Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2913 results about "Photocurrent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
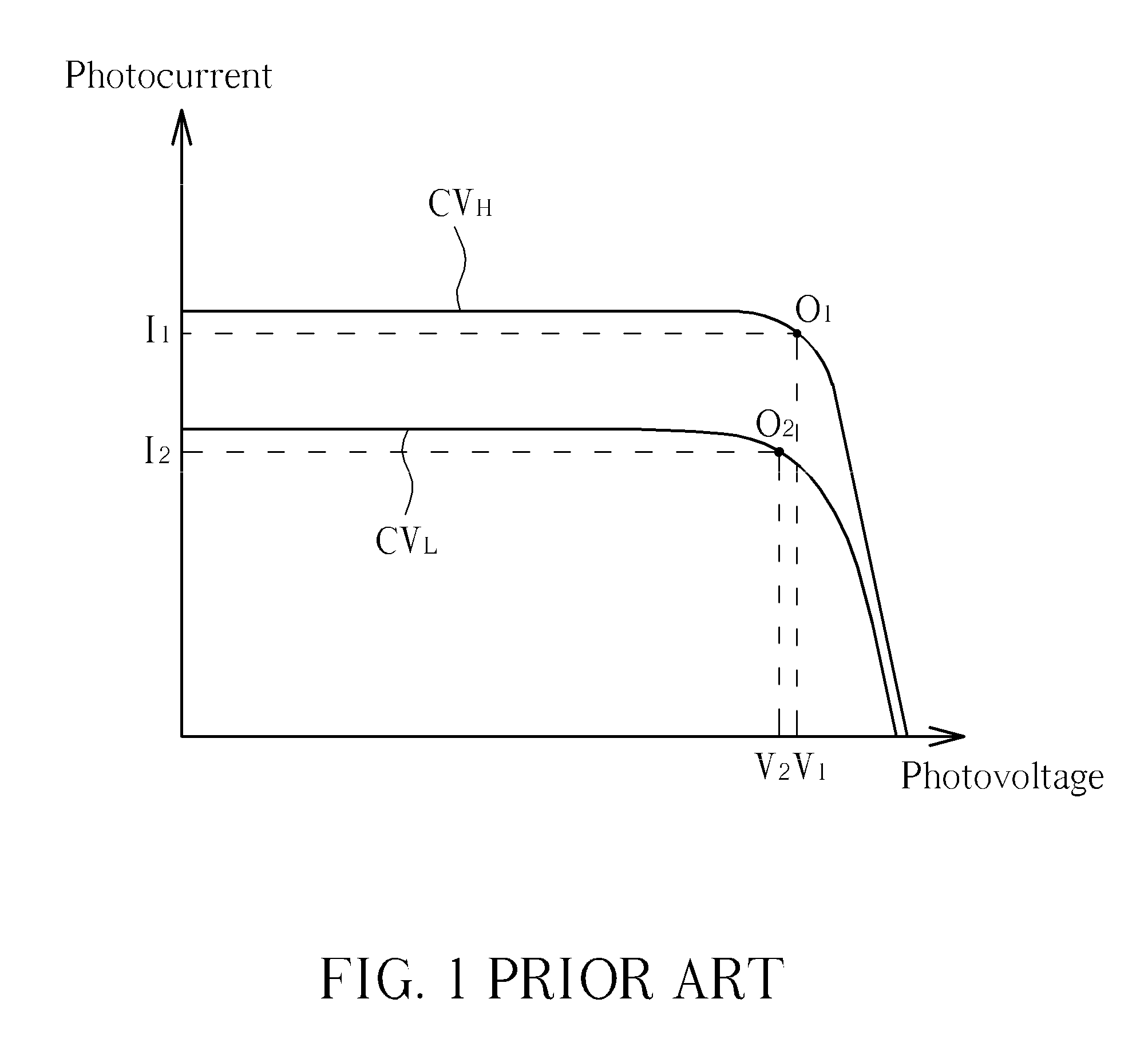
Photocurrent is the electric current through a photosensitive device, such as a photodiode, as the result of exposure to radiant power. The photocurrent may occur as a result of the photoelectric, photoemissive, or photovoltaic effect.
Silicon-based visible and near-infrared optoelectric devices
InactiveUS7057256B2Promote generationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsSurface layer
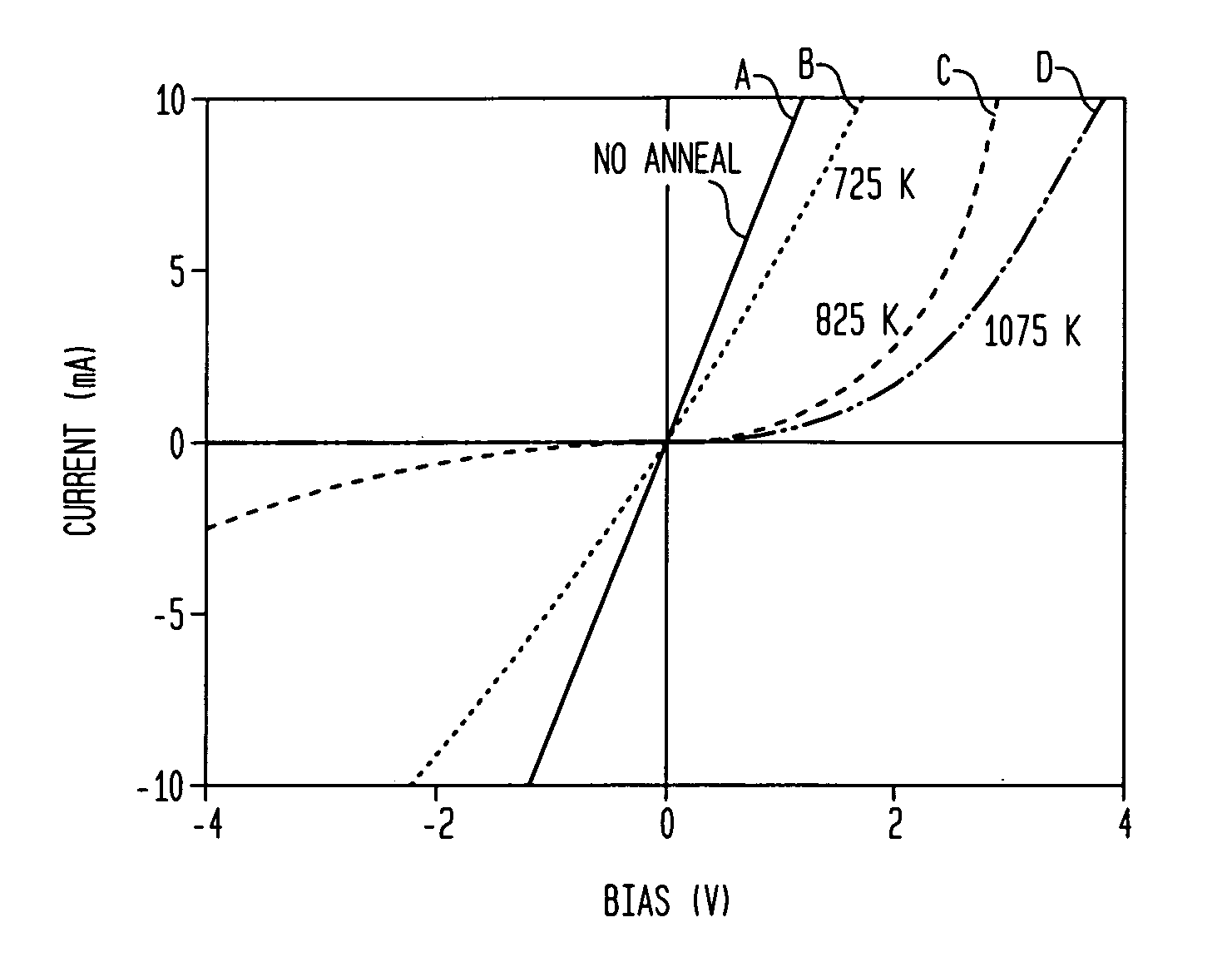
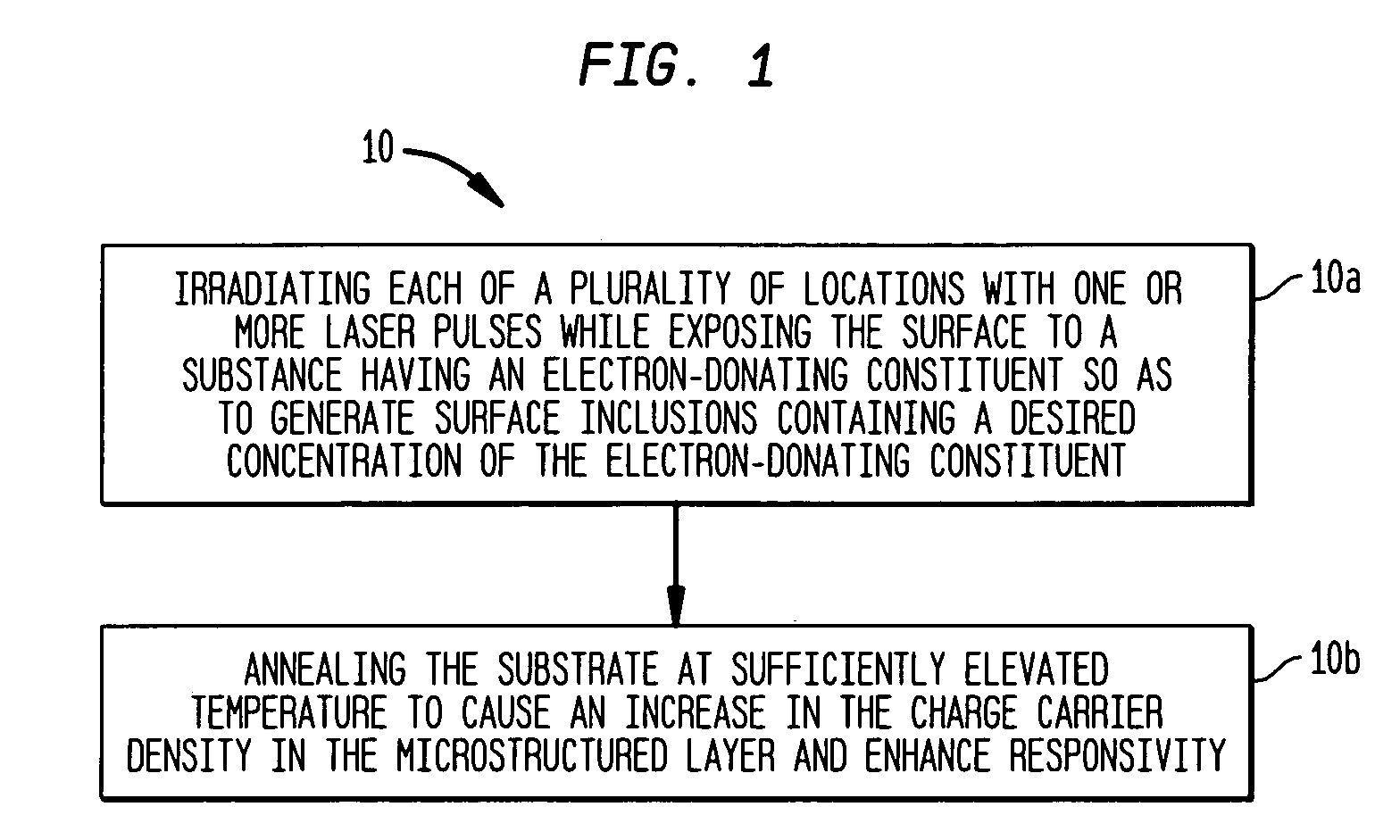
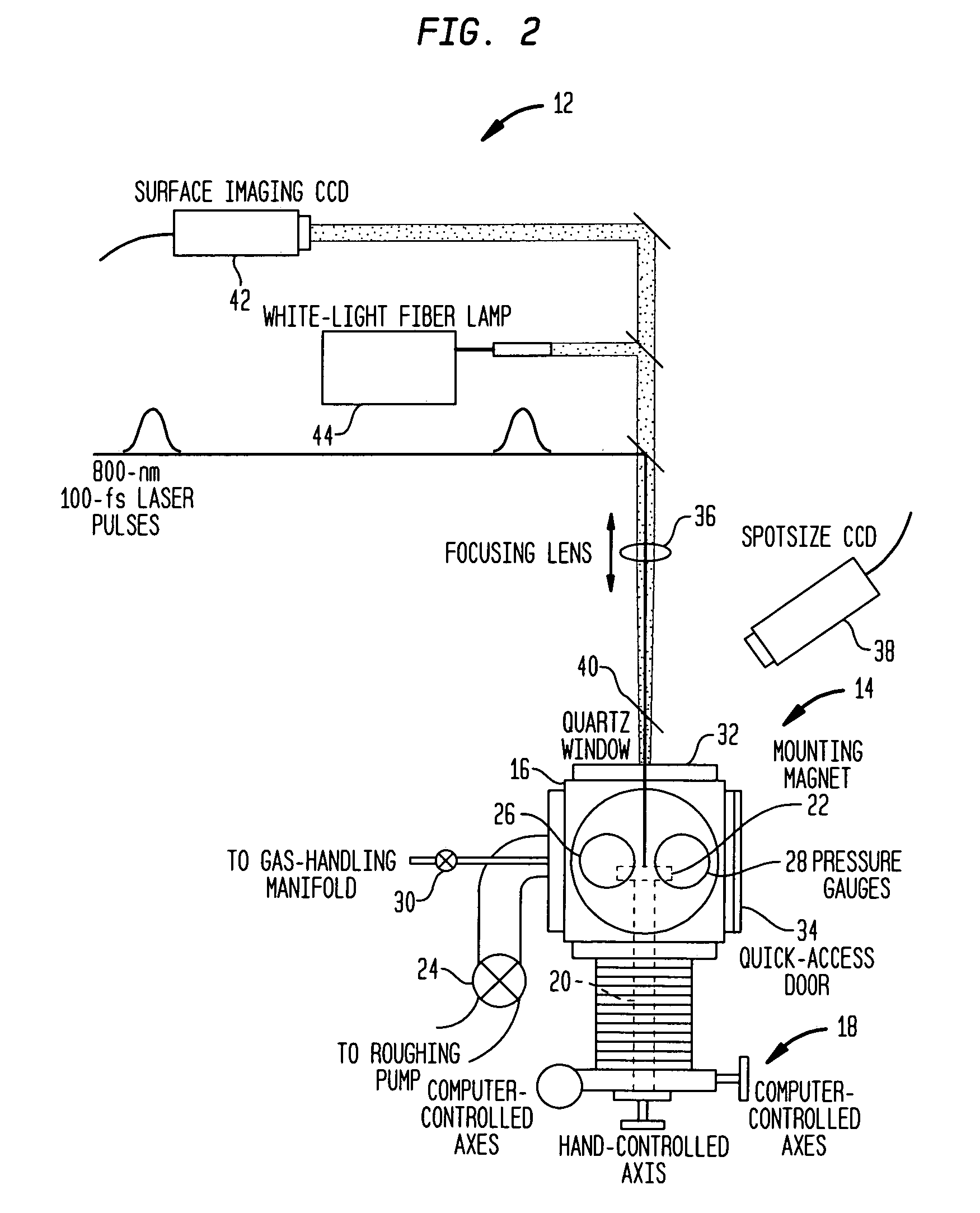
In one aspect, the present invention provides a silicon photodetector having a surface layer that is doped with sulfur inclusions with an average concentration in a range of about 0.5 atom percent to about 1.5 atom percent. The surface layer forms a diode junction with an underlying portion of the substrate. A plurality of electrical contacts allow application of a reverse bias voltage to the junction in order to facilitate generation of an electrical signal, e.g., a photocurrent, in response to irradiation of the surface layer. The photodetector exhibits a responsivity greater than about 1 A / W for incident wavelengths in a range of about 250 nm to about 1050 nm, and a responsivity greater than about 0.1 A / W for longer wavelengths, e.g., up to about 3.5 microns.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
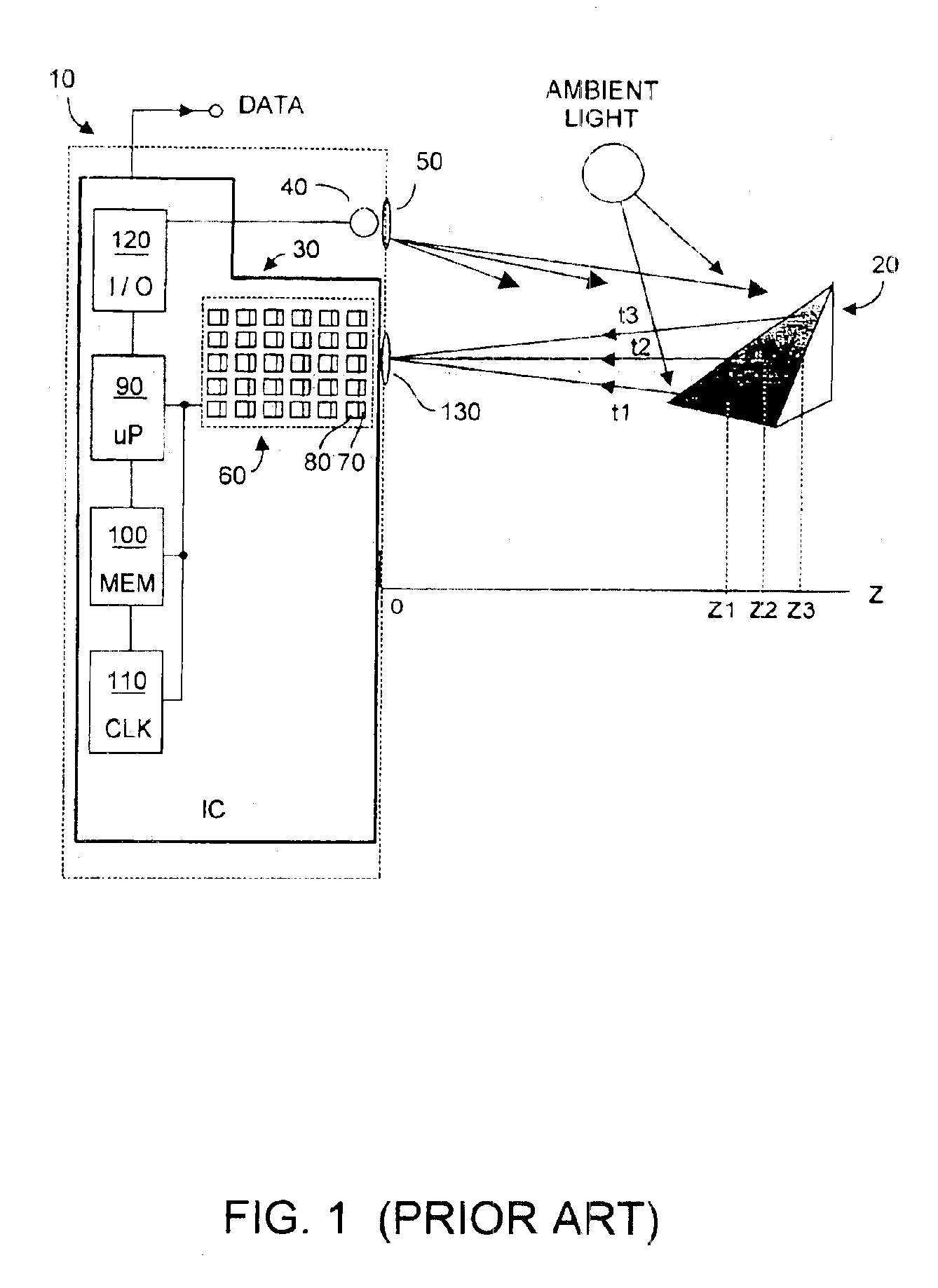
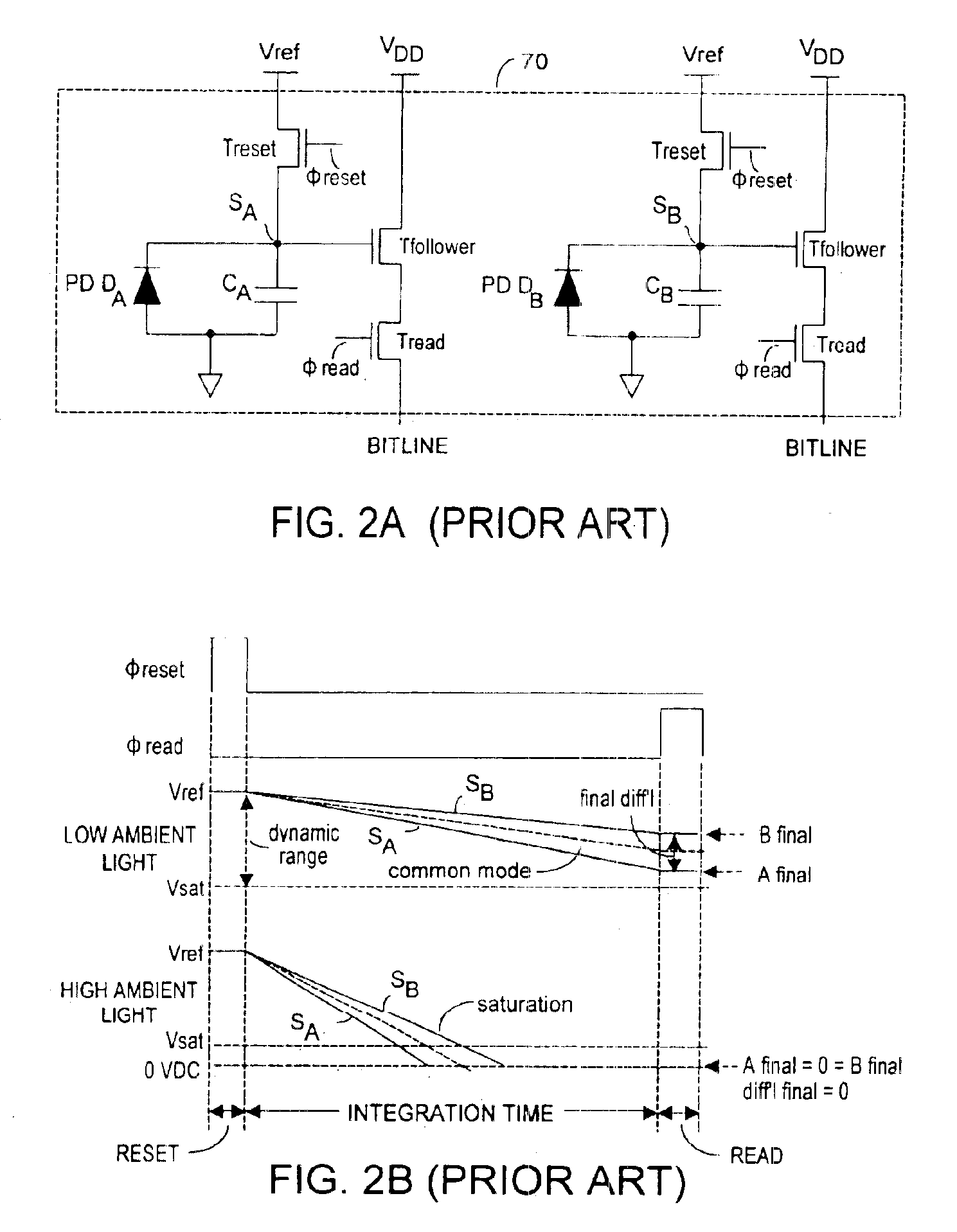
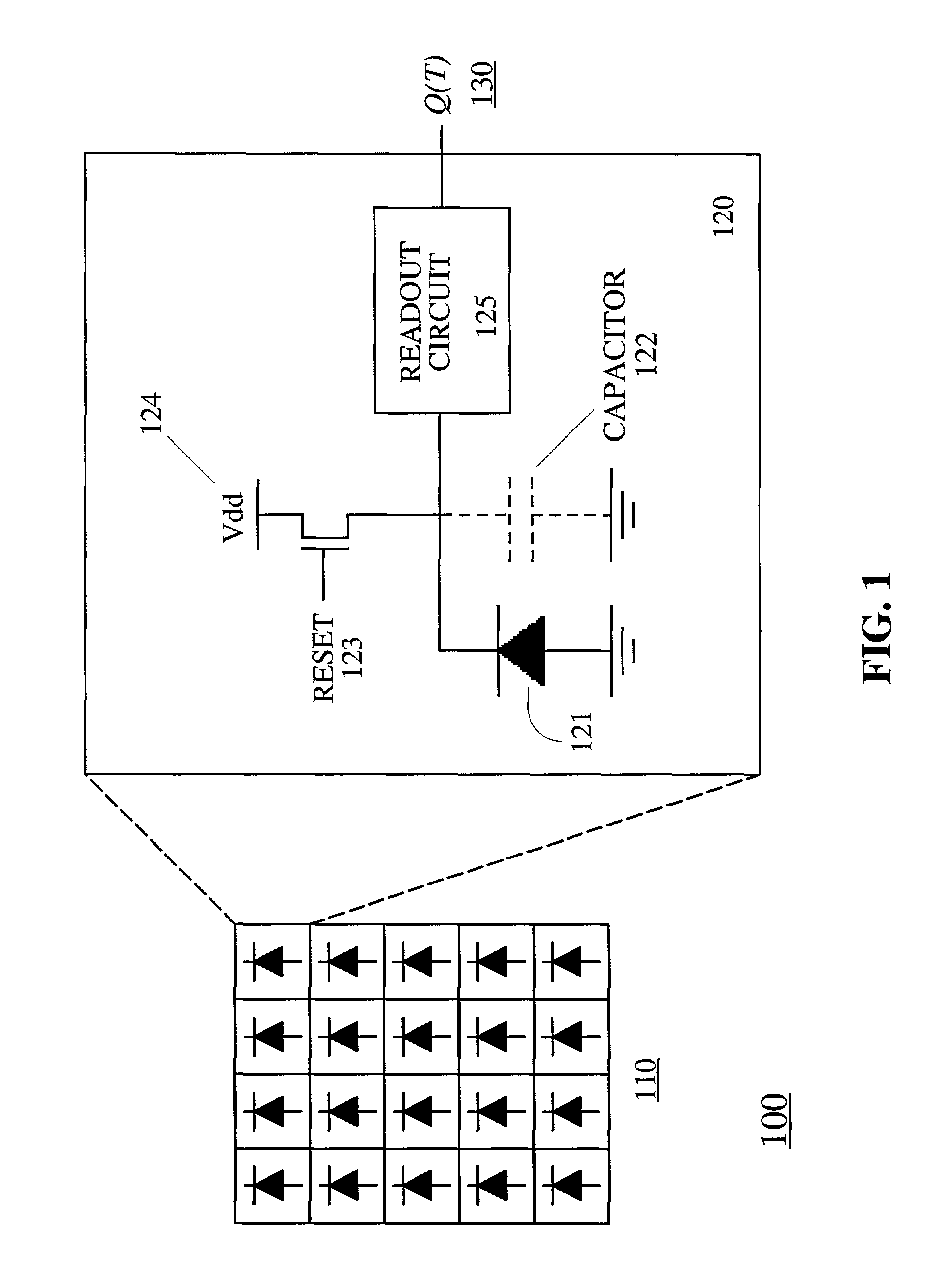
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range
InactiveUS6919549B2Effective dynamic rangeInhibition effectTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
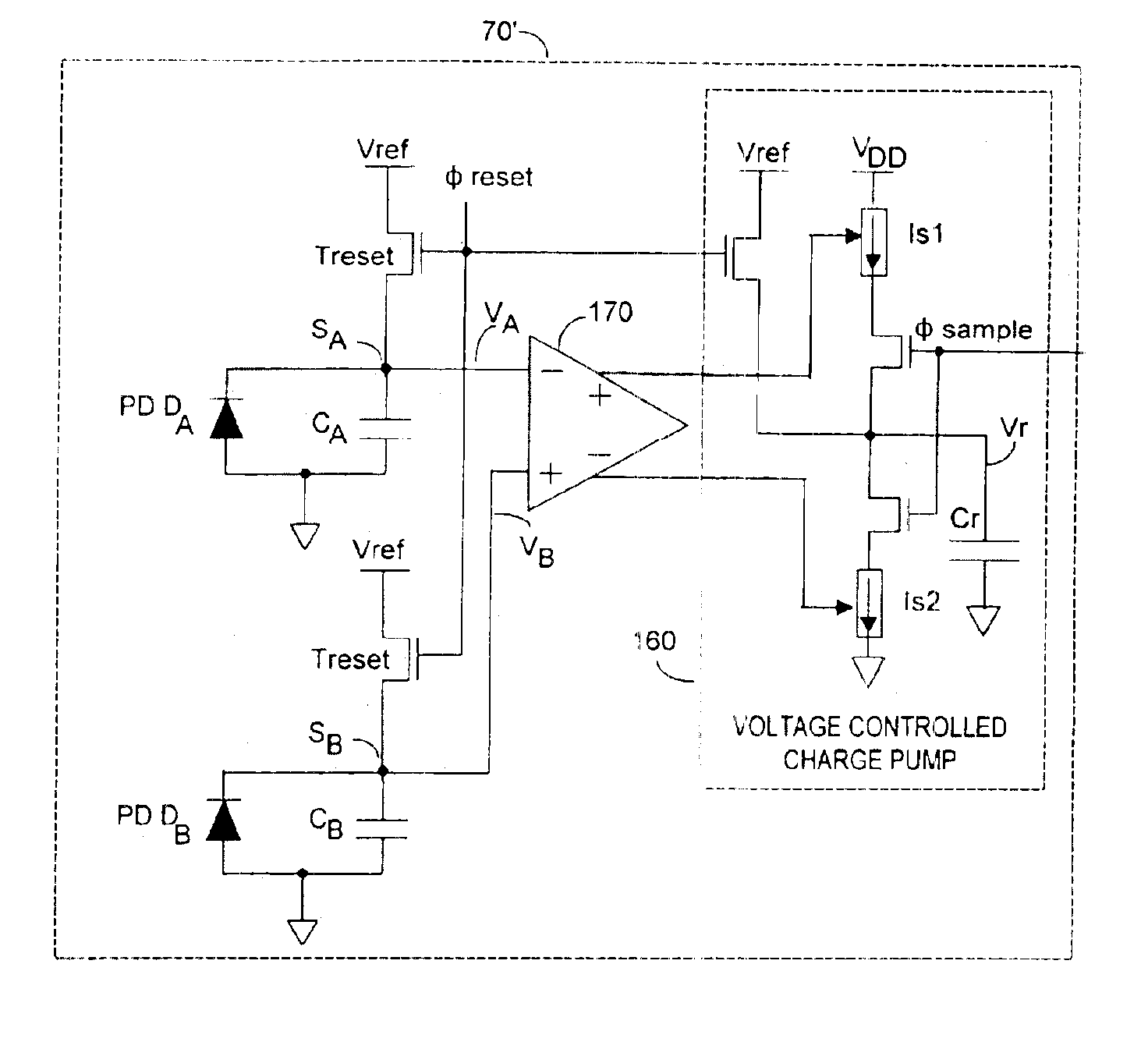
Effective differential dynamic range in a differential pixel detector is increased by avoiding saturation effects due to common mode contribution in optical energy to be detected. Photocurrent generated by each photodetector pair is directly integrated by an associated capacitor over an integration time T. Within time T, before either integrated capacitor voltage reaches Vsat for the photodetector, at least one of the capacitors is reset to a voltage such that the desired differential detector signal is still determinable. Reset may be generated externally or internally to the differential pixel detector.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
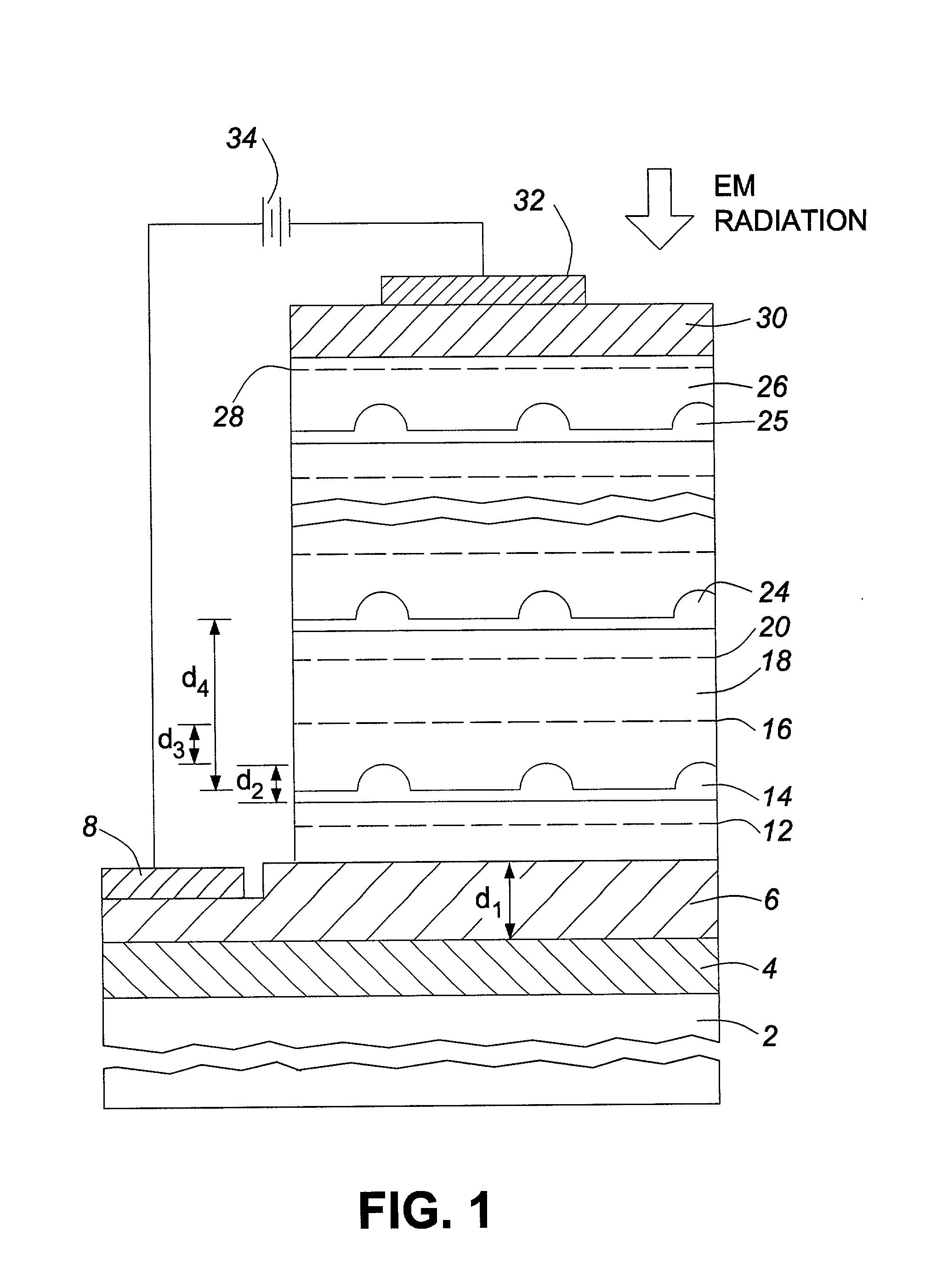
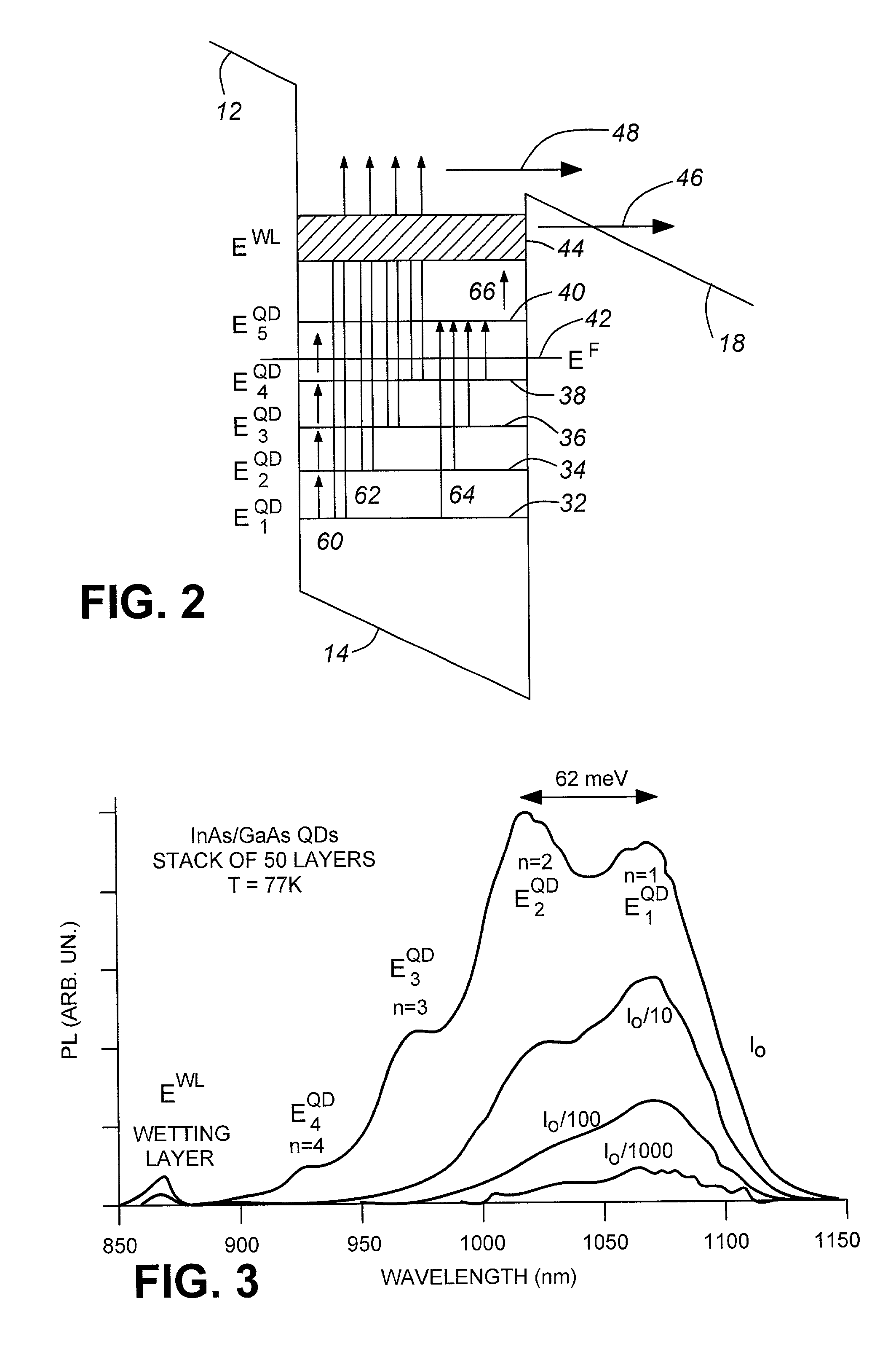
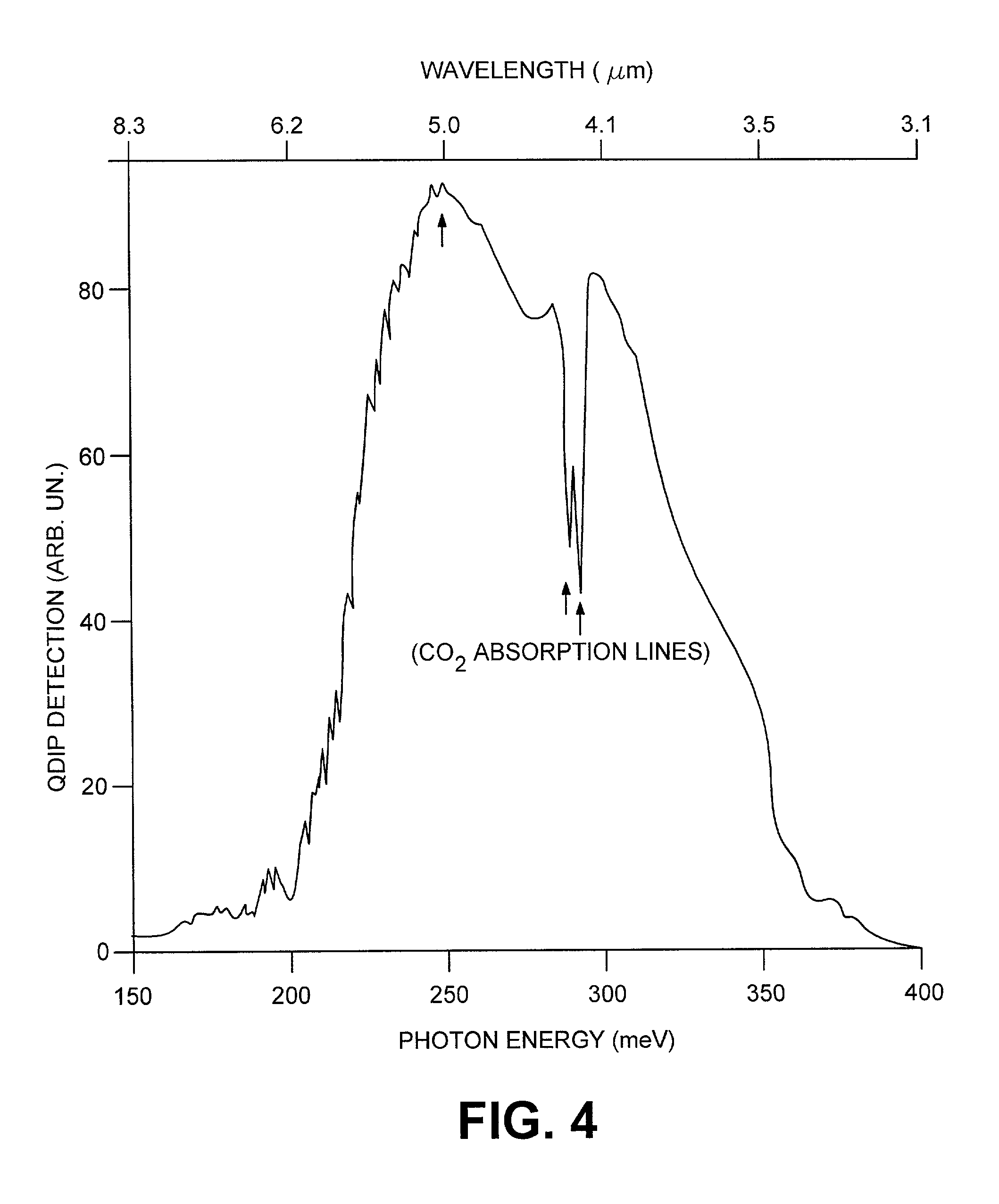
Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIP)
InactiveUS6239449B1Quality improvementNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum dot infrared photodetectorsPhotodetector
