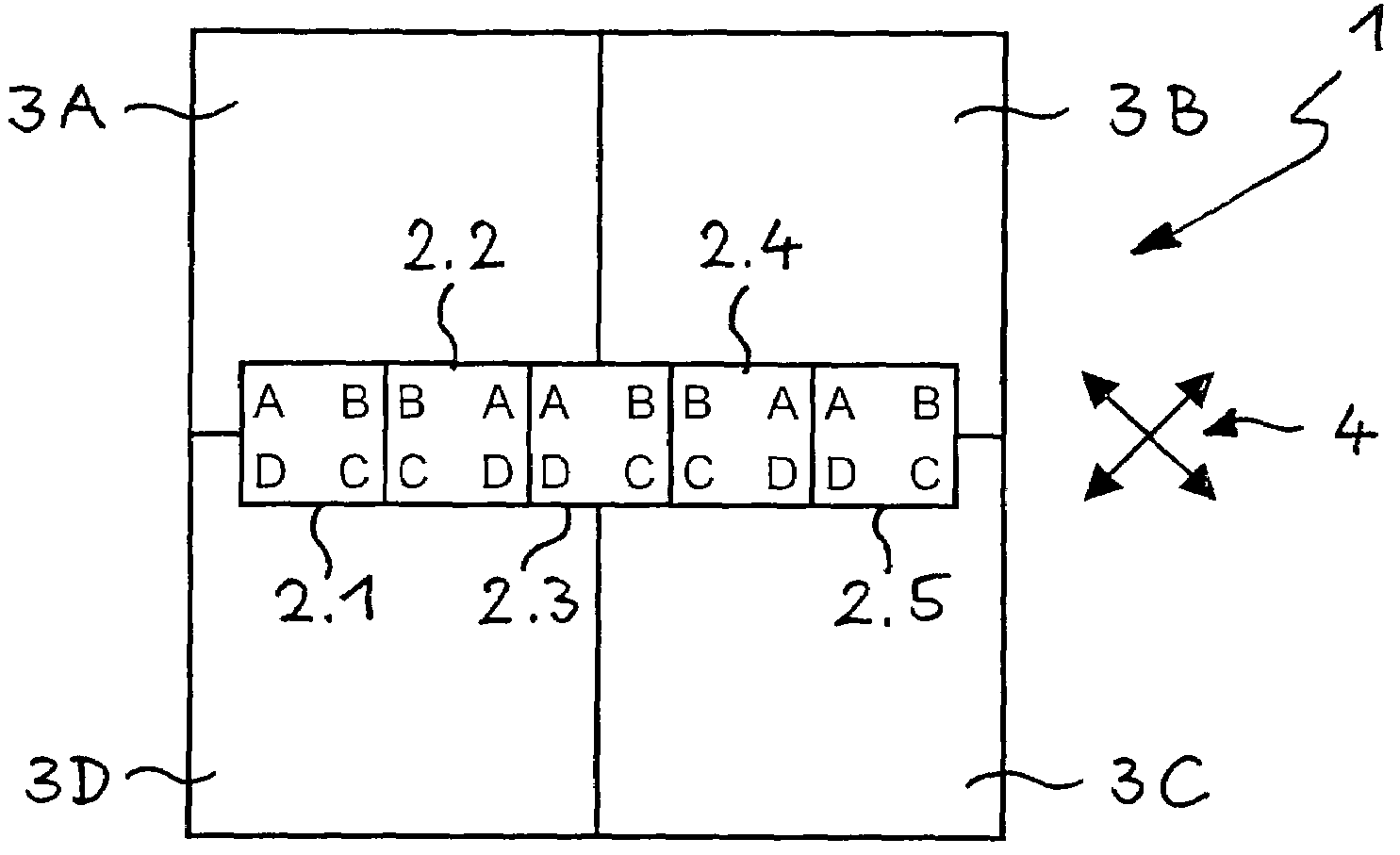
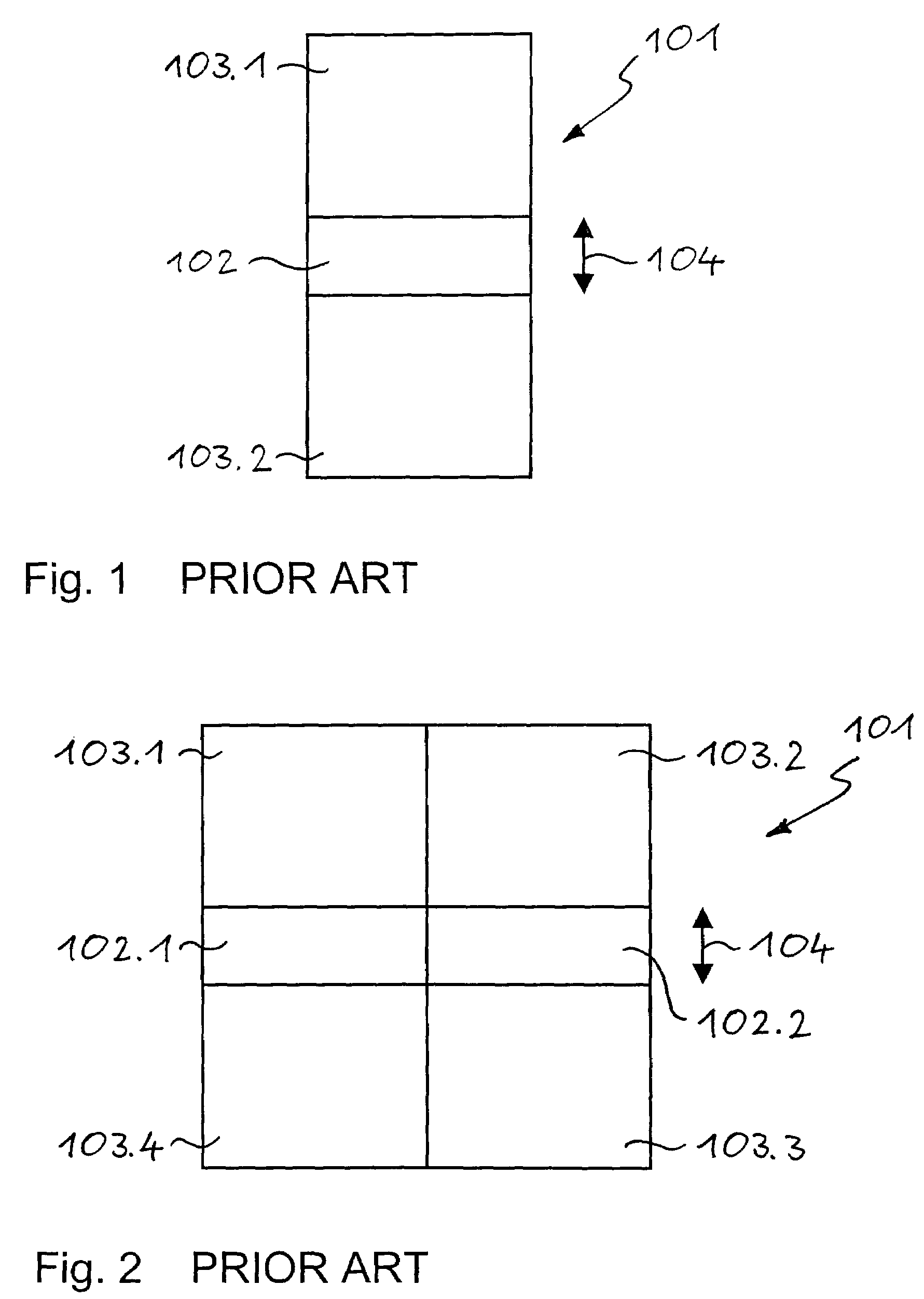
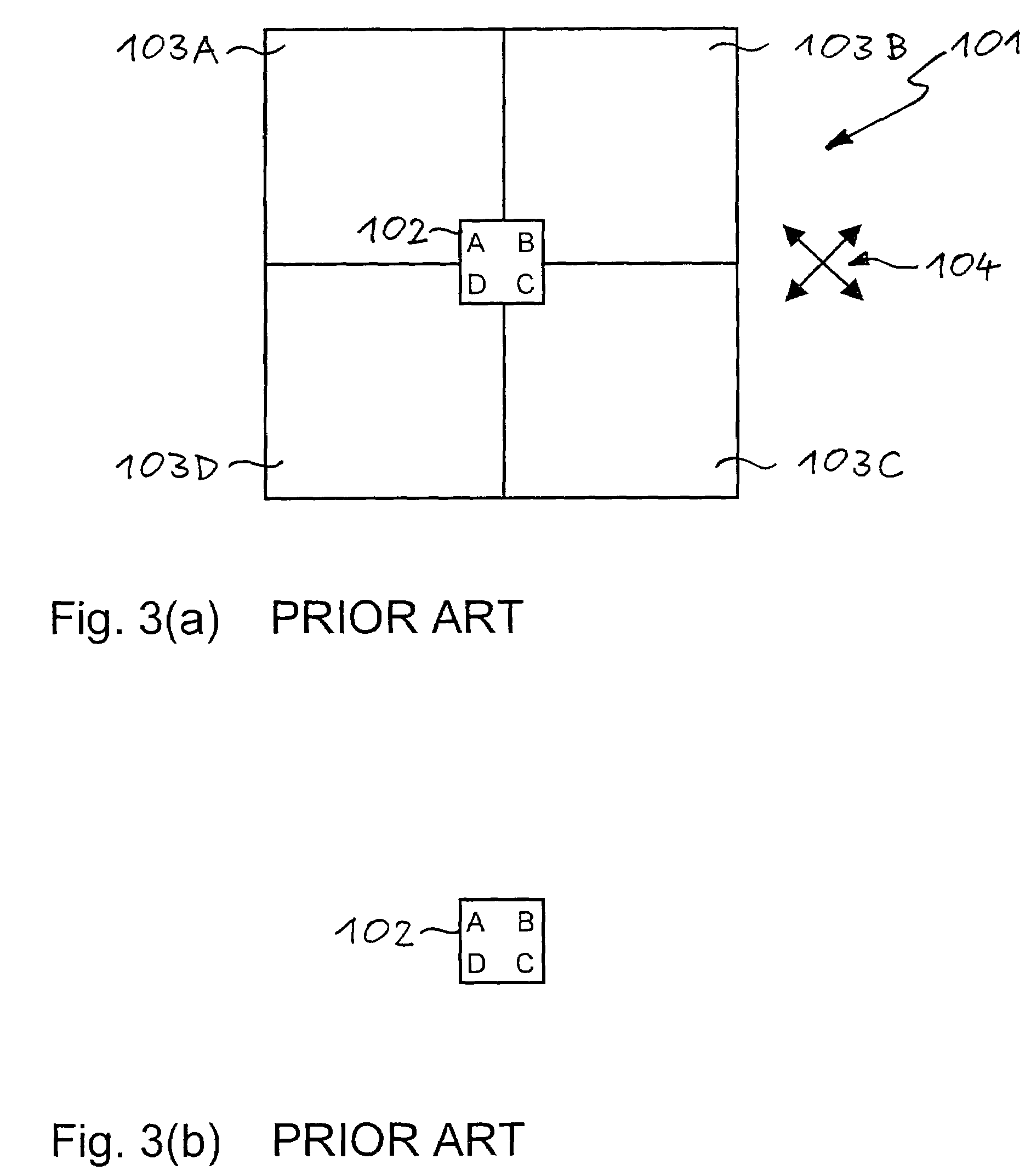
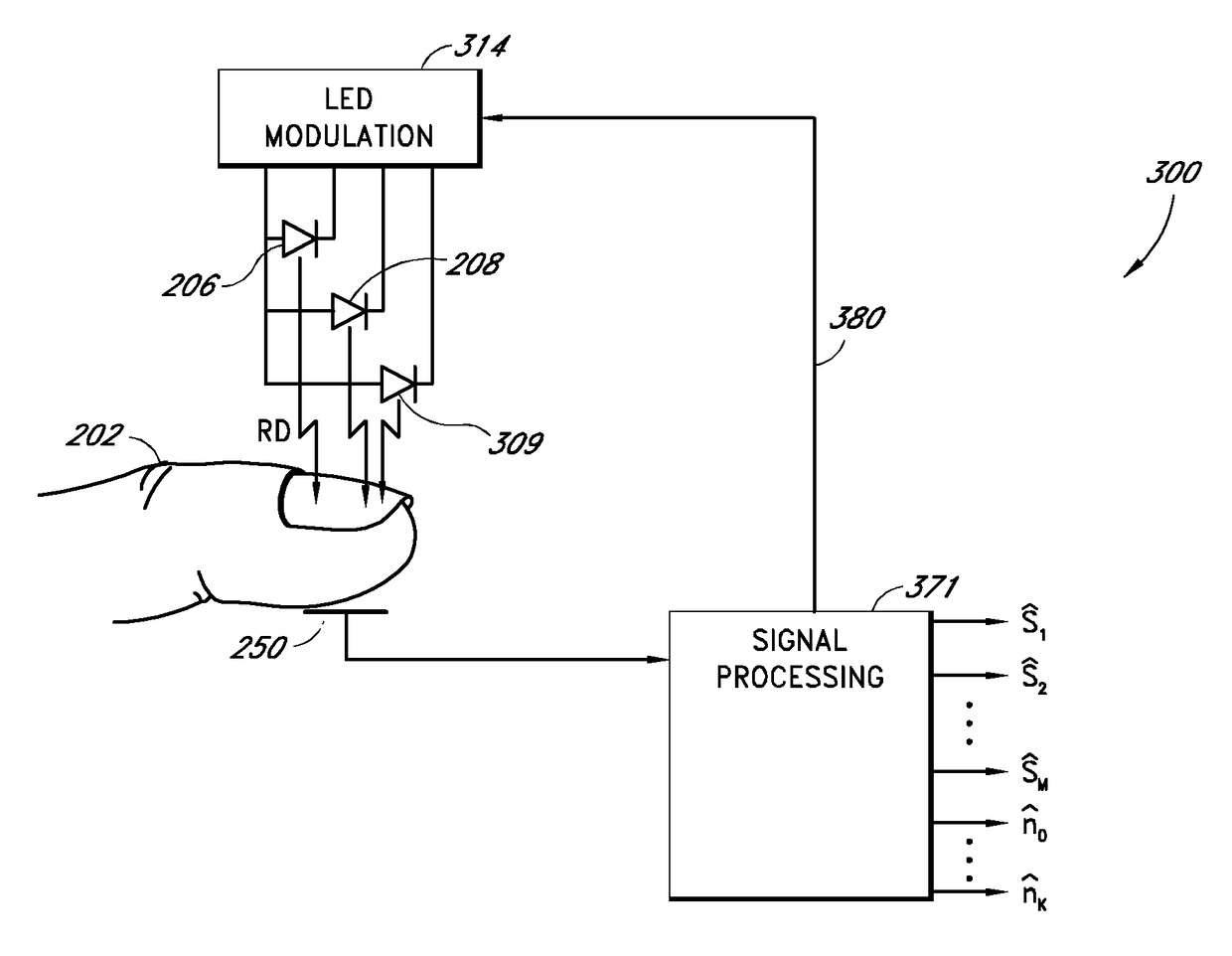
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
17134 results about "Demodulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Demodulation is extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. There are many types of modulation so there are many types of demodulators. The signal output from a demodulator may represent sound (an analog audio signal), images (an analog video signal) or binary data (a digital signal).
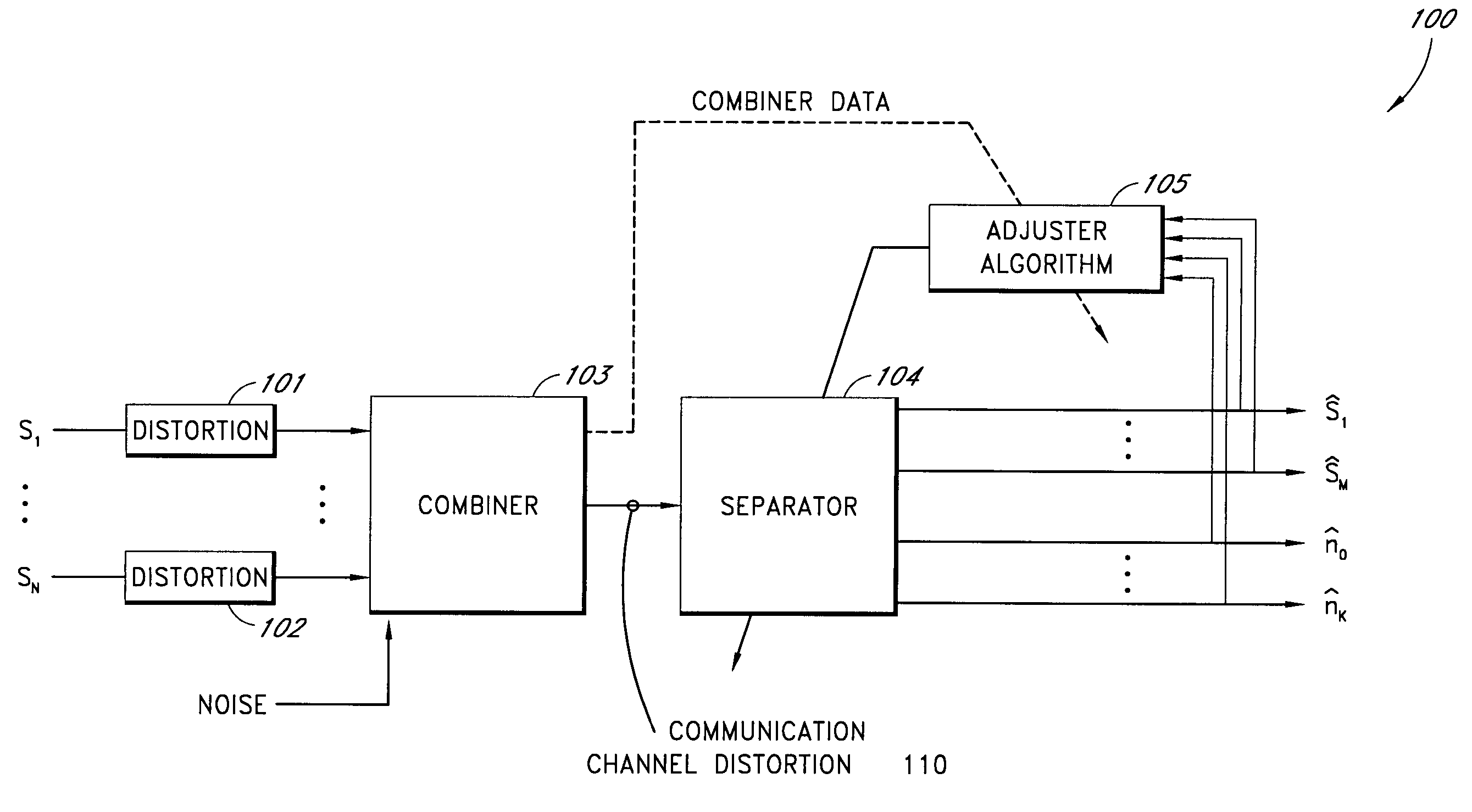
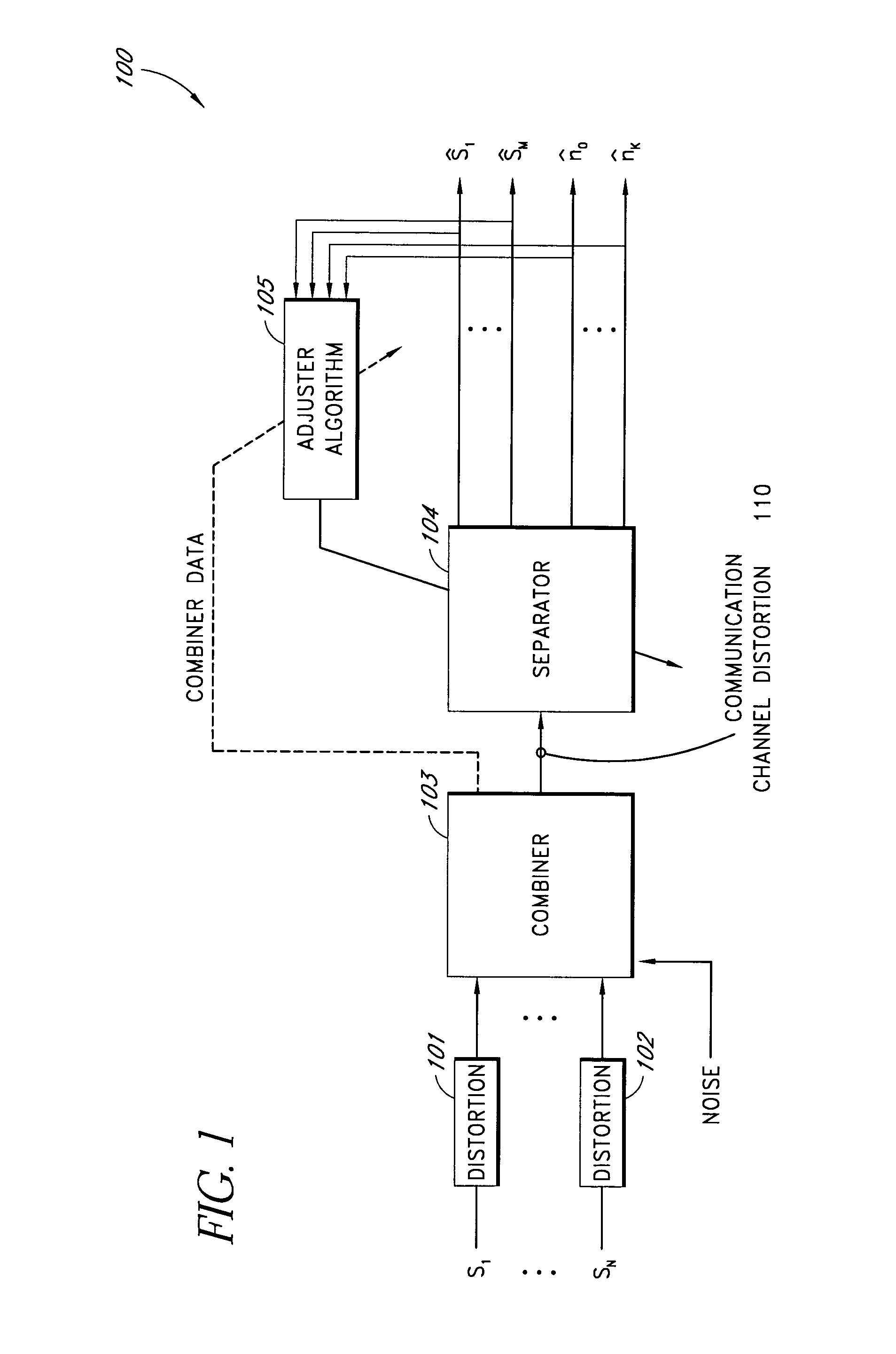
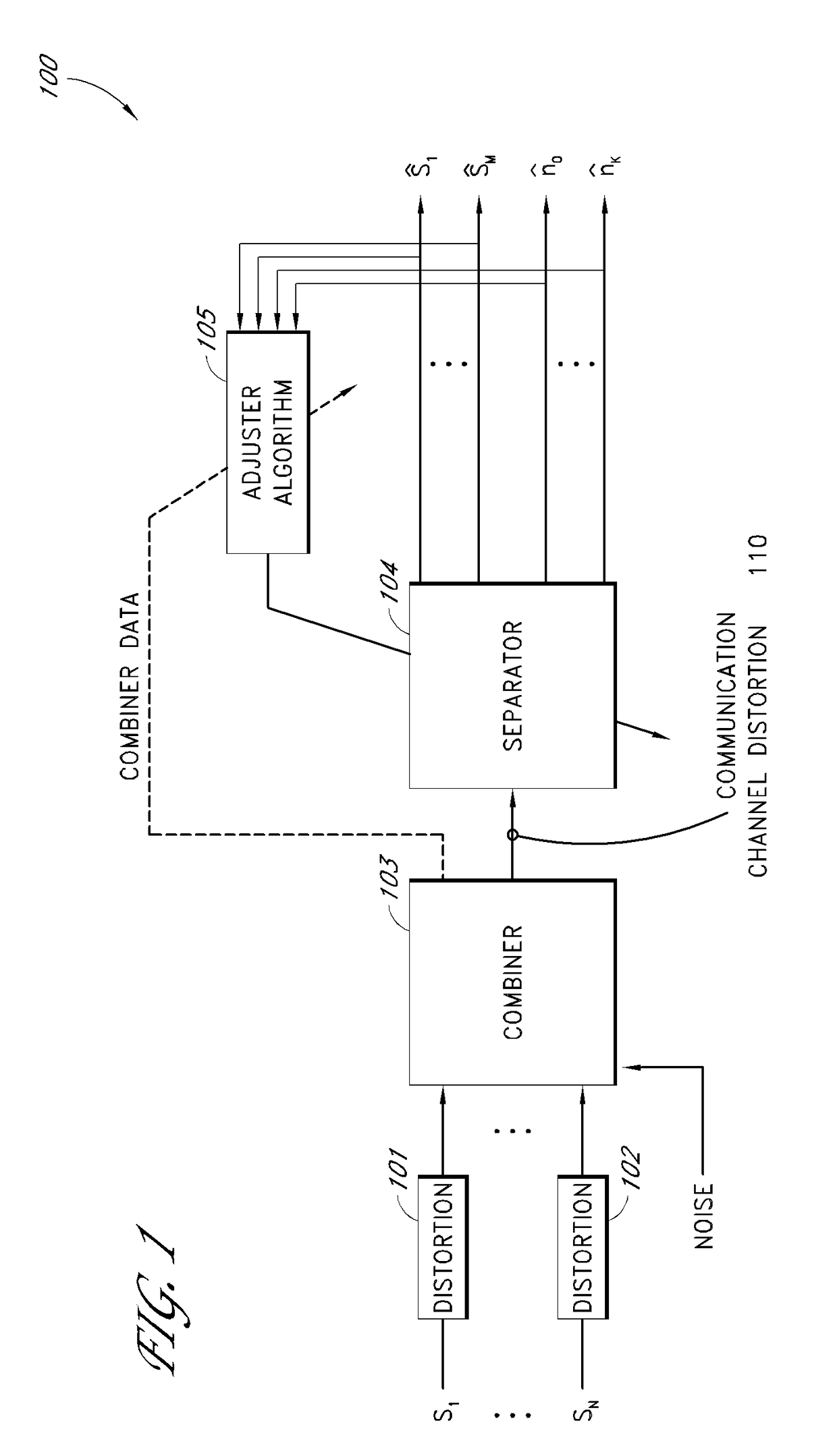
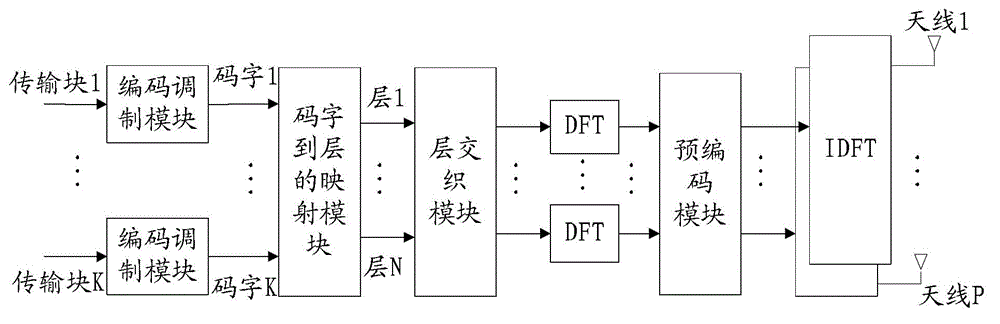
Method and apparatus for reducing coupling between signals
InactiveUS7003338B2Reduces crosstalk and other contaminationCrosstalk in the multi-channel demodulator is reducedDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical sensorsComputer moduleSignal processing
A method and an apparatus for separating a composite signal into a plurality of signals is described. A signal processor receives a composite signal and separates a composite signal in to separate output signals. Feedback from one or more of the output signals is provided to a configuration module that configures the signal processor to improve a quality of the output signals. In one embodiment, the signal processor separates the composite signal by applying a first demodulation signal to the composite signal to generate a first output signal. In one embodiment, the signal processor also applies a second demodulation signal to the composite signal to generate a second output signal. In one embodiment, a phase and / or amplitude of the first demodulation signal and a phase and / or amplitude of the second demodulation signal are selected to reduce crosstalk. In one embodiment, the composite signal is obtained from a detector in a system for measuring one or more blood constituents.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
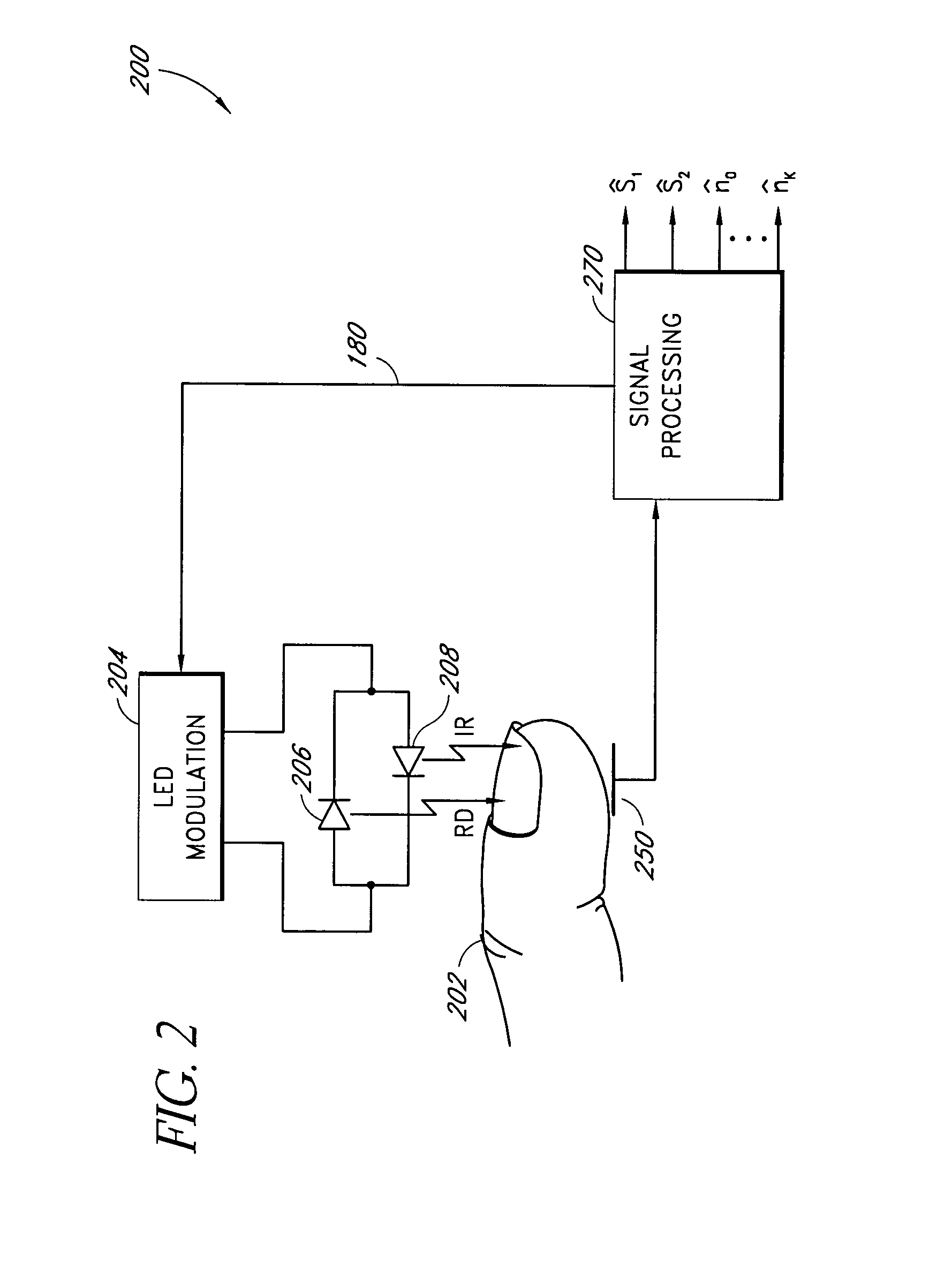
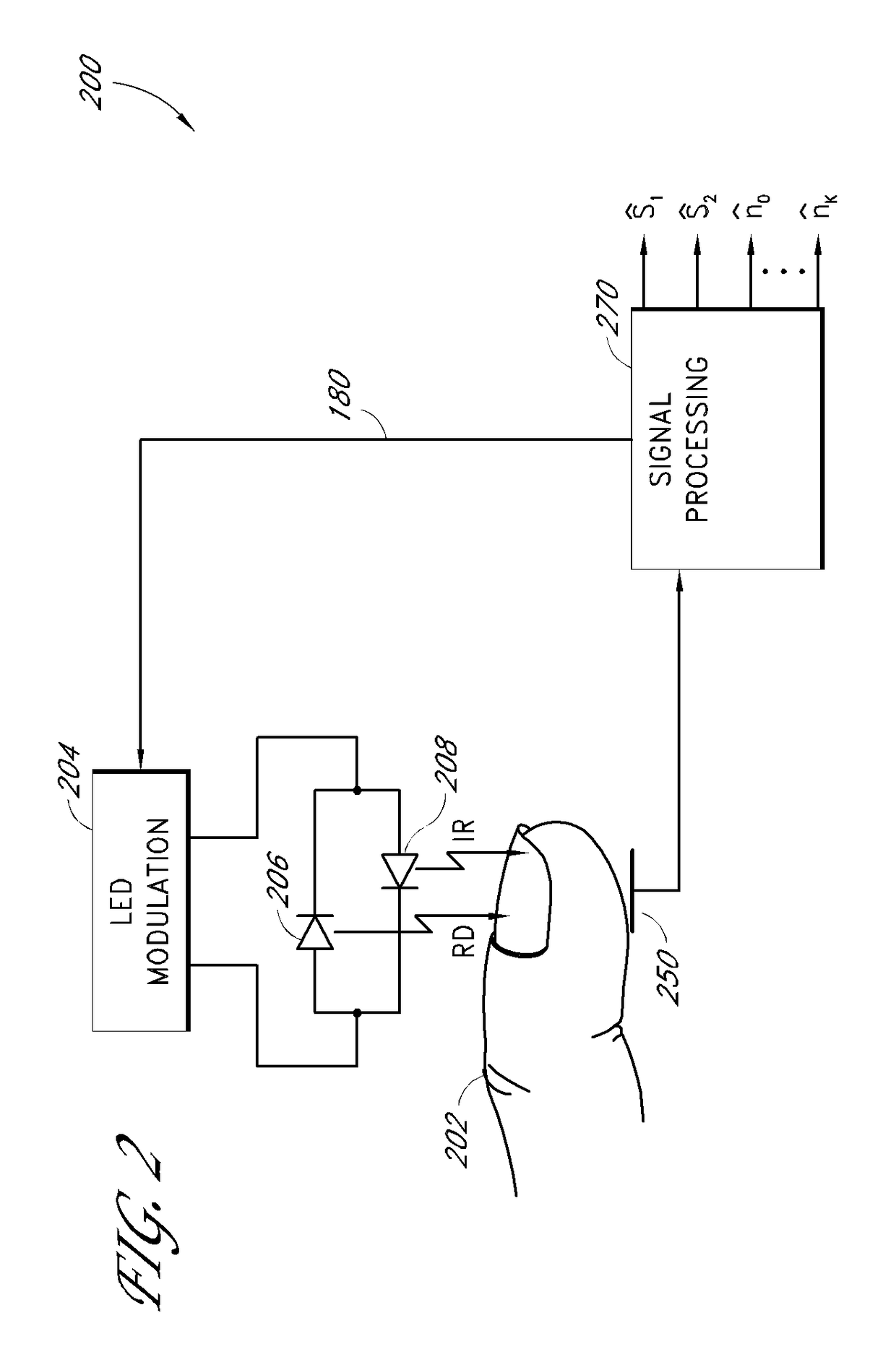
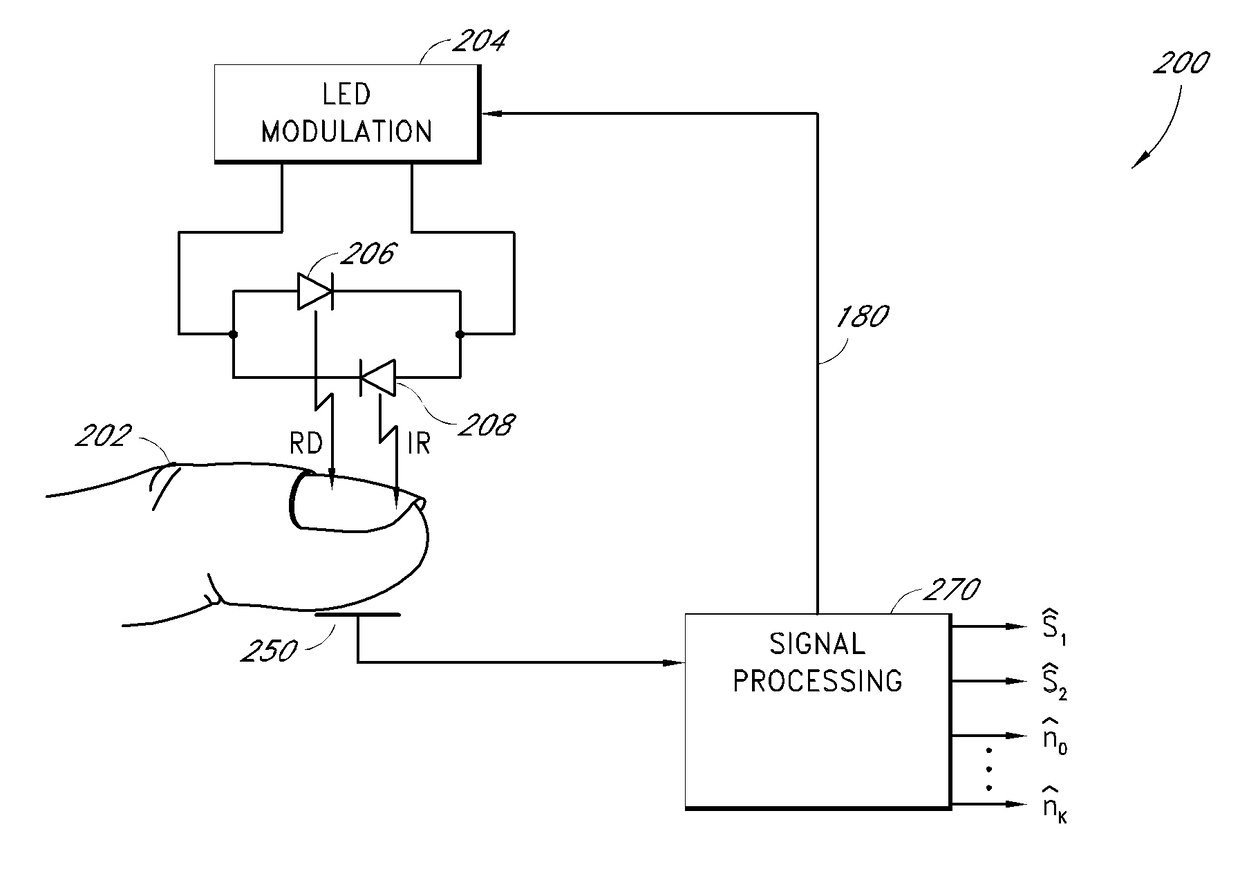
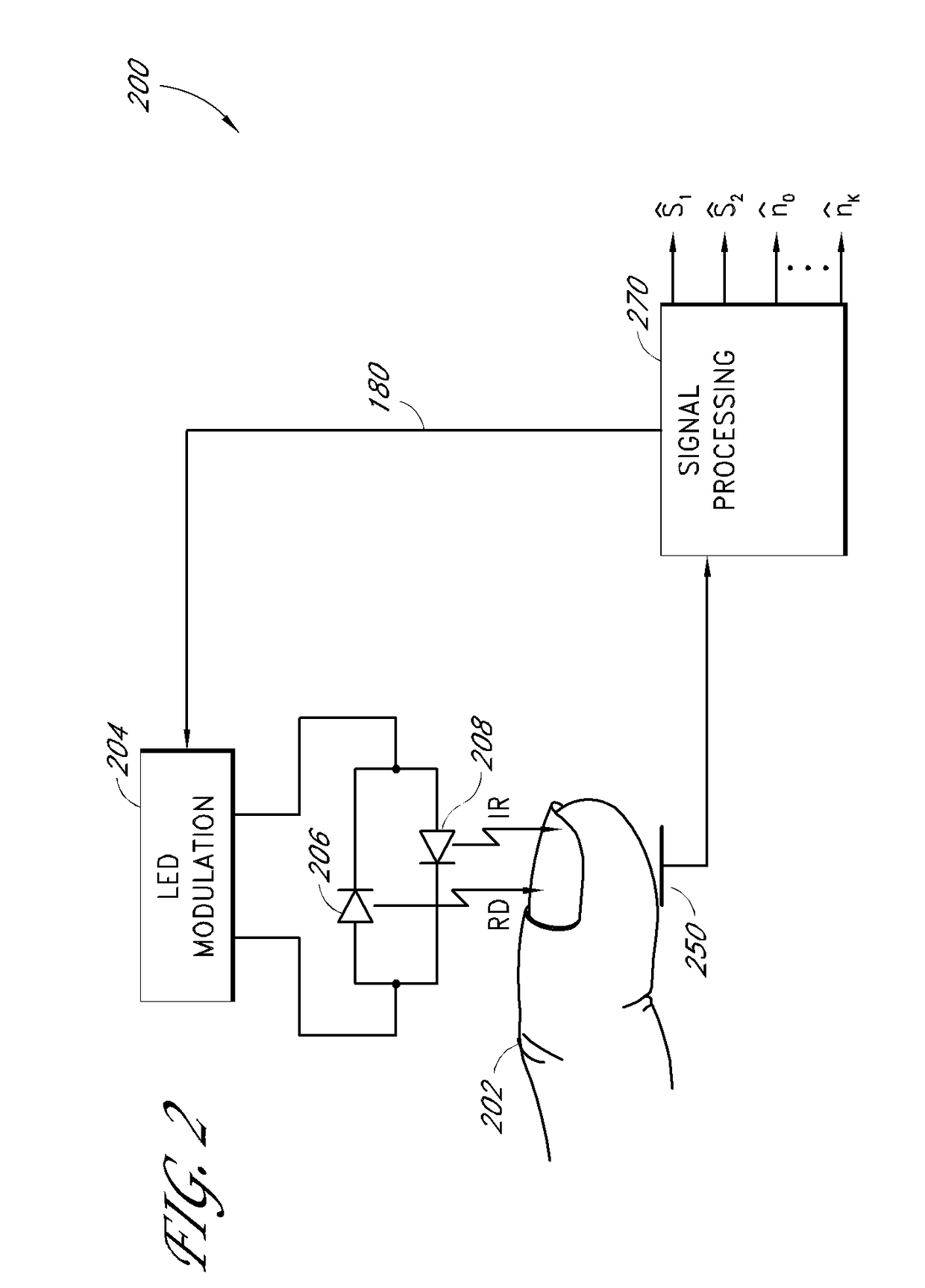
Method and apparatus for demodulating signals in a pulse oximetry system
InactiveUS7003339B2Reduce distractionsHigh resolutionTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexHarmonicBlood oxygenation
A method and an apparatus measure blood oxygenation in a subject. A first signal source applies a first input signal during a first time interval. A second signal source applies a second input signal during a second time interval. A detector detects a first parametric signal responsive to the first input signal passing through a portion of the subject having blood therein. The detector also detects a second parametric signal responsive to the second input signal passing through the portion of the subject. The detector generates a detector output signal responsive to the first and second parametric signals. A signal processor receives the detector output signal and demodulates the detector output signal by applying a first demodulation signal to a signal responsive to the detector output signal to generate a first output signal responsive to the first parametric signal. The signal processor applies a second demodulation signal to the signal responsive to the detector output signal to generate a second output signal responsive to the second parametric signal. The first demodulation signal and the second demodulation signal both include at least a first component having a first frequency and a first amplitude and a second component having a second frequency and a second amplitude. The second frequency is a harmonic of the first frequency. The second amplitude is related to the first amplitude to minimize crosstalk from the first parametric signal to the second output signal and to minimize crosstalk from the second parametric signal to the first output signal.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
