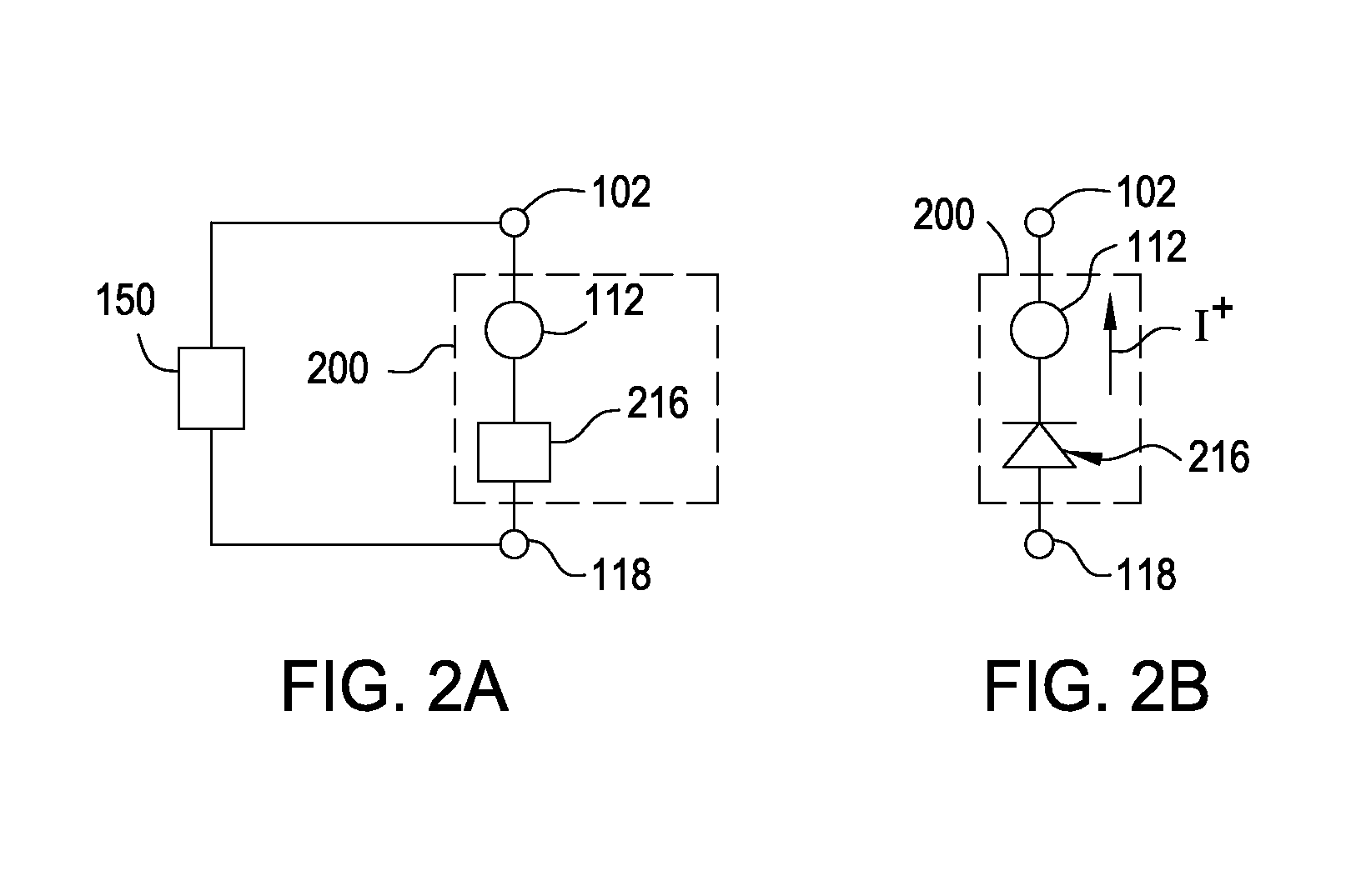
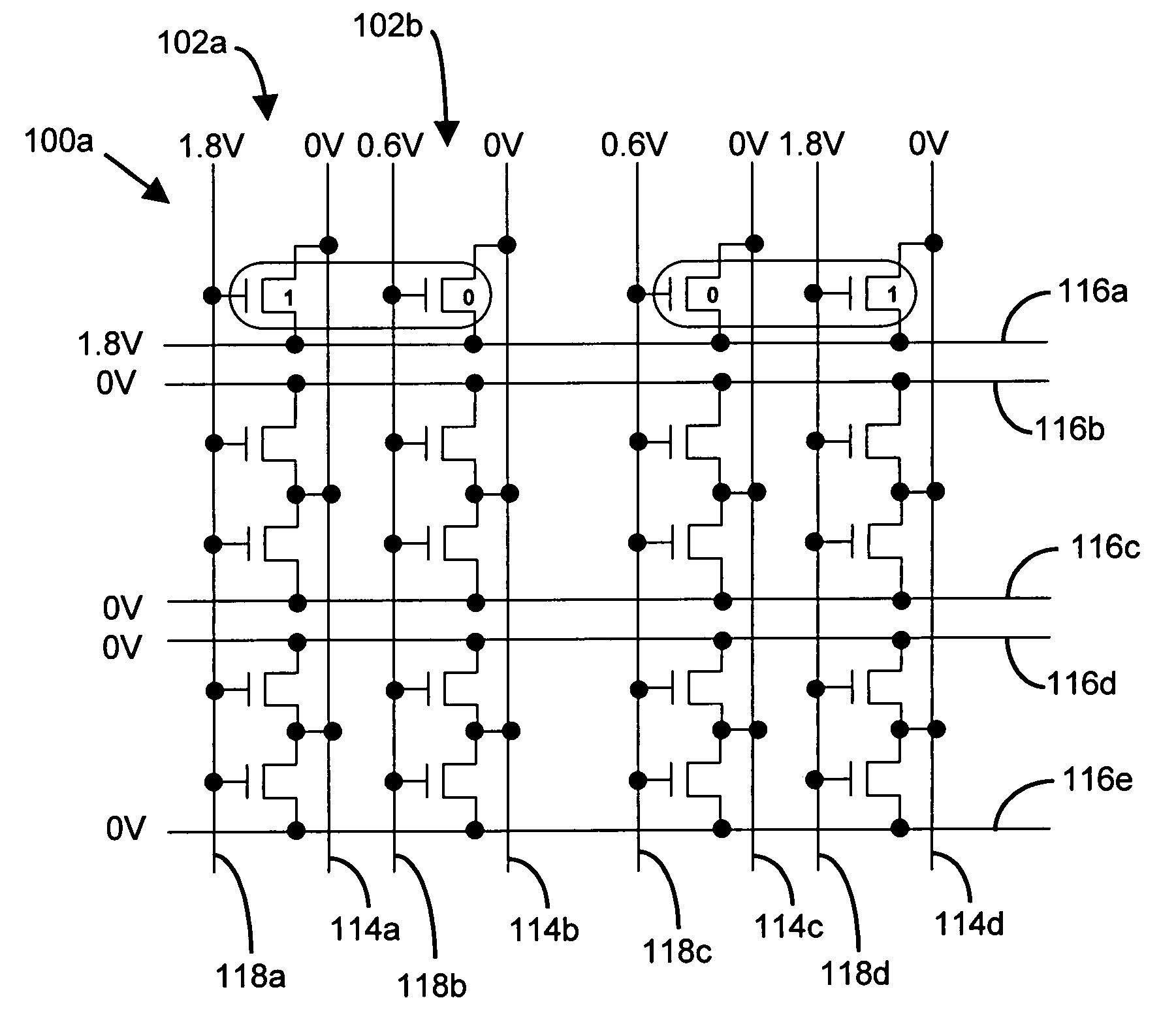
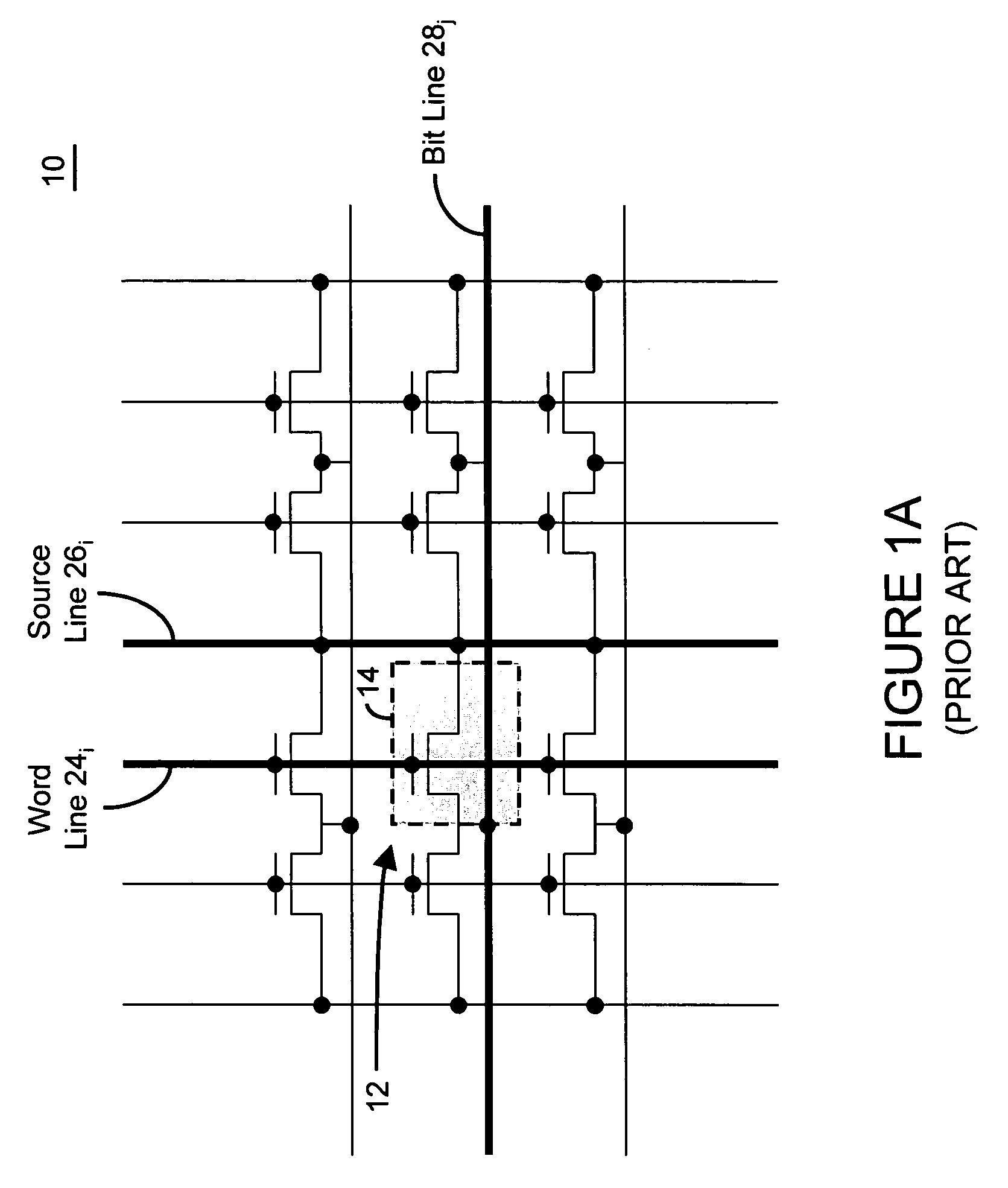
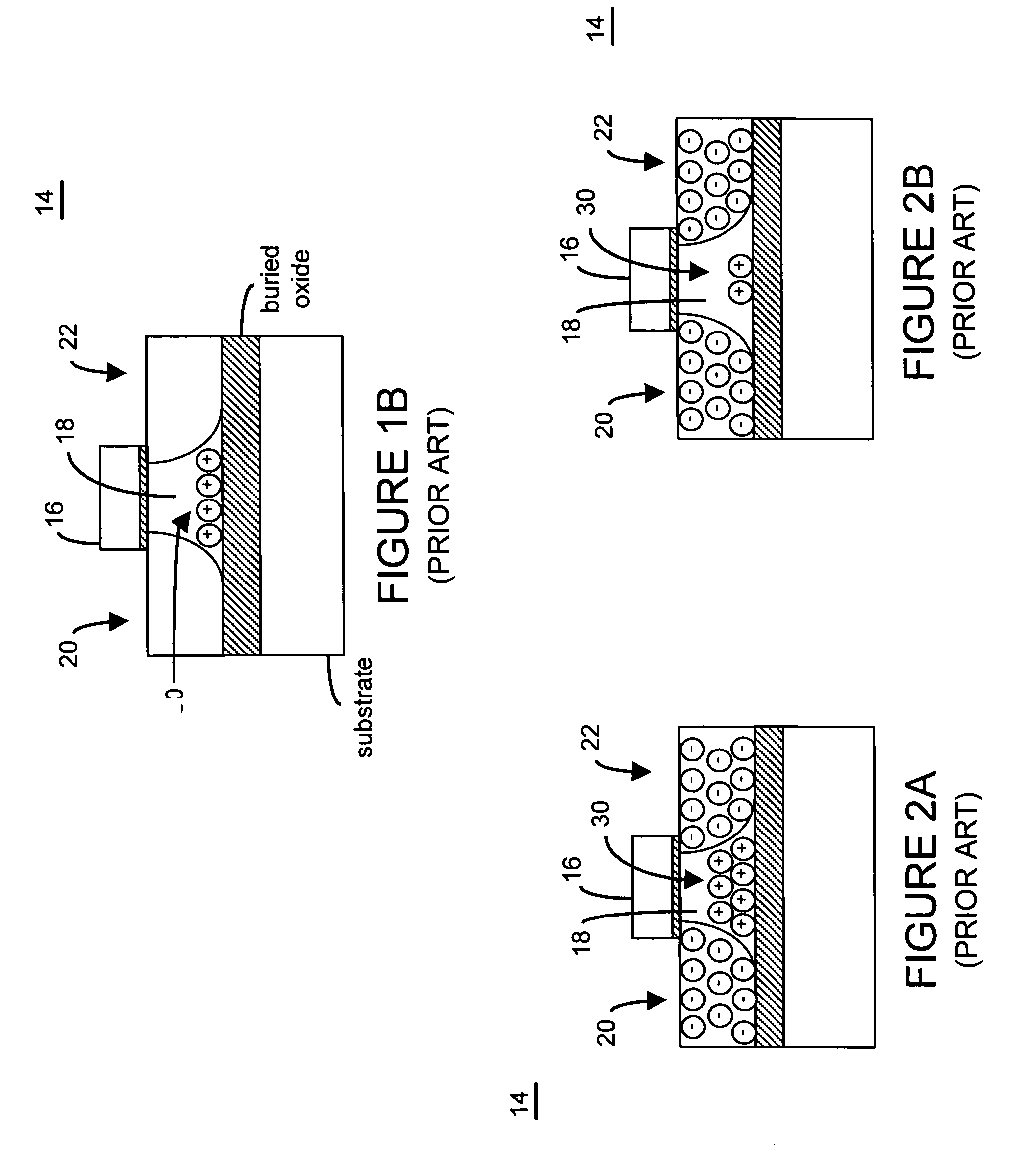
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1577 results about "Logic state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
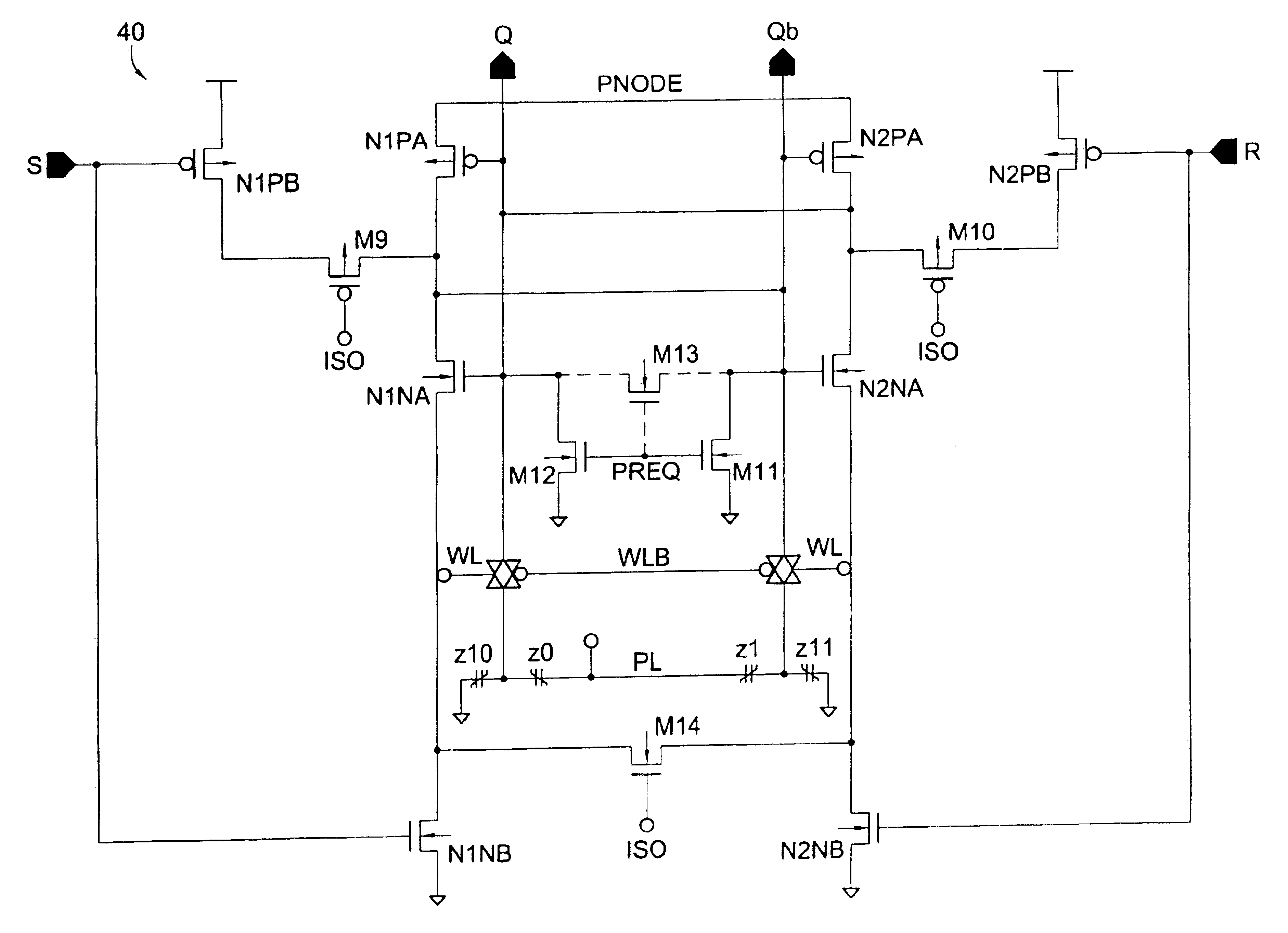
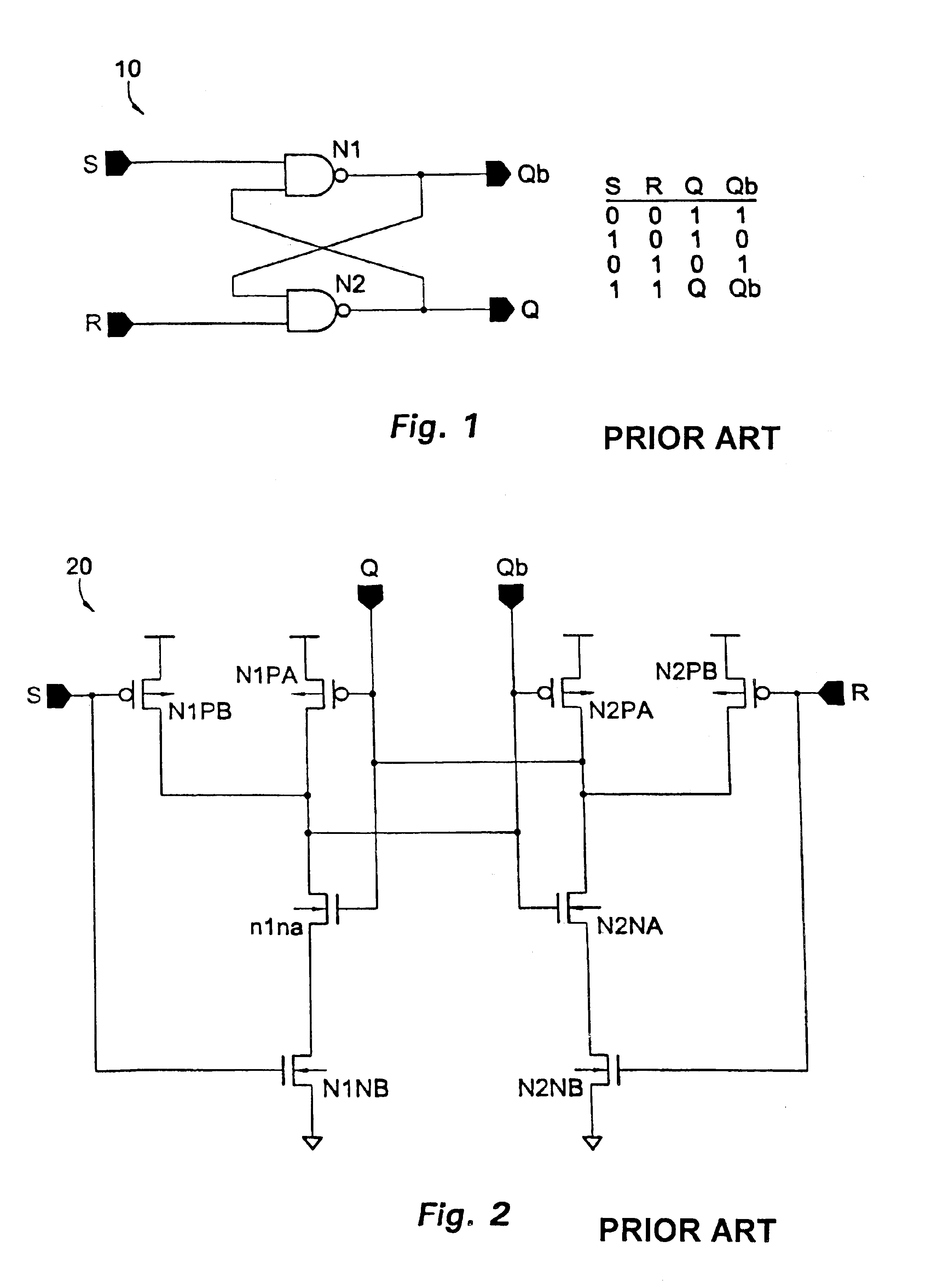
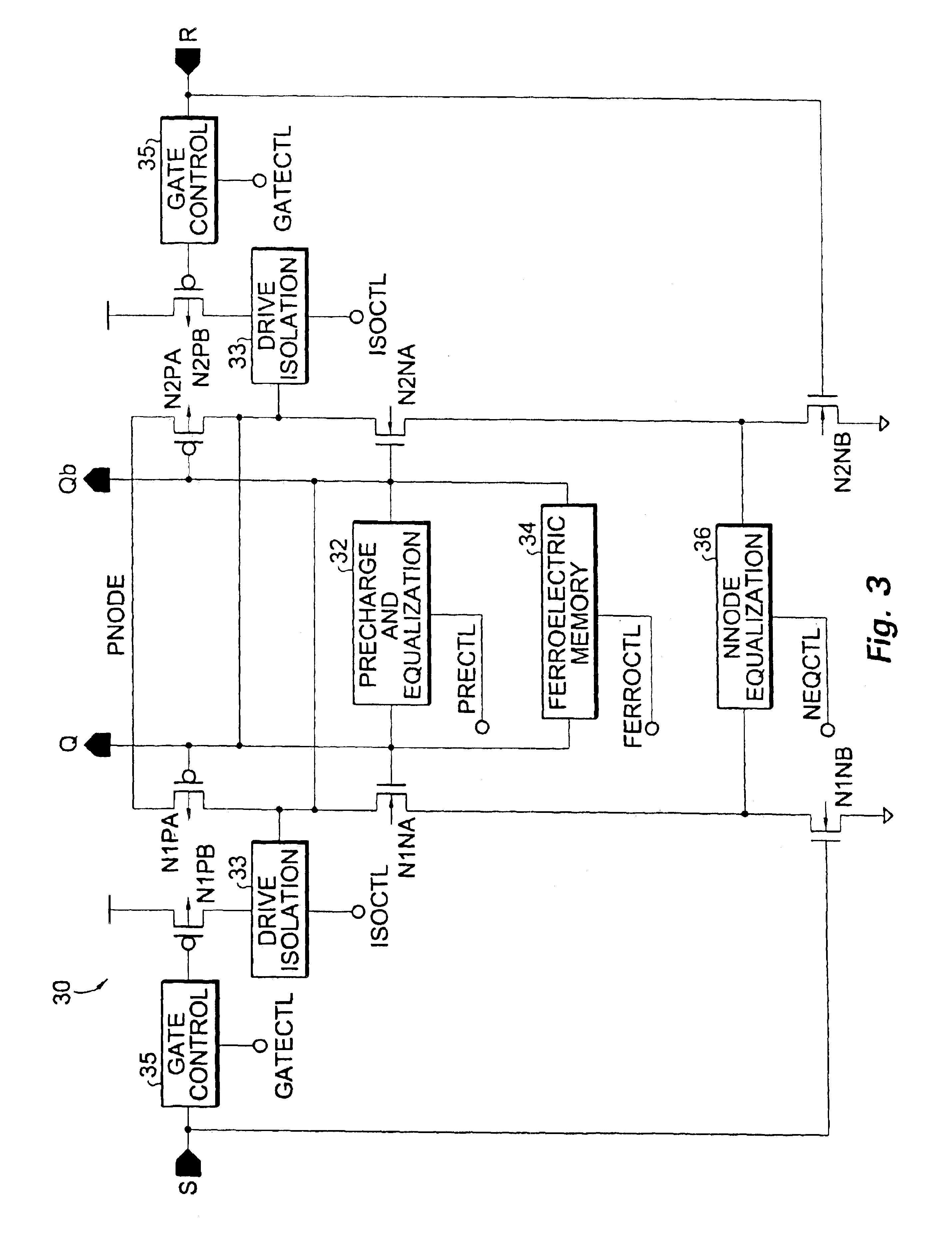
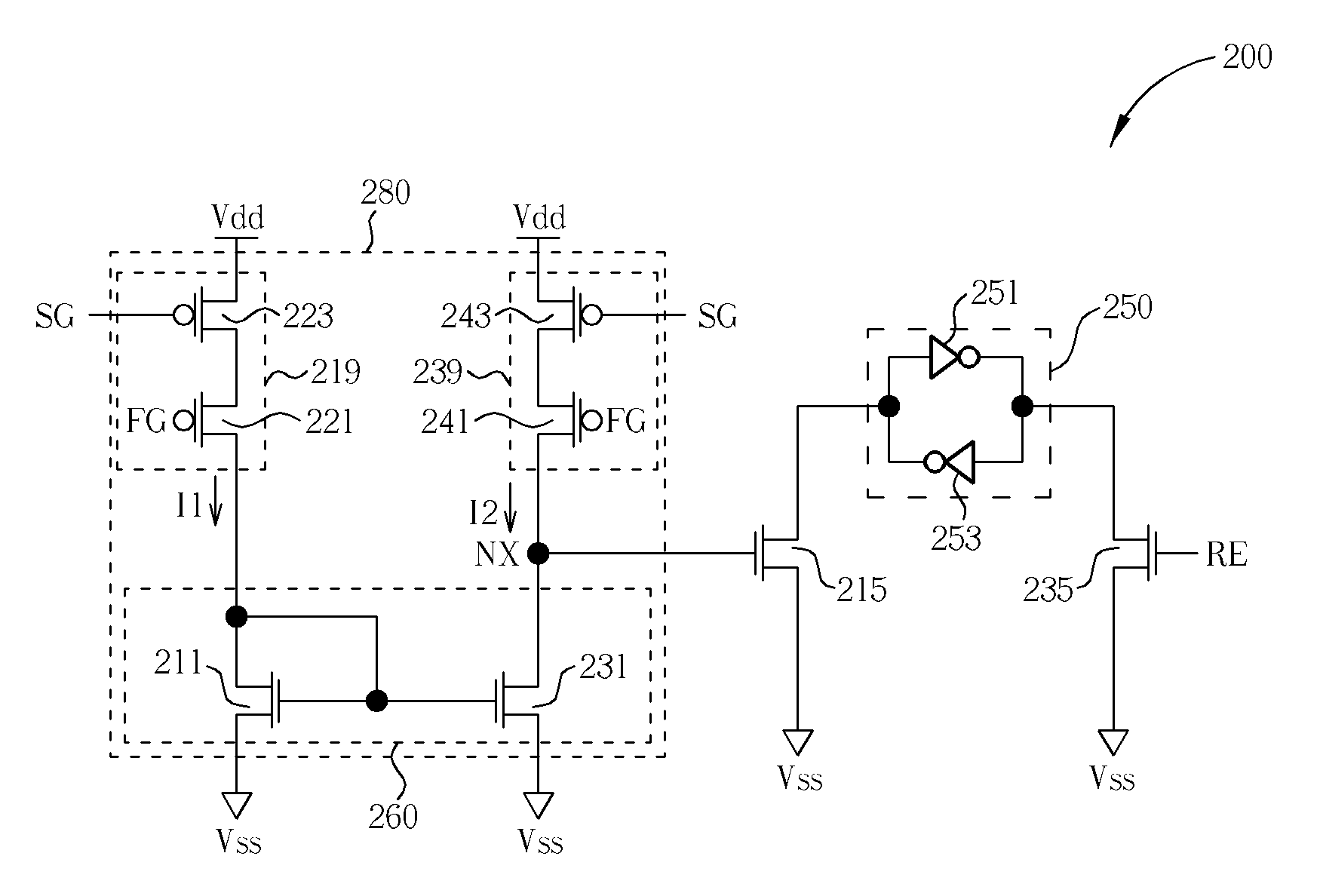
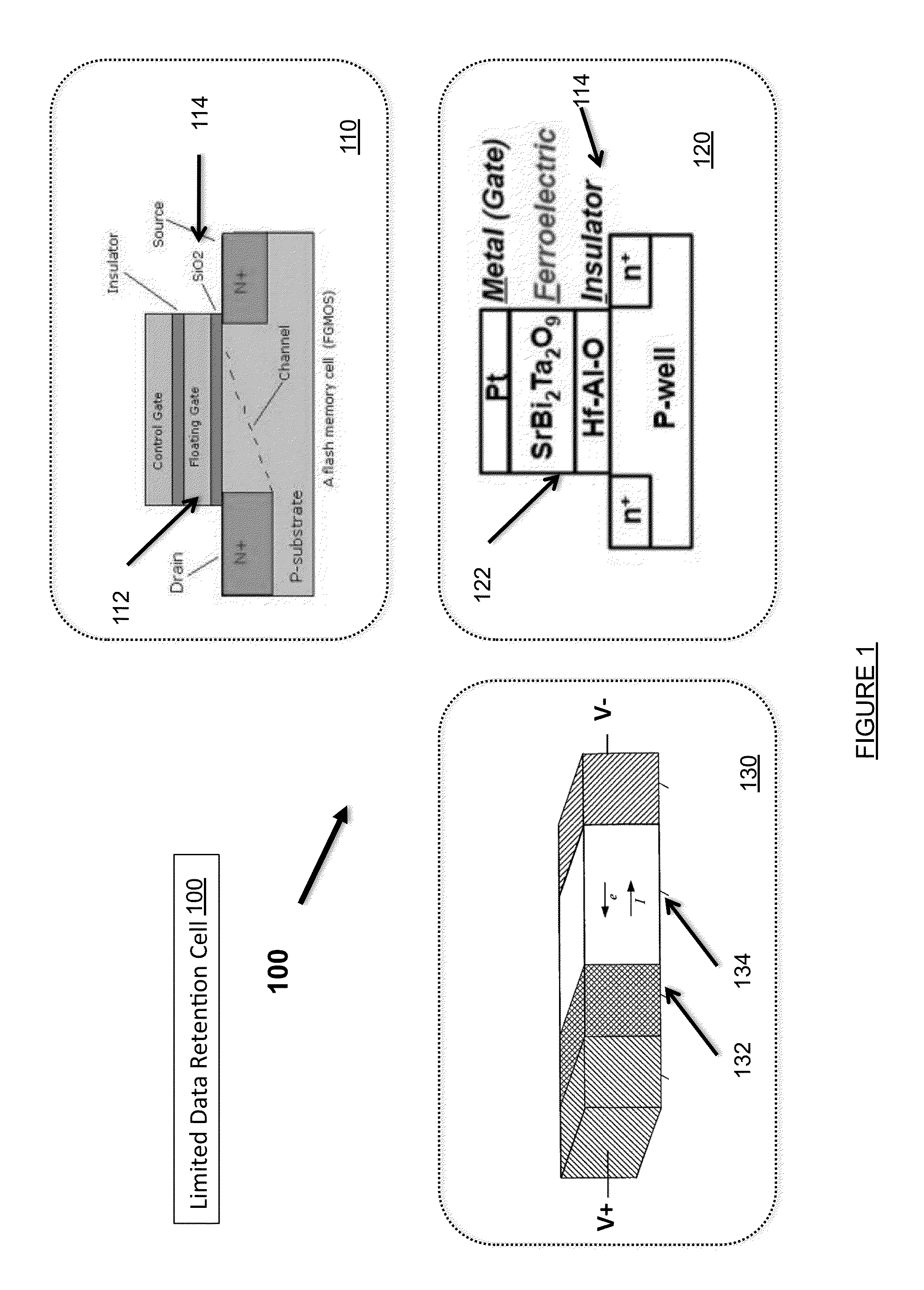
Ferroelectric non-volatile logic elements
InactiveUS6894549B2Easy translationImprove performanceTransistorPulse generation by non-linear magnetic/dielectric devicesShift registerAudio power amplifier
Various logic elements such as SR flip-flops, JK flip-flops, D-type flip-flops, master-slave flip-flops, parallel and serial shift registers, and the like are converted into non-volatile logic elements capable of retaining a current output logic state even though external power is removed or interrupted through the strategic addition of ferroelectric capacitors and supporting circuitry. In each case, the building blocks of a cross-coupled sense amplifier are identified within the logic element and the basic cell is modified and / or optimized for sensing performance.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Sense amplifier circuit having current mirror architecture
A sense amplifier circuit for use in a semiconductor memory device has complemented logic states at opposite sides of the latch circuit in the sense amplifier circuit determinate all the time in operation. The sense amplifier circuit takes advantage of a current mirror circuit for ascending or descending a voltage level at the gate of a transistor by charge accumulation or charge dissipation, which turns on or off the transistor so as to control the logic states at opposite sides of the latch circuit in the sense amplifier circuit.
