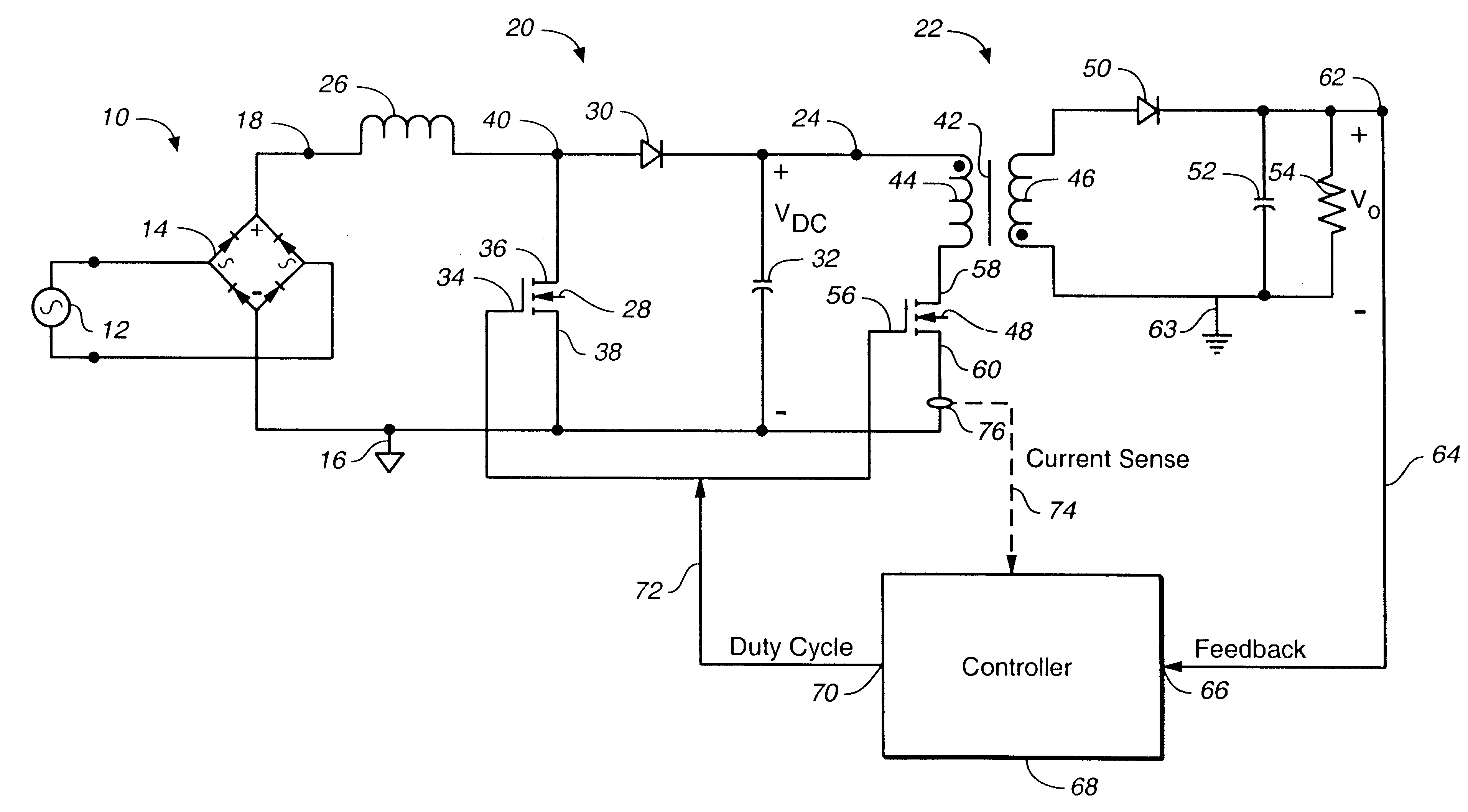
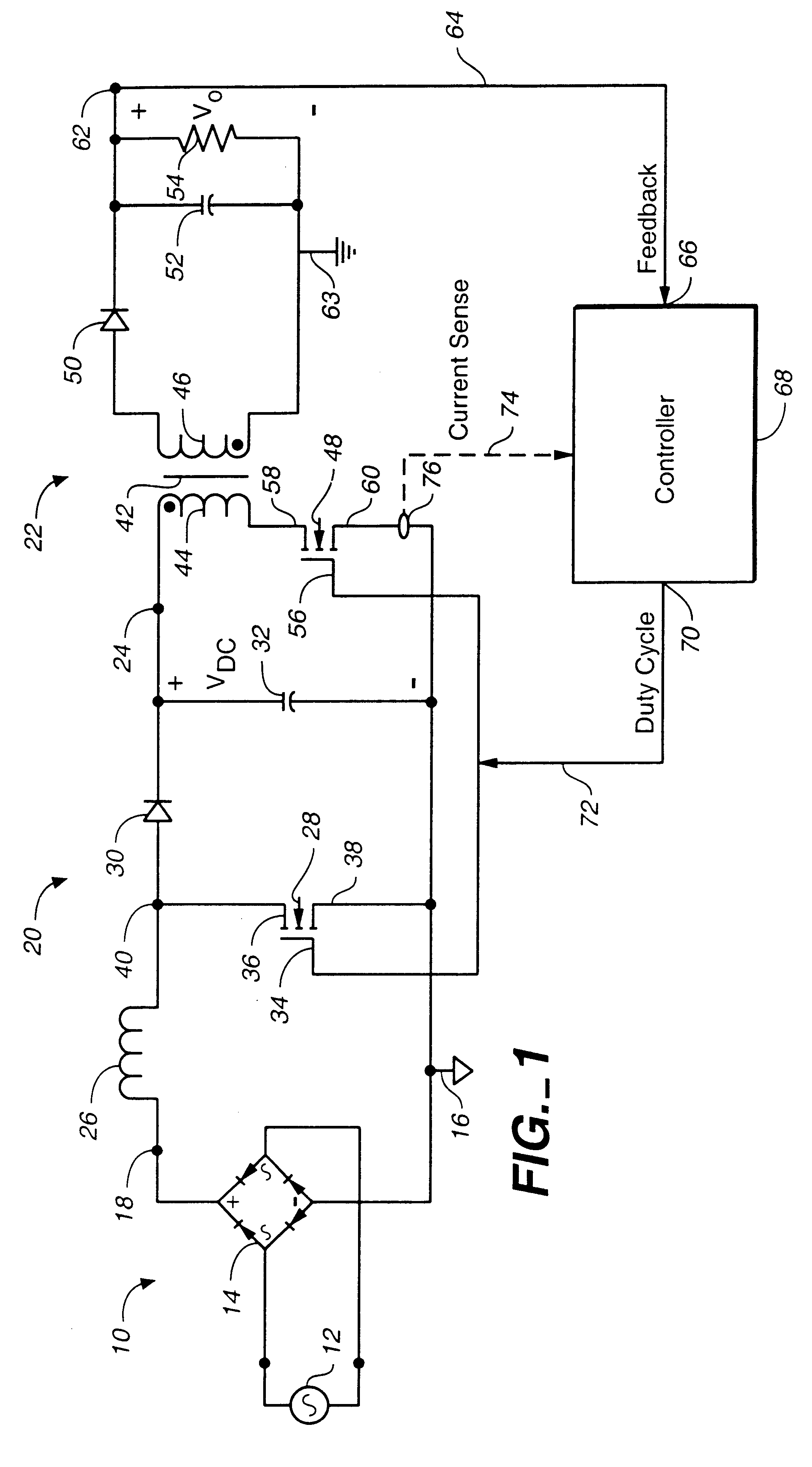
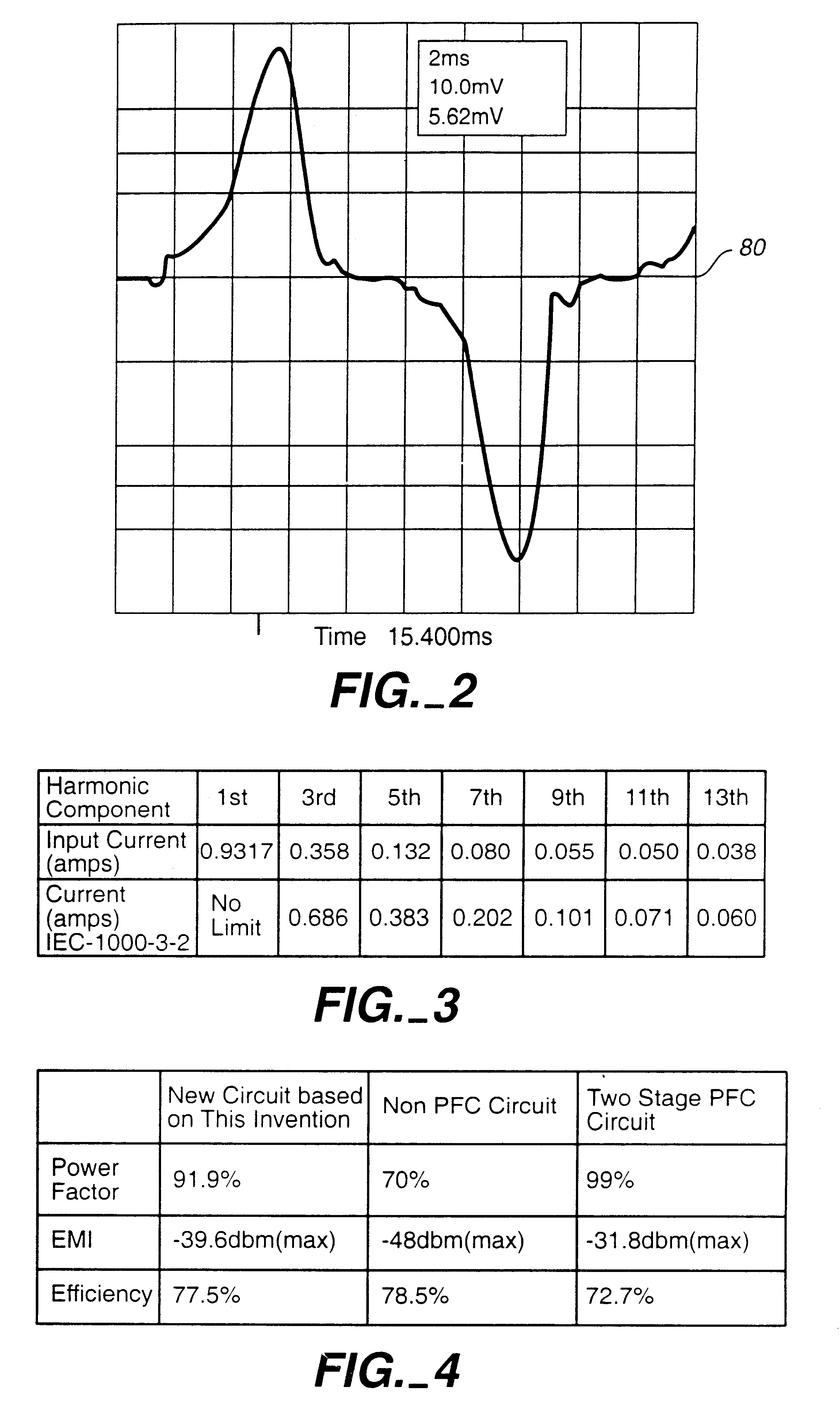
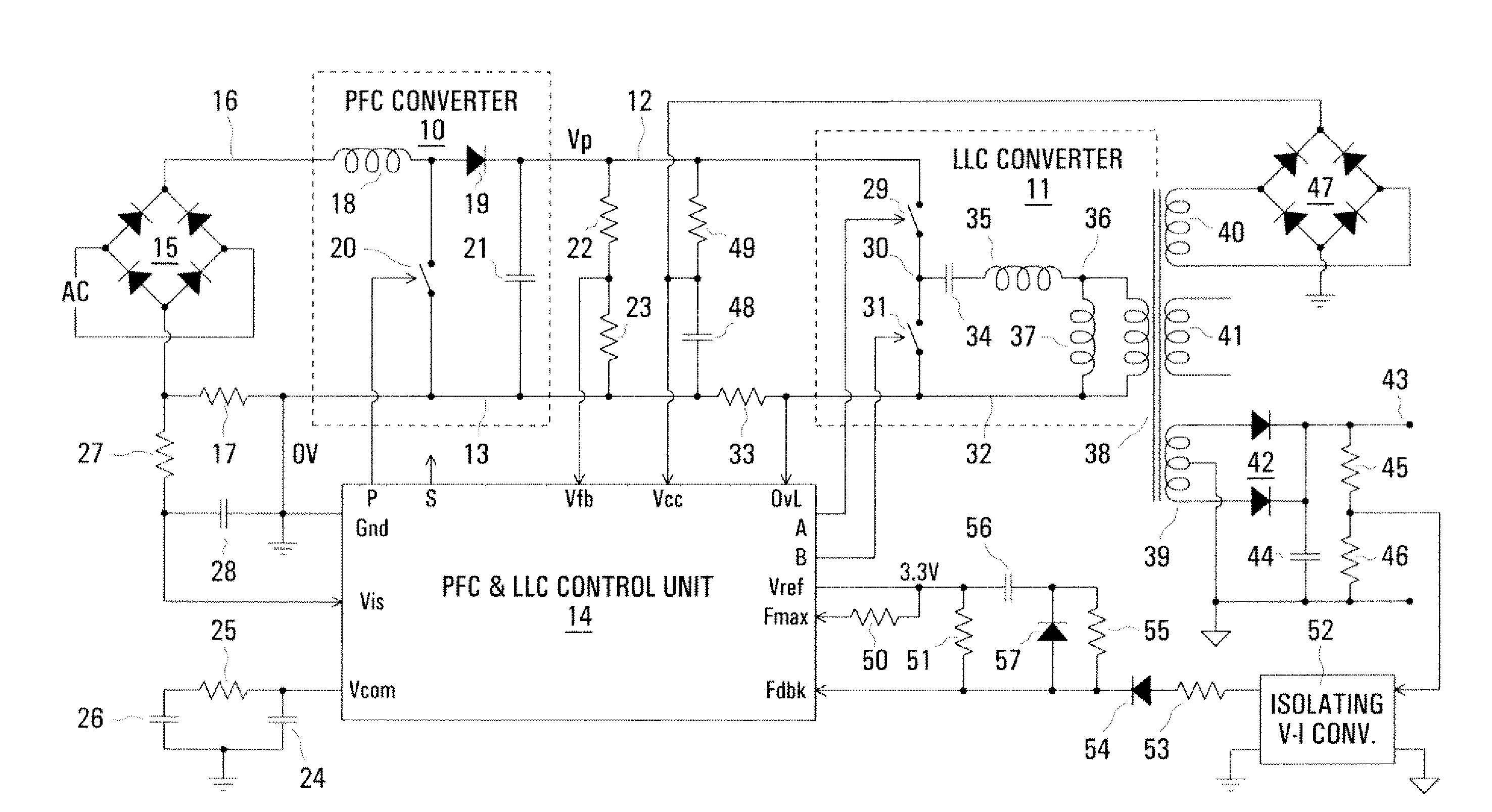
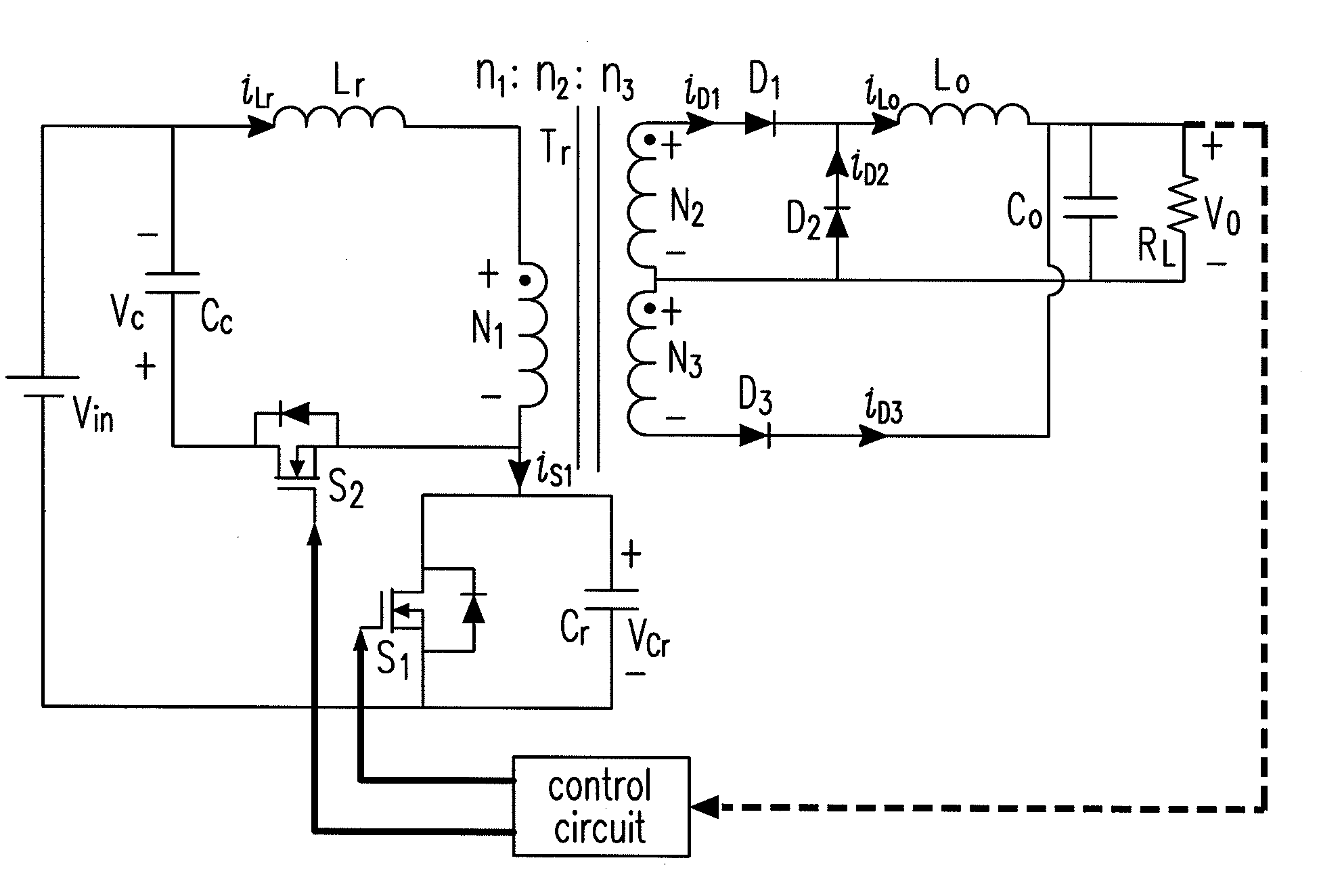
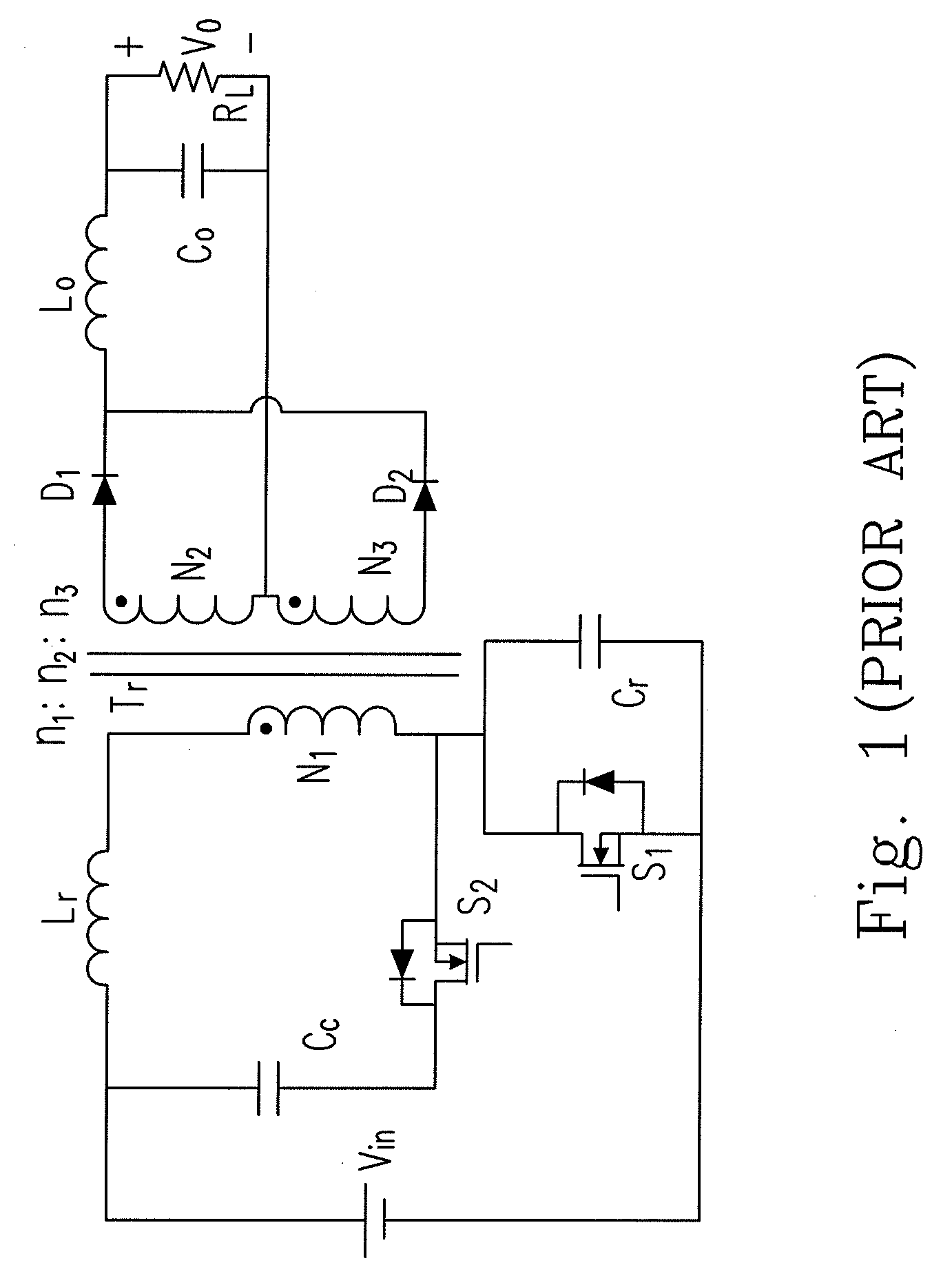
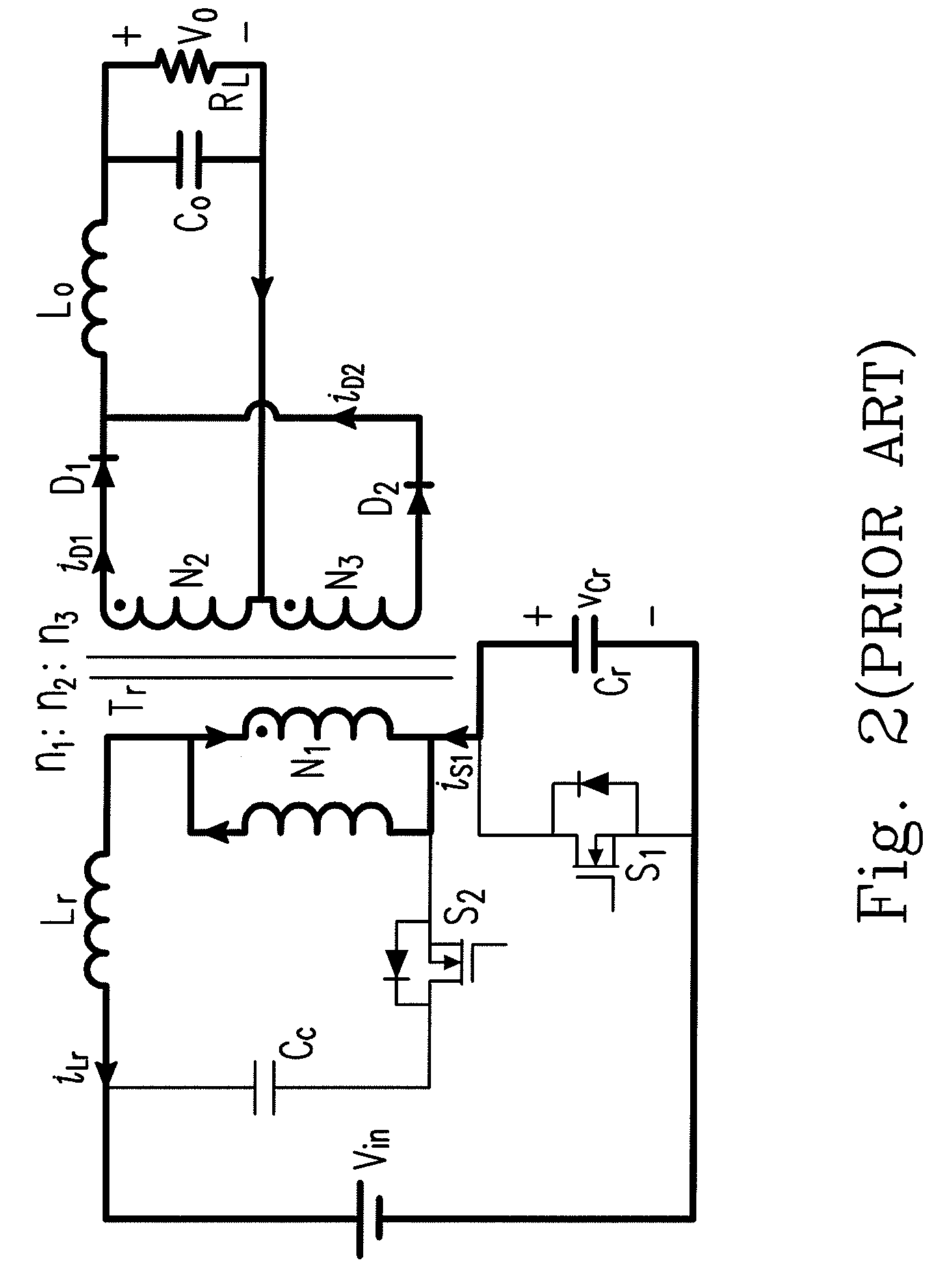
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2975 results about "Transverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In radio engineering, a transverter is a radio frequency device that consists of an upconverter and a downconverter in one unit. Transverters are used in conjunction with transceivers to change the range of frequencies over which the transceiver can communicate.
