Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
354 results about "Reflectometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
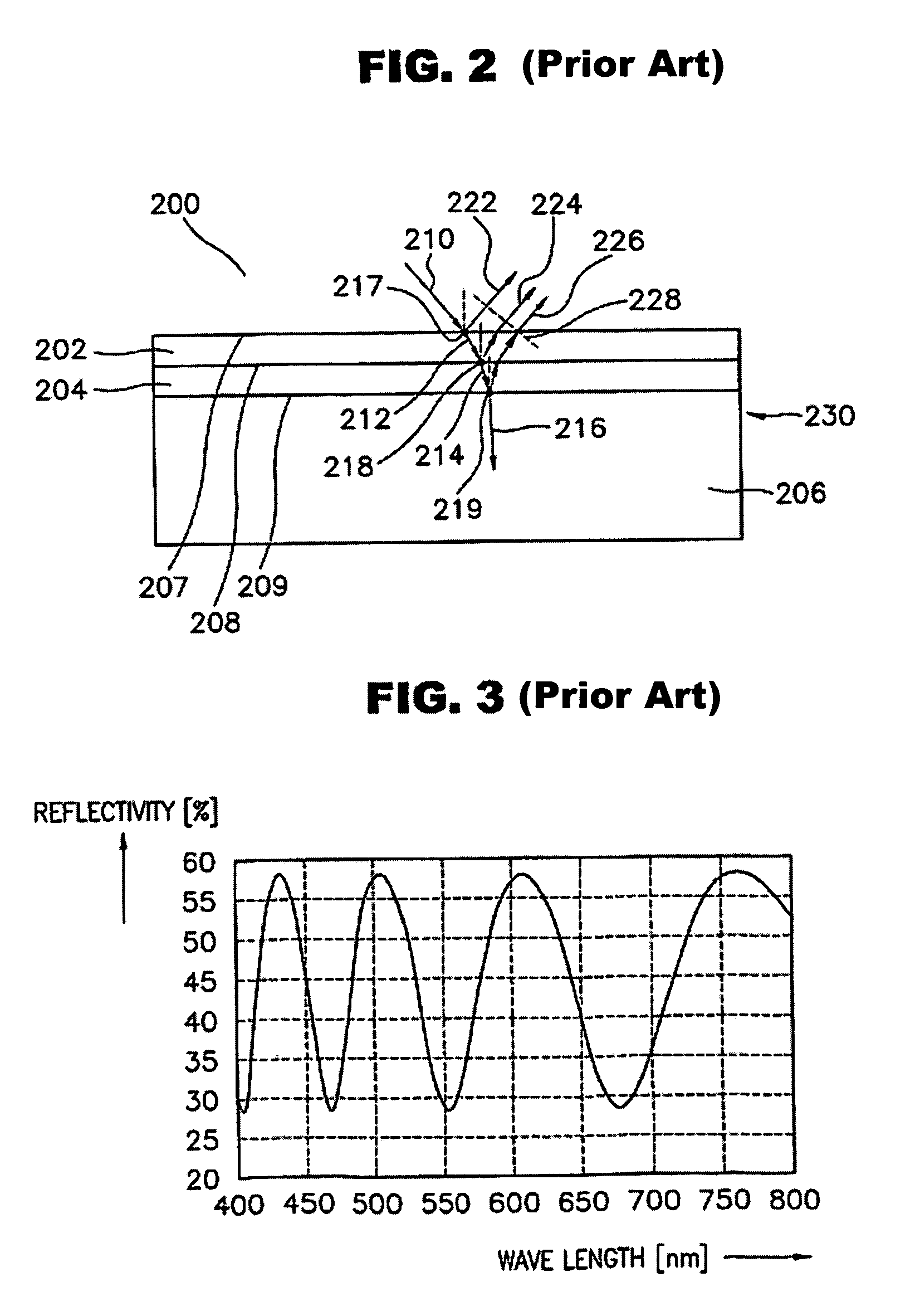
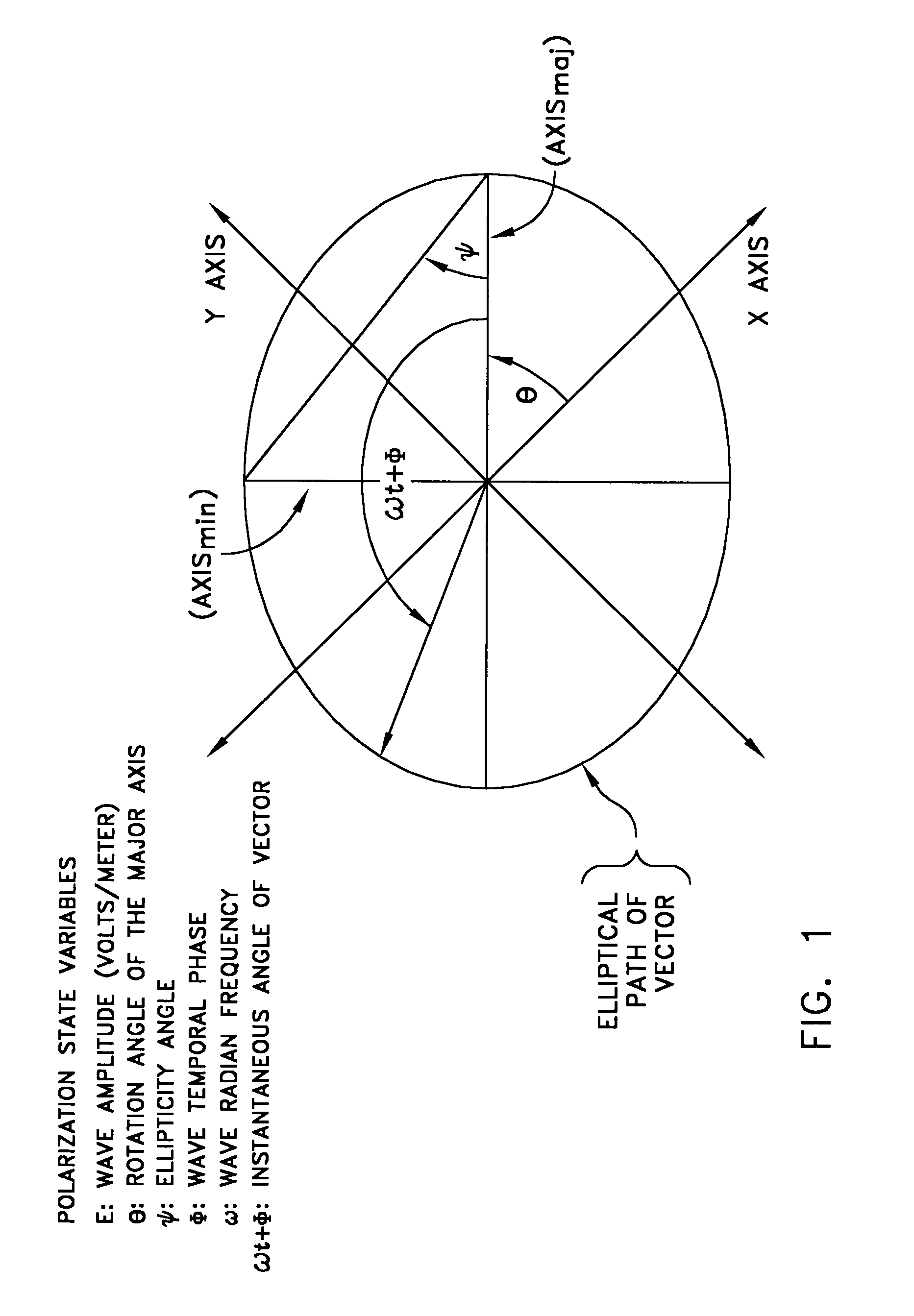
Reflectometry uses the reflection of waves at surfaces and interfaces to detect or characterize objects. There are many different forms of reflectometry. They can be classified in several ways: by the used radiation (electromagnetic, ultrasound, particle beams), by the geometry of wave propagation (unguided versus wave guides or cables), by the involved length scales (wavelength and penetration depth versus size of the investigated object), by the method of measurement (continuous versus pulsed, polarization resolved, ...), and by the application domain.
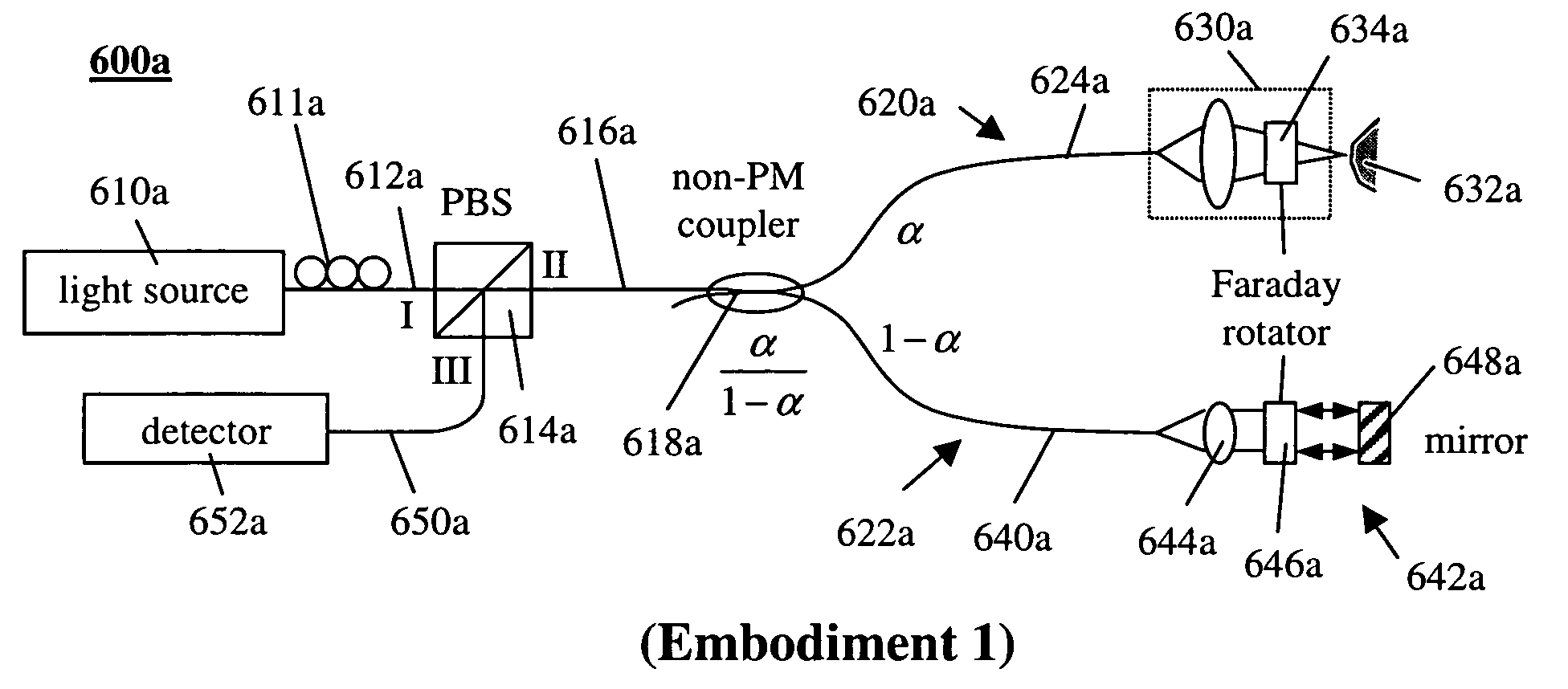
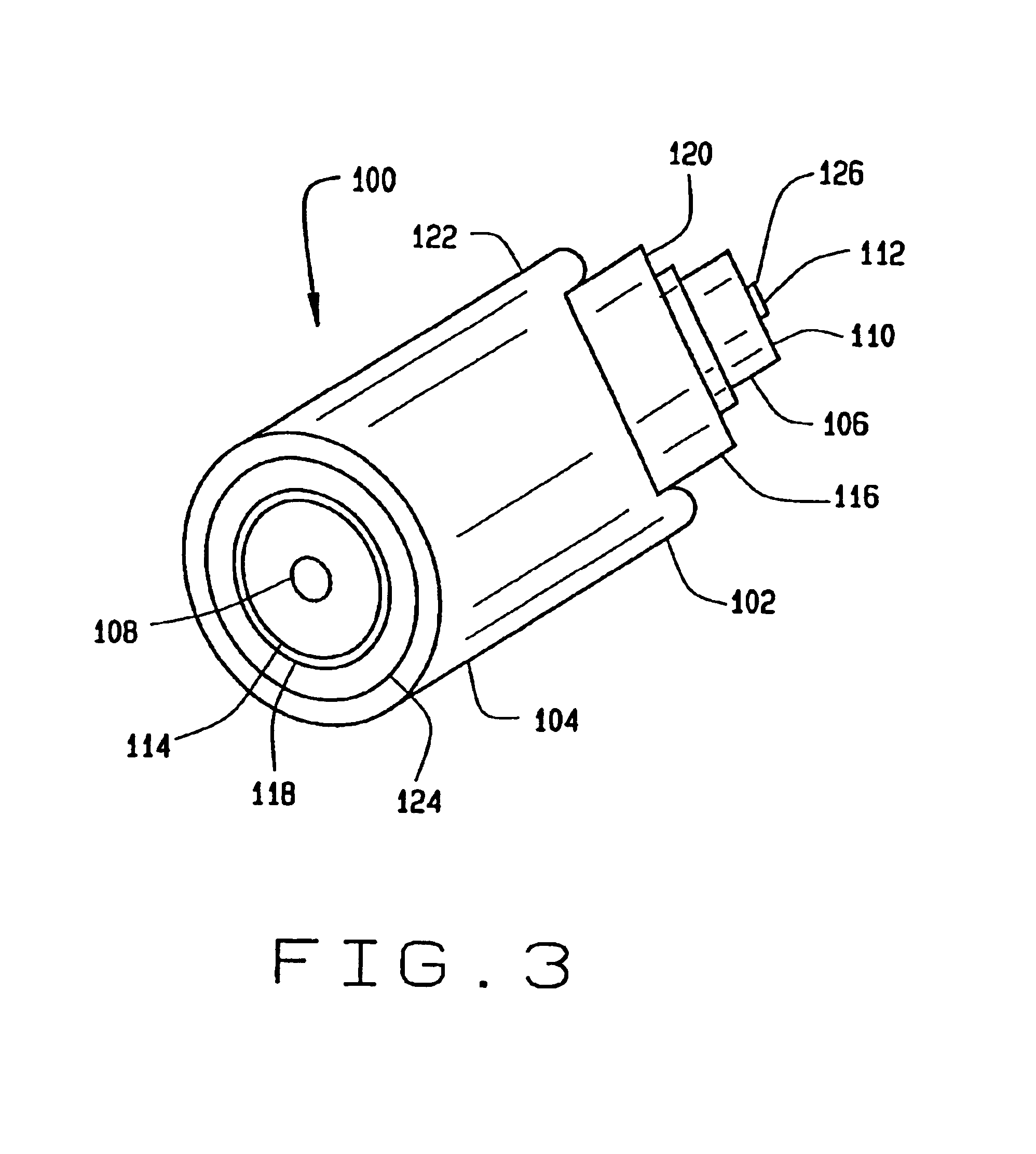
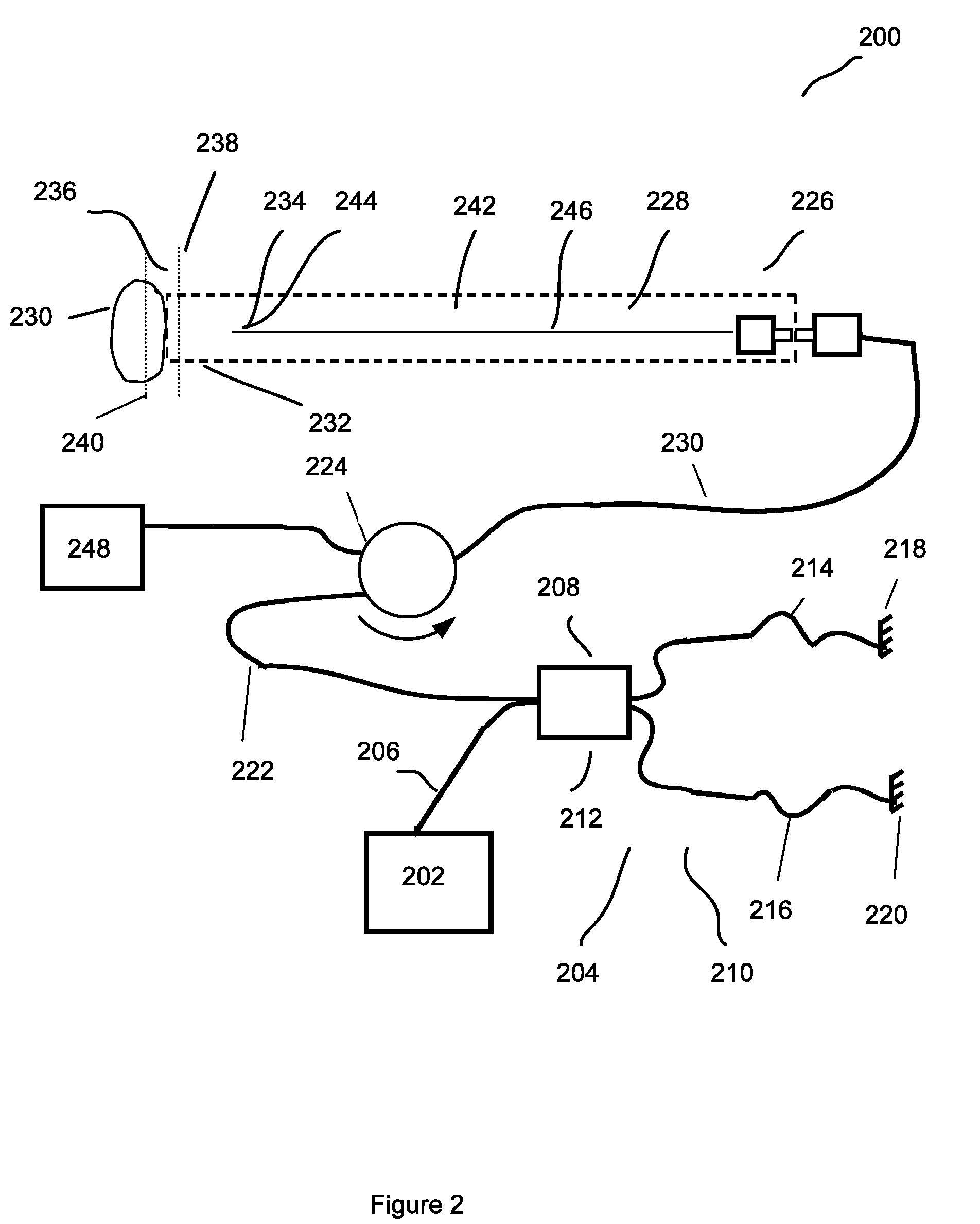
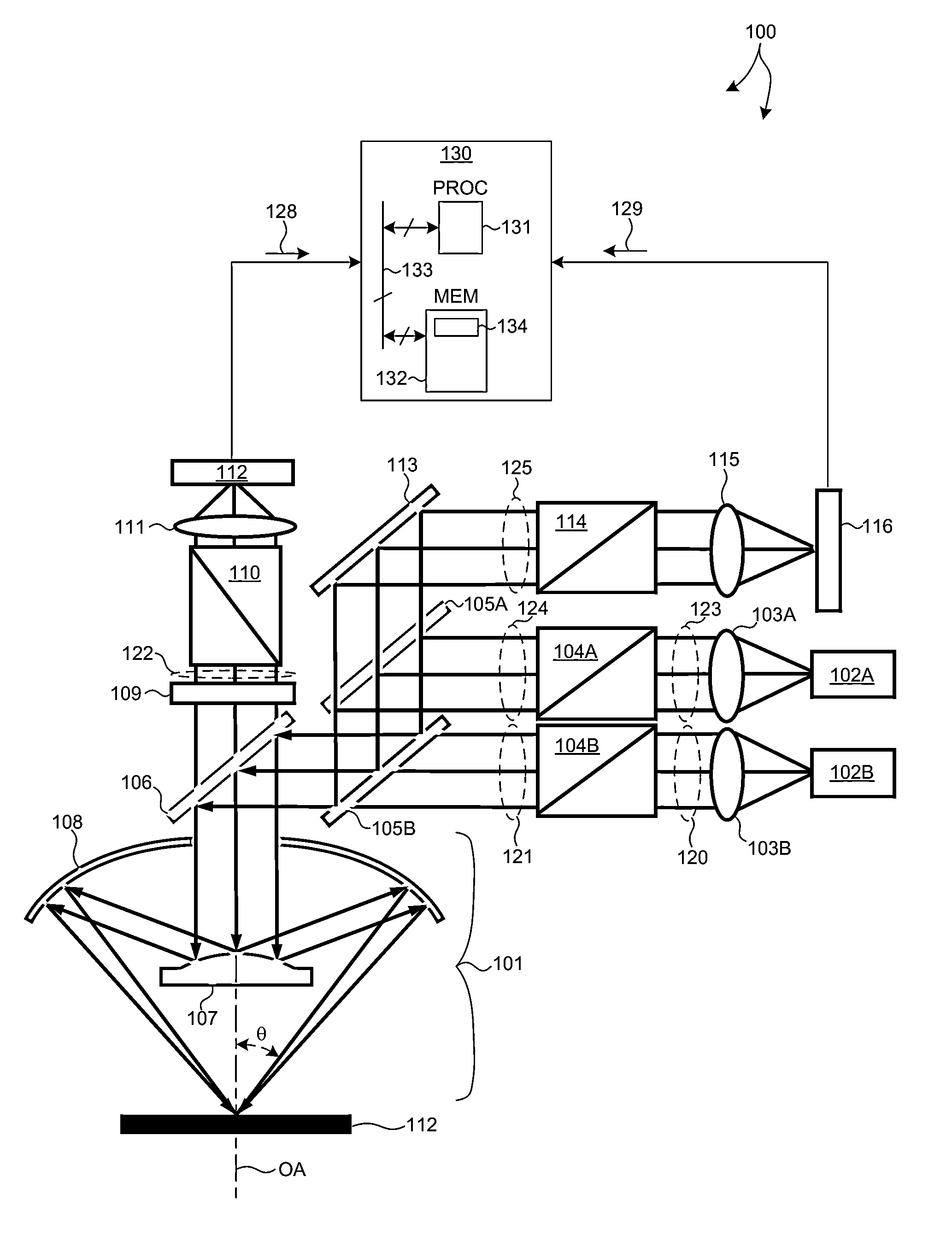
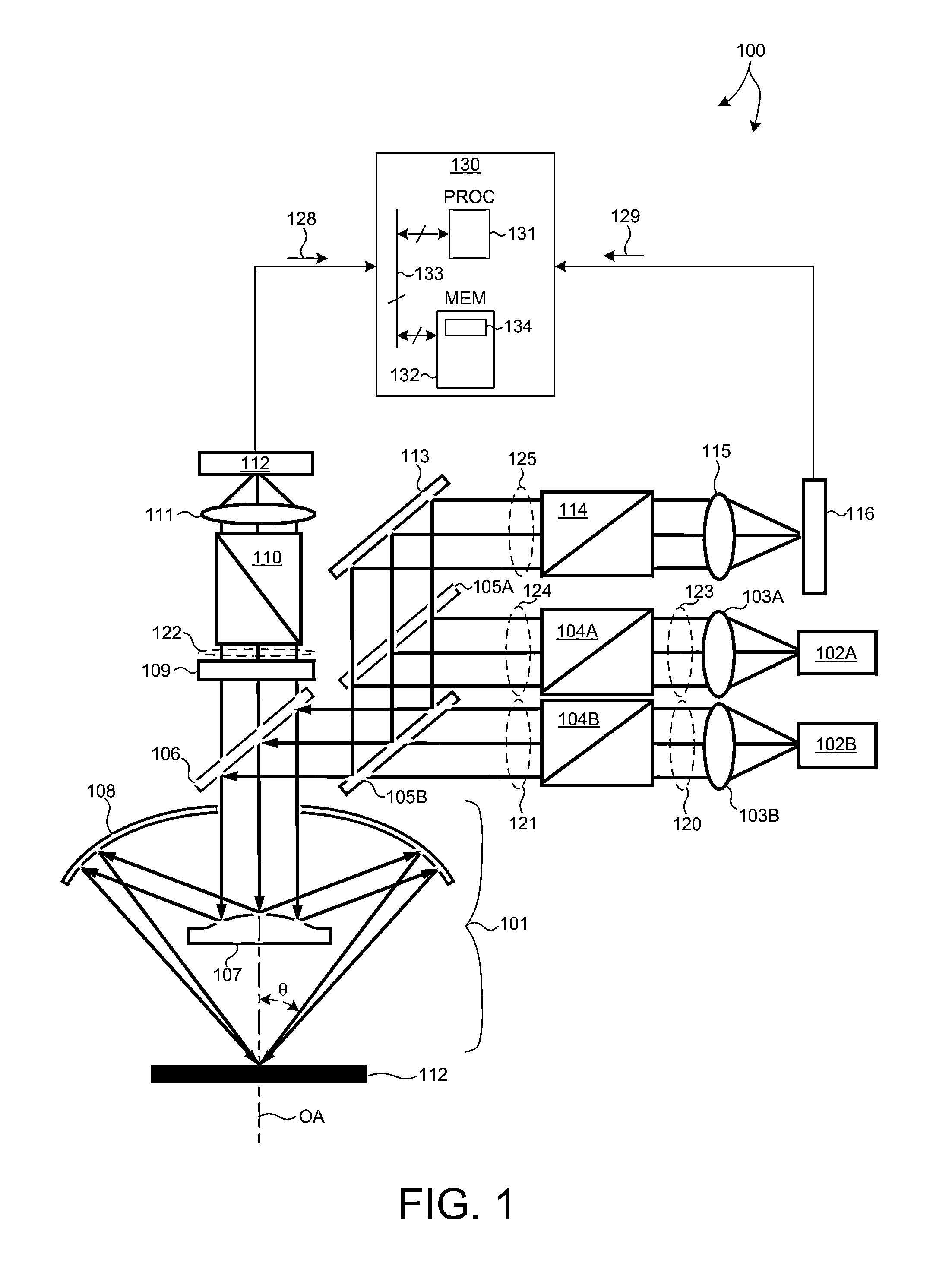
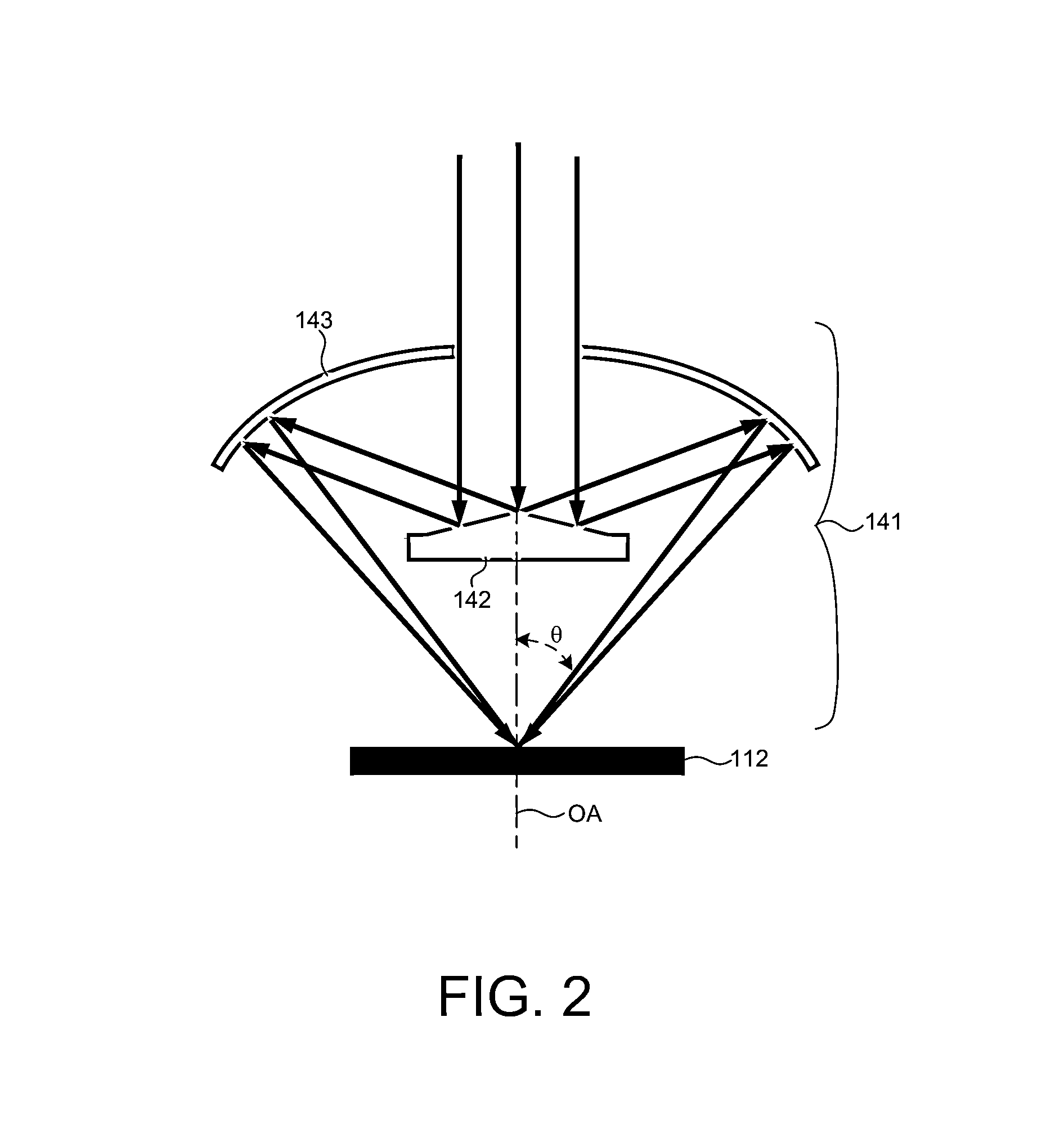
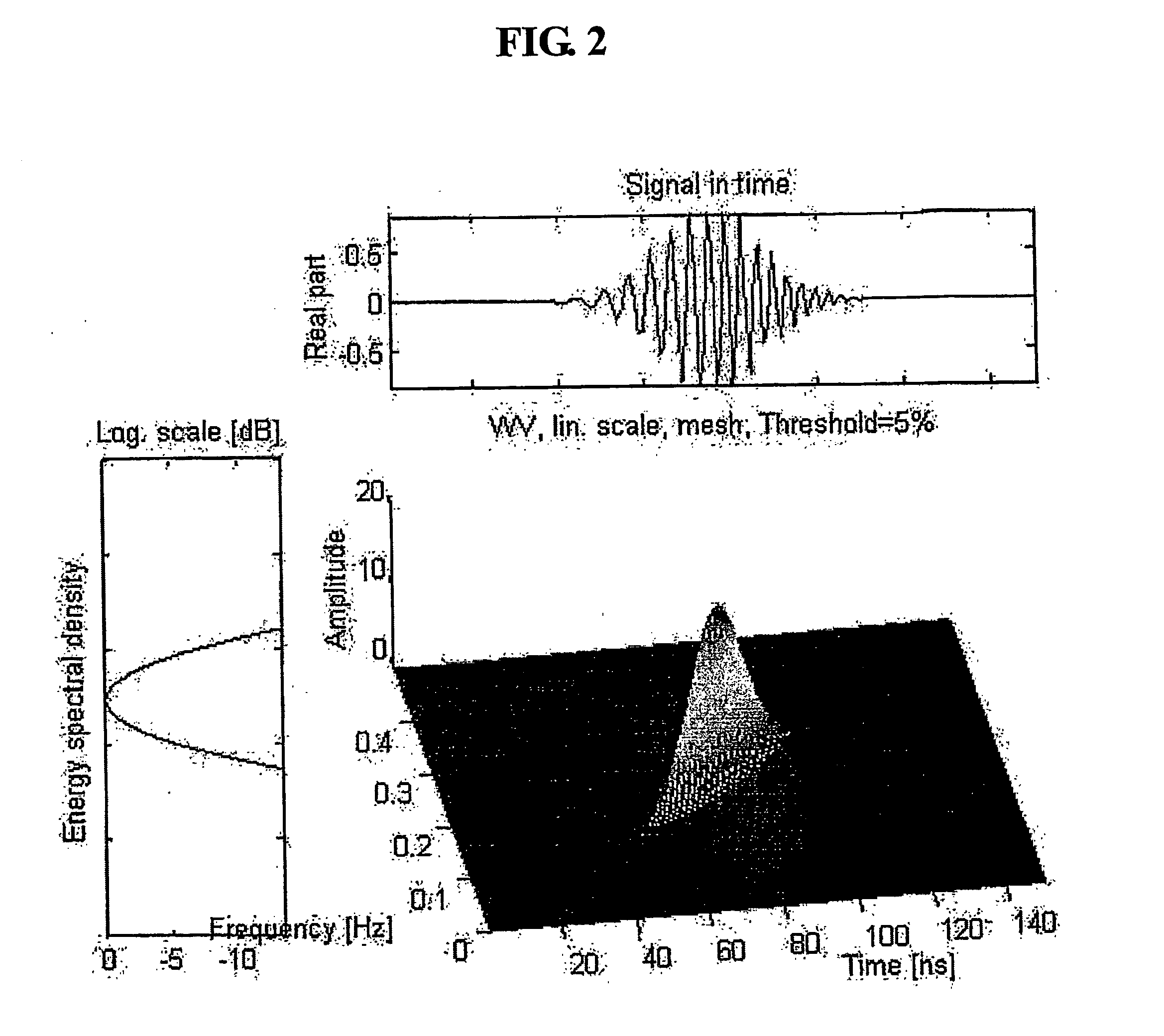
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS20050213103A1Reduce system costLow costReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
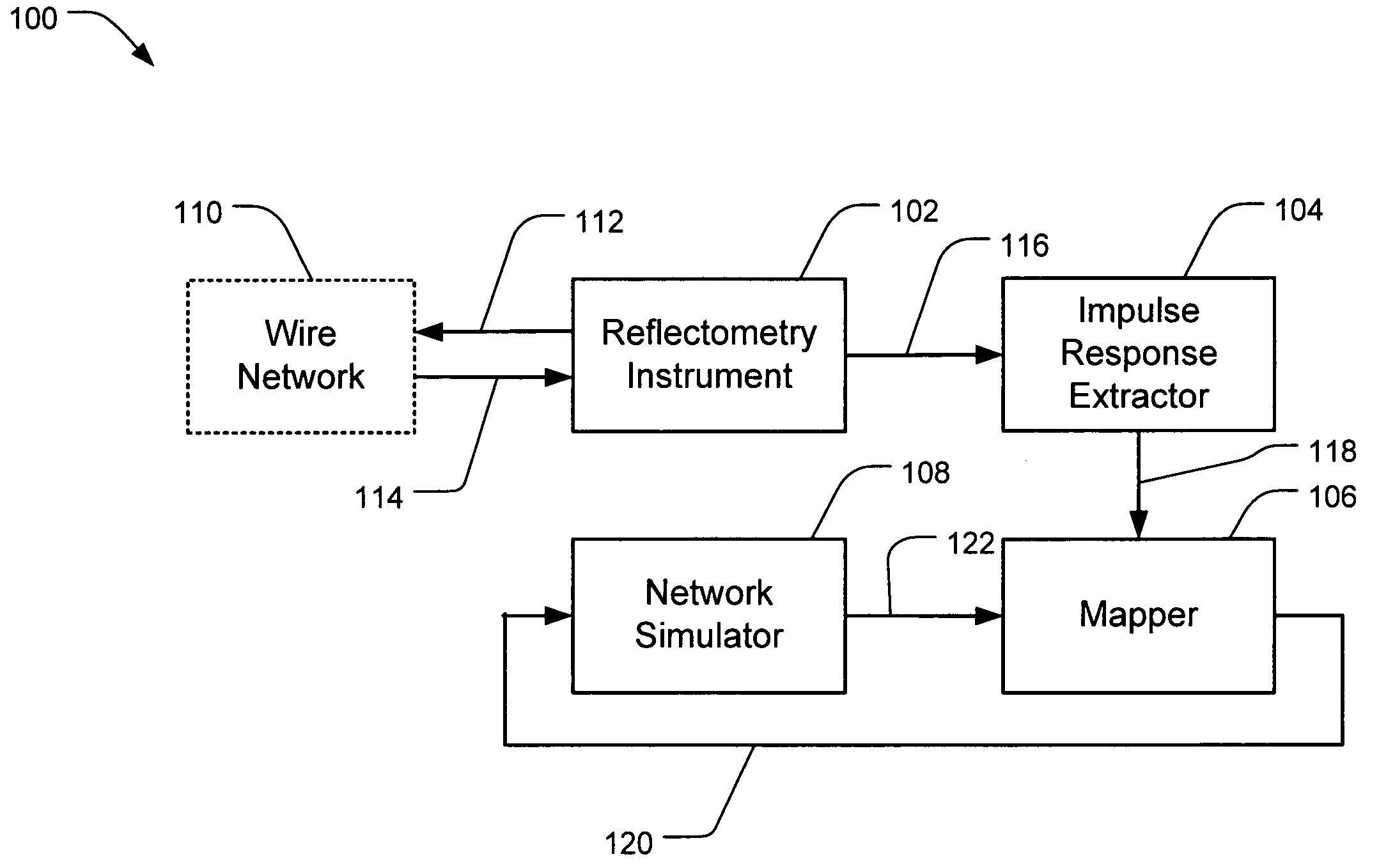
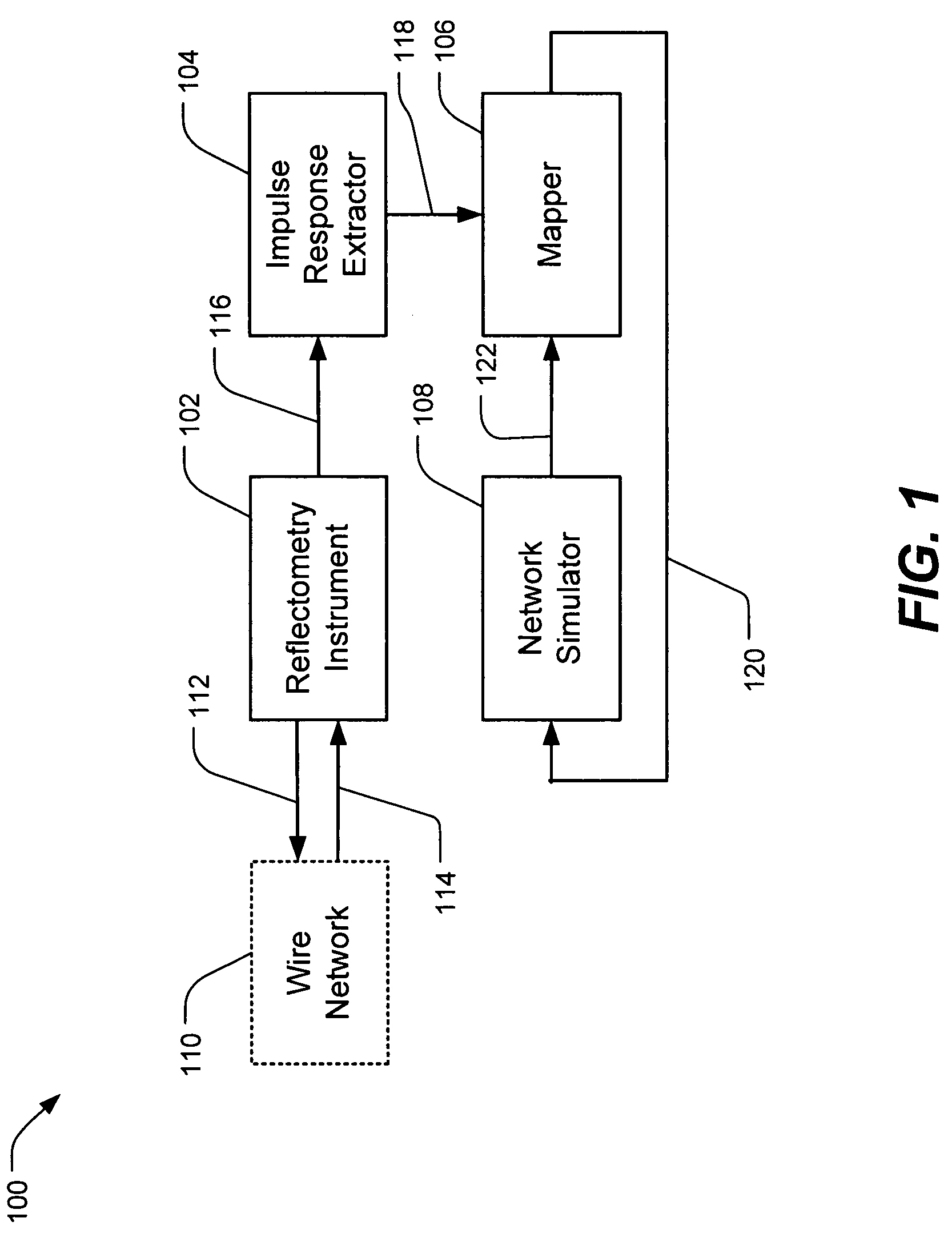
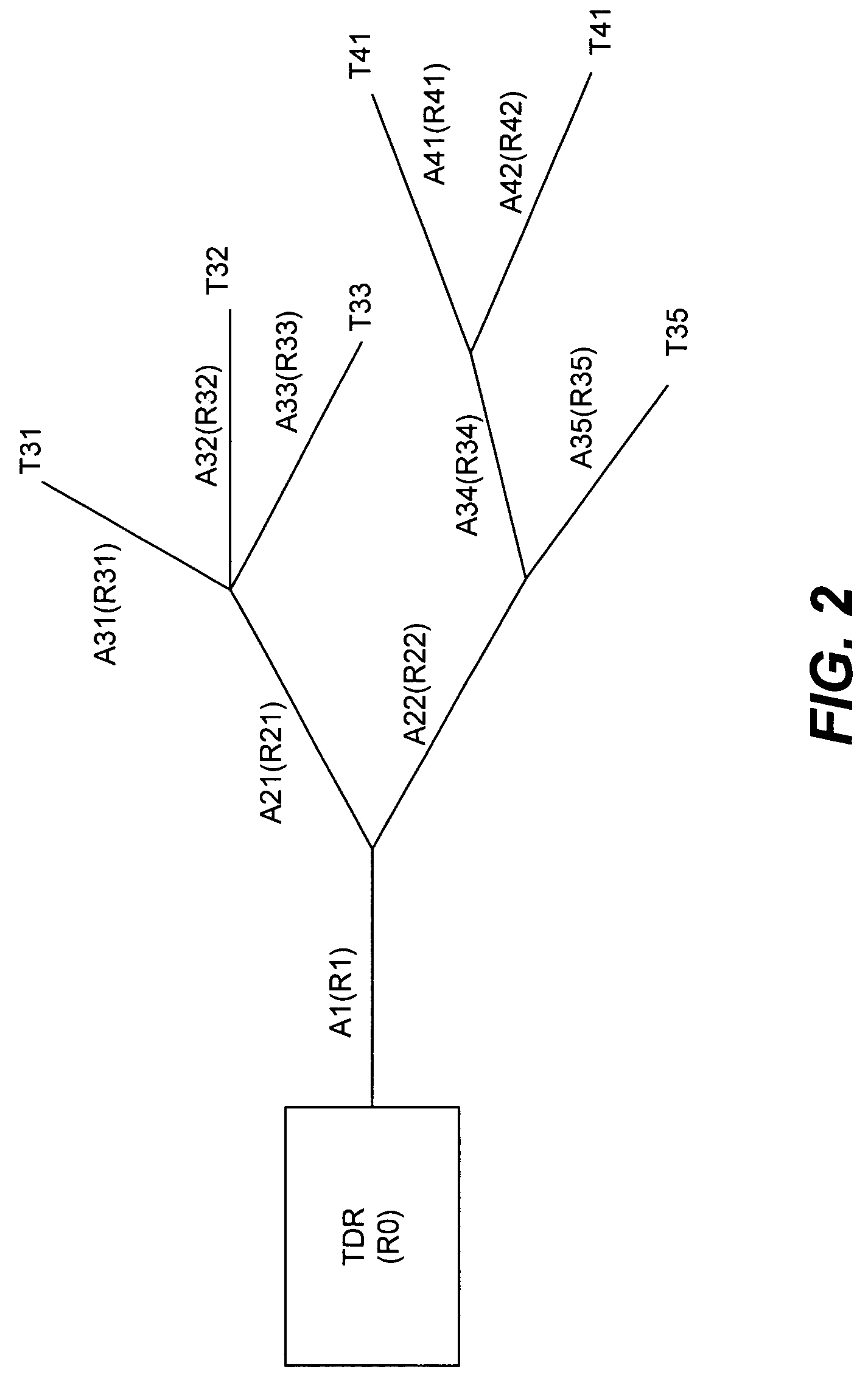
Wire network mapping method and apparatus using impulse responses
ActiveUS7282922B2Reduce the differenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsFinite impulse responseNetwork model
A method and apparatus for mapping a wire network is disclosed. The method includes obtaining a reflectometry test signal of the wire network. An estimated network impulse response is estimated from the reflectometry response. A wire network model is then initialized, and iteratively improved by simulating an impulse response of the wire network model and adjusting the wire network model to reduce differences between the simulated impulse response and estimated network impulse response.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Radio frequency guide wire assembly with optical coherence reflectometry guidance
A guide wire assembly includes a guide wire, an optical fiber, and an insulating coating. The guide wire has a distal end, a proximal end, and a bore extending through the wire between the distal and proximal ends. The an optical fiber also includes a distal end and a proximal end and is located within the bore of the guide wire. The optical fiber extends at least between the distal and proximal ends of the guide wire. The insulating coating is around an outside diameter of the guide wire, and is applied such that the distal ends of the guide wire and optical fiber are exposed.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS7126693B2Improve efficiencySimple configurationReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