A photodetector capable of normal incidence detection over a broad range of long wavelength light signals to efficiently convert infrared light into electrical signals. It is capable of converting long wavelength light signals into electrical signals with direct normal incidence sensitivity without the assistance of light coupling devices or schemes. In the apparatus, stored charged carriers are ejected by photons from quantum dots, then flow over the other barrier and quantum dot layers with the help of an electric field produced with a voltage applied to the device, producing a detectable photovoltage and photocurrent. The photodetector has multiple layers of materials including at least one quantum dot layer between an emitter layer and a collector layer, with a barrier layer between the quantum dot layer and the emitter layer, and another barrier layer between the quantum dot layer and the collector.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
LADAR transmitting and receiving system and method
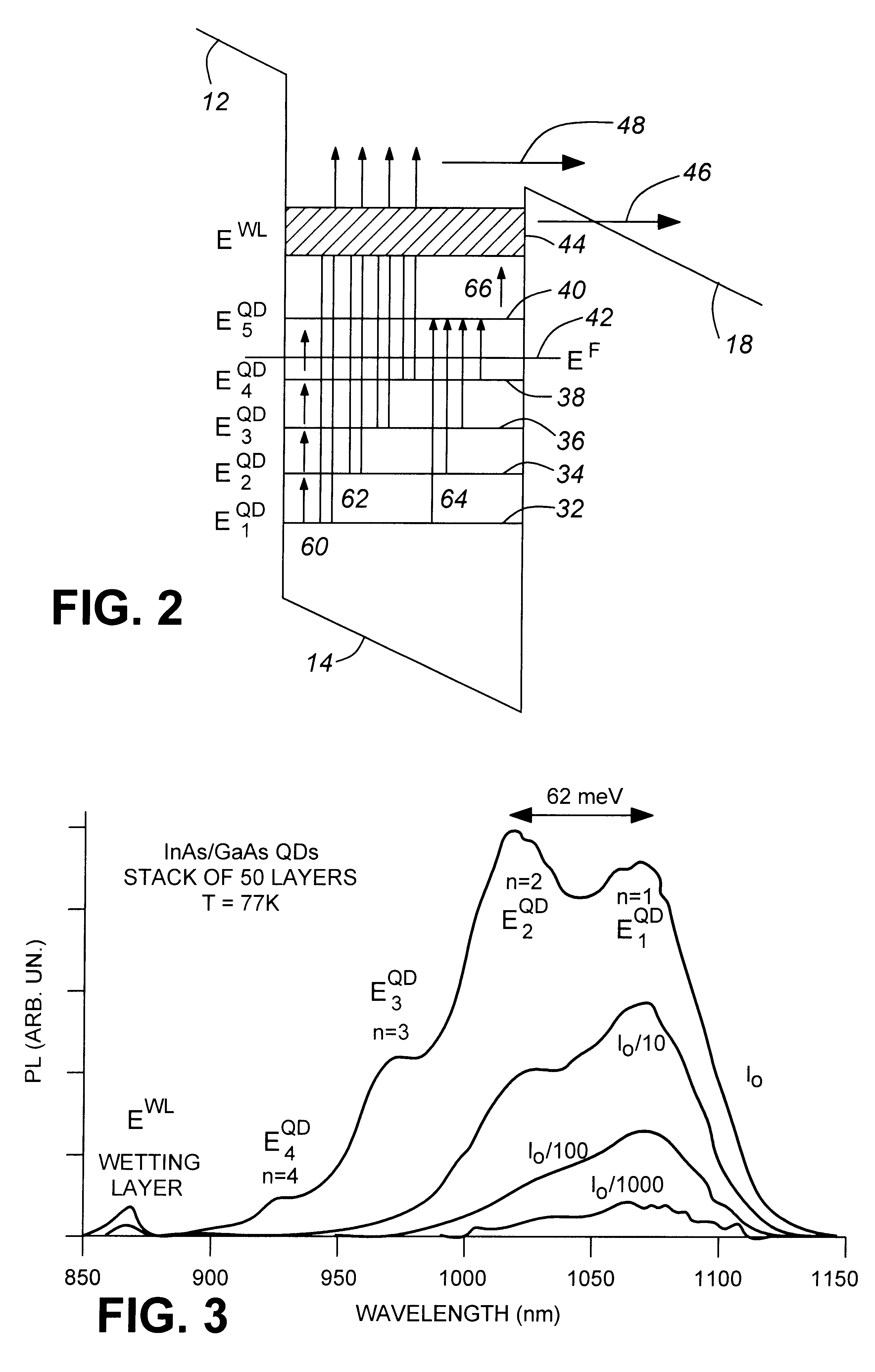
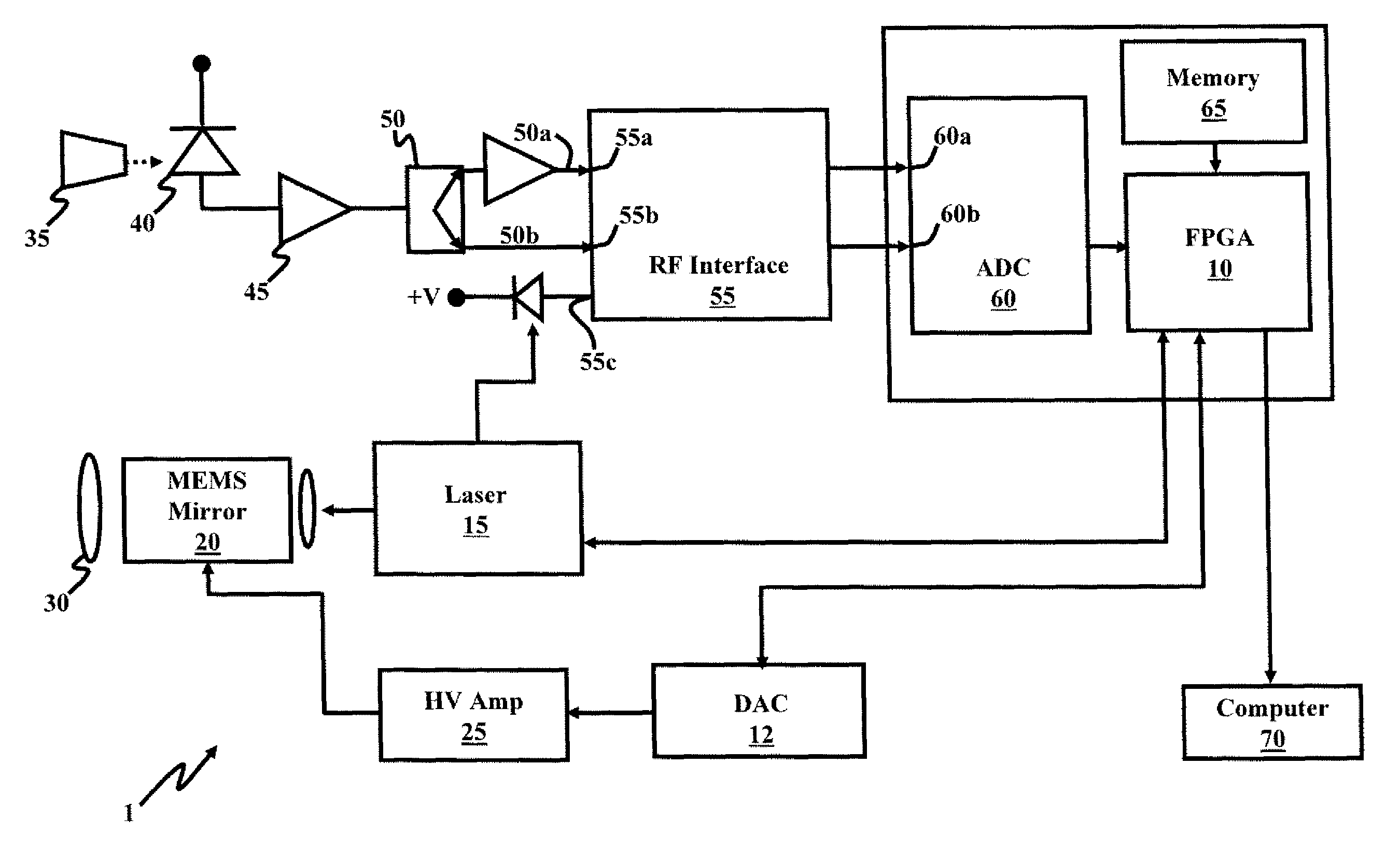
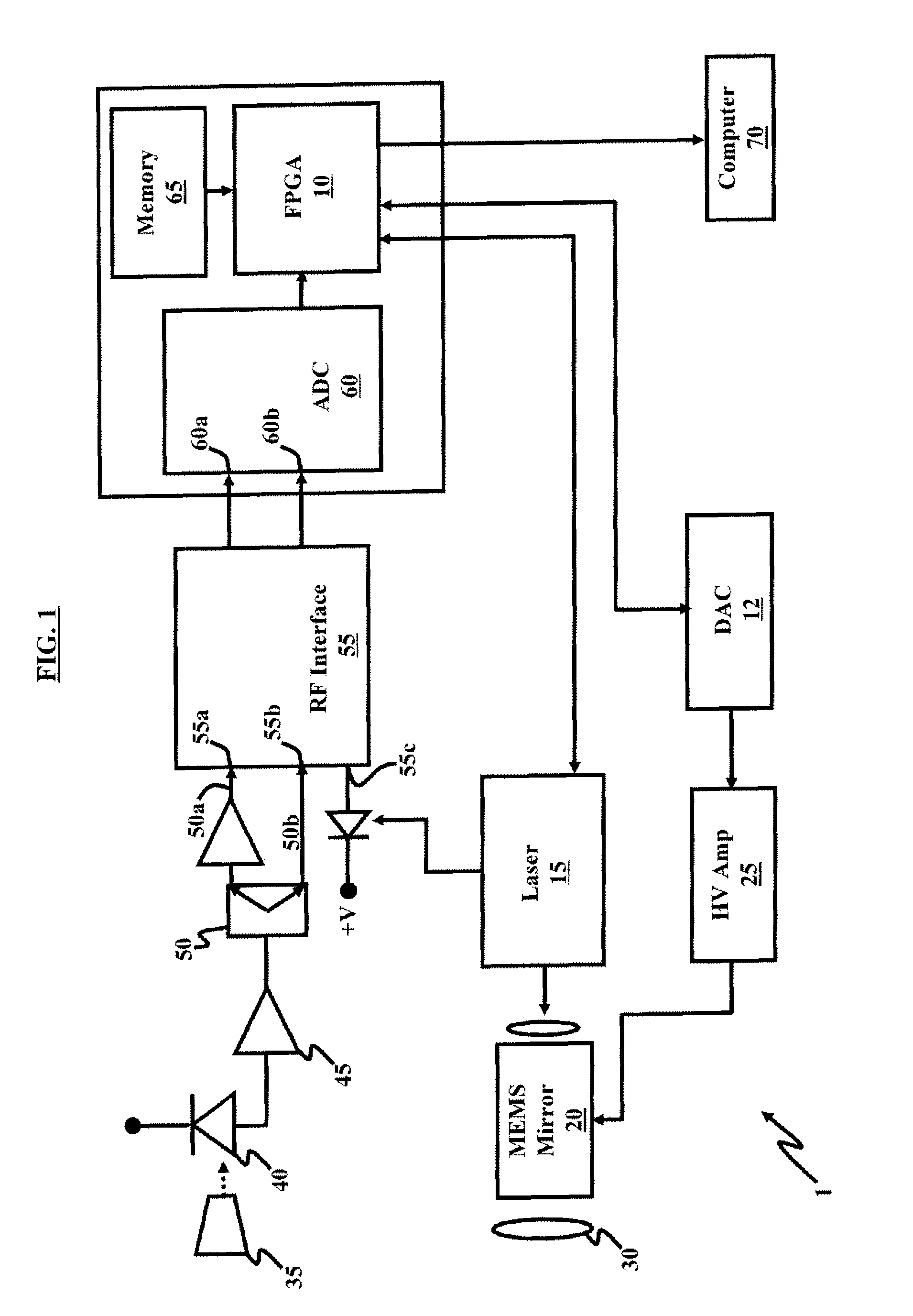
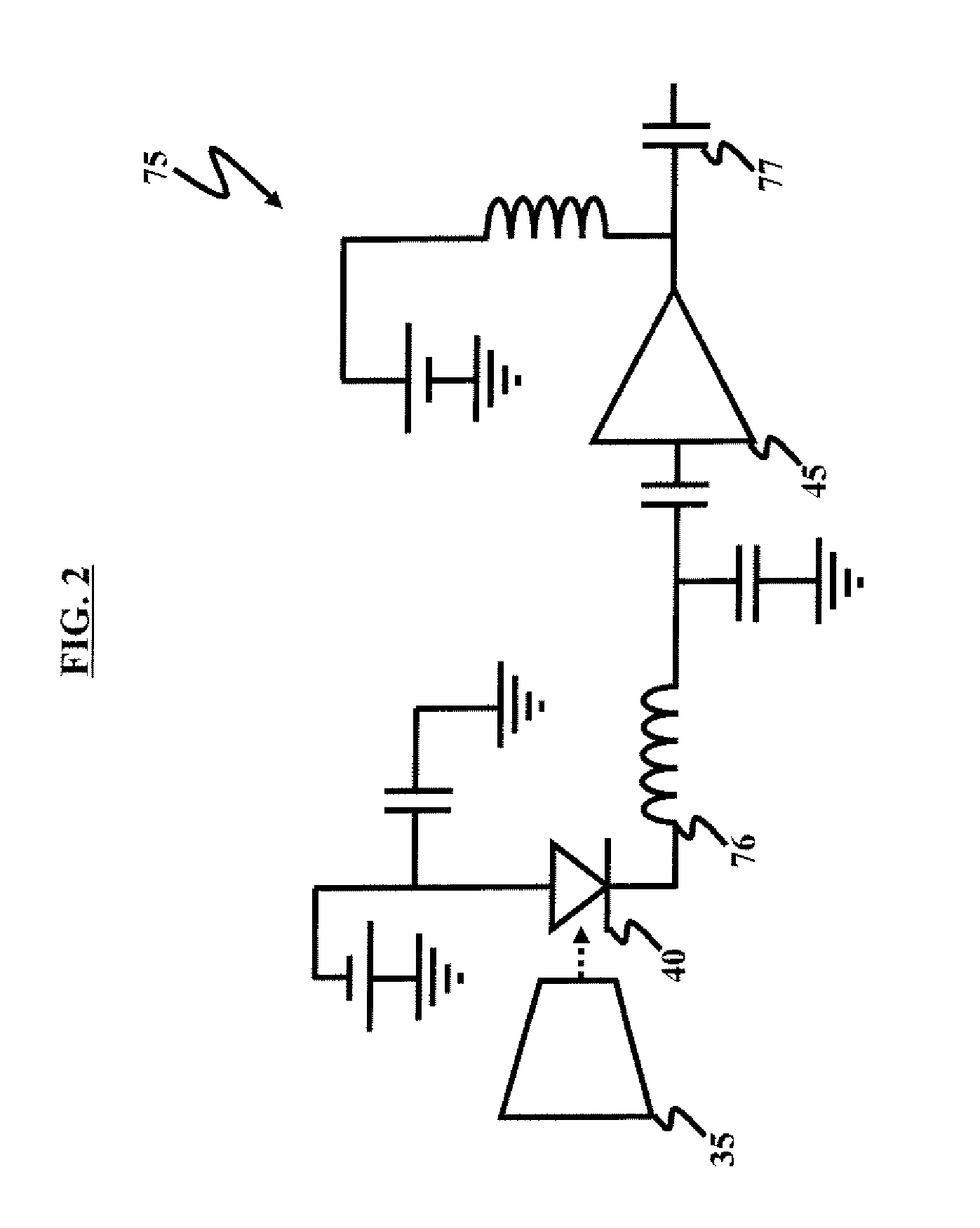
A compact LADAR transmitting and receiving apparatus includes a pulse laser generating pulses of light; a transmitter collimating and directing the pulses of light toward a target; a receiver collecting reflected pulses of light, the reflected pulses of light having been reflected from the target, the receiver comprising a tapered fiber bundle; a sensor operatively connected to the tapered fiber bundle, where the sensor comprises a photosensitive region and outputs a photocurrent; an amplifier amplifying the photocurrent; and a power divider splitting the amplified photocurrent between a high gain channel and a low gain channel; a RF interface accepting the high gain channel, the low gain channel, and an undelayed sample of a pulse of light generated from the pulse laser as input; a processing unit accepting output from the RF interface; and a display unit displaying output from the processing unit.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
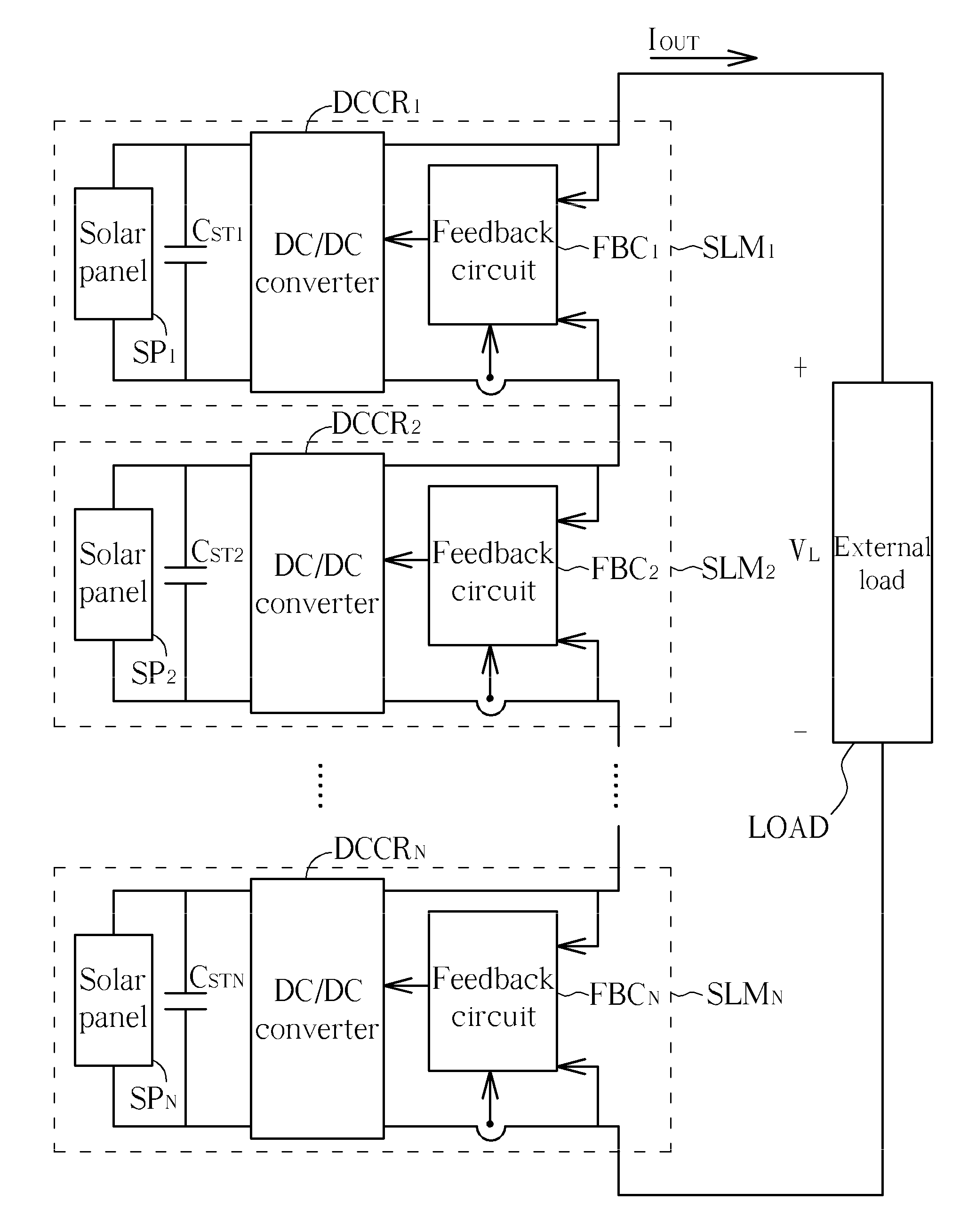
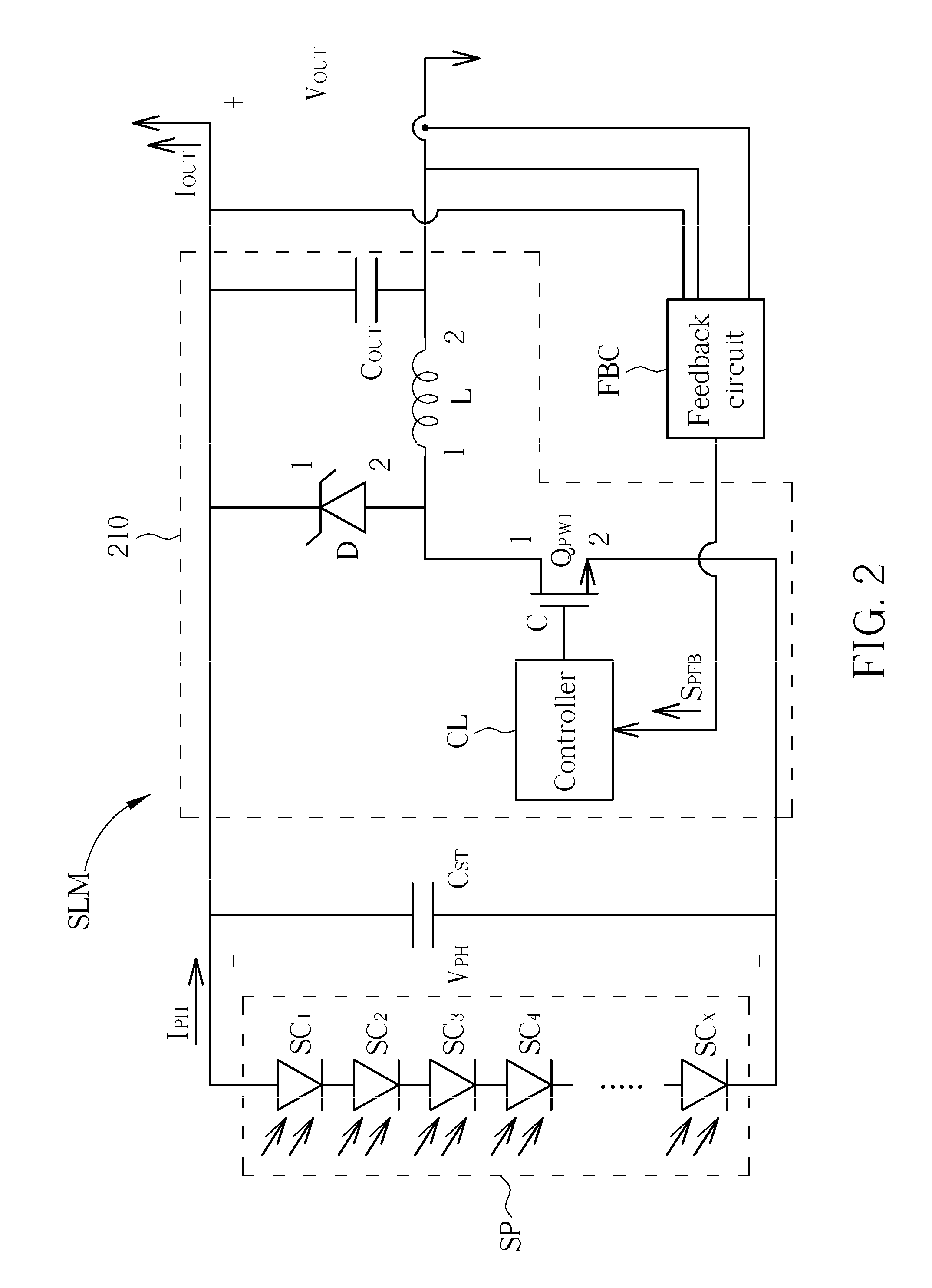
Series solar system with current-matching function
InactiveUS20110056533A1Increase powerDc network circuit arrangementsPV power plantsElectricityOperating point
A series solar system with current-matching function includes a plurality of solar modules. The plurality of the solar modules is electrically connected in series. Each solar module includes a DC / DC converter and a solar panel electrically connected in parallel. The photocurrent generated by the solar panel is matched with the current generated by the solar panel operating at the optimum operating point by means of adjusting the duty cycle of the DC / DC converter, so that the solar panel can generate maximum output power. Therefore, in the series solar system, even a solar module is covered, causing the received light intensity of the solar module is reduced, and the series solar system still can generate maximum output power.