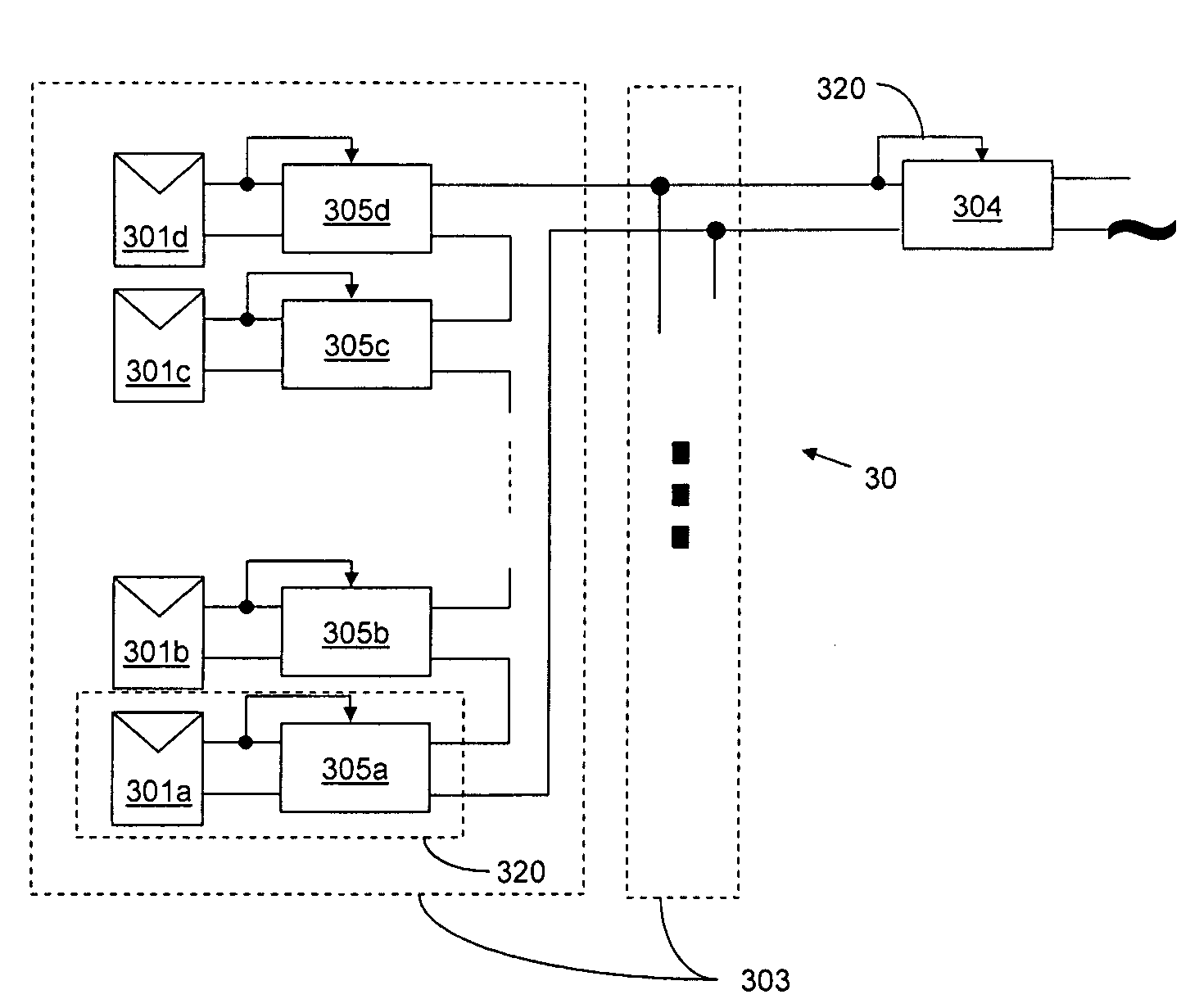
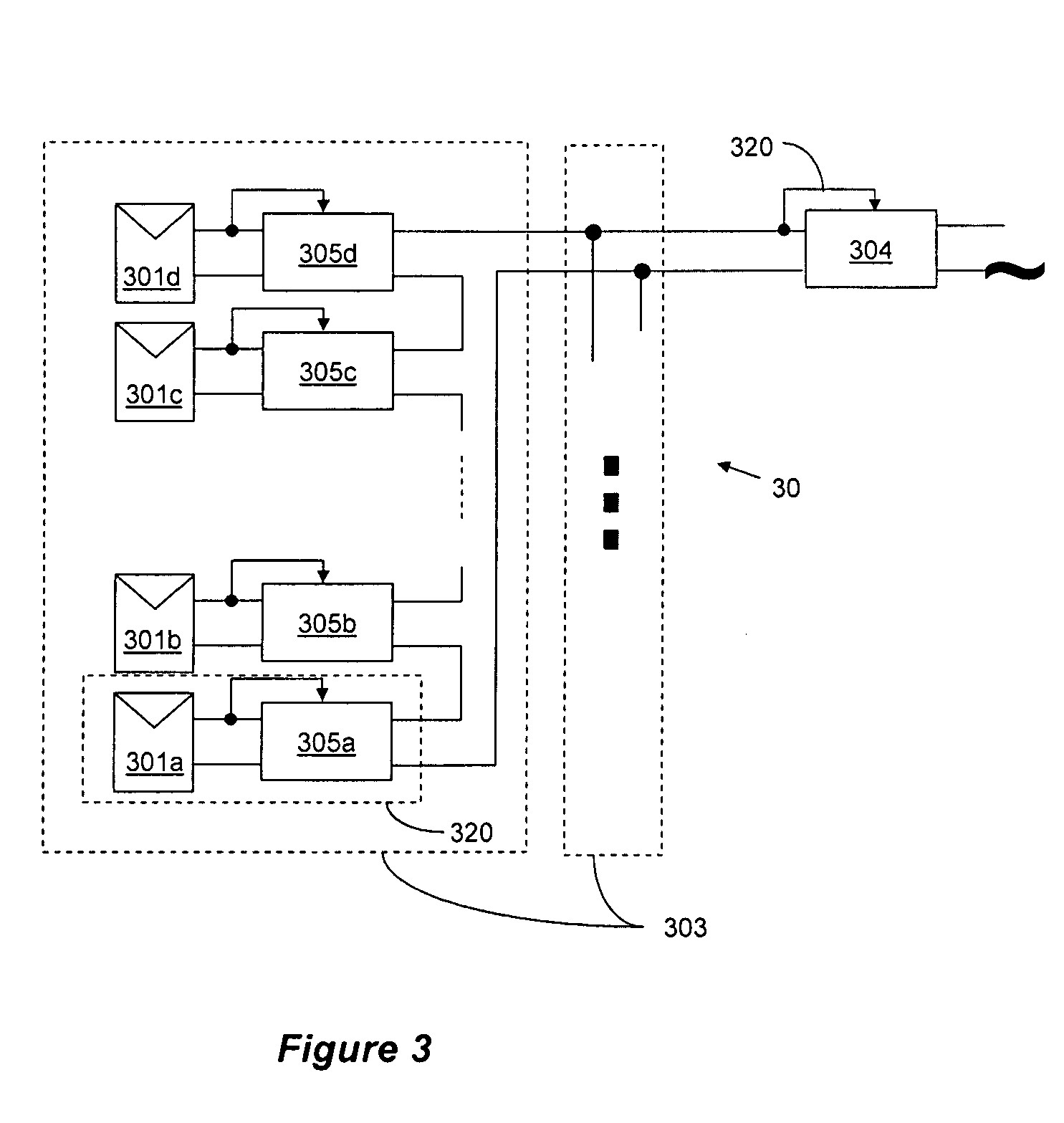
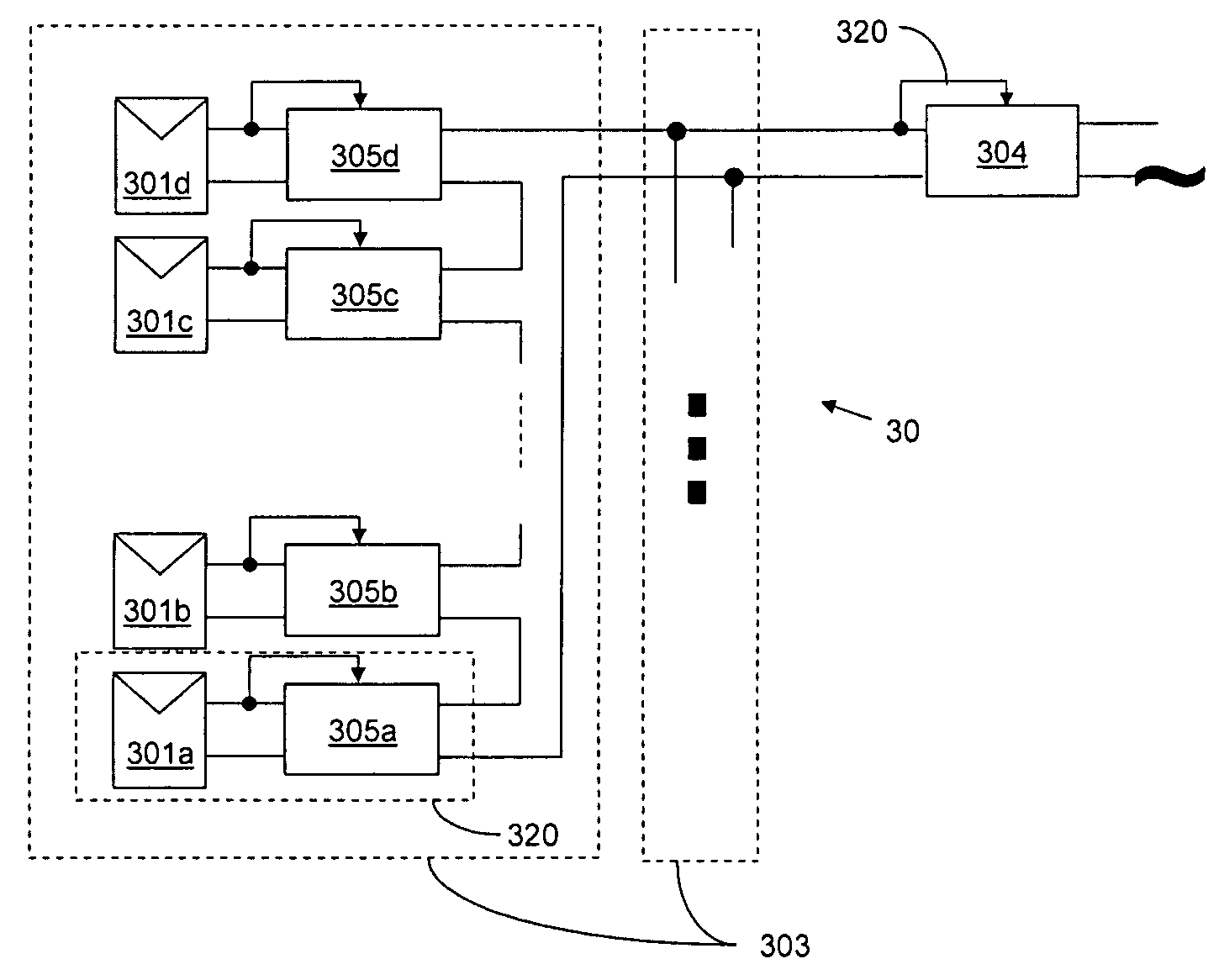
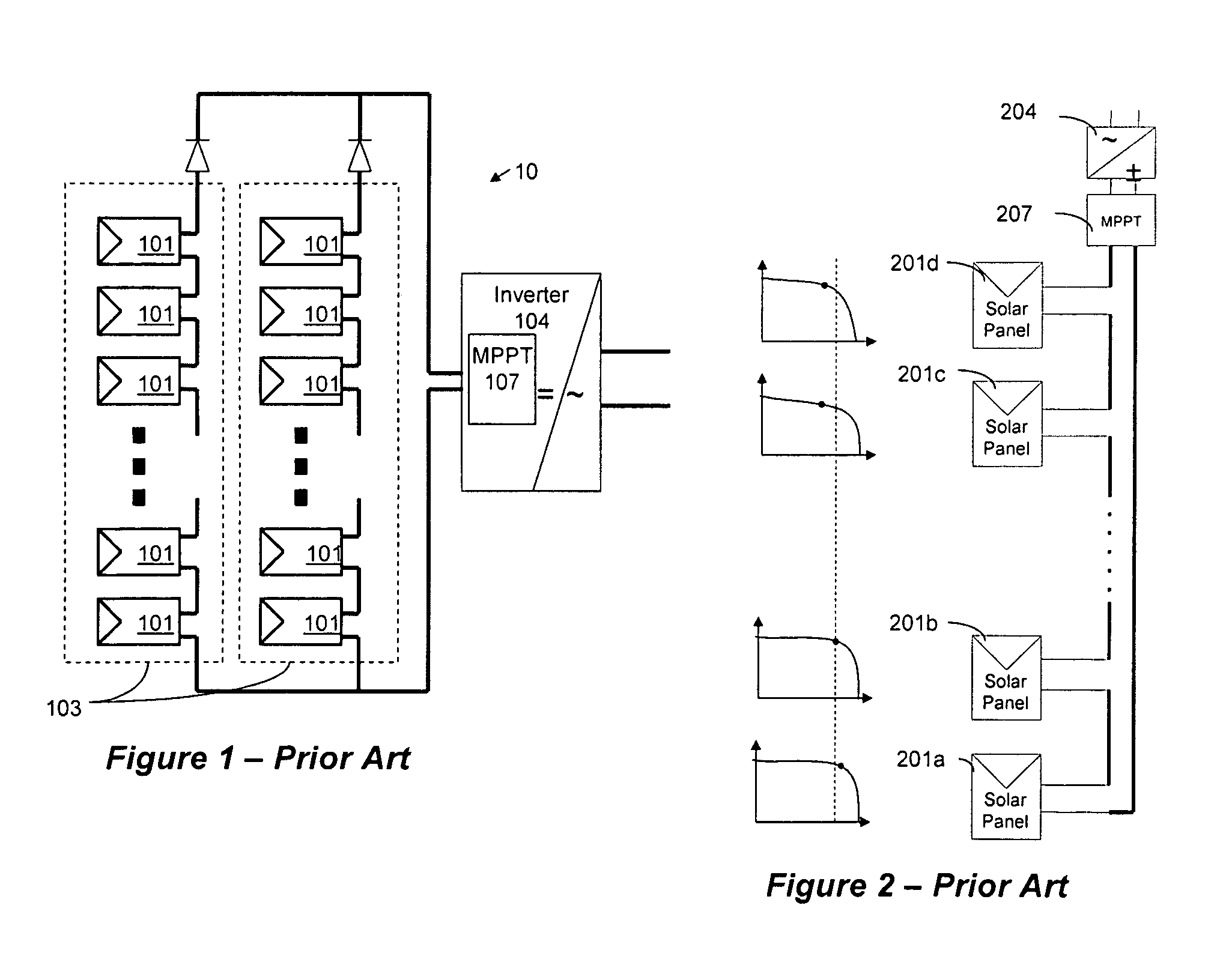
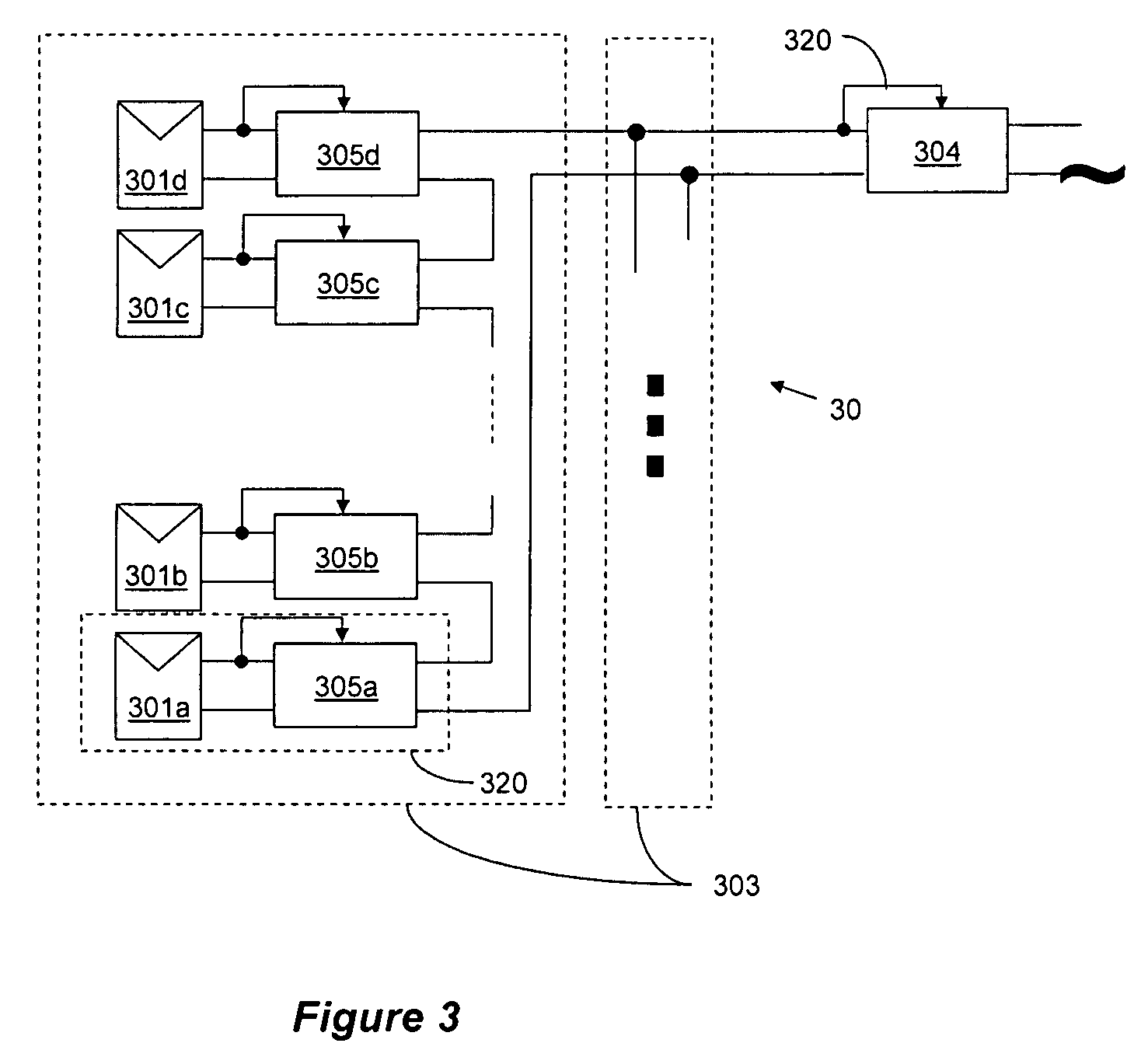
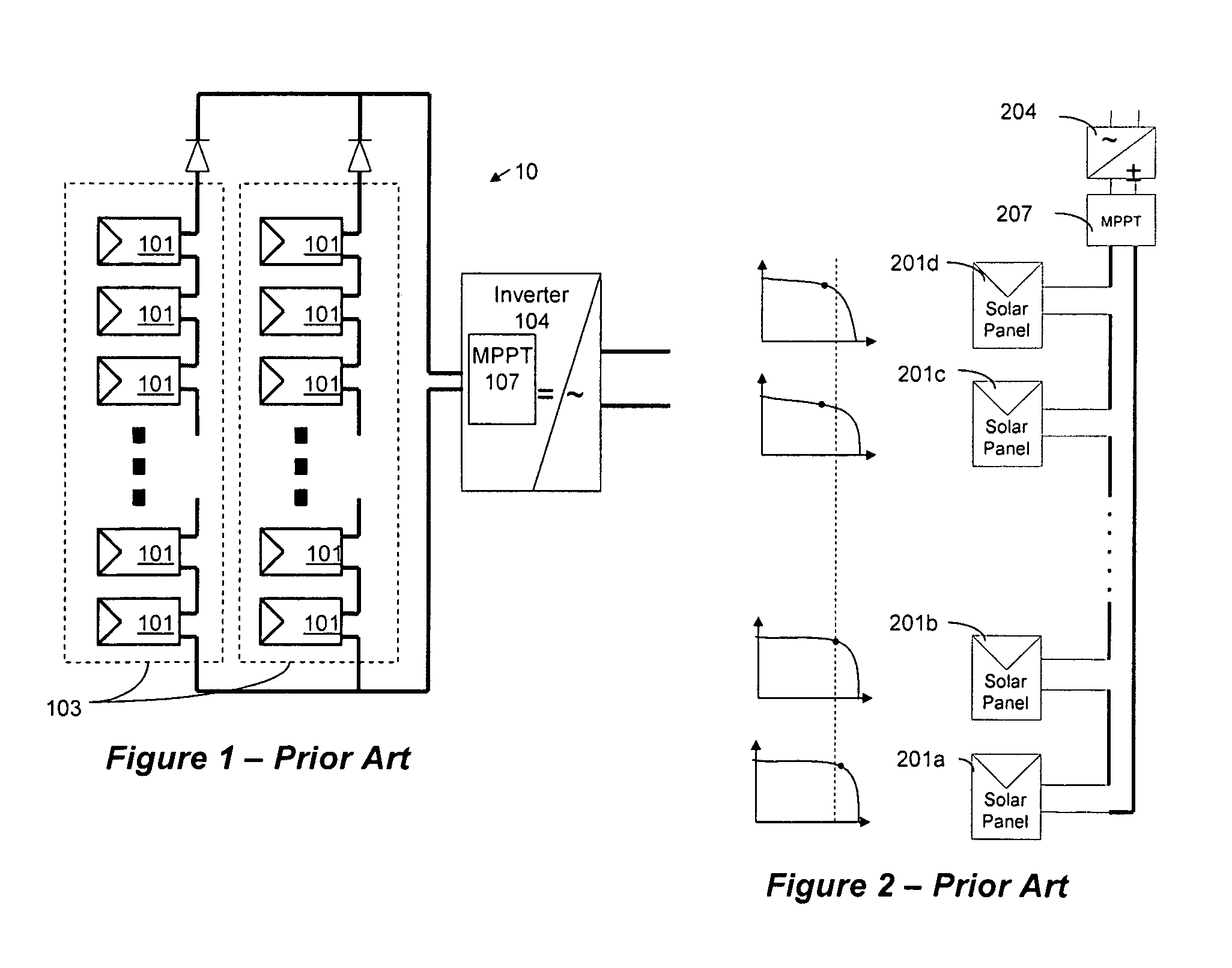
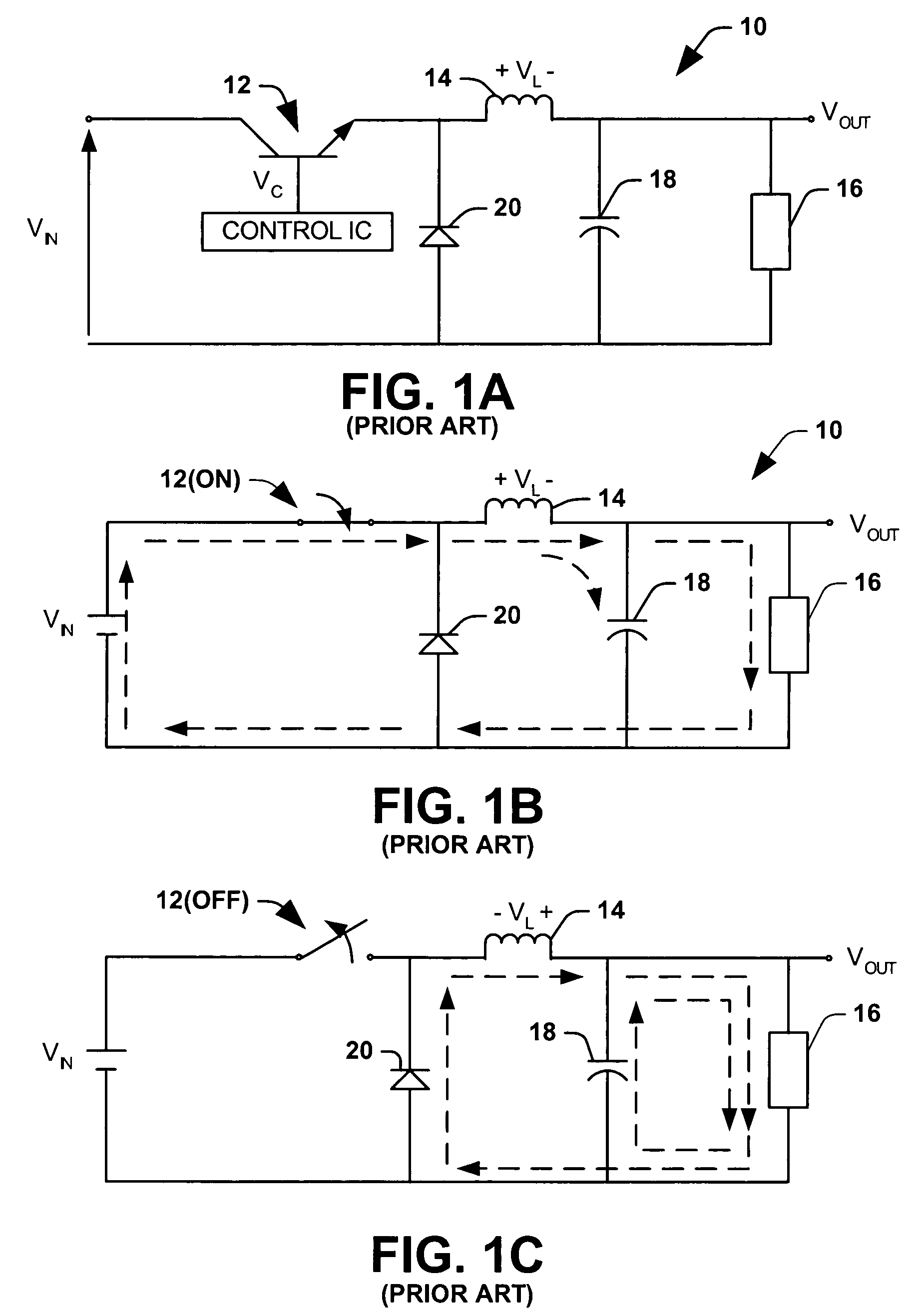
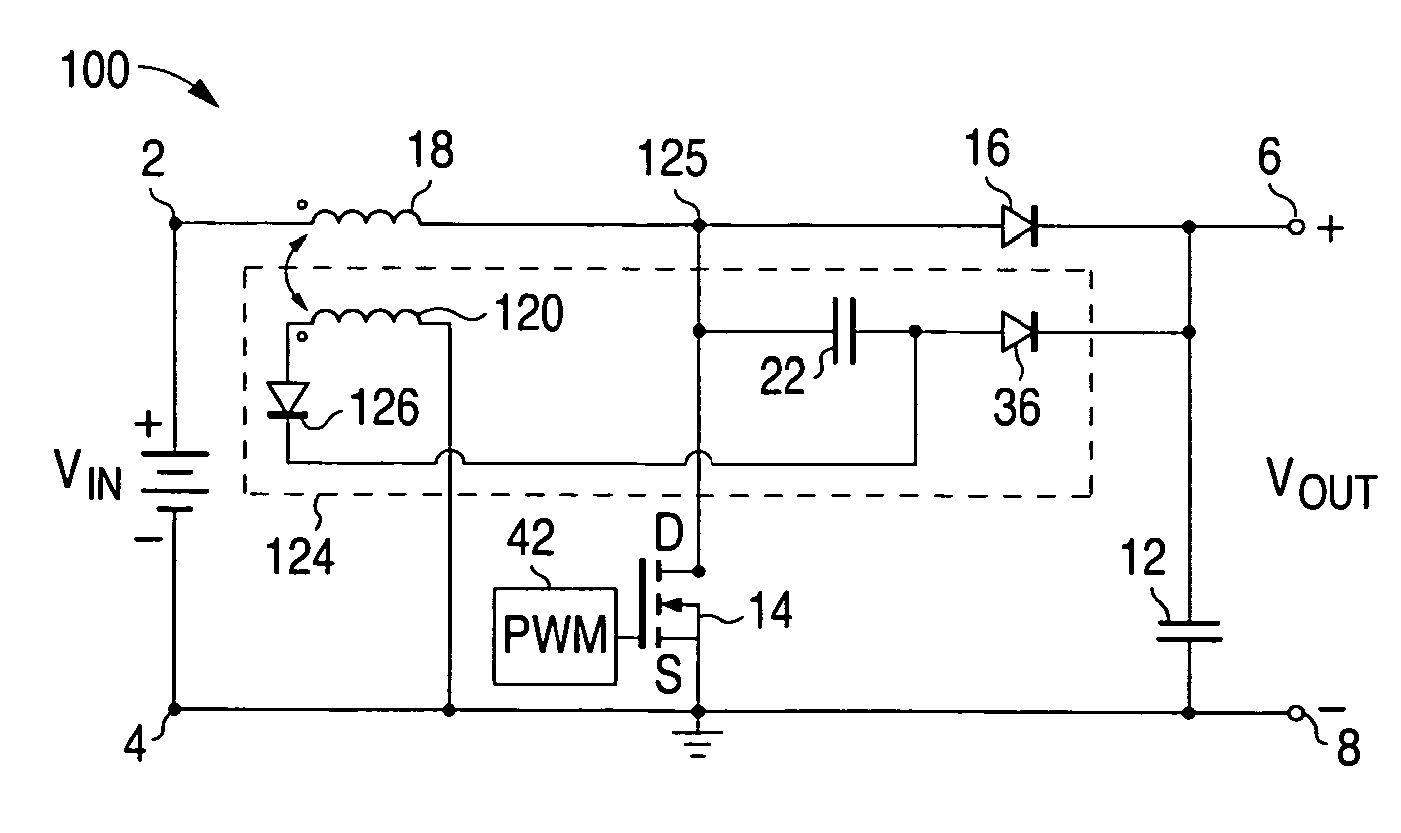
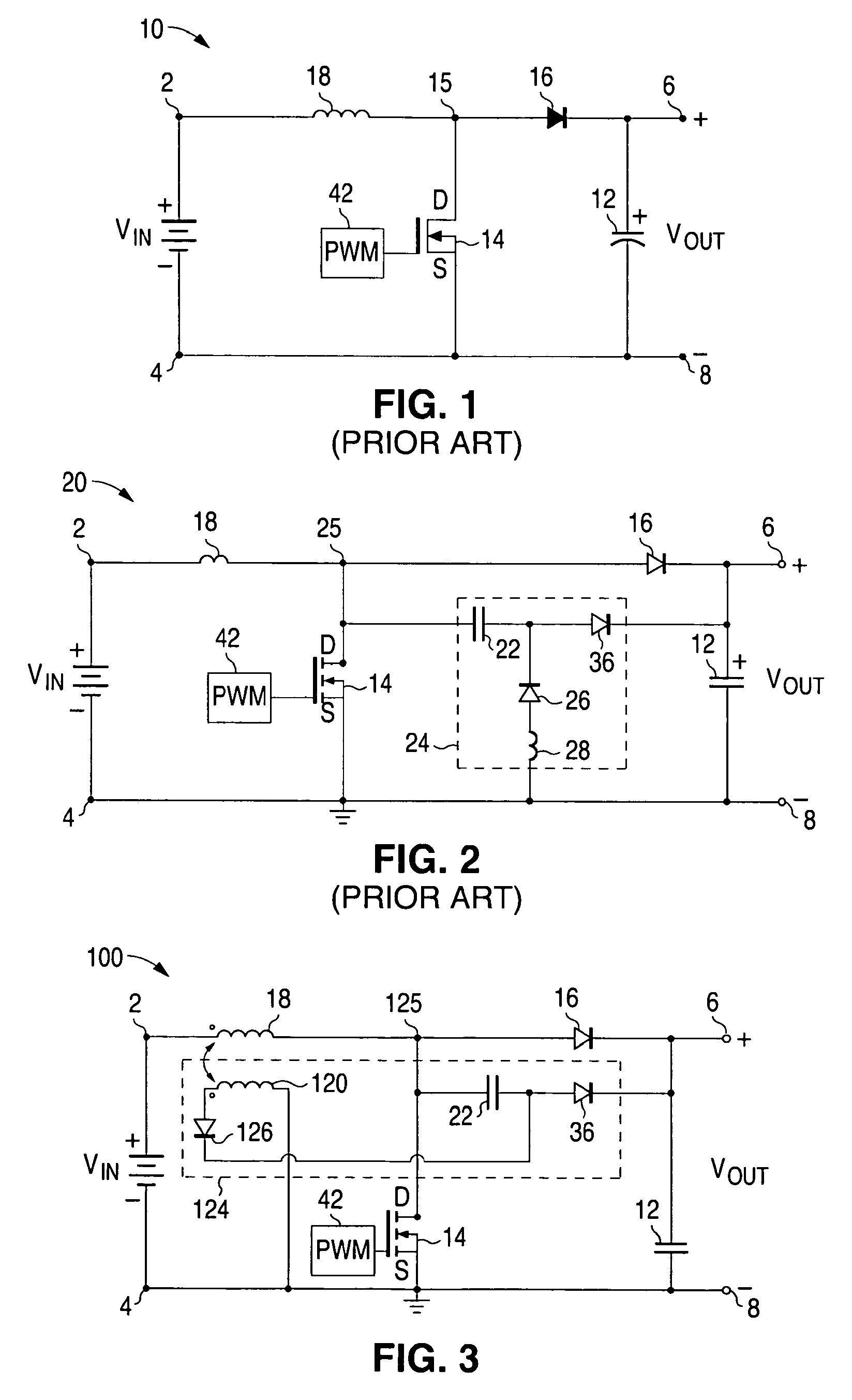
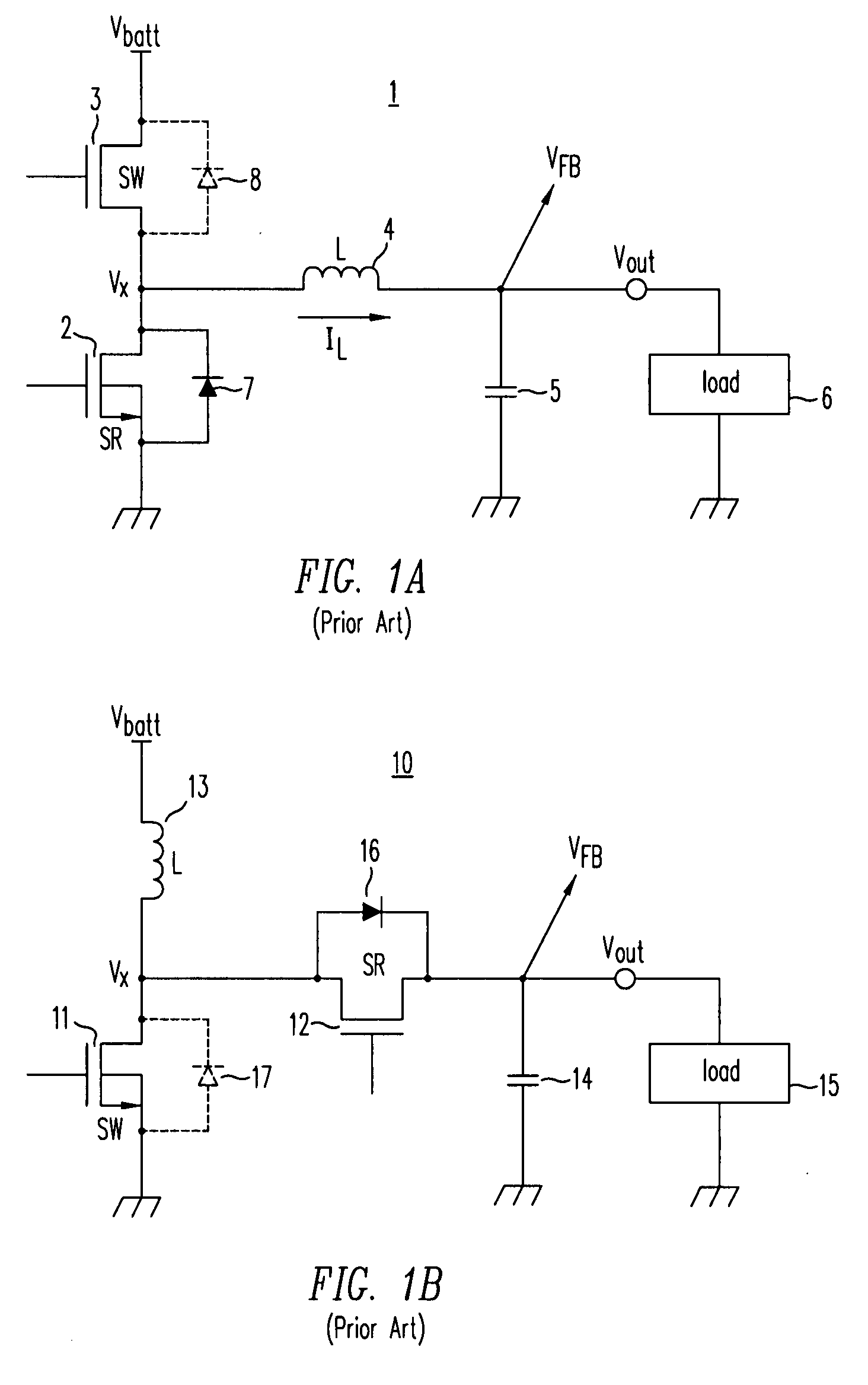
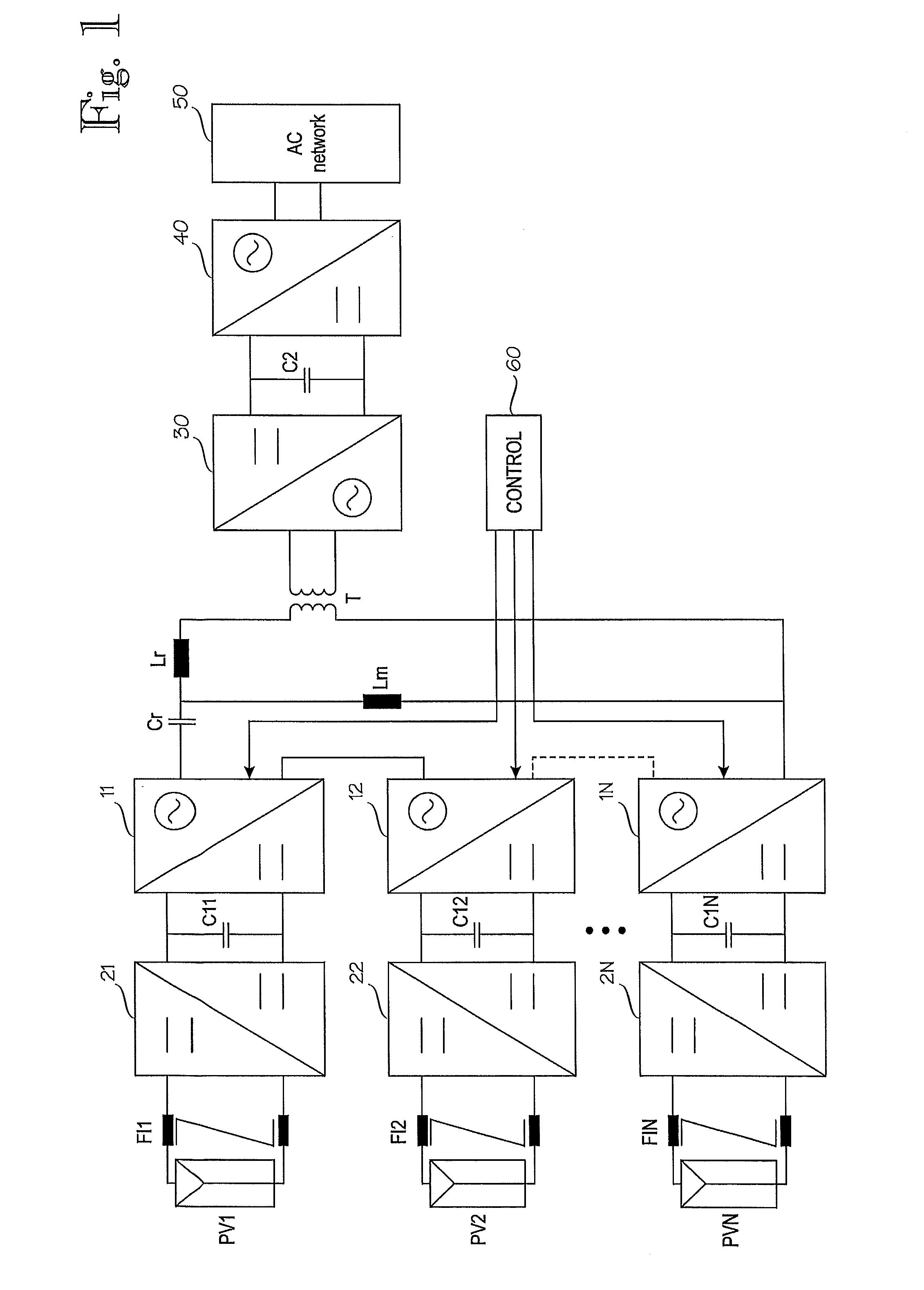
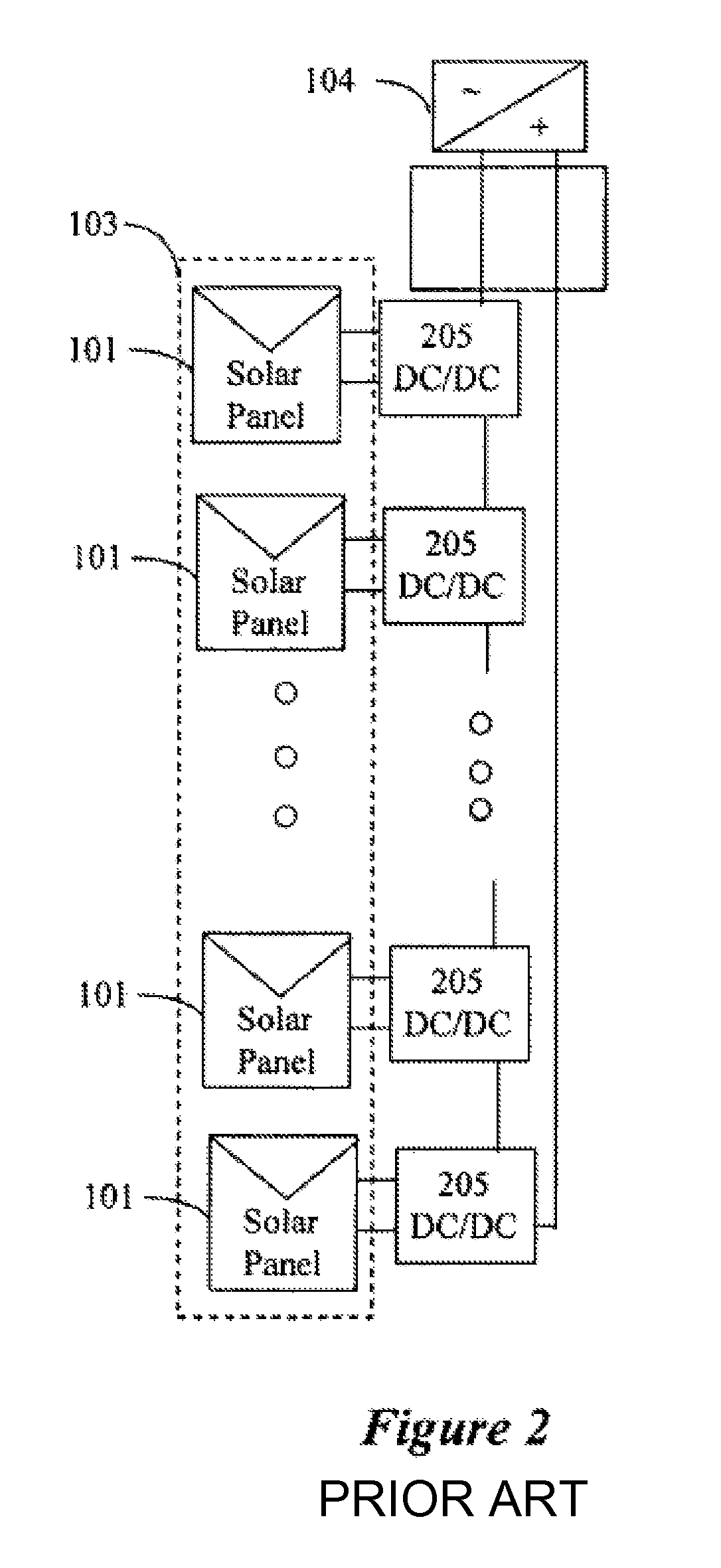
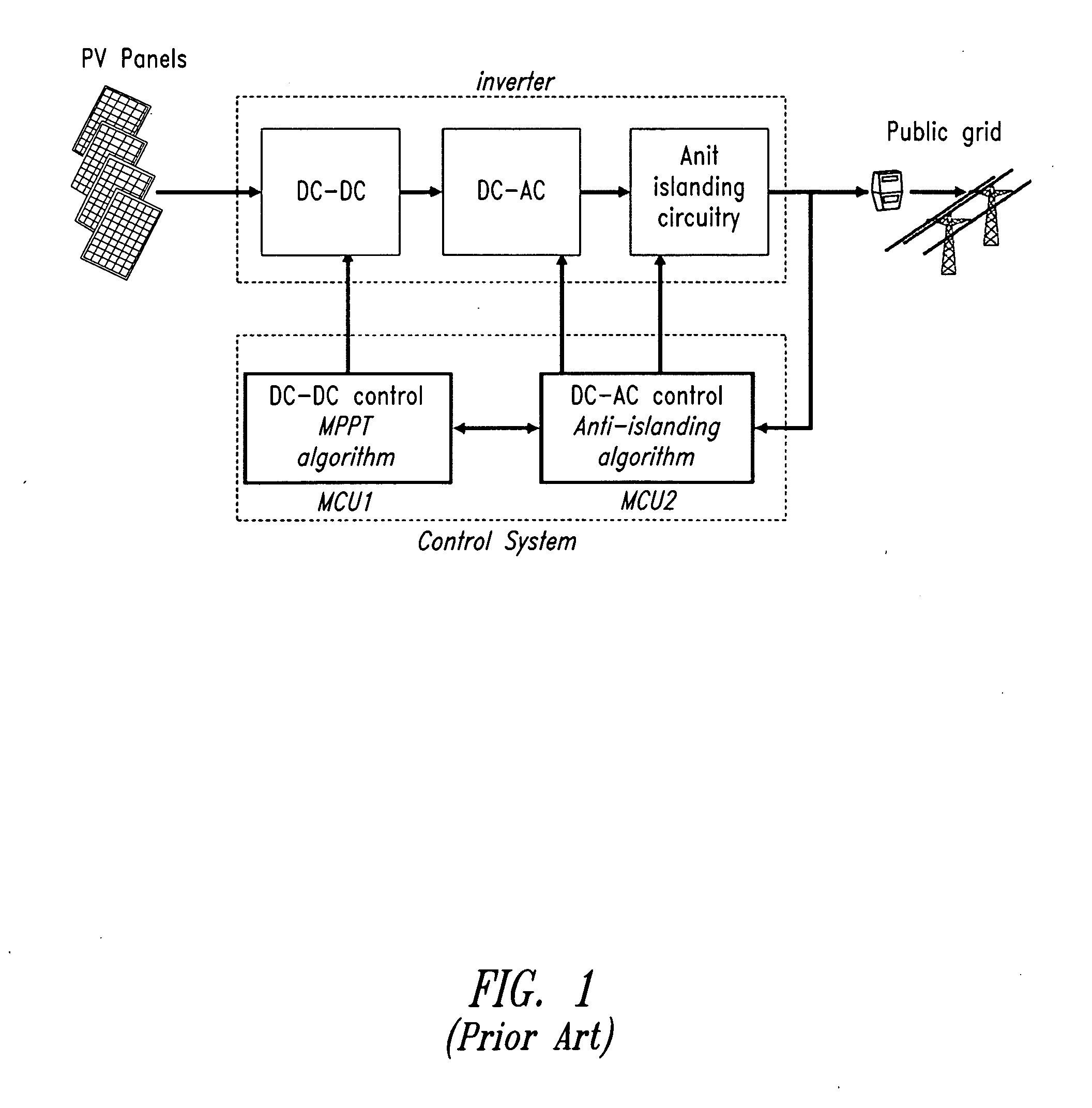
Distributed power harvesting systems using DC power sources
ActiveUS20080143188A1Improve reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransverterVoltage variation
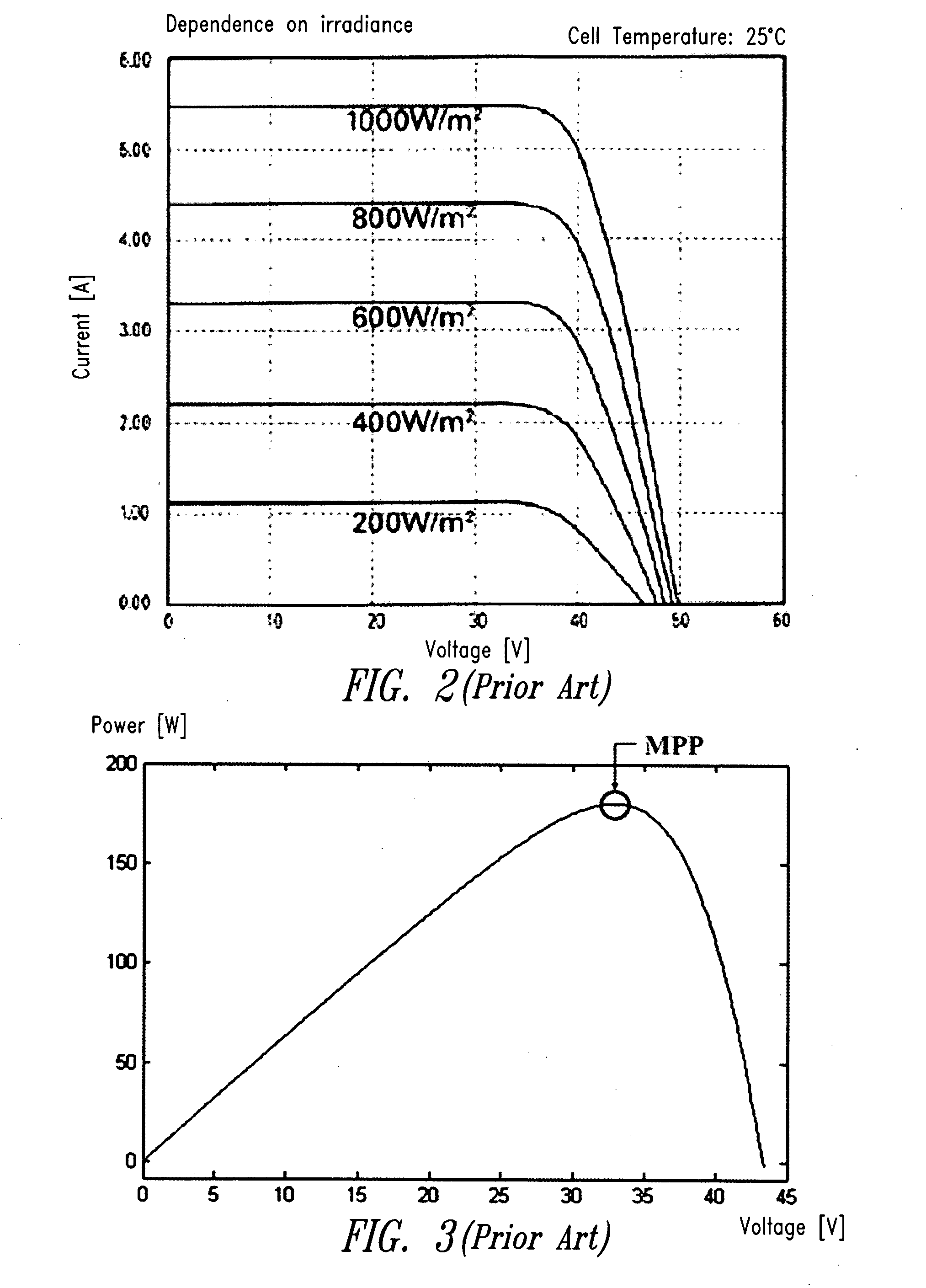
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
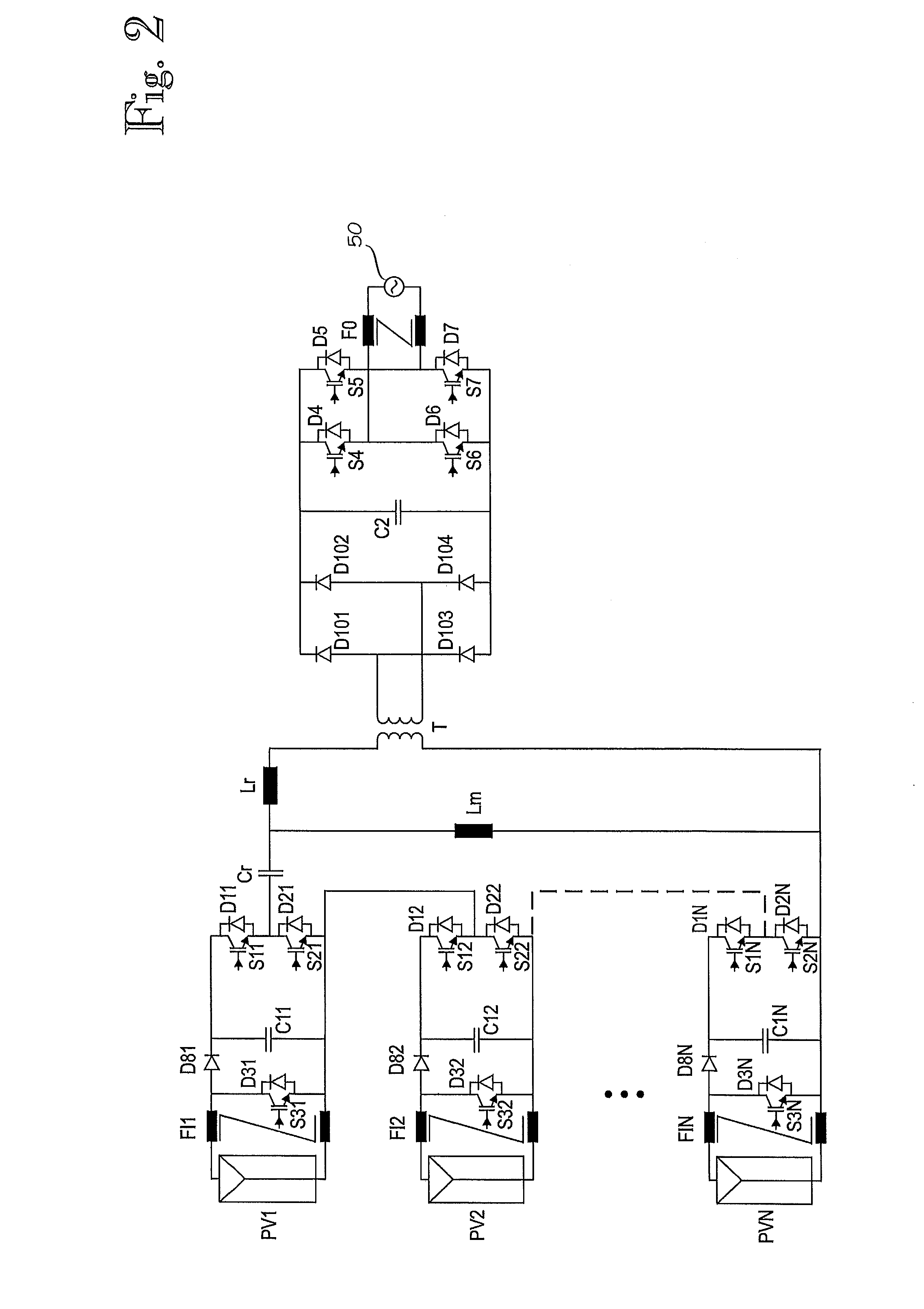
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS20080150366A1Improve reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS8013472B2Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
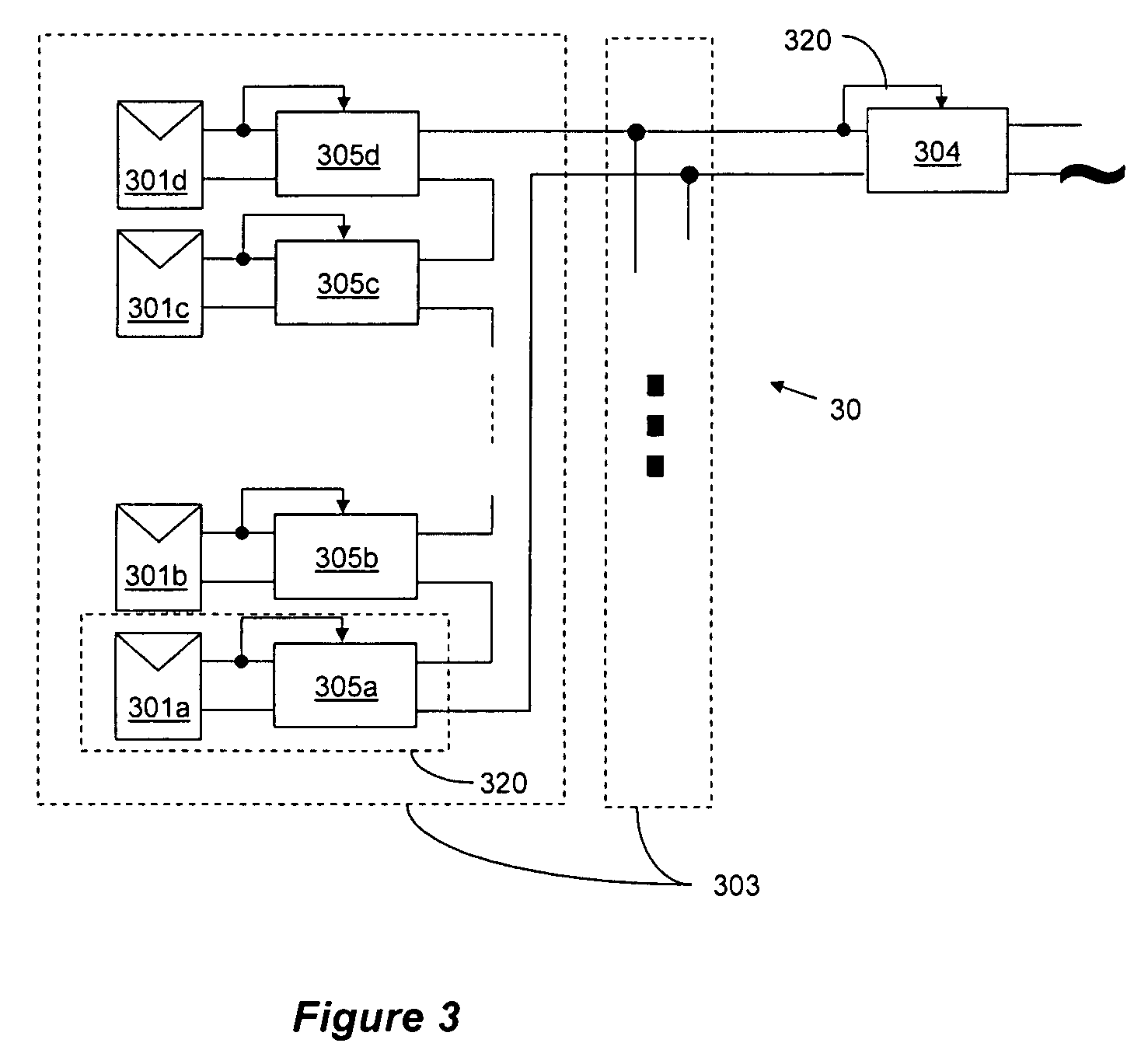
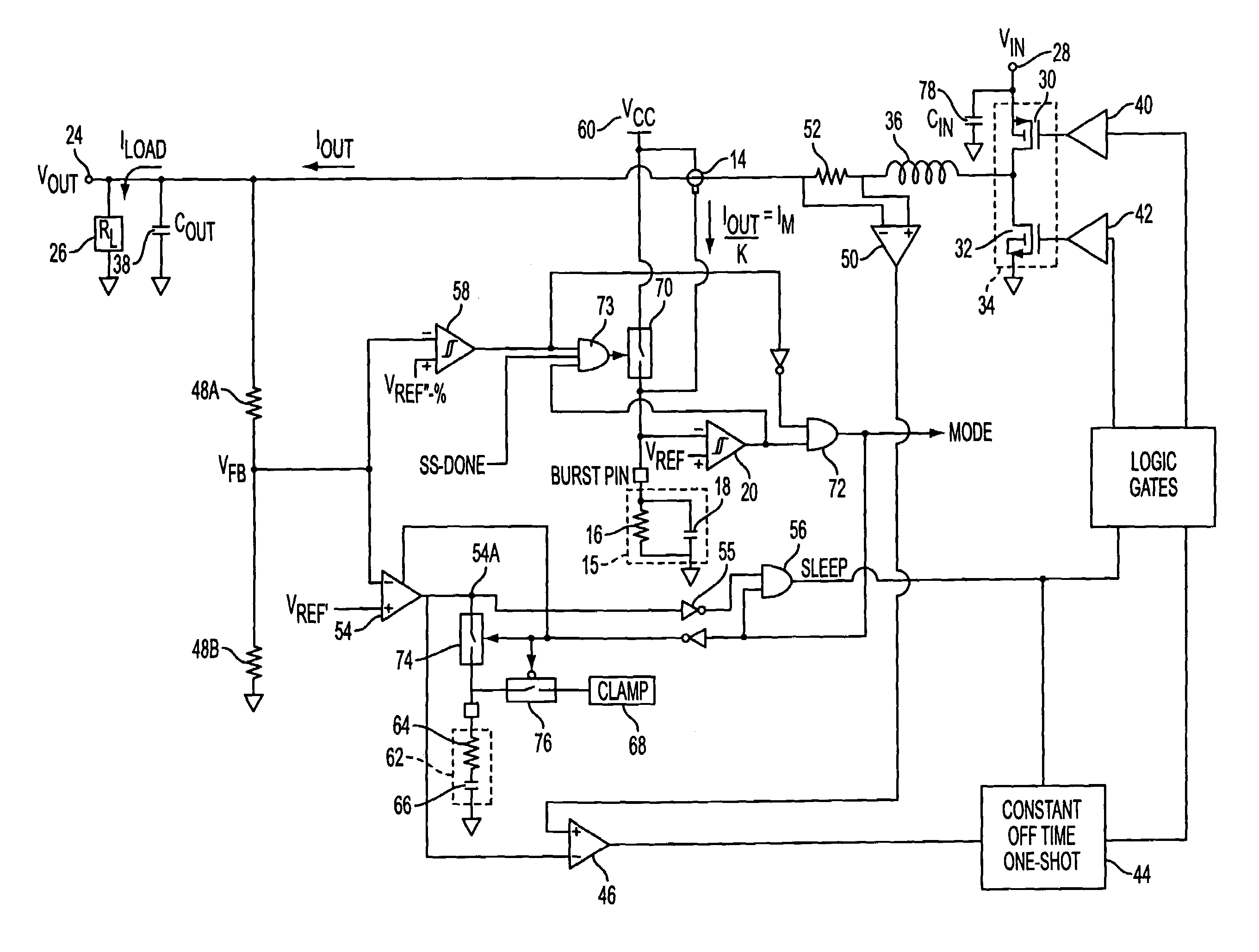
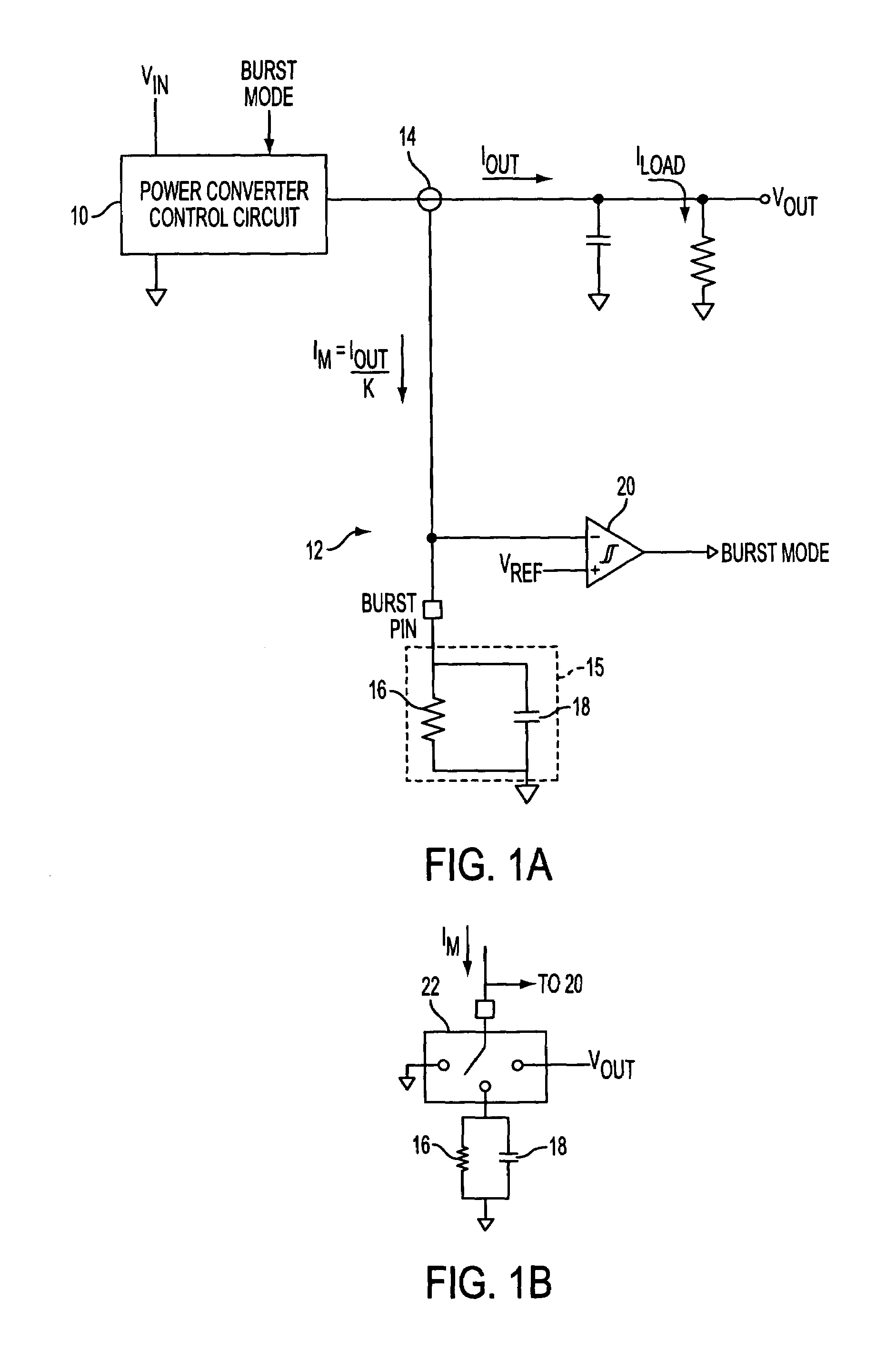
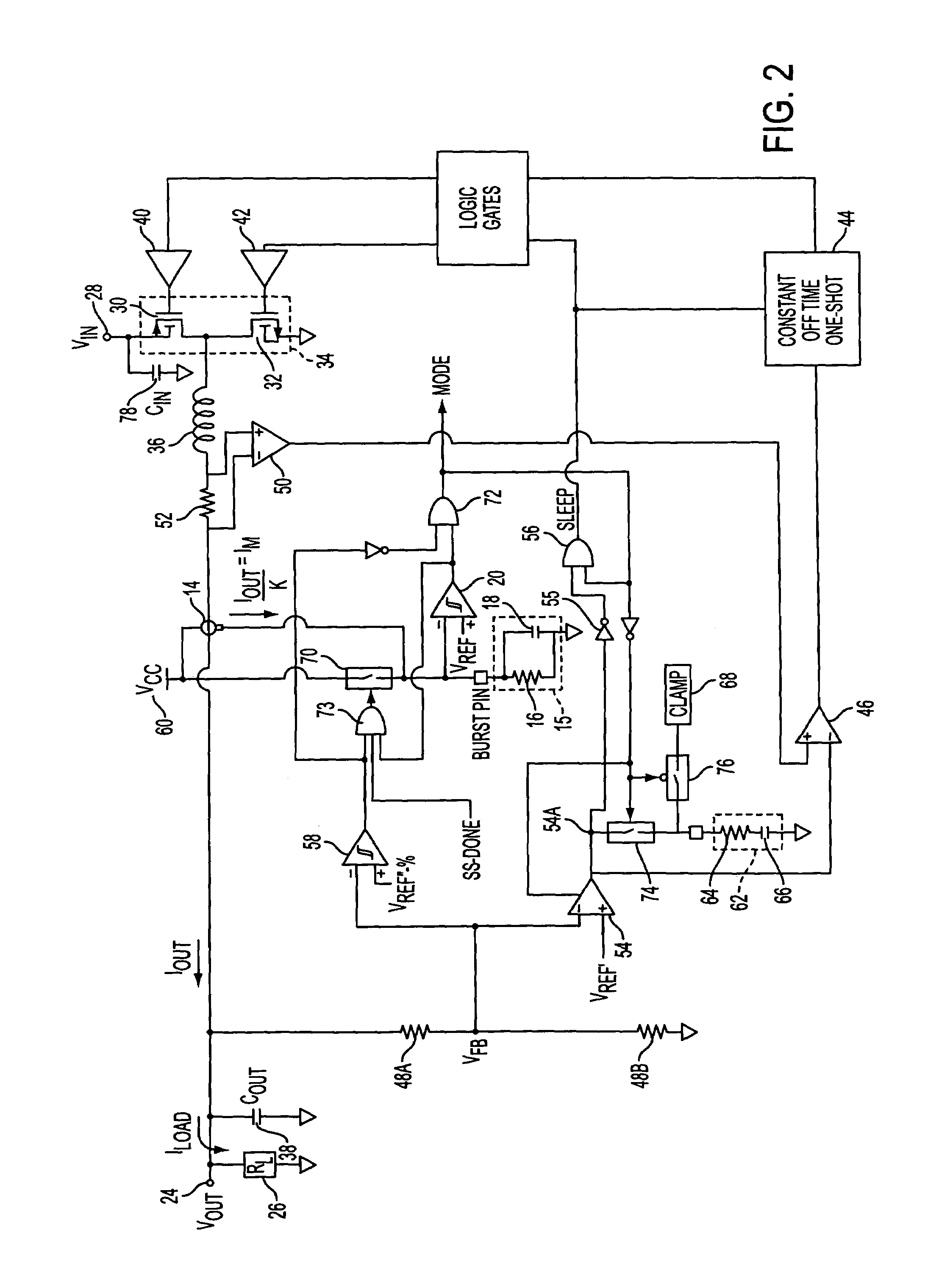
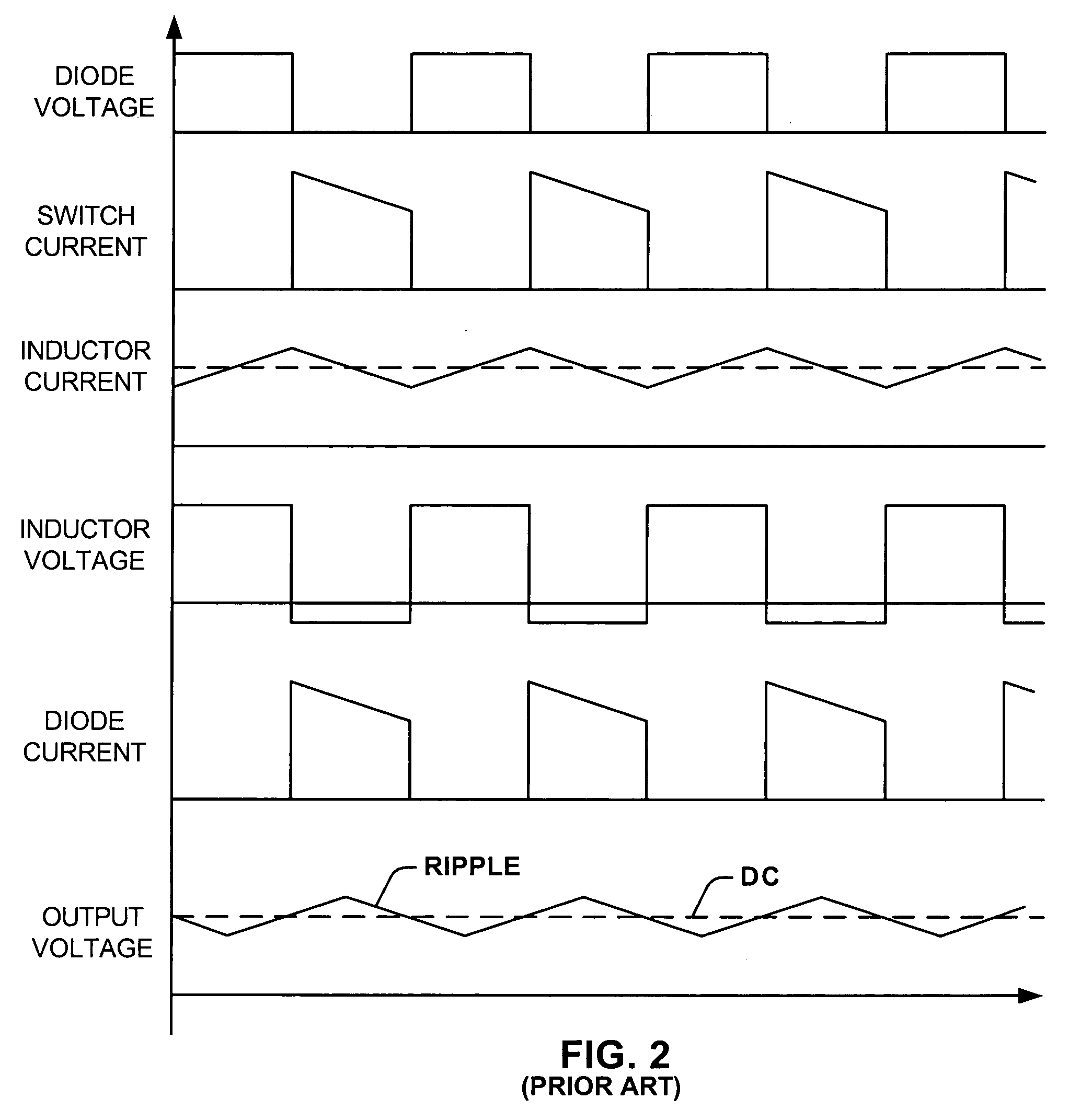
Methods and circuits for programmable automatic burst mode control using average output current
ActiveUS7030596B1Smooth and repeatable transitionEasy programmingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMode controlTransverter
The present invention comprises a user-programmable control circuit for use in a power converter to automatically transition the converter into BURST mode when load current demand is low. The control circuit senses load current demand by monitoring the output current of the converter, and generating a signal representative of the monitored output current. The control circuit may automatically transition the converter into BURST mode when the signal indicative of the average monitored output current decreases below a user-programmable threshold. BURST mode may increase overall converter efficiency by turning OFF a plurality of electronic components, and maintaining the converter's output voltage at a regulated level by energy stored in an output capacitor.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
