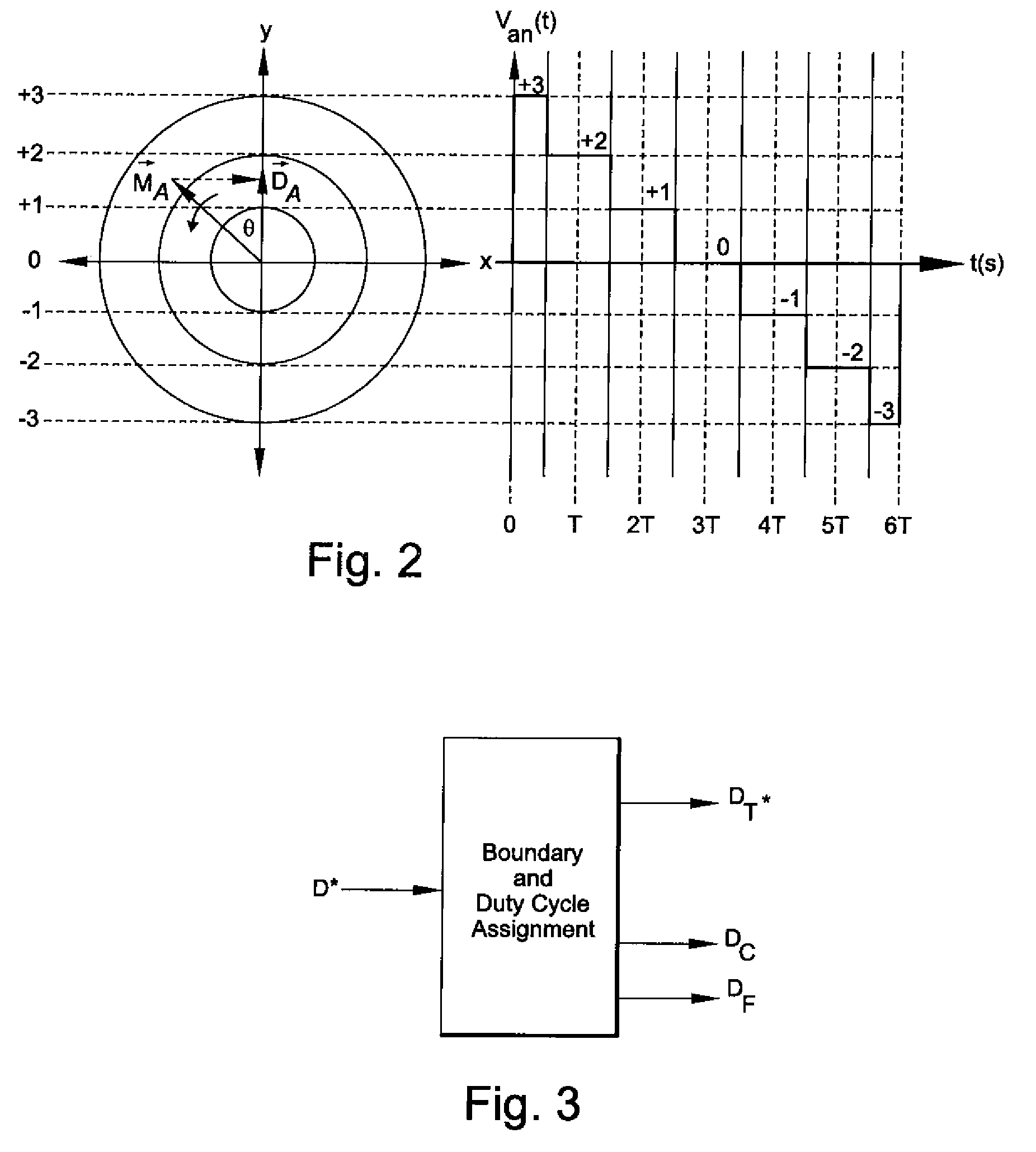
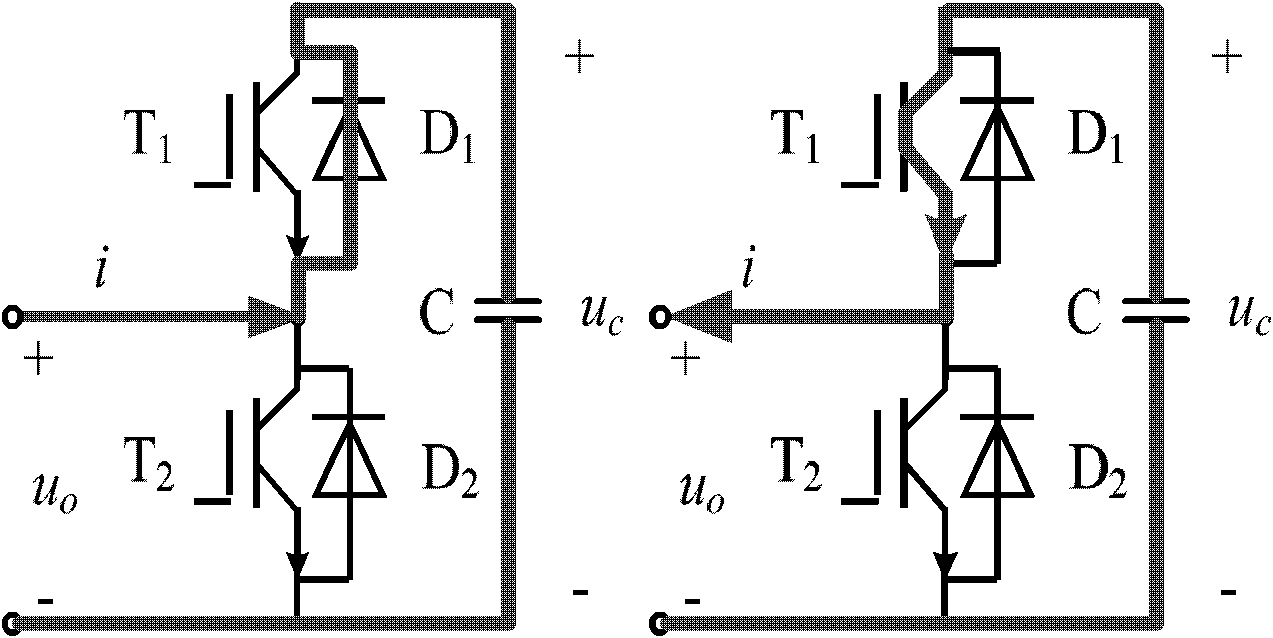
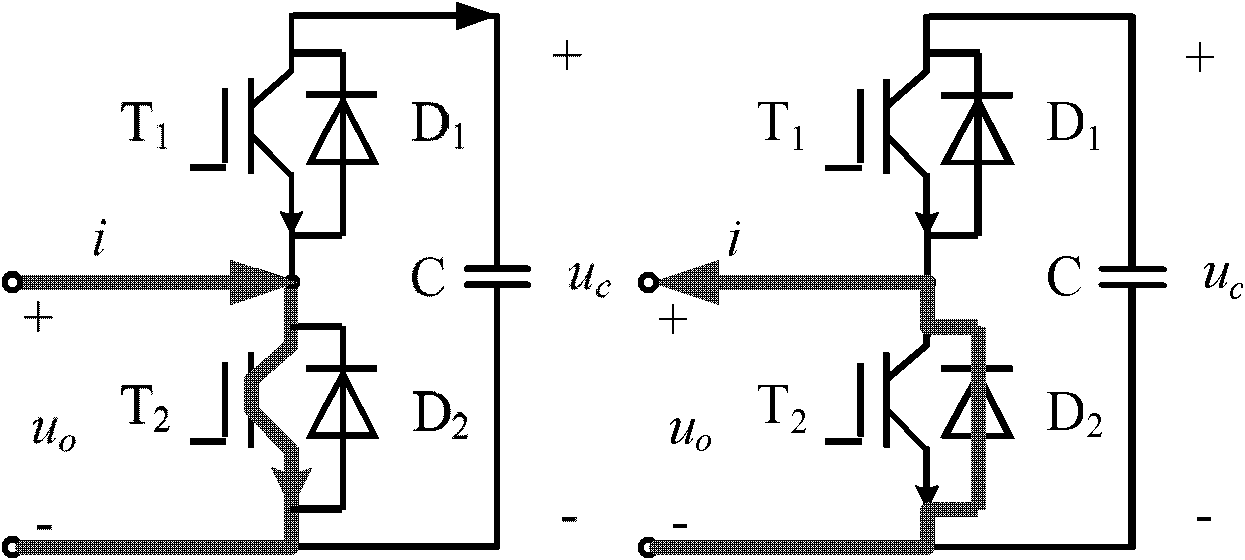
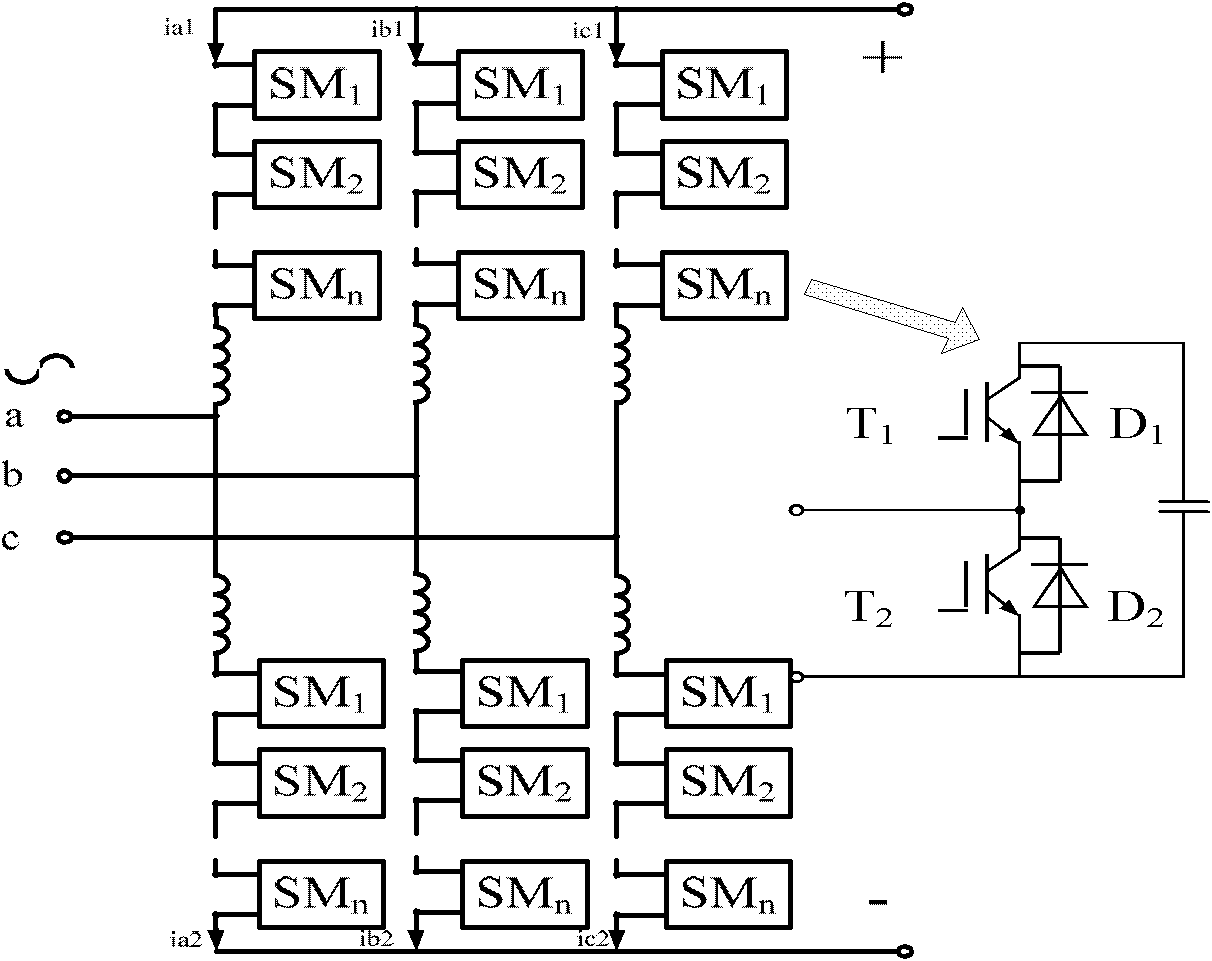
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2703 results about "Capacitor voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS7211081B2Reducing switching transientPromote resultsSurgical instruments for heatingCapacitor voltageEngineering
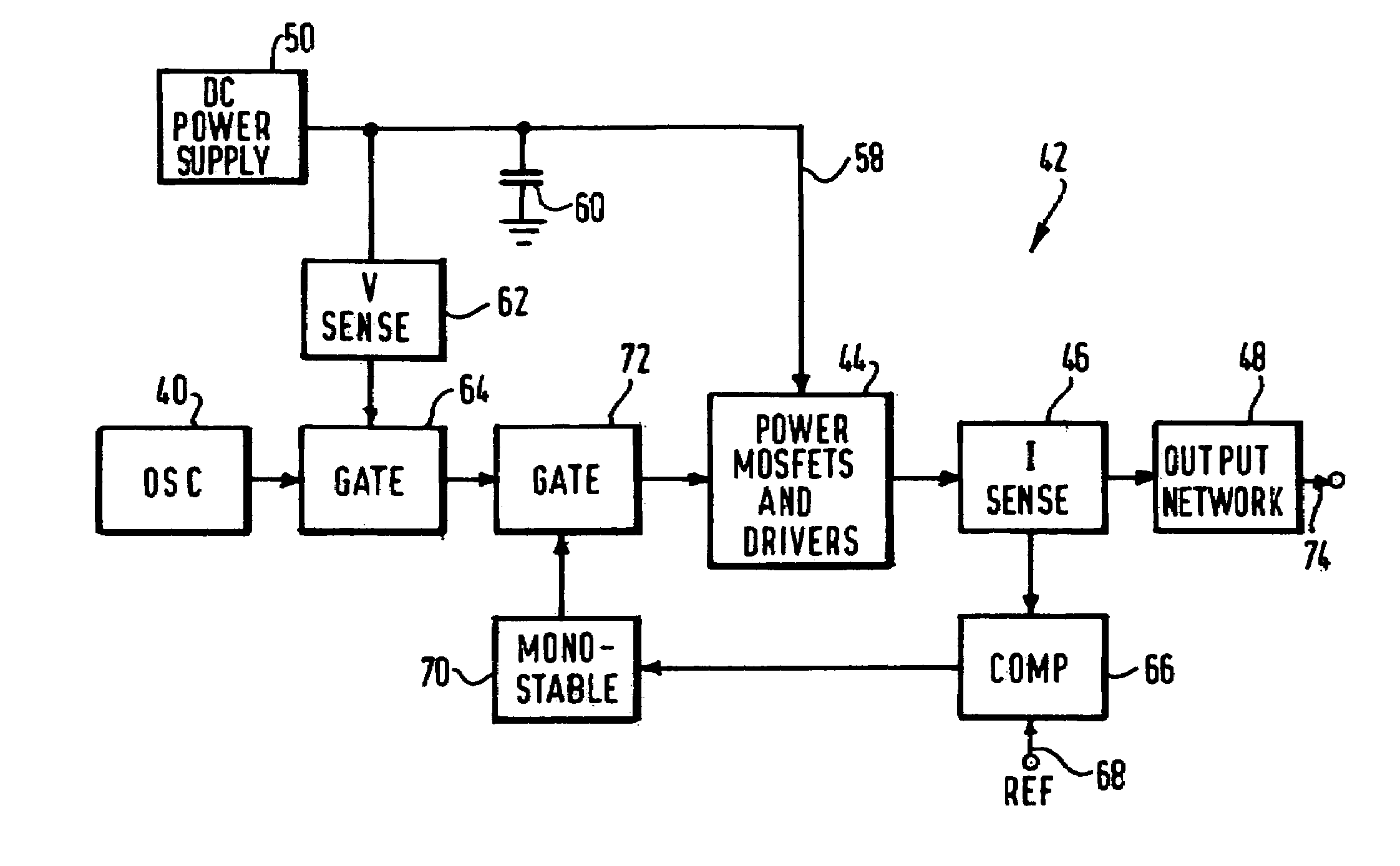
An electrosurgical generator for supplying RF power to an electrosurgical instrument for cutting or vaporising tissue has an RF output stage (42) with an RF power bridge (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4), a pair of output lines (74) and a series-resonant output network (48). The output impedance of the output stage (42) at the output lines (74) is less than 200 / √P ohms, where P is the maximum continuous RF output power of the generator. The generator offers improved cutting and vaporising performance, especially in relation to the reliability with which an arc can be struck when presented with an initial low impedance load. Overloading of the output stage is prevented by rapidly operating protection circuitry responsive to a predetermined electrical condition such as a substantial short-circuit across the output lines. In the preferred embodiment, the output stage is capable of maintaining output pulses at least 1kW peak by supplying the power bridge from a large reservoir capacitor (60). Pulsing is dynamically variable in response to load conditions by controlling the maximum energy per pulse in response to the reservoir capacitor voltage.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range
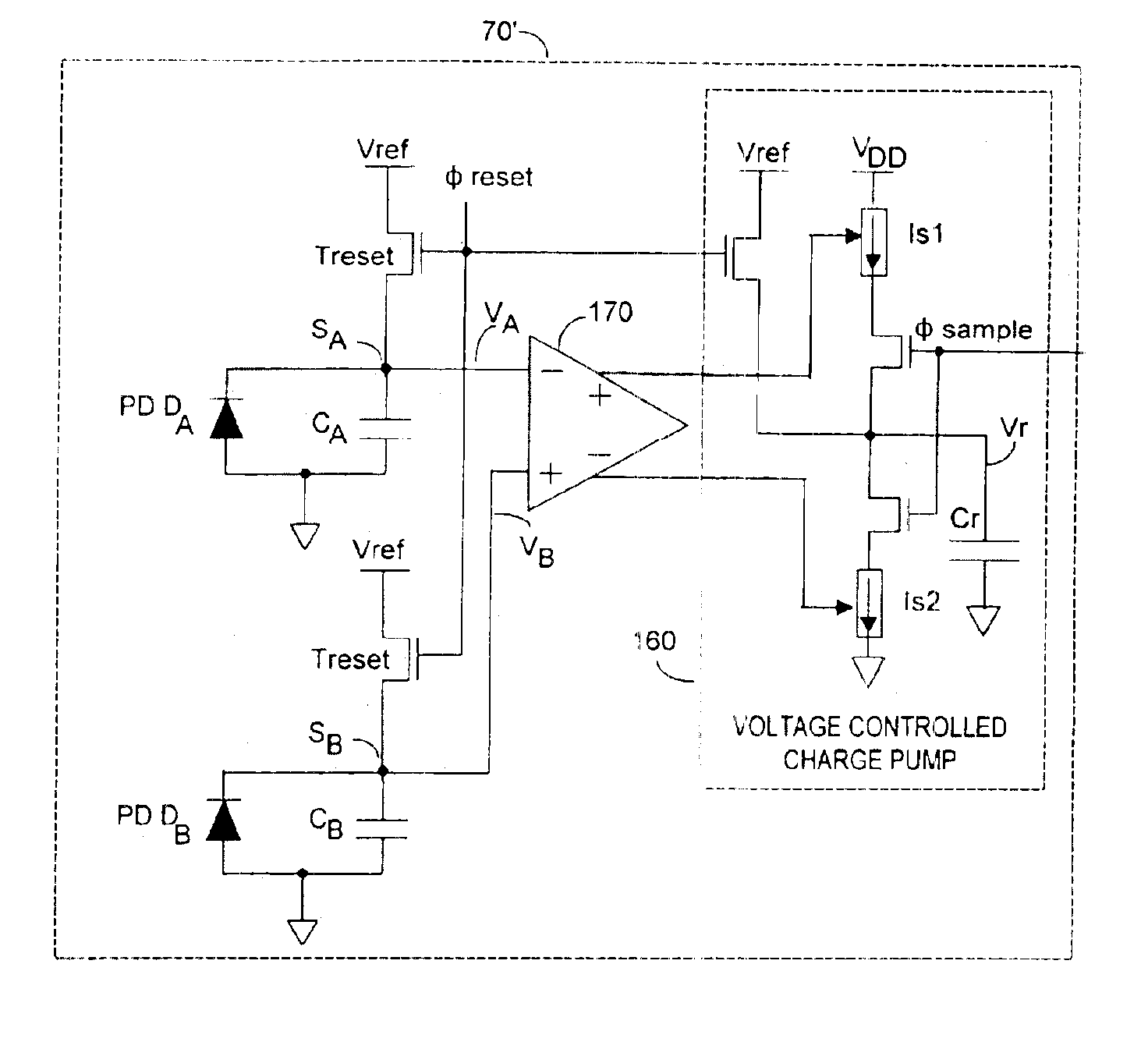
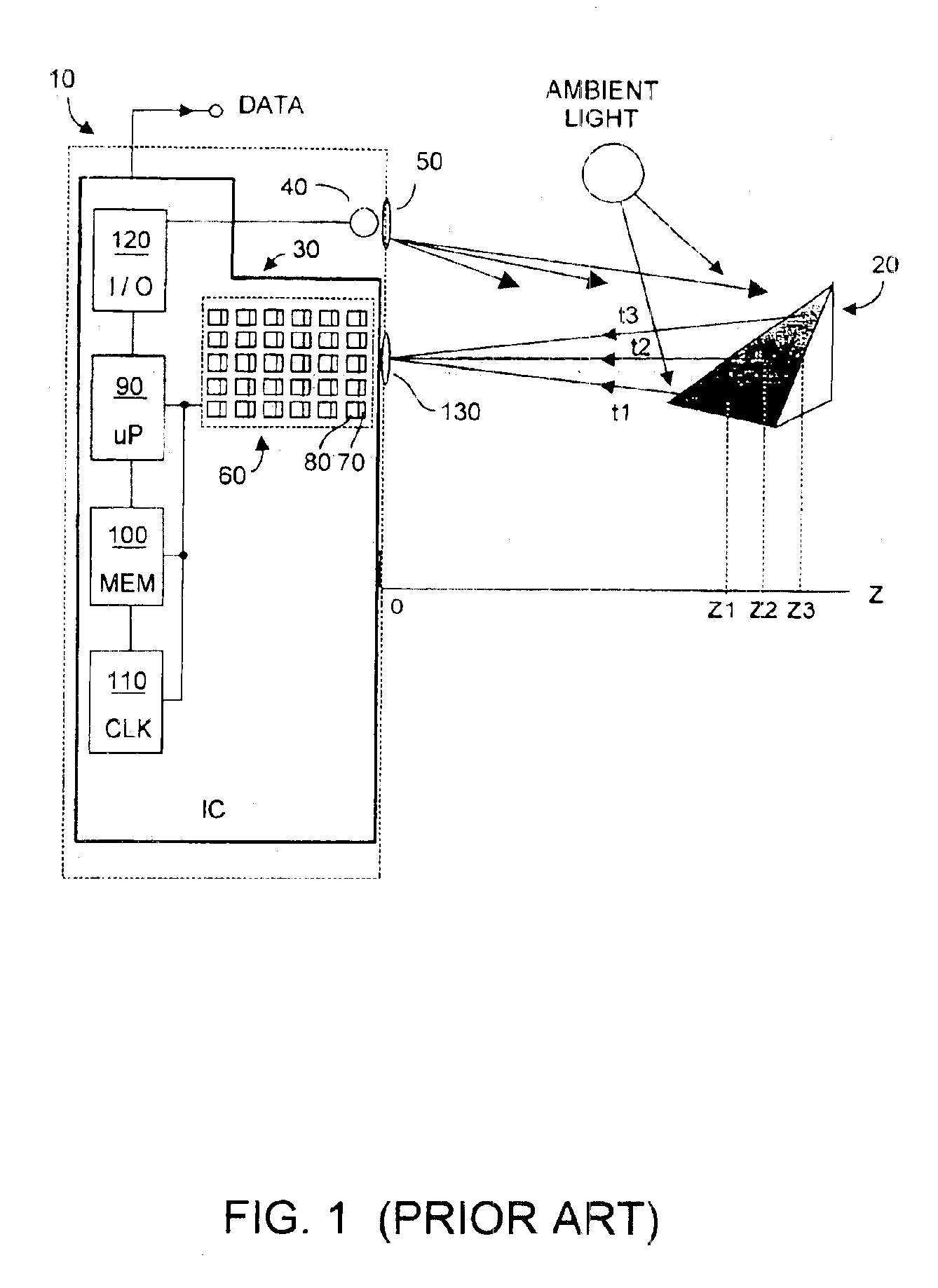
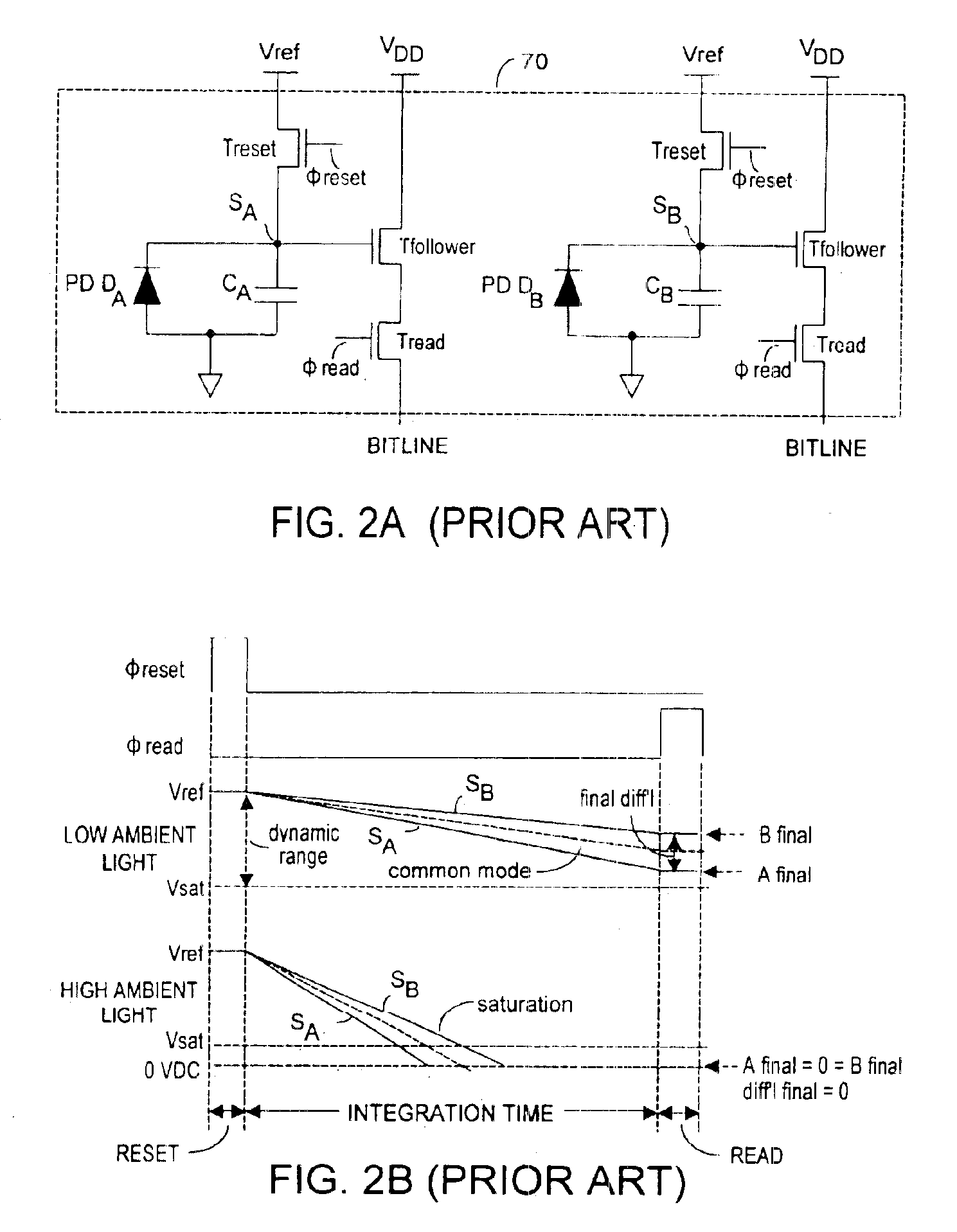
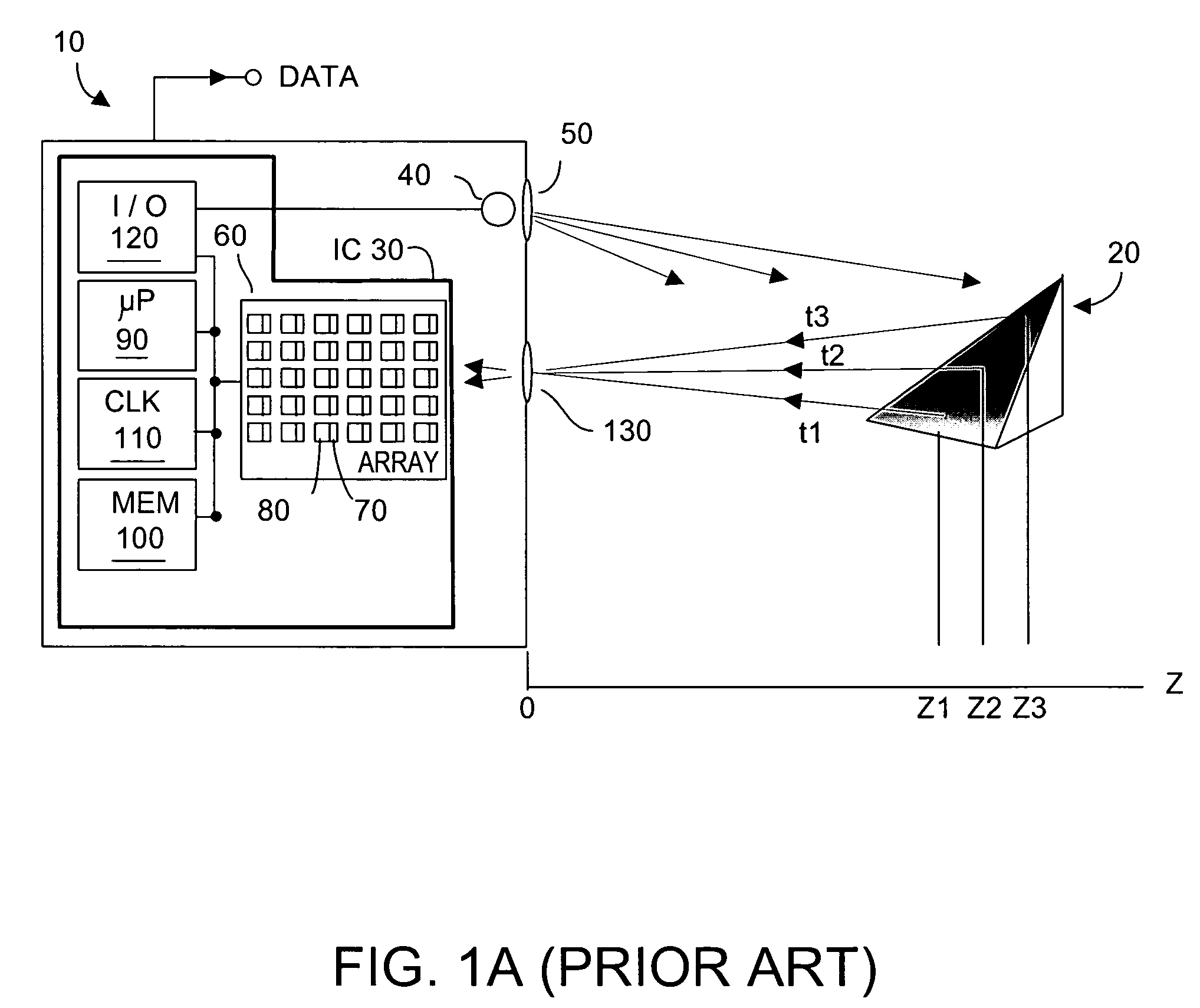
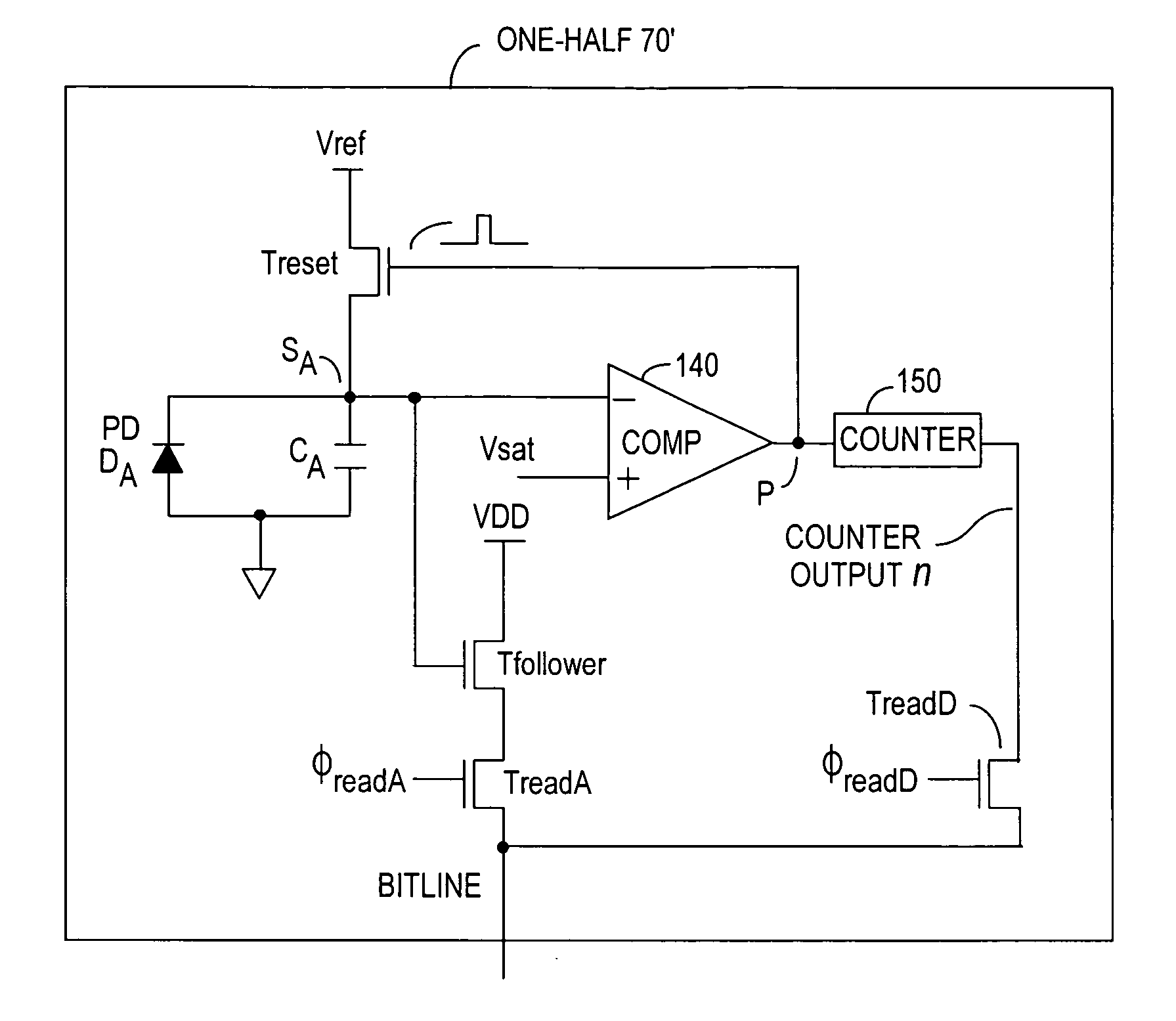
InactiveUS6919549B2Effective dynamic rangeInhibition effectTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Effective differential dynamic range in a differential pixel detector is increased by avoiding saturation effects due to common mode contribution in optical energy to be detected. Photocurrent generated by each photodetector pair is directly integrated by an associated capacitor over an integration time T. Within time T, before either integrated capacitor voltage reaches Vsat for the photodetector, at least one of the capacitors is reset to a voltage such that the desired differential detector signal is still determinable. Reset may be generated externally or internally to the differential pixel detector.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
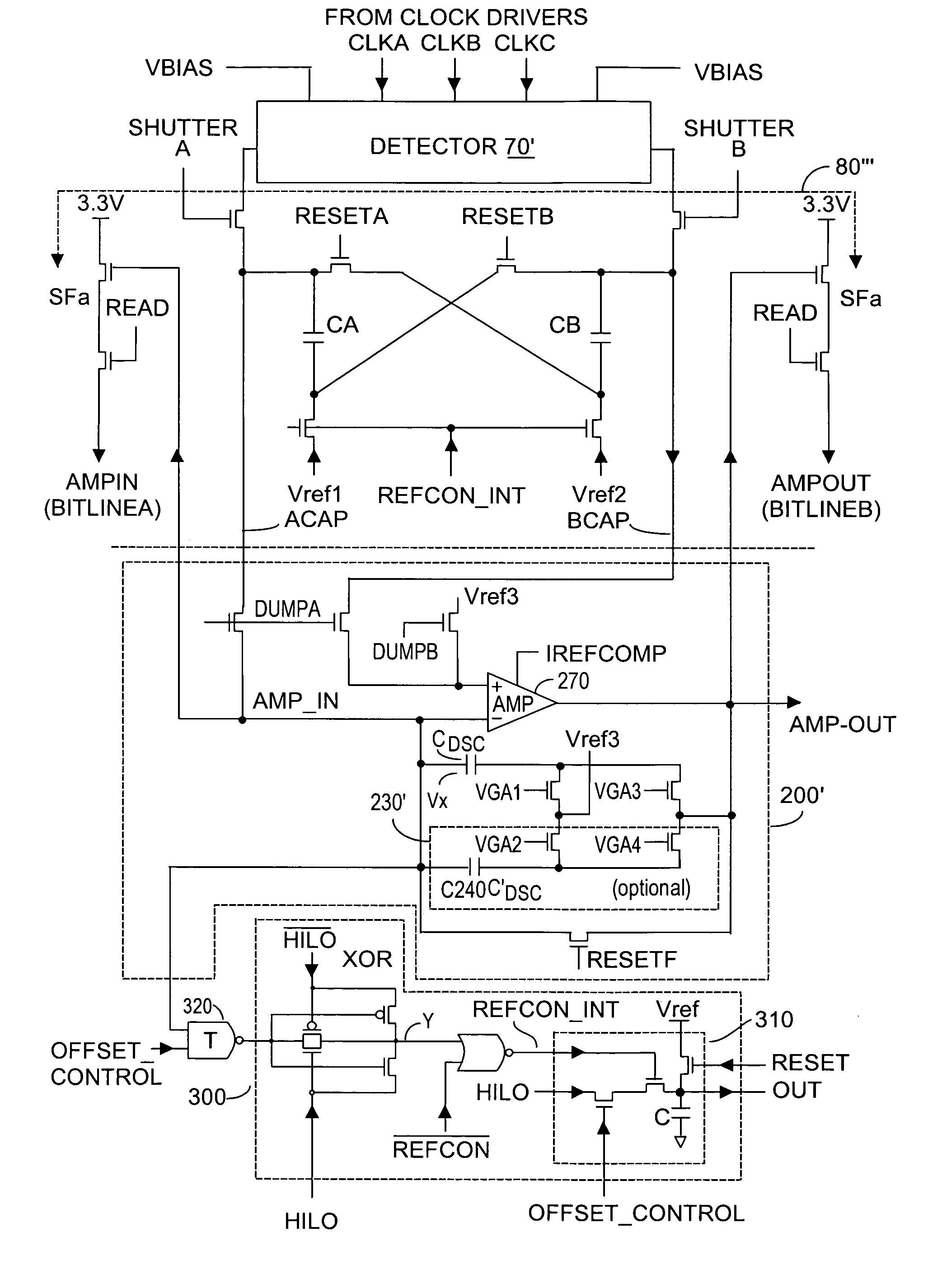
ActiveUS7157685B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSCapacitor voltage
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Liquid crystal display device, driving circuit, driving method, and electronic devices
InactiveUS6897845B2Integrated reductionMiniaturizationCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayCapacitor voltage
The voltage swing of a data signal, which is supplied to a data line, is maintained to be small, thereby reducing the power consumption. When a scanning signal supplied to a scanning line is set to an on-voltage, a data signal with a voltage, depending on the density and depending on the writing polarity, is applied to a data line. In this case, a TFT is turned on. Thus, a liquid crystal capacitor and storage capacitor store the charge corresponding to the voltage of the data signal. Then, the scanning signal is set to an off-voltage to turn the TFT off, and the voltage of the other terminal of the storage capacitor is raised from the low-level of capacitor voltage to the high-level, and the charge corresponding to the raised voltage amount is redistributed to the liquid crystal capacitor. Thus, the effective voltage value applied to the liquid crystal capacitor can correspond to the voltage swing of the data signal or more.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
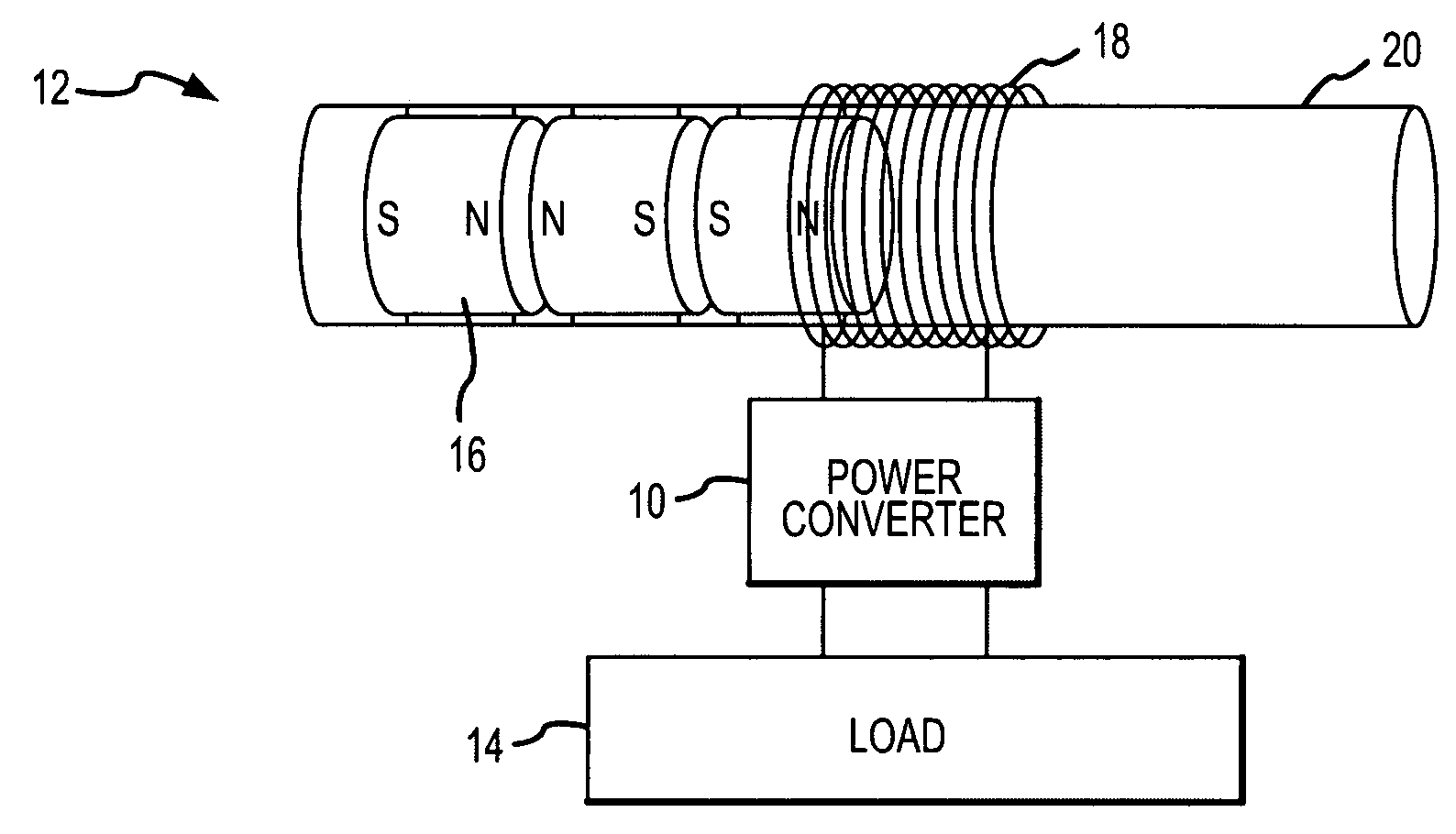
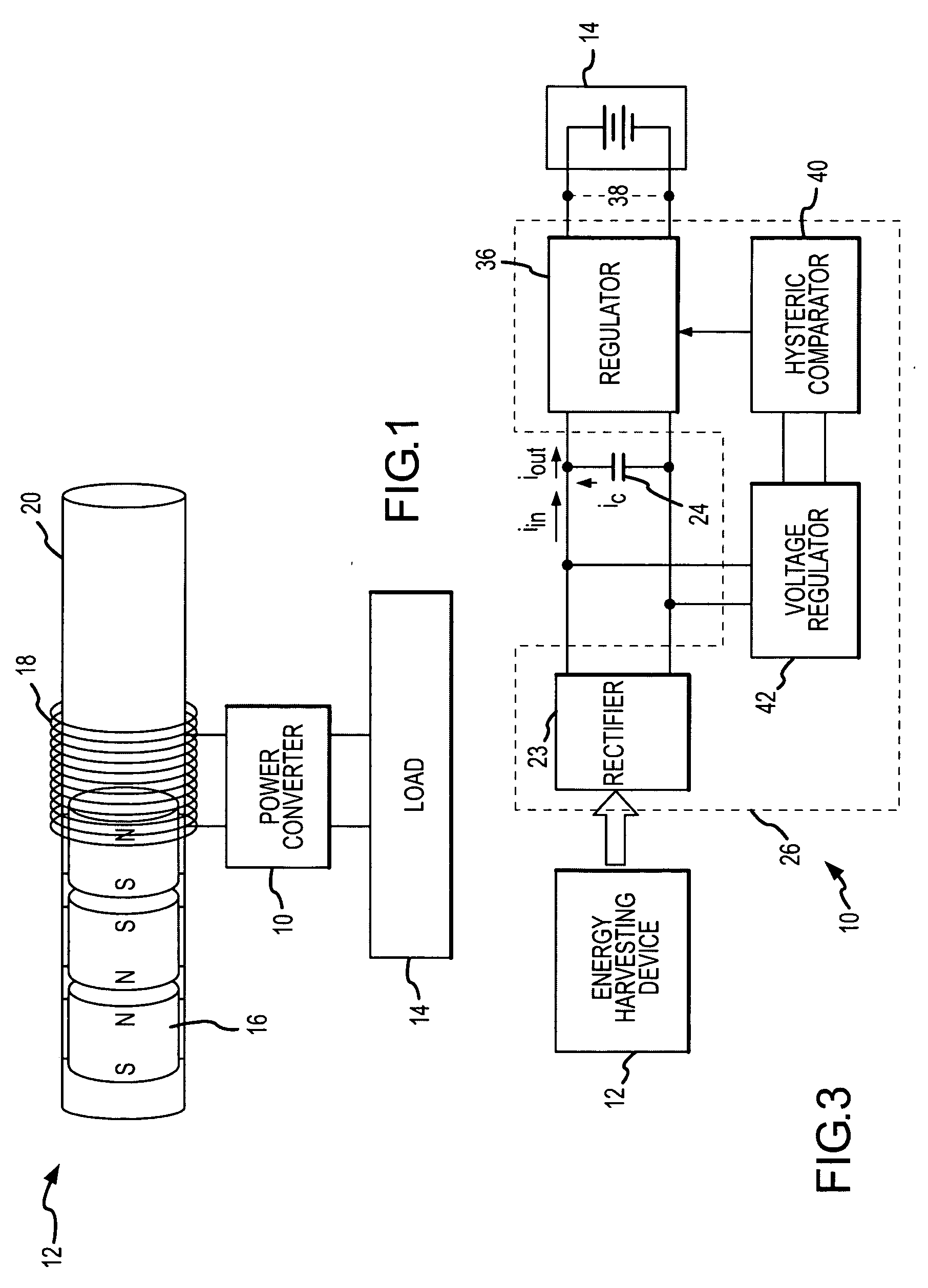
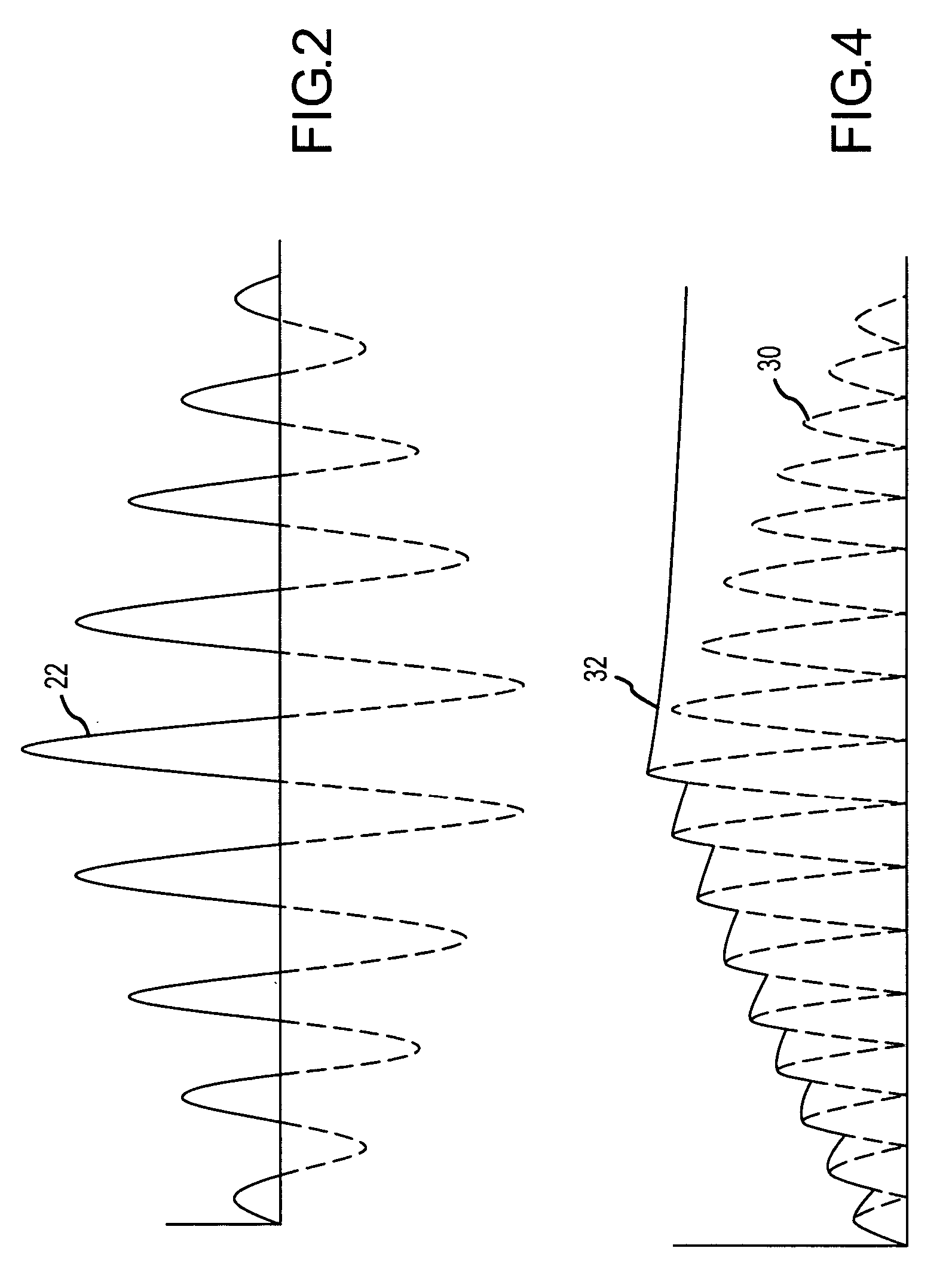
