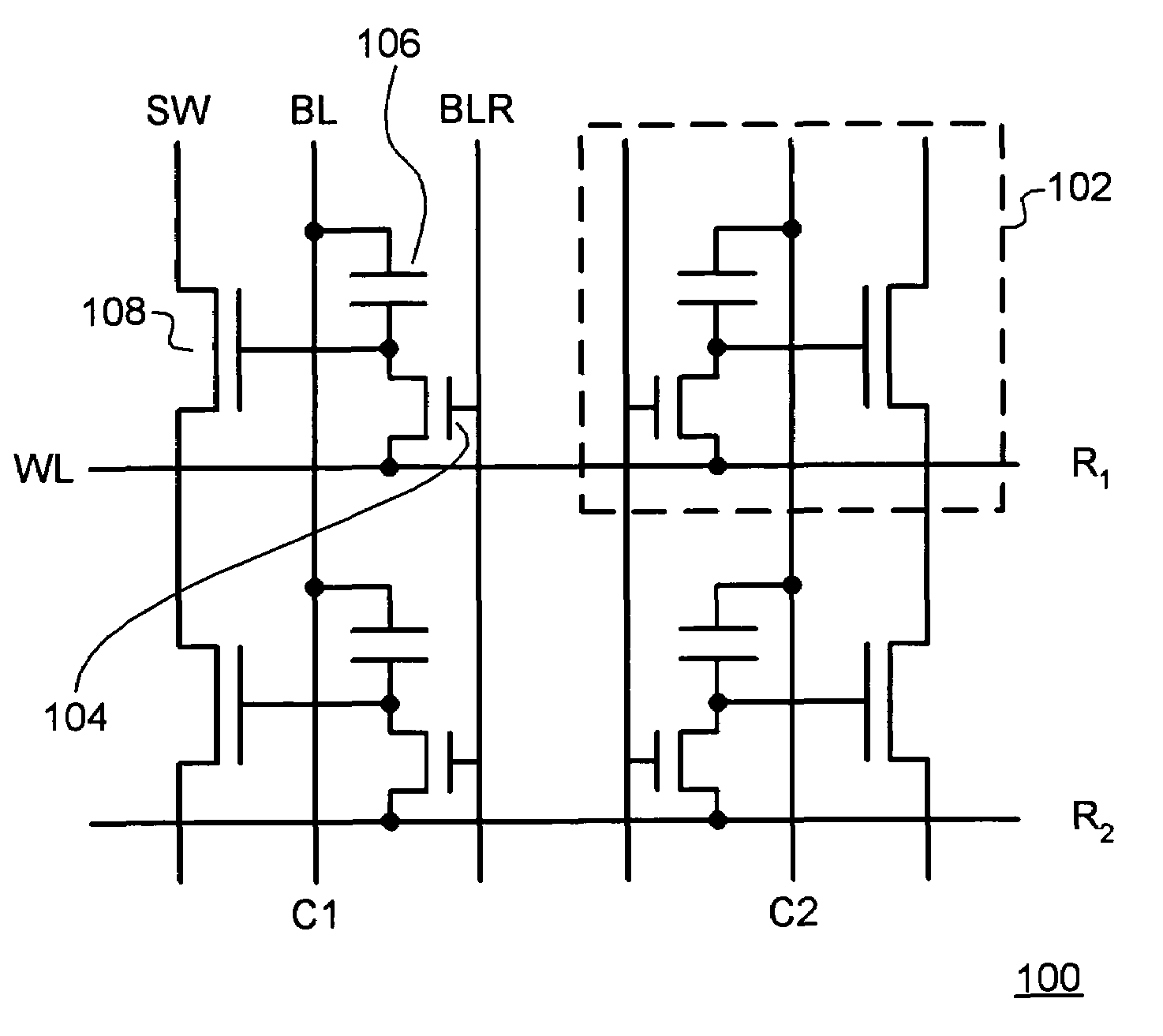
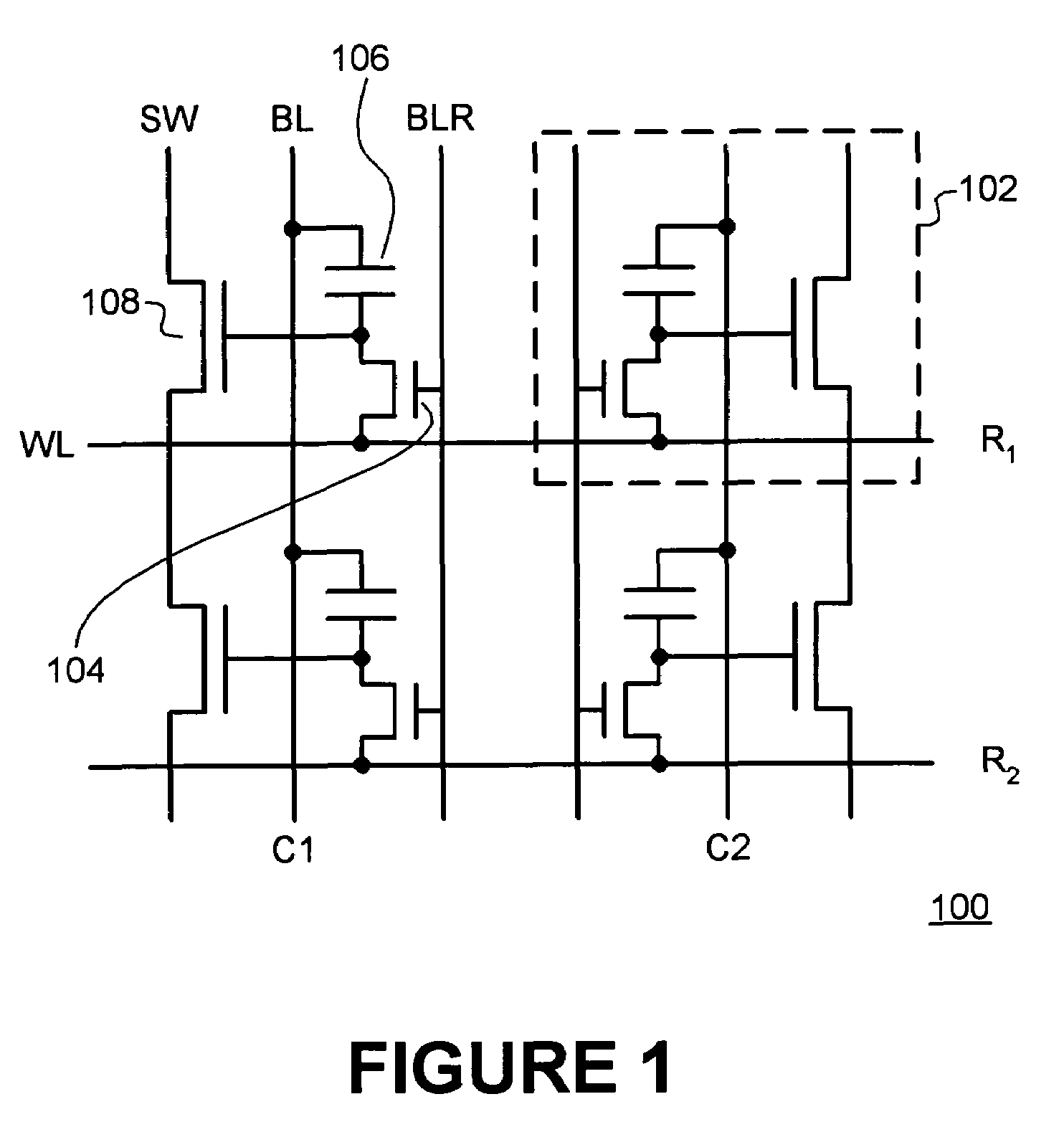
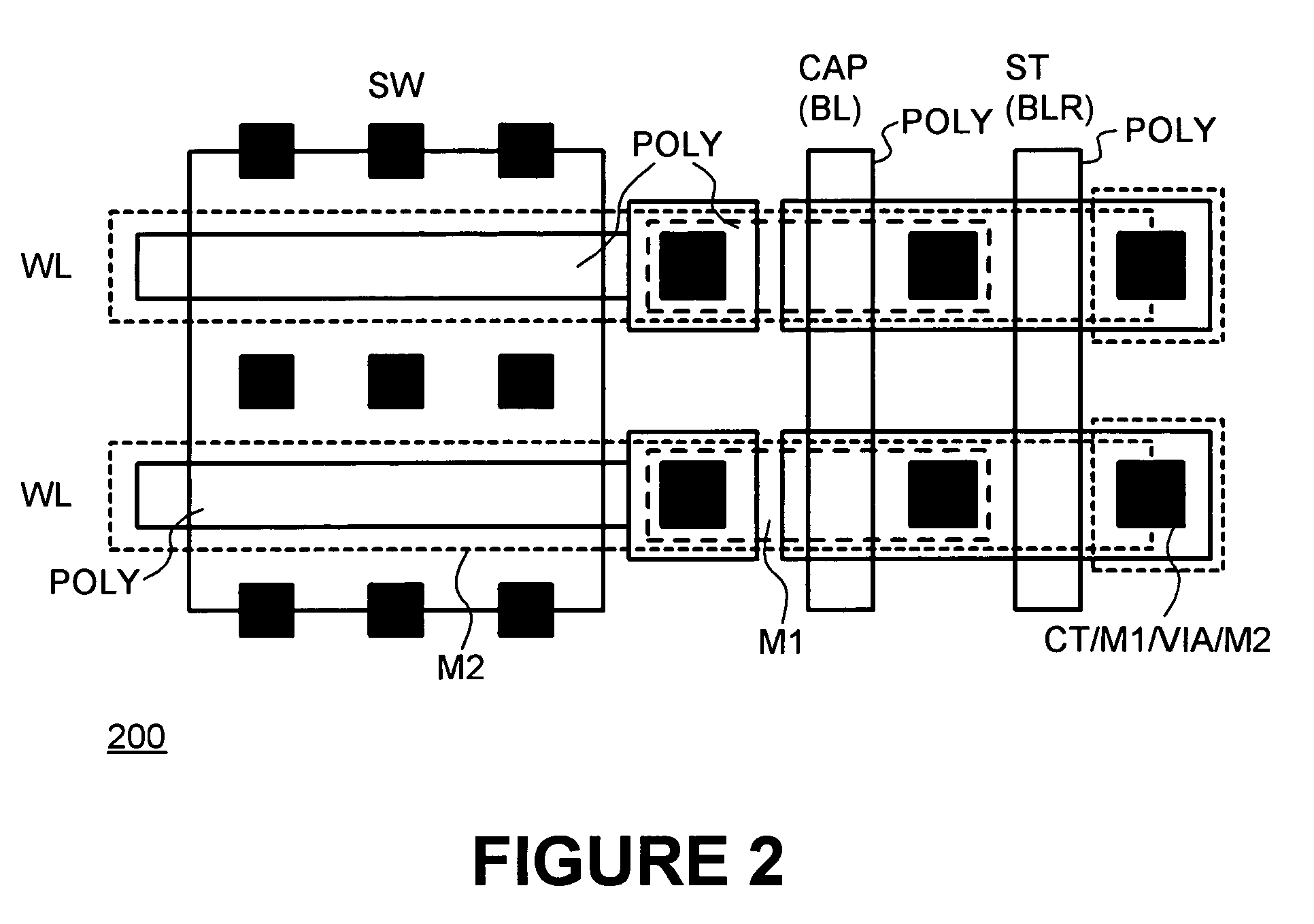
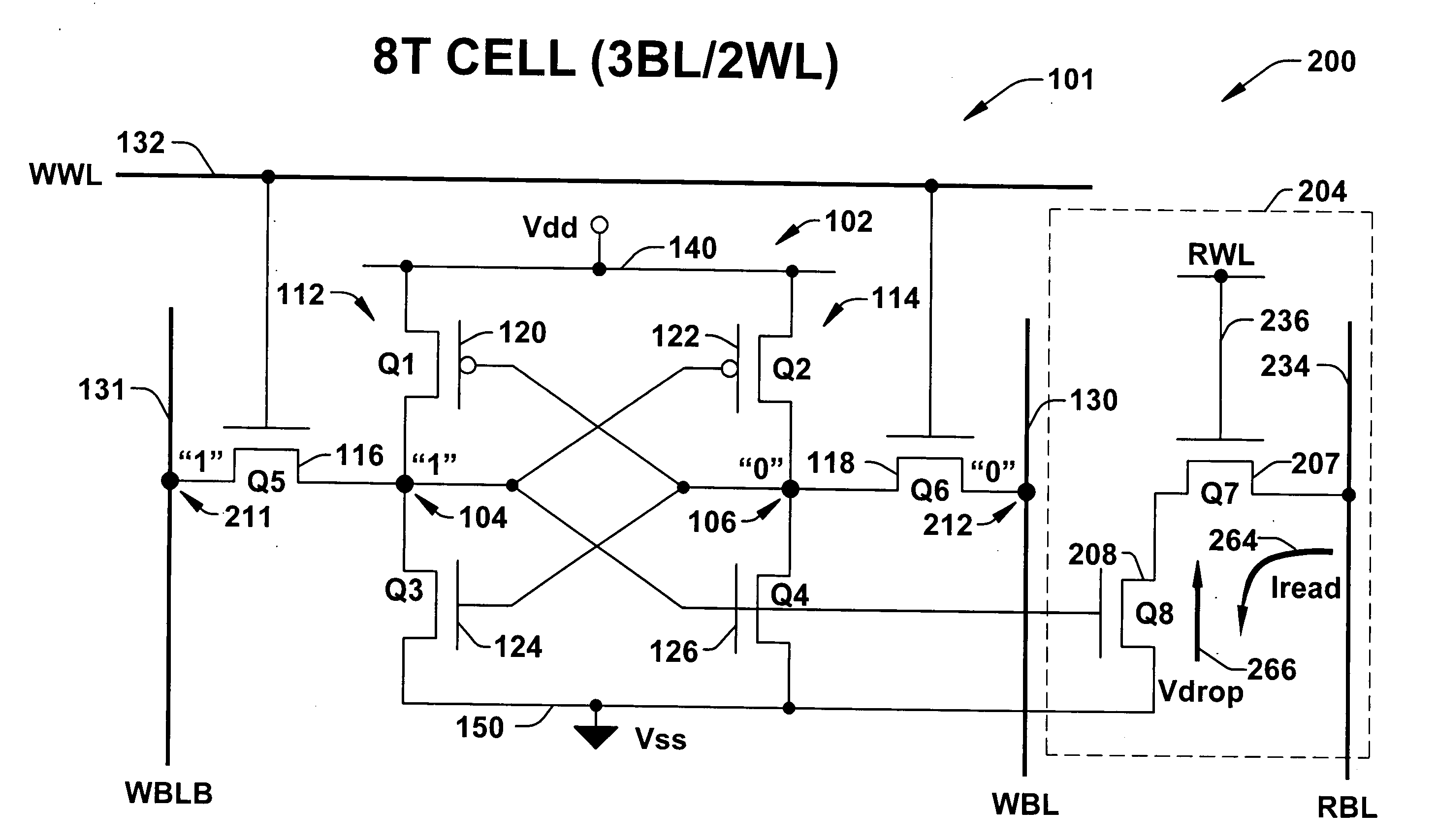
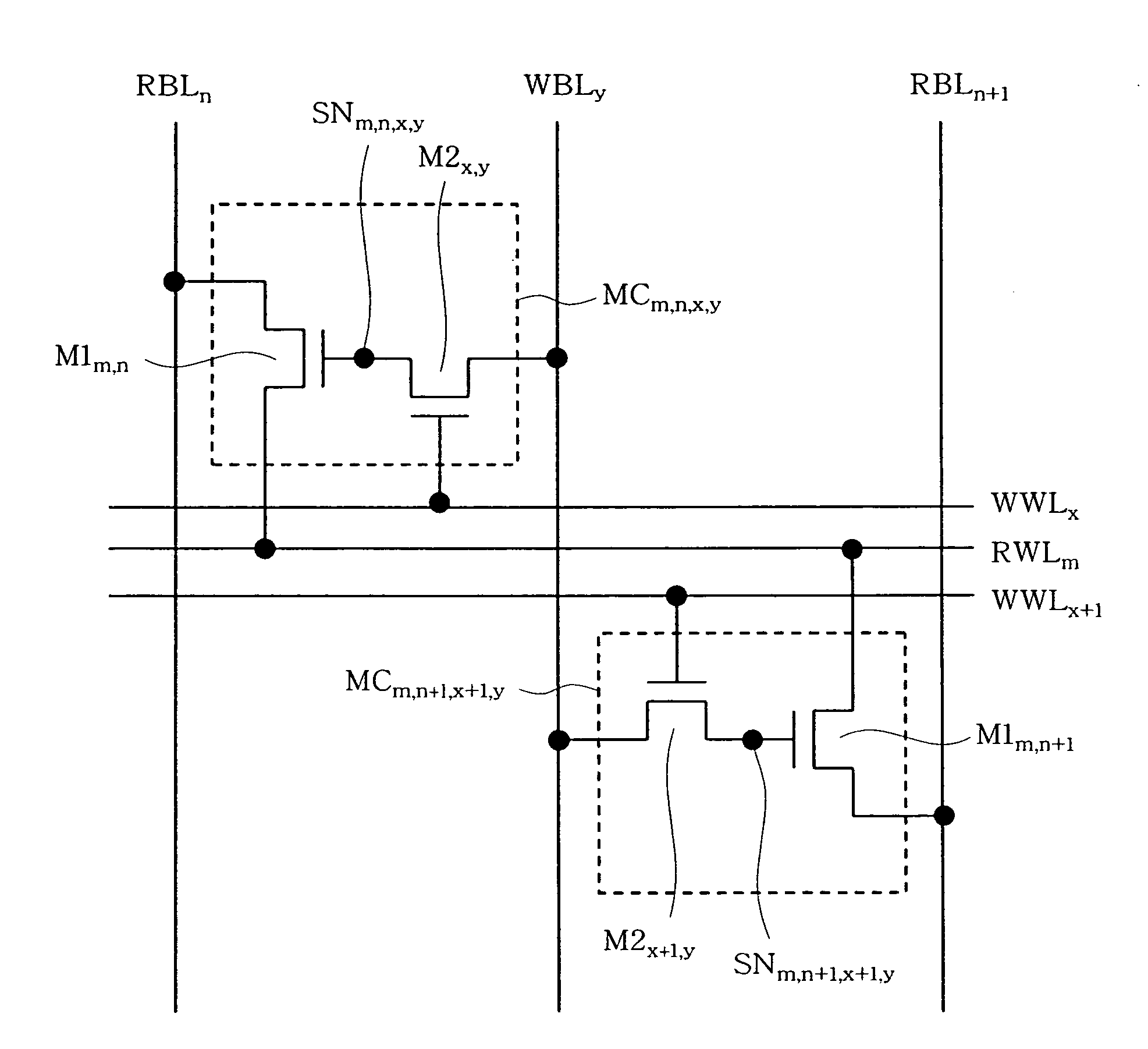
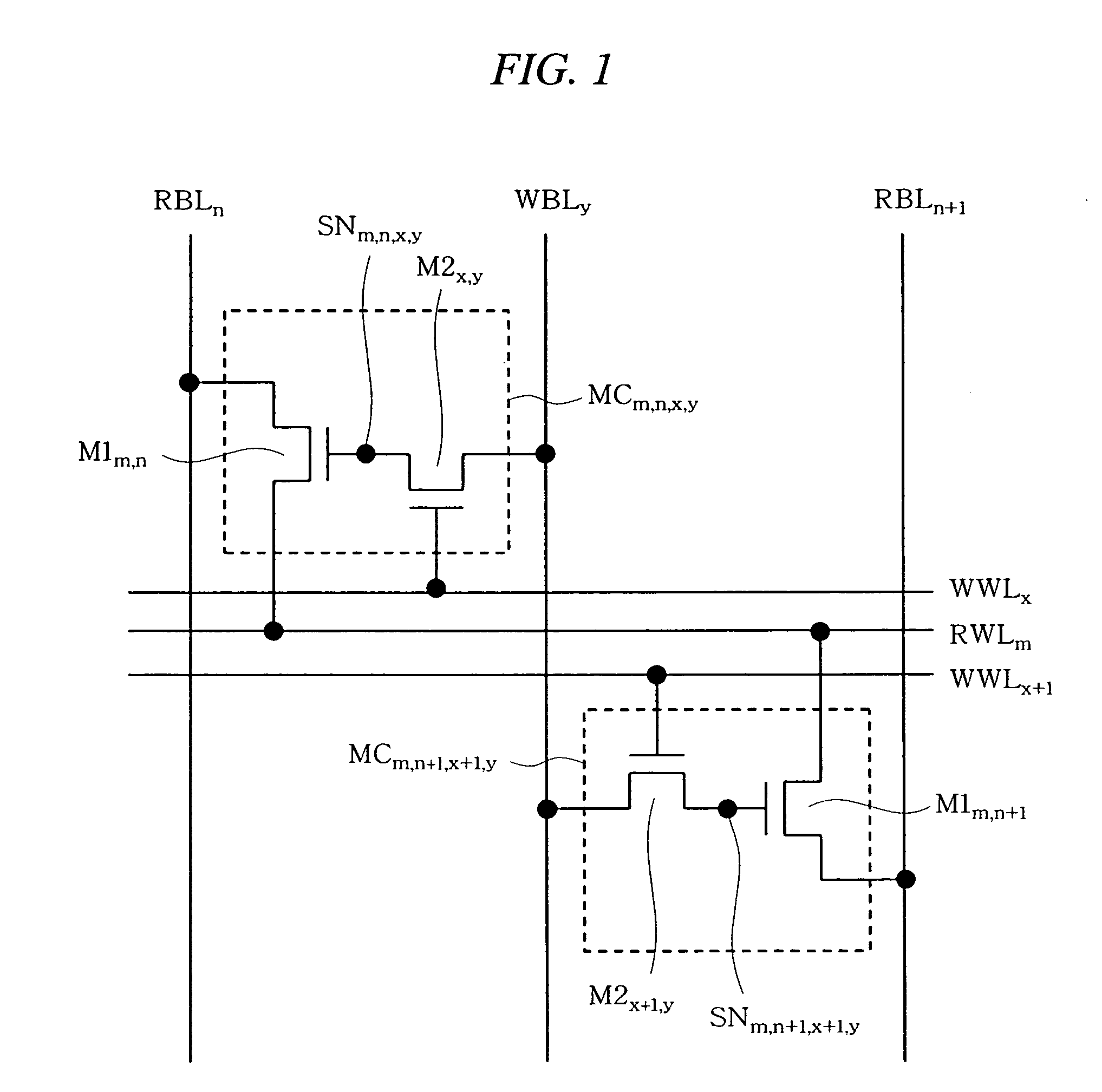
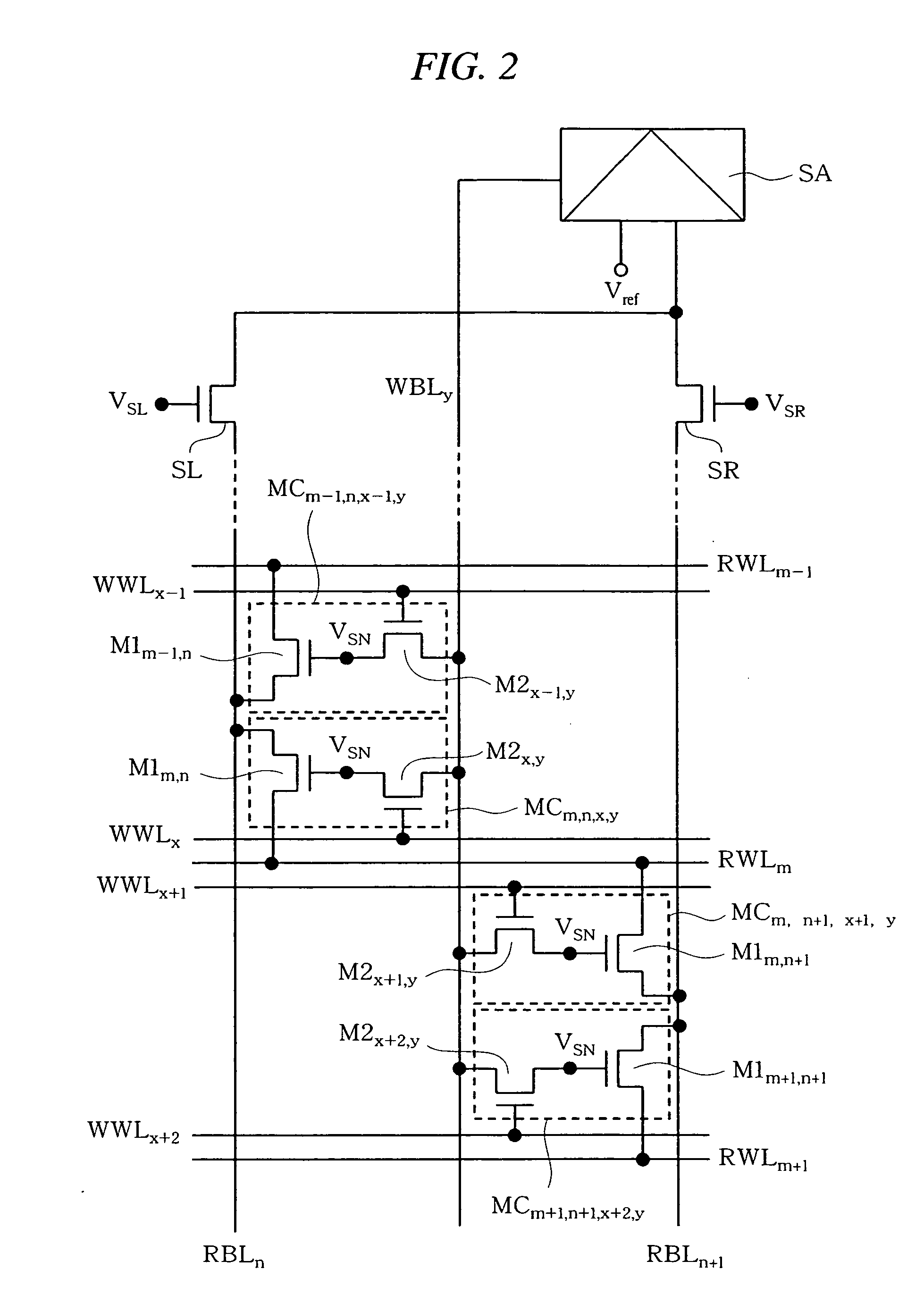
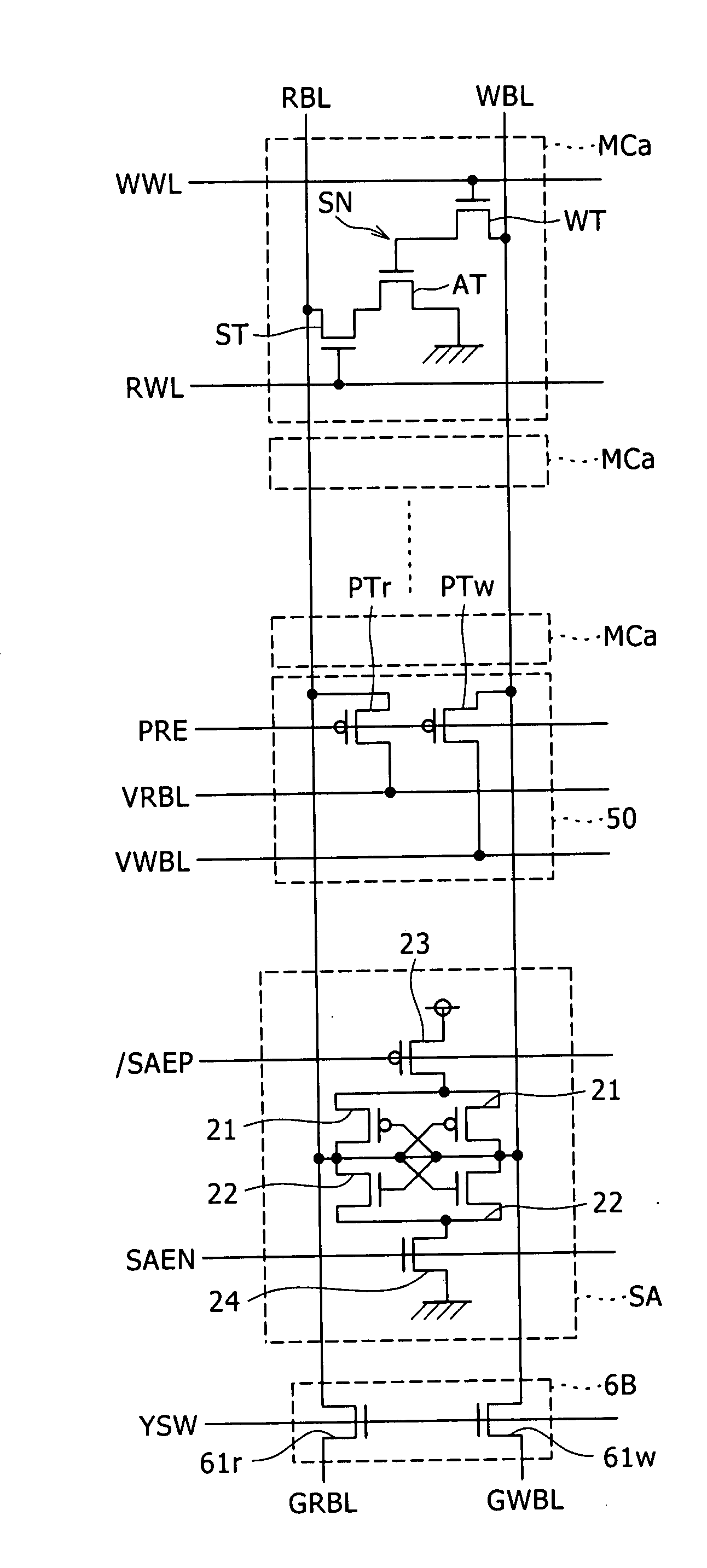
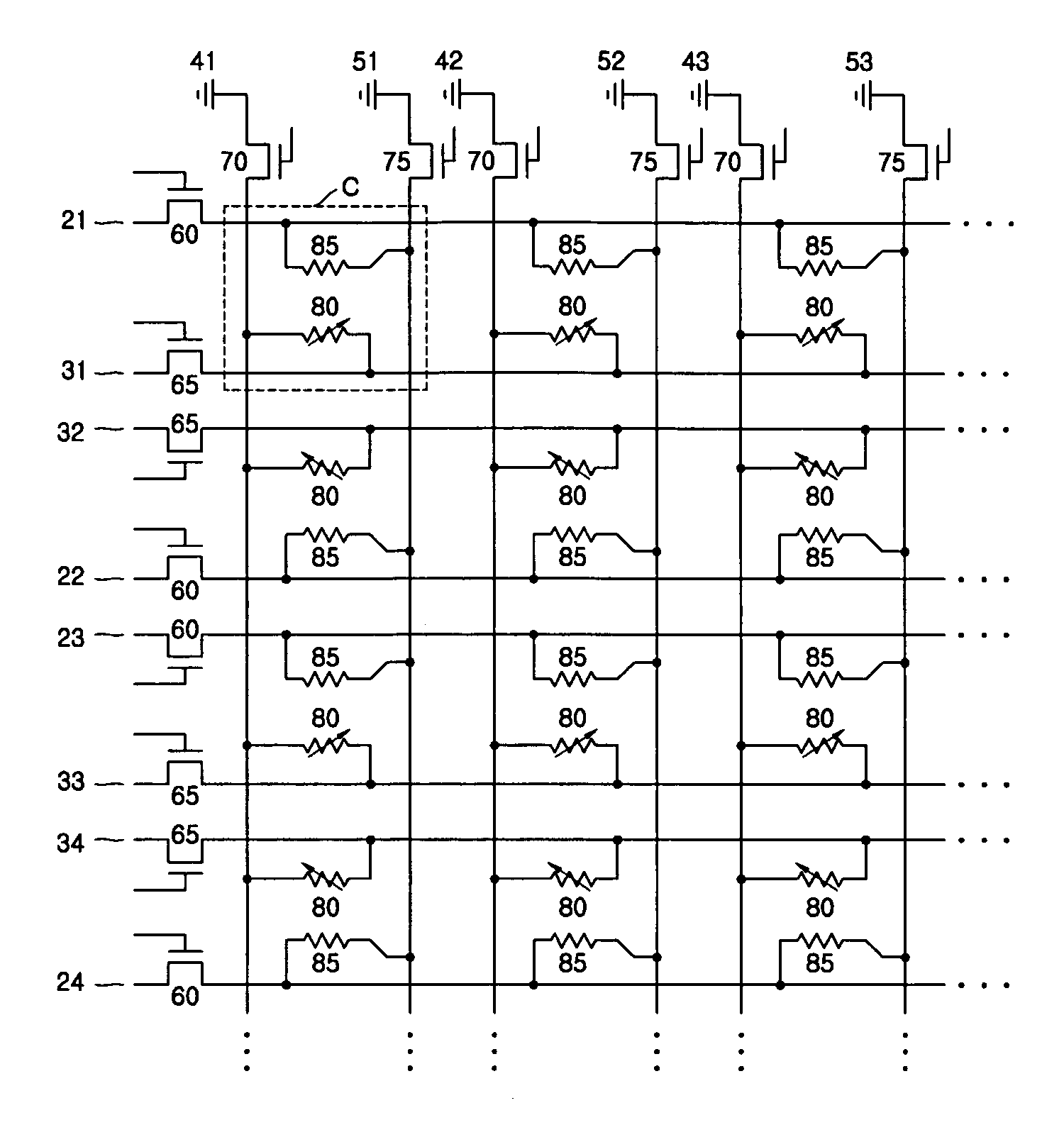
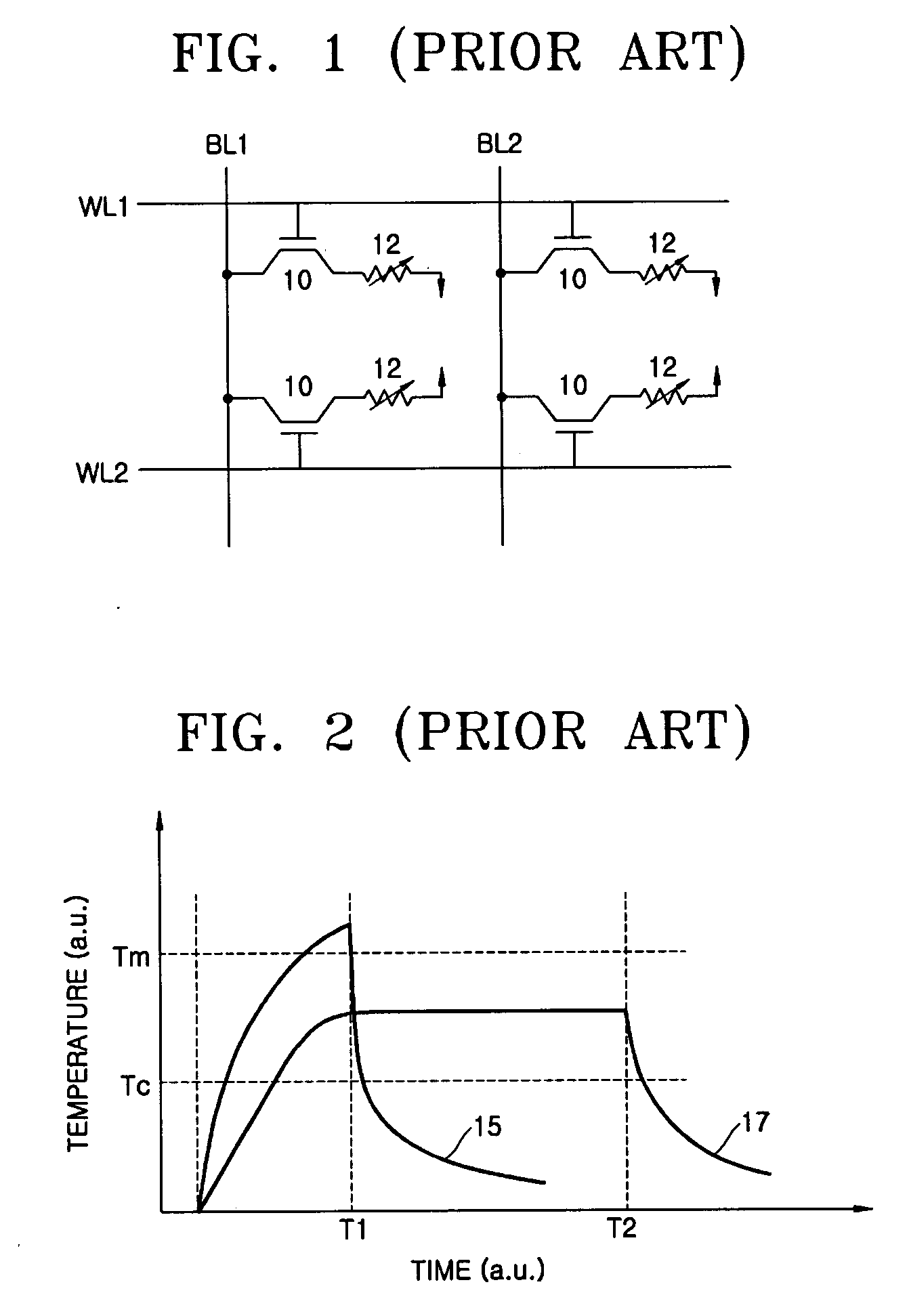
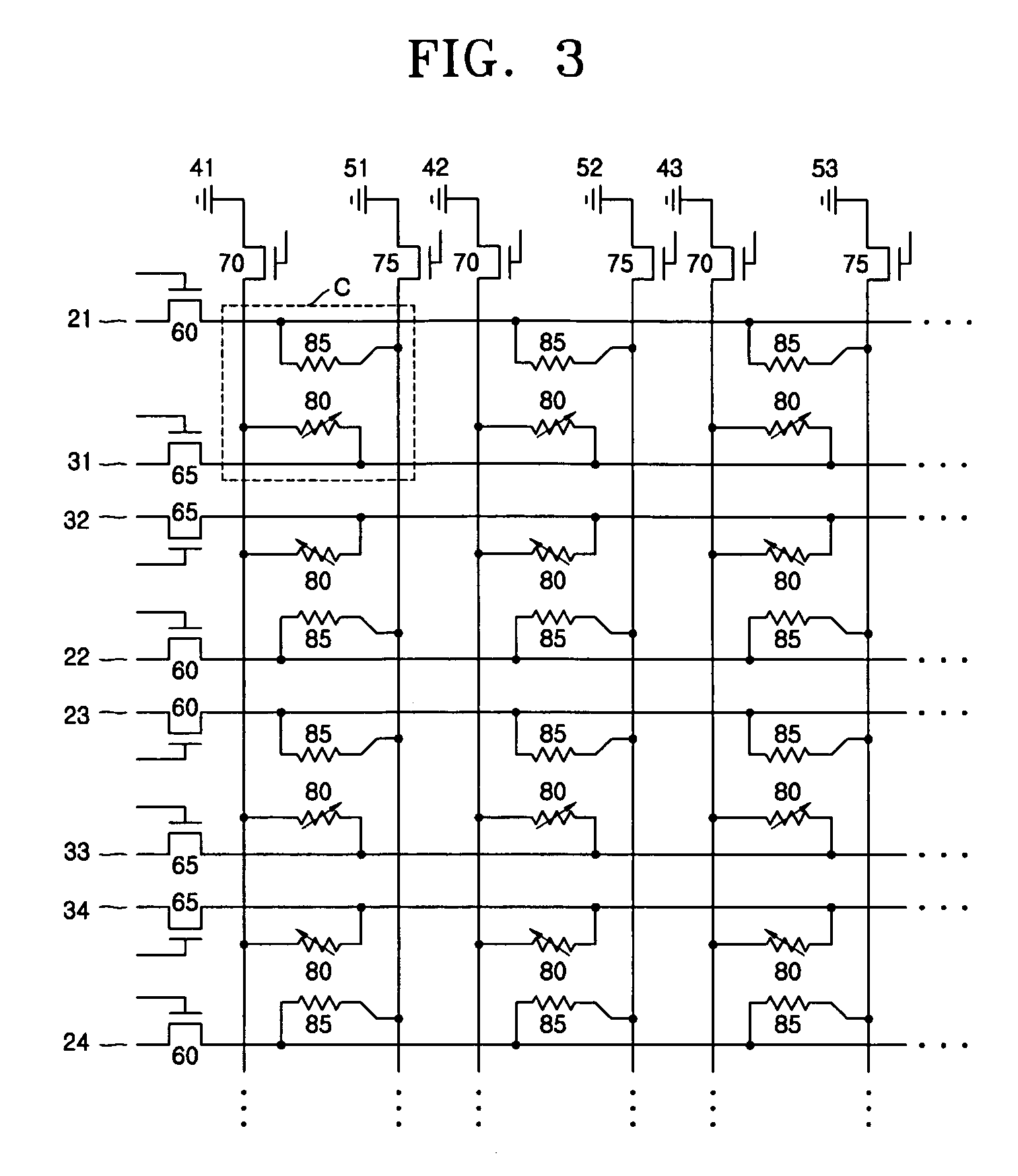
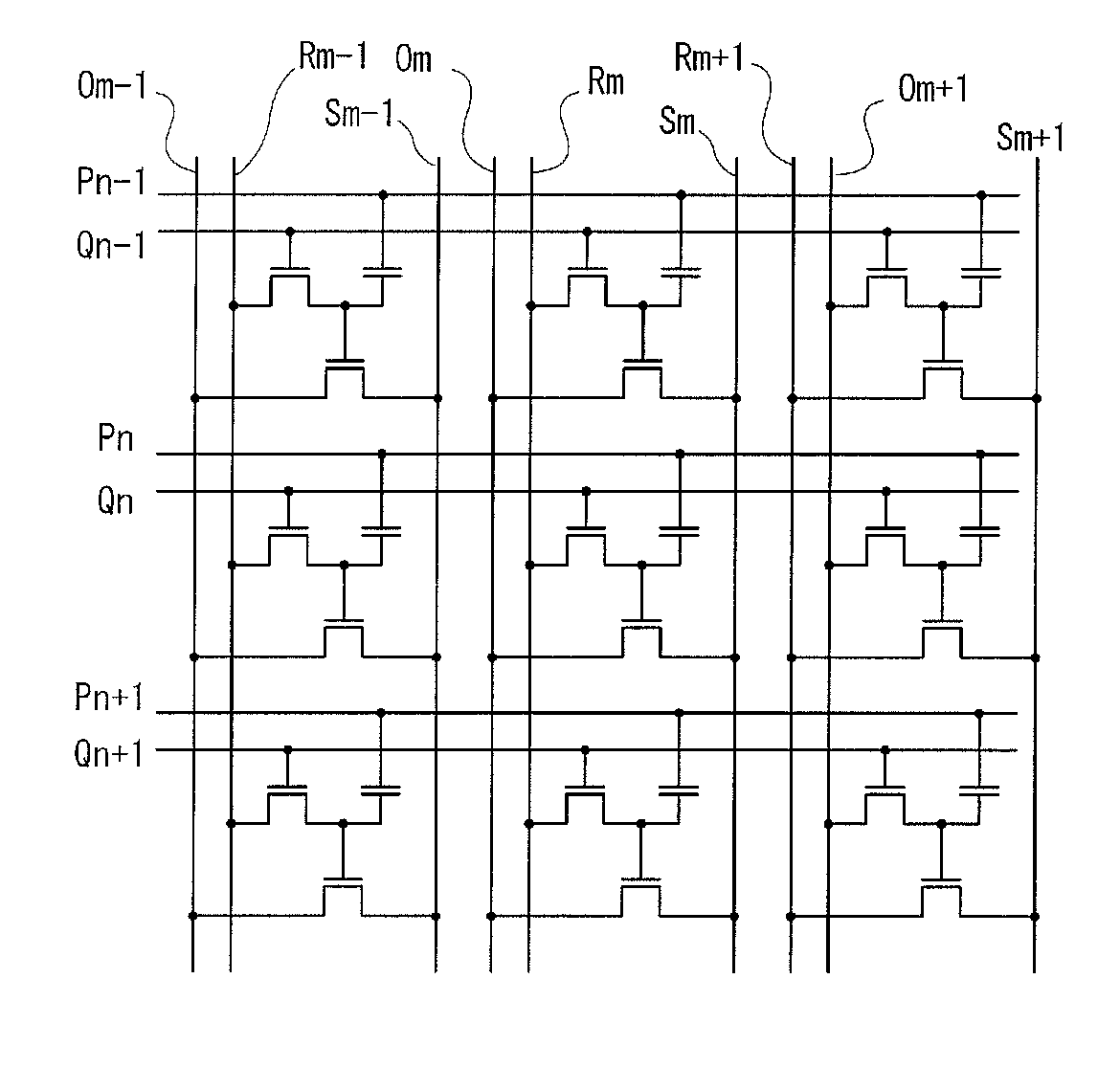
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
339 results about "Read bit line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
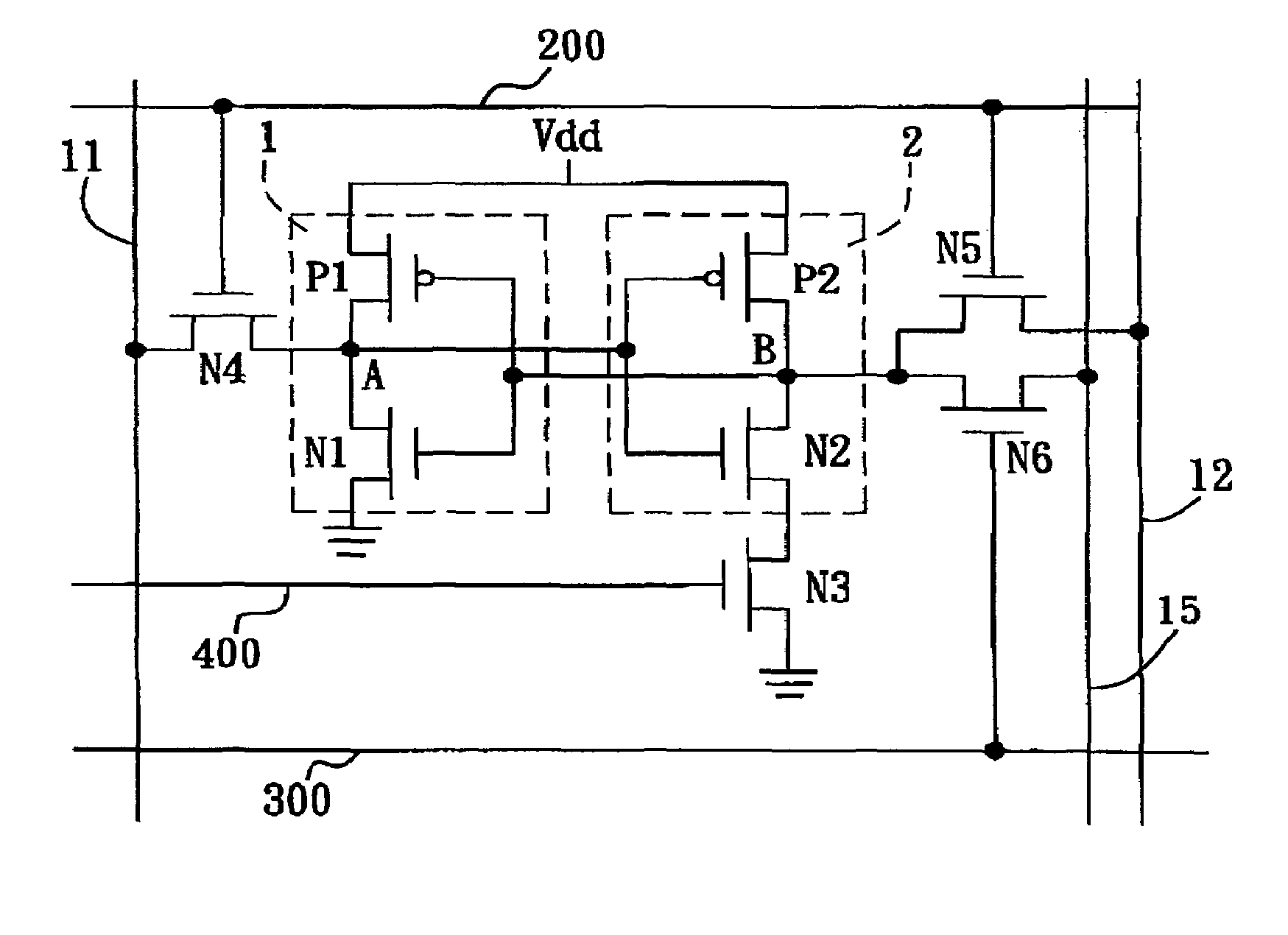
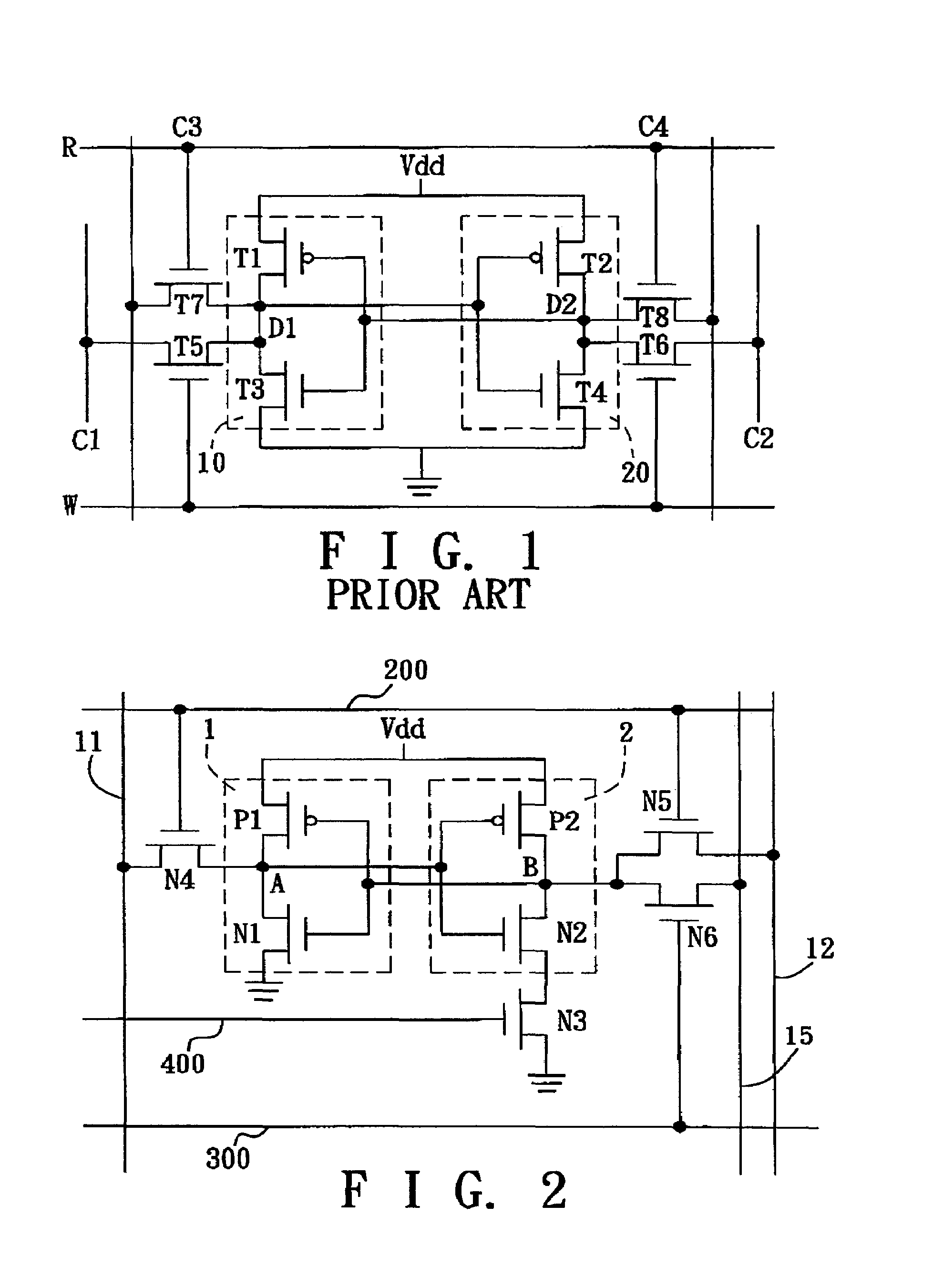
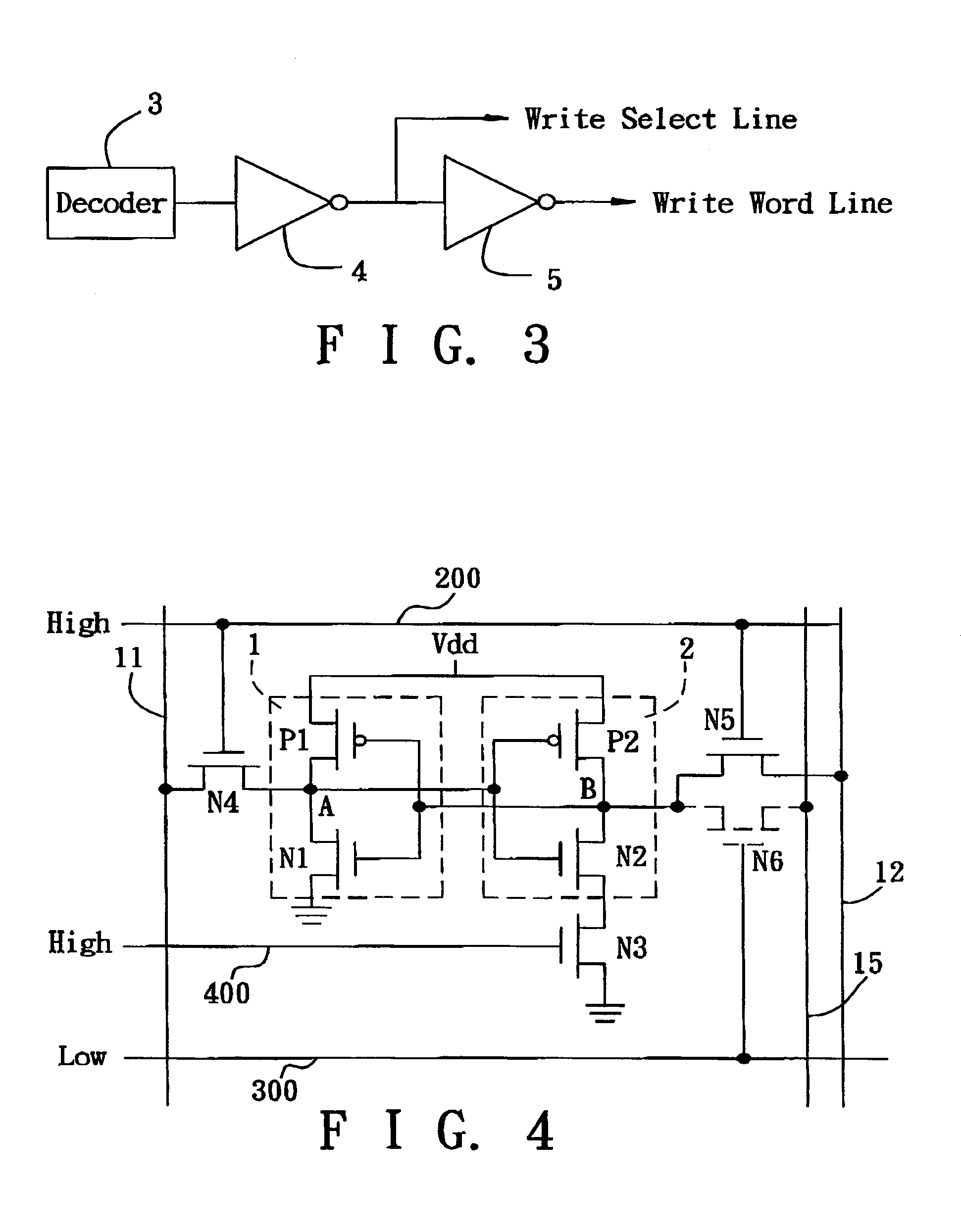
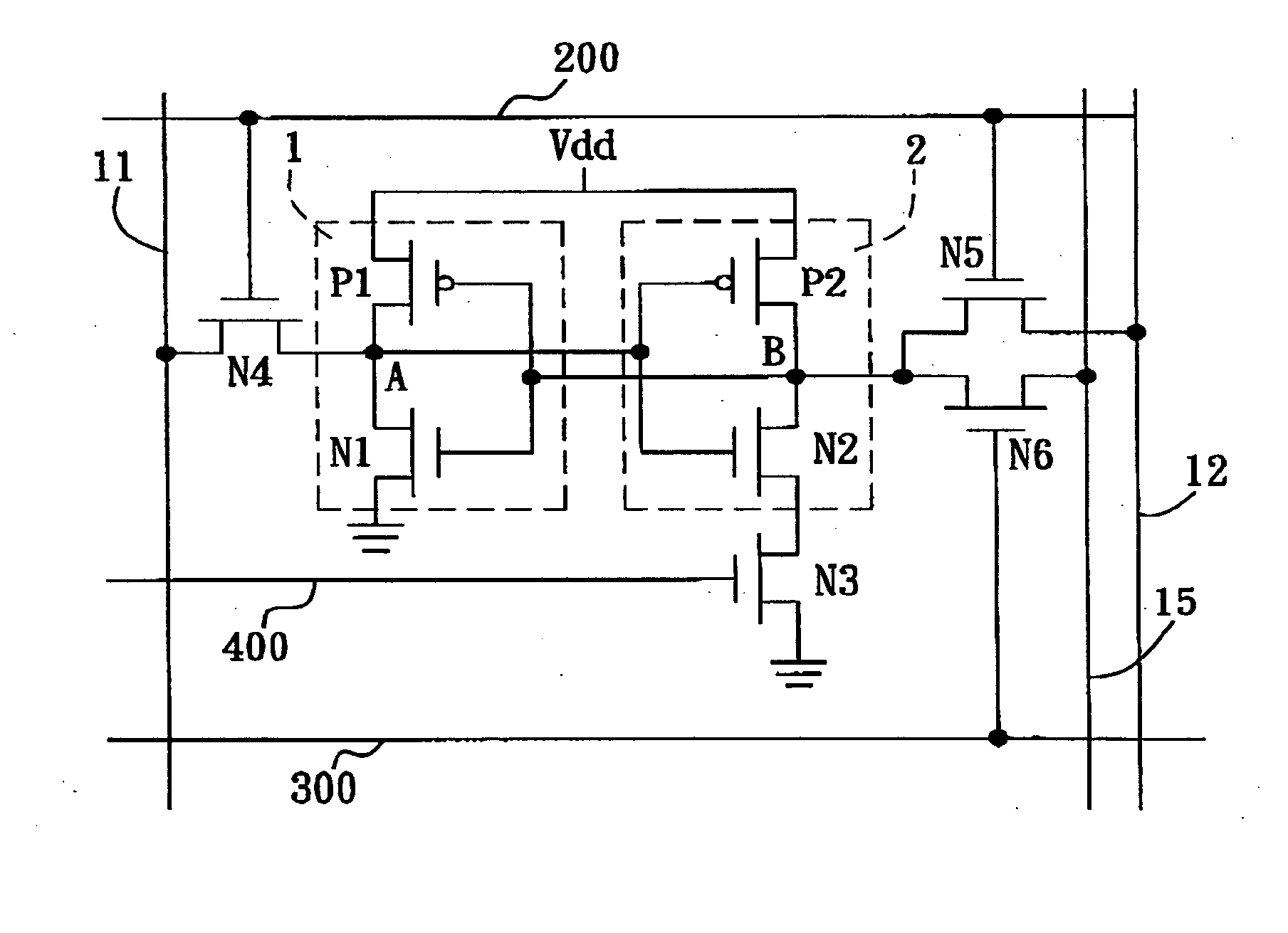
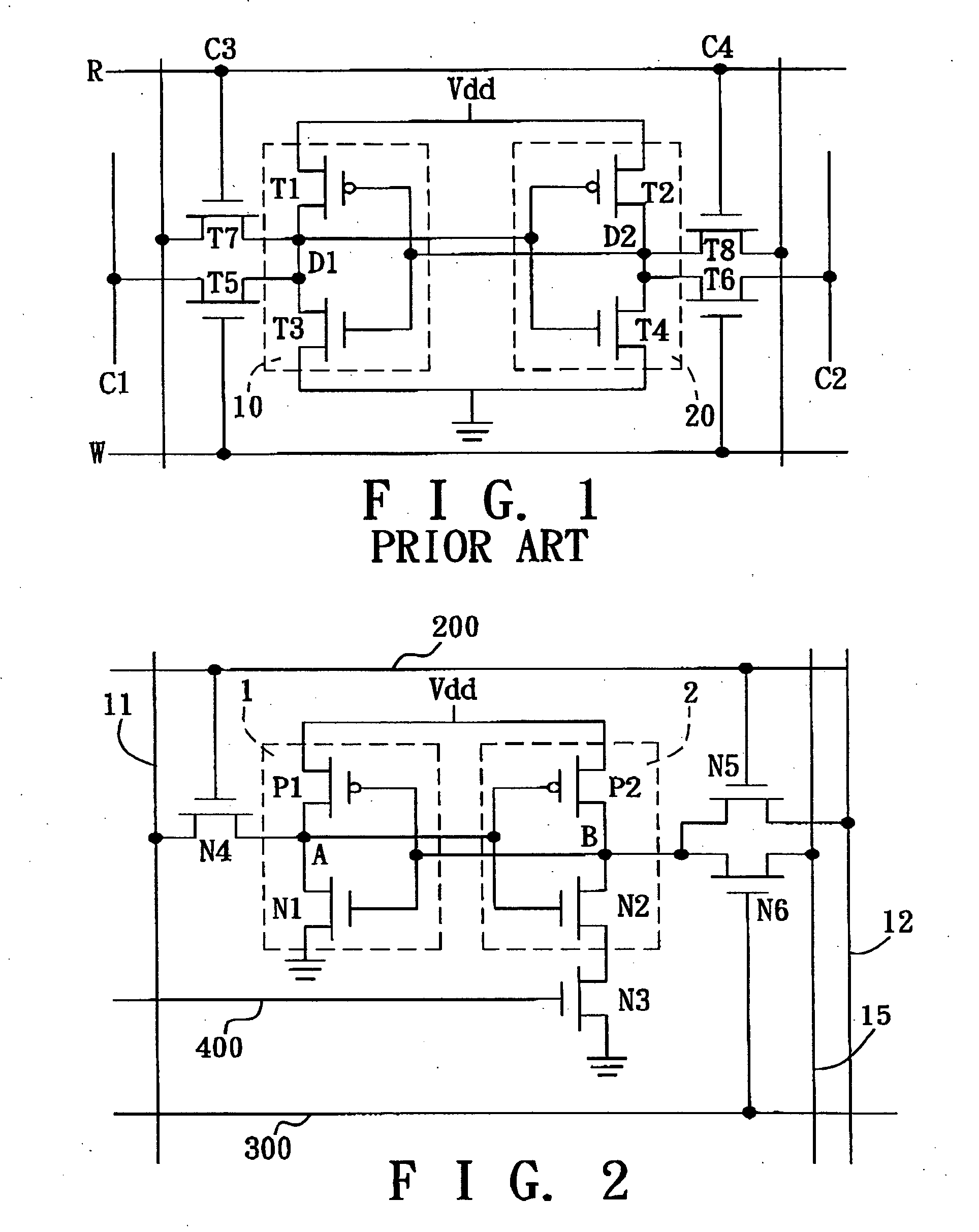
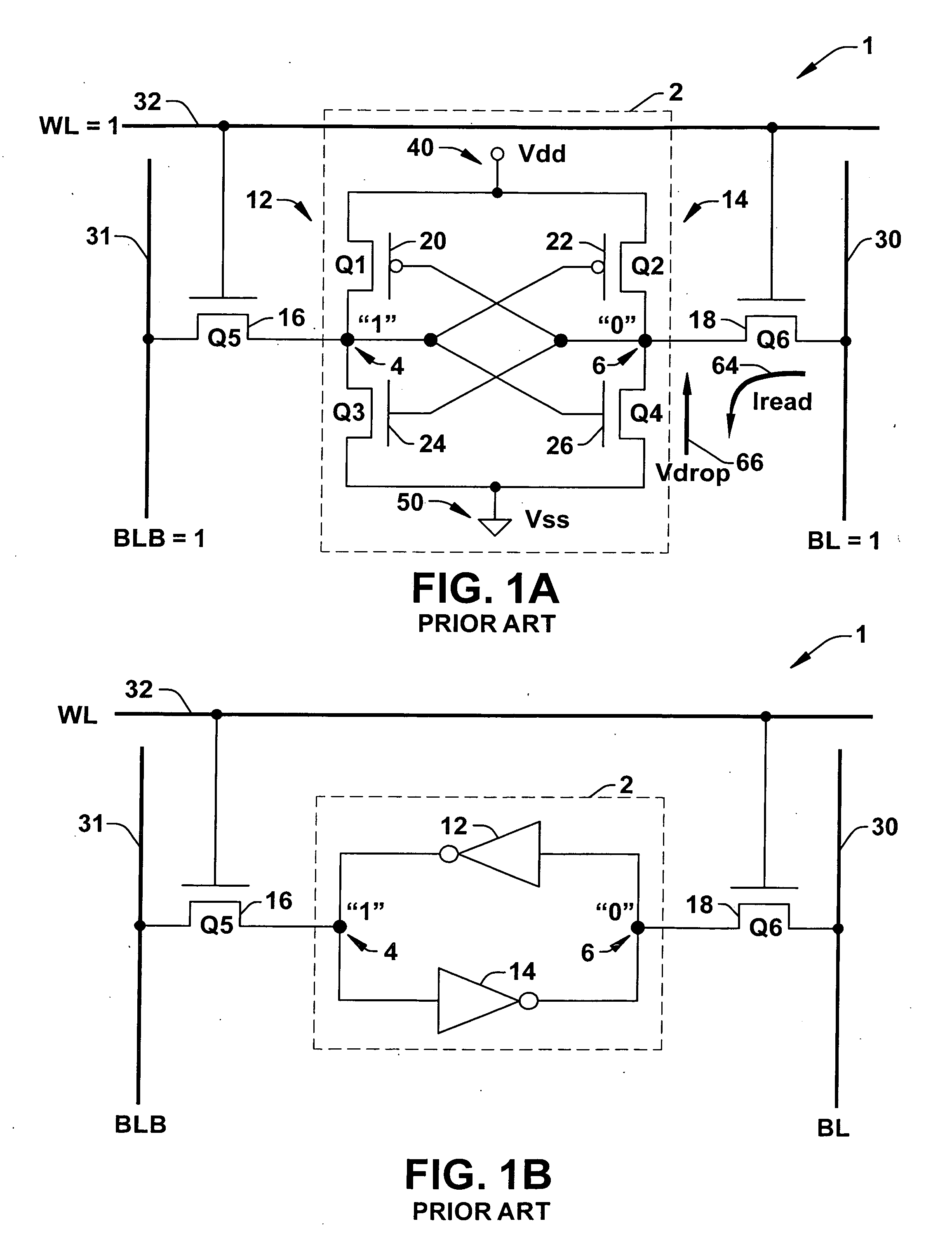
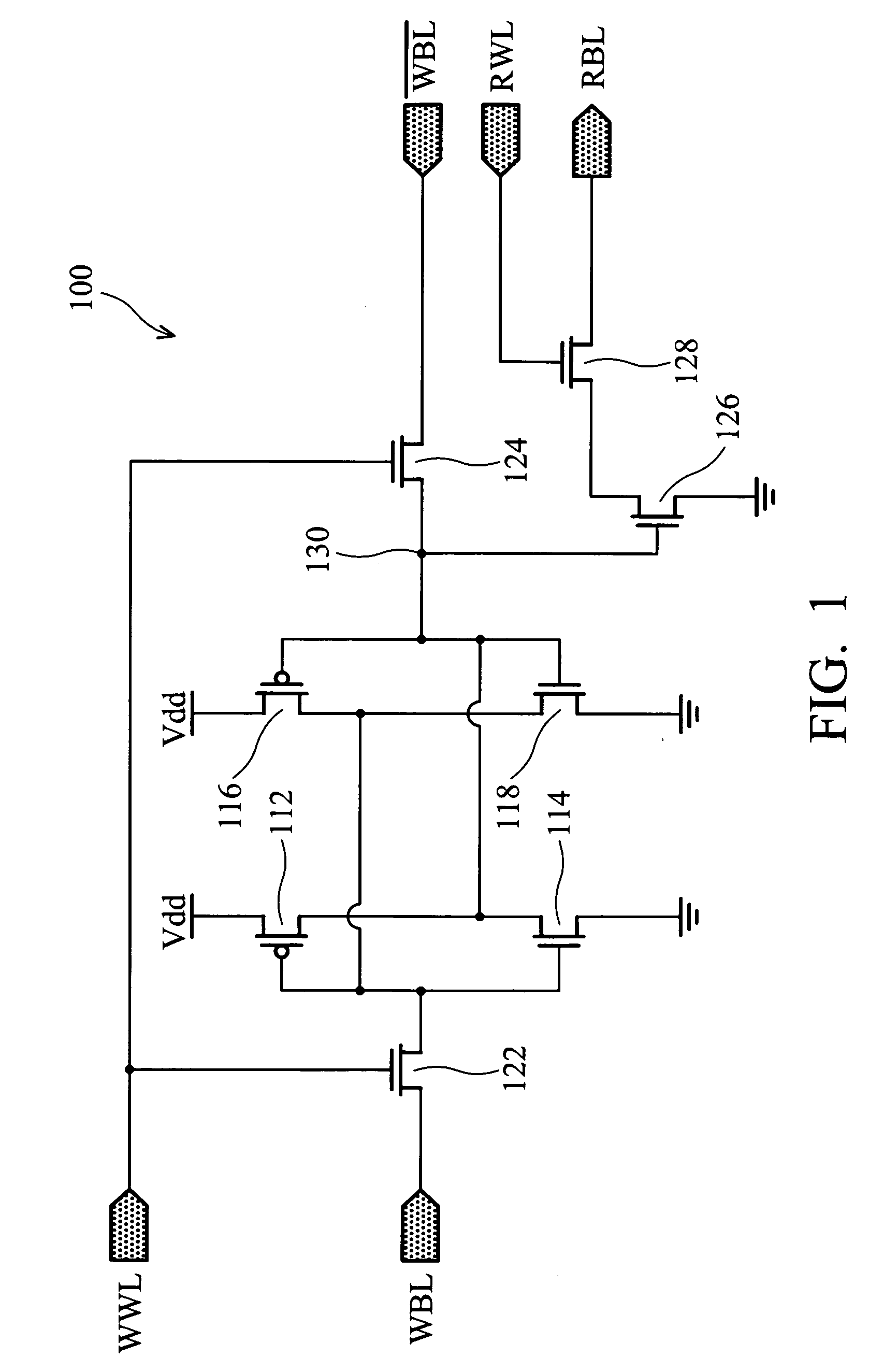
Low-power SRAM memory cell
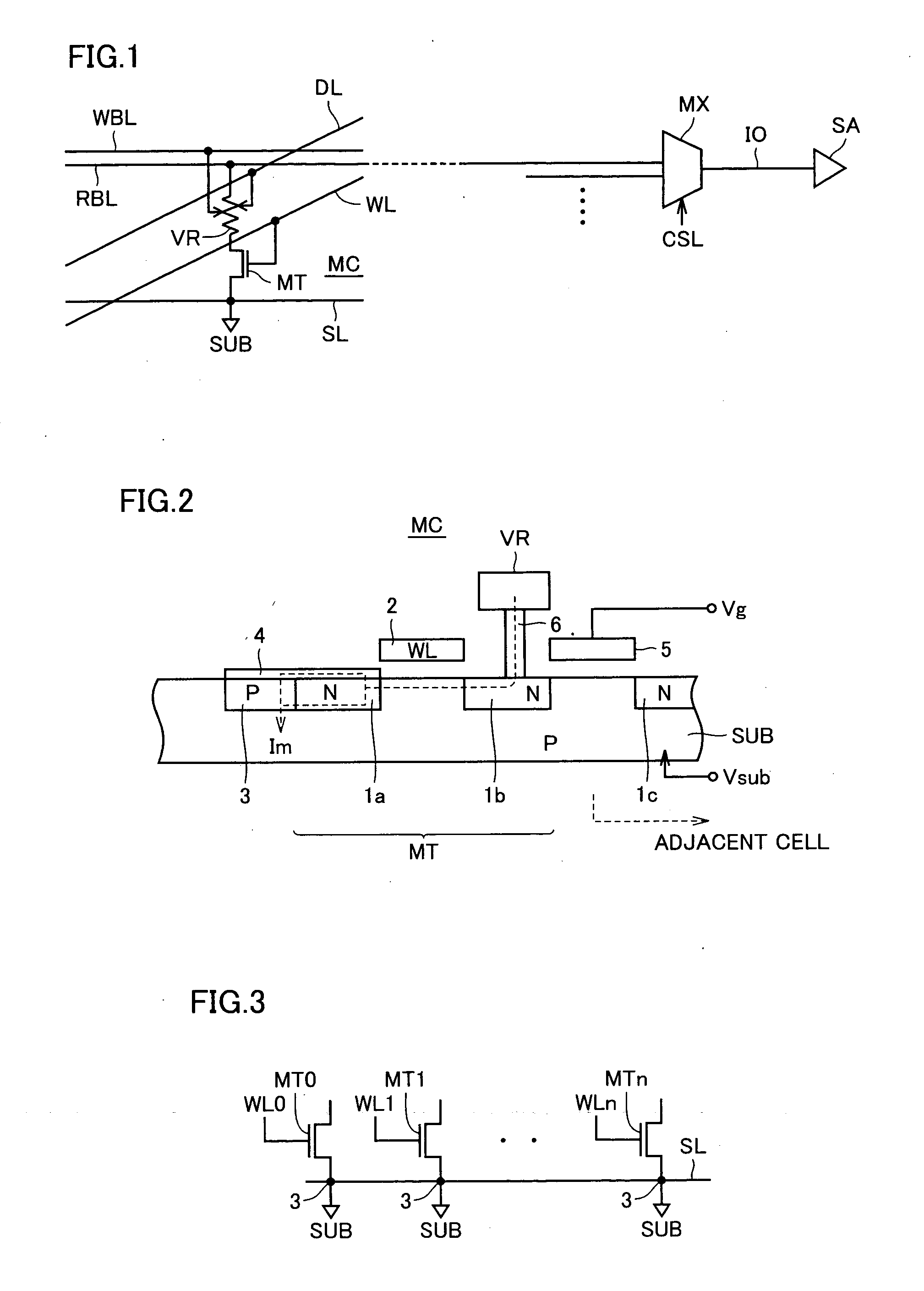
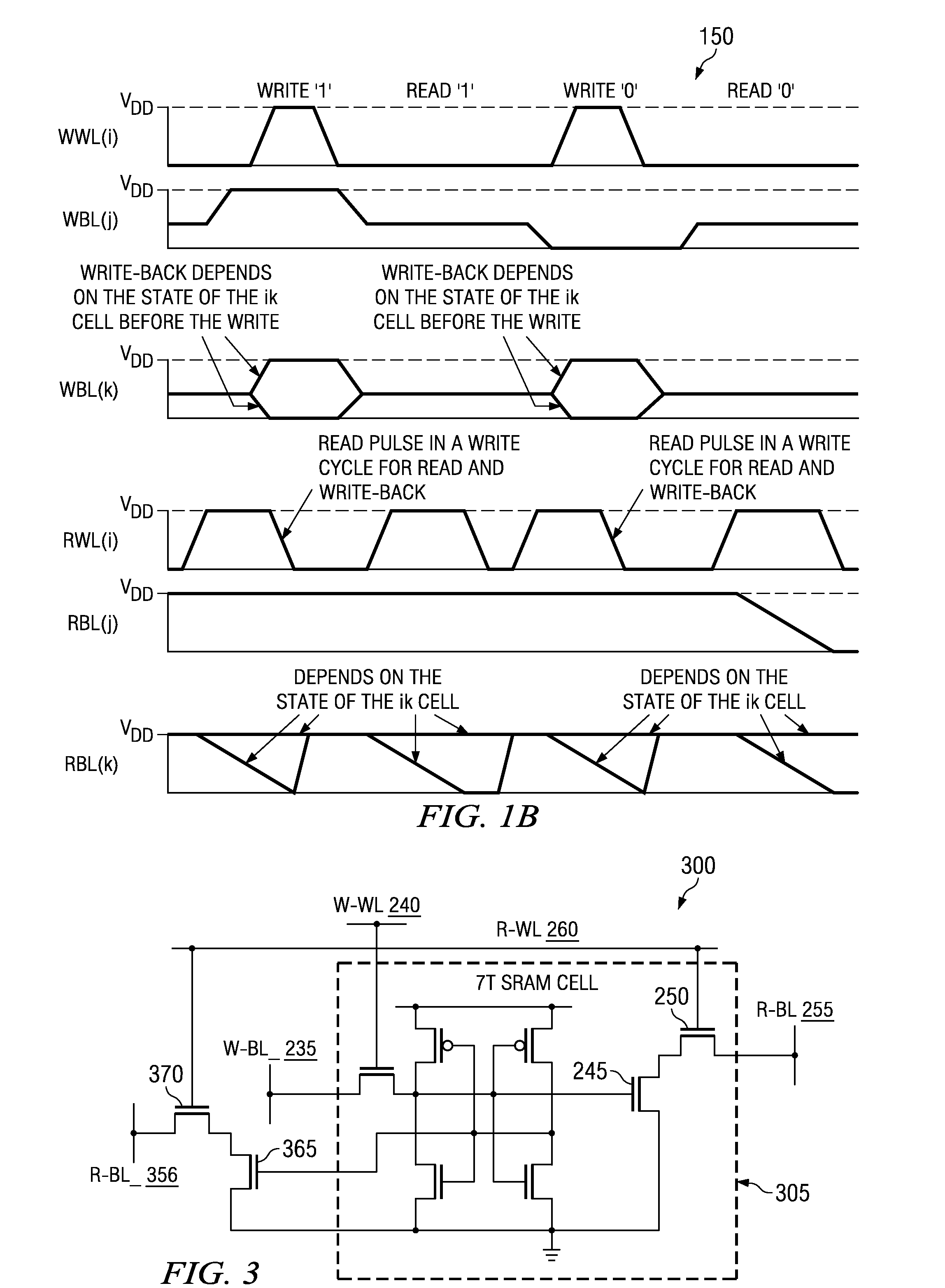
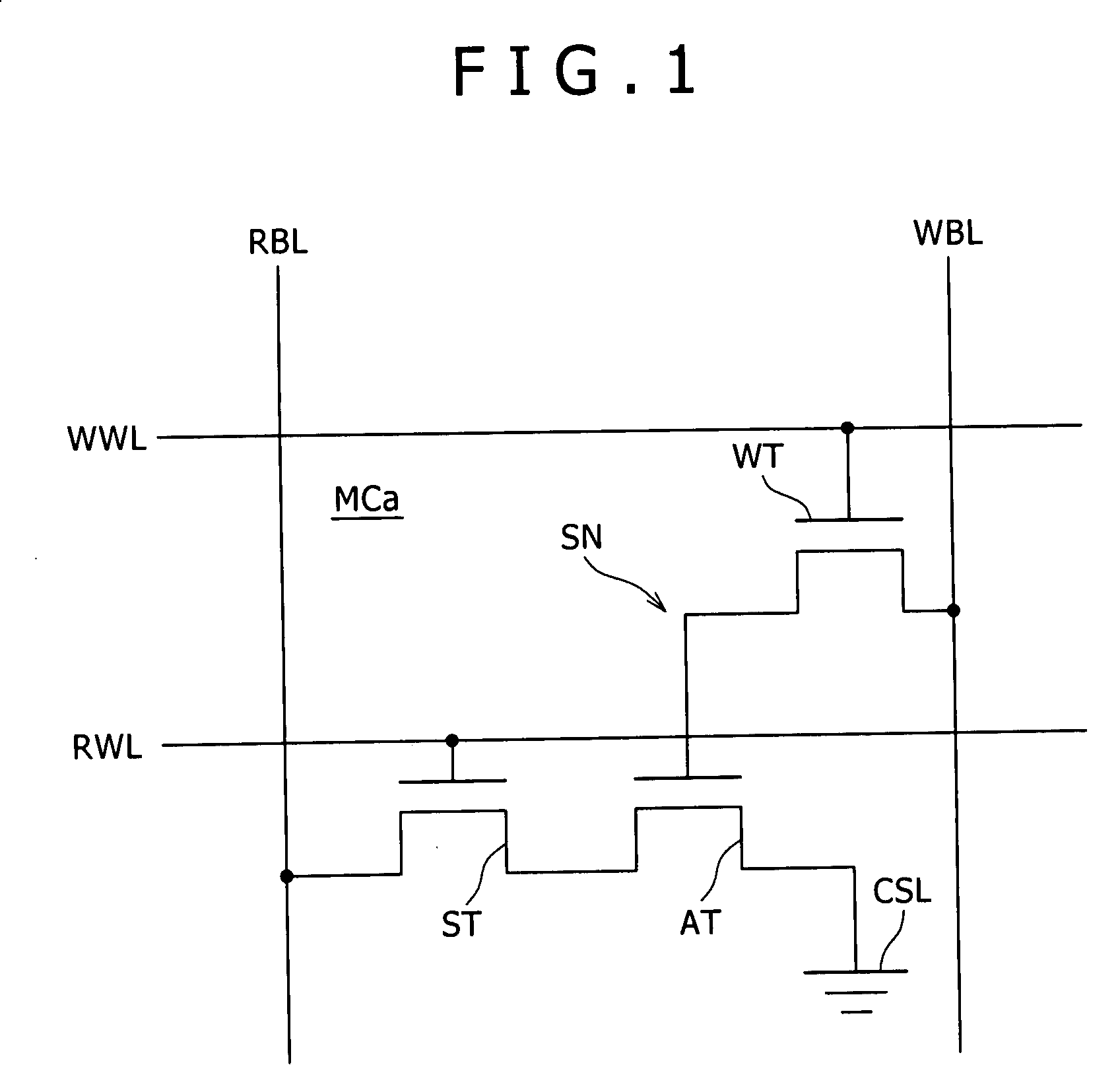
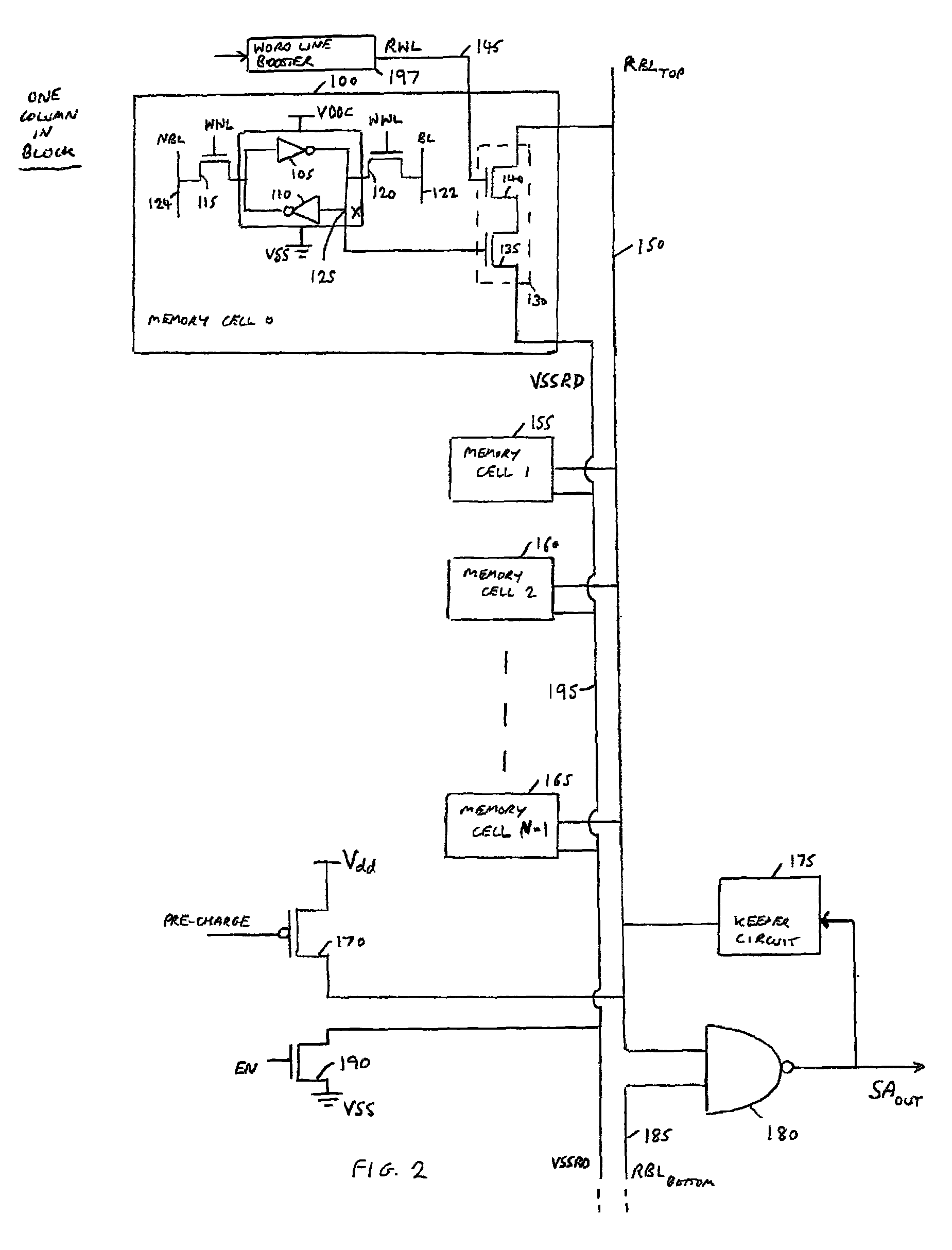
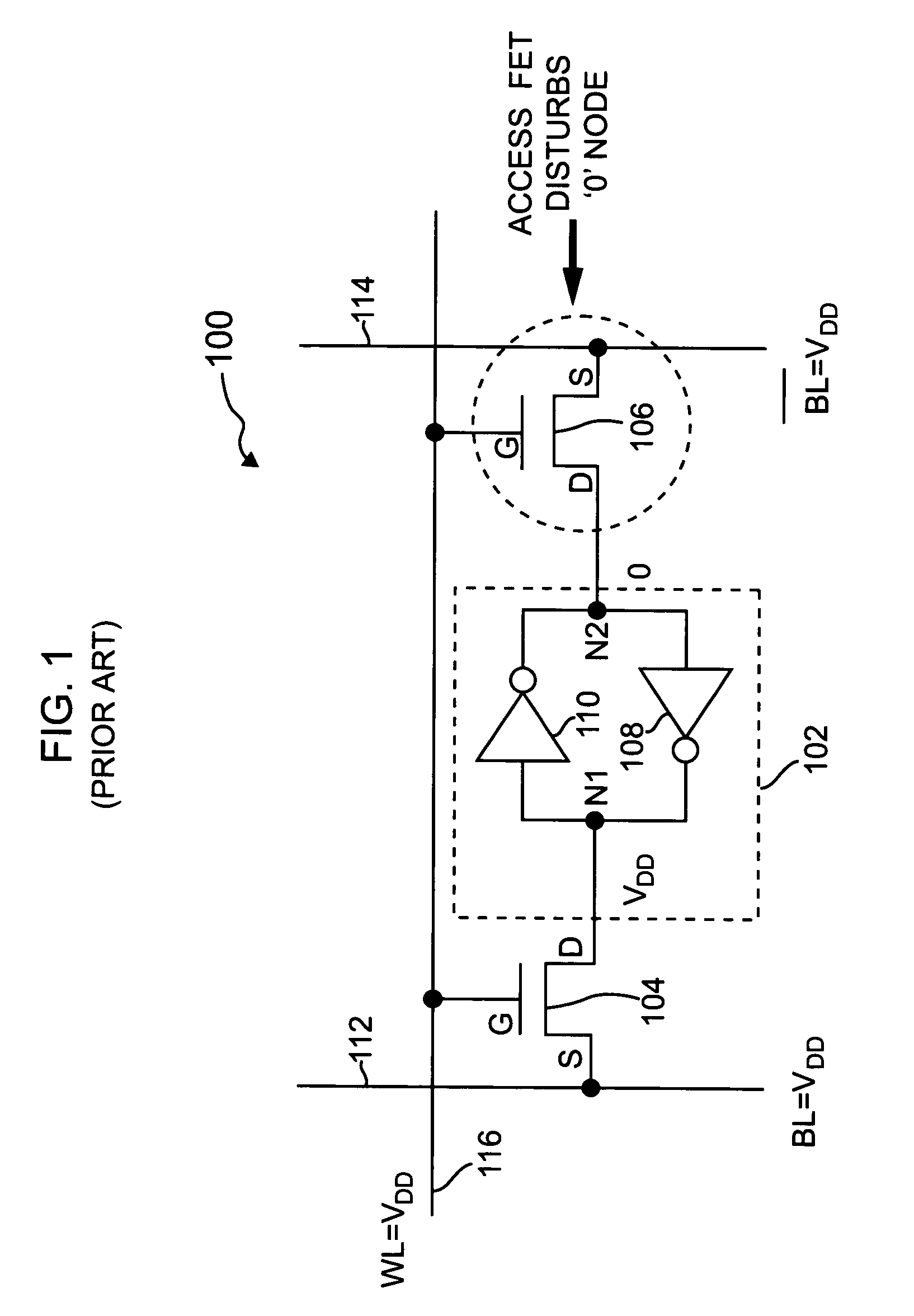
An SRAM memory cell that has a relatively small power consumption when writing a write value of ‘0’ to the memory cell includes cross-coupled first and second inverters, at least one read access transistor for selectively coupling a respective read bit line to a common connection node of a respective one of the first and second inverters, a switching transistor for selectively coupling the second inverter to a ground terminal, and a write access transistor for selectively coupling the common connection node of the second inverter to a write bit line.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Low-power SRAM memory cell