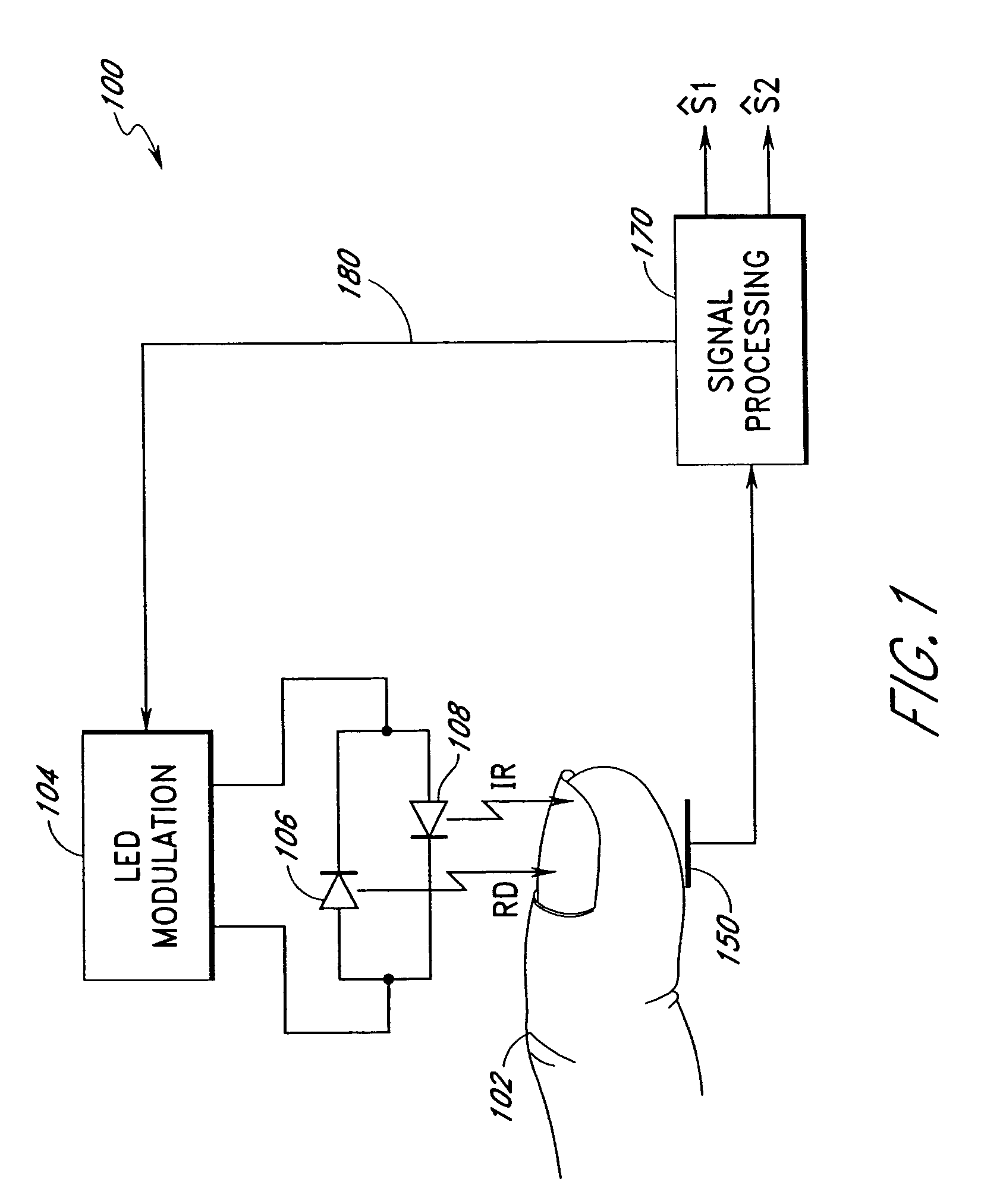
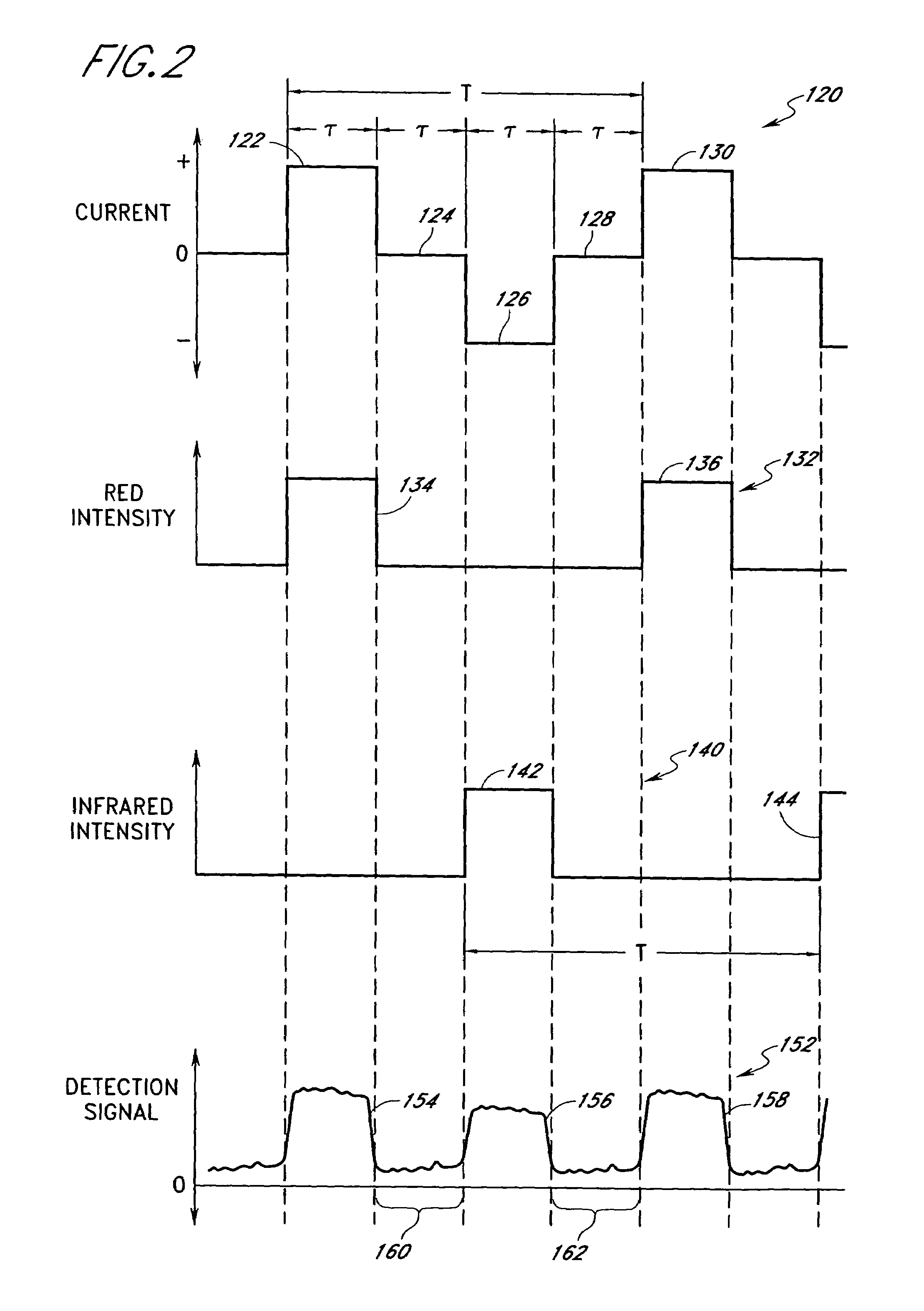
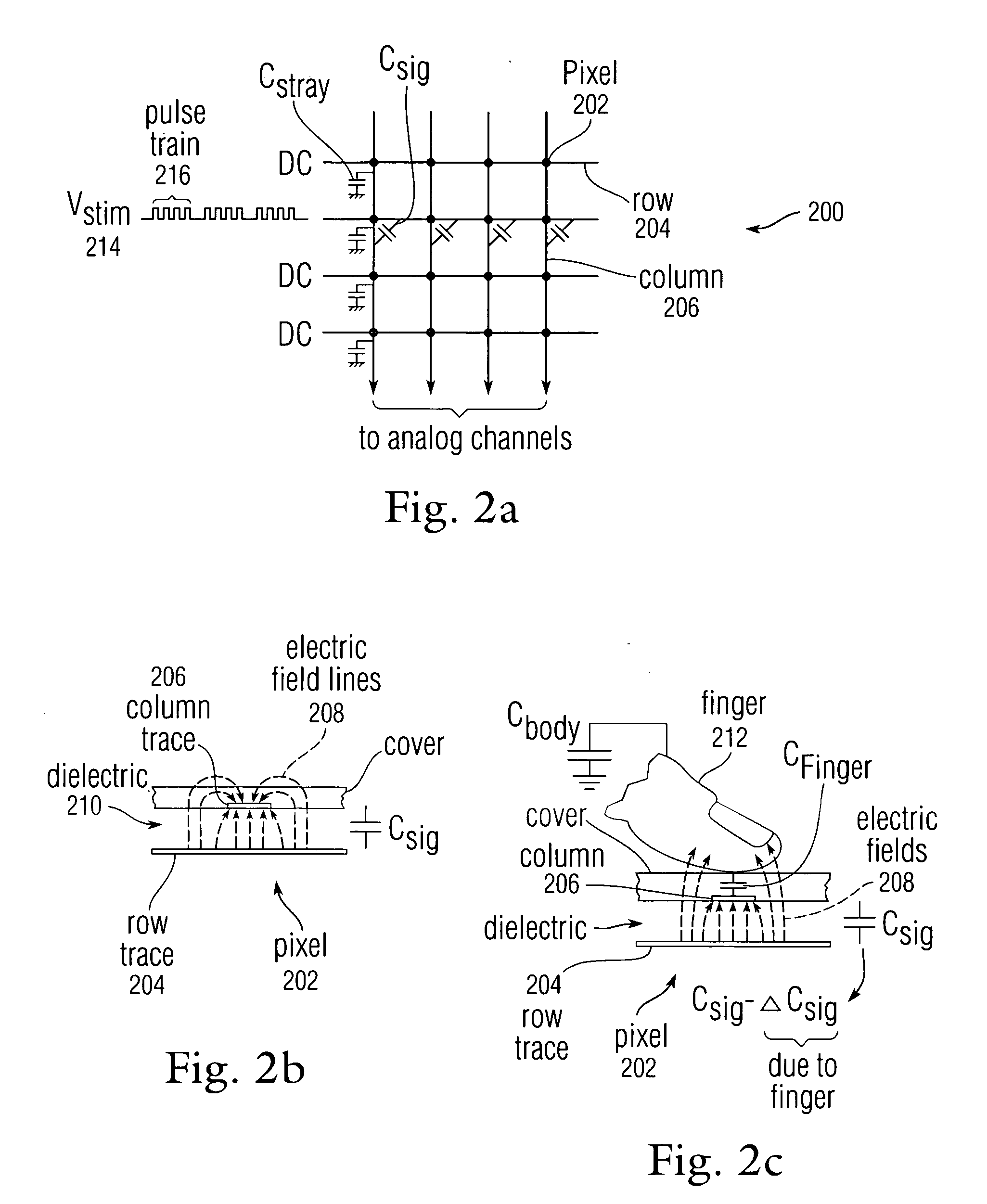
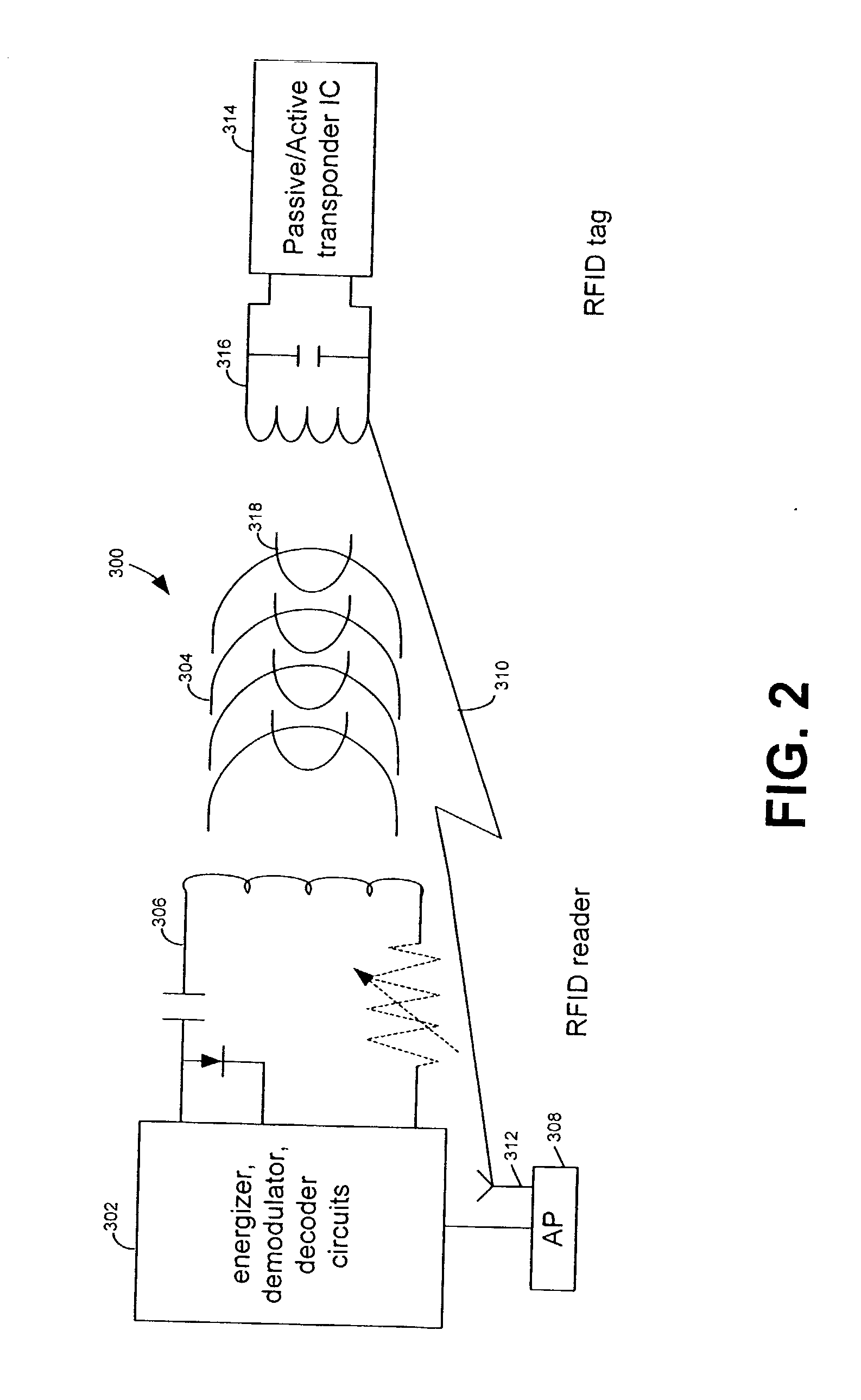
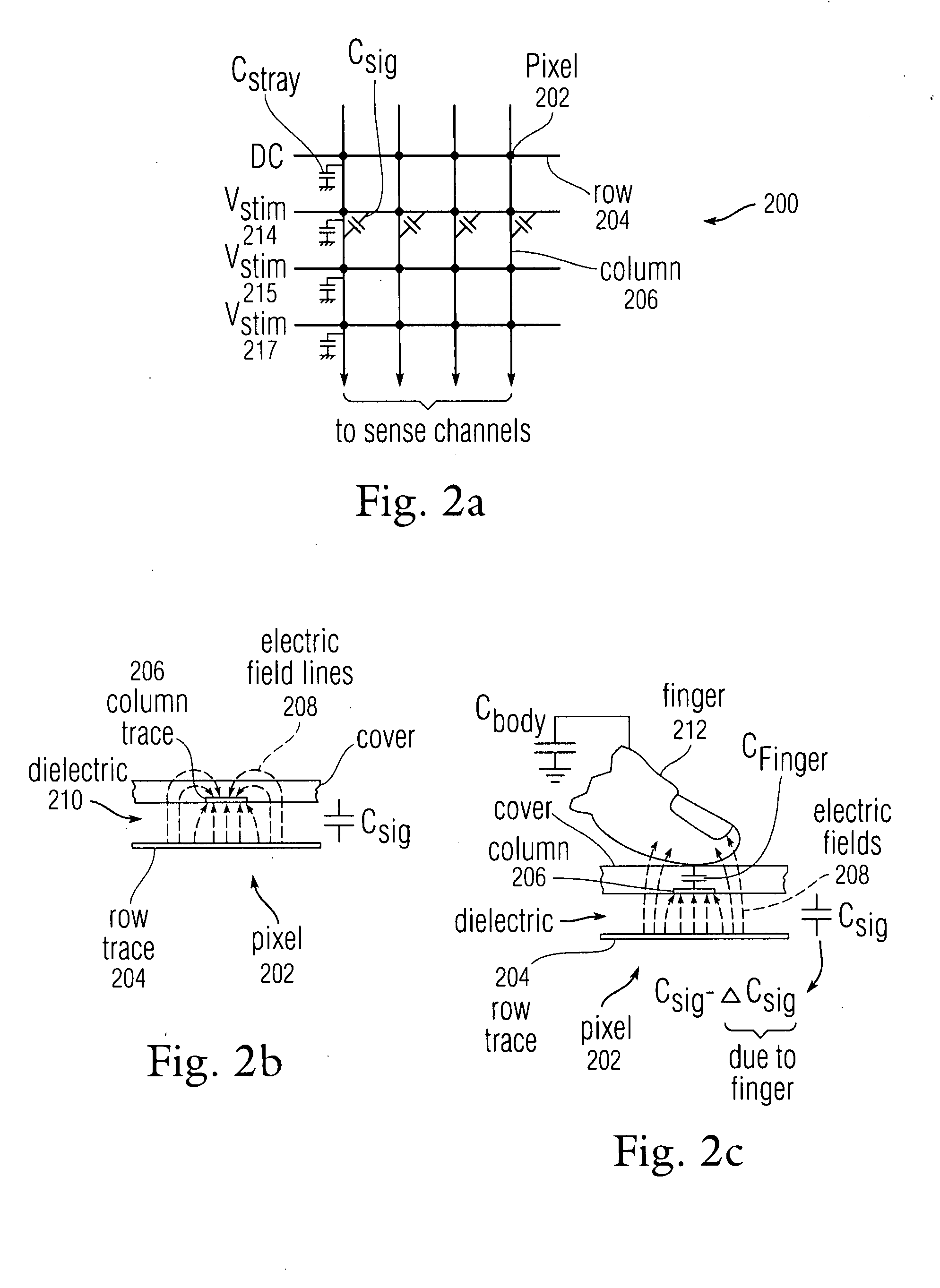
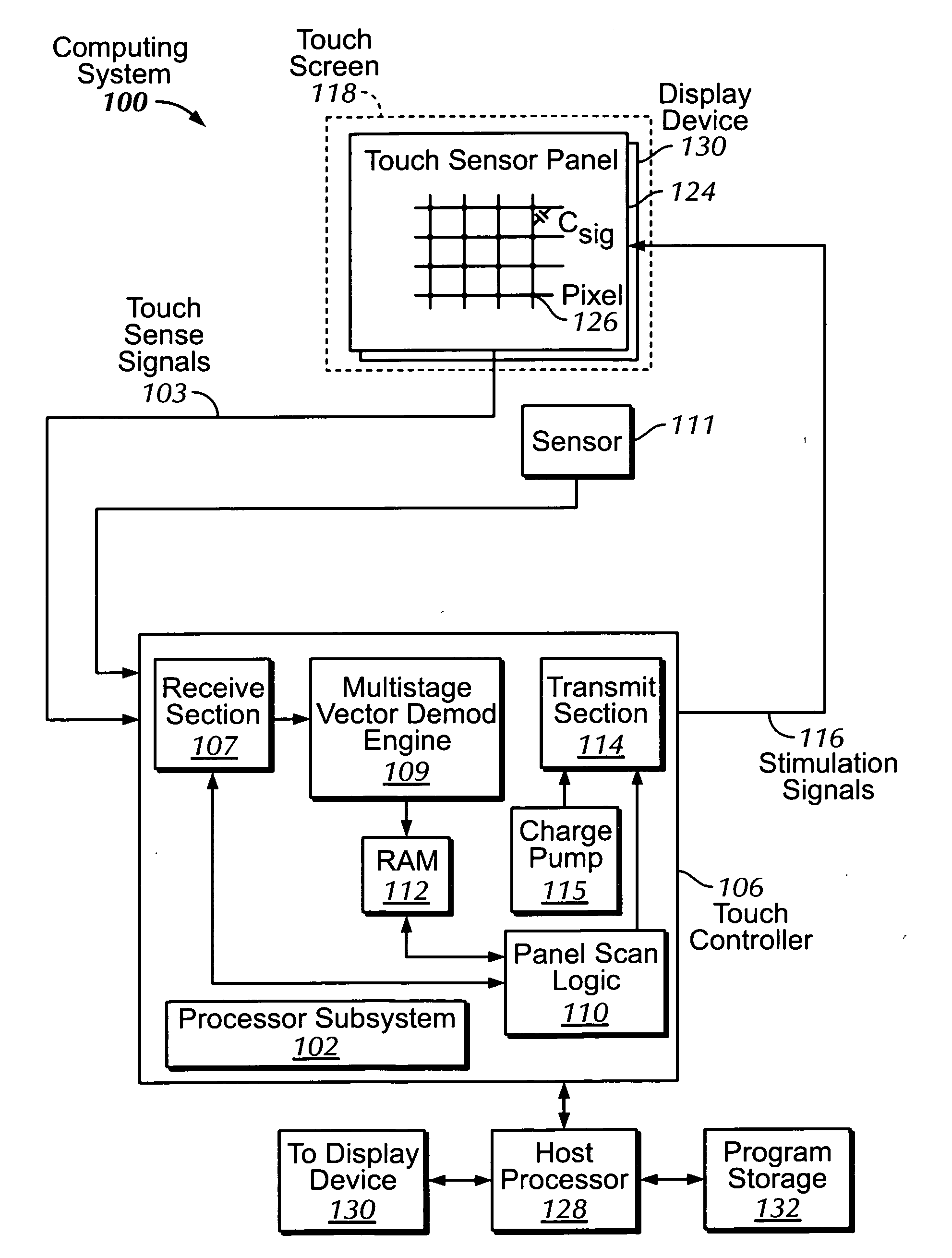
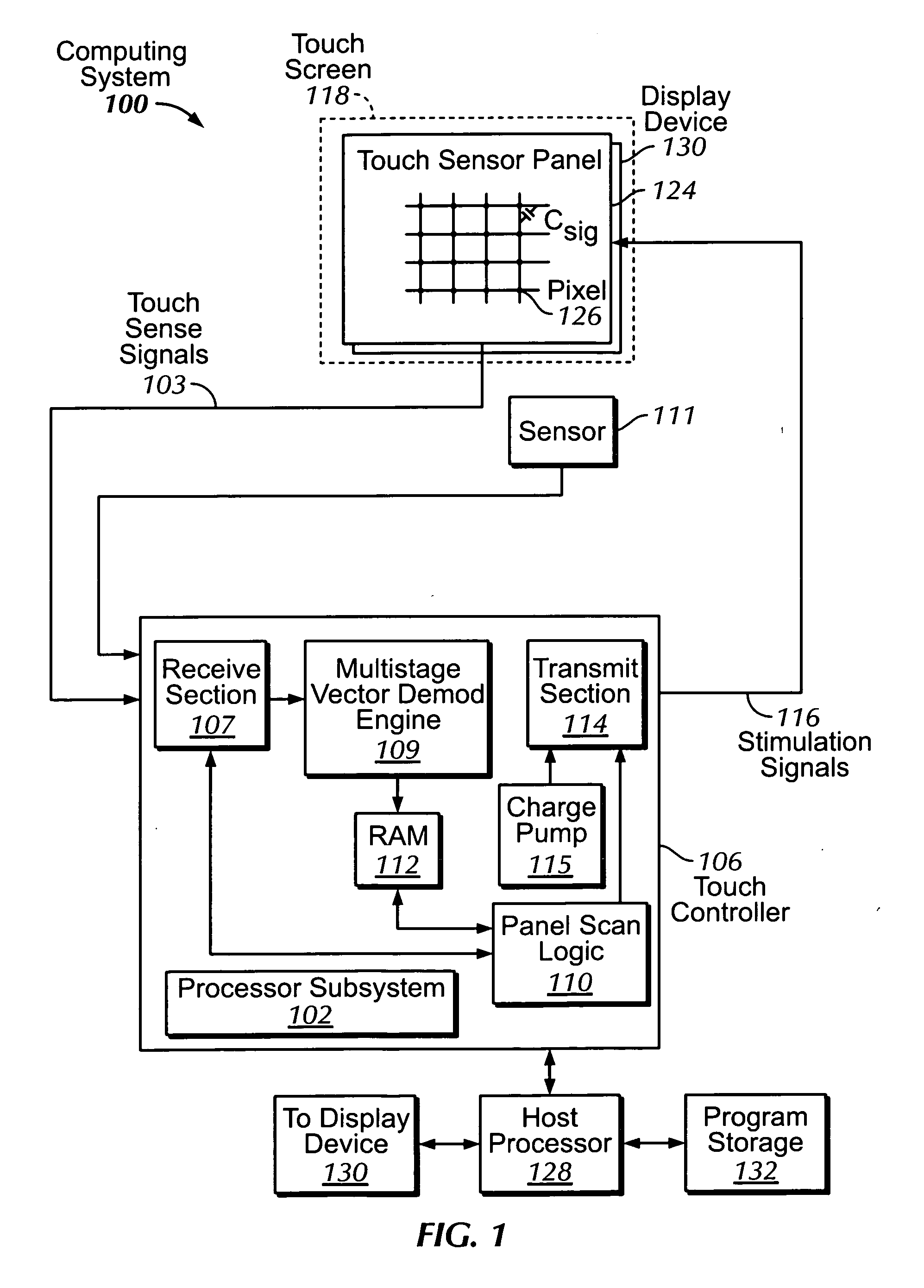
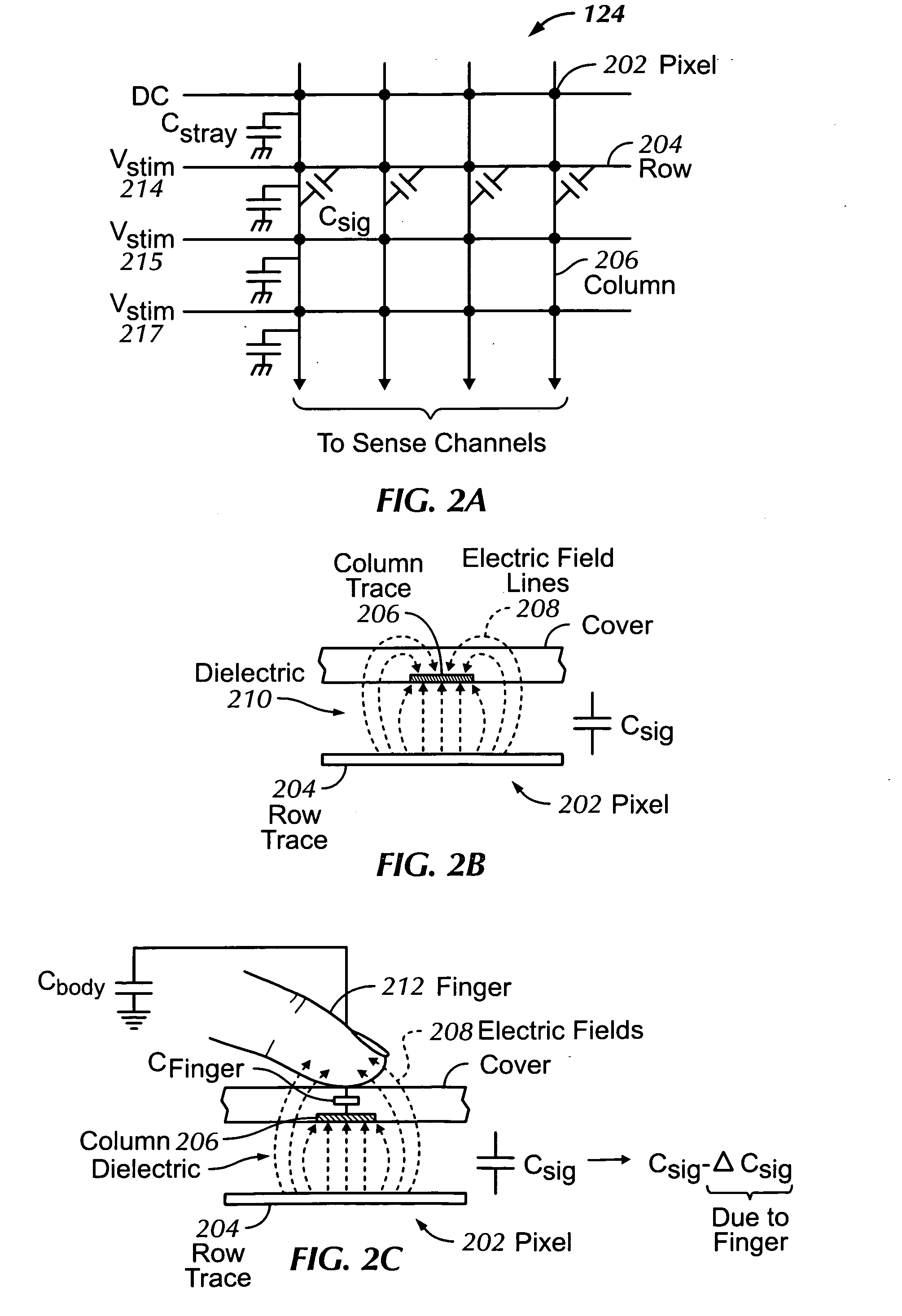
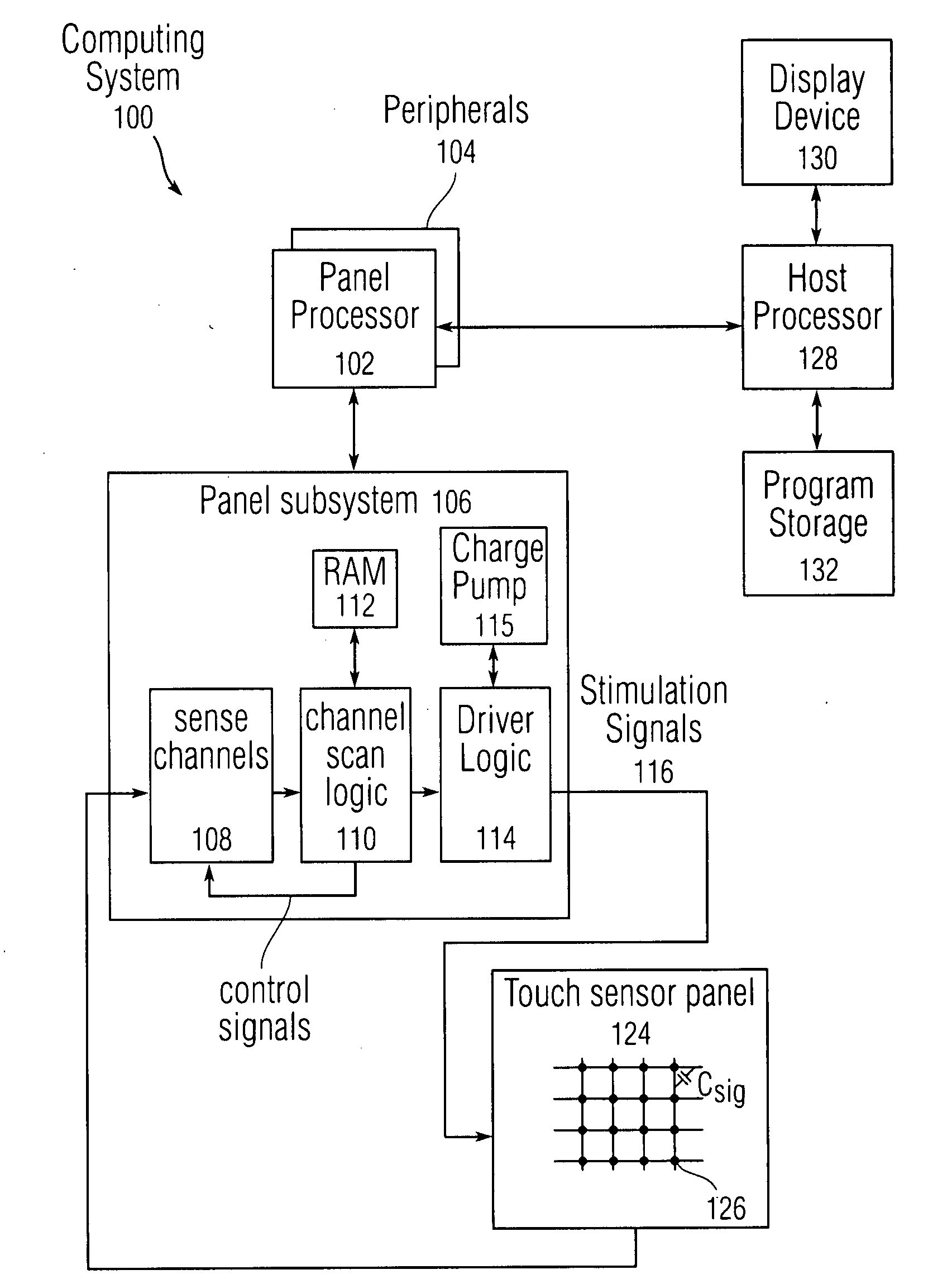
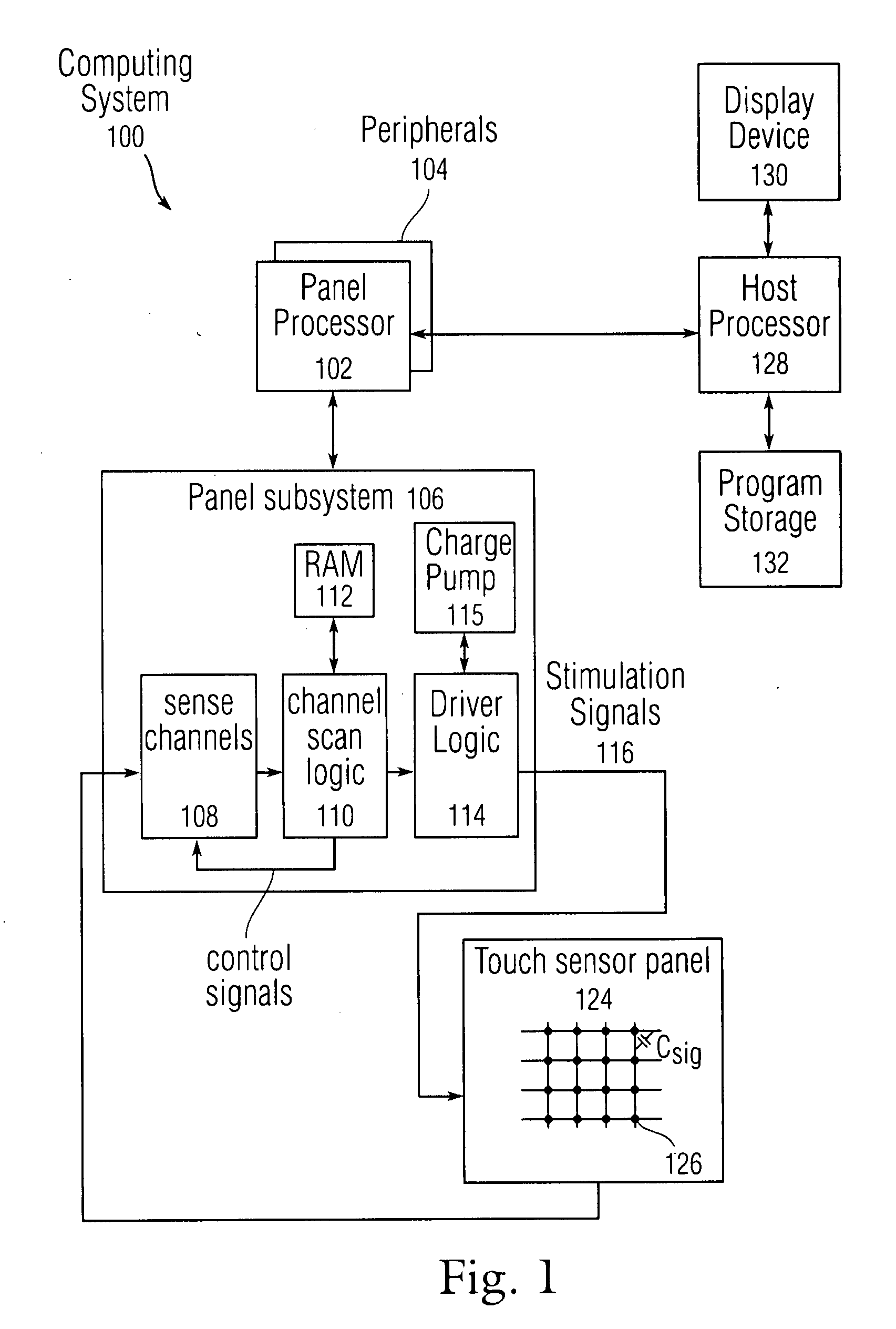
Proximity and multi-touch sensor detection and demodulation
ActiveUS20080158172A1Brightening displayDisplay delayEnergy efficient ICTPower network operation systems integrationProximity sensorEngineering
The use of one or more proximity sensors in combination with one or more touch sensors in a multi-touch panel to detect the presence of a finger, body part or other object and control or trigger one or more functions in accordance with an “image” of touch provided by the sensor outputs is disclosed. In some embodiments, one or more infrared (IR) proximity sensors can be driven with a specific stimulation frequency and emit IR light from one or more areas, which can in some embodiments correspond to one or more multi-touch sensor “pixel” locations. The reflected IR signal, if any, can be demodulated using synchronous demodulation. In some embodiments, both physical interfaces (touch and proximity sensors) can be connected to analog channels in the same electrical core.
Owner:APPLE INC
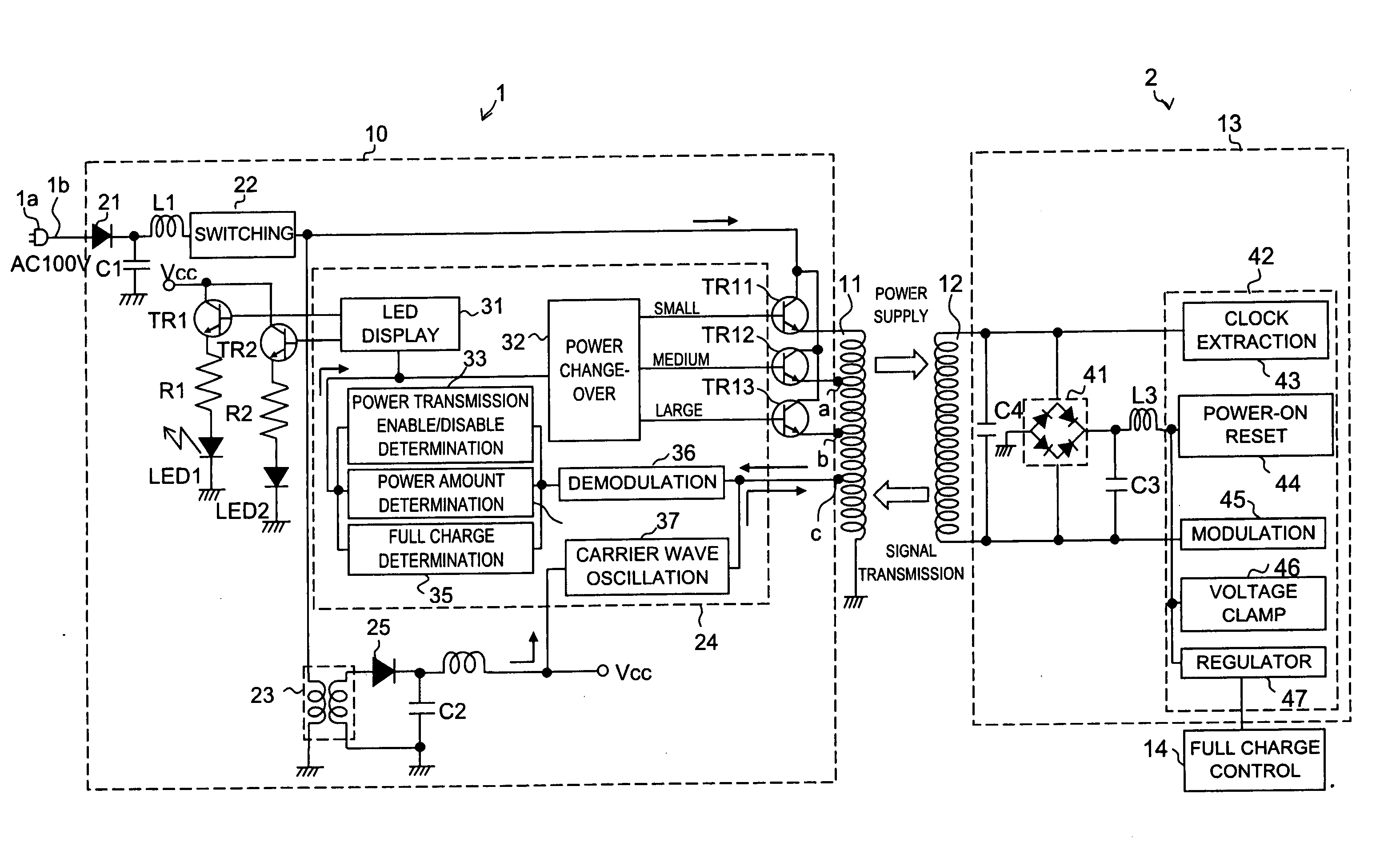
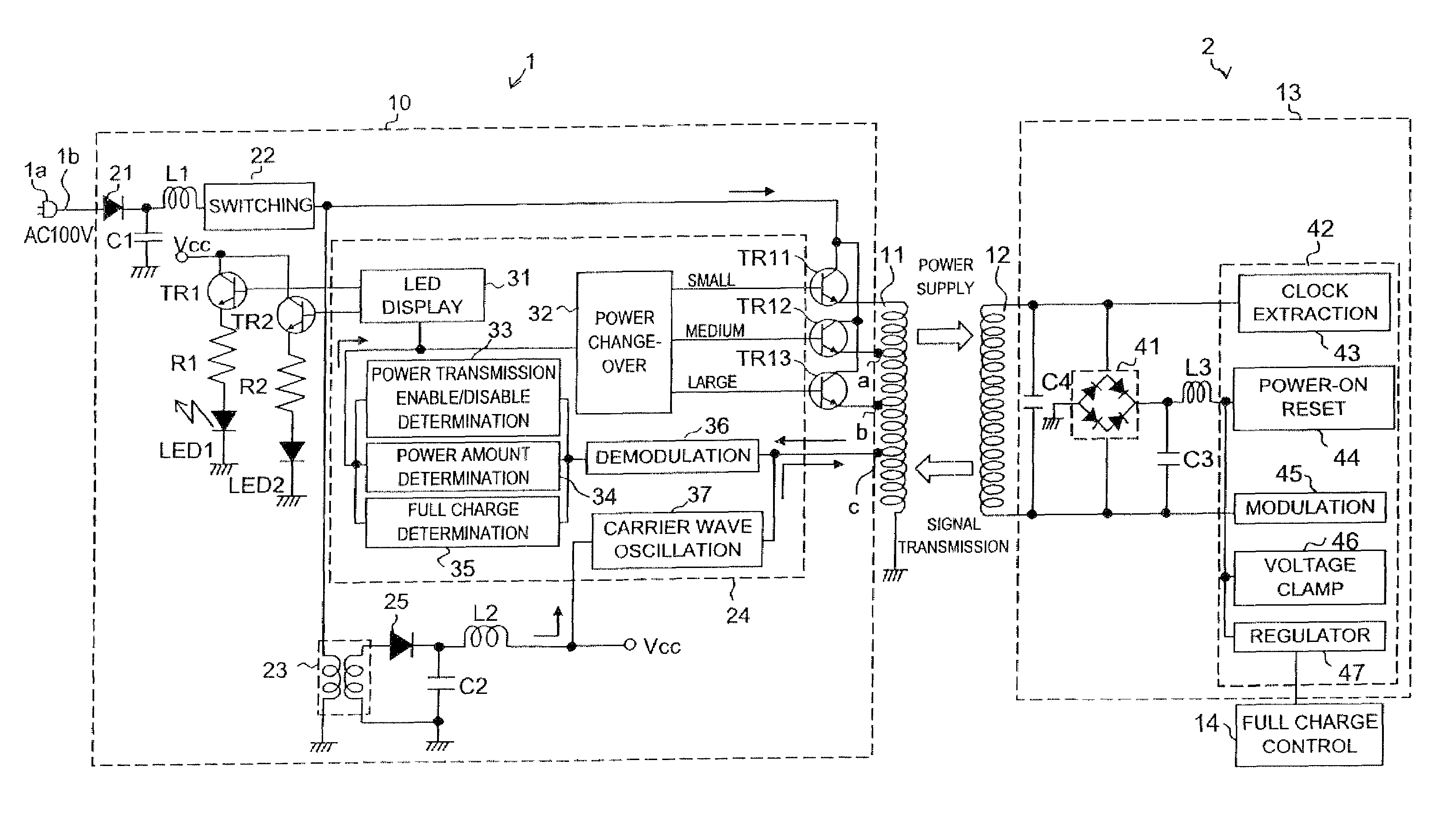
Power supply system
InactiveUS20050068019A1Save spaceDc network circuit arrangementsCircuit monitoring/indicationElectric forceElectricity
A power supply system according to the present invention comprises: a primary side coil; a power transmission apparatus having a primary side circuit for feeding a pulse voltage resulted from switching a DC voltage which is obtained by rectifying and smoothing a commercial power supply to the primary side coil; a secondary side coil magnetically coupled to the primary side coil; and power reception equipment having a secondary side circuit for rectifying and smoothing voltage induced across the secondary side coil, wherein there is provided a power adjusting section for adjusting a level of power to be transmitted according to power required by the power reception equipment. The power adjusting section has, in the primary side circuit, a carrier wave oscillation circuit for supplying a carrier wave to the primary side coil, a demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal transmitted from the secondary circuit and received by the primary side coil, and a power change-over section for selecting a level of power to be transmitted according to an information signal from the power reception equipment and demodulated by the demodulation circuit. The power adjusting section has, in the secondary side circuit, a modulation circuit for modulating the carrier wave fed from the carrier wave oscillation circuit and received by the secondary side coil with the information signal from the power reception equipment and transmitting the modulated signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
