Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
167 results about "Test pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
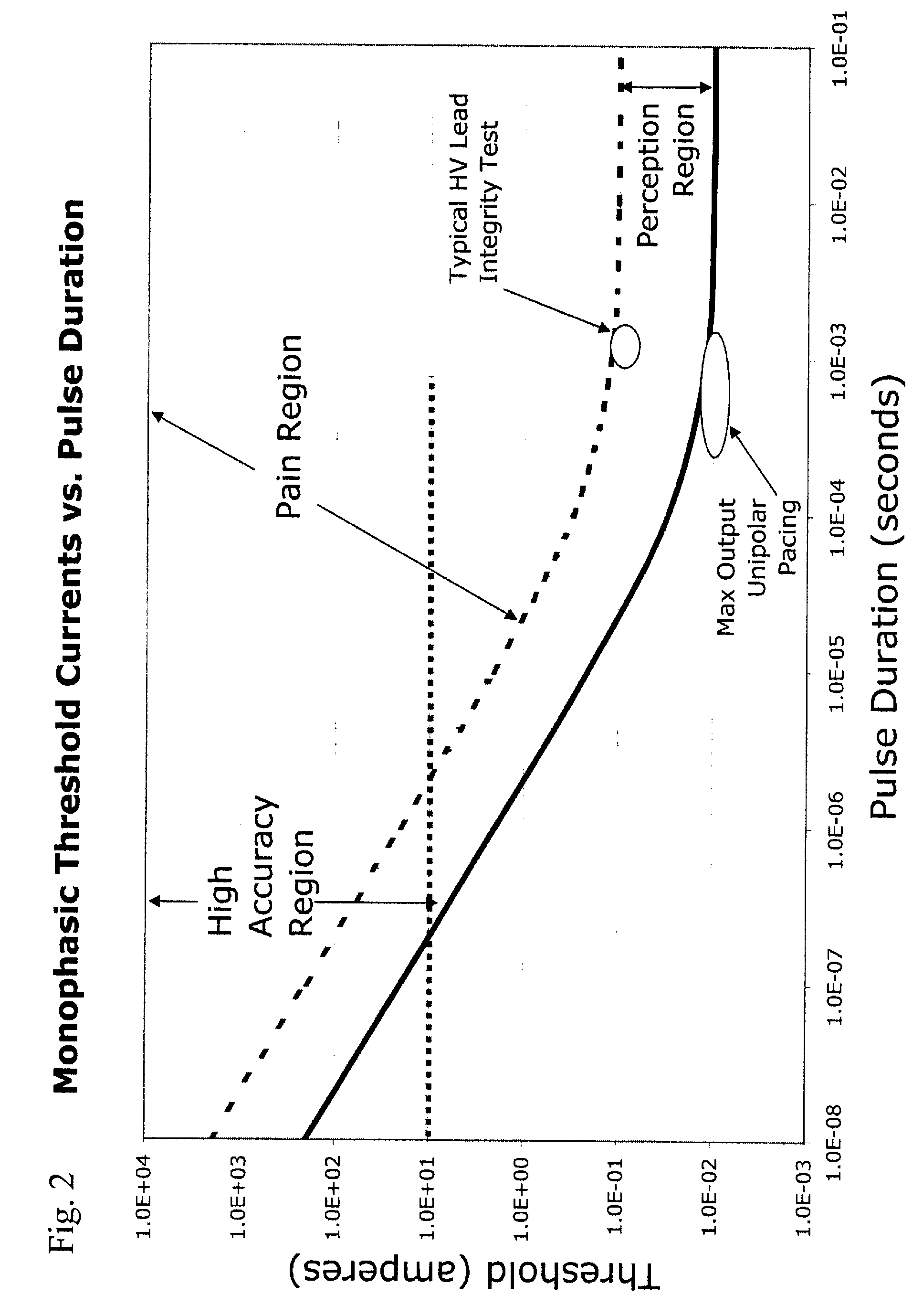
The pulse test’s effectiveness is based on the observation that energy toxins accelerate the pulse rate. An individual's radial pulse can be measured from the wrist. The average pulse of an infant is 100 to 160 beats per minute. A person's pulse can be affected by the presence of thyroid disorders.
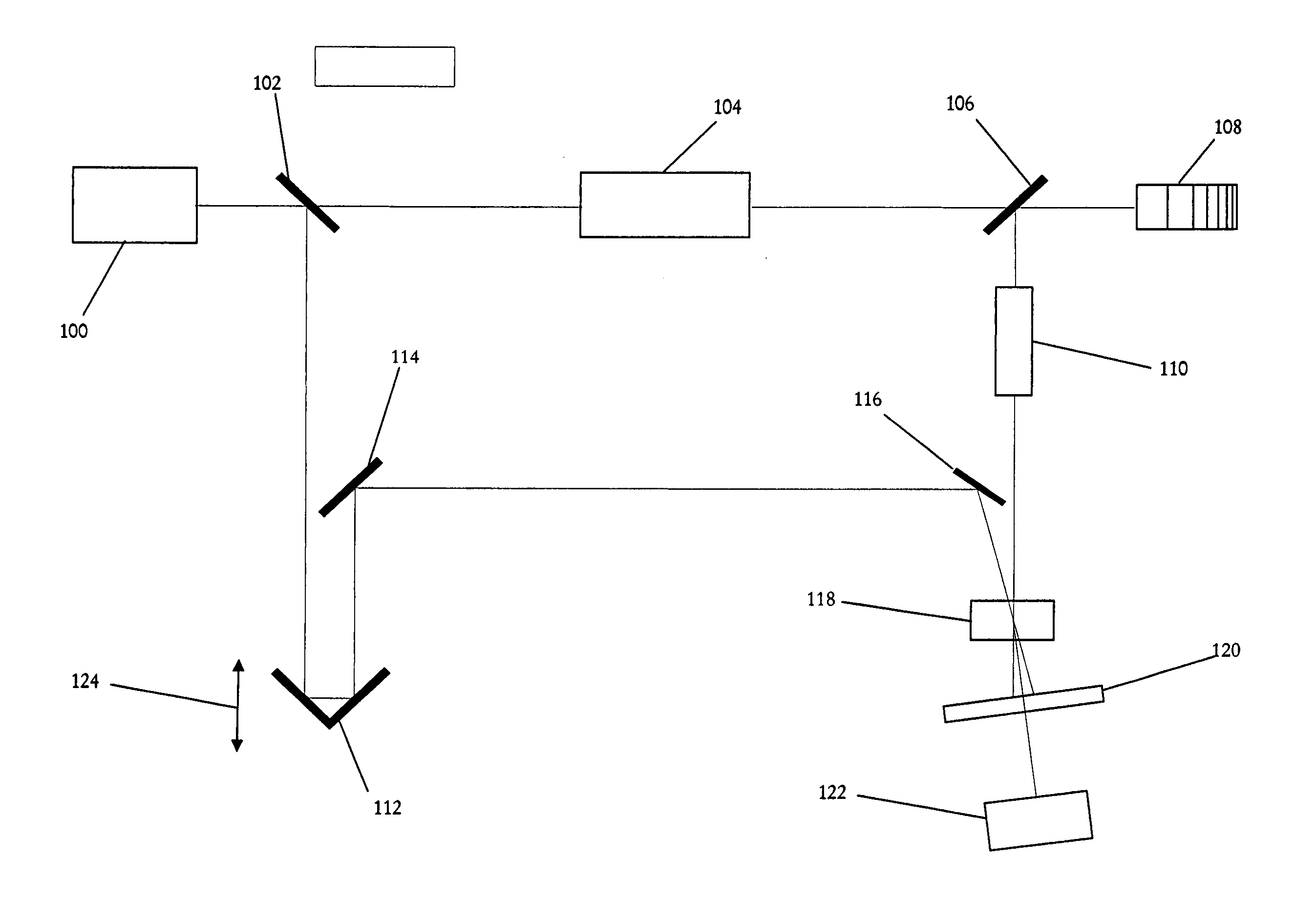
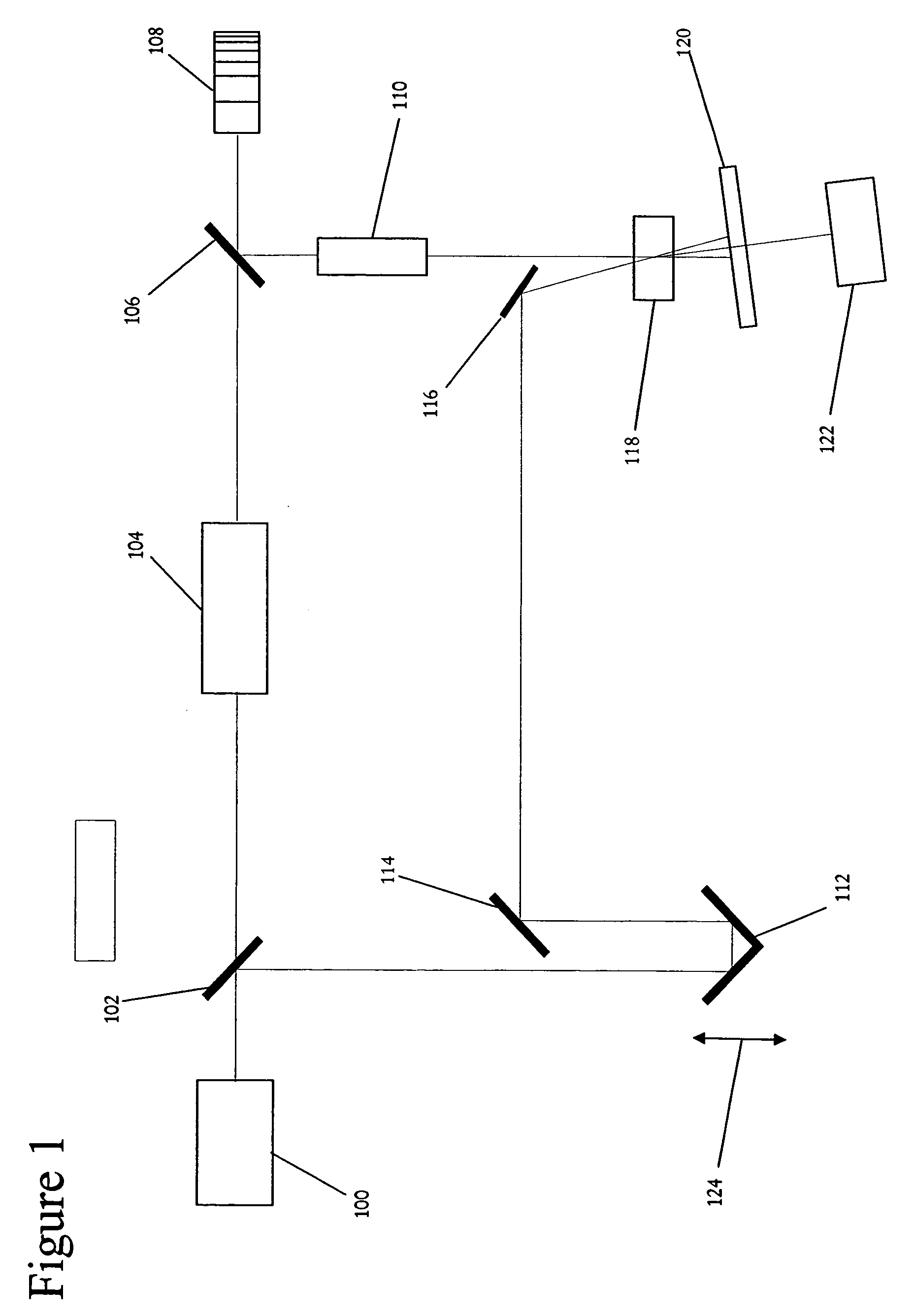
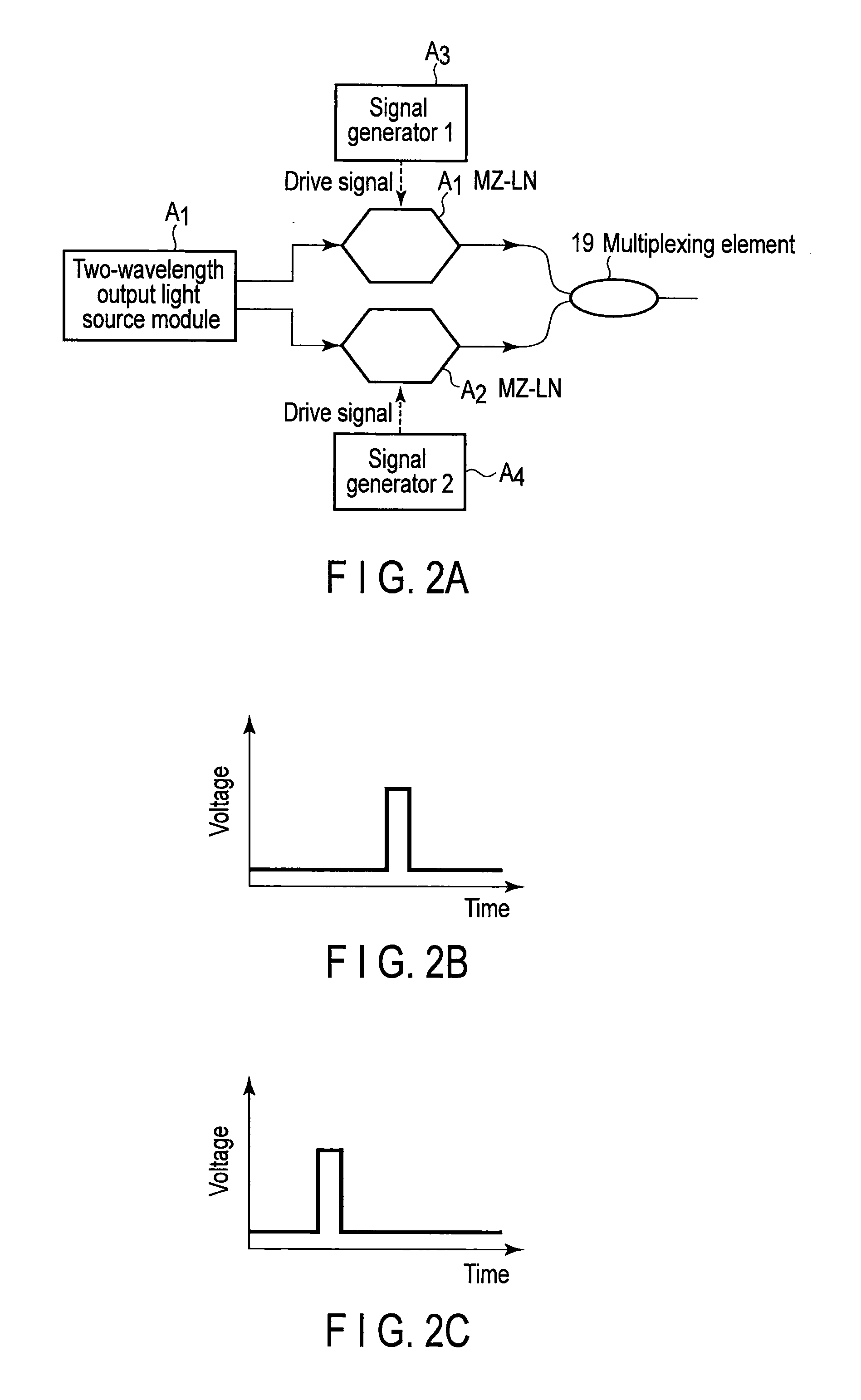
Smart linear pulsed laser diode driver, and method
ActiveUS20110085576A1Improve efficiencySmall sizeLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitor voltageEngineering
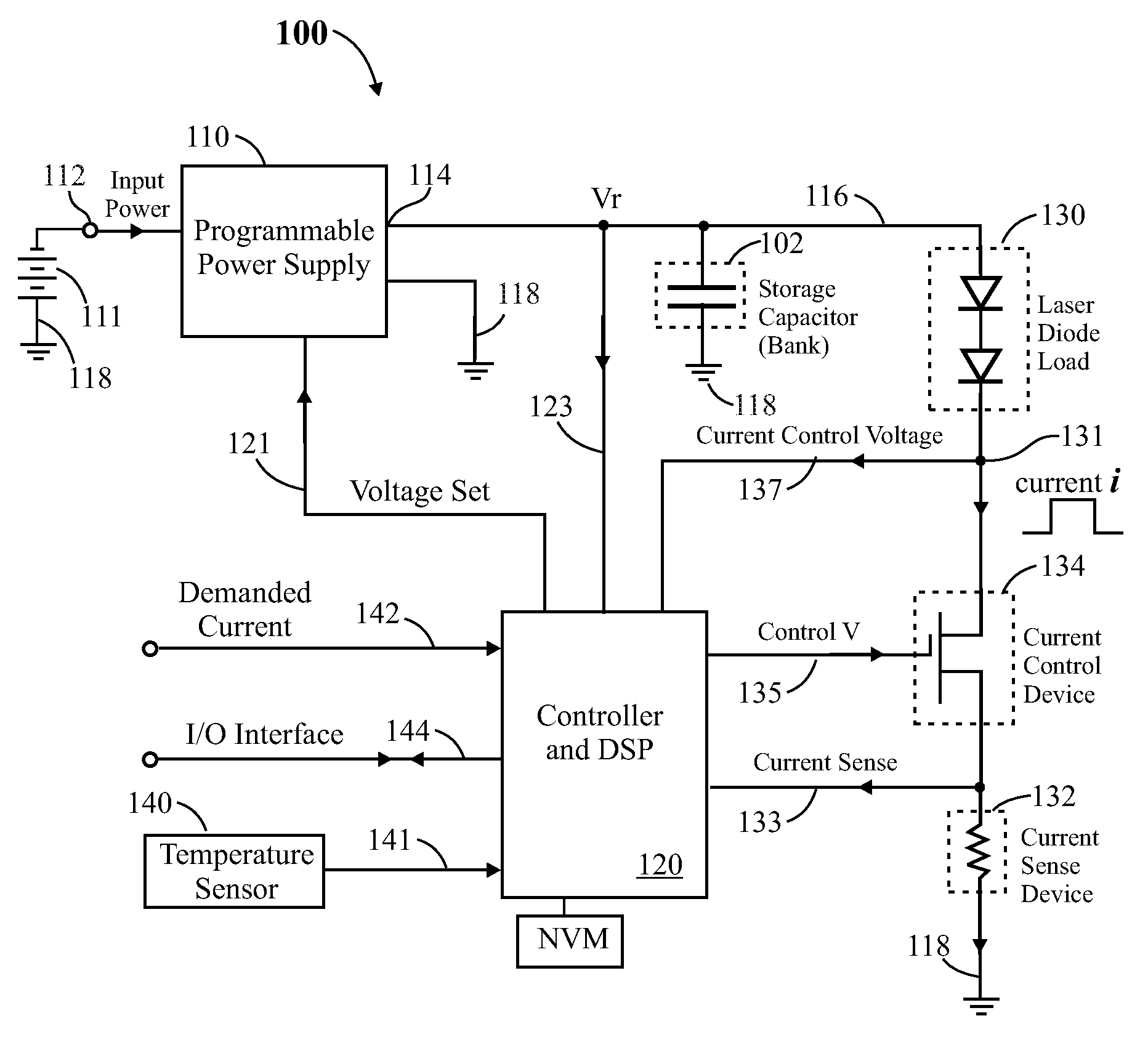
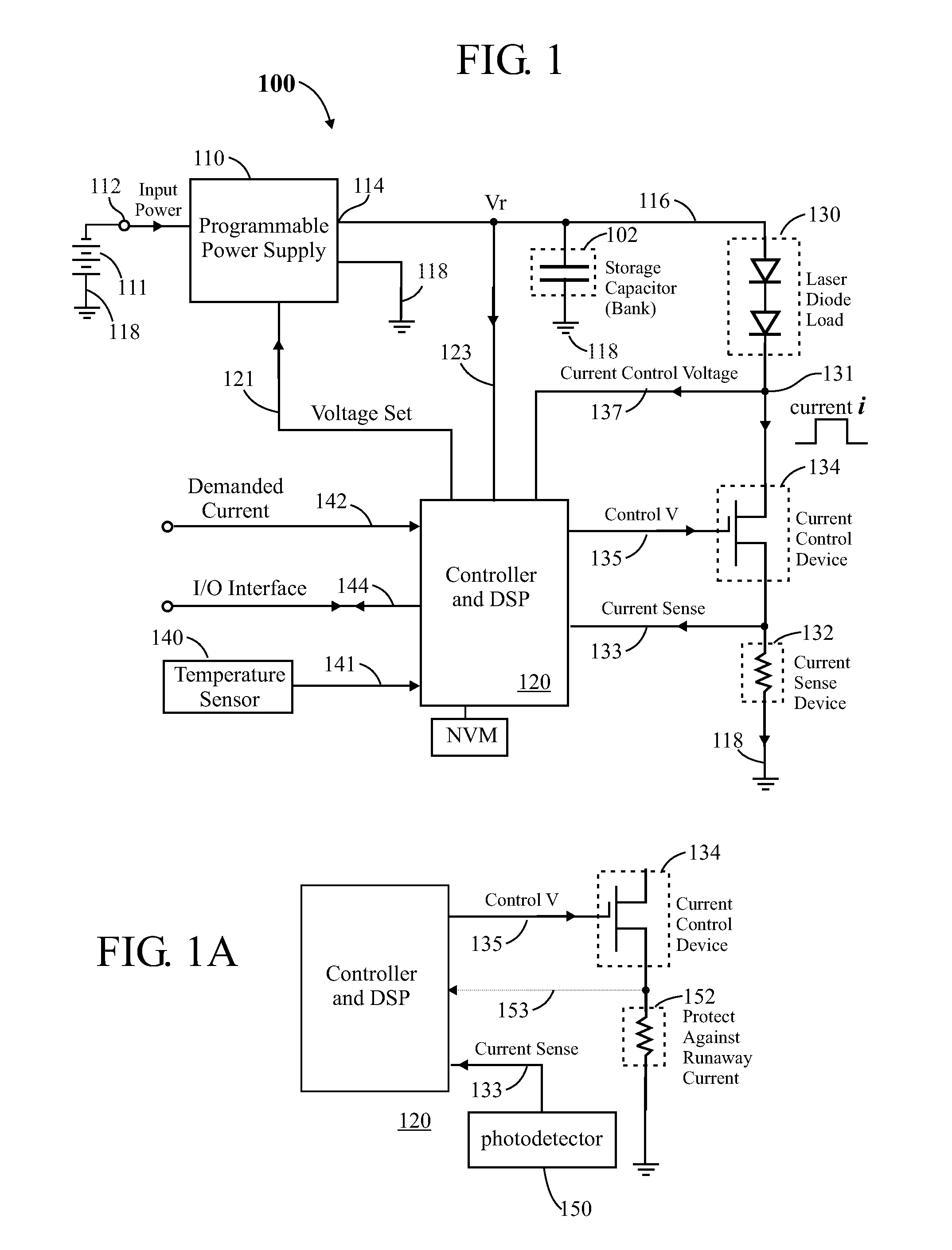
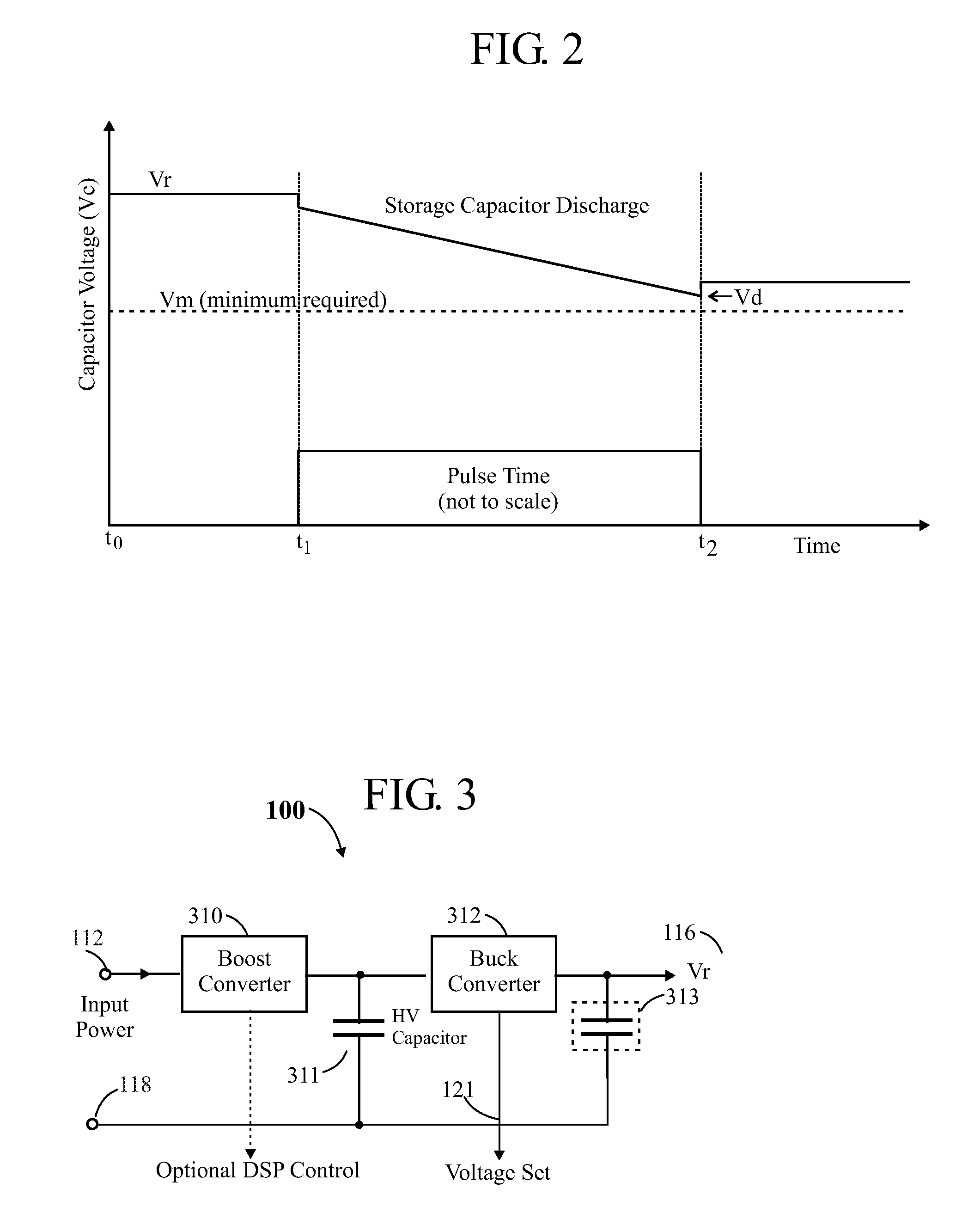
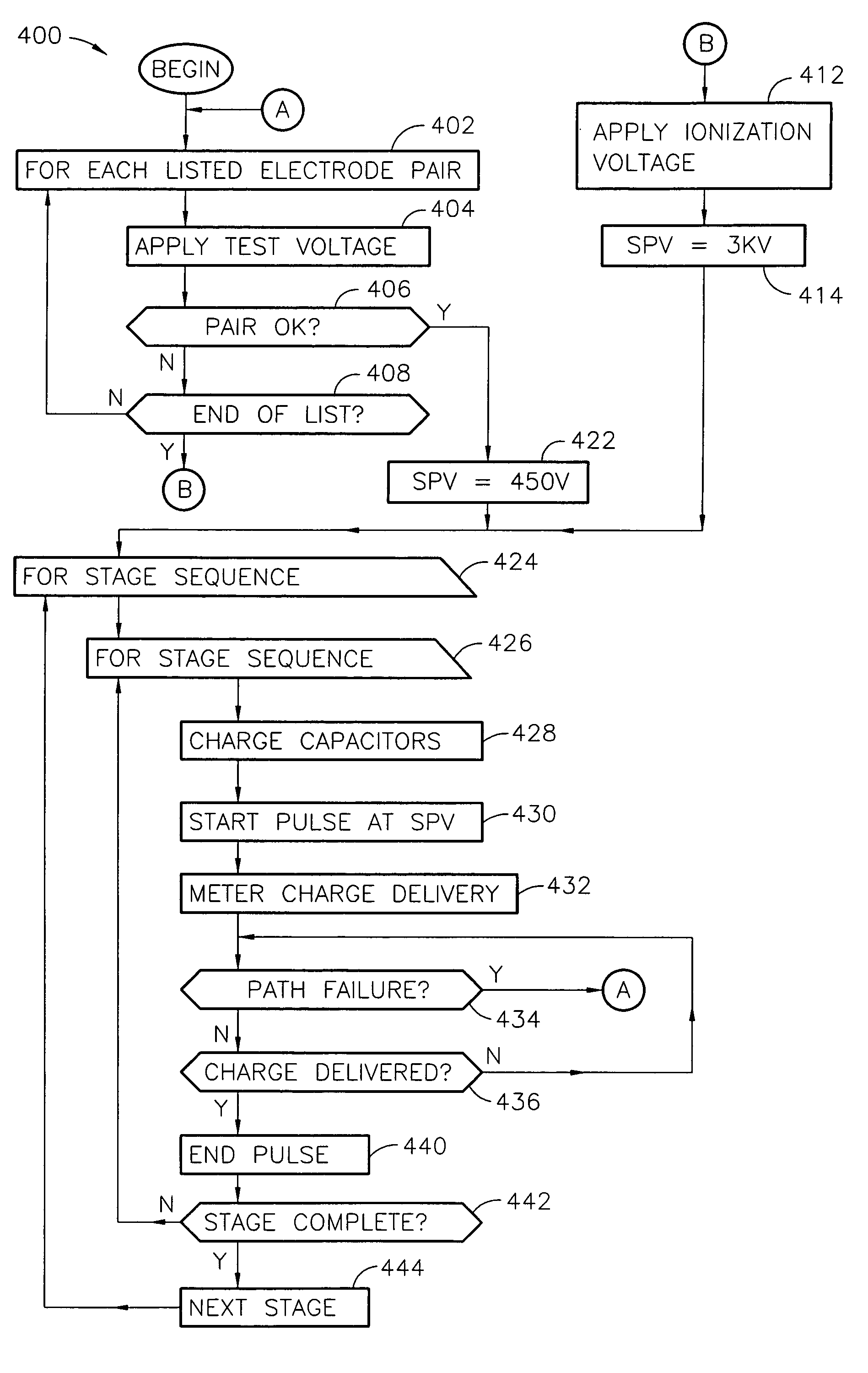
