Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11096 results about "Secondary side" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
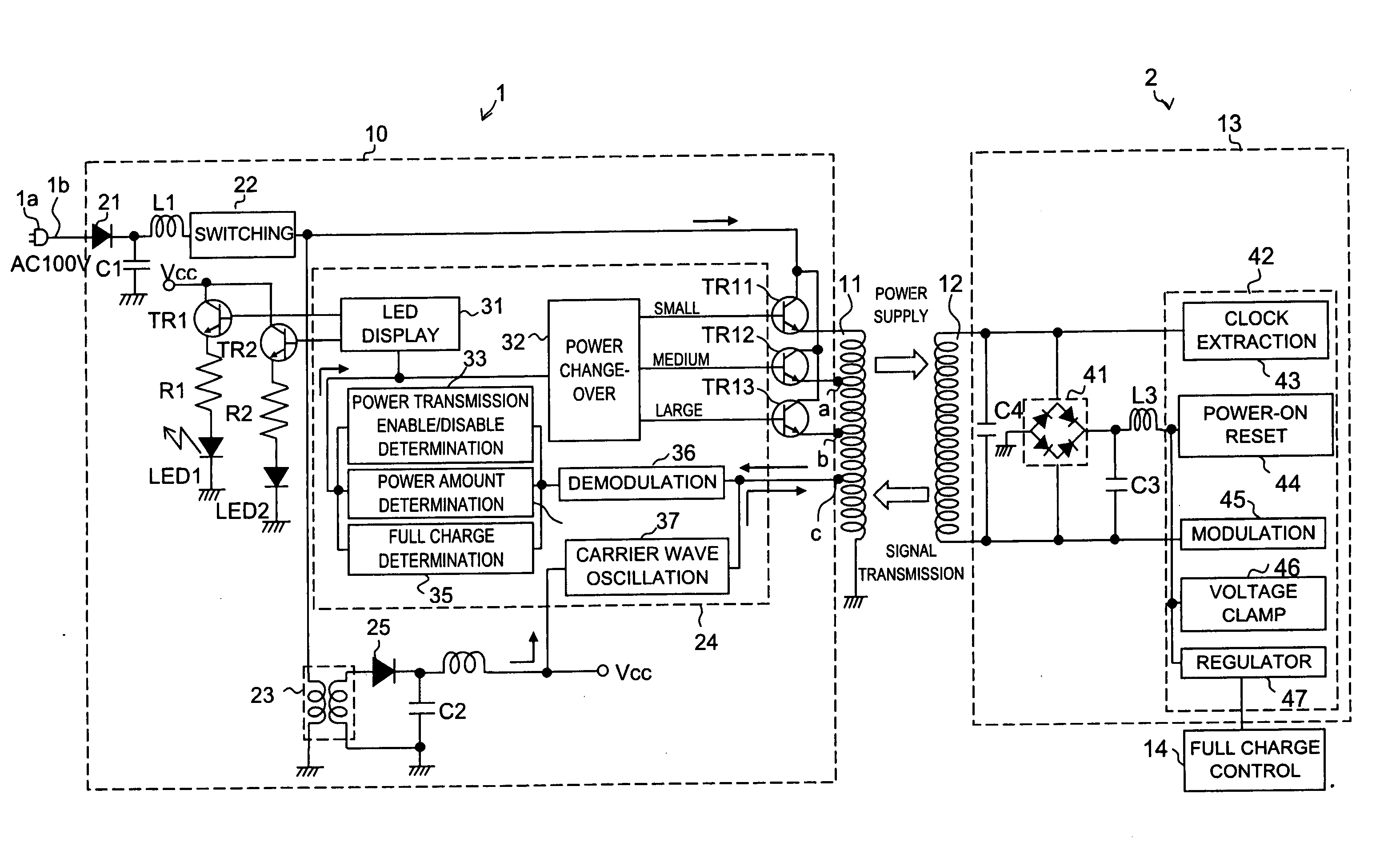
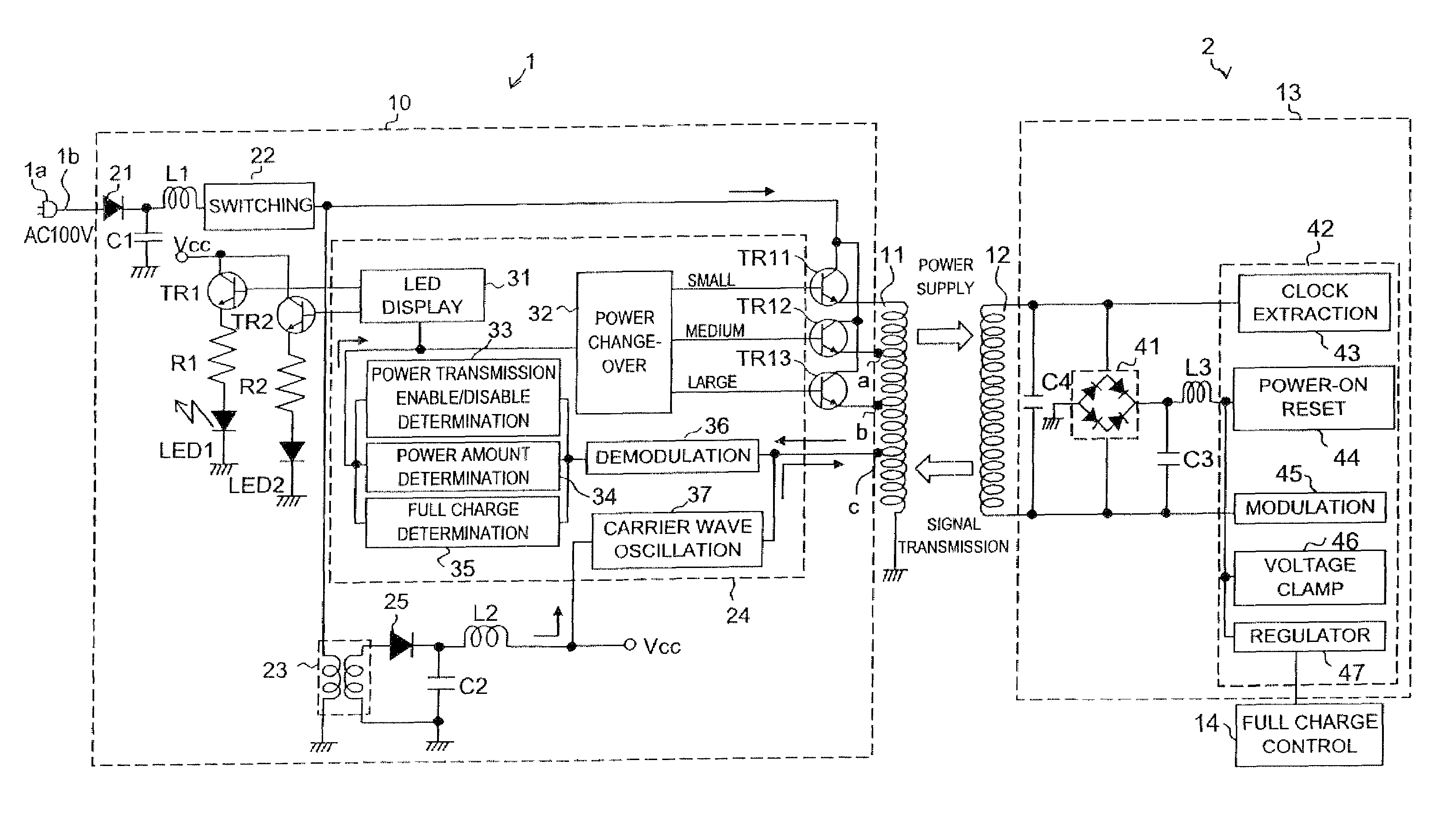
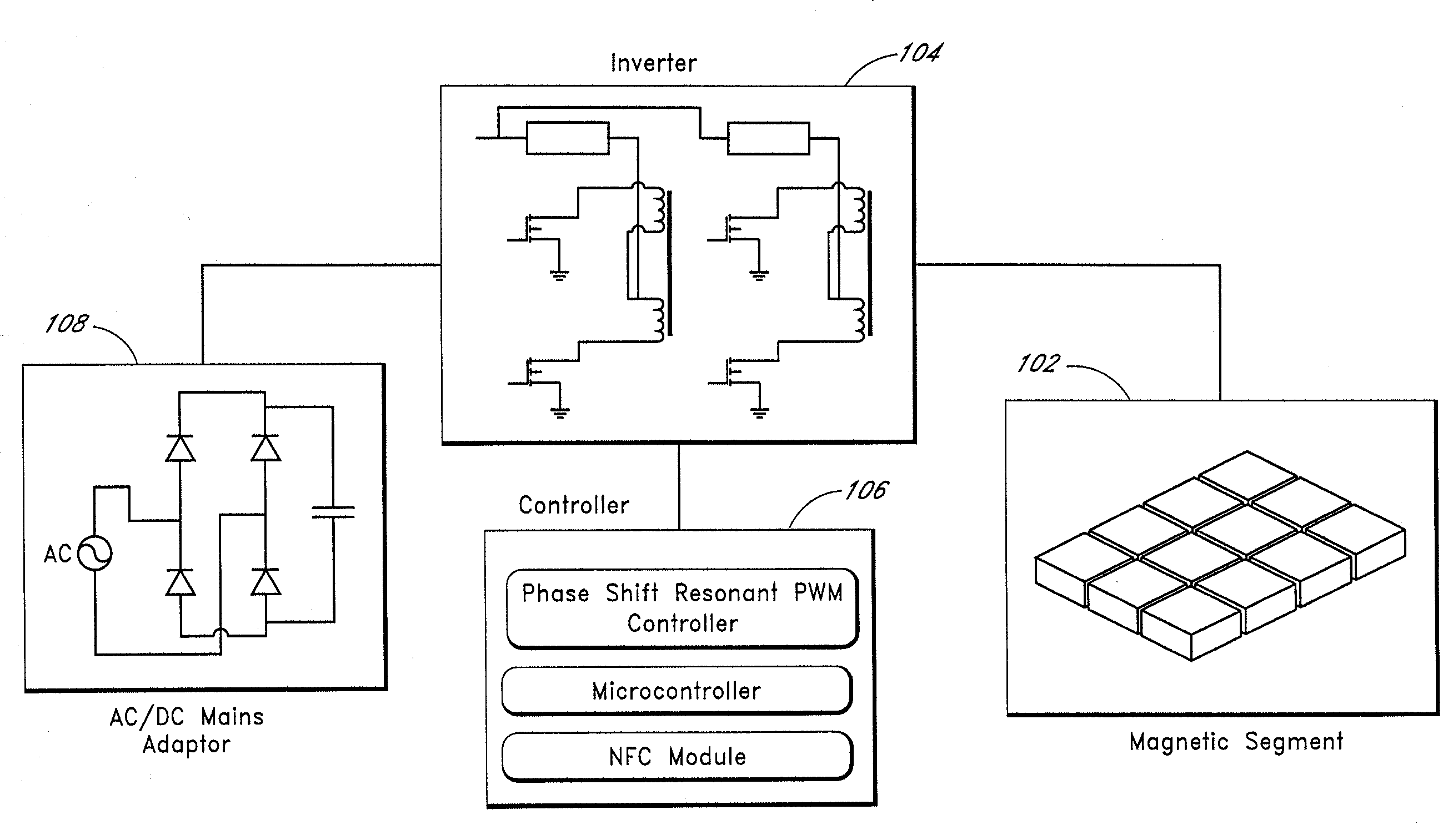
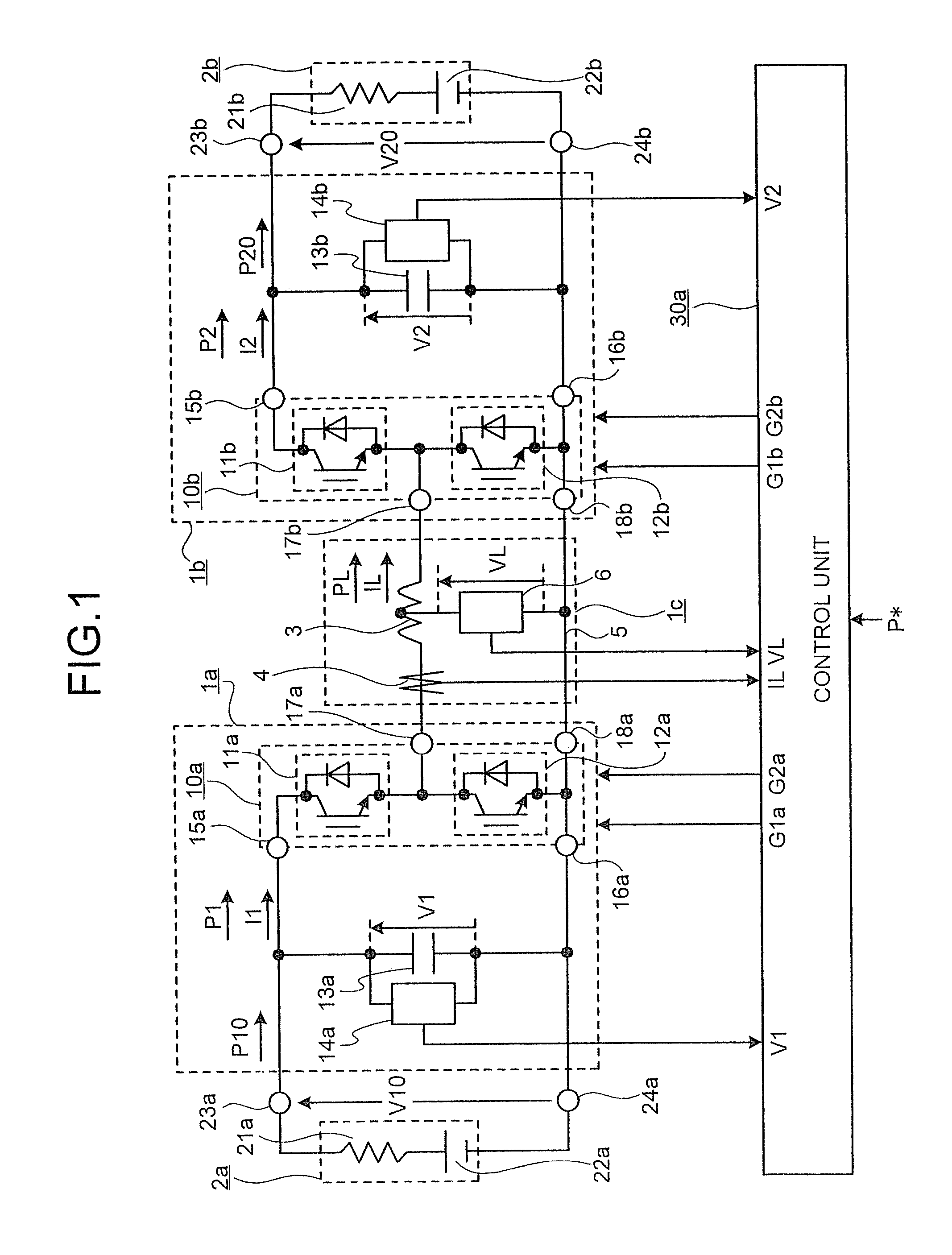
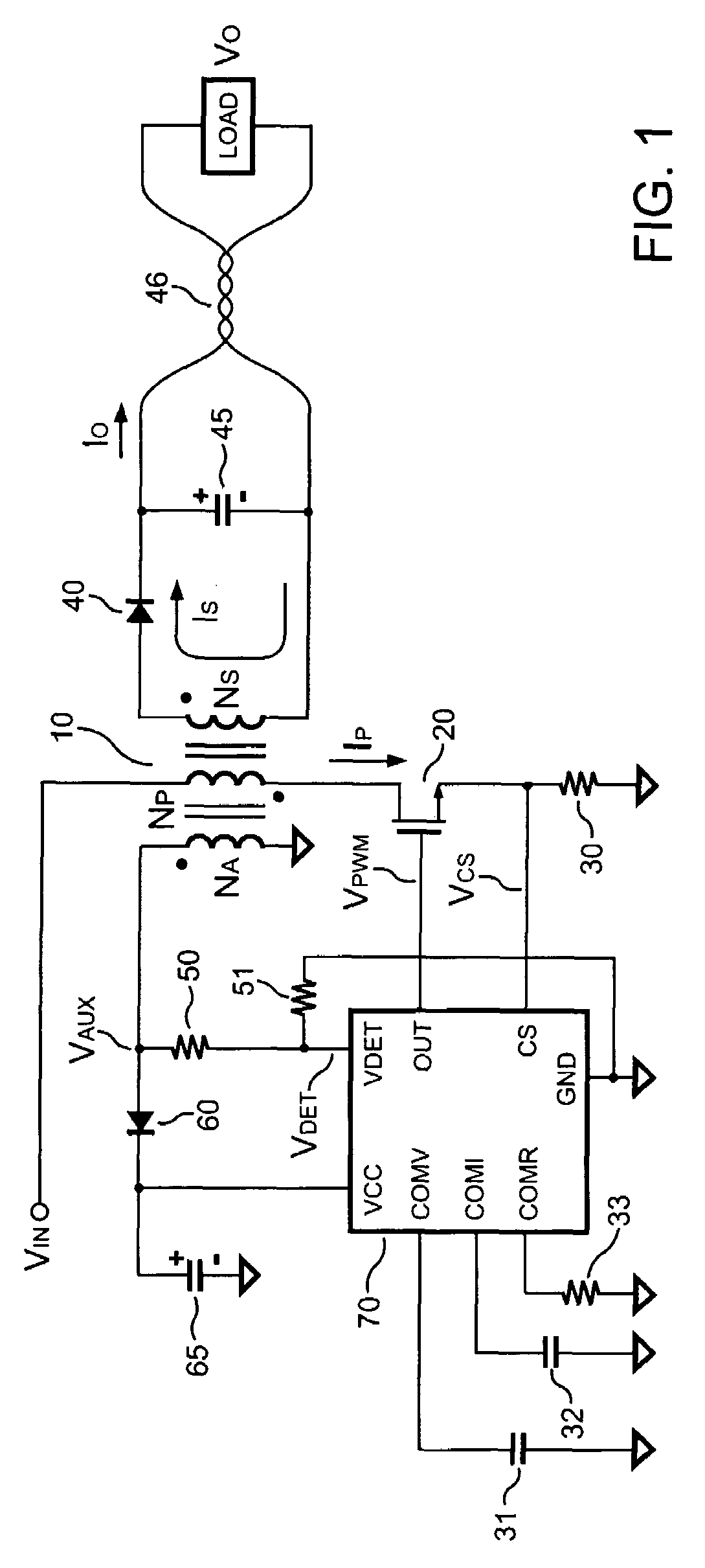
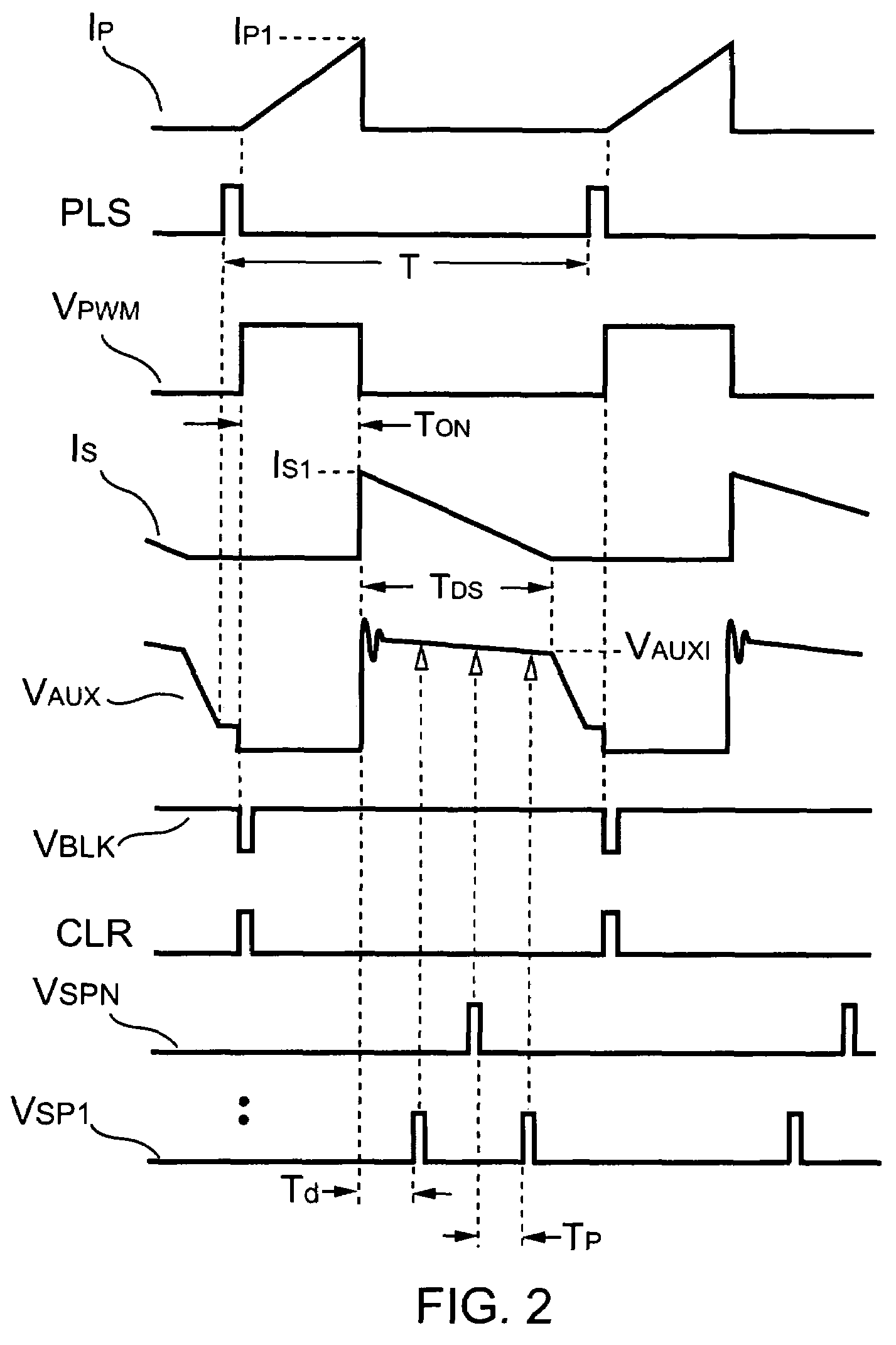
Power supply system
InactiveUS20050068019A1Save spaceDc network circuit arrangementsCircuit monitoring/indicationElectric forceElectricity
A power supply system according to the present invention comprises: a primary side coil; a power transmission apparatus having a primary side circuit for feeding a pulse voltage resulted from switching a DC voltage which is obtained by rectifying and smoothing a commercial power supply to the primary side coil; a secondary side coil magnetically coupled to the primary side coil; and power reception equipment having a secondary side circuit for rectifying and smoothing voltage induced across the secondary side coil, wherein there is provided a power adjusting section for adjusting a level of power to be transmitted according to power required by the power reception equipment. The power adjusting section has, in the primary side circuit, a carrier wave oscillation circuit for supplying a carrier wave to the primary side coil, a demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal transmitted from the secondary circuit and received by the primary side coil, and a power change-over section for selecting a level of power to be transmitted according to an information signal from the power reception equipment and demodulated by the demodulation circuit. The power adjusting section has, in the secondary side circuit, a modulation circuit for modulating the carrier wave fed from the carrier wave oscillation circuit and received by the secondary side coil with the information signal from the power reception equipment and transmitting the modulated signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
Power supply system
InactiveUS7233137B2Save spaceCircuit monitoring/indicationVolume/mass flow measurementElectric power transmissionCarrier signal
A power supply system is provided, having: a primary side coil; a power transmission apparatus having a primary side circuit for feeding a pulse voltage resulted from switching a DC voltage which is obtained by rectifying and smoothing a commercial power supply to the primary side coil; a secondary side coil magnetically coupled to the primary side coil; and power reception equipment having a secondary side circuit for rectifying and smoothing voltage induced across the secondary side coil, wherein there is provided a power adjusting section for adjusting a level of power to be transmitted according to power required by the power reception equipment. The power adjusting section has, in the primary side circuit, a carrier wave oscillation circuit for supplying a carrier wave to the primary side coil, a demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal transmitted from the secondary circuit and received by the primary side coil, and a power change-over section for selecting a level of power to be transmitted according to an information signal from the power reception equipment and demodulated by the demodulation circuit. The power adjusting section has, in the secondary side circuit, a modulation circuit for modulating the carrier wave fed from the carrier wave oscillation circuit and received by the secondary side coil with the information signal from the power reception equipment and transmitting the modulated signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
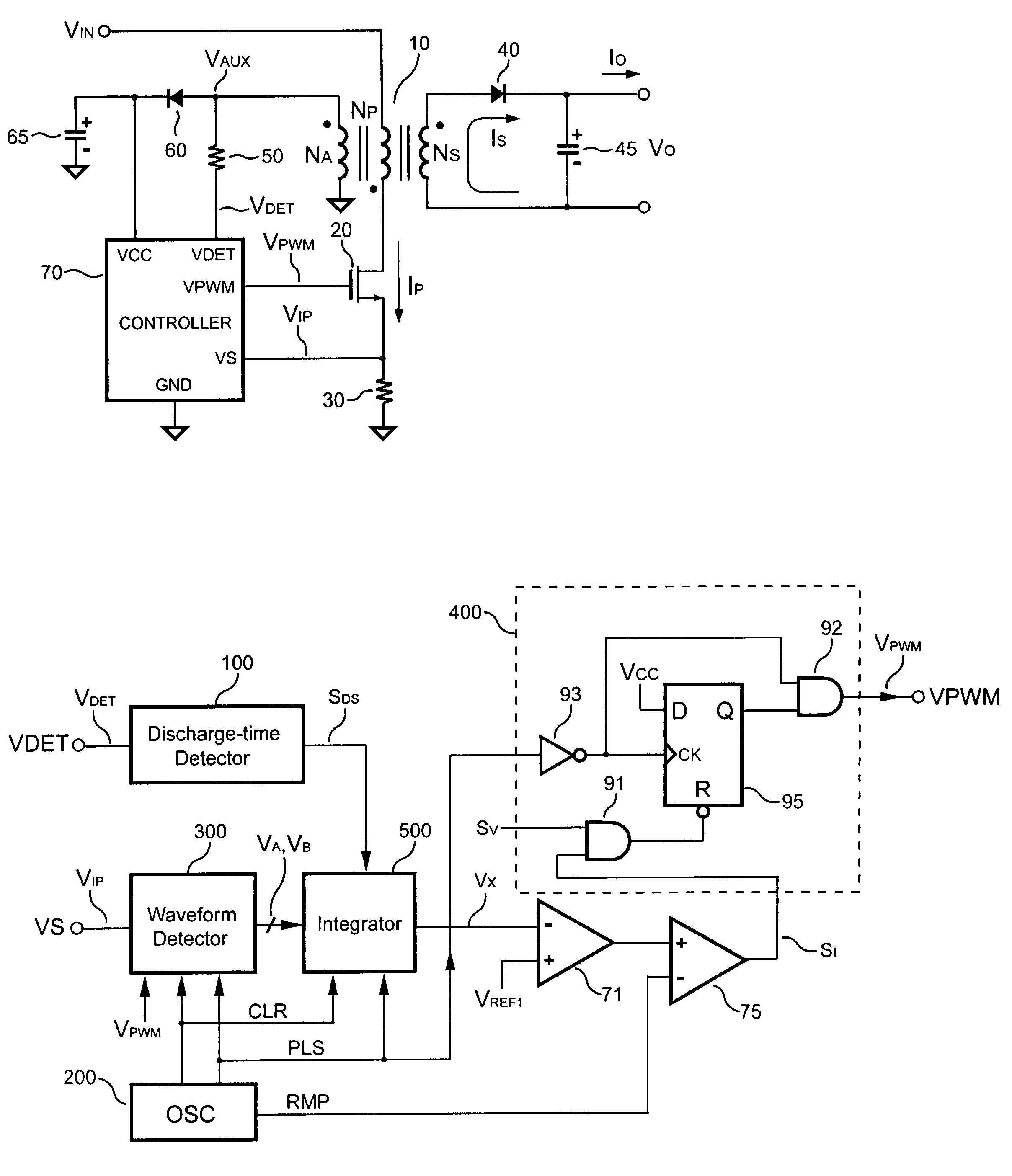
Control circuit for controlling output current at the primary side of a power converter
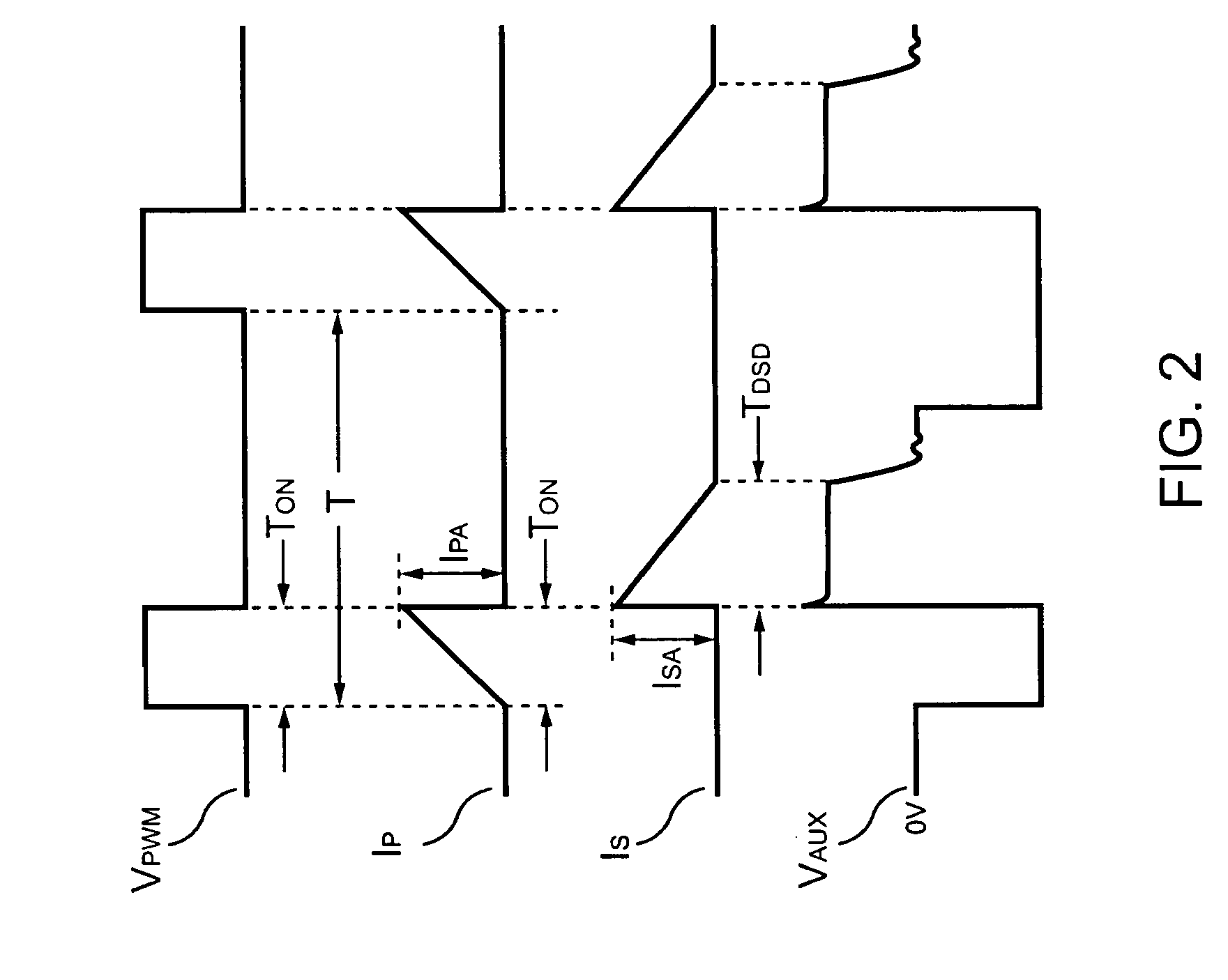
A control circuit controlling output current at the primary side of a power converter is provided. A waveform detector generates a current-waveform signal. A discharge-time detector detects a discharge-time of a secondary side switching current. An oscillator generates an oscillation signal for determining the switching frequency of the switching signal. An integrator generates an integrated signal by integrating an average current signal with the discharge-time. The average current signal is generated in response to the current-waveform signal. The time constant of the integrator is correlated with the switching period of the switching signal, therefore the integrated signal is proportional to the output current. An error amplifier amplifies the integrated signal and provides a loop gain for output current control. A comparator controls the pulse width of the switching signal in reference to the output of the error amplifier. Therefore, the output current of the power converter can be regulated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Implantable medical device with contactless power transfer housing
InactiveUS20050288743A1Minimizing surgeryMinimizing subsequent treatmentElectrotherapyElectromagnetic wave systemTransmitted powerElectrical battery
A transcutaneous recharging system for providing power to an implantable medical device comprises a primary side circuit for transmitting power in the form of magnetic flux; and a secondary side circuit integral to the implantable medical device for receiving the power transmitted from the primary side circuit and for providing the received power to recharge a battery in the implantable medical device, wherein the primary and secondary side circuits are not physically coupled. A variety of attachment configurations are disclosed for attaching and shielding the secondary circuit directly onto the housing of the implantable medical device, inclusive of flexible printed circuit coils and wire coils recessed into helical notches.