High efficiency power converter for energy harvesting devices
A high-efficiency power converter converts the unregulated AC electrical energy generated by an energy harvesting device to regulated quasi-continuous DC or AC power delivered to a load. A DC link capacitor stores energy from the AC input. Control electronics alternately transfers regulated power to the load and recharges the capacitor in accordance with a hysteresis window in the capacitor energy. The control electronics terminates transfer of regulated power to the load and initiates recharging of the capacitor when the capacitor voltage, hence energy falls below a lower threshold and terminates capacitor charging and initiates power transfer when the capacitor voltage, hence energy exceeds an upper threshold.
Owner:TELEDYNE LICENSING
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS7321111B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Smart linear pulsed laser diode driver, and method
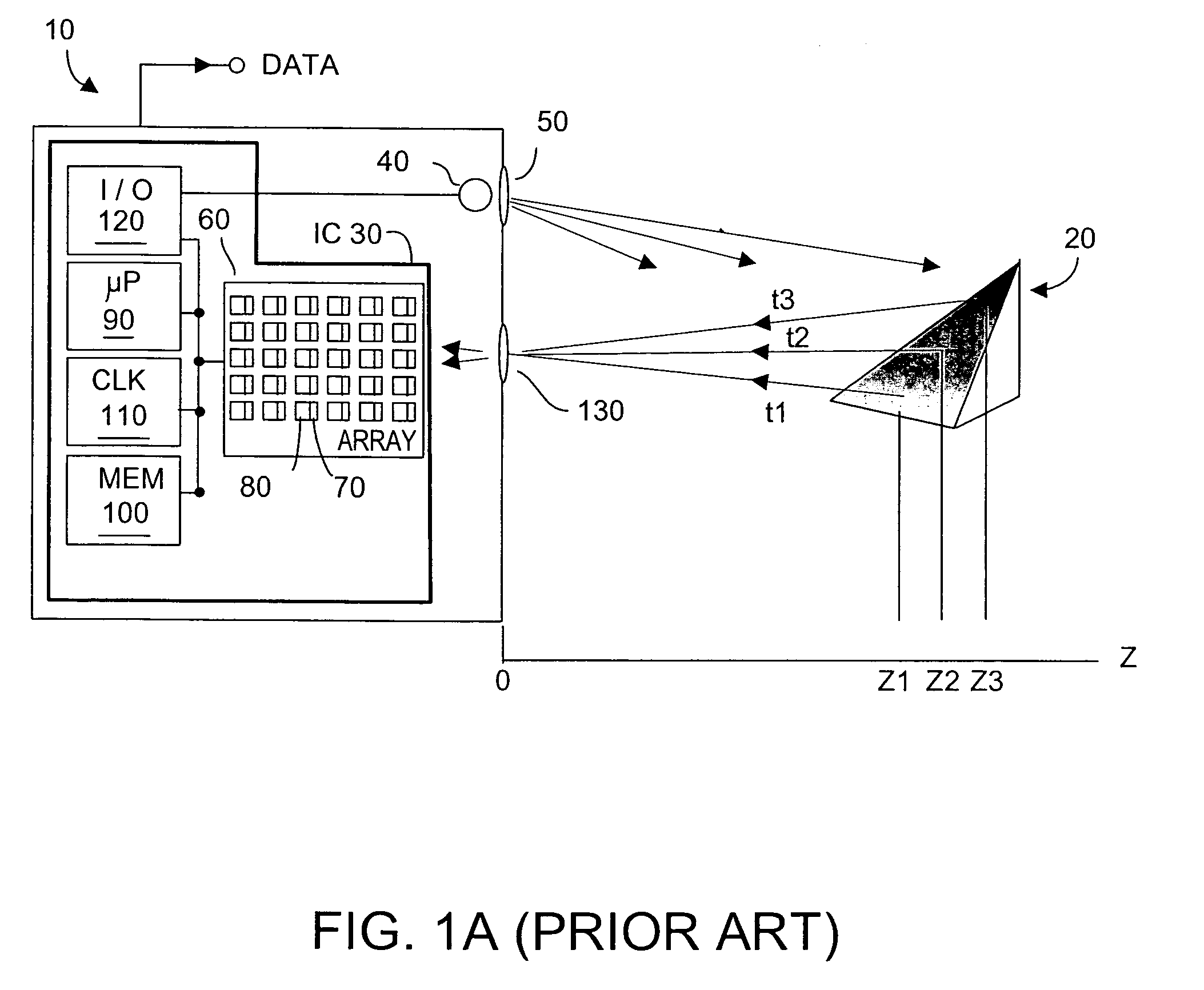
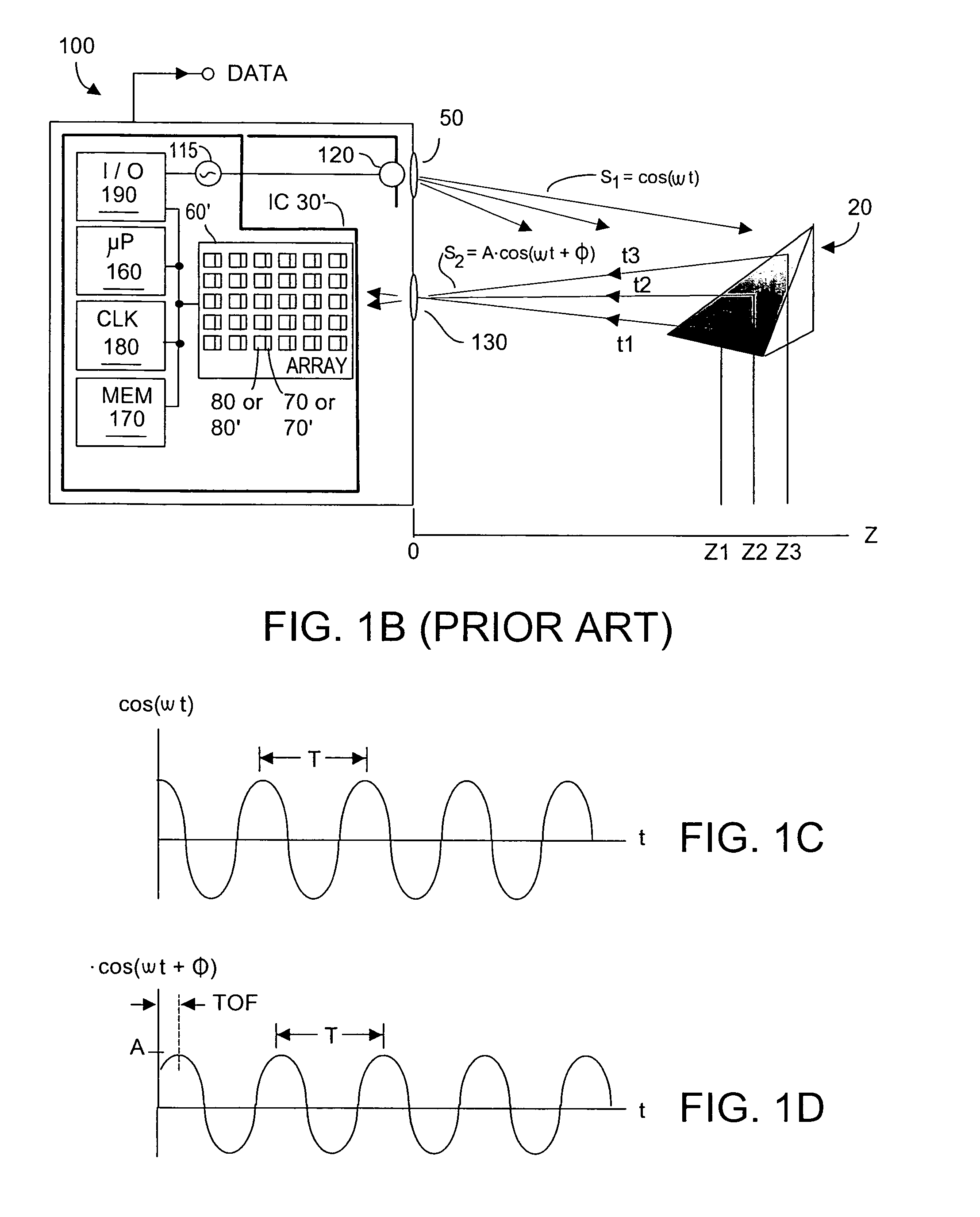
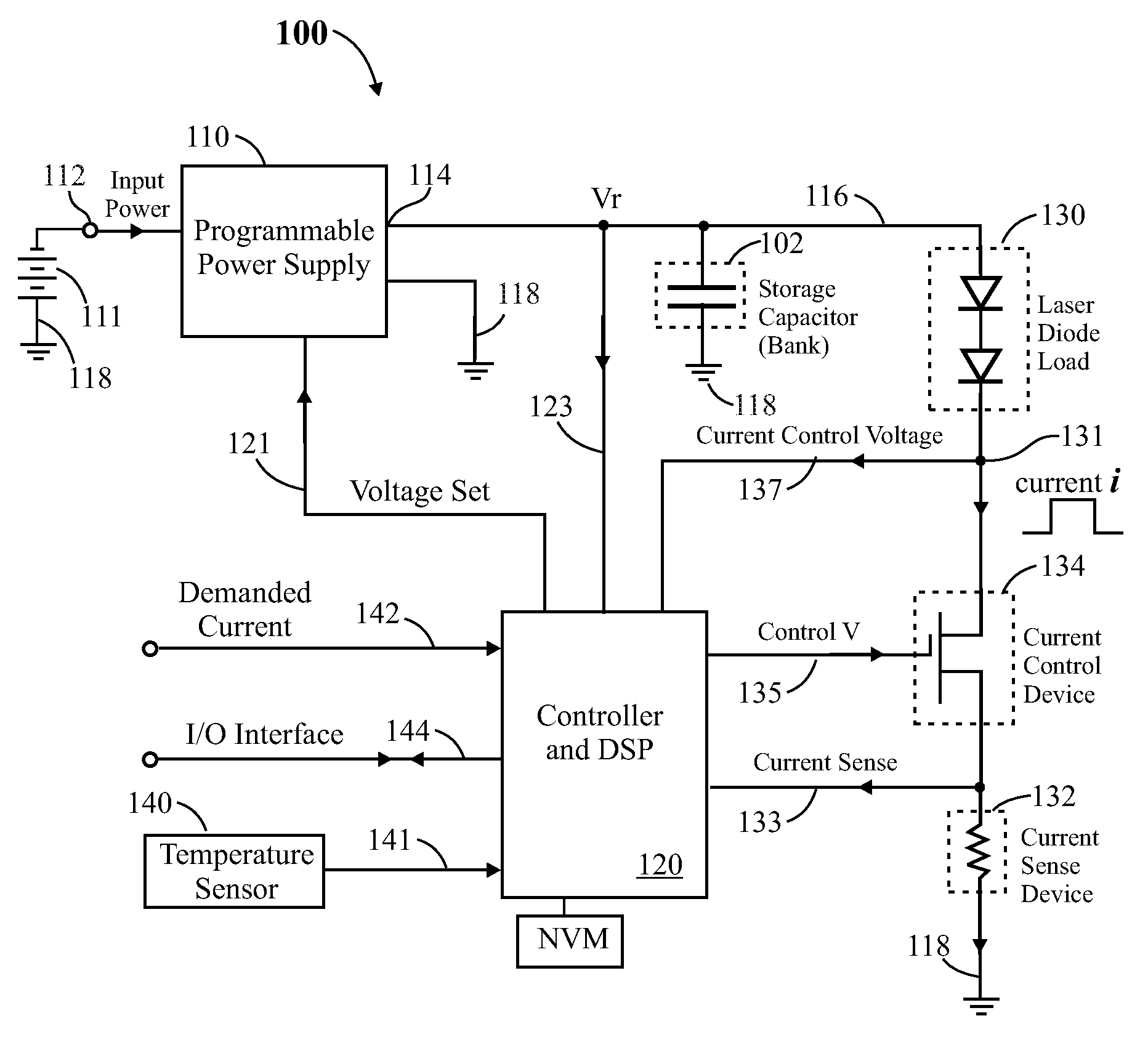
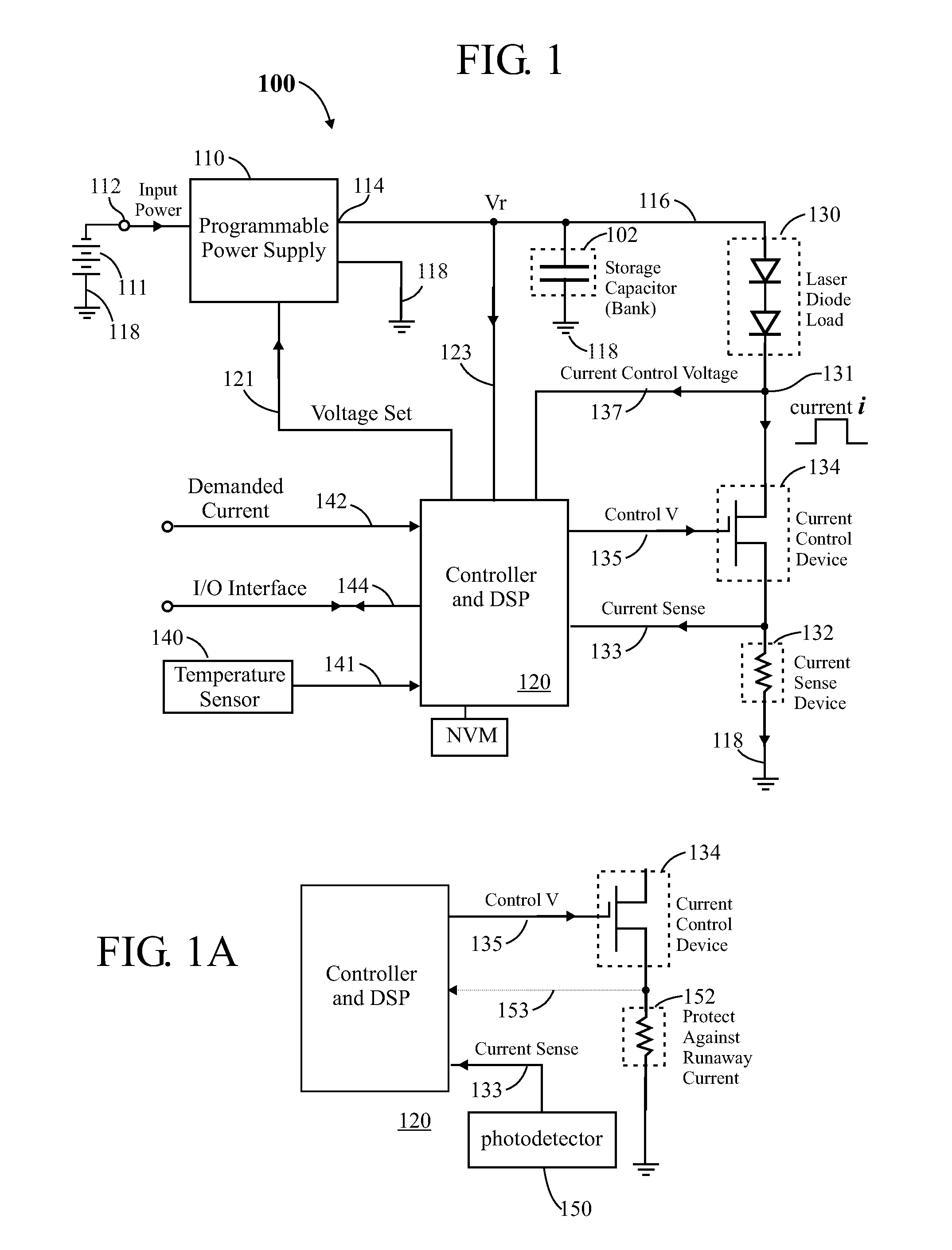
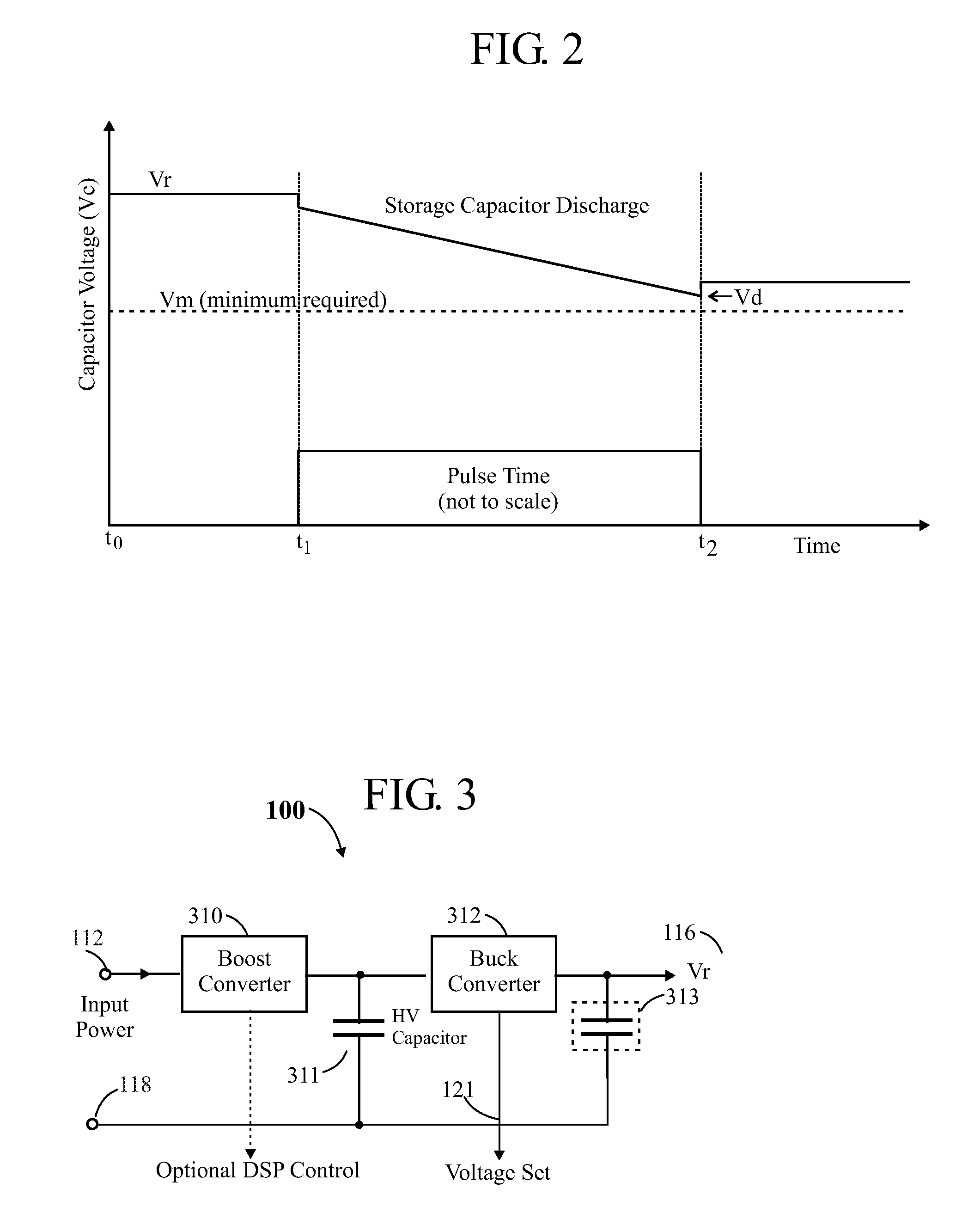
ActiveUS20110085576A1Improve efficiencySmall sizeLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitor voltageEngineering
In a pulsed laser diode driver an energy storage capacitor is continuously being charged to a supply voltage Vr. When a pulse is initiated, energy stored in the capacitor is delivered to the laser diode load. The capacitor voltage Vd at the end of a pulse is used to control Vr to ensure that Vd is maintained above a minimum voltage Vm required to ensure operation of a current control device (such as FET) just above saturation. Test pulses (such as with attenuated currents or reduced pulsewidth) may be fired to determine an initial optimum value for Vr. After a test pulse, a slightly high estimate for Vr may be used and may be iterated (incremented) down to an optimum value Vm during a firing burst. A digital processor may be used to calculate and store data to optimize the performance. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ANALOG MODULES
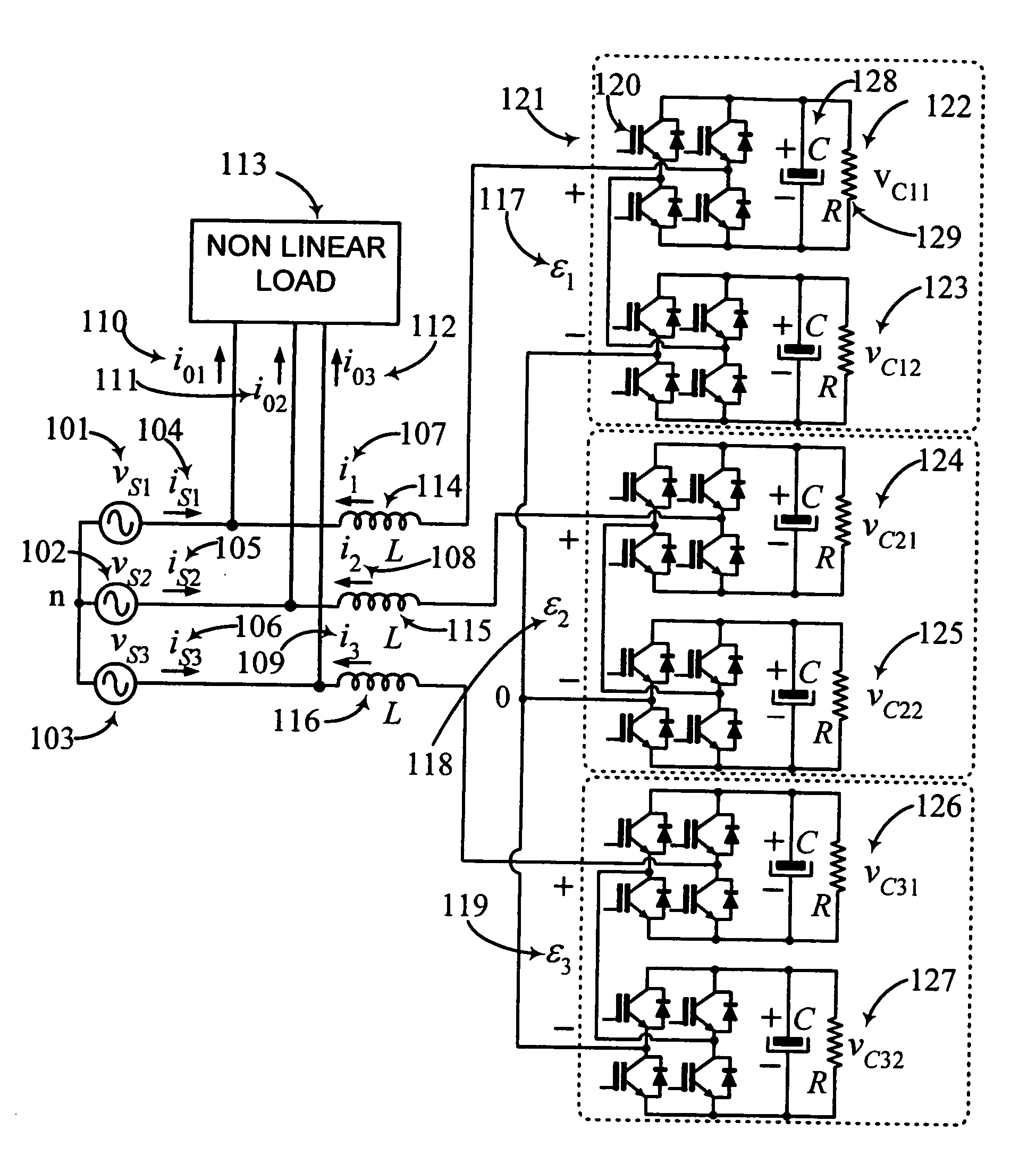
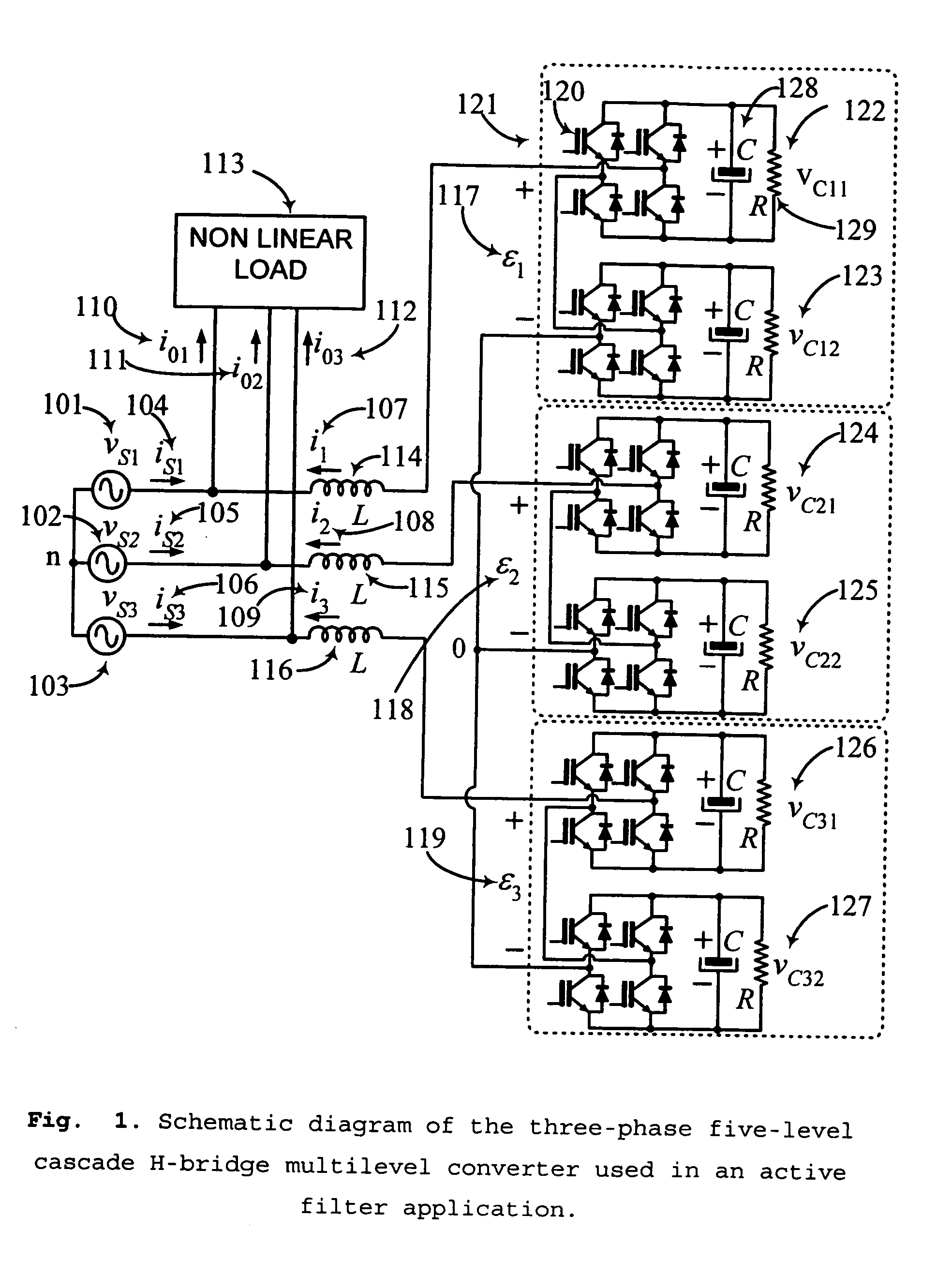
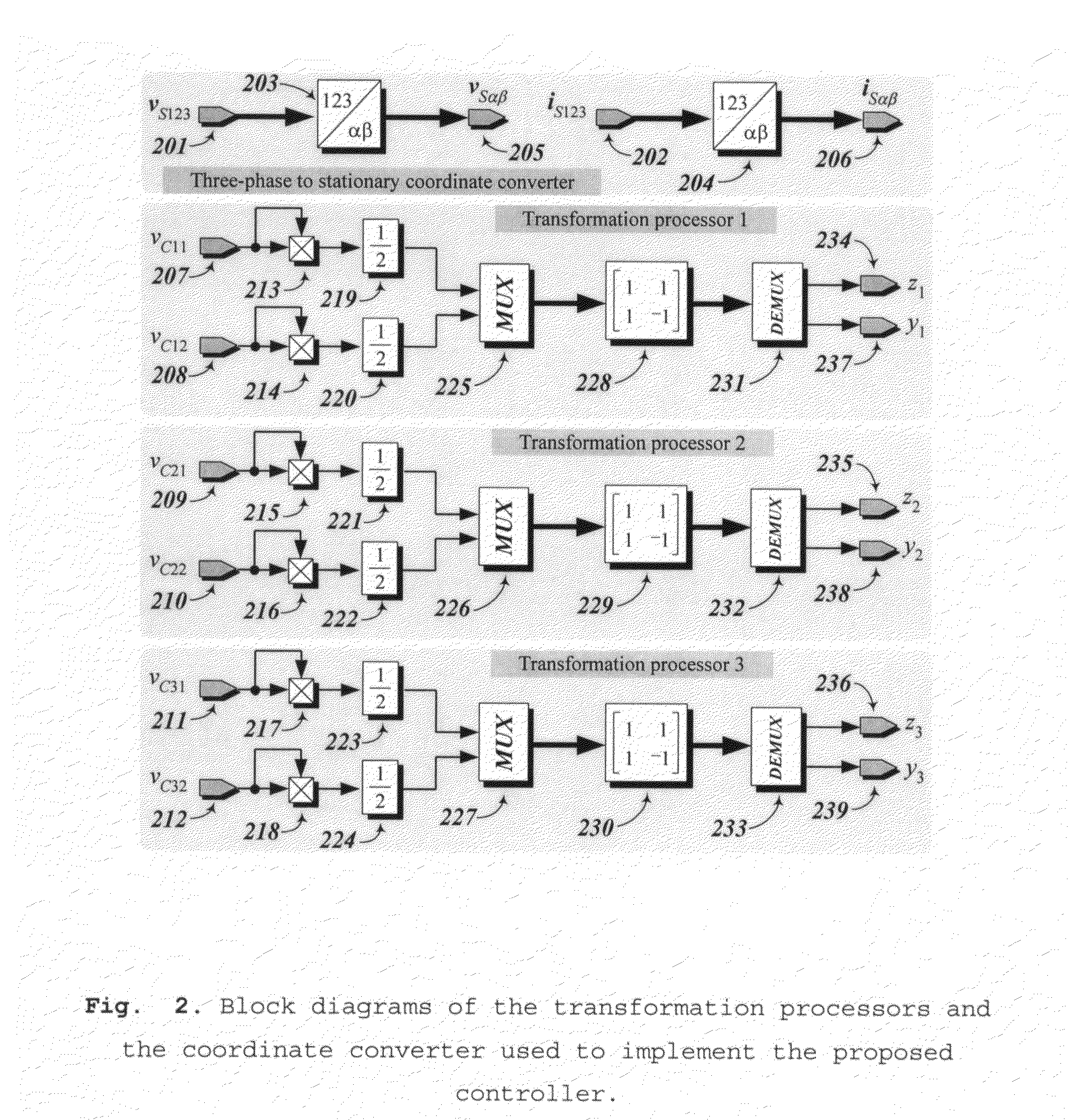
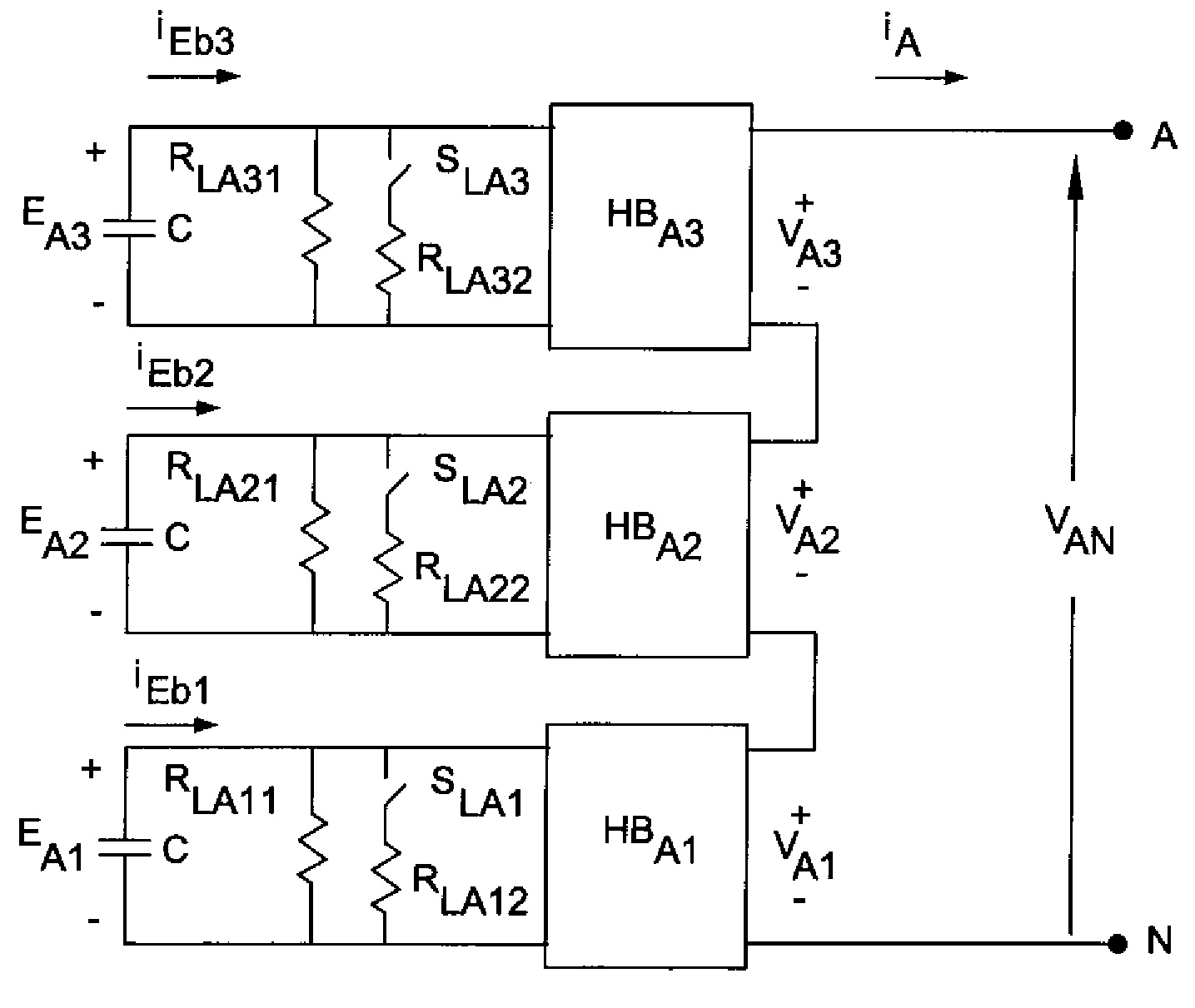
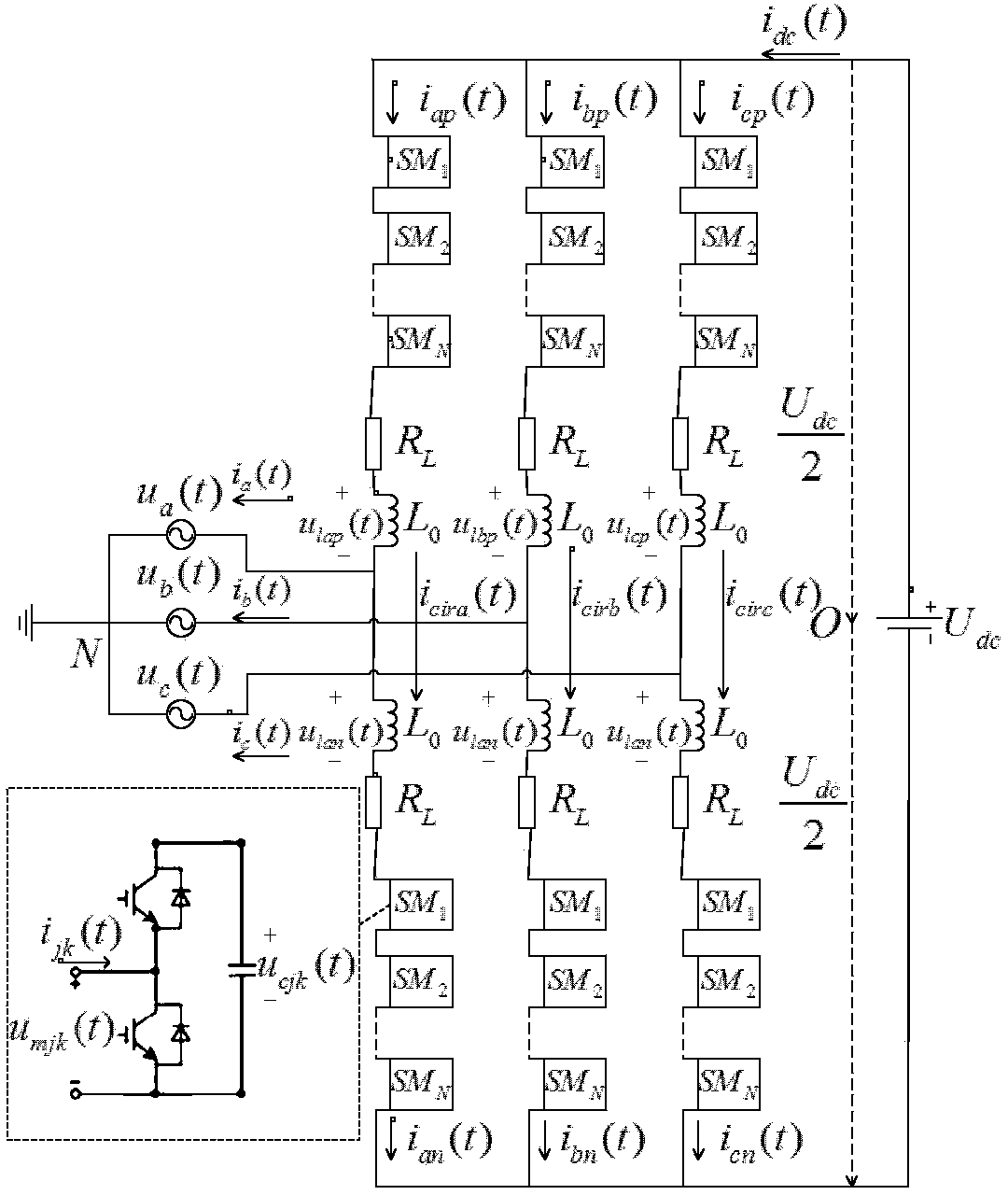
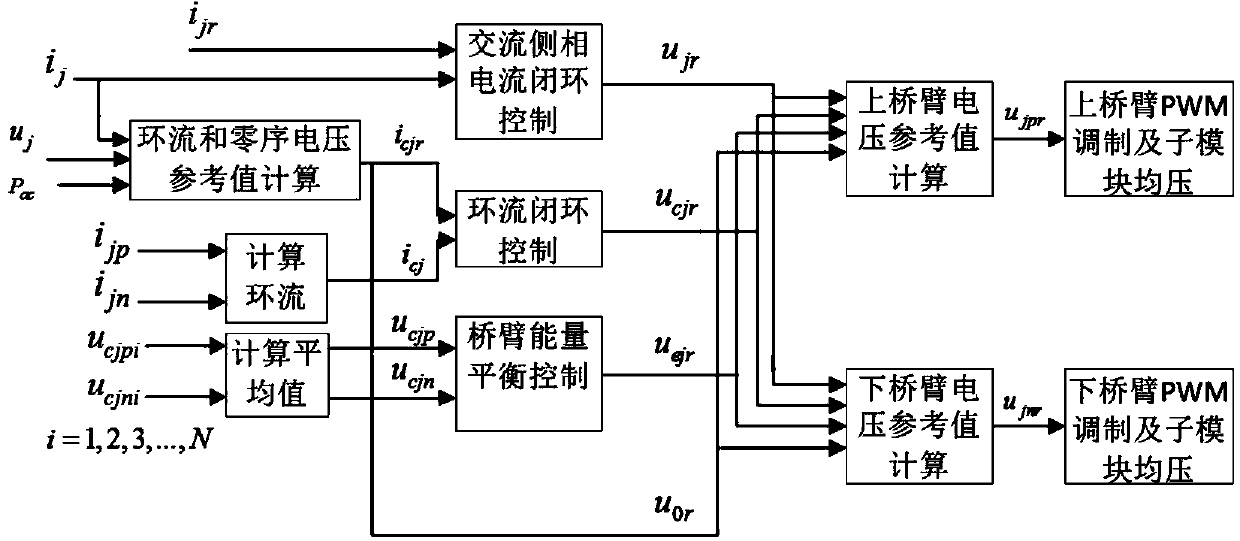
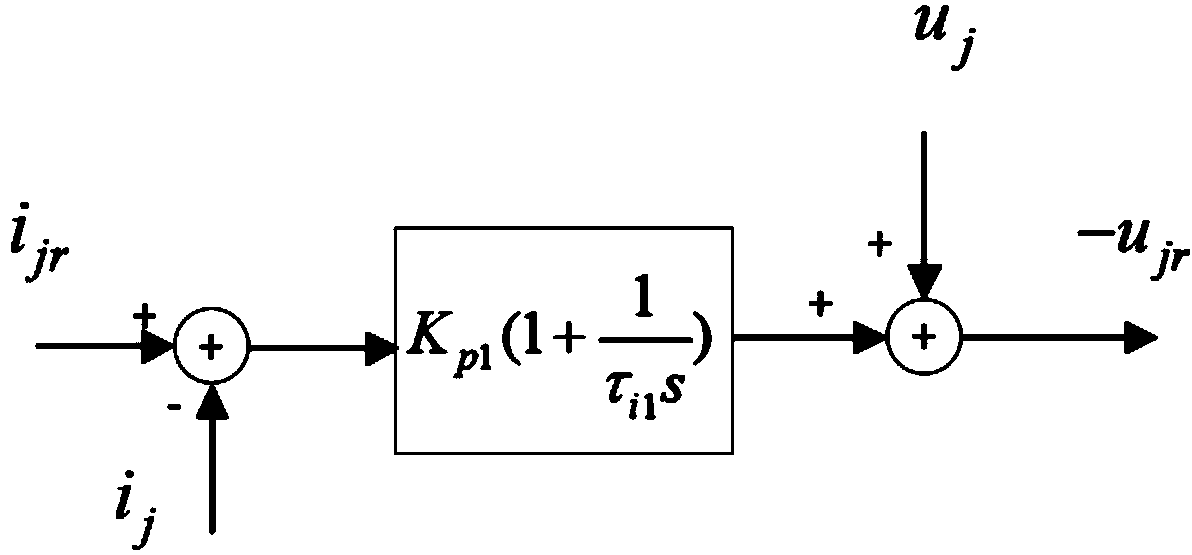
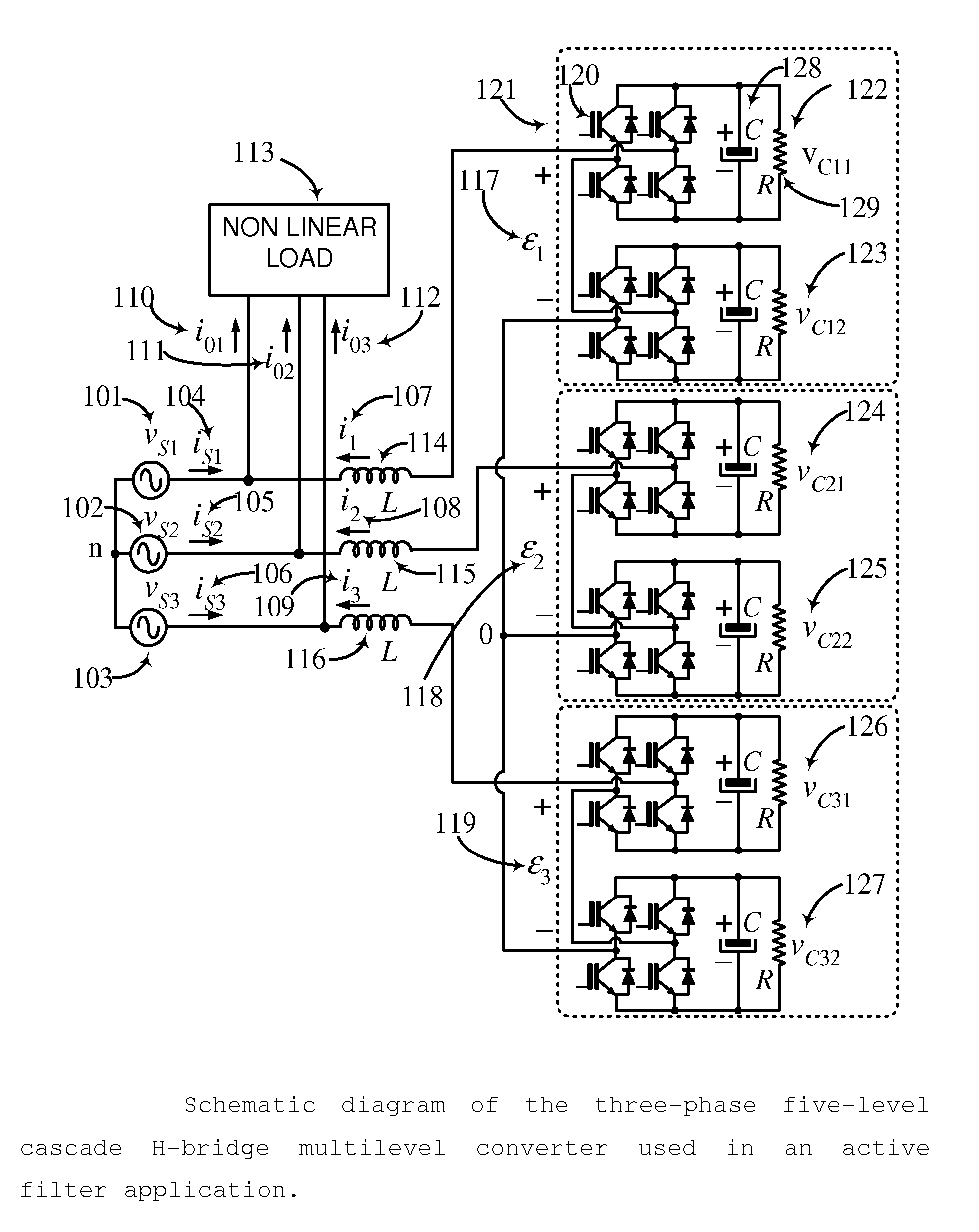
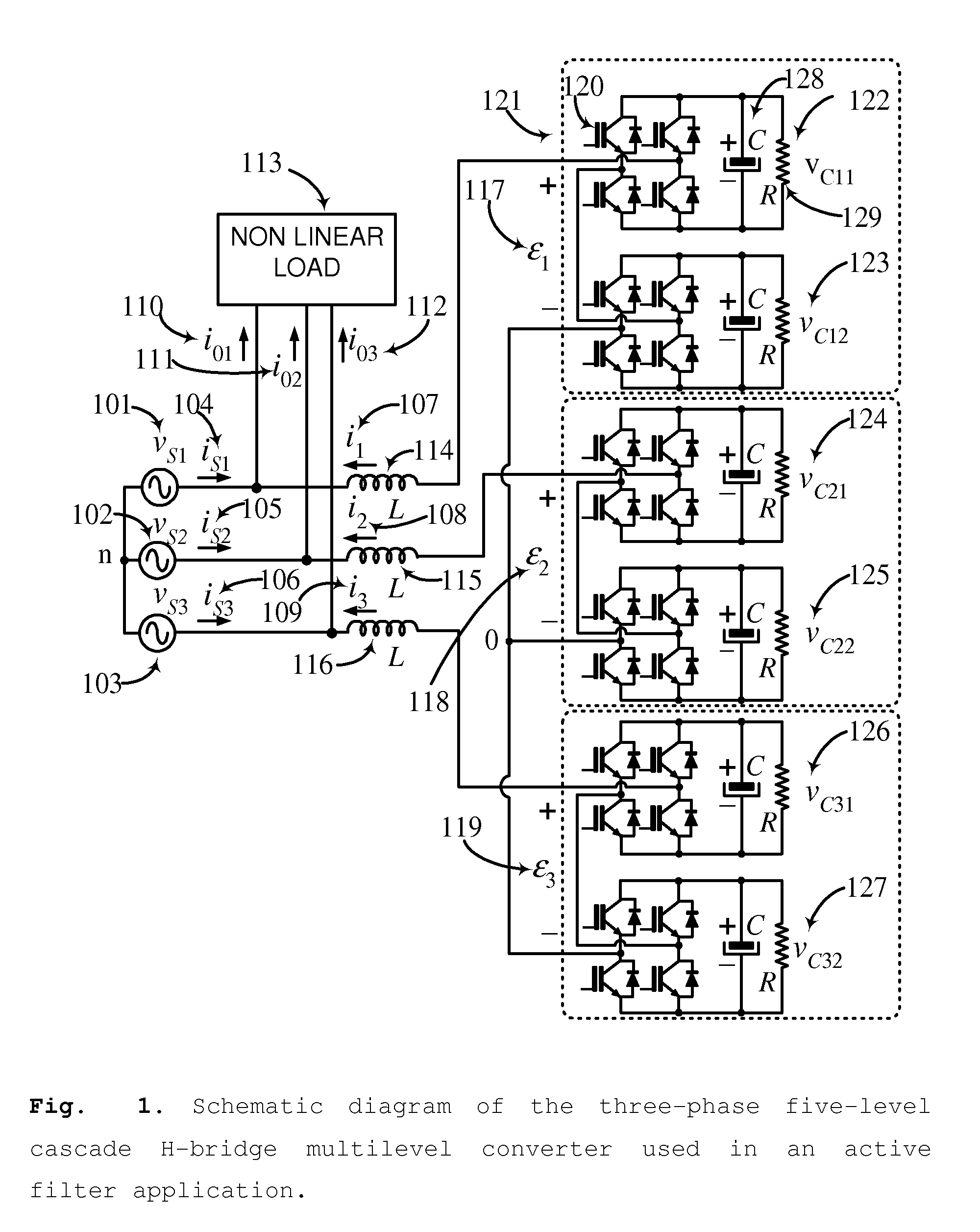
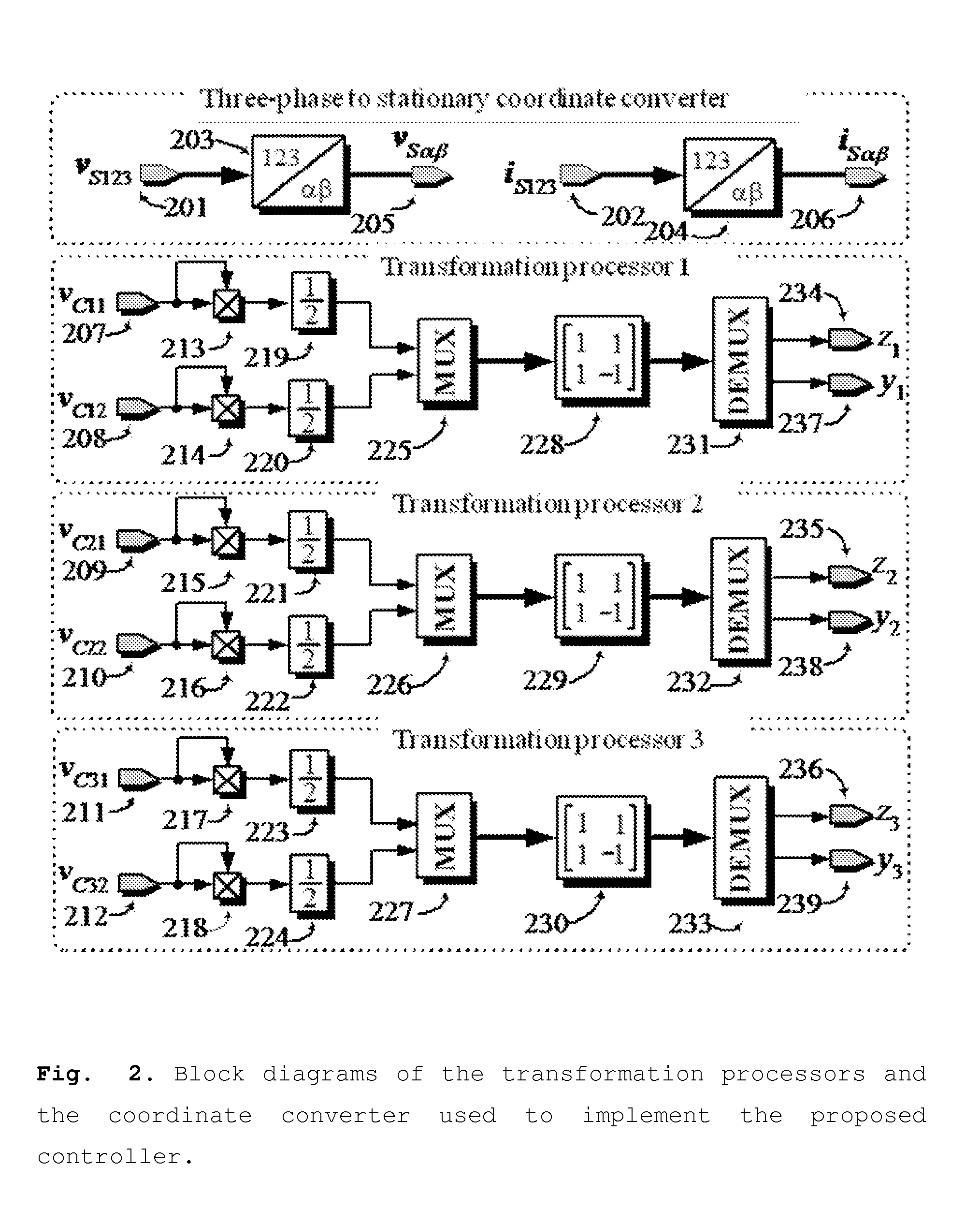
Controller for the three-phase cascade multilevel converter used as shunt active filter in unbalanced operation with guaranteed capacitors voltages balance
InactiveUS20090102436A1Increase the switching frequencyDesigning can be facilitatedActive power filteringElectric variable regulationNonlinear distortionCapacitor voltage
The present invention comprises a controller for the cascade H-bridge three-phase multilevel converter used as a shunt active filter. Based on the proposed mathematical model, the controller is designed to compensate harmonic distortion and reactive power due to a nonlinear distorting load. Simultaneously, the controller guarantees regulation and balance of all capacitor voltages. The idea behind the controller is to allow distortion of the current reference during the transients to guarantee regulation and balance of the capacitors voltages. The controller provides the duty ratios for each H-bridge of the cascade multilevel converter.
Owner:INST POTOSINO DE INVESTIGACION CIENTIFICA Y TECHCA A C
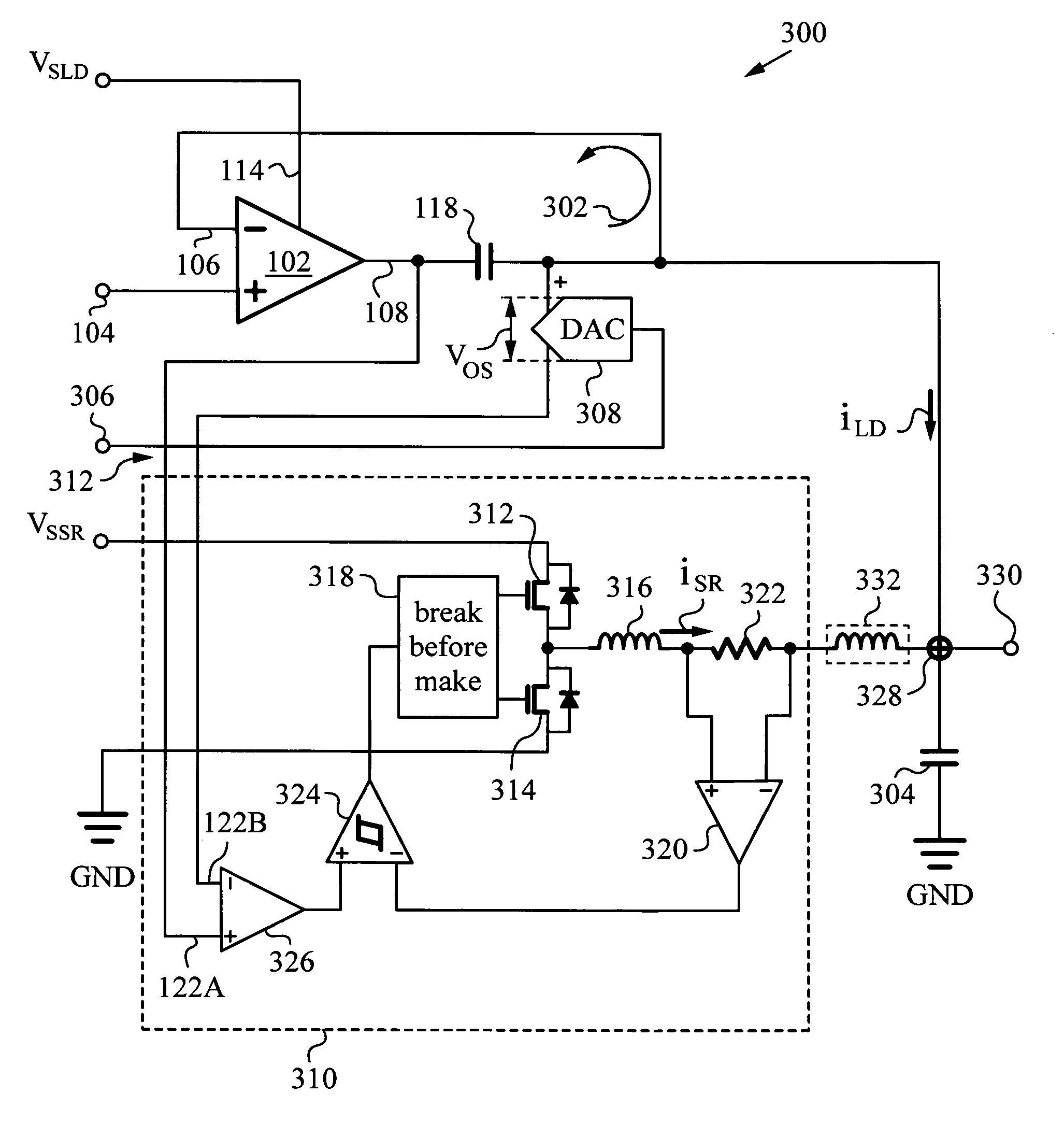
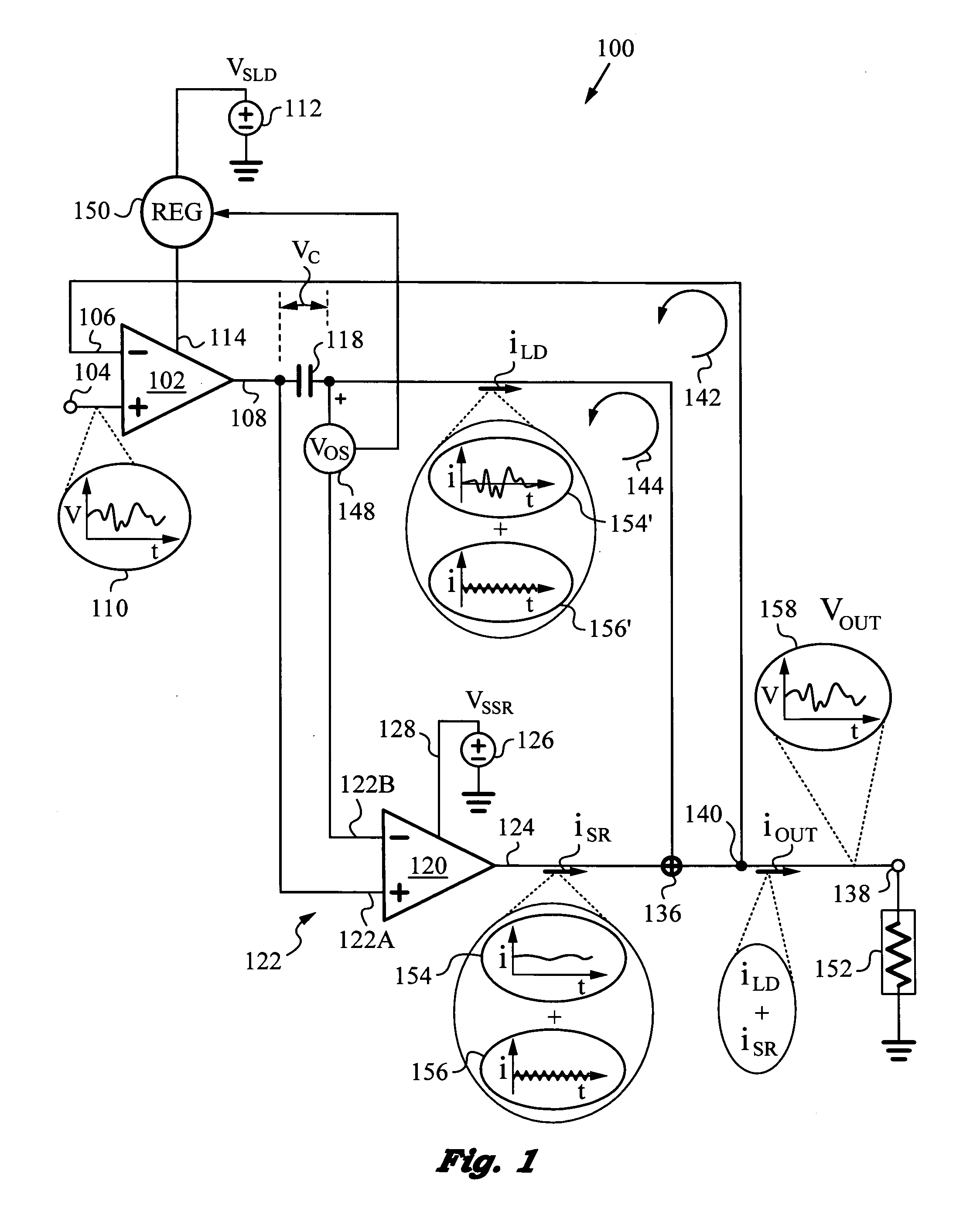
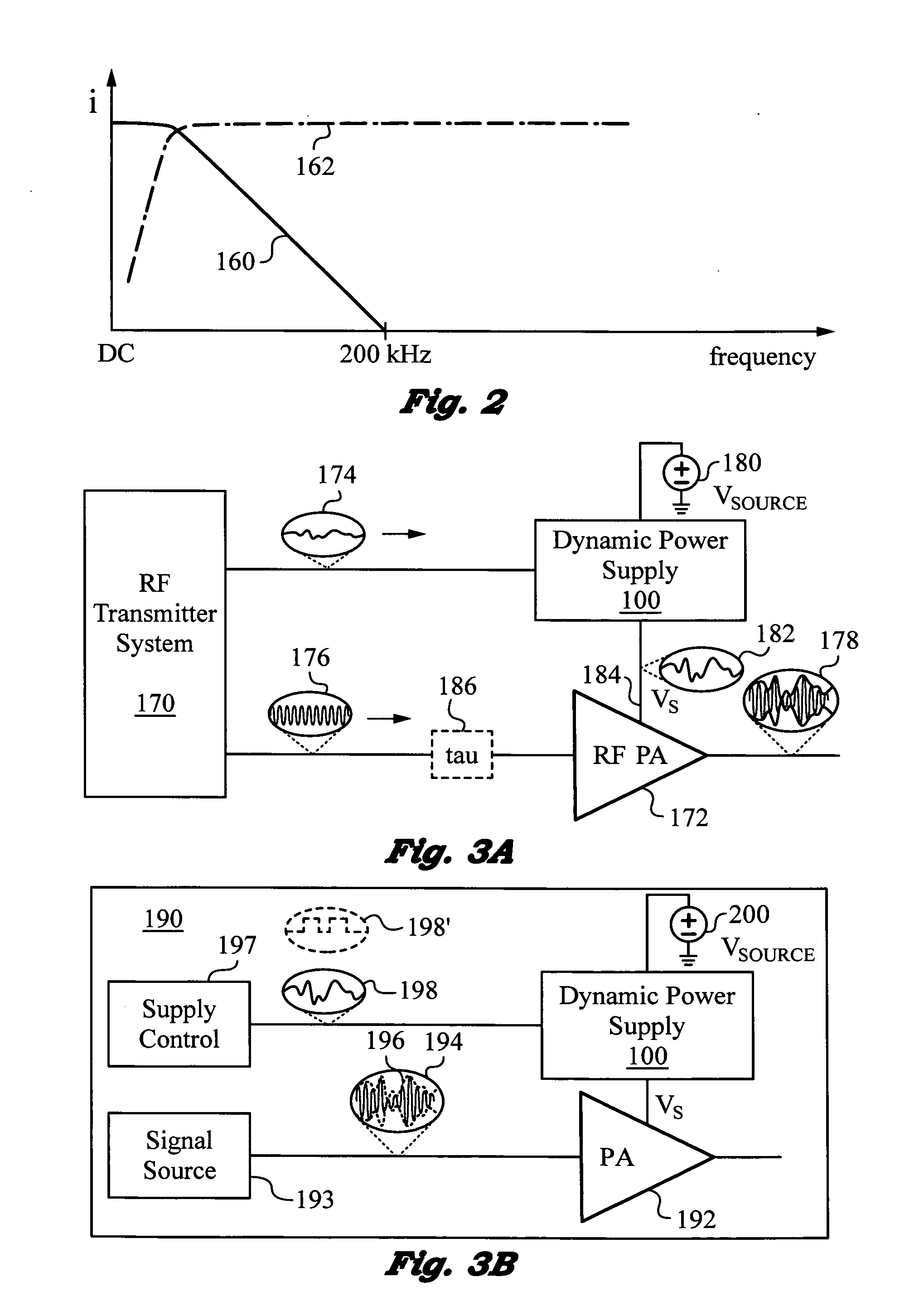
Dynamic power supply employing a linear driver and a switching regulator
ActiveUS20130214858A1Reduce power supply voltageImprove efficiencyGain controlDc-dc conversionNegative feedbackCapacitor voltage
