Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
670 results about "Dram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
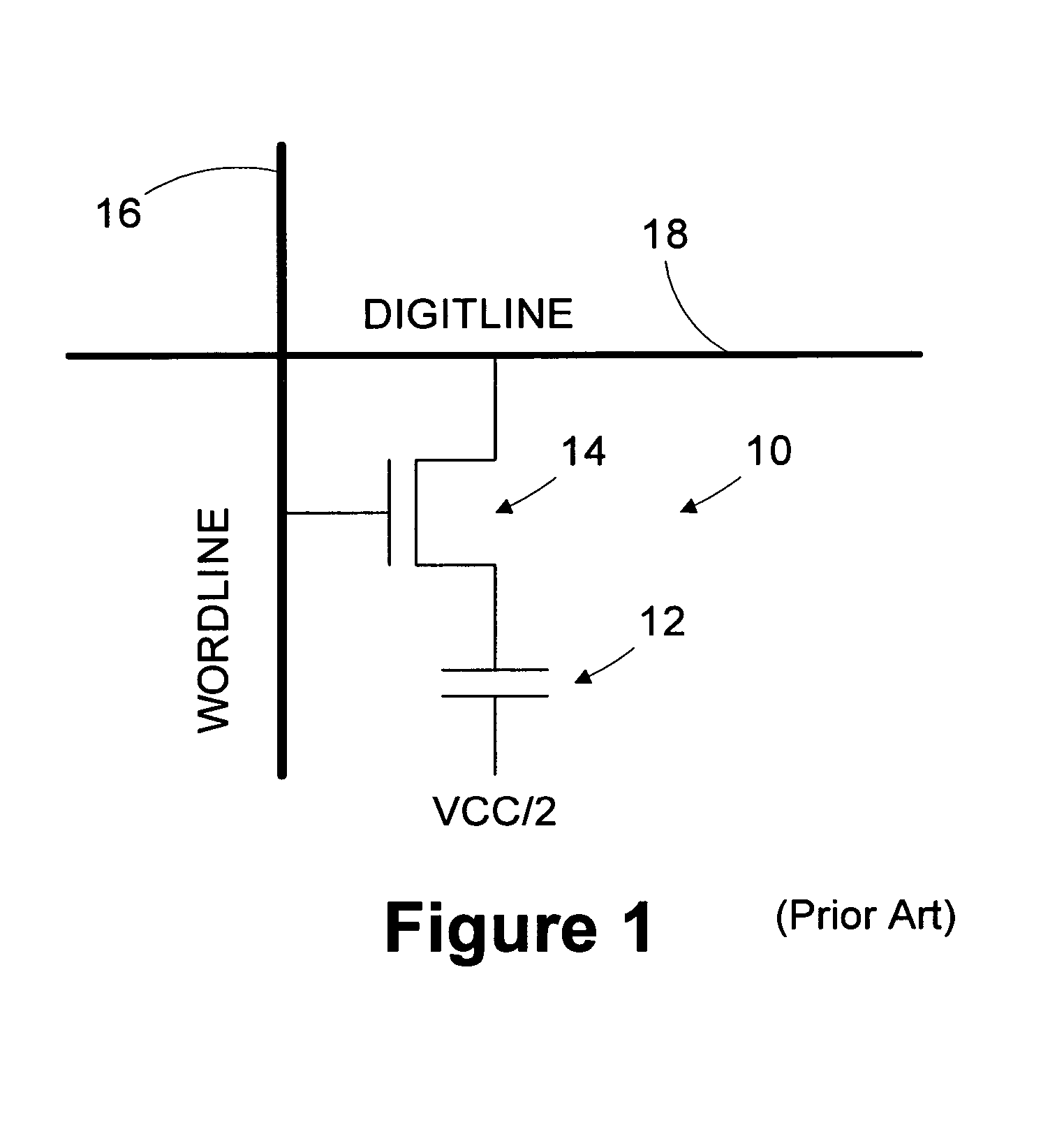
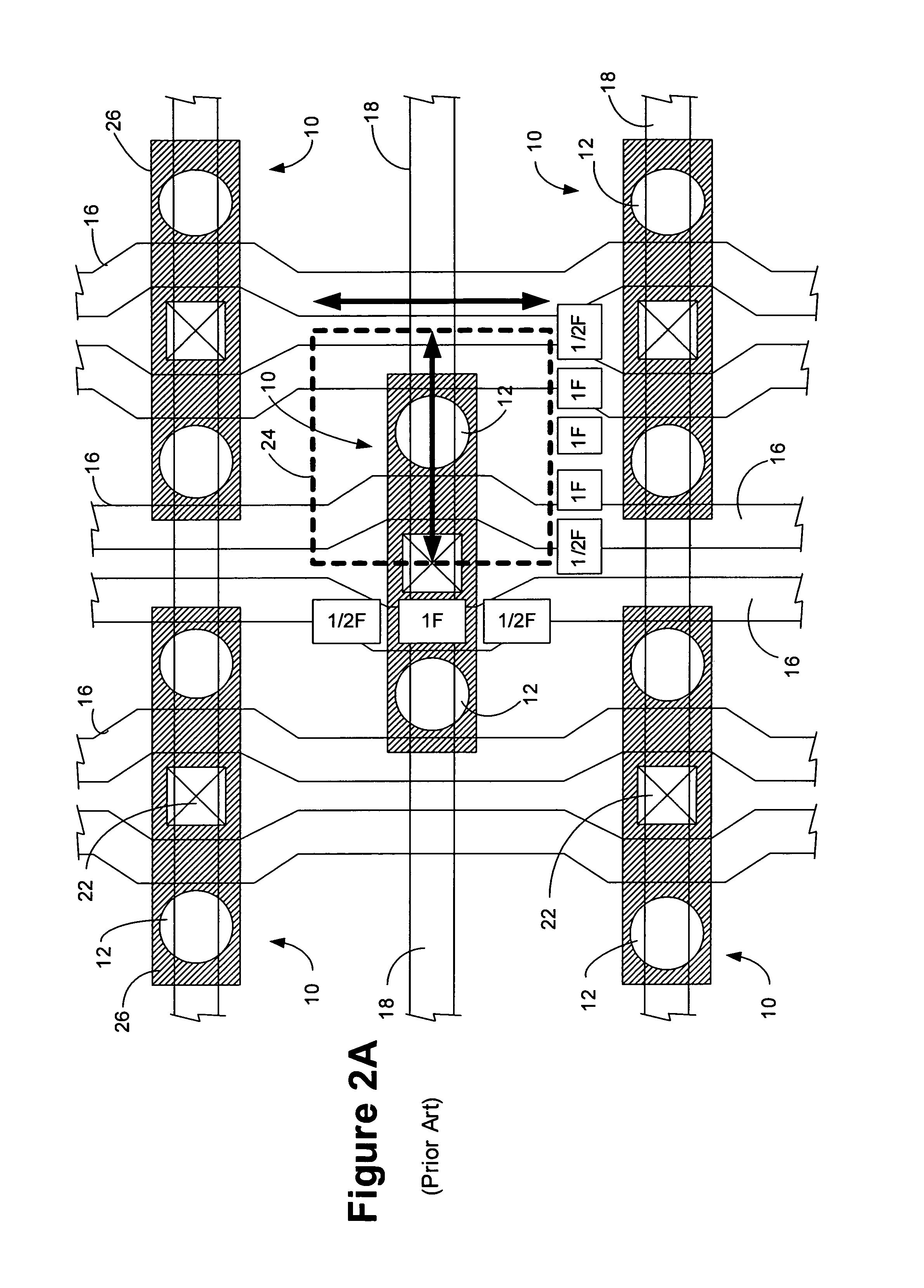
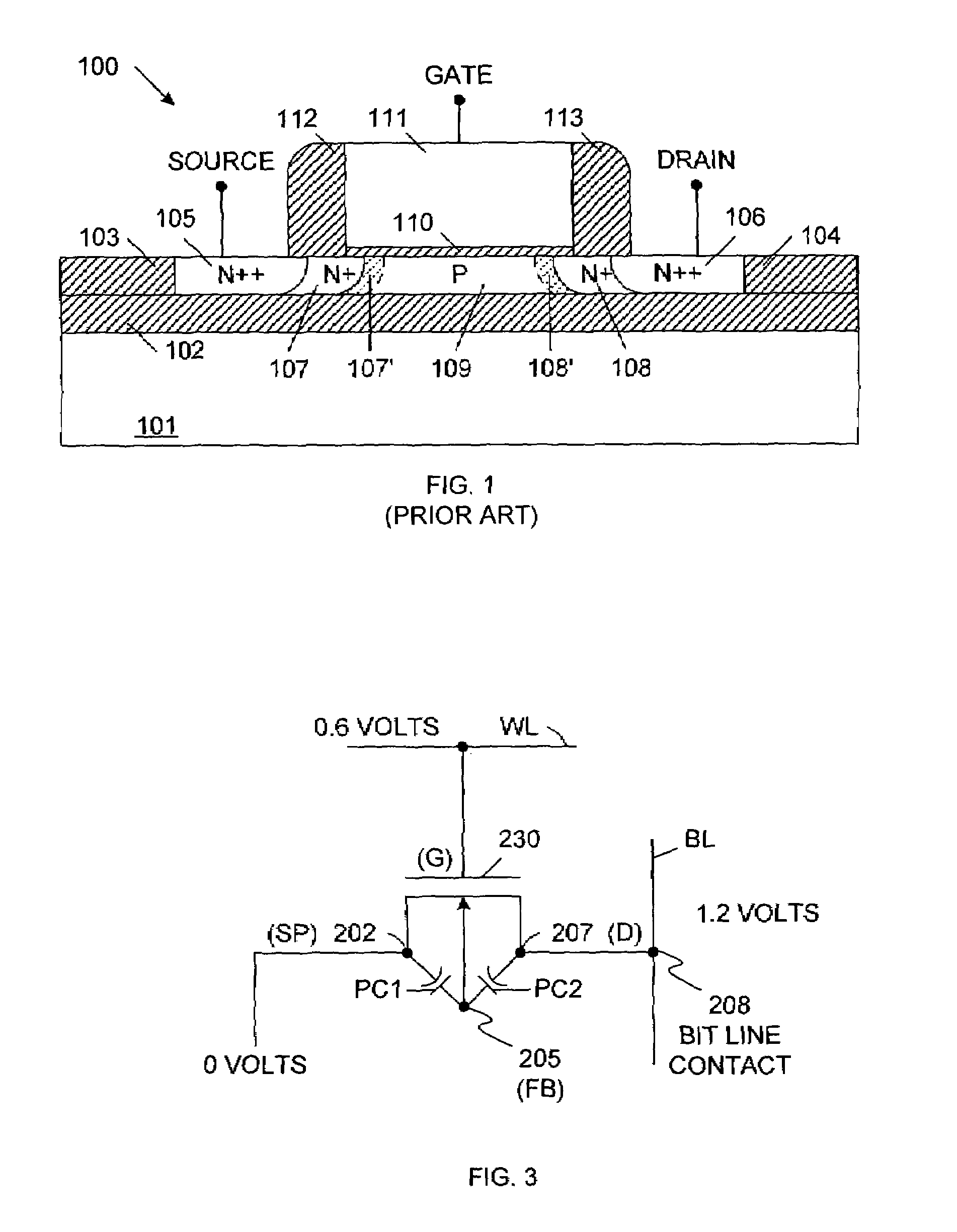
The dram (alternative British spelling drachm; apothecary symbol ʒ or ℨ; abbreviated dr) is a unit of mass in the avoirdupois system, and both a unit of mass and a unit of volume in the apothecaries' system. It was originally both a coin and a weight in ancient Greece. The unit of volume is more correctly called a fluid dram, fluid drachm, fluidram or fluidrachm (abbreviated fl dr, ƒ 3, or fʒ).
Processor Arrays Made of Standard Memory Cells
Owner:GSI TECH
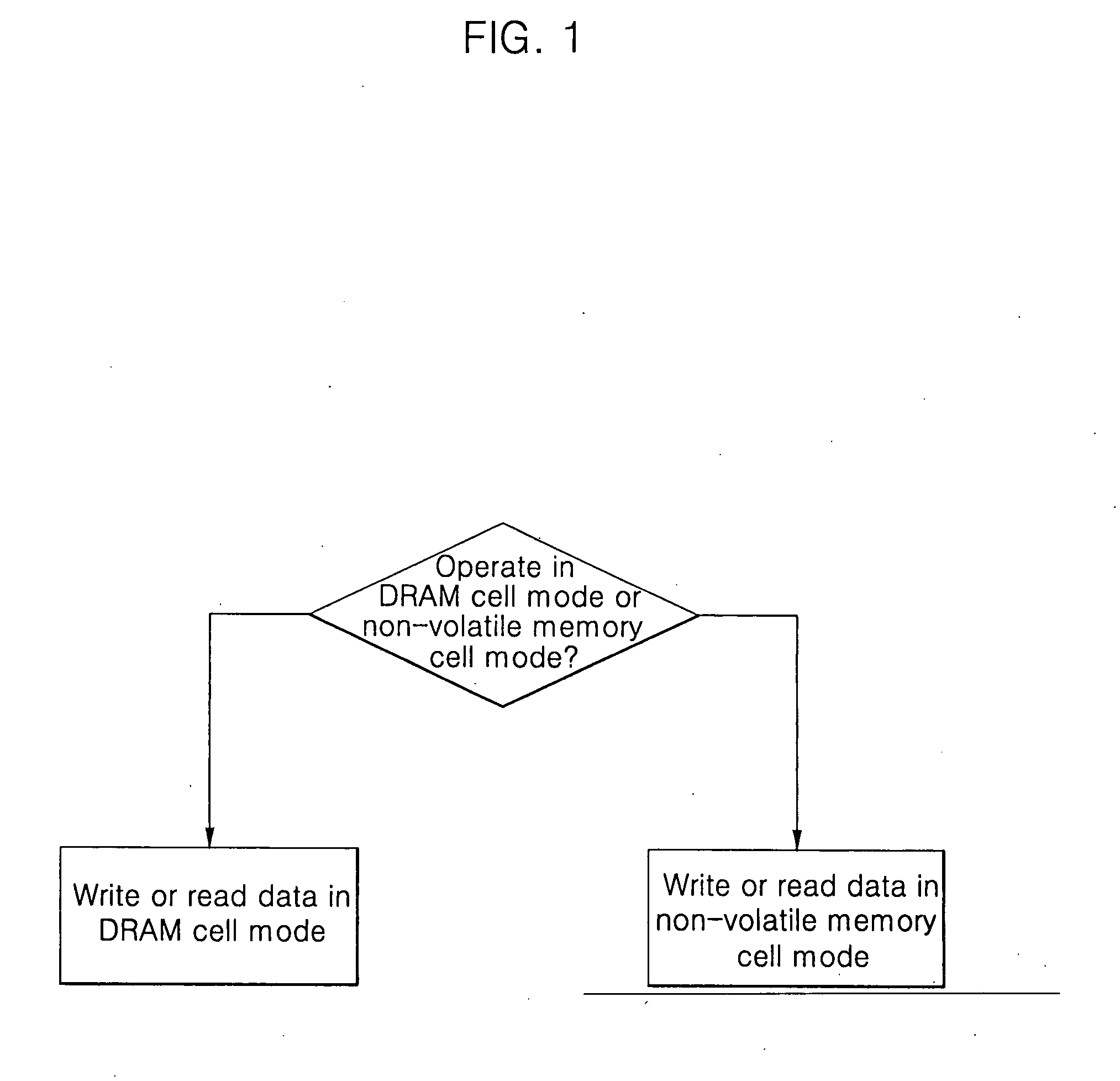
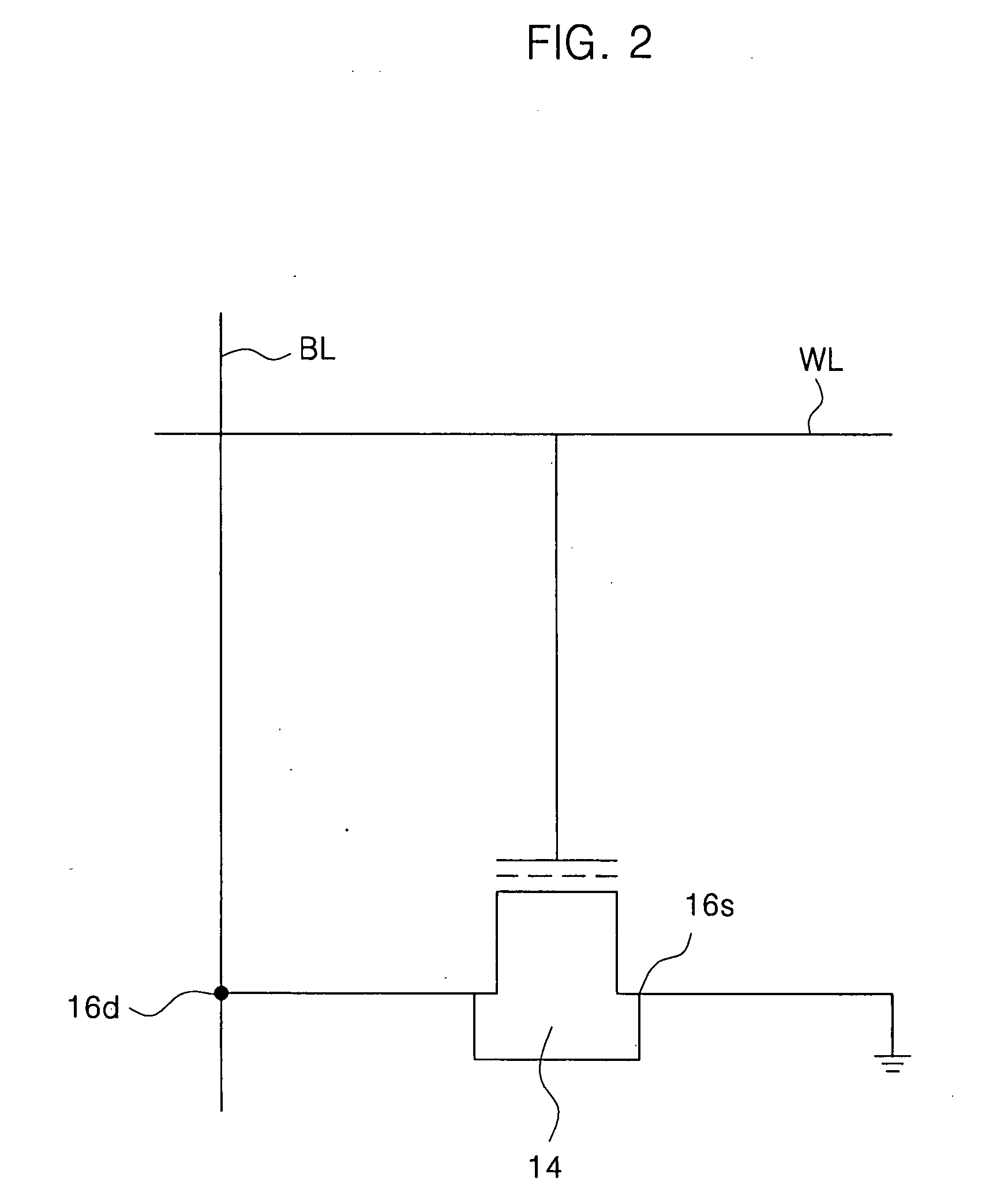
Semiconductor memory device having DRAM cell mode and non-volatile memory cell mode and operation method thereof
A semiconductor memory device may have a DRAM cell mode and a non-volatile memory cell mode without a capacitor, including multiple transistors arranged in an array and having floating bodies, word lines connected to gate electrodes of the transistors, bit lines at a first side of the gate electrodes connected to drains of the transistors, source lines at a second side of the gate electrodes, different from the first side, and connected to sources of the transistors on the semiconductor substrate, and charge storage regions between the gate electrodes and the floating bodies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
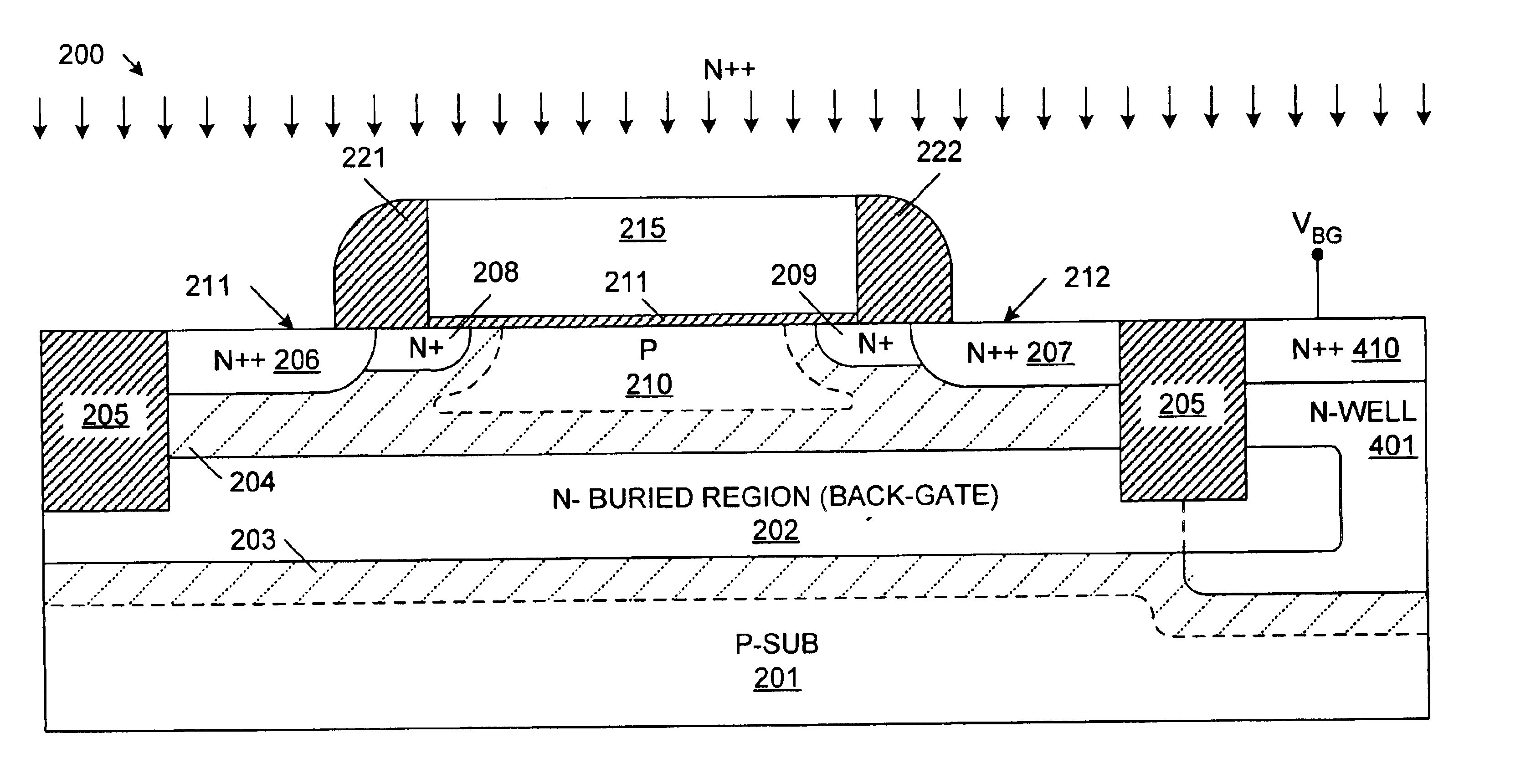
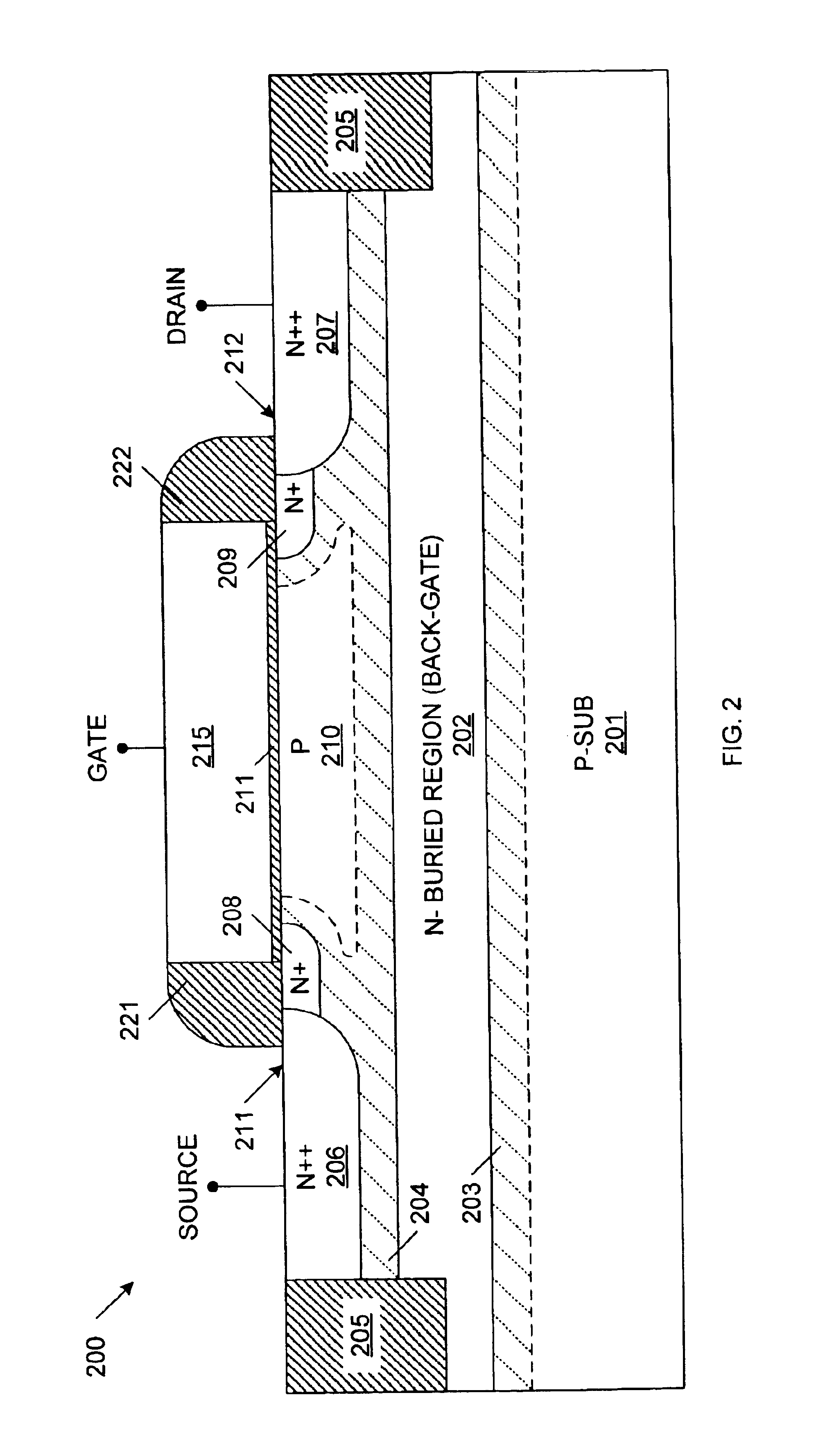
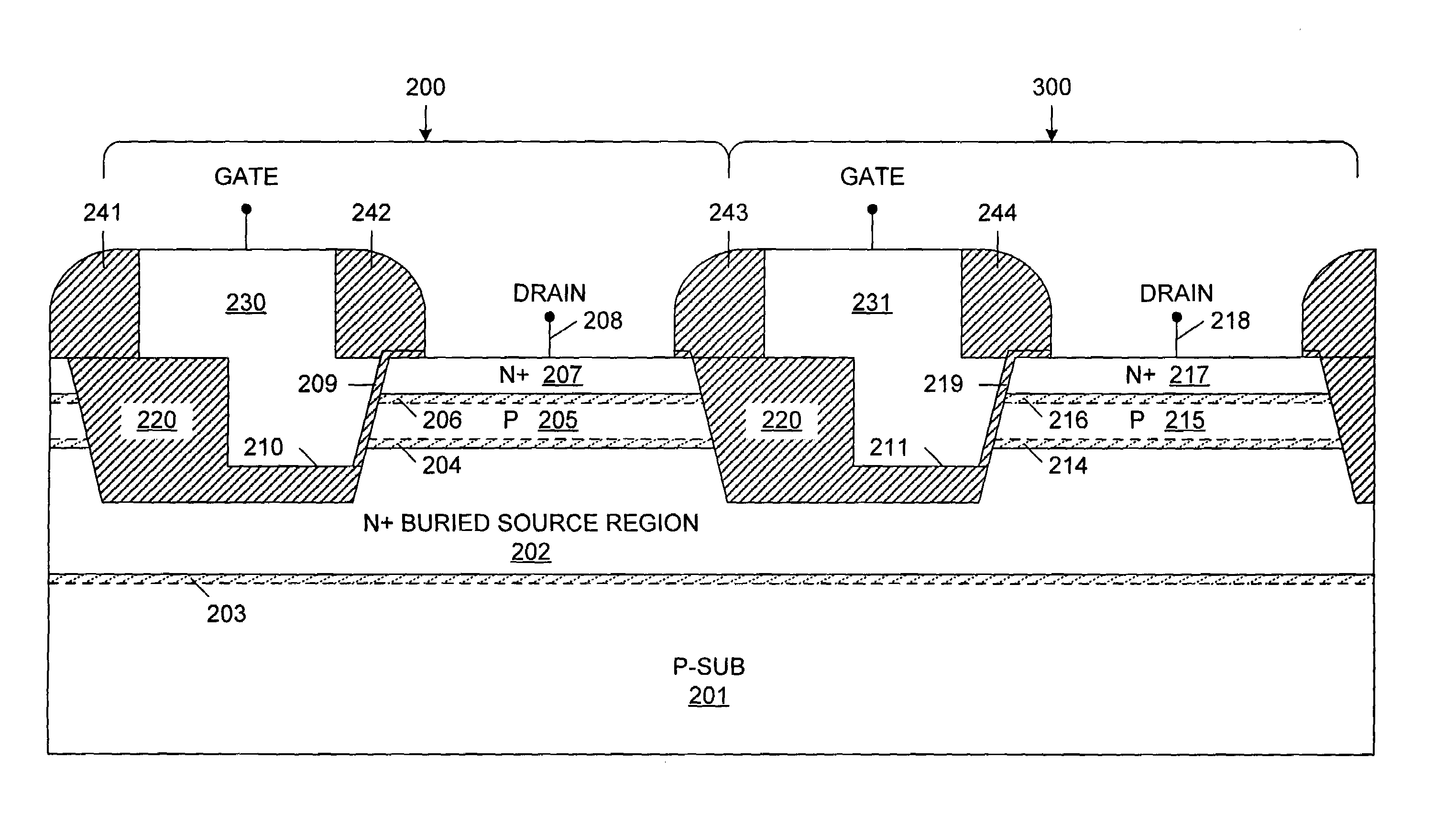
Method of fabricating a one transistor floating-body DRAM cell in bulk CMOS process with electrically isolated charge storage region
InactiveUS6913964B2Limiting leakage currentEnsure adequate isolationTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
A one-transistor, floating-body (1T / FB) dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell is provided that includes a field-effect transistor fabricated using a process compatible with a standard CMOS process. The field-effect transistor includes a source region and a drain region of a first conductivity type and a floating body region of a second conductivity type, opposite the first conductivity type, located between the source region and the drain region. A buried region of the first conductivity type is located under the source region, drain region and floating body region. The buried region helps to form a depletion region, which is located between the buried region and the source region, the drain region and the floating body region. The floating body region is thereby isolated by the depletion region. A bias voltage can be applied to the buried region, thereby controlling leakage currents in the 1T / FB DRAM cell.