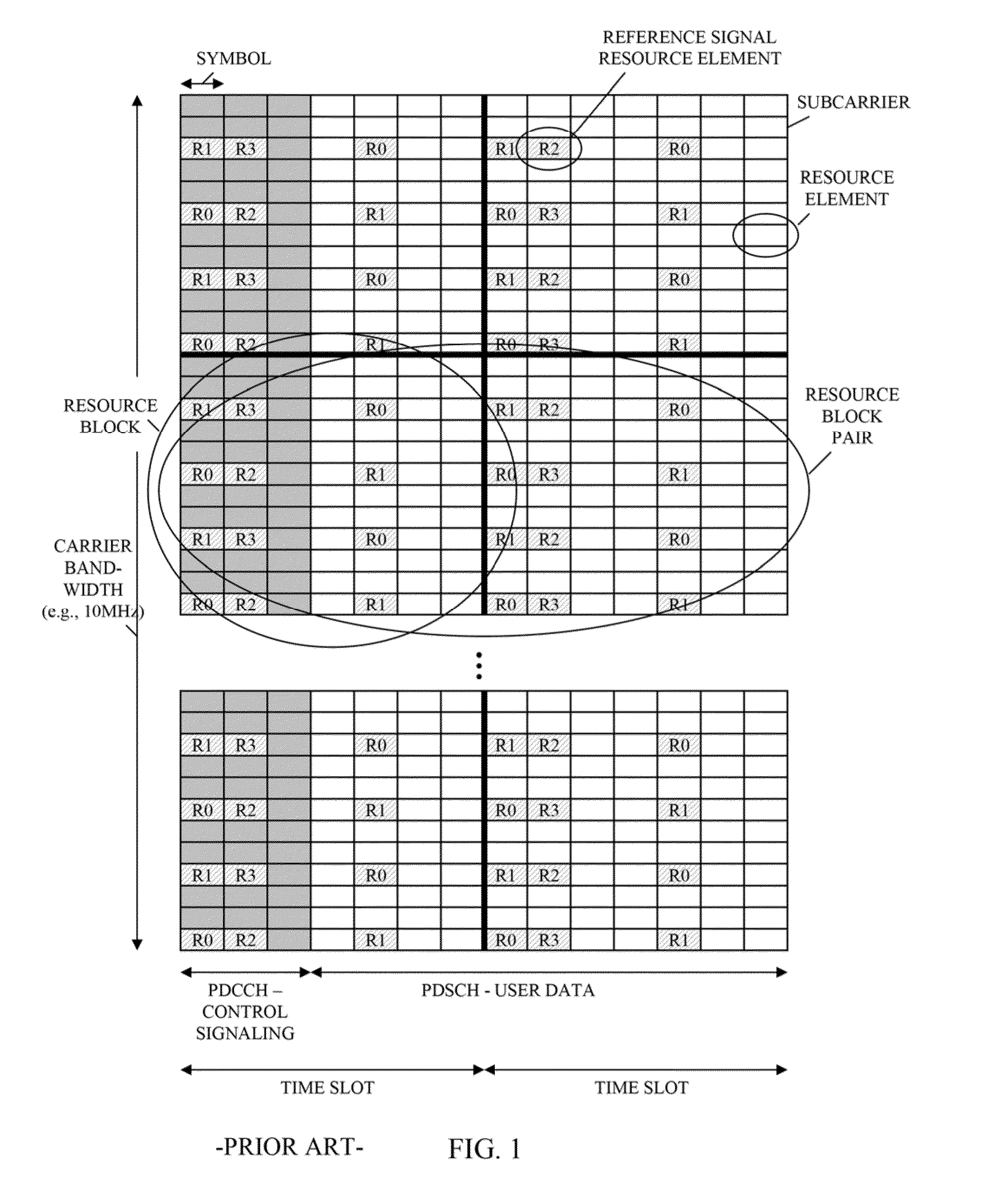
Apparatus for OFDMA transmission and reception for coherent detection in uplink of wireless communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS20050135324A1Improve channel estimation performanceFrequency-division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemResource block
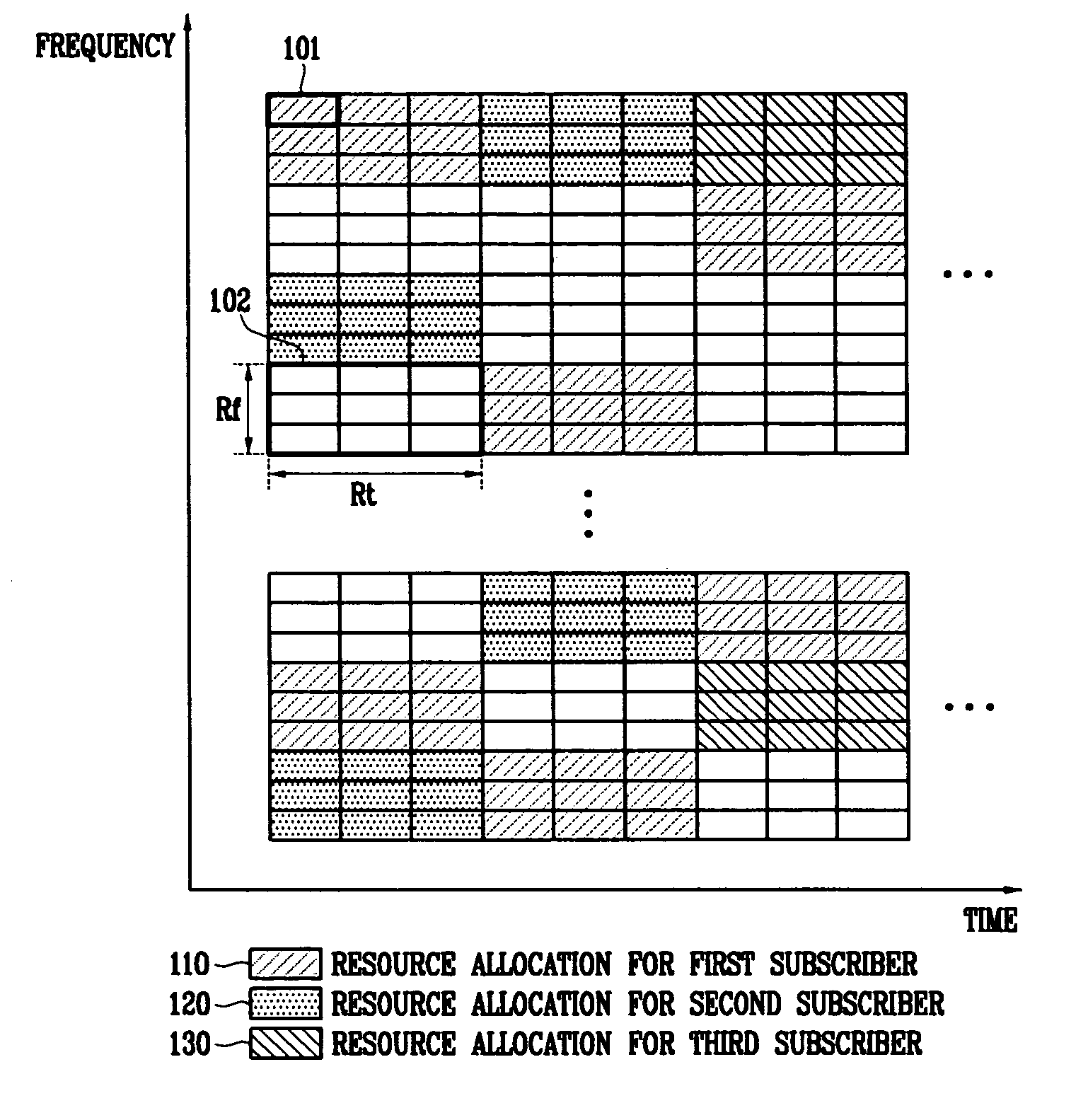
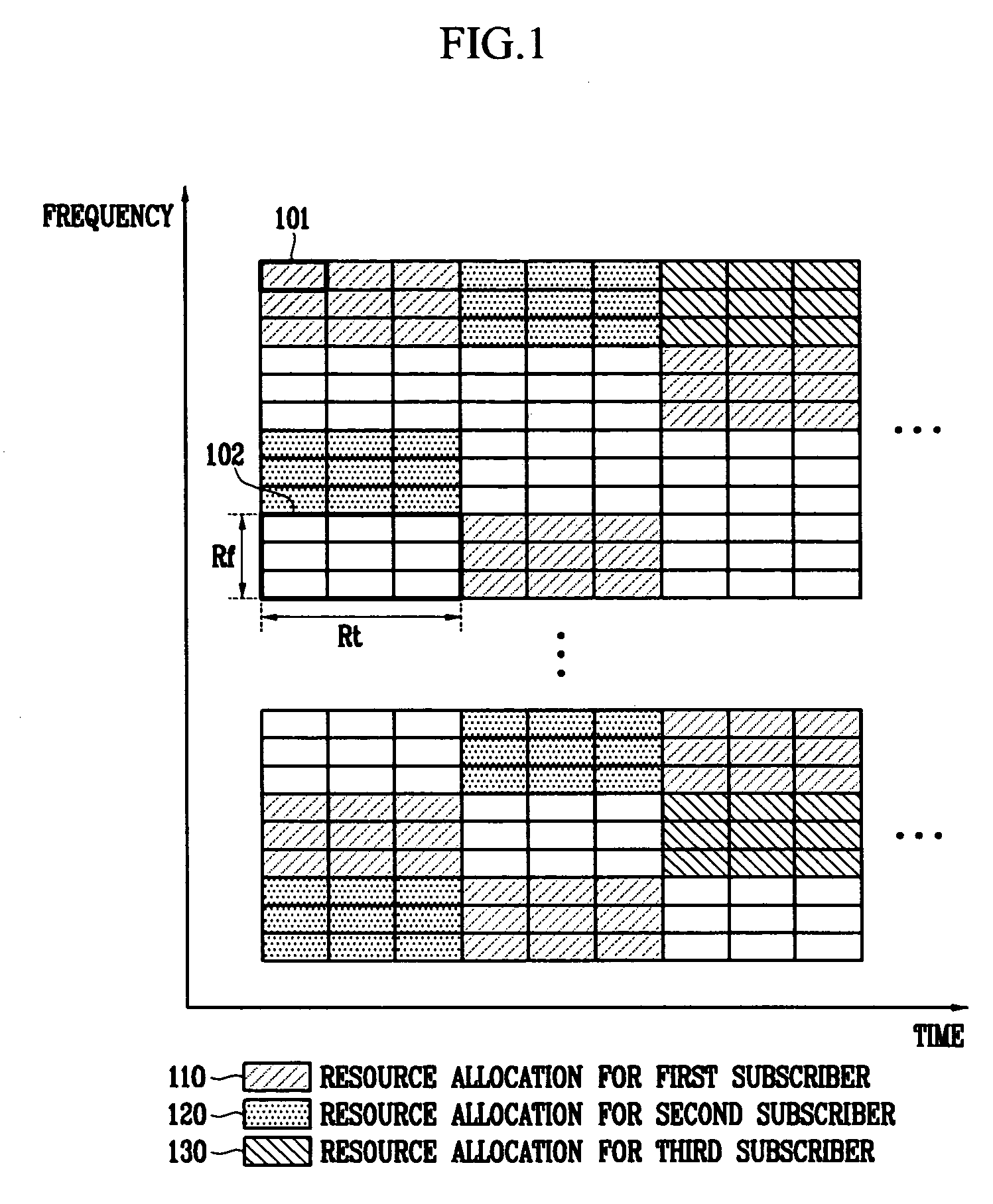
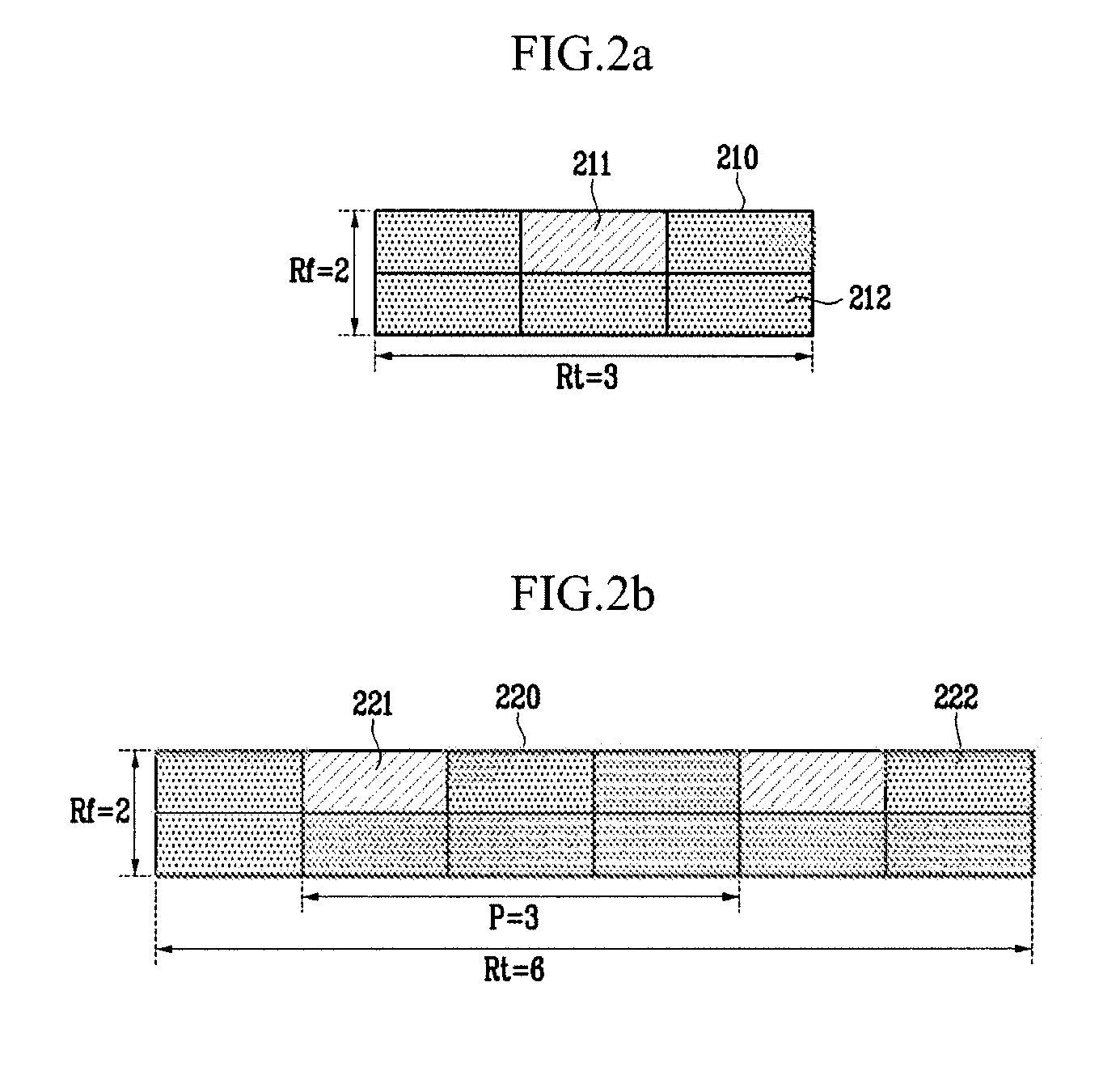
In the resource mapping method for data transmission, a time-frequency resource of a slot interval including OFDM symbols is divided into traffic channels and shared among the subscribers, the traffic channel including resource blocks uniformly distributed in the whole transmit frequency band, the resource block including consecutive subcarriers of consecutive received symbols having at least one inserted pilot symbol. The pilot symbols and the channel-encoded and modulated data symbols are processed by time-frequency mapping according to the resource-block-based mapping method to generate received symbols. The receiver separates the received symbols by subscribers according to the resource-block-based mapping method in a frequency domain, and performs iterative channel estimation, demodulation, and decoding by using the pilot and a data reference value after decoding for each traffic channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of modulated electromagnetic waves
InactiveUS7060957B2Low lighting powerExtend integration timePrismsSolid-state devicesPulse radiationData acquisition
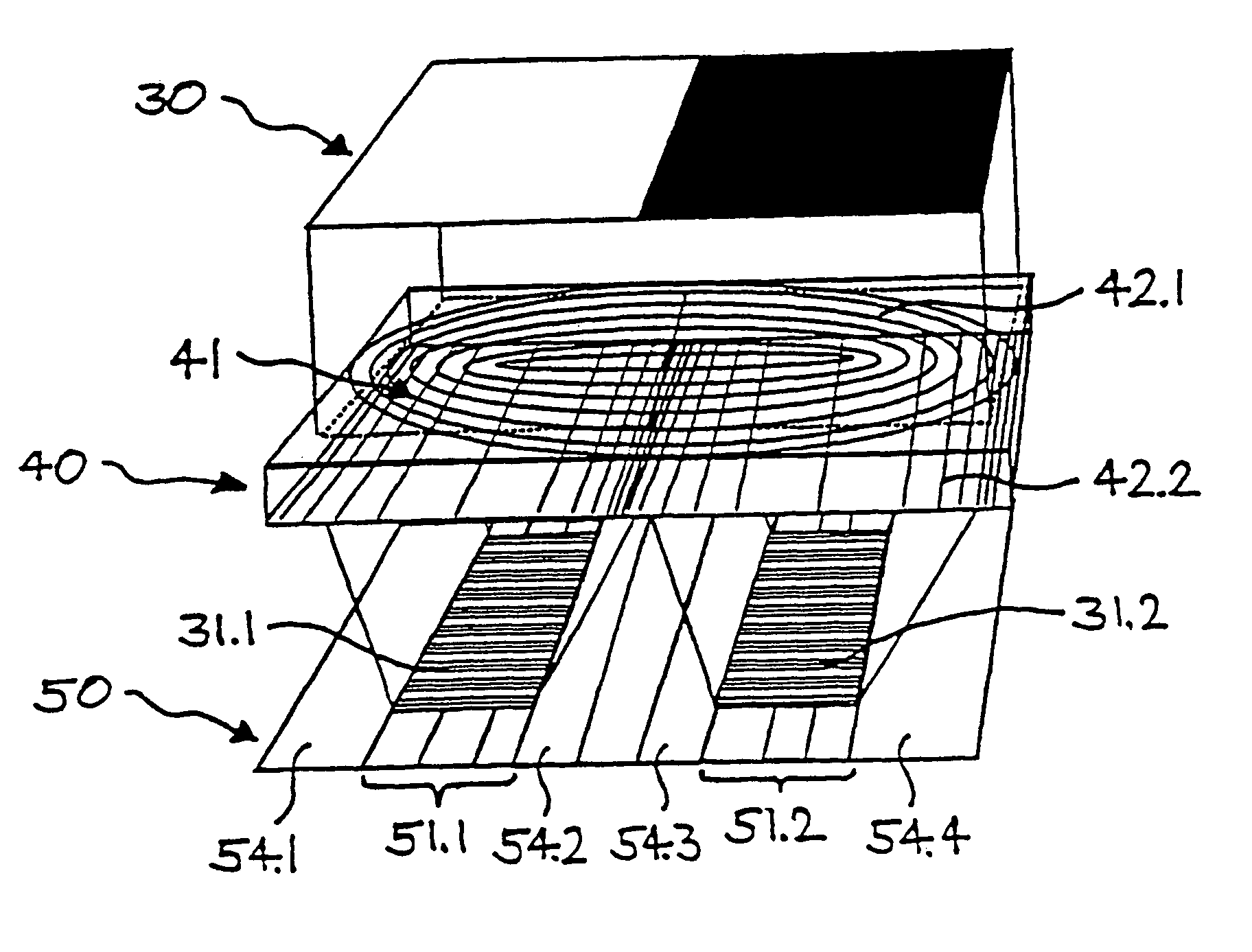
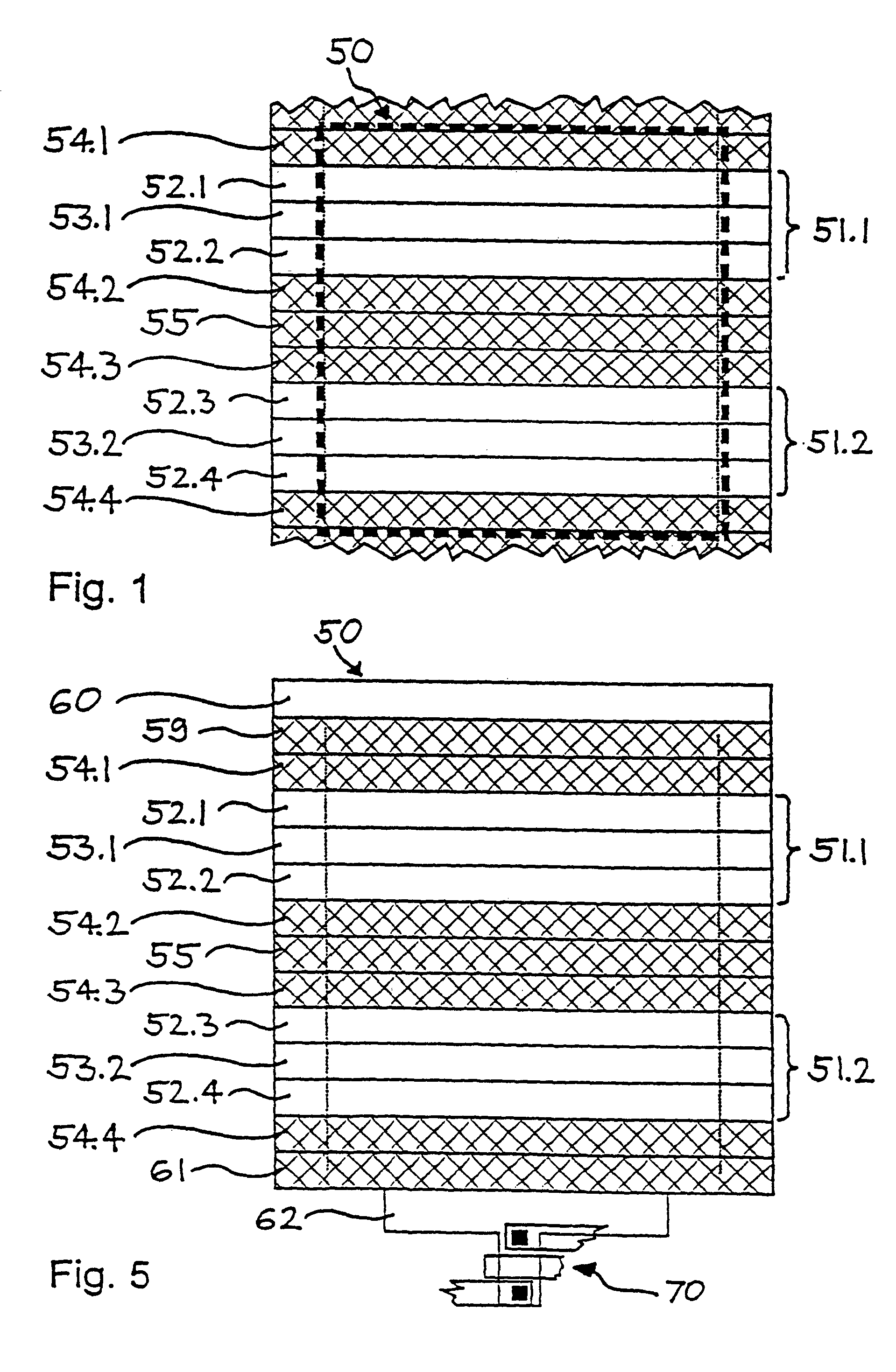
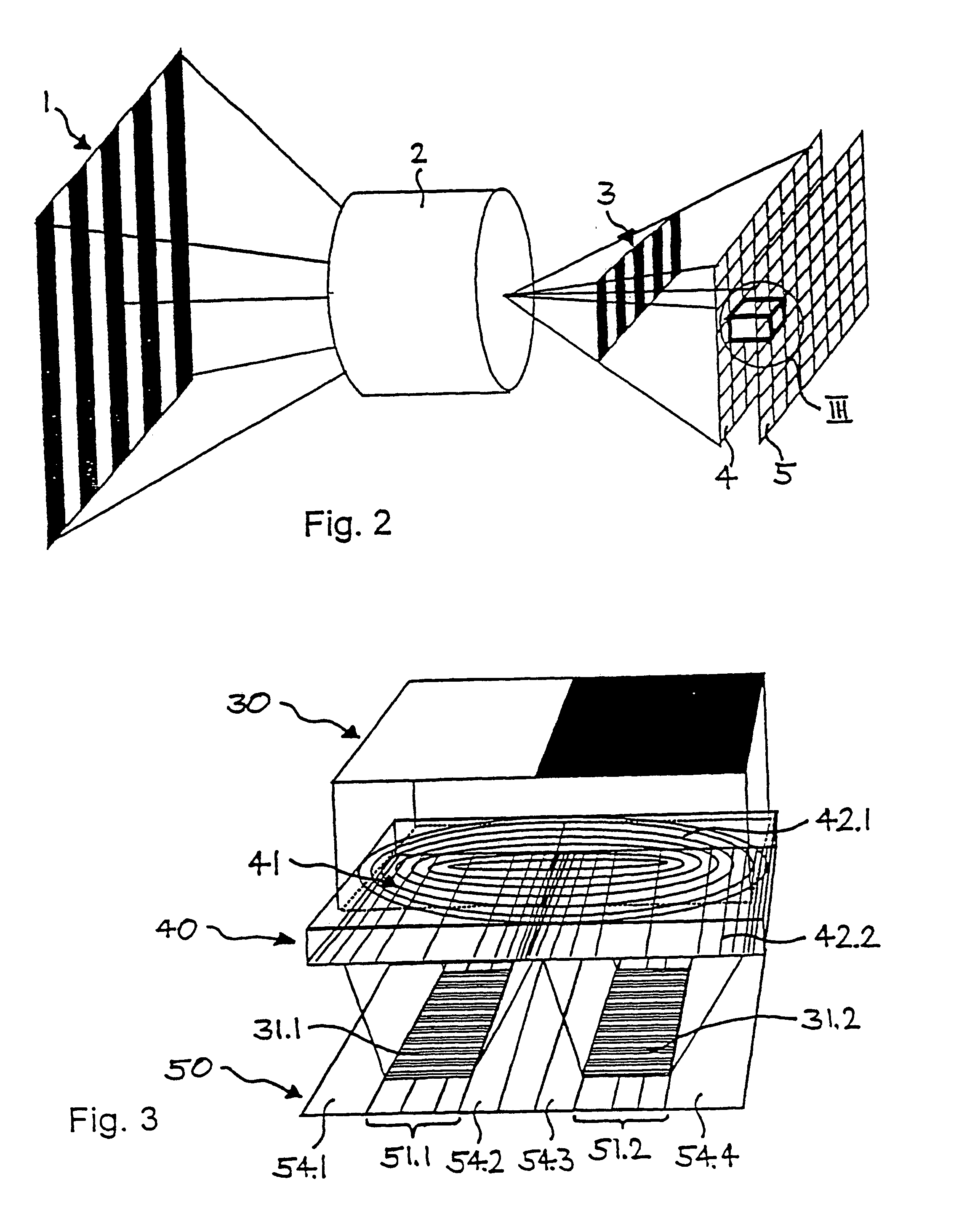
A device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of temporally modulated electromagnetic waves makes it possible to measure phase, amplitude and offset of a temporally modulated, spatially coded radiation field. A micro-optical element (41) spatially averages a portion (30) of the scene and equally distributes the averaged intensity on two photo sites (51.1.51.2) close to each other. Adjacent to each of these photo sites (51.1) are two storage areas (54.1, 54.2) into which charge from the photo site can be moved quickly (with a speed of several MHz to several tens or even hundreds of MHz) and accumulated essentially free of noise. This is possible by employing the charge-coupled device (CCD) principle. The device combines a high optical fill factor, insensitivity to offset errors, high sensitivity even with little light, simultaneous data acquisition, small pixel size, and maximum efficiency in use of available signal photons for sinusoidal as well as pulsed radiation signals. The device and method may be used in a time-of-flight (TOF) range imaging system without moving parts, offering 2D or 3D range data.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
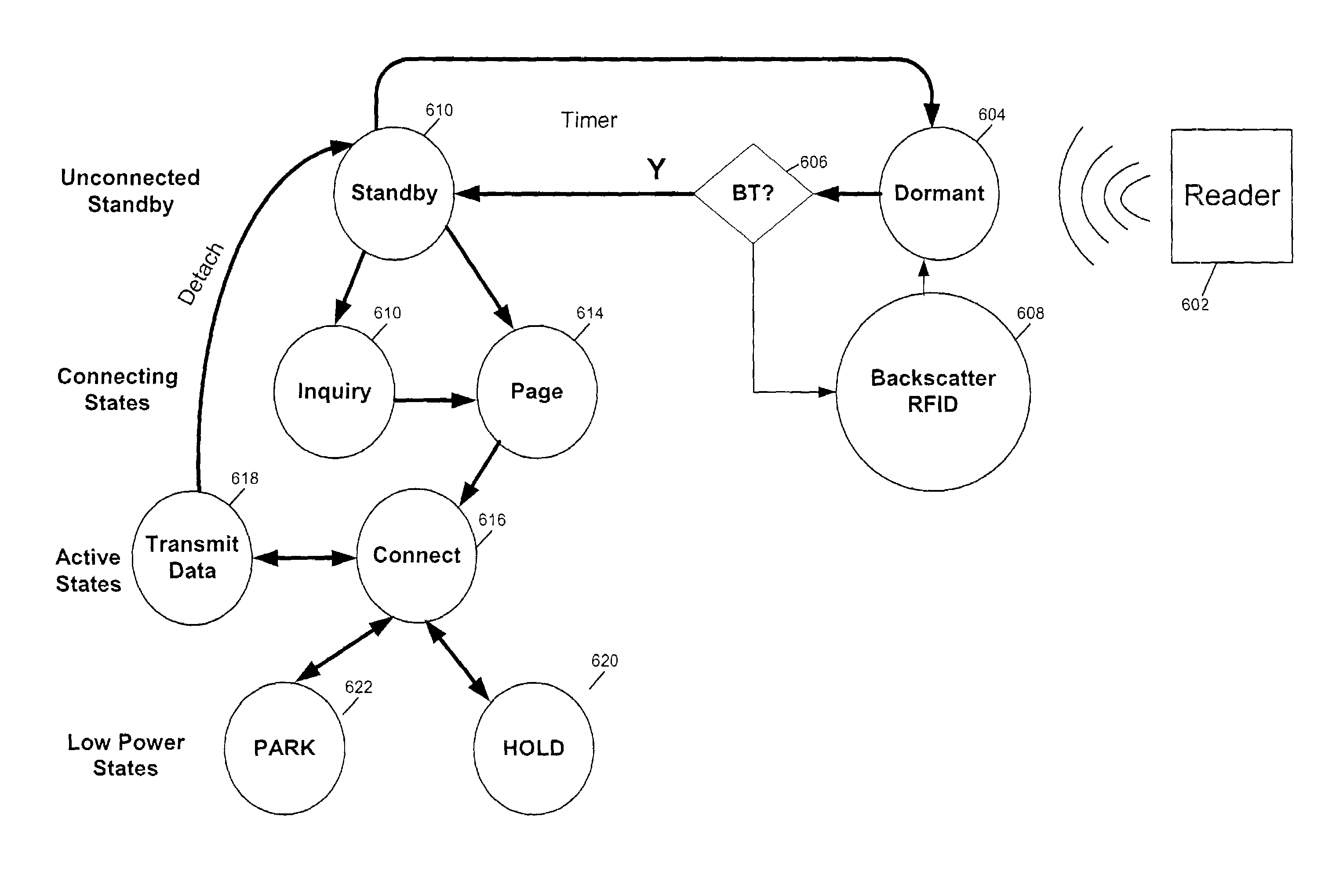
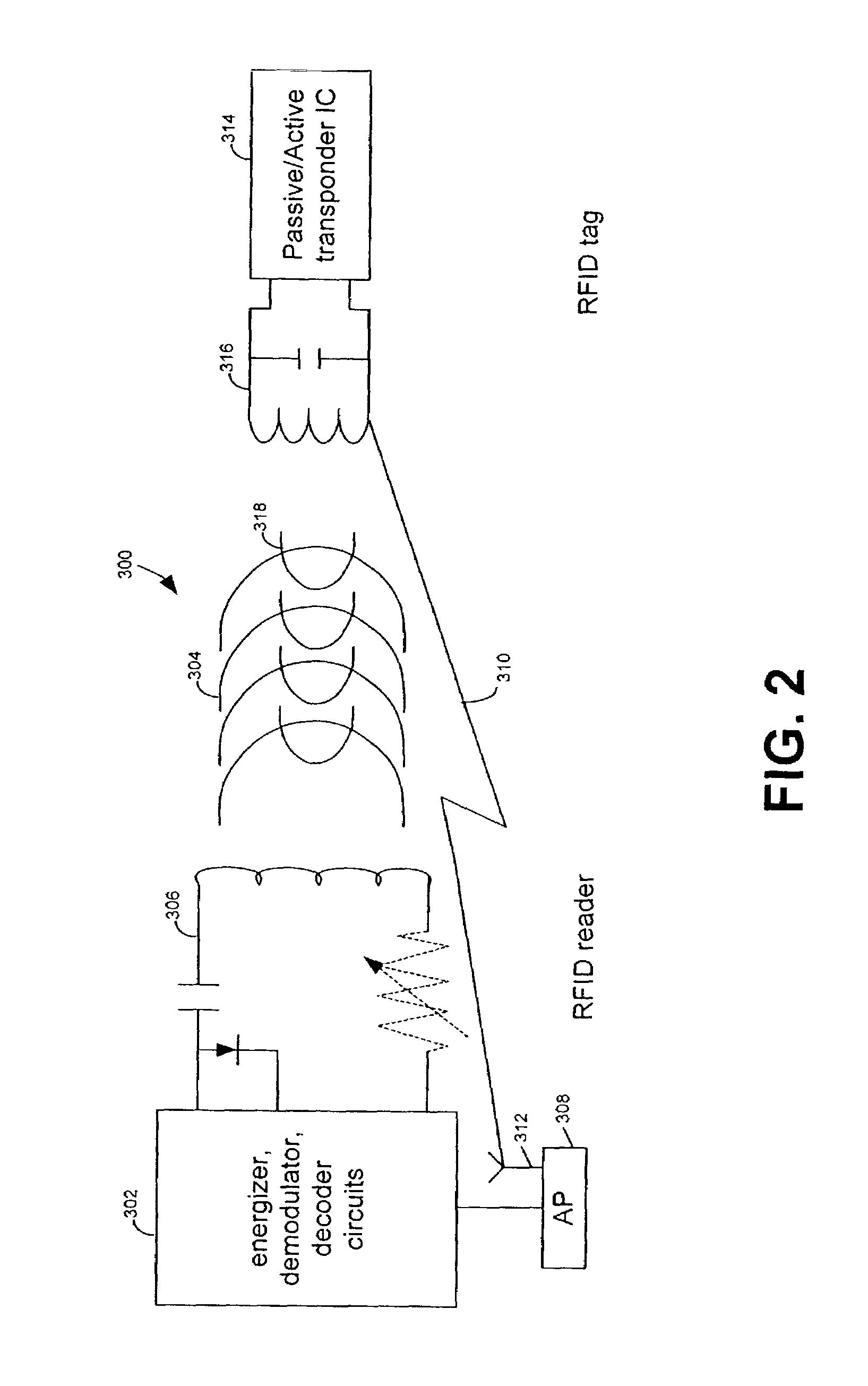
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS20030104848A1Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
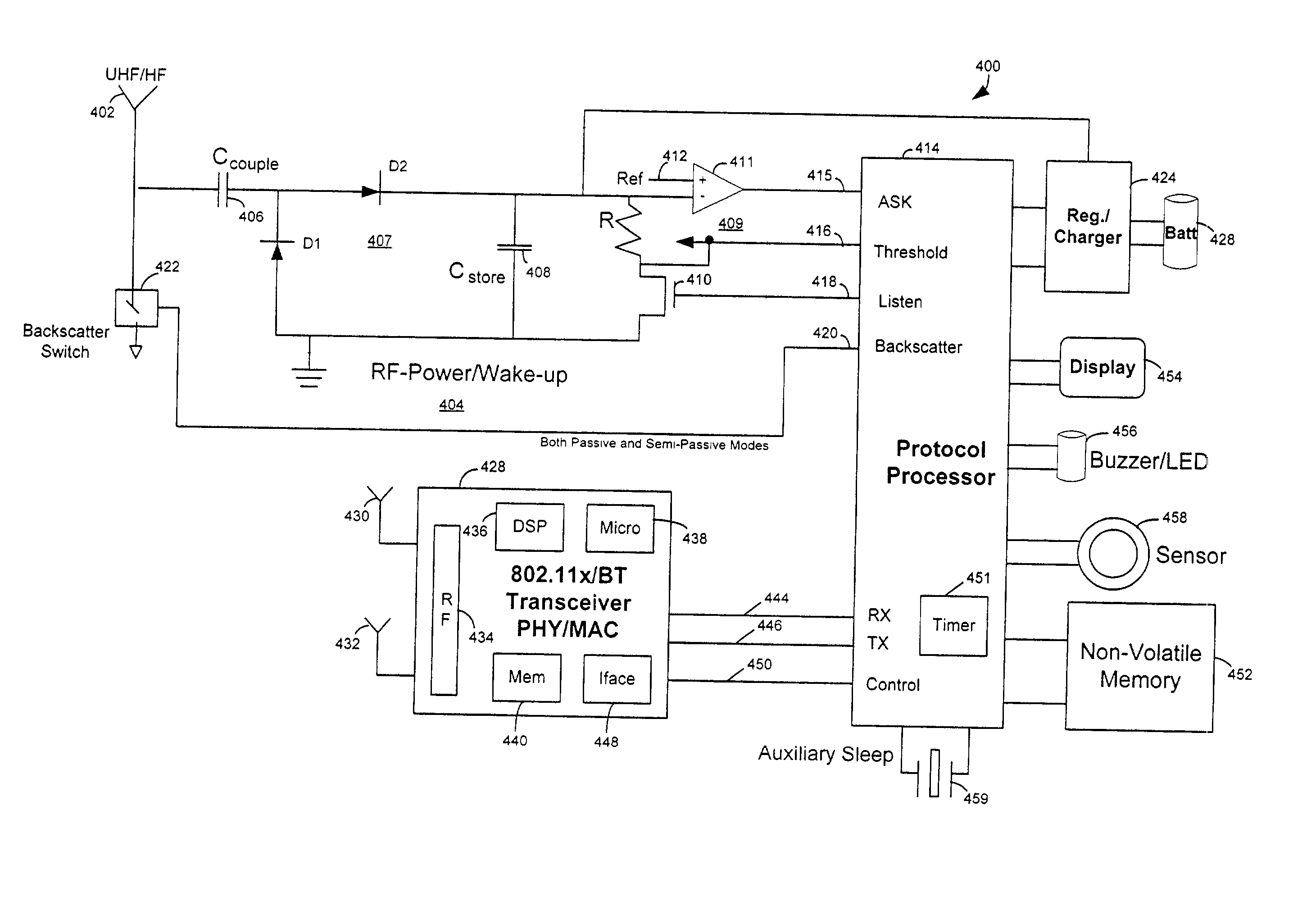
