Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1510 results about "Semiconductor storage devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
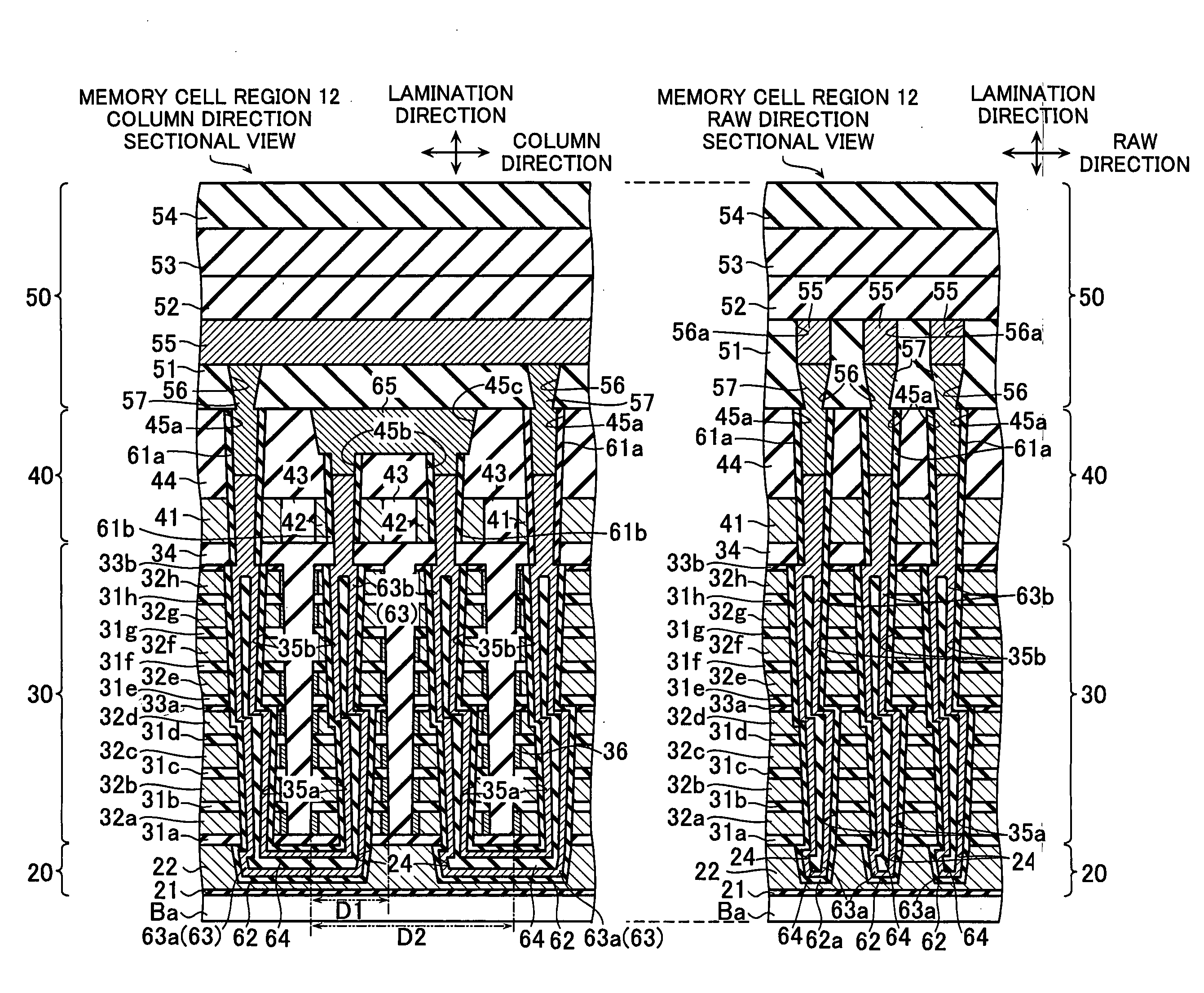
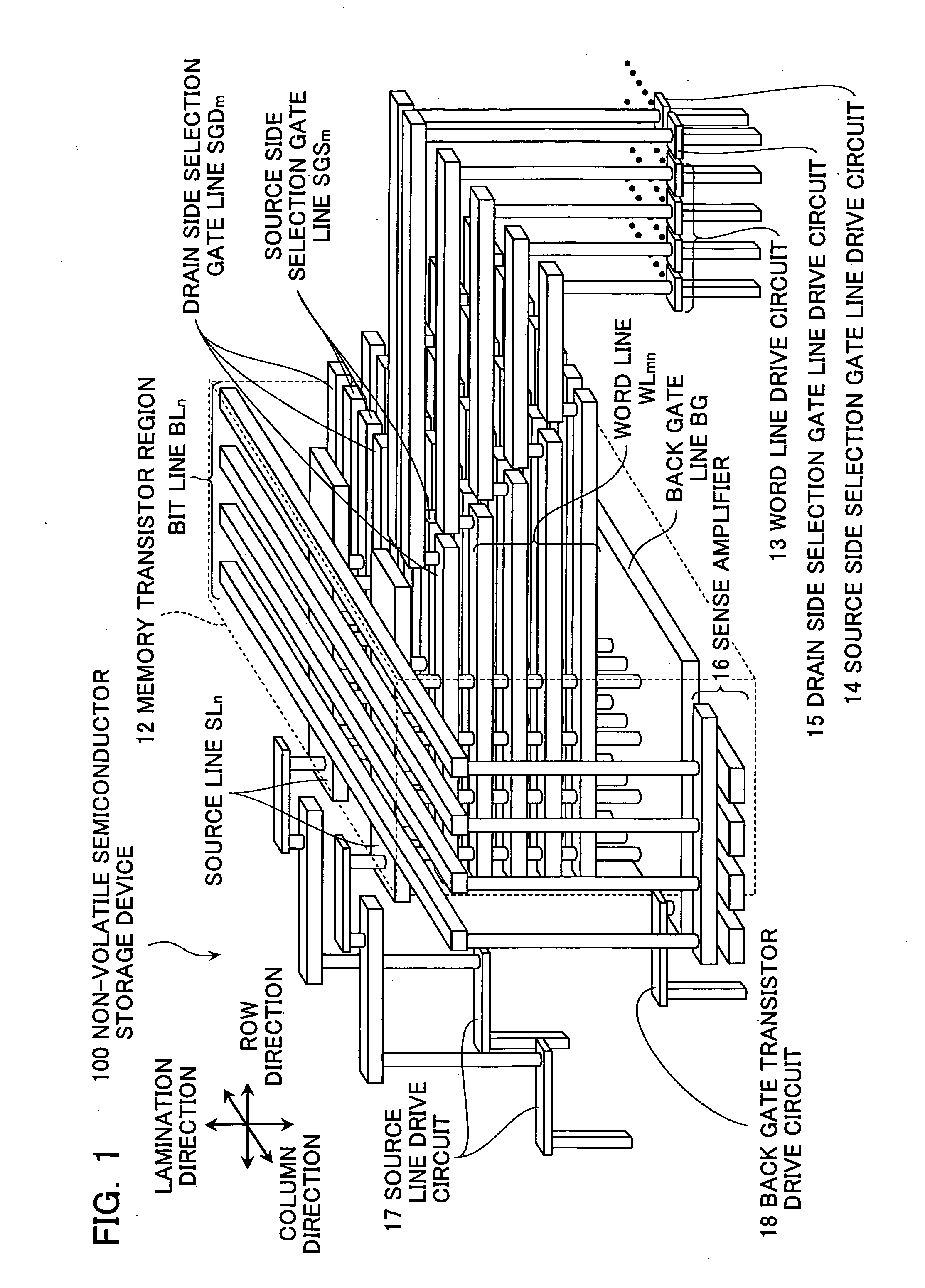
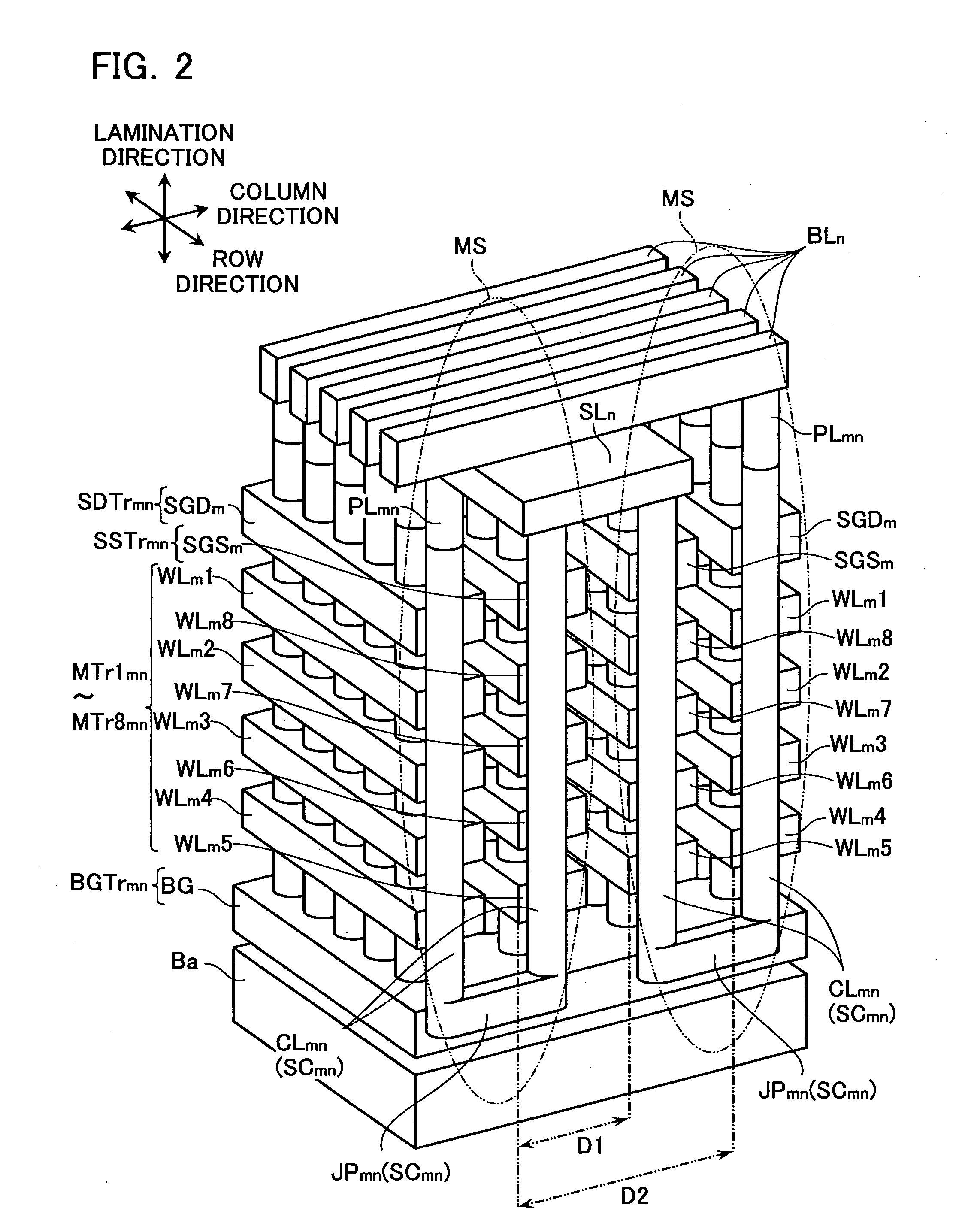
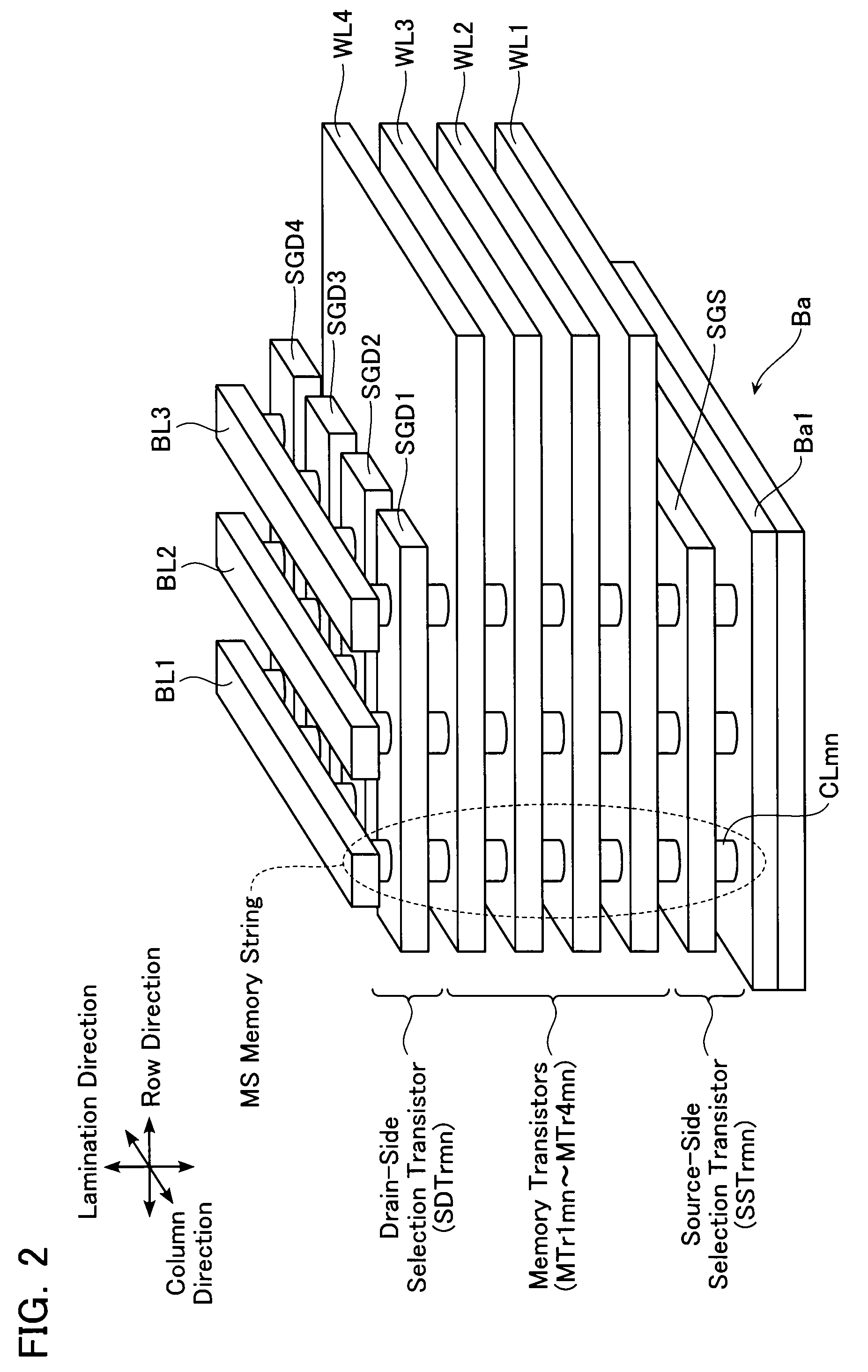
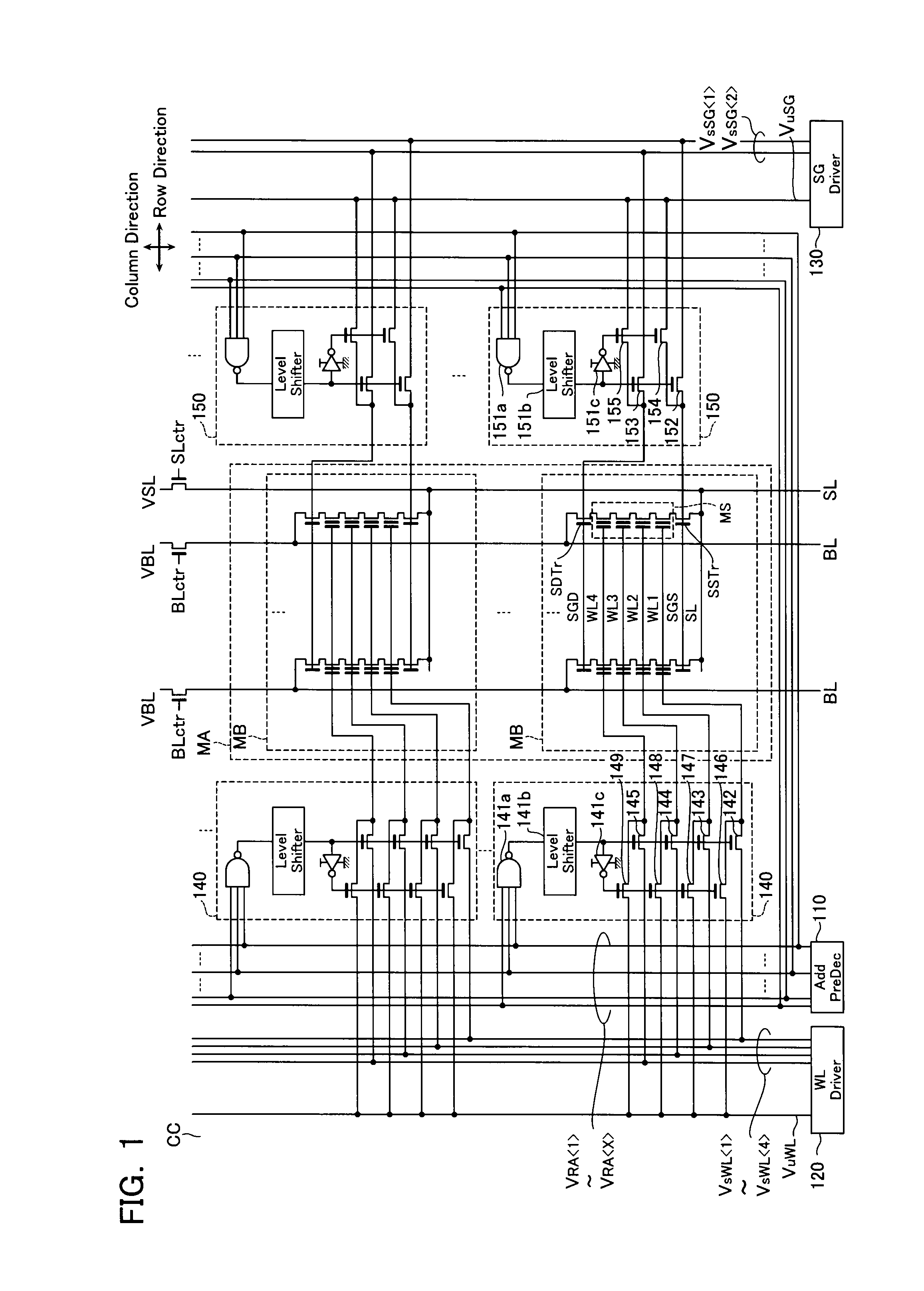
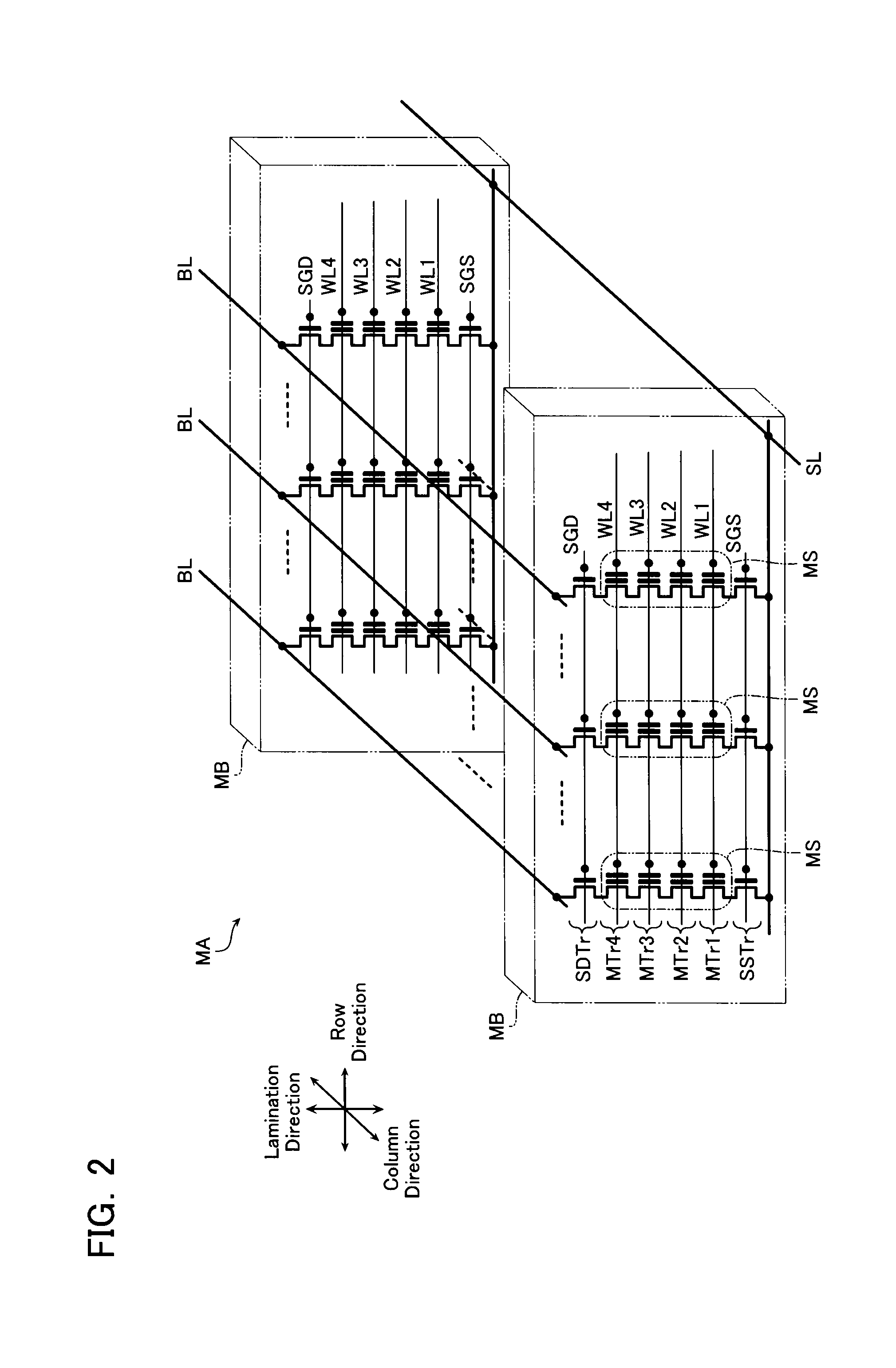
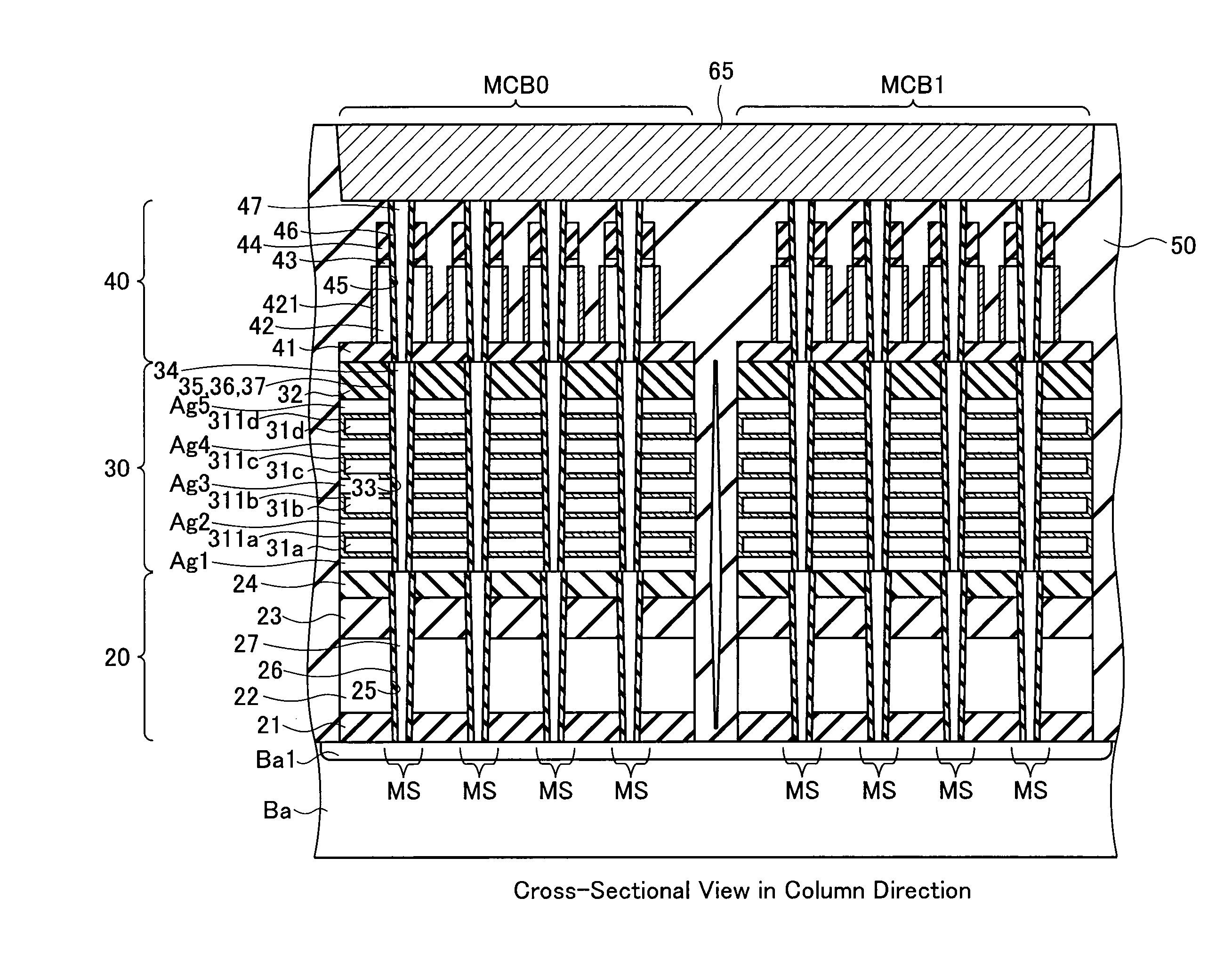
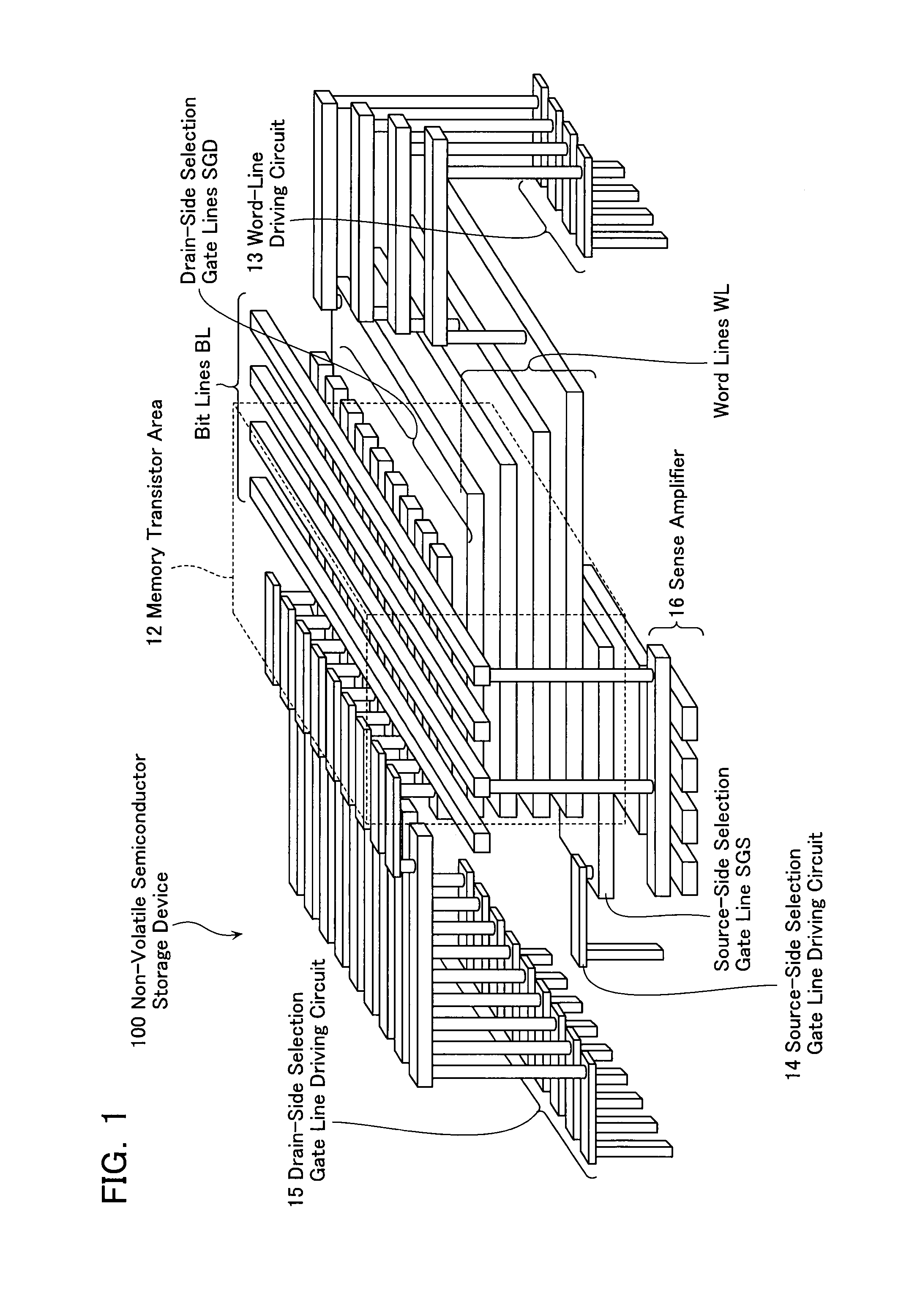
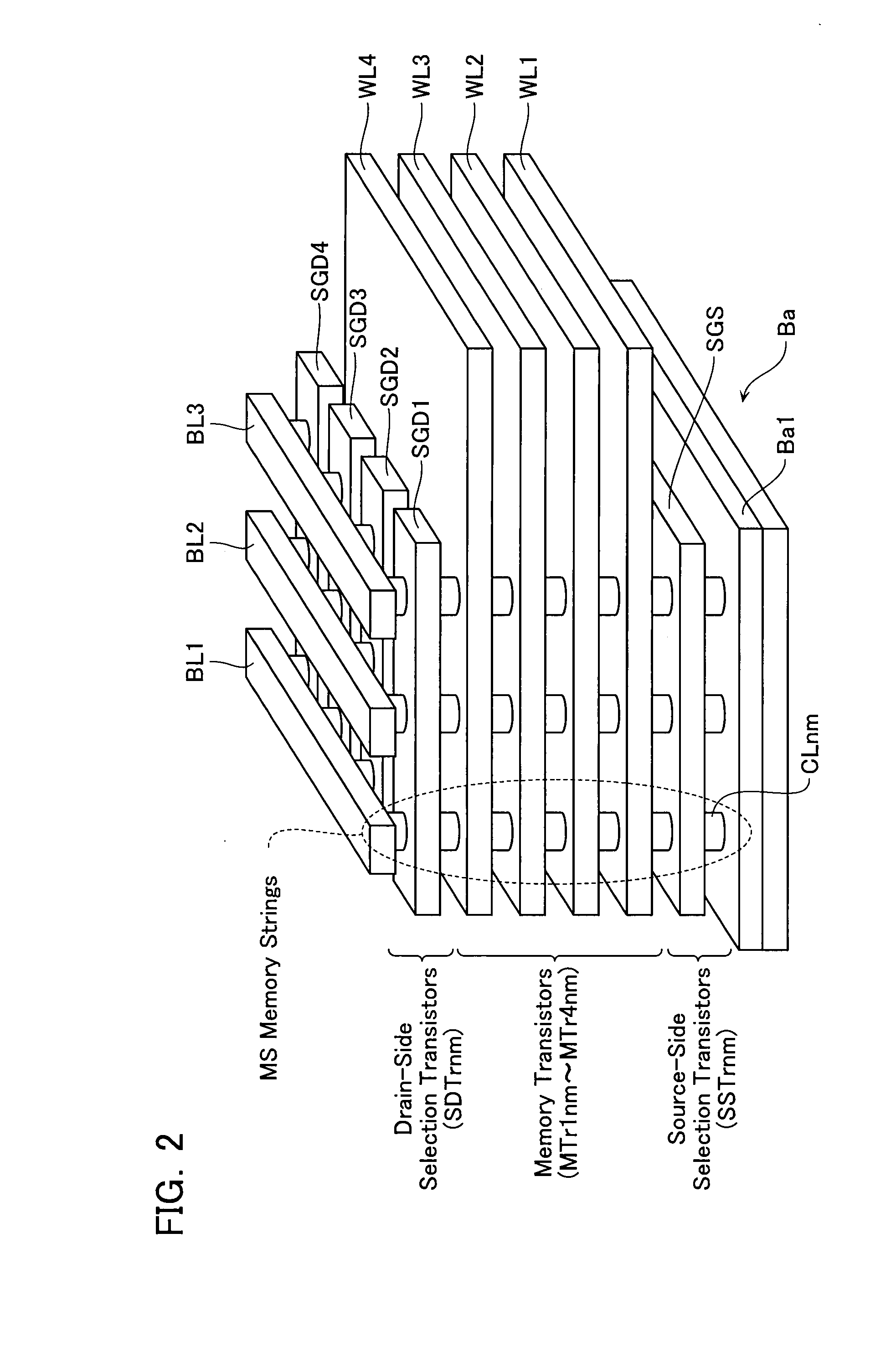
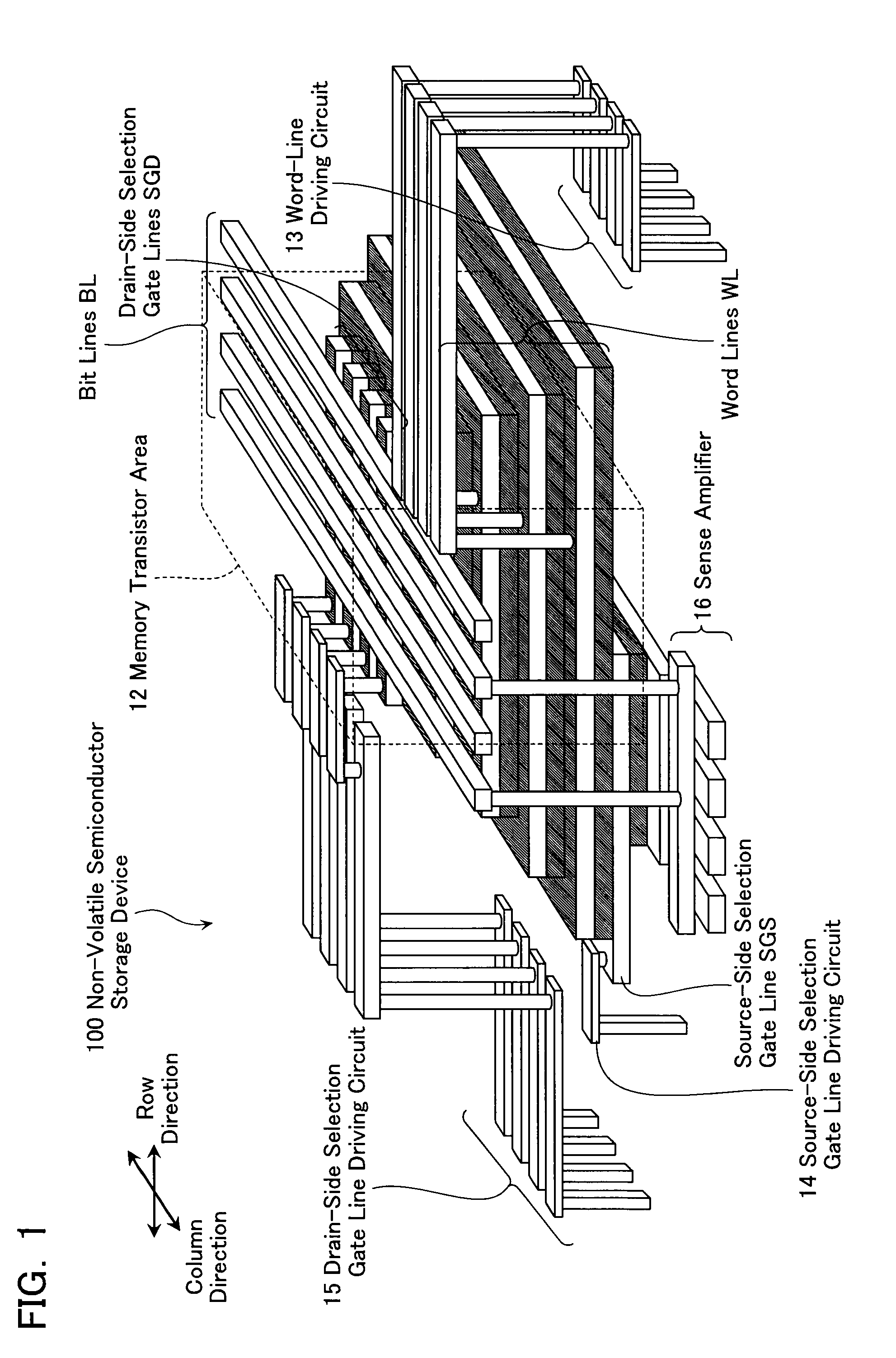
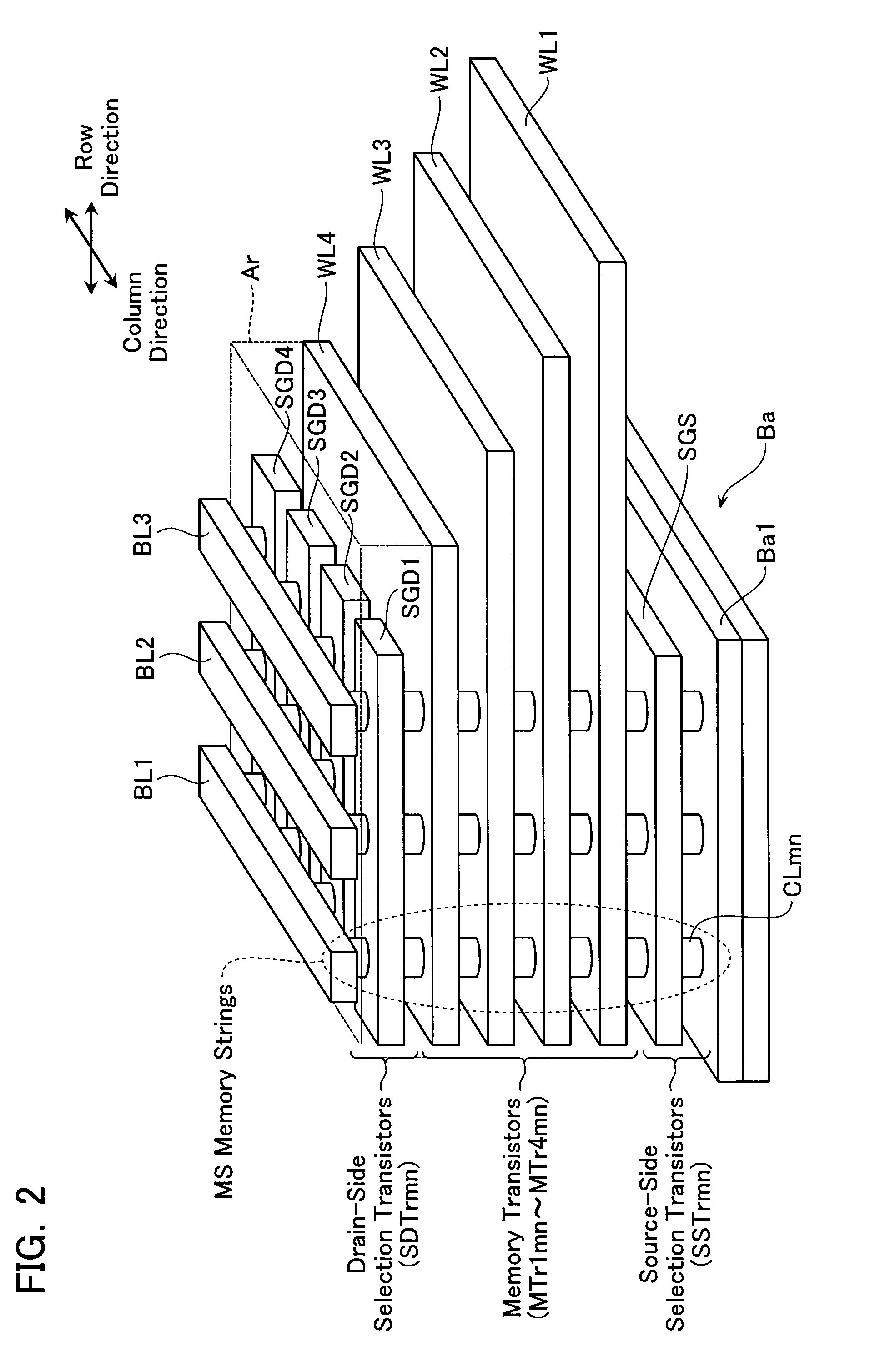
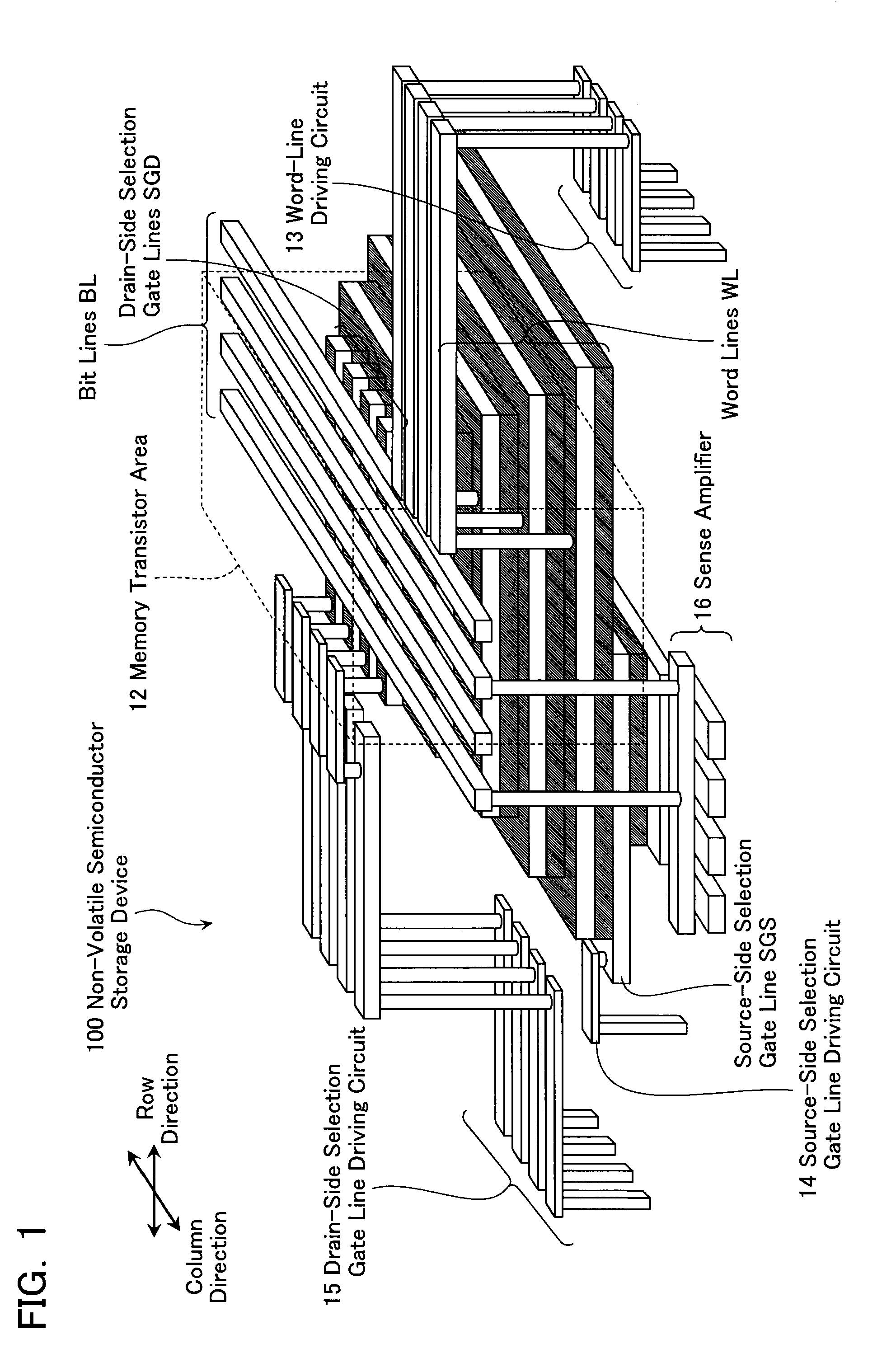
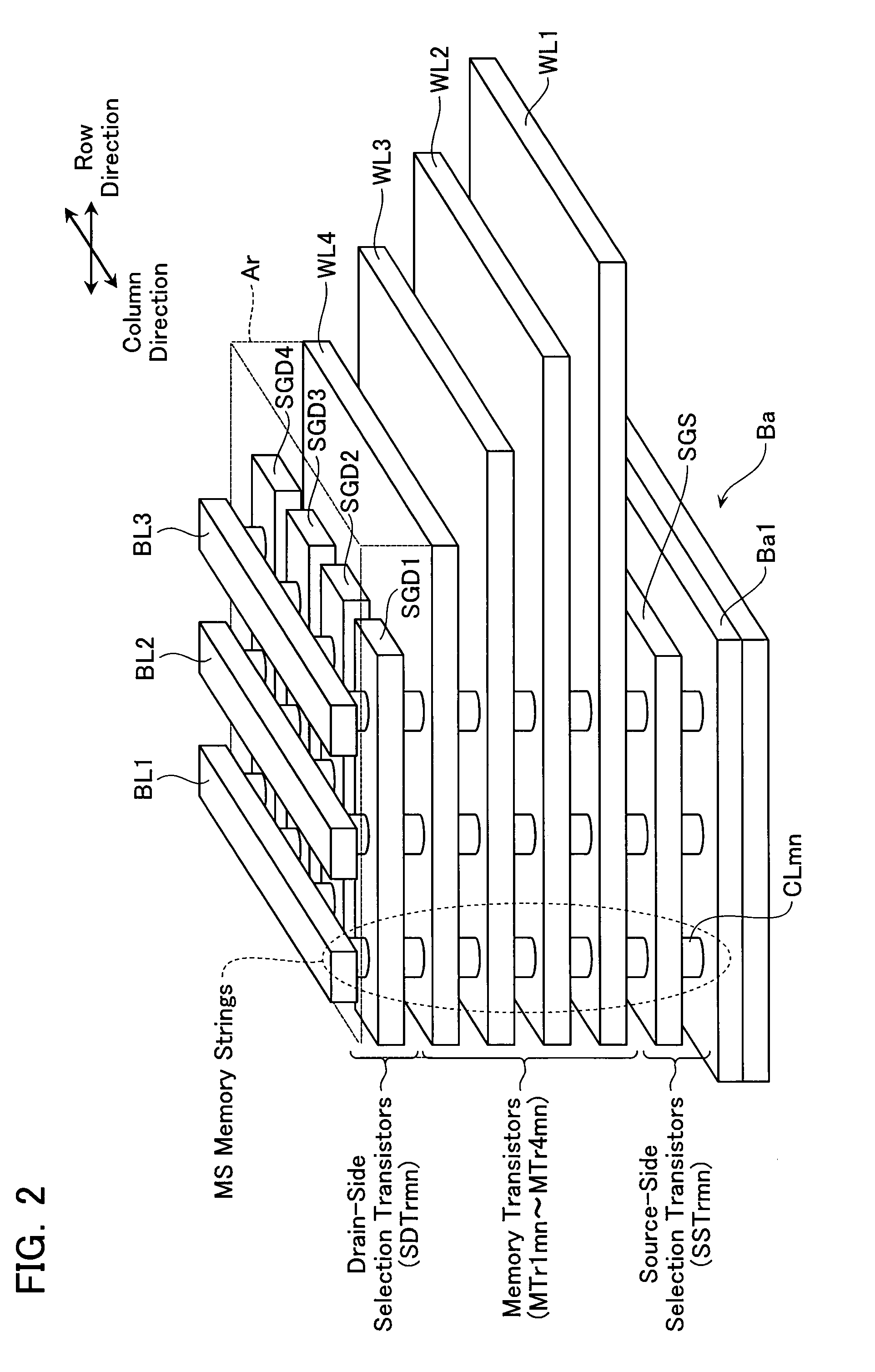
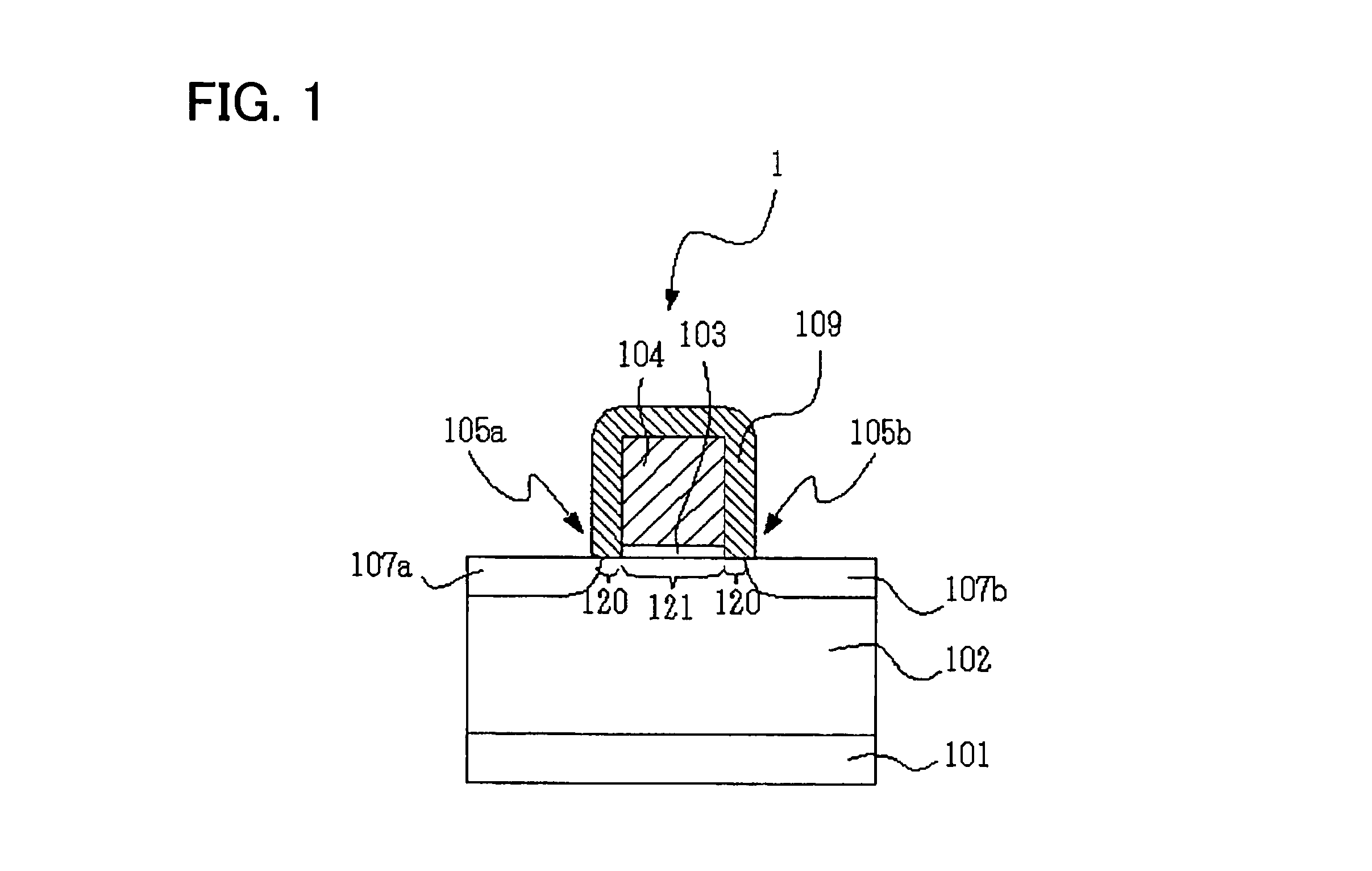
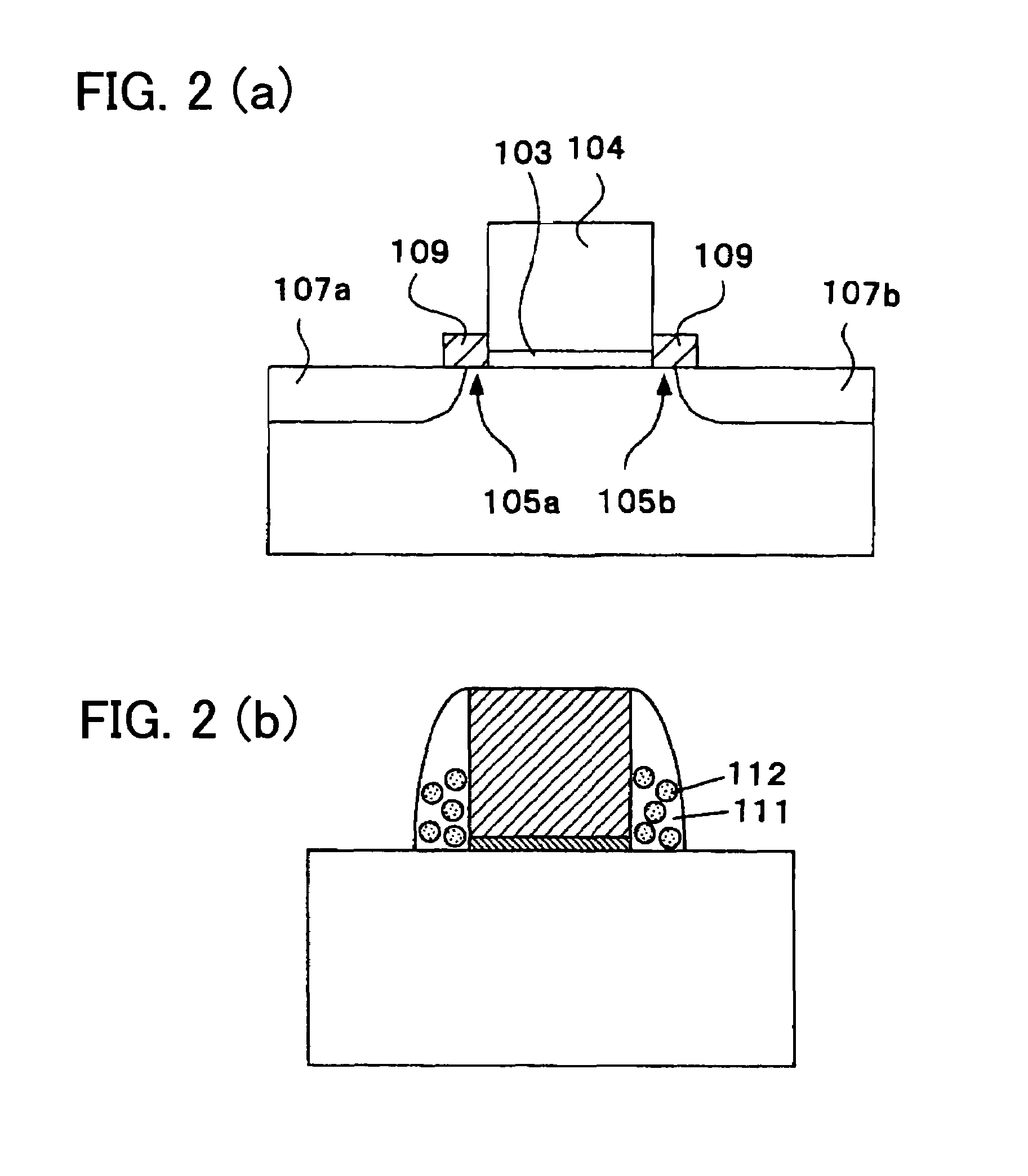
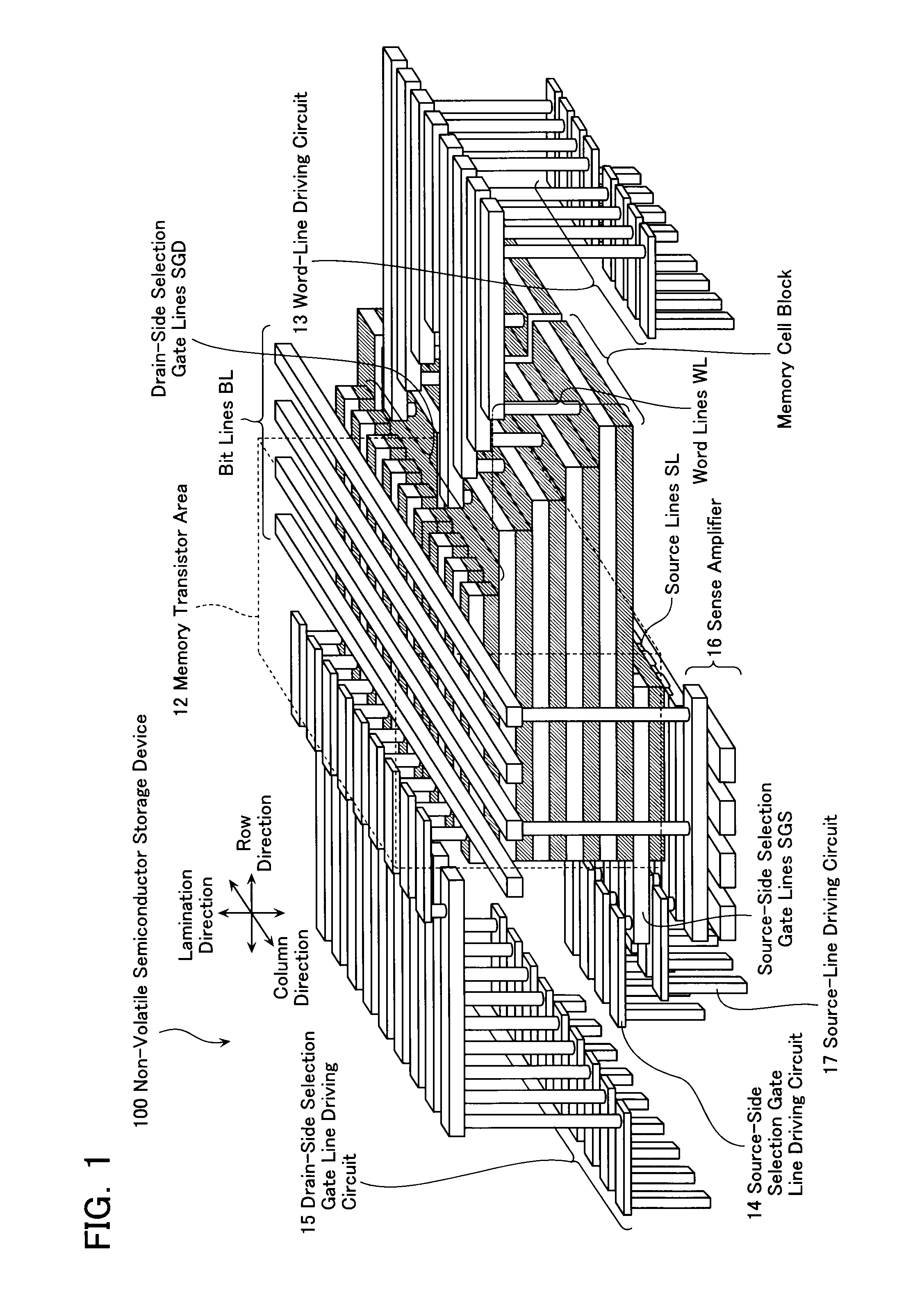
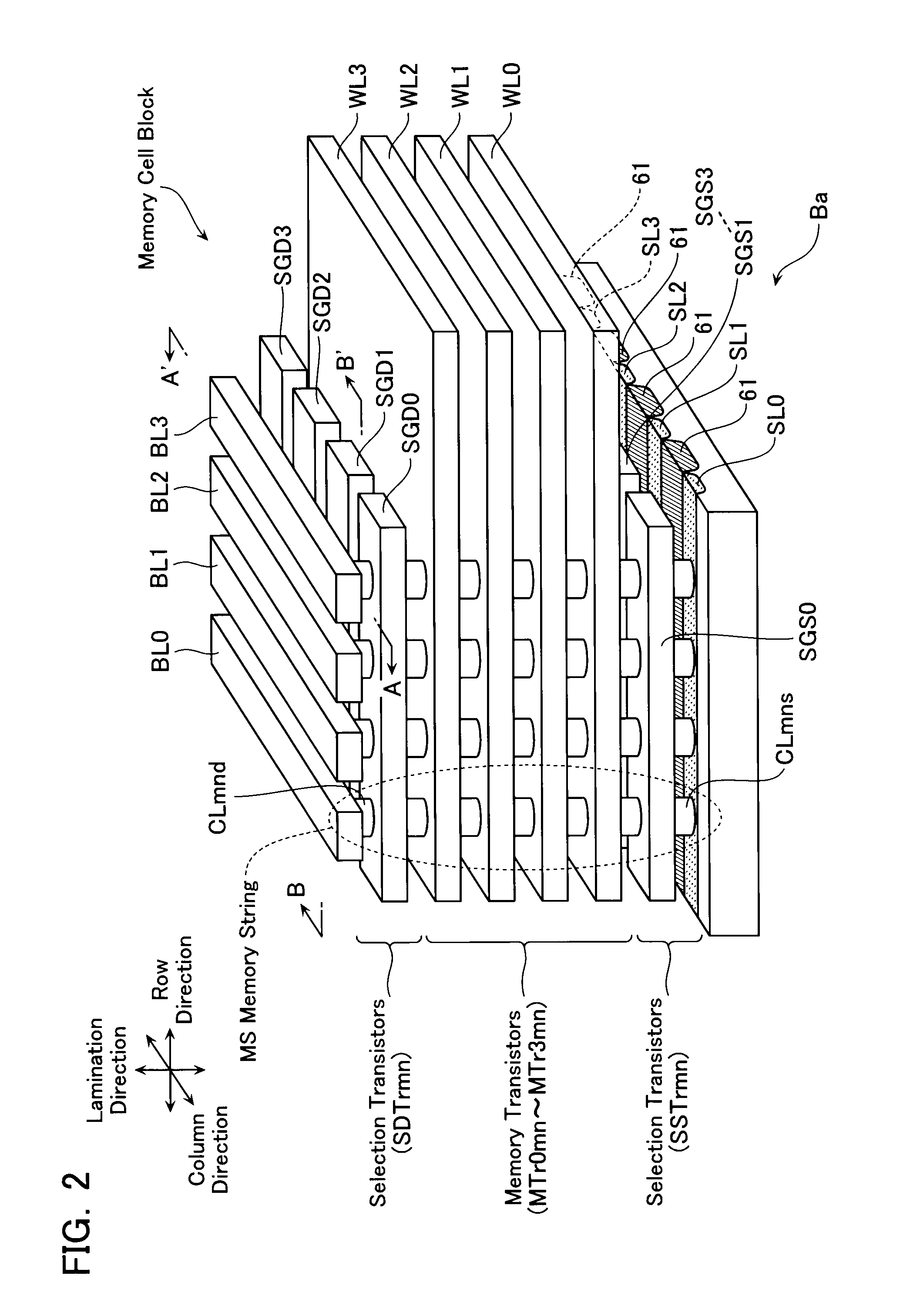
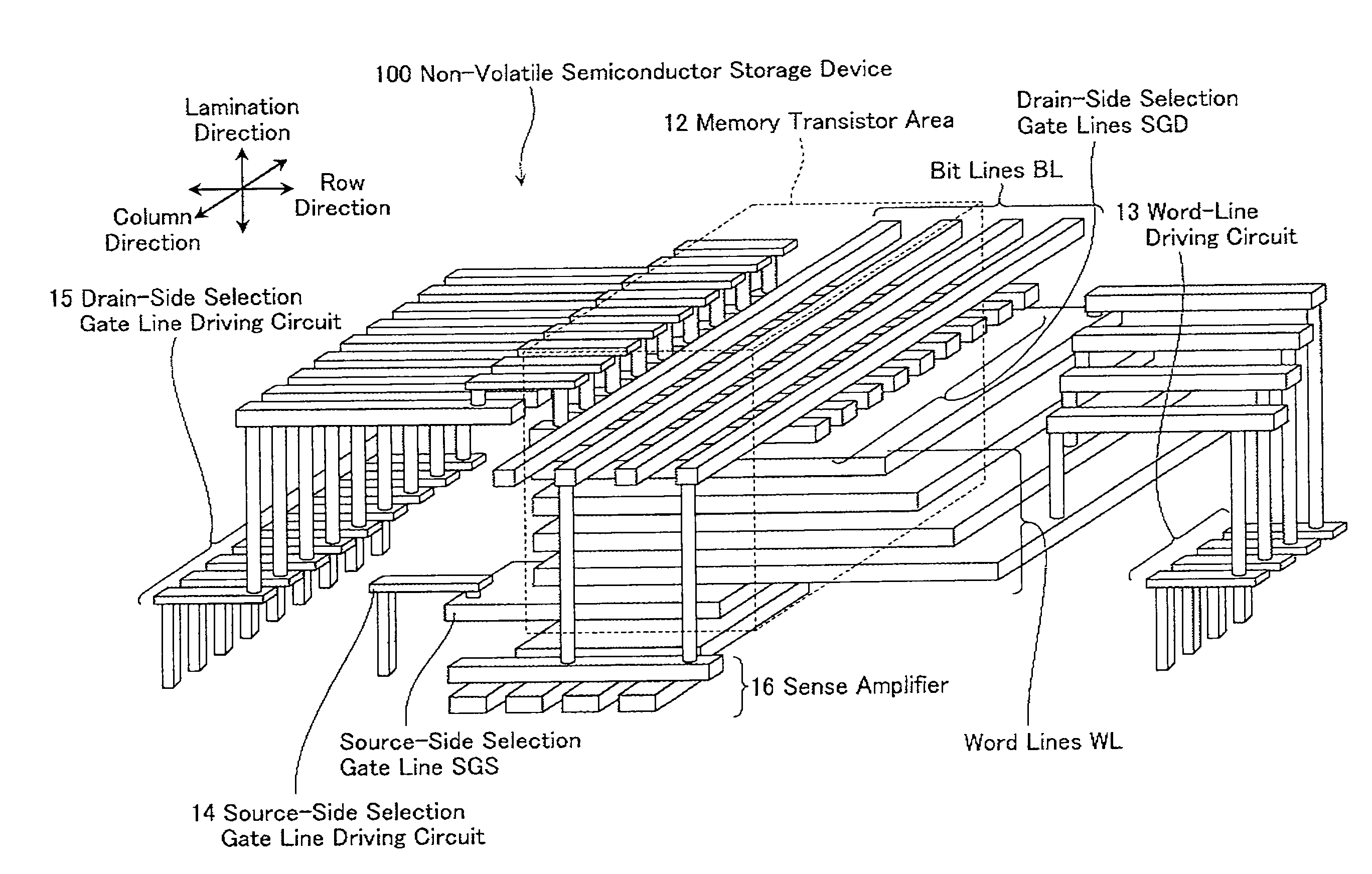
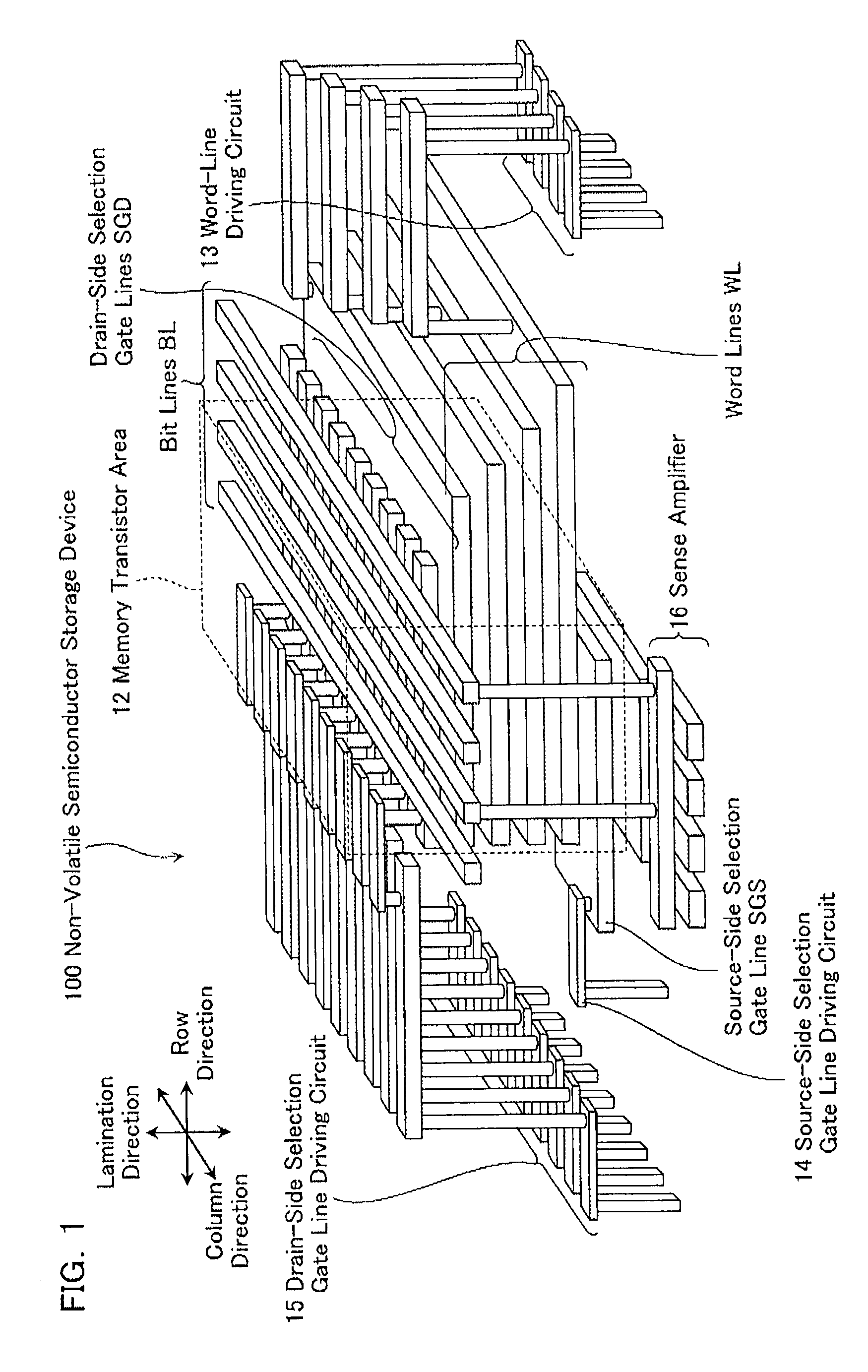
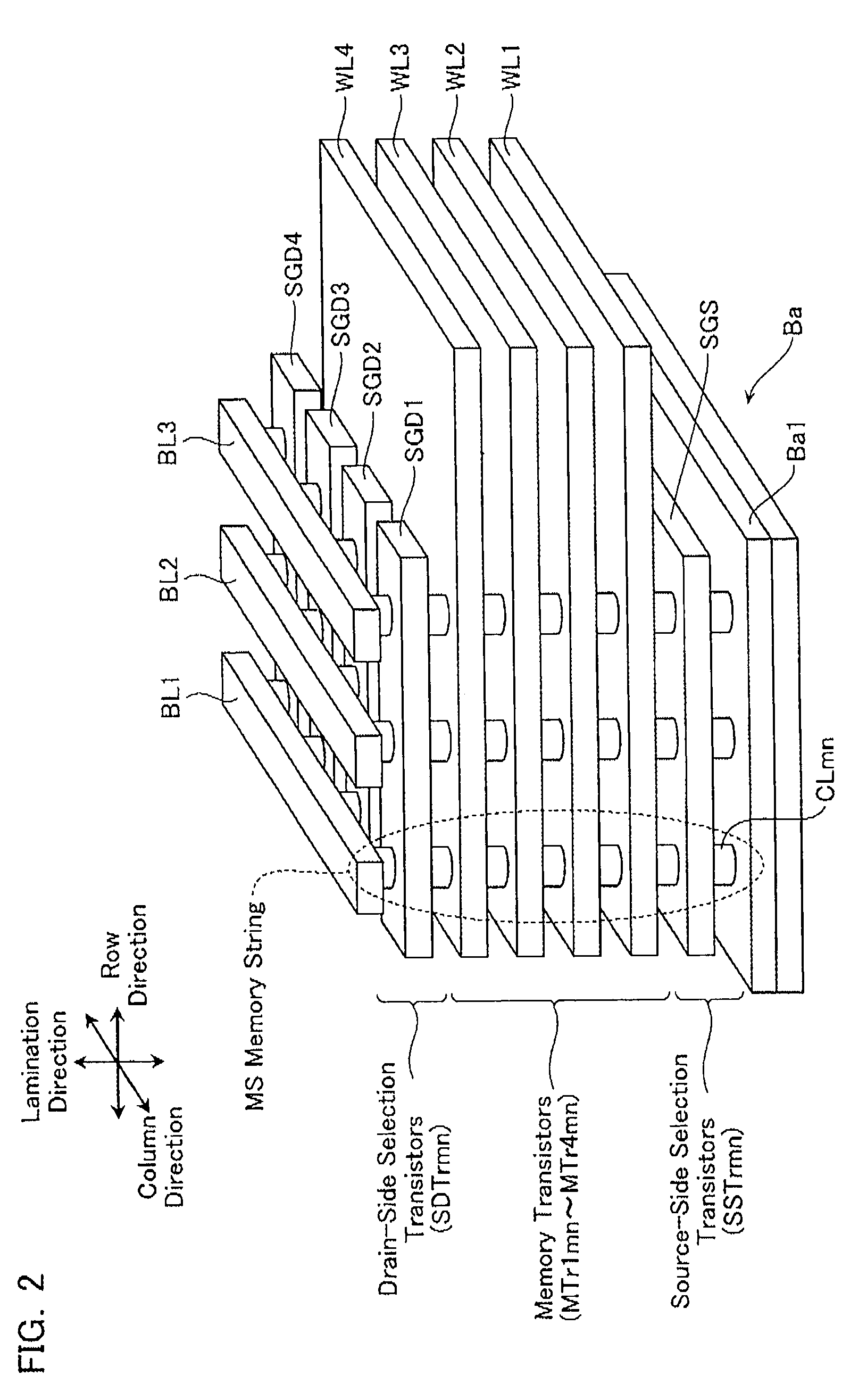
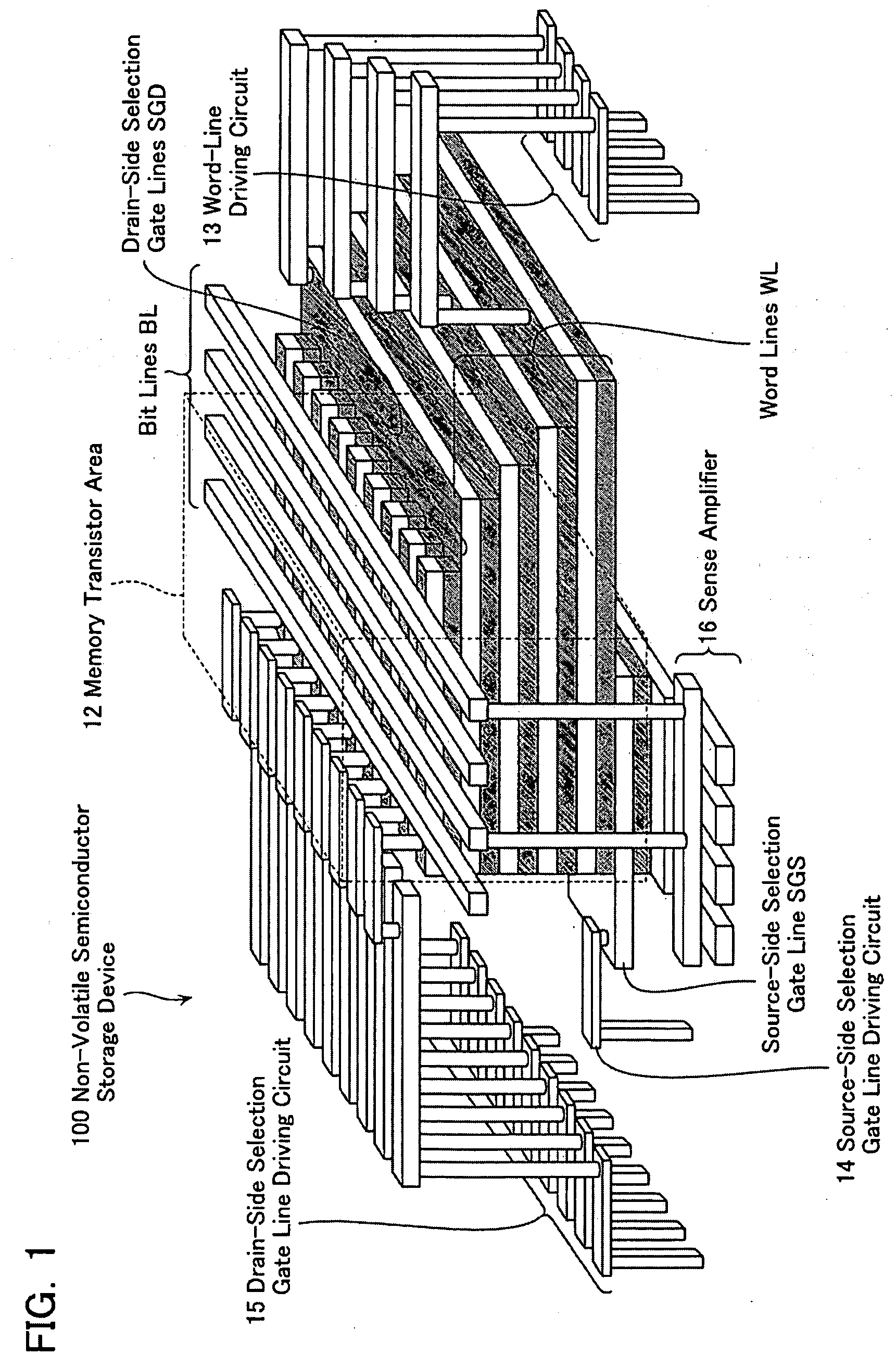
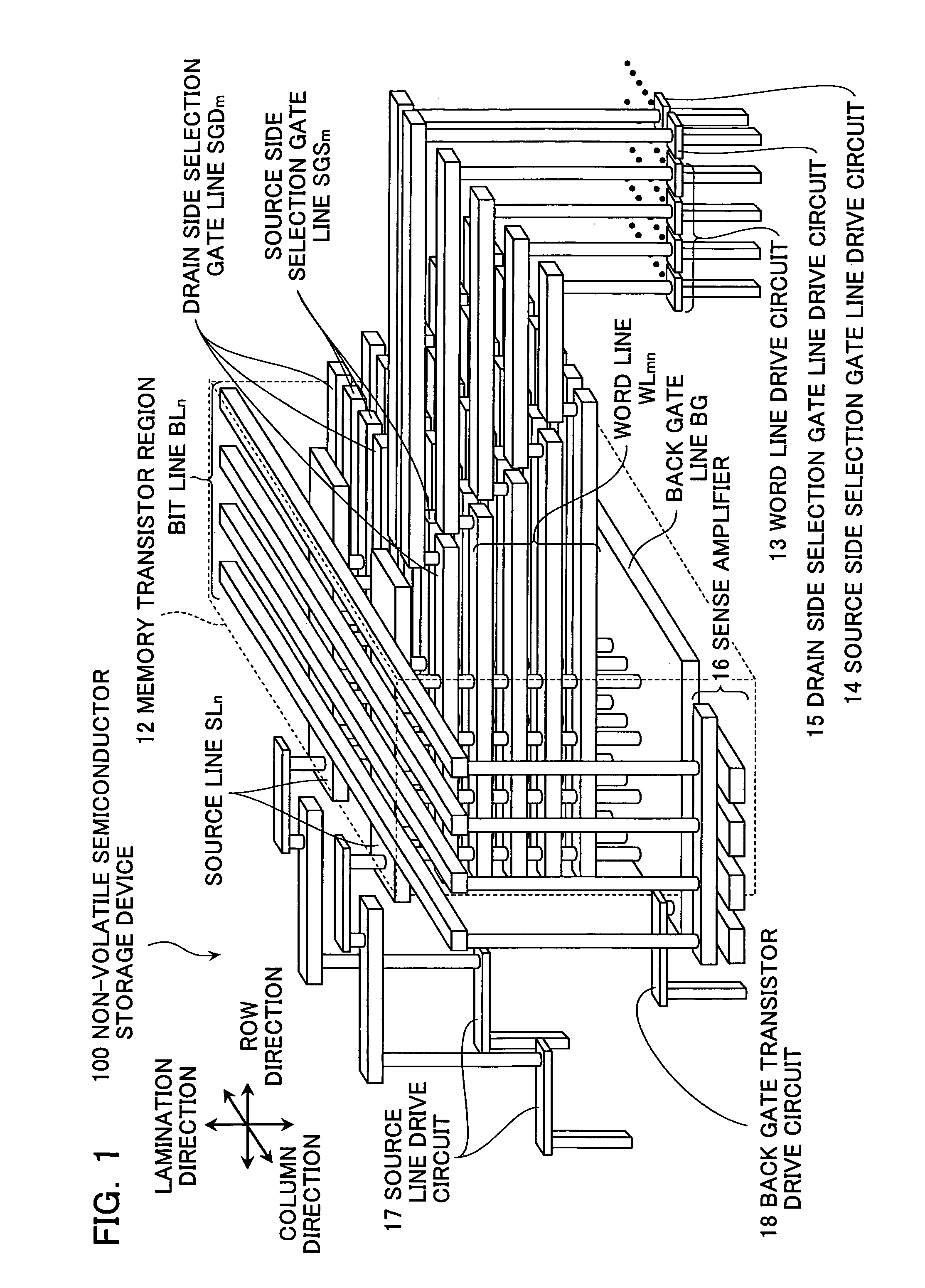
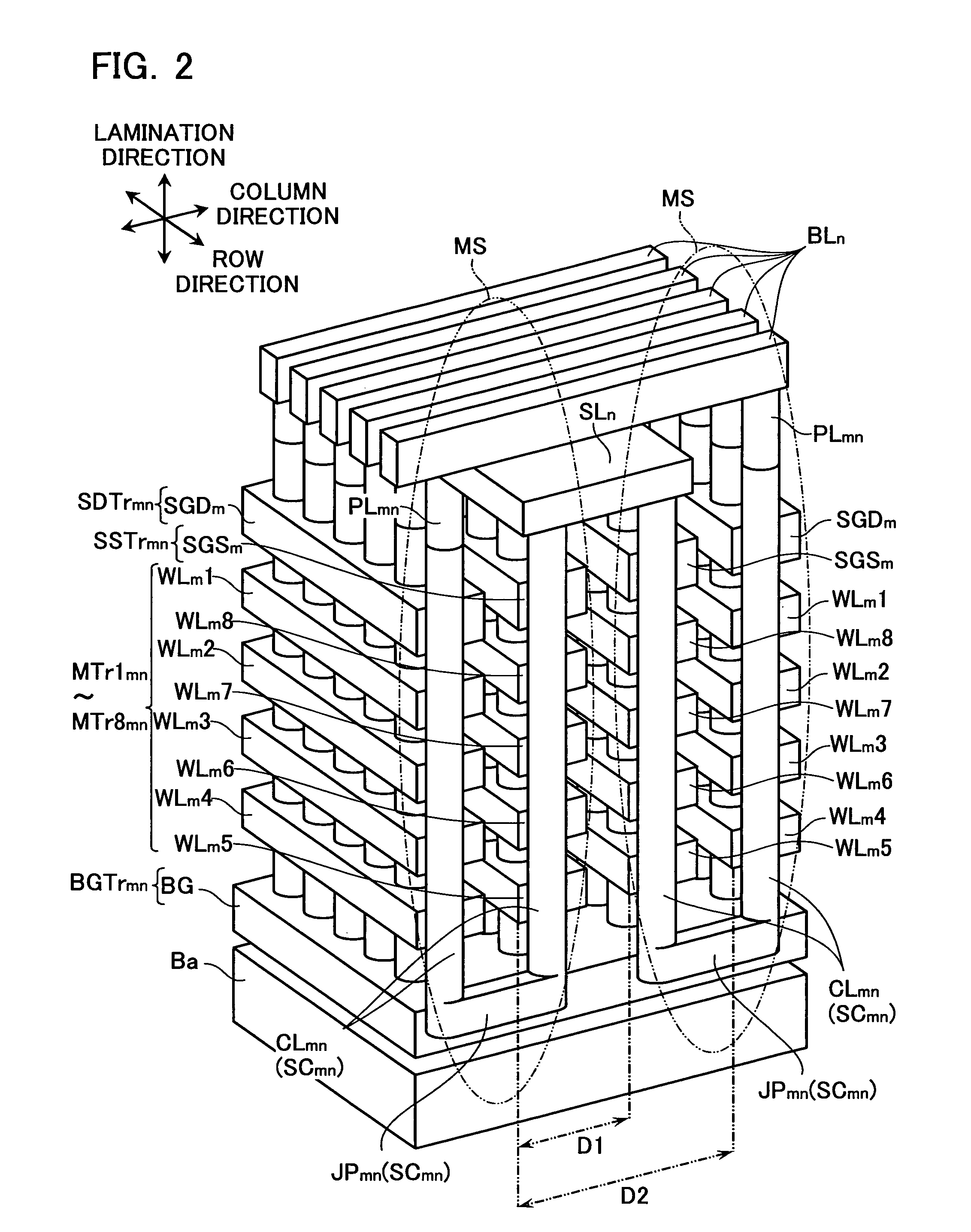
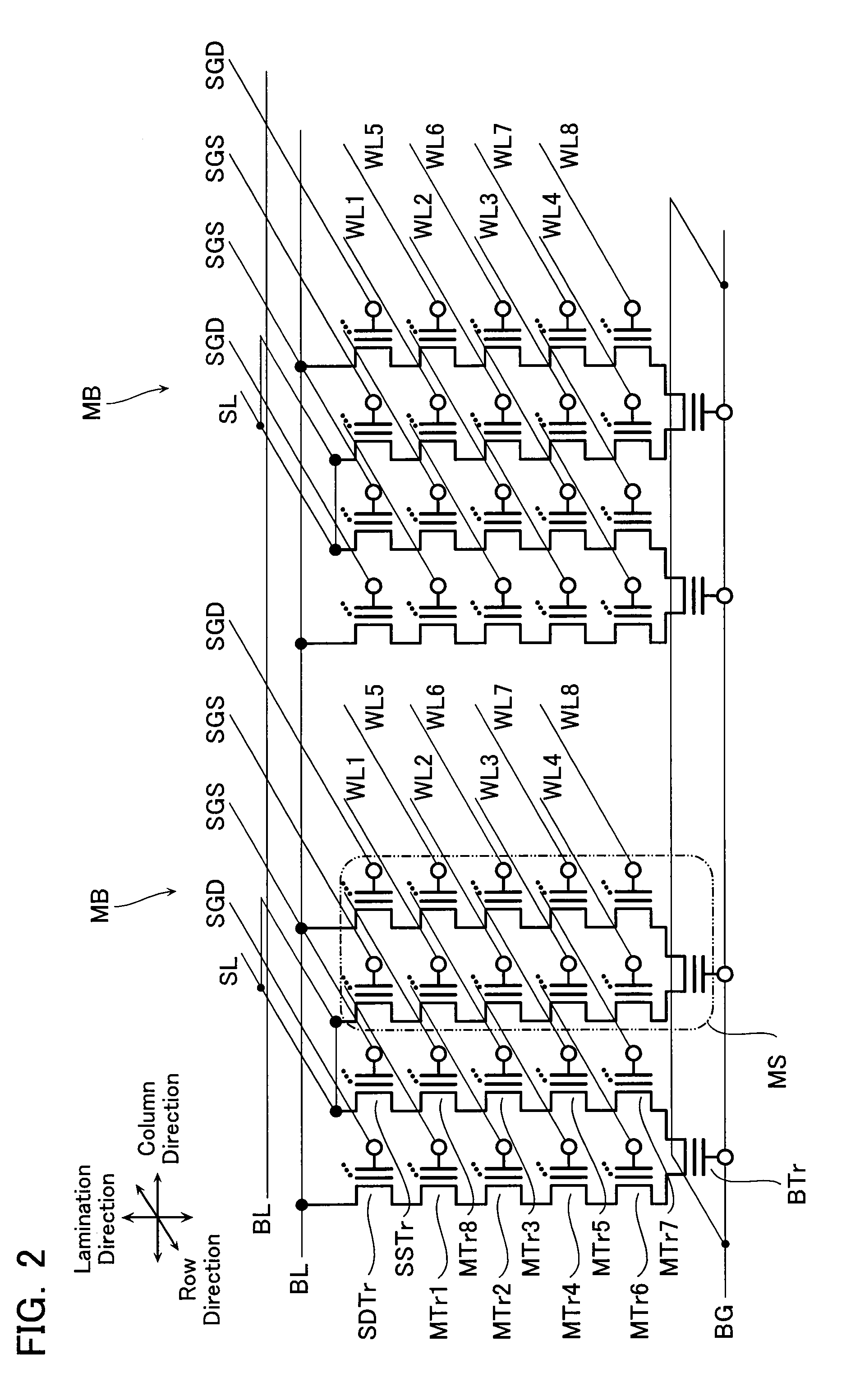
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
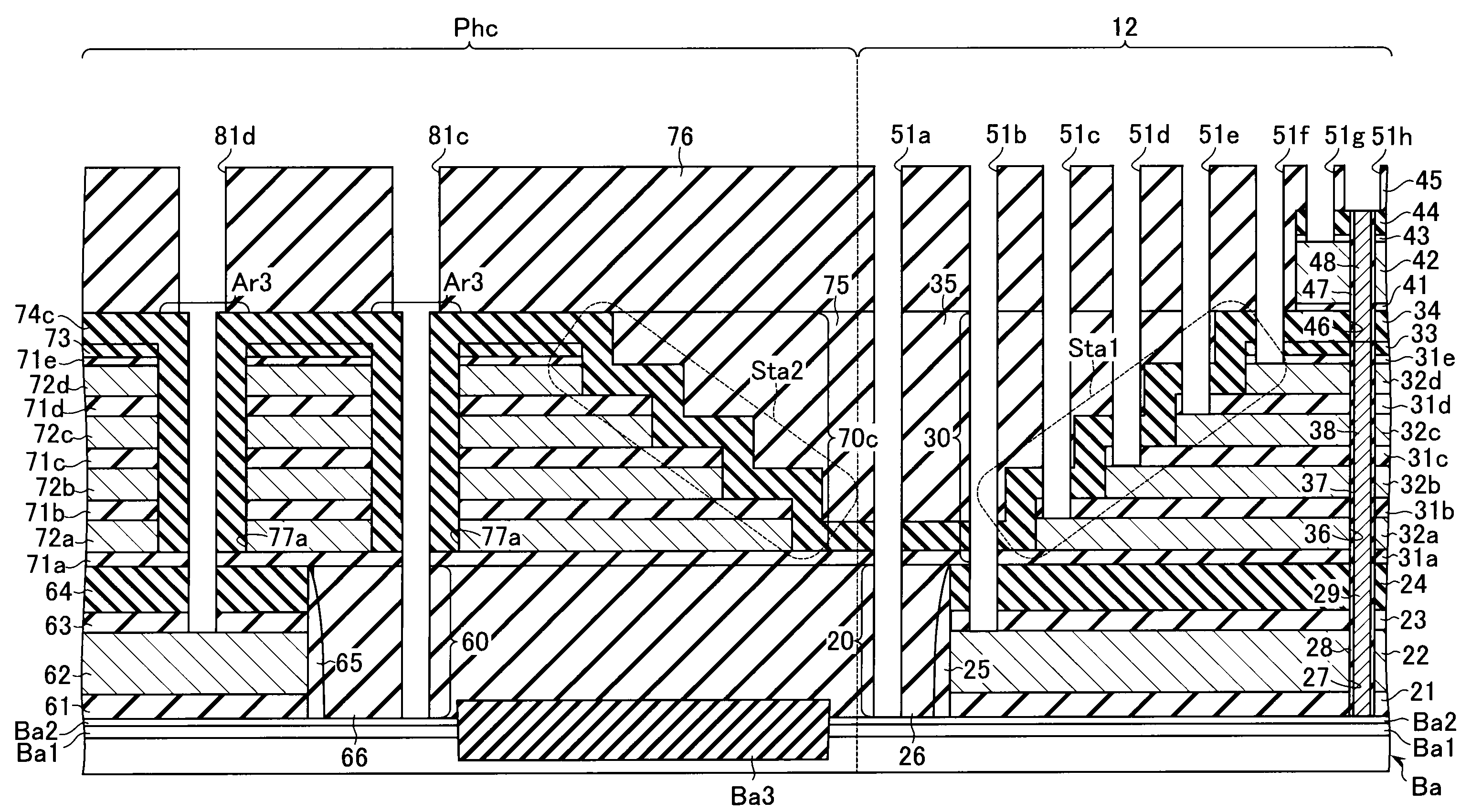
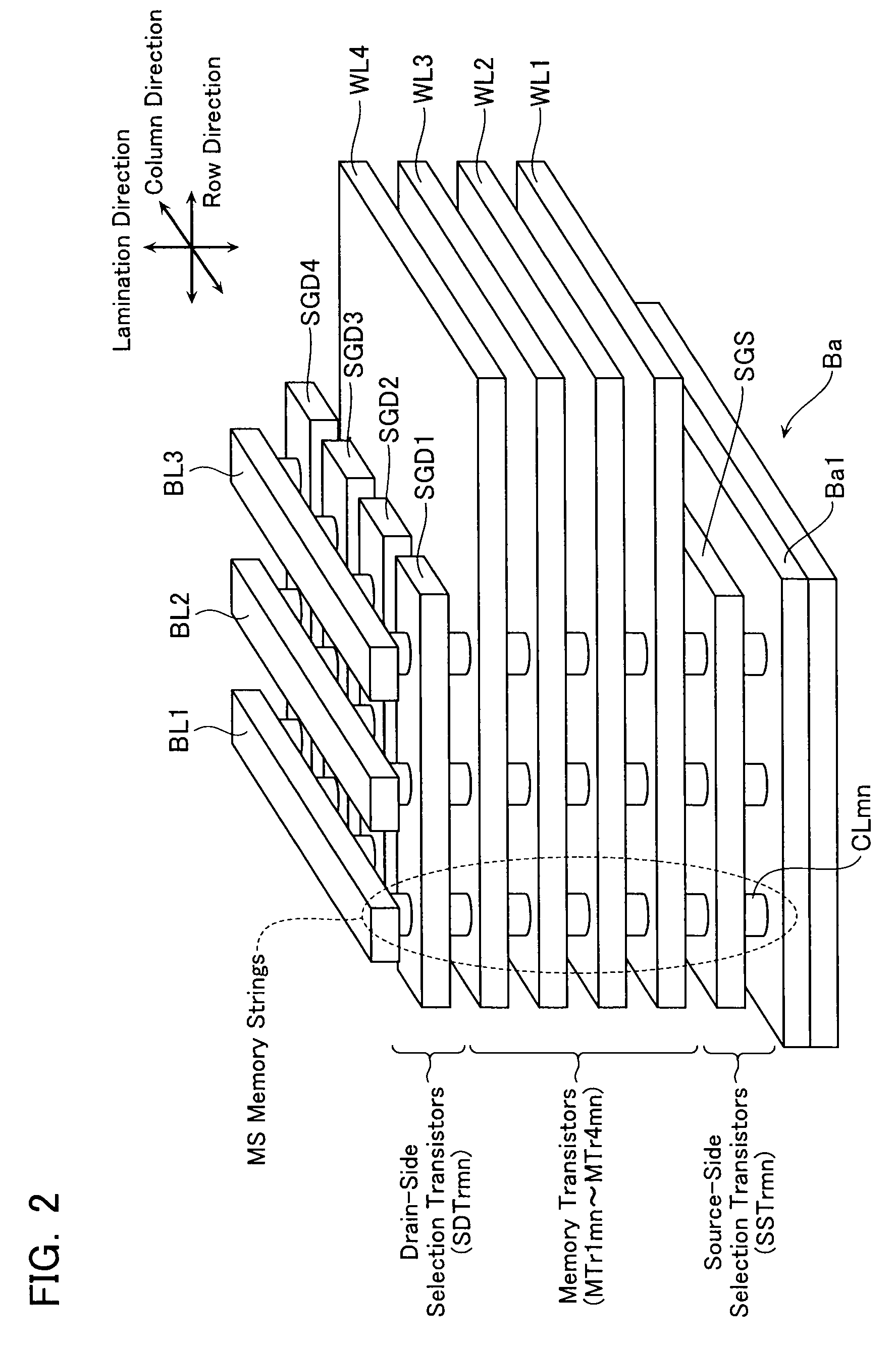
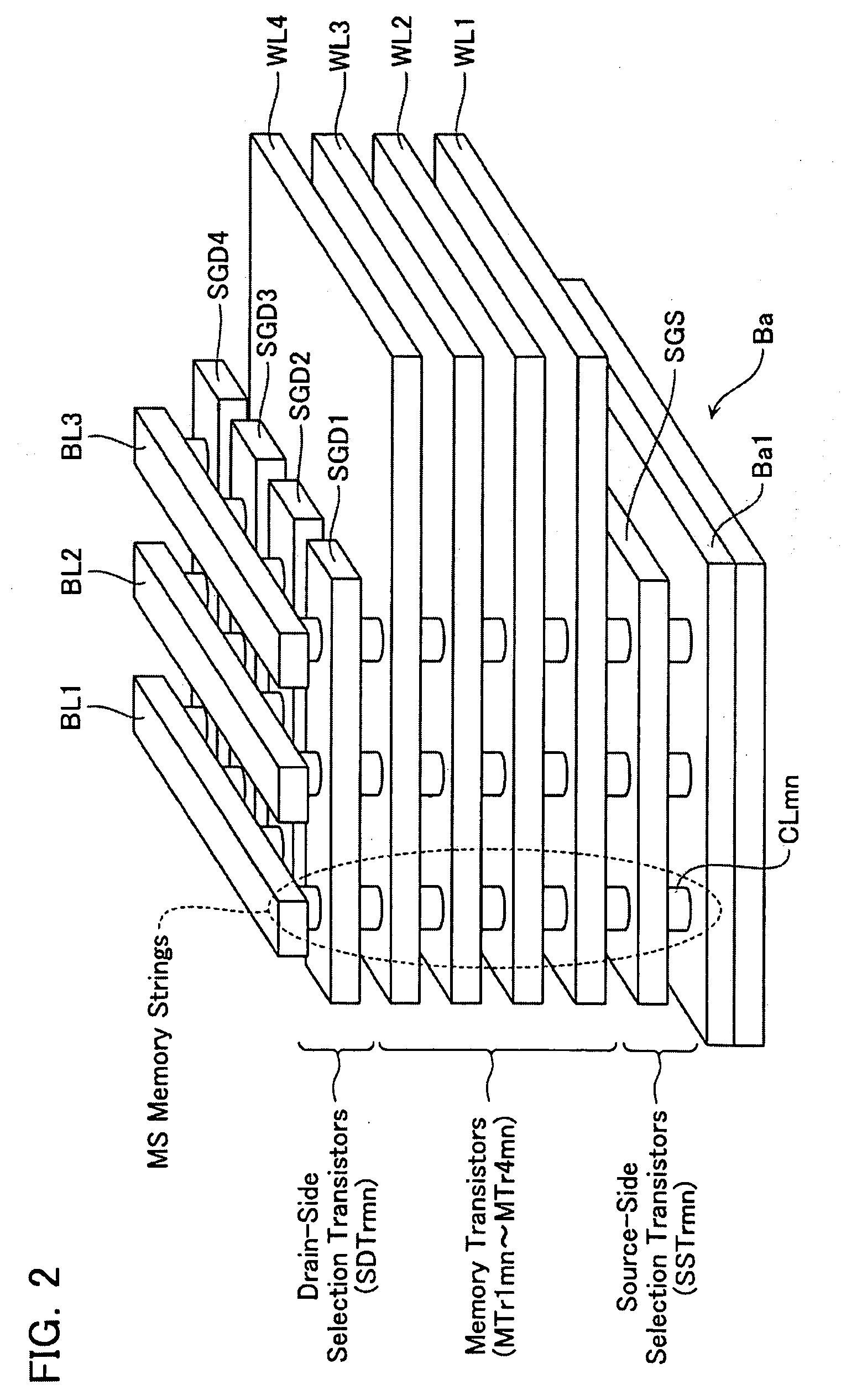
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings to each of which a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells are connected in series. Each of the memory strings includes first semiconductor layers each having a pair of columnar portions