Owner:MOSYS INC
One transistor DRAM cell structure and method for forming
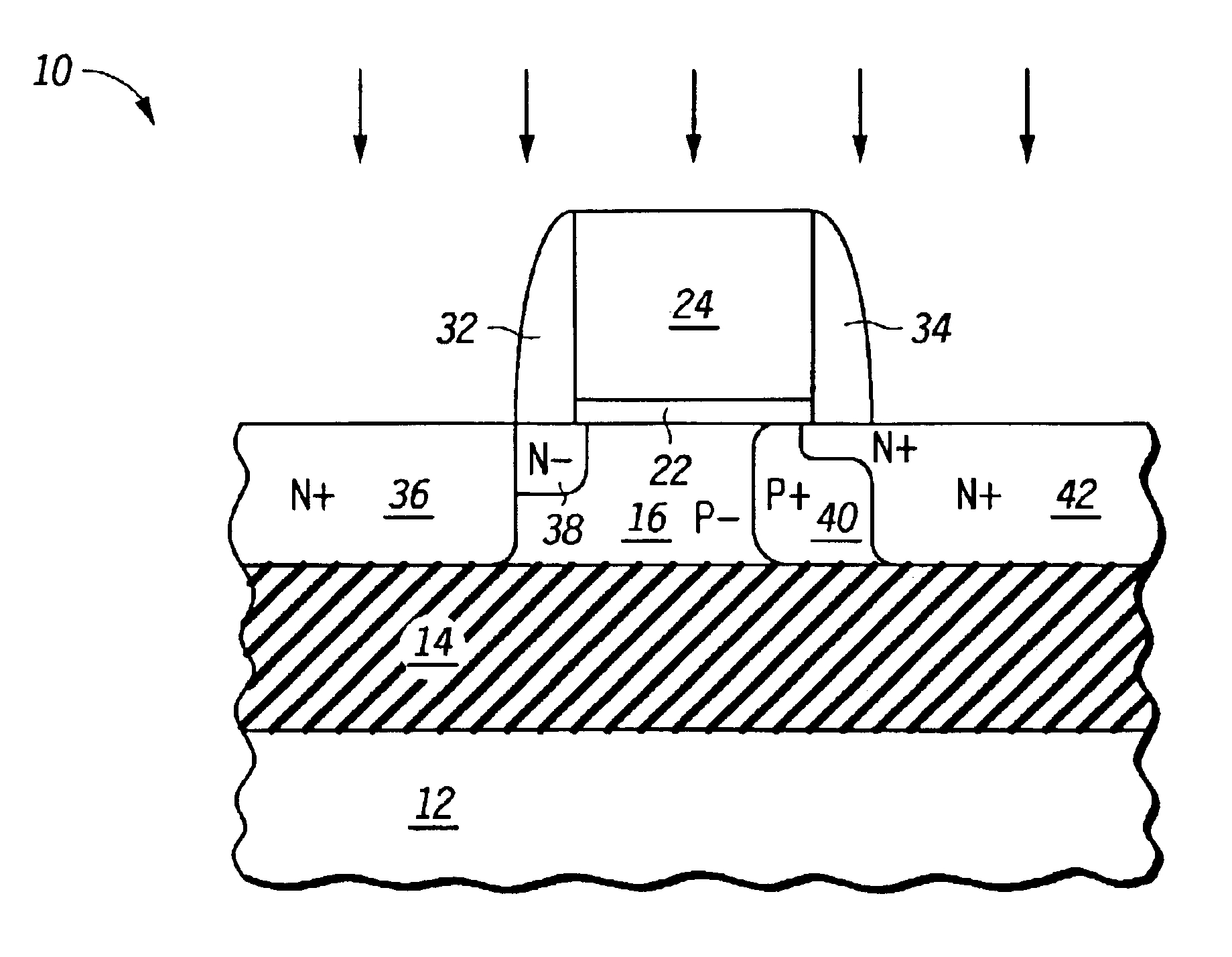
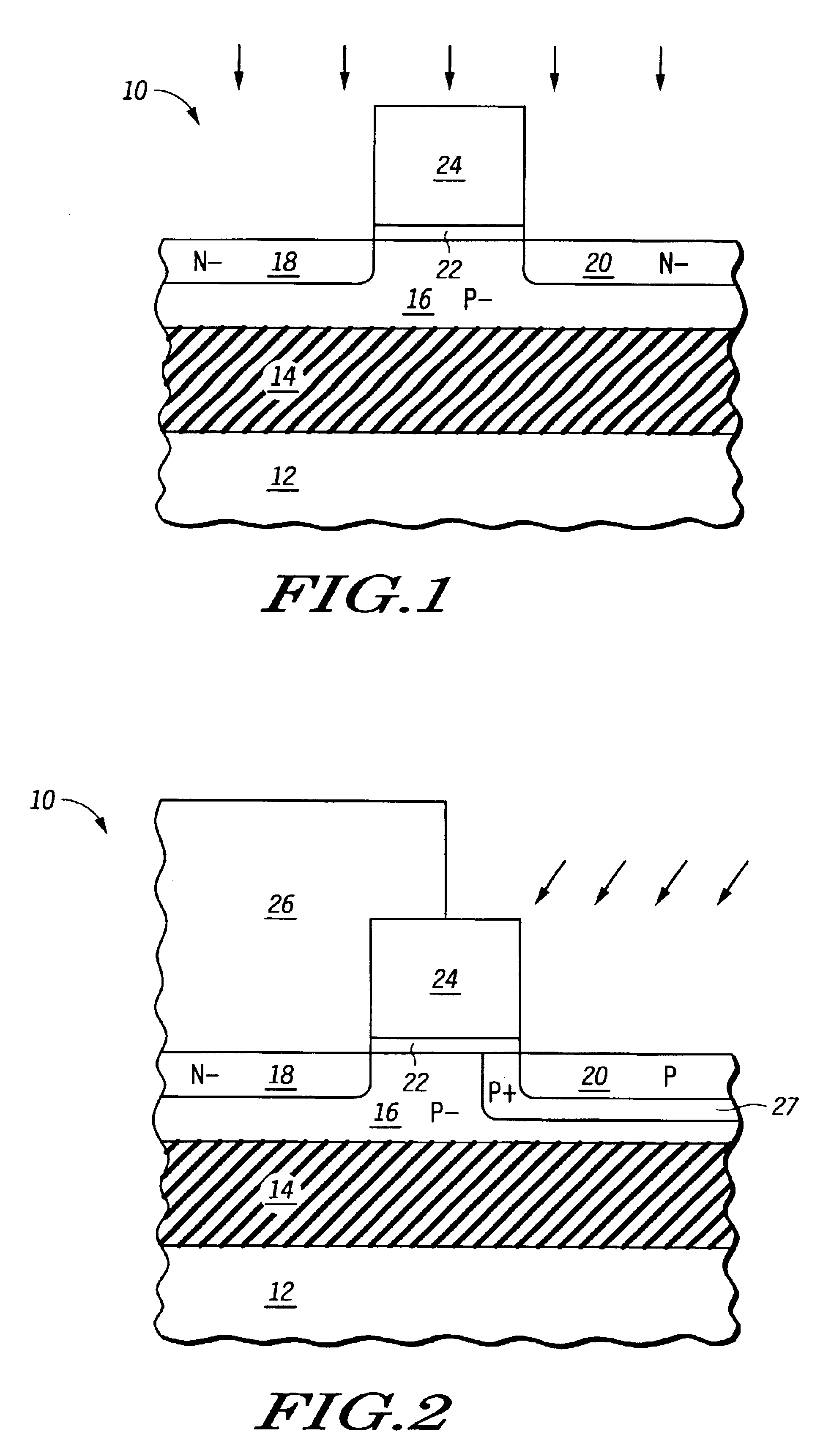
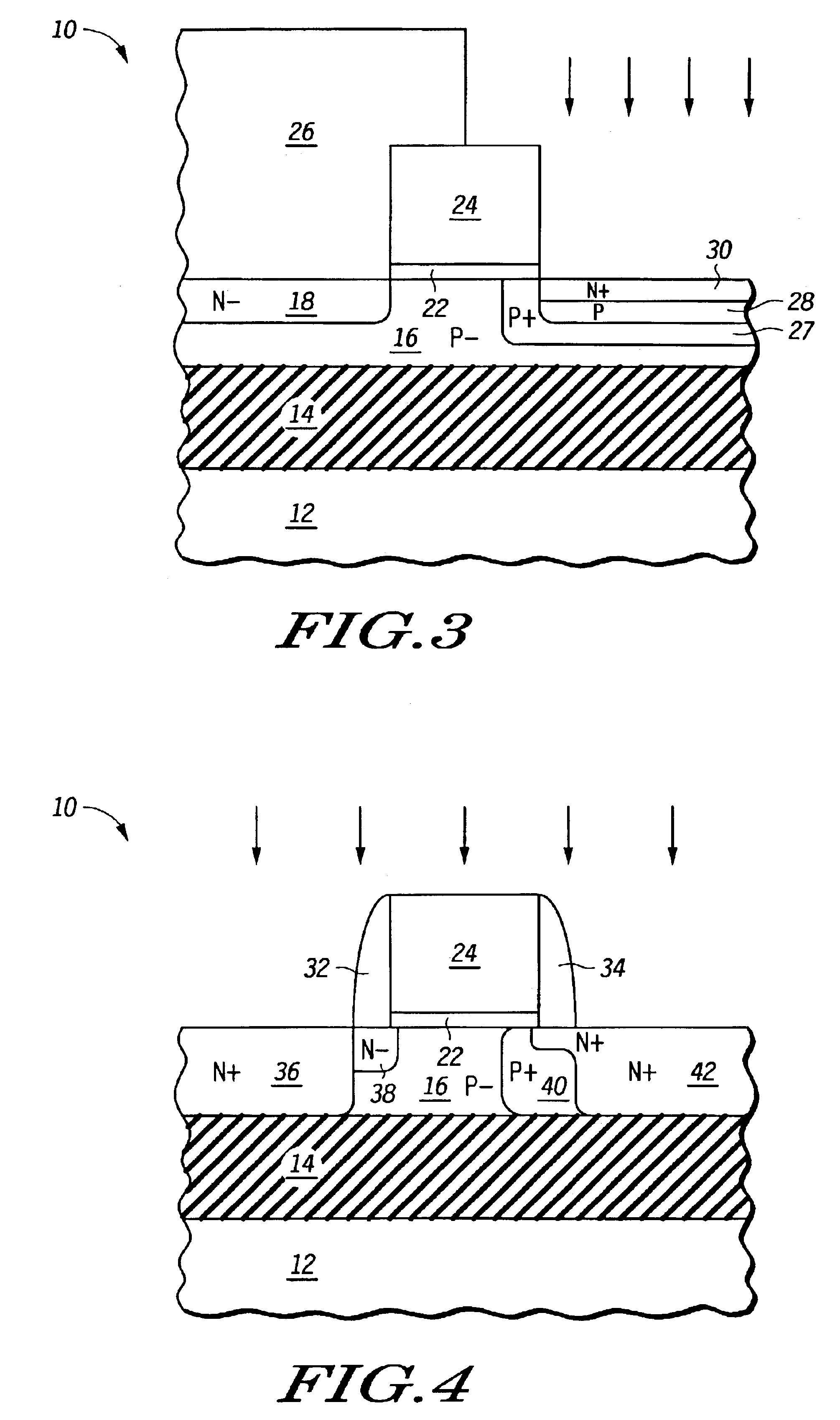
A single transistor DRAM cell is formed in a SOI substrate so that the DRAM cells are formed in bodies that are electrically isolated from each other. Each cell has doped regions that act as source and drain contacts. Between the drain contact and the body is a region, which aids in impact ionization and thus electron / hole formation during programming that is the same conductivity type as the body but of a higher concentration than the body. Adjacent to the source contact and to the body is a region, which aids in diode current during erase, that is the same conductivity type as the source contact but of a lower concentration than the source contact.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
DRAM controller for graphics processing operable to enable/disable burst transfer
ActiveUS7562184B2Reduce in quantityReduce overheadMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsComputer science
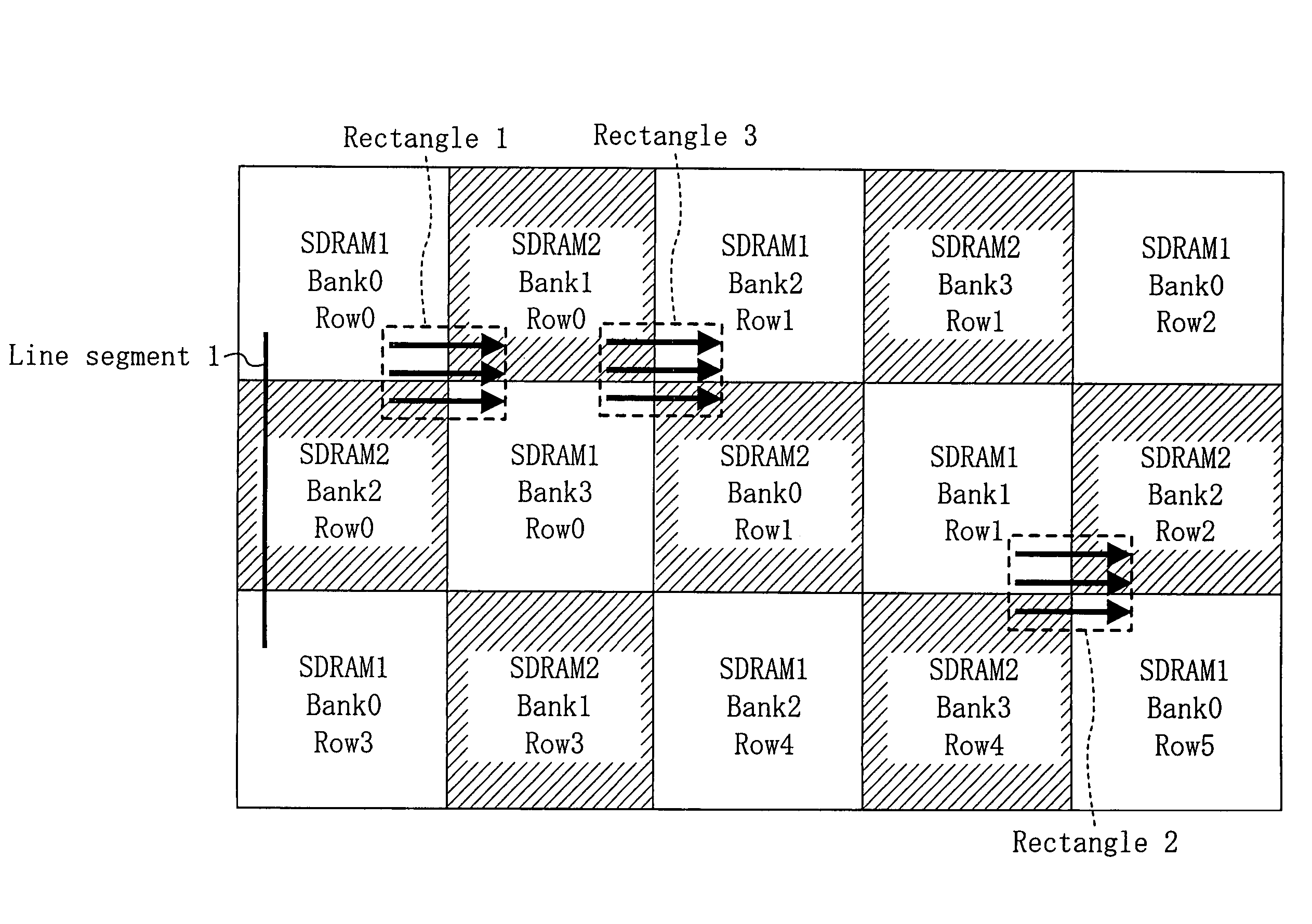
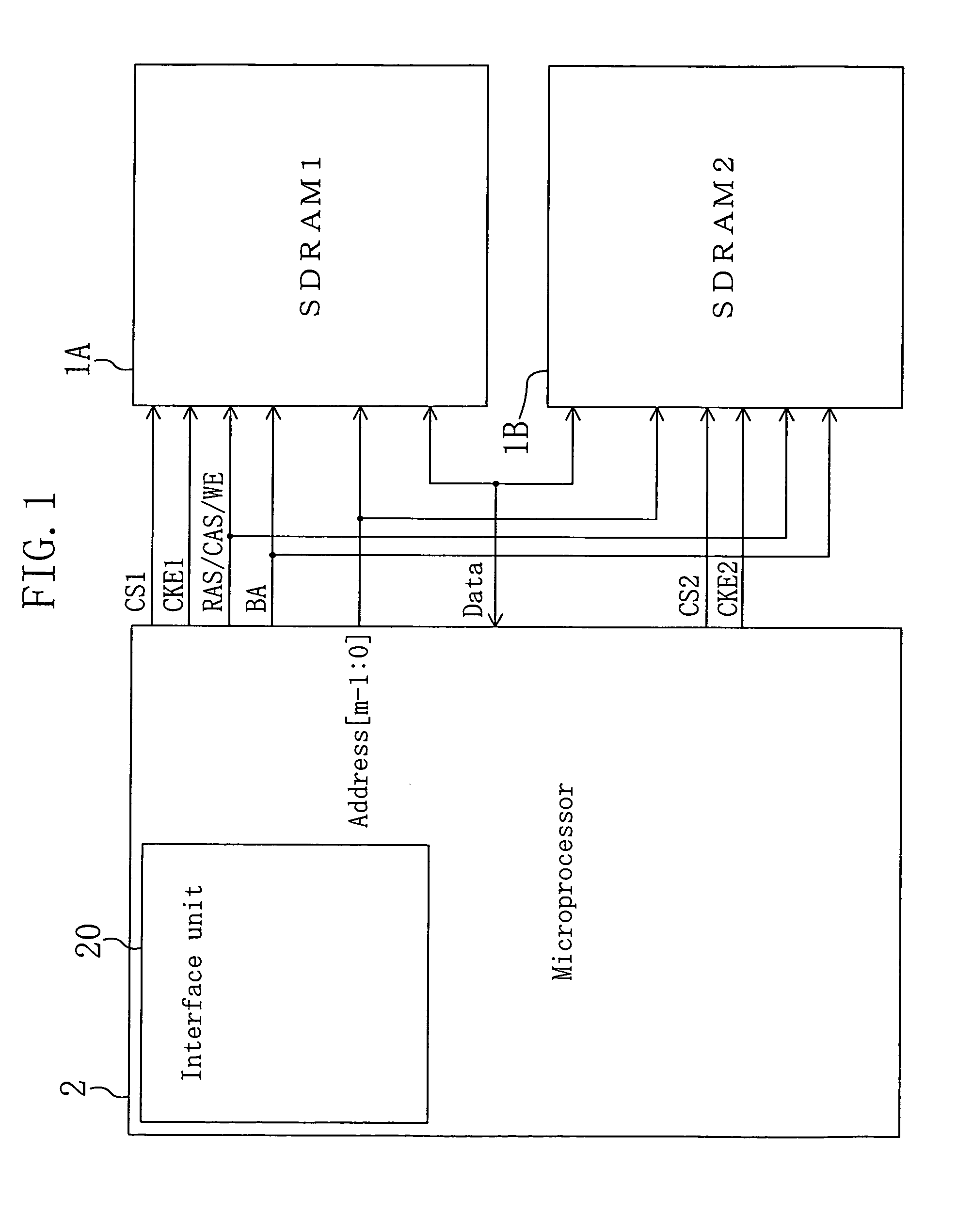
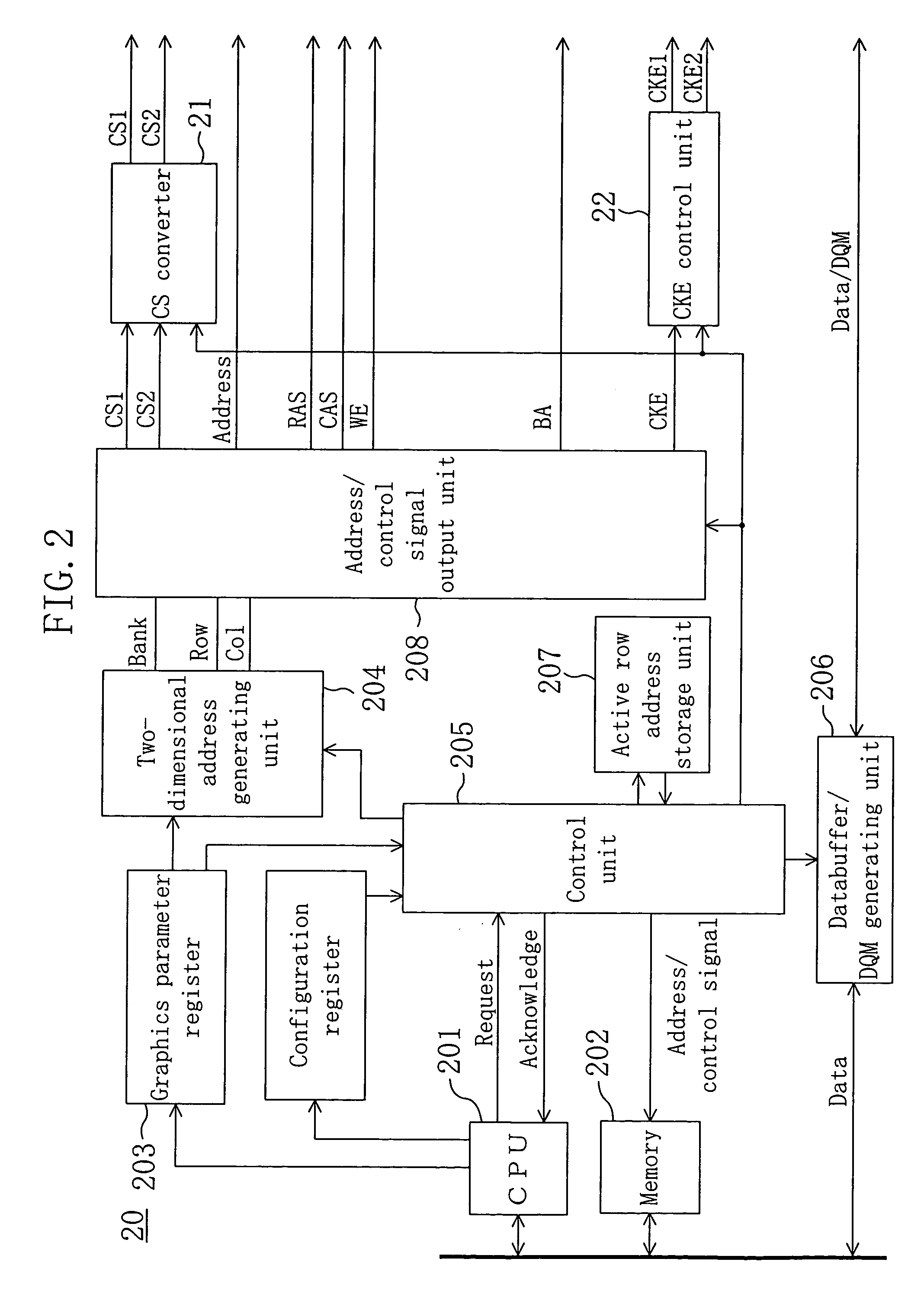
An interface unit 20 assigns different SDRAMs 1 and 2 to adjacent drawing blocks in a frame-buffer area. In processing that extends across the adjacent drawing blocks, active commands, for example, are issued alternately to the SDRAMs 1 and 2 to reduce waiting cycles resulting from the issue interval restriction. Furthermore, since individual clock enable signals CKE1 and CKE2 are output to the SDRAMs 1 and 2 so that burst transfers of the SDRAMs 1 and 2 can be stopped individually, no cycle is necessary to stop the burst transfers.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
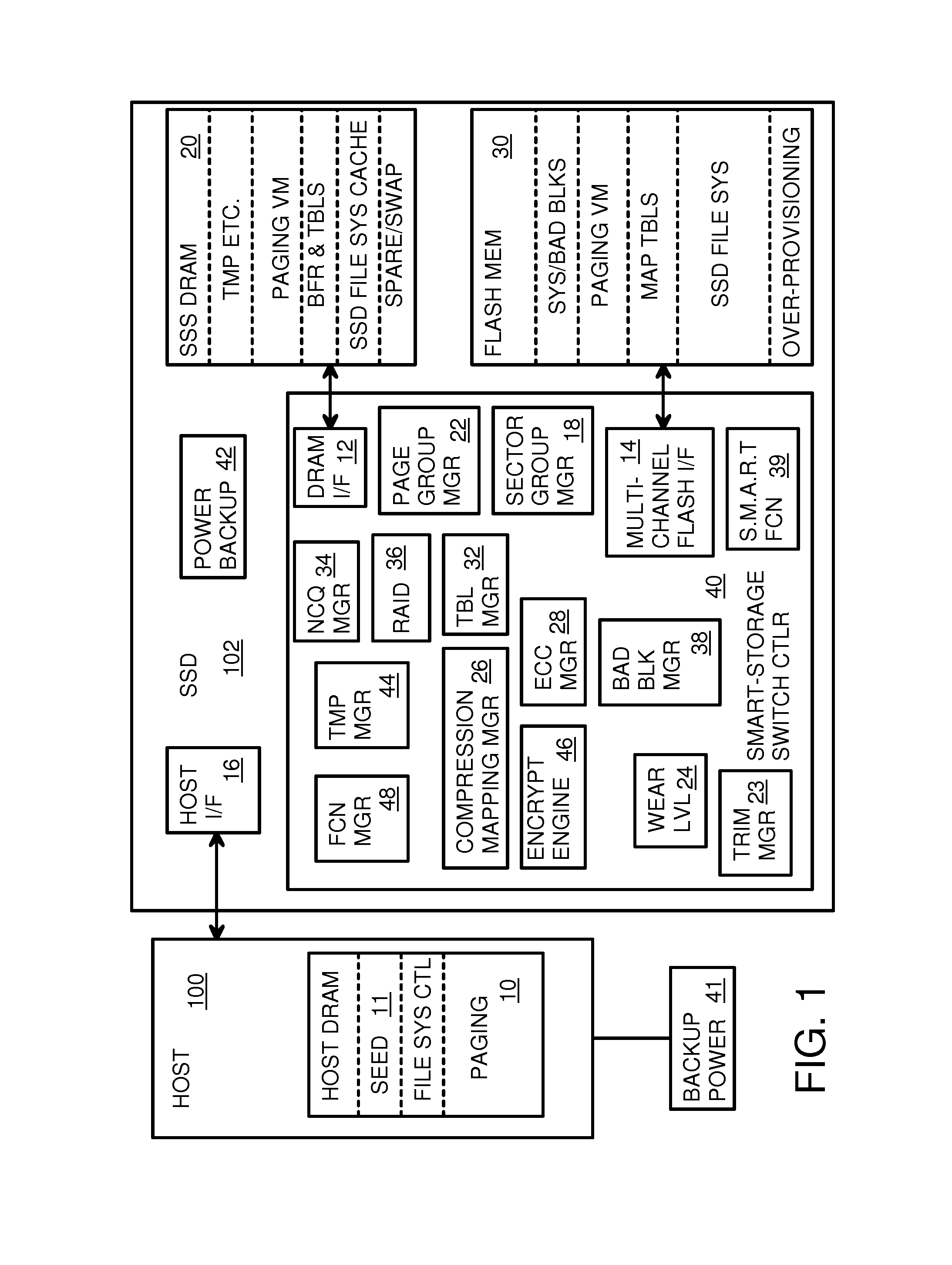
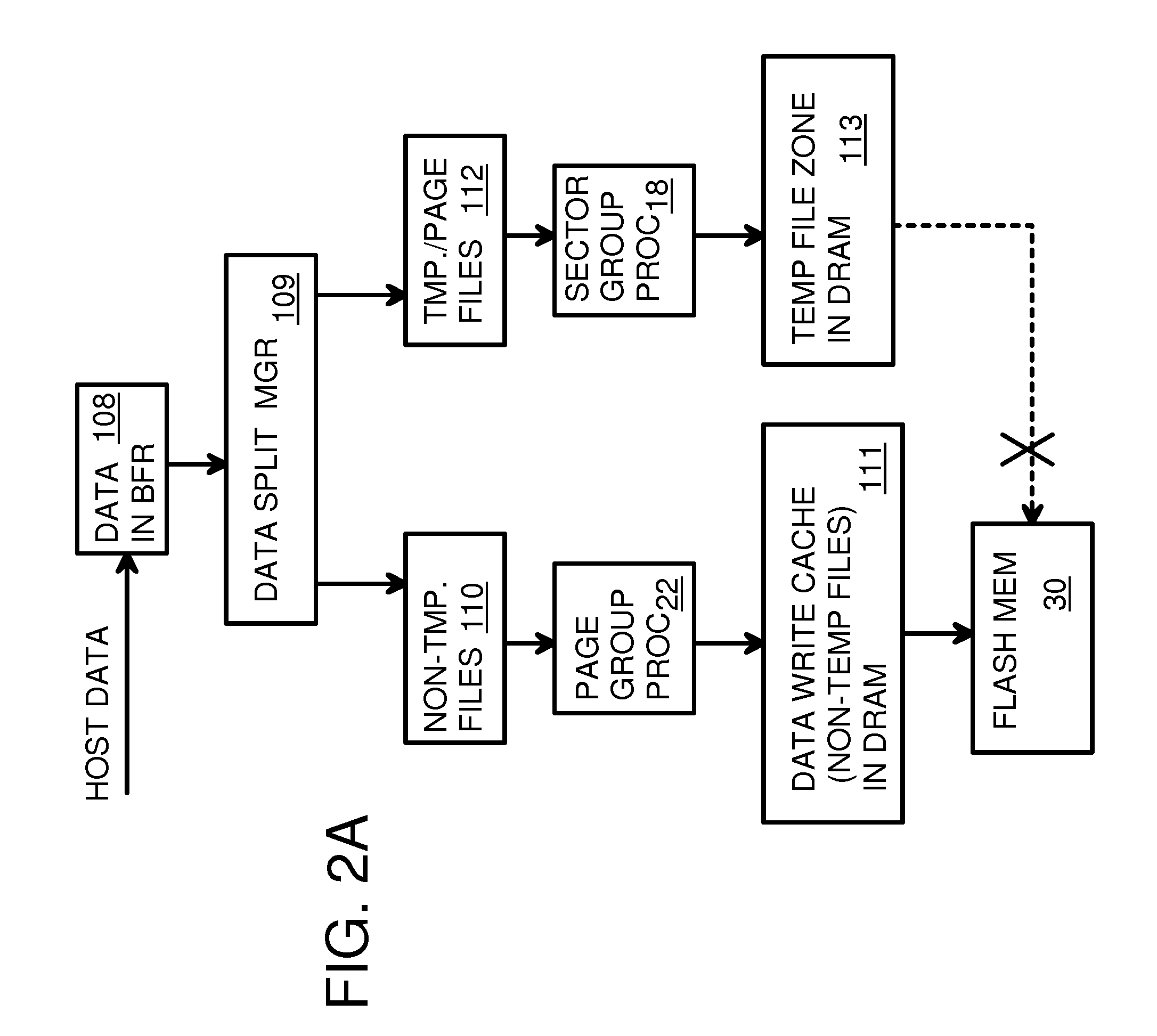
Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) and Diversion of Temp Files for Reduced Flash Wear of a Super-Endurance Solid-State Drive
ActiveUS20150106556A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFilename extensionData file
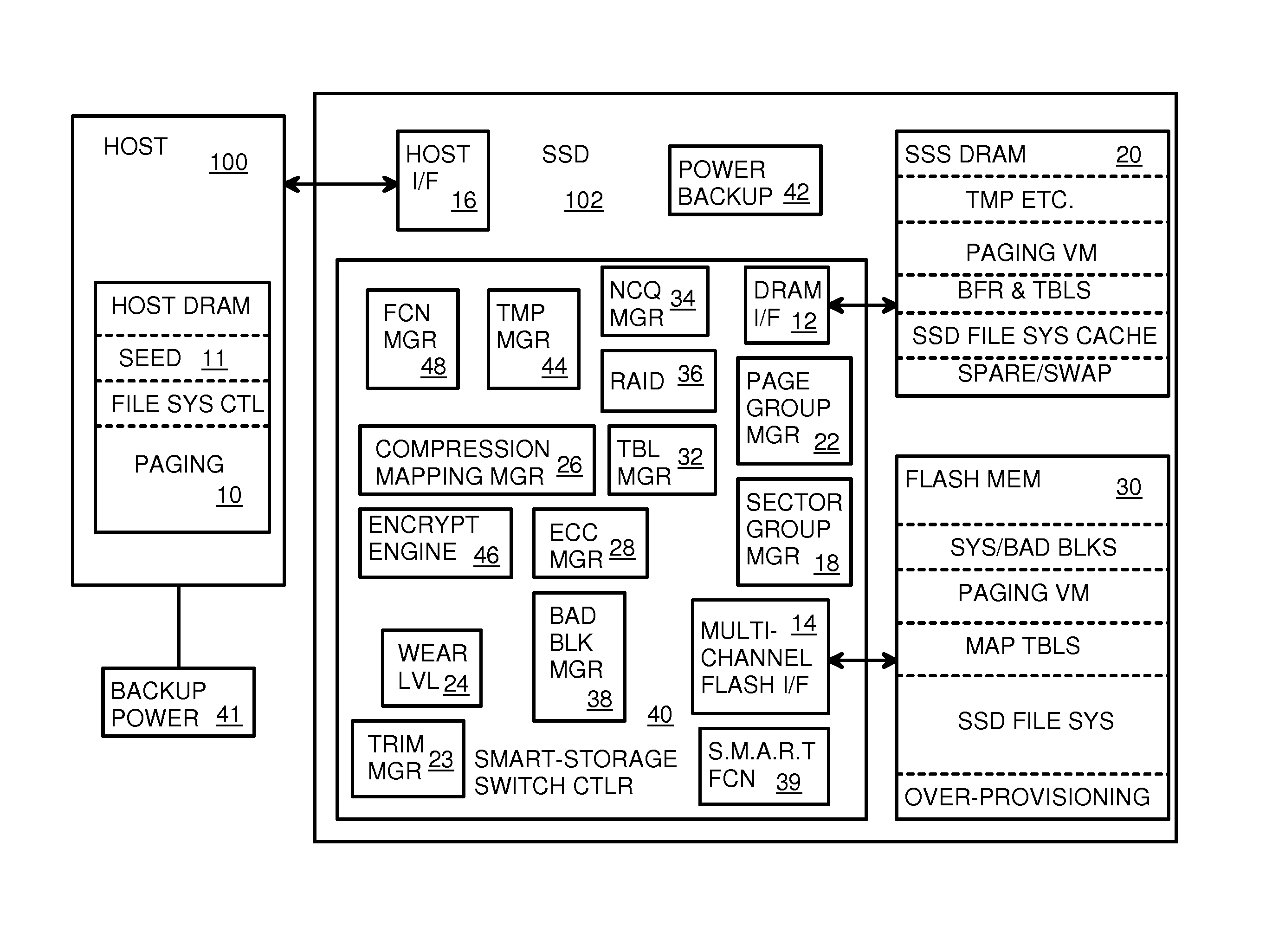
A flash drive has increased endurance and longevity by reducing writes to flash. An Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) is created in a DRAM buffer and provides temporary storage to reduce flash wear. A Smart Storage Switch (SSS) controller assigns data-type bits when categorizing host accesses as paging files used by memory management, temporary files, File Allocation Table (FAT) and File Descriptor Block (FDB) entries, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from FAT. Paging files and temporary files are never written to flash. Partial-page data is packed and sector mapped by sub-sector mapping tables that are pointed to by a unified mapping table that stores the data-type bits and pointers to data or tables in DRAM. Partial sectors are packed together to reduce DRAM usage and flash wear. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
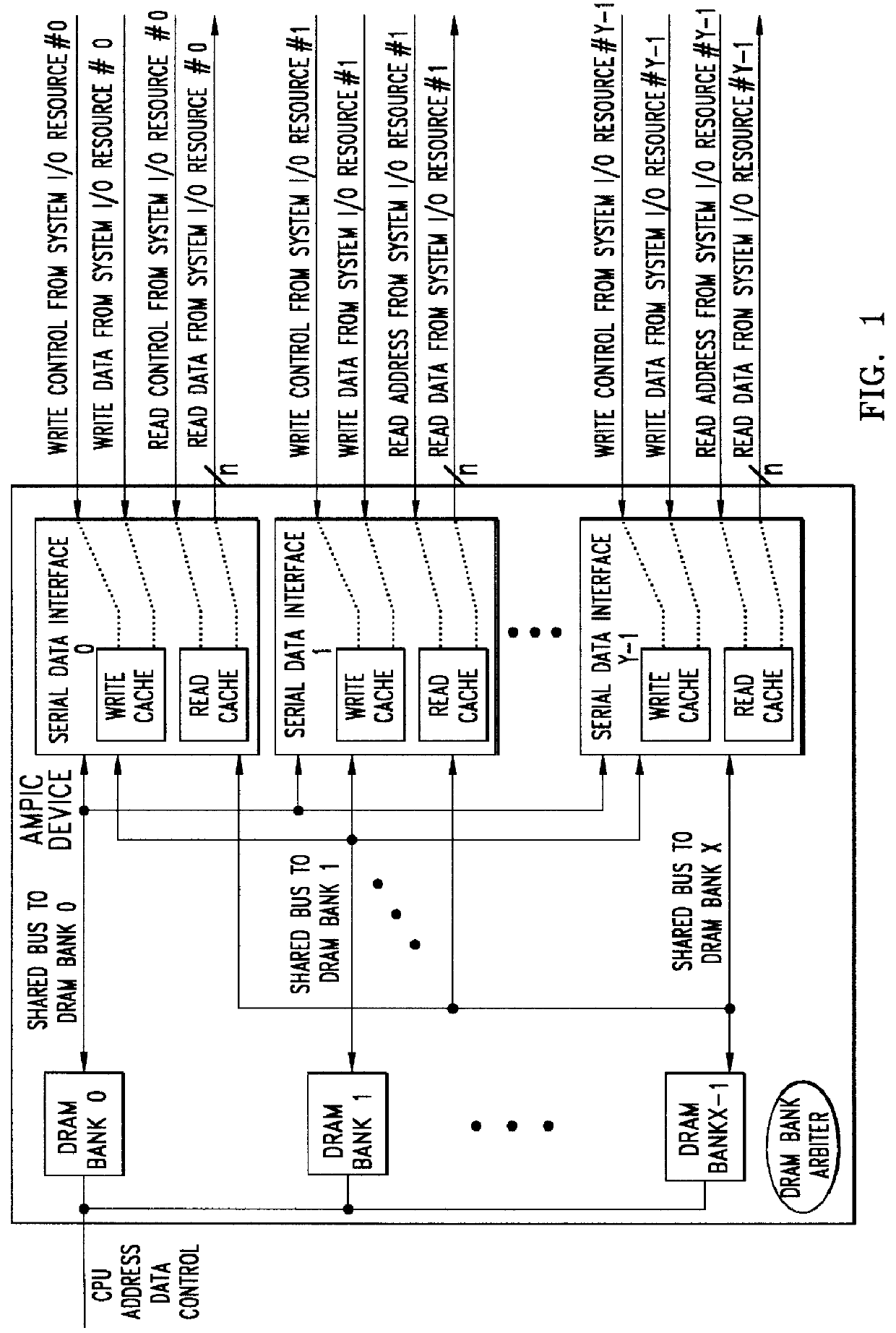
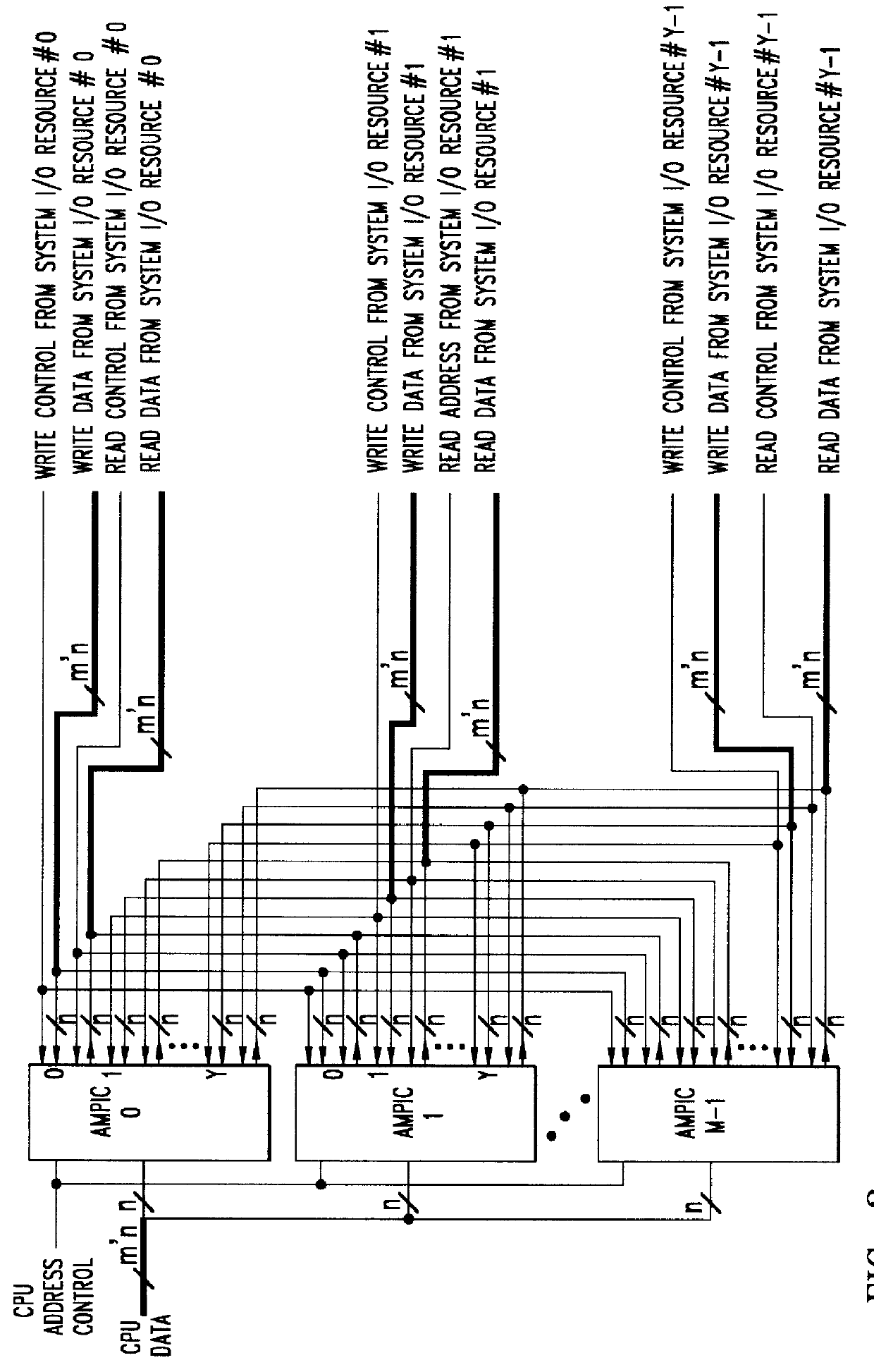
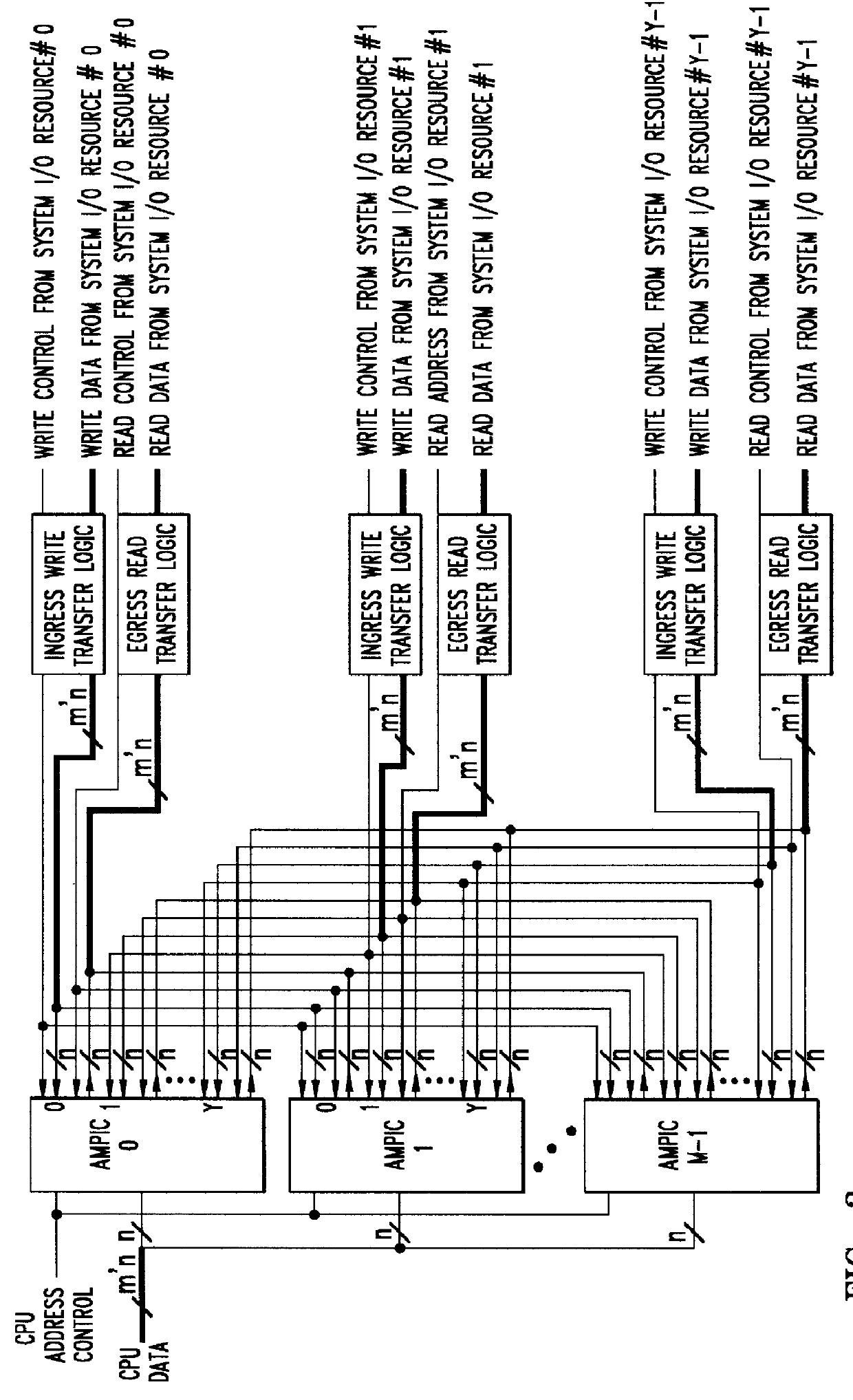
Method of and apparatus for validating data read out of a multi port internally cached dynamic random access memory (AMPIC DRAM)
InactiveUS6085290AEliminates race conditionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData validationStatic random-access memory
An apparatus for and method of enhancing the performance of a multi-port internal cached DRAM (AMPIC DRAM) by providing an internal method of data validation within the AMPIC memories themselves to guarantee that only valid requested data is returned from them, or properly marked invalid data. A modified technique for identifying bad data that has been read out of AMPIC memory devices in the system.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS +1
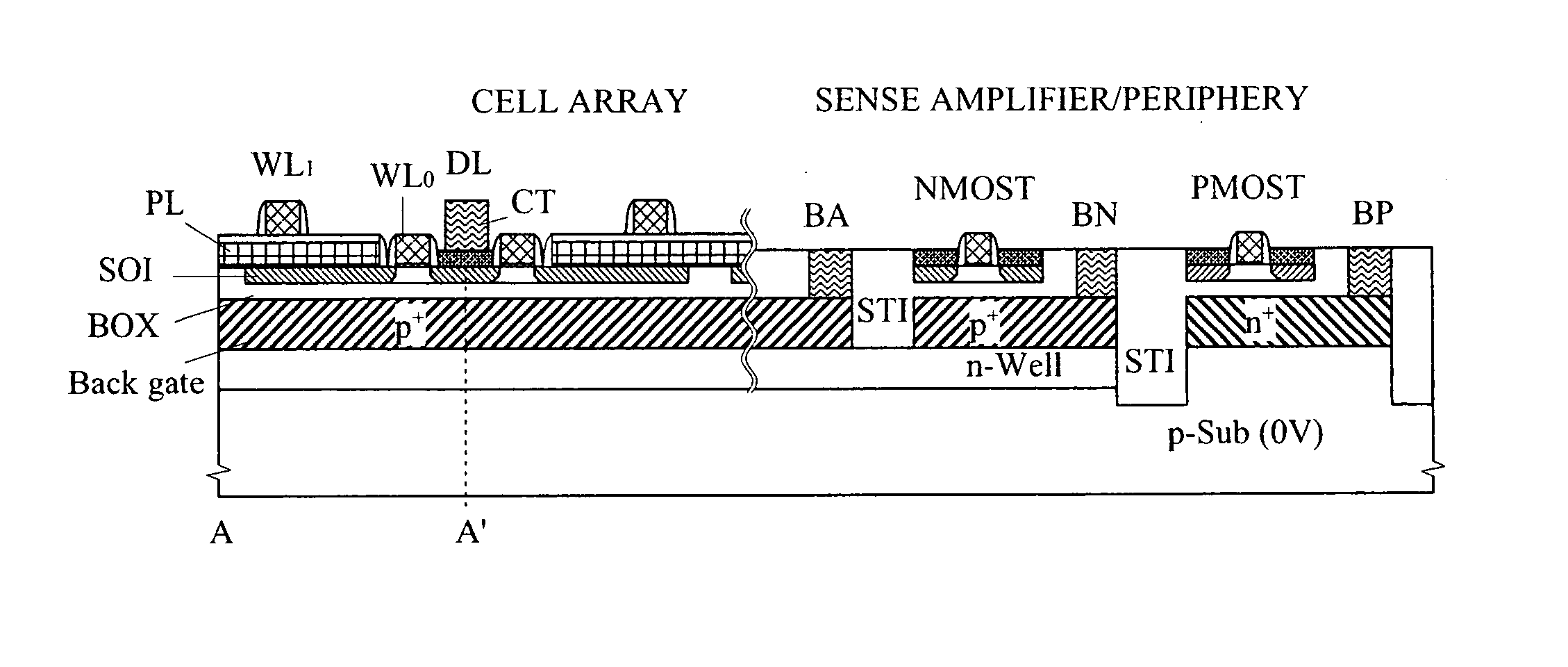
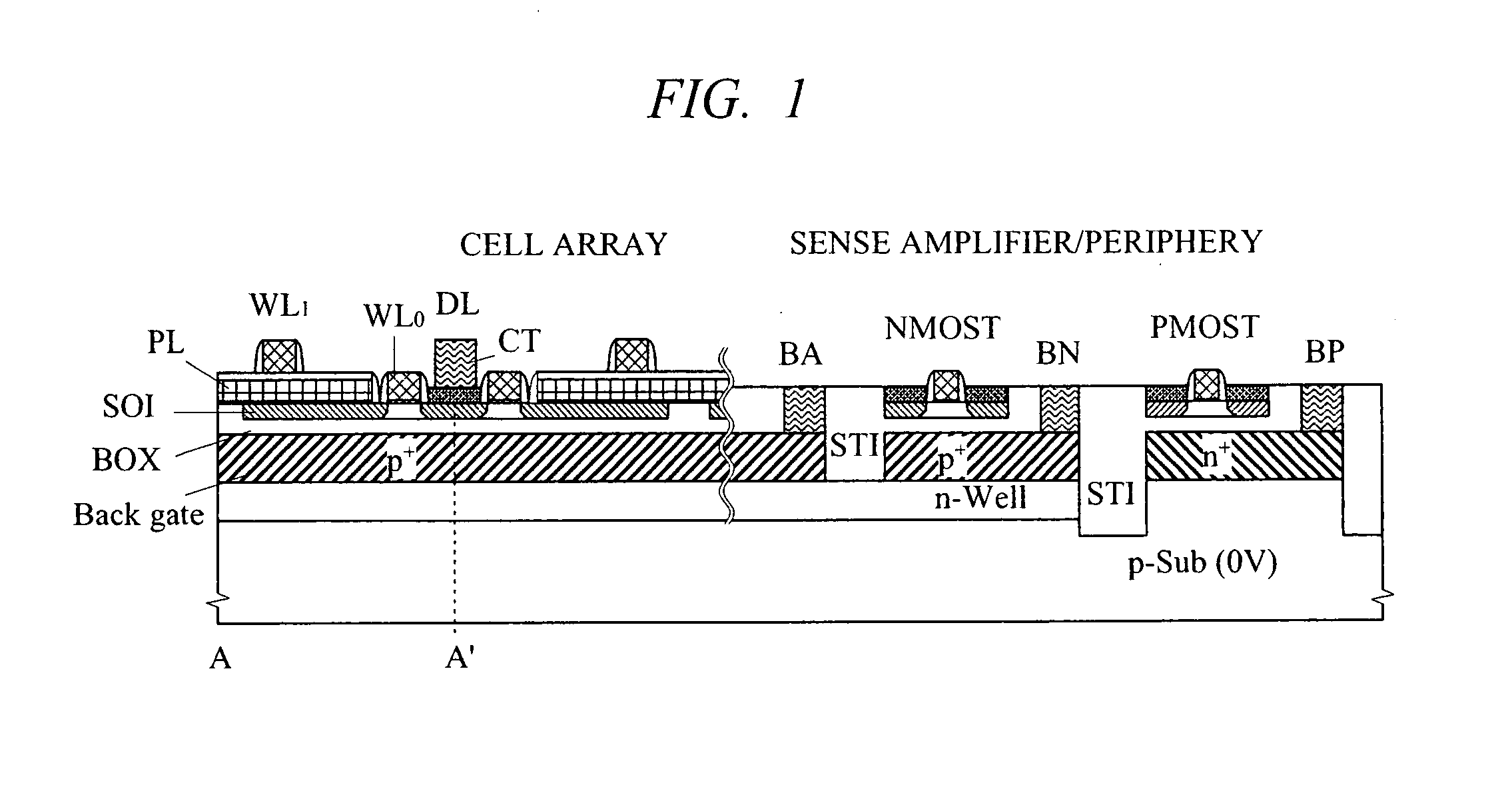
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090003105A1Run at high speedSmall sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageAudio power amplifier
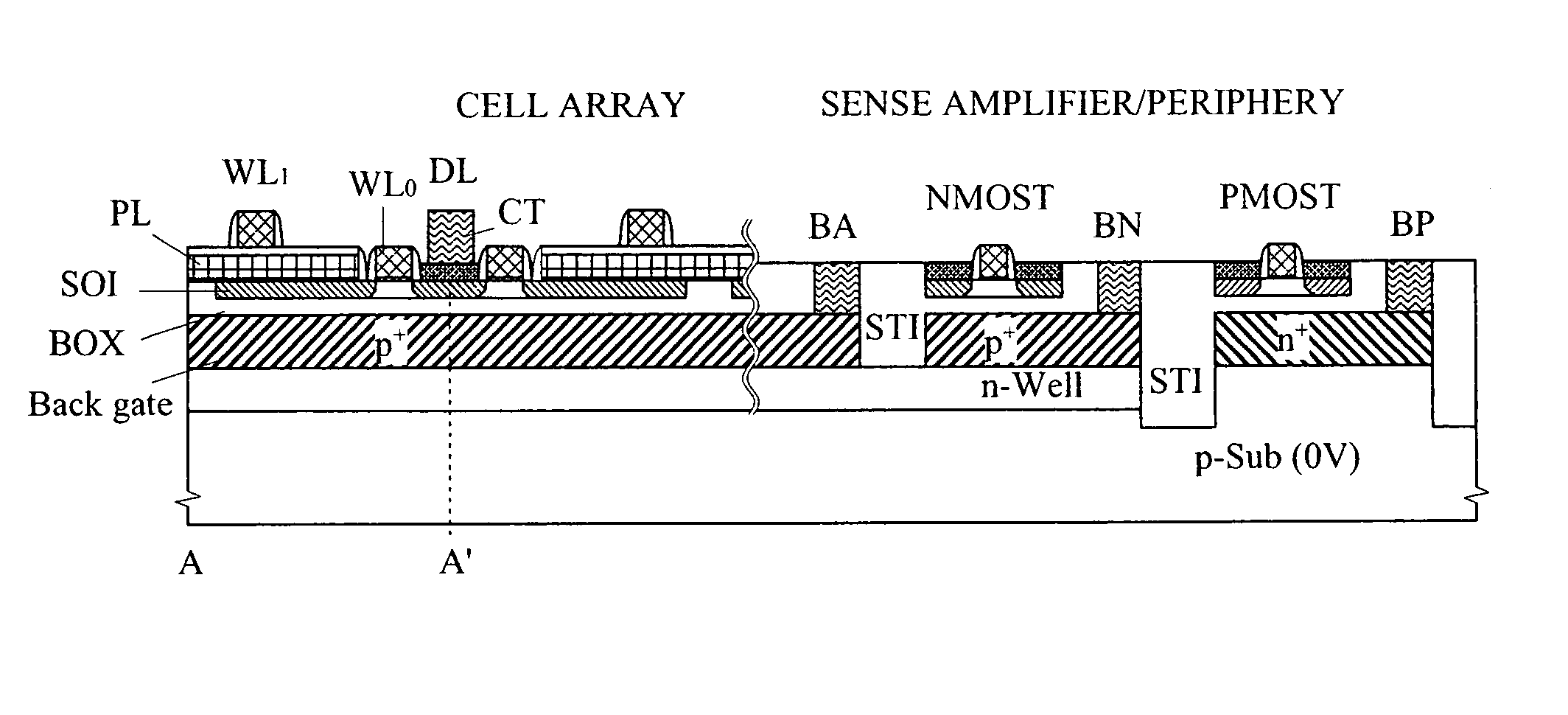
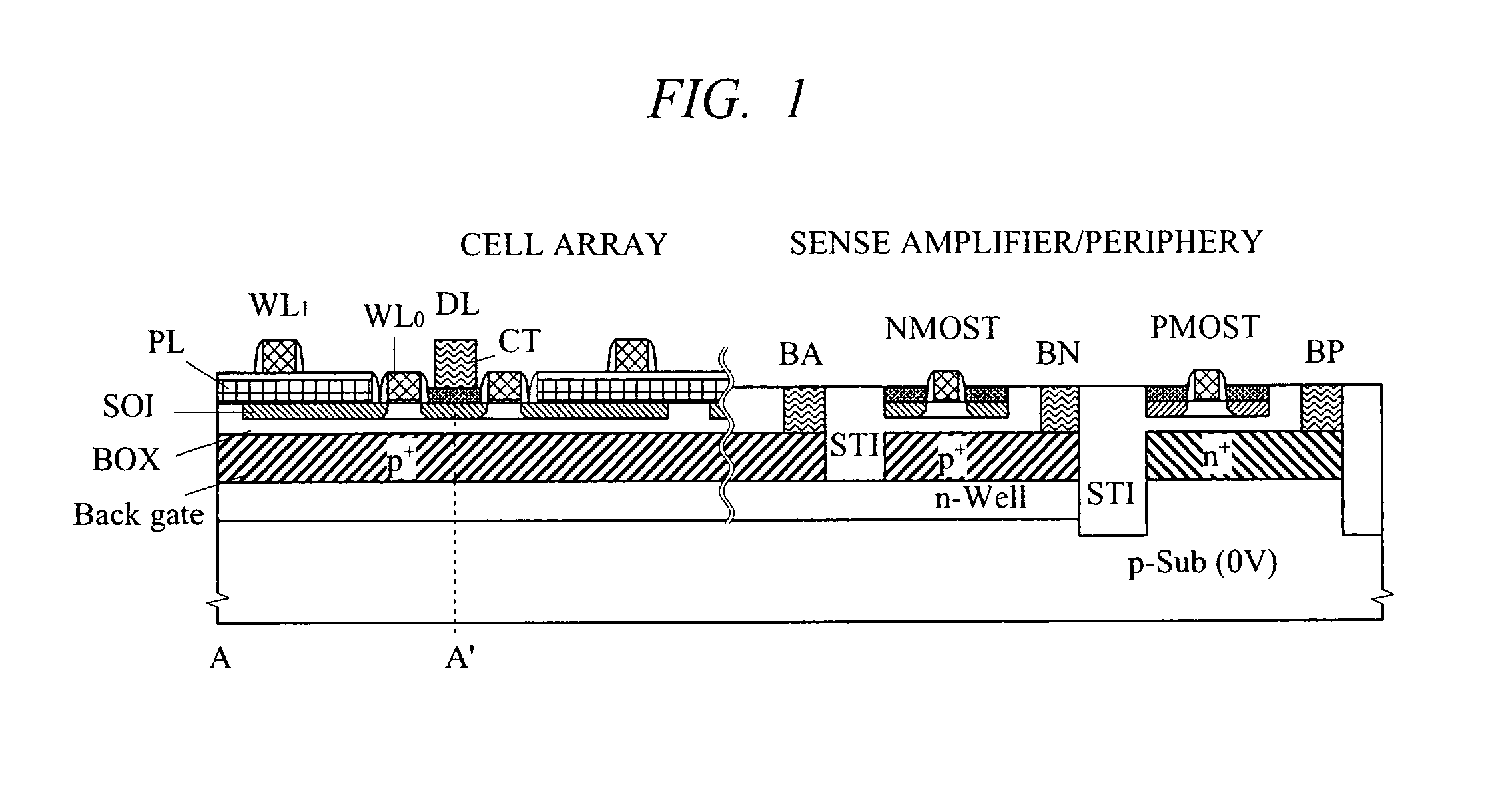
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of integrating volatile and non-volatile memory cells on the same substrate and a semiconductor memory device thereof
InactiveUS6670234B2Simple processMinimizes stepSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle chipDram
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
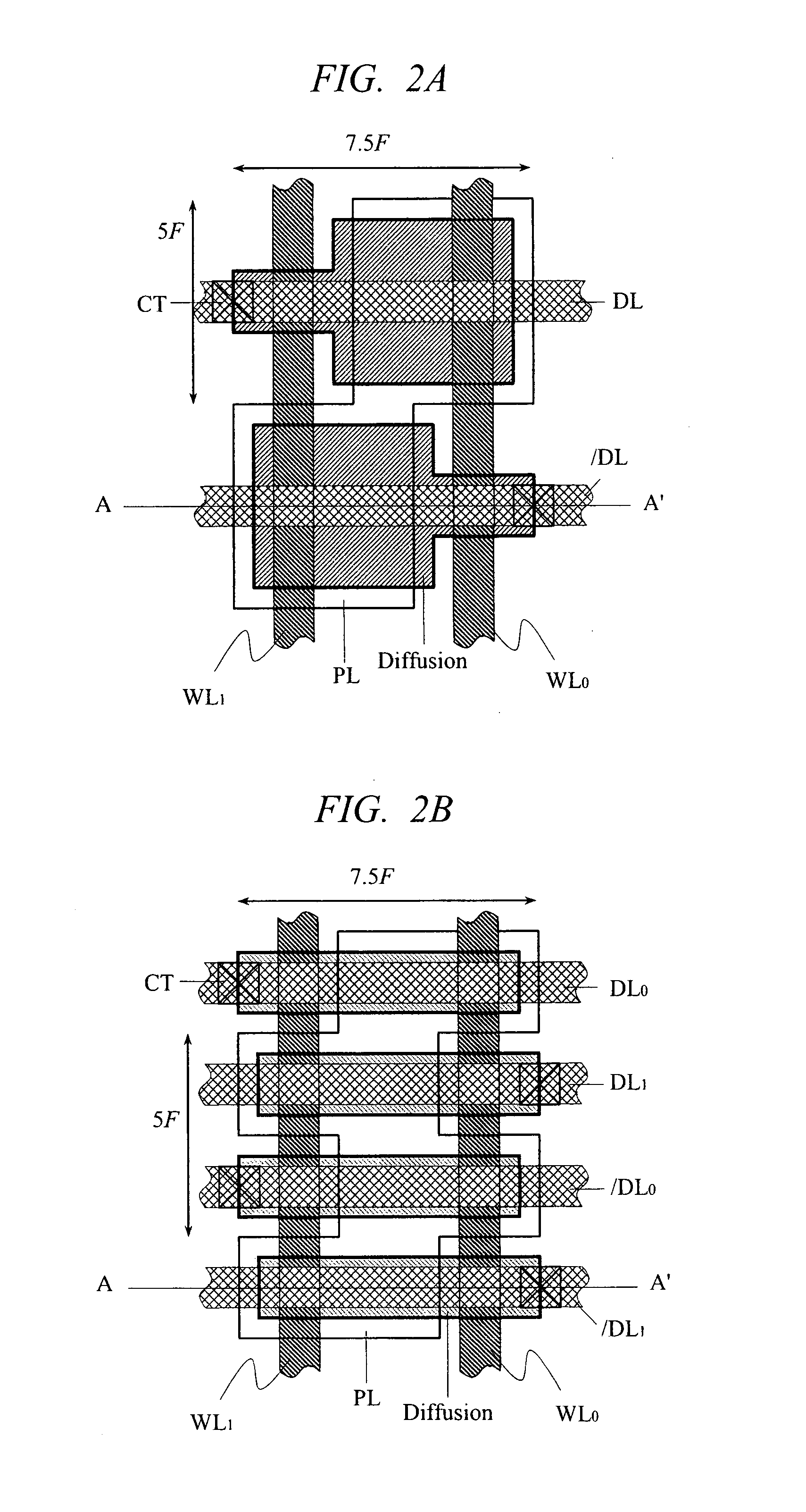
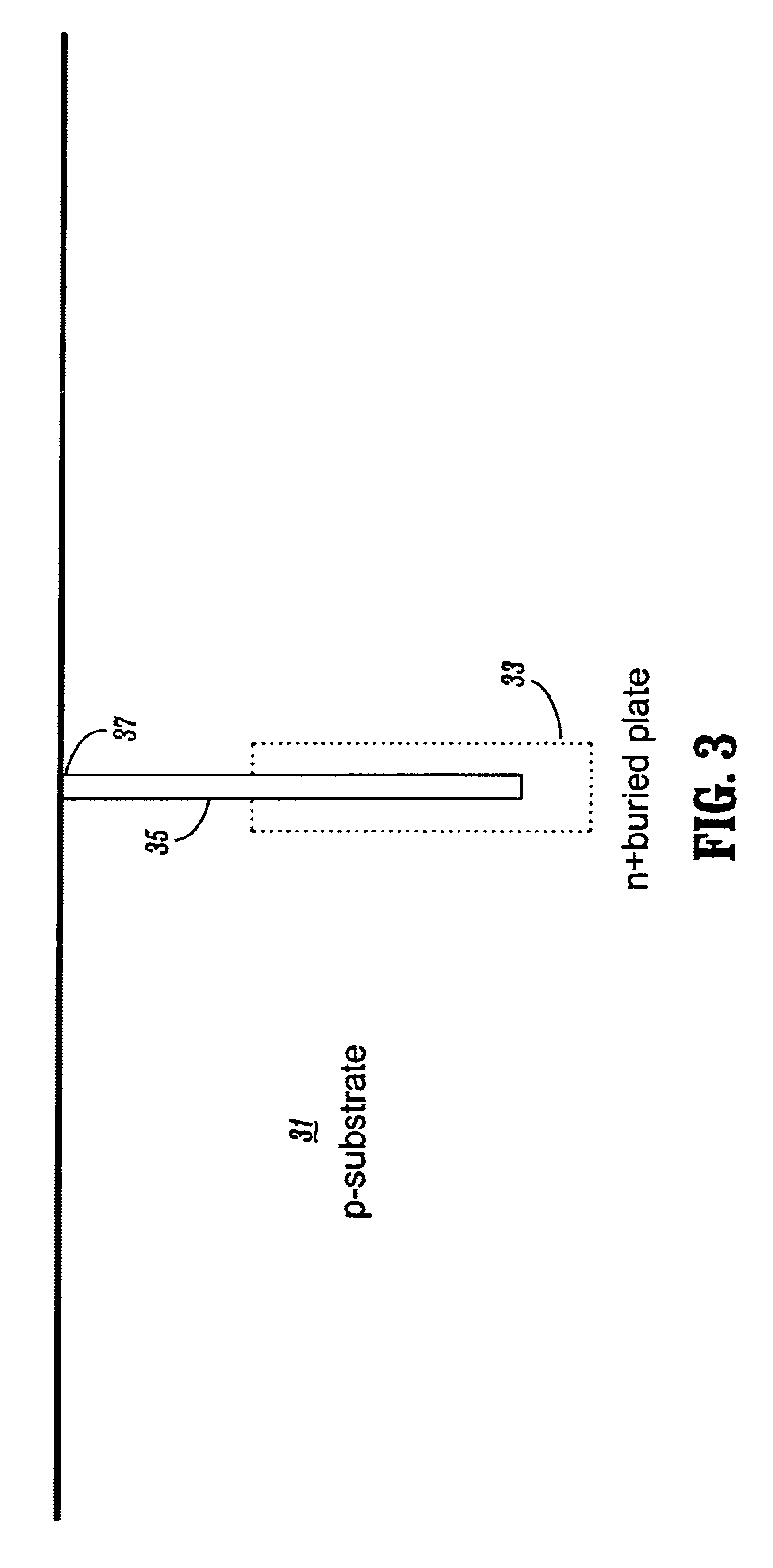
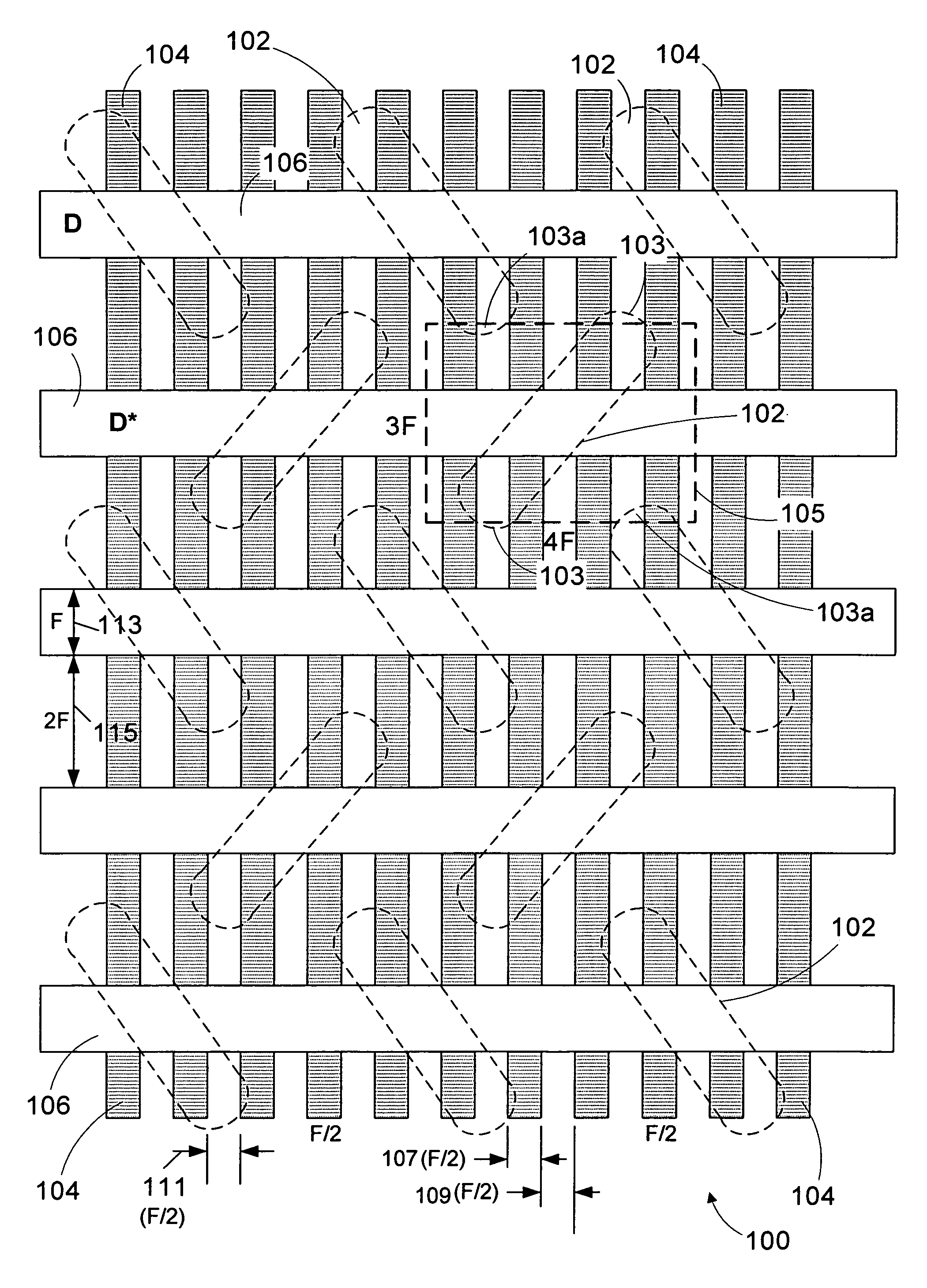
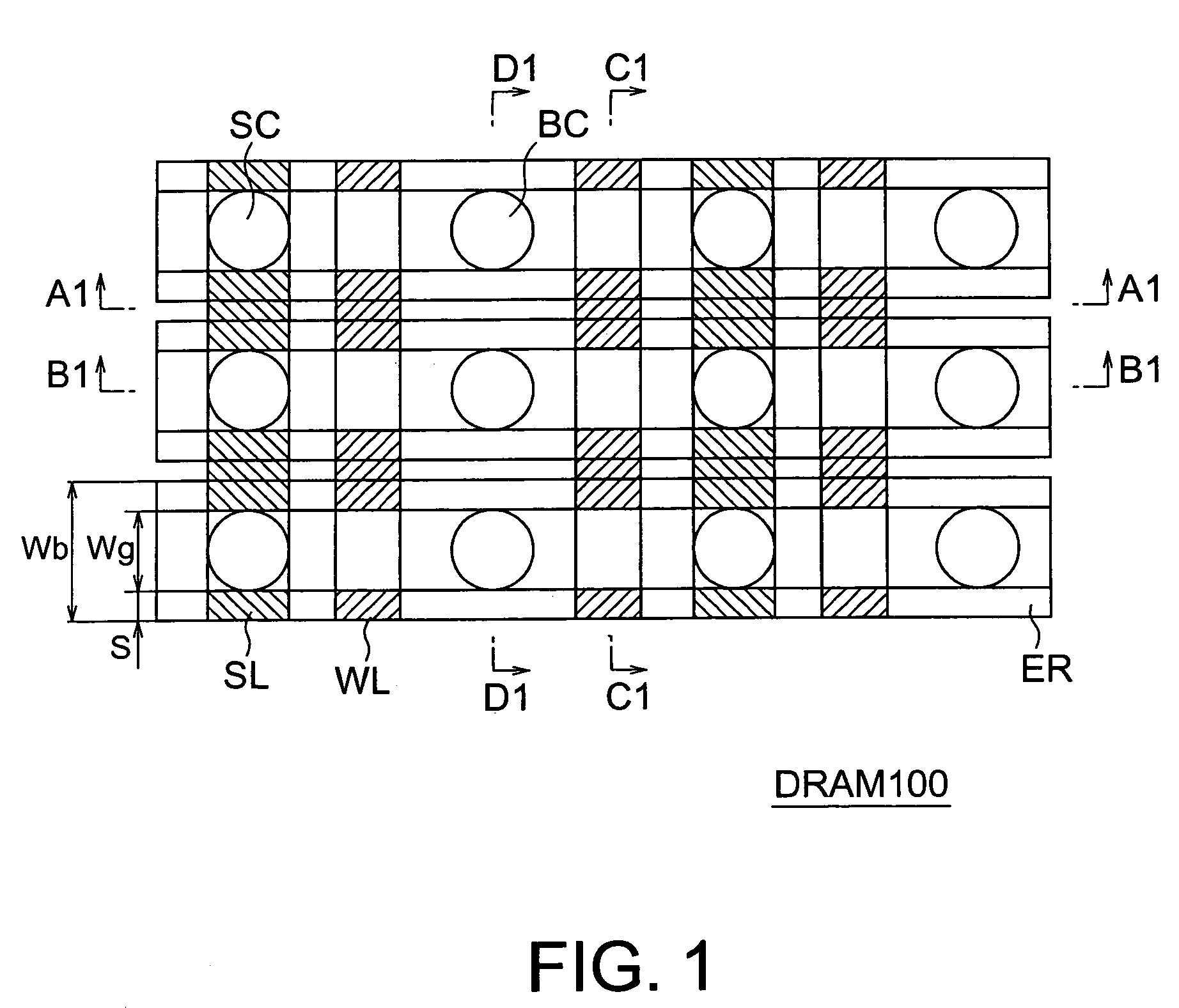
6F2 DRAM cell design with 3F-pitch folded digitline sense amplifier
The present invention is generally directed to a DRAM cell design with folded digitline sense amplifier. In one illustrative embodiment, a memory array having a plurality of memory cells having an effective size of 6F2 is disclosed which has a plurality of dual bit active areas, each of the active areas having a substantially longitudinal axis, and a plurality of digitlines on a 3F-pitch arranged in a folded digitline architecture, wherein the active areas are positioned such that the longitudinal axis of the active areas is oriented at an angle with respect to a centerline of the digitlines.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Monolithic 3-d dynamic memory and method