An RFID system includes a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol-compatible with existing 802.11x / Bluetooth Standards as well as RFID standards. The tag is linked to a multi-protocol Interrogator via a generated RF Continuous Wave (CW) field. The tag includes an antenna coupled to an RFID and a Bluetooth / 802.11x transceiver section. A Protocol Processor services RFID and transceiver sections and is coupled to the antenna via a backscatter switch. The Interrogator can switch the tag to an RFID backscatter radiation mode where the processor switches the antenna impedance to reflect the CW signal. For transceiver operation the processor switches antenna impedance in synchronization with a frame organized bit stream. For reception, the RFID section utilizes demodulation techniques, typically Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), and provides a wake up mode within a predetermined distance of the Interrogator. The transceiver may operate in a backscatter or regular mode as directed by an Access Point.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Individual channel phase delay scheme
ActiveUS20080157867A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsPhase-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringNoise suppression
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to processing an incoming signal by using a demodulation signal, while controlling the phase of the demodulation signal in relation to the incoming signal. The incoming signal can be processed by being mixed with the modulation signal at a mixer. The mixing may thus cause various beneficial modifications of the incoming signal, such as noise suppression of the incoming signal, rectification of the incoming signal, demodulation of the incoming signal, etc.
Owner:APPLE INC
Highly sensitive, fast pixel for use in an image sensor
ActiveUS7560701B2Overcomes speed limitationReasonable sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectric signalDemodulation
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for calibration to reduce coupling between signals in a measurement system
ActiveUS9861305B1Reduce crosstalkReduces other contaminationDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical sensorsData setCoupling
A method and an apparatus for separating a composite signal into a plurality of signals is described. A signal processor receives a composite signal and separates a composite signal into separate output signals. Feedback from one or more of the output signals is provided to a configuration module that configures the signal processor to improve a quality of the output signals. In one embodiment, calibration data from multiple calibration data sets is used to configure the demodulation of the composite signal into separate output signals.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Multiple simultaneous frequency detection
ActiveUS20080309625A1Wireless commuication servicesTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency mixerFrequency detection
The use of multiple stimulation frequencies and phases to generate an image of touch on a touch sensor panel is disclosed. Each of a plurality of sense channels can be coupled to a column in a touch sensor panel and can have multiple mixers. Each mixer in the sense channel can utilize a circuit capable generating a demodulation frequency of a particular frequency. At each of multiple steps, various phases of selected frequencies can be used to simultaneously stimulate the rows of the touch sensor panel, and the multiple mixers in each sense channel can be configured to demodulate the signal received from the column connected to each sense channel using the selected frequencies. After all steps have been completed, the demodulated signals from the multiple mixers can be used in calculations to determine an image of touch for the touch sensor panel at each frequency.
