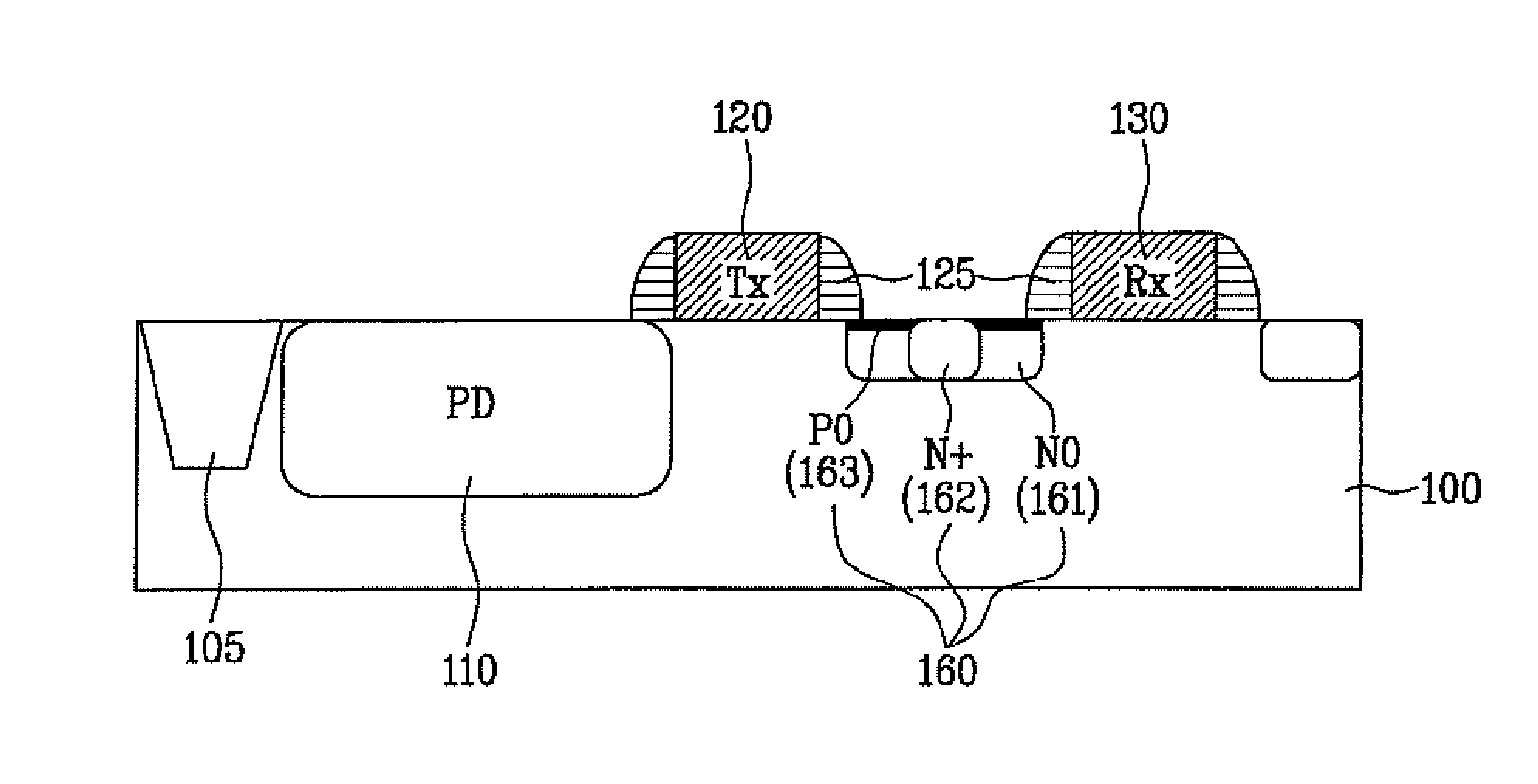
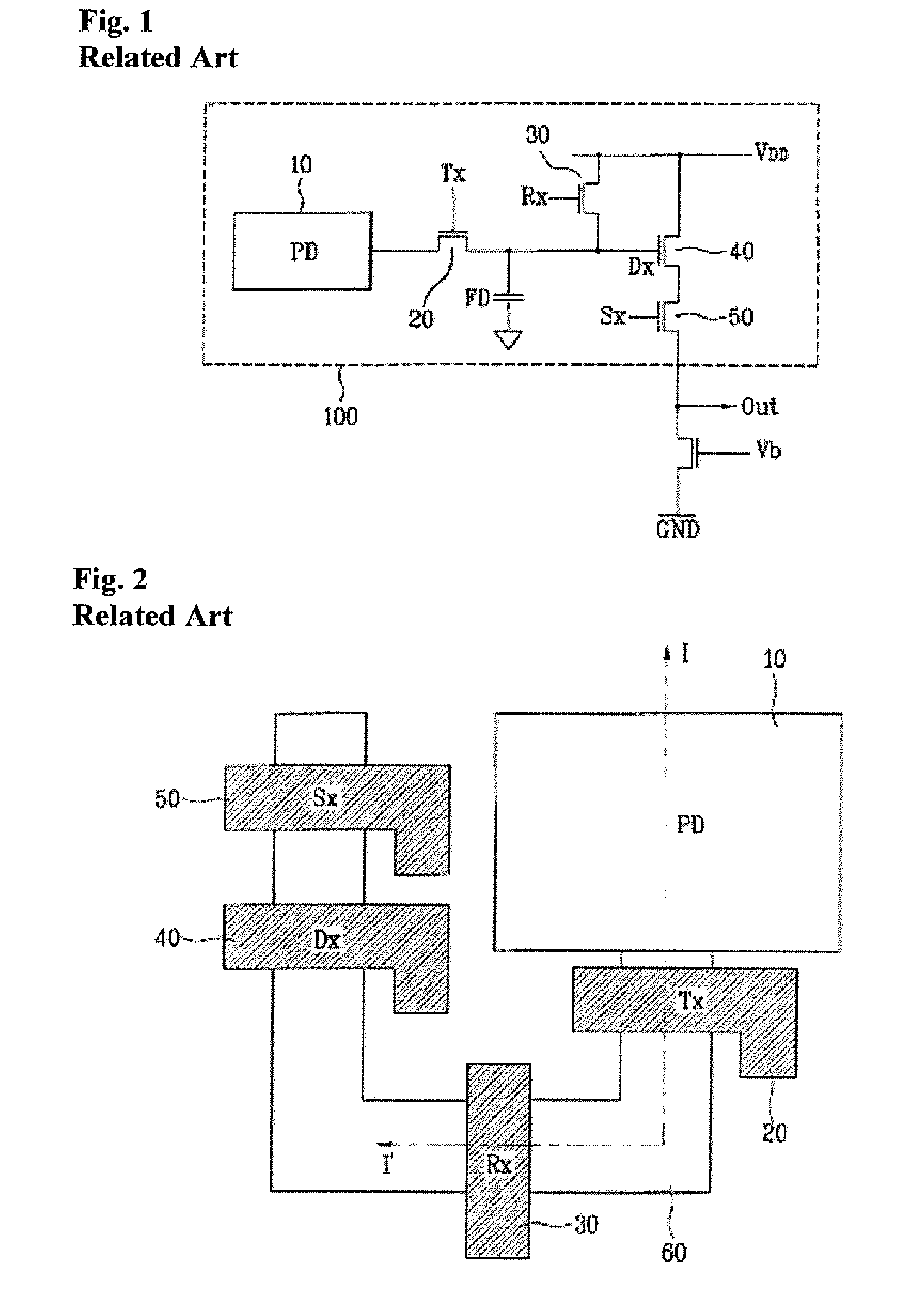
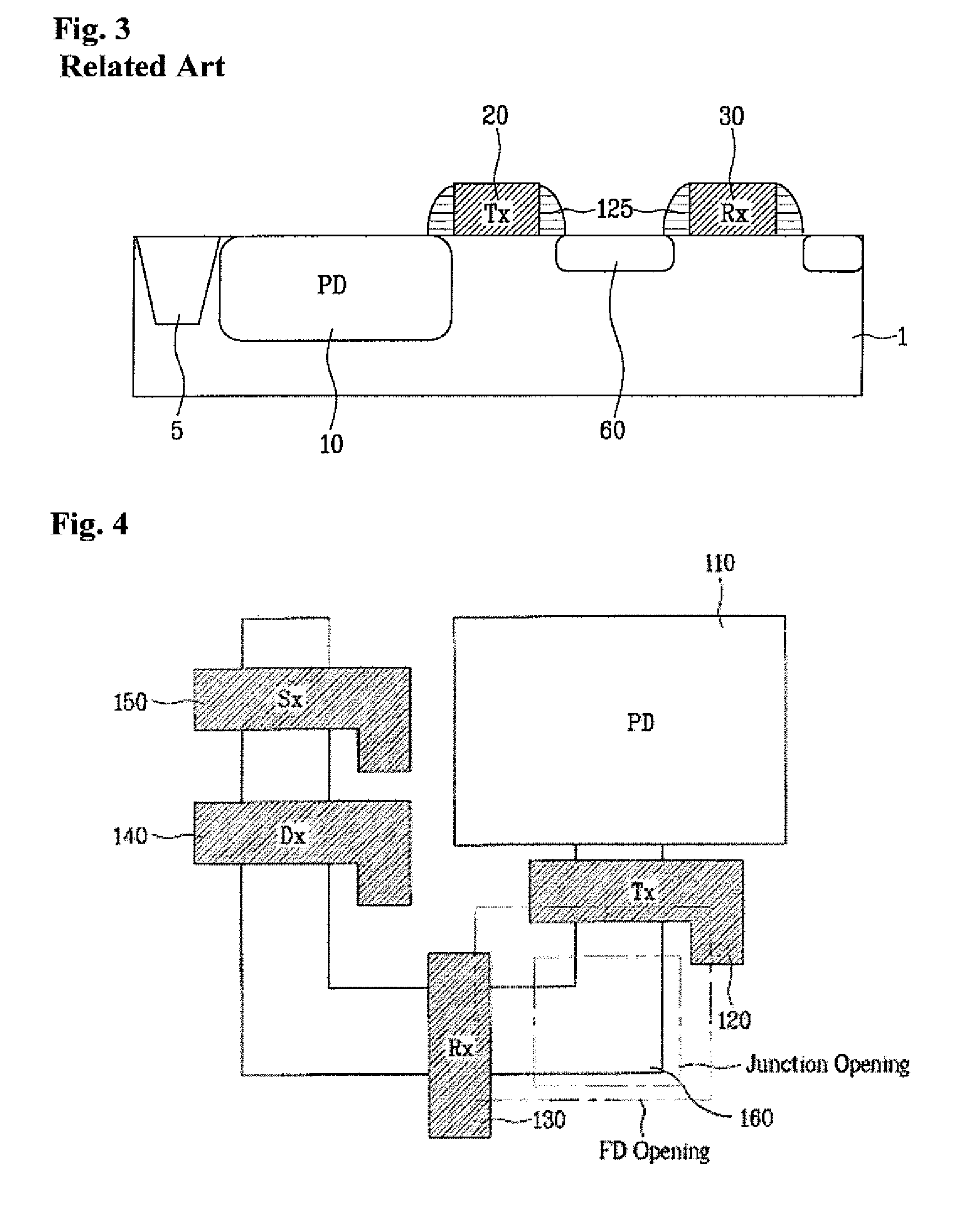
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
256 results about "Junction leakage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
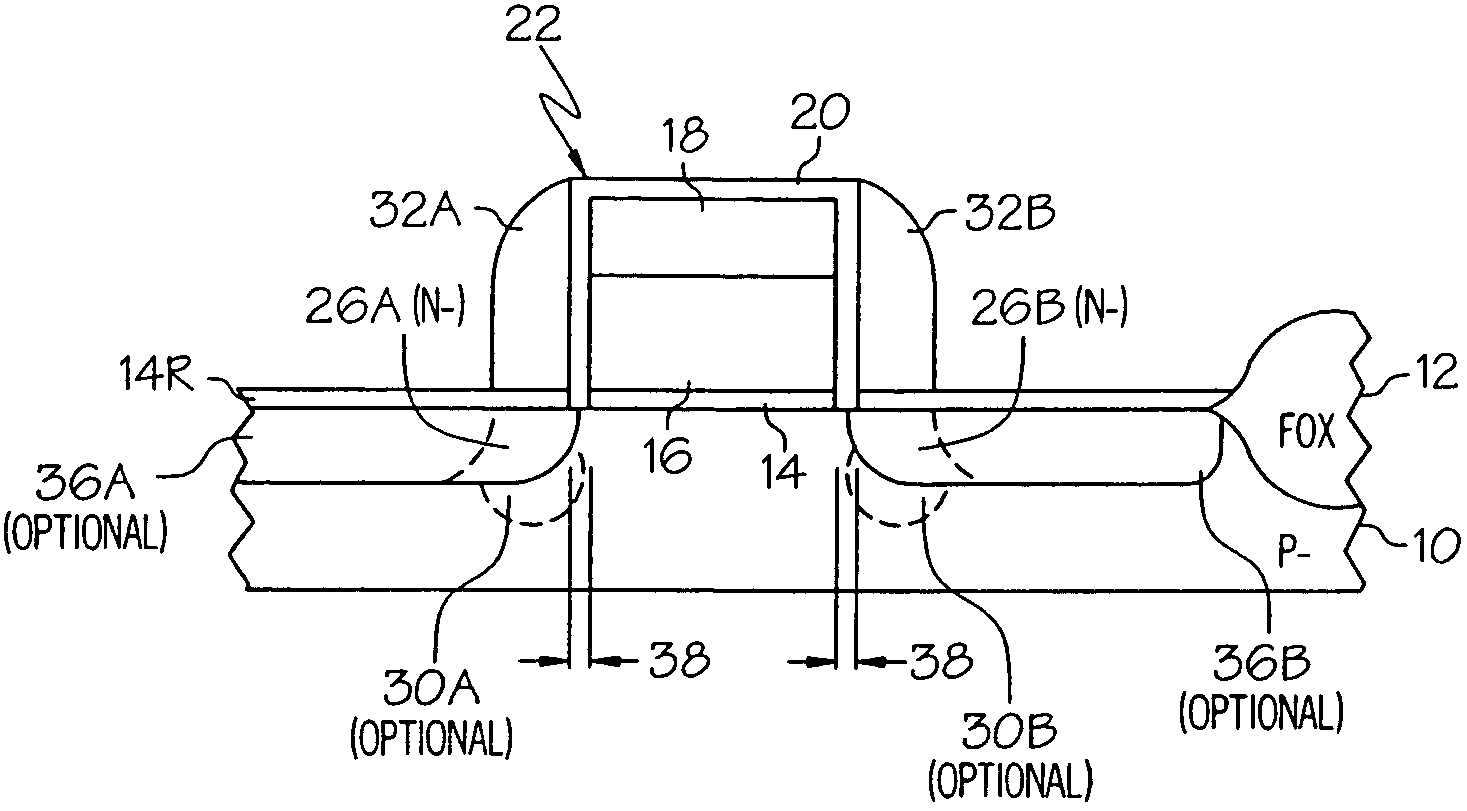
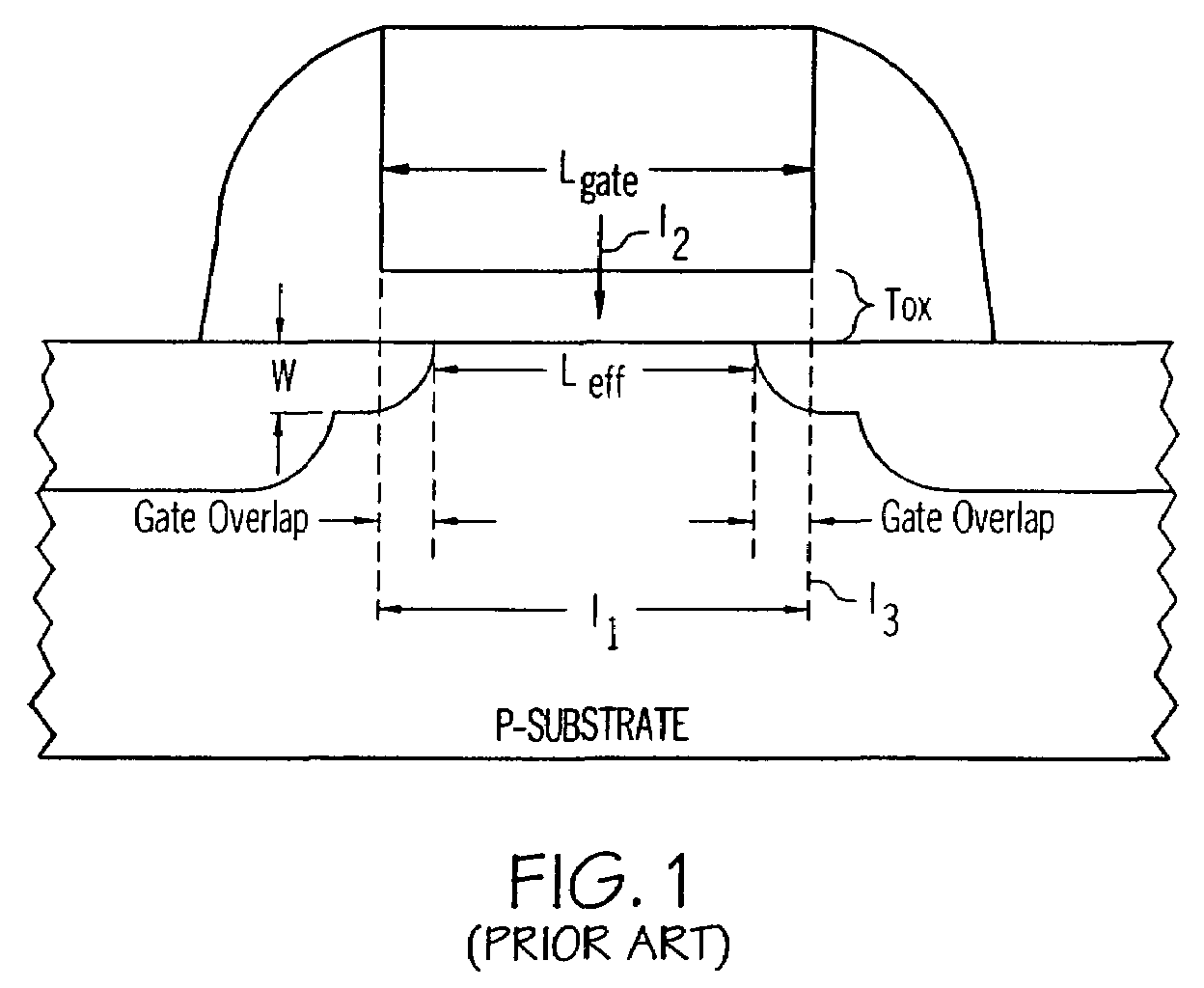
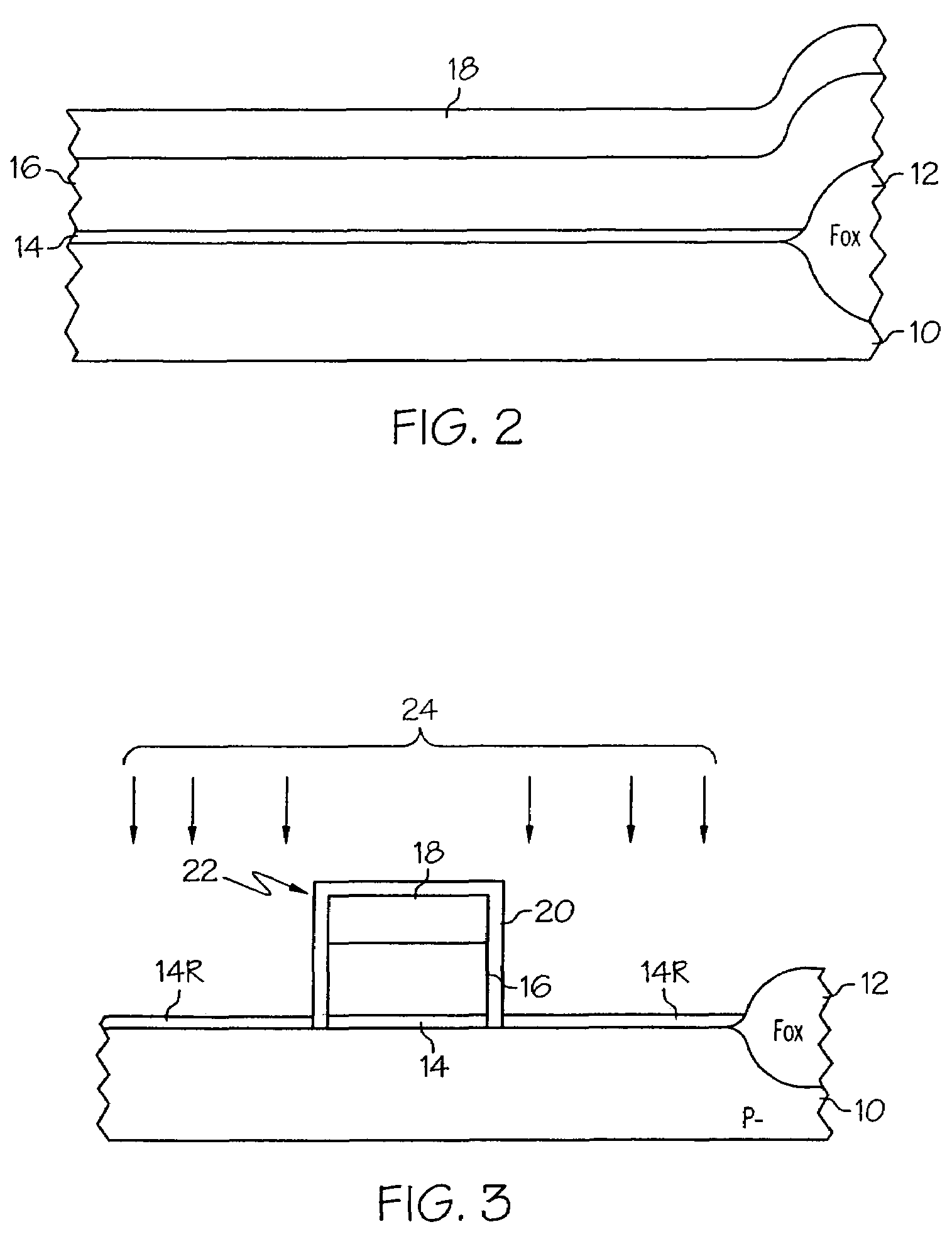
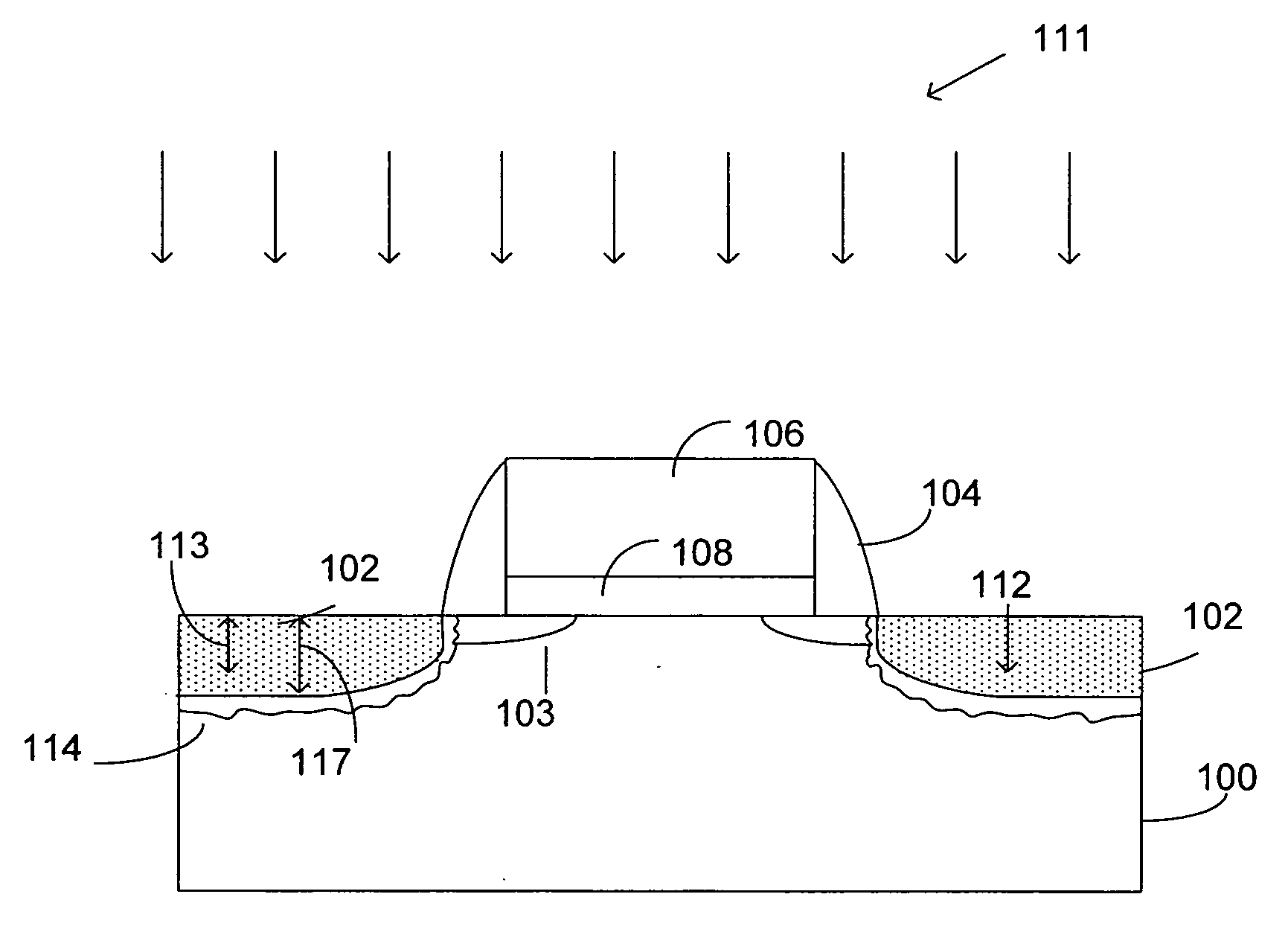
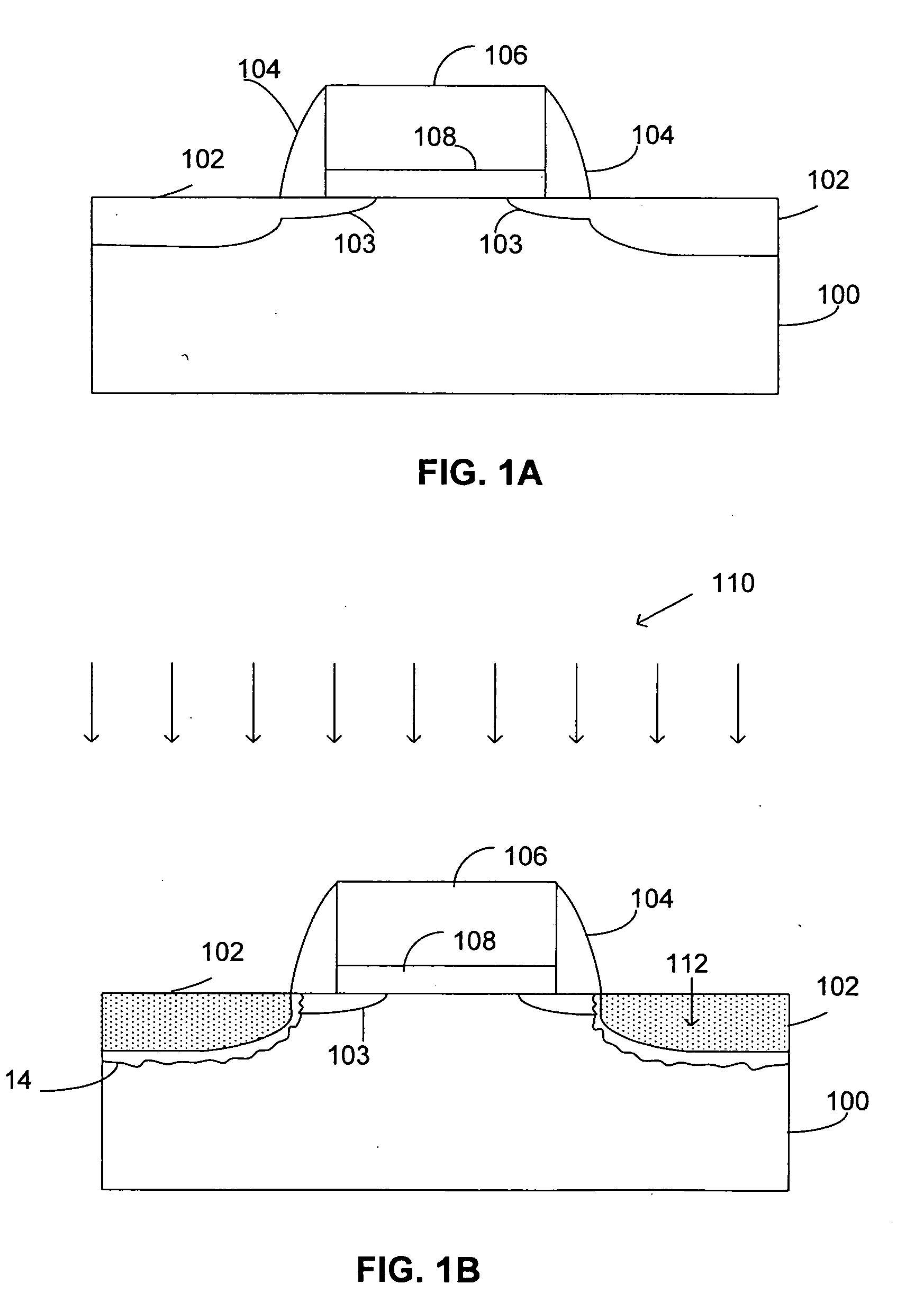
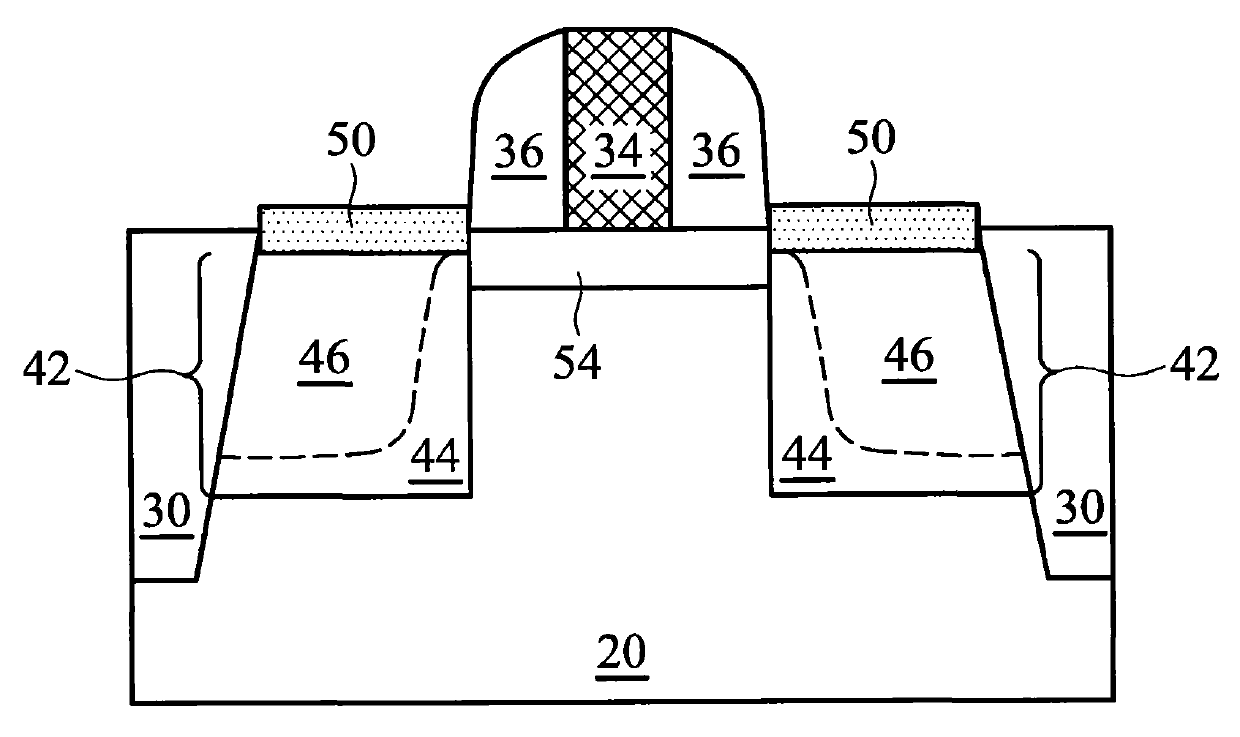
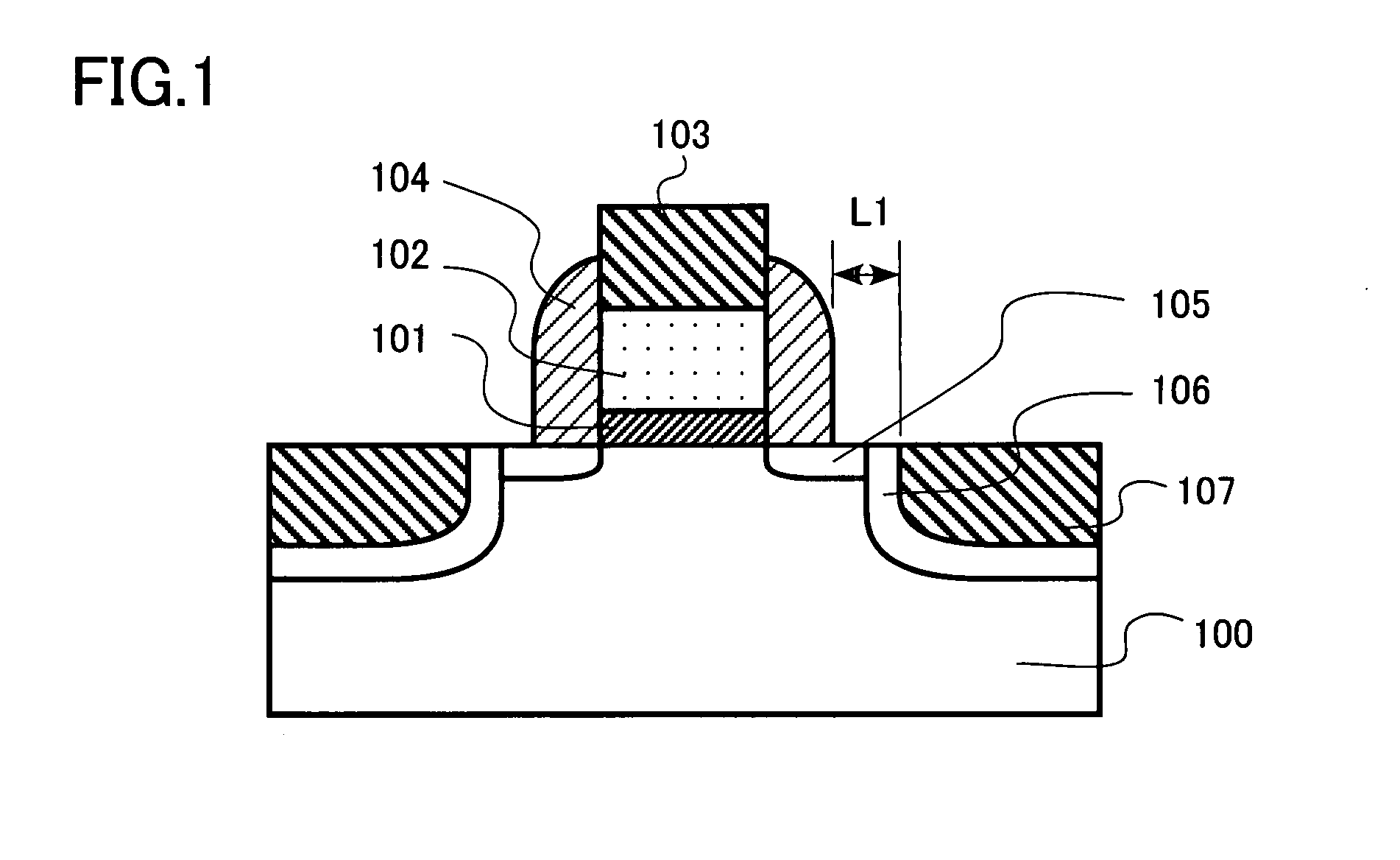
If a potential is applied from collector to emitter, then one junction is reverse-biased, so a tiny leakage will occur. The other junction is forward-biased, so will have a low resistance.
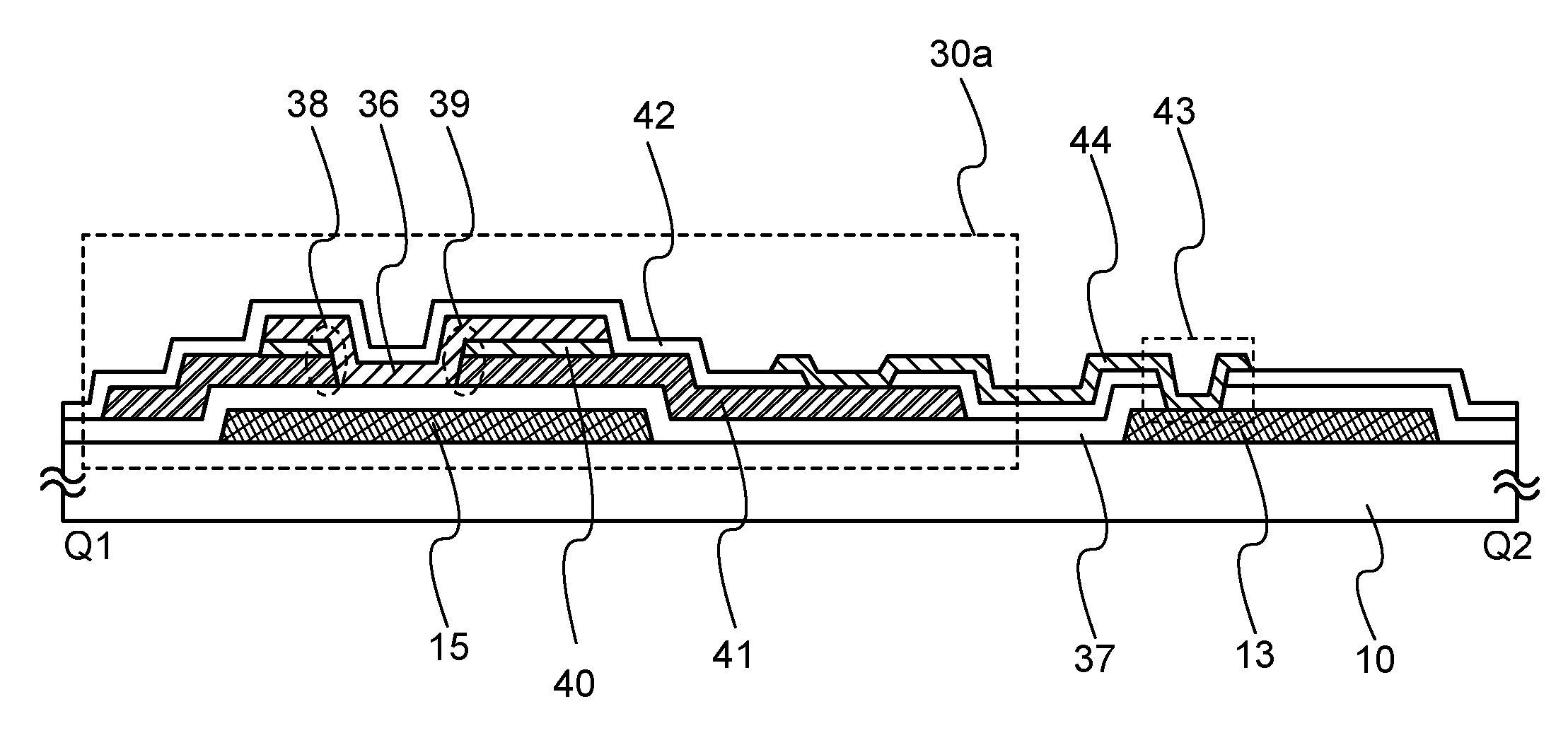
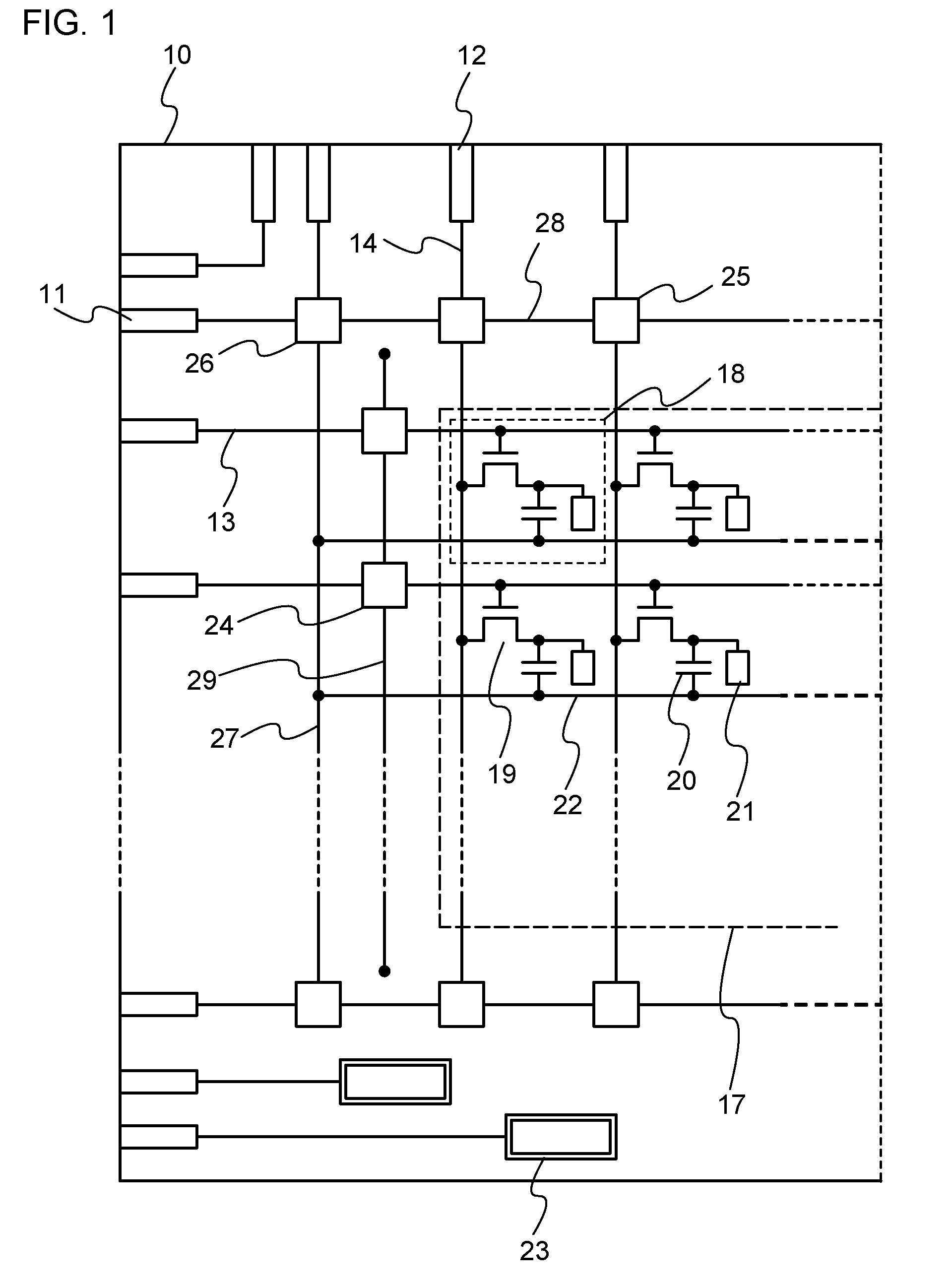
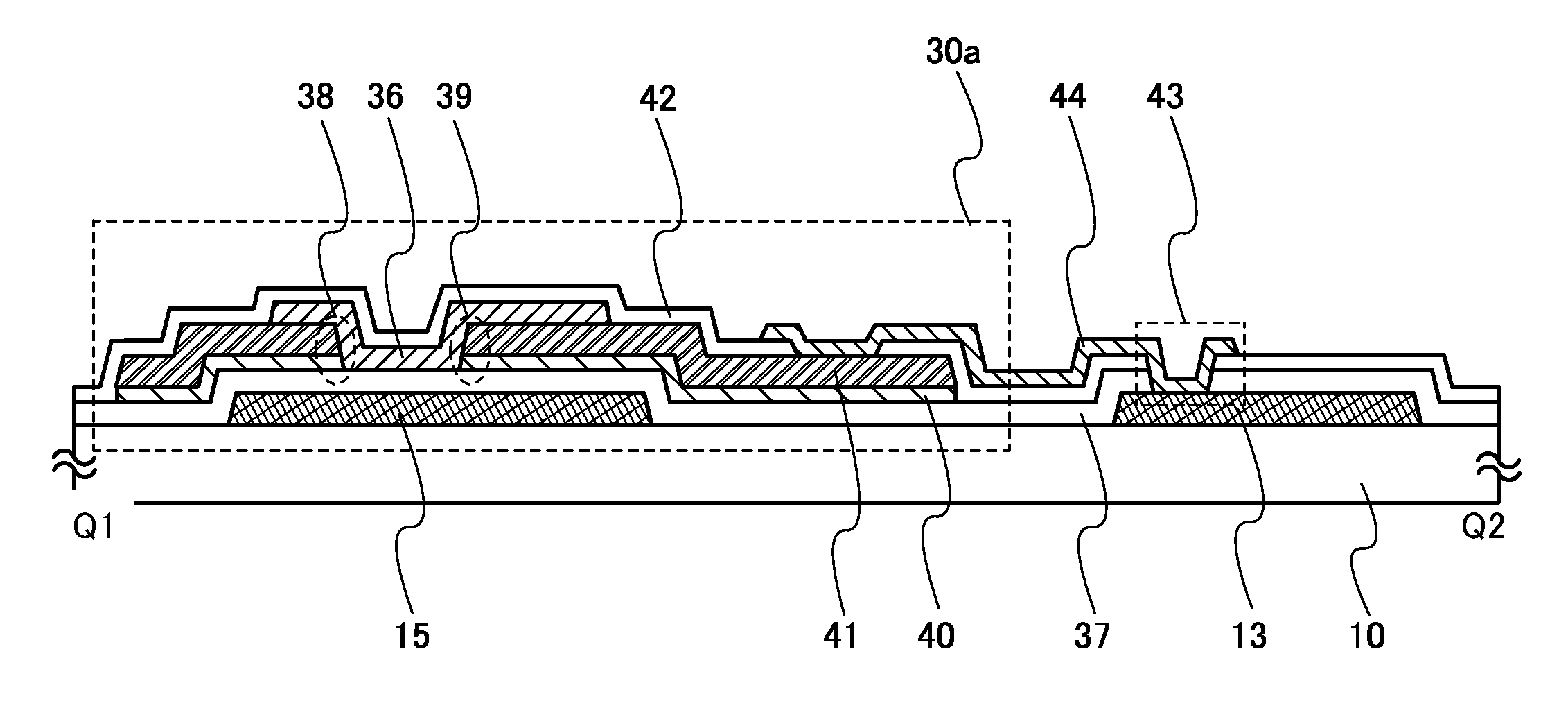
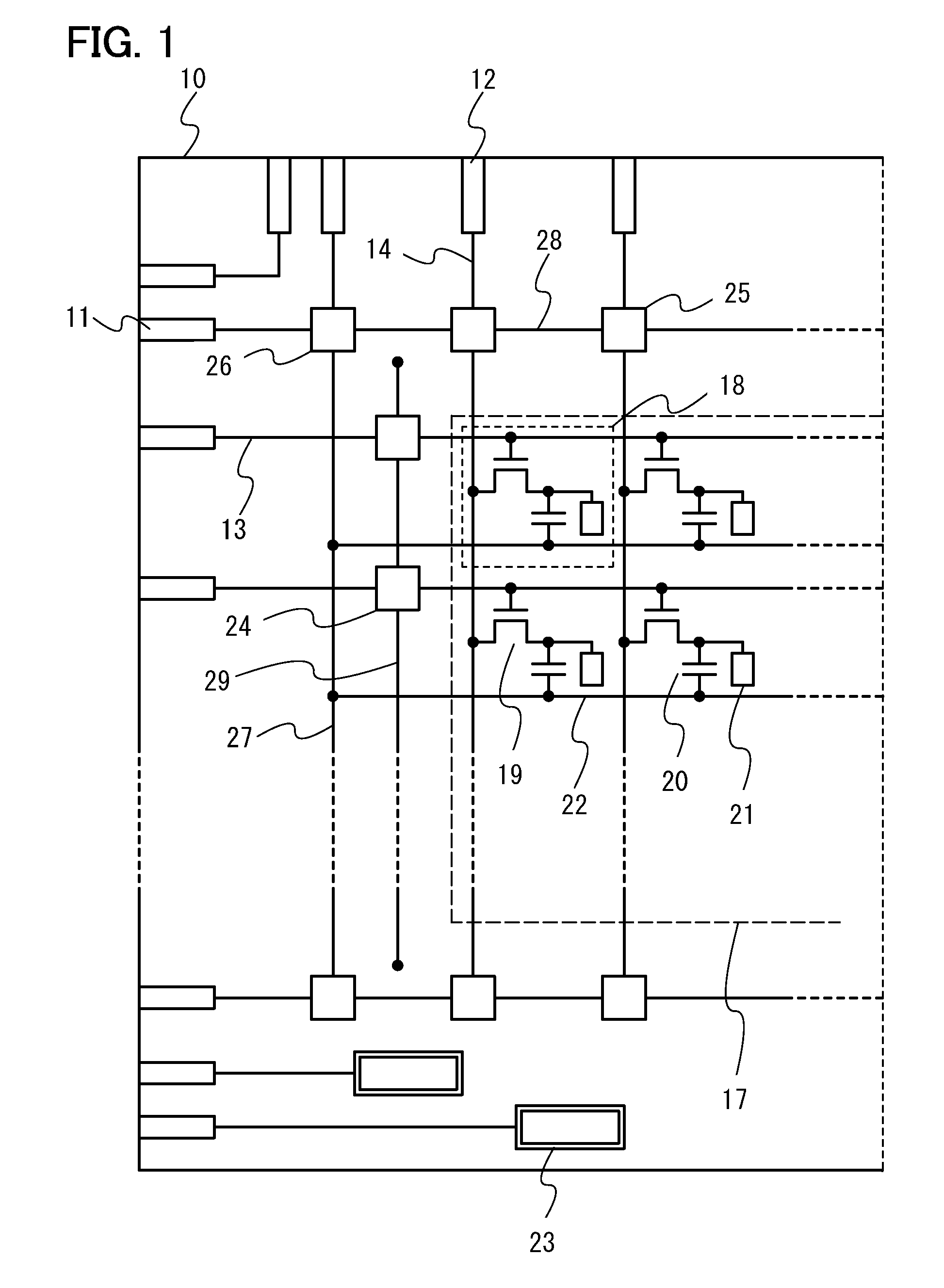
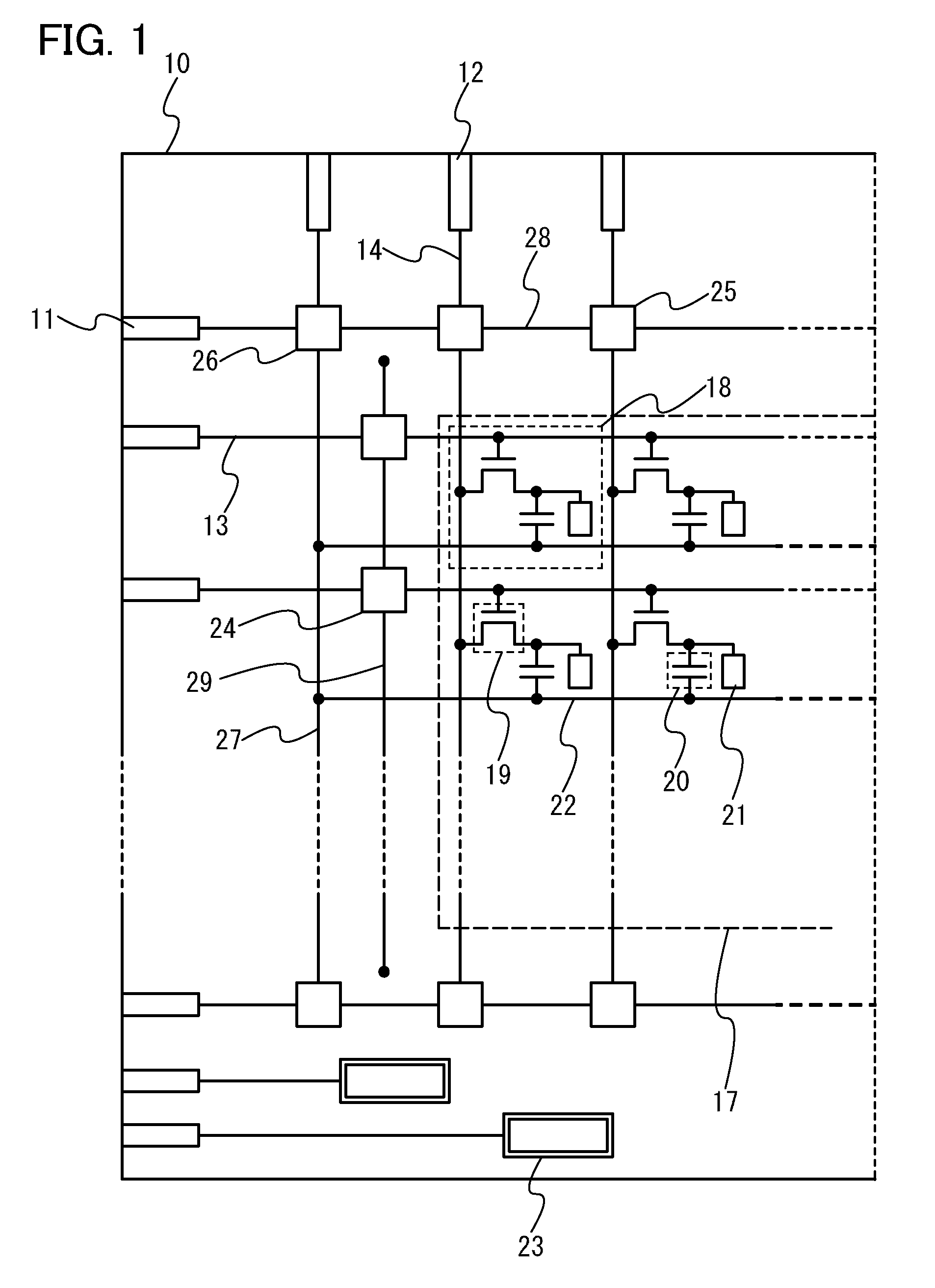
Display device
InactiveUS20100065840A1Improve conductivityGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageLinear element
A protective circuit includes a non-linear element, which further includes a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer covering the gate electrode, a pair of first and second wiring layers whose end portions overlap with the gate electrode over the gate insulating layer and in which a conductive layer and a second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked, and a first oxide semiconductor layer which overlaps with at least the gate electrode and which is in contact with side face portions of the gate insulating layer and the conductive layer of the first wiring layer and the second wiring layer and a side face portion and a top face portion of the second oxide semiconductor layer. Over the gate insulating layer, oxide semiconductor layers with different properties are bonded to each other, whereby stable operation can be performed as compared with Schottky junction. Thus, the junction leakage can be decreased and the characteristics of the non-linear element can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device
ActiveUS20100065839A1Suitable structureAvoid defectsSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsJunction leakageLinear element
A protective circuit includes a non-linear element, which includes a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer covering the gate electrode, a pair of first and second wiring layers whose end portions overlap with the gate electrode over the gate insulating layer and in which a second oxide semiconductor layer and a conductive layer are stacked, and a first oxide semiconductor layer which overlaps with at least the gate electrode and which is in contact with the gate insulating layer, side face portions and part of top face portions of the conductive layer and side face portions of the second oxide semiconductor layer in the first wiring layer and the second wiring layer. Over the gate insulating layer, oxide semiconductor layers with different properties are bonded to each other, whereby stable operation can be performed as compared with Schottky junction. Thus, the junction leakage can be decreased and the characteristics of the non-linear element can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Vertical semiconductor device with tunnel insulator in current path controlled by gate electrode
InactiveUS6873009B2Suppress lowering of driving forceLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentJunction leakage