extending in a vertical direction with respect to a substrate and a coupling portion formed to couple the lower ends of the pair of columnar portions; a charge storage layer formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions; and first conductive layers formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions and the charge storage layer. The first conductive layers functions as gate electrodes of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
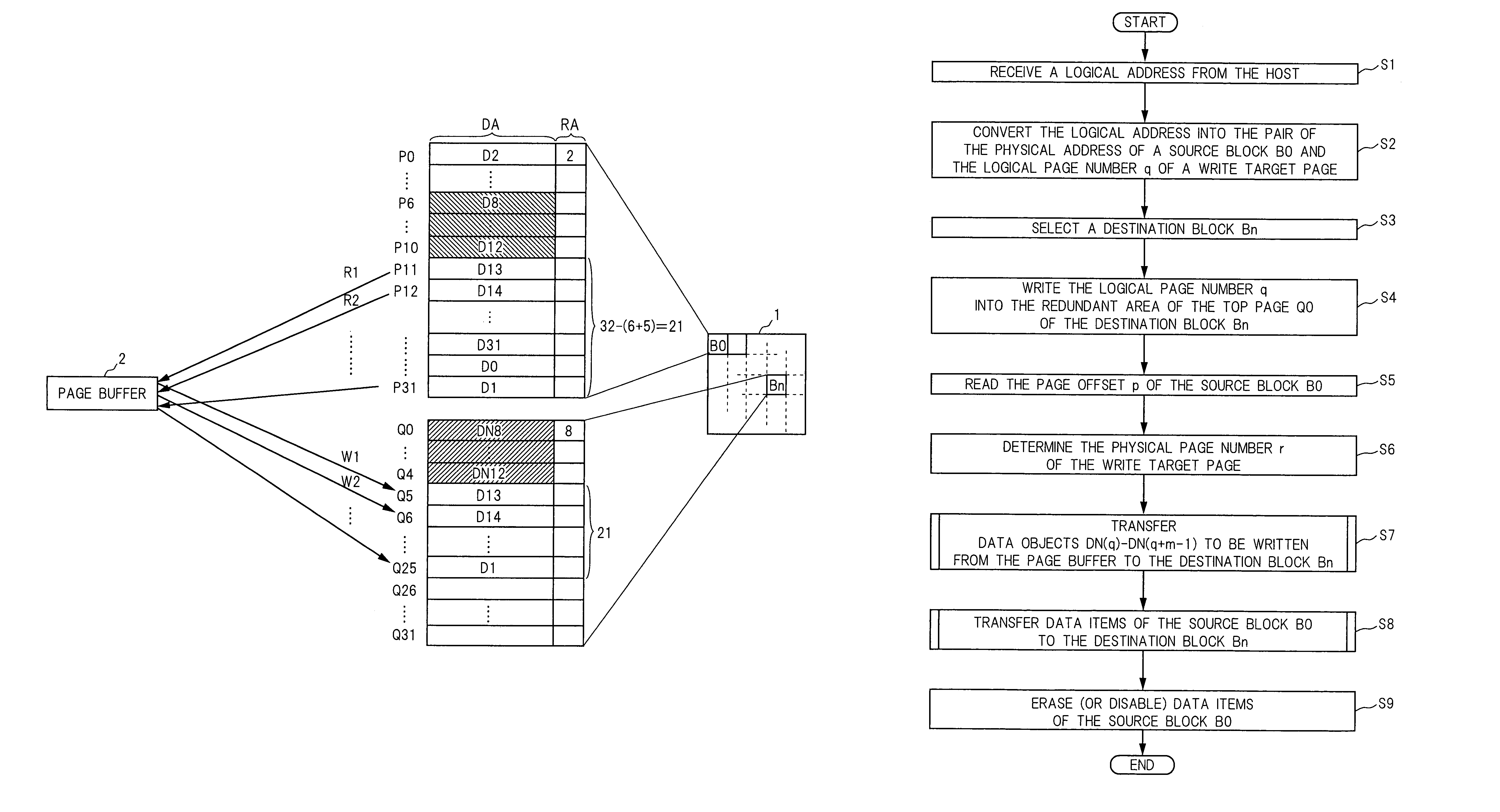
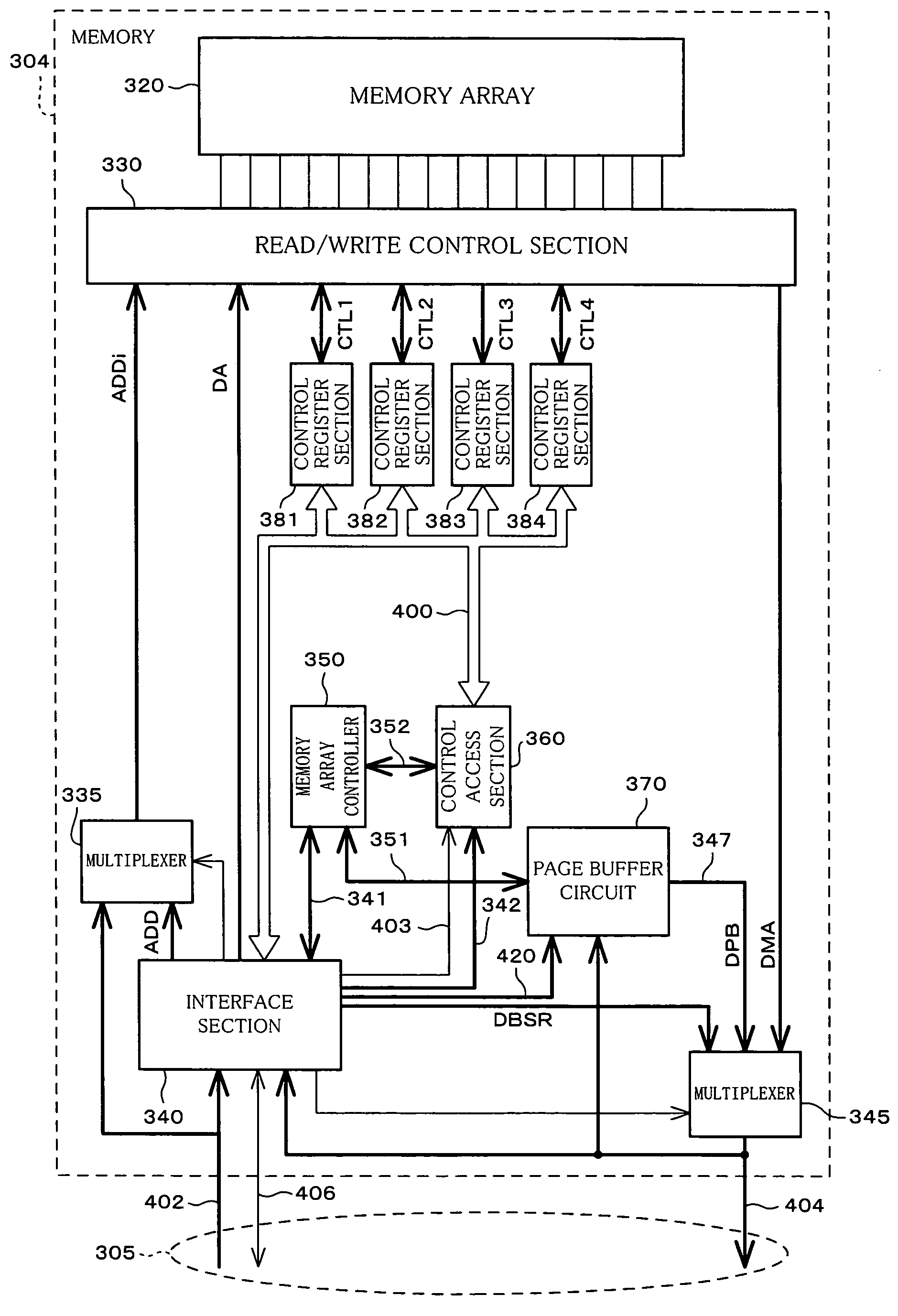
Semiconductor memory device and method for writing data into flash memory
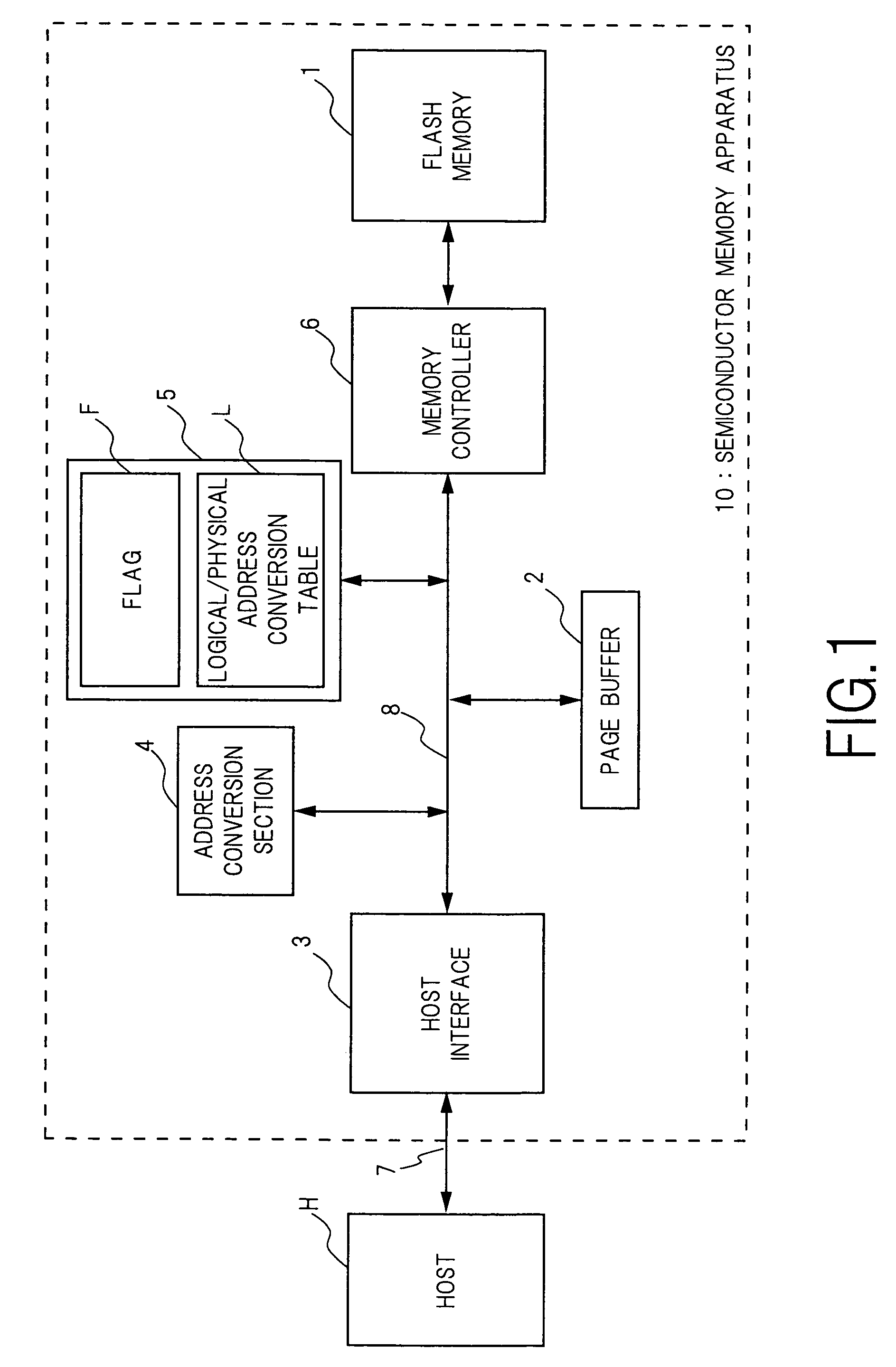
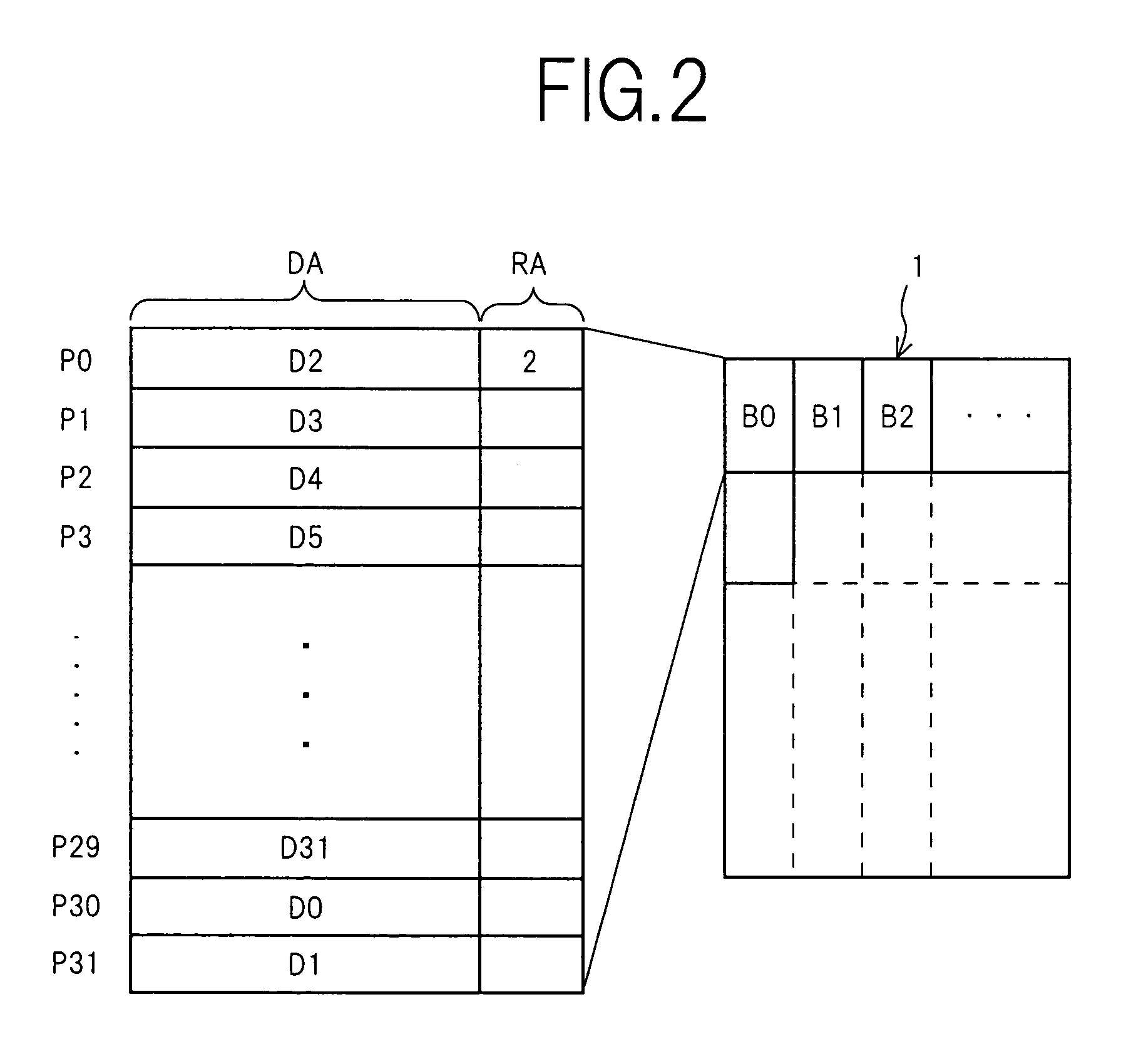
ActiveUS7107389B2Small sizeReduce waiting timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHome pageDatabase
A source block (B0) and the logical page number (“8”) of a write target page are identified from the logical address of the write target page. Data objects (DN8, DN9, . . . , DN12) to be written, which a host stores in a page buffer (2), are written into the data areas (DA) of the pages (Q0, Q1, . . . , Q4) of a destination block (Bn), starting from the top page (Q0) in sequence. The logical page number (“8”) of the write target page is written into the redundant area (RA) of the top page (Q0). The physical page number (“6=8−2”) of the write target page is identified, based on the logical page number (“8”) of the write target page and the page offset (“2”) of the source block (B0). When notified by the host of the end of the sending of