Owner:APPLE INC
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS7215976B2Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Power supply system
InactiveUS7233137B2Save spaceCircuit monitoring/indicationVolume/mass flow measurementElectric power transmissionCarrier signal
A power supply system is provided, having: a primary side coil; a power transmission apparatus having a primary side circuit for feeding a pulse voltage resulted from switching a DC voltage which is obtained by rectifying and smoothing a commercial power supply to the primary side coil; a secondary side coil magnetically coupled to the primary side coil; and power reception equipment having a secondary side circuit for rectifying and smoothing voltage induced across the secondary side coil, wherein there is provided a power adjusting section for adjusting a level of power to be transmitted according to power required by the power reception equipment. The power adjusting section has, in the primary side circuit, a carrier wave oscillation circuit for supplying a carrier wave to the primary side coil, a demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal transmitted from the secondary circuit and received by the primary side coil, and a power change-over section for selecting a level of power to be transmitted according to an information signal from the power reception equipment and demodulated by the demodulation circuit. The power adjusting section has, in the secondary side circuit, a modulation circuit for modulating the carrier wave fed from the carrier wave oscillation circuit and received by the secondary side coil with the information signal from the power reception equipment and transmitting the modulated signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
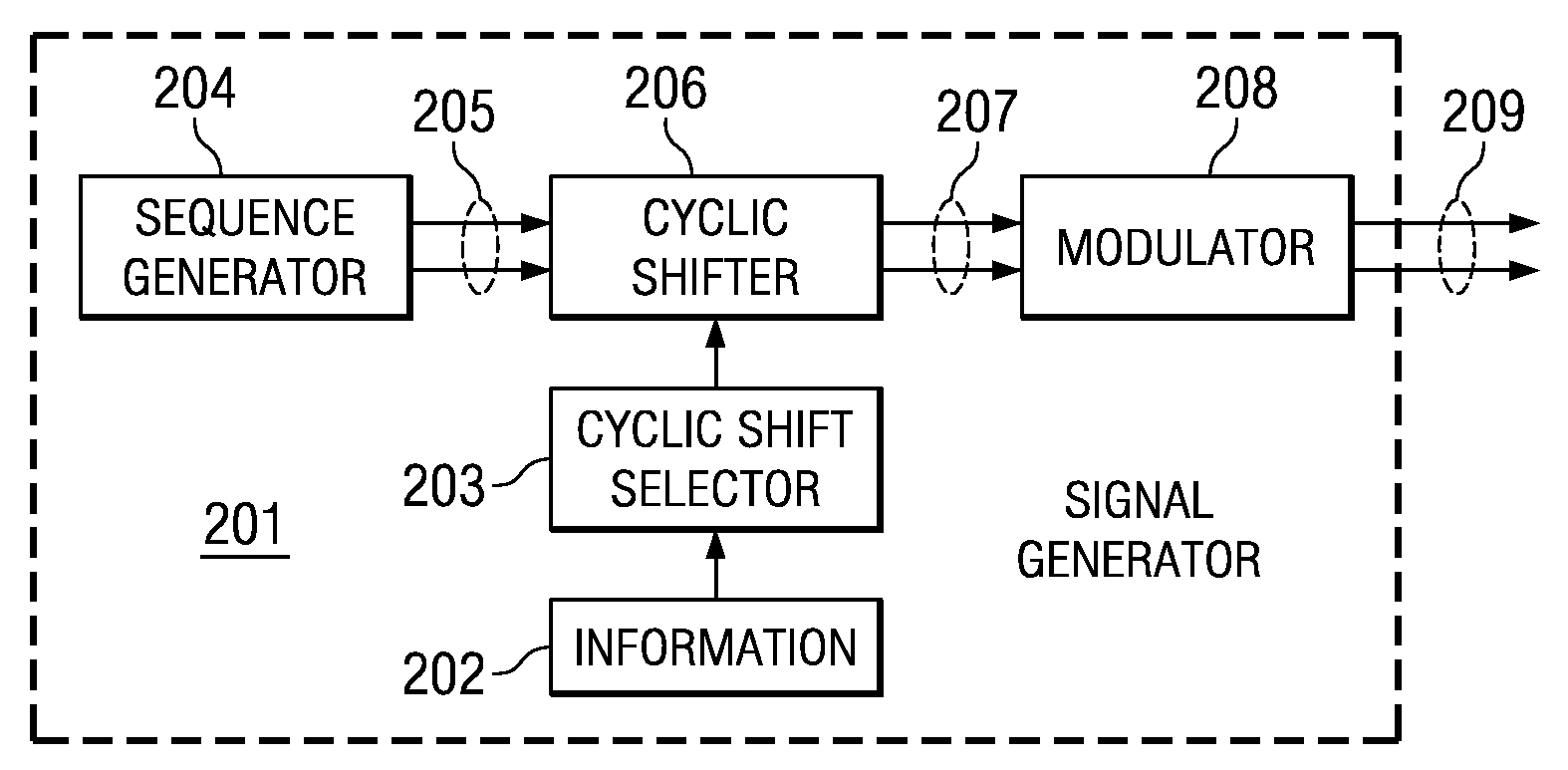
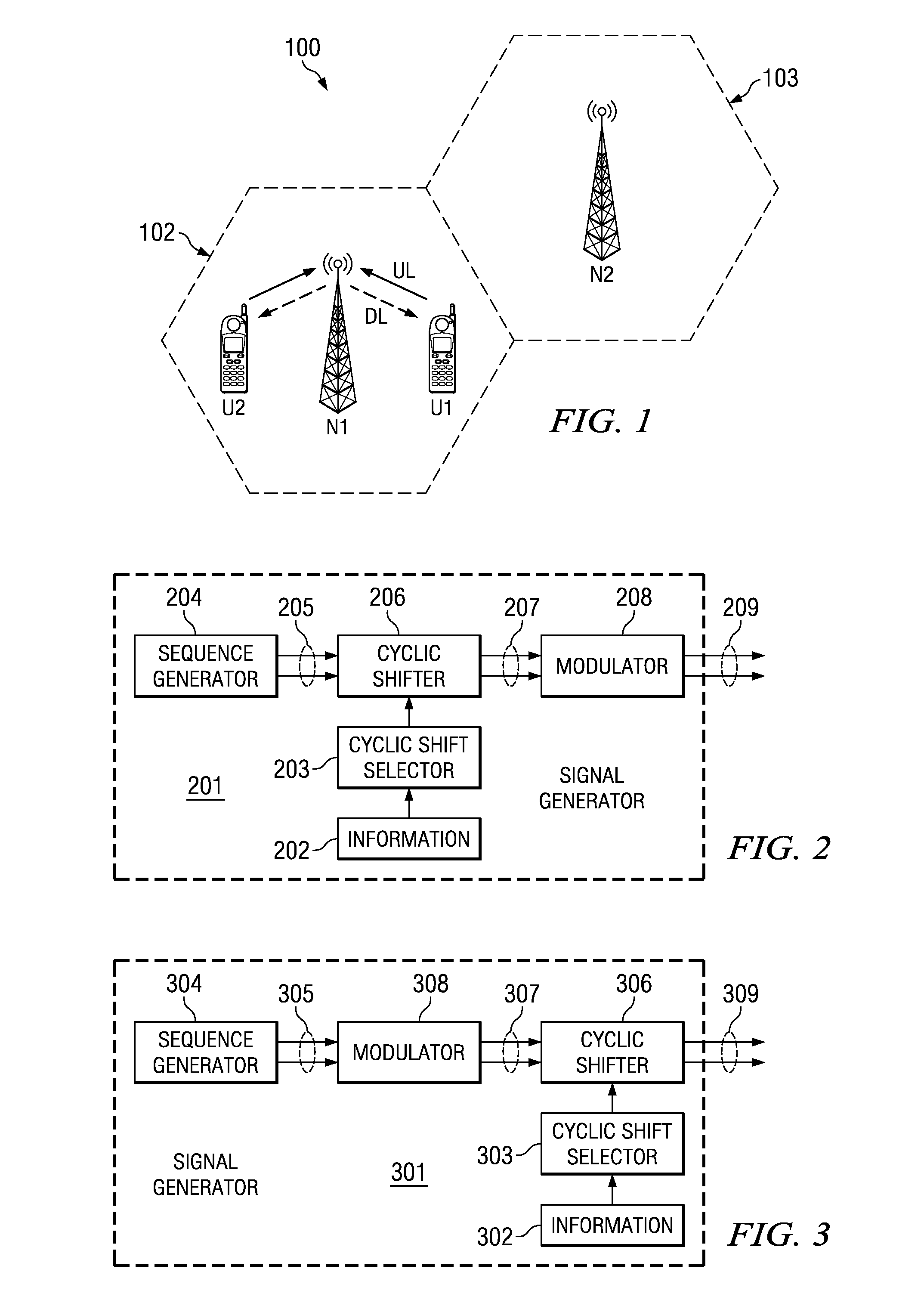
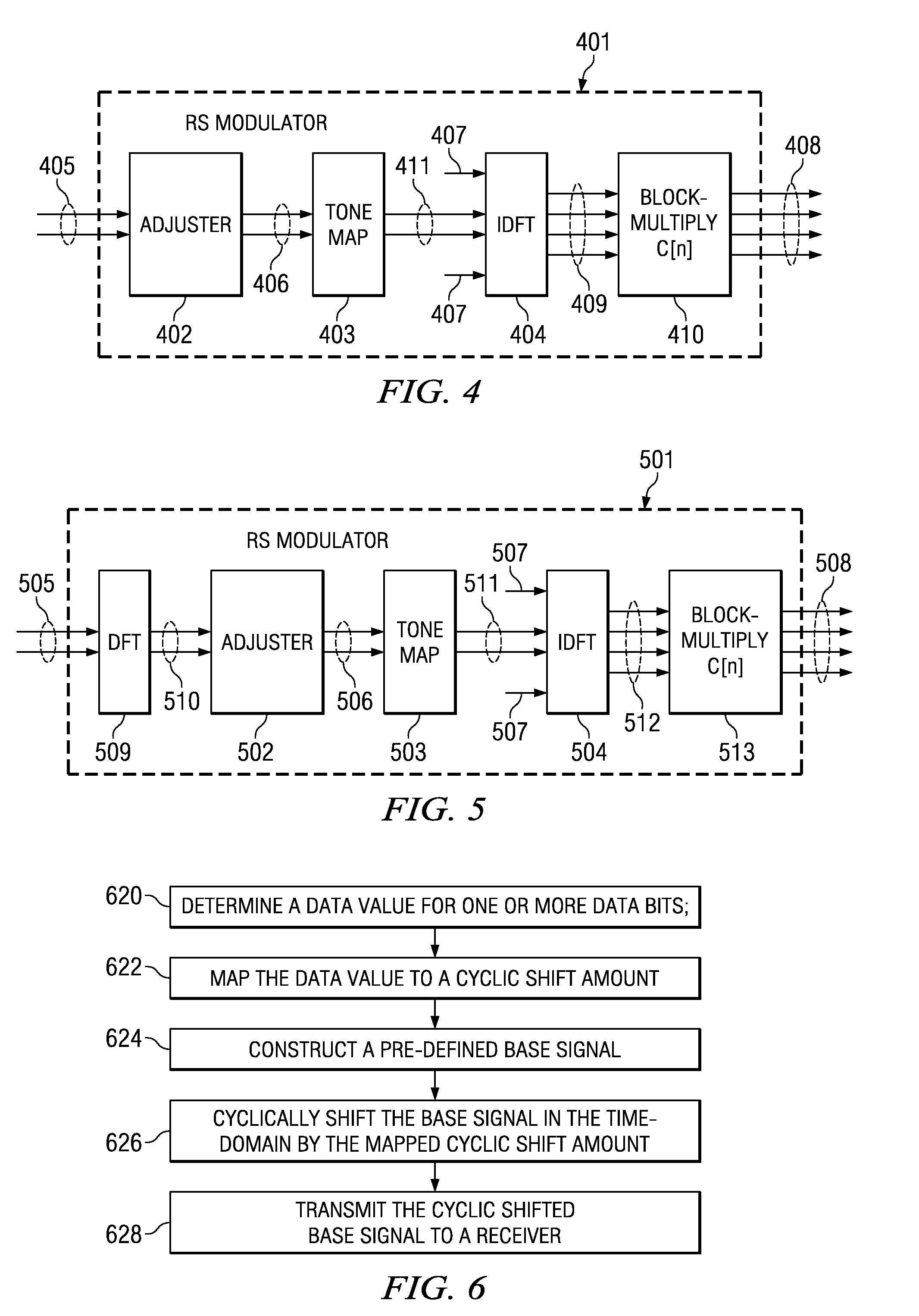
Transmission of ACK/NACK Bits and their Embedding in the Reference Signal
ActiveUS20080075184A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionWireless cellular networksData value
Transmitting a ACK / NACK response in a wireless cellular network by mapping the data value into a cyclic shifted version of a reference signal. A subframe is formed with a plurality of symbols with certain symbols designated as reference signal (RS) symbols. The receiver and transmitter both know when an ACK / NACK response is expected. If an ACK / NACK response is not expected, then an RS is inserted in the duration of symbols designated as RS symbols. If an ACK / NACK response is expected, then the ACK / NACK response is embedded in one or more of the symbols designated as RS symbols. The subframe is transmitted to a receiver, and the receiver can determine the ACK / NACK value in the RS symbol, if present, and also use the RS symbol for coherent demodulation of a CQI (channel quality indicator) or data.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
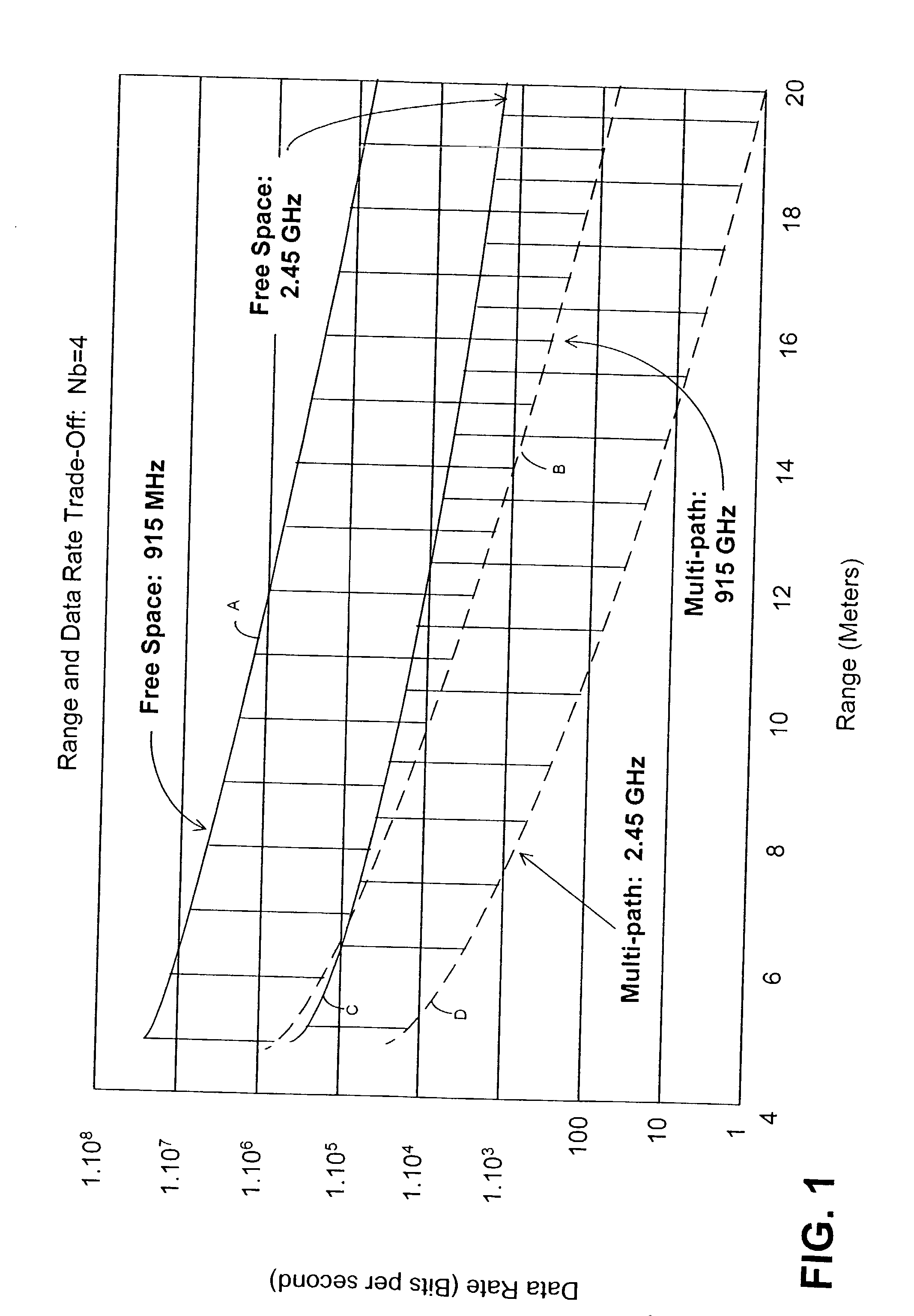
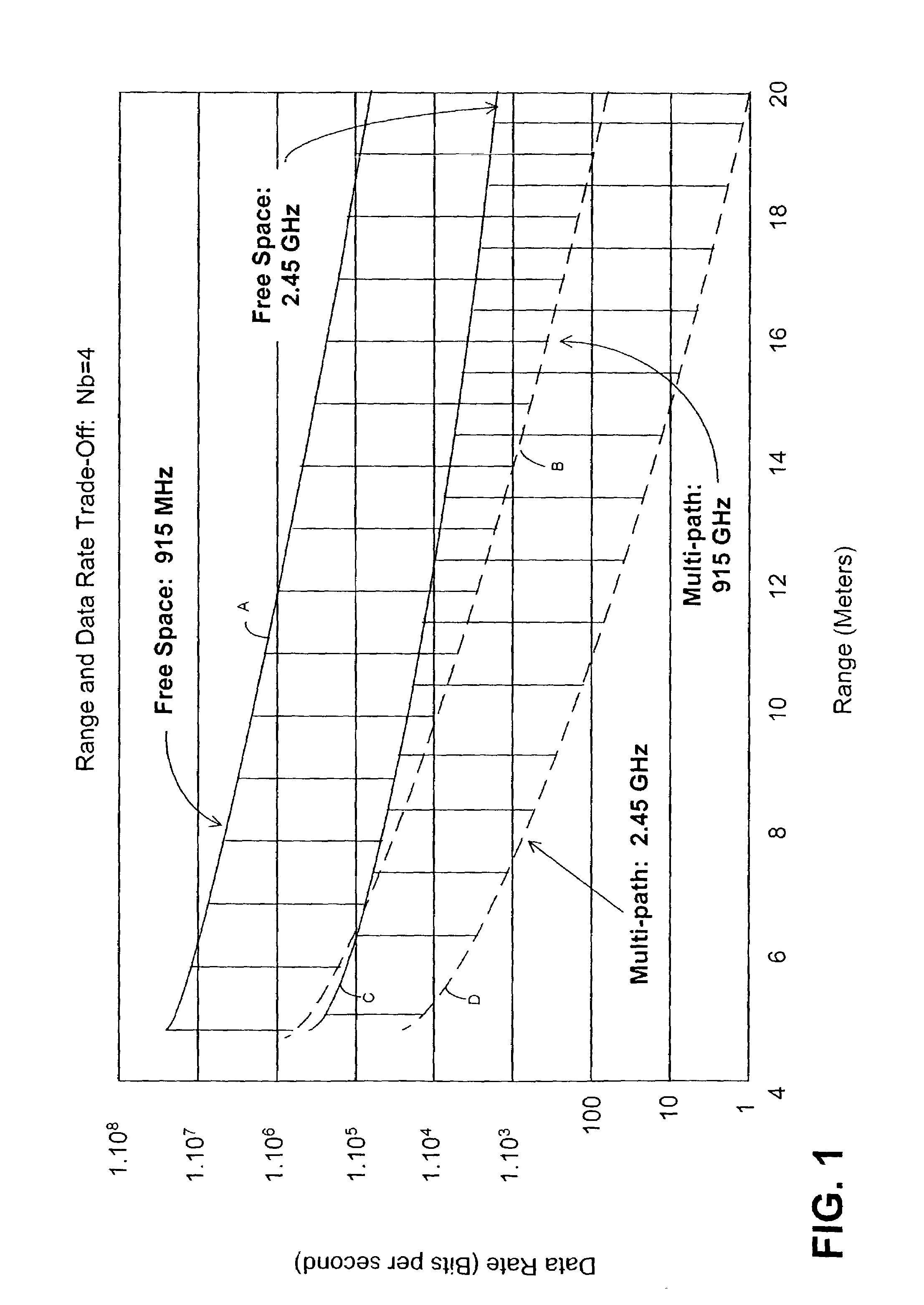
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
Location finder, tracker, communication and remote control system
ActiveUS7260369B2Expand coverageImprove performanceTelevision system detailsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsRemote controlControl system
A radio frequency identification (RFID) device, locator, wired and / or wireless communicator system comprising one or more than one antennas for receiving Radio Frequency (RF) signals from one or more RFID and or location determining and / or communication transmitters. The system has one or more receivers and demodulators for reception and demodulation of signals to baseband signals. A processor circuit processes the baseband signals and provides them to a cross-correlator circuit for cross-correlating the processed baseband signals and for generation of cross-correlated baseband signals. One or more modulators modulate the baseband signals and provide them to one or more transmitters. circuitry.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
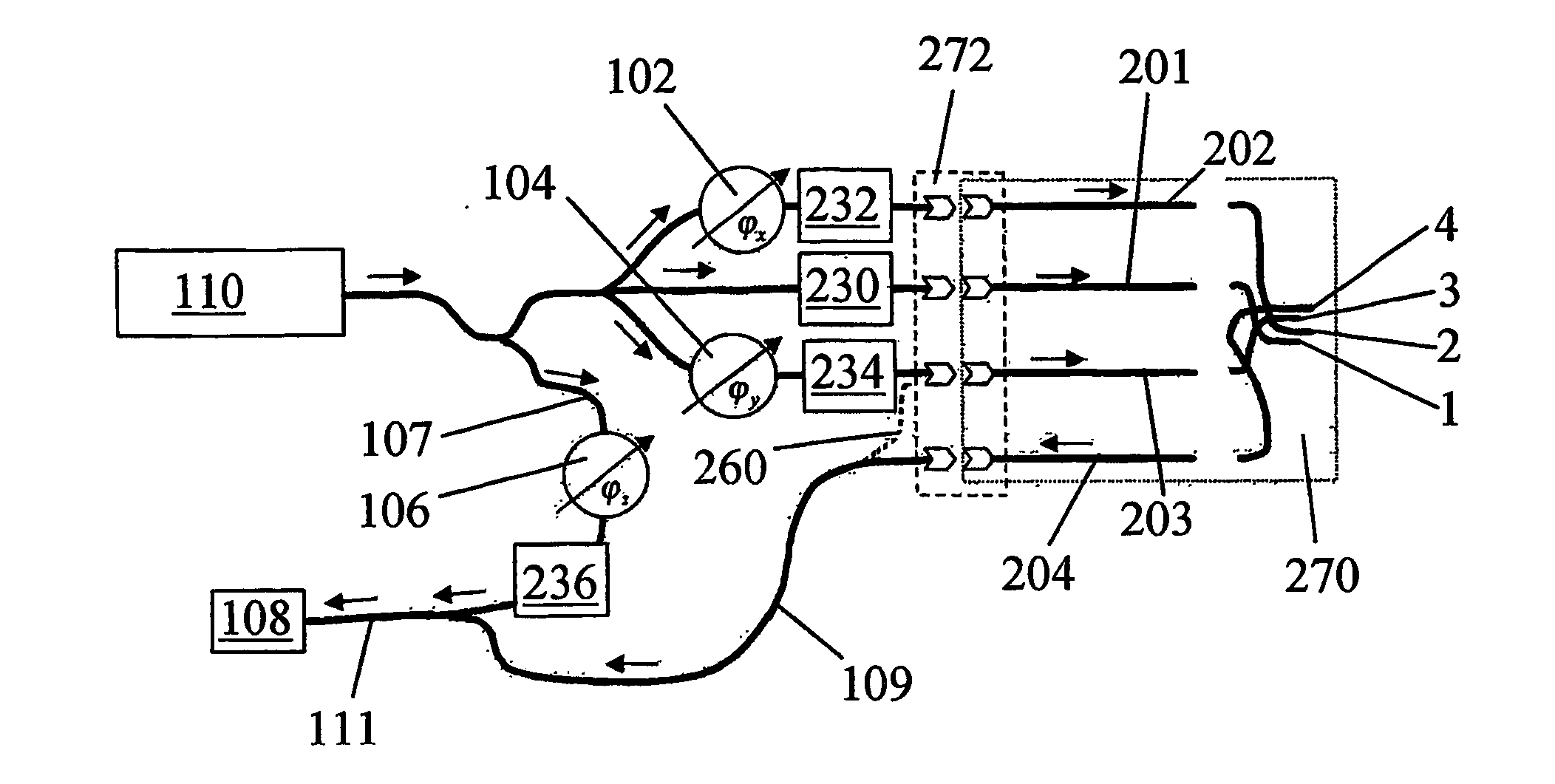
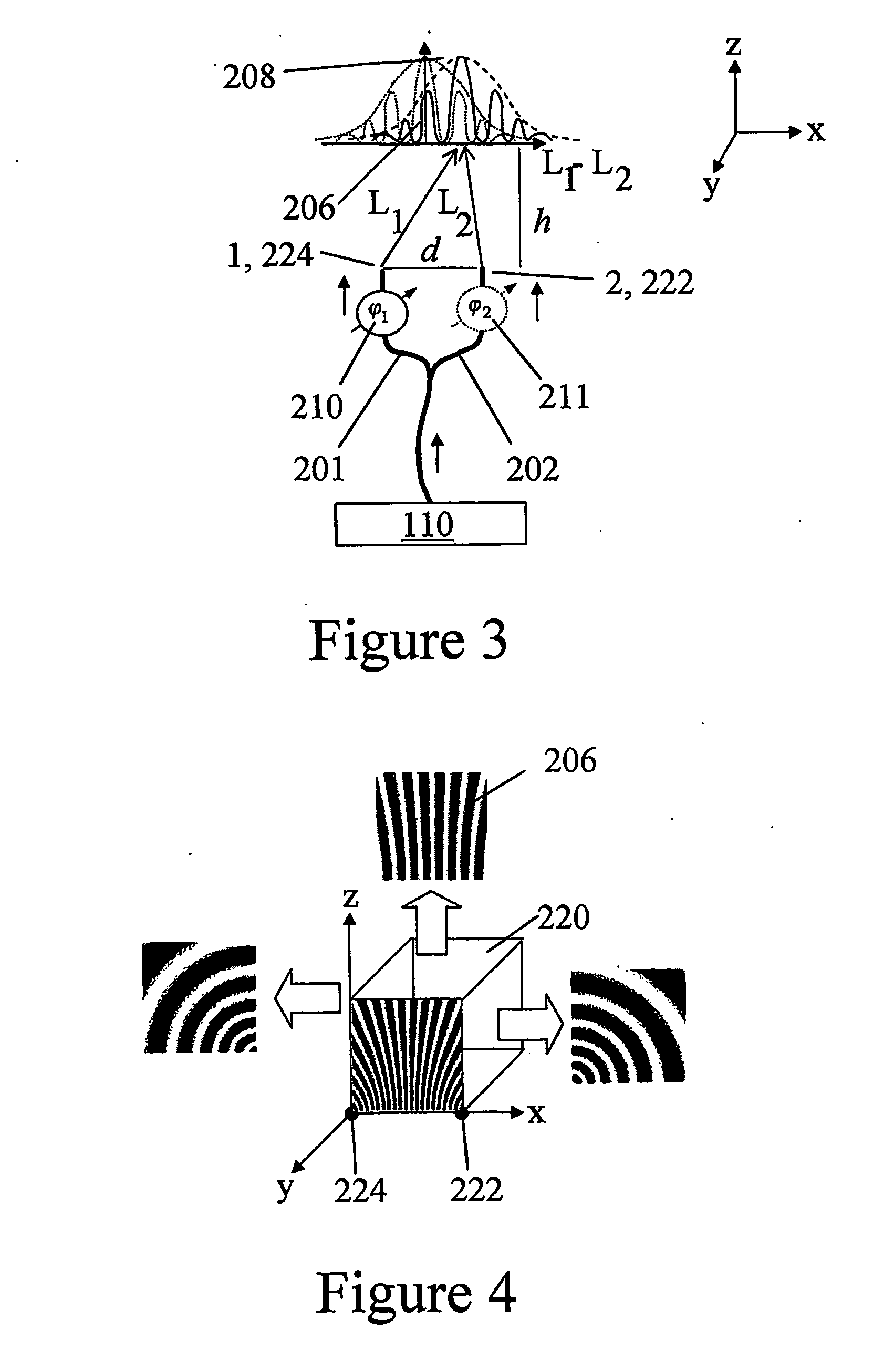
Optical coherence tomography with 3d coherence scanning
Optical coherence tomography with 3D coherence scanning is disclosed, using at least three fibers (201, 202, 203) for object illumination and collection of backscattered light. Fiber tips (1, 2, 3) are located in a fiber tip plane (71) normal to the optical axis (72). Light beams emerging from the fibers overlap at an object (122) plane, a subset of intersections of the beams with the plane defining field of view (266) of the optical coherence tomography apparatus. Interference of light emitted and collected by the fibers creates a 3D fringe pattern. The 3D fringe pattern is scanned dynamically over the object by phase shift delays (102, 104) controlled remotely, near ends of the fibers opposite the tips of the fibers, and combined with light modulation. The dynamic fringe pattern is backscattered by the object, transmitted to a light processing system (108) such as a photo detector, and produces an AC signal on the output of the light processing system (108). Phase demodulation of the AC signal at selected frequencies and signal processing produce a measurement of a 3D profile of the object.
Owner:APPLIED SCI INNOVATIONS +1
Rfid Apparatus
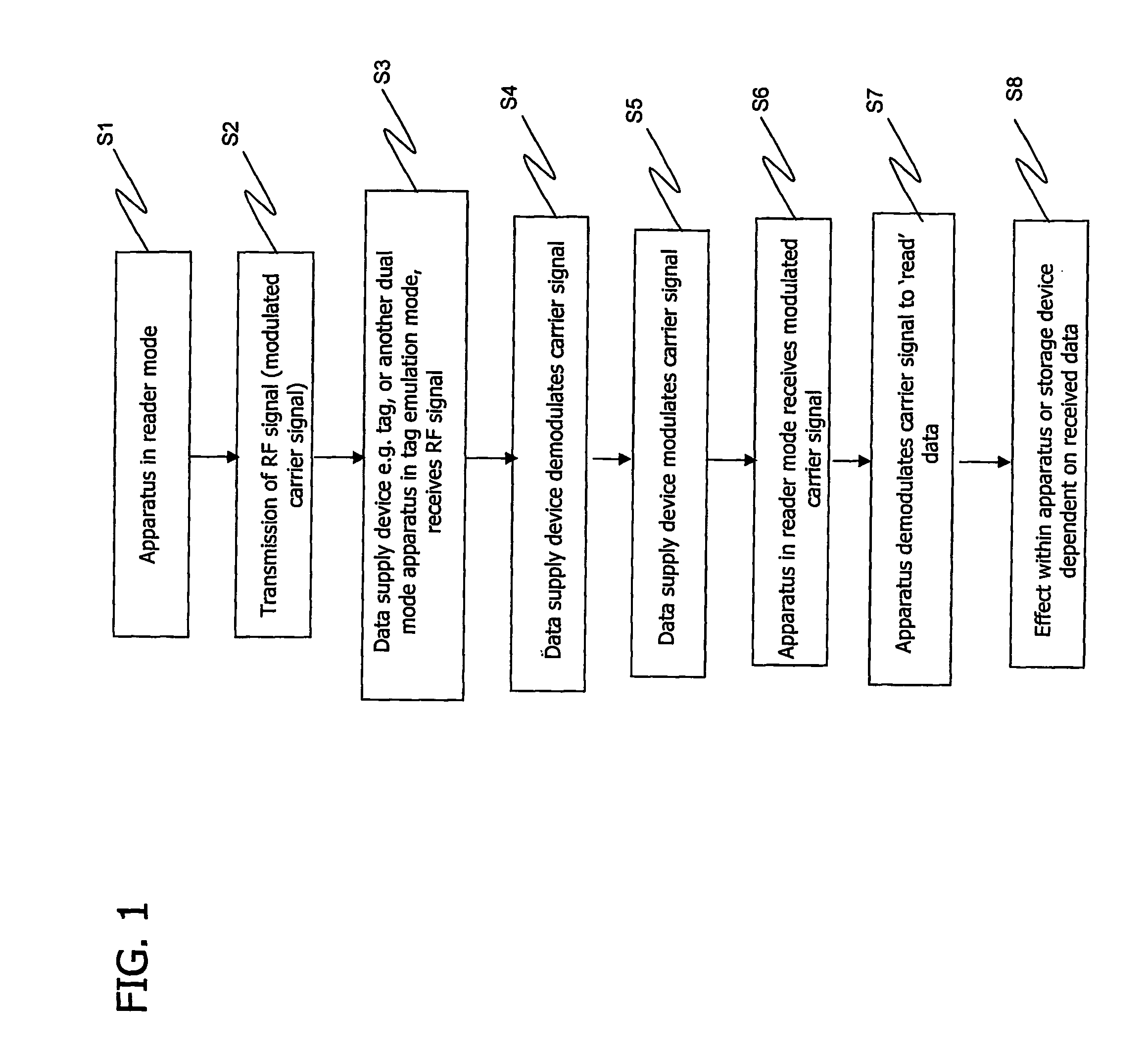
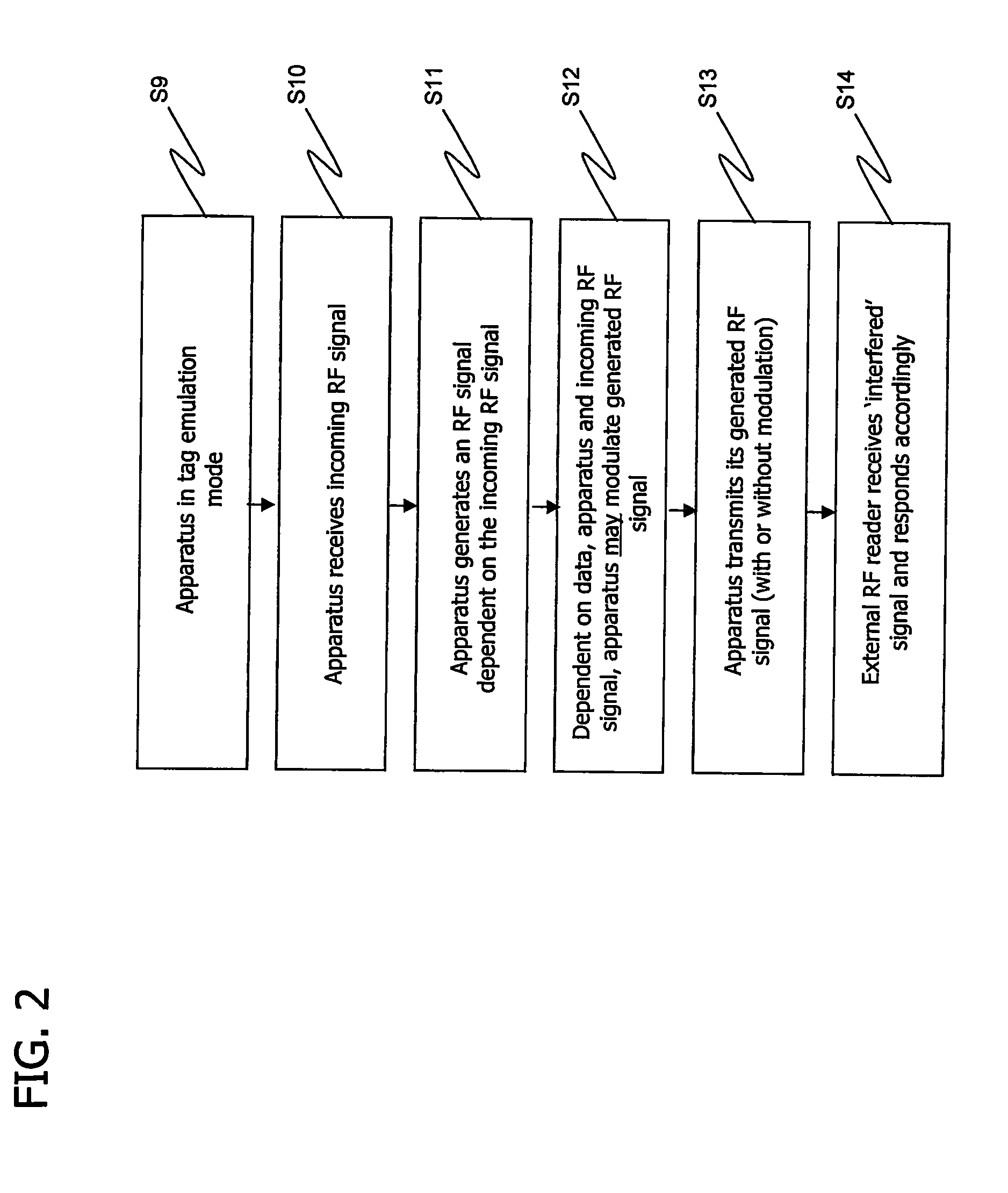
ActiveUS20080018433A1Different propertyUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsDemodulation
RFID apparatus includes transmission means for transmitting an RF signal; reception means for receiving a modulated RF signal; and demodulation means for demodulating a received modulated signal. The apparatus comprises generating means for generating a RF signal dependent on an incoming RF signal, the incoming RF signal being generated by different apparatus, and the apparatus is arranged to transmit the generated RF signal such that the generated RF signal interferes with the incoming RF signal. The RFID apparatus has both the means to respond to an RF reader device, in tag emulation mode, and means to function as an RF reader device, in reader mode.