Owner:INERGY TECH
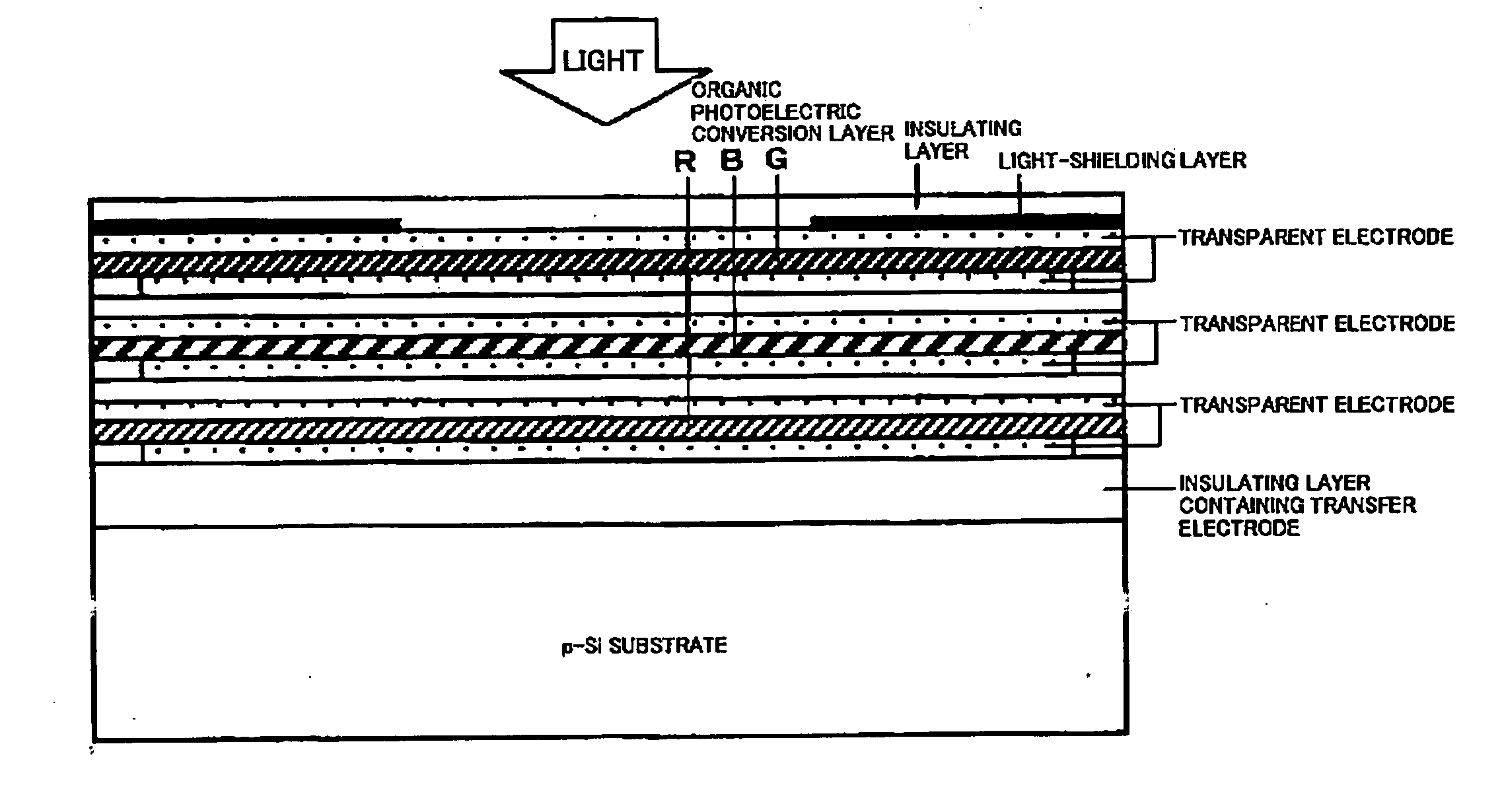
Organic photoelectric conversion device and stack type photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20070120045A1Total current dropReduce noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansOrganic layerPhotoelectric conversion
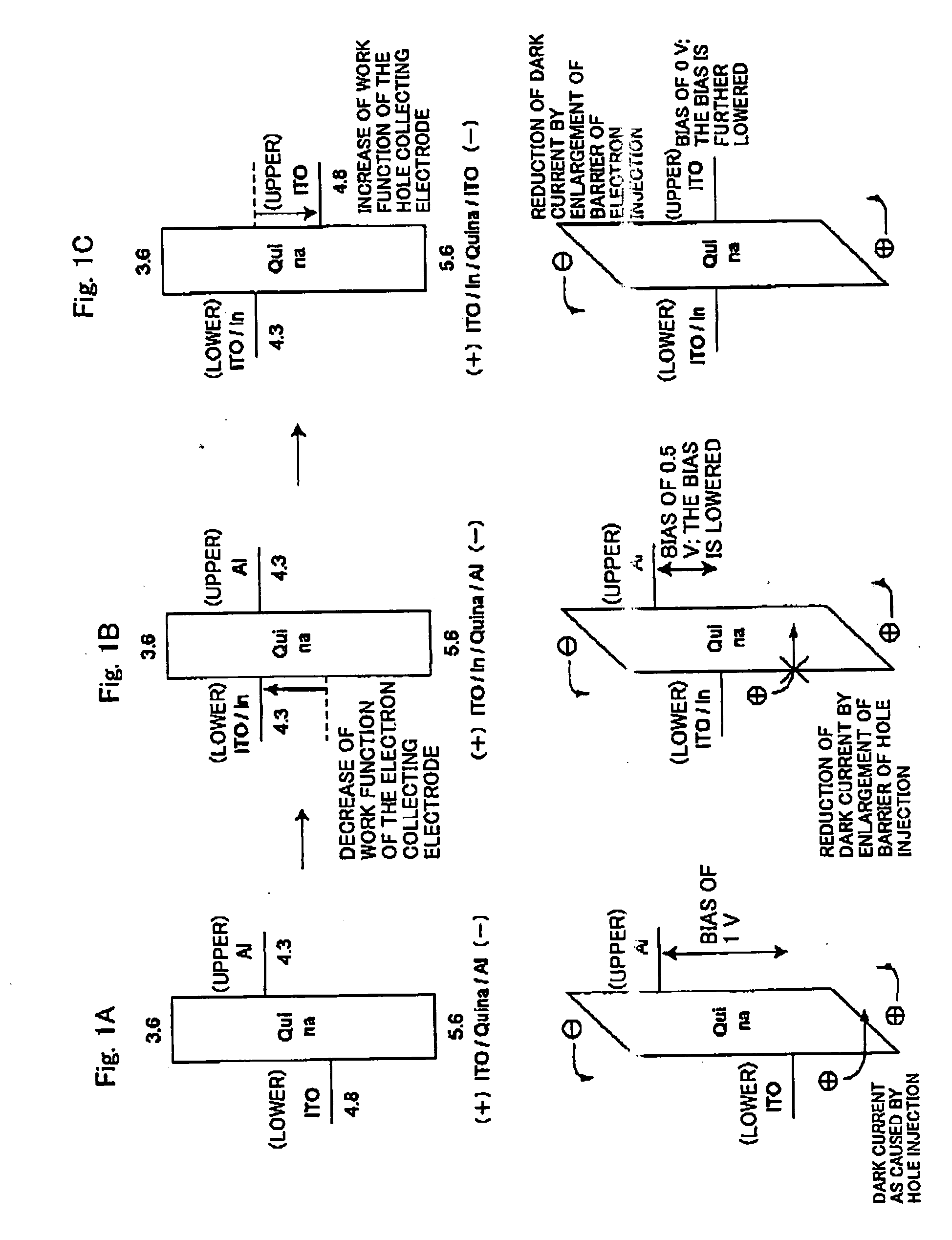
An organic photoelectric conversion device comprising; a lower electrode; an organic layer; and an upper electrode provided in this order, in which at least one of the lower electrode and the upper electrode is a transparent electrode and an electron is collected in a side of one of the lower electrode and the upper electrode and a hole is collected in a side of other of the lower electrode and the upper electrode so as to read out photocurrent, wherein the electrode in the side of collecting an electron is the transparent electrode and has a word function of 4.5 eV or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Solid state photosensitive devices which employ isolated photosynthetic complexes
ActiveUS20050098726A1Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementPhotosynthetic ComplexesSemiconductor materials
Solid state photosensitive devices including photovoltaic devices are provided which comprise a first electrode and a second electrode in superposed relation; and at least one isolated Light Harvesting Complex (LHC) between the electrodes. Preferred photosensitive devices comprise an electron transport layer formed of a first photoconductive organic semiconductor material, adjacent to the LHC, disposed between the first electrode and the LHC; and a hole transport layer formed of a second photoconductive organic semiconductor material, adjacent to the LHC, disposed between the second electrode and the LHC. Solid state photosensitive devices of the present invention may comprise at least one additional layer of photoconductive organic semiconductor material disposed between the first electrode and the electron transport layer; and at least one additional layer of photoconductive organic semiconductor material, disposed between the second electrode and the hole transport layer. Methods of generating photocurrent are provided which comprise exposing a photovoltaic device of the present invention to light. Electronic devices are provided which comprise a solid state photosensitive device of the present invention.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Monolithic photovoltaic energy conversion device
InactiveUS20070137698A1Solid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A multijunction, monolithic, photovoltaic (PV) cell and device (600) is provided for converting radiant energy to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The PV cell includes an array of subcells (602), i.e., active p / n junctions, grown on a compliant substrate, where the compliant substrate accommodates greater flexibility in matching lattice constants to adjacent semiconductor material. The lattice matched semiconductor materials are selected with appropriate band-gaps to efficiently create photovoltage from a larger portion of the solar spectrum. Subcell strings (601, 603) from multiple PV cells are voltage matched to provide high output PV devices. A light emitting cell and device is also provided having monolithically grown red-yellow and green emission subcells and a mechanically stacked blue emission subcell.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Communication using bi-directional LEDs
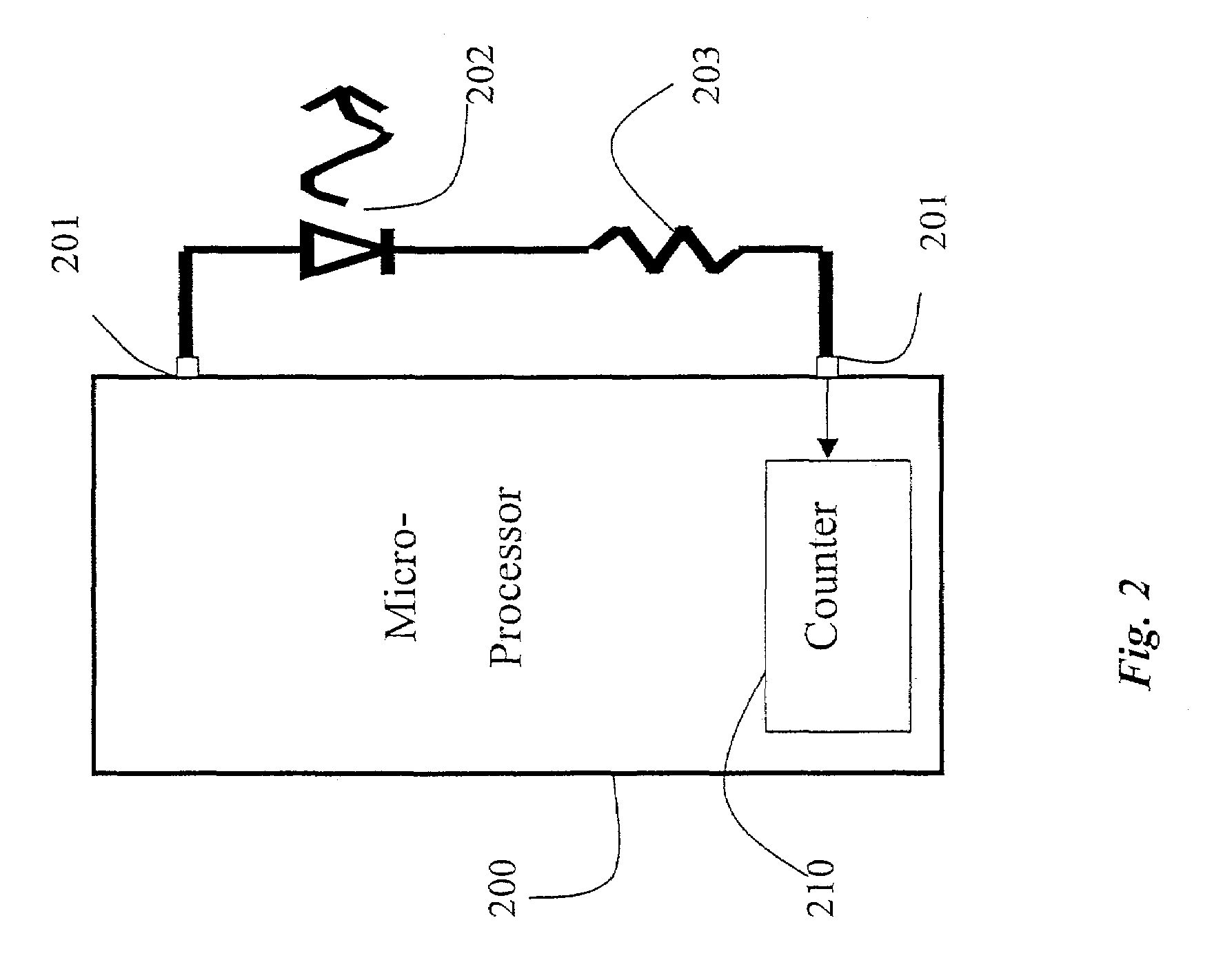
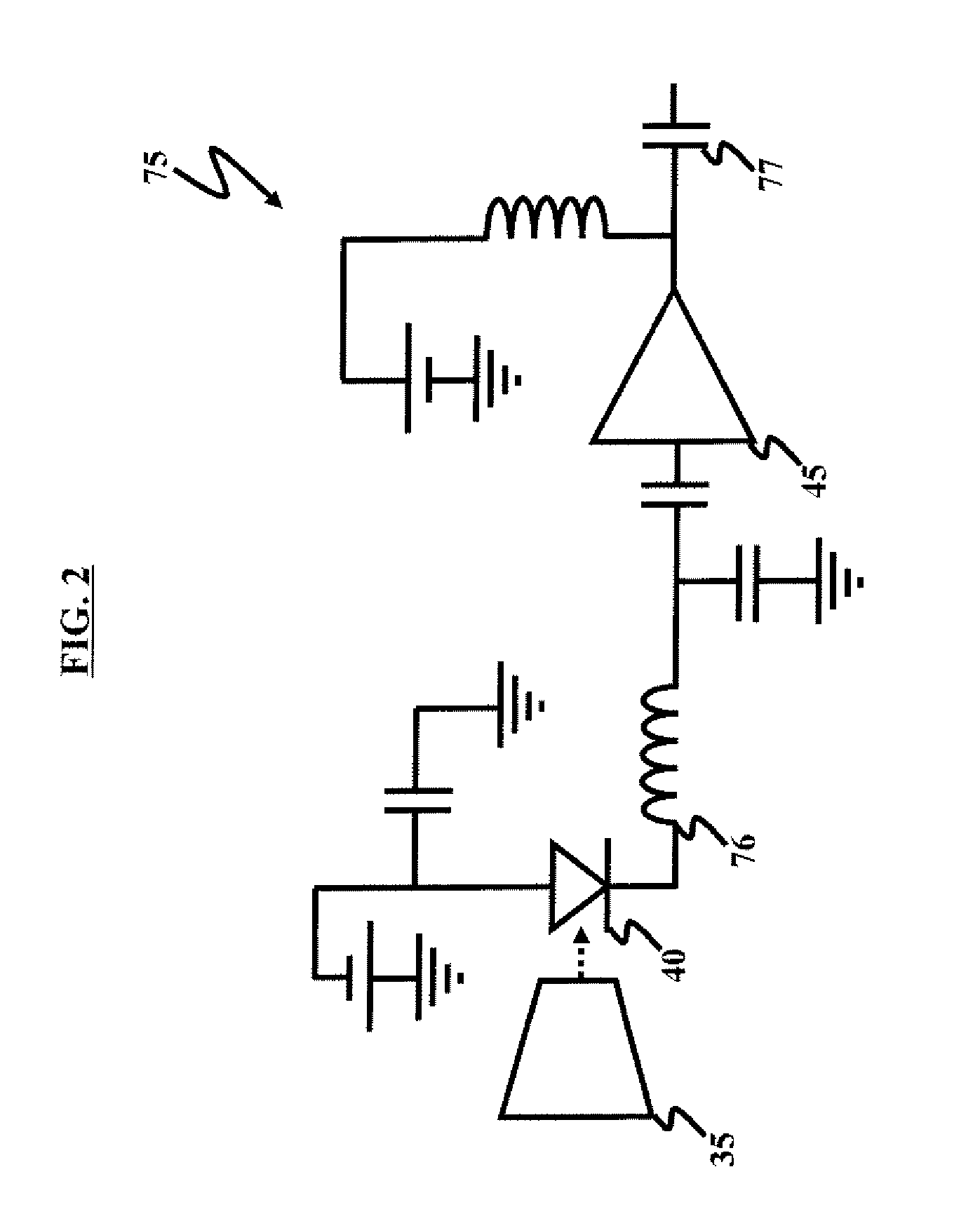
An optical communications transceiver includes an LED coupled in series with a resistor. A microprocessor has one I / O pin connected to the LED. In a first mode or transmit mode, the LED is periodically driving in forward bias to emit light to transmit data. In a second or receive mode, the LED is periodically not driven in reverse bias, e.g., reverse bias or zero bias. Then, the LED is allowed to change charge of the capacitance of the LED's junction using a photo-current. The change in charge is measured using a timer. When the change in charge exceeds a predetermined threshold, input light is sensed. Thus, the LED can be used to receive data in the second mode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Flame sensor with dynamic sensitivity adjustment