In a pulsed laser diode driver an energy storage capacitor is continuously being charged to a supply voltage Vr. When a pulse is initiated, energy stored in the capacitor is delivered to the laser diode load. The capacitor voltage Vd at the end of a pulse is used to control Vr to ensure that Vd is maintained above a minimum voltage Vm required to ensure operation of a current control device (such as FET) just above saturation. Test pulses (such as with attenuated currents or reduced pulsewidth) may be fired to determine an initial optimum value for Vr. After a test pulse, a slightly high estimate for Vr may be used and may be iterated (incremented) down to an optimum value Vm during a firing burst. A digital processor may be used to calculate and store data to optimize the performance. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ANALOG MODULES
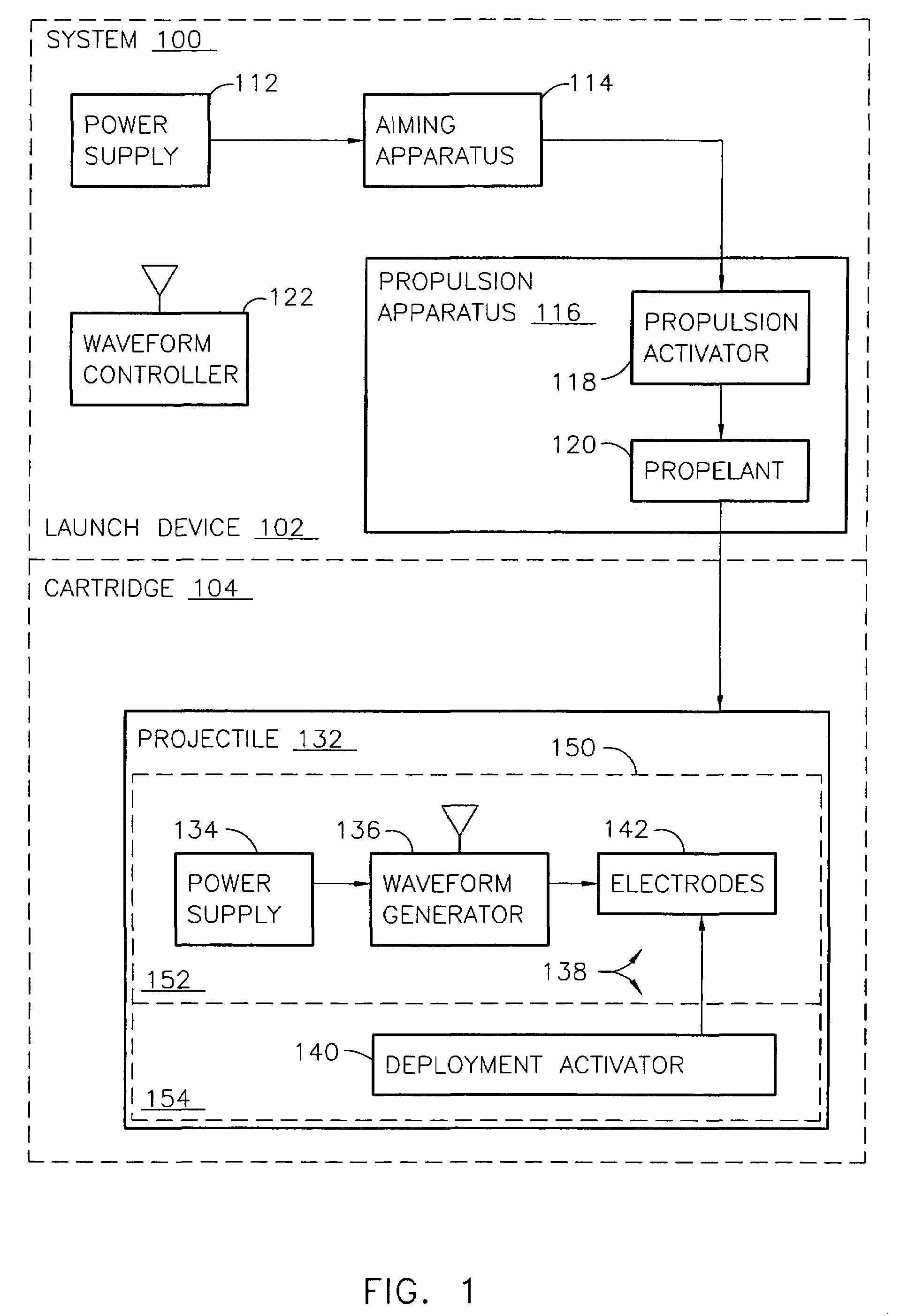
Systems and methods for immobilization using selected electrodes
ActiveUS7057872B2Effectively fixedReduce riskAmmunition projectilesElectrical apparatusHemt circuitsBiomedical engineering