Owner:AHN IN +2
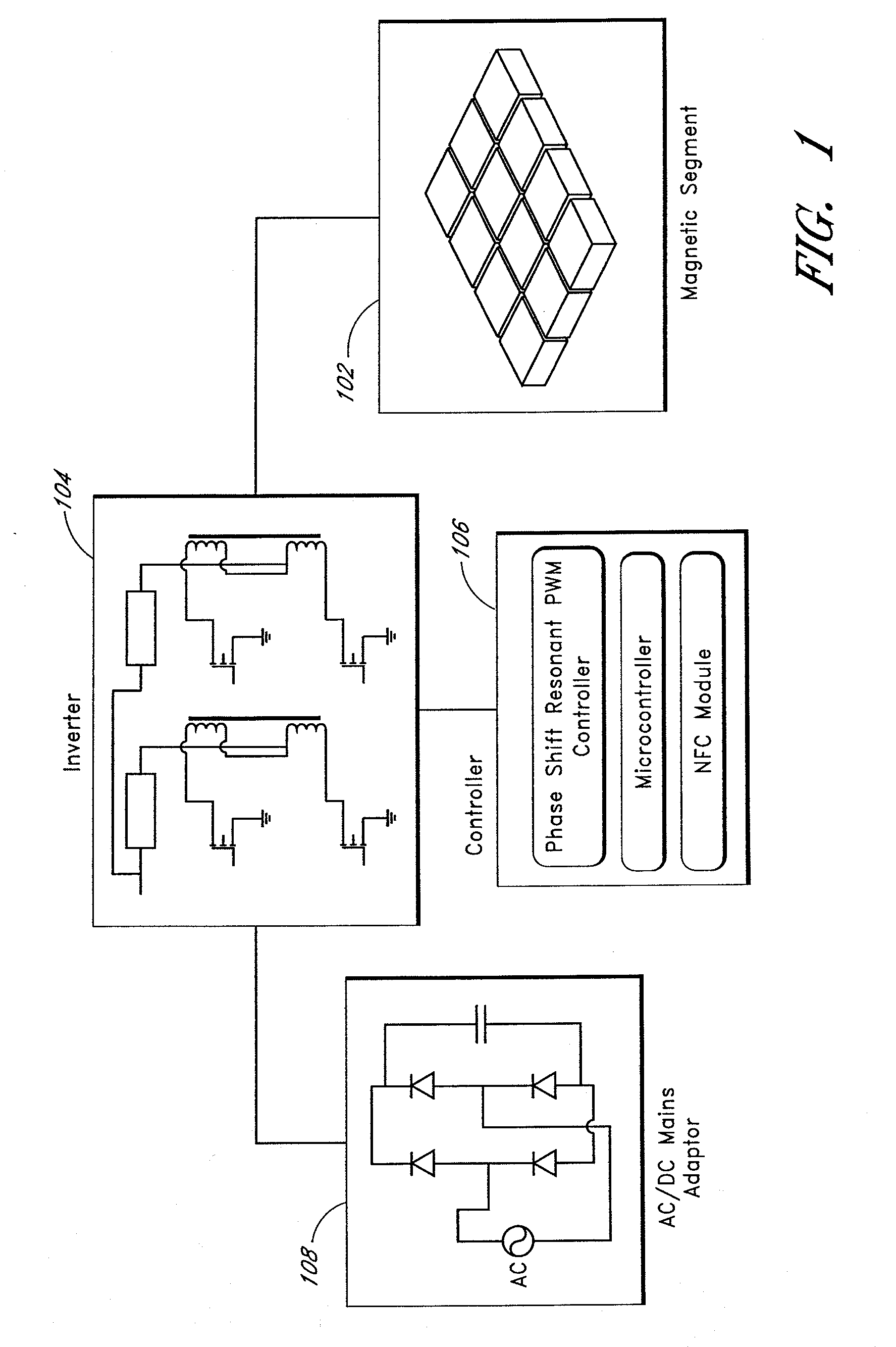
Systems and methods for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS20080116847A1Relax requirementsEasy to customizeTransformersTransformers/inductances circuitsEngineeringMagnetic amplifier
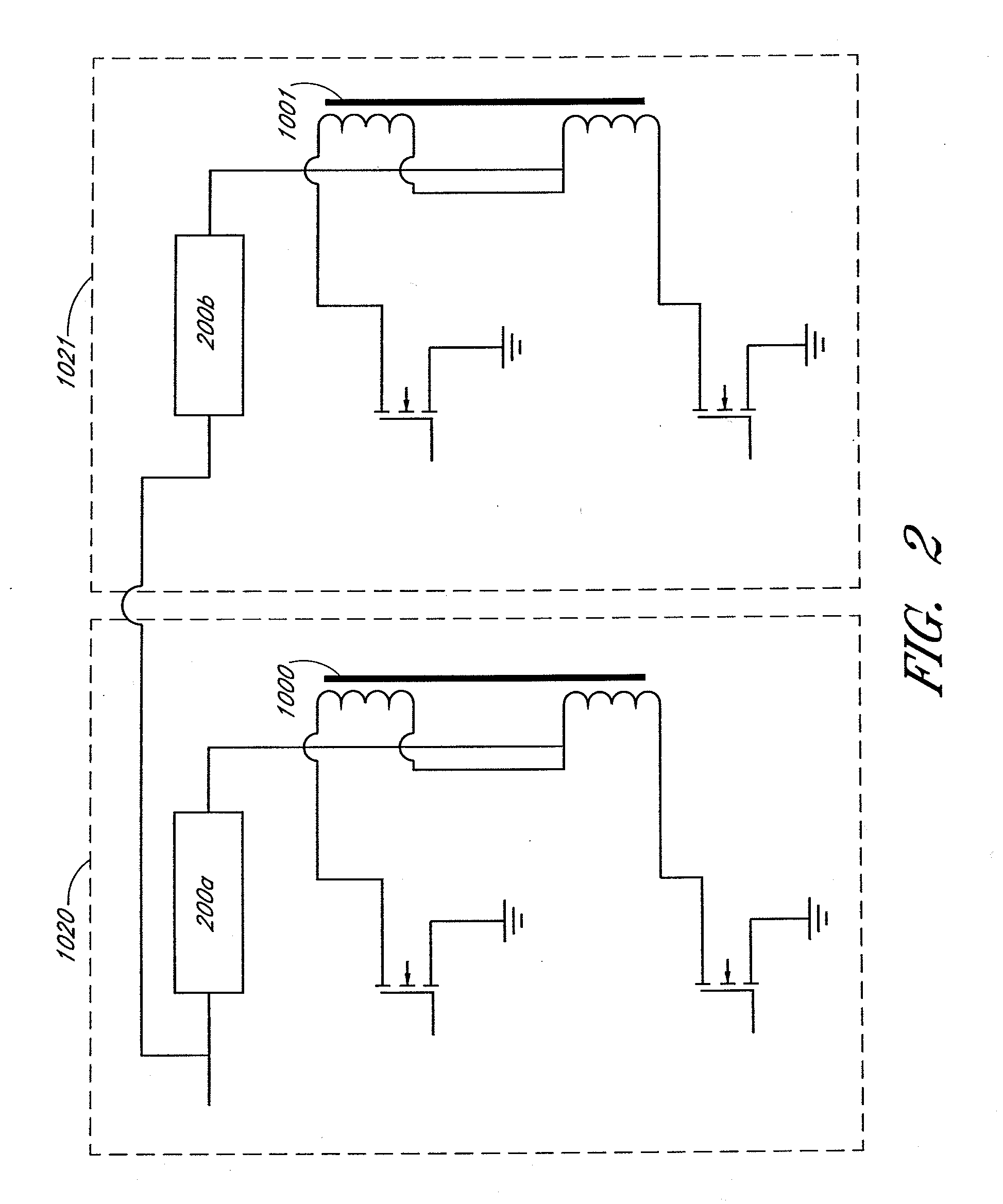
Systems and methods for wireless power transfer are disclosed. Primary windings generate magnetic fields which are inductively coupled to secondary windings to transfer power in a wireless manner. One embodiment includes a plurality of tiles of magnetic cores and windings for the primary windings. The tiles can be arranged in a magnetic segment with windings of tiles being orthogonal with respect to windings of adjacent tiles. For example, a winding of a first tile can be horizontal, and windings of adjacent tiles can be vertical. One embodiment further groups these magnetic segments into larger entities, wherein each magnetic segment can be independently activated. One embodiment includes a magnetic amplifier or an electronic device for secondary side control of power. This permits multiple devices to be powered or charged to be able to regulate power or charging independently from one another.
Owner:BIO AIM TECH HLDG
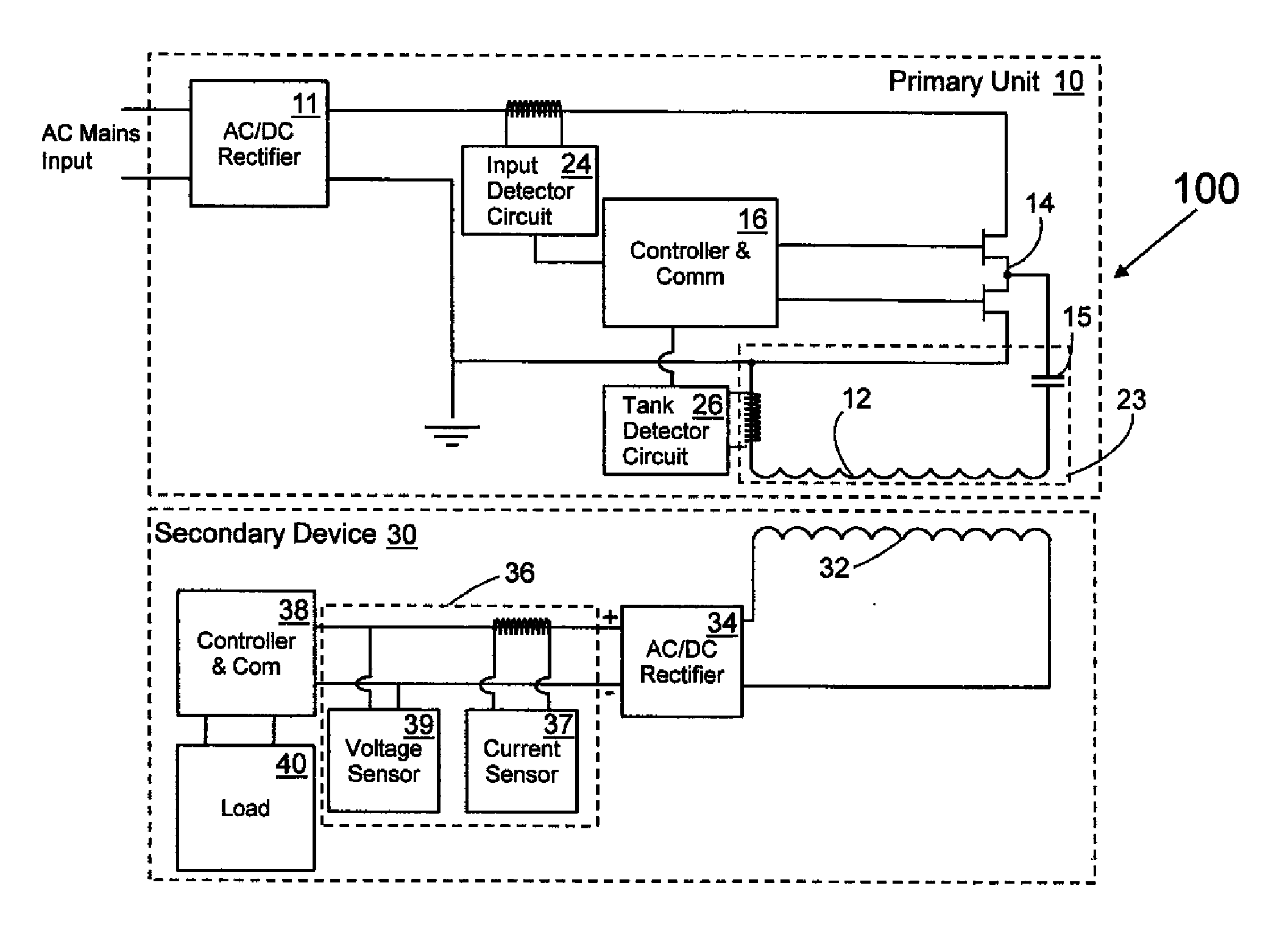
Input parasitic metal detection
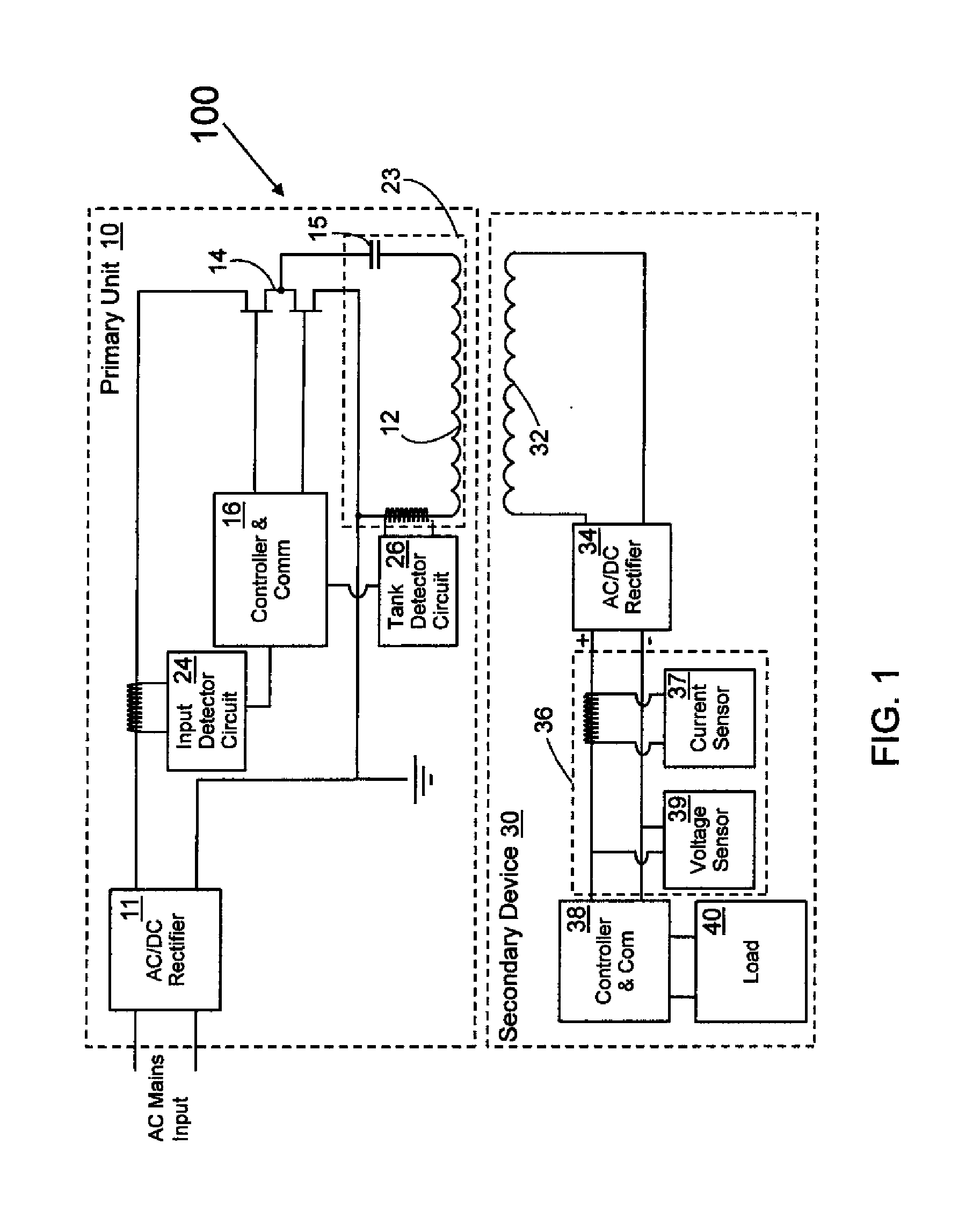
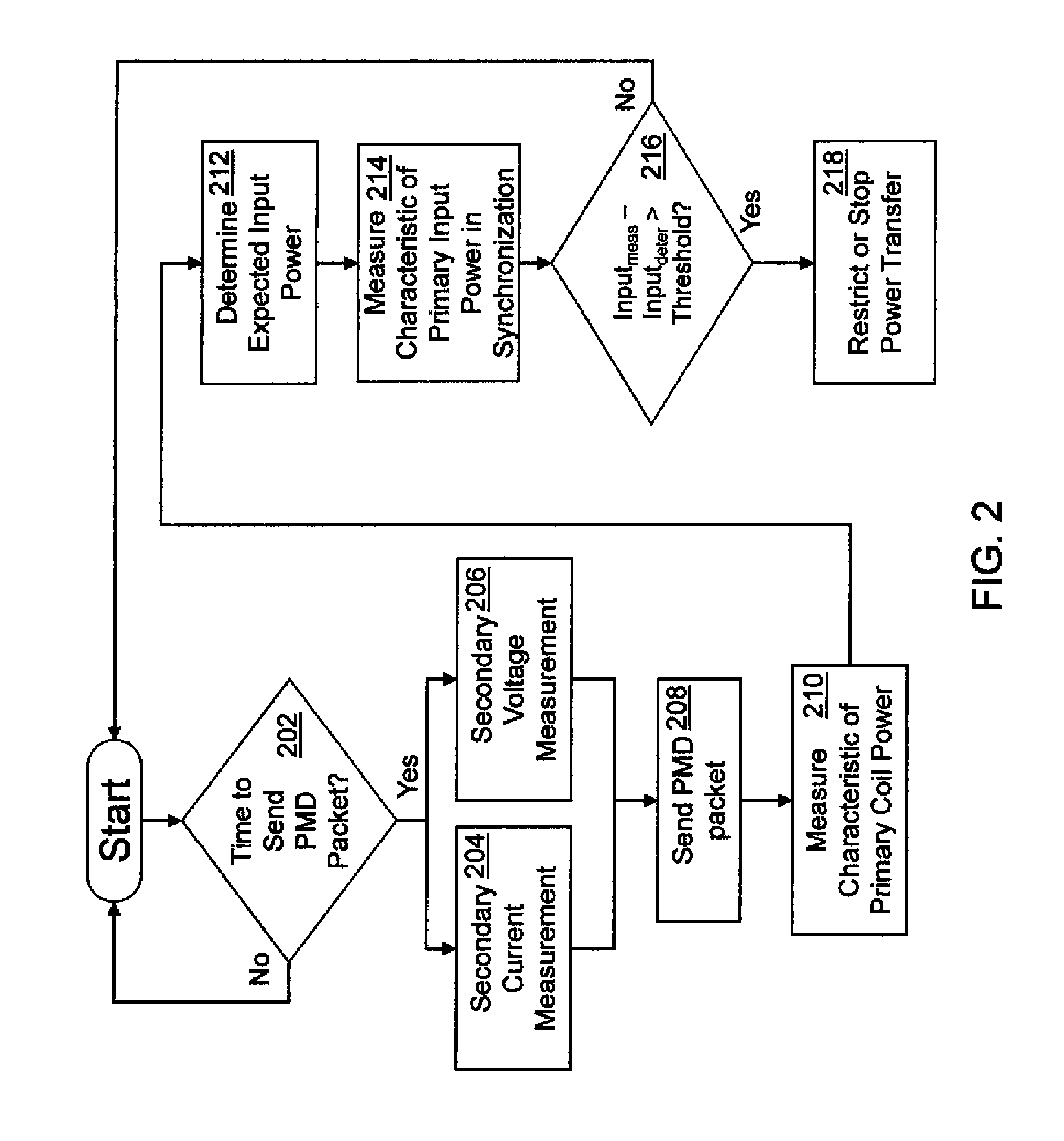
A system and method of controlling inductive power transfer in an inductive power transfer system and a method for designing an inductive power transfer system with power accounting. The method of controlling inductive power transfer including measuring a characteristic of input power, a characteristic of power in the tank circuit, and receiving information from a secondary device. Estimating power consumption based on the measured characteristic of tank circuit power and received information and comparing the measured characteristic of input power, the information from the secondary device, and the estimated power consumption to determine there is an unacceptable power loss. The method for designing an inductive power transfer system with power accounting including changing the distance between a primary side and a secondary side and changing a load of the secondary side. For each distance between the primary side and the secondary side and for each load, measuring a circuit parameter on the primary side in the tank circuit and a circuit parameter on the secondary side during the transfer of contactless energy. The method further including selecting a formula to describe power consumption in the system during the transfer of contactless energy based on coefficients and the circuit parameters, and determining the coefficients using the measured circuit parameters.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
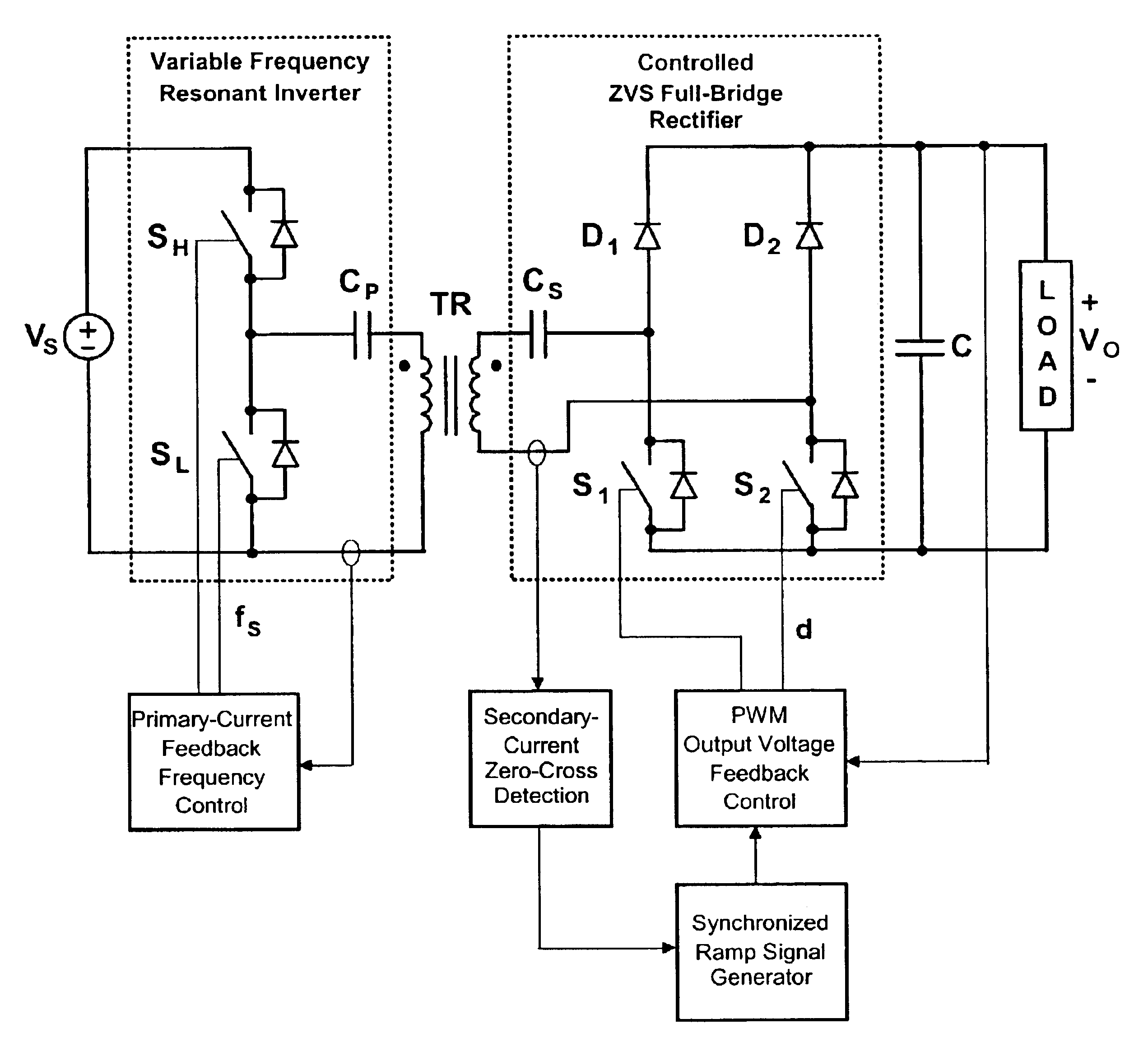
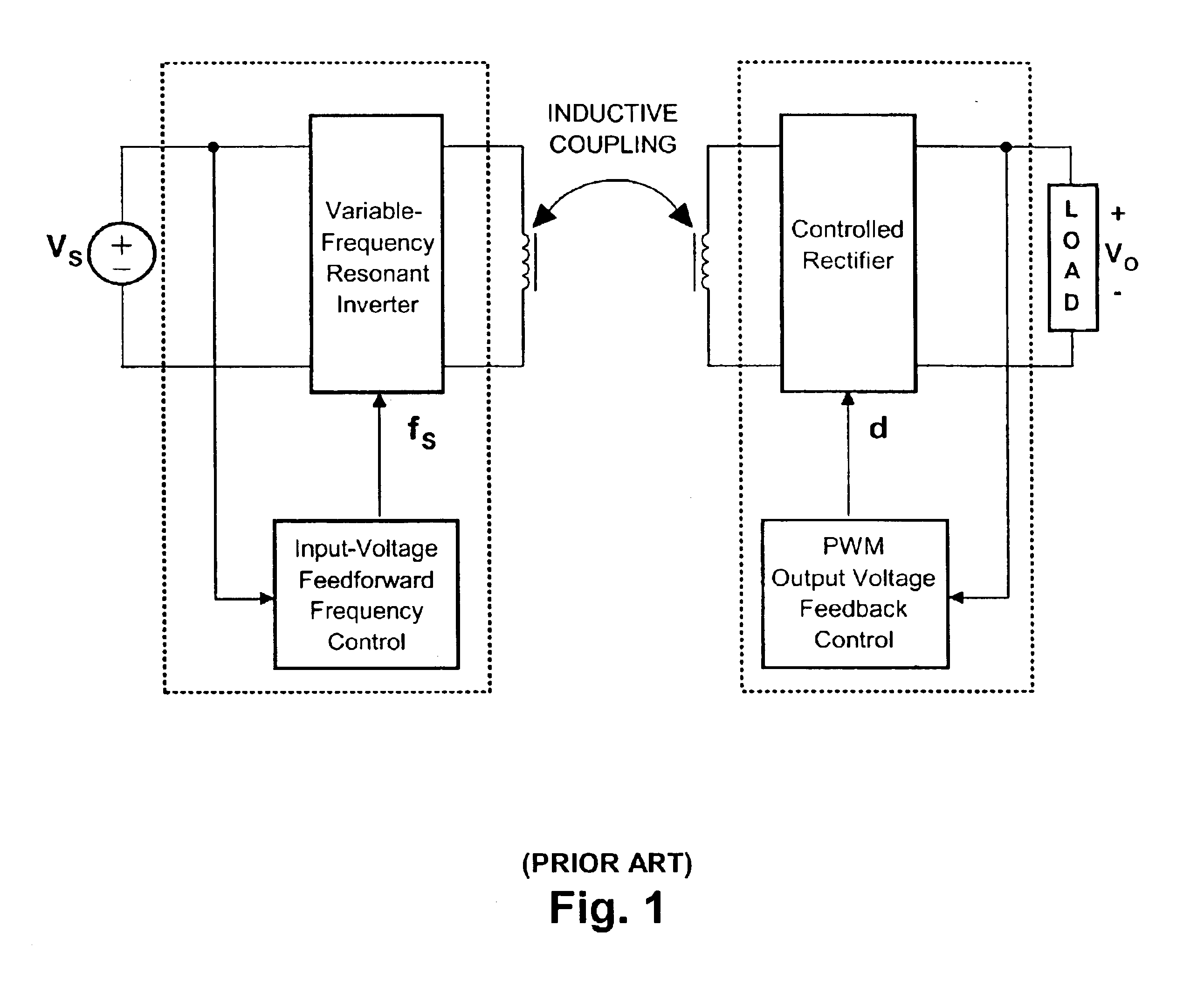
Contactless electrical energy transmission system having a primary side current feedback control and soft-switched secondary side rectifier
ActiveUS6934167B2Energy can transferEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching frequencyEngineering
A contactless electrical energy transmission system includes a transformer having a primary winding that is coupled to a power source through a primary resonant circuit and a secondary winding that is coupled to a load through a secondary resonant circuit. The primary and secondary resonant circuits are inductively coupled to each other. A primary control circuit detects current changes through the primary resonant circuit to control the switching frequency of a controllable switching device for maintaining a substantially constant energy transfer between the primary winding and secondary winding in response to at least one of a power source voltage change and a load change. As a result, excessive circulating energy of the CEET system is minimized providing a tight regulation of the output voltage over the entire load and input voltage ranges without any feedback connection between the primary side and the secondary side.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Contactless power transfer system
