Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
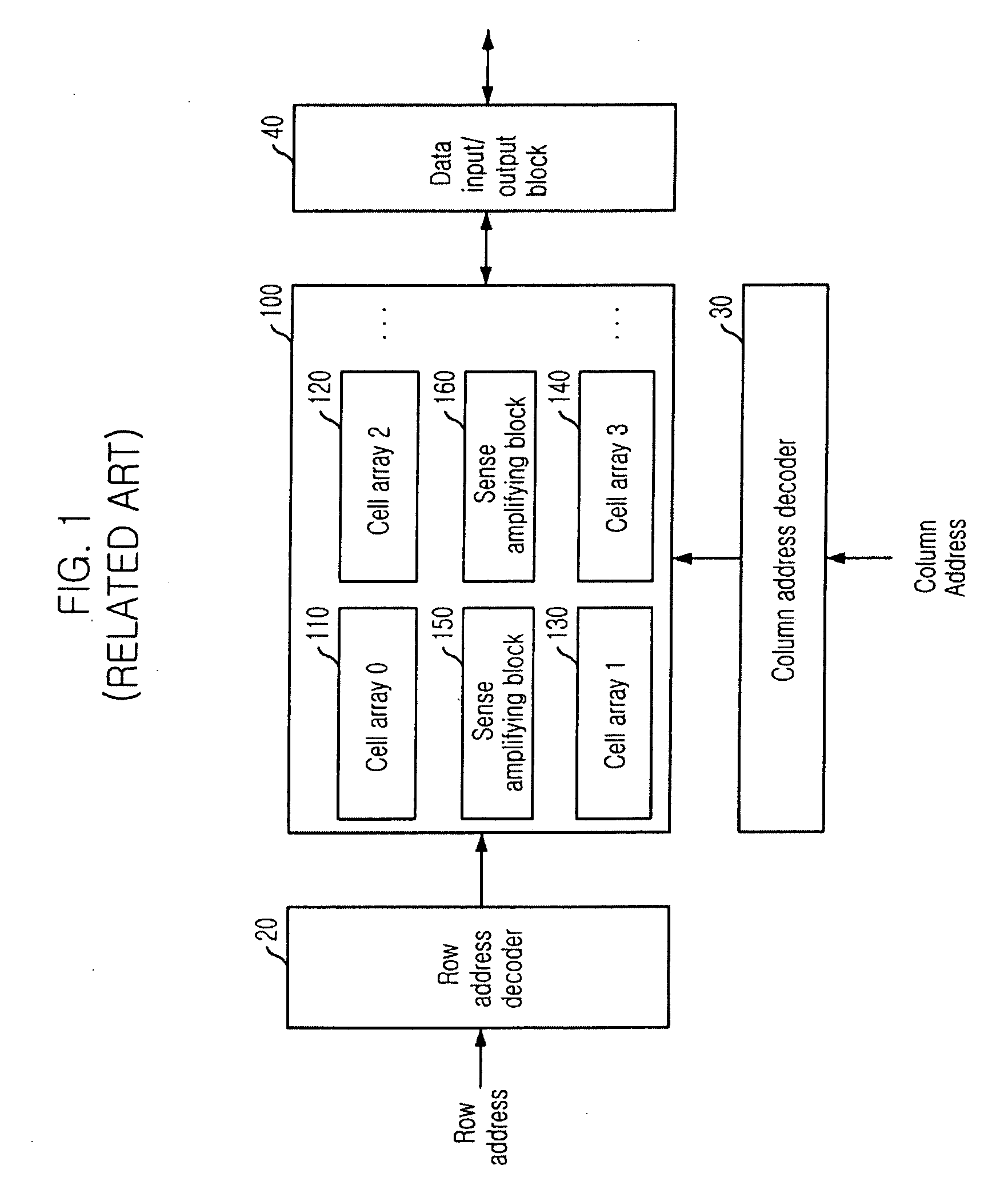
14251 results about "Semiconductor memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) memory, where data is stored within MOSFET (MOS field-effect transistor) memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit chip. There are numerous different types of implementations using various technologies.
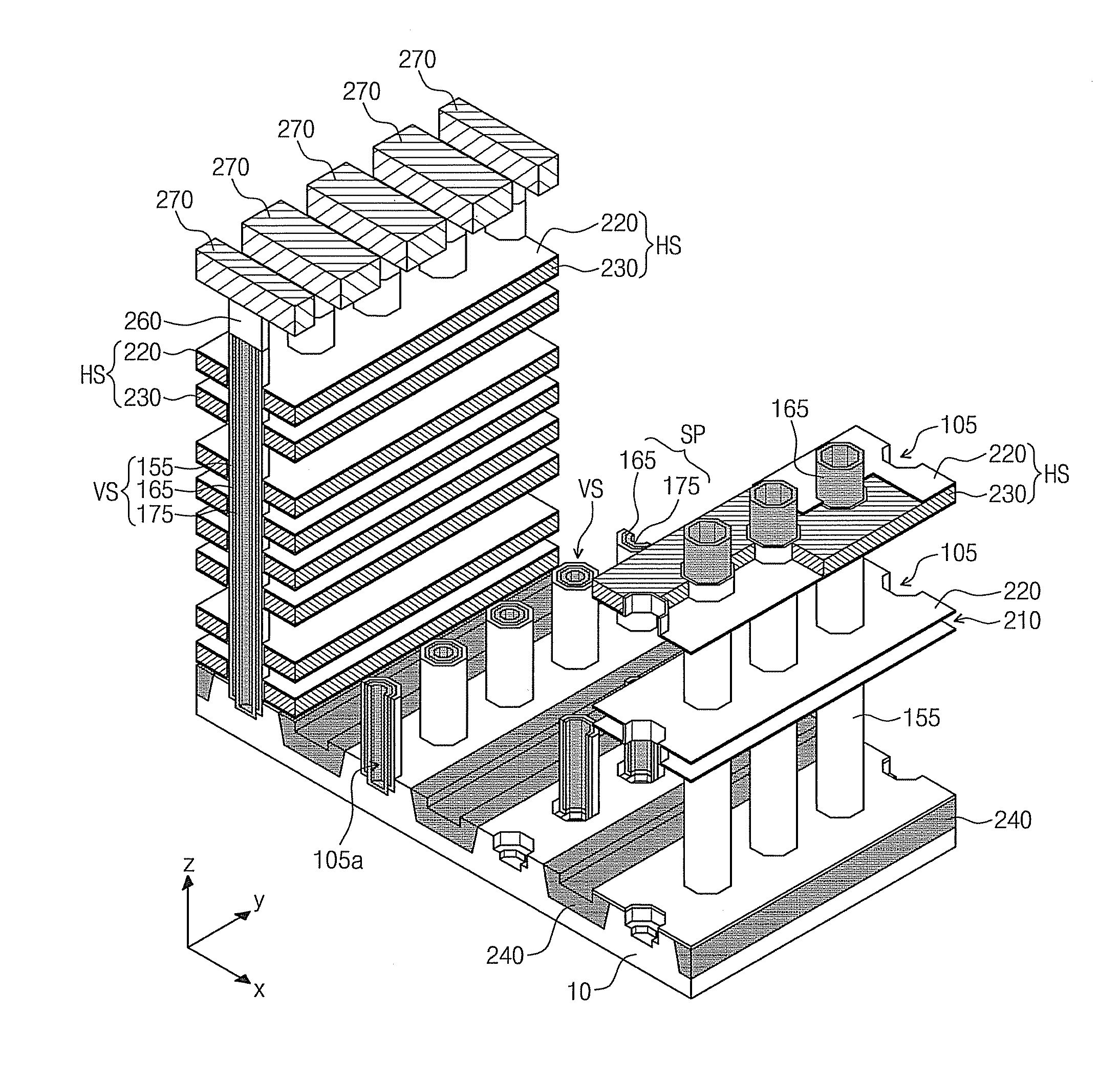
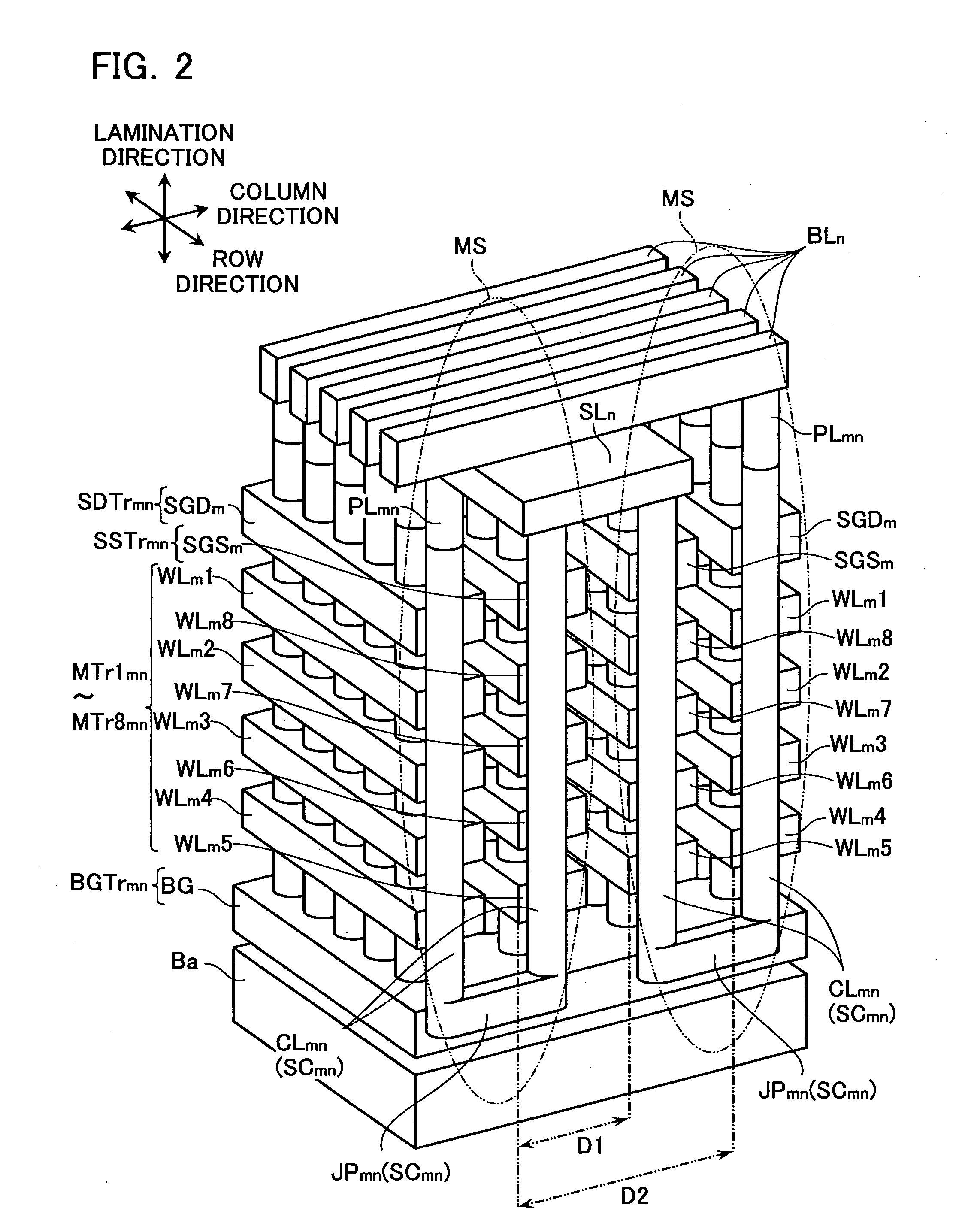
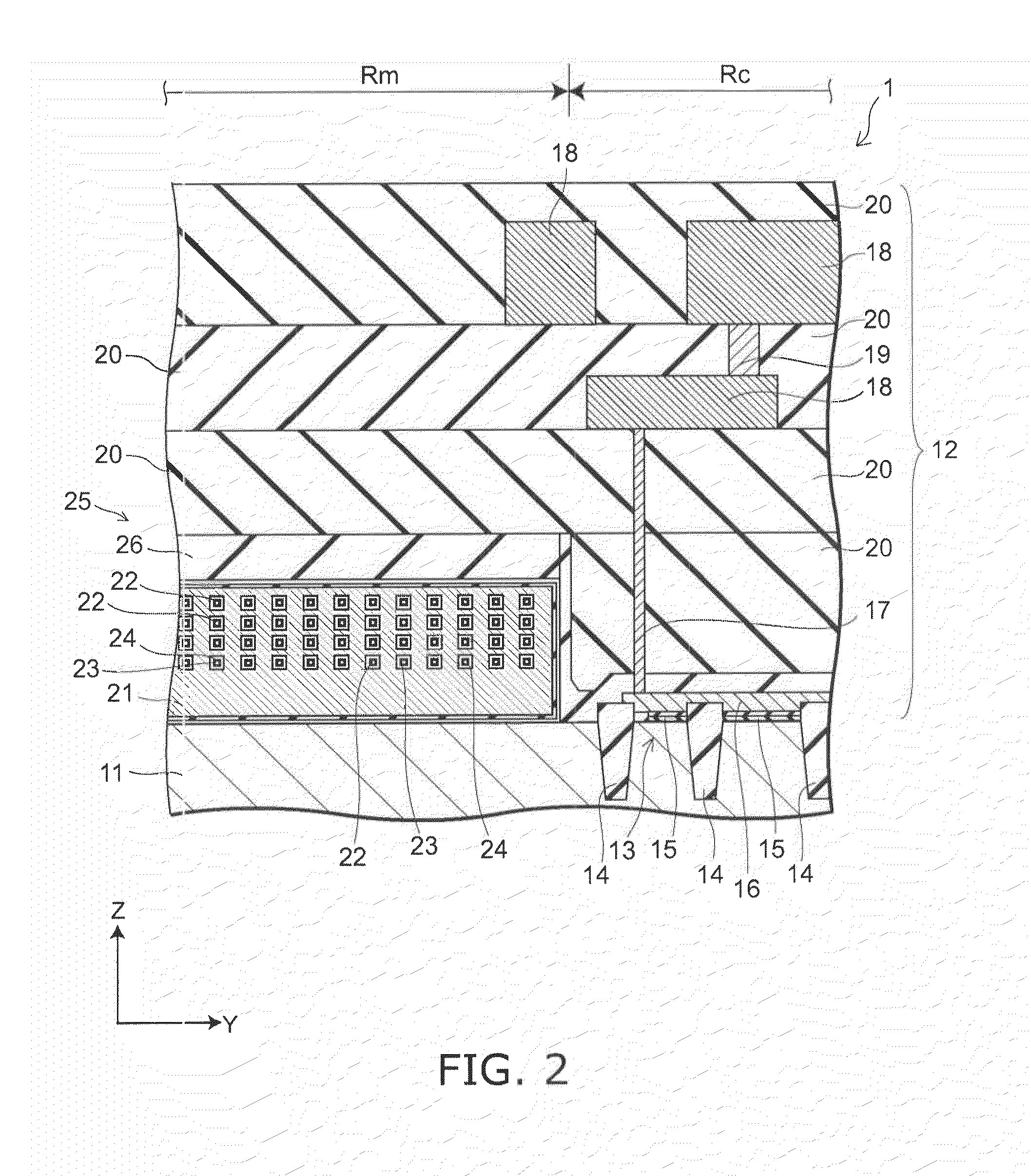
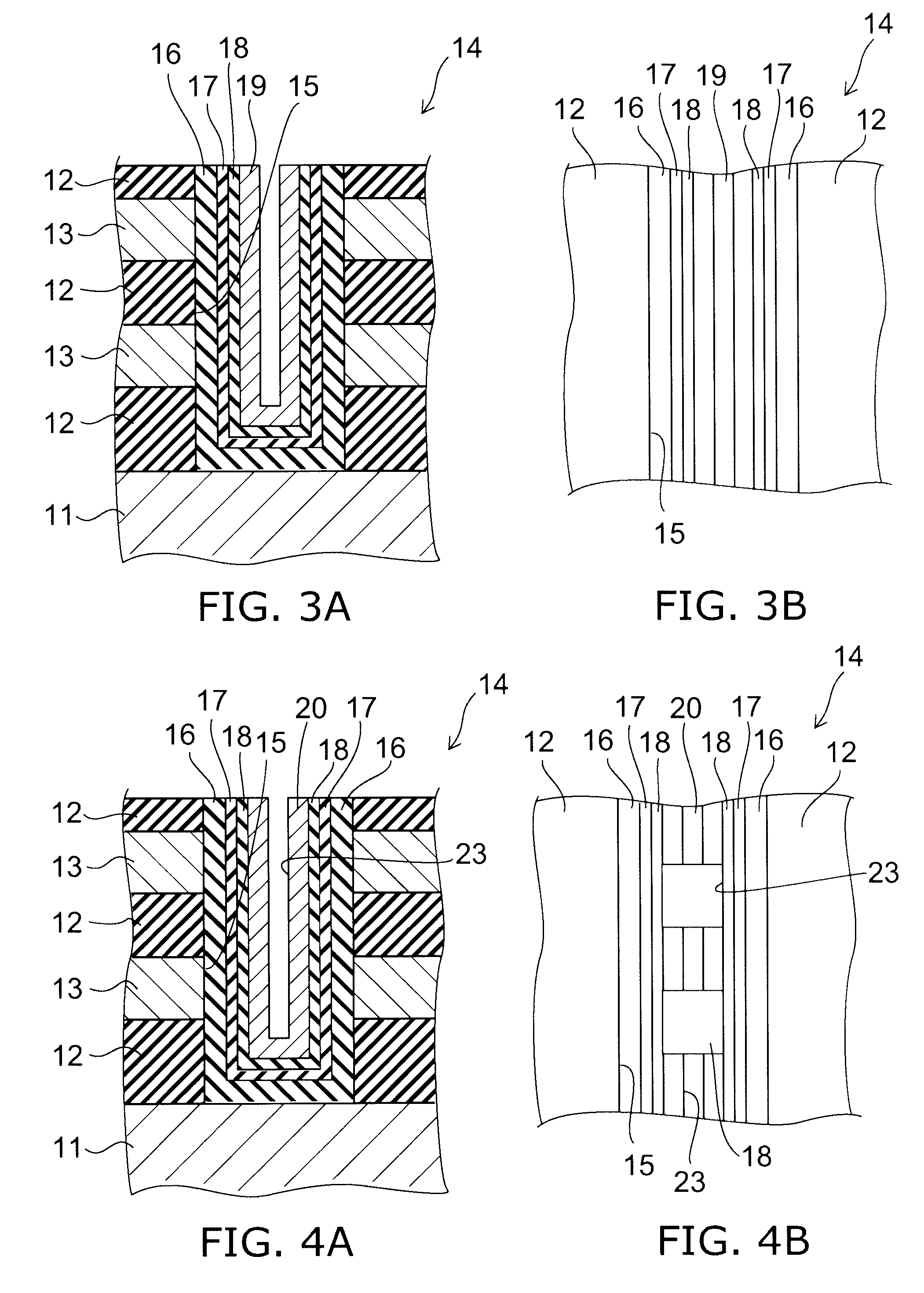
Three-Dimensional Semiconductor Memory Devices And Methods Of Fabricating The Same
ActiveUS20110233648A1Increasing the thicknessReduce resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Three-dimensional semiconductor memory devices and methods of fabricating the same. The three-dimensional semiconductor devices include an electrode structure with sequentially-stacked electrodes disposed on a substrate, semiconductor patterns penetrating the electrode structure, and memory elements including a first pattern and a second pattern interposed between the semiconductor patterns and the electrode structure, the first pattern vertically extending to cross the electrodes and the second pattern horizontally extending to cross the semiconductor patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
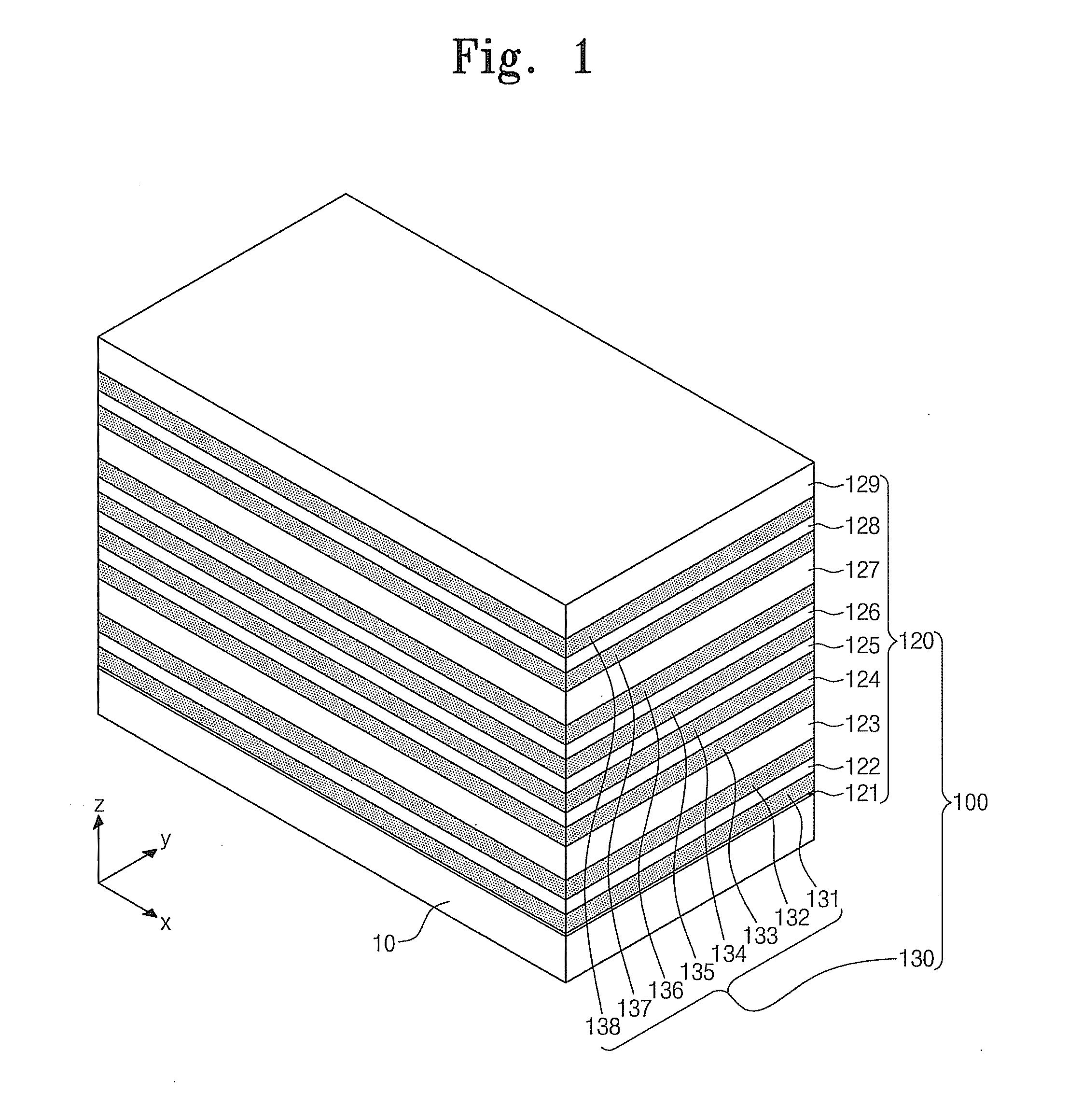
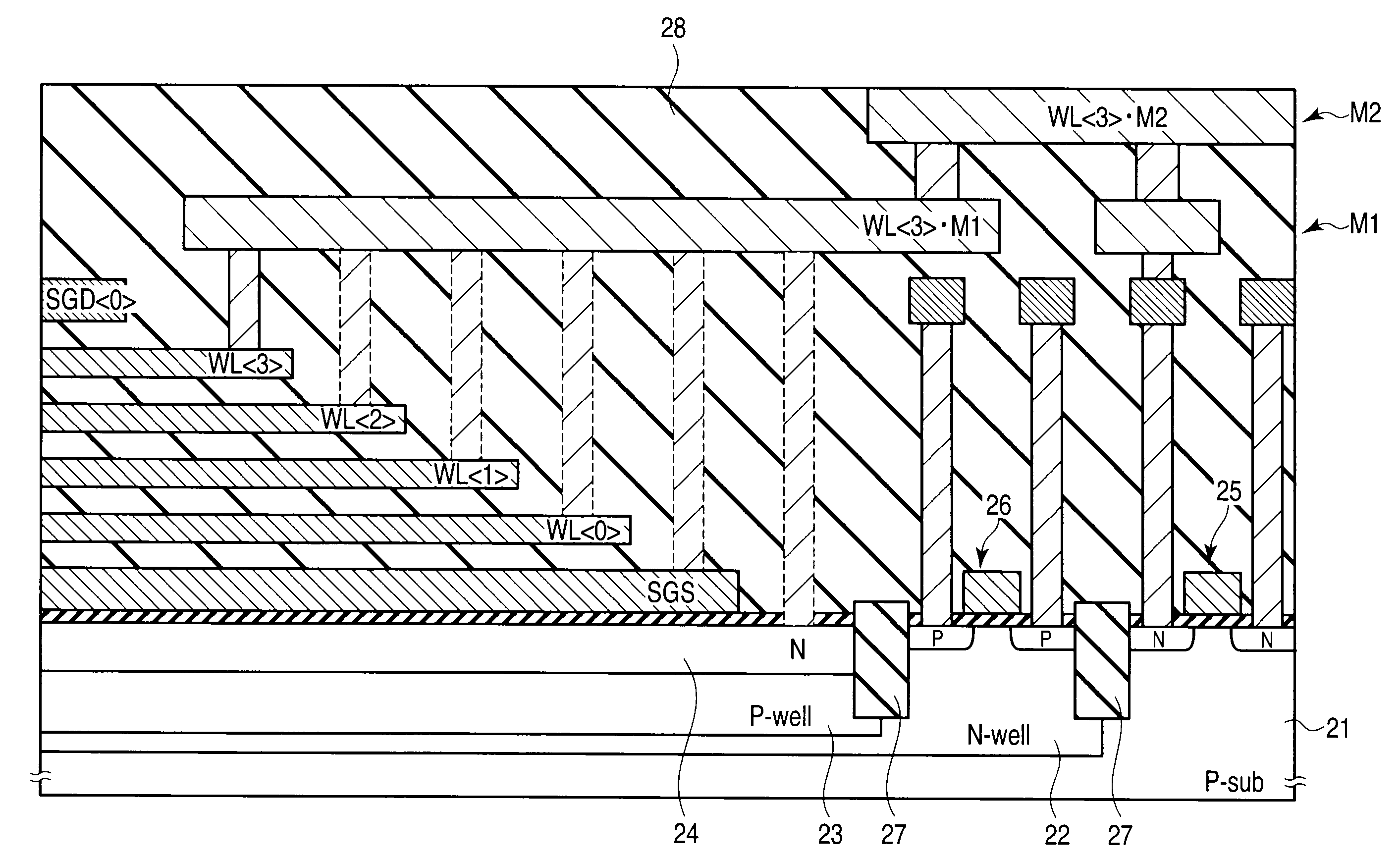
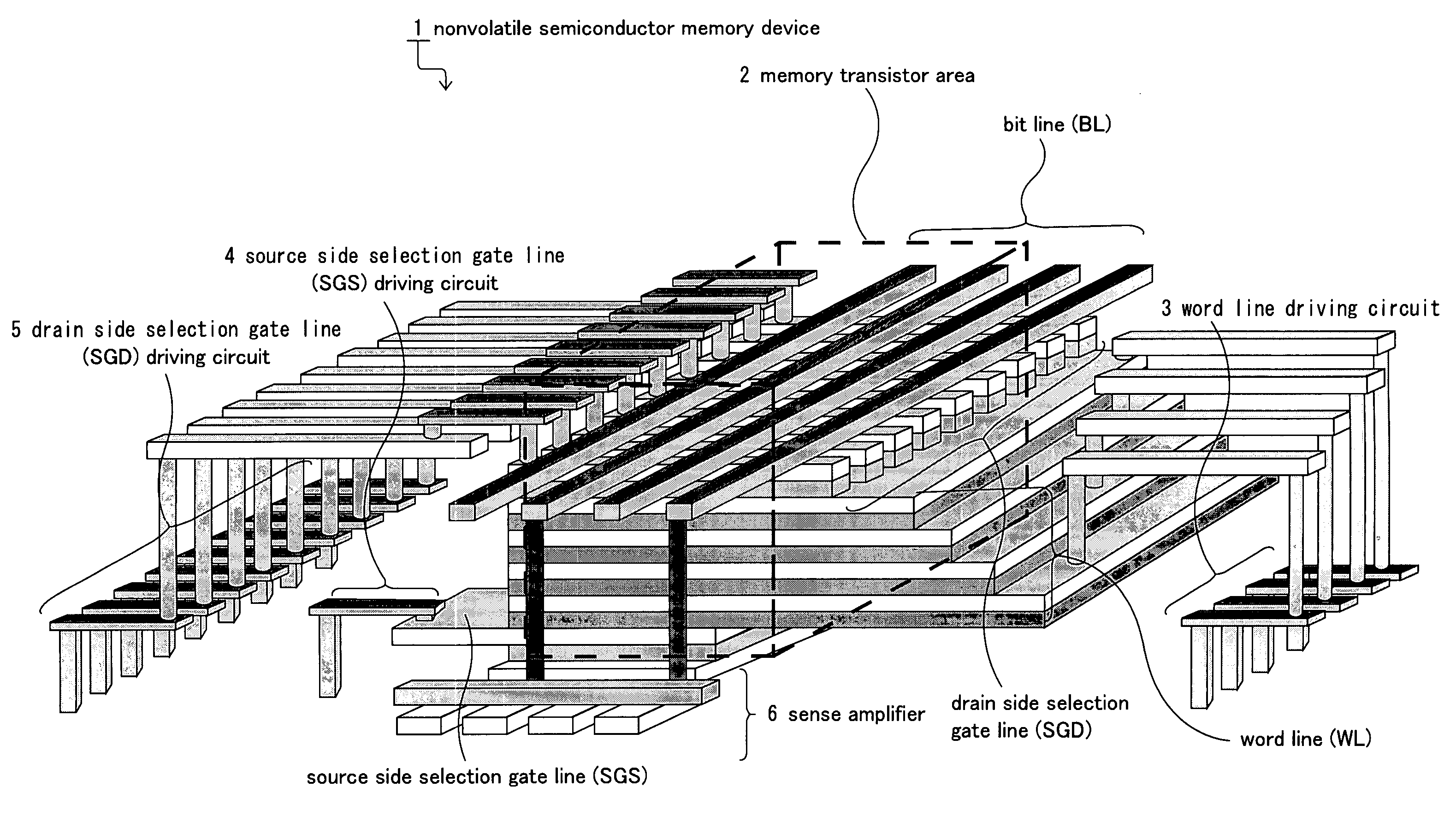
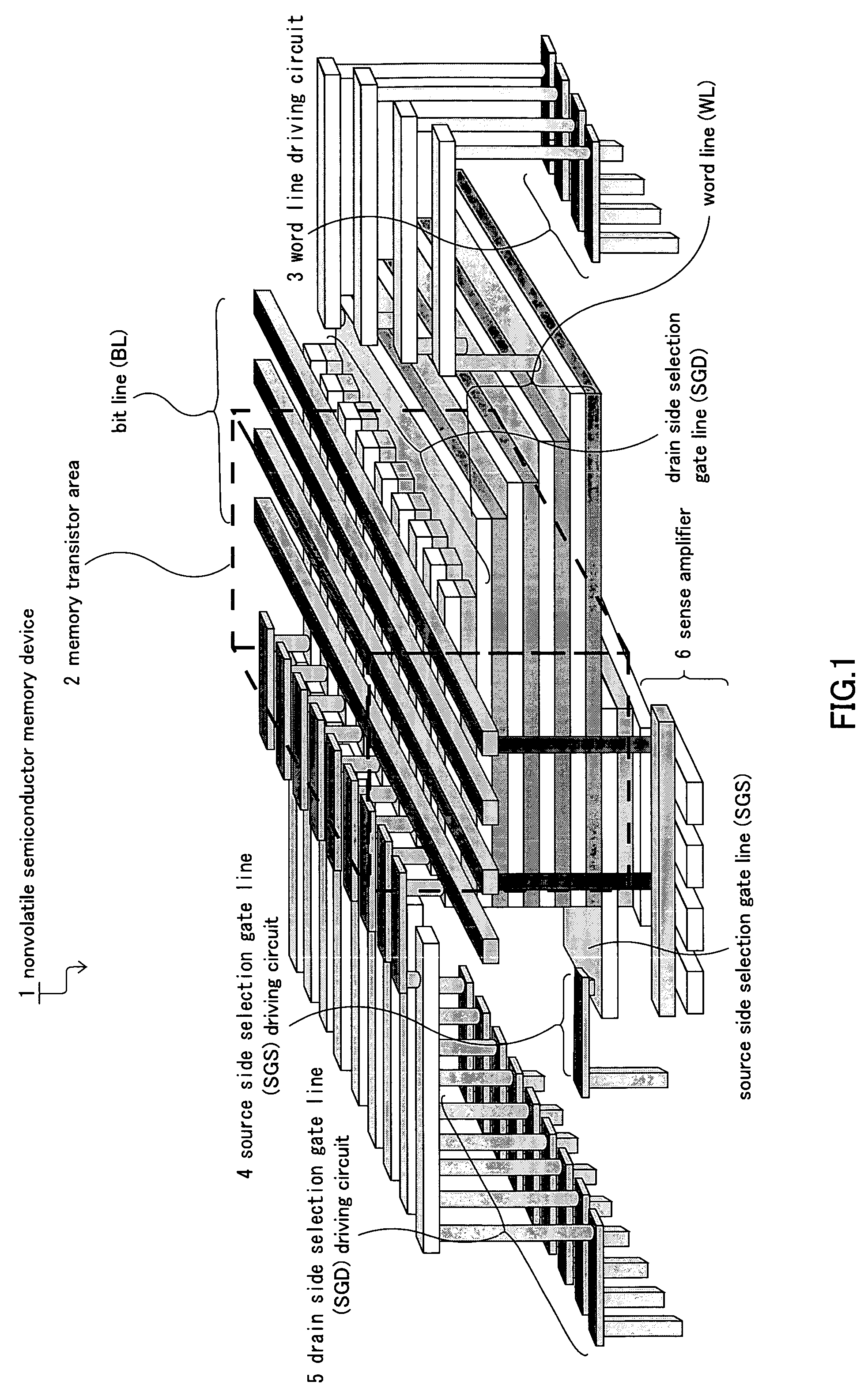
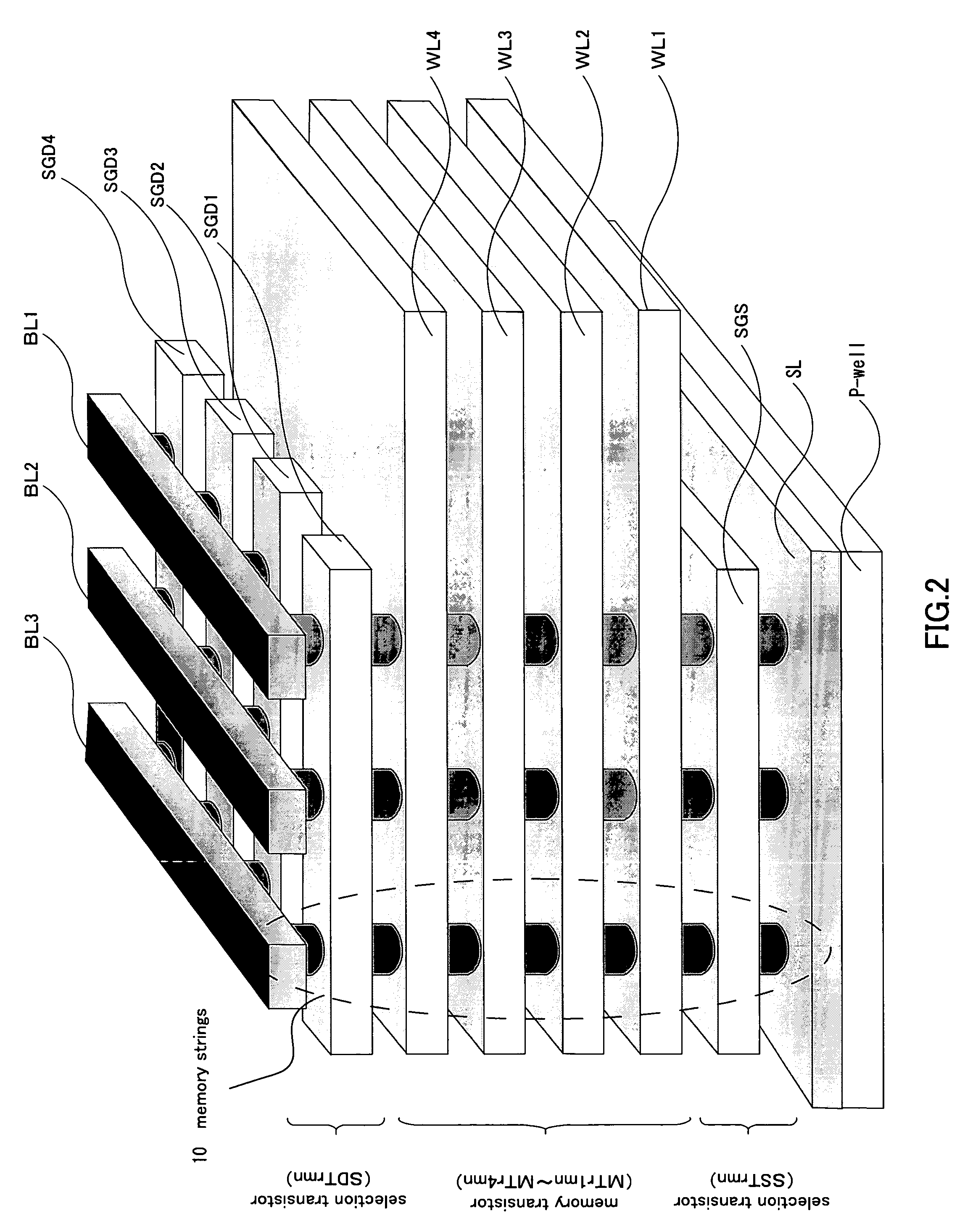
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
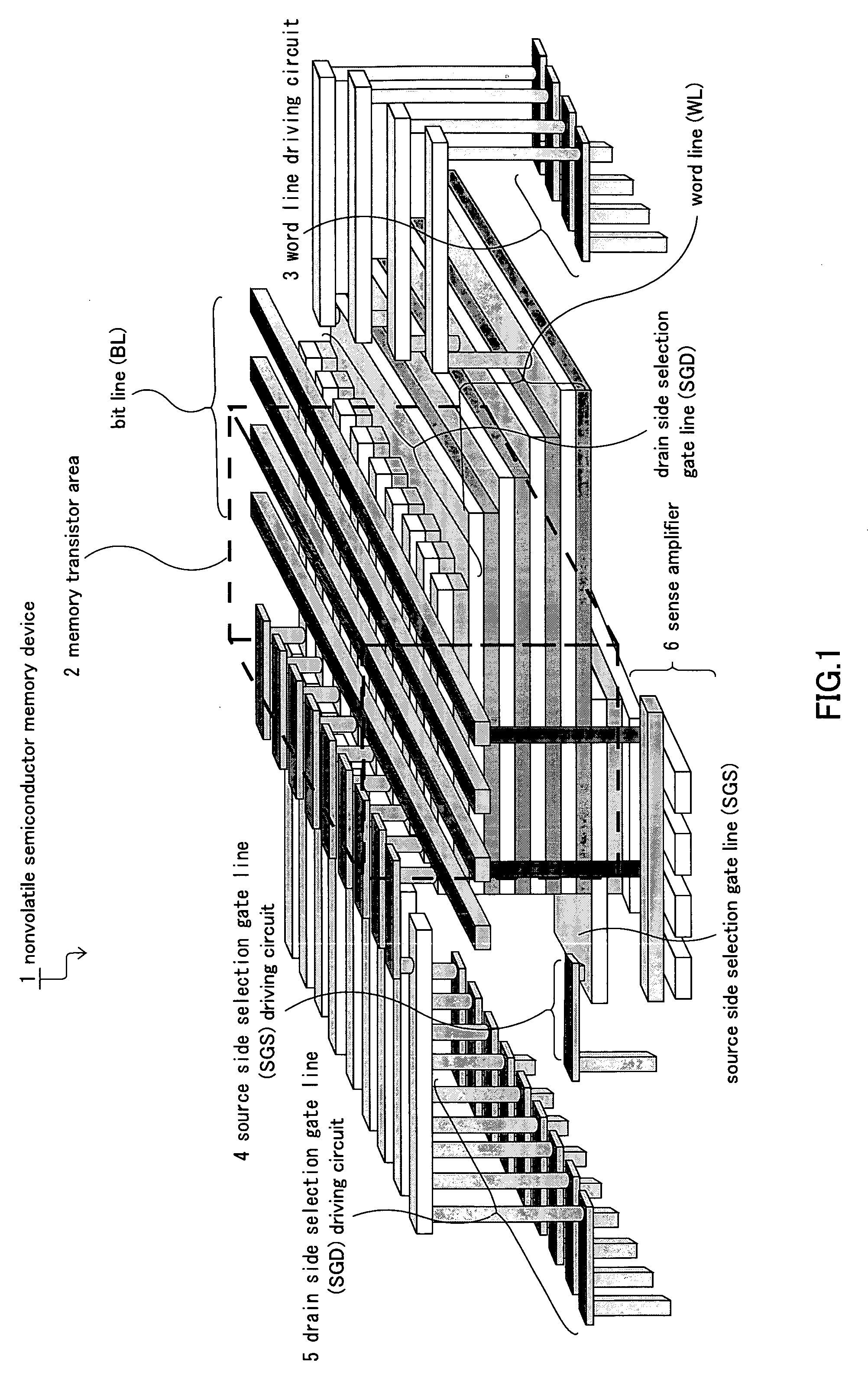
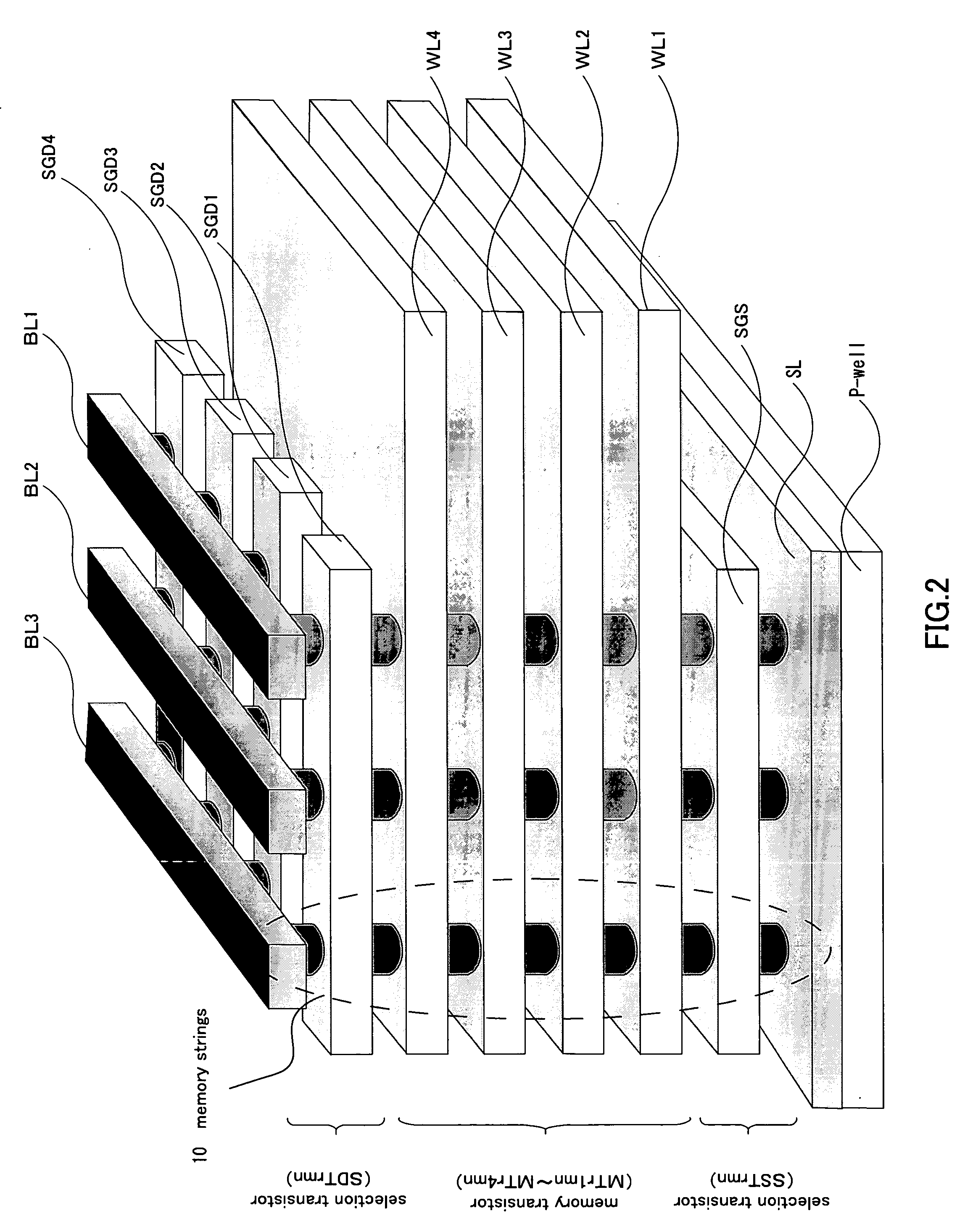
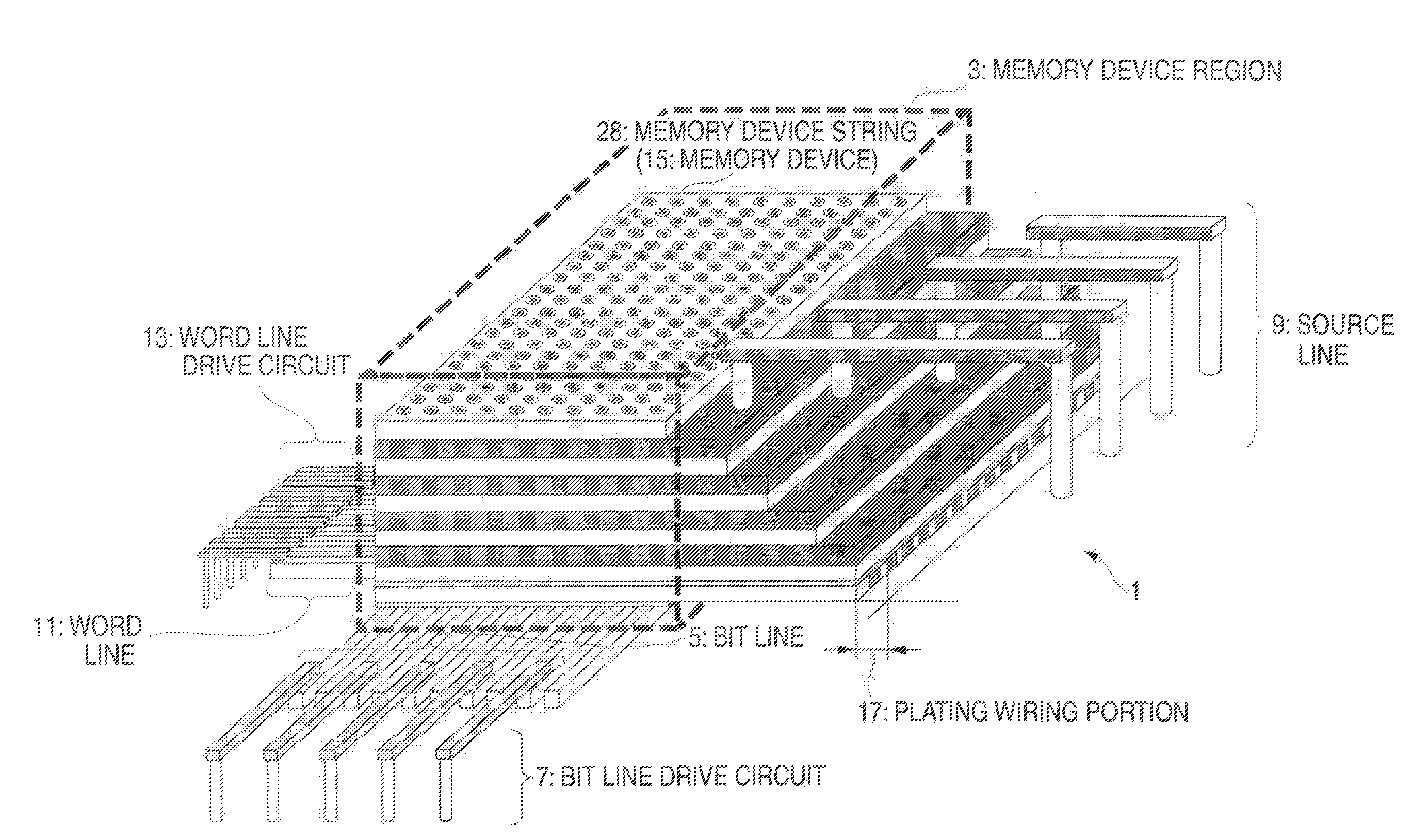
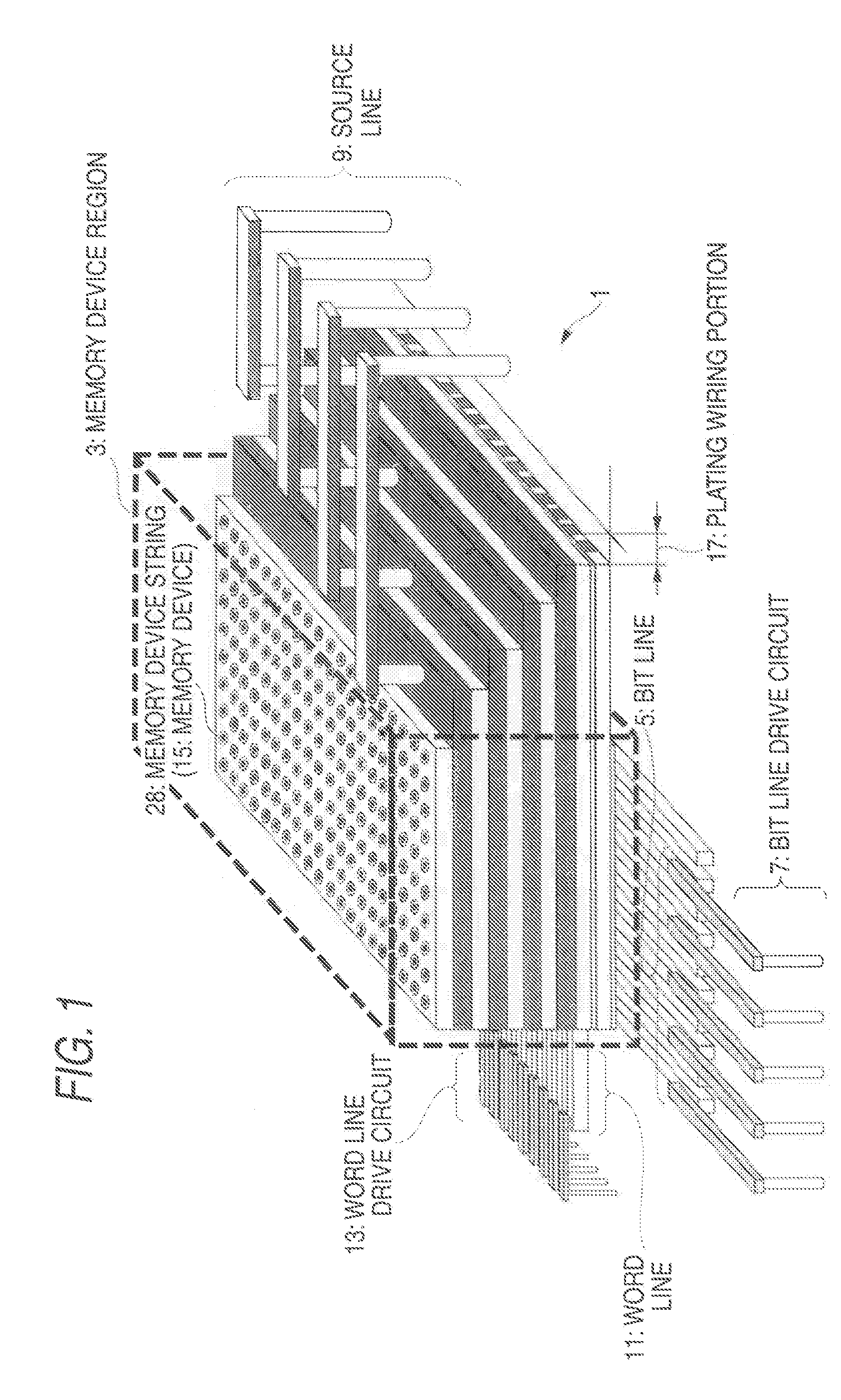
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device that have a new structure are provided, in which memory cells are laminated in a three dimensional state so that the chip area may be reduced. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of the present invention is a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device that has a plurality of the memory strings, in which a plurality of electrically programmable memory cells is connected in series. The memory strings comprise a pillar shaped semiconductor; a first insulation film formed around the pillar shaped semiconductor; a charge storage layer formed around the first insulation film; the second insulation film formed around the charge storage layer; and first or nth electrodes formed around the second insulation film (n is natural number more than 1). The first or nth electrodes of the memory strings and the other first or nth electrodes of the memory strings are respectively the first or nth conductor layers that are spread in a two dimensional state.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