Owner:NXP USA INC
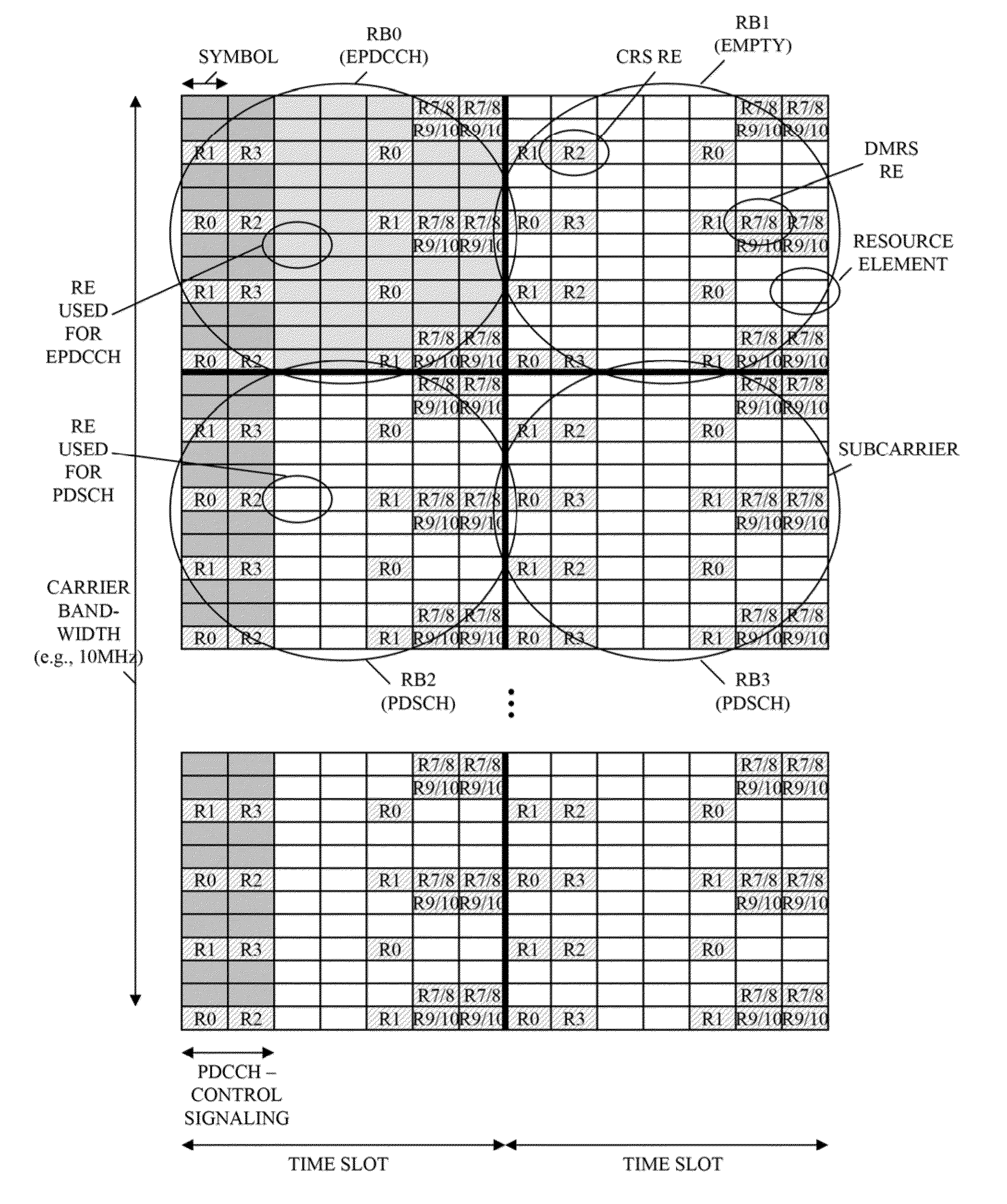
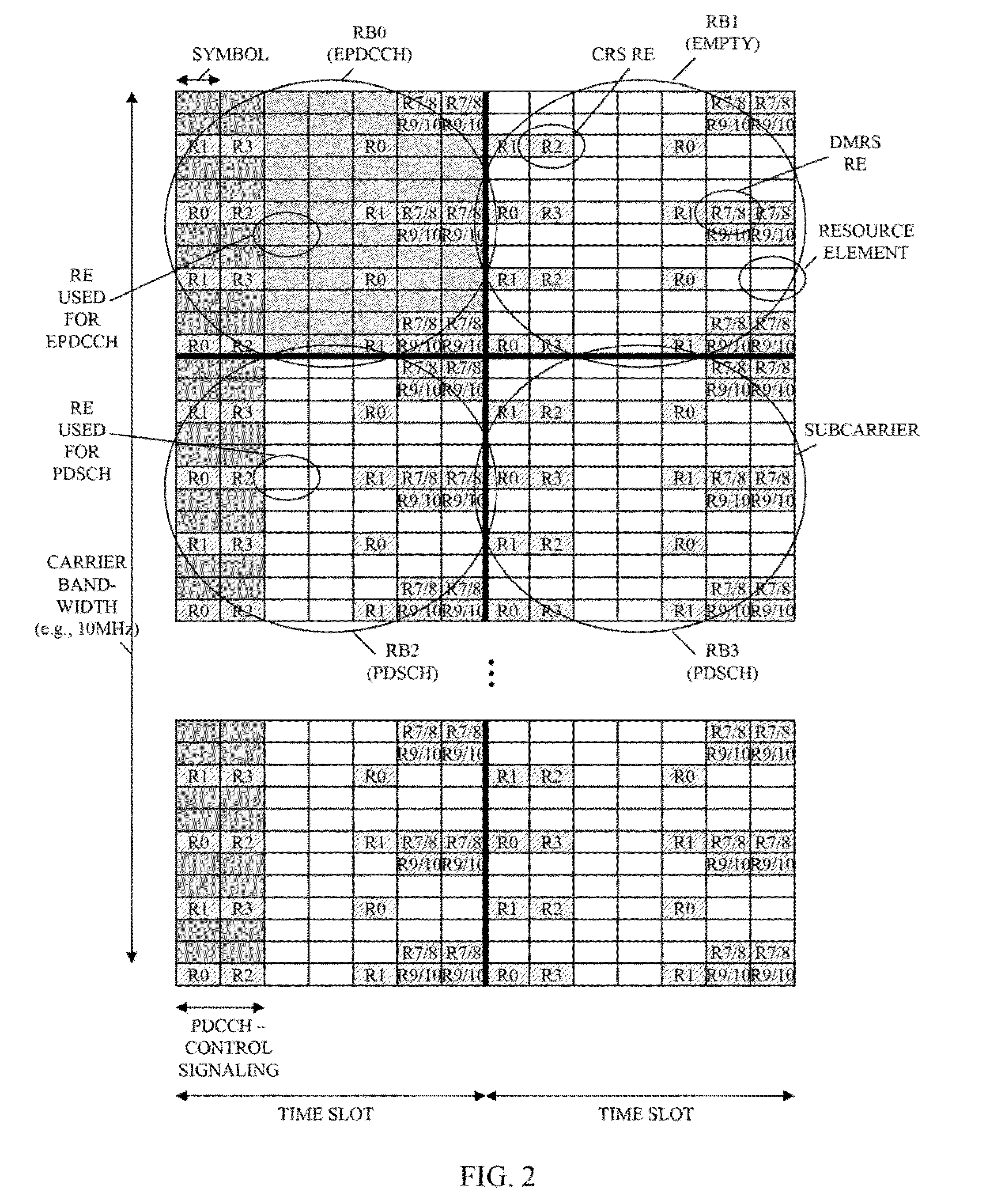
Uplink DMRS transmitting method, device and system/ Transmitting method, device and system used for uplink DMRS
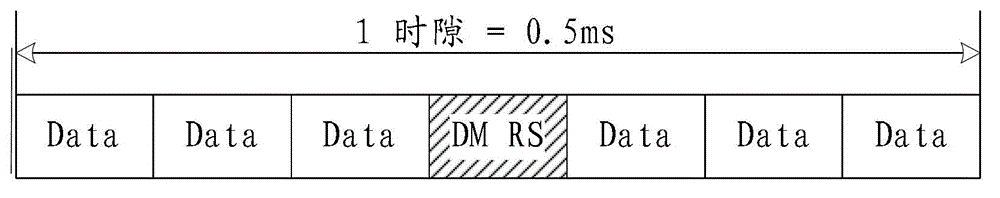
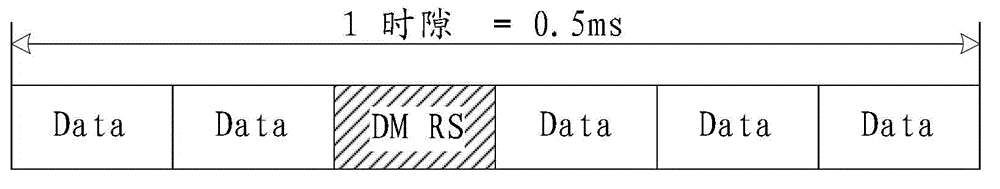
ActiveCN103944665ASolve excessive overheadTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDemodulation
The invention relates to the field of communication, provides an uplink DMRS (Demodulation Reference Signal) transmitting method, device and system and solves the problem that the time-frequency resource overhead of the uplink demodulation reference signal is excessive. The method comprises the steps that a base station configures a resource, a pattern or a parameter set required for transmitting the uplink DMRS for a user terminal; and the base station transmits or indicates the resource, the pattern or the parameter set required for transmitting the uplink DMRS to the user terminal via a bit domain or a high-level signaling of downlink control information. The resource, the pattern or the parameter set comprises a time domain position, a frequency domain position, a subframe configuration or a cycle, and a hopping mode. The technical scheme is applicable to a long term evolution system, and an uplink DMRS transmitting mechanism with the low time-frequency resource overhead is realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for calibration to reduce coupling between signals in a measurement system
ActiveUS20180153448A1Reduces crosstalk and other contaminationCrosstalk in the multi-channel demodulator is reducedDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical sensorsData setCoupling
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Method for providing high-speed data service and voice service
InactiveUS6970502B2Increase speedInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplexDigital subscriber lineTransport system
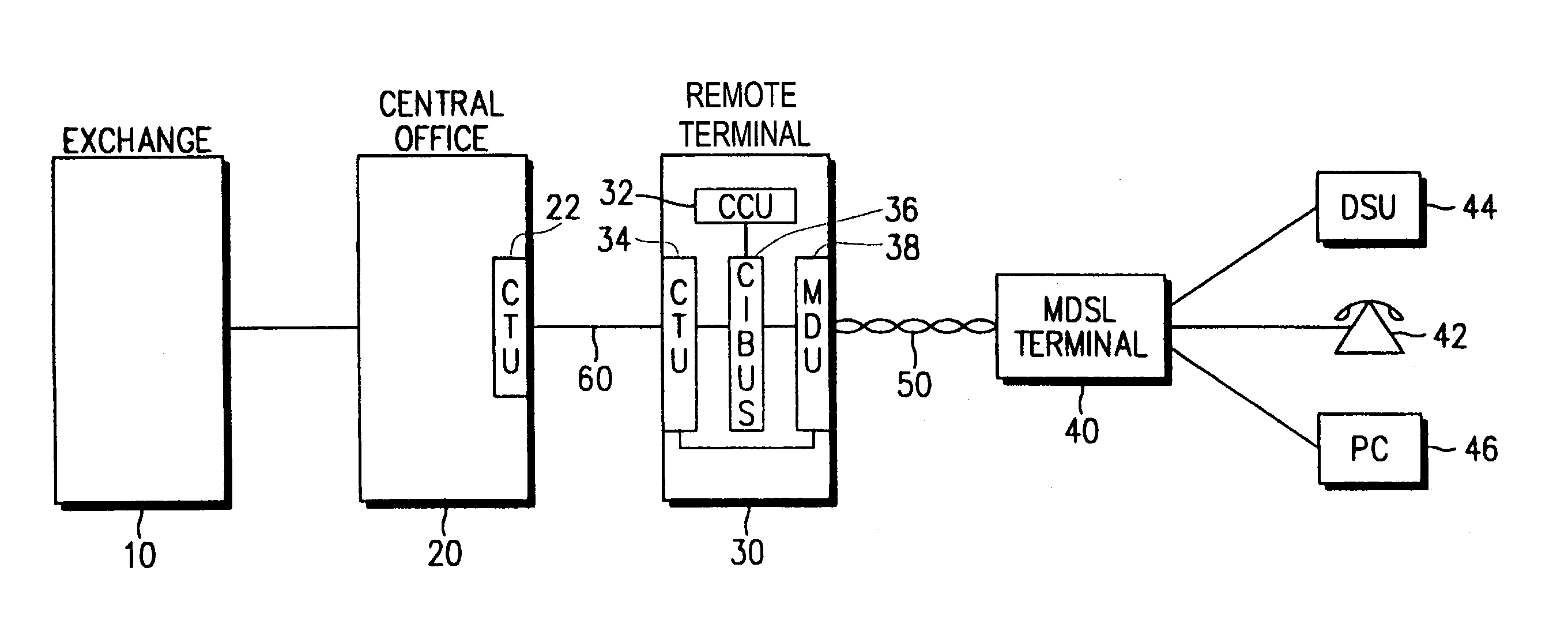
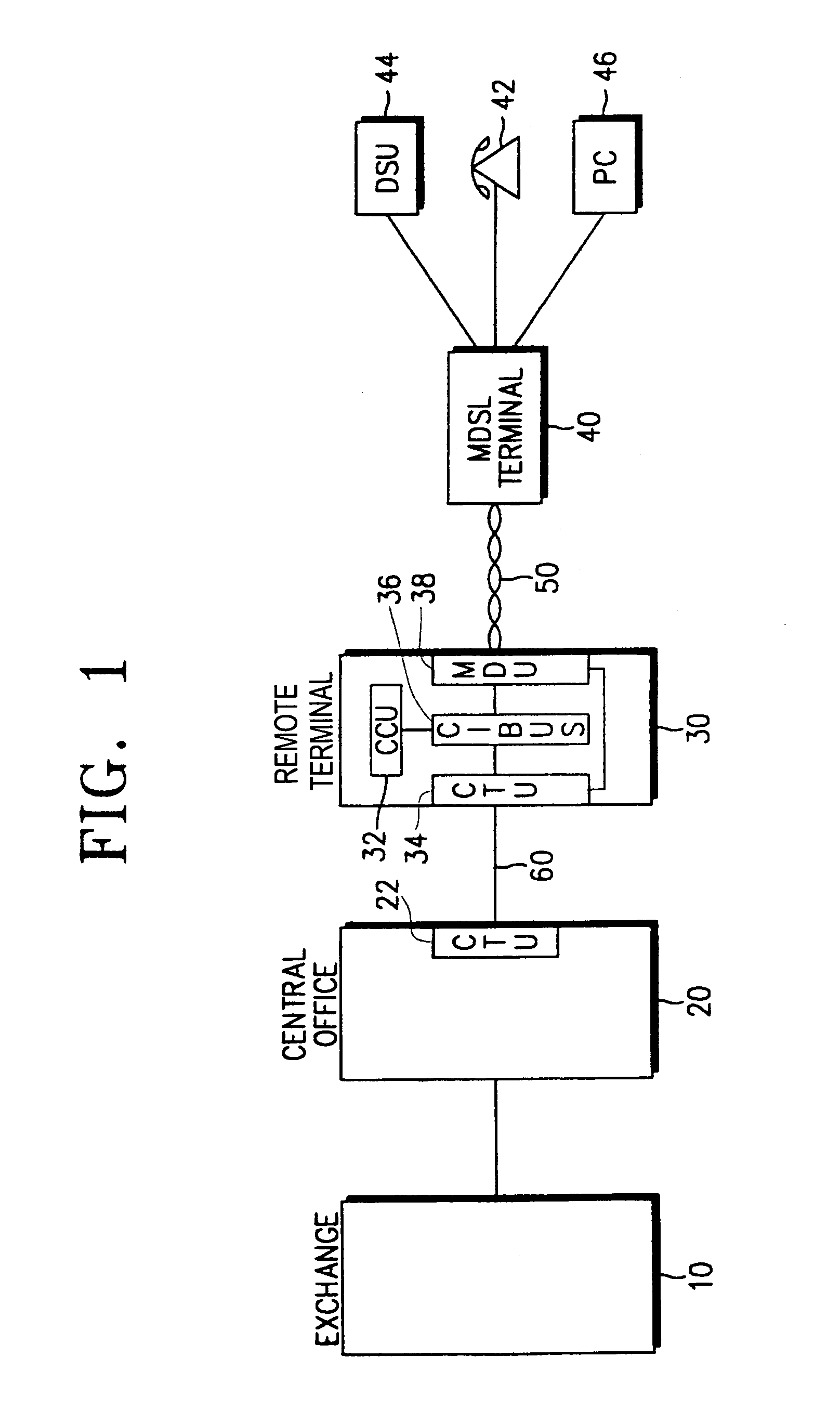
Providing a high-speed data service and voice service in a transmission system employing two binary, one quarternary (2B1Q) modulation / demodulation, using a high-speed data service remote terminal, a plurality of user data service and voice service terminals, and a multi-rate digital subscriber line (MDSL) terminal connected to the remote terminal through a twisted pair line, and to the user terminals. During downstream voice service, the remote terminal assembles and transmits an high bit rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) frame by including signaling signals for the voice service and signal processing mode information in a user-defined interval of the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame, to the multi-rate digital subscriber line terminal through the twisted pair line. During upstream voice service, the remote terminal receives the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame and transmits the signaling signals received to an exchange.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
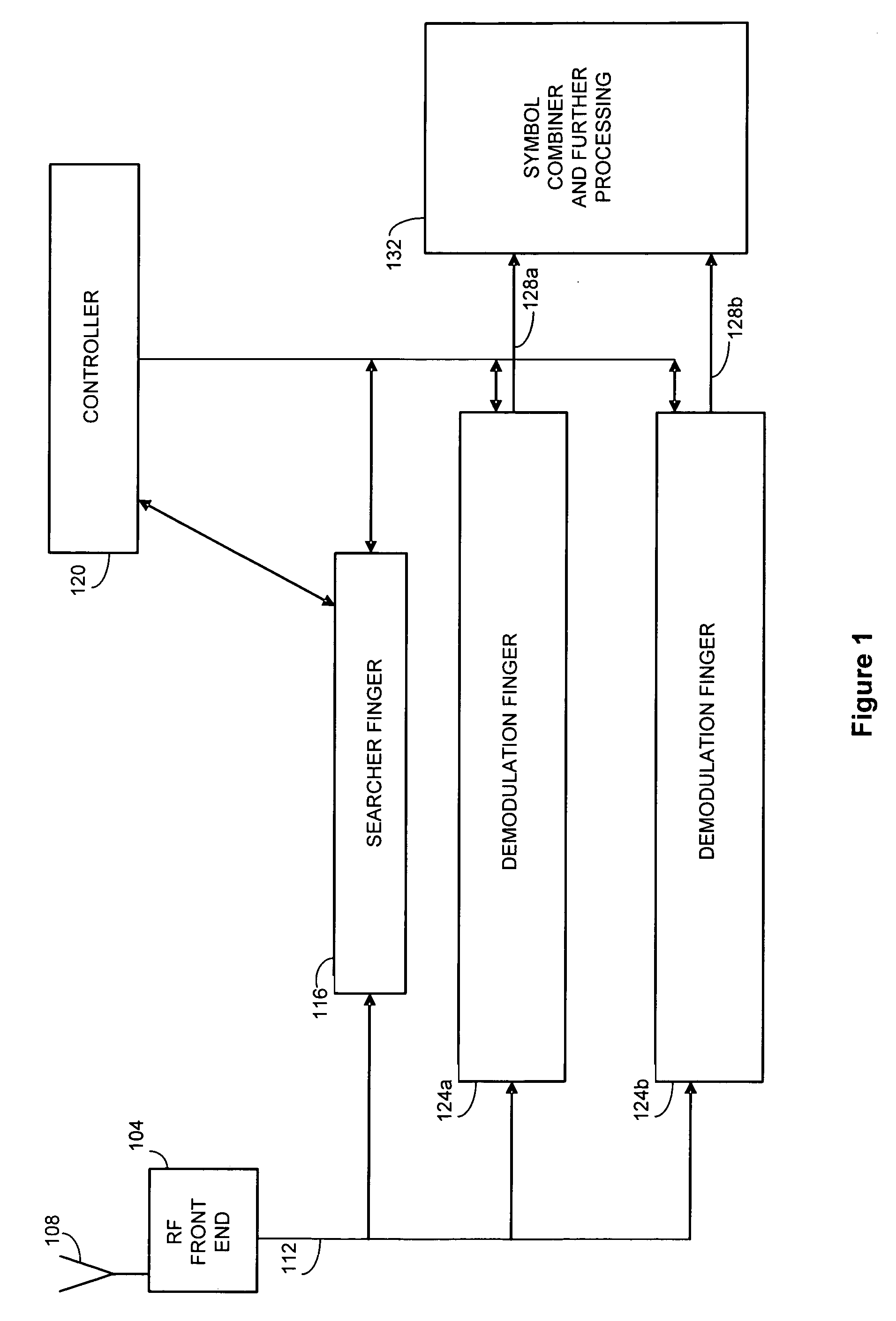
Method and apparatus for selectively applying interference cancellation in spread spectrum systems
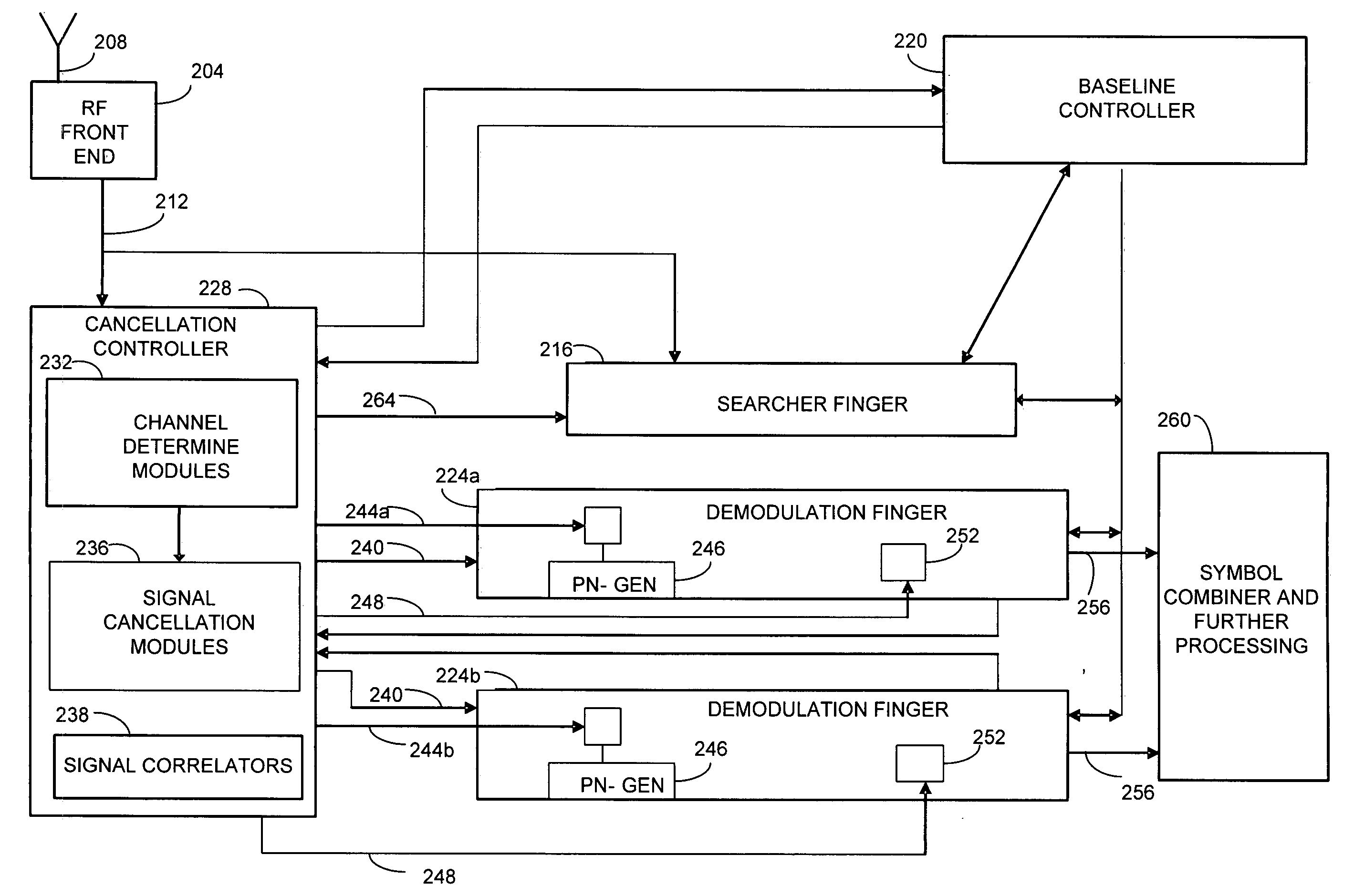
ActiveUS20070183483A1High strengthIncrease signal strengthError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal cancellationEngineering
The present invention is directed to the selective provision of interference canceled signal streams to demodulating fingers in a communication receiver. According to the present invention, potential interferer signal paths are identified. Signal streams having one or more potential interferer signals removed or canceled are created, and a correlation is performed to determine whether the strength of a desired signal path increased as a result. If the correlation indicates that the strength of a desired signal path was increased by the signal cancellation, the interference canceled signal stream is provided to the demodulation finger assigned to track the desired signal path. If the correlation determines that the strength of the desired signal path did not increase as a result of performing interference cancellation, the raw or a different interference canceled signal stream is provided to the demodulation finger.