ActiveUS7197113B1Radiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric power transmissionTransfer system
In accordance with one embodiment, a contactless power transfer system is provided that comprises a stationary member including a power input configured to receive power at first voltage from a power supply. The system further includes a rotating member rotatably coupled to the stationary member and a rotary transformer. The rotary transformer has primary and secondary sides, with the primary side being disposed on the stationary member. The primary side has a primary winding that receives power at the first voltage from the power input. The secondary side is disposed on the rotating member and produces power at a second voltage. The secondary side has a rotating core and separate secondary sub-windings, each of which has forward and return paths that are circumferentially disposed about the rotating core. The forward and return paths of each of the sub-windings rotate proximate to, and are disposed a substantially equal distance from, the primary winding disposed on the stationary member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Active-clamp current-source push-pull dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20070247877A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePush pull
Provided is a current-source push-pull DC-DC converter using an active clamp circuit for reusing energy of leakage inductances by not only diodes on a secondary side of a transformer being zero-current switched using a series-resonant full-wave rectifier, but also the active clamp circuit on a primary side of the transformer, which provides a discharge path of the energy stored in the leakage inductances, increases power conversion efficiency even for a wide input voltage range and reduces a switch voltage stress as compared to a conventional current-source push-pull circuit by operating even for a duty ratio below 0.5 by flowing a current of an input inductor through capacitors of the active clamp circuit when both main switches are off.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Biosensor
InactiveUS6719887B2Improve solubilityNot easy to dissolveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerEngineering
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
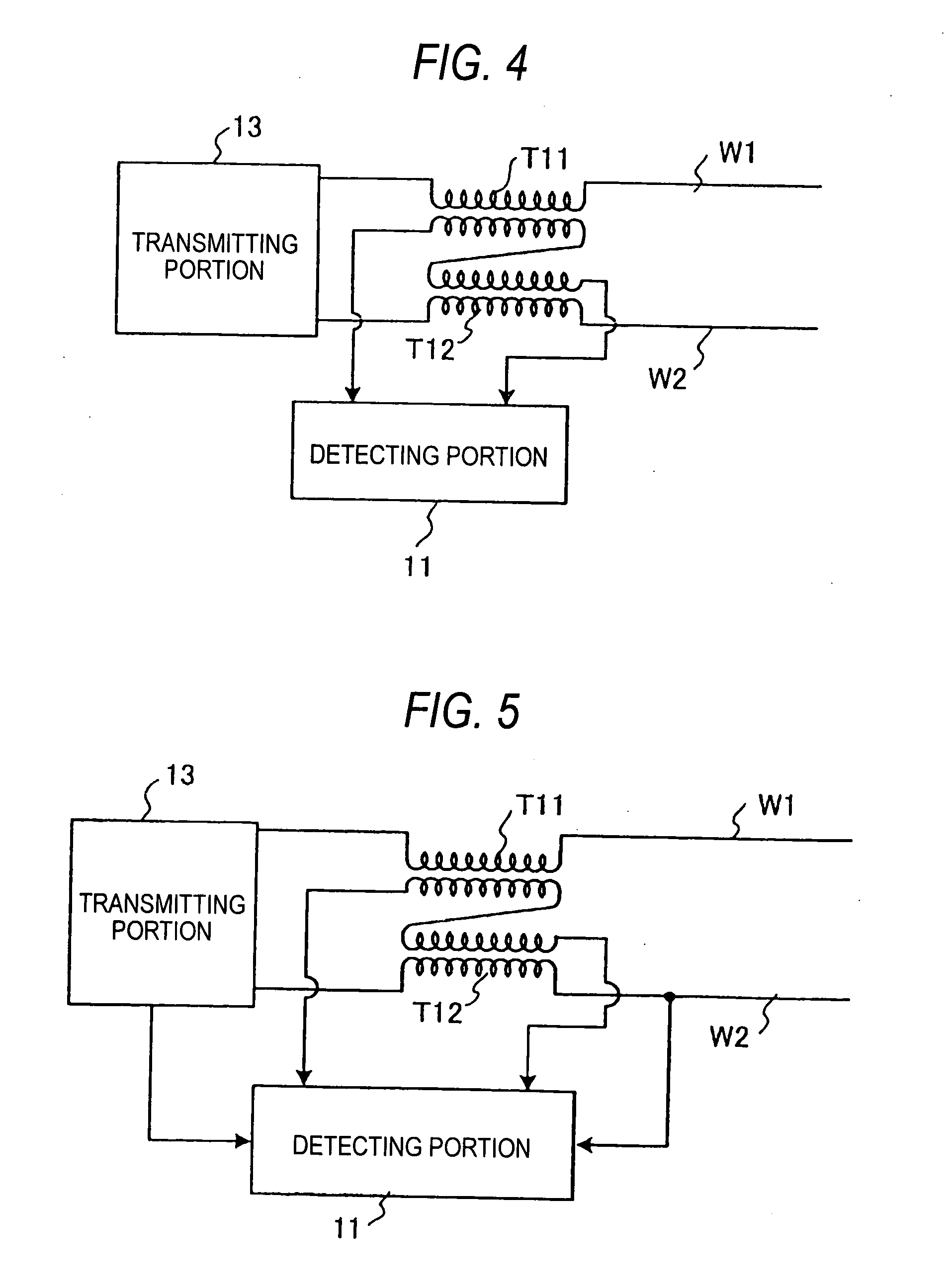
Line state detecting apparatus and transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus of balanced transmission system
InactiveUS20050232412A1Promote balance between supply and demandSystems using filtering and bypassingSubstations coupling interface circuitsElectrical conductorSecondary side
A line state detecting apparatus provided in a balanced transmission system includes, in transmission lines comprising a pair of conductors W1, W2 connected to a transmitting portion 13, current transformers T11, T12 primary sides of which are inserted to respectives thereof in series therewith and secondary sides of which are connected in series to cancel currents or voltages of the two transformer by each other, and a detecting portion 11 for detecting currents or voltages on secondary sides of the current transformers T11, T12. By an output of the detecting portion 11, a difference of currents or voltages of the conductors W1, W2 of the transmission lines is provided and an unbalance component between the conductors W1, W2 is detected.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bi-directional inductive power transfer
