Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1668 results about "Lattice constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
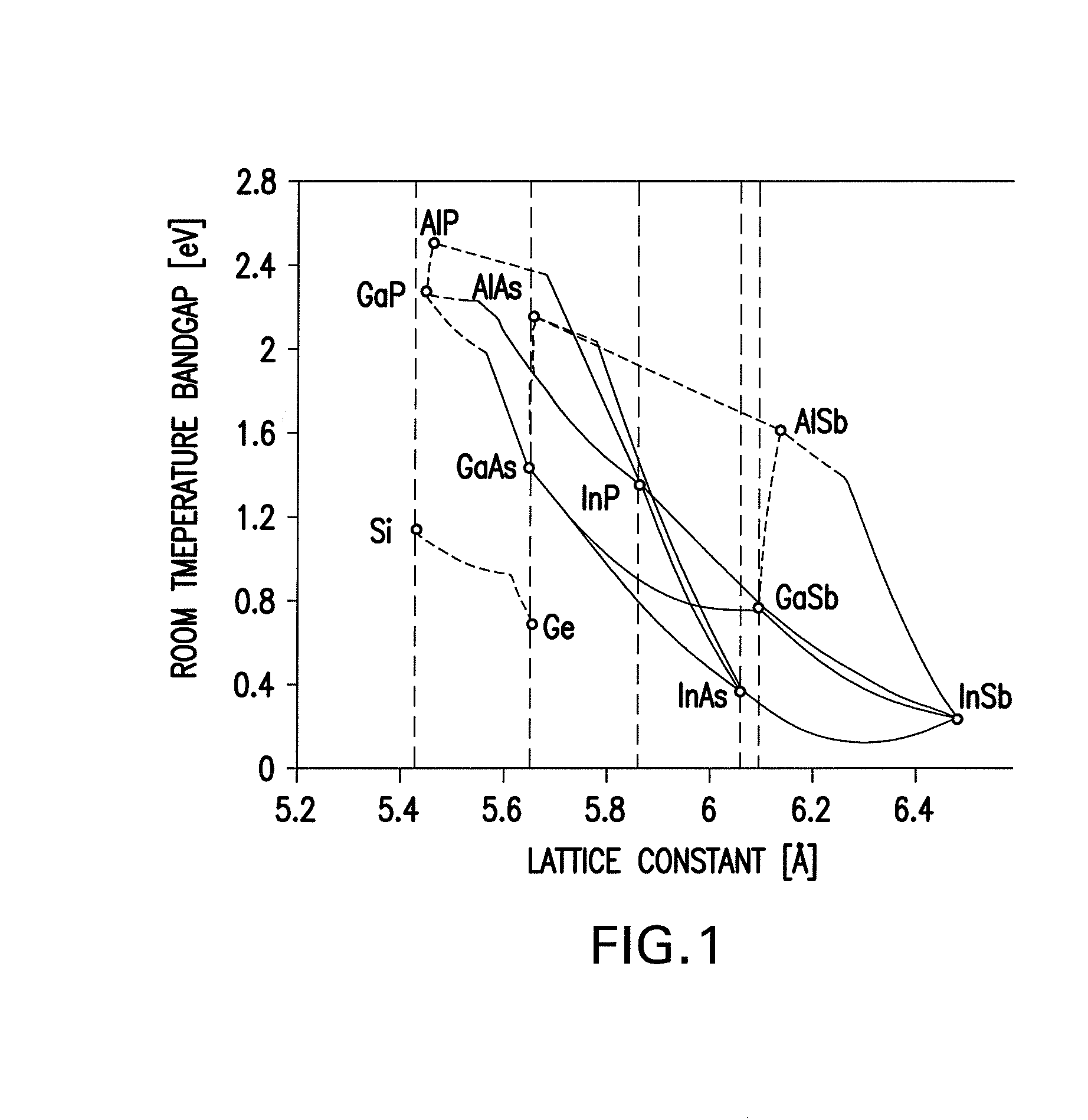
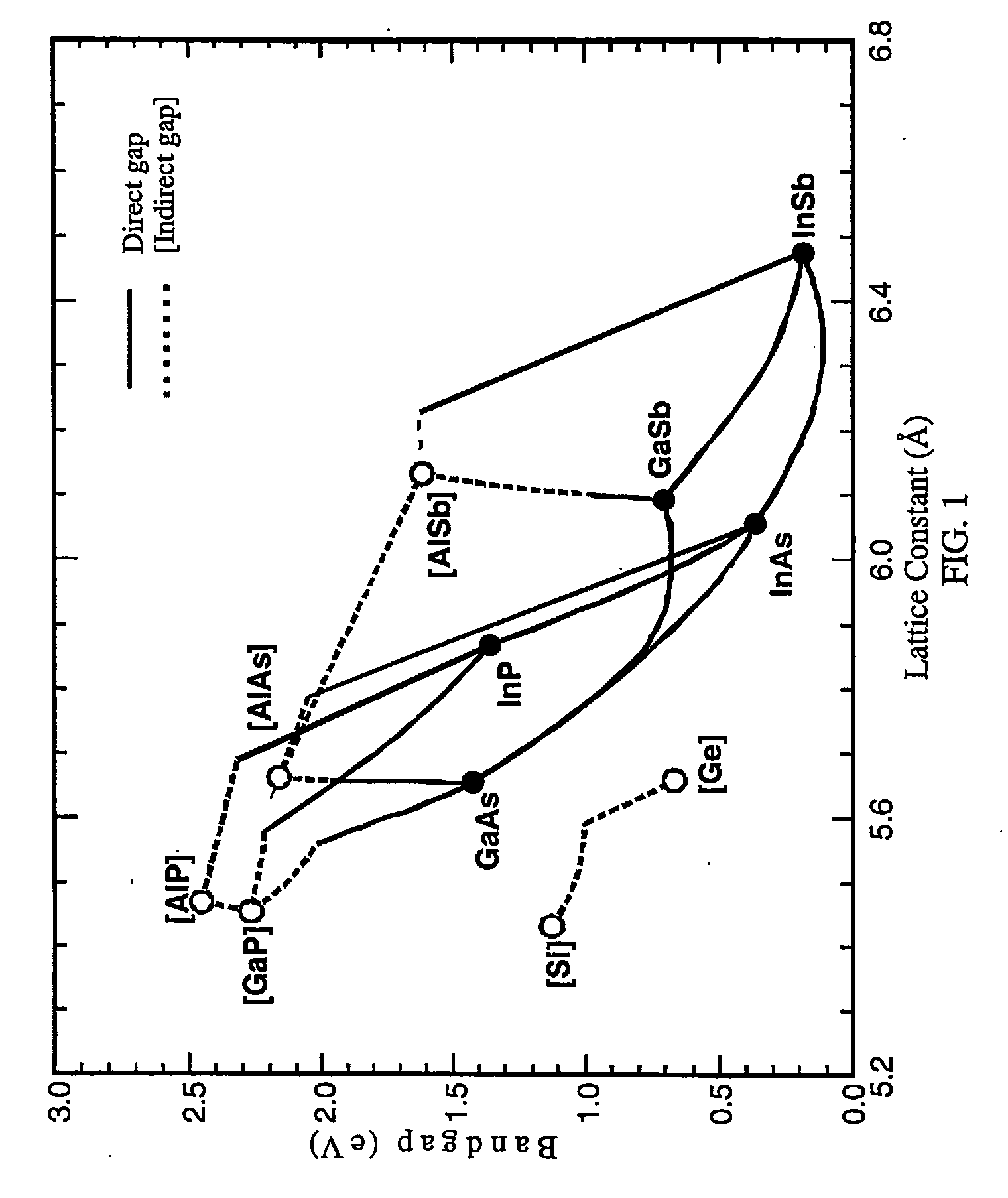
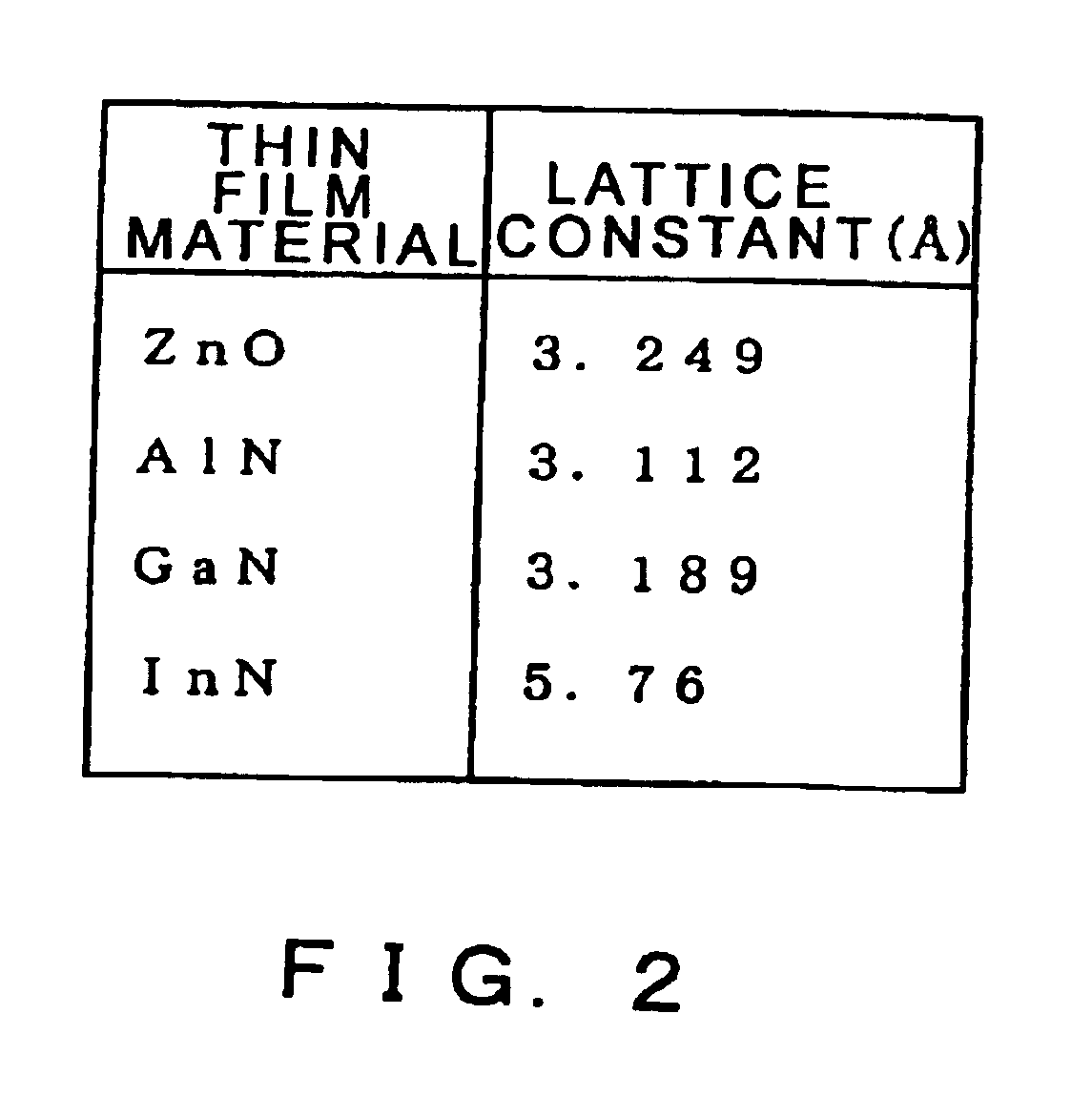
The lattice constant, or lattice parameter, refers to the physical dimension of unit cells in a crystal lattice. Lattices in three dimensions generally have three lattice constants, referred to as a, b, and c. However, in the special case of cubic crystal structures, all of the constants are equal and are referred to as a. Similarly, in hexagonal crystal structures, the a and b constants are equal, and we only refer to the a and c constants. A group of lattice constants could be referred to as lattice parameters. However, the full set of lattice parameters consist of the three lattice constants and the three angles between them.
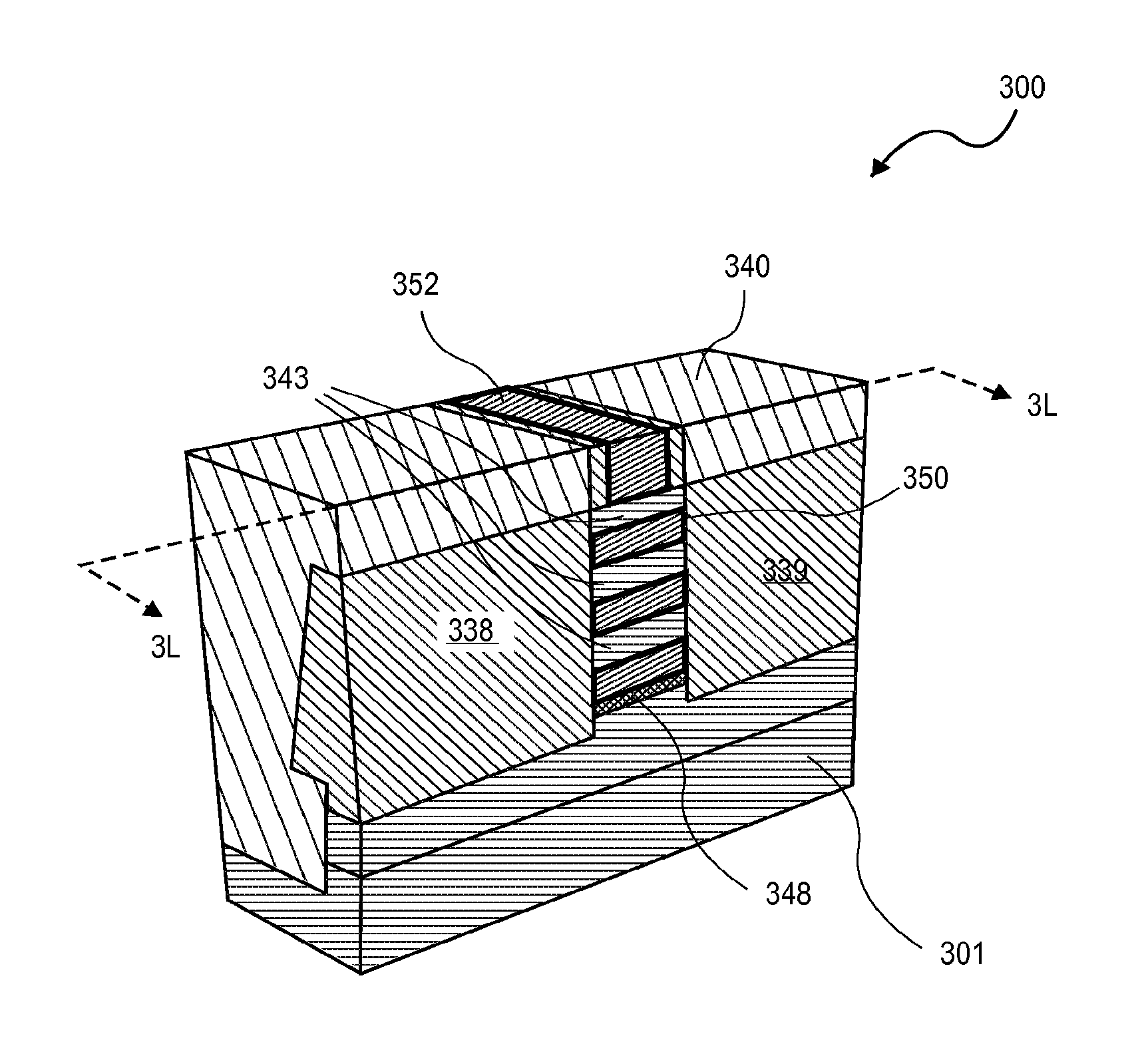
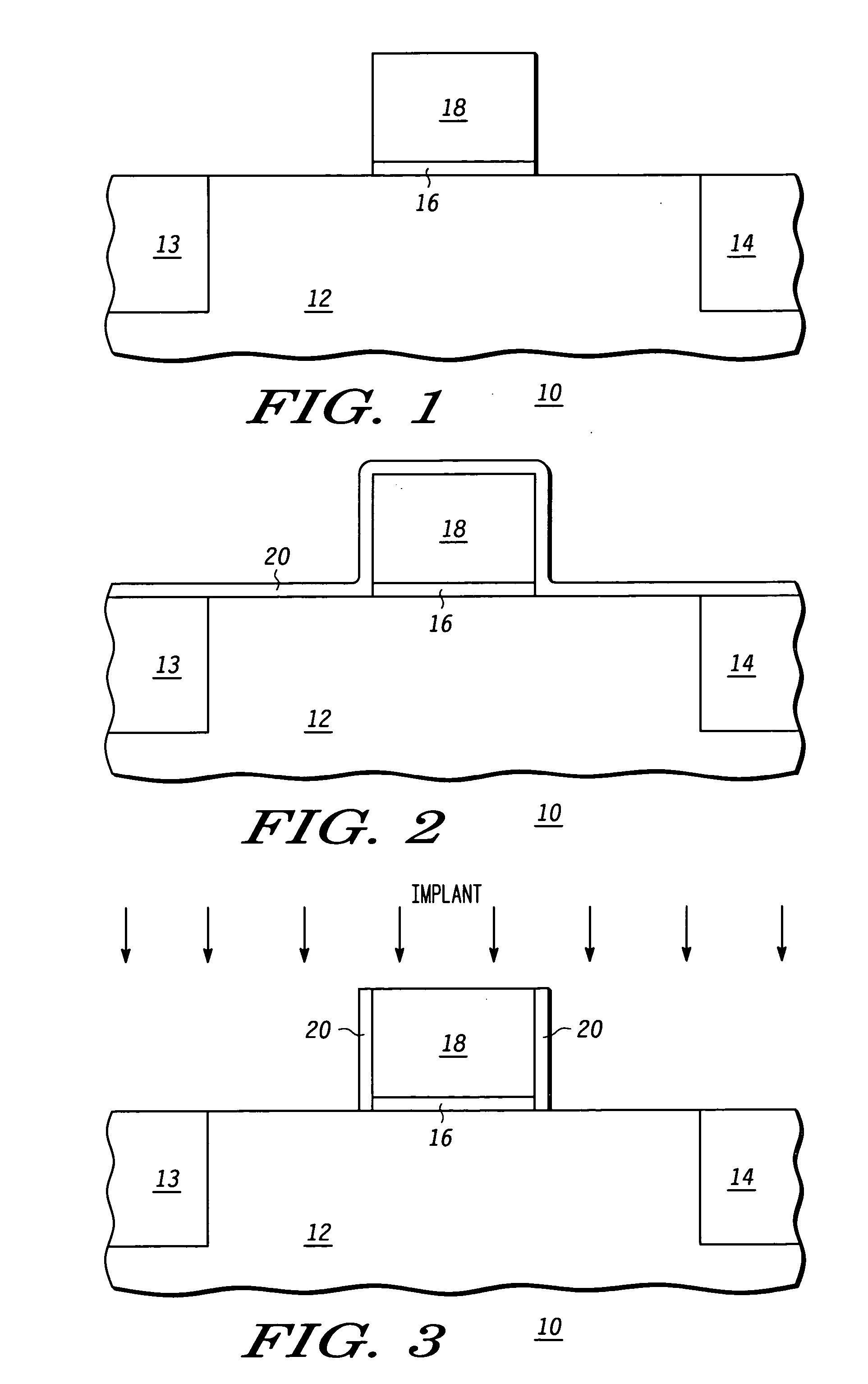
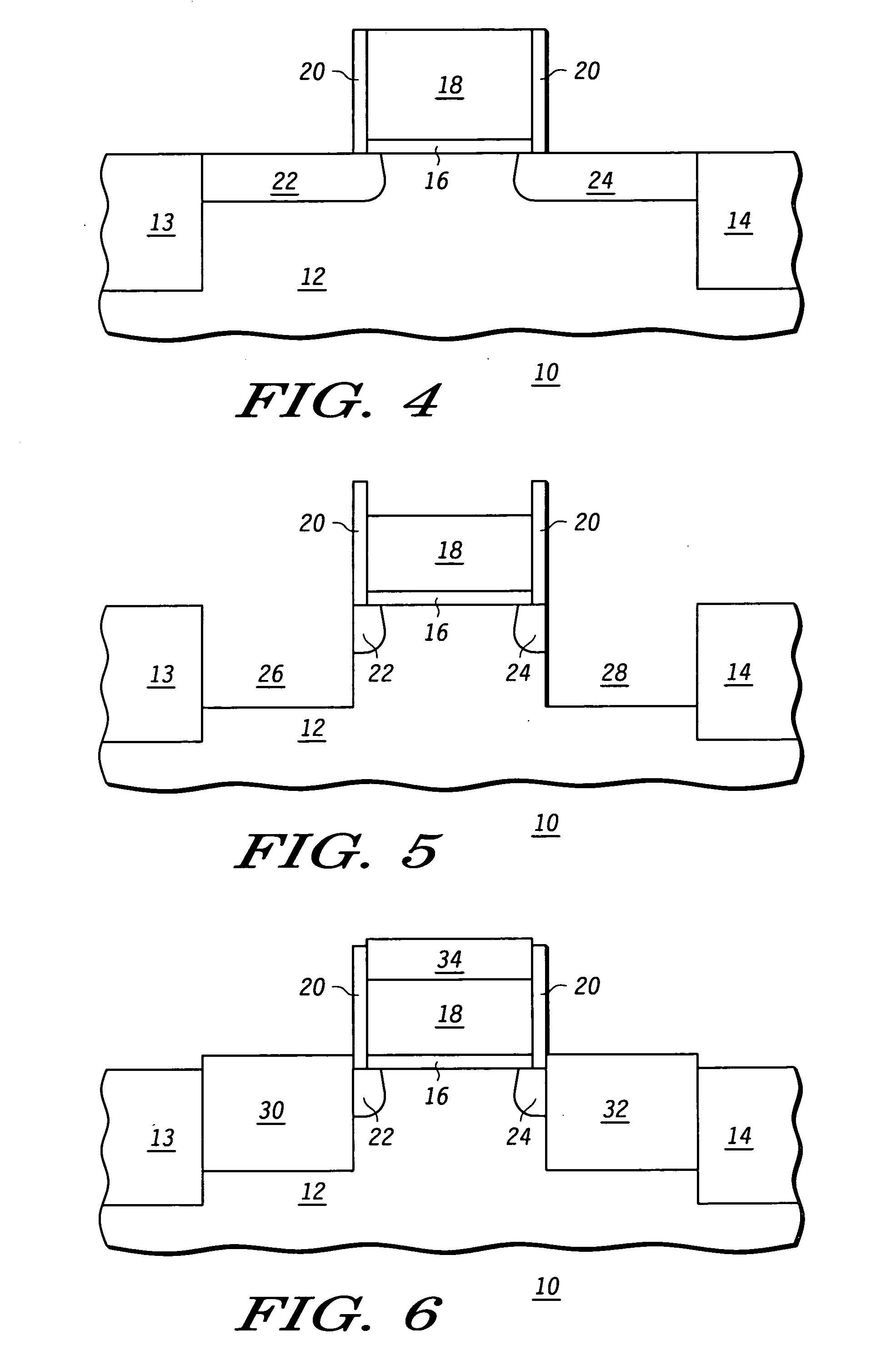
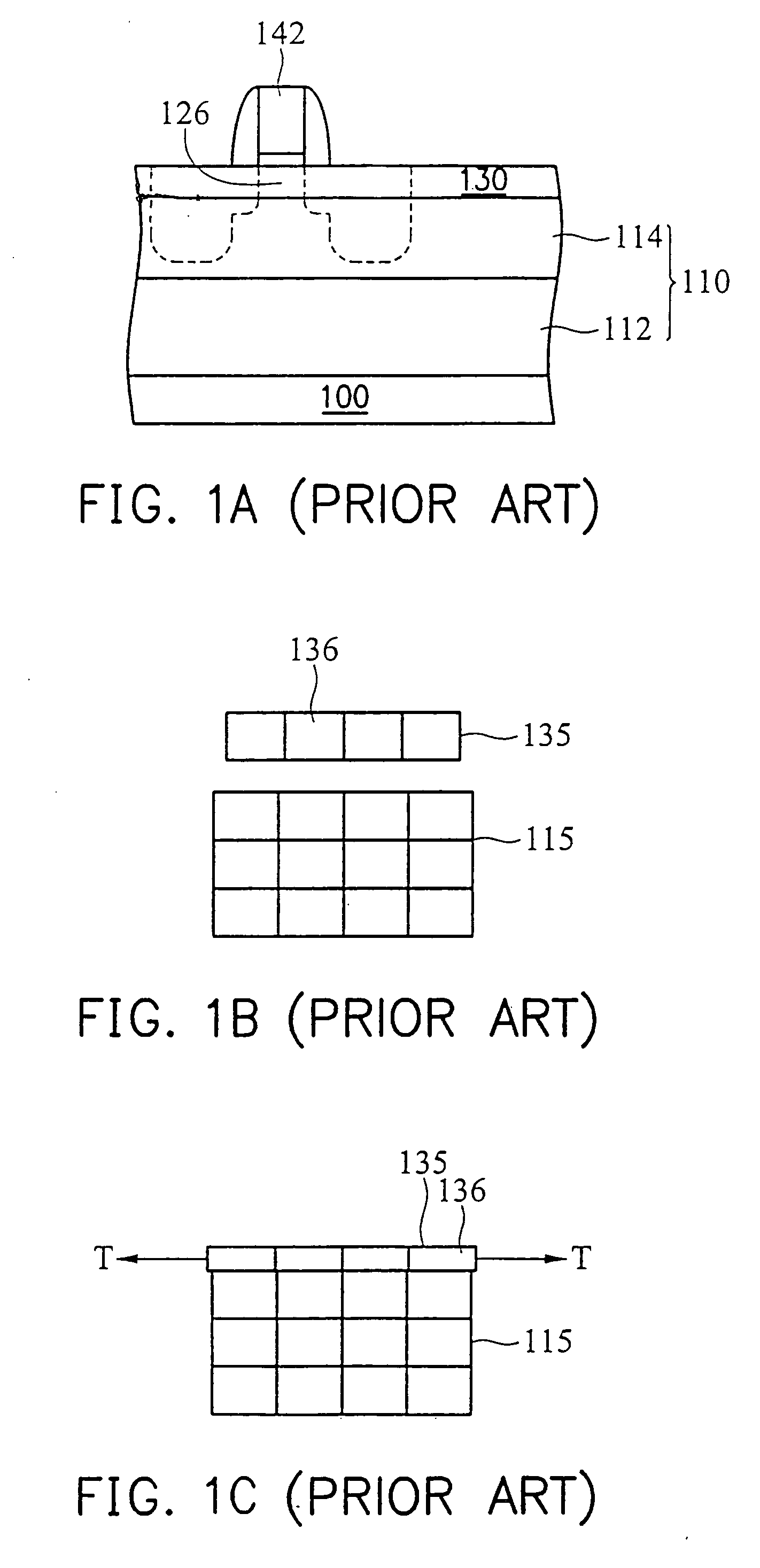
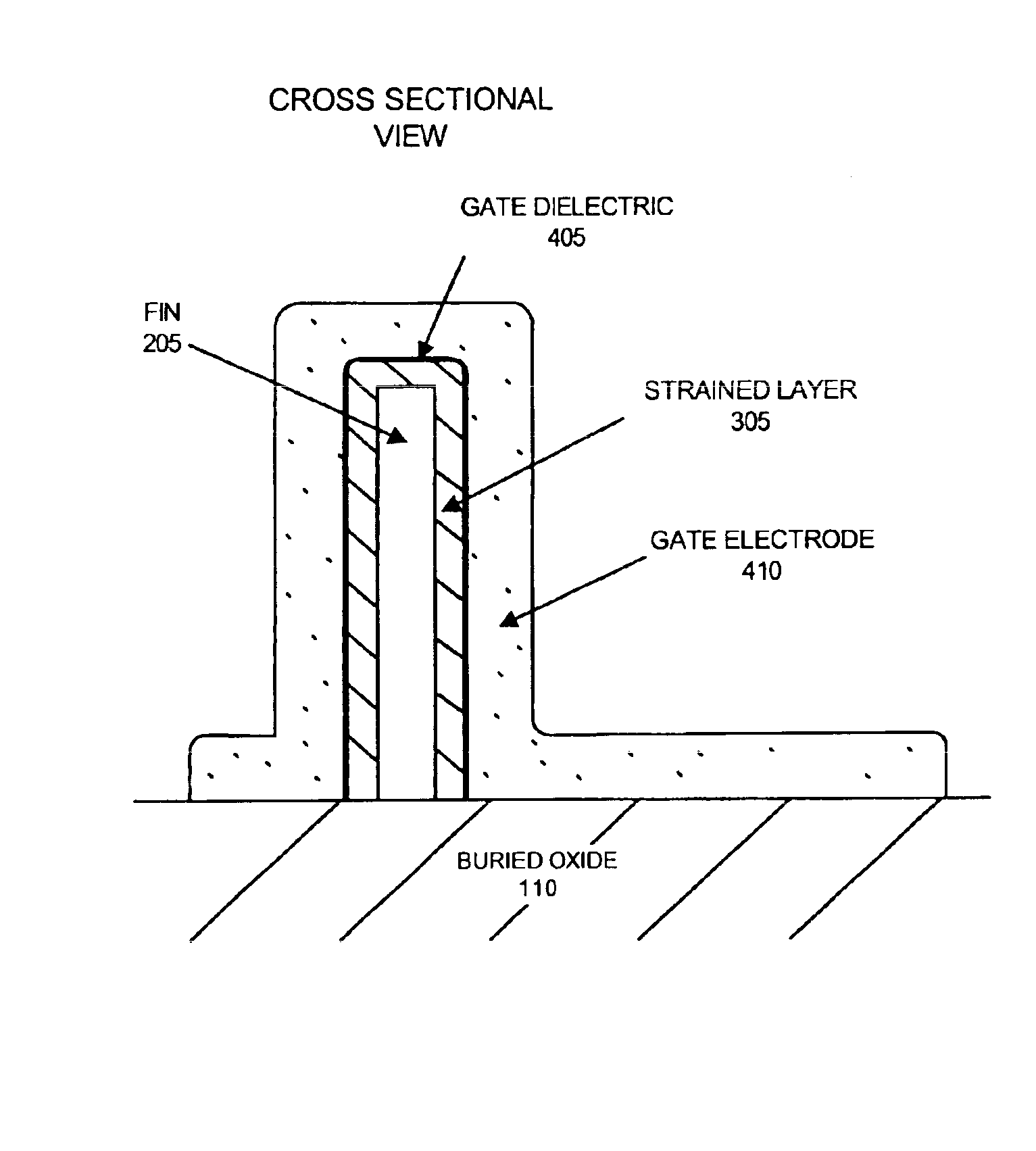
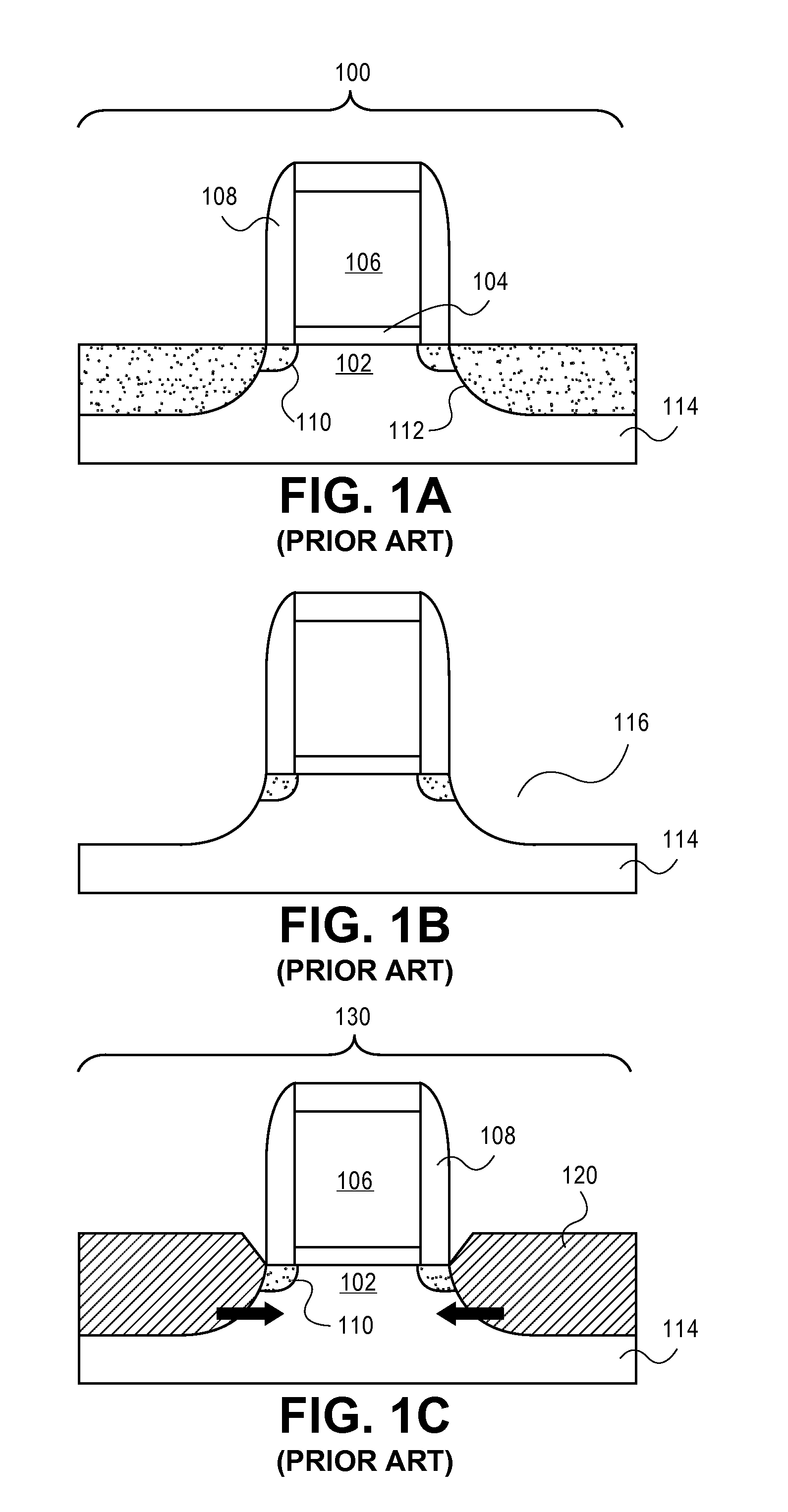
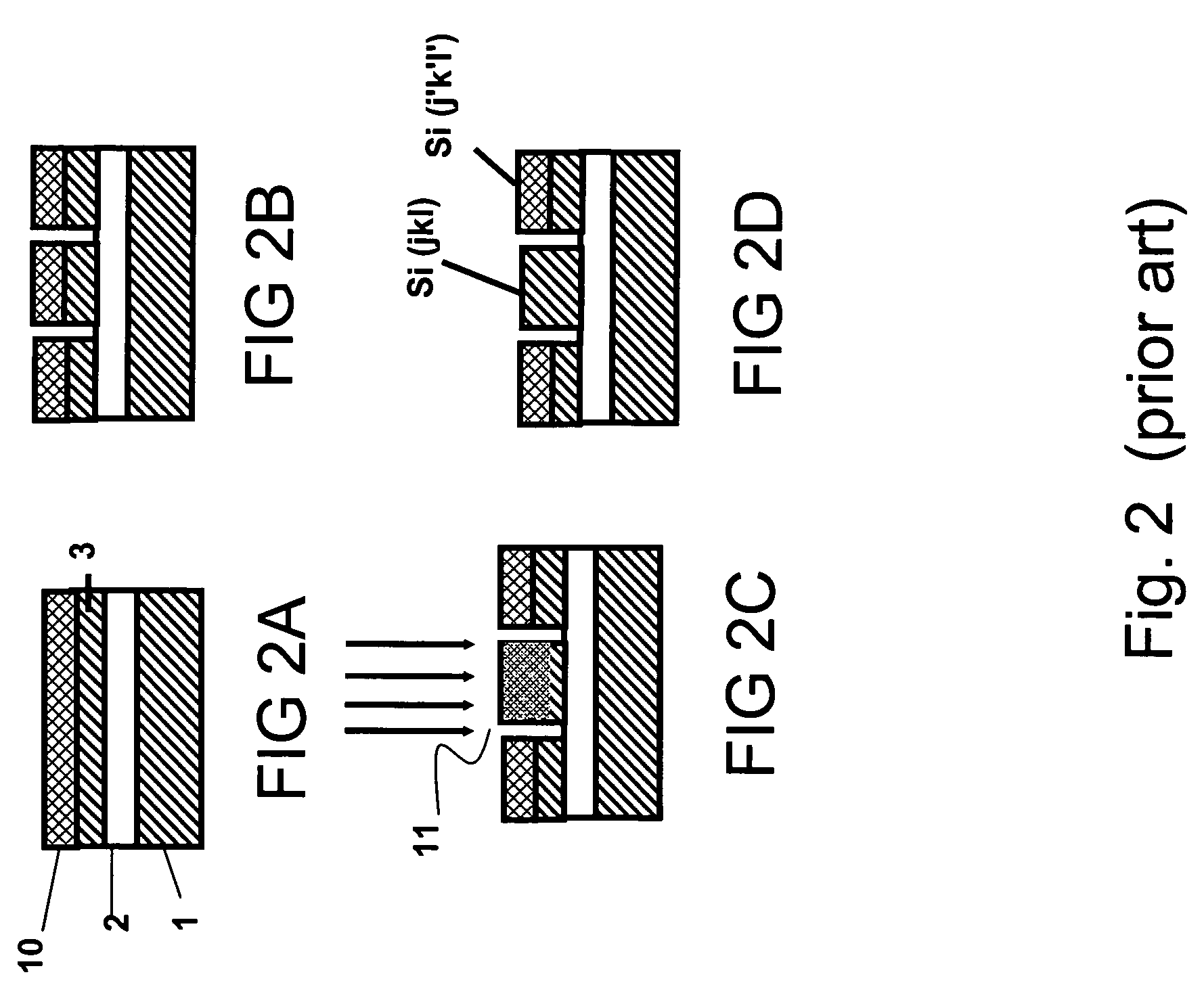
Non-planar gate all-around device and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS20140225065A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireGate dielectric
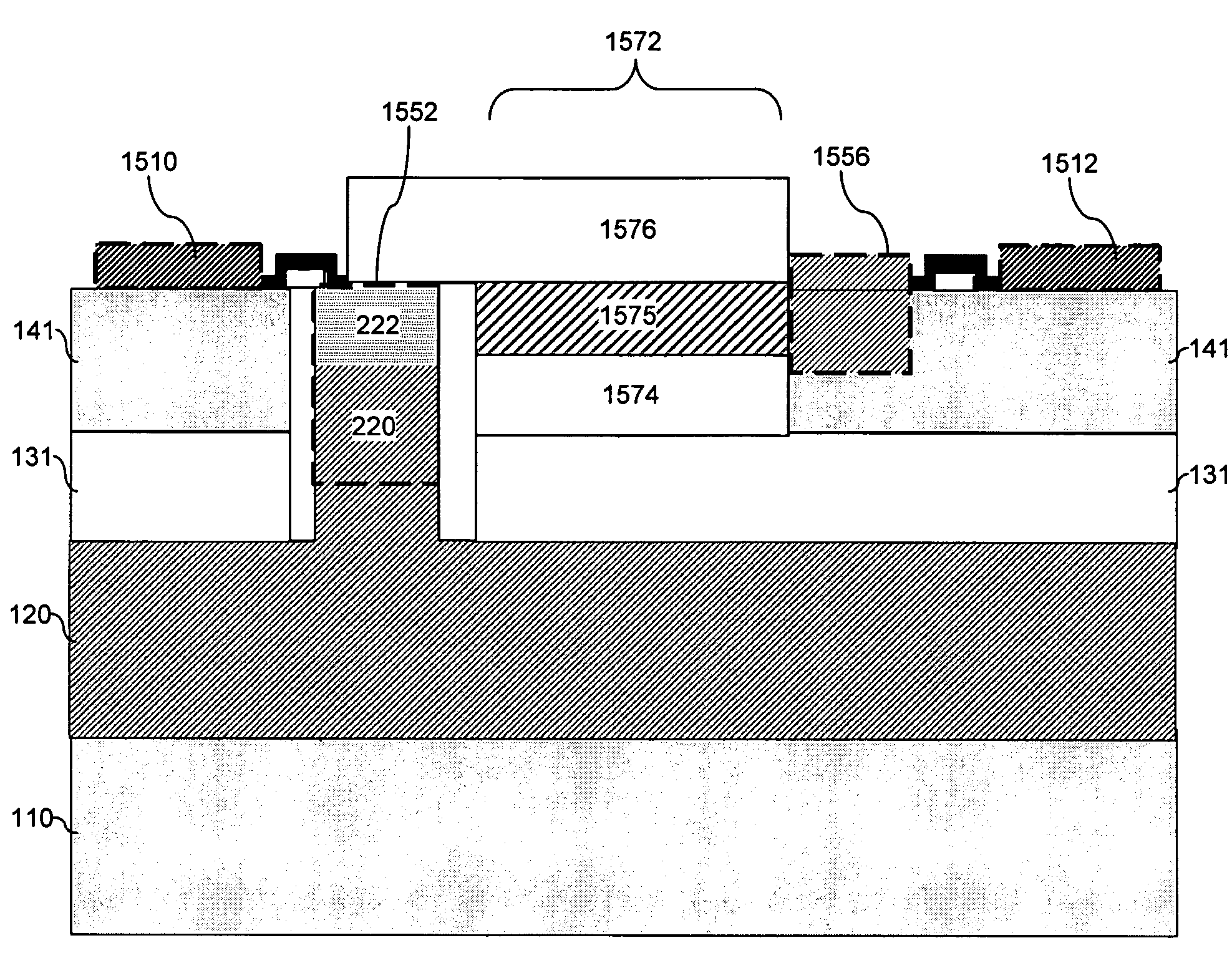
A non-planar gate all-around device and method of fabrication thereby are described. In one embodiment, the device includes a substrate having a top surface with a first lattice constant. Embedded epi source and drain regions are formed on the top surface of the substrate. The embedded epi source and drain regions have a second lattice constant that is different from the first lattice constant. Channel nanowires having a third lattice are formed between and are coupled to the embedded epi source and drain regions. In an embodiment, the second lattice constant and the third lattice constant are different from the first lattice constant. The channel nanowires include a bottom-most channel nanowire and a bottom gate isolation is formed on the top surface of the substrate under the bottom-most channel nanowire. A gate dielectric layer is formed on and all-around each channel nanowire. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric layer and surrounding each channel nanowire.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for making a semiconductor device with strain enhancement
InactiveUS20060228863A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice constantSemiconductor
A semiconductor device with strain enhancement is formed by providing a semiconductor substrate and an overlying control electrode having a sidewall. An insulating layer is formed adjacent the sidewall of the control electrode. The semiconductor substrate and the control electrode are implanted to form first and second doped current electrode regions, a portion of each of the first and second doped current electrode regions being driven to underlie both the insulating layer and the control electrode in a channel region of the semiconductor device. The first and second doped current electrode regions are removed from the semiconductor substrate except for underneath the control electrode and the insulating layer to respectively form first and second trenches. An insitu doped material containing a different lattice constant relative to the semiconductor substrate is formed within the first and second trenches to function as first and second current electrodes of the semiconductor device.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