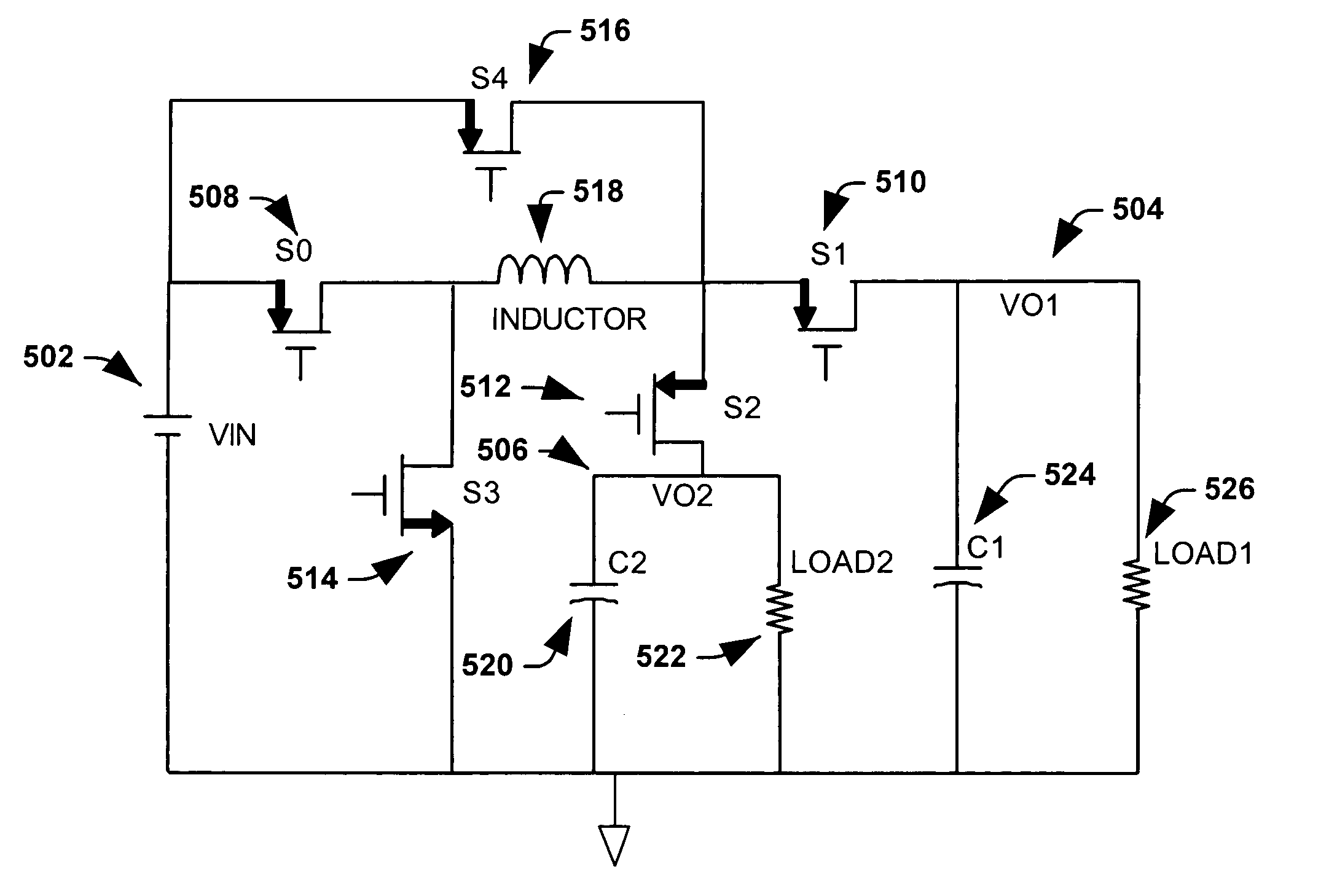
Single inductor dual output buck converter with frequency and time varying offset control
ActiveUS7061214B2Convenient sourcePromote conversionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterTransverter
A single-inductor dual-output buck converter and control method that facilitates power conversion by converting a single DC power source / supply into two separate DC outputs, each of which can be configured to provide a selected / desired voltage by selection of respective duty cycles. The topology of the inverter includes a pair of diodes or switches that can selectively re-circulate inductor current. The converter is generally operated at a fixed frequency with four stages of operation. A first and third stage of operation provide power to a first and second output, respectively. A second and fourth stage of operation re-circulate inductor current and can partially recharge a battery type power source. The power output for each stage (voltage and current) can be selectively obtained by computing and employing appropriate time periods for the stages of operation that correspond to appropriate duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
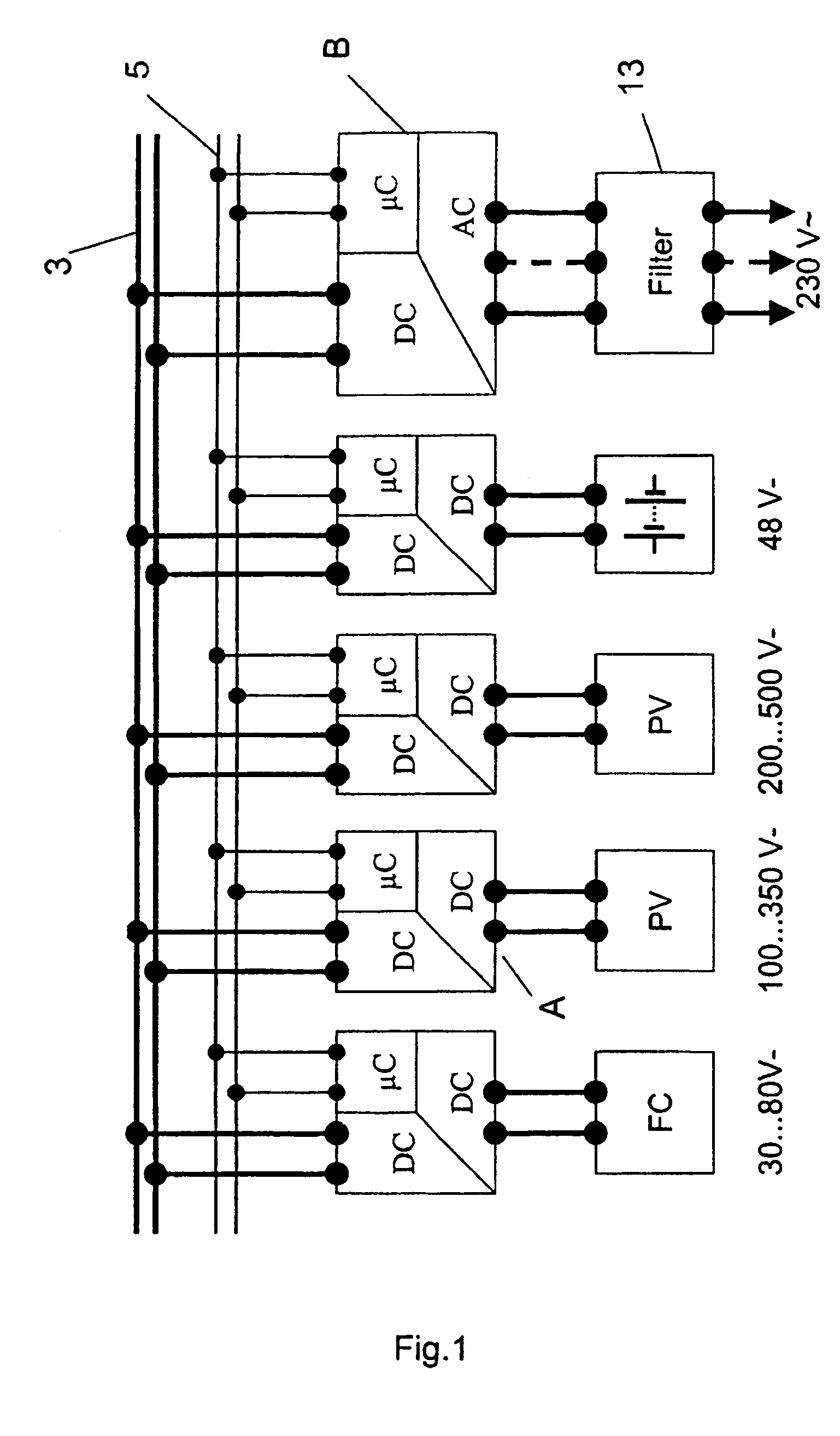
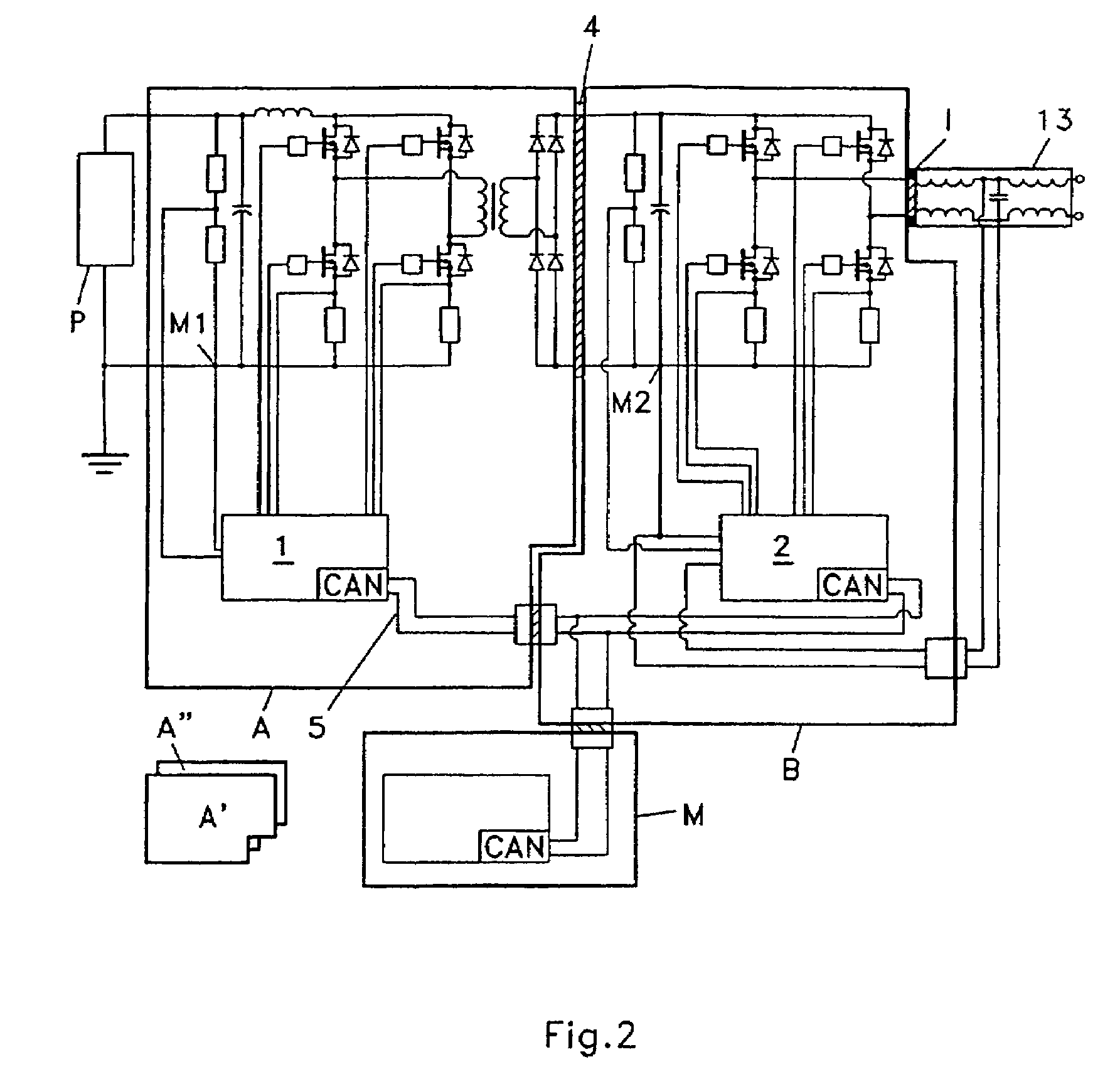
Power converter
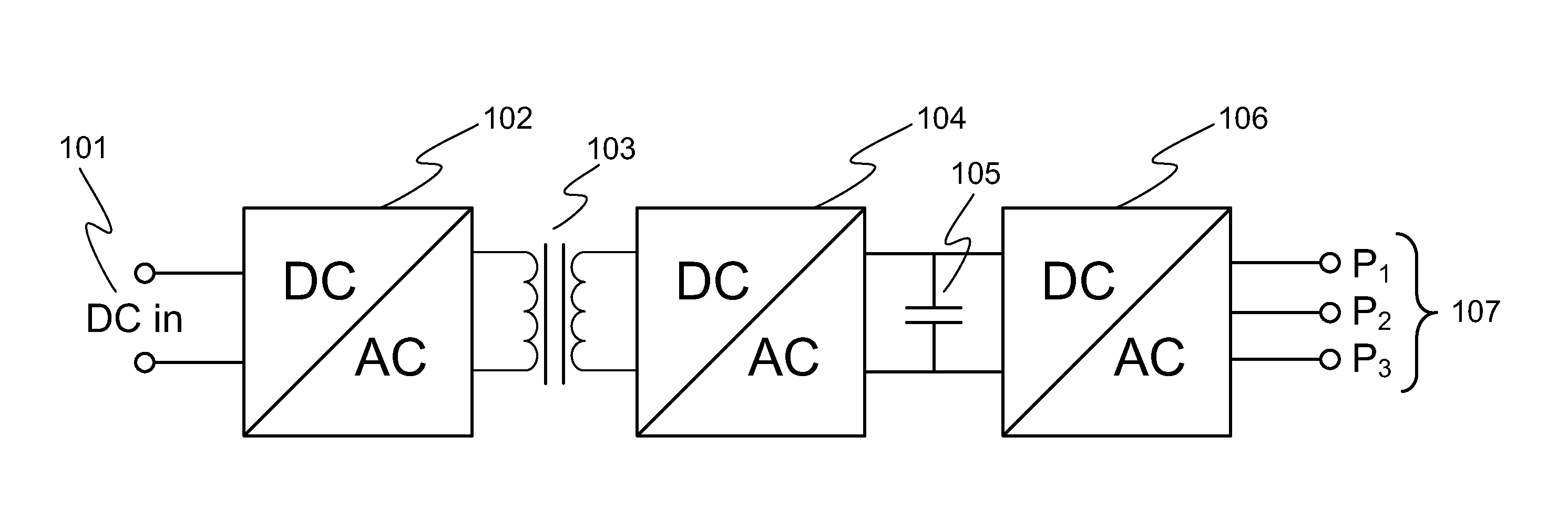
ActiveUS7339287B2Easy to controlDc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransformerEngineering
A power converter for converting energy from a green power unit as e.g. a solar cell into energy fed into the commercial grid is described. The object is to provide a versatile modularized power converter with eased access to control of the power switches. Another object is to improve the electrical efficiency. This is