Owner:EMEMORY TECH INC
Nonvolatile memory device using a varistor as a current limiter element
ActiveUS20130214232A1Reduce voltageTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineeringMusic player
Embodiments of the invention include a method of forming a nonvolatile memory device that contains a resistive switching memory element that has improved device switching performance and lifetime, due to the addition of a current limiting component disposed therein. The electrical properties of the current limiting component are configured to lower the current flow through the variable resistance layer during the logic state programming steps by adding a fixed series resistance in the resistive switching memory element of the nonvolatile memory device. In some embodiments, the current limiting component comprises a varistor that is a current limiting material disposed within a resistive switching memory element in a nonvolatile resistive switching memory device. Typically, resistive switching memory elements may be formed as part of a high-capacity nonvolatile memory integrated circuit, which can be used in various electronic devices, such as digital cameras, mobile telephones, handheld computers, and music players.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
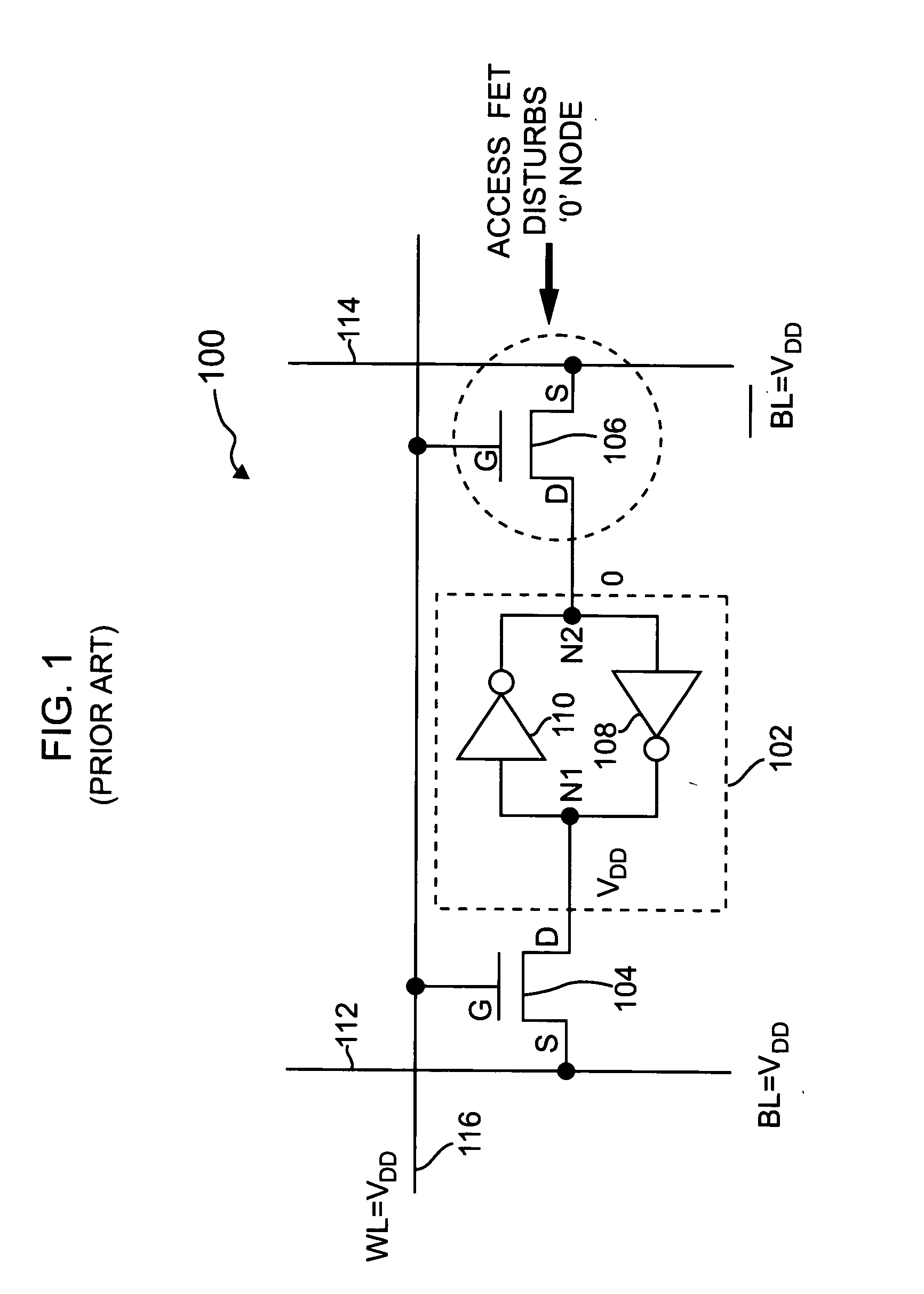
Semiconductor memory cell, array, architecture and device, and method of operating same
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In a first aspect, the present invention is directed to a memory cell and technique of reading data from and writing data into that memory cell. In this regard, in one embodiment of this aspect of the invention, the memory cell includes two transistors which store complementary data states. That is, the two-transistor memory cell includes a first transistor that maintains a complementary state relative to the second transistor. As such, when programmed, one of the transistors of the memory cell stores a logic low (a binary “0”) and the other transistor of the memory cell stores a logic high (a binary “1”). The data state of the two-transistor complementary memory cell may be read and / or determined by sampling, sensing measuring and / or detecting the polarity of the logic states stored in each transistor of complementary memory cell. That is, the two-transistor complementary memory cell is read by sampling, sensing measuring and / or detecting the difference in signals (current or voltage) stored in the two transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Floating-body DRAM in tri-gate technology
A floating-body dynamic random access memory device may include a semiconductor body having a top surface and laterally opposite sidewalls formed on a substrate. A gate dielectric layer may be formed on the top surface of the semiconductor body and on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body. A gate electrode may be formed on the gate dielectric on the top surface of the semiconductor body and adjacent to the gate dielectric on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body. The gate electrode may only partially deplete a region of the semiconductor body, and the partially depleted region may be used as a storage node for logic states.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Programmable resistive device and memory using diode as selector
Building programmable resistive devices in contact holes at the crossover of a plurality of conductor lines in more than two vertical layers is disclosed. There are plurality of first conductor lines and another plurality of second conductor lines that can be substantially perpendicular to each other, though in two different vertical layers. A diode and / or a programmable resistive element can be fabricated in the contact hole between the first and second conductor lines. The programmable resistive element can be coupled to another programmable resistive device or shared between two programmable devices whose diodes conducting currents in opposite directions and / or coupled to a common conductor line. The programmable resistive memory can be configured to be programmable by applying voltages to conduct current flowing through the programmable resistive element to change its resistance for a different logic state.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