An SRAM memory cell that has a relatively small power consumption when writing a write value of ‘0’ to the memory cell includes cross-coupled first and second inverters, at least one read access transistor for selectively coupling a respective read bit line to a common connection node of a respective one of the first and second inverters, a switching transistor for selectively coupling the second inverter to a ground terminal, and a write access transistor for selectively coupling the common connection node of the second inverter to a write bit line.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
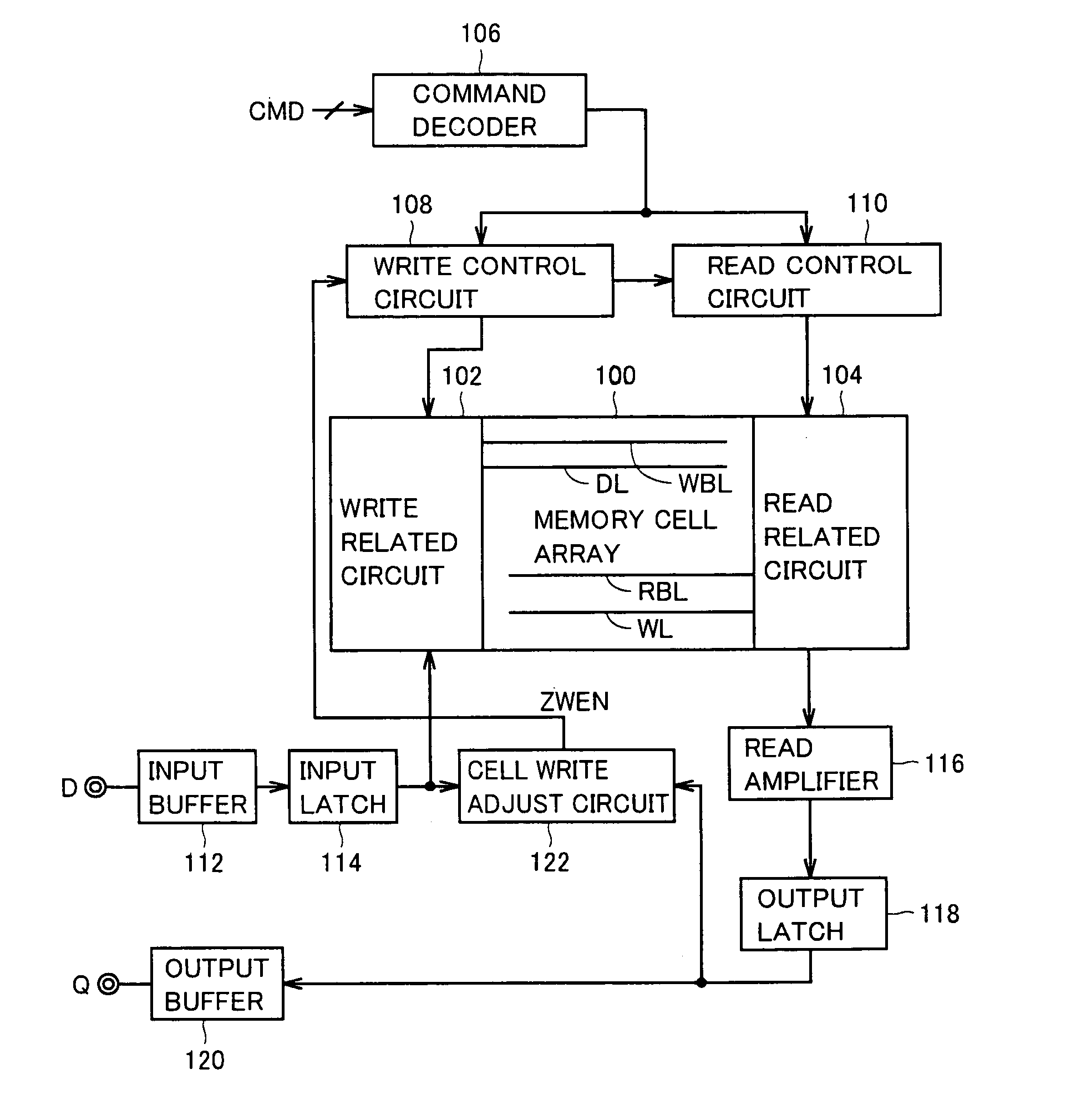
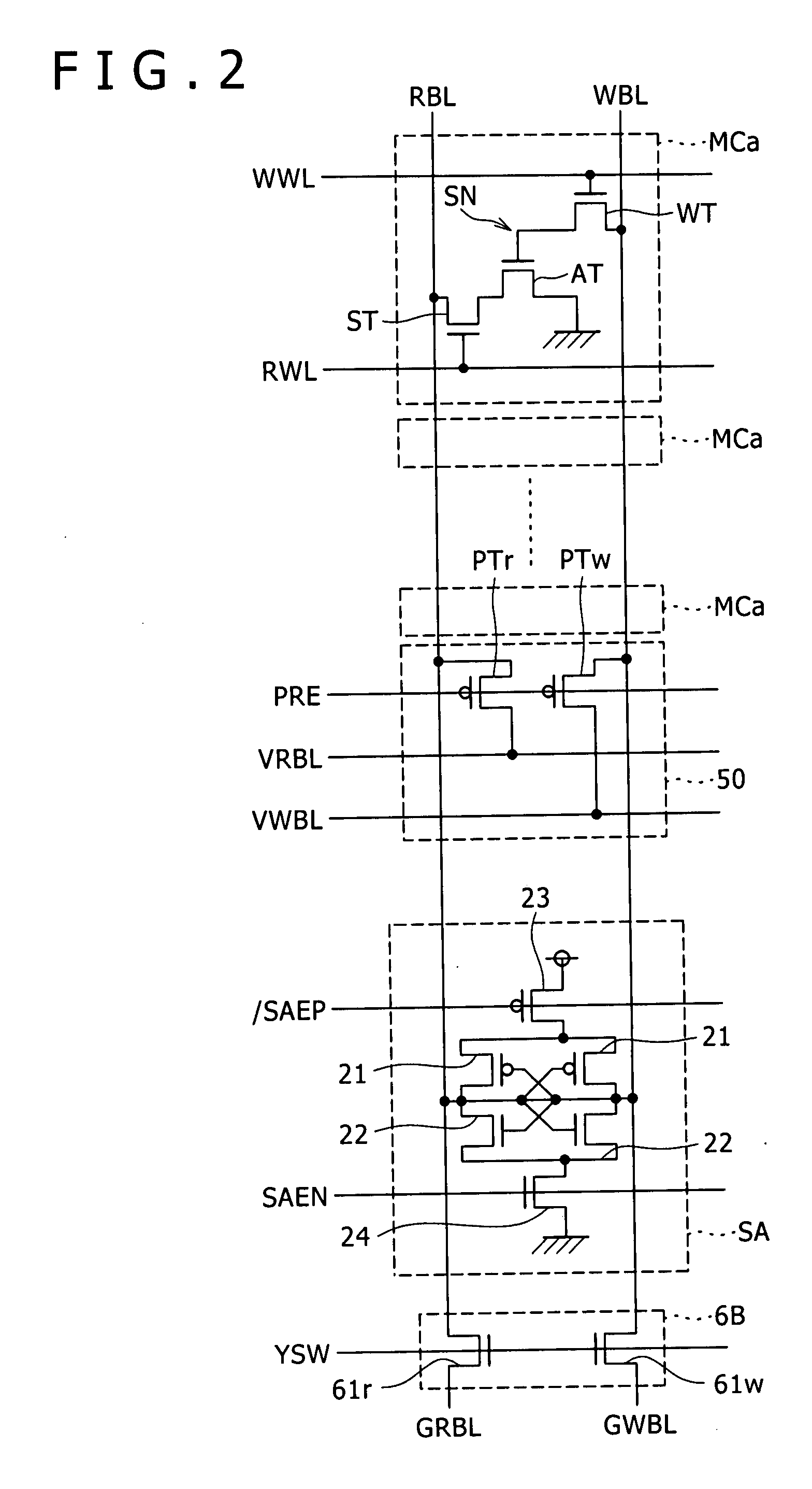
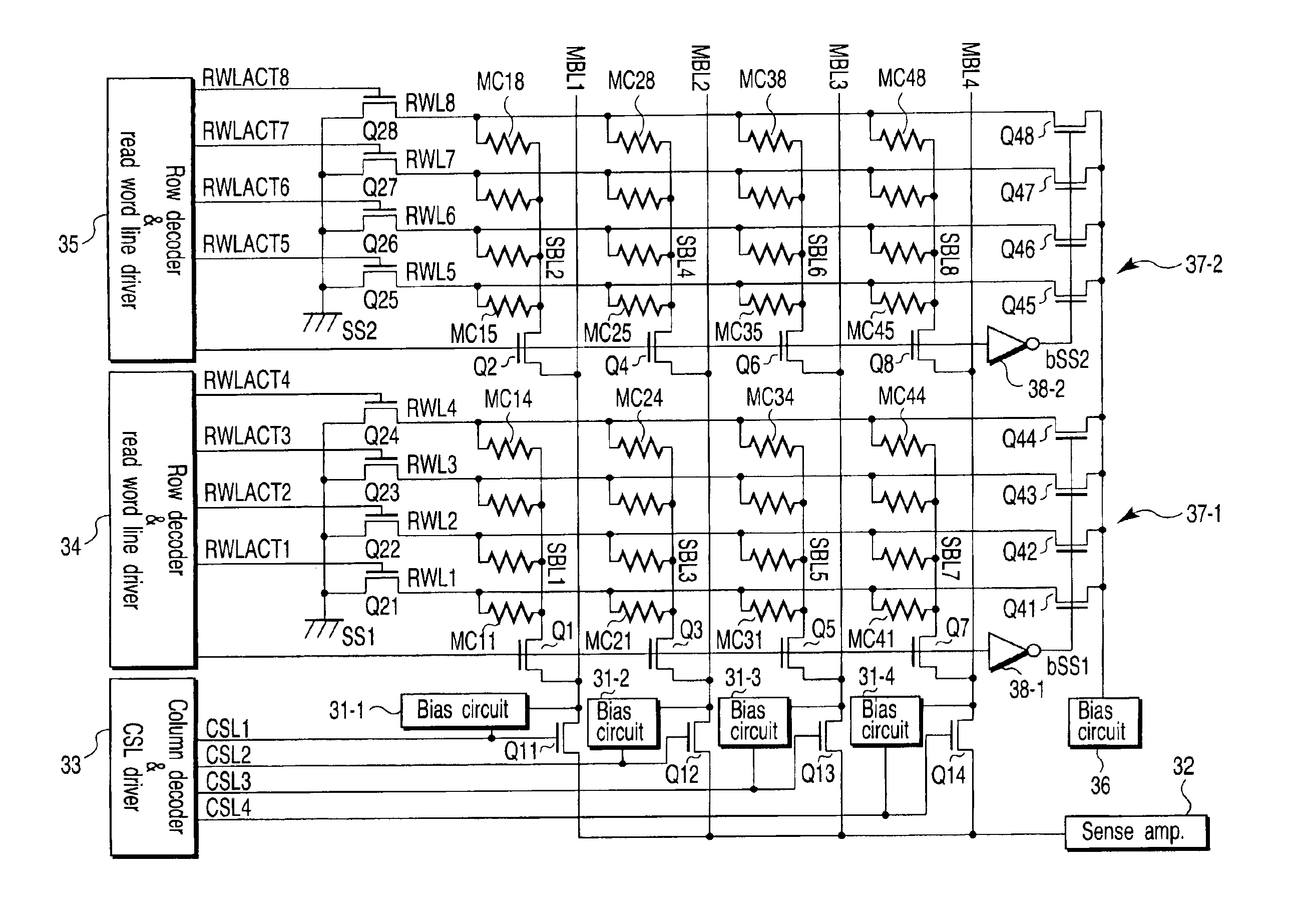
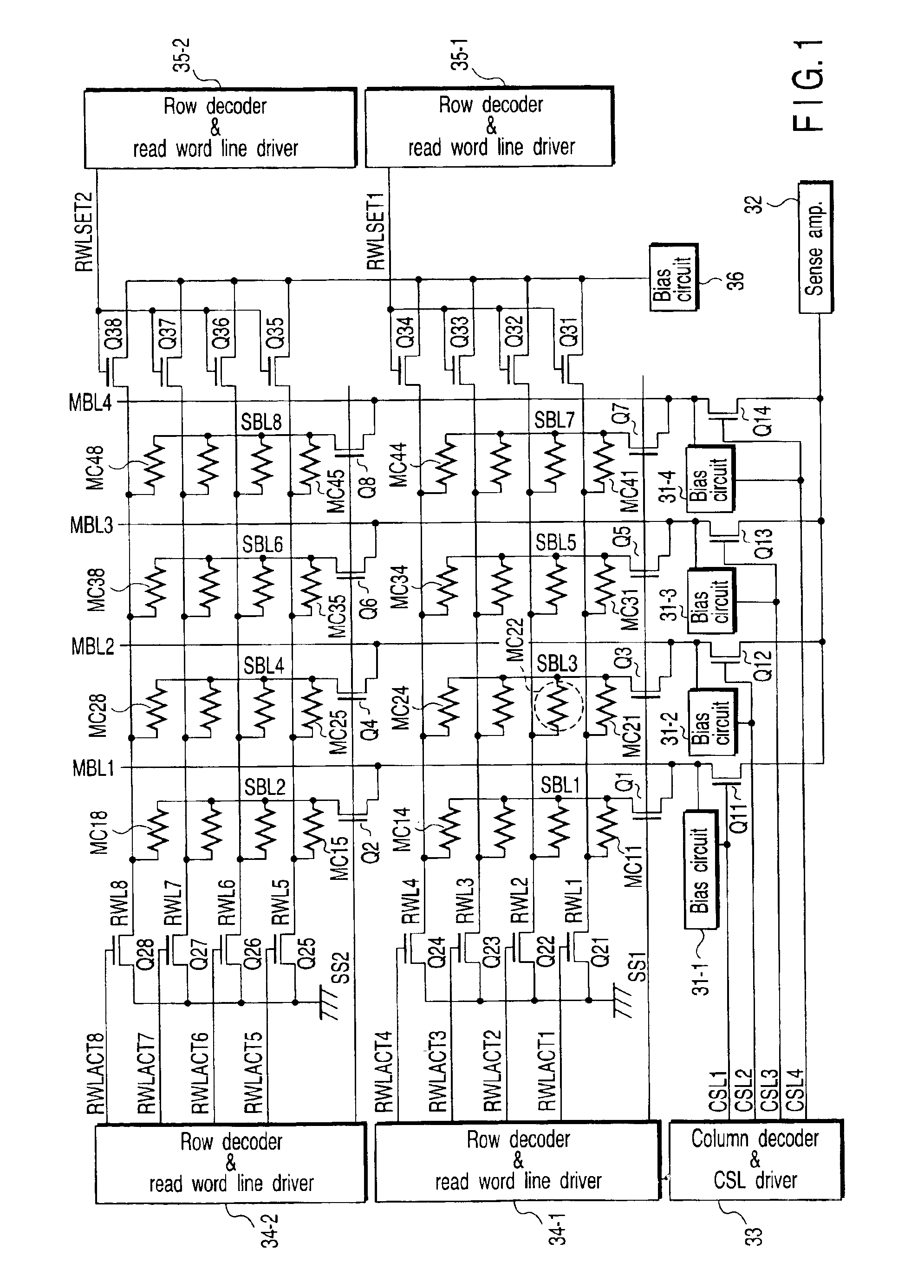
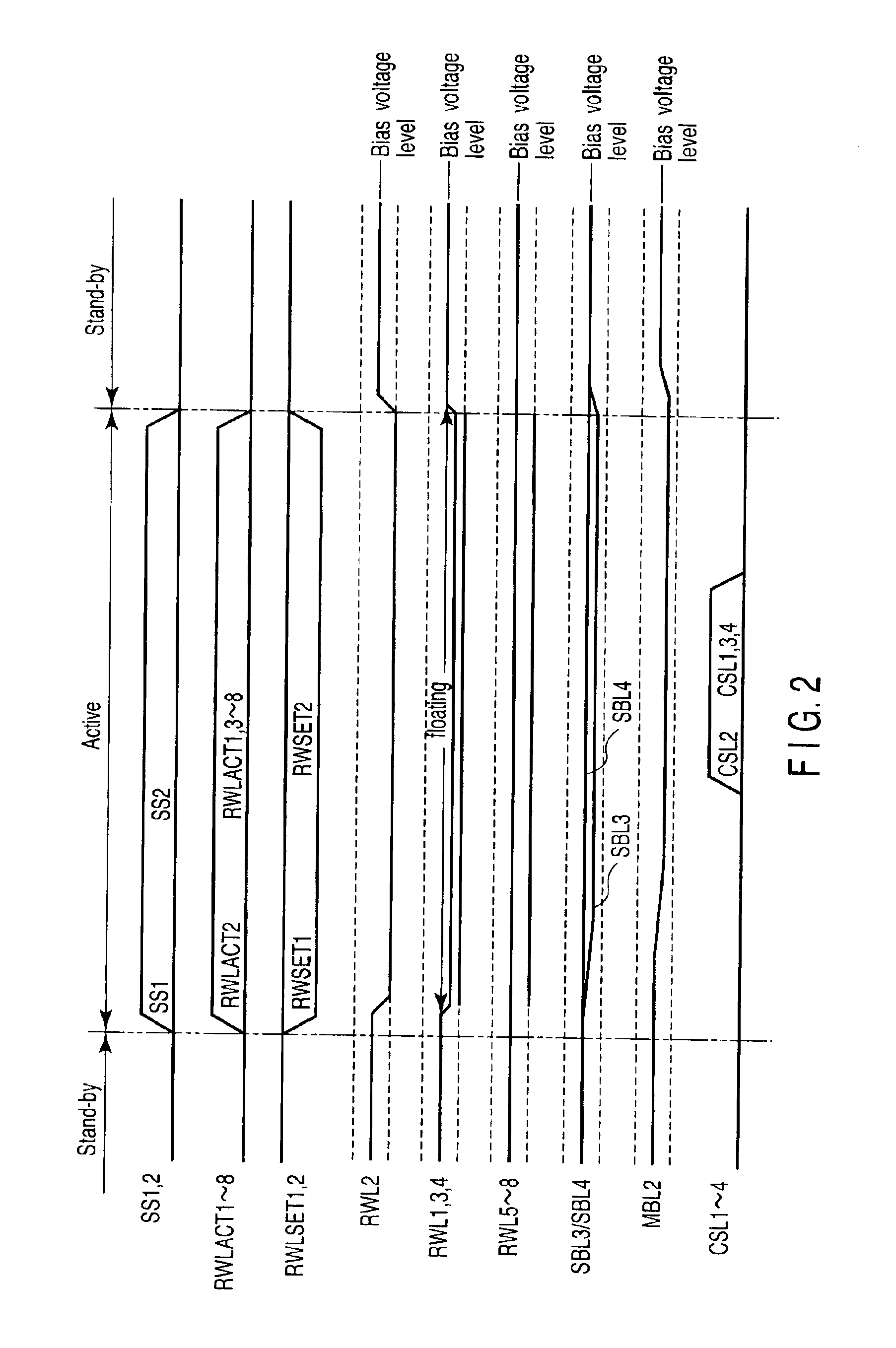
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device allowing concurrent data writing and data reading
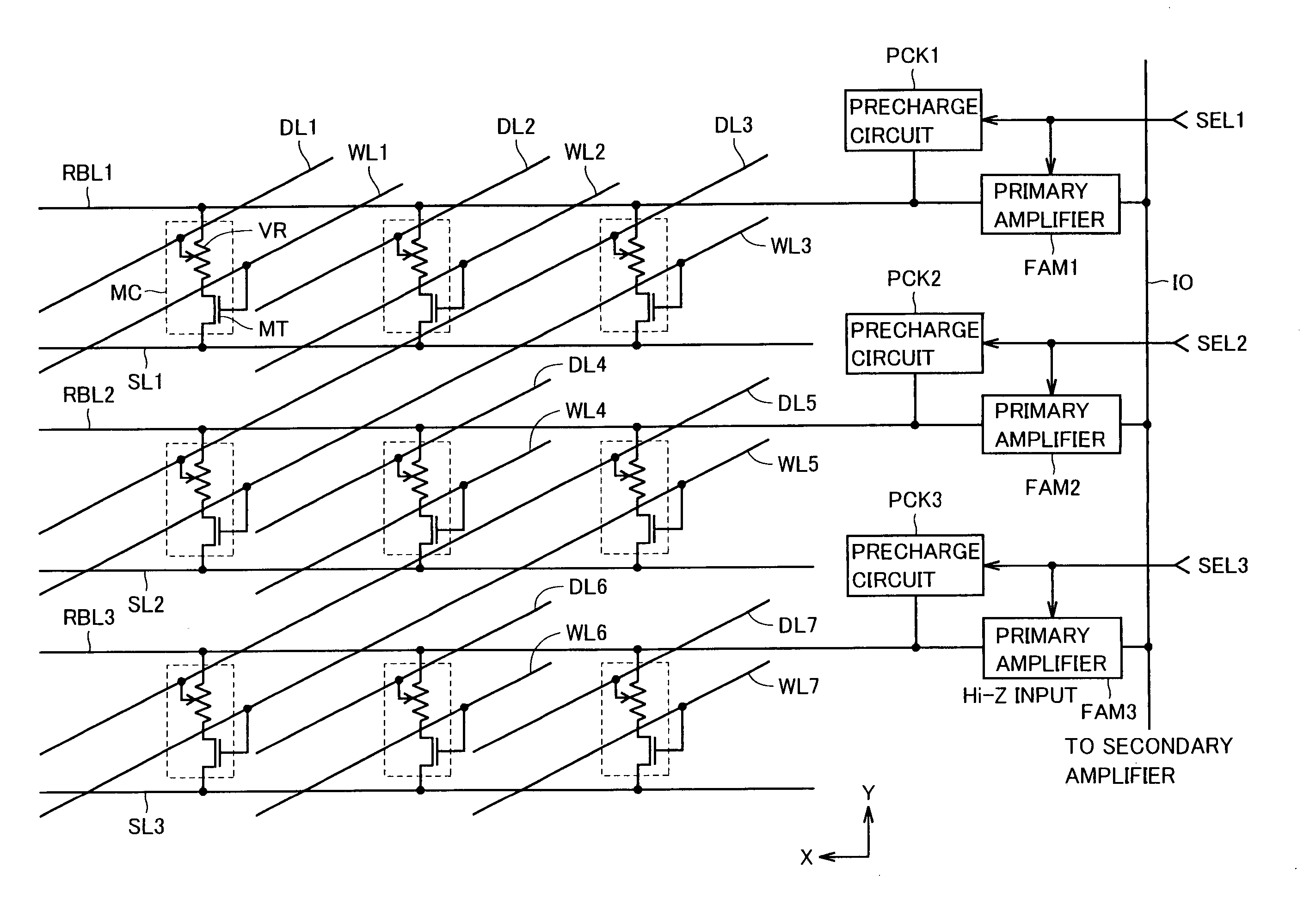
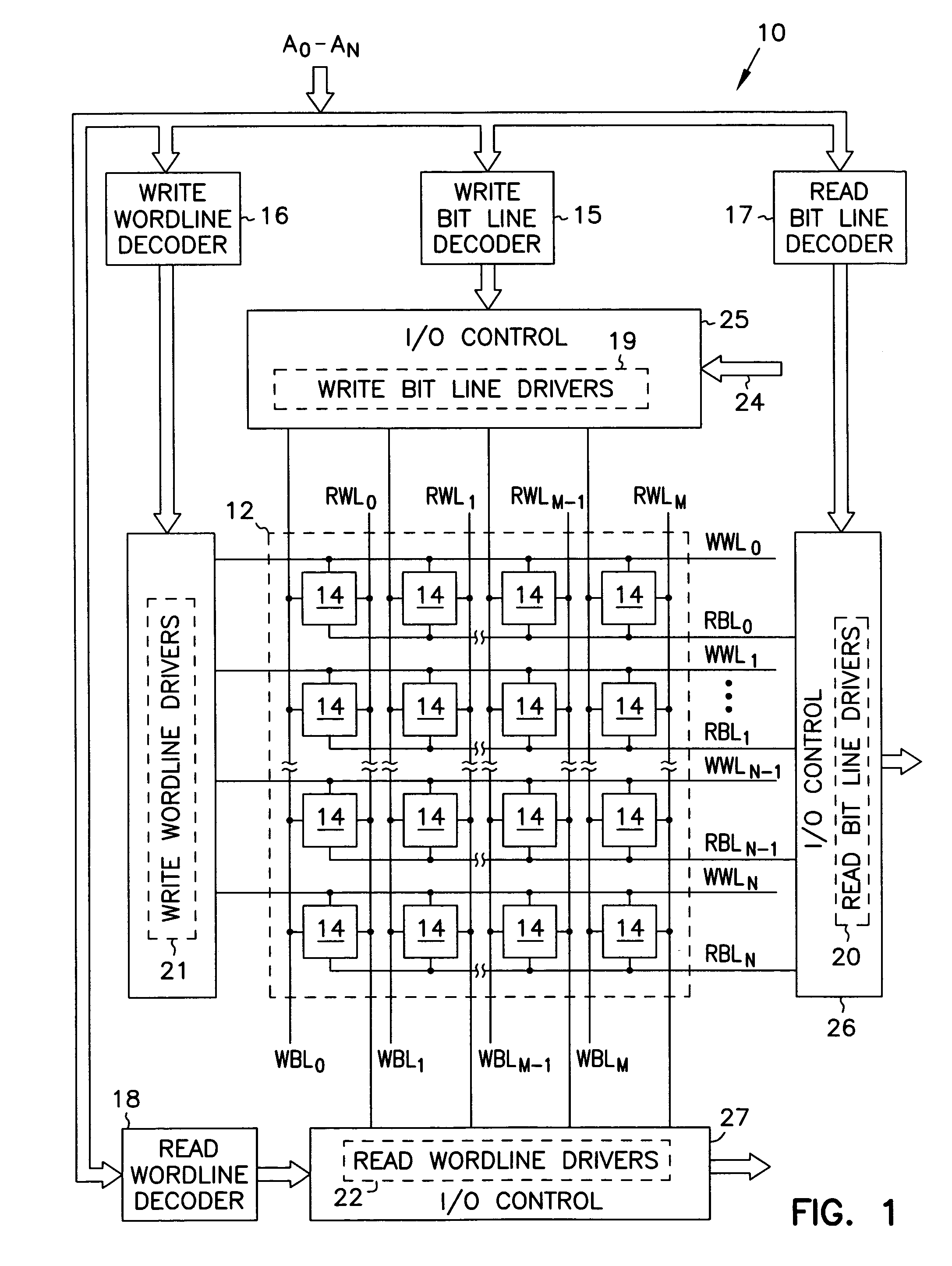
A write bit line and a read bit line are provided separately for a memory cell. A source line connecting to the memory cell is formed of a source impurity region the same in conductivity type as a substrate region. A memory cell transistor and the source impurity region are connected by a metal interconnection line of a low resistance. A rise in the source line potential can be prevented, and a memory cell current can reliably be generated according to storage data. Further, fast data reading can be achieved. Additionally, by performing precharging and data amplification in a unit of read bit line, the load of the read bit line can be alleviated to achieve fast reading. An accessing time of a non-volatile semiconductor memory device that uses a variable resistance element as a storage element is reduced without increasing the current consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20110182110A1Reduce power consumptionNovel structureSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesWrite bitEngineering
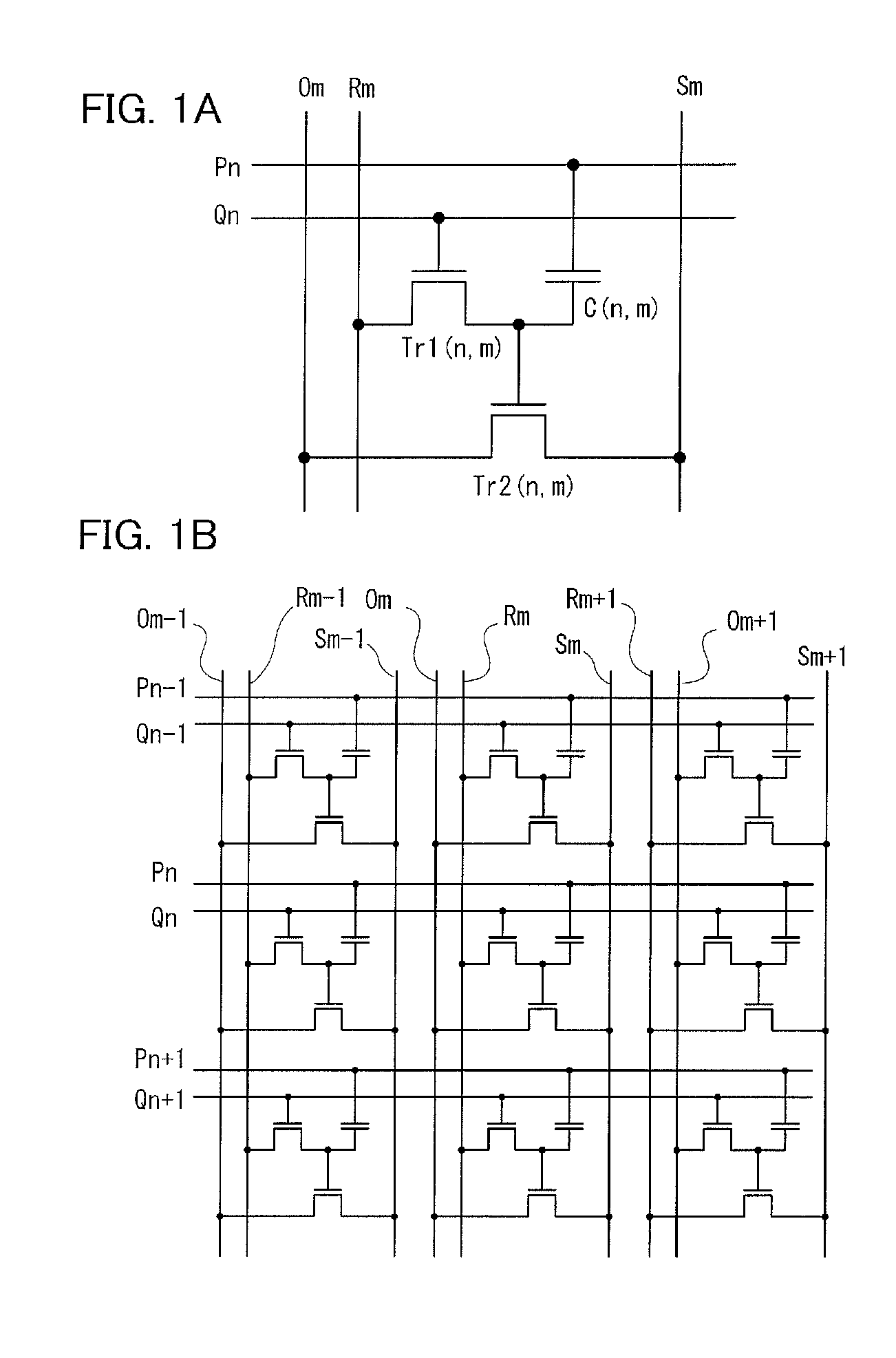
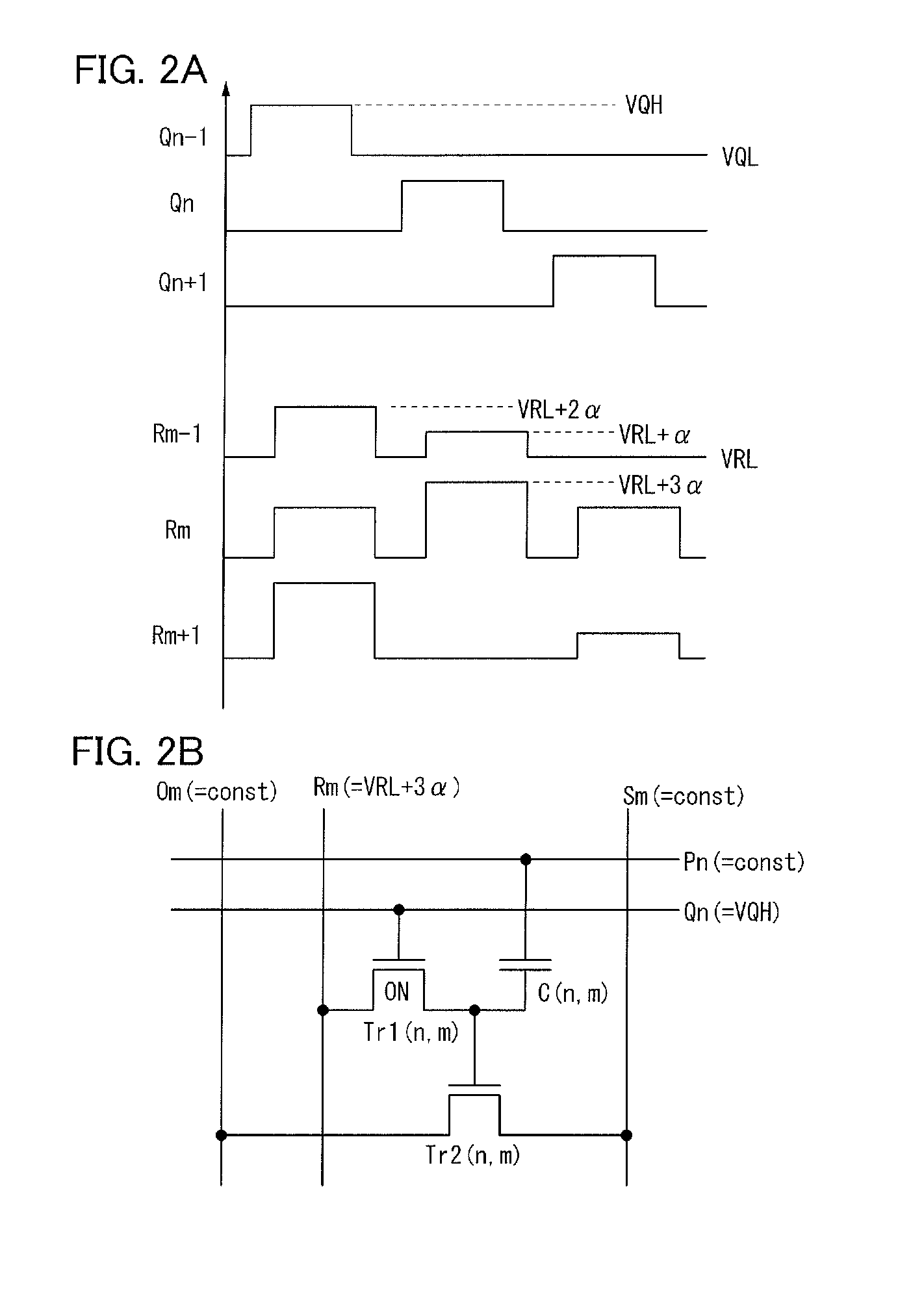
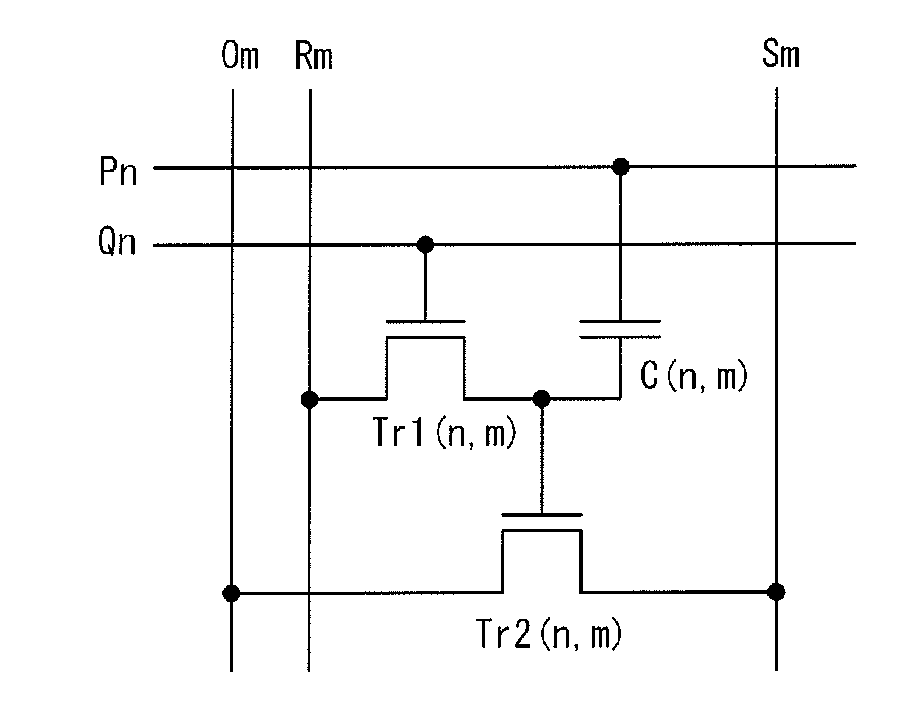
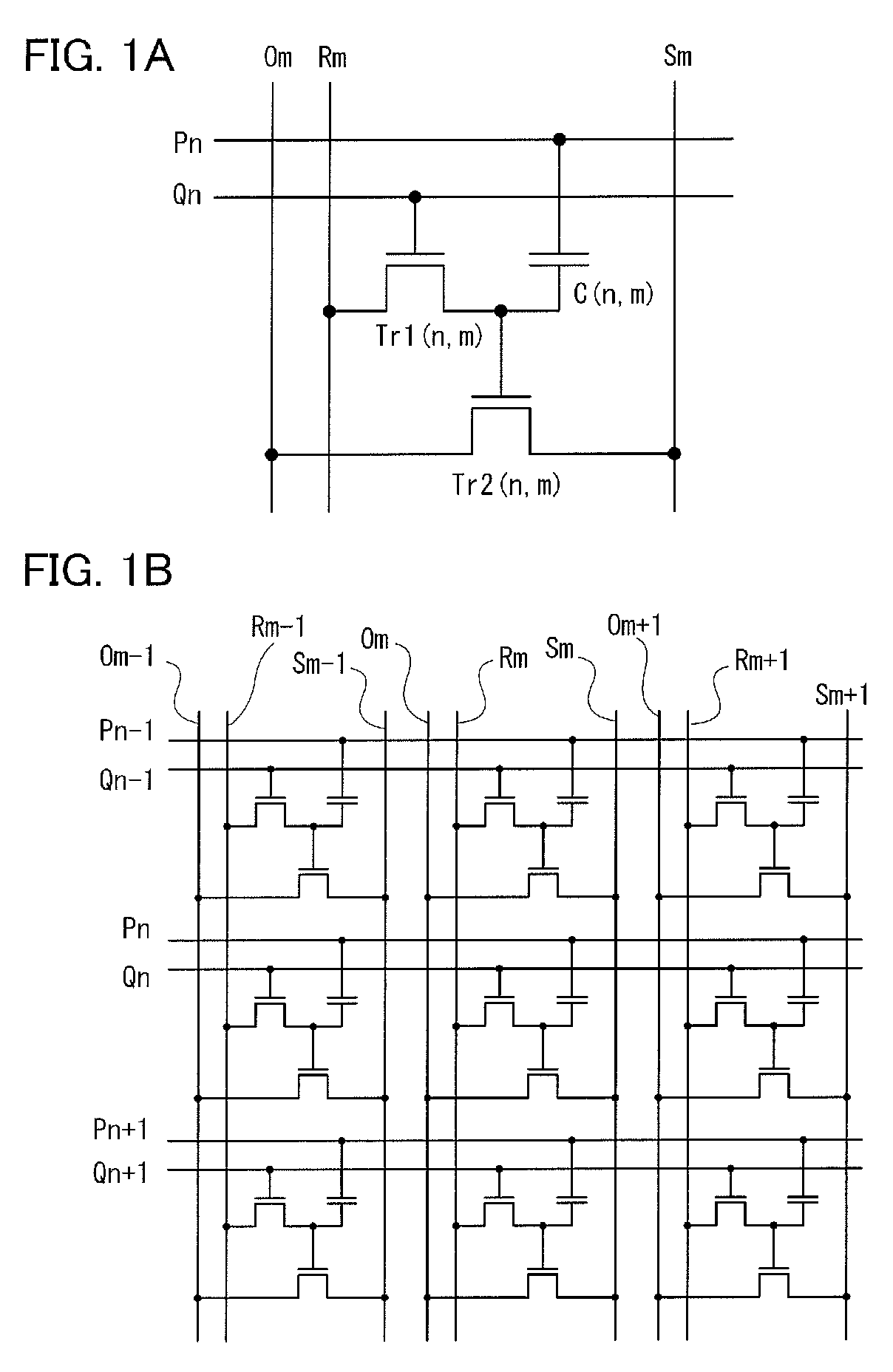
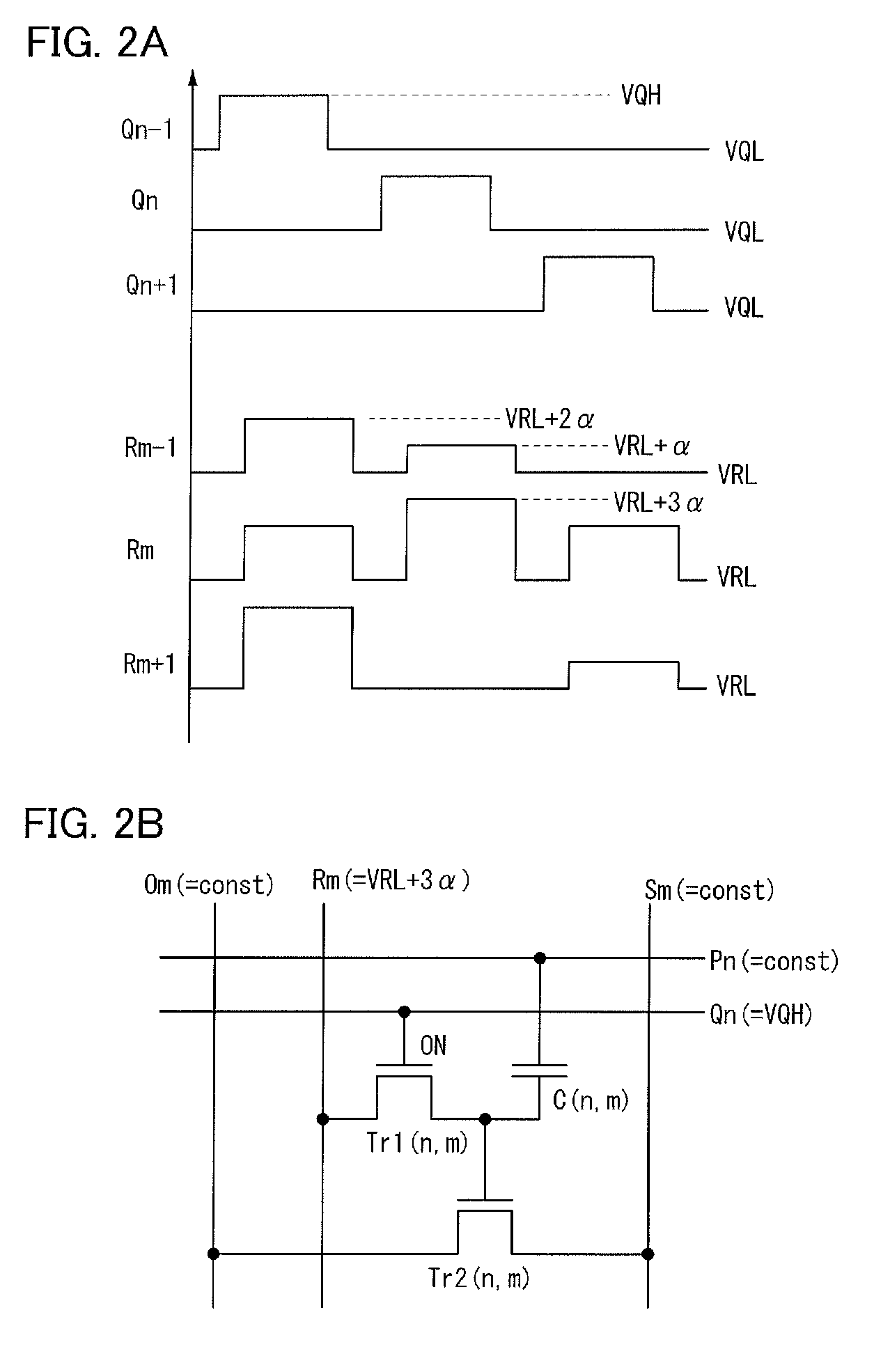
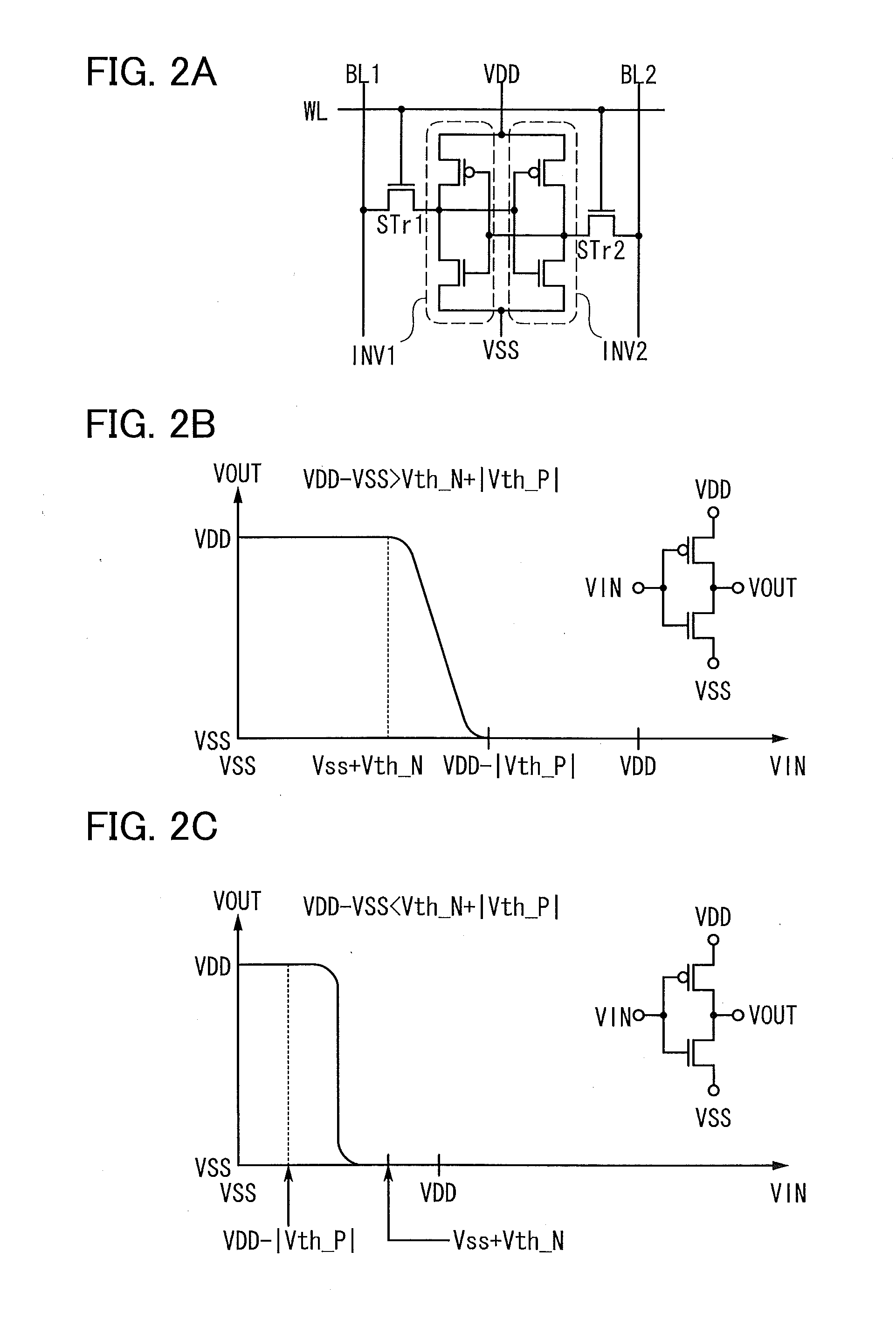