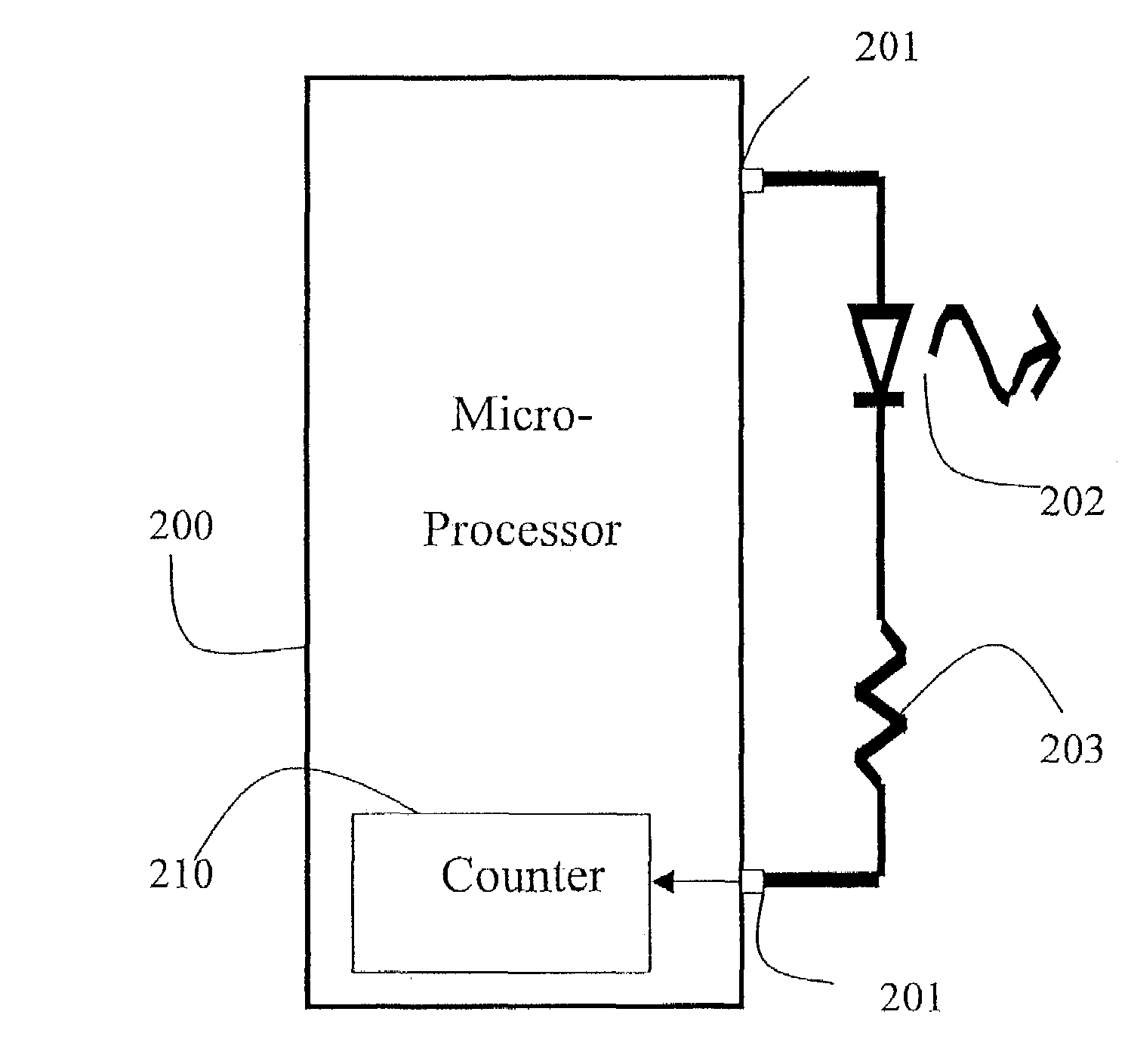
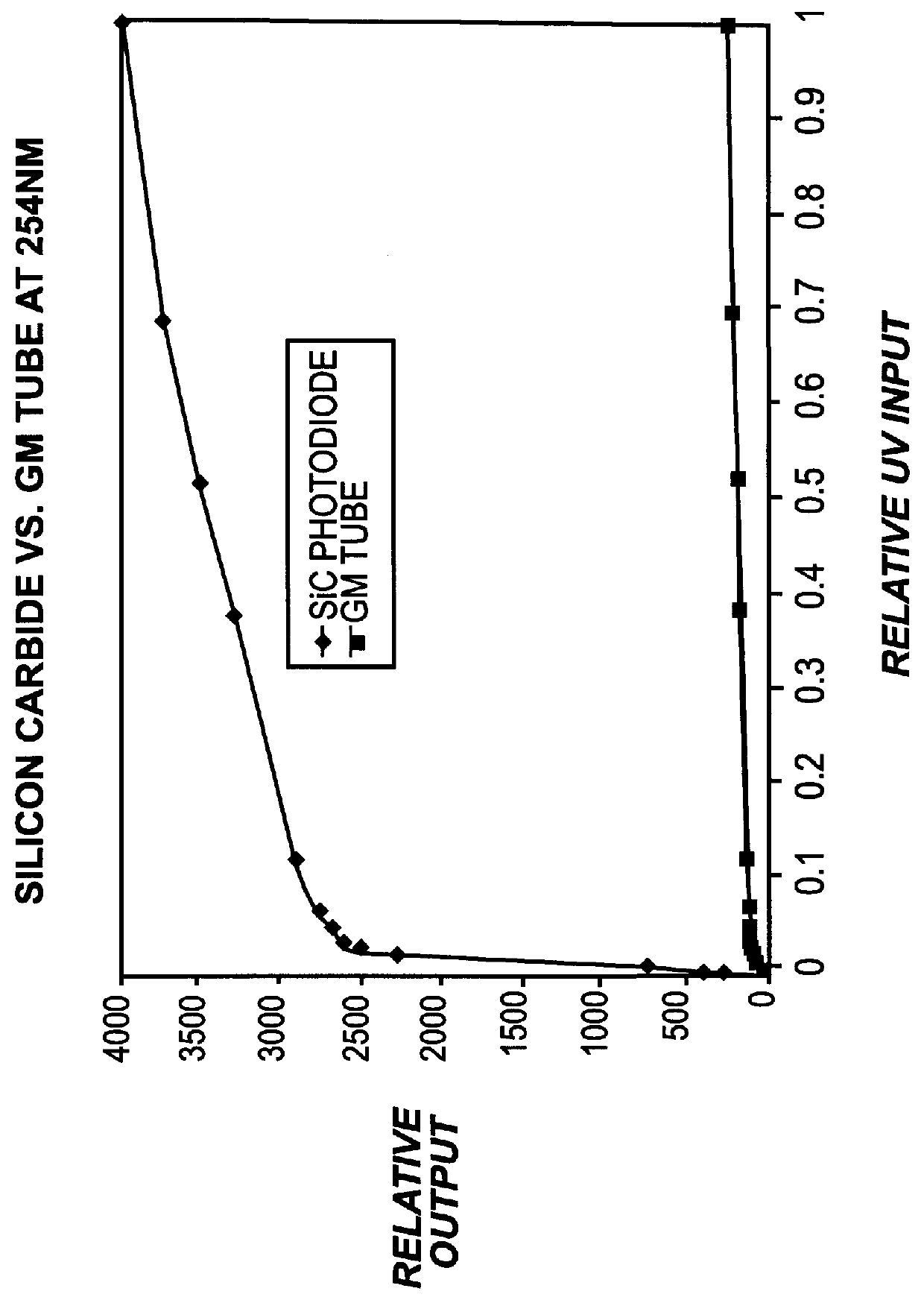
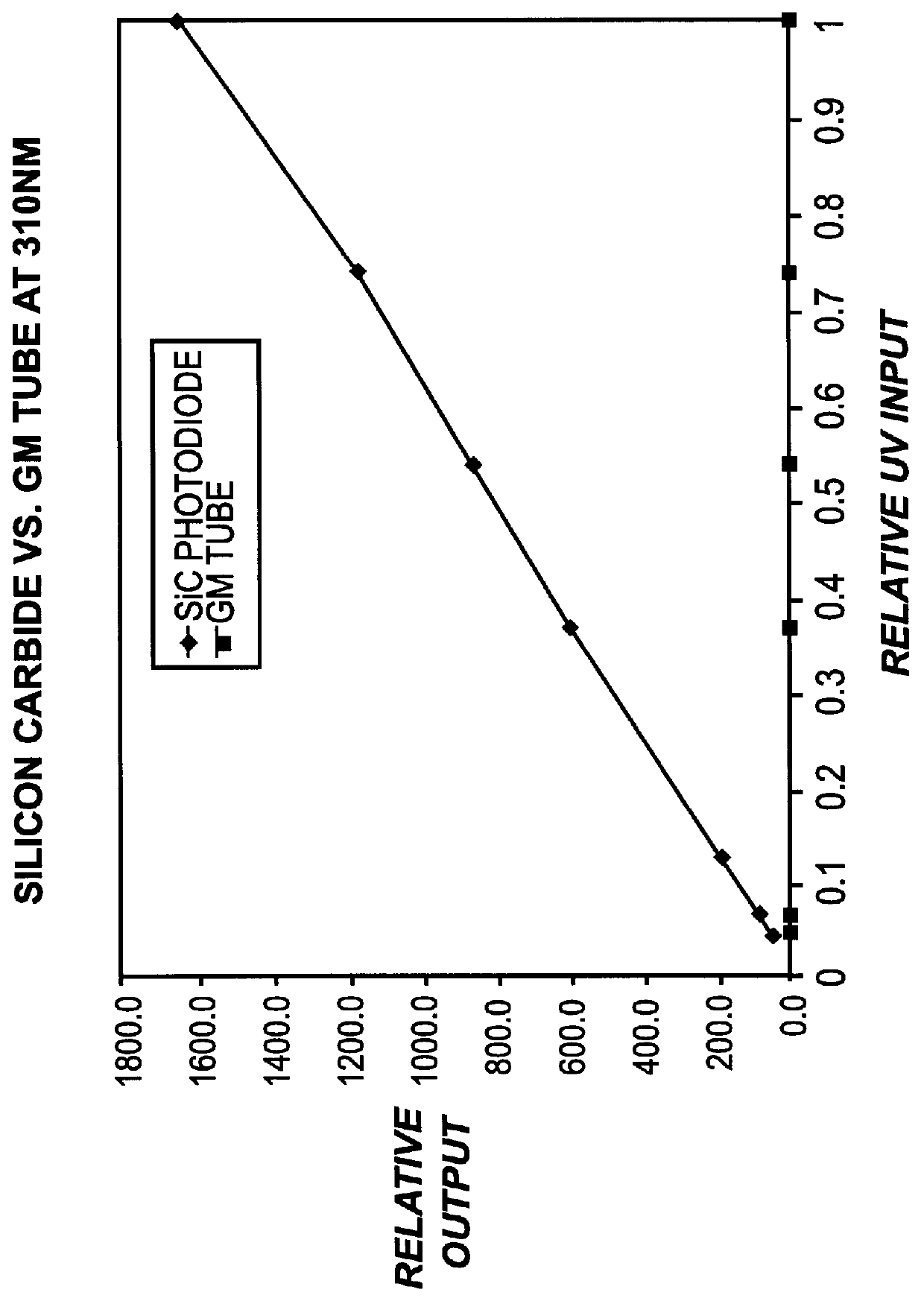
InactiveUS6013919AIncreased ultraviolet sensitivityEliminate needInternal-combustion engine testingContinuous combustion chamberSignal conditioning circuitsUltraviolet lights
The present invention provides a flame sensor having dynamic sensitivity adjustment, wherein the sensitivity of the flame detector can be adjusted by varying the gain of a signal conditioning circuit associated with the flame detector. The flame detector includes a photodiode, such as, for example, a silicon carbide (SiC) photodiode, that, when exposed to electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength in the range of from about 190-400 nanometers, and preferably within the ultraviolet range. The photodiode generates a photocurrent proportional to the ultraviolet light intensity to which it is exposed. The output of the photodiode is processed and amplified by signal conditioning circuitry to produce a signal indicative of the presence of a flame. Moreover, a cutoff wavelength for silicon carbide photodiodes is preferably in the range of about 400 nanometers, which renders the photodiode "blind" to potentially interfering blackbody radiation from the walls of the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
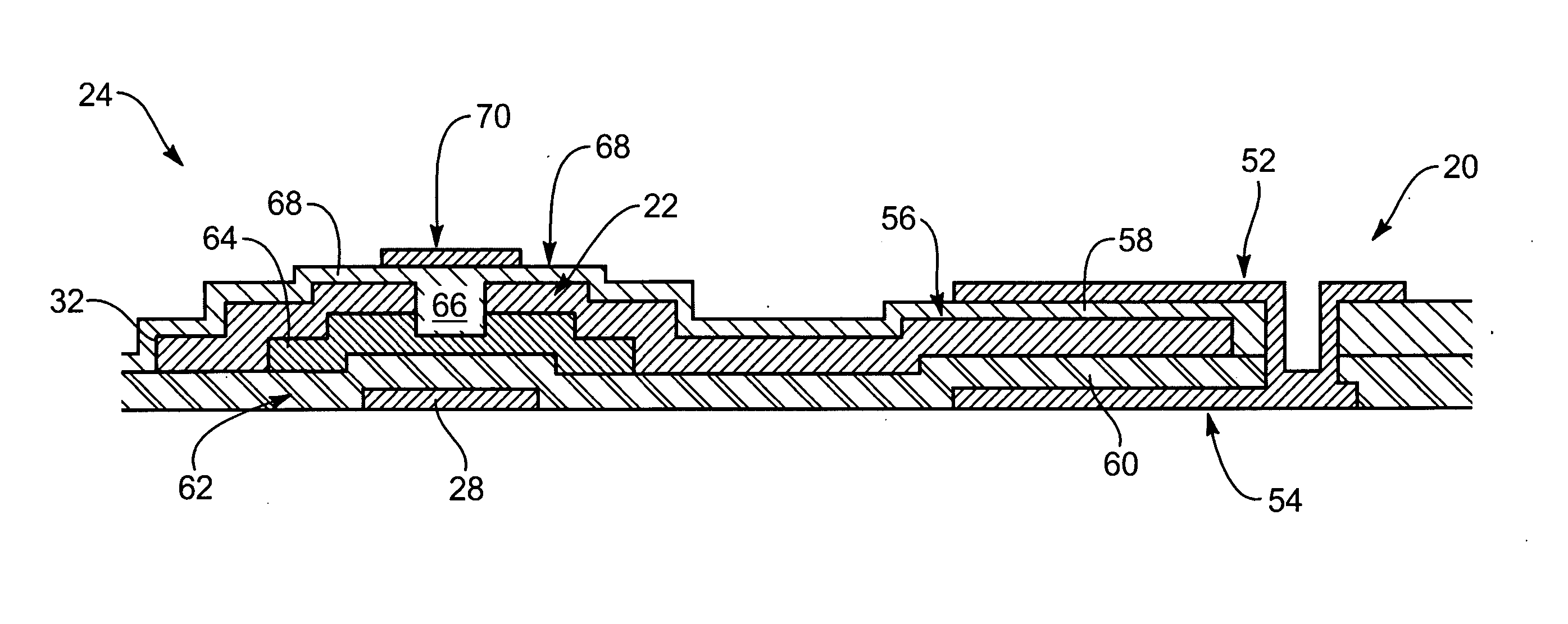
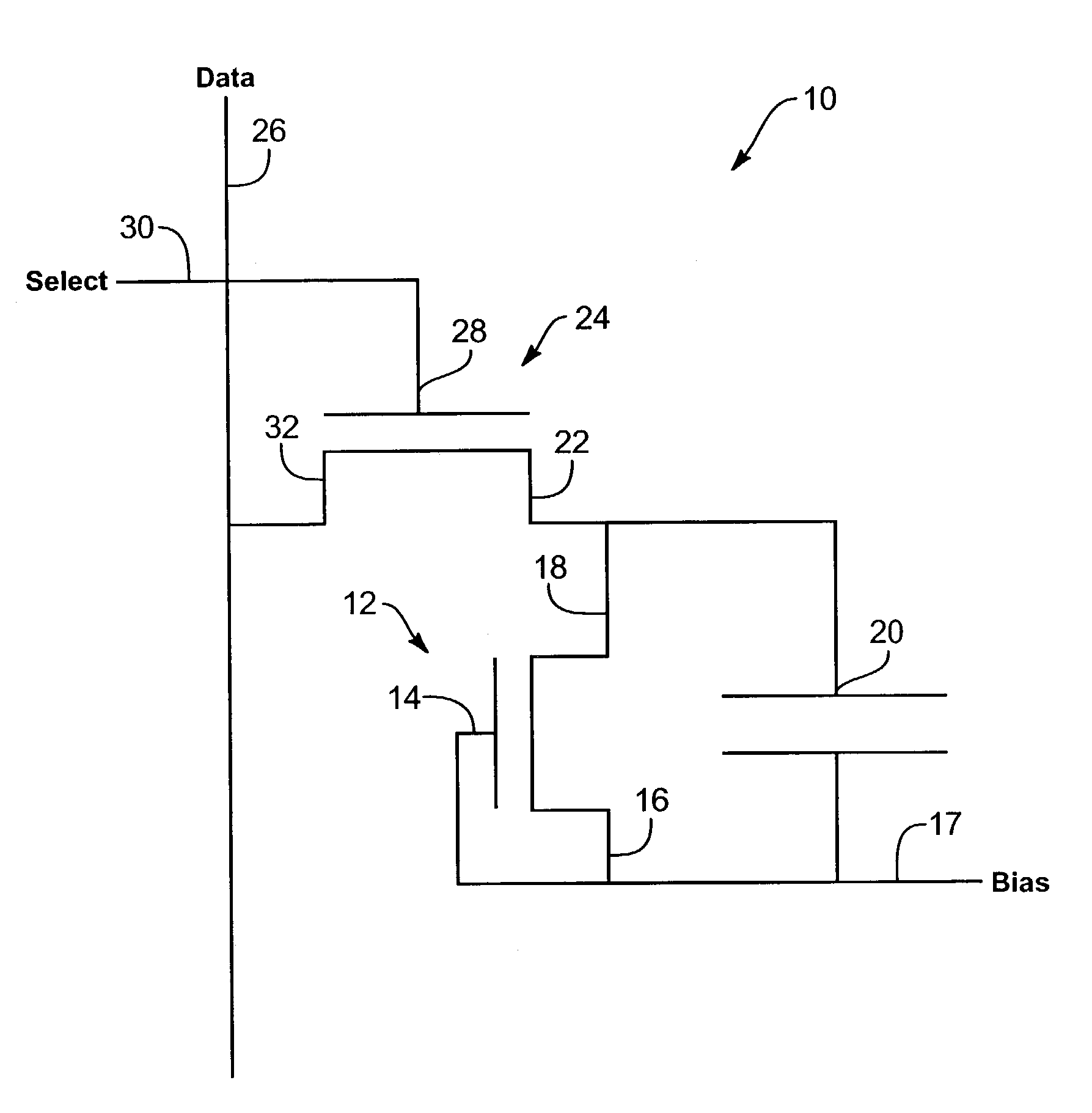
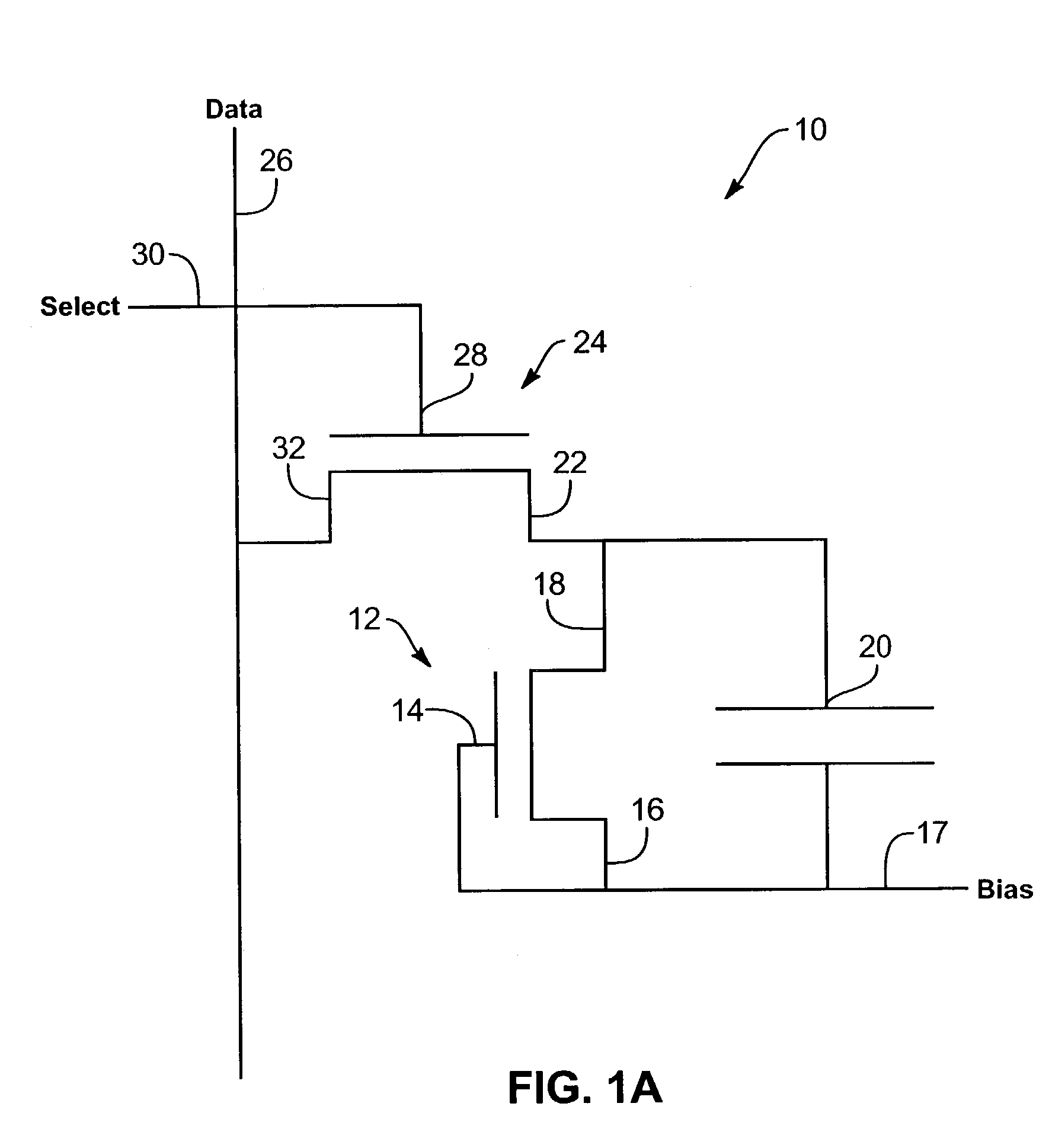
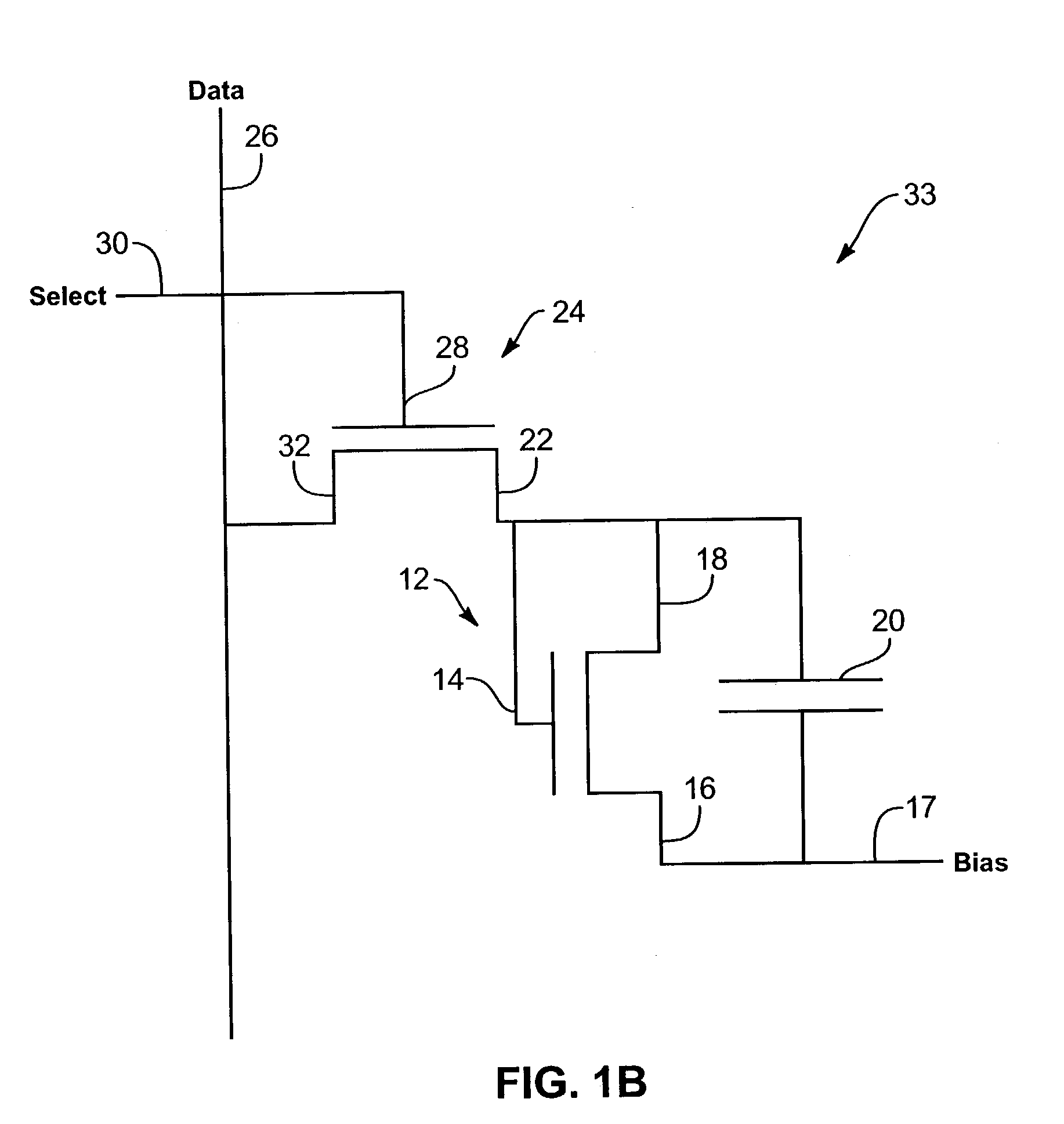
Image sensor with photosensitive thin film transistors and dark current compensation
InactiveUS20050231656A1Increase photosensitivityReduce impactTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotocurrentCapacitor
An image sensor array includes image sensors having photo TFTs to generate photocurrent in response to received images. The photo TFTs each have their respective gate electrodes and source electrodes independently biased to reduce the effects of dark current. Storage capacitors are coupled to each photo TFT and discharged upon generation of a photocurrent. Each storage capacitor is coupled to a readout TFT that passes a current from the storage capacitor to a data line. The photo TFT may be disposed above the storage capacitor to increase the exposed surface area of the photo TFT.
Owner:APPLE INC
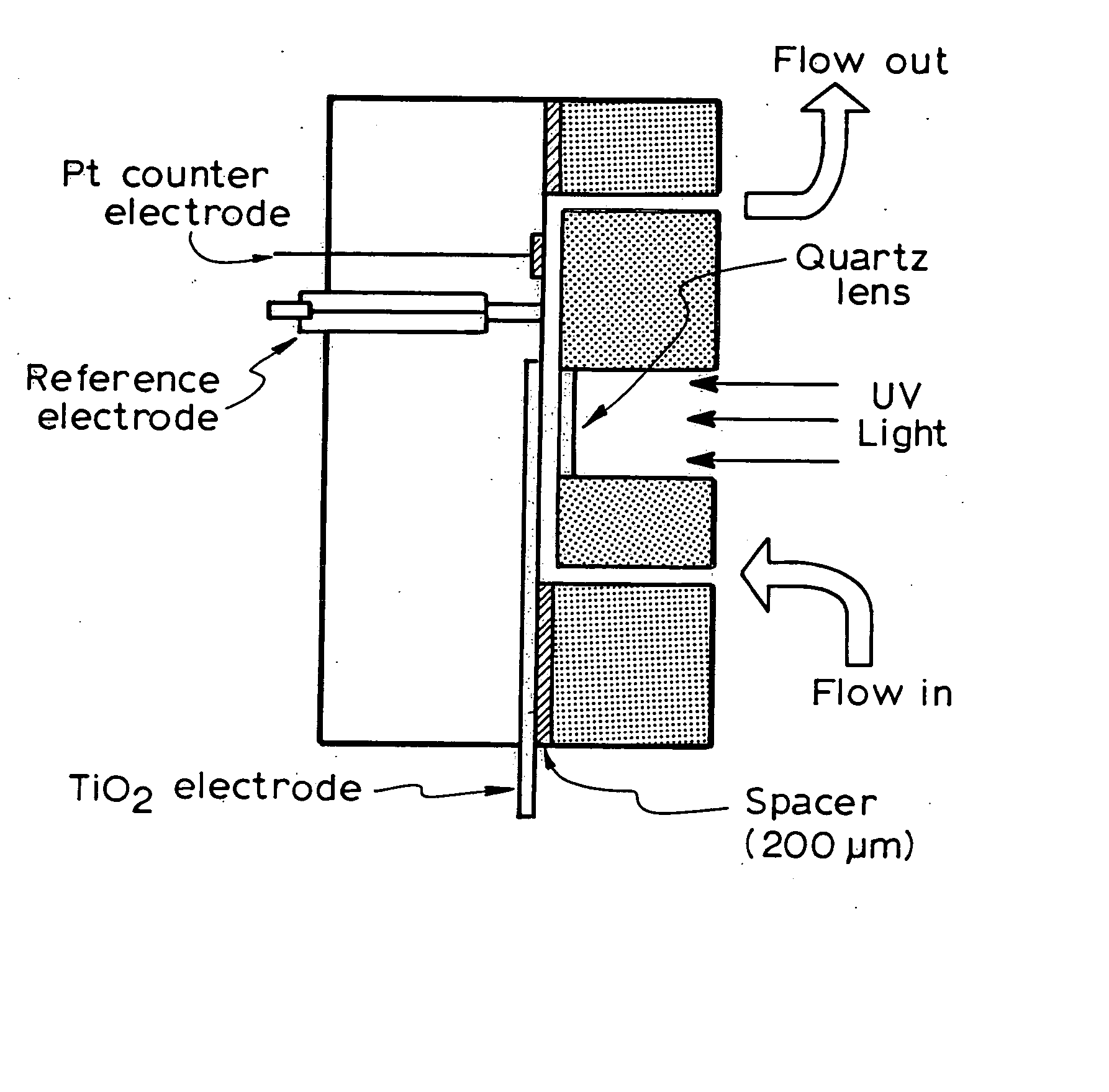
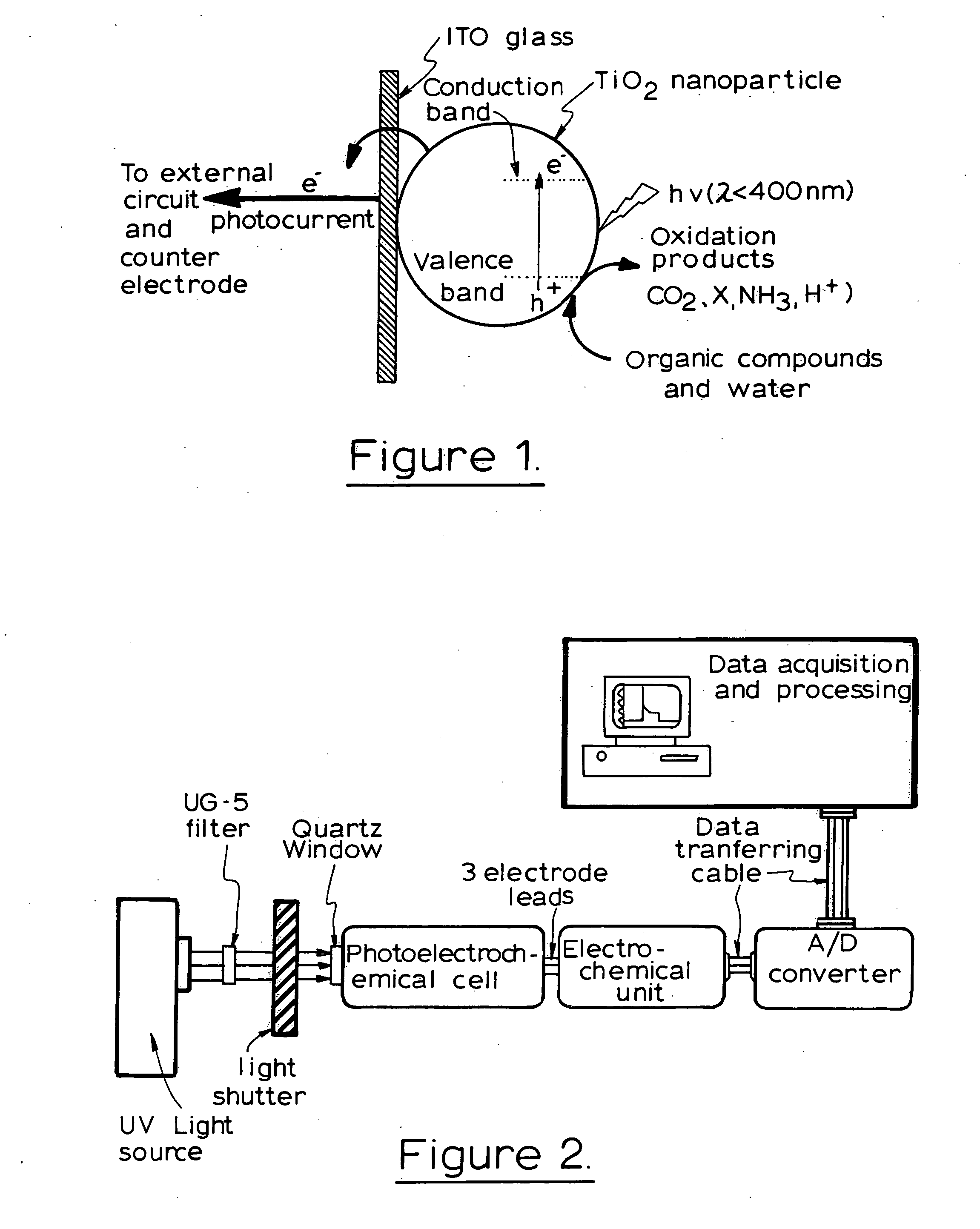
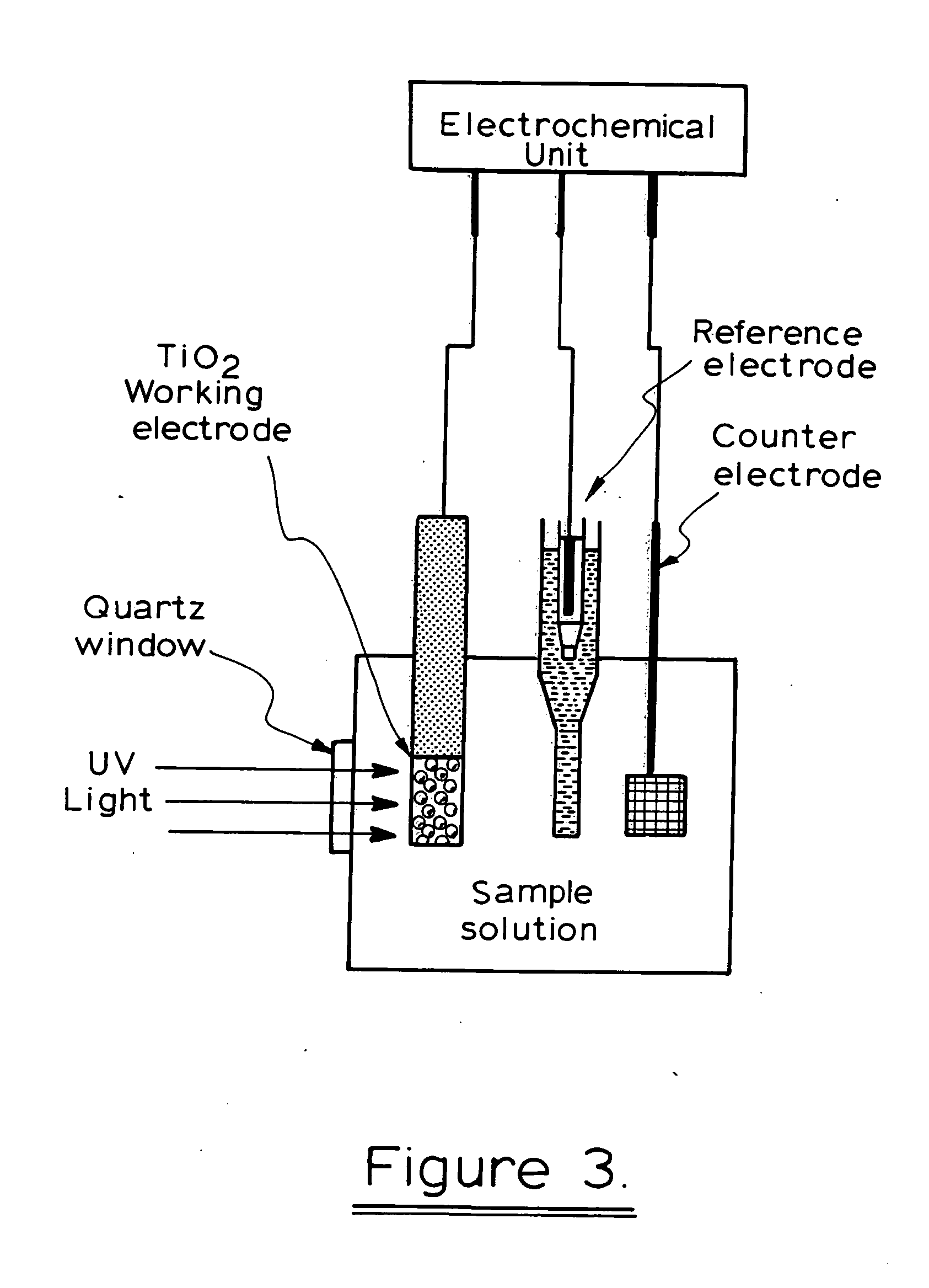
Photoelectrochemical determination of chemical oxygen demand
ActiveUS20060240558A1High sensitivityWide linear rangeChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using combustionSupporting electrolytePotential measurement
A photoelectrochemical assay apparatus for determining chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a water sample which consists of a) a measuring cell for holding a sample to be analysed b) a titanium dioxide nanoparticle photoelectric working electrode and a counter electrode disposed in said cell, c) a UV light source adapted to illuminate the photoelectric working electrode d) control means to control the illumination of the working electrode e) potential measuring means to measure the electrical potential at the working and counter electrodes f) analysis means to derive a measure of oxygen demand from the measurements made by the potential measuring means. The method of determining chemical oxygen demand of a water sample, comprises the steps of a) applying a constant potential bias to a photoelectrochemical cell, containing a supporting electrolyte solution; b) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the background photocurrent produced at the working electrode from the supporting electrolyte solution; c) adding a water sample, to be analysed, to the photoelectrochemical cell; d) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the total photocurrent produced; e) determining the chemical oxygen demand of the water sample according to the type of degradation conditions employed. The determination may be under exhaustive degradation conditions, in which all organics present in the water sample are oxidised or under non-exhaustive degradation conditions, in which the organics present in the water sample are partially oxidised.