Owner:III HLDG 1
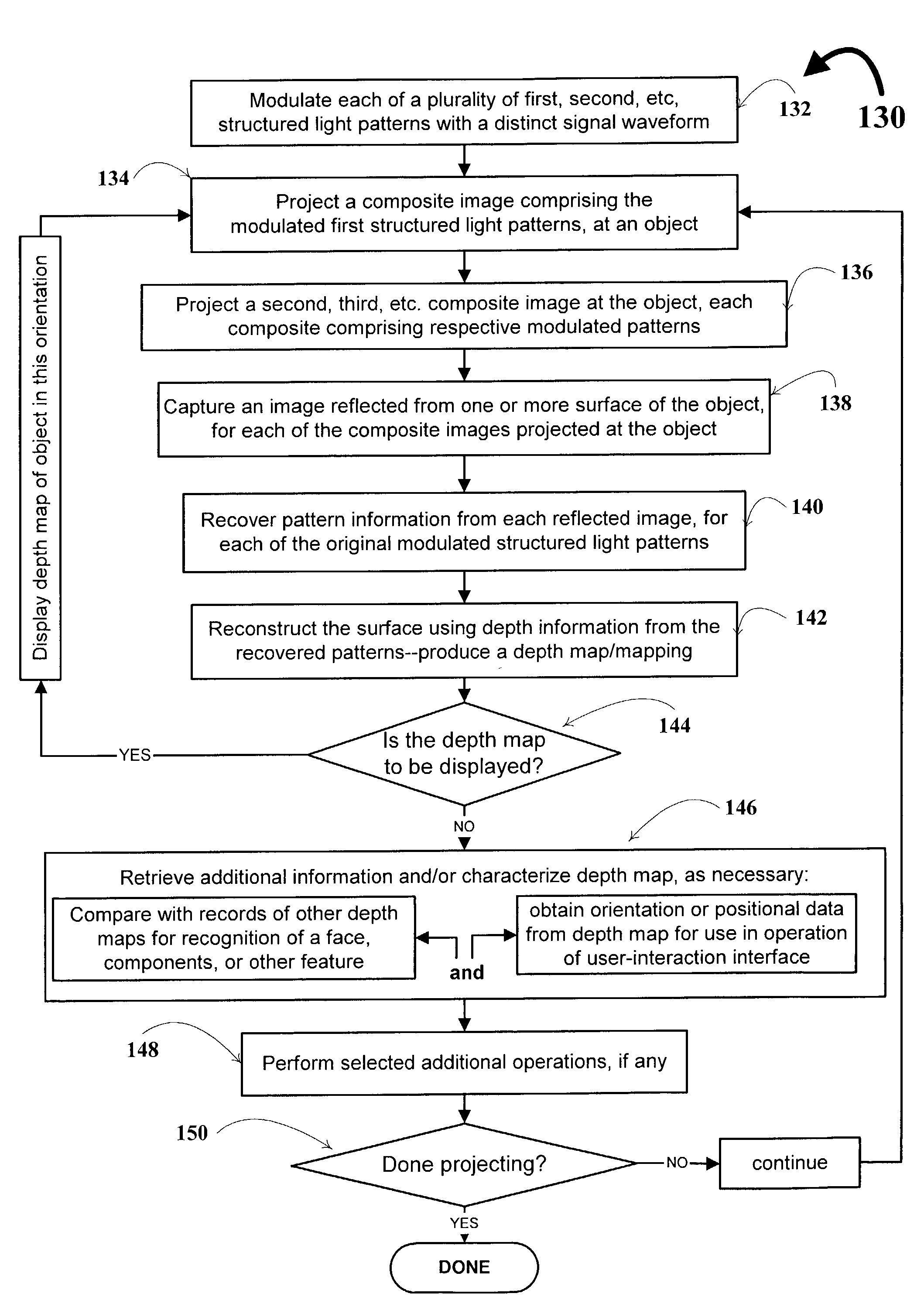
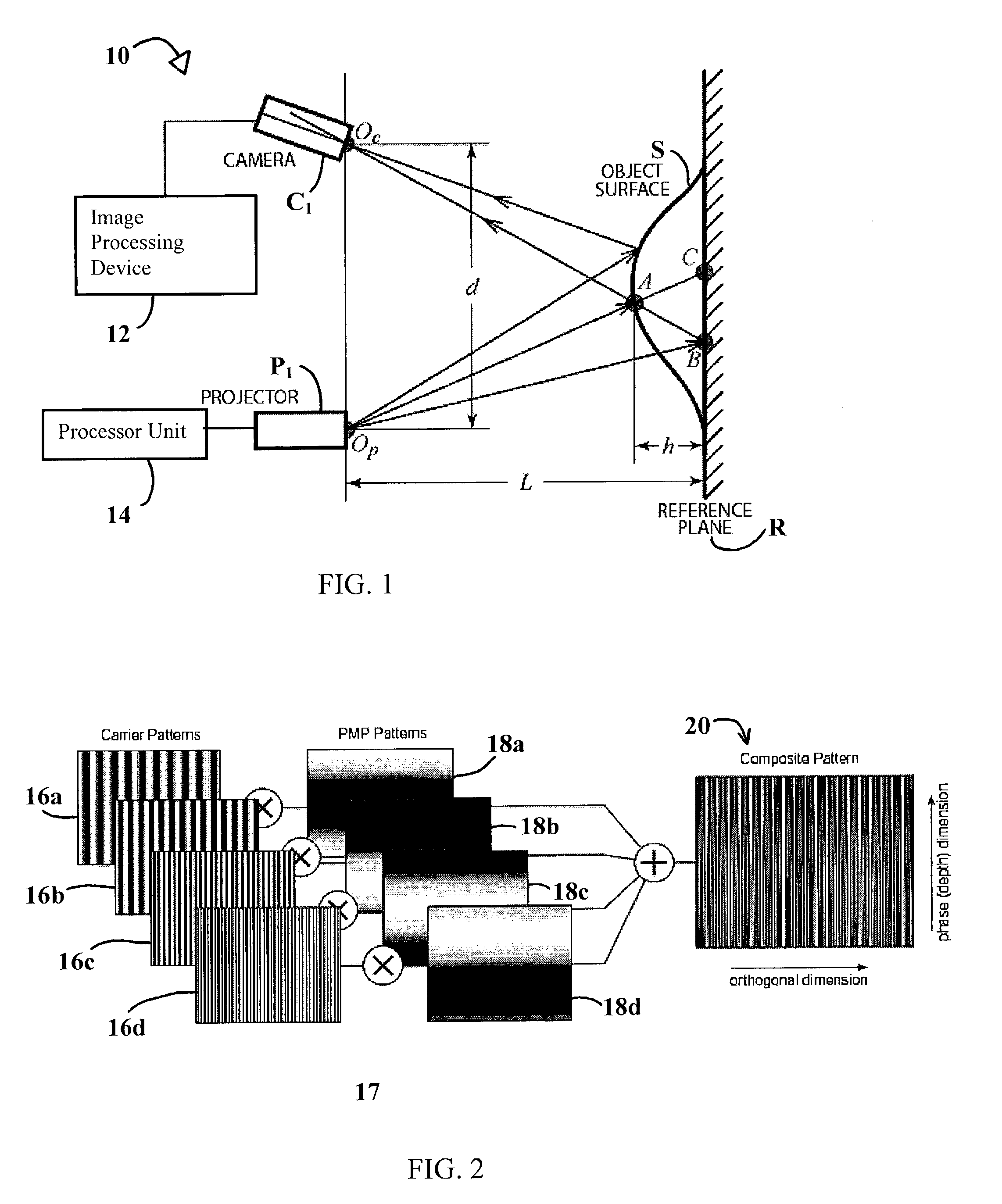
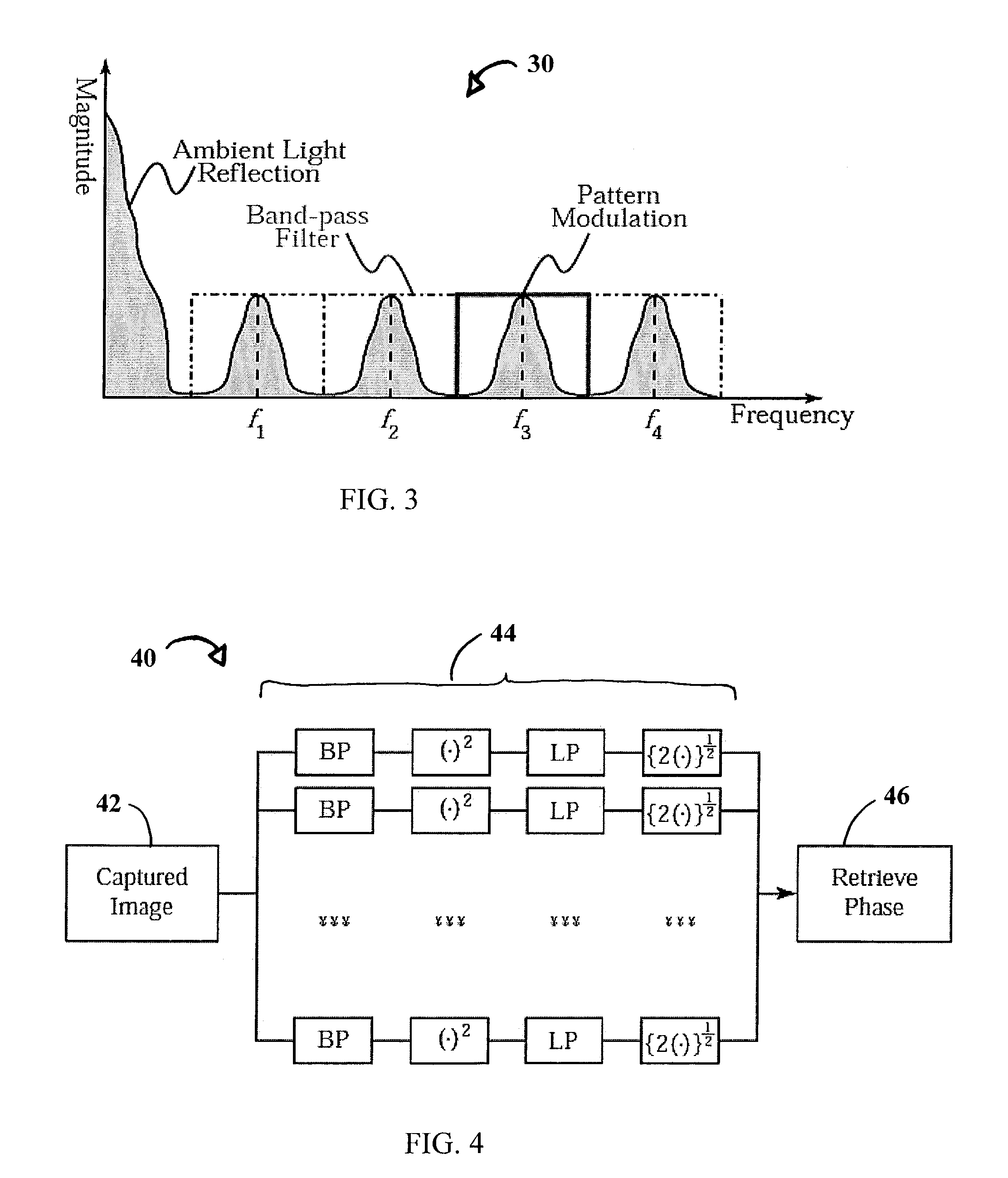
System and technique for retrieving depth information about a surface by projecting a composite image of modulated light patterns
InactiveUS7440590B1More detailed and large depth mappingLimited bandwidthProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInteraction interfaceTelecollaboration
A technique, associated system and program code, for retrieving depth information about at least one surface of an object. Core features include: projecting a composite image comprising a plurality of modulated structured light patterns, at the object; capturing an image reflected from the surface; and recovering pattern information from the reflected image, for each of the modulated structured light patterns. Pattern information is preferably recovered for each modulated structured light pattern used to create the composite, by performing a demodulation of the reflected image. Reconstruction of the surface can be accomplished by using depth information from the recovered patterns to produce a depth map / mapping thereof. Each signal waveform used for the modulation of a respective structured light pattern, is distinct from each of the other signal waveforms used for the modulation of other structured light patterns of a composite image; these signal waveforms may be selected from suitable types in any combination of distinct signal waveforms, provided the waveforms used are uncorrelated with respect to each other. The depth map / mapping to be utilized in a host of applications, for example: displaying a 3-D view of the object; virtual reality user-interaction interface with a computerized device; face—or other animal feature or inanimate object—recognition and comparison techniques for security or identification purposes; and 3-D video teleconferencing / telecollaboration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
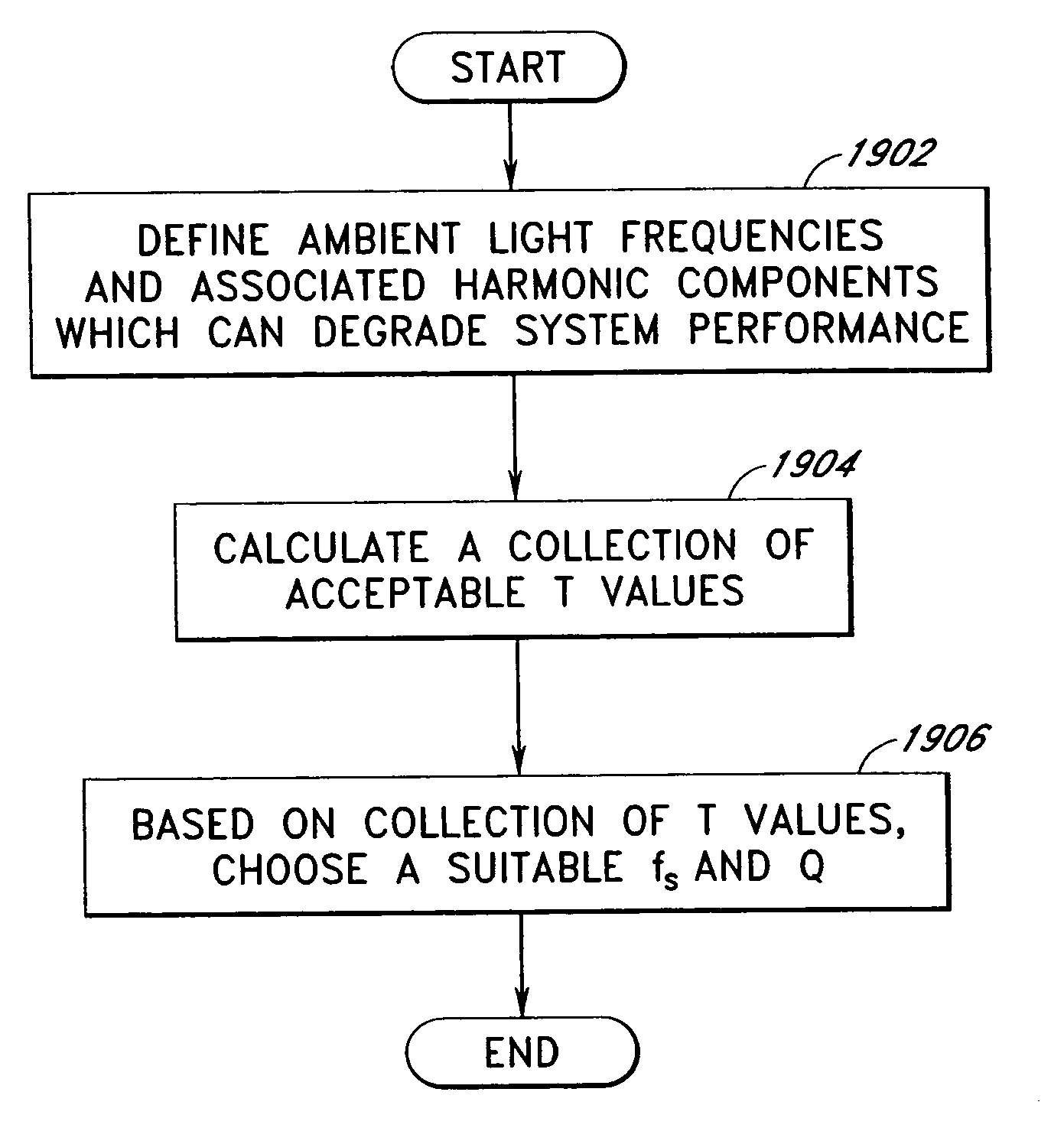
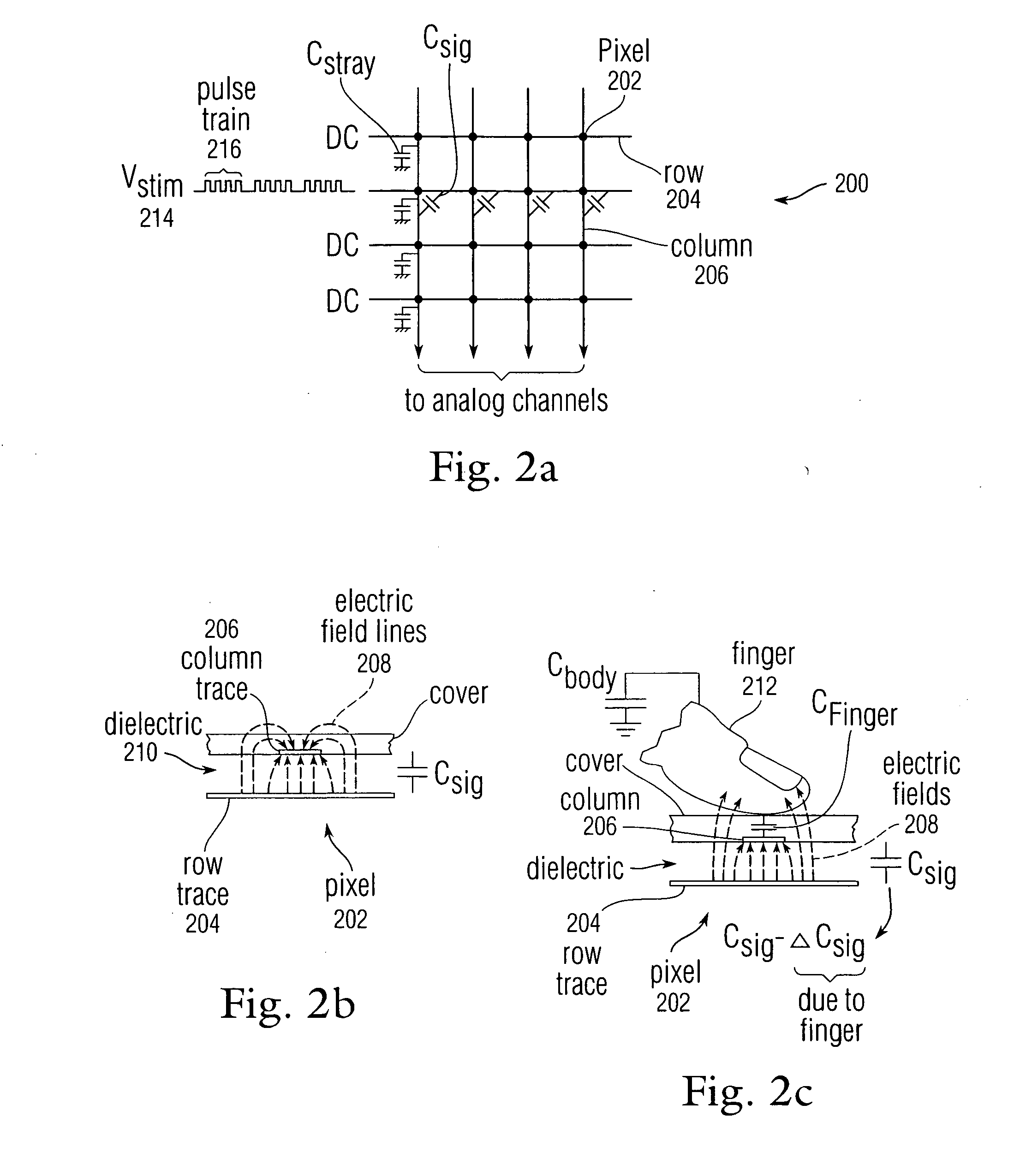
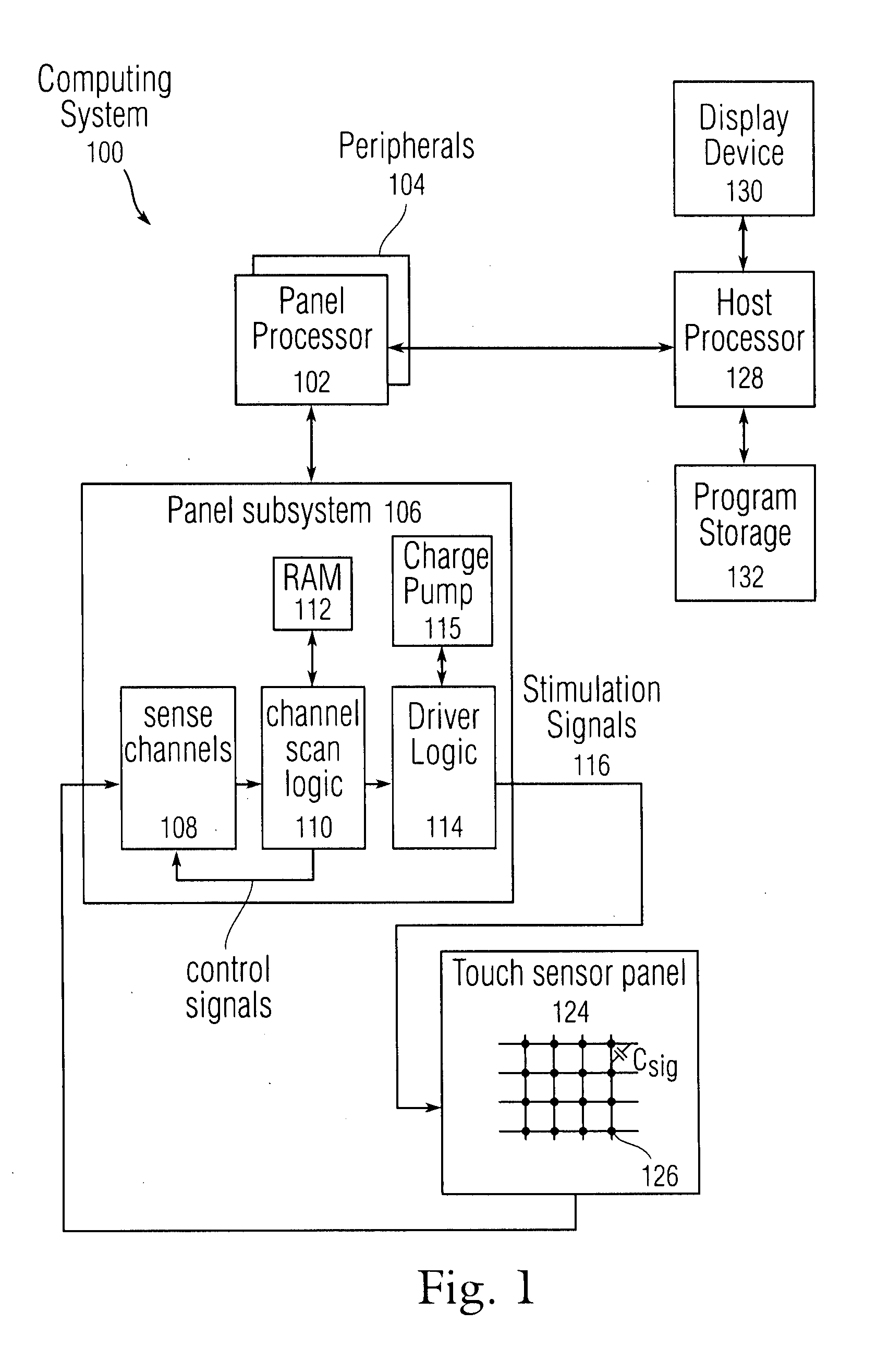
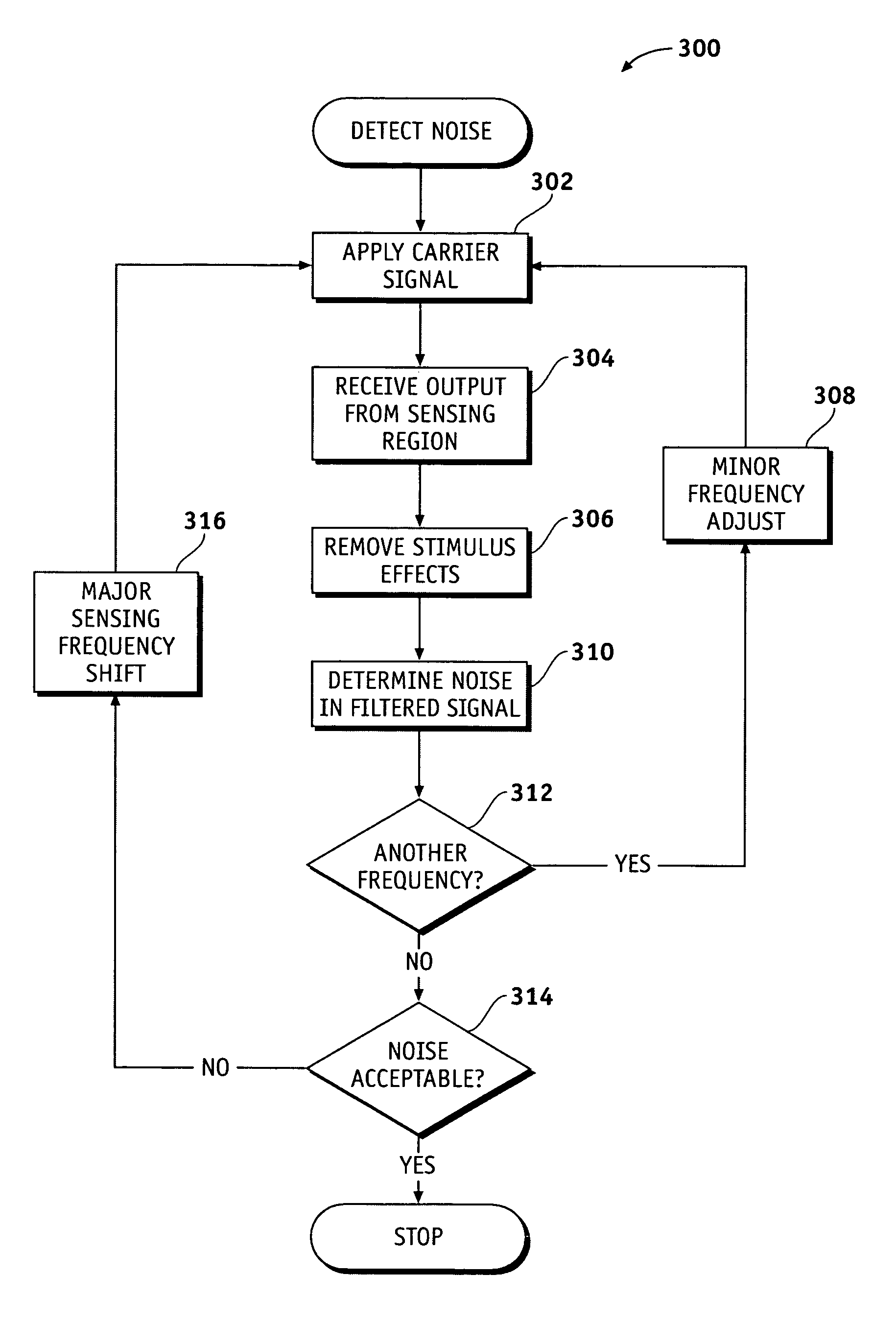
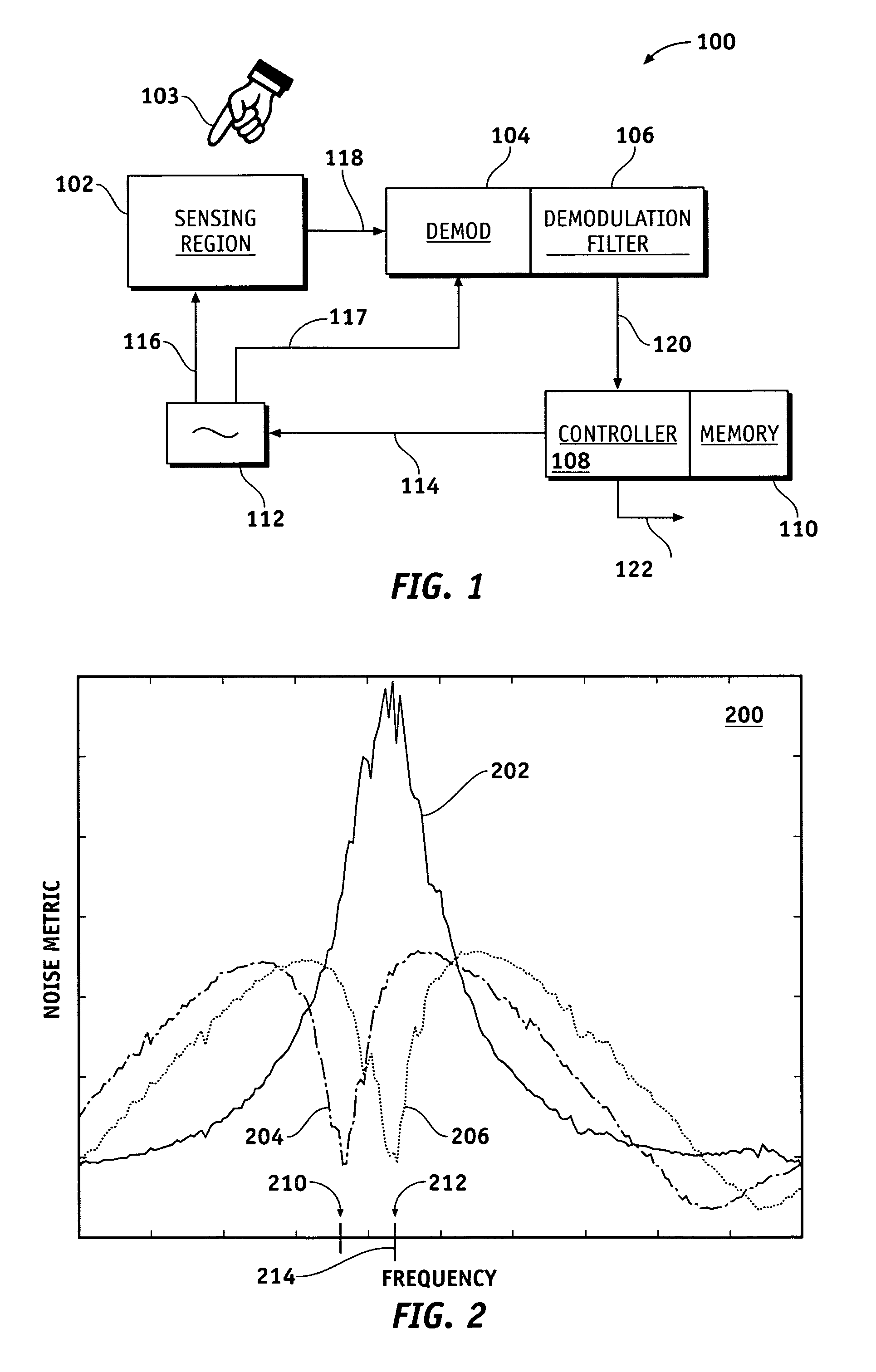
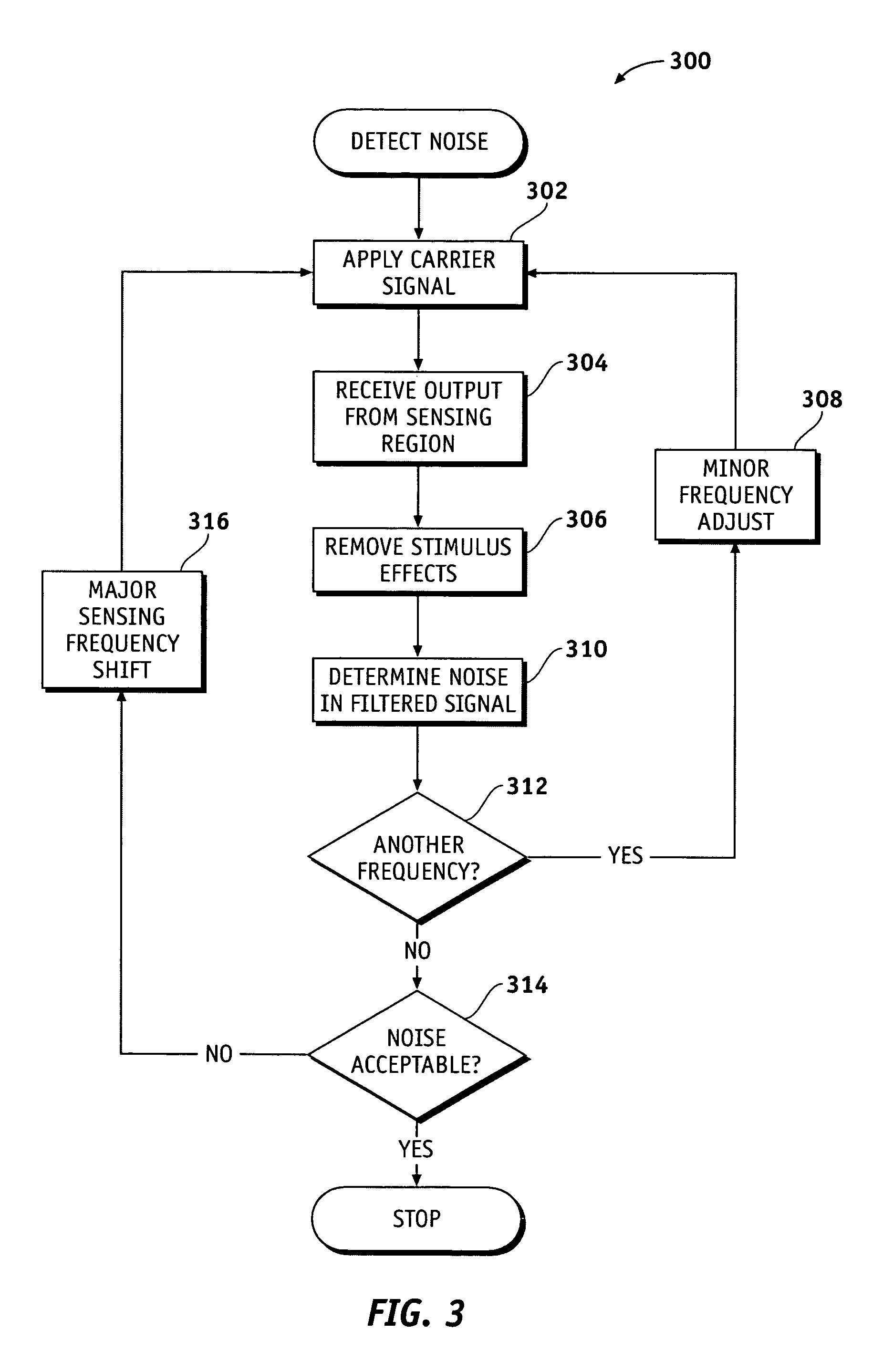
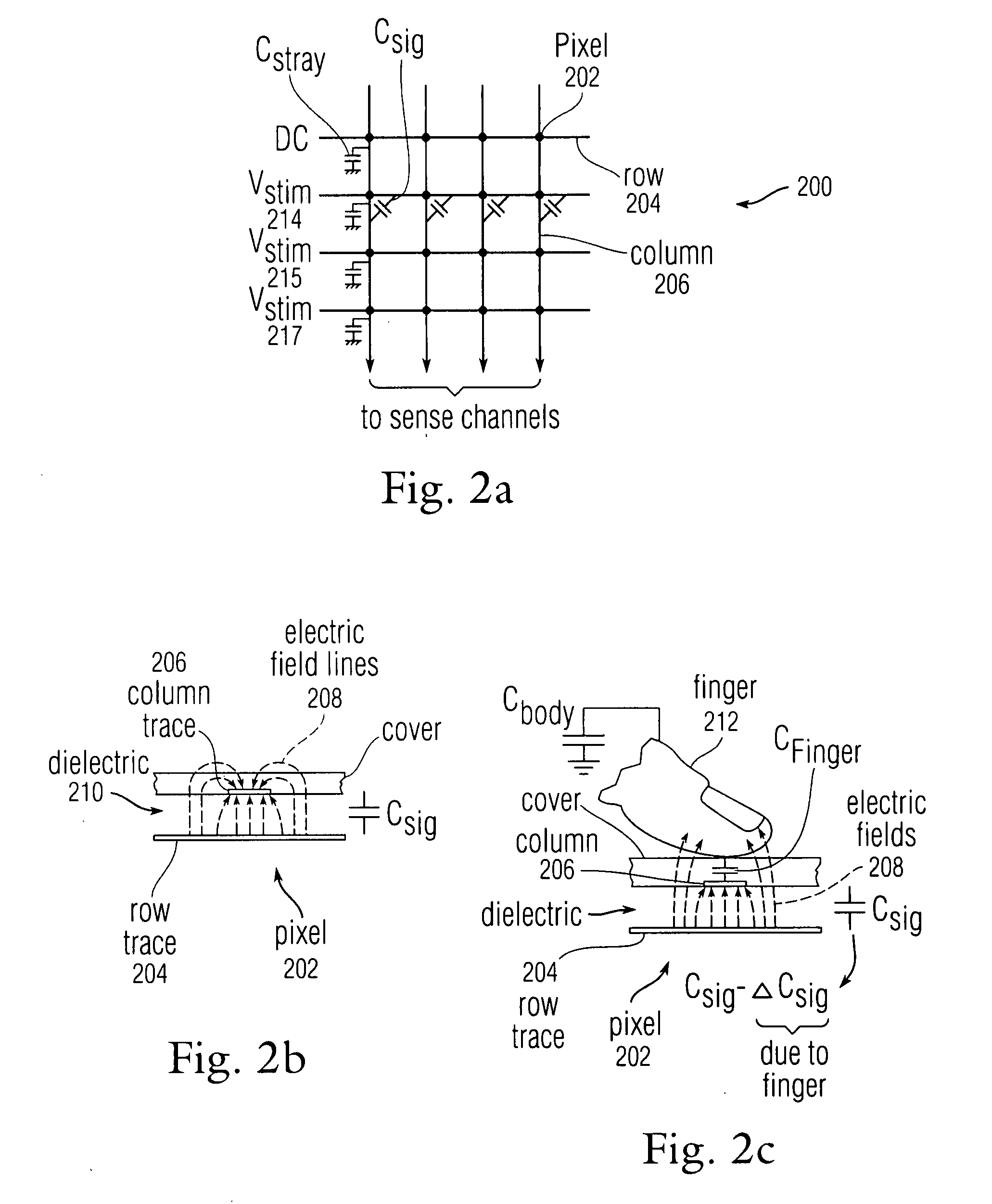
Methods and systems for detecting noise in a position sensor using minor shifts in sensing frequency
ActiveUS7031886B1Measurement devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCarrier signalTouchpad
Methods, systems and devices are described for detecting noise in a touchpad or other sensor that produces an output in response to a stimulus that is applied at or near a sensing region. According to various embodiments, a carrier signal is applied to the sensing region at two or more frequencies to thereby produce an output from the sensing region at each frequency. Each of the outputs is demodulated and filtered by a demodulation filter having a demodulation filter bandwidth. The various frequencies applied to the carrier signal are selected such that a difference between the frequencies is less than the demodulation filter bandwidth. At least some of the effects of the stimulus are removed from the outputs produced by the various carrier frequencies to produce two or more filtered outputs. The filtered outputs are then added, combined or otherwise processed to detect noise contained therein. If noise contained in one or more of the filtered outputs reaches an unacceptable level, the carrier signal may be shifted to a new sensing frequency for subsequent operation of the sensor.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Apparatus for OFDMA transmission and reception for coherent detection in uplink of wireless communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS7639660B2Improve channel estimation performanceFrequency-division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemResource block
In the resource mapping method for data transmission, a time-frequency resource of a slot interval including OFDM symbols is divided into traffic channels and shared among the subscribers, the traffic channel including resource blocks uniformly distributed in the whole transmit frequency band, the resource block including consecutive subcarriers of consecutive received symbols having at least one inserted pilot symbol. The pilot symbols and the channel-encoded and modulated data symbols are processed by time-frequency mapping according to the resource-block-based mapping method to generate received symbols. The receiver separates the received symbols by subscribers according to the resource-block-based mapping method in a frequency domain, and performs iterative channel estimation, demodulation, and decoding by using the pilot and a data reference value after decoding for each traffic channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
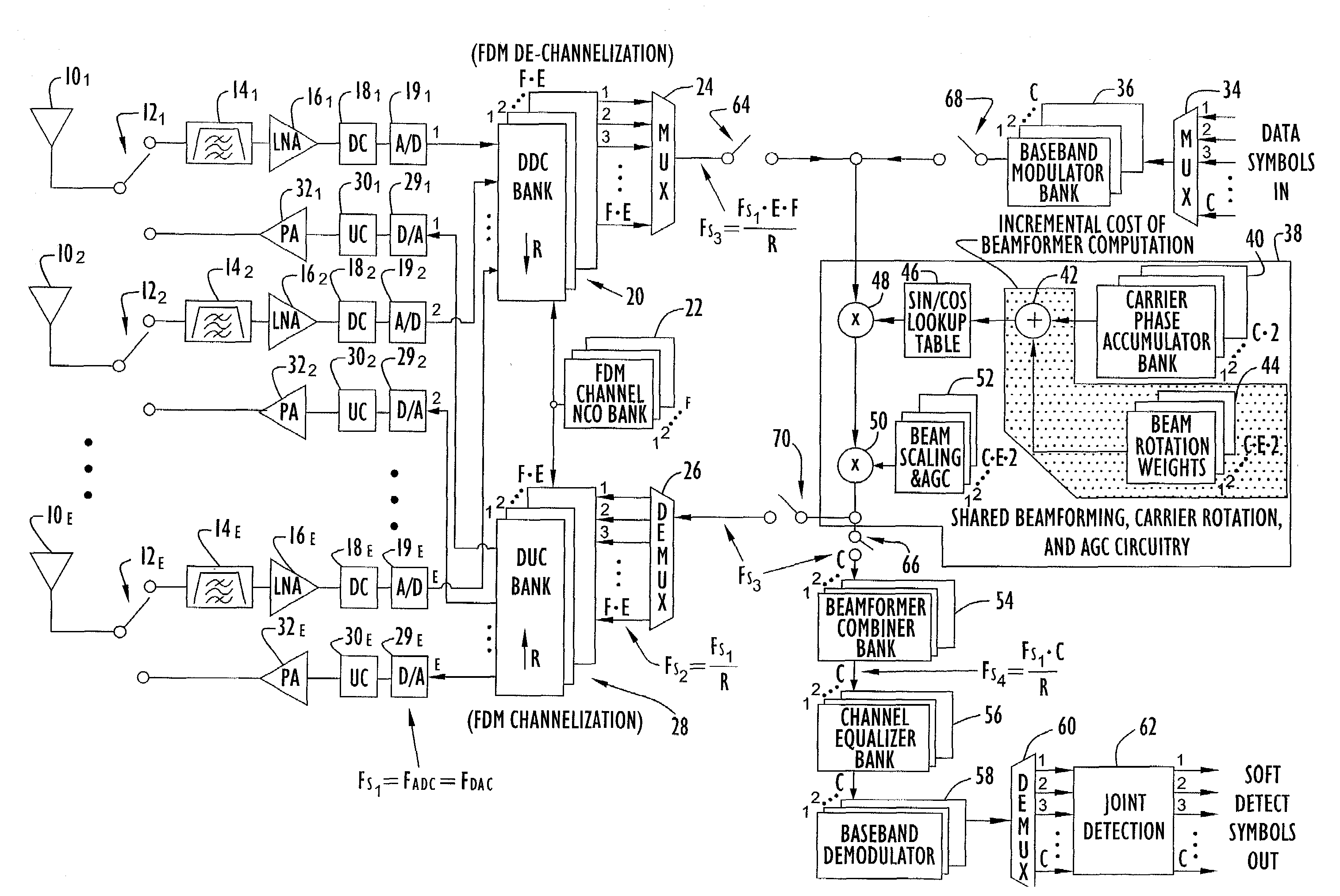
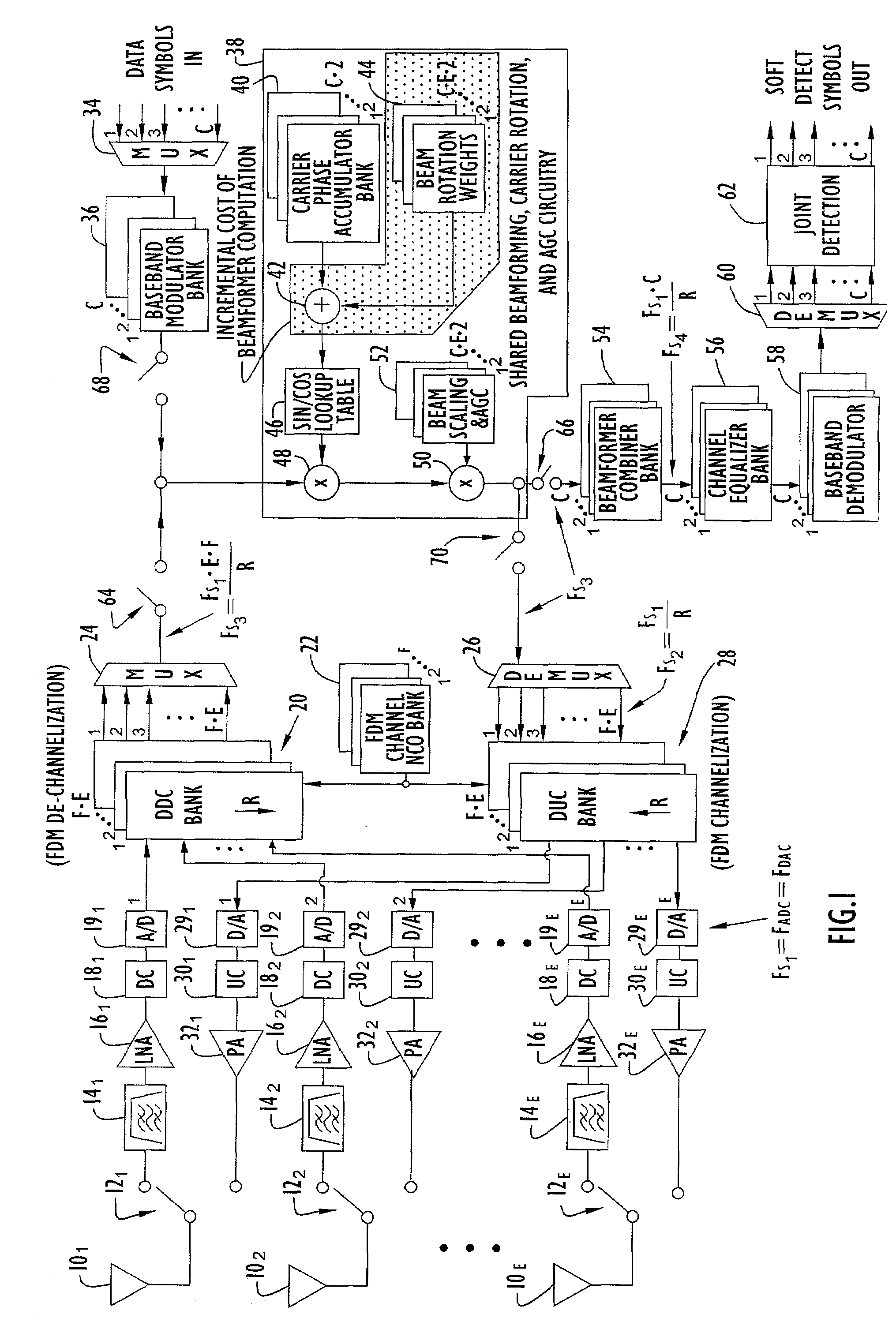
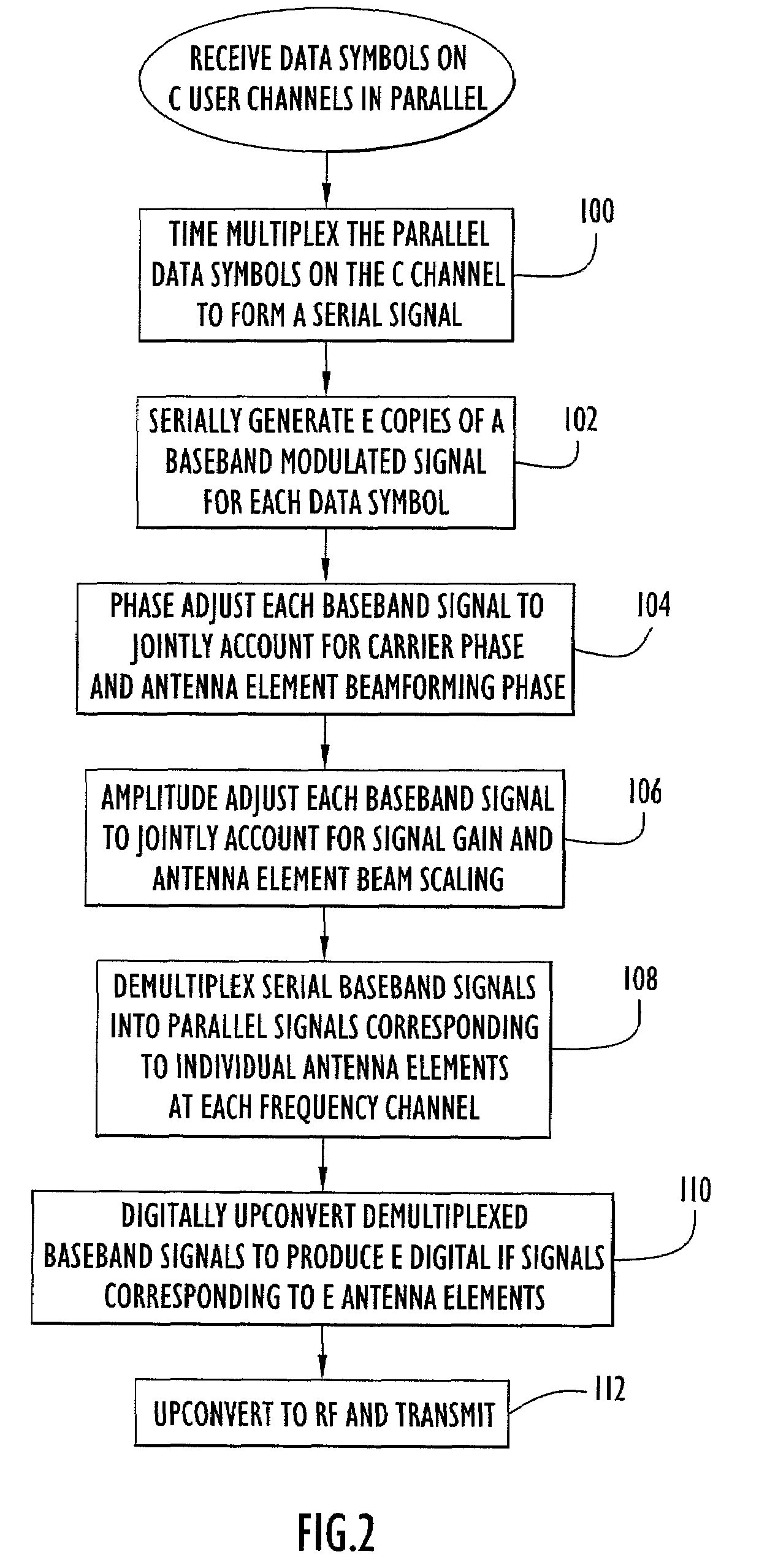
Integrated beamformer/modem architecture
ActiveUS7260141B2High computational complexityDecreasing computational rateSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTransceiverModem device
A transceiver employing a steerable phased-array antenna includes a modem architecture in which signals from each antenna element in the array are independently processed down to the individual baseband channel level, and digital beamforming is performed at baseband. The data rate reduction from IF to baseband permits parallel signal data from multiple antenna elements to be time multiplexed and serially processed at acceptable data rates at baseband with minimal modem hardware requirements. Both for transmit signal modulation and received signal demodulation, the computation of carrier tracking, automatic gain control (AGC) / power-control, and beamforming are shared by the same processing circuitry for all channels when performed at baseband. The resulting baseband circuitry is only incrementally larger than that required for carrier tracking and AGC alone, yet accomplishes independent beamforming for each antenna element on each user channel.