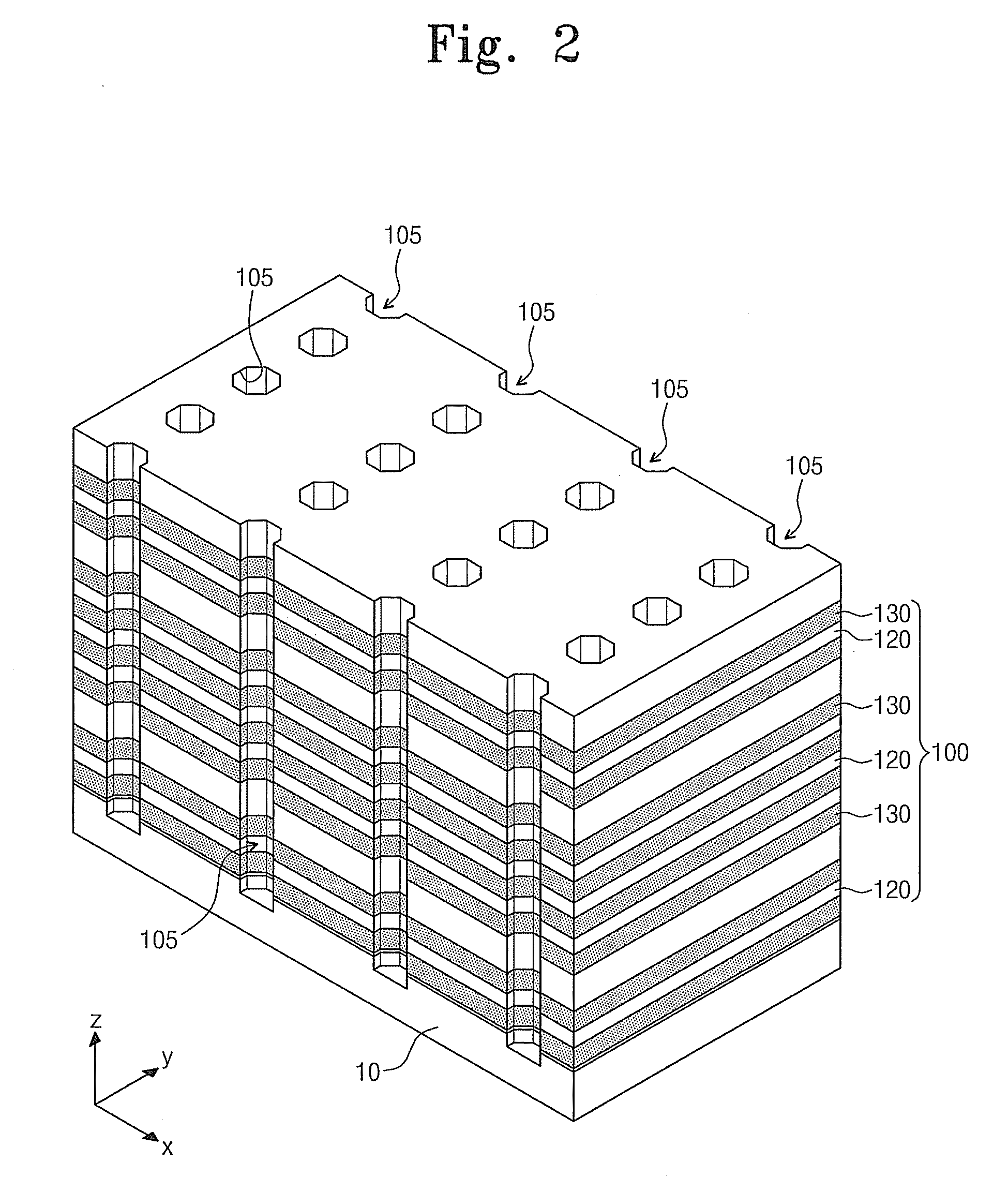
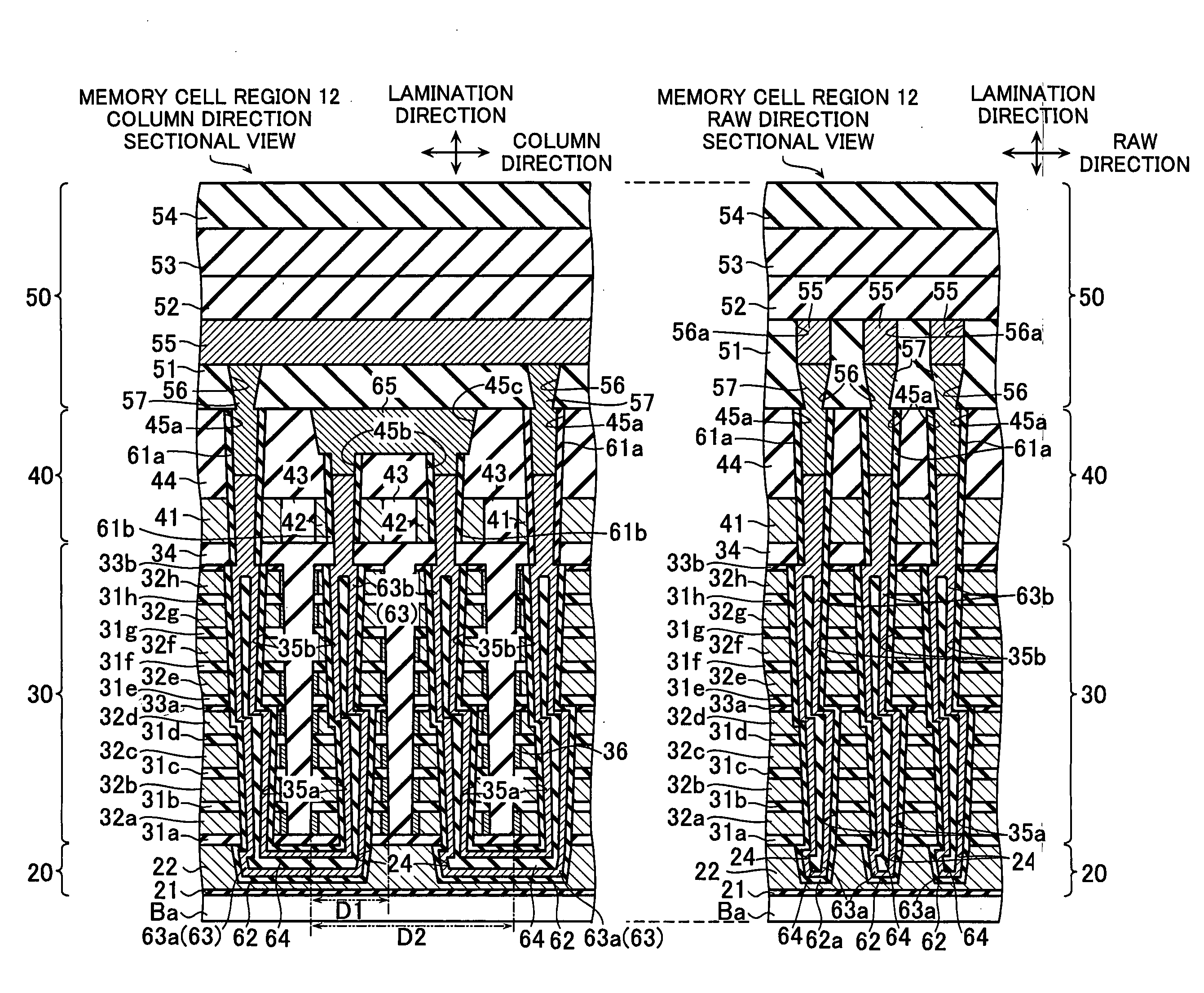
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings to each of which a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells are connected in series. Each of the memory strings includes first semiconductor layers each having a pair of columnar portions extending in a vertical direction with respect to a substrate and a coupling portion formed to couple the lower ends of the pair of columnar portions; a charge storage layer formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions; and first conductive layers formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions and the charge storage layer. The first conductive layers functions as gate electrodes of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
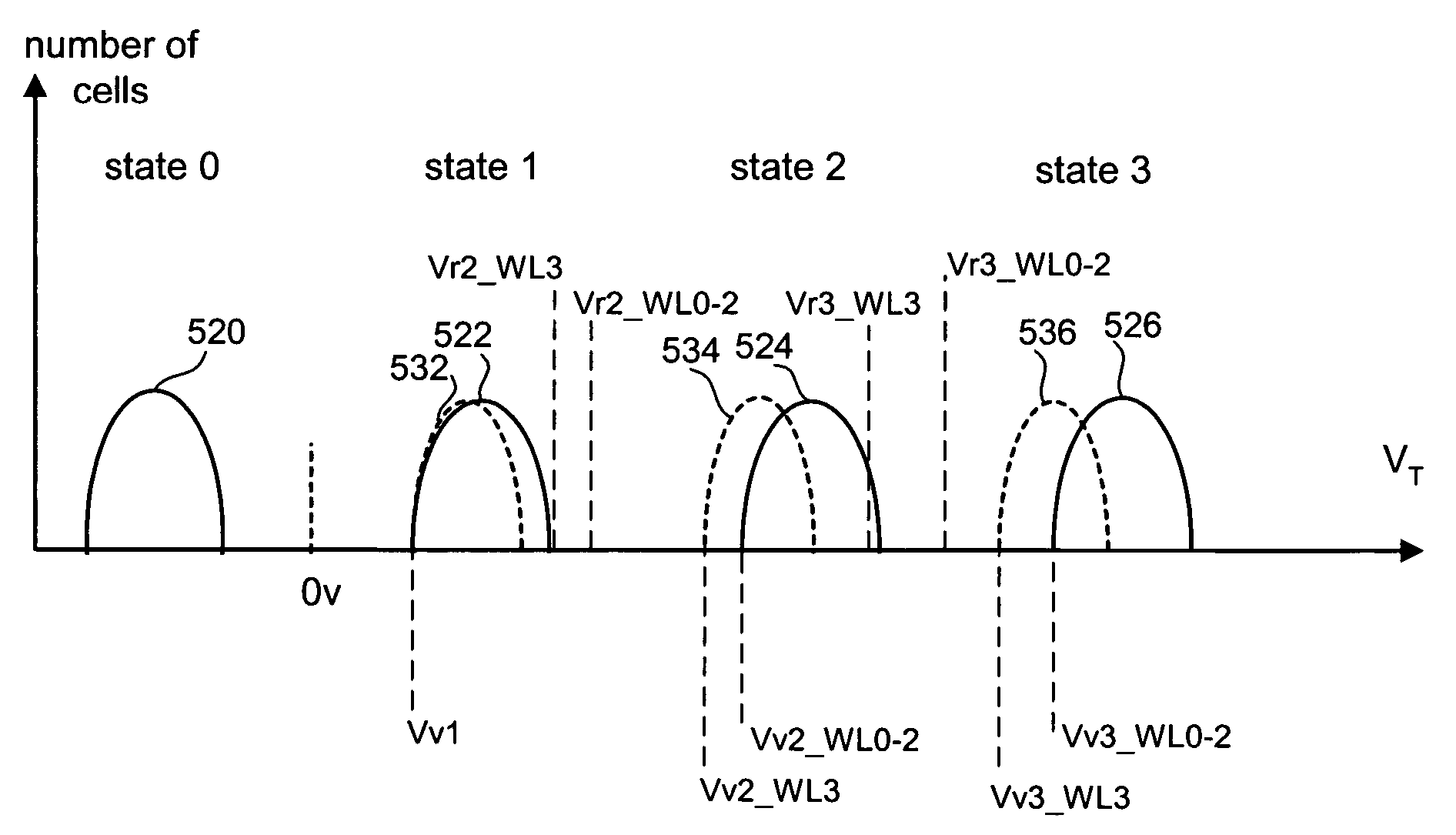
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Source side self boosting technique for non-volatile memory
InactiveUS6859397B2Improve performanceMinimize program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePre-chargeProgramming process
A non-volatile semiconductor memory system (or other type of memory system) is programmed in a manner that avoids program disturb. In one embodiment that includes a flash memory system using a NAND architecture, program disturb is avoided by increasing the channel potential of the source side of the NAND string during the programming process. One exemplar implementation includes applying a voltage (e.g. Vdd) to the source contact and turning on the source side select transistor for the NAND sting corresponding to the cell being inhibited. Another implementation includes applying a pre-charging voltage to the unselected word lines of the NAND string corresponding to the cell being inhibited prior to applying the program voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
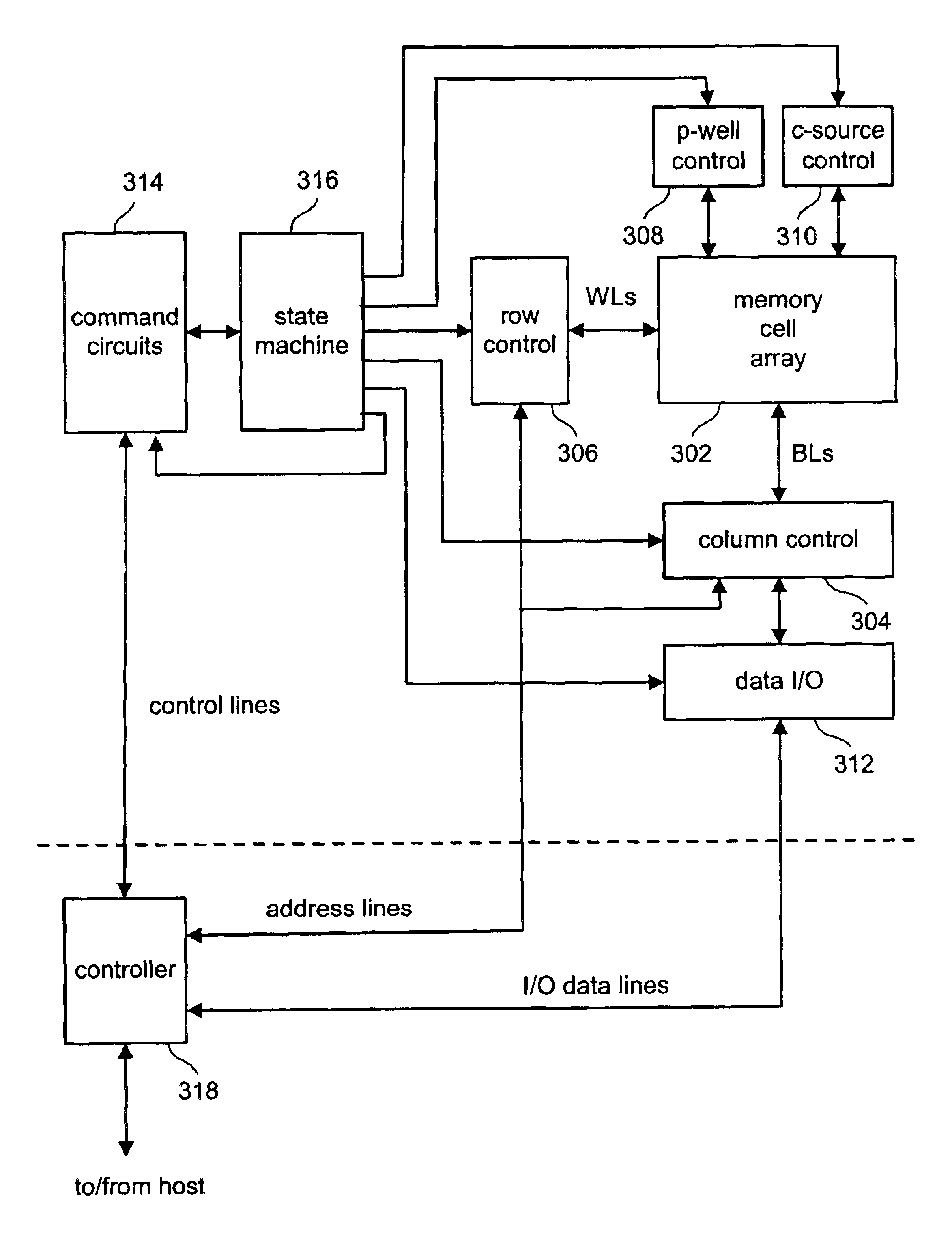
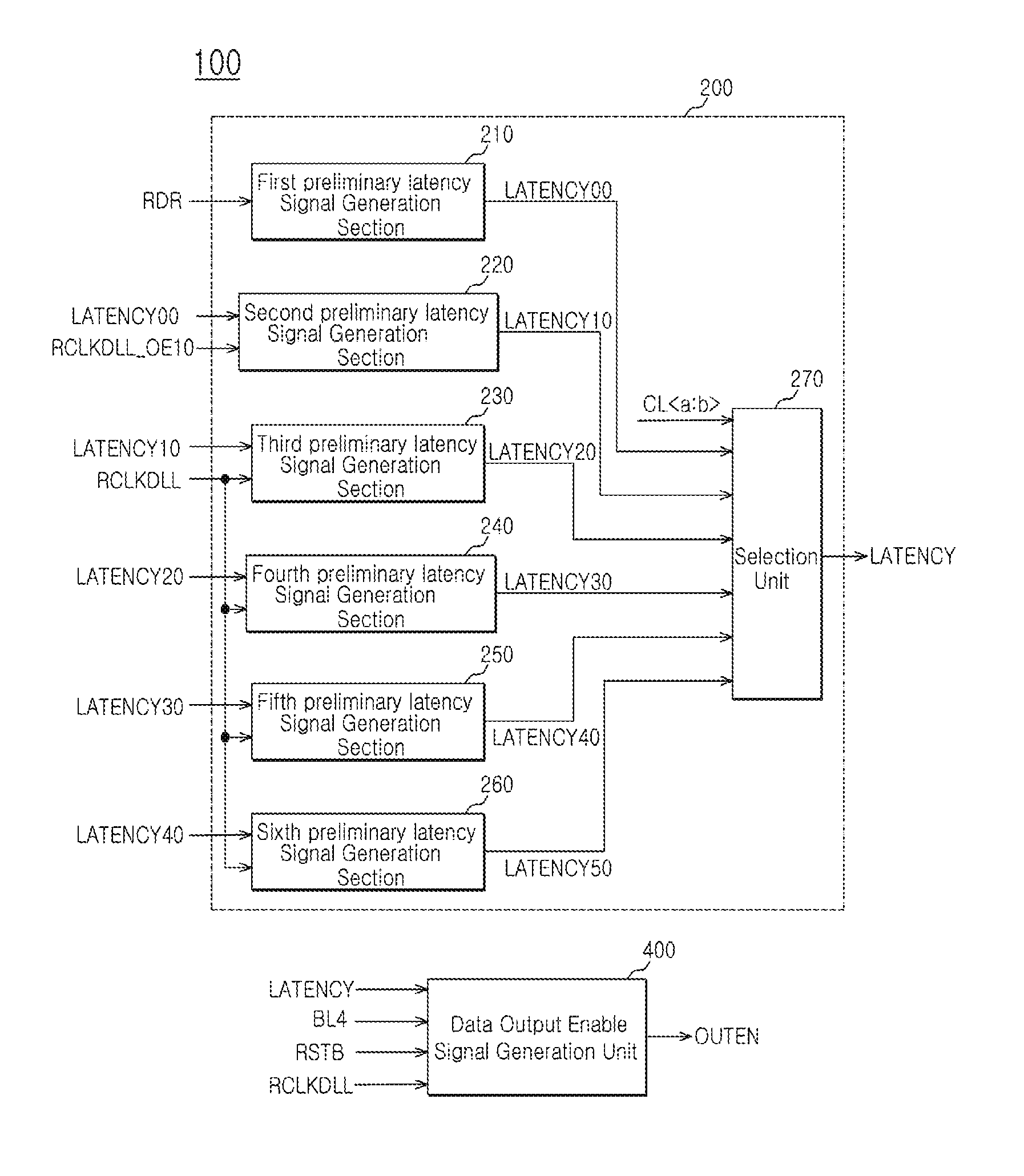
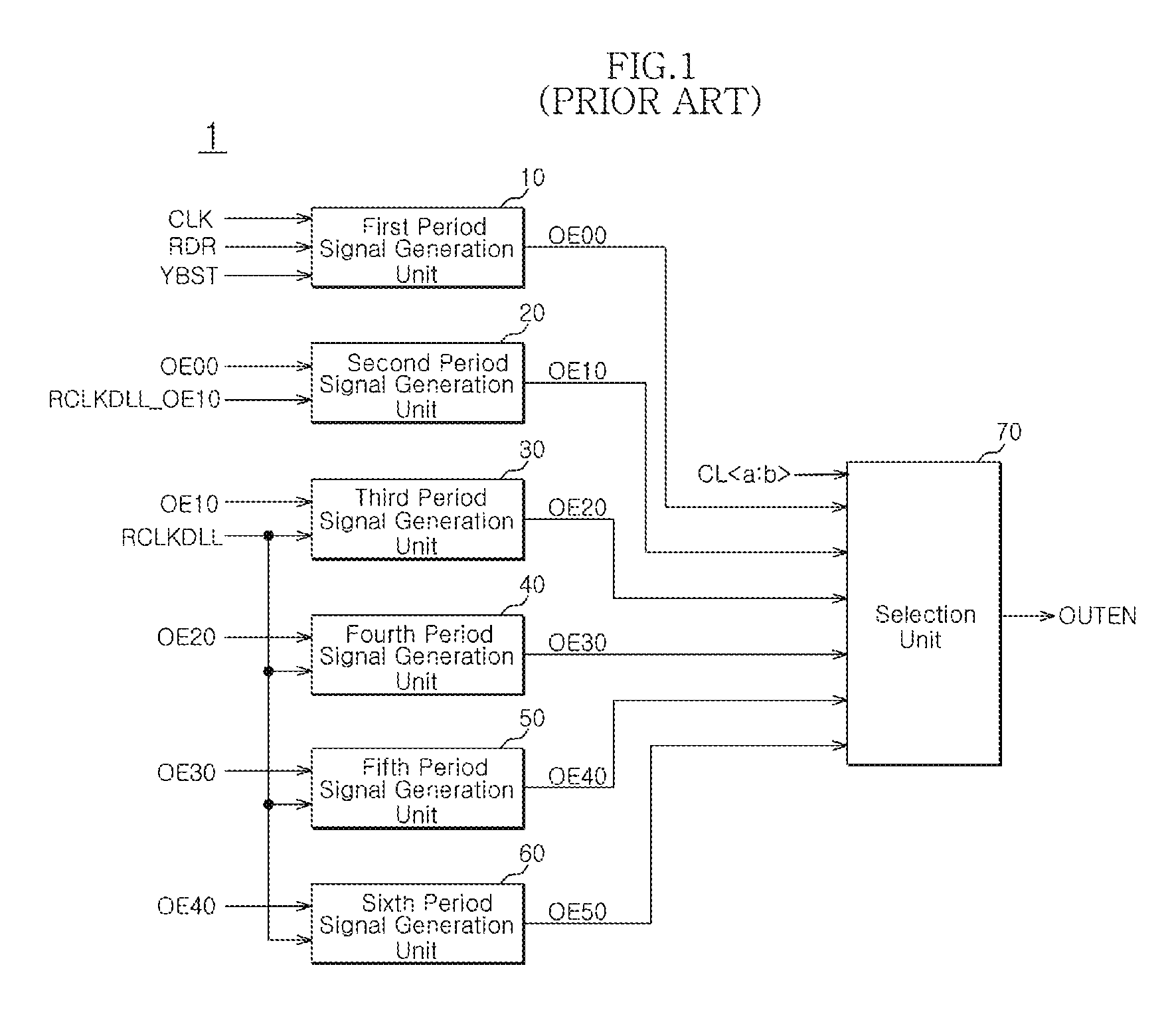
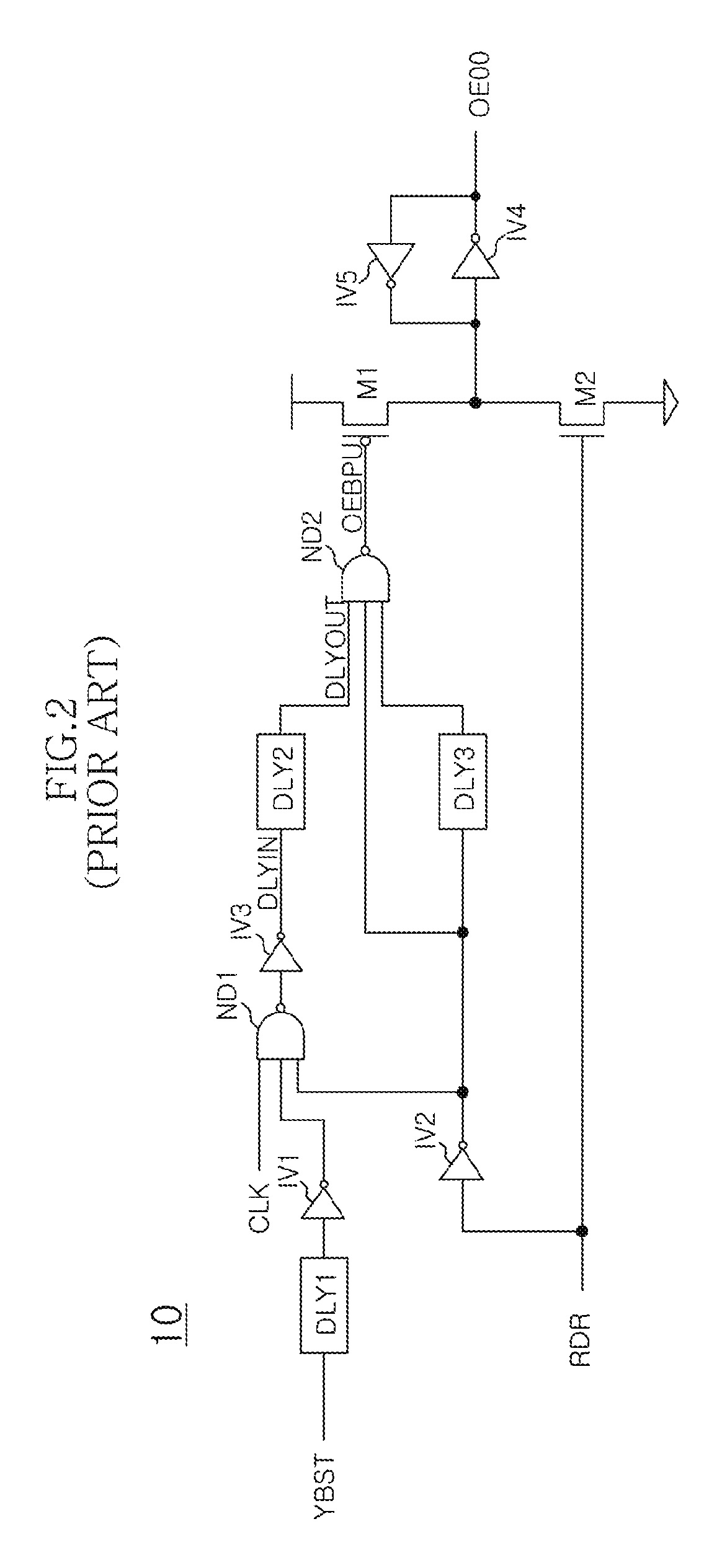
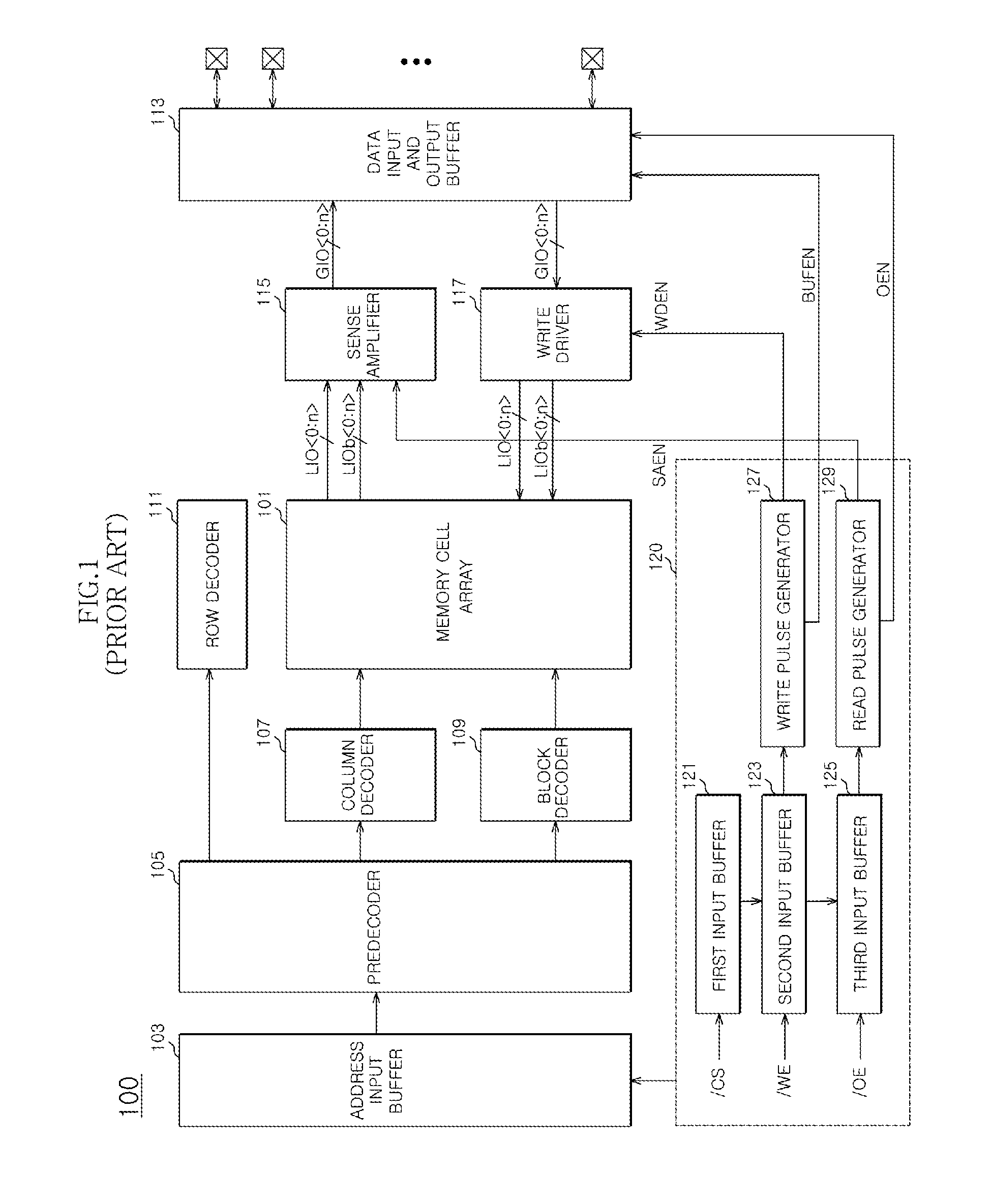
Output enable signal generation circuit of semiconductor memory
An output enable signal generation circuit of a semiconductor memory includes: a latency signal generation unit configured to generate a latency signal for designating activation timing of a data output enable signal in response to a read signal and a CAS latency signal; and a data output enable signal generation unit configured to control the activation timing and deactivation timing of the data output enable signal in response to the latency signal and a signal generated by shifting the latency signal based on a burst length (BL).
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
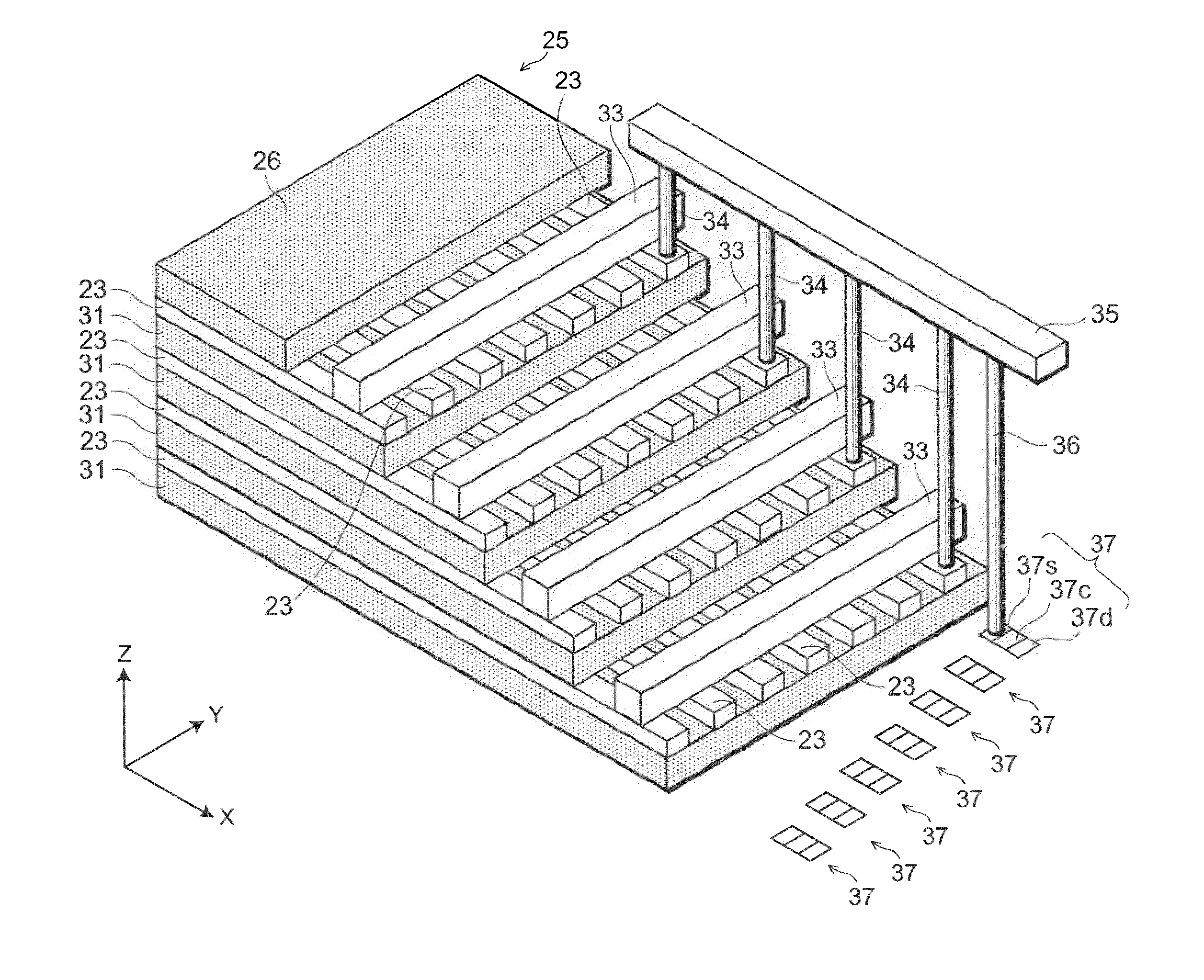