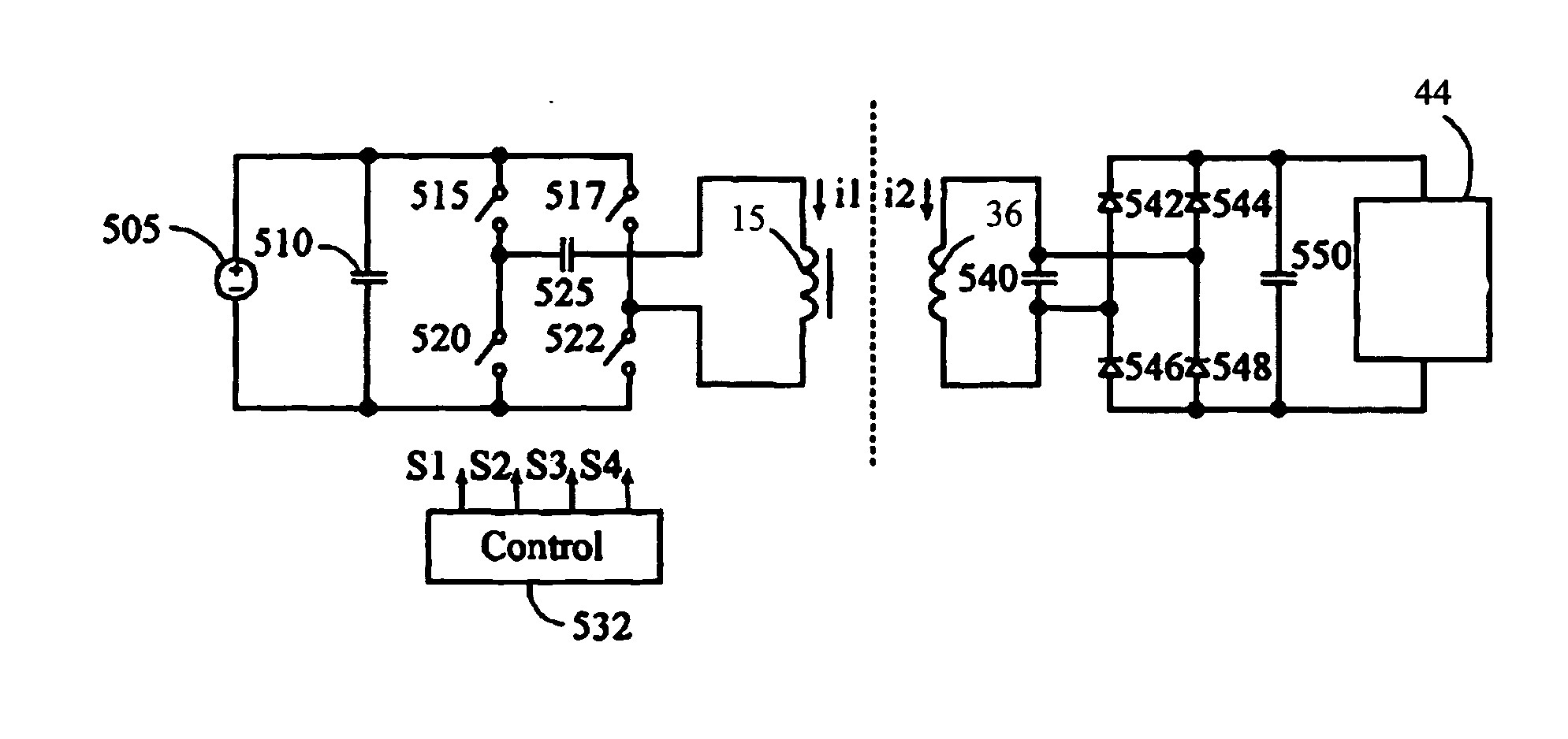
A method, apparatus, and system are provided which enables the control of contactless power transfer in an inductive power transfer system using a phase control technique. The method comprises adjusting the phase of a secondary-side converter output voltage with respect to that of a primary-side converter. The magnitude of power transfer is determined by the relative phase angle, and the direction of power transfer is determined by whether the secondary converter output voltage leads or lags the input converter voltage, thereby enabling bi-directional power transfer between the primary and secondary sides of the system. According to alternative embodiments, the method may also be used for uni-directional power transfer only, and / or the secondary converter may be operated to maintain a constant relative phase angle.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
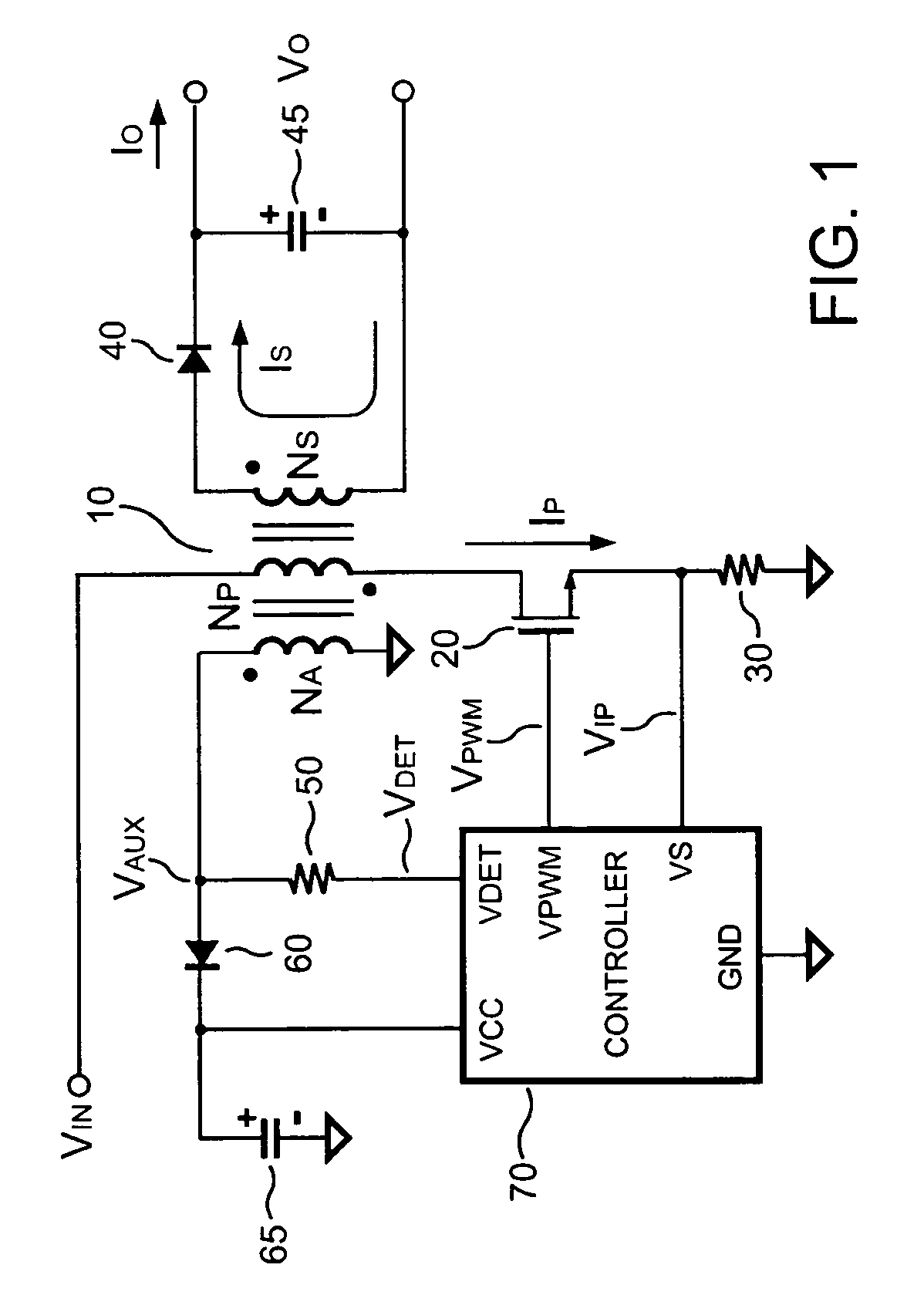
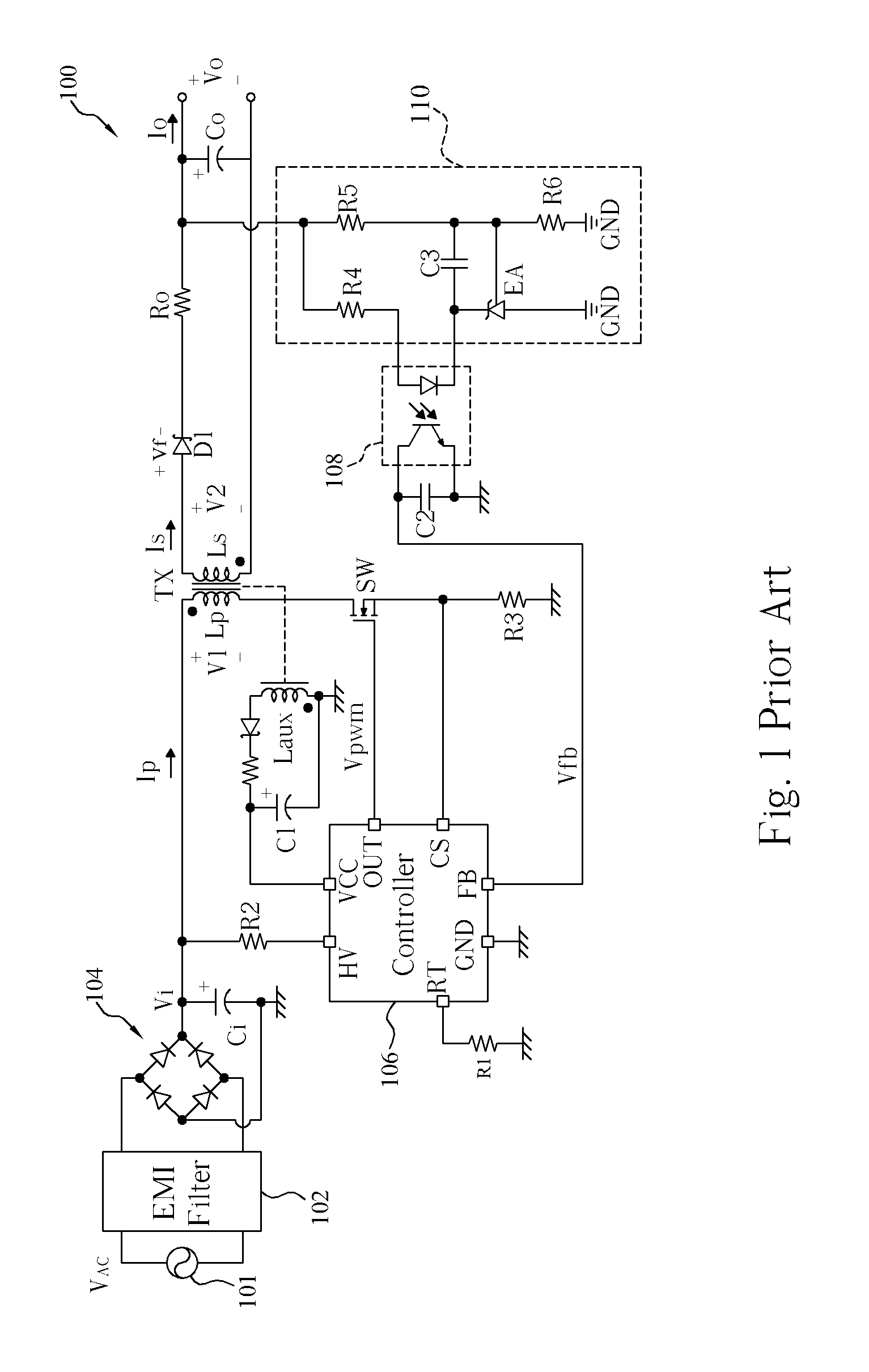
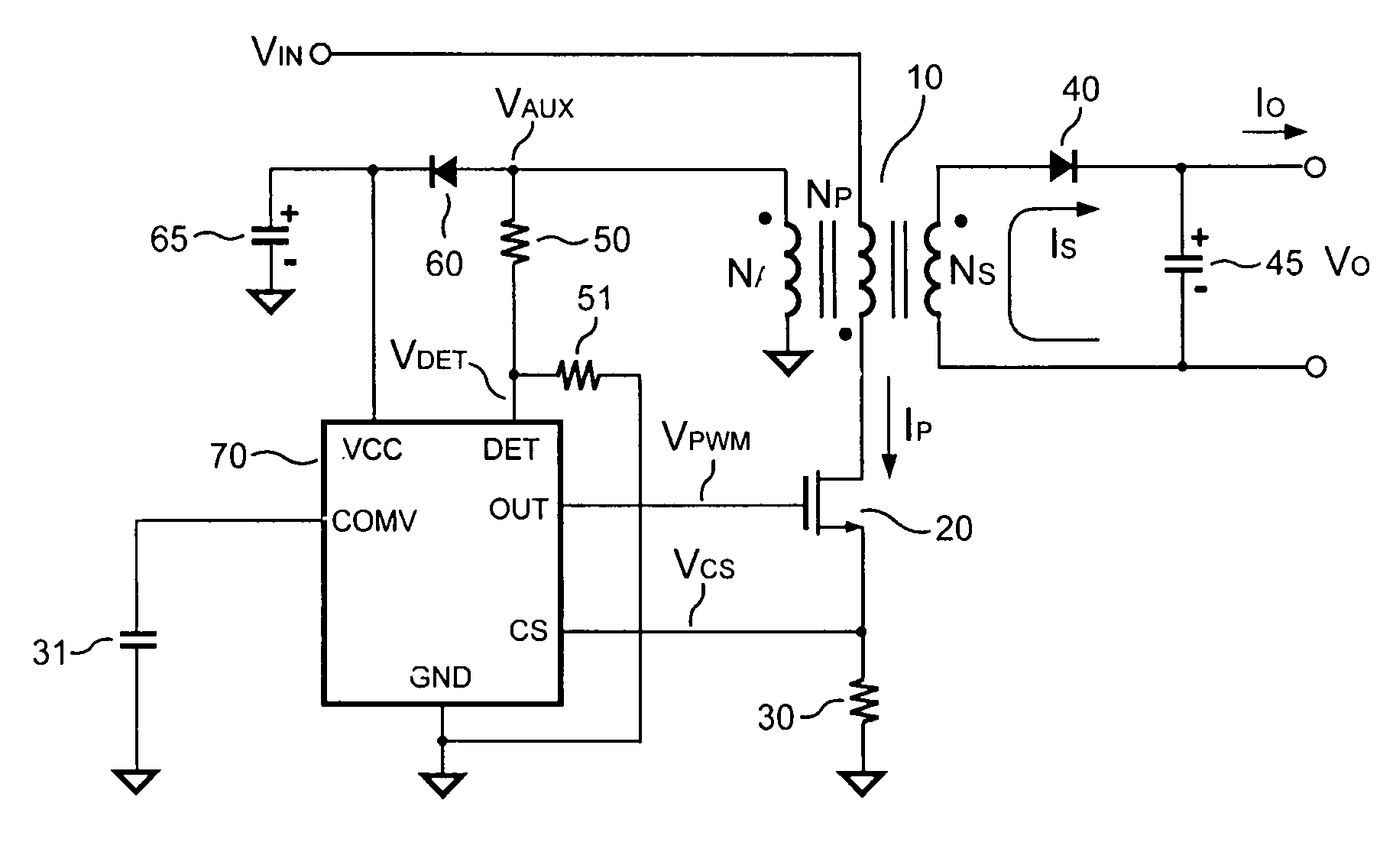
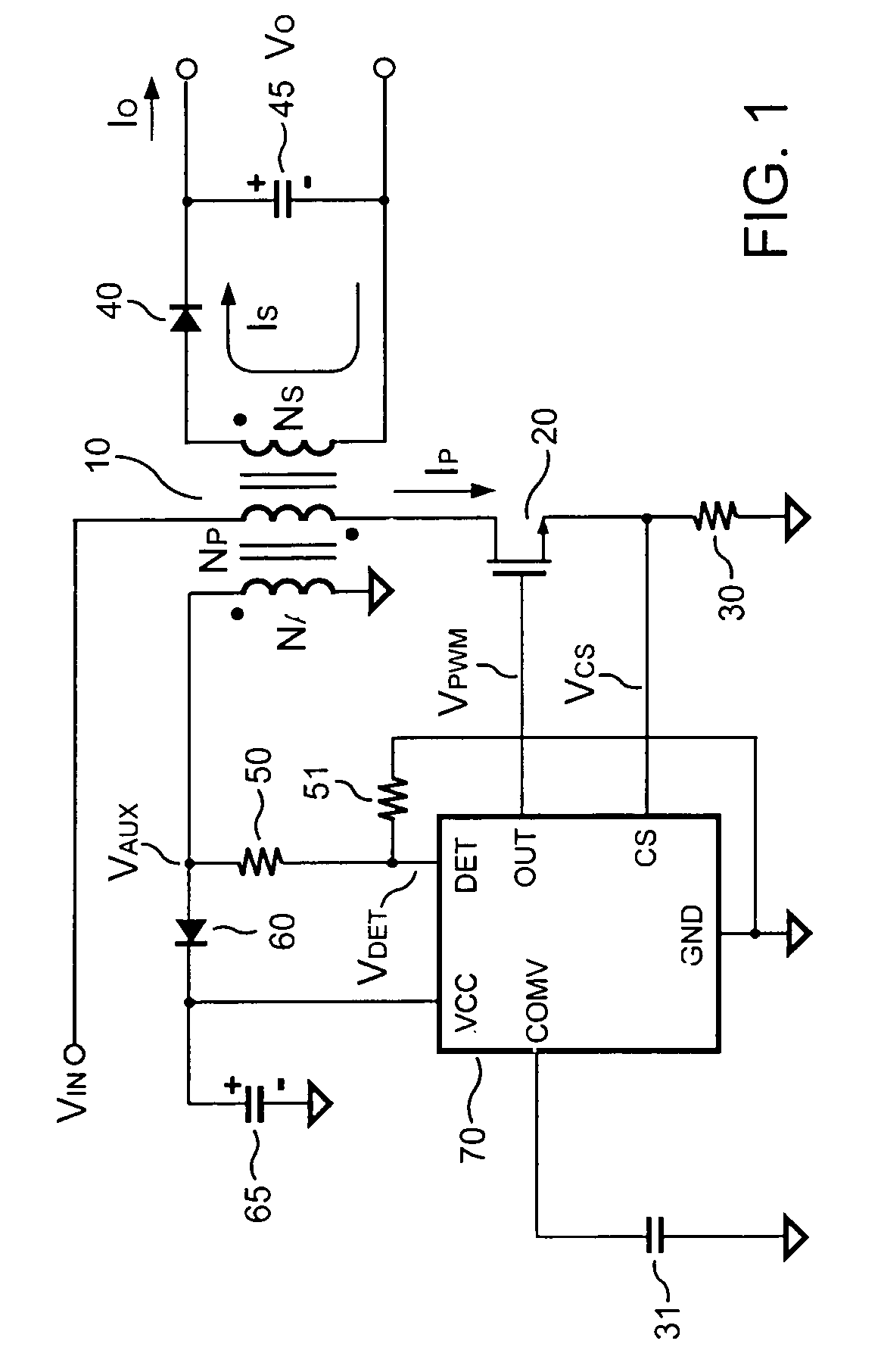
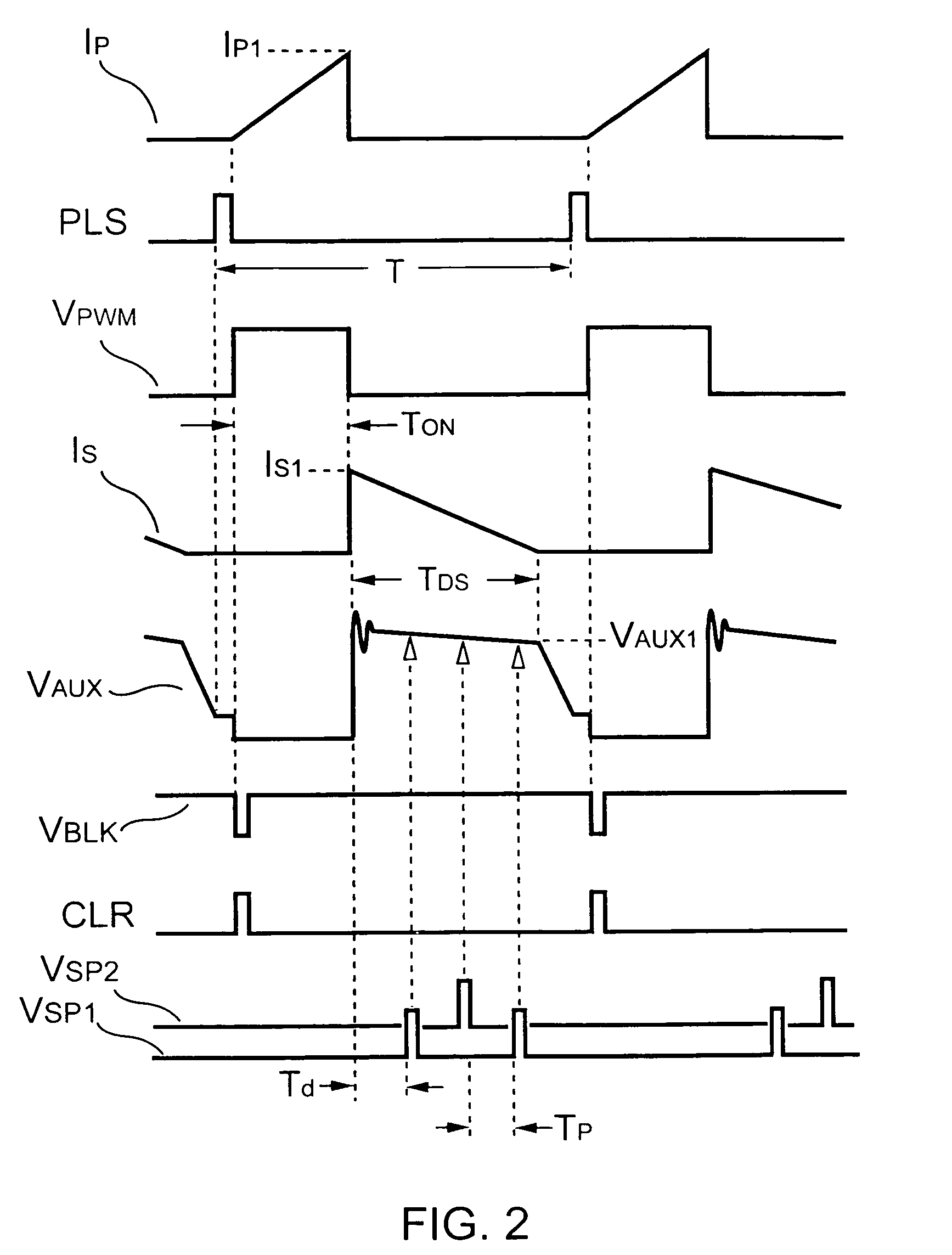
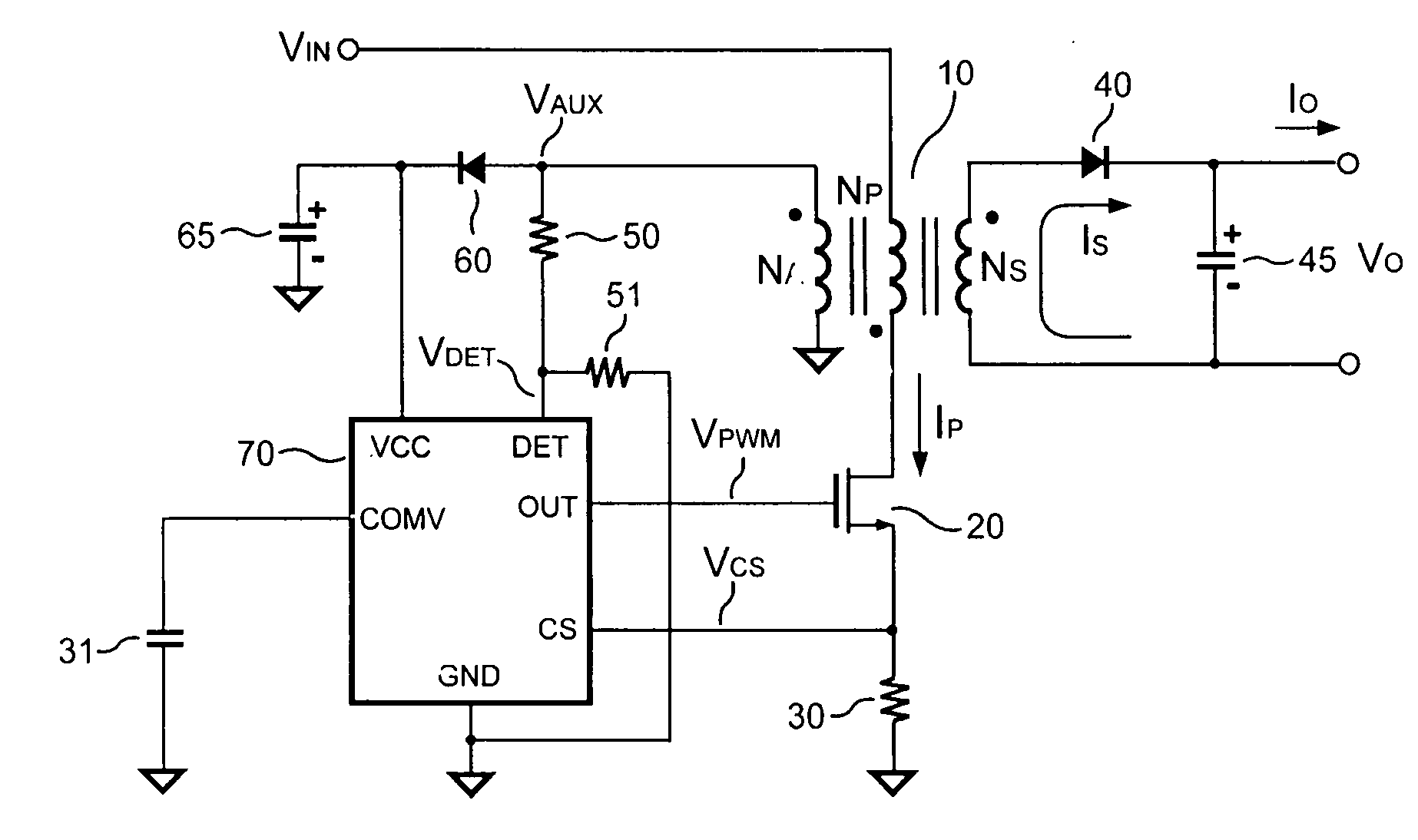
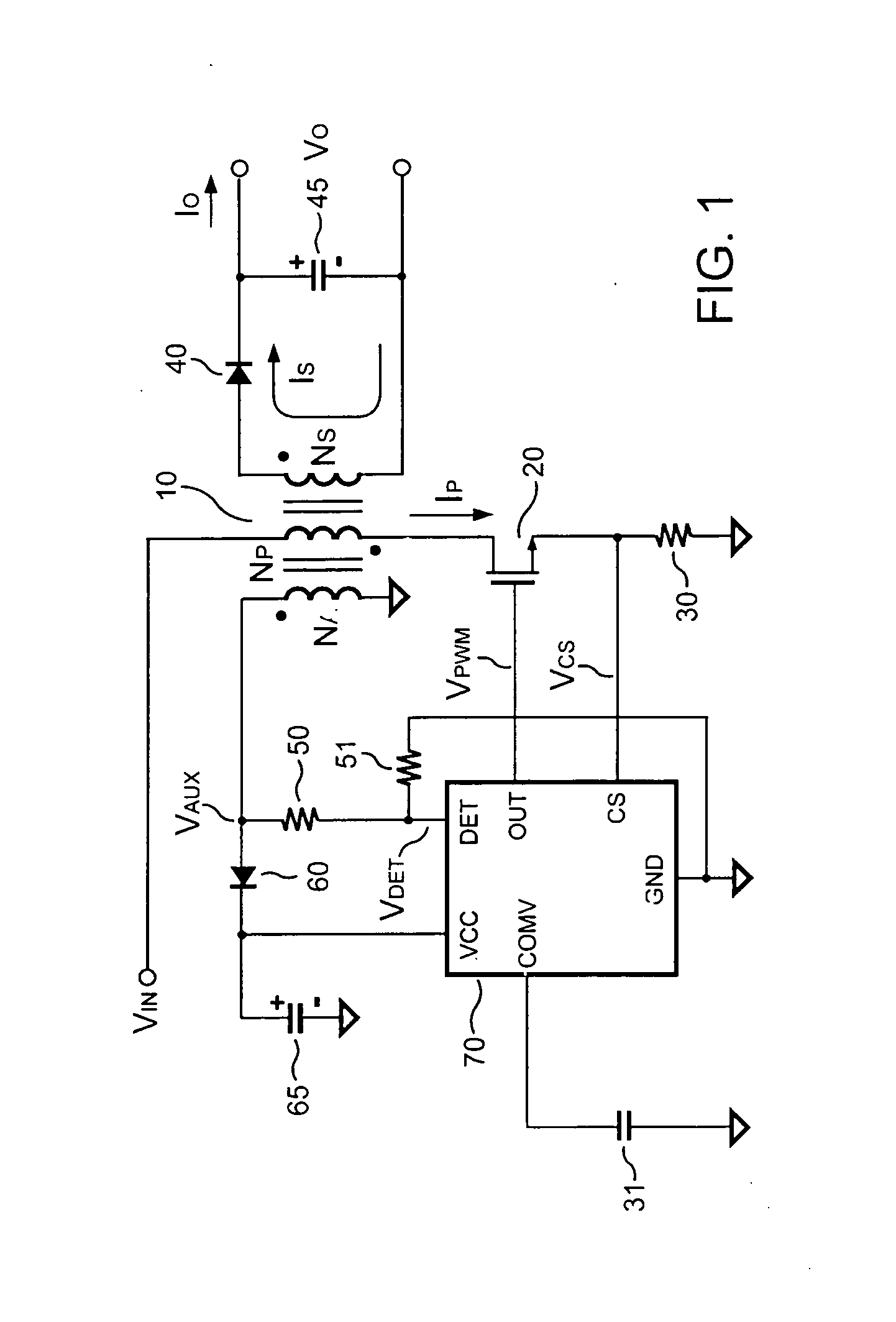
Switching-mode power converter and pulse-width-modulation control circuit with primary-side feedback control
A pulse-width-modulation control circuit of a switching-mode power converter with a primary-side feedback control is disclosed. The switching-mode power converter includes a transformer, a power switch, a current sensing resistor and the pulse-width-modulation control circuit. The transformer includes a primary-side winding, a secondary-side winding and an auxiliary winding. The pulse-width-modulation control circuit includes a sample and hold circuit, a transconductor circuit, an error amplifier and a pulse-width-modulation generator.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
Biosensor
InactiveUS6706232B2Avoid destructionNot easy to dissolveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWhole blood unitsEngineering
There is provided a cholesterol sensor with high-accuracy and excellent response, whose object to be measured is whole blood, where plasma with hemocytes therein filtered can rapidly reach an electrode system. In a biosensor where plasma with hemocytes therein filtered with a filter is sucked into a sample solution supply pathway due to capillarity, there are formed: a first pressing part for holding a primary side portion of the filter from the bottom; a second pressing part for holding a secondary side portion of the filter from the top and the bottom; a third pressing part for holding the central portion of the filter from the top; and a void for surrounding the filter between the second pressing part and third pressing part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
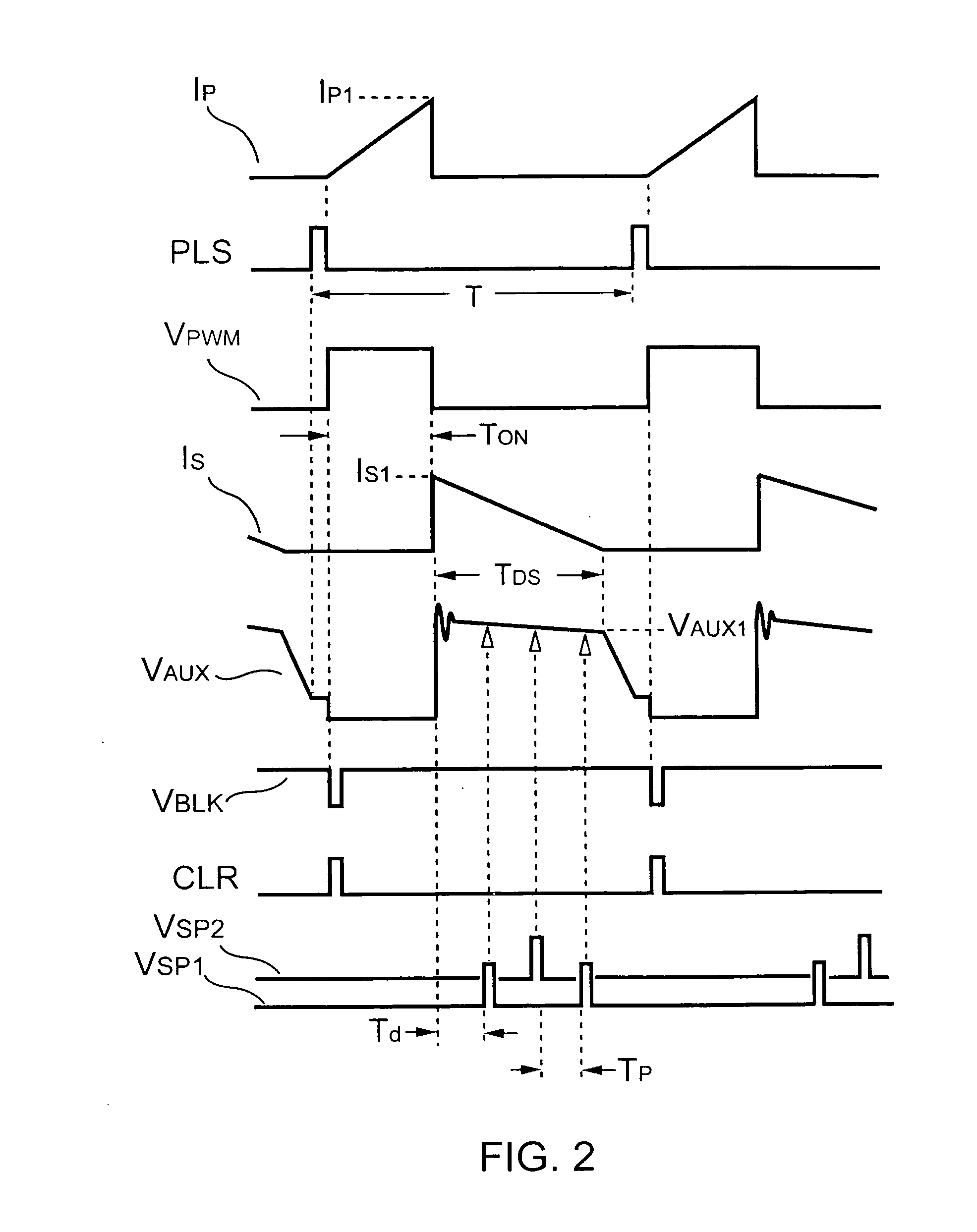
Switching control circuit having off-time modulation to improve efficiency of primary-side controlled power supply
ActiveUS7362593B2Save power consumptionLight load conditionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionAudio power amplifierControl signal
A voltage-waveform detector produces a voltage-feedback signal and a discharge-time signal by multi-sampling a voltage signal of a transformer. The discharge-time signal represents a discharge time of a secondary-side switching current. A voltage-loop error amplifier amplifies the voltage-feedback signal and generates a control signal. An off-time modulator correspondingly generates a discharge-current signal and a standby signal in response to the control signal and an under-voltage signal. The under-voltage signal indicates a low supply voltage of the controller. An oscillator produces a pulse signal in response to the discharge-current signal. The pulse signal determines the off-time of the switching signal. A PWM circuit generates the switching signal in response to the pulse signal and the standby signal. The standby signal further controls the off-time of the switching signal and maintains a minimum switching frequency. The switching signal is used for regulating the output of the power supply.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
