Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8692 results about "Charge current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Current is defined as the rate of flow of charges through a medium. These charges are usually in the form of electrons. The SI unit for current is ampere, which is named in honor of Andre-Marie Ampere.
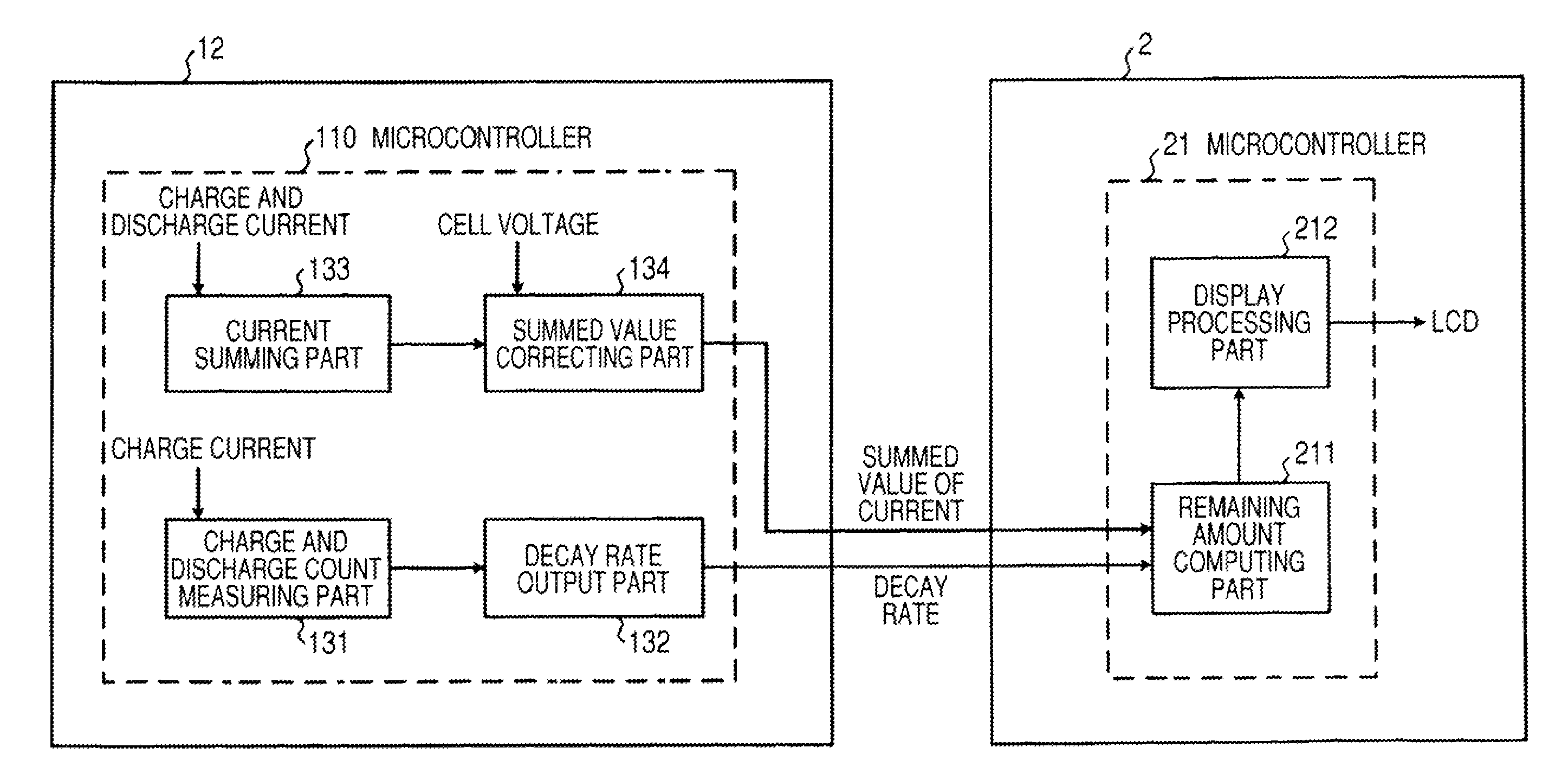
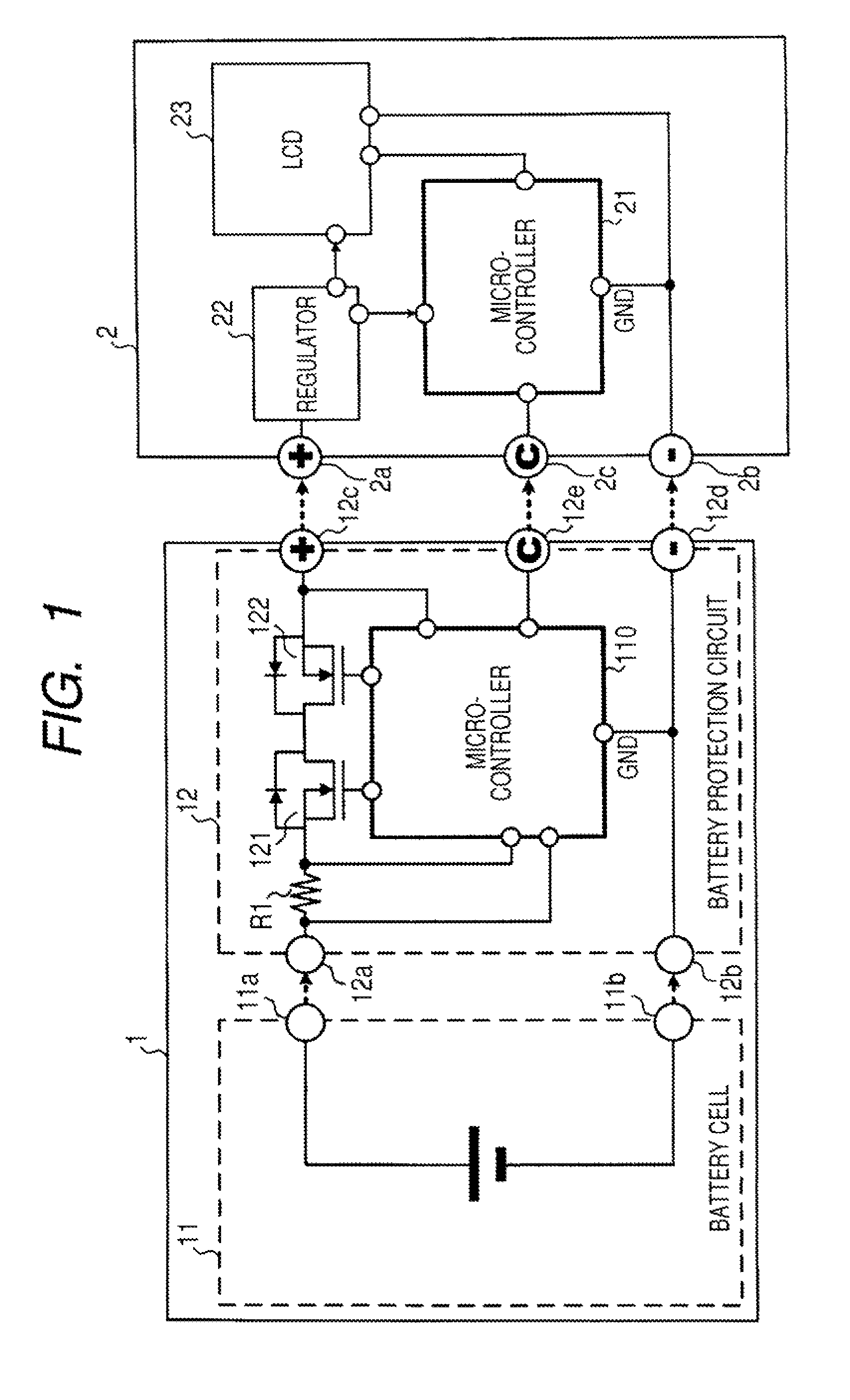
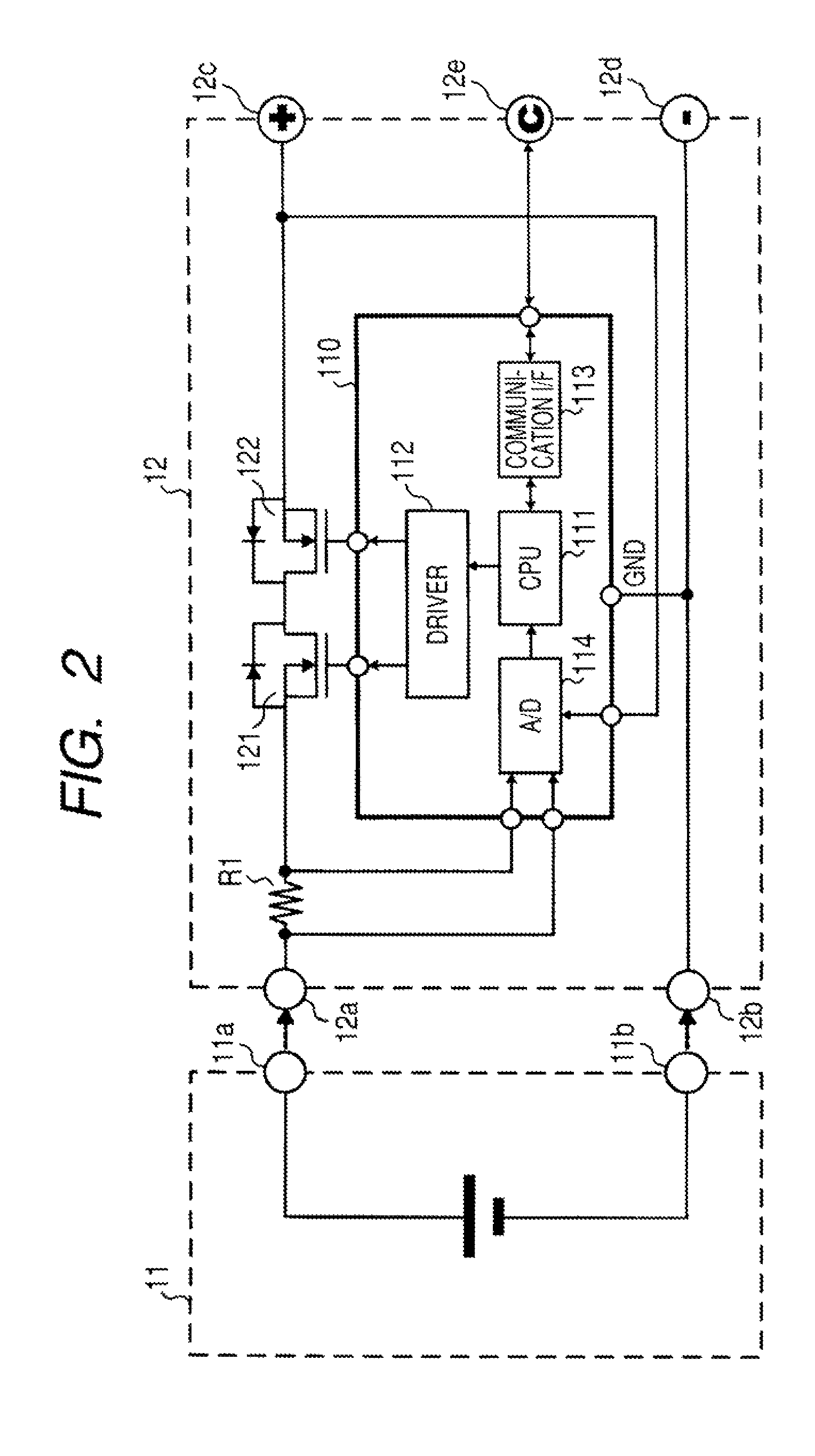
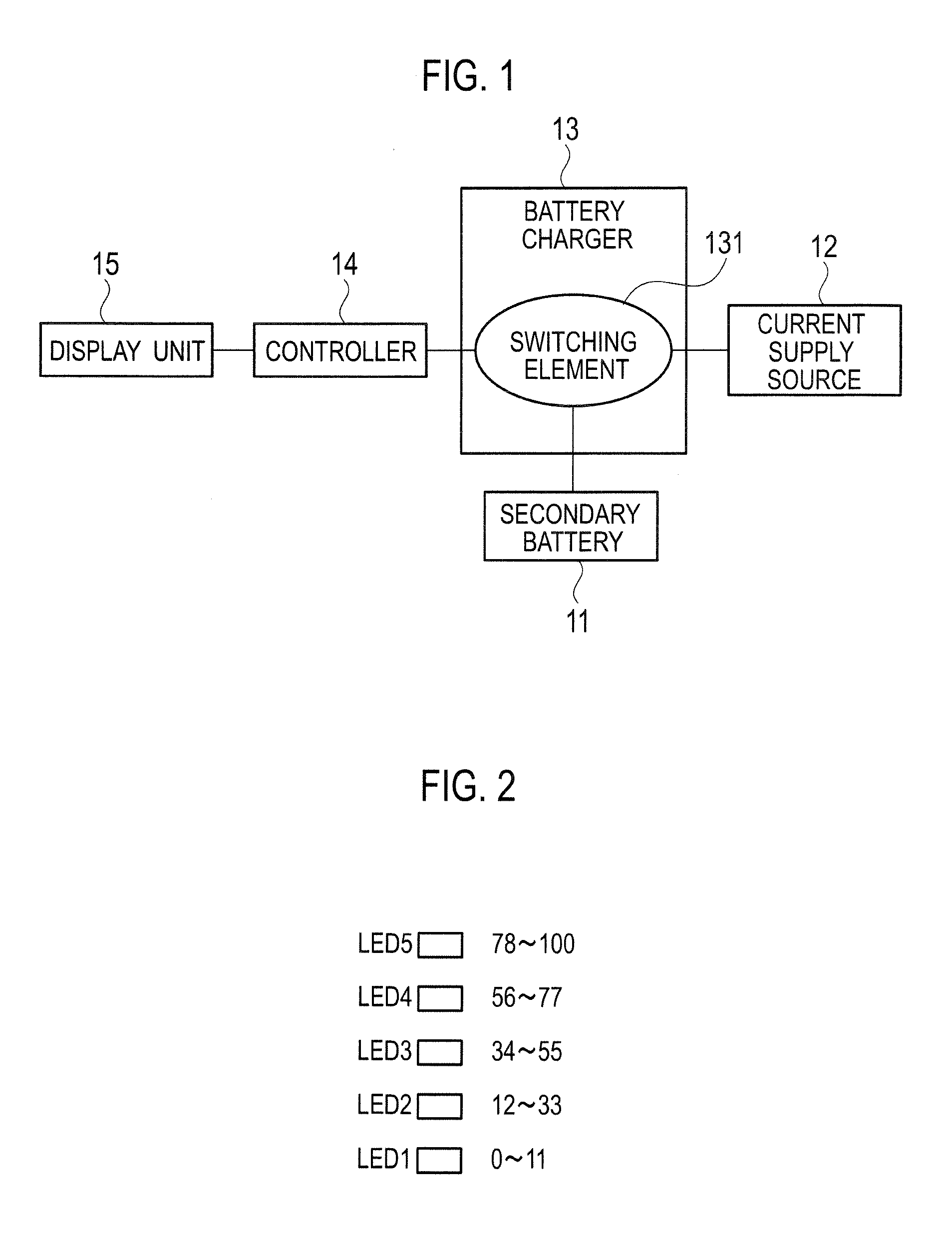
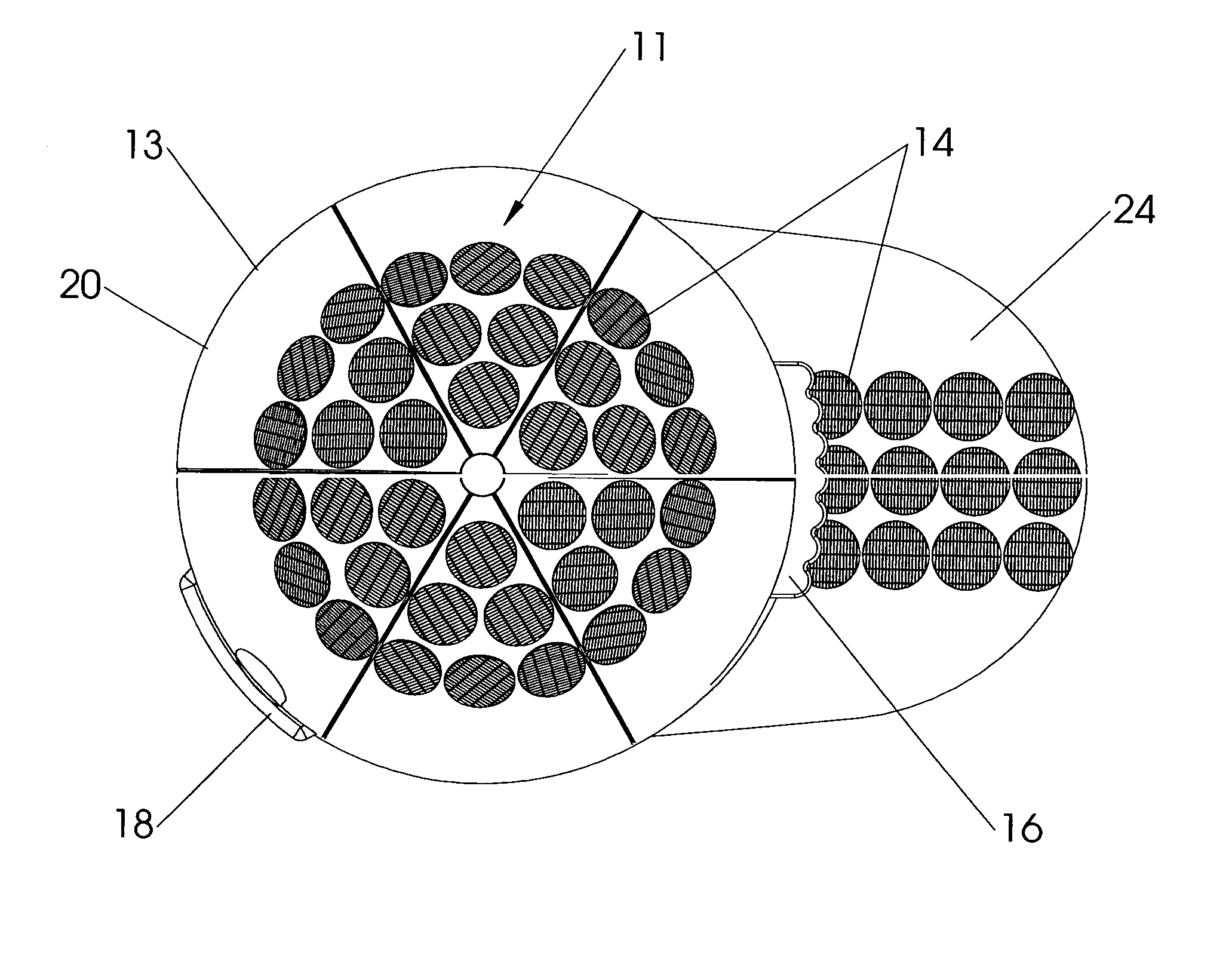
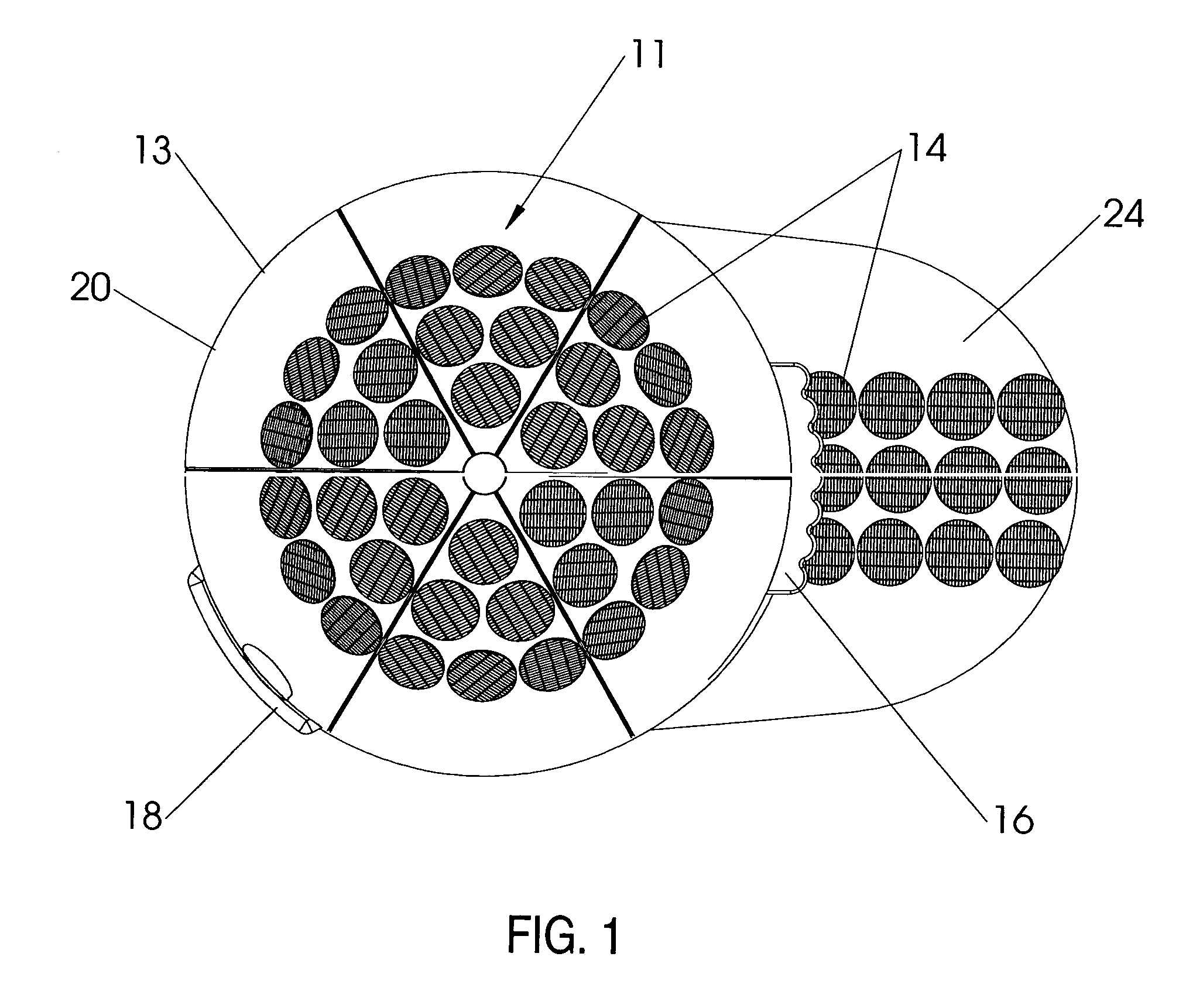
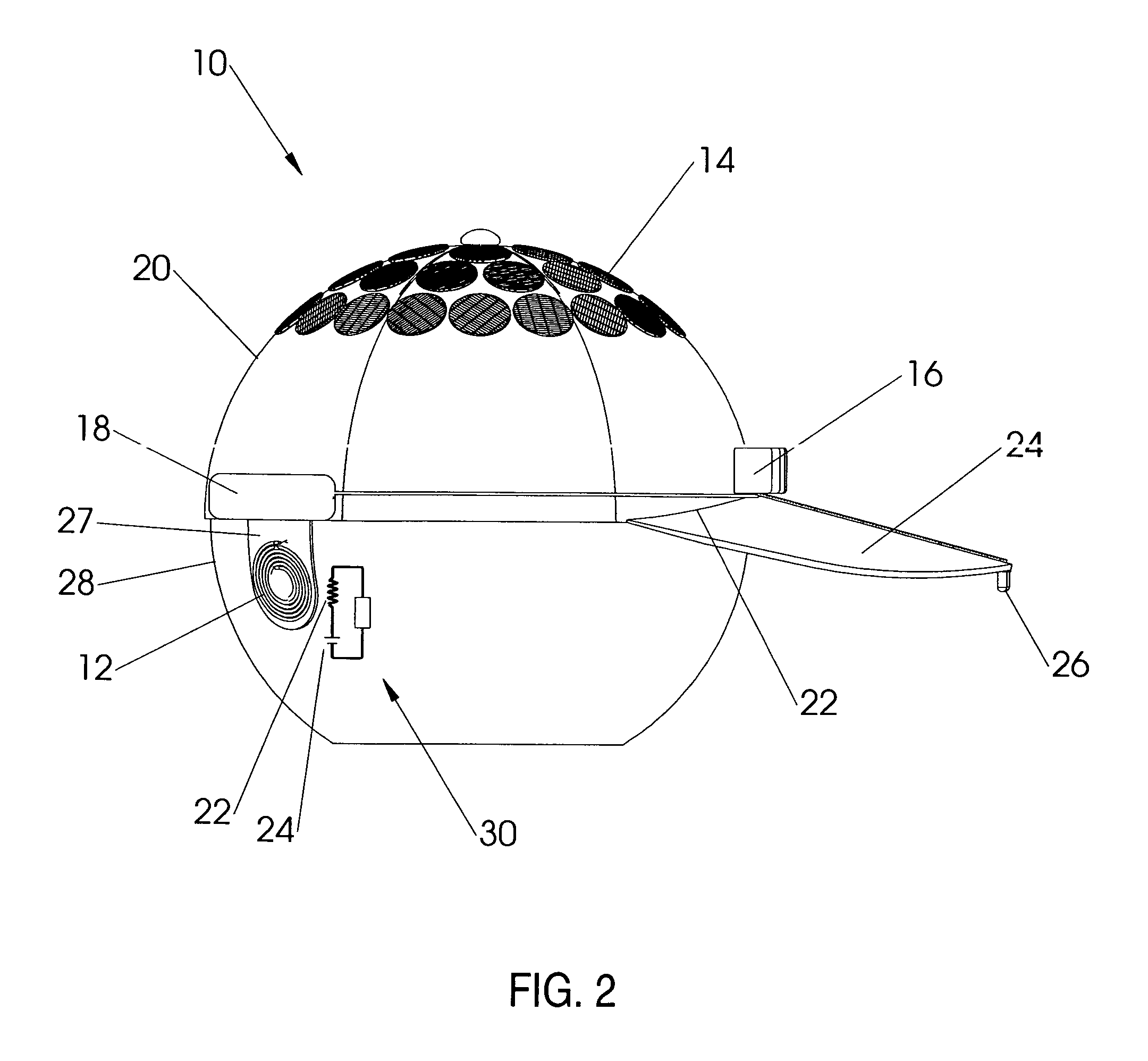
Battery pack, electronic appliance, and method of detecting remaining amount of battery
InactiveUS8359174B2Accurate detectionCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingPower flowCharge current
A battery pack has a charge and discharge count measuring part (131) configured to measure the number of times of charges and discharges of a secondary battery based on the summed value of the charge current for the secondary battery, and a decay rate output part (132) configured to compute a decay rate that indicates a degree of decay of the secondary battery based on the number of times of charges and discharges measured by the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) and to output it to a device being a discharge load. For example, the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) repeatedly sums the detected values of the charge current to a predetermined threshold, and counts up the number of times of charges and discharges every time when the summed value reaches the threshold. Accordingly, even though charges and discharges are repeated at finer steps in a relatively narrow voltage range, the number of times of charges and discharges can be counted accurately, and the computing accuracy of the decay rate is improved. In the battery pack in which the secondary battery is accommodated, parameters for detecting the remaining amount of the battery are detected more accurately.