It is an object of the present invention to provides a field effect transistor with extremely low leakage current. It is another object of the invention to provide a semiconductor memory device having an excellent information holding characteristic. It is a further object of the invention to provide a method for manufacturing in a simple manner a novel field effect transistor or semiconductor memory device with extremely low leakage current. According to a typical basic configuration of the present invention, a thin insulating film is inserted in a vertically disposed Schottky junction to form source and drain electrodes and a tunnel of the insulating film in the junction is controlled by a gate electrode. The gate electrode is disposed on each of both sides of a vertical channel, permitting a field effect to be exerted effectively on the junction, whereby a junction leakage in an OFF state can be made extremely low.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Soi transistor having a reduced body potential and a method of forming the same
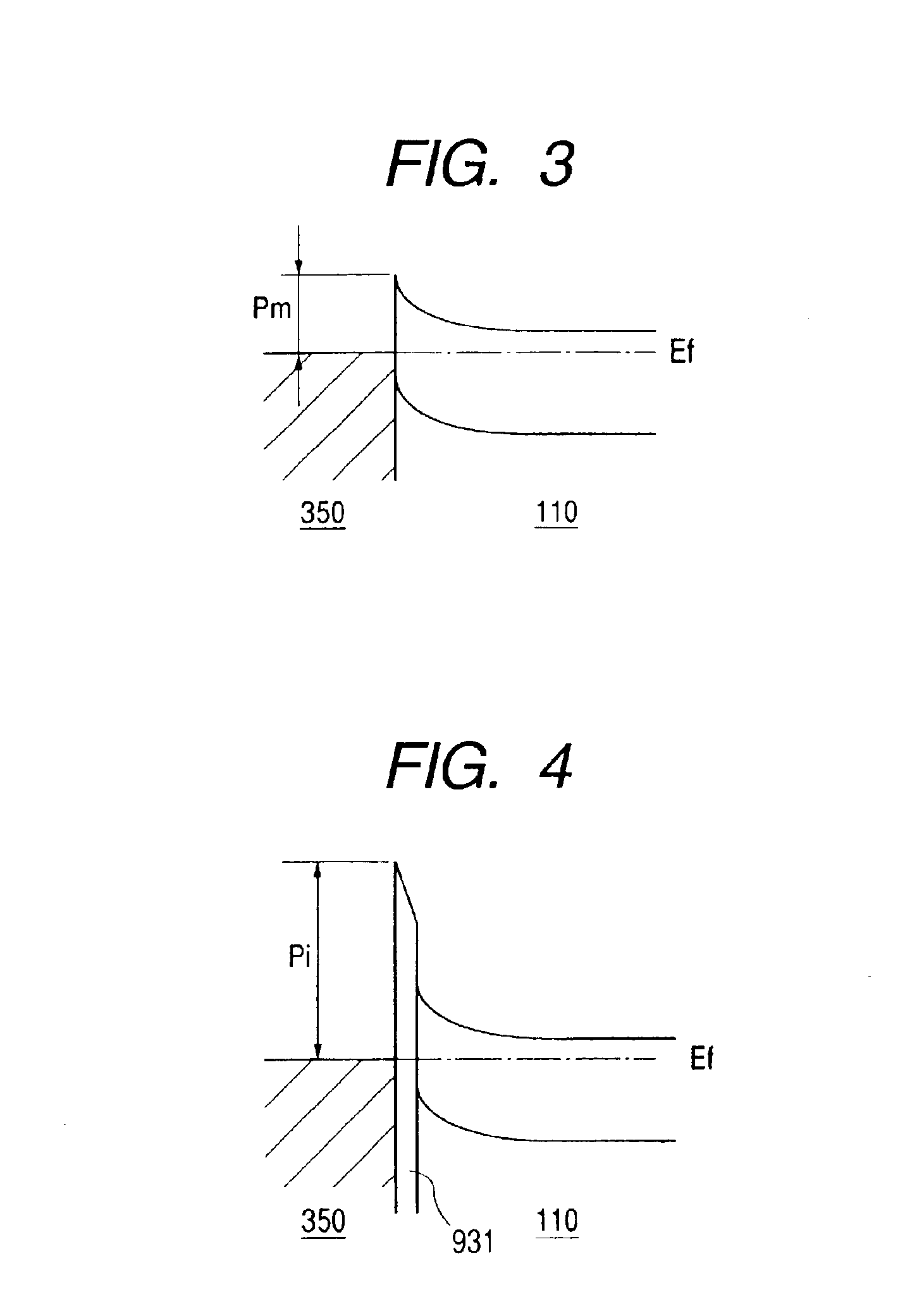
ActiveUS20070252205A1Reduce hysteresis effectsImprove compatibilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction leakageCharge carrier
By introducing a atomic species, such as carbon, fluorine and the like, into the drain and source regions, as well as in the body region, the junction leakage of SOI transistors may be significantly increased, thereby providing an enhanced leakage path for accumulated minority charge carriers. Consequently, fluctuations of the body potential may be significantly reduced, thereby improving the overall performance of advanced SOI devices. In particular embodiments, the mechanism may be selectively applied to threshold voltage sensitive device areas, such as static RAM areas.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Structure and method for making low leakage and low mismatch nmosfet
An improved SRAM and fabrication method are disclosed. The method comprises use of a nitride layer to encapsulate PFETs and logic NFETs, protecting the gates of those devices from oxygen exposure. NFETs that are used in the SRAM cells are exposed to oxygen during the anneal process, which alters the effective work function of the gate metal, such that the threshold voltage is increased, without the need for increasing the dopant concentration, which can adversely affect issues such as mismatch due to random dopant fluctuation, GIDL and junction leakage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090003105A1Run at high speedSmall sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageAudio power amplifier
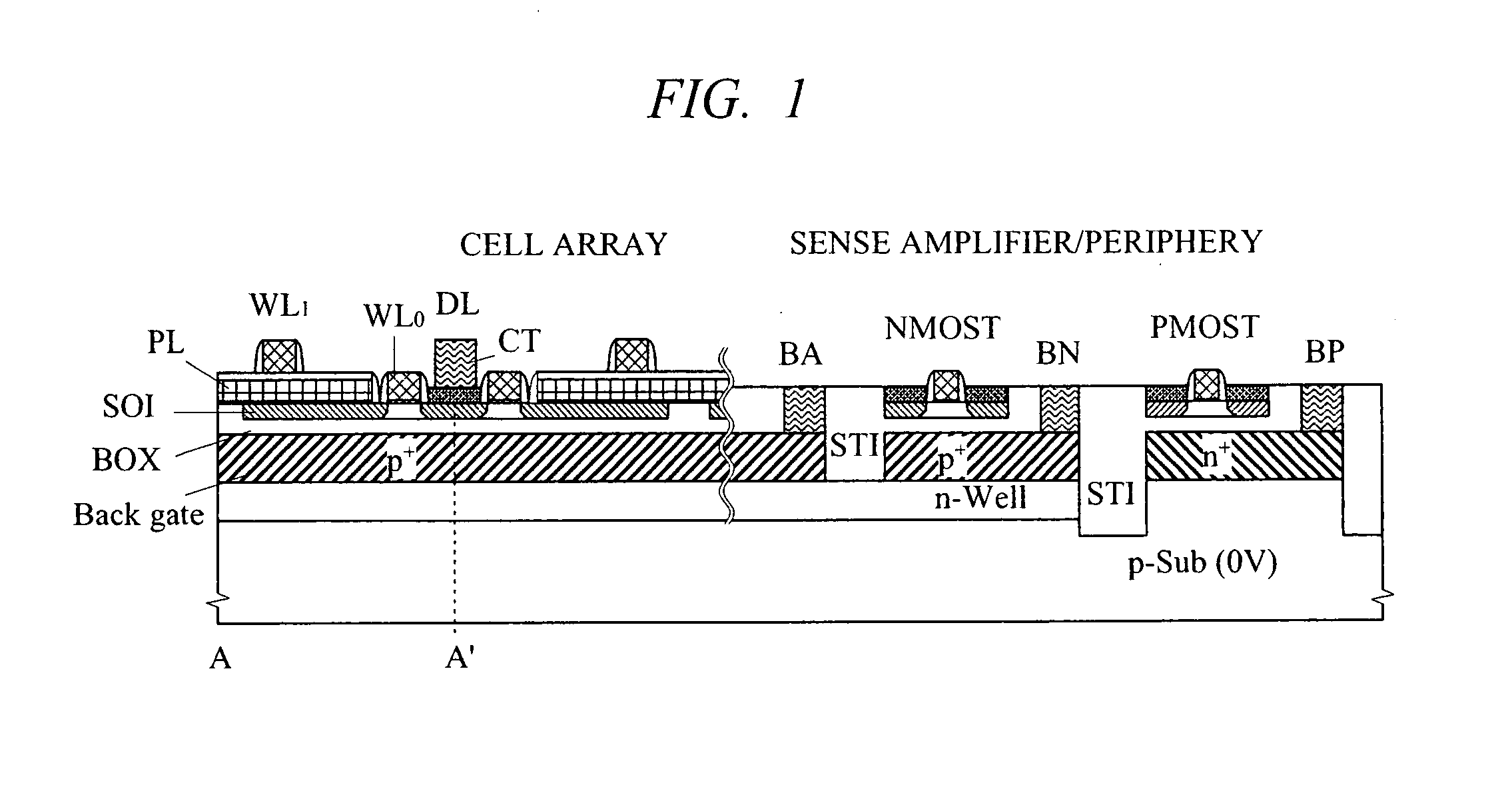
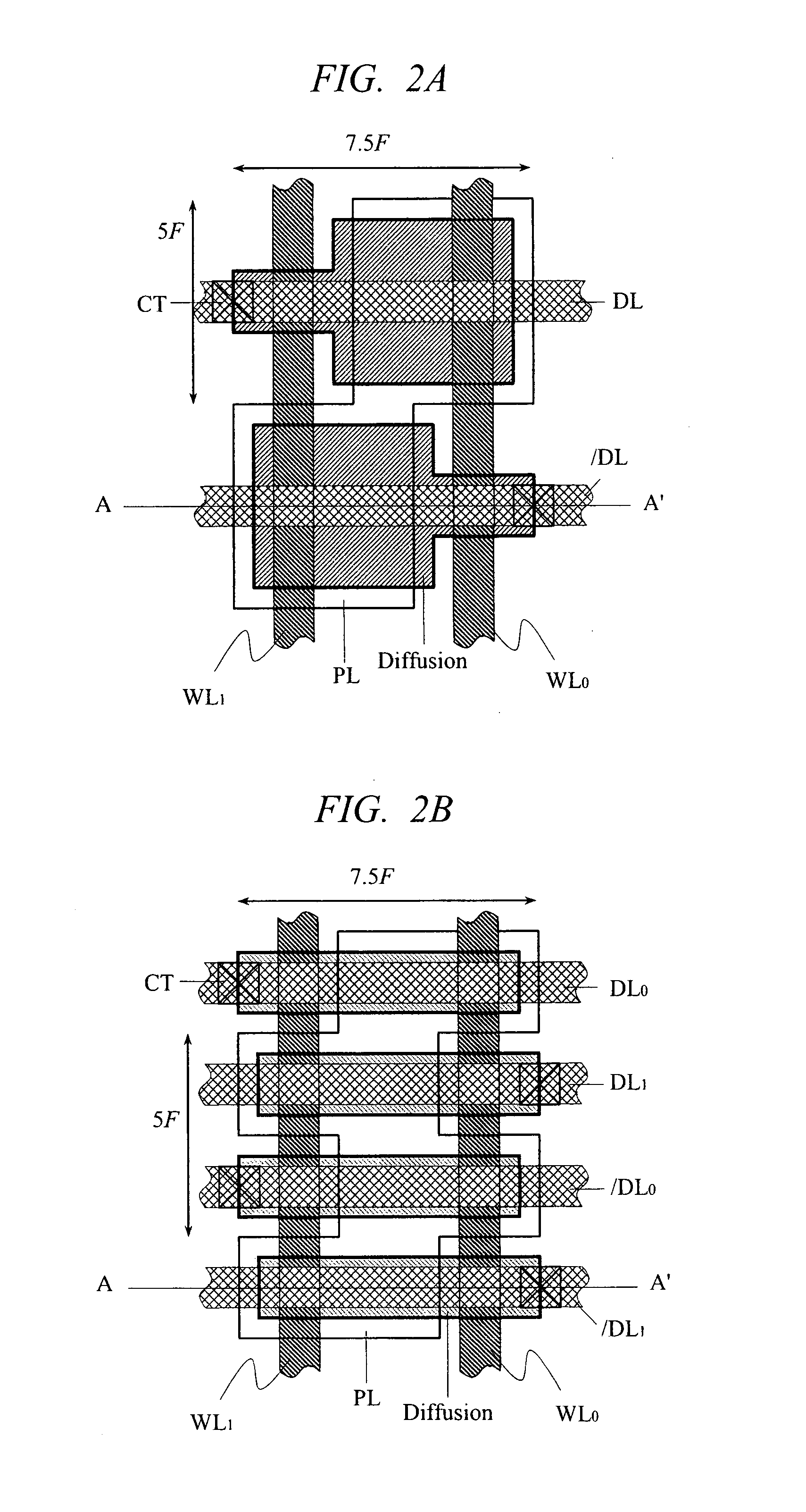
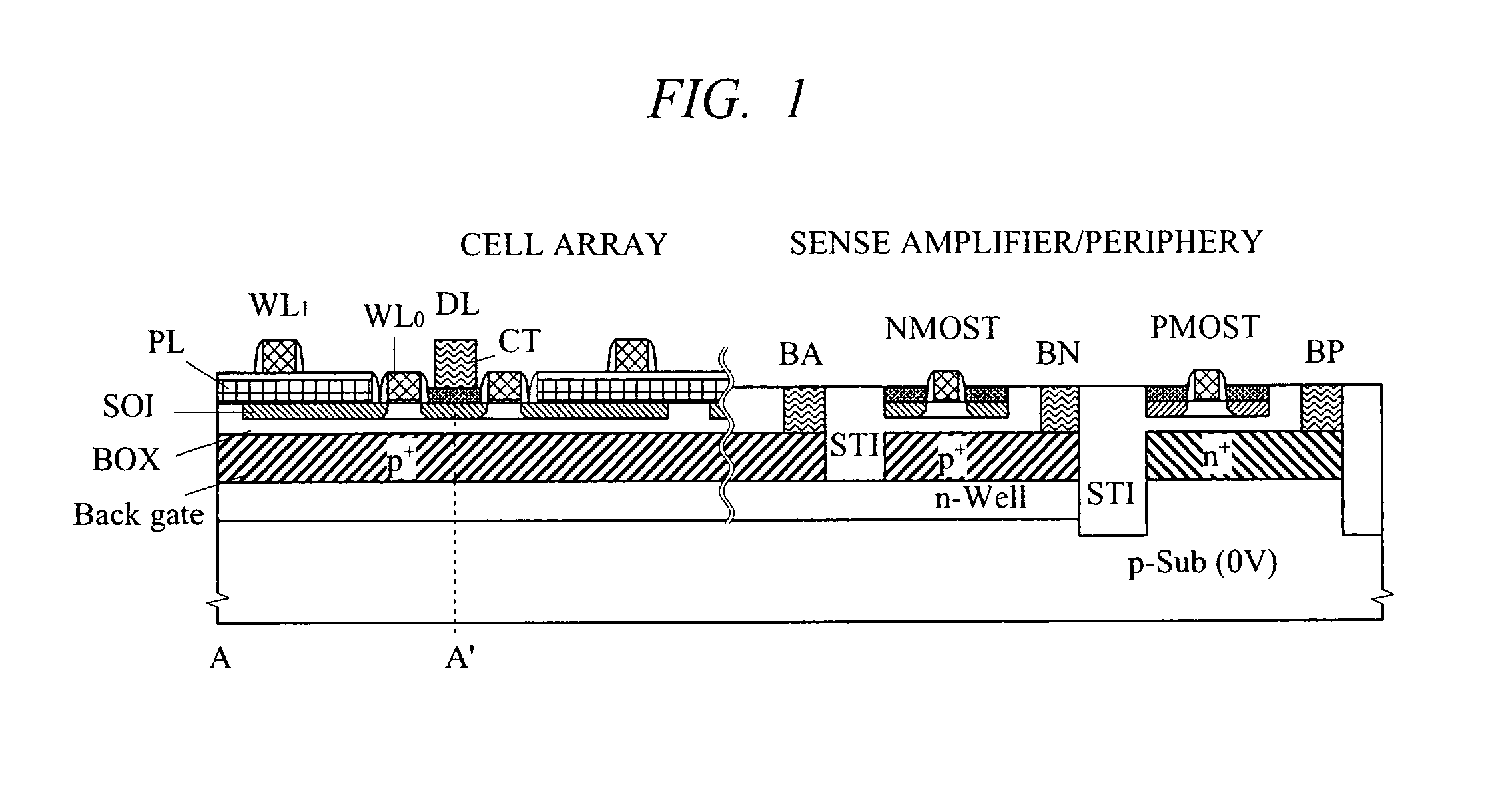
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device
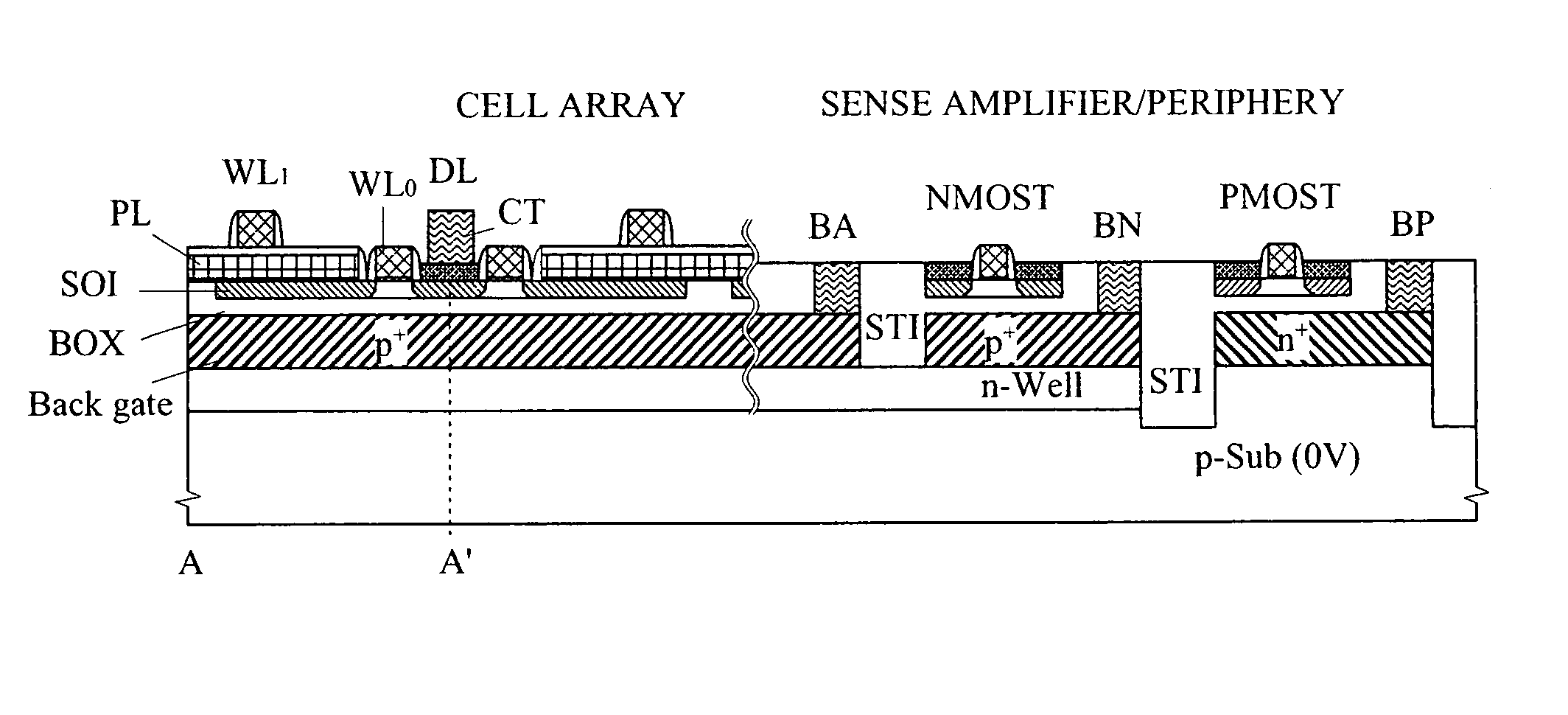
A high-speed and low-voltage DRAM memory cell capable of operating at 1 V or less and an array peripheral circuit are provided. A DRAM cell is comprised of a memory cell transistor and planar capacitor which utilize a FD-SOI MOST structure. Since there is no junction leakage current, loss of stored charge is eliminated, and the low-voltage operation can be realized. Further, a gate and a well in a cross-coupled type sense amplifier using FD-SOI MOSTs are connected. By this means, a threshold value dynamically changes and high-speed sensing operation can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Display device
InactiveUS20100072470A1Improve conductivityGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageLinear element
A protective circuit includes a non-linear element which includes a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer covering the gate electrode, a first oxide semiconductor layer overlapping with the gate electrode over the gate insulating layer, a channel protective layer overlapping with a channel formation region of the first oxide semiconductor layer, and a pair of a first wiring layer and a second wiring layer whose end portions overlap with the gate electrode over the channel protective layer and in which a conductive layer and a second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked. Over the gate insulating layer, oxide semiconductor layers with different properties are bonded to each other, whereby stable operation can be performed as compared with Schottky junction. Thus, the junction leakage can be reduced and the characteristics of the non-linear element can be improved.