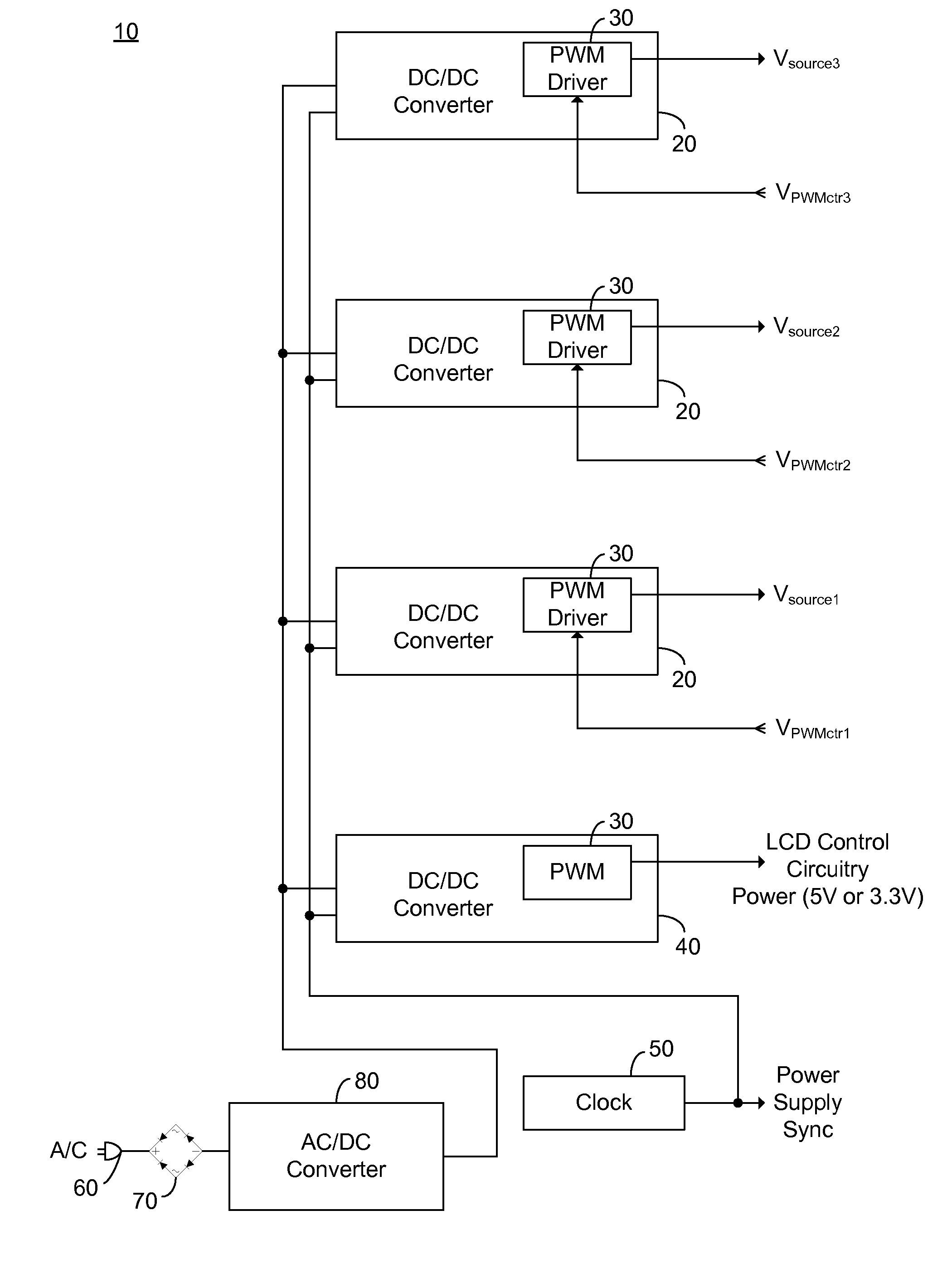
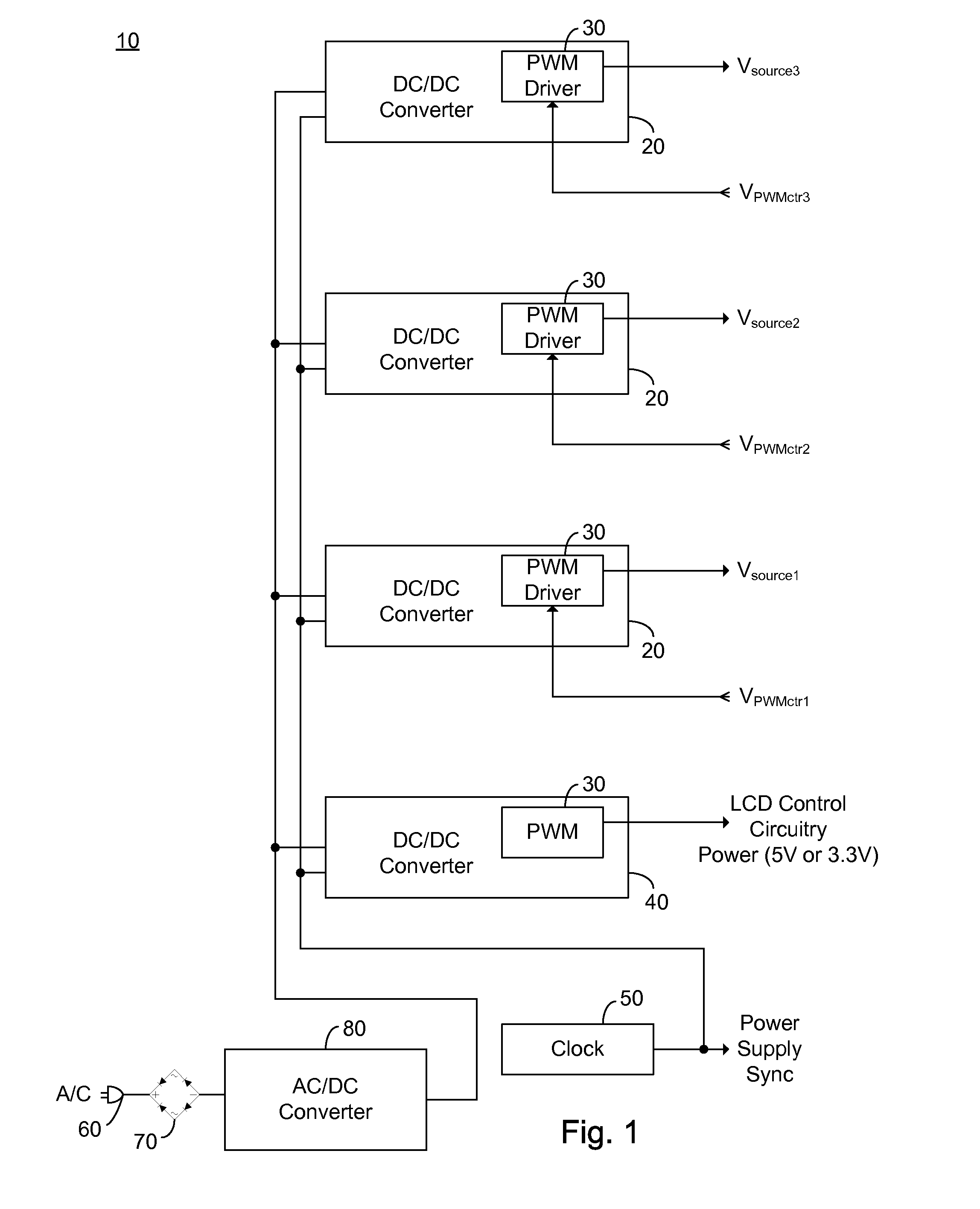
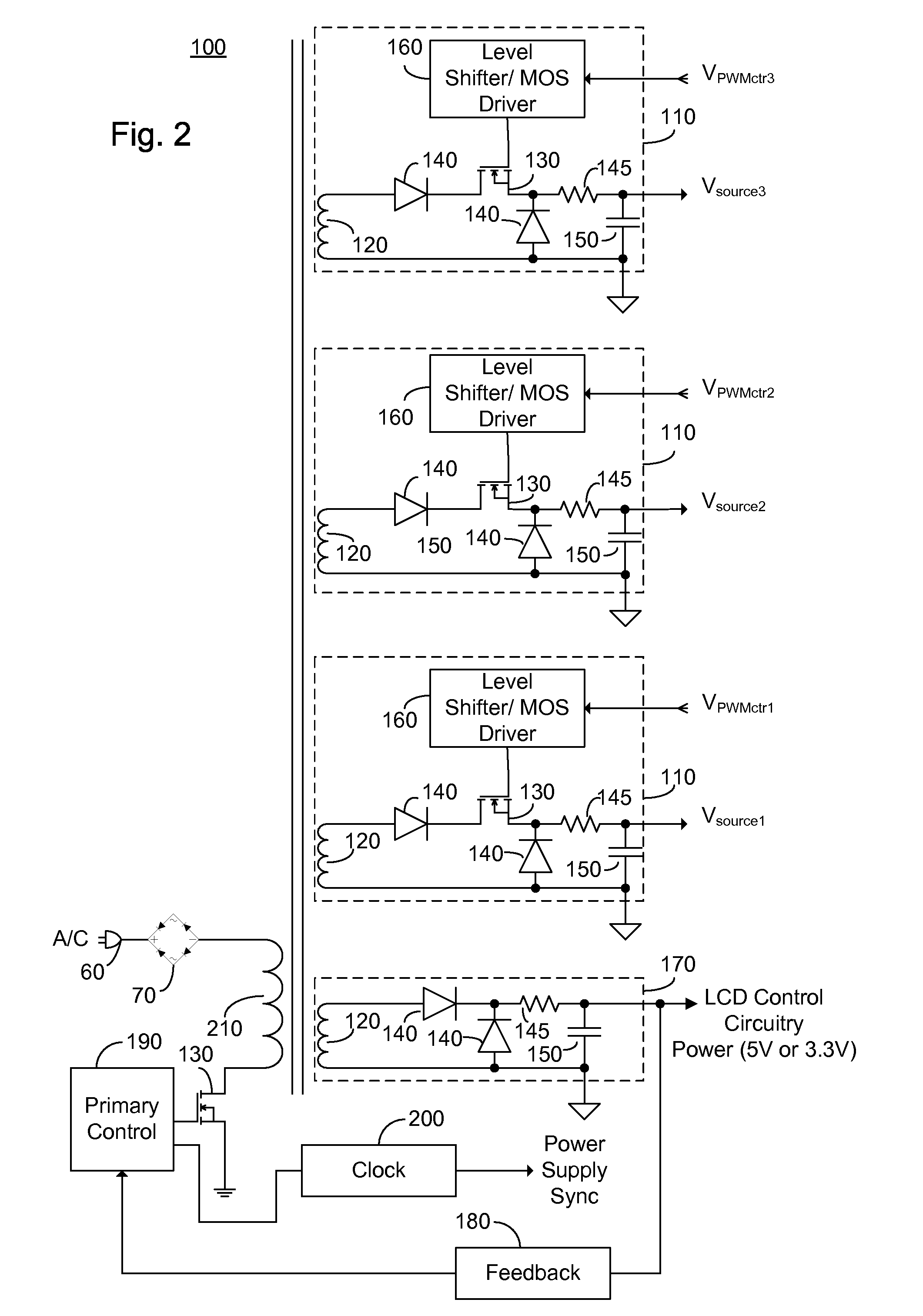
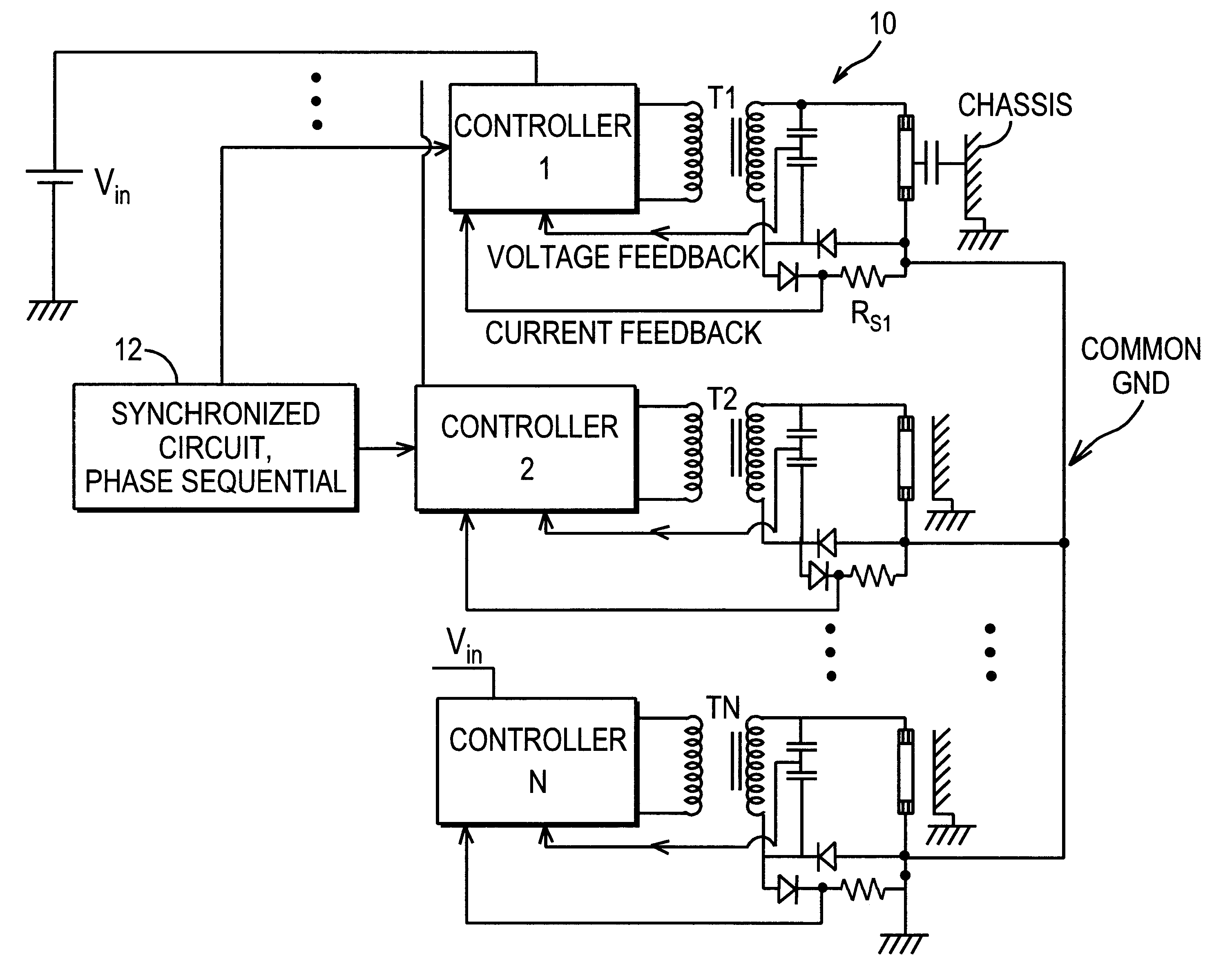
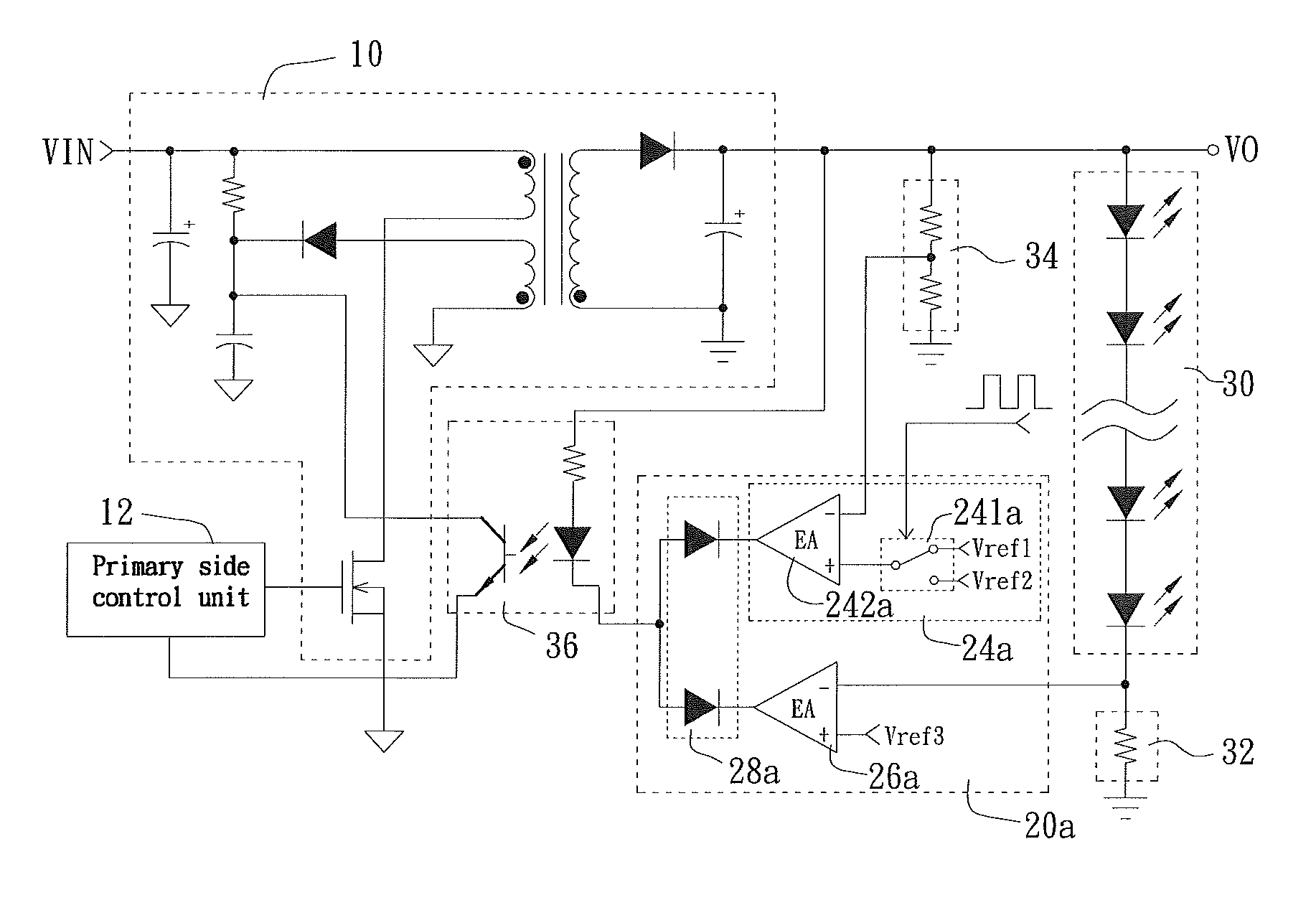
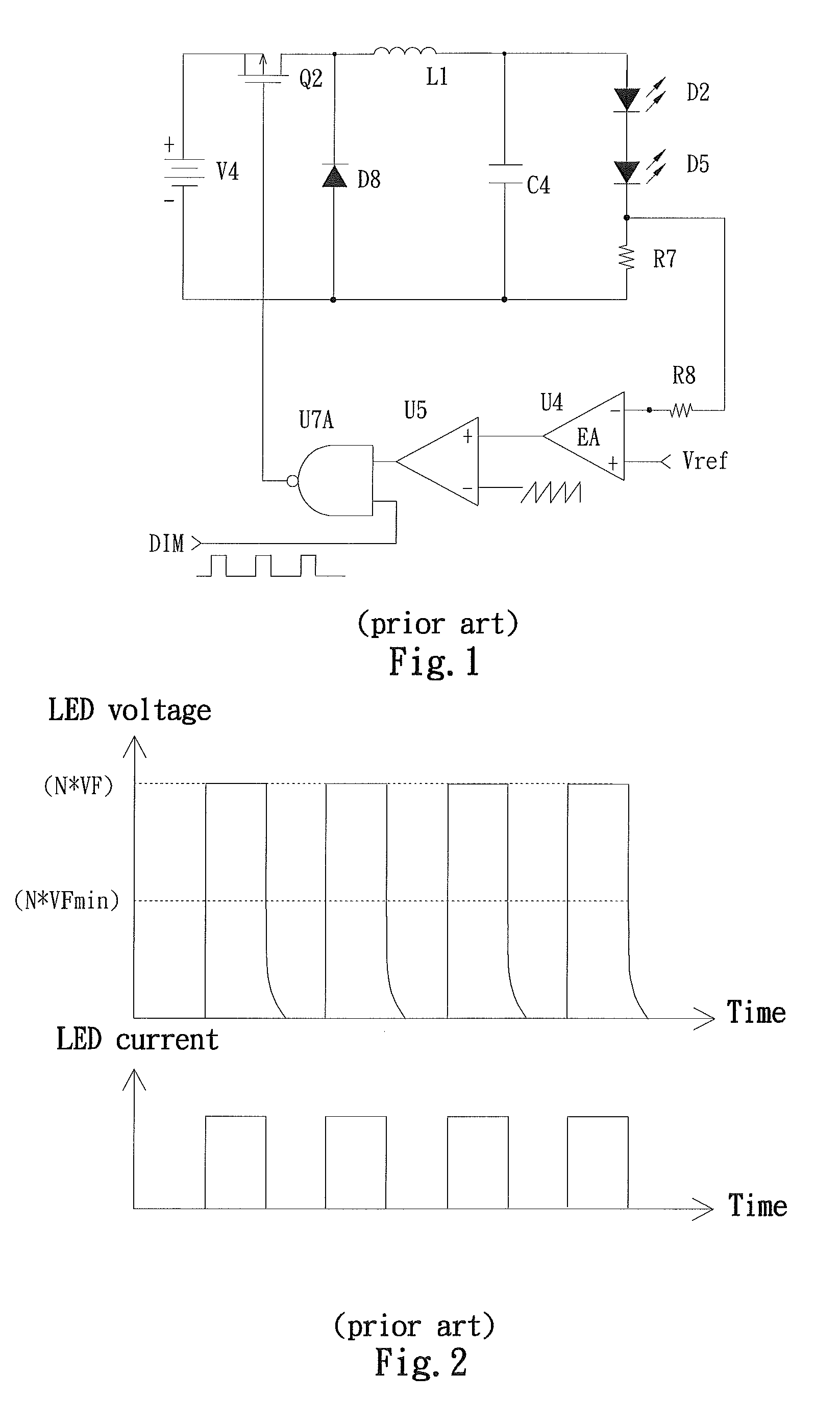
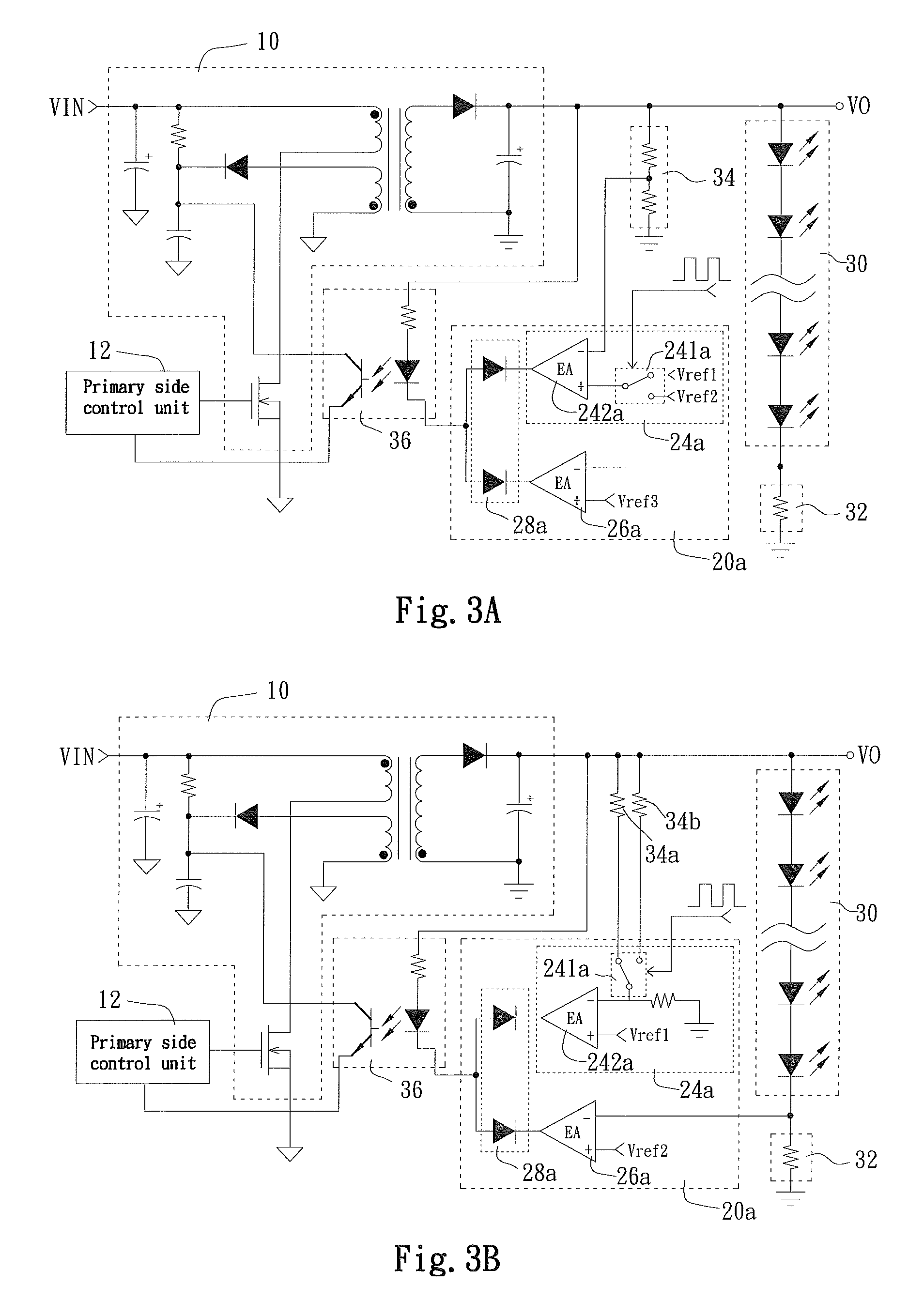
Secondary Side Post Regulation for LED Backlighting
A secondary side post regulator arrangement for a plurality of LED strings. For each secondary winding, a first electronically controlled switch is provided arranged to control the power output, and a LED string is connected thereto. A second electronically controlled switch is further connected in series with the LED string, arranged to receive a PWM signal, thereby pulsing current through the LED string. A current sensing element is further provided outputting a voltage representation of the current through the LED string, and a synchronized sampling circuit is provided arranged to sample the voltage representation during the on period of the second electronically controlled switch. The sampled and held voltage representation is compared with a reference signal and fed back to control the first electronically controlled switch. The voltage output associated with each secondary winding is controlled, responsive to the reference voltage.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
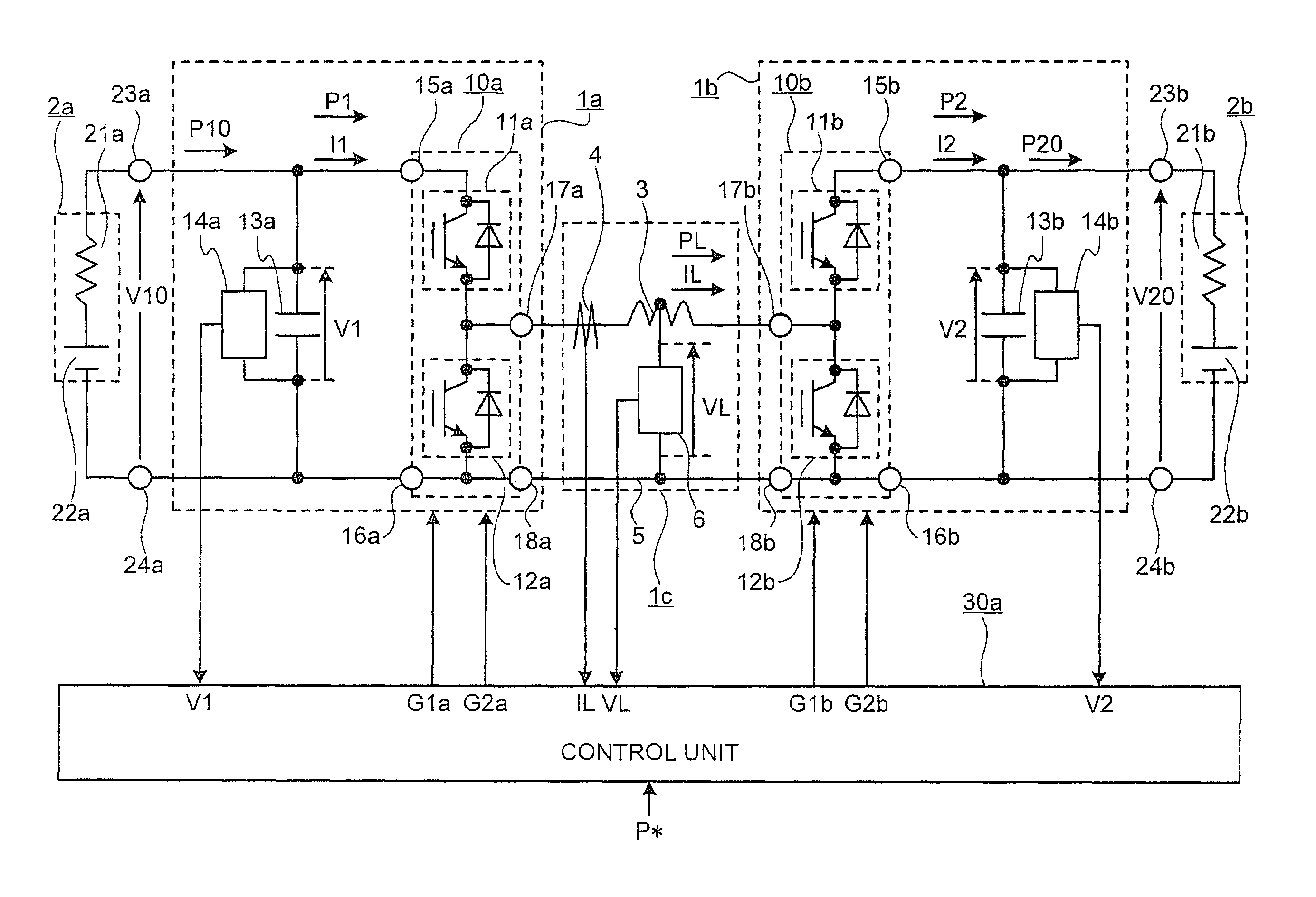
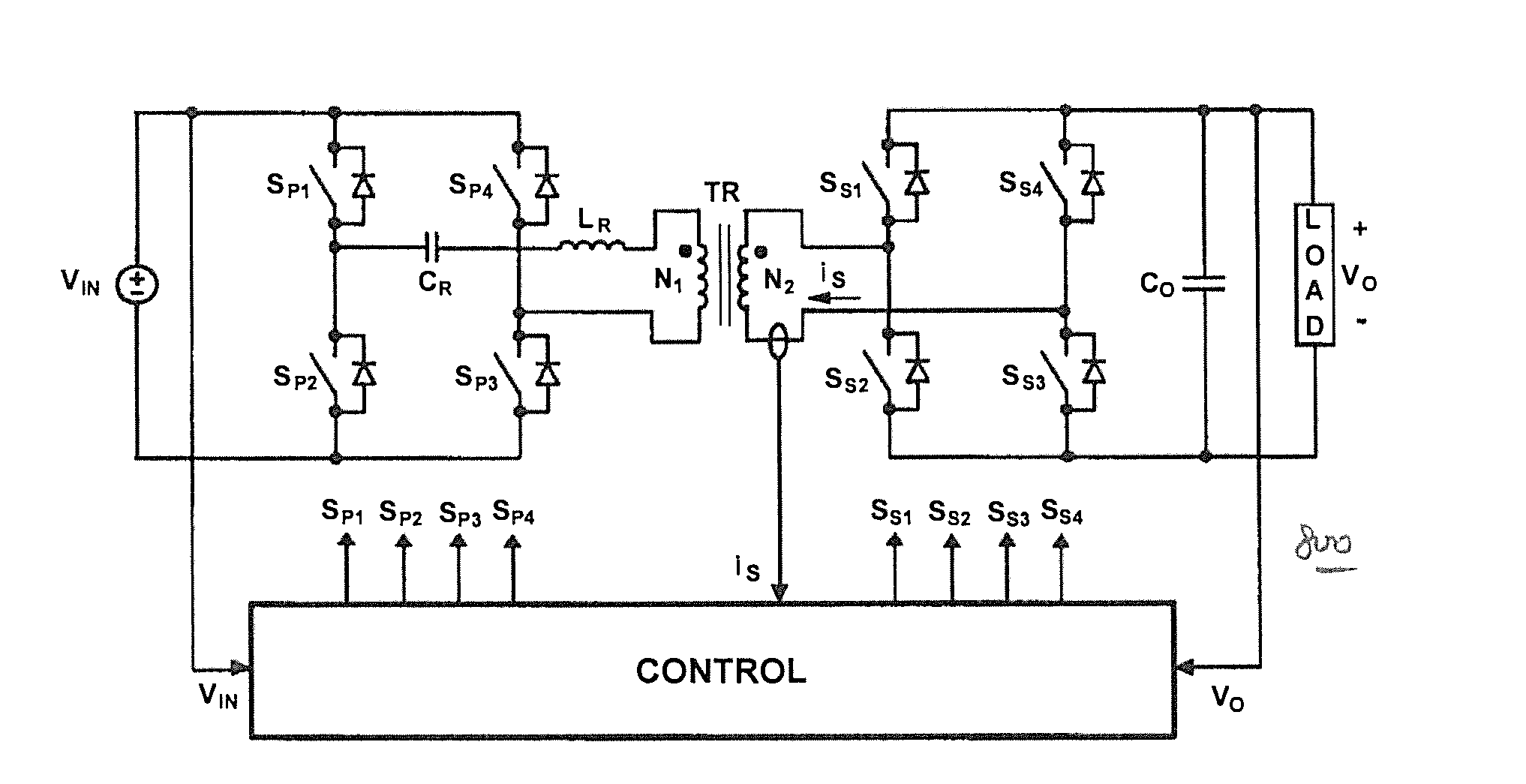
Bidirectional buck boost DC-DC converter, railway coach drive control system, and railway feeder system
InactiveUS7723865B2Electric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsAutomatic controlDc dc converter
According to the present invention, a bidirectional buck boost DC-DC converter can be obtained, in which power can flow bidirectionally from a primary side to a secondary side and from the secondary side to the primary side, regardless of a magnitude relation between a secondary-side voltage and a primary-side voltage in a state where different DC voltage sources are connected to the primary side and the secondary side in the DC-DC converter. A direction and a magnitude of the power can be automatically controlled to a desired value continuously on instantaneous value basis.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
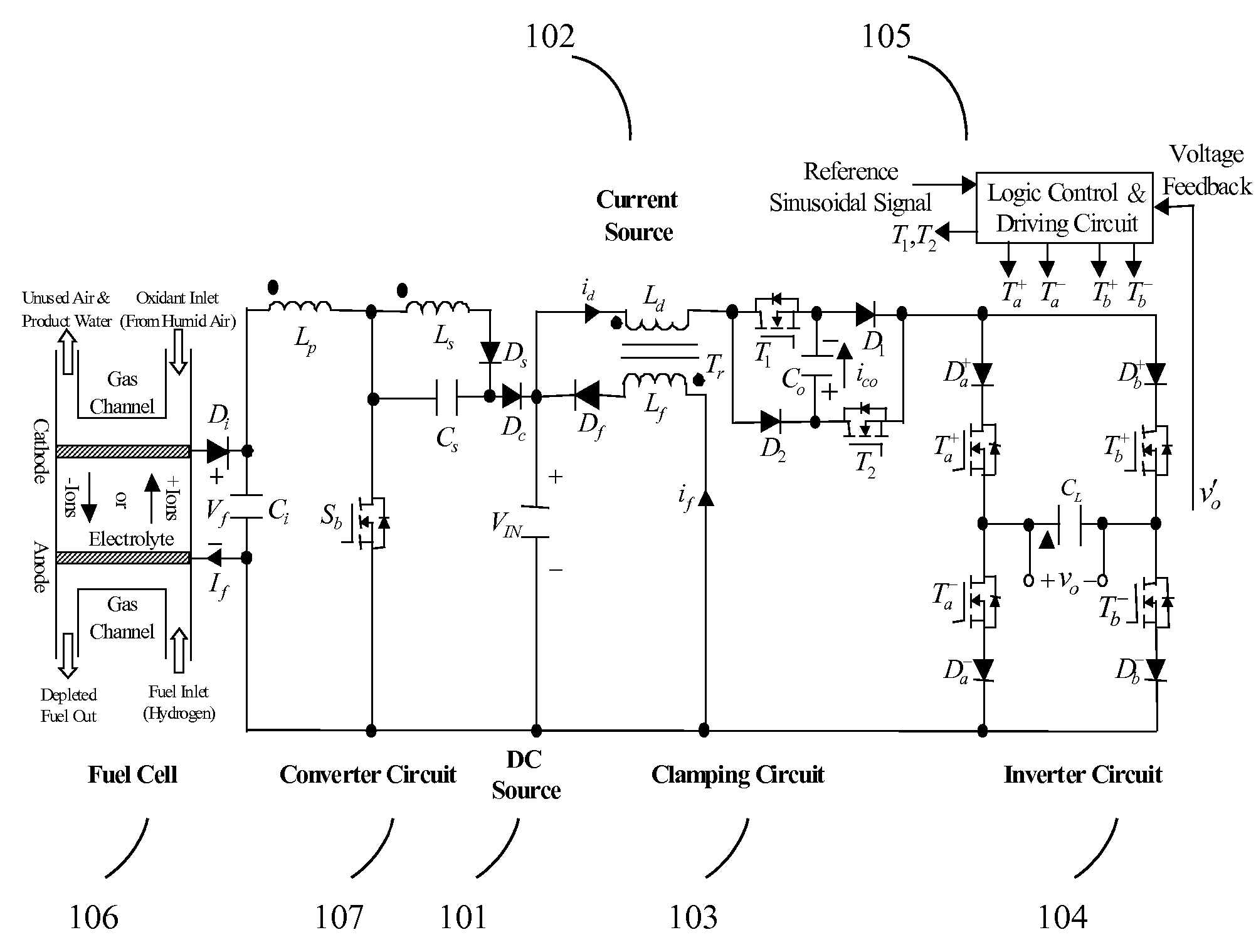
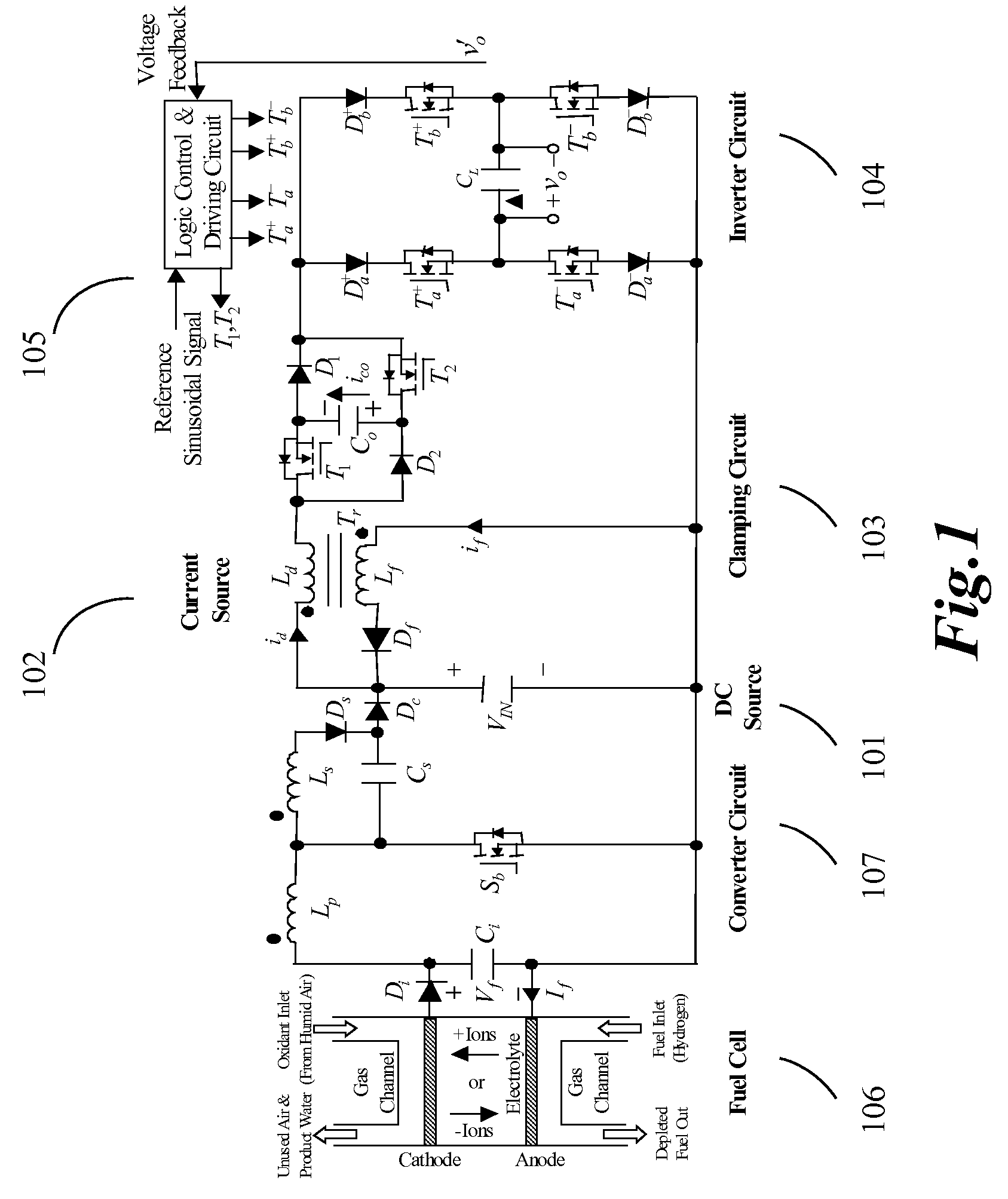
Current source wave voltage inverter voltage-clamping and soft-switching techniques, and fuel cell system using the same
ActiveUS7262979B2Lower component costsEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingEngineering
A current-source sine-wave voltage inverter for converting a direct current (DC) voltage to an alternating (AC) voltage includes a DC source for providing a DC voltage, a current source circuit having a primary side inductance of a transformer, a clamping circuit, an inverting circuit, and a control and driving circuit. The clamping circuit includes a first switch cascaded with a first diode, a second diode cascaded with a second switch, a first capacitor connected between an anode of the first diode and a cathode of the second diode, a secondary side inductance of the transformer cascaded with a third diode, the secondary side inductance of the transformer and the third diode connected to two ends of the DC source, and a cathode of the third diode connected to an anode of the DC source. The present invention also provides a fuel cell system.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Switching control circuit having off-time modulation to improve efficiency of primary-side controlled power supply