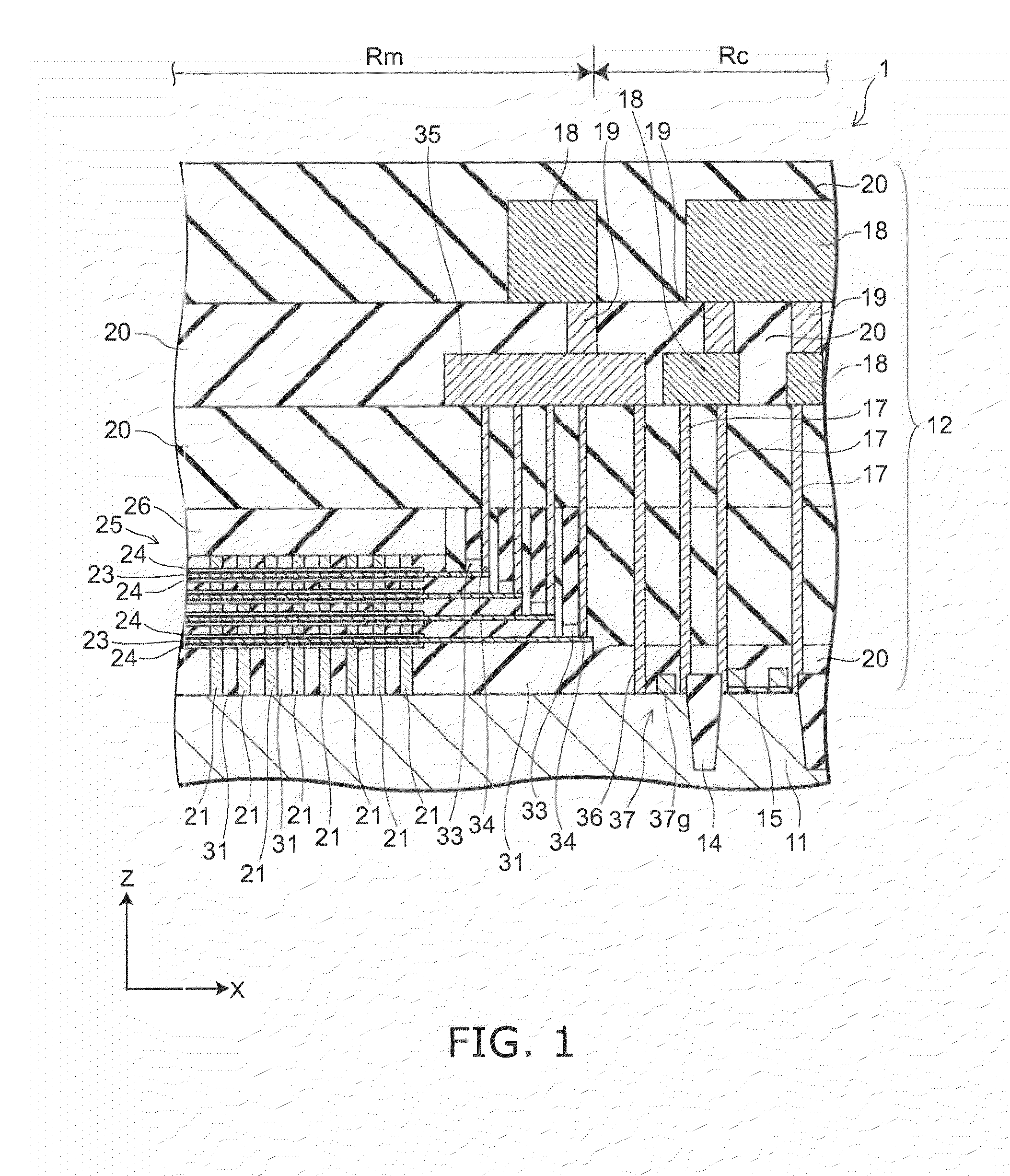
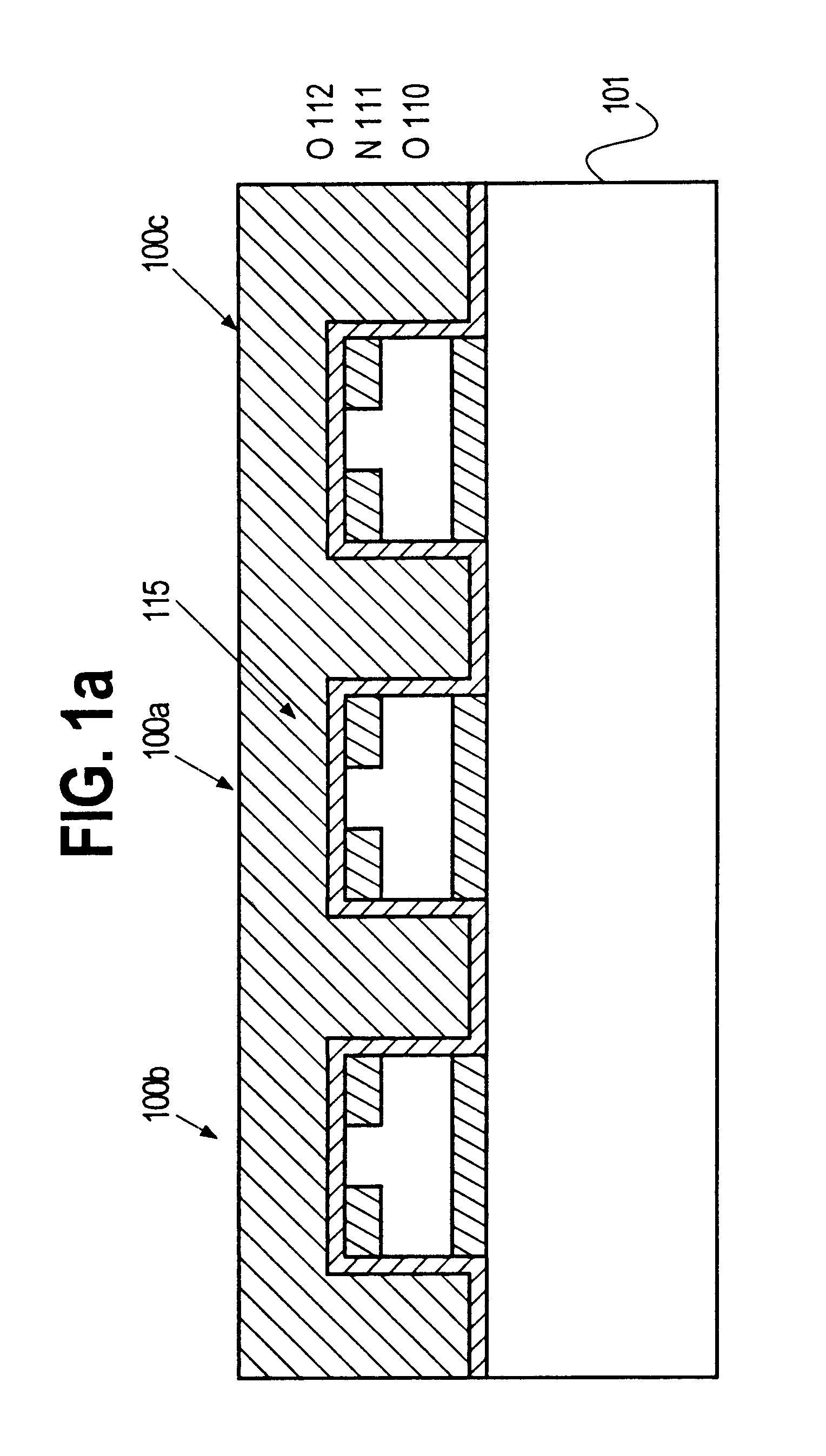
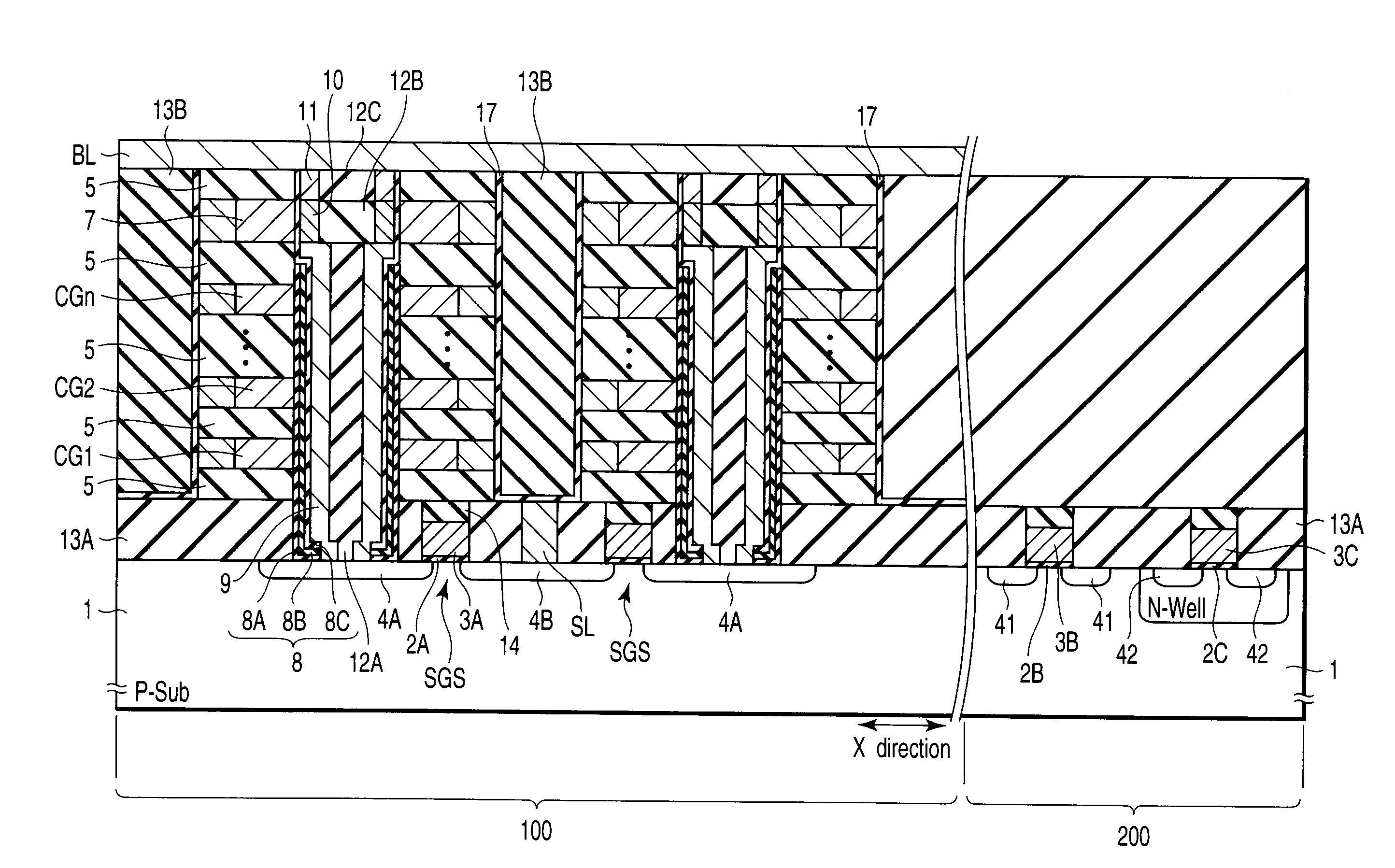
Semiconductor memory and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20110284946A1Increase bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSilicon
A semiconductor memory capable of increasing bit density by three-dimensional arrangement of cells and a method for manufacturing the same are provided.In a semiconductor memory 1, gate electrode films 21 are provided on a silicon substrate 11. The gate electrode films 21 are arranged in one direction parallel to the upper surface of the silicon substrate 11 (X direction). Each gate electrode film 21 has a lattice plate-like shape, having through holes 22 in a matrix form as viewed in the X direction. Silicon beams 23 are provided passing through the through holes 22 of the gate electrode films 21 and extending in the X direction. Further, an ONO film 24 including a charge storage layer is provided between the gate electrode film 21 and the silicon beam 23.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
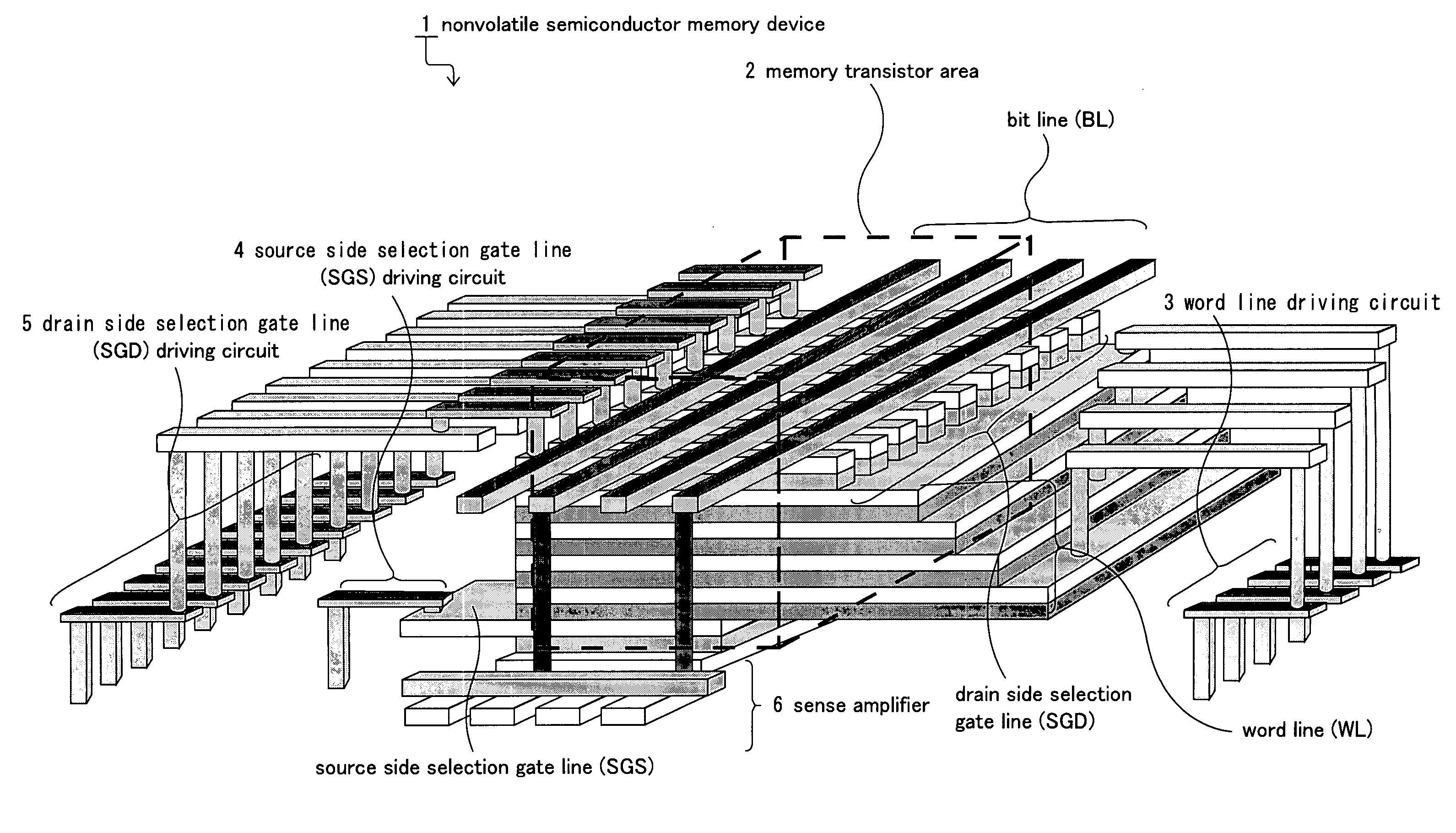
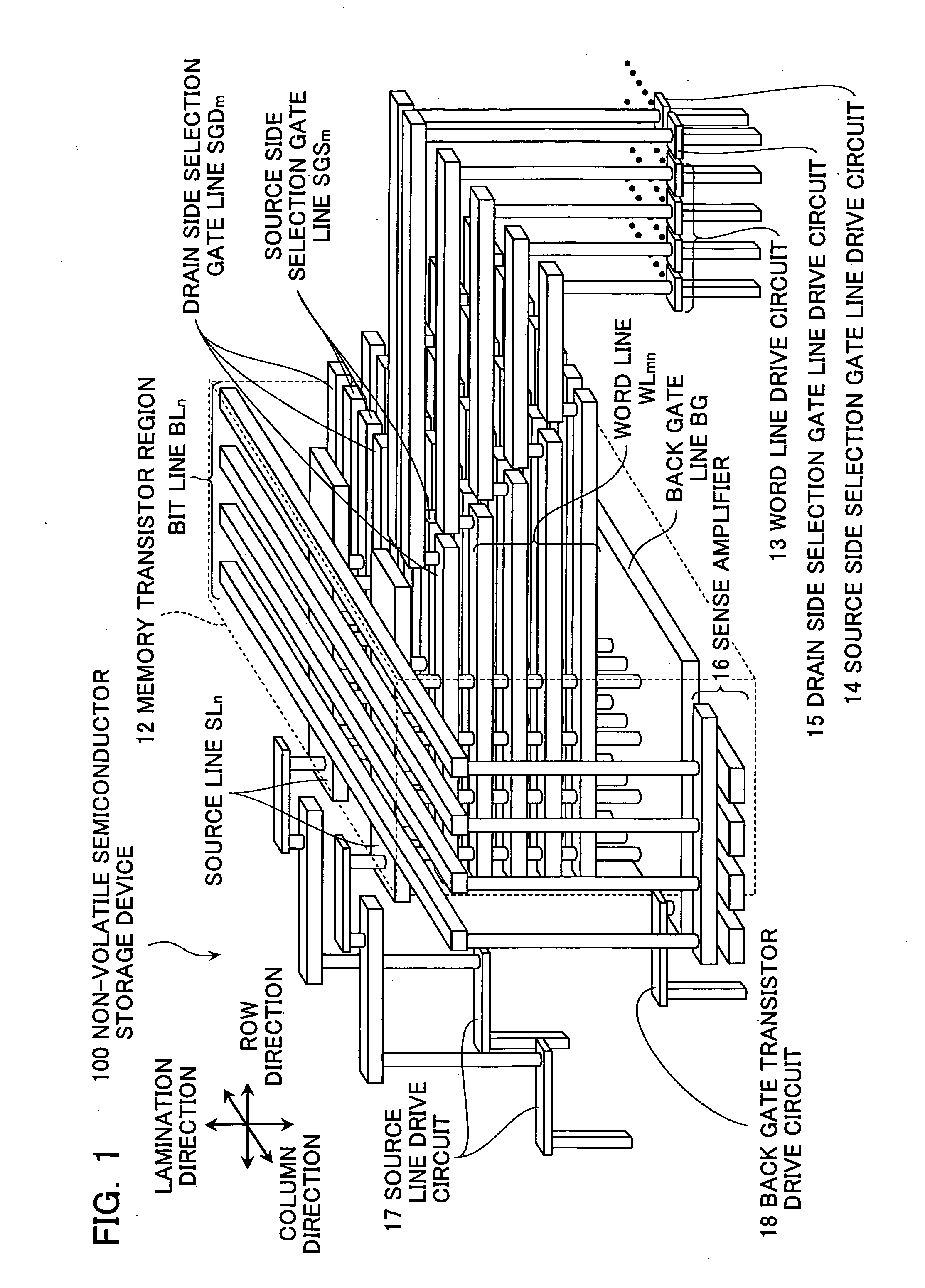
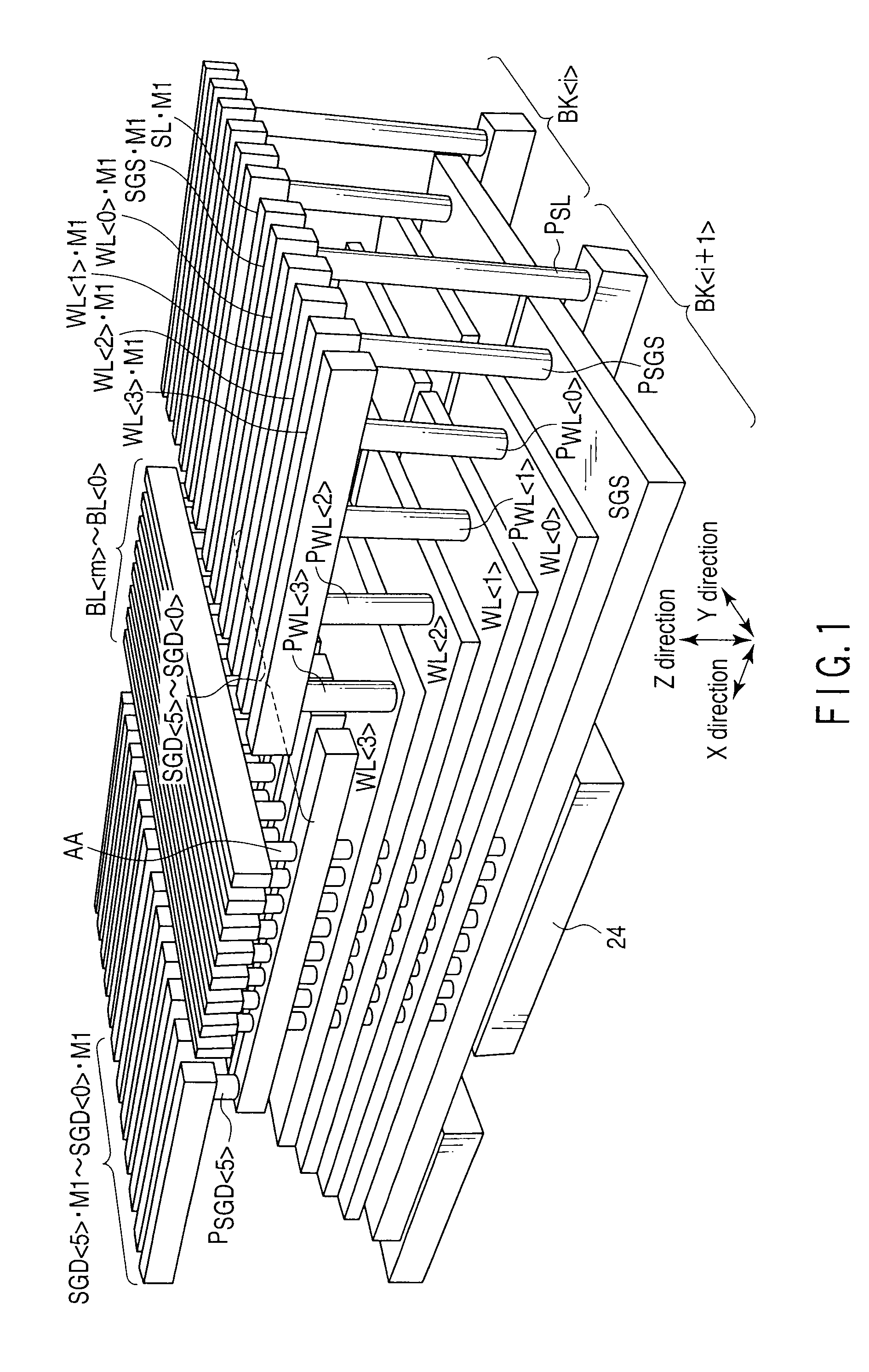
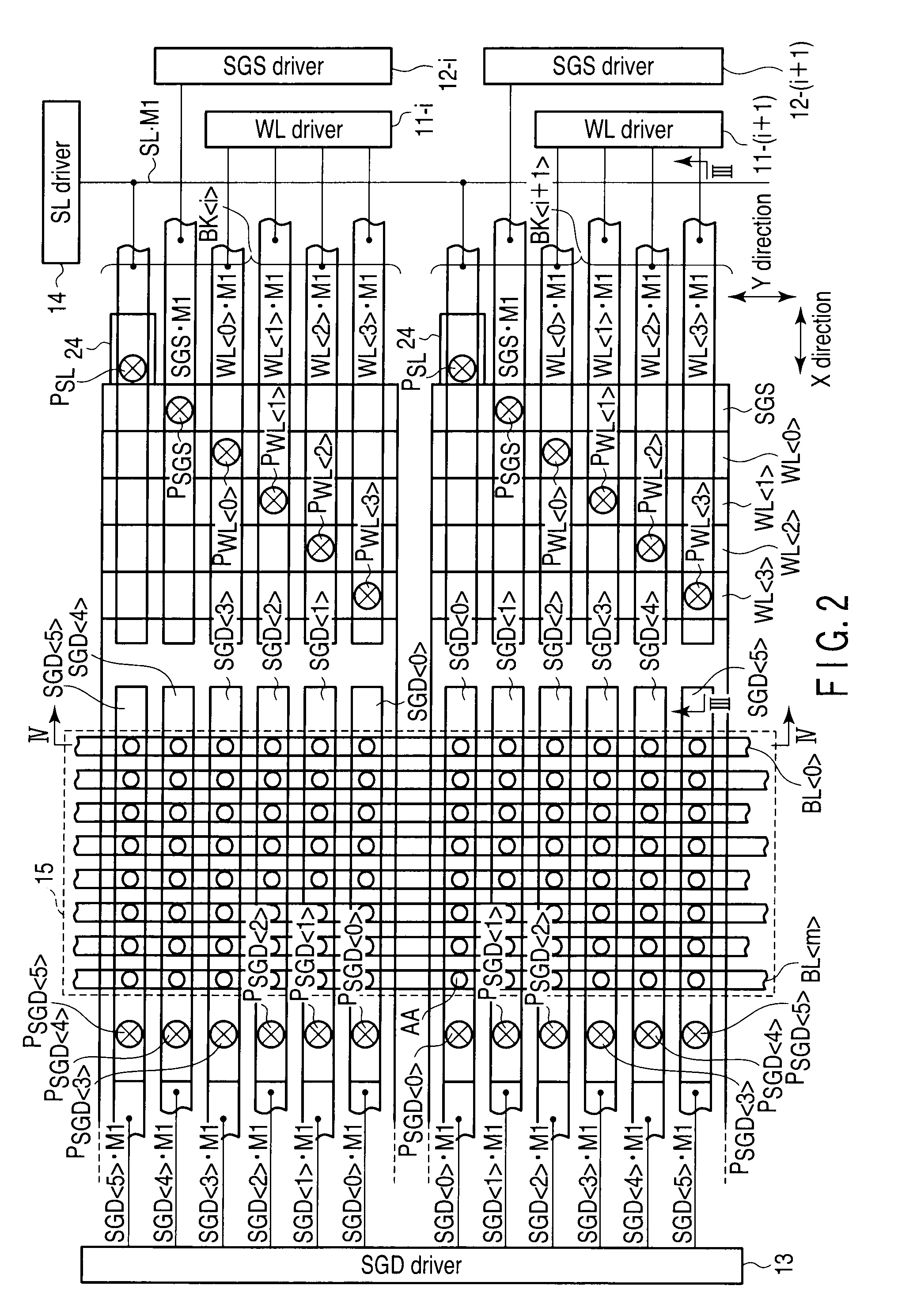
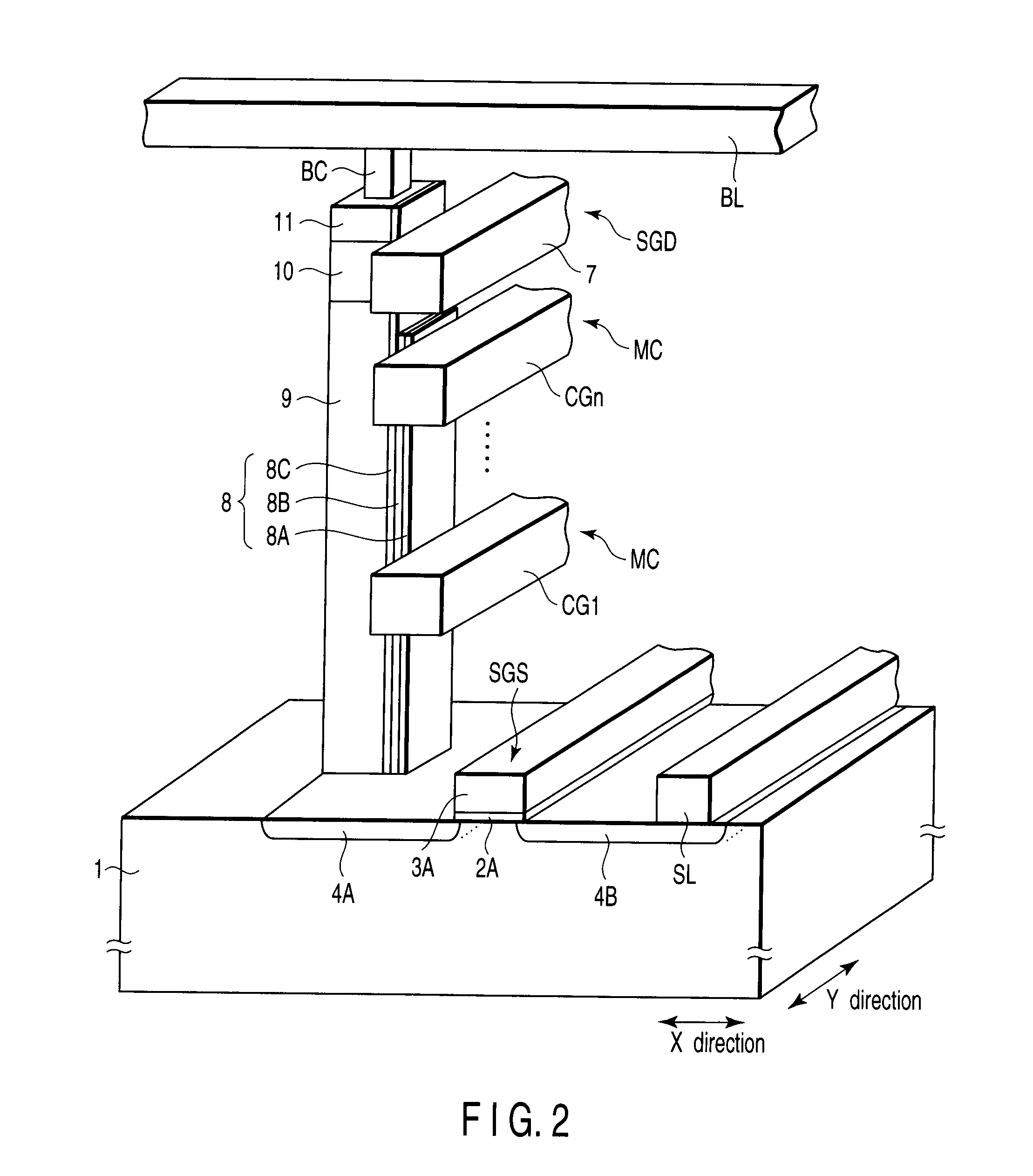
Three dimensional stacked nonvolatile semiconductor memory
A three dimensional stacked nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to an example of the present invention includes a memory cell array comprised of first and second blocks disposed side by side in a first direction, and a driver disposed on one end of the memory cell array in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction. A source diffusion layer, which is common to the first and second blocks, is disposed in a semiconductor substrate, and a contact plug, which has a lower end connected to the source diffusion layer and an upper end connected to a source line disposed above at least three conductive layers, is interposed between the first and second blocks.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor memory and method for manufacturing the same
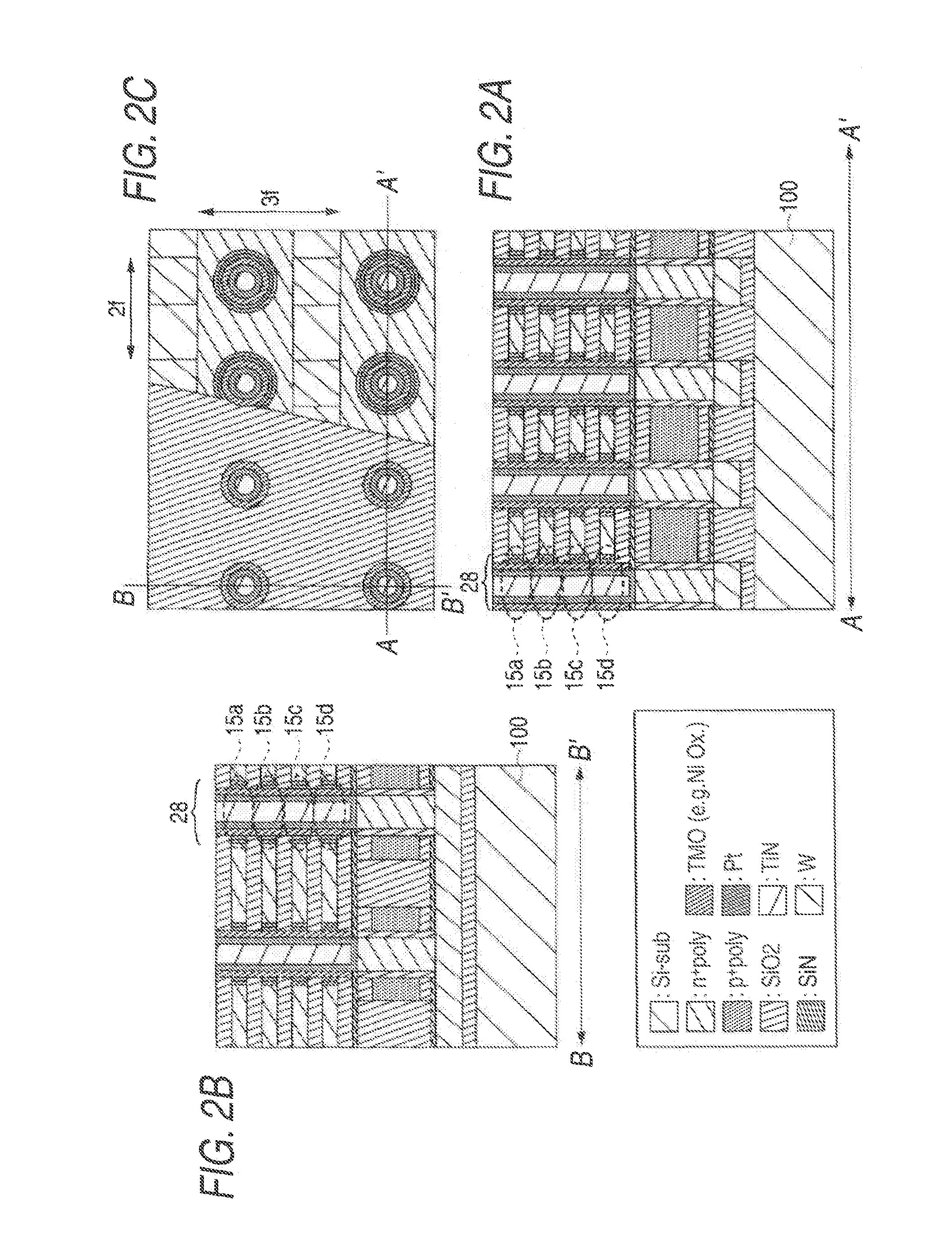
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a nonvolatile semiconductor memory including: a plurality of memory devices each having: a resistance change element, and a diode connected serially to the resistance change element; and a source conductive layer spreading two-dimensionally to be connected to one ends of the plurality of memory devices.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Vertical memory device structures
Vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are added to a separately fabricated substrate that includes electrical devices and / or interconnect. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are physically separated from each other, and are not disposed within the same semiconductor body. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells can be added to the separately fabricated substrate as a thin layer including several doped semiconductor regions which, subsequent to attachment, are etched to produce individual doped stack structures, which are then supplied with various dielectric coatings, gate electrodes, and contacts by means of further processing operations. Alternatively, the plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells may be completely fabricated prior to attachment. DRAMs, SRAMs, non-volatile memories, and combinations of memory types can be provided.
Owner:BESANG
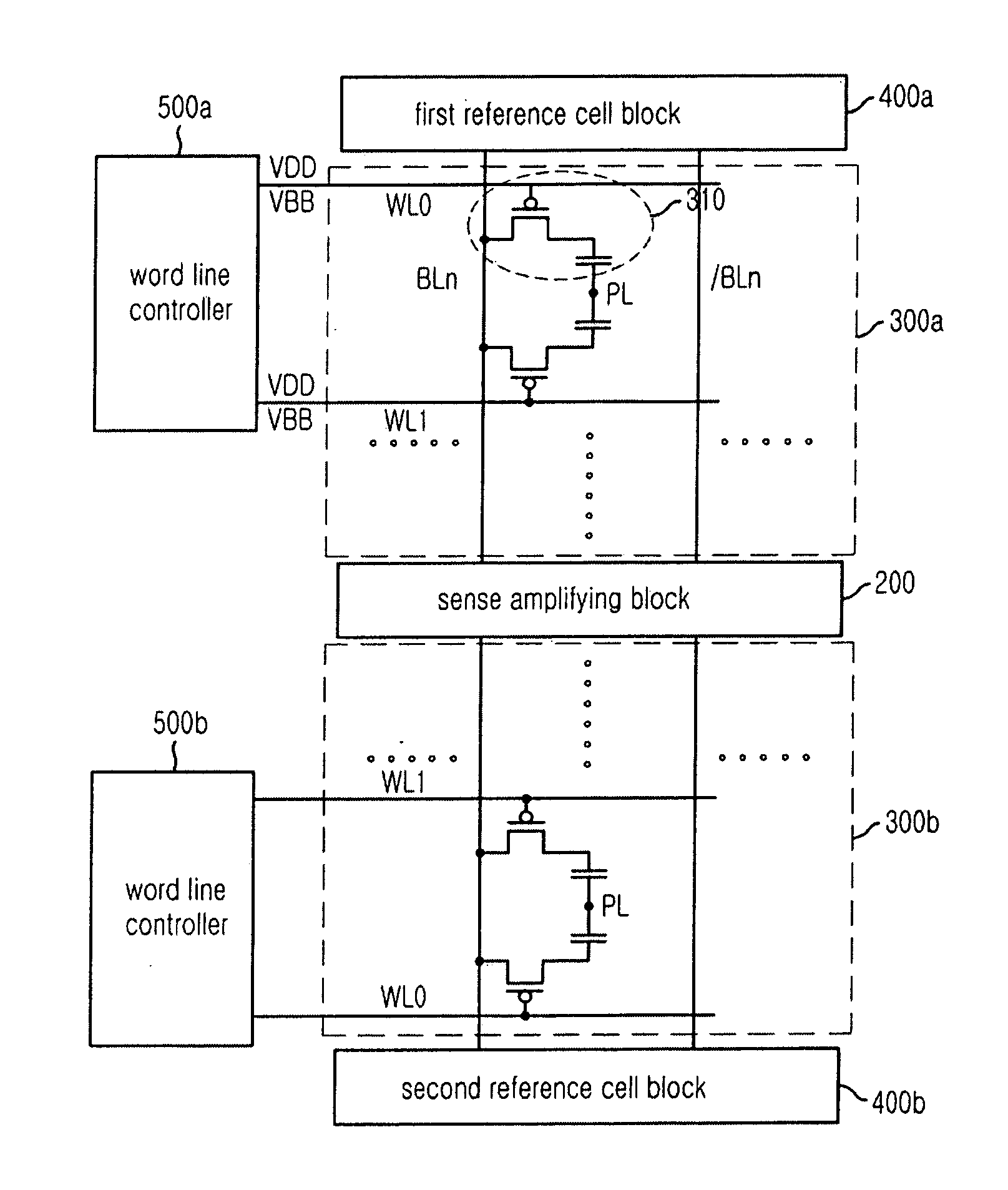
Semiconductor memory device for low voltage
A semiconductor memory device includes a first cell array including a plurality of unit cells and a bit line sense amplifying unit for sensing and amplifying data signals stored in the unit cells. Each unit cell is provided with a PMOS transistor and a capacitor. Therefore, the semiconductor memory device efficiently operates with low voltage without any degradation of operation speed.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
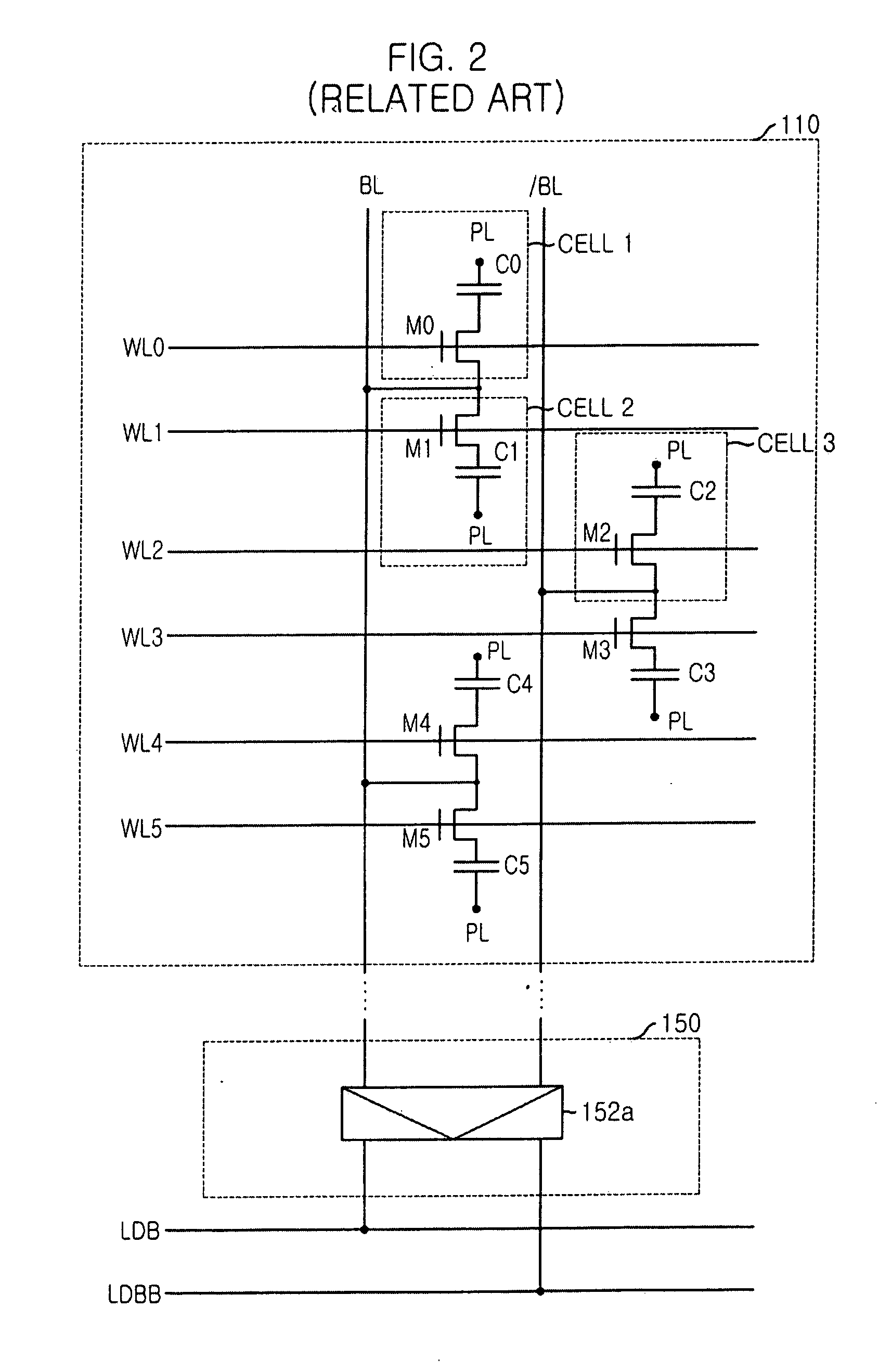
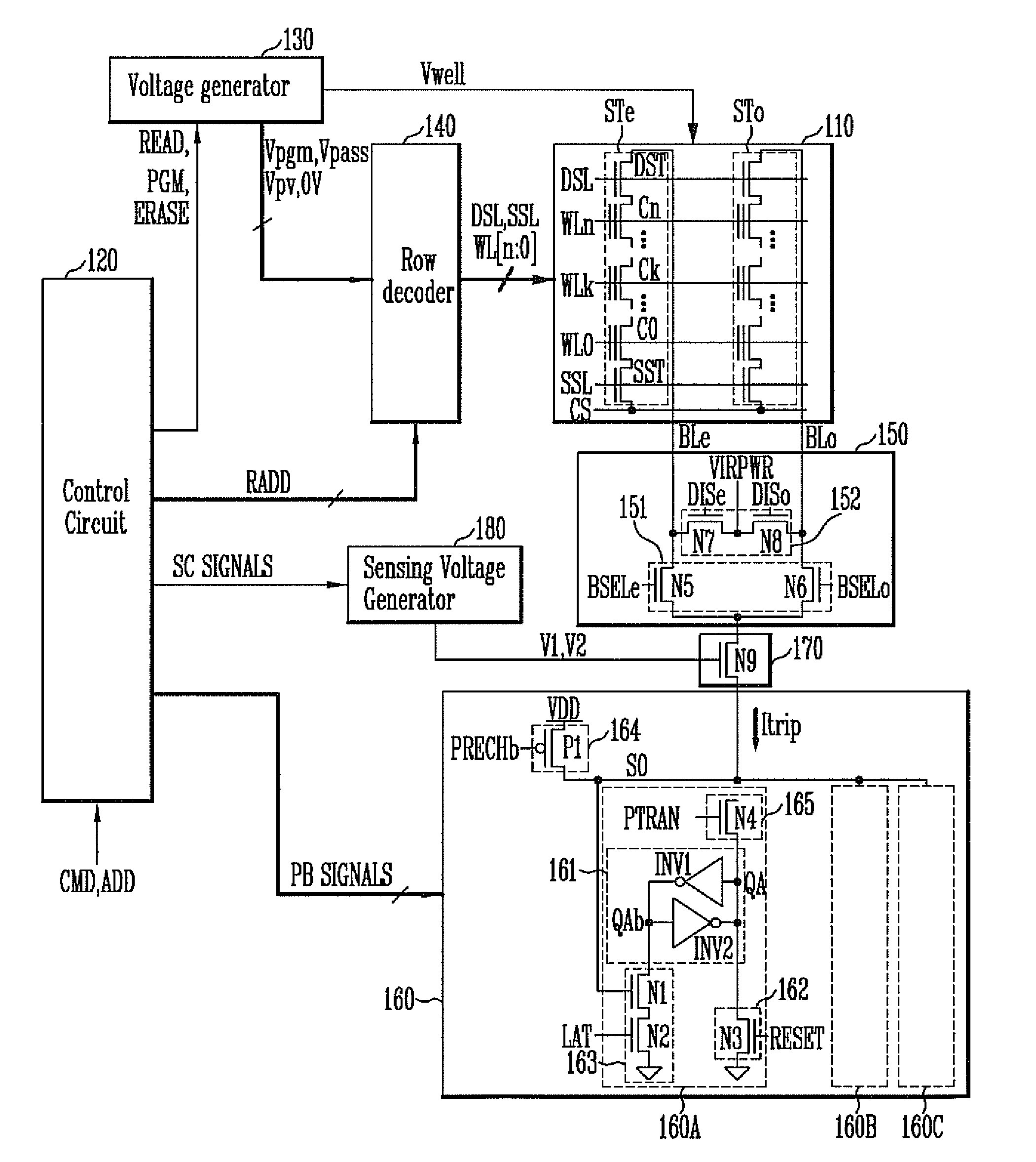
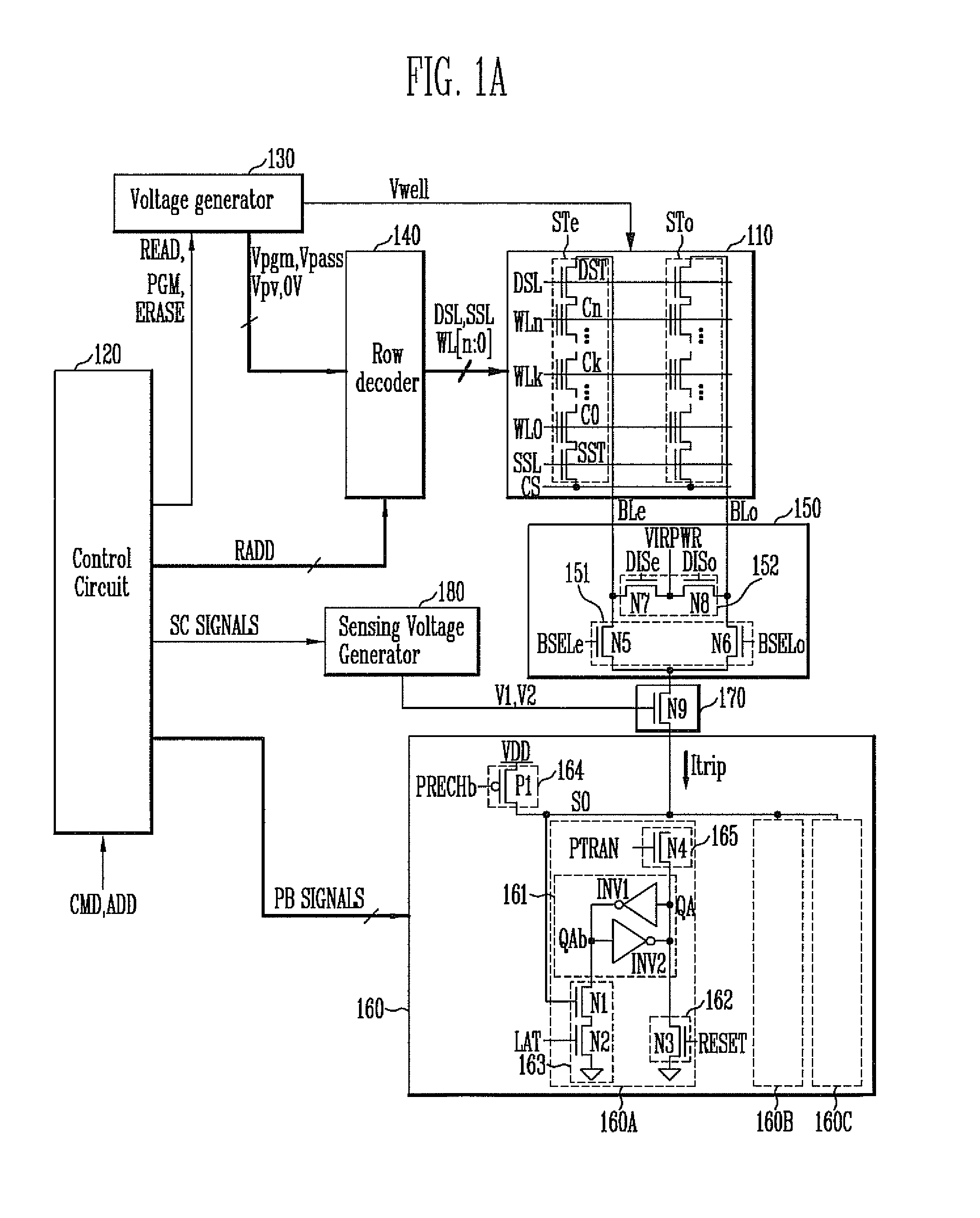
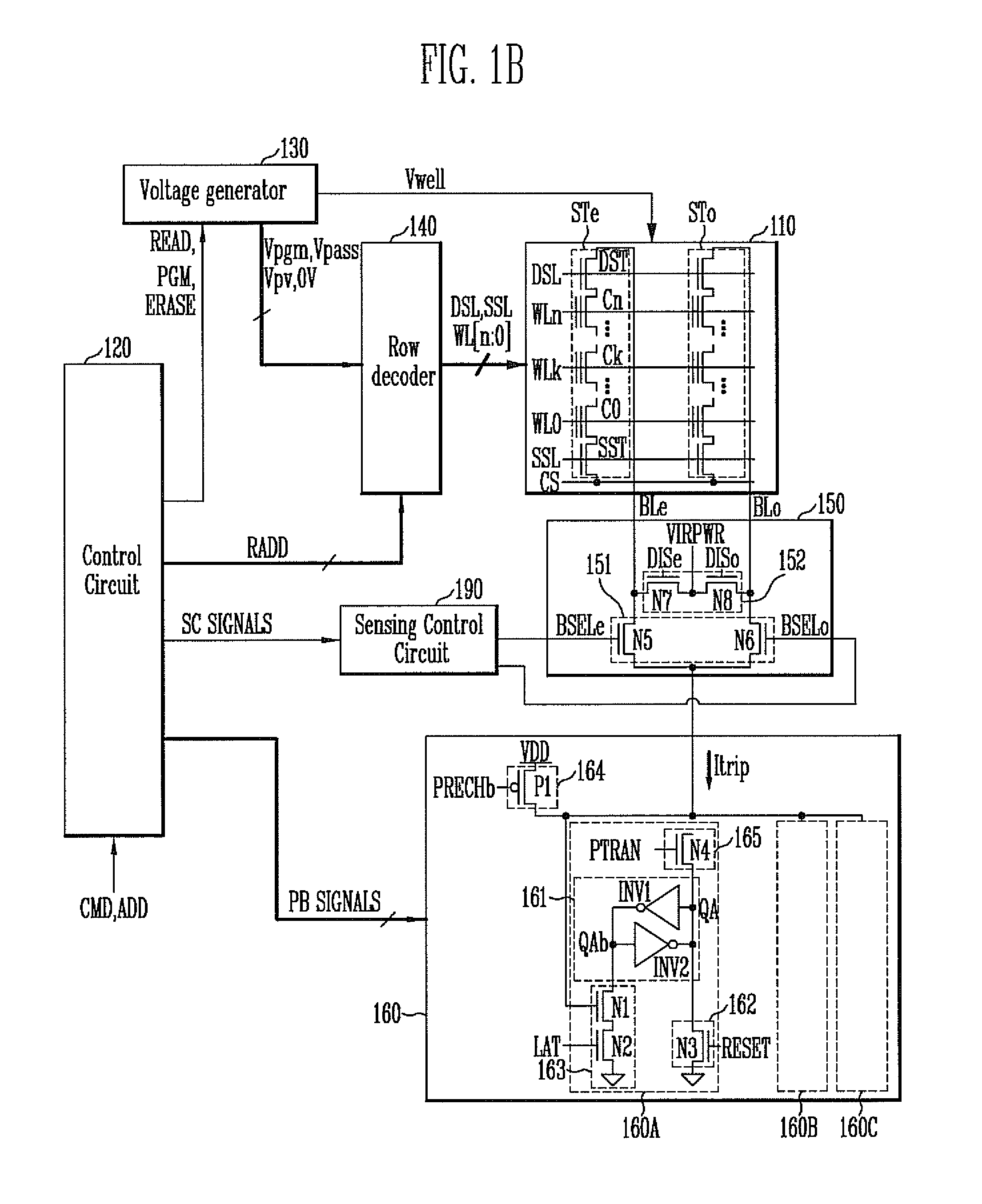
Semiconductor memory device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8526239B2Minimizing deteriorationImprove reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureControl circuit
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory string coupled to a bit line, a page buffer configured to sense a sensing current of the bit line in an erase verification operation or a program verification operation, and a sensing control circuit configured to differently set a level of the sensing current in the erase verification operation and the program verification operation in order to sense the threshold voltage level of a selected memory cell of the memory string.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Dielectric film and formation method thereof, semiconductor device, non-volatile semiconductor memory device, and fabrication method for a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080277715A1Improve wiring speedLow working voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricHydrogen
Owner:FOUND FOR ADVANCEMENT OF INT SCI
Semiconductor memory device and method of operation the same
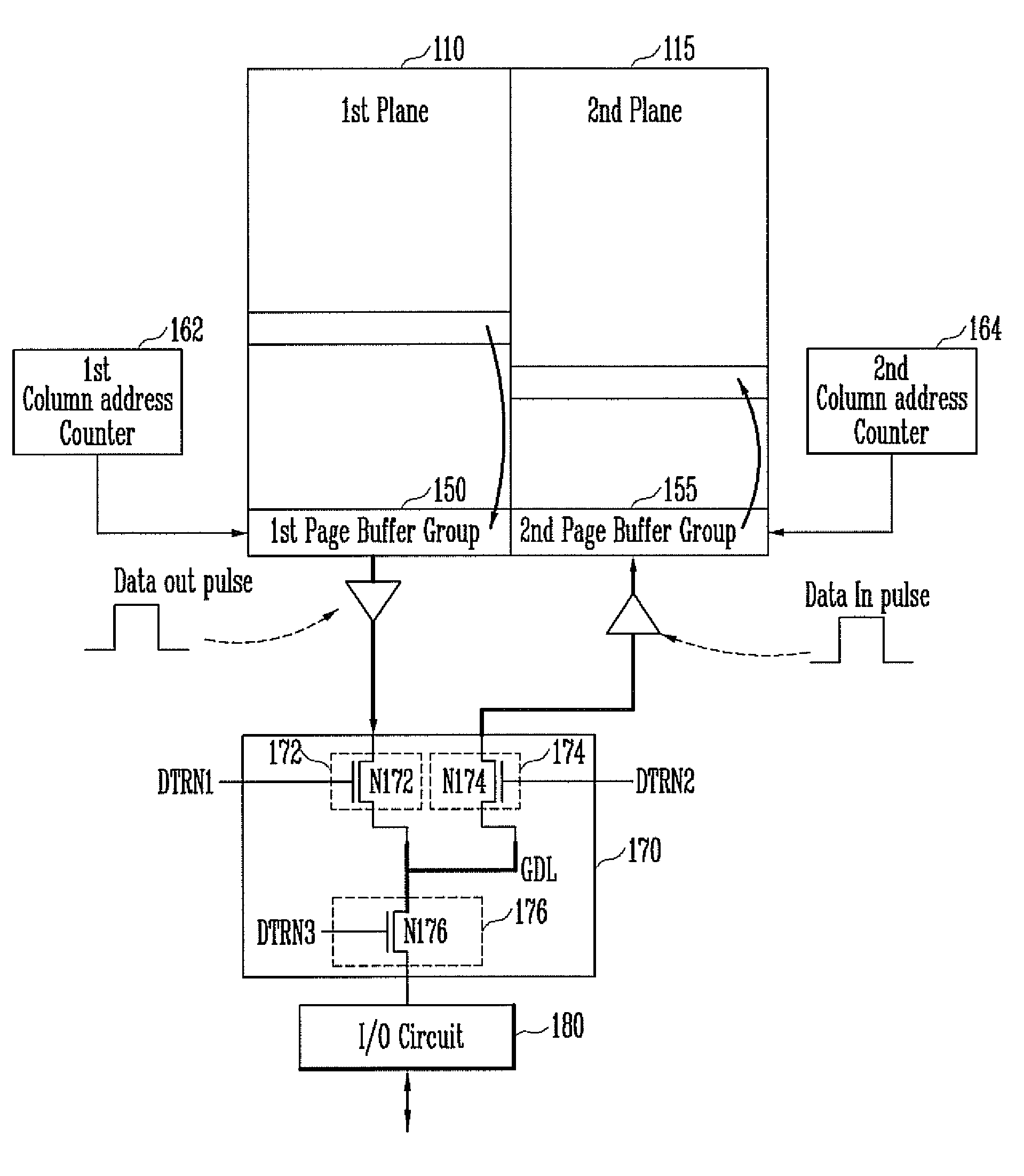
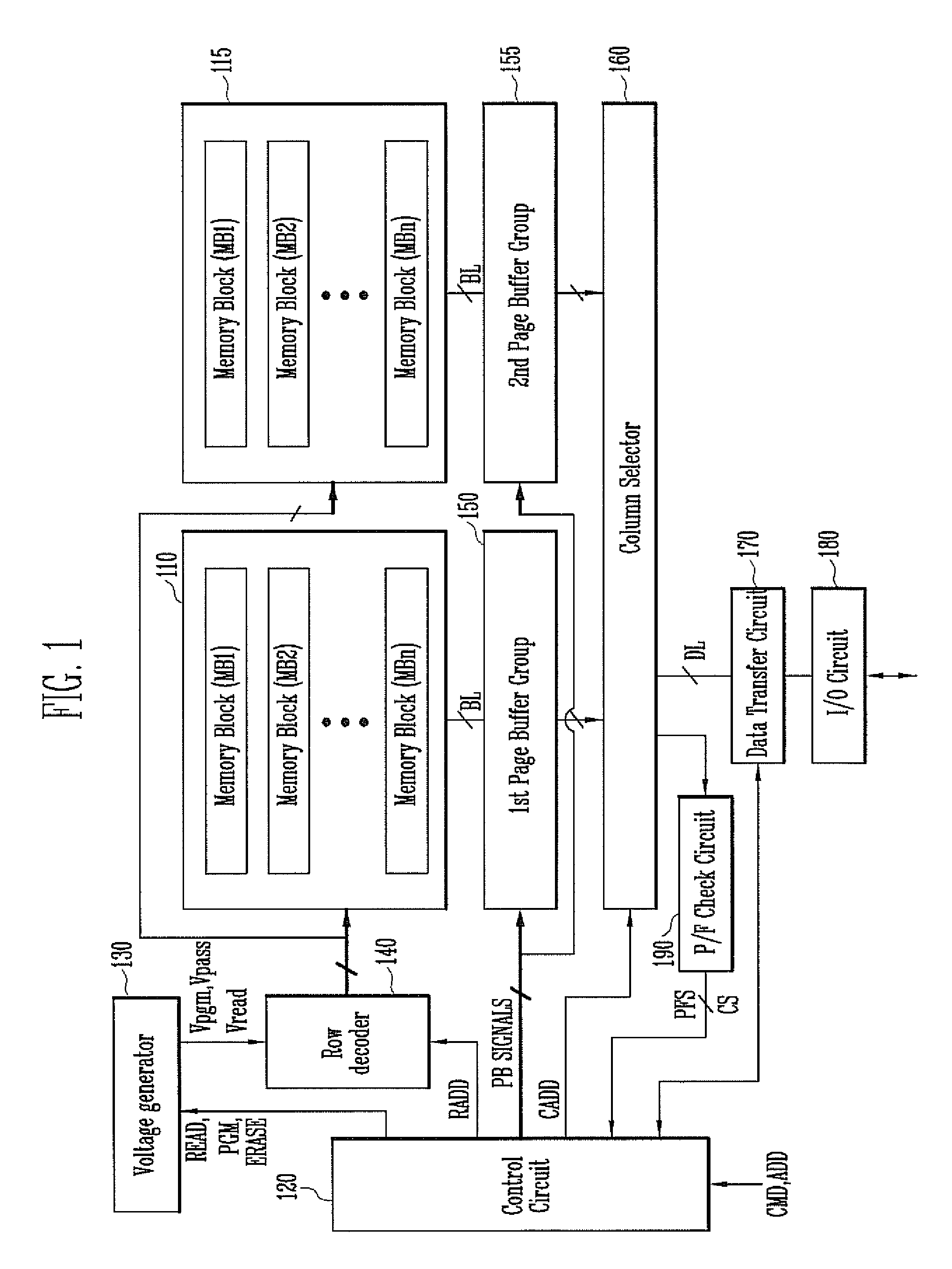
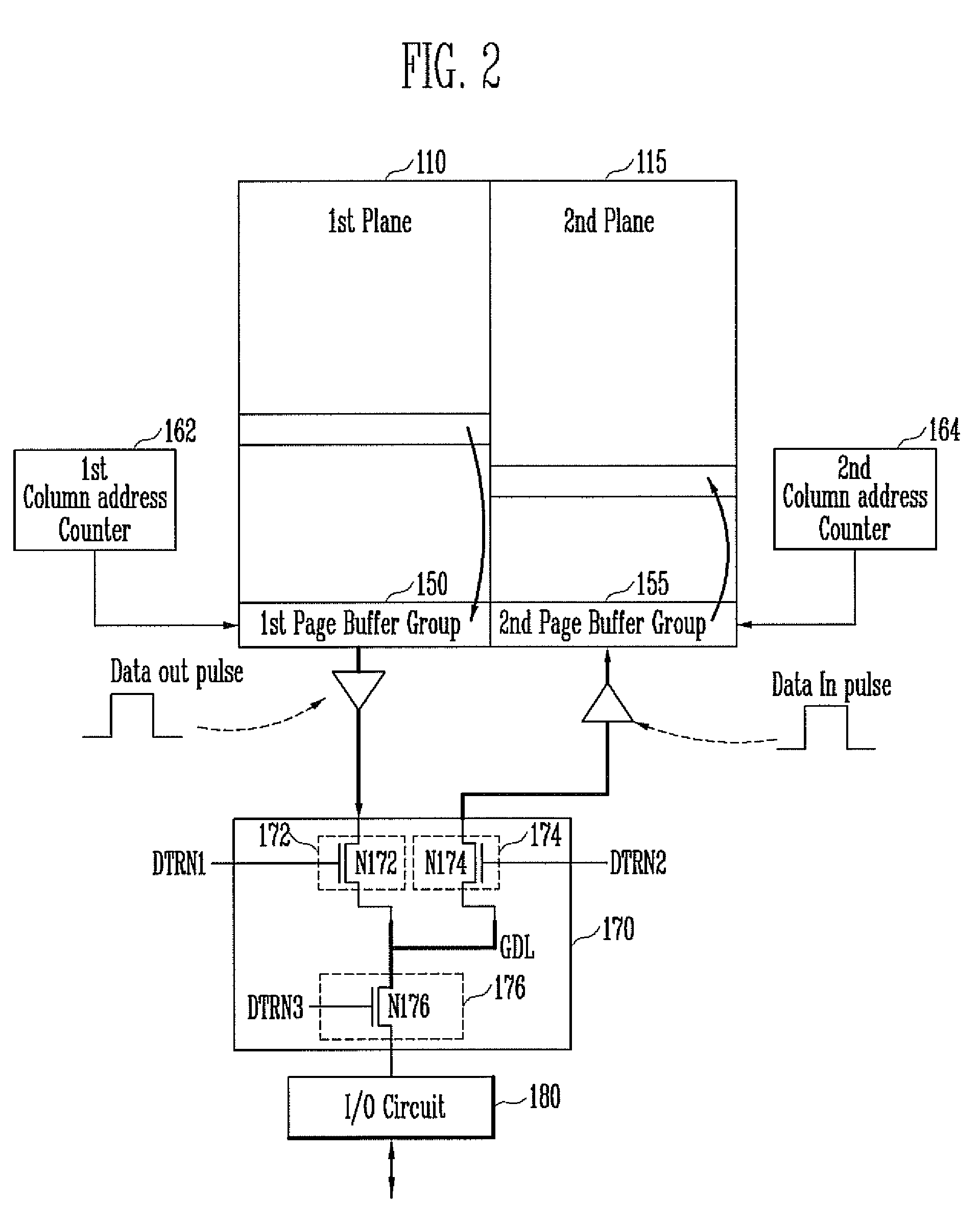