Owner:AXON ENTERPRISE INC
System and method for detecting a device requiring power
A system and technique for detecting a device that requires power is implemented with a power detection station. The power detection system includes a detector having an output and a return which are coupled together by the device when the device requires power. The detector includes a word generator for generating test pulses for transmission to the device via the detector output, and a comparator for comparing the detector output with the detector return. The power detection station has a wide variety of applications, including by way of example, a switch or hub.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
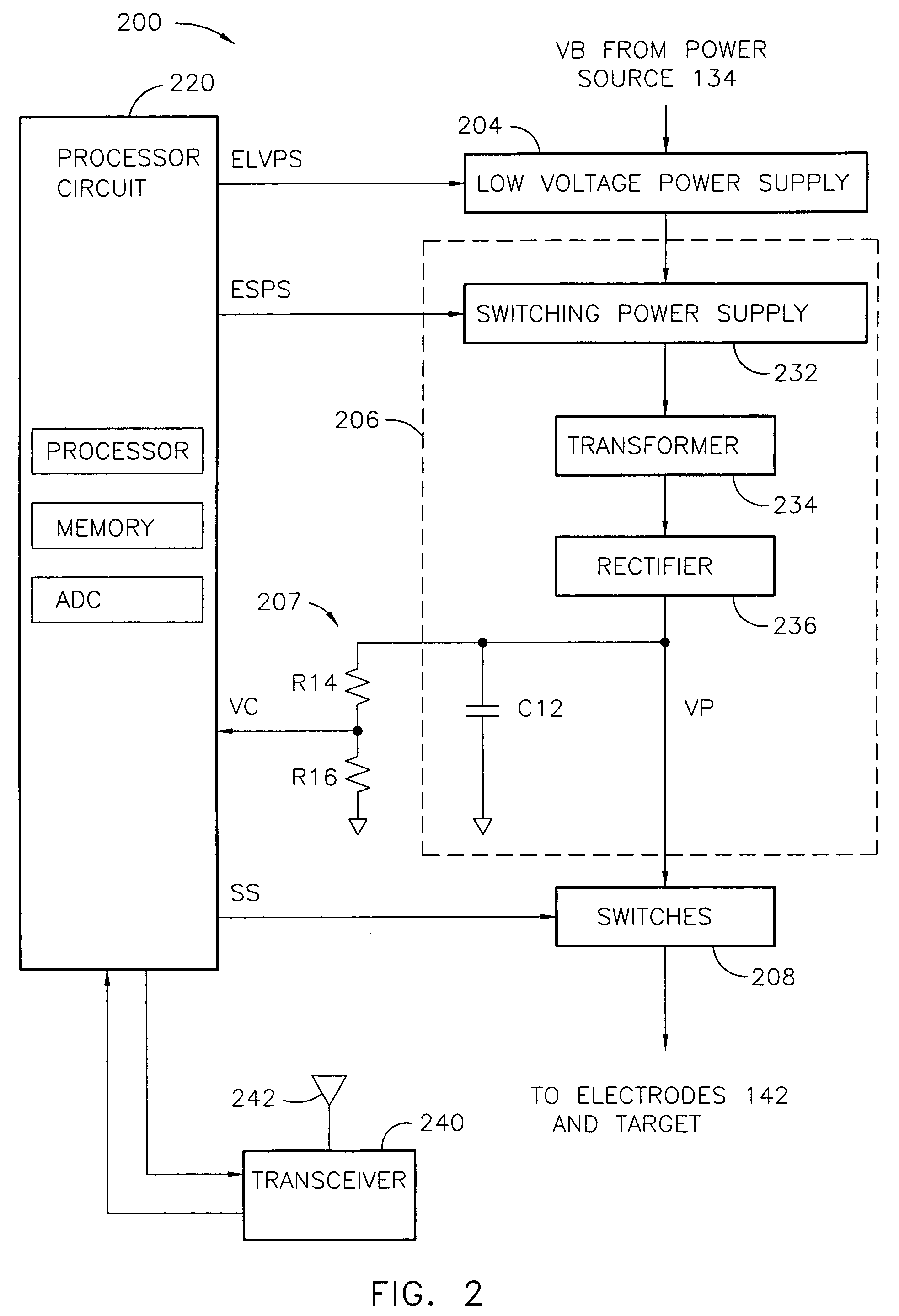
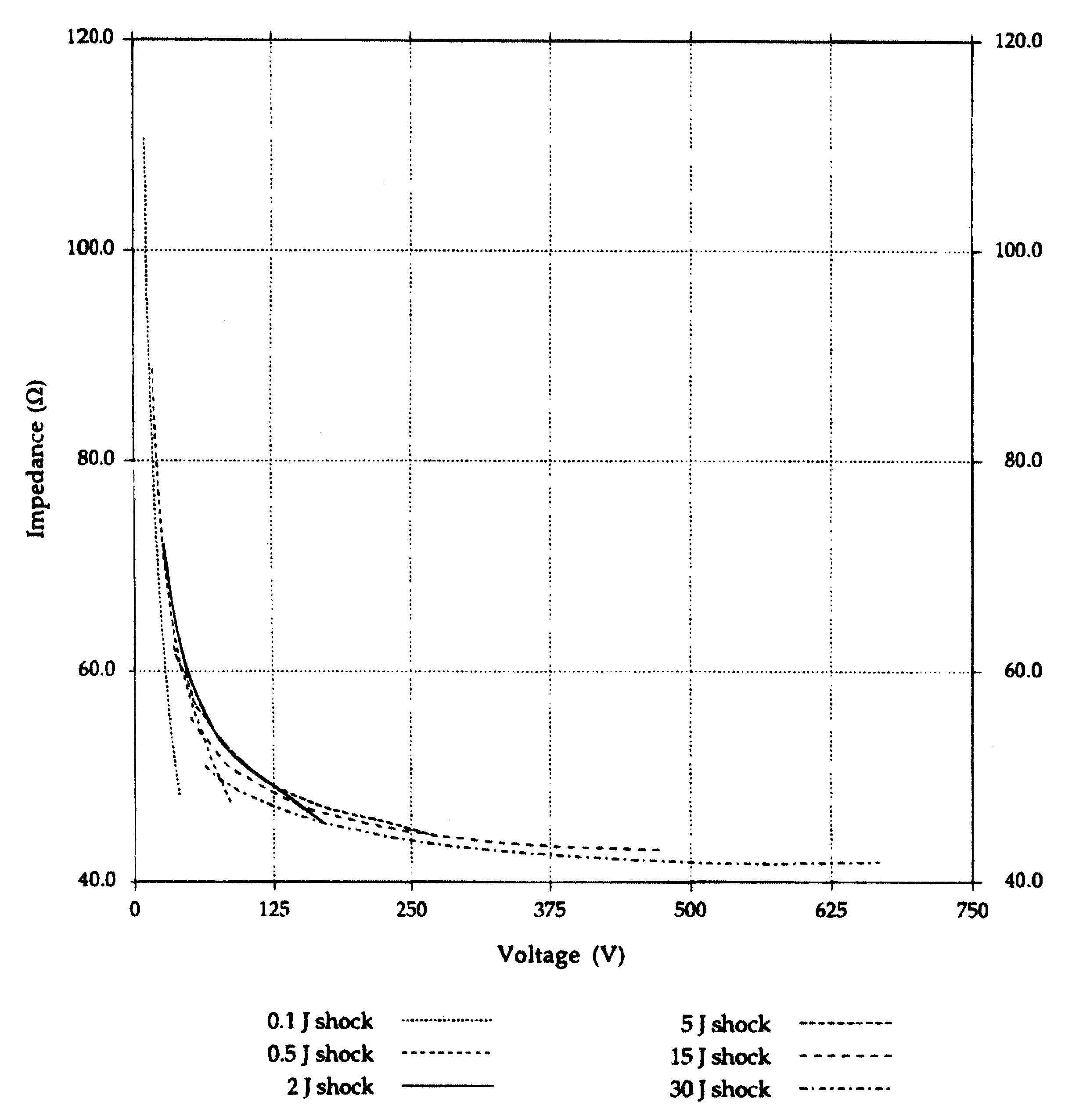
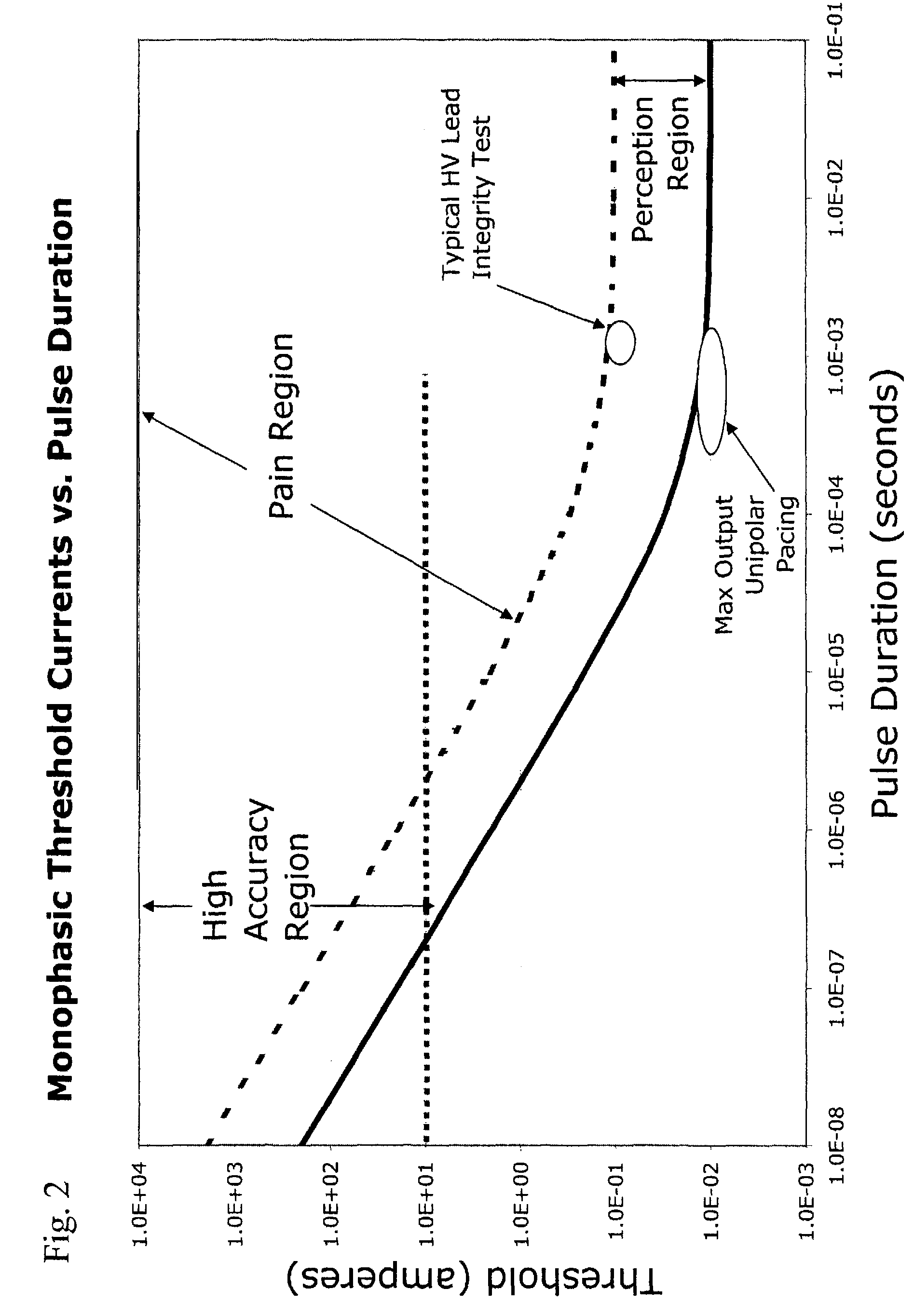
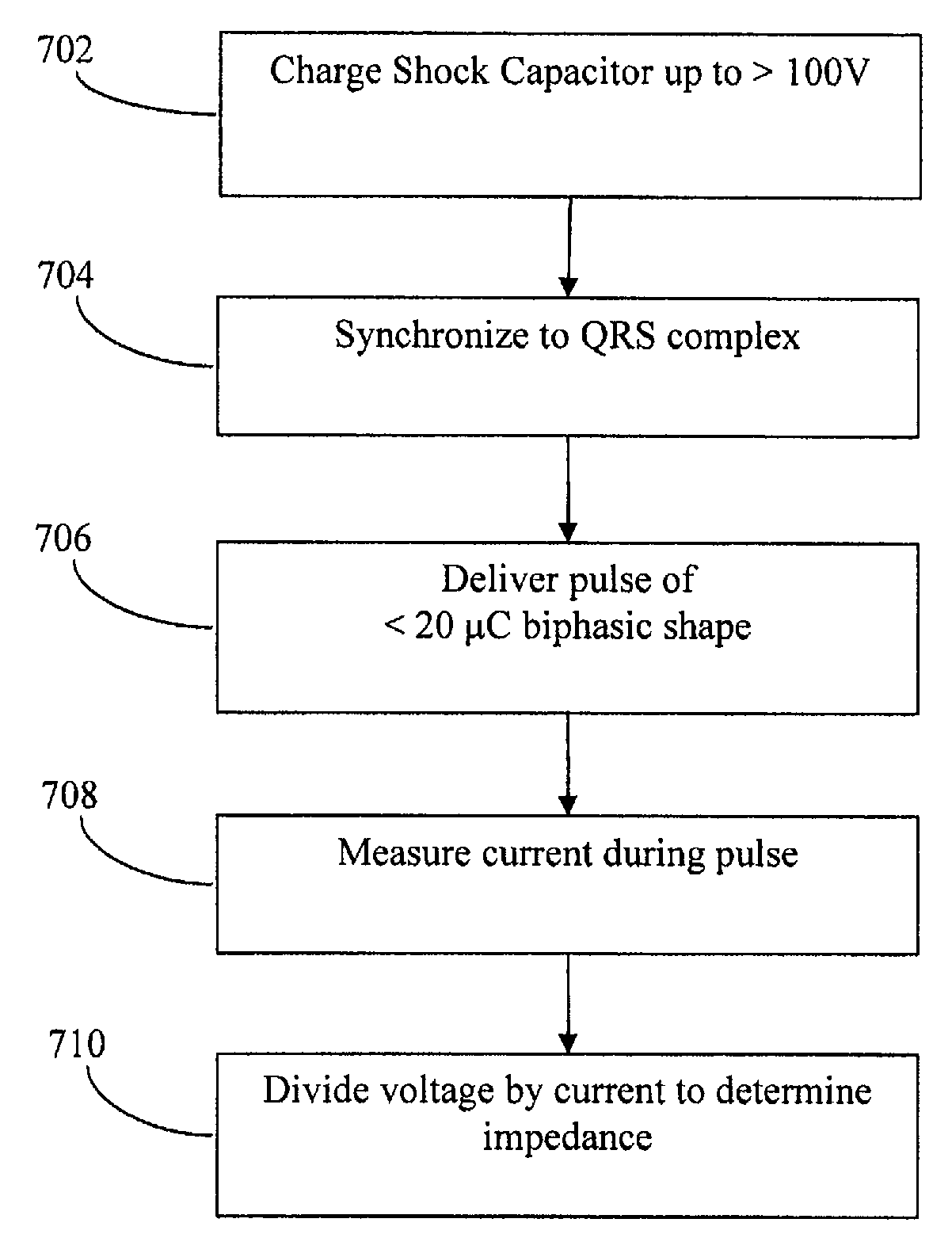
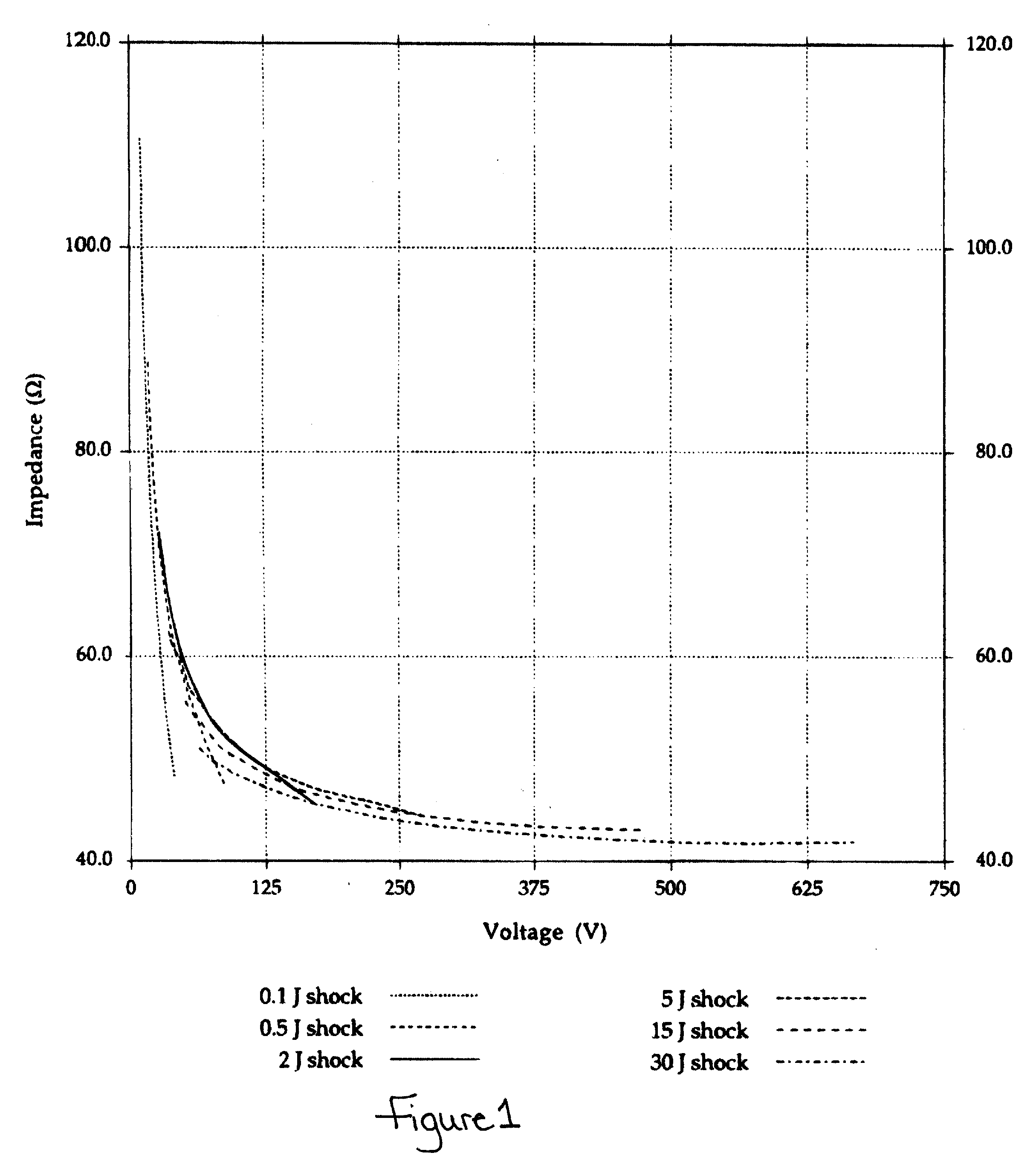
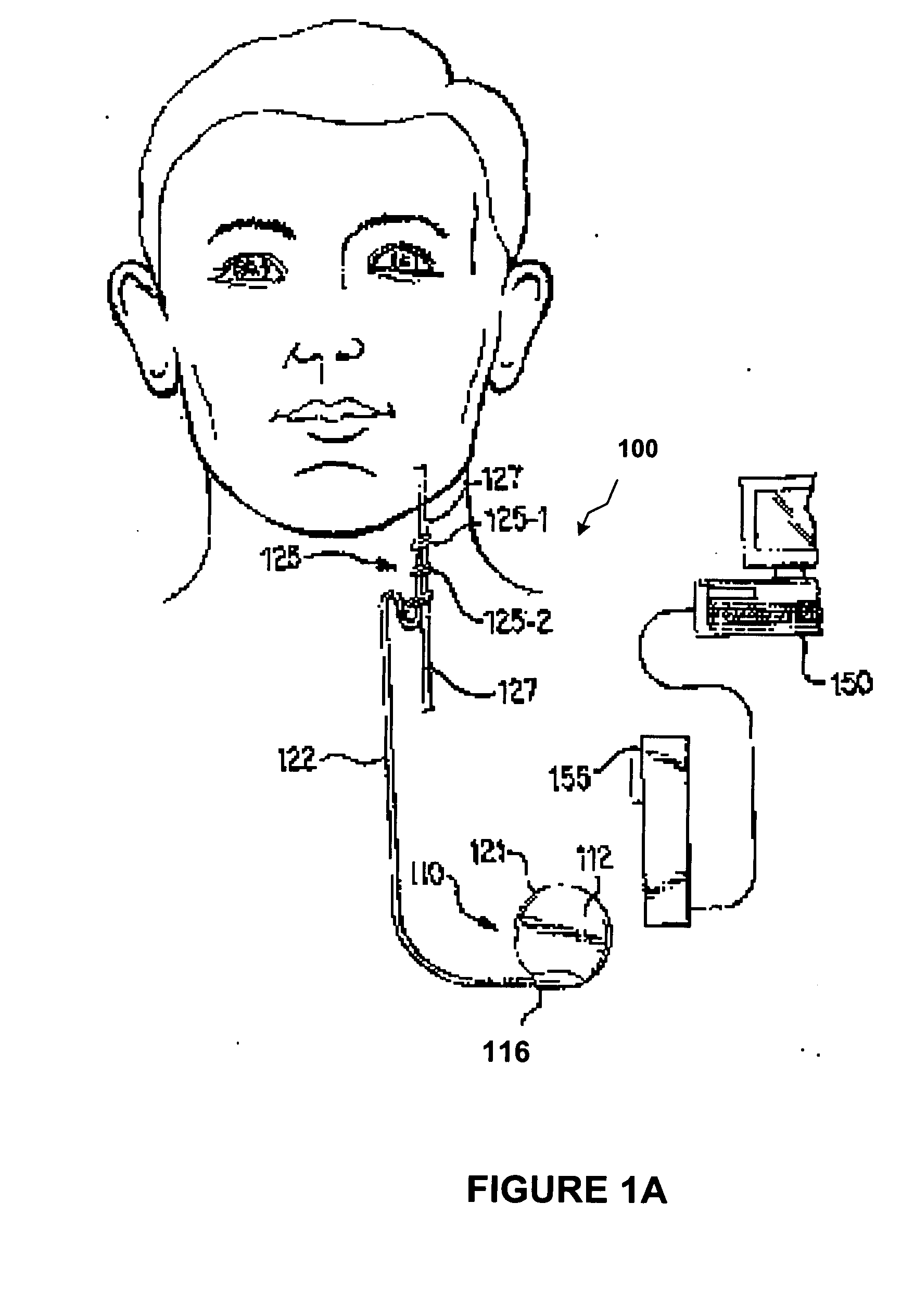