achieved by using an independent controller on a DC / DC module and an independent controller on a DC / AC module, whereby the two independent controllers communicate with each other and the outside world by means of a communication bus. Further, the DC / DC module of the power converter comprises a transformer which transfers energy from the DC / DC module to the DC / AC module. This design enables independent control of the modules and eases controllability of the power switches in order to suppress retroaction from pulsations generated on the mains when supplying energy to a single phase grid. Hereby the electrical efficiency of the power converter is increased. Also, an active snubber circuit is described which further increase the efficiency.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
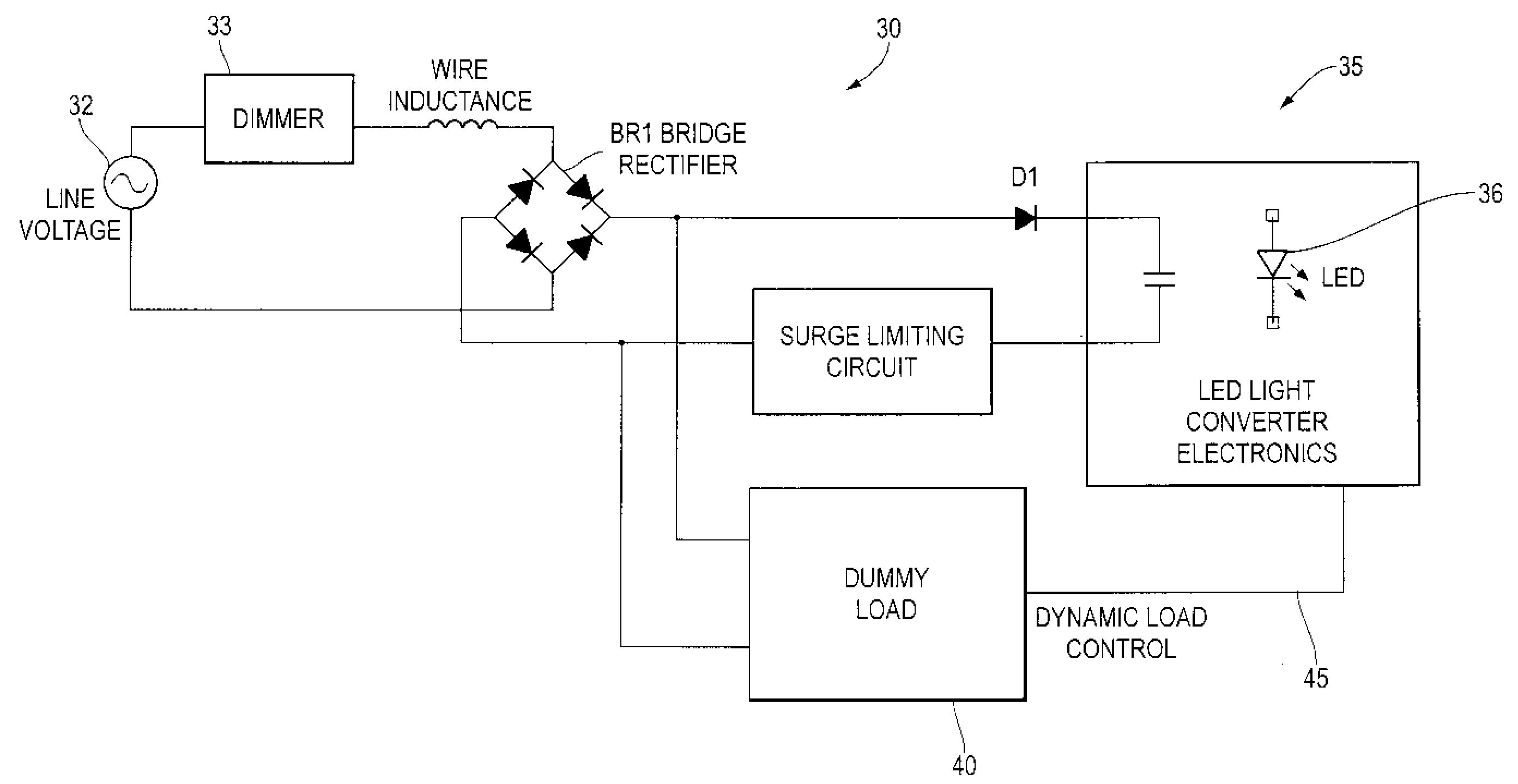
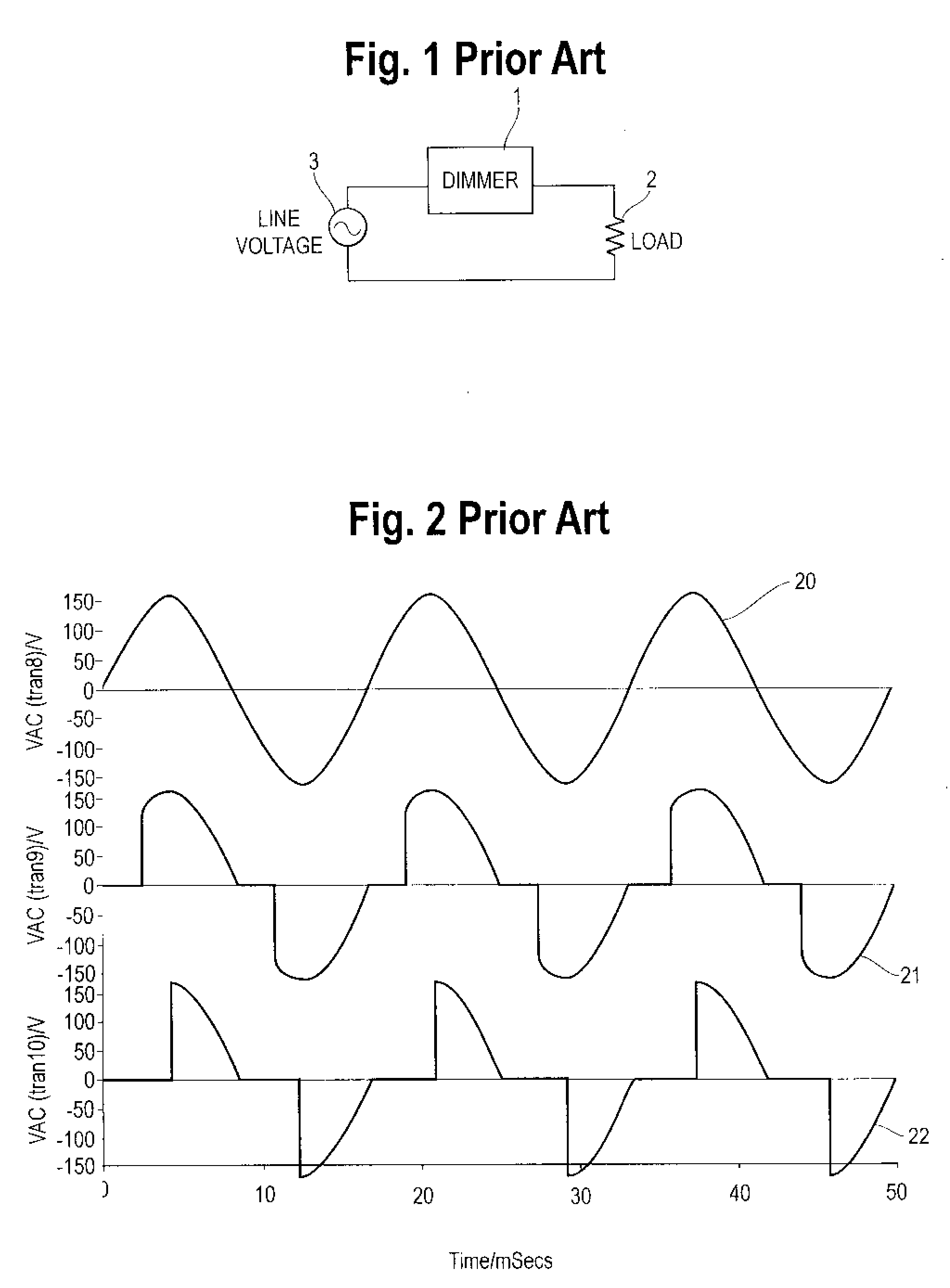
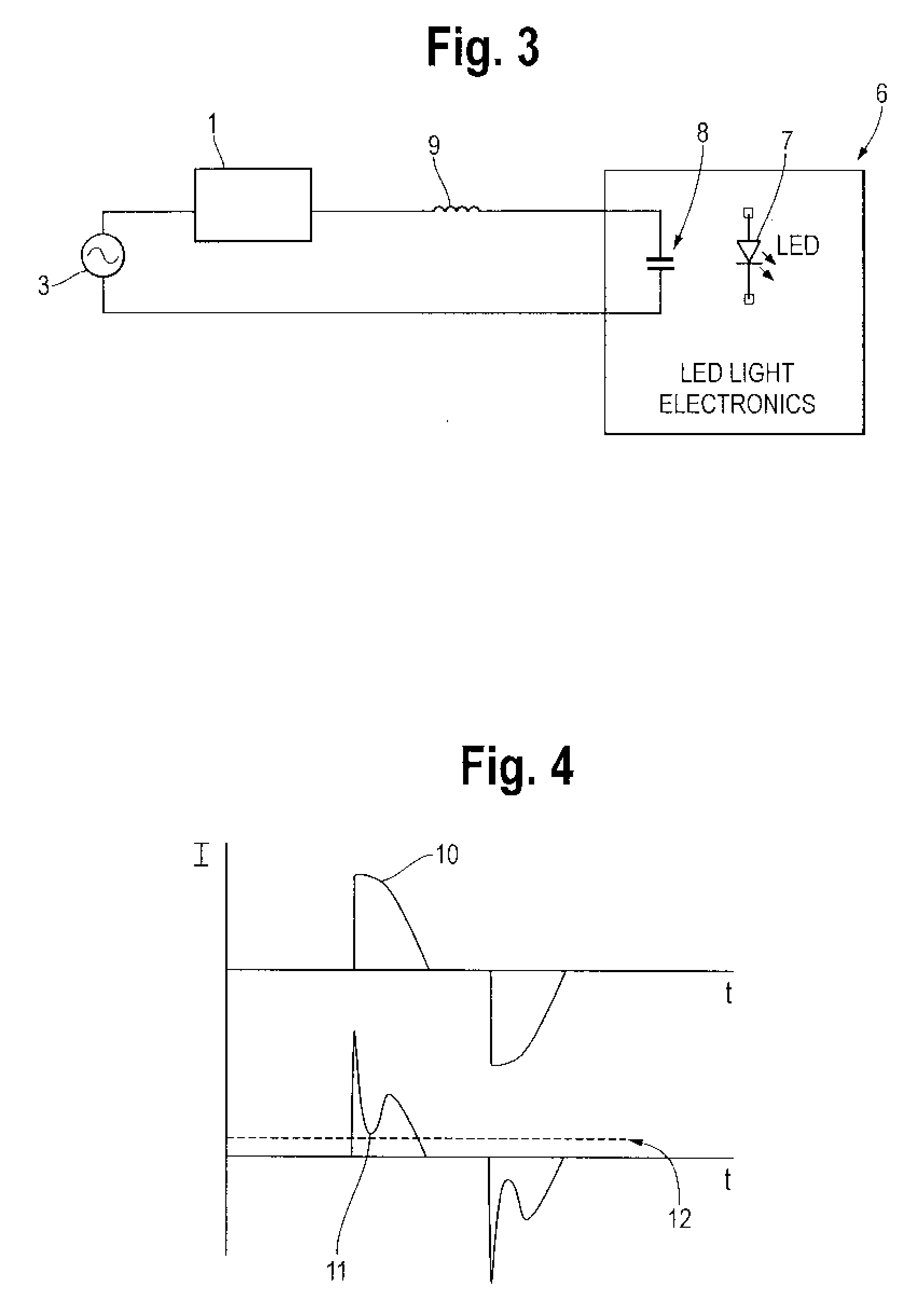
Dimming Circuit for Led Lighting Device With Means for Holding Triac in Conduction
InactiveUS20080258647A1Sufficient currentElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesEffect lightEngineering
The invention disclosed herein is a dynamic dummy load to allow a phase control dimmer to be used with LED lighting. The invention includes providing a dynamic dummy load to provide a load to the dimmer when the LED electronics do not provide sufficient load due to start up issues or ringing in the circuit, the dynamic dummy load providing a reduced flow of current when the LED and its converter electronics provide sufficient current draw from the dimmer. The system generally includes a power source electrically connected to a phase control dimmer, the phase control dimmer electrically connected to converter circuitry to convert the AC power output of the dimmer to DC power output for powering the LED lighting, a dynamic dummy load electrically connected in parallel with the converter circuitry, the dummy load varying its current draw in response to operation of the converter circuitry.