A semiconductor memory device includes a first plane and a second plane each configured to include a plurality of memory cells, and a data transfer circuit configured to transfer first data, stored in the memory cells of the first plane, to the second plane and transfer second data, stored in the memory cells of the second plane, to the first plane when a copyback operation is performed and to transfer the first data or the second data to an I / O circuit when a read operation is performed.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device
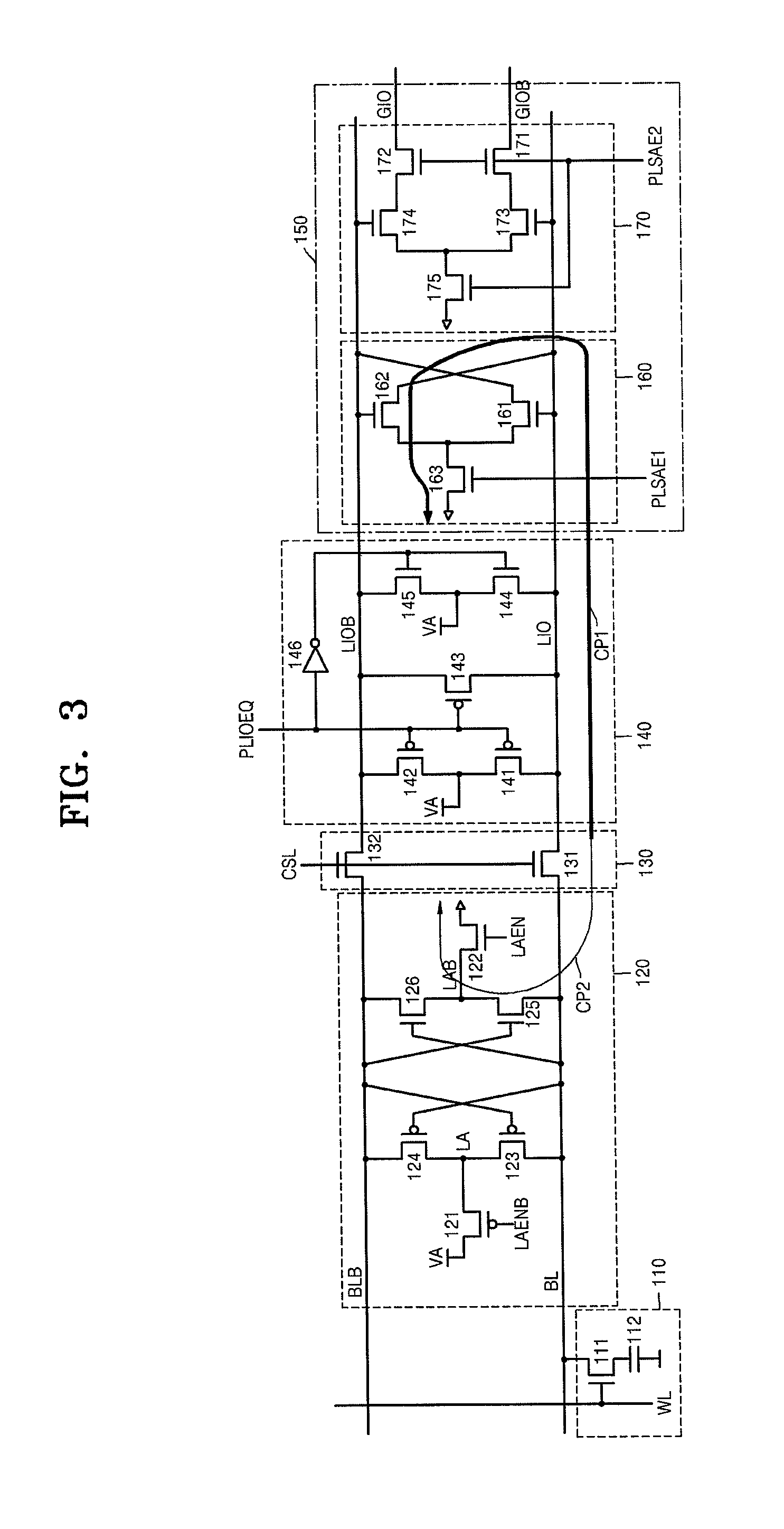
A semiconductor memory device includes a bitline sensing amp detecting and amplifying data of a pair of bitlines from a memory cell, a column selecting unit transmitting the data of the pair of bitlines to a pair of local datalines in response to a column selecting signal, a dataline precharging unit precharging the pair of local datalines to a precharging voltage level in response to a precharging signal, and a dataline sensing amp detecting and amplifying data transmitted to the pair of local datalines. The dataline sensing amp includes a charge sync unit discharging the pair of local datalines at the precharging voltage level in response to a first dataline sensing enabling signal and data of the pair of local datalines, and a data sensing unit transmitting data of the pair of local datalines to a pair of global datalines in response to a second dataline sensing enabling signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
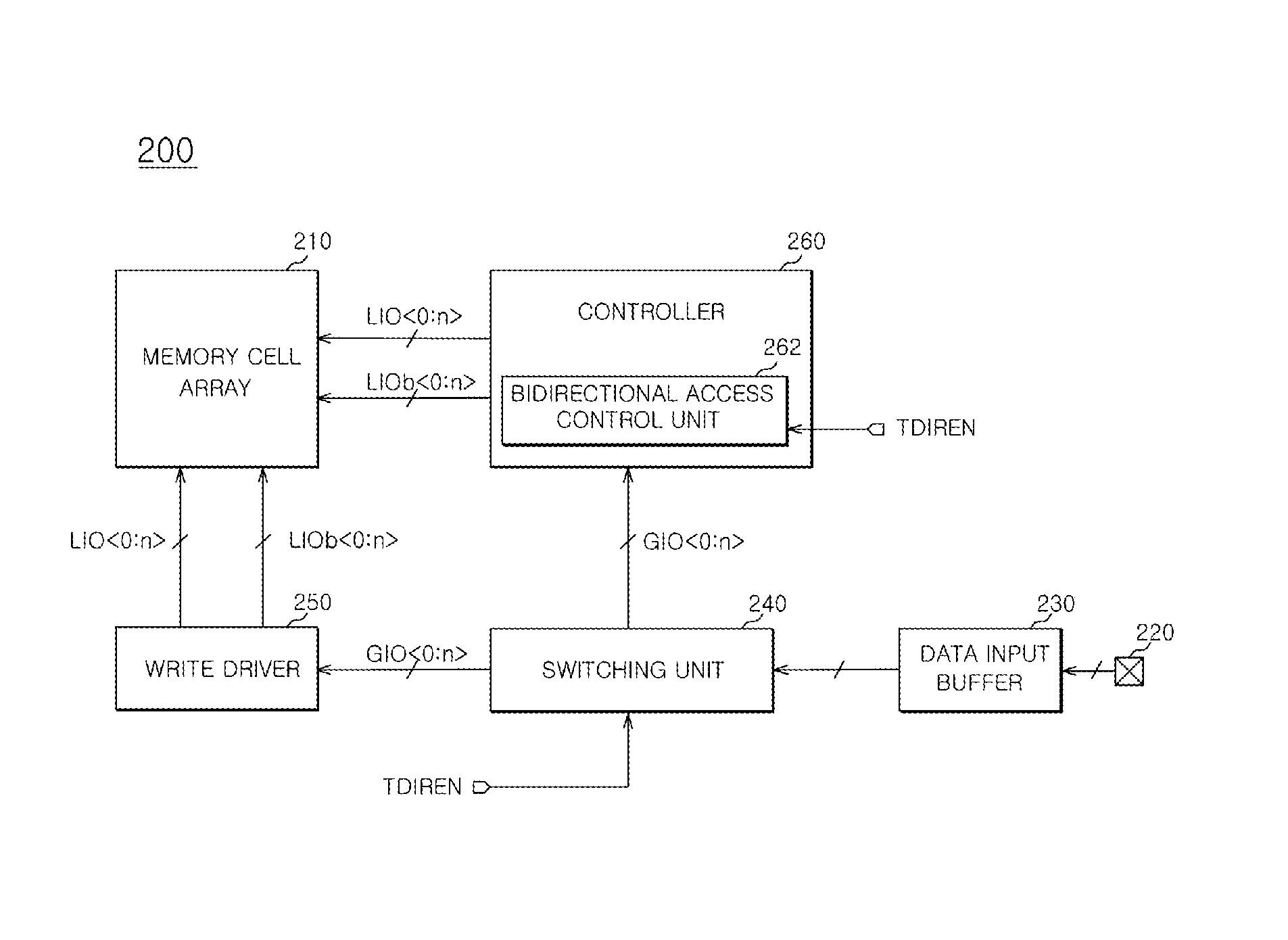
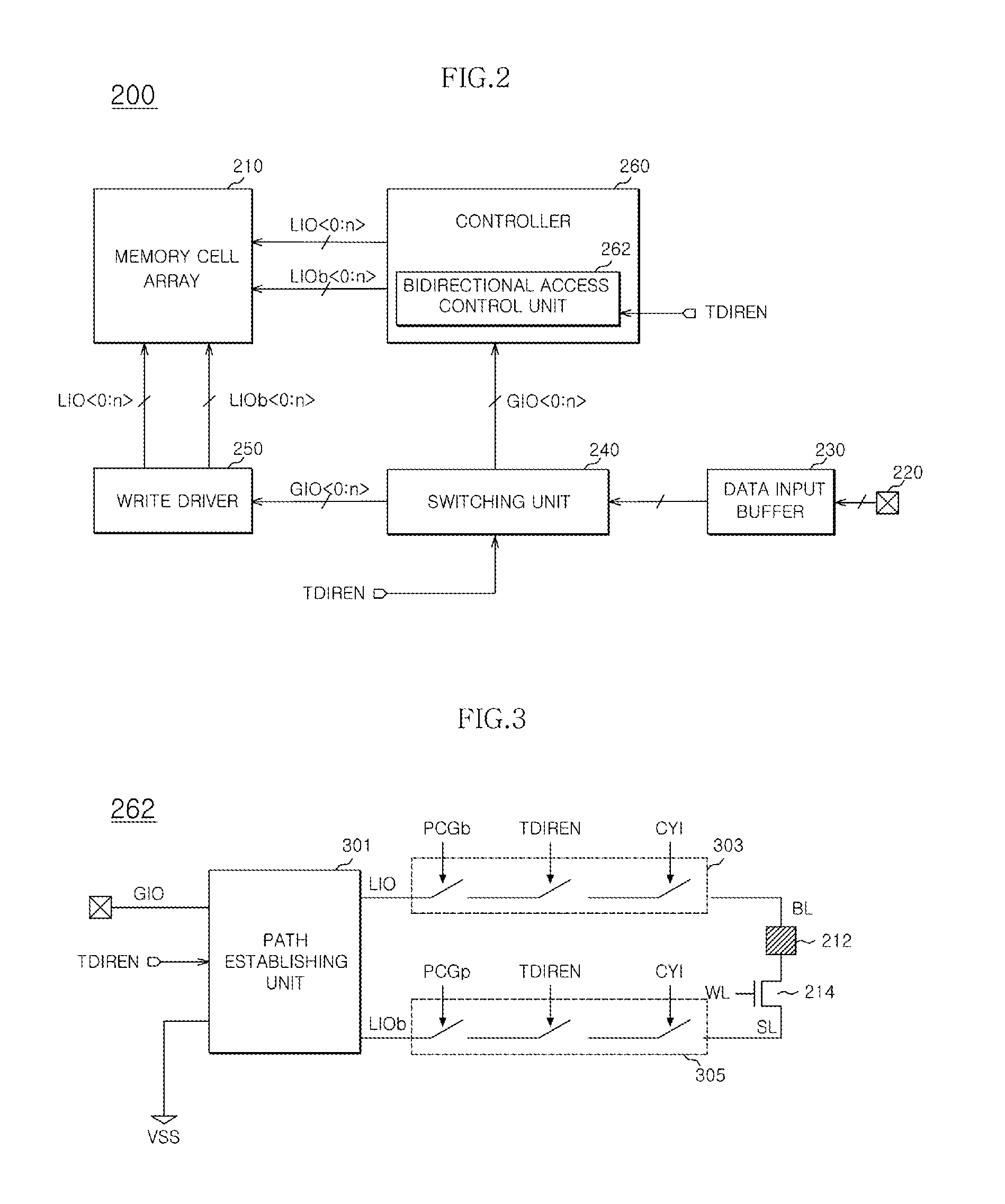
Semiconductor memory apparatus and test circuit therefor
Disclosed is a semiconductor memory apparatus, including: a memory cell array configured to include a plurality of memory cells; a switching unit configured to be coupled to data input and output pads and control a data transfer path of data applied to the data input and output pads in response to a test mode signal; a write driver configured to drive data transferred from the switching unit and write the data in the memory cell array at a normal mode; and a controller configured to transfer the data from the switching unit to the memory cell at a test mode.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
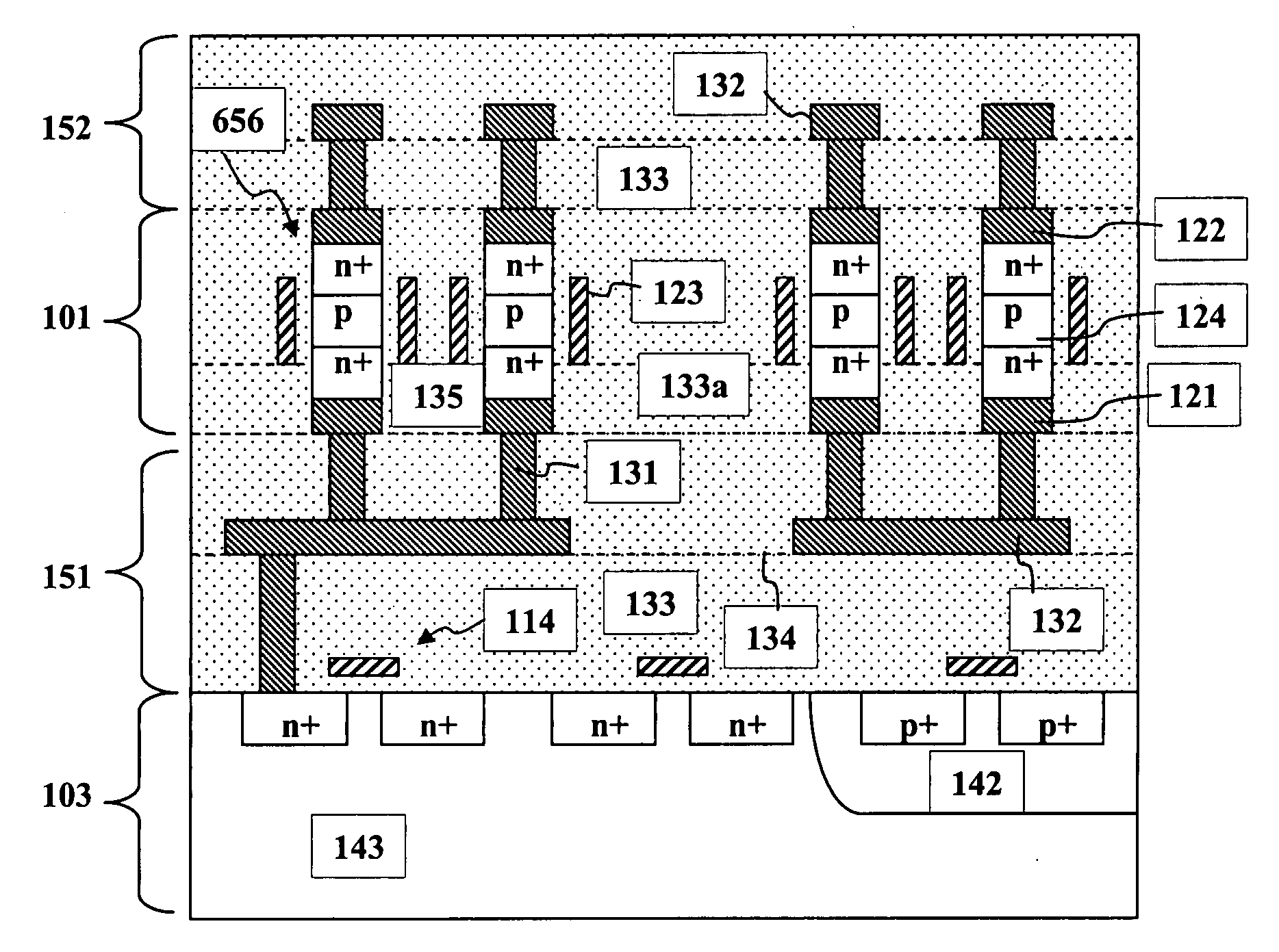
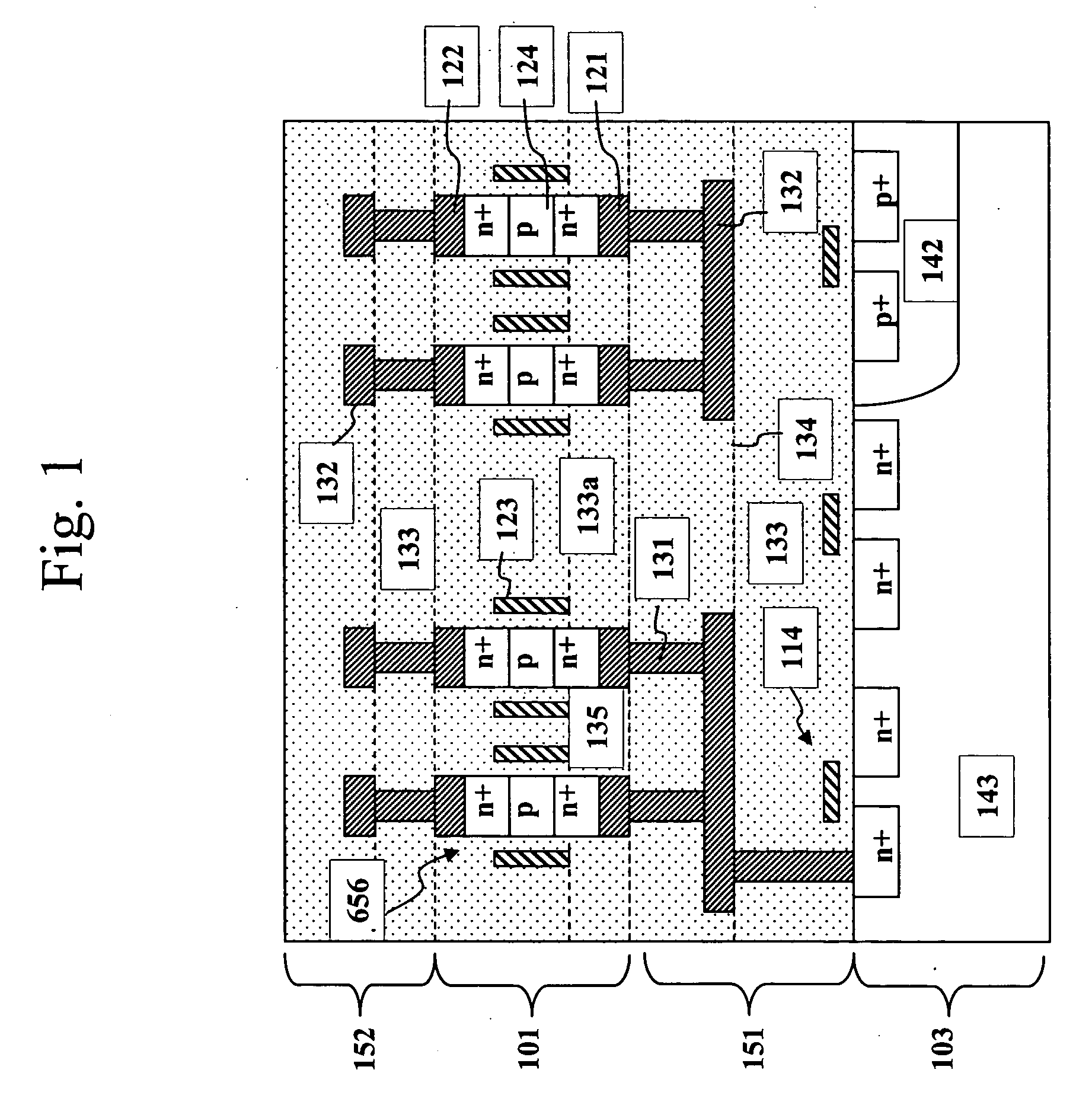
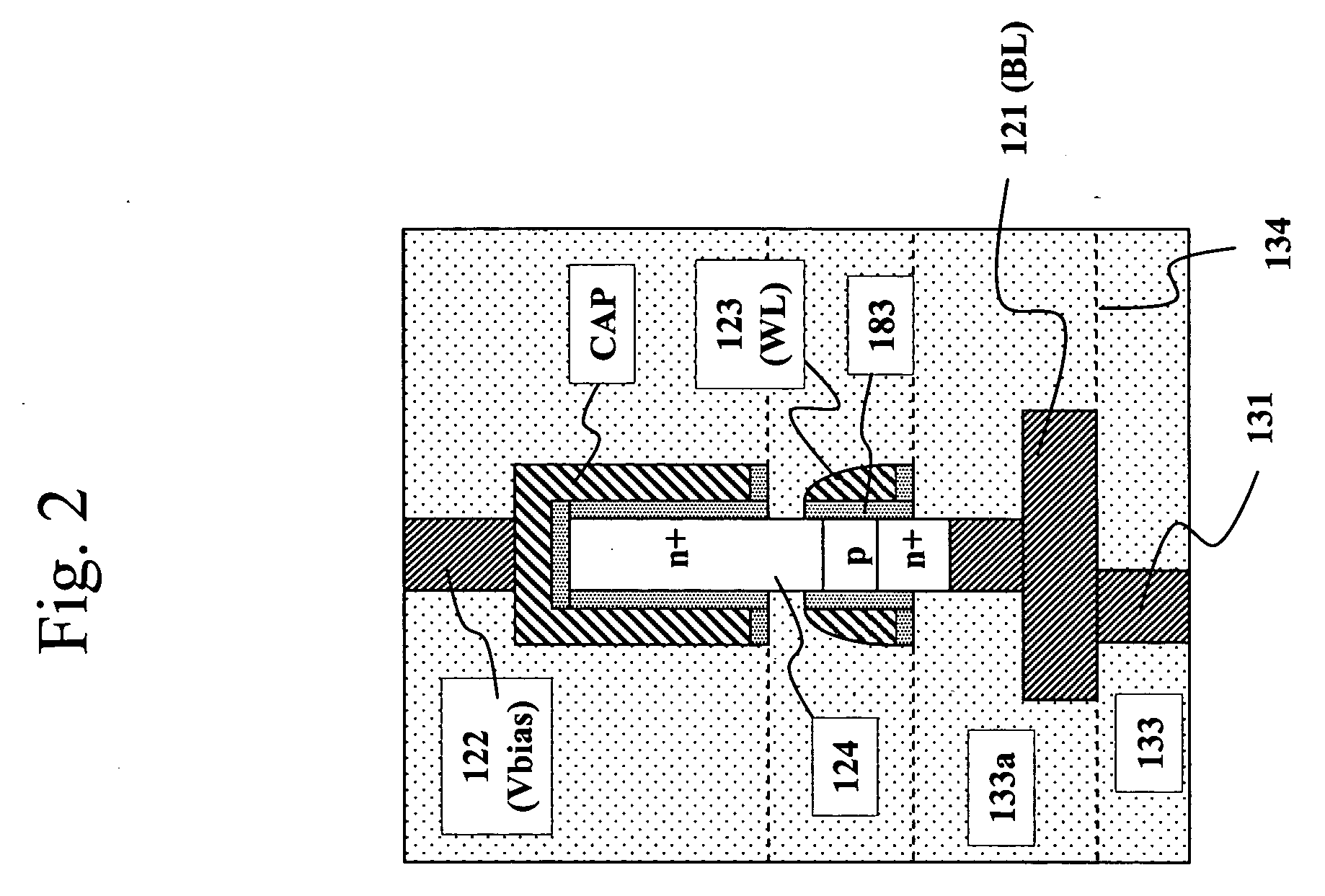
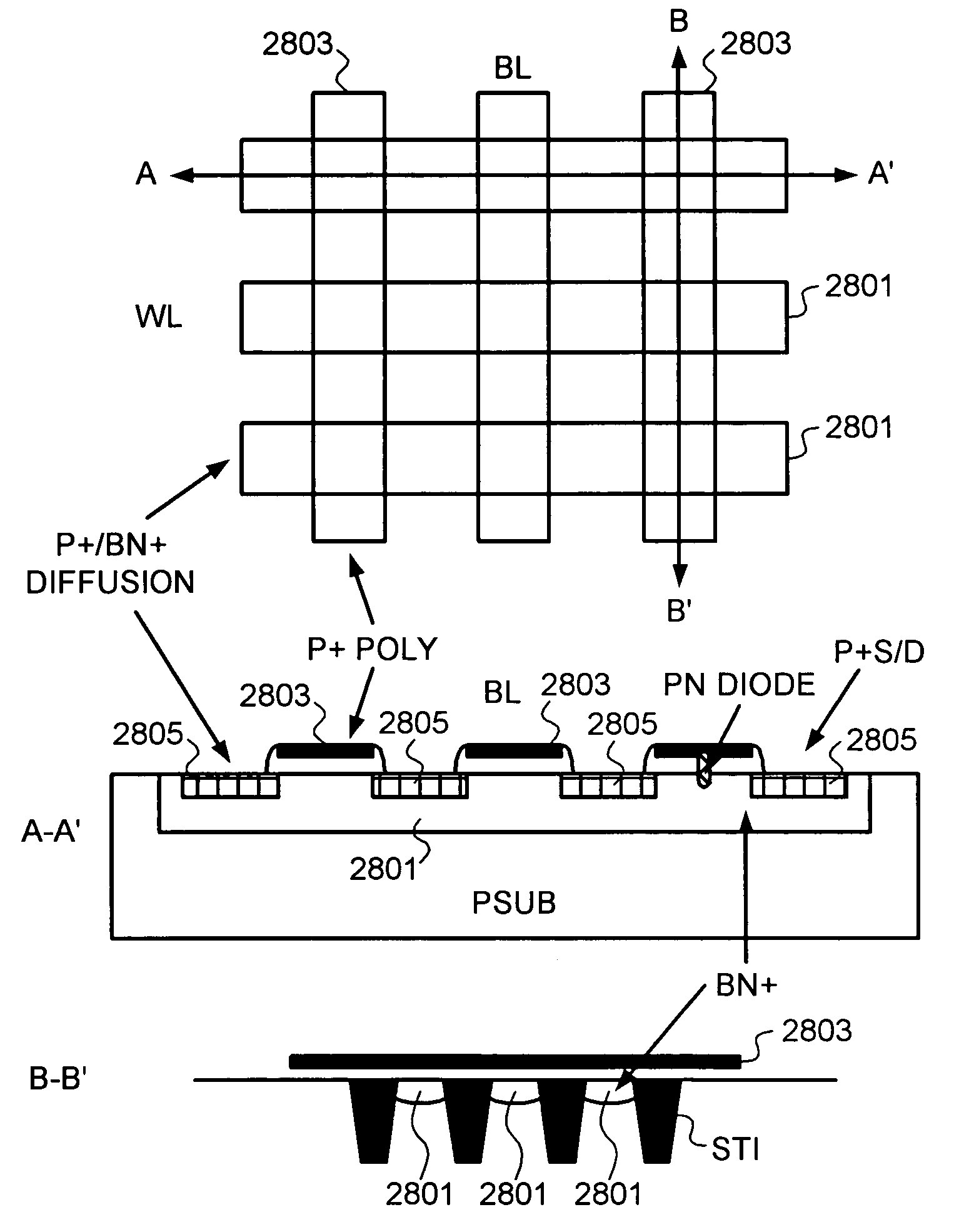
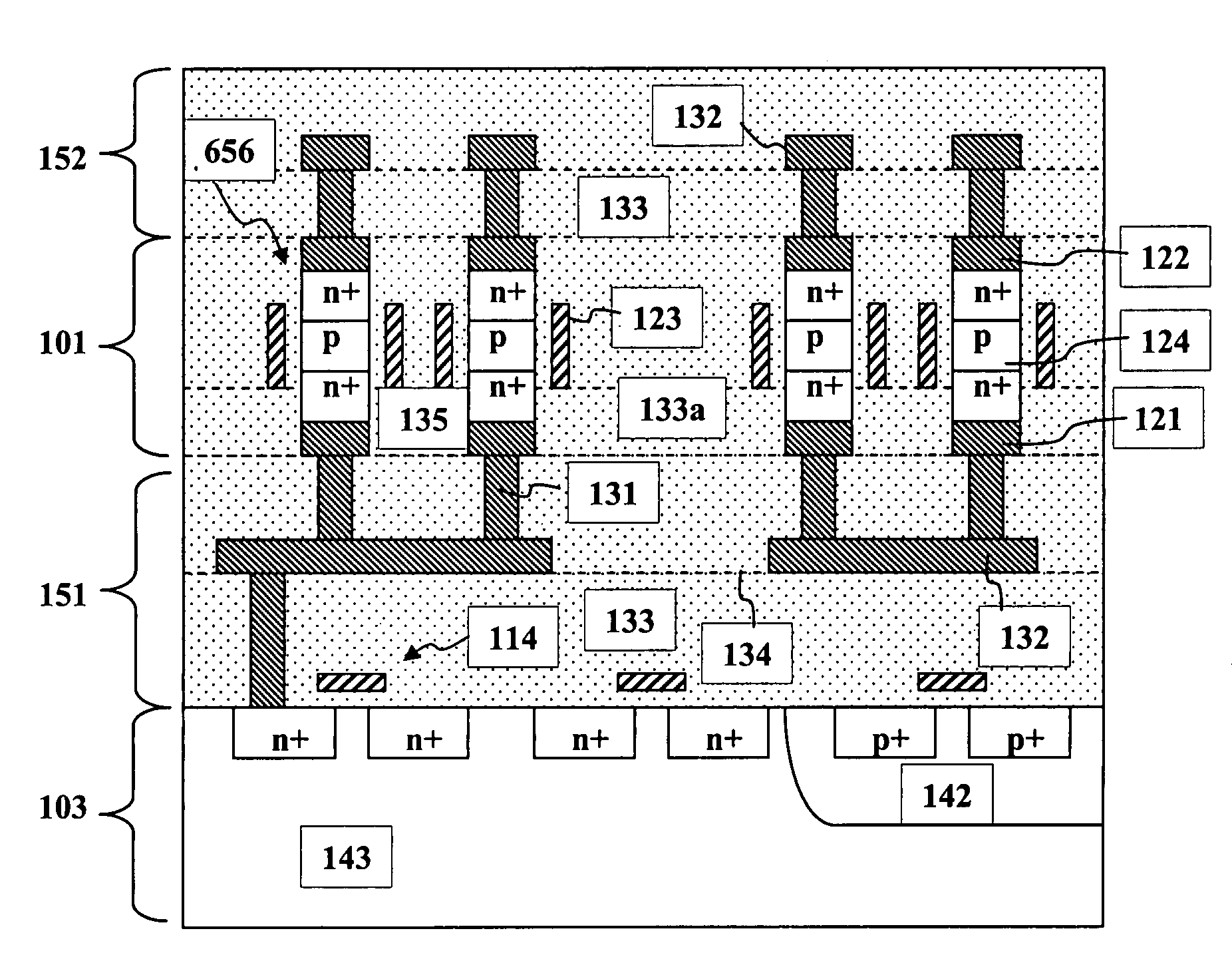
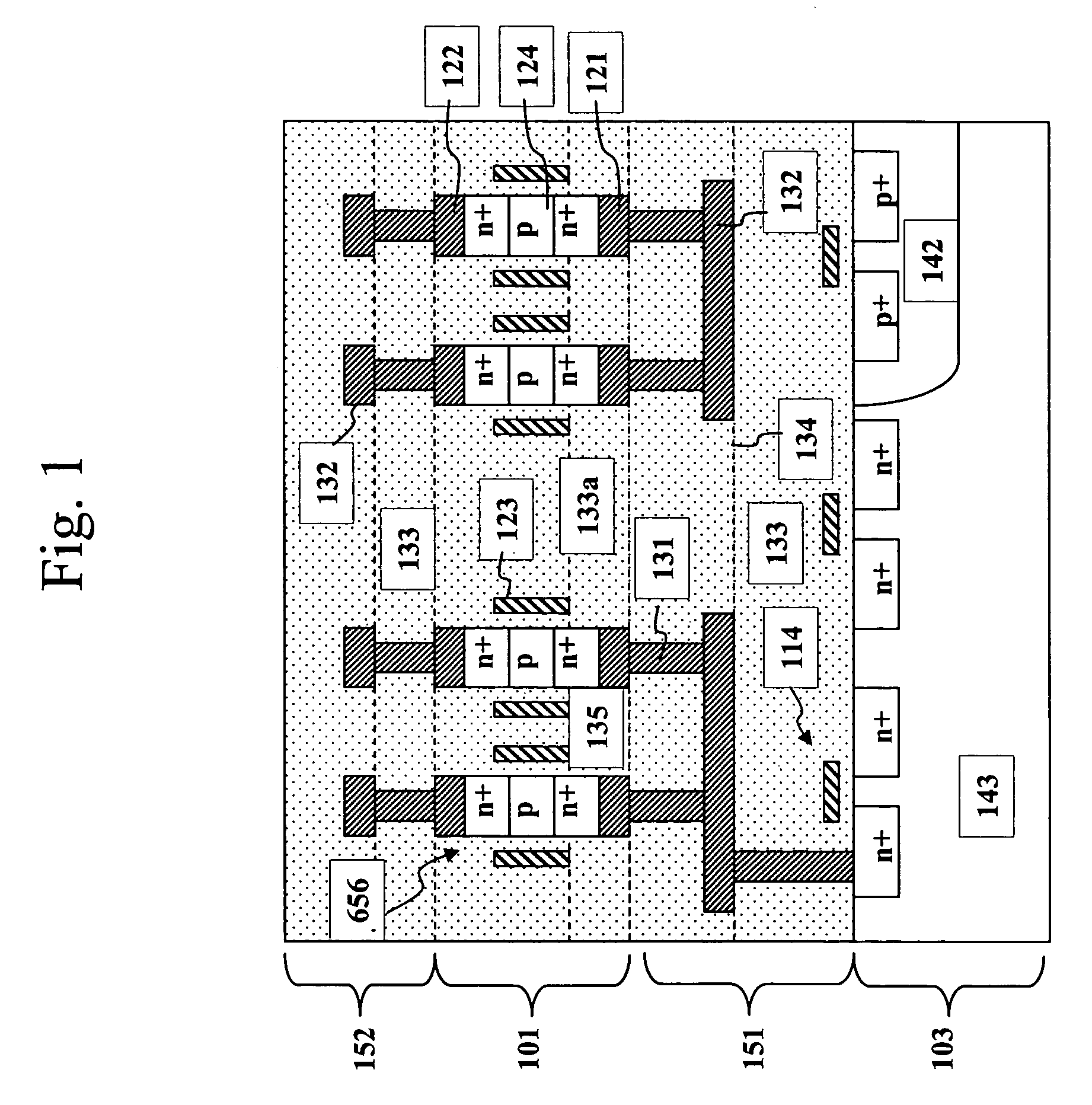
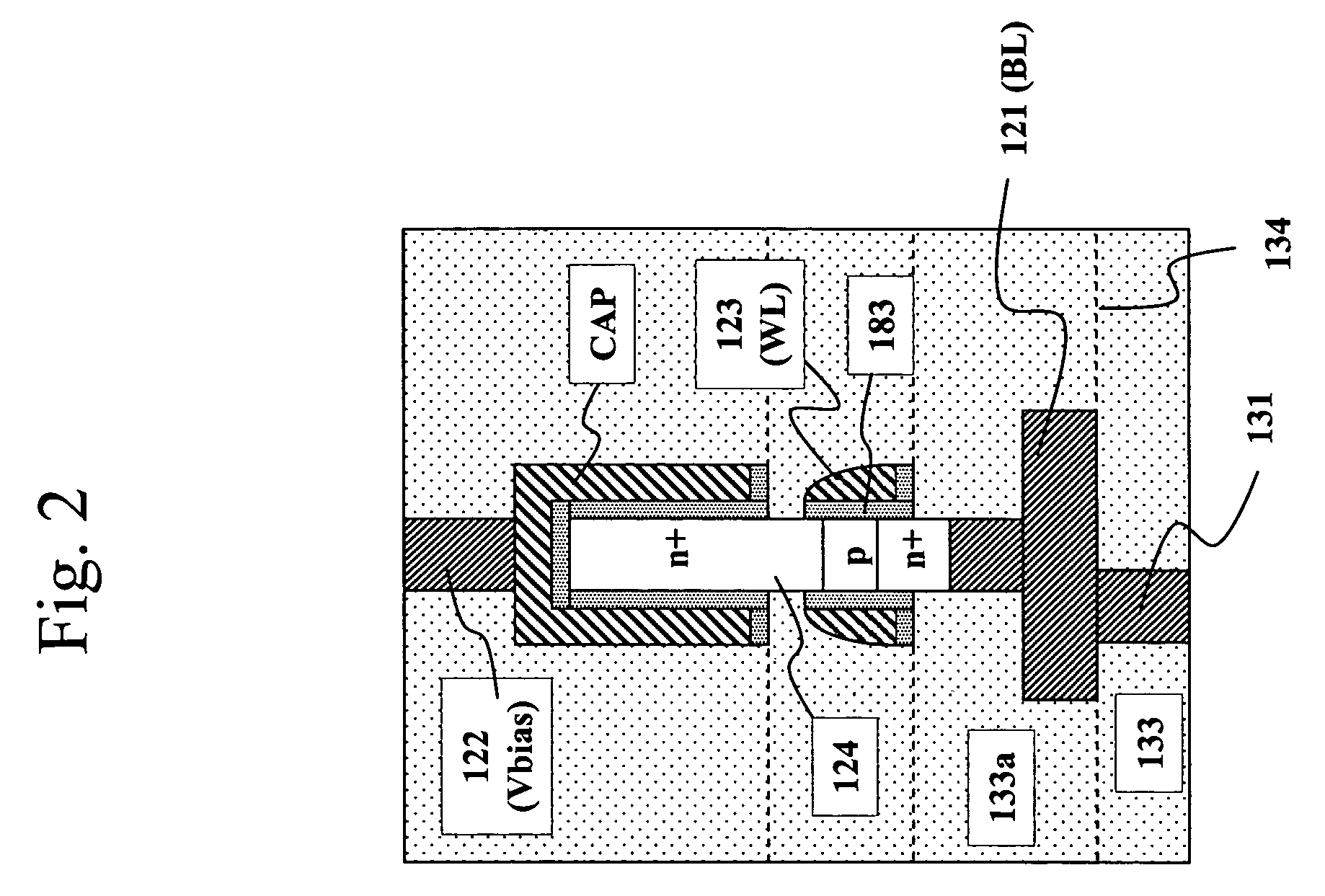
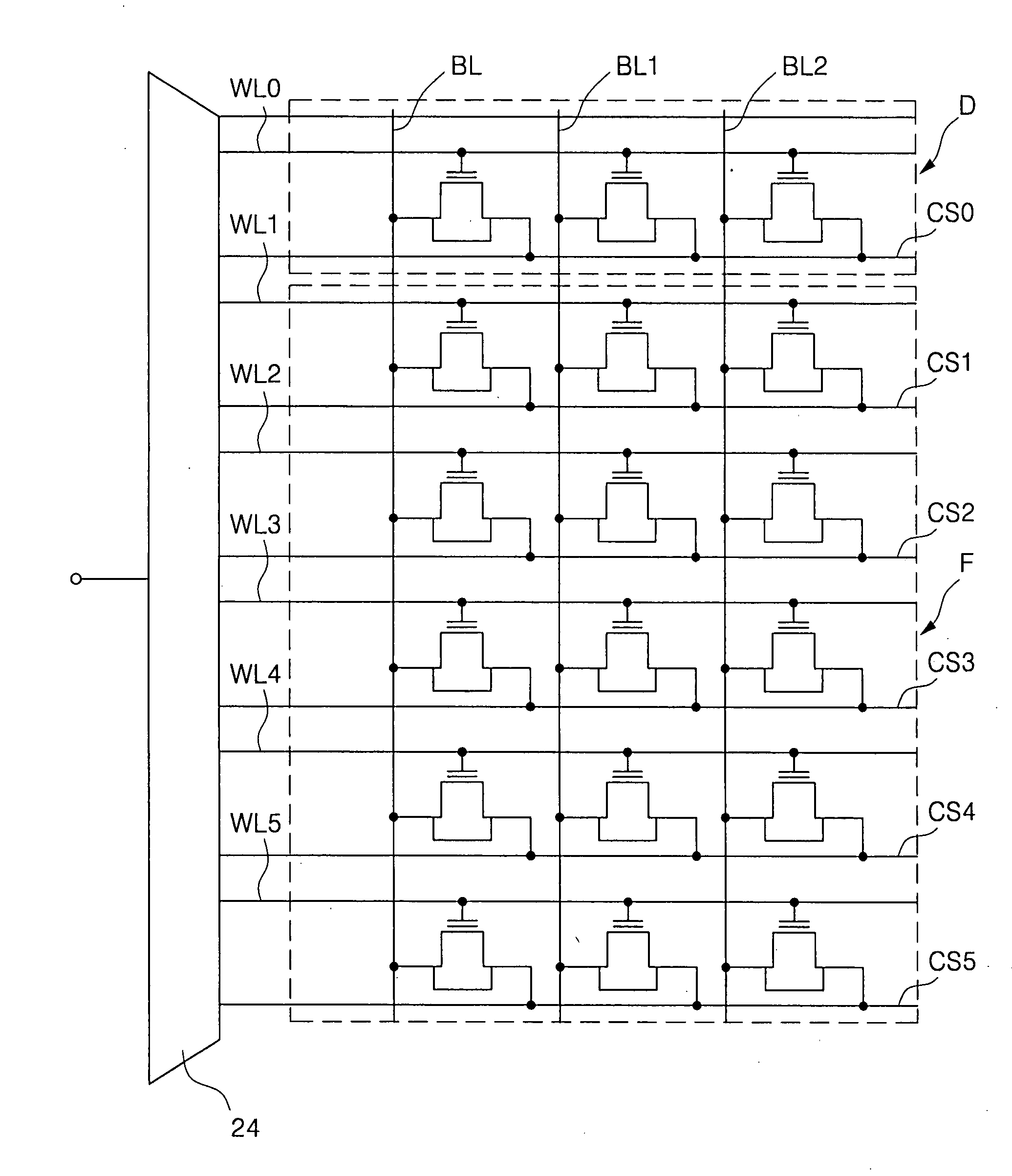
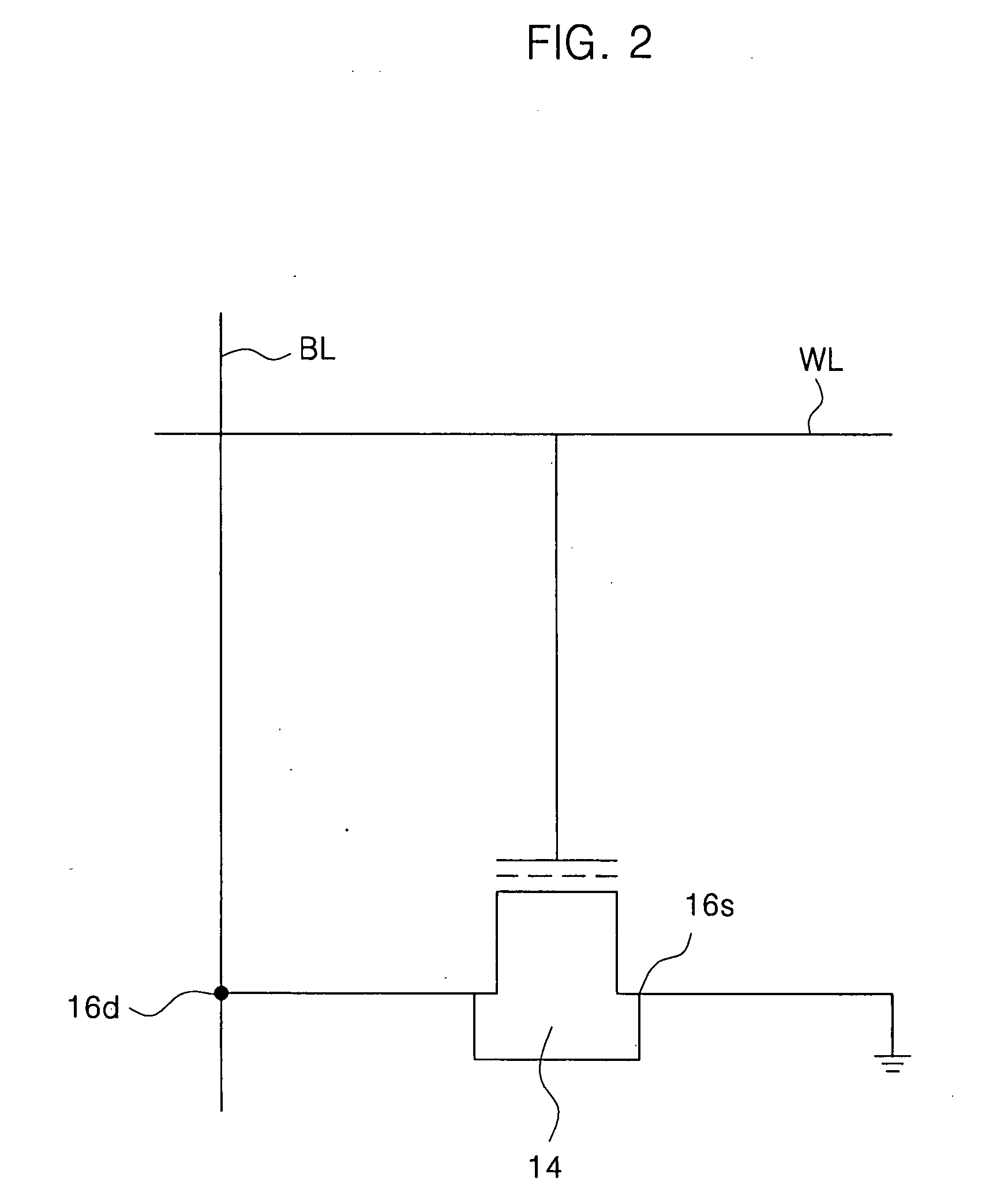
High density semiconductor memory cell and memory array using a single transistor and having counter-doped poly and buried diffusion wordline