ActiveUS20060055433A1Save power consumptionLight load conditionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalSwitching frequency
A voltage-waveform detector produces a voltage-feedback signal and a discharge-time signal by multi-sampling a voltage signal of a transformer. The discharge-time signal represents a discharge time of a secondary-side switching current. A voltage-loop error amplifier amplifies the voltage-feedback signal and generates a control signal. An off-time modulator correspondingly generates a discharge-current signal and a standby signal in response to the control signal and an under-voltage signal. The under-voltage signal indicates a low supply voltage of the controller. An oscillator produces a pulse signal in response to the discharge-current signal. The pulse signal determines the off-time of the switching signal. A PWM circuit generates the switching signal in response to the pulse signal and the standby signal. The standby signal further controls the off-time of the switching signal and maintains a minimum switching frequency. The switching signal is used for regulating the output of the power supply.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
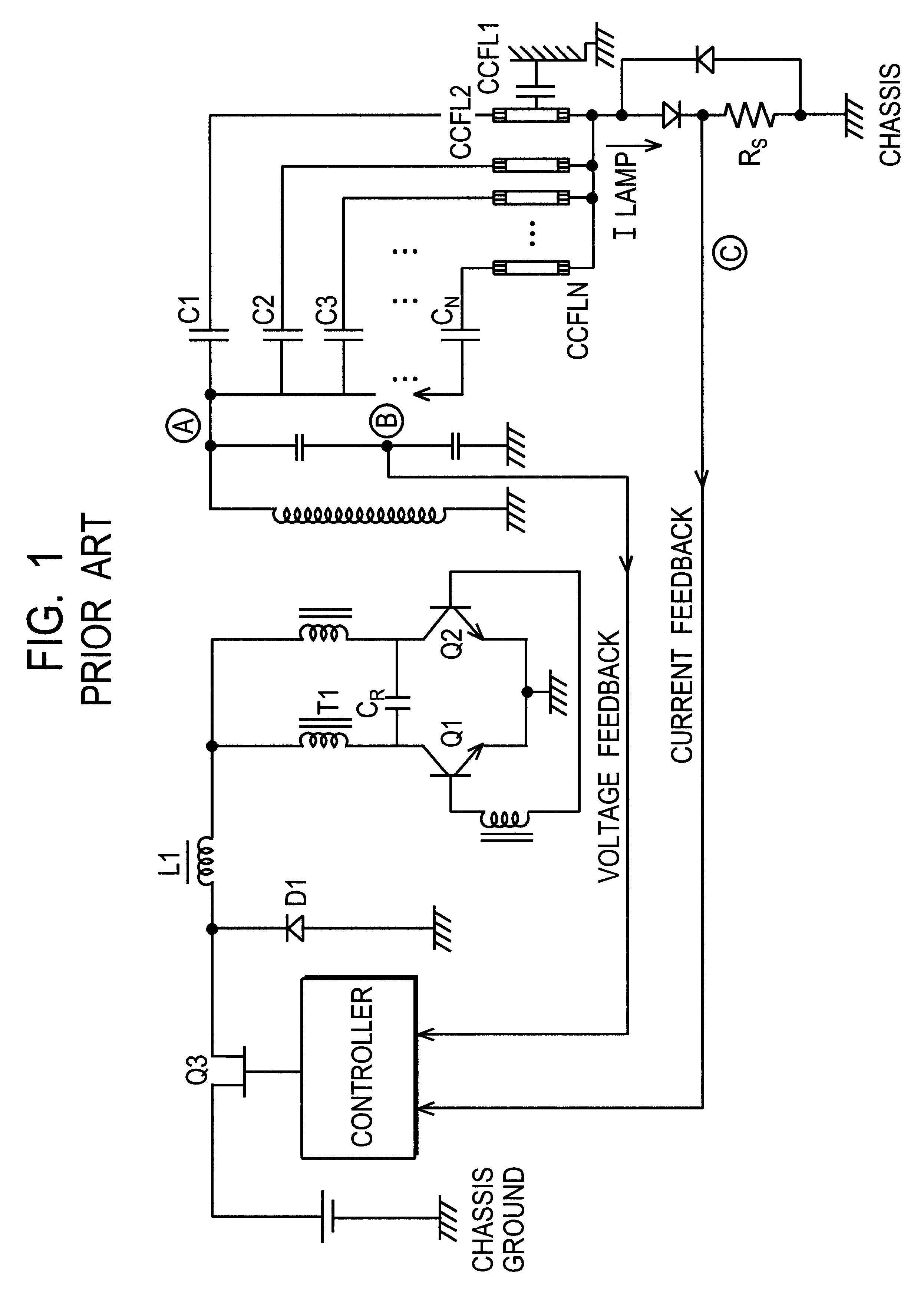
Lamp grounding and leakage current detection system
InactiveUS6570344B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionGround systemEngineering
A common ground system and methodology for one or more loads. In exemplary embodiments, a lamp load is regulated by providing a common ground on the secondary side of the transformer and the load. Lamp regulation is provided, in part, via a current feedback loop provided on the secondary side that is commonly grounded between the bottom of the transformer and the bottom of the lamp through the current feedback loop. In this manner, a feedback signal is developed that includes the leakage current of the lamp.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Resonant converters and control methods thereof
ActiveUS20150229225A1Improve performanceReducing switching-frequency rangeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTime delaysEngineering
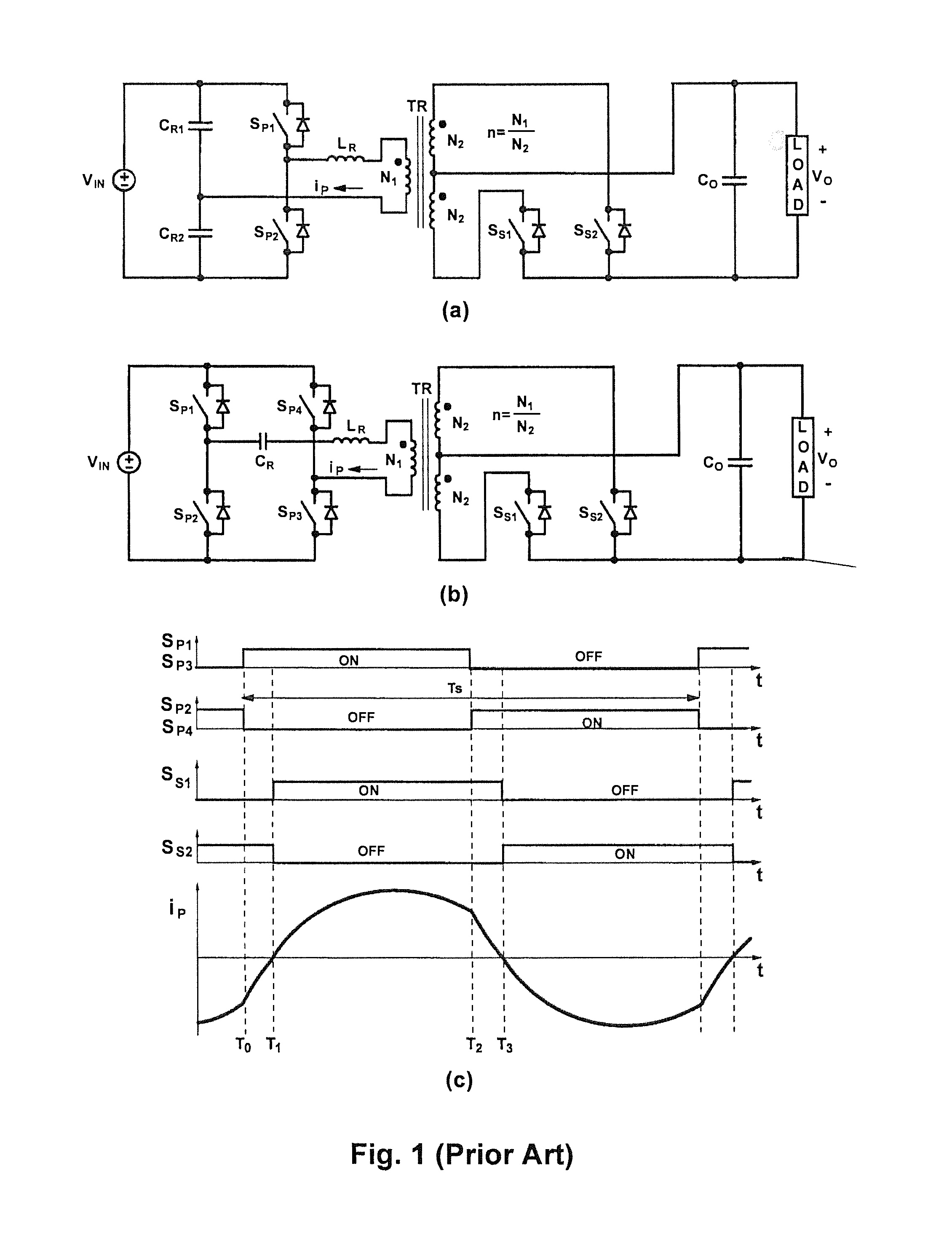
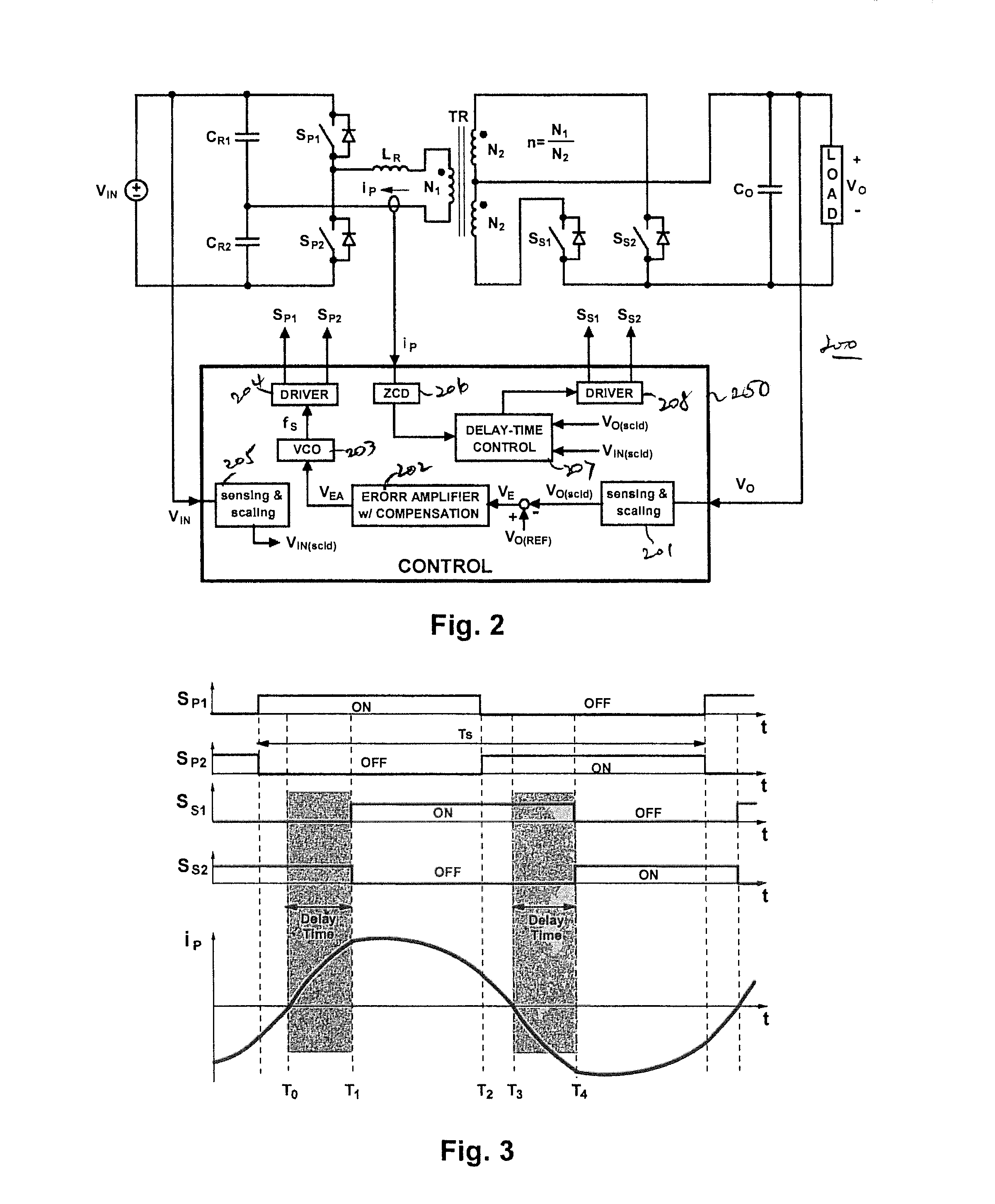
Control methods for resonant converters offer improved performance in resonant converters that operate with a wide input-voltage range or a wide output-voltage range (or both) by substantially reducing the switching-frequency range. Reduction in the switching frequency range is achieved by controlling the output voltage with a combination of variable-frequency control and time-delay control. Variable-frequency control may be used to control the primary switches of an isolated resonant converter, while delay-time control may be used to control secondary-side rectifier switches provided in place of diode rectifiers. The secondary-side control may be implemented by sensing the secondary current or the primary current (or both) and by delaying the turning-off of the corresponding secondary switch with respect to the zero crossings in the secondary current or the primary current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
System and method for synchronous rectifier drive that enables converters to operate in transition and discontinuous mode
ActiveUS20100027298A1Inhibition transitionWithout significant lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterSecondary side
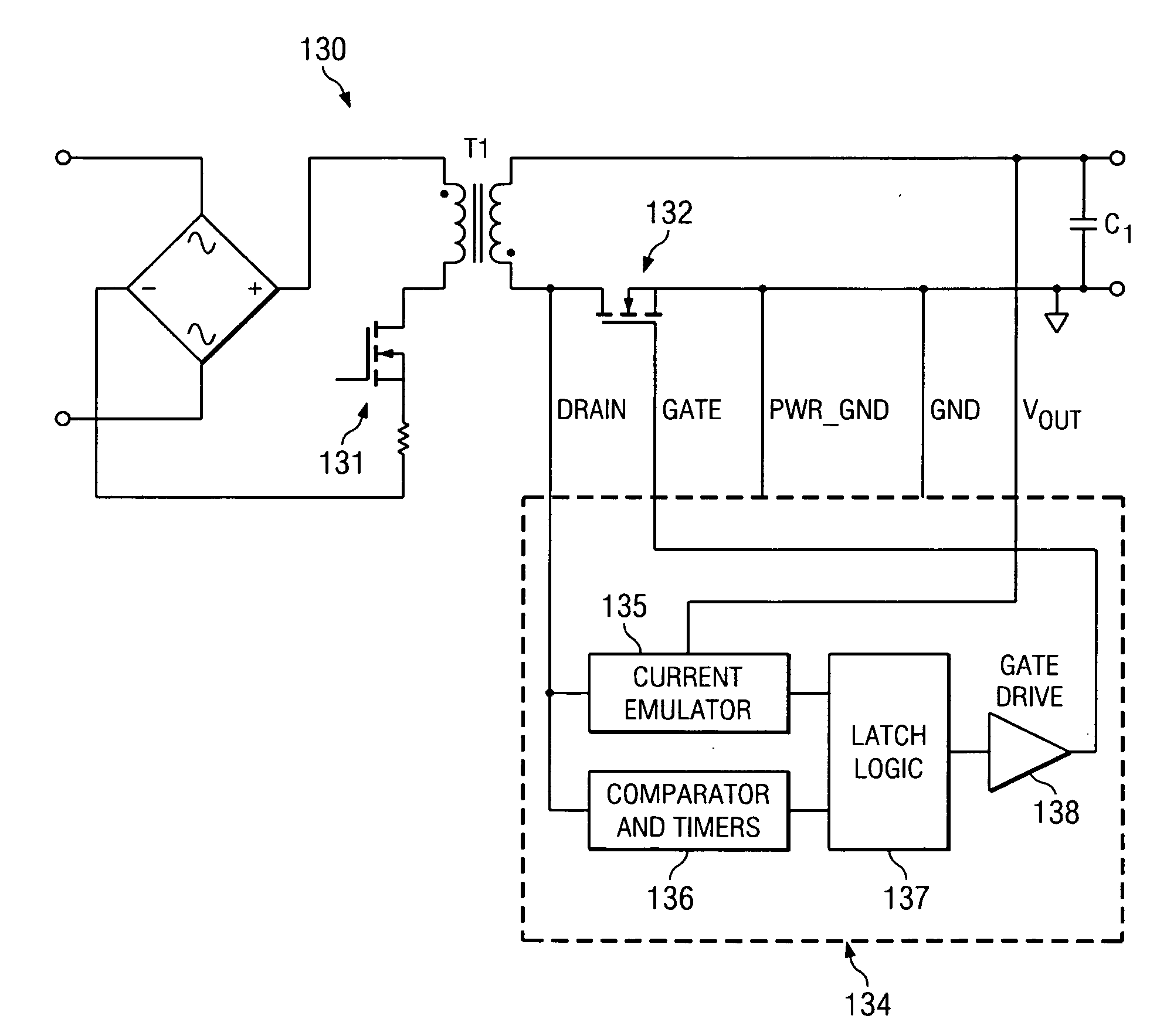
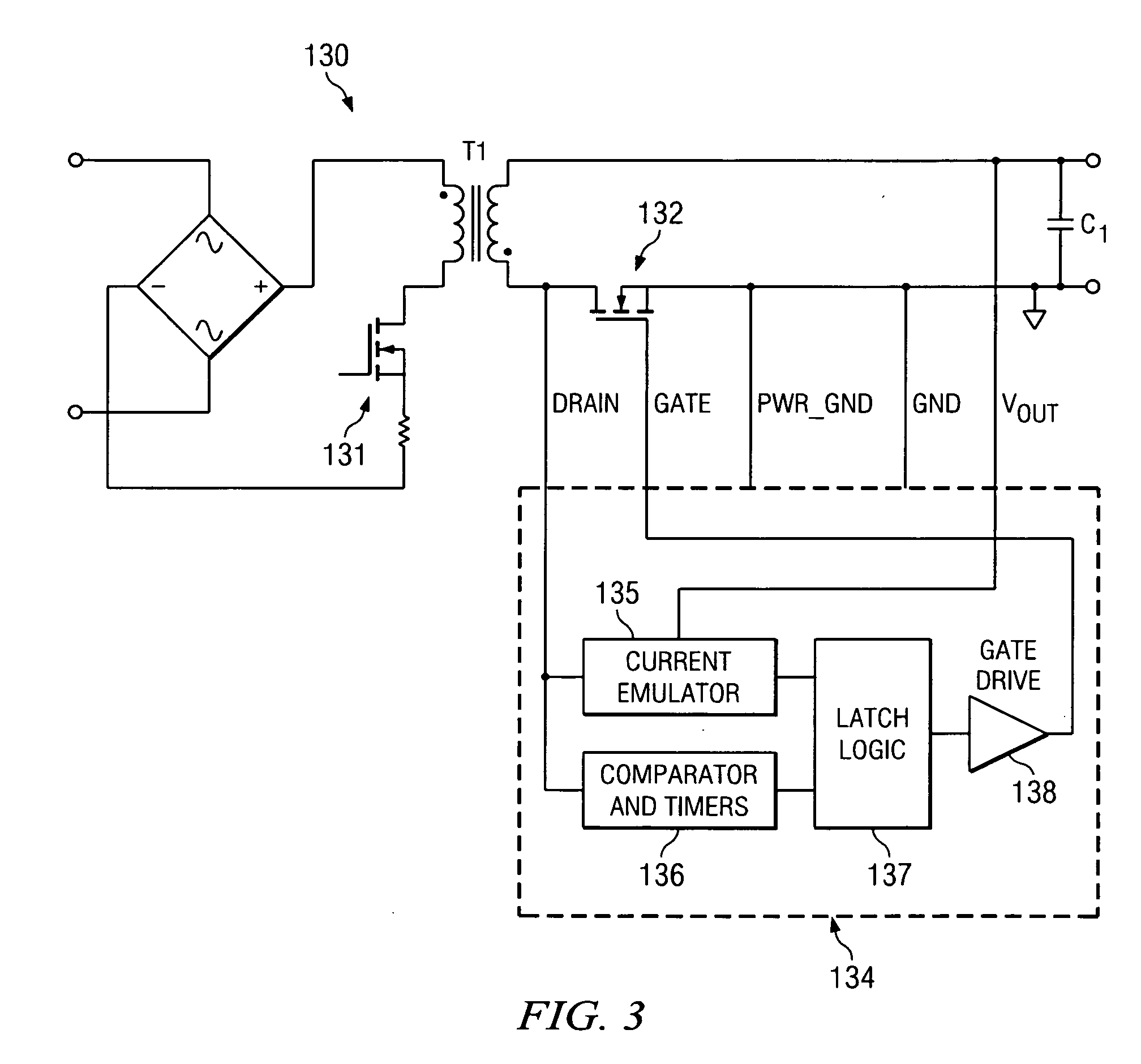