Owner:DYNAMIC LED TECH LLC
Wireless energy transfer for vehicle applications
InactiveUS20120112538A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferTransverter
A vehicle powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load configured to power the drive system of a vehicle using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed upon the vehicle and configured to be coupled to the load by a converter capable of converting energy captured by the second electromagnetic resonator into a form usable by the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
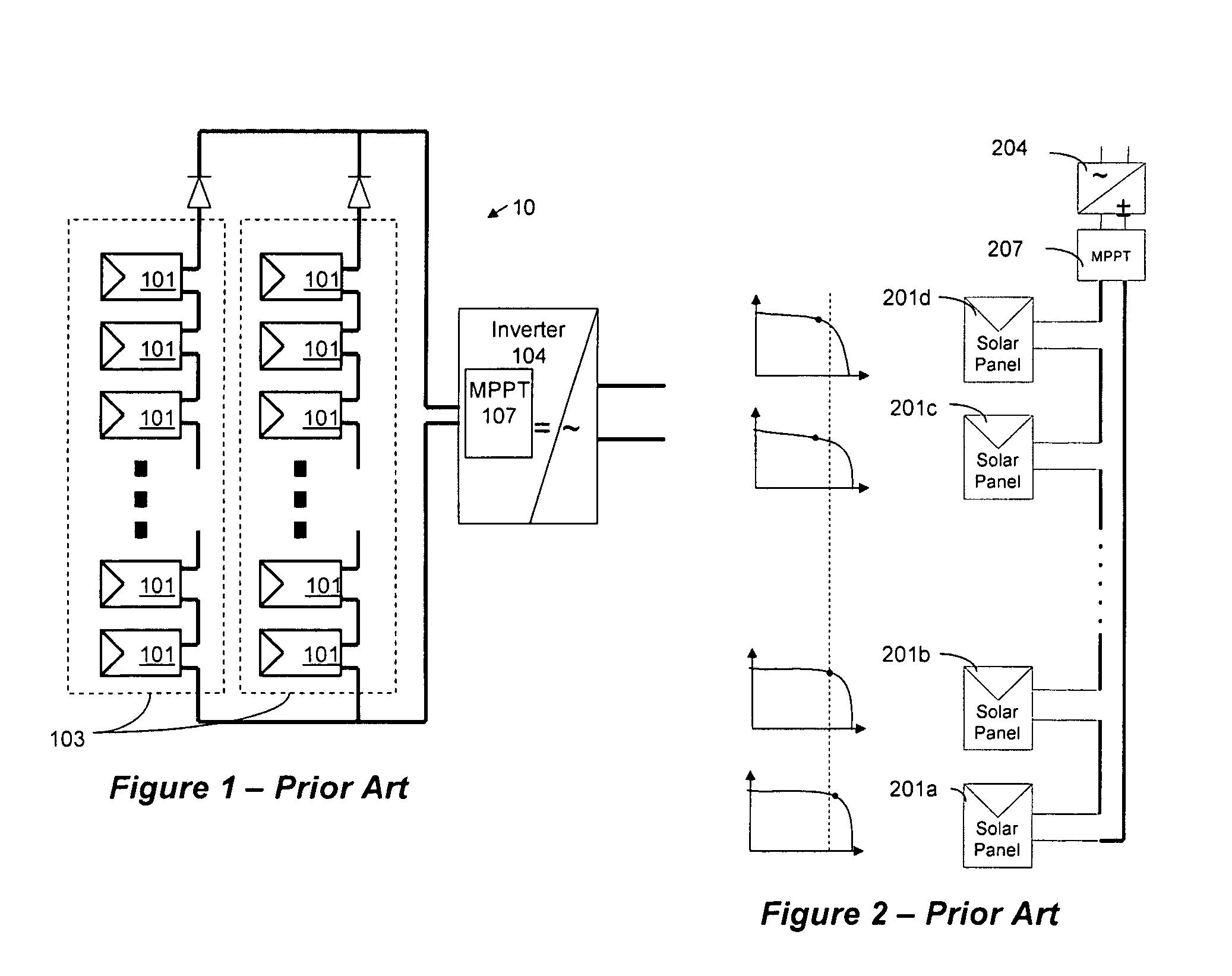
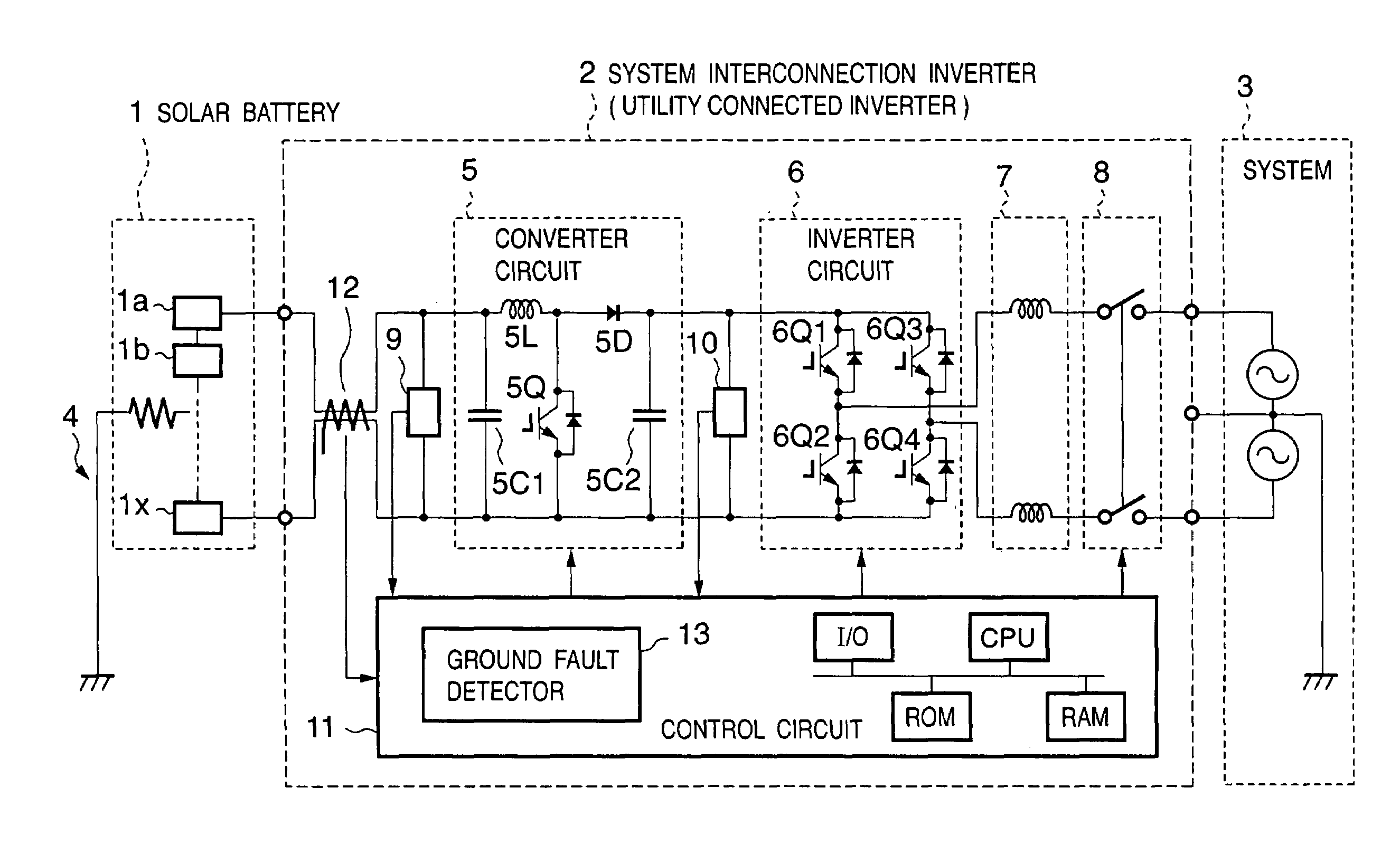
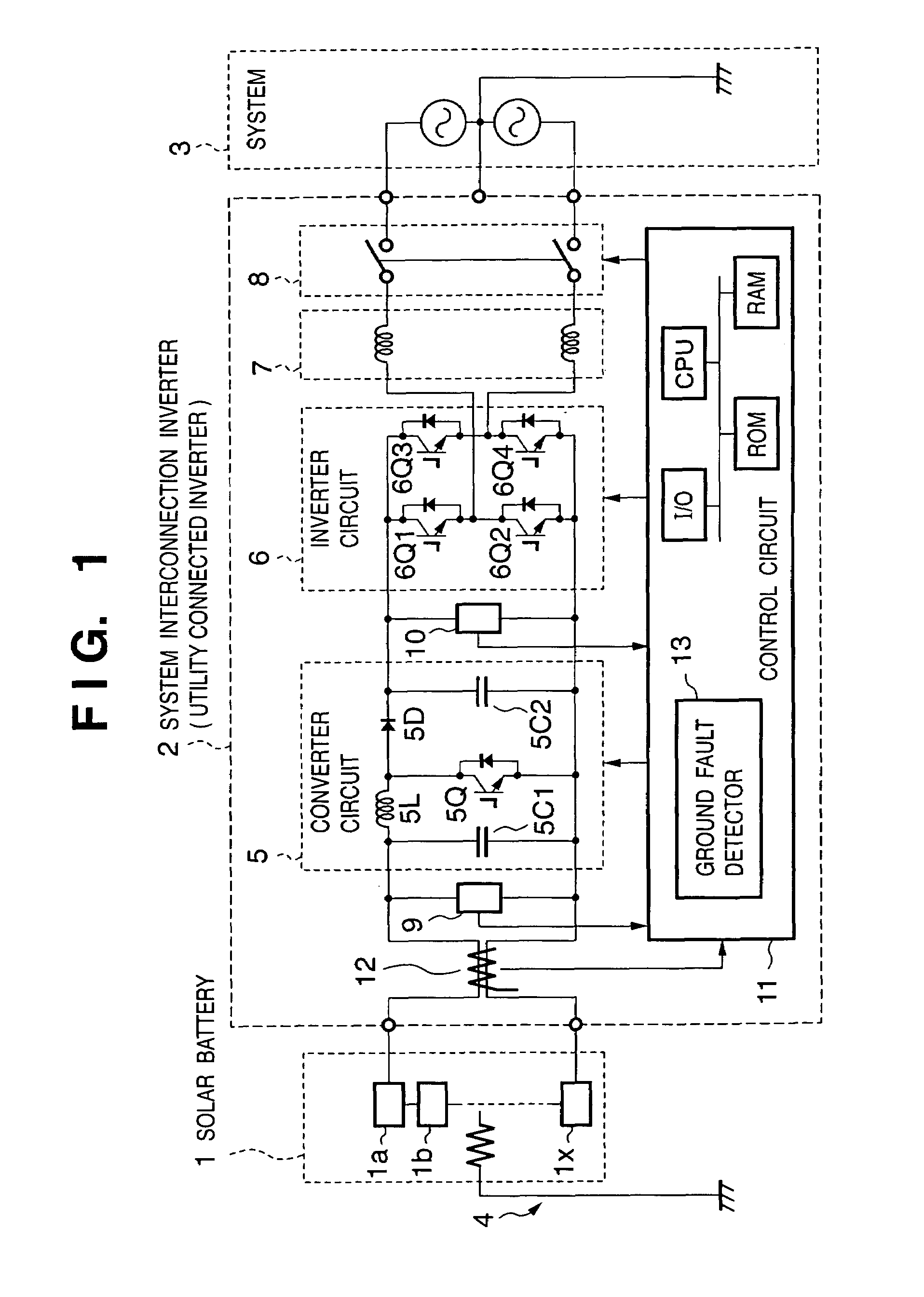
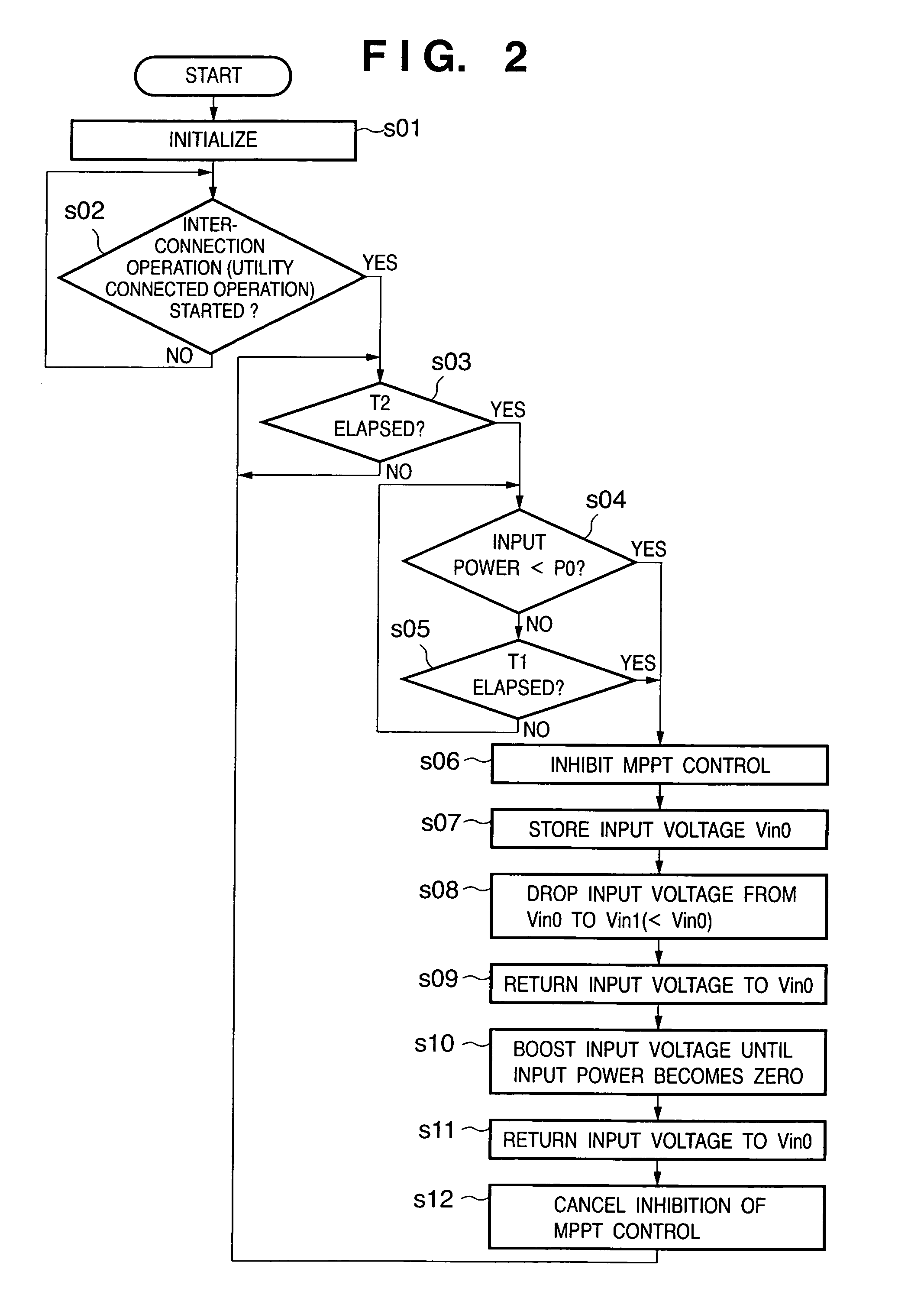
Power converting apparatus, control method therefor, and solar power generation apparatus
InactiveUS7079406B2Short timePower supply linesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical batteryTransverter
The object is to reliably detect a ground fault of a solar battery. To detect a ground fault position to take an efficient measure against the ground fault, DC power input from a solar battery is converted into AC power and supplied to a system. In a system interconnection inverter (utility connected inverter) having non-insulated input and output, the input voltage of a converter circuit and / or the intermediate voltage between the converter circuit and an inverter circuit are varied to control the potential to ground at each portion of the solar battery to a value other than a value close to zero.
Owner:CANON KK
Circuit for conditioning a supply at the maximum power point
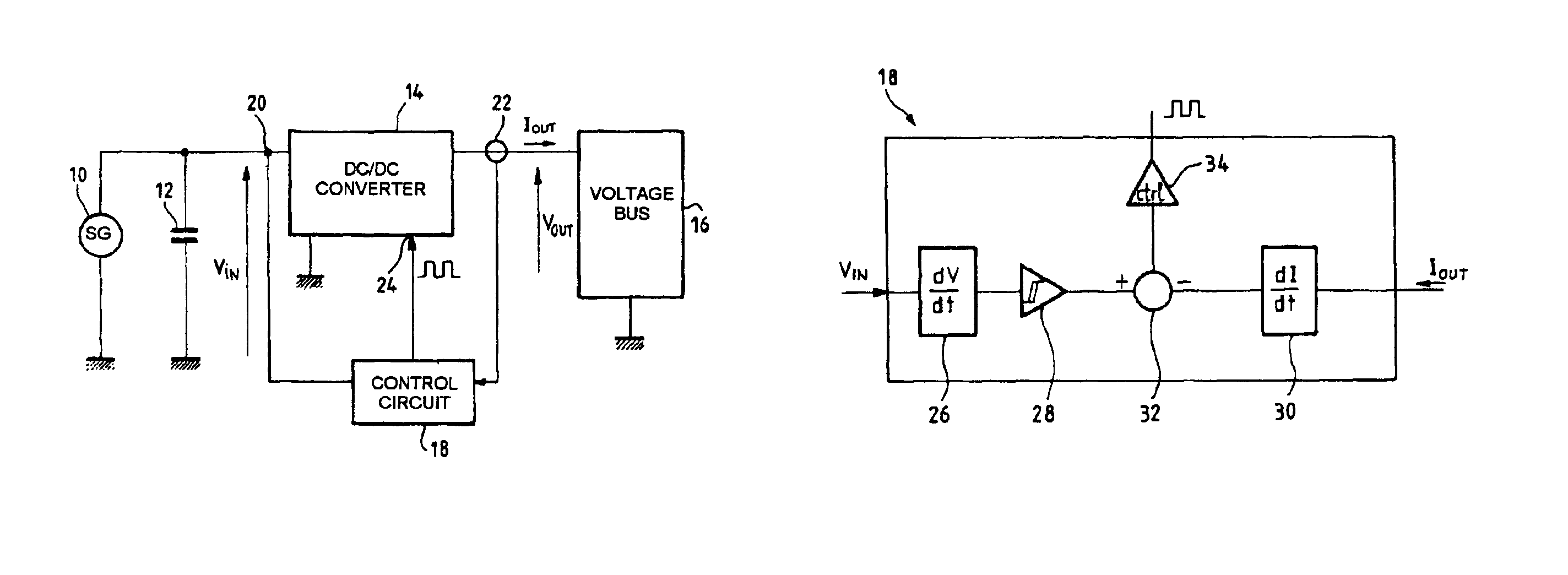
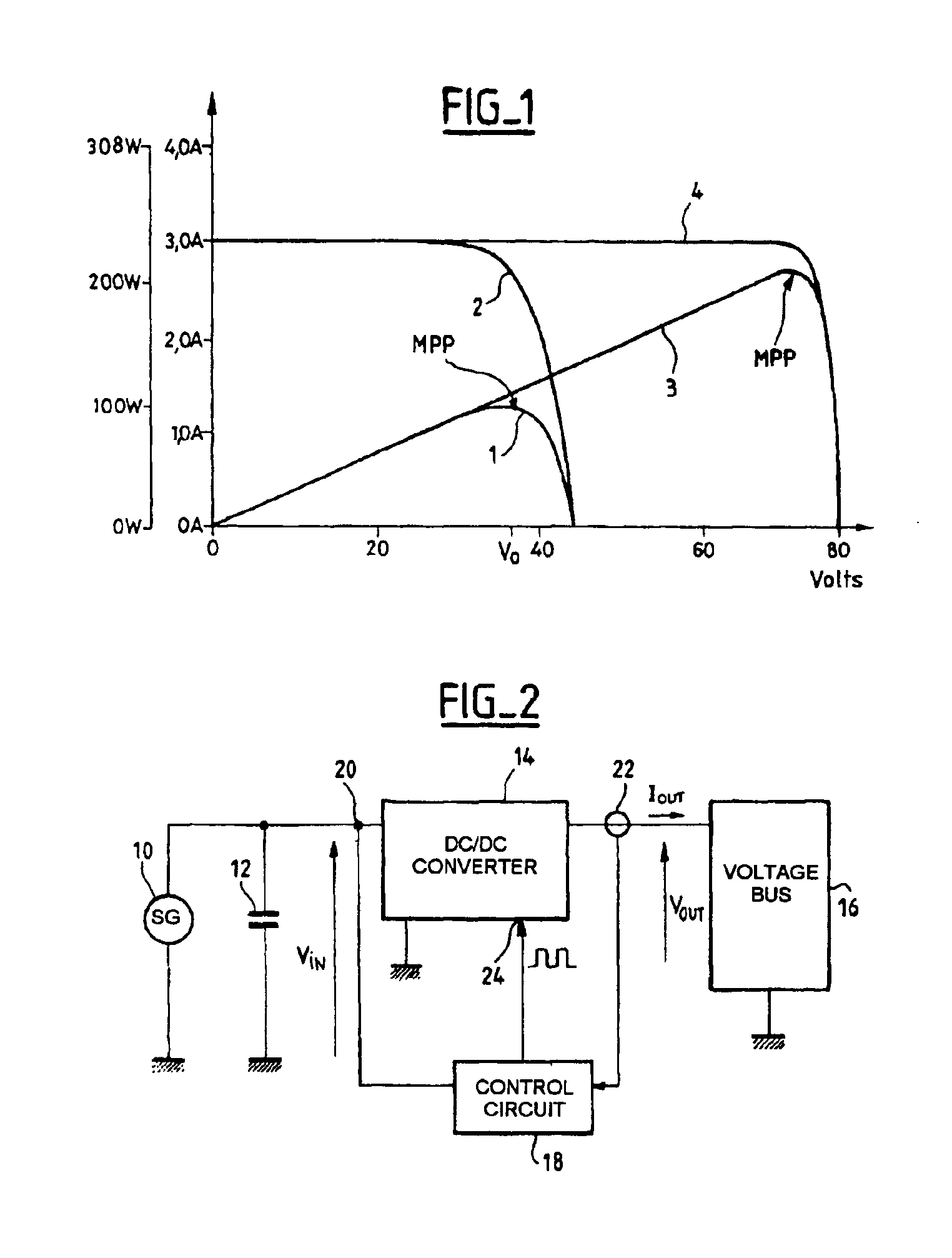
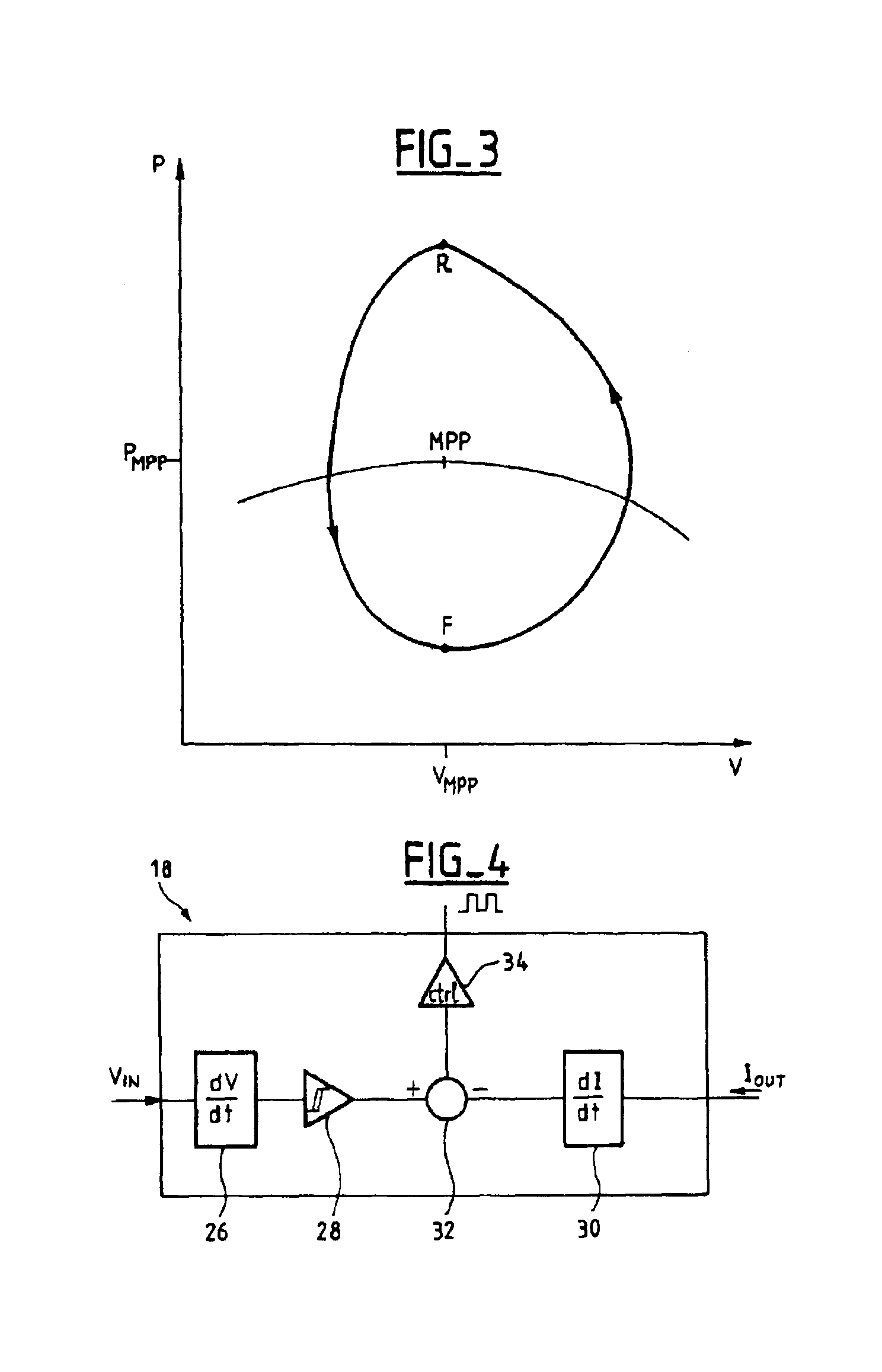
InactiveUS6919714B2Vast supplyBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply linesTransverterControl circuit
A circuit for conditioning a power supply whose graph of the power supplied as a function of the voltage at the terminals of the supply features a maximum comprises a DC / DC converter with an input to which power is supplied by the power supply and an output from which power is supplied to a load. A control circuit controls the converter in accordance with a power set point applied to the converter. The set point is a rising set point when the time derivative of the converter input voltage is higher than a negative first threshold value and a falling set point when the time derivative of the converter input voltage is lower than a positive second threshold voltage. The rate of variation of the average power when the set point is a rising set point is lower than the opposite of the rate of variation of the average power when the set point is a falling set point. The conditioning circuit enables the supply to deliver power at the maximum power point and is simple to implement.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
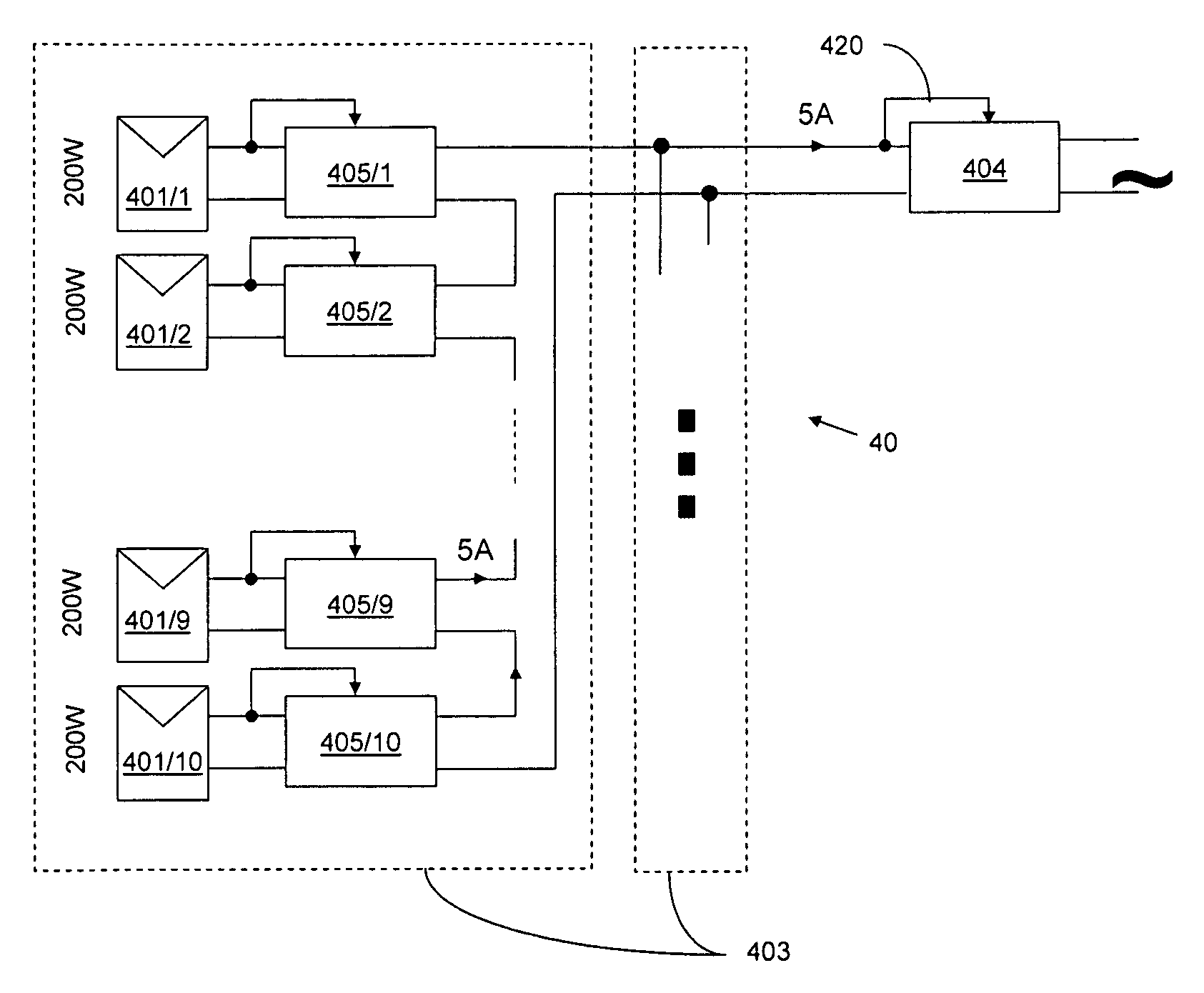
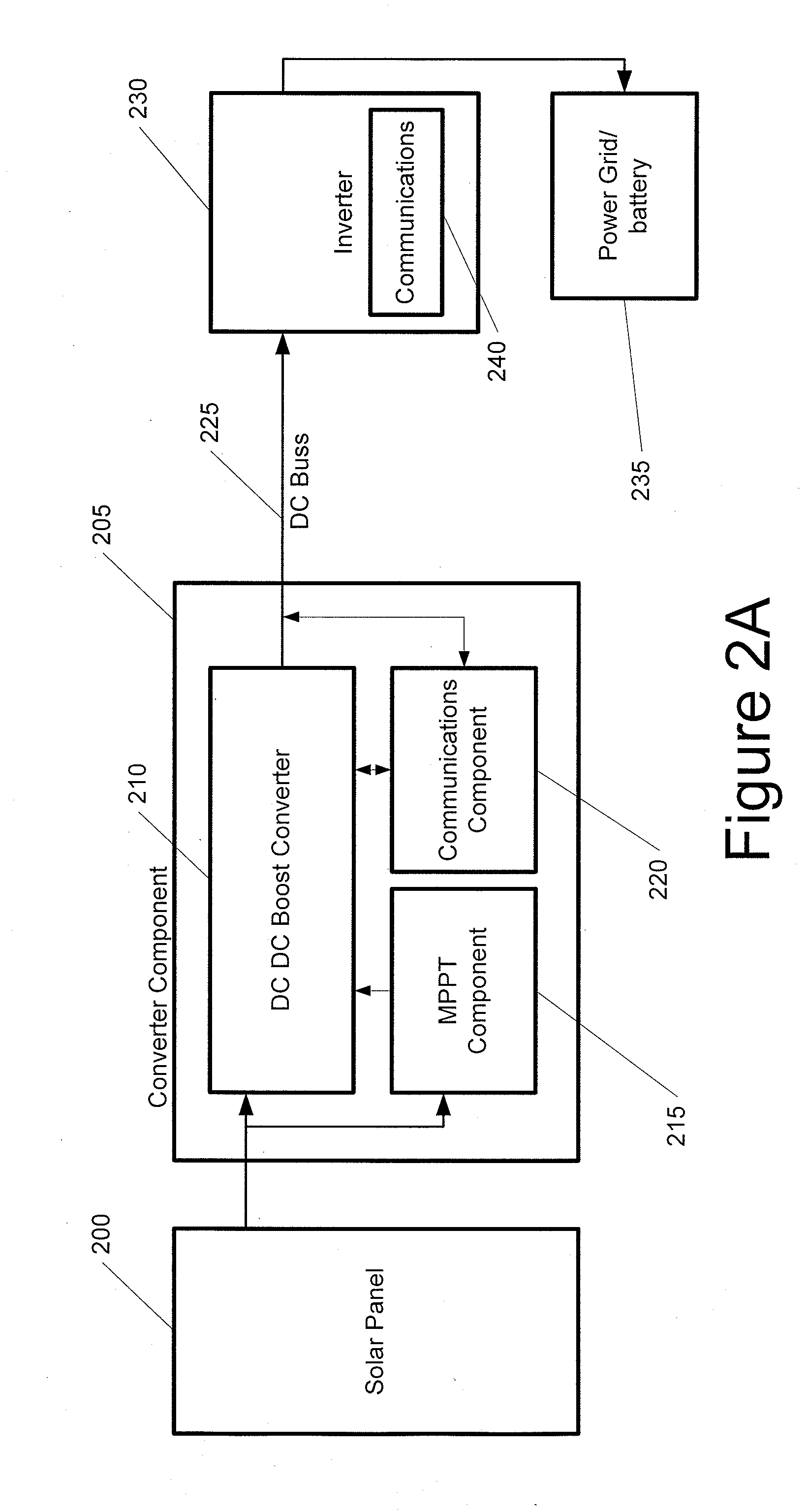
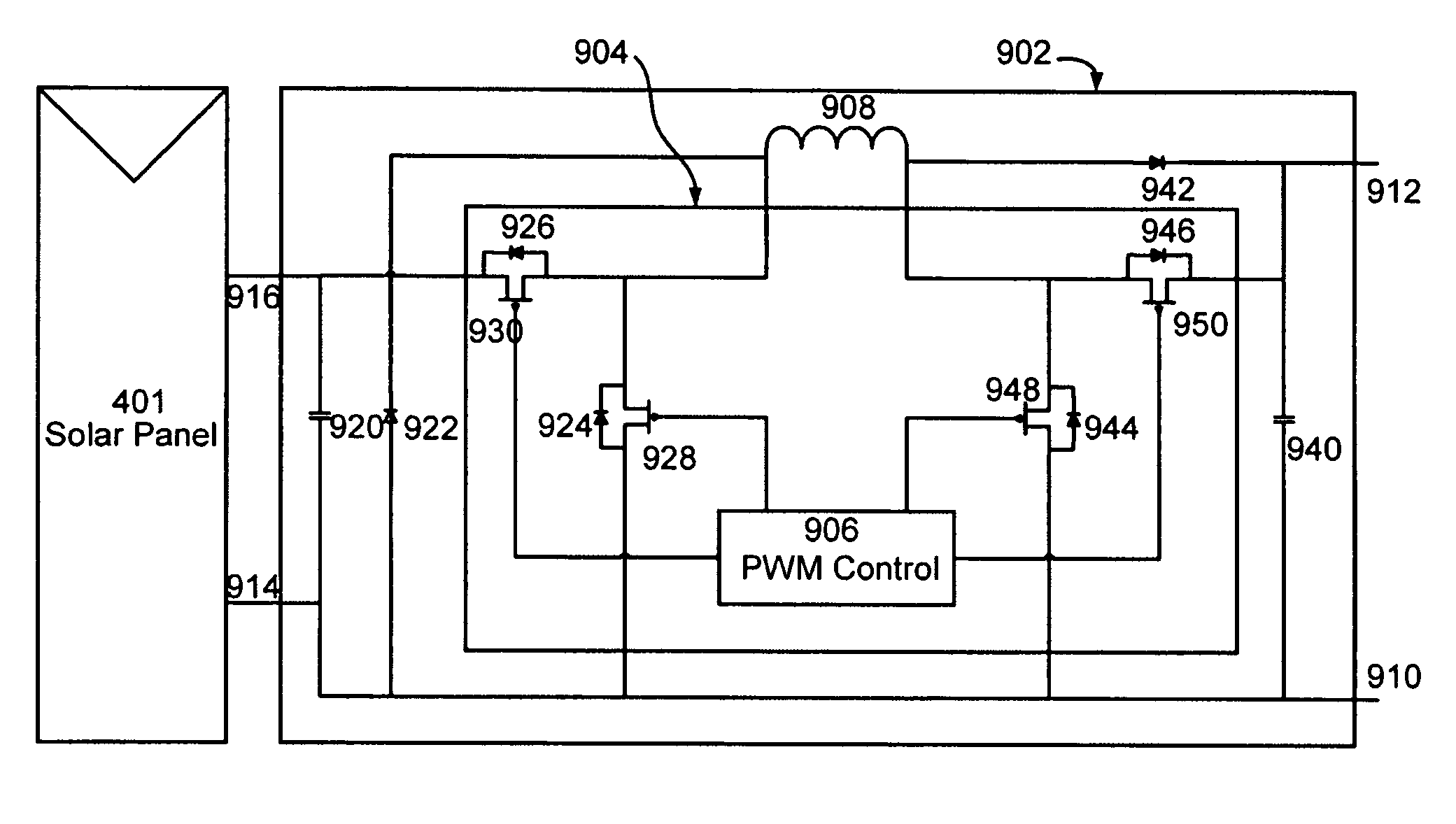
Advanced Renewable Energy Harvesting
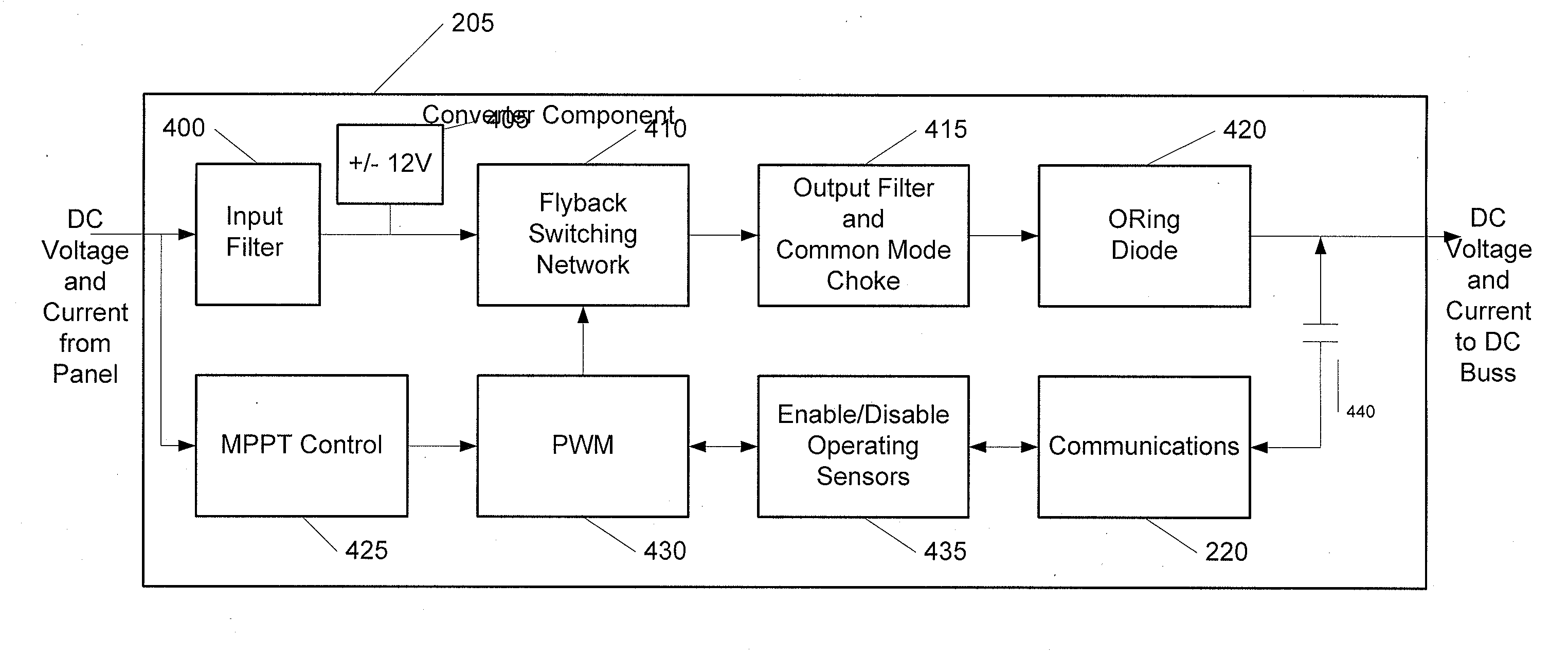
InactiveUS20090160258A1Power maximizationMinimize transmission wire lossBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransverterInput impedance
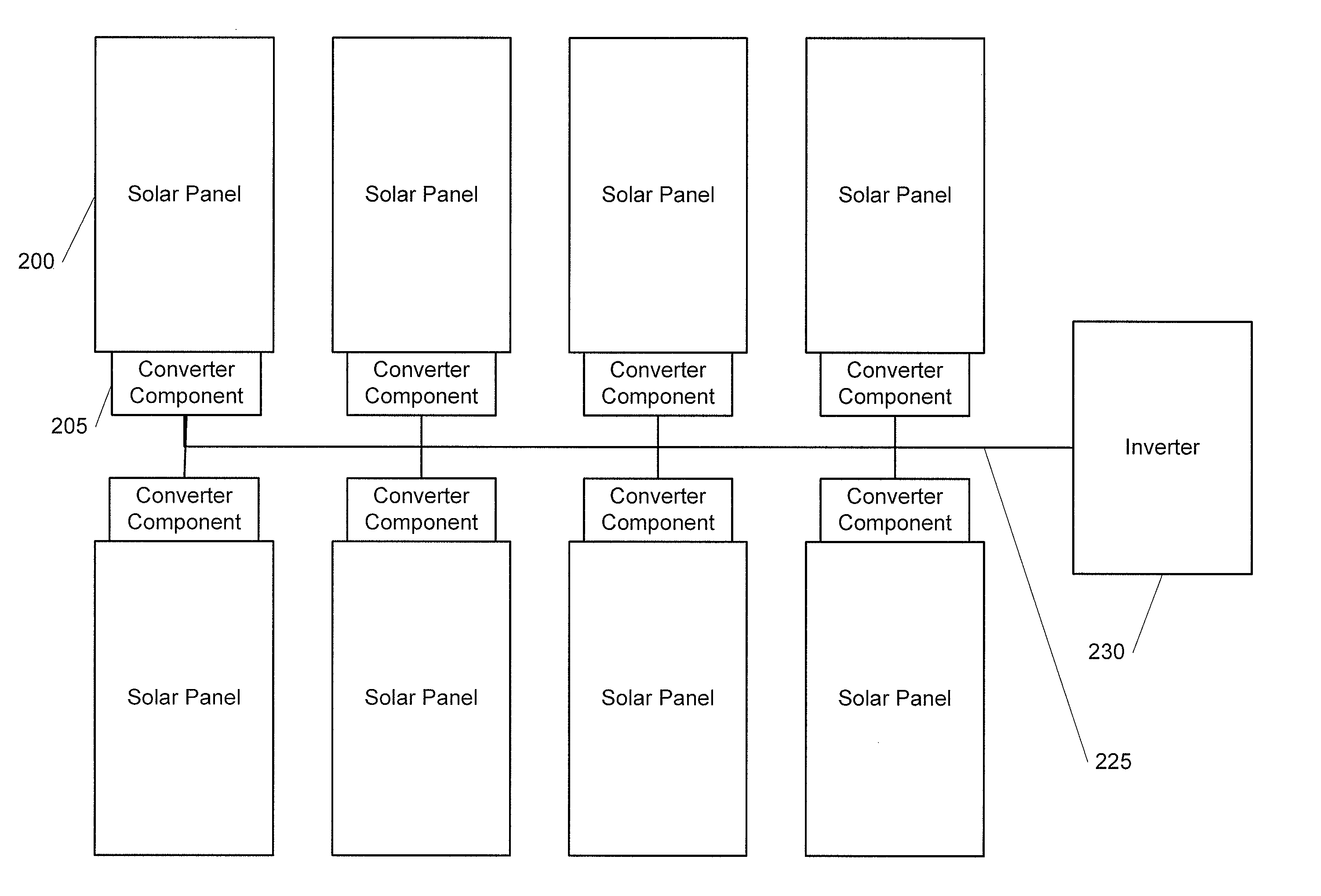
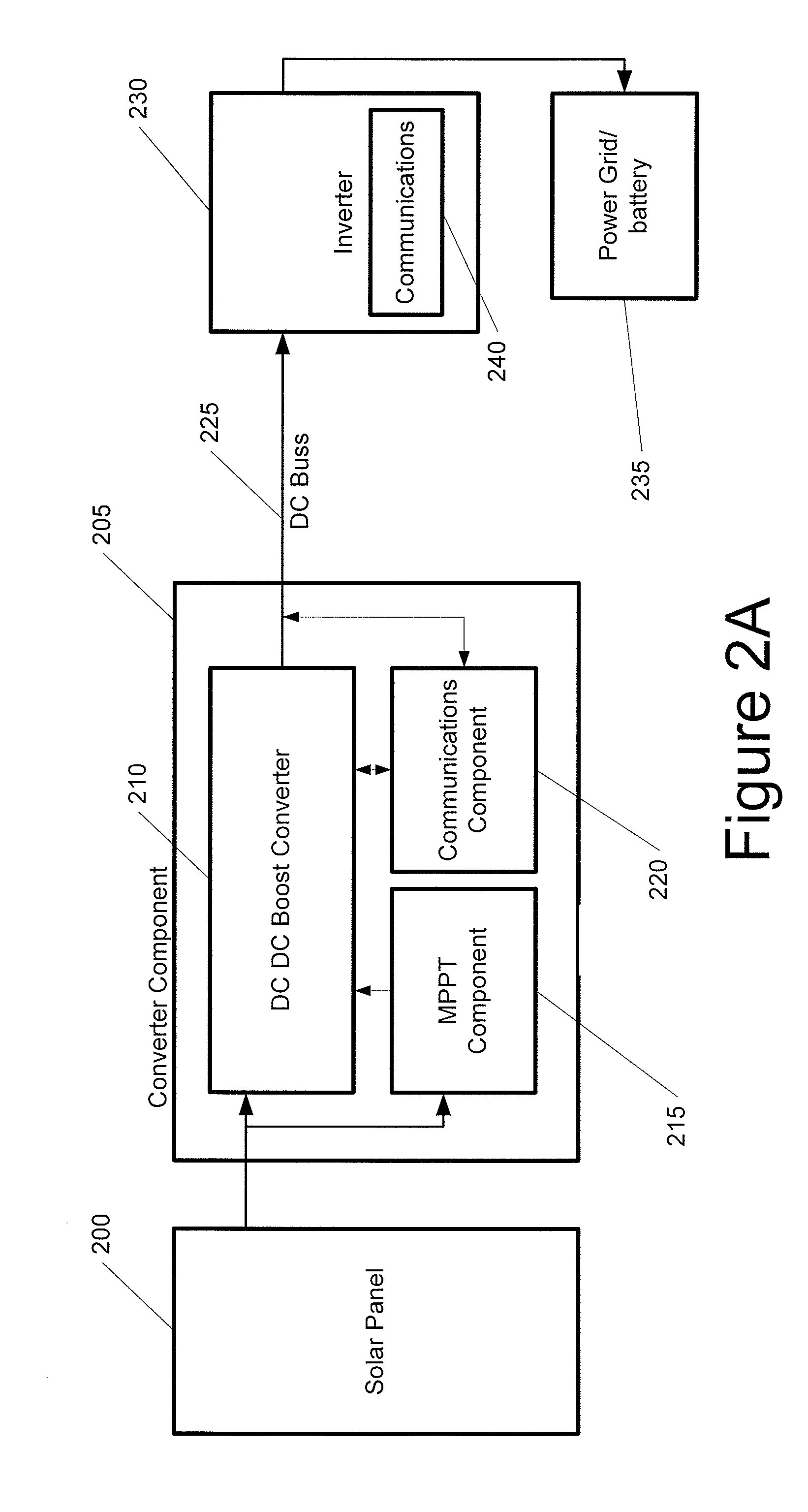
The power of DC electrical sources is combined onto a DC buss, such that each source behaves independently from any other source attached to the buss. In one embodiment, a converter module is attached to each of a plurality of solar photovoltaic panels and its output is attached in a parallel manner to a common buss that forms the input to a DC AC inverter. The converter module includes a Maximum Power Point Tracking component that matches the output impedance of the panels to the input impedance of the converter module. The converter also includes a communication component that provides parametric data and identification to a central inverter. Data generated by each converter module is transmitted over the power line or by wireless means and is collected at the inverter and forwarded to a data collection and reporting system.