Display device
ActiveUS20100072471A1Improve conductivityGuaranteed uptimeTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesJunction leakageLinear element
A protective circuit includes a non-linear element which includes a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer covering the gate electrode, a first oxide semiconductor layer overlapping with the gate electrode over the gate insulating layer, and a first wiring layer and a second wiring layer whose end portions overlap with the gate electrode over the first oxide semiconductor layer and in which a conductive layer and a second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked. Over the gate insulating layer, oxide semiconductor layers with different properties are bonded to each other, whereby stable operation can be performed as compared with Schottky junction. Thus, the junction leakage can be reduced and the characteristics of the non-linear element can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
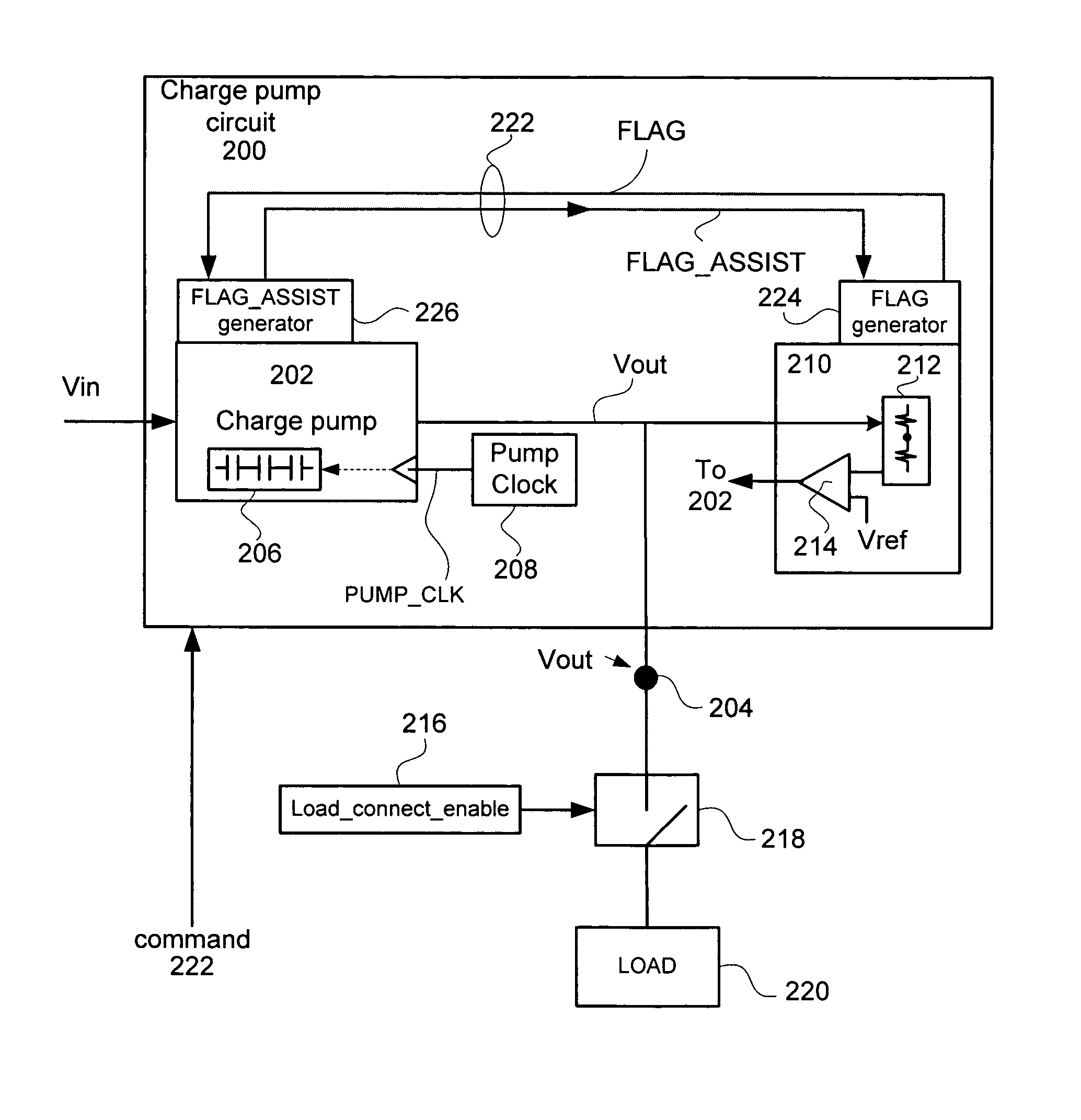
Implementation of output floating scheme for hv charge pumps
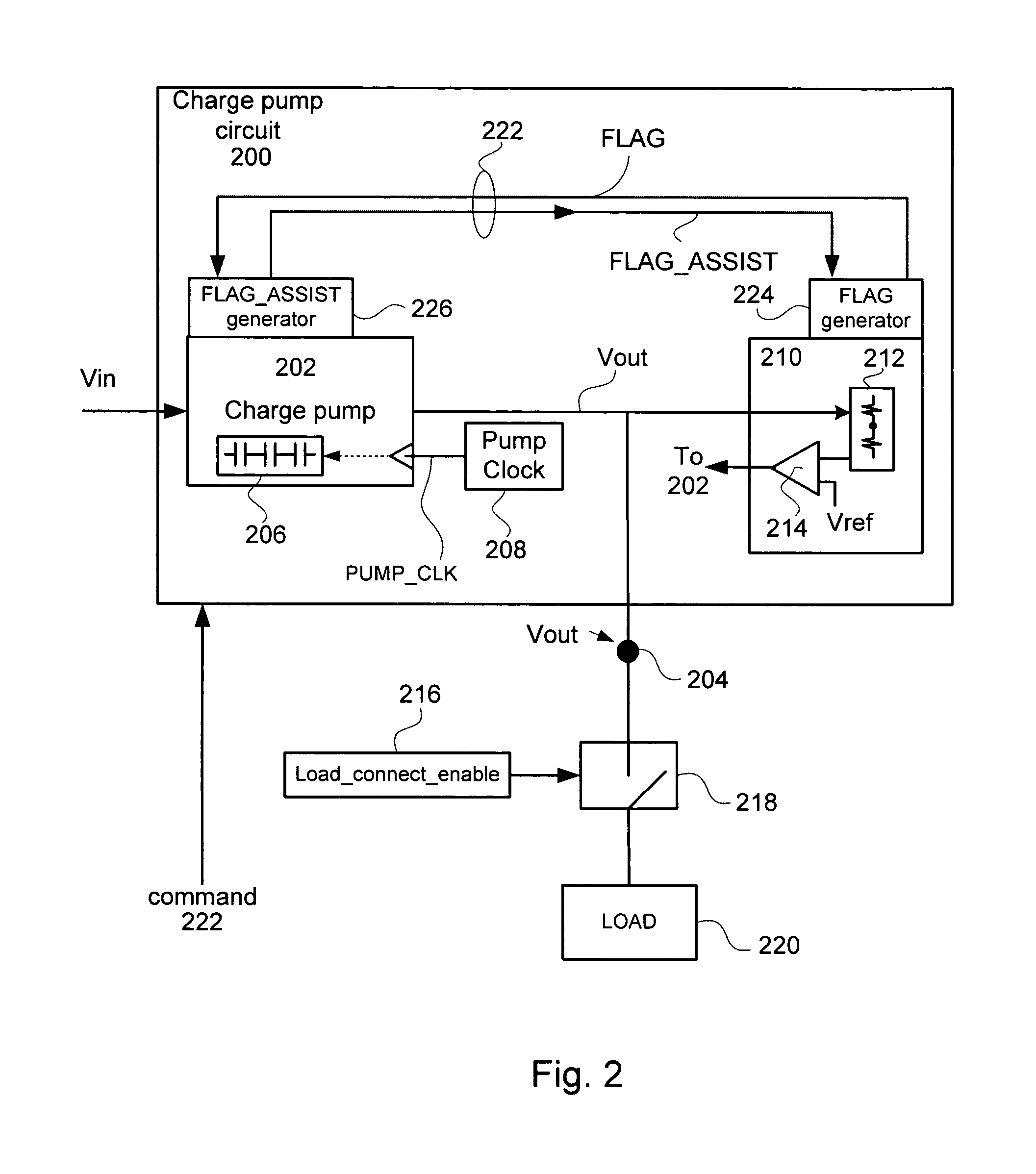
According to different embodiments of the present invention, various methods, devices and systems are described for managing power in charge pumps in a non-volatile memory system having a high voltage charge pump and associated regulator. A method includes the following operations, receiving an operation command corresponding to an operation, pumping up a charge pump output voltage to a desired output voltage, turning off the regulator and the charge pump when the output voltage is approximately the desired output voltage compensating for charge sharing by turning on the charge pump and setting a pump clock rate to a slow clock rate in order to avoid overshooting the desired output voltage by the charge pump while the operation is being carried out, and compensating for junction leakage by turning on the regulator and the charge pump until the charge pump output voltage is the desired output voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertical semiconductor device with tunnel insulator in current path controlled by gate electrode
It is an object of the present invention to provides a field effect transistor with extremely low leakage current. It is another object of the invention to provide a semiconductor memory device having an excellent information holding characteristic. It is a further object of the invention to provide a method for manufacturing in a simple manner a novel field effect transistor or semiconductor memory device with extremely low leakage current. According to a typical basic configuration of the present invention, a thin insulating film is inserted in a vertically disposed Schottky junction to form source and drain electrodes and a tunnel of the insulating film in the junction is controlled by a gate electrode. The gate electrode is disposed on each of both sides of a vertical channel, permitting a field effect to be exerted effectively on the junction, whereby a junction leakage in an OFF state can be made extremely low.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Silicide gate transistors and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7067379B2Improve performanceEliminate depletionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction leakageGate dielectric
A method in which a gate and raised source / drain (S / D) regions are fully silicided in separate steps to avoid degrading the resistance or junction leakage is described. A gate dielectric layer, gate, and spacers are formed over a semiconductor layer that is preferably Si, SiGe, or SiGeC on a buried insulator. Raised S / D regions are formed by selective epitaxy between spacers and isolation regions. The gate is protected with a mask while the raised S / D regions are covered with a first metal layer. A first anneal affords fully silicided S / D regions. A dielectric stack is deposited on the substrate and planarized to be coplanar with the top of the spacers. The mask is removed and a second metal layer is deposited. A second anneal yields a fully silicided gate electrode. The invention is also an SOI transistor with silicided raised S / D regions and a fully silicided and optionally recessed gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Soi transistor having an embedded strain layer and a reduced floating body effect and a method for forming the same