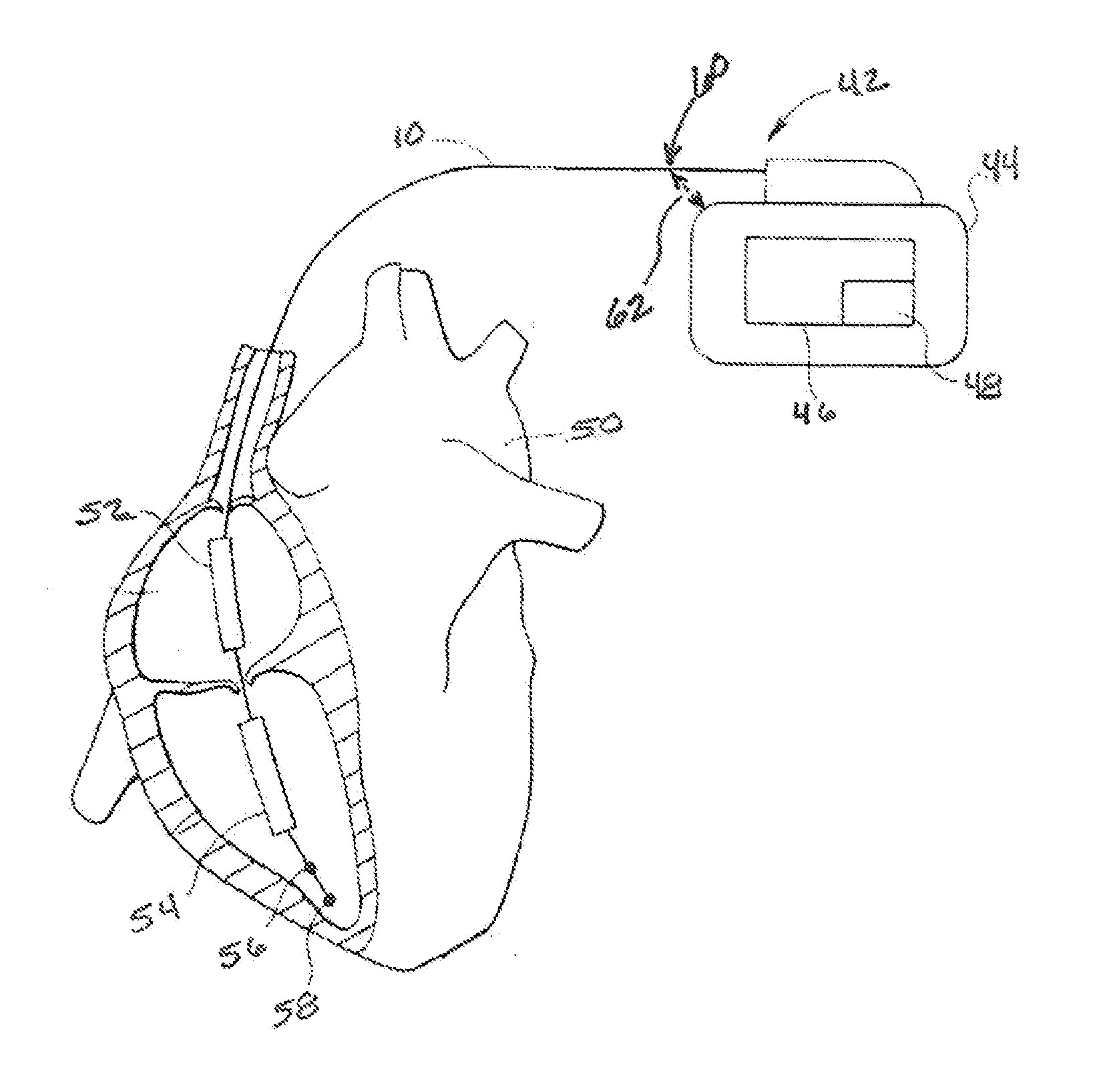
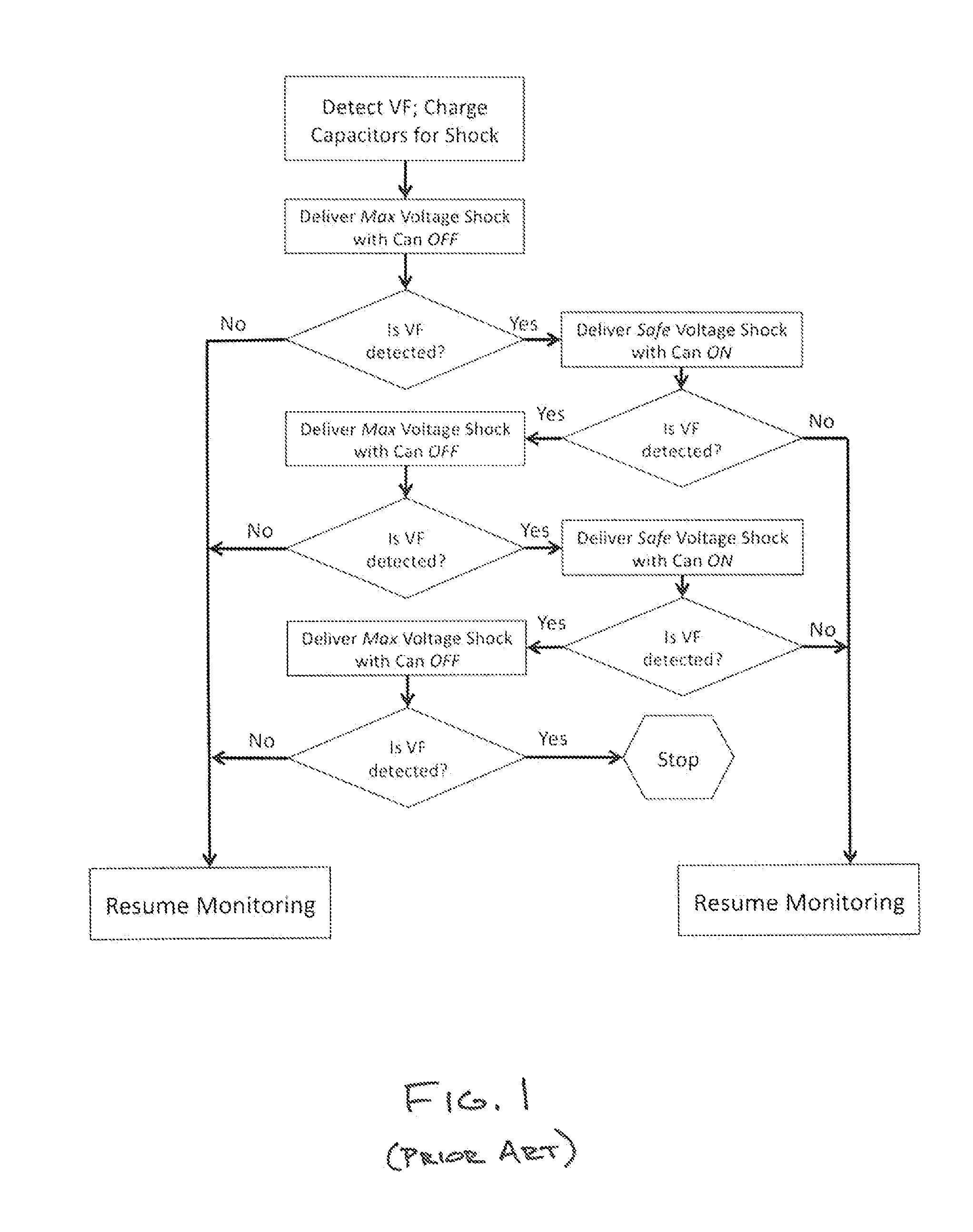
Apparatus and methods for measuring defibrillation lead impedance via a high magnitude, short duration current pulse
ActiveUS8352033B2Exact impedanceNot painful to the patientElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringLead impedanceHigh voltage capacitors
Methods and apparatus for accurately and painlessly measuring the impedance between defibrillation electrodes implanted in a patient utilize a high current test pulse delivered with a sufficiently high current to produce an accurate measurement of the defibrillation electrode impedance while limiting the duration of the test pulse such that the pain sensing cells in the patient do not perceive the test pulse. In one embodiment, the test pulse is generated from the high voltage transformer without storing energy in the high voltage capacitors and is delivered to the defibrillation electrodes in the patient utilizing the high voltage switching circuitry.