Owner:EIQ ENERGY INC
Snubber circuit for a power converter
InactiveUS7385833B2Easy to controlHigh voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterEngineering
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
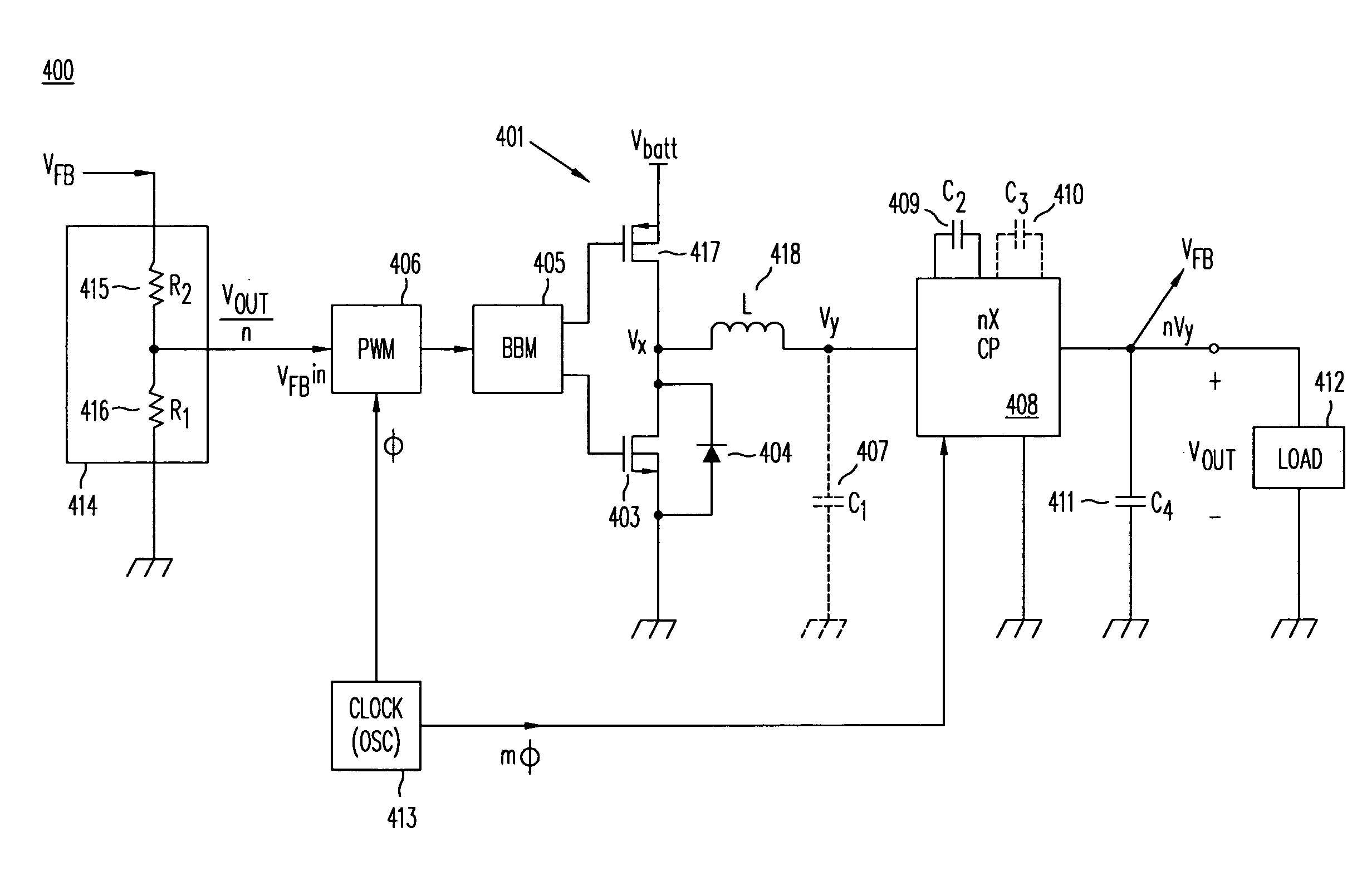
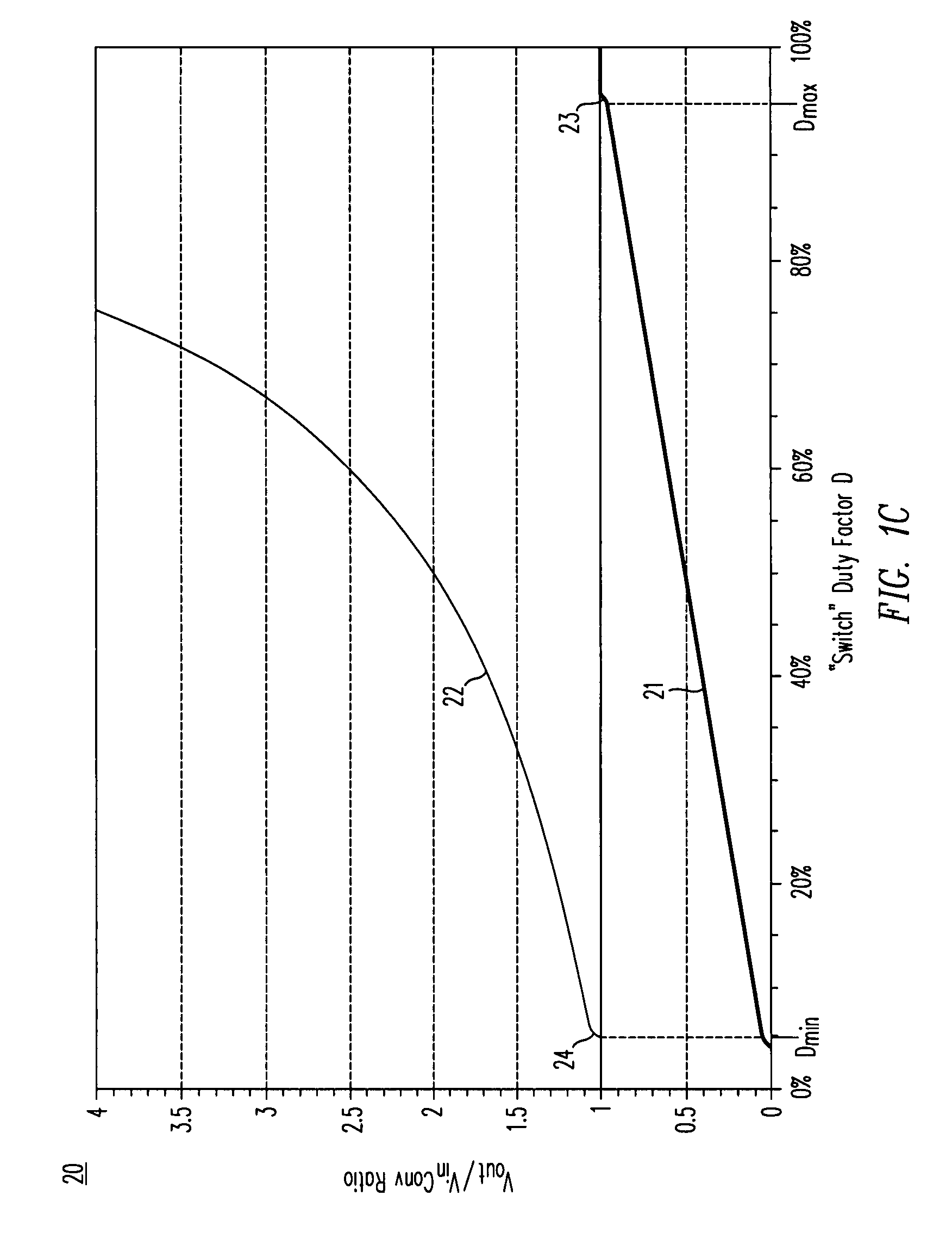
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
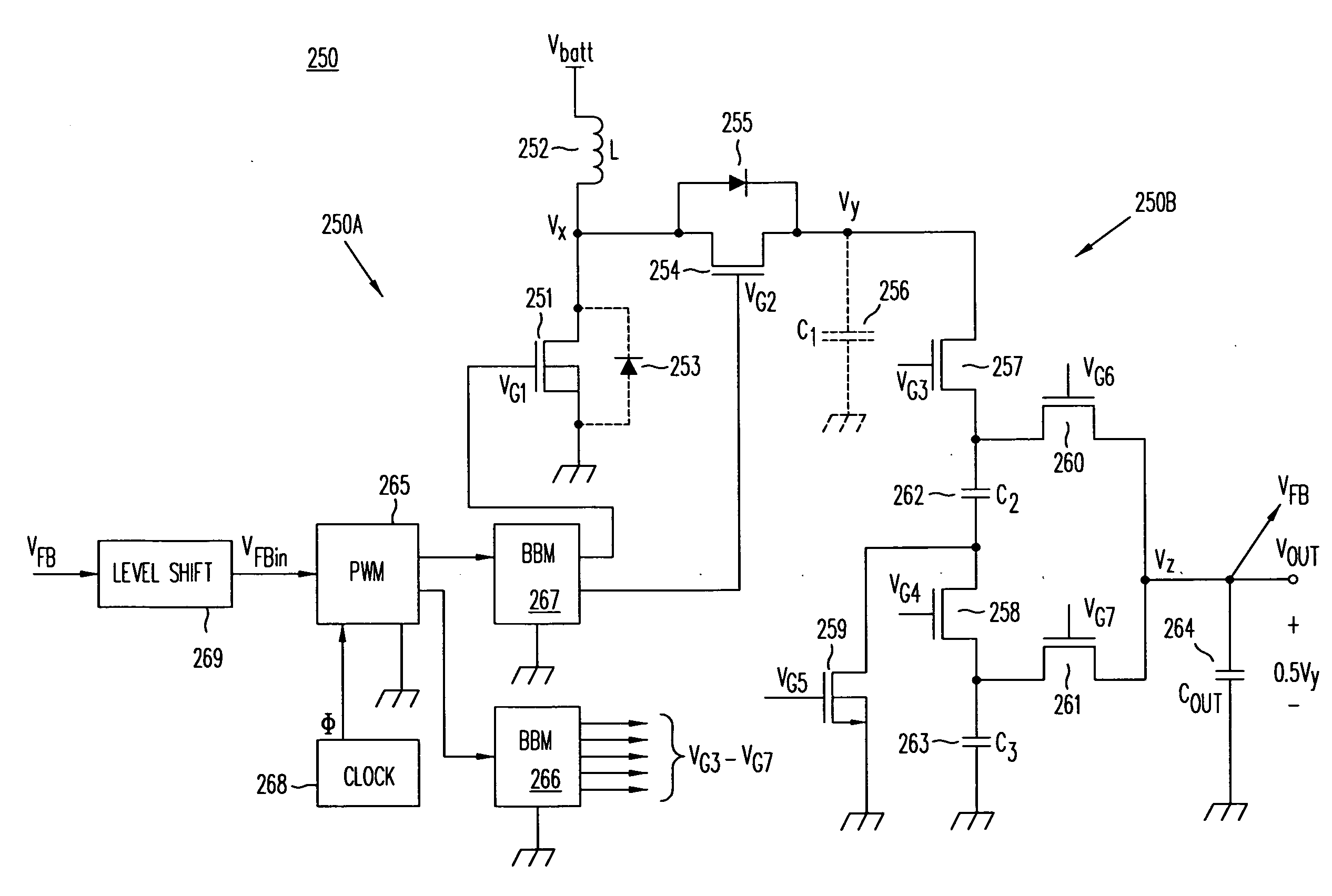
ActiveUS20080158915A1Poor regulationAvoid problemsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
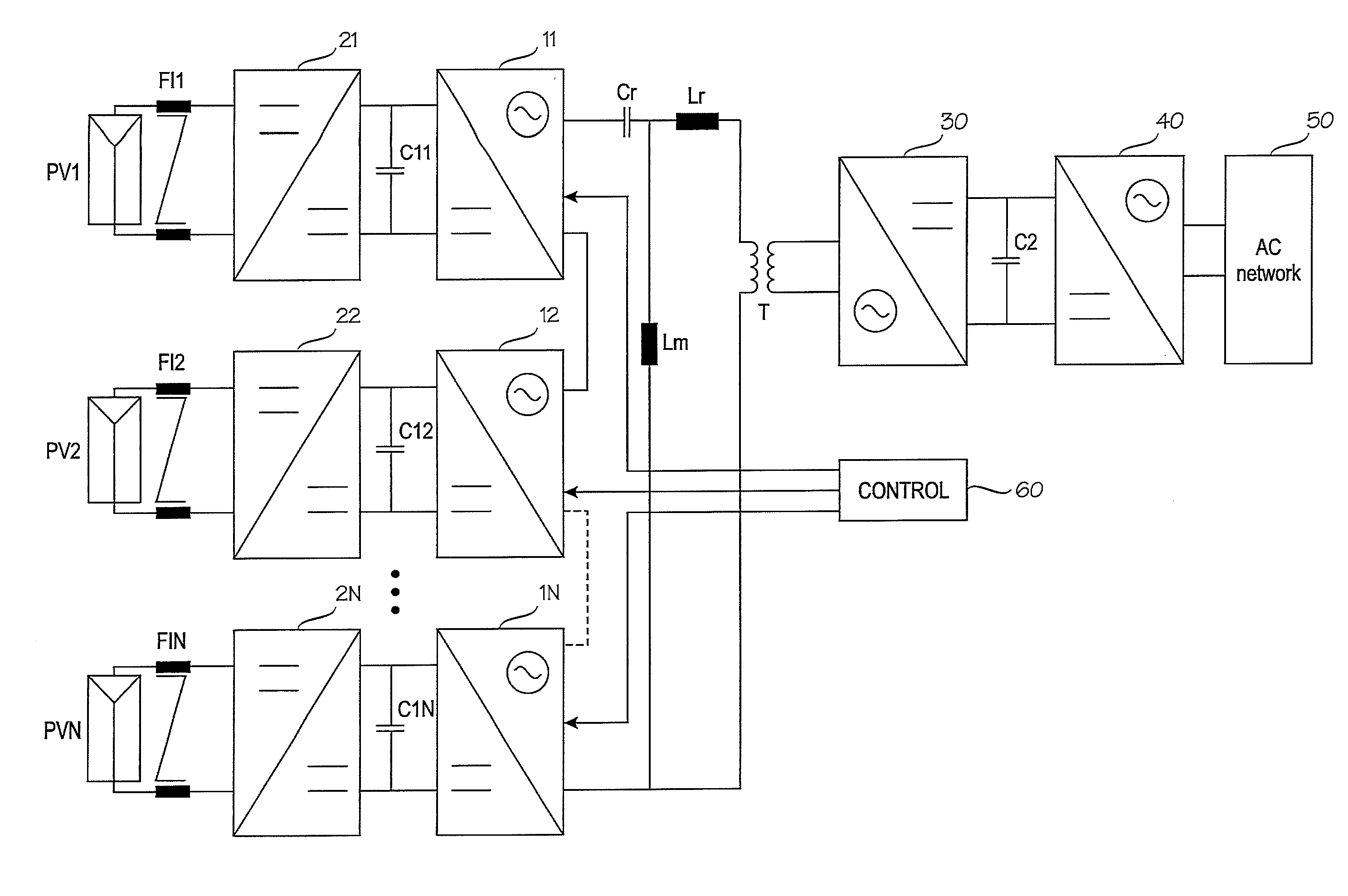
Method for controlling single-phase dc/ac converters and converter arrangement
ActiveUS20100244575A1More compactLess expensiveDc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationTransverterControl theory
A method is disclosed for controlling single-phase DC / AC converters, along with a converter arrangement having at least two single-phase DC / AC converters. A controller is provided which can control the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters, and an isolation transformer, wherein outputs of the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters are cascade-connected with each other and an input of the isolation transformer. The controller is configured to control the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters to deliver power from their inputs to their outputs by turns.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Current bypass for distributed power harvesting systems using DC power sources
ActiveUS7900361B2Improve reliabilityGuaranteed functionDc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationEngineeringElectric power
A converter circuit providing multiple current bypass routes between the output leads to provide reliability in a series connection of several converters. If the converter malfunctions due to component failure, the current bypass routes provide a path for the current that views the malfunctioning converter as substantially a short. Diodes prevent backflow into the power source connected to the converter. Redundancy is provided in the bypass portions of the converter circuit that provides alternate parallel paths in case a defective component in one of the paths opens the circuit along that path. In one example, the converter is implemented as a buck plus boost converter where either the buck or the boost portion or both are operative responsive to a controller controlling the switches of both portions. Most of the converter circuit may be implemented in an integrated circuit.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
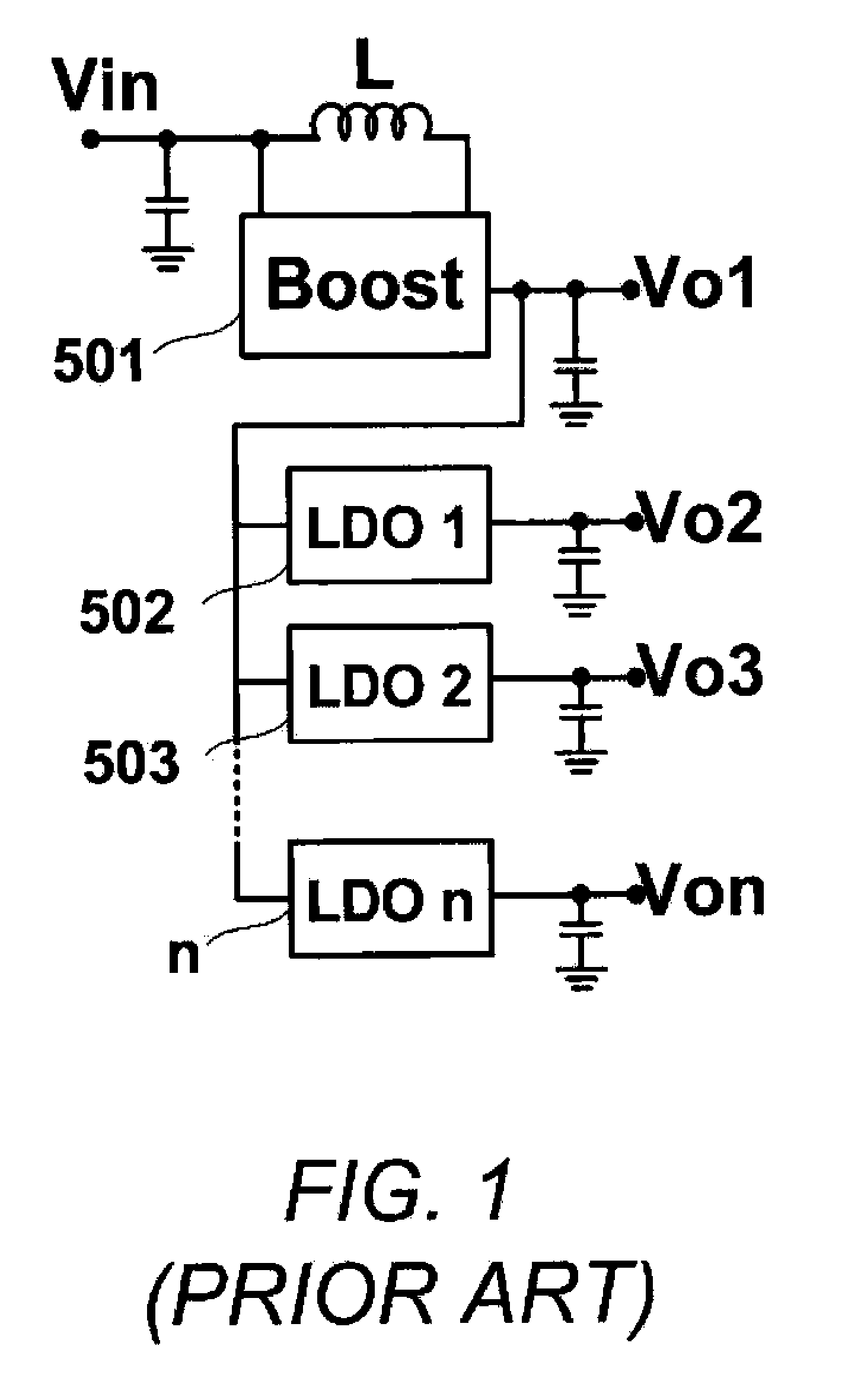
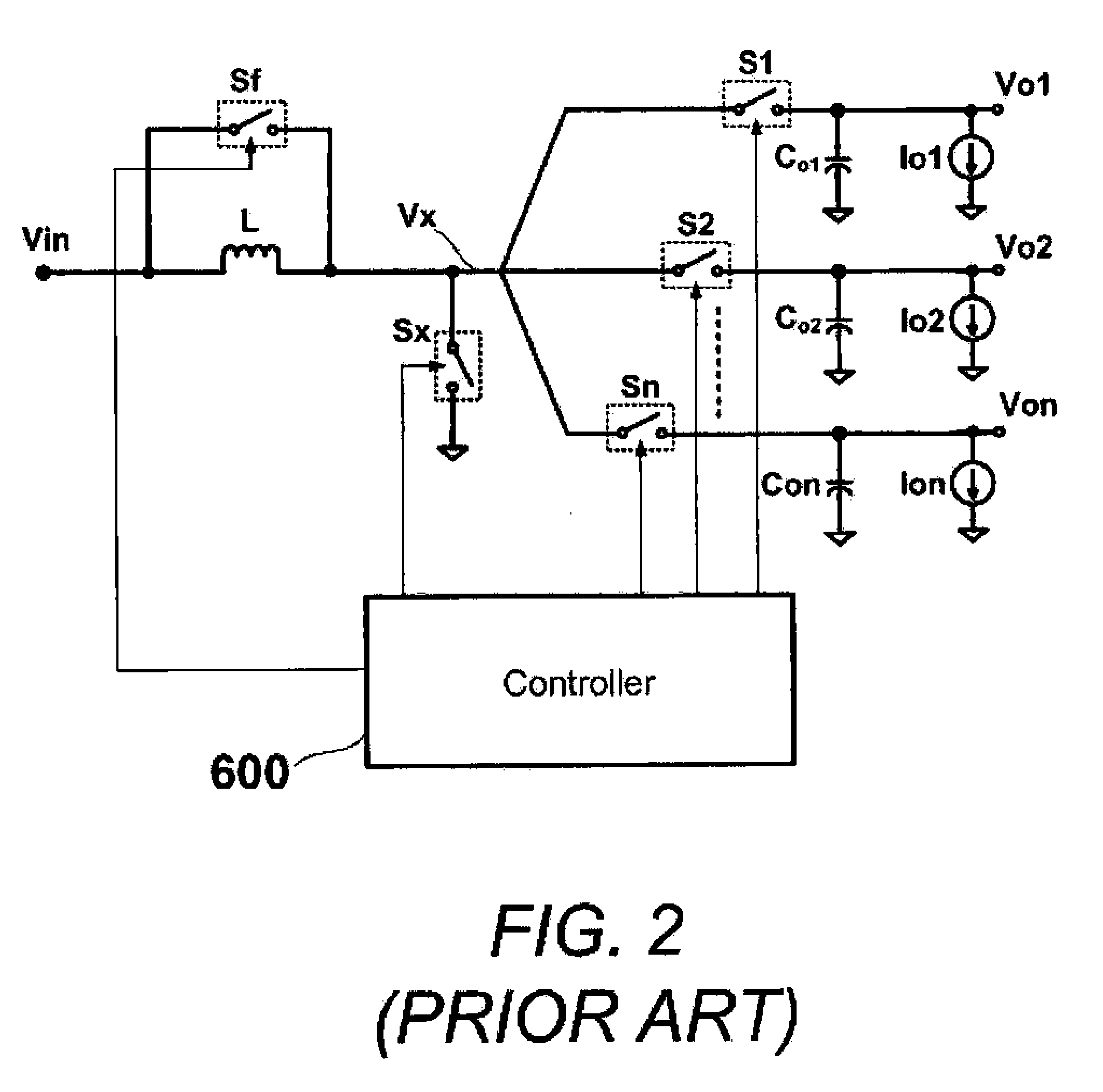
Multiple-Output DC-DC Converter
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter design. The converter requires only one single inductor to draw energy from one input source and distribute it to more than one outputs, employing Flexible-Order Power-Distributive Control (FOPDC). It include a single inductor, a number of power switches, comparators, only one error amplifier, a detecting circuit and a control block to regulate outputs. This converter can correctly regulate multiple outputs with fast transient response, low cross regulation, and effective switching frequency for each output. It can work in both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM). Moreover, with FOPDC, future output extension is simple, making a shorter time-to-market process for next versions of the converter. The design can be applied to different types of DC-DC converter.