X-ray reflectometry with small-angle scattering measurement
InactiveUS6895075B2Improve featuresUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionElevation angleDetector array
Apparatus for inspection of a sample includes a radiation source and an array of detector elements arranged to receive radiation from the surface due to irradiation of an area of the surface by the radiation source. The array has a first operative configuration for resolving the received radiation along a first axis perpendicular to the surface, and a second operative configuration for resolving the received radiation along a second axis parallel to the surface. A signal processor processes the signal from the detector array in the two configurations so as to determine a reflectance of the surface as a function of elevation angle relative to the surface and a scattering profile of the surface as a function of azimuthal angle in a plane of the surface.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
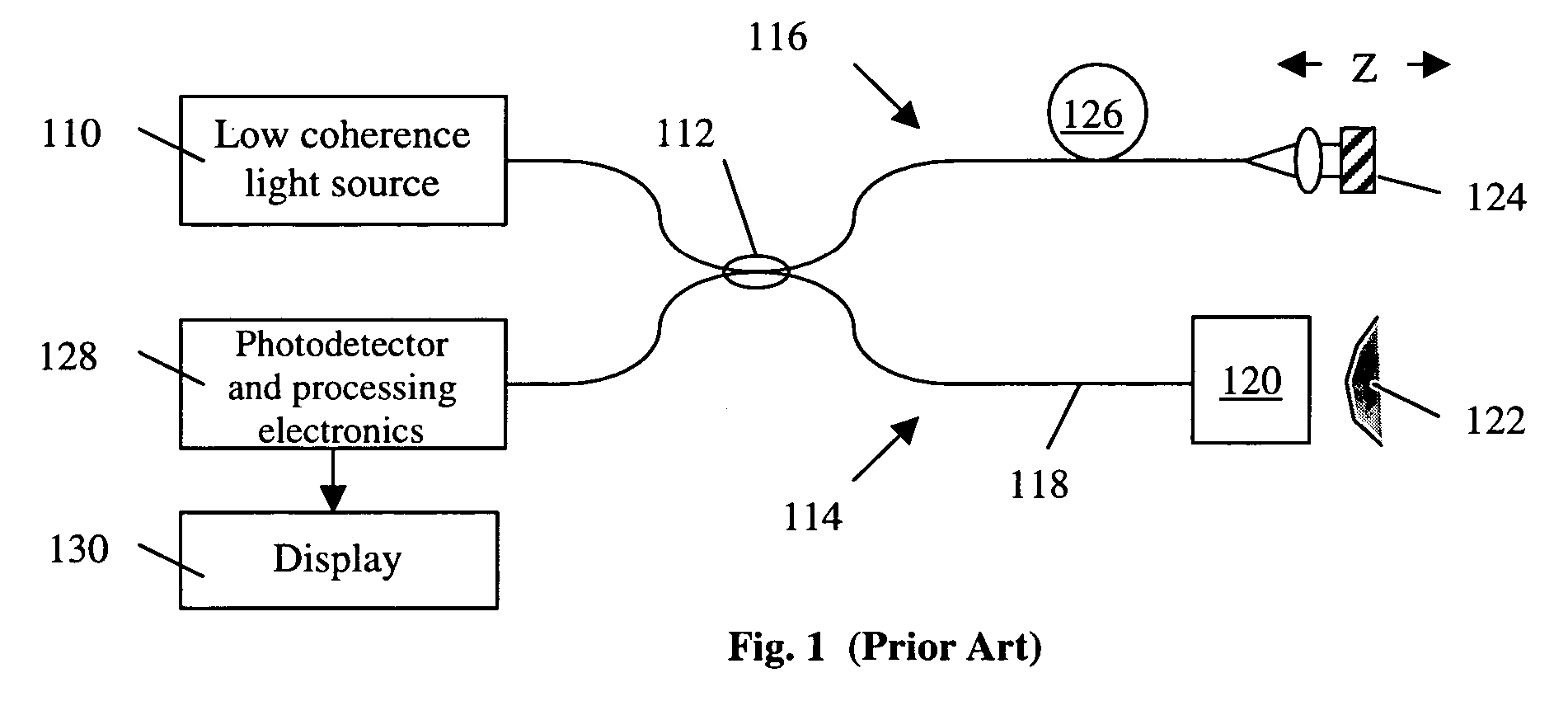
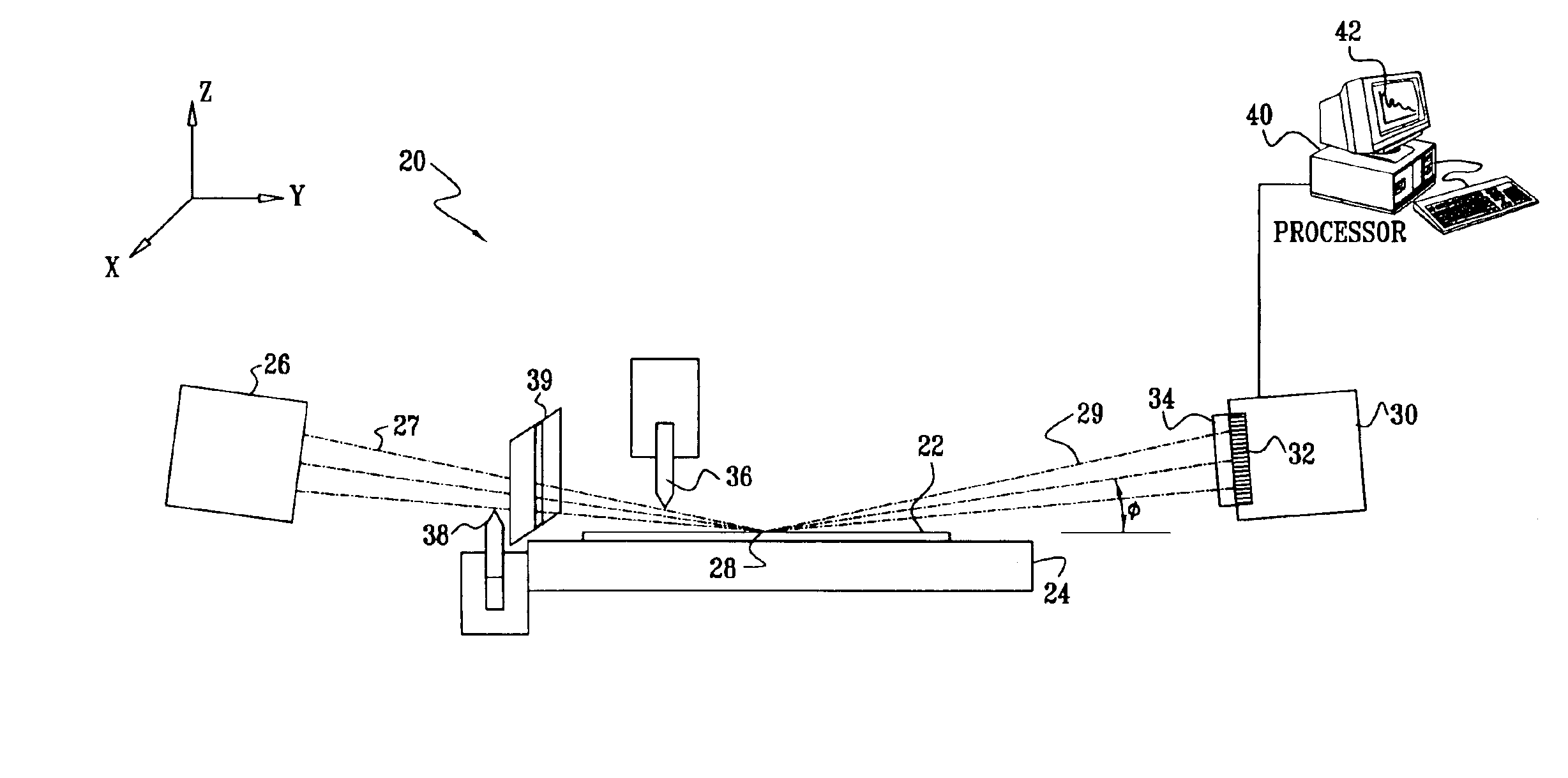
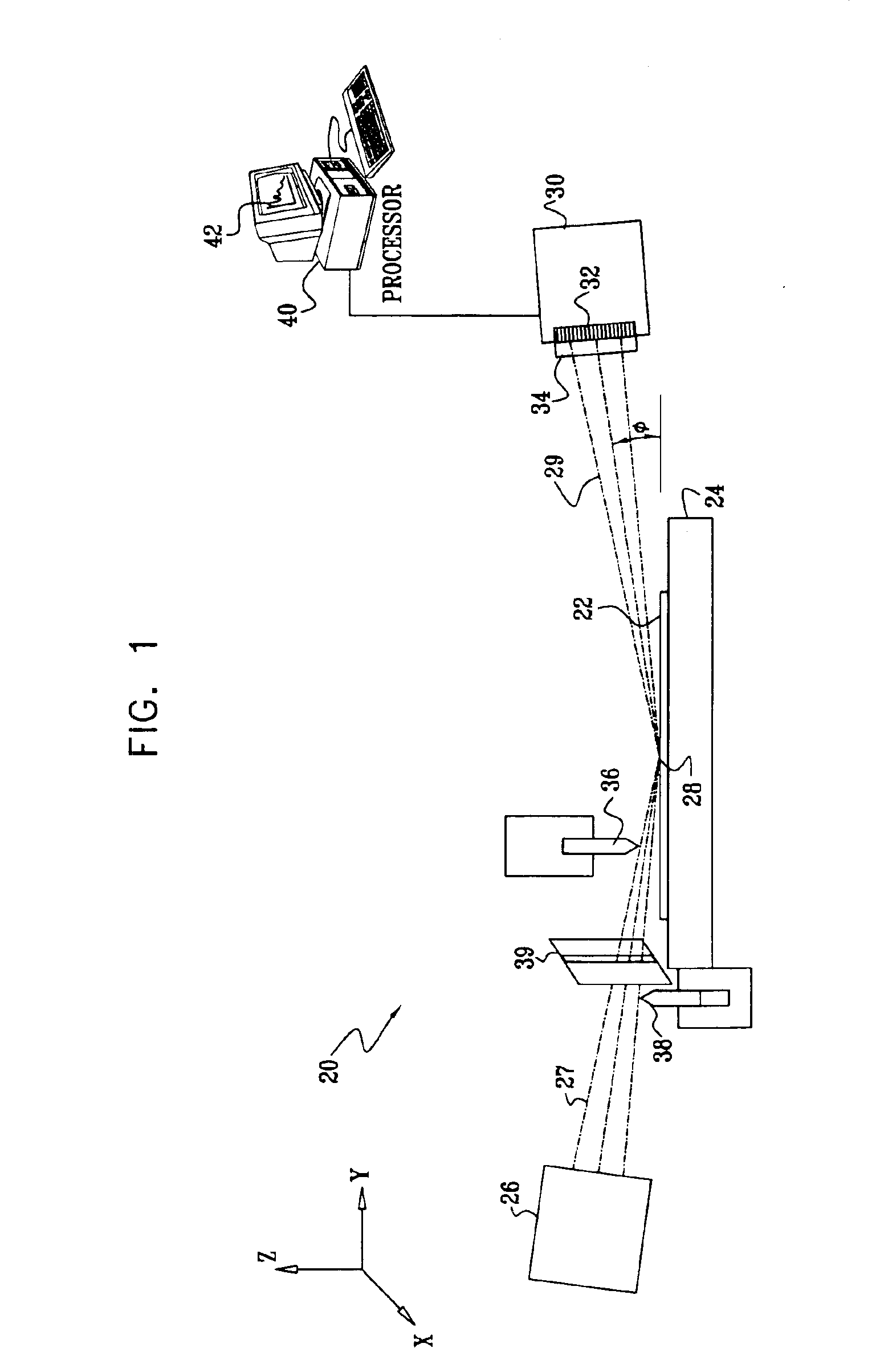
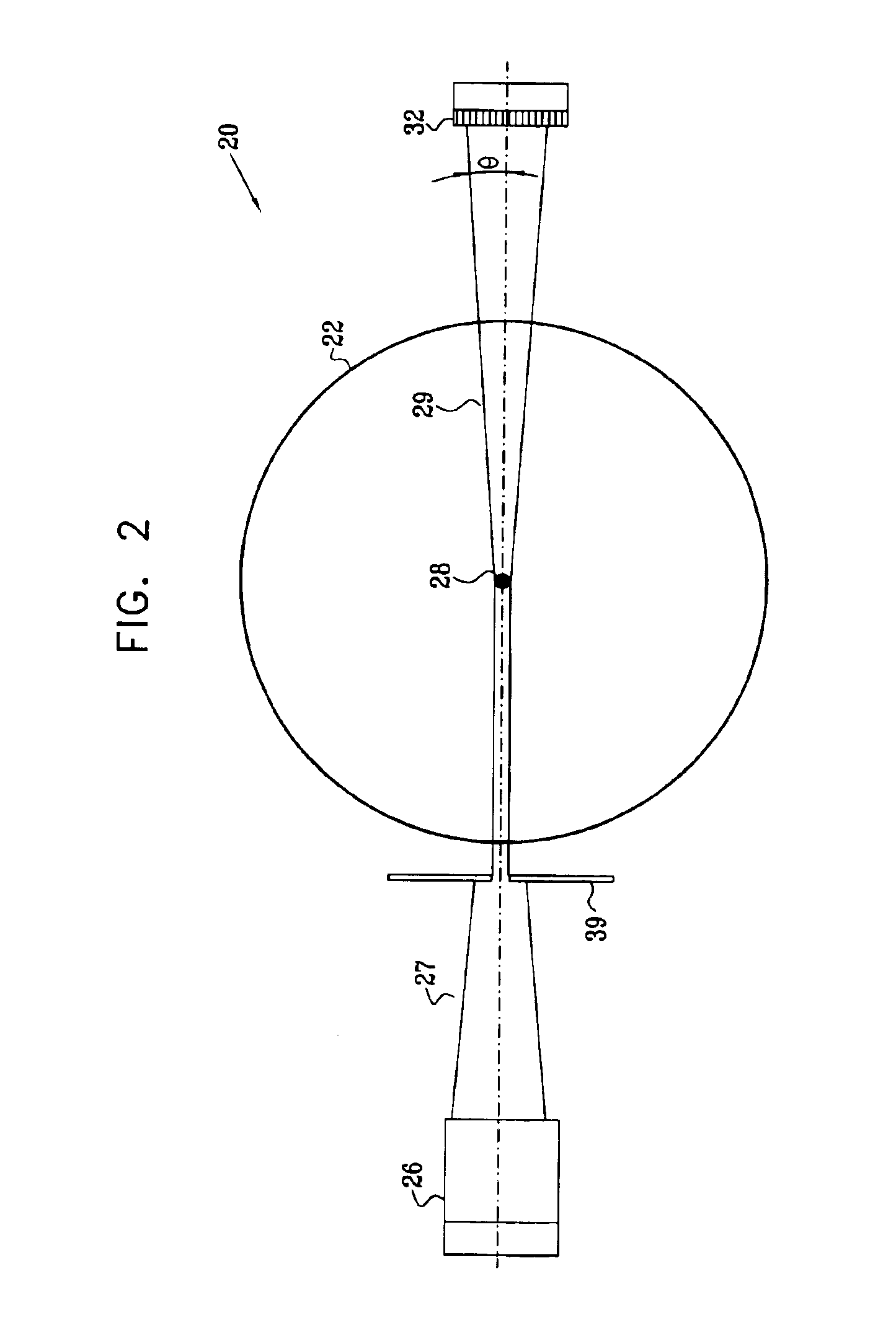
Method and apparatus for measuring optical reflectivity and imaging through a scattering medium
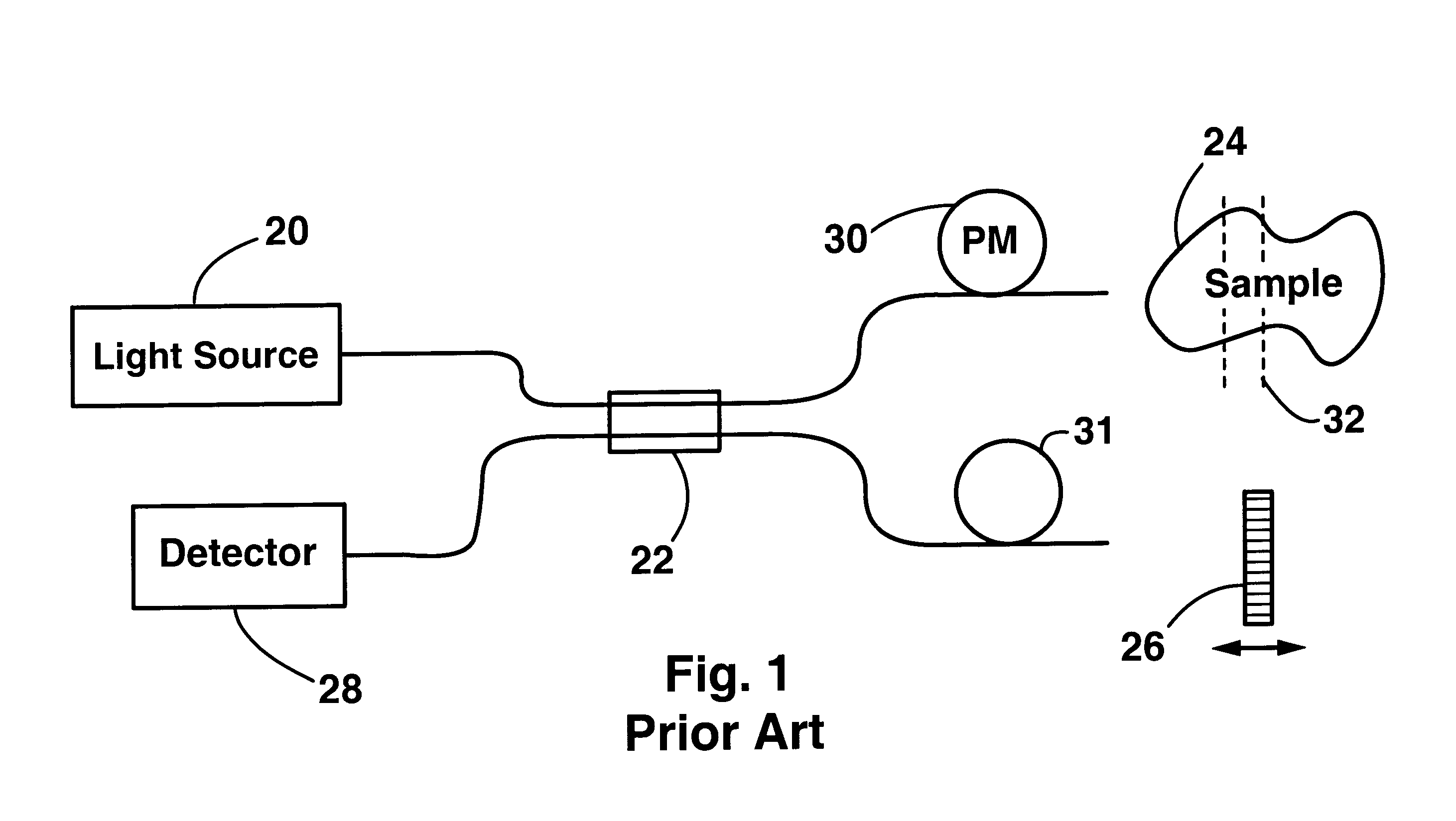
InactiveUS6201608B1Short data acquisition timeImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
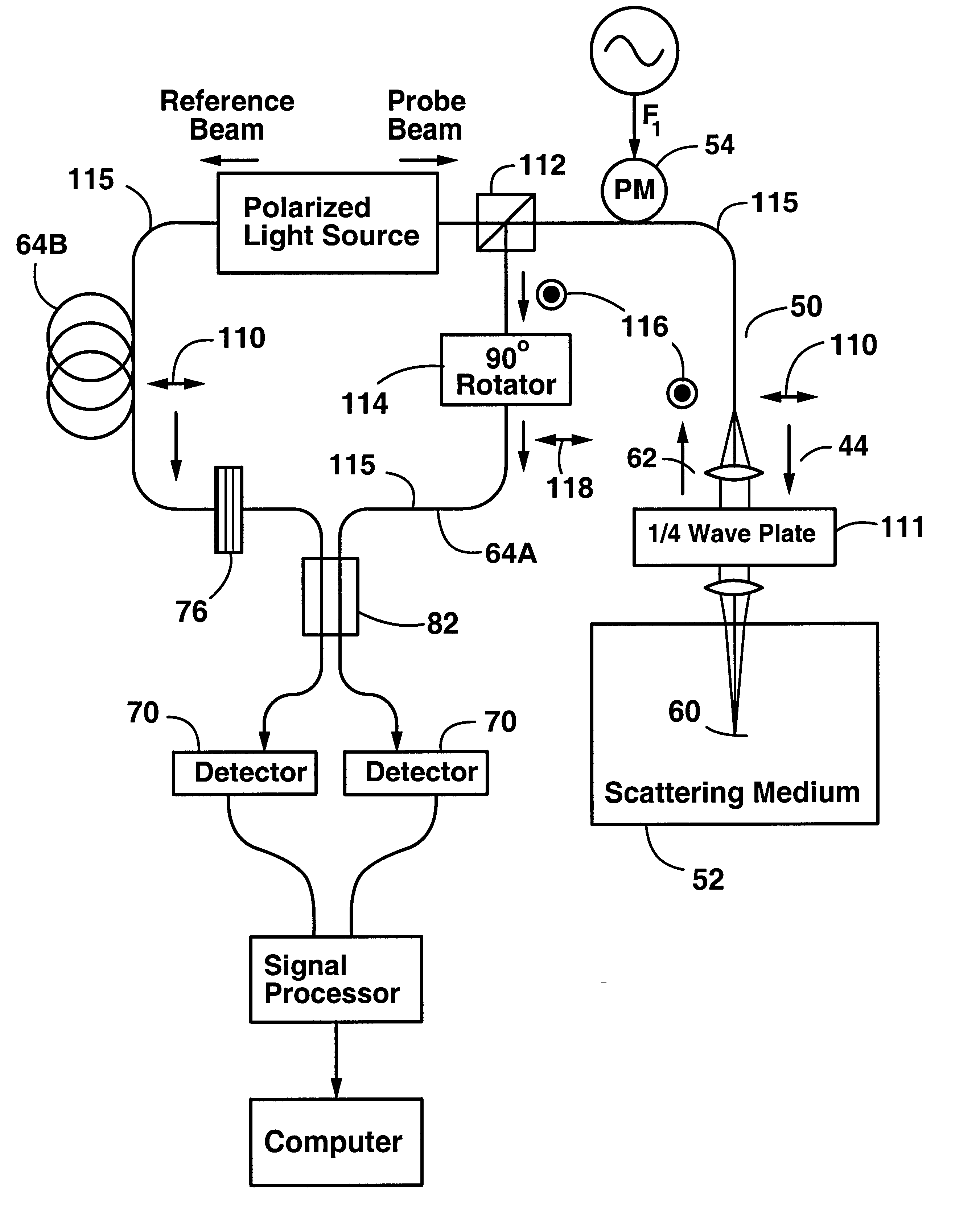
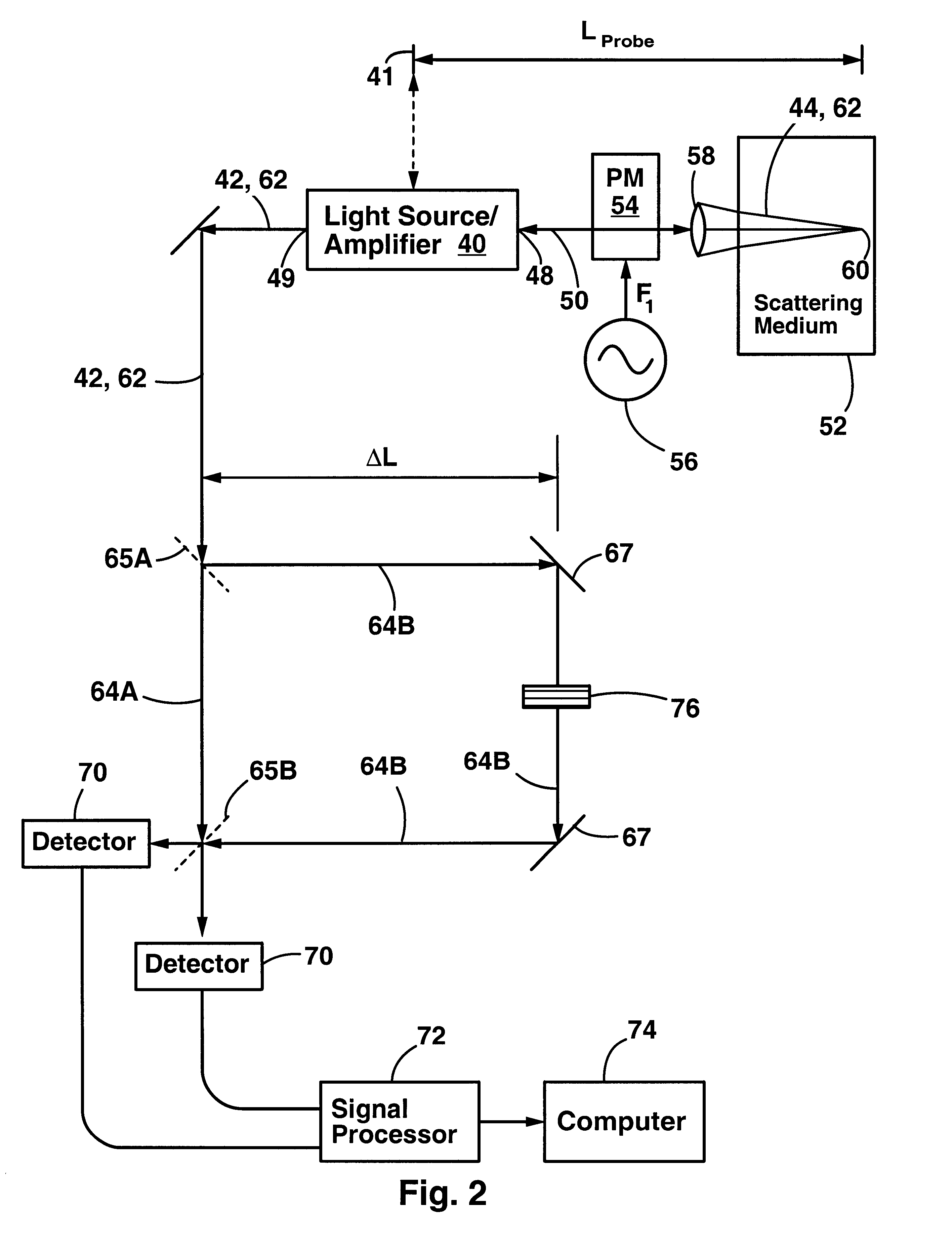
An apparatus and method for performing optical coherence domain reflectometry. The apparatus preferably includes a single output light source to illuminate a sample with a probe beam and to provide a reference beam. The reference beam is routed into a long arm of an interferometer by a polarizing beamsplitter. A reflected beam is collected from the sample. A 90.degree. double pass polarization rotation element located between the light source and the sample renders the polarizations of the probe beam and reflected beam orthogonal. The polarizing beamsplitter routes the reflected beam into a short arm of the interferometer. The interferometer combines the reference beam and the reflected beam such that coherent interference occurs between the beams. The apparatus ensures that all of the reflected beam contributes to the interference, resulting in a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:OPTICAL BIOPSY TECH
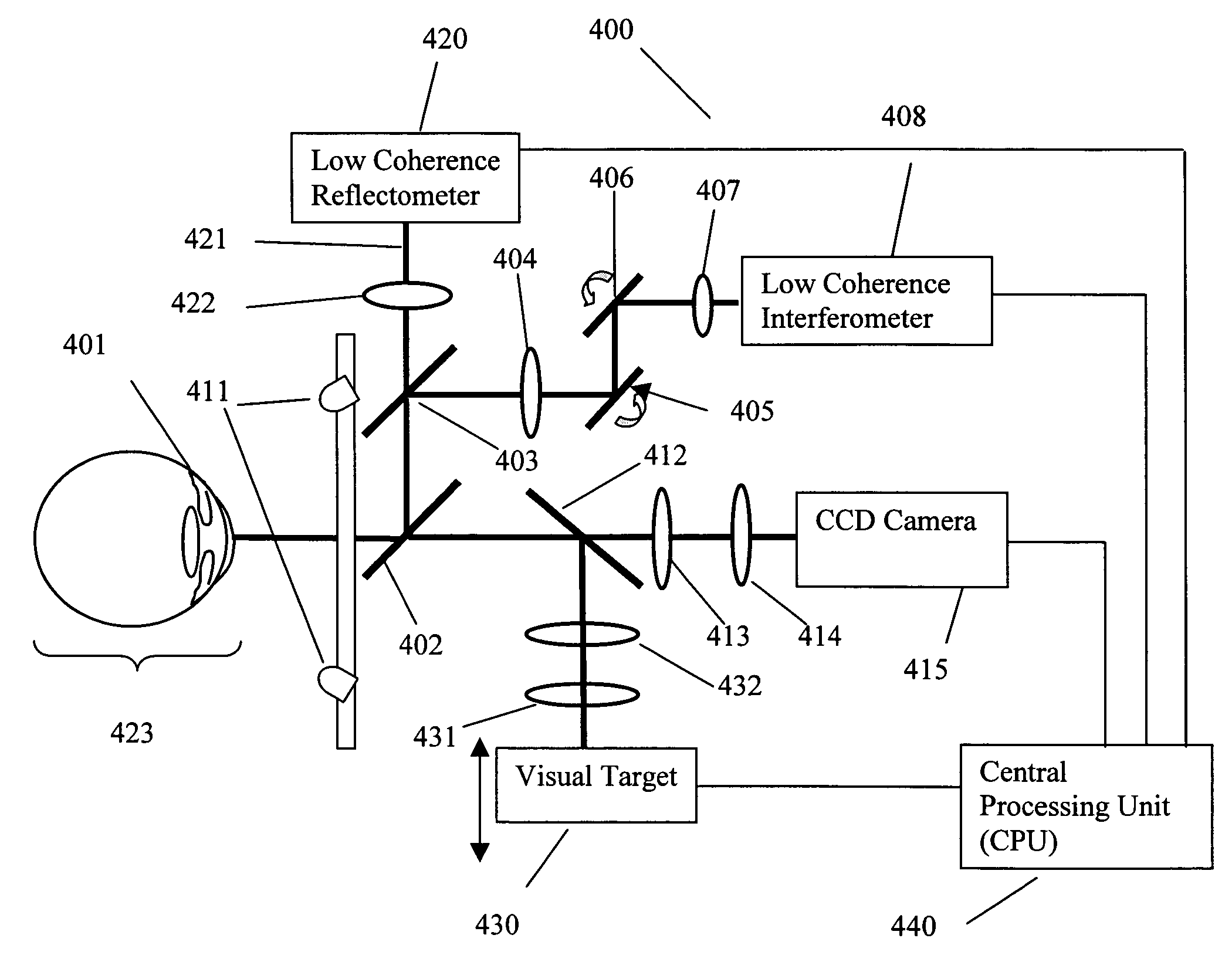
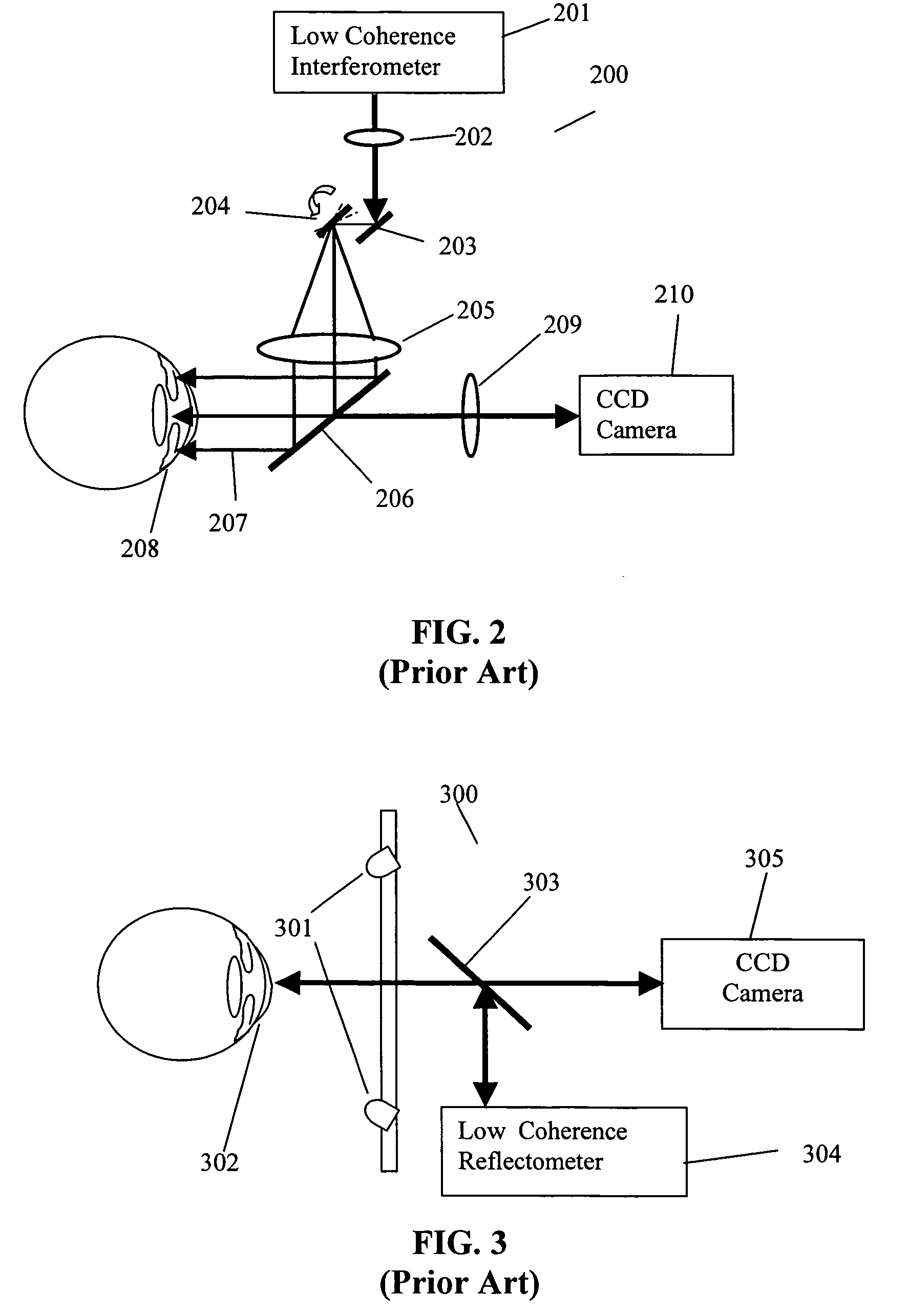
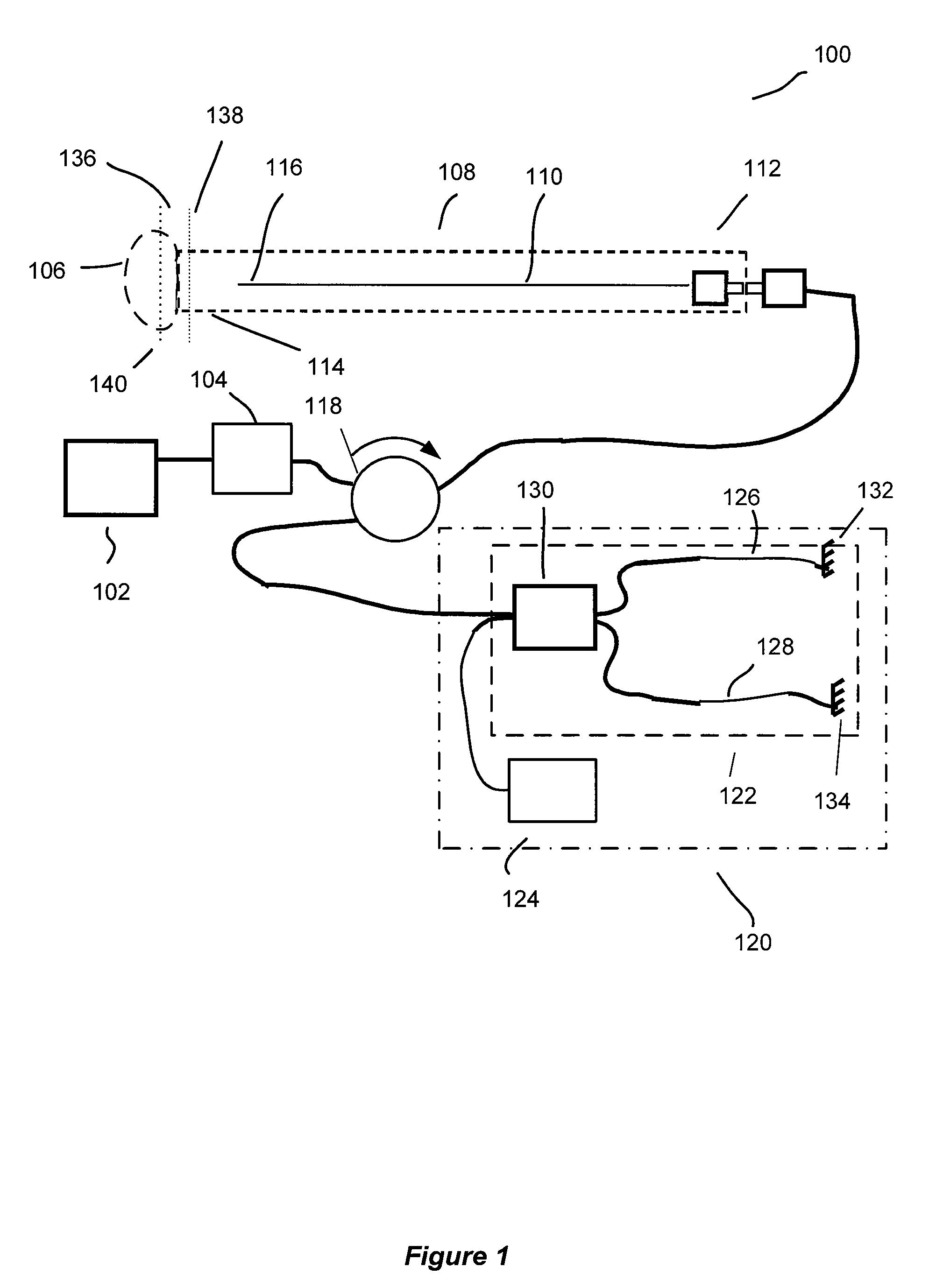
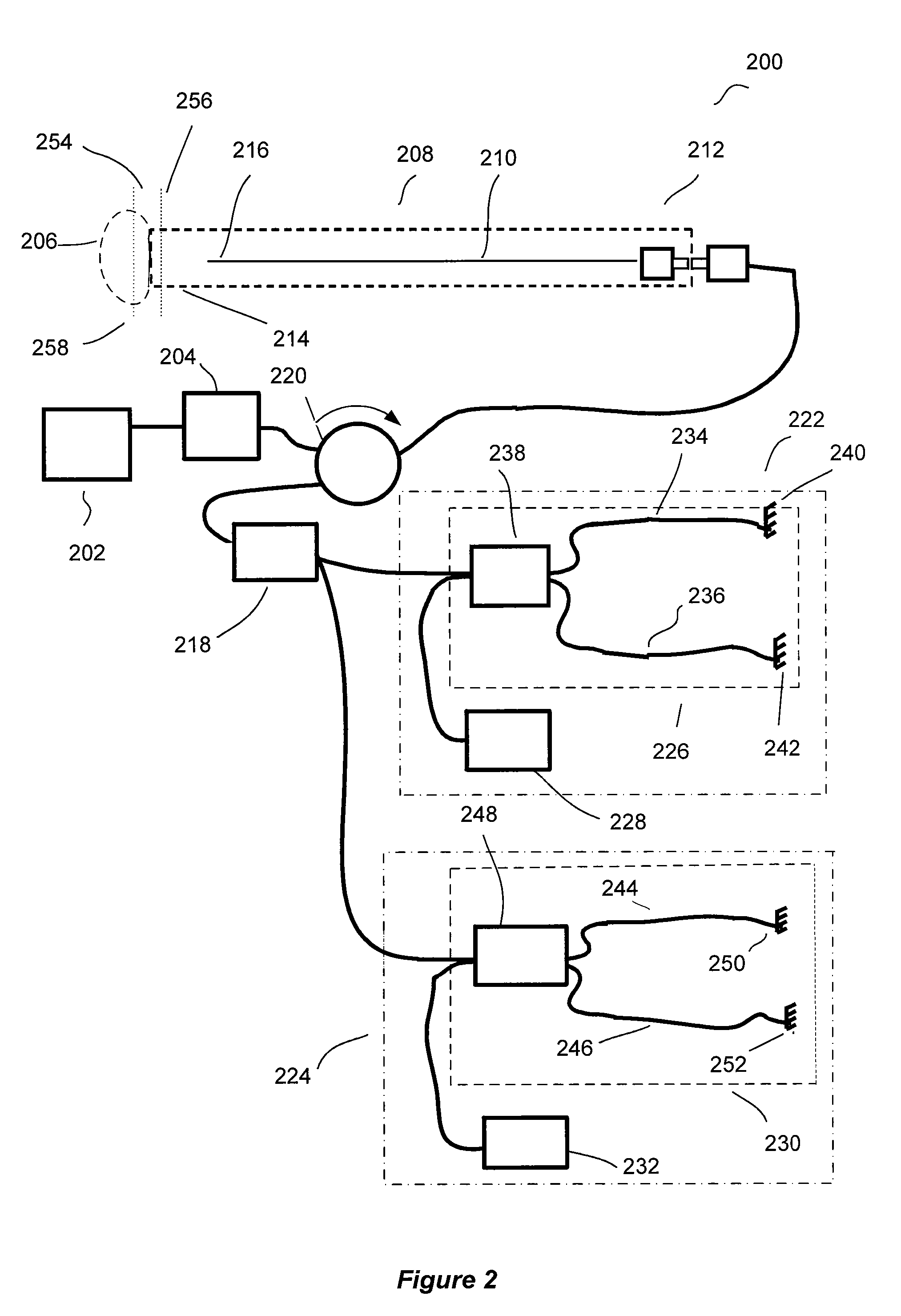
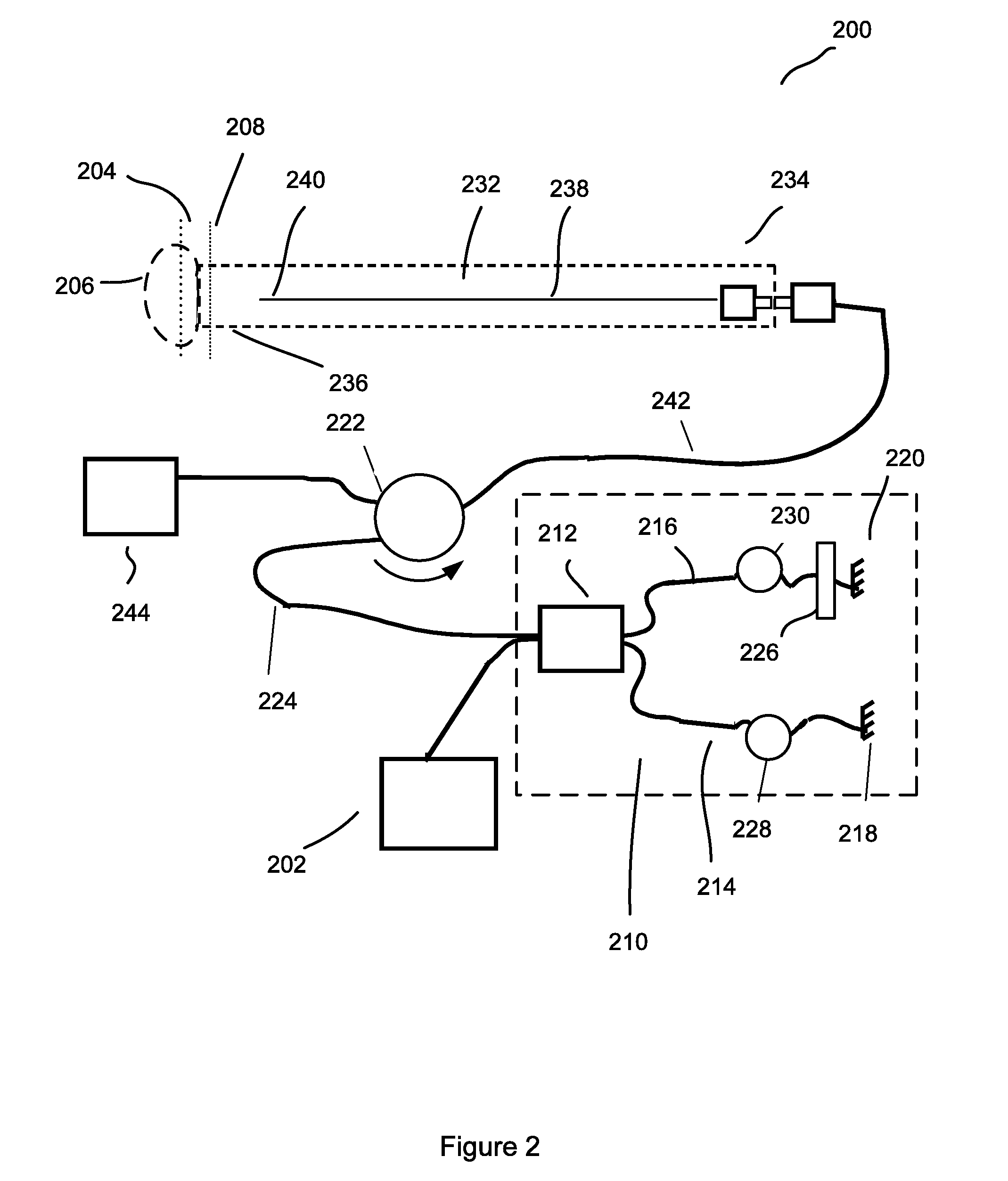
Optical apparatus and methods for performing eye examinations