InactiveUS20070252204A1Improve performanceEfficient dischargeTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentFloating body effect
By forming a portion of a PN junction within strained silicon / germanium material in SOI transistors with a floating body architecture, the junction leakage may be significantly increased, thereby reducing floating body effects. The positioning of a portion of the PN junction within the strained silicon / germanium material may be accomplished on the basis of implantation and anneal techniques, contrary to conventional approaches in which in situ doped silicon / germanium is epitaxially grown so as to form the deep drain and source regions. Consequently, high drive current capability may be combined with a reduction of floating body effects.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
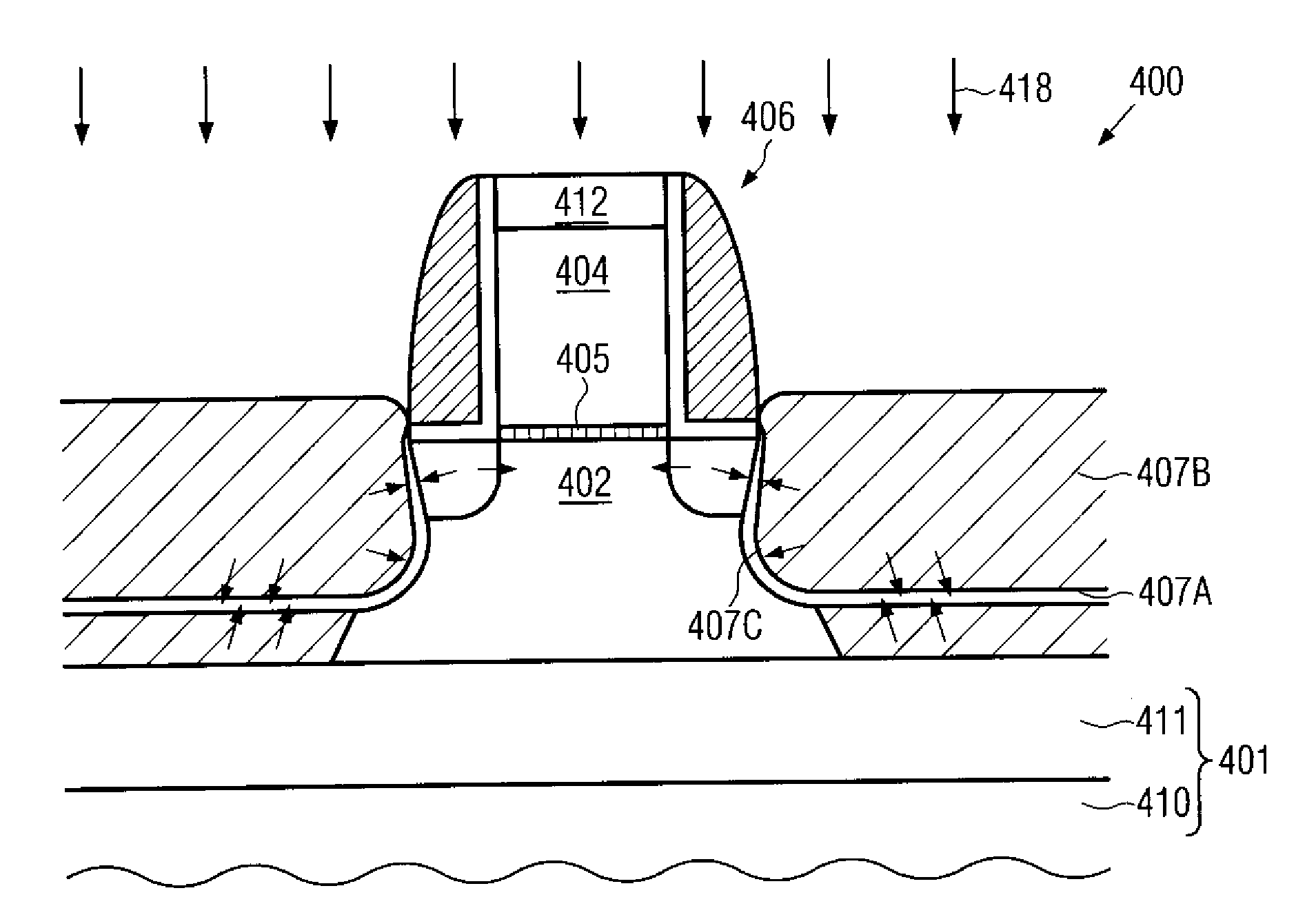
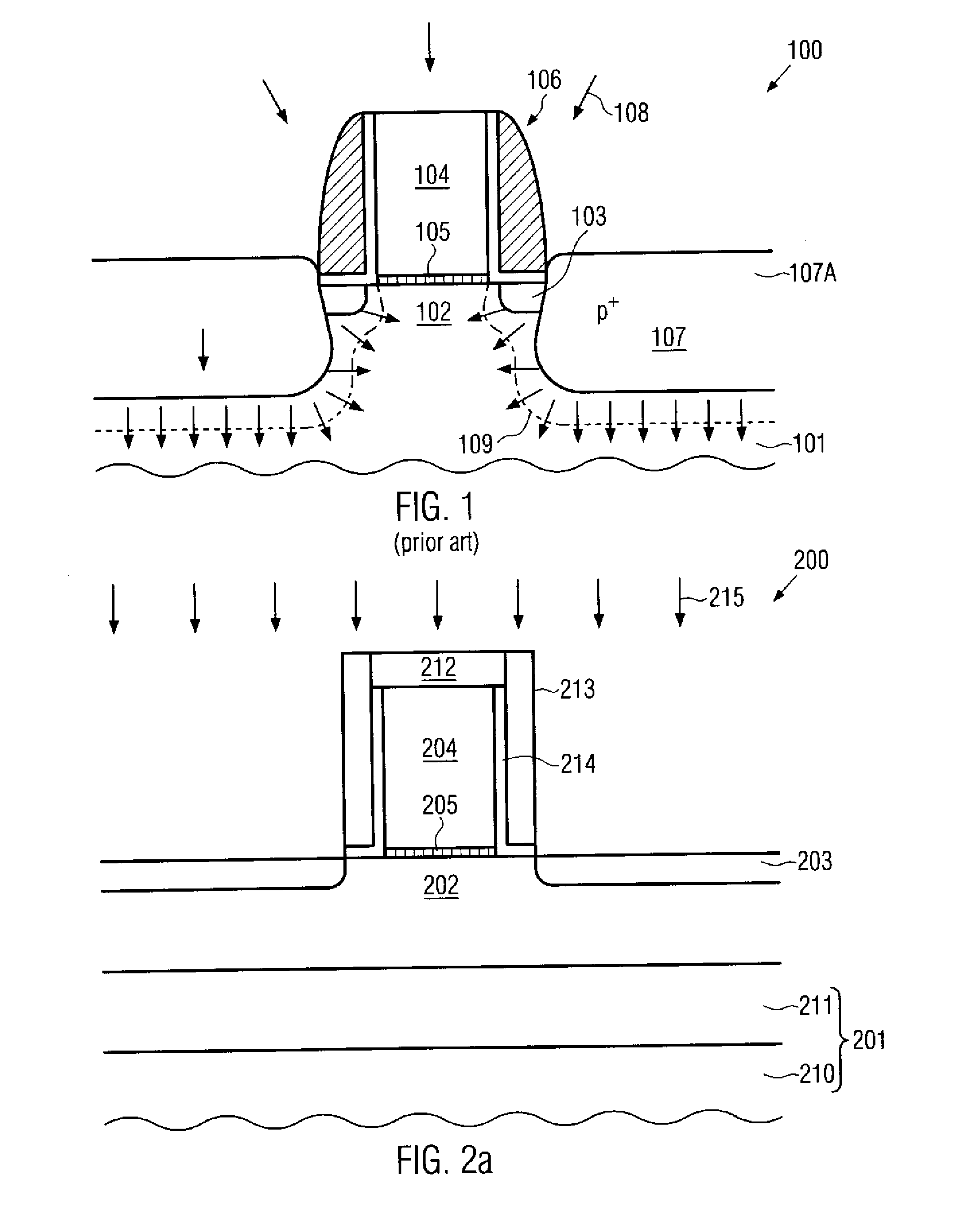
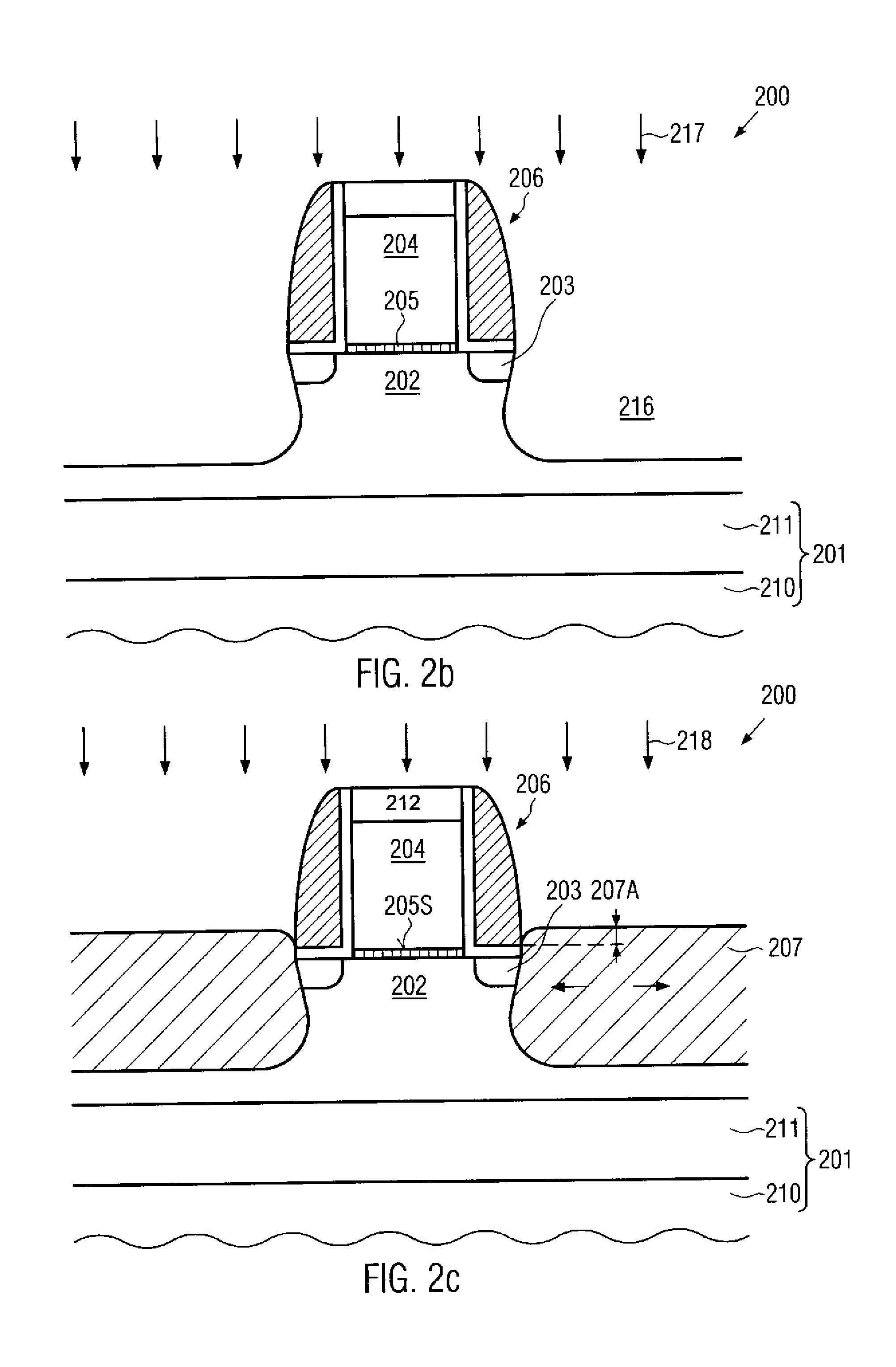
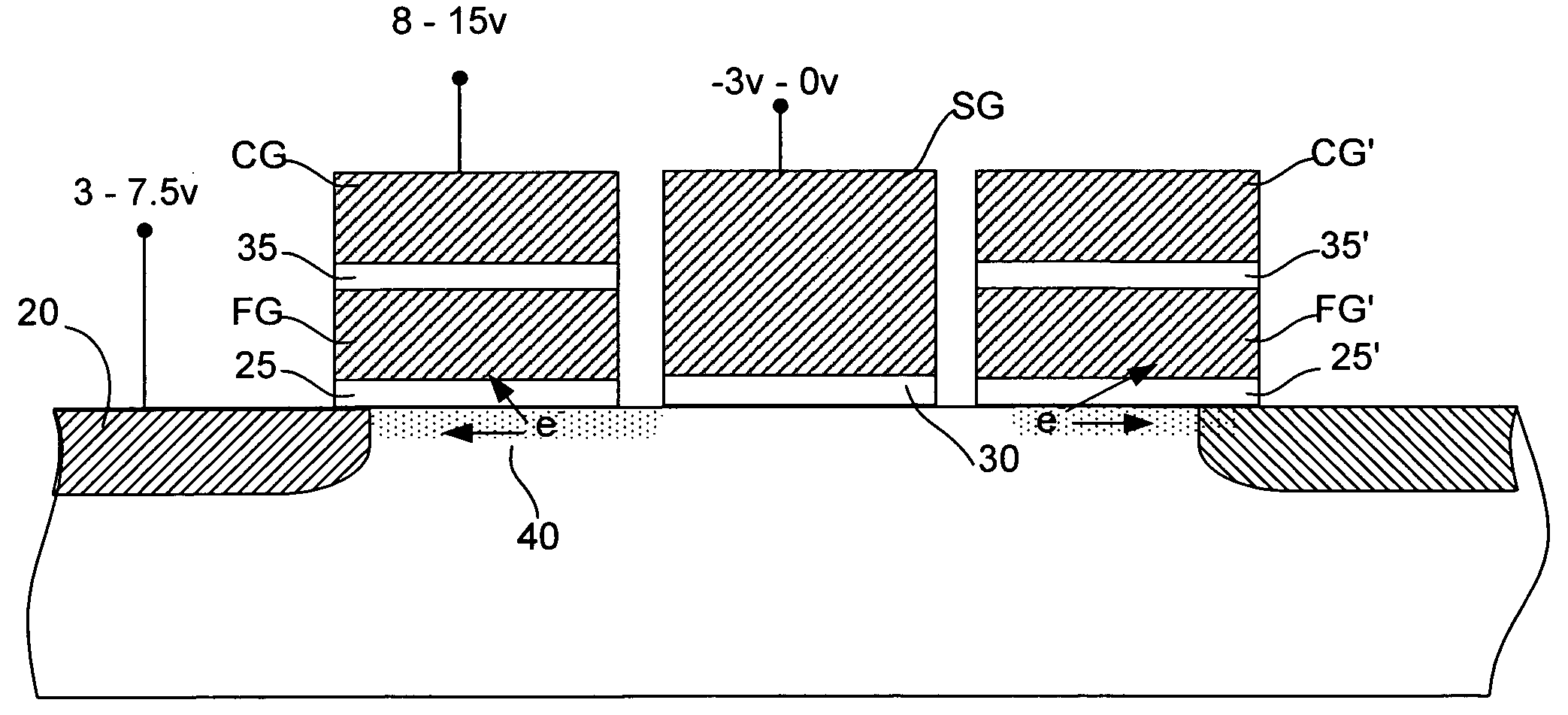
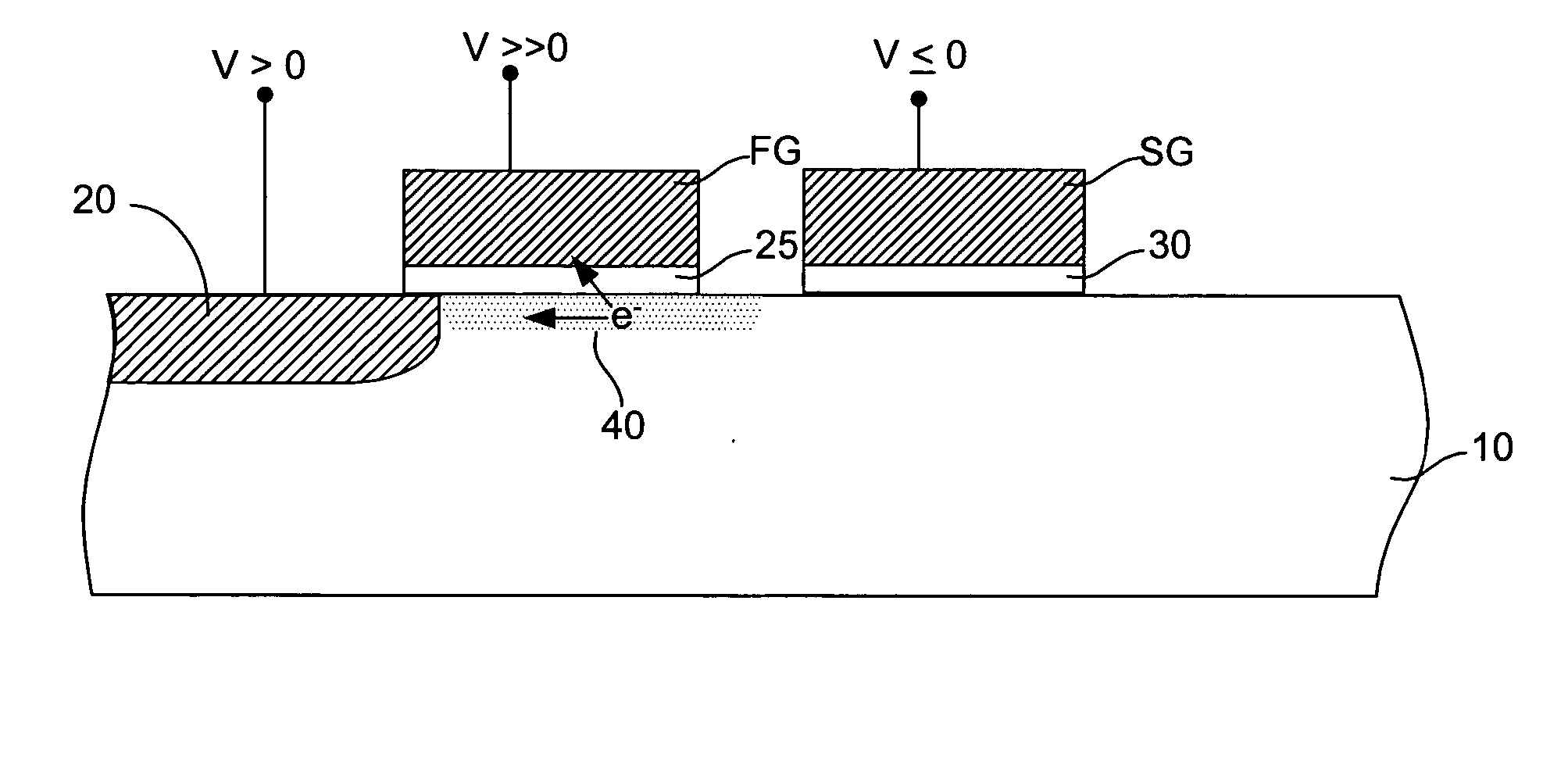
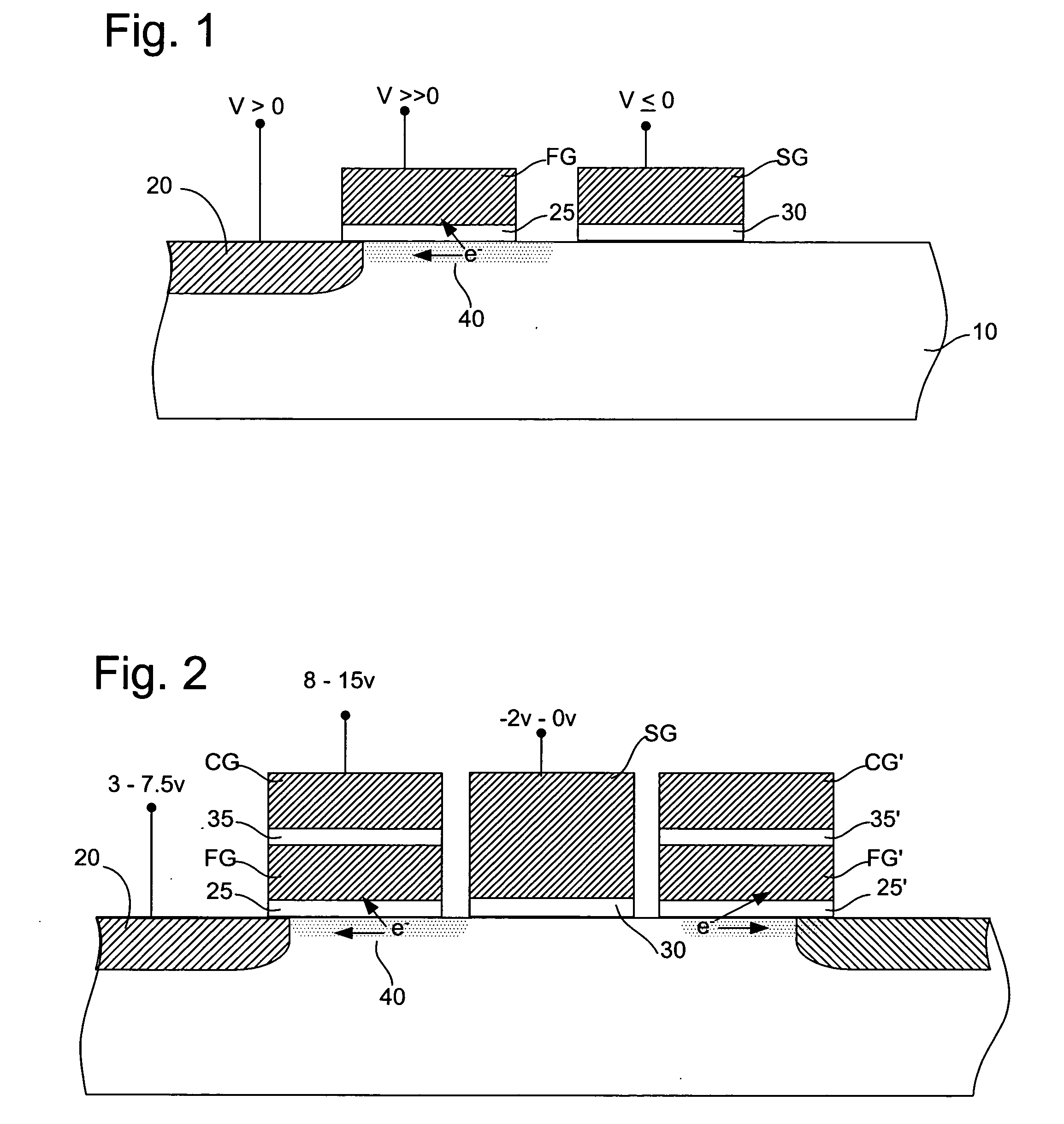
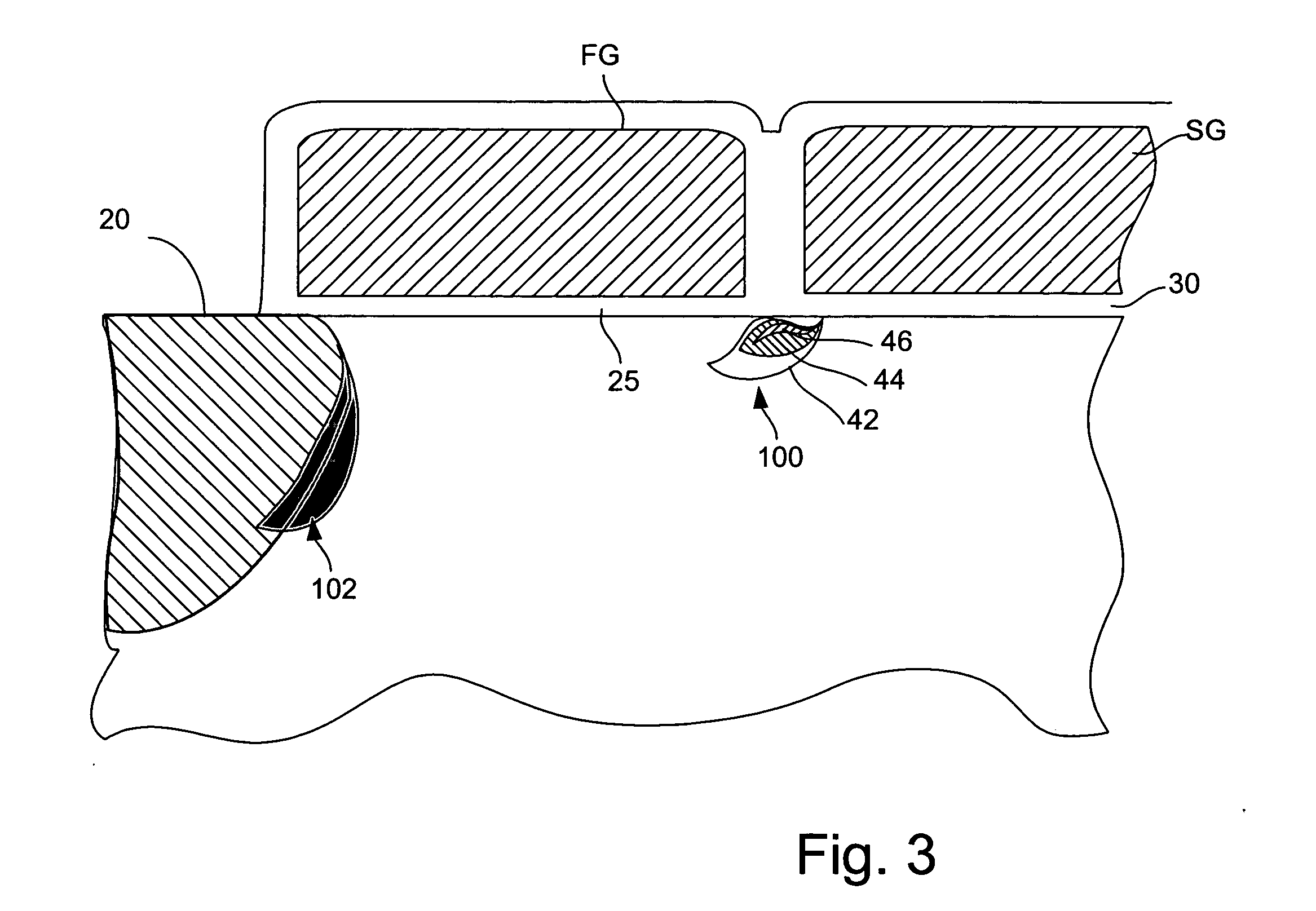
Flash memory programming using gate induced junction leakage current
A method for programming a storage element and a storage element programmed using gate induced junction leakage current are provided. The element may include at least a floating gate on a substrate, an active region in the substrate, and a second gate adjacent to the floating gate. The method may include the steps of: creating an inversion region in the substrate below the floating gate by biasing the first gate; and creating a critical electric field adjacent to the second gate. Creating a critical electric field may comprise applying a first positive bias to the active region; and applying a bias less than the first positive bias to the second gate. The element further includes a first bias greater than zero volts applied to the active region and a second bias greater than the first bias applied to the floating gate and a third bias less than or equal to zero applied to the second gate. The first and third bias are selected to create leakage current in the substrate between the floating gate and the select gate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Transistor using impact ionization and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060125041A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricOhmic contact
A transistor using impact ionization and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. A gate dielectric layer, a gate, and first and second spacers are formed on a semiconductor substrate. A first impurity layer is formed spaced from the first spacer and a second impurity layer is formed expanding and overlapping with the second spacer therebelow, by performing slant ion-implantation on the semiconductor substrate using the gate and the first and second spacers as a mask. A source and a drain are formed on the semiconductor substrate to be self-aligned with the first and second spacers, respectively, thereby defining an ionization region between the source and the drain in the semiconductor substrate. The source includes a first silicide layer to form a schottky junction with the ionization region. The drain includes a portion of the second impurity layer overlapping with the second spacer and a second silicide layer which is aligned with the second spacer to form an ohmic contact with the second impurity layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Nitrogen implantation using a shadow effect to control gate oxide thickness in DRAM semiconductor