A semiconductor device which stores data by using a transistor whose leakage current between source and drain in an off state is small as a writing transistor. In a matrix including a plurality of memory cells in which a drain of the writing transistor is connected to a gate of a reading transistor and the drain of the writing transistor is connected to one electrode of a capacitor, a gate of the writing transistor is connected to a writing word line; a source of the writing transistor is connected to a writing bit line; and a source and a drain of the reading transistor are connected to a reading bit line and a bias line. In order to reduce the number of wirings, the writing bit line or the bias line is substituted for the reading bit line in another column.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Combination field programmable gate array allowing dynamic reprogrammability and non-votatile programmability based upon transistor gate oxide breakdown
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP +1
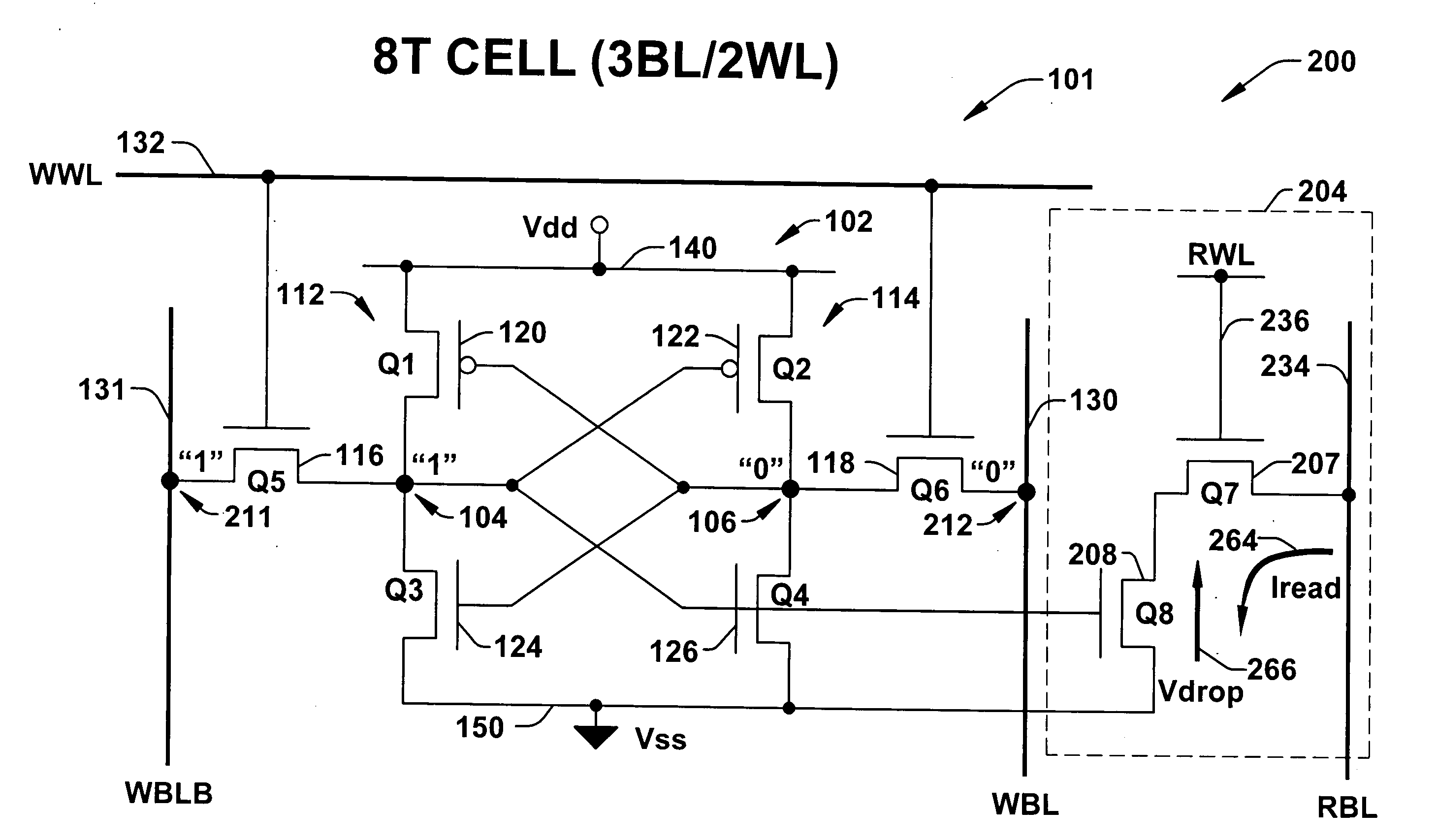
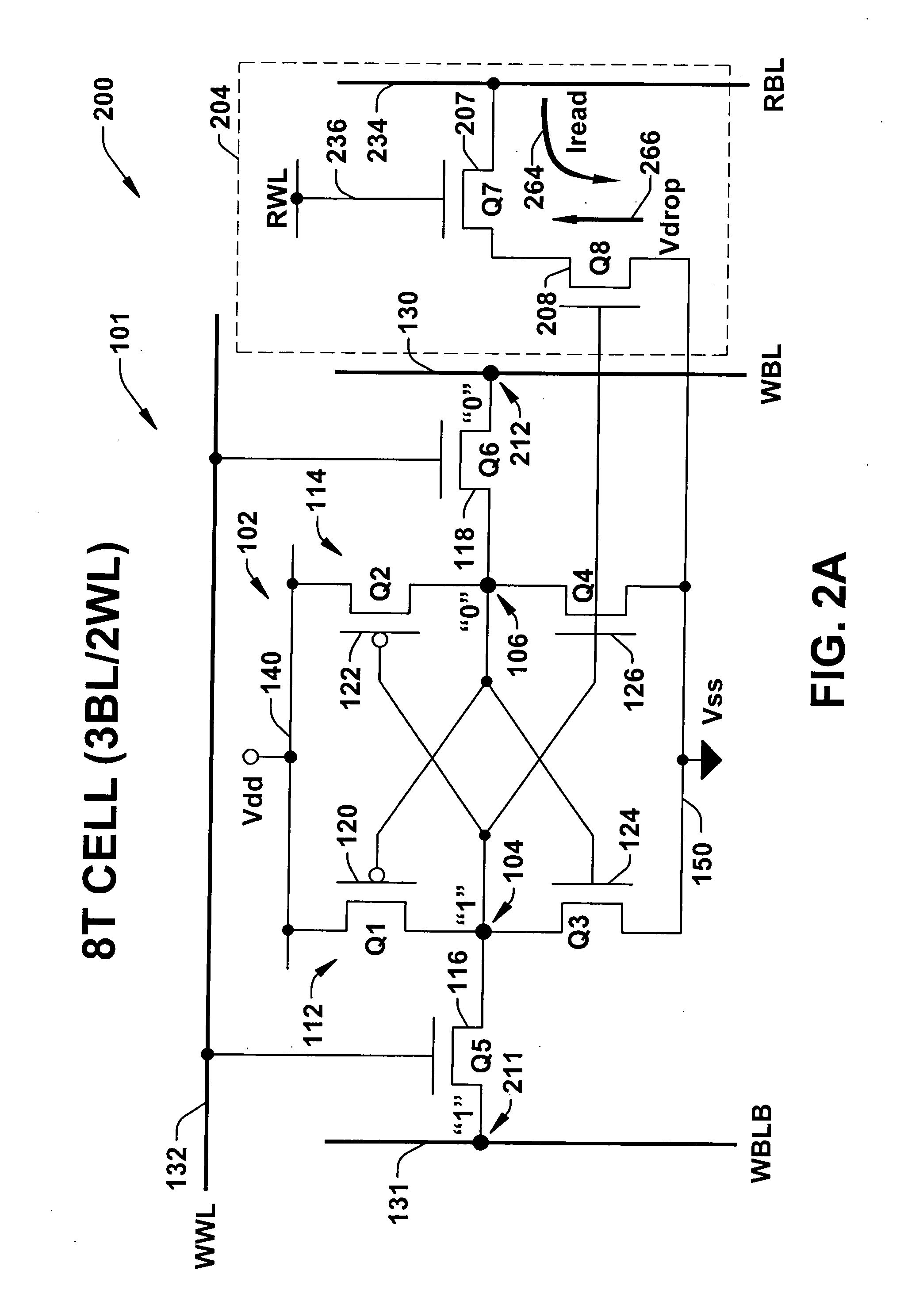
8T SRAM cell with higher voltage on the read WL
ActiveUS20070279966A1Avoid dataHigh voltageDigital storageSemiconductor devicesHemt circuitsVoltage source
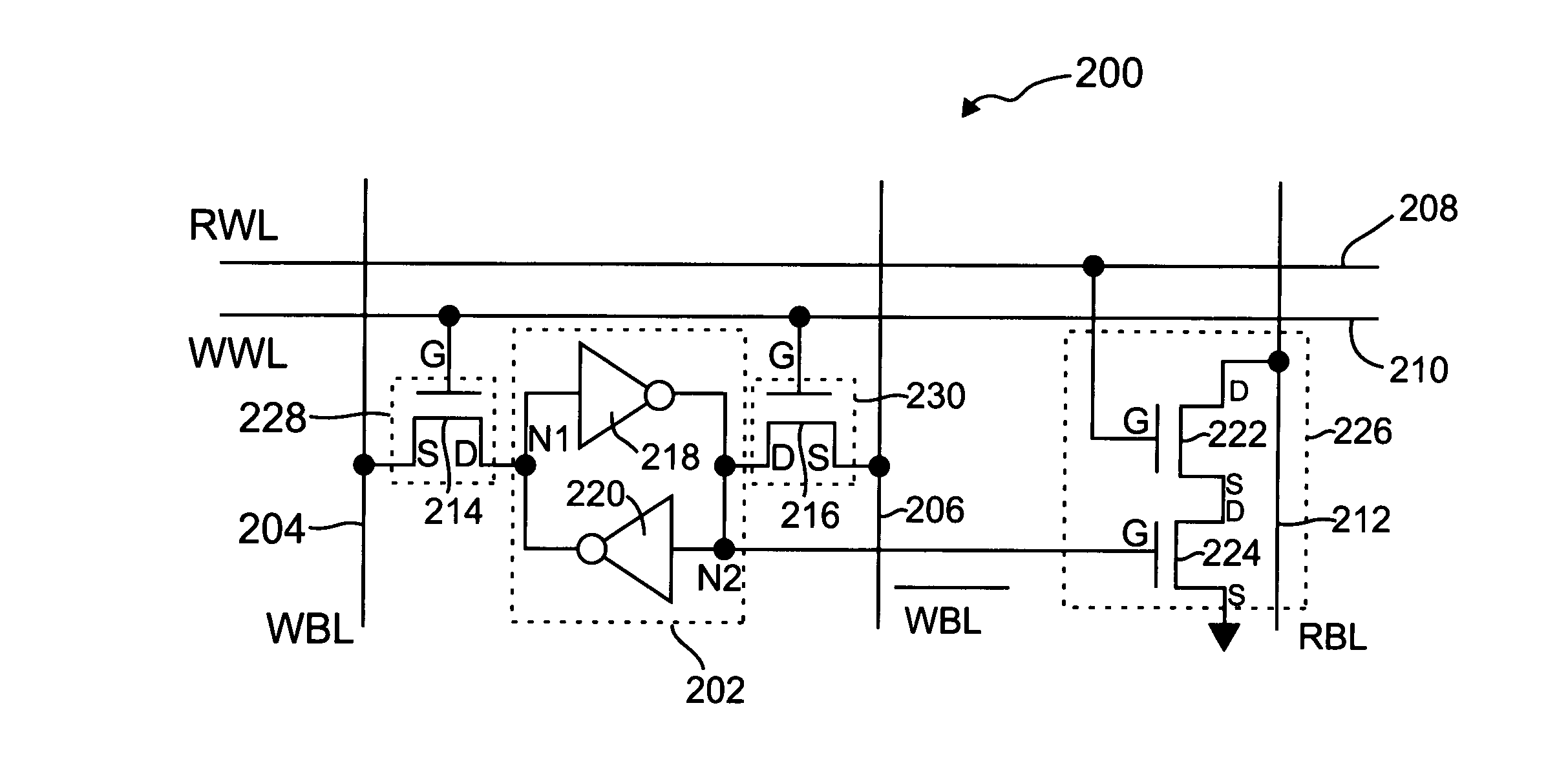
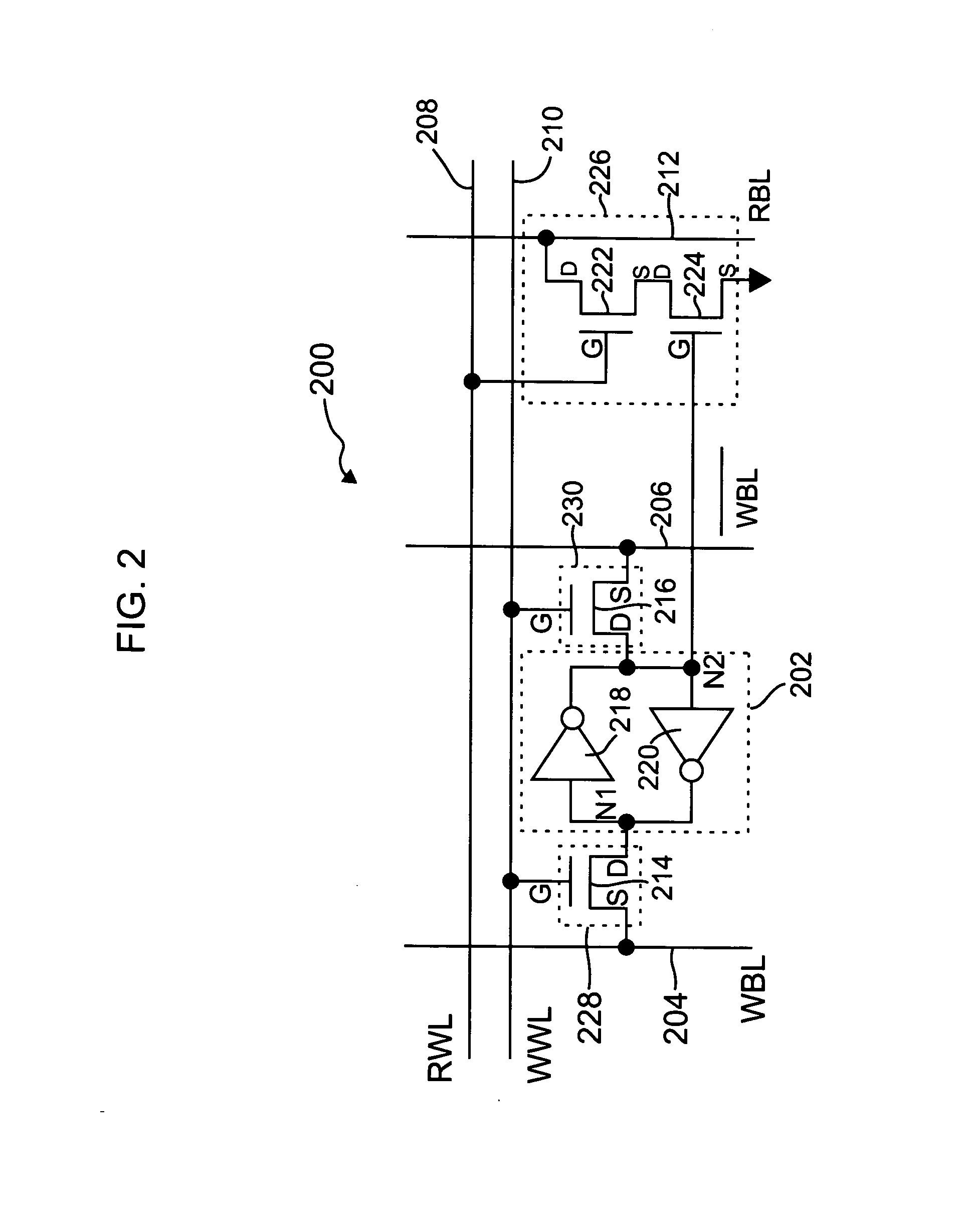
The present invention provides circuitry for writing to and reading from an SRAM cell core, an SRAM cell, and an SRAM device. In one aspect, the circuitry includes a write circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core that includes a write transistor gated by a write word line. The circuitry also includes a read buffer circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core to read the cell without disturbing the state of the cell. The read buffer circuit includes a read transistor gated by a read word line, the read transistor coupled between a read bit-line and a read driver transistor that is further coupled to a voltage source Vss. The read driver transistor and a first driver transistor of the cell core are both gated by one output of the cell core. The read transistor has an electrical characteristic that differs from that of the core cell first driver transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Magnetic random access memory