Owner:KROLL MARK
Radio frequency power amplifier protection system
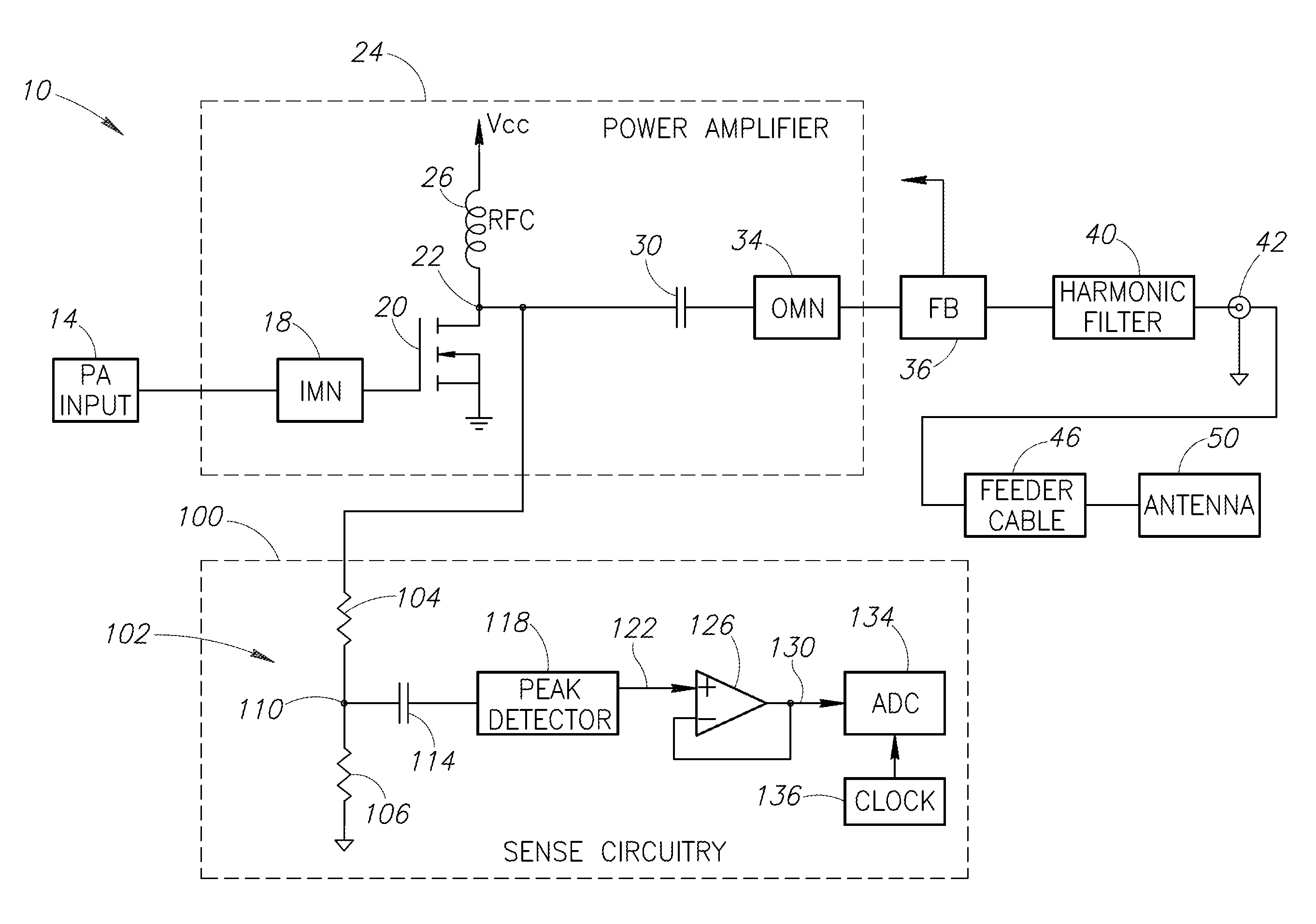
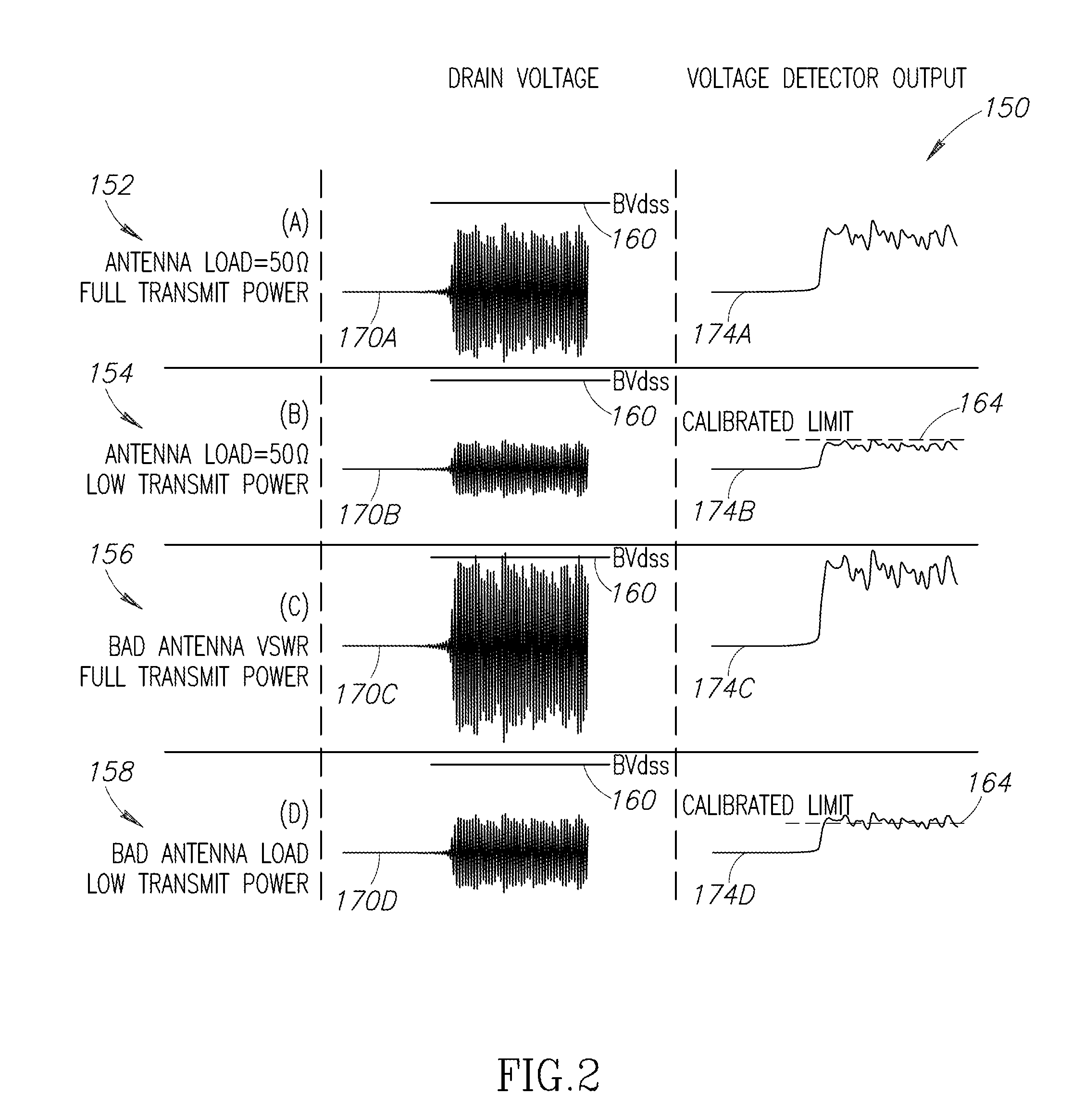
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier protection system for a radio. The protection system utilizes a resistive tap connected to the drain of a power amplifier transistor and a high speed voltage detector. The protection system uses short, low-power tests pulses to determine the quality of an antenna load upon tuning the radio to an RF carrier frequency by transmitting the short test pulse. If the measured voltage value exceeds a calibrated value, the power of the RF transmitter is reduced for subsequent operation or the RF transmitter is shut down completely. The invention also includes a system and method for detecting when an antenna is disconnected from a radio using an low frequency AC signal to measure the resistance of an antenna connected to an RF transmitter.
Owner:SPECTRALUX
High Accuracy Painless Method for Measuring Defibrillation Lead Impedance
ActiveUS20090099615A1Exact impedanceNot painful to the patientHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringLead impedanceHigh voltage capacitors
Methods and apparatus for accurately and painlessly measuring the impedance between defibrillation electrodes implanted in a patient utilize a high current test pulse delivered with a sufficiently high current to produce an accurate measurement of the defibrillation electrode impedance while limiting the duration of the test pulse such that the pain sensing cells in the patient do not perceive the test pulse. In one embodiment, the test pulse is generated from the high voltage transformer without storing energy in the high voltage capacitors and is delivered to the defibrillation electrodes in the patient utilizing the high voltage switching circuitry.
Owner:KROLL MARK
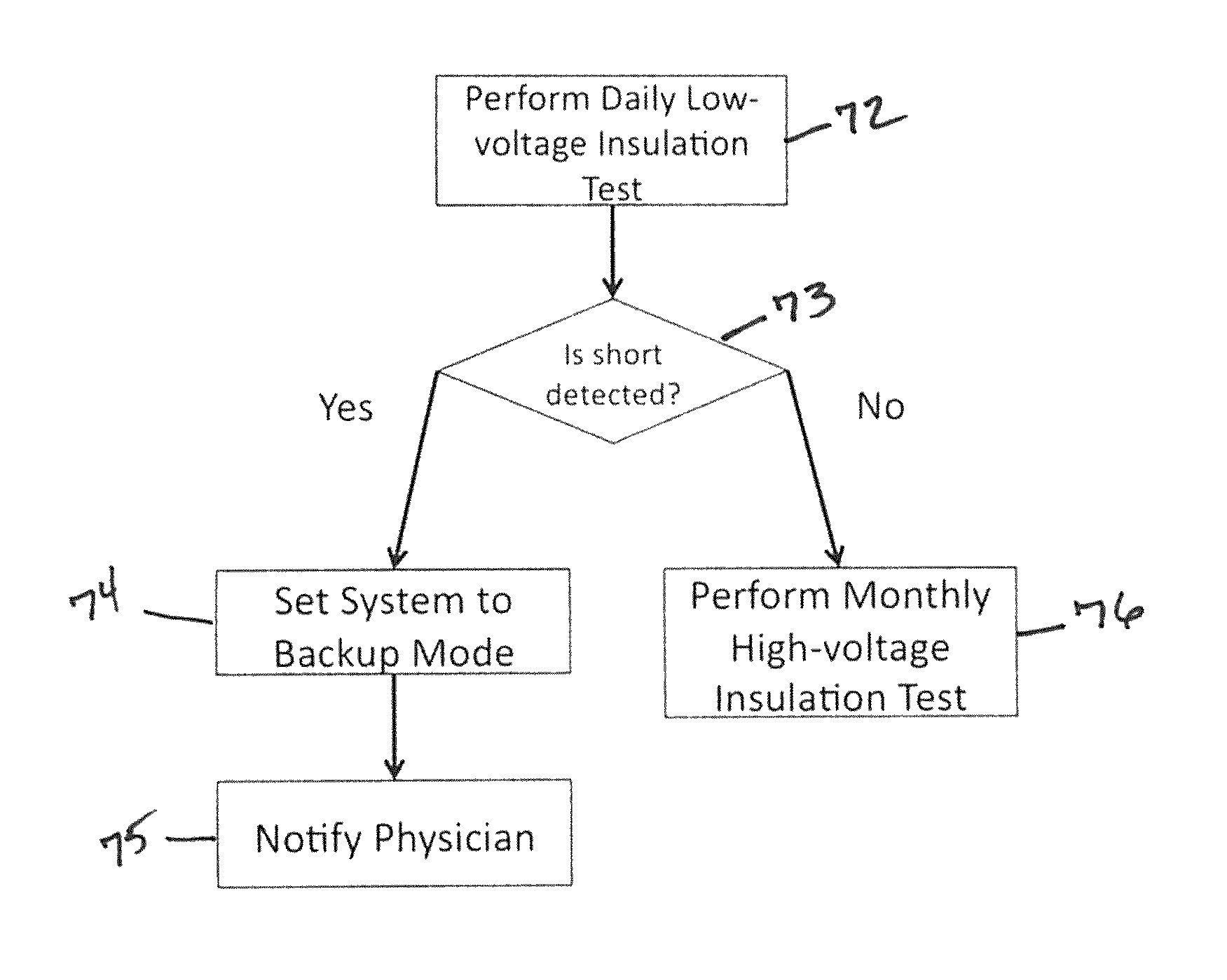
Method for detecting and treating insulation lead-to-housing failures
Disclosed is a method for the diagnosis of conductor anomalies, such as an insulation failure resulting in a short circuit, in an implantable medical device, such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). Upon determining if a specific defibrillation pathway is shorted, the method excludes the one electrode from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between functioning defibrillation electrodes. Protection can be provided against a short in the right-ventricular coil-CAN defibrillation pathway of a pectoral, transvenous ICD with a dual-coil defibrillation lead. If a short caused by an in-pocket abrasion is present, the CAN is excluded from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between the right-ventricular and superior vena cava defibrillation coils. Determination that the defibrillation pathway is shorted may be made by conventional low current measurements or delivery of high current extremely short test pulses.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Lead condition assessment for an implantable medical device
A method, system, and apparatus for performing a lead condition assessment and / or a lead orientation determination associated with an implantable medical device (IMD). A first impedance is determined. The first impedance relates to the impedance relative to a first electrode and a portion of the IMD. A second impedance is determined. The second impedance relates to the impedance relative to a second electrode and the portion of the IMD. The first impedance is compared with the second impedance to determine an impedance difference. A determination is made whether the impedance difference is outside a predetermined tolerance range. Furthermore, artifact measured during impedance measurements or test pulses may be compared to assess lead orientation. An indication of a lead condition error is provided in response to determining that the impedance difference is outside the predetermined tolerance range.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
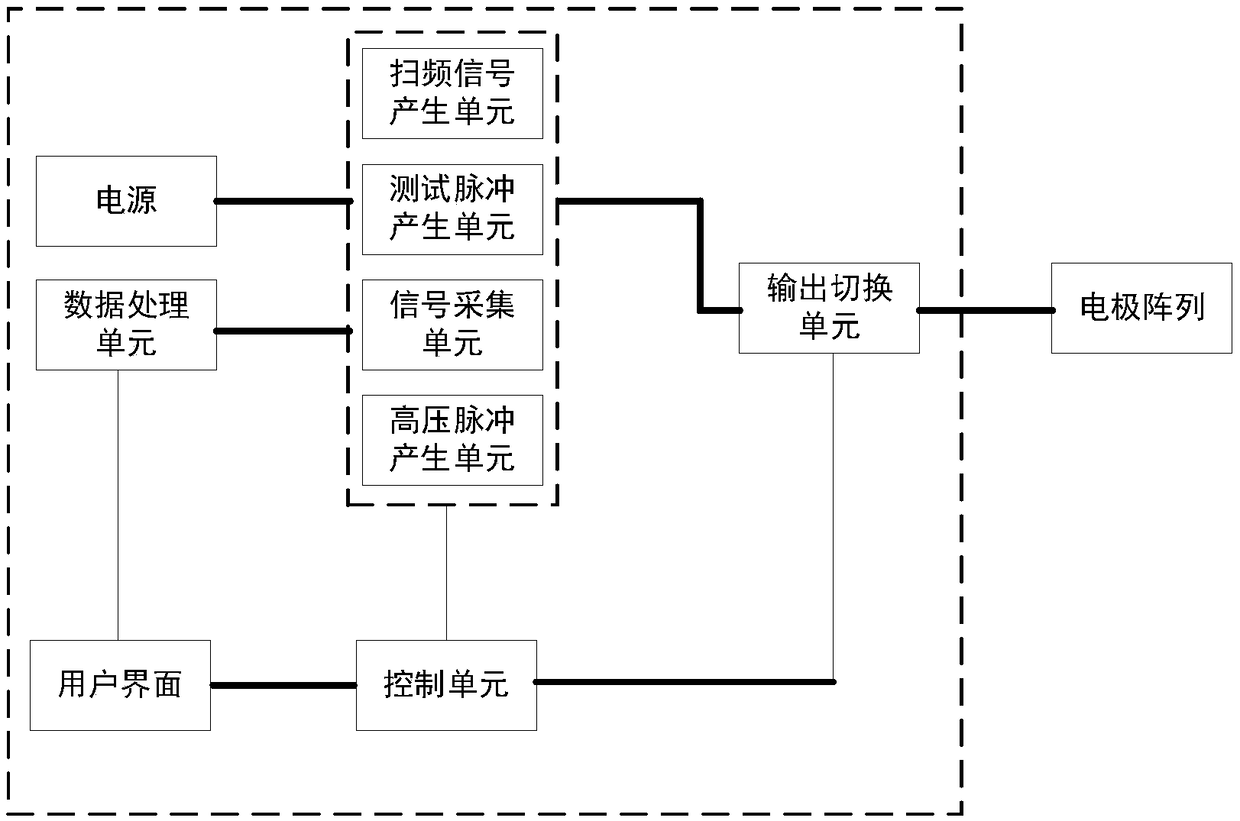
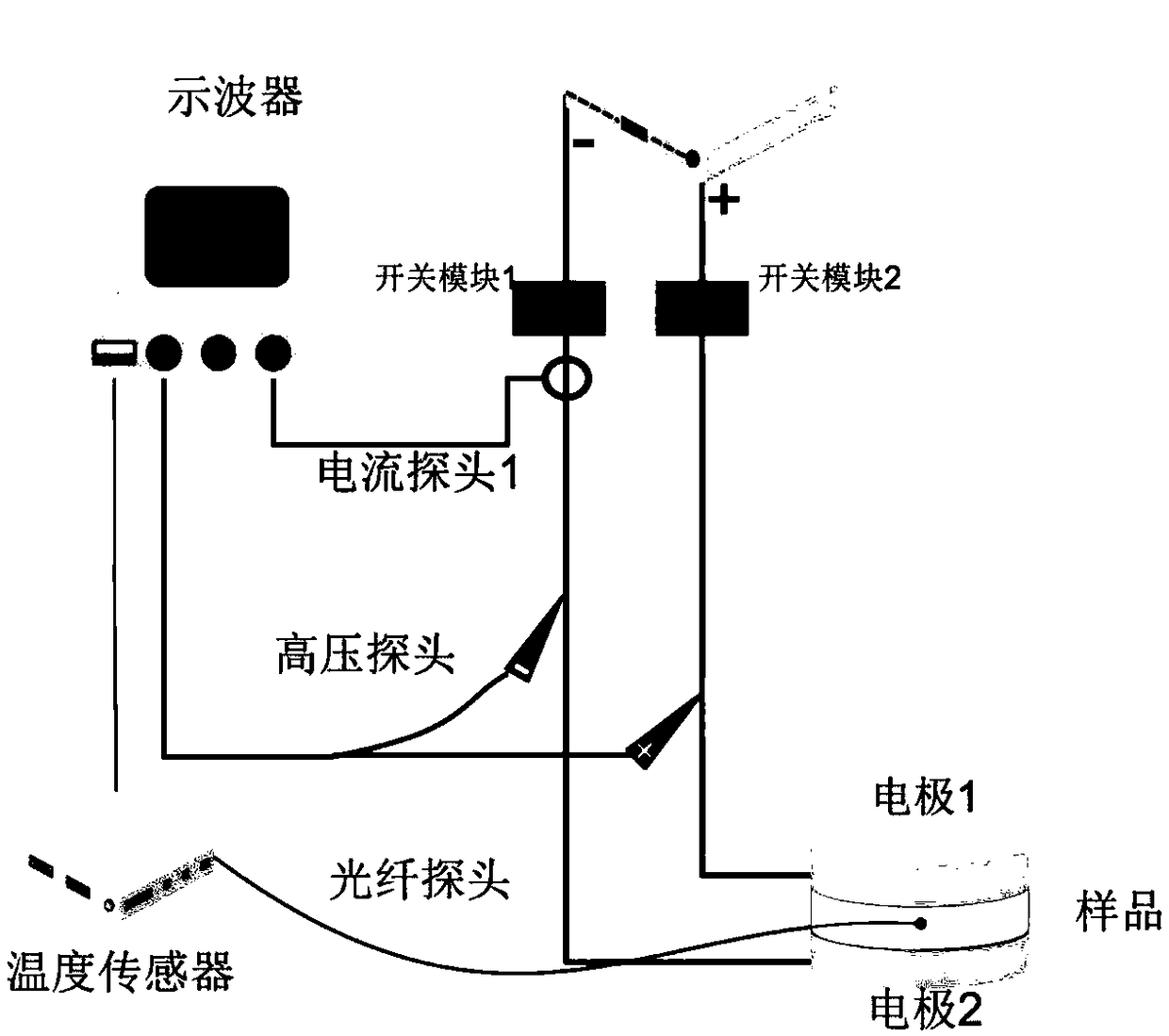
Dynamic real-time evaluation equipment for irreversible electroporation tissue ablation
InactiveCN109157280AAvoid stabilityAvoid problems reflecting limited ablation areaSurgical instruments for heatingMathematical modelDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses dynamic real-time evaluation equipment for irreversible electroporation tissue ablation, which utilizes an electrode in an irreversible electroporation tumor treatment primarypulse application process to detect tissue impedance spectrum changes before and after pulse treatment. As that instability of the impedance spectrum signal measure by the applied pulse electrode andthe problem of reflect the limited ablation area are effectively avoided, the relationship between the impedance spectrum measured by different electrode pairs and the actual ablation size is established aft subsequent data processing according to the impedance spectrum variation measured by different electrode pairs. At the same time, the change of tissue electrical properties was obtained by applying small signal test pulse during the treatment, and the mathematical model was established to judge the tissue ablation condition. At that same time, the invention can combine the advantage of thesweep frequency method and the test pulse method respectively, and solve the important problem of dynamic monitoring of curative effect in the treatment process of ablation effect aft irreversible electroporation pulse treatment and immediate evaluation of curative effect after treatment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
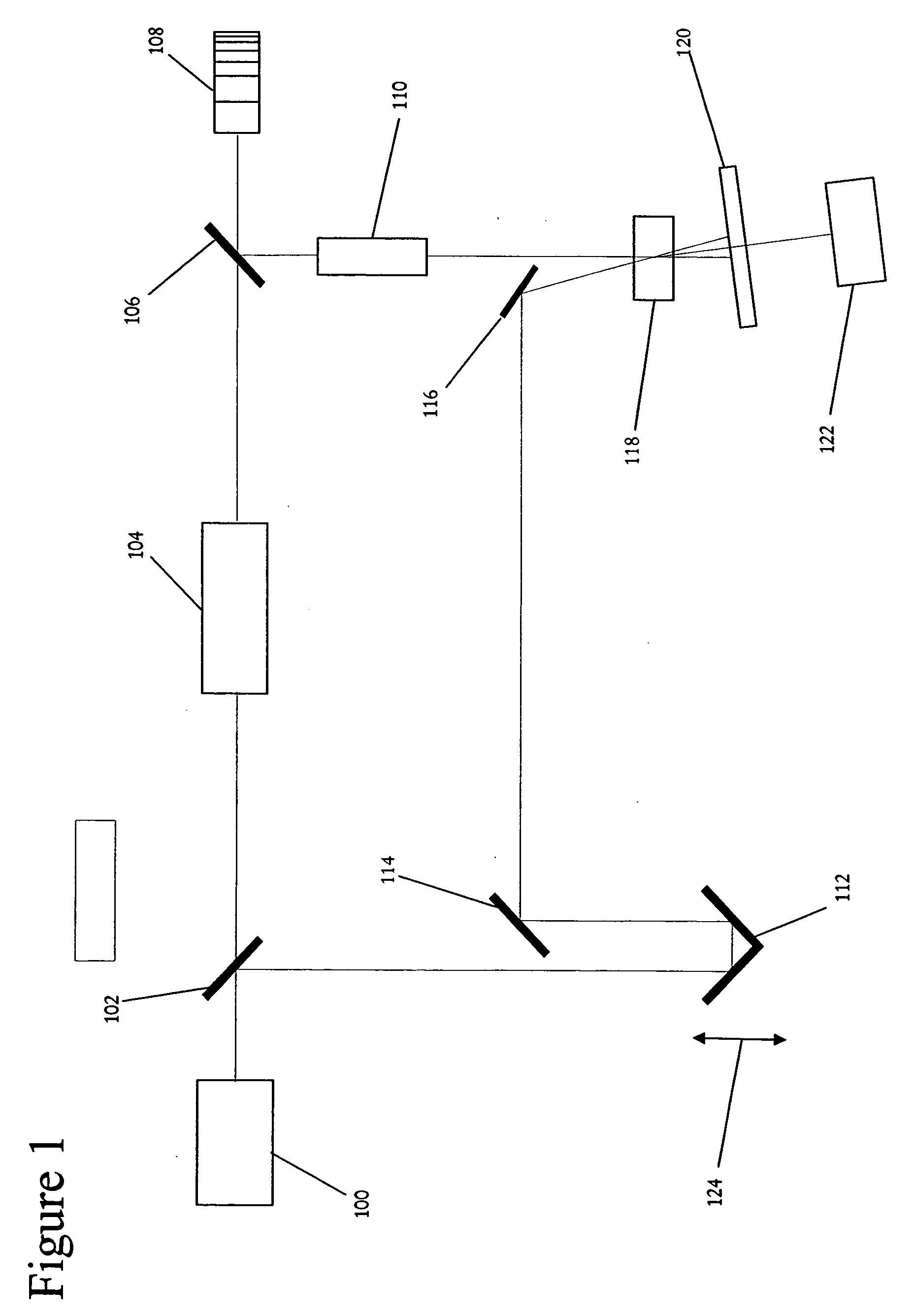
Ultrafast laser pulse shape measurement method and system
A laser pulse shape measuring system to measure the pulse shape of pulses generated by a pulsed laser. Each pulse includes a pulse width and a peak wavelength. The system includes: a beam splitter coupled to the laser to separate each of the pulses into a test pulse and a probe pulse; a pulse width compression means coupled to the beam splitter to compress the pulse width of each probe pulse; a controllable delay means to control a time offset between each test pulse and a corresponding probe pulse; a nonlinear optical medium arranged such that the test beam path and the probe beam path intersect within it to generate wavelength converted pulses corresponding to intersecting pairs of pulses; a detector coupled to the nonlinear optical medium to detect the pulse energies of the wavelength converted pulses; and a processor to determine the pulse shape of the laser pulses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for detecting and treating insulation lead-to-housing failures