Owner:JDA TECH
Multi-cellular photovoltaic panel system with dc-dc conversion replicated for groups of cells in series of each panel and photovoltaic panel structure
ActiveUS20090179500A1Improve efficiencySimple processClimate change adaptationDc source parallel operationDc dc converterMppt algorithm
A photovoltaic energy conversion system includes a distributed control structure for groups of cells of each multi-cellular panel, the components of which are entirely physically integrated in the photovoltaic panel. Each multi-cellular photovoltaic panel has a DC bus, supplied in parallel by a plurality of DC-DC converters, each provided with a controller that controls the working point of the photovoltaic cells coupled to the input of the DC-DC converter for a maximum yield of electric power by implementing a relatively simple MPPT algorithm. The controller includes a logic circuit and A / D converters of analog signals representing the input voltage and the input current generated by the group of cells that is coupled to the input of the DC-DC converter and optionally also of the output voltage of the converter, and a relatively simple D / A converter of the drive control signal of the power switch of the DC-DC converter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Advanced renewable energy harvesting
InactiveUS8138631B2Power maximizationEfficiently invertingBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransverterInput impedance
The power of DC electrical sources is combined onto a DC buss, such that each source behaves independently from any other source attached to the buss. In one embodiment, a converter module is attached to each of a plurality of solar photovoltaic panels and its output is attached in a parallel manner to a common buss that forms the input to a DC AC inverter. The converter module includes a Maximum Power Point Tracking component that matches the output impedance of the panels to the input impedance of the converter module. The converter also includes a communication component that provides parametric data and identification to a central inverter. Data generated by each converter module is transmitted over the power line or by wireless means and is collected at the inverter and forwarded to a data collection and reporting system.
Owner:EIQ ENERGY INC
Topology and control method for power factor correction
InactiveUS6344986B1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceReduce output voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterInductor
In a power factor corrected AC-to-DC power supply system, a DC-to-DC power converter is coupled to the output of an AC-to-DC power converter in order to produce a regulated DC output signal from a rectified AC input signal. The AC-to-DC power converter and the DC-to-DC power converter each includes a switch for controlling the operation of their respective power converter. The AC-to-DC converter includes an inductor. The system provides power factor correction for minimizing harmonic distortion by including a controller that receives the regulated DC output voltage as a feedback signal, and in response, produces a series of drive pulses having predetermined constant duty cycle. These pulses are simultaneously fed to each switch, to operate the respective converters alternately between ON and OFF states. When the AC-to-DC converter is driven by a fixed duty cycle of the series of pulses, power factor correction is improved since the current flowing through the inductor is substantially proportional to the waveform of the rectified AC input signal. By preselecting the value of the inductor, the AC-to-DC converter is operable in a discontinuous mode when the instantaneous rectified AC input signal is low and in a continuous mode when the instantaneous rectified AC input signal is high.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Control arrangement for a resonant mode power converter
InactiveUS20080198638A1Minimize such dead timeMinimize timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCharge currentControl signal
The switching frequency of an LLC converter is controlled by a control unit to which a feedback circuit provides a first current dependent upon the output voltage of the converter. An oscillator circuit produces a sawtooth waveform at a frequency dependent upon the first current, up to a limit equal to a second current set by a resistor. Two complementary switch control signals are produced for controlling two switches of the converter for conduction in alternate cycles of the sawtooth waveform. A timer produces dead times between the two complementary switch control signals in dependence upon the second current. Another resistor provides a current constituting a minimum value of the first current, and a charging current of a capacitor in series with a resistor modifies the first current for soft starting of the converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
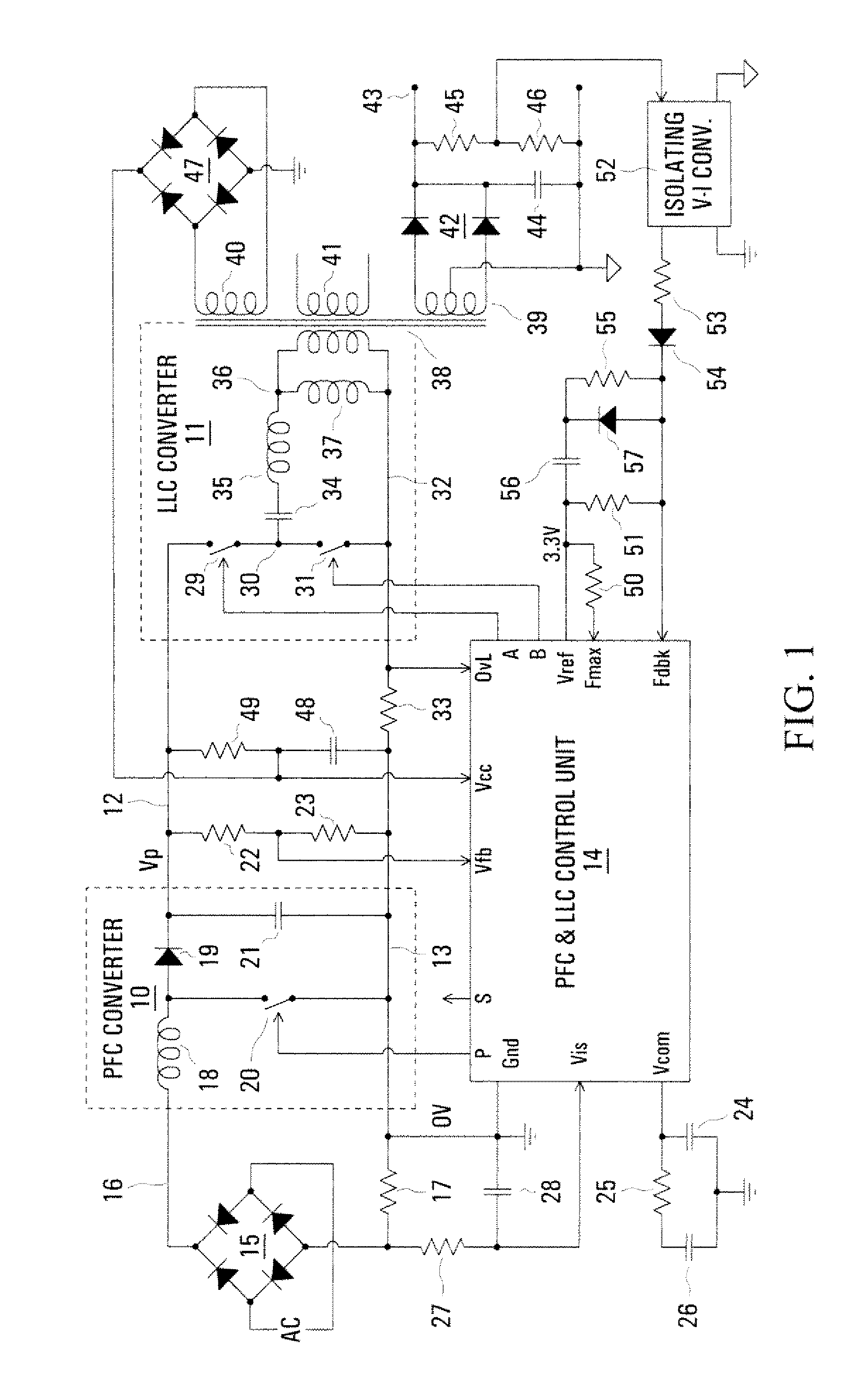
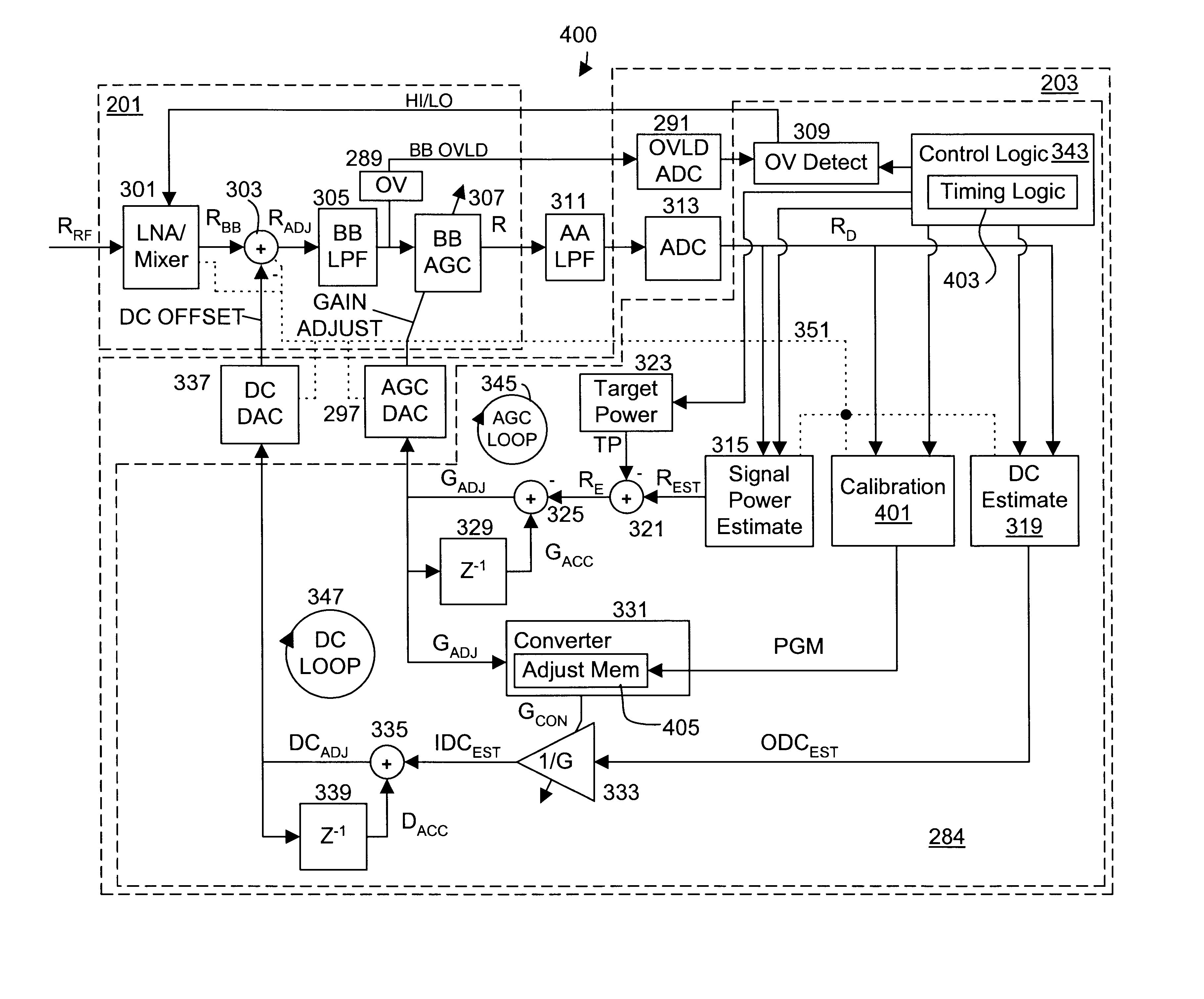
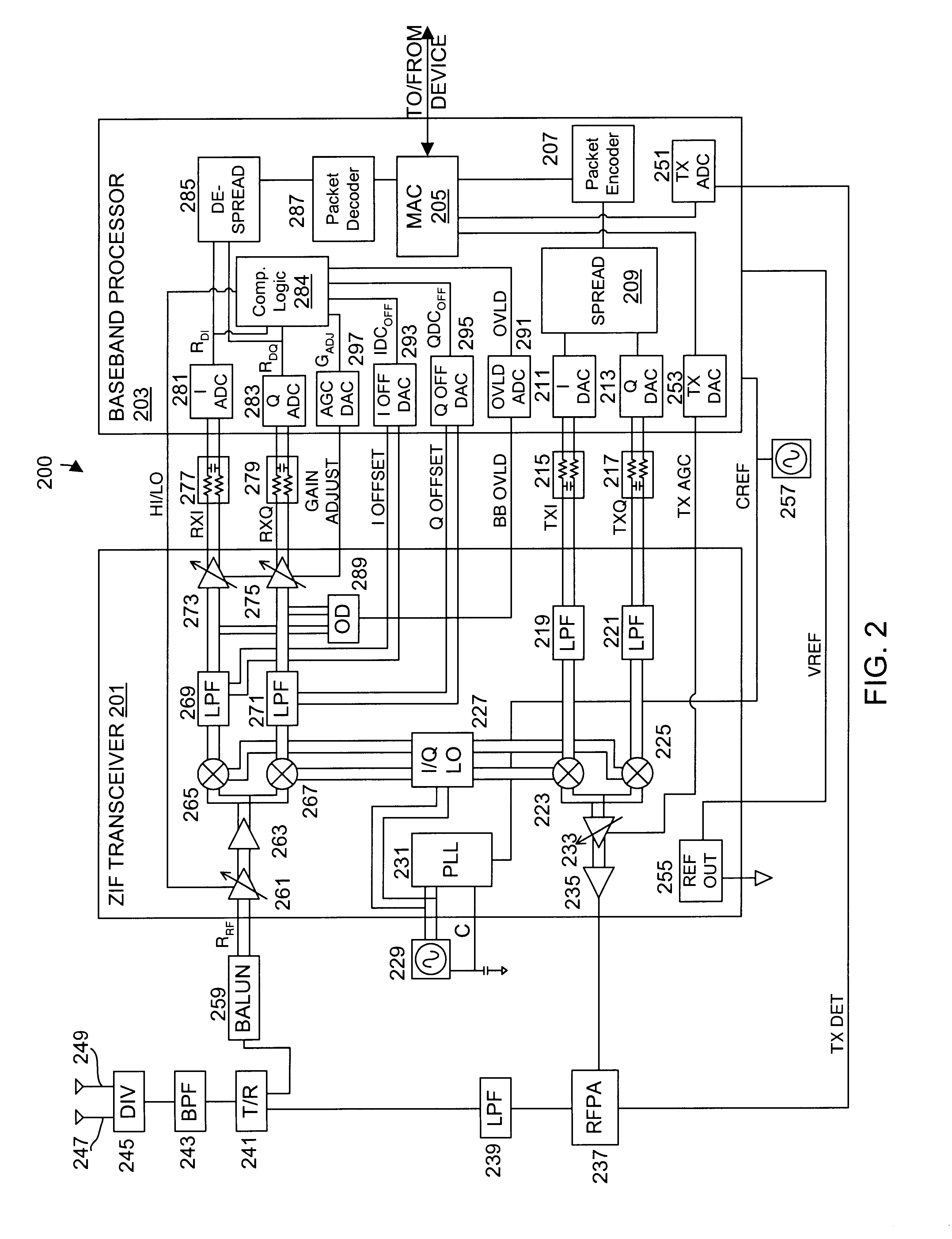
Calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6735422B1Low costMaximum performancePulse automatic controlGain controlTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) architecture. The device includes a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor, which further includes a calibrator that periodically performs a calibration procedure. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic, a gain converter and the calibrator. The gain converter converts gain between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The calibrator programs the gain converter with values determined during the calibration procedure. The gain converter may be a lookup table that stores gain conversion values based on measured gain of a baseband gain amplifier of the ZIF transceiver. The gain control logic may further include a gain adjust limiter that limits change of a gain adjust signal during operation based on a maximum limit or on one or more gain change limits. A second lookup table stores a plurality of DC adjust values, which are added during operation to further reduce DC offset. The calibration procedure includes sampling an output signal for each gain step of the baseband amplifier at two predetermined range values and corresponding DC offsets using successive approximation. The data is used to calculate gain, DC offset and DC differential values, which are used to determine the conversion values programmed into the lookup tables or the gain adjust limiter.
Owner:M RED INC
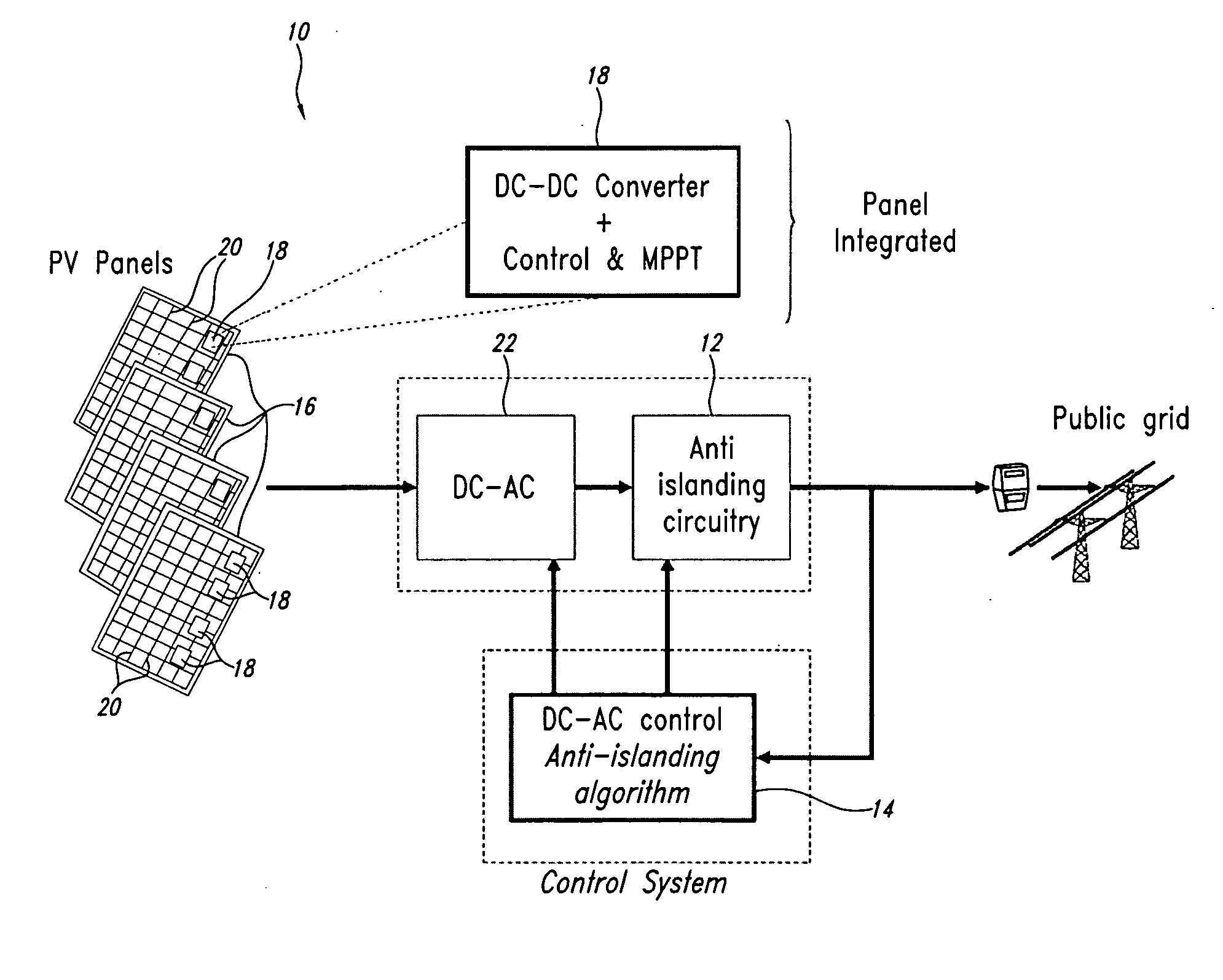
Photovoltaic module-mounted ac inverter
ActiveUS20080285317A1Total current dropIncrease the ripple frequencyConversion constructional detailsElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringTransistor
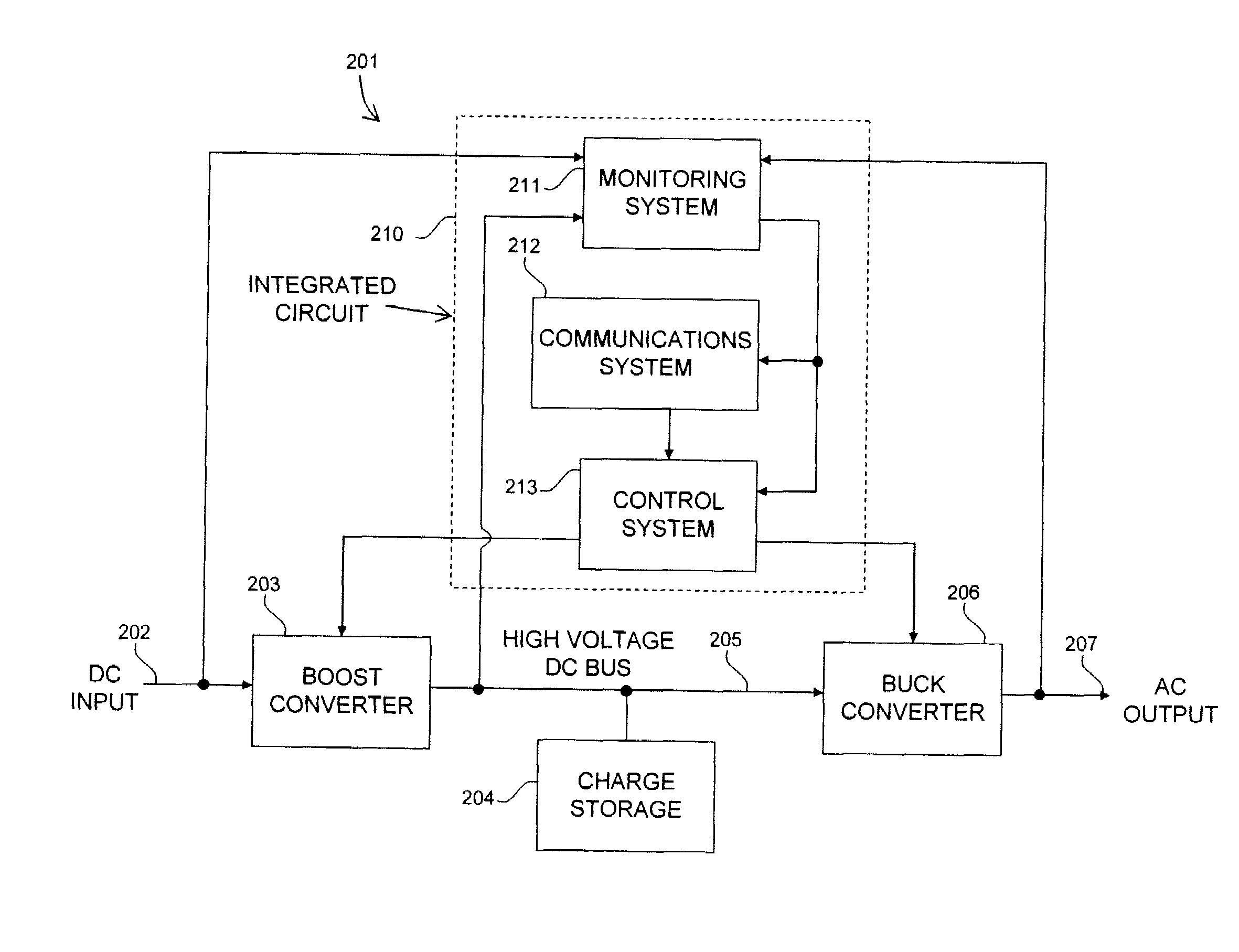