A highly efficient, high control bandwidth and high-speed power supply with a linear driver and a switching regulator for regulating an output based on a control signal. The linear driver has a first input for receiving the control signal and a second input connected to the output for receiving negative feedback. The driver's output is controlled by its two inputs and has a capacitor connected in series with it to generate a capacitor voltage VC responsive to the DC and low frequency components in the driver's output. The switching regulator has a control input and a regulator output connected in a regulator feedback loop. The control input receives capacitor voltage VC and the regulator feedback loop minimizes capacitor voltage VC. Thus, switching regulator takes over the generation of DC and low frequency components, while the linear driver provides high frequency output current components.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Method and circuit for cascaded pulse width modulation
InactiveUS7230837B1Eliminate DC-capacitor voltage imbalanceActive power filteringConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitor voltageDc capacitor
A method of balancing the voltage of DC links in a cascaded multi-level converter (CMC) semiconductor circuit, including the steps of providing a plurality of H-bridge converters per phase in the CMC circuit and utilizing a three phase duty cycle value from the main controller to determine a normalized duty cycle value, a ceiling duty cycle value and a floor duty cycle value. The normalized duty cycle value and an output current of the CMC is used to determine the direction and polarity of a capacitor current, and utilizing the capacitor current to determine a plurality of output capacitor voltages. A voltage summation result and direction is obtained from a ceiling index pointer and a floor index pointer and the voltage summation result, direction from the ceiling index pointer and a floor index pointer are used to create a combined switching table for the H-bridge converters. A pulse width modulator is utilized to balance the voltage of the DC links and thereby eliminate DC-capacitor voltage imbalance.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC +2
Voltage balancing control method for multi-level modular converter
ActiveCN102130619AAvoid randomnessReduce switching frequencyDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitor voltageComputer module
The invention relates to a voltage balancing control method for a multi-level modular converter, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) judging whether the current direction of a bridge arm is a positive direction or a negative direction; 2) searching for a sub-module with the highest capacitor voltage amplitude value from the sub-modules in an output state, and simultaneously searching for the sub-module with the lowest capacitor voltage amplitude values from the sub-modules in a bypass state; and 3) judging whether to use or bypass the sub-modules or not. By the method, sub-module switching randomness is completely avoided, and the switching frequency of the sub-module is reduced; and the sub-module capacitor voltage balancing control method is more applicable in the field of high-voltage high-capacity converters with a great number of sub-modules.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Electric power converter
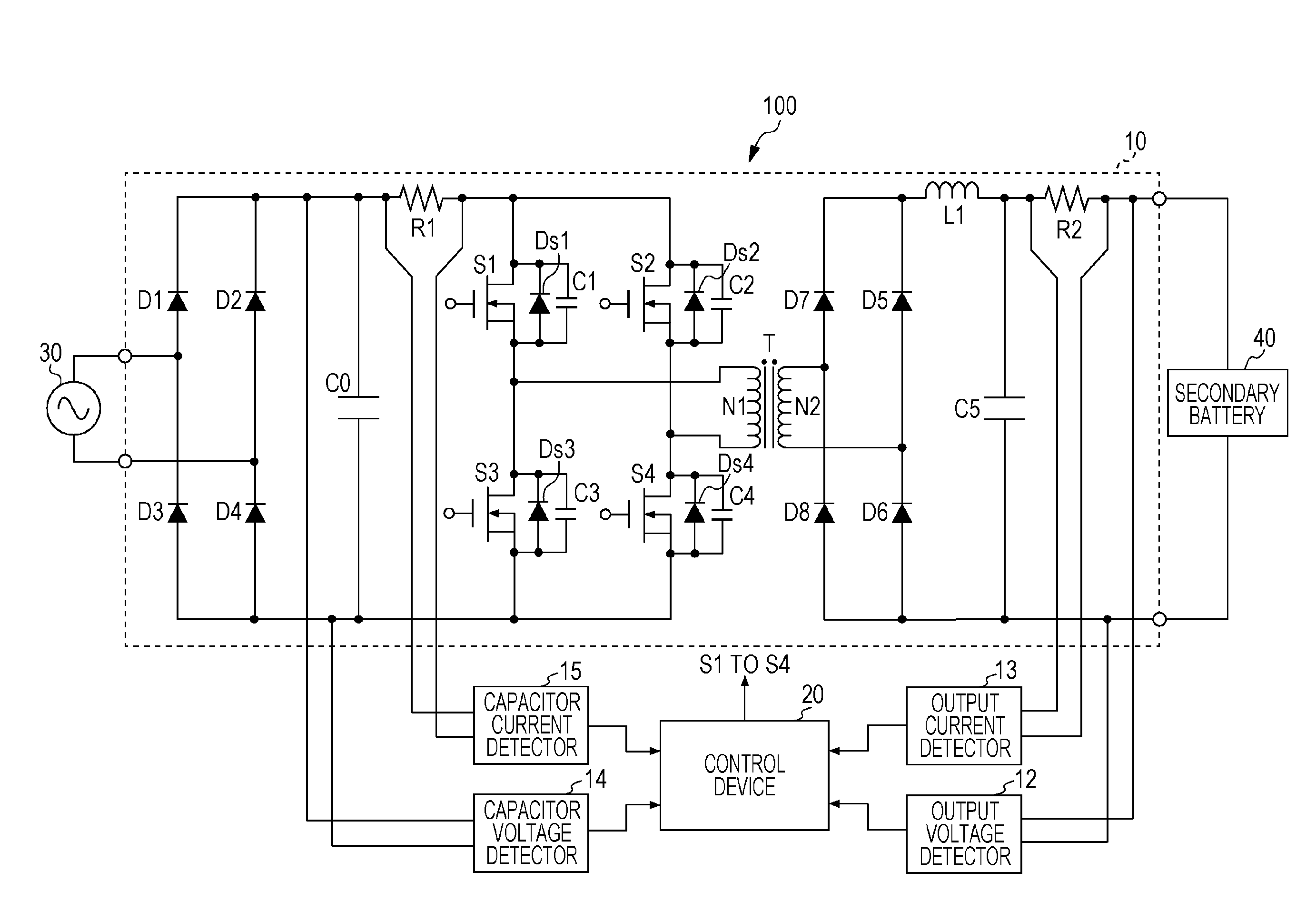
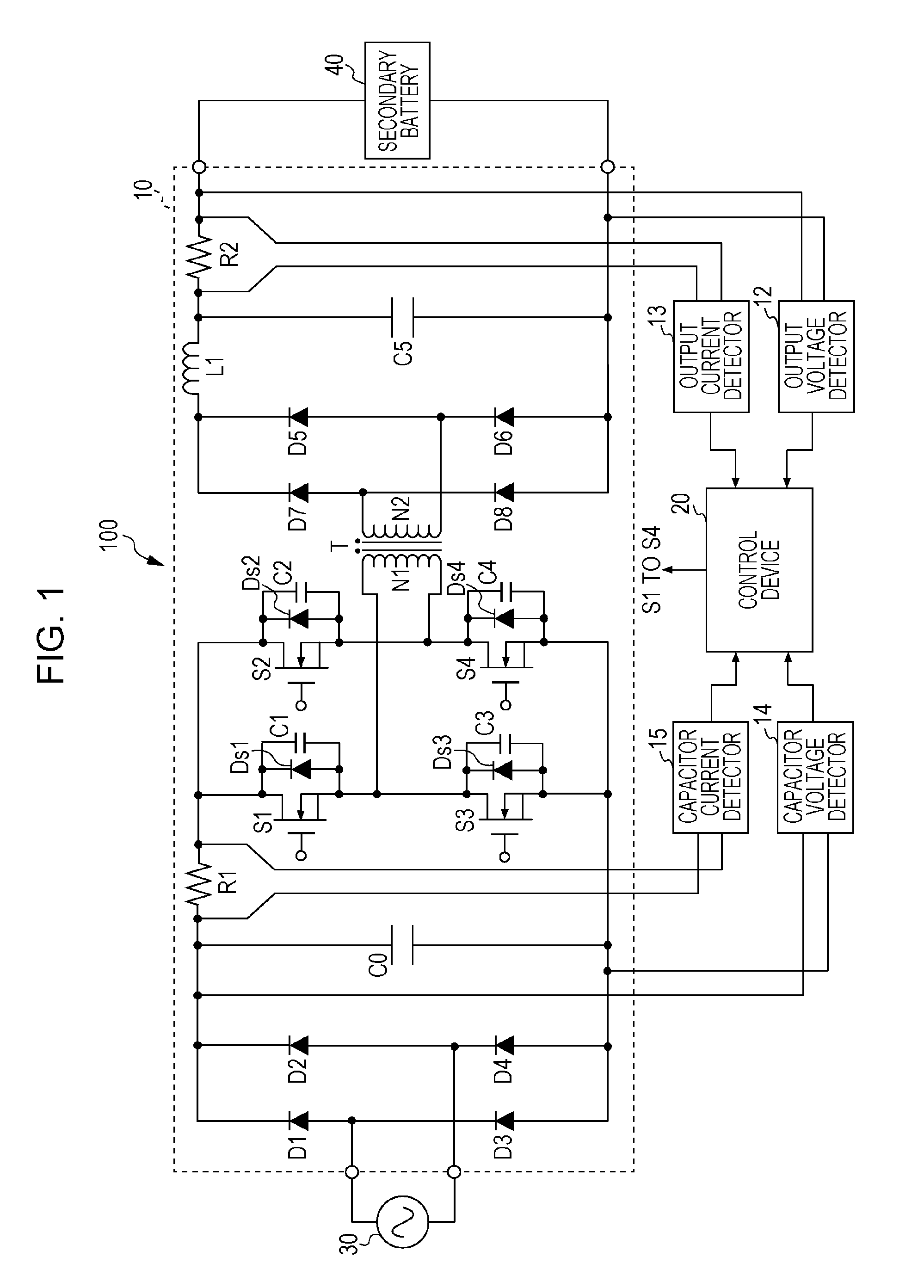
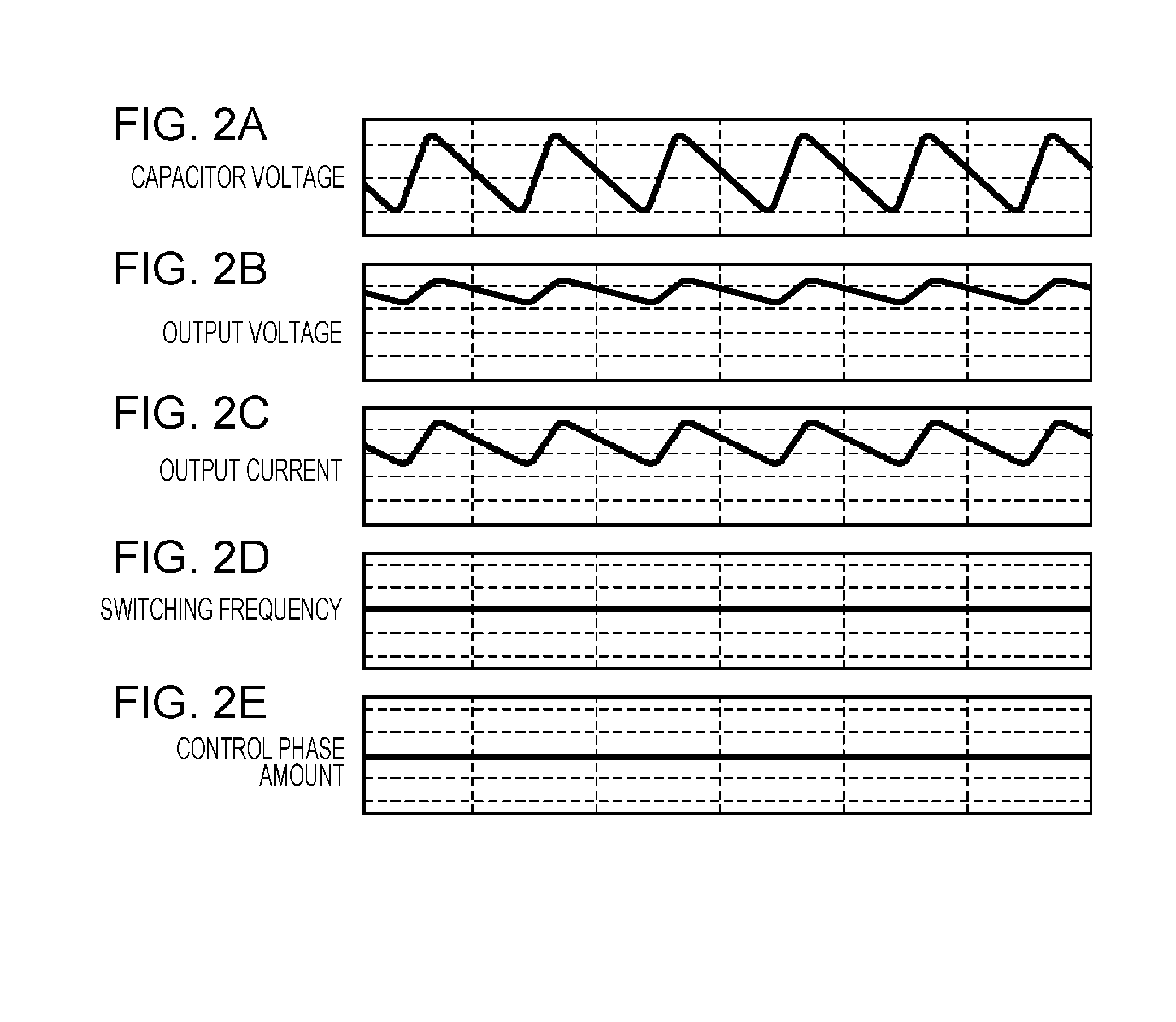
ActiveUS20150180356A1Reduce rippleCharging stationsElectric devicesCapacitor voltageSwitching frequency
An electric power converter includes a capacitor, a bridge circuit that includes a plurality of switching elements, a transformer, a secondary side rectifier circuit, a smoothing circuit, a detector that detects a value based on at least one of a capacitor voltage and a current flowing from the capacitor, and a control device that outputs a primary side drive signal to turns on / off each of the plurality of switching elements at a switching frequency, the control device increasing the switching frequency when the detected value increases, the control device reducing the switching frequency when the detected value decreases.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring current as in sensing a memory cell
InactiveUS6930942B2Increase rangeShorten the counting processElectric analogue storesDigital storageAudio power amplifierCapacitor voltage