An eye examination system is presented that obtains several parameters of the eye. A system according to some embodiments of the present invention include a keratometry system, a low coherence reflectometry system, and a low coherence interferometry system co-coupled to the eye. In some embodiments, the low coherence interferometry system can provide interferometric tomography data. A processor can be coupled to receive data from the keratometry system, the low coherence reflectometry system, and the low coherence interferometry system and calculate at least one parameter of the eye from that data.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
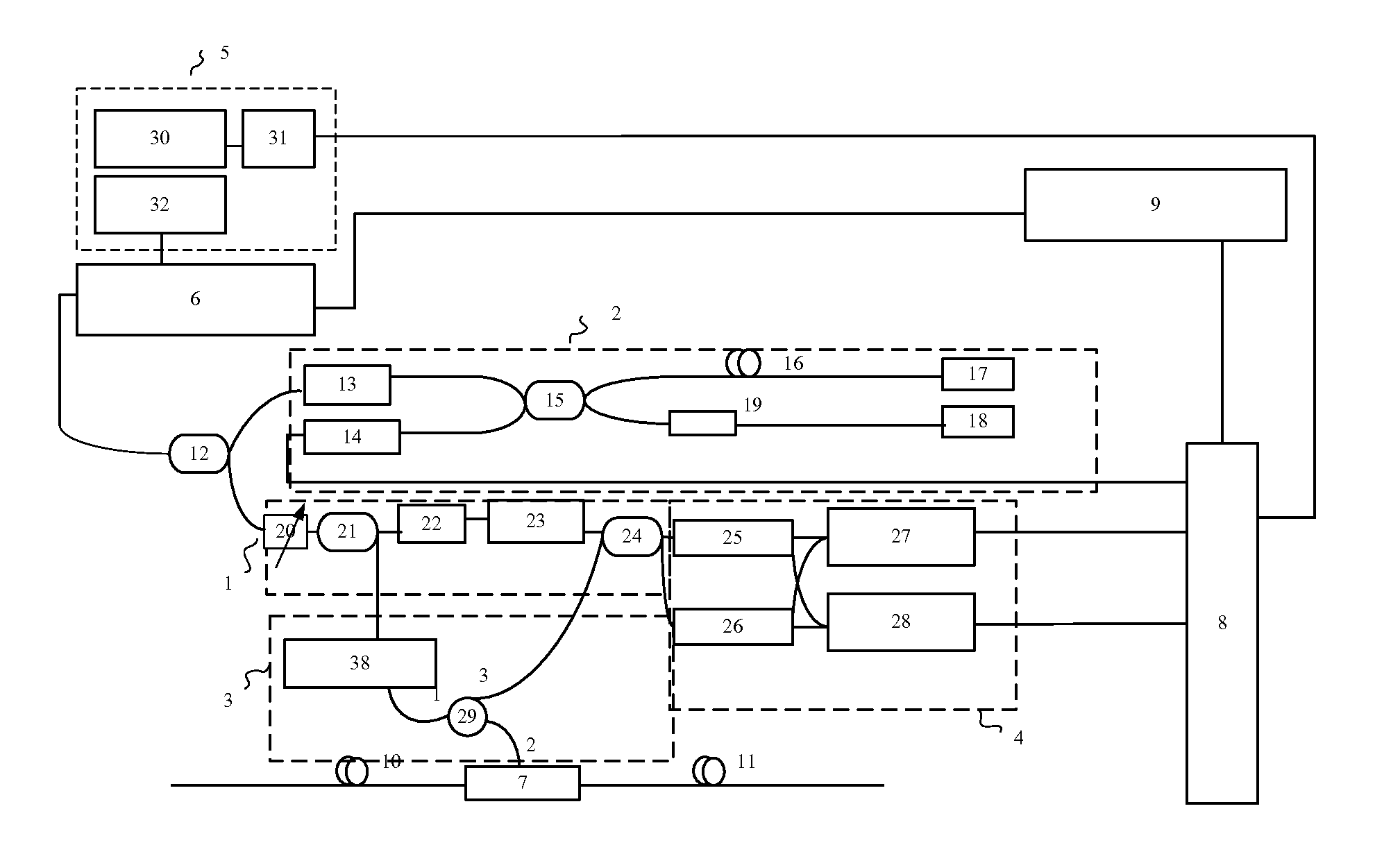
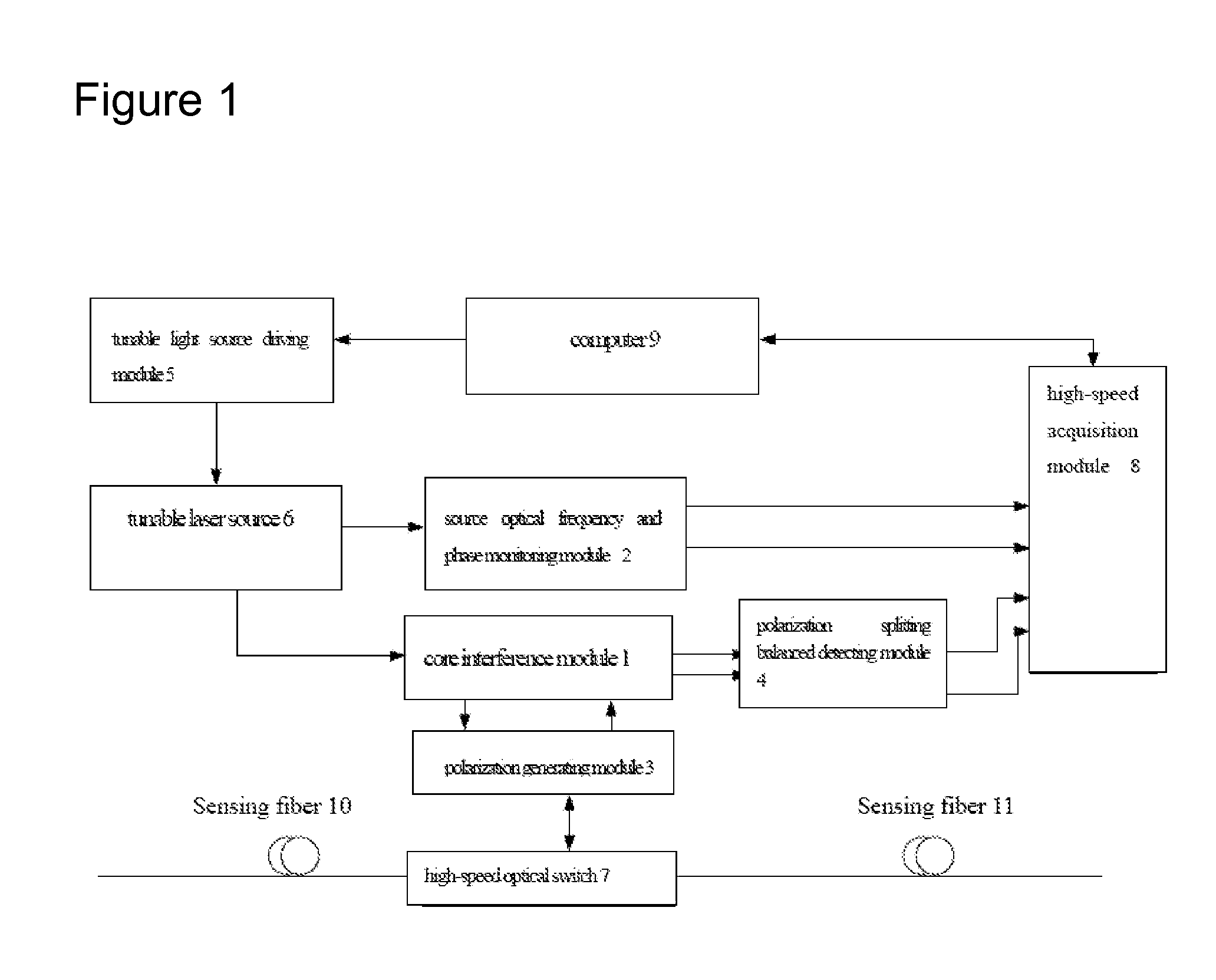
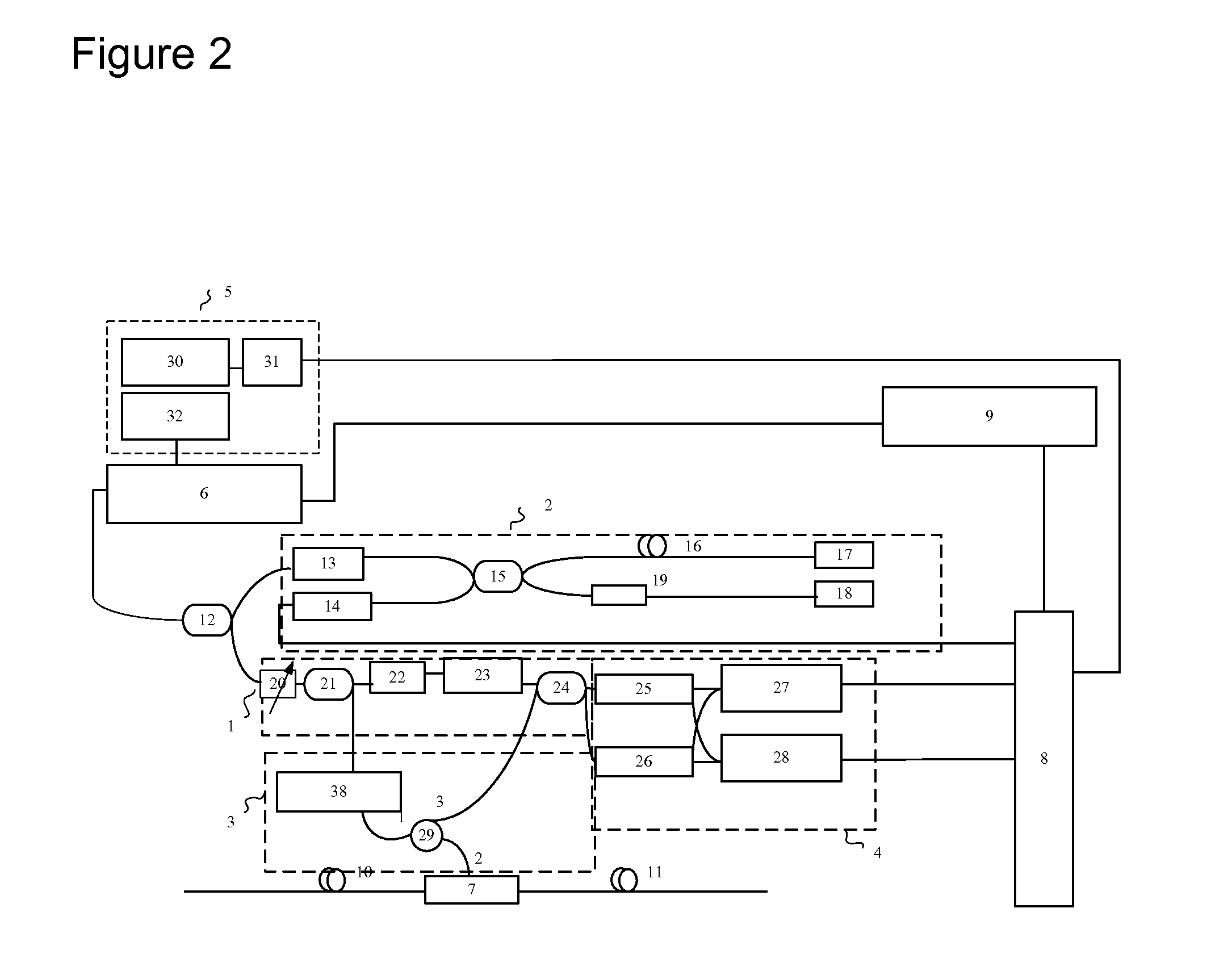
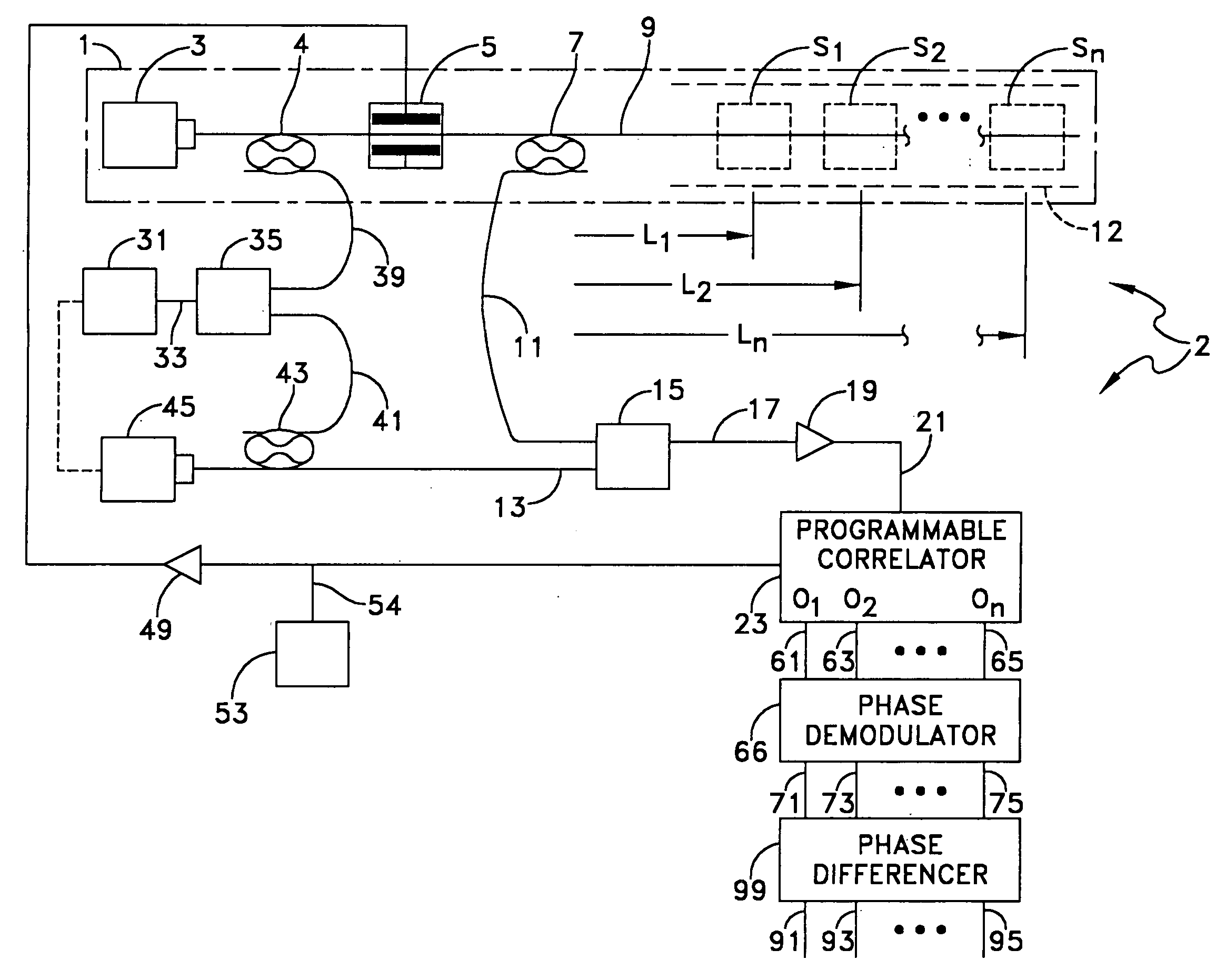
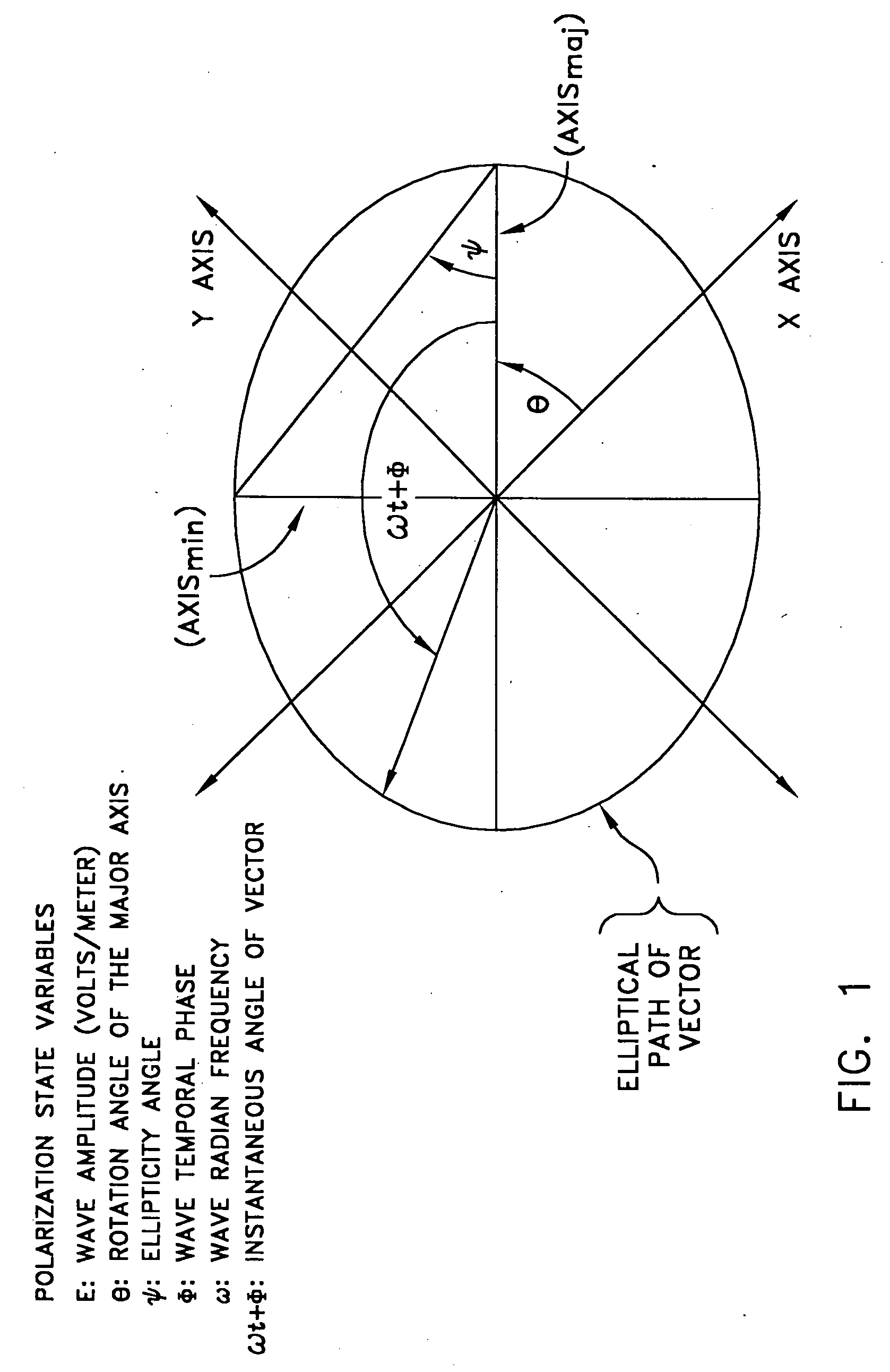
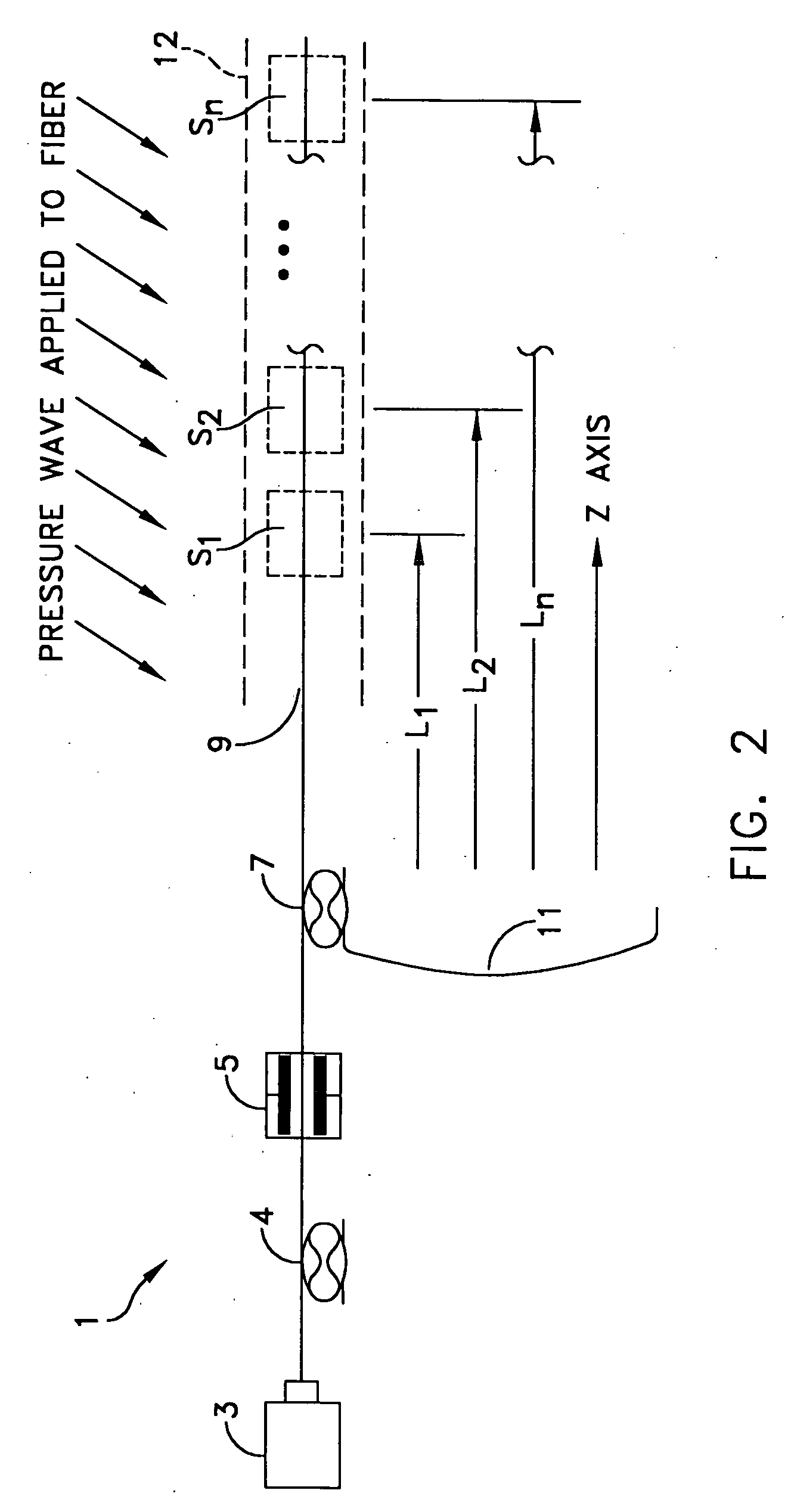
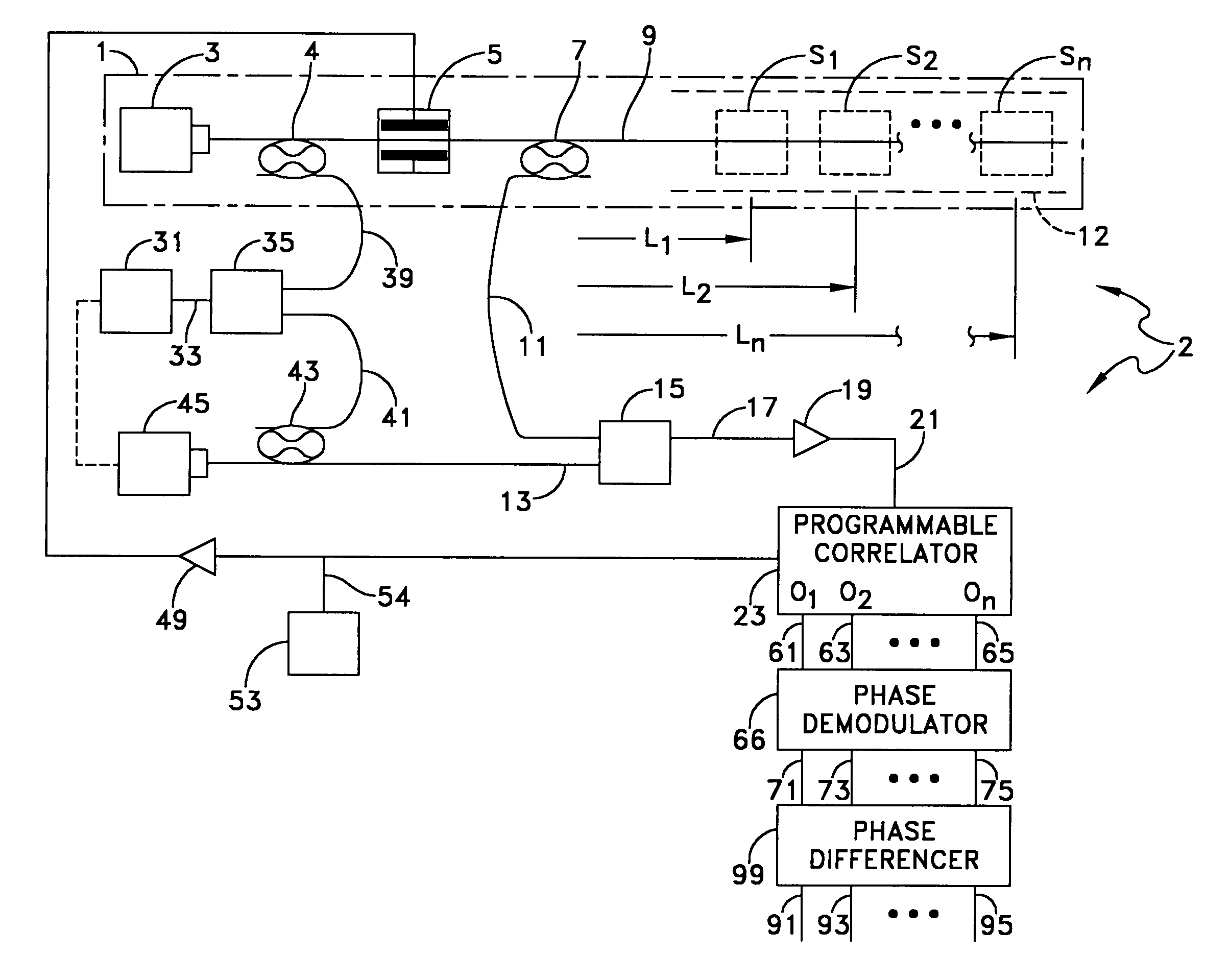
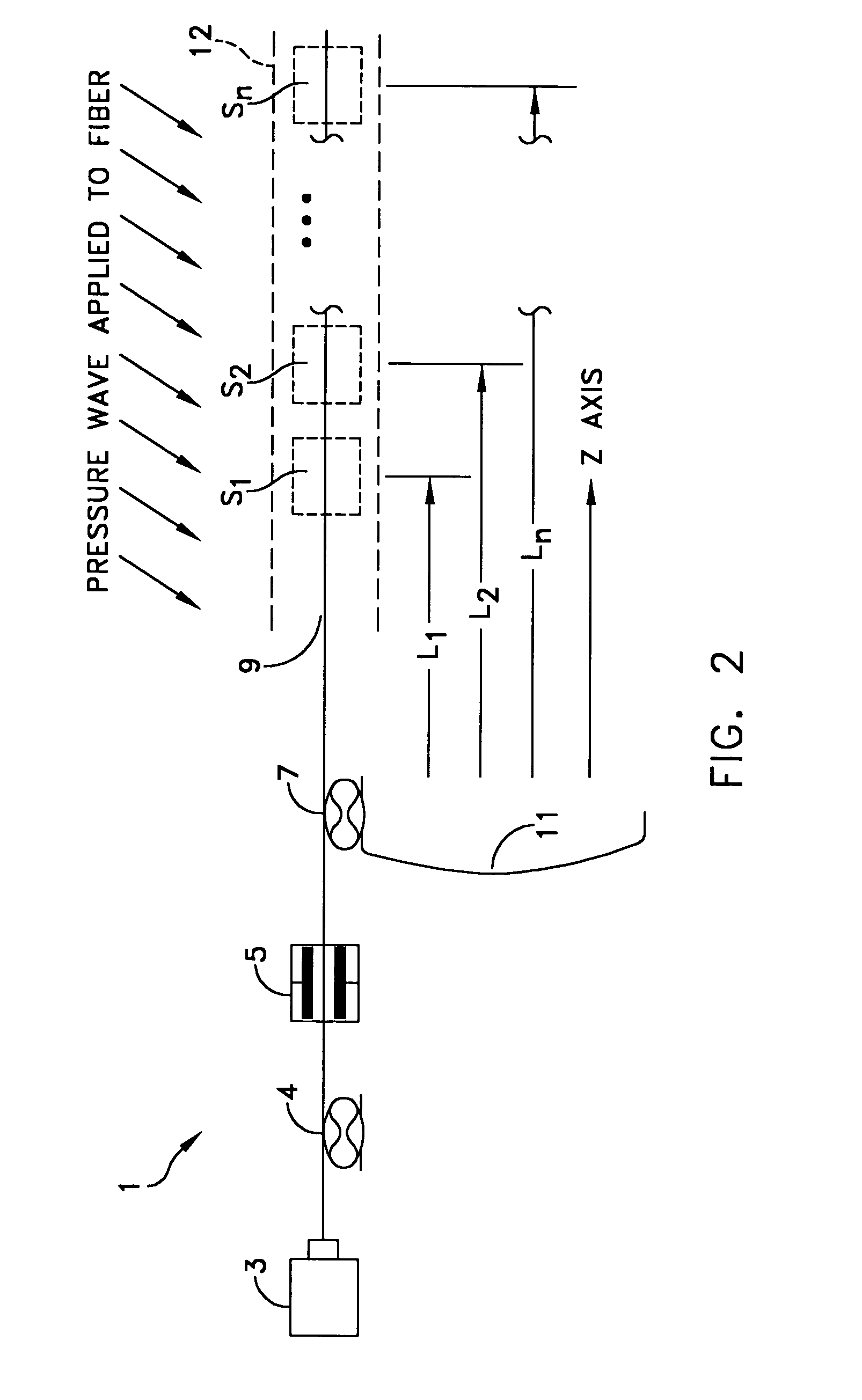
Distributed disturbance sensing device and the related demodulation method based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry
ActiveUS20140176937A1Long test distanceImprove spatial resolutionReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementInformation analysisS-matrix
This invention relates to a distributed disturbance sensing device based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry (OFDR) and the related demodulation thereof. The device, adopting OFDR, polarization controlling and analysis techniques, consists of a ultra-narrow linewidth tunable laser source module, polarization generating and polarization splitting balanced detecting module, laser source optical frequency and phase monitoring module, high-speed optical switch and so on to establish a large-scale and long-distance optical sensing network. The demodulation method consists of analysis the polarization information from sensing optical fiber, the method of suppressing and compensating of the non-linear optical frequency and the laser phase noise, super-resolution analyzing, advanced denoising method and the polarization information analysis method based on Jones and Mueller's matrices using distributed wave plate model of optical fiber.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Optical catheter configurations combining raman spectroscopy with optical fiber-based low coherence reflectometry
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for sample analysis, such as tissue analysis, that integrate high wavenumber (HW) Raman spectroscopy for chemical composition analysis and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide depth and morphological information. The invention also provides side-viewing optical probes that are based on a single double clad optical fiber for performing the combined HW Raman spectroscopy and OCT. Intravascular catheter embodiments and related vascular diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