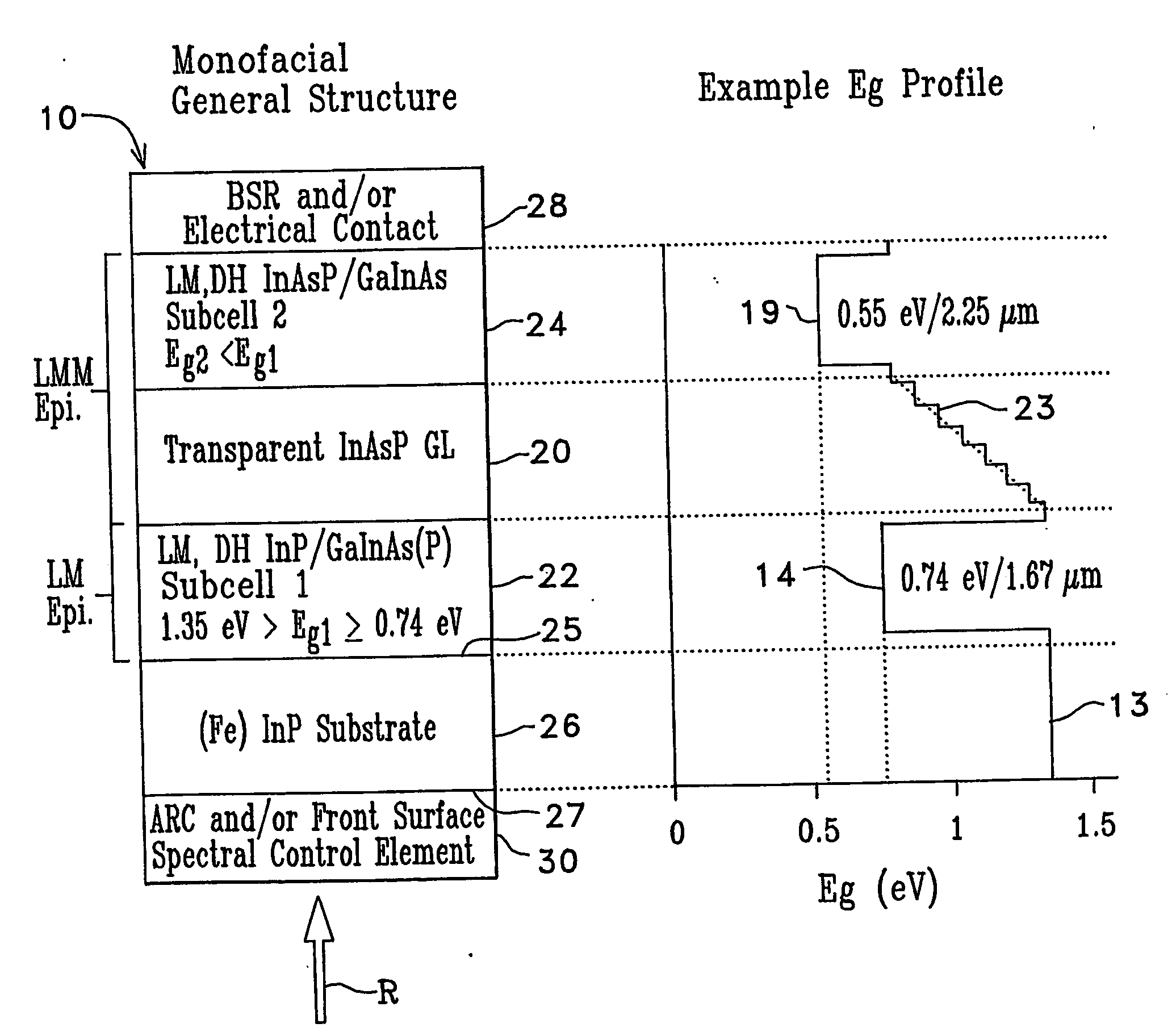
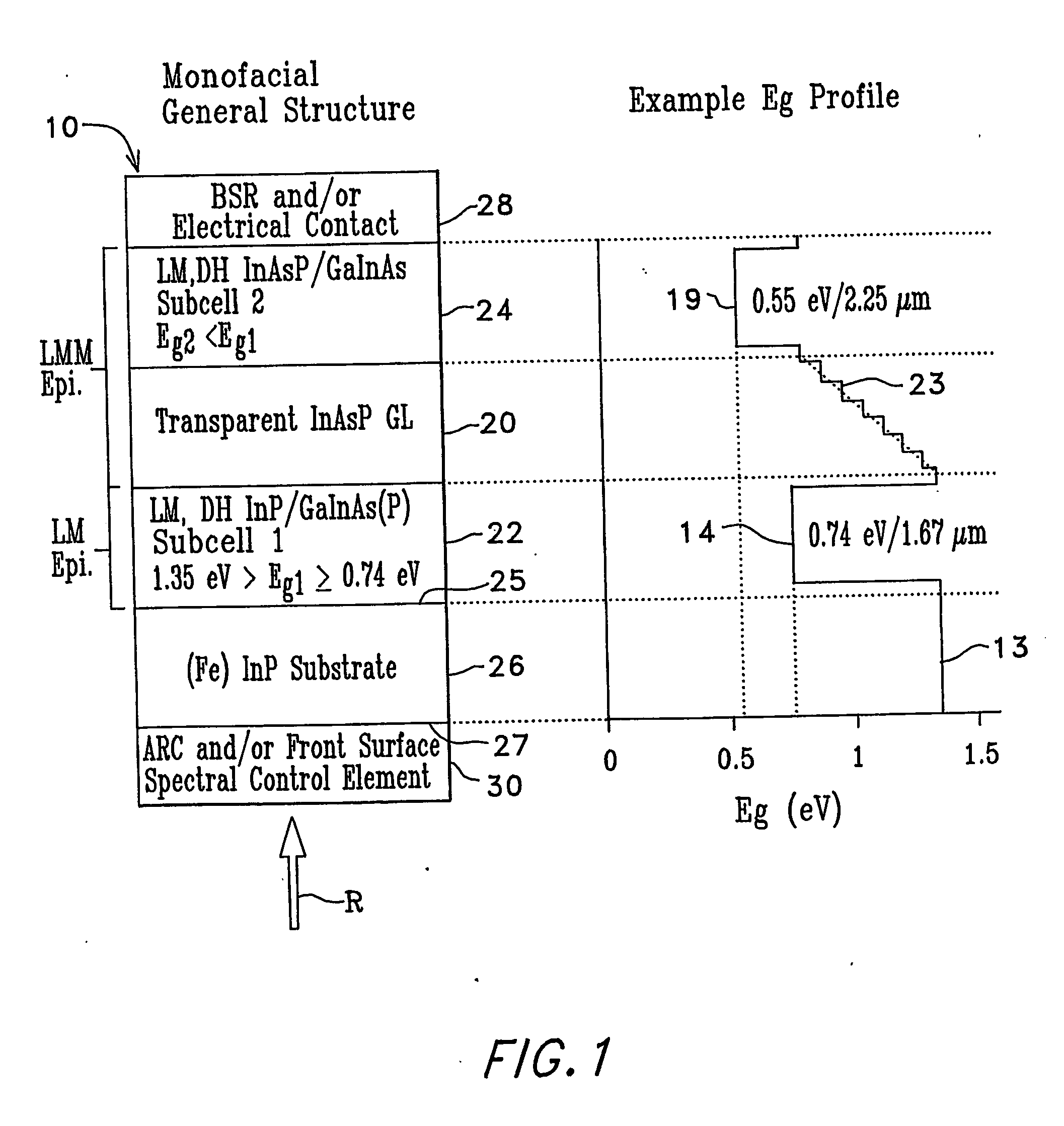
Low bandgap, monolithic, multi-bandgap, optoelectronic devices
InactiveUS20060162768A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
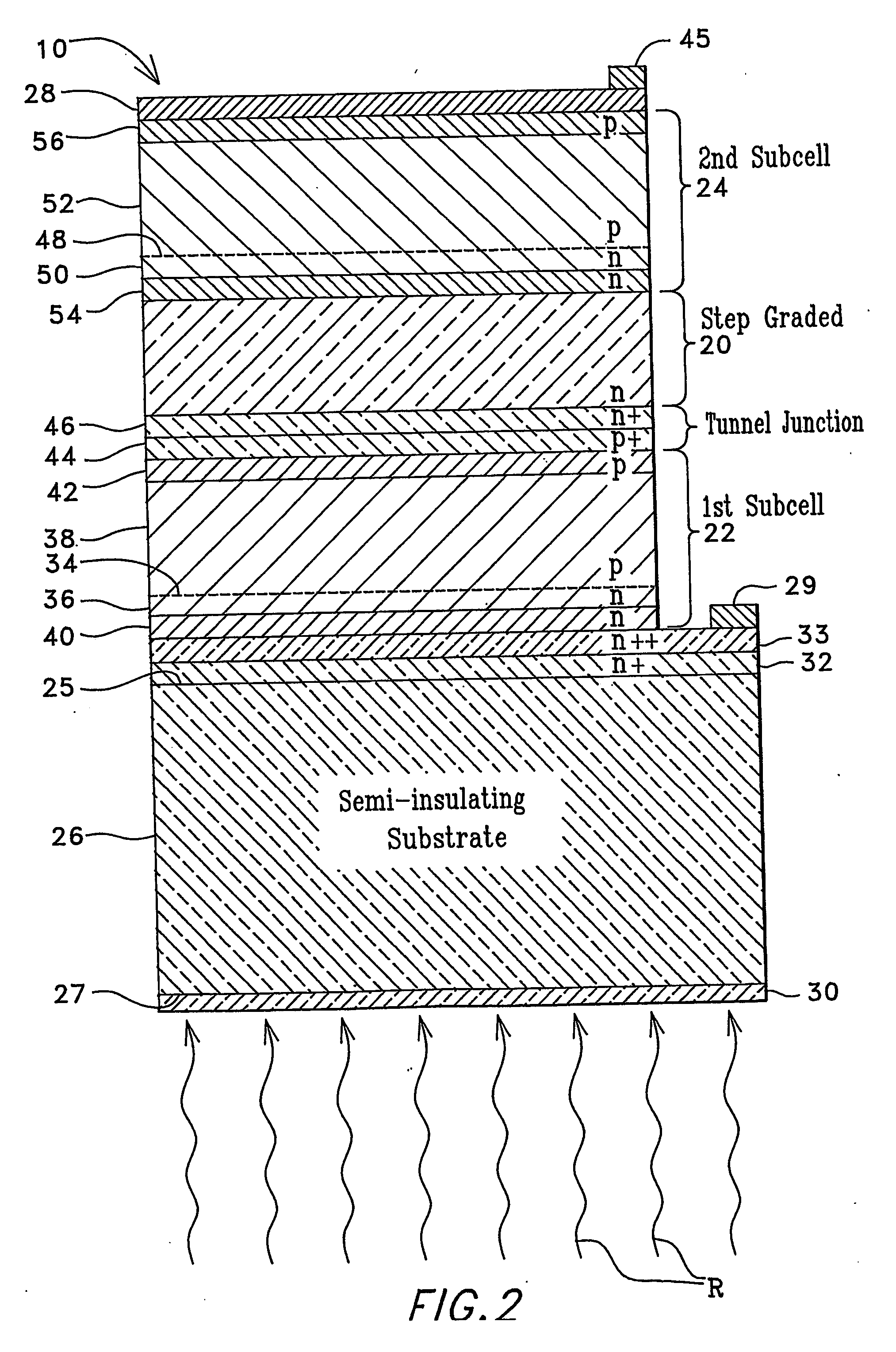
Low-bandgap, monolithic, multi-bandgap, optoelectronic devices (10), including PV converters, photodetectors, and LED's, have lattice-matched (LM), double-heterostructure (DH), low-bandgap GaInAs(P) subcells (22, 24) including those that are lattice-mismatched (LMM) to InP, grown on an InP substrate (26) by use of at least one graded lattice constant transition layer (20) of InAsP positioned somewhere between the InP substrate (26) and the LMM subcell(s) (22, 24). These devices are monofacial (10) or bifacial (80) and include monolithic, integrated, modules (MIMs) (190) with a plurality of voltage-matched subcell circuits (262, 264, 266, 270, 272) as well as other variations and embodiments.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070254414A1Sufficient carrier mobilityImpurity will diffuseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface layerConcentration gradient
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes: the first step of forming a gate electrode over a silicon substrate, with a gate insulating film; and the second step of digging down a surface layer of the silicon substrate by etching conducted with the gate electrode as a mask. The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device further includes the third step of epitaxially growing, on the surface of the dug-down portion of the silicon substrate, a mixed crystal layer including silicon and atoms different in lattice constant from silicon so that the mixed crystal layer contains an impurity with such a concentration gradient that the impurity concentration increases along the direction from the silicon substrate side toward the surface of the mixed crystal layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
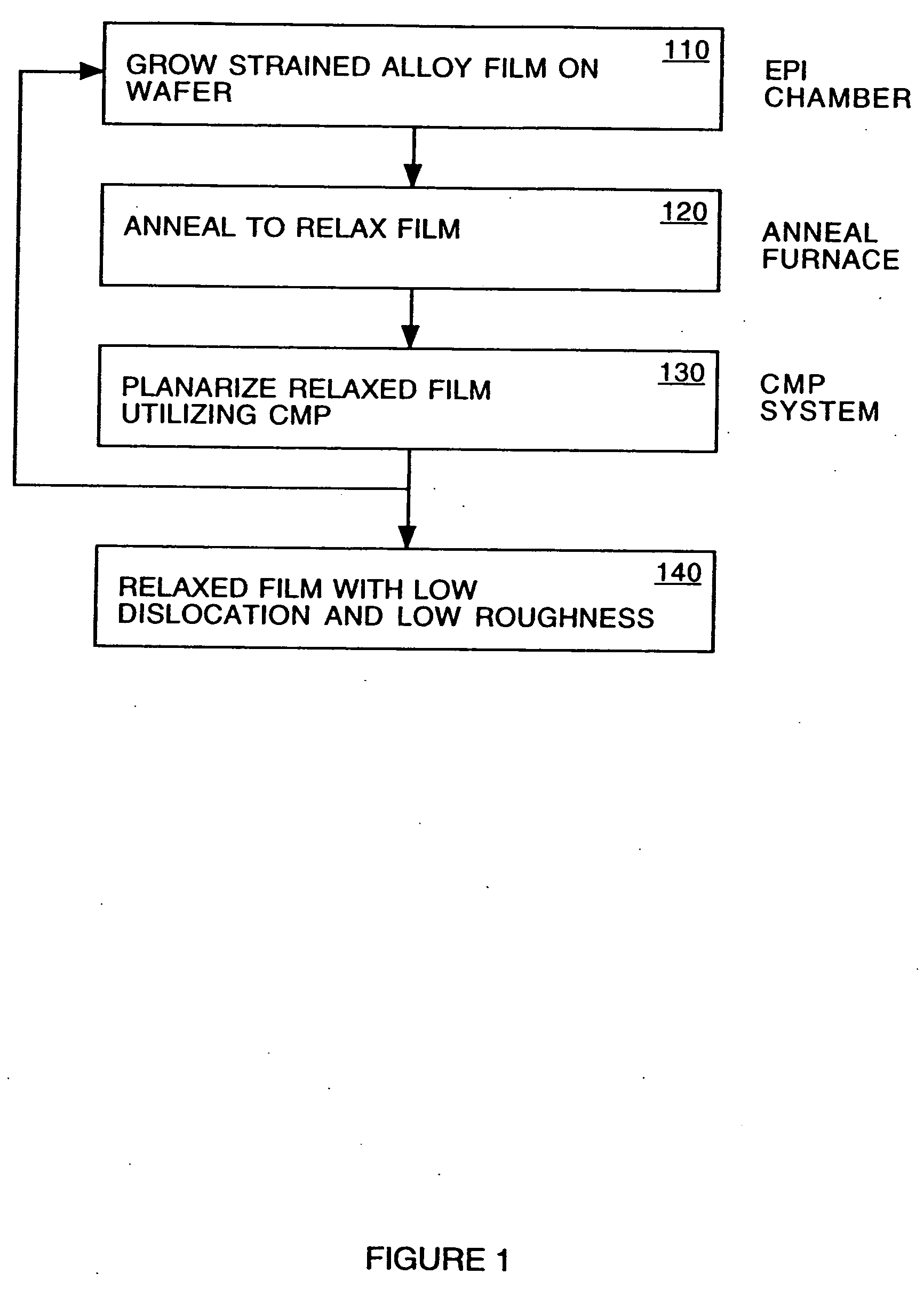
Non-contact etch annealing of strained layers
InactiveUS20070051299A1Reduce misalignmentReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantElectrical conductor
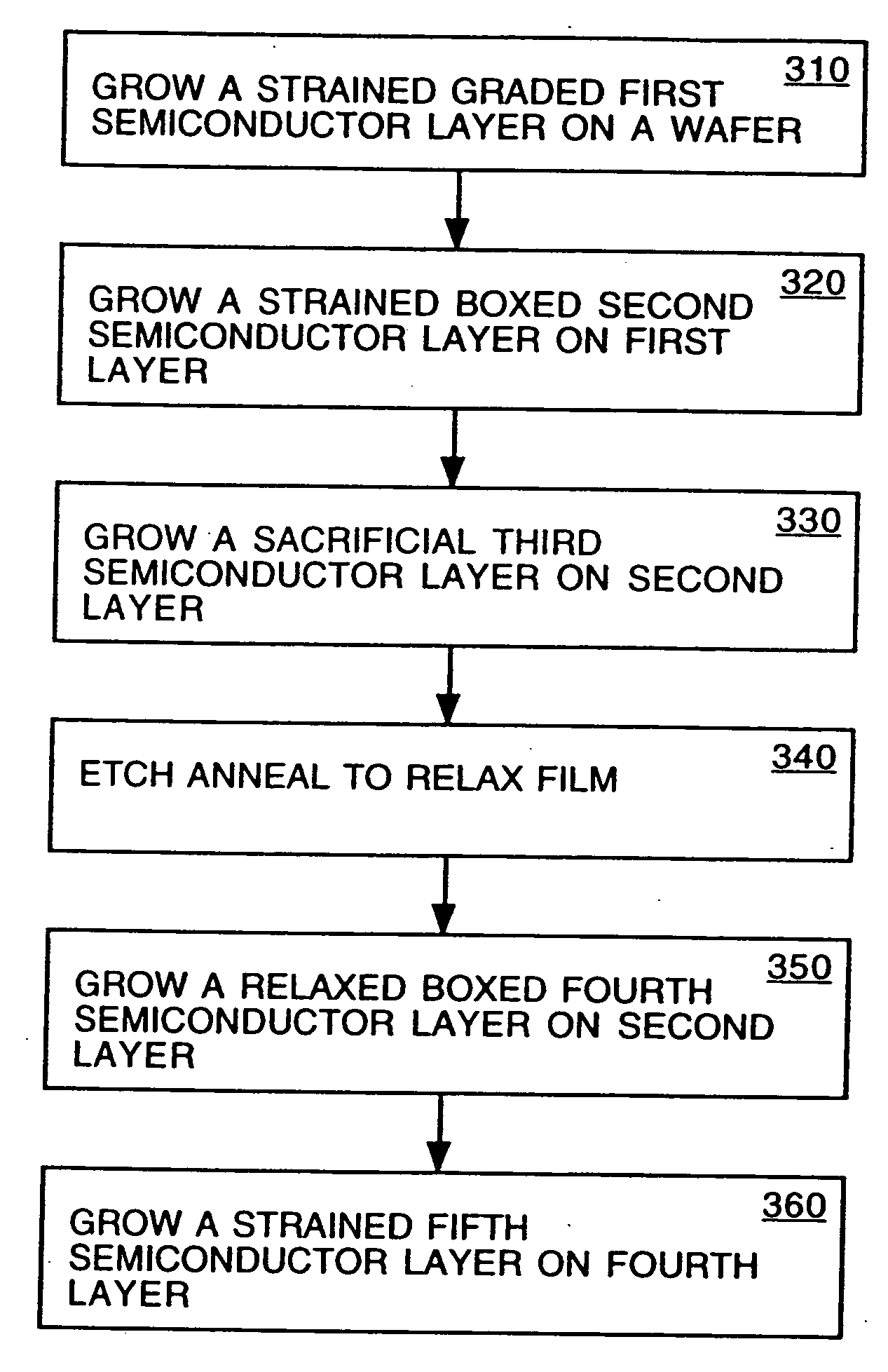
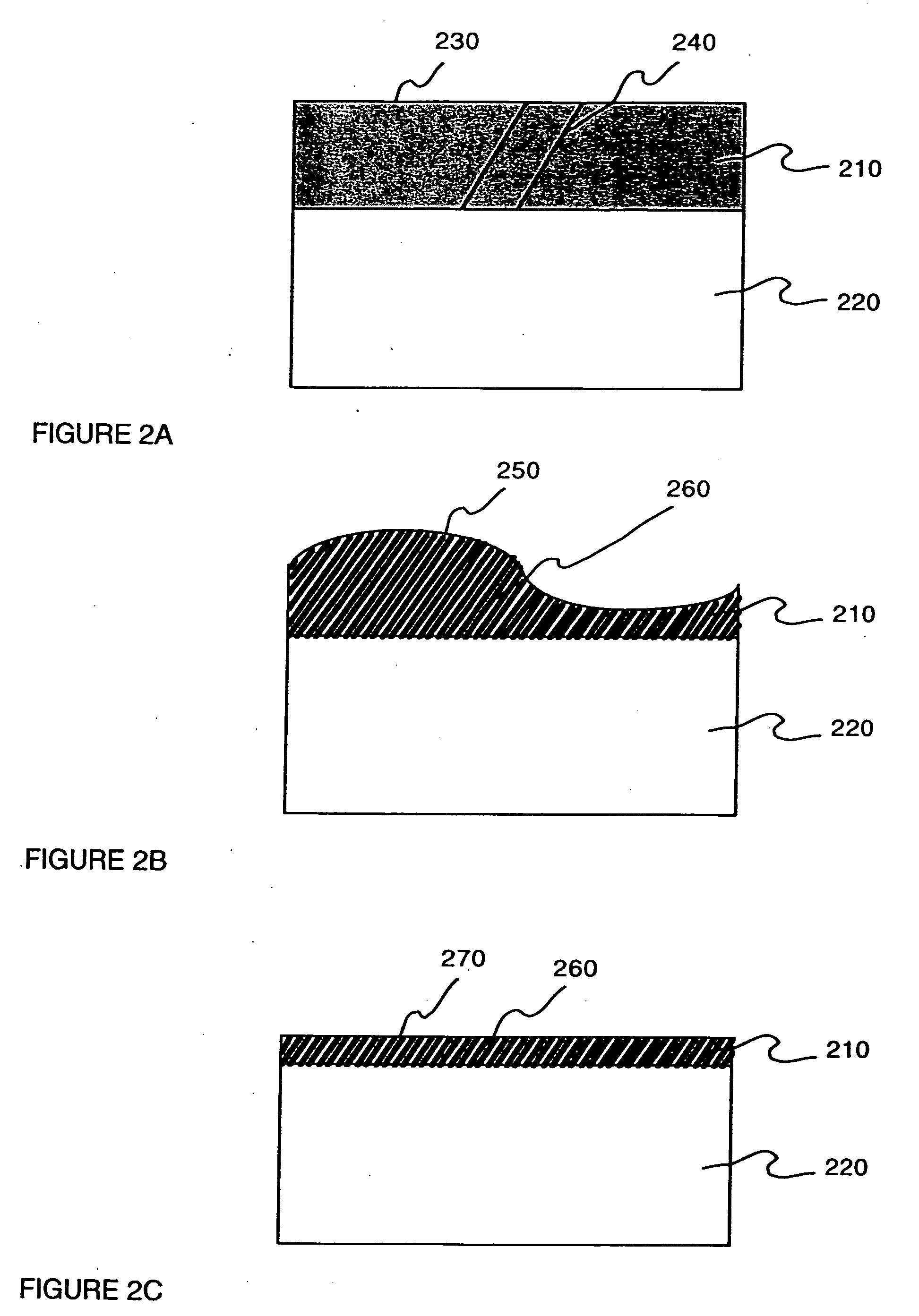
The present invention provides a method of forming a strained semiconductor layer. The method comprises growing a strained first semiconductor layer, having a graded dopant profile, on a wafer, having a first lattice constant. The dopant imparts a second lattice constant to the first semiconductor layer. The method further comprises growing a strained boxed second semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the first semiconductor layer and growing a sacrificial third semiconductor layer having the first lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer. The method further comprises etch annealing the third and second semiconductor layer, wherein the third semiconductor layer is removed and the second semiconductor layer is relaxed. The method may further comprises growing a fourth semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer, wherein the fourth semiconductor layer is relaxed, and growing a strained fifth semiconductor layer having the first semiconductor lattice constant on the fourth semiconductor layer. The method controls the surface roughness of the semiconductor layers. The method also has the unexpected benefit of reducing dislocations in the semiconductor layers.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
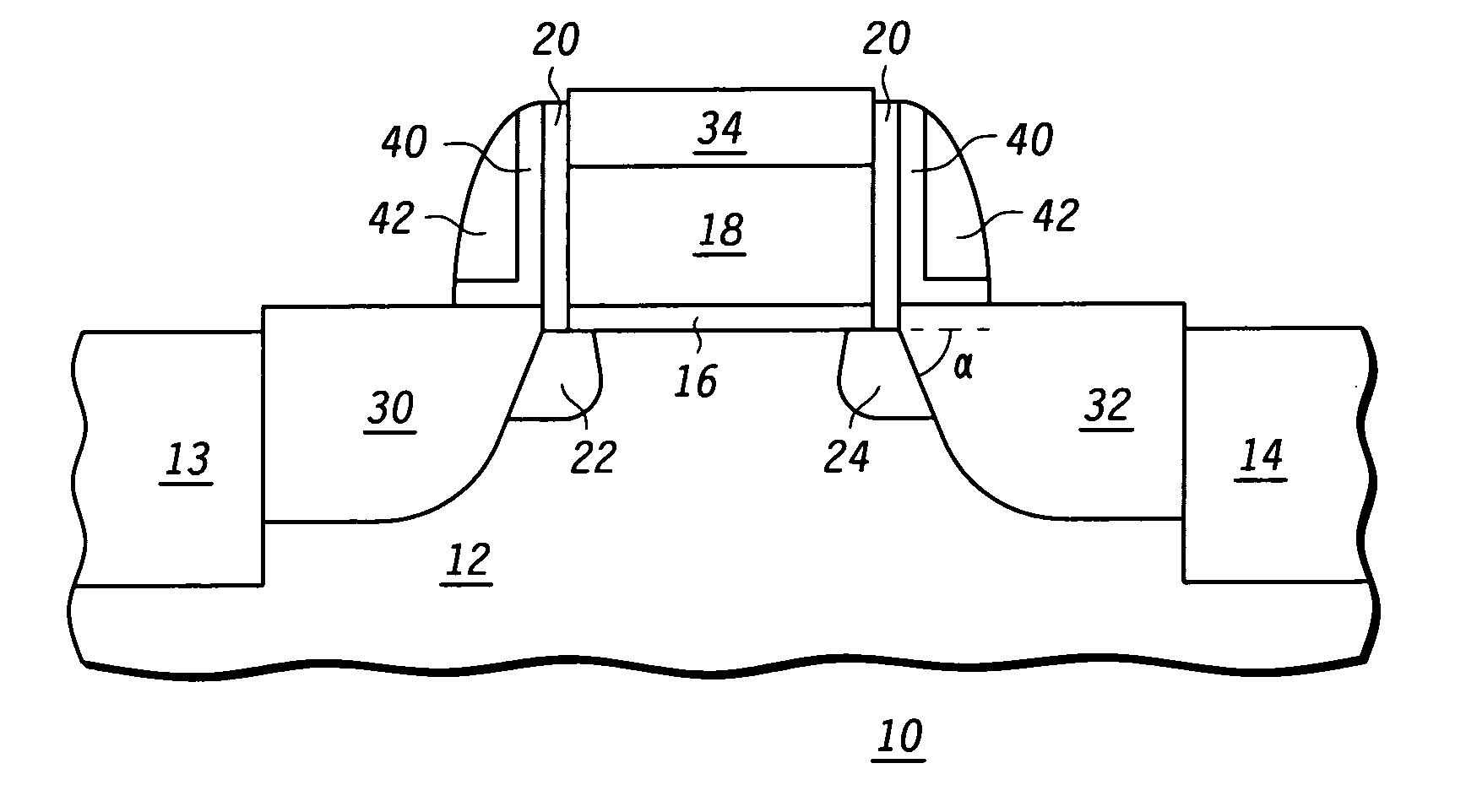
Strained-channel transistor structure with lattice-mismatched zone