A programmable memory cell comprised of a transistor located at the crosspoint of a column bitline and a row wordline is disclosed. The transistor has its gate formed from the column bitline and its source connected to the row wordline. The memory cell is programmed by applying a voltage potential between the column bitline and the row wordline to produce a programmed p+ region to form a p-n diode in the substrate underlying the gate of the transistor. Further, the wordline is formed from a buried diffusion N+ layer while the column bitline is formed from a counterdoped polysilicon layer.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
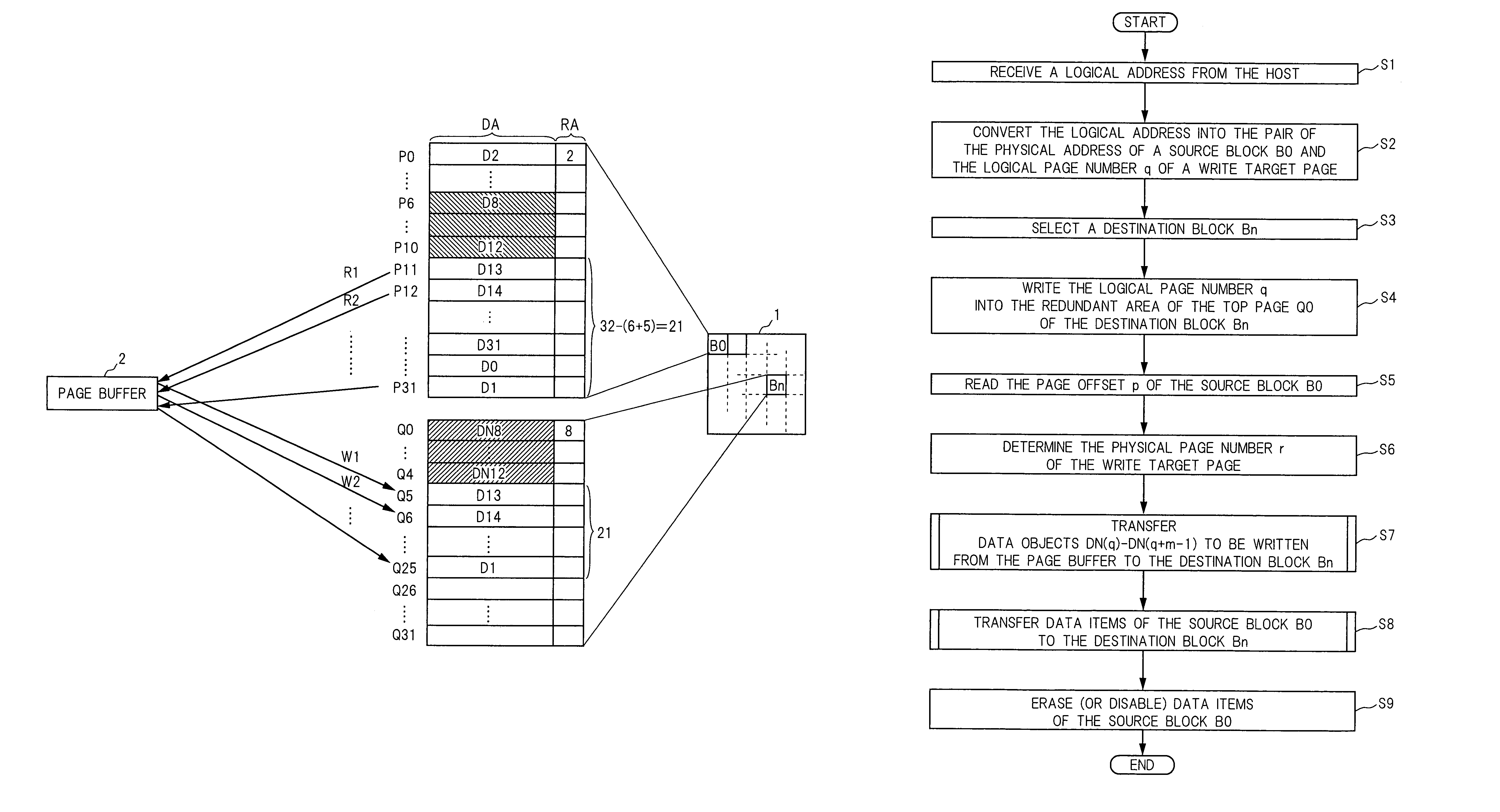
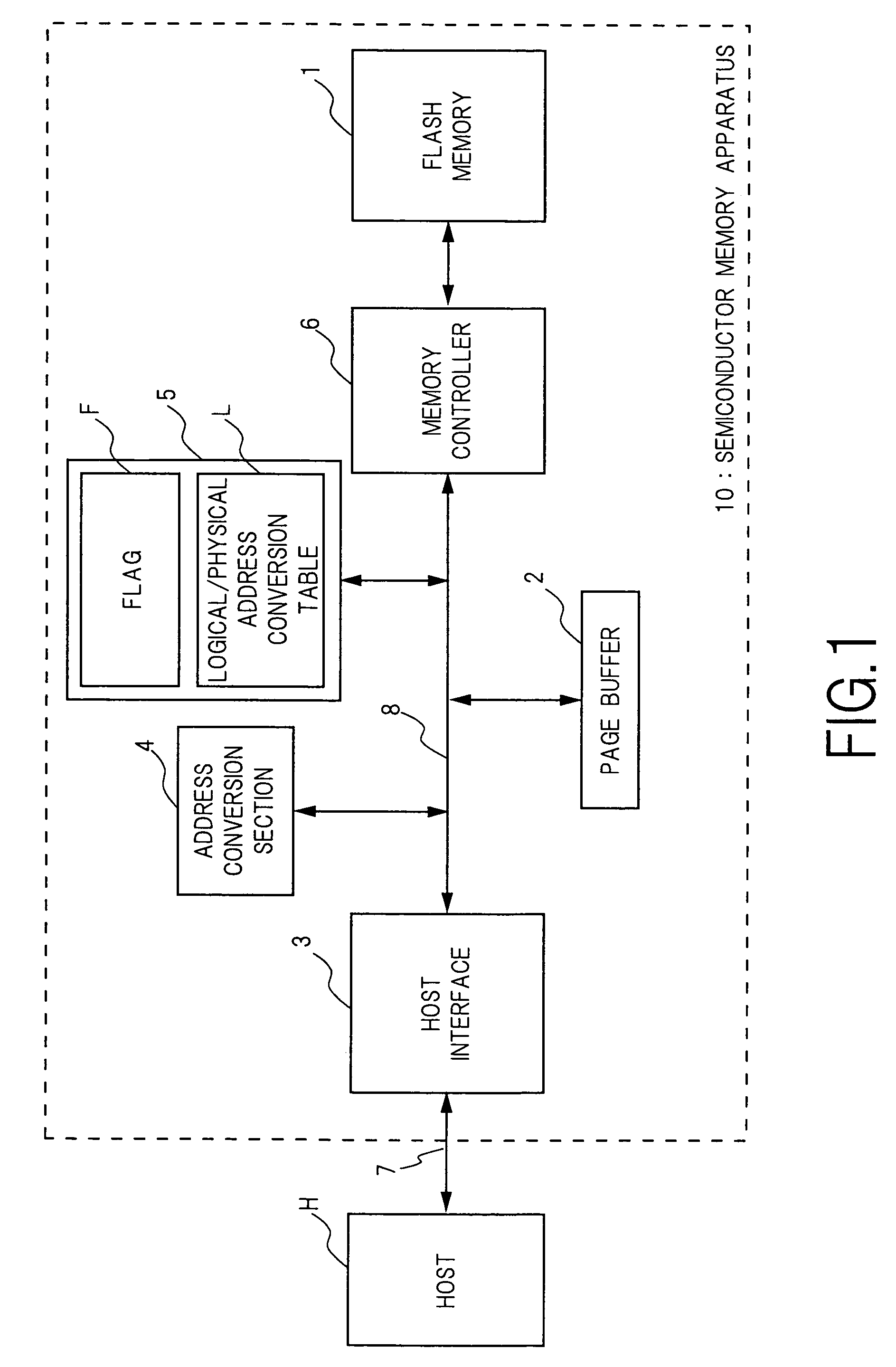
Semiconductor memory device and method for writing data into flash memory
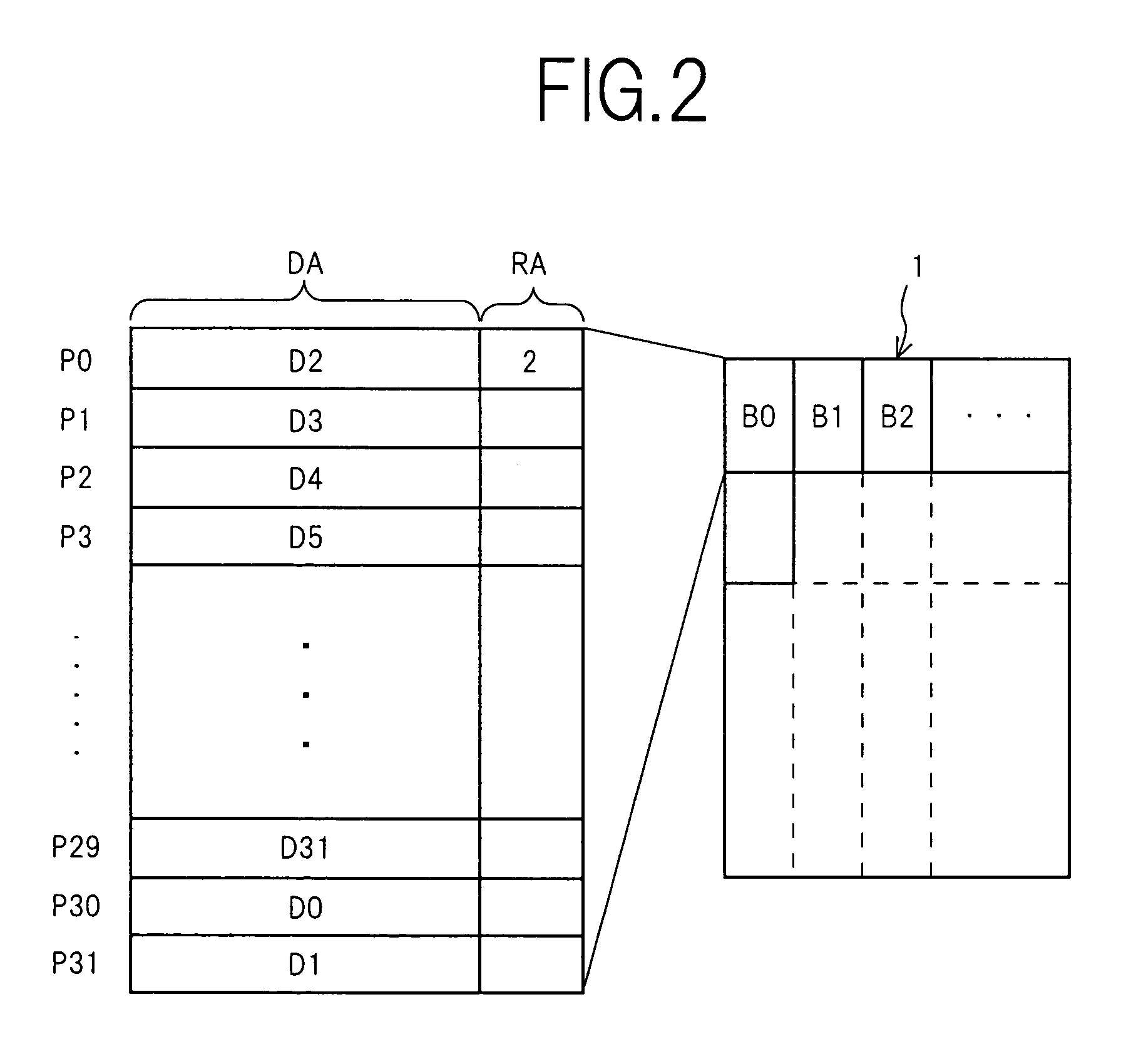
ActiveUS7107389B2Small sizeReduce waiting timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHome pageDatabase
A source block (B0) and the logical page number (“8”) of a write target page are identified from the logical address of the write target page. Data objects (DN8, DN9, . . . , DN12) to be written, which a host stores in a page buffer (2), are written into the data areas (DA) of the pages (Q0, Q1, . . . , Q4) of a destination block (Bn), starting from the top page (Q0) in sequence. The logical page number (“8”) of the write target page is written into the redundant area (RA) of the top page (Q0). The physical page number (“6=8−2”) of the write target page is identified, based on the logical page number (“8”) of the write target page and the page offset (“2”) of the source block (B0). When notified by the host of the end of the sending of the data objects (DN8, . . . , DN12), the data items (D13, . . . , D31, D0, D1, . . . , D7) in the source block (B0) are transferred to the pages (Q5, Q6, . . . , Q31) in the destination block (Bn) via the page buffer (2) sequentially and cyclically, starting from the page (P11) situated cyclically behind the write target page (P6) by the number (“5”) of pages of the data objects (DN8, . . . , DN12).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Vertical memory device structures
Vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are added to a separately fabricated substrate that includes electrical devices and / or interconnect. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are physically separated from each other, and are not disposed within the same semiconductor body. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells can be added to the separately fabricated substrate as a thin layer including several doped semiconductor regions which, subsequent to attachment, are etched to produce individual doped stack structures, which are then supplied with various dielectric coatings, gate electrodes, and contacts by means of further processing operations. Alternatively, the plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells may be completely fabricated prior to attachment. DRAMs, SRAMs, non-volatile memories, and combinations of memory types can be provided.