InactiveUS20170278858A1Accelerated programReduced P/E voltageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringDram
A monolithic 3-D dynamic memory structure includes independently addressable strings of dual-gate devices. In each dual-gate device charge is deliberately stored on one side of the dual-gate. Although the stored charge may leak away, the stored charge in a dual-gate device of the present invention need only be refreshed at much longer intervals than conventional DRAM cells.
Owner:SCHILTRON
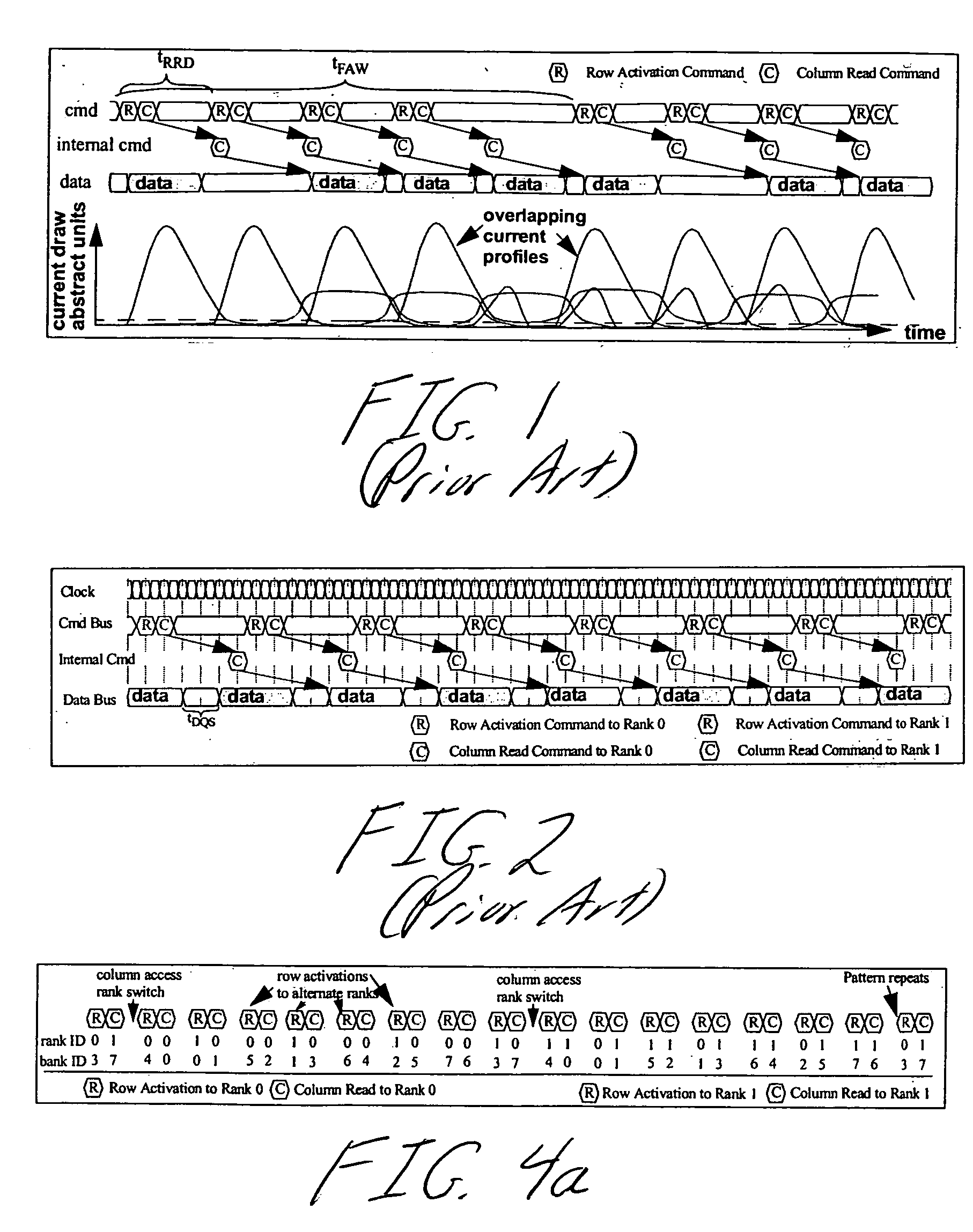
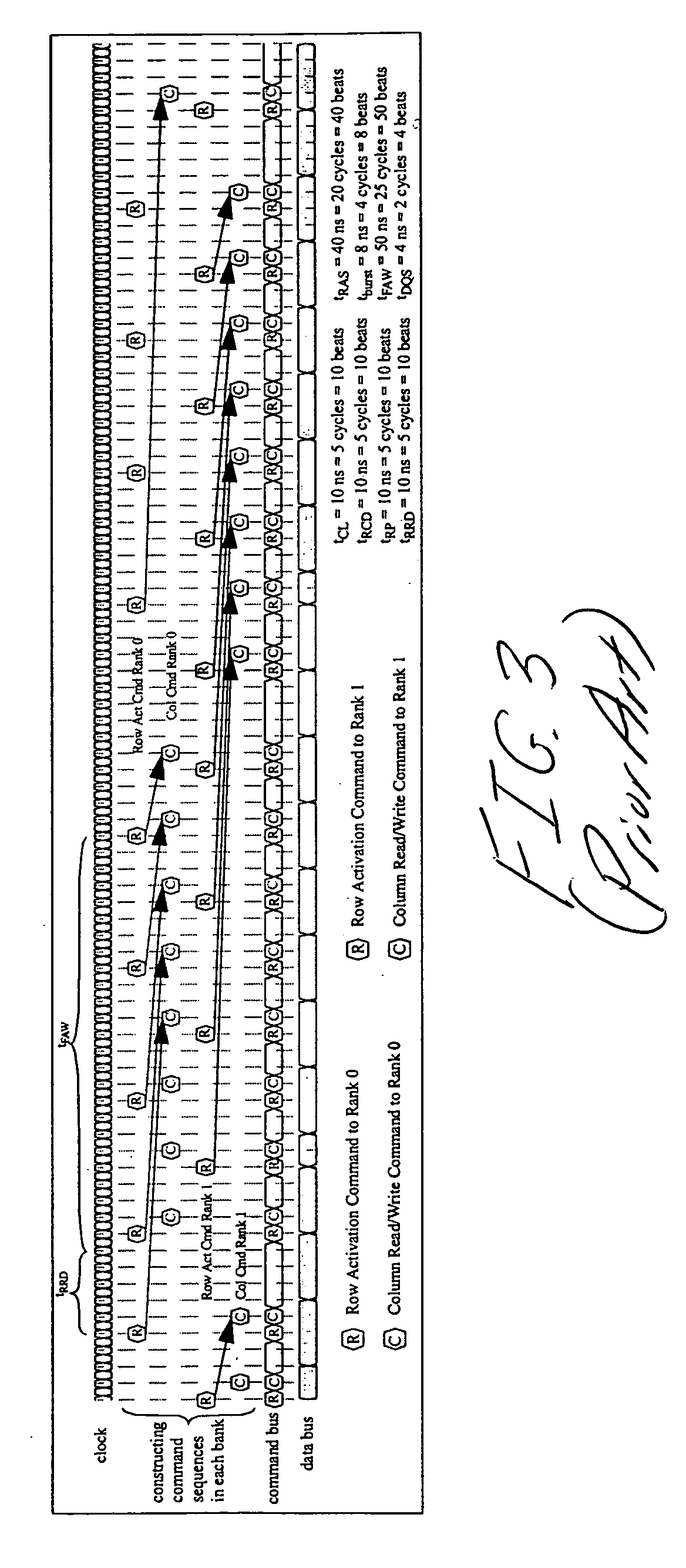
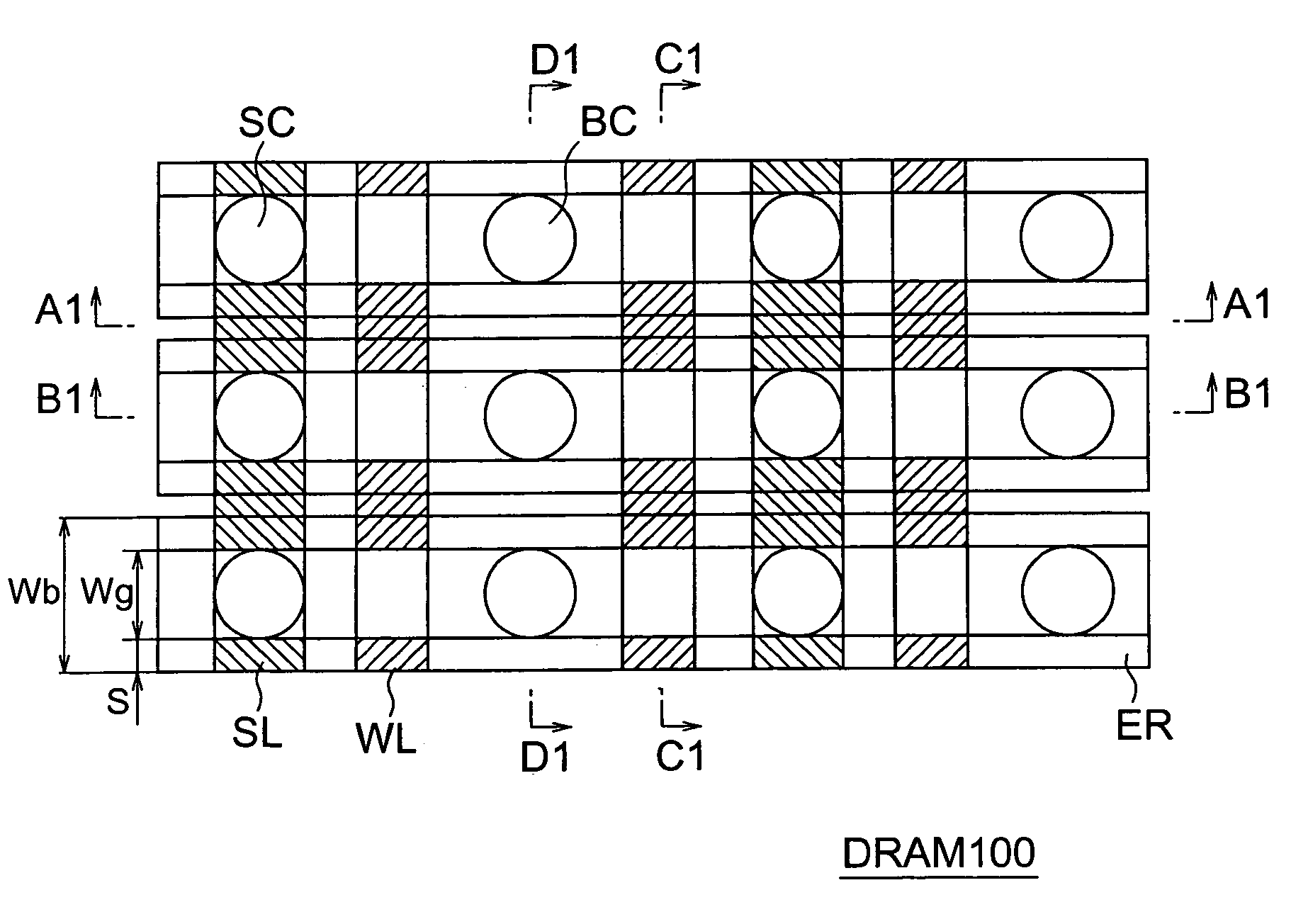
System and method for performing multi-rank command scheduling in DDR SDRAM memory systems
InactiveUS20060248261A1Better bandwidth utilizationMinimize bandwidth impactMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankGroup scheduling
A DRAM command scheduling algorithm is presented that is designed to alleviate various constraints imposed upon high performance, high datarate, short channel DDRx SDRAM memory systems. The algorithm amortizes the overhead costs of rank-switching time and schedules around the tFAW bank activation constraint. A multi-rank DDRx memory system is also presented having at least two ranks of memory each having a number of banks and at least one memory controller configured for performing the hardware-implemented step of DRAM command scheduling for row access commands and column access commands. The step of command scheduling includes decoupling the row access commands from the column access commands; alternatively scheduling the decoupled row access commands to different ranks of memory; and group scheduling the decoupled column access commands to each bank of the number of banks of a given rank of the different ranks of memory.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
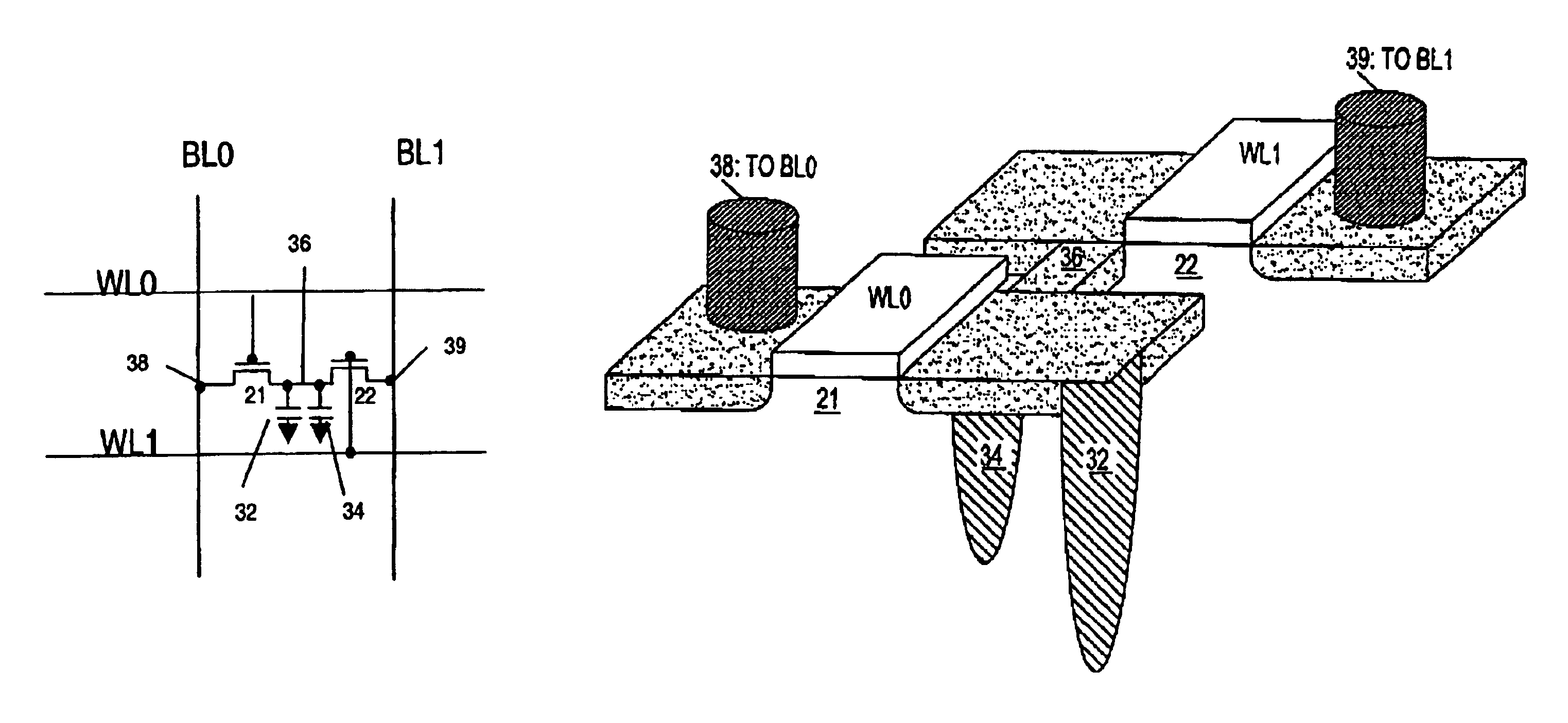
Floating body-type DRAM cell with increased capacitance
A semiconductor memory device includes transistors, each including a first-conductivity-type semiconductor layer formed on a semiconductor substrate via a first insulating film, a second-conductivity-type source / drain regions formed in the semiconductor layer, a first-conductivity-type body region formed between the source region and the drain region in the semiconductor layer, the body region being electrically floating, and a gate electrode formed on a surface of a central