the data objects (DN8, . . . , DN12), the data items (D13, . . . , D31, D0, D1, . . . , D7) in the source block (B0) are transferred to the pages (Q5, Q6, . . . , Q31) in the destination block (Bn) via the page buffer (2) sequentially and cyclically, starting from the page (P11) situated cyclically behind the write target page (P6) by the number (“5”) of pages of the data objects (DN8, . . . , DN12).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
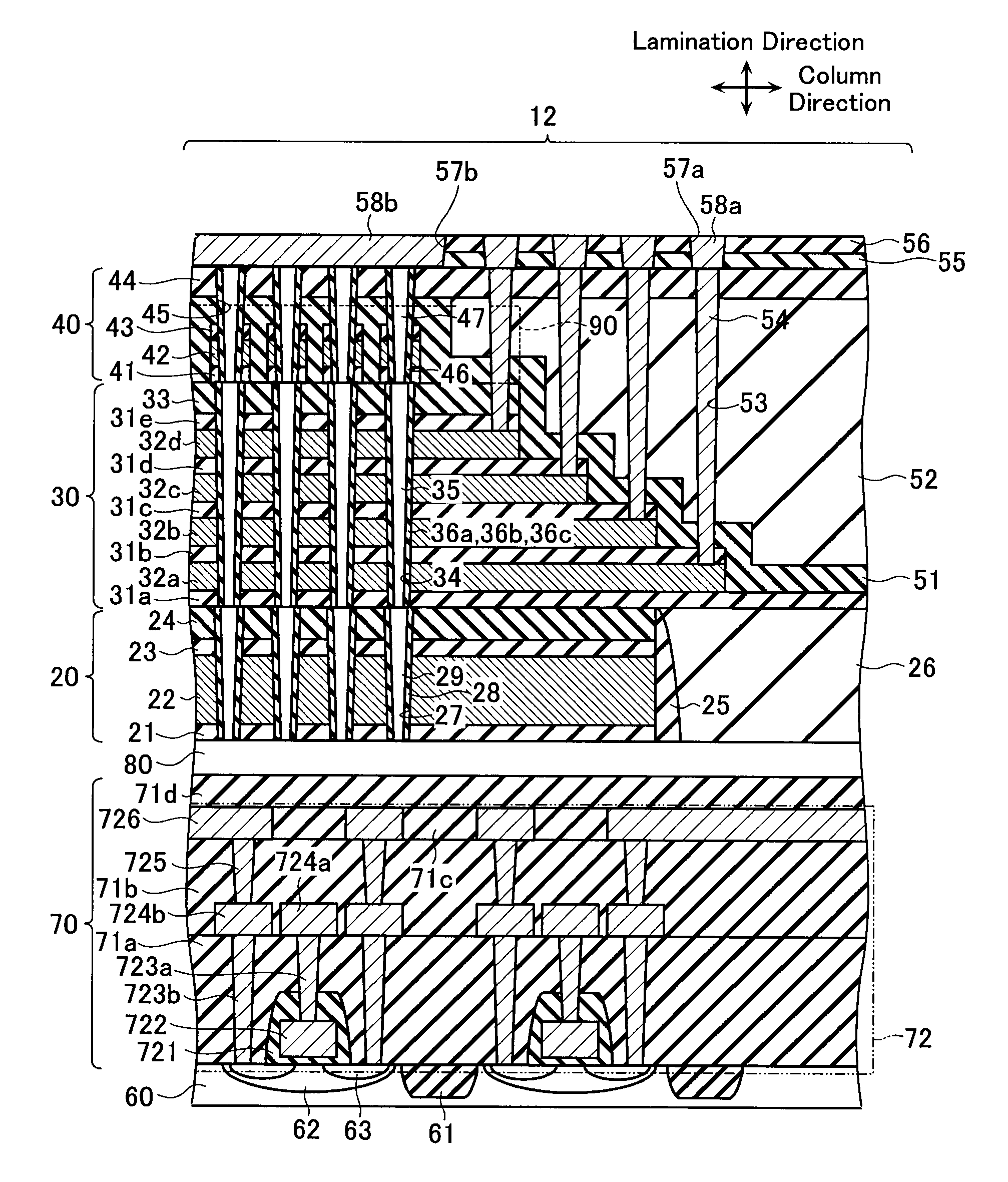
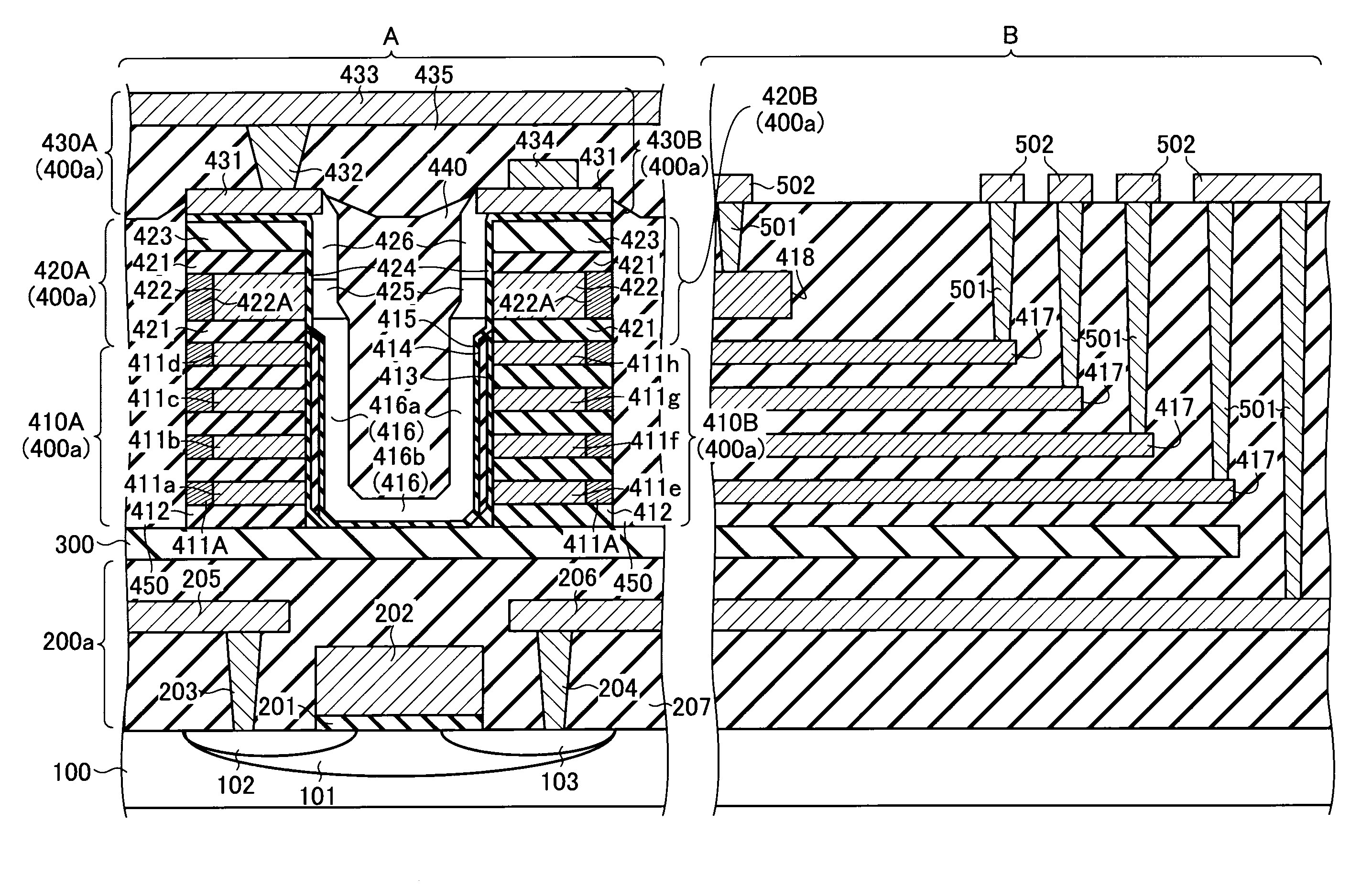
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090267135A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorInsulation layer
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device includes a first layer and a second layer. The first layer includes: a plurality of first conductive layers extending in parallel to a substrate and laminated in a direction perpendicular to the substrate; a first insulation layer formed on an upper layer of the plurality of first conductive layers; a first semiconductor layer formed to penetrate the plurality of first conductive layers; and a charge accumulation layer formed between the first conductive layers and the first semiconductor layer. Respective ends of the first conductive layers are formed in a stepwise manner in relation to each other in a first direction. The second layer includes: a plurality of second conductive layers extending in parallel to the substrate and laminated in a direction perpendicular to the substrate, the second conductive layers being formed