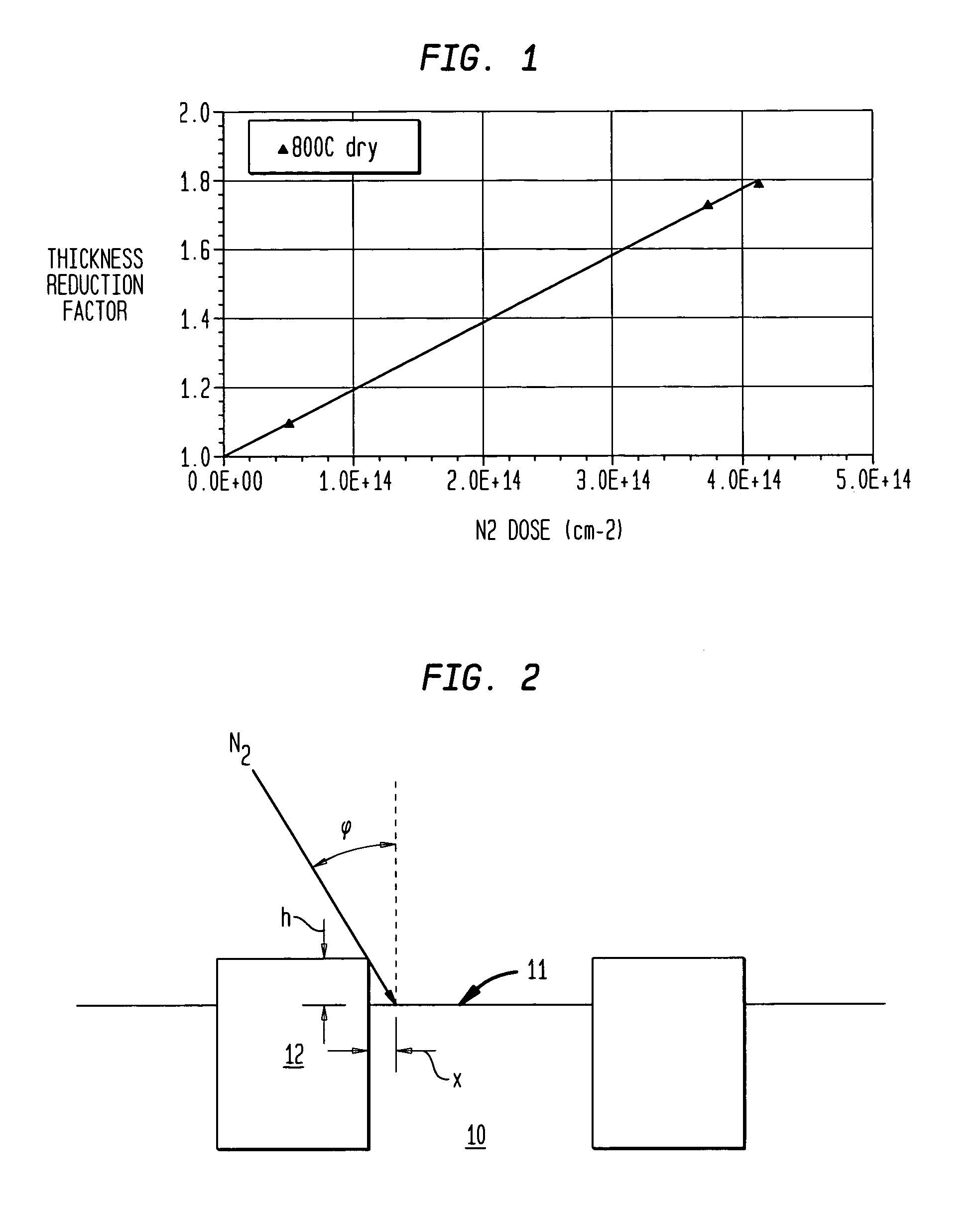
Process for forming dual gate oxides for DRAMS by incorporating different thicknesses of gate oxides by using nitrogen implantation. Either angled nitrogen implantation or nitride spacers is used to create a “shadow effect” or area, which limits the nitrogen dose close to the edges of the active area. The reduction of nitrogen dose leads to an increased gate oxide thickness at the active area (AA) adjacent to the shallow trench, increases the threshold of the parasitic corner device and reduces sub Vt (threshold voltage) and junction leakage.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method of manufacturing a multilayered doped conductor for a contact in an integrated circuit device
InactiveUS7195995B2Increase the doping concentrationLess susceptibleTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantElectrical conductor
A method of manufacturing a memory device addressing reliability and refresh characteristics through the use of a multilayered doped conductor, and a method making is described. The multilayered doped conductor creates a high dopant concentration in the active area close to the channel region. The rich dopant layer created by the multilayered doped conductor is less susceptible to depletion from trapped charges in the oxide. This improves device reliability at burn-in and lowers junction leakage, thereby providing a longer period between refresh cycles.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method to reduce junction leakage through partial regrowth with ultrafast anneal and structures formed thereby
InactiveUS20080121882A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantJunction leakage
Methods and associated structures of forming a microelectronic device are described. Those methods may include creating an amorphous region in source / drain regions of a substrate by ion implantation with an electrically neutral dopant, annealing with a first anneal that removes defects without completely re-crystallizing the amophous region, ion implantation of electrically active dopant to a depth shallower than the remaining amorphous region, followed by a second anneal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
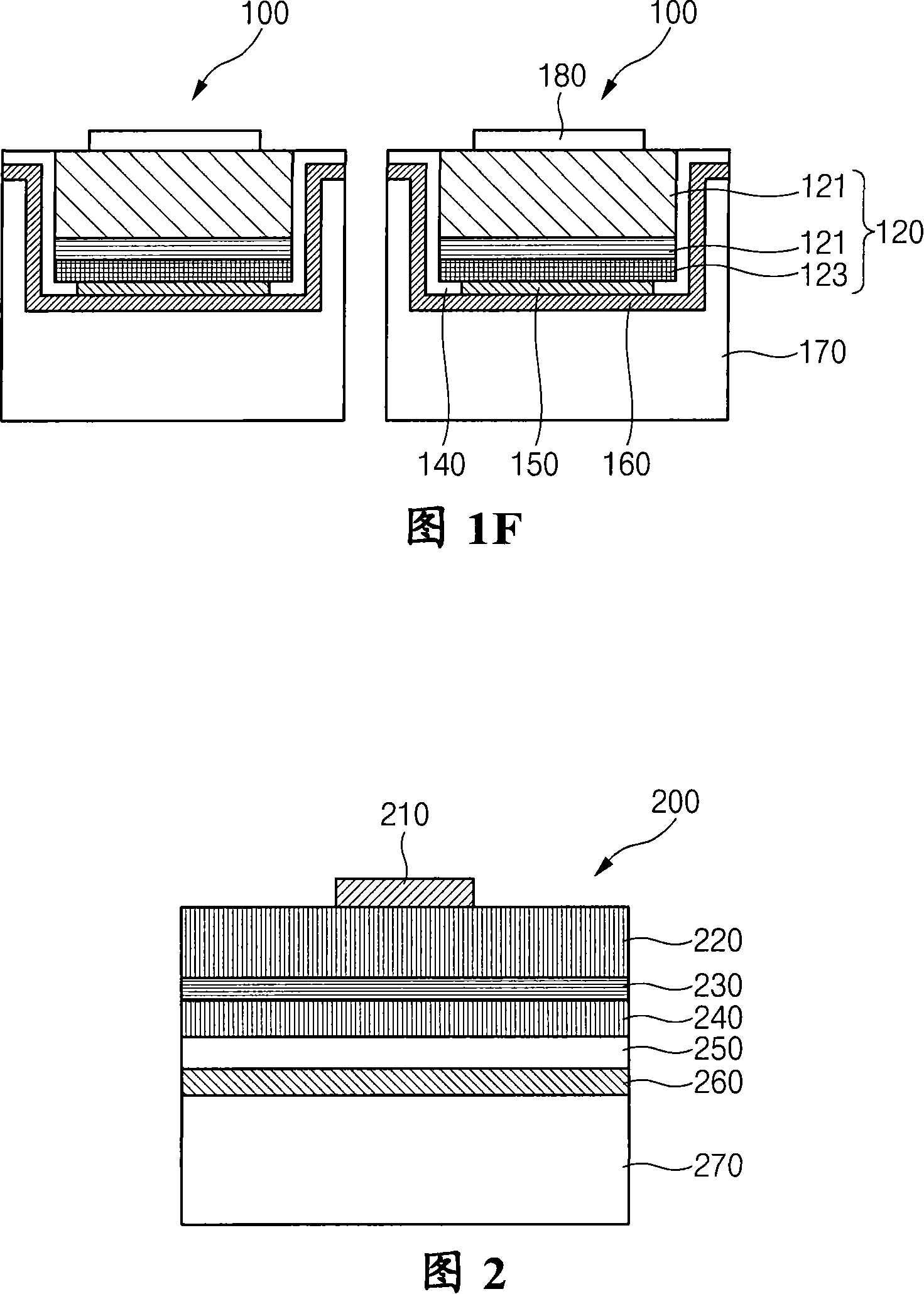
Vertical gallium nitride-based light emitting diode and method of manufacturing the same
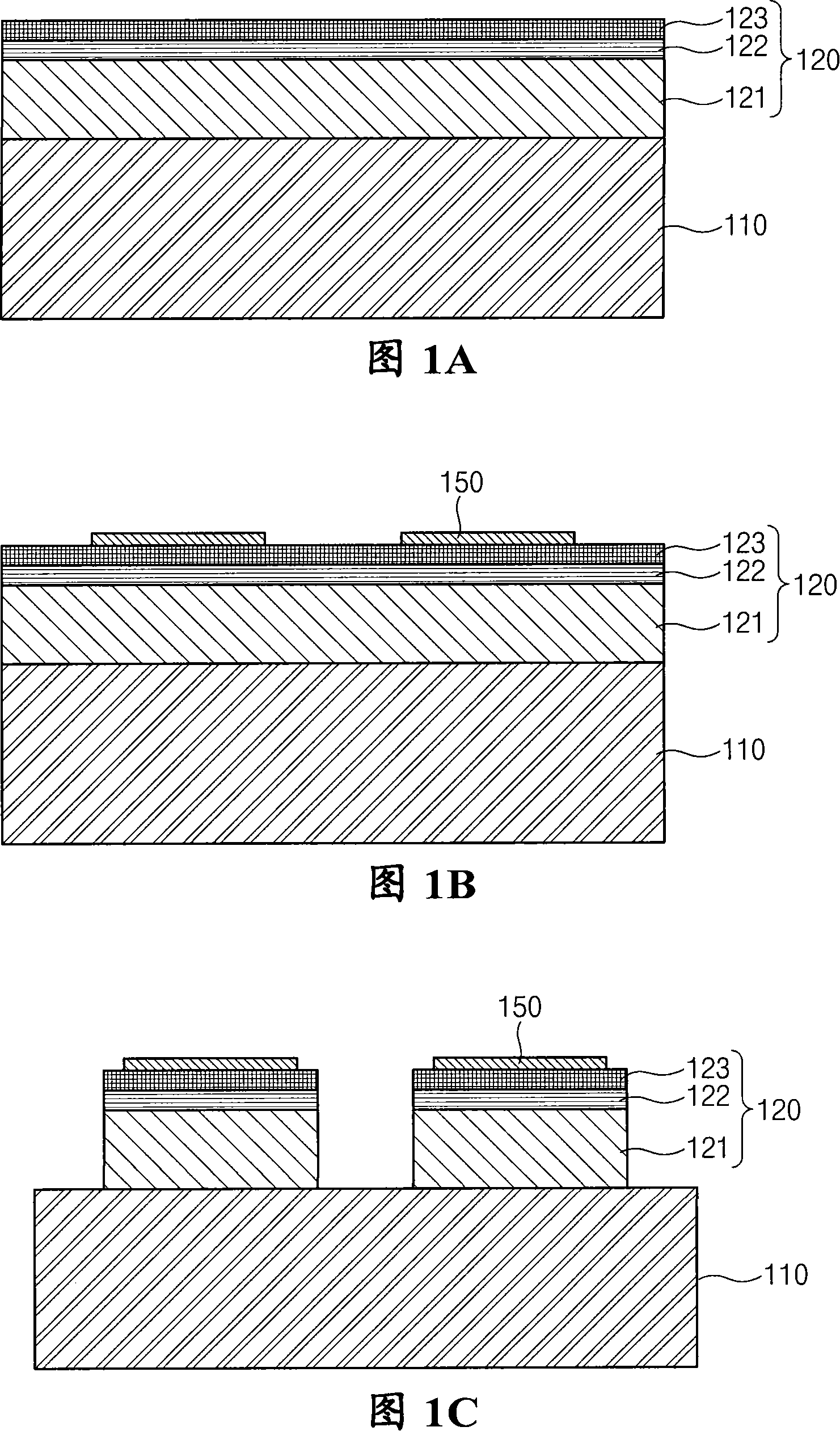
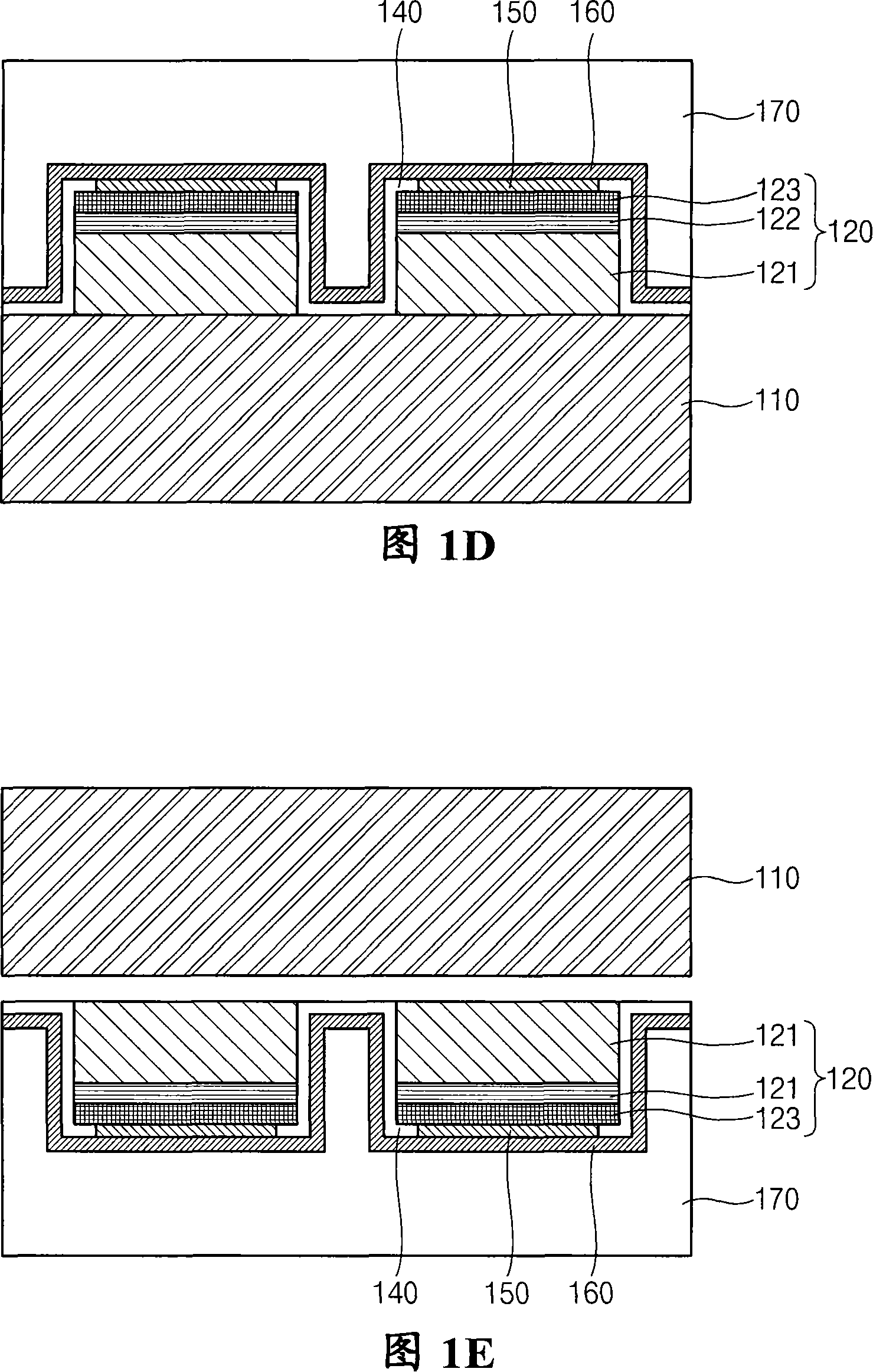
ActiveCN101132040AImprove reliabilityAvoid bendingSemiconductor devicesJunction leakageConductive materials
A vertical gallium nitride-based light emitting diode and a manufacturing method thereof are provided to prevent junction leakage and a short circuit by preventing atoms composing a metal seed layer from penetrating into an active layer. A light emission structure(120) comprising an n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer(121), an active layer, and a p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer(123) is formed on a substrate, and then is etched to divide the light emission structure into units of LED(100). A p-electrode(150) is formed on each of the divided light emission structures, and a non-conductive material is filled between the divided light emission structures. A metal seed layer(160) is formed on the structure, and a first plated layer(170a) is formed on the metal seed layer excluding a region between the light emission structures. A second plated layer(170b) is formed on the metal seed layer between the first plated layers. The substrate is separated from the light emission structures, and then the non-conductive material is removed between the light emission structures exposed by separating the substrate. An n-electrode(180) is formed on the n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer, and then portions of the metal seed layer and the second plated layer are removed between the light emission structures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