portion of the body region via a second insulating film. In a section along a word line, which connects the gate electrodes together, a length of a boundary between the central portion of the body region and the second insulating film is smaller than a length of a boundary between the body region and the first insulating film. A second-conductivity-type counter impurity is doped in a surface portion of the central portion of the body region on which the second insulating film is formed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
A semiconductor memory device comprises select transistors formed on side surfaces of plural silicon columns defined by a grid-like trenches on a surface of a silicon substrate, each select transistor having a source and a drain on the top surface and the bottom of the silicon column. A capacitor is formed on the top surface of the silicon column to form a DRAM cell. The source / drain layers on the bottom of a greater number of memory cells are commonly connected, or the source / drain layers on the bottom of adjacent memory cells are commonly connected, to be brought out to the surface of the silicon substrate by a connection line to be connected to a constant voltage or a bit line.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
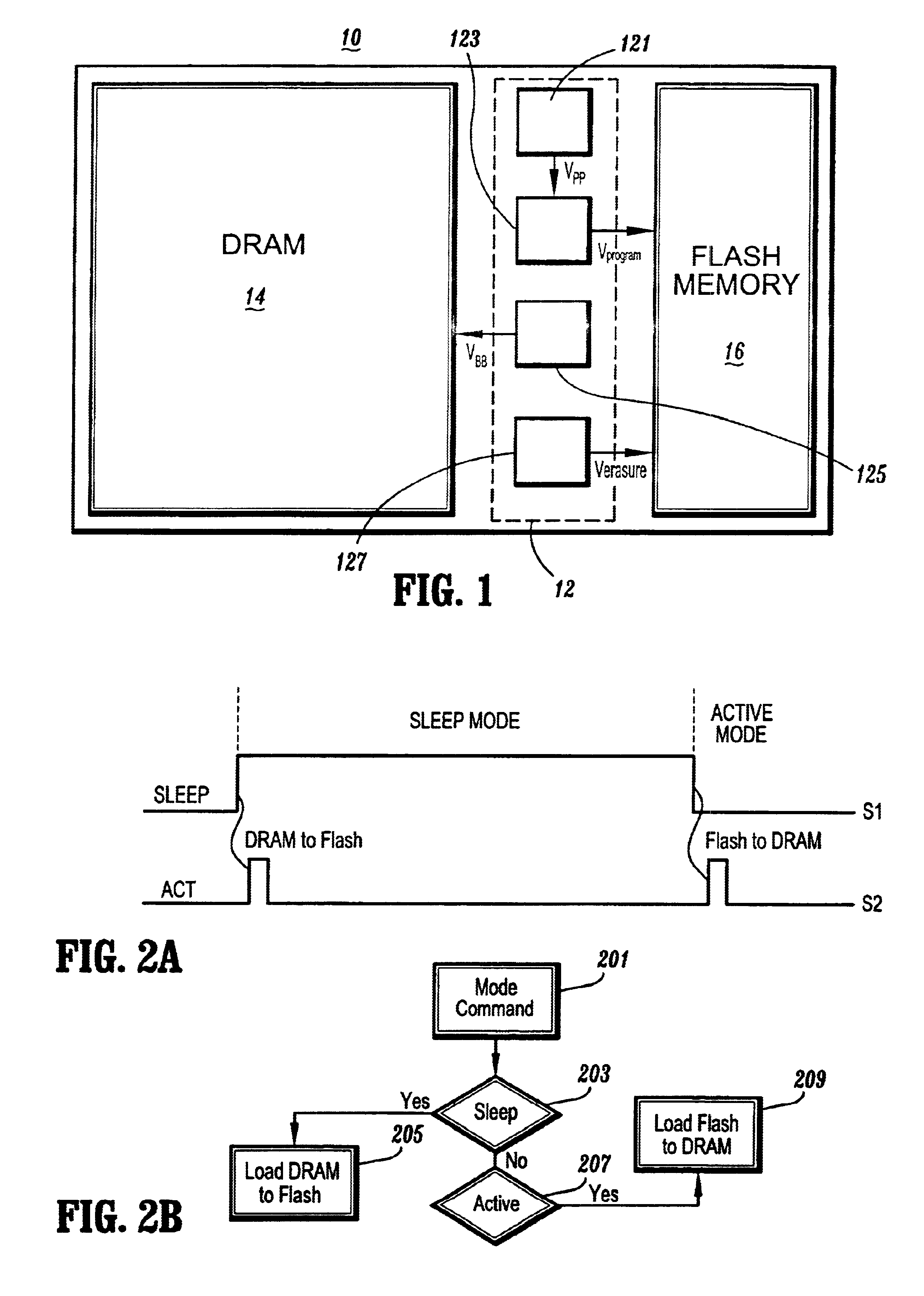
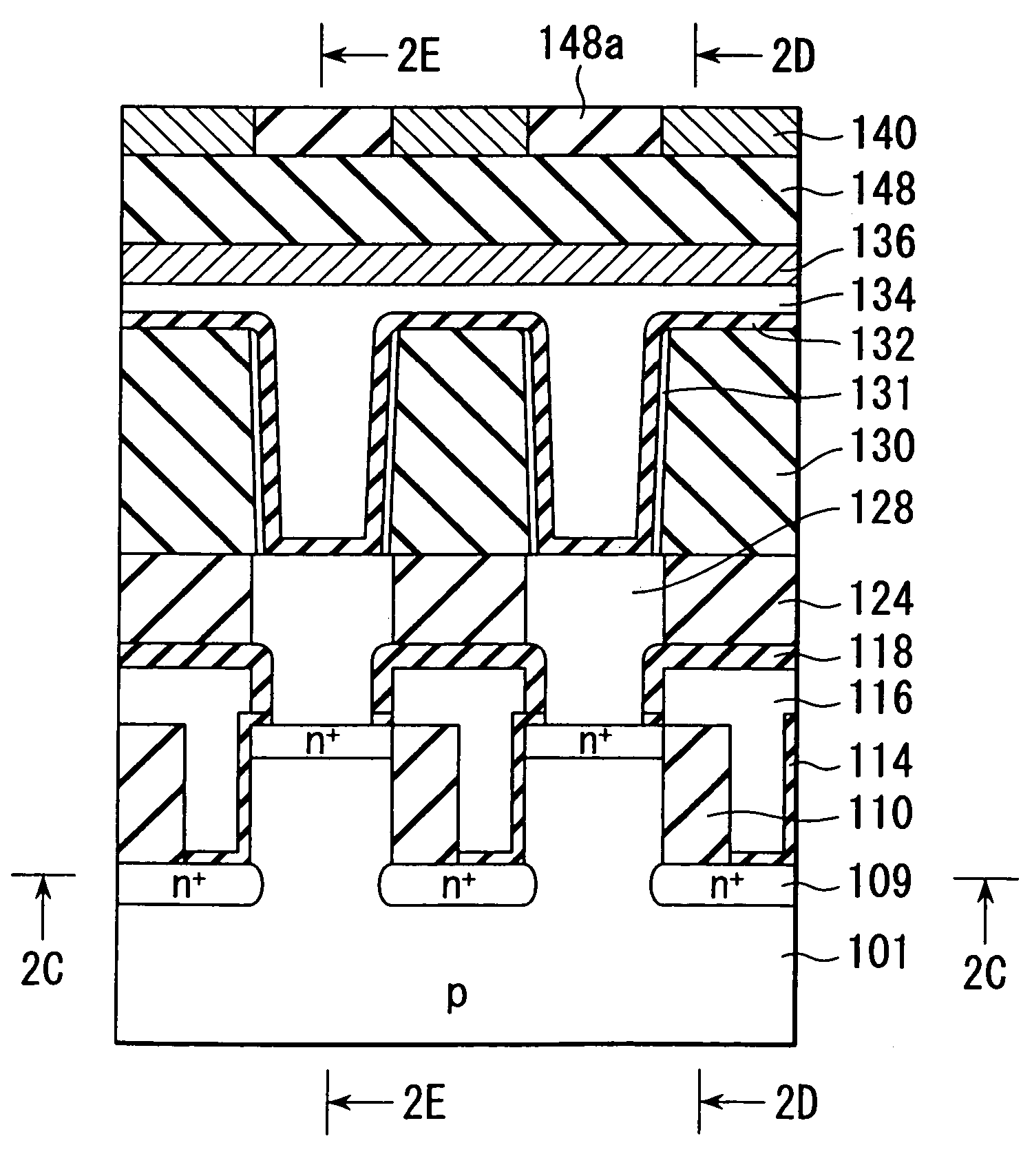
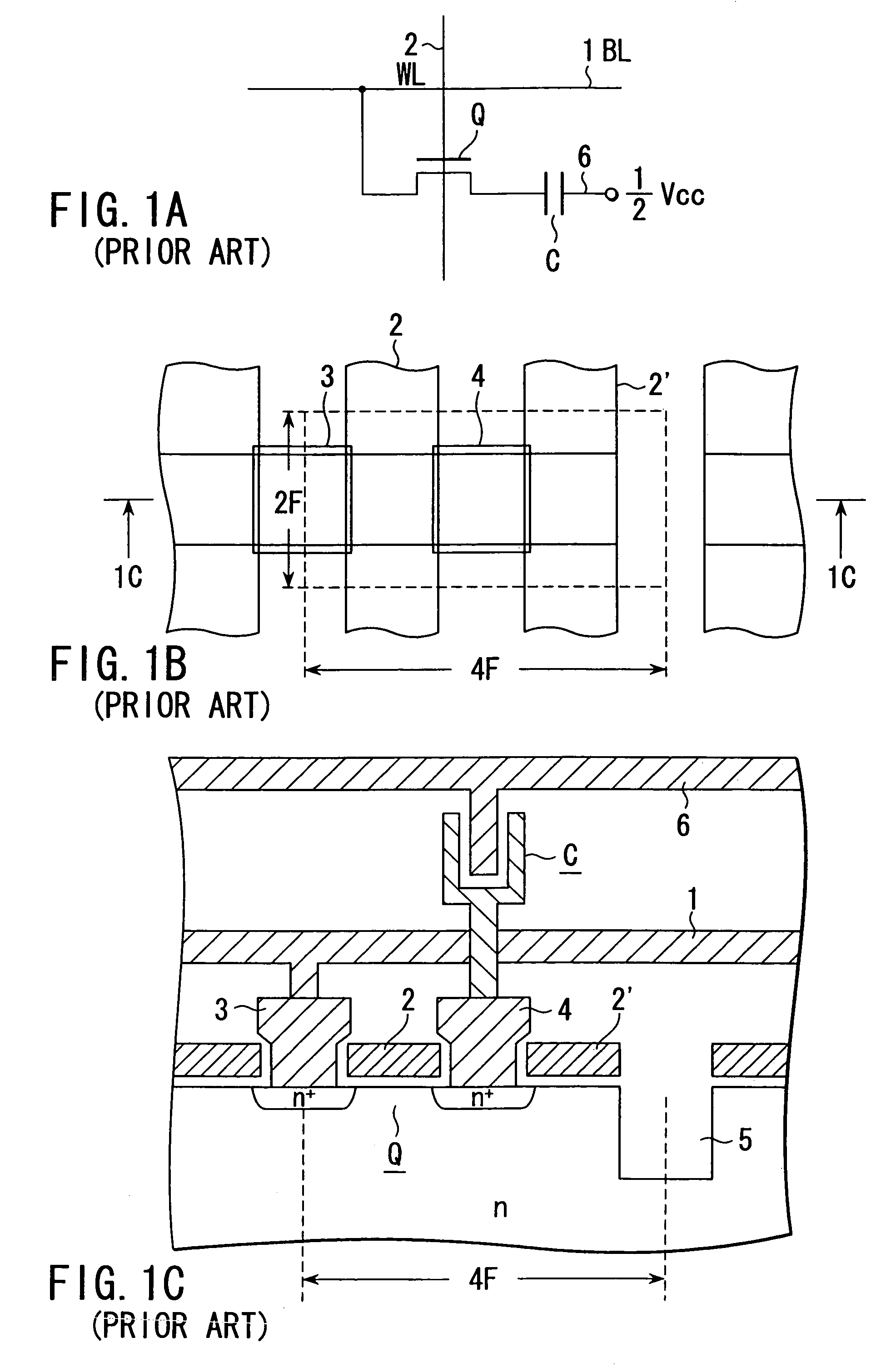
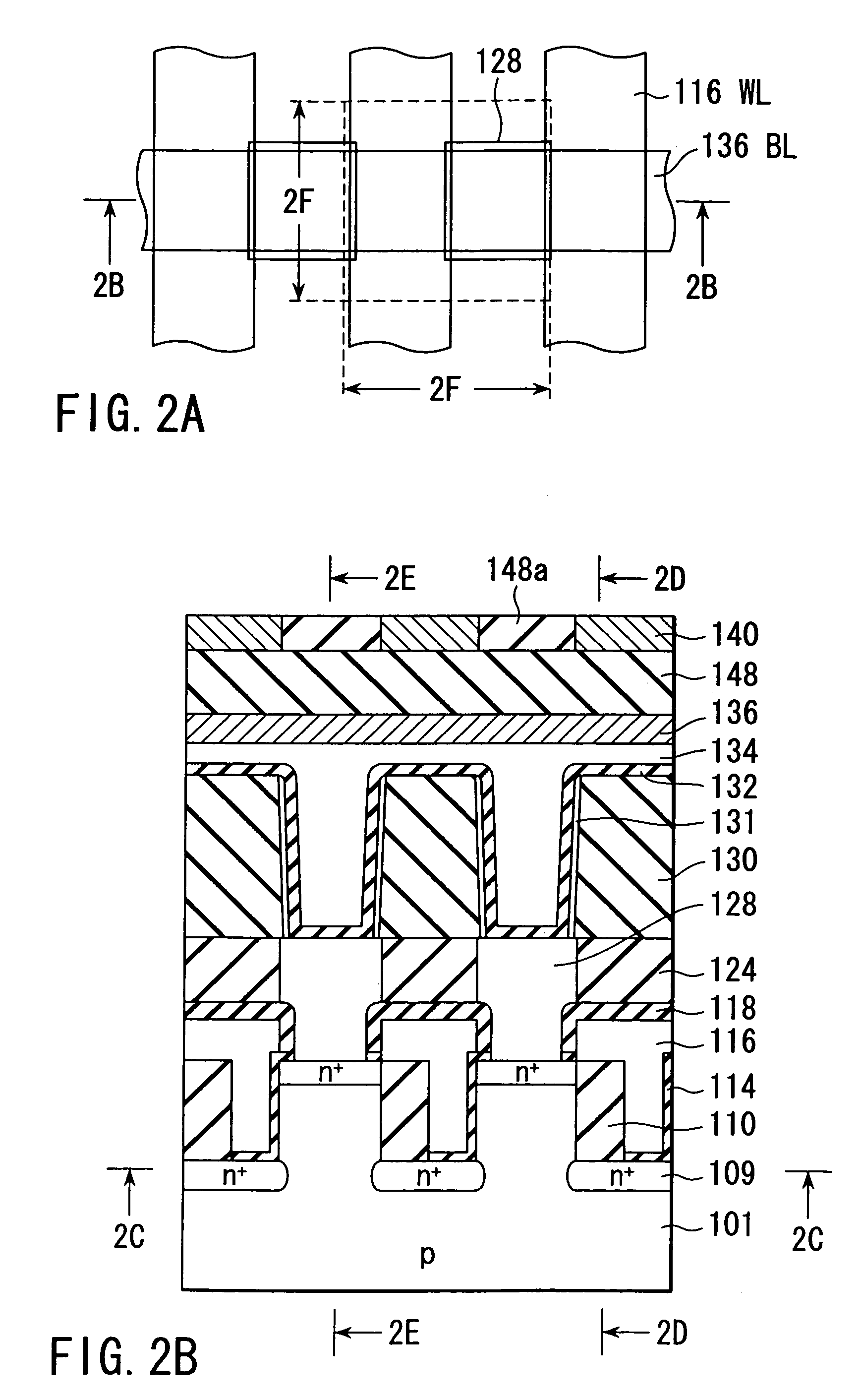
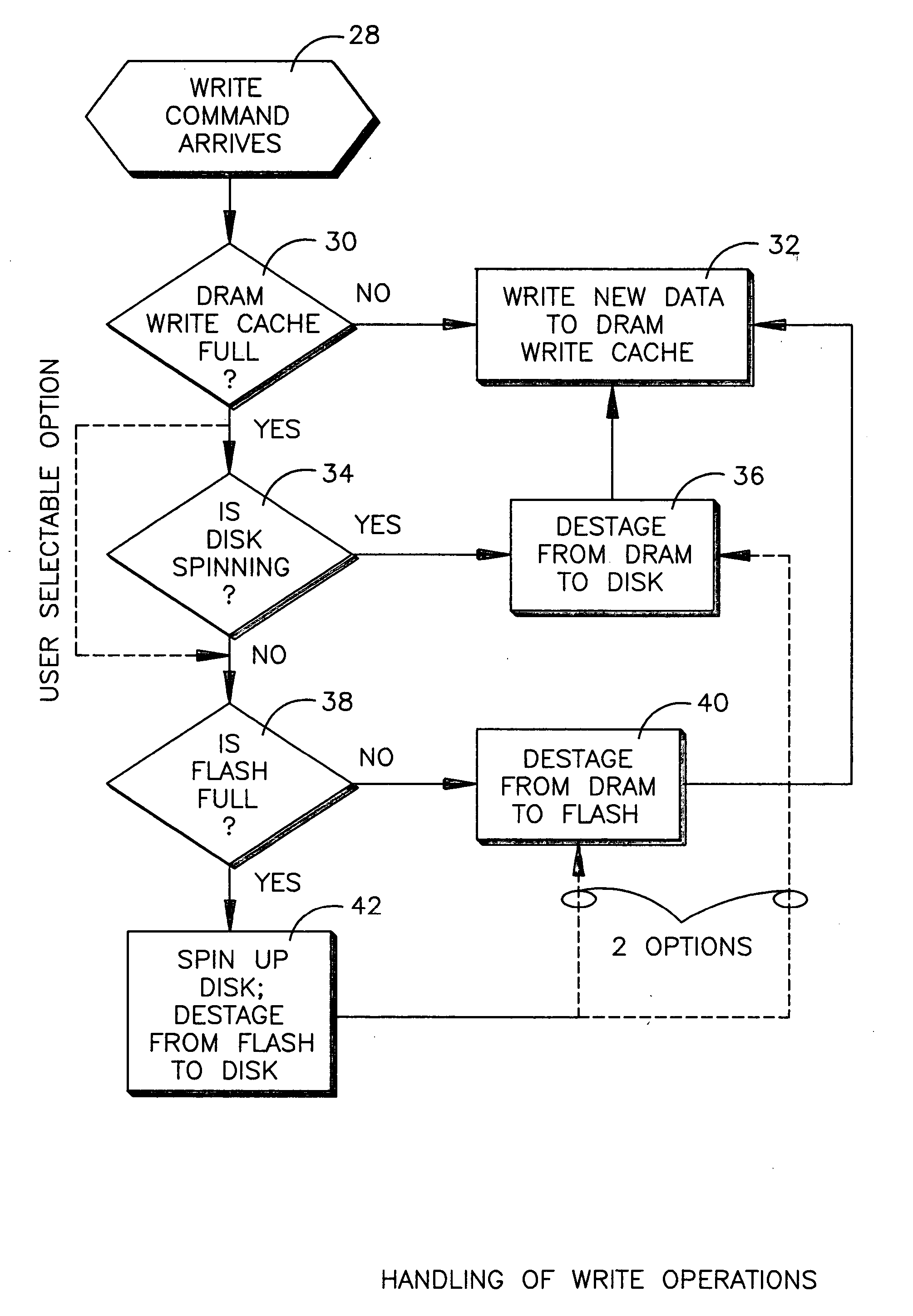
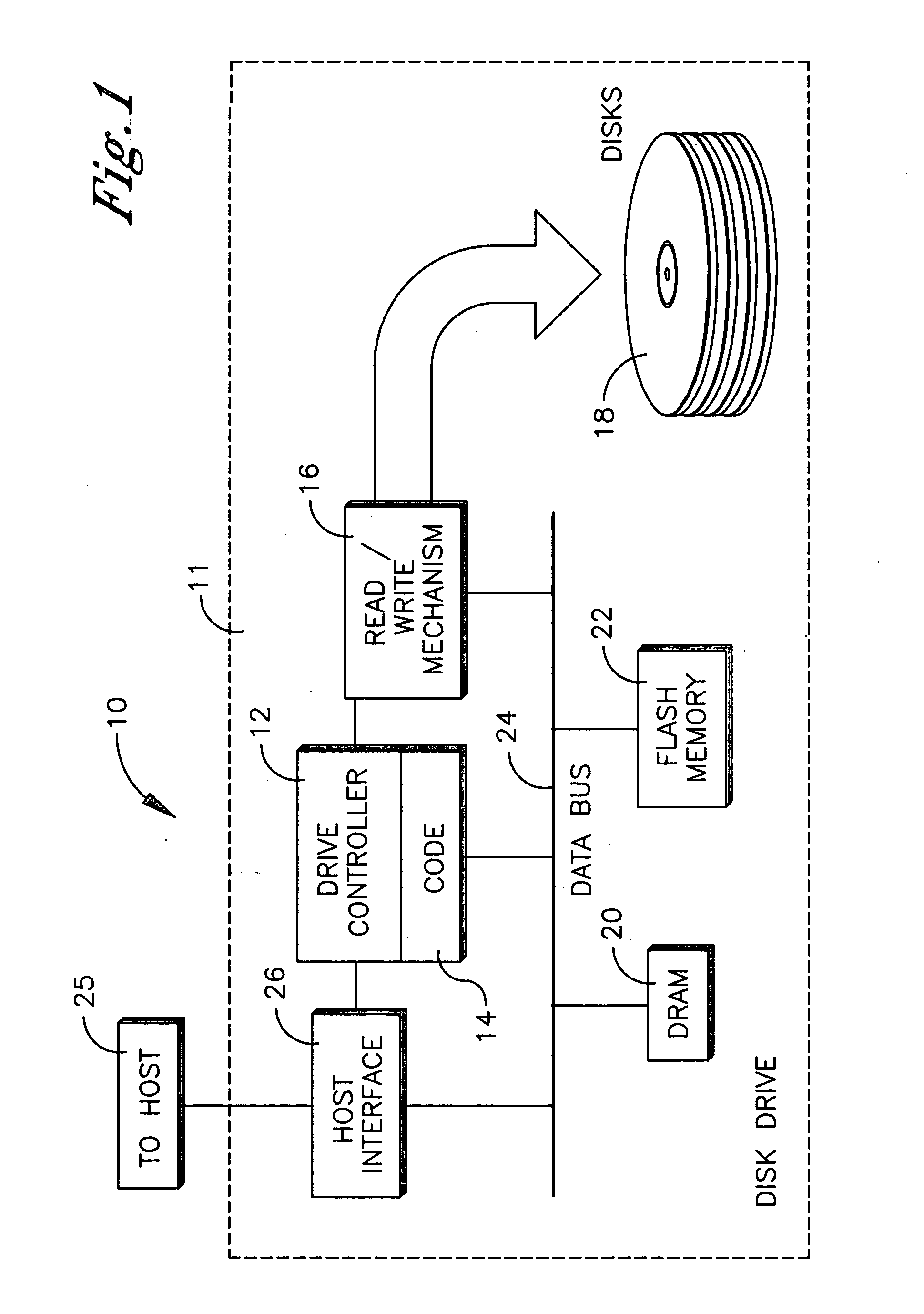
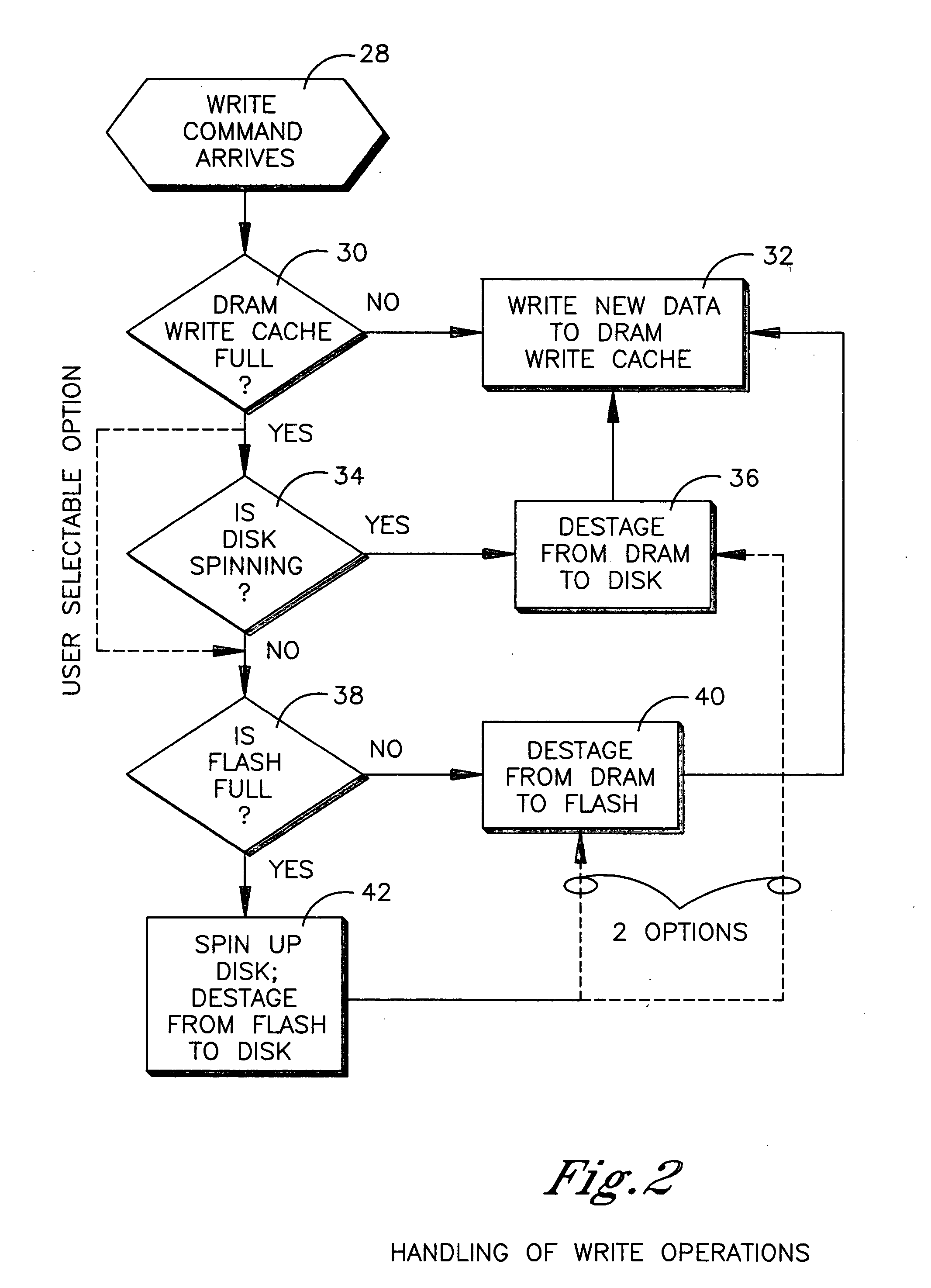
HDD having both dram and flash memory
InactiveUS20060080501A1Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveMobile computing
A mobile computing hard disk drive has both a flash memory device and a DRAM device, with the HDD controller managing data storage between disk, DRAM, and flash both when write requests arrive and when the HDD is idle to optimize flash memory device life and system performance.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
DRAM cell with enhanced SER immunity
A memory cell that has first and second fully depleted transfer devices each having a body region and first and second diffused electrodes. The cell has a differential storage capacitor having at least one node abutting and in electrical contact with one of the first and second diffused electrodes of each of the transfer devices. The storage capacitor has a primary capacitance and a plurality of inherent capacitances, wherein the primary capacitance has a capaictive value that is at least approximately five times greater than that of the plurality of inherent capacitances.