Disclosed is a method for the diagnosis of conductor anomalies, such as an insulation failure resulting in a short circuit, in an implantable medical device, such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). Upon determining if a specific defibrillation pathway is shorted, the method excludes the one electrode from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between functioning defibrillation electrodes. Protection can be provided against a short in the right-ventricular coil-CAN defibrillation pathway of a pectoral, transvenous ICD with a dual-coil defibrillation lead. If a short caused by an in-pocket abrasion is present, the CAN is excluded from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between the right-ventricular and superior vena cava defibrillation coils. Determination that the defibrillation pathway is shorted may be made by conventional low current measurements or delivery of high current extremely short test pulses.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Lead condition assessment for an implantable medical device
A method, system, and apparatus for performing a lead condition assessment and / or a lead orientation determination associated with an implantable medical device (IMD). A first impedance is determined. The first impedance relates to the impedance relative to a first electrode and a portion of the IMD. A second impedance is determined. The second impedance relates to the impedance relative to a second electrode and the portion of the IMD. The first impedance is compared with the second impedance to determine an impedance difference. A determination is made whether the impedance difference is outside a predetermined tolerance range. Furthermore, artifact measured during impedance measurements or test pulses may be compared to assess lead orientation. An indication of a lead condition error is provided in response to determining that the impedance difference is outside the predetermined tolerance range.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Process for determining the operating parameters of an injection device
ActiveUS7269500B2Expand the scope of operationThe result is accurateAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl signalEngineering
A process for determining the operating parameters of an injection device of a combustion engine includes the steps of: (a) selecting an injector to test; (b) calculating a mean velocity associated with a preceding injector arranged before the injector to test; c) applying to the injector to test an injection control signal including at least one test pulse having an adjustable parameter; (d) calculating a mean velocity associated with the injector to test; (e) calculating a difference between the mean velocity calculated in step d) and the mean velocity calculated in step b); (f) repeating steps b) to d) for at least another engine cycle, each time varying the parameter of the test pulse; (g) determining a value of the parameter of the test pulse for which the mean velocity difference exceeds a predetermined threshold; and storing the parameter value.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
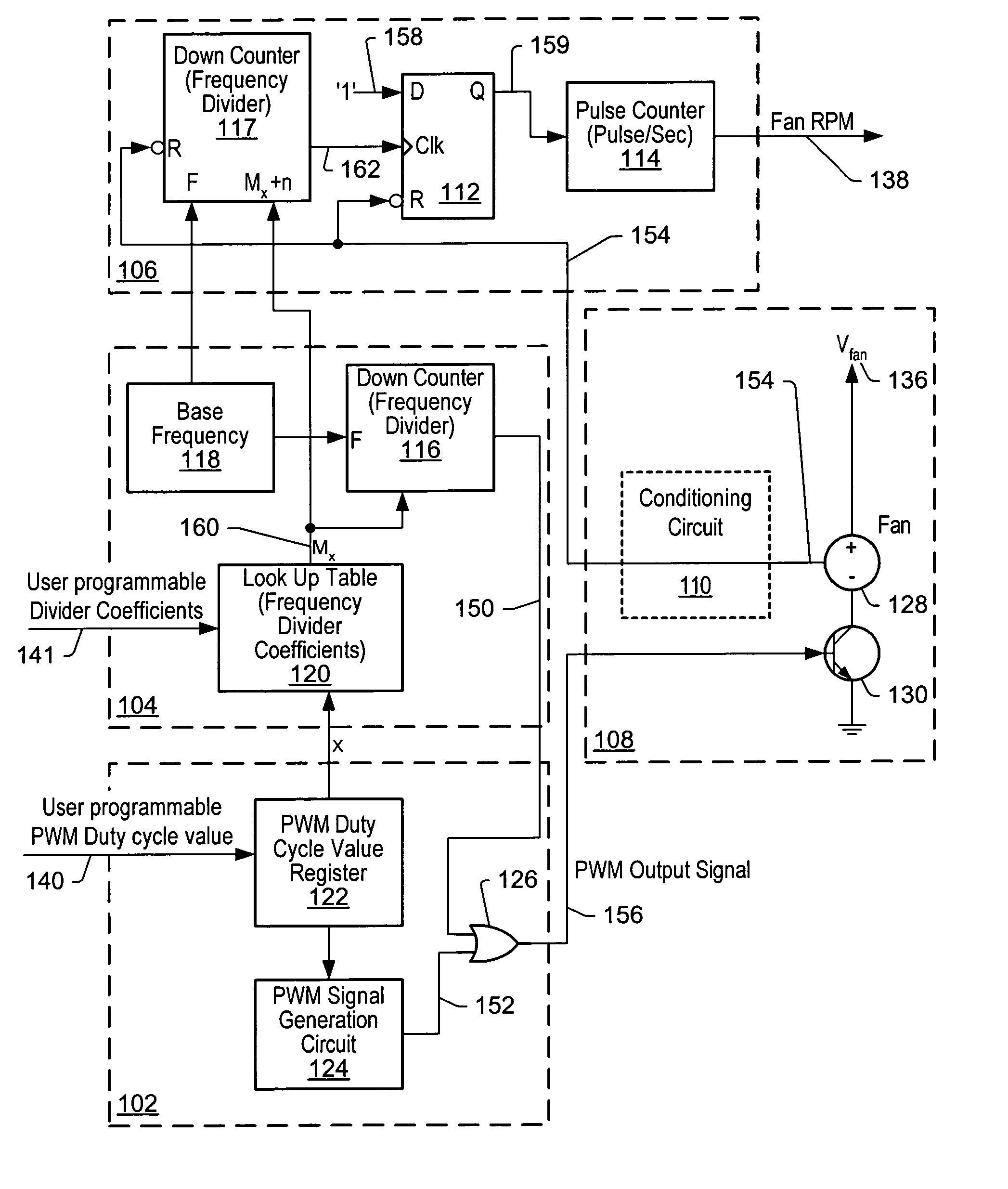
Method and apparatus to achieve accurate fan tachometer with programmable look-up table
ActiveUS7092623B2Shorten speedHigh frequencySynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPwm signalsPulse width modulated
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Component interface module
InactiveUS6842669B2Maintain reliabilityLevel controlElectric testing/monitoringFunctional testingPulse test
A component interface module (CIM) arbitrates through priority logic component command signals from redundant systems and integrates the selected priority command signal with component feedback signals in component logic to generate a control signal for a component in a complex plant. The non-software based CIM is programmable for use with a variety of plant components. The component logic includes blocking logic that prevents or terminates generation of the control signal such as when component activation has been completed. Diagnostics incorporated into the CIM include: an input port interface test, a pulse test that continuously checks for proper propagation of test pulses through the priority and component logic, and a test of the functioning of the CIM output device such as a relay.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
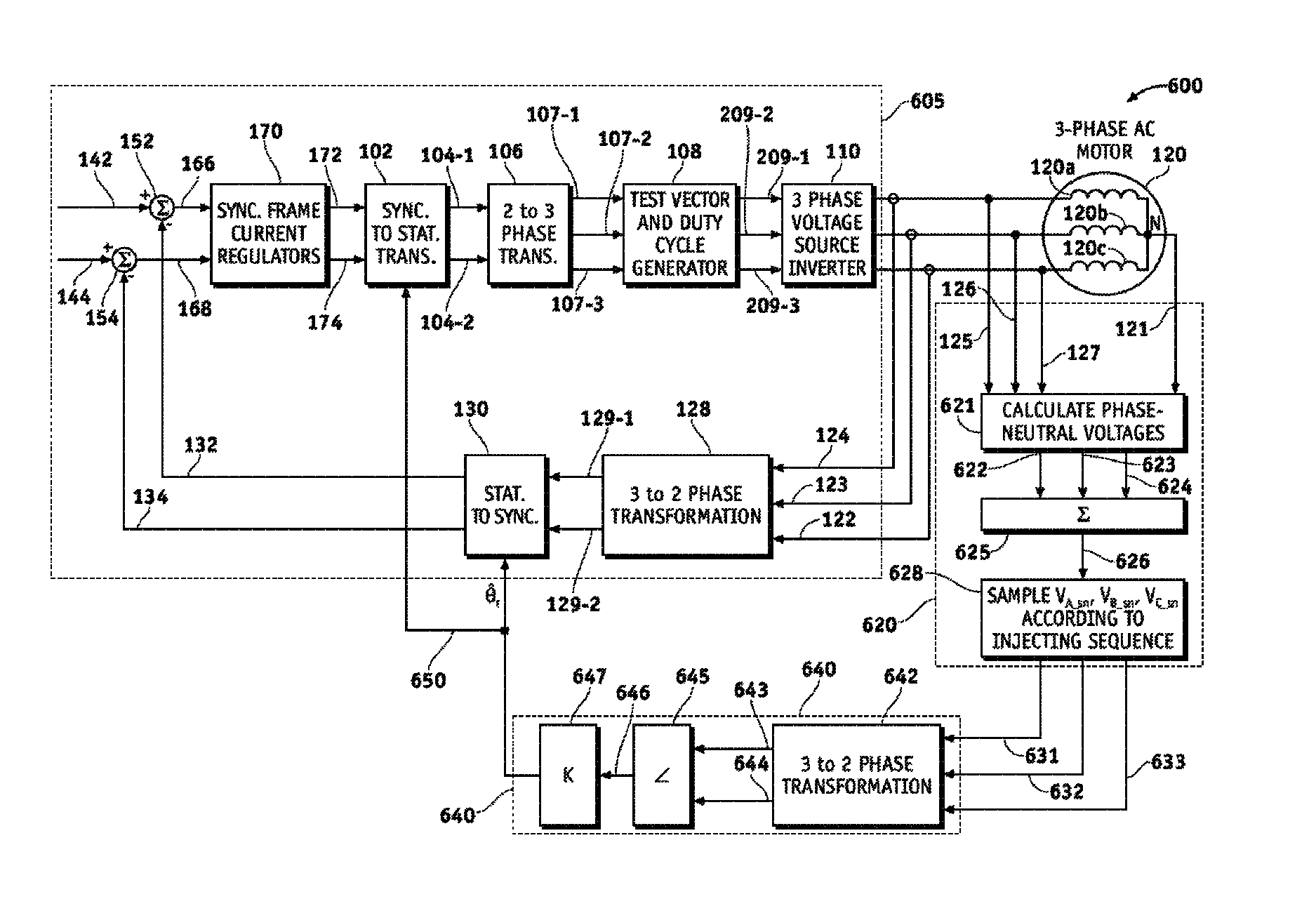
Vector controlled motor drive system implementing pulse width modulated (PWM) waveforms
ActiveUS8253360B2Reduce switching lossesDecreased numberAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveWave shape
A vector controlled motor drive system is provided that includes a test vector and duty cycle generator module designed to receive a set of three-phase voltage command signals and designed to generate a set of pulse width modulated (PWM) waveforms. The set of PWM waveforms comprise: a first modified switching vector signal for a first motor phase that comprises at least two test pulses over three consecutive PWM cycles. The first modified switching vector signal has a first amplitude value that changes between a high amplitude value and a low amplitude value during the three consecutive PWM cycles. A number of transitions by the first modified switching vector signal between the low amplitude value and the high amplitude value over the three consecutive PWM cycles is greater than six and less than twelve.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Smart linear pulsed laser diode driver, and method
ActiveUS8184670B2Improve efficiencySmall sizeLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitor voltageEngineering
In a pulsed laser diode driver an energy storage capacitor is continuously being charged to a supply voltage Vr. When a pulse is initiated, energy stored in the capacitor is delivered to the laser diode load. The capacitor voltage Vd at the end of a pulse is used to control Vr to ensure that Vd is maintained above a minimum voltage Vm required to ensure operation of a current control device (such as FET) just above saturation. Test pulses (such as with attenuated currents or reduced pulsewidth) may be fired to determine an initial optimum value for Vr. After a test pulse, a slightly high estimate for Vr may be used and may be iterated (incremented) down to an optimum value Vm during a firing burst. A digital processor may be used to calculate and store data to optimize the performance. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ANALOG MODULES
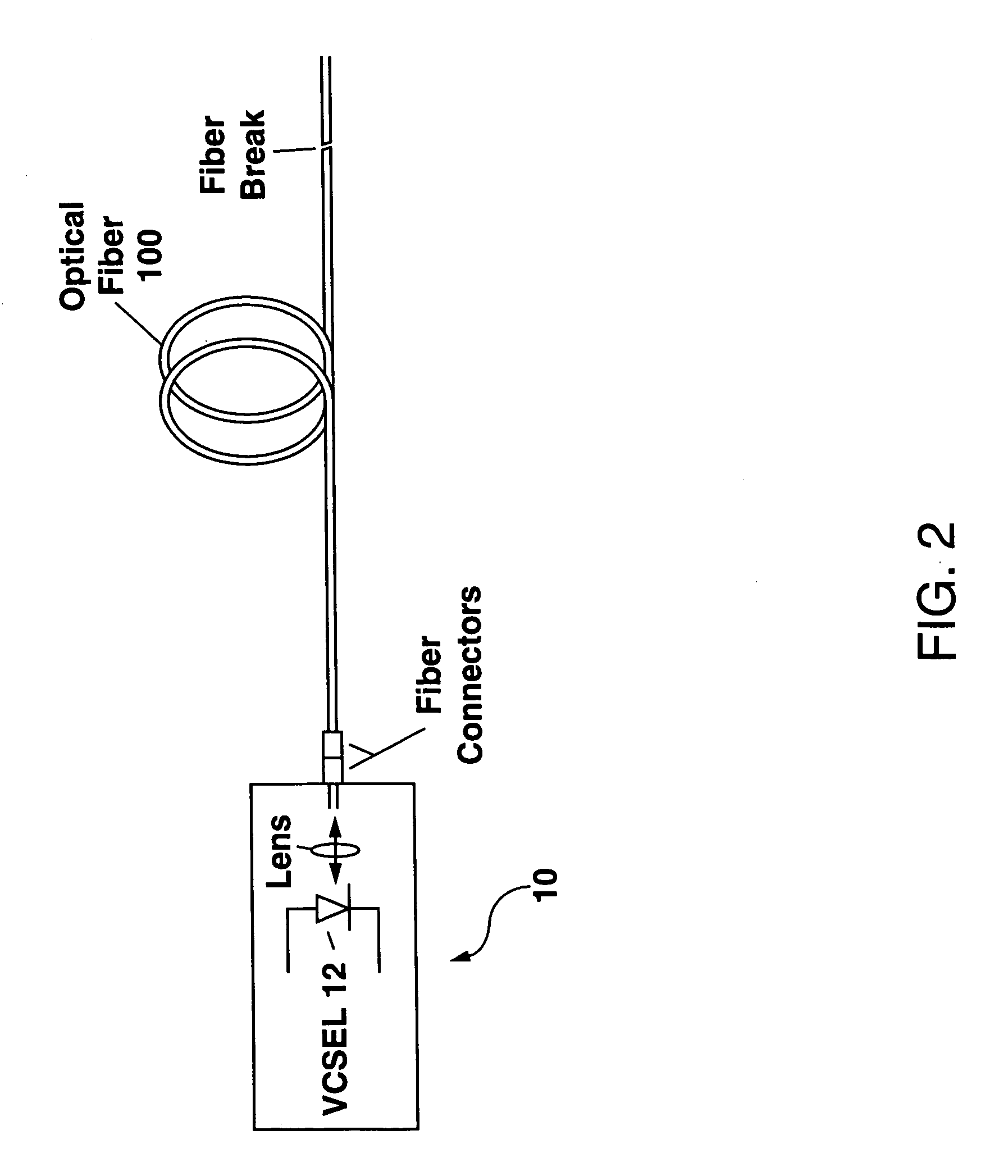
VCSEL fault location apparatus and method