in the same layer as the plurality of first conductive layers; and a second insulation layer formed on an upper layer of the plurality of second conductive layers. Respective ends of the second conductive layers are formed to align along a straight line extending in a direction substantially perpendicular to the substrate at a predetermined area.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
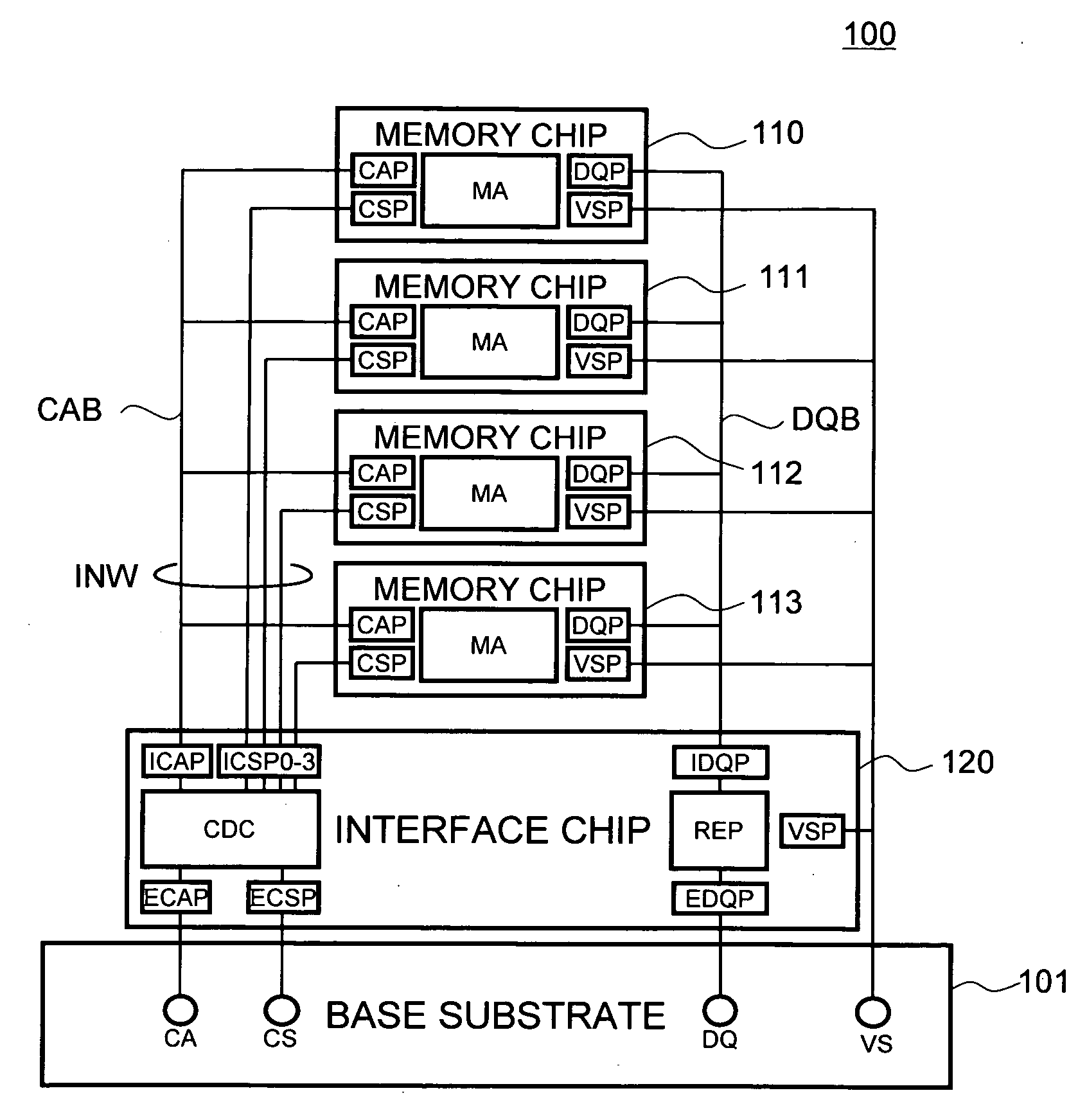
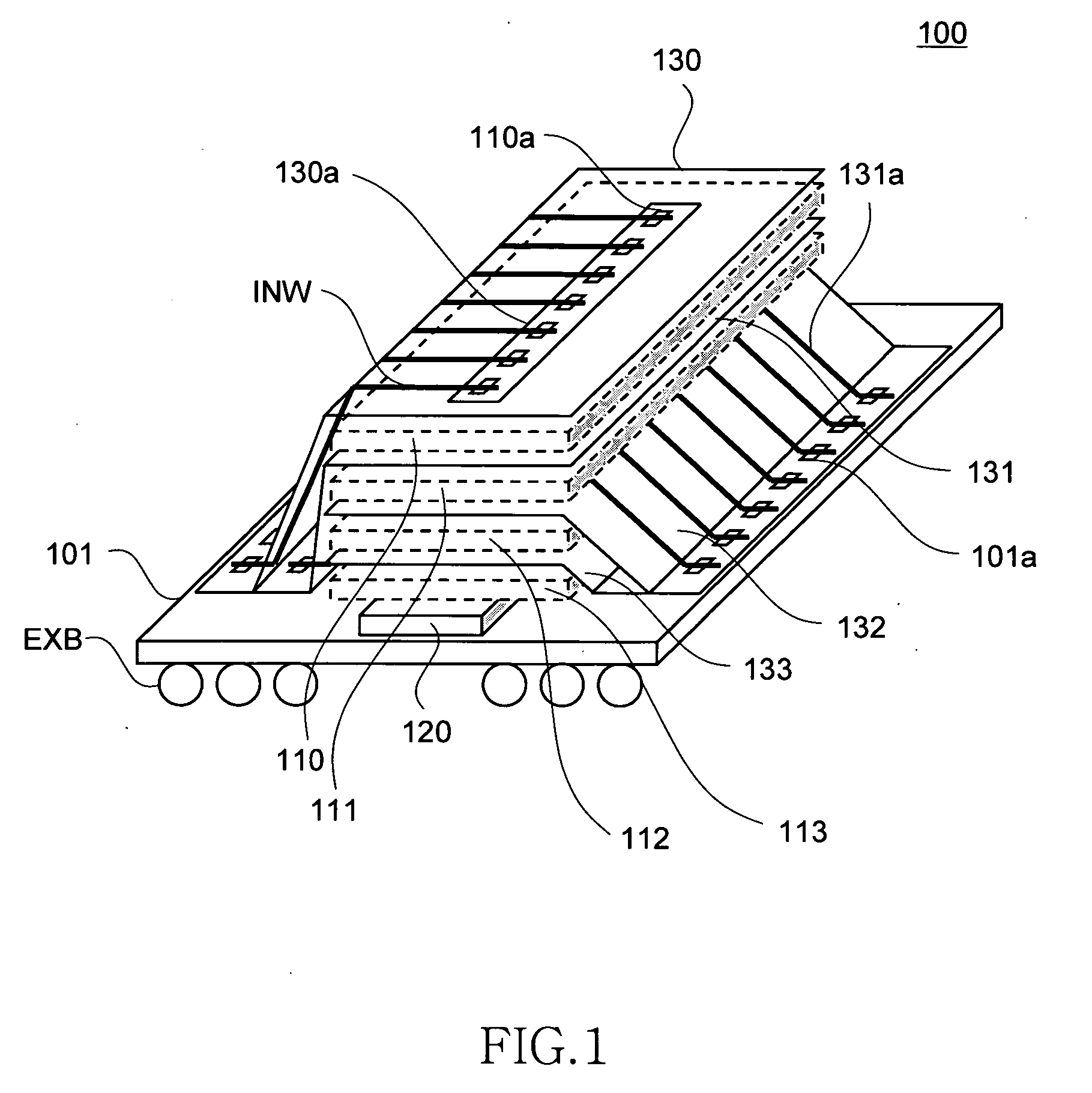
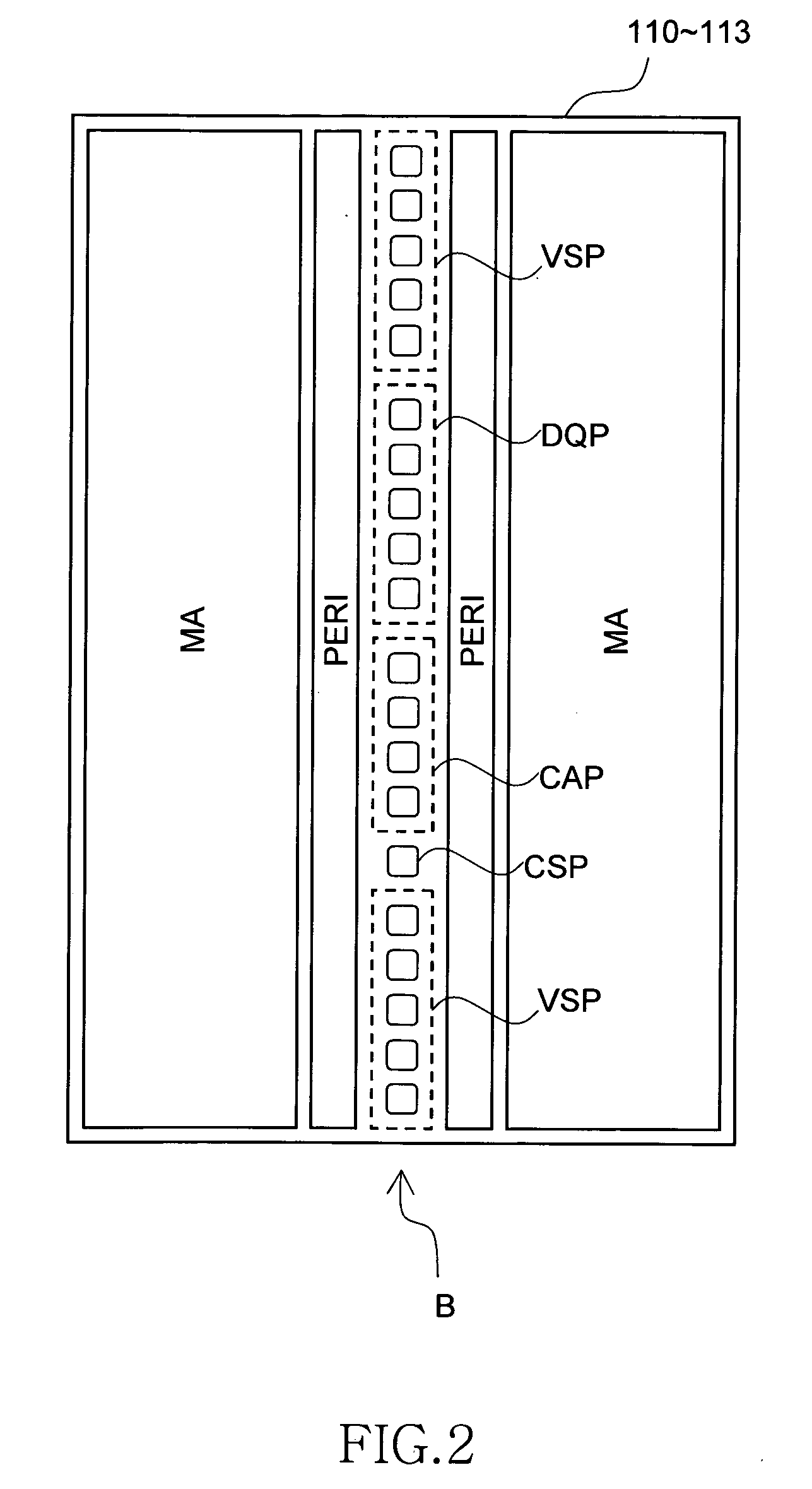
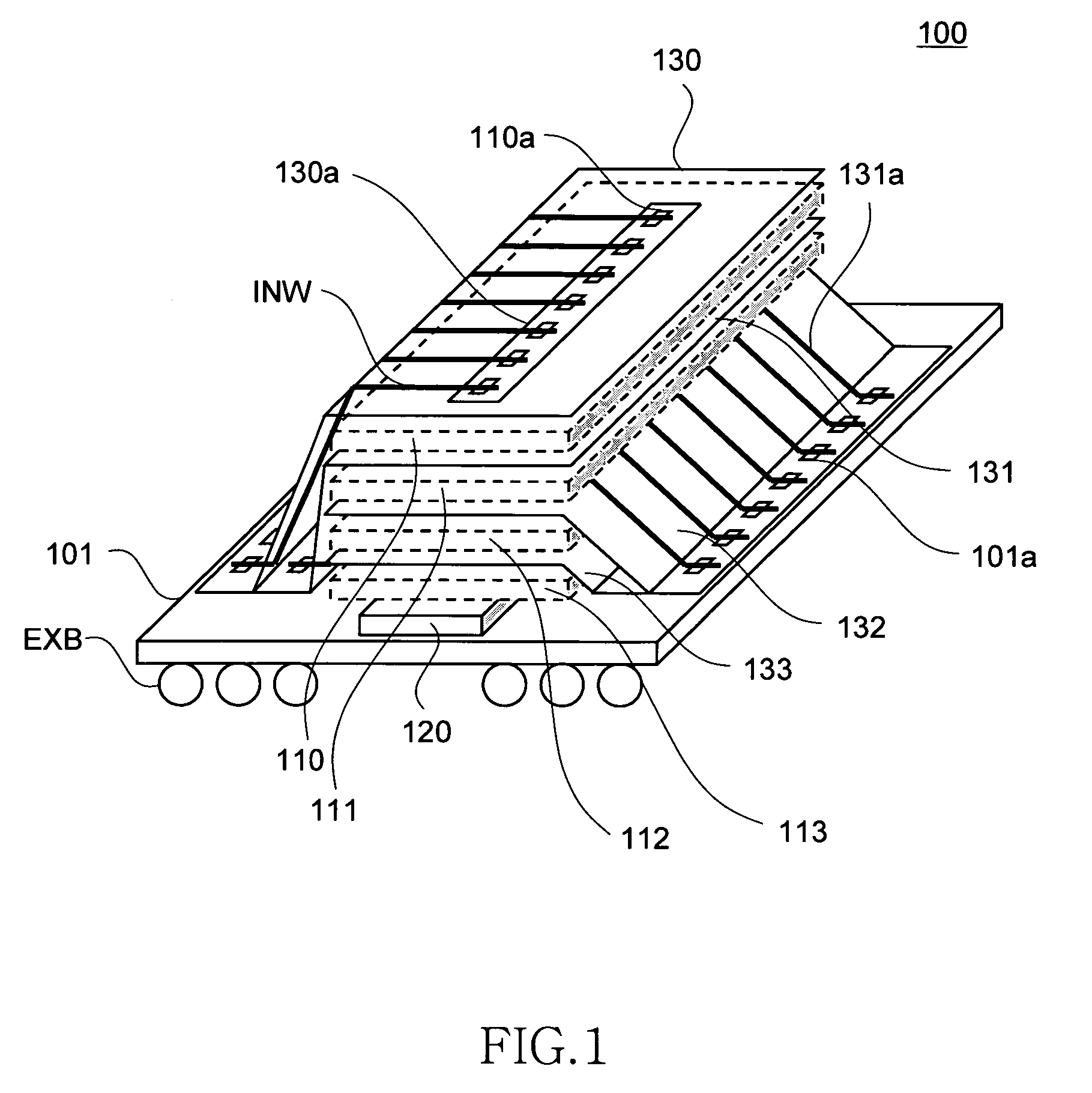
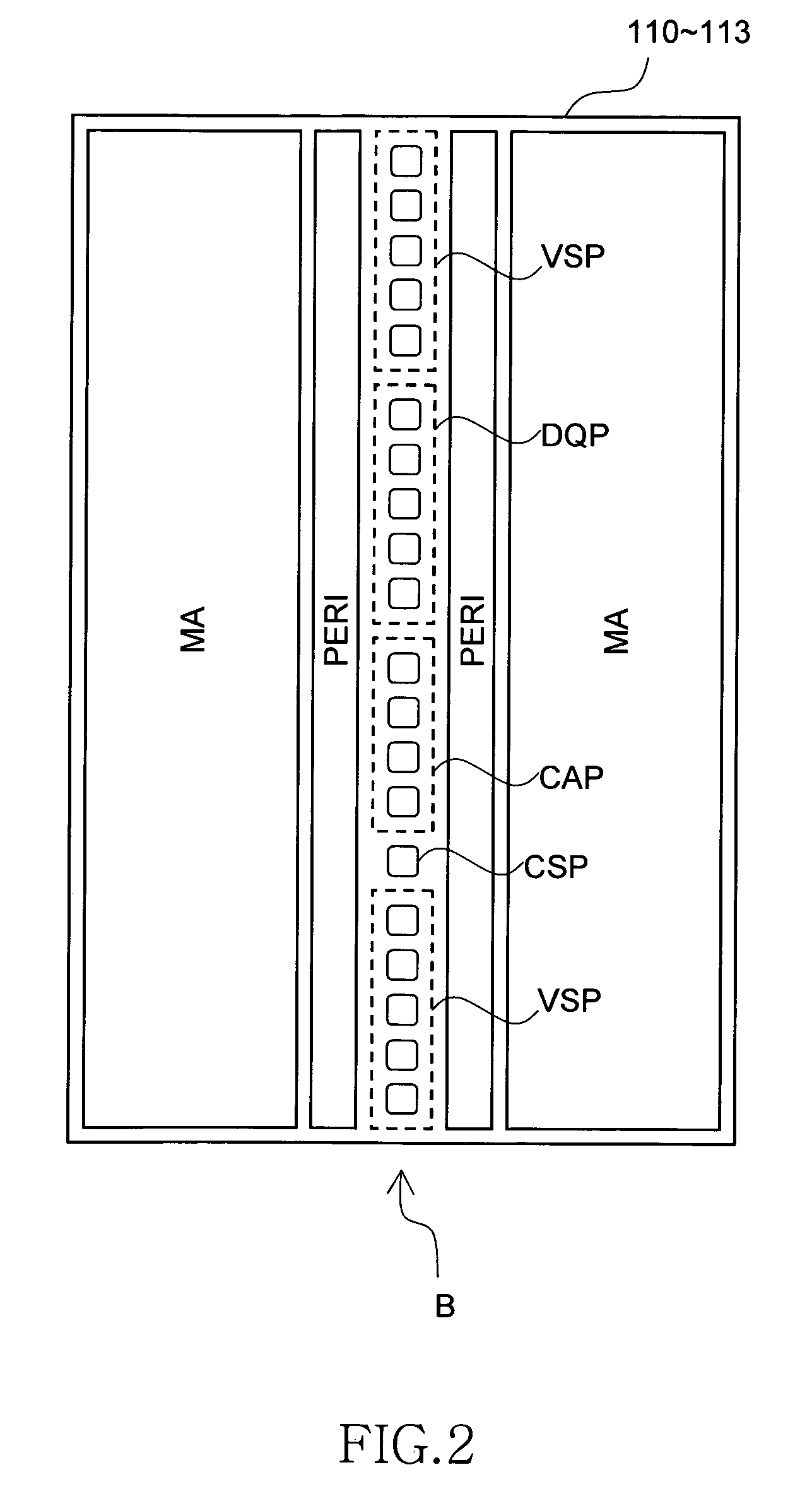
Semiconductor storage device having a plurality of stacked memory chips
ActiveUS20060233012A1Reduce in quantityReduction in wiring capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipChip select
A semiconductor storage employs a base substrate (101) having a command / address external terminal group (CA), a data input / output external terminal group (DQ), and a single chip select external terminal (CS), and also comprises a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) mounted on a base substrate (101), each of which can individually carry out read and write operations. The terminals (CA), (DQ), and (CS) are connected to an interface chip (120). The interface chip (120) has a chip select signal generation circuit that can individually activate a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) on the basis of an address signal fed by way of the terminal (CA) and on the basis of a chip select signal fed by way of the terminal (CS).