Owner:IBM CORP
DRAM cells with repressed floating gate memory, low tunnel barrier interpoly insulators
Structures and methods for memory cells having a volatile and a non-volatile component in a single memory cell are provided. The memory cell includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The memory cell is adapted to operate in a first and a second mode of operation. The first mode of operation is a dynamic mode of operation and the second mode of operation is a repressed memory mode of operation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
A high speed dram architecture with uniform access latency
A Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) performs read, write, and refresh operations. The DRAM includes a plurality of sub-arrays, each having a plurality of memory cells, each of which is coupled with a complementary bit line pair and a word line. The DRAM further includes a word line enable device for asserting a selected one of the word lines and a column select device for asserting a selected one of the bit line pairs. A timing circuit is provided for controlling the word line enable device, the column select device, and the read, write, and refresh operations in response to a word line timing pulse. The read, write, and refresh operation are performed in the same amount of time.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
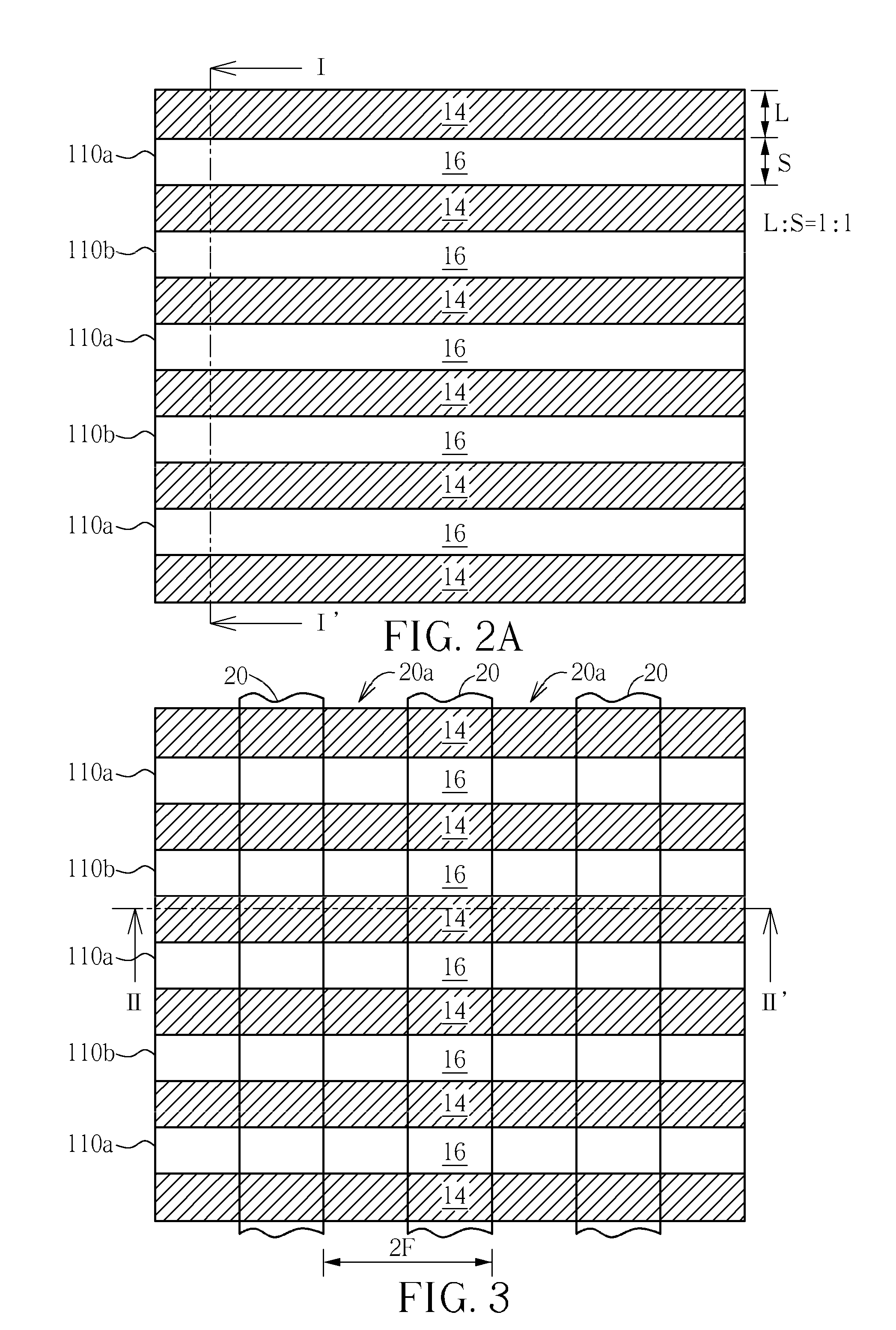
DRAM layout with vertical FETs and method of formation
DRAM cell arrays having a cell area of about 4F2 comprise an array of vertical transistors with buried bit lines and vertical double gate electrodes. The buried bit lines comprise a silicide material and are provided below a surface of the substrate. The word lines are optionally formed of a silicide material and form the gate electrode of the vertical transistors. The vertical transistor may comprise sequentially formed doped polysilicon layers or doped epitaxial layers. At least one of the buried bit lines is orthogonal to at least one of the vertical gate electrodes of the vertical transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
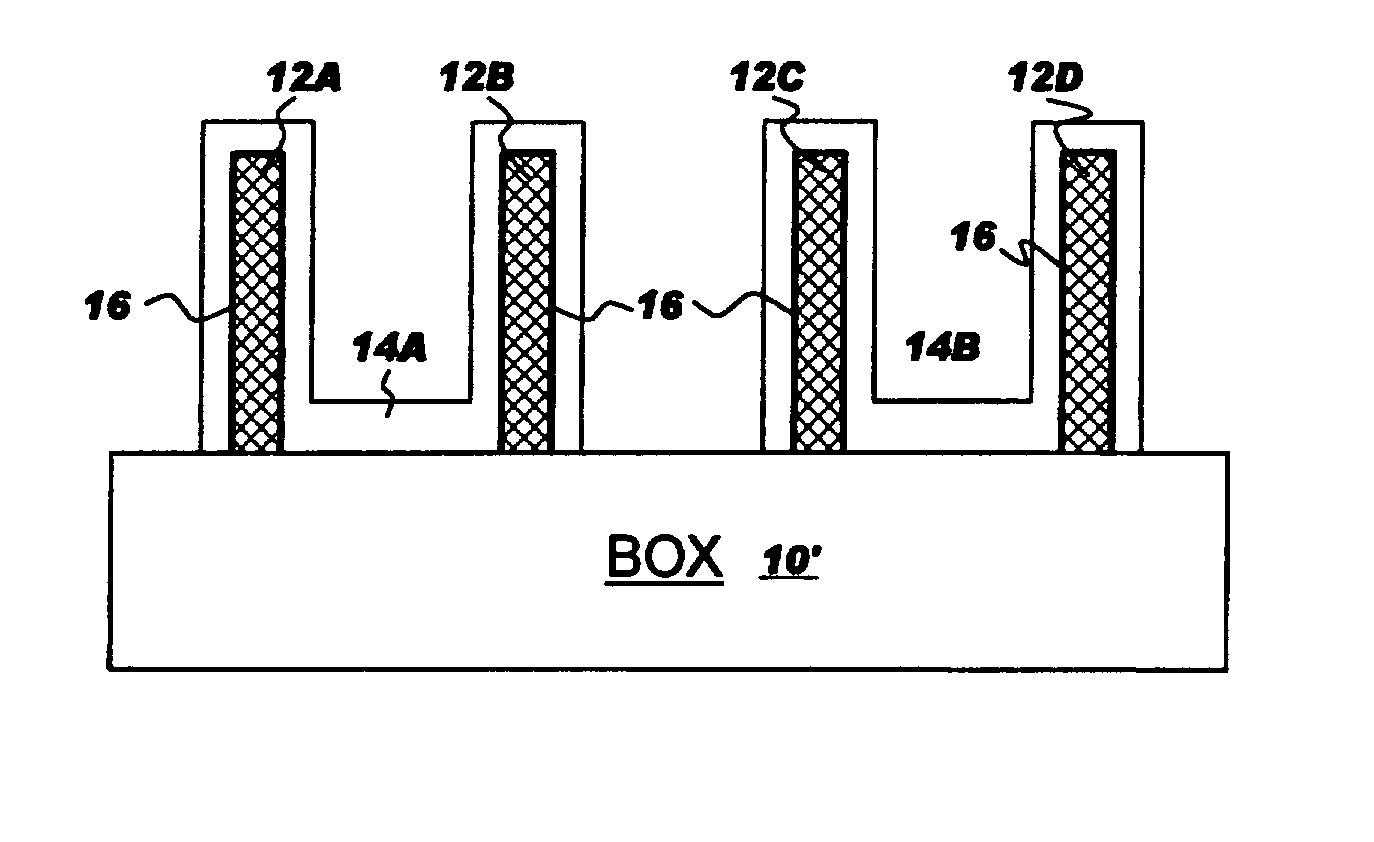
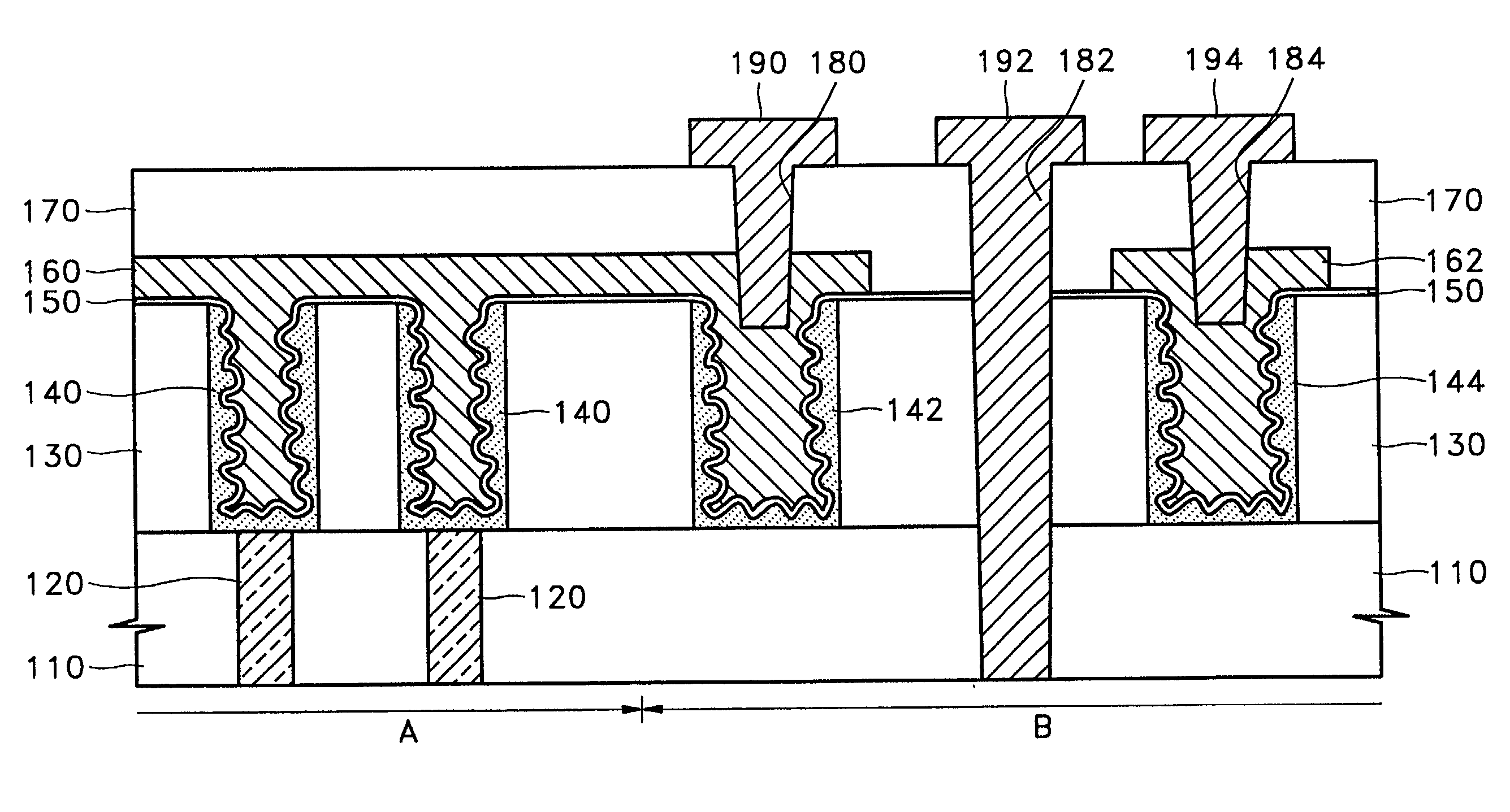
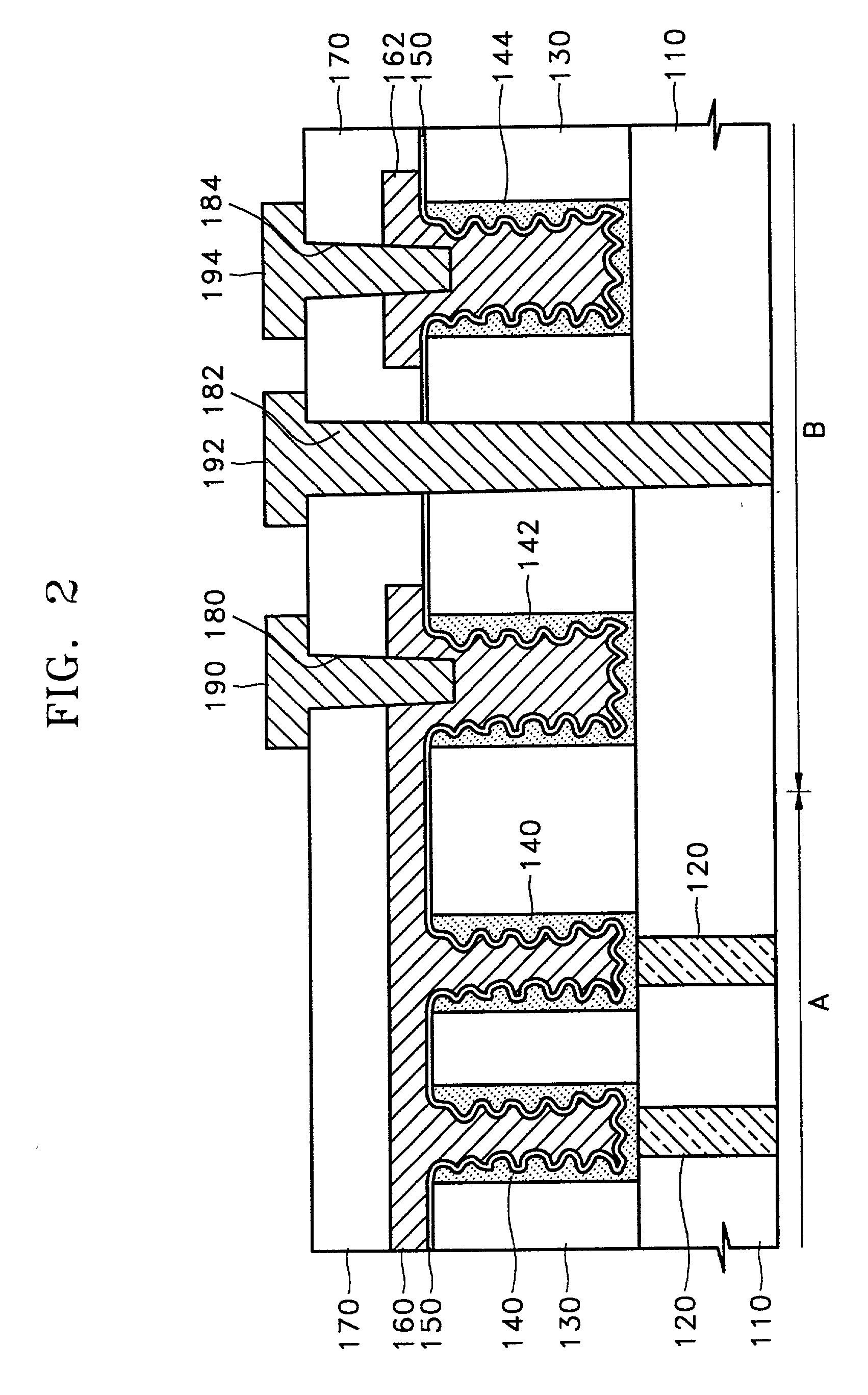
Contact structure with a lower interconnection having t-shaped portion in cross section and method for forming the same
InactiveUS20020153589A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionDielectric layer
A contact structure in a semiconductor device including a dynamic random access memory (DRAM) and a method of forming the same are provided. The contact structure, which is formed in a peripheral circuit area or a logic circuit area of a semiconductor device including a DRAM having a cell array area with a plurality of DRAM cells and the peripheral or logic circuit area, includes a lower interconnection formed of the same material as a capacitor upper electrode of each of the plurality of DRAM cells; an interlayer dielectric layer formed on the lower interconnection and having a contact hole exposing a predetermined portion of the lower interconnection; and an upper interconnection formed on the interlayer dielectric layer and electrically connected to the lower interconnection through the contact hole. The lower portion of the lower interconnection has a larger area than the bottom of the contact hole and extends downward so that the lower interconnection has a T-shape in a cross-section view. By forming the lower interconnection under a shallow contact hole to have a T-shape extending downward when forming contact holes having a large difference in depth, the lower interconnection can be prevented from being pierced when the contact holes are formed. Consequently, stable and uniform contact resistance can be obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating vertical one-transistor floating-body DRAM cell in bulk CMOS process with electrically isolated charge storage region
InactiveUS6964895B2Preventing undesirable current leakage and shortingTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDram
A vertical one-transistor, floating-body DRAM cell is fabricated by forming an isolation region in a semiconductor substrate, thereby defining a semiconductor island in the substrate. A buried source region is formed in the substrate, wherein the top / bottom interfaces of the buried source region are located above / below the bottom of the isolation region, respectively. A recessed region is etched into the isolation region, thereby exposing sidewalls of the semiconductor island, which extend below the top interface of the buried source region. A gate dielectric is formed over the exposed sidewalls, and a gate electrode is formed in the recessed region, over the gate dielectric. A drain region is formed at the upper surface of the semiconductor island region, thereby forming a floating body region between the drain region and the buried source region. Dielectric spacers are formed adjacent to the gate electrode, thereby covering exposed edges of the gate dielectric.
Owner:MOSYS INC
Dram cell with double-gate fin-fet, dram cell array and fabrication method thereof
A transistor structure includes a semiconductor substrate having a top surface and sidewalls extending downward from the top surface, wherein each of the sidewall comprises a vertical upper sidewall surface and a lower sidewall recess laterally etched into the semiconductor substrate. A trench fill dielectric region is inlaid into the top surface of the semiconductor substrate. Two source / drain regions are formed into the top surface of the semiconductor substrate and are sandwiched about the trench fill region. A buried gate electrode is embedded in the lower sidewall recess. A gate dielectric layer is formed on surface of the lower sidewall recess between the semiconductor substrate and the buried gate electrode.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
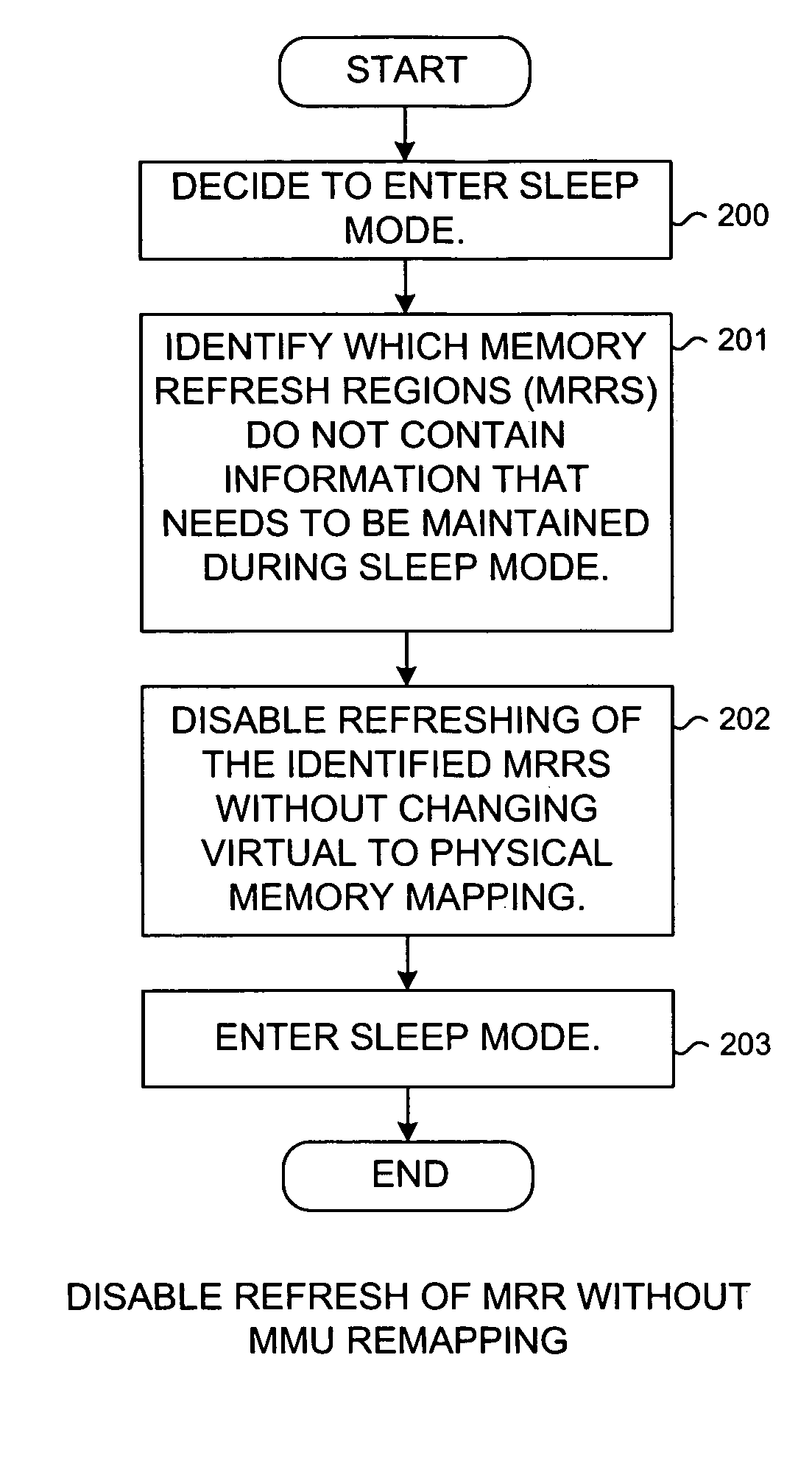
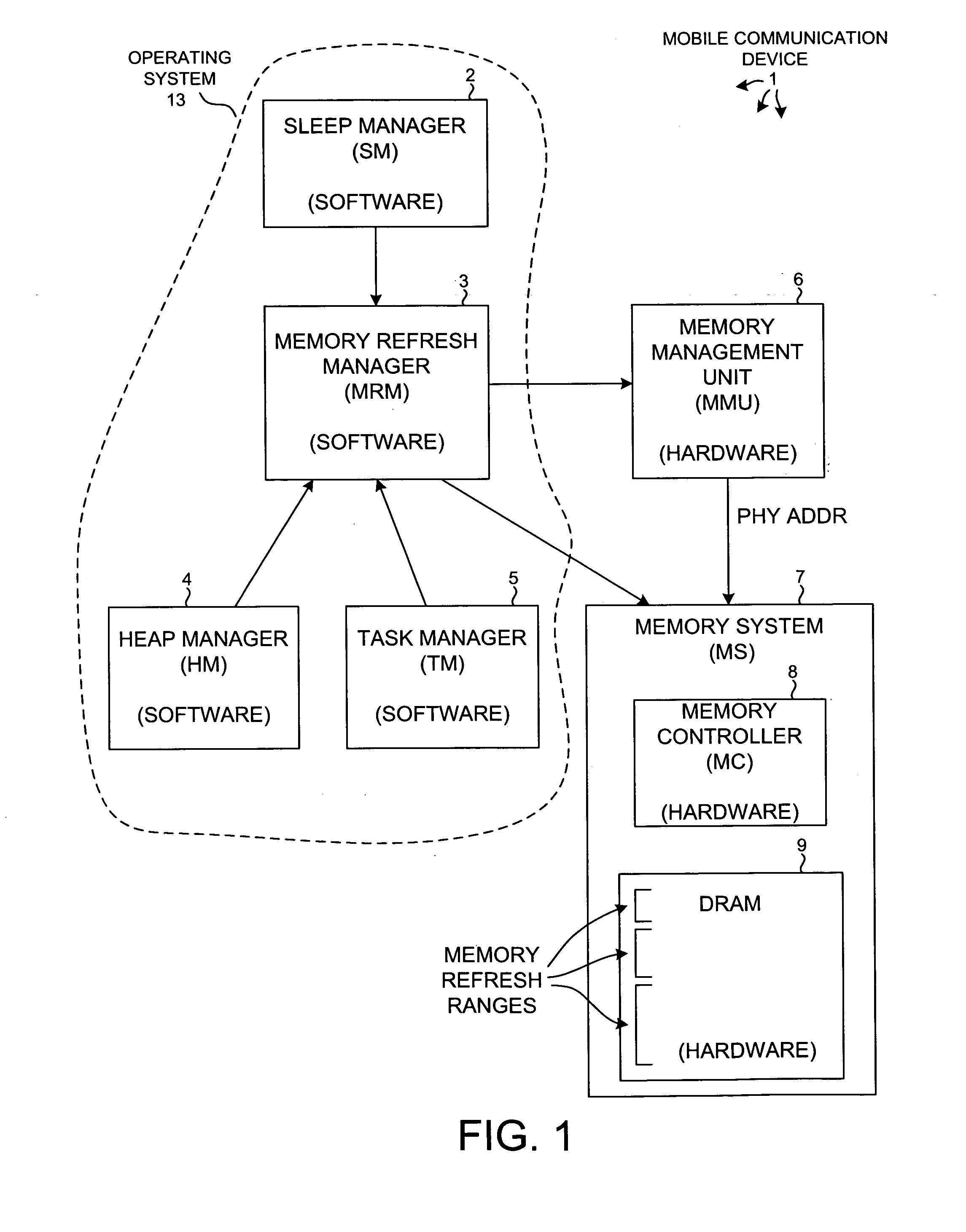
Reducing power consumption by disabling refresh of unused portions of DRAM during periods of device inactivity
InactiveUS20070180187A1Average power consumptionReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTVirtual memoryComputer architecture
Power consumption of a mobile communication device is reduced by disabling refreshing of unused portions of DRAM. DRAM includes multiple separately refreshable memory refresh ranges (MRRs). A memory refresh manager (MRM) within the device's operating system identifies ranges of virtual memory that will not be used during subsequent sleep mode operation. The MRM remaps virtual to physical memory space to conglomerate the physical memory pages (associated with virtual memory that will not be used) in certain MRRs such that the contents of entire MRRs need not be maintained in sleep mode. Information in any remapped physical page that needs to be maintained during sleep mode is copied so that it resides at the same virtual address after the remapping as before. Other software operates in virtual memory space and is not affected by the remapping. Refreshing of the certain MRRs is then disabled for sleep mode, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
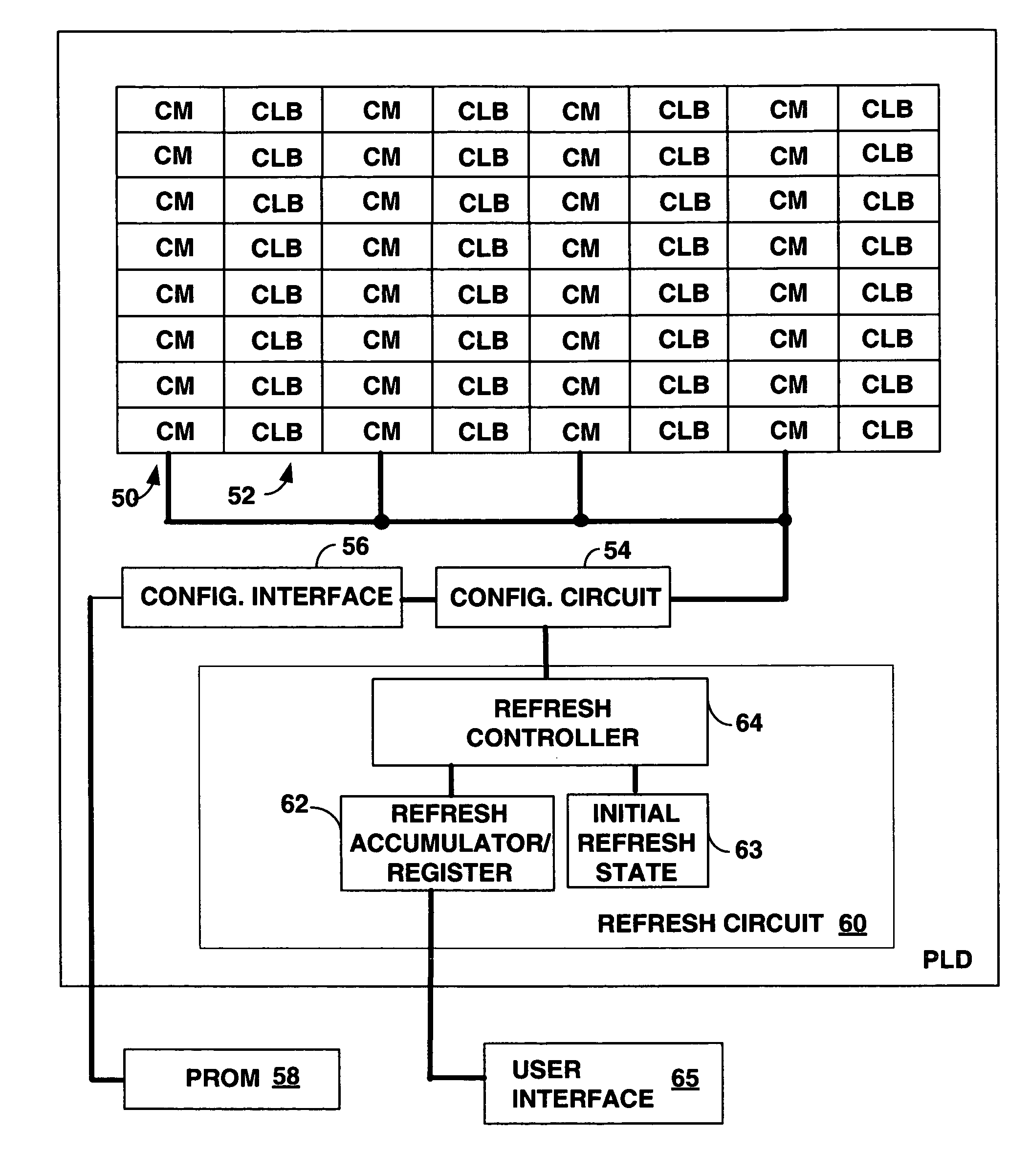
Programmable logic device (PLD) with memory refresh based on single event upset (SEU) occurrence to maintain soft error immunity
ActiveUS7764081B1Reduce memory cell densityMinimized circuitReliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsProgrammable logic deviceSingle event upset
A Programmable Logic Device (PLD) is provided with configuration memory cells displaying a superior soft error immunity by combating single event upsets (SEUs) as the configuration memory cells are regularly refreshed from non-volatile storage depending on the rate SEUs may occur. Circuitry on the PLD uses a programmable timer to set a refresh rate for the configuration memory cells. Because an SEU which erases the state of a small sized memory cell due to collisions with cosmic particles may take some time to cause a functional failure, periodic refreshing will prevent the functional failure. The configuration cells can be DRAM cells which occupy significantly less space than the SRAM cells. Refresh circuitry typically provided for DRAM cells is reduced by using the programming circuitry of the PLD. Data in the configuration cells of the PLD are reloaded from either external or internal soft-error immune non-volatile memory.