Apparatus and methods sense or measure an input current, such as a current indicating a logic state of a memory cell. A sensing circuit includes an amplifier, a capacitor, a current source circuit, a clocked comparator and a clocked counter. The current source circuit operates responsive to an output of the comparator to supply or withdraw current to and from the capacitor during respective charging and discharging intervals. The count in the clocked counter results from periodic comparisons of the capacitor voltage with a reference voltage and is, therefore, related to the logic state of the memory cell. The magnitude of current supplied during charging is less than the magnitude withdrawn during discharging, allowing use of a smaller counter.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Modularized multi-level converter with auxiliary diode
InactiveCN102832841ASimple structureSimplify the control problemActive power filteringAc-dc conversionCapacitor voltageHigh pressure
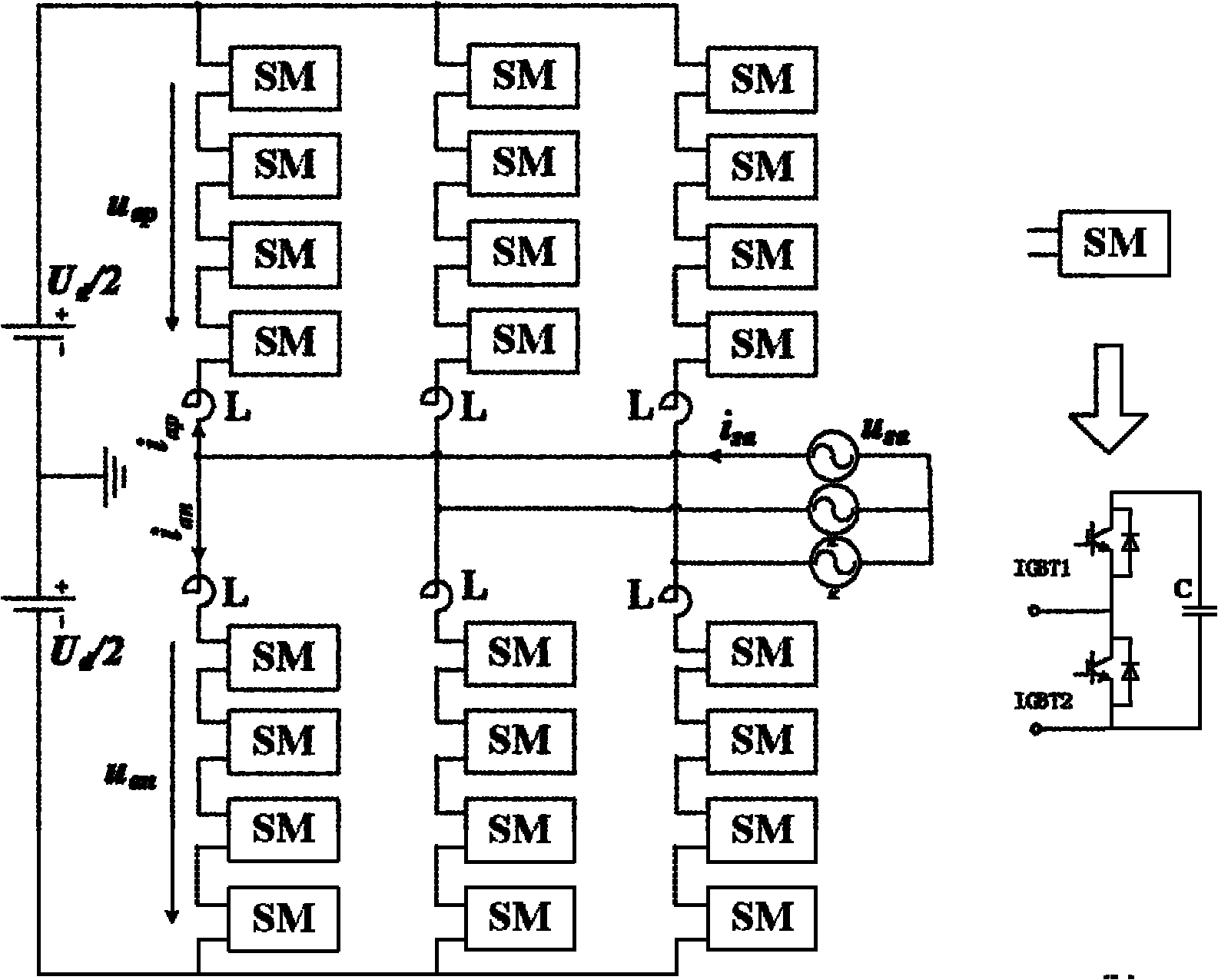
The invention relates to a modularized multi-level converter with an auxiliary diode. The modularized multi-level converter comprises a three-phase valve body, and three active energy feedback circuits respectively connected to the three-phase valve body, wherein each phase of valve body comprises 2M half-bridge inversion units and 2M-1 auxiliary diodes; direct current capacitors of the 1-(2M-1)th serially connected half-bridge inversion units are respectively connected with one auxiliary diode, and the final (2M)th half-bridge inversion unit is serially connected to form the valve body; the 1-Mth half-bridge inversion units form the upper-half part of the valve body to output a negative polarity voltage; and the (M+1)th to 2Mth half-bridge inversion units form the lower-half part of the valve body to output a positive polarity voltage. The auxiliary diodes and the active energy feedback circuits form a capacitor voltage sharing loop, the modularized multi-level converter realizes capacitance self voltage sharing effect, and realizes that the unit capacitance voltage is measured by using less direct current voltage sensors, thus the detection and the control of multi-level topology are greatly simplified. The modularized multi-level converter can be used in occasions such as reaction compensation and harmonic treatment of a medium-voltage or high-voltage power grid.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Switching-mode power supply having a synchronous rectifier
InactiveUS7120036B2Save the problemImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitor voltageFeedback circuits
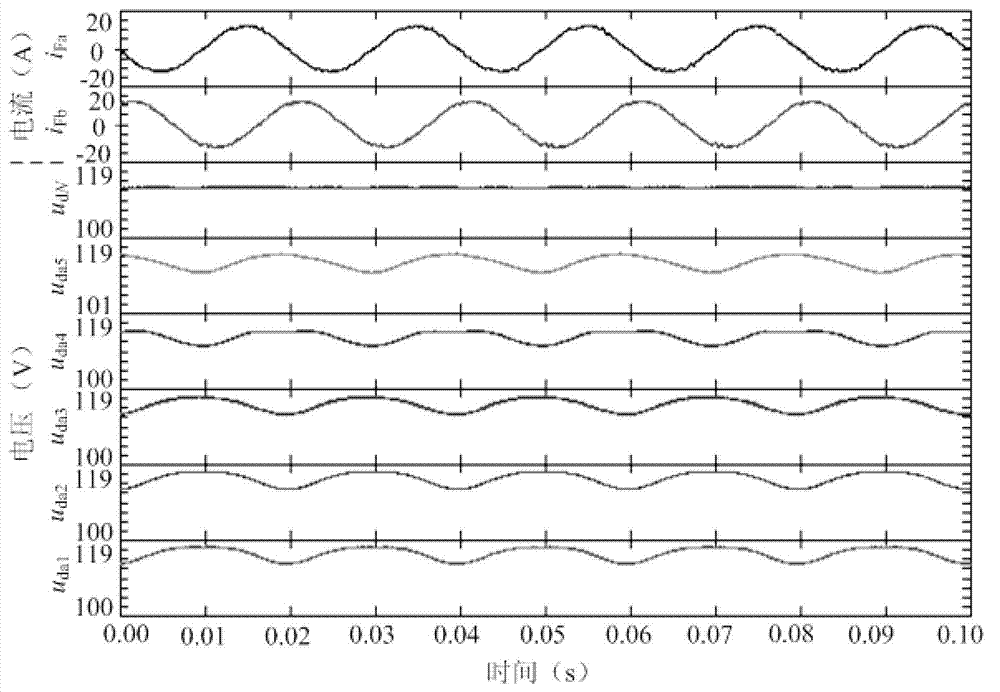
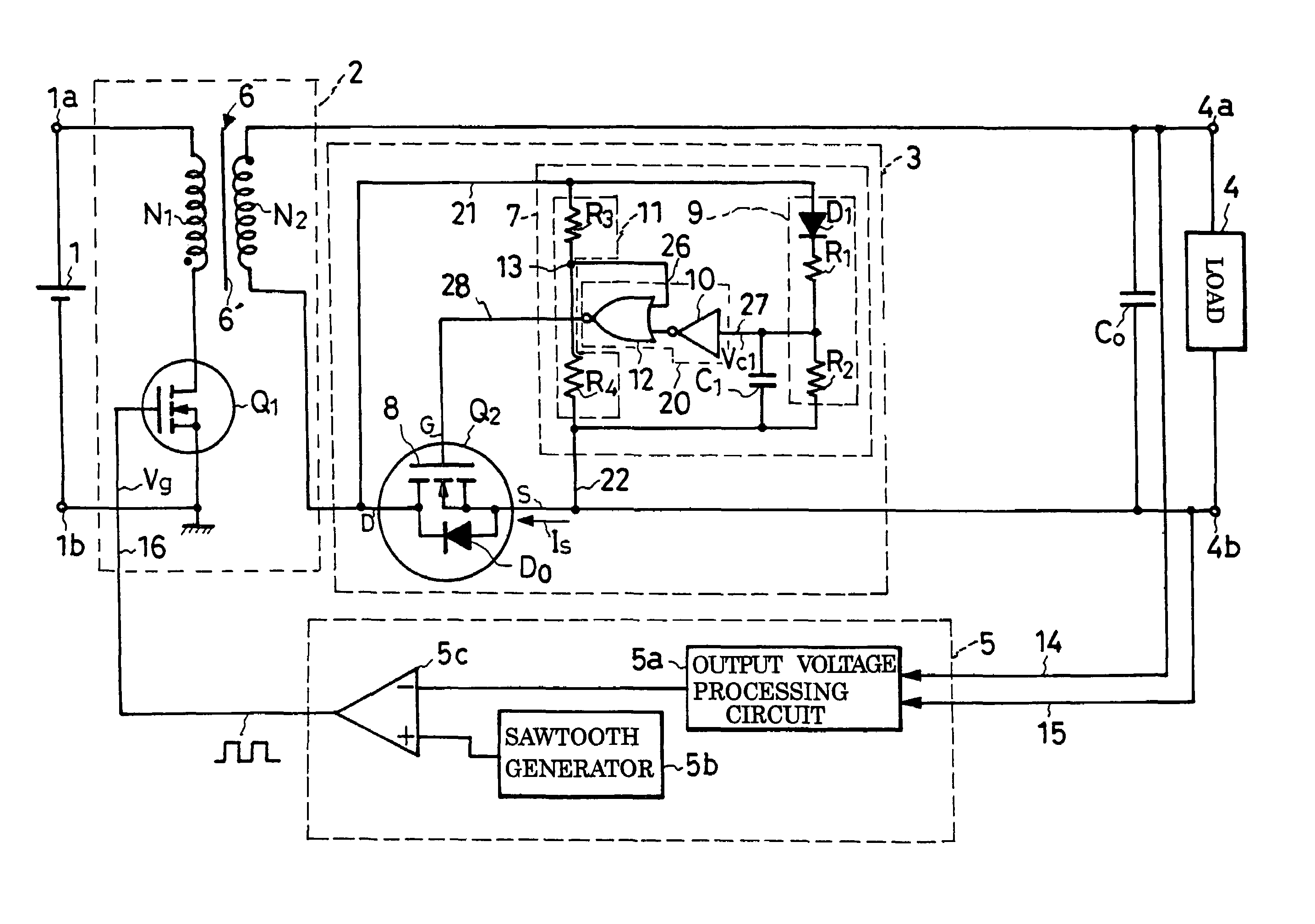
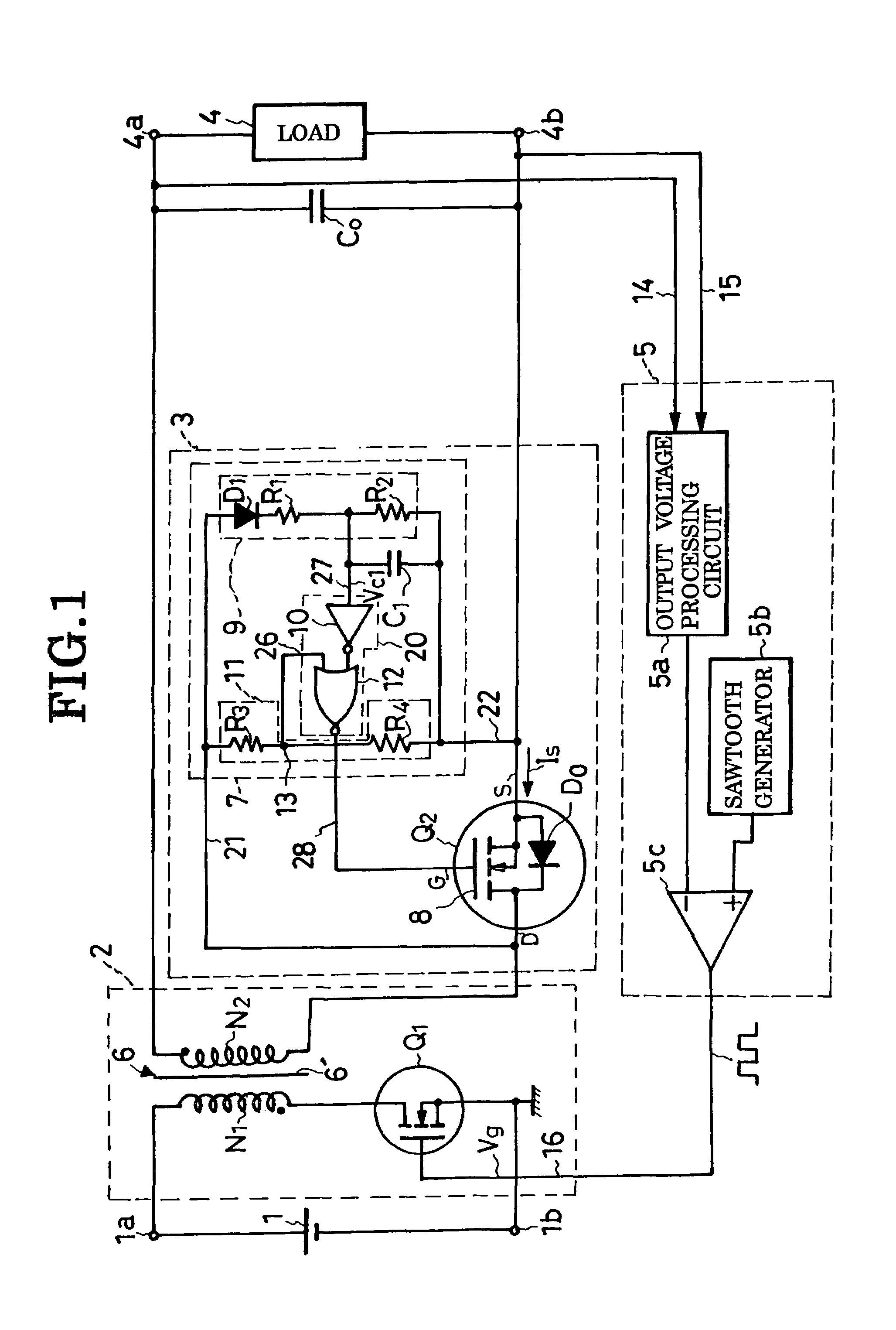
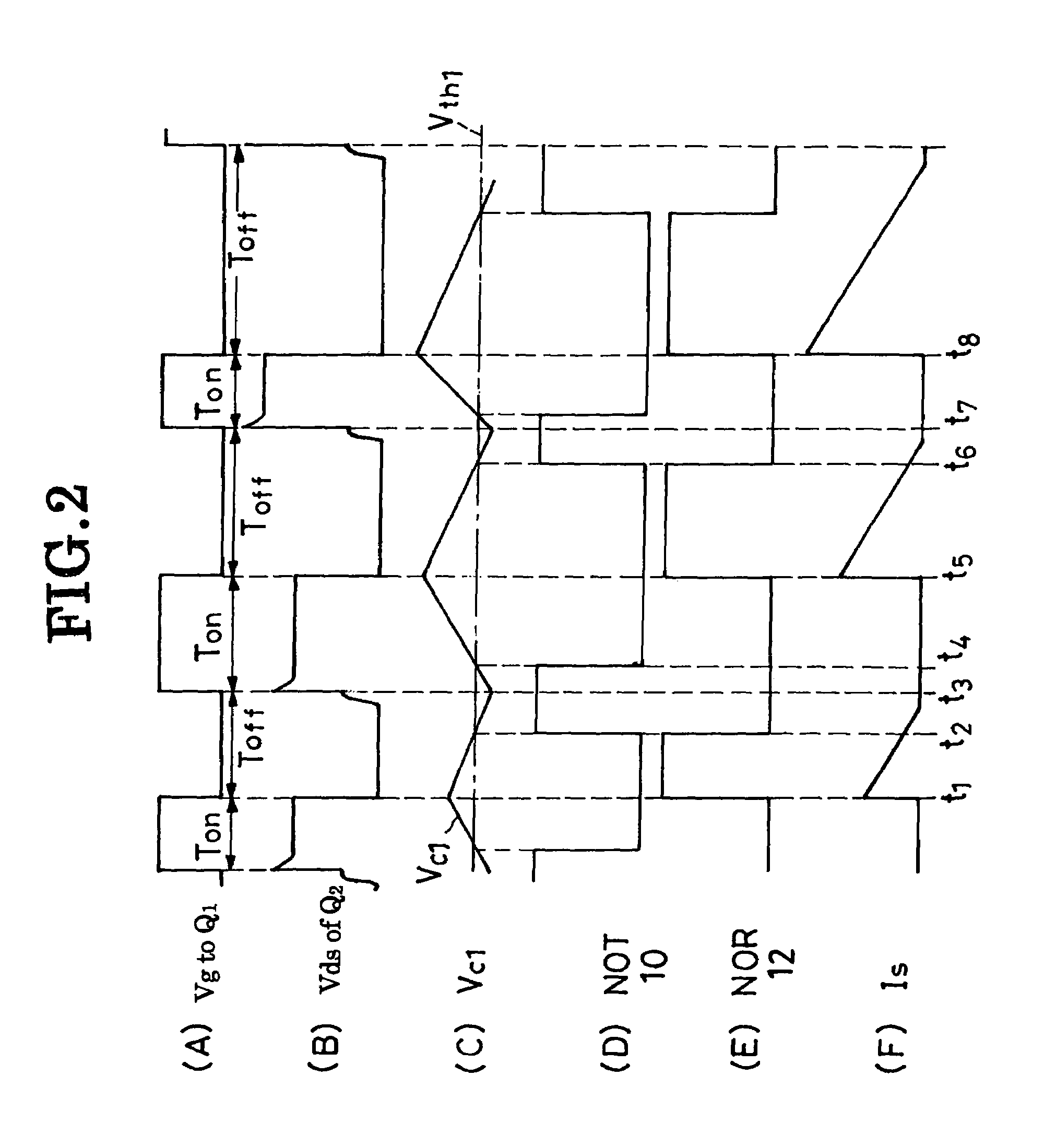
A DC-to-DC converter incorporates a transformer having a primary winding connected to a pair of DC input terminals via an active switch, which turns on and off under the control of a feedback circuit, and a secondary winding connected to a pair of DC output terminals via a synchronous rectifier and a smoothing capacitor. The synchronous rectifier is a parallel connection of a synchronous rectifier switch and a diode. A synchronous rectifier control circuit is connected to the synchronous rectifier switch for causing conduction therethrough while the active switch is off. The synchronous rectifier control circuit comprises a capacitor for determination of the conducting periods of the synchronous rectifier switch, and a logic network for on / off control of the synchronous rectifier switch according to whether the active switch is on or off and whether the capacitor voltage is higher than a predefined threshold or not.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sub-module fault diagnosis method of modular multilevel converter
InactiveCN103235219AEasy to implementQuick implementationAc-dc conversionElectrical testingFreewheelCapacitance