Owner:579453 ONTARIO INC
Silicon-based visible and near-infrared optoelectric devices
InactiveUS20050127401A1Promote generationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerPhotovoltaic detectors
In one aspect, the present invention provides a silicon photodetector having a surface layer that is doped with sulfur inclusions with an average concentration in a range of about 0.5 atom percent to about 1.5 atom percent. The surface layer forms a diode junction with an underlying portion of the substrate. A plurality of electrical contacts allow application of a reverse bias voltage to the junction in order to facilitate generation of an electrical signal, e.g., a photocurrent, in response to irradiation of the surface layer. The photodetector exhibits a responsivity greater than about 1 A / W for incident wavelengths in a range of about 250 nm to about 1050 nm, and a responsivity greater than about 0.1 A / W for longer wavelengths, e.g., up to about 3.5 microns.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
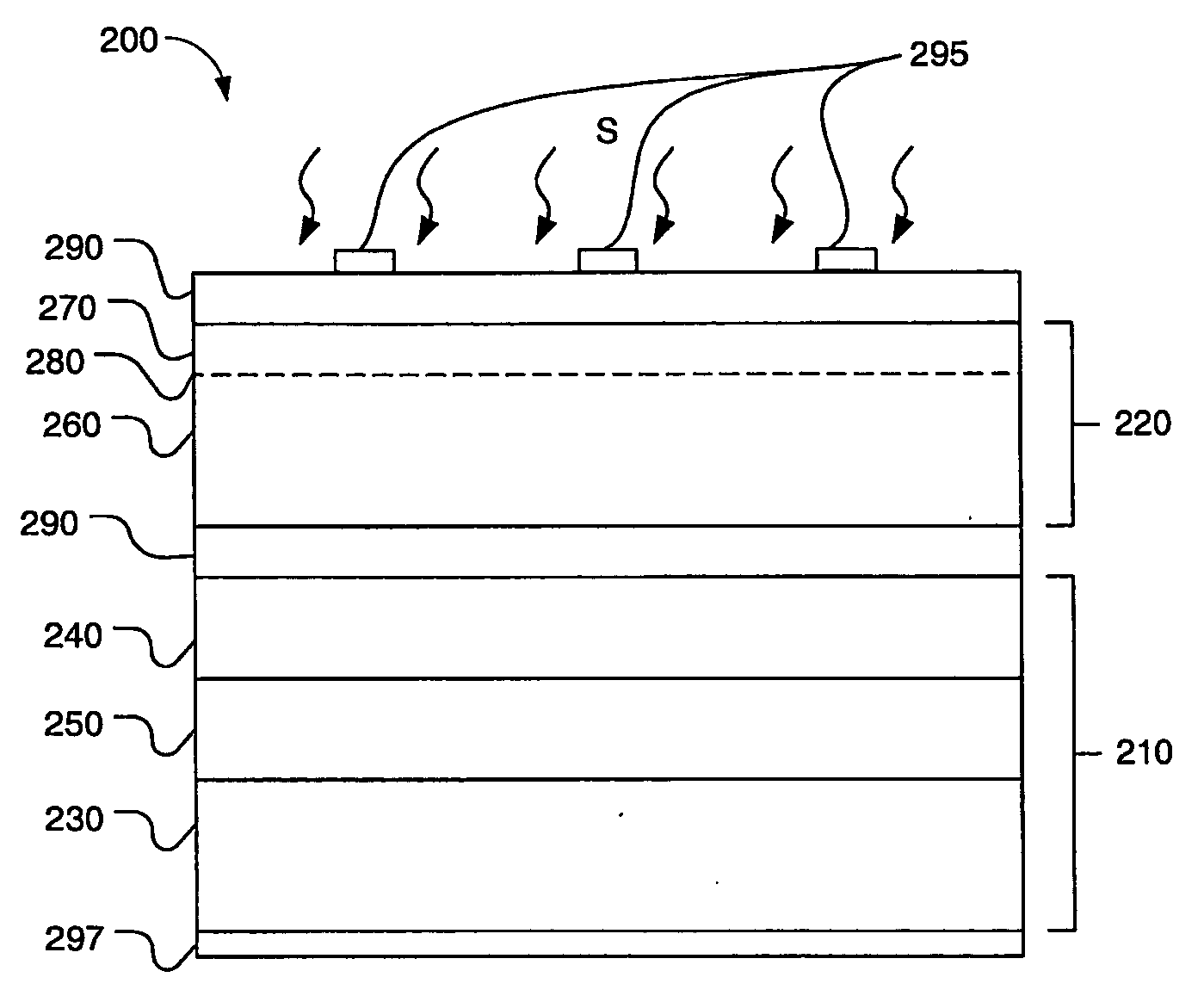
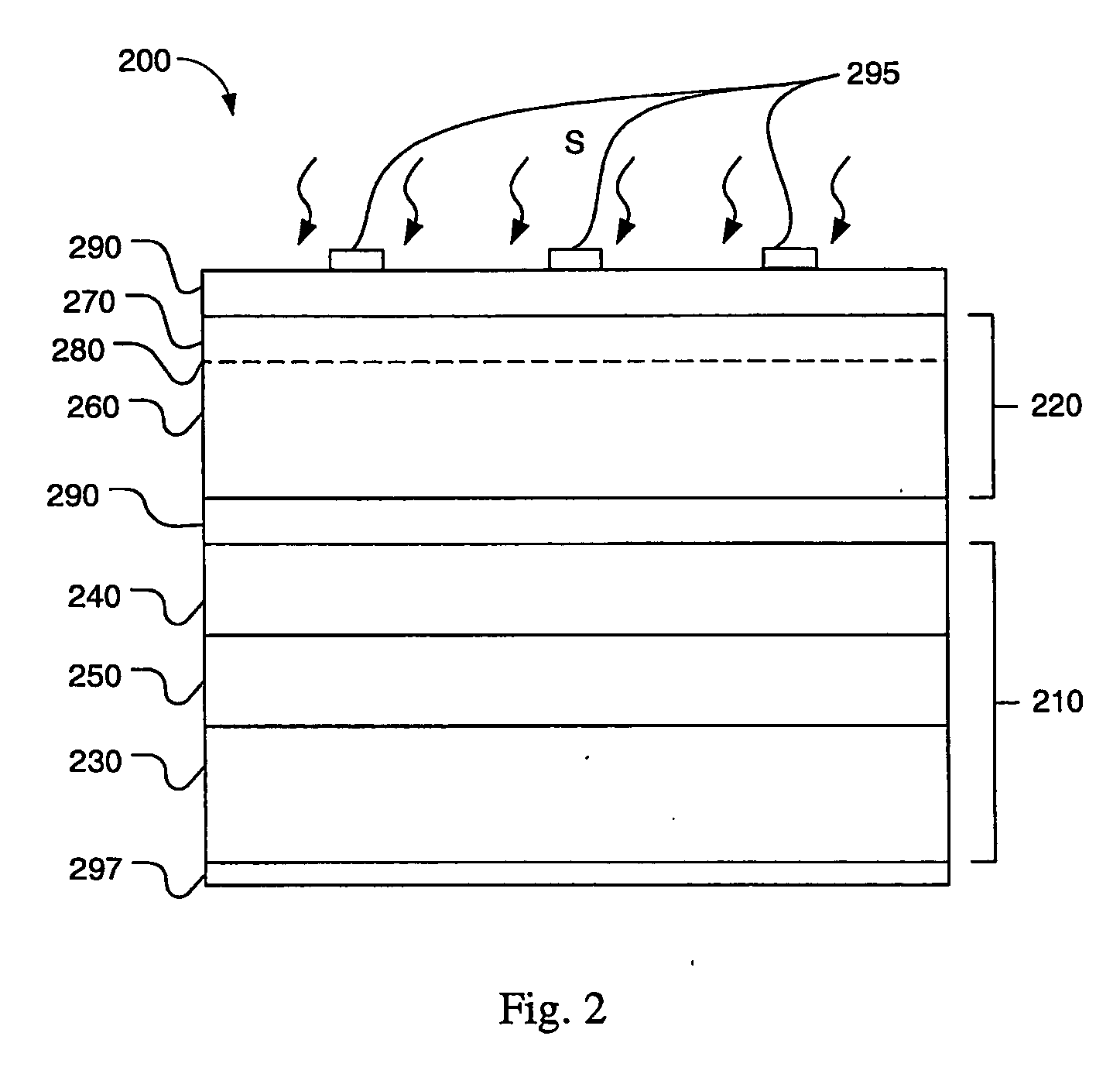
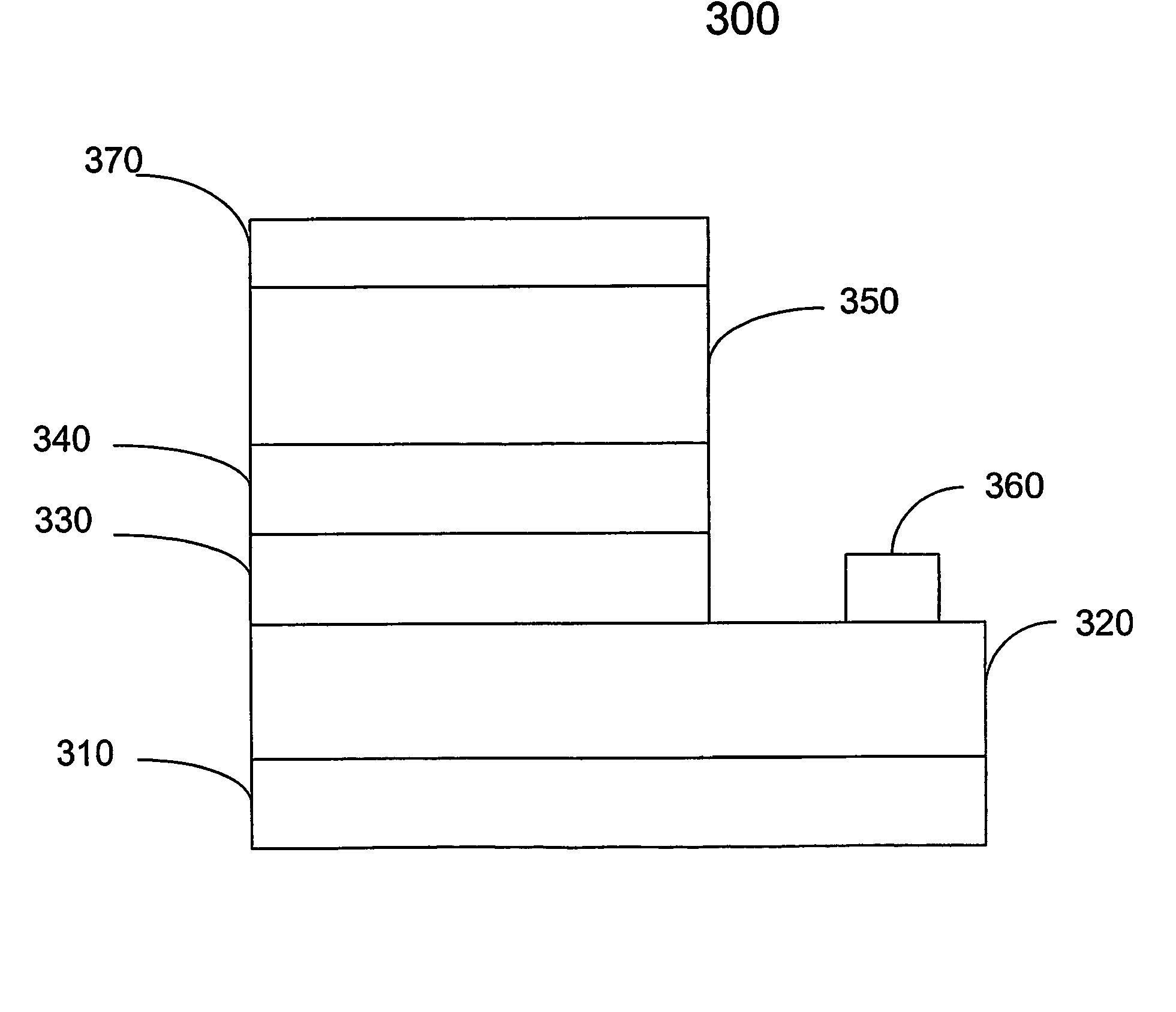
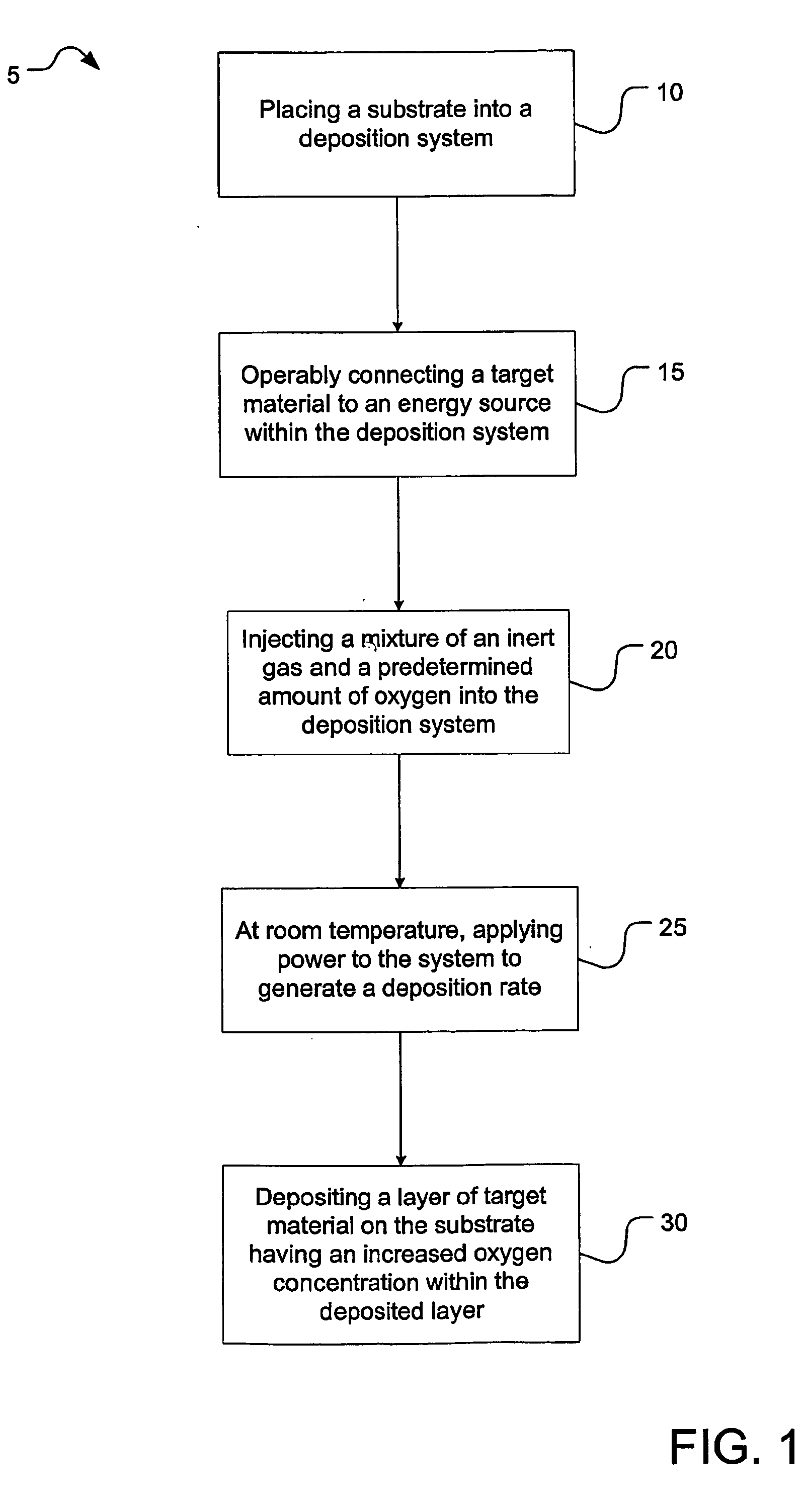
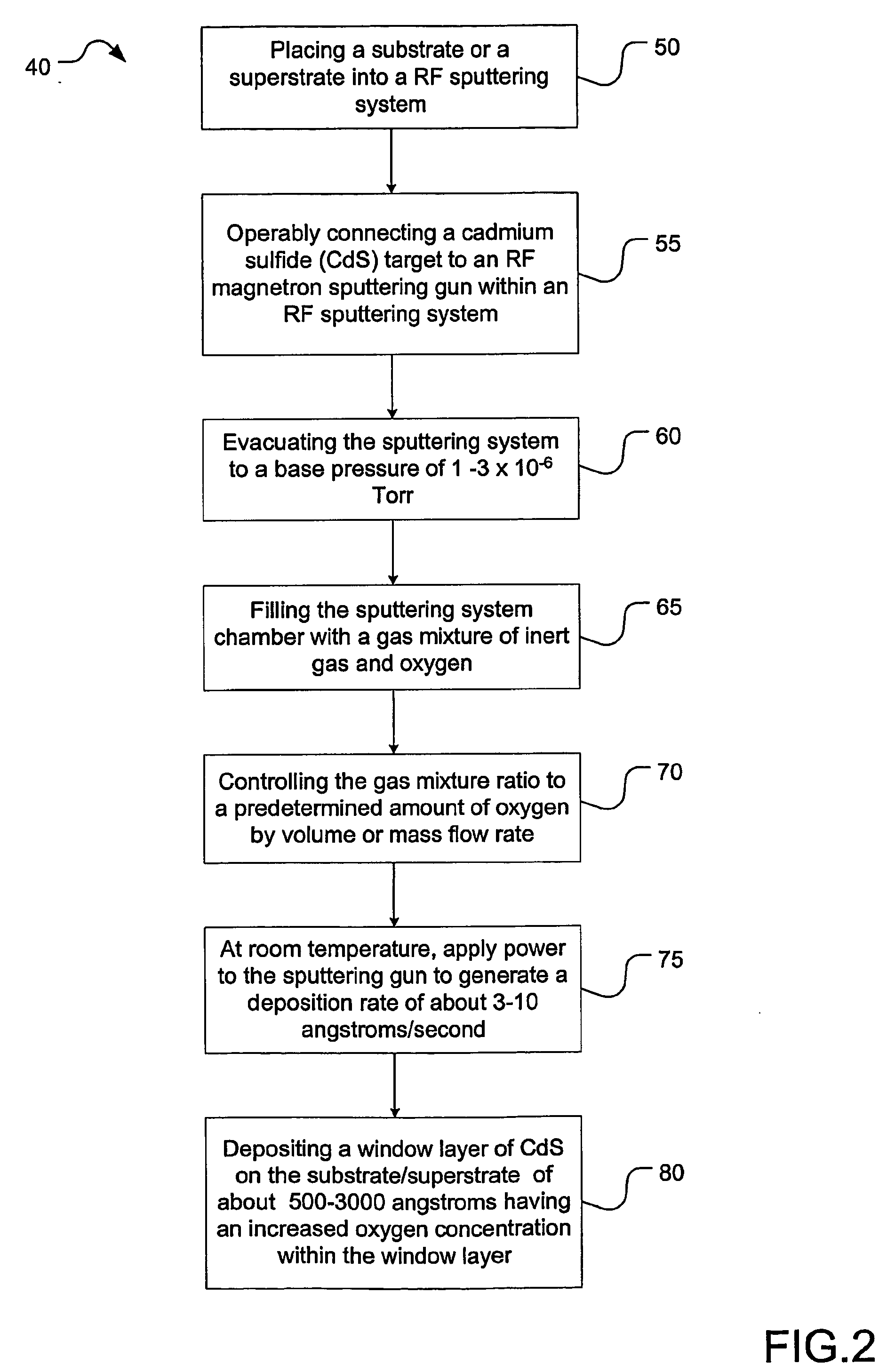
Semiconductor device with higher oxygen (02) concentration within window layers and method for making
InactiveUS20050009228A1Improve efficiencyIncrease oxygen concentrationVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionDevice material
A method for making a heterojunction photovoltaic device (200) is provided for converting solar radiation to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The method and apparatus include an improved window layer (230) having an increased oxygen (140) concentration with higher optical bandgap and photo to dark conductivity ratio. The improved photovoltaic device (200) is made using a deposition method which incorporates the use of a gas mixture of an inert gas (115) and a predetermined amount of oxygen (140), deposited at or near room temperature. Window layers contemplated by the present invention include, but are not limited to, cadmium sulfide (CdS) and various alloys of zinc cadmium sulfide (ZnxCd1-xS). To further increase the efficiency of the resultant photovoltaic device (200), deposition parameters are controlled and monitored to improve the deposited window layer (230).
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Method of and apparatus for electro-optical distance measurement
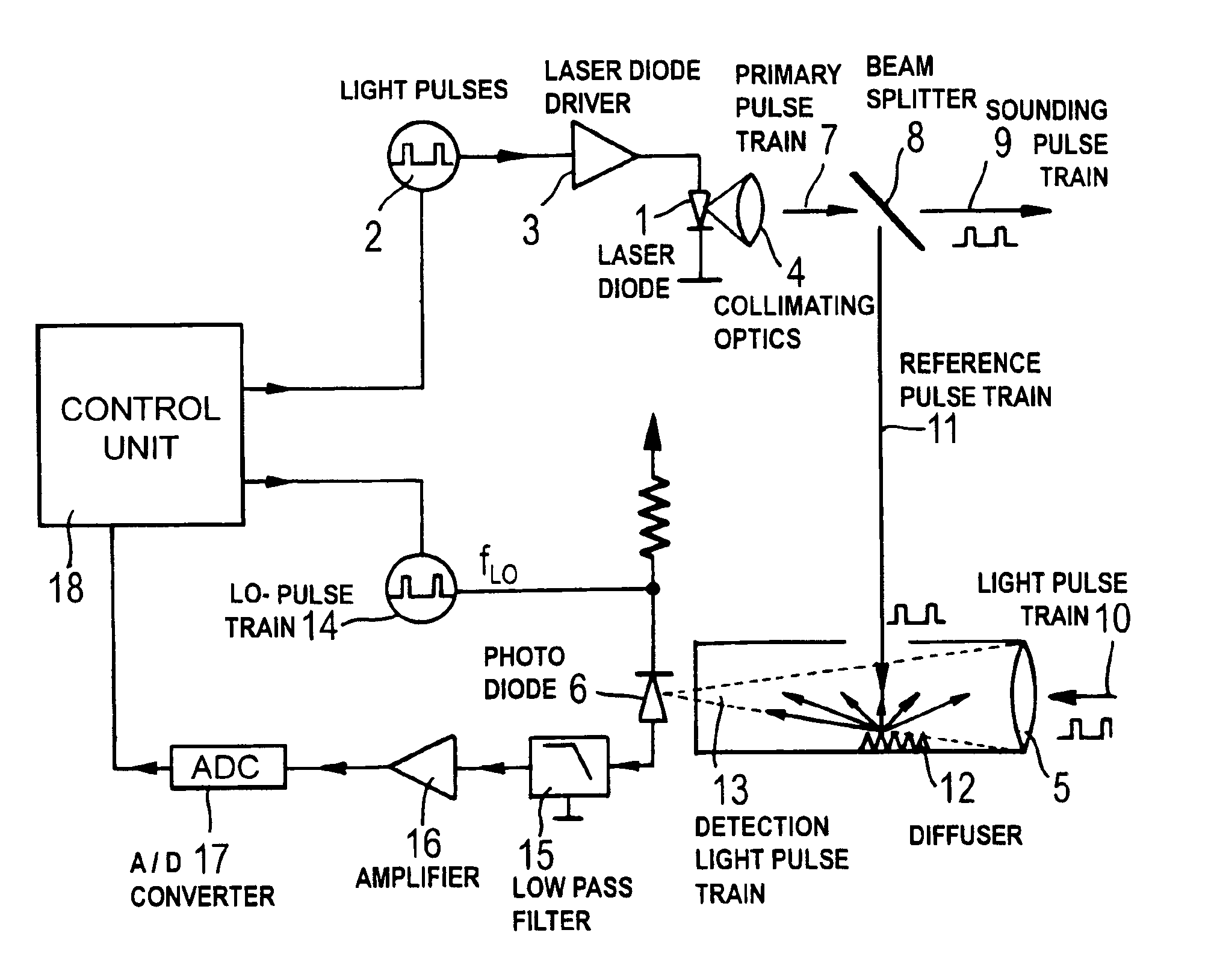
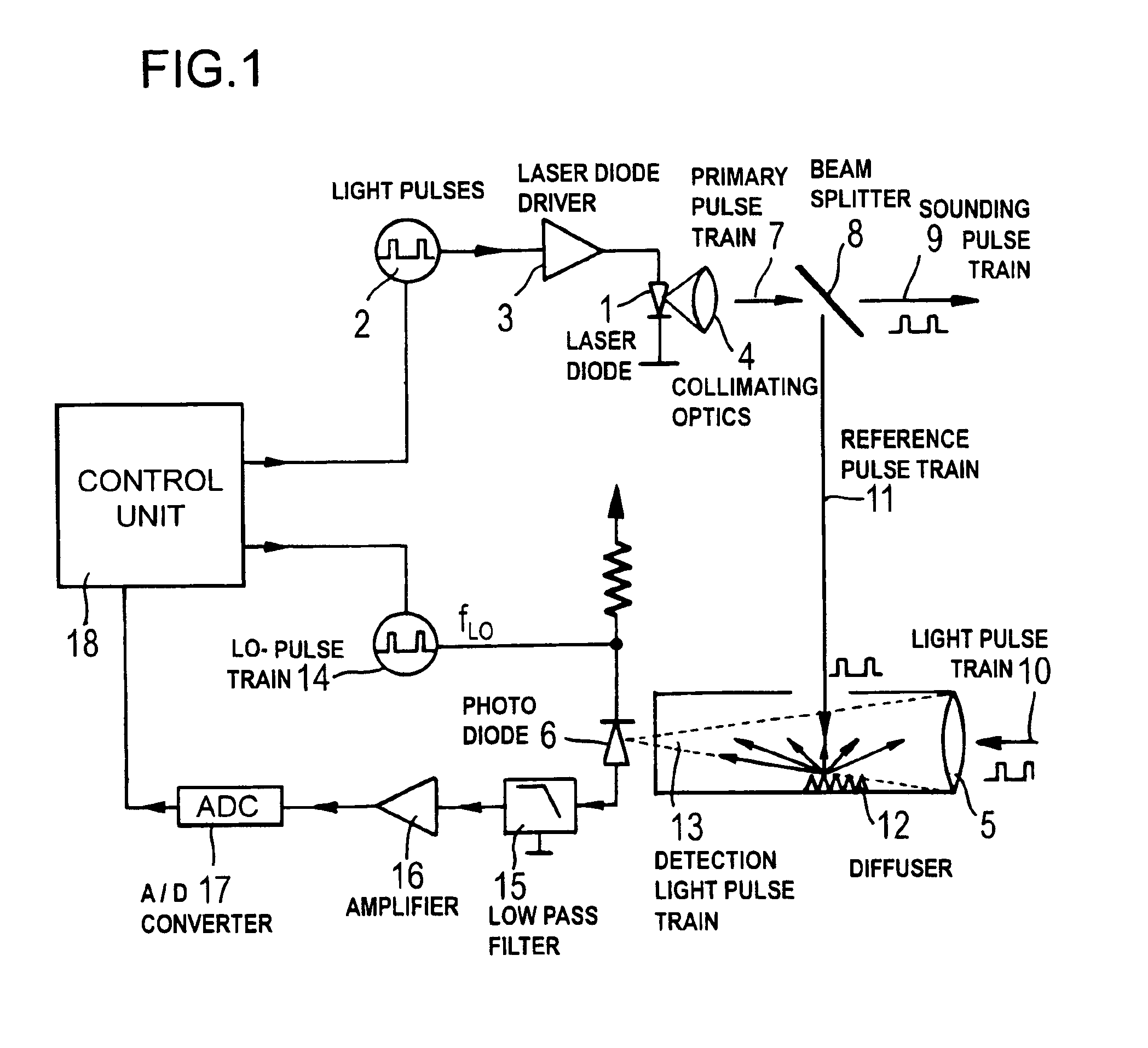
InactiveUS6917415B2Low costReduce frequencyOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLocal oscillatorPulse sequence
A method of and an apparatus for an electro-optical distance measurement in which a laser beam of a laser diode (1) is directed as an intensity modulated train of emitted light pulses onto an object, the reflected measurement pulse train (10) is detected by a light detector (6), which generates, in response to the detection of a measurement pulse train, a first photo-current component, a smaller portion of the intensity modulated pulse train is branched out as a reference pulse train and, after passing a known reference path, is also detected by the light detector (6), which generates in response to this detection a second photo current component, and the light detector converts the measurement pulses, together with a mixer pulse train generated by a local oscillator, into a comparatively low-frequency IF-region that determines, after a corresponding conversion, the measured distance.
Owner:HILTI AG +1
High density photodiodes
InactiveUS20080067622A1Improve uniformityHigh densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBatch processingHigh density
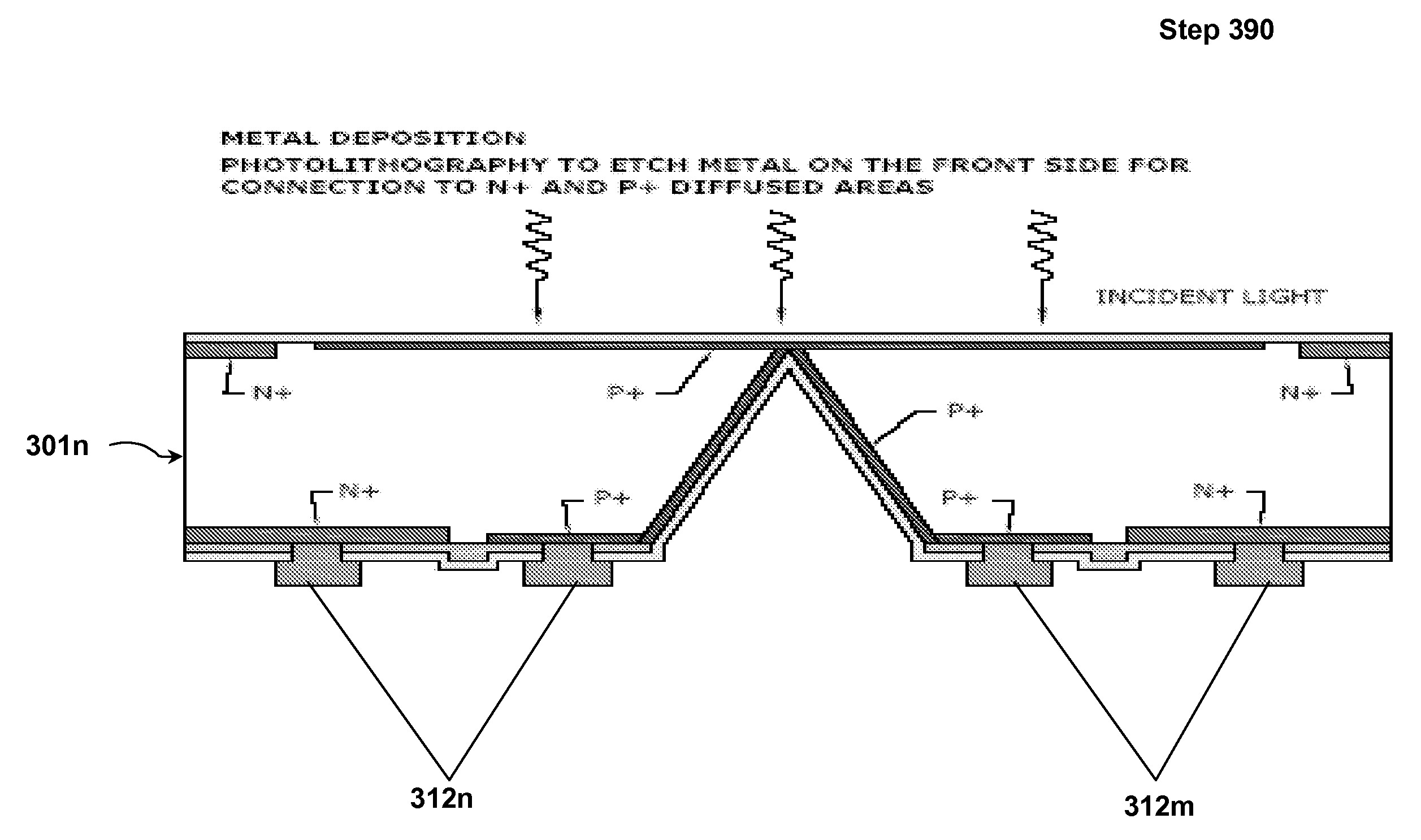
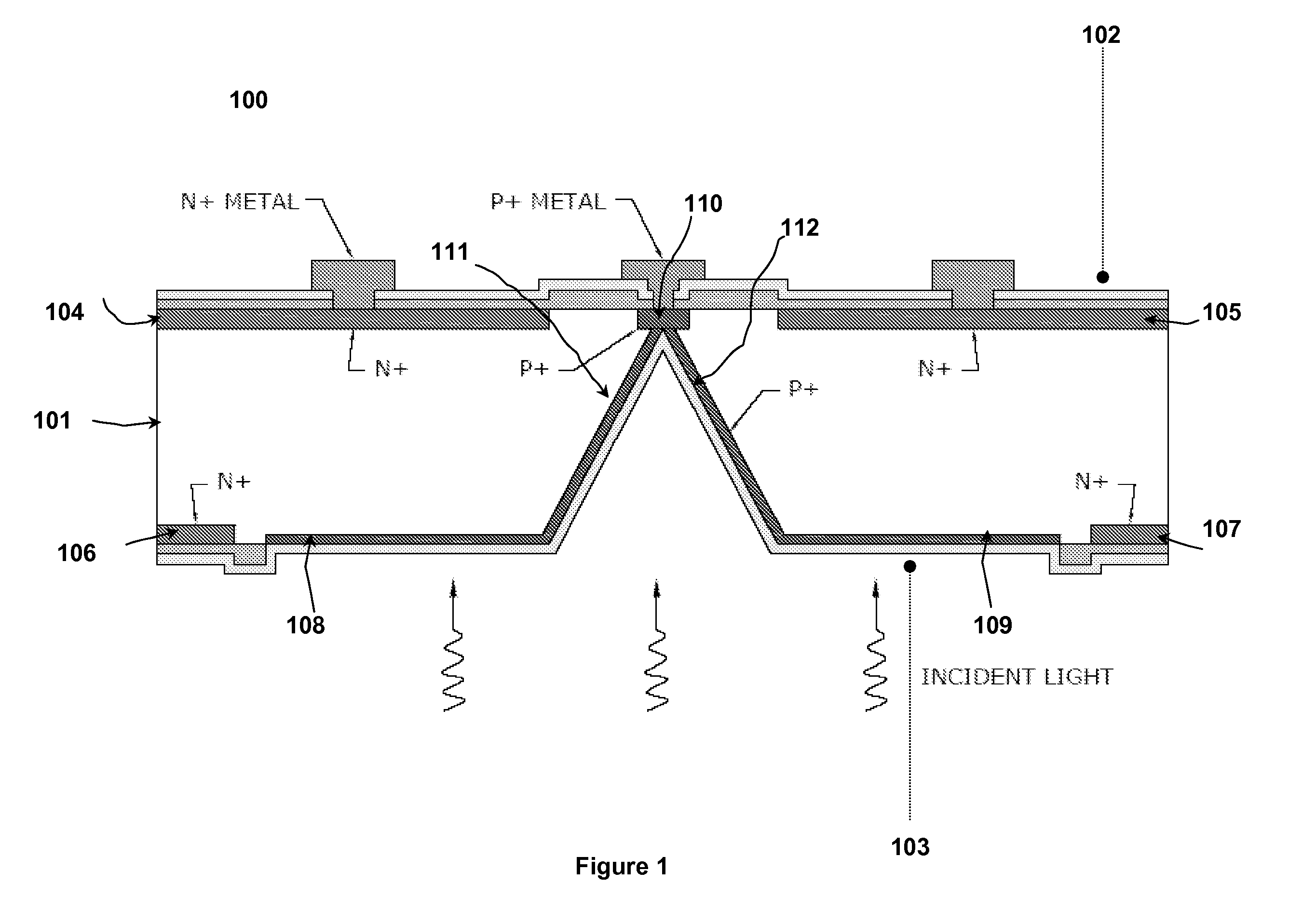
The present invention is a front-side contact, back-side illuminated (FSC-BSL) photodiode arrays and front-side illuminated, back-side contact (FSL-BSC) photodiode arrays having improved characteristics, including high production throughput, low-cost manufacturing via implementation of batch processing techniques; uniform, as well as high, photocurrent density owing to presence of a large continuous homogeneous, heavily doped layer; and back to front intrachip connections via the homogenous, heavily doped layers on the front and back sides of the substrate.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
Systems and methods for dimming of a light source
ActiveUS20140176016A1Good dimming effectReduce flickerElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesWork cycleDimmer
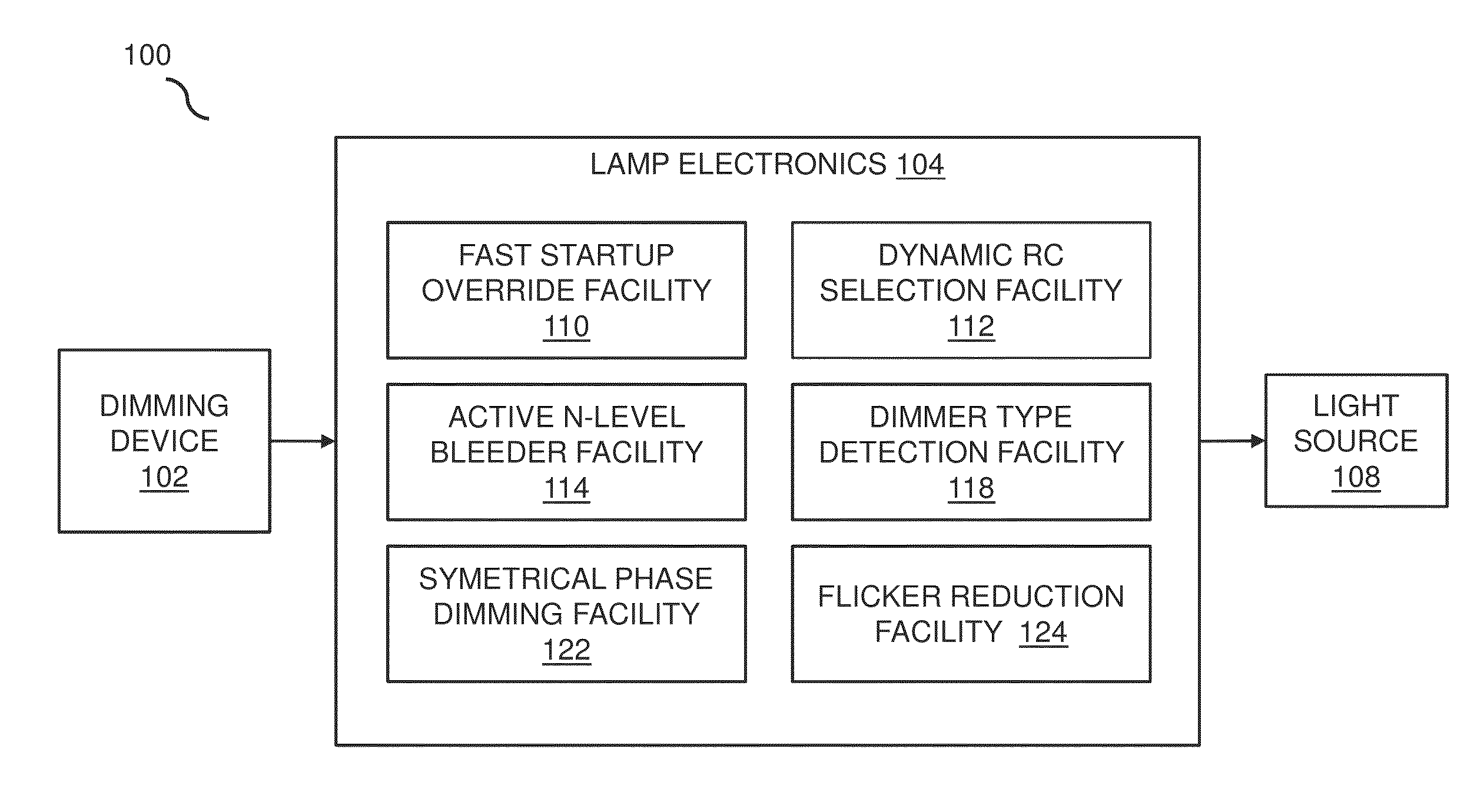
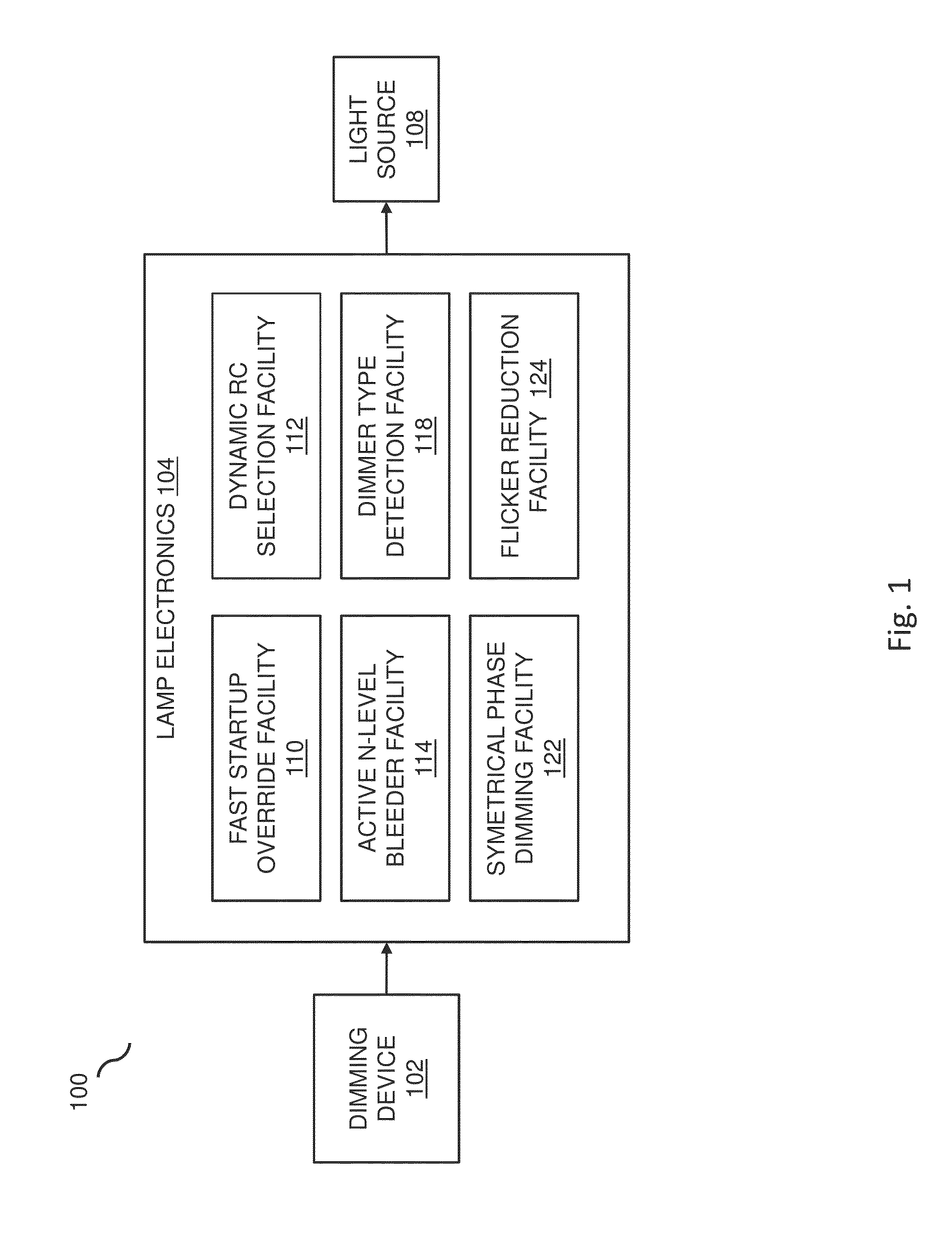
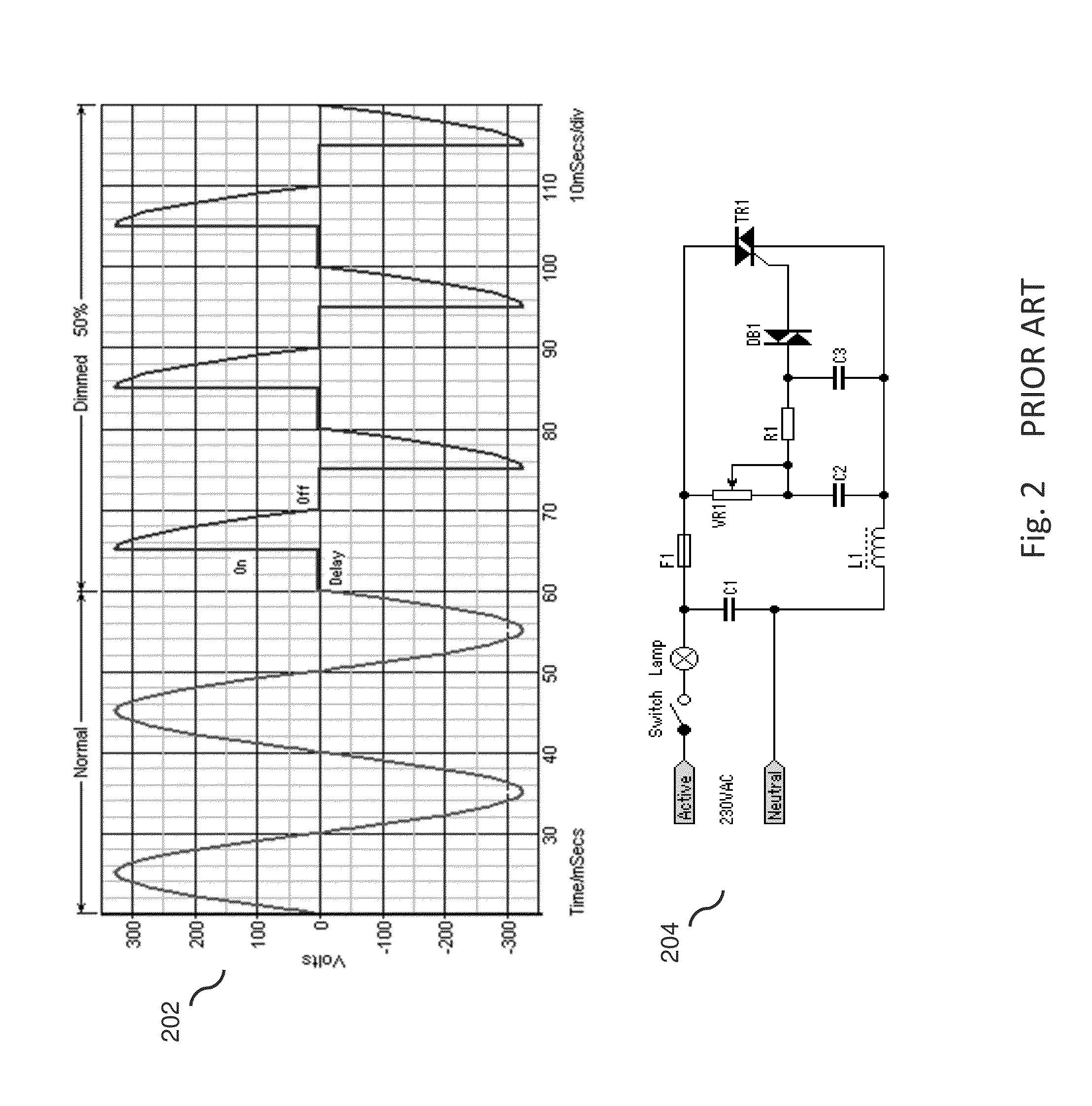
In embodiments, improved capabilities are described for dimming performance of lighting methods and systems, such as the improvement of dimming LED lamps that are dimmed from standard external dimming devices. Methods and systems for improving dimming performance include a fast startup override facility for overriding a default dimming function of the lamp's electronics through forcing the lamp electronics to operate with a higher than normal duty cycle to ensure the lamp electronics can deliver higher than normal power to an LED module during a dimming current level startup condition. Dimming facilities may also include a dynamic RC selection facility, an active N-level bleeder facility, a dimmer-type detection facility, an improved dimming linearity through symmetrical phase cutting facility, and a flicker reduction facility.