Owner:XILINX INC
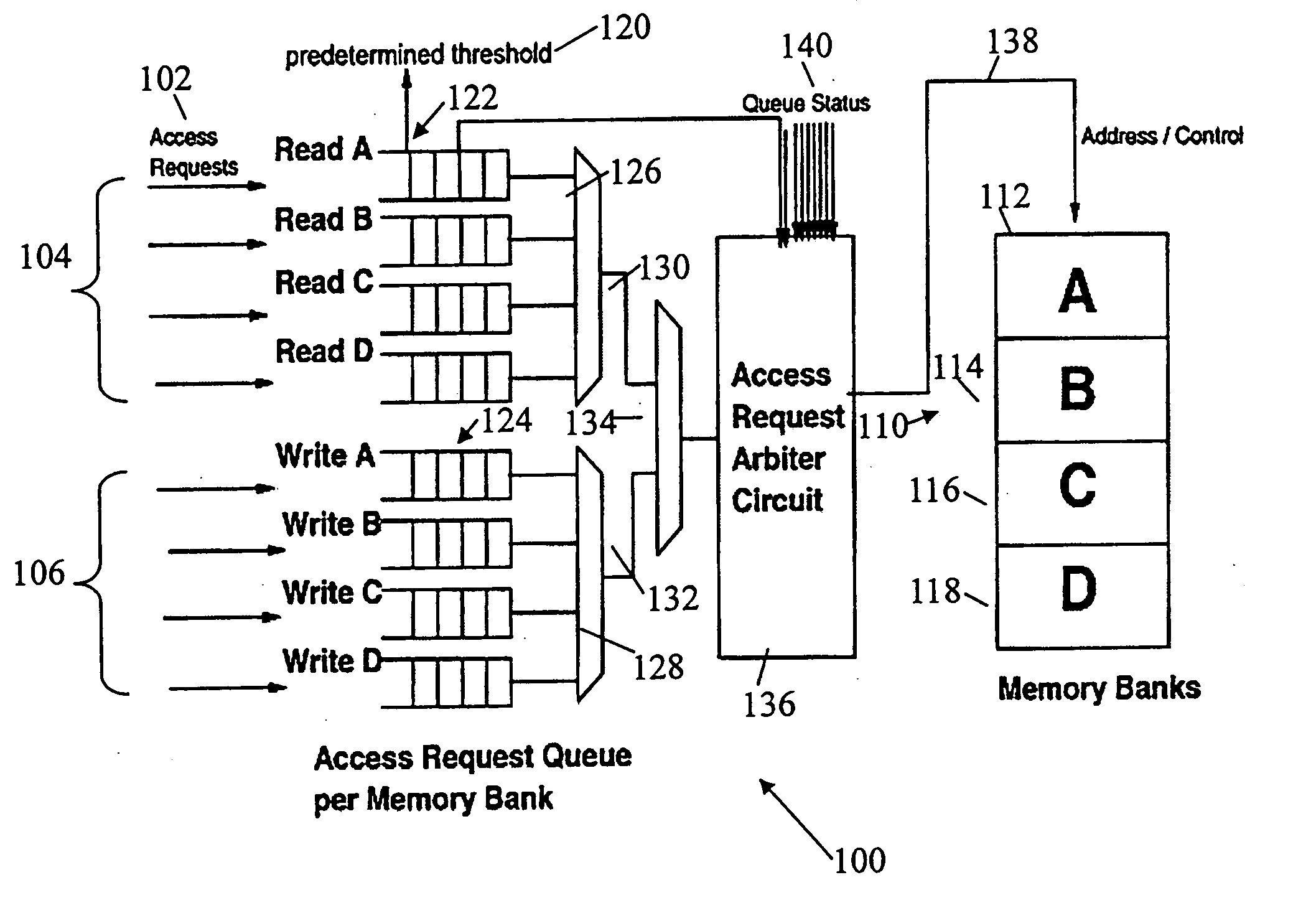
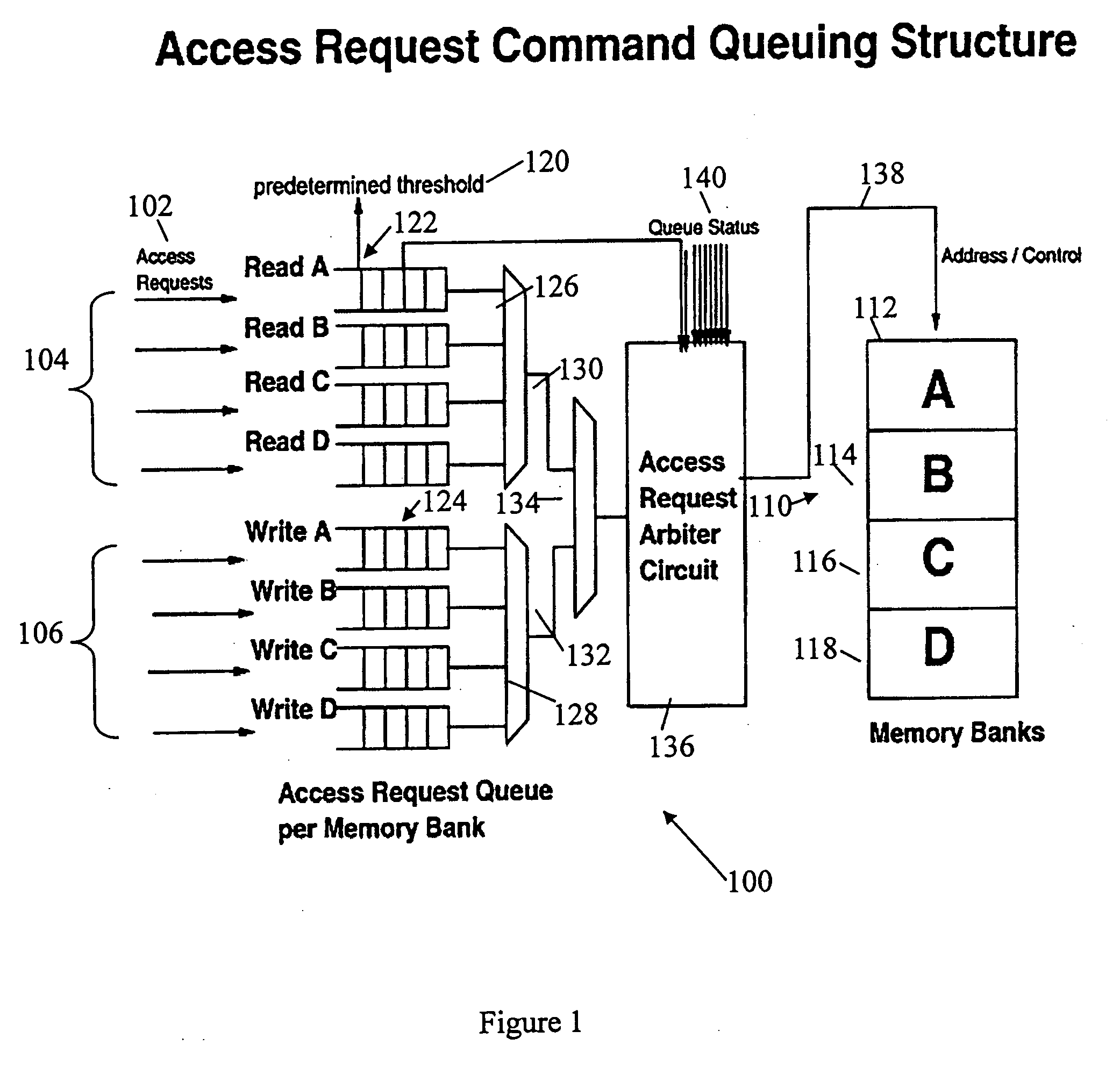
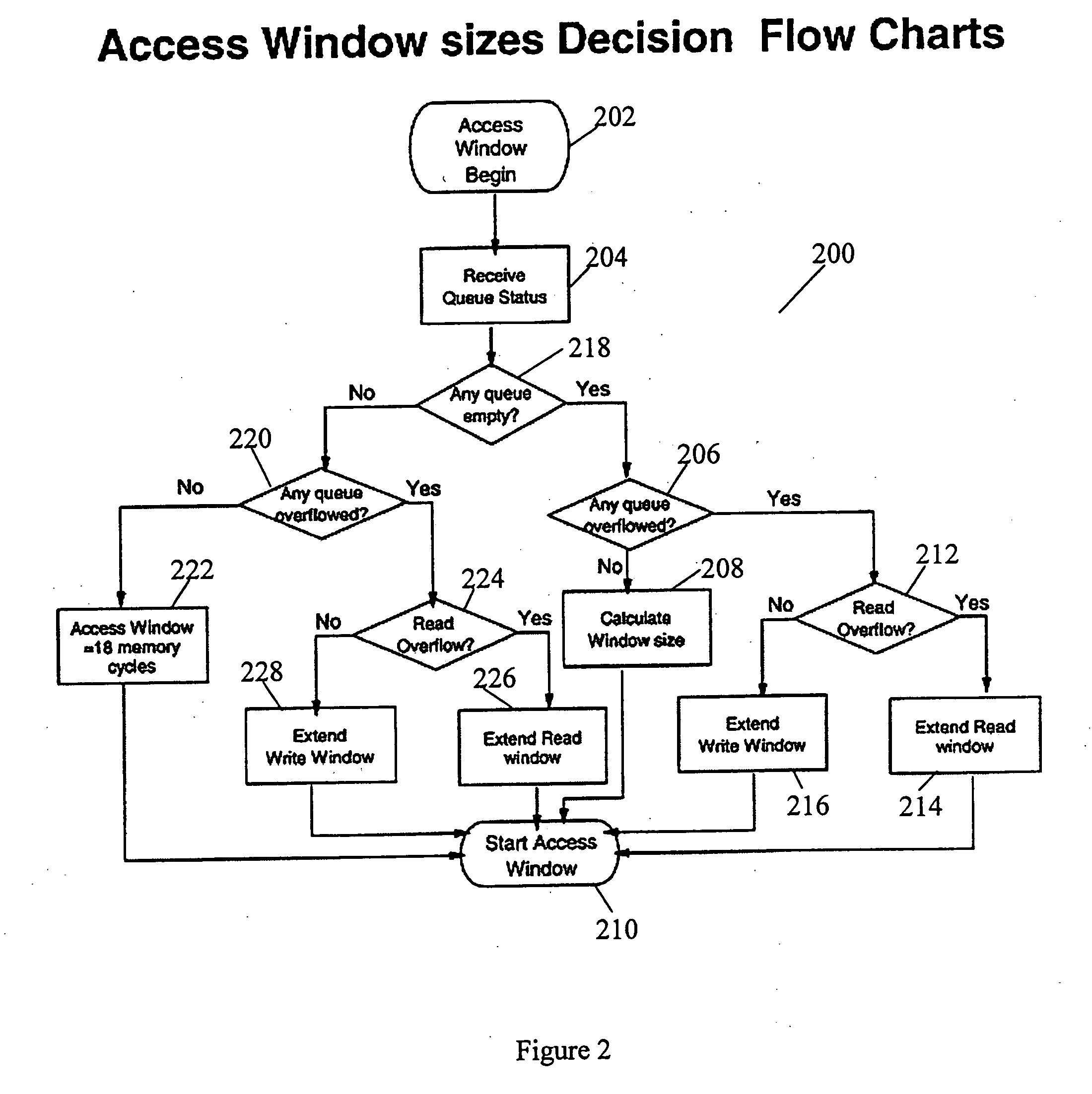
DRAM access command queuing structure
ActiveUS20060026342A1Solve insufficient bandwidthAvoid bottleneck and conflictMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory systemsMemory bankDram memory
Access arbiters are used to prioritize read and write access requests to individual memory banks in DRAM memory devices, particularly fast cycle DRAMs. This serves to optimize the memory bandwidth available for the read and the write operations by avoiding consecutive accesses to the same memory bank and by minimizing dead cycles. The arbiter first divides DRAM accesses into write accesses and read accesses. The access requests are divided into accesses per memory bank with a threshold limit imposed on the number of accesses to each memory bank. The write receive packets are rotated among the banks based on the write queue status. The status of the write queue for each memory bank may also be used for system flow control. The arbiter also typically includes the ability to determine access windows based on the status of the command queues, and to perform arbitration on each access window.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
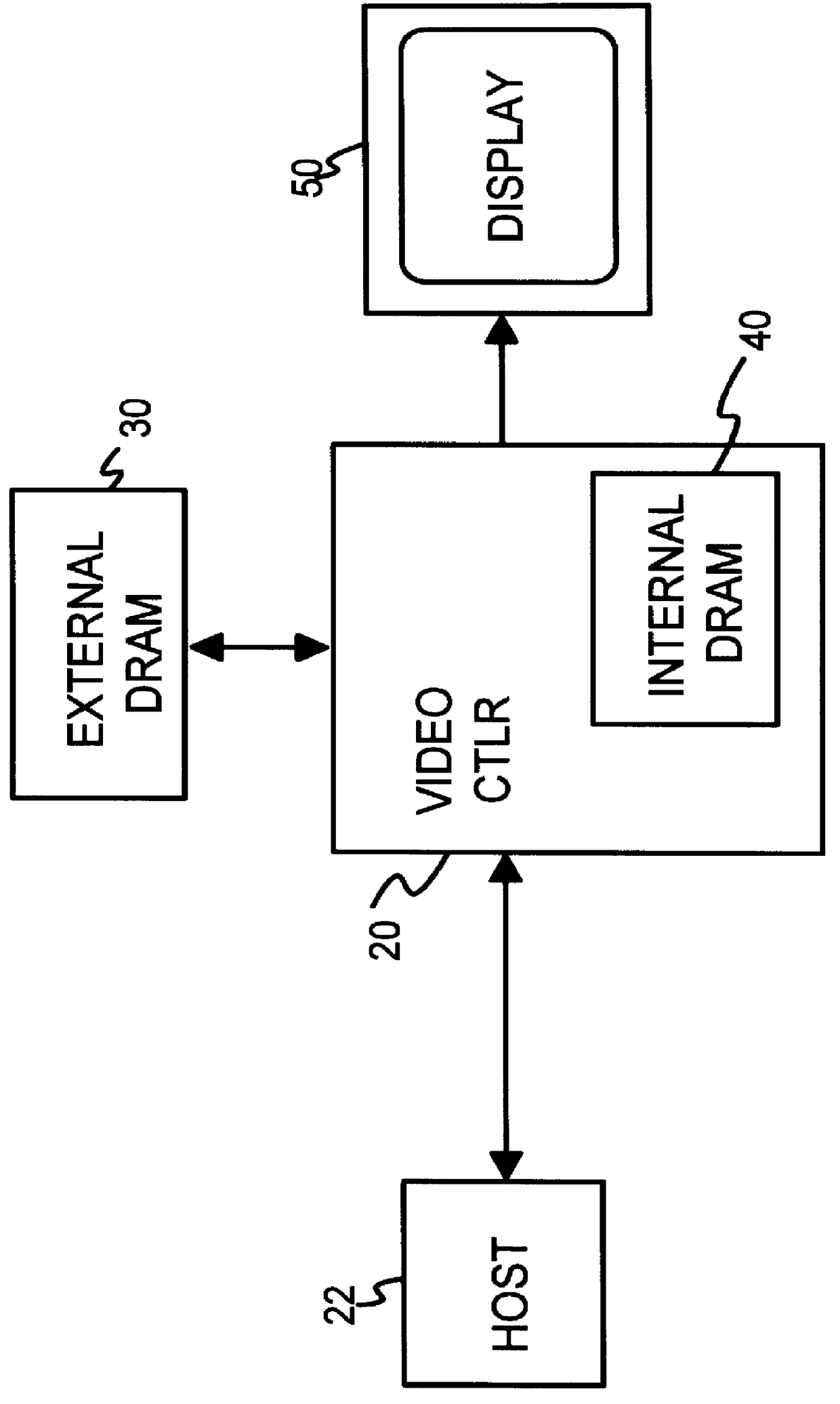
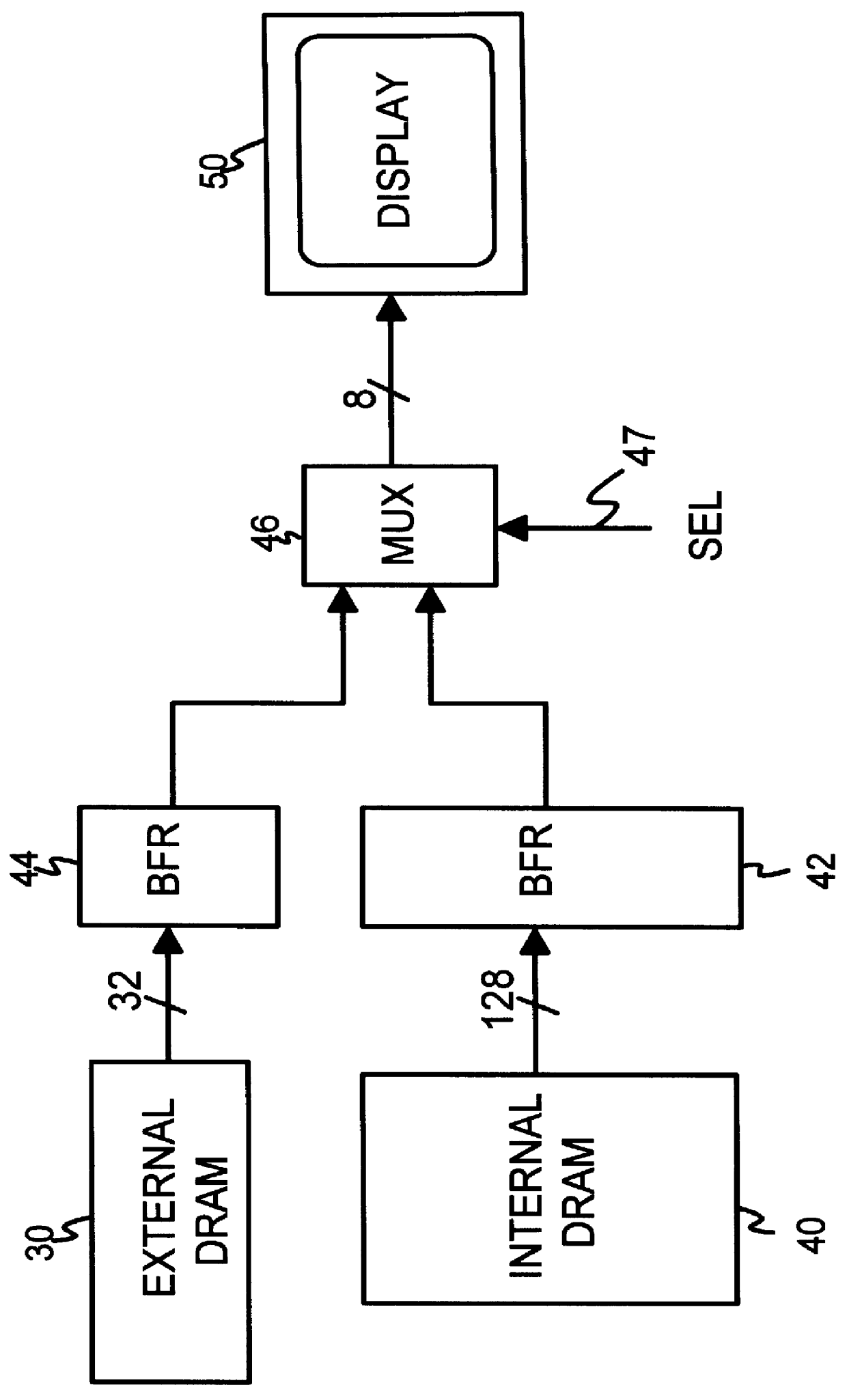
Testable interleaved dual-DRAM architecture for a video memory controller with split internal/external memory
A video sub-system features reduced power consumption by integrating a video memory onto the same chip as the video memory controller. The video memory is preferably a small DRAM sufficiently large to store all pixel data for lower resolutions, but insufficient for higher resolutions. At higher resolutions, an external DRAM supplements the internal DRAM. The amount of external DRAM needed depends upon the resolution to be supported. The internal DRAM has a wide data bus and thus high bandwidth, since no external I / O pins are needed. The external DRAM is narrow to minimize pincount and power consumption. Since the external DRAM is slower and lower in bandwidth, pixel data from both internal and external DRAMs are interleaved together for each horizontal scan line. Thus the lower bandwidth of the external DRAM is masked by the high bandwidth of the wide internal DRAM. Either the internal or the external DRAM, or both, are automatically tested with a pseudo-random number generator that writes pseudo-random numbers to the DRAM while simultaneously supplying pixel data to the graphics data path for display. A checksum of the pixel data output from the graphics data path is generated for the first screen of pixels or frame, while on the second frame the pseudo-random number generator is disabled and the DRAM supplies the same pixel data that was written to it by the pseudo-random number generator during the first frame. The checksums for the first and second frames should match if the DRAM is free of faults.
Owner:FAUST COMMUNICATIONS LLC
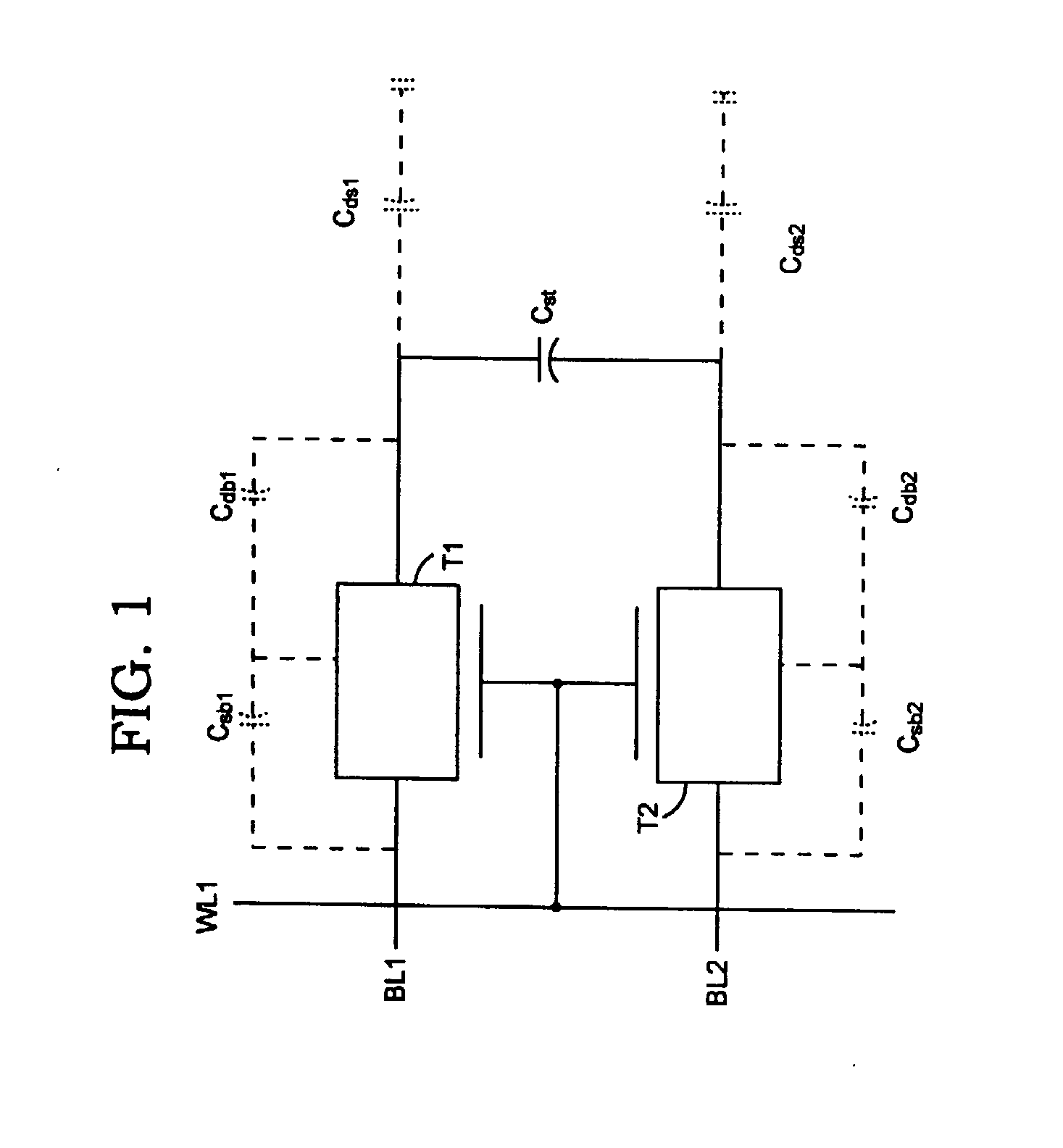
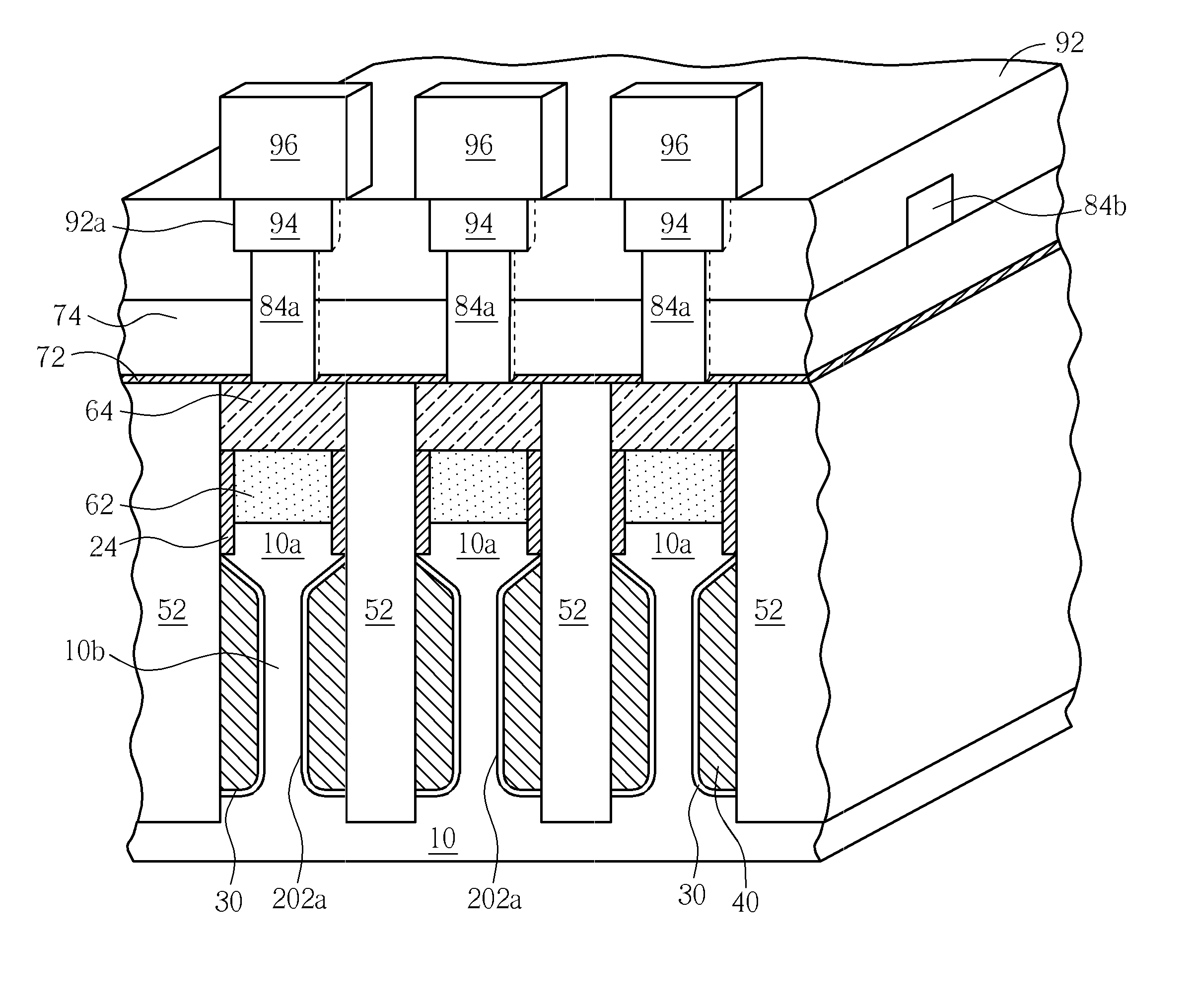
Structure and system-on-chip integration of a two-transistor and two-capacitor memory cell for trench technology
InactiveUS6845033B2Lower performance requirementsReducing storage chargeTransistorJoints with sealing surfacesRandom access memoryEngineering
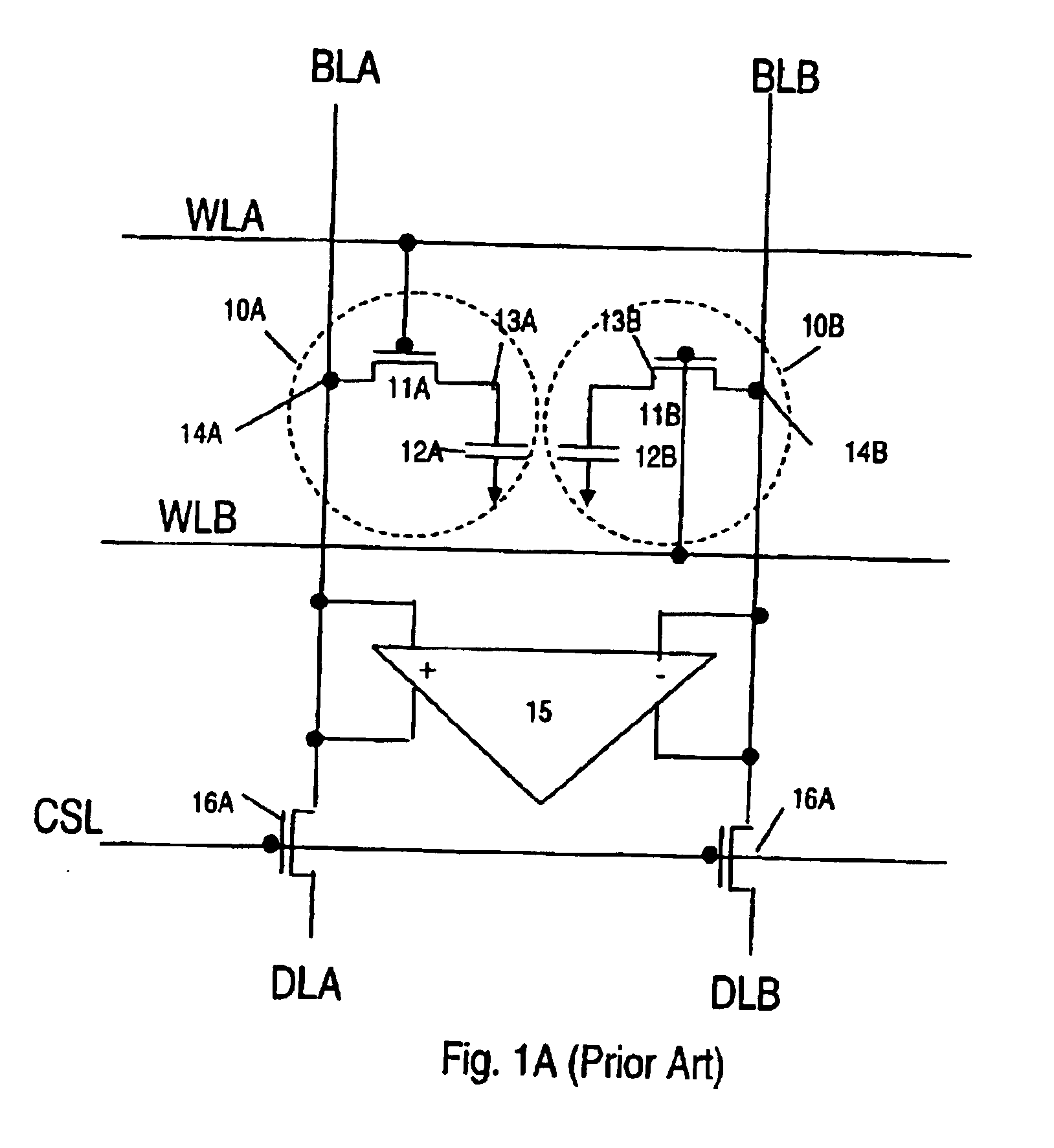
A two-port dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell consisting of two transistors and two trench capacitors (2T and 2C DRAM cell) connecting two one transistor and one capacitor DRAM cell (1T DRAM cell) is described. The mask data and cross-section of the 2T 2C DRAM and 1T DRAM cells are fully compatible to each other except for the diffusion connection that couples two storage nodes of the two 1T DRAM cells. This allows a one-port memory cell with 1T and 1C DRAM cell and a two-port memory cell with 2T and 2C DRAM cell to be fully integrated, forming a true system-on chip architecture. Alternatively, by halving the capacitor, the random access write cycle time is further reduced, while still maintaining the data retention time. The deep trench process time is also reduced by reducing by one-half the trench depth.