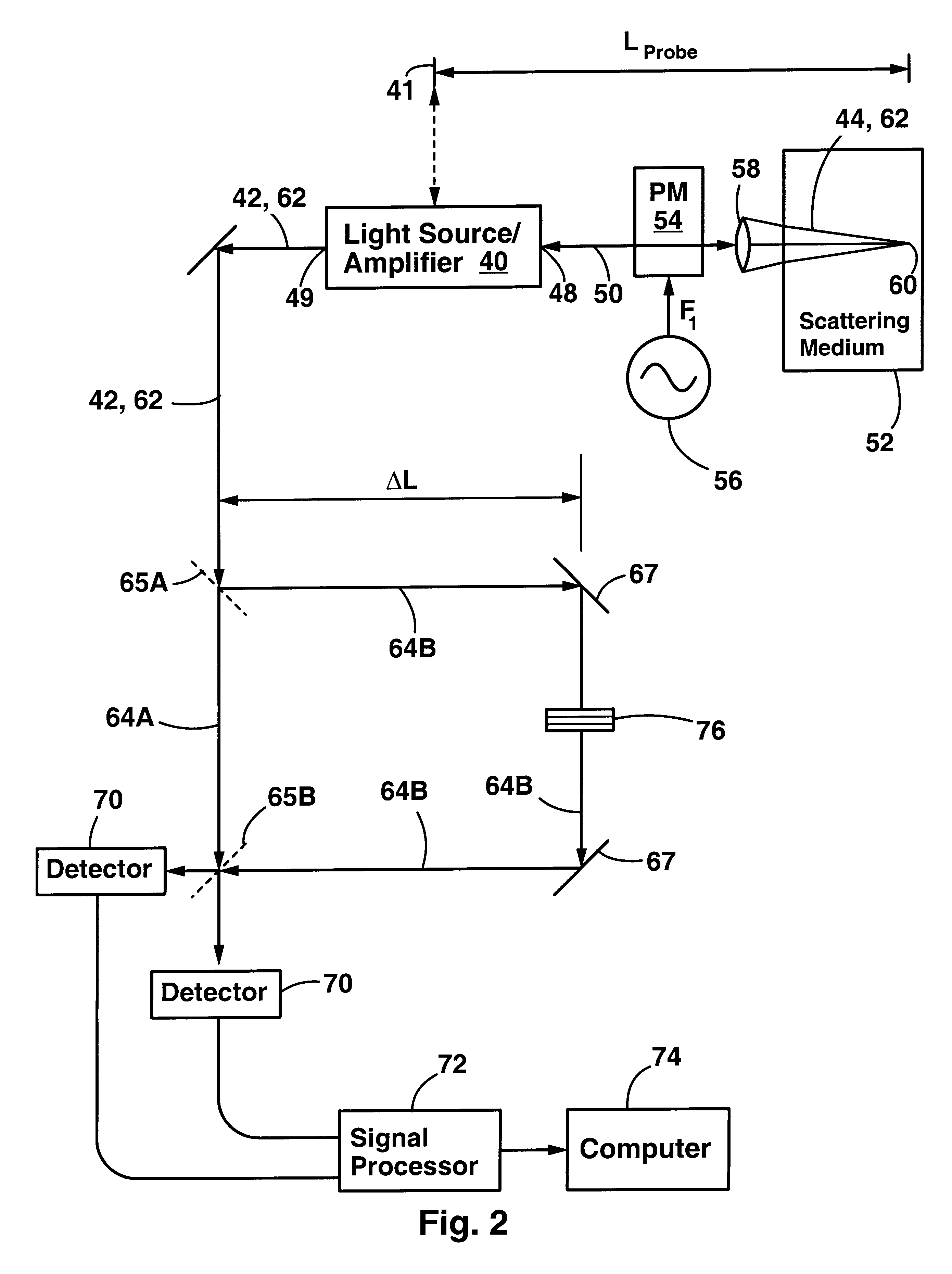
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
InactiveUS7428053B2Relieving the requirements to the spectral resolutionEliminate the problemInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical radiationData acquisition
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography devices include a portion of optical fiber with predetermined optical properties adapted for producing two eigen modes of the optical radiation propagating therethrough with a predetermined optical path length difference. The two replicas of the optical radiation outgoing from the portion of the optical fiber are then delivered to an associated sample by an optical fiber probe. The tip of the optical fiber serves as a reference reflector and also serves as a combining element that produces a combination optical radiation by combining an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from the reference reflector. The topology of the devices allows for registering a cross-polarized or a parallel-polarized component of the optical radiation reflected or backscattered from the associated sample. Having the optical path length difference for the two eigen modes of the optical radiation (which is an equivalent of an interferometer offset in previously known devices) differ from the reference offset in the devices of the present invention allows for relieving the requirements to the spectral resolution of the FD OCT engine and / or data acquisition and processing system, and substantially eliminates depth ambiguity problems.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Apparatus for measuring characteristics of thin film by means of two-dimensional detector and method of measuring the same
InactiveUS7286242B2Simple structurePhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansNon destructiveTwo dimensional detector
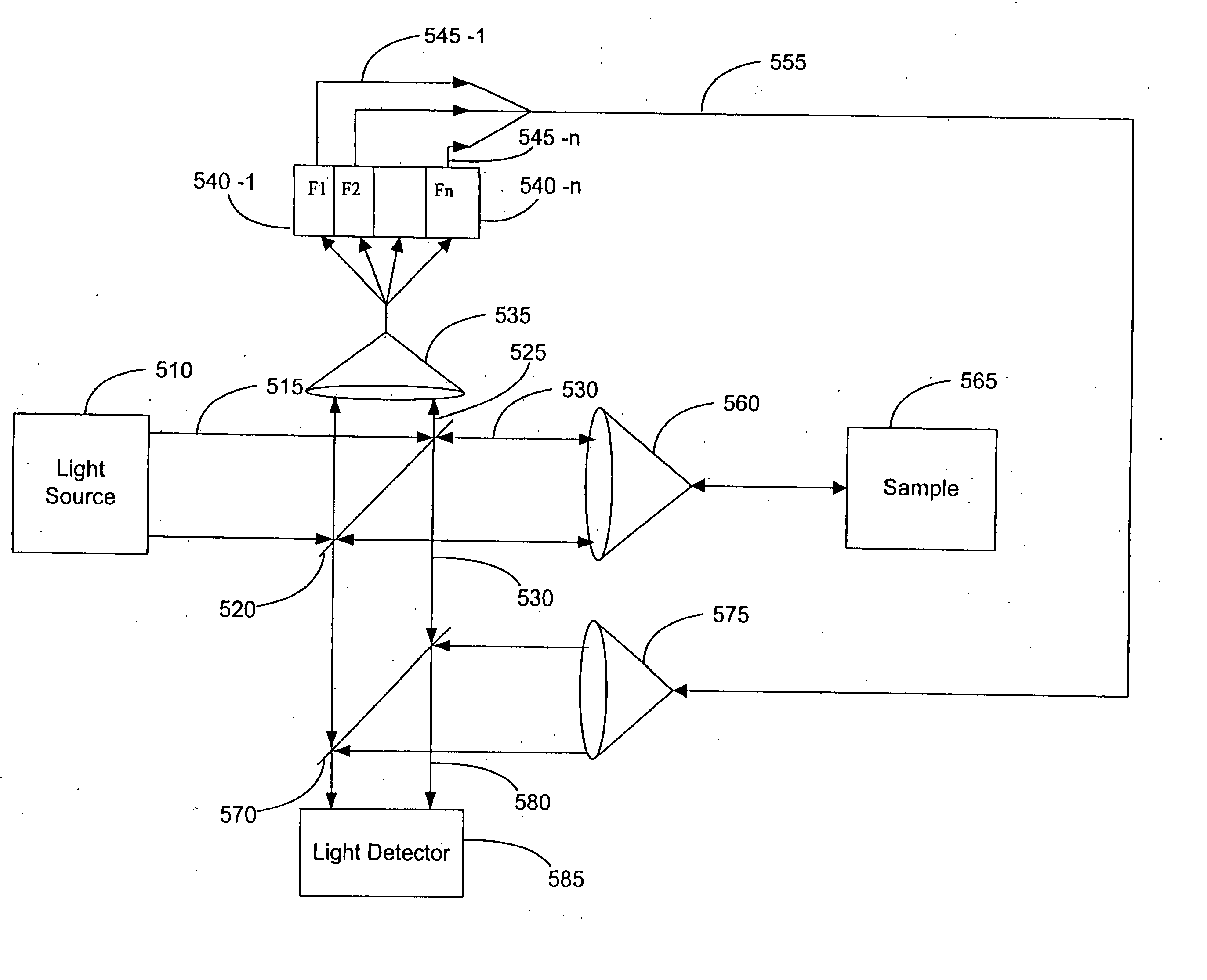
The present invention relates to a non-contact, non-destructive measuring apparatus that measures thickness profile and refractive index distribution of a single or multiple layers of thin films by means of the principle of reflectometry. According to the present invention, by employing more than one narrow band-pass optical filters and a two-dimensional array of CCD sensors, and by finding an optimal solution for the nonlinear functional relationship between the thickness of said thin film or thin films and the corresponding refractive indexes by using an iterative numerical computation method, said apparatus simultaneously measures local area-wise thickness profile and refractive index distribution among others of said a single layer or multiple layers of thin films on a substrate.