InactiveUS20040173815A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor materials
A strained-channel transistor structure with lattice-mismatched zone and fabrication method thereof. The transistor structure includes a substrate having a strained channel region, comprising a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant, in a surface, a gate dielectric layer overlying the strained channel region, a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric layer, and a source region and drain region oppositely adjacent to the strained channel region, with one or both of the source region and drain region comprising a lattice-mismatched zone comprising a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant different from the first natural lattice constant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Strained silicon fin structure
InactiveUS20060113522A1Suppression of short channel effectsIncrease currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentLattice mismatch
Disclosing is a strained silicon finFET device having a strained silicon fin channel in a double gate finFET structure. The disclosed finFET device is a double gate MOSFET consisting of a silicon fin channel controlled by a self-aligned double gate for suppressing short channel effect and enhancing drive current. The silicon fin channel of the disclosed finFET device is a strained silicon fin channel, comprising a strained silicon layer deposited on a seed fin having different lattice constant, for example, a silicon layer deposited on a silicon germanium seed fin, or a carbon doped silicon layer deposited on a silicon seed fin. The lattice mismatch between the silicon layer and the seed fin generates the strained silicon fin channel in the disclosed finFET device to improve hole and electron mobility enhancement, in addition to short channel effect reduction characteristic inherently in a finFET device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Multi-core holey fiber and optical transmission system
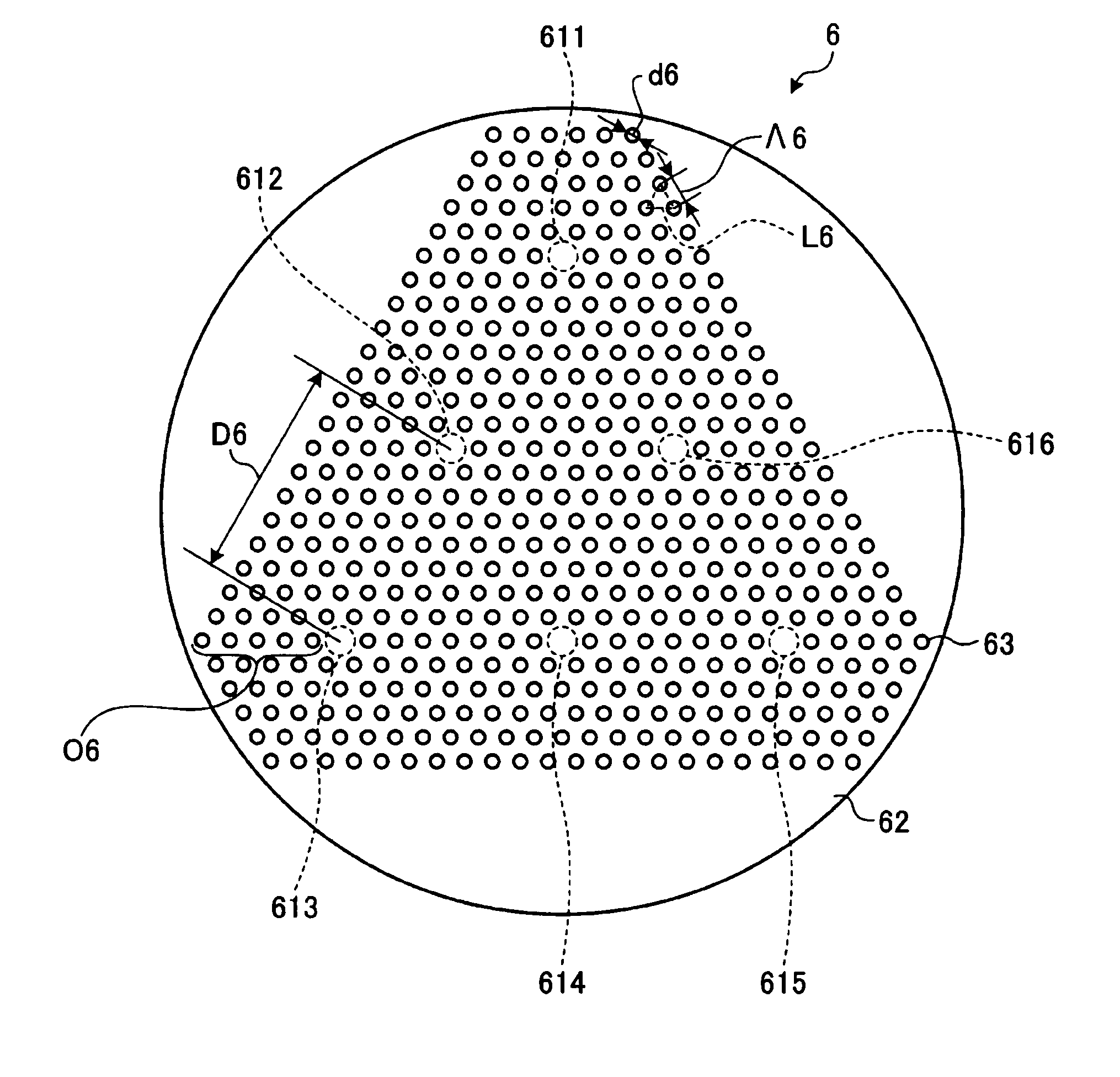
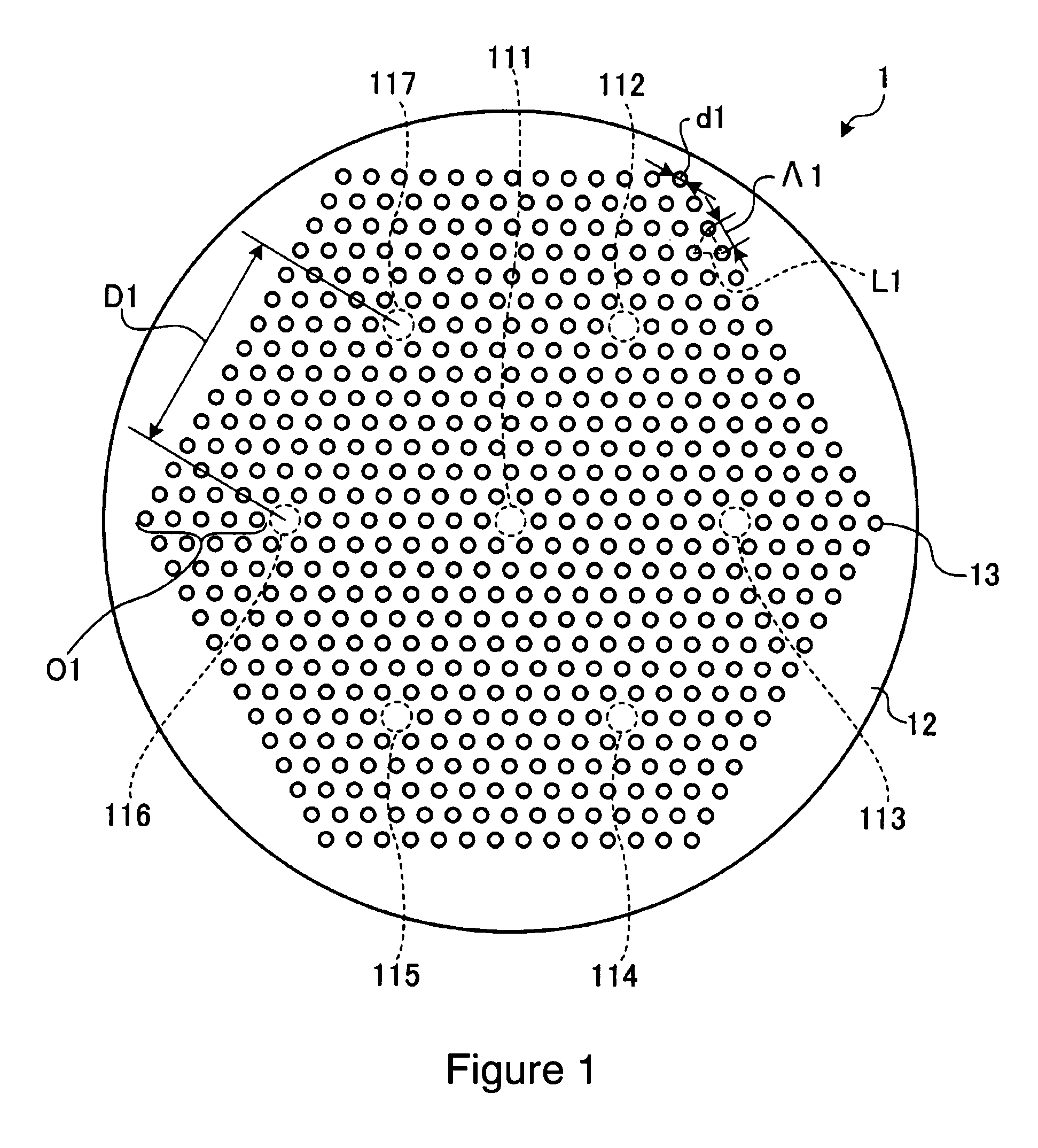
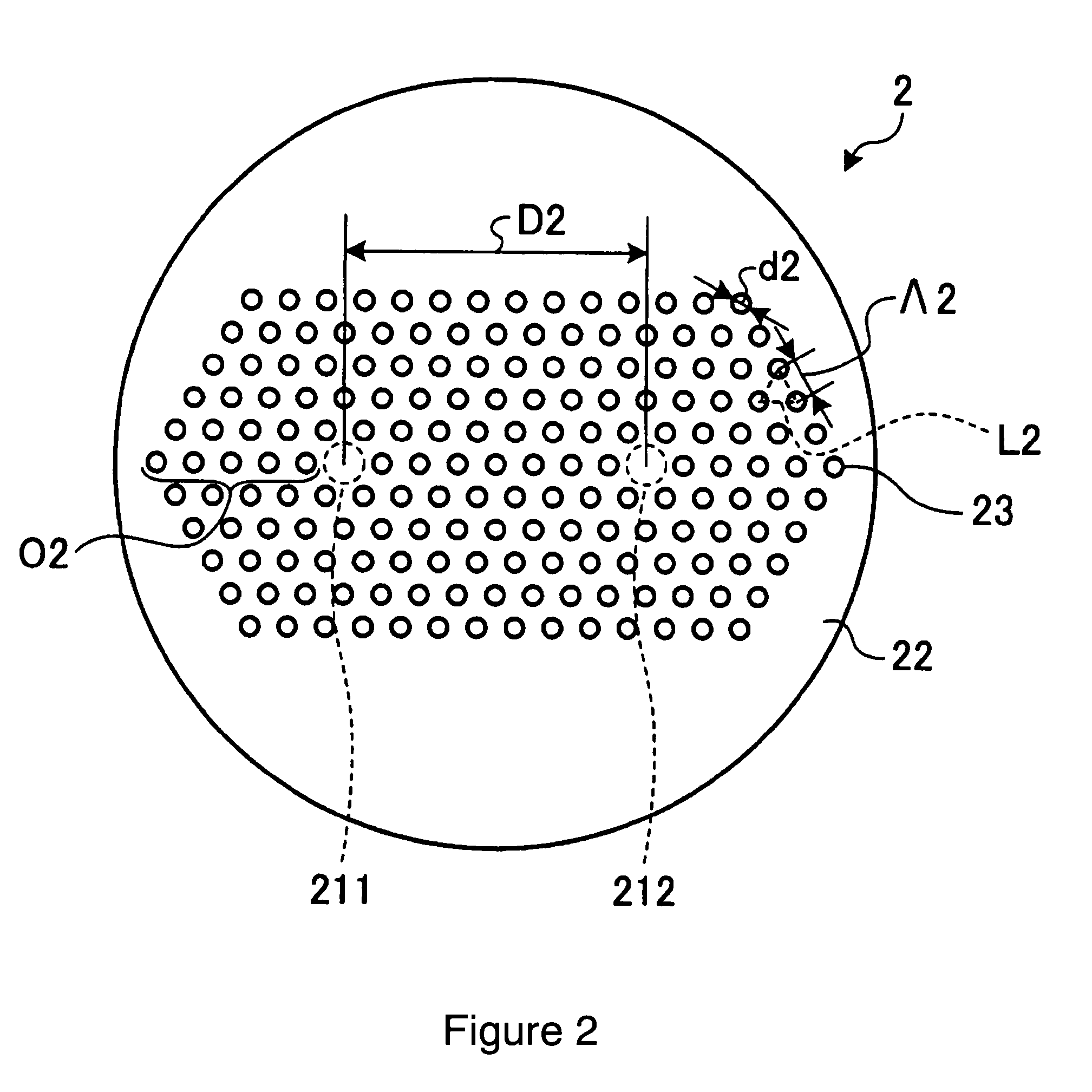
A multi-core holey fiber with suppression of crosstalk deterioration among transmitted optical signals in a plurality of cores, and an optical transmission system using the fiber are disclosed. The multi-core holey fiber comprises a plurality of cores arranged separately from each other, and a cladding surrounding the plurality of cores wherein the cladding has plurality of holes arranged in a triangular lattice shape to create hole layers around the plurality of cores. Additionally, d / Λ is not more than 0.5, where Λ [μm] is lattice constant of the triangular lattice, d [μm] is diameter of each of the holes; a distance between adjacent cores is equivalent to not less than six hole layers; the cores arranged farthest from the center of the multi-core holey fiber is surrounded by not less three hole layers; and the sum of the coupling coefficients between the adjacent cores is not more than 1.6×10−5 / m.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Monolithically integrated light emitting devices
ActiveUS7535089B2Layered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSingle crystalLattice constant