Owner:IBM CORP
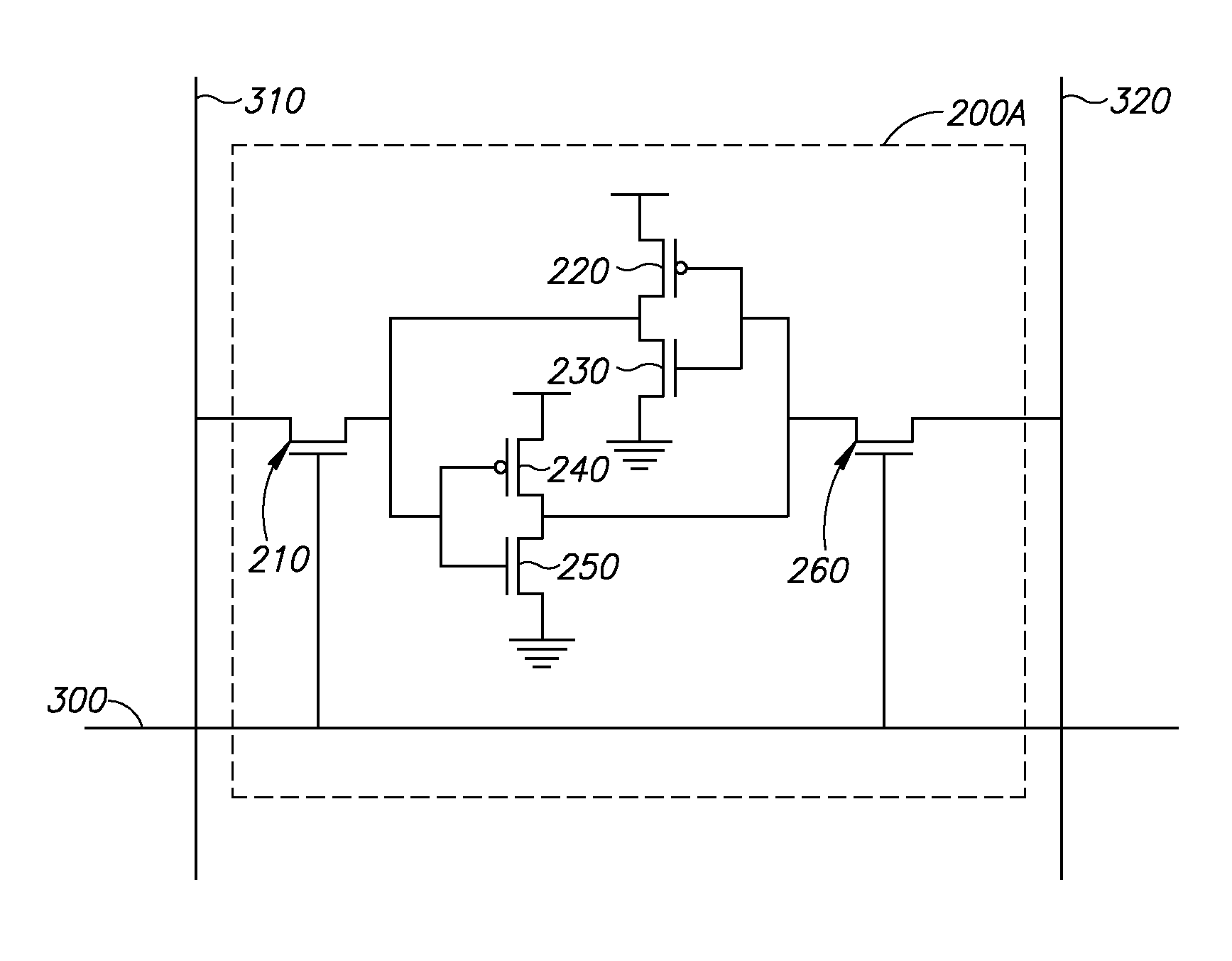
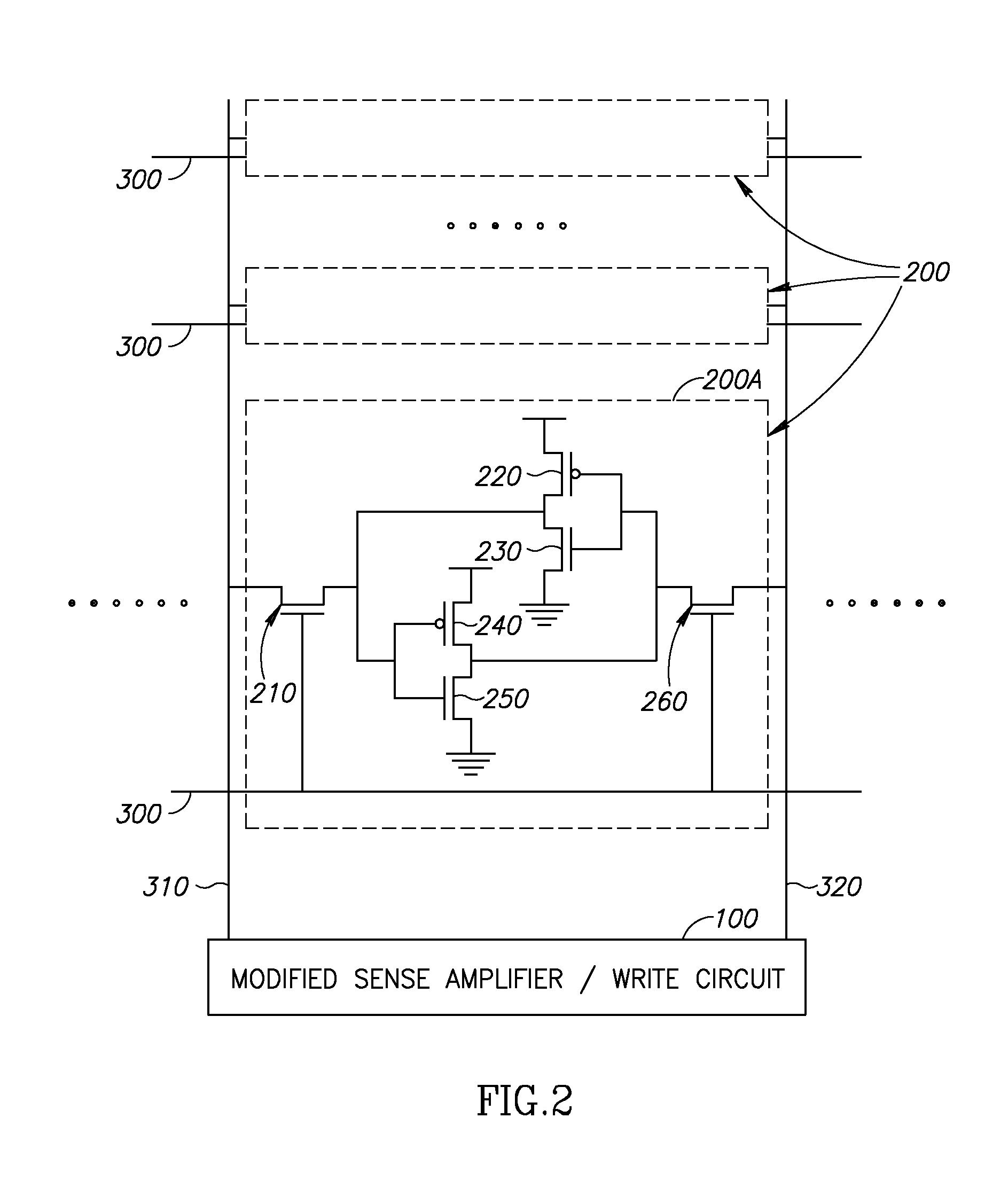
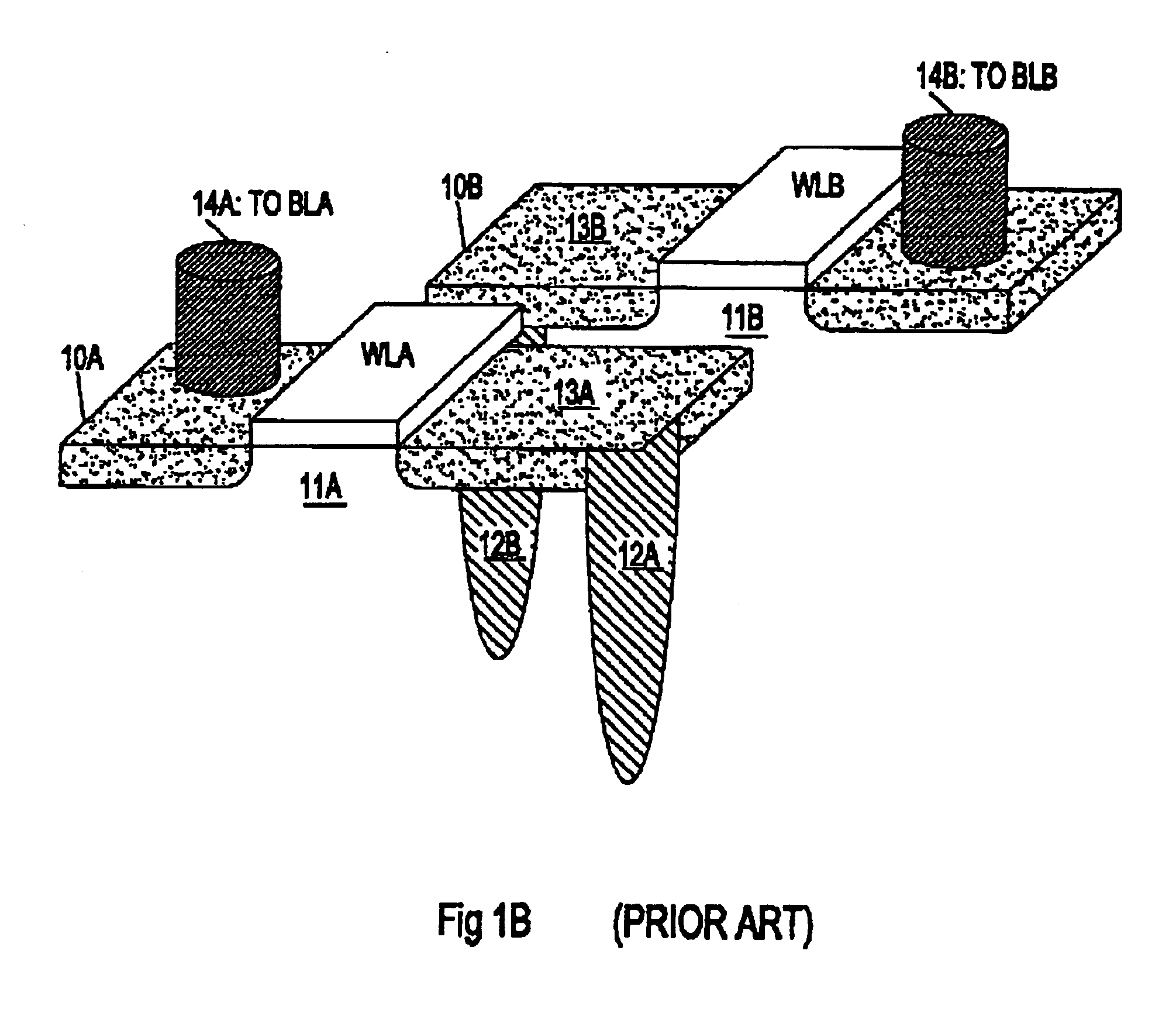
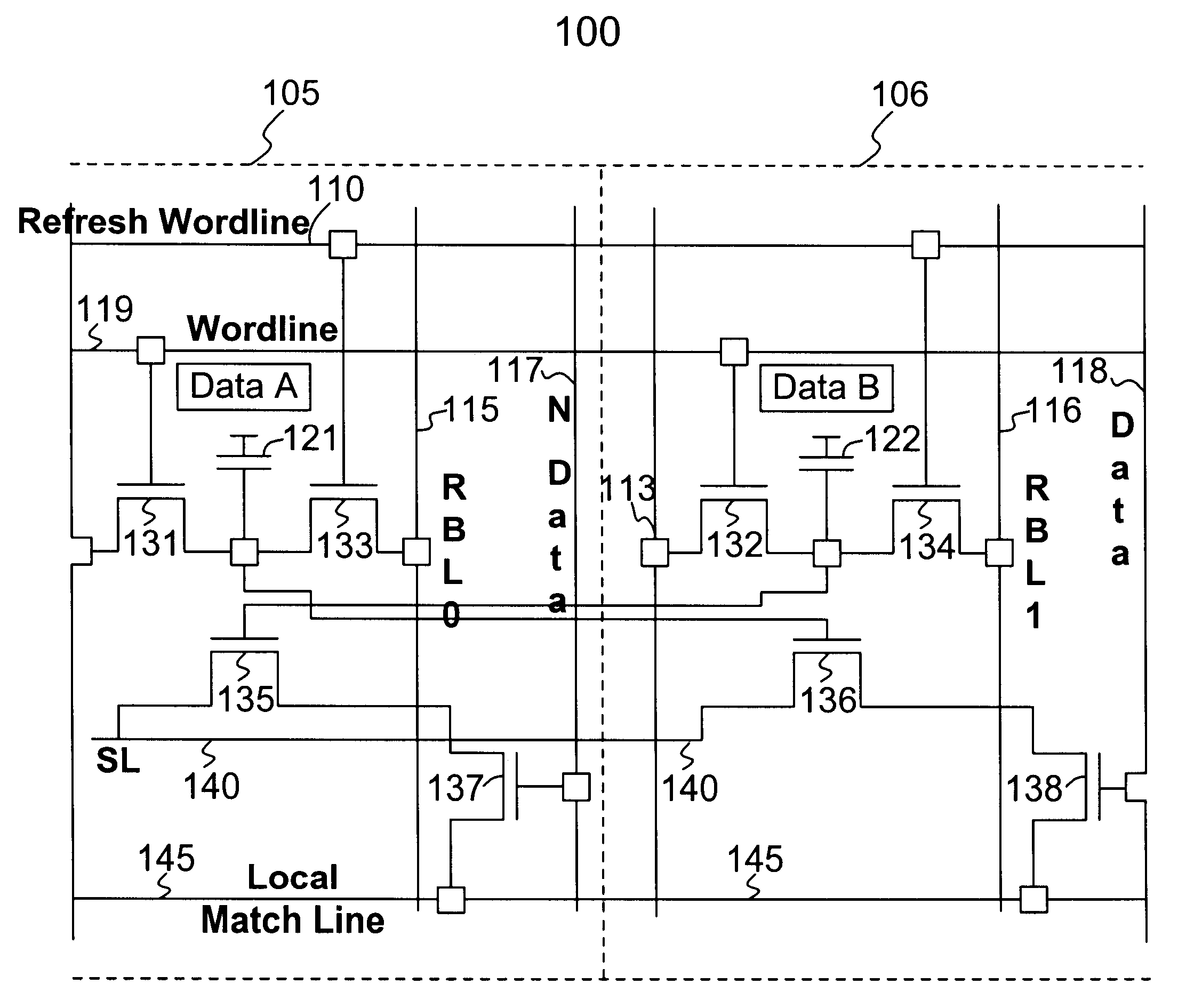
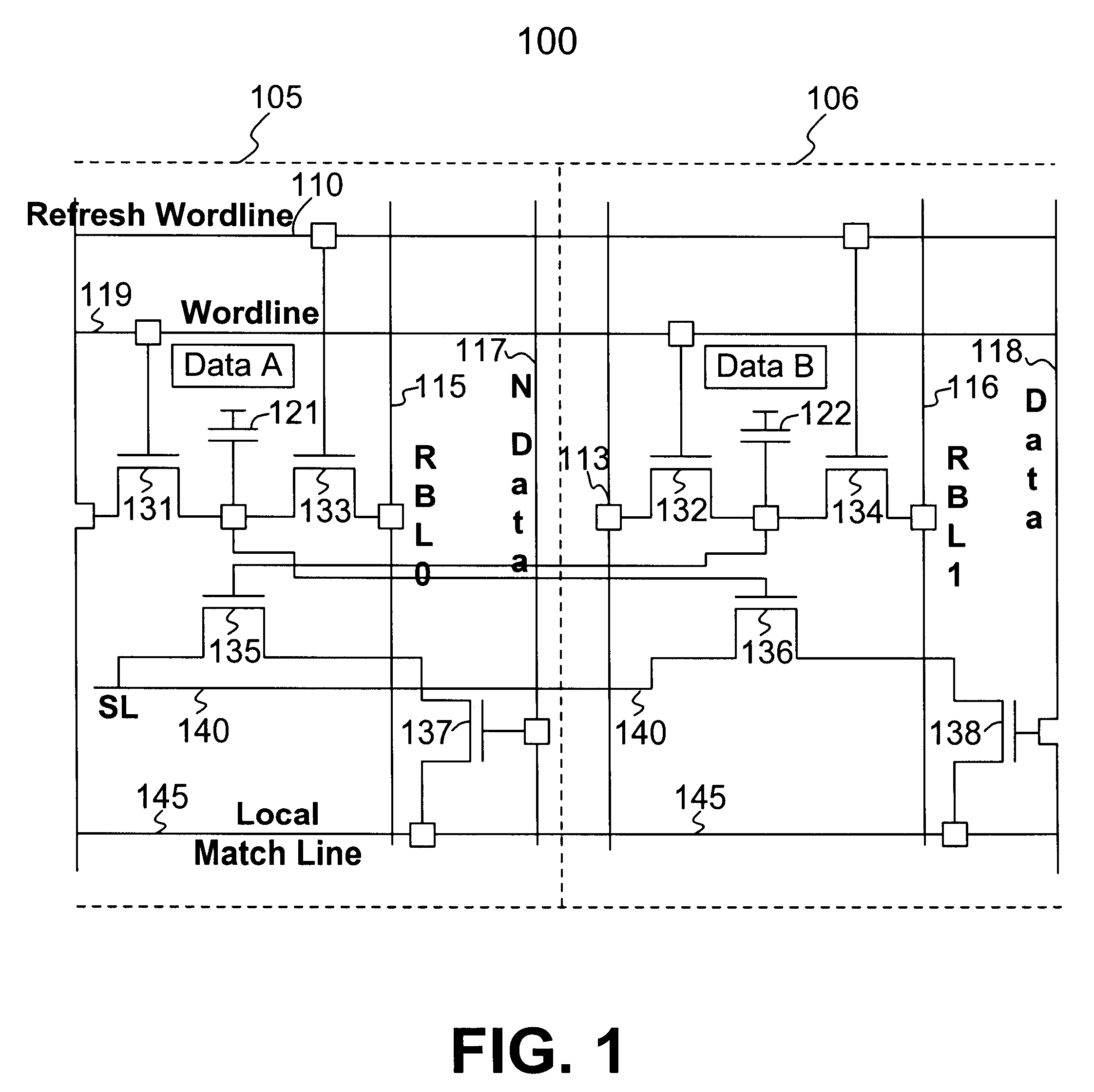
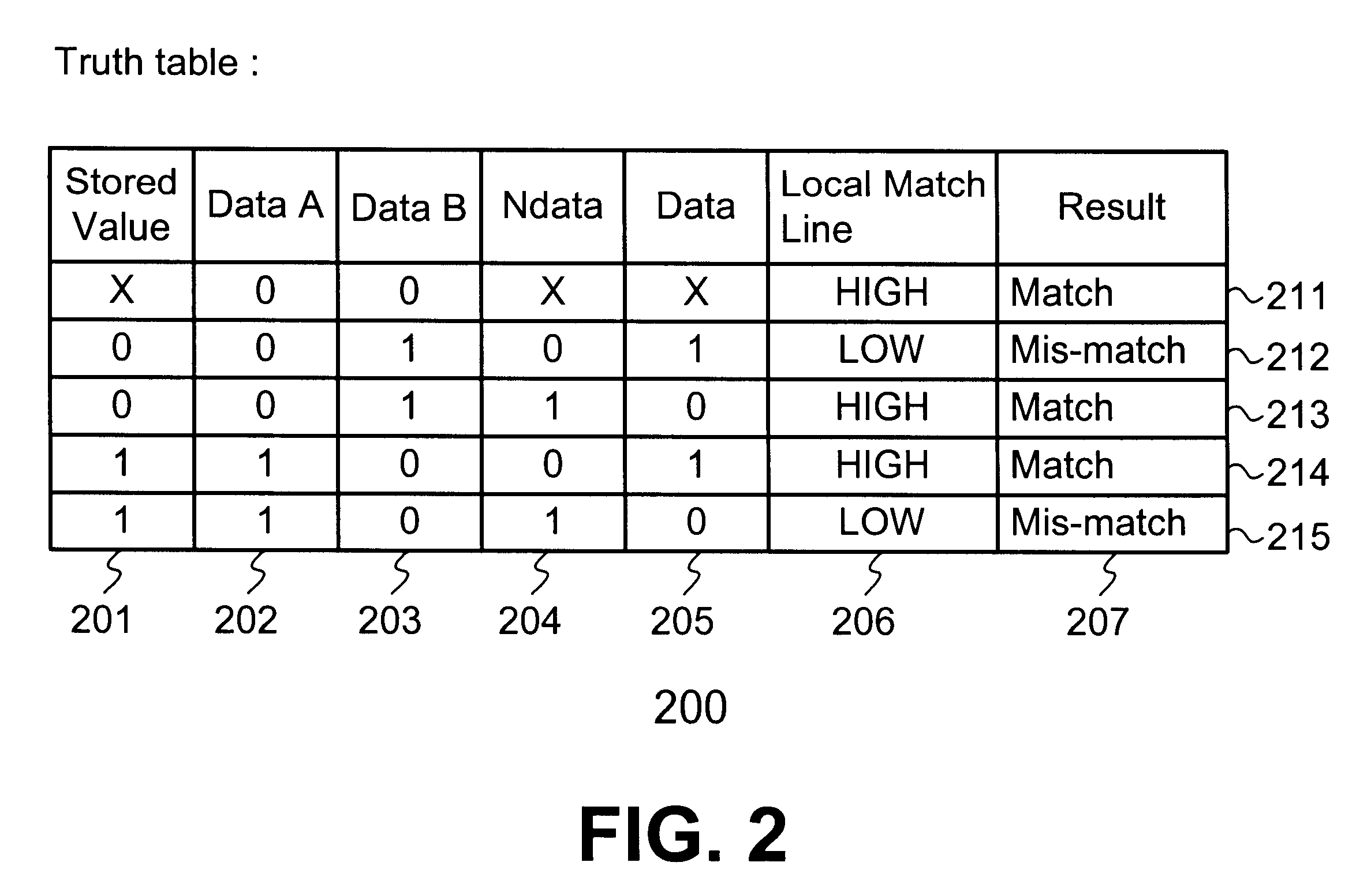
DRAM based refresh-free ternary CAM
A ternary state content addressable memory (CAM) cell that includes two DRAM cells. In addition to a port for controlling and transmitting data to the CAM, another port is exclusively used for refreshing the DRAM cells. A refresh word line is coupled to the two DRAM cells for performing DRAW cell refresh. A refresh bit line is coupled to the first of the two DRAM cells for refreshing this first DRAM cell. A refresh bit line is coupled to the second of the two DRAM cells for refreshing this second DRAM cell. Problematic power consumption and voltage swing found in a conventional CAM are overcome in the CAM. A swing line (SL) is coupled to said first and second DRAM cells and a local match line (LML) of said CAM cell, said SL having an adjustable voltage level for changing voltage swing in said LML to regulate trade-off between power consumption and speed of said CAM cell.
Owner:ATEL VENTURE FUND LLC
Nitrided STI liner oxide for reduced corner device impact on vertical device performance
ActiveUS6998666B2Reduces corner effectReduces dopant depletionTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETElectrical conductor
A method of fabricating an integrated circuit device comprises etching a trench in a substrate and forming a dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell having a storage capacitor at a lower end and an overlying vertical metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) comprising a gate conductor and a boron-doped channel. The method includes forming trenches adjacent the DRAM cell and a silicon-oxy-nitride isolation liner on either side of the DRAM cell, adjacent the gate conductor. Isolation regions are then formed in the trenches on either side of the DRAM cell. Thereafter, the DRAM cell, including the boron-containing channel region adjacent the gate conductor, is subjected to elevated temperatures by thermal processing, for example, forming a support device on the substrate adjacent the isolation regions. The nitride-containing isolation liner reduces segregation of the boron in the channel region, as compared to an essentially nitrogen-free oxide-containing isolation liner.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com