The invention discloses a sub-module fault diagnosis method of a modular multilevel converter in the technical field of power transmission and distribution. According to the technical scheme, the method includes: firstly, performing fault feature analysis aiming at typical faults of sub-modules; secondly, configuring an SFDU (sub-module fault diagnosis unit) in an SMC (sub-module controller), and combining provided sub-module fault diagnosis indexes by the aid of capacitor voltage, bridge arm current and trigger signals at the moment so as to achieve diagnosis of faults of sub-module IGBT (insulated gate bipolar translator) short circuit, IGBT open circuit, FWD (freewheel diode) short circuit, capacitor failure and the like; and finally, adopting an exclusive method in a VBC (valve base controller) to achieve diagnosis of faults of sub-module FWD open circuit, capacitor open circuit failure, connection line open circuit and the like. The method has the advantages that diagnosis of sub-module faults is achieved on the base of software, additional measuring points are not added to an original control protection system, and the method is easy to implement, has quick and efficient sub-module fault diagnosis capability, and has coordination with other protection settings.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Optimal pressure equalizing control method of modular multilevel converter type direct current transmission system
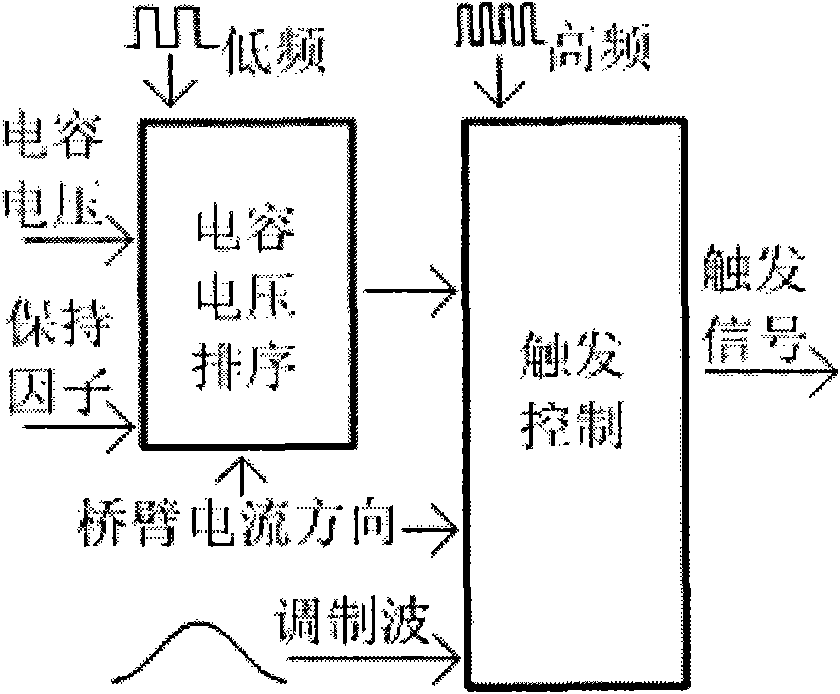
InactiveCN101860203AReduce switching frequencyDoes not slow down trackingAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLower limitCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses an optimal pressure equalizing control method of a modular multilevel converter type direct current transmission system. By setting an upper limit and a lower limit on voltage, the pressure equalizing control is mainly carried out on submodules with out-of-limit capacitor voltage, and capacitor voltage sequencing for submodules with no out-of-limit capacitor voltage is processed by combing the charging / discharging conditions of bridge arm current so as to increase the probability of maintaining an original switching state for the submodules with no out-of-limit capacitor voltage when the next action is in triggering control and lower the switching frequency of devices. The introduction of the pressure equalizing control can not lower the working frequency of triggering control and the tracking speed of a converter by using submodule capacitor voltage sequencing and triggering control to work at different frequencies. The optimal pressure equalizing control method of the invention can greatly lower the switching frequency of the devices on the premise of having no obvious increment on submodule capacitor voltage fluctuation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
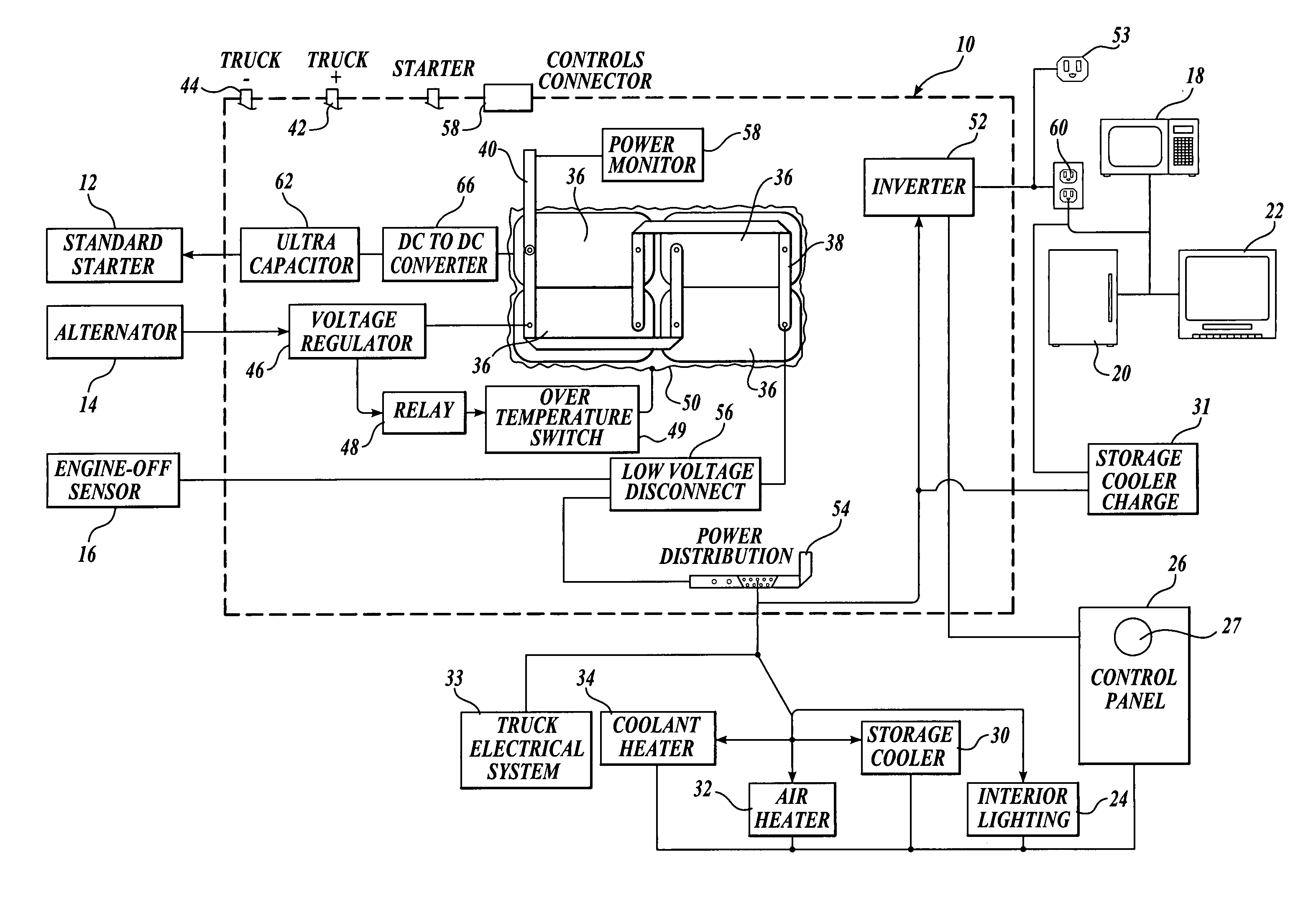
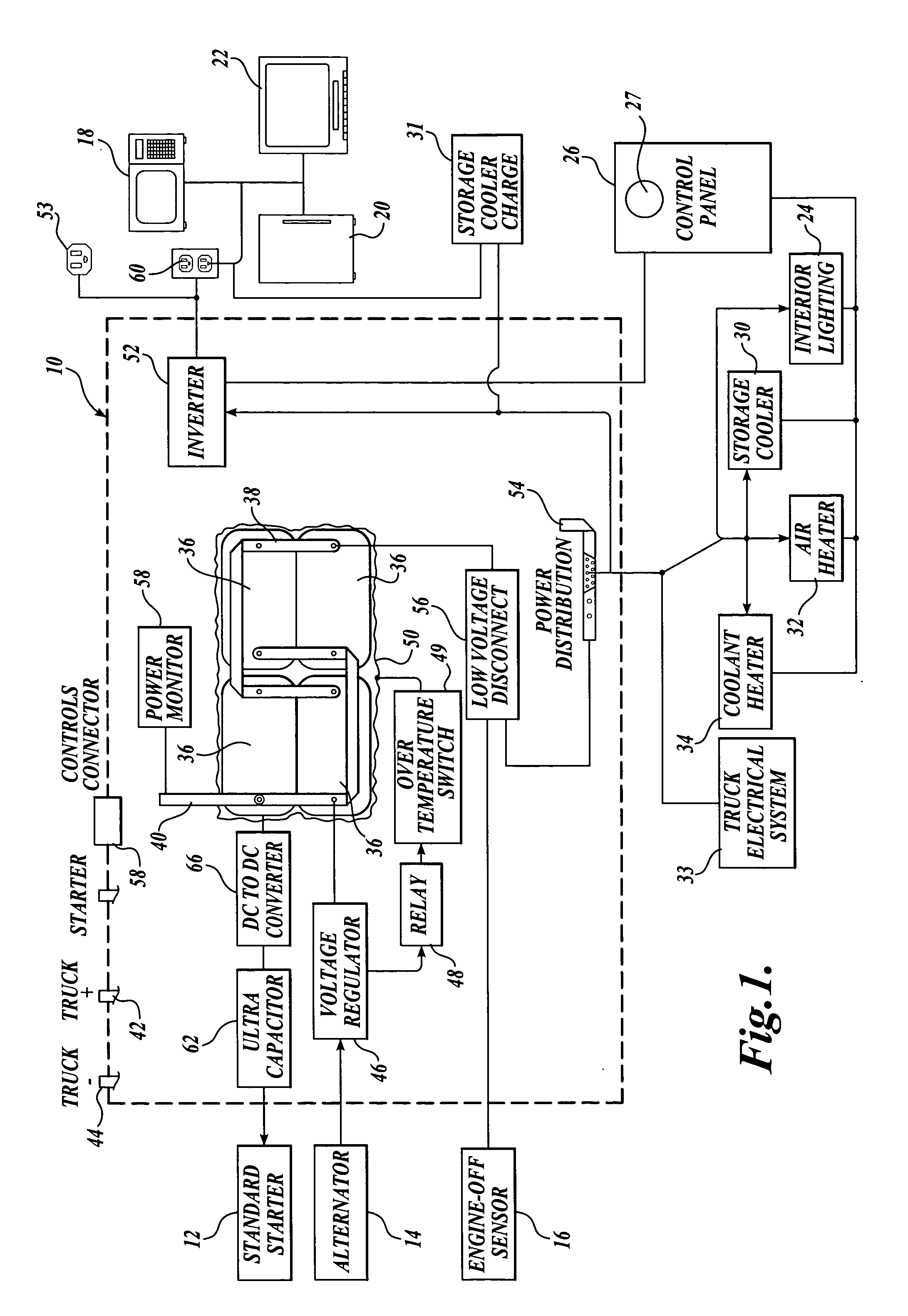
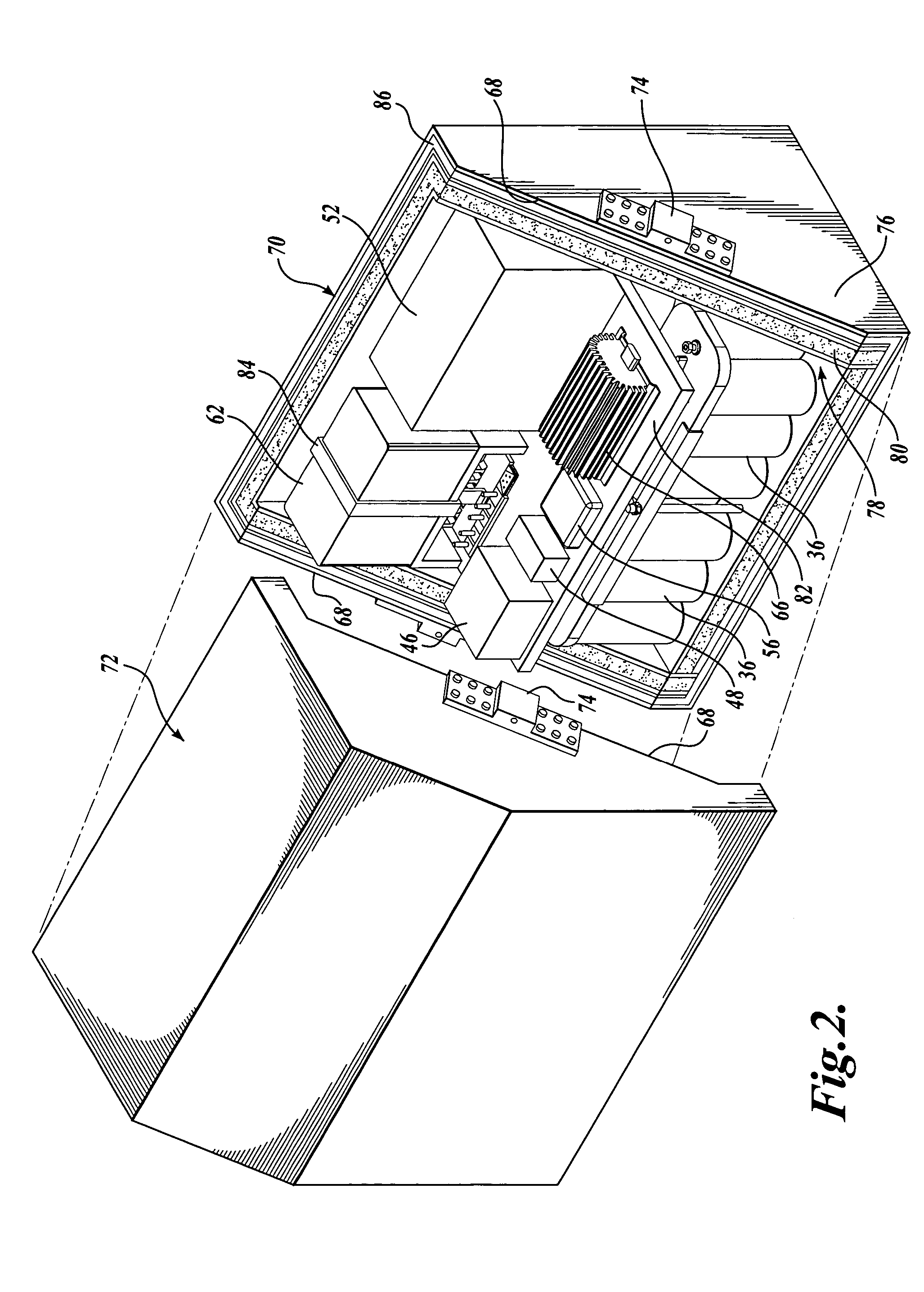
Electrical power system for vehicles requiring electrical power while the vehicle engine is not in operation
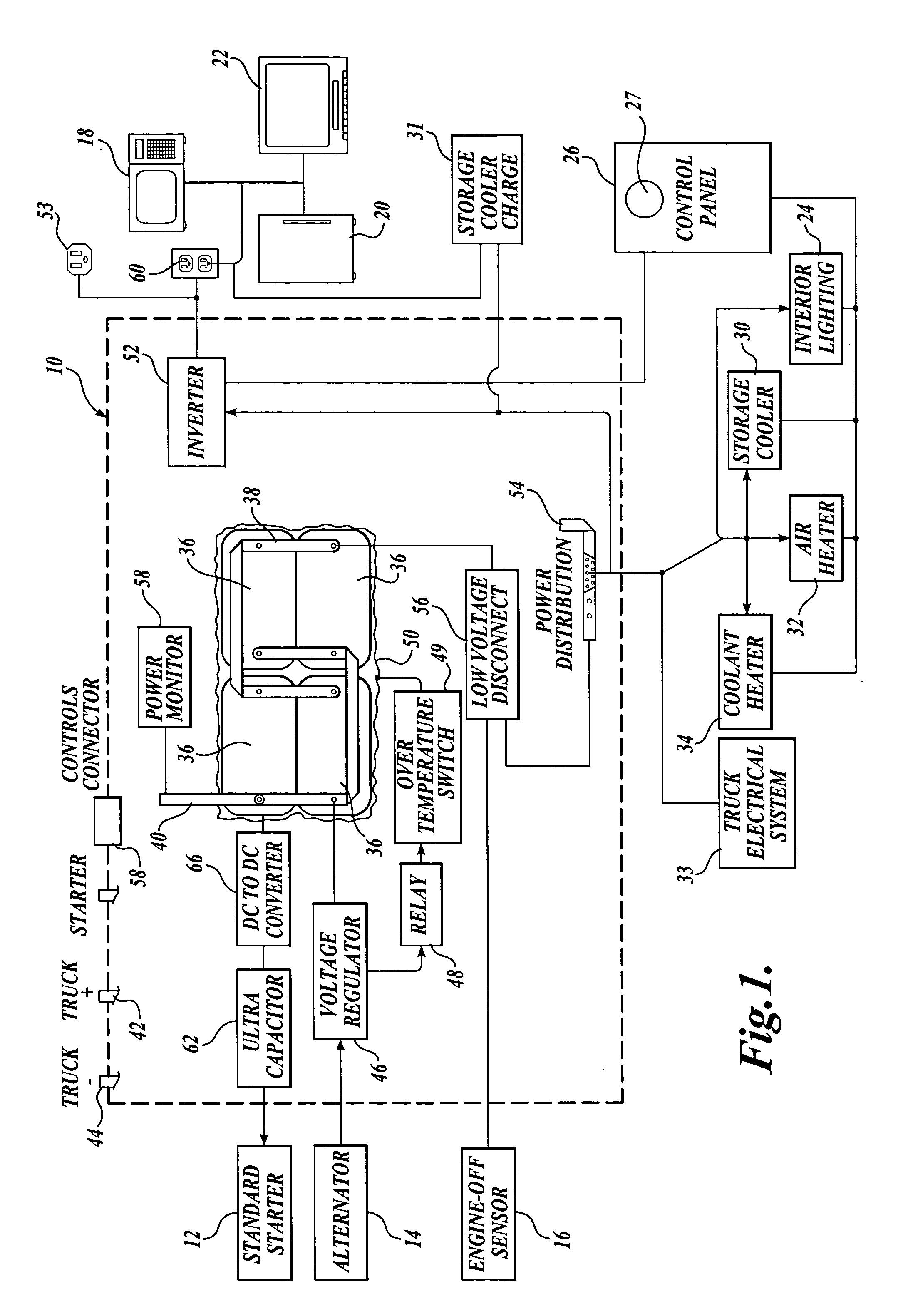
ActiveUS20060023480A1Increased power capacityReduce capacityConverter typesVehicle heating/cooling devicesCharge currentLow voltage
A system for supplying electrical power for use when the vehicle engine is shut down and configurations of long-haul trucks employing the system are disclosed. The power system is a battery bank contained within an insulated enclosure. The batteries are heated when the truck is in operation with the insulated enclosure maintaining battery temperature sufficient to provide high battery power capacity for an extended period after the vehicle is shut down. A large capacitor, rather than the batteries, provides current for starting the vehicle engine. A dc-to-dc converter controls the fully charged capacitor voltage and provides capacitor charging current even when the batteries have been discharged to a low-voltage condition. The disclosed long-haul truck configurations include a storage cooler that employs a phase-change medium that is thermally charged to a low temperature while the truck is in operation and is used to provide sleeper unit cooling air. Additional provision is made for heating the sleeper unit and for powering a coolant heater that can warm the truck engine block and truck fuel when the engine is shut down during cold weather.
Owner:PACCAR INC