Owner:KORRUS INC
Exposure control in electronic cameras by detecting overflow from active pixels
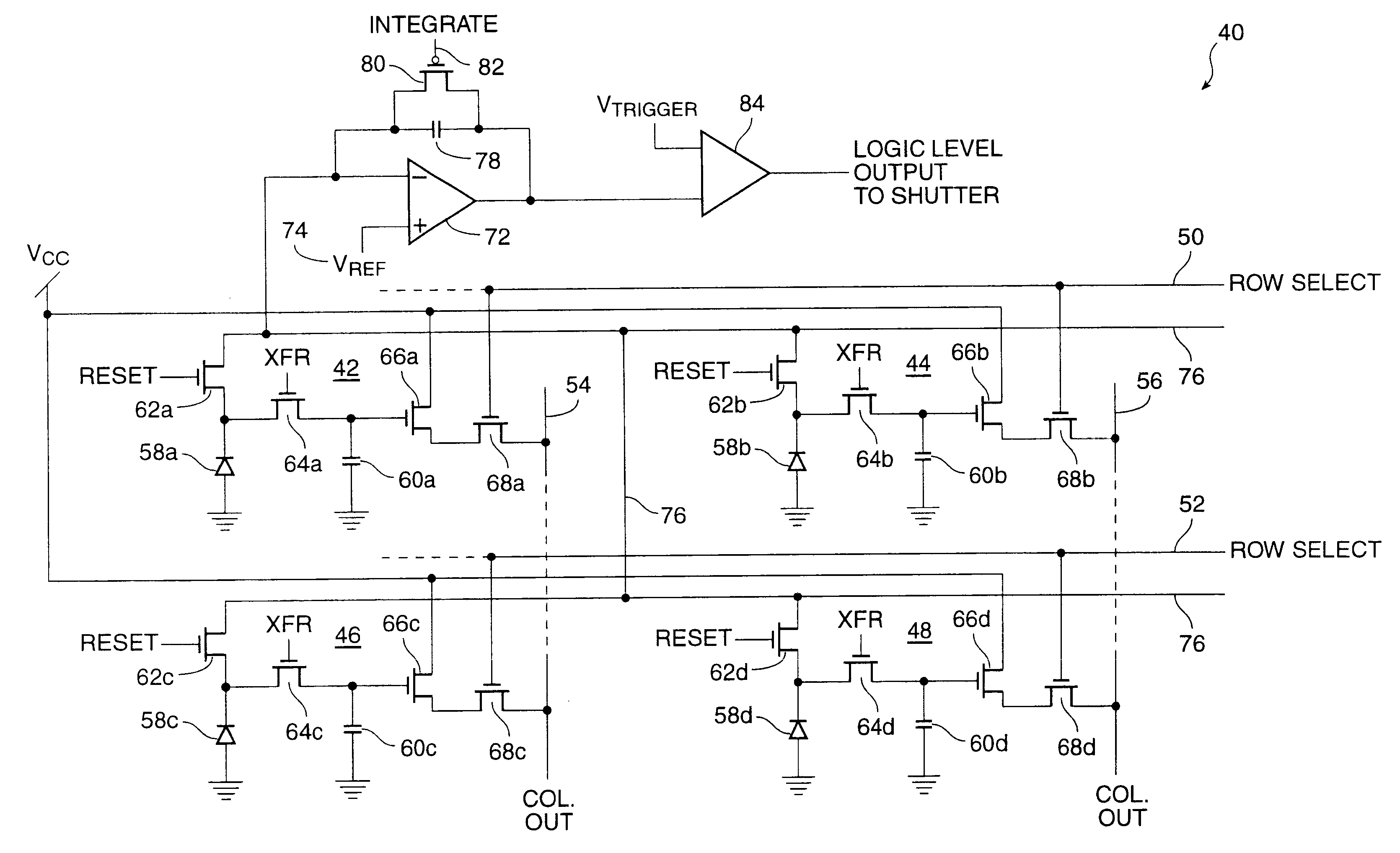
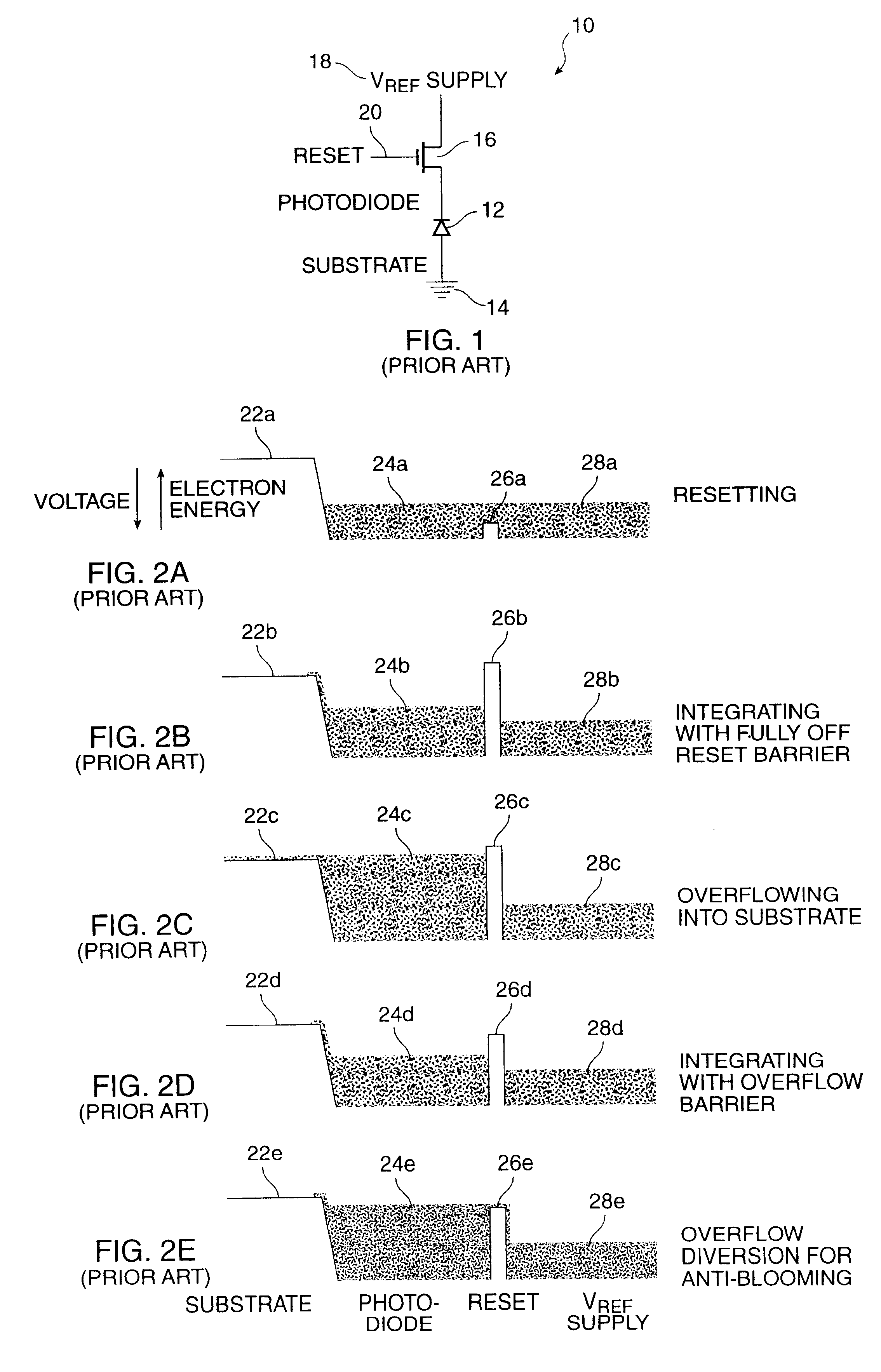
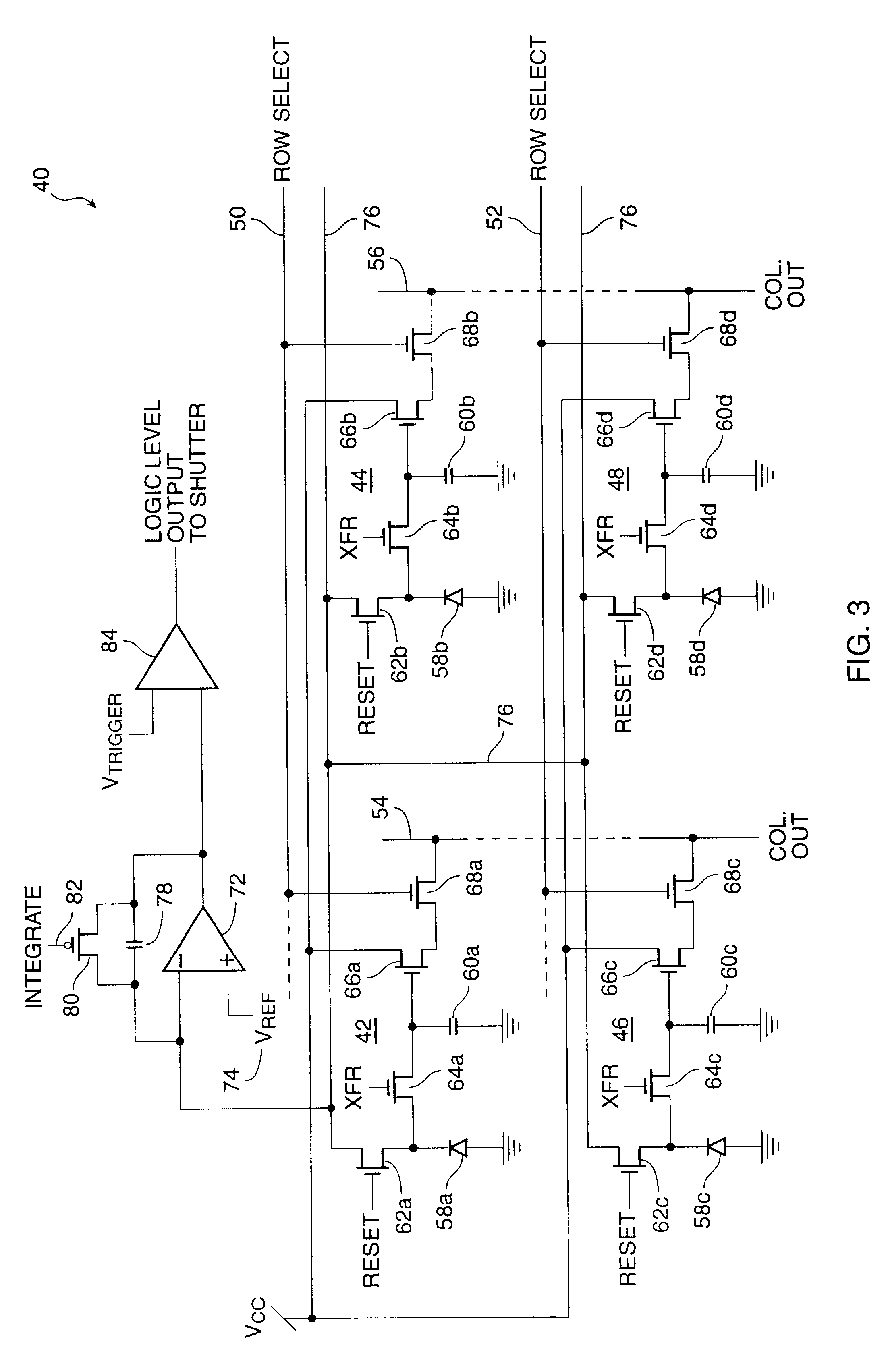
InactiveUS6452633B1Improve dynamic rangeReduce pattern noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl electronicsExposure control
A method for controlling the exposure of an active pixel array electronic still camera includes the steps of: integrating photocurrent in each pixel during an integration time period; collecting overflow charge from all pixels in the array during the integration time period; developing an overflow signal as a function of the overflow charge; and terminating the integration time period when the overflow signal exceeds a preset threshold level selected to represent a desired reference exposure level. Apparatus for performing the method of the present invention includes circuitry for integrating photocurrent in each pixel during a integration time period; circuitry for diverting and detecting overflow charge from all pixels in the array during the integration time period; circuitry for developing an overflow signal as a function of the overflow charge; and circuitry for terminating said integration time period when the overflow signal exceeds a preset threshold level selected to represent a desired reference exposure level.
Owner:FOVEON
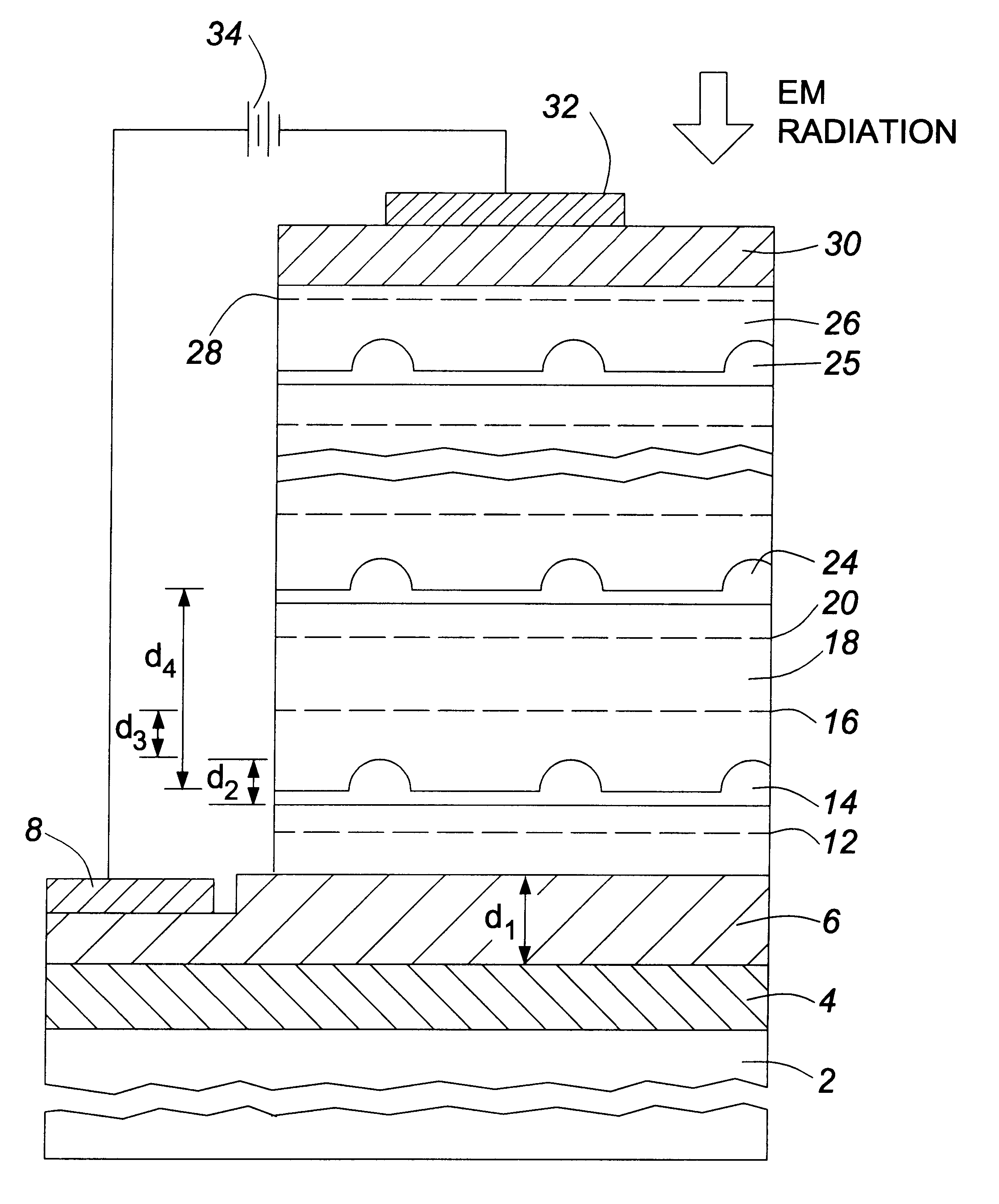
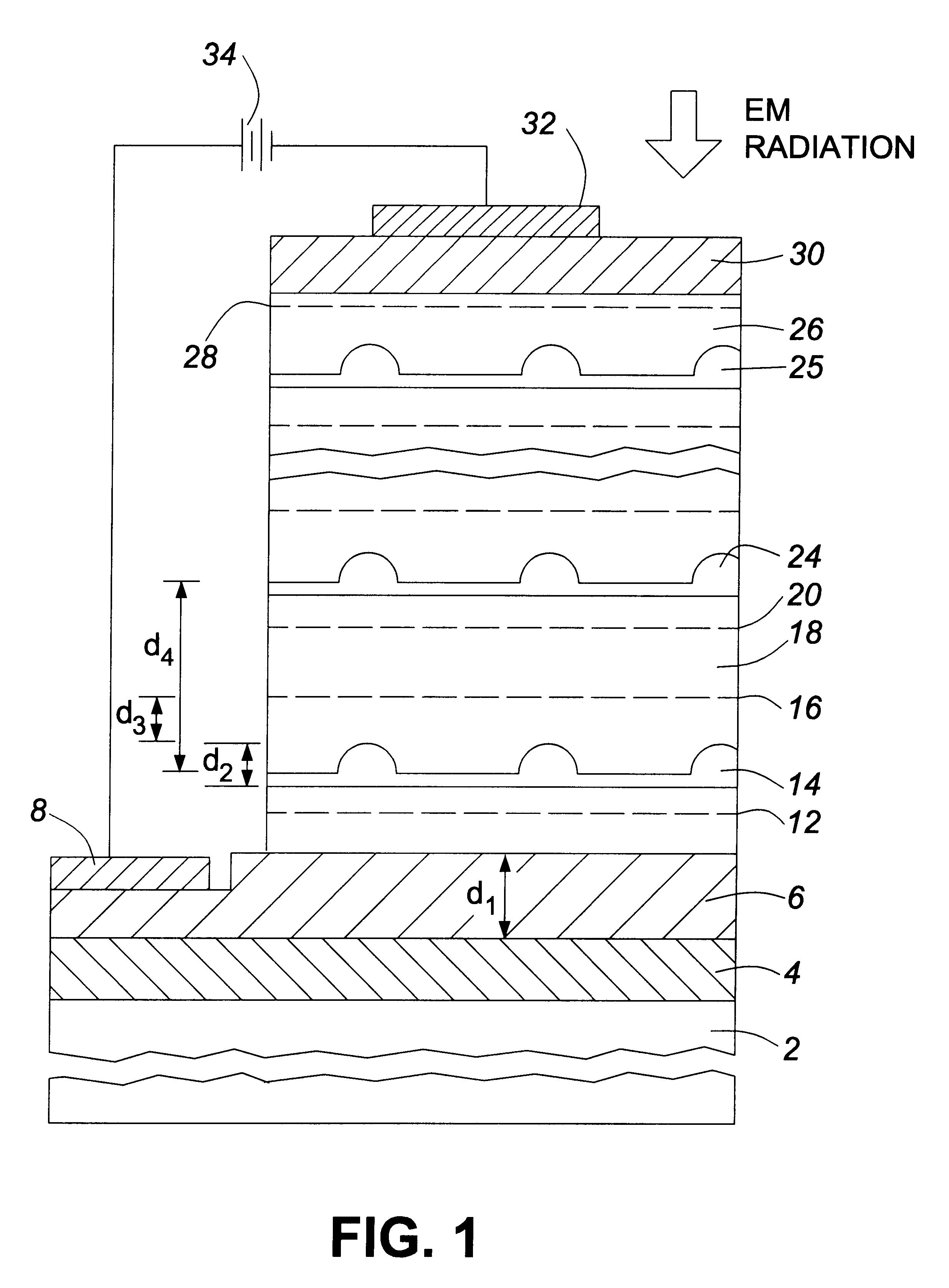
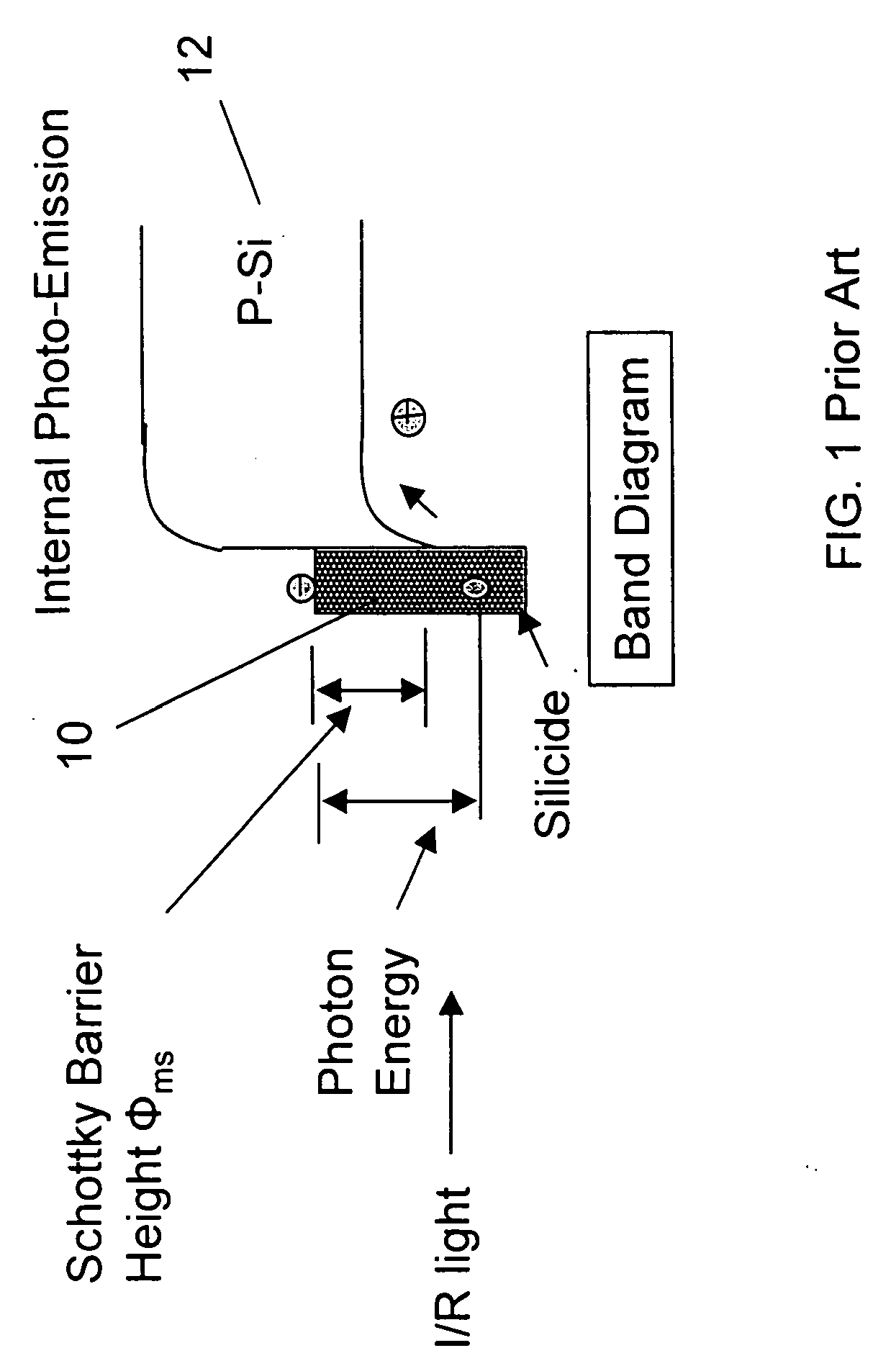
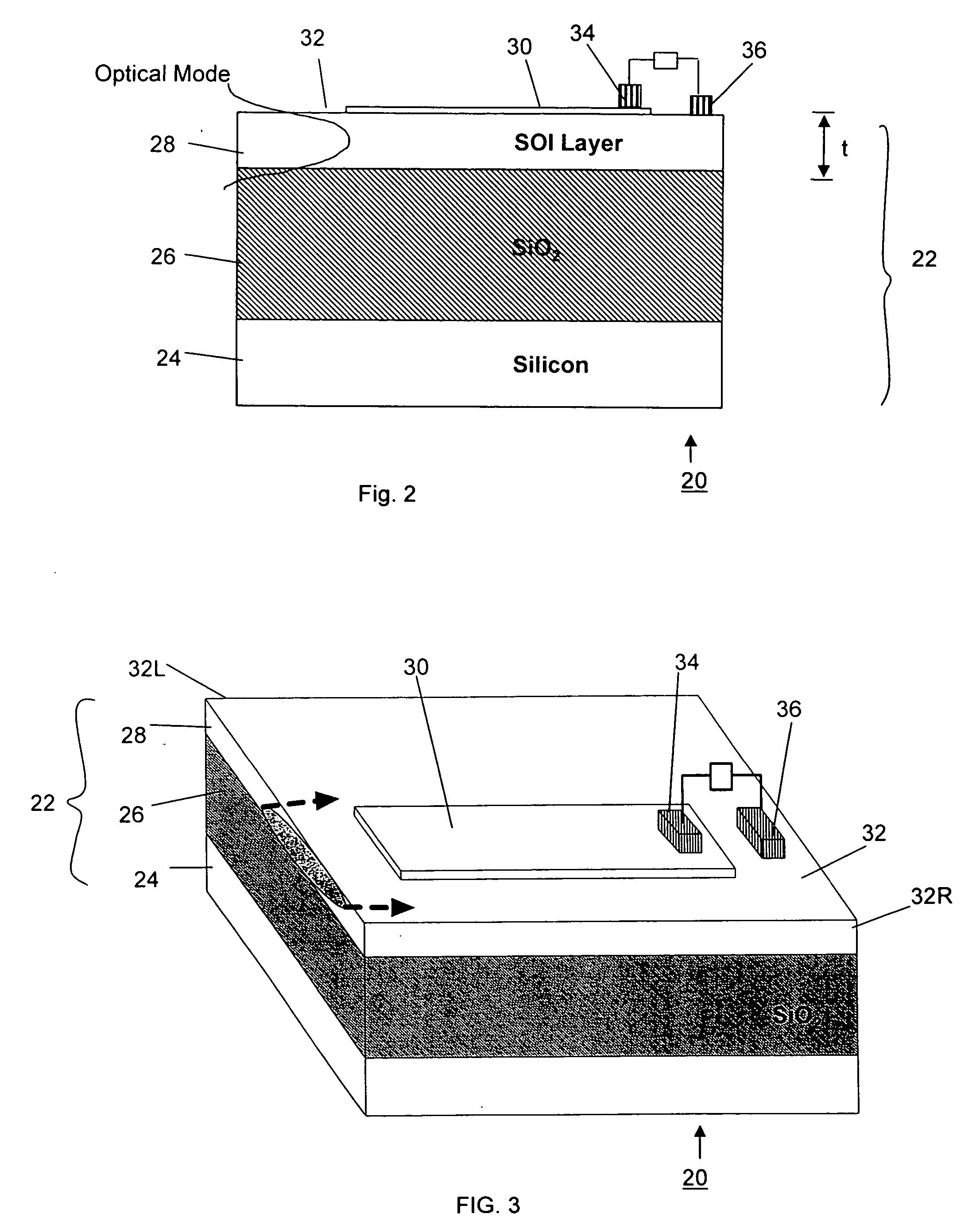
Silicon-based Schottky barrier infrared optical detector
ActiveUS20050110108A1Reduce dark currentEasy to operateOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic energy generationSchottky barrierPhotodetector
A silicon-based IR photodetector is formed within a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) structure by placing a metallic strip (preferably, a silicide) over a portion of an optical waveguide formed within a planar silicon surface layer (i.e., “planar SOI layer”) of the SOI structure, the planar SOI layer comprising a thickness of less than one micron. Room temperature operation of the photodetector is accomplished as a result of the relatively low dark current associated with the SOI-based structure and the ability to use a relatively small surface area silicide strip to collect the photocurrent. The planar SOI layer may be doped, and the geometry of the silicide strip may be modified, as desired, to achieve improved results over prior art silicon-based photodetectors.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Quantum dot infrared photodetector (QDIP) and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20010028055A1Quality improvementNanoinformaticsSemiconductor devicesQuantum dot infrared photodetectorsPhotodetector
A photodetector capable of normal incidence detection over a broad range of long wavelength light signals to efficiently convert infrared light into electrical signals. It is capable of converting long wavelength light signals into electrical signals with direct normal incidence sensitivity without the assistance of light coupling devices or schemes. In the apparatus, stored charged carriers are ejected by photons from quantum dots, then flow over the other barrier and quantum dot layers with the help of an electric field produced with a voltage applied to the device, producing a detectable photovoltage and photocurrent. The photodetector has multiple layers of materials including at least one quantum dot layer between an emitter layer and a collector layer, with a barrier layer between the quantum dot layer and the emitter layer, and another barrier layer between the quantum dot layer and the collector.