Methods and structures for monolithically integrating monocrystalline silicon and monocrystalline non-silicon materials and devices are provided. In one structure, a monolithically integrated semiconductor device structure comprises a silicon substrate and a first monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over the silicon substrate, wherein the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from a lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure further includes an insulating layer disposed over the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a first region and a monocrystalline silicon layer disposed over the insulating layer in the first region. The structure includes at least one silicon-based electronic device including an element including at least a portion of the monocrystalline silicon layer. The structure also includes a second monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over at least a portion of the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a second region and absent from the first region, wherein the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from the lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure includes at least one III-V light-emitting device including an active region including at least a portion of the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method to control source/drain stressor profiles for stress engineering
ActiveUS20070235802A1Reduce duplicationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedGate dielectric
An example embodiment of a strained channel transistor structure comprises the following: a strained channel region comprising a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant; a gate dielectric layer overlying the strained channel region; a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric layer; and a source region and drain region oppositely adjacent to the strained channel region, one or both of the source region and drain region are comprised of a stressor region comprised of a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant different from the first natural lattice constant; the stressor region has a graded concentration of a dopant impurity and / or of a stress inducing molecule. Another example embodiment is a process to form the graded impurity or stress inducing molecule stressor embedded S / D region, whereby the location / profile of the S / D stressor is not defined by the recess depth / profile.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
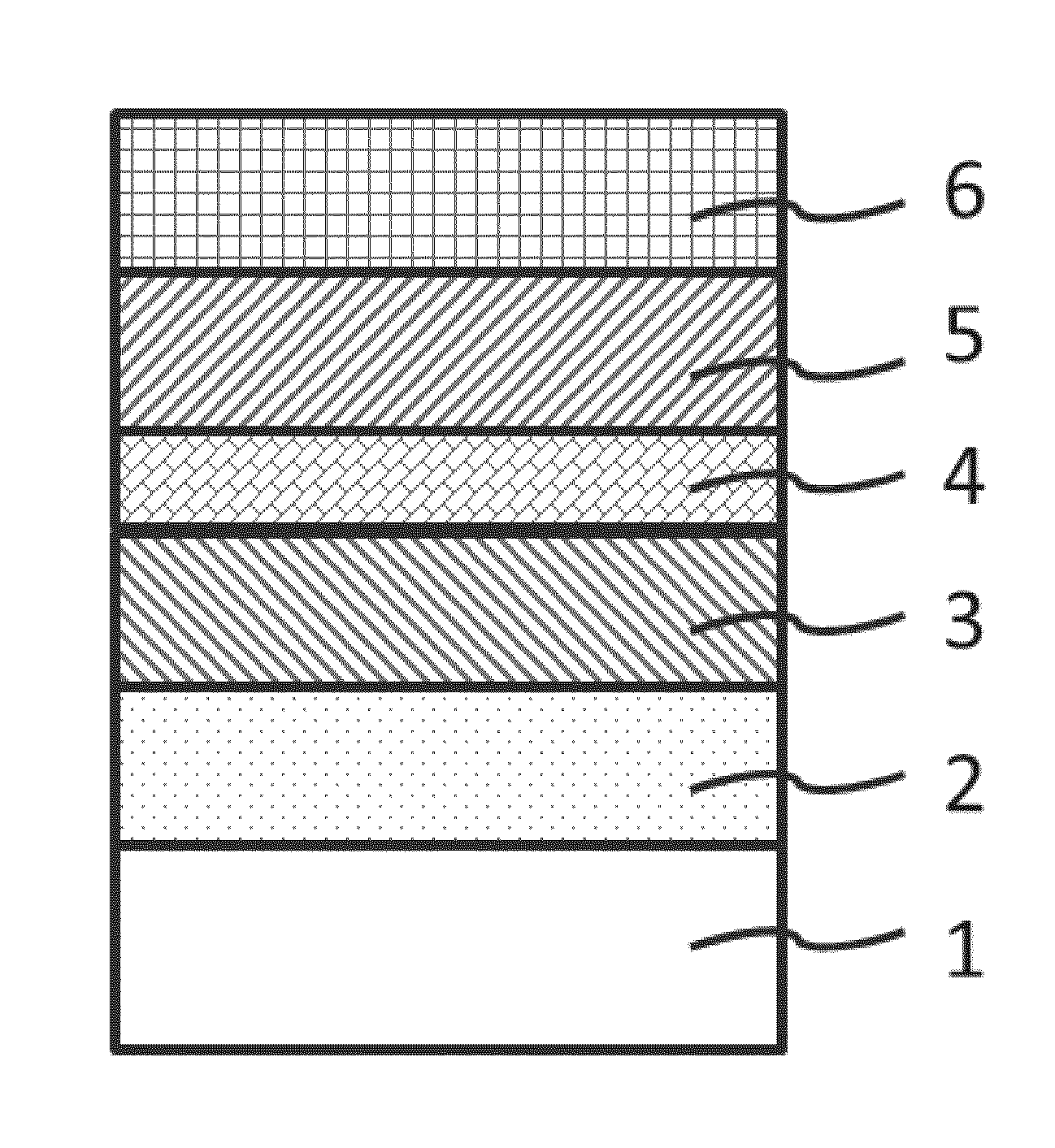
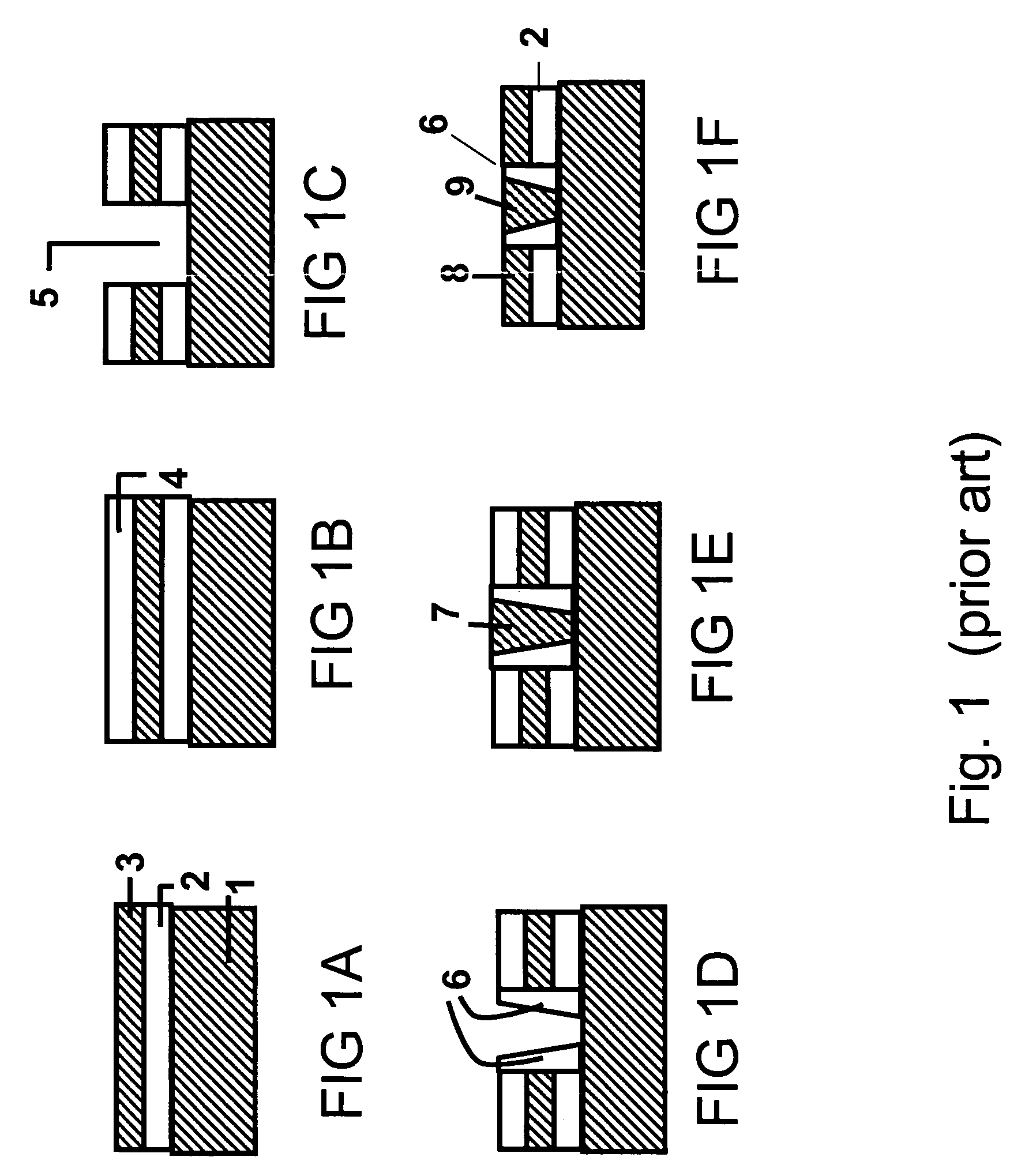
Nitride-based semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
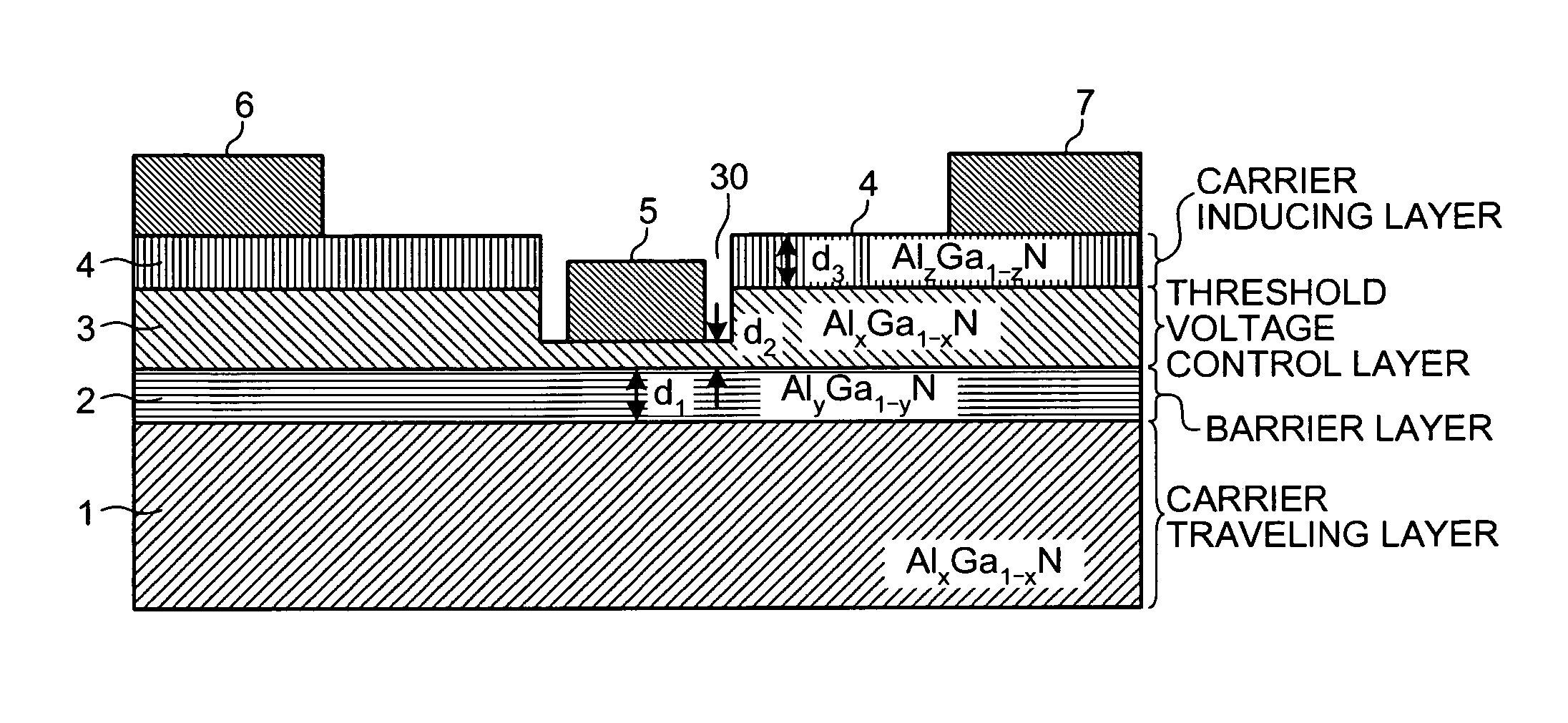
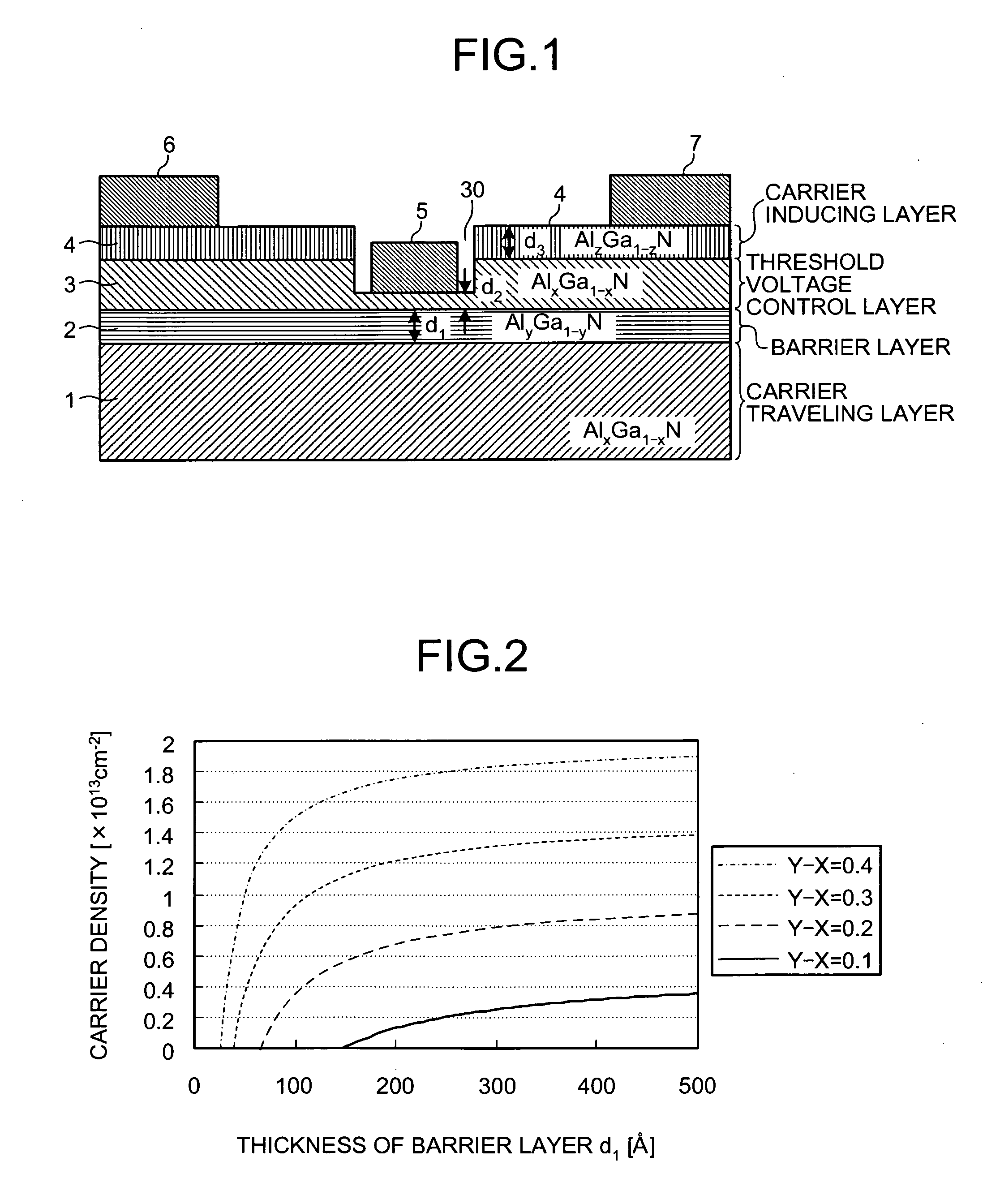
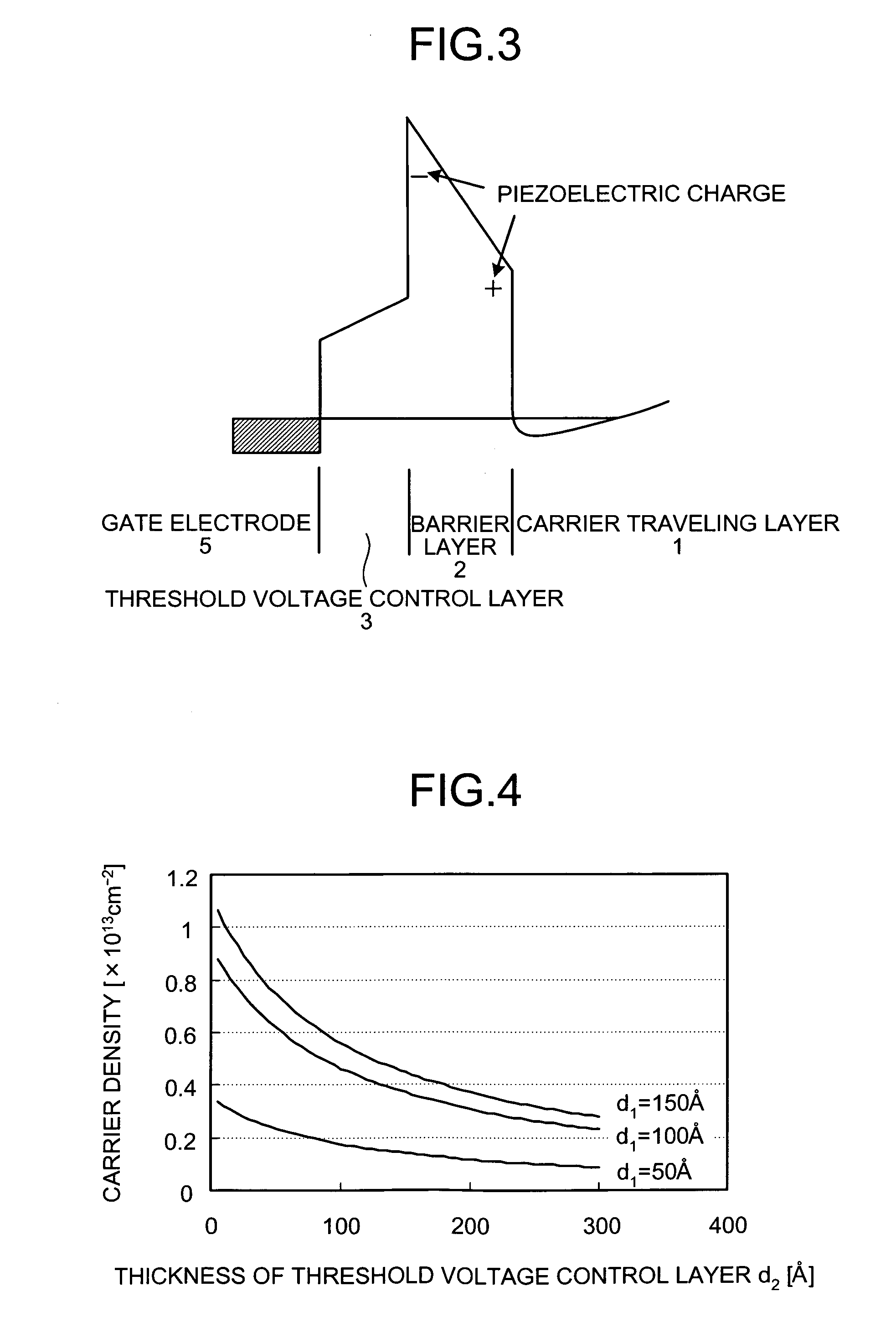
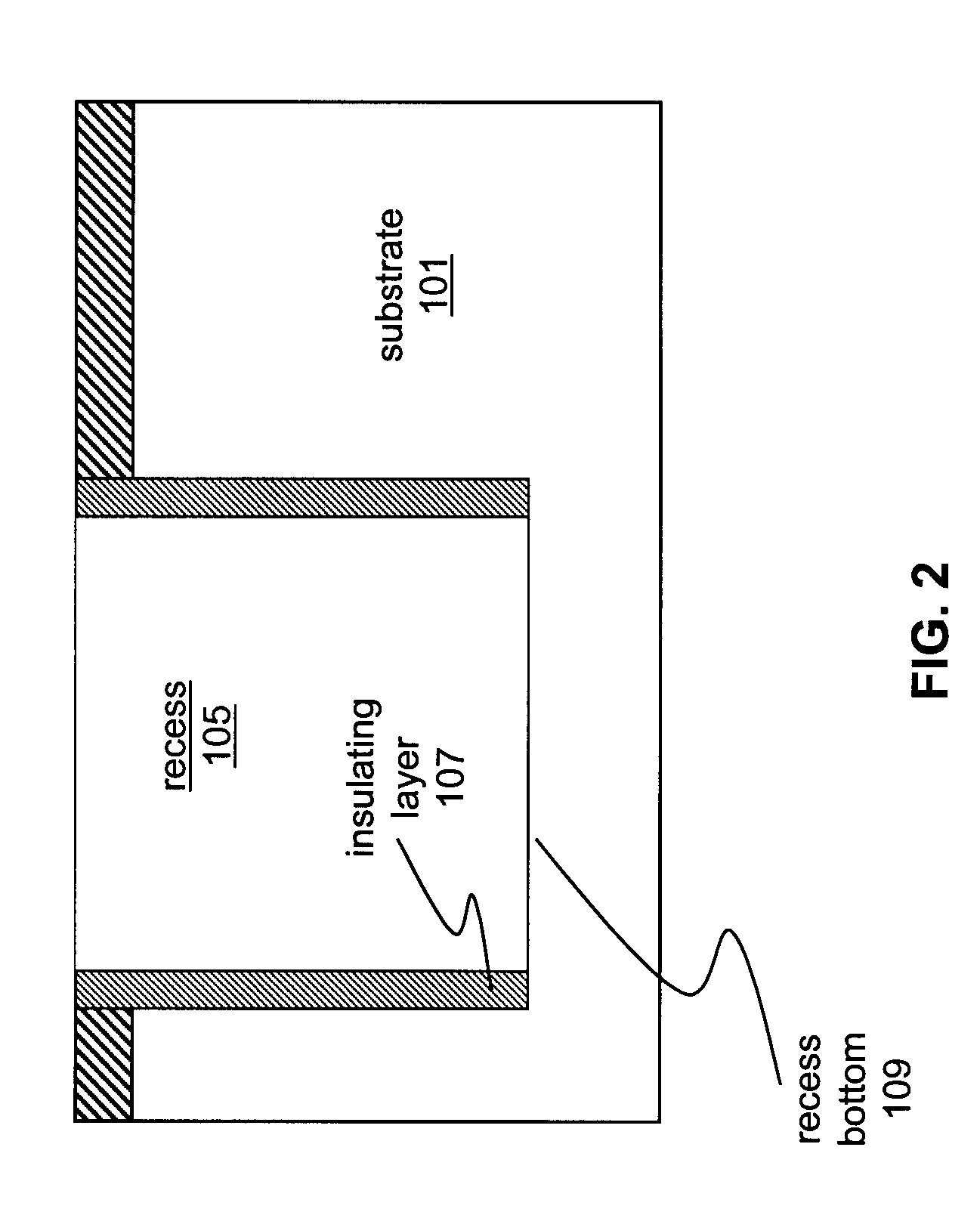
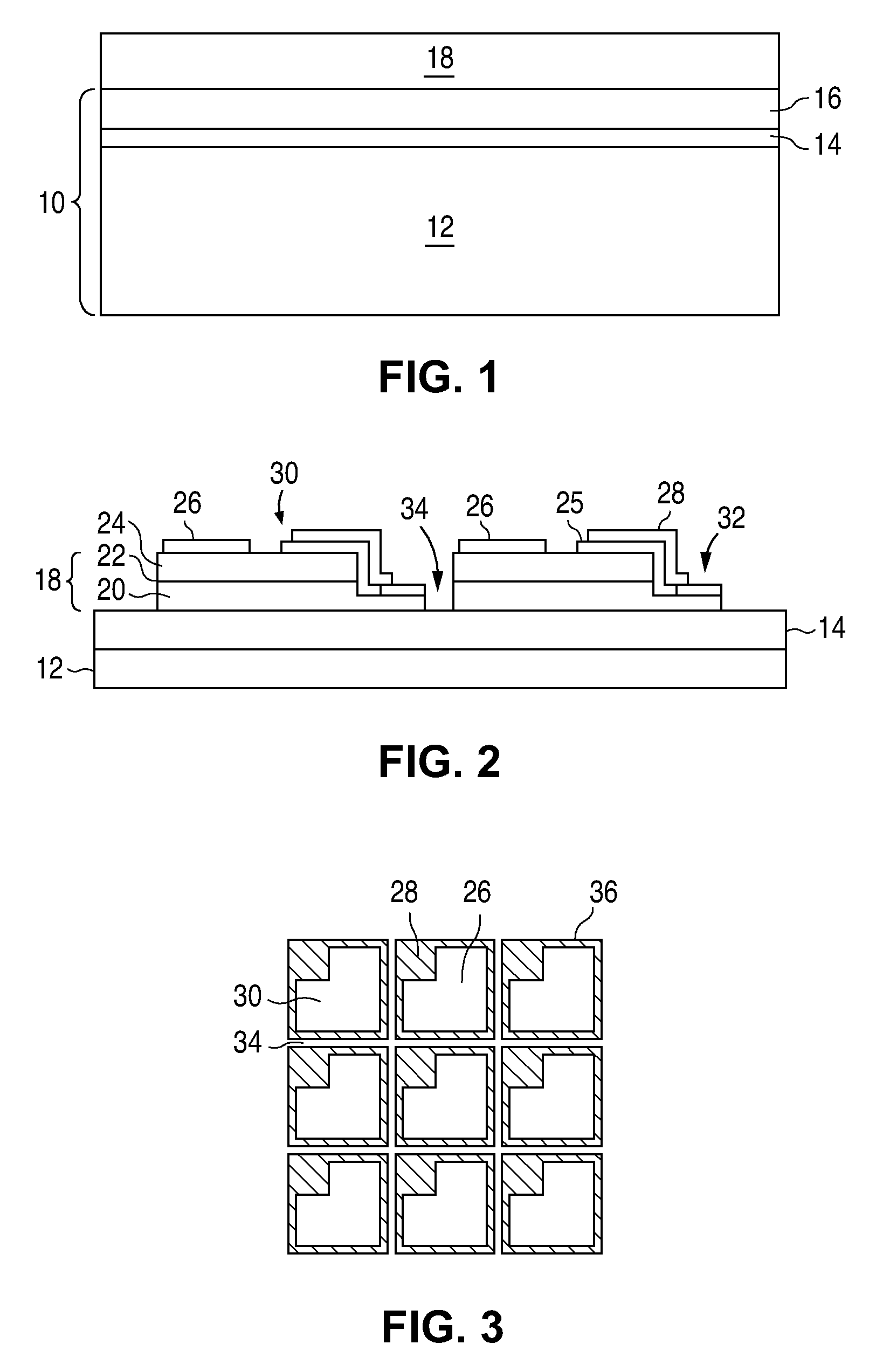
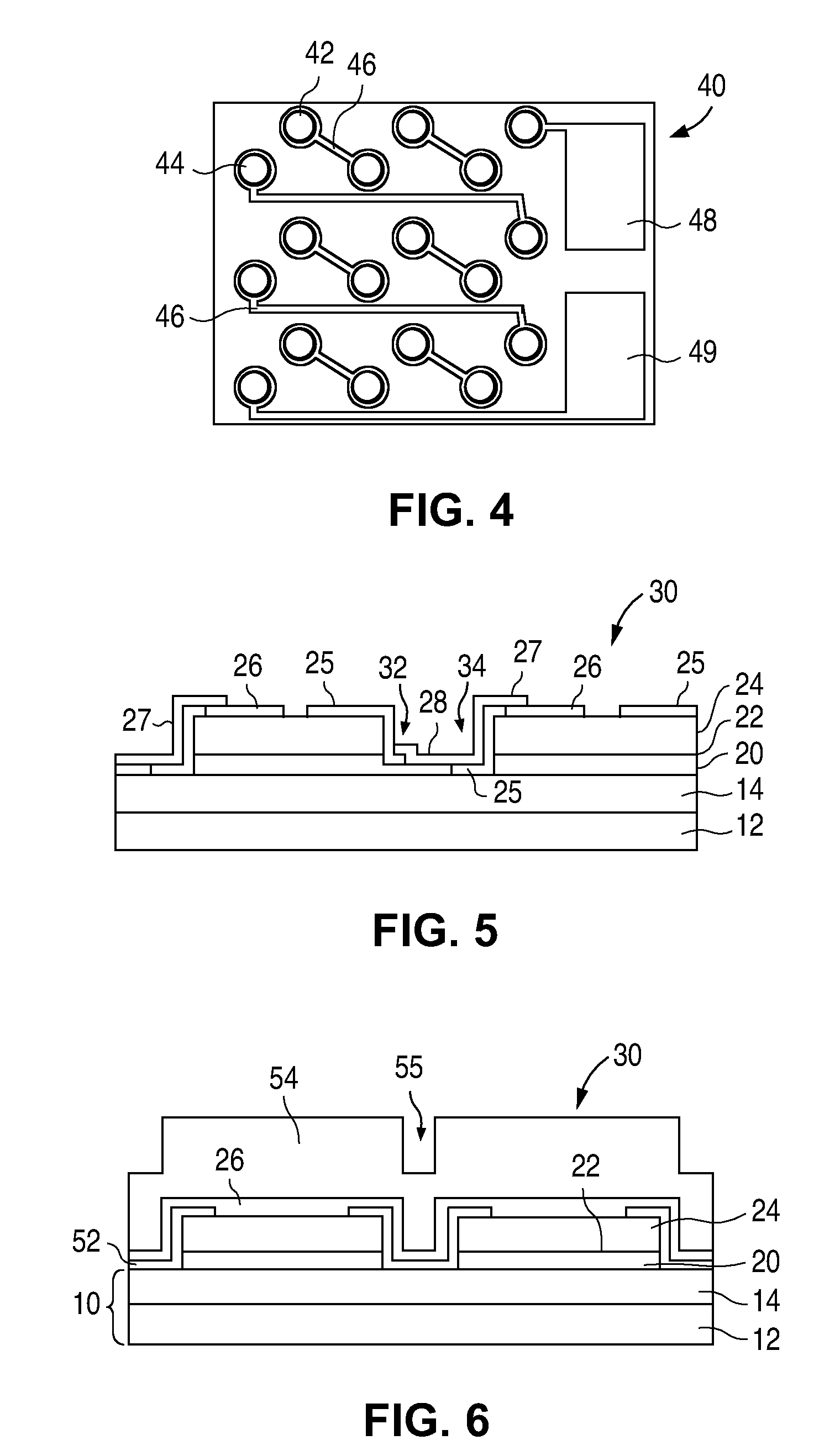
The nitride-based semiconductor device includes a carrier traveling layer 1 composed of non-doped AlxGa1-xN (0≦X<1); a barrier layer 2 formed on the carrier traveling layer 1 and composed of non-doped or n-type AlYGa1-YN (0<Y≦1, X<Y) having a lattice constant smaller than that of the carrier traveling layer 1; a threshold voltage control layer 3 formed on the barrier layer 2 and composed of a non-doped semiconductor having a lattice constant equal to that of the carrier traveling layer 1; and a carrier inducing layer 4 formed on the threshold voltage control layer 3 and composed of a non-doped or n-type semiconductor having a lattice constant smaller than that of the carrier traveling layer 1. The nitride-based semiconductor device further includes a gate electrode 5 formed in a recess structure, a source electrode 6 and a drain electrode 7.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
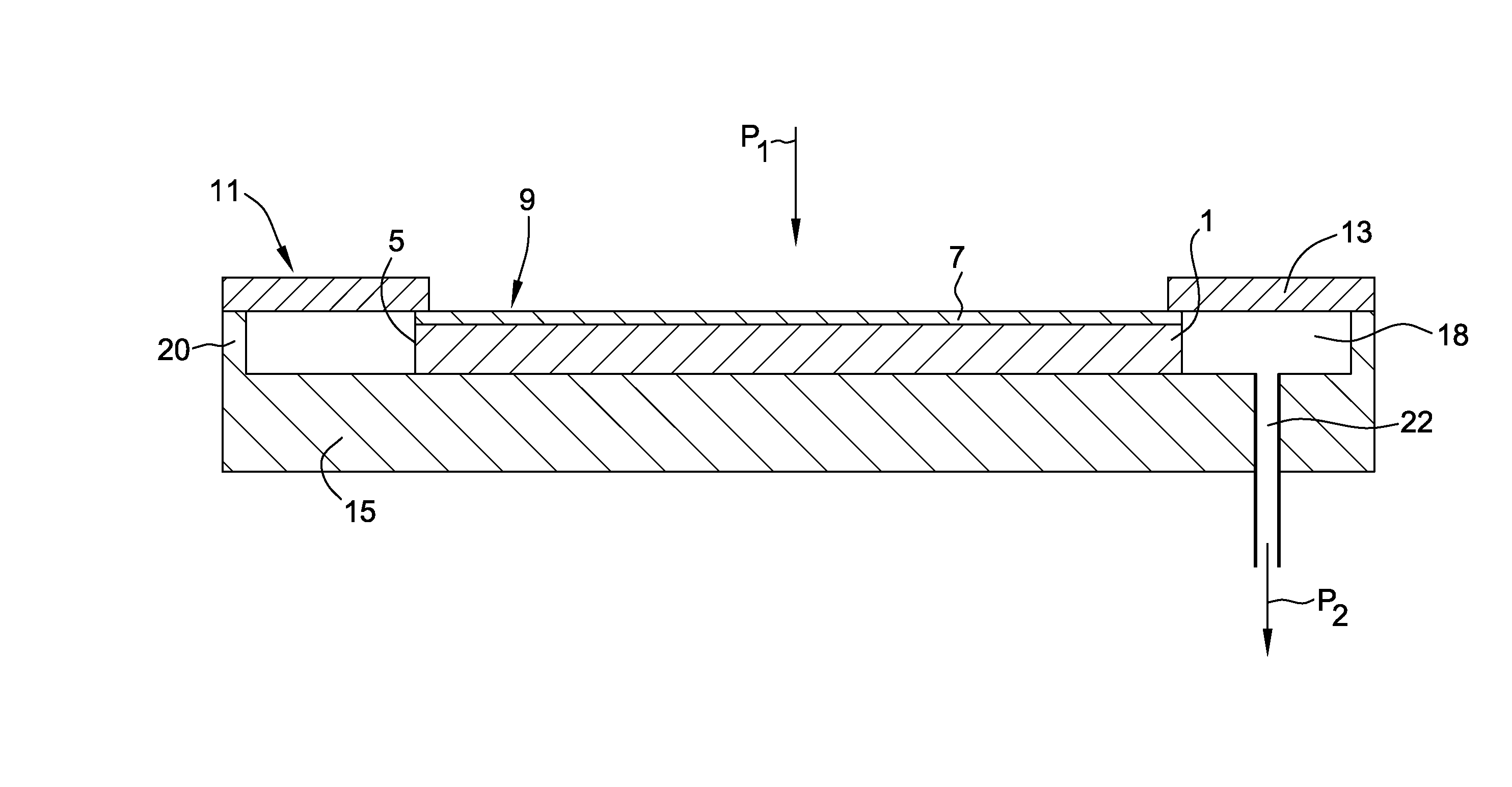
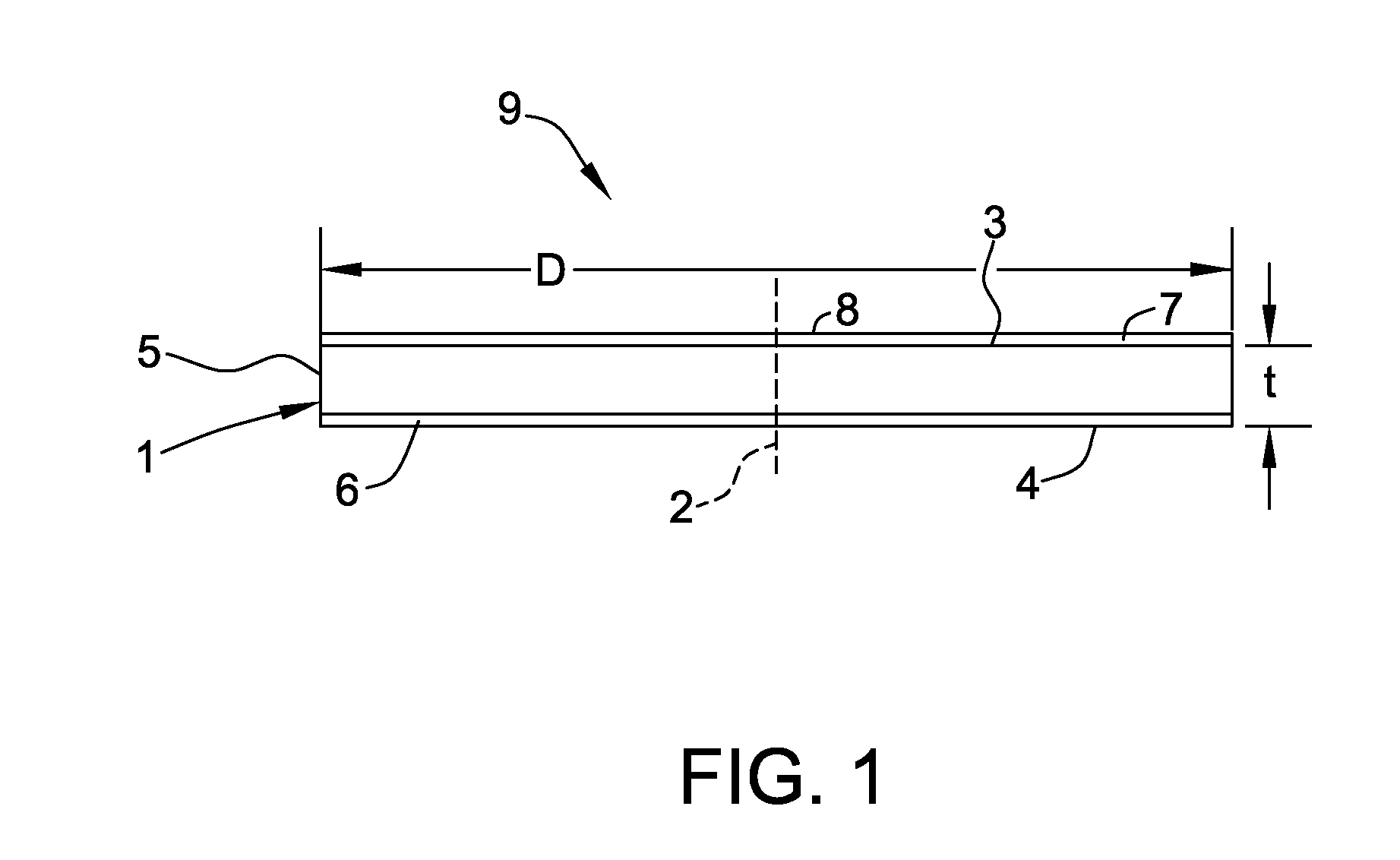
Processes and Apparatus for Preparing Heterostructures with Reduced Strain by Radial Distension