Pixel and organic light emitting display using the same
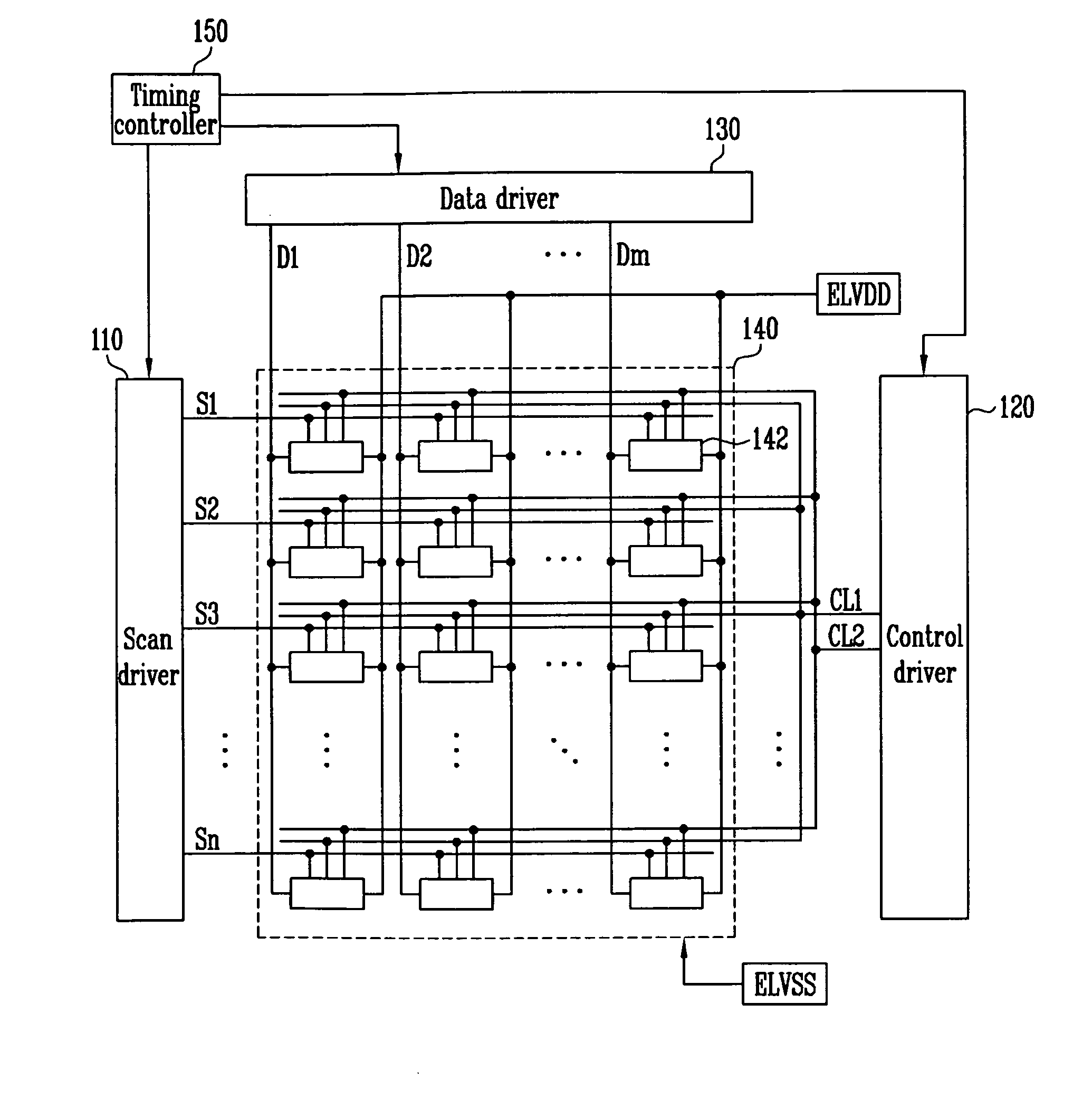
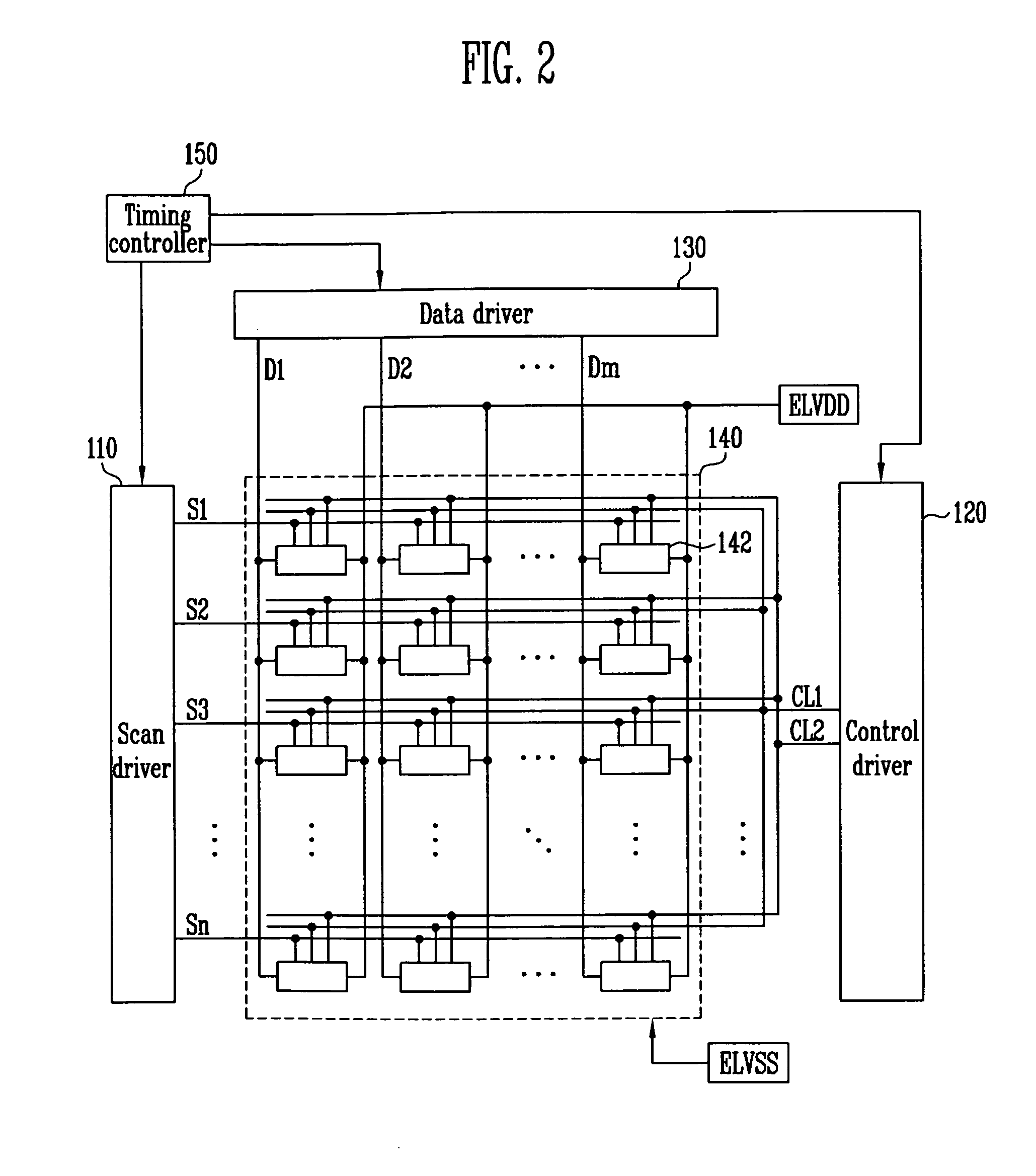
ActiveUS20120113077A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPower flowCapacitor voltage
A pixel may include an organic light emitting diode (OLED) with a cathode electrode coupled to a second power source, a first transistor with a first electrode coupled to a data line, with a second electrode coupled to a first node, the first transistor being turned on when a scan signal is supplied to a scan line, a first capacitor coupled between the first node and a third power source to charge a first capacitor voltage corresponding to a data signal supplied from the data line, and a pixel circuit charged by the first capacitor voltage to supply current corresponding to a charged first power source voltage from a first power source to the second power source via the OLED.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Voltage balancing control method for modular multilevel converter
InactiveUS20140002048A1Reduce switching frequencyAvoid switchingAc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationHigh voltage igbtCapacitor voltage
The present invention relates to Voltage balancing control method for modular multilevel converter is characterized that, it includes some steps as follows:1) Determine the leg current direction is positive or negative;2) Find out the highest sub module on output state whose capacitor voltage amplitude is the maximum, and find out that on bypass state whose capacitor voltage amplitude is the minimum;3) Determine whether the sub module inputs or bypass operation; this method avoided switching arbitrariness of the sub module, and decreased the switching frequency of the sub module. The capacitor voltage balancing control of the sub module proposed by the method is more suitable to be applied in the field of high voltage and large capacity converter that has large numbers of sub modules.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20070046619A1Easy to controlOutput fluctuationCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay boardLiquid-crystal display
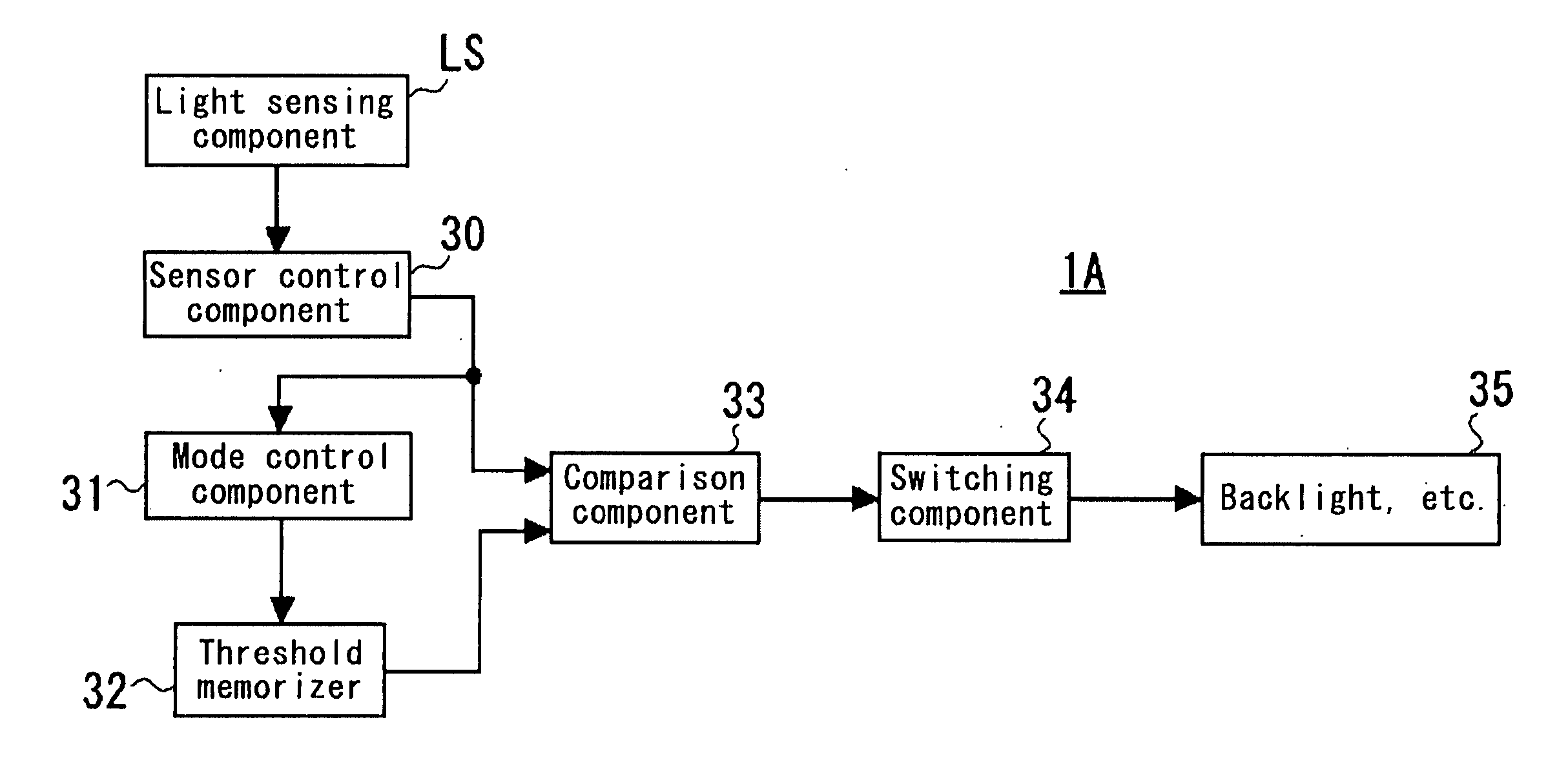
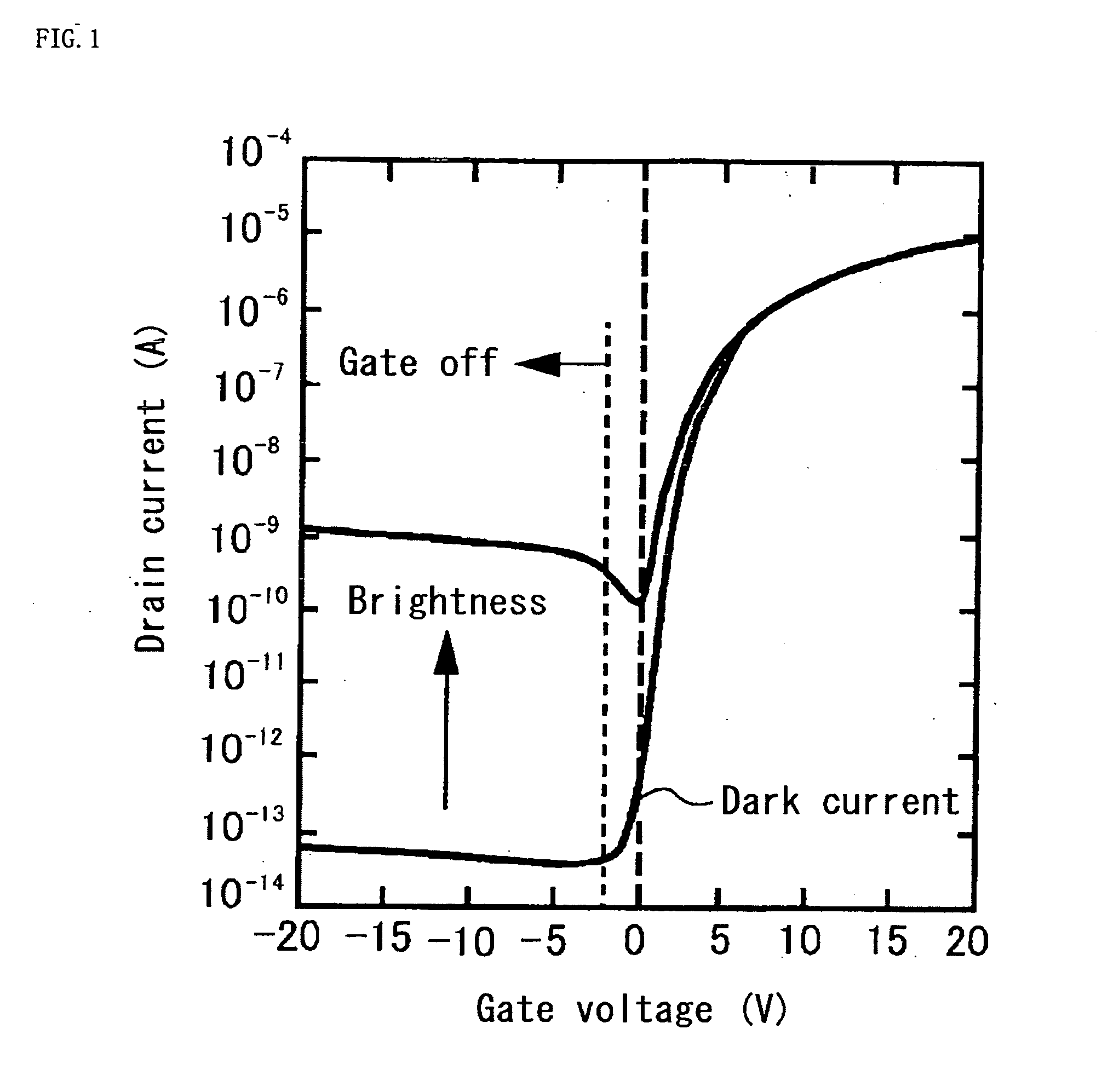
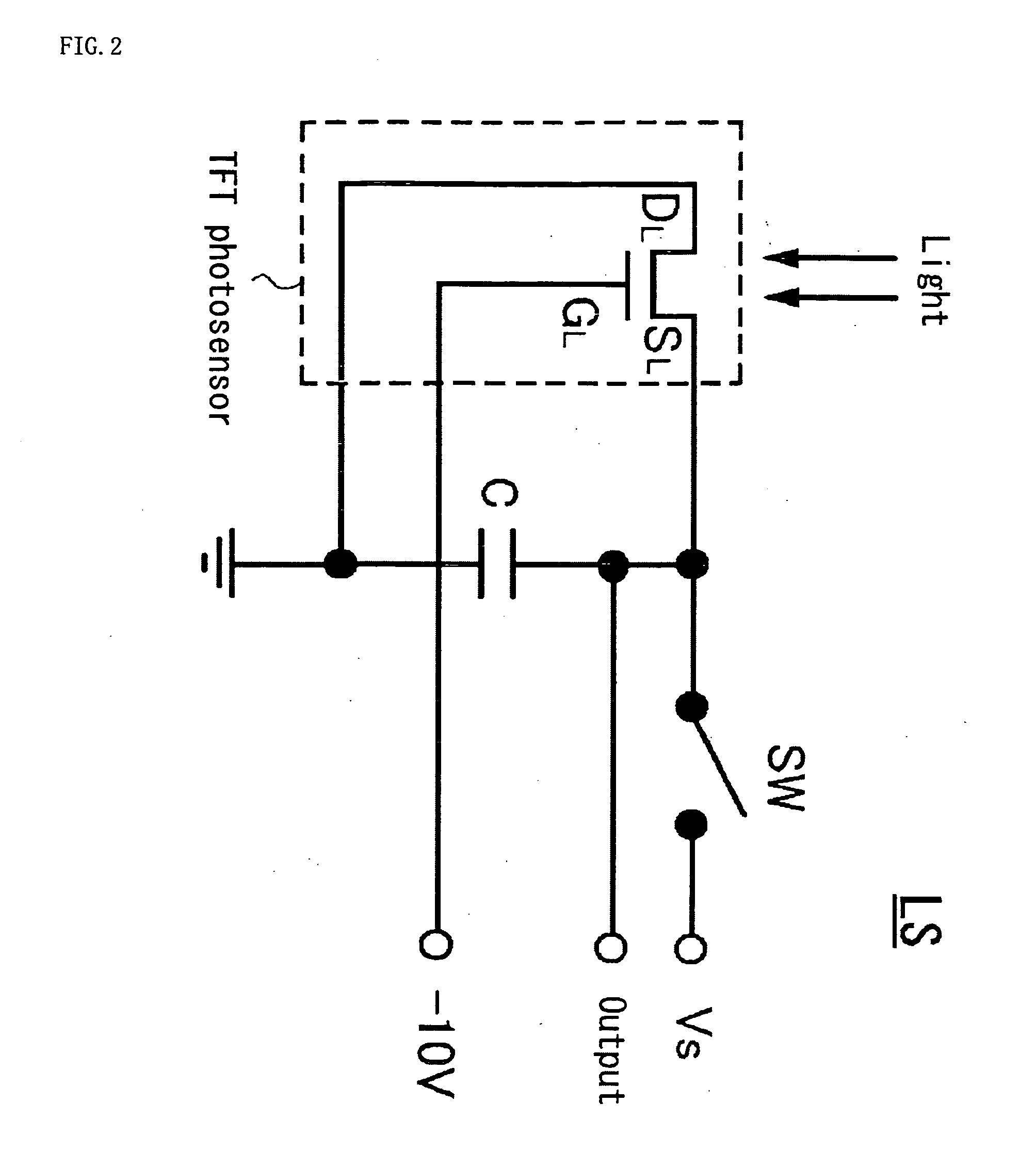
A liquid crystal display device 1 of the invention has a liquid crystal display panel in which a liquid crystal layer 14 is provided between a TFT substrate 2 and a CF substrate 25 that has a common electrode 26, a light sensing component LS1 with a TFT photosensor that senses external light, and an illuminating means controlled according to the output of the light sensing component. The light sensing component is deployed at the periphery of the TFT substrate's display area DA and uses a thin film transistor as photosensor. A capacitor C is connected between source and drain electrodes SL, DL for such TFT photosensor. One of the capacitor's terminals is connected to a standard voltage source VS via a switch element SW, and the other to the common electrode 26. Voltage that is always lower than the voltage applied to the common electrode by an amount corresponding to a reverse bias voltage is applied to the gate electrode GL for the TFT photosensor. The capacitor's voltage a certain time after the switch element turns off is output. As a result, it will be possible to provide a liquid crystal display device in which the light sensing component incorporated in the liquid crystal display panel is not susceptible to the influence of the drive signals for the display panel, and in which the light sensing component does not induce deterioration of the liquid crystals.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
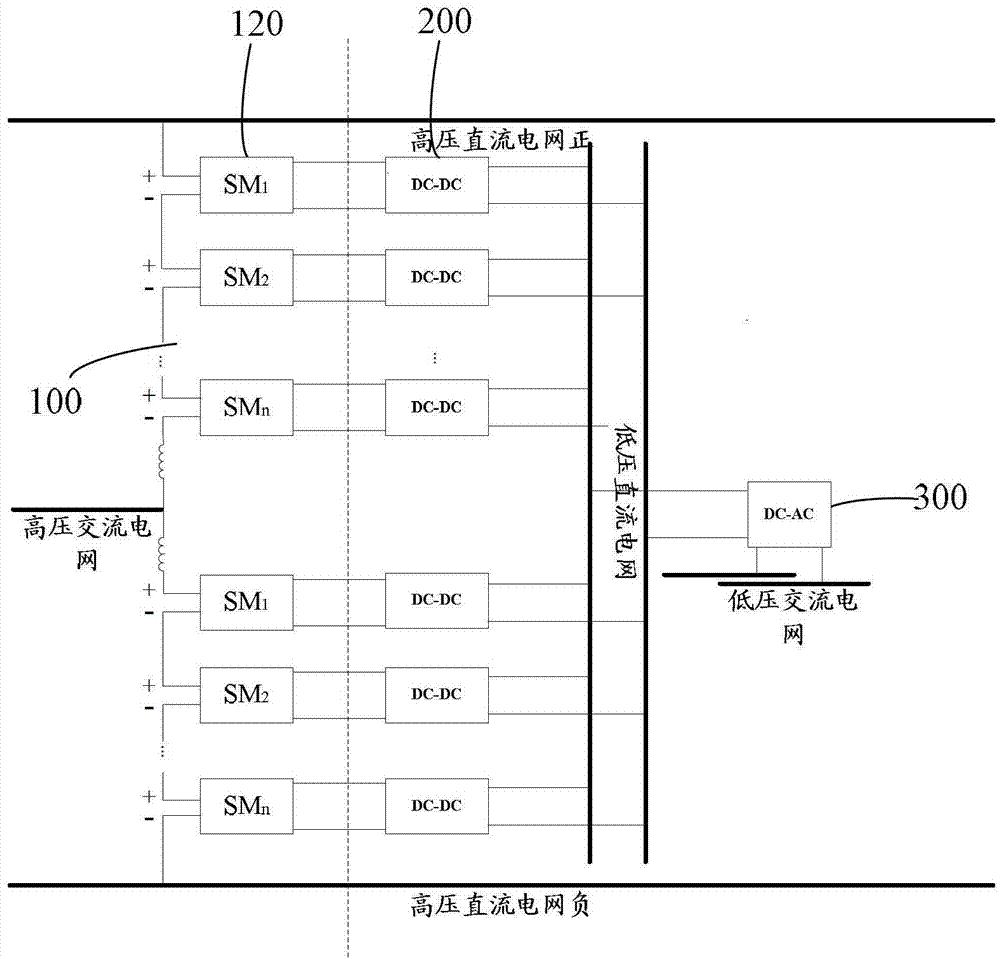
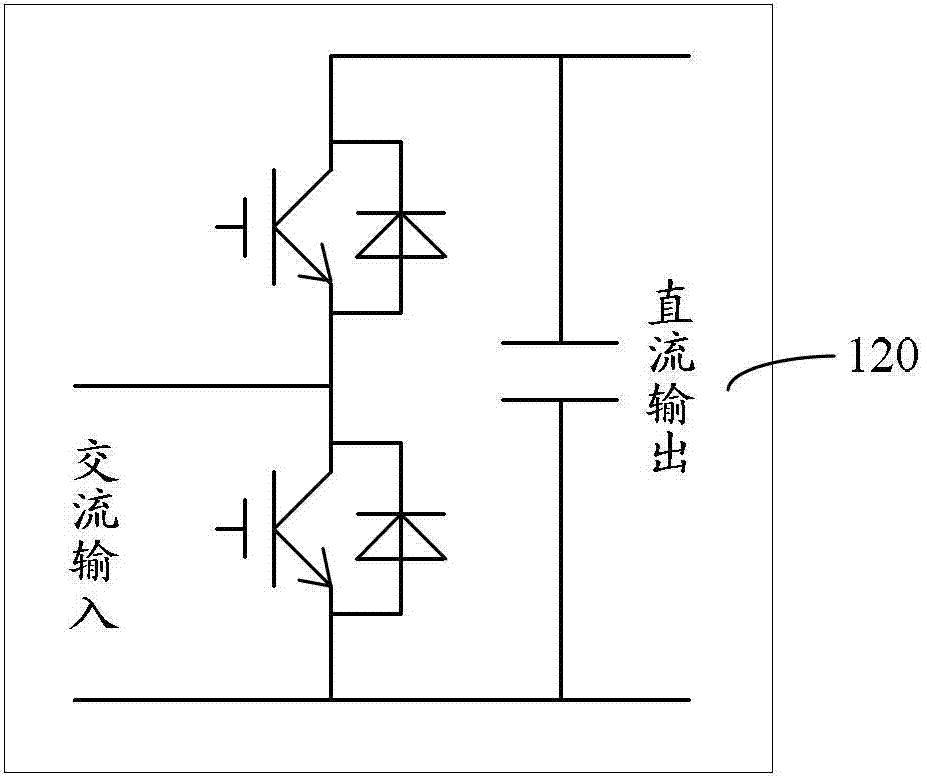
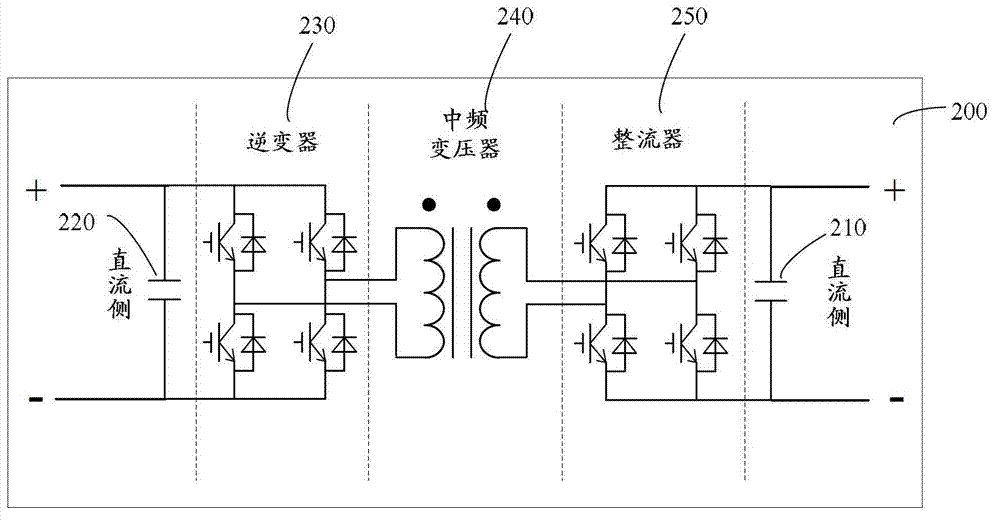
Electronic power transformer based on multi-media card (MMC)