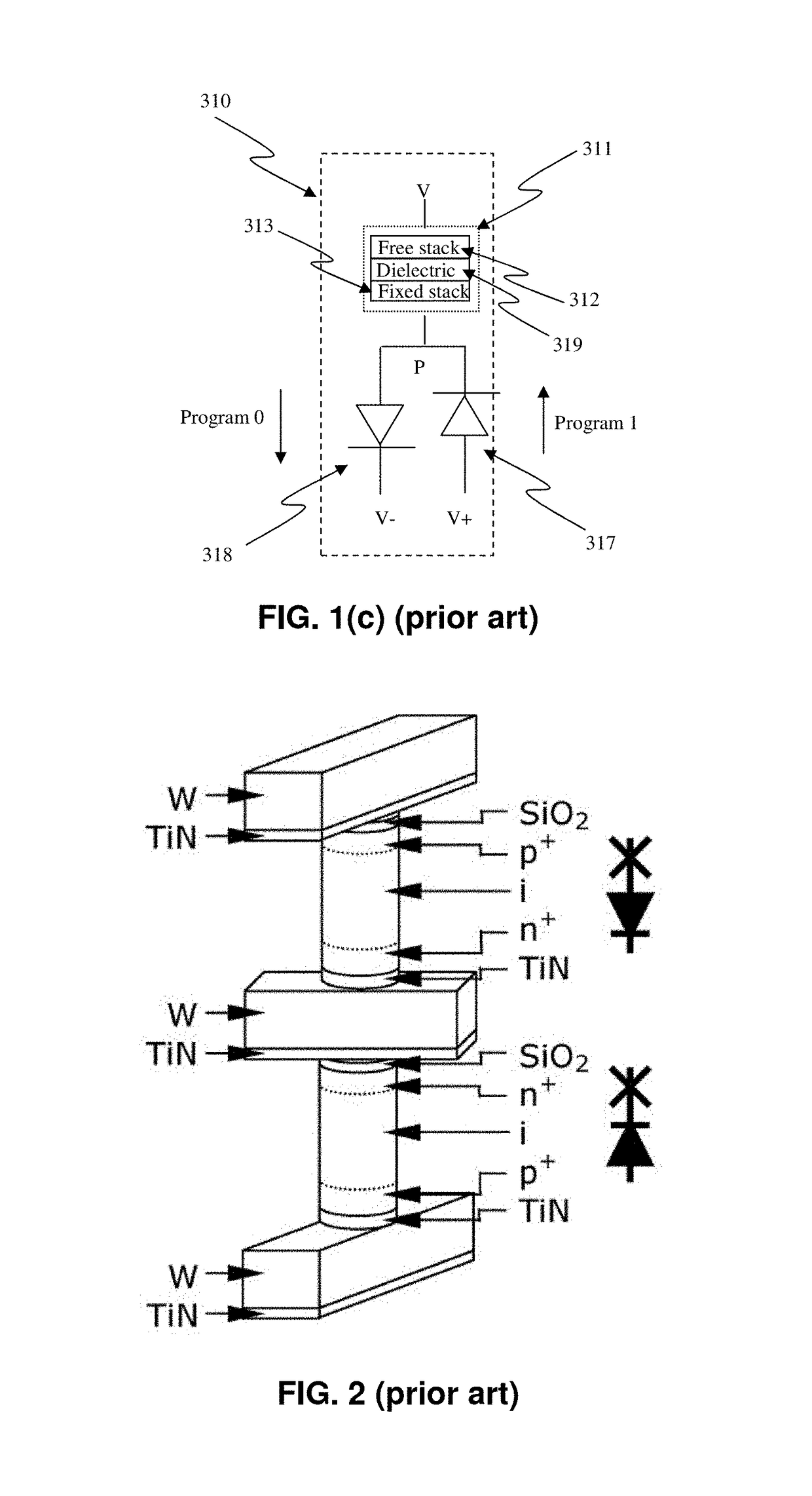
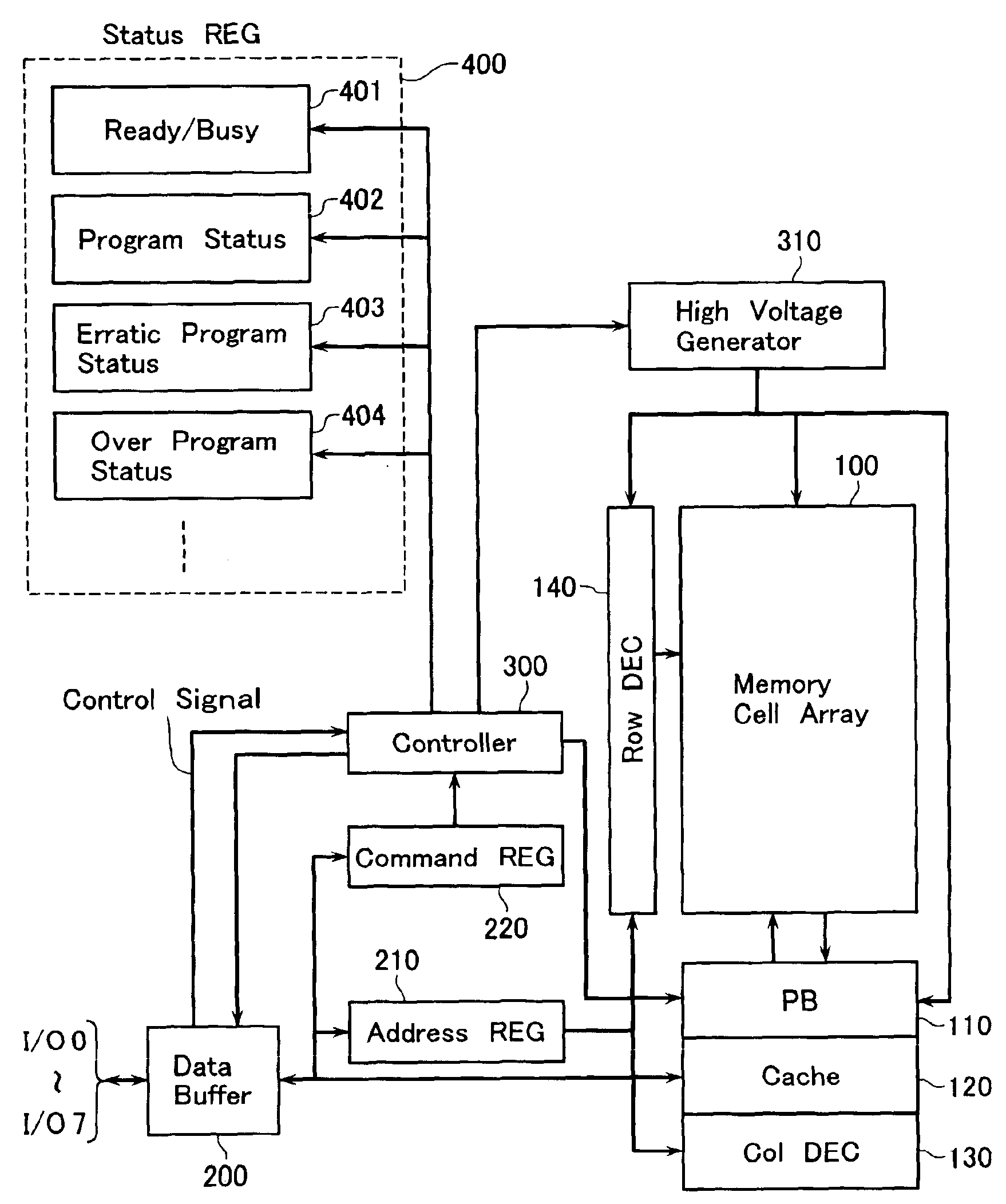
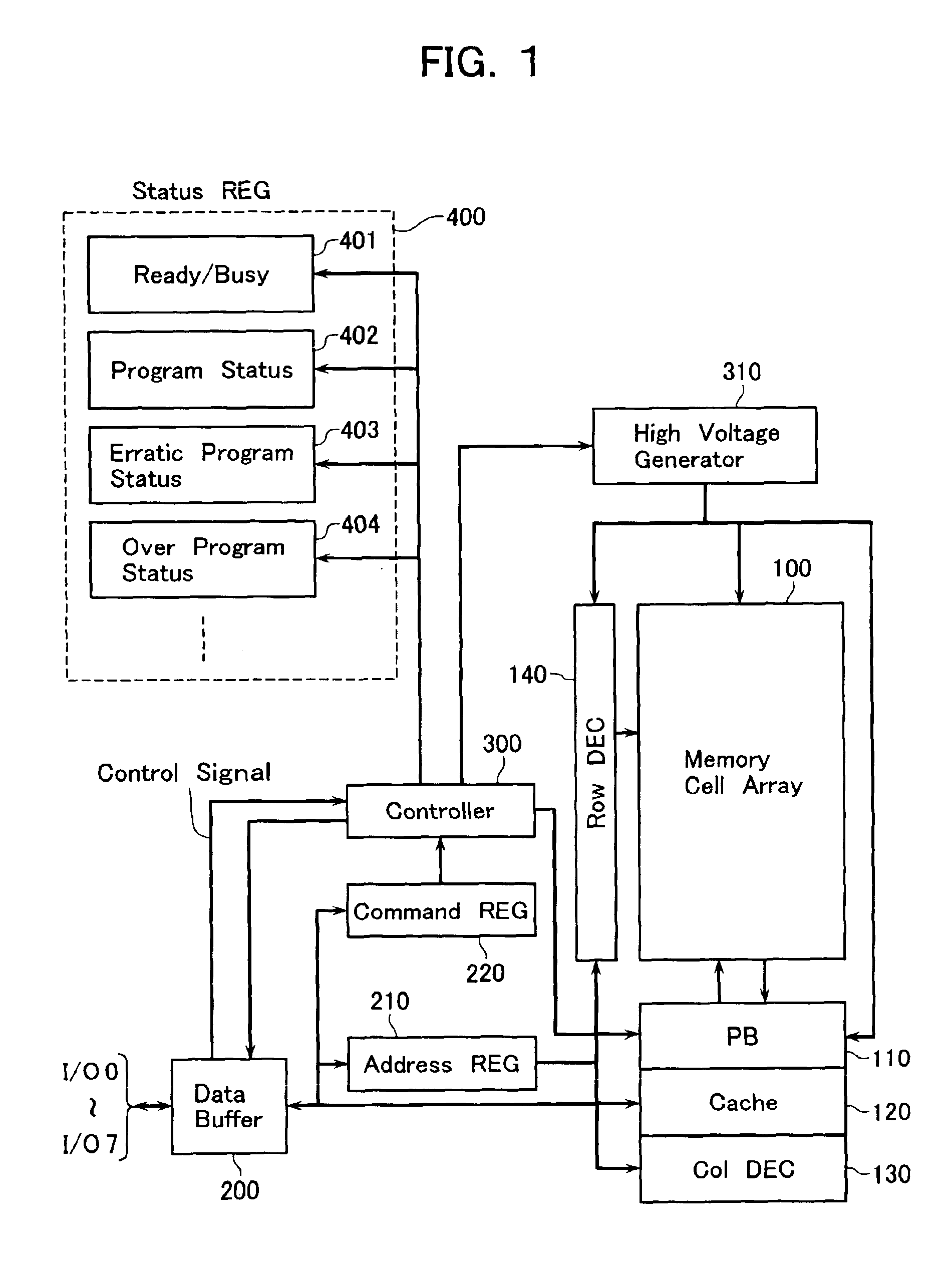
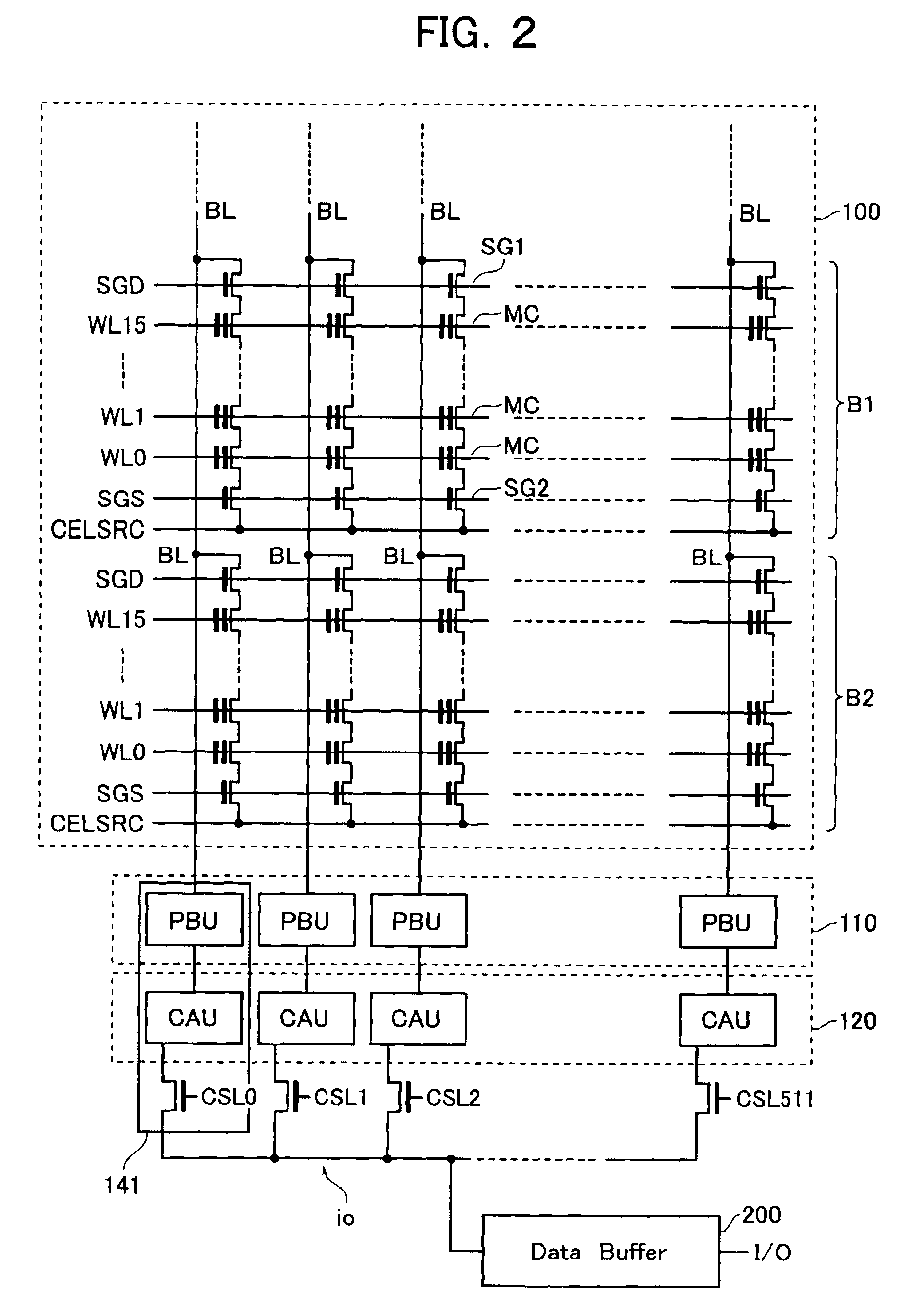
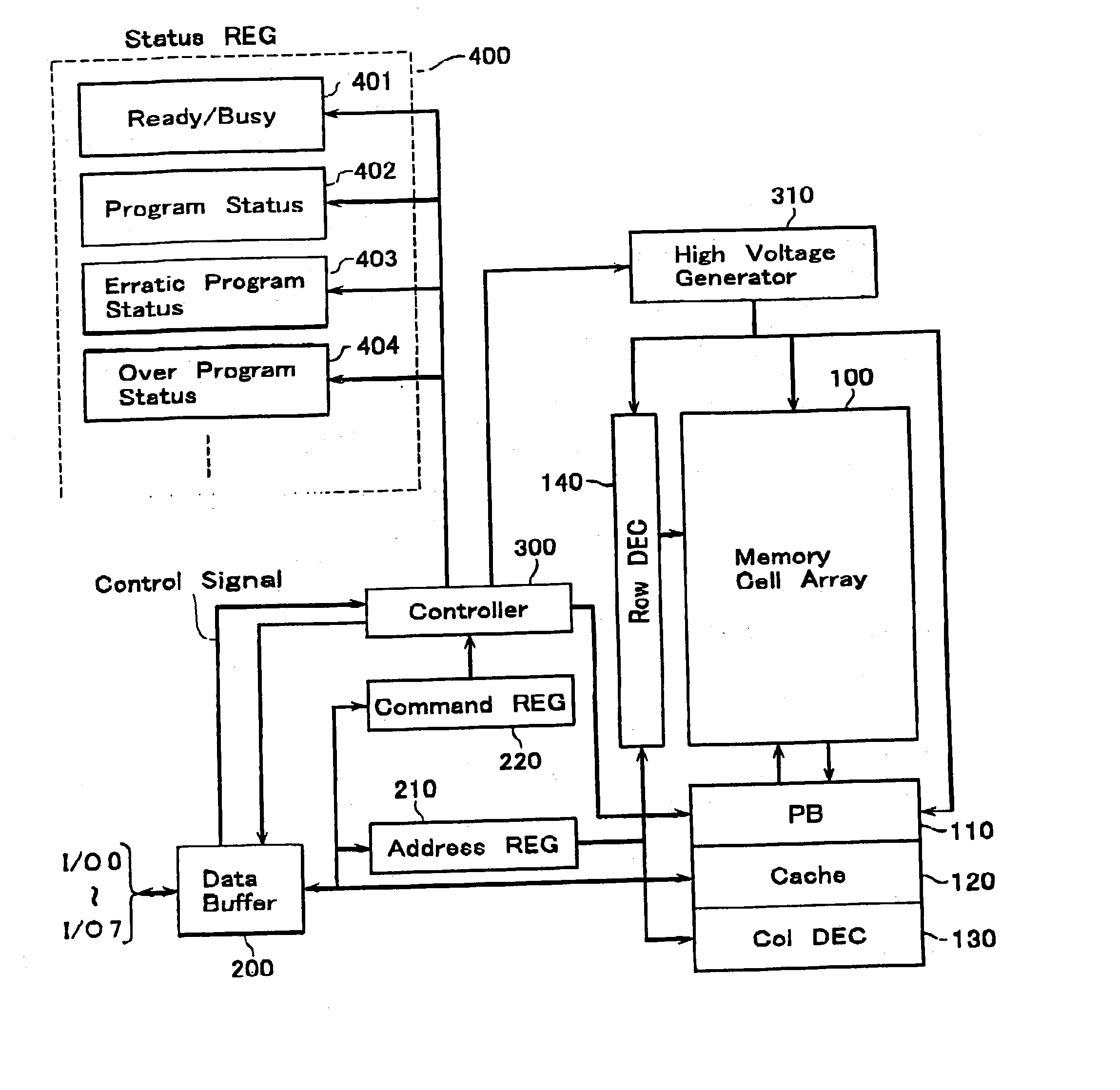
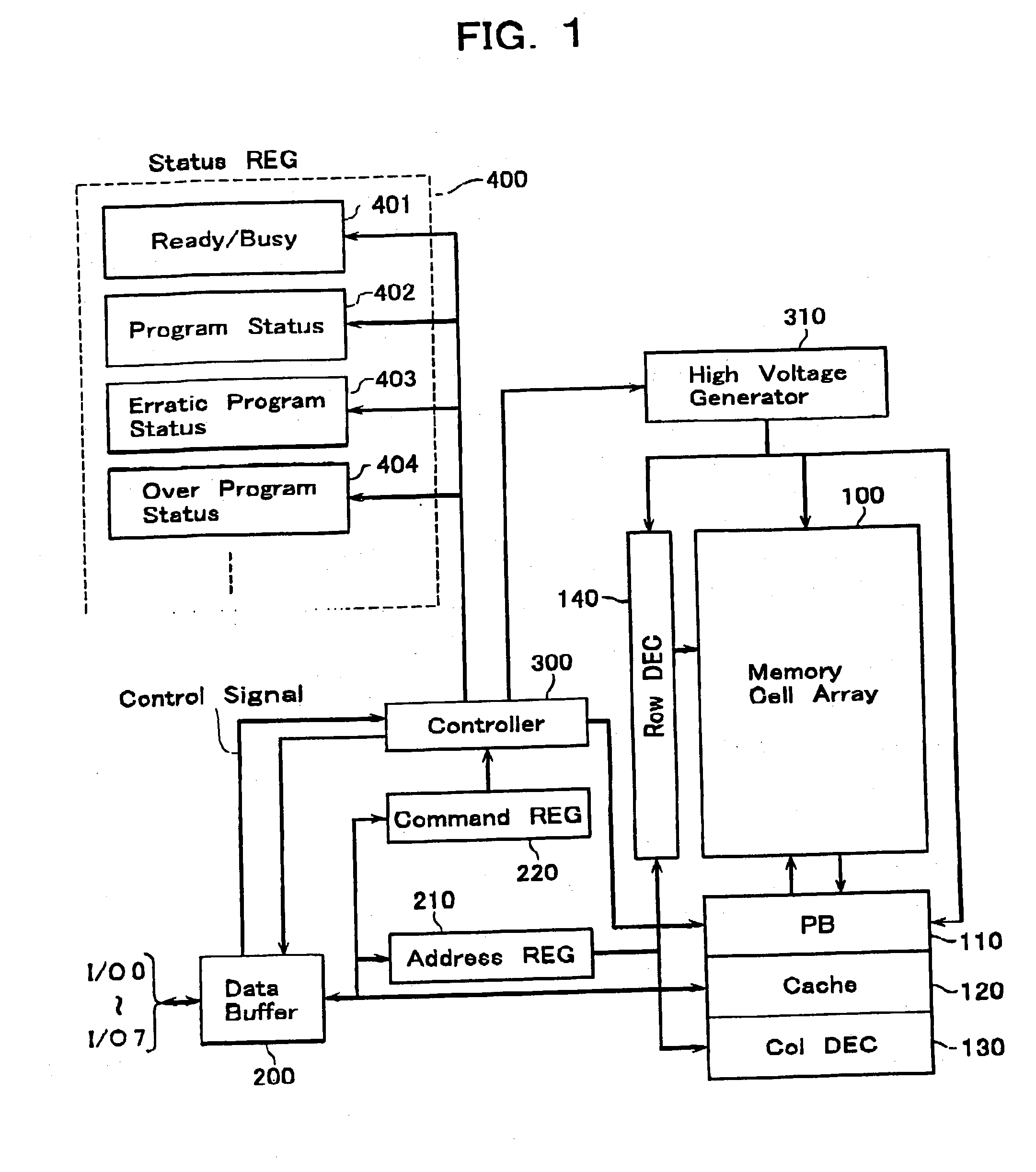
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array, a data hold circuit, and a controller A program control function applies a program voltage to a selected memory cell to let data shift from a first logic state to a second logic state. A program verify control function verifies that a programmed data of the selected memory cell shifted to the second logic state. An erratic program verify control function checks that a threshold voltage of a memory cell to be held in the first logic state does not exceed a third value set as an upper limit value of a variation of the first logic state. An over-program verify control function checks that a threshold voltage of the selected memory cell shifted to the second logic state does not exceed a fourth value set as an upper limit thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
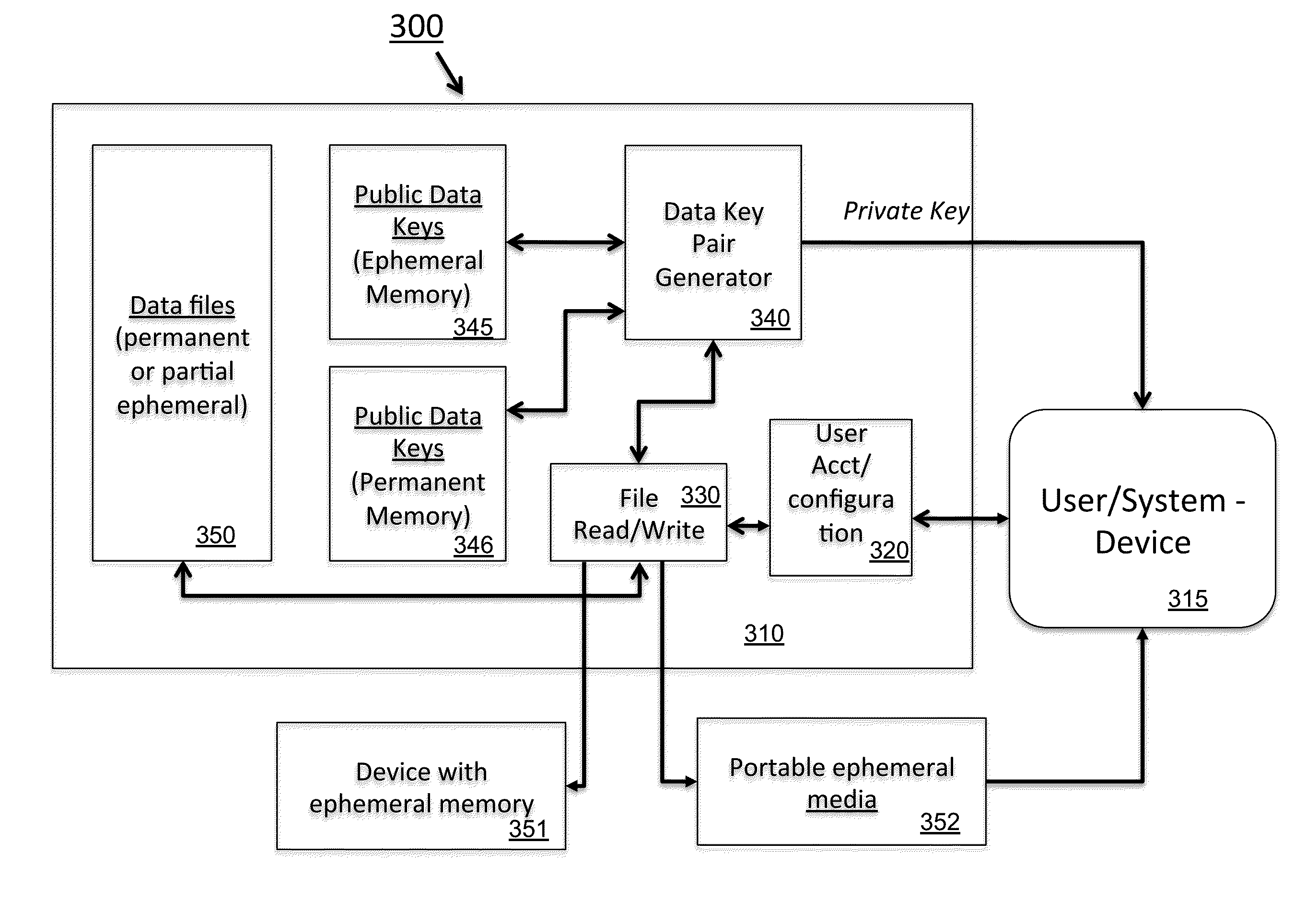
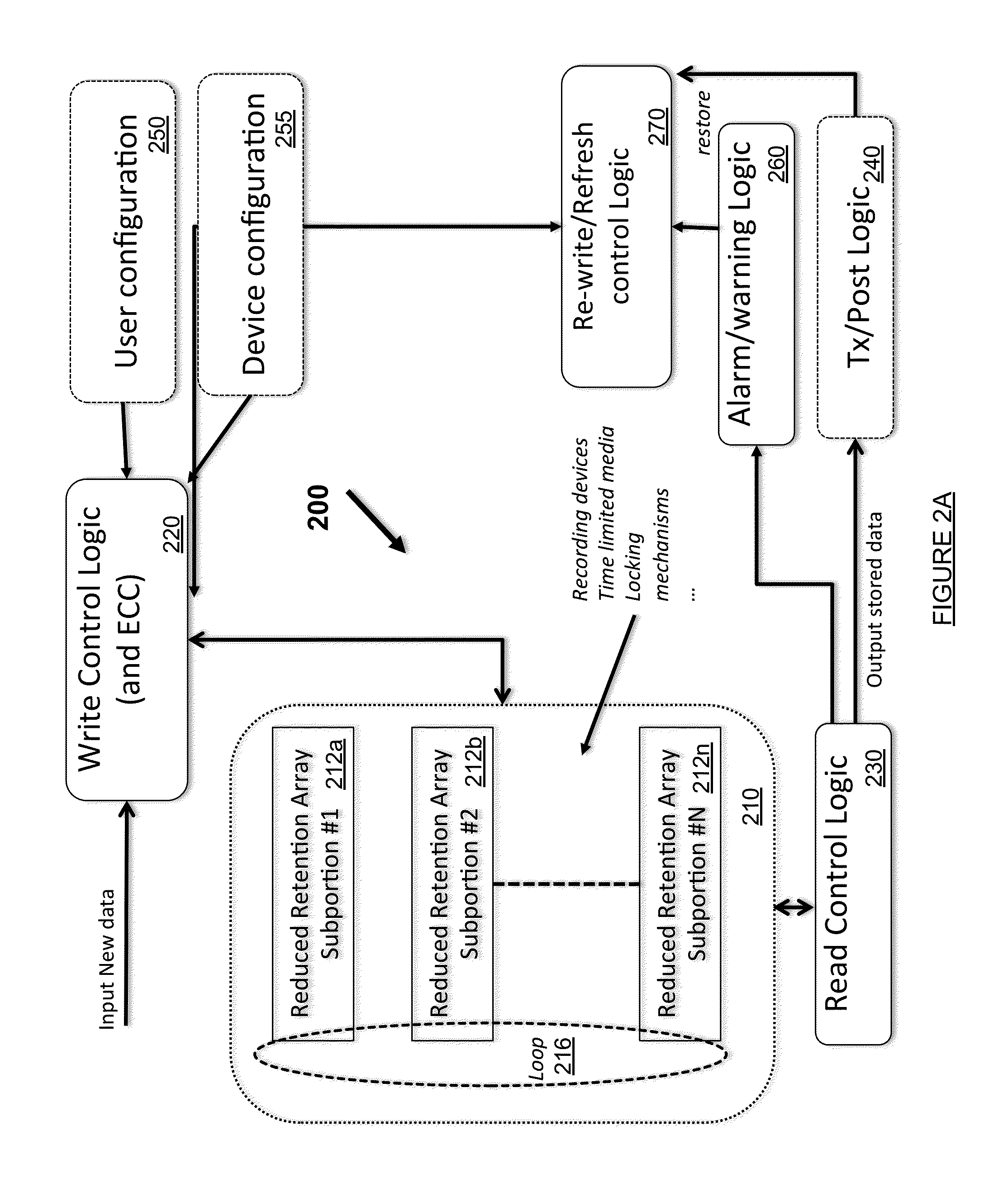
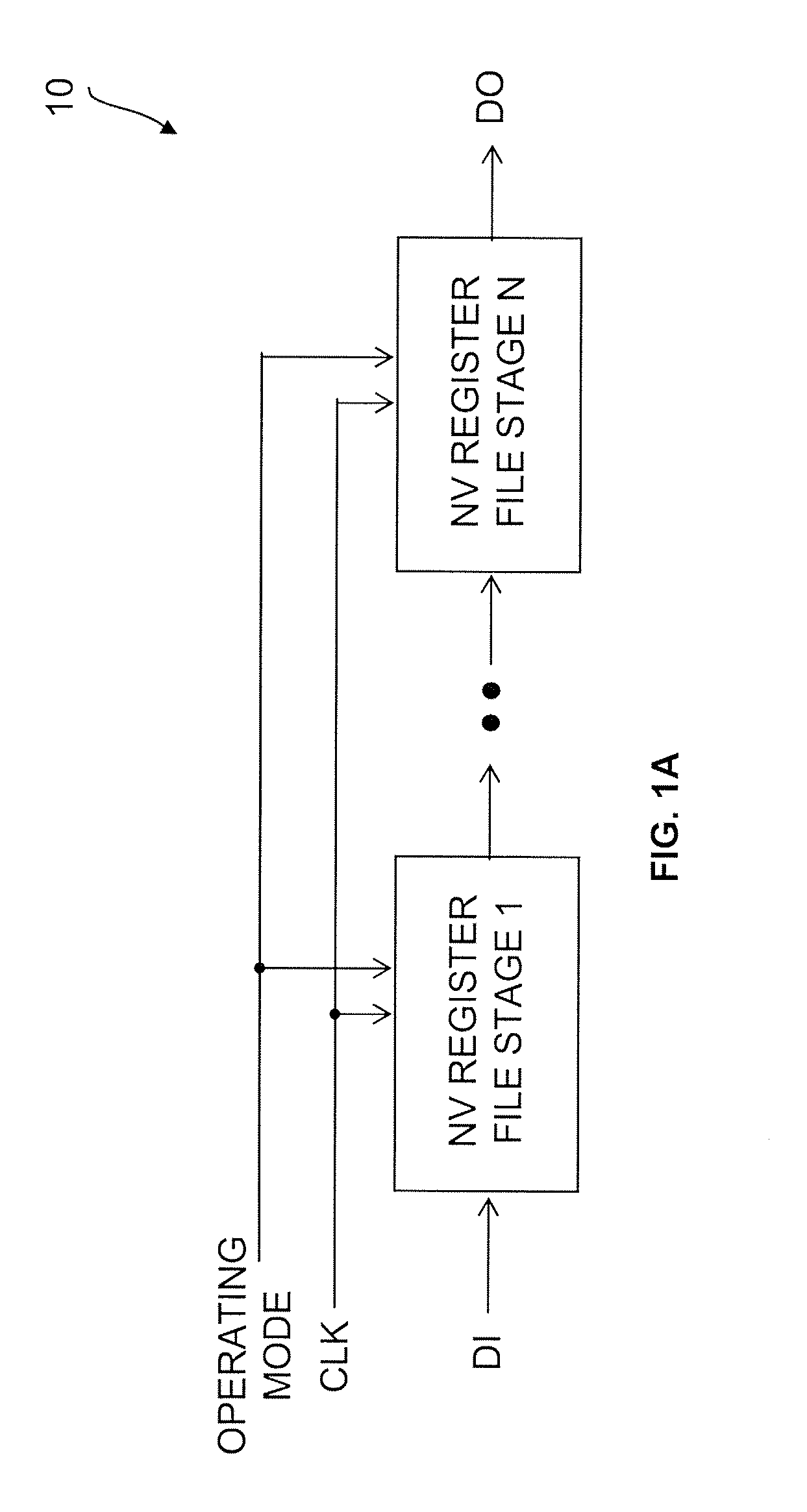
Ephemeral Storage Elements, Circuits, and Systems
An array of programmable non-volatile devices are is adapted such that their logic state is controllably altered over time by quiescent changes, slow controlled changes, scheduled changes, or some combination thereof imposed at a physical level. This allows for improved security and privacy for data to be permanently deleted. In some applications a data refresh and / or automatic backup can be implemented as well.
Owner:JONKER
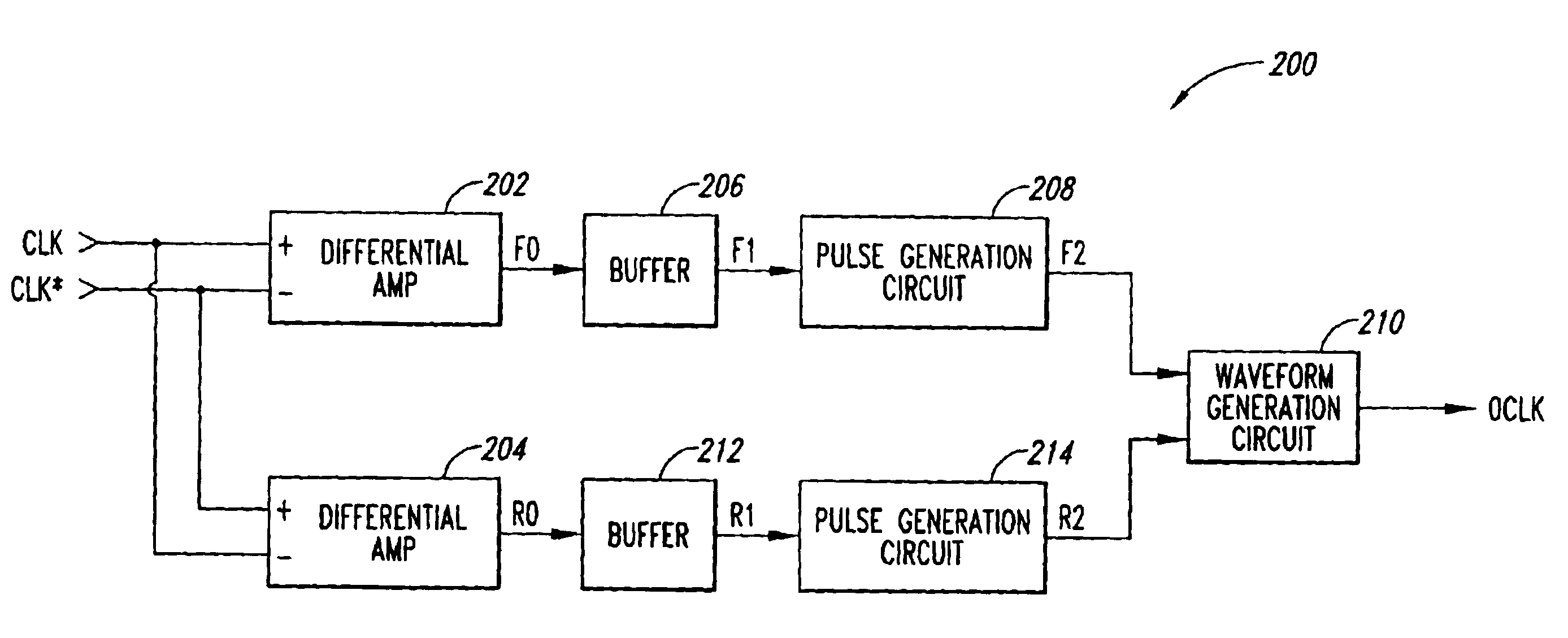
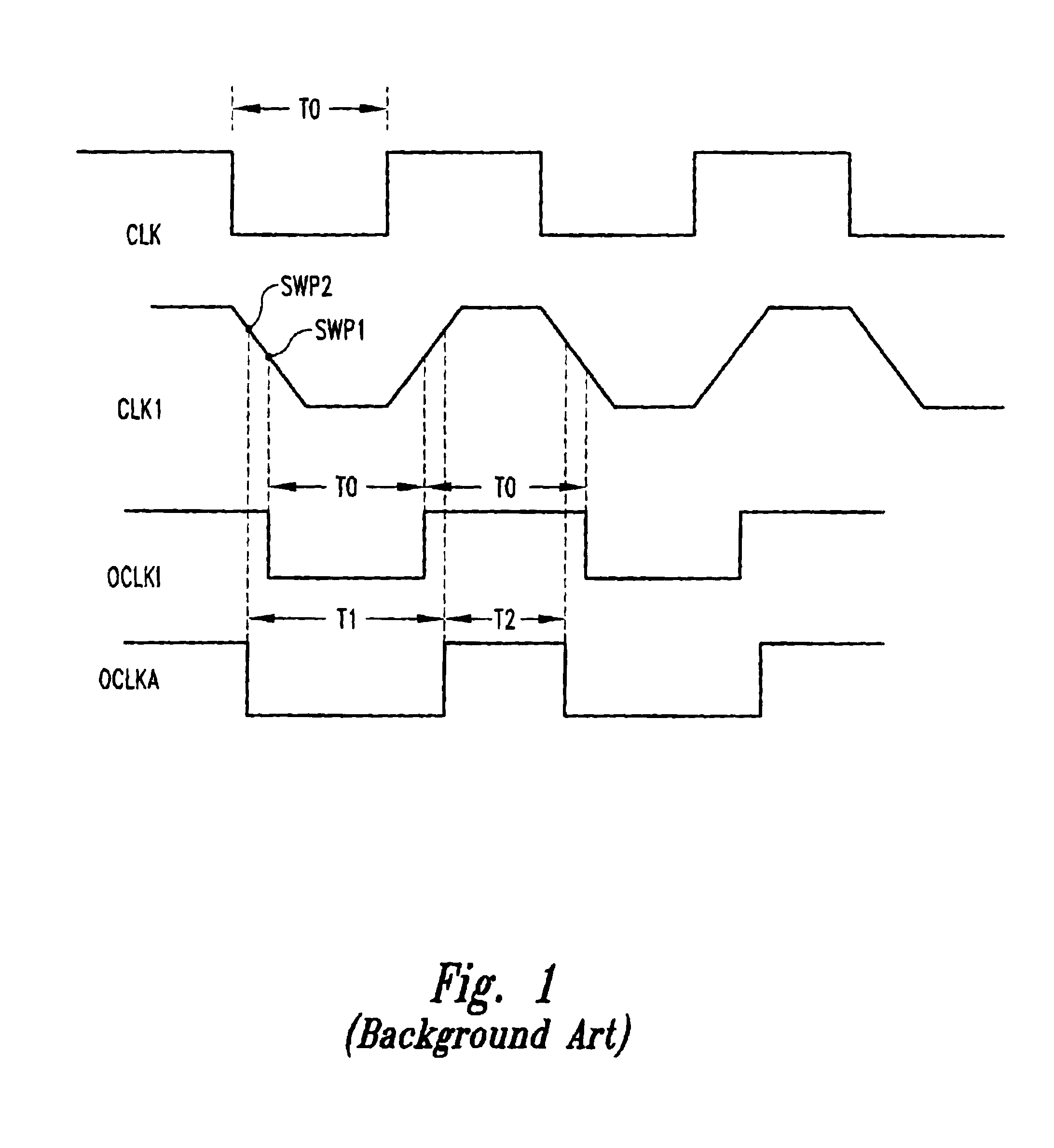
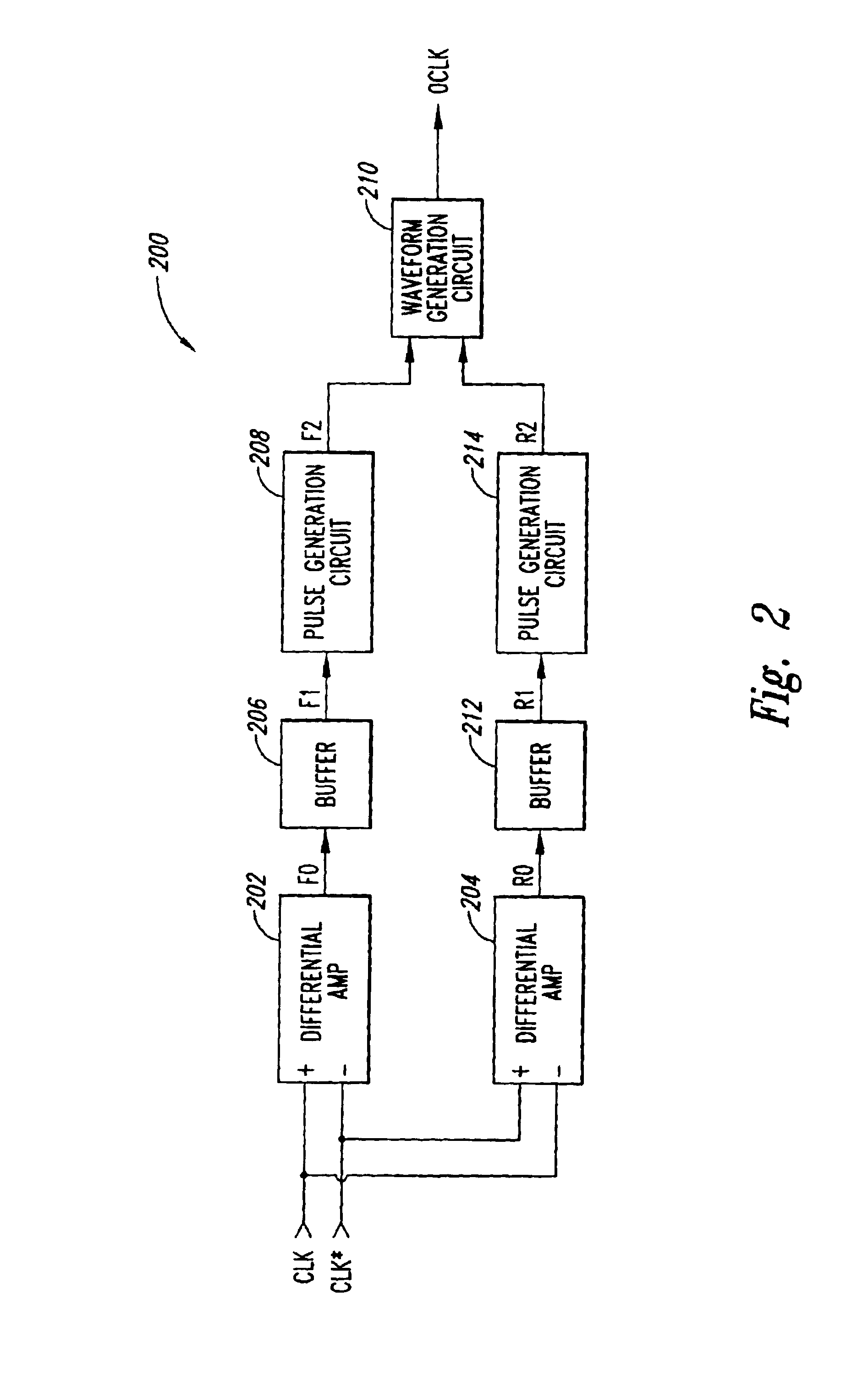
Low skew clock input buffer and method
InactiveUS6847582B2Reliability increasing modificationsDigital storageAudio power amplifierLogic state
An input buffer includes first and second cross-coupled differential amplifiers. Each amplifier drives a buffer signal from a first logic state to a second logic state at a first slew rate when input signal transitions from a first logic state to a second logic state and a complementary input signal transitions from the second logic state to the first logic state, and drives the buffer signal from the second logic state to the first logic state at a second slew rate when the signal transitions are the complement of these previous transitions. An output circuit generates a first edge of an output signal when the buffer signal from the first amplifier transitions from the first logic state to the second logic state and generates a second edged of the output signal when the buffer signal from the second amplifier transitions from the first to the second logic state.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
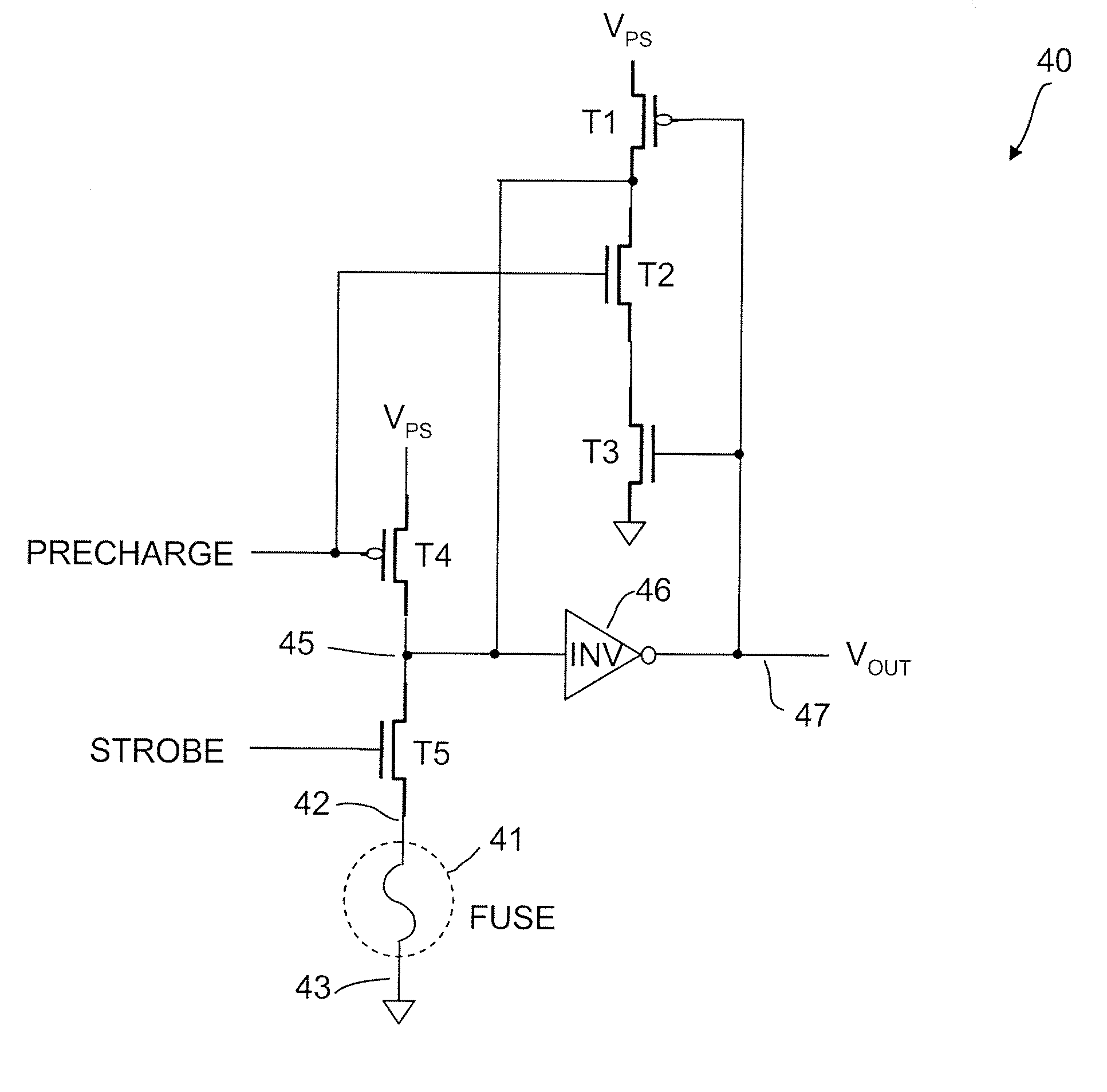
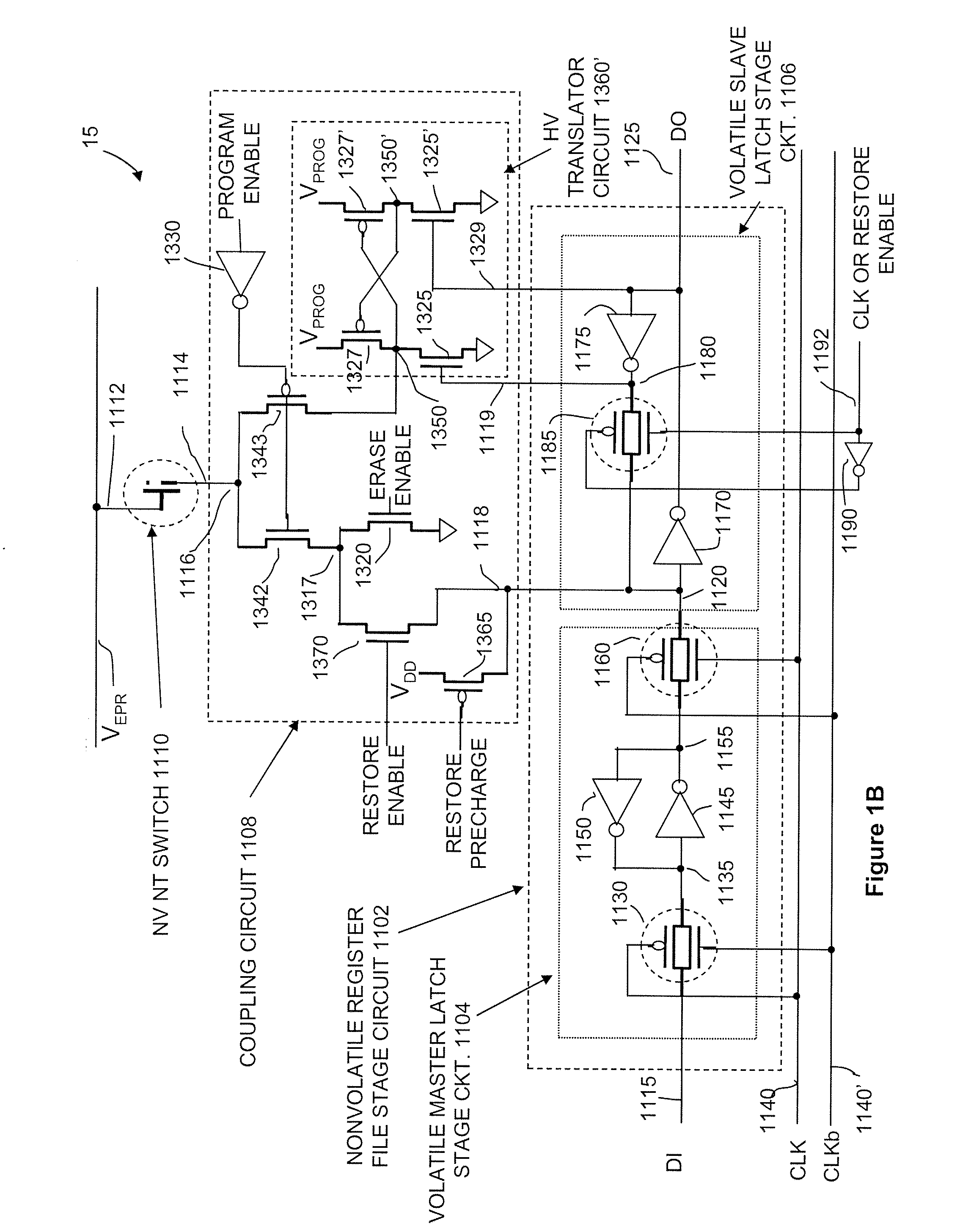
Latch circuits and operation circuits having scalable nonvolatile nanotube switches as electronic fuse replacement elements
ActiveUS20080159042A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsProcessor registerHemt circuits
A non-volatile latch circuit is provided. The non-volatile latch circuit includes a nanotube switching element capable of switching between resistance states and non-volatilely retaining the resistance state. The non-volatile latch circuit includes a volatile latch circuit is capable of receiving and volatilely storing a logic state. When the nanotube switching element is a resistance state, the volatile latch circuit retains a corresponding logic state and outputs that corresponding logic state at an output terminal. A non-volatile register file configuration circuit for use with a plurality of non-volatile register files is also provided. The non-volatile register file configuration circuit includes a selection circuitry and a plurality of nanotube fuse elements, each in electrical communication with one of a plurality of non-volatile register files. The selection circuitry is capable of applying electrical stimulus to each of the selected nanotube fuse elements to selectively bypass the corresponding register file.