A synchronous rectifier is switched in accordance with a primary switch transition and a reference signal representing current in a current storage device to which the synchronous rectifier is coupled. A current emulator provides a signal representing current in the current storage device as a volt-second product so that current stored in the current storage device while the primary switch is on is discharged by the synchronous rectifier. The use of a current emulator provides an inexpensive solution for controlling synchronous rectifier transitions without resorting to more expensive current sensing solutions that are commercially impracticable. Blanking intervals are provided for avoiding false transitions of the synchronous rectifier when the primary switch turns on and after the synchronous rectifier turns off. The disclosed system and method can be applied to flyback converters for a synchronous rectifier on the secondary side of a transformer, or the inductor of buck converters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
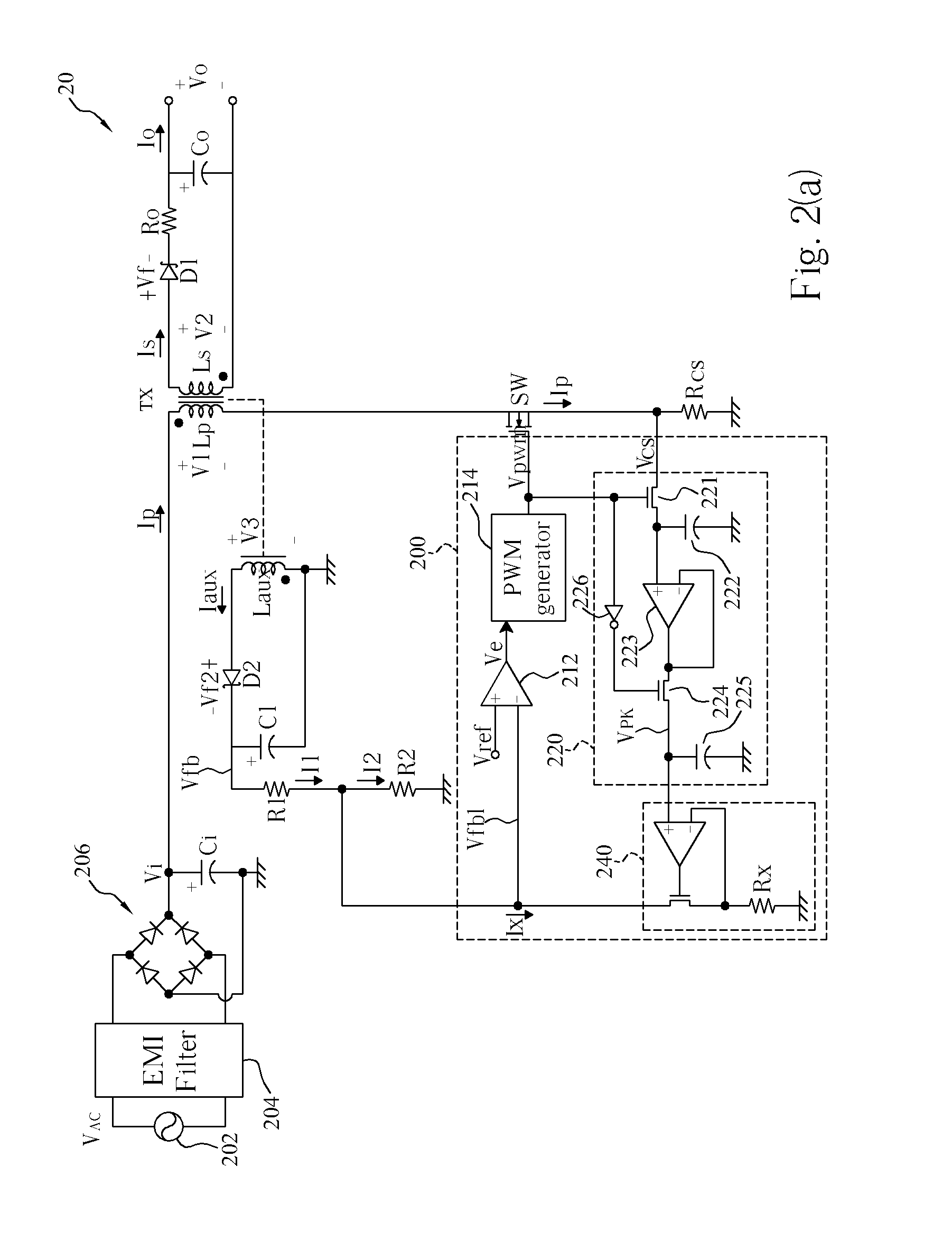
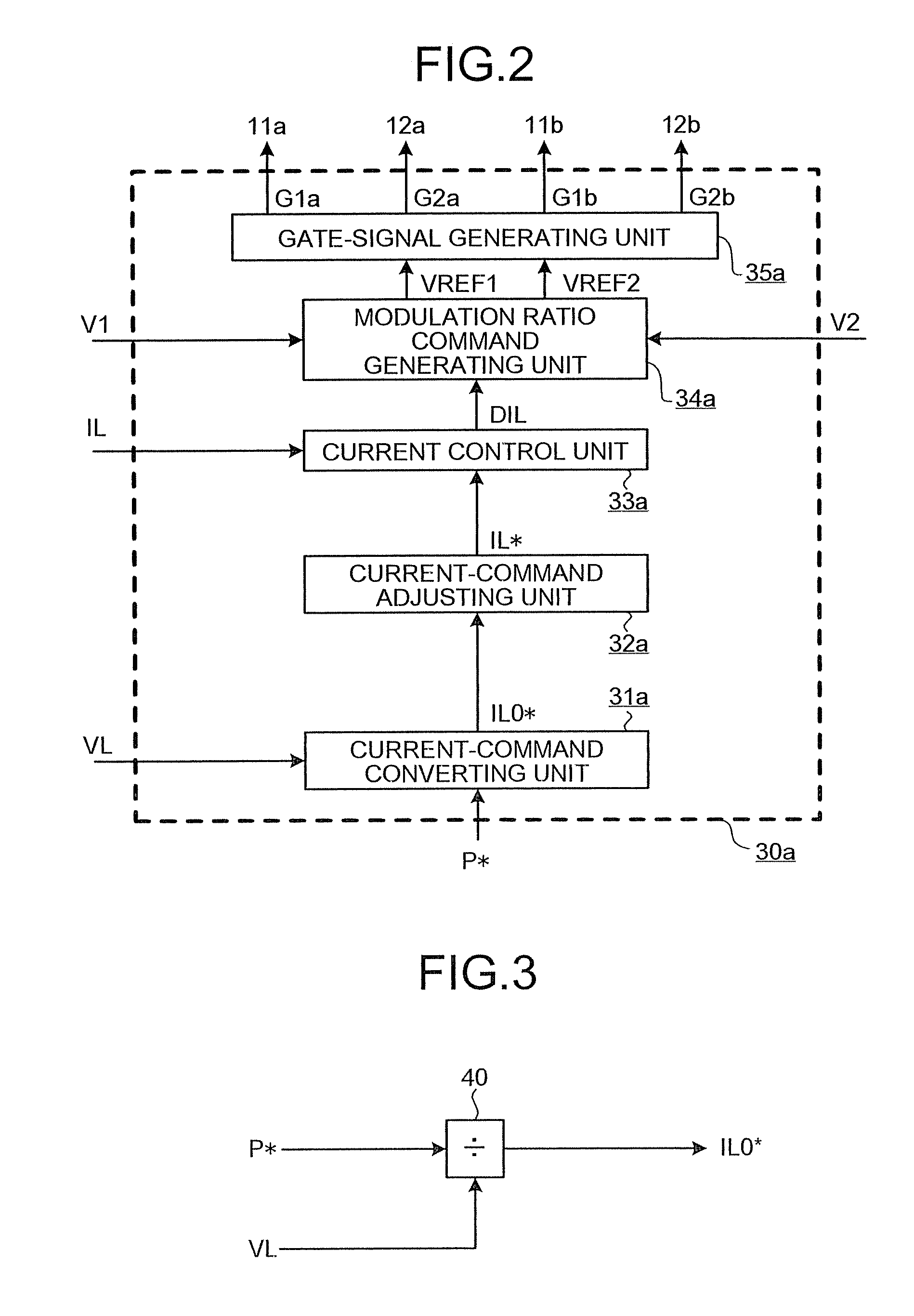
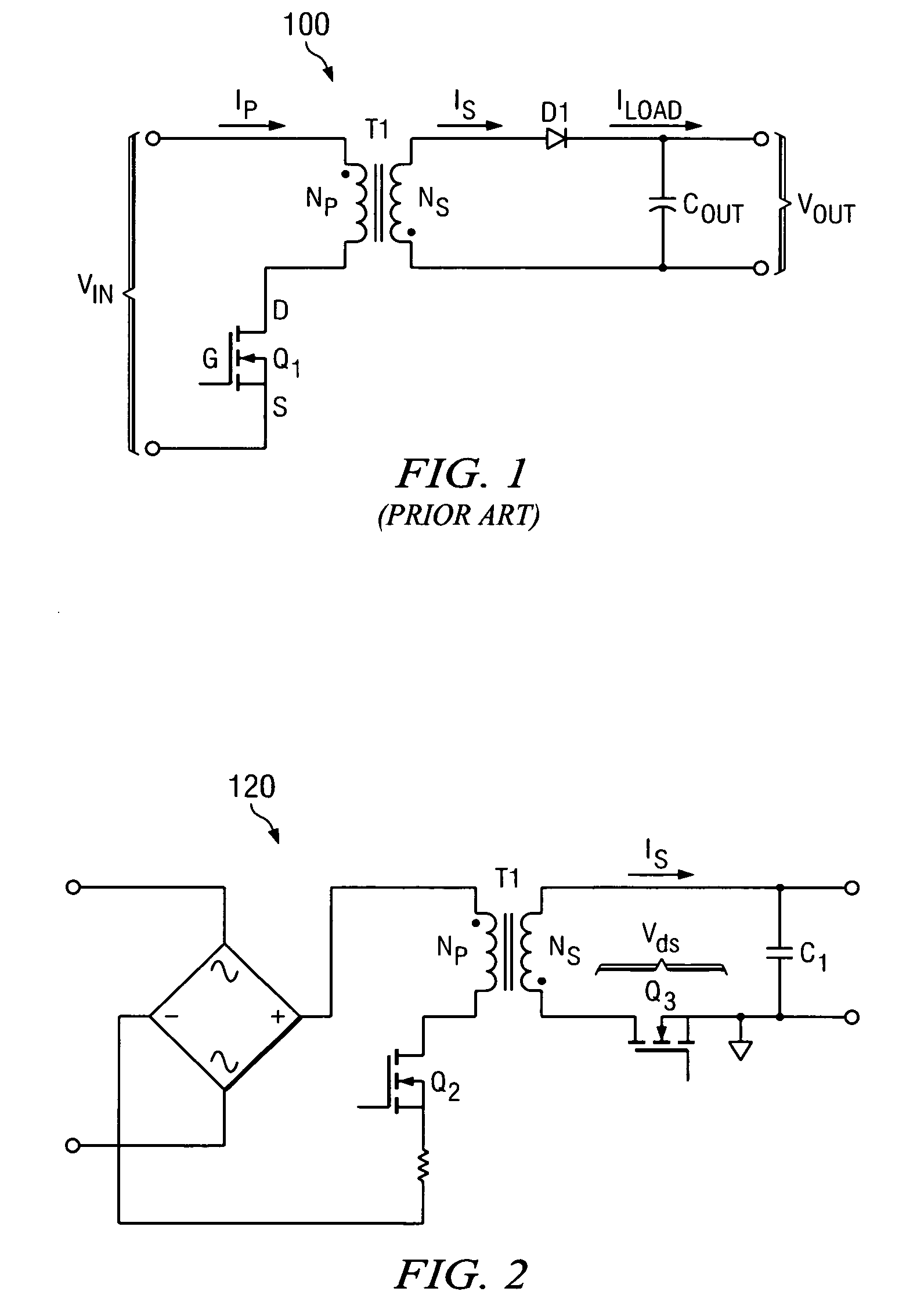
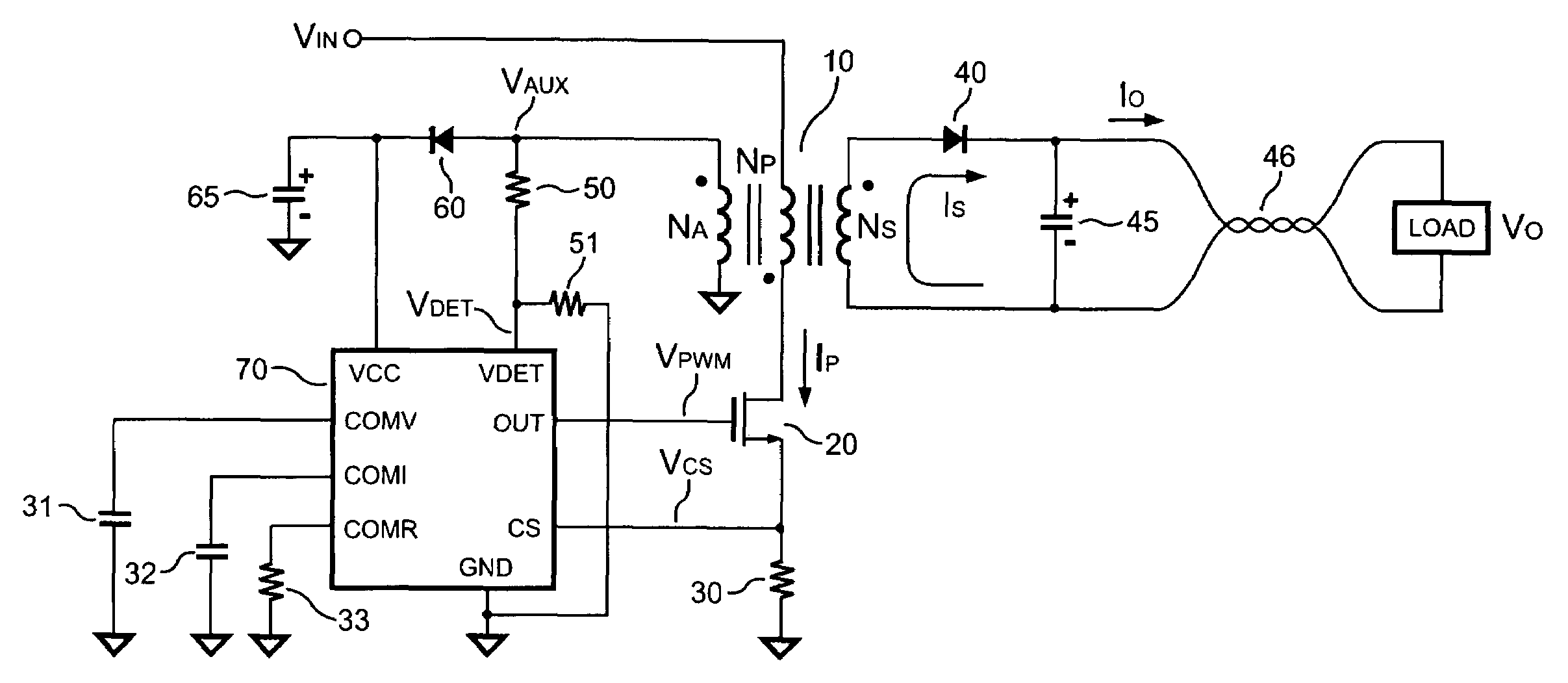
Primary-side based control of secondary-side current for a transformer
A power control system includes a transformer and a controller regulates a current on a secondary-side of the transformer based on a primary-side signal value. In at least one embodiment, the secondary-side current is a current out of a filter coupled to a rectifier and the secondary-side of the transformer and into a load. In at least one embodiment, the primary-side signal value is a sample of a current in the primary-side windings of the transformer. In at least one embodiment, the primary-side signal value represents a sample value of a primary-side transformer current. Proper timing of sampling the primary-side signal value substantially eliminates contributions of a transformer magnetizing current from the primary-side transformer current sample. Sampling the primary-side signal value when contributions of the transformer magnetizing current are substantially eliminated allows at least an average of the secondary-side current to be determined from the primary-side signal value.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
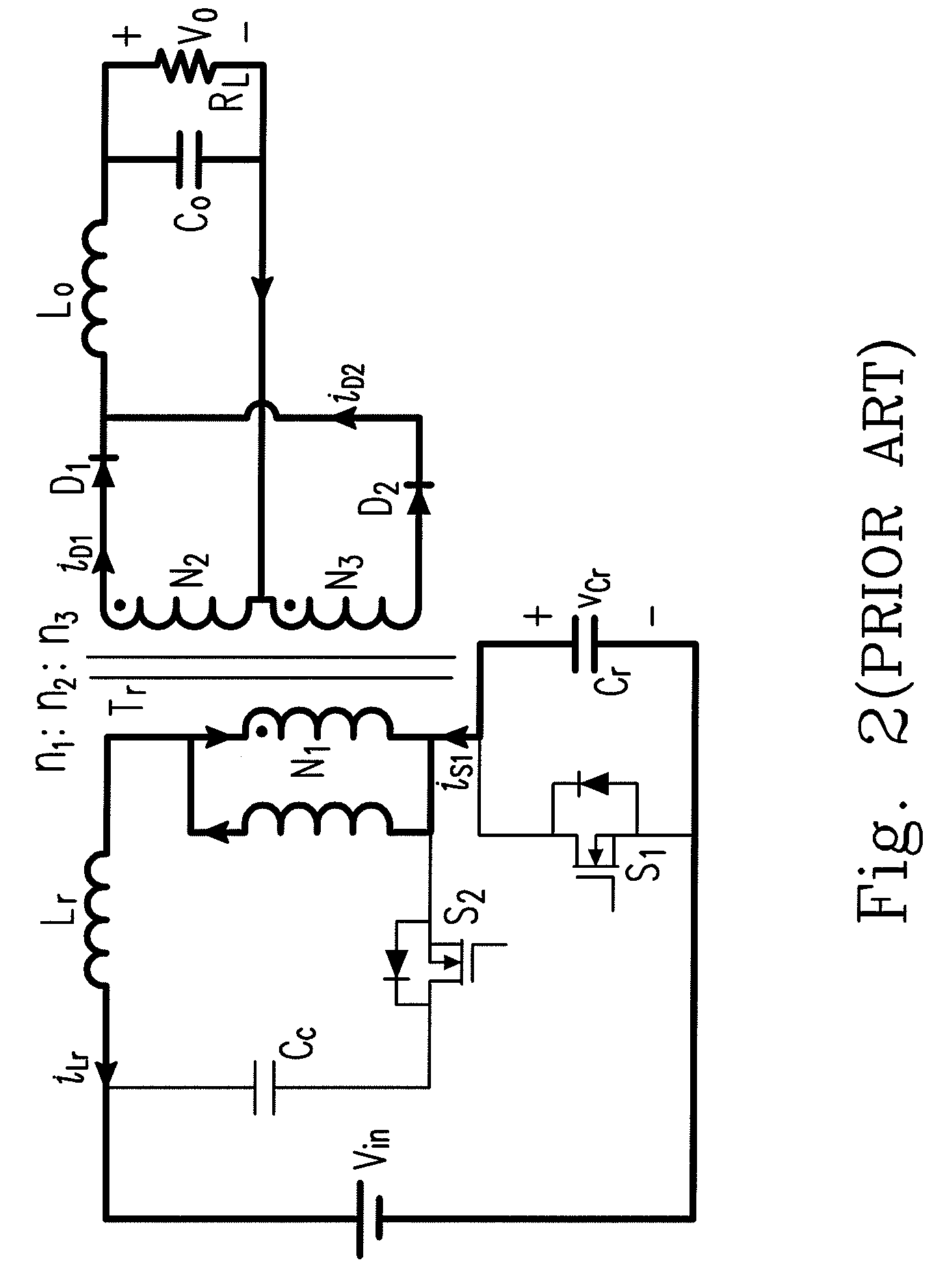
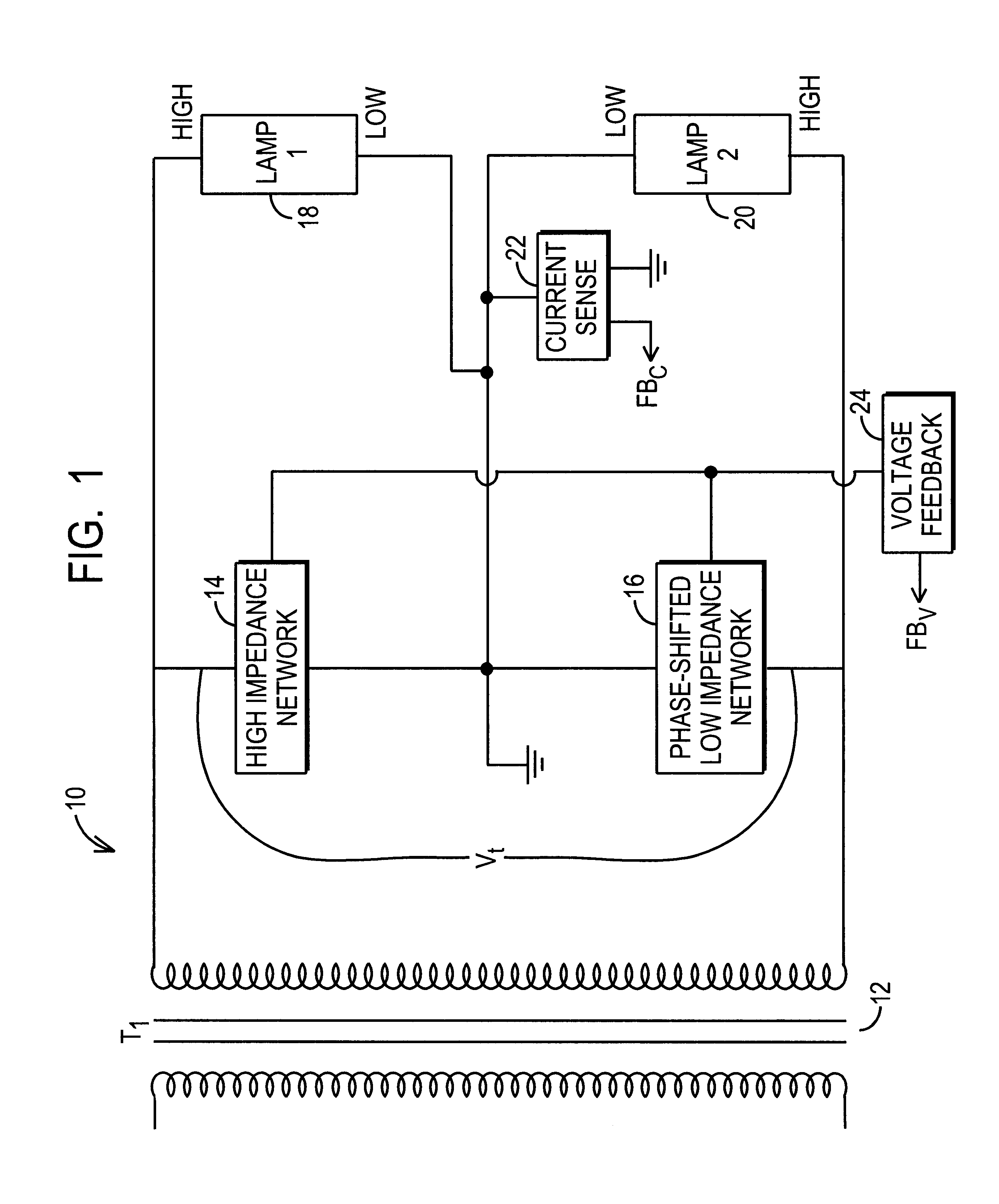
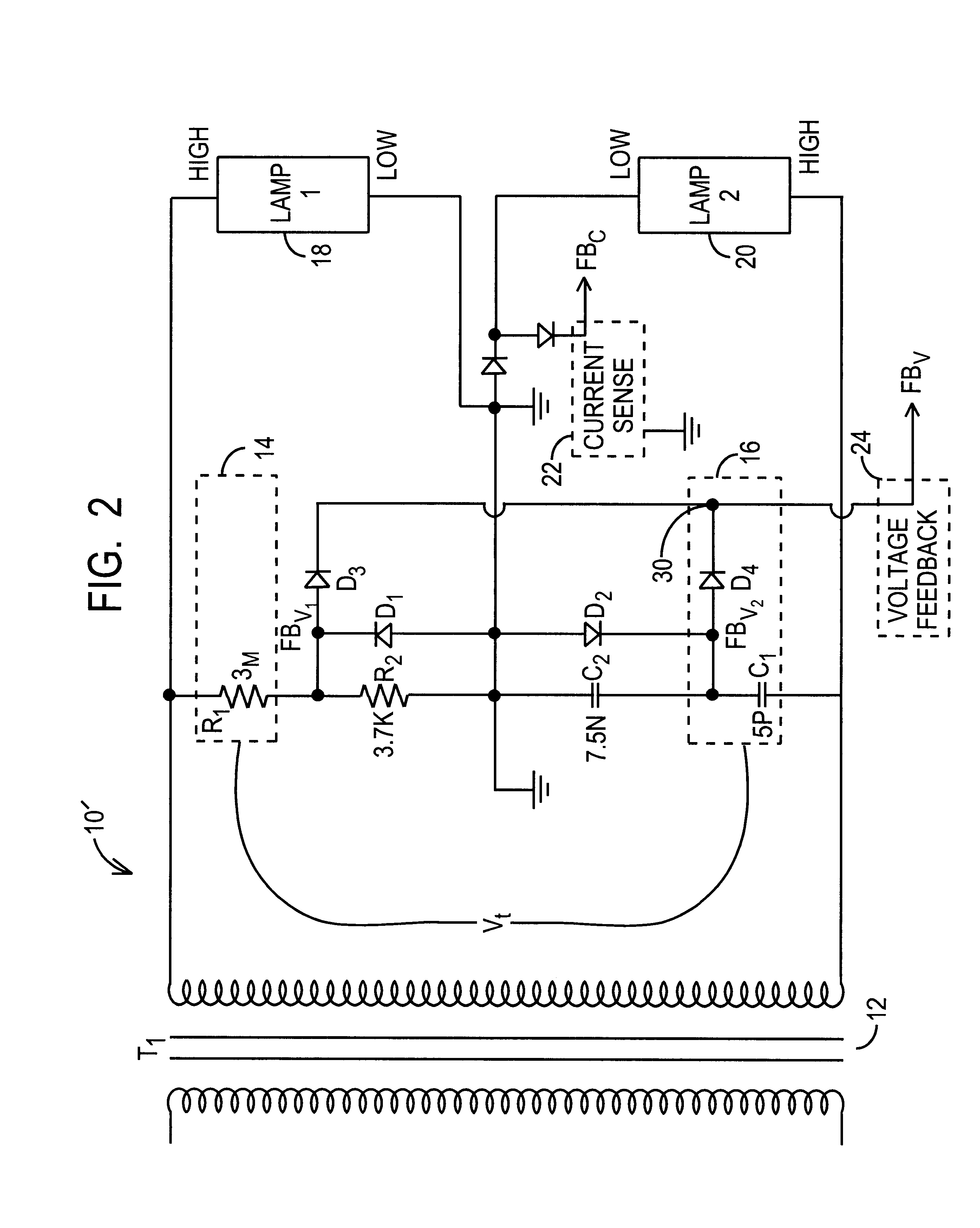
Lamp driving topology
InactiveUS6559606B1Low voltage requirementLess developmentElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementPhase shiftedEngineering
A lamp driving system that includes a first impedance and a second impedance coupled to the secondary side of a transformer, where the second impedance has a phase shifted value compared to the first impedance. Two lamp loads are connected in series together, and in parallel to the first and second impedances and to the transformer. The phase shift between the impedances ensures that the transformer need not supply double the striking voltage to strike the series-connected lamps. A difference in the resistance between the first and second impedances ensures that the lamps ignite in a specified sequence.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
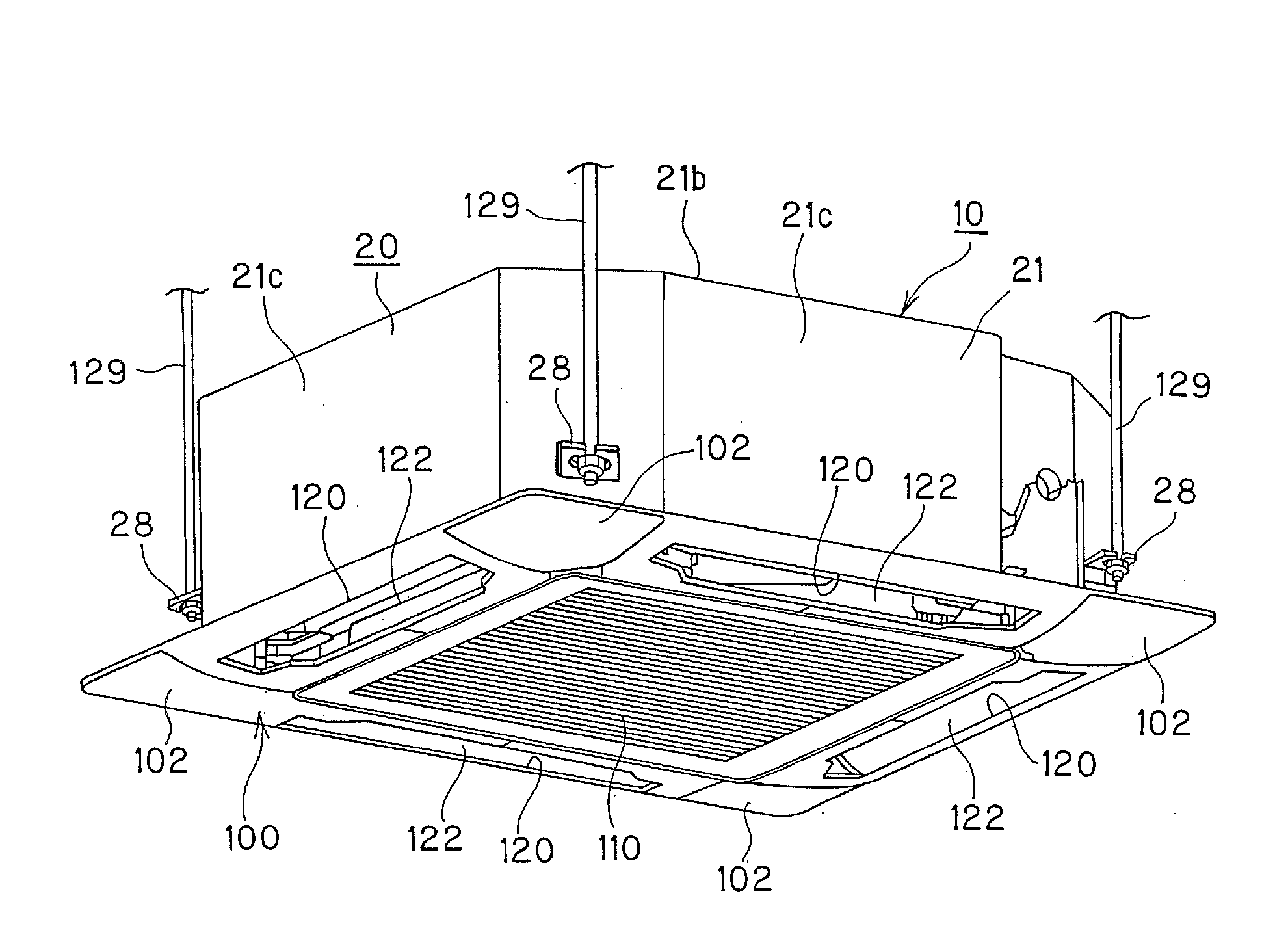
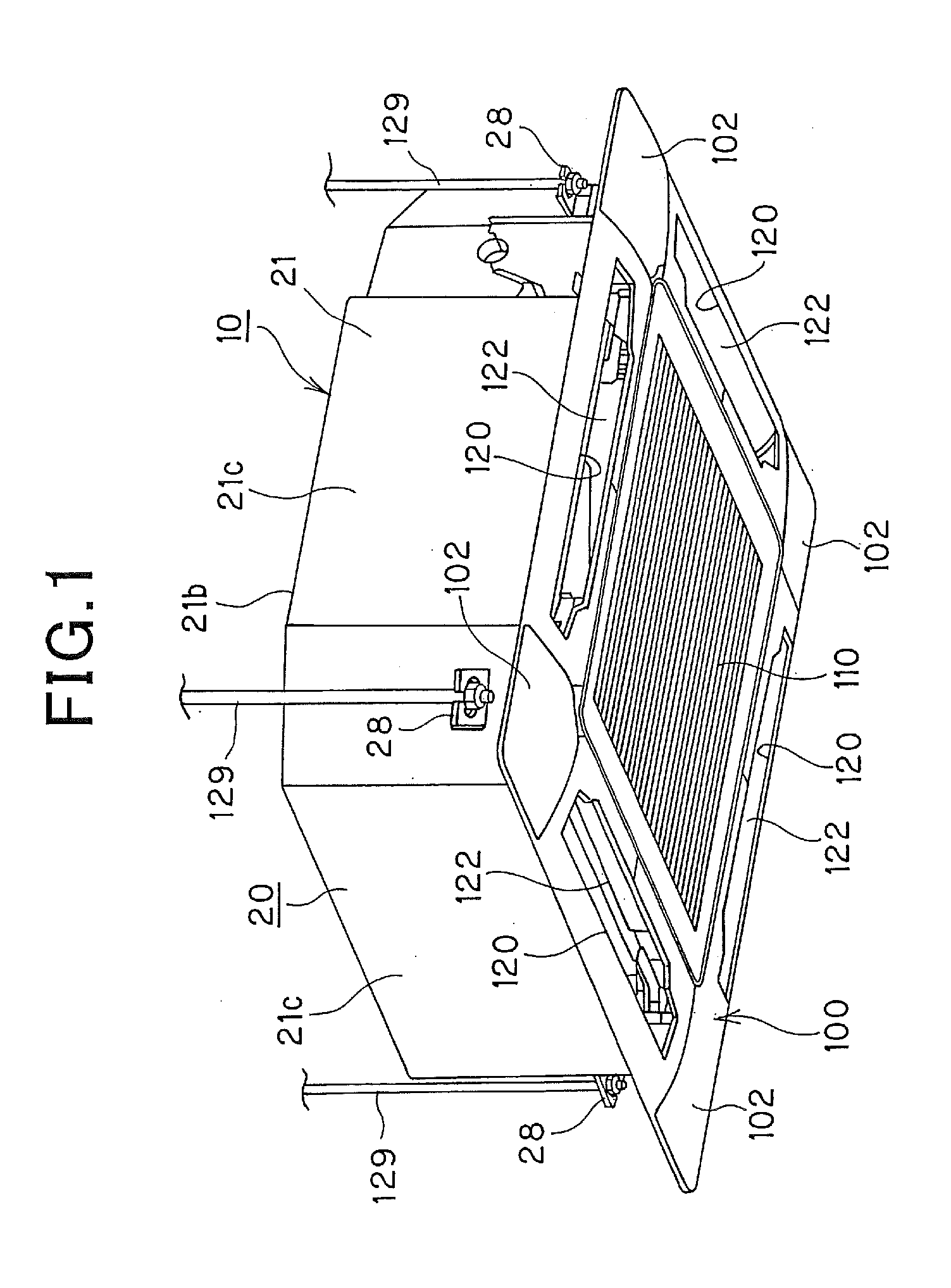
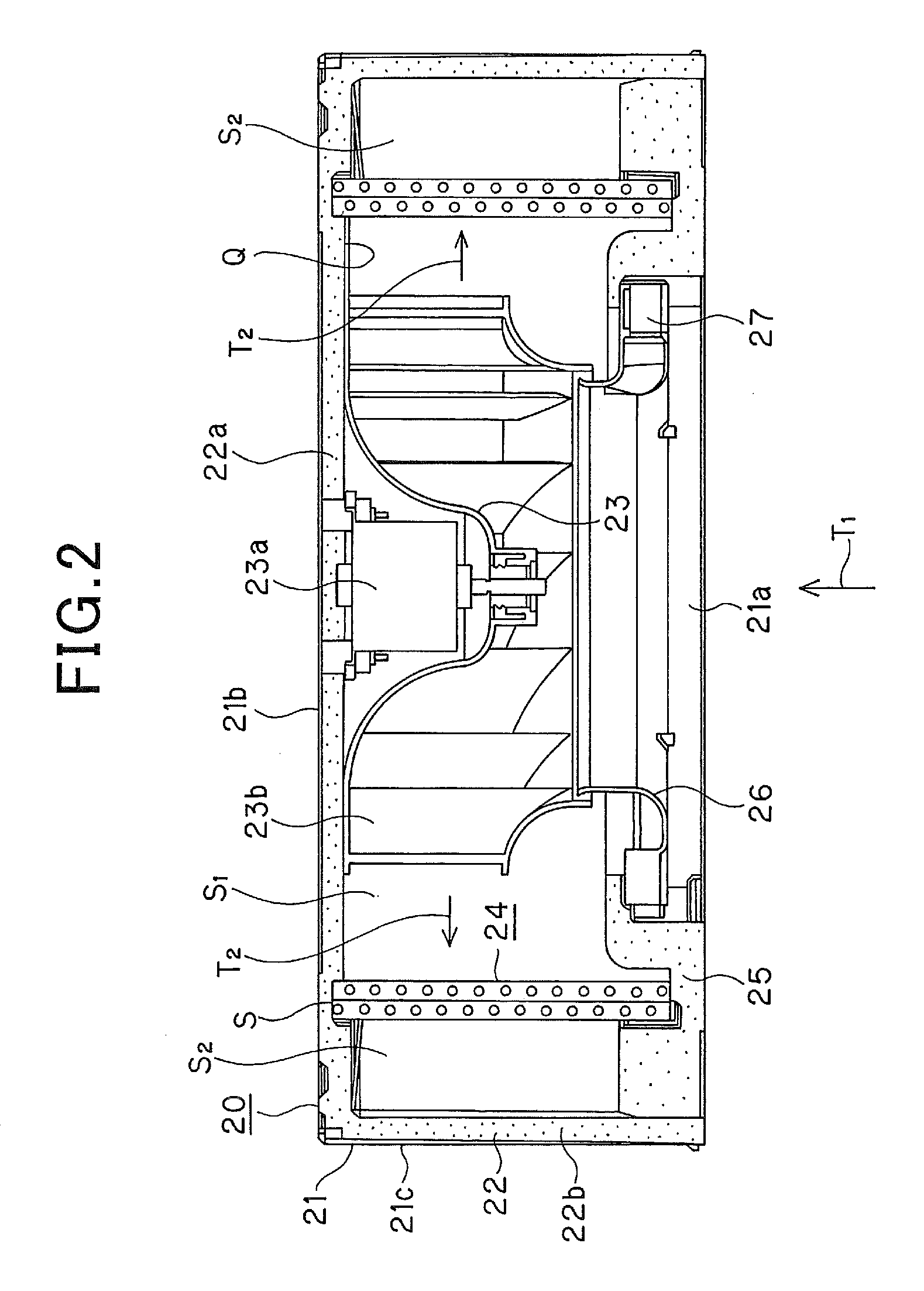
In-ceiling mount type air conditioner and indoor unit thereof
ActiveUS20090025414A1Add dimensionReduce displacementLighting and heating apparatusHeating and ventilation casings/coversEngineeringAir blower