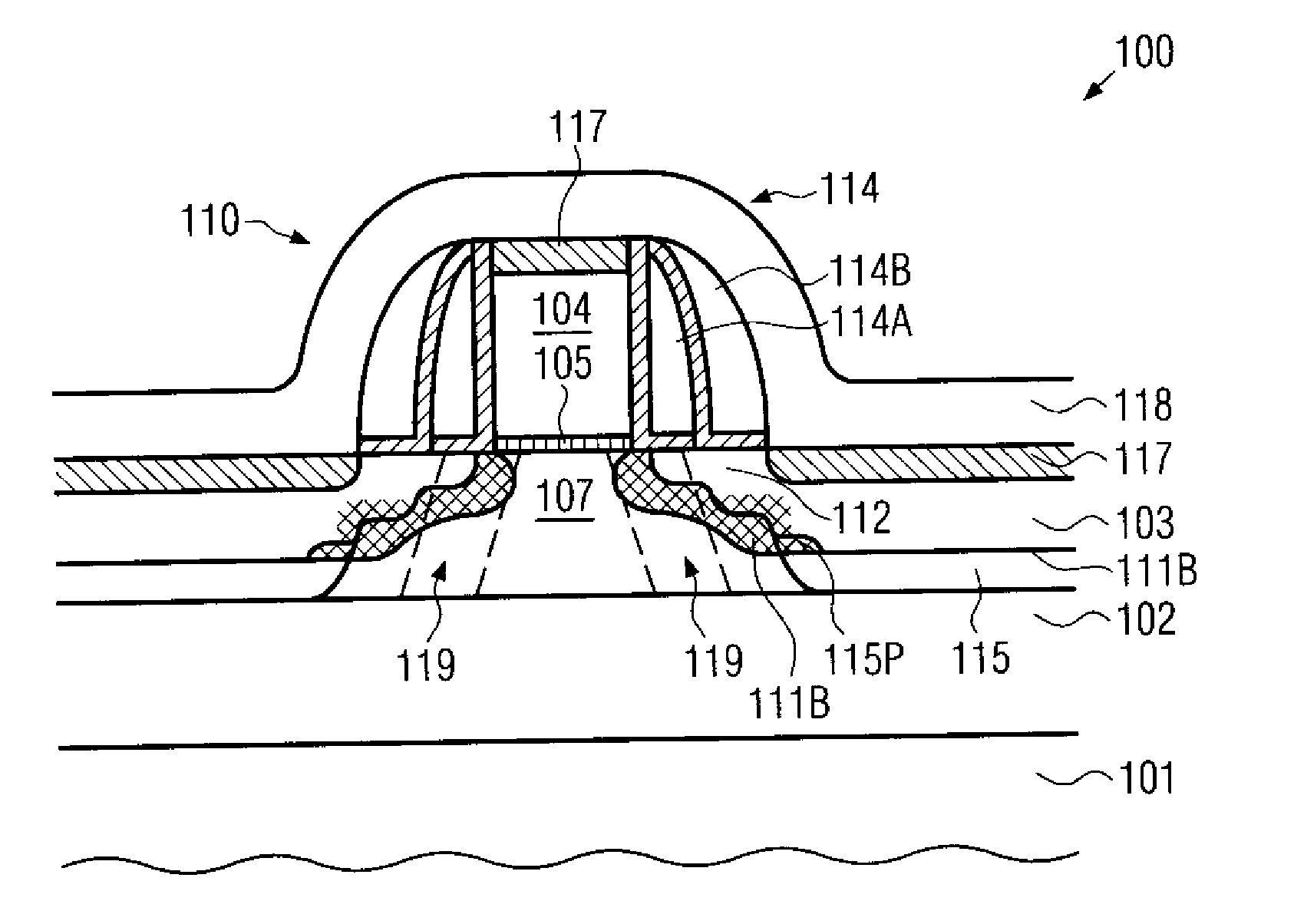
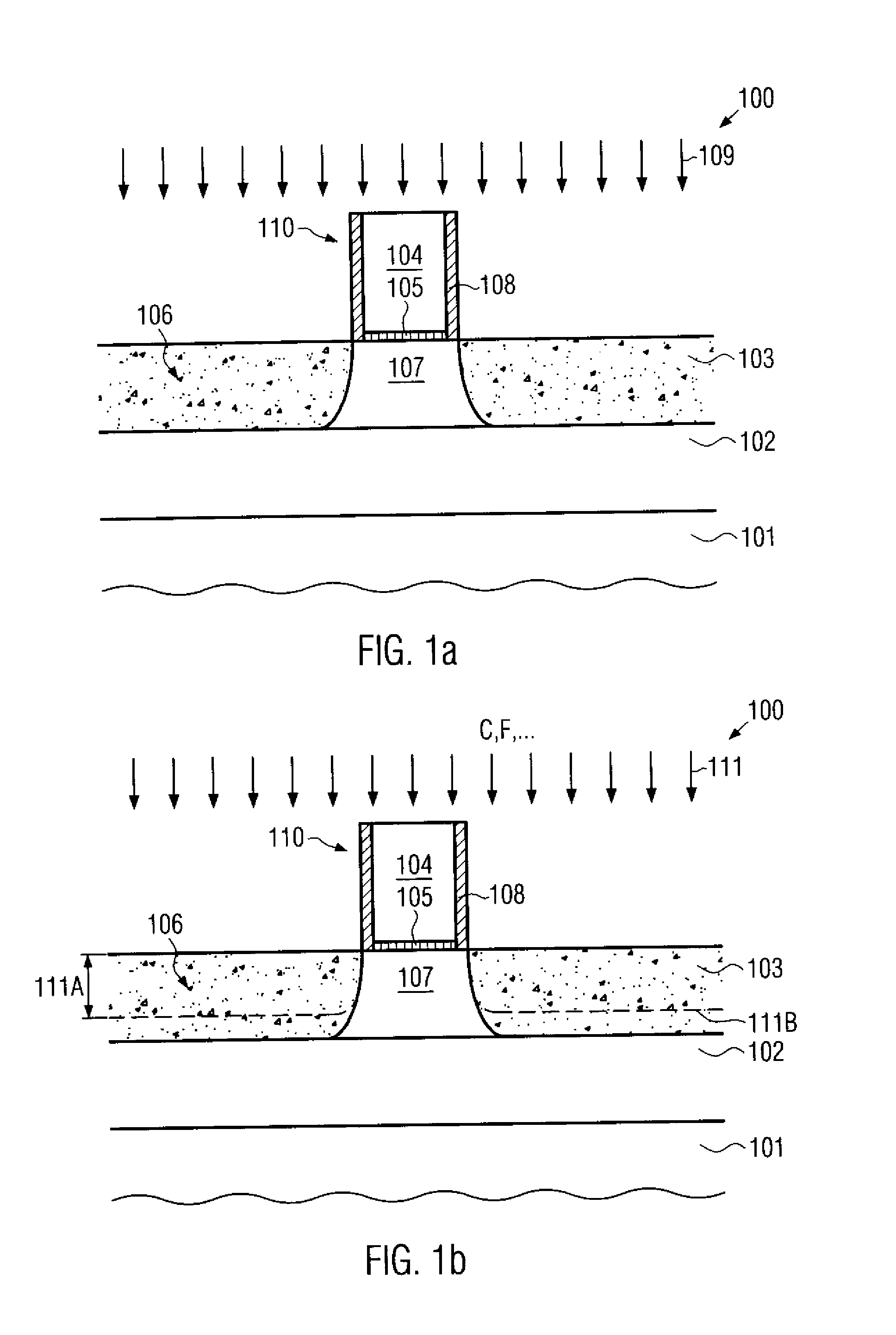
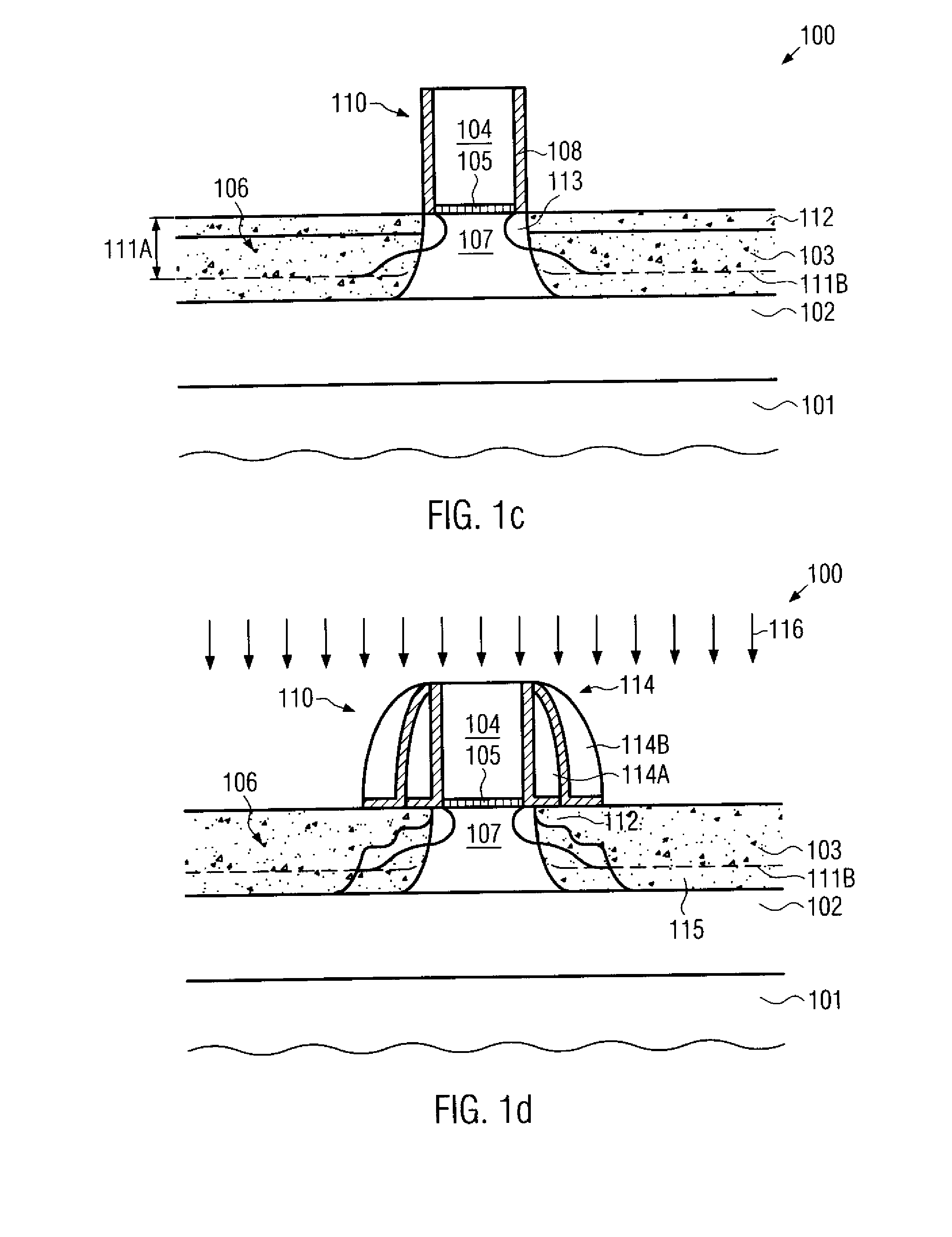
Soi field effect transistor having asymmetric junction leakage
InactiveUS20090032845A1Narrow widthFloating body effect is reduced and eliminatedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFloating body effectJunction leakage
A source trench and a drain trench are asymmetrically formed in a top semiconductor layer comprising a first semiconductor in a semiconductor substrate. A second semiconductor material having a narrower band gap than the first semiconductor material is deposited in the source trench and the drain trench to form a source side narrow band gap region and a drain side narrow band gap region, respectively. A gate spacer is formed and source and drain regions are formed in the top semiconductor layer. A portion of the boundary between an extended source region and an extended body region is formed in the source side narrow band gap region. Due to the narrower band gap of the second semiconductor material compared to the band gap of the first semiconductor material, charge formed in the extended body region is discharged through the source and floating body effects are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of manufacturing complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor
InactiveUS7595210B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFloating diffusion
A method of manufacturing a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor is provided. The method can include the steps of: providing a semiconductor substrate having an active region and an isolation region defined thereon; forming a photodiode at a photodiode area of the active region; forming first and second gate polys on a transistor region of the active region; forming a floating diffusion region on the semiconductor substrate between the first and second gate polys for receiving electrons transferred from the photodiode; and forming a floating diffusion node region at a part of the floating diffusion region for forming a metal contact. The floating diffusion region can be formed independently of the floating diffusion node region, so that a junction leakage current generated from the floating diffusion node region can be controlled.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
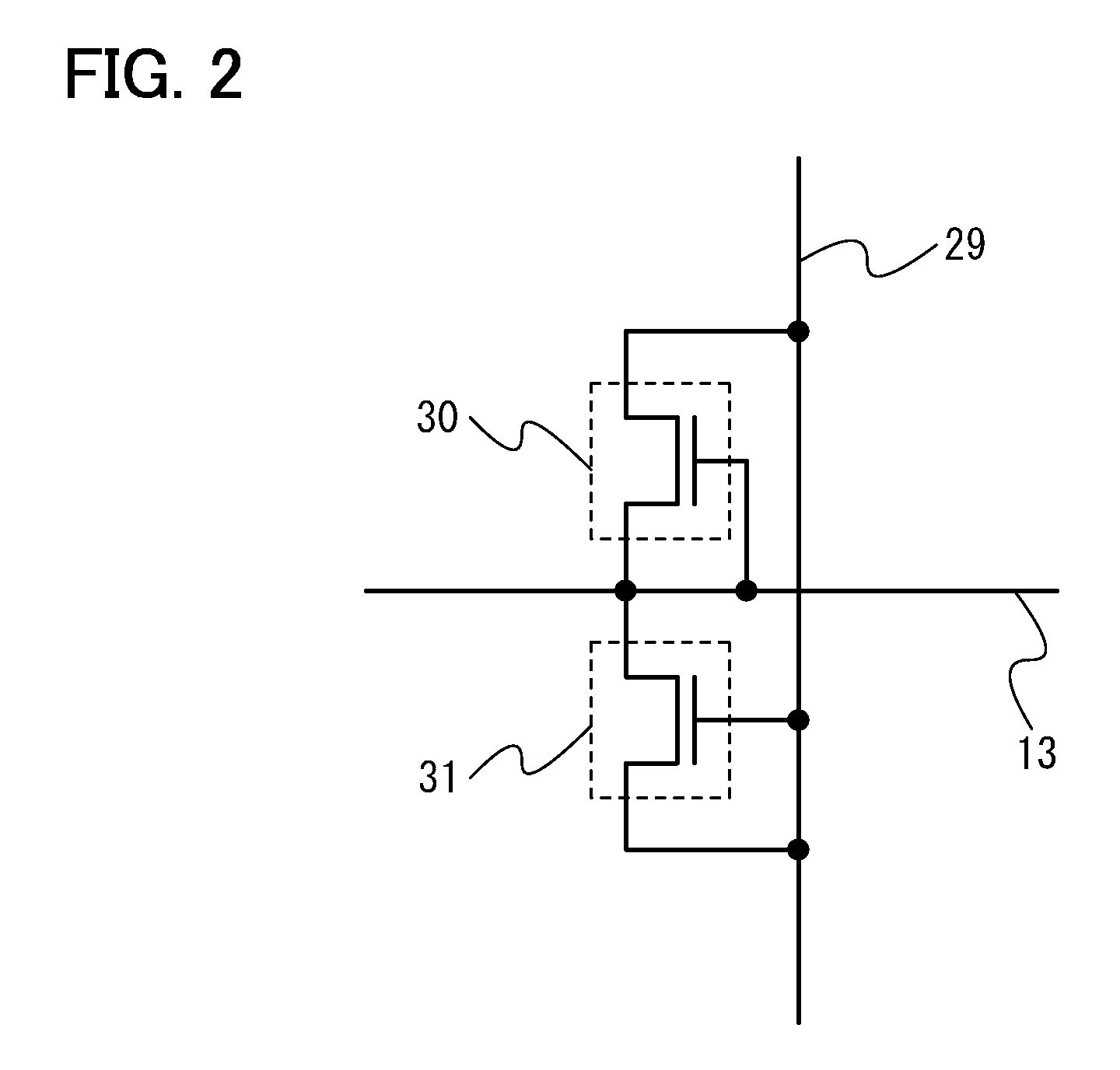
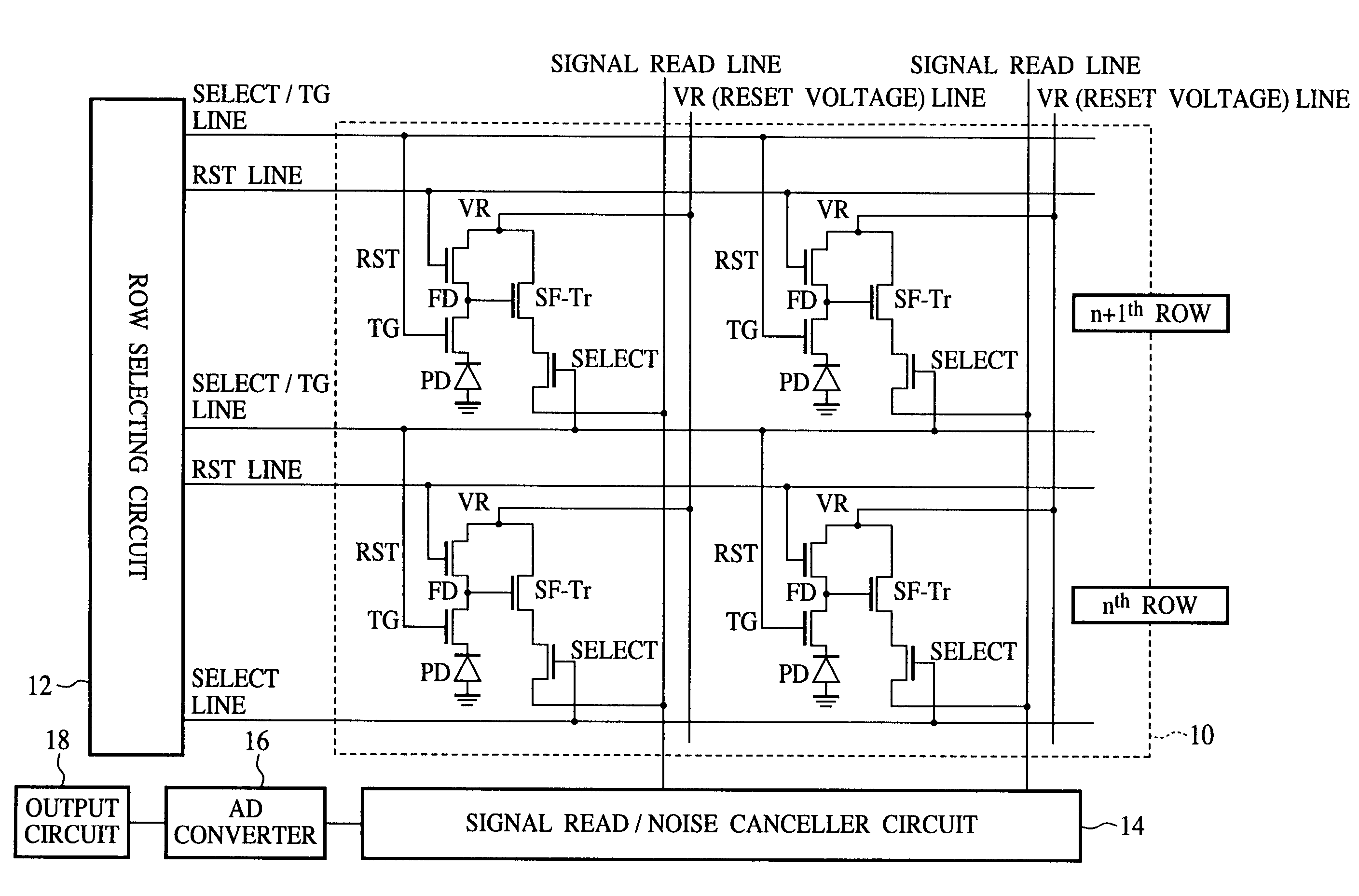
Solid-state image sensor and image reading method
InactiveUS7391453B2Increase the areaReduce junctionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsJunction leakageEngineering
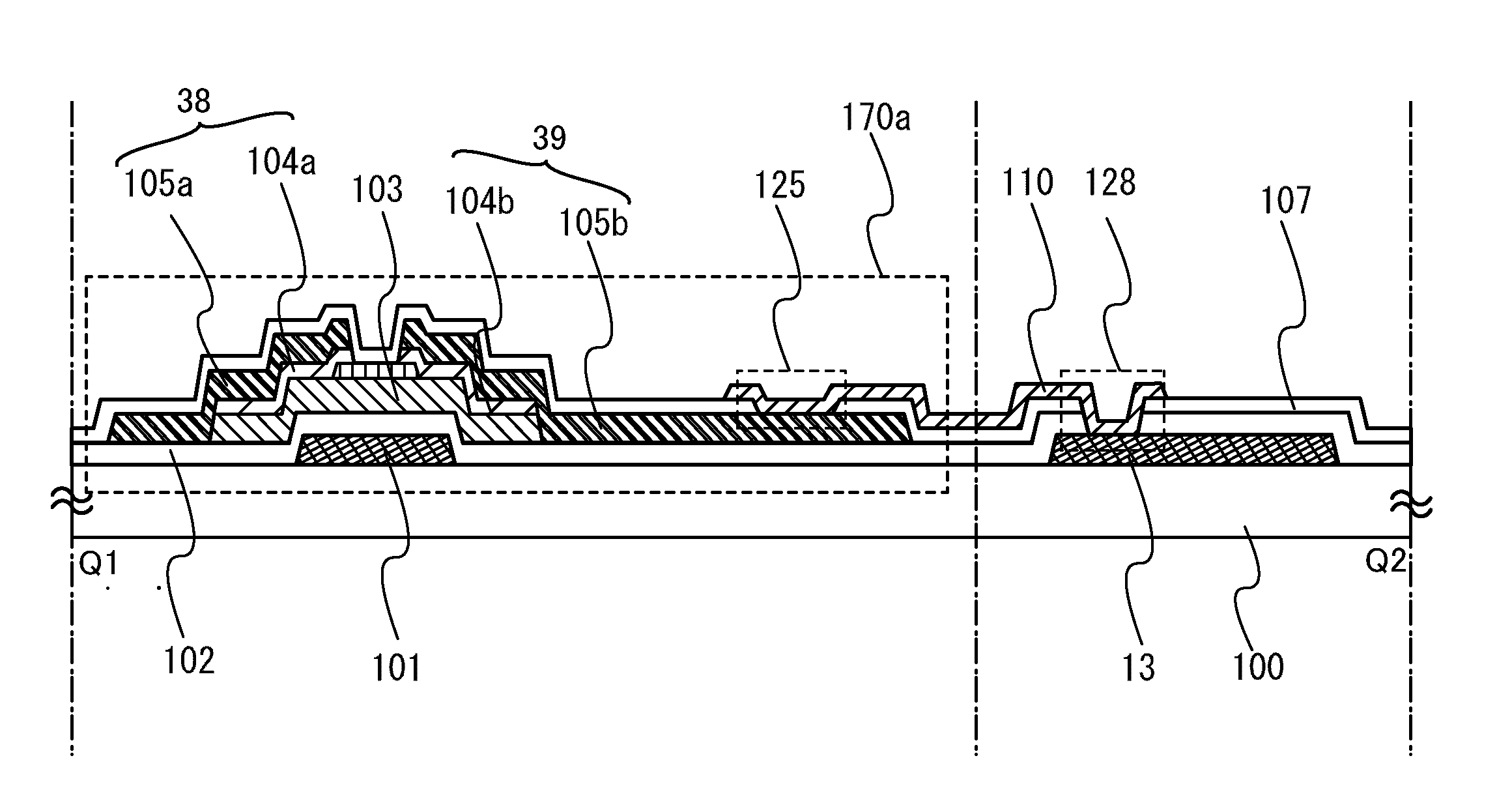
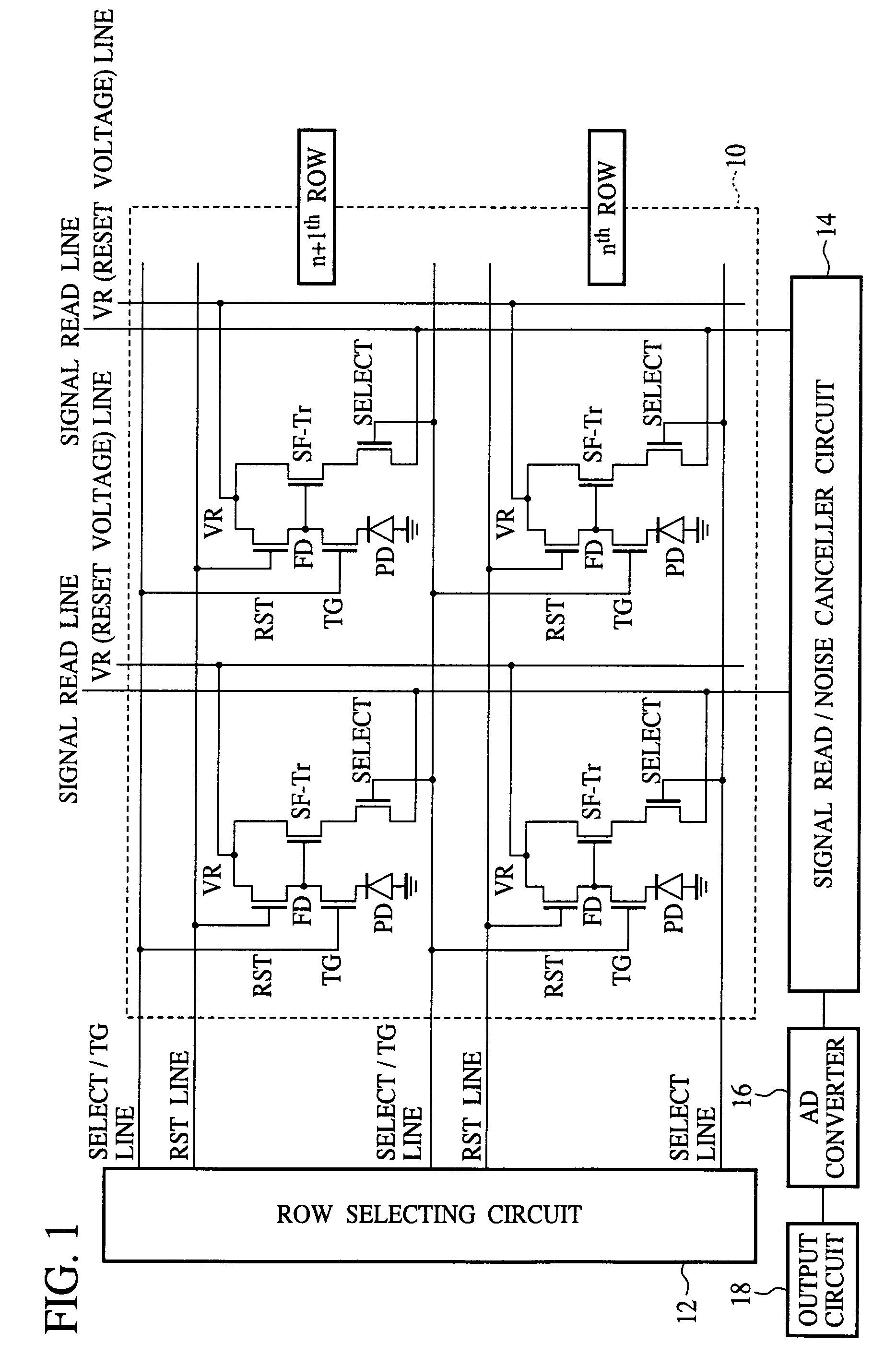
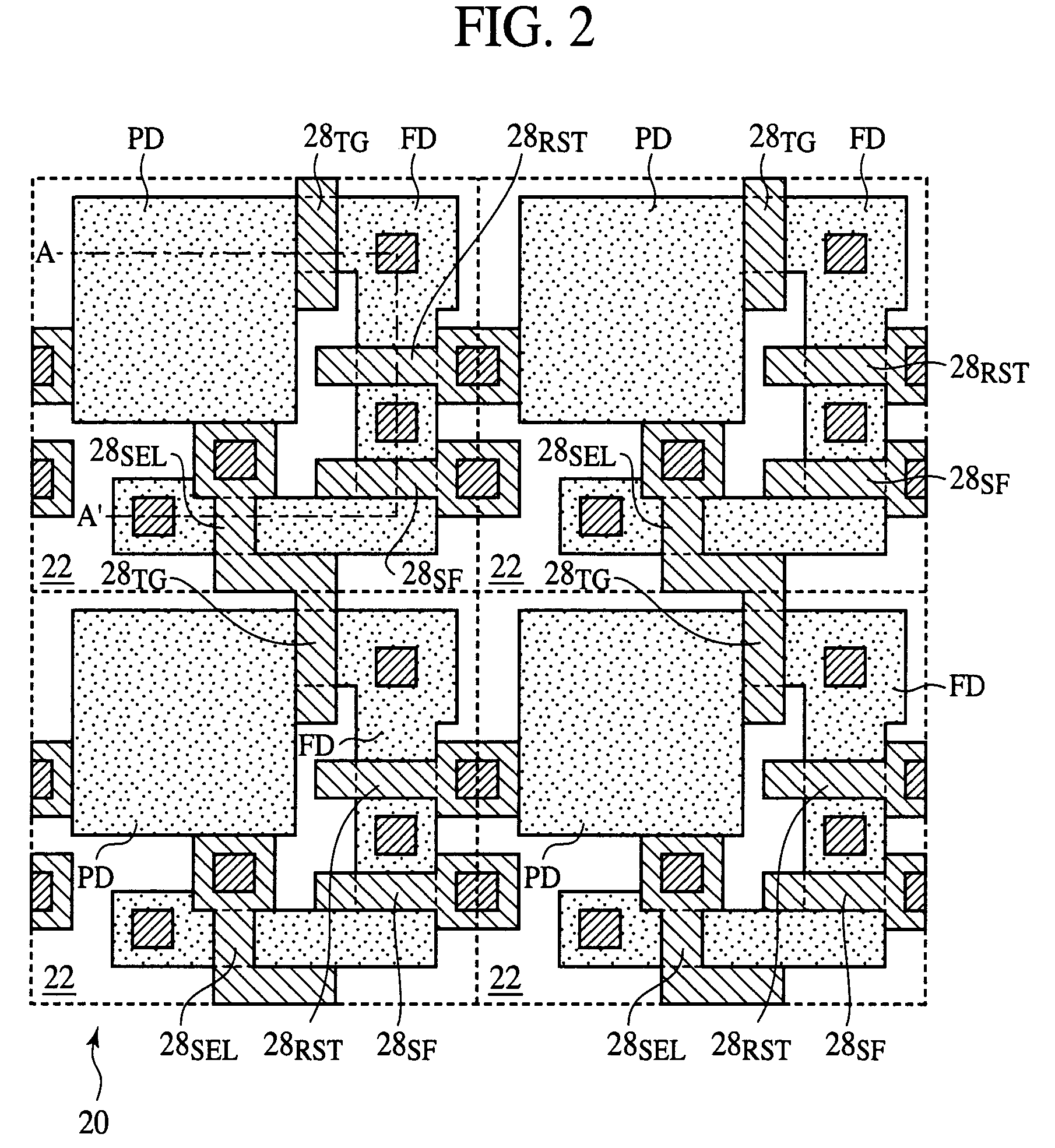
In the solid-state image sensor comprising 4-Tr-pixels, TG lines connecting the gate electrodes 28TG of the transfer transistors of the pixel units of the nth row, and select lines connecting the gate electrodes 28SEL of the select transistors of the pixel units of the n+1th row are formed of a common signal line, and the gate electrodes 28TG of the pixels of the nth row and the gate electrodes 28SEL of the pixel units of the n+1th row are formed in one continuous pattern of the same conducting layer. Whereby allowance can be given to layouts of the metal interconnection layers. Accordingly, the floating diffusions FD can be effectively shielded from light. Furthermore, allowance can be given to the area. Accordingly, the floating diffusions FD can have the area increased, whereby the junction leakage can be reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Integrated circuit structure
ActiveCN101908543ALower resistanceImprove drive currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentSemiconductor materials