Owner:LIONRA TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for control channel transmission and reception
A communication system is provided wherein a user equipment (UE) receives control information from a wireless network. The UE monitors control channel candidates using common reference signals (CRS) and monitors enhanced control channel candidates using demodulation reference signals (DMRS) when the UE is configured in a first transmission mode, such as transmission mode 9, for receiving a downlink shared traffic channel based on DMRS. The UE monitors control channel candidates only using CRS when the UE is configured in a second transmission mode, such as any of transmission modes 1-6, for receiving a downlink shared traffic channel based on CRS. The UE then receives downlink control information (DCI) in a subframe in one of the monitored control channel candidates or enhanced control channel candidates in the subframe.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
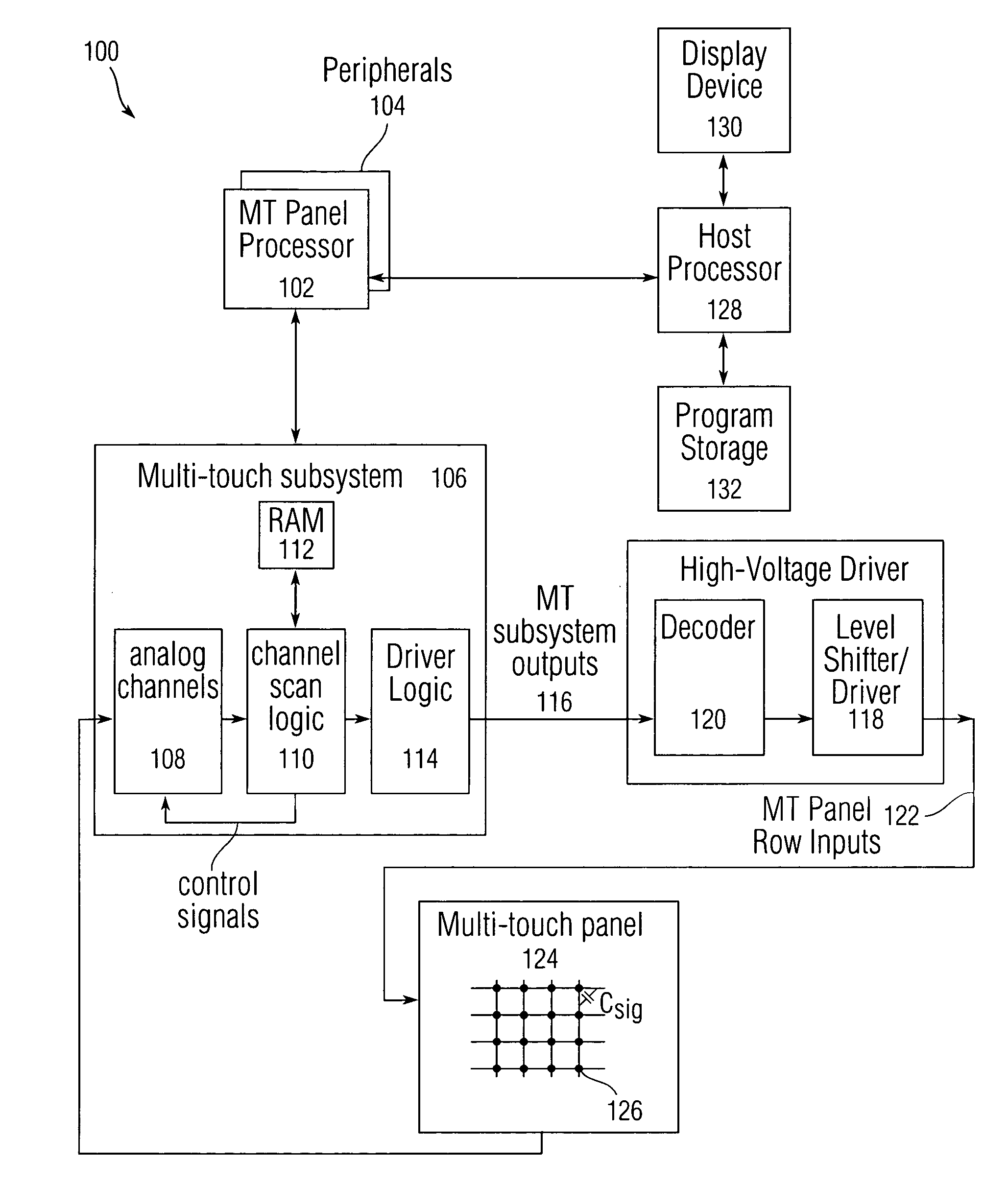
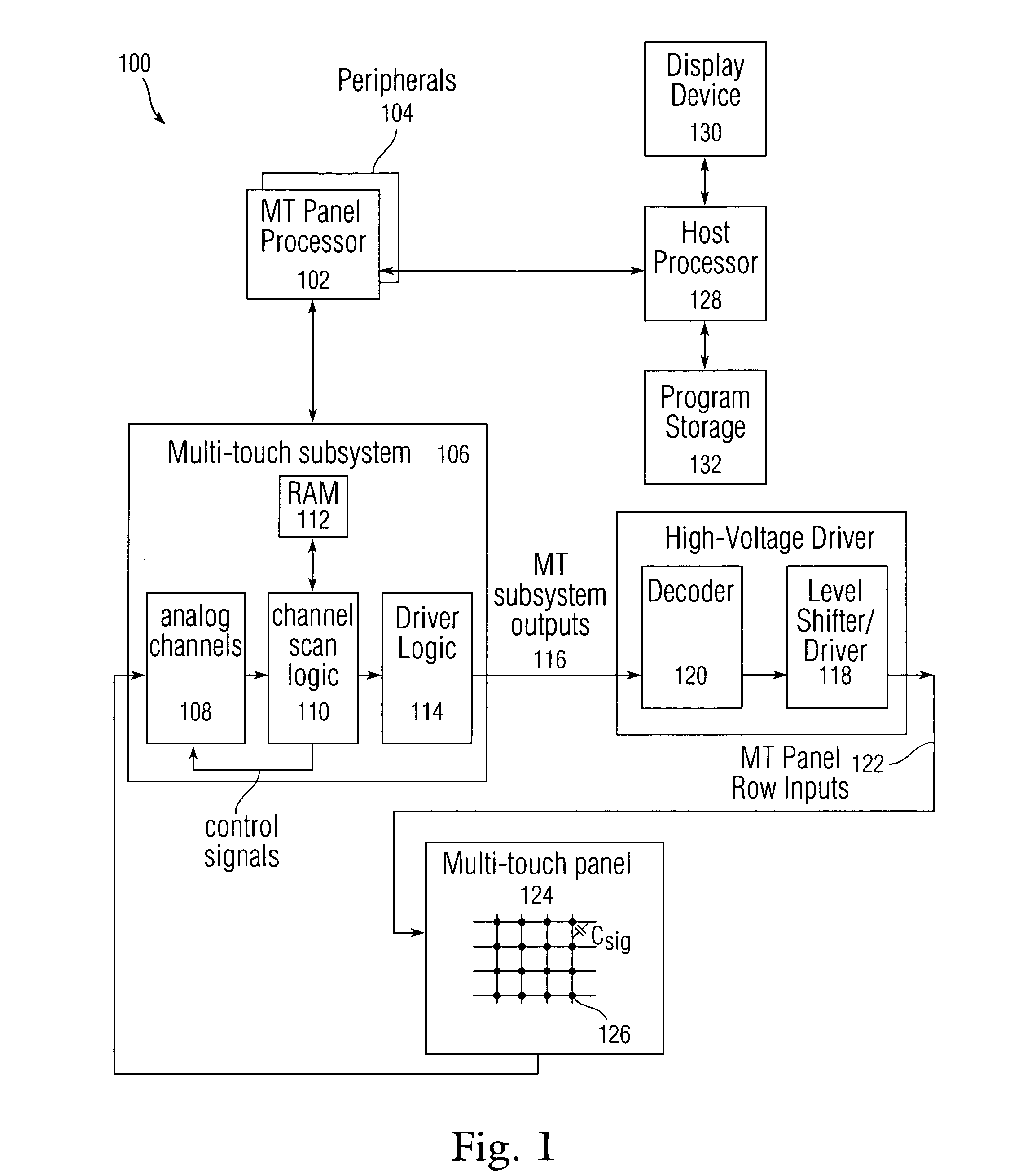
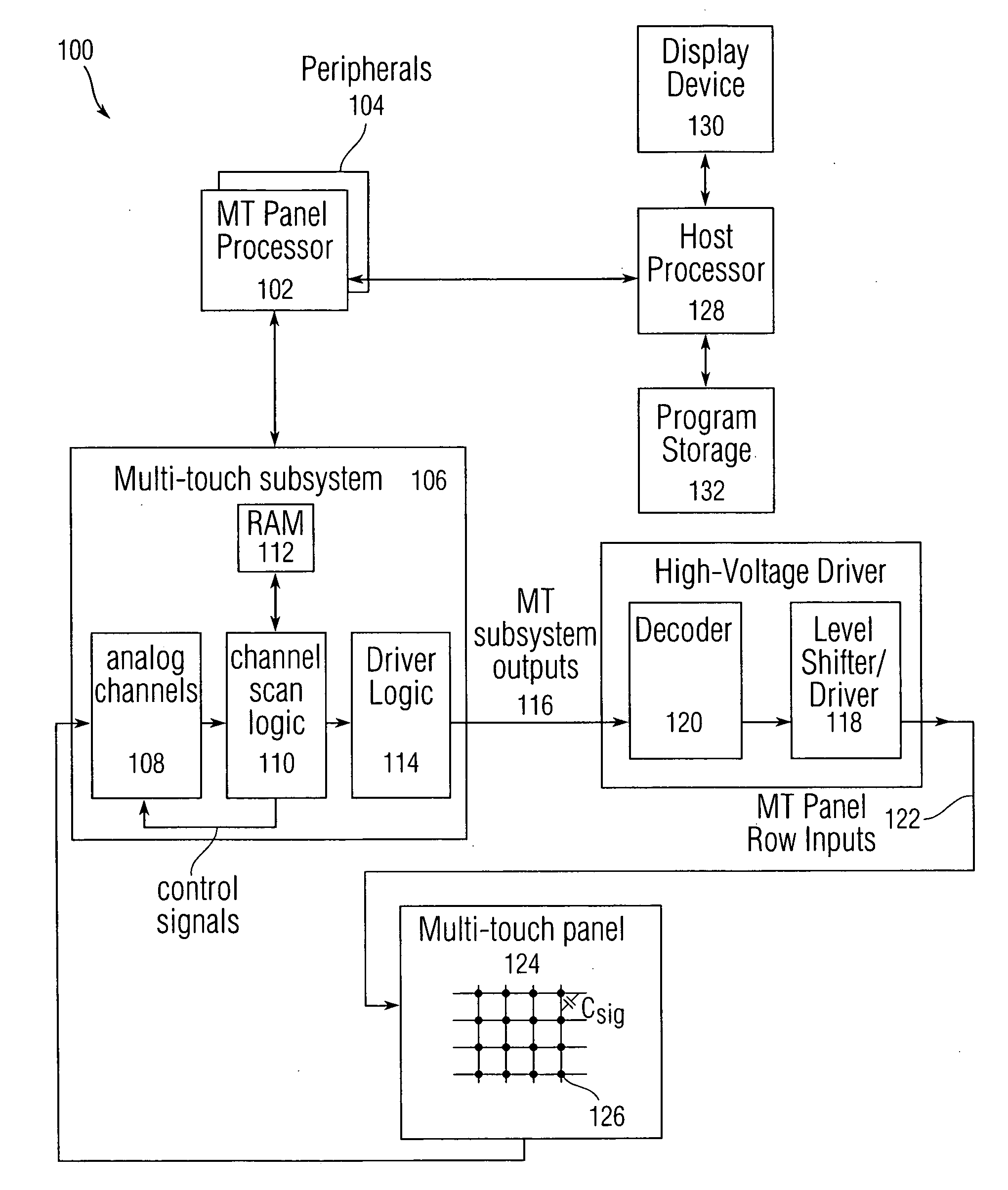
Single-chip multi-stimulus sensor controller
ActiveUS20100059295A1Transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSingle chipFrequency demodulation
A multi-stimulus controller for a multi-touch sensor is formed on a single integrated circuit (single-chip). The multi-stimulus controller includes a transmit oscillator, a transmit signal section that generates a plurality of drive signals based on a frequency of the transmit oscillator, a plurality of transmit channels that transmit the drive signals simultaneously to drive the multi-touch sensor, a receive channel that receives a sense signal resulting from the driving of the multi-touch sensor, a receive oscillator, and a demodulation section that demodulates the received sense signal based on a frequency of the receive oscillator to obtain sensing results, the demodulation section including a demodulator and a vector operator.
Owner:APPLE INC
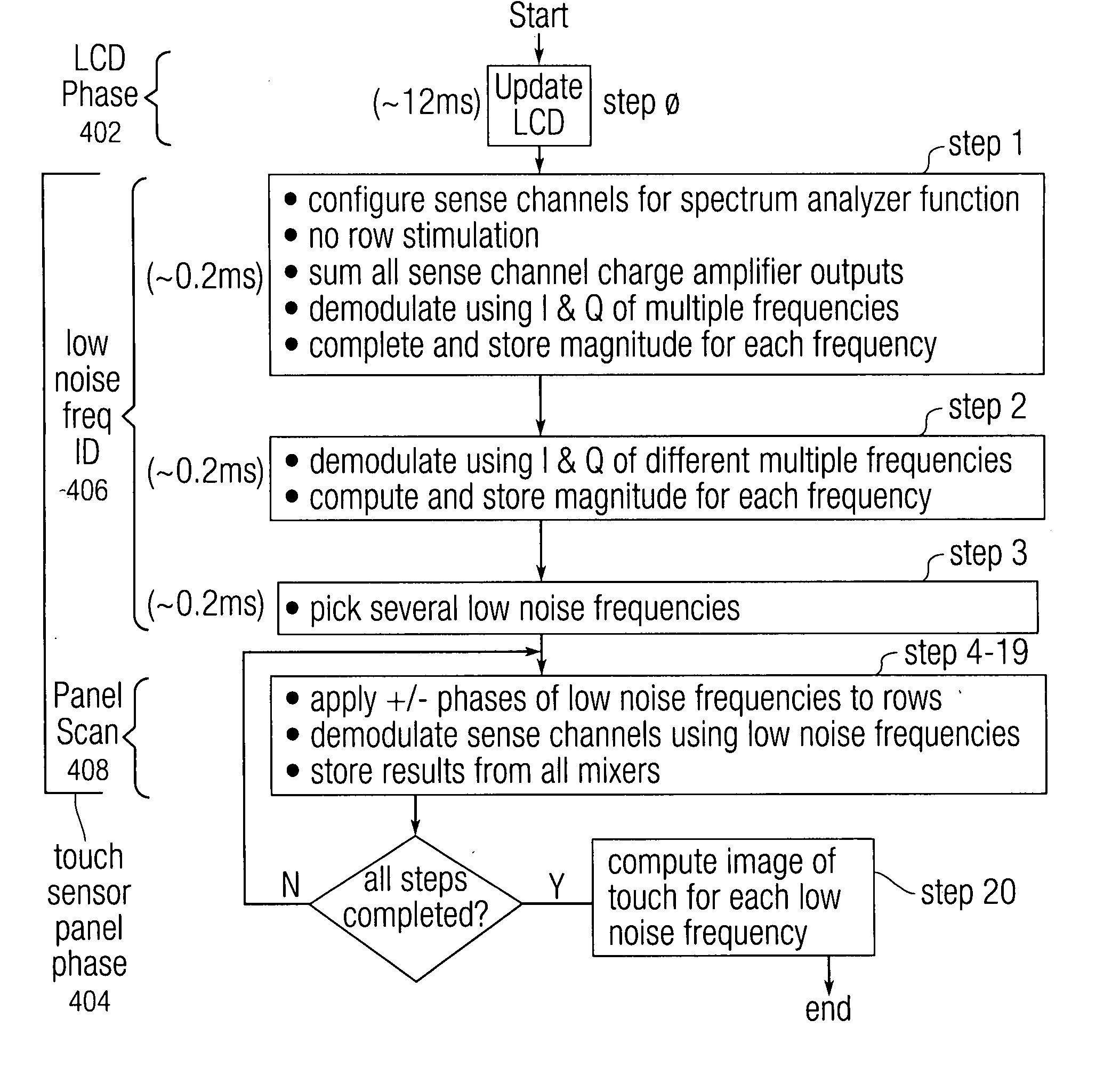
Detection of low noise frequencies for multiple frequency sensor panel stimulation
ActiveUS20080309628A1Reduce noiseSubstation equipmentSpecial data processing applicationsLow noiseFrequency mixer
The identification of low noise stimulation frequencies for detecting and localizing touch events on a touch sensor panel is disclosed. Each of a plurality of sense channels can be coupled to a separate sense line in a touch sensor panel and can have multiple mixers, each mixer using a demodulation frequency of a particular frequency, phase and delay. With no stimulation signal applied to any drive lines in the touch sensor panel, pairs of mixers can demodulate the sum of the output of all sense channels using the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) signals of a particular frequency. The demodulated outputs of each mixer pair can be used to calculate the magnitude of the noise at that particular frequency, wherein the lower the magnitude, the lower the noise at that frequency. Several low noise frequencies can be selected for use in a subsequent touch sensor panel scan function.
Owner:APPLE INC
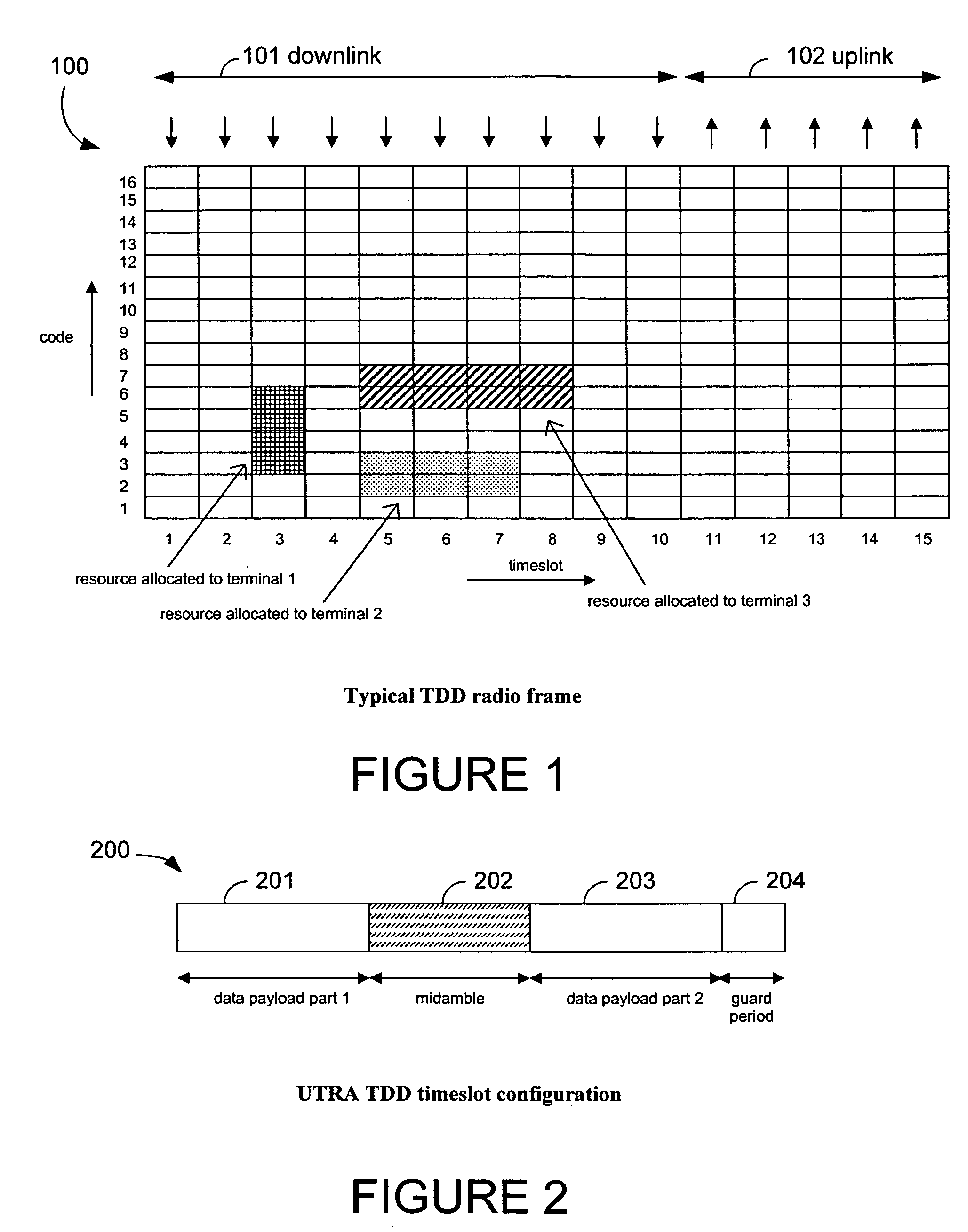
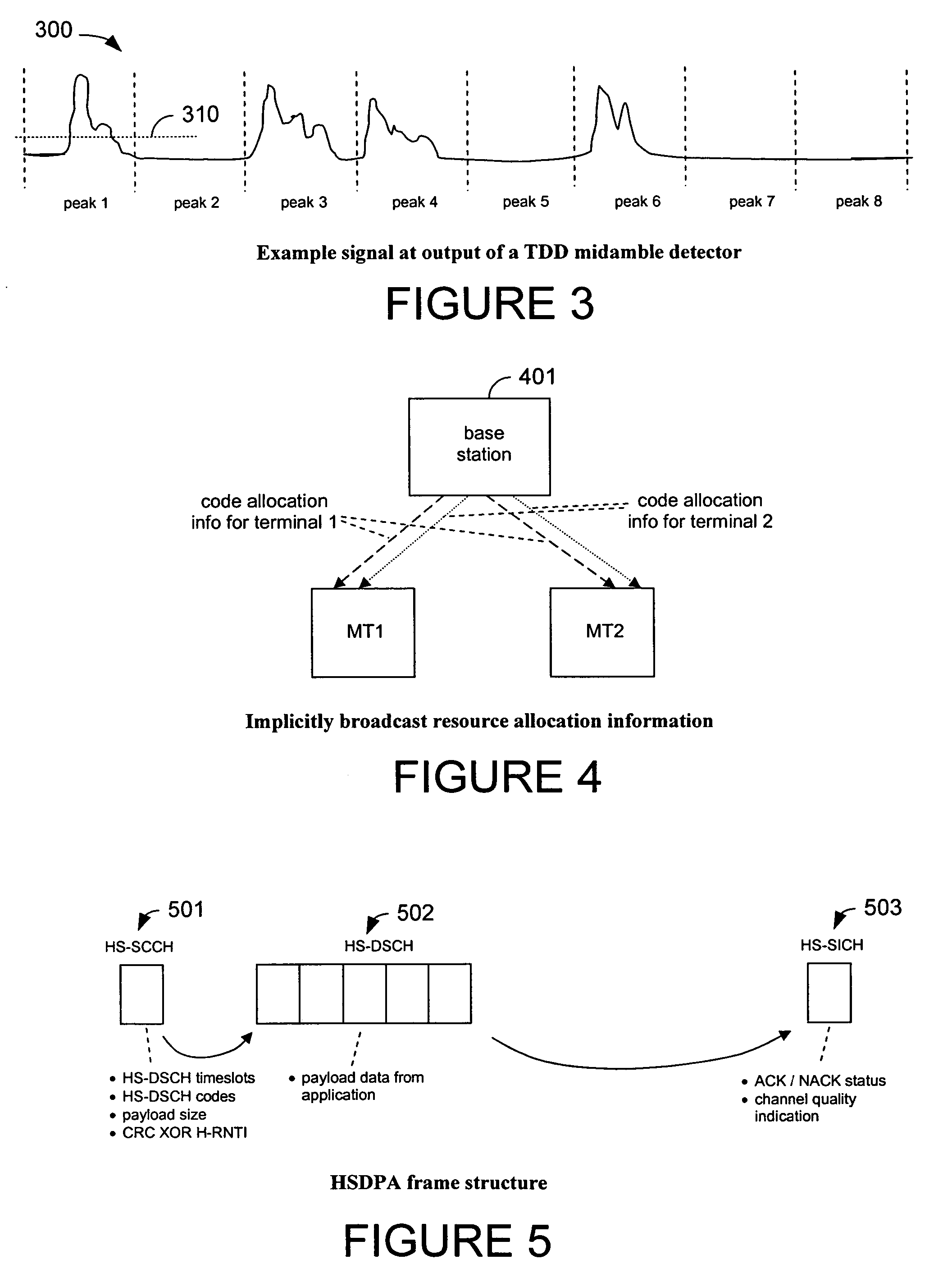
Signalling MIMO allocations
ActiveUS20050250506A1Improve abilitiesPower managementSpatial transmit diversityBase stationDemodulation
The present invention relates to demodulation of radio signals from a base station having collocated transmit antennas, and more particularly to signaling allocation information from a base station to a mobile terminal. The allocation information may include timeslot and code information of allocation to other mobile terminals. Some embodiments of the present invention facilitate a mobile terminal's ability to receive and demodulate a signal containing multiple interfering signals by communicating codes allocated to other mobile terminals.
Owner:SISVEL INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com