ActiveUS7218388B1Reduce electrical impedanceHigh impedanceMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainResonant cavityFiber
An apparatus for locating a fault within an optical fiber is disclosed. The apparatus, which can be formed as a part of a fiber-optic transmitter or as a stand-alone instrument, utilizes a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) to generate a test pulse of light which is coupled into an optical fiber under test. The VCSEL is subsequently reconfigured by changing a bias voltage thereto and is used as a resonant-cavity photodetector (RCPD) to detect a portion of the test light pulse which is reflected or scattered from any fault within the optical fiber. A time interval Δt between an instant in time when the test light pulse is generated and the time the reflected or scattered portion is detected can then be used to determine the location of the fault within the optical fiber.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for detecting and treating insulation lead-to-housing failures
ActiveUS20150151118A1High resolutionHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesElectrical conductorDual coil
Disclosed is a method for the diagnosis of conductor anomalies, such as an insulation failure resulting in a short circuit, in an implantable medical device, such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). Upon determining if a specific defibrillation pathway is shorted, the method excludes the one electrode from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between functioning defibrillation electrodes. Protection can be provided against a short in the right-ventricular coil-CAN defibrillation pathway of a pectoral, transvenous ICD with a dual-coil defibrillation lead. If a short caused by an in-pocket abrasion is present, the CAN is excluded from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between the right-ventricular and superior vena cava defibrillation coils. Determination that the defibrillation pathway is shorted may be made by conventional low current measurements or delivery of high current extremely short test pulses.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Radio frequency power amplifier protection system
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier protection system for a radio. The protection system utilizes a resistive tap connected to the drain of a power amplifier transistor and a high speed voltage detector. The protection system uses short, low-power tests pulses to determine the quality of an antenna load upon tuning the radio to an RF carrier frequency by transmitting the short test pulse. If the measured voltage value exceeds a calibrated value, the power of the RF transmitter is reduced for subsequent operation or the RF transmitter is shut down completely. The invention also includes a system and method for detecting when an antenna is disconnected from a radio using an low frequency AC signal to measure the resistance of an antenna connected to an RF transmitter.
Owner:SPECTRALUX
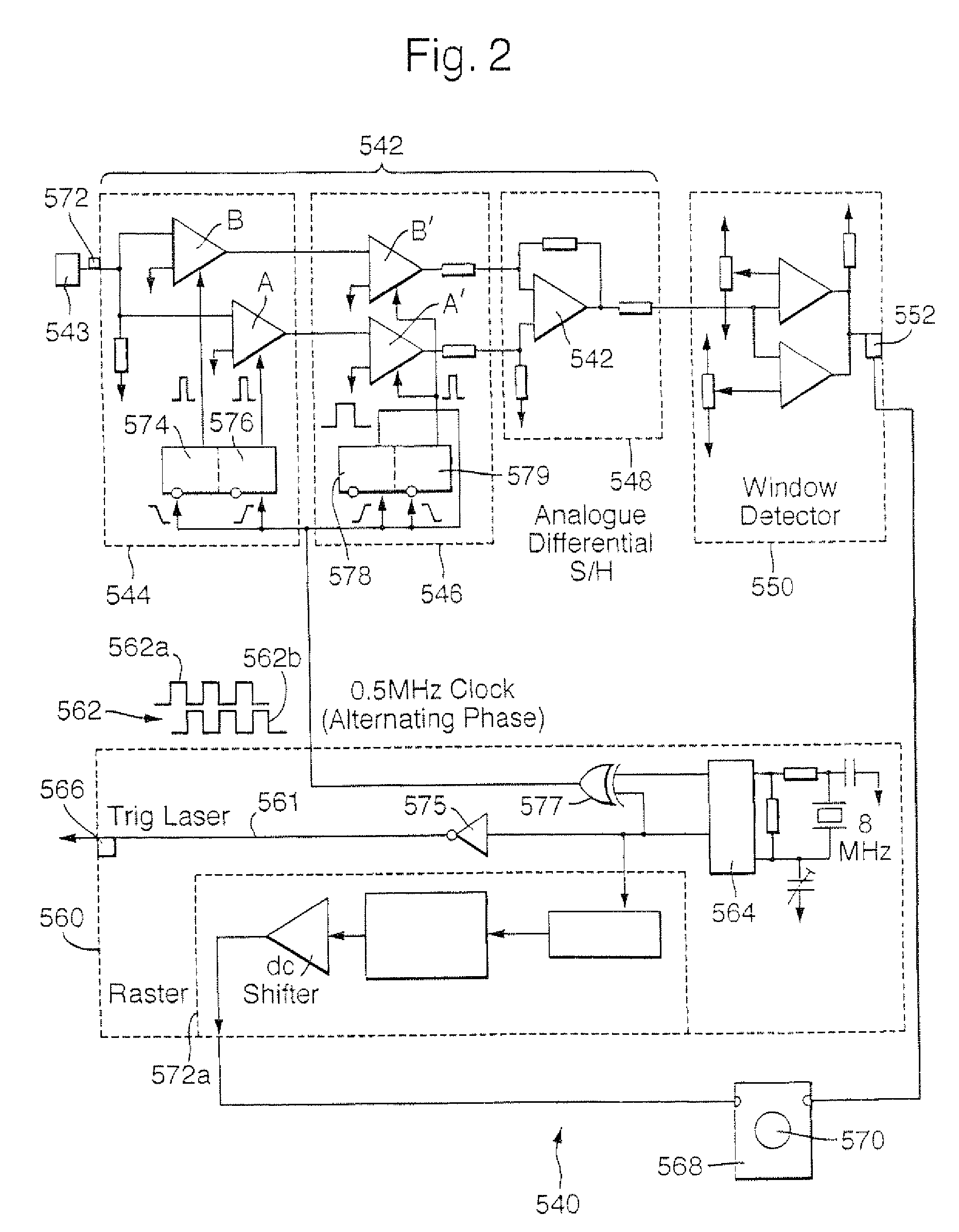
Evaluating the position of disturbance
ActiveCN1938575AConverting sensor output opticallyReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in frequency-domainTime domainOptical link
The present invention relates to a method of and apparatus for evaluating the position of a disturbance on an optical link, in particular where the disturbance is a time-varying disturbance. An optical time domain reflectometry technique is used in which a series of low coherence test pulses is launched by means of an optical pulse source (18) into an the optical link (16), and the backscattered return signal is monitored. The test pulses pass through an unbalanced Mach Zhender interferometer (20) with the result that for each test pulse, a pair of time-displaced pulse copies is launched onto the link (16). The backscattered return signal is passed through the same interferometer (20), which causes the pulse copes of each pair to become realigned and to interfere with one another. A time-varying disturbance (x) is likely to affect each pulse copy of a pair differently. As a result, an abnormality such as a step is likely occur in the backscattered signal. From the time position of an abnormality, the distance of the disturbance responsible is evaluated.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Evaluating the position of a disturbance
The position of a disturbance on an optical link is evaluated, in particular where the disturbance is a time-varying disturbance. An optical time domain reflectometry technique is used in which a series of low coherence test pulses is launched by means of an optical pulse source into an the optical link, and the backscattered return signal is monitored. The test pulses pass through an unbalanced Mach Zhender interferometer with the result that for each test pulse, a pair of time-displaced pulse copies is launched onto the link. The backscattered return signal is passed through the same interferometer, which causes the pulse copies of each pair to become realigned and to interfere with one another. A time-varying disturbance is likely to affect each pulse copy of a pair differently. As a result, an abnormality such as a step is likely to occur in the backscattered signal. From the time position of an abnormality, the distance of the disturbance responsible is evaluated.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Ultrafast laser pulse shape measurement method and system
A laser pulse shape measuring system to measure the pulse shape of pulses generated by a pulsed laser. Each pulse includes a pulse width and a peak wavelength. The system includes: a beam splitter coupled to the laser to separate each of the pulses into a test pulse and a probe pulse; a pulse width compression means coupled to the beam splitter to compress the pulse width of each probe pulse; a controllable delay means to control a time offset between each test pulse and a corresponding probe pulse; a nonlinear optical medium arranged such that the test beam path and the probe beam path intersect within it to generate wavelength converted pulses corresponding to intersecting pairs of pulses; a detector coupled to the nonlinear optical medium to detect the pulse energies of the wavelength converted pulses; and a processor to determine the pulse shape of the laser pulses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor memory apparatus and method for controlling programming current pulse