A photovoltaic module-mounted AC inverter circuit uses one or more integrated circuits, several power transistors configured as switches, several solid-dielectric capacitors for filtering and energy storage, several inductors for power conversion and ancillary components to support the above elements in operation. The integrated circuit includes all monitoring, control and communications circuitry needed to operate the inverter. The integrated circuit controls the activity of pulse-width modulated power handling transistors in both an input boost converter and a single-phase or multi-phase output buck converter. The integrated circuit also monitors all power processing voltages and currents of the inverter and can take appropriate action to limit power dissipation in the inverter, maximize the available power from the associated PV module and shut down the inverter output if the grid conditions so warrant. The integrated circuit implements power line communications by monitoring the AC wiring for signals and generating communications signals via the same pulse-width modulation system used to generate the AC power. Communications is used to report inverter and PV module status information, local identification code and to allow for remote control of inverter operation.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including up inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS20080157733A1Poor regulationIncrease heightEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceTransverter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a boost converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage up by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Dc-dc converters
ActiveUS20110018516A1Easy to controlTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterPower flow
Methods and apparatus for control of DC-DC converters. The DC-DC converter is operable so that the low side supply switch may be inhibited from turning on in a cycle following the high side supply switch turning off. Turn on of the low side switch is inhibited if the time between turn off of the high side switch and the inductor (L) current reaching zero is less than a predetermined duration. Inhibiting the low side switch from turning on can prevent the inductor current from going negative, which would reduce the efficiency of the converter. When turn on of the low side switch is inhibited the inductor current flows through a parallel path, such as a parasitic body diode associated with the low side switch, which allows current flow in one direction only.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
System and Method for Exchangeable Capacitor Modules for High Power Inverters and Converters
ActiveUS20130094262A1Facilitate notificationAc-dc conversion without reversalCapacitor testingElectric power transmissionTransverter
A method of and system for monitoring condition of a large capacitor connected across an output of a rectifier circuit in an operating electrical power transmission circuit in order to anticipate capacitor failure and facilitate appropriate corrective action is disclosed. The method includes measuring a ripple voltage on the capacitor and ripple current through the capacitor, determining from a representative signal whether the signal exceeds a predetermined threshold; and sending an output to a controller on a system operator if the signal exceeds the predetermined threshold. The ripple current and ripple voltage measurements may be provided as inputs to a digital to analog converter which produces and sends the representative signal to a microprocessor to generate the output to the controller.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
System and method for synchronous rectifier drive that enables converters to operate in transition and discontinuous mode
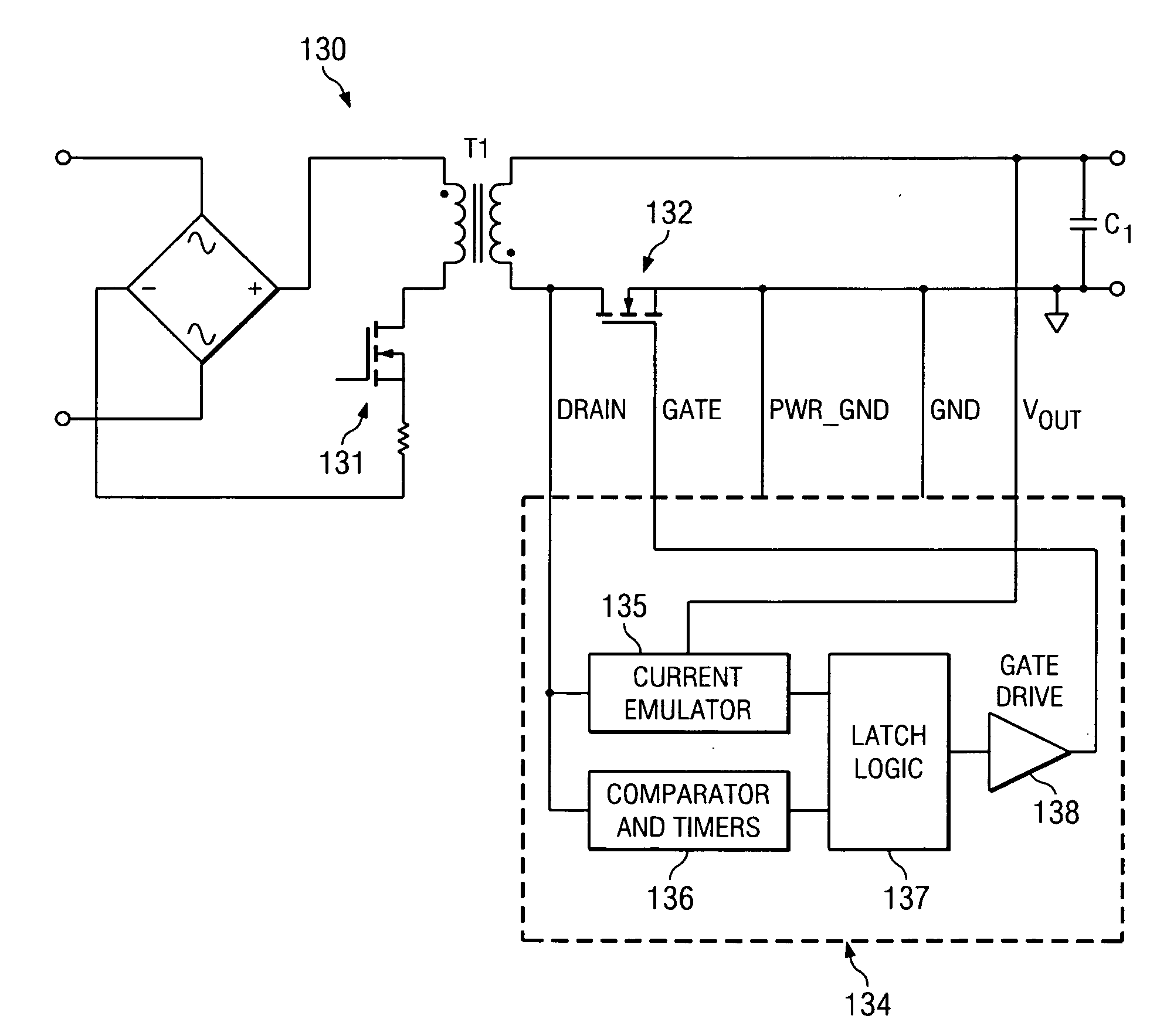
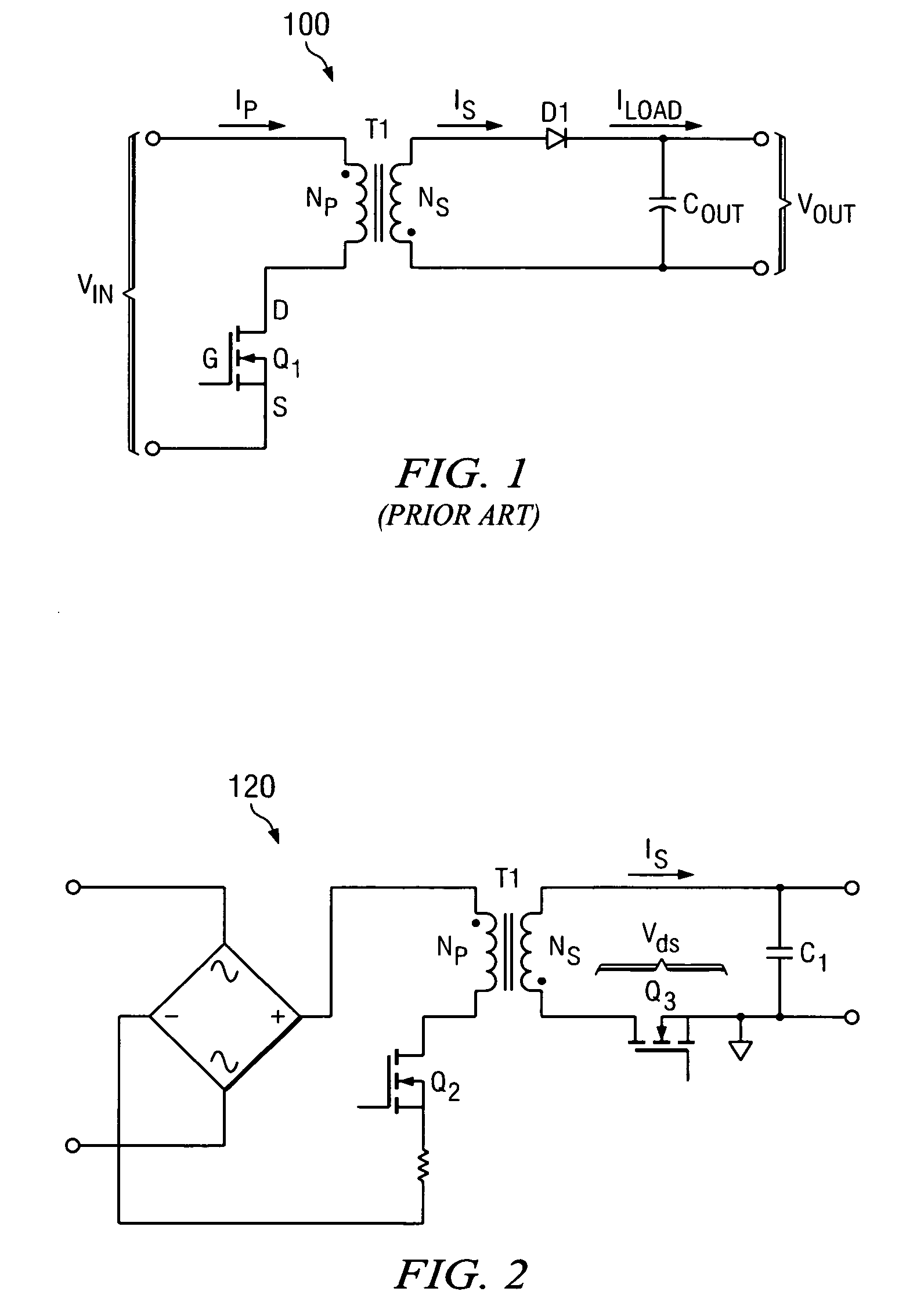
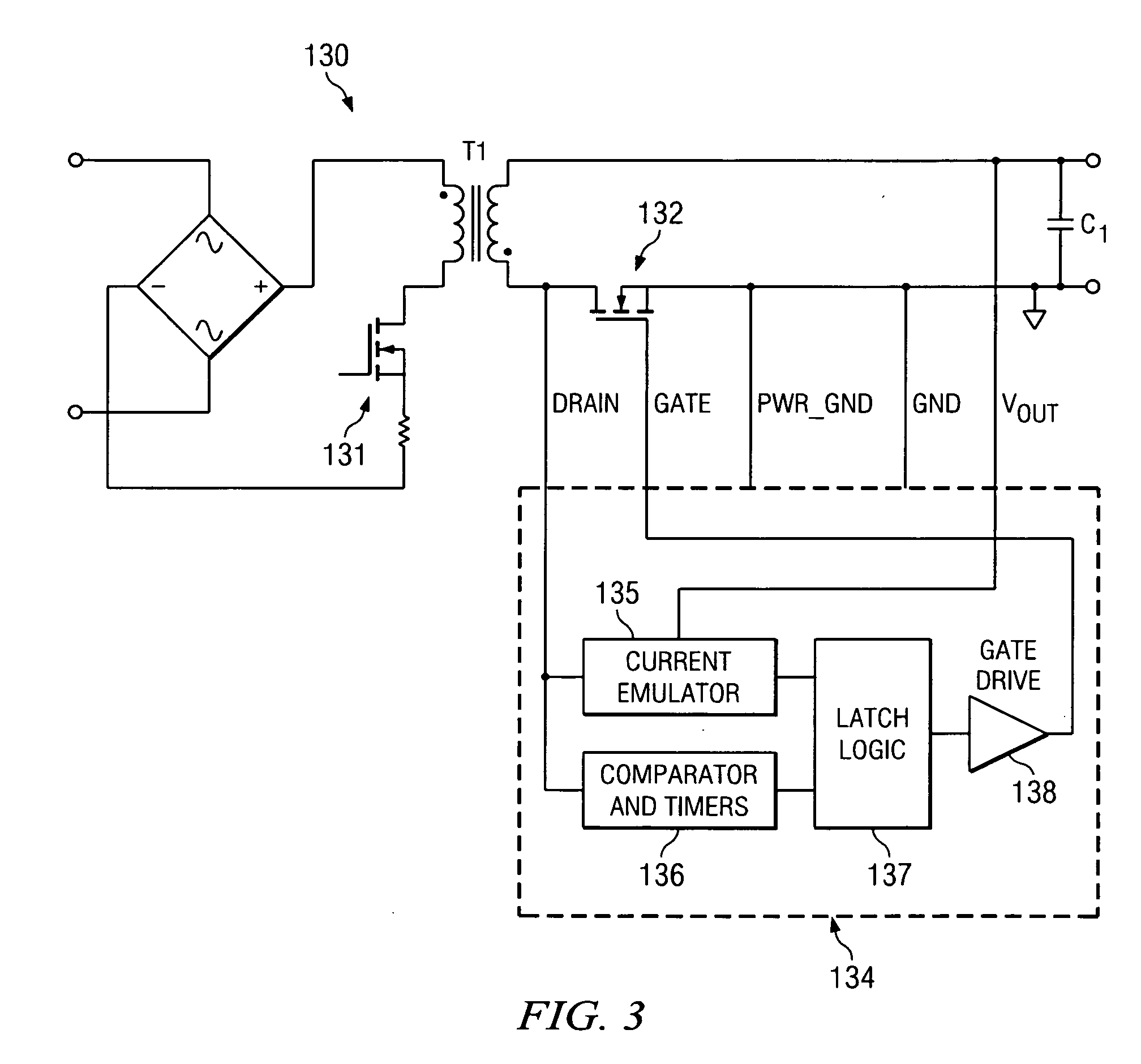
ActiveUS20100027298A1Inhibition transitionWithout significant lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterSecondary side
A synchronous rectifier is switched in accordance with a primary switch transition and a reference signal representing current in a current storage device to which the synchronous rectifier is coupled. A current emulator provides a signal representing current in the current storage device as a volt-second product so that current stored in the current storage device while the primary switch is on is discharged by the synchronous rectifier. The use of a current emulator provides an inexpensive solution for controlling synchronous rectifier transitions without resorting to more expensive current sensing solutions that are commercially impracticable. Blanking intervals are provided for avoiding false transitions of the synchronous rectifier when the primary switch turns on and after the synchronous rectifier turns off. The disclosed system and method can be applied to flyback converters for a synchronous rectifier on the secondary side of a transformer, or the inductor of buck converters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
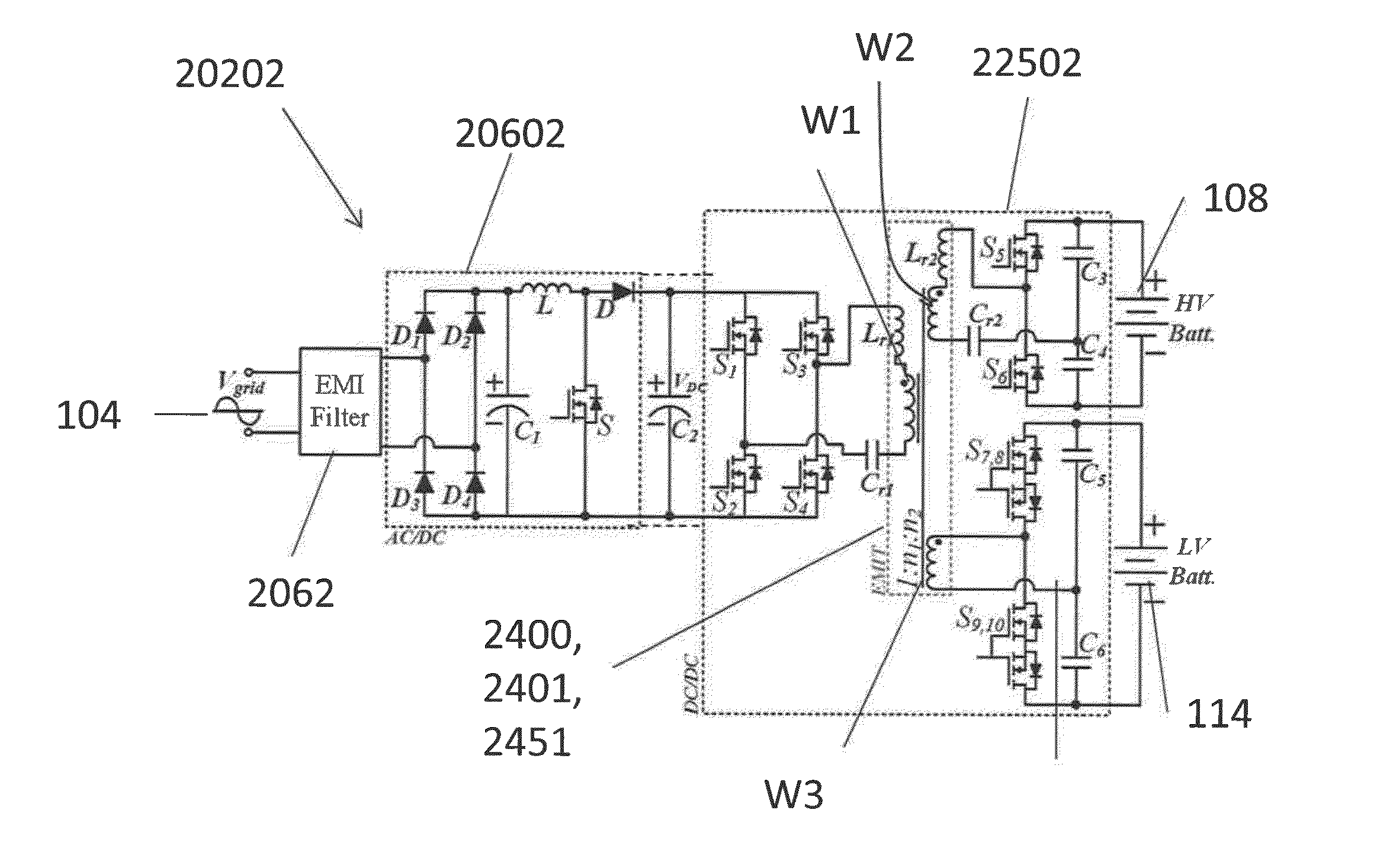
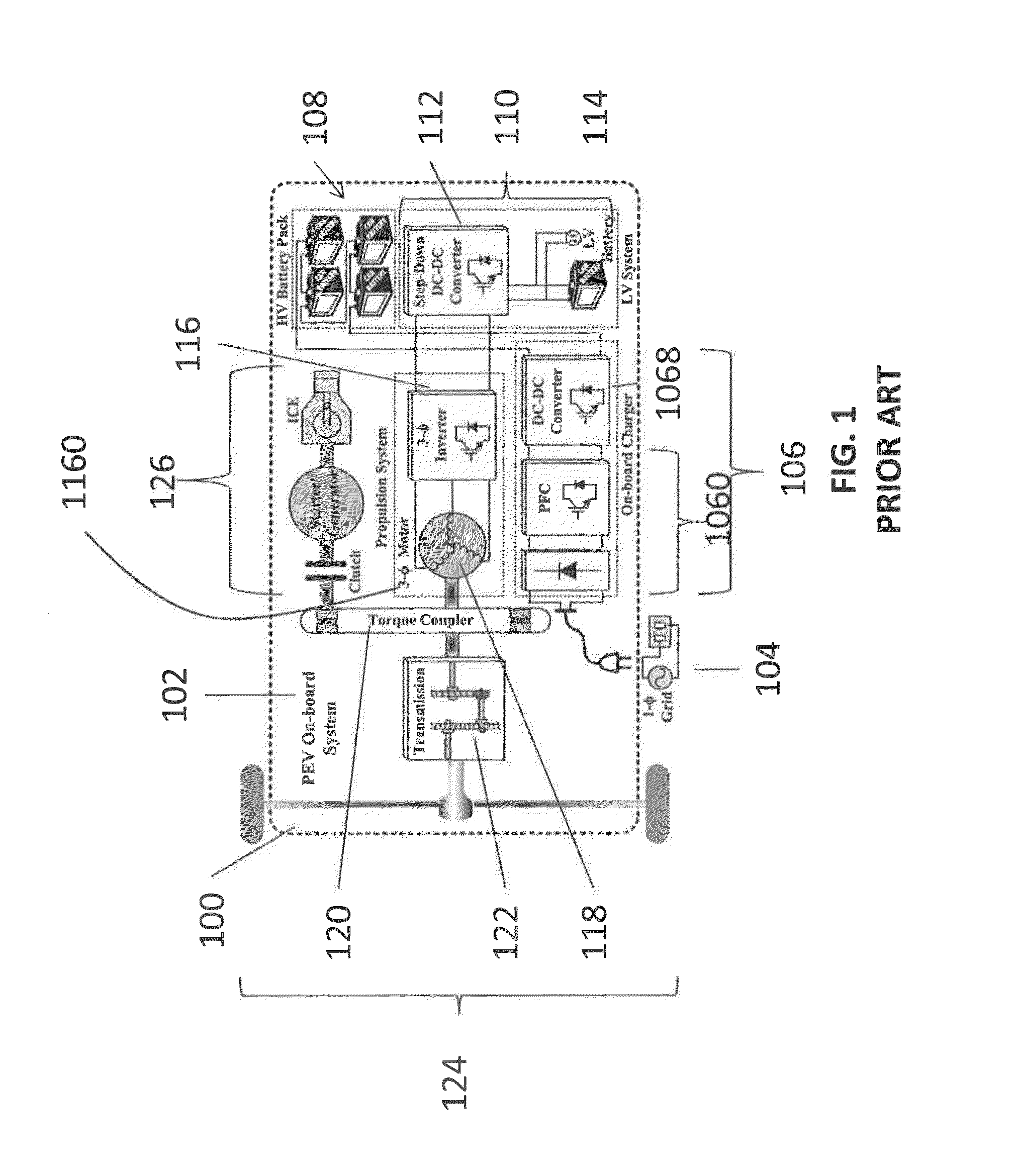
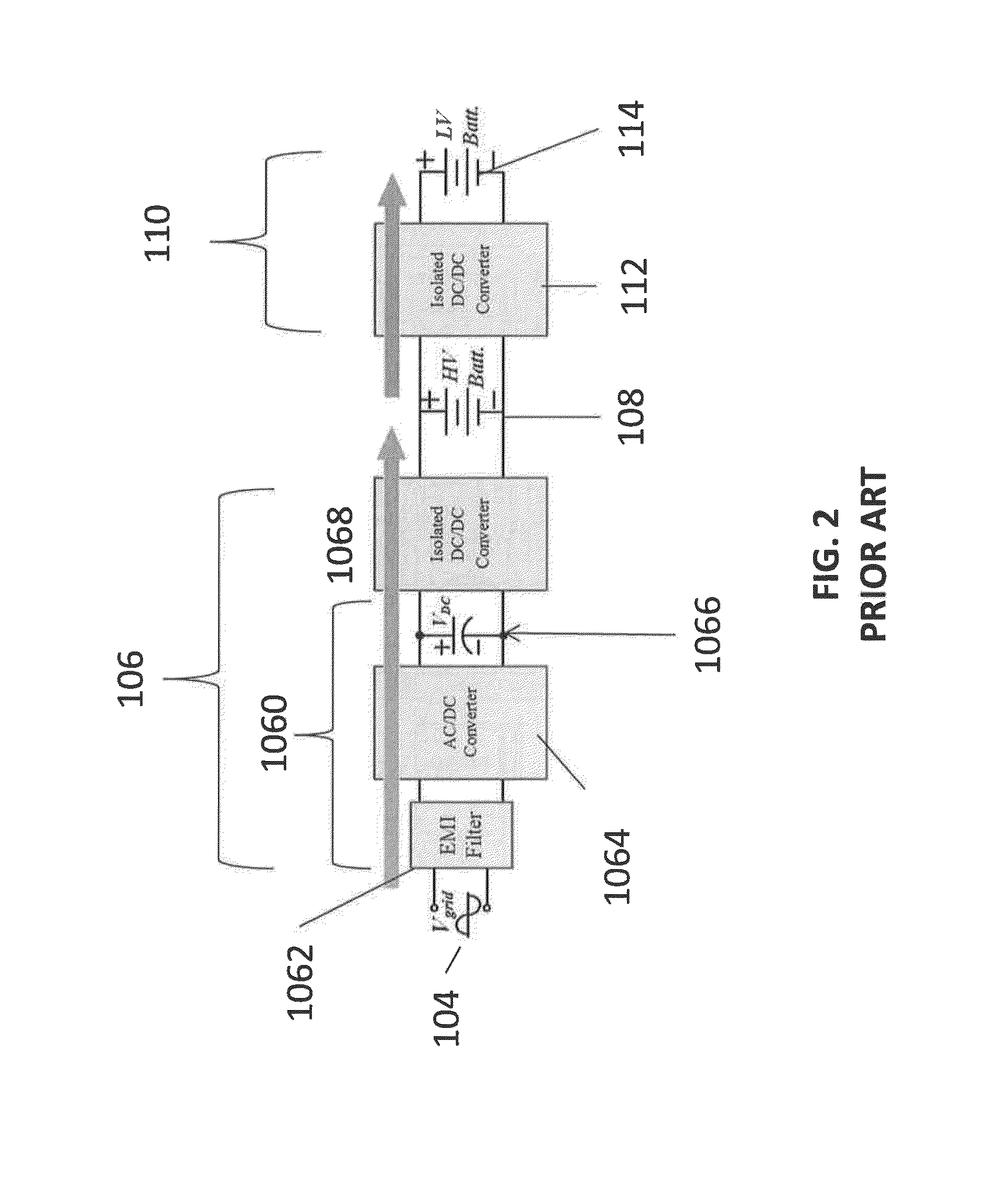
An integrated dual-output grid-to-vehicle (G2V) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles
ActiveUS20160016479A1Improve power densitySmall sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresElectrical batteryLow voltage
An integrated and isolated onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles, includes an ac-dc converter and a dual-output dc-dc resonant converter, for both HV traction batteries and LV loads. In addition, the integrated and isolated onboard charger may be configured as unidirectional or bidirectional, and is capable of delivering power from HV traction batteries to the grid for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. To increase the power density of the converter, the dual-output DC-DC resonant converter may combine magnetic components of resonant networks into a single three-winding electromagnetically integrated transformer (EMIT). The resonant converter may be configured as a half-bridge topology with split capacitors as the resonant network components to further reduce the size of converter. The integrated charger may be configured for various operating modes, including grid to vehicle (G2V), vehicle to grid (V2G) and high voltage to low voltage, HV-to-LV (H2L) charging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
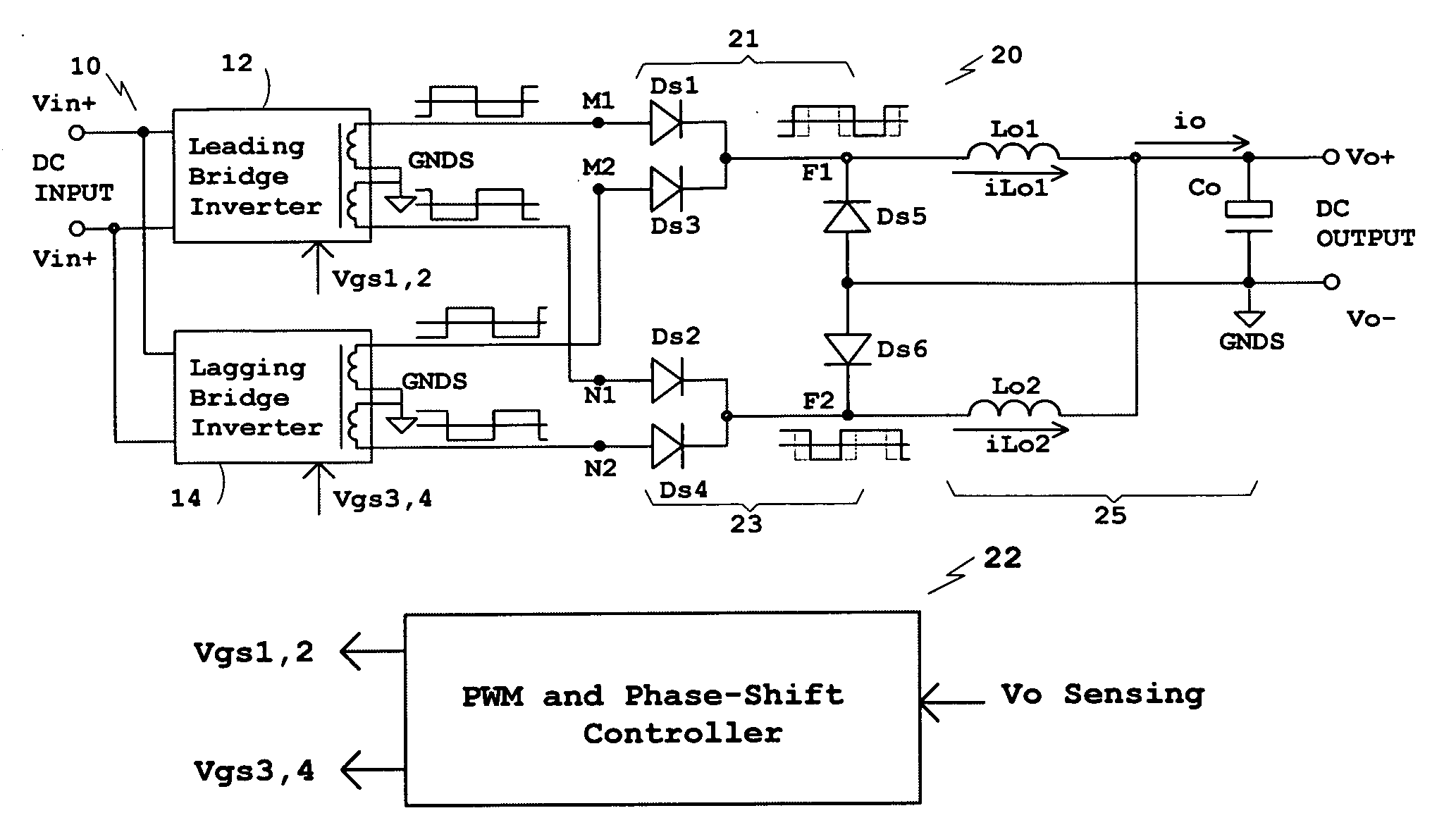
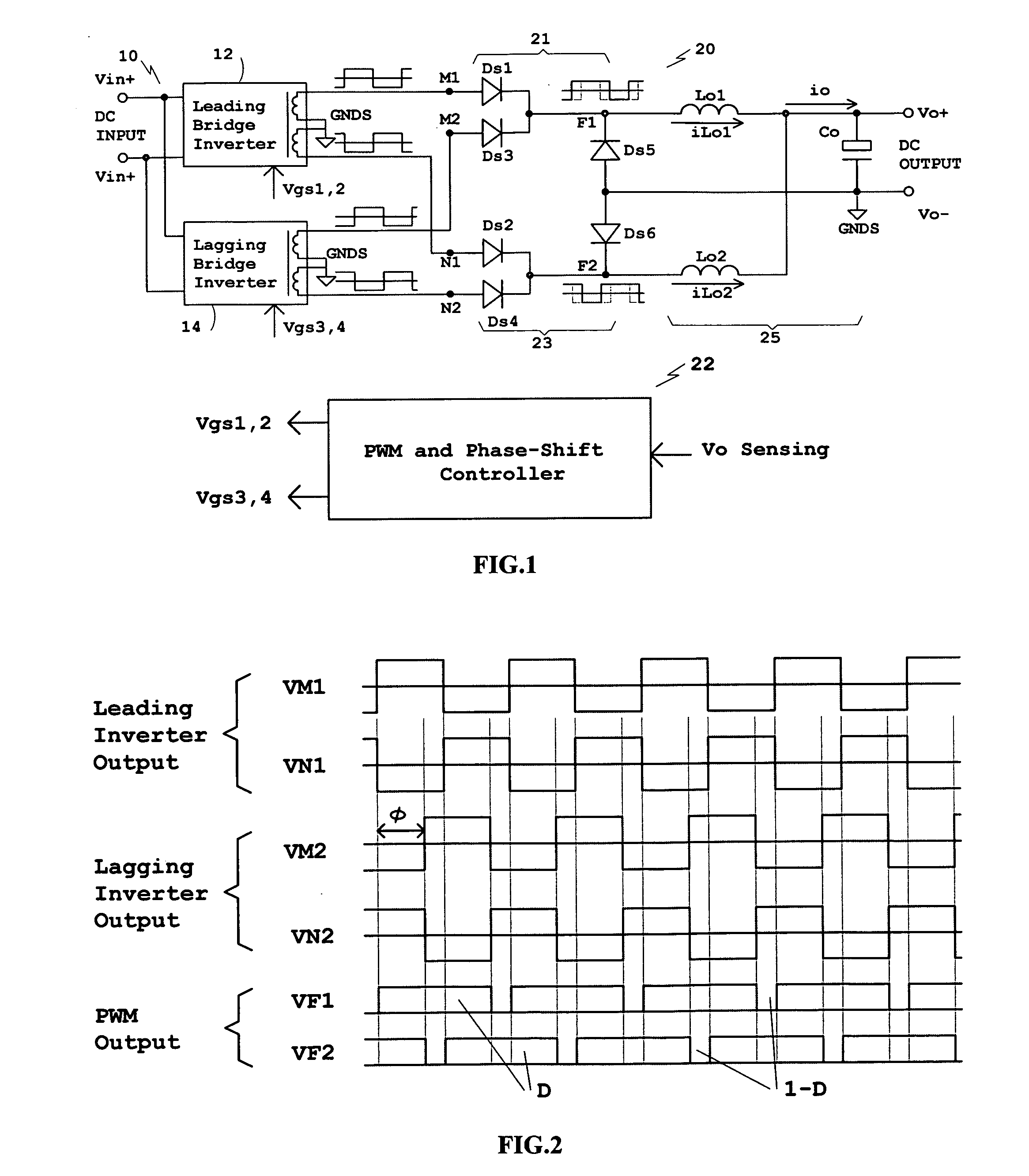
Phase-shifted dual-bridge DC/DC converter with wide-range ZVS and zero circulating current
ActiveUS20090196072A1Solve insufficient storage spaceMinimizes voltage ringingAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePhase difference
Disclosed is a family of new DC / DC converters and a new control method. The converter comprises two bridge inverters, two full-wave rectification circuits and a current-doubler filter. Each inverter is able to generate a symmetrical and isolated AC output voltage. Phase-shift control is employed to control the phase difference between the two bridge inverters. By shifting the phase, the converter changes the two inverters' output voltage overlapping area to regulate its output voltage. The bridge inverters always operate at 50% duty cycle, like an open loop Bus Converter, to achieve wide-range zero voltage switching and eliminate circulating current for normal operation. For low output voltage regulation and soft start, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control is used. The converters and the control method improve power conversion efficiency, maximize magnetic component utilization, reduce semiconductor stress and decrease EMI emission.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Distributed Power Harvesting Systems Using DC Power Sources
InactiveUS20120175963A1Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransverterEngineering
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com