The invention provides an electronic power transformer based on a multi-media card (MMC). The electronic power transformer based on the MMC comprises the MMC and a direct current-direct current (DC-DC) isolator. The MMC comprises a plurality of sub-modules which are connected in series, the direct current output side and the direct current input side of the DC-DC isolator are respectively connected with capacitors in parallel, the direct current output side of the DC-DC isolator is connected with a low voltage direct current power grid, the direct current input side of the DC-DC isolator is connected with the direct current output ends of the sub-modules, and each sub-module comprises a half-bridge circuit and a capacitor, wherein the half-bridge circuits and the capacitors are connected in parallel. When direct current capacitor voltage of the MMC is unbalanced, the sub-modules with high capacitor voltage in the MMC charge the capacitors with low voltage to raise voltage values through the DC-DC isolator with the help of the low voltage direct current power grid and then through the DC-DC isolator again, stability of voltage on the direct current side is guaranteed, and therefore automatic balance of the direct current capacitor voltage of the MMC is achieved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Complex control system and method of modular multi-level converter
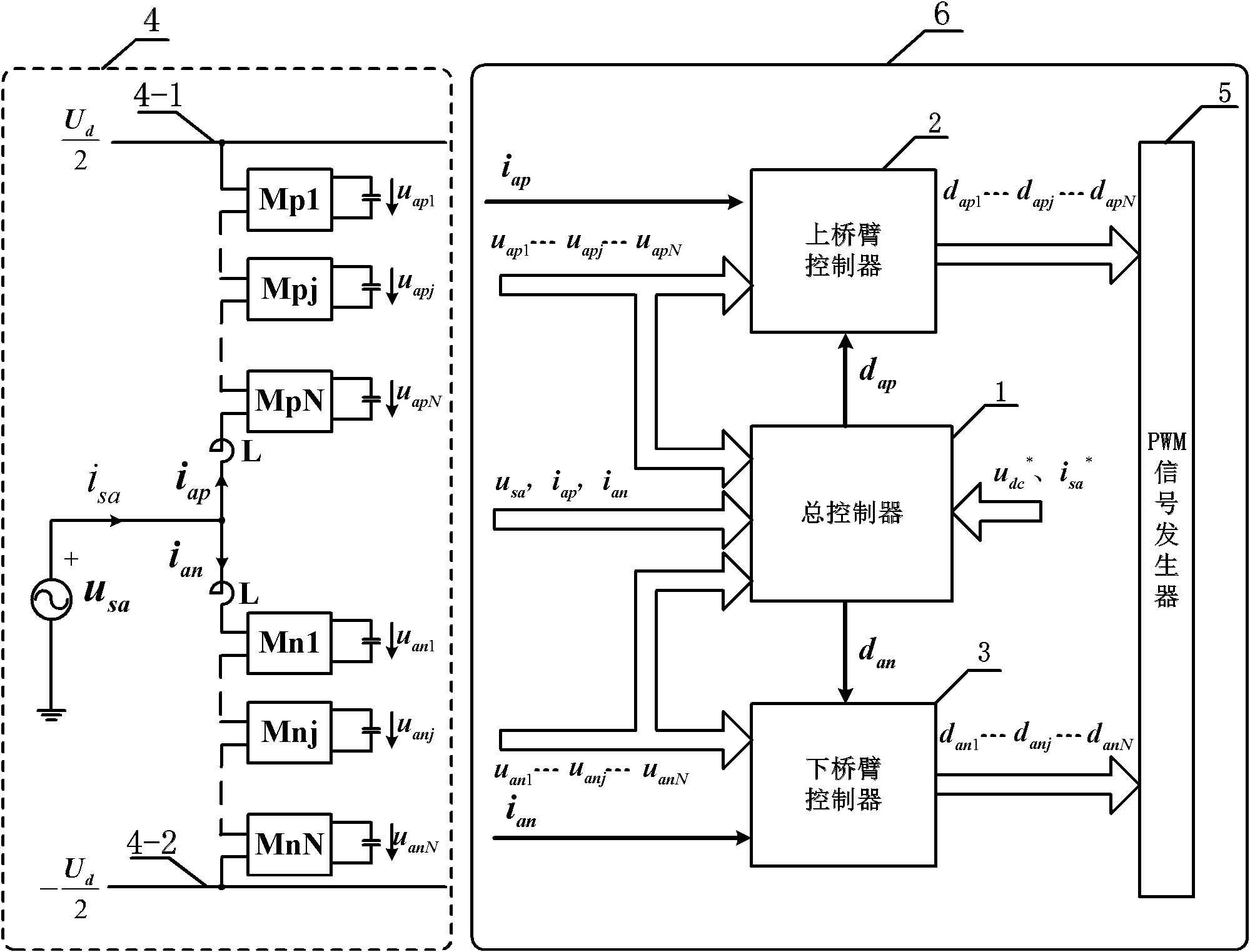
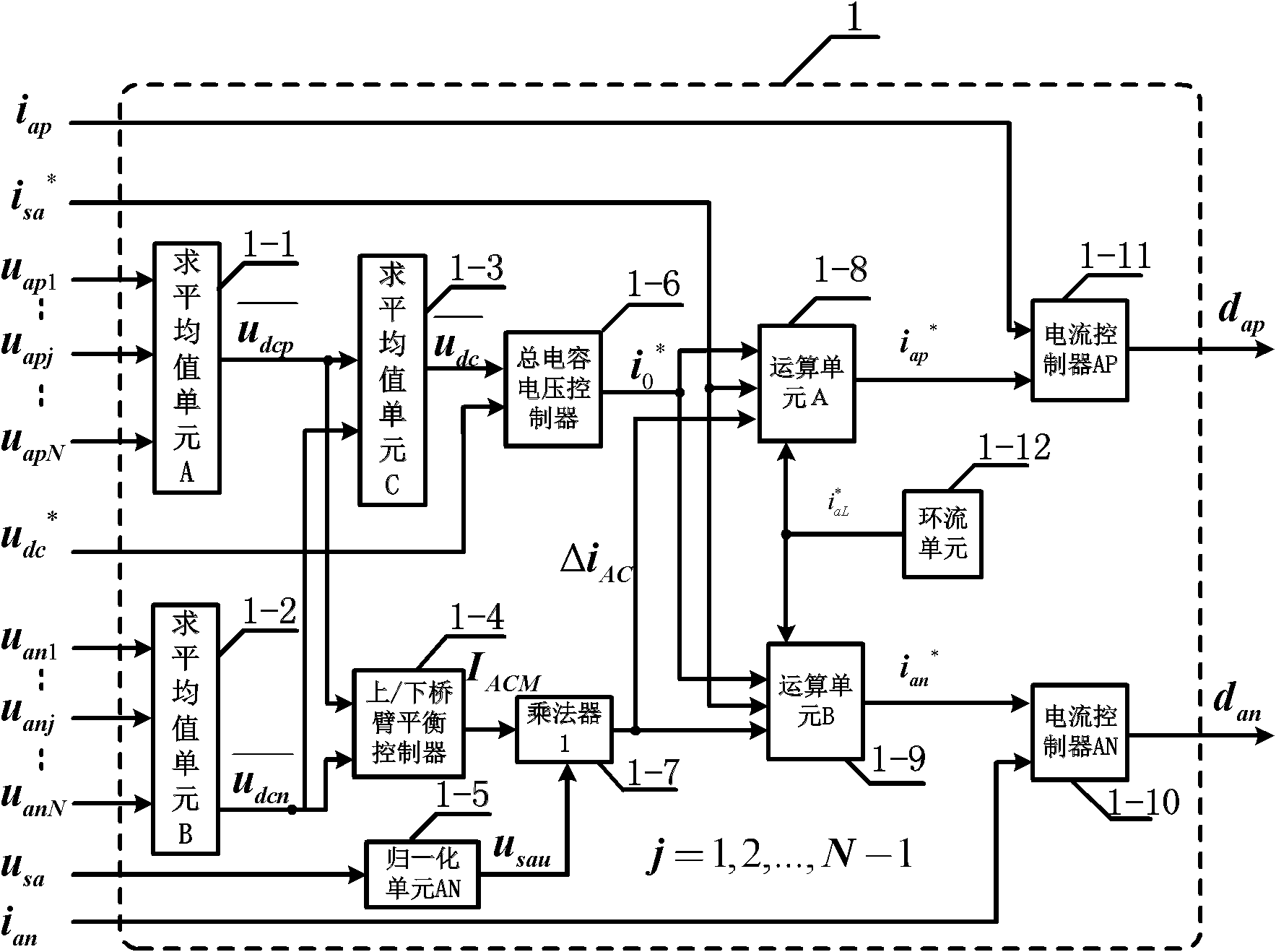
InactiveCN102158112AAchieve currentTo achieve voltage controlAc-dc conversionCapacitanceCapacitor voltage
The invention relates to a complex control system and method of a modular multi-level converter. The method is characterized in that each submodule capacitor voltage of an upper bridge arm and a lower bridge arm on the modular multi-level converter, currents of the upper and lower bridge arms and a power supply voltage of an alternating current (AC) side are detected, and a master controller carries out an operation on each submodule capacitor voltage, the currents of the upper and lower bridge arms and the power supply voltage of the AC side to obtain the public pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty ratio of the upper and lower bridge arms; an upper and lower bridge arm controller carries out an operation on each submodule capacitor voltage of the upper and lower bridge arms and the public PWM duty ratio of the upper and lower bridge arms to obtain the PWM duty ratio of each submodule of the upper and lower bridge arms; and the PWM duty ratio of each submodule is processed by a PWM signal generator so as to generate PWM control signals of each submodule, thus realizing balance control of each submodule capacitor voltage of the convertor and current and voltage control of the convertor. The complex control system is not required to use a special charge-discharge power circuit for a capacitor, can be applied to any PWM node, controls circulating flow flexibly, meets special demands, and is specific in physical significance and sufficient in theoretical foundation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Electrical power system for vehicles requiring electrical power while the vehicle engine is not in operation
ActiveUS7145788B2Reduce capacitySave energyConverter typesVehicle heating/cooling devicesCapacitor voltageLow voltage
A system for supplying electrical power for use when the vehicle engine is shut down and configurations of long-haul trucks employing the system are disclosed. The power system is a battery bank contained within an insulated enclosure. The batteries are heated when the truck is in operation with the insulated enclosure maintaining battery temperature sufficient to provide high battery power capacity for an extended period after the vehicle is shut down. A large capacitor, rather than the batteries, provides current for starting the vehicle engine. A dc-to-dc converter controls the fully charged capacitor voltage and provides capacitor charging current even when the batteries have been discharged to a low-voltage condition. The disclosed long-haul truck configurations include a storage cooler that employs a phase-change medium that is thermally charged to a low temperature while the truck is in operation and is used to provide sleeper unit cooling air. Additional provision is made for heating the sleeper unit and for powering a coolant heater that can warm the truck engine block and truck fuel when the engine is shut down during cold weather.