A semiconductor memory apparatus includes a write control code generation unit configured to generate a write control code which is updated at each pulsing timing of an external test pulse signal applied through a pad; and a data write unit configured to output a programming current pulse which has a magnitude corresponding to the code value of the write control code.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method and apparatus to achieve accurate fan tachometer with programmable look-up table
ActiveUS20050238336A1Reduce frequencyAccurate measurementMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPwm signalsSignal multiplexing
A system and method for measuring the speed of a fan is presented. The duty cycle of a pulse width modulated (PWM) power signal may control speed of the fan. The fan may generate tachometer pulses used for monitoring RPM of the fan. Very low frequency test pulses may be generated and provided via a test signal multiplexed with the PWM signal to obtain tachometer pulses present even when the PWM signal is deasserted. The frequency of the test signal may be determined based on the duty cycle of the PWM signal and may be dynamically updated using frequency divider values stored in a user programmable look-up table. The tachometer pulses may be used to reset a flip-flop whose data input is held high and a down counter, which may be operated at a frequency slightly lower than the frequency of the test signal, with the output of the down counter clocking the flip-flop. The output of the flip-flop may provide recreated tachometer pulses to a pulse counter that counts the number of pulses within a determined period of time, providing a measured RPM of the fan.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
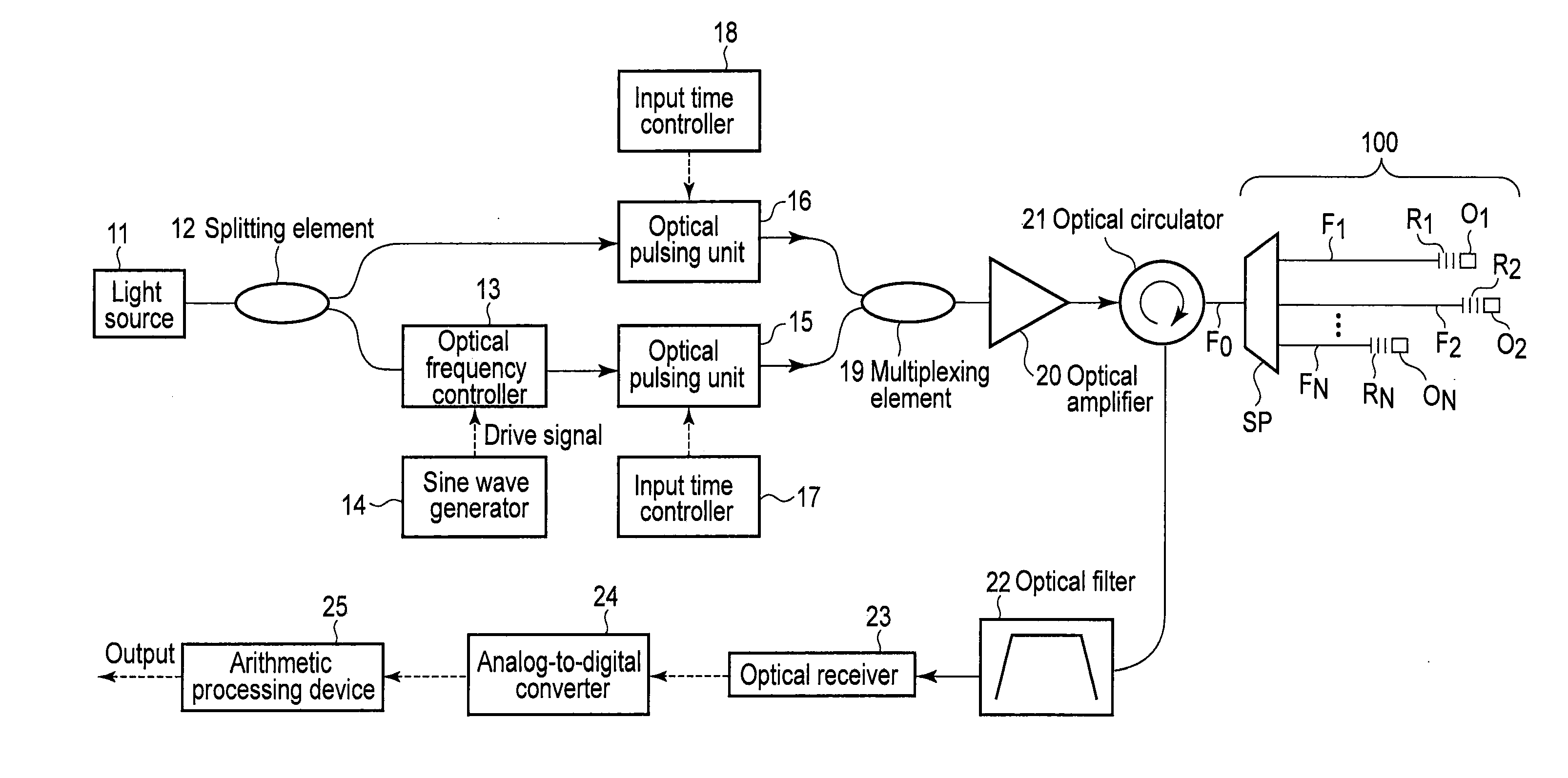
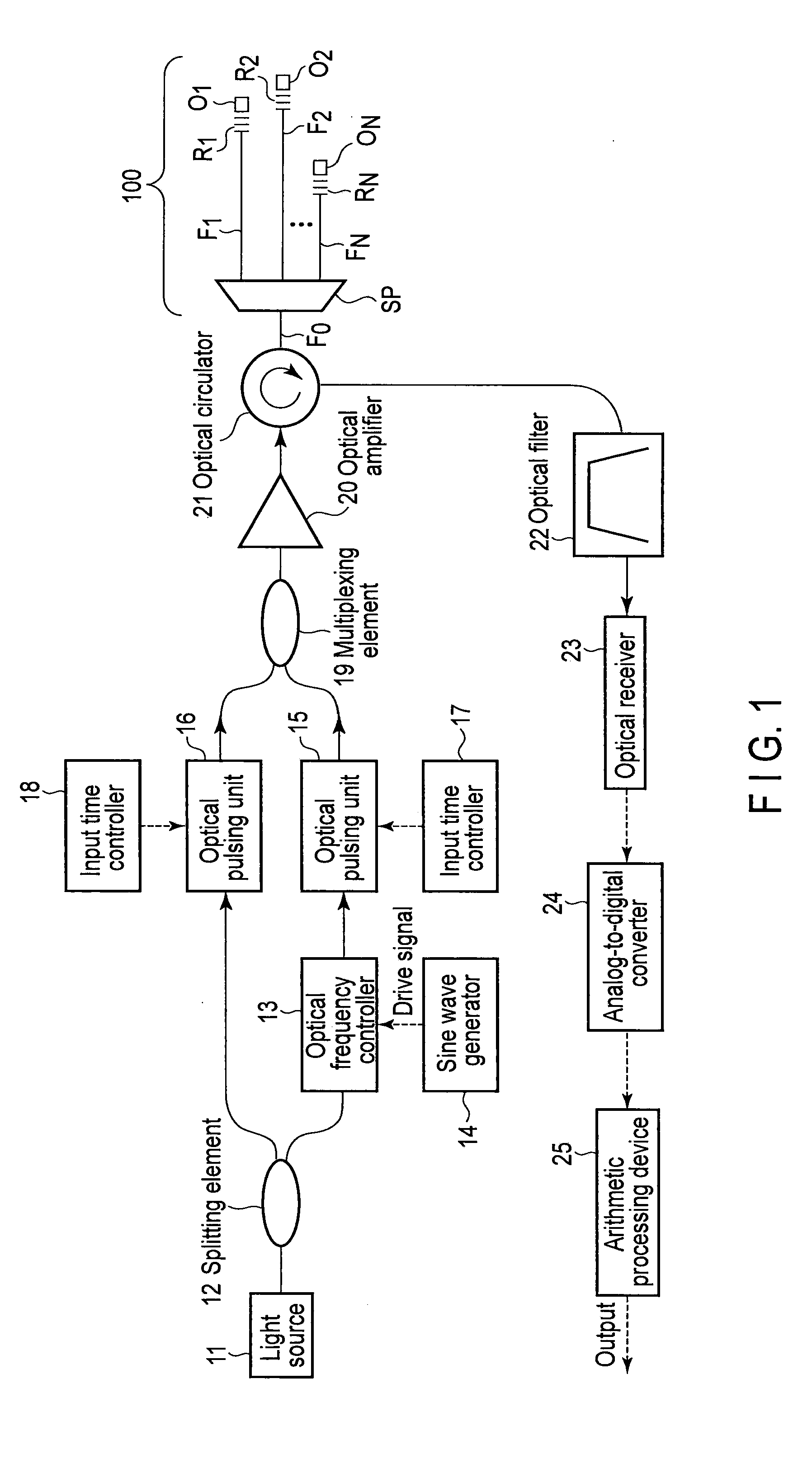
Optical fiber line characteristic analysis apparatus and analysis method thereof
ActiveUS20140098362A1Inexpensive analysisReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansTarget fibersVIT signals
A test pulse is generated from a first and a second test light beam pulse with different wavelengths, with a predetermined time difference applied between the first and the second test light beam pulse. A circulator inputs the test pulse to a trunk fiber of a measurement target fiber line. A reflected light is extracted which is output from an input end of the trunk fiber. A filter extracts stimulated Brillouin backscattered light. A receiver receives and converts the scattered light into an electrical signal. A processing device carries out the signal to determine in which of N branched fibers the stimulated Brillouin scattered light is generated, while varying a time difference between the first and the second test pulse.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
A mobile terminal testing heartbeat and its measurement method
InactiveCN101150615AAdd heartbeat measurement functionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateComputer moduleComputer terminal
The invention discloses a mobile terminal for testing palmus and a measuring method therefor, comprising: a pulse detection module which is used for testing pulse jitter of a user and converting the jitter information into a detection signal can be identified by a mobile terminal base-band chip; a mobile terminal base-band chip which is used for base-band testing, calculating of the detection signal and judging stationarity of the user palmus. The invention increases palmus testing function on the mobile terminal, which is suitable to users with heart disease, has the advantages of low cost, which is convenient to test and carry.
Owner:SHENZHEN KESHENG COMM TECH
Method and device to measure the temperature of microwave components
InactiveUS6431749B1Easy to understandSimple circuitThermometer detailsThermometers using mean/integrated valuesMicrowaveMeasurement point
In a method and a device for the measurement of the mean temperature of components, a sequence of test pulses of increasing duration is applied to the component, the power of the pulses representing a state of operation of the component, a measurement of junction temperature being performed at the end of each pulse to obtain a curve representing the progress of the junction temperature of the component as a function of time on the basis of the temperature measurement points obtained at the end of each pulse. The disclosed method and device can be applied especially to determine the junction temperature of microwave electronic components working in continuous mode or in pulsed mode.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
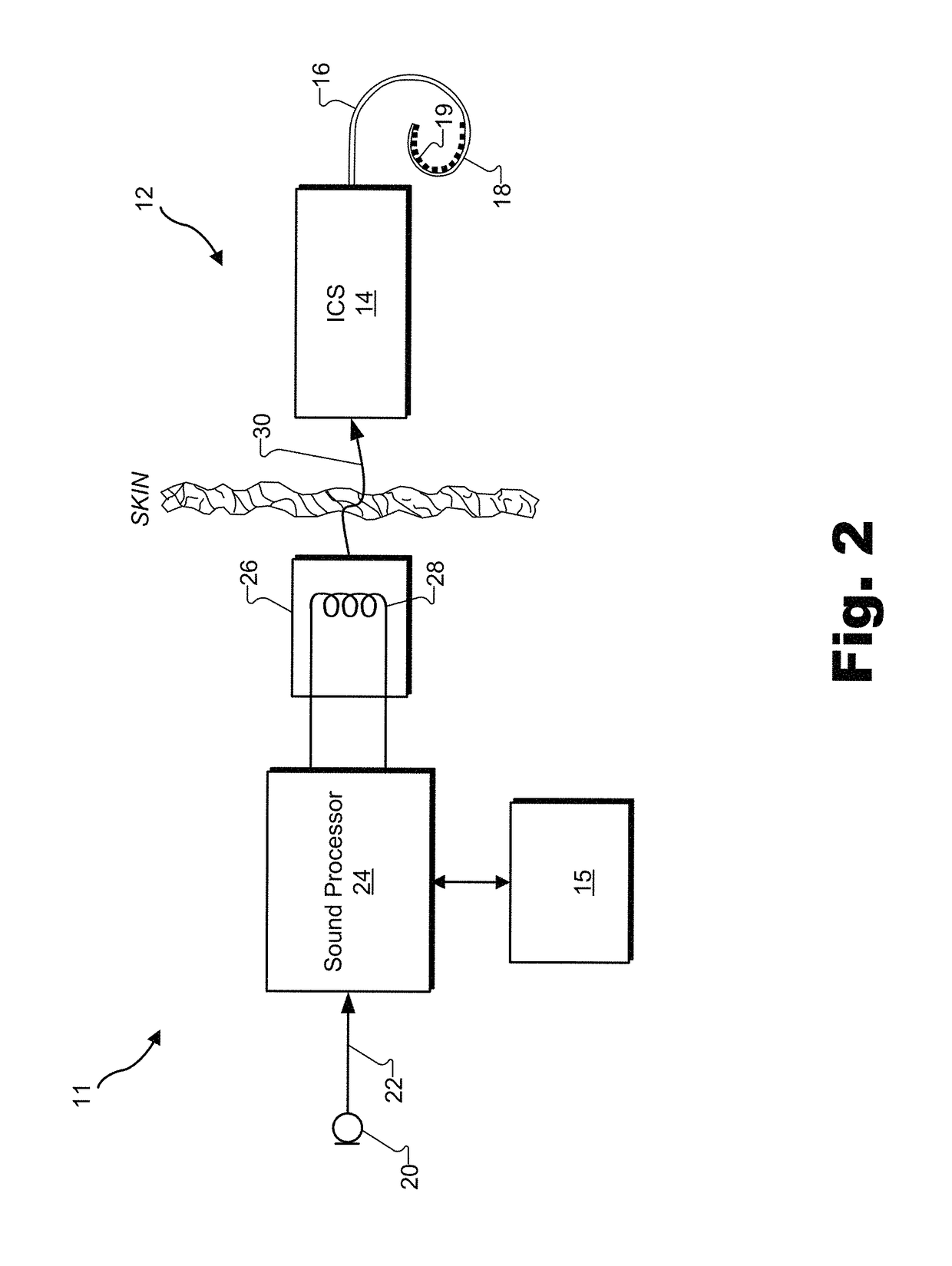
System and method for neural cochlea stimulation
ActiveUS9744358B2Minimize power consumptionHead electrodesAudiometeringMeasurement deviceCochlear implantation
A system having a device for neural stimulation of a patient's cochlea, an in-situ device for measuring a patient's response to the neural stimulation of the cochlea, and a programming unit for adjusting the stimulation device; the stimulation device having a stimulation signal unit for generating a stimulation signal formed of pulses having a shape determined by a shape parameter set including at least one shape parameter; a cochlear implant stimulation arrangement with a plurality of stimulation channels for stimulating the cochlea based on the stimulation signal; the measuring device providing patient-specific response data concerning the stimulation response to a programming unit that controls the stimulation signal unit by subsequently supplying a plurality of different test shape parameter sets to the stimulation signal unit for causing the stimulation signal unit to generate corresponding test pulses, the programming unit evaluating each test shape parameter set based on stimulation response data.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Liquid crystal display and dead pixel test circuit and method for liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display includes a liquid crystal display panel and a test circuit. The liquid crystal panel includes a number of scanning lines and a number of data lines cooperatively forming a pixel cell. The test circuit includes a control unit, a gate driving circuit, a data driving circuit and a detecting circuit. The gate driving circuit and the data driving circuit respectively provide a scan pulse and a test pulse to the pixel cells. The test pulse includes a first voltage. After a predefined period for providing the scan pulse and the test pulse to the pixel cells, the detecting circuit detects a voltage of the data lines, and determines the pixel cell is damaged if the voltage of the data lines is equal to the first voltage. A test circuit and a test method for detecting damaged pixel cells are also provided.
Owner:FU TAI HUA IND SHENZHEN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com