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
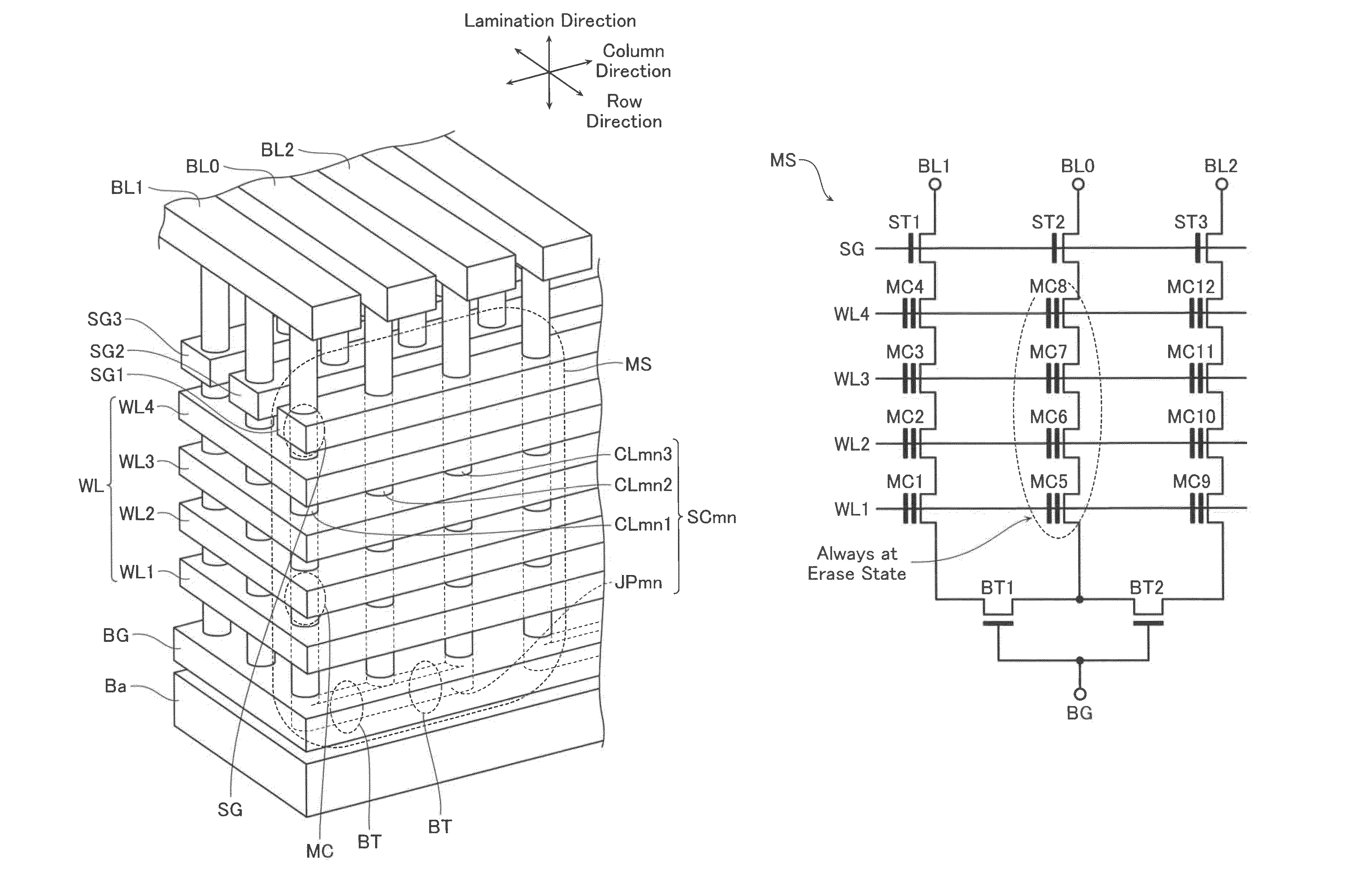
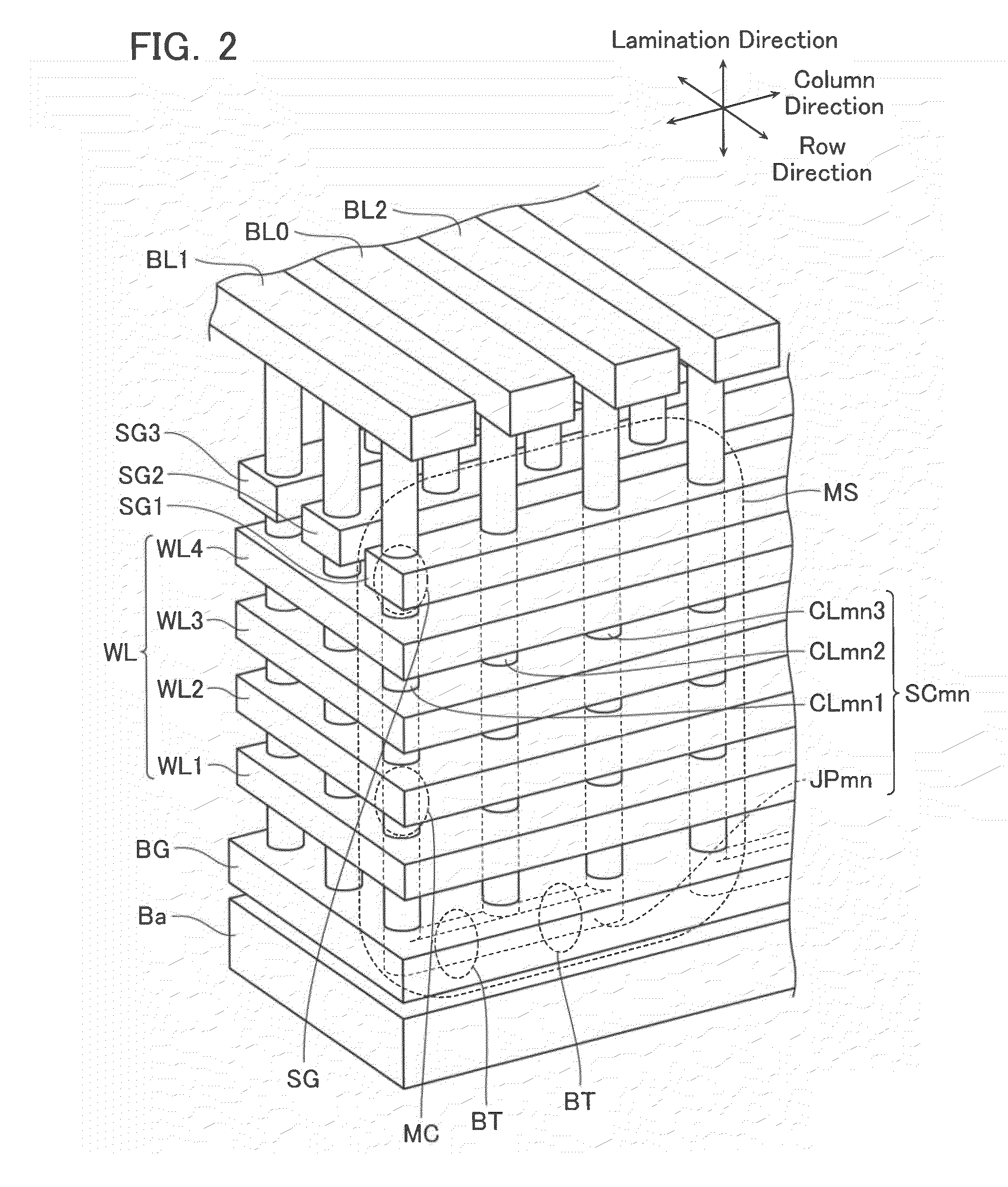
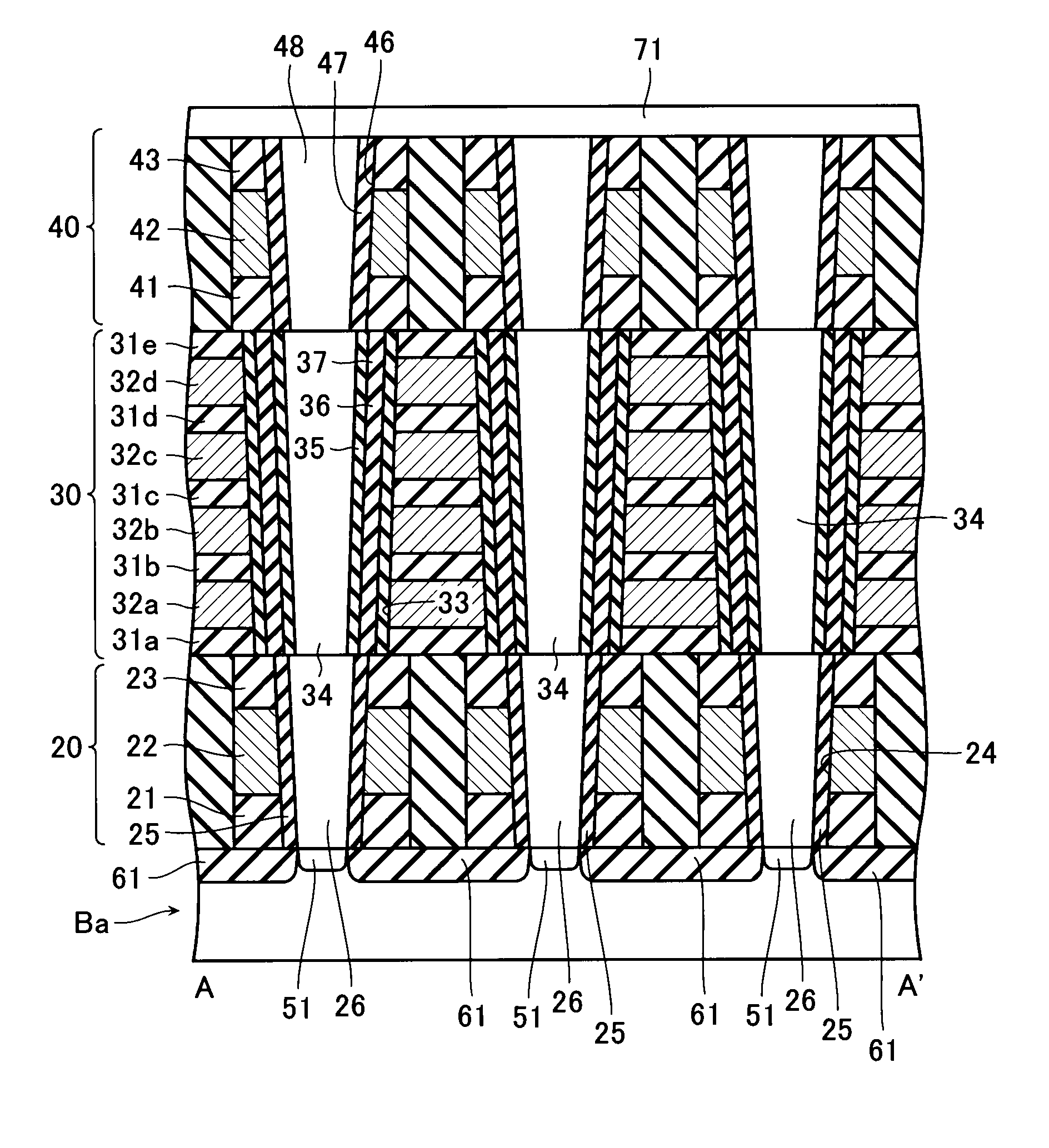
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device includes a control circuit performing an erase operation to erase data from a selected one of memory transistors. The control circuit applies a first voltage to the other end of selected one of selection transistors, causes the selected one of the selection transistors to turn on, and causes any one of the memory transistors to turn on that is closer to the selection transistor than the selected one of the memory transistors. The control circuit also applies a second voltage lower than the first voltage to a gate of the selected one of the memory transistors. Such a potential difference between the first voltage and the second voltage causing a change in electric charges in the electric charge storage layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
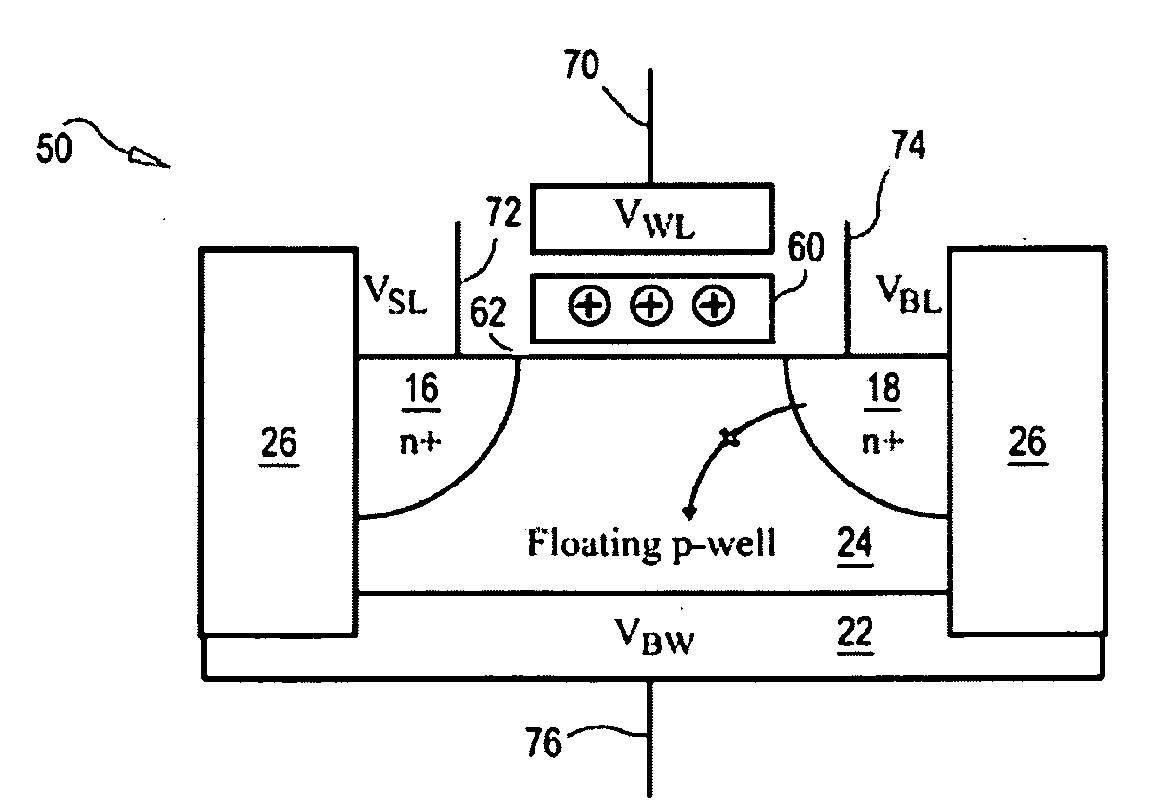
Method of operating semiconductor memory device with floating body transistor using silicon controlled rectifier principle
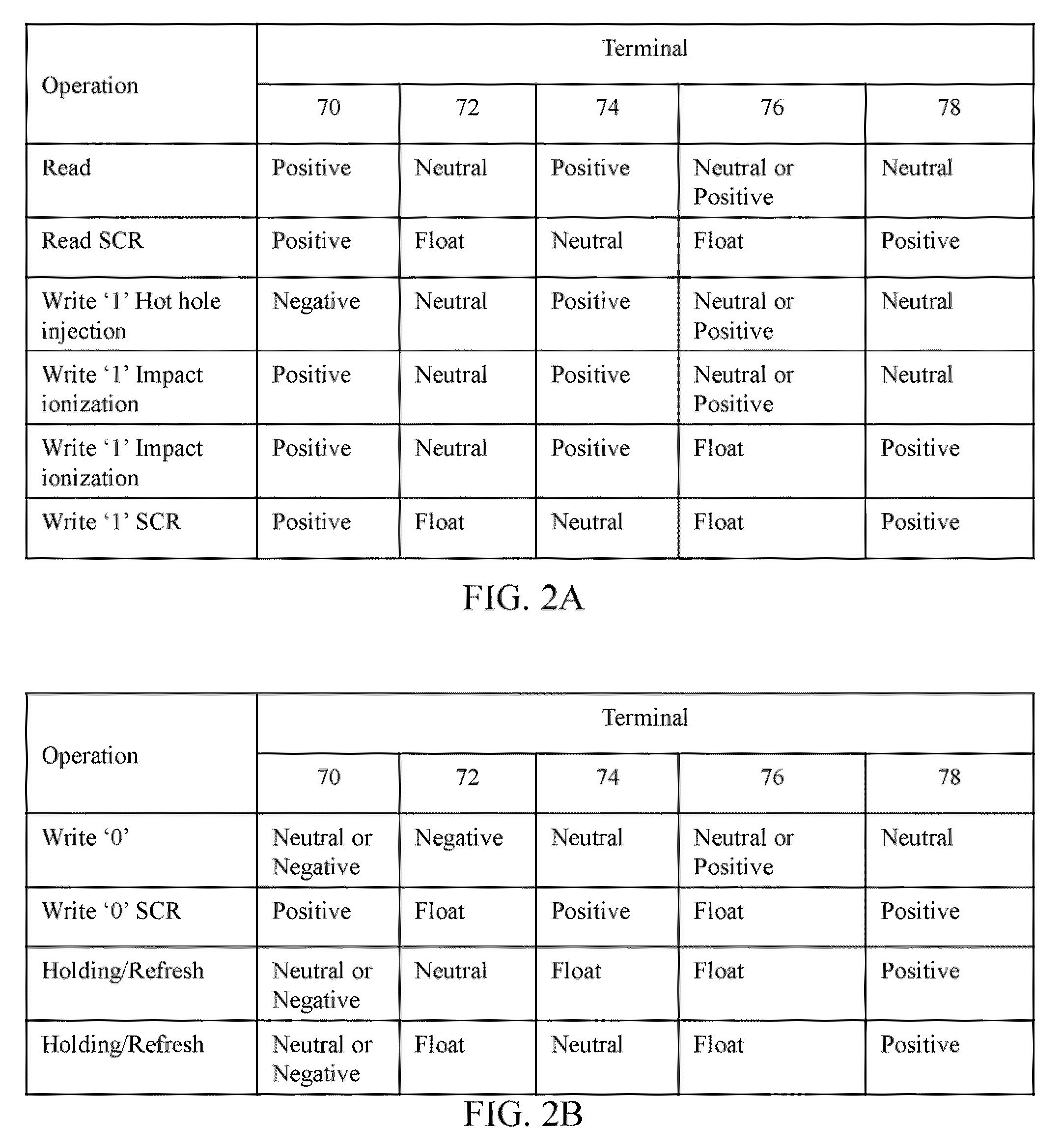
Methods of operating semiconductor memory devices with floating body transistors, using a silicon controlled rectifier principle are provided, as are semiconductor memory devices for performing such operations. A method of maintaining the data state of a semiconductor dynamic random access memory cell is provided, wherein the memory cell comprises a substrate being made of a material having a first conductivity type selected from p-type conductivity type and n-type conductivity type; a first region having a second conductivity type selected from the p-type and n-type conductivity types, the second conductivity type being different from the first conductivity type; a second region having the second conductivity type, the second region being spaced apart from the first region; a buried layer in the substrate below the first and second regions, spaced apart from the first and second regions and having the second conductivity type; a body region formed between the first and second regions and the buried layer, the body region having the first conductivity type; and a gate positioned between the first and second regions and adjacent the body region. The memory cell is configured to store a first data state which corresponds to a first charge in the body region in a first configuration, and a second data state which corresponds to a second charge in the body region in a second configuration. The method includes: providing the memory cell storing one of the first and second data states; and applying a positive voltage to a substrate terminal connected to the substrate beneath the buried layer, wherein when the body region is in the first state, the body region turns on a silicon controlled rectifier device of the cell and current flows through the device to maintain configuration of the memory cell in the first memory state, and wherein when the memory cell is in the second state, the body region does not turn on the silicon controlled rectifier device, current does not flow, and a blocking operation results, causing the body to maintain the second memory state.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Semiconductor storage device
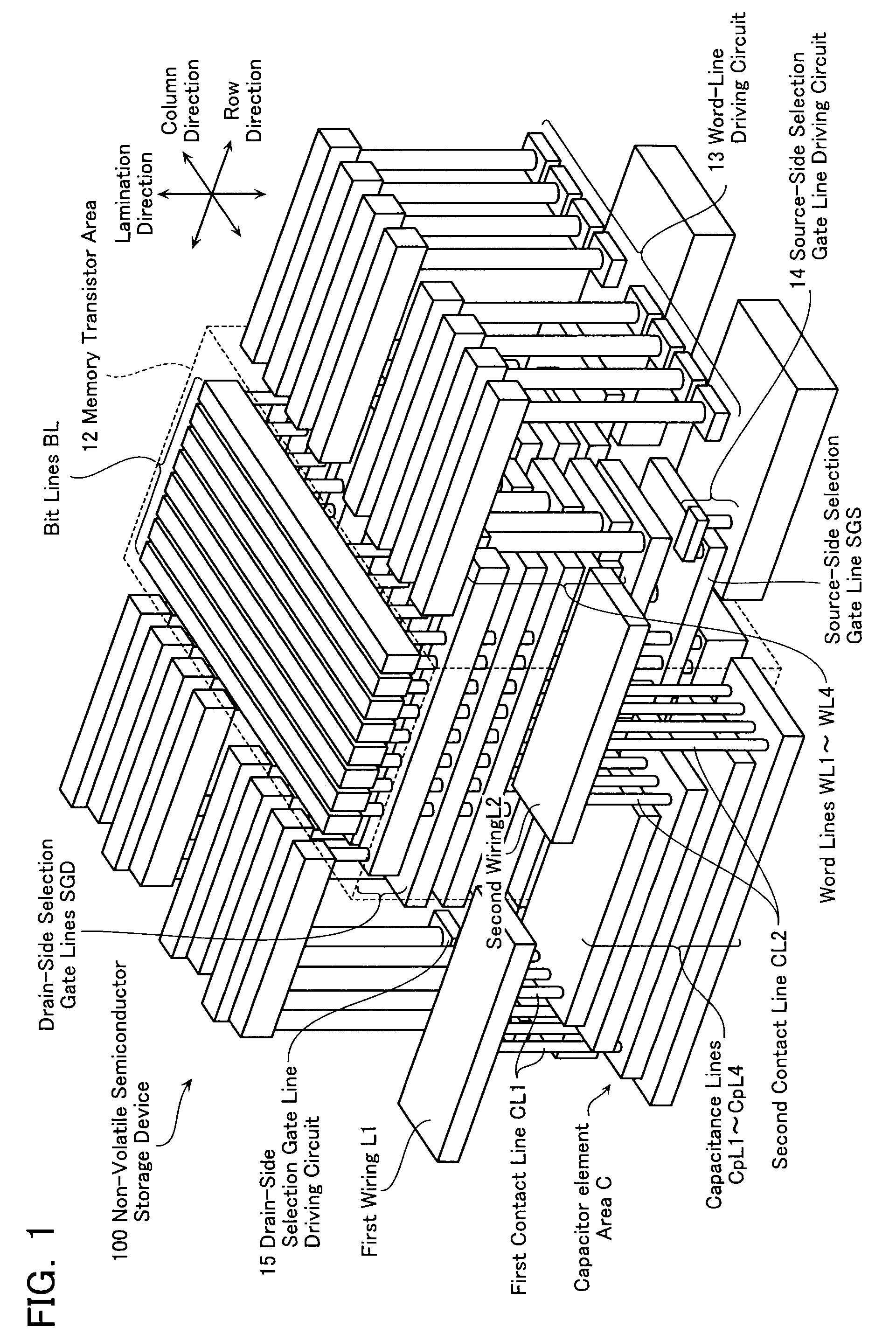
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has: a plurality of memory strings with a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells connected in series; and a capacitor element area including capacitor elements. Each of the memory strings includes: a plurality of first conductive layers laminated on a substrate; and a plurality of first interlayer insulation layers formed between the plurality of first conductive layers. The capacitor element area includes: a plurality of second conductive layers laminated on a substrate and formed in the same layer as the first conductive layers; and a plurality of second interlayer insulation layers formed between the plurality of second conductive layers and formed in the same layer as the first interlayer insulation layers. A group of the adjacently-laminated second conductive layers is connected to a first potential, while another group thereof is connected to a second potential.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
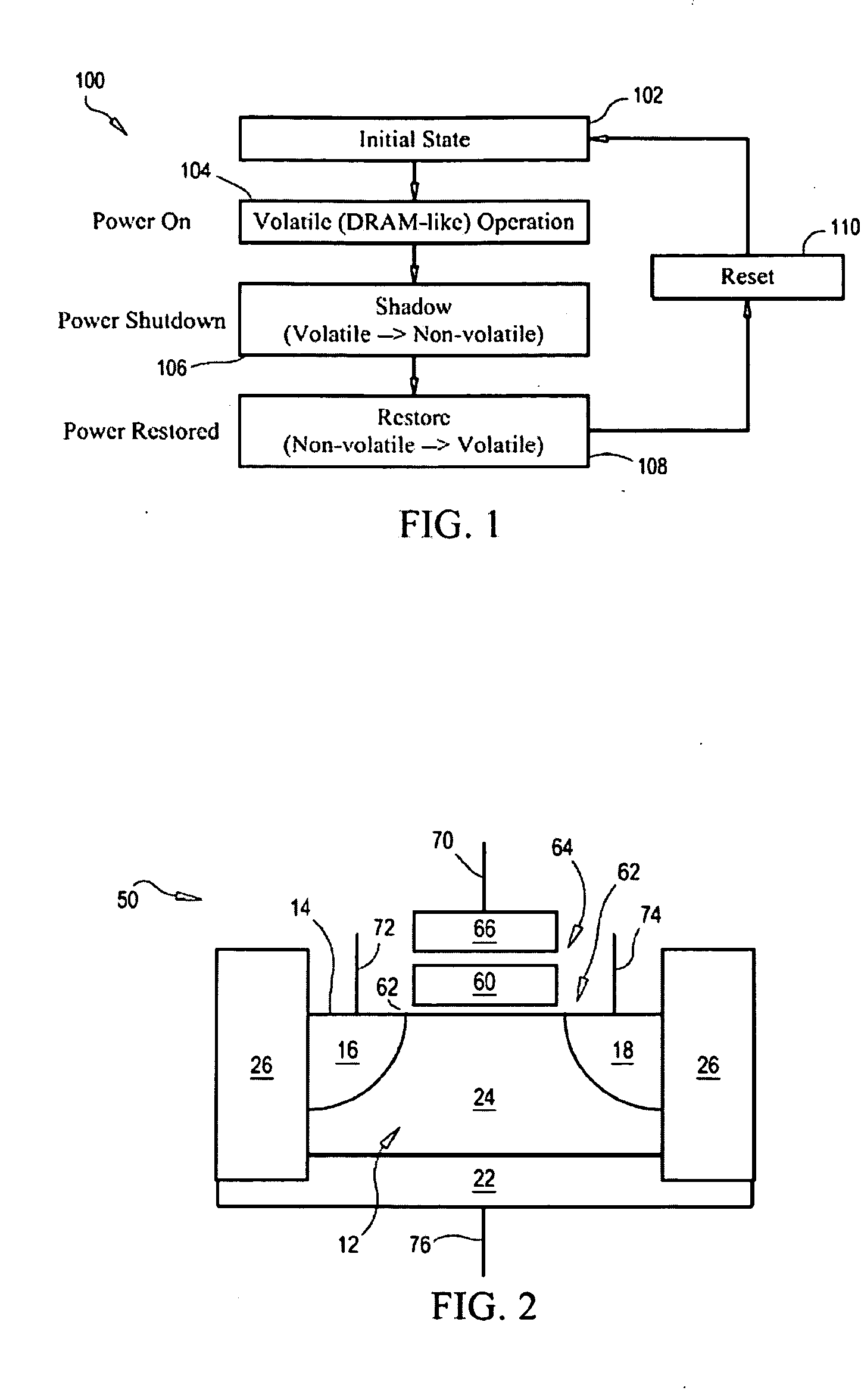
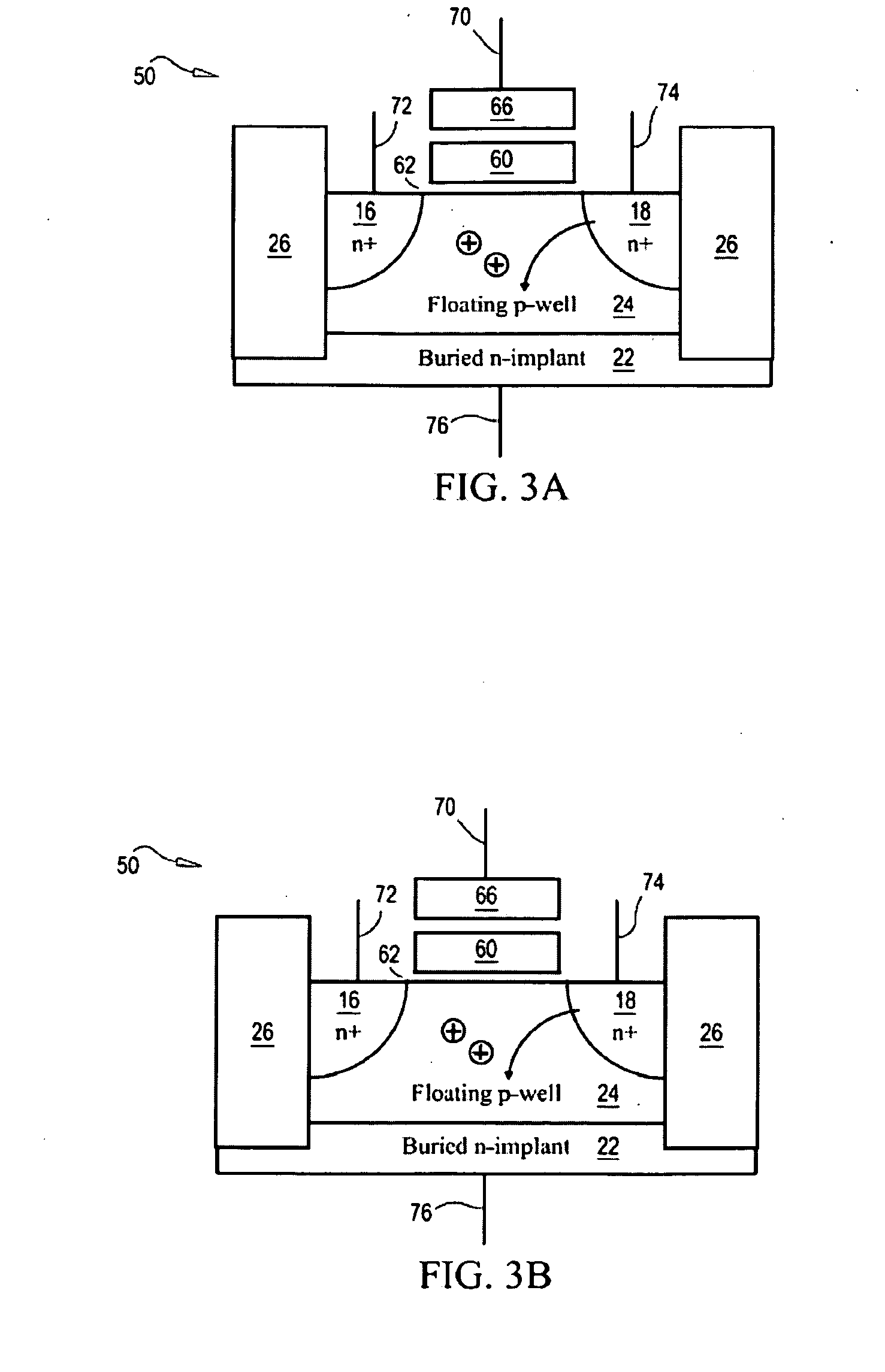
Semiconductor memory having both volatile and non-volatile functionality and method of operating
Semiconductor memory having both volatile and non-volatile modes and methods of operation. A semiconductor storage device includes a plurality of memory cells each having a floating body for storing, reading and writing data as volatile memory. The device includes a floating gate or trapping latter for storing data as non-volatile memory, the device operating as volatile memory when power is applied to the device, and the device storing data from the volatile memory, as non-volatile memory when power to the device is interrupted.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
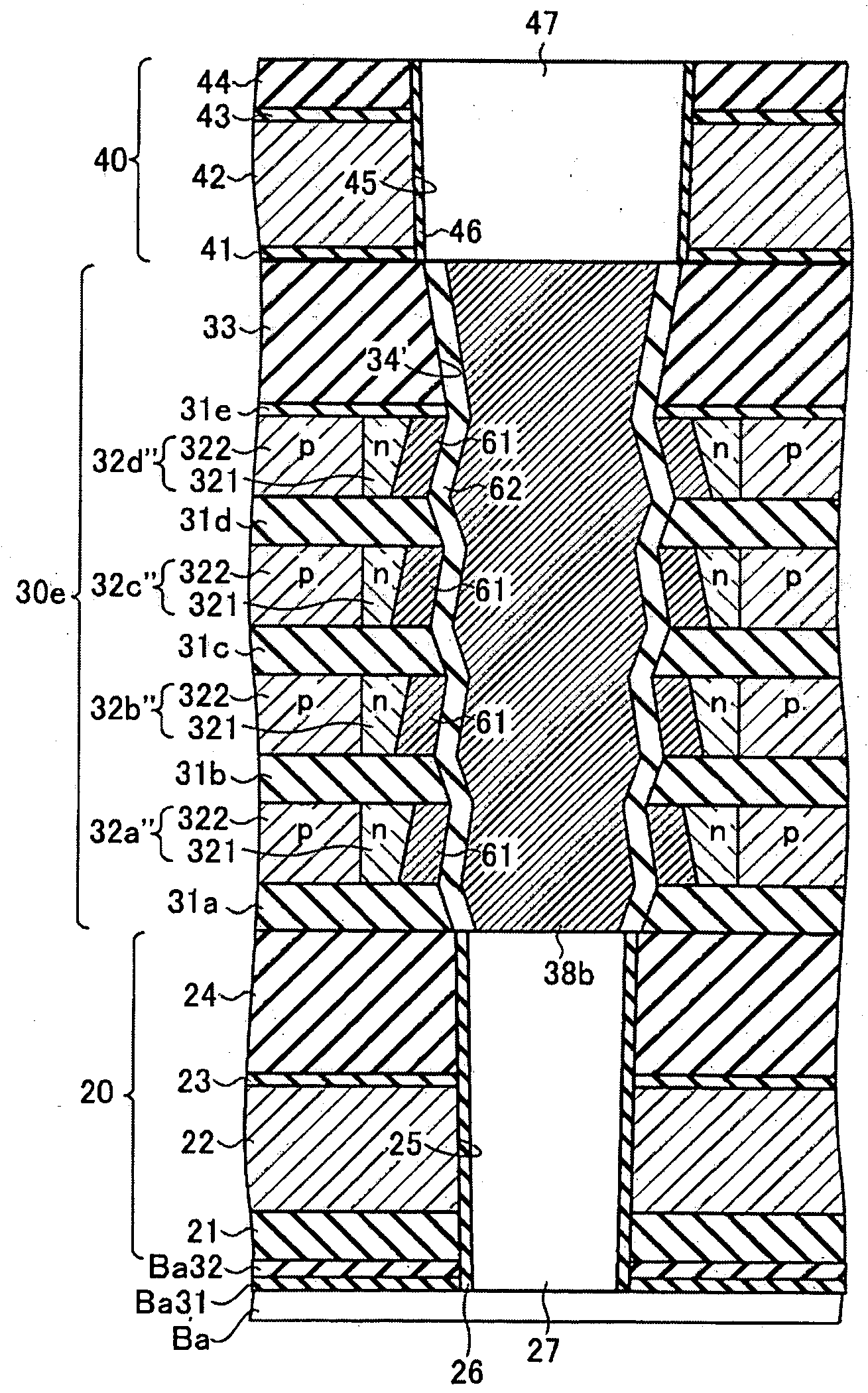
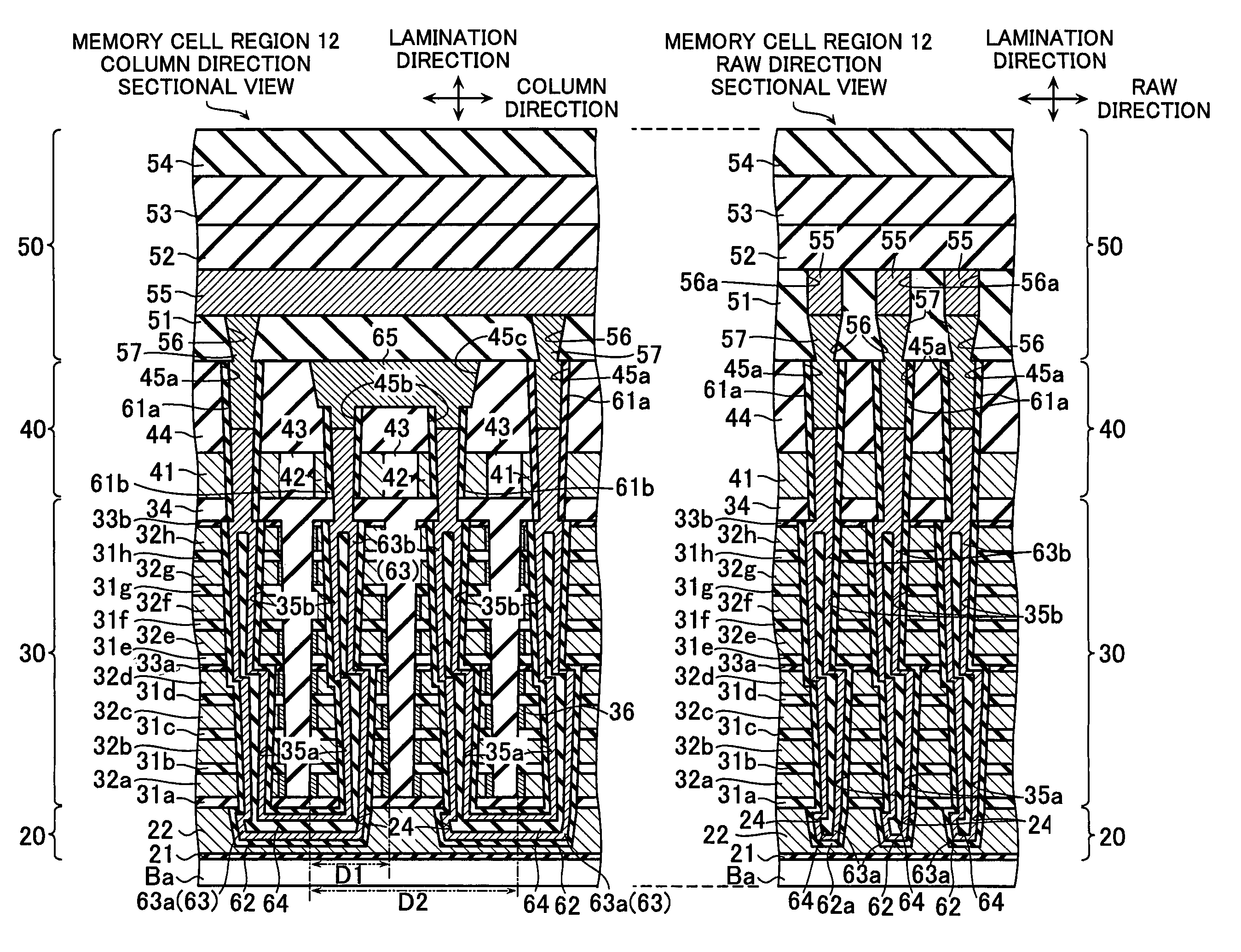
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090242967A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSemiconductor storage devices
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings with a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells connected in series. Each of the memory strings comprises: a first columnar semiconductor layer extending in a vertical direction to a substrate; a charge accumulation layer formed around the first columnar semiconductor layer via a first insulation layer; and a first conductive layer formed around the charge accumulation layer via a second insulation layer. Each of the first conductive layers is formed to expand in a two-dimensional manner, and air gaps are formed between the first conductive layers located there above and there below.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7910432B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSemiconductor storage devices
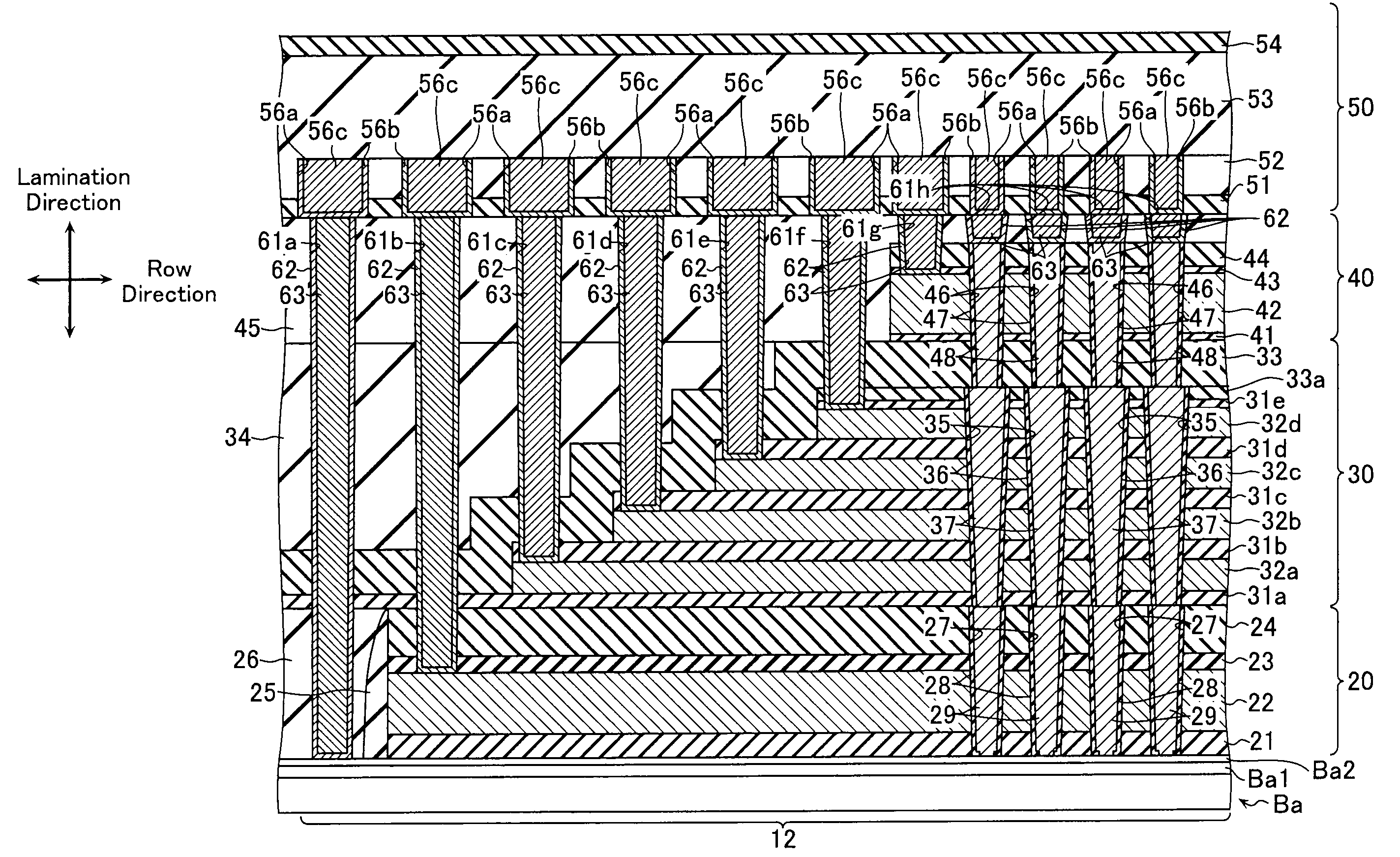
Each of the memory strings includes: a first columnar semiconductor layer extending in a vertical direction to a substrate; a plurality of first conductive layers formed to sandwich an insulation layer with a charge trap layer and expand in a two-dimensional manner; a second columnar semiconductor layer formed in contact with the top surface of the first columnar semiconductor layer and extending in a vertical direction to the substrate; and a plurality of second conductive layers formed to sandwich an insulation layer with the second columnar semiconductor layer and formed in a stripe pattern extending in a first direction orthogonal to the vertical direction. Respective ends of the plurality of first conductive layers in the first direction are formed in a stepwise manner in relation to each other, entirety of the plurality of the second conductive layers are formed in an area immediately above the top layer of the first conductive layers, and the plurality of first conductive layers and the plurality of second conductive layers are covered with a protection insulation layer that is formed continuously with the plurality of first conductive layers and the second conductive layers.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS20080128780A1TransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor storage devices