Owner:HB SOLUTION CO LTD
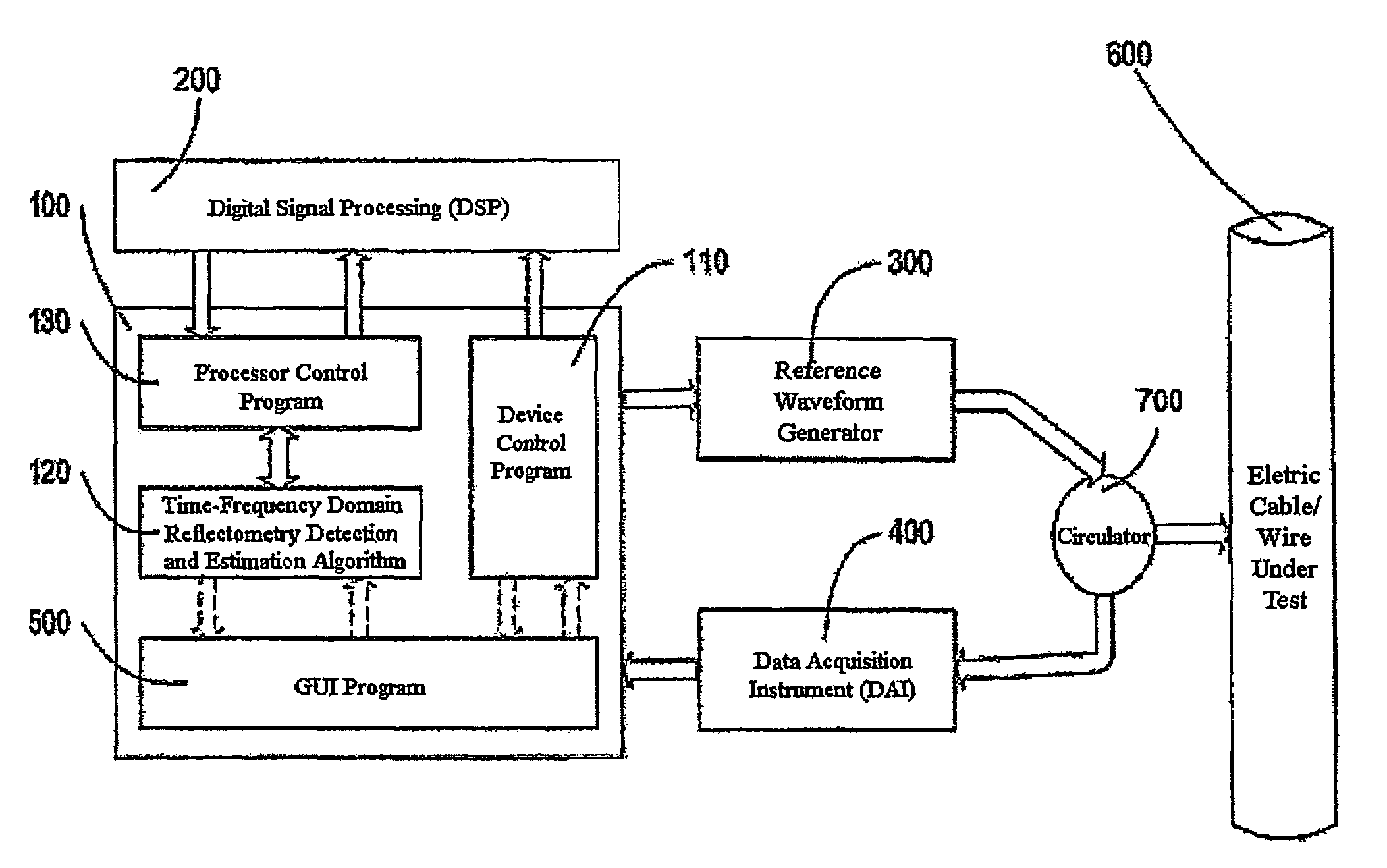
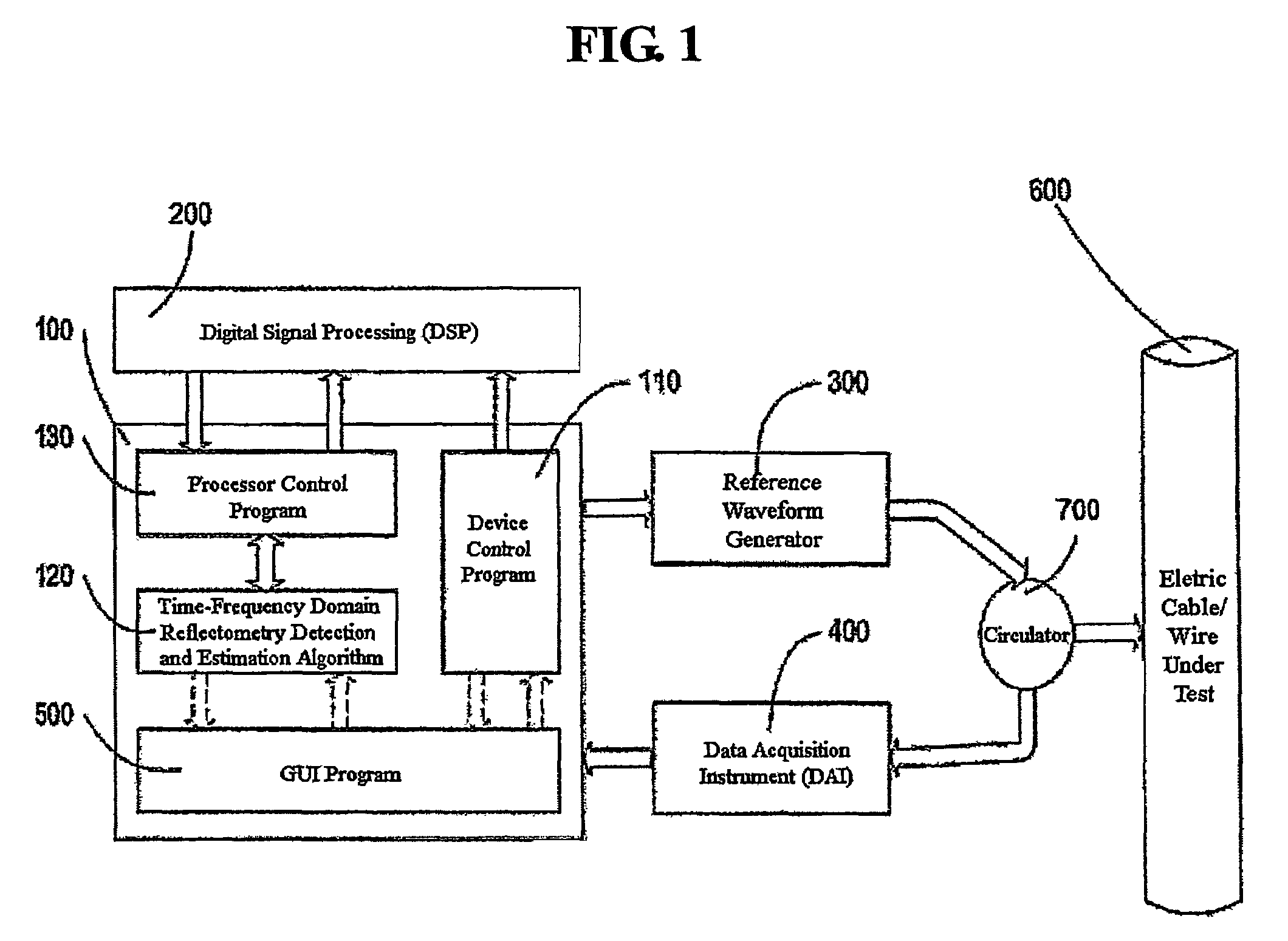
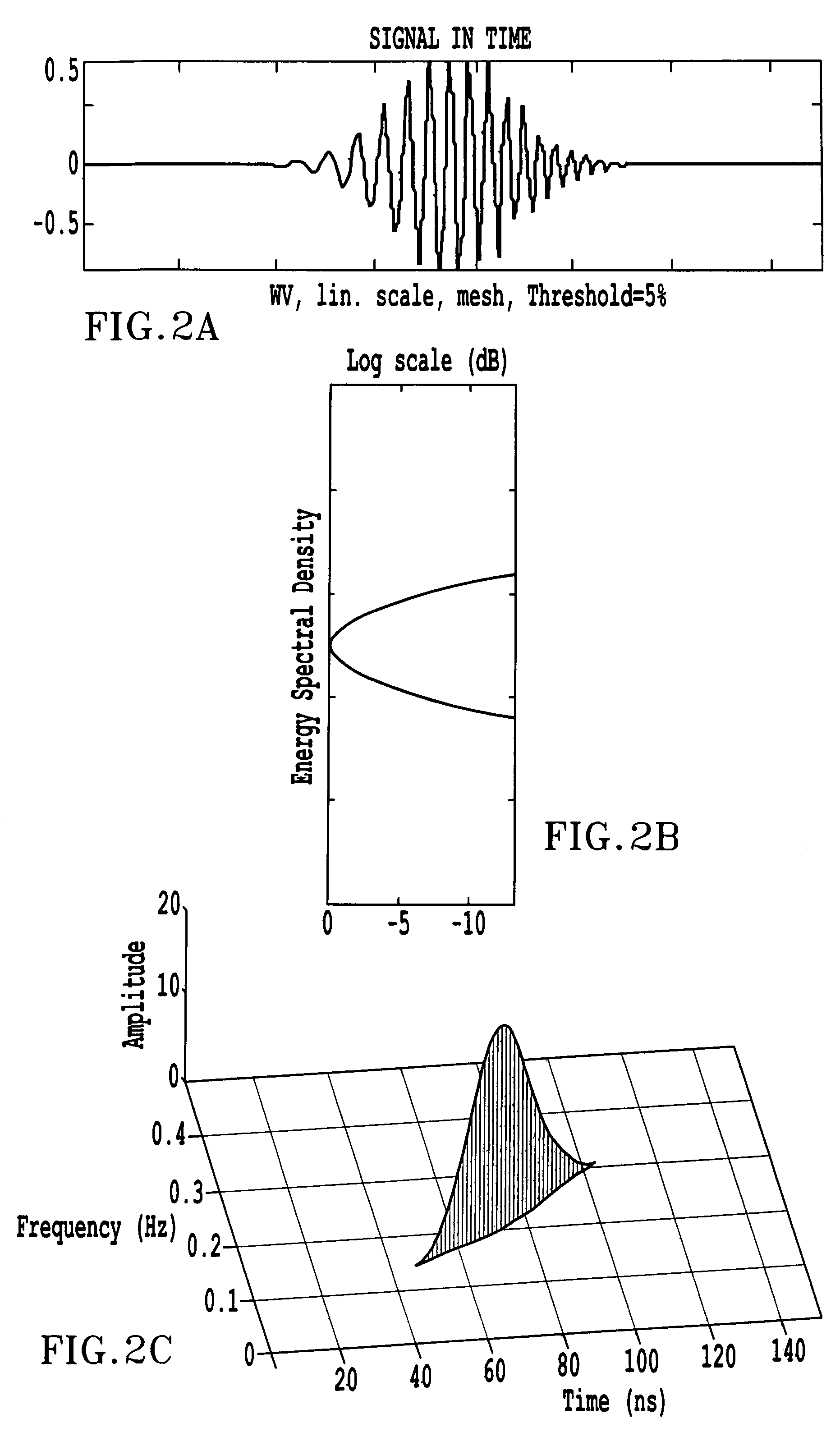
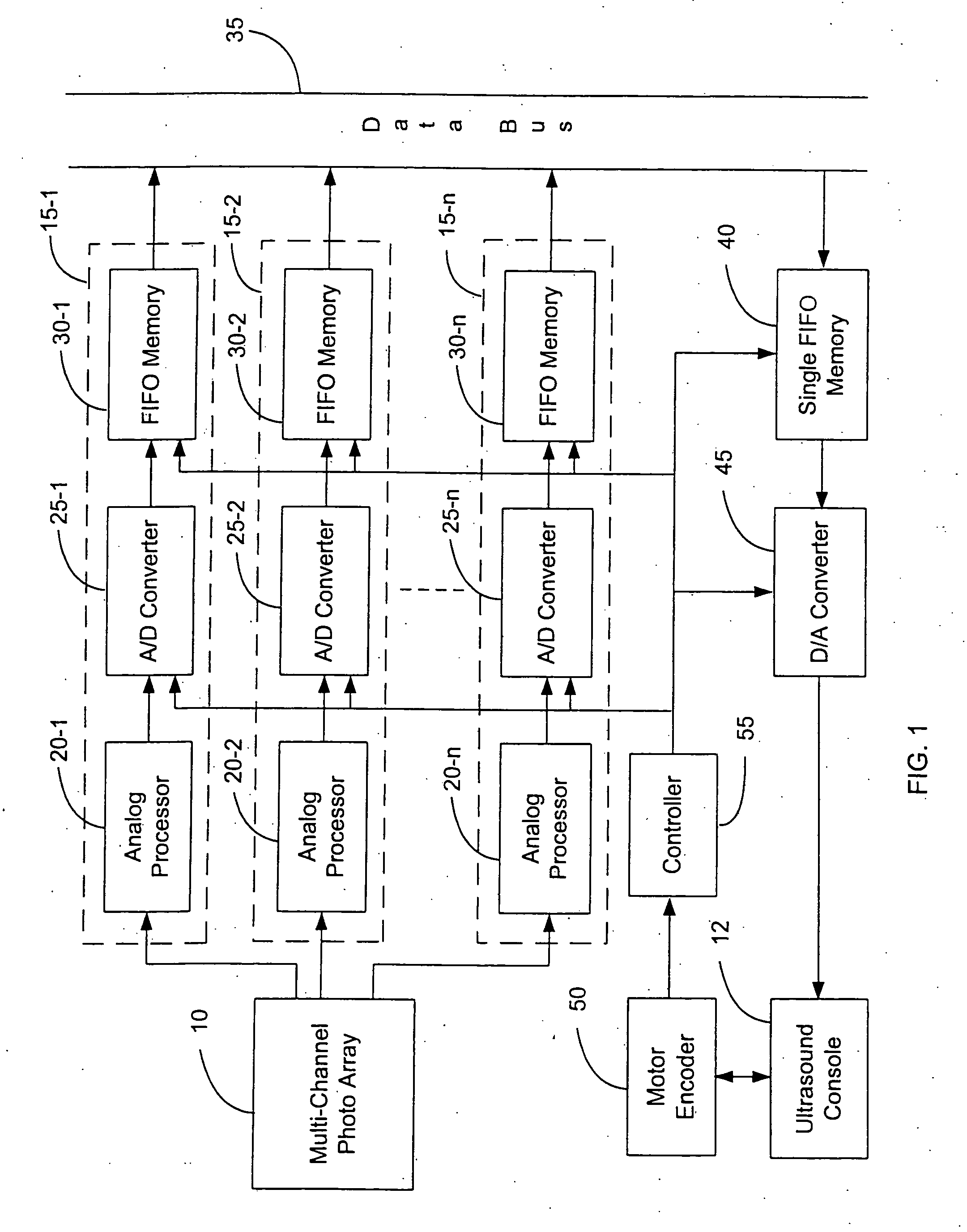
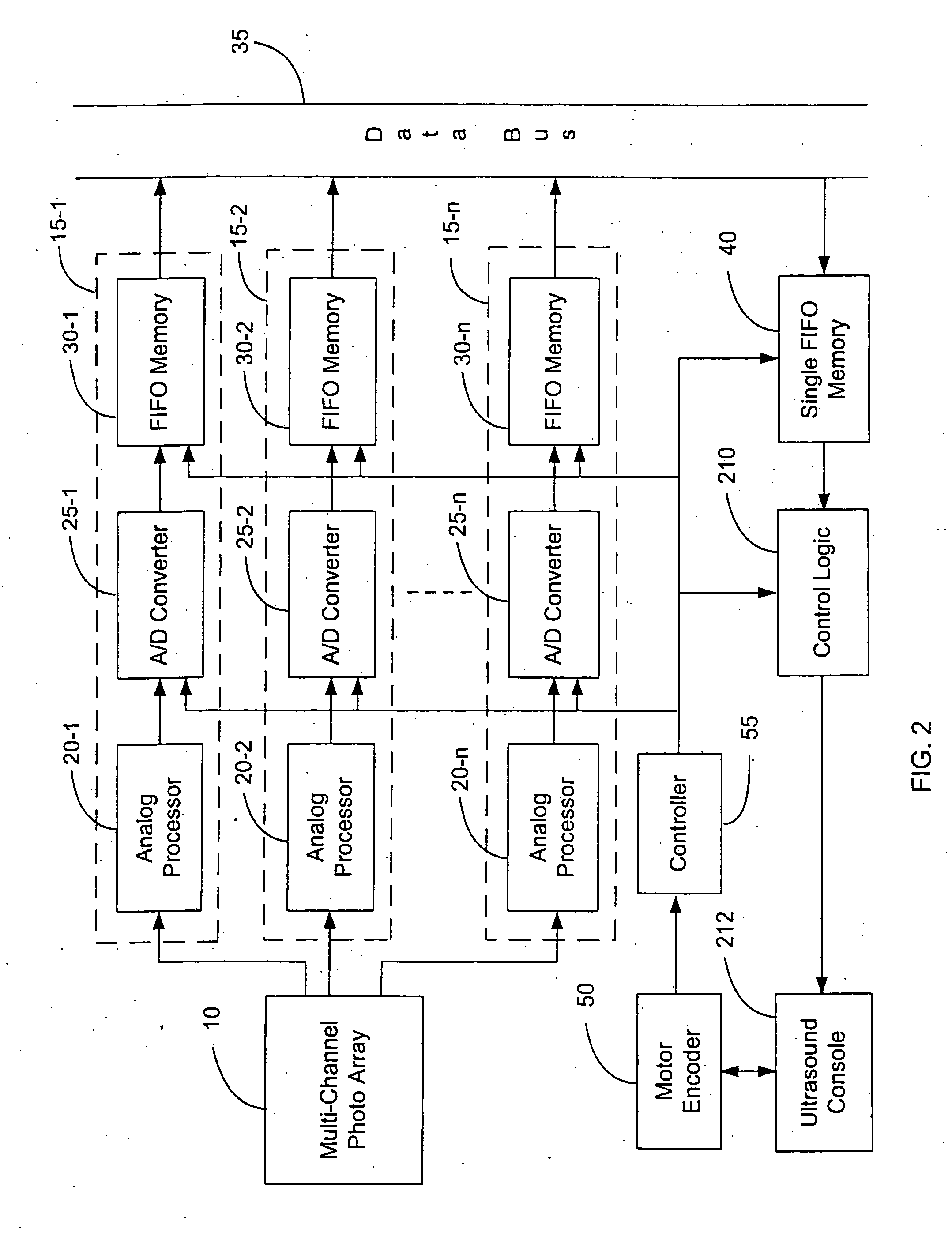
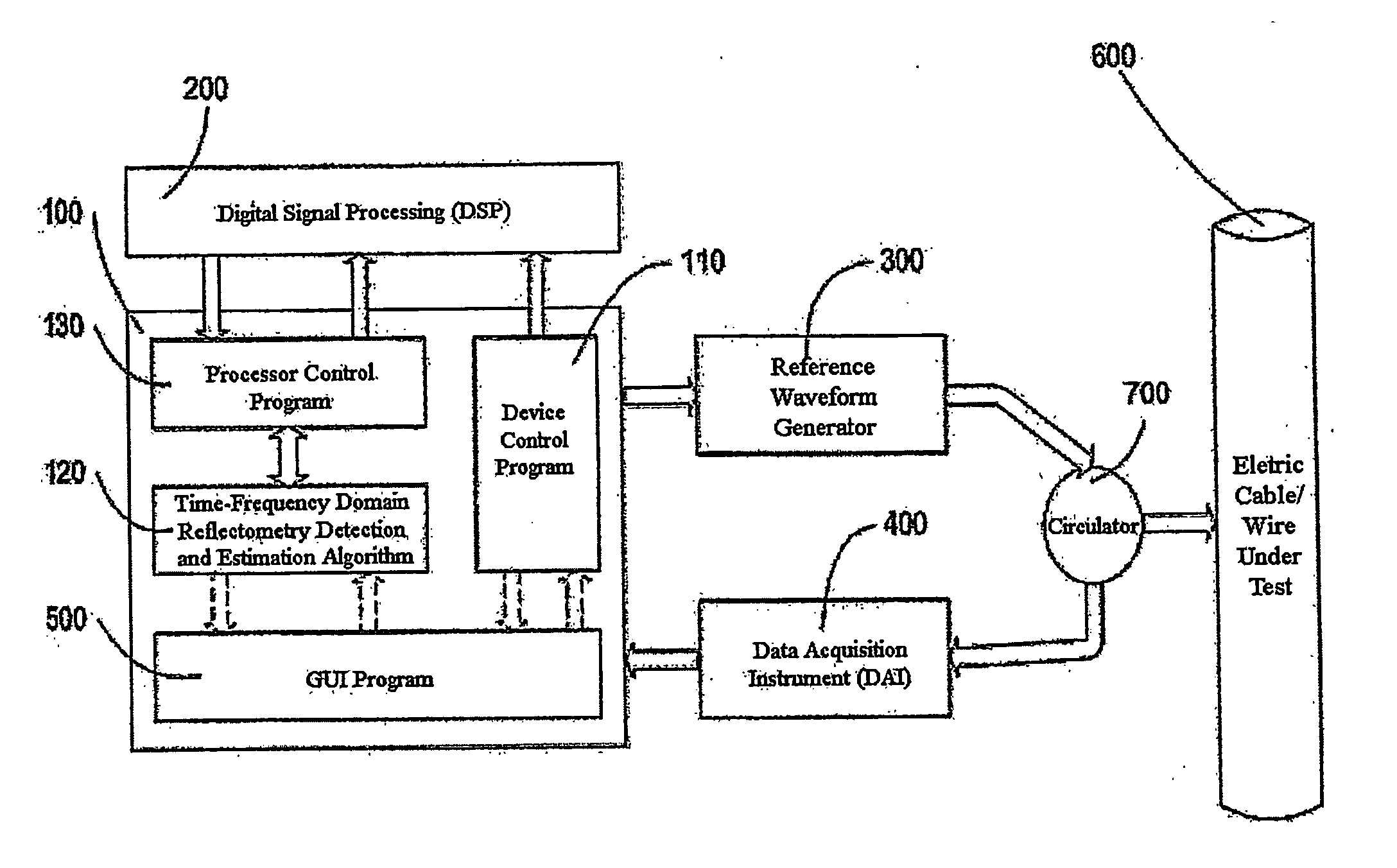
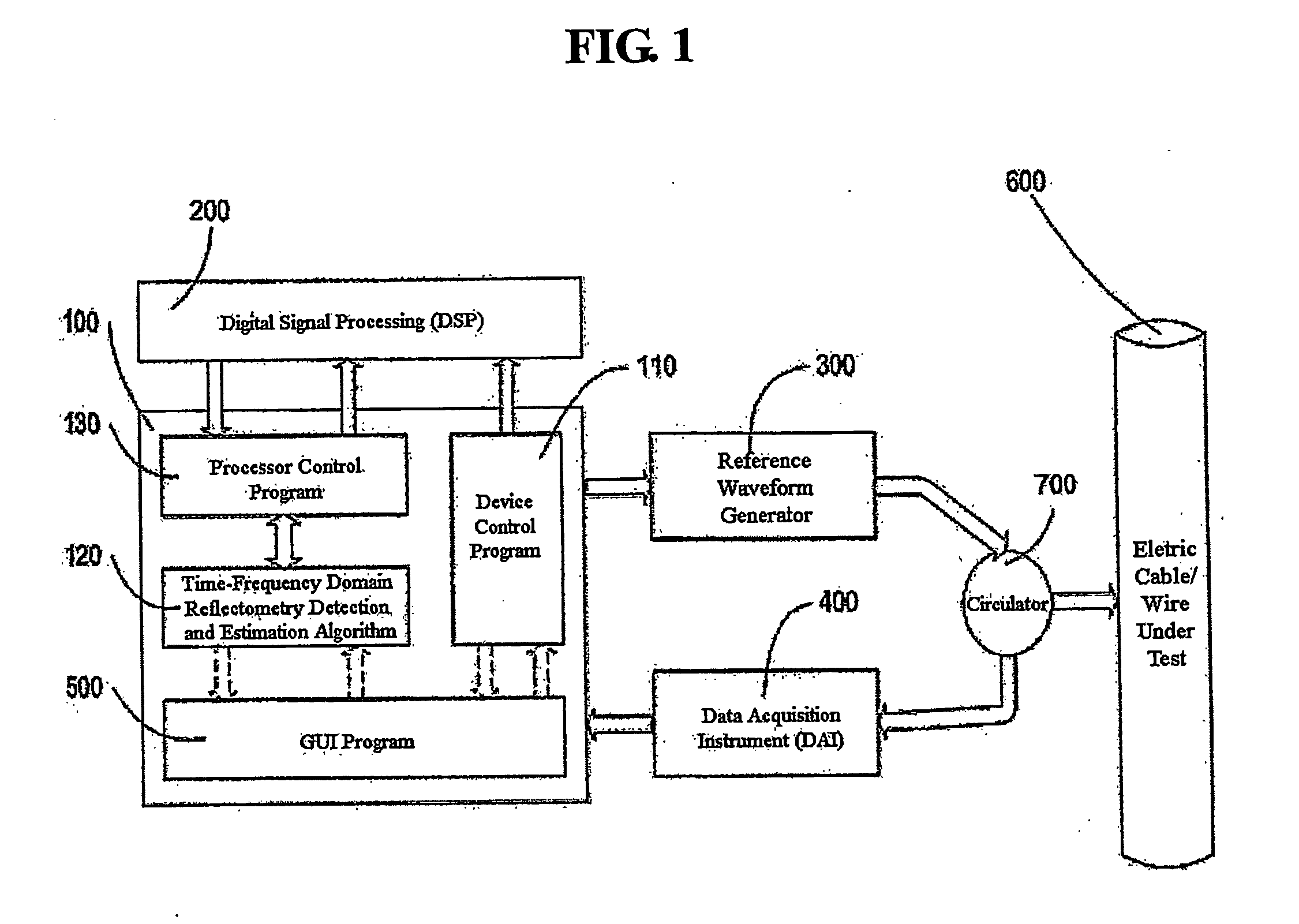
Time-frequency domain reflectometry apparatus and method
InactiveUS7337079B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsMeasurement deviceTime delays
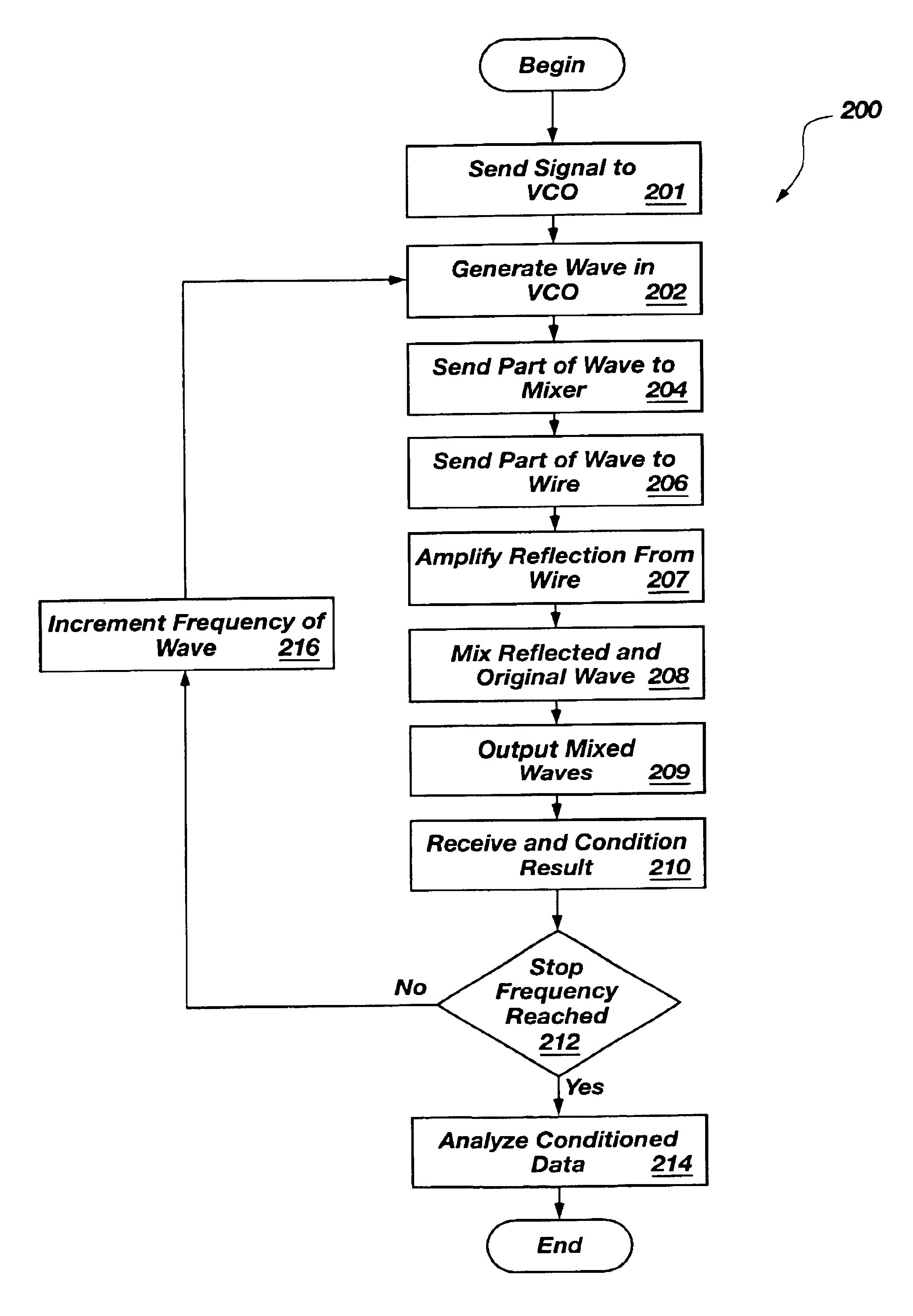
An apparatus and method for high-resolution reflectometry that operates simultaneously in both the time and frequency domains, utilizing time-frequency signal analysis and a chirp signal multiplied by a Gaussian time envelope. The Gaussian envelope provides time localization, while the chirp allows one to excite the system under test with a swept sinewave covering a frequency band of interest. High resolution in detection of the reflected signal is provided by a time-frequency cross correlation function. The high-accuracy localization of faults in a wire / cable can be achieved by measurement of time delay offset obtained from the frequency offset of the reflected signal. The apparatus enables one to execute an automated diagnostic procedure of a wire / cable under test by control of peripheral devices.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
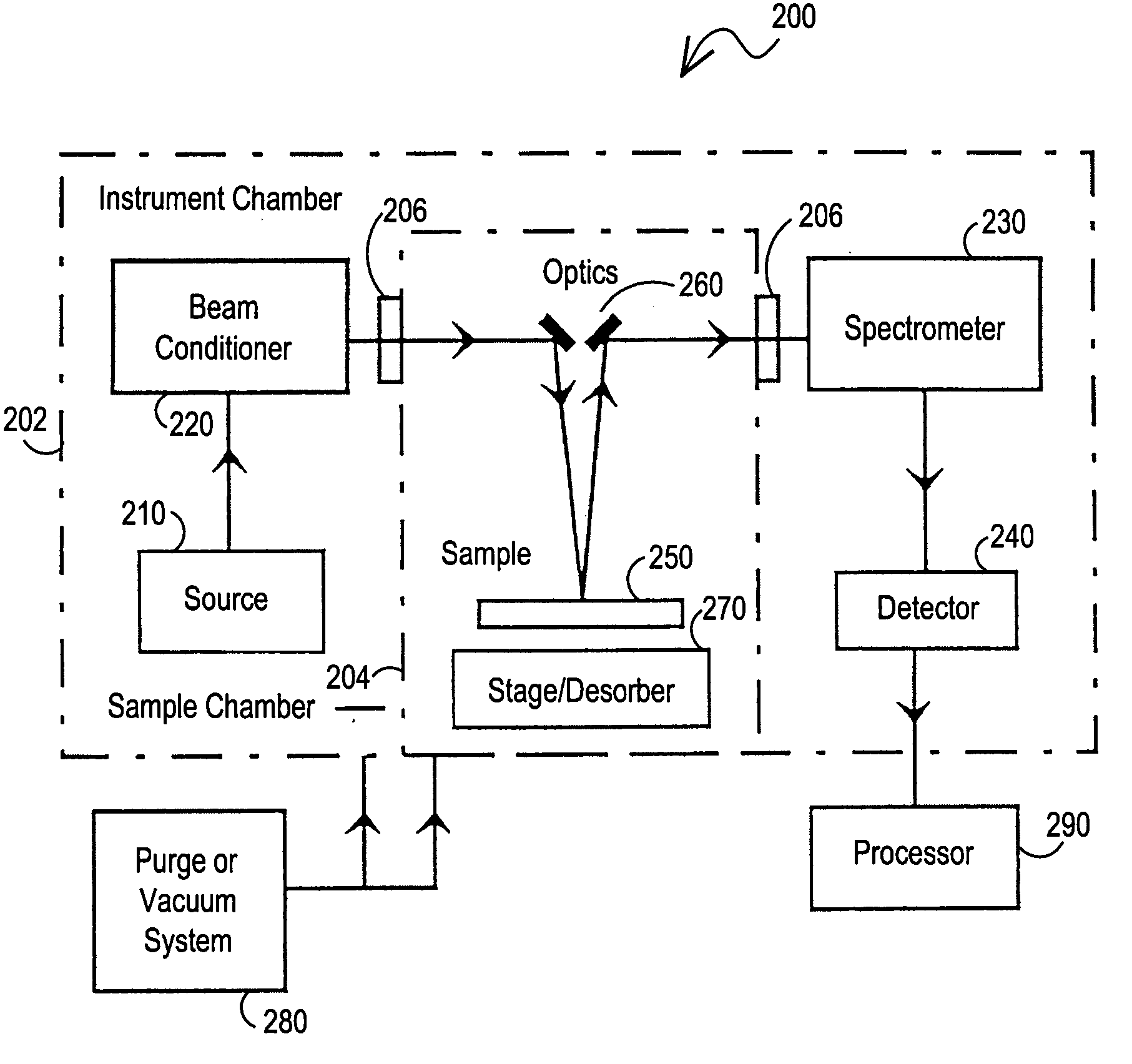
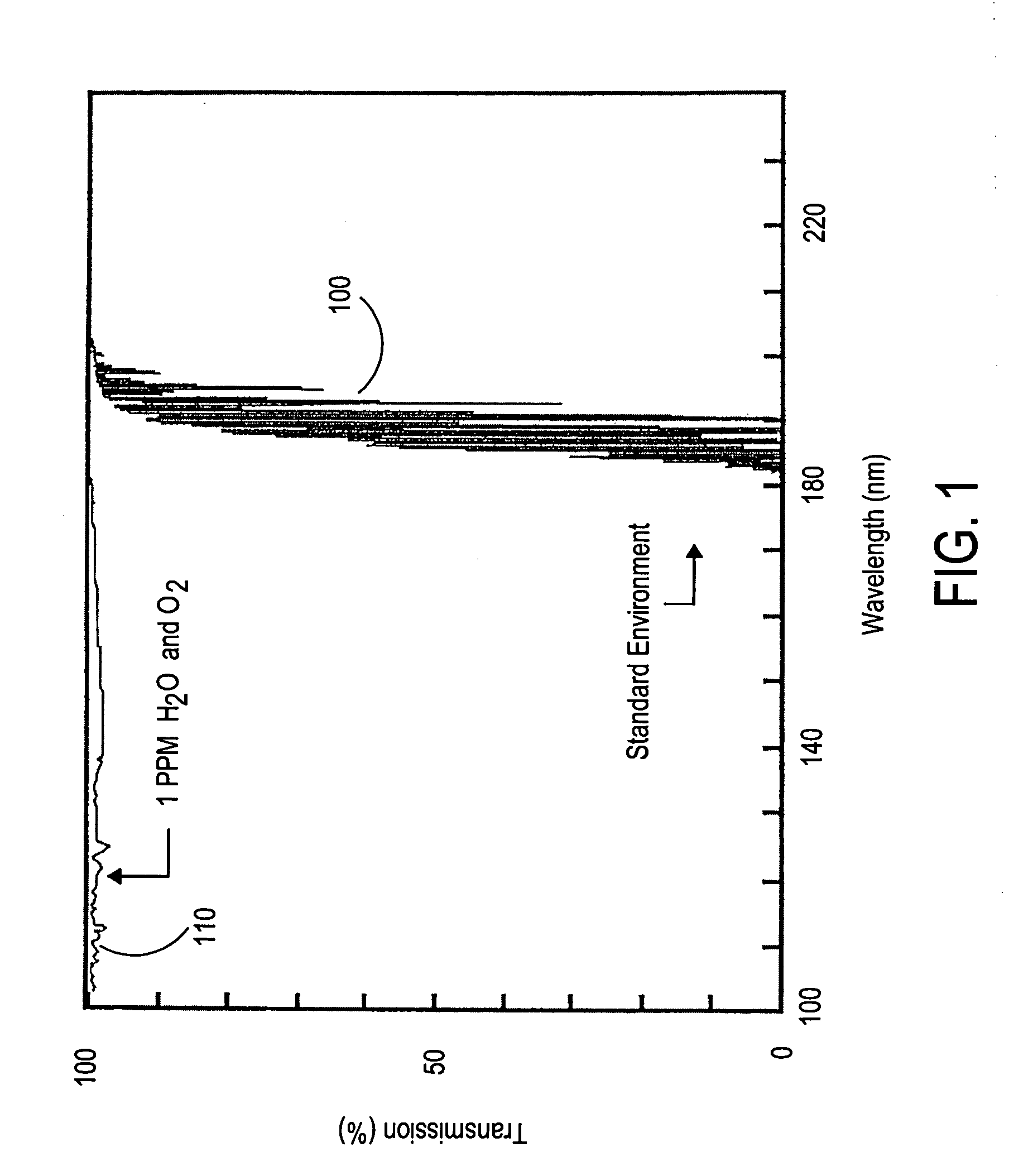
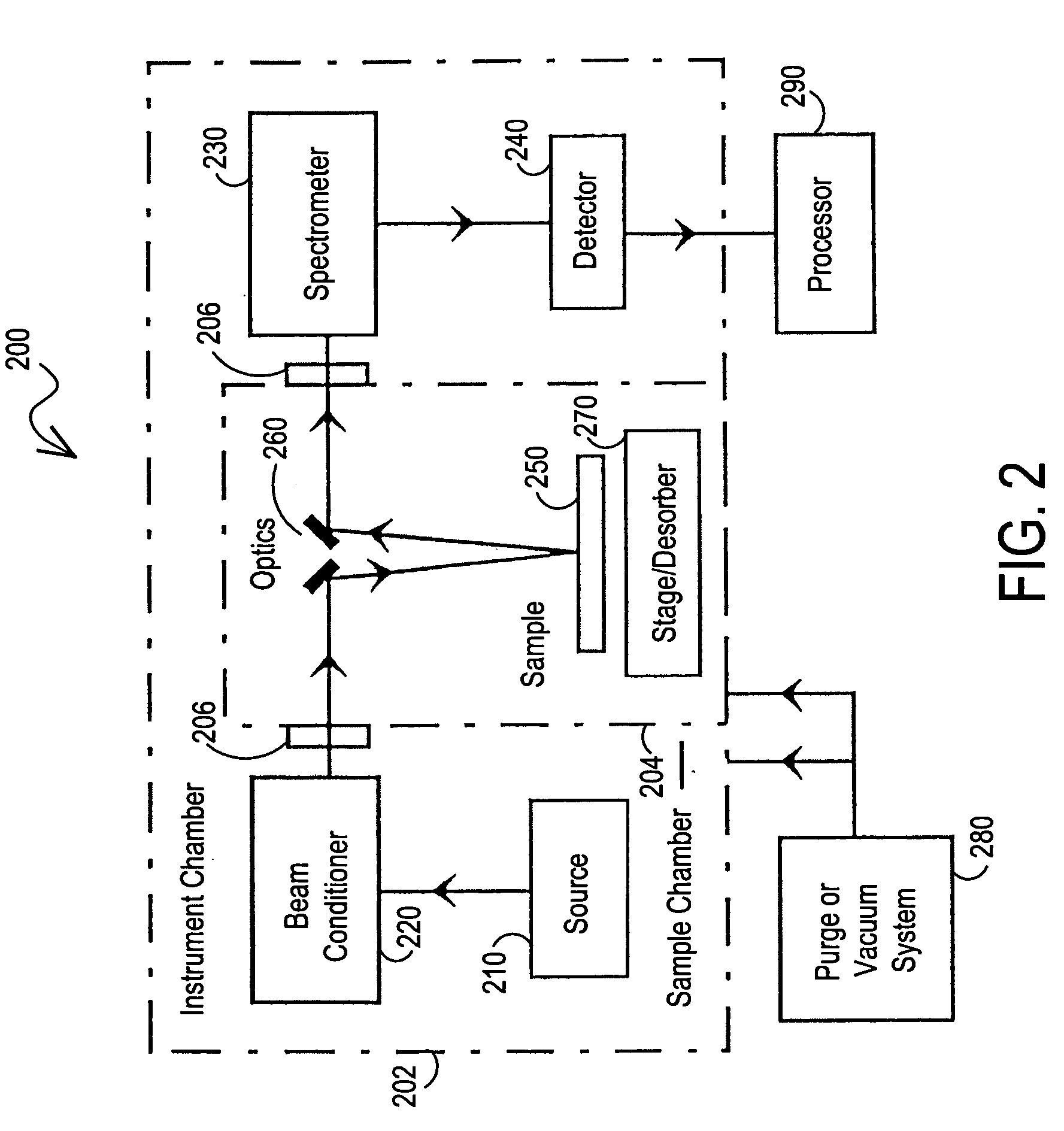
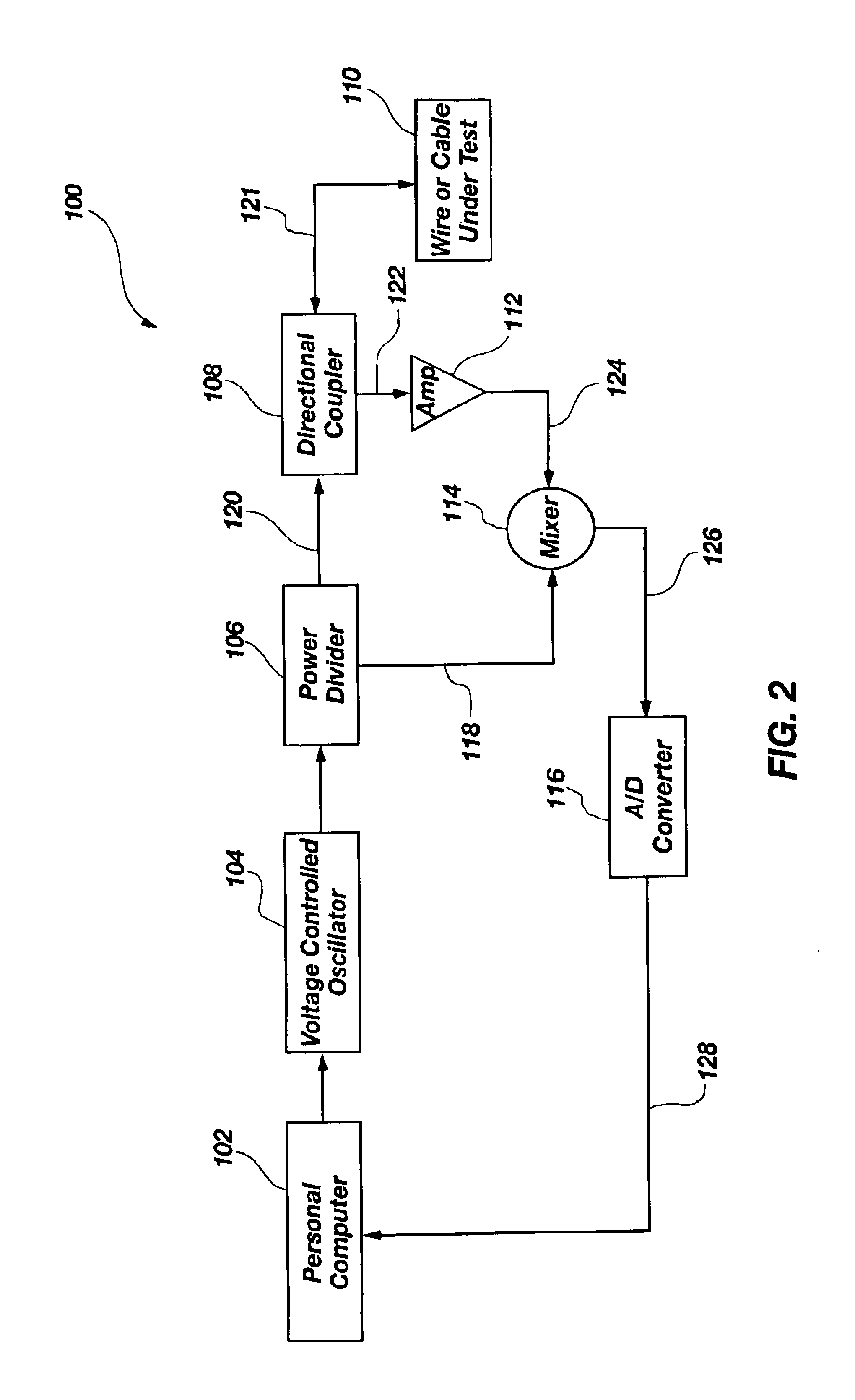
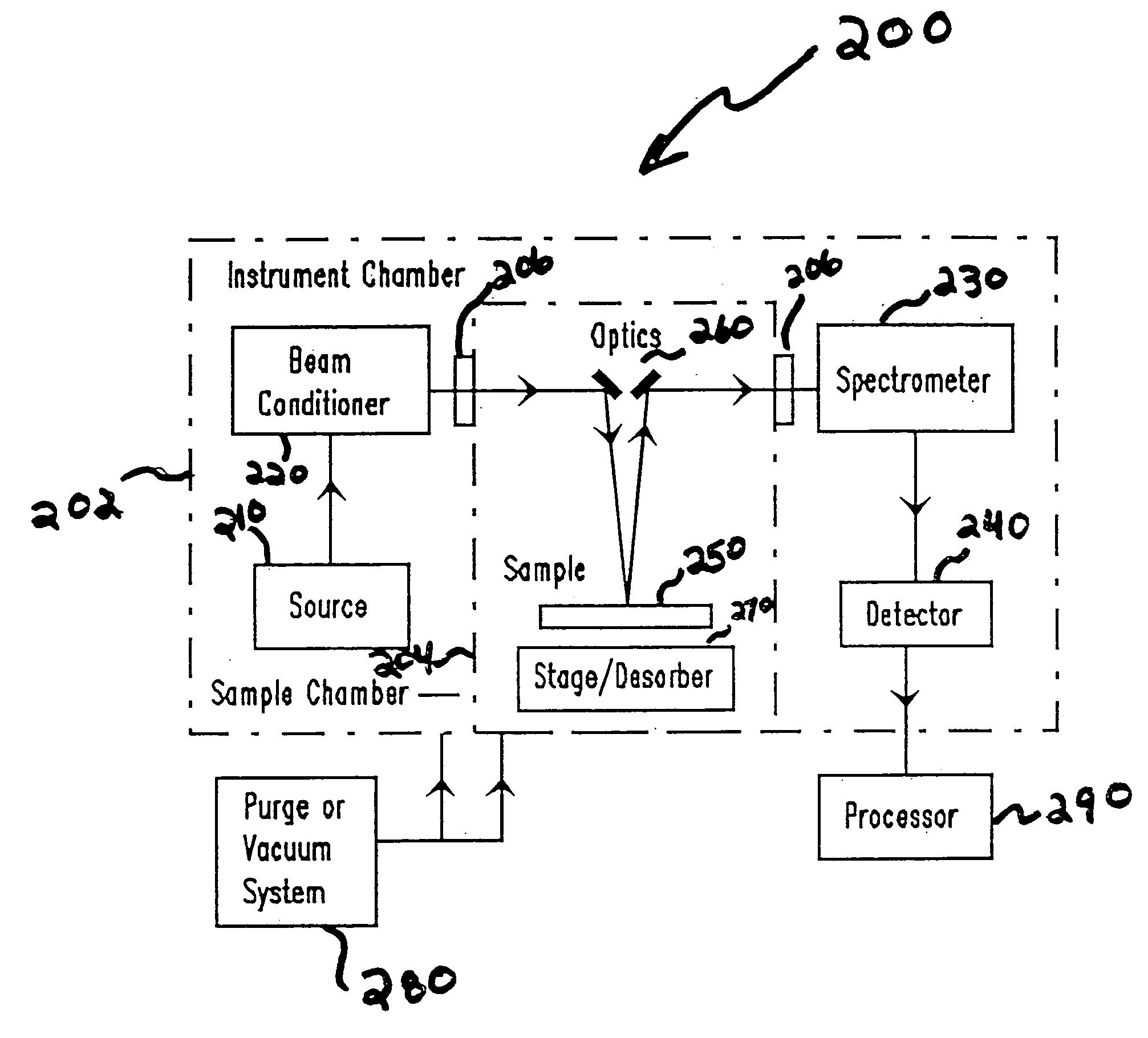
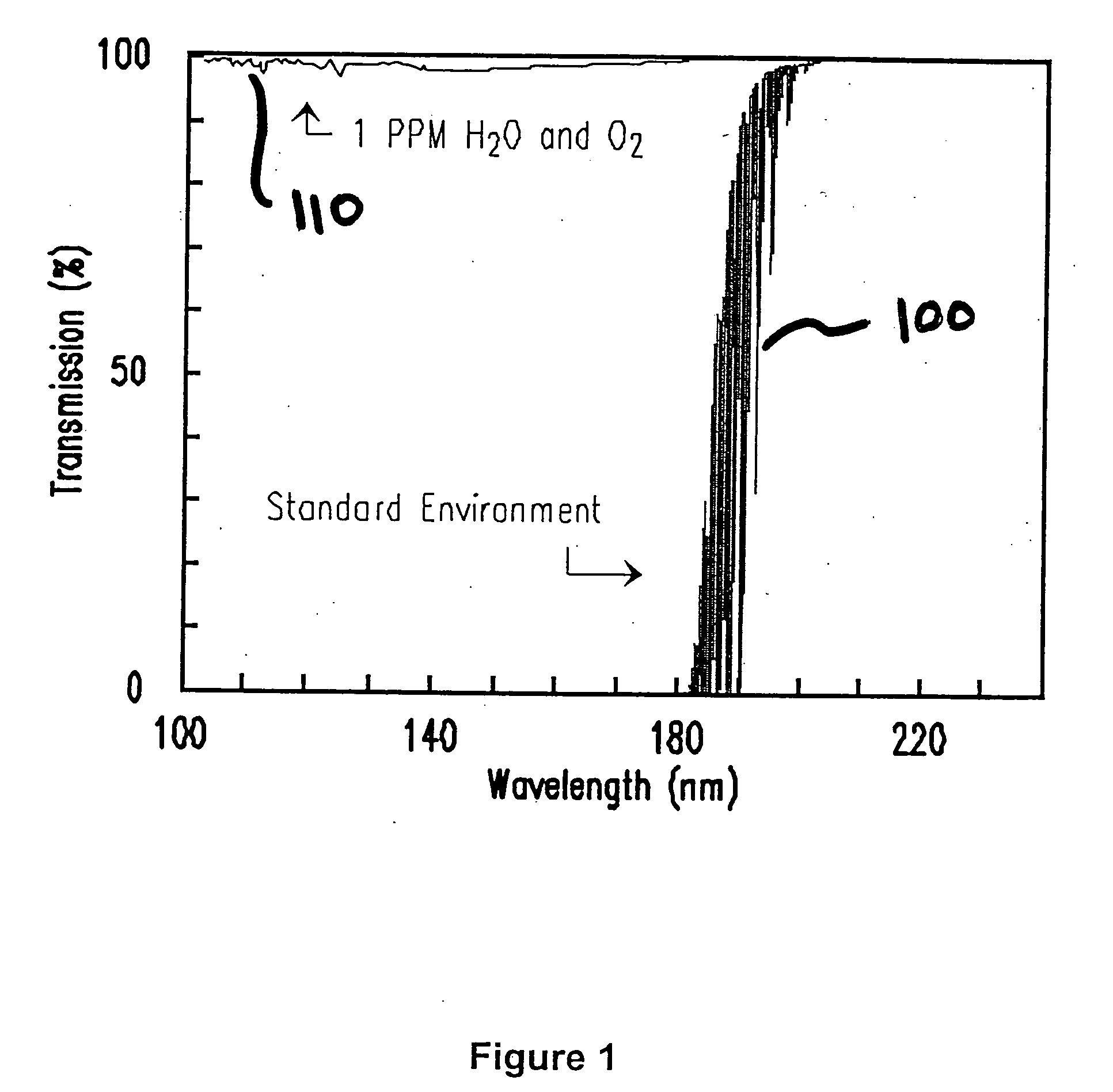
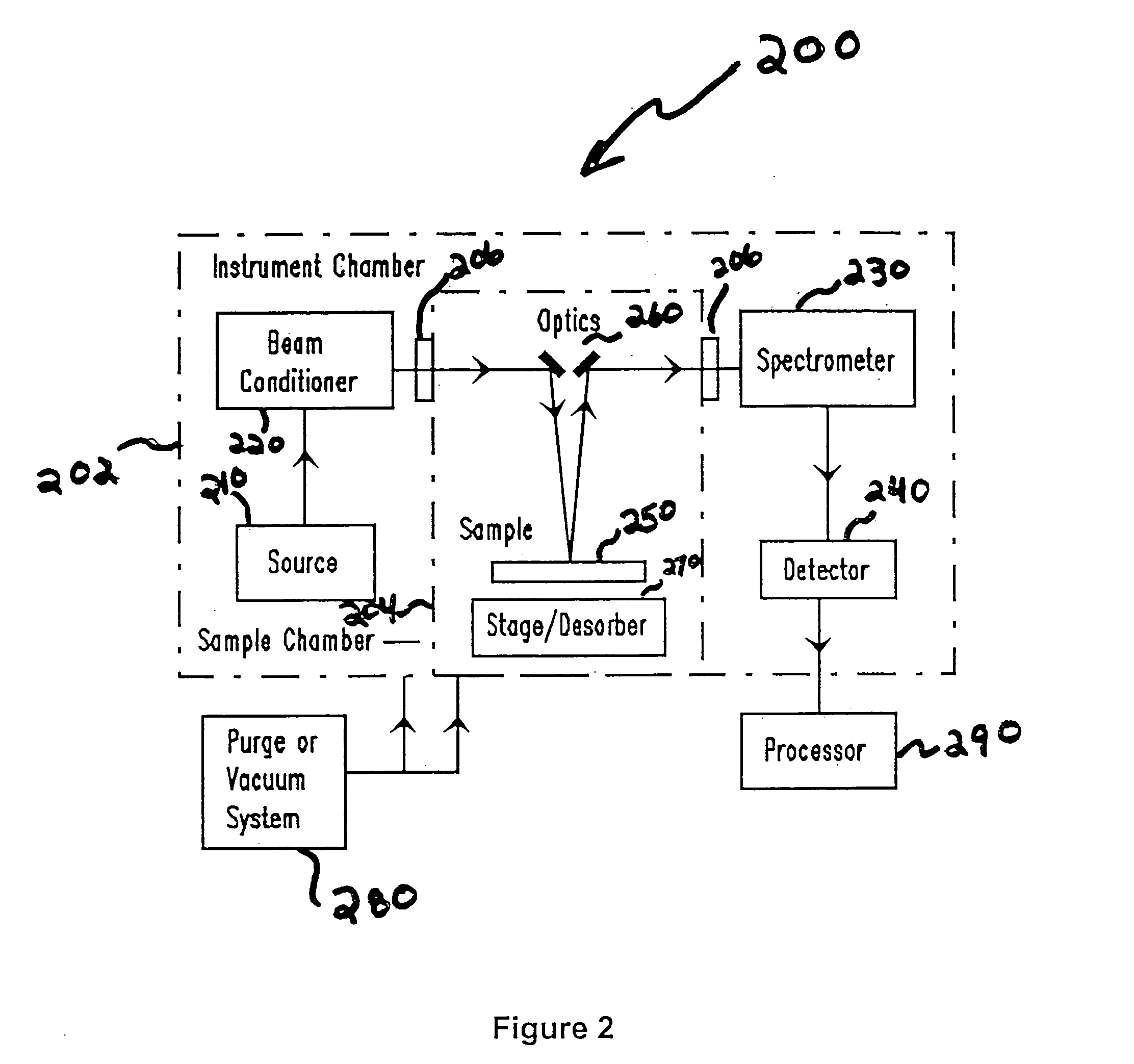
Vacuum ultraviolet reflectometer system and method
ActiveUS7067818B2Change levelThin layerSpectrum investigationPolarisation-affecting propertiesMetrologyUltraviolet
A spectroscopy system is provided which operates in the vacuum ultra-violet spectrum. More particularly, a system utilizing reflectometry techniques in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum is provided for use in metrology applications. The system may further include the use of an array detector in combination with an imaging spectrometer. In this manner data for multiple wavelengths may be simultaneously collected. Moreover, the multiple wavelengths of data may be collected simultaneously for a two dimensional sample area. The system may further include the use of a fixed diffraction grating and does not require the use of polarizing elements. To ensure accurate and repeatable measurement, the environment of the optical path is controlled. The optical path may include a controlled environmental chamber in which non-absorbing purge gases are present or in which vacuum evacuation techniques are utilized. The controlled environment may further include a separate instrument chamber and a separate sample chamber. The controlled environment limits in a repeatable manner the absorption of VUV photons.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
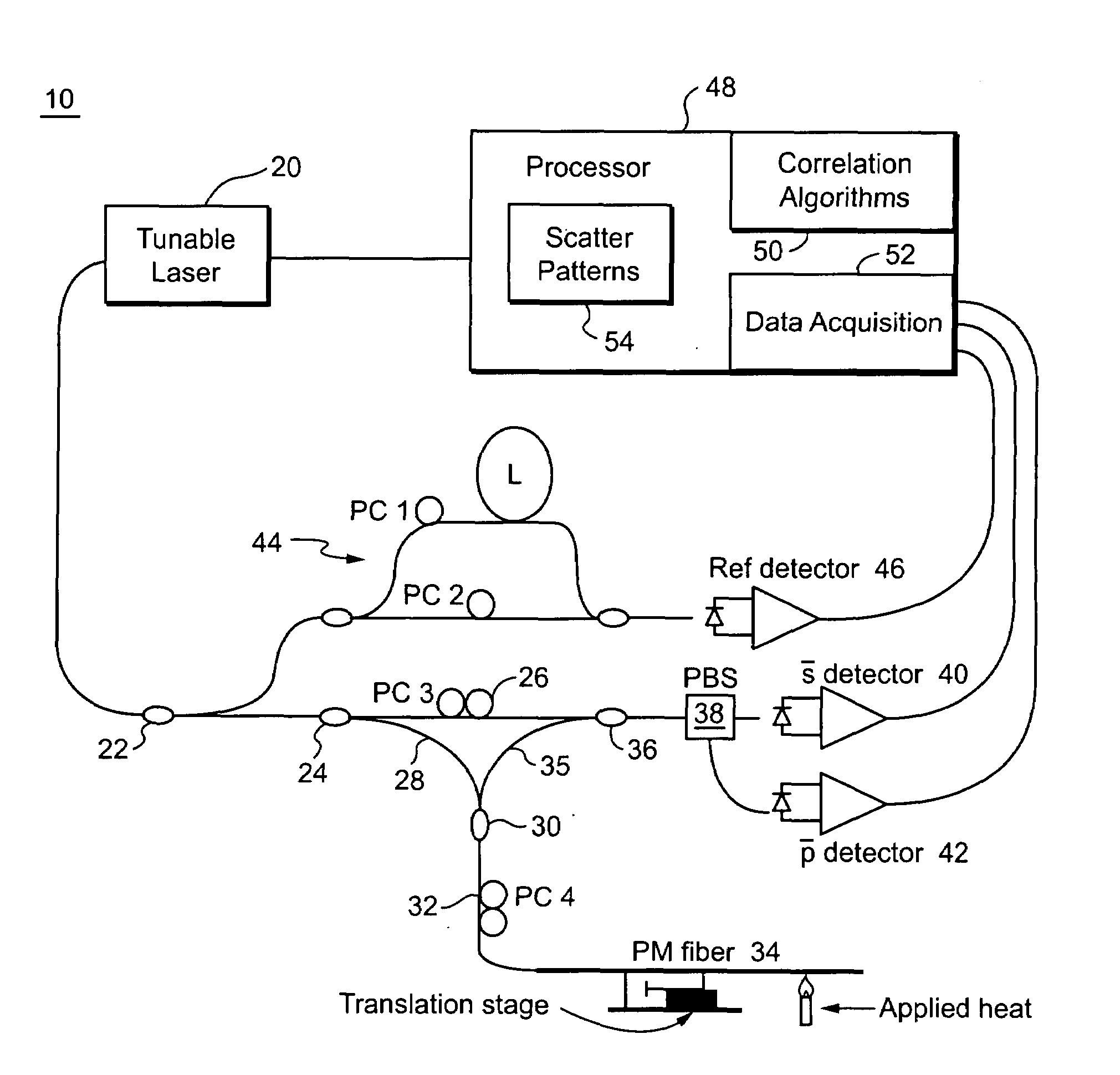
Distributed strain and temperature discrimination in polarization maintaining fiber
ActiveUS7538883B2Force measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberSpectral response