A read block is constituted of a plurality of TMR elements arranged in a lateral direction. One end of each of the TMR elements in the read block is connected in common, and connected to a source line via a read select switch. The other ends of TMR elements are independently connected to read bit lines / write word lines. The read bit lines / write word lines are connected to common data lines via a row select switch. The common data lines are connected to a read circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
A write bit line and a read bit line are provided separately for a memory cell. A source line connecting to the memory cell is formed of a source impurity region the same in conductivity type as a substrate region. A memory cell transistor and the source impurity region are connected by a metal interconnection line of a low resistance. A rise in the source line potential can be prevented, and a memory cell current can reliably be generated according to storage data. Further, fast data reading can be achieved. Additionally, by performing precharging and data amplification in a unit of read bit line, the load of the read bit line can be alleviated to achieve fast reading. An accessing time of a non-volatile semiconductor memory device that uses a variable resistance element as a storage element is reduced without increasing the current consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
8T SRAM cell with higher voltage on the read WL
ActiveUS7400523B2Avoid dataHigh voltageDigital storageSemiconductor devicesHemt circuitsVoltage source
The present invention provides circuitry for writing to and reading from an SRAM cell core, an SRAM cell, and an SRAM device. In one aspect, the circuitry includes a write circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core that includes a write transistor gated by a write word line. The circuitry also includes a read buffer circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core to read the cell without disturbing the state of the cell. The read buffer circuit includes a read transistor gated by a read word line, the read transistor coupled between a read bit-line and a read driver transistor that is further coupled to a voltage source Vss. The read driver transistor and a first driver transistor of the cell core are both gated by one output of the cell core. The read transistor has an electrical characteristic that differs from that of the core cell first driver transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
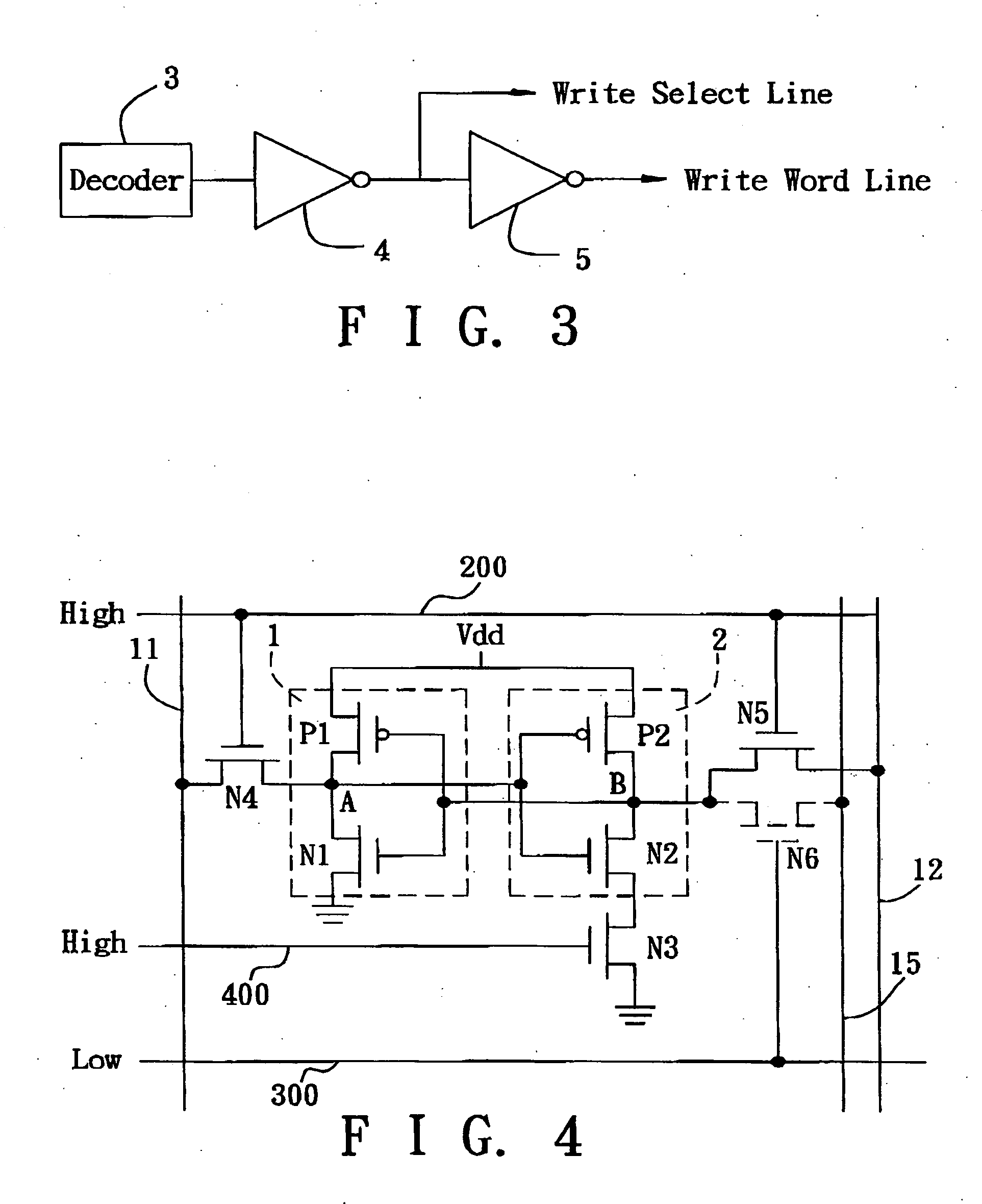
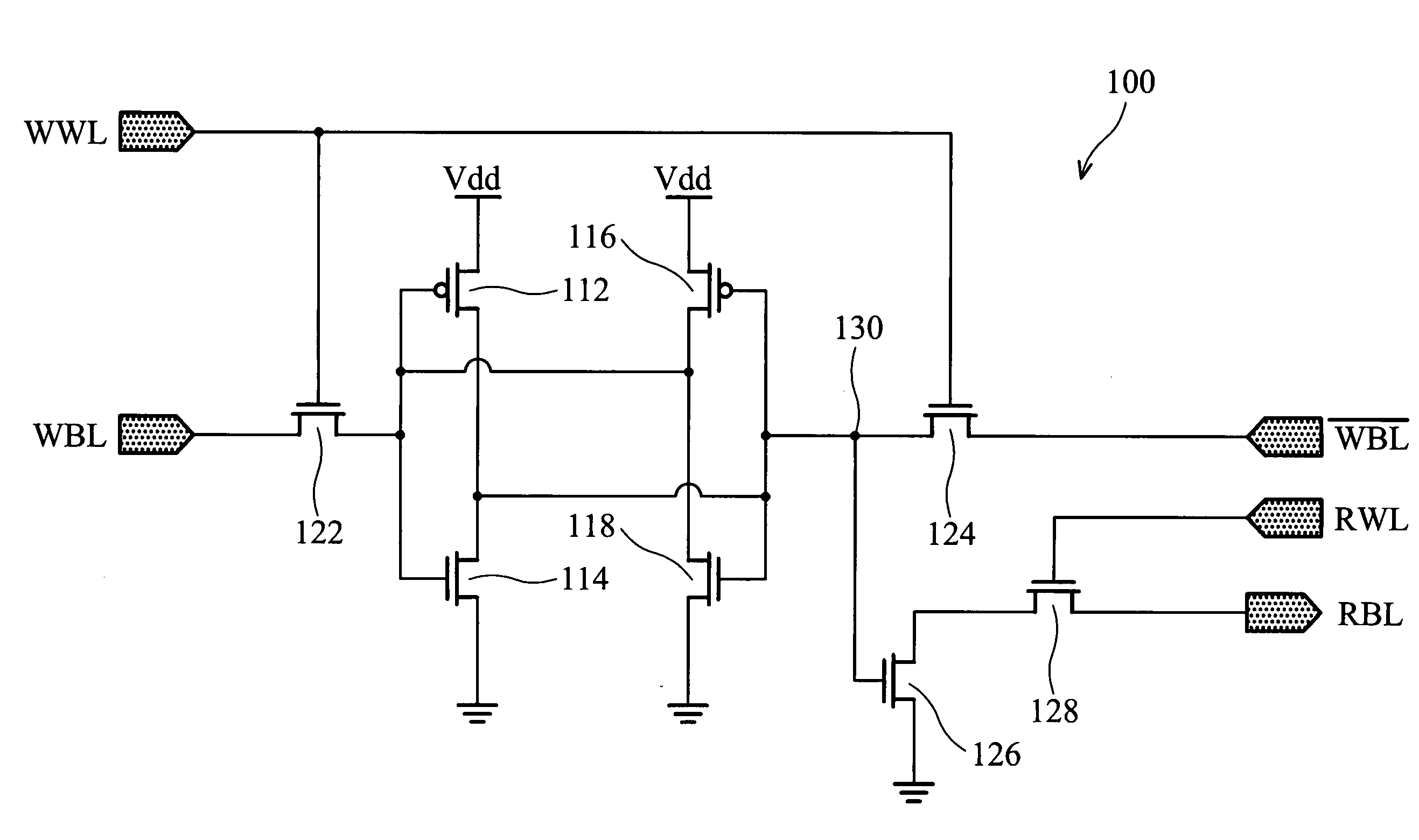
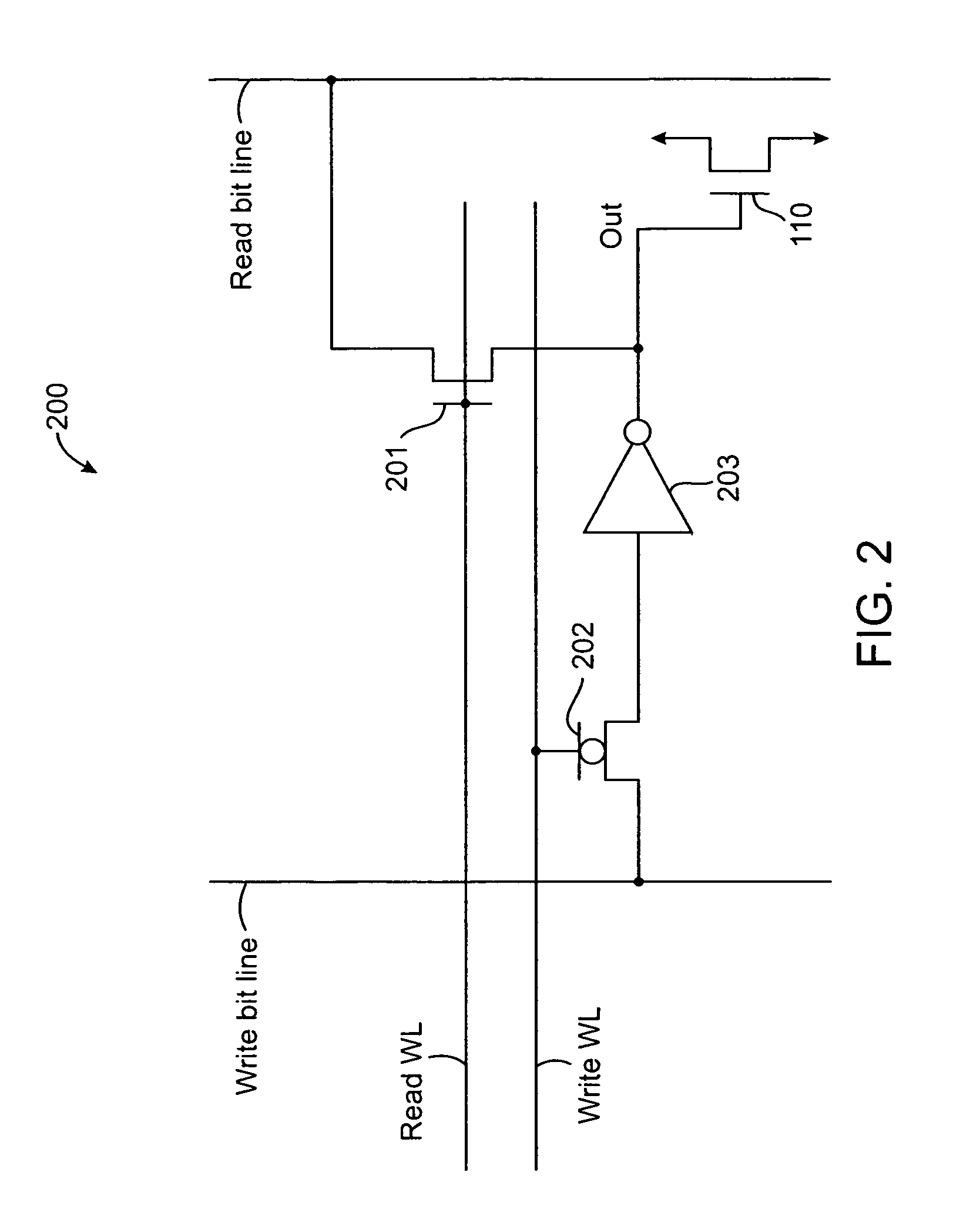
Circuit and Method for a High Speed Memory Cell
InactiveUS20100165704A1Easy to operateHigh operating requirementsDigital storageWrite bitHigh speed memory
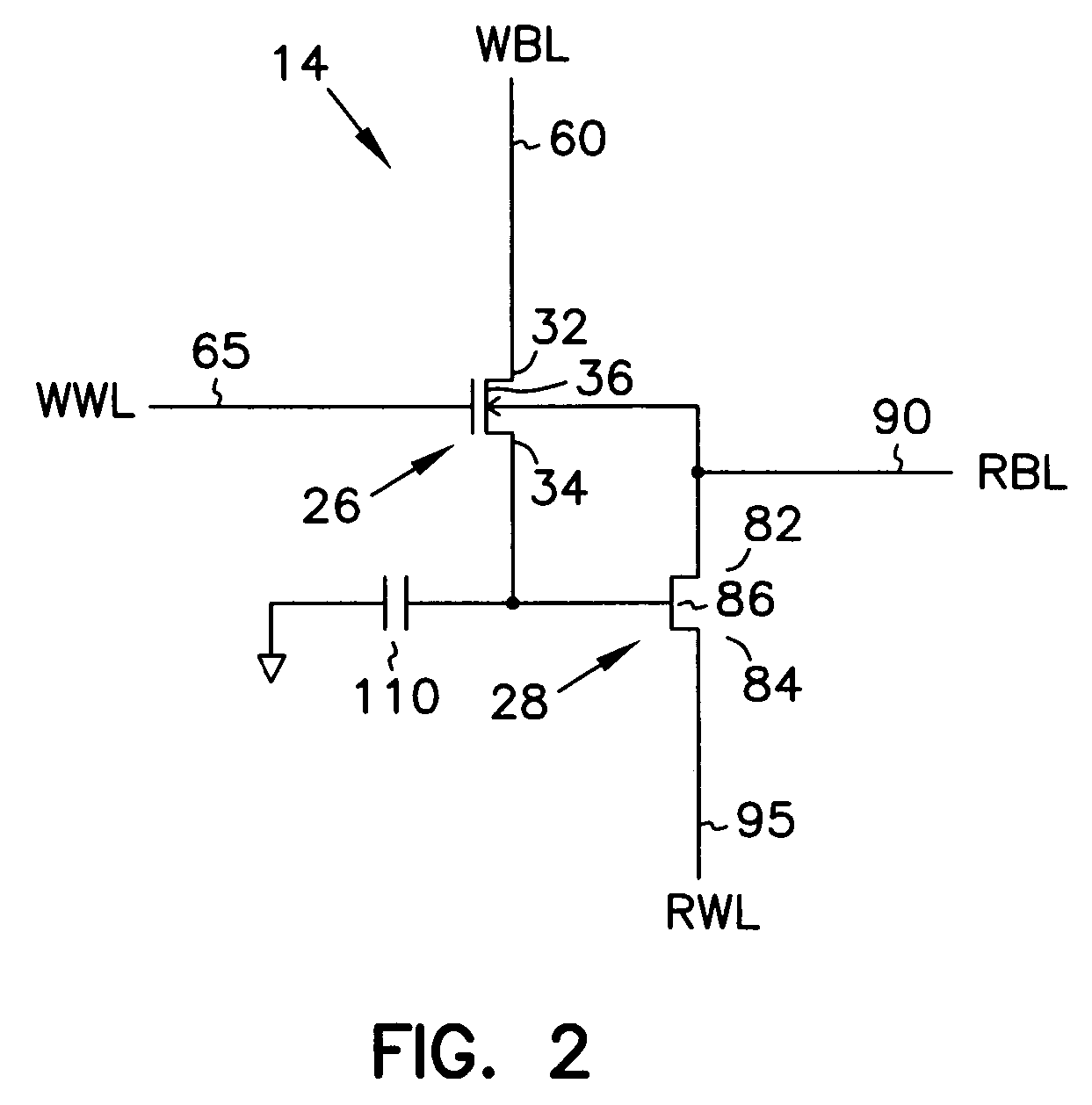
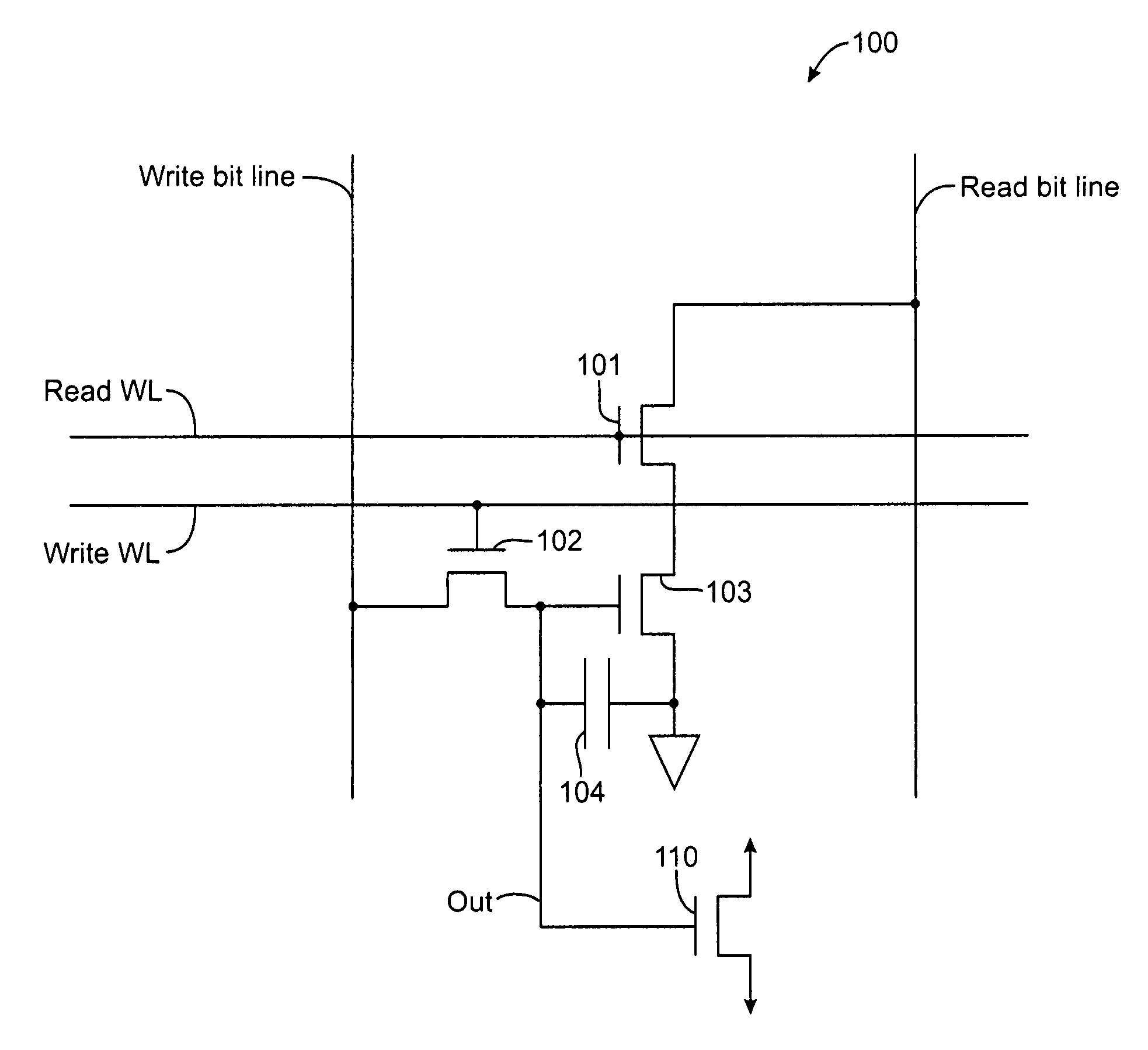
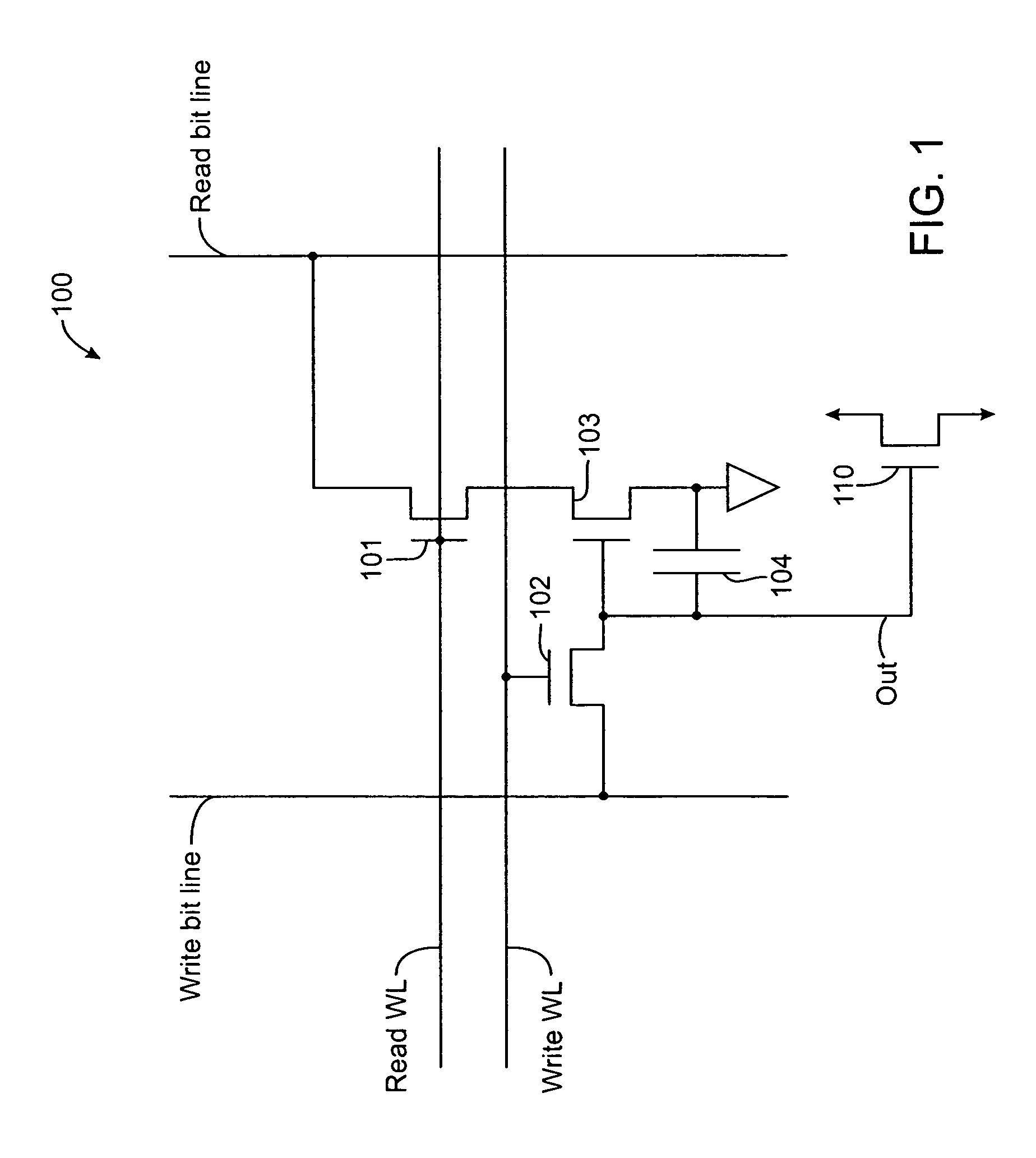
A memory cell is disclosed, including a write access transistor coupled between a storage node and a write bit line, and active during a write cycle responsive to a voltage on a write word line; a read access transistor coupled between a read word line and a read bit line, and active during a read cycle responsive to a voltage at the storage node; and a storage capacitor coupled between the read word line and the storage node. Methods for operating the memory cell are also disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Seven transistor SRAM cell
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Magnetic random access memory
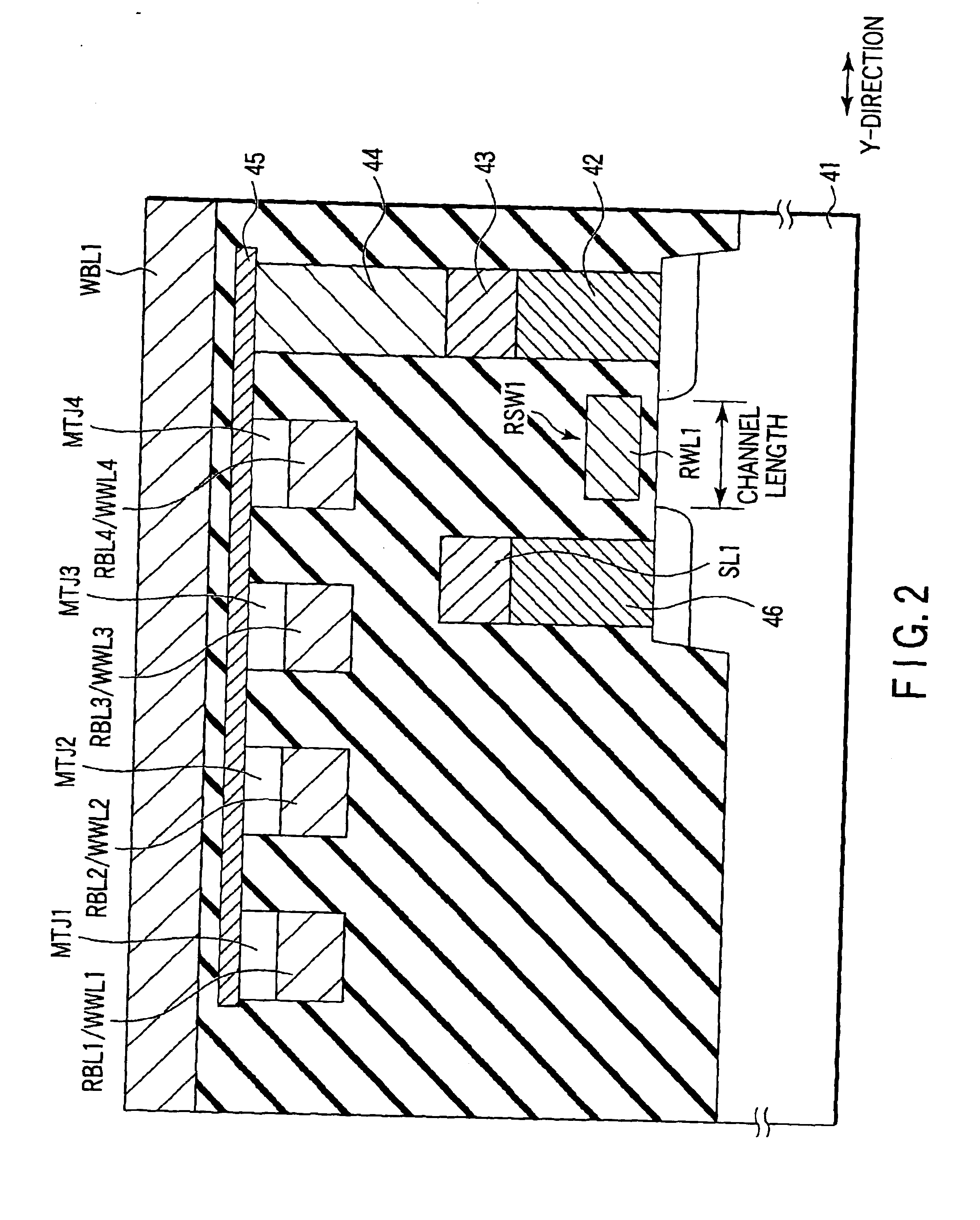
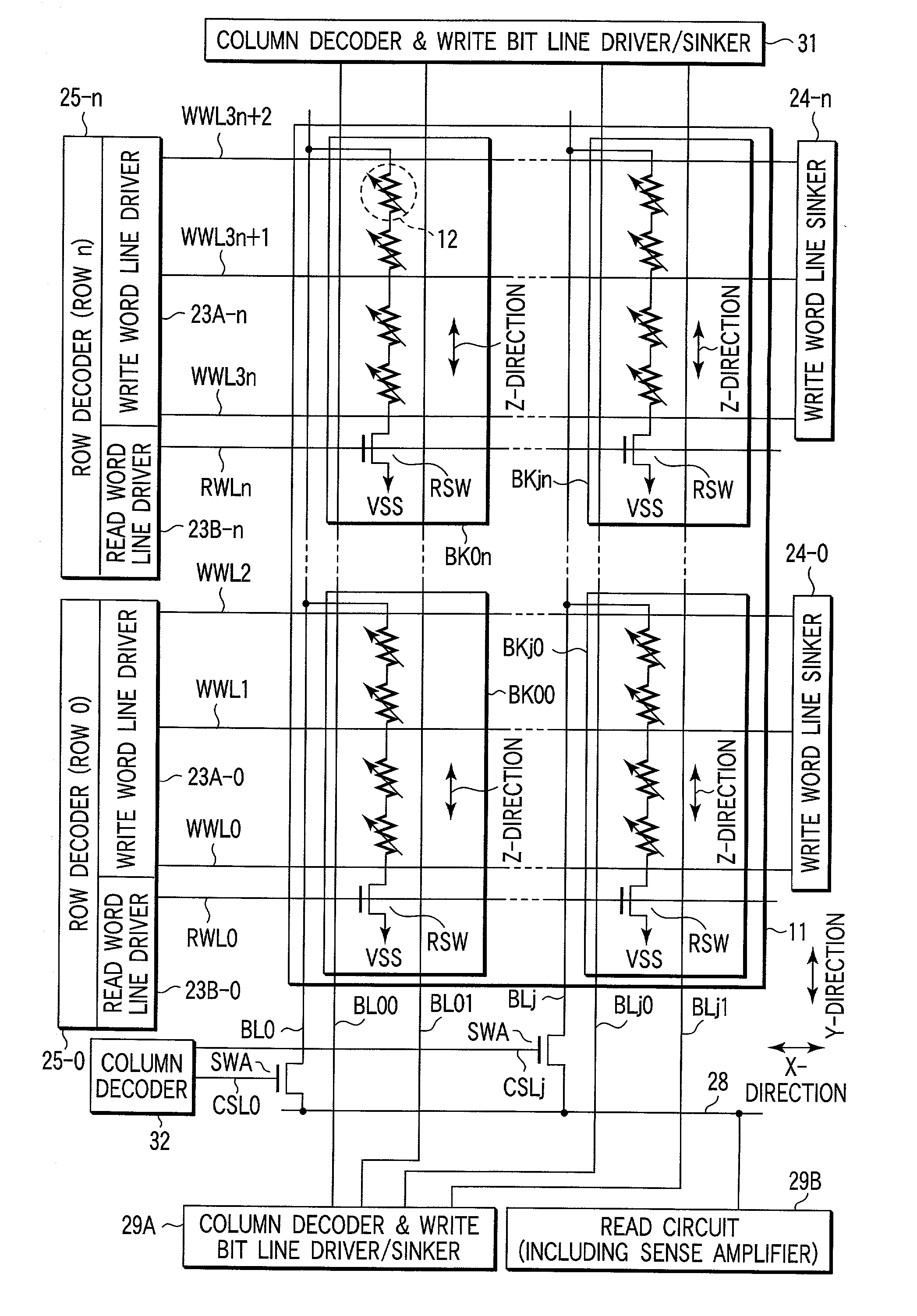
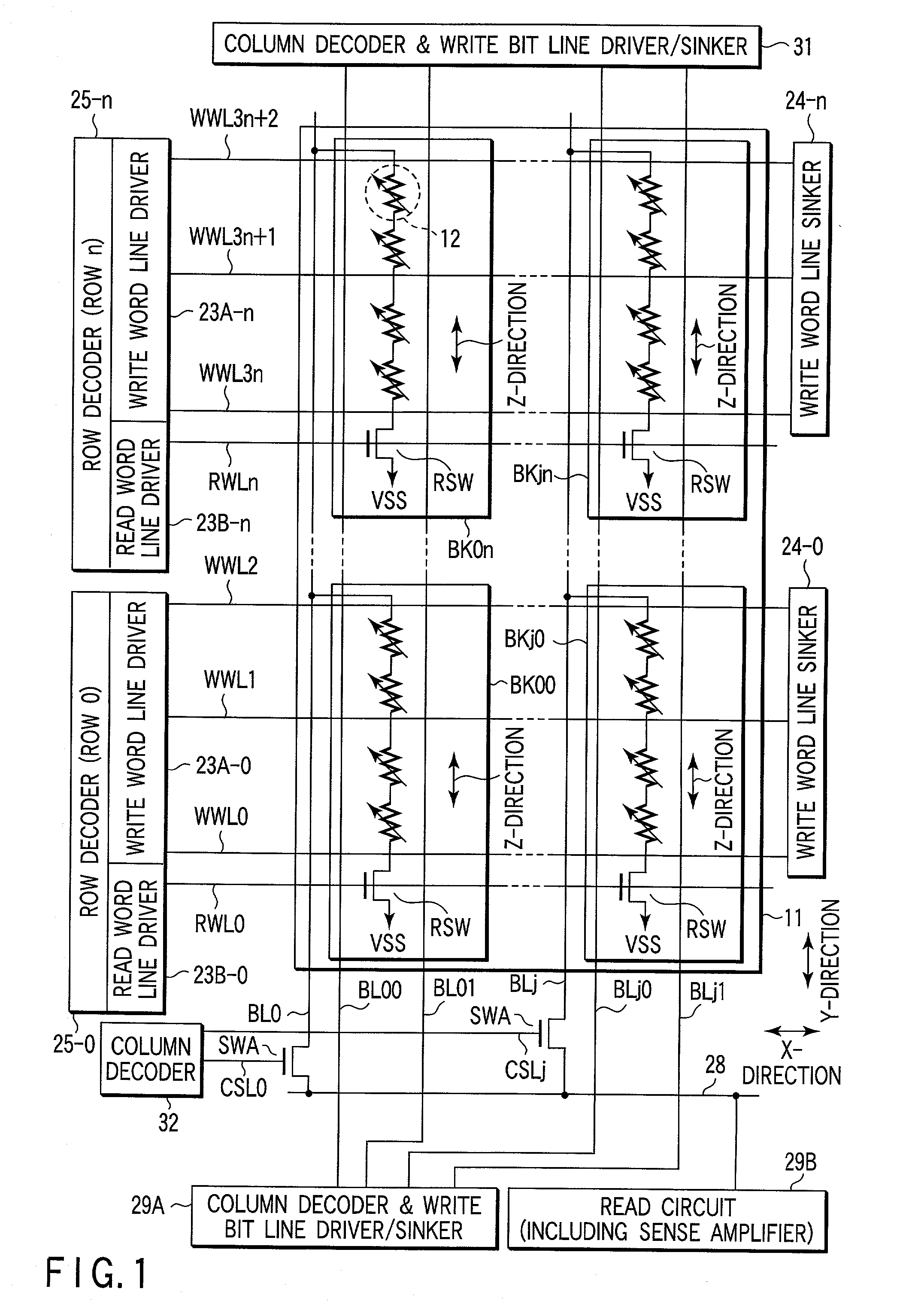