A three-dimensional non-volatile semiconductor storage device which realizes both increased packing density and improved performance is disclosed. According to one aspect, there is provided a non-volatile semiconductor storage device comprising a first non-volatile memory cell provided on a first insulator, which includes a first semiconductor layer, and a first gate stack provided above the first semiconductor layer and including a first charge storage layer and a first control gate electrode, and a second non-volatile memory cell provided above the first non-volatile memory cell, which includes a second semiconductor layer, and a second gate stack provided above the second semiconductor layer and including a second charge storage layer and a second control gate electrode, the second gate stack being positioned to be aligned with the first gate stack, and wherein the first control gate electrode functions as a back gate electrode to the second non-volatile memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
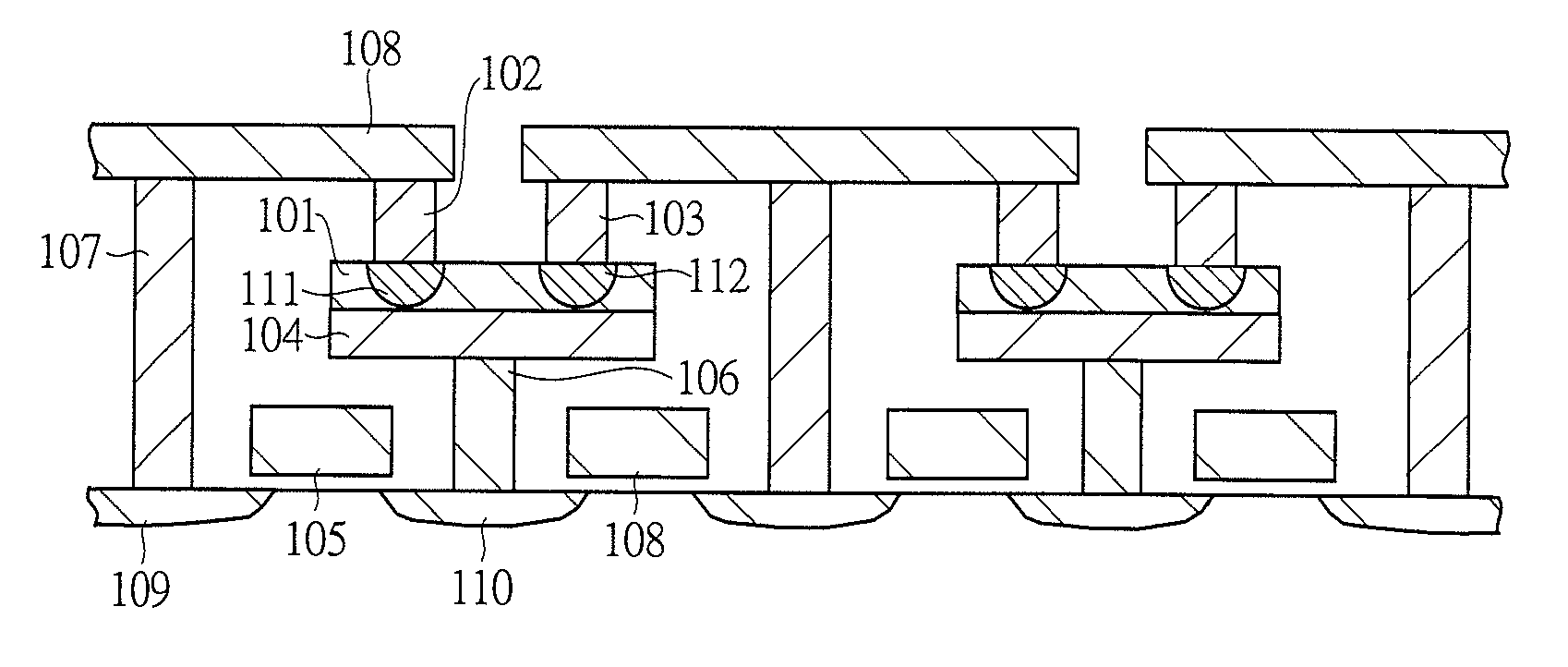
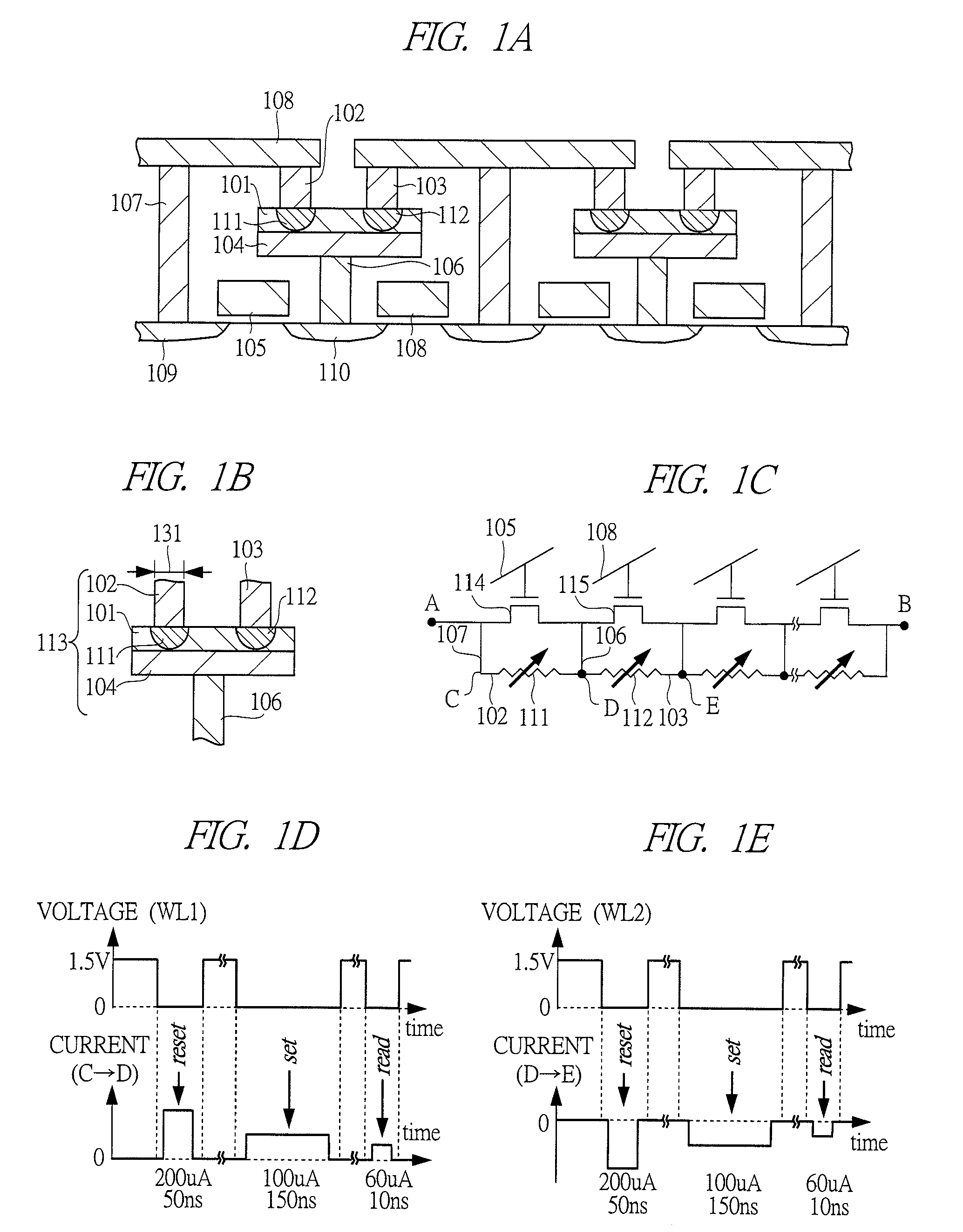
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS7864568B2Solid-state devicesDigital storagePhase-change memorySemiconductor storage devices
In a semiconductor storage device such as a phase change memory, a technique which can realize high integration is provided. The semiconductor storage device includes a phase change thin film 101 having two stable phases of a crystal state with low electric resistance and an amorphous state with high electric resistance, upper plug electrodes 102 and 103 provided on one side of the phase change thin film 101, a lower electrode 104 provided on the other side of the phase change thin film 101, a selecting transistor 114 whose drain / source terminals are connected to the upper plug electrode 102 and the lower electrode 104, and a selecting transistor 115 whose drain / source terminals are connected to the upper plug electrode 103 and the lower electrode 104, and a first memory cell is configured with the selecting transistor 114 and a phase change region 111 in the phase change thin film 101 sandwiched between the upper plug electrode 102 and the lower electrode 104, and a second memory cell is configured with the selecting transistor 115 and a phase change region 112 in the phase change thin film 101 sandwiched between the upper plug electrode 103 and the lower electrode 104.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090230462A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSemiconductor storage devices
Each of the memory strings includes: a first columnar semiconductor layer extending in a vertical direction to a substrate; a plurality of first conductive layers formed to sandwich an insulation layer with a charge trap layer and expand in a two-dimensional manner; a second columnar semiconductor layer formed in contact with the top surface of the first columnar semiconductor layer and extending in a vertical direction to the substrate; and a plurality of second conductive layers formed to sandwich an insulation layer with the second columnar semiconductor layer and formed in a stripe pattern extending in a first direction orthogonal to the vertical direction. Respective ends of the plurality of first conductive layers in the first direction are formed in a stepwise manner in relation to each other, entirety of the plurality of the second conductive layers are formed in an area immediately above the top layer of the first conductive layers, and the plurality of first conductive layers and the plurality of second conductive layers are covered with a protection insulation layer that is formed continuously with the plurality of first conductive layers and the second conductive layers.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
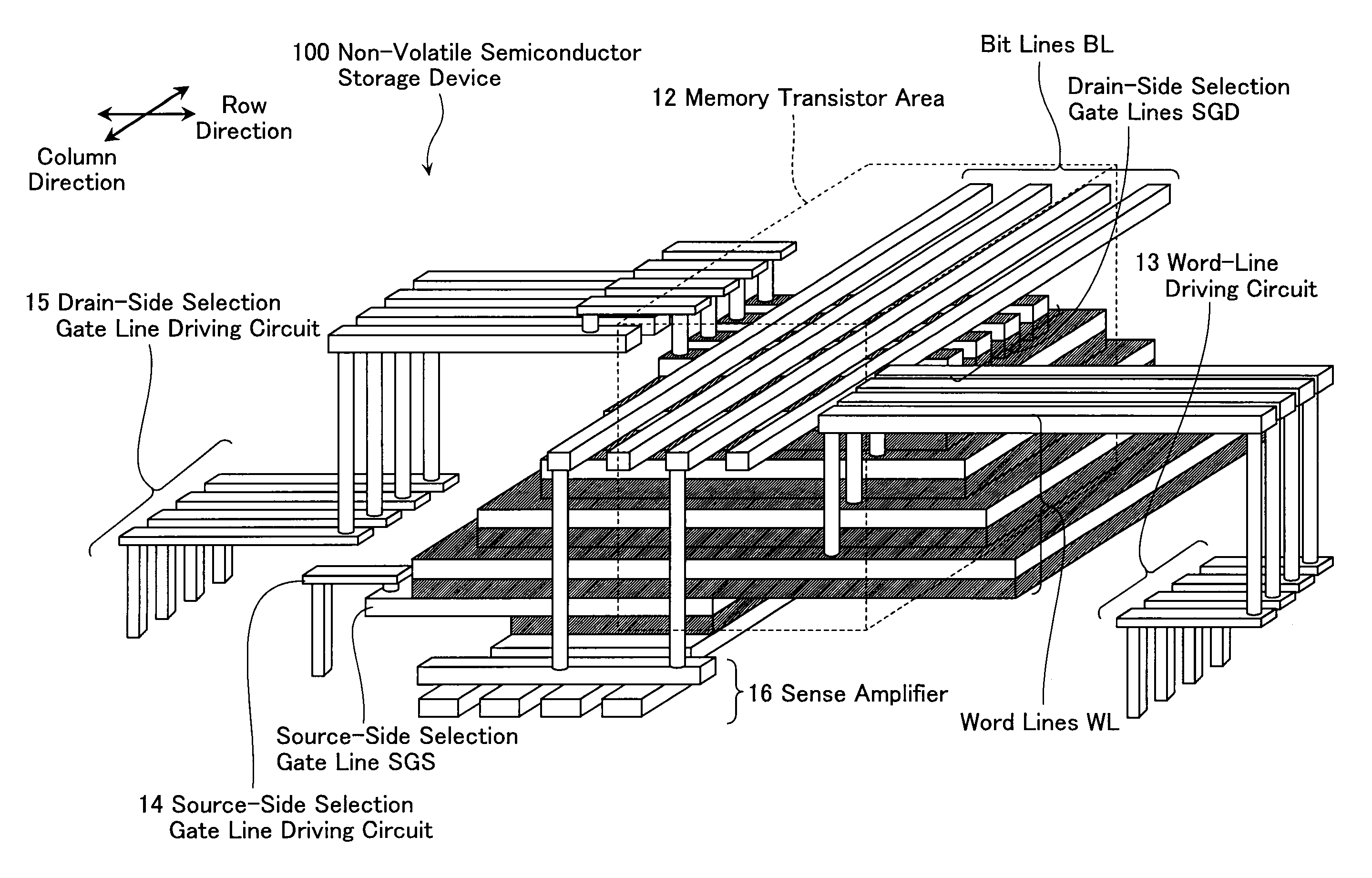
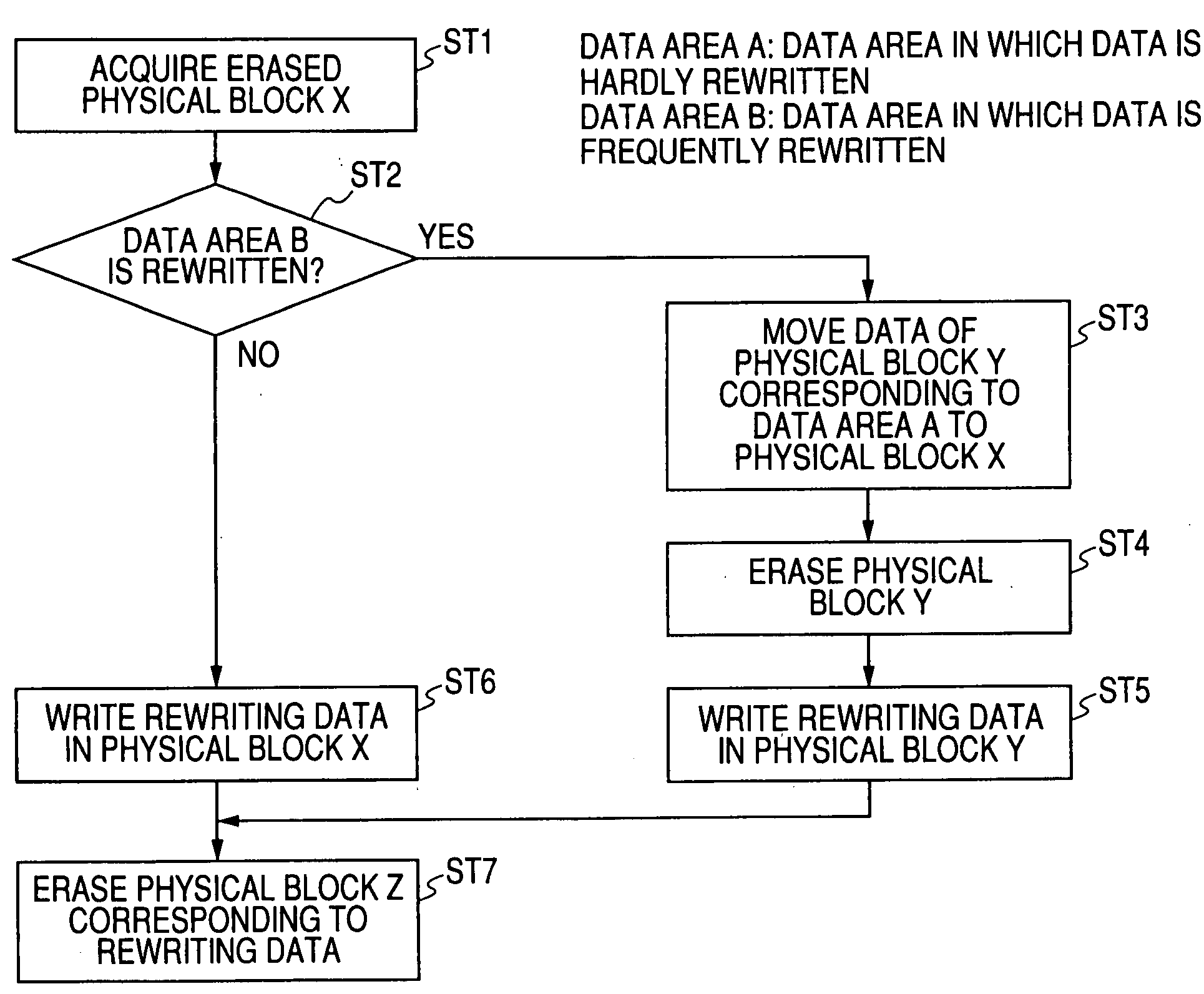
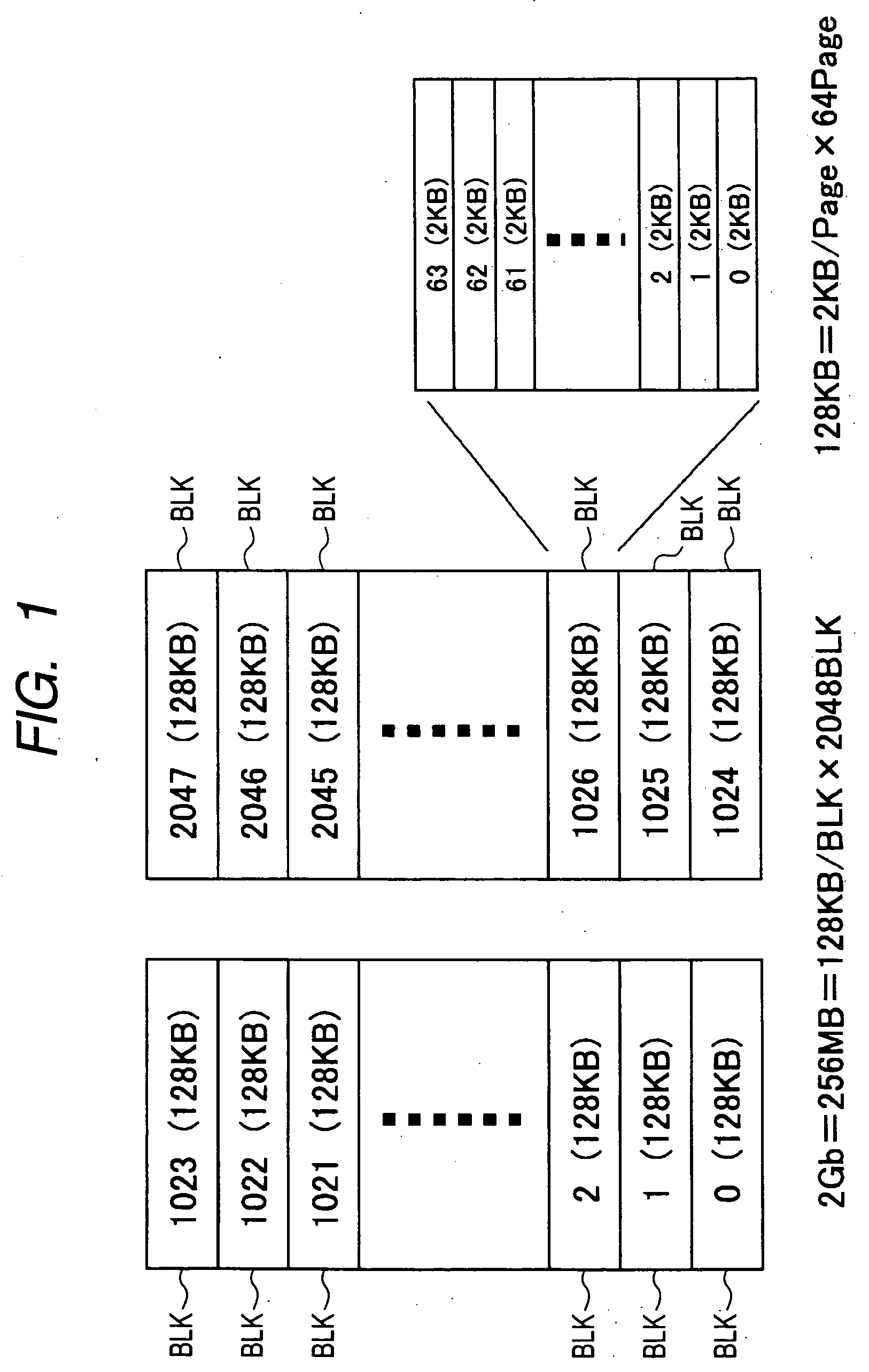
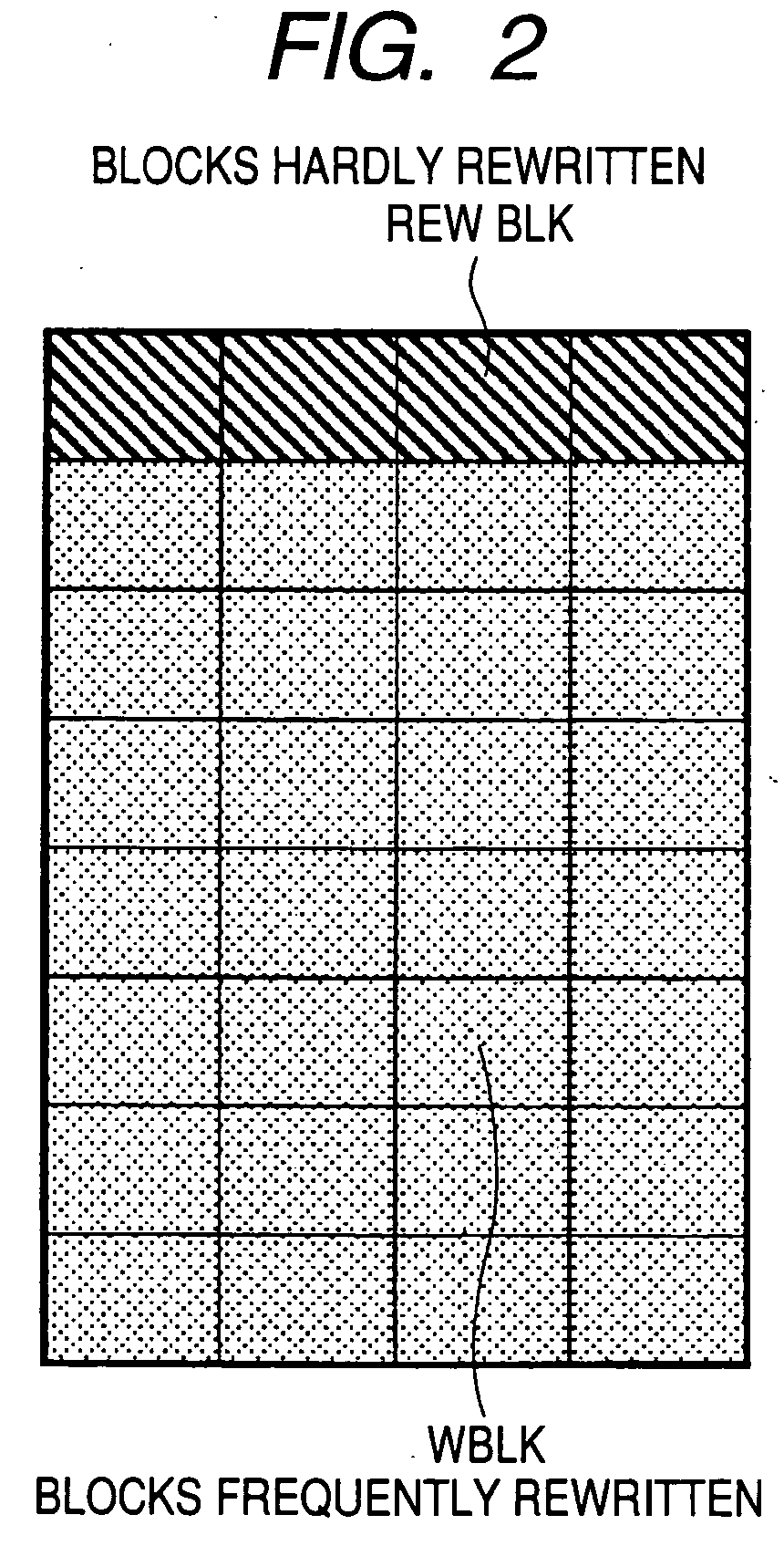
Memory system
ActiveUS20070103992A1Extend effective lifeEasy to controlMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesLogical block addressingSemiconductor storage devices
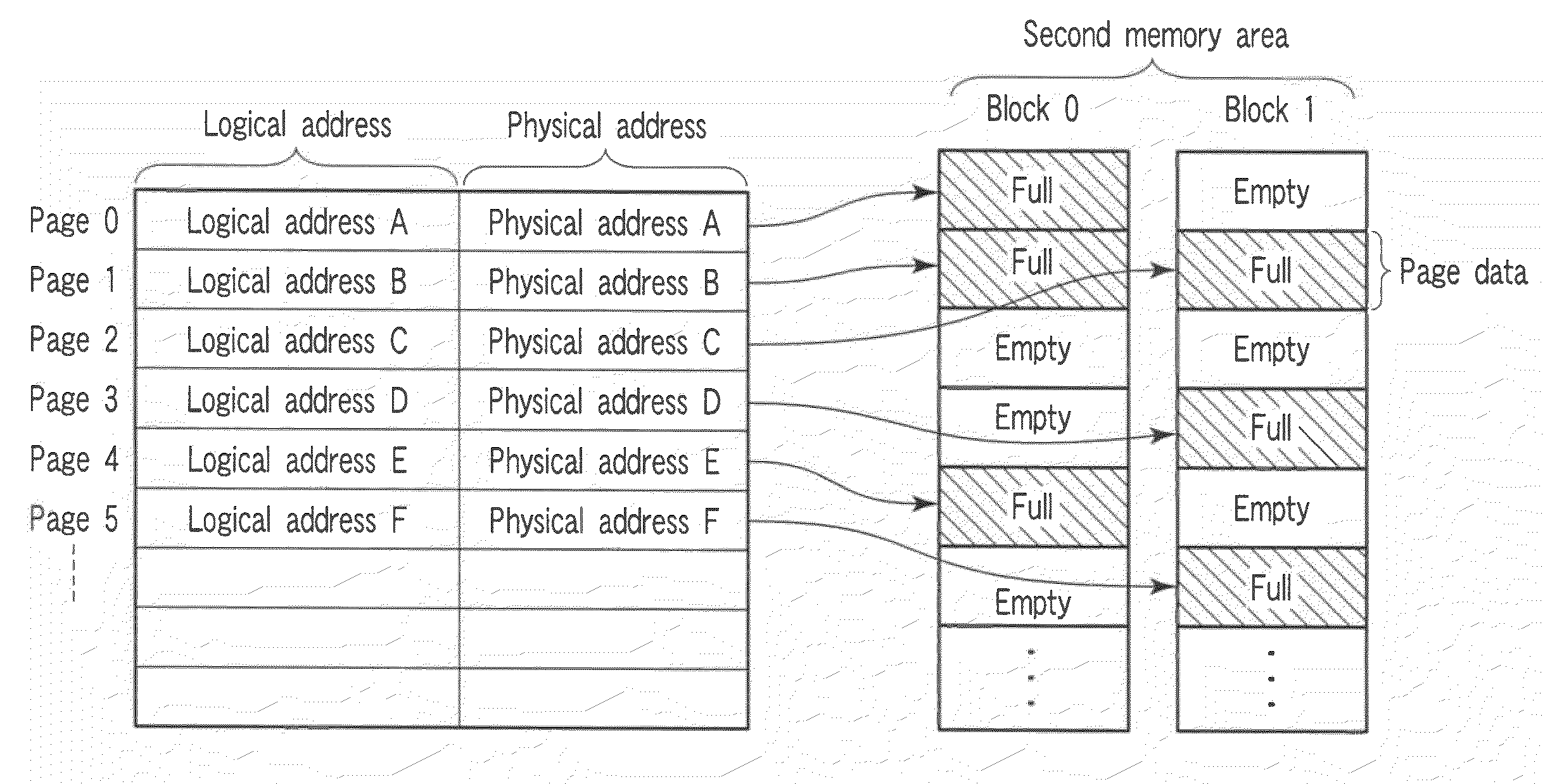
A memory system including a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device includes: a nonvolatile memory unit that includes a first data area in which data is frequently rewritten and a second data area in which data is hardly rewritten; and a control unit. The control unit sequentially selects logical block addresses in the second data area in which data is hardly rewritten and updates physical block addresses at new rewriting destinations in the first data area in which data is frequently rewritten to physical block addresses corresponding to the logical block addresses selected.
Owner:SONY CORP
Writing control method and writing control system of semiconductor storage device, and portable electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050002263A1Easily-realized finerSpeedup of writingTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor storage devicesEngineering
A writing control system providing high-speed writing to a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device, includes (a) a plurality of memory elements each having: a gate electrode provided on a semiconductor layer with an intervening gate insulating film; a channel region provided beneath the gate electrode; a diffusion region provided on both sides of the channel region, having an opposite polarity to the channel region; and a memory functioning member, provided on both sides of the gate electrode, having a function of holding electric charges, (b) a memory array including a page buffer circuit, and (c) CPU controlling writing to the memory array. The CPU loads a first plane of the page buffer circuit with a first byte of data and writes with the first byte of data stored in the first plane. Further, the CPU writes a second byte of data into the second plane and writes the second byte of data having been stored in the second plane while writing the first byte of data having been stored in the first plane into the memory array.
Owner:SHARP KK
Writing control method and writing control system of semiconductor storage device, and portable electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7050337B2The implementation process is simpleSpeedup of writingTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor storage devicesHemt circuits
A writing control system providing high-speed writing to a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device, includes (a) a plurality of memory elements each having: a gate electrode provided on a semiconductor layer with an intervening gate insulating film; a channel region provided beneath the gate electrode; a diffusion region provided on both sides of the channel region, having an opposite polarity to the channel region; and a memory functioning member, provided on both sides of the gate electrode, having a function of holding electric charges, (b) a memory array including a page buffer circuit, and (c) CPU controlling writing to the memory array. The CPU loads a first plane of the page buffer circuit with a first byte of data and writes with the first byte of data stored in the first plane. Further, the CPU writes a second byte of data into the second plane and writes the second byte of data having been stored in the second plane while writing the first byte of data having been stored in the first plane into the memory array.