A portion of a polarization maintaining (PM) optical fiber having two polarization states is analyzed. First and second spectral responses of the PM fiber portion are determined. In a preferred implementation, the spectral responses are determined using Optical Frequency Domain Reflectometry (OFDR). Each polarization state of the PM fiber portion has a corresponding spectral component in the first spectral response. First and second spectral analyses of the PM fiber portion are performed using the first and second spectral responses. Based on those spectral analyses of the PM fiber portion, a first physical characteristic affecting the PM fiber portion is determined that is distinct from a second different physical characteristic affecting the fiber portion. Example physical characteristics include temperature and strain. An output signal related to the first physical characteristics affecting the fiber portion is provided, e.g., for display, further processing, etc.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometer and common path frequency domain optical coherence tomography device
InactiveUS7426036B2Improve fluencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansData acquisitionHandling system
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography devices with an additional interferometer are suggested. The additional interferometer offset is adjusted such, that it is ether less than the reference offset, or exceeds the distance from the reference reflector to the distal boundary of the longitudinal range of interest. This adjustment allows for relieving the requirements to the spectral resolution of the frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography engine and / or speed of the data acquisition and processing system, and eliminates depth ambiguity problems. The new topology allows for including a phase or frequency modulator in an arm of the additional interferometer improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the devices. The modulator is also capable of substantially eliminating mirror ambiguity, DC artifacts, and autocorrelation artifacts. The interference signal is produced either in the interferometer or inside of the optical fiber probe leading to the sample.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Multisensor probe for tissue identification
A multisensor probe for continuous real-time tissue identification. The multisensor probe includes a tissue penetrating needle, a plurality of sensors useful in characterizing tissue and a position sensor to measure the depth of the needle into the tissue being diagnosed. The sensors include but are not limited to an optical scattering and absorption spectroscopy sensor, an optical coherence domain reflectometry sensor, an electrical impedance sensor, a temperature sensor, a pO2 sensor, a chemical sensor and other sensors useful in identifying tissue. The sensors may take the form of a plurality of optical fibers extending through said needle. A retractable sheath may be disposed around the distal section of the needle to protect the needle when not in use. The sheath retracts when the probe is inserted into tissue and the position of the sheath relative to the needle may be measured to determine the needle's depth. Systems and methods for tissue identification are also provided.