Owner:BESANG
Semiconductor memory devices including an air gap and methods of fabricating the same
Provided are a semiconductor memory device and a method of fabricating the same, the semiconductor memory device may include a semiconductor substrate with a first trench defining active regions in a first region and a second trench provided in a second region around the first region, a gate electrode provided on the first region to cross the active regions, a charge storing pattern disposed between the gate electrode and the active regions, a blocking insulating layer provided between the gate electrode and the charge storing pattern and extending over the first trench to define a first air gap in the first trench, and an insulating pattern provided spaced apart from a bottom surface of the second trench to define a second air gap in the second trench.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
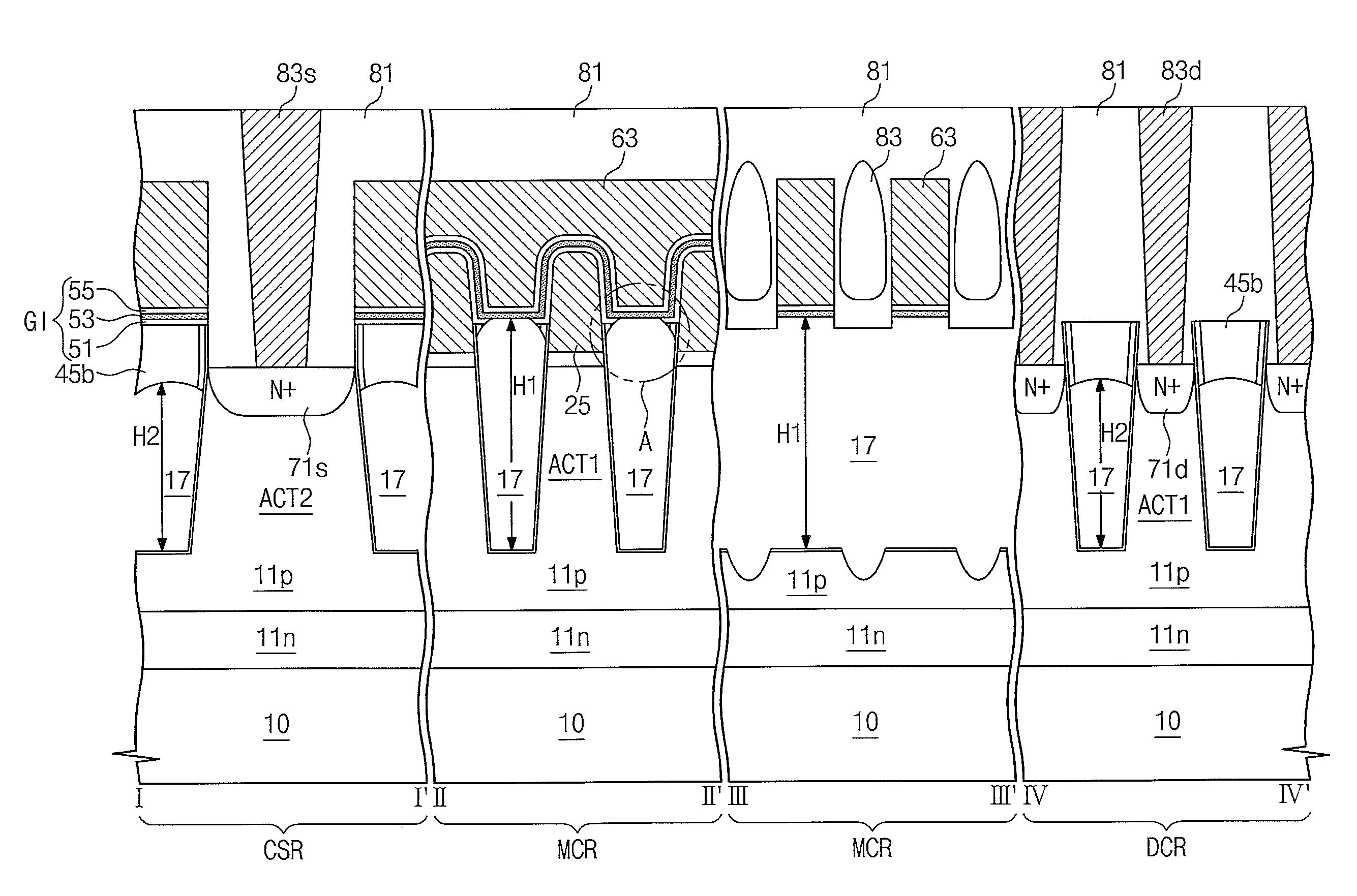
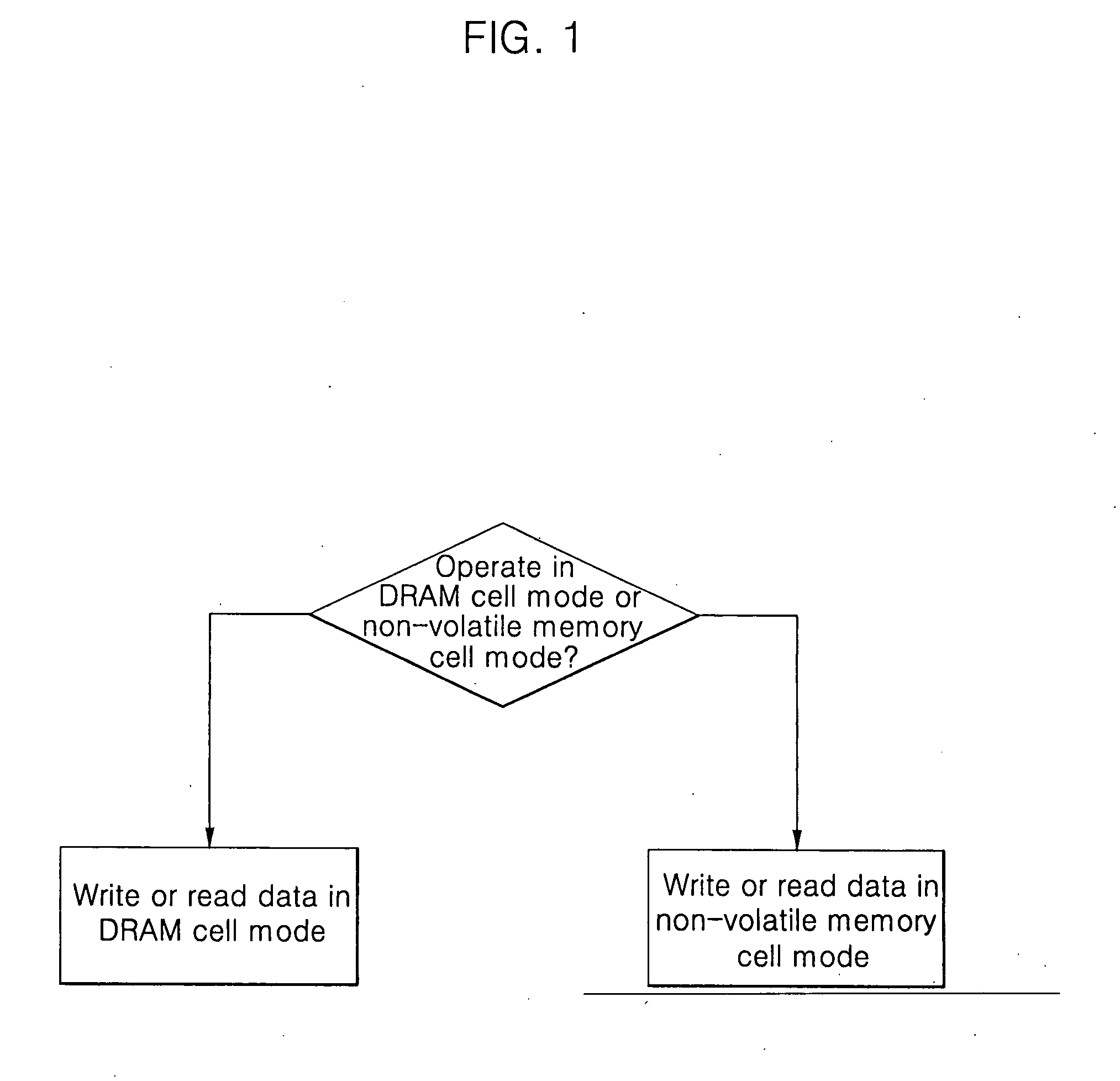
Semiconductor memory device having DRAM cell mode and non-volatile memory cell mode and operation method thereof
A semiconductor memory device may have a DRAM cell mode and a non-volatile memory cell mode without a capacitor, including multiple transistors arranged in an array and having floating bodies, word lines connected to gate electrodes of the transistors, bit lines at a first side of the gate electrodes connected to drains of the transistors, source lines at a second side of the gate electrodes, different from the first side, and connected to sources of the transistors on the semiconductor substrate, and charge storage regions between the gate electrodes and the floating bodies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memory using doped select transistor channel
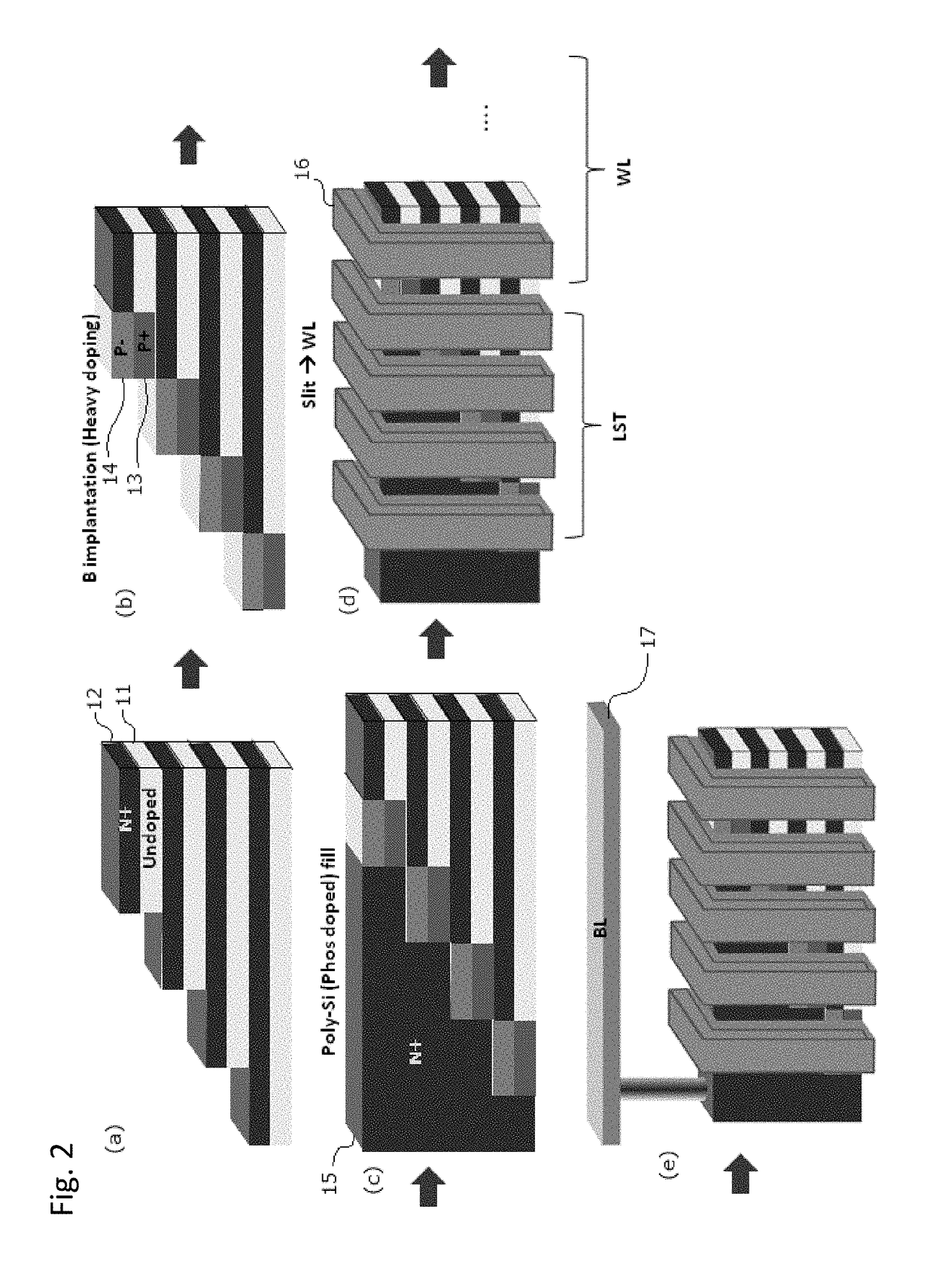
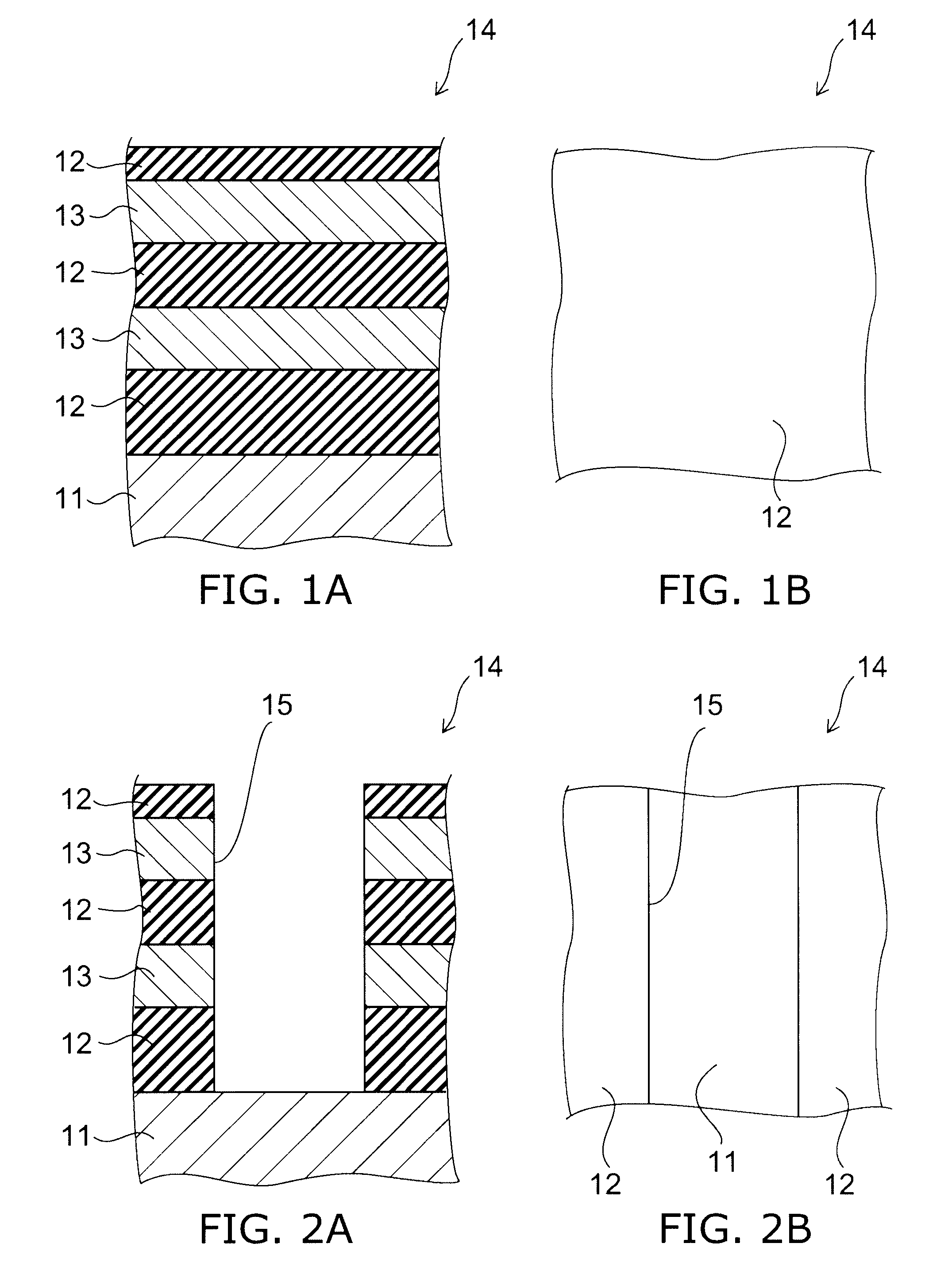
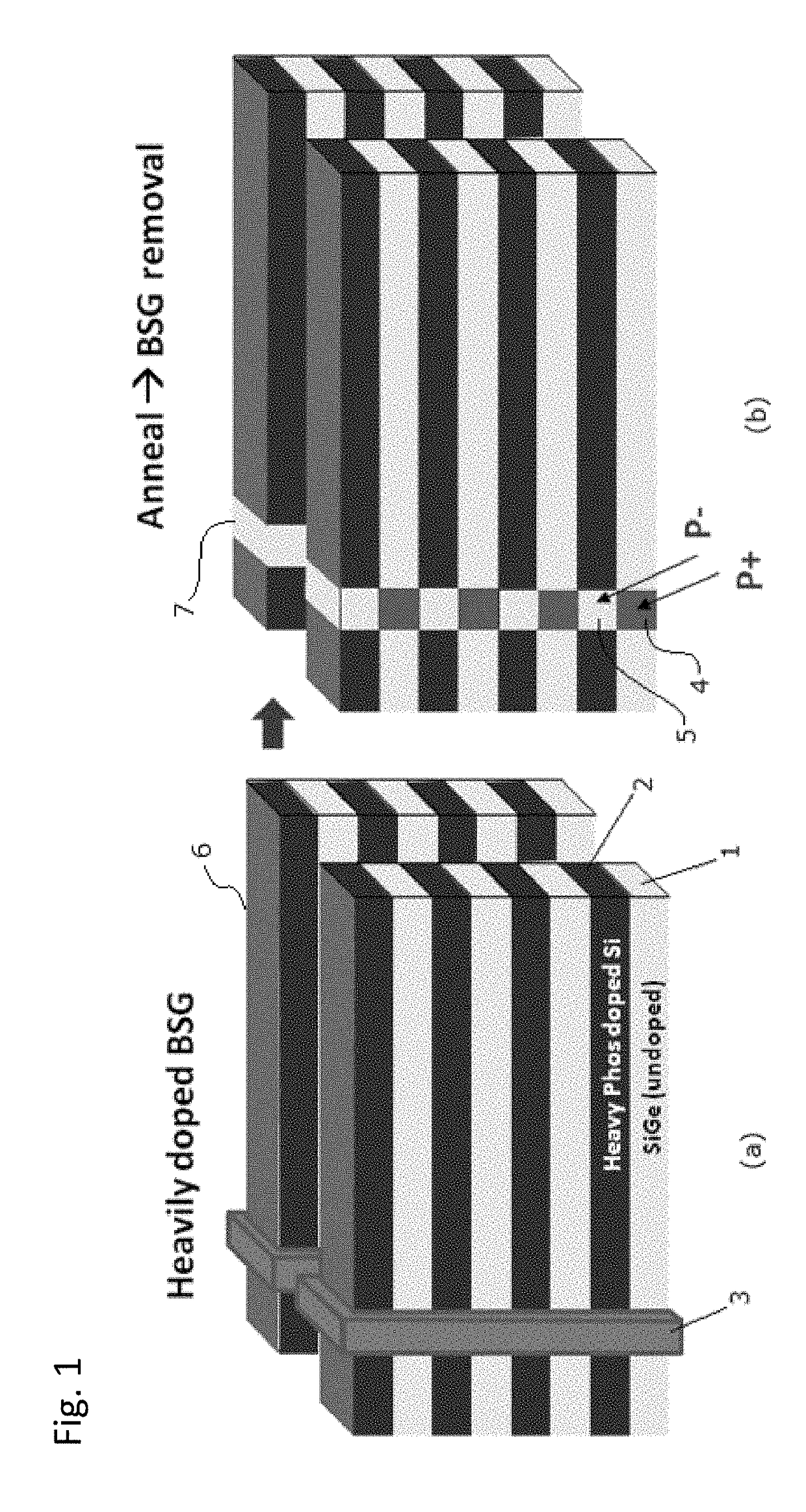
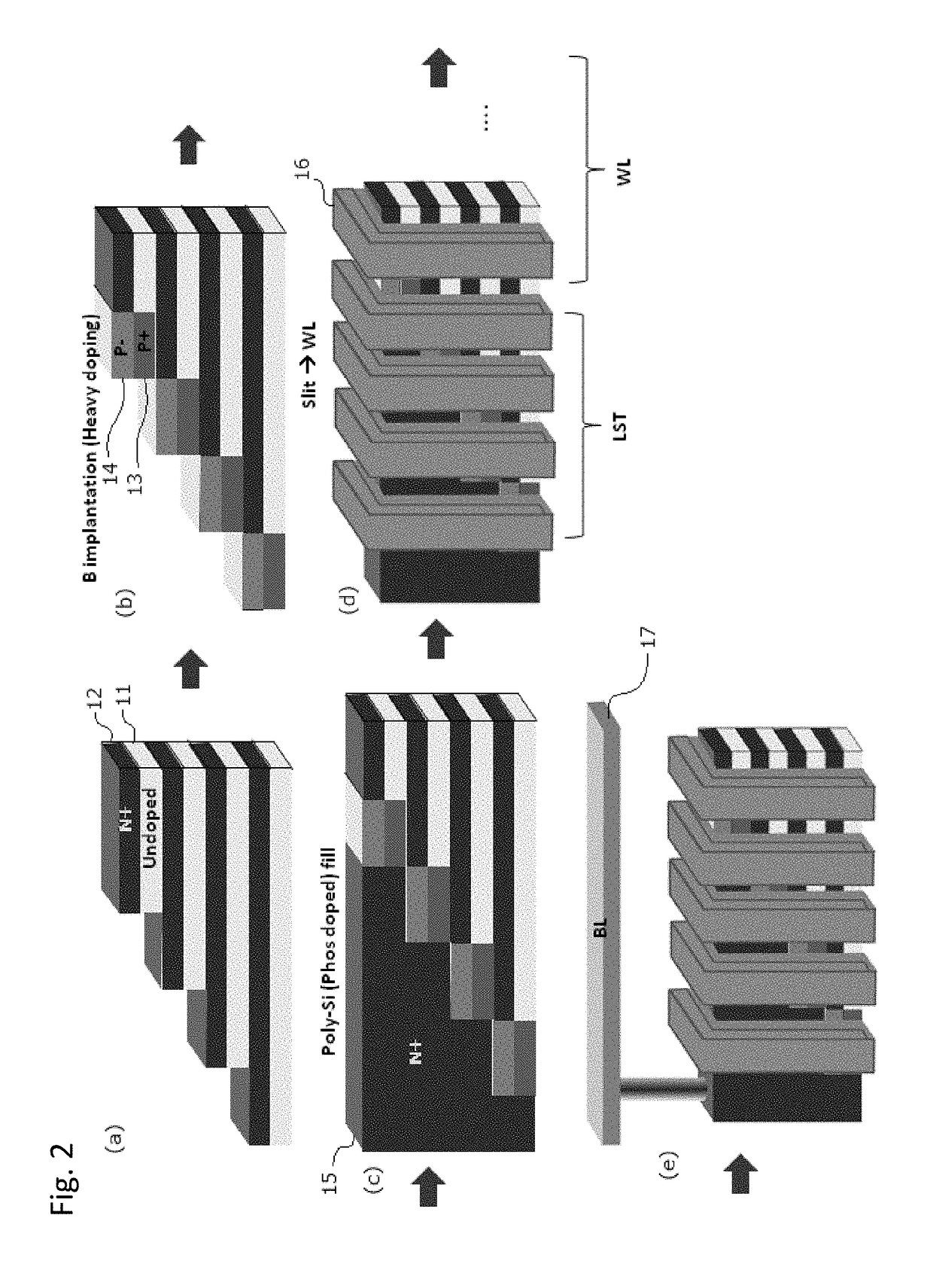
ActiveUS10090316B2Suitable threshold voltageAccurate isolationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
In 3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memories including NAND and NOR flash memories, a lightly boron-doped layer is formed on top of a heavily boron-doped layer to form a select transistor, wherein the former serves as a channel of the select transistor and the latter serves as an isolation region which isolates the select transistor from a memory transistor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100140684A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideThermal treatment
On a silicon substrate is formed a stacked body by alternately stacking a plurality of silicon oxide films and silicon films, a trench is formed in the stacked body, an alumina film, a silicon nitride film and a silicon oxide film are formed in this order on an inner surface of the trench, and a channel silicon crystalline film is formed on the silicon oxide film. Next, a silicon oxide layer is formed at an interface between the silicon oxide film and the channel silicon crystalline film by performing thermal treatment in an oxygen gas atmosphere.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
8 bit per cell non-volatile semiconductor memory structure utilizing trench technology and dielectric floating gate
The present application discloses a non-volatile semiconductor memory device for storing up to eight-bits of information. The device has a semiconductor substrate of one conductivity type, a central bottom diffusion region on top of a portion of the semiconductor substrate, a second semiconductor layer on top of the bottom diffusion region, and left and right diffusion regions formed in the second semiconductor layer apart from the central bottom diffusion region thus forming a first vertical channel between the right and central bottom diffusion regions. The device further includes a trapping dielectric layer formed over exposed portions of the semiconductor substrate, left, central and right bottom diffusion regions and second semiconductor layer and a wordline formed over the trapping dielectric layer. A methods of fabricating this novel cell using trench technology is also disclosed.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory and process of producing the same