Owner:NANTERO
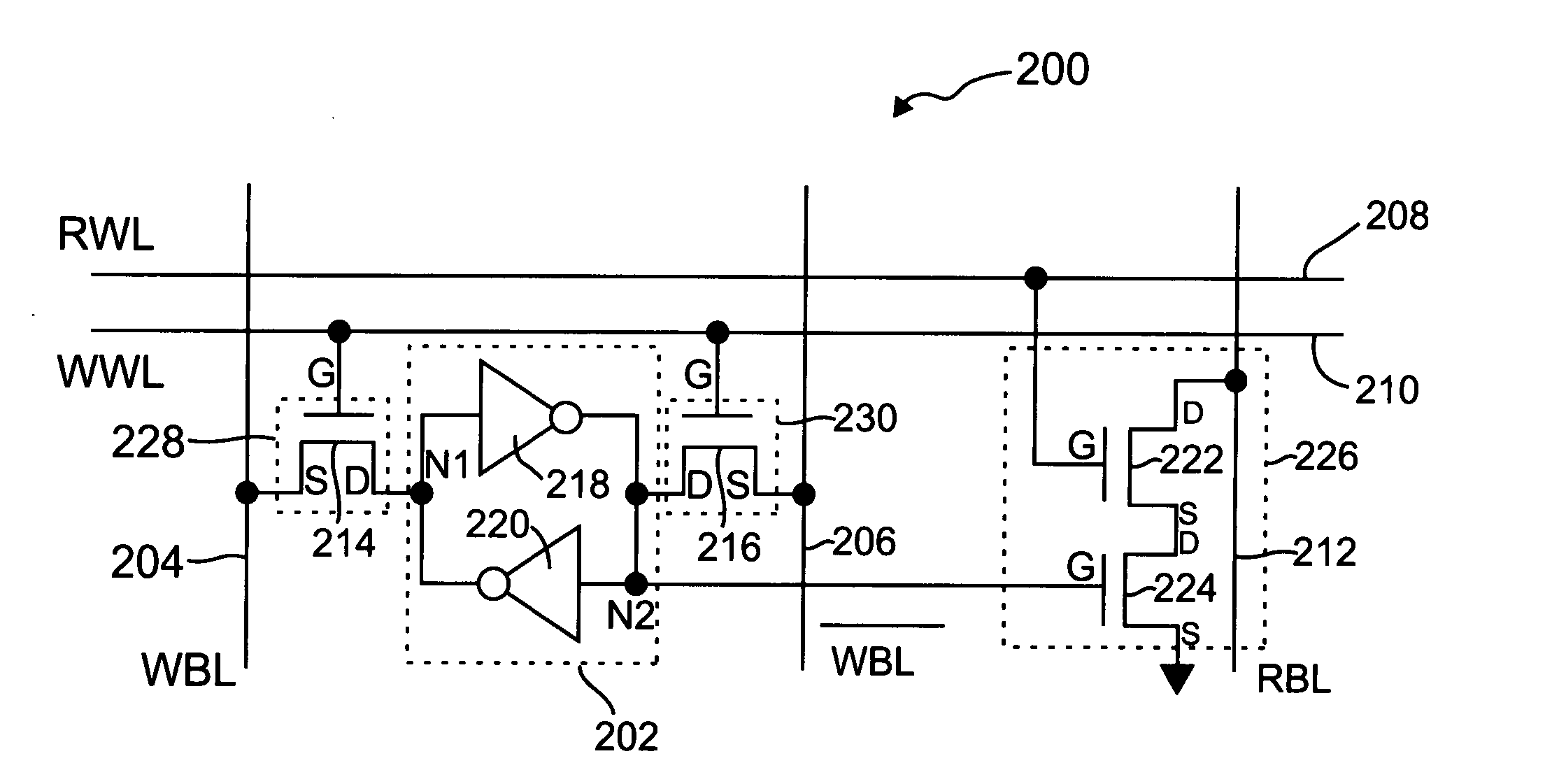
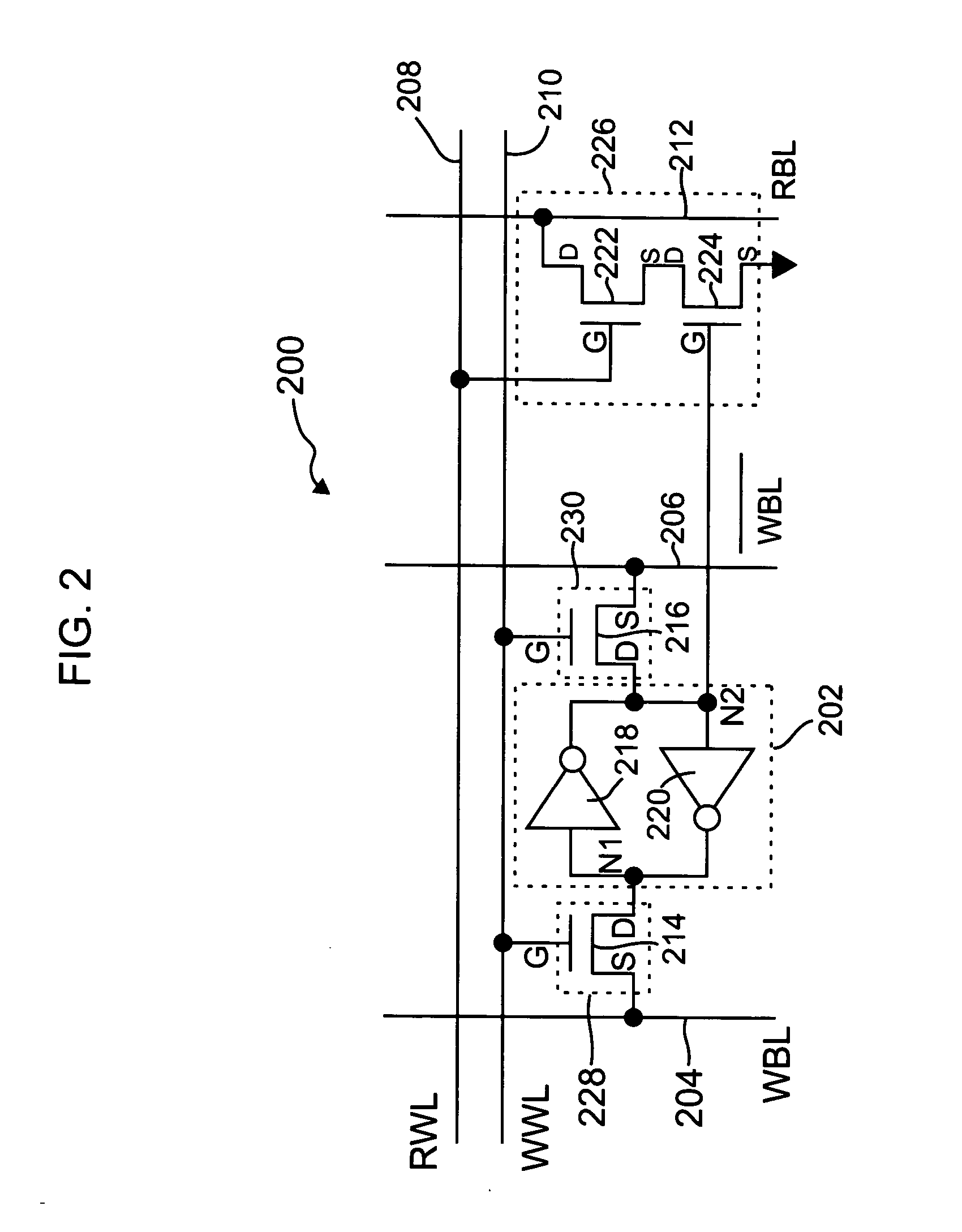
Memory cell having improved read stability
ActiveUS20060146638A1Virtually eliminates disturbs of the memory cellTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh impedanceStorage cell
A memory cell for use in a memory array includes a storage element for storing a logical state of the memory cell, a write circuit and a read circuit. The write circuit is operative to selectively connect a first node of the storage element to at least a first write bit line in the memory array in response to a write signal for selectively writing the logical state of the memory cell. The read circuit includes a substantially high impedance input node connected to the storage element and an output node connectable to a read bit line of the memory array. The read circuit is configured to generate an output signal at the output node which is representative of the logical state of the storage element in response to a read signal applied to the read circuit. The memory cell is configured such that the write circuit is disabled during a read operation of the memory cell so as to substantially isolate the storage element from the first write bit line during the read operation. A strength of at least one transistor device in the storage element is separately optimized relative to a strength of at least one transistor device in the write circuit and / or the read circuit.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20090194839A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsBit lineHigh density
Owner:NANTERO
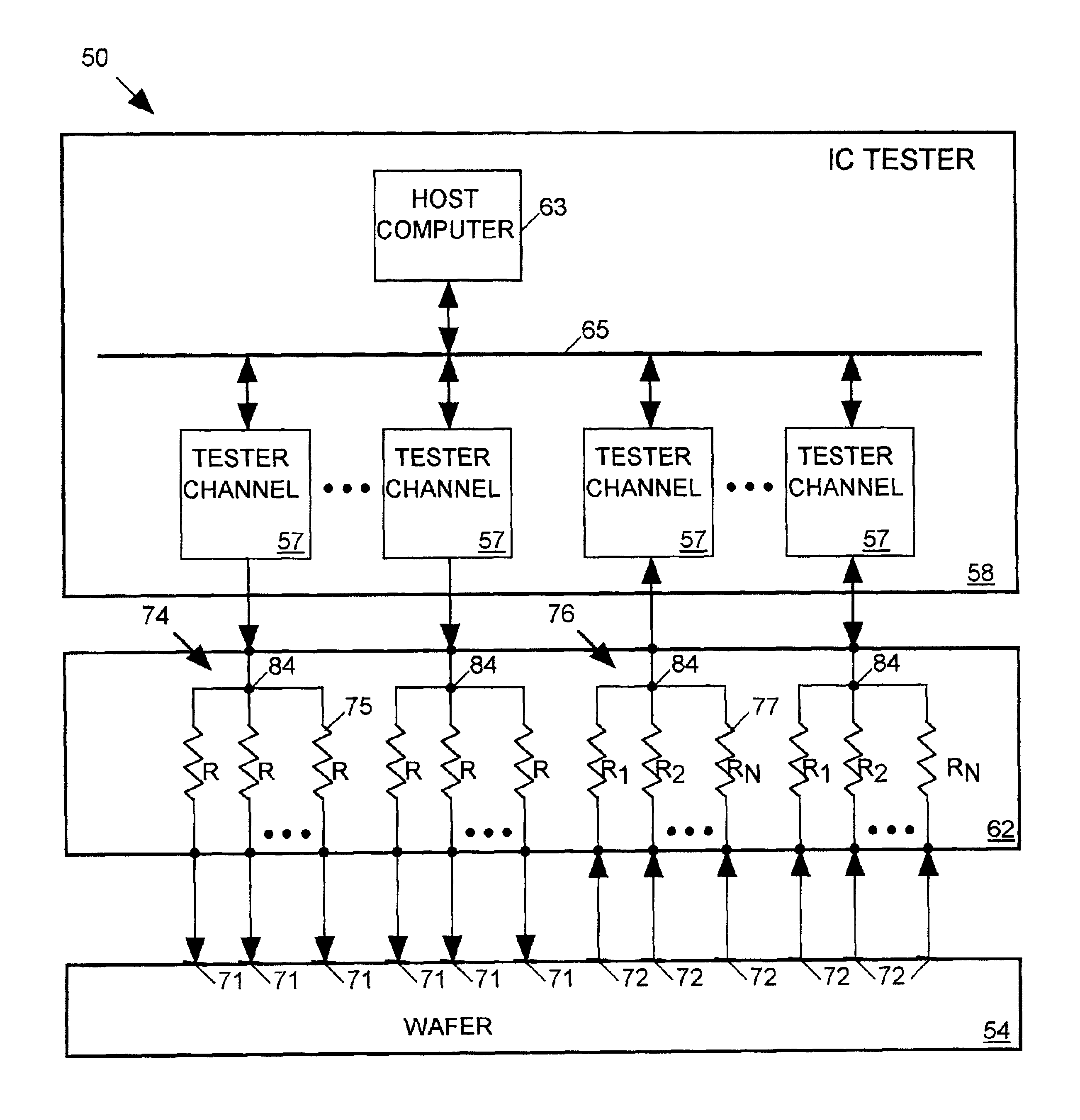
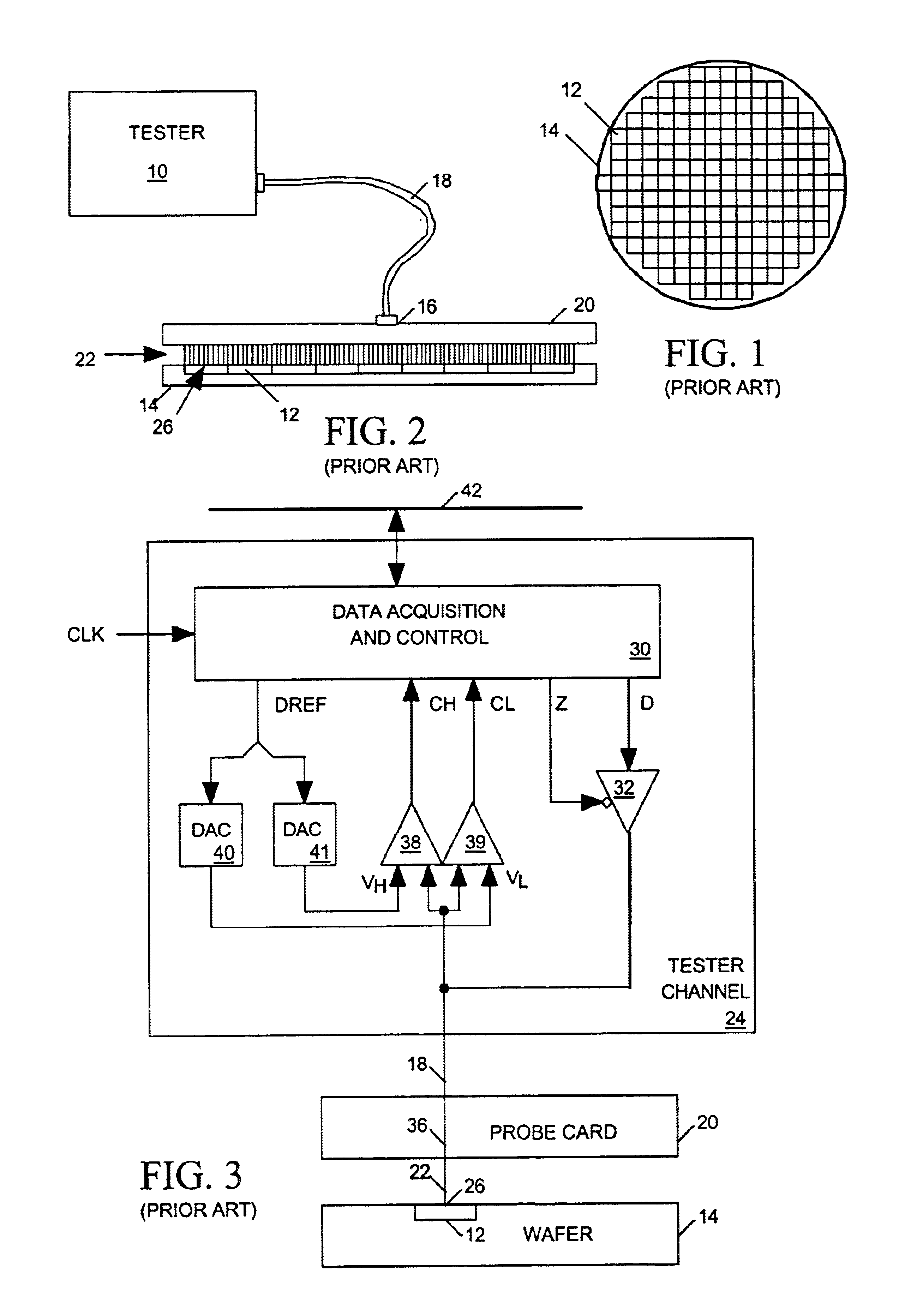
Tester channel to multiple IC terminals
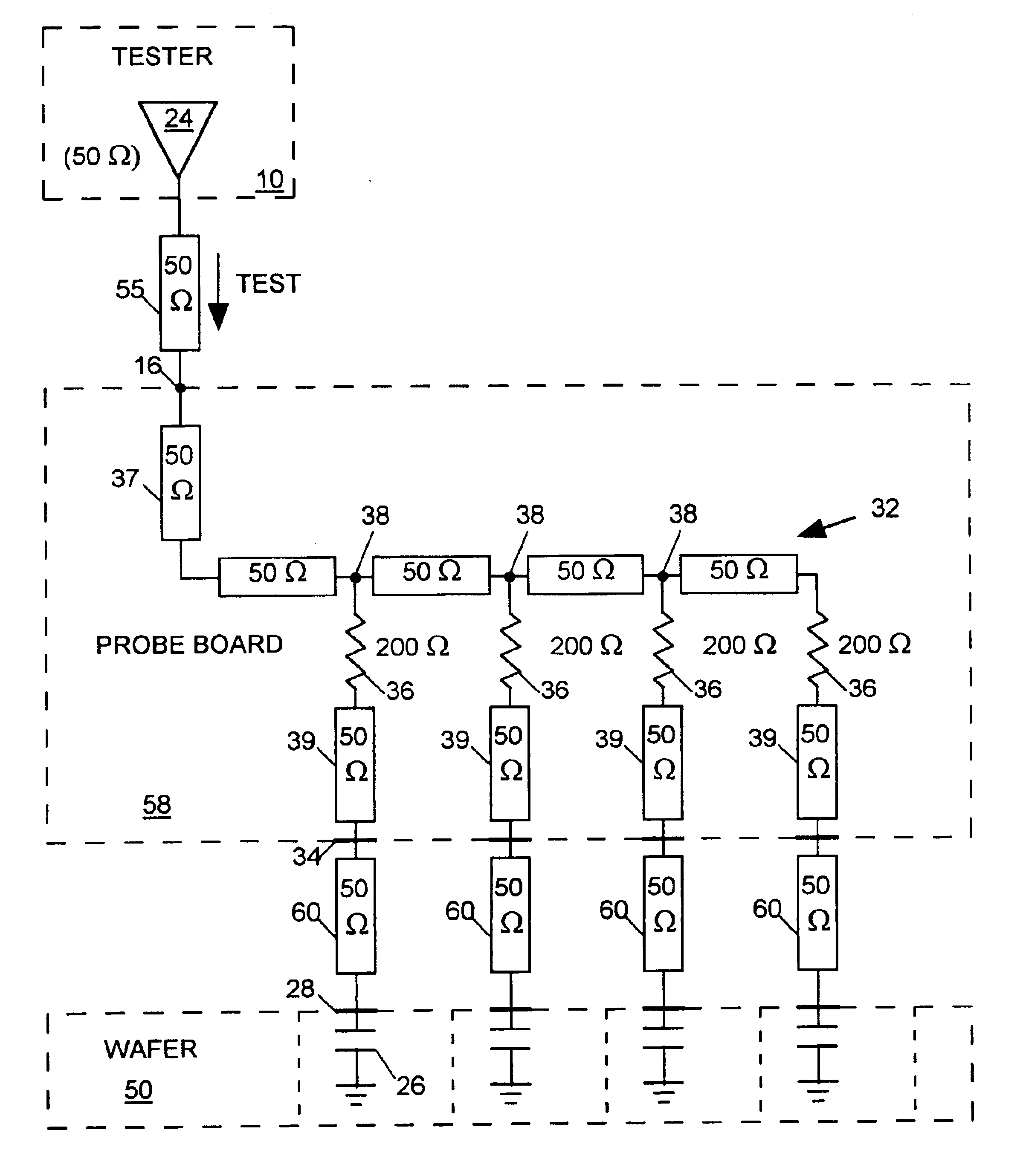
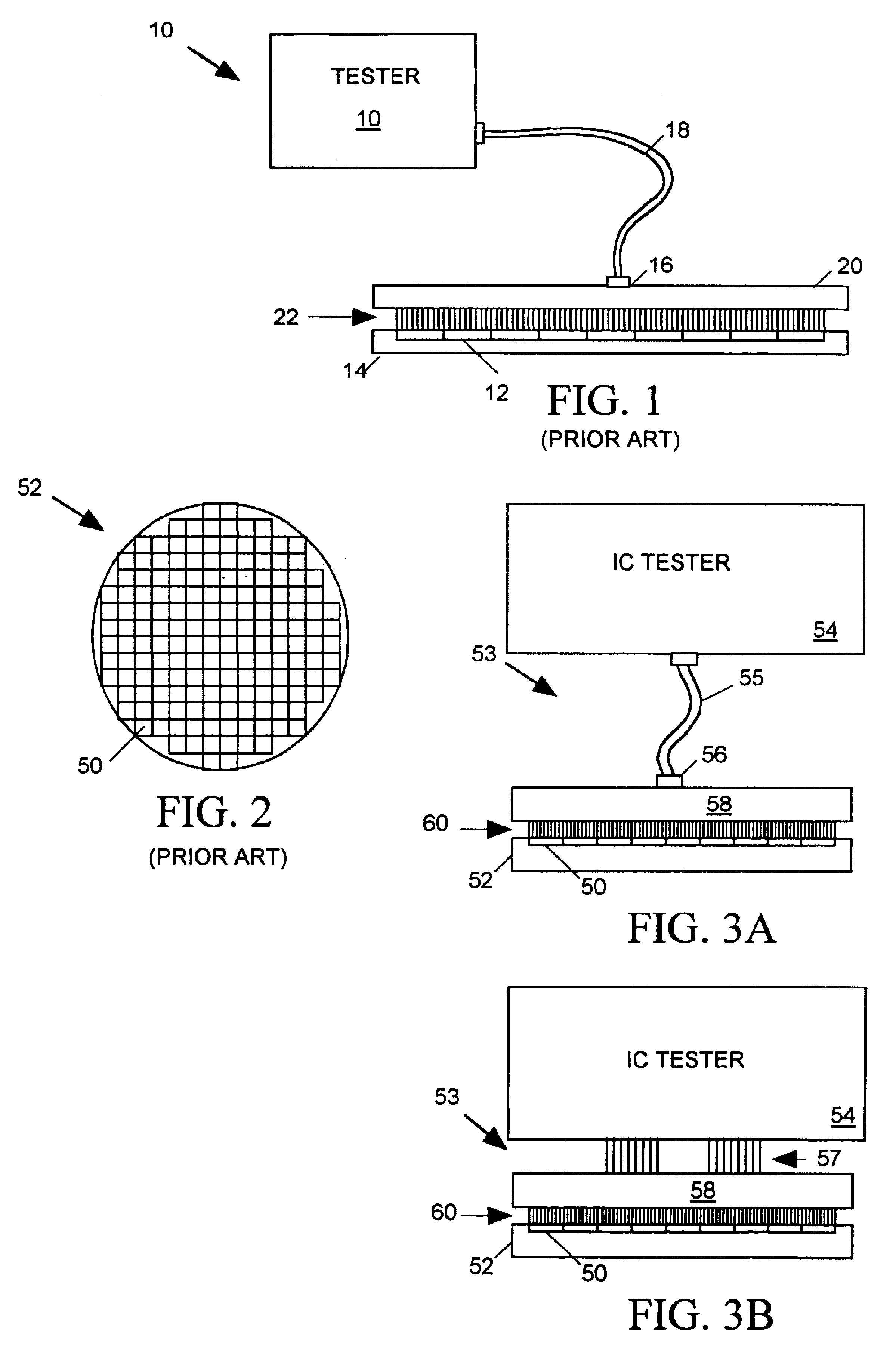
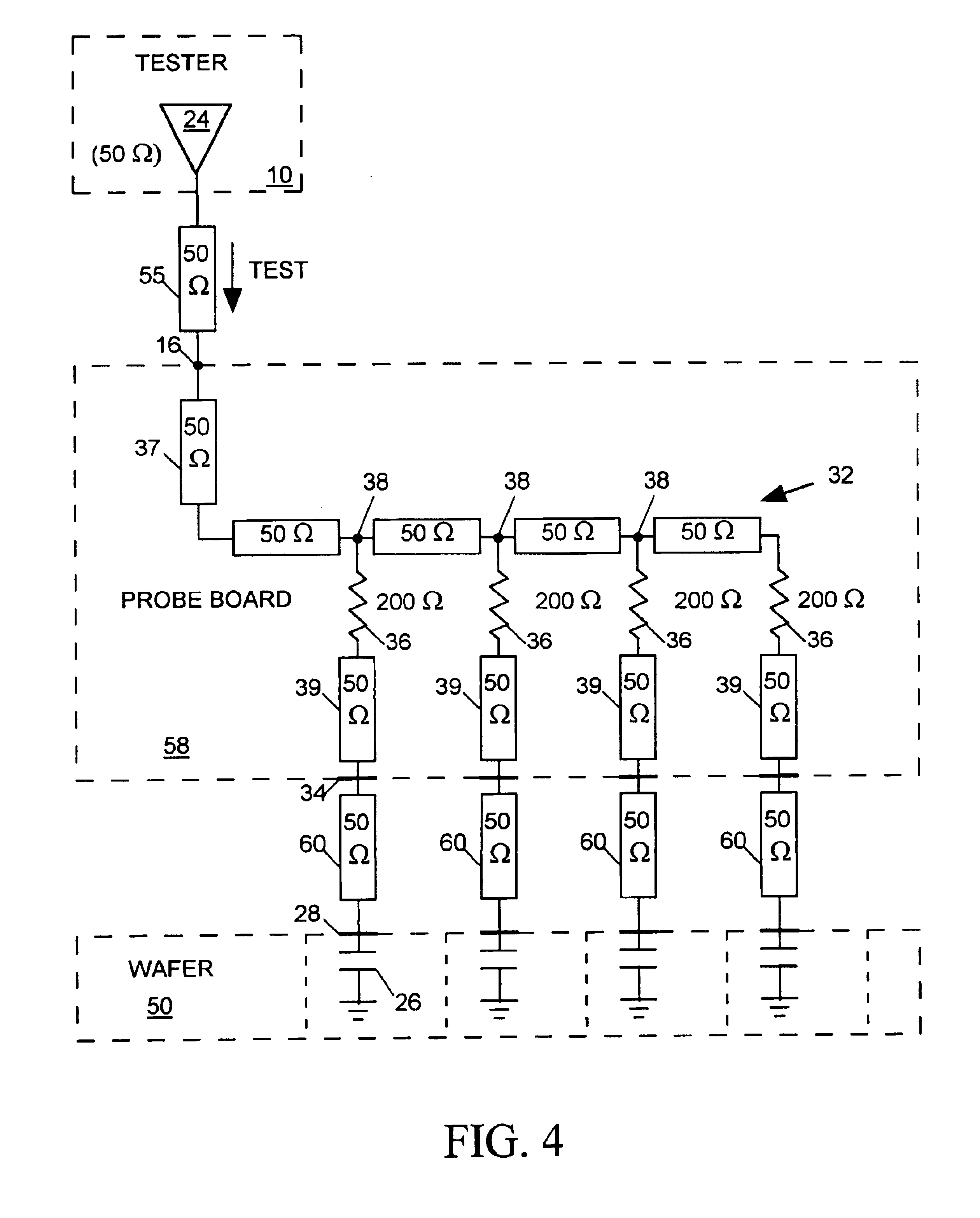
InactiveUS6798225B2Digital circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceProbe card
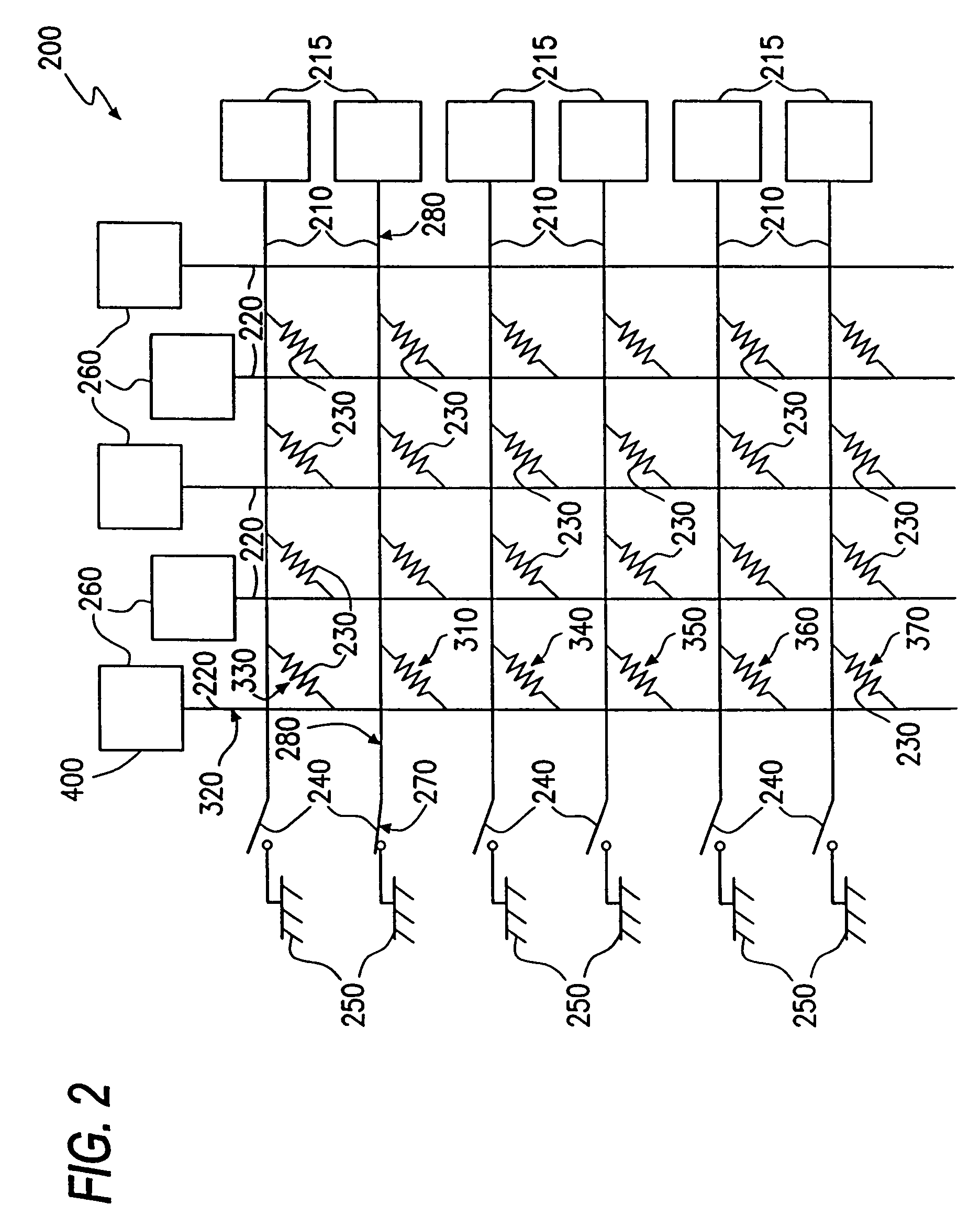
A probe card provides signal paths between integrated circuit (IC) tester channels and probes accessing input and output pads of ICs to be tested. When a single tester channel is to access multiple (N) IC pads, the probe card provides a branching path linking the channel to each of the N IC input pads. Each branch of the test signal distribution path includes a resistor for isolating the IC input pad accessed via that branch from all other branches of the path so that a fault on that IC pad does not substantially affect the voltage of signals appearing on any other IC pad. When a single tester channel is to monitor output signals produced at N IC pads, the resistance in each branch of the signal path linking the pads of the tester channel is uniquely sized to that the voltage of the input signal supplied to the tester channel is a function of the combination of logic states of the signals produced at the N IC pads. The tester channel measures the voltage of its input signal so that the logic state of the signals produced at each of the N IC output pads can be determined from the measured voltage.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Phase shifter with reduced linear dependency
InactiveUS6874109B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionCircuit complexityLinear dependency
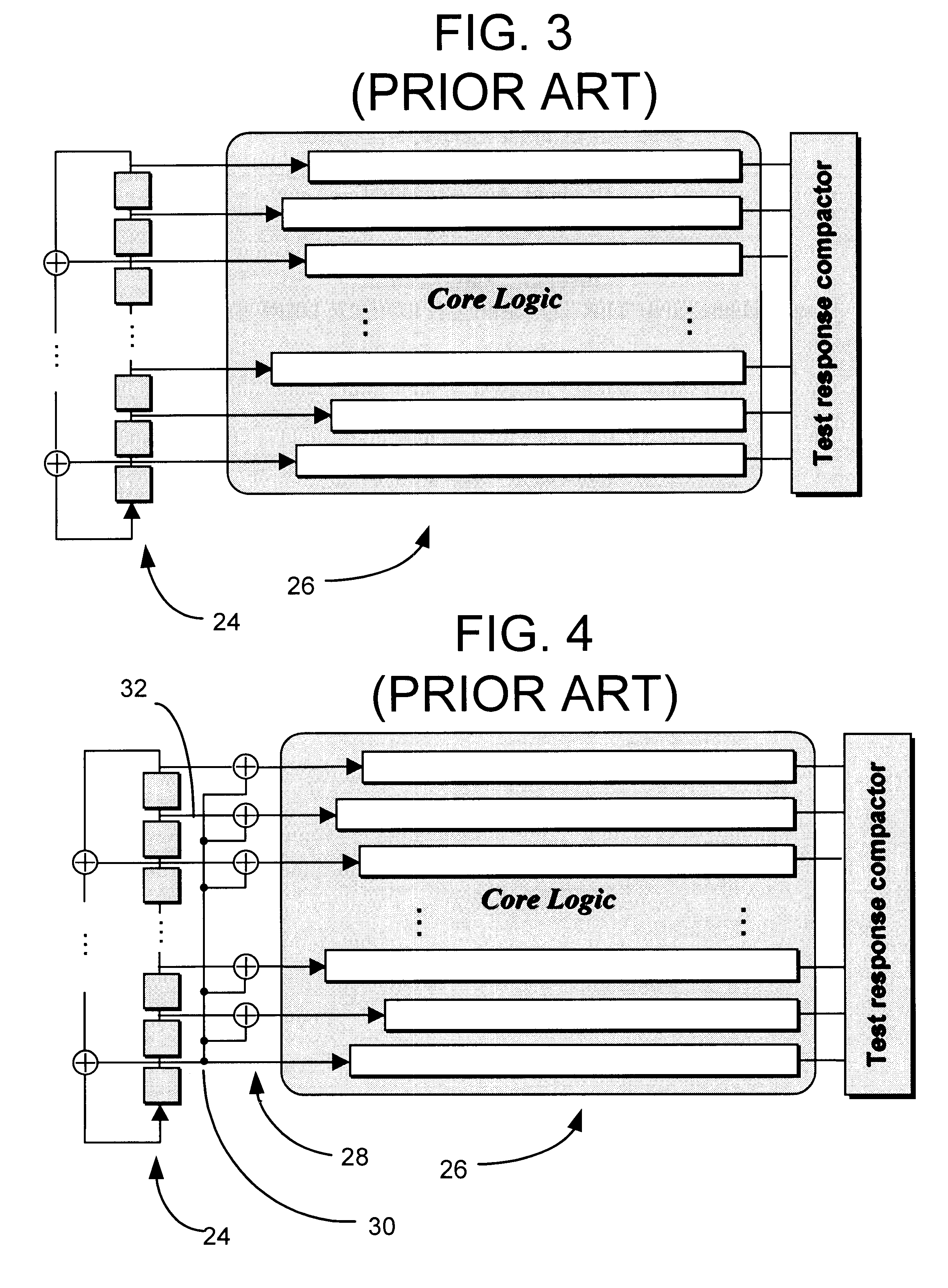
A method is disclosed for the automated synthesis of phase shifters. Phase shifters comprise circuits used to remove effects of structural dependencies featured by pseudo-random test pattern generators driving parallel scan chains. Using a concept of duality, the method relates the logical states of linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) and circuits spacing their inputs to each of the output channels. The method generates a phase shifter network balancing the loads of successive stages of LFSRs and satisfying criteria of reduced linear dependency, channel separation and circuit complexity.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