Blocks are connected to a read bit line. One block has MTJ elements which are connected to each other in series between the read bit line and a ground terminal. A MTJ elements are superposed on, e.g., a semiconductor substrate. A read bit line is arranged on the superposed MTJ elements. A write word line extending in a X-direction and a write bit line extending in a Y-direction are arranged in the vicinity of the MTJ elements in the block.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20060227648A1Increase the number ofArea of memory cell is increasedTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite bitComputer science
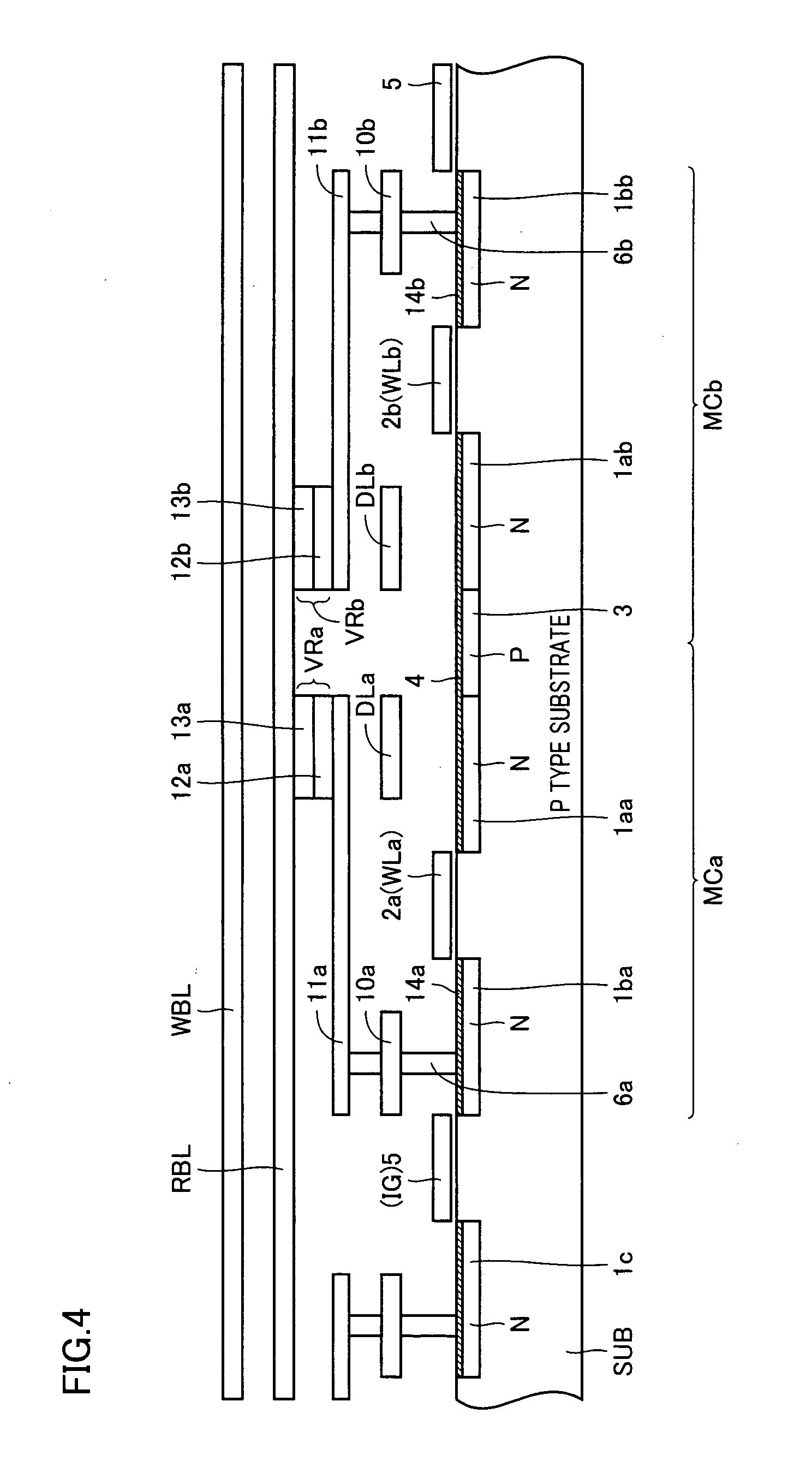
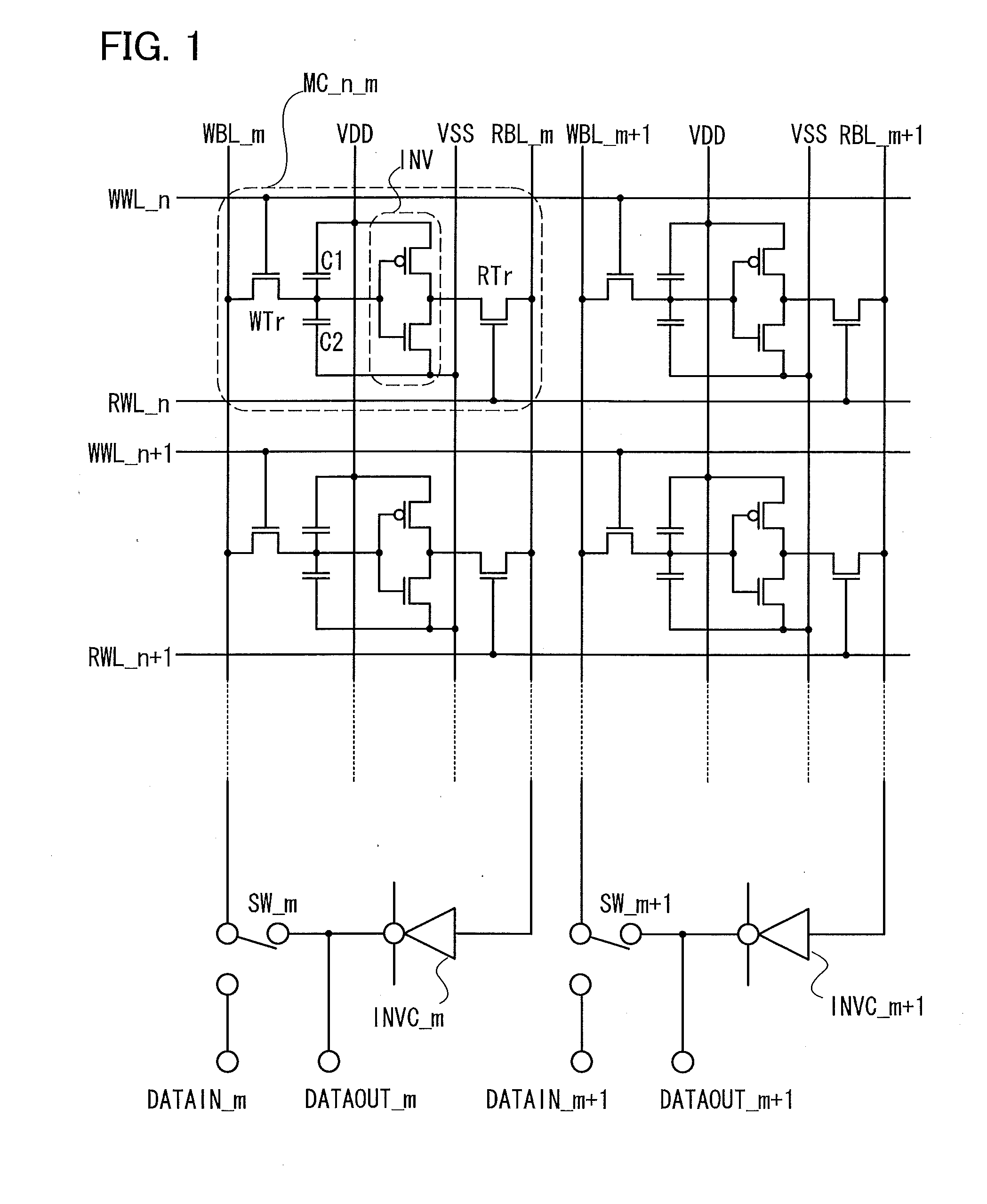
In a two-transistor gain cell structure, a semiconductor memory device capable of stable reading without malfunction and having small-area memory cells is provided. In a two-transistor gain cell memory having a write transistor and a read transistor, a write word line, a read word line, a write bit line, and a read bit line are separately provided, and voltages to be applied are independently set. Furthermore, a memory cell is connected to the same read word line and write bit line as those of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20080025113A1Speedup of readSpeedup of write operationDigital storageWrite bitWrite buffer
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor memory device including, a memory array with memory cells array-like arranged, a read bit line connected to a data output node of the memory cells and shared by a plurality of the memory cells arranged in one direction in the memory array, a write bit line connected to a data input node of the memory cells and shared by a plurality of the memory cells, a sense amplifier for sensing a voltage of the reading bit line, a first sense line and a second sense line connected to the sense amplifier, a read bit line switch for controlling electrical connection and disconnection between the first sense line and the read bit line, a write buffer connected between the second sense line and the write bit line, capable of controlling electrical connection and disconnection between the second sense line and the write bit line.