Owner:FAFARD SIMON +1
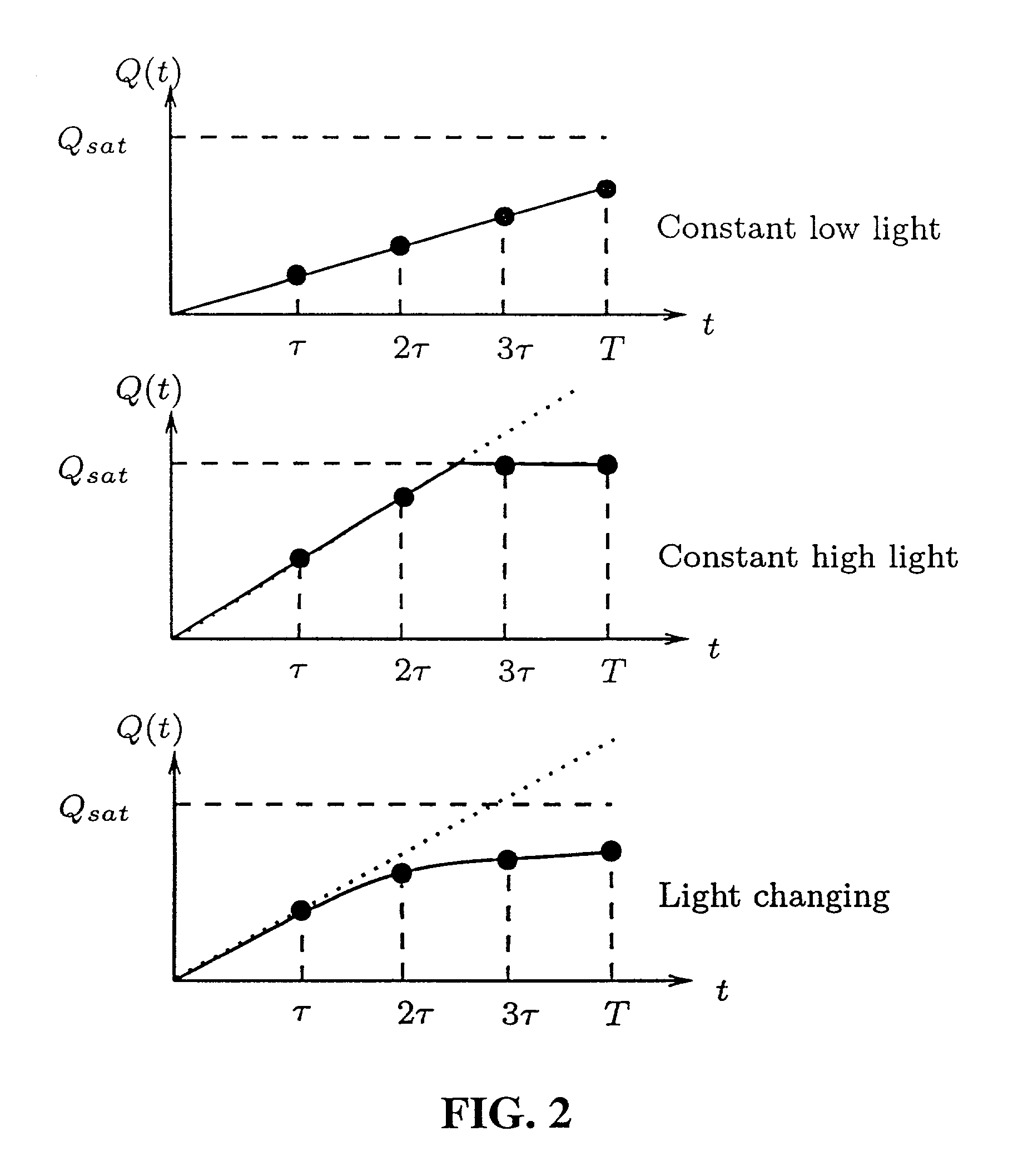
Motion/saturation detection system and method for synthesizing high dynamic range motion blur free images from multiple captures
ActiveUS7061524B2Improve dynamic rangeEasy to optimizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingSingle chip
Motion / Saturation detection system and method for synthesizing high dynamic range motion blur free images from multiple captures, the system and method utilizing photocurrent estimation to reduce read noise and enhance dynamic range at the low illumination end, saturation detection to enhance dynamic range at the high illumination end, and motion blur detection to ensure the photocurrent estimation is not corrupted by motion. Motion blur detection also makes it possible to extend exposure time and to capture more images, which can be used to further enhance dynamic range at the low illumination end. The present invention operates completely locally, making it well suited for single chip digital camera implementations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Ladar transmitting and receiving system and method
A compact LADAR transmitting and receiving apparatus includes a pulse laser generating pulses of light; a transmitter collimating and directing the pulses of light toward a target; a receiver collecting reflected pulses of light, the reflected pulses of light having been reflected from the target, the receiver comprising a tapered fiber bundle; a sensor operatively connected to the tapered fiber bundle, where the sensor comprises a photosensitive region and outputs a photocurrent; an amplifier amplifying the photocurrent; and a power divider splitting the amplified photocurrent between a high gain channel and a low gain channel; a RF interface accepting the high gain channel, the low gain channel, and an undelayed sample of a pulse of light generated from the pulse laser as input; a processing unit accepting output from the RF interface; and a display unit displaying output from the processing unit.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
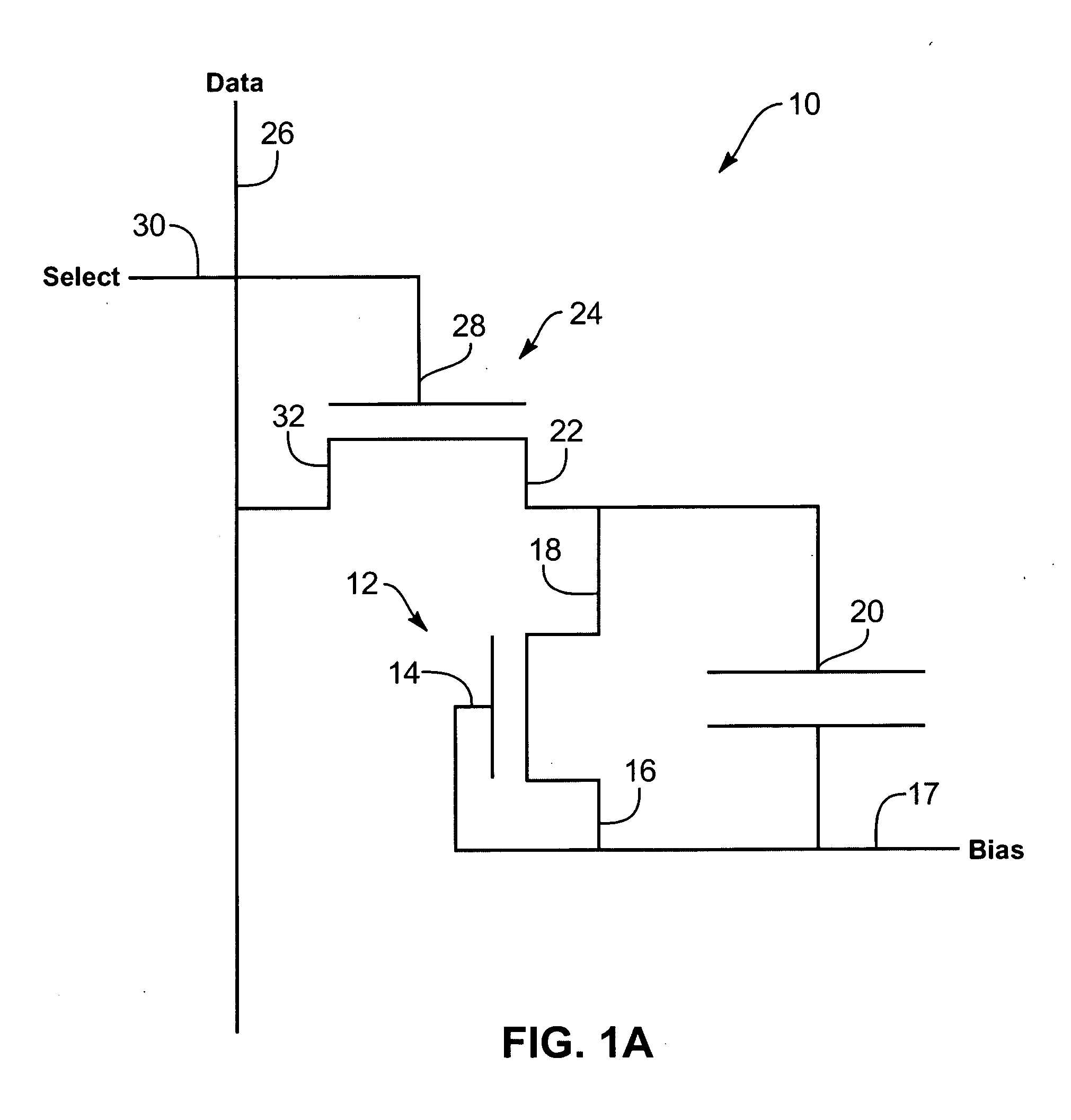
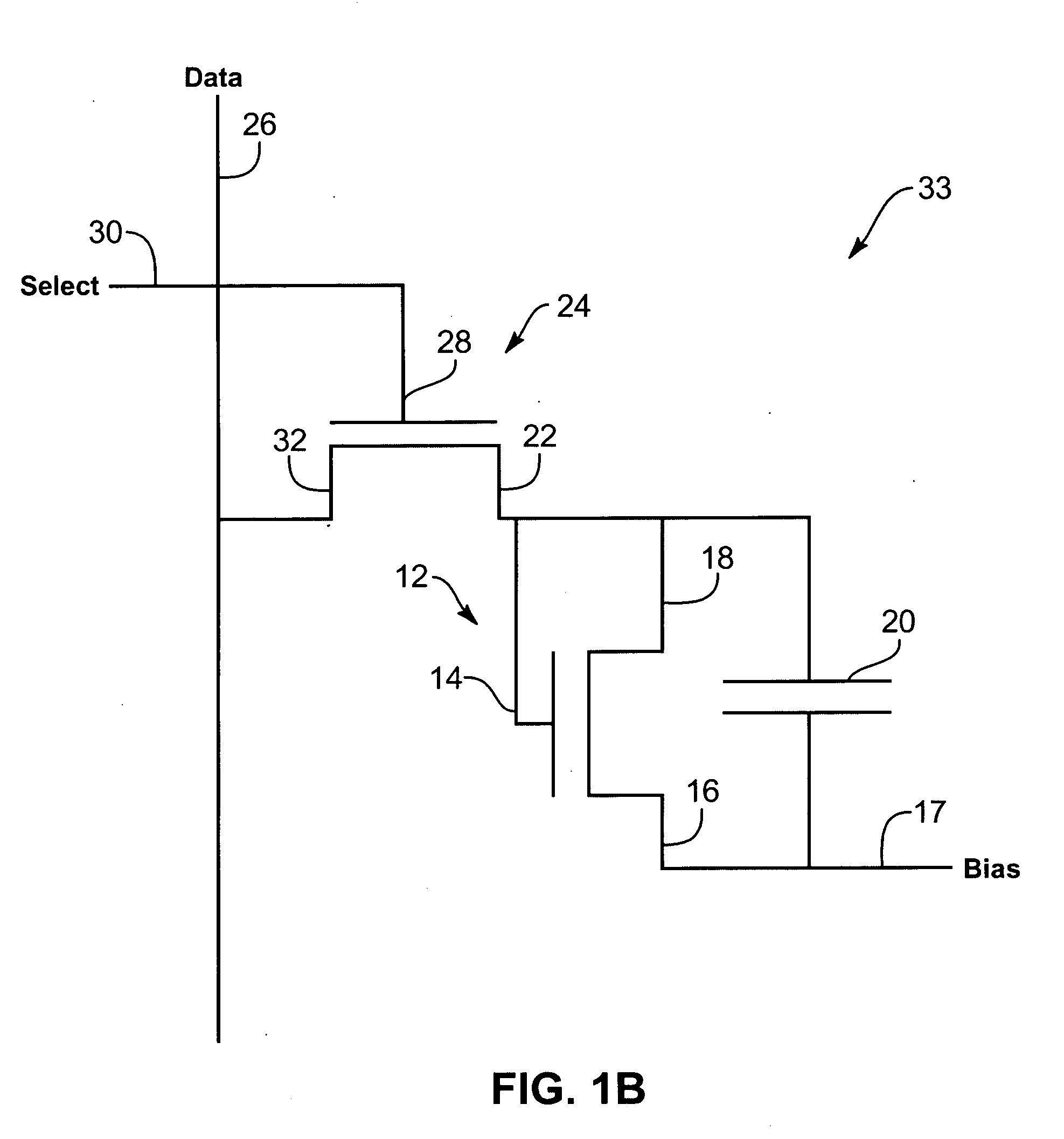
Image sensor with photosensitive thin film transistors
InactiveUS7023503B2Increase photosensitivityPrevent leakageStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPhotocurrentCapacitor
An image sensor array includes image sensors having photo TFTs to generate photocurrent in response to received images. The photo TFTs each have their respective gate electrodes shorted to source electrodes to increase generated photocurrent. Storage capacitors are coupled to each photo TFT and discharged upon generation of a photocurrent. Each storage capacitor is coupled to a readout TFT that passes a current from the storage capacitor to a data line. Data lines indicate location of the received image on the image sensor array.
Owner:APPLE INC
Nanowire photodetector and image sensor with internal gain
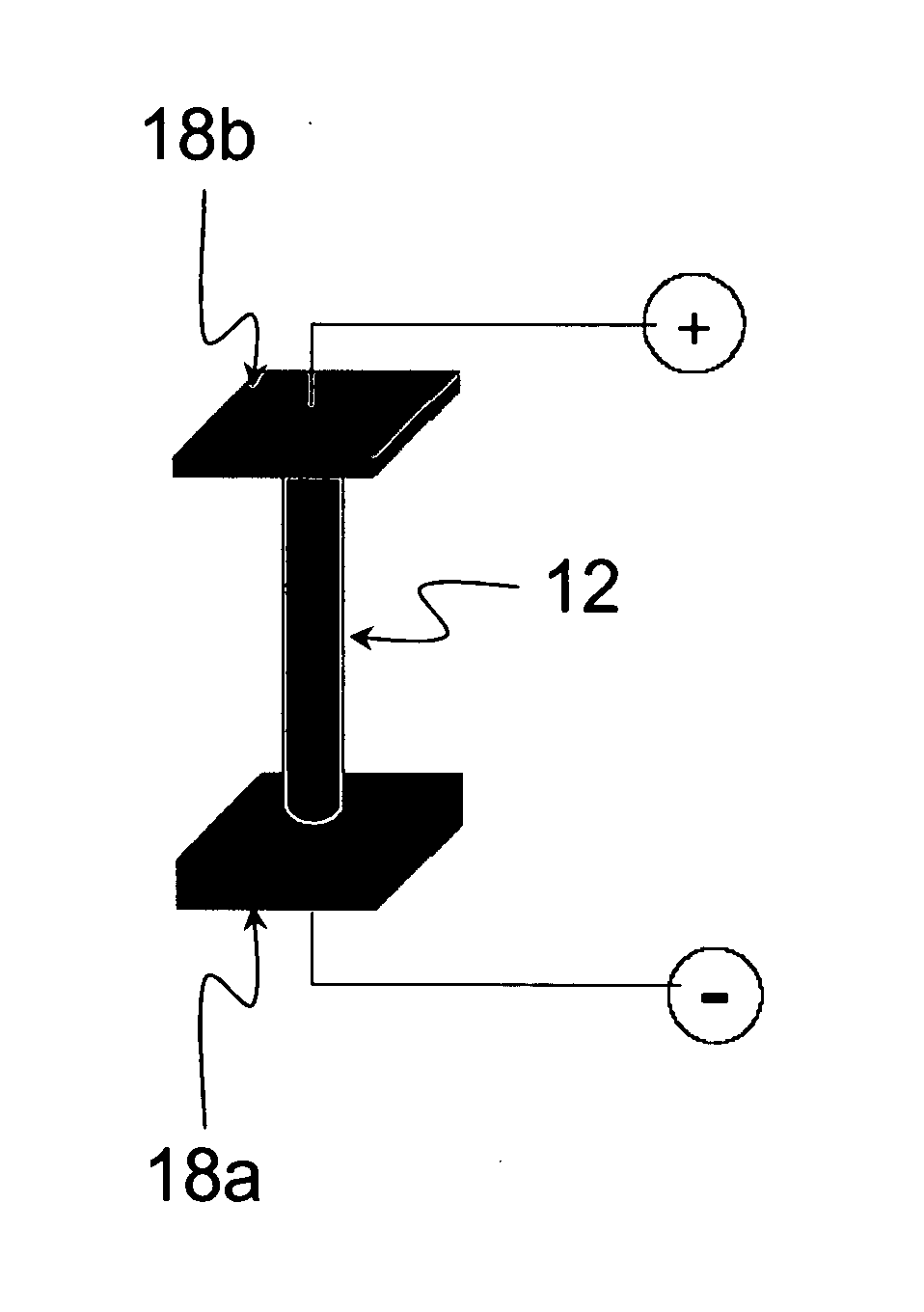
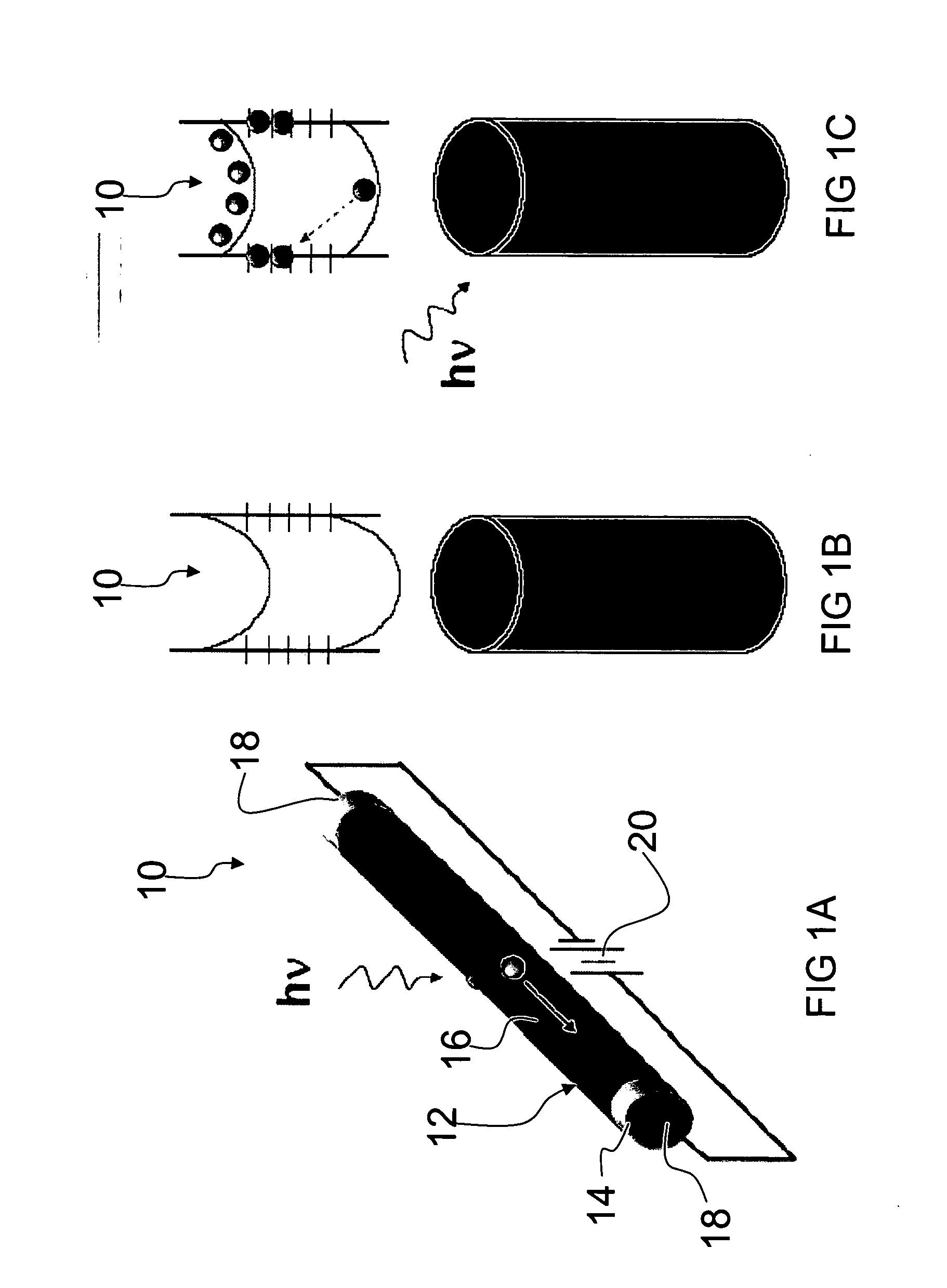
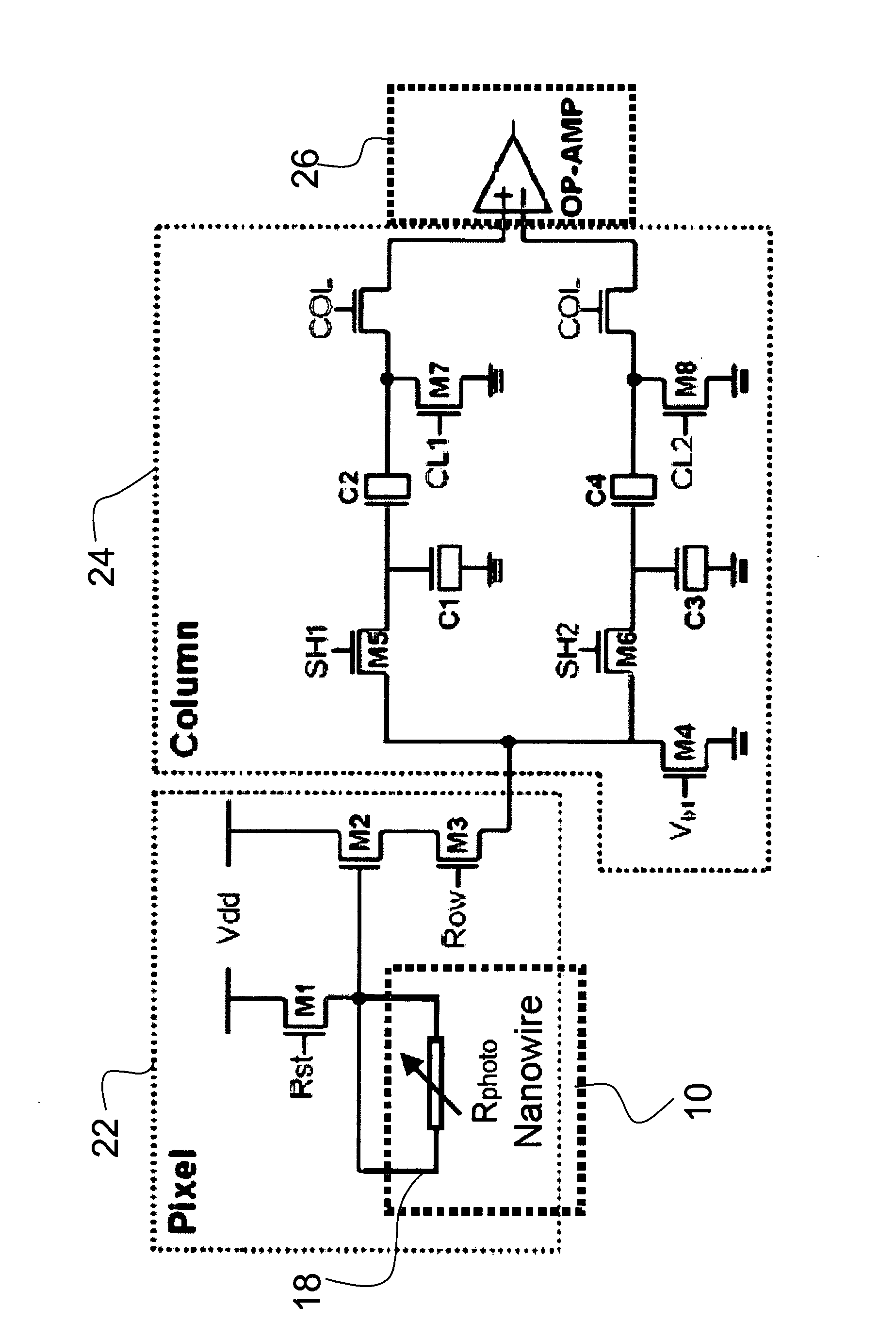
InactiveUS20100295019A1High gainHigh photocurrent responseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsResistNanowire
A practical ID nanowire photodetector with high gain that can be controlled by a radial electric field established in the ID nanowire. A ID nanowire photodetector device of the invention includes a nanowire that is individually contacted by electrodes for applying a longitudinal electric field which drives the photocurrent. An intrinsic radial electric field to the nanowire inhibits photo-carrier recombination, thus enhancing the photocurrent response. The invention further provides circuits of ID nanowire photodetectors, with groups of photodetectors addressed by their individual ID nanowires electrode contacts. The invention also provides a method for placement of ID nanostructures, including nanowires, with registration onto a substrate. A substrate is patterned with a material, e.g., photoresist, and trenches are formed in the patterning material at predetermined locations for the placement of ID nanostructures. The ID nanostructures are aligned in a liquid suspension, and then transferred into the trenches from the liquid suspension. Removal of the patterning material places the ID nanostructures in predetermined, registered positions on the substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Display device
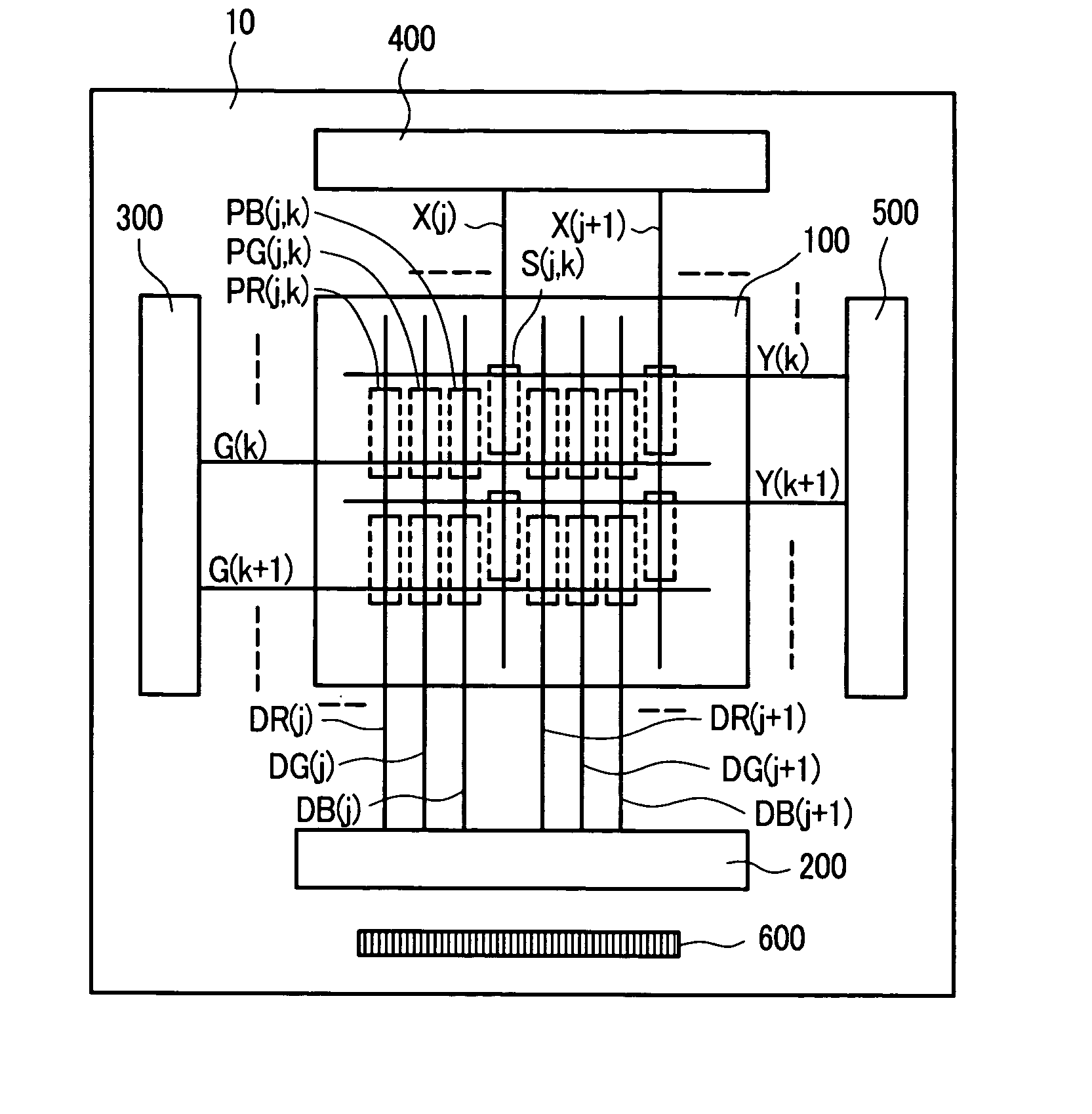
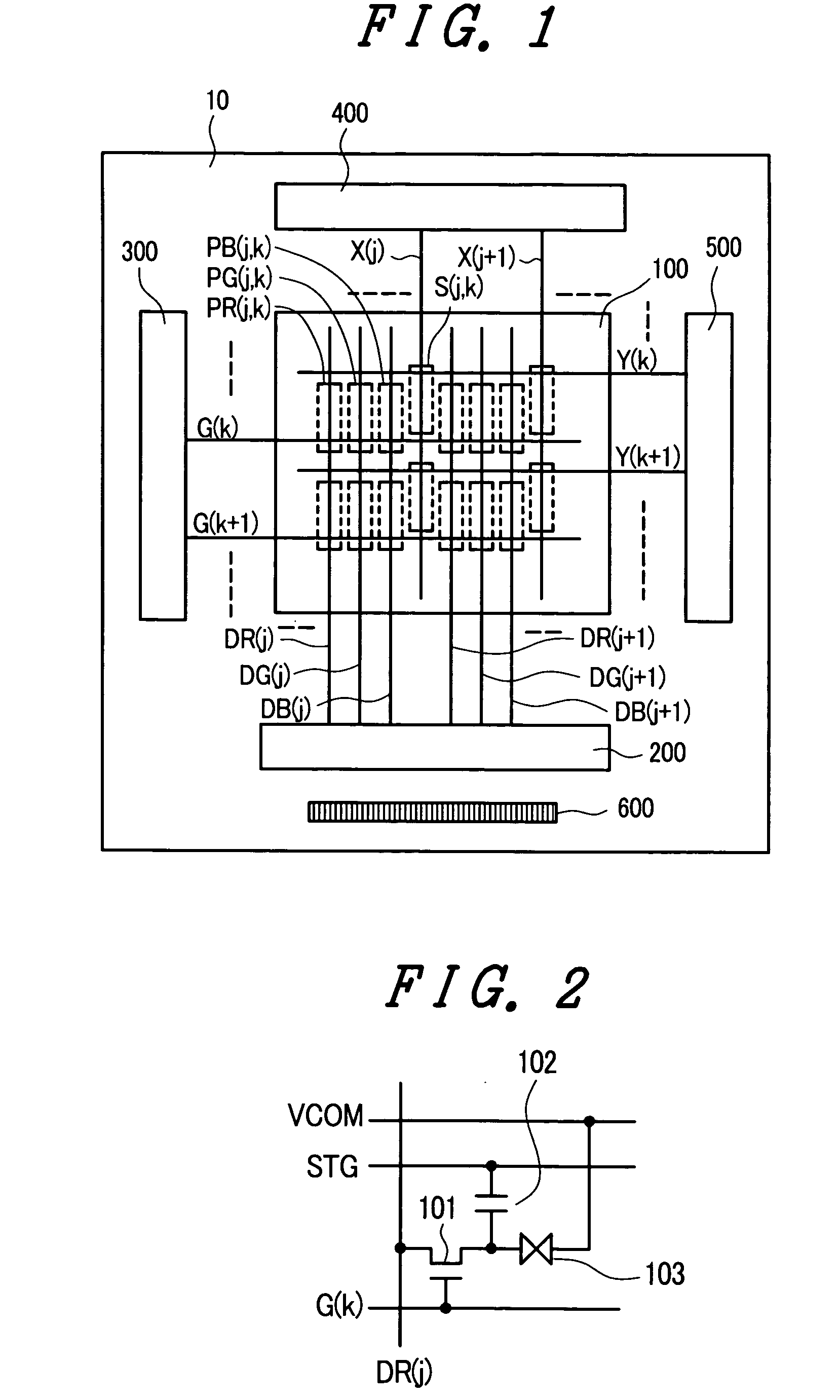
ActiveUS20070070056A1Reduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceDisplay device
A display device which incorporates a touch panel function therein can reduce the number of elements which constitute a photo sensor circuit and can accurately detect an input coordinate position without requiring a particular coordinate arithmetic circuit. In a display device which includes: a display part on which a plurality of pixels are arranged in a matrix array; and a plurality of photo detection circuits which are arranged in a matrix array in the inside of the display part, each photo detection circuit of the plurality of photo detection circuits includes: a photo sensor which converts an incident light into a optical current corresponding to intensity of the incident light; an integral capacitance which integrates the optical current converted by the photo sensor; and a comparator to which a voltage of the integral capacitance is inputted; and the comparator includes a transistor of an open drain output type with a grounded source.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