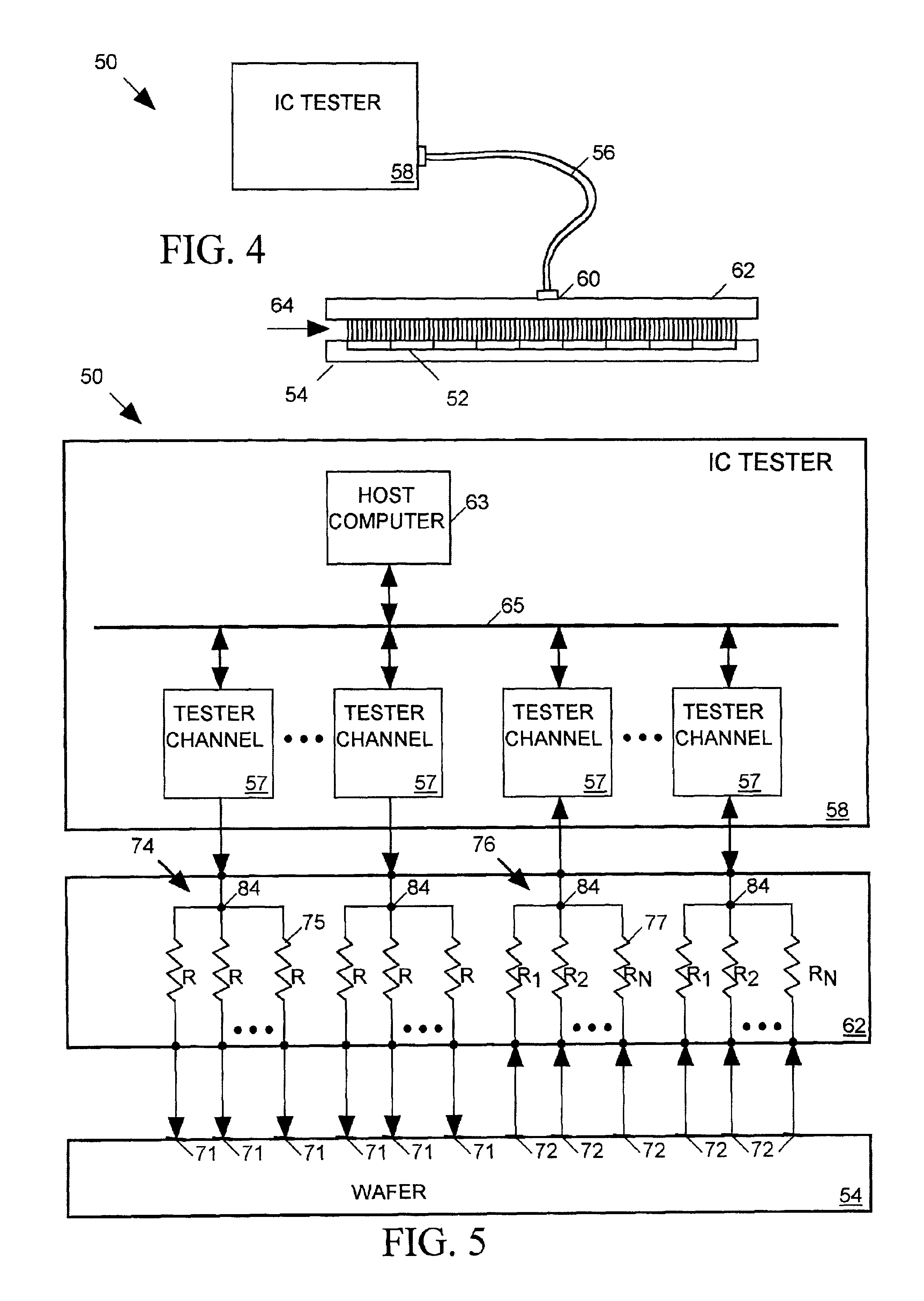
Test signal distribution system for IC tester
InactiveUS6784674B2Digital circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsDistribution systemEngineering
A probe board provides signal paths between an integrated circuit (IC) tester and probes accessing terminals on the surfaces of ICs formed on a semiconductor wafer for receiving test signals form the IC tester. A branching signal path within the probe board distributes a test signal produced by one channel of the IC tester to several probes. Resistors within the branching signal path resistively isolate the probes from one another so that a fault occurring at any one IC terminal will not affect the logic state of the test signal arriving at any other IC terminal. The isolation resistors are sized relative to signal path characteristic impedances so as to substantially minimize test signal reflections at the branch points.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
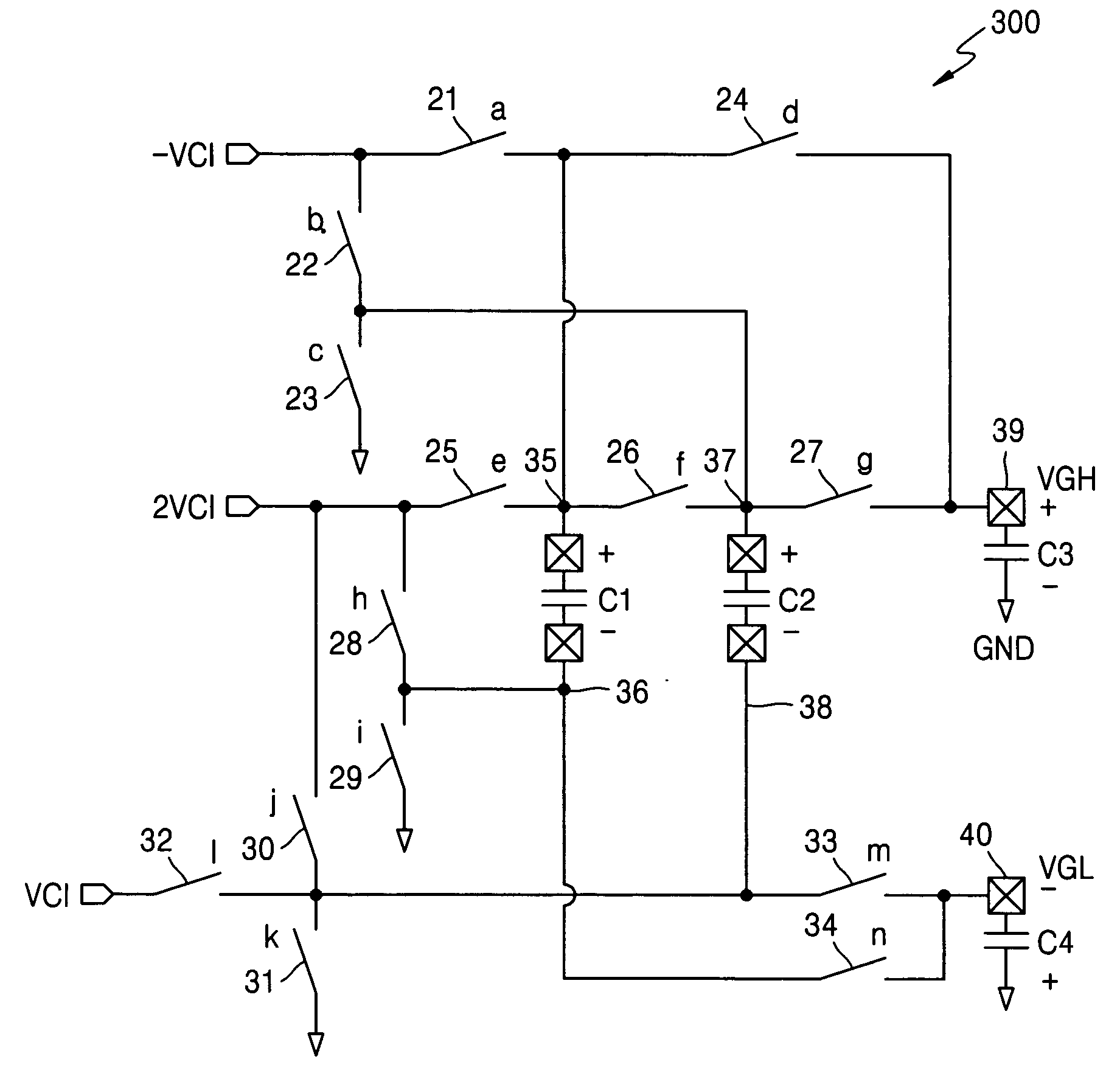
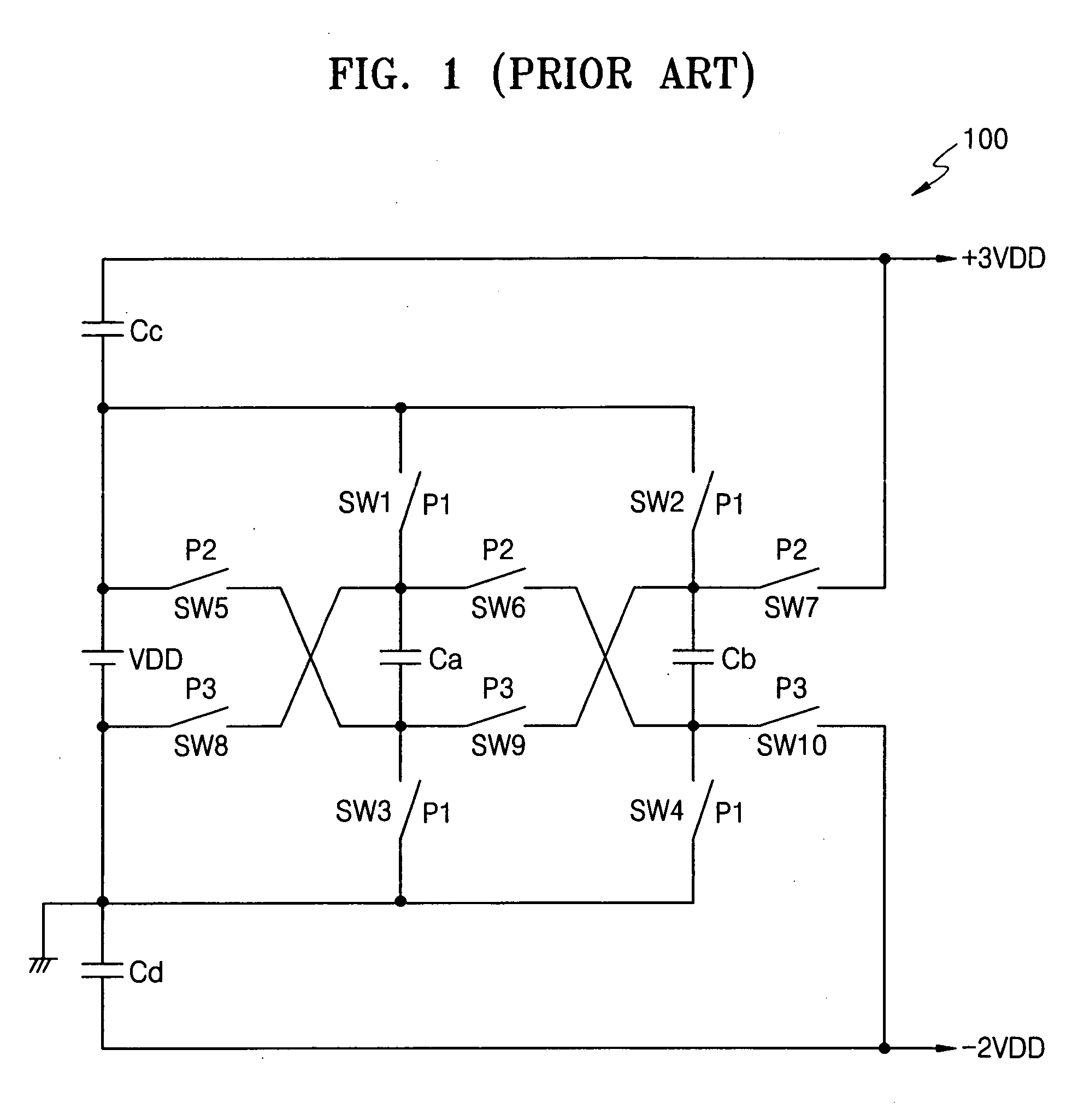
Voltage boosting circuit and method
ActiveUS20050047180A1Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitancePhase control
A voltage boosting circuit, boosting power supply unit and methods thereof are provided. A boosting power supply unit includes a boosting circuit having a small number of externally-mounted capacitors, which generates stepped-up and stepped-down boosted voltages through charging and pumping under two-phase control, so that the simultaneous output of the stepped-up voltage and the stepped-down voltage, the output of only the stepped-up voltage, the output of only the stepped-down voltage, and the cut-off of the output of the stepped-up voltage and the stepped-down voltage can be controlled on the basis of the phase control signal generated from the enable signals of which the logic states are changed in accordance with an amount of load.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
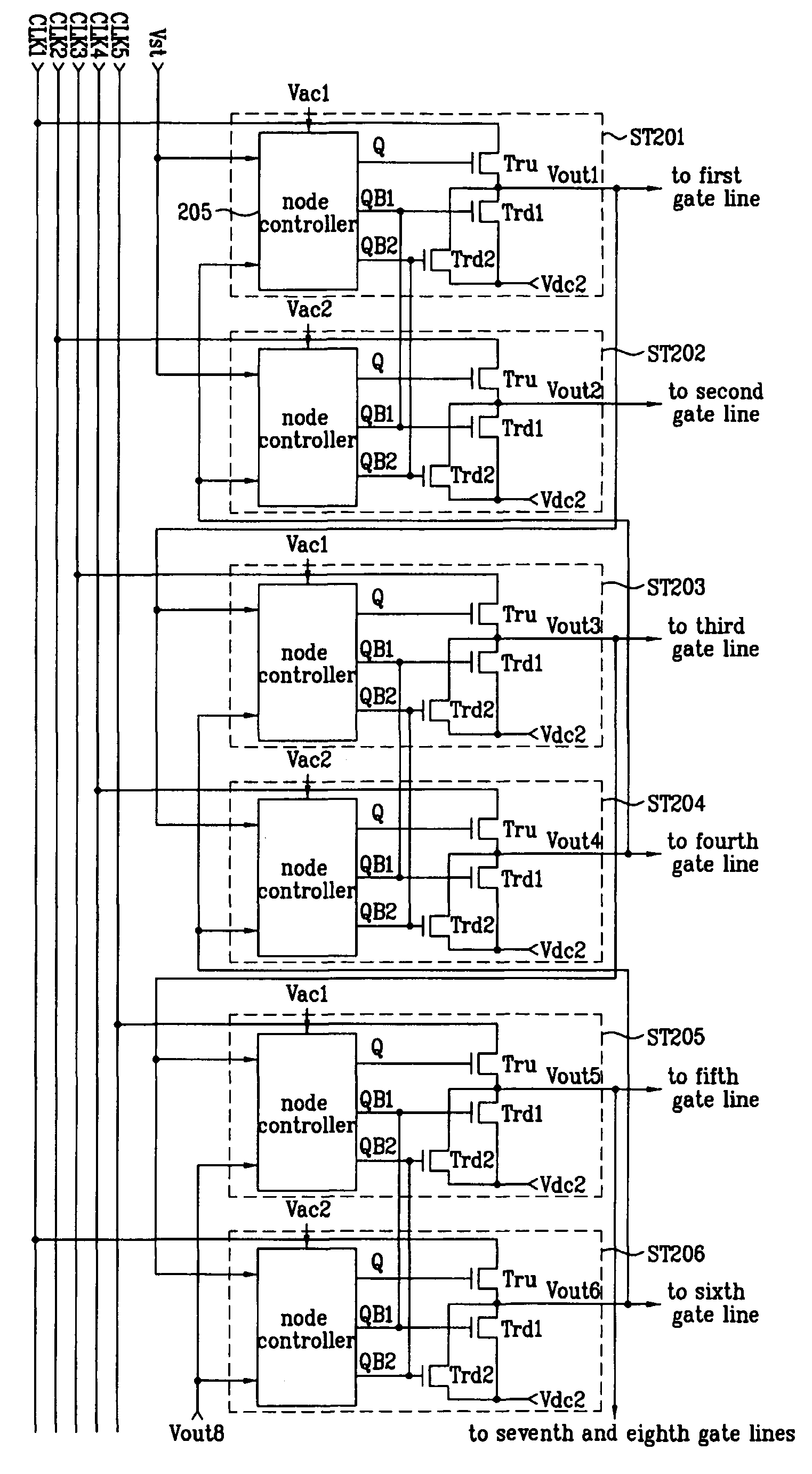
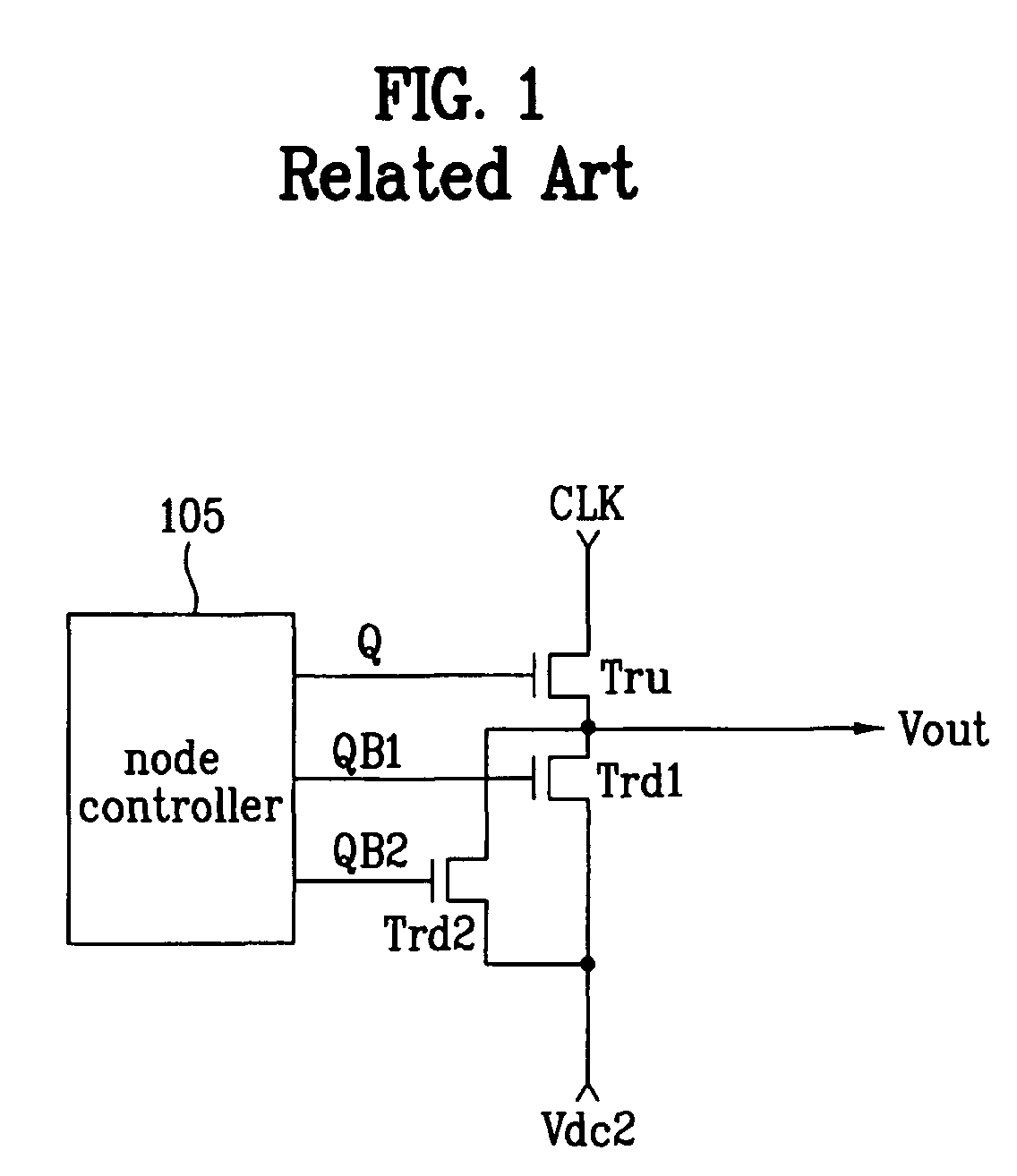
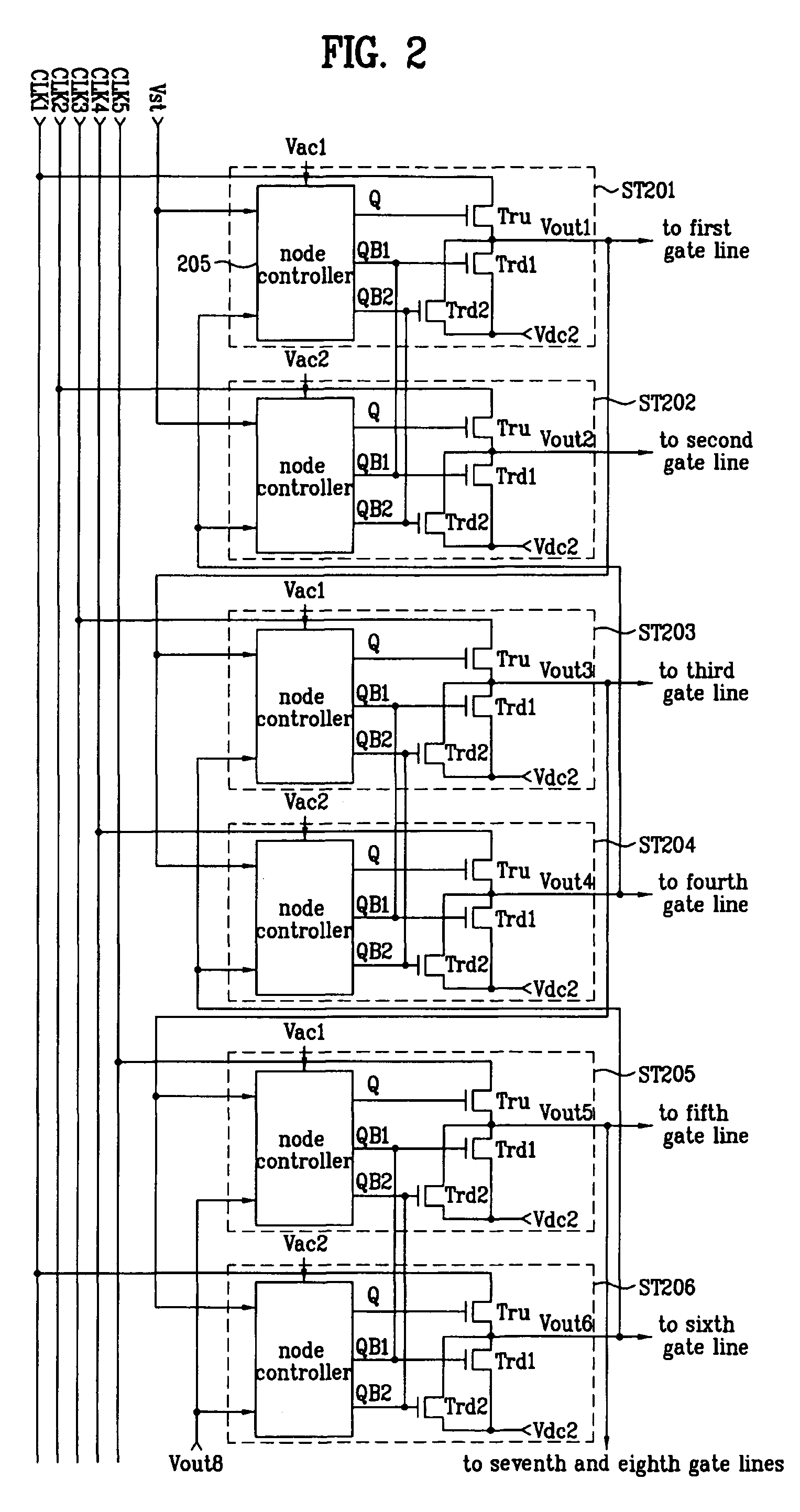
Shift register
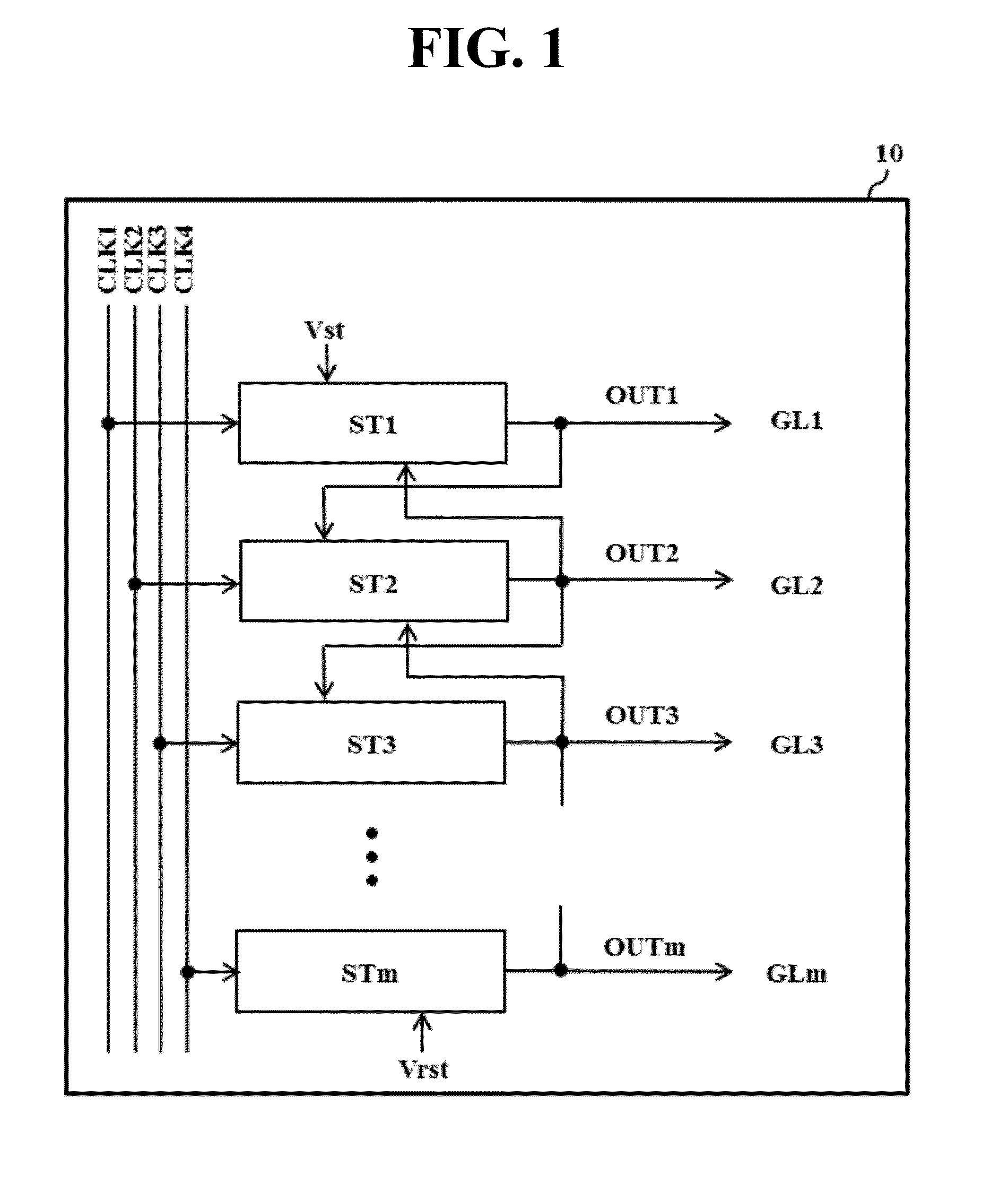
ActiveUS20070104307A1Reduce in quantityReduce manufacturing costDigital storageShift registerLogic state
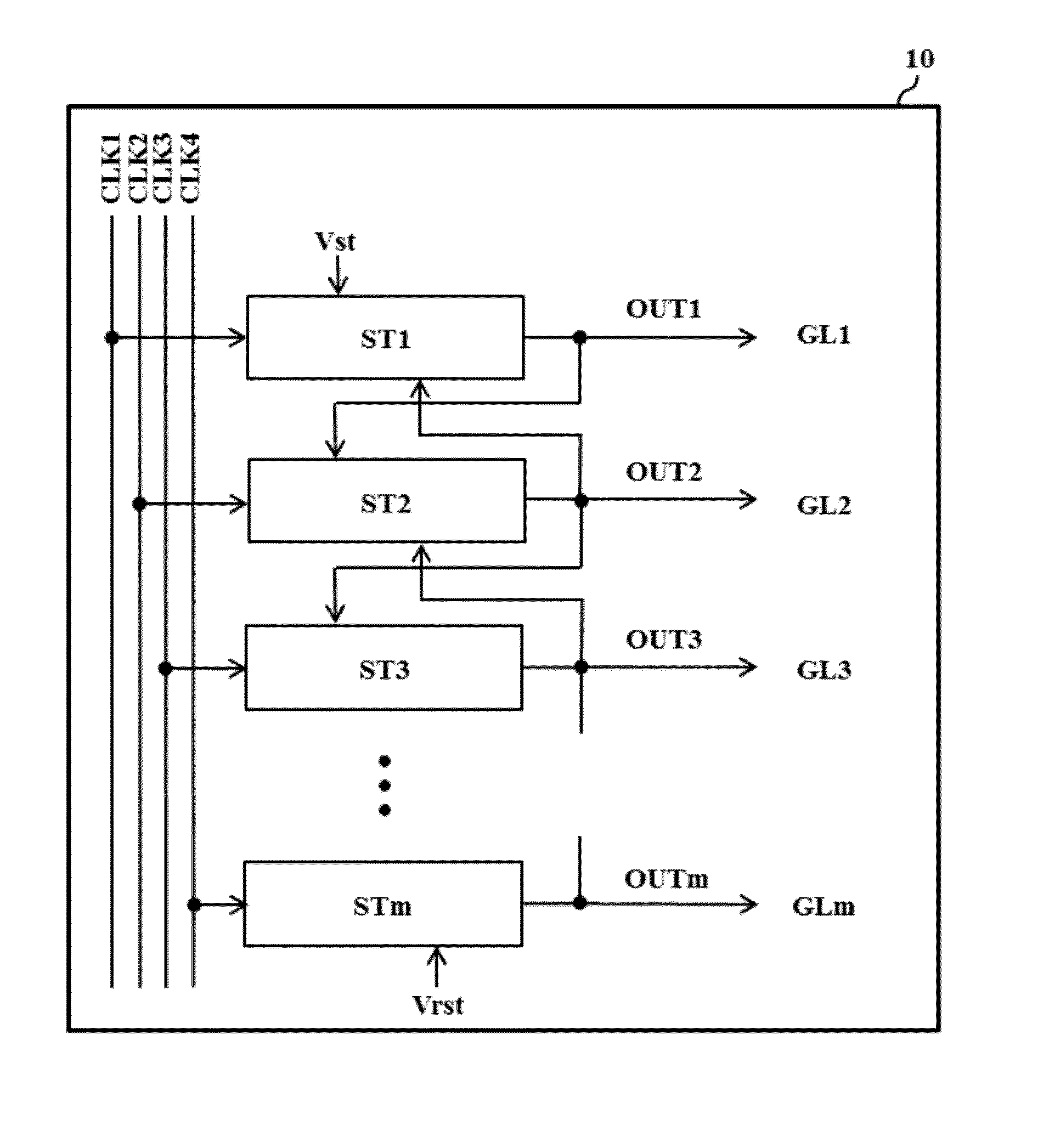
A shift register includes first and second stages for sequentially outputting scan pulses to drive first and second gate lines. One of the first and second stages includes a pull-up switching device connected to an enabling node of the one of the first and second stages; a first pull-down switching device connected to a first disabling node of the one of the first and second stages; a second pull-down switching device connected to a second disabling node of the one of the first and second stages; and a node controller. The node controller of the first stage controls the logic state of each of the enabling node of the first stage, the first disabling node of the first stage and the first disabling node of the second stage. The node controller of the second stage controls the logic state of each of the enabling node of the second stage, the second disabling node of the second stage and the second disabling node of the first stage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Cross-point memory architecture with improved selectivity
InactiveUS7046550B1High selectivityImproved cross-point memory arrayRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineElectricity
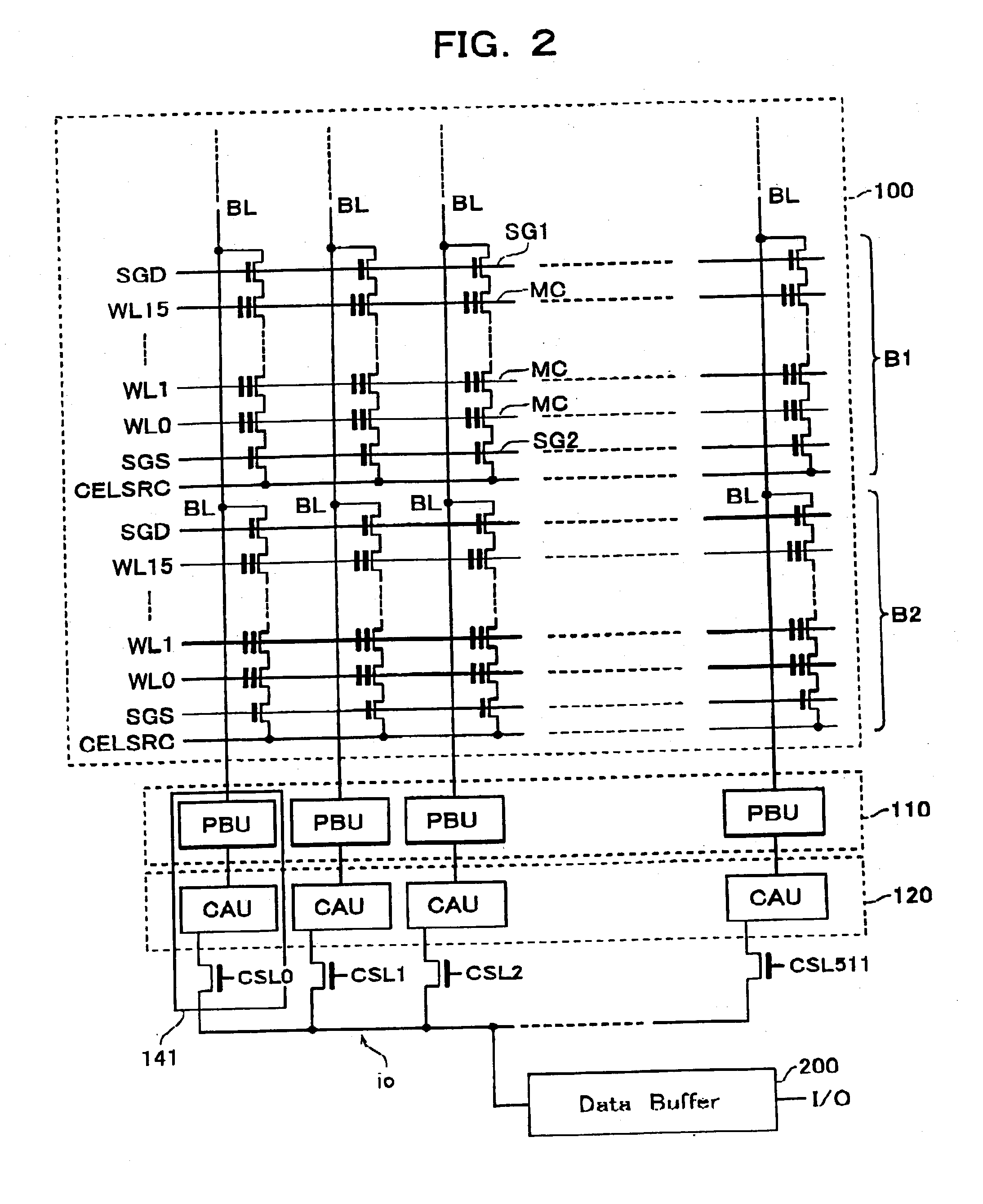
A cross-point memory includes a plurality of memory cells, a plurality of global word lines, a plurality of local word lines, and a plurality of global bit lines. At least a given one of the global word lines is configurable for conveying a write current for selectively writing a logical state of one or more of the memory cells. Each of the local word lines is connected to at least one of the memory cells for assisting in writing a logical state of the at least one memory cell corresponding thereto. Each of the global bit lines is connected to at least one of the memory cells for writing a logical state of the memory cell corresponding thereto. The memory further includes a plurality of selection circuits, each of the selection circuits being operative to electrically connect a given one of the local word lines to a given one of the global word lines in response to a control signal applied thereto. During a write operation directed to at least one selected memory cell, the write current passes through the selected memory cell for writing the logical state of the selected memory cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
Output buffer with time varying source impedance for driving capacitively-terminated transmission lines
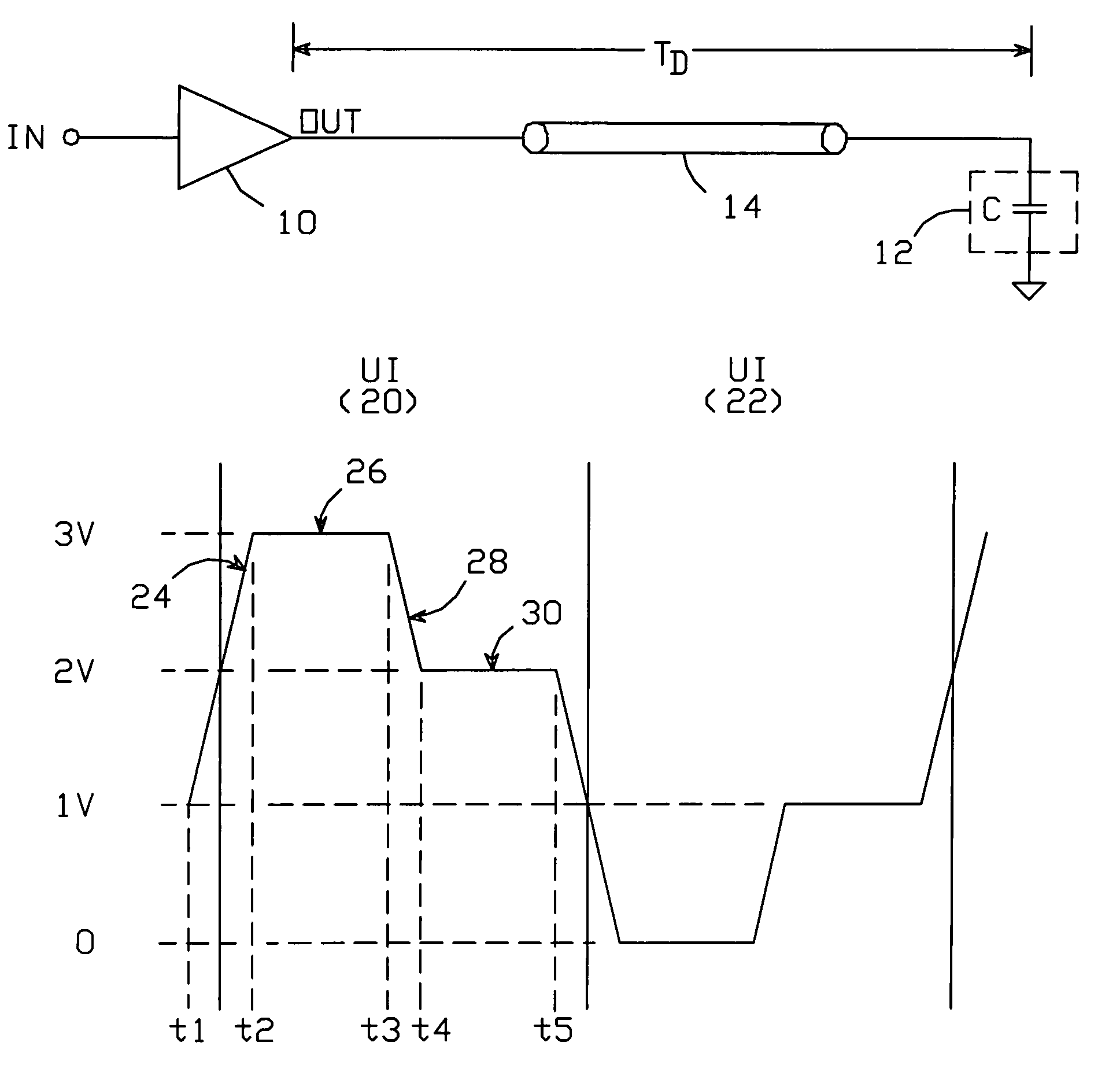
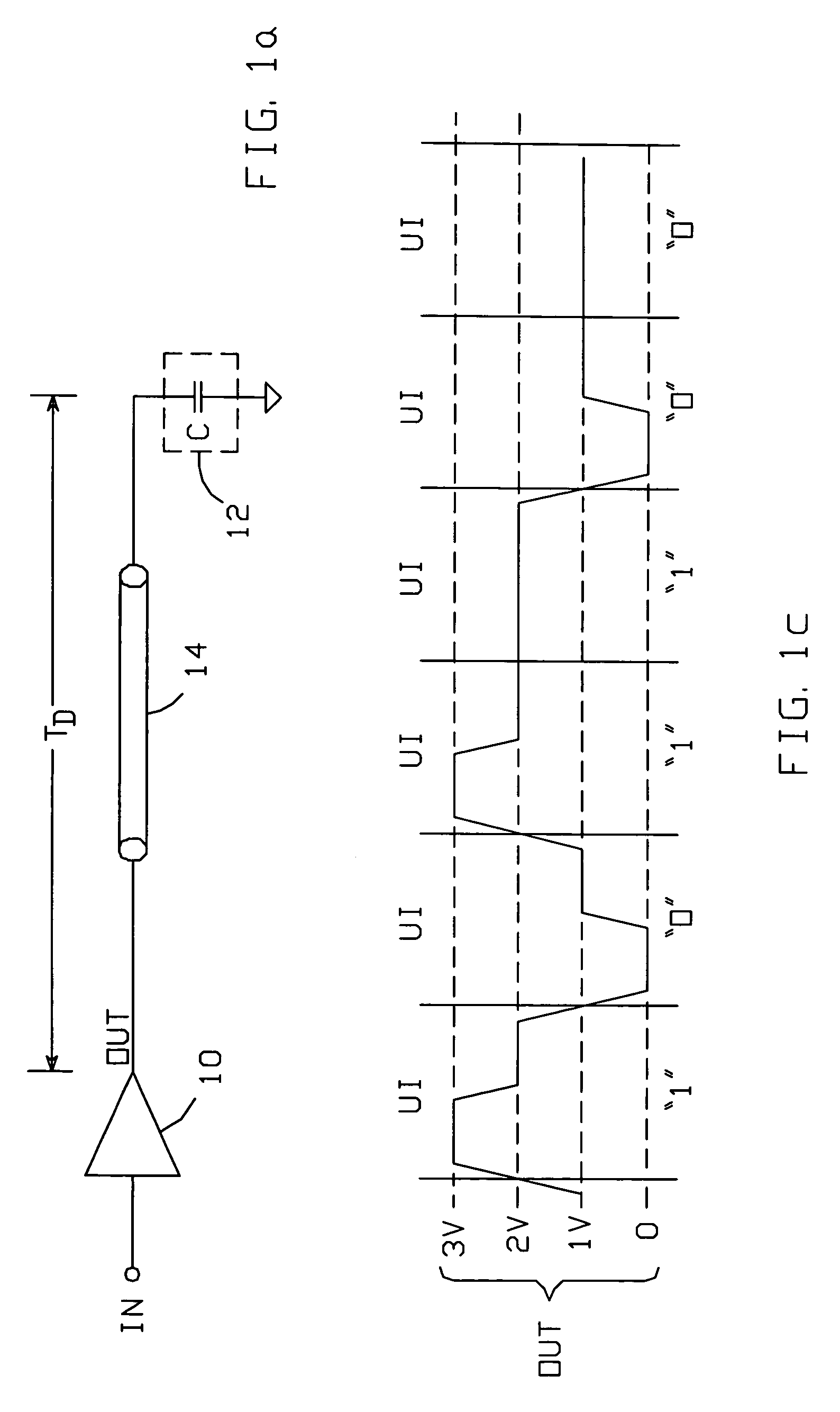
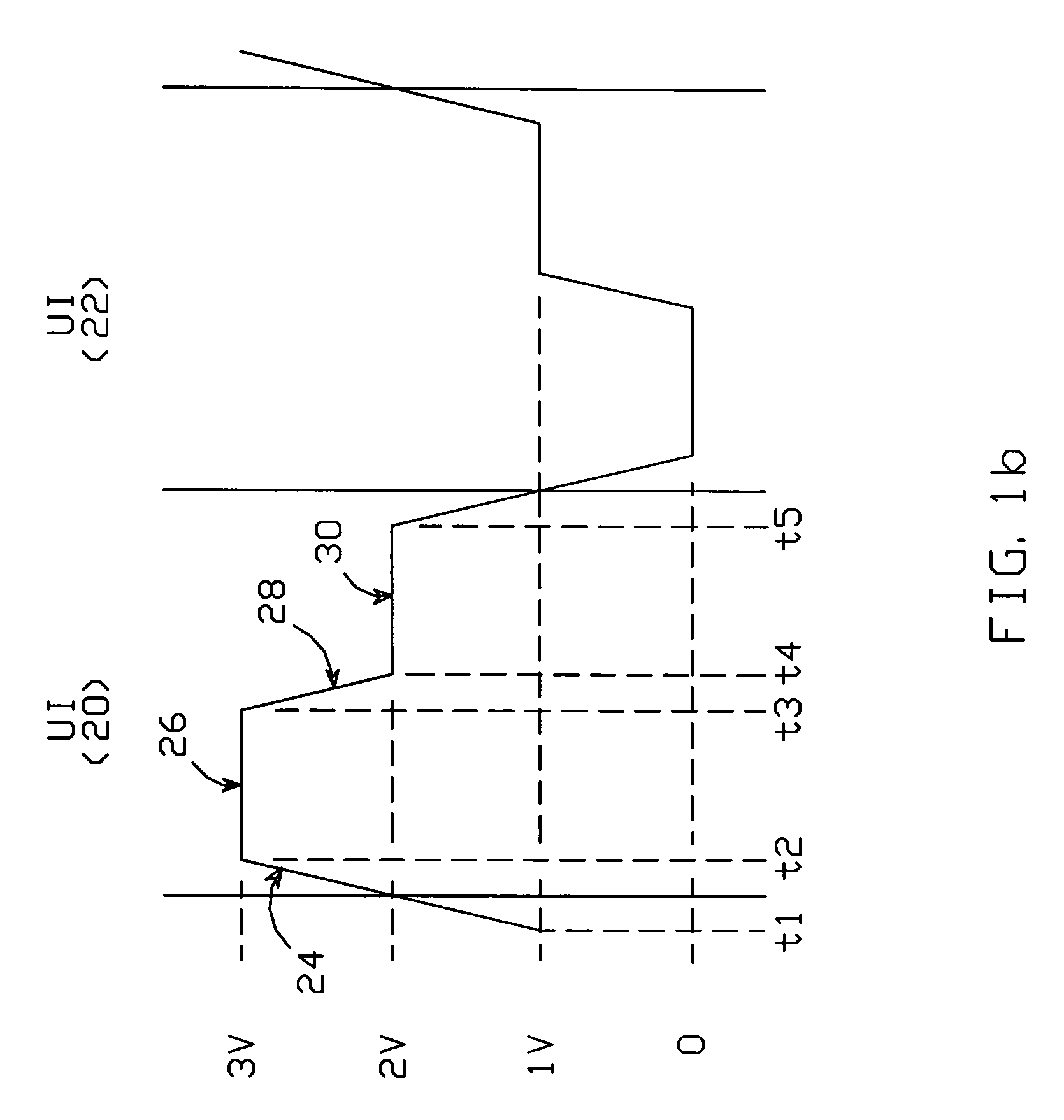
ActiveUS6980021B1Reduce impactFast chargingReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuit coupling arrangementsEngineeringLogic state
An output buffer for driving a capacitively-terminated transmission line produces a waveform which comprises a first portion during which the waveform transitions from a voltage V1 to a voltage V2; a second portion during which it remains fixed at V2; a third portion during which it transitions to a voltage V3; and a fourth portion during which it remains fixed at V3. The waveform is created within a unit interval whenever successive data bits transition between logic states. The first and second portions are generated with circuitry arranged such that V2 is maximized by reducing the buffer's output impedance. The fourth portion is generated with circuitry which has a non-zero output impedance preferably equal to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, to absorb transitions reflected back to the source circuitry by the capacitive termination.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
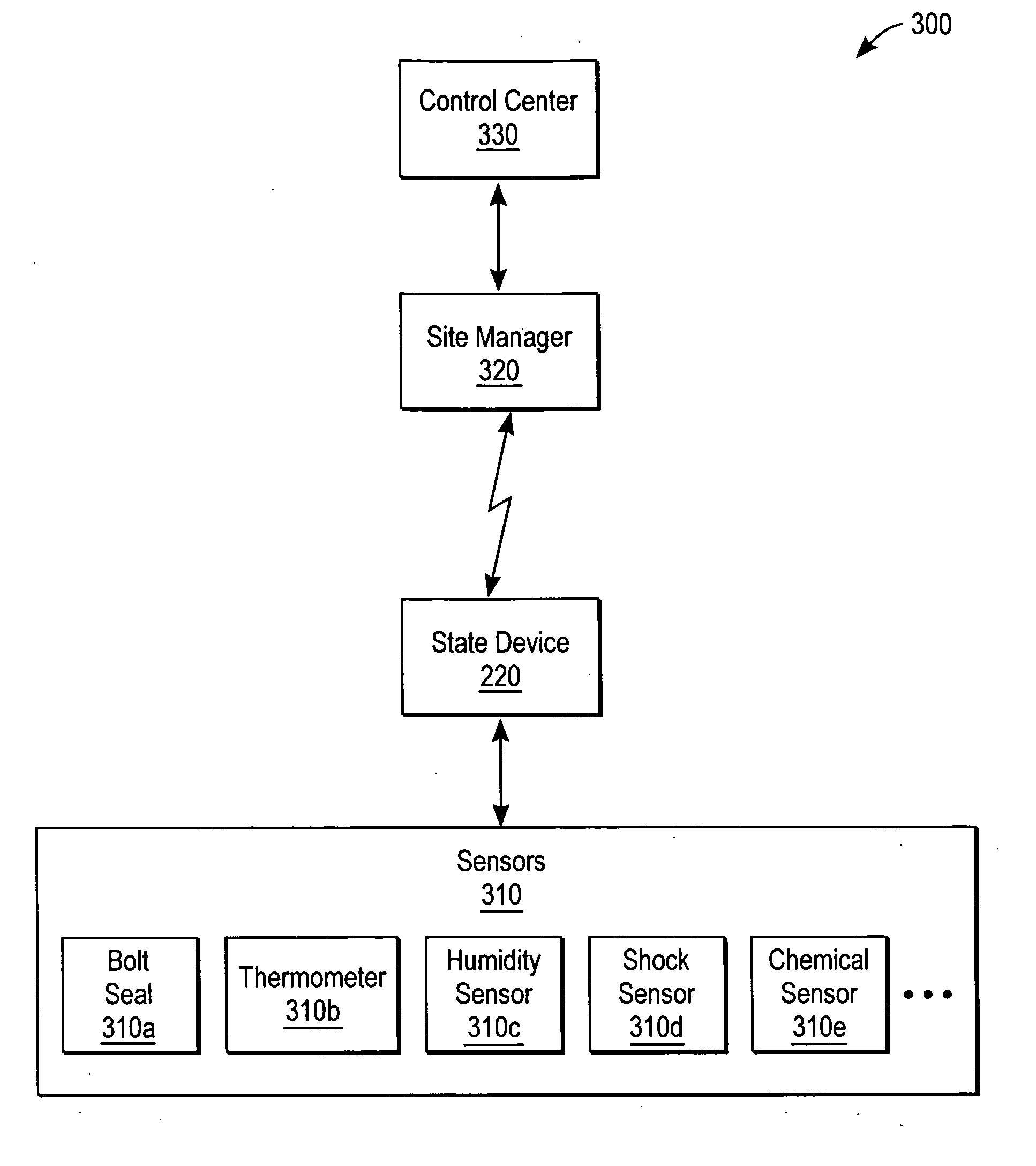
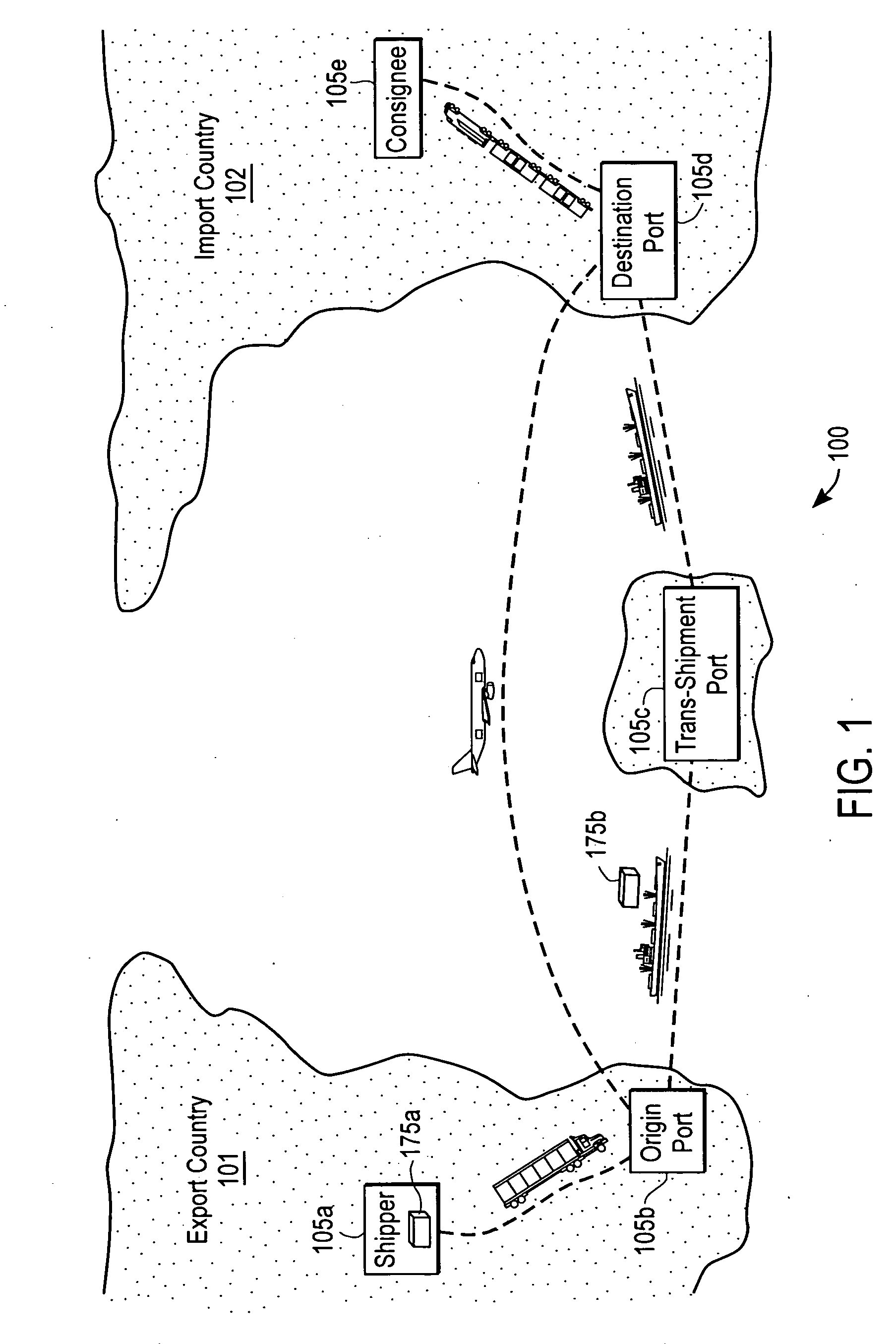
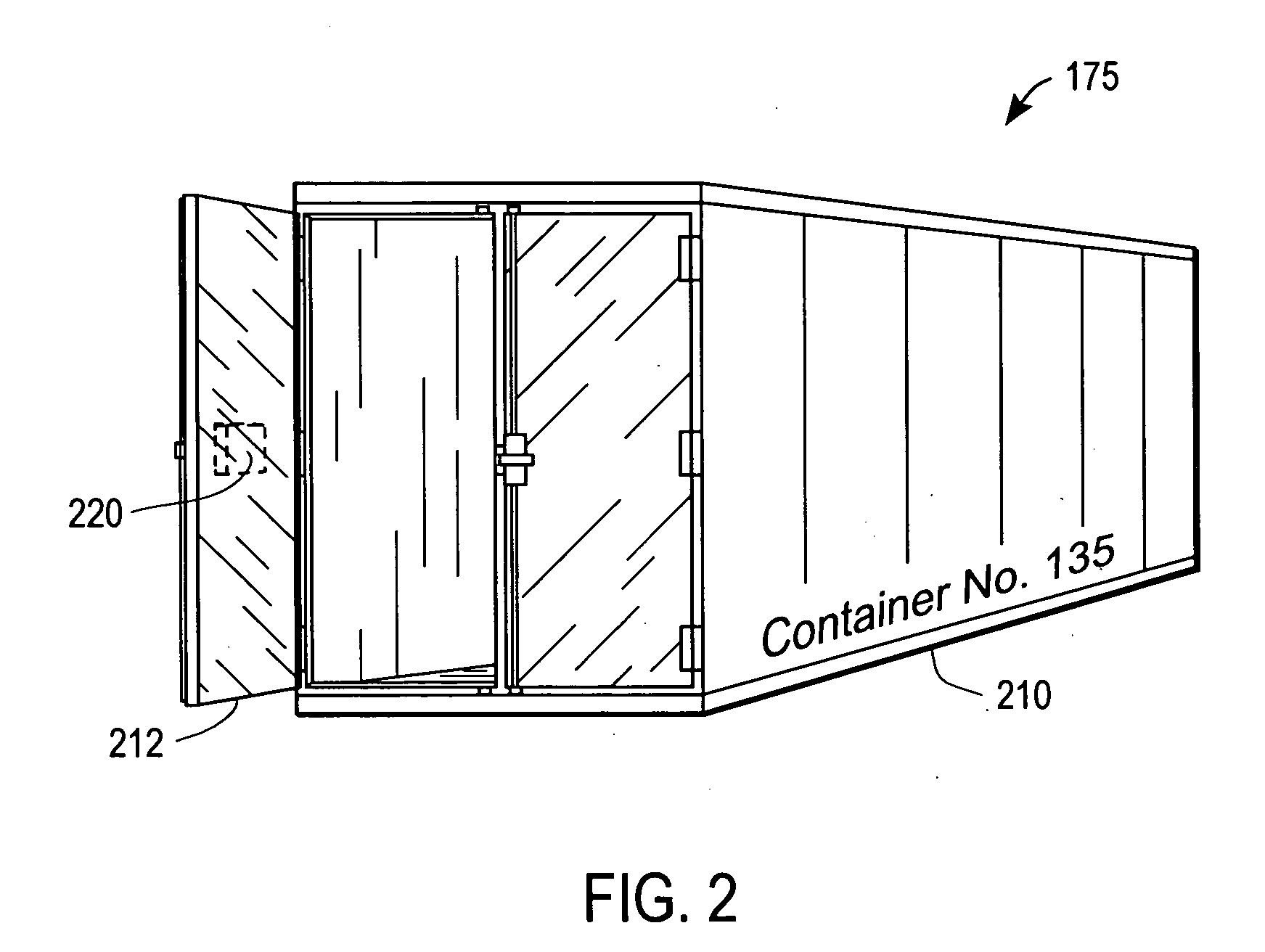
State monitoring of a container
A container for locally determining a container state using a state device. The state device detects unexpected events by comparing expected event information with actual event information related to a container condition. The container condition includes, for example, environmental conditions, logistical or location conditions, and physical or security conditions. Thus, the container is able to intelligently monitor its state and raise an alert without intervention from a central system. The container can also be programmed and reprogrammed with updated logic, states, and / or expected event information. A sensor in the state device gathers input information for comparison to expected event information. A communication port in the state device receives event information. For example, a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver can determine a current location for comparison to an expected location at the current time. In another example, an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) receiver and transmitter automatically uploads state information to a central system.