Owner:SONY CORP
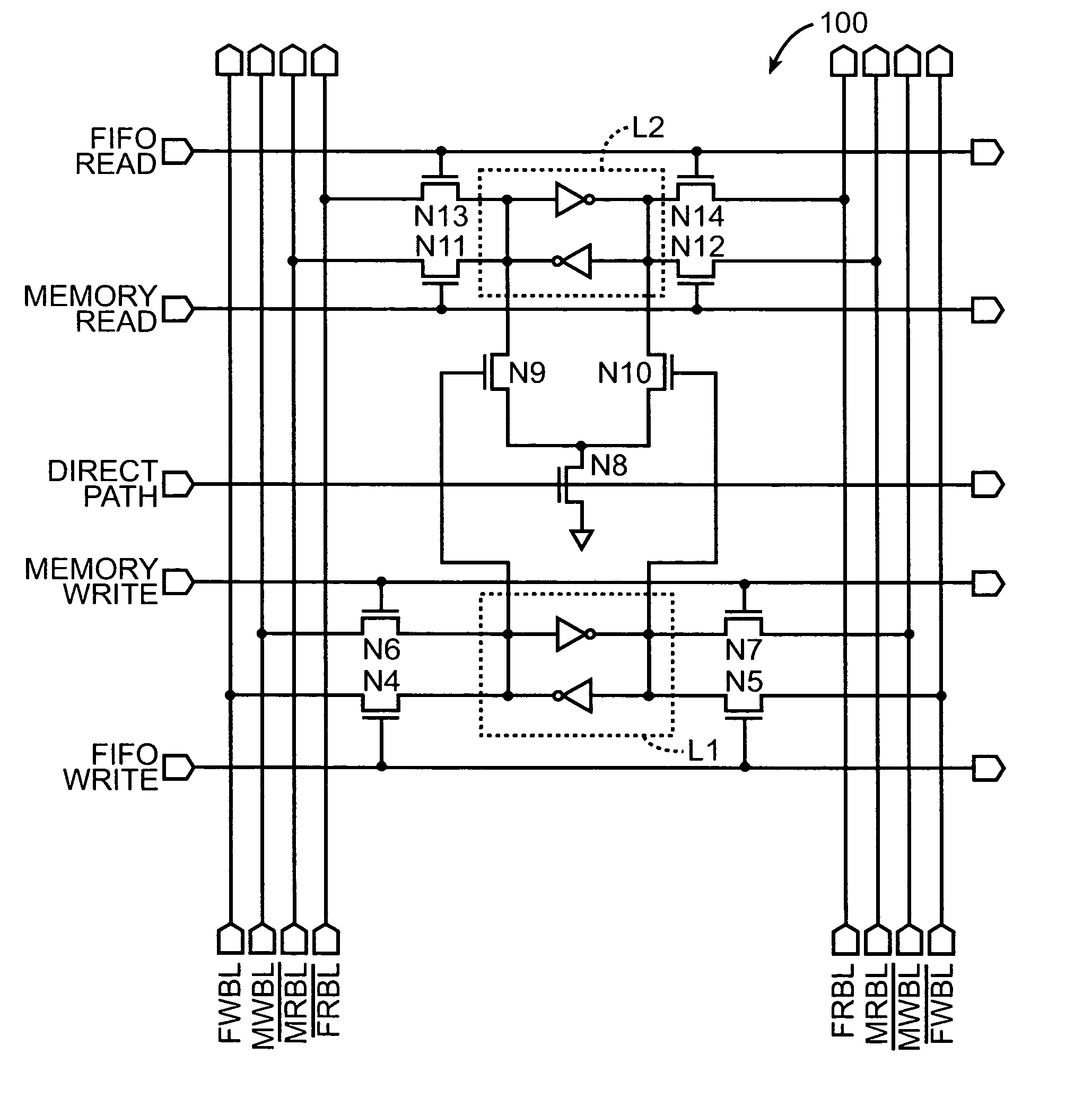
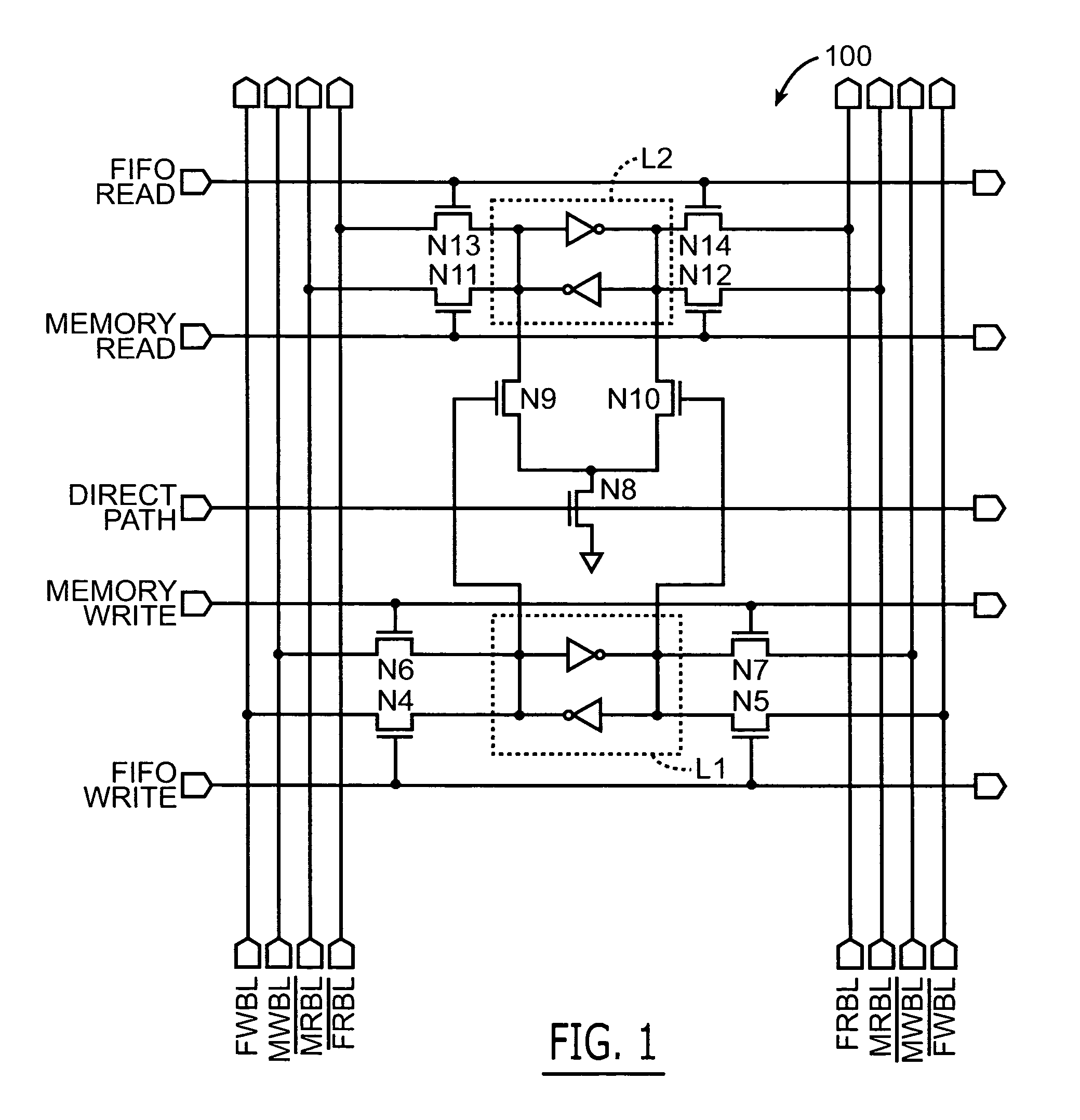
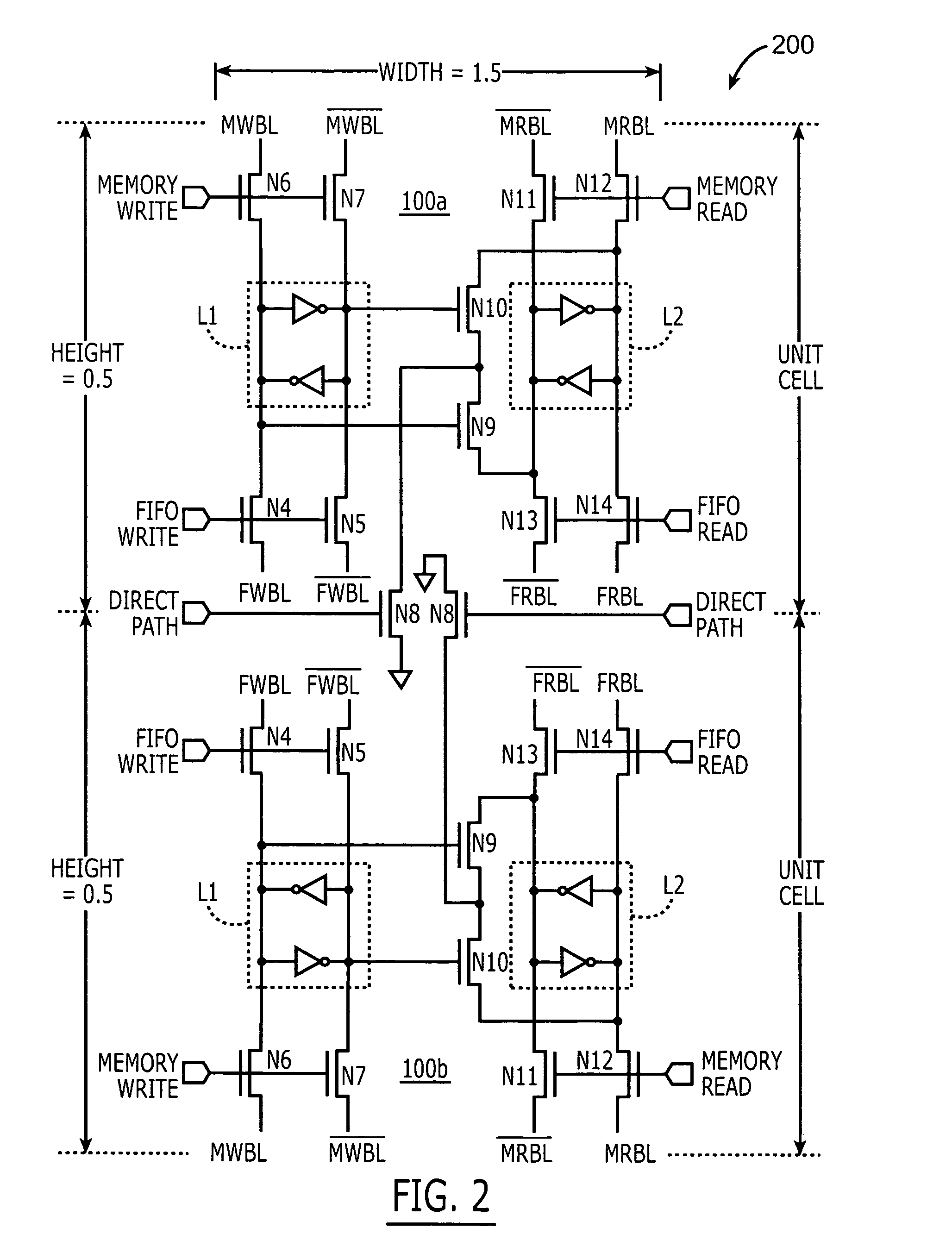
Multi-port memory cells for use in FIFO applications that support data transfers between cache and supplemental memory arrays
A multi-port memory cell includes a first SRAM element having a first pair of access transistors electrically coupled to a pair of FIFO write bit lines. A second dual-port SRAM element is also provided. This second dual-port SRAM element has a second pair of access transistors electrically coupled to a pair of FIFO read bit lines and a third pair of access transistors electrically coupled to a pair of memory read bit lines. A direct path data transfer circuit is provided. This transfer circuit is configured to support a unidirectional data transfer path that extends from first storage nodes within the first SRAM element to second storage nodes within the second dual-port SRAM element. This transfer circuit is also responsive to a direct path word line signal.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
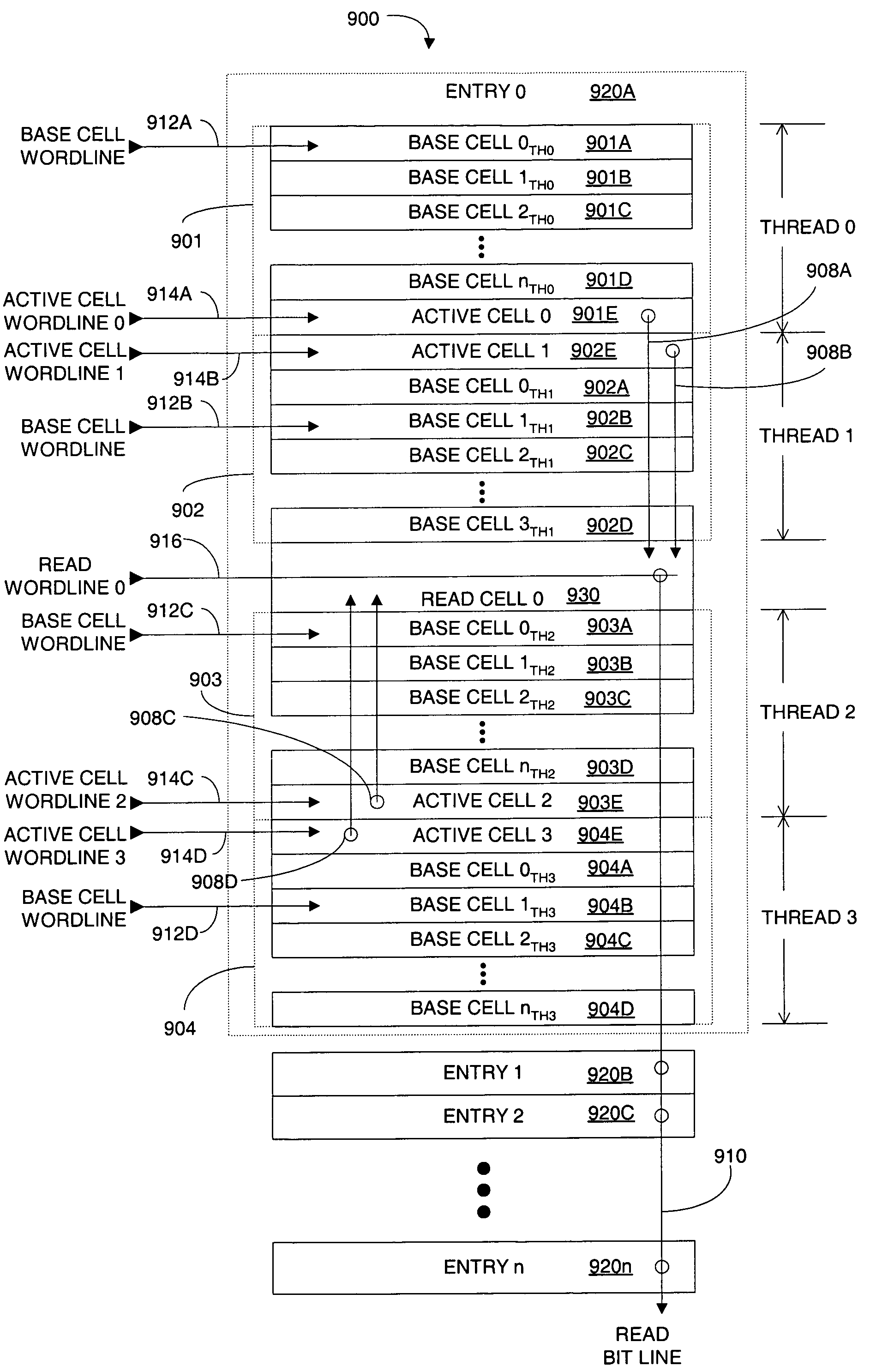
Efficient implementation of a read scheme for multi-threaded register file
ActiveUS7203100B2Faster, smaller area multi-threaded memory read schemeRead-only memoriesDigital storageActive cellMemory systems
A multi-threaded memory system including a plurality of entries, each one of the plurality of entries including a plurality of threads, each one of the plurality of threads including an active cell and a shared read cell. The shared read cell has an output coupled to a read bit line and a corresponding plurality of inputs coupled to an output of the corresponding active cells in each one of the plurality of threads. A multi-threaded memory system is also described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
MRAM having memory cell array in which cross-point memory cells are arranged by hierarchical bit line scheme and data read method thereof
A memory cell array is of a hierarchical bit line scheme in which cross-point memory cells that exhibit a magnetoresistive effect are laid out in a matrix, and a read bit line to be used in a data read mode is constituted by a main bit line and a sub bit line. A column select circuit selects a main bit line and connects it to a sense amplifier. A row select circuit selects a word line for each cell unit, and in read operation, sets, in a floating state, word lines to which unselected memory cells connected to the sub bit line to which a selected memory cell is connected are connected, and sets the remaining word lines connected to sub bit lines which do not include the selected memory cell to a potential substantially equal to the main bit line.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
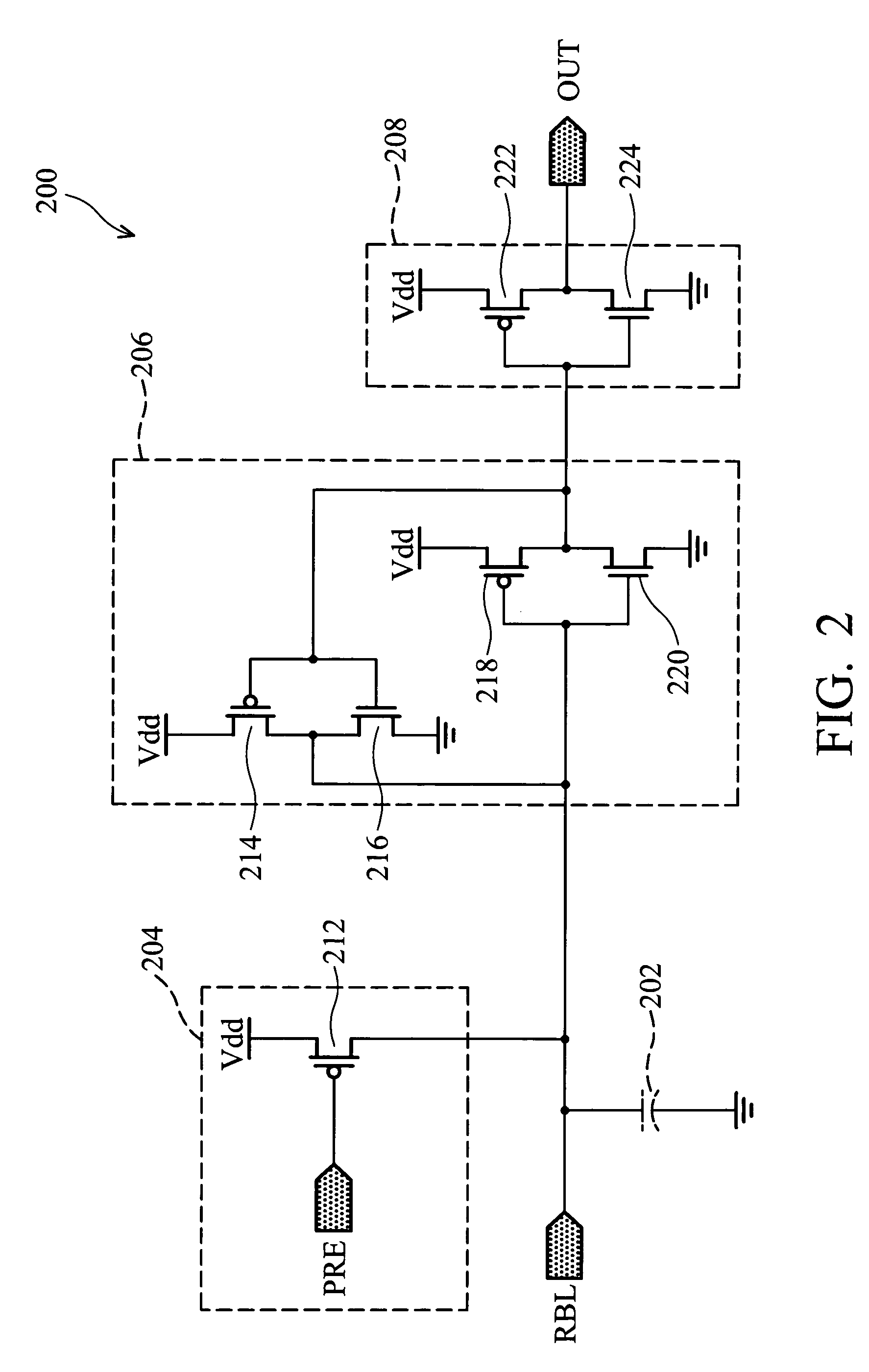
Output circuit of a memory and method thereof
ActiveUS20070115739A1Shorten access timeImprove performanceDigital storageComputer hardwareAudio power amplifier
An output circuit of a memory is provided. The output circuit includes a first pre-charge circuit, coupled to a read bit line which is coupled to a plurality of memory cells, pre-charging the voltage of the read bit line to a logic high level before a stored bit of a target memory cell is read to the read bit line, wherein the target memory cell is one of the plurality of memory cells, and a sense amplifier, coupled to the read bit line, detecting the voltage of the read bit line after the stored bit of the target memory cell is read to the read bit line, and comparing the voltage of the read bit line with the logic high level to respectively generate a comparison result signal and an inverse comparison result signal to a first output node and a second output node.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Memory device and method of controlling leakage current within such a memory device
ActiveUS9171634B2Reduce leakage currentImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureDrain current
A memory device includes an array of memory cells arranged as a plurality of rows and columns, each row being coupled to an associated read word line, and each column forming at least one column group, where the memory cells of each column group are coupled to an associated read bit line. Each column has an active mode of operation where a read operation may be performed on an activated memory cell within that column group, and a non-active mode of operation where the read operation is not performable. Precharge circuitry is used, for each column group, to precharge the associated read bit line to a first voltage level prior to the read operation. Each memory cell includes coupling circuitry connected between the associated read bit line and a reference line associated with the column group containing that memory cell.
Owner:ARM LTD
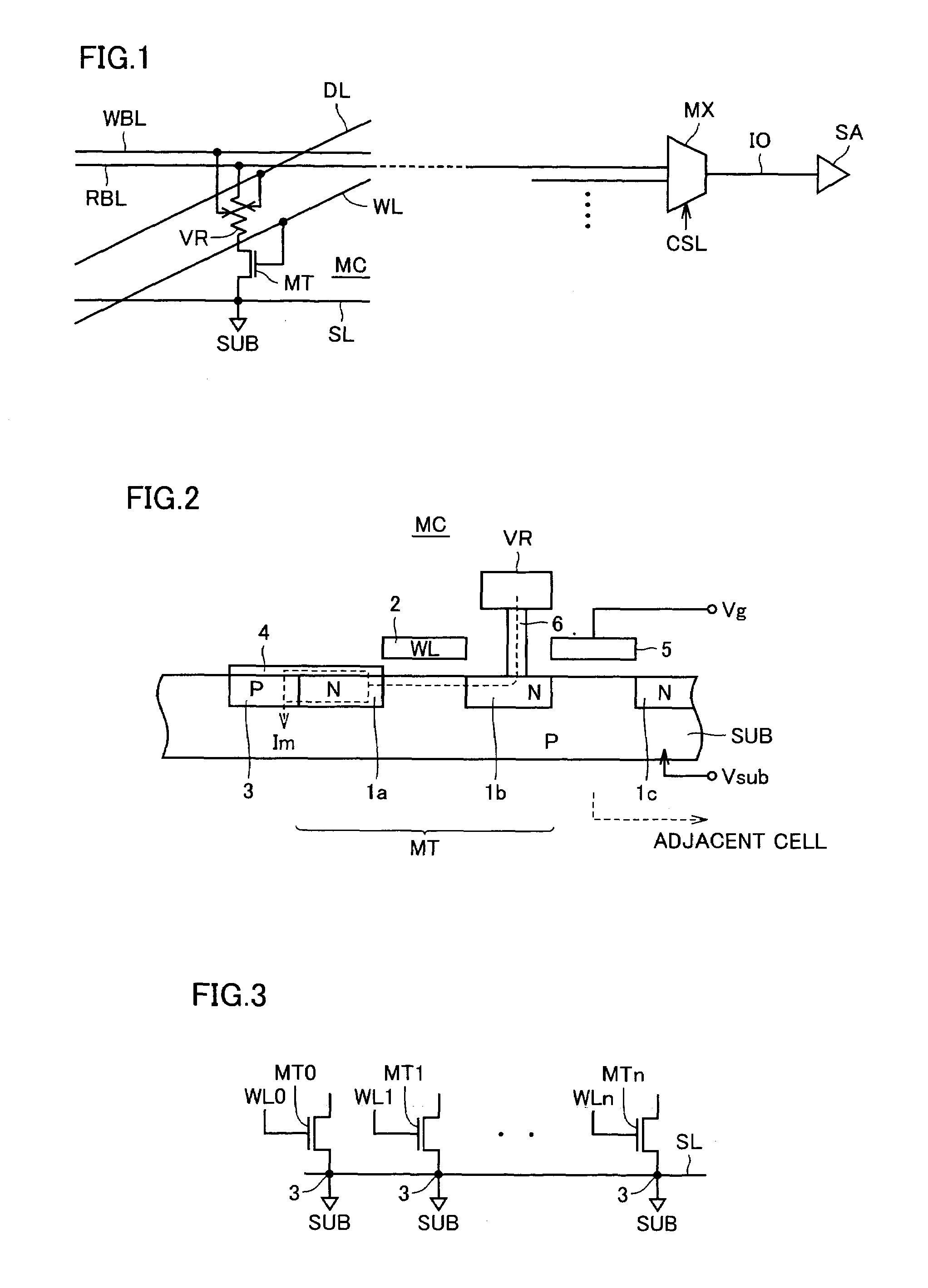
Vertical gain cell and array for a dynamic random access memory and method for forming the same
InactiveUS7049196B2Increase cell densityGreat data retention timeTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETSemiconductor materials
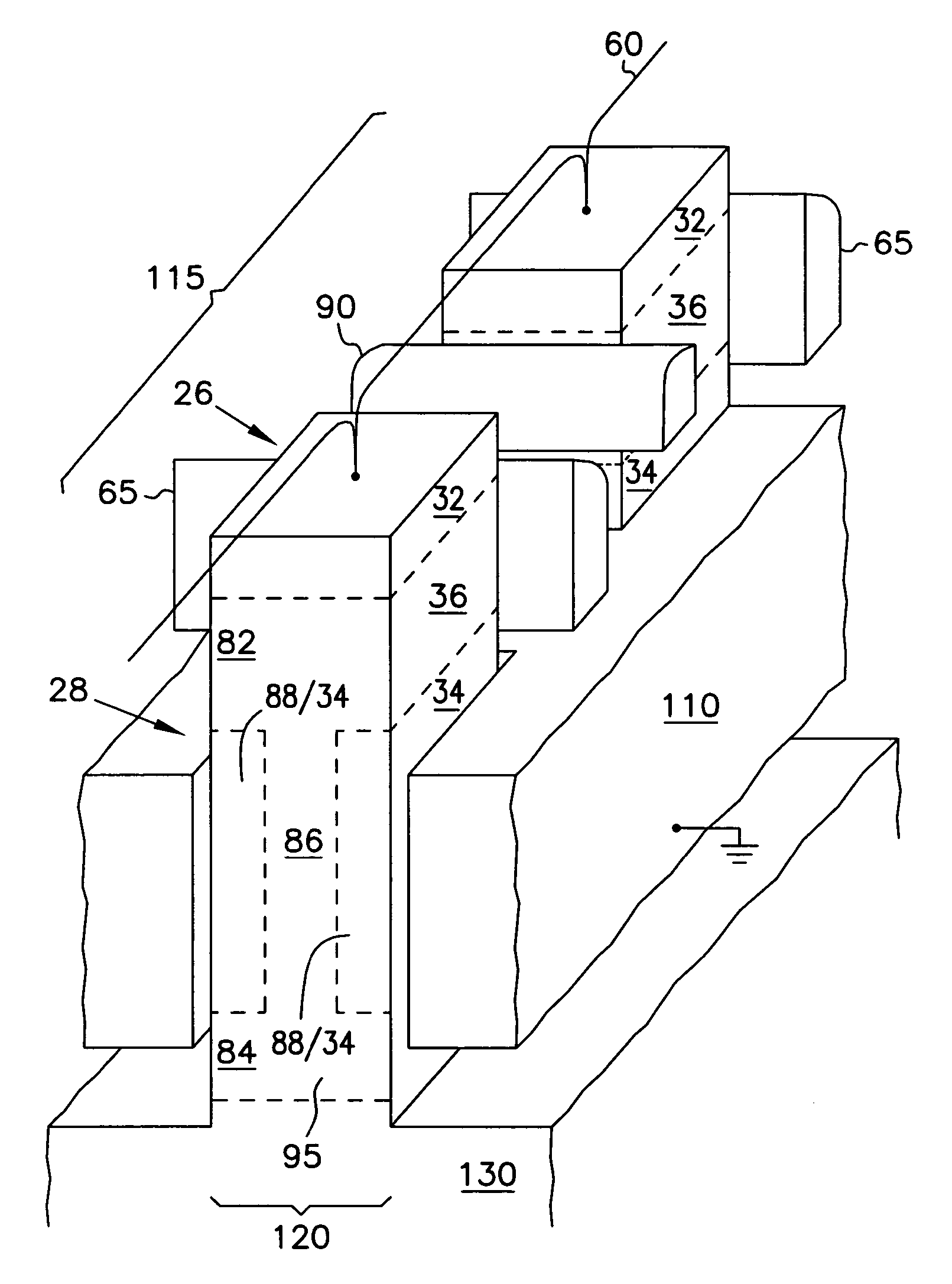
A vertical gain memory cell including an n-channel metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) and p-channel junction field-effect transistor (JFET) transistors formed in a vertical pillar of semiconductor material is provided. The body portion of the p-channel transistor is coupled to a second source / drain region of the MOSFET which serves as the gate for the JFET. The second source / drain region of the MOSFET is additionally coupled to a charge storage node. Together the second source / drain region and charge storage node provide a bias to the body of the JFET that varies as a function of the data stored by the memory cell. A non destructive read operation is achieved. The stored charge is sensed indirectly in that the stored charge modulates the conductivity of the JFET so that the JFET has a first turn-on threshold for a stored logic “1” condition and a second turn-on threshold for a stored logic “0” condition. The charge storage node is a plate capacitor which surrounds the second source / drain region of the MOSFET. The vertical gain cell is fabricated so that the write word line, read bit line, read word line and capacitor are buried beneath the silicon surface. As a result the cell can be fabricated in an area as small as four (4) lithographic feature squares.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Phase change memory device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20060092694A1Improve reliabilityImprove integrityRead-only memoriesDigital storagePhase-change memoryComputer science
A phase change memory device and a method of operating the same are provided. The phase change memory device may include a plurality of unit cells arranged in a matrix composed of rows and columns; a plurality of program bit lines and read bit lines arranged in rows, each of the program and read bit lines having a row selection transistor formed at one end thereof; and a plurality of program word lines and read word lines arranged in columns, each of the program and read word lines having a column selection transistor formed at one end thereof. Each of the unit cells may include a phase change resistor and an exothermal resistor used to heat the phase change resistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device, driving method thereof, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110205774A1Reduce power consumptionHighly integratedTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite bitEngineering