Owner:PACCAR INC
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS20060157643A1Increase elasticityFunction providedTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a fixed compensating offset (ΔV) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. The number (N) of ΔV offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo+N·ΔV, where Vo is capacitor voltage. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Discharging control device for electric power conversion system
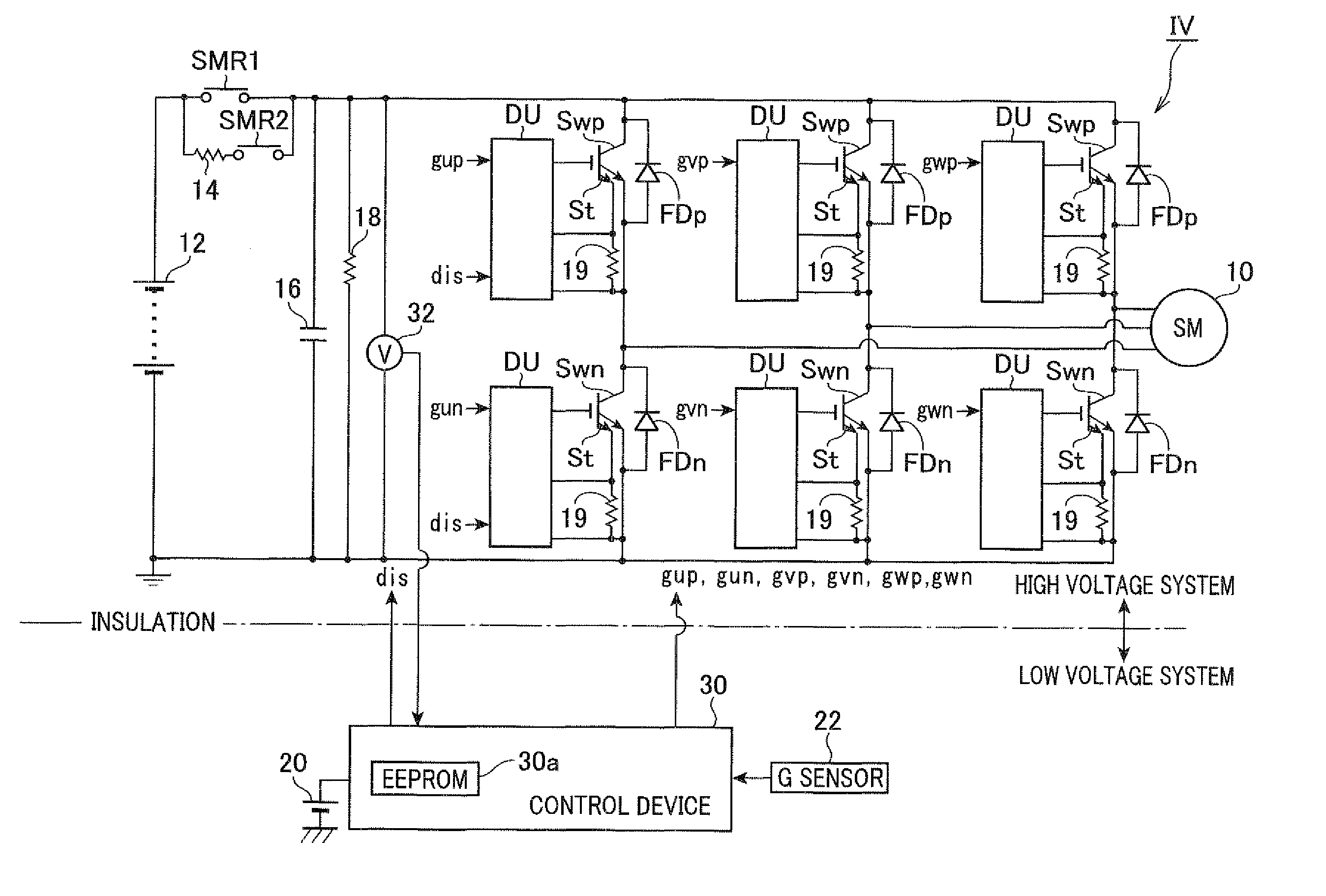
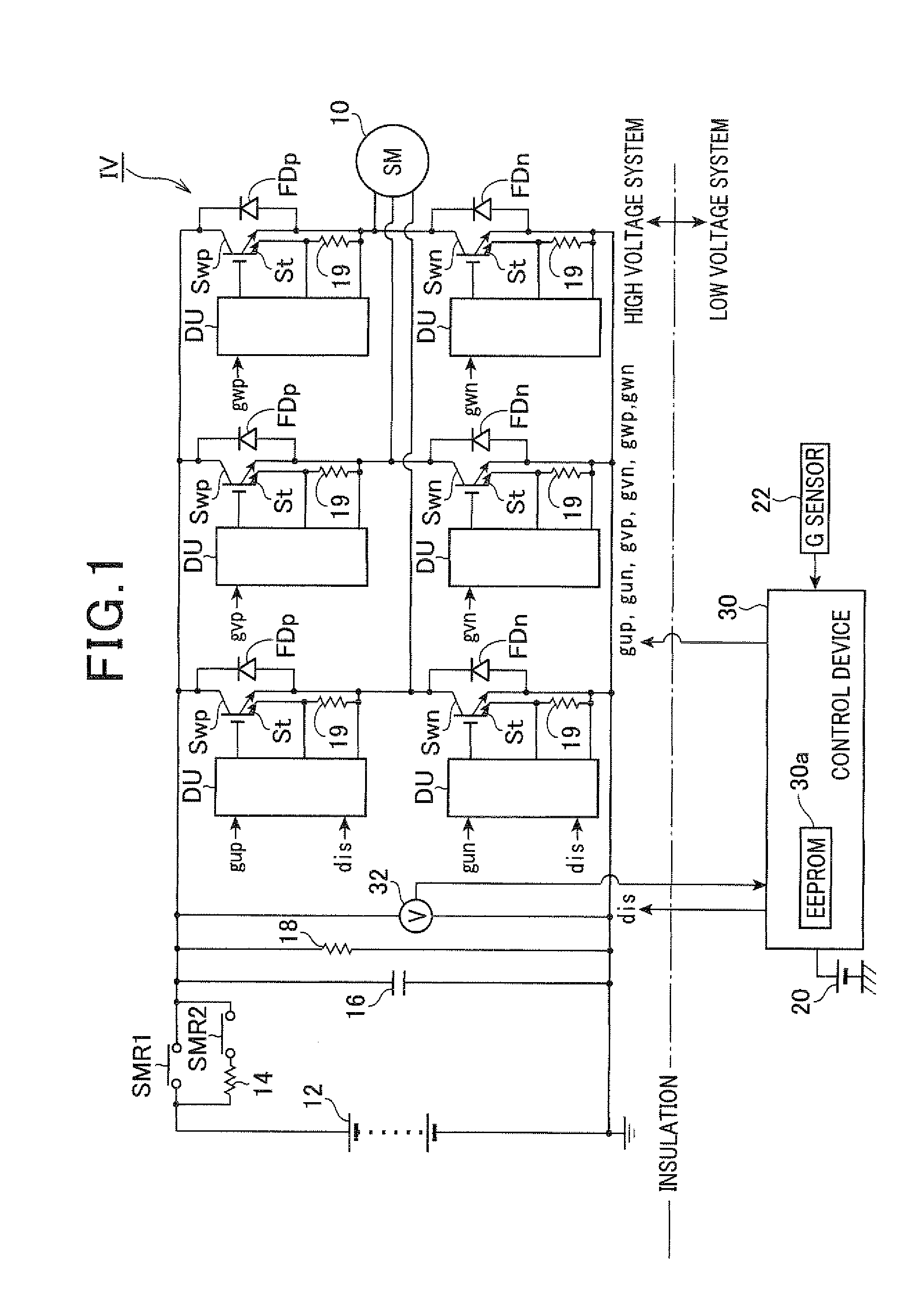
ActiveUS20110221374A1Avoid diagnostic resultReduce heatAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitor voltageLow voltage
A discharge control device in an electric power conversion system mounted to a motor vehicle turns off a relay in order to instruct an electric power conversion circuit to supply a reactive current into a motor generator, and thereby to decrease a capacitor voltage to a diagnostic voltage. After this process, the discharge control device outputs an emergency discharging instruction signal dis in order to turn on both power switching elements at high voltage side and a low voltage side in the electric power conversion circuit. This makes a short circuit between the electrodes of the capacitor in order to discharge the capacitor, and executes a discharging control to detect whether or not an emergency discharging control is correctly executed and completed. The discharge control device detects whether or not the electric power stored in the capacitor is discharged on the basis of the voltage of a voltage sensor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Discharge Lamp Lighting Device, and Lighting Equipment and Lighting System Using the Device
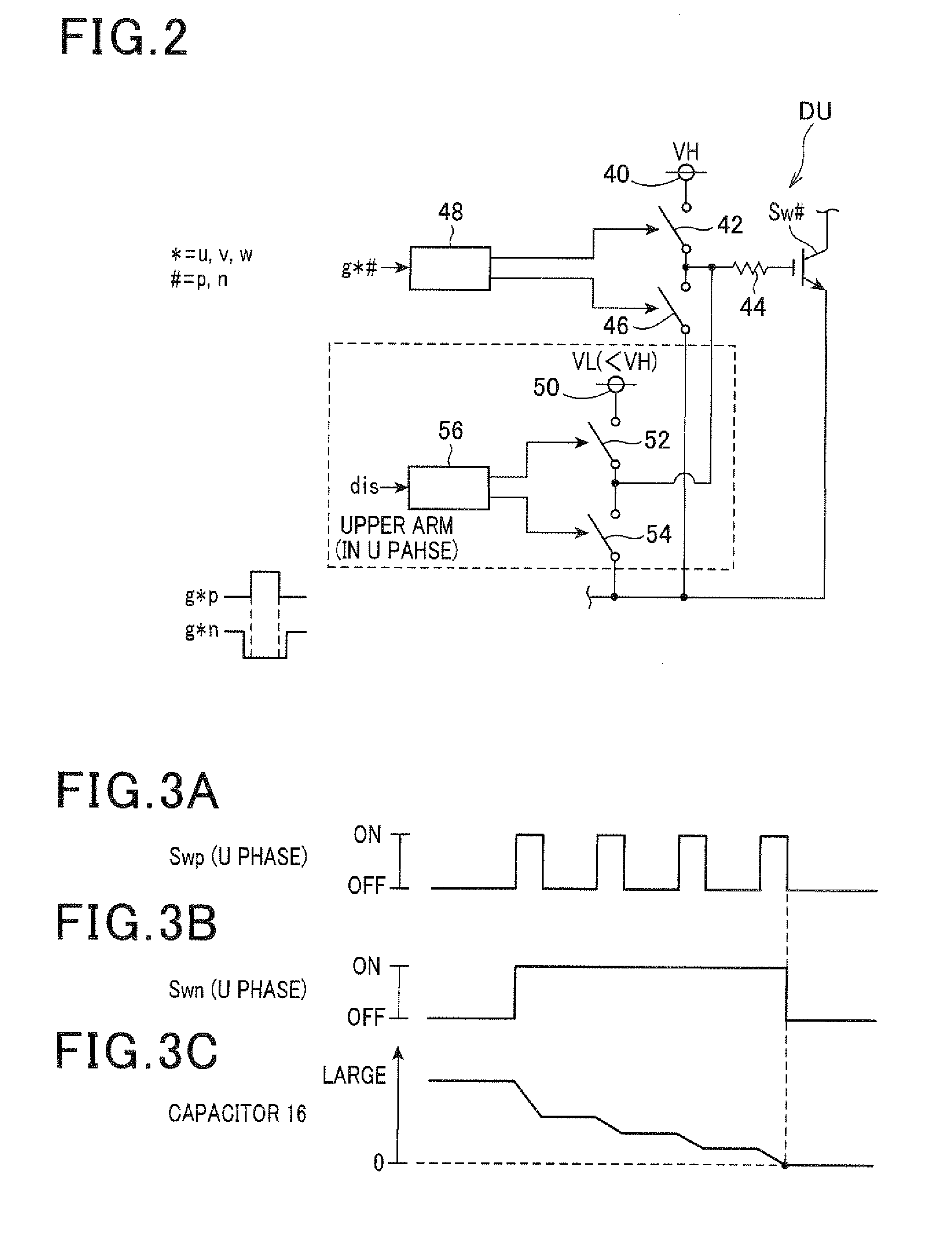
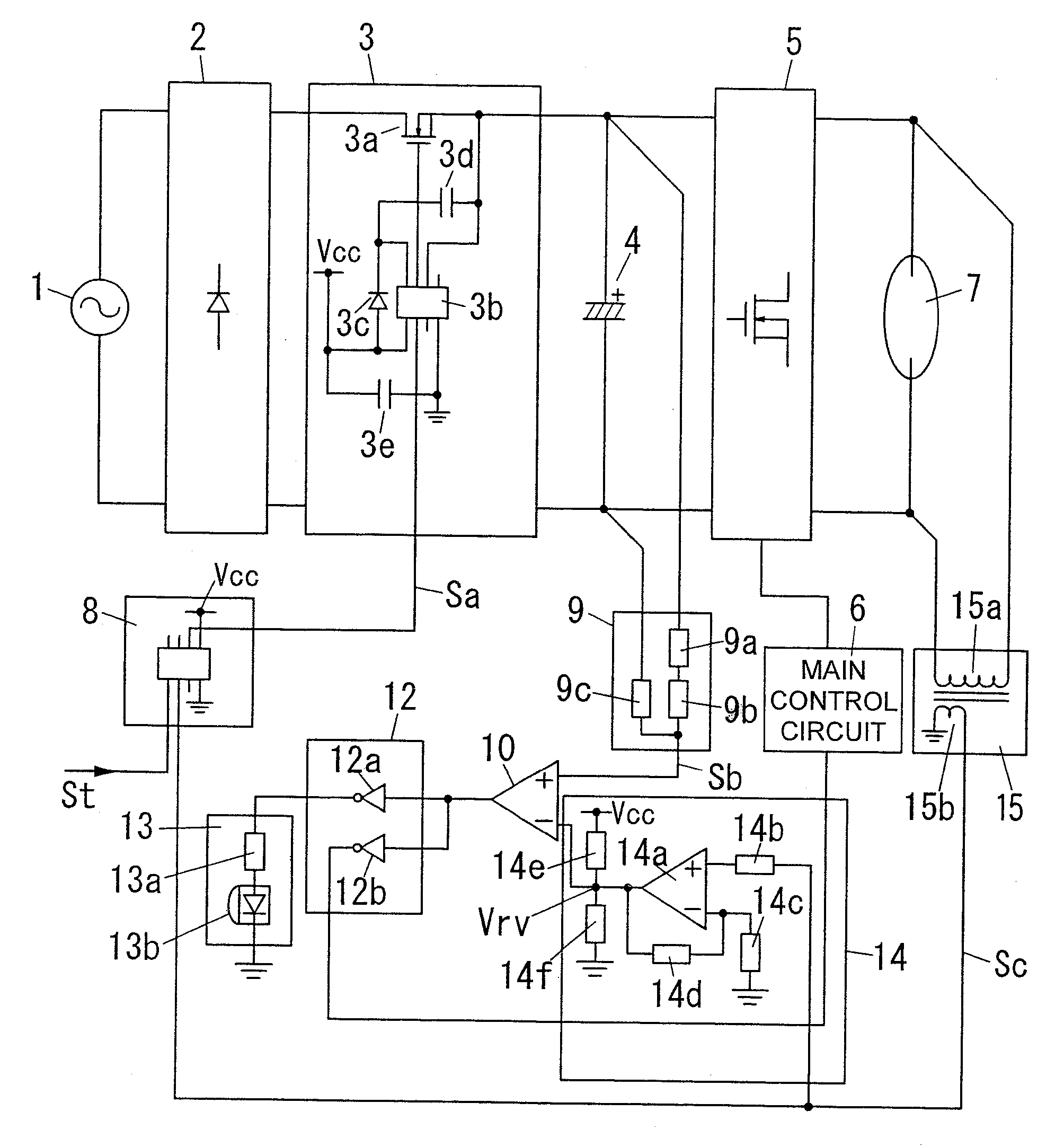
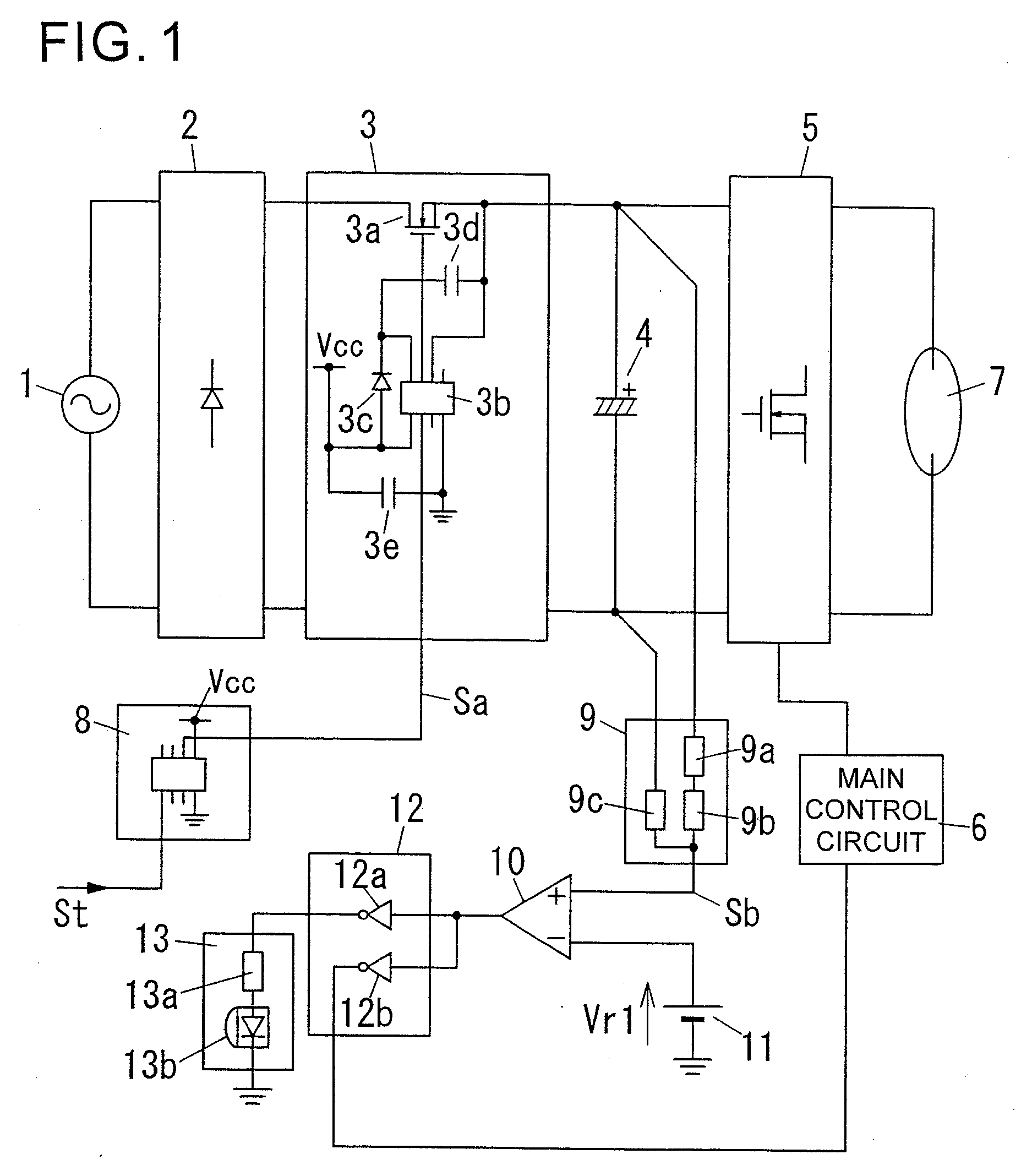
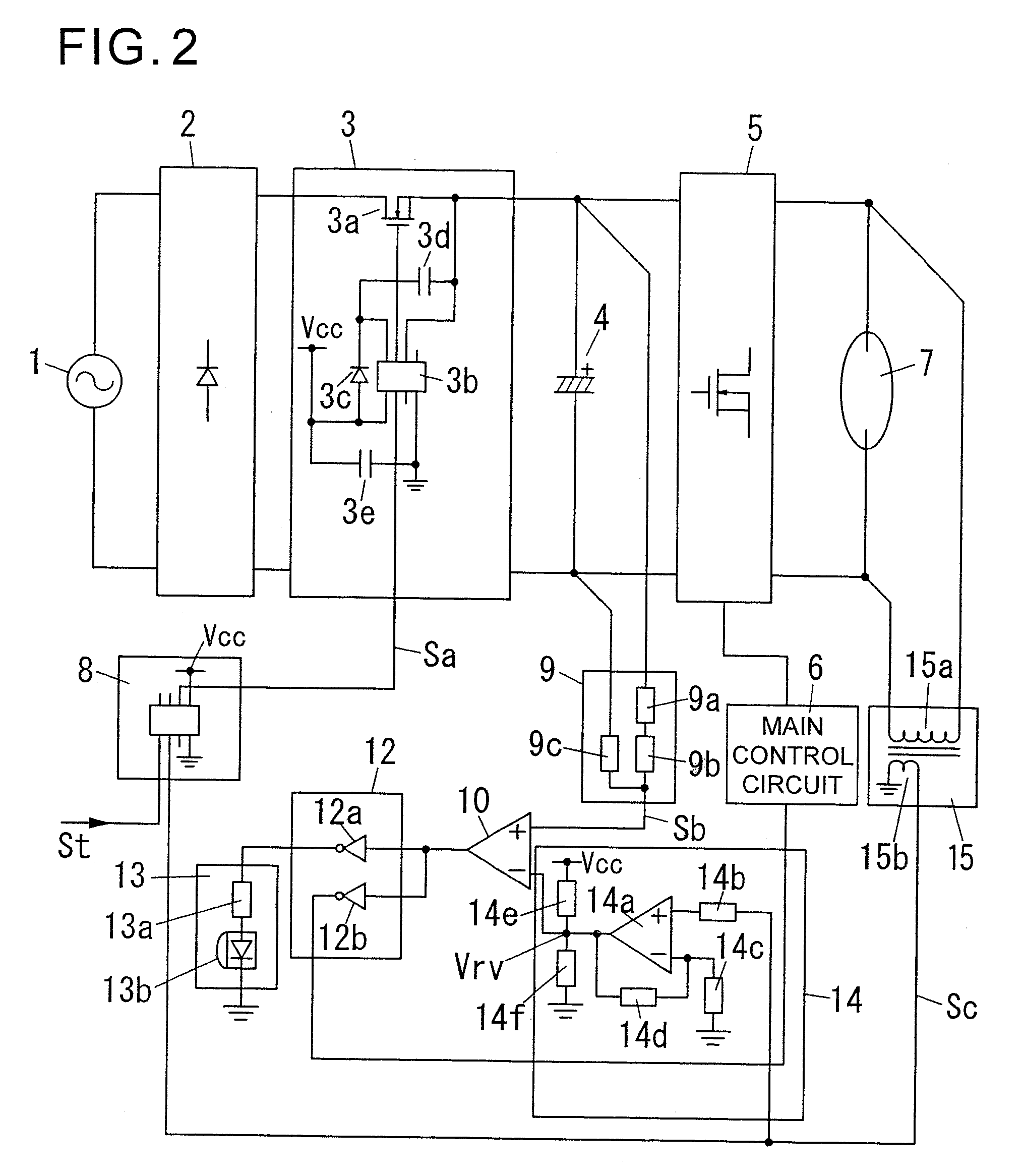
InactiveUS20080030143A1Simple configurationEnsure correct executionDischarge tube testingBatteries circuit arrangementsMOSFETLight equipment
A level shift IC (3b) of a power supply / shutoff section (3) is operable, when a shutoff signal (Sa) is input from a timer circuit (8) for a time T during an ON state of a discharge lamp (7), to turn off a MOSFET (3a) so as to shut off power supply to a smoothing capacitor (4). When a detection signal (Sb) of a capacitor voltage is lowered to a value less than a reference voltage Vr1 during input of the shutoff signal (Sa), an output of a comparator (10) is changed from an H level to an L level in an inverted manner. In conjunction with this change, respective outputs of an auxiliary control circuit (12) and a NOT element (12a, 12b) are changed from an L level to an H level in an inverted manner. As a result, a current flows from the NOT element (12a) to an LED (13b) through a resistor (13a) to turn on the LED (13b). Thus, a life end of the smoothing capacitor 4 is annunciated, and a main control circuit (6) is operable to suppress an output of an inverter main circuit (5).
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Modular multi-level converter capacitor voltage fluctuation inhibition method under low-frequency working condition
ActiveCN103701350AGuaranteed symmetrySymmetry helpsDc-ac conversion without reversalPhase currentsCapacitor voltage
The invention relates to a modular multi-level converter capacitor voltage fluctuation inhibition method under a low-frequency working condition, and belongs to the technical field of power electronics and motor drive. The method comprises the following steps: the alternating-current side three-phase phase current which meets the low-frequency working need is obtained by performing closed-loop control on the modular multi-level converter alternating-current side three-phase phase current; loop current only contains a direct-current component and a high-frequency alternating-current component by closed-loop control of the three-phase loop current, and a bridge arm voltage contains a high-frequency zero sequence component by overlapping high-frequency voltage at the midpoint electric potential at the direct-current side; the amplitude values, the frequencies and the phases of the loop current high-frequency alternating-current component and the bridge arm voltage high-frequency zero sequence component are obtained by operation, so that the phase voltage and the phase current of the alternating-current side do not contain high-frequency harmonic waves, moreover, the cycles of charging and discharging submodules are shortened, and the effect of inhibiting the capacitor voltage vibration of the submodules is realized; the electrical quantity of each bridge arm is kept to be balanced by the balancing control on the bridge arm energy so as to guarantee that the modular multi-level converter runs symmetrically and stably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Controller for the three-phase cascade multilevel converter used as shunt active filter in unbalanced operation with guaranteed capacitors voltages balance
InactiveUS7710082B2Active power filteringDc-ac conversion without reversalNonlinear distortionCapacitor voltage
The present invention comprises a controller for the cascade H-bridge three-phase multilevel converter used as a shunt active filter. Based on the proposed mathematical model, the controller is designed to compensate harmonic distortion and reactive power due to a nonlinear distorting load. Simultaneously, the controller guarantees regulation and balance of all capacitor voltages. The idea behind the controller is to allow distortion of the current reference during the transients to guarantee regulation and balance of the capacitors voltages. The controller provides the duty ratios for each H-bridge of the cascade multilevel converter.
Owner:INST POTOSINO DE INVESTIGACION CIENTIFICA Y TECHCA A C
Power supply device and method for detecting non-contact state of load connected to power supply device
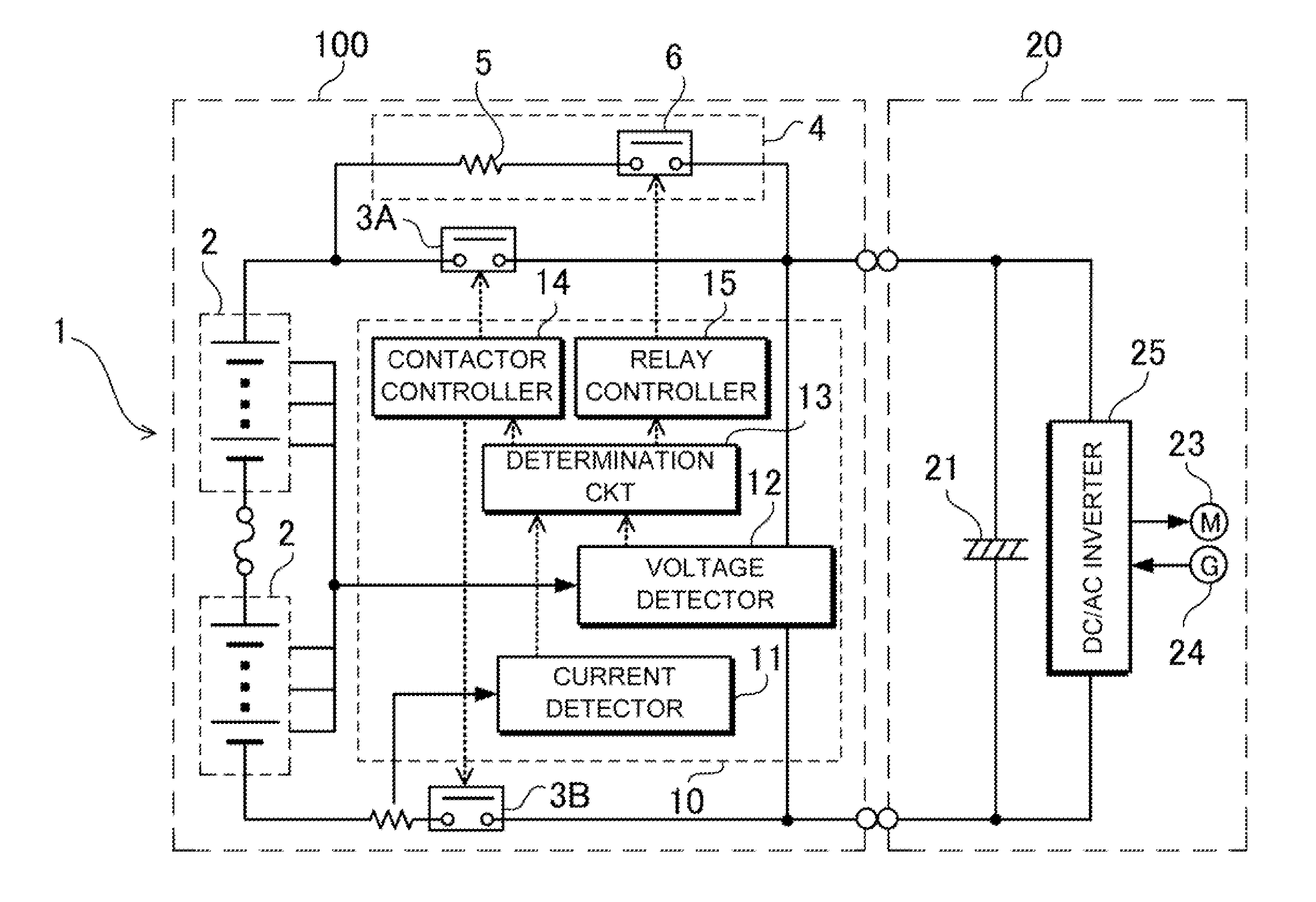
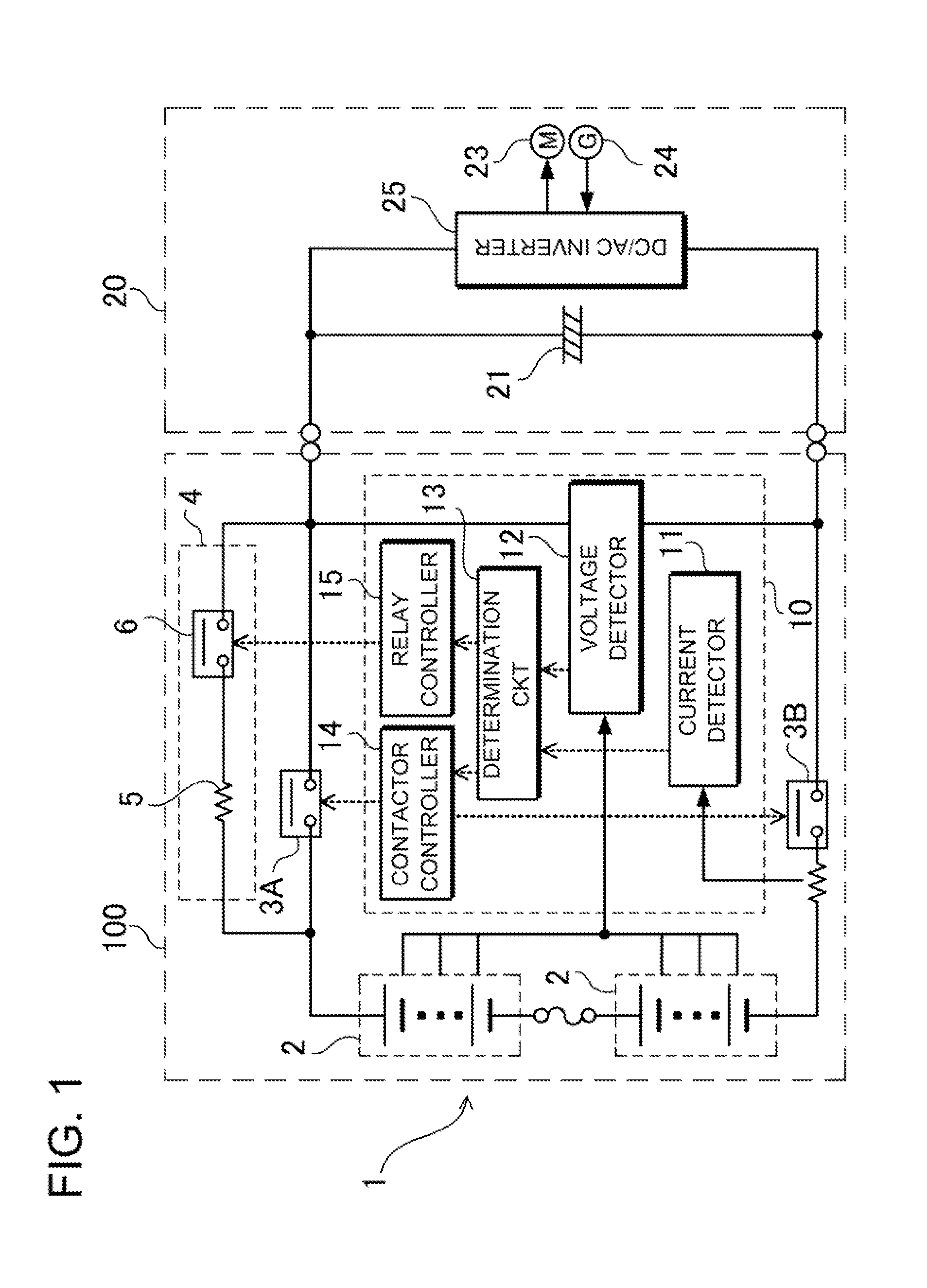
ActiveUS20110210746A1For direct connectionSure easyCharging stationsElectric devicesElectrical batteryCapacitor voltage
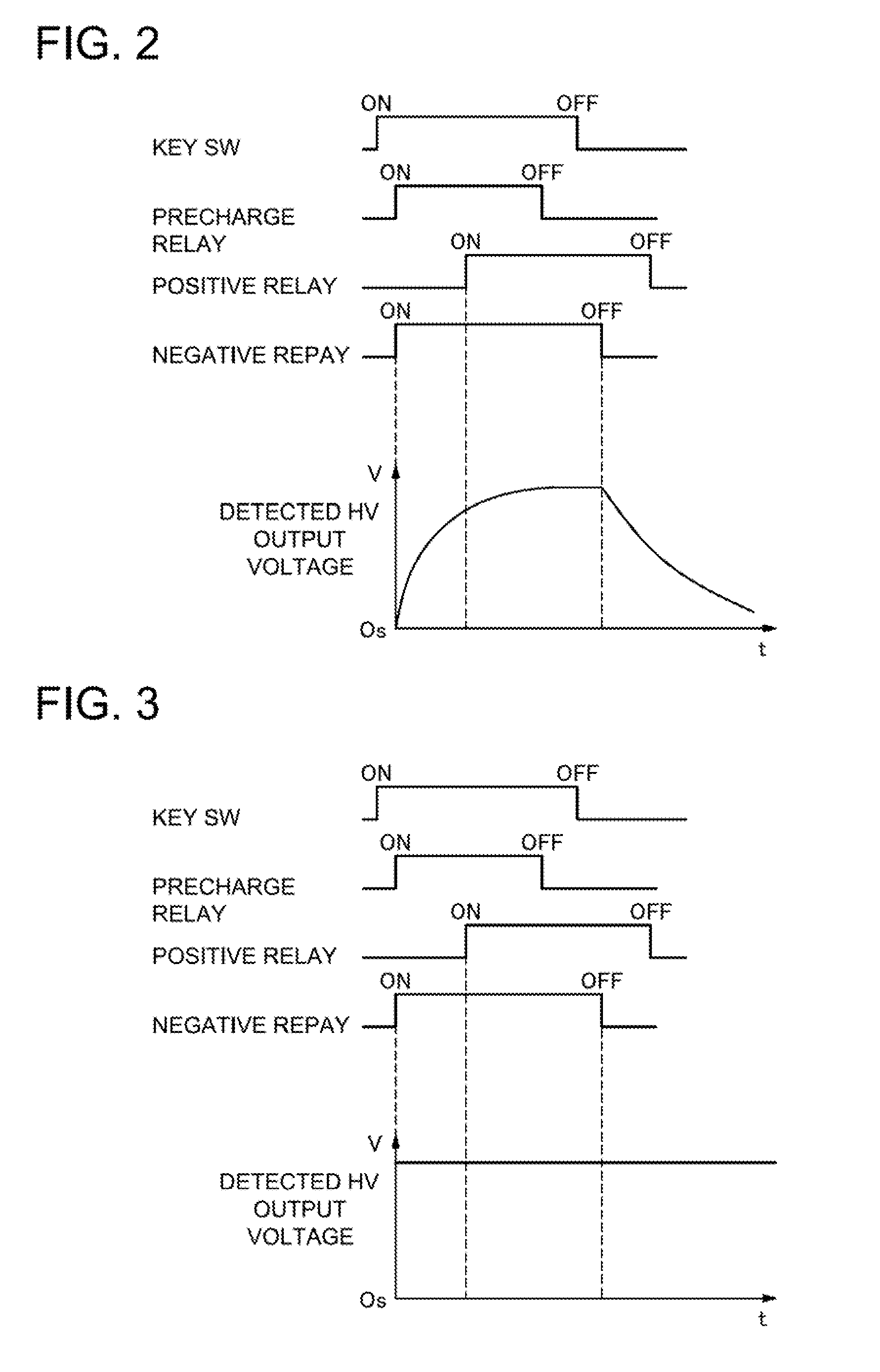
A power supply device includes a battery 1, positive and negative-side contactors 3A and 3B, and a controller 10. The battery 1 supplies power to a load 20. The positive-side contactor 3A is serially connected to the positive side of the battery 1. The negative-side contactor 3B is serially connected to the negative side of the battery 1. The controller 10 determines whether the load 20 connected to the output sides of the positive-side contactor 3A and the negative-side contactor 3B is in a connected or non-contact state. The controller 10 includes a voltage detecting circuit 12 that detects the capacitor voltage of a capacitor 21 connected to the output sides of the positive-side contactor 3A and the negative-side contactor 3B, and a determination circuit 13 that compares the detected voltage with a predetermined voltage and determines the connected state of the load 20.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com