Owner:SHARP KK
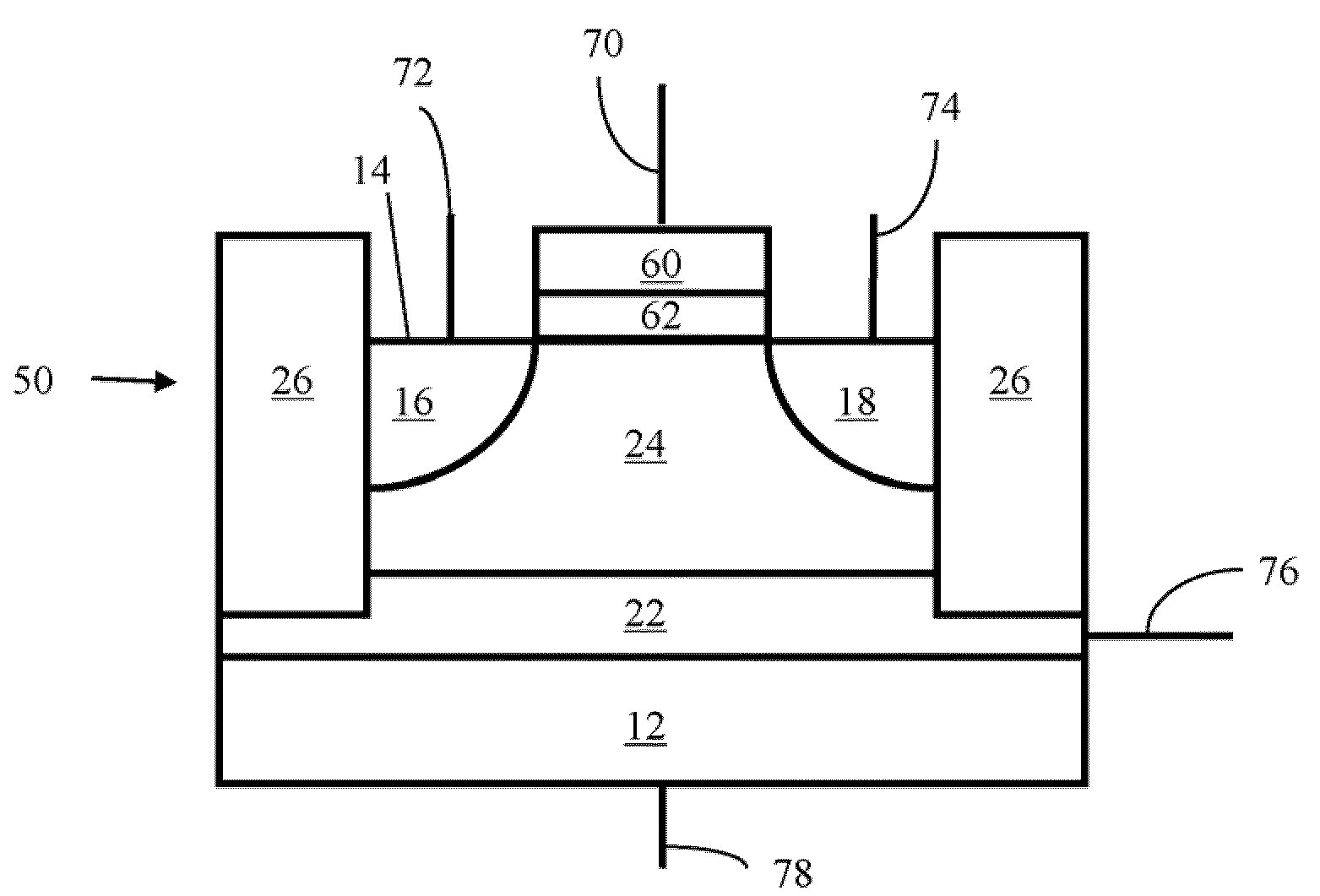
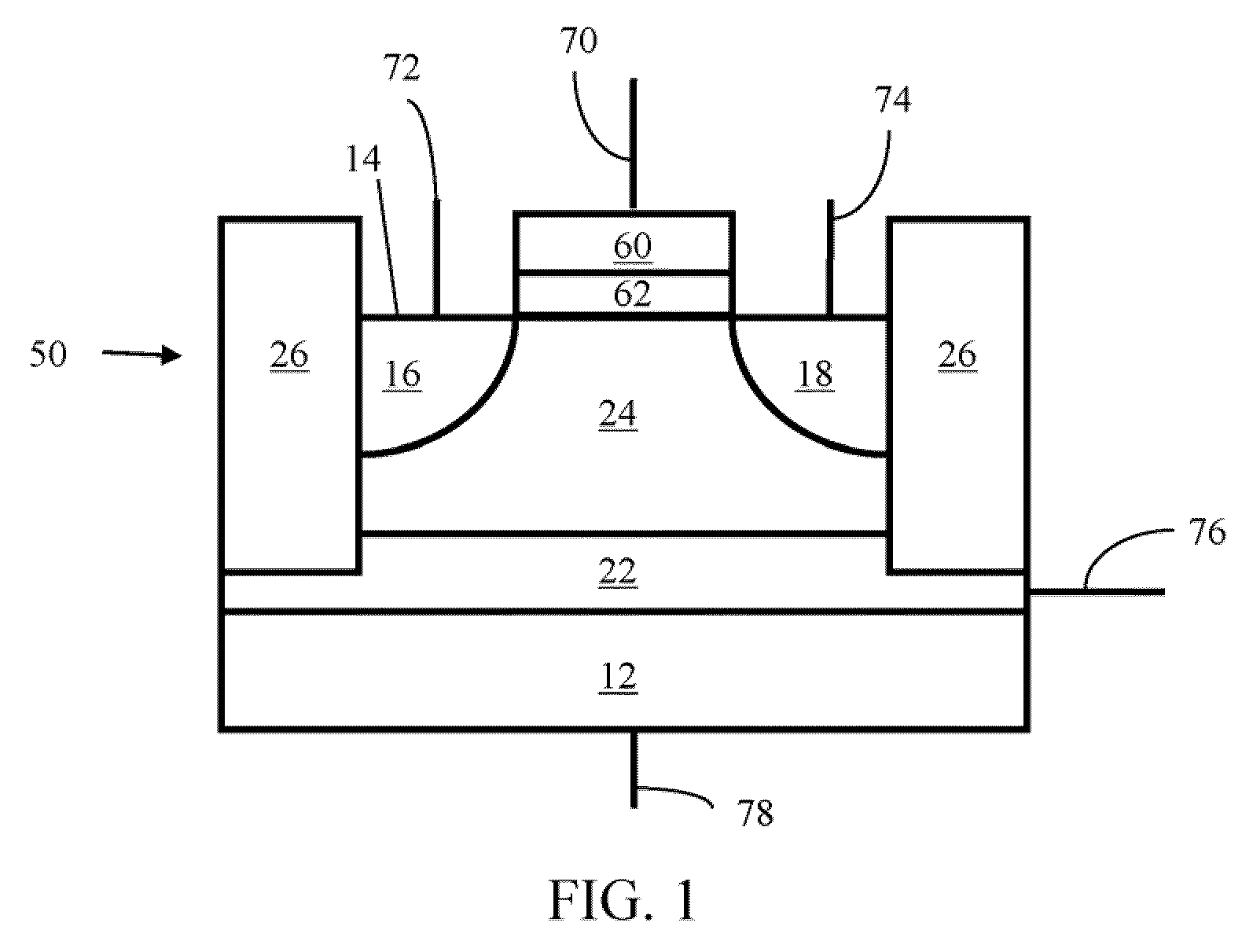
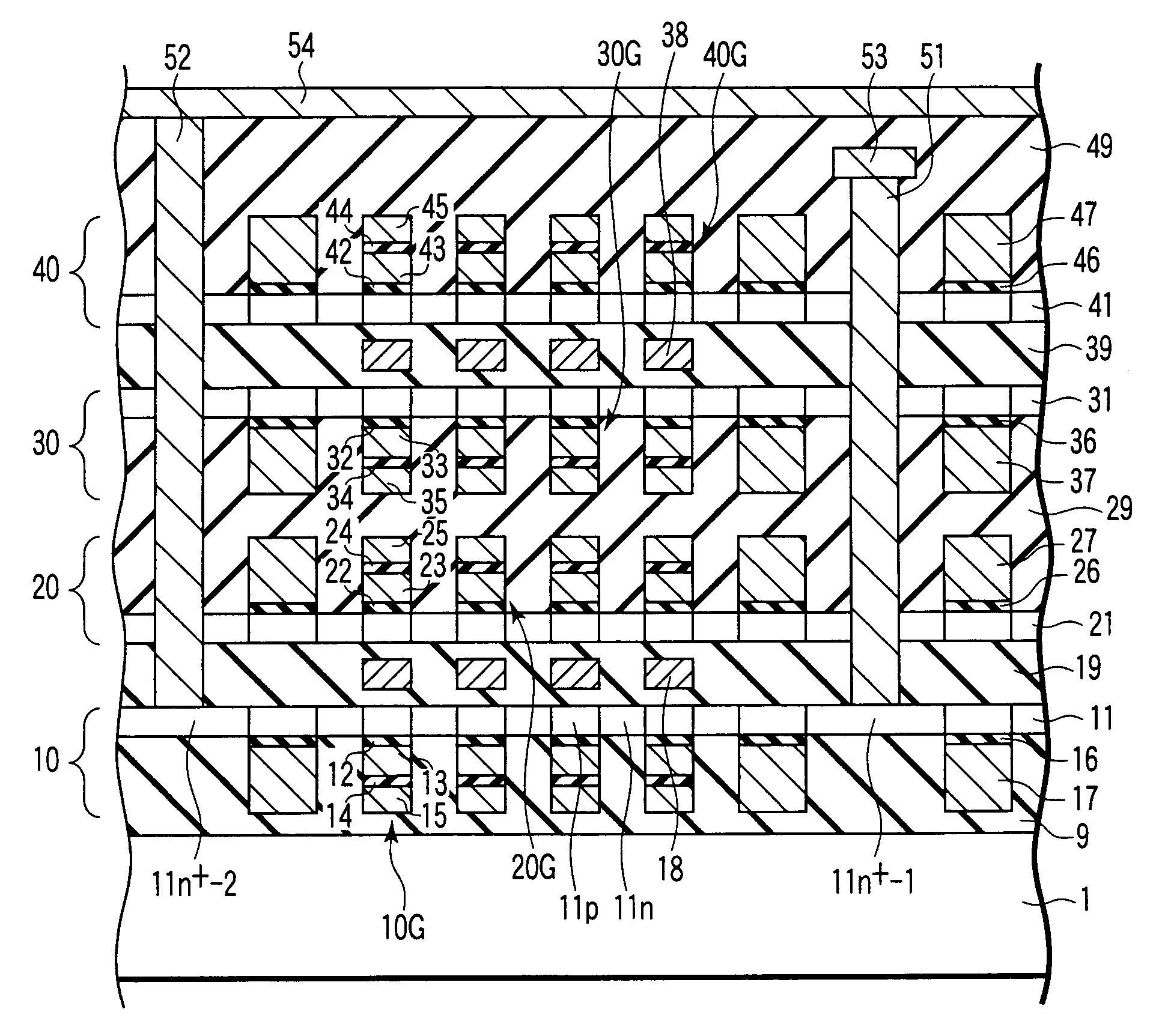
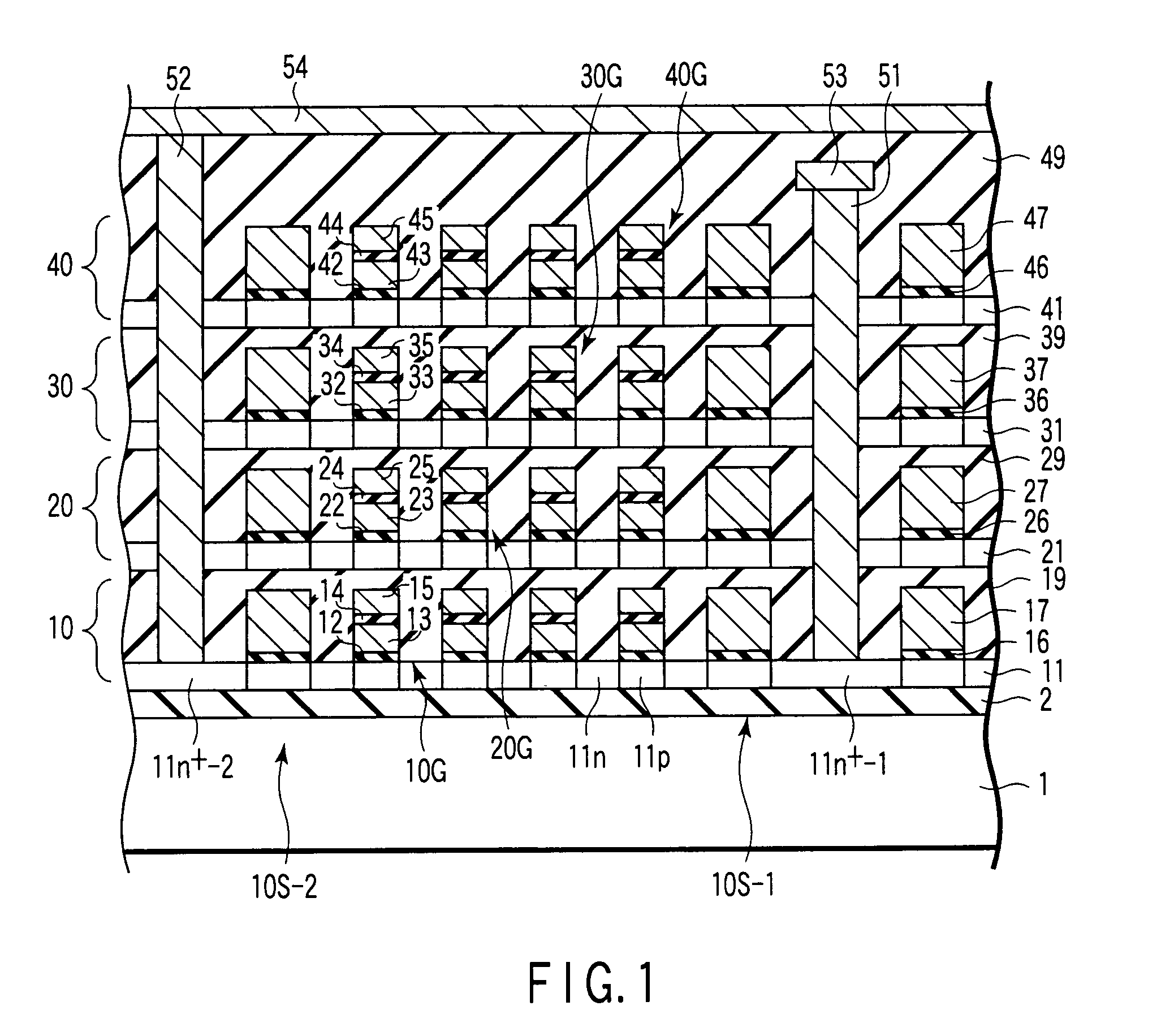
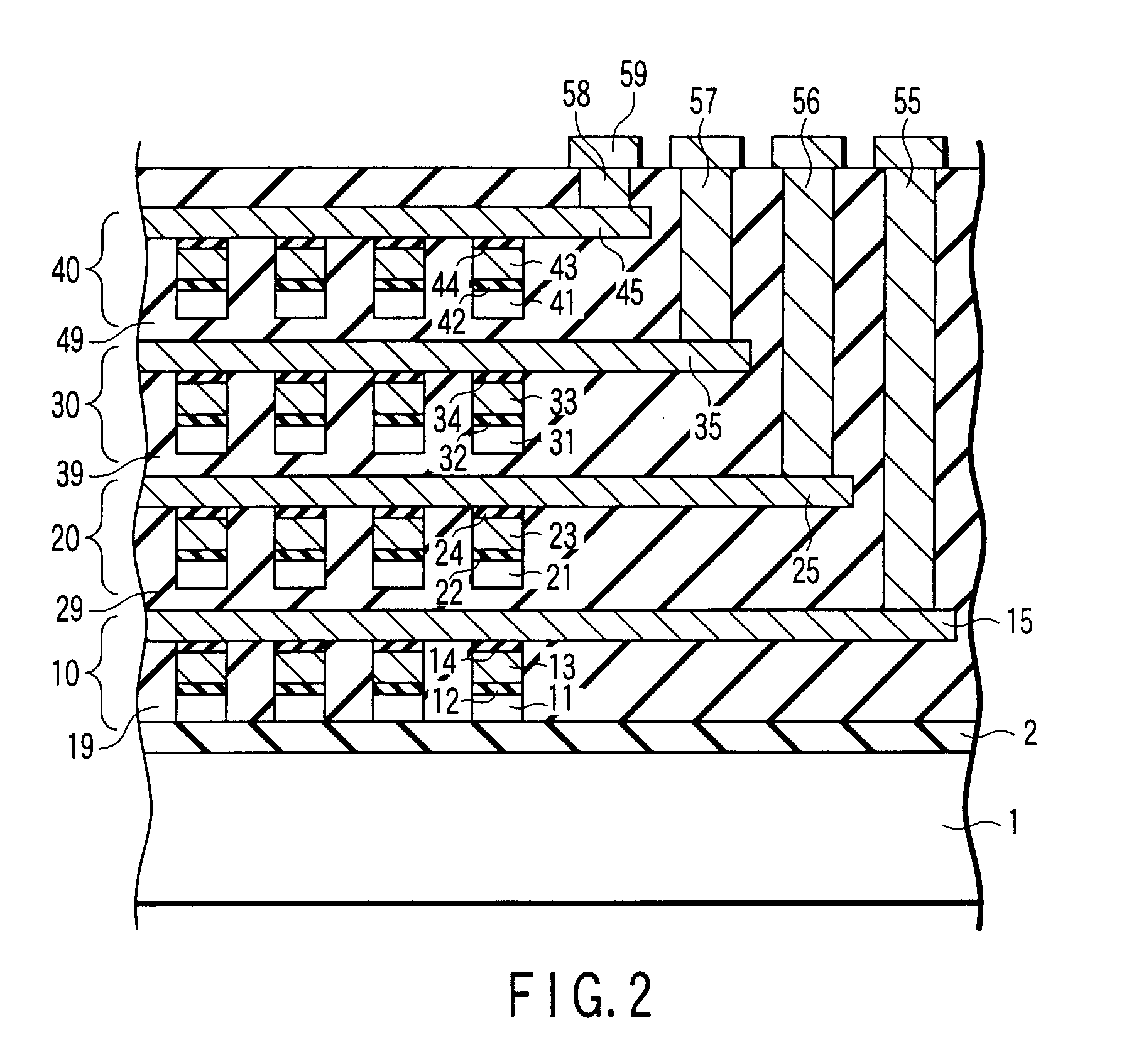
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
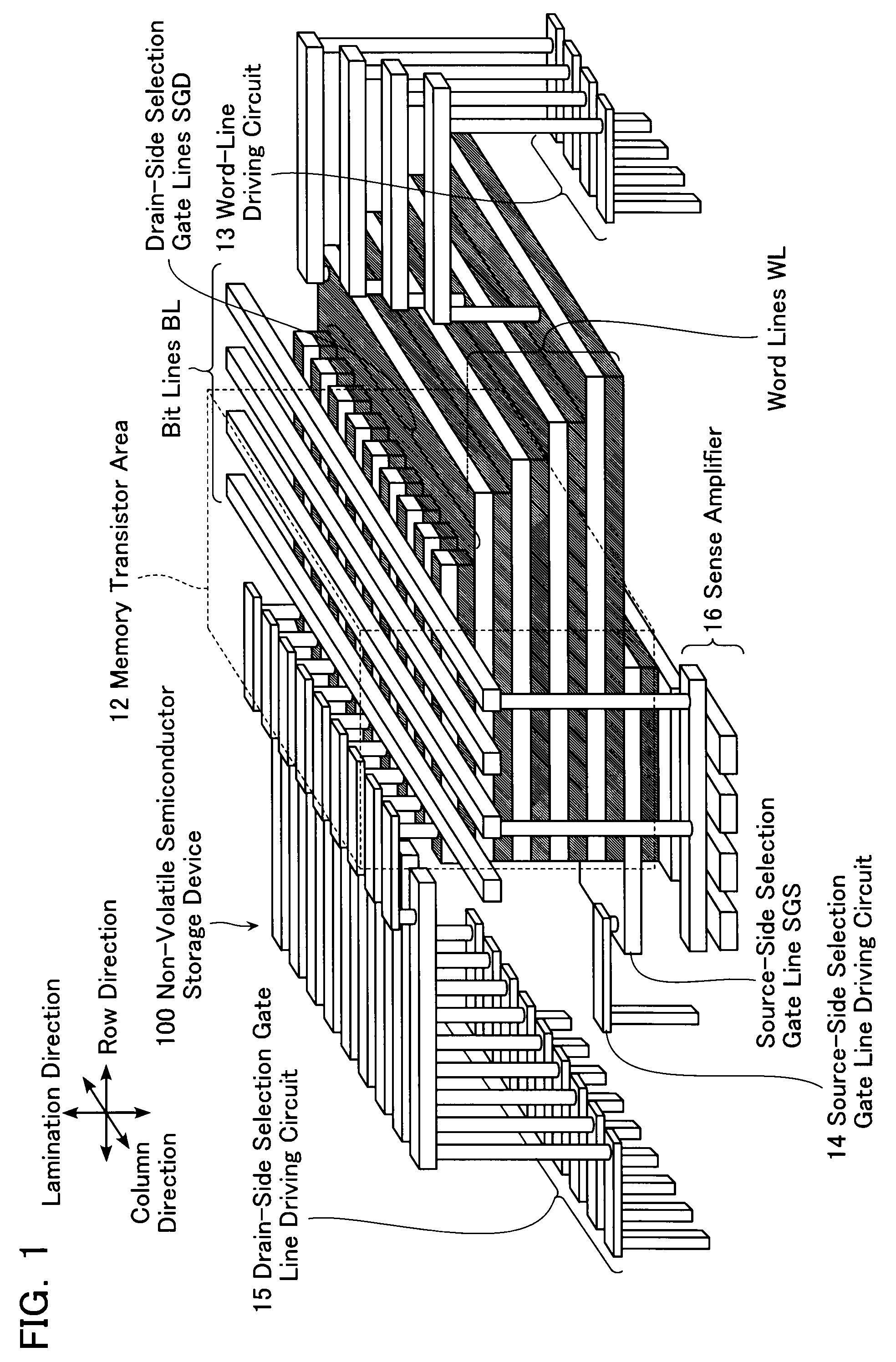
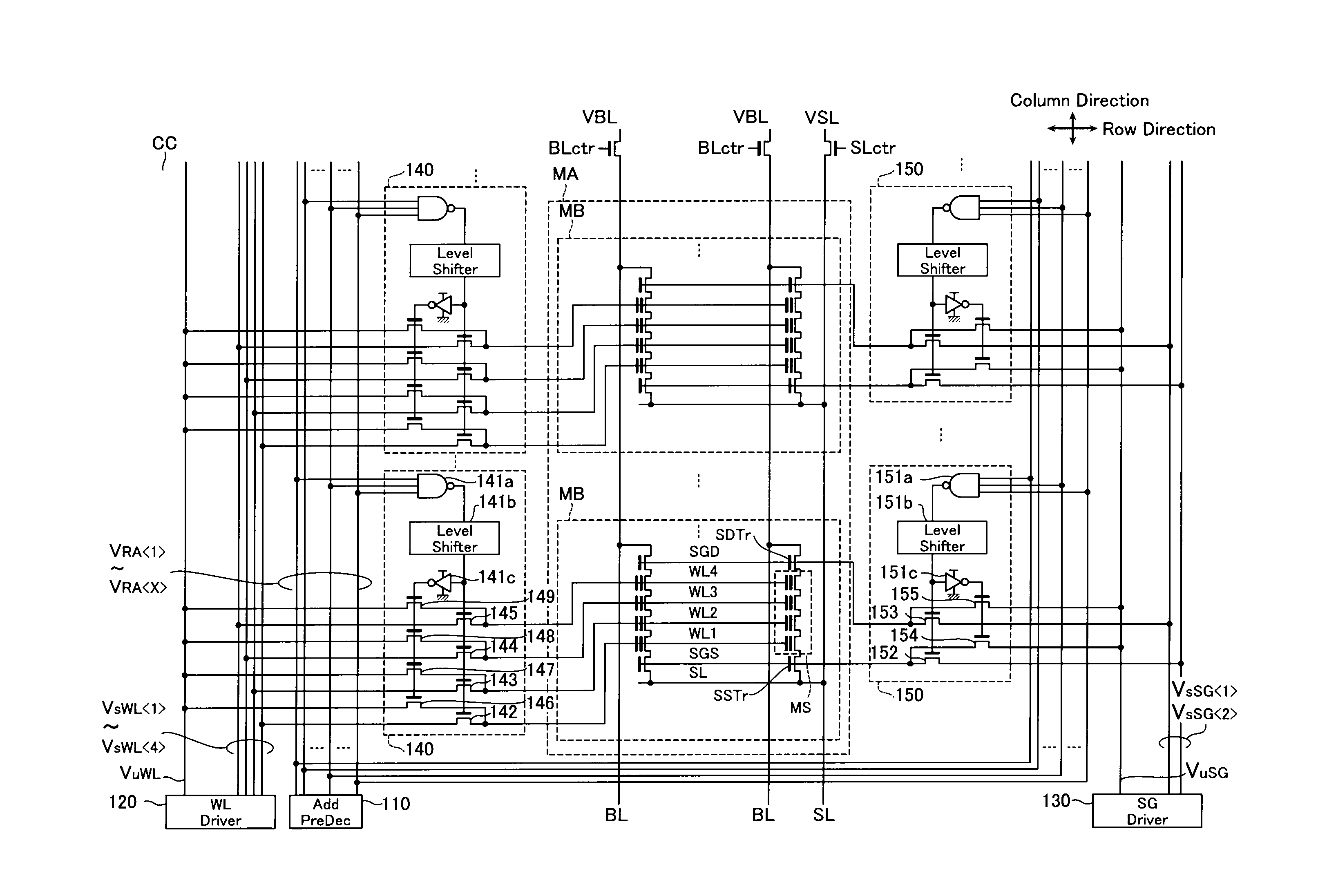
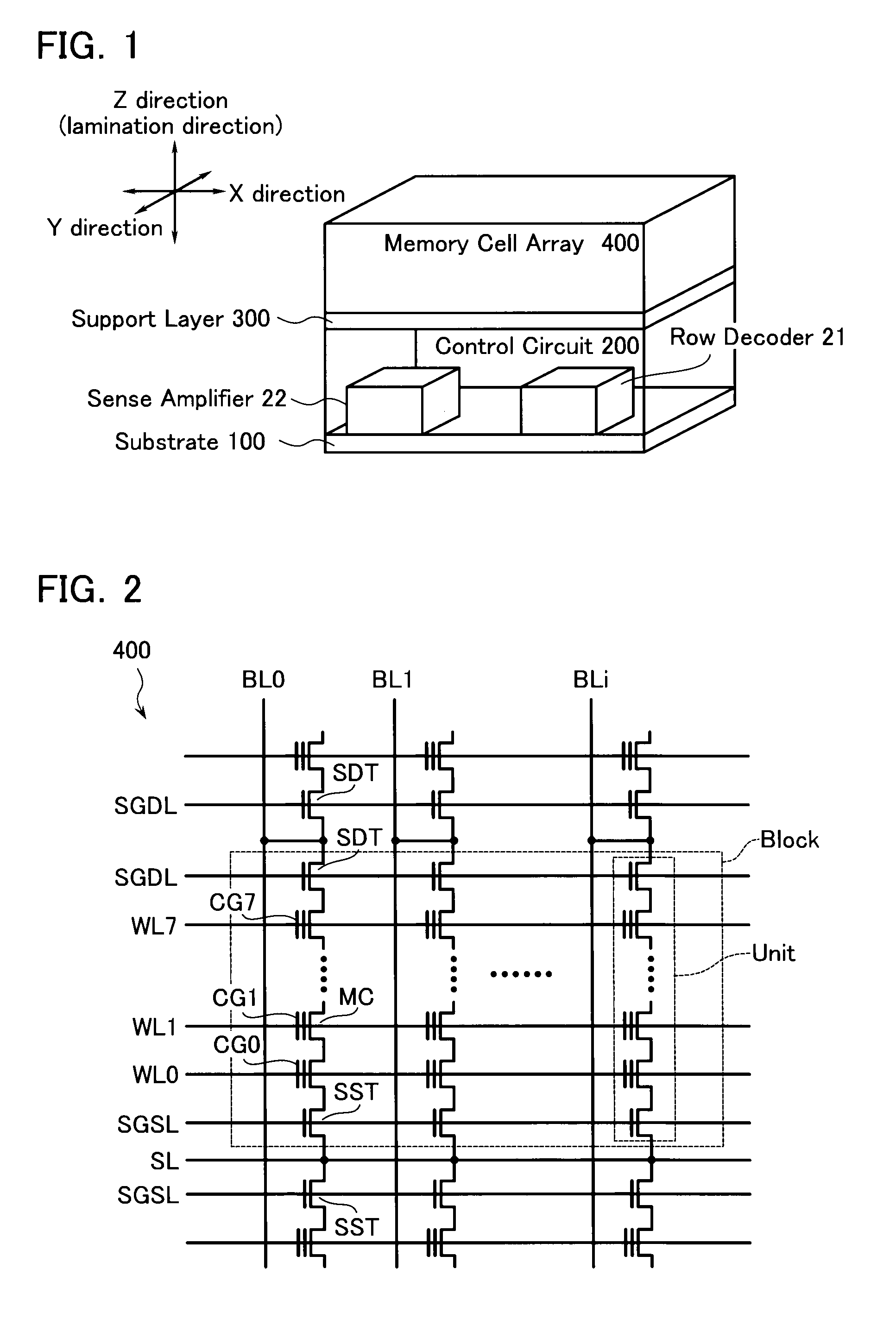
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device includes: a substrate; a control circuit layer provided on the substrate; a support layer provided on the control circuit layer; and a memory cell array layer provided on the support layer. The memory cell array layer includes: a first lamination part having first insulation layers and first conductive layers alternately laminated therein; and a second lamination part provided on either the top or bottom surface of the respective first lamination part and laminated so as to form a second conductive layer between second insulation layers. The control circuit layer includes at least any one of: a row decoder driving word lines provided in the memory cell array layer, and a sense amplifier sensing and amplifying a signal from bit lines provided in the memory cell array layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
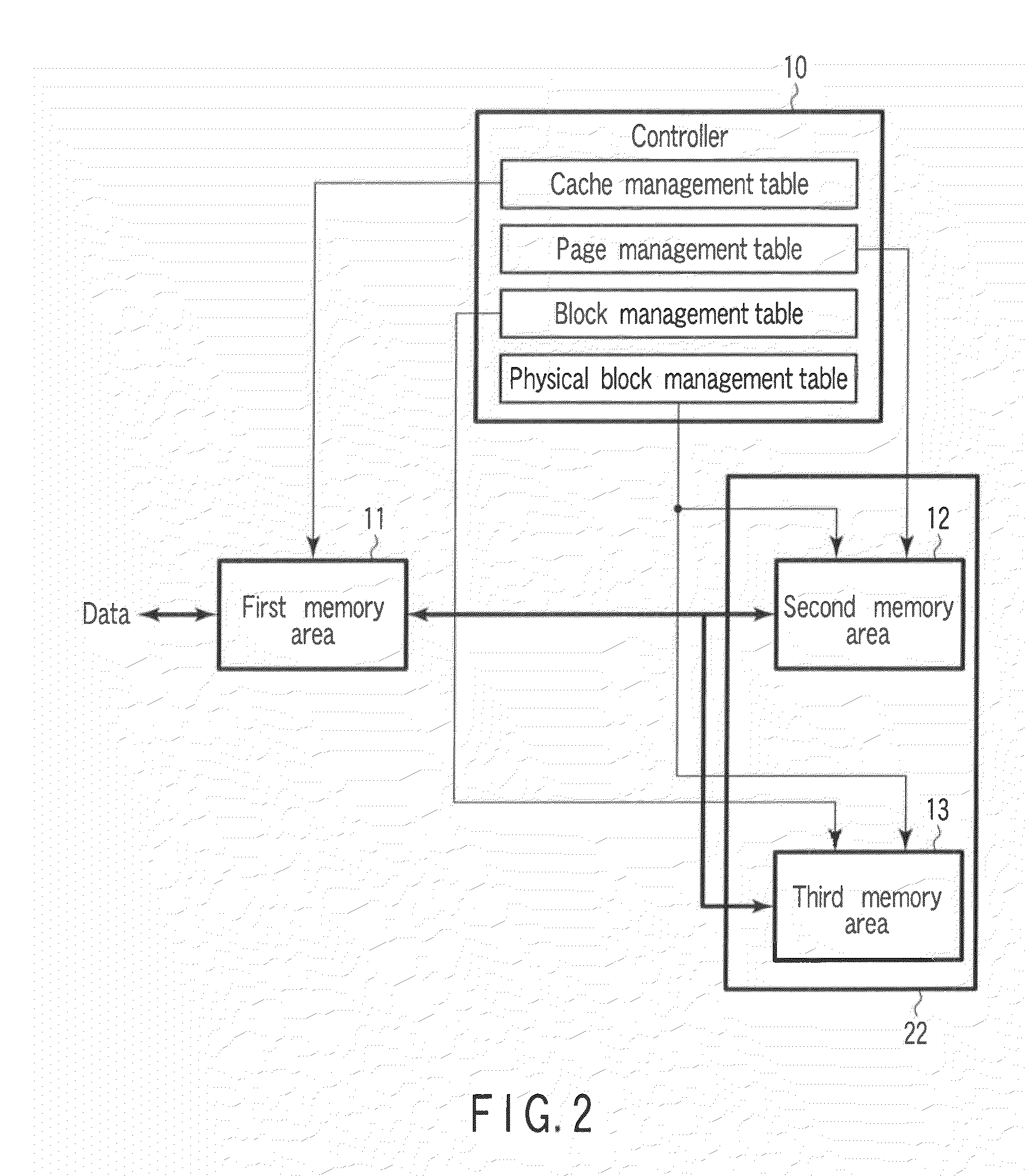
Semiconductor storage device, method of controlling the same, controller and information processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100037009A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInformation processingManagement unit
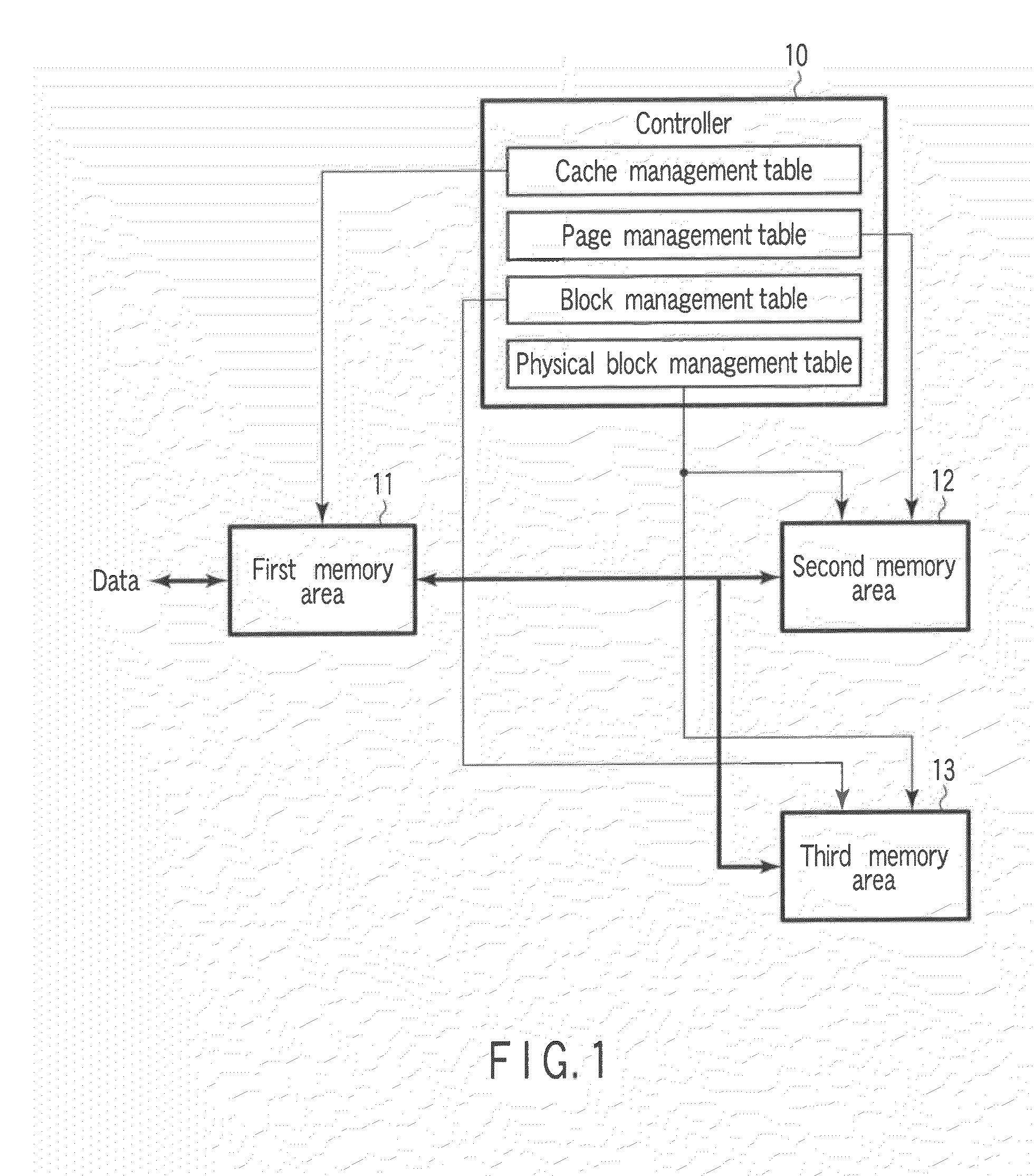
A semiconductor storage device includes a first memory area configured in a volatile semiconductor memory, second and third memory areas configured in a nonvolatile semiconductor memory, and a controller which executes following processing. The controller executes a first processing for storing a plurality of data by the first unit in the first memory area, a second processing for storing data outputted from the first memory area by a first management unit in the second memory area, and a third processing for storing data outputted from the first memory area by a second management unit in the third memory area.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
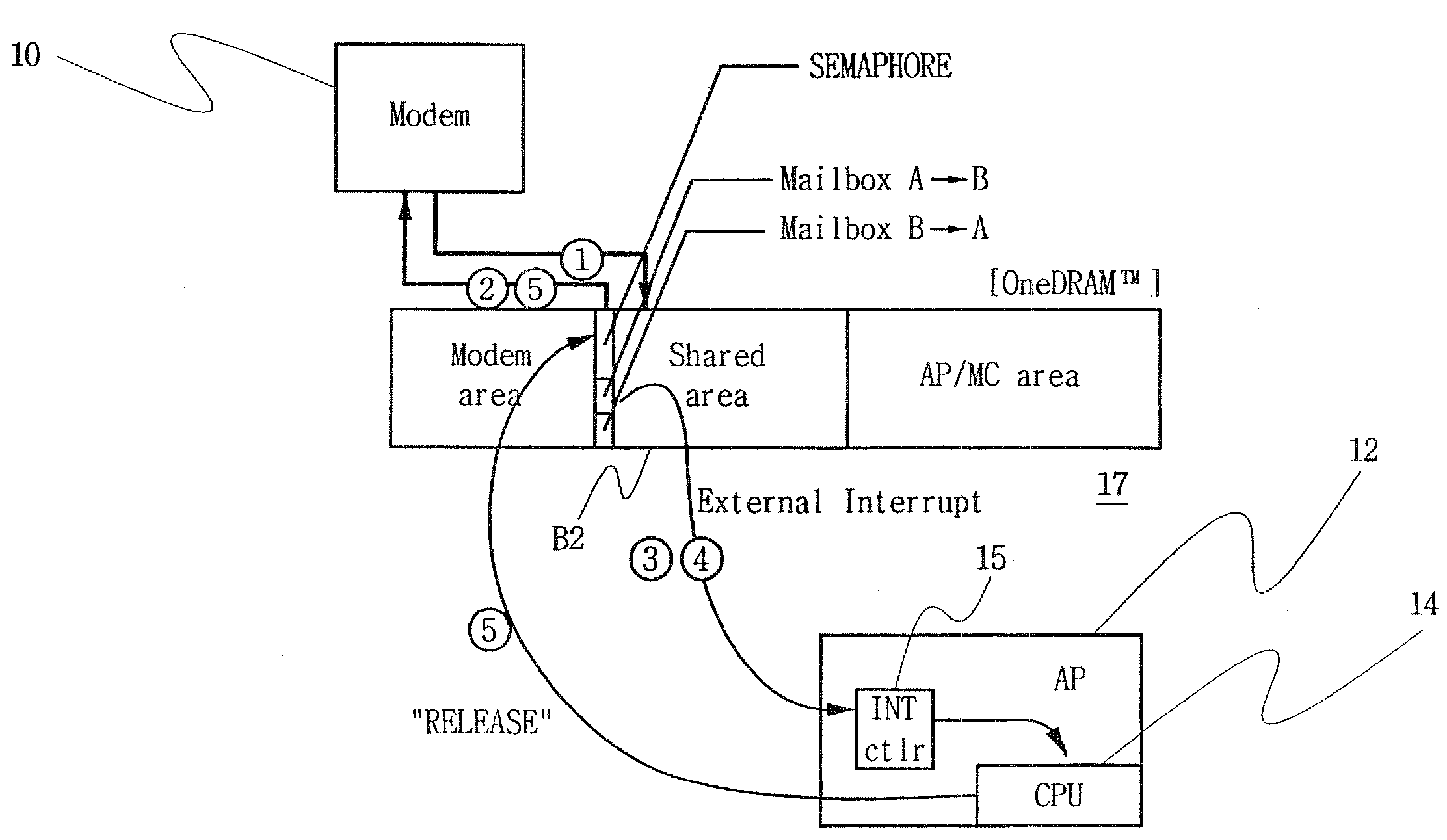
Multipath accessible semiconductor memory device with host interface between processors
ActiveUS20080077937A1Low costIncrease speedGeneral purpose stored program computerDigital storageMulti processorData access
A multipath accessible semiconductor memory device provides an interface function between processors. The memory device may include a memory cell array having a shared memory area operationally coupled to two or more ports that are independently accessible by two or more processors, an access path forming unit to form a data access path between one of the ports and the shared memory area in response to external signals applied by the processors, and an interface unit having a semaphore area and mailbox areas accessible in the shared memory area by the two or more processors to provide an interface function for communication between the two or more processors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
When a data erase operation is performed in one memory cell block, a first voltage is applied to one source line selected from m source lines in the one memory cell block. A second voltage equal to a voltage of the source lines before the data erase operation begins is applied to the other source lines. Then, after a certain time delay from application of the first voltage, a third voltage smaller than the first voltage is applied to a third conductive layer of a source-side selection transistor connected to a selected source line. Then, a hole current is produced near a third gate insulation layer due to a potential difference between the first and third voltage. A fourth voltage is applied to one of first conductive layers connected to one of the memory transistor to be erased. The other first conductive layers are brought into a floating state.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090146206A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesInsulation layerSemiconductor storage devices
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings with a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells connected in series. Each of the memory strings includes: a first columnar semiconductor layer extending in a direction perpendicular to a substrate and having a first hollow extending downward from its upper end; a first insulation layer formed in contact with the outer wall of the first columnar semiconductor layer; a second insulation layer formed on the inner wall of the first columnar semiconductor layer so as to leave the first hollow; and a plurality of first conductive layers formed to sandwich the first insulation layer with the first columnar semiconductor layer and functioning as control electrodes of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090230458A1Long distanceSmall distanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSemiconductor storage devices
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor storage device
A semiconductor storage device according to one embodiment of the present invention, comprising: FBCs (Floating Body Cells) which store data by accumulating a majority carrier in a floating channel body; and sense amplifiers which perform control reading out data stored in said FBC, wherein each of said sense amplifier includes: a pair of sense nodes provided corresponding to a bit line pair to which said FBC is connected; a pair of load which flow currents through said pair of sense nodes; latch circuits which latch potentials of said pair of sense nodes when a potential difference between said pair of sense nodes reaches a predetermined value; and an output control circuit which outputs latched outputs of said latch circuits at a predetermined timing and feeds back the latched outputs to said bit line pair side to again write it into said FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
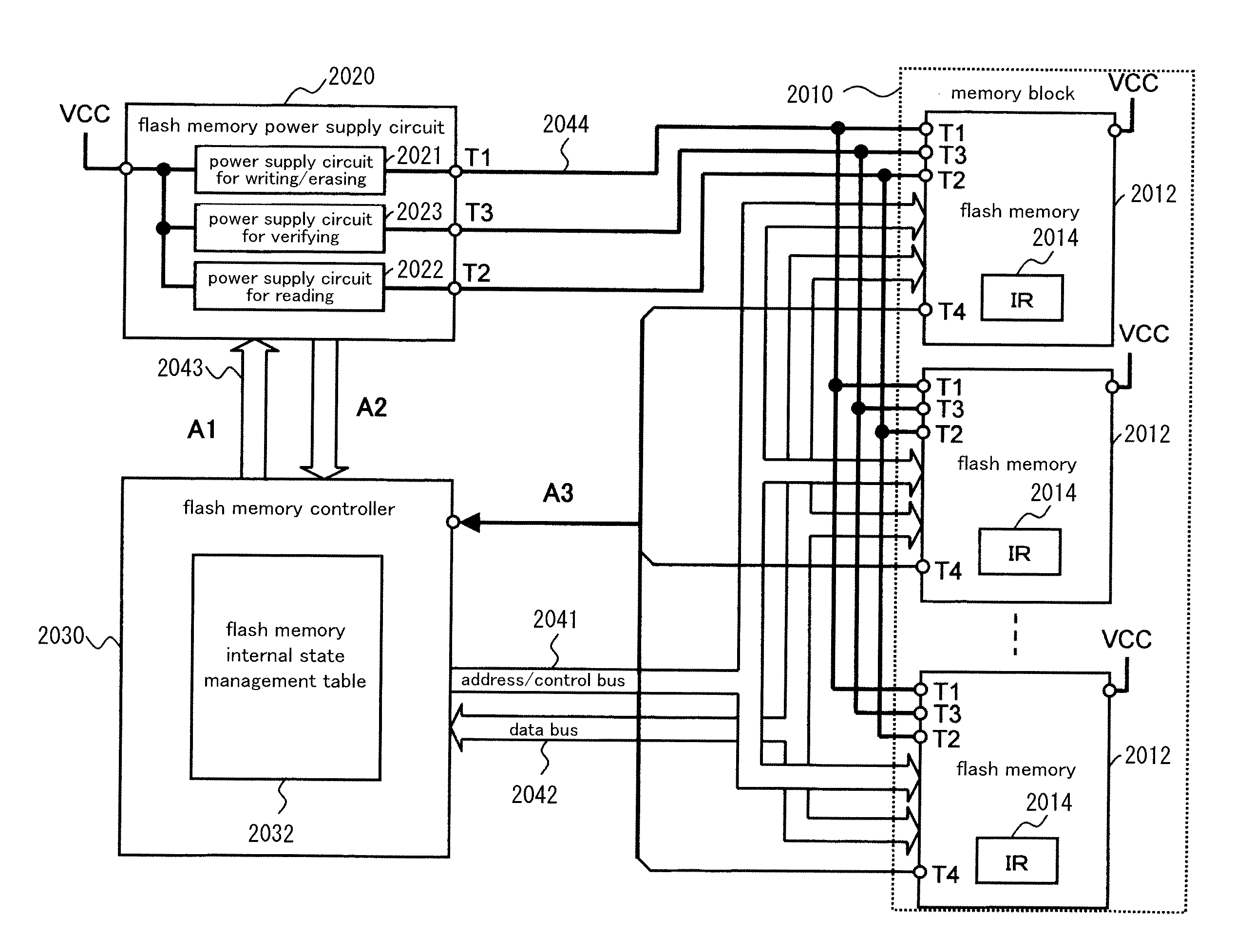