ActiveUS20140187022A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCeramic shaping apparatusSurface layerSemiconductor structure
Apparatus and processes for preparing heterostructures with reduced strain are disclosed. The heterostructures may include a semiconductor structure that conforms to a surface layer having a different crystal lattice constant than the structure to form a relatively low-defect heterostructure.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
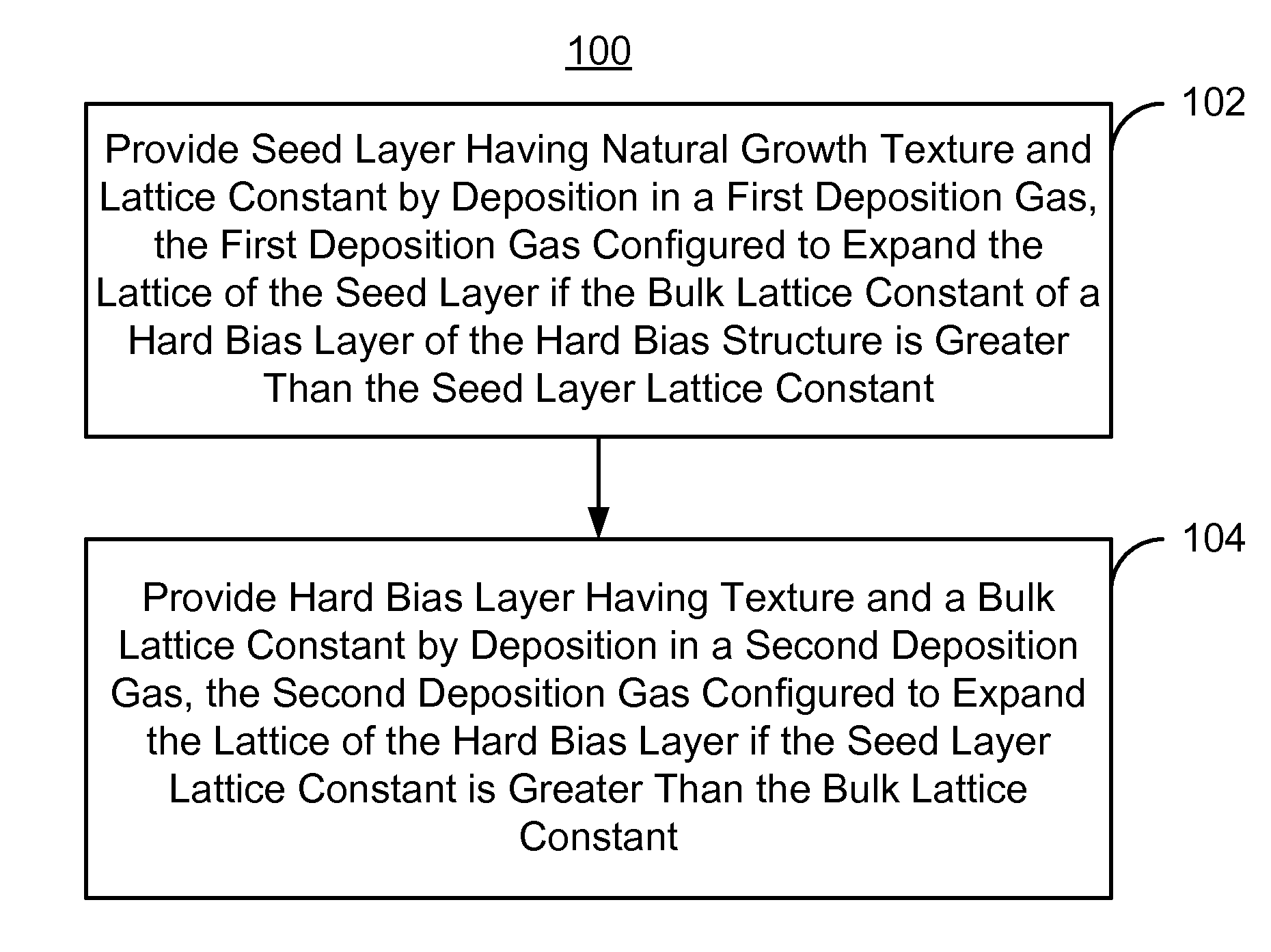
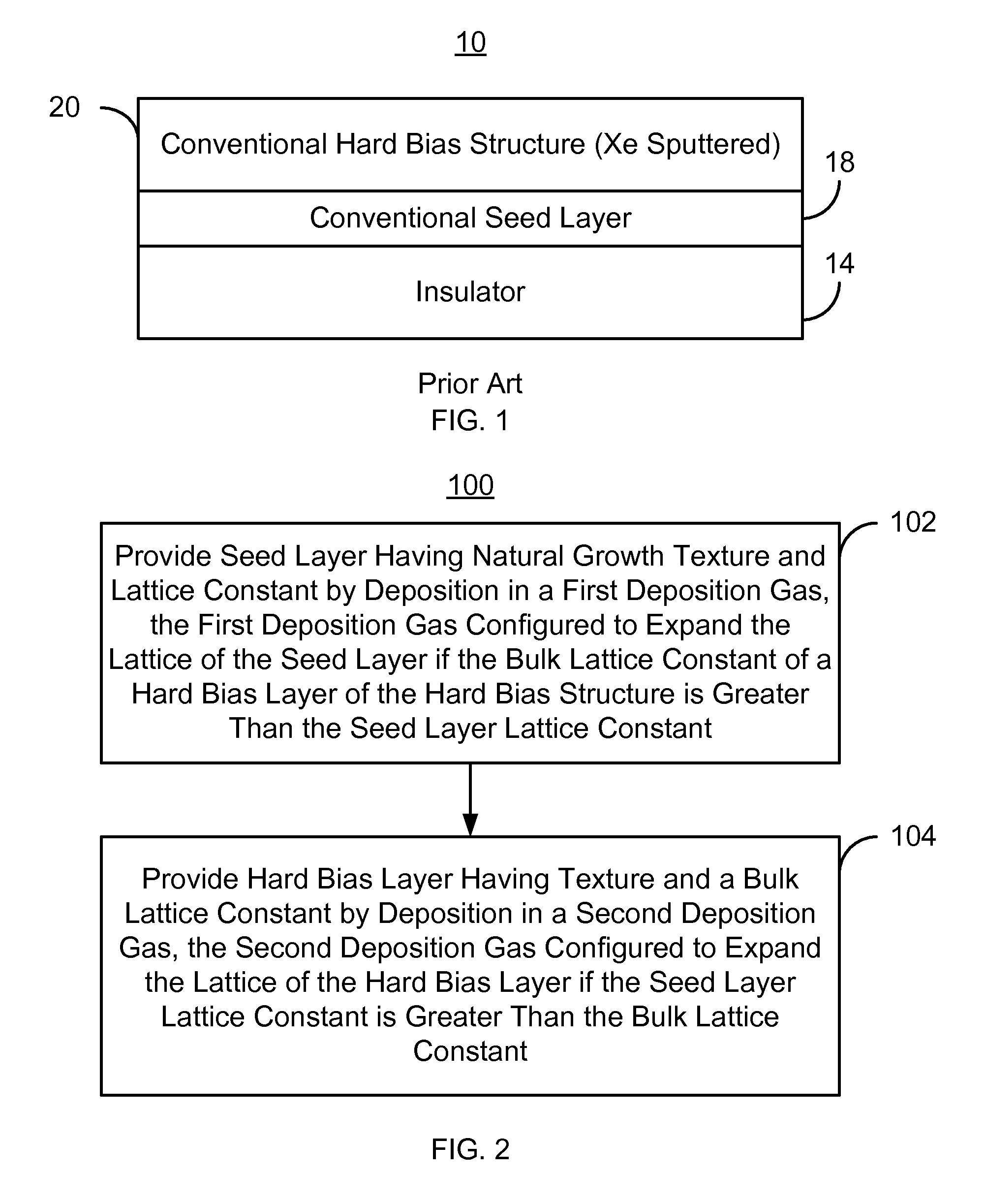
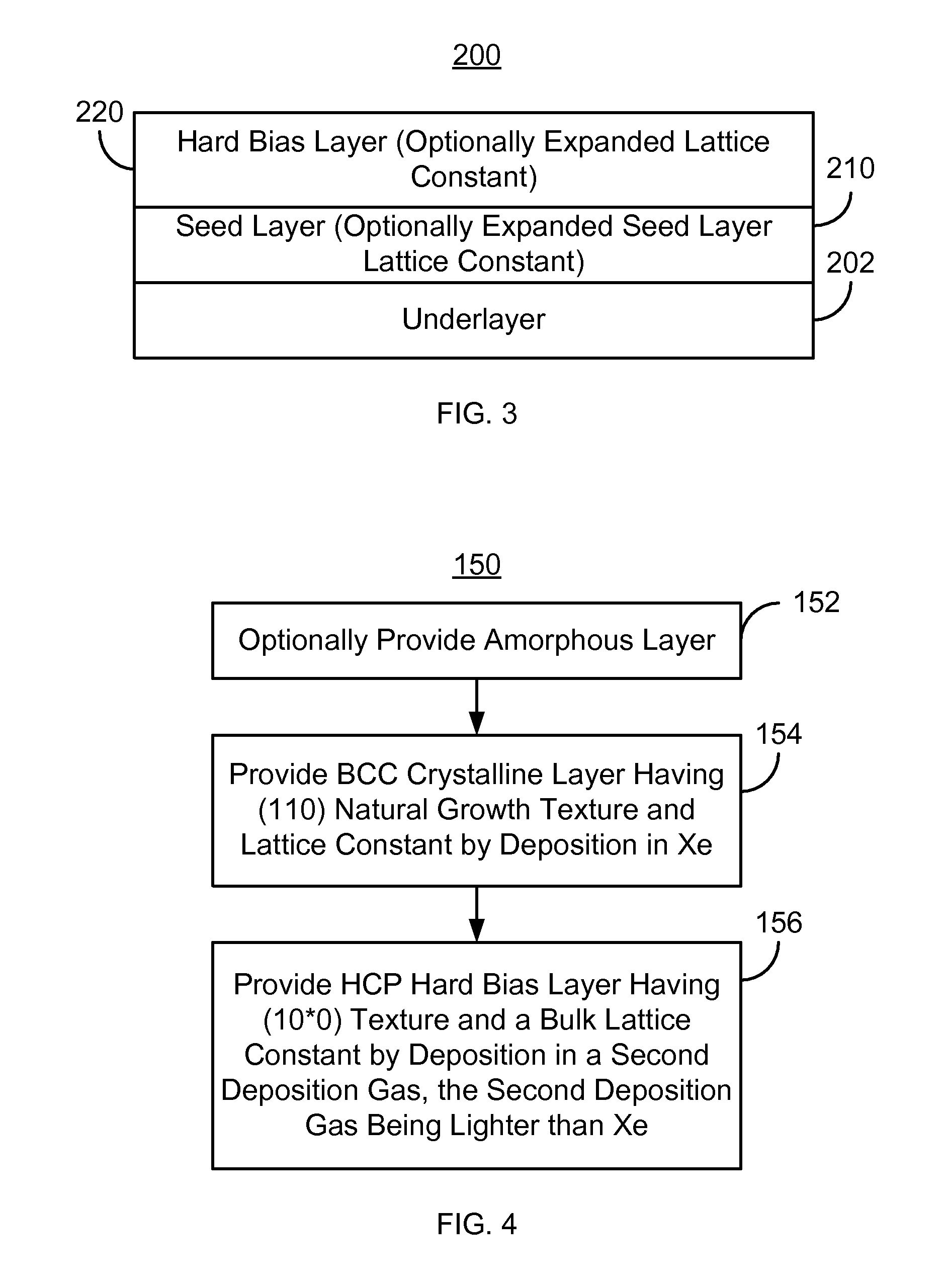
Method for providing an improved hard bias structure
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
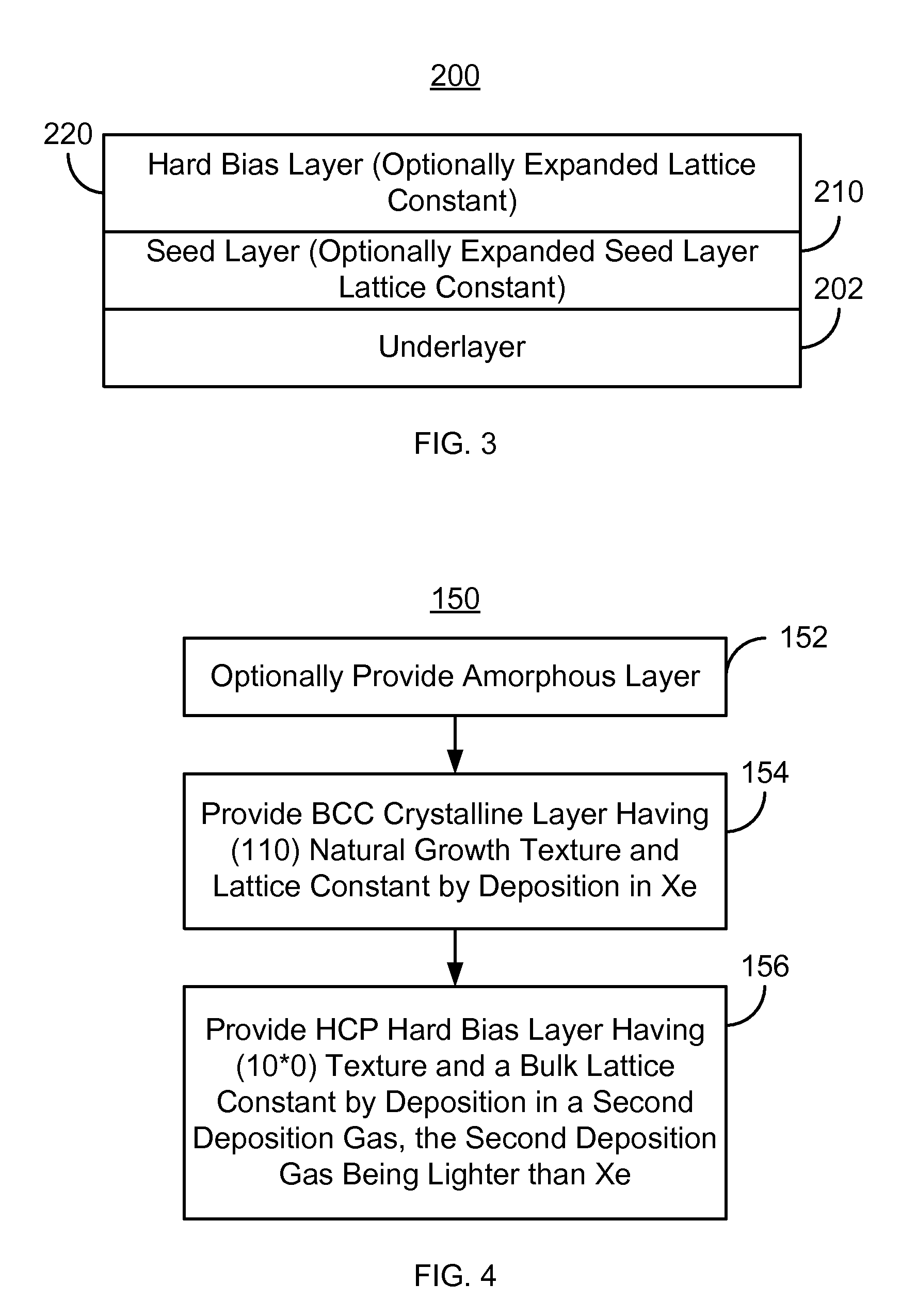
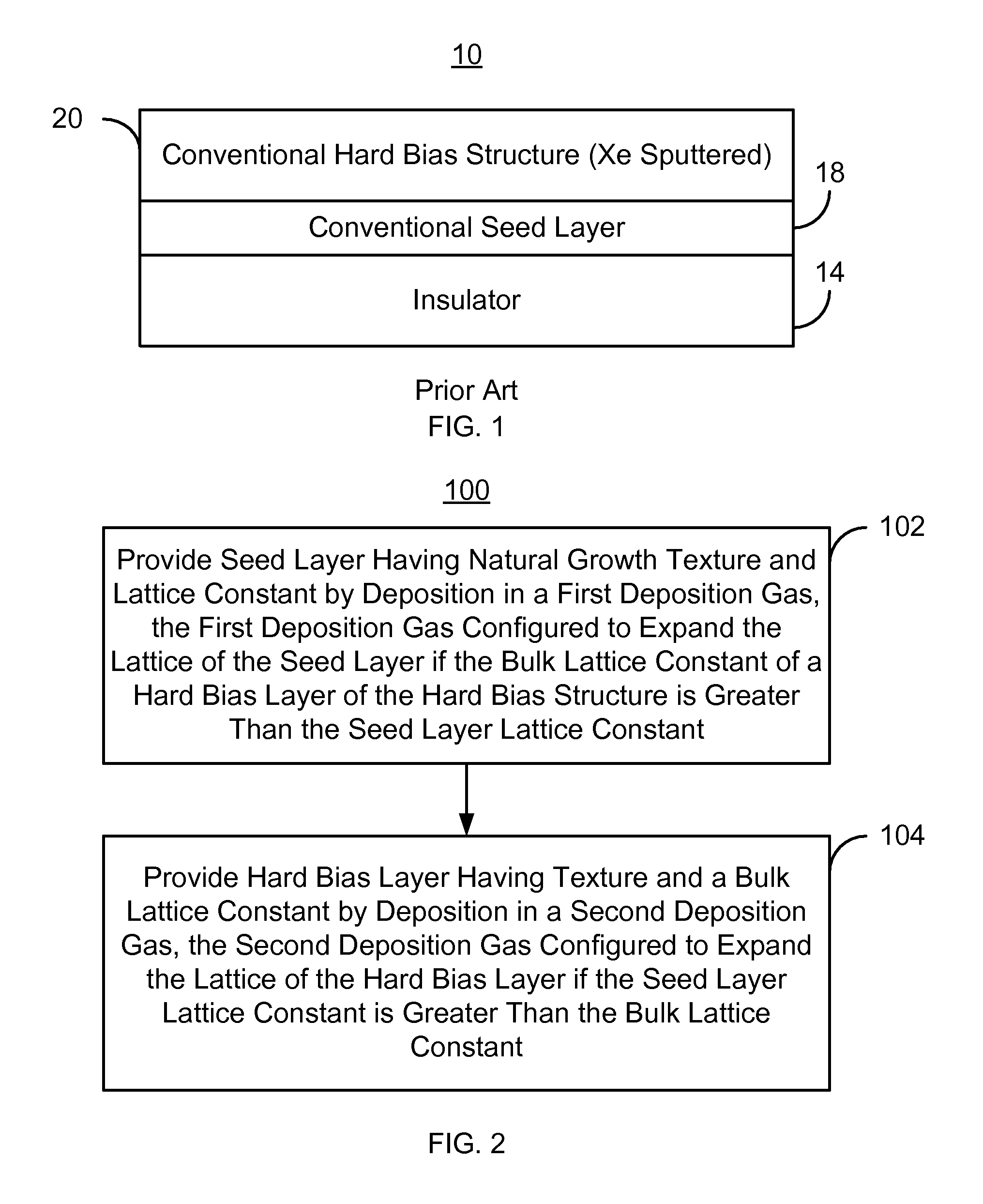
Method and system for providing an improved hard bias structure
ActiveUS8270126B1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsLattice constantEnvironmental geology
A method and system for providing a hard bias structure include providing a seed layer for a hard bias structure. The seed layer has a lattice constant and a natural growth texture. The method and system further include depositing the hard bias layer for the hard bias structure on the seed layer. The natural growth texture of the seed layer corresponds to a texture for the hard bias layer. The hard bias layer has a bulk lattice constant. Providing the seed layer includes forming a first plasma of a first deposition gas configured to expand the seed layer lattice constant if the bulk lattice constant is greater than the seed layer constant. Depositing the hard bias layer further includes forming a second plasma of a second deposition gas configured to expand the bulk lattice constant if the seed layer lattice constant is greater than the bulk lattice constant.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Monolithically integrated light emitting devices
ActiveUS20070105256A1Layered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSingle crystal
Methods and structures for monolithically integrating monocrystalline silicon and monocrystalline non-silicon materials and devices are provided. In one structure, a monolithically integrated semiconductor device structure comprises a silicon substrate and a first monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over the silicon substrate, wherein the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from a lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure further includes an insulating layer disposed over the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a first region and a monocrystalline silicon layer disposed over the insulating layer in the first region. The structure includes at least one silicon-based electronic device including an element including at least a portion of the monocrystalline silicon layer. The structure also includes a second monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over at least a portion of the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a second region and absent from the first region, wherein the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from the lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure includes at least one III-V light-emitting device including an active region including at least a portion of the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Strained-channel semiconductor structure and method of fabricating the same