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory of an aspect of the present invention comprises a semiconductor substrate, a pillar-shaped semiconductor layer extending in the vertical direction with respect to the surface of the semiconductor substrate, a plurality of memory cells arranged in the vertical direction on the side surface of the semiconductor layer and having a charge storage layer and a control gate electrode, a first select gate transistor arranged on the semiconductor layer at an end of the memory cells on the side of the semiconductor substrate, and a second select gate transistor arranged on the semiconductor layer on the other end of the memory cells opposite to the side of the semiconductor substrate, wherein the first select gate transistor includes a diffusion layer in the semiconductor substrate and is electrically connected to the pillar-shaped semiconductor layer by way of the diffusion layer that serves as the drain region.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memory using doped select transistor channel
ActiveUS20180061851A1Without deterioration of reading latencyAccurate isolationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
In 3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memories including NAND and NOR flash memories, a lightly boron-doped layer is formed on top of a heavily boron-doped layer to form a select transistor, wherein the former serves as a channel of the select transistor and the latter serves as an isolation region which isolates the select transistor from a memory transistor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Detecting over programmed memory
ActiveUS6917542B2Lower requirementRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureThreshold voltage
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
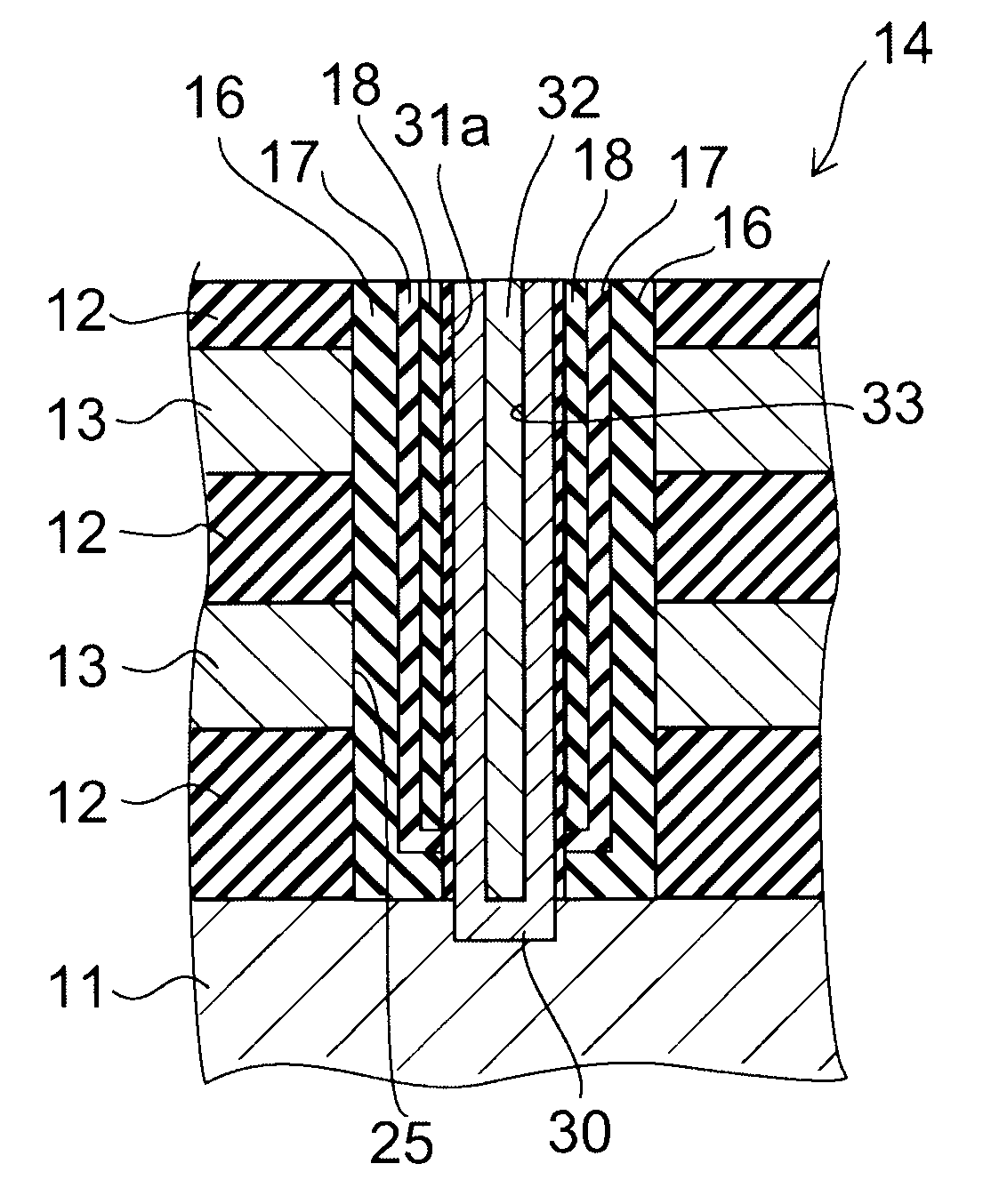
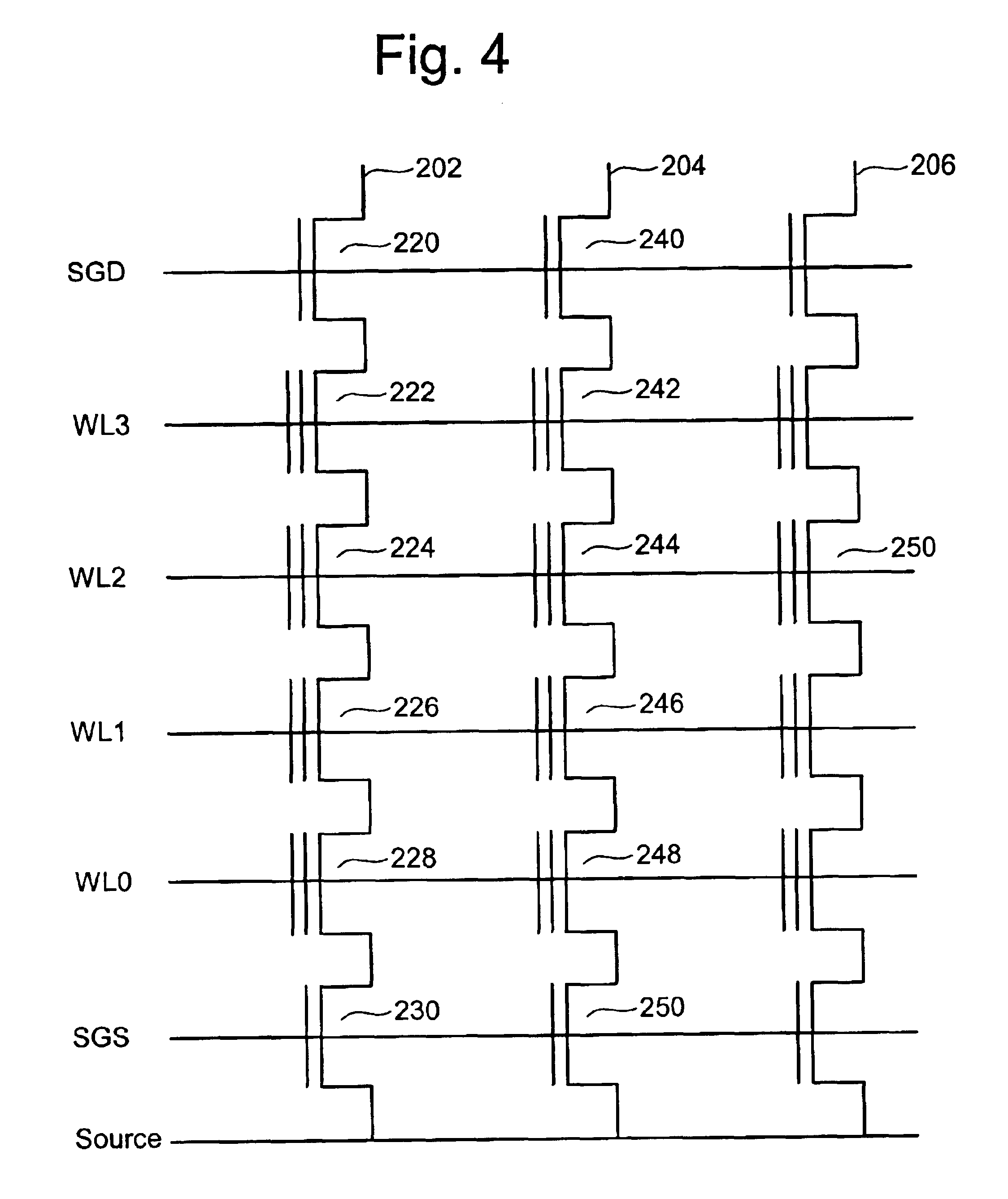
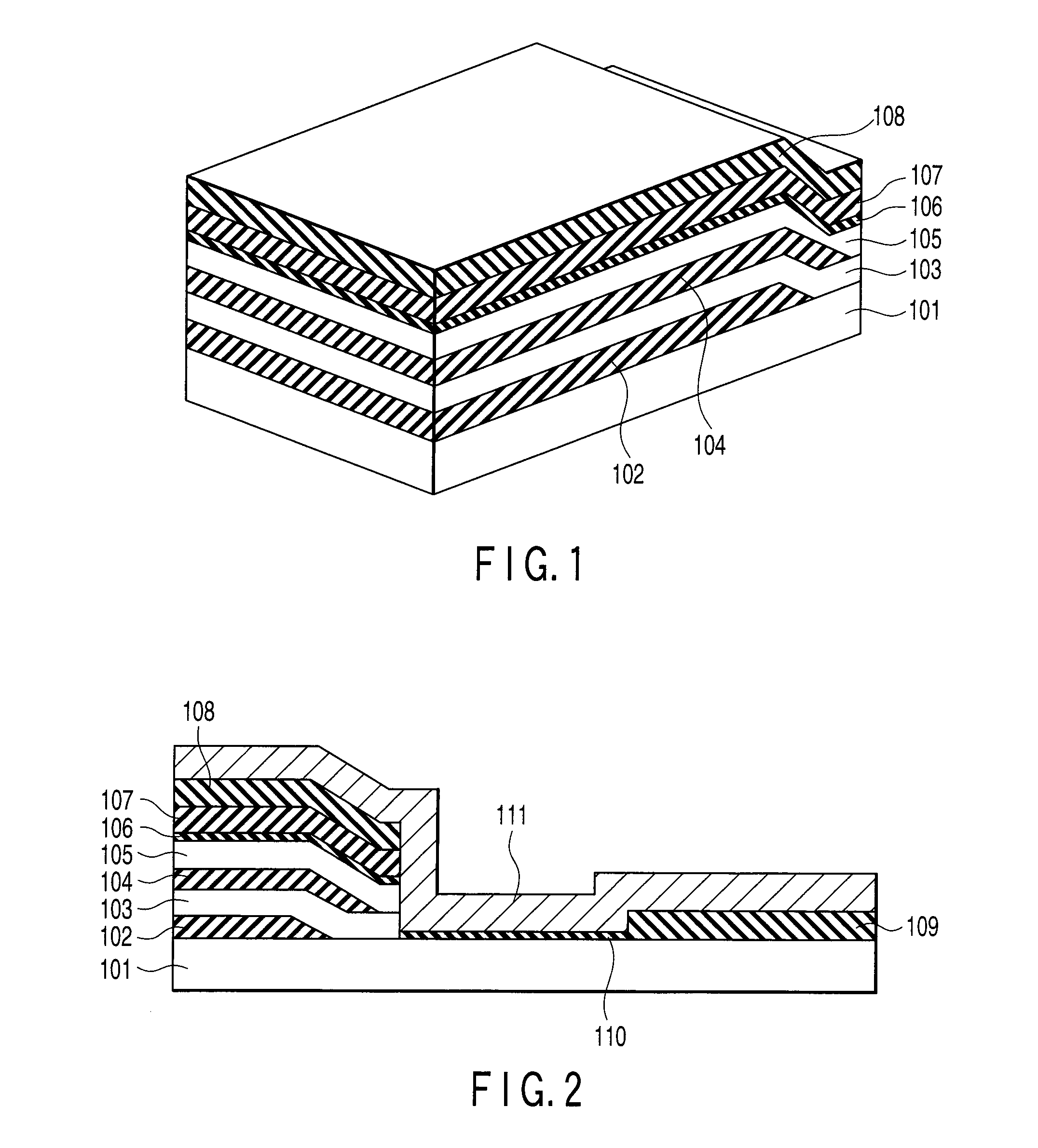
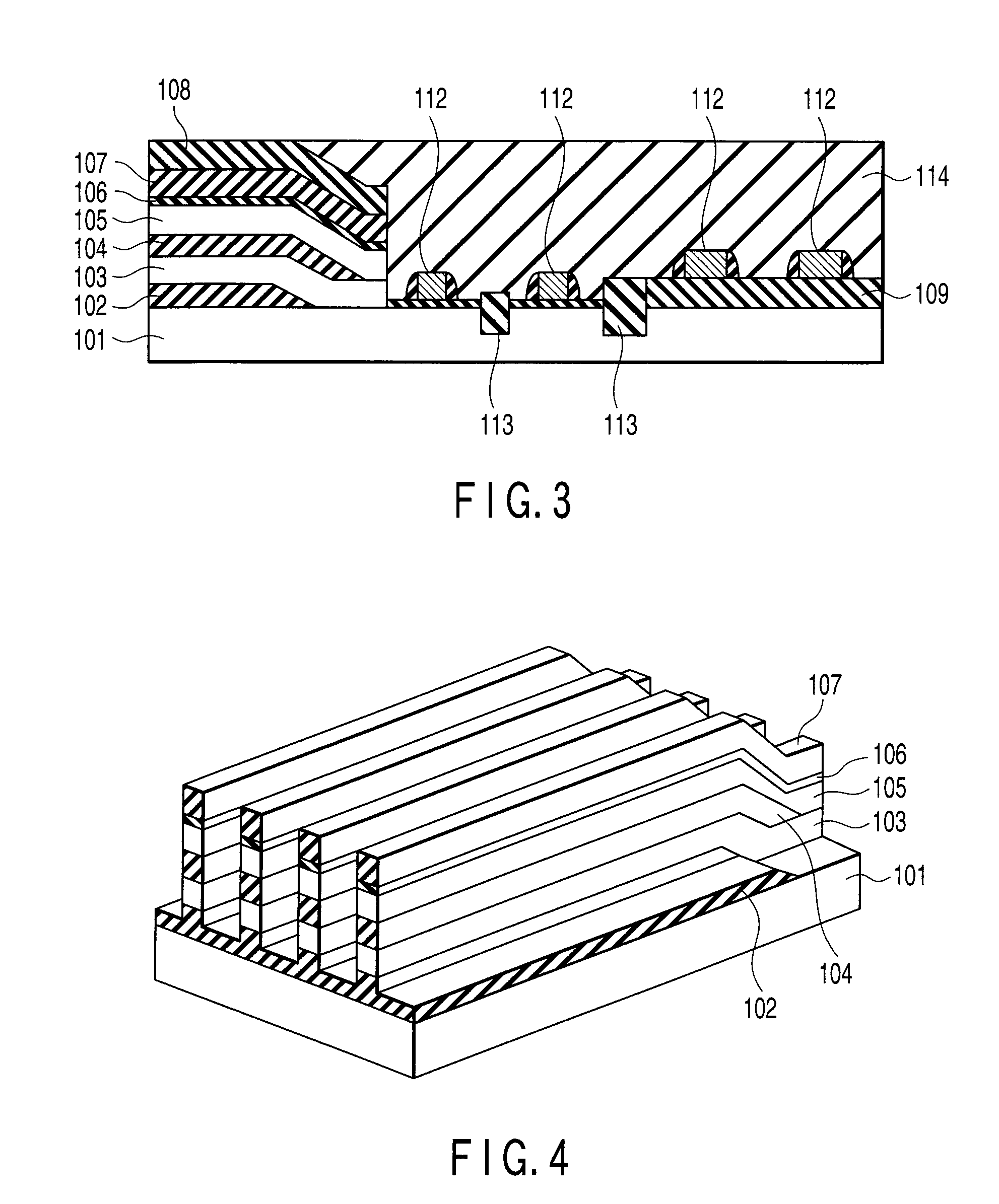
Semiconductor Memory and Method of Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20080073635A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor memory includes a plurality of stripe-like active areas formed by stacking, in a direction perpendicular to a substrate, a plurality of layers extending parallel to the substrate, a first gate electrode formed on first side surfaces of the active areas, the first side surfaces being perpendicular to the substrate, a second gate electrode formed on second side surfaces of the active areas, the second side surfaces being perpendicular to the substrate. The layers are patterned in self-alignment with each other, intersections of the active areas and the first gate electrode form a plurality of memory cells, and the plurality of memory cells in an intersecting plane share the first gate electrode.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
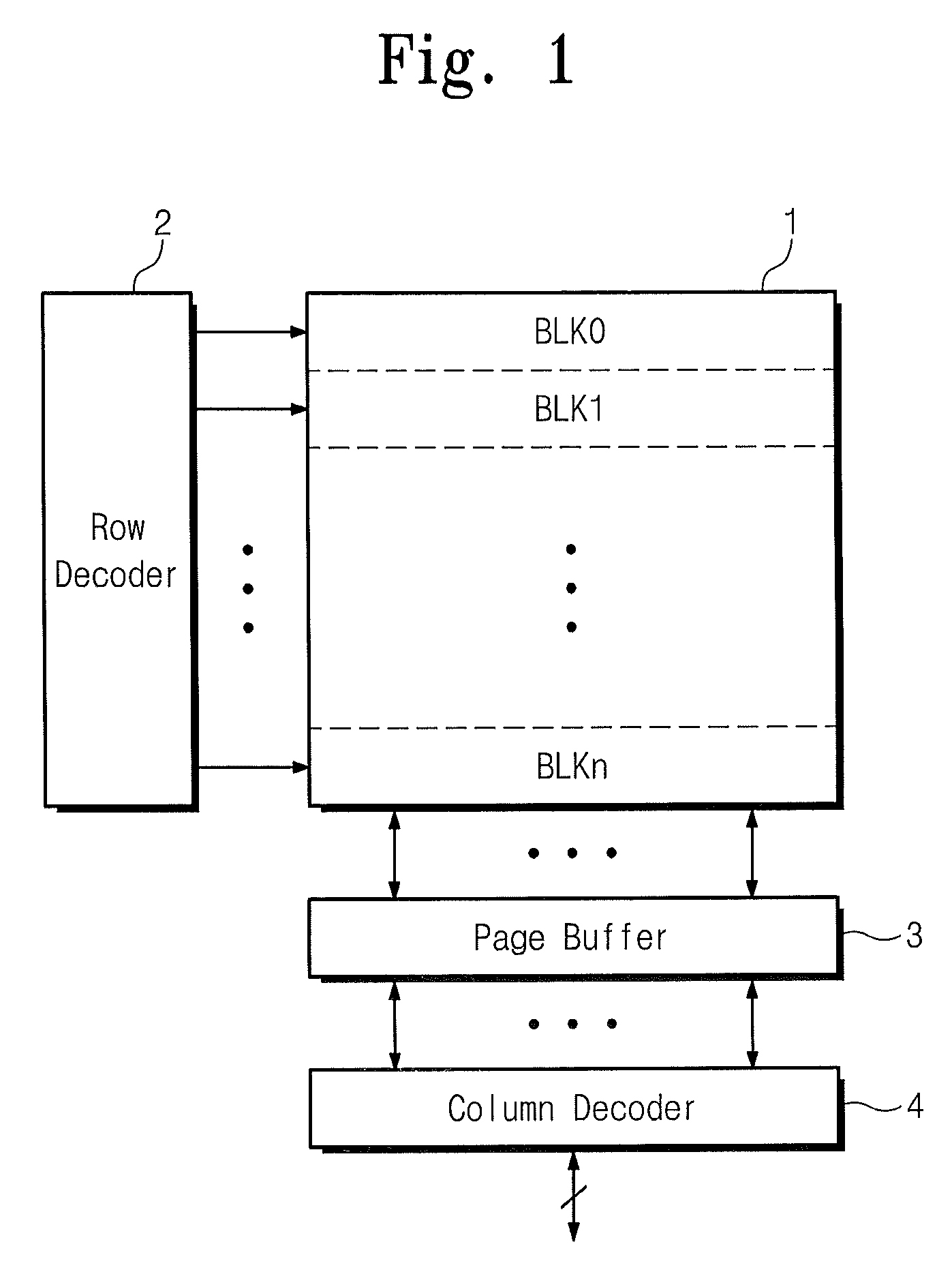
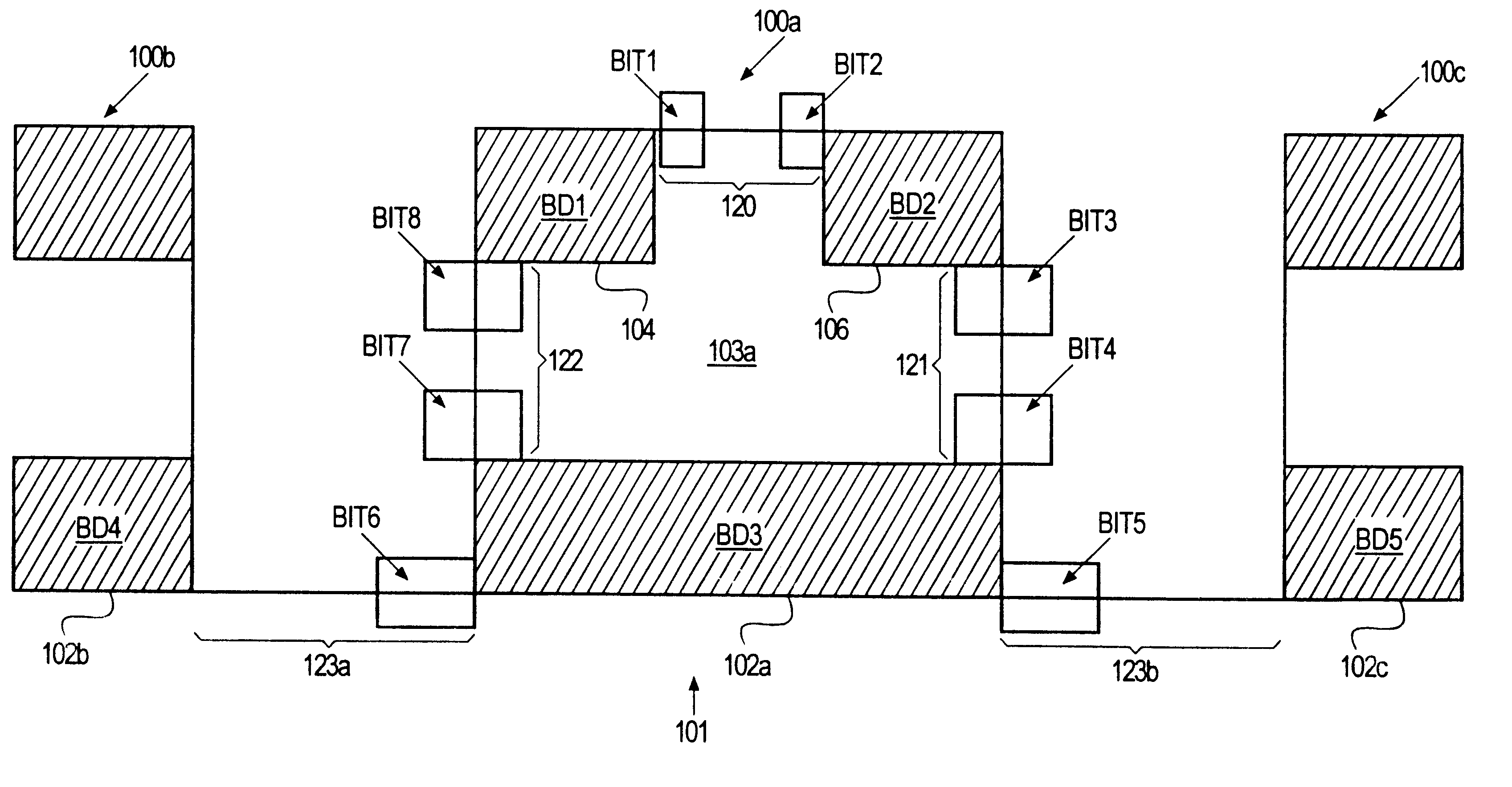
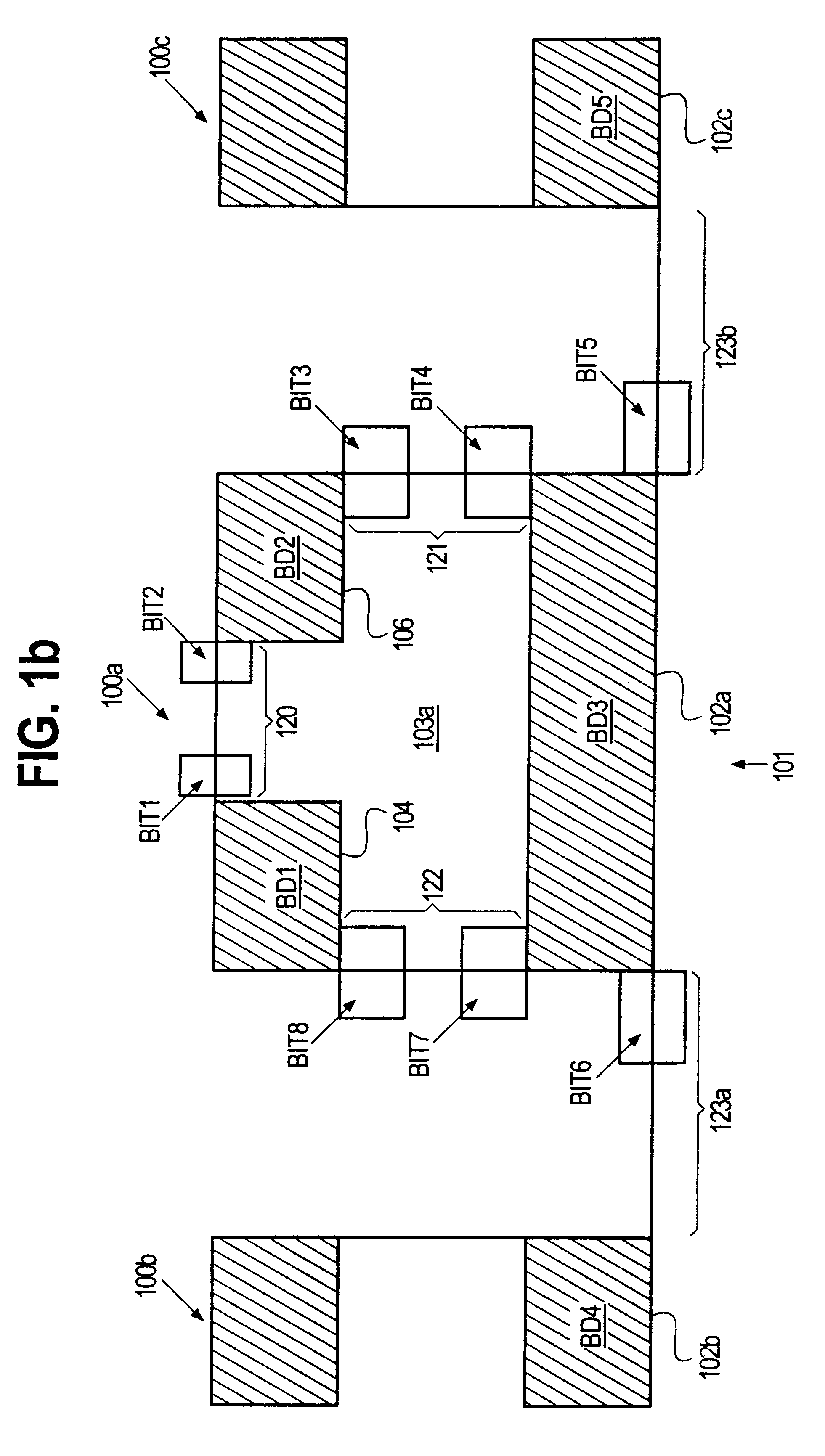
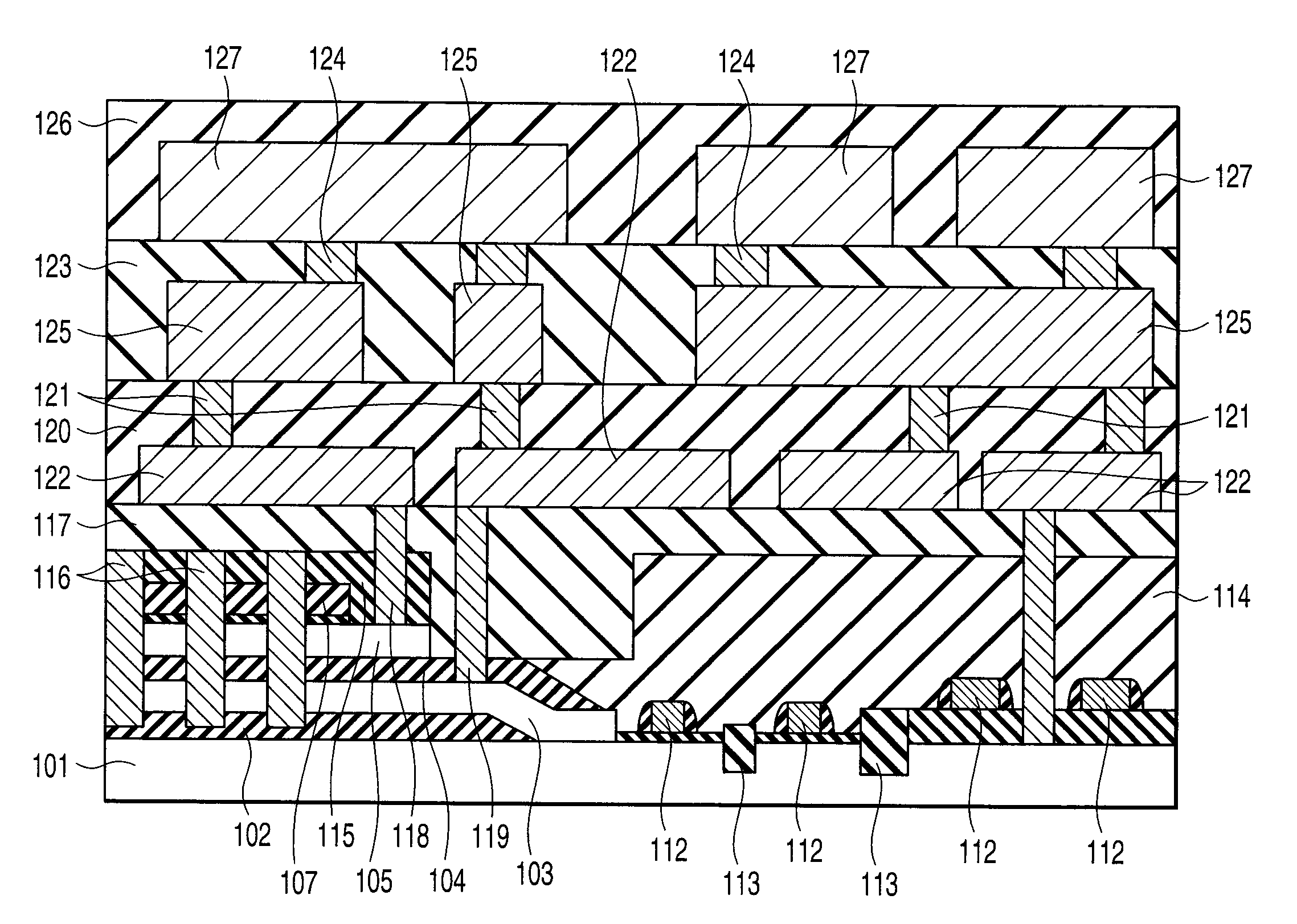
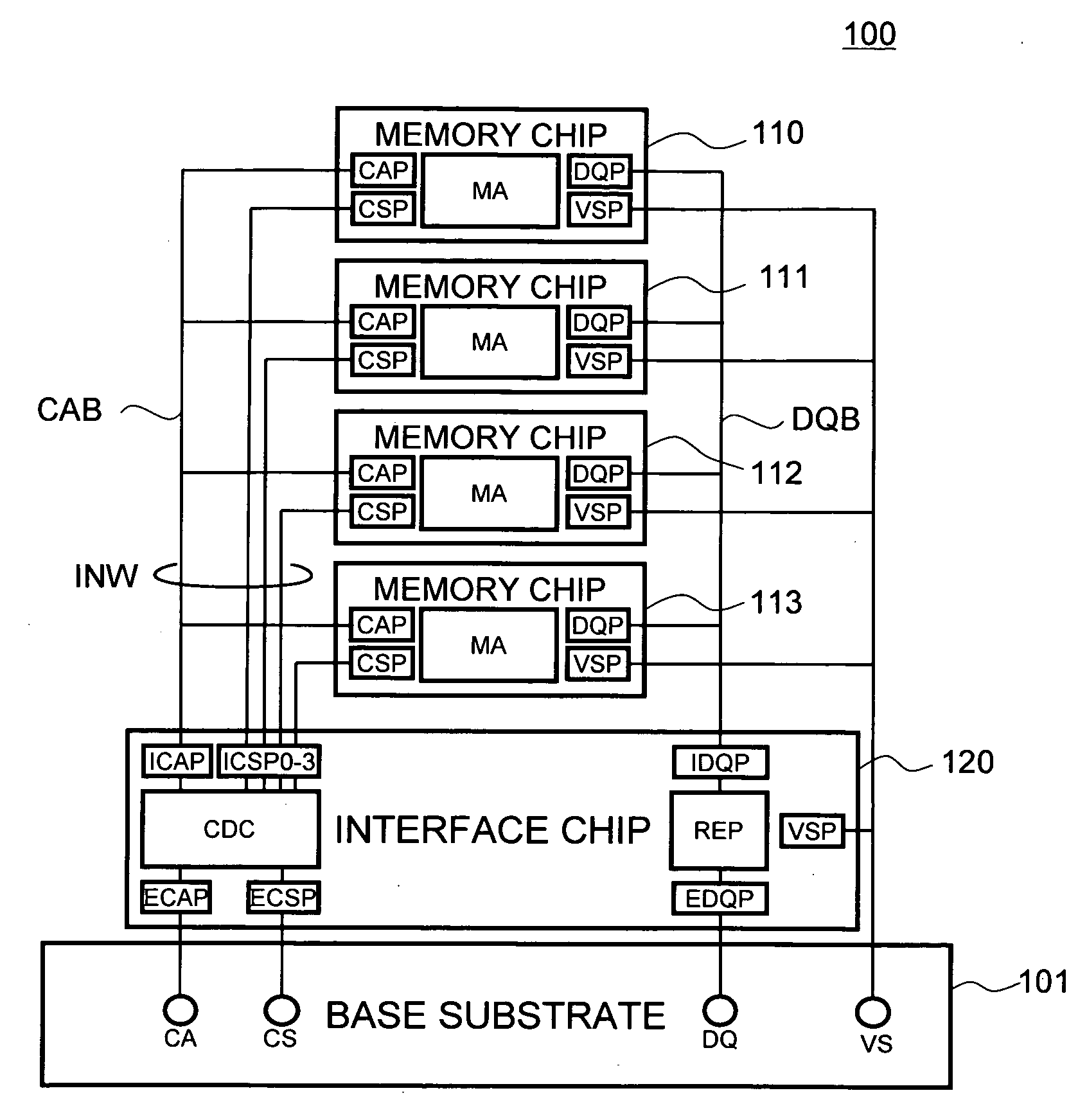
Semiconductor storage device having a plurality of stacked memory chips
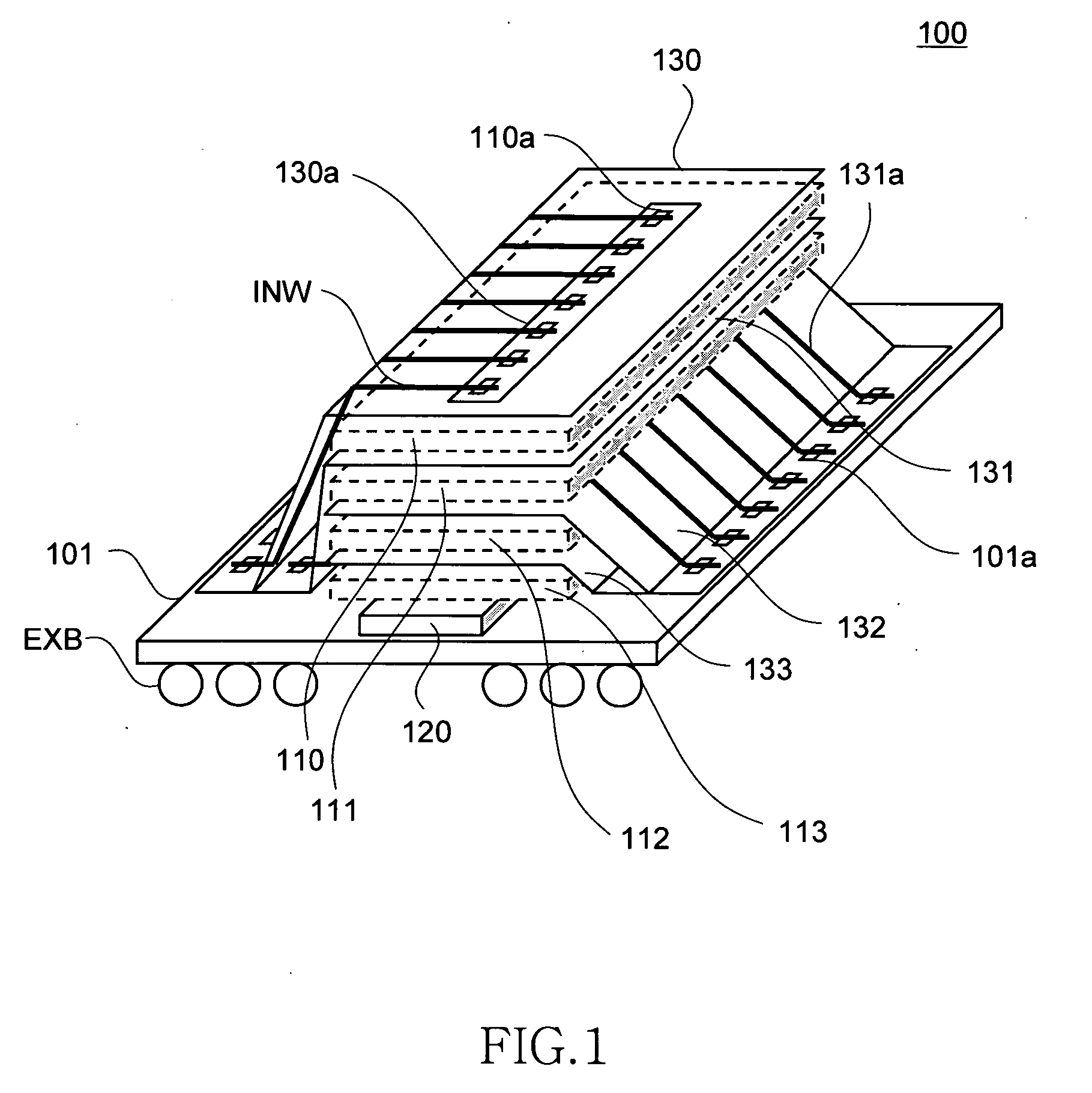
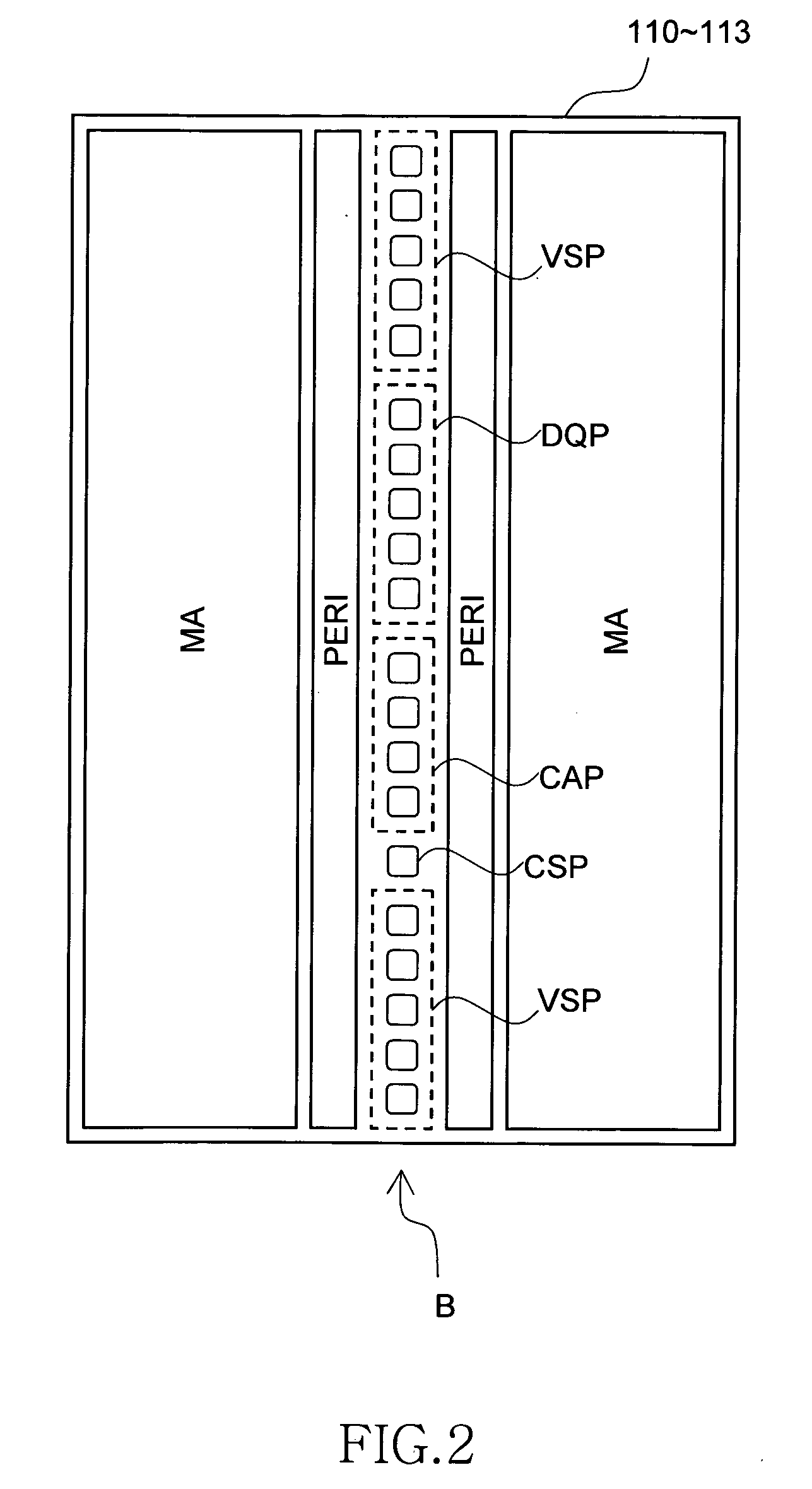
ActiveUS20060233012A1Reduce in quantityReduction in wiring capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipChip select
A semiconductor storage employs a base substrate (101) having a command / address external terminal group (CA), a data input / output external terminal group (DQ), and a single chip select external terminal (CS), and also comprises a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) mounted on a base substrate (101), each of which can individually carry out read and write operations. The terminals (CA), (DQ), and (CS) are connected to an interface chip (120). The interface chip (120) has a chip select signal generation circuit that can individually activate a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) on the basis of an address signal fed by way of the terminal (CA) and on the basis of a chip select signal fed by way of the terminal (CS).
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com