A matrix is formed using a plurality of memory cells in each of which a drain of the writing transistor is connected to a gate of a reading transistor and one electrode of a capacitor. A gate of the writing transistor, a source of the writing transistor, a source of the reading transistor, and a drain of the reading transistor are connected to a writing word line, a writing bit line, a reading bit line, and a bias line, respectively. The other electrode of the capacitor is connected to a reading word line. In order to decrease the number of wirings, the writing bit line is substituted for the reading bit line. The reading bit line is formed so as to be embedded in a groove-like opening formed over a substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
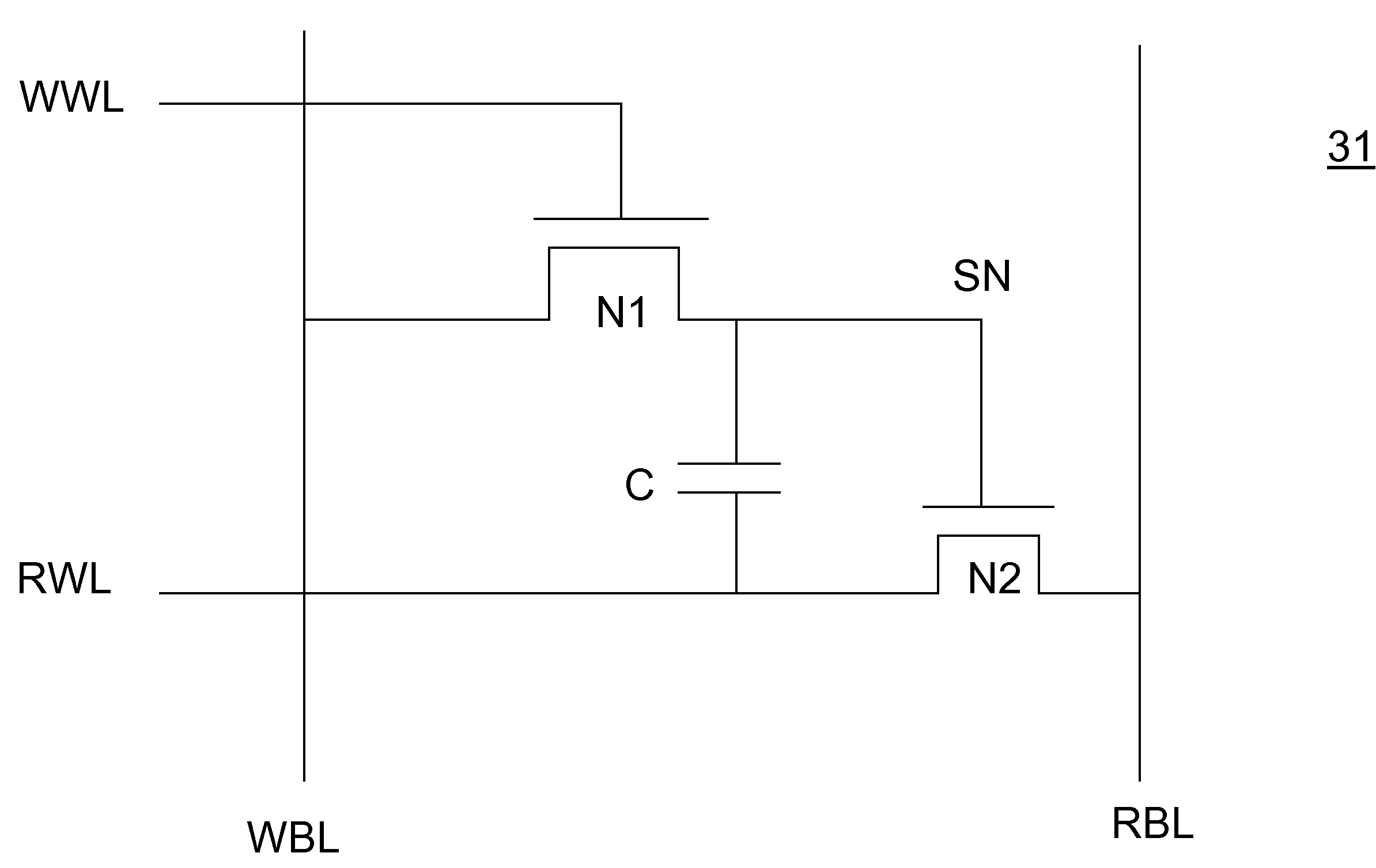
Dynamic RAM storage techniques
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) cells are provided. Data can be read from a DRAM cell without draining the stored charge stored in the cell. During a read cycle, current flows between a Read Bit line and a supply voltage, and charge is not drained directly from the DRAM storage node. Each DRAM cell has a small number of transistors. The DRAM cell can be used to store configuration data on a programmable integrated circuits (IC). Pass gates are used on programmable ICs to drive signals across the chip. Data stored in DRAM cells is provided directly to the pass gates at the full supply voltage to prevent signal degradation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
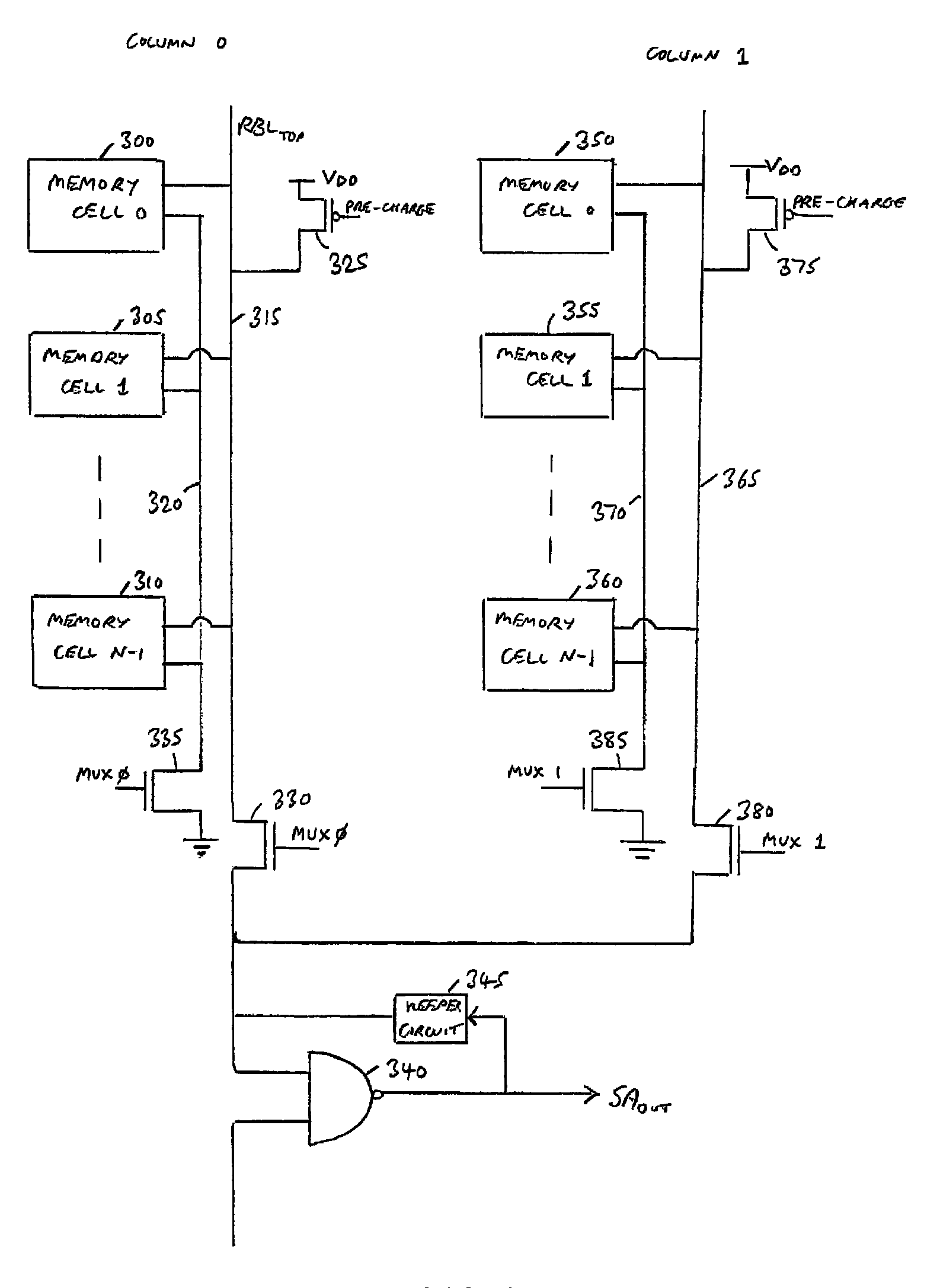
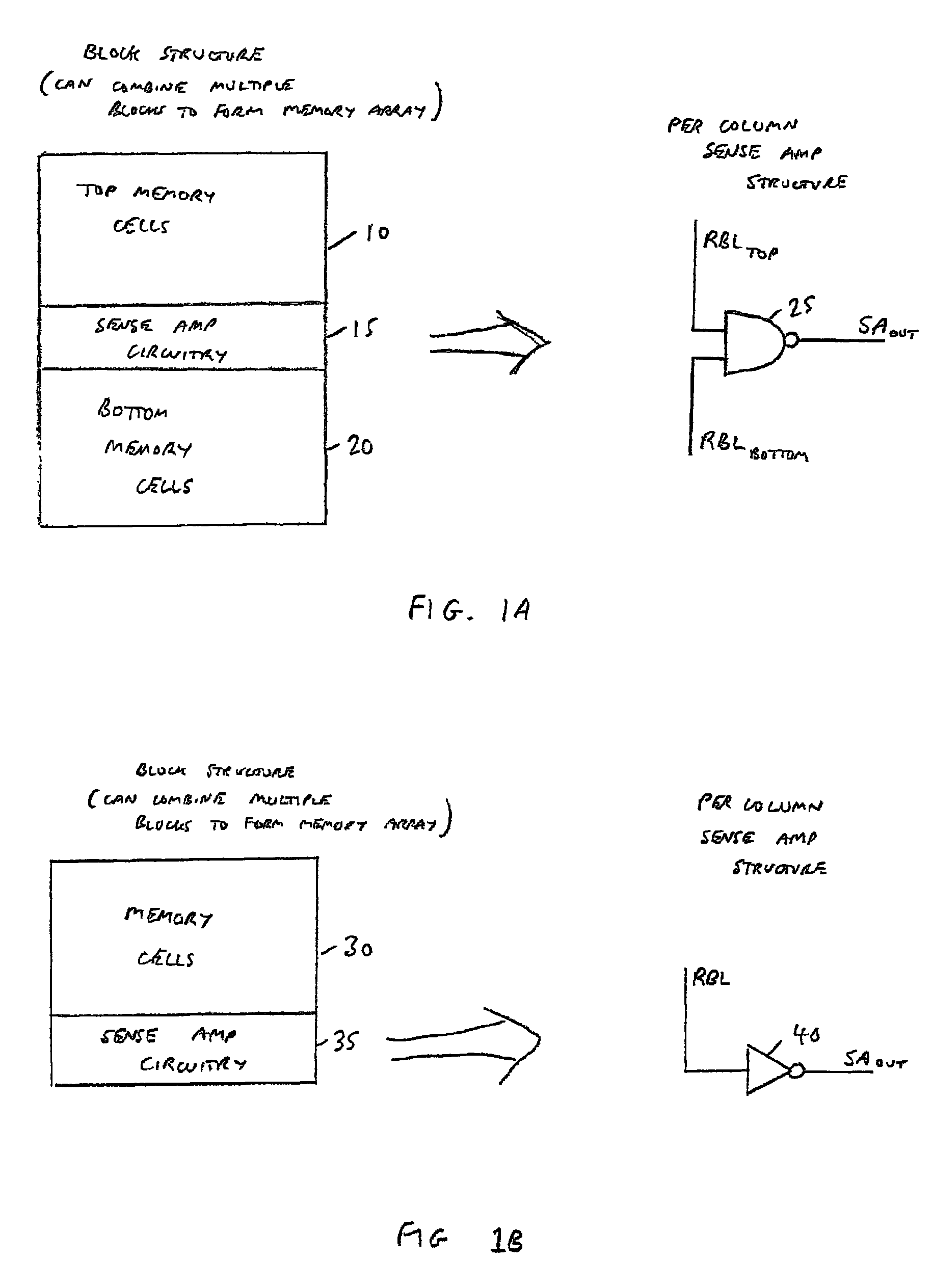
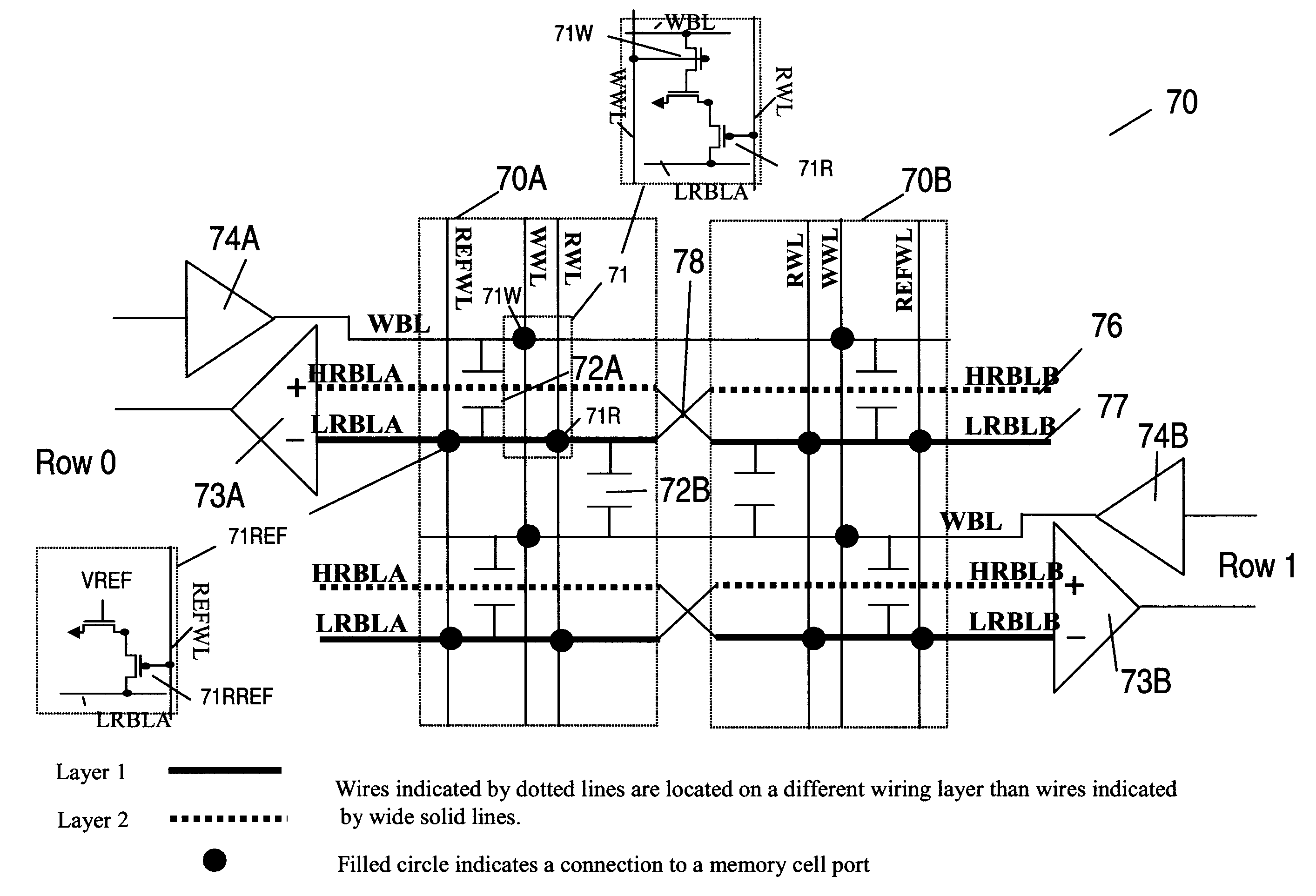
Multi-port memory architecture
A multi-port memory architecture utilizing an open bitline configuration for the read bitline is described. The memory is sub-divided into two arrays (A and B) consisting of memory gain cells arranged in a matrix formation, the cells having two general ports or separate read and write ports to enable simultaneous a read and write operation. Each memory array includes a reference wordline coupled to reference cells. When the reference cell is accessed, the read bitline (RBL) discharges to a level at half the value taken by a cell storing a 0 or 1. Each pair of RBLB in the same column of the two arrays is coupled to a differential sense amplifier, and each write bitline (WBL) in the two arrays is linked to write drivers WBLs in the two arrays are driven to the same voltage and at the same slew rate. The WBL swing in each array creates coupling noise by the bitline-to-bitline capacitors. For a given sense amplifier and its associated RBLs, the coupling creates an identical coupling noise on RBLA and RBLB that are positioned in the two arrays A and B. This common mode noise is rejected by the differential sense amplifier. Thus, a read sense amplifier can accurately discriminate between the signal by activating the cell by way of RWL, and the reference cell by way of REFWL.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS8395931B2Reduce power consumptionNovel structureRead-only memoriesDigital storageWrite bitEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20120099360A1Less power consumptionReduce power consumptionDigital storagePower inverterPotential difference
In a memory cell, a transistor with extremely high off-resistance is used as a write transistor; a drain and a source of the write transistor are connected to a write bit line and an input of an inverter, respectively; and a drain and a source of a read transistor are connected to a read bit line and an output of the inverter, respectively. Capacitors may be intentionally disposed to the source of the write transistor. Alternatively, parasitic capacitance may be used. Since the data retention is performed using charge stored on these capacitors, a potential difference between power sources for the inverter can be 0. This eliminates leakage current between the positive and negative electrodes of the inverter, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Silicon germanium read port for a static random access memory register file
ActiveUS20160064068A1Faster rateAvoid conductionTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryProcessor register
A static random access memory (SRAM) circuit includes a write port and a read port coupled to the write port. The read port includes a read bit line and a first p-type metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor having a silicon germanium (SiGe) channel. The read port also includes a second PMOS transistor having a second SiGe channel, where the second PMOS transistor is coupled to the first PMOS transistor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Memory cell having improved read stability
ActiveUS7106620B2Virtually eliminates disturbs of the memory cellTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite bitMemory cell
A memory cell for use in a memory array includes a storage element for storing a logical state of the memory cell, a write circuit and a read circuit. The write circuit is operative to selectively connect a first node of the storage element to at least a first write bit line in the memory array in response to a write signal for selectively writing the logical state of the memory cell. The read circuit includes a substantially high impedance input node connected to the storage element and an output node connectable to a read bit line of the memory array. The read circuit is configured to generate an output signal at the output node which is representative of the logical state of the storage element in response to a read signal applied to the read circuit. The memory cell is configured such that the write circuit is disabled during a read operation of the memory cell so as to substantially isolate the storage element from the first write bit line during the read operation. A strength of at least one transistor device in the storage element is separately optimized relative to a strength of at least one transistor device in the write circuit and / or the read circuit.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS7123498B2Improve reliabilityHighly reliable reading of informationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectric analogue storesWrite bitComputer science
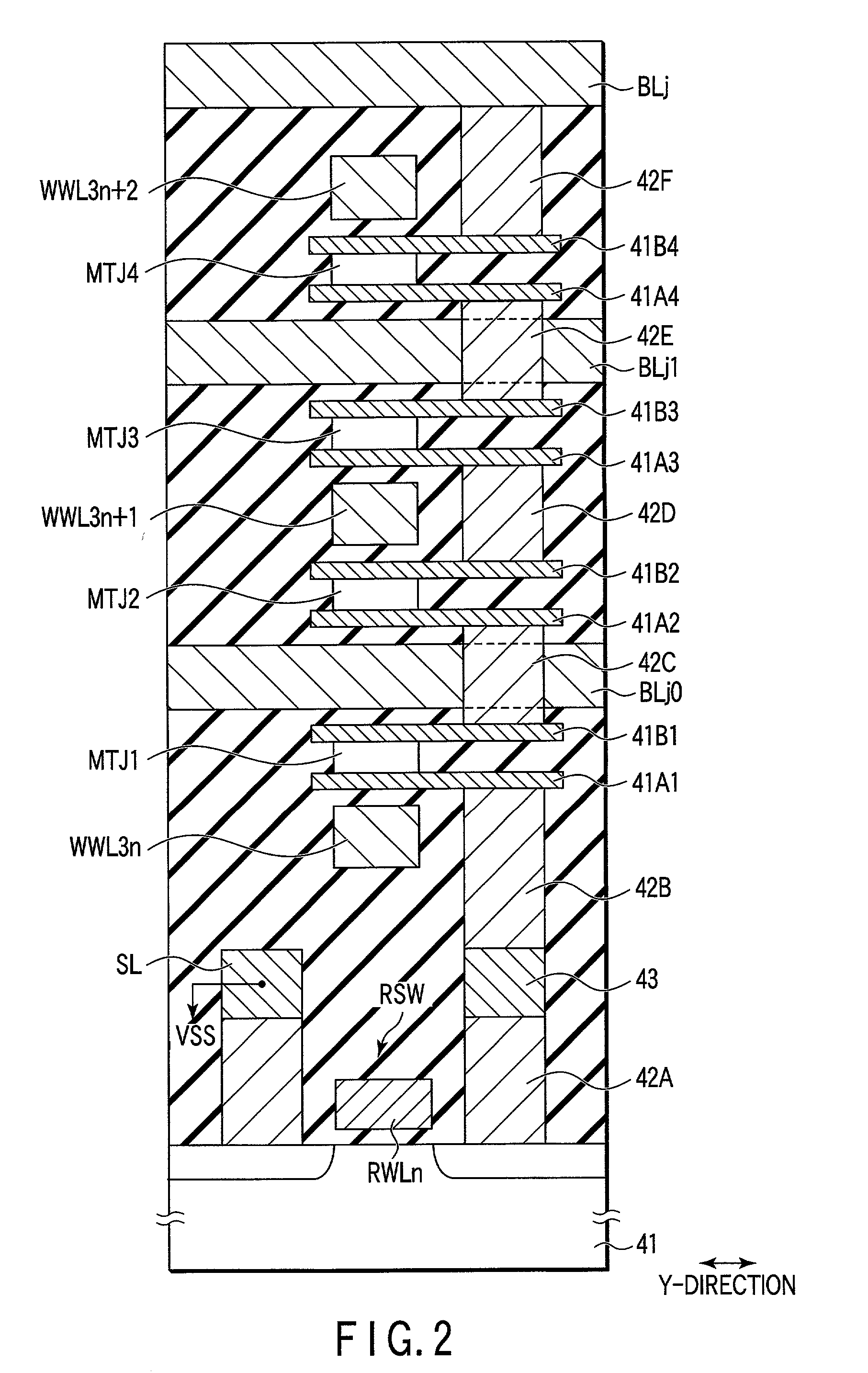
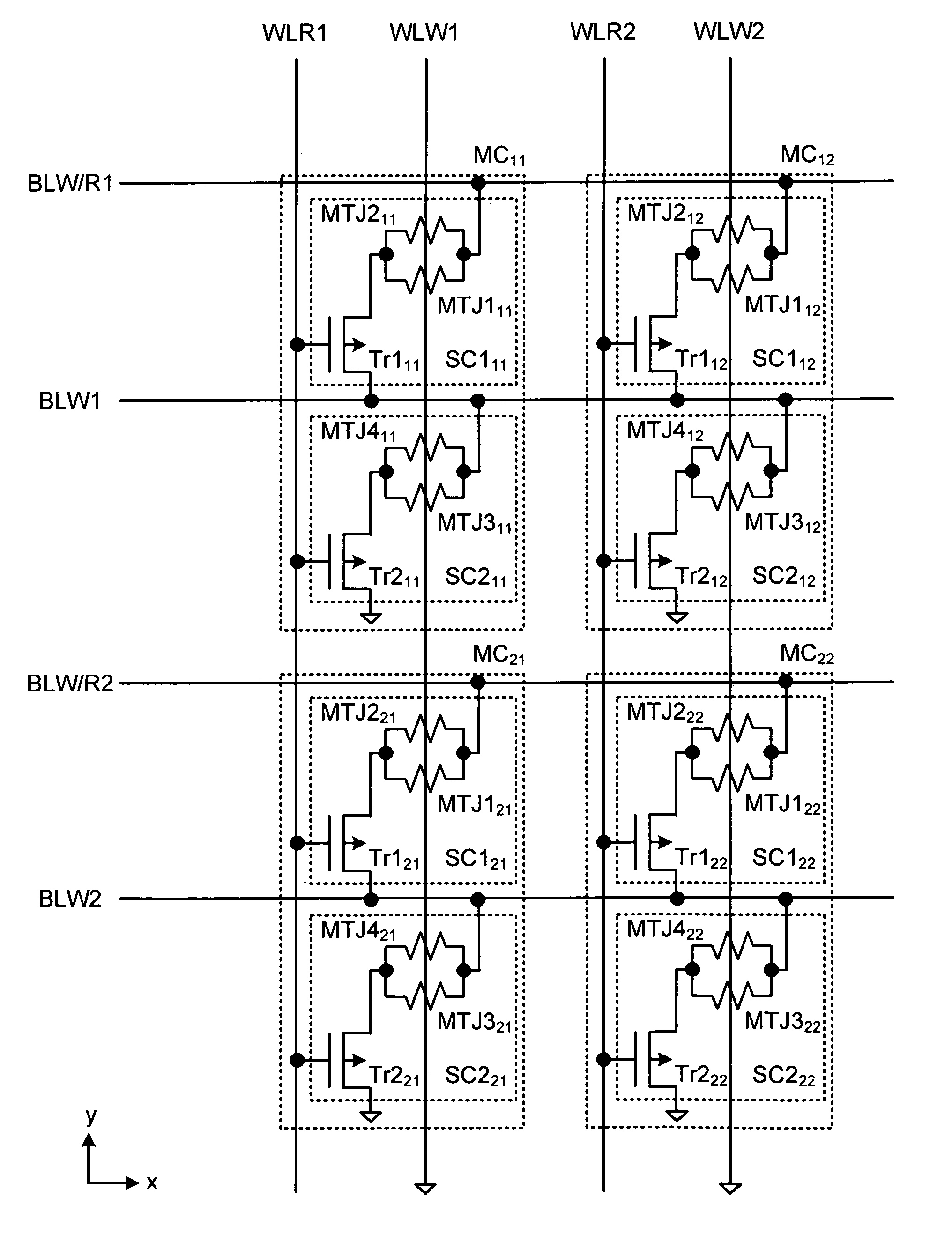
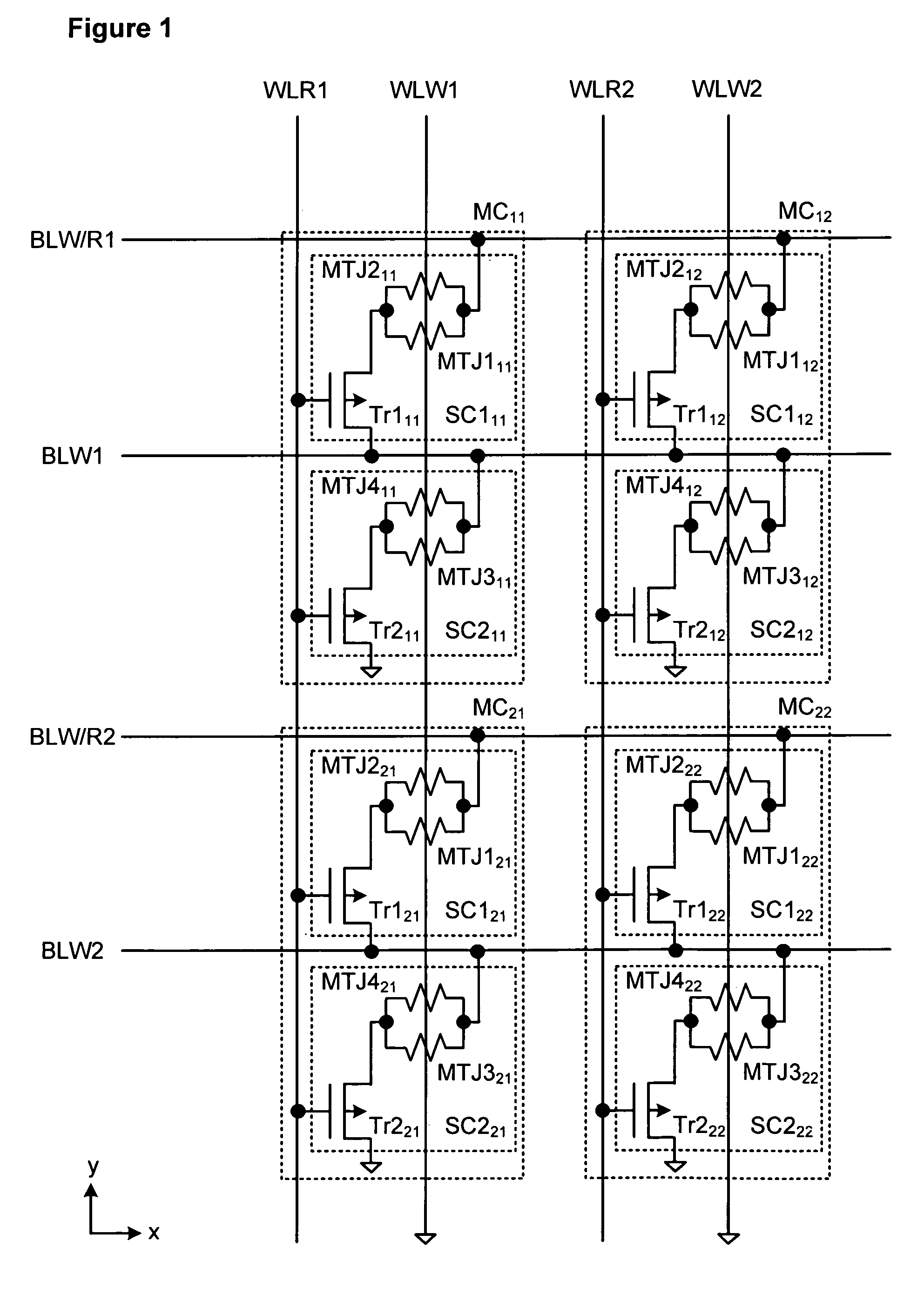
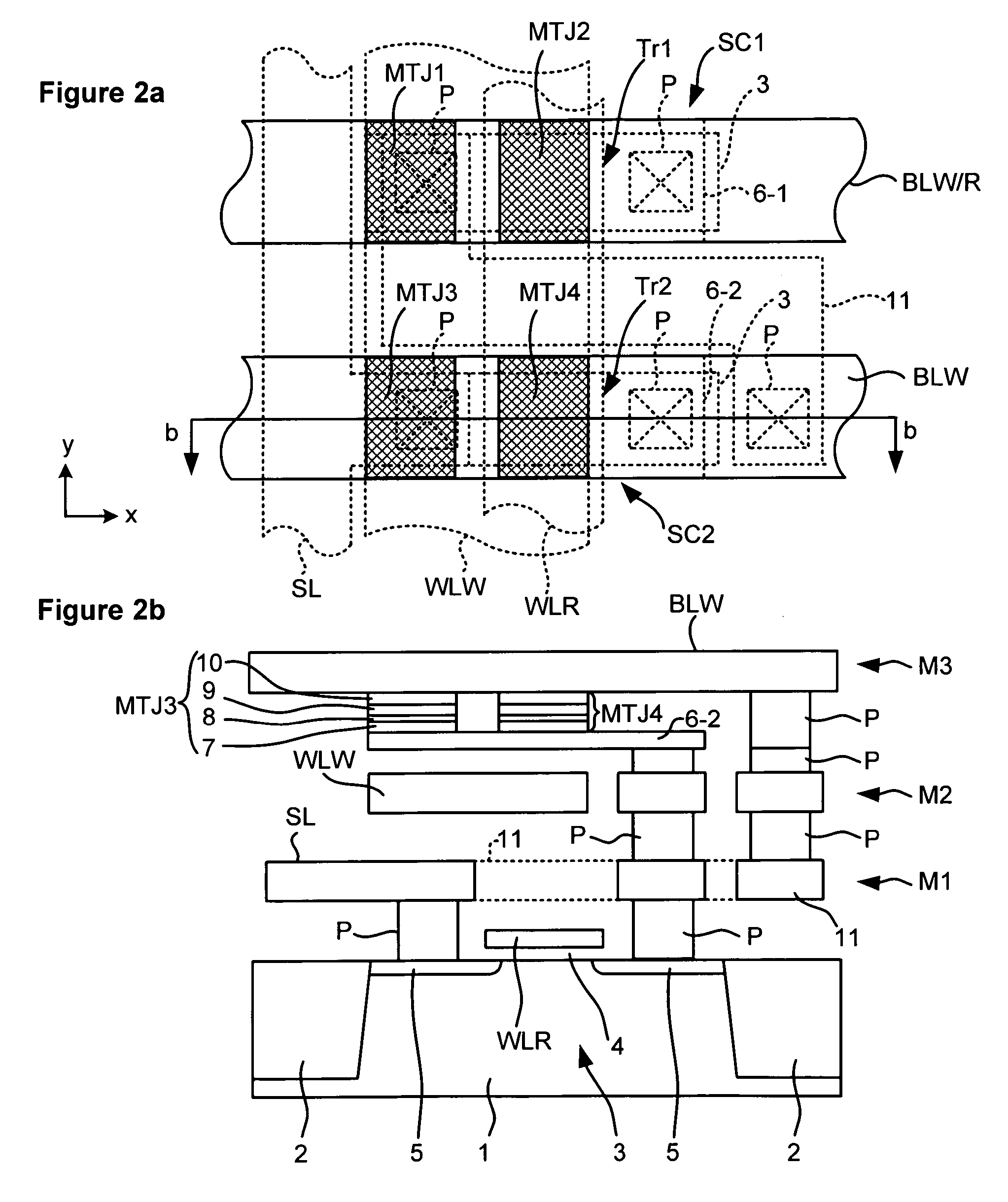
MRAM has read word lines WLR and write word line WLW extending in the y direction, write / read bit line BLW / R and write bit line BLW extending in the x direction, and the memory cells MC disposed at the points of the intersection of these lines. The memory MC includes sub-cells SC1 and SC2. The sub-cell SC1 includes magneto resistive elements MTJ1 and MTJ2 and a selection transistor Tr1, and the sub-cell SC2 includes magneto resistive elements MTJ3 and MTJ4 and a selection transistor Tr2. The magneto resistive elements MTJ1 and MTJ2 are connected in parallel, and the magneto resistive elements MTJ3 and MTJ4 are also connected in parallel. Further, the sub-cells SC1 and SC2 are connected in series between the write / read bit line BLW / R and the ground.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Apparatus for and Method of Current Leakage Reduction in Static Random Access Memory Arrays
InactiveUS20090175107A1Improve developmentLess powerDigital storageStable stateStatic random-access memory
A novel and useful mechanism for reducing current leakage in a static random access memory array which significantly reduces the power requirements of the memory array. The method enables the steady state of all local and global bit lines in an SRAM array to be discharged during both active and inactive modes. The memory array consists of memory cells having an N channel field effect transistor read stack. A mechanism is provided to evaluate data from memory cells where the steady state of local and global read bit lines is discharged.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com