A strained-channel semiconductor structure and method of fabricating the same. The strained-channel semiconductor structure comprises a substrate composed of a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant. A channel region is disposed in the substrate and a gate stack is disposed over the strained channel region A pair of source / drain regions are oppositely disposed in the substrate adjacent to the channel region, wherein each of the source / drain regions comprises a lattice-mismatched zone comprising a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant rather than the first natural lattice constant, an inner side and an outer side corresponding to the gate stack, and at least one outer sides laterally contacts the first semiconductor material of the substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
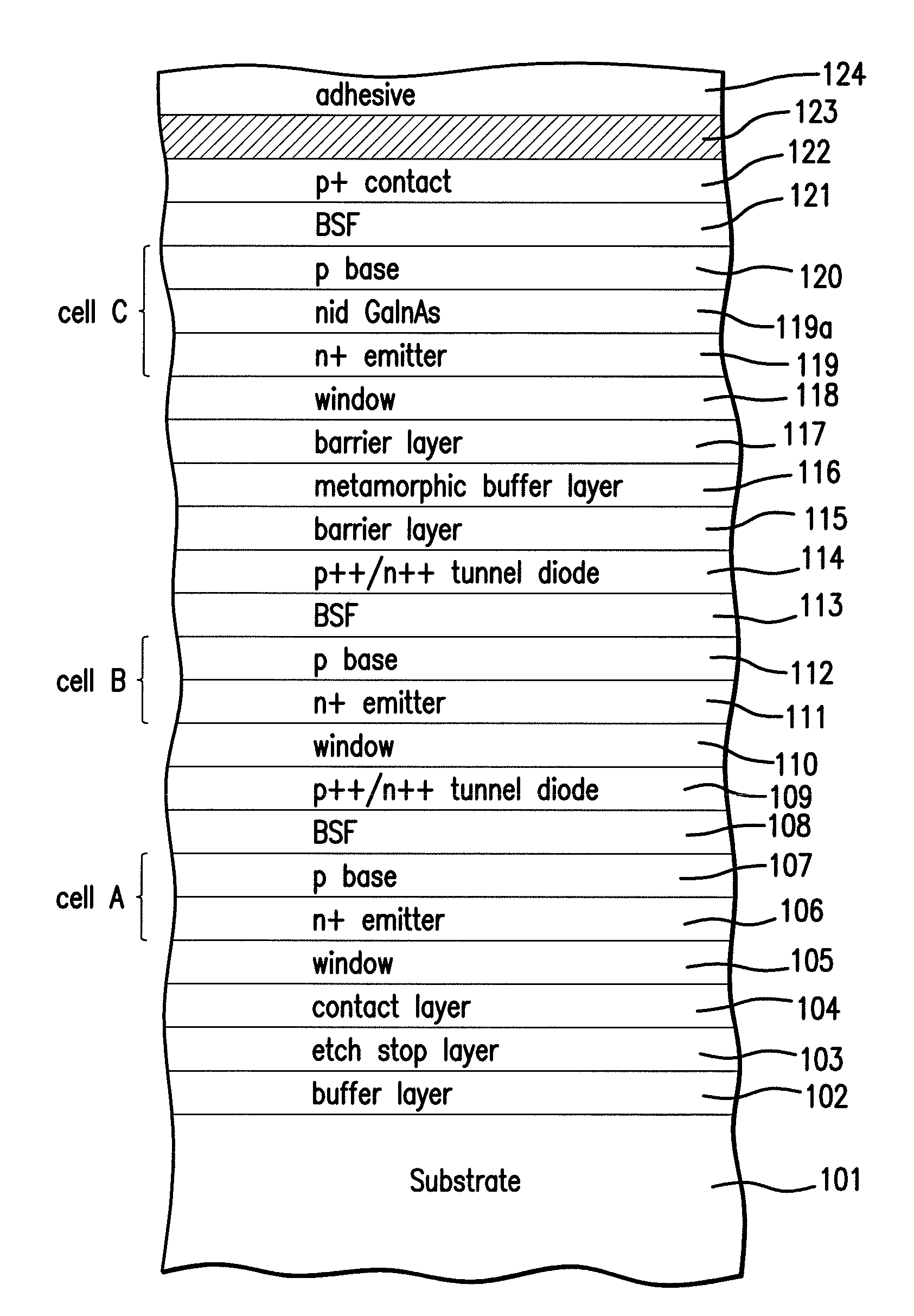
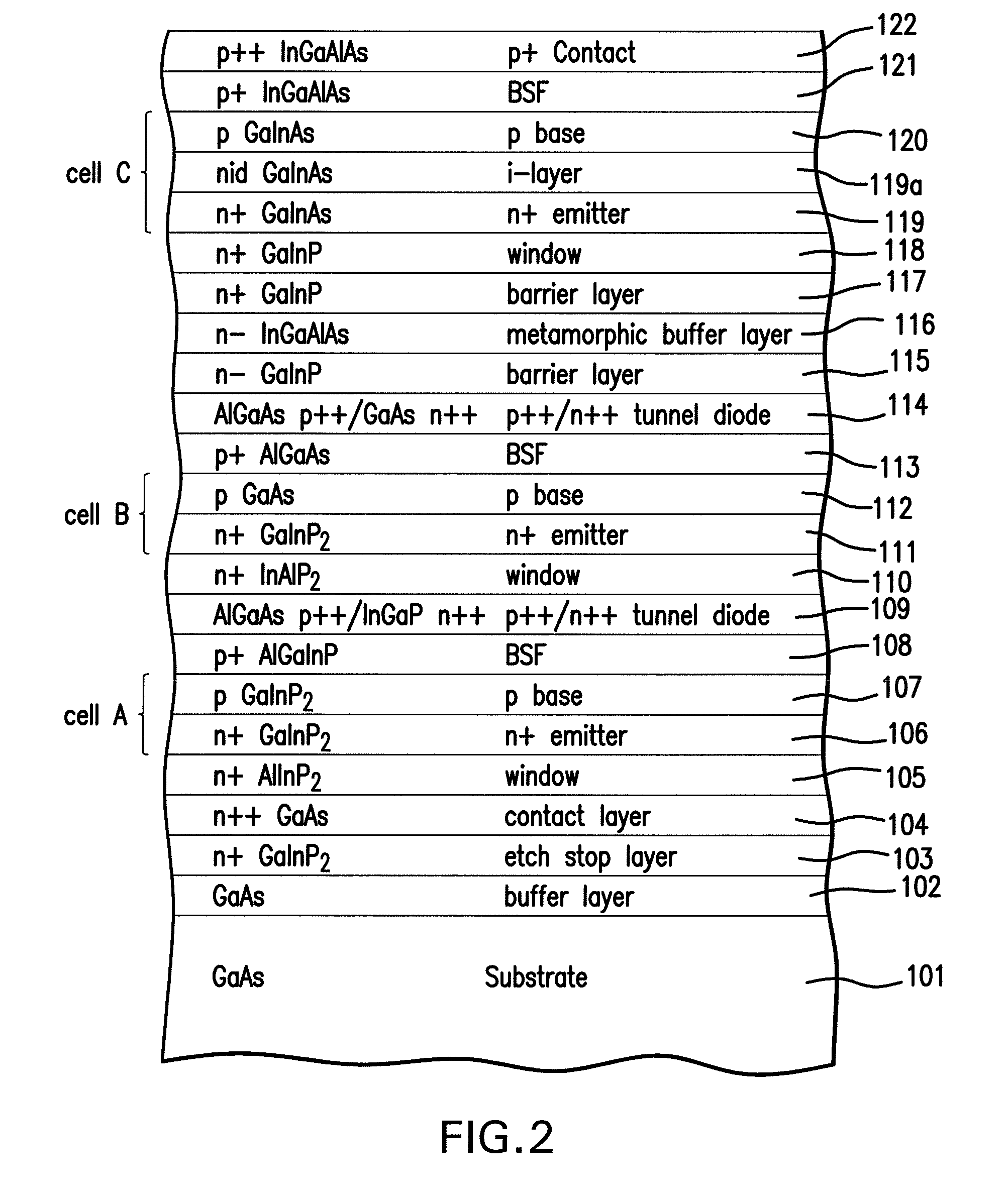
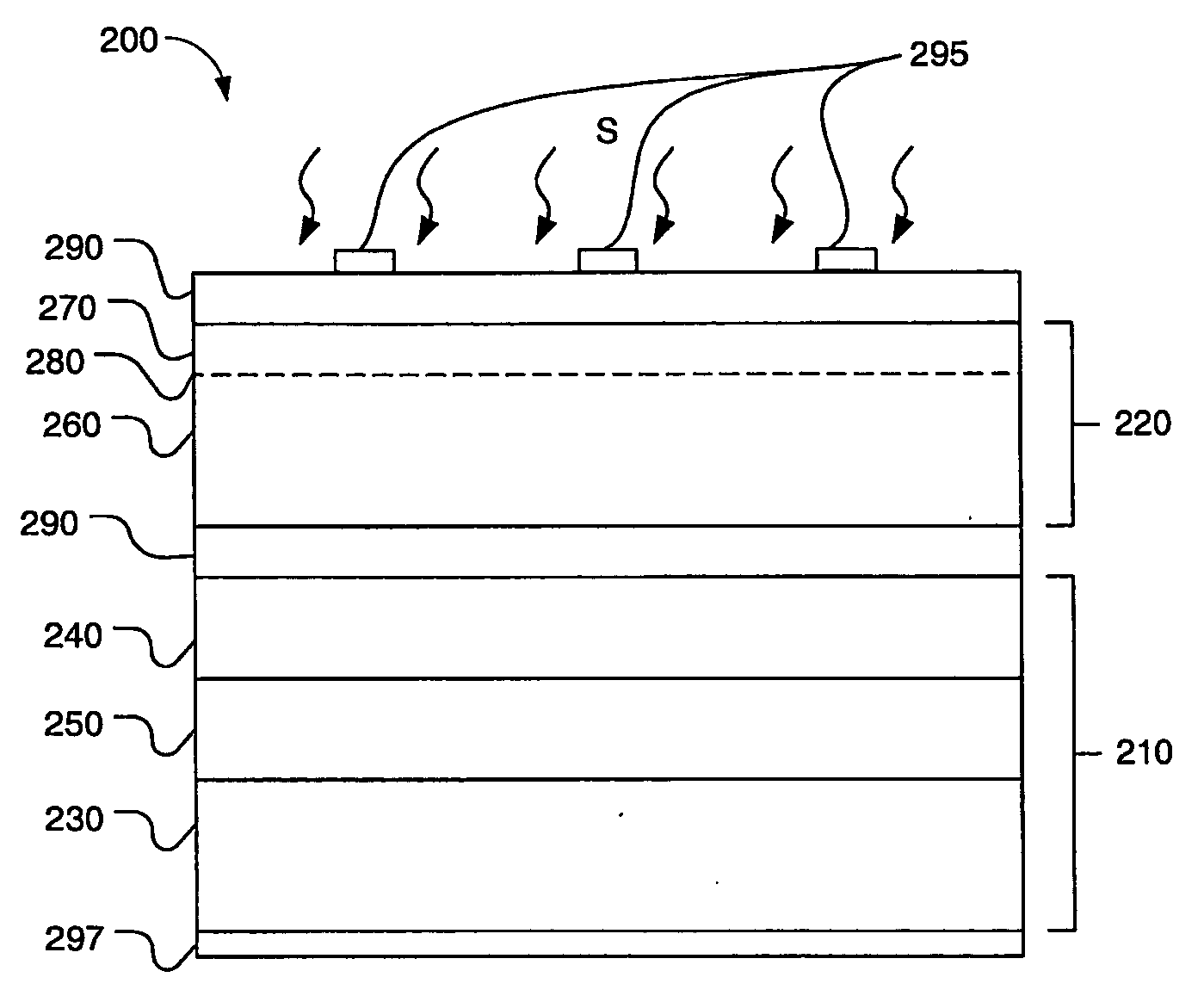
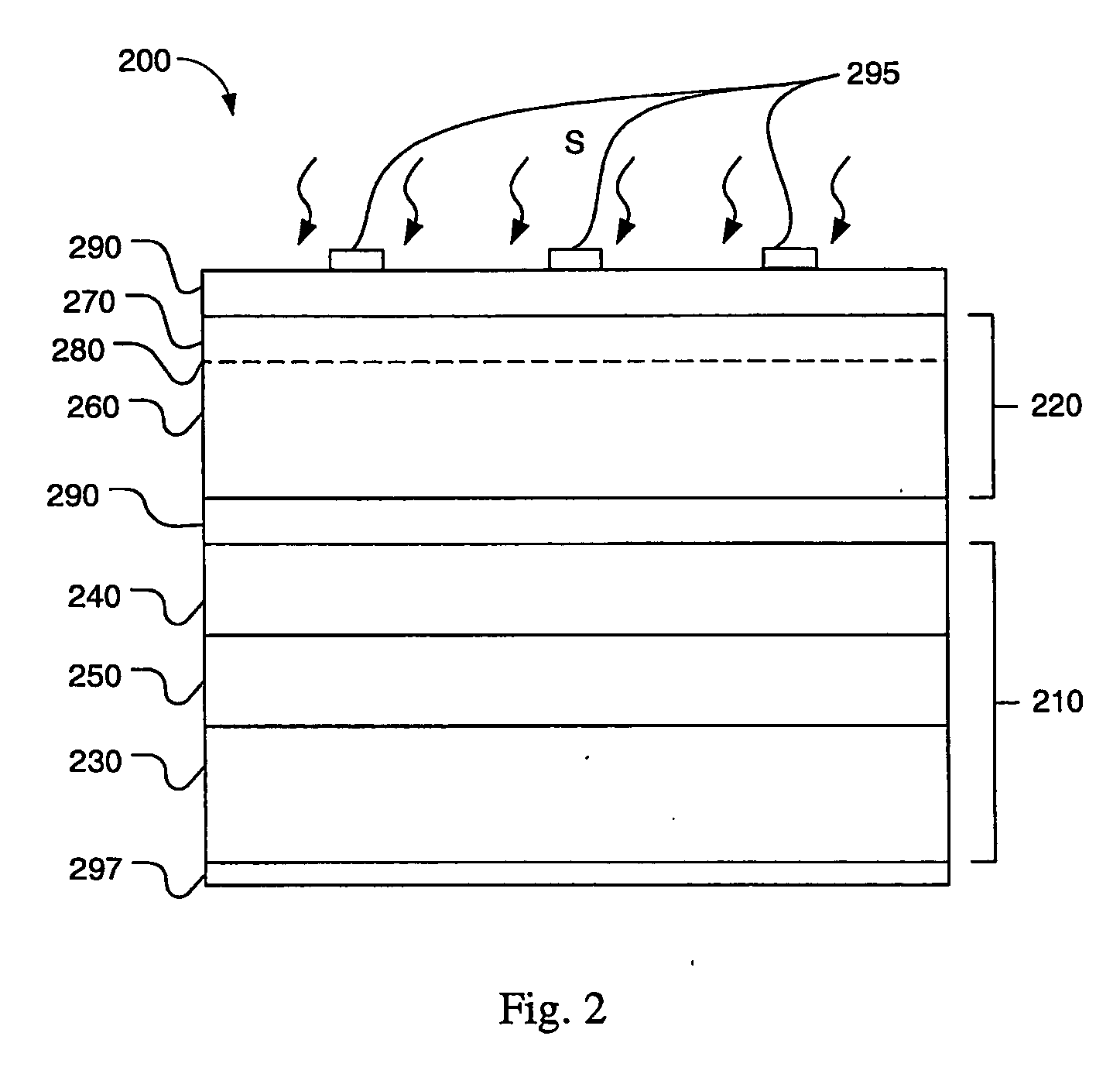
Strain Balanced Multiple Quantum Well Subcell In Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cell
InactiveUS20090272438A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSolar cell
A method of manufacturing a solar cell by providing a first semiconductor substrate for the epitaxial growth of semiconductor material; forming a first subcell on the substrate with a first semiconductor material with a first band gap and a first lattice constant; forming a second subcell with a second semiconductor material with a second band gap and a second lattice constant, wherein the second band gap is less than the first band gap and the second lattice constant is greater than the first lattice constant; the second subcell including a strain balanced quantum well structure; and forming a lattice constant transition material positioned between the first subcell and the second subcell, the lattice constant transition material having a lattice constant that changes gradually from the first lattice constant to the second lattice constant.
Owner:EMCORE SOLAR POWER
Monolithically integrated silicon and III-V electronics
Methods and structures for monolithically integrating monocrystalline silicon and monocrystalline non-silicon materials and devices are provided. In one structure, a monolithically integrated semiconductor device structure comprises a silicon substrate and a first monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over the silicon substrate, wherein the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from a lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure also includes an insulating layer disposed over the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a first region and a monocrystalline silicon layer disposed over the insulating layer in the first region. The structure includes at least one silicon-based electronic device comprising an element including at least a portion of the monocrystalline silicon layer. The structure includes a second monocrystalline semiconductor layer disposed over at least a portion of the first monocrystalline semiconductor layer in a second region and absent from the first region, wherein the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer has a lattice constant different from the lattice constant of relaxed silicon. The structure also includes at least one III-V electronic device comprising an element including at least a portion of the second monocrystalline semiconductor layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Patterned strained semiconductor substrate and device
ActiveUS20060019462A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice constantSemiconductor