Owner:SAVI TECH INC
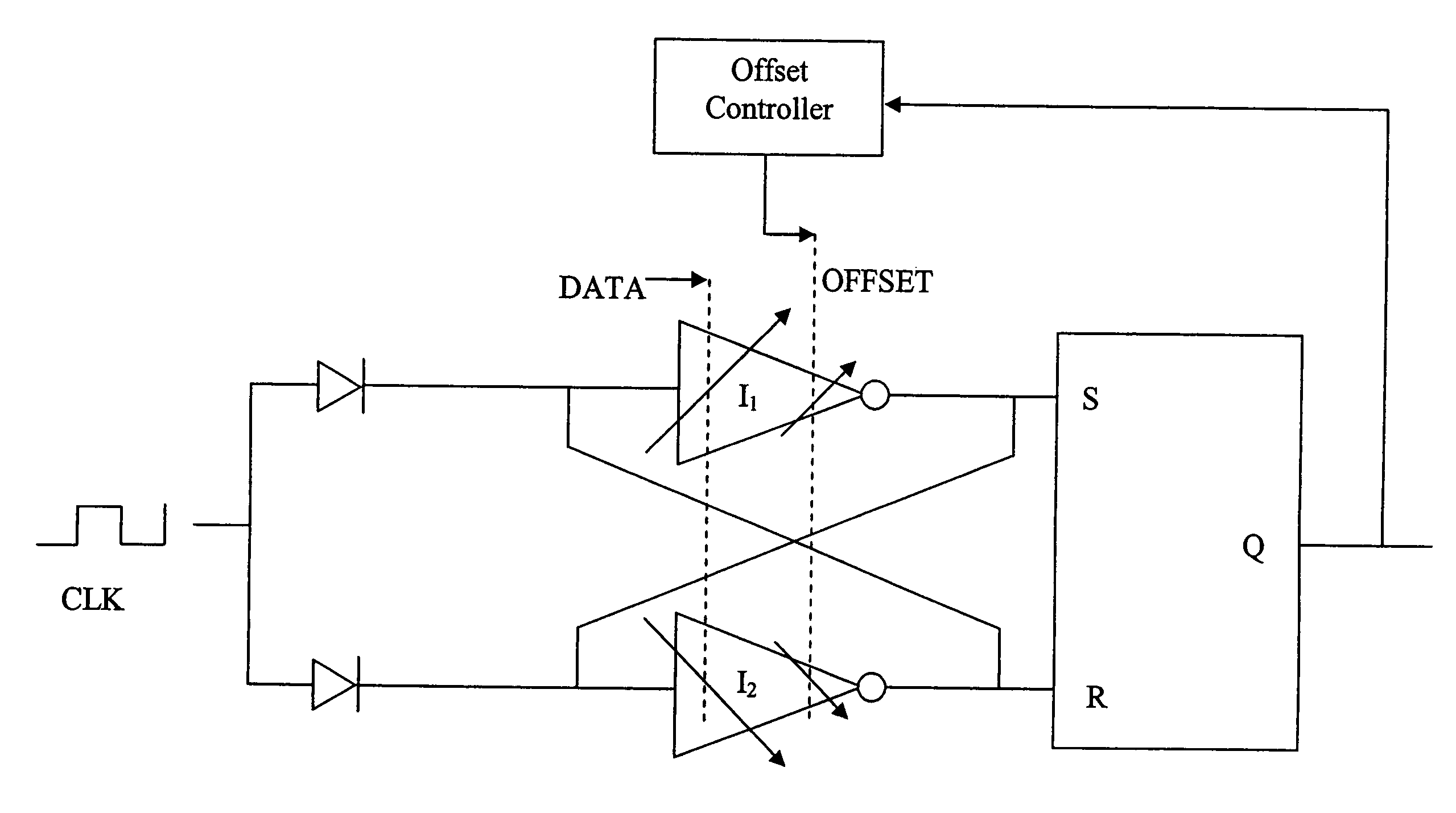
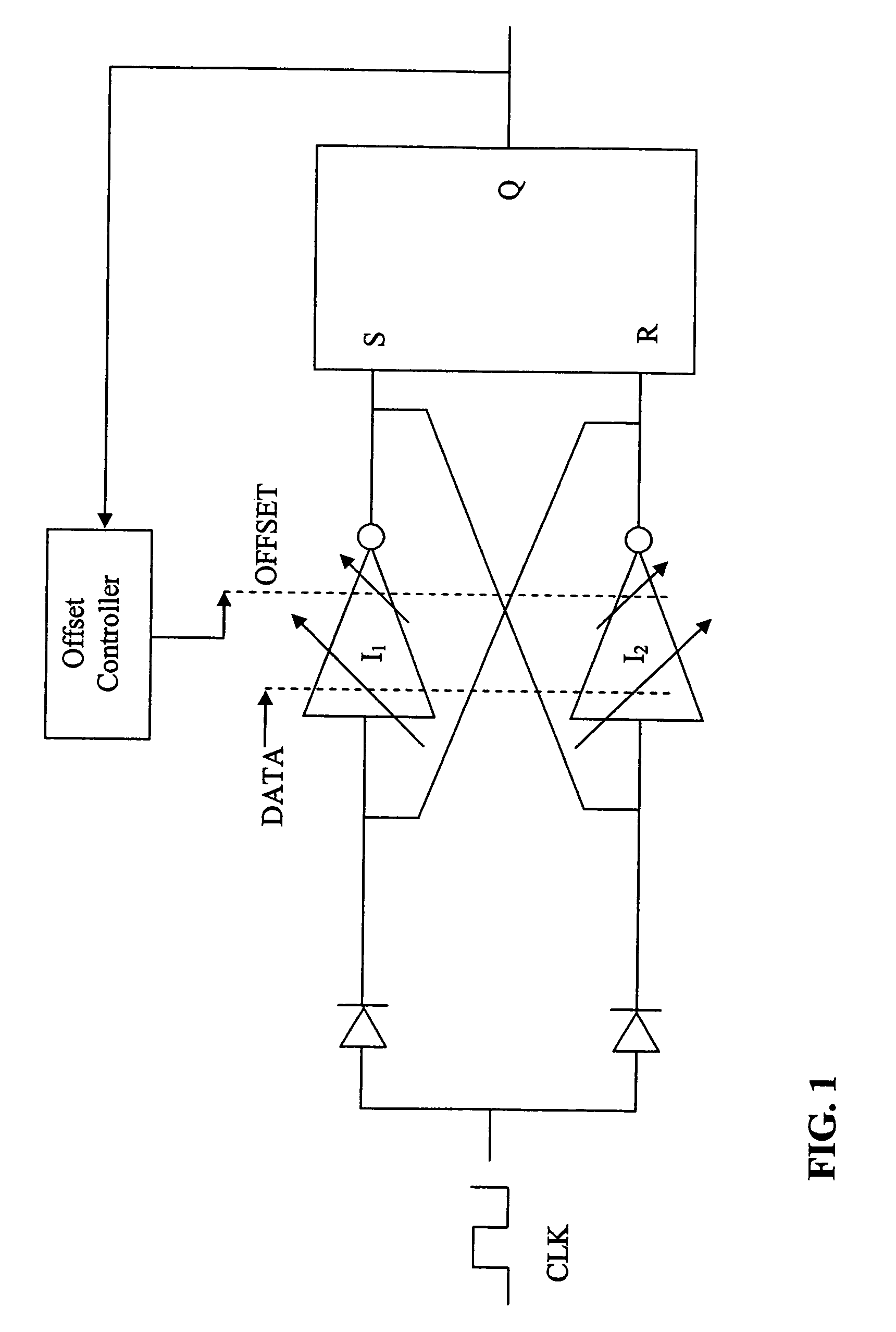
High-speed data sampler with input threshold adjustment
InactiveUS7813460B2High bandwidthQuick fixPulse automatic controlSpeech analysisControl signalData signal
Method and apparatus for sampling a high-speed digital signal include providing a data signal to a differential data input circuit, an offset control signal, and a strobe pulse. In response to the strobe pulse, the data signal is resolved into an output logic state based to a relatively greater extent on the differential data signal and to a relatively lesser extent on the offset control signal.
Owner:SLT LOGIC
System and method for sensing data stored in a resistive memory element using one bit of a digital count
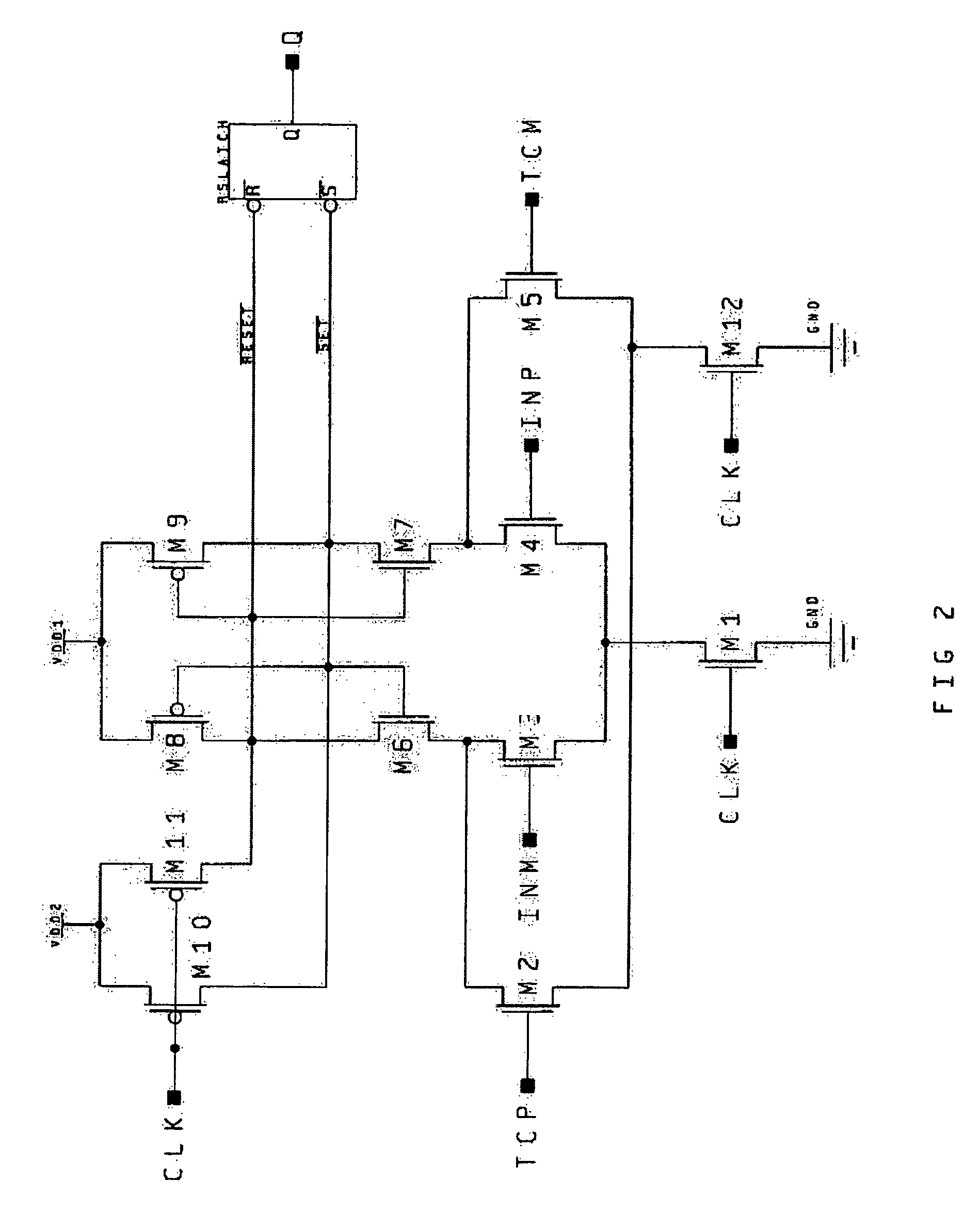
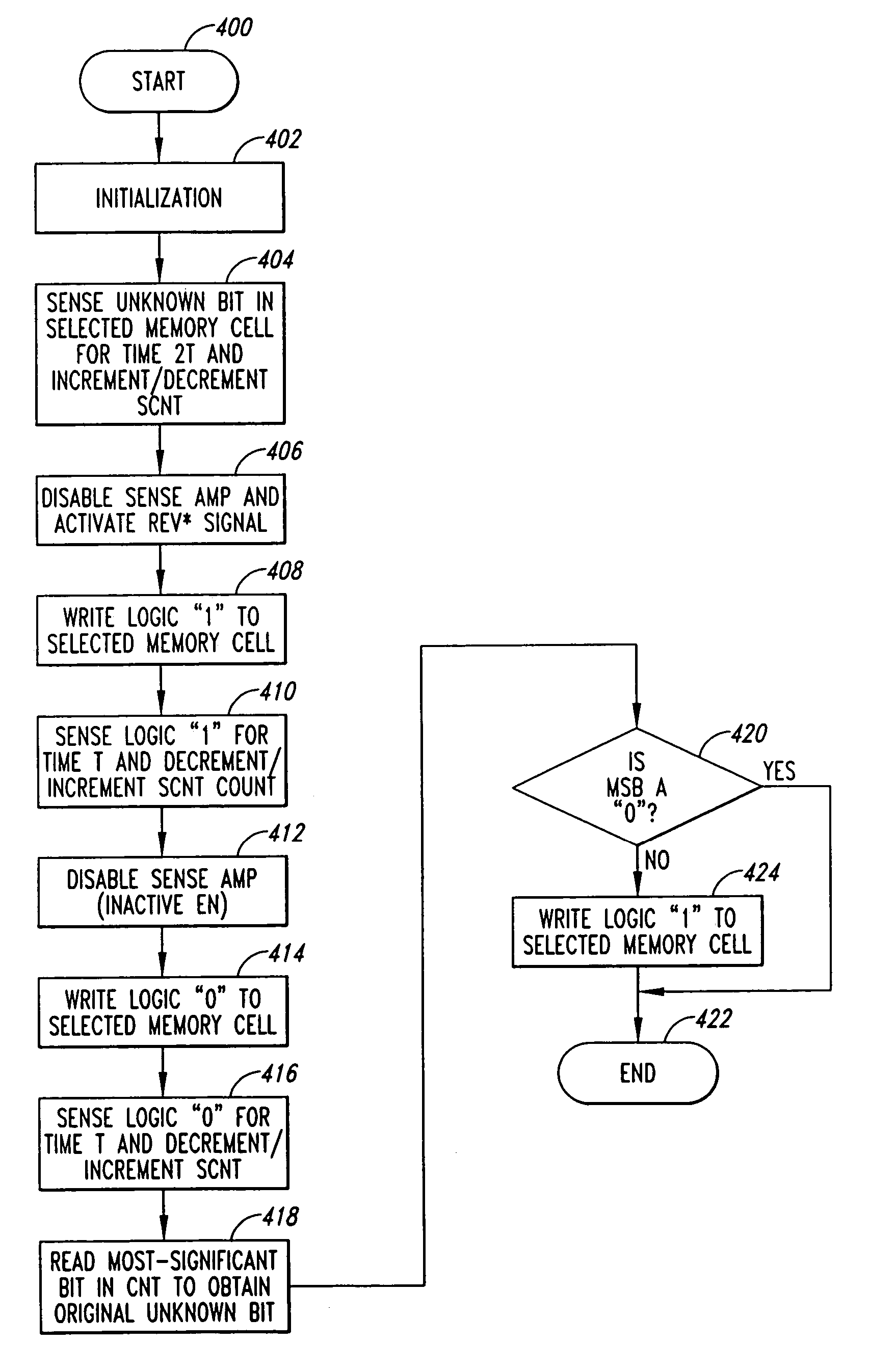
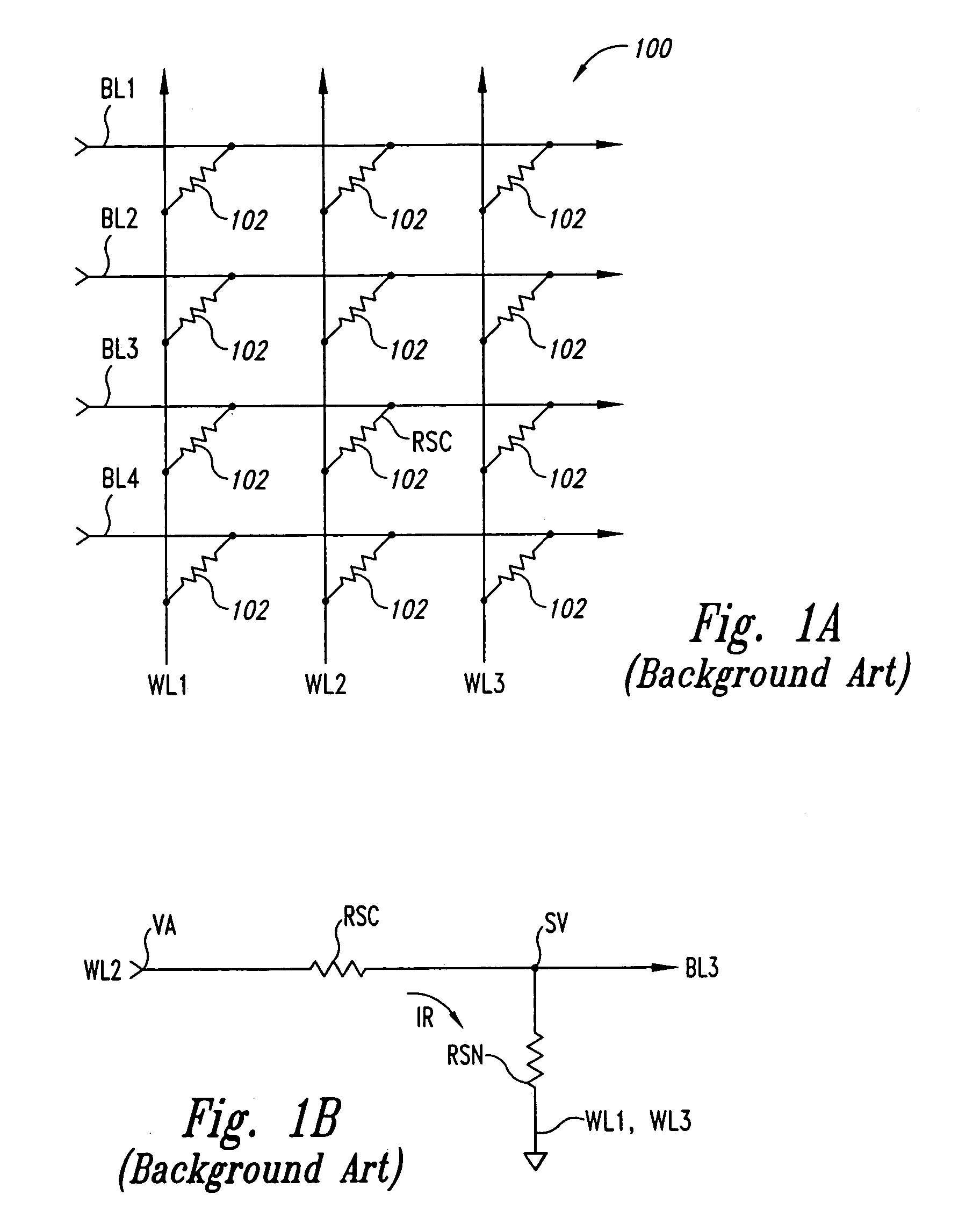
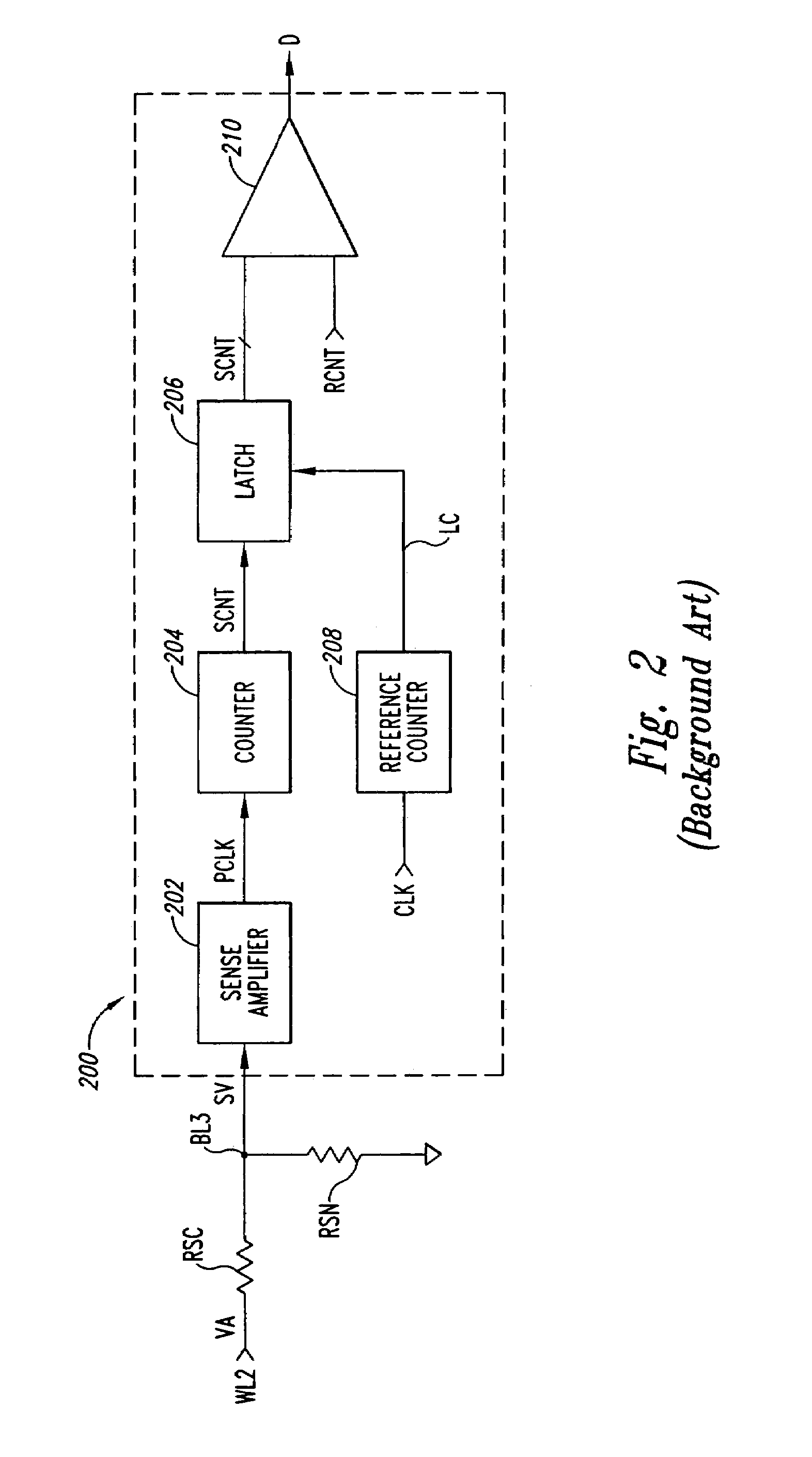
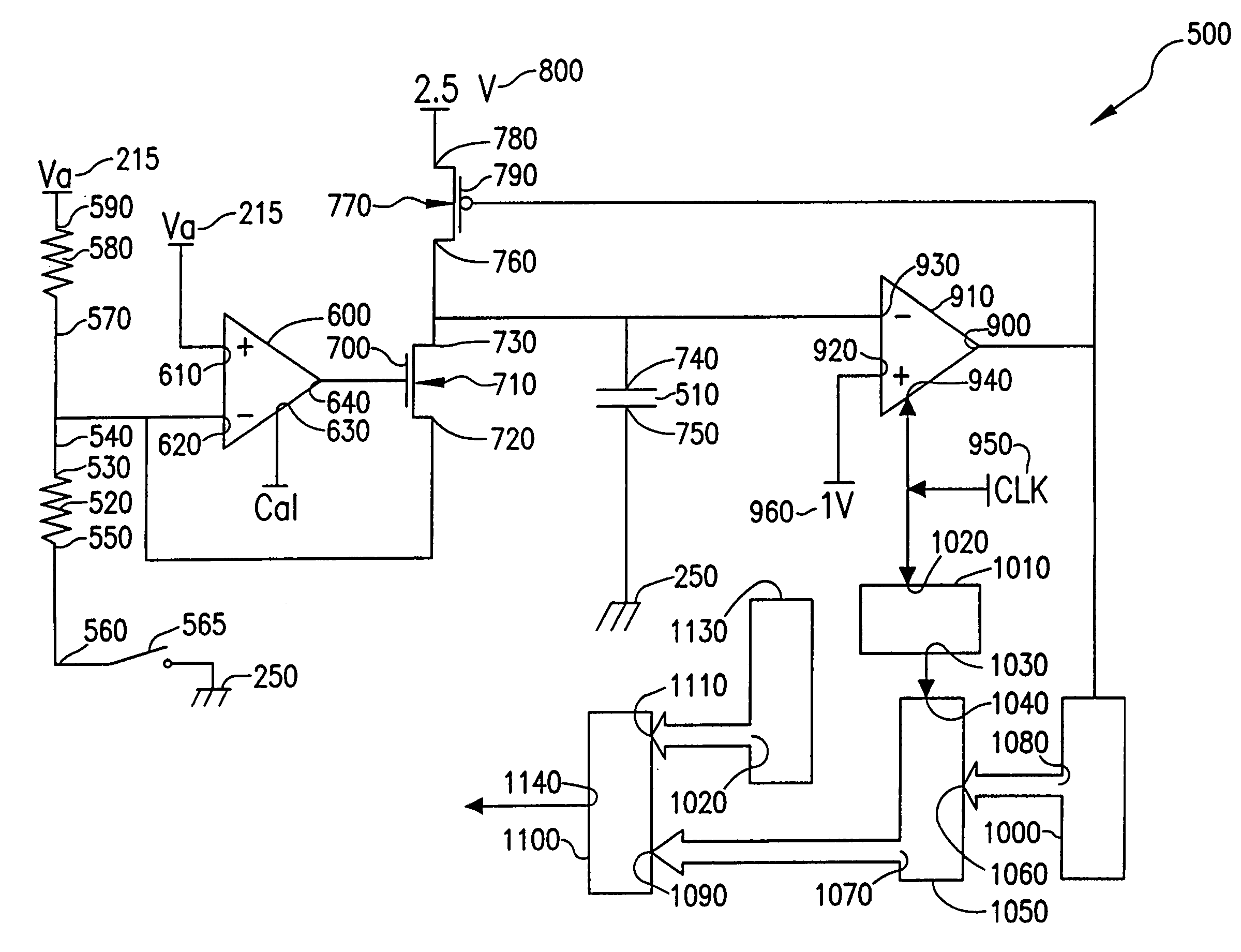
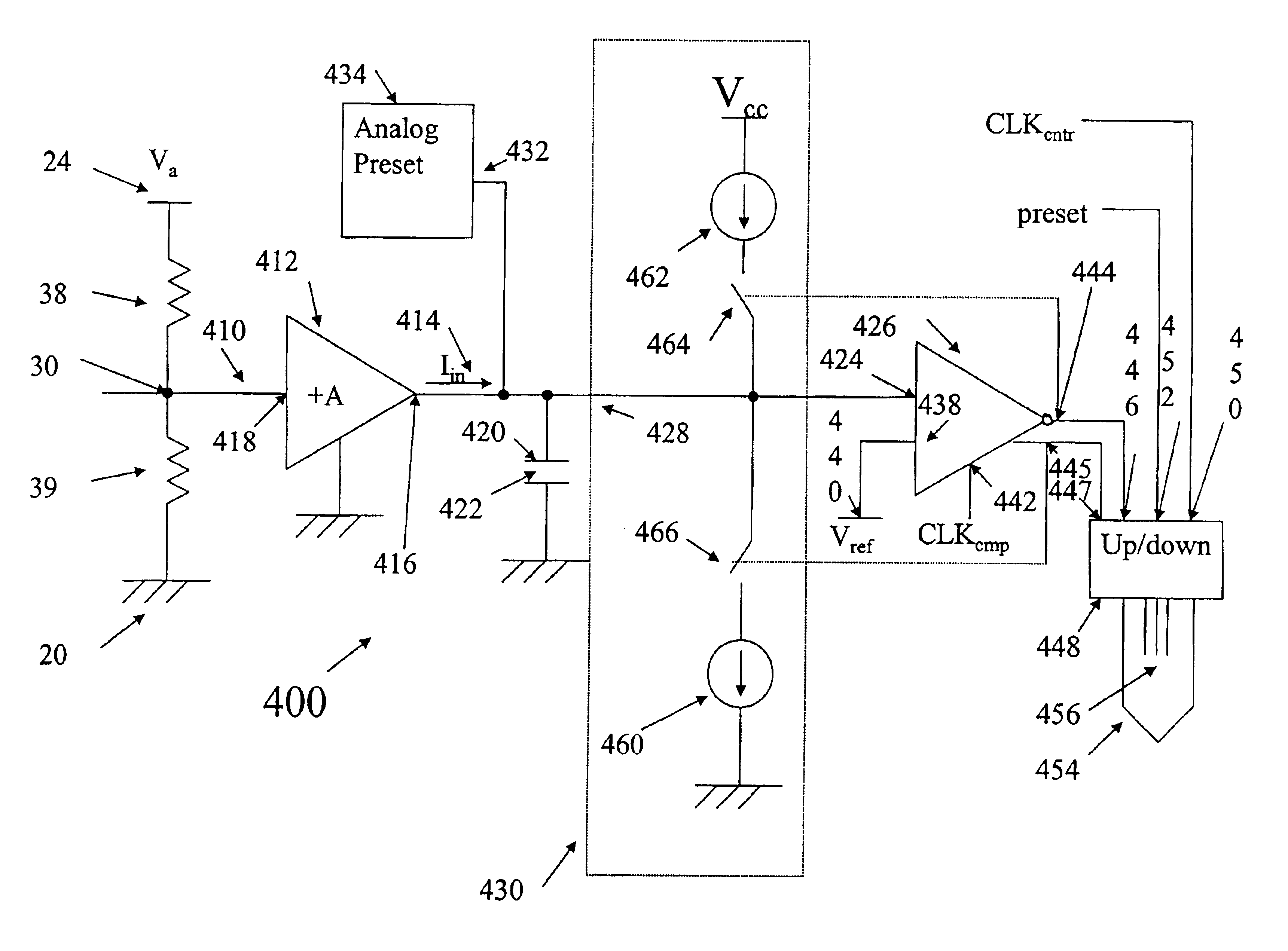
A method and system sense the logic state of an unknown initial data bit stored in a selected resistive memory cell. According to one method, a first count representing the logic state of the unknown initial data bit stored in the selected memory cell is generated. A second count is then generated, and represents a data bit having a first known logic state stored in the selected memory cell. A third count is then generated, and represents a data bit having a second known logic state stored in the selected memory cell. The logic state of the initial unknown data bit stored in the selected memory cell is then determined from the first, second, and third counts.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array in which electrically erasable and programmable memory cells are arrayed, each of the memory cells storing therein a first logic state with a threshold voltage lower than or equal to a first value or a second logic state with a threshold voltage higher than or equal to a second value that is higher than the first value, a data hold circuit for holding program data and sensing data as read out of the memory cell array, and a controller configured to control a program sequence, wherein the controller has the control functions of: a program control function for applying a program voltage to a selected memory cell of the memory cell array to let the data shift from the first logic state to the second logic state; a program verify control function for verifying that the programmed data of the selected memory cell shifted to the second logic state; an erratic program verify control function for checking that the threshold voltage of a memory cell to be held in the first logic state does not exceed a third value set as an upper limit value of a variation of the first logic state; and an over-program verify control function for checking that the threshold voltage of the selected memory cell shifted to the second logic state does not exceed a fourth value set as an upper limit thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Shift Register and Display Device Using the Same
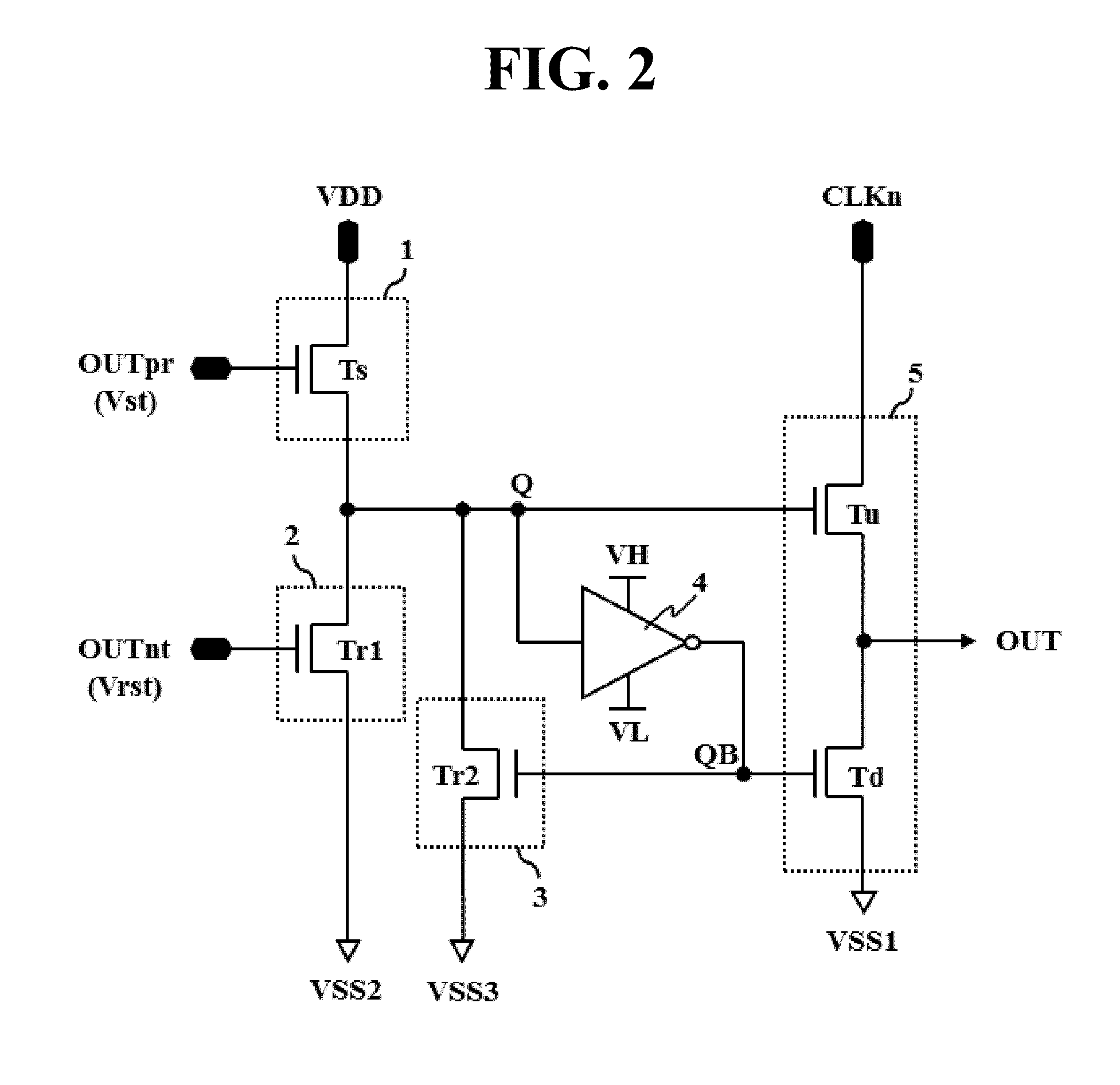
ActiveUS20150317954A1Stable display deviceStable outputCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageShift registerDisplay device
A shift register capable of preventing leakage current and a display device using the same are disclosed. The shift register includes a plurality of stages. Each stage includes a set unit setting a Q node in response to a start pulse or previous output, an inverter for controlling a QB node to have a logic state opposite to that of the Q node, an output unit for outputting any one input clock or a gate off voltage in response to the logic states of the Q and QB nodes, a reset unit including a reset switching element, the reset switching element resetting the Q node with a first reset voltage in response to a reset pulse or next output, and a noise cleaner resetting the Q node with a second reset voltage in response to the QB node. When the reset switching element is turned off, the first reset voltage is greater than a voltage of the reset pulse or the next output for the current.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
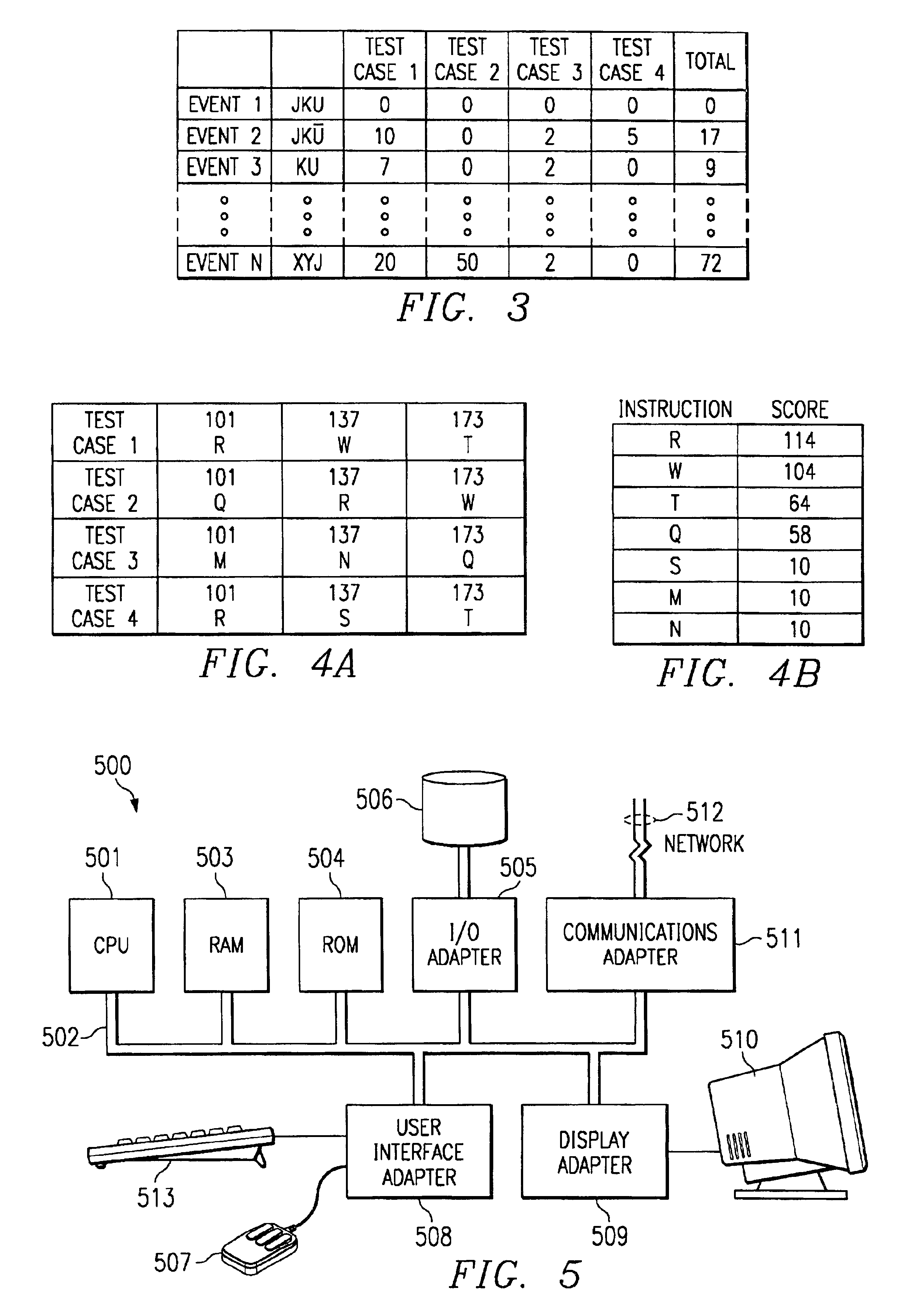
Method and apparatus for generating transaction-based stimulus for simulation of VLSI circuits using event coverage analysis
InactiveUS6859770B2Improve trustElectronic circuit testingAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSpecific testAlgorithm
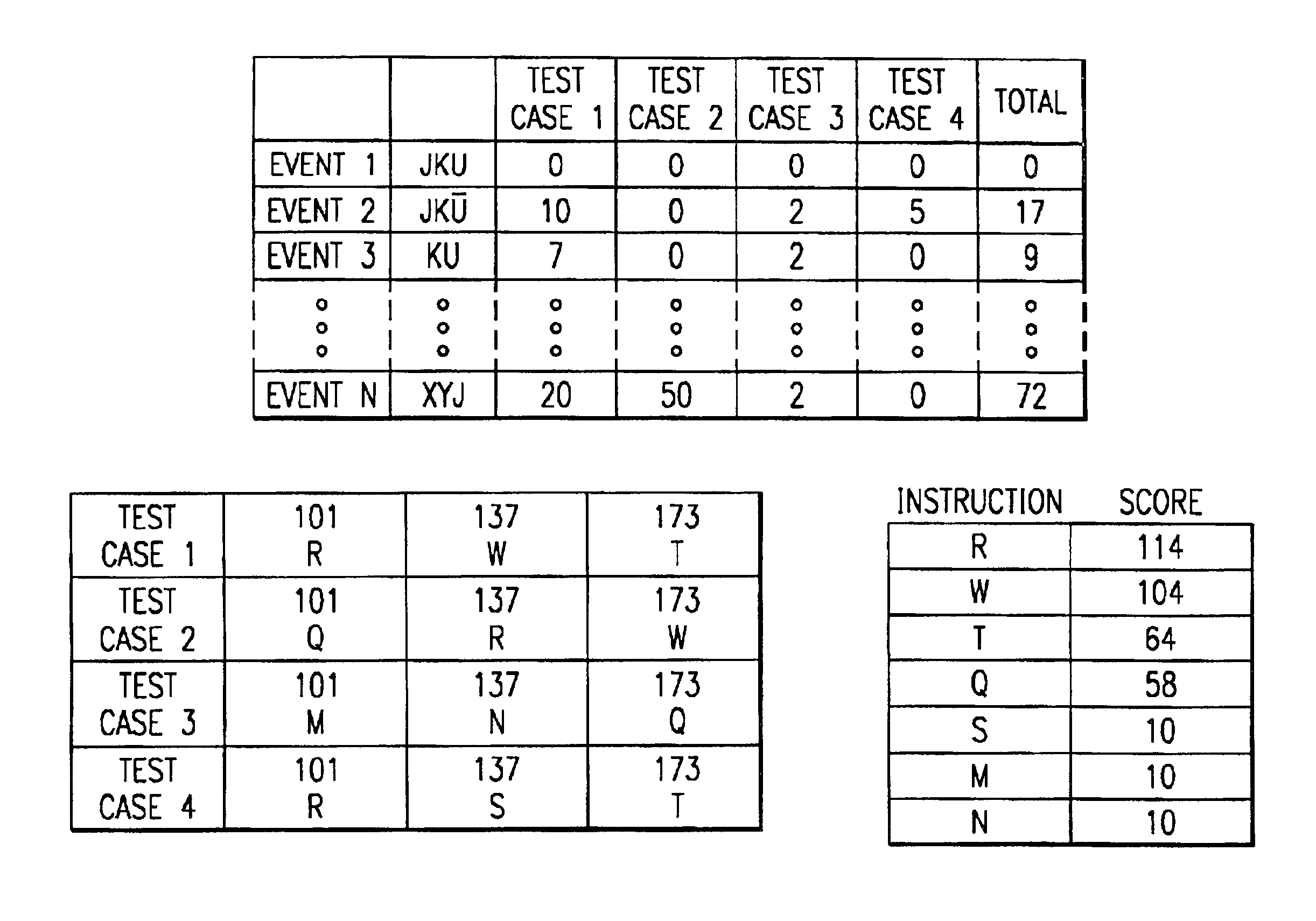
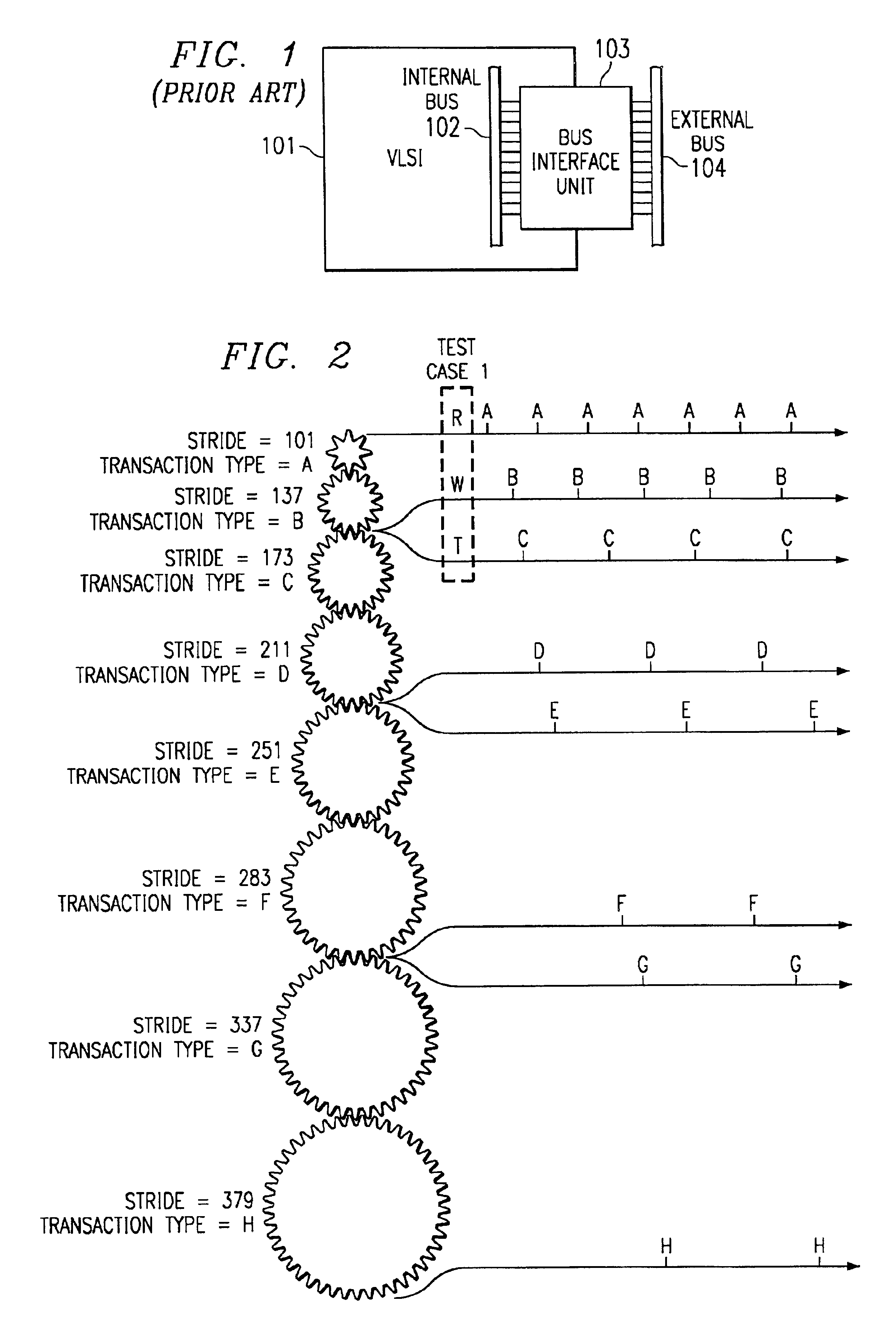
The present invention applies genetic algorithmic generation of test cases the simulation of VLSI logic circuit blocks. The present invention generates a number of original test cases. This aggregate of solutions is provided to a circuit simulator. The results of the simulator are maintained in a matrix or table. The results detail the number of times that particular logic states or events associated with the VLSI block have been stimulated by particular test cases. The aggregate of solutions and the simulation results are then analyzed by the genetic algorithm. The genetic algorithm preferably identifies states associated with the circuit simulation that have not been produced by the original test cases. The genetic algorithm then combines characteristics of various test cases to generate new test cases. The new test cases are provided to the circuit simulator thereby providing a higher degree of confidence that the entire VLSI chip design has been simulated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