An integrated circuit structure includes a substrate, and a channel over the substrate. The channel includes a first III-V compound semiconductor material formed of group III and group V elements. A gate structure is over the channel. A source / drain region is adjacent the channel and includes a group-IV region formed of a doped group-IV semiconductor material selected from the group consisting essentially of silicon, germanium, and combinations thereof. By re-growing silicon / germanium source / drain regions, the existing silicidation technique can be used to reduce the source / drain resistance and to improve drive currents of the resulting transistors. Buffer layers have the effect of smoothening the lattice constant transition between the channel of the transistor and the source / drain regions, resulting in a reduced defect density and reduced junction leakage currents.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method to reduce junction leakage current in strained silicon on silicon-germanium devices
InactiveUS6846720B2Reduce connection areaReduce junction leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETJunction leakage
A MOSFET device in strained silicon-on-SiGe and a method of forming the device are described. The said device achieves reduced junction leakage due to the lower band-gap values of SiGe. The method consists of forming isolation trenches in a composite strained-Si / SiGe substrate and growing a liner oxide by wet oxidation such that oxidation is selective to SiGe only, with negligible oxidation of silicon surfaces. Selective oxidation results in oxide encroachment under strained-Si, thereby reducing the junction area after device fabrication is completed. Reduced junction area leads to reduced n+ / p or p+ / n junction leakage current.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Epitaxial buffer layer for finfet source and drain junction leakage reduction
A semiconductor device including a gate structure on a channel region portion of a fin structure, and at least one of an epitaxial source region and an epitaxial drain region on a source region portion and a drain region portion of the fin structure. At least one of the epitaxial source region portion and the epitaxial drain region portion include a first concentration doped portion adjacent to the fin structure, and a second concentration doped portion on the first concentration doped portion. The second concentration portion has a greater dopant concentration than the first concentration doped portion. An extension dopant region extending into the channel portion of the fin structure having an abrupt dopant concentration gradient of n-type or p-type dopants of 7 nm per decade or greater.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080001224A1Improve performanceIncrease injection rateTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction leakageField-effect transistor
A semiconductor device which can effectively suppress a short channel effect and junction leakage is provided. A semiconductor device includes a field effect transistor. The field effect transistor includes a first semiconductor region of a first conductivity type, a gate electrode formed on a gate insulating film, and source and drain electrodes. The field effect transistor also includes second semiconductor regions of a second conductivity type. The field effect transistor further includes third semiconductor regions of the second conductivity type having an impurity concentration higher than that of the second semiconductor region and formed between the source electrode and the first and second semiconductor regions and between the drain electrode and the first and second semiconductor regions, and side wall insulating films formed on both the side surfaces of the gate electrode. The source electrode and the drain electrode are separated from the side wall insulating films.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Flash memory programming using gate induced junction leakage current
ActiveUS20050099849A1Increase electron-hole pair generationIncreasing pair generationRead-only memoriesDigital storageJunction leakageElectric field