An indoor unit of an in-ceiling mount type air conditioner including a box-shaped housing having a top plate portion, a side plate portion and an opening portion at the lower portion thereof, a face panel detachably mounted on the opening portion of the housing, an indoor heat exchanger through which the inside of the housing is compartmented into a primary side and a secondary side, and an air blower secured to the top plate portion of the housing that faces the primary side, has a primary side heat insulating material is provided to the top plate portion so as to face the primary side of the housing and a secondary side heat insulating material provided to the side plate portion so as to face the secondary side of the housing, wherein the primary side heat insulating material is provided with an opening portion through which the air blower is fixed to the top plate portion.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Multi-Sided Media Viewer and Technique for Media Association
Owner:NBCUNIVERSAL
Light-emitting diode driving circuit and secondary side controller for controlling the same
InactiveUS7855520B2Low costLayout on a printed circuit board (PCB) may be simplifiedElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitEffect light
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
Non-effective earthing distribution system fault locating method based on neutral point of transient traveling wave
InactiveCN101232176ASolve hard-to-reach puzzlesFix speed inconsistenciesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationTransient stateDistribution transformer
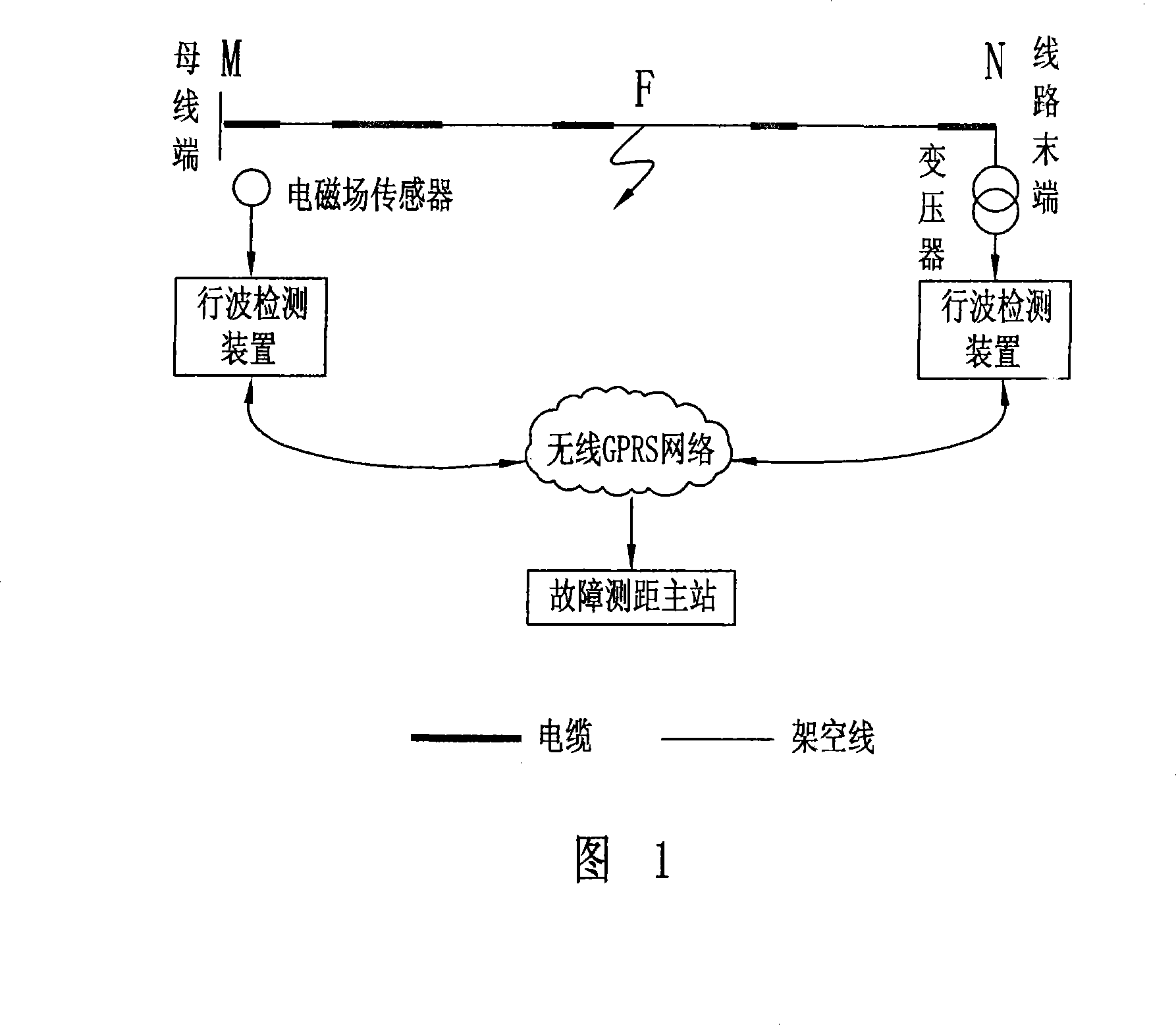
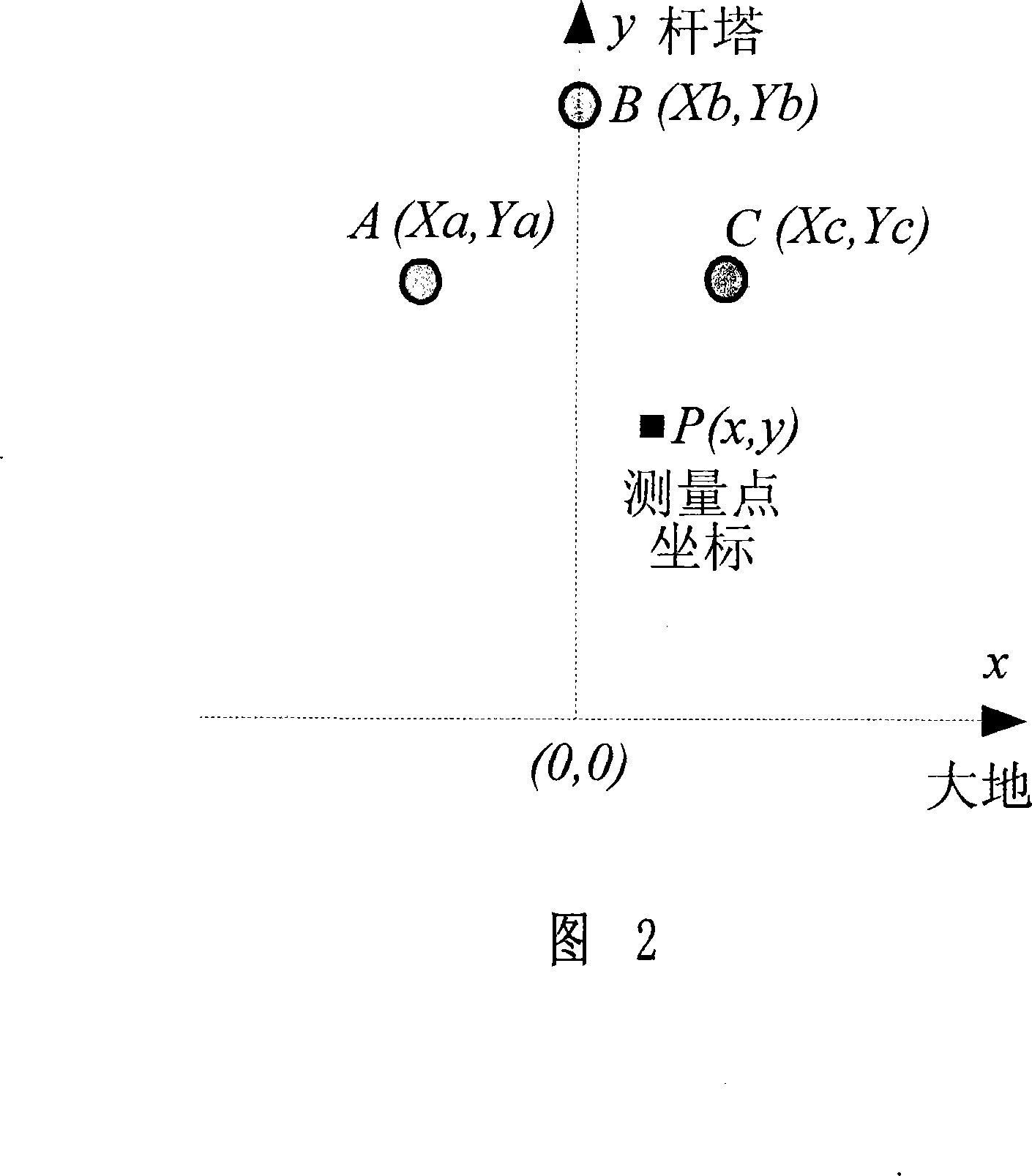
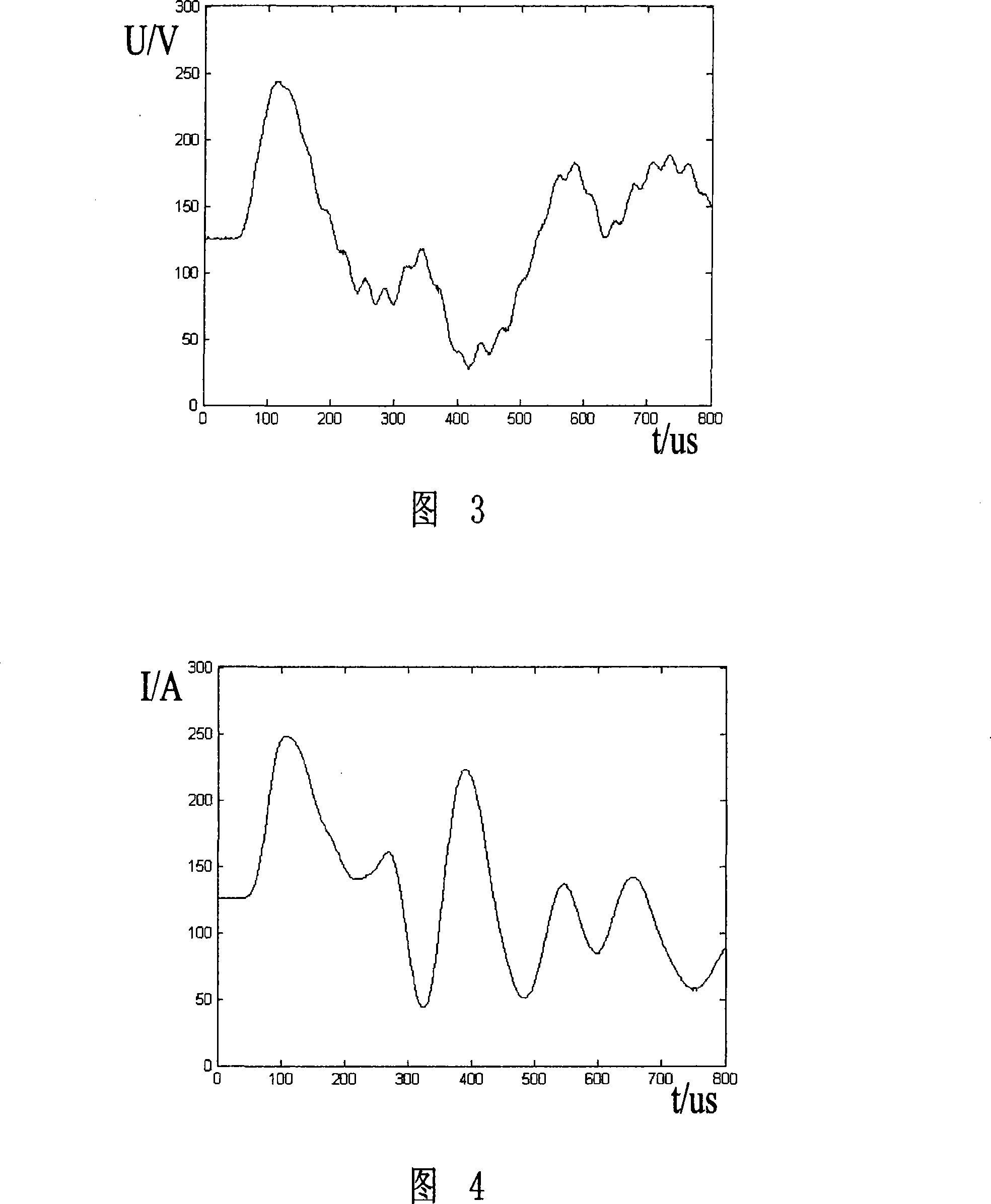
The invention discloses a method for locating fault of power distribution system with ineffectively grounded neutral point based on transient traveling wave, which can acquire required traveling wave signals and relatively higher detection reliability by arranging equipment only on both sides of circuit. According to the actual site condition, a non-contact electromagnetic field sensor is arranged in a transformer substation to acquire transient voltage and current traveling wave, a power distribution transformer arranged on the tail end of the circuit transmits voltage-variable traveling wave to solve the problem in acquisition of tail-end voltage traveling wave signals, and the type of the fault of the circuit can be rapidly recognized according to the amplitude and the polarity characteristics of a fault traveling wave recorded by the secondary side of the transformer. The invention provides a new fault search algorithm based on the midpoint of time to solve the problem of noncontinuous wave speed of aerial wire and cable. Accordingly, the proposal can achieve the assembly and the operation of the equipment without adding extra primary equipment of the system and powering off the circuit, thus saving the cost and reducing the complex degree of the project. Practical operation shows that the method can locate a fault within a range of plus or minus 100 m.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIVERSITY
Primary-side controlled switching regulator
A switching regulator includes a switching device to switch a transformer from a primary-side to secondary side. A control circuit generates a switching signal for regulating output of the switching regulator. The control circuit includes a first circuit to generate a first signal and a timing signal by measuring a reflected signal of the transformer. A second circuit produces a second signal by integrating a current signal with the timing signal. The current signal represents a primary-side switching current of the transformer. A first feedback circuit produces a first feedback signal in response to the first signal and the reference signal, in which the reference signal is varied in response to the change of the second signal. Furthermore, a second feedback circuit generates a second feedback signal in response to the second signal. A switching control circuit generates the switching signal in response to the feedback signals.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com