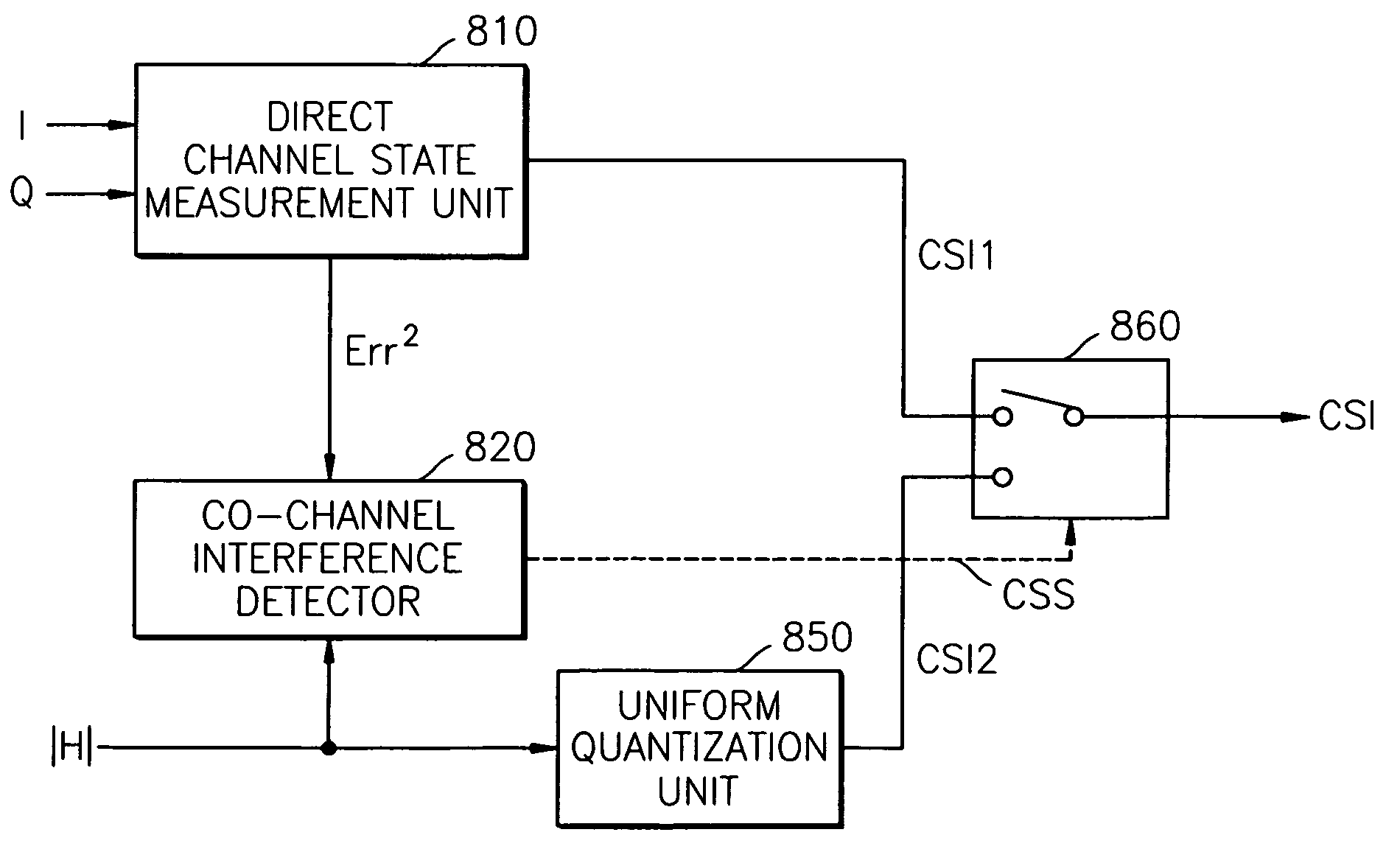
Method and apparatus for providing channel state information
ActiveUS7430256B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionChannel state informationControl signal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Resistive memory element sensing using averaging
A system for determining the logic state of a resistive memory cell element, for example an MRAM resistive cell element. The system includes a controlled voltage supply, an electronic charge reservoir, a current source, and a pulse counter. The controlled voltage supply is connected to the resistive memory cell element to maintain a constant voltage across the resistive element. The charge reservoir is connected to the voltage supply to provide a current through the resistive element. The current source is connected to the charge reservoir to repeatedly supply a pulse of current to recharge the reservoir upon depletion of electronic charge from the reservoir, and the pulse counter provides a count of the number of pulses supplied by the current source over a predetermined time. The count represents a logic state of the memory cell element.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for measuring current as in sensing a memory cell
InactiveUS6930942B2Increase rangeShorten the counting processElectric analogue storesDigital storageAudio power amplifierCapacitor voltage
Apparatus and methods sense or measure an input current, such as a current indicating a logic state of a memory cell. A sensing circuit includes an amplifier, a capacitor, a current source circuit, a clocked comparator and a clocked counter. The current source circuit operates responsive to an output of the comparator to supply or withdraw current to and from the capacitor during respective charging and discharging intervals. The count in the clocked counter results from periodic comparisons of the capacitor voltage with a reference voltage and is, therefore, related to the logic state of the memory cell. The magnitude of current supplied during charging is less than the magnitude withdrawn during discharging, allowing use of a smaller counter.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Processing high-speed digital signals
ActiveUS7187738B2Reduce controlMeet high-speed operationChannel dividing arrangementsPulse automatic controlData synchronizationData stream
A first transparent latch receives a first synchronised signal changing its logic state synchronously with respect to a clock signal. A second transparent latch receives a second synchronised signal output by the first latch. When the clock signal has a first logic state the first latch has a non-responsive state and the second latch has a responsive state, and when the clock signal has a second logic state the first latch has the responsive state and the second latch has the non-responsive state. The change in logic state of a third synchronised signal output by the second latch is guaranteed to occur in a particular half-cycle of the clock signal, irrespective of process / voltage / temperature (PVT) variations of the circuitry. Clock recovery circuitry may have rising-edge and falling-edge latches; circulating control pattern verification circuitry; data synchronising circuitry for converting parallel data clocked by a first clock signal into serial data clocked by a second clock signal asynchronous with the first clock signal; and data recovery circuitry for producing an offset clock signal which suits a data eye shape of a received serial data stream.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Process for presenting a user state using several pieces of communication equipment
InactiveUS20060034430A1Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersLogic stateHuman–computer interaction
A process for presenting a state of availability of a user for communications using a plurality of telecommunication devices including at least one means for the production of the presentation associated with an intelligent platform, including acquiring first data composed of characteristics of a user including at least one identification of the user, at least two terminals to which the user can be associated with at least one characteristic of a connection mode and including storage at an address accessible to the intelligent platform of the characteristics, updating second data representative of a physical and / or logic state of a terminal of a user and / or of a general physical and / or logic state of the user with requests for the updating of the physical and / or logic state of an associated terminal and / or of the user by virtue of identification of a user and / or of the user's terminal by a system and / or an authorized user and including optional storage at an address accessible to the intelligent platform of the second data representative of the physical and / or logic state of the terminal or of the physical and / or logic state of the user, and determining the presentation of the first and the second data for a user from the first and the second data which user is registered in the service for presenting the state of a user of the intelligent platform and who made the request.
Owner:LIAKIS PANAGIOTIS MR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com