Owner:BIOLUMINATE
Polarization-sensitive common path optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
Polarization sensitive common path OCT / OCR devices are presented. Optical radiation from a source is converted into two cross-polarized replicas propagating therethrough with a predetermined optical path length difference. The two cross-polarized replicas are then delivered to an associated sample by a delivering device, which is, preferably, an optical fiber probe. A combination optical radiation is produced in at least one secondary interferometer by combining a corresponding portion of an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from a tip of an optical fiber of the optical fiber probe. Subject to a preset optical path length difference of the arms of the at least one secondary interferometer, a cross-polarized component, and / or a parallel-polarized component of the combined optical radiation, are selected. The topology of the devices allows for time domain, as well as for frequency domain registration.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Common path time domain optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
InactiveUS7538886B2Reduce necessityInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical radiationTomography
In common path time domain OCT / OCR devices optical radiation from a source is first split into two replicas, which are then delivered to an associated sample by an optical fiber probe. The tip of the optical fiber probe serves as a reference reflector and also serves as a combining element that produces a combination optical radiation by combining an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from the reference reflector. The topology of the devices eliminates the necessity of using Faraday mirrors, and also allows for registering a cross-polarized component of the optical radiation reflected or backscattered from the associated sample, as well as a parallel-polarized component.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
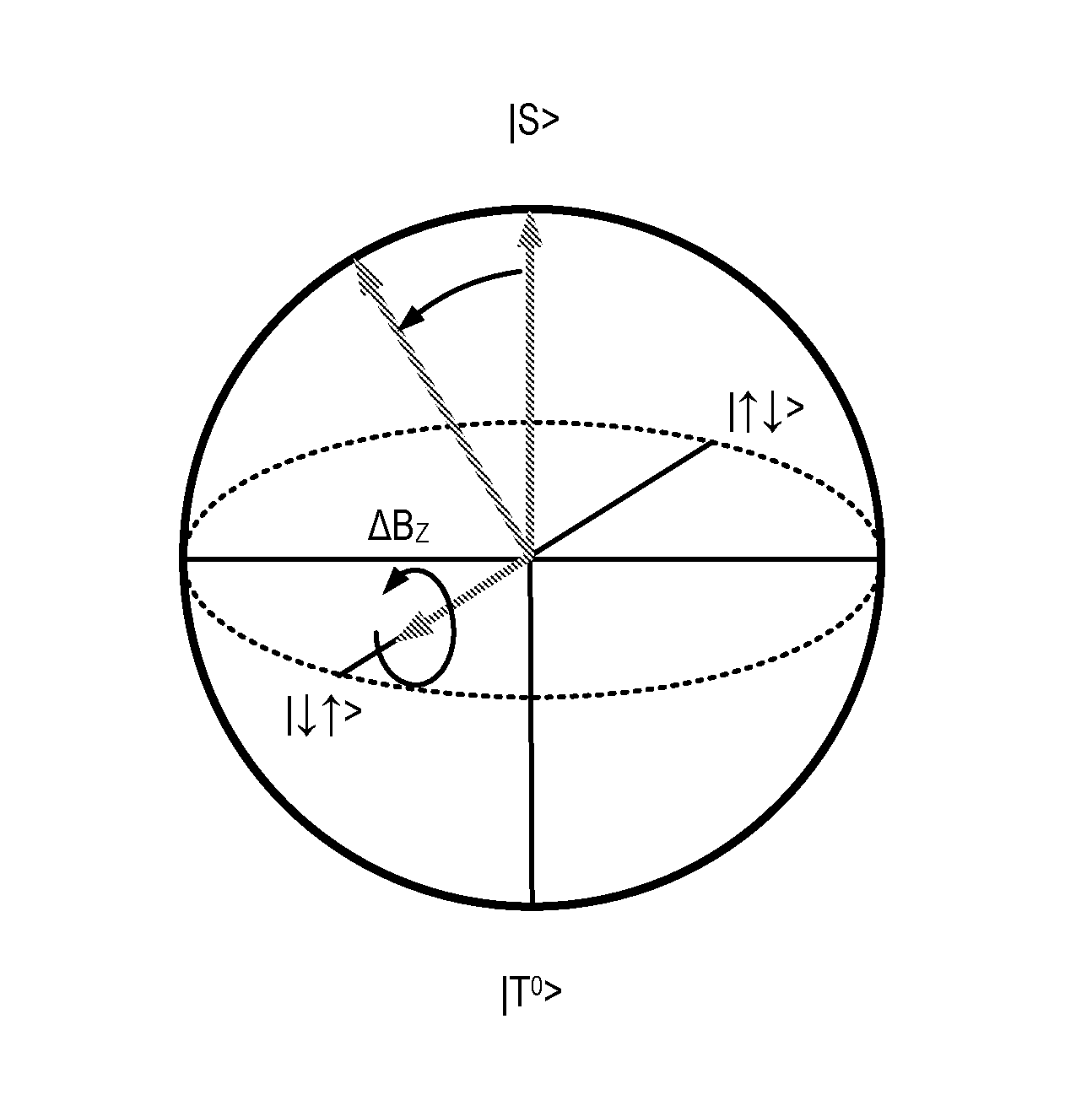
Quantum information processing
Quantum information processing apparatus and methods are described. The apparatus comprises a device for defining a qubit and a reflectometry circuit for reading out a state of the qubit. The device comprises a semiconductor nanowire extending along a first direction having first and second obtuse or acute edges running along the first direction, gate dielectric overlying the first and second edges of the nanowire and a split gate running across a section of the nanowire in a second, transverse direction, the split gate comprising first and second gates overlying the first and second edges respectively. The reflectometry circuit comprises a resonator coupled to the first or second gate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
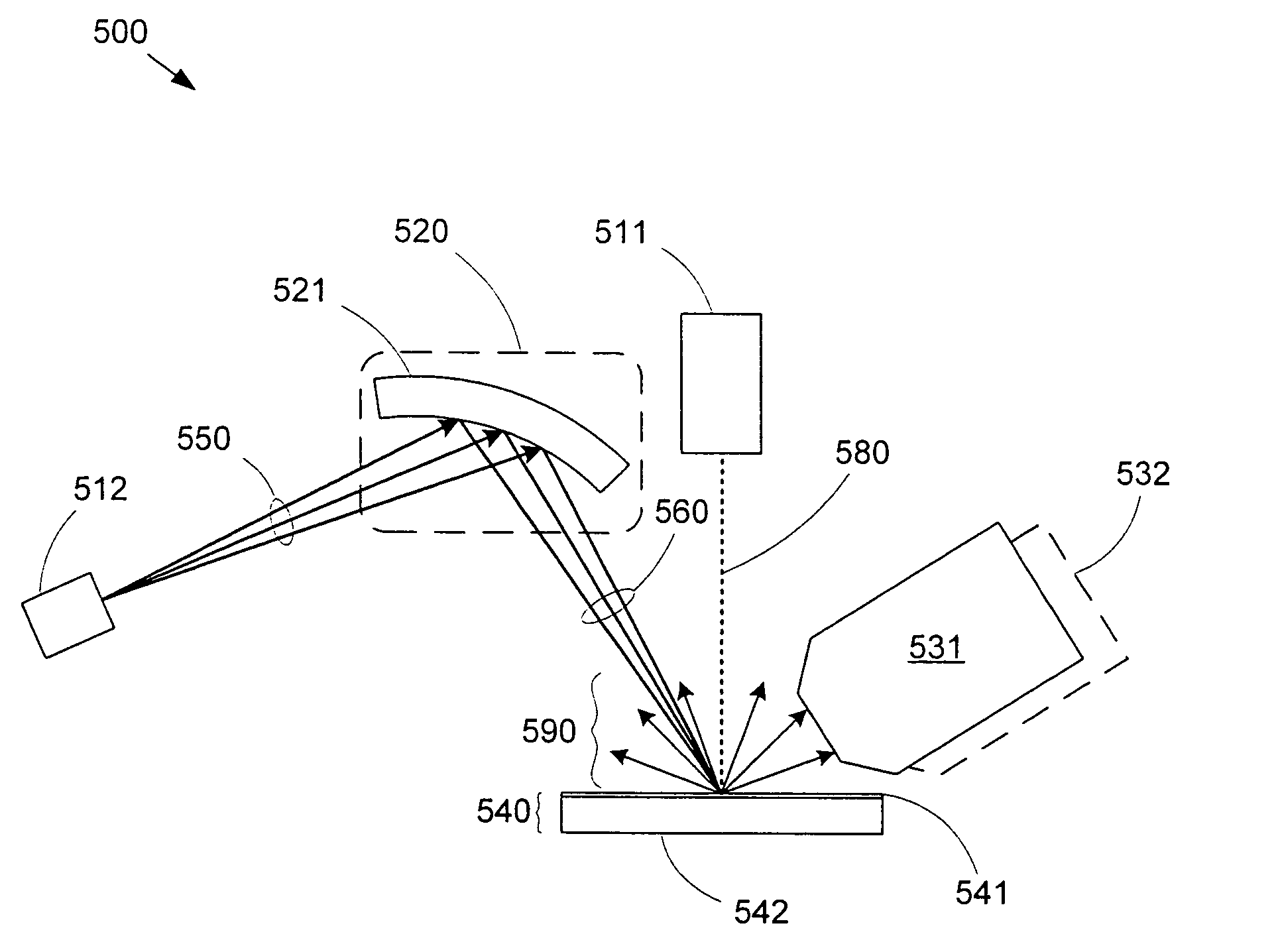
Small Spot Size Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
ActiveUS20130321810A1High measurement sensitivityIncrease the number ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusAngle of incidenceMetrology
Methods and systems for small angle CD metrology with a small spot size are introduced to increase measurement sensitivity while maintaining adequate throughput necessary for modern semiconductor manufacture. A small angle CD metrology system includes a small angle spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) subsystem combined with a small angle spectroscopic reflectometry system, both operated at small angles of incidence. The small angle SE subsystem is configured to operate in a complete Mueller Matrix mode to further improve measurement sensitivity. The small angle CD metrology system includes an objective having all reflective surfaces in the light path. In some embodiments, the all-reflective objective is a Schwartzschild objective having an axicon mirror element to further reduce measurement spot size. In some embodiments, the small angle CD metrology system includes a dynamic aperture subsystem to isolate specific ranges of angles of incidence and azimuth for improved measurement sensitivity.
Owner:KLA CORP
Wire fault detection
InactiveUS20040230385A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
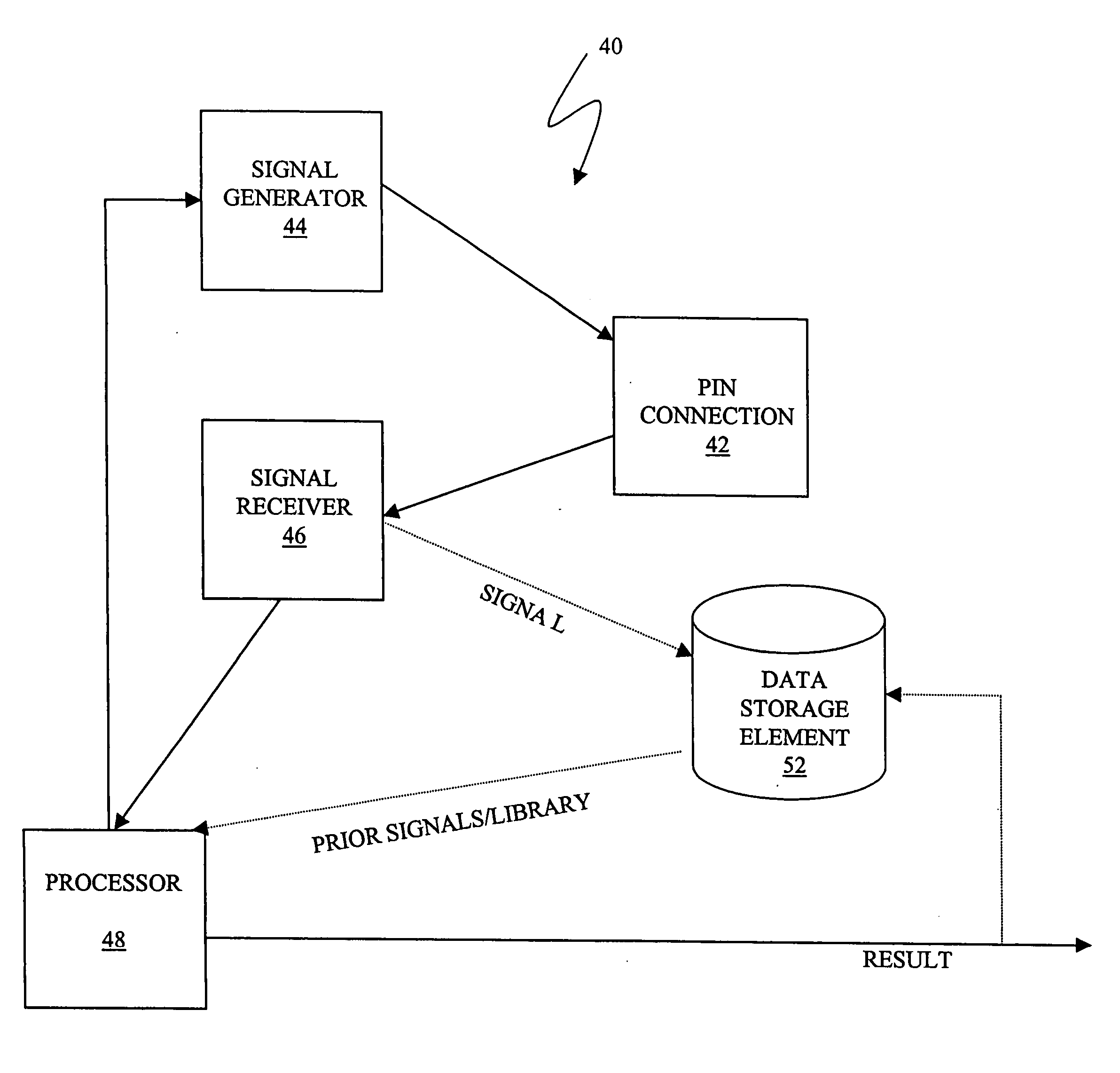
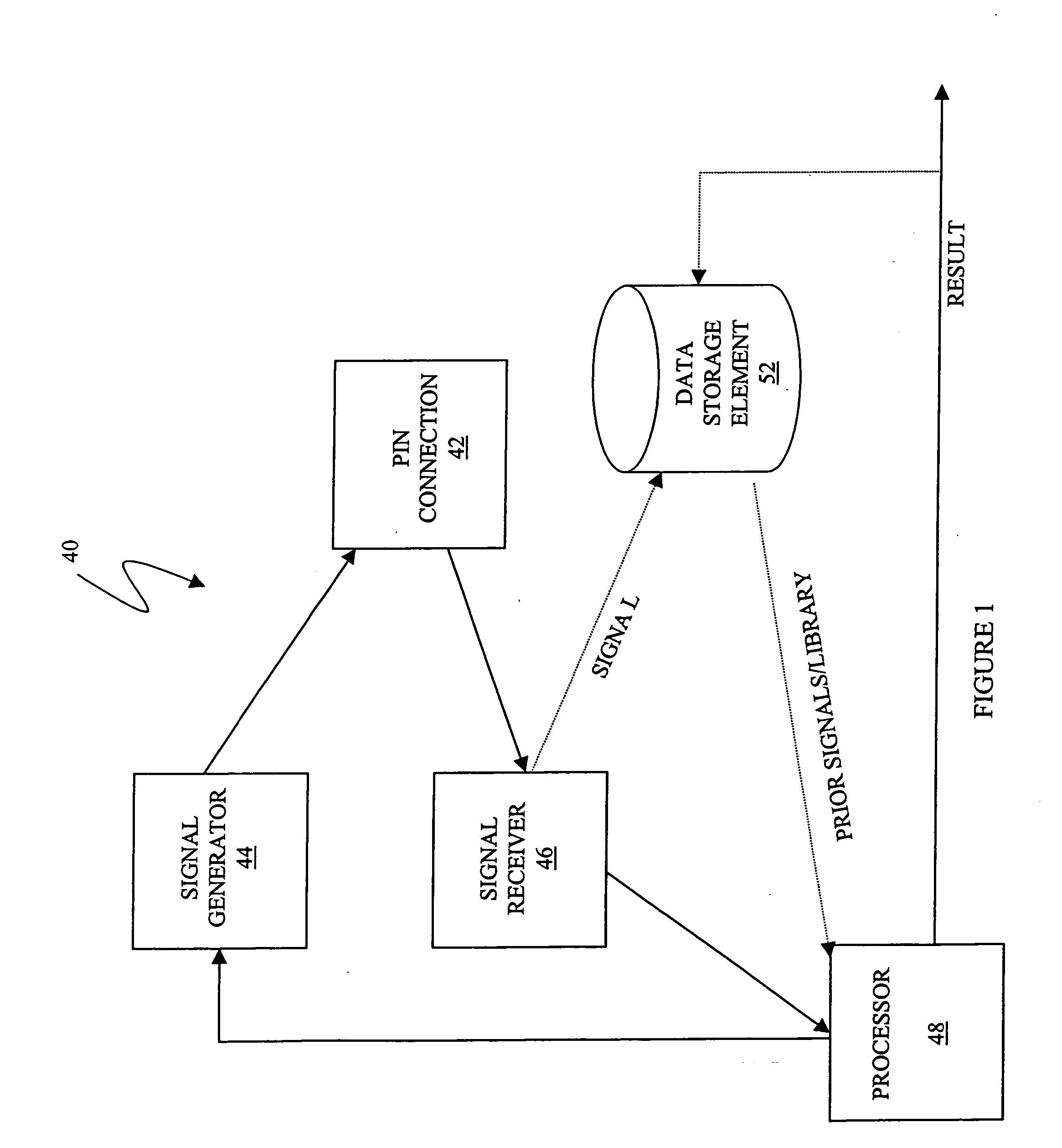
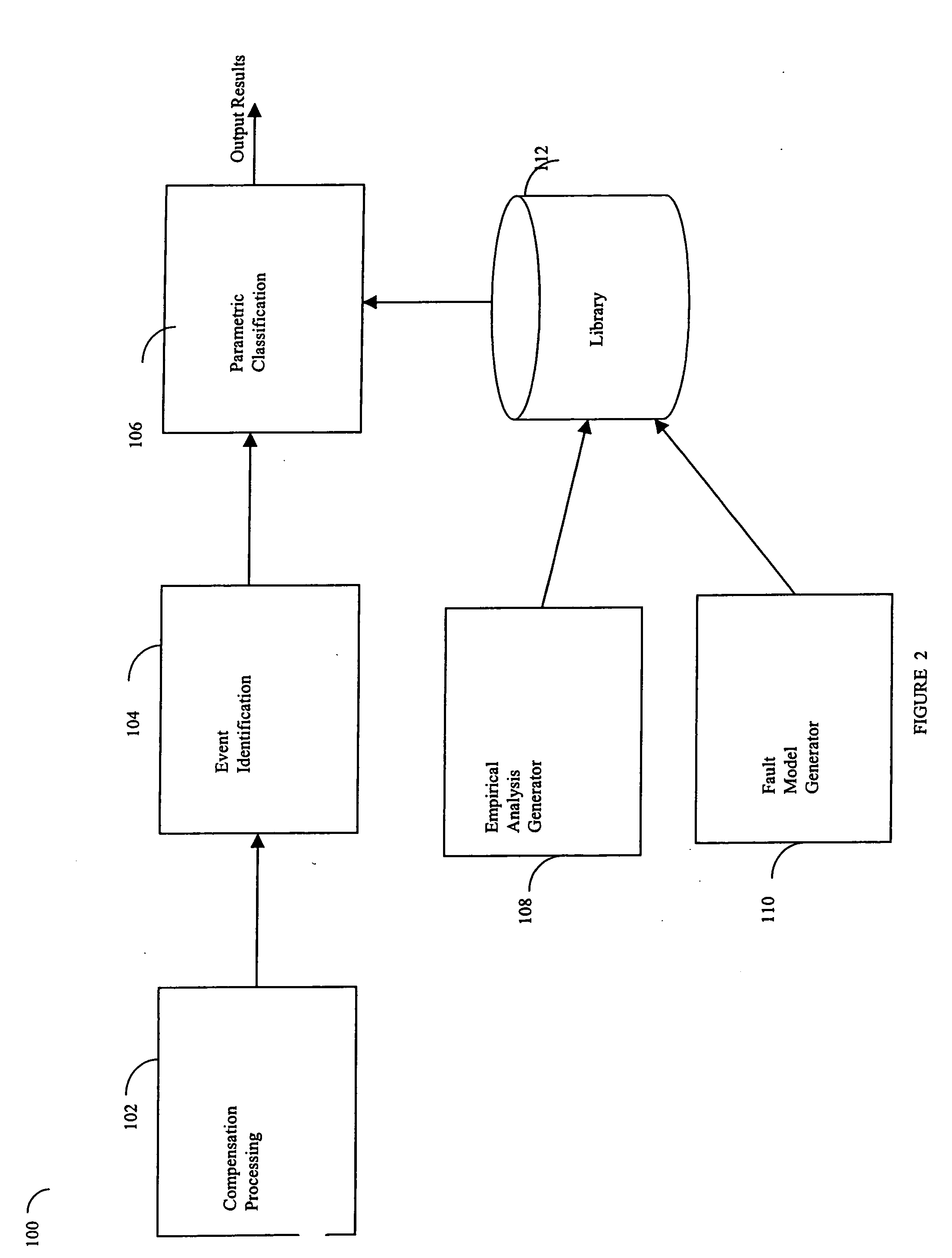
Described are techniques used in a wire diagnostics system to detect events, such as defects, that may occur within a wire or cable under test. An incident voltage signal is sent out on the wire and a measured voltage signal is obtained which includes the incident voltage and the reflected voltage. Compensation processing is performed on the measured waveform to remove unwanted reflective components. Additionally, the waveform is then subject to attenuation processing and event detection processing. Detected events, such as defects, are classified and output as results. Events are classified by parametric classification using a library of known events or faults. The library of known events or faults is previously generated using empirical analysis and modeling techniques. Additionally, joint time-frequency domain reflectometry (TFDR) techniques are described for event identification and classification for a wire under test.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
Frequency domain reflectometry system for testing wires and cables utilizing in-situ connectors, passive connectivity, cable fray detection, and live wire testing
InactiveUS6868357B2Less costlyResistance/reactance/impedenceTesting electric installations on transportCapacitanceEngineering
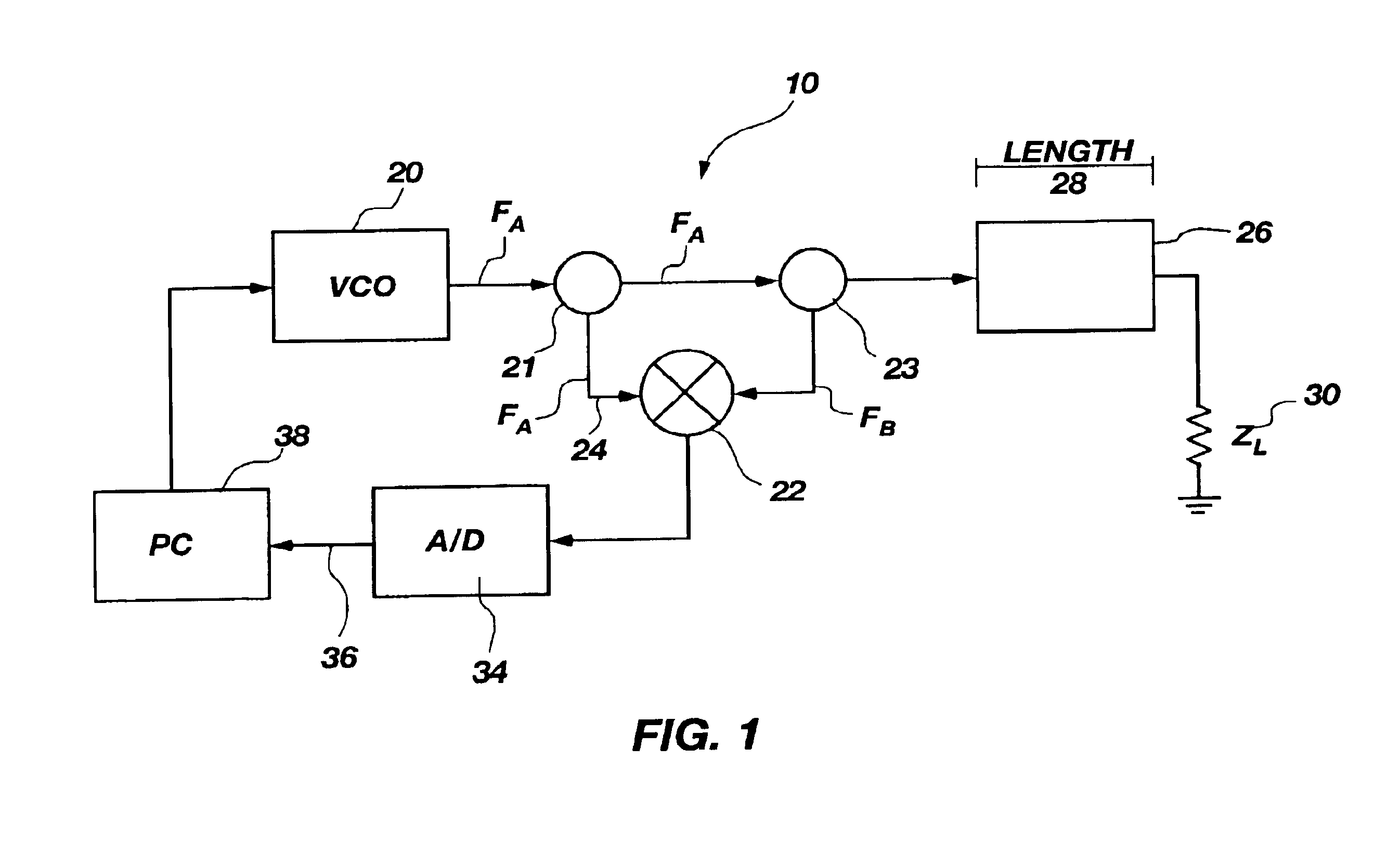
A frequency domain reflectometer that is in electrical communication with a cable under test in order to determine cable characteristics including cable length and load characteristics such as capacitance, inductance, resistance, impedance (which is characterized as an open or short circuit condition), and the location of an open or short circuit, wherein the FDR cable testing is performed in-situ when the system is installed at the time of installation of the cable to thereby enable testing of cable without having to remove it and risk damage, wherein FDR cable testing is performed passively so as not to interfere with normal operation of the cable even if the FDR cable testing system should fail, wherein a system is taught that can detect faults that are difficult to detect out of an operating environment, and wherein FDR cable testing is performed to detect cable fray conditions, wherein the cable may be grounded or coupled to air.