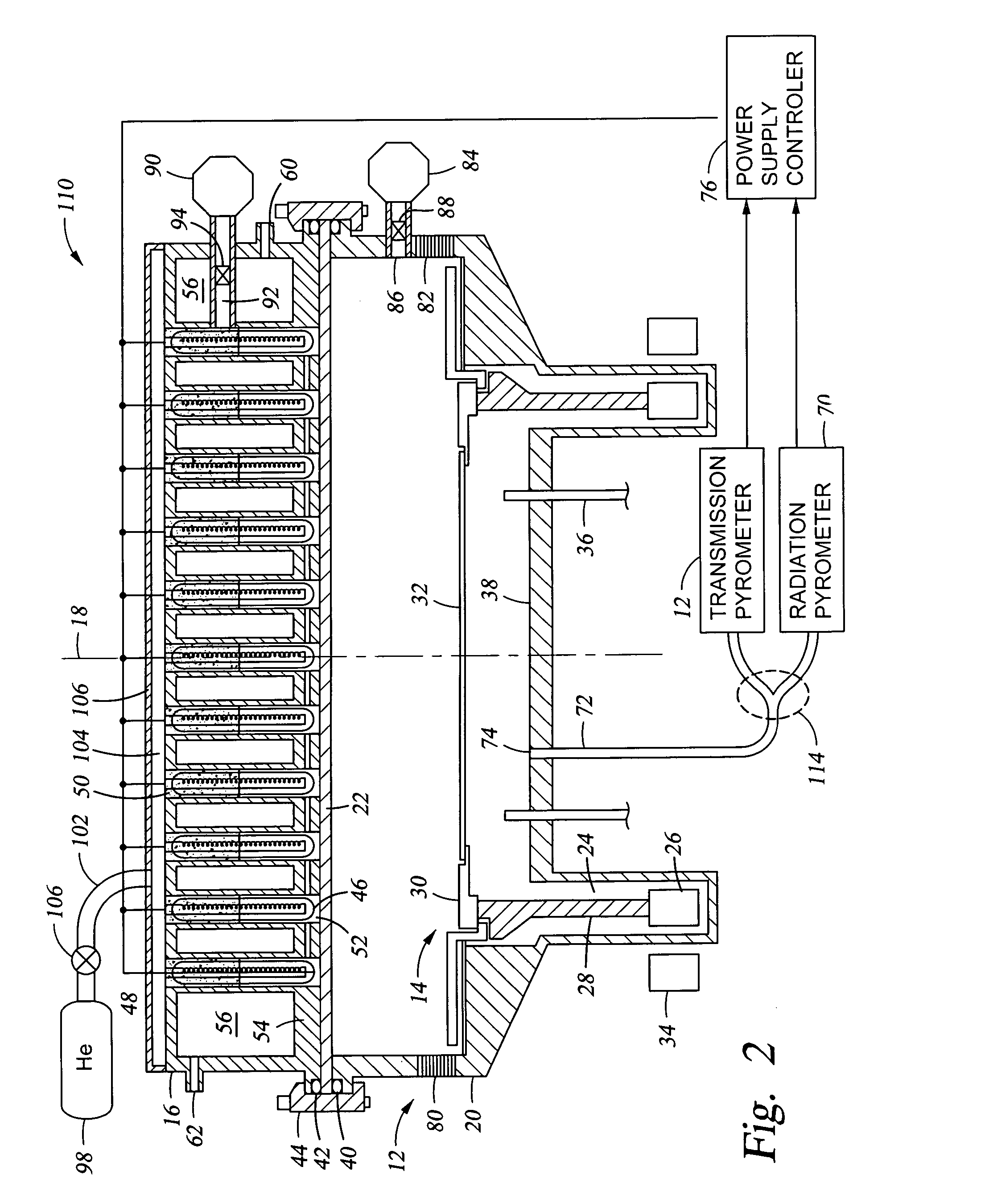
Method and apparatus for low temperature pyrometry useful for thermally processing silicon wafers
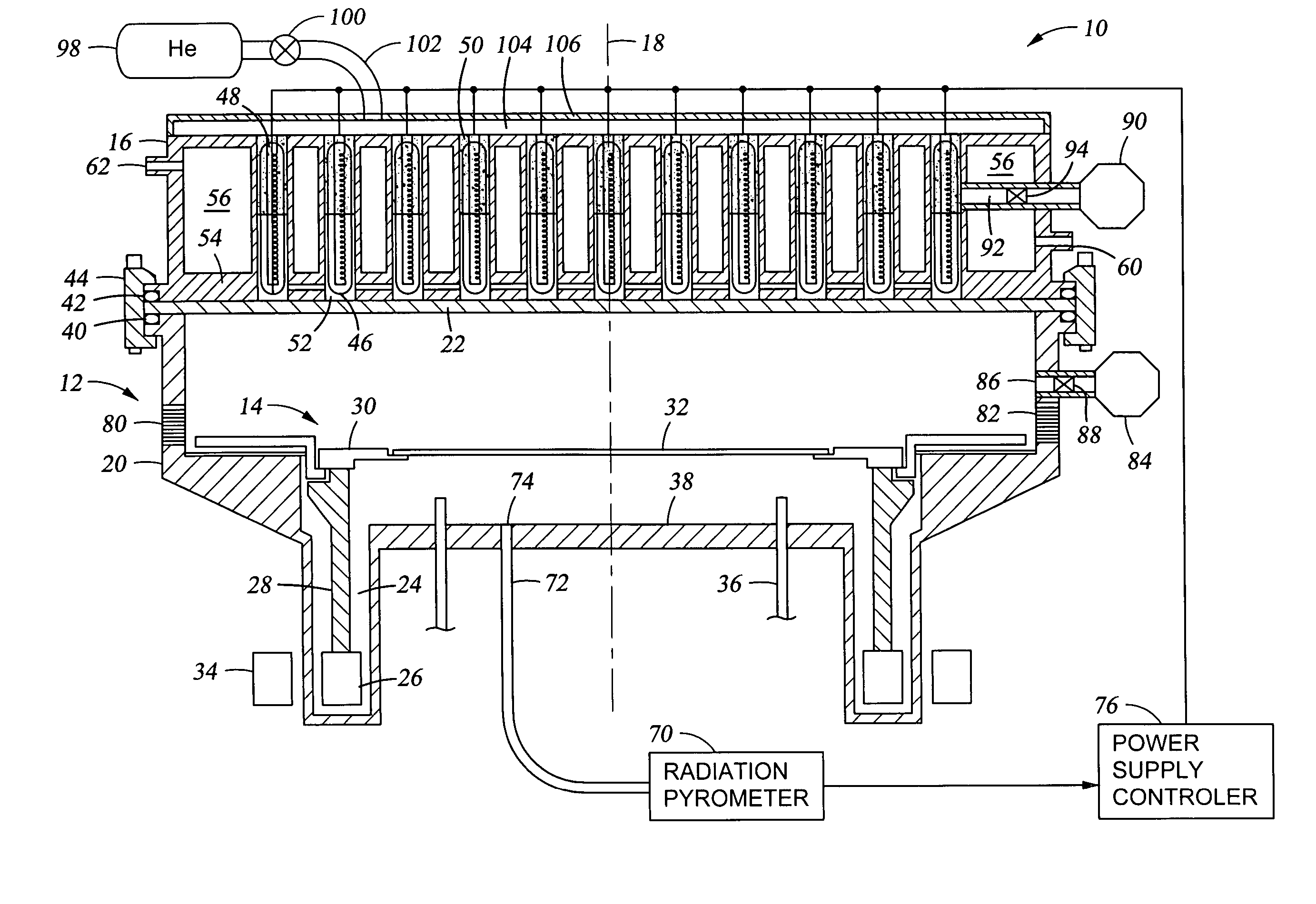
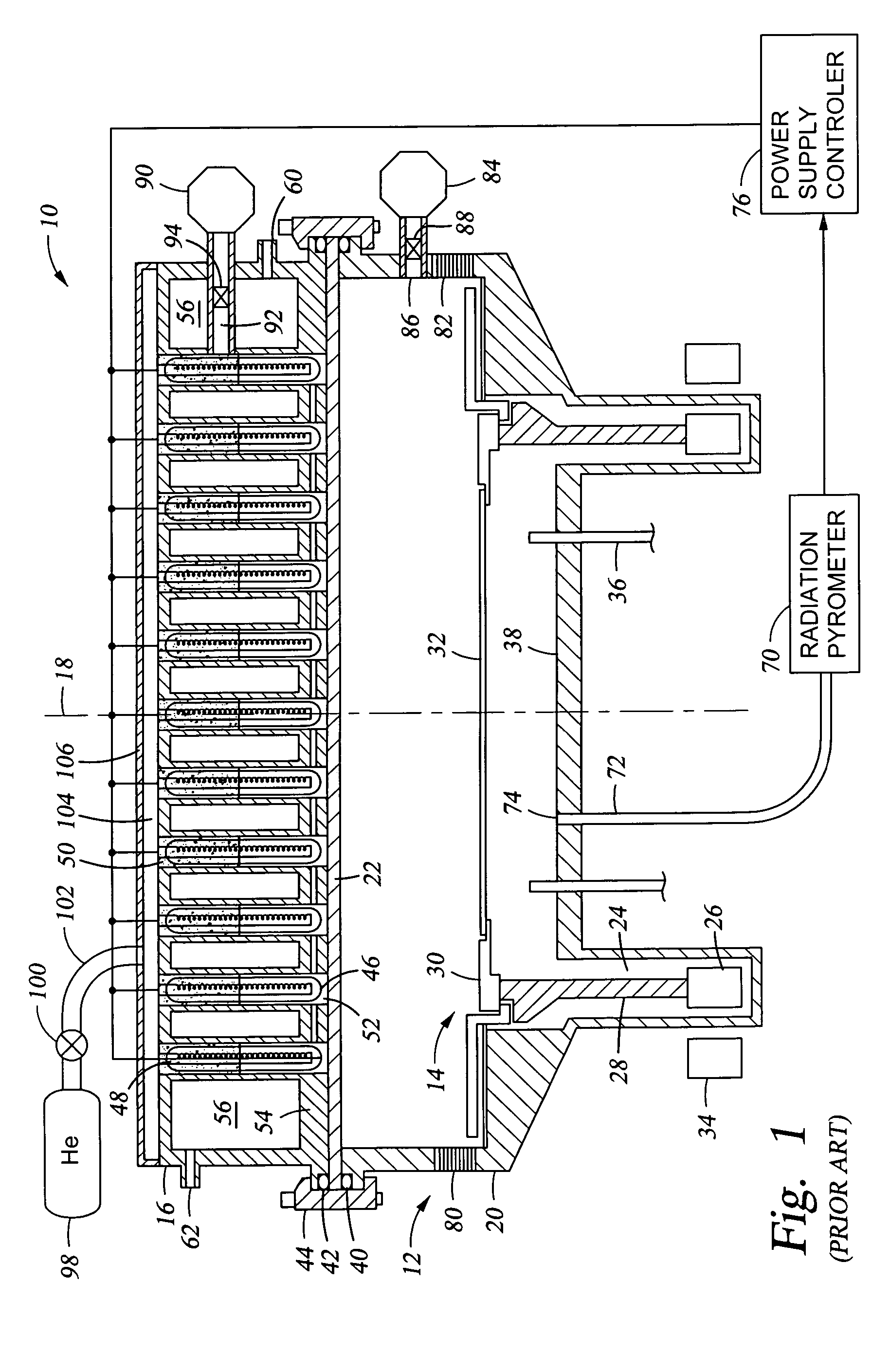
A rapid thermal processing (RTP) system including a transmission pyrometer monitoring the temperature dependent absorption of the silicon wafer for radiation from the RTP lamps at a reduced power level. A look-up table is created relating unnormalized values of photodetector photocurrents with wafer and radiant lamp temperatures. A calibrating step measures the photocurrent with known wafer and lamp temperatures and all photocurrents measured thereafter are accordingly normalized. The transmission pyrometer may be used for closed loop control for thermal treatments below 500° C. or used in the pre-heating phase for a higher temperature process including radiation pyrometry in closed loop control. The pre-heating temperature ramp rate may be controlled by measuring the initial ramp rate and readjusting the lamp power accordingly. Radiation and transmission pyrometers may be included in an integrated structure with a beam splitter dividing radiation from the wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
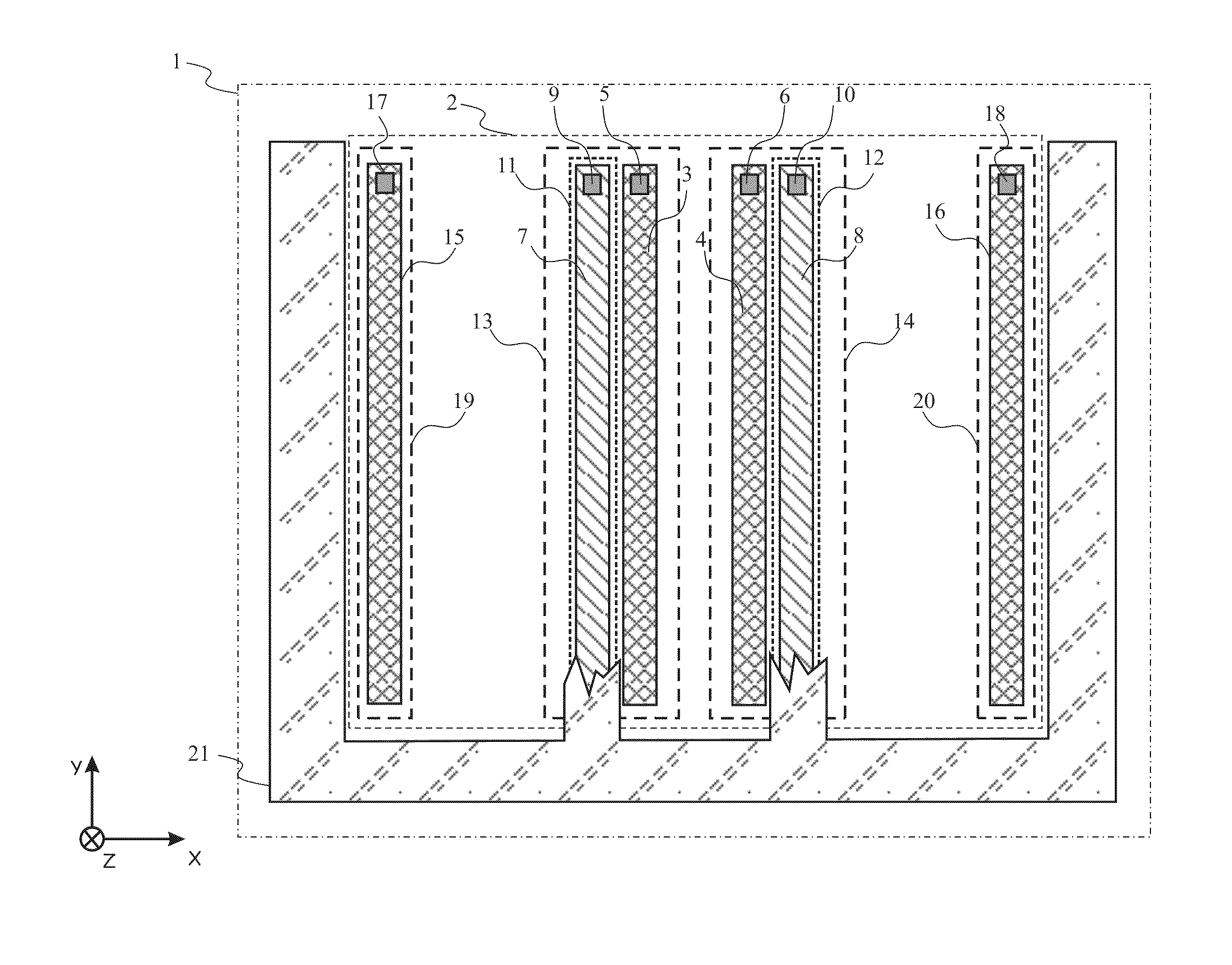
Photonic mixer and use thereof
ActiveUS20110255071A1High resolutionSmall sizeOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesDopantPhotonics
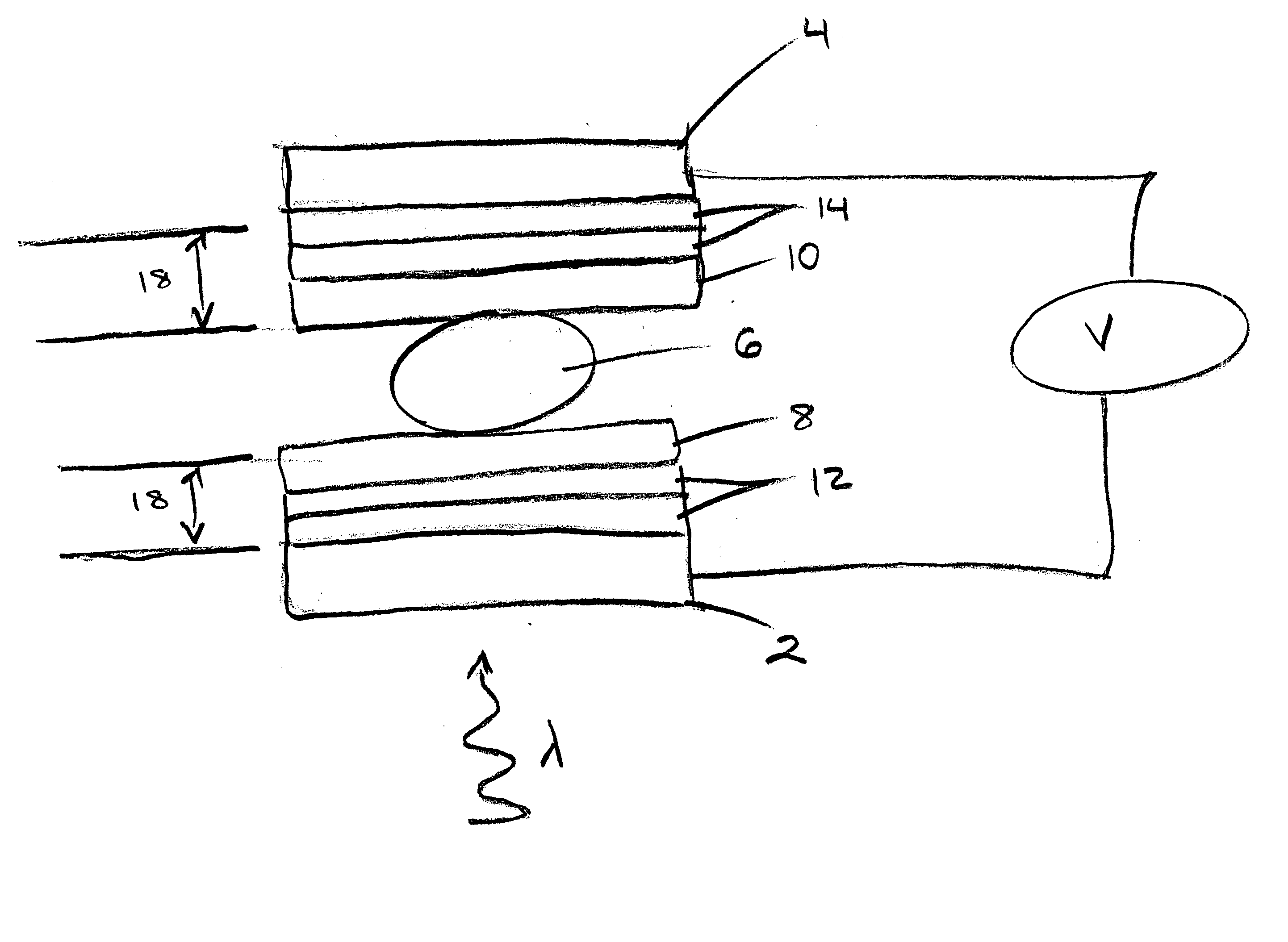
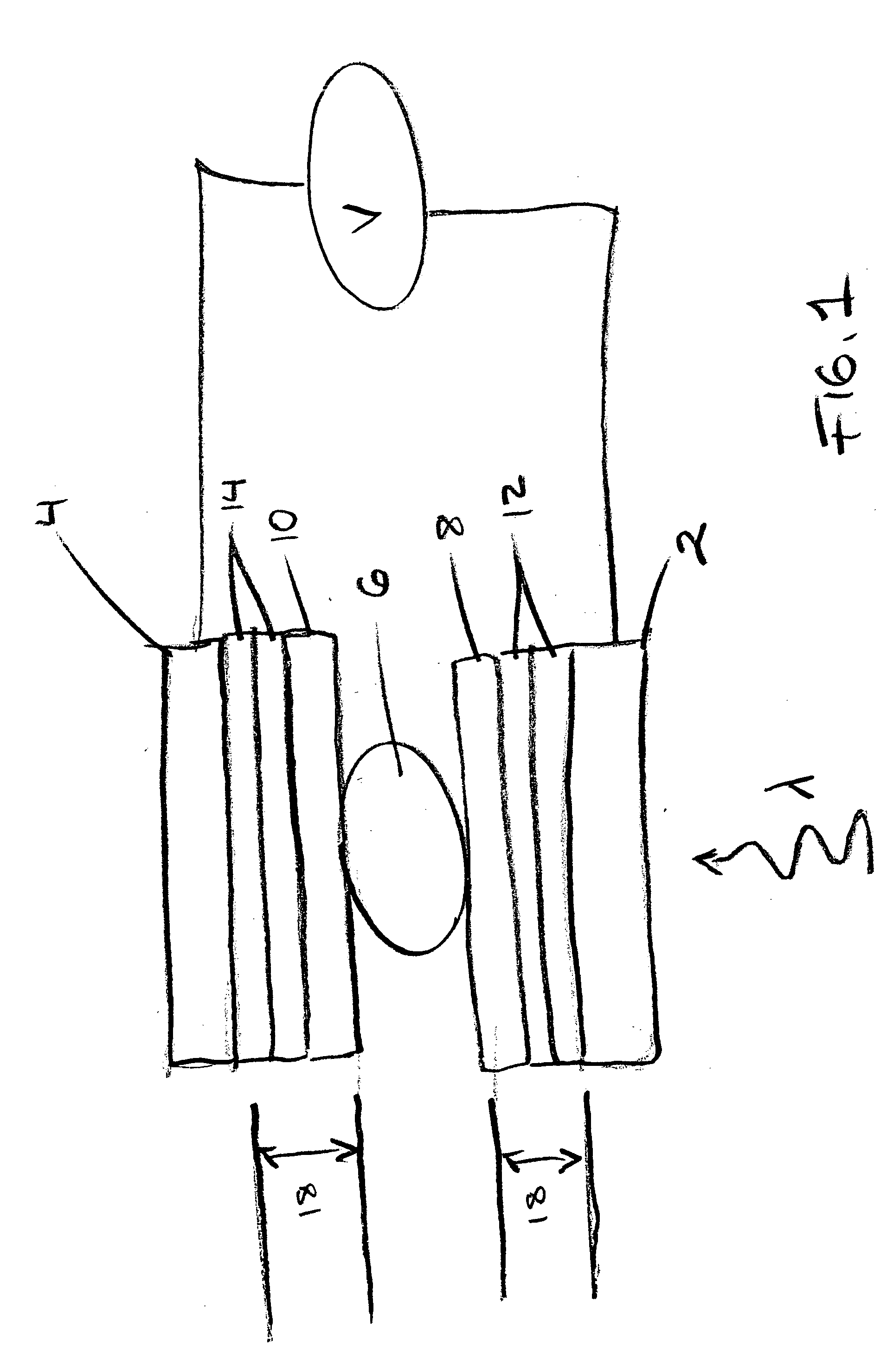
The photonic mixer comprises a couple of an injecting contact region (3,4) for injecting the majority carrier current into the semiconductor substrate (1) and a detector region (7,8) for collecting the photocurrent. The injecting contact region (3,4) is doped with a dopant of the first conductivity type (p+) at a higher dopant concentration than the semiconductor substrate (1). The detector region (7,8) is doped with a dopant of a second conductivity type (n+) opposite the first conductivity type and has a junction (11,12) with the semiconductor substrate (1), a zone of the semiconductor substrate (1) around said junction (11,12) being a depleted substrate zone (101, 102). The couple further comprises a field shaping zone (13, 14) of the first conductivity type (p−) defining a lateral edge of the couple and having a dopant concentration higher than the dopant concentration of the semiconductor substrate (1), for example between the dopant concentrations of the semiconductor substrate (1) and the injecting contact region (3,4), which field shaping zone (13, 14) is designed to limit said depleted substrate zone (101, 102) laterally.
Owner:SOFTKINETIC SENSORS +1
TFT array panel, liquid crystal display including same, and method of manufacturing TFT array panel
InactiveUS20060243979A1Avoid leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A thin film transistor (TFT) array panel effectively minimizing light leakage current and a liquid crystal display including the same. The panel includes a transistor structure having a gate electrode formed on an insulating substrate; a semiconductor layer formed on and insulated from the gate electrode; a light blocking layer formed around and overlapping a portion of the gate electrode; a data line intersecting the gate line to form a source electrode, which overlaps a portion of the semiconductor layer; a drain electrode opposing to the source electrode and overlapping a portion of the semiconductor layer, and a pixel electrode formed on and insulated from the transistor structure and electrically connected to the drain electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Back-contact photovoltaic cell comprising a thin lamina having a superstrate receiver element
InactiveUS20100229928A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPhotocurrent
A photovoltaic assembly comprises a thin semiconductor lamina and a receiver element, where the receiver element serves as a superstrate in the completed device. The photovoltaic assembly includes a photovoltaic cell. The photovoltaic cell is a back-contact cell; photocurrent passes into and out of the back surface of the cell, but does not pass through the light-facing surface. The lamina is typically substantially crystalline and has a thickness less than about 100 microns, in some embodiments 10 microns or less.
Owner:GTAT CORPORATION
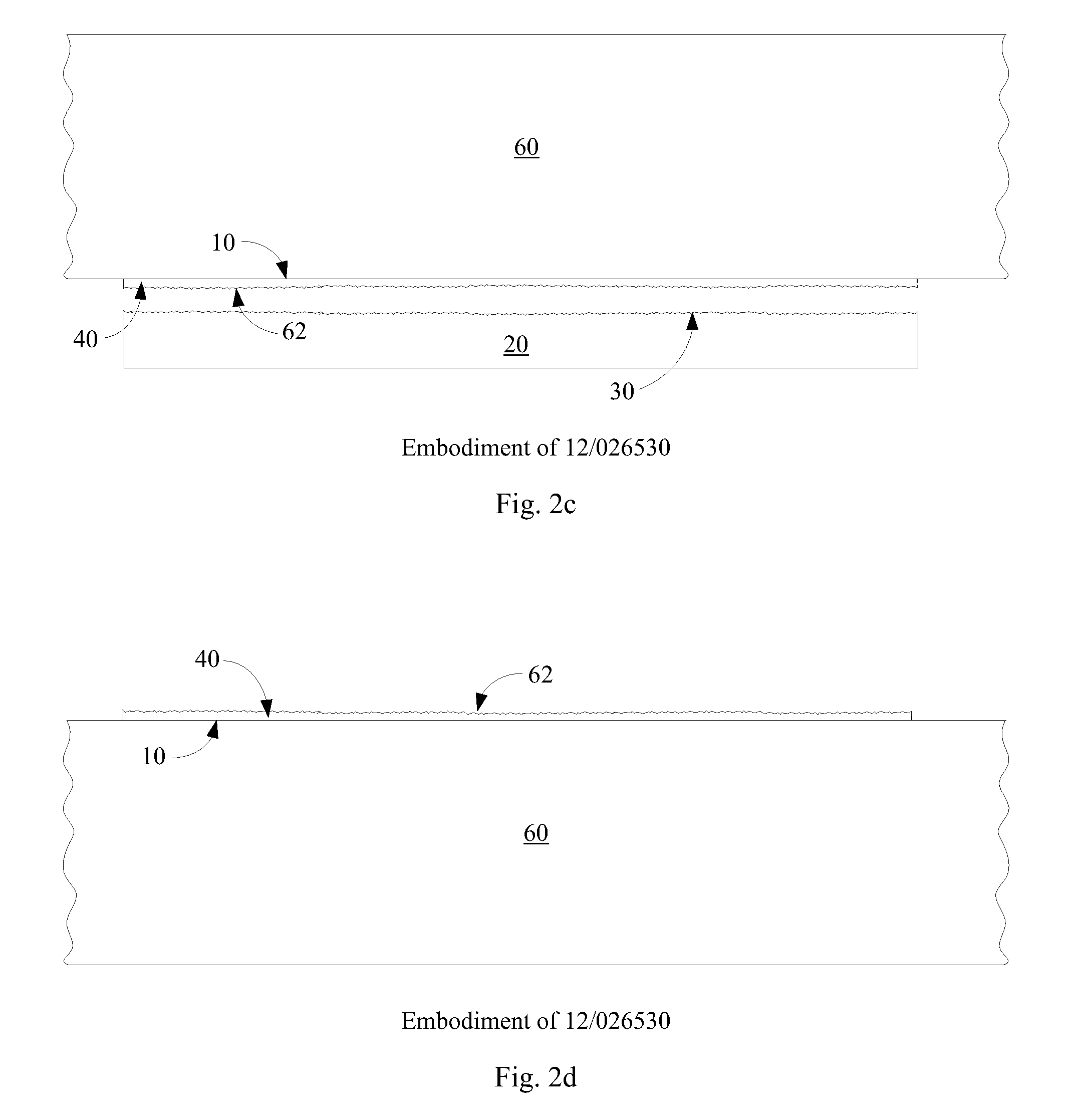
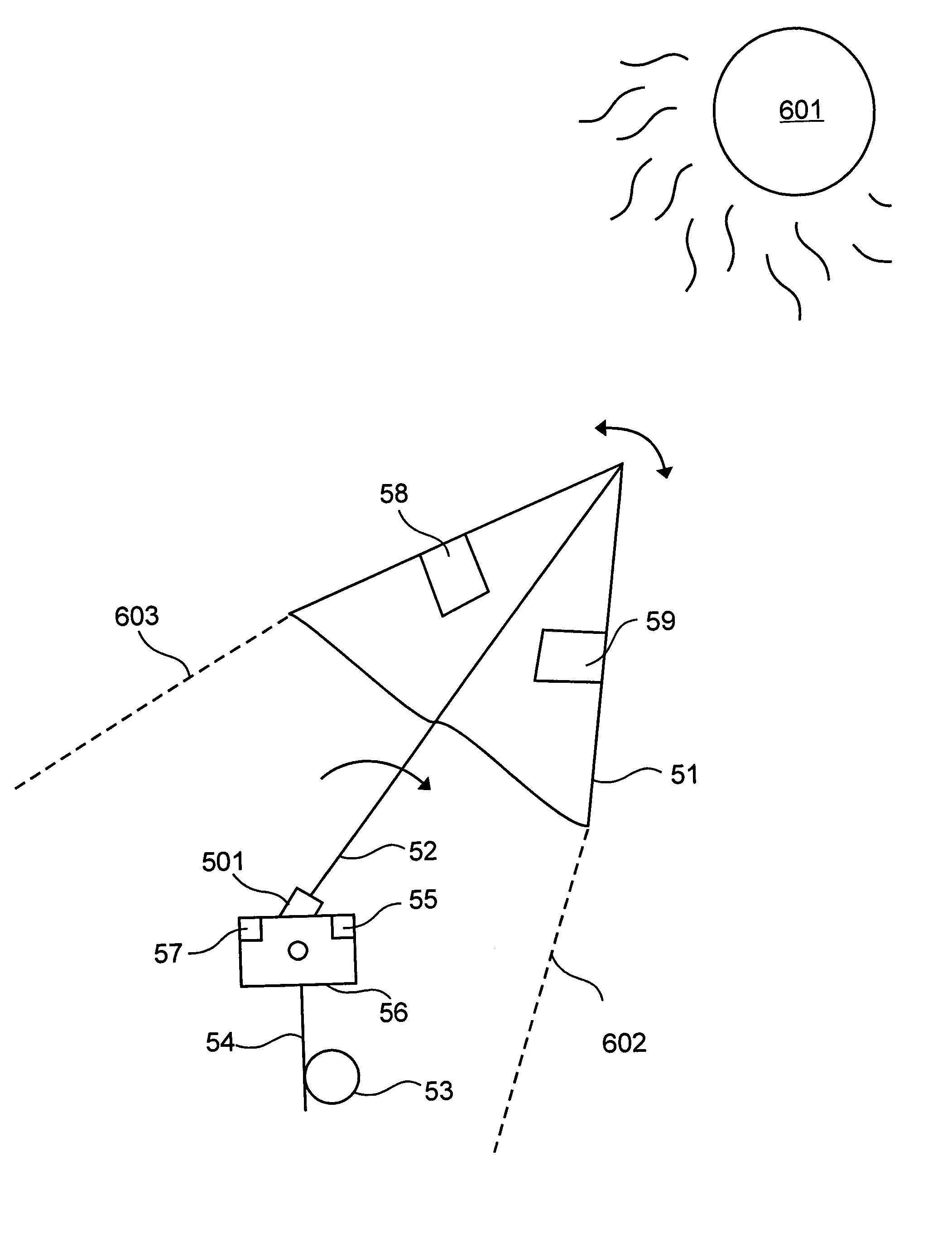
Automated canopy positioning system
An automated canopy positioning system for providing solar protection is disclosed. The automated canopy positioning system orients the canopy of the umbrella in relation to the sun so that a shade at a predetermined location is provided thereunder. The system has a canopy for providing shade in response to light impacting the upper surface, a first photodetector for detecting the amount of light in the shaded area and for generating a photocurrent in response to the light incident thereon, a control circuit for receiving the photocurrent and for generating a control signal in dependence thereon, and a positioning mechanism coupled with the canopy for spatially orienting the canopy in response to the control signal.
Owner:TWISTED INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com