A method that includes forming a pattern of strained material and relaxed material on a substrate; forming a strained device in the strained material; and forming a non-strained device in the relaxed material is disclosed. In one embodiment, the strained material is silicon (Si) in either a tensile or compressive state, and the relaxed material is Si in a normal state. A buffer layer of silicon germanium (SiGe), silicon carbon (SiC), or similar material is formed on the substrate and has a lattice constant / structure mis-match with the substrate. A relaxed layer of SiGe, SiC, or similar material is formed on the buffer layer and places the strained material in the tensile or compressive state. In another embodiment, carbon-doped silicon or germanium-doped silicon is used to form the strained material. The structure includes a multi-layered substrate having strained and non-strained materials patterned thereon.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Monolithic photovoltaic energy conversion device
InactiveUS20070137698A1Solid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A multijunction, monolithic, photovoltaic (PV) cell and device (600) is provided for converting radiant energy to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The PV cell includes an array of subcells (602), i.e., active p / n junctions, grown on a compliant substrate, where the compliant substrate accommodates greater flexibility in matching lattice constants to adjacent semiconductor material. The lattice matched semiconductor materials are selected with appropriate band-gaps to efficiently create photovoltage from a larger portion of the solar spectrum. Subcell strings (601, 603) from multiple PV cells are voltage matched to provide high output PV devices. A light emitting cell and device is also provided having monolithically grown red-yellow and green emission subcells and a mechanically stacked blue emission subcell.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
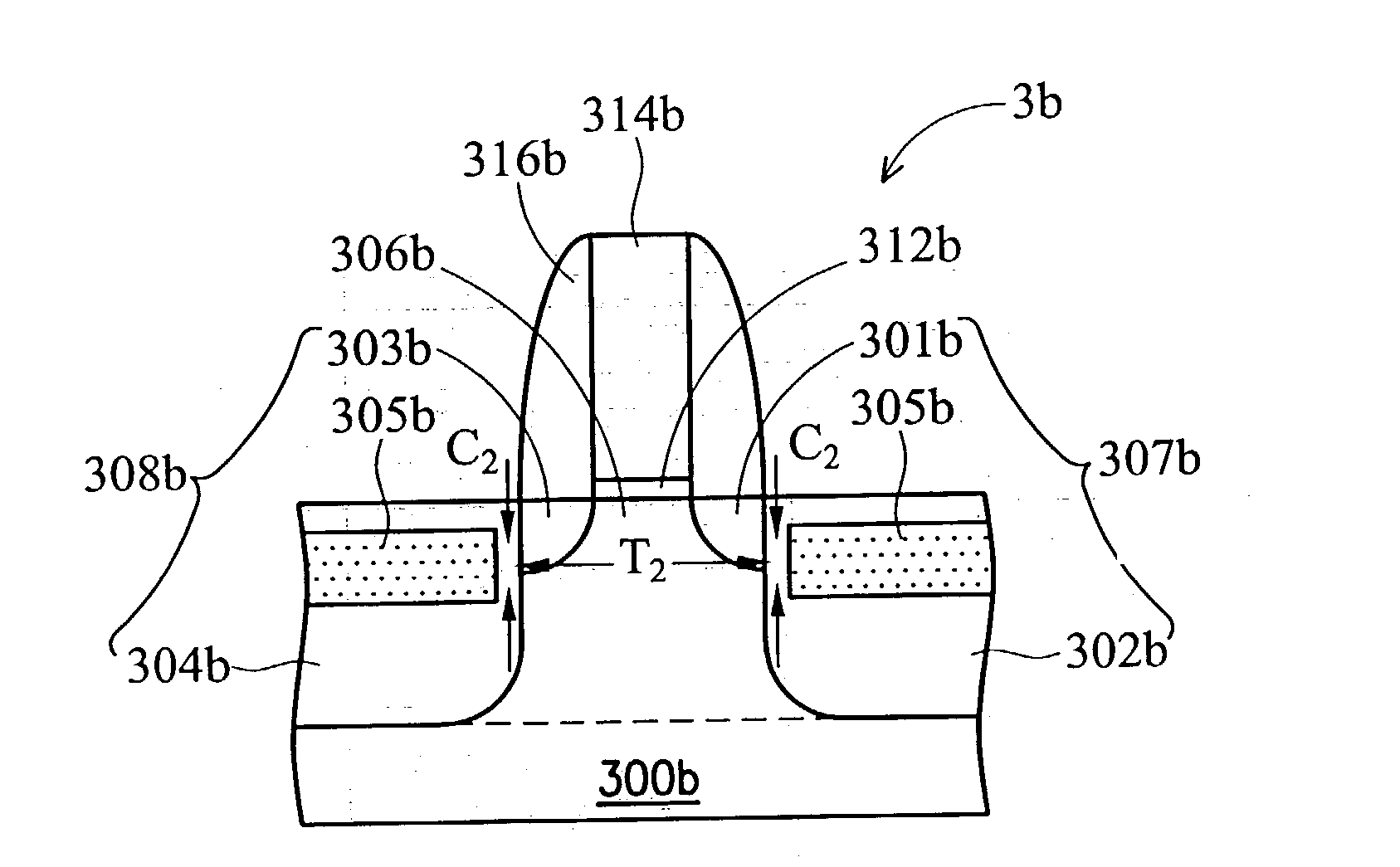
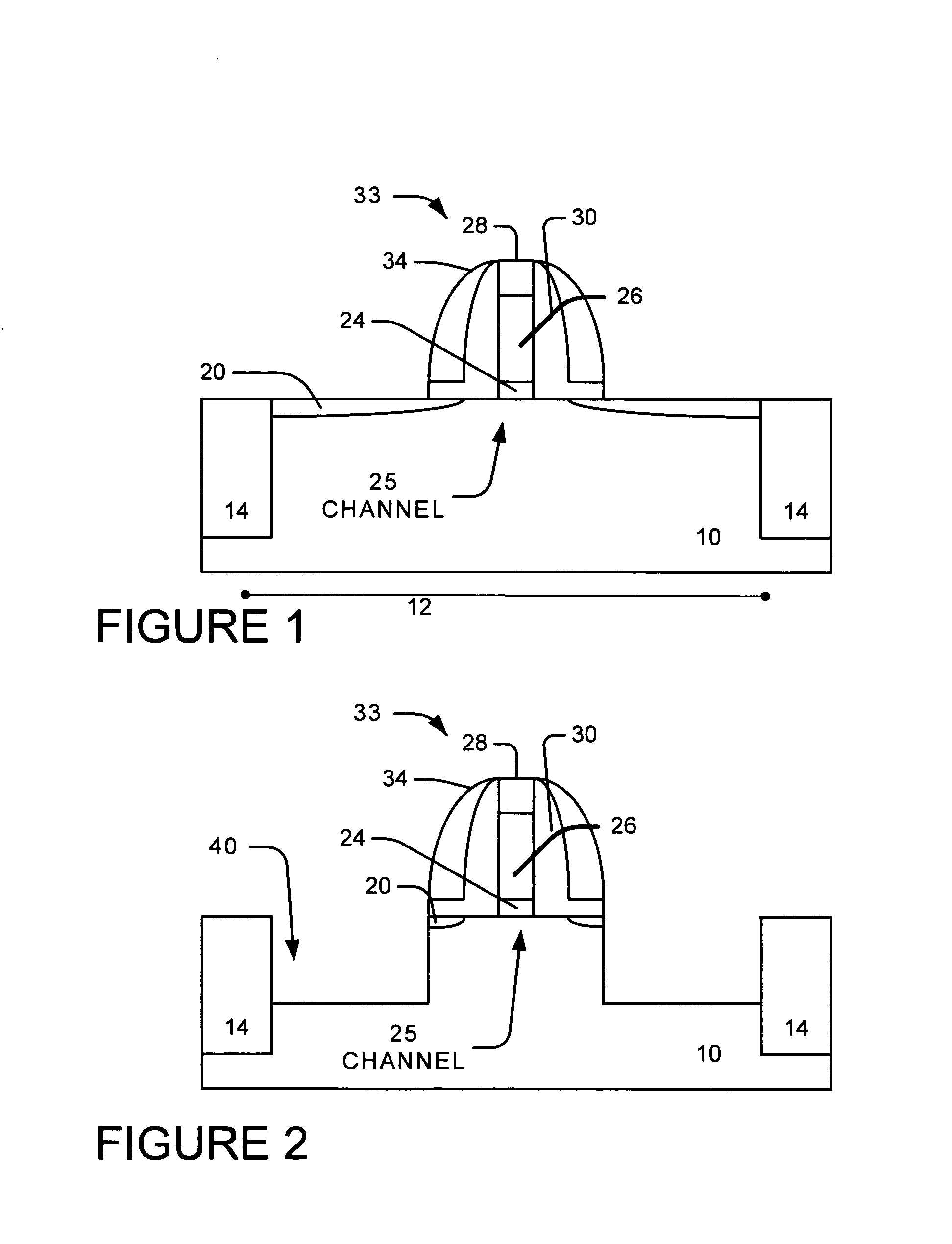
Strained channel FinFET
InactiveUS6897527B2High carrier mobilityImproving FinFET performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesTensile strainCrystalline materials
A semiconductor device includes a fin and a layer formed on at least a portion of the fin. The fin includes a first crystalline material. The layer includes a second crystalline material, where the first crystalline material has a larger lattice constant than the second crystalline material to induce tensile strain within the layer.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
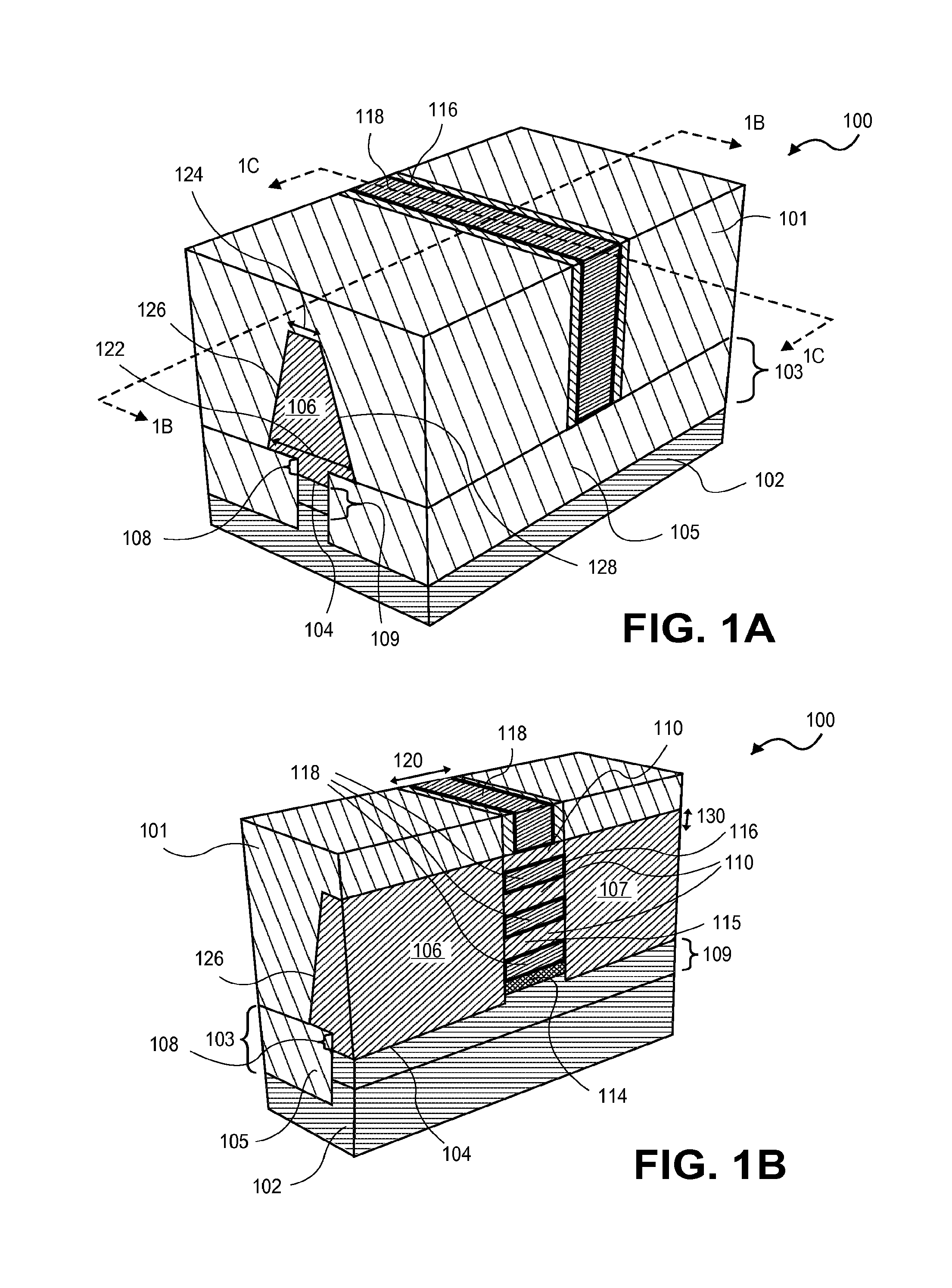
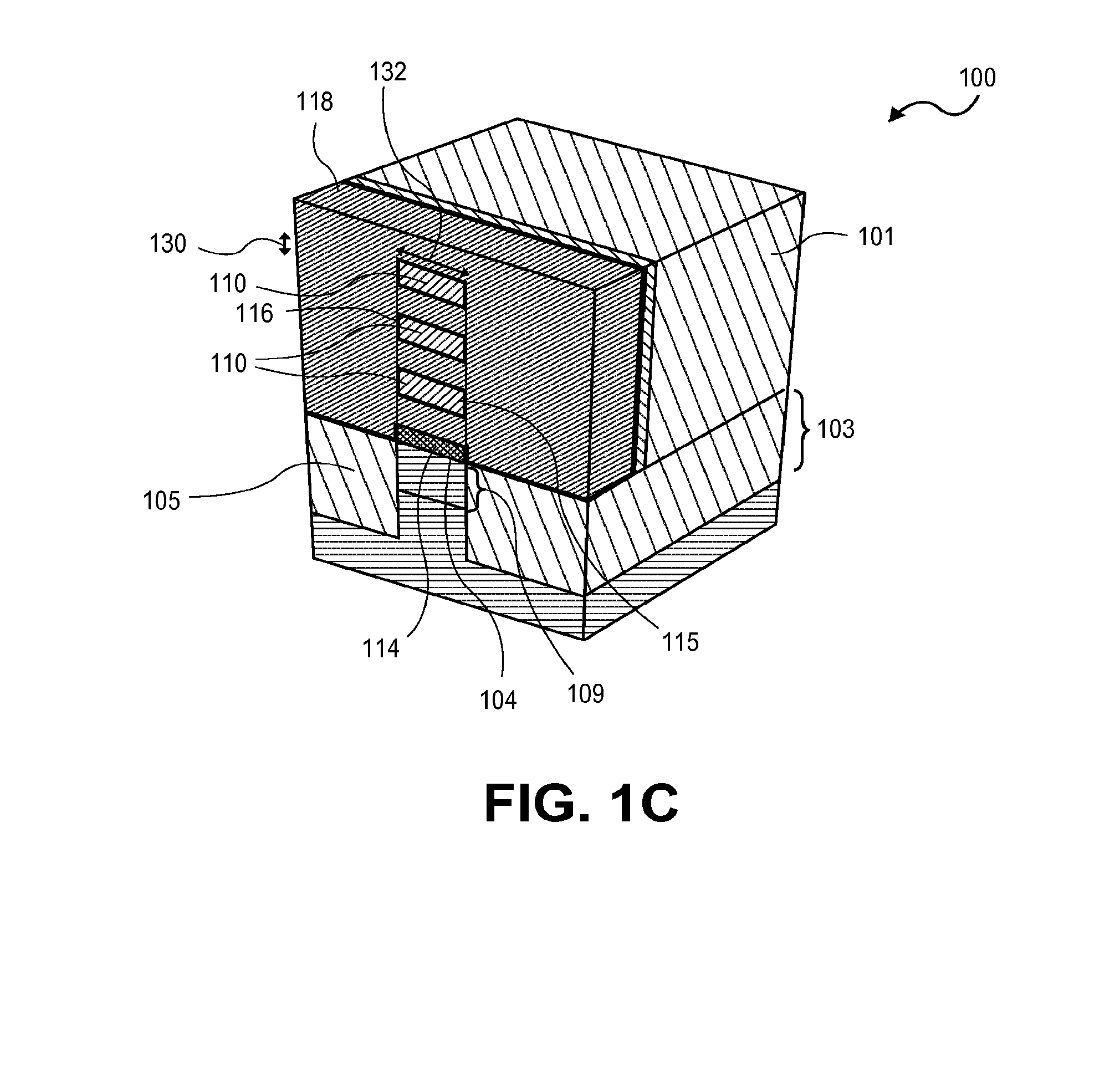
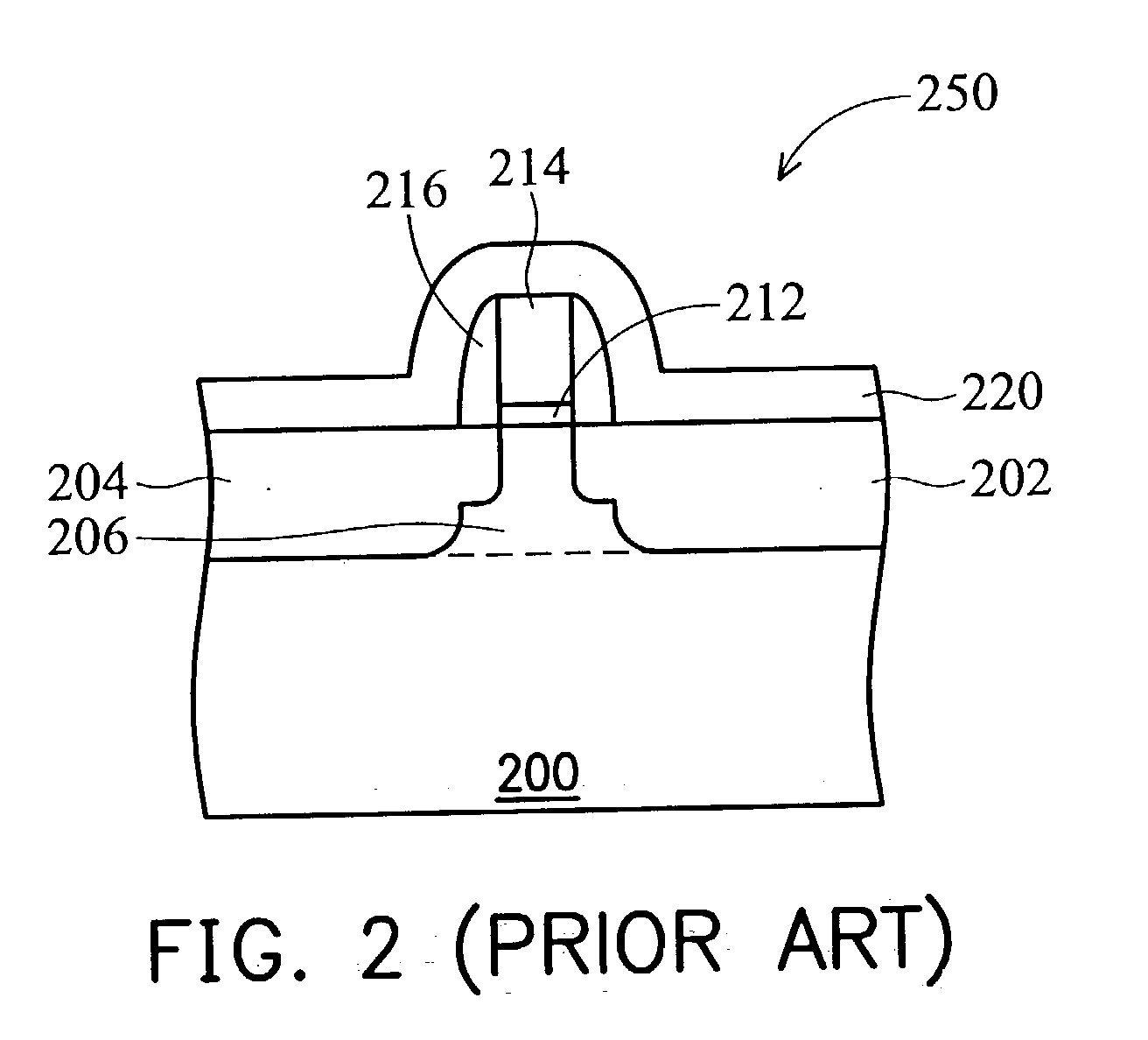
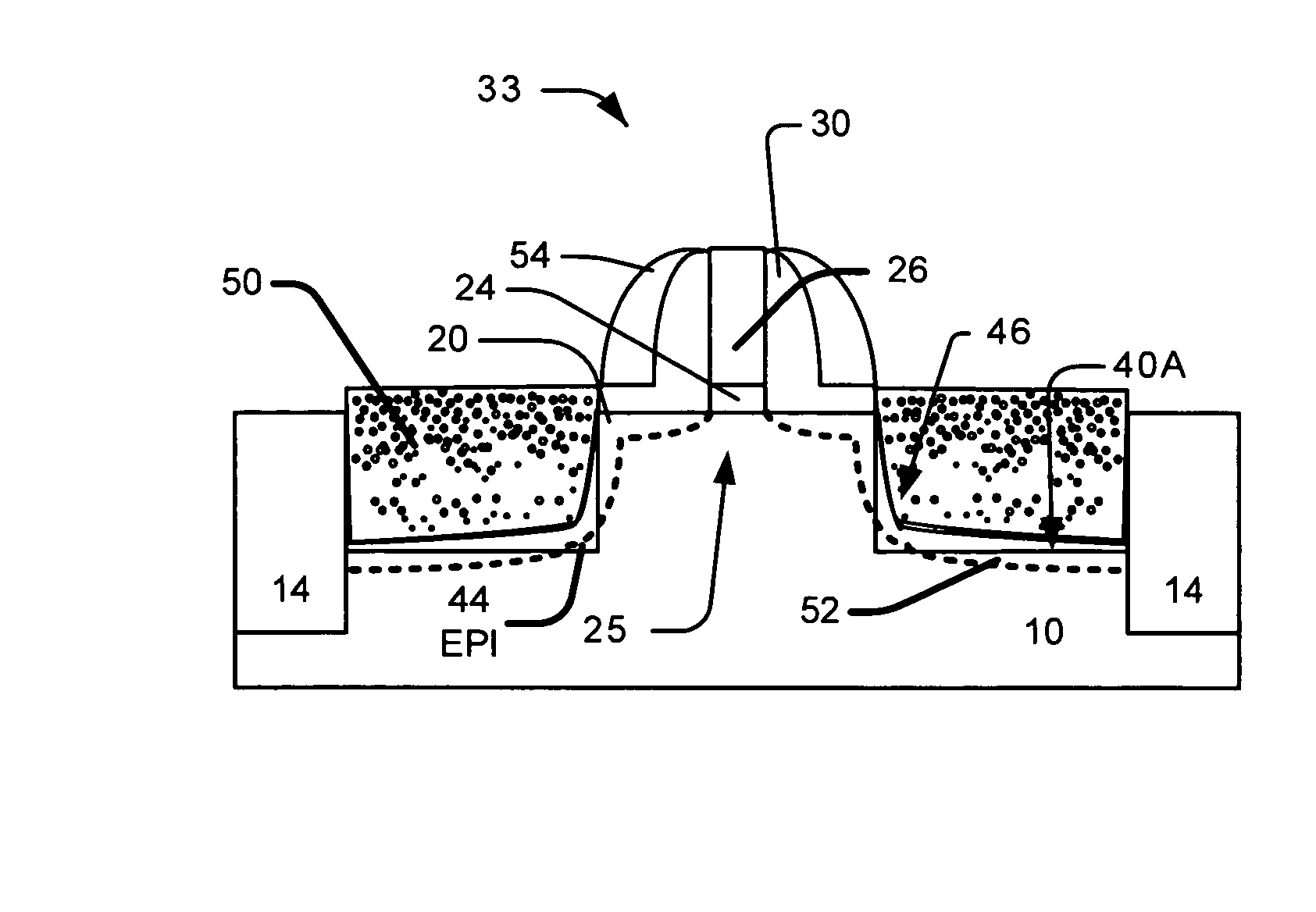
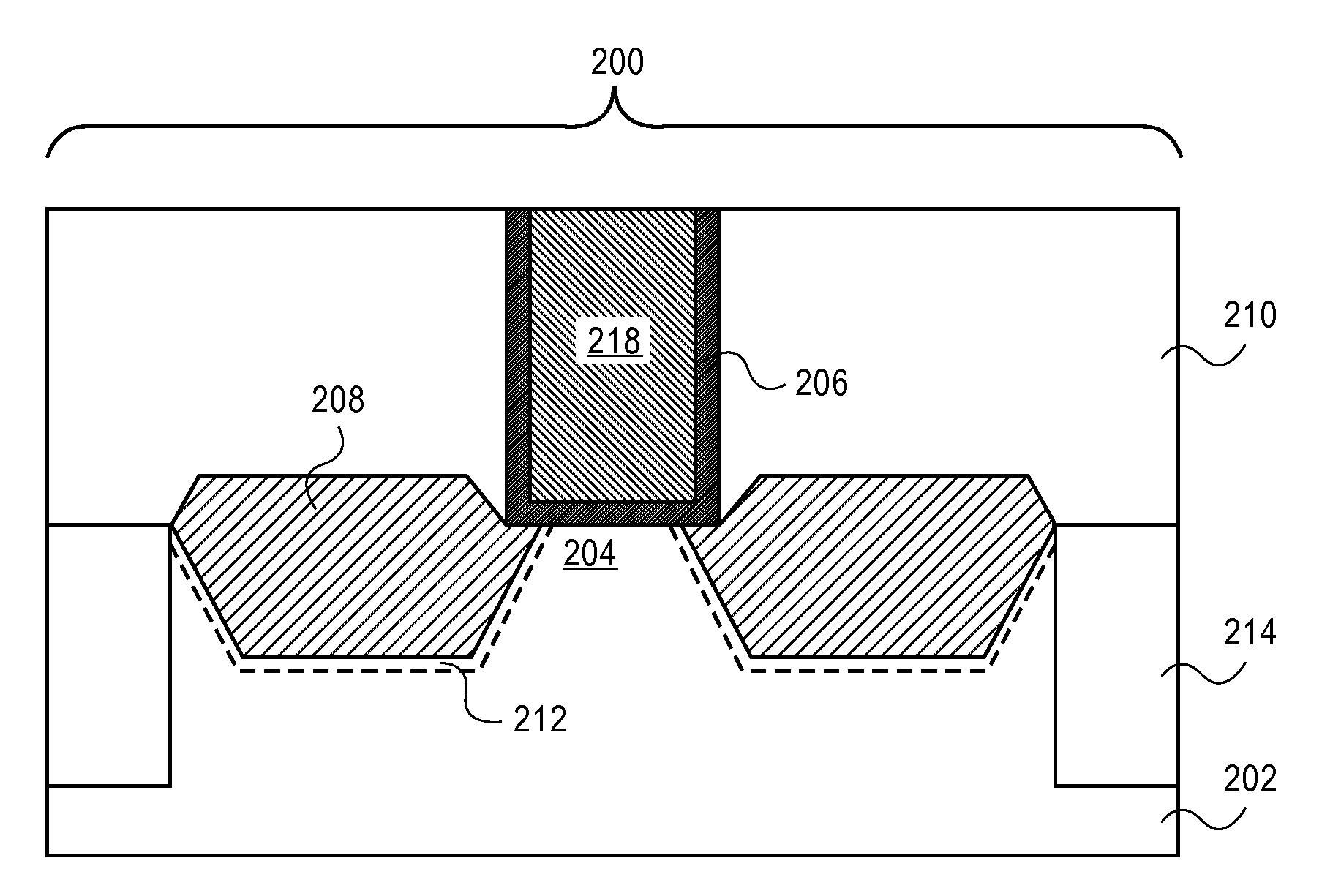
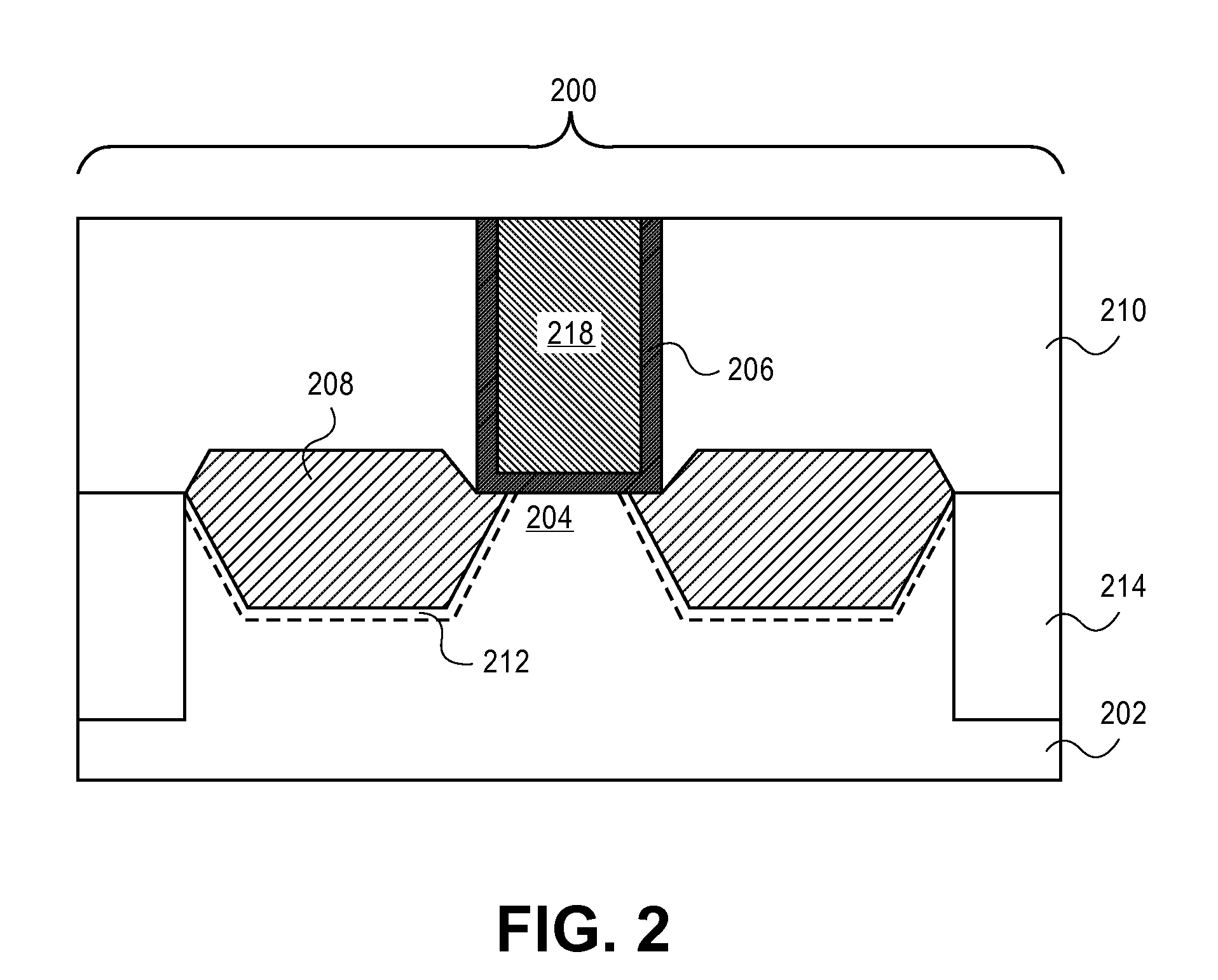
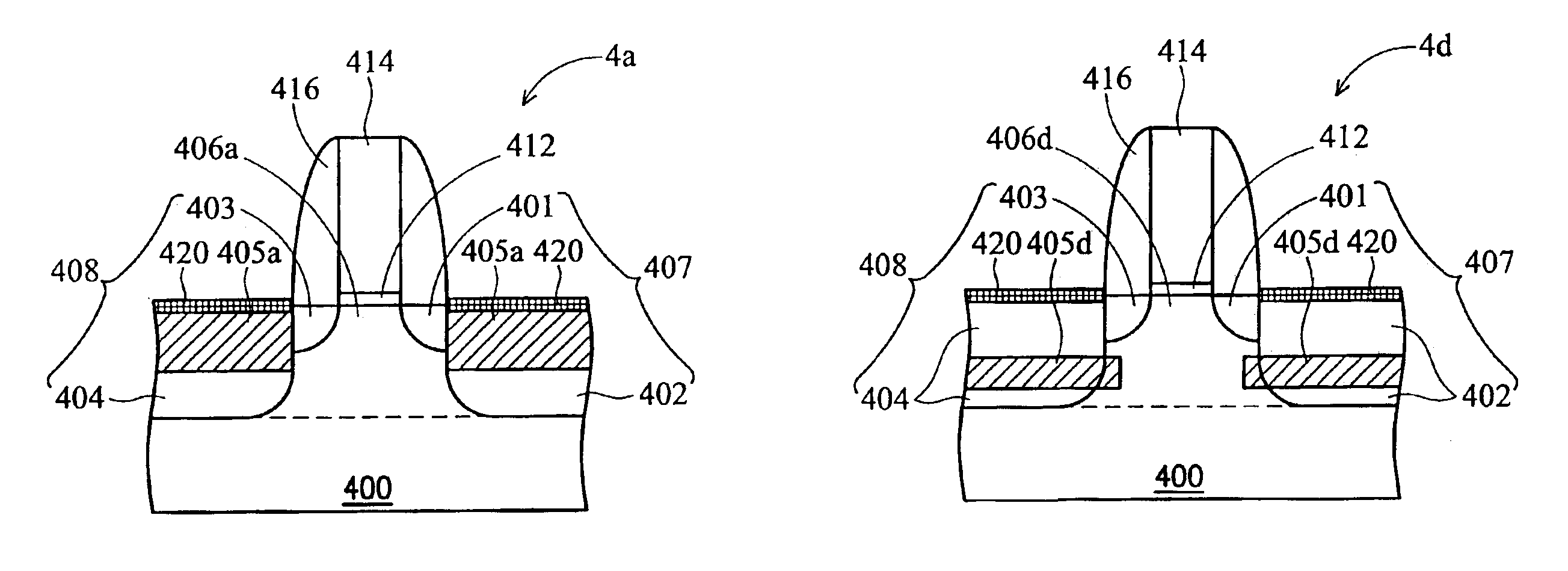
Semiconductor device having tipless epitaxial source/drain regions
ActiveUS20080283906A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricGate stack
A semiconductor device having tipless epitaxial source / drain regions and a method for its formation are described. In an embodiment, the semiconductor device comprises a gate stack on a substrate. The gate stack is comprised of a gate electrode above a gate dielectric layer and is above a channel region in the substrate. The semiconductor device also comprises a pair of source / drain regions in the substrate on either side of the channel region. The pair of source / drain regions is in direct contact with the gate dielectric layer and the lattice constant of the pair of source / drain regions is different than the lattice constant of the channel region. In one embodiment, the semiconductor device is formed by using a dielectric gate stack placeholder.