Owner:LIVEWIRE INNOVATION
Broad band referencing reflectometer
ActiveUS20050006590A1Fast convergenceThe result is accurateRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesData setOptical Module
A spectroscopy system is provided which is optimized for operation in the VUV region and capable of performing well in the DUV-NIR region. Additionally, the system incorporates an optical module which presents selectable sources and detectors optimized for use in the VUV and DUV-NIR. As well, the optical module provides common delivery and collection optics to enable measurements in both spectral regions to be collected using similar spot properties. The module also provides a means of quickly referencing measured data so as to ensure that highly repeatable results are achieved. The module further provides a controlled environment between the VUV source, sample chamber and VUV detector which acts to limit in a repeatable manner the absorption of VUV photons. The use of broad band data sets which encompass VUV wavelengths, in addition to the DUV-NIR wavelengths enables a greater variety of materials to be meaningfully characterized. Array based detection instrumentation may be exploited to permit the simultaneous collection of larger wavelength regions.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
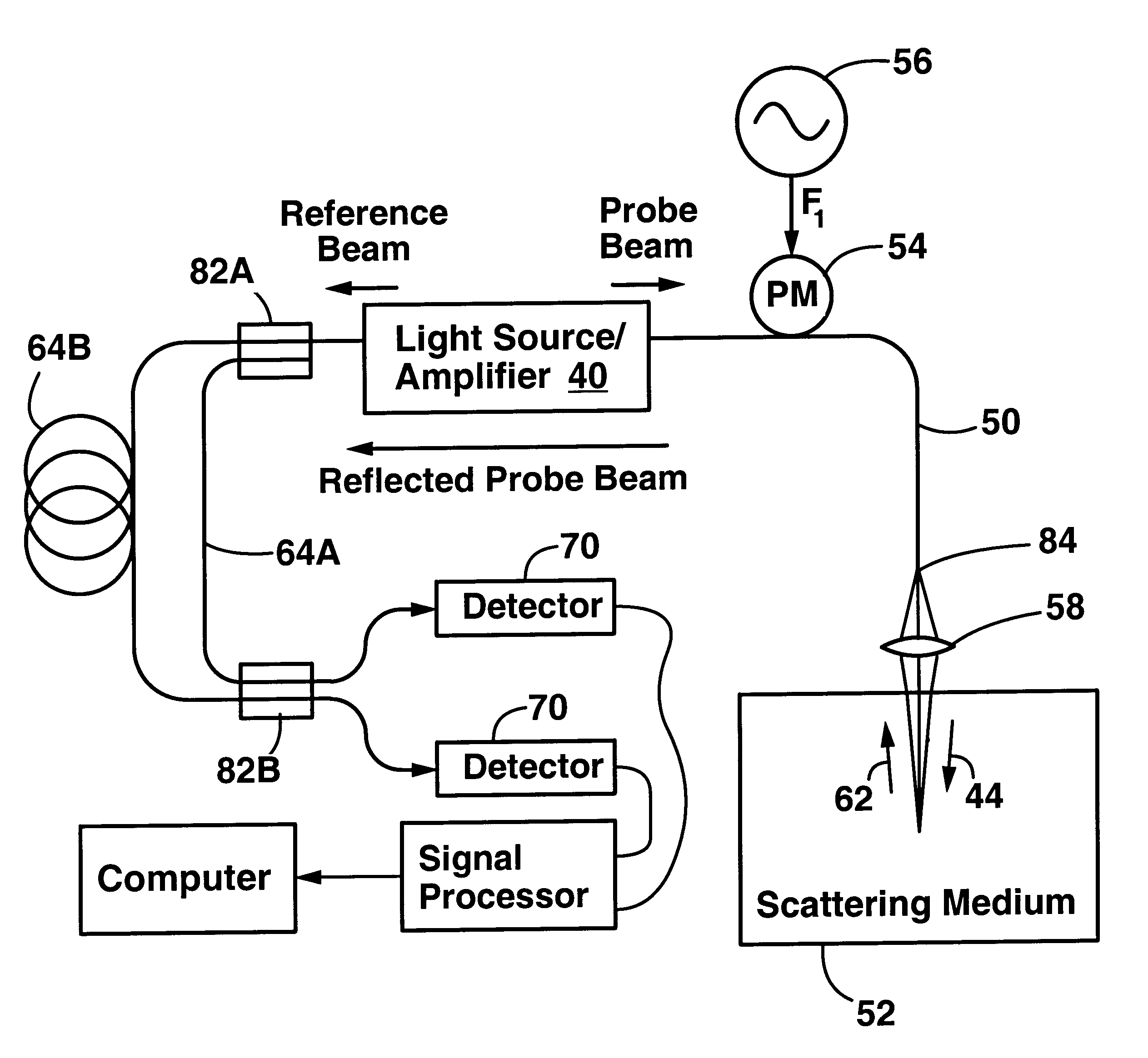
Method and apparatus for performing optical coherence-domain reflectometry and imaging through a scattering medium
InactiveUS6233055B1Enhanced signalImprove spatial resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringUsing optical meansSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
An apparatus and method for performing optical coherence domain reflectometry. The apparatus preferably includes a single output light source to illuminate a sample with a probe beam and to provide a reference beam. The reference beam is routed into a long arm of an interferometer by a polarizing beamsplitter. A reflected beam is collected from the sample. A 90.degree. double pass polarization rotation element located between the light source and the sample renders the polarizations of the probe beam and reflected beam orthogonal. The polarizing beamsplitter routes the reflected beam into a short arm of the interferometer. The interferometer combines the reference beam and the reflected beam such that coherent interference occurs between the beams. The apparatus ensures that all of the reflected beam contributes to the interference, resulting in a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:OPTICAL BIOPSY TECH
Electronically scanned optical coherence tomography with frequency modulated signals
An improved Optical Coherence Domain Reflectometry (OCDR) system is provided. One embodiment of this OCDR system outputs a detector signal carrying image depth information on multiple modulation frequencies, where each modulation frequency corresponds to a different image depth. The image depth information from the detector signal may be resolved by tuning to the desired modulation frequency. Another system for imaging body tissue uses multiple frequency modulators such that the light beam does not travel from an optical fiber to free space.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Time-frequency domain reflectometry apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060097730A1Wide applicationResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsMeasurement deviceTime delays
An apparatus and method for high-resolution reflectometry that operates simultaneously in both the time and frequency domains, utilizing time-frequency signal analysis and a chirp signal multiplied by a Gaussian time envelope. The Gaussian envelope provides time localization, while the chirp allows one to excite the system under test with a swept sinewave covering a frequency band of interest. High resolution in detection of the reflected signal is provided by a time-frequency cross correlation function. The high-accuracy localization of faults in a wire / cable can be achieved by measurement of time delay offset obtained from the frequency offset of the reflected signal. The apparatus enables one to execute an automated diagnostic procedure of a wire / cable under test by control of peripheral devices.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
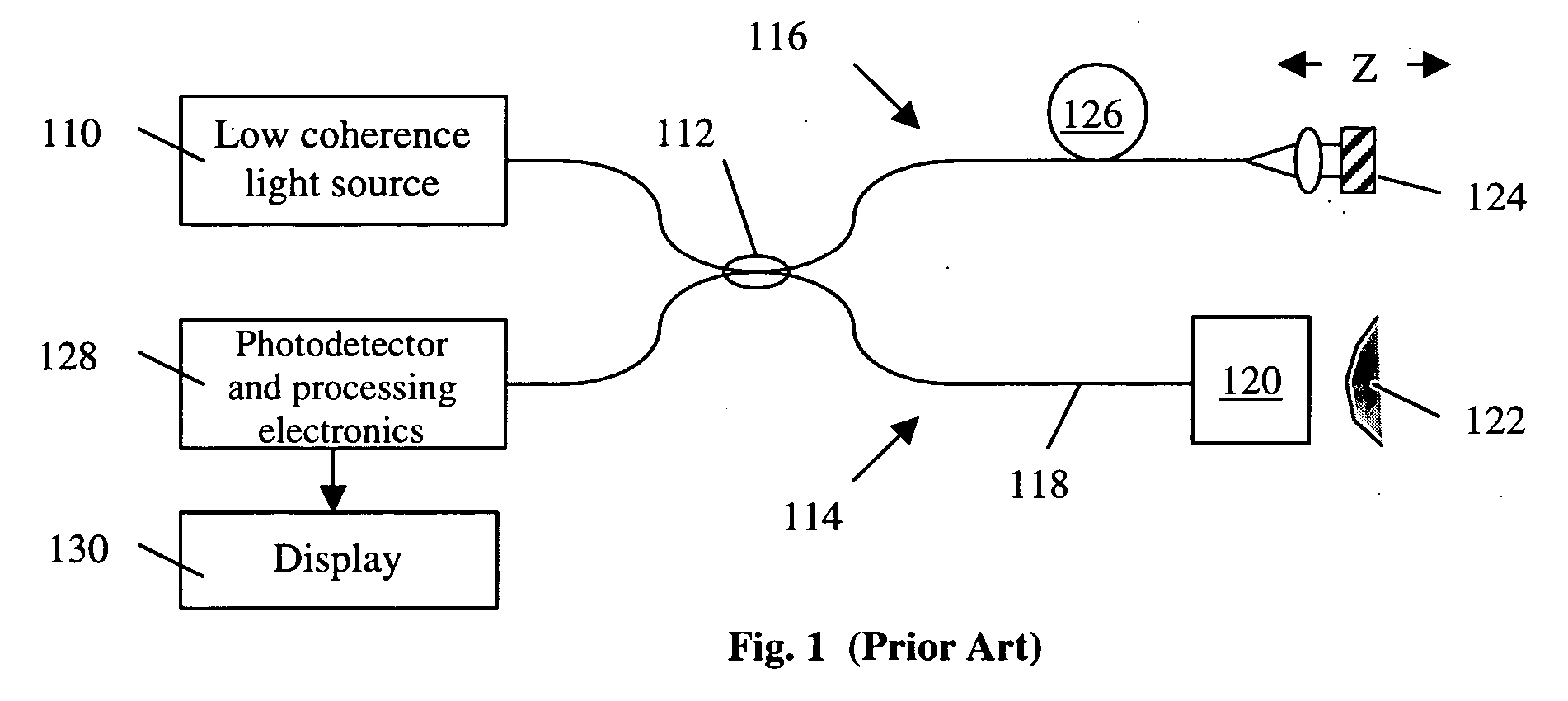
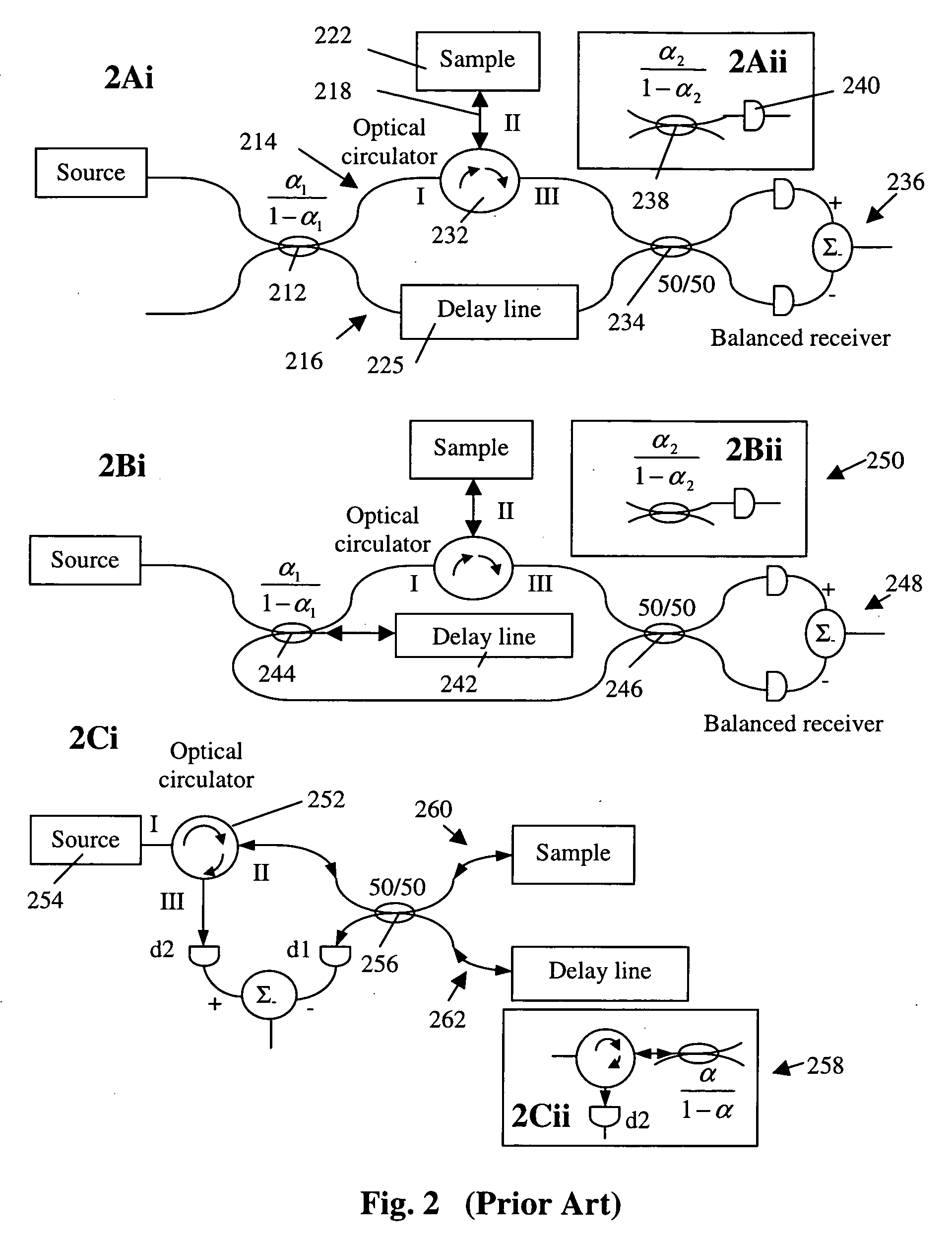
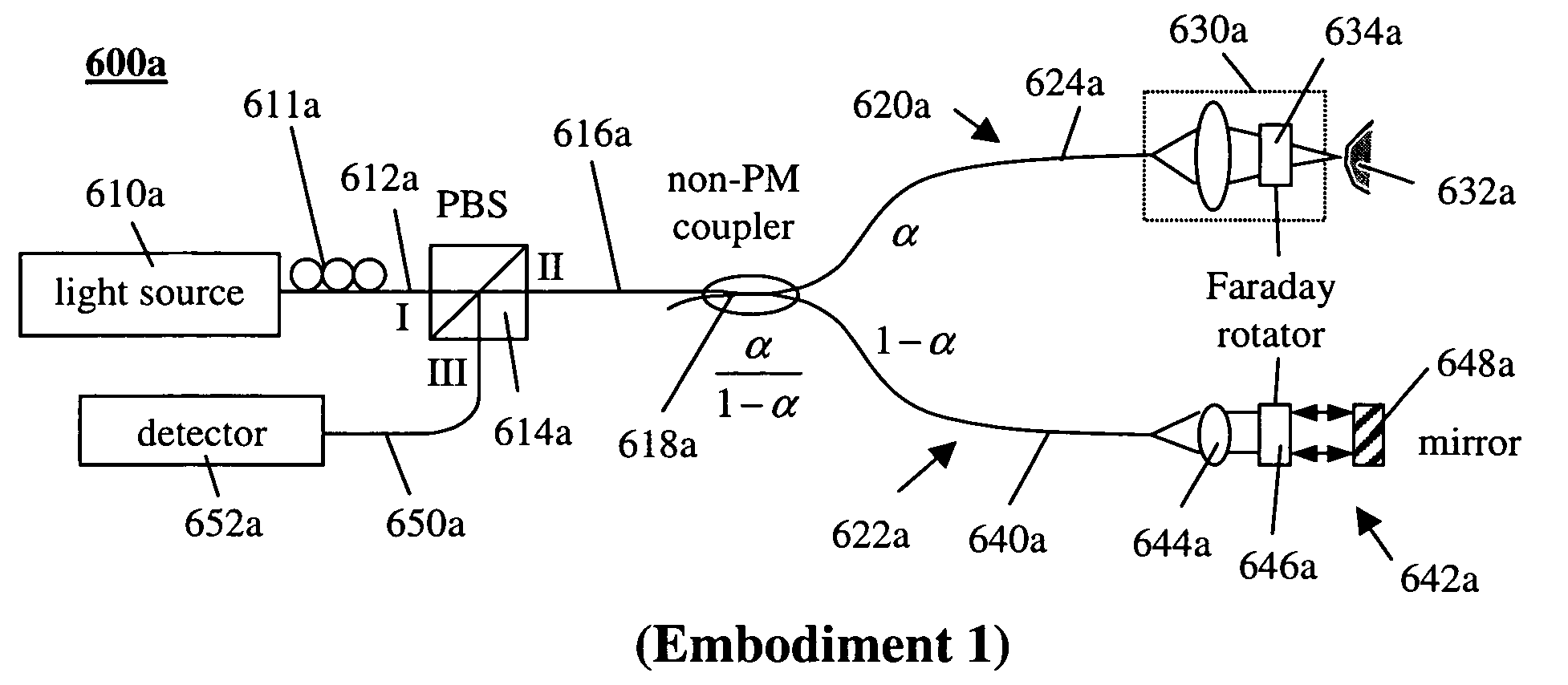
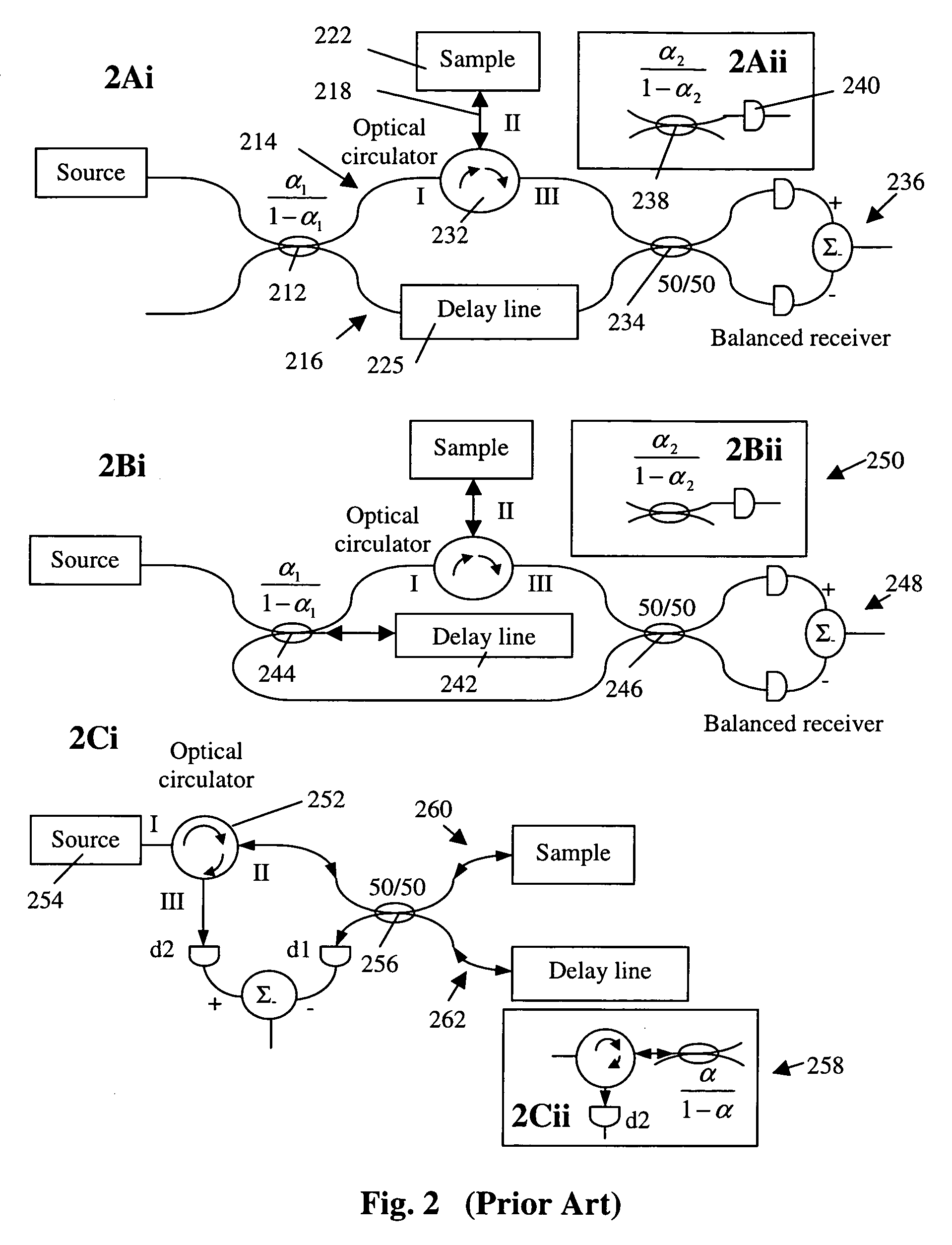
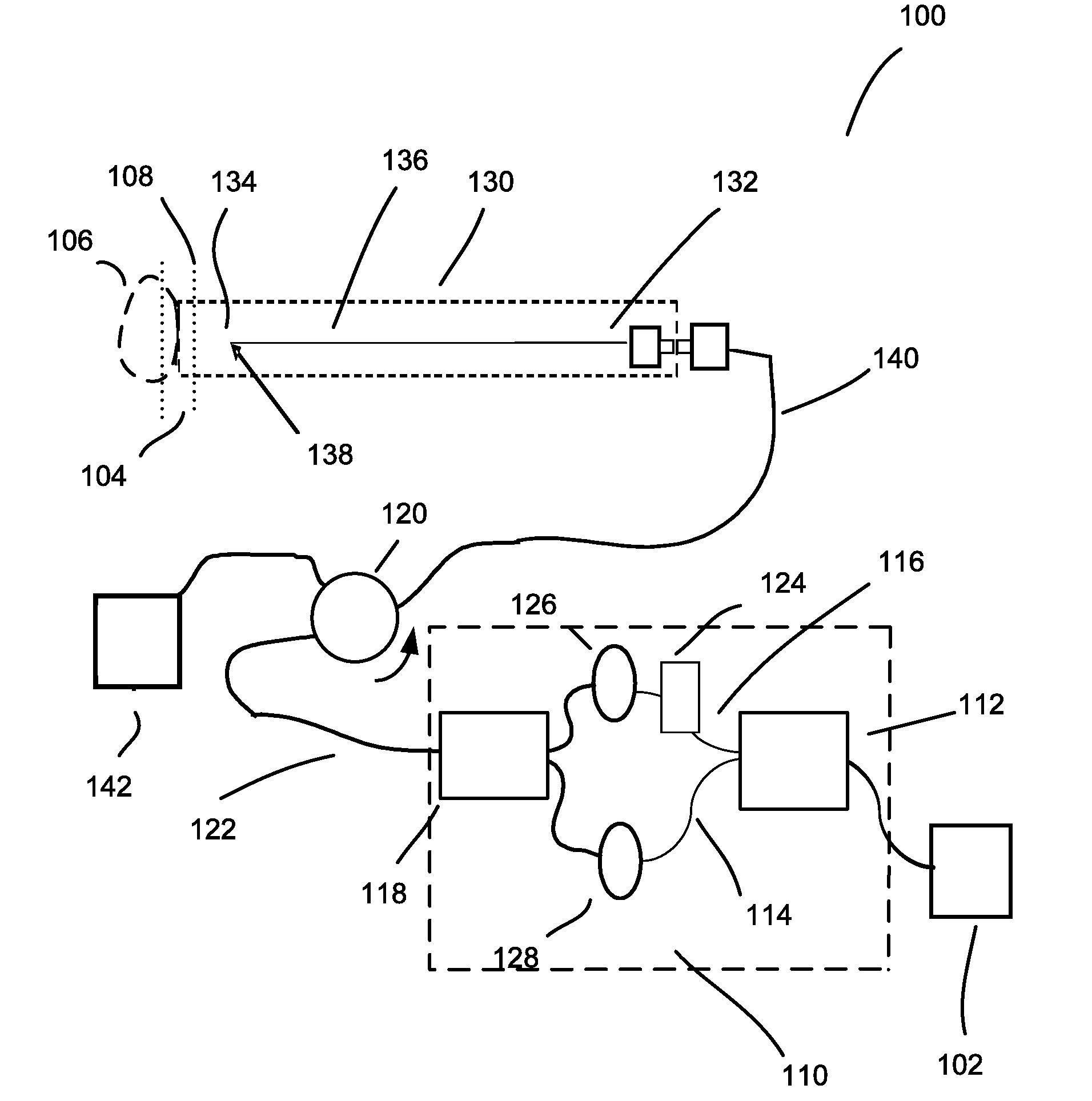
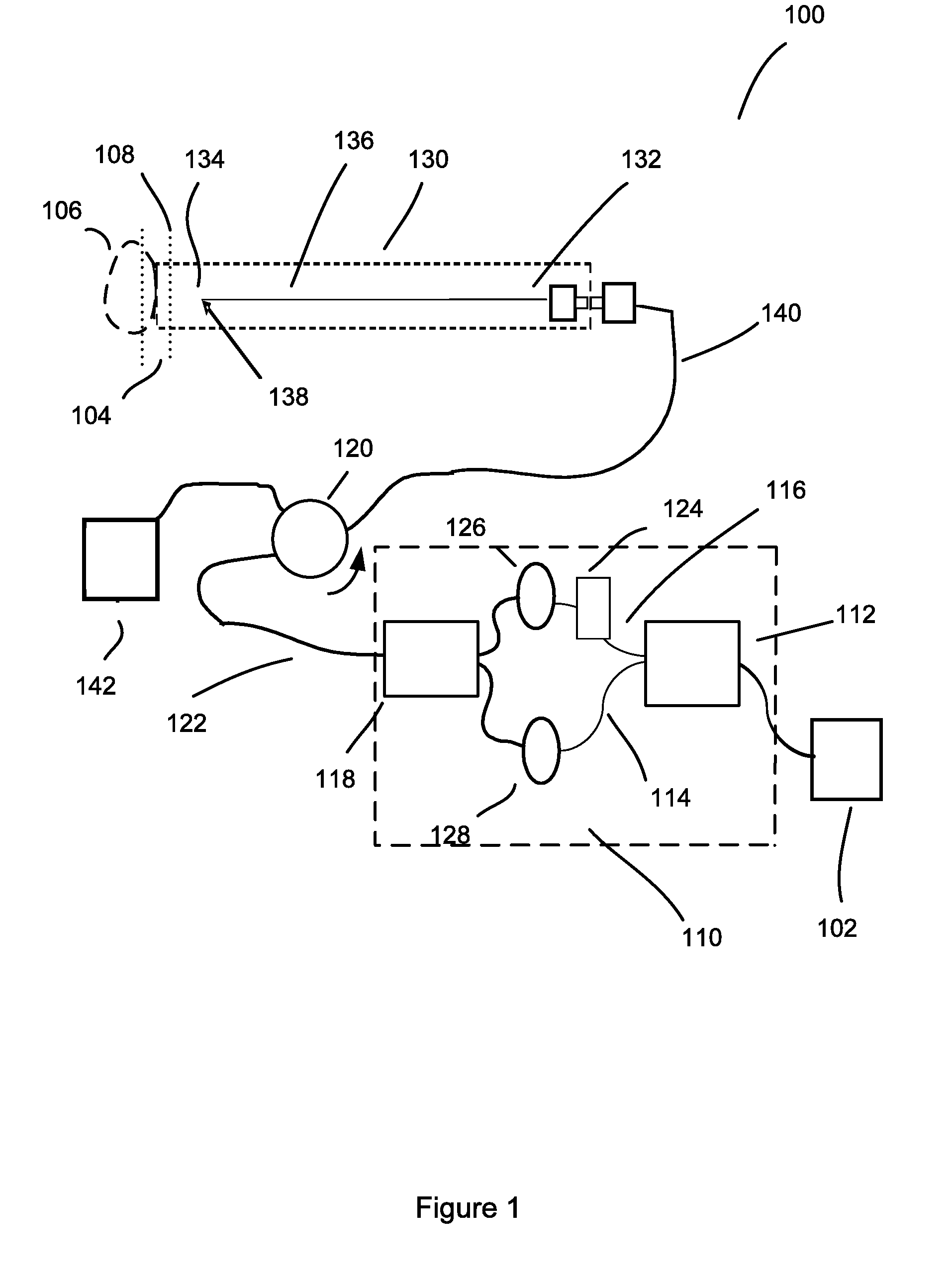
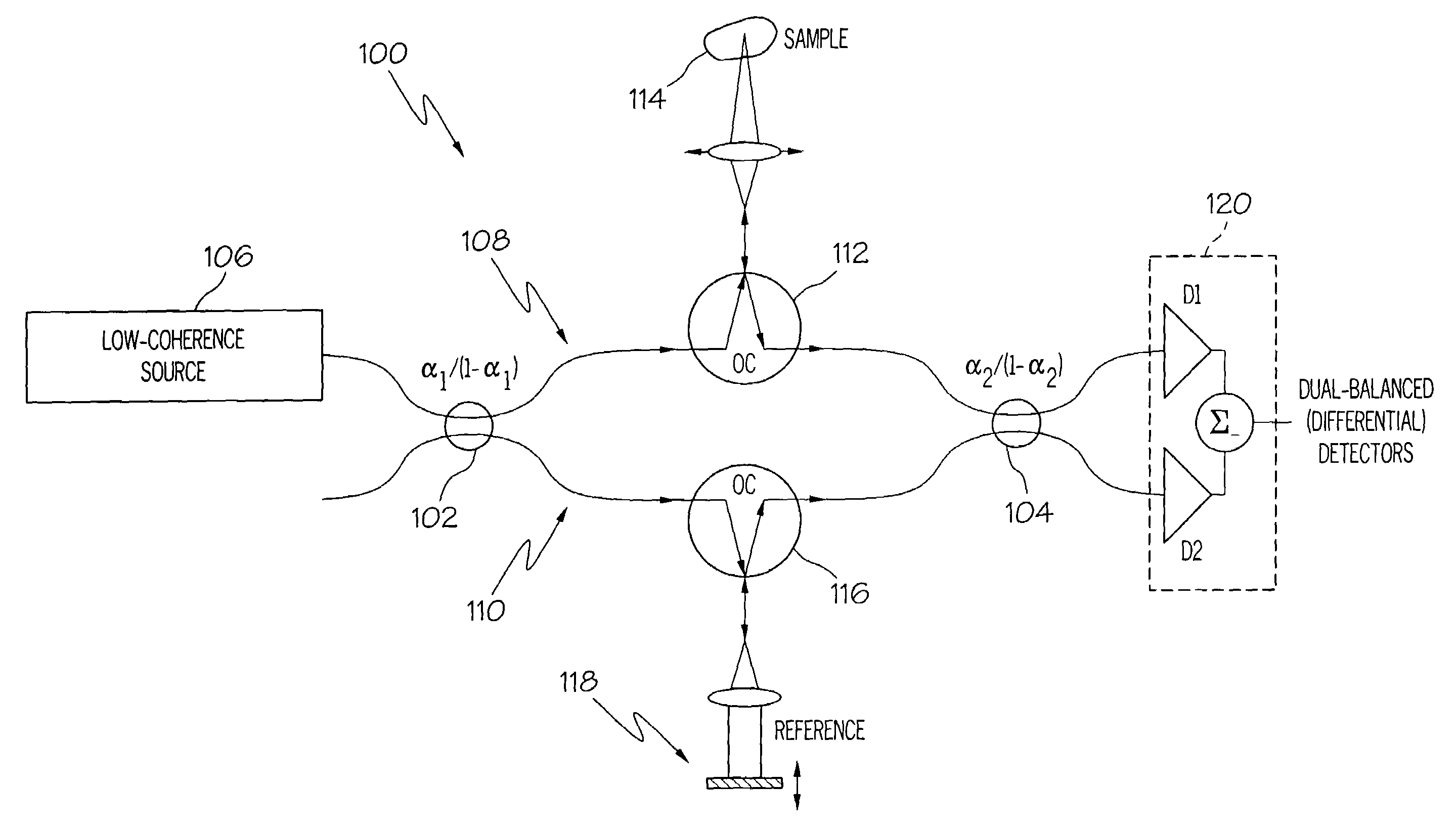
Interferometers for optical coherence tomography and reflectometry
An interferometer system includes an optical radiation source, an optical circulator connected between the optical radiation source and a sample location for transmitting optical radiation from the optical radiation source to the sample location, an output of the optical circulator connected to direct optical radiation to an optical detector. Various embodiments of such a system are possible. A method of performing OCDR or OCT imaging of a sample which involves the steps of: (a) producing low coherence optical radiation; (b) directing at least some of the low coherence optical radiation through an optical circulator to the sample; (c) reflecting at least some of the low coherence optical radiation off of the sample; and (d) detecting at least some of the reflected low coherence optical radiation and producing an electrical signal corresponding thereto.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC +2
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS7030971B1To offer comfortLow costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringTime delays
A CW lightwave modulated by a continuously reiterated binary pseudorandom code sequence is launched into an end of a span of ordinary optical fiber cable. Portions of the launched lightwave back propagate to the launch end from a continuum of locations along the span because of innate fiber properties including Rayleigh scattering. This is picked off the launch end and heterodyned to produce a r.f. beat signal. The r.f. beat signal is processed by a plurality (which can be thousands) of correlator type binary pseudonoise code sequence demodulators respectively operated in different delay time relationships to the timing base of the reiterated modulation sequences. The outputs of the demodulators provide r.f. time-domain reflectometry outputs representative of signals (e.g., acoustic pressure waves) incident to virtual sensors along the fiber at positions corresponding to the various time delay relationships.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE OFFICE OF NAVAL RES
Multi-technique thin film analysis tool
InactiveUS7039158B1Low costImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansElectron probe microanalysisComposition analysis
A thin film analysis system includes multi-technique analysis capability. Grazing incidence x-ray reflectometry (GXR) can be combined with x-ray fluorescence (XRF) using wavelength-dispersive x-ray spectrometry (WDX) detectors to obtain accurate thickness measurements with GXR and high-resolution composition measurements with XRF using WDX detectors. A single x-ray beam can simultaneously provide the reflected x-rays for GXR and excite the thin film to generate characteristic x-rays for XRF. XRF can be combined with electron microprobe analysis (EMP), enabling XRF for thicker films while allowing the use of the faster EMP for thinner films. The same x-ray detector(s) can be used for both XRF and EMP to minimize component count. EMP can be combined with GXR to obtain rapid composition analysis and accurate thickness measurements, with the two techniques performed simultaneously to maximize throughput.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com