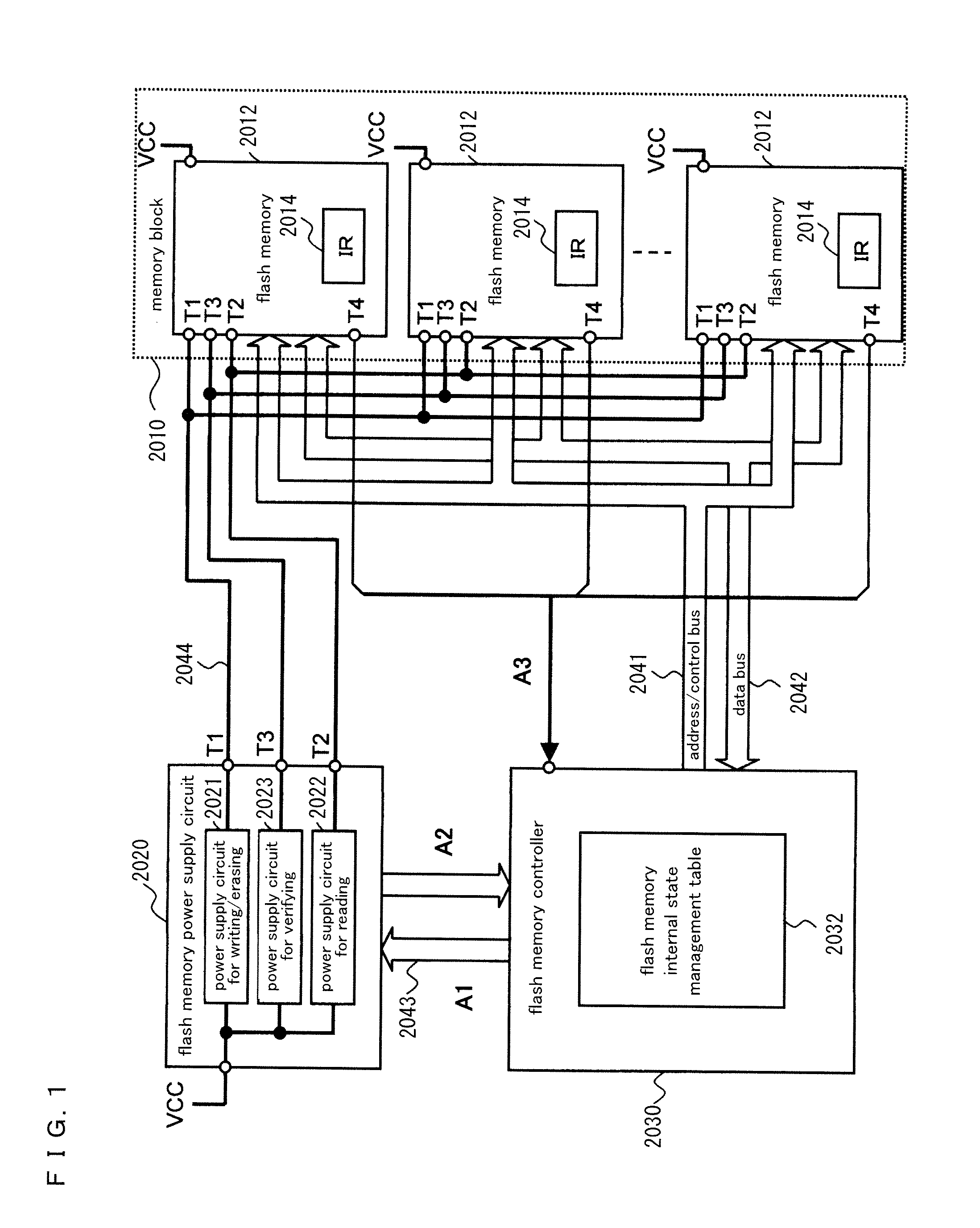
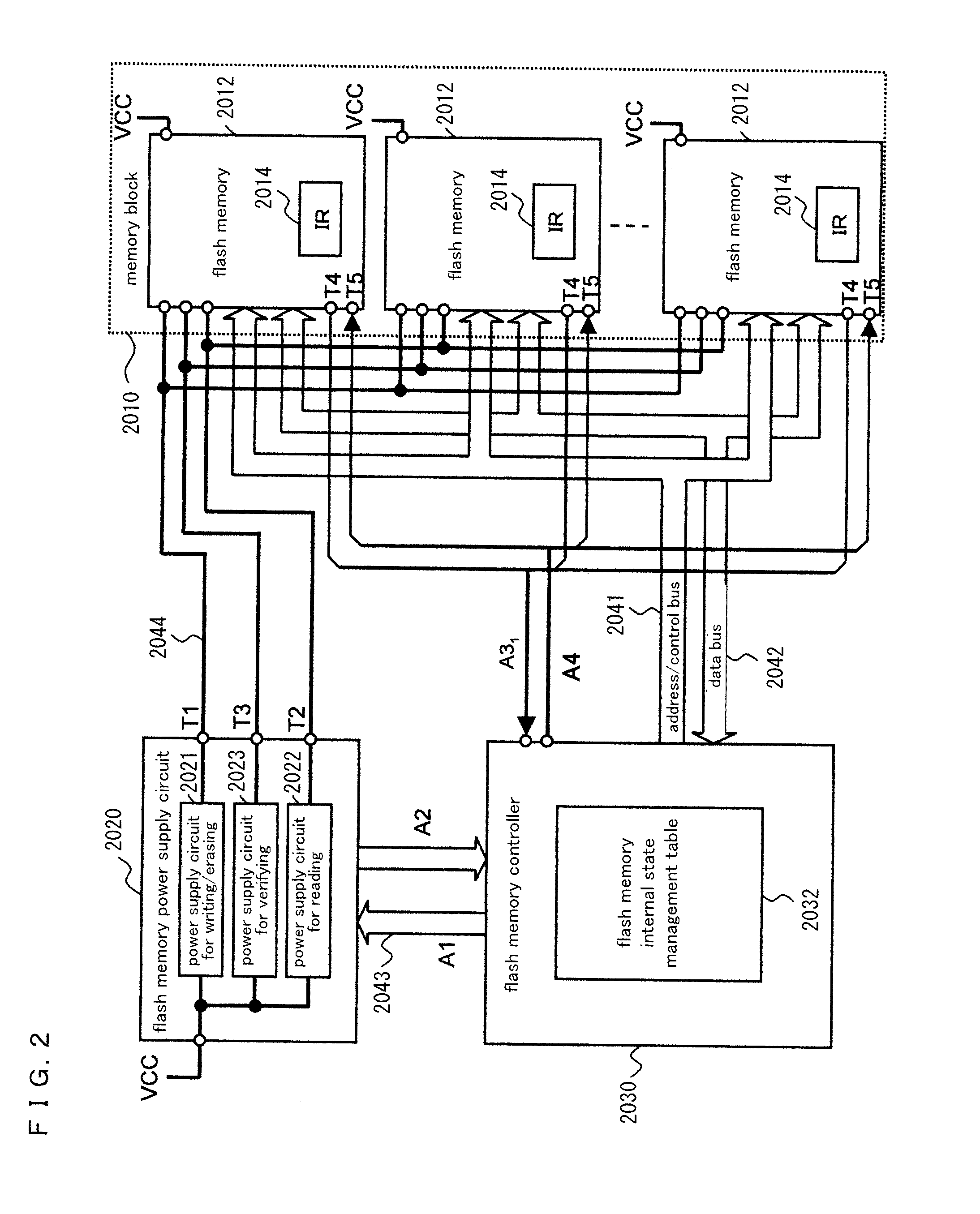
Nonvolatile storage system, power supply circuit for memory system, flash memory, flash memory controller, and nonvolatile semiconductor storage device
ActiveUS20130124888A1Stably execute processReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSemiconductor storage devicesFlash memory controller
Disclosed is a nonvolatile storage system including: a memory block having a plurality of flash memories; a flash memory power supply circuit outside of the memory block; and a flash memory controller. The flash memory power supply circuit has a plurality of types of power supply circuits for process execution, the power supply circuits for process execution generating and supplying power at a plurality of voltage levels needed to execute processes in the flash memories. The flash memory controller monitors changes of the internal states of the flash memories by communicating with the flash memories, thereby controlling the power supply circuits for process execution and the flash memories.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
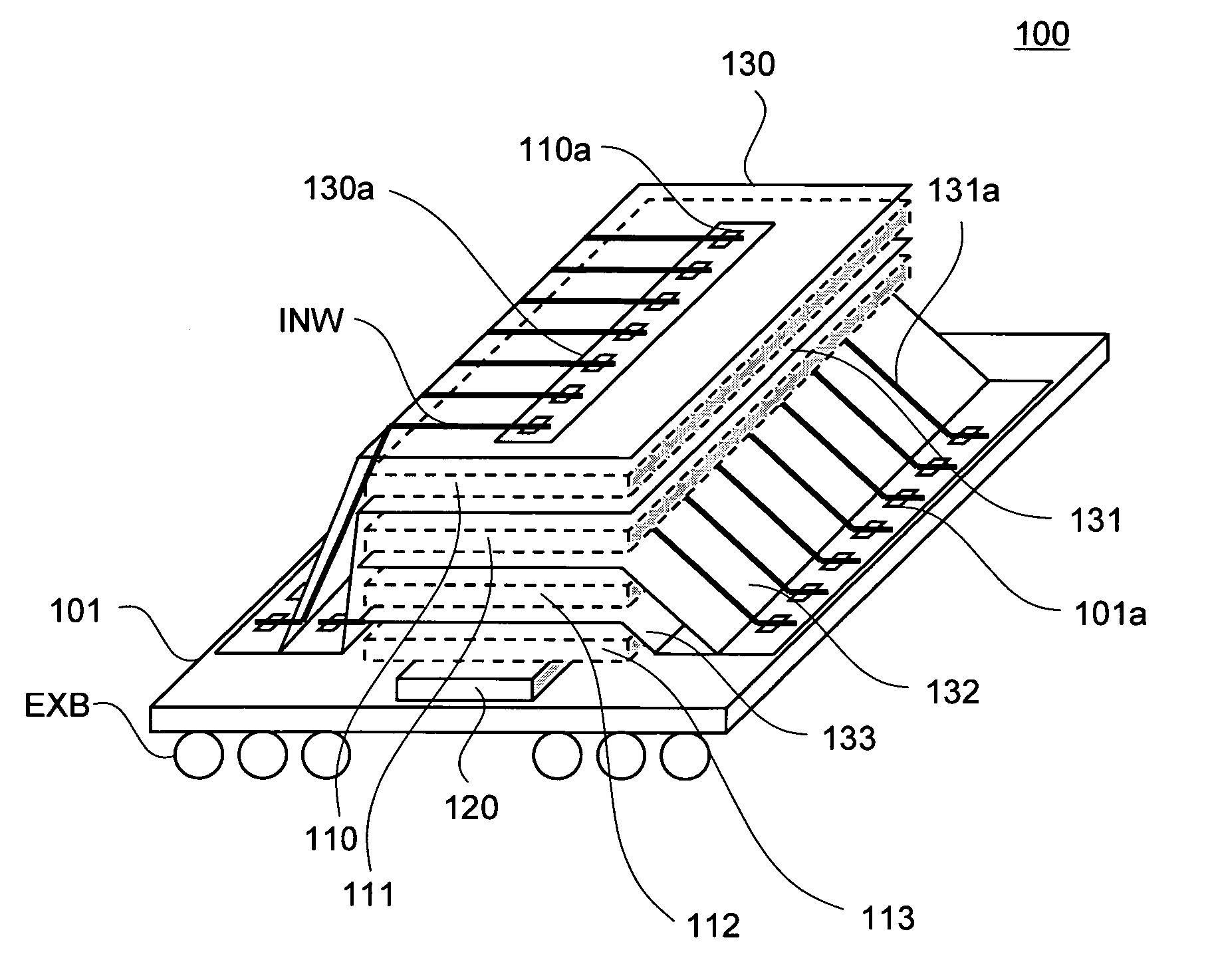
Semiconductor storage device having a plurality of stacked memory chips
ActiveUS7466577B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceAssure compatibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage employs a base substrate (101) having a command / address external terminal group (CA), a data input / output external terminal group (DQ), and a single chip select external terminal (CS), and also comprises a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) mounted on a base substrate (101), each of which can individually carry out read and write operations. The terminals (CA), (DQ), and (CS) are connected to an interface chip (120). The interface chip (120) has a chip select signal generation circuit that can individually activate a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) on the basis of an address signal fed by way of the terminal (CA) and on the basis of a chip select signal fed by way of the terminal (CS).
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings to each of which a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells are connected in series. Each of the memory strings includes first semiconductor layers each having a pair of columnar portions extending in a vertical direction with respect to a substrate and a coupling portion formed to couple the lower ends of the pair of columnar portions; a charge storage layer formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions; and first conductive layers formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions and the charge storage layer. The first conductive layers function as gate electrodes of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
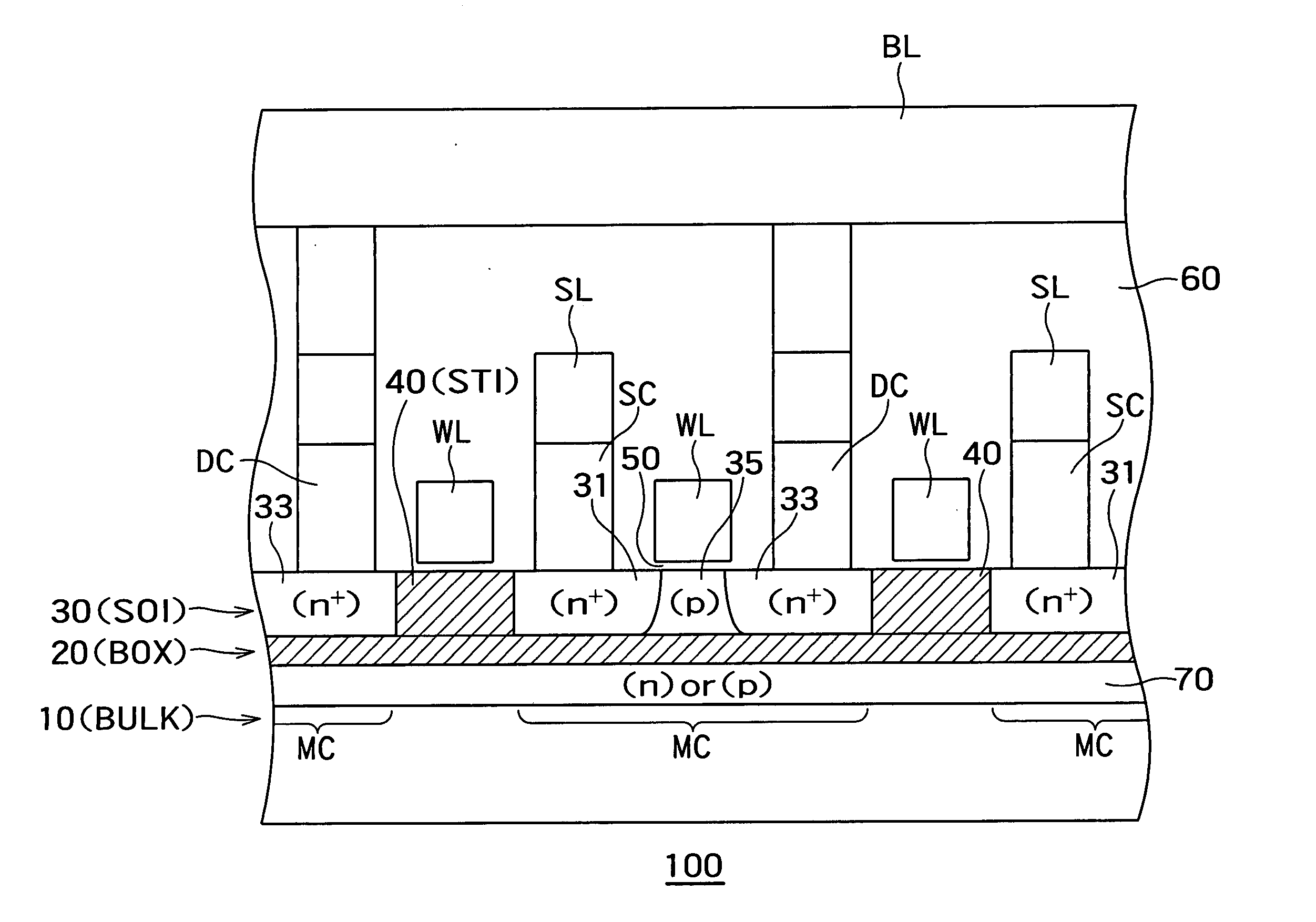
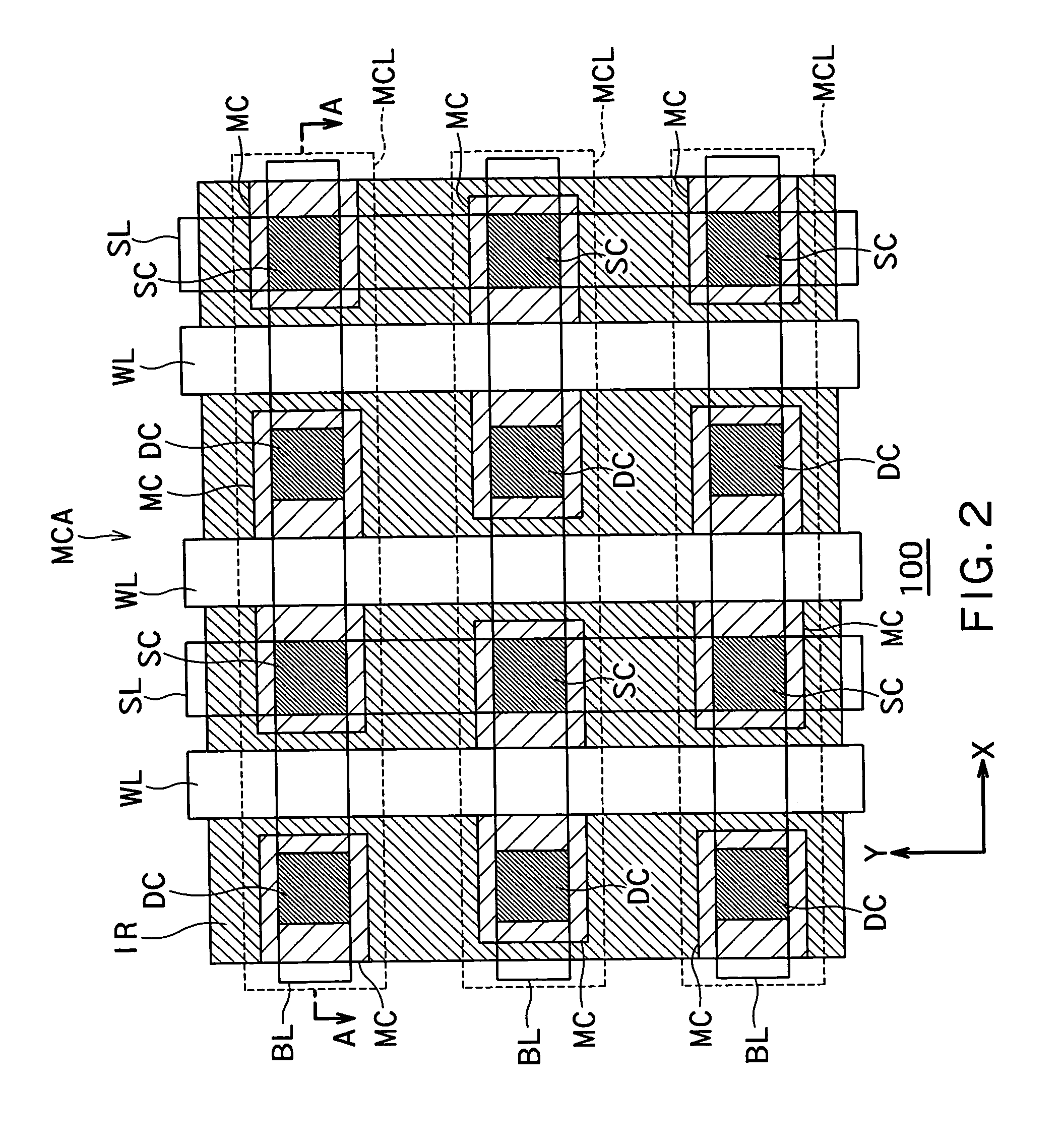
Semiconductor storage device
A semiconductor storage device comprises a semiconductor substrate; an insulating layer formed on the semiconductor substrate; a first semiconductor layer formed on the insulating layer and insulated from the semiconductor substrate; memory cells each having a source region of a first conduction type and a drain region of the first conduction type both formed in the first semiconductor layer, and having a body of a second conduction type formed in the first semiconductor layer between the source region and the drain region, said memory cells being capable of storing data by accumulating or releasing electric charge in or from their respective body regions; memory cell lines each including a plurality of said memory cells aligned in the channel lengthwise direction; and a memory cell array including a plurality of said memory cell lines aligned in a channel widthwise direction of the memory cells, wherein said memory cells on a common memory cell line are aligned to uniformly orient the directions from their source regions to the drain regions whereas directions of said memory cells from their source regions to the drain regions on said memory cell line are opposite from those of memory cells on neighboring said memory cell lines.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
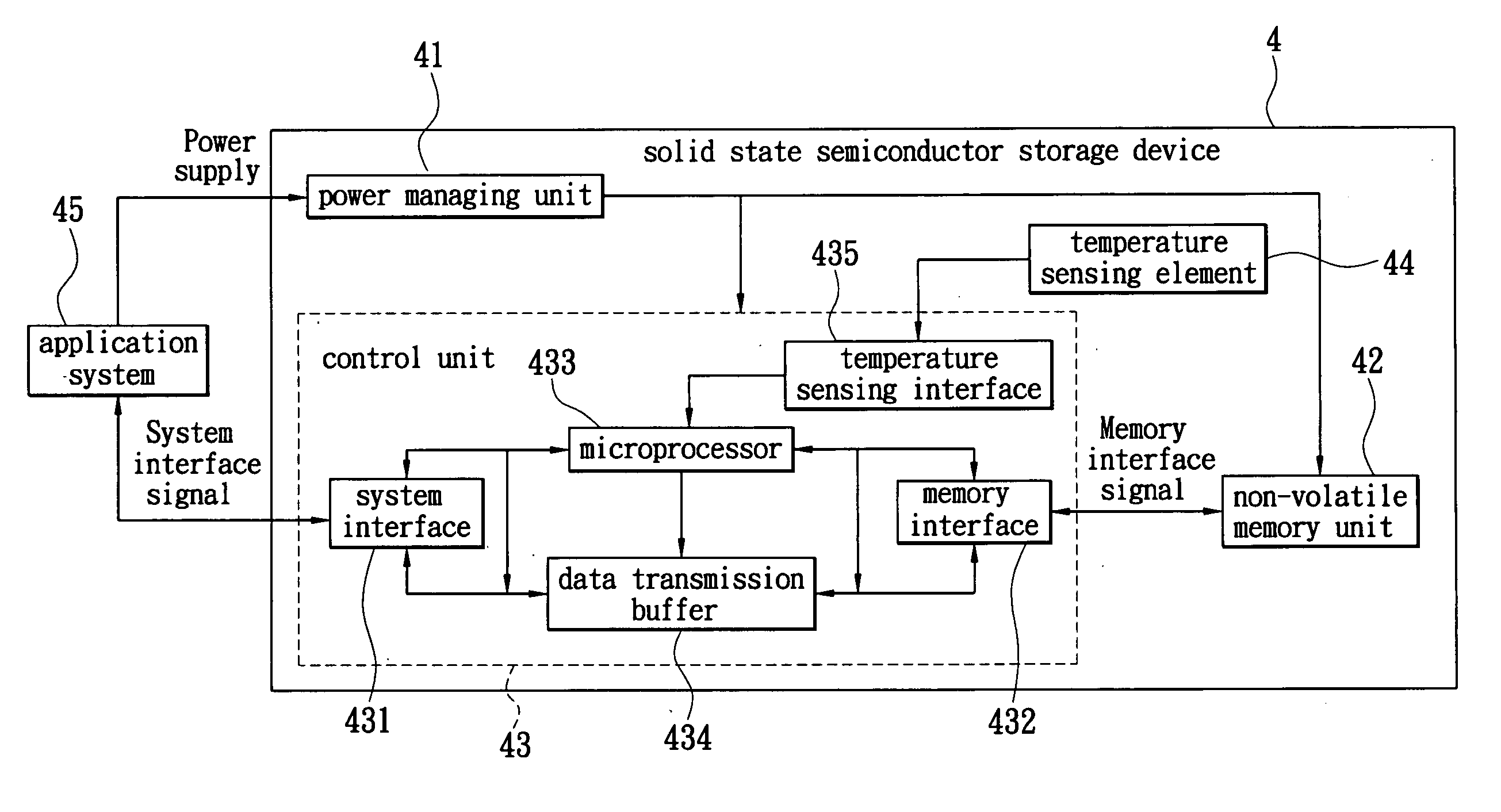
Solid state semiconductor storage device with temperature control function, application system thereof and control element thereof
ActiveUS20090091996A1Effective temperature controlDigital storageTemperature controlSemiconductor storage devices
A solid state semiconductor storage device with temperature control function comprises a non-volatile memory unit, a temperature sensing element, and a control unit. The temperature sensing element is used for sensing the operation temperature of the solid state semiconductor storage device so as to provide a temperature sensing signal to the control unit. According to the temperature sensing signal, the control unit controls the operation mode of the solid state semiconductor storage device for achieving the function of temperature control.
Owner:ADATA
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100171162A1TransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor storage devices
Each of memory strings comprising: a first semiconductor layer having a pair of columnar portions extending in a vertical direction to a substrate and a joining portion formed to join lower ends of the pair of columnar portions; an electric charge accumulation layer formed to surround a side surface of the first semiconductor layer; and a first conductive layer formed to surround a side surface of the electric charge accumulation layer. The columnar portions are aligned at a first pitch in a first direction orthogonal to the vertical direction, and arranged in a staggered pattern at a second pitch in a second direction orthogonal to the vertical and first directions. The first conductive layers are configured to be arranged at the first pitch in the first direction, and extend to curve in a wave-like fashion in the second direction along the staggered-pattern arrangement.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com