A method for programming a storage element and a storage element programmed using gate induced junction leakage current are provided. The element may include at least a floating gate on a substrate, an active region in the substrate, and a second gate adjacent to the floating gate. The method may include the steps of: creating an inversion region in the substrate below the floating gate by biasing the first gate; and creating a critical electric field adjacent to the second gate. Creating a critical electric field may comprise applying a first positive bias to the active region; and applying a bias less than the first positive bias to the second gate. The element further includes a first bias greater than zero volts applied to the active region and a second bias greater than the first bias applied to the floating gate and a third bias less than or equal to zero applied to the second gate. The first and third bias are selected to create leakage current in the substrate between the floating gate and the select gate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
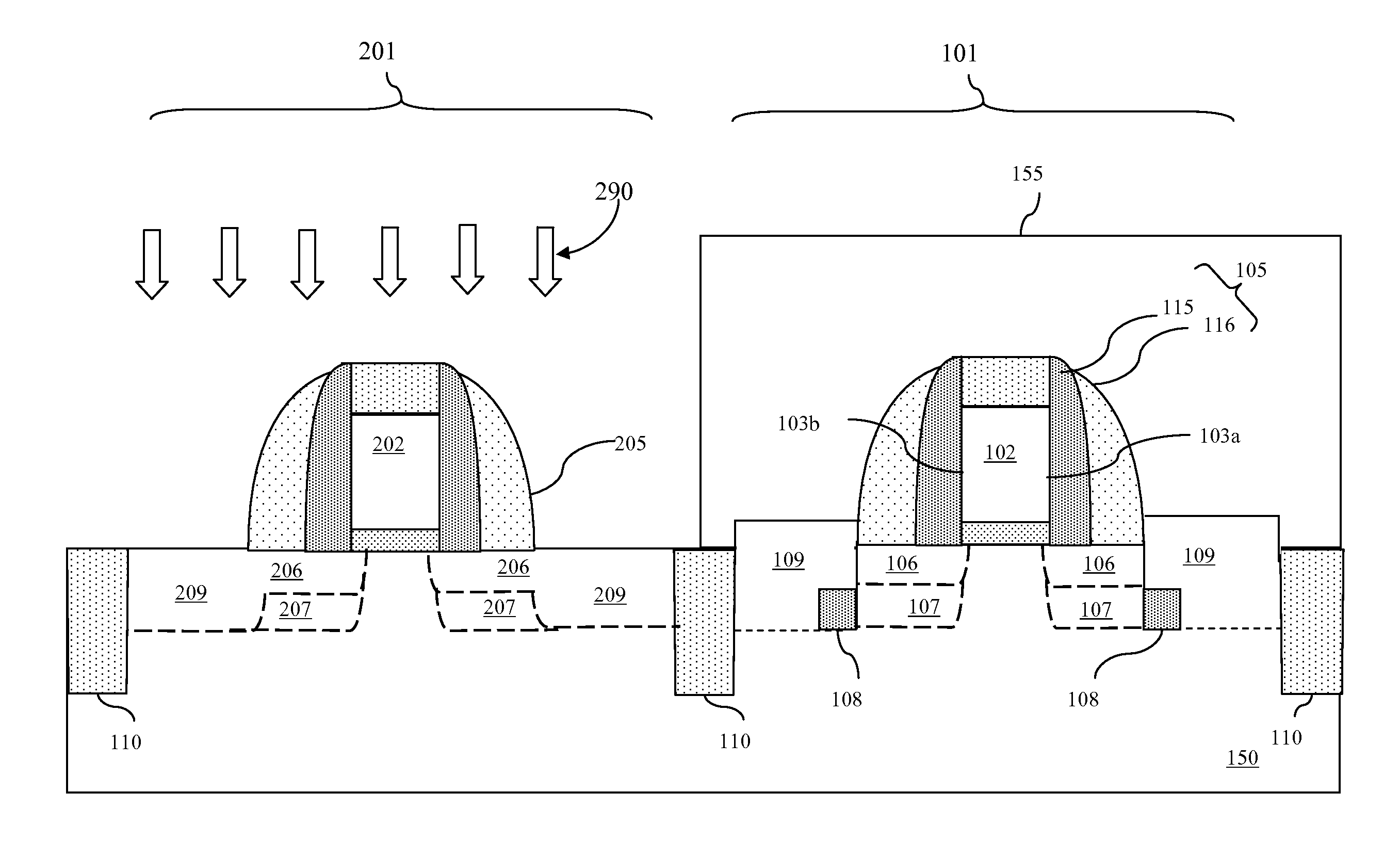
Structure and method to improve short channel effects in metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors
InactiveUS20080121985A1Suppression of short channel effectsCapacitance minimizedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceCMOS
Disclosed are embodiments of improved MOSFET and CMOS structures that provides for increased control over short channel effects. Also disclosed are embodiments of associated methods of forming these structures. The embodiments suppress short channel effects by incorporating buried isolation regions into a transistor below source / drain extension regions and between deep source / drain regions and the channel region and, particularly, between deep source / drain regions and the halo regions. Buried isolation regions between the deep source / drain regions and the channel region minimize drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) as well as punch through. Additionally, because the deep source / drain regions and halo regions are separated by the buried isolation regions, side-wall junction capacitance and junction leakage are also minimized.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
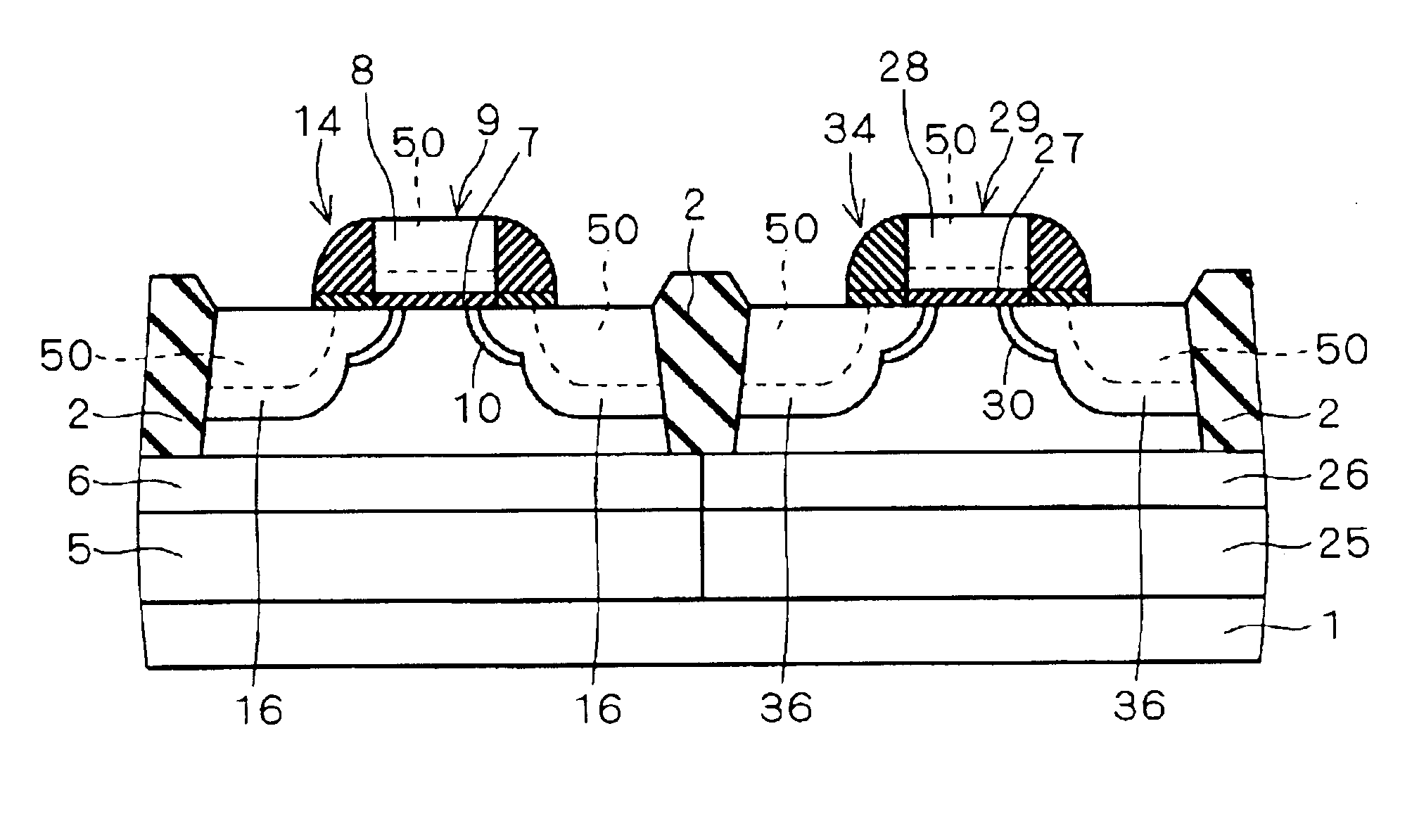
InactiveUS6872642B2Improve performanceIncrease productionTransistorSolid-state devicesJunction leakageEngineering
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device is provided which can suppress leakage current increases by making into silicide. Impurity that suppresses silicide formation reaction (suppression impurity), such as germanium, is introduced into source / drain regions (16, 36) from their upper surfaces. In the source / drain regions (16, 36), a region shallower than a region where the suppression impurity is distributed (50) is made into silicide, so that a silicide film (51) is formed in the source / drain regions (16, 36). Thus, by making the region shallower than the region (50) into silicide, it is possible to suppress that silicide formation reaction extends to the underside of the region to be made into silicide. This enables to reduce the junction leakage between the source / drain regions (16, 36) and a well region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
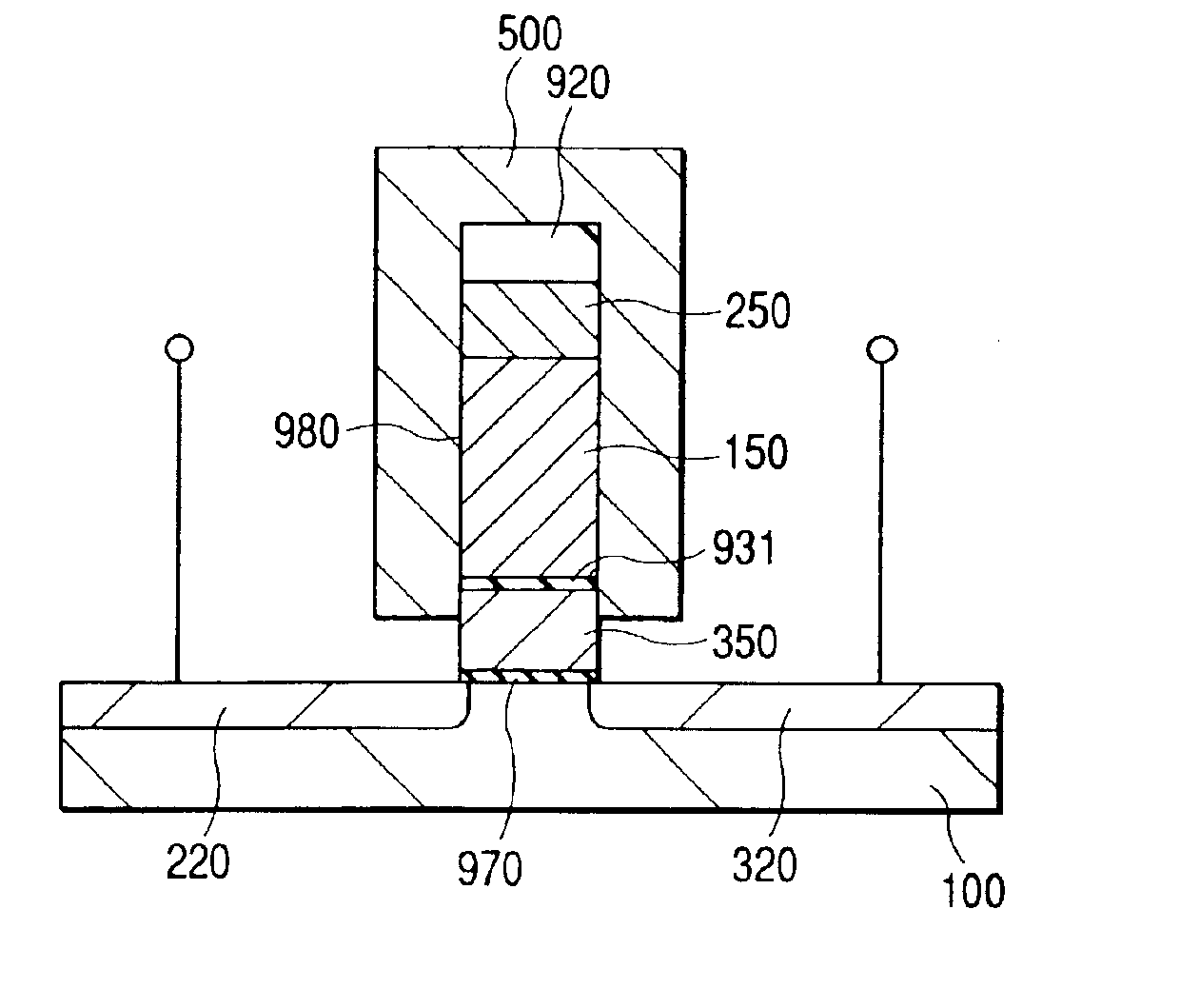
Device and method of reducing junction leakage
InactiveUS20110291202A1Reduce junction leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantJunction leakage
A device and method for reducing junction leakage in a semiconductor junction includes forming a faceted raised structure in a source / drain region of the device. Dopants are diffused from the faceted raised structure into a substrate below the faceted raised structure to form source / drain regions. A sprinkle implantation is applied on the faceted raised structure to produce a multi-depth dopant profile in the substrate for the source / drain regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com