Owner:INTEL CORP
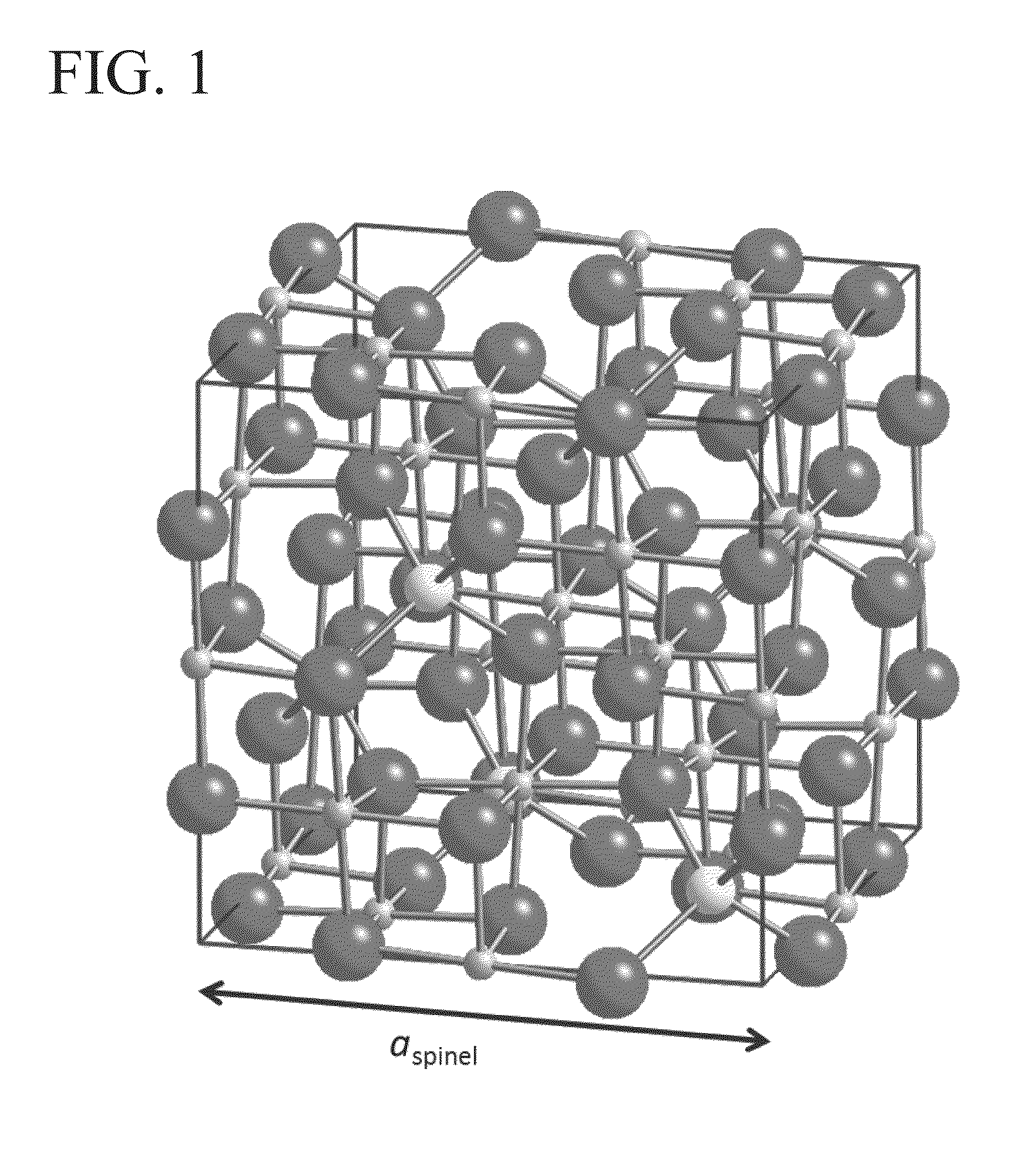
Ferromagnetic Tunnel Junction Structure and Magnetoresistive Effect Device and Spintronics Device Utilizing Same
ActiveUS20130221461A1High TMR valueQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCrystalline oxideSpace group
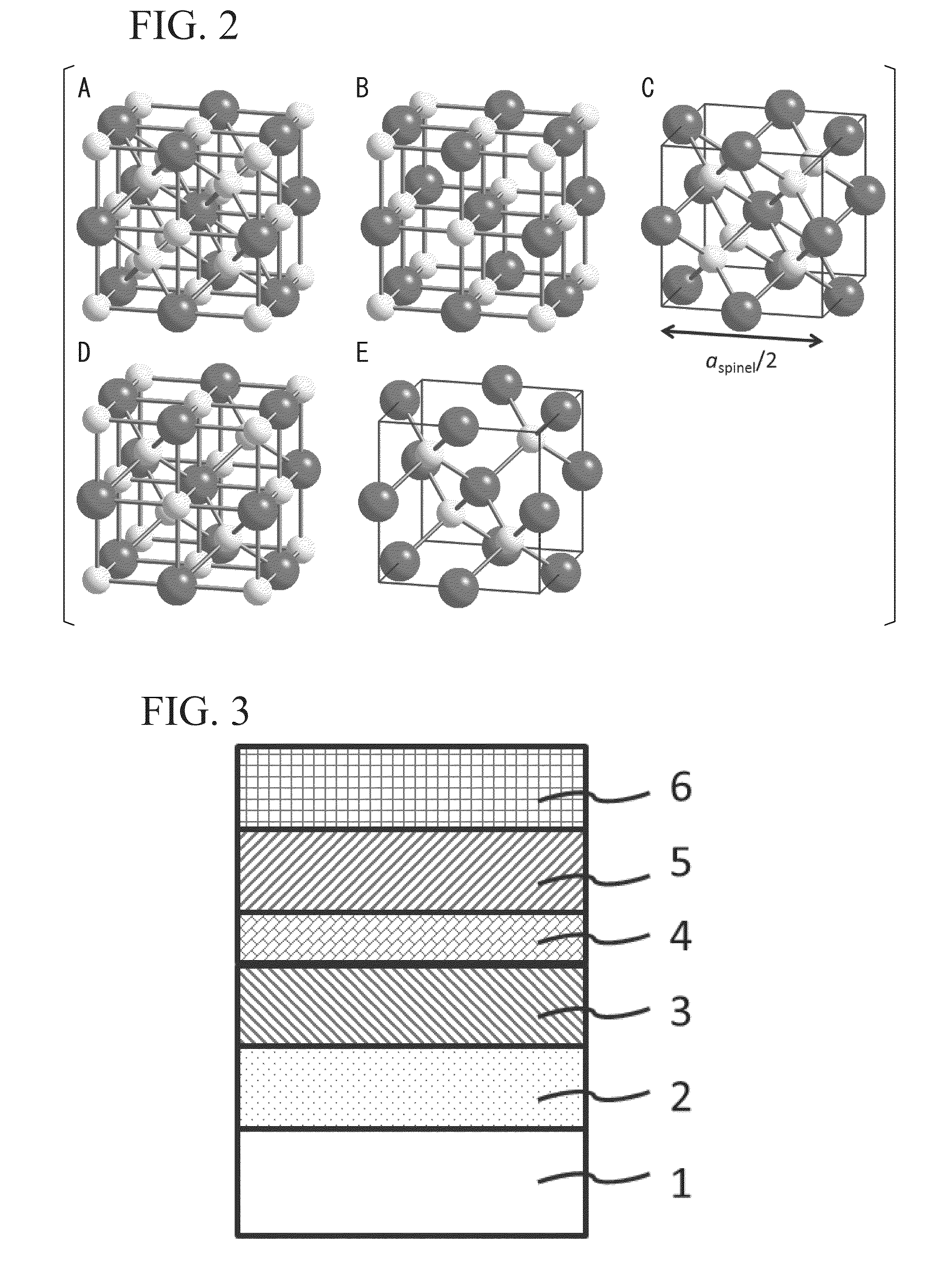
A ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure comprising a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, and a tunnel barrier layer that is interposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer, wherein the tunnel barrier layer includes a crystalline non-magnetic material having constituent elements that are similar to those of an crystalline oxide that has spinel structure as a stable phase structure; the non-magnetic material has a cubic structure having a symmetry of space group Fm-3m or F-43m in which atomic arrangement in the spinel structure is disordered; and an effective lattice constant of the cubic structure is substantially half of the lattice constant of the oxide of the spinel structure.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Strained-channel transistor structure with lattice-mismatched zone
InactiveUS6921913B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor materials
A strained-channel transistor structure with lattice-mismatched zone and fabrication method thereof. The transistor structure includes a substrate having a strained channel region, comprising a first semiconductor material with a first natural lattice constant, in a surface, a gate dielectric layer overlying the strained channel region, a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric layer, and a source region and drain region oppositely adjacent to the strained channel region, with one or both of the source region and drain region comprising a lattice-mismatched zone comprising a second semiconductor material with a second natural lattice constant different from the first natural lattice constant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
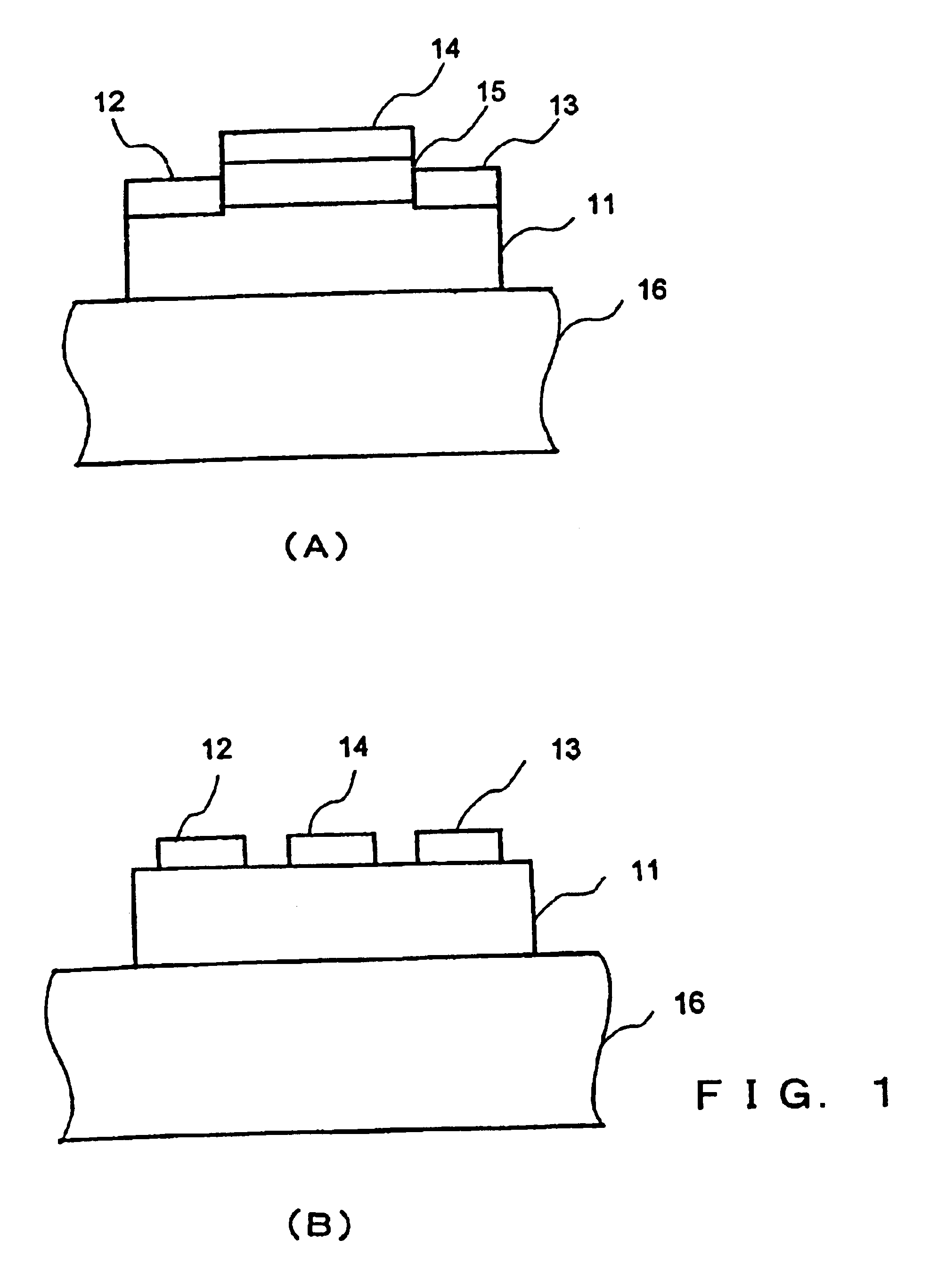
Semiconductor device
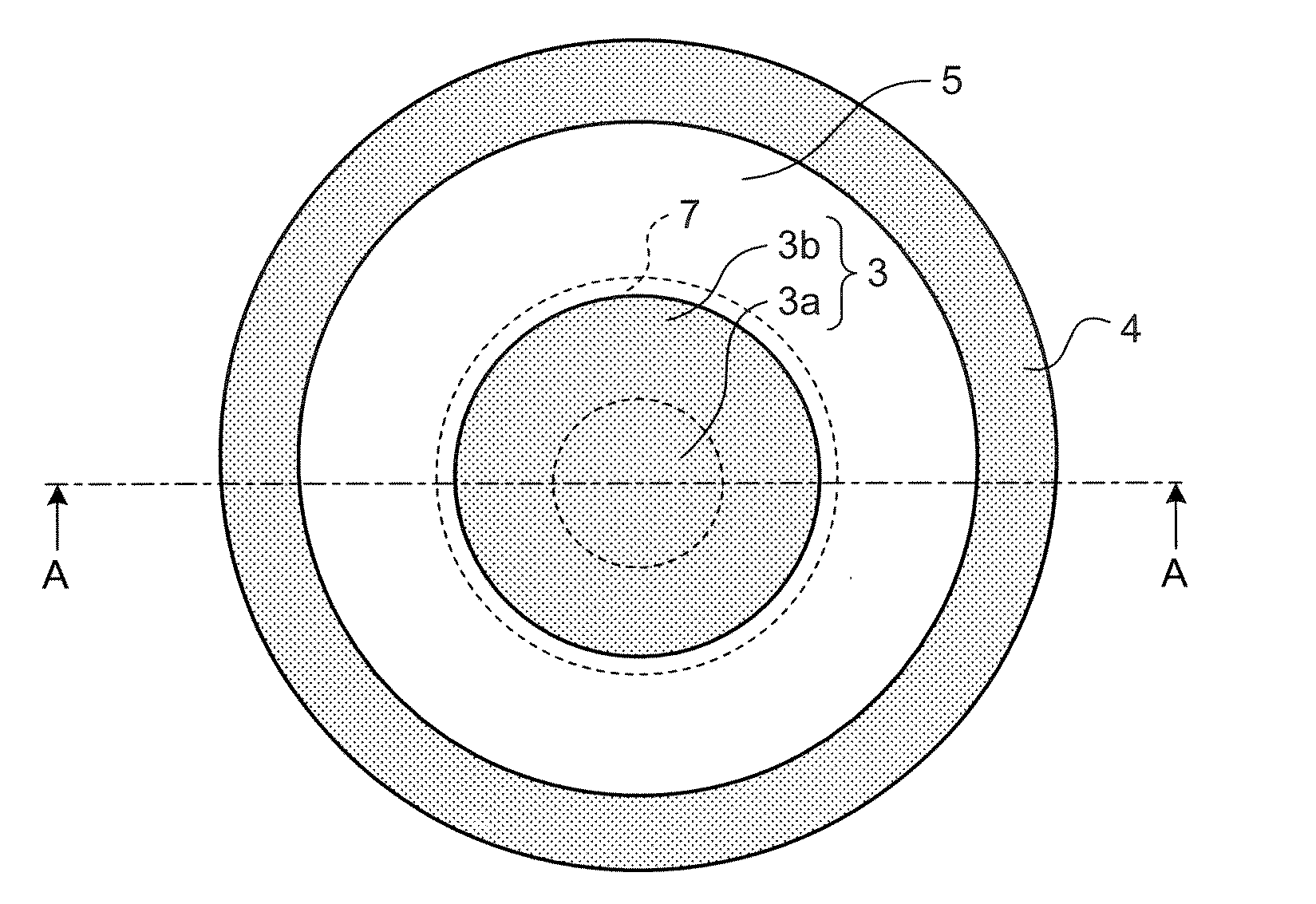
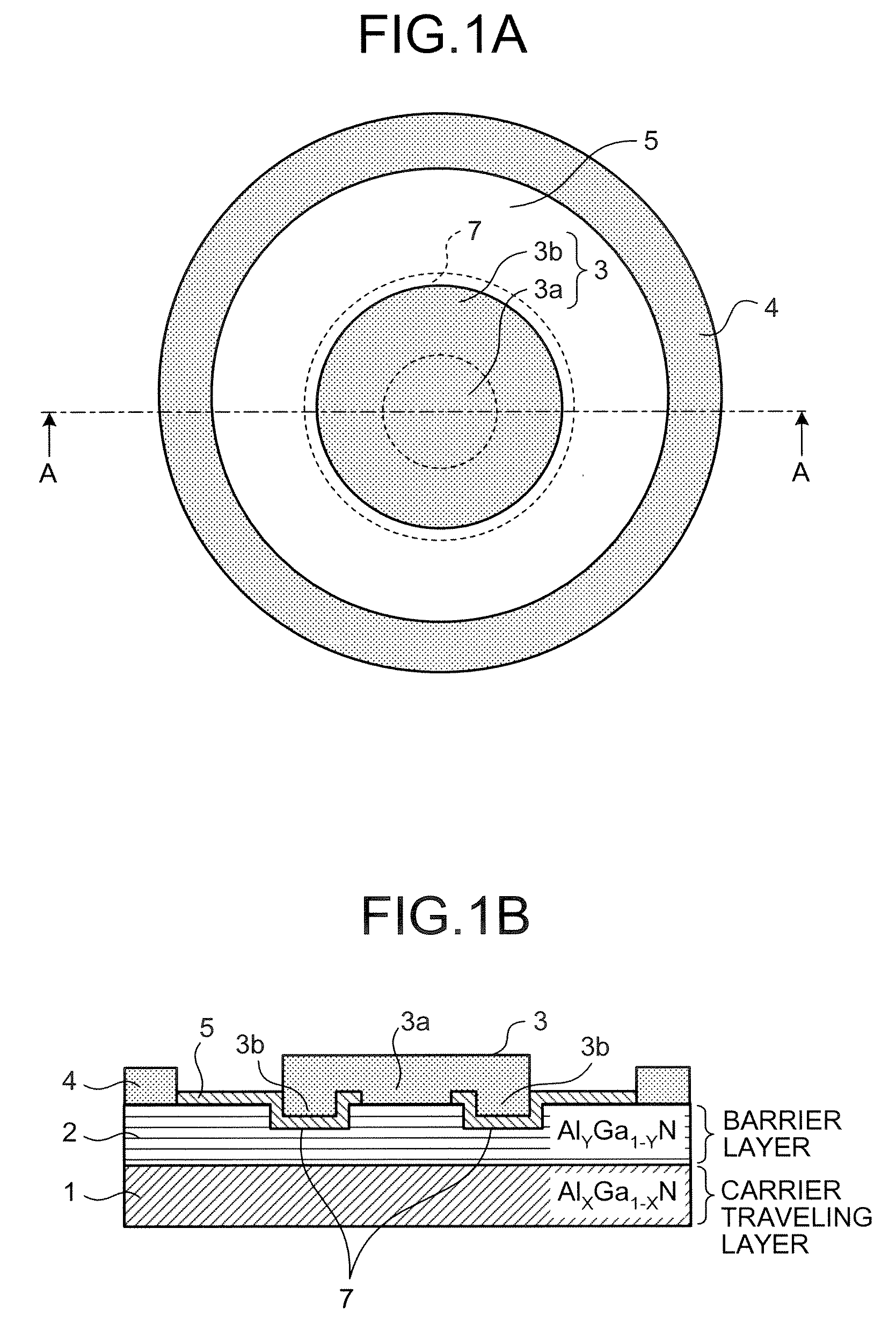
The present invention provides a high quality thin film comparable to a bulk single crystal and providres a semiconductor device with superior characteristics. A channel layer 11, for example, is formed of a semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO or the like. A source 12, a drain 13, a gate 14 and a gate insulating layer 15 are formed on the channel layer 111 to form an FET. For a substrate 16, a proper material is selected depending on a thin film material of the channel layer 11 in consideration of compatibility of both lattice constants. For example, if ZnO is used for the semiconductor of the channel layer as a base material, ScAlMgO4 or the like can be used for the substrate 16.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Mixed orientation and mixed material semiconductor-on-insulator wafer
The present disclosure relates, generally, to a semiconductor substrate with a planarized surface comprising mixed single-crystal orientation regions and / or mixed single-crystal semiconductor material regions, where each region is electrically isolated. In accordance with one embodiment of the disclosure CMOS devices on SOI regions are manufactured on semiconductors having different orientations. According to another embodiment, an SOI device is contemplated as having a plurality of semiconductor regions having at least one of a different semiconductor material, crystalline lattice constant or lattice strain. Methods and processes for fabricating the different embodiments of the invention is also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
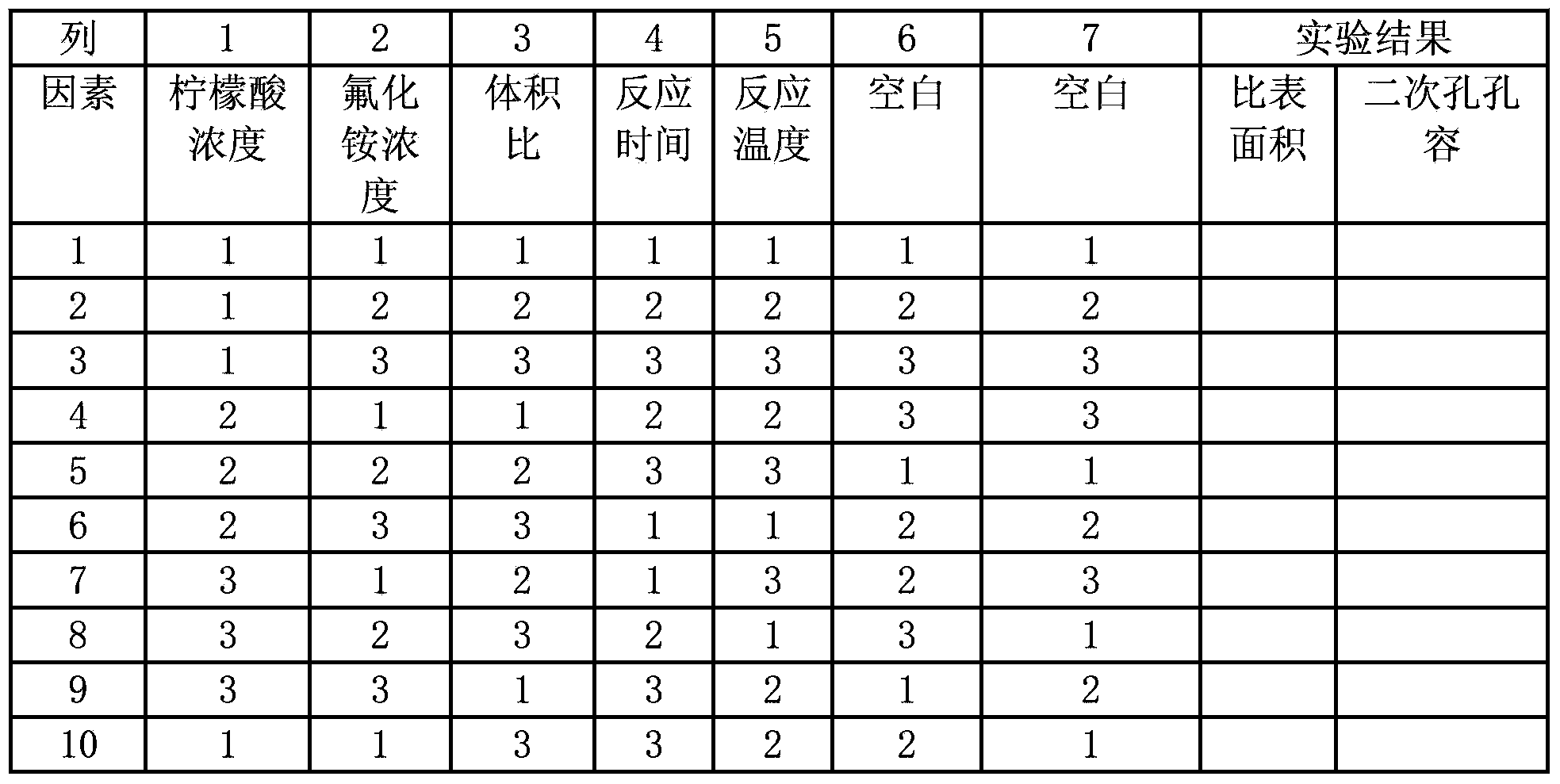
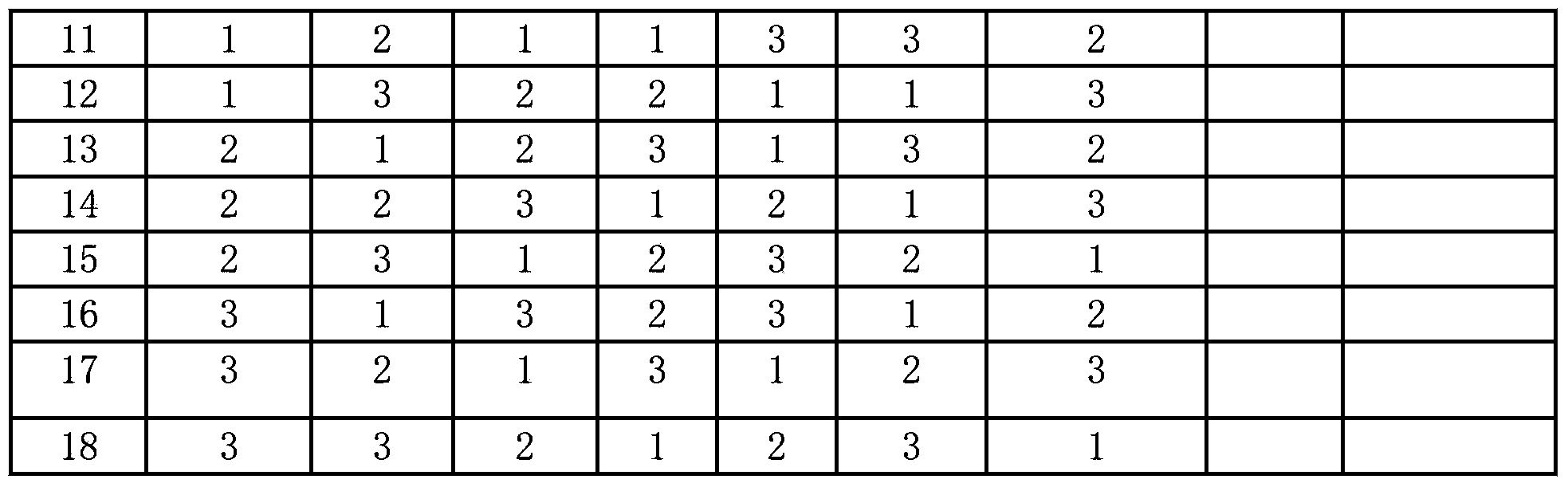
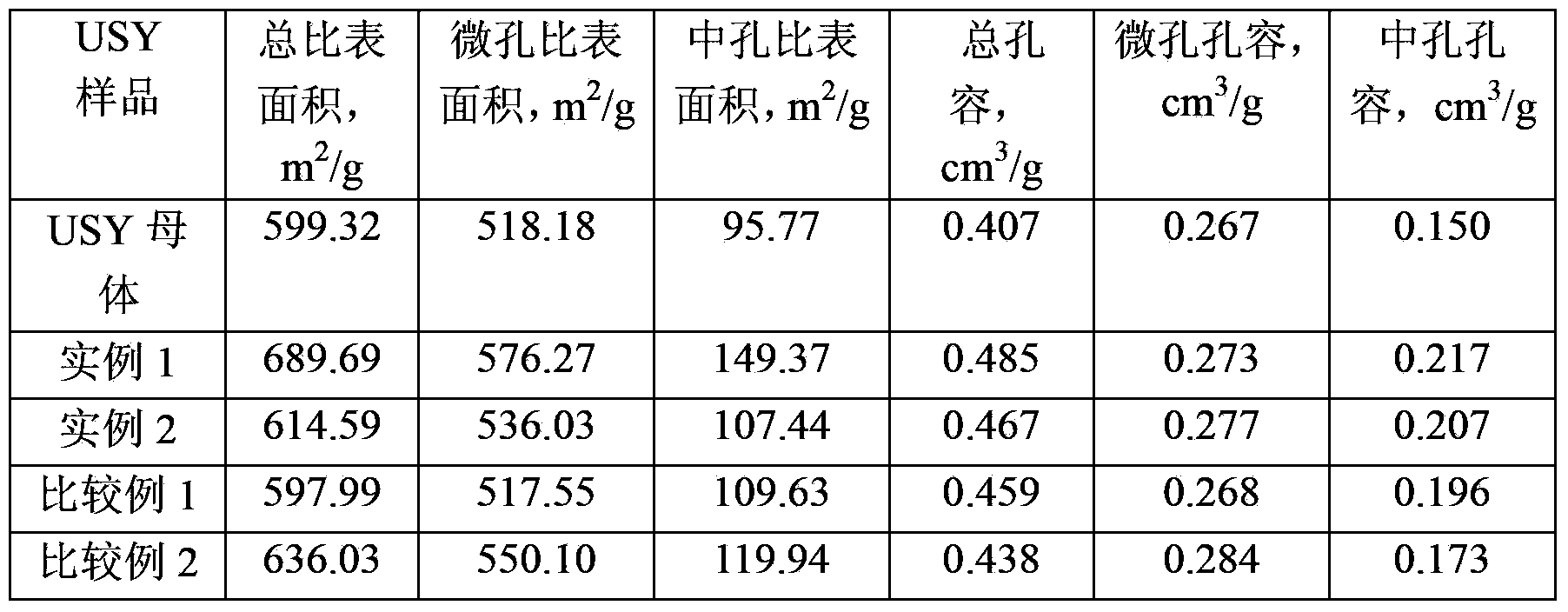
Method for modifying mesoporous-rich USY (Ultra-Stable Y) molecular sieve in combined manner
InactiveCN104229823ASmall cell constantIncreased secondary pore contentFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteInorganic saltsMolecular sieve
The invention relates to a method for modifying a USY (Ultra-Stable Y) molecular sieve. The method is characterized in that organic acid and an inorganic salt dealuminizing reagent are simultaneously added in a modifying process for organic acid-inorganic salt combined modification, and optimum process conditions, namely optimum concentration, volume ratio, reaction time, reaction temperature and the like, of an organic acid and an inorganic salt solution are determined by virtue of an orthogonal test. Compared with an industrial USY molecular sieve, the USY molecular sieve obtained by adopting the method disclosed by the invention is obviously increased in secondary pore content, can be kept at higher crystallinity and is enhanced in silica-alumina ratio, reduced in lattice constant and suitable for high-medium oil type hydrocracking catalyst carriers.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
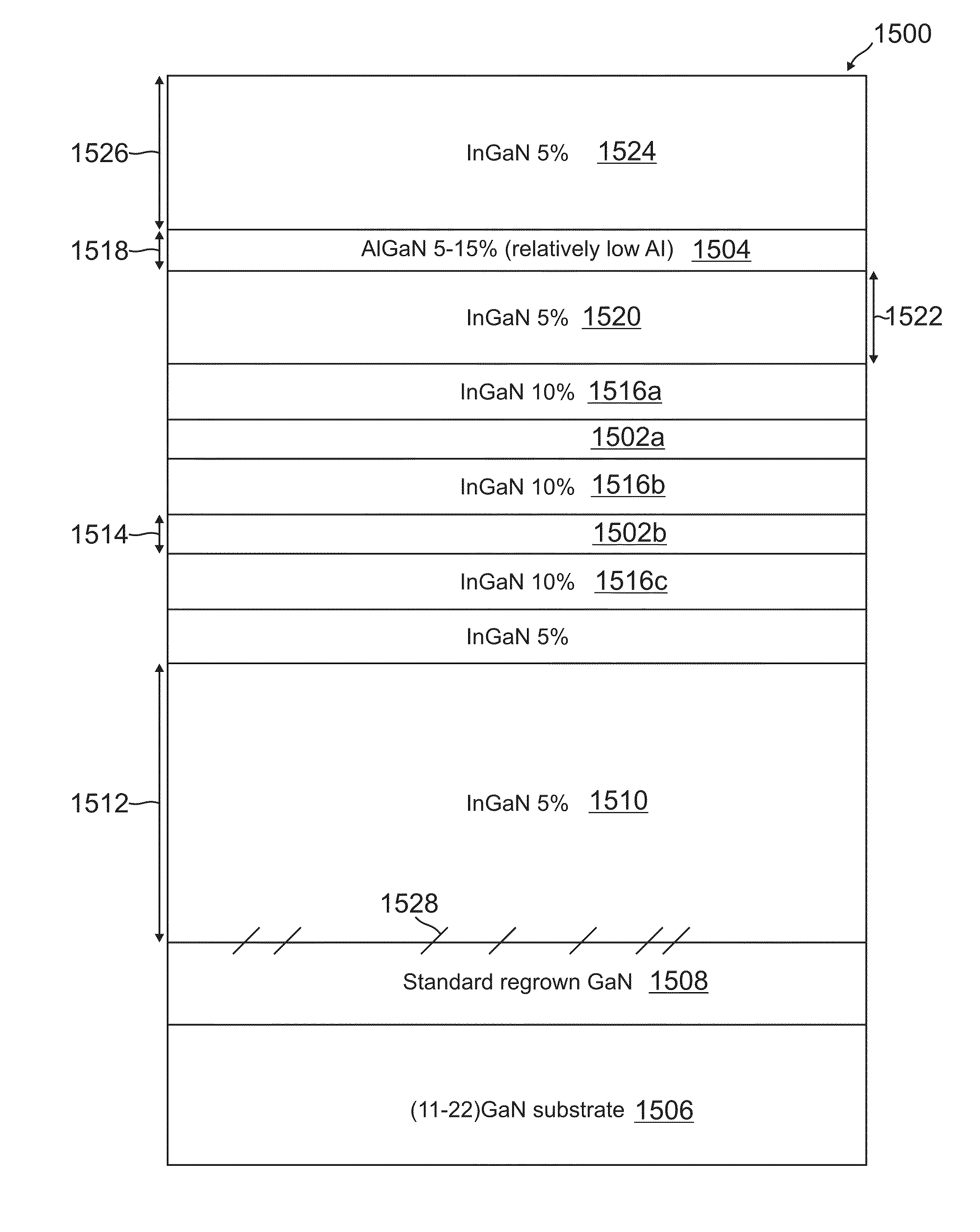
Semipolar nitride-based devices on partially or fully relaxed alloys with misfit dislocations at the heterointerface
ActiveUS20110064103A1Quality improvementImprovement ingredientsPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsAlloyLattice constant
A dislocation-free high quality template with relaxed lattice constant, fabricated by spatially restricting misfit dislocation(s) around heterointerfaces. This can be used as a template layer for high In composition devices. Specifically, the present invention prepares high quality InGaN templates (In composition is around 5-10%), and can grow much higher In-composition InGaN quantum wells (QWs) (or multi quantum wells (MQWs)) on these templates than would otherwise be possible.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor light emitting devices grown on composite substrates
ActiveUS20100072489A1Relieve pressureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureComposite substrate
A plurality of III-nitride semiconductor structures, each comprising a light emitting layer disposed between an n-type region and a p-type region, are grown on a composite substrate. The composite substrate includes a plurality of islands of III-nitride material connected to a host by a bonding layer. The plurality of III-nitride semiconductor structures are grown on the III-nitride islands. The composite substrate may be formed such that each island of III-nitride material is at least partially relaxed. As a result, the light emitting layer of each semiconductor structure has an a-lattice constant greater than 3.19 angstroms.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Nitride-based semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070145390A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialNon doped
A nitride-based semiconductor device includes a diode provided on a semiconductor substrate. The diode contains a first nitride-based semiconductor layer made of non-doped AlXGa1-XN (0≦X<1); a second nitride-based semiconductor layer made of non-doped or n-type AlYGa1-YN (0≦Y≦1, X<Y) having a lattice constant smaller than that of the first nitride-based semiconductor layer; a first electrode formed on the second nitride-based semiconductor layer; a second electrode formed on the second nitride-based semiconductor layer; and an insulating film that covers the second nitride-based semiconductor layer below a peripheral portion of the first electrode. In the diode, a recess structure portion is formed at a position near the peripheral portion of the first electrode on the second nitride-based semiconductor layer, and the first electrode covers the second nitride-based semiconductor layer and at least a part of the insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com