Owner:SONY CORP
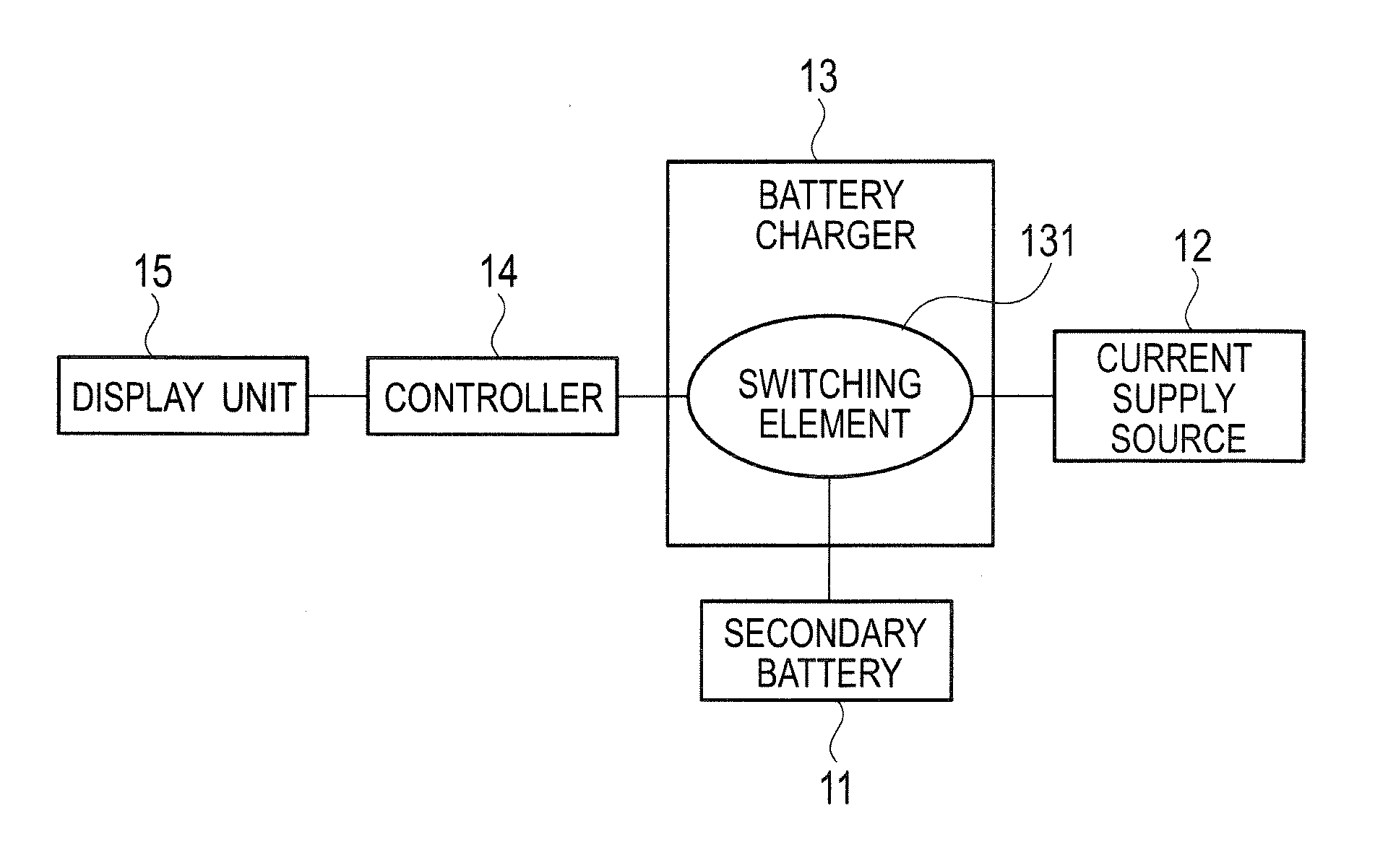
Rechargeable electric device
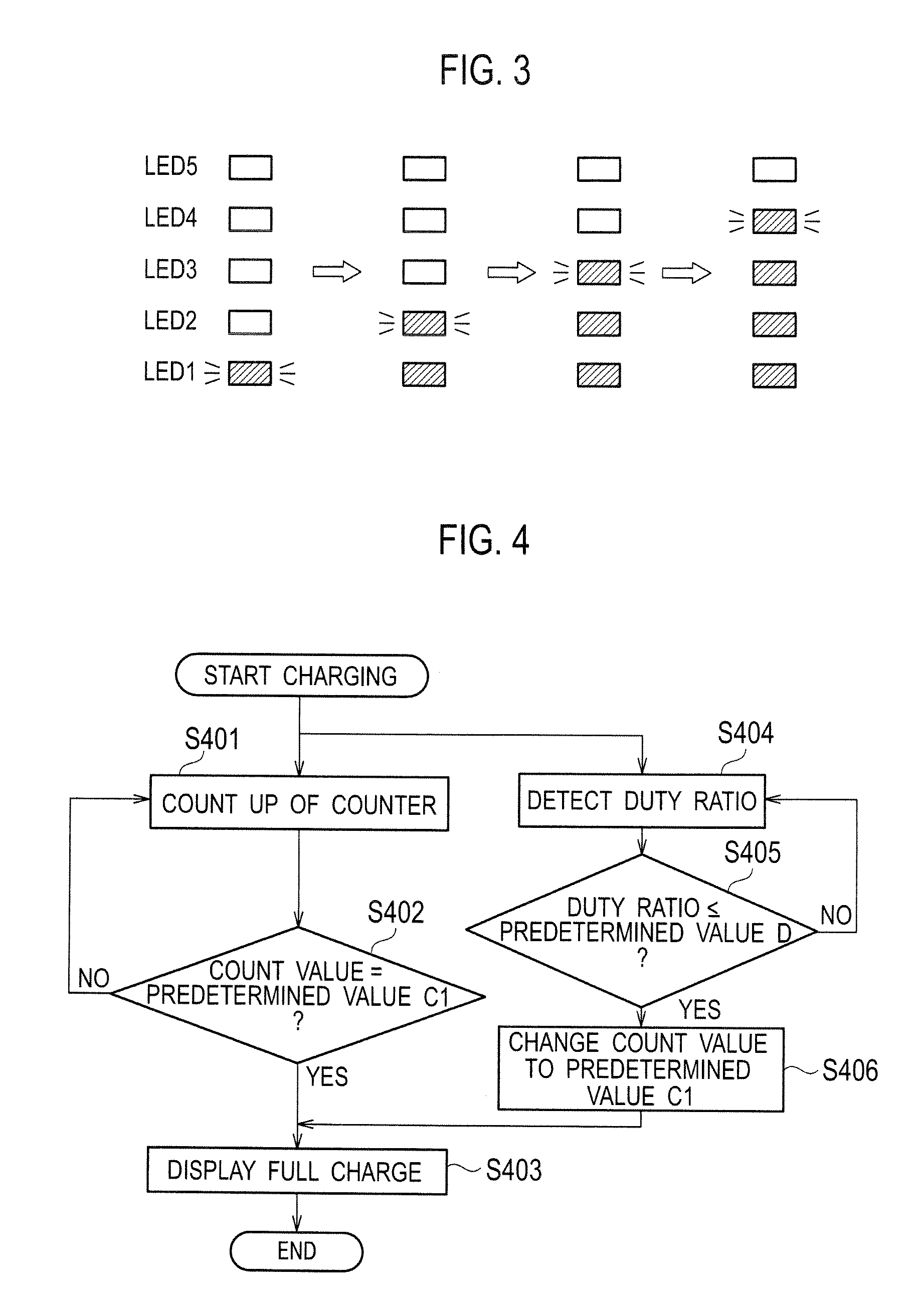
InactiveUS20130169217A1Accurate displayImprove accuracyCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingCharge currentSwitching signal
Under a control by a controller (14), a rechargeable electric device makes a full charge display to display on a display unit (15) that a secondary battery (11) is fully charged, after a start of charging the secondary battery (11) in a case where either when a count value of a counter reaches a first predetermined value (C1) corresponding to the full charge of the secondary battery (11), or when a duty ratio of switching signals which make an on / off control of a switching element (131) becomes smaller than or equal to a predetermined value (D) corresponding to the charge current obtained at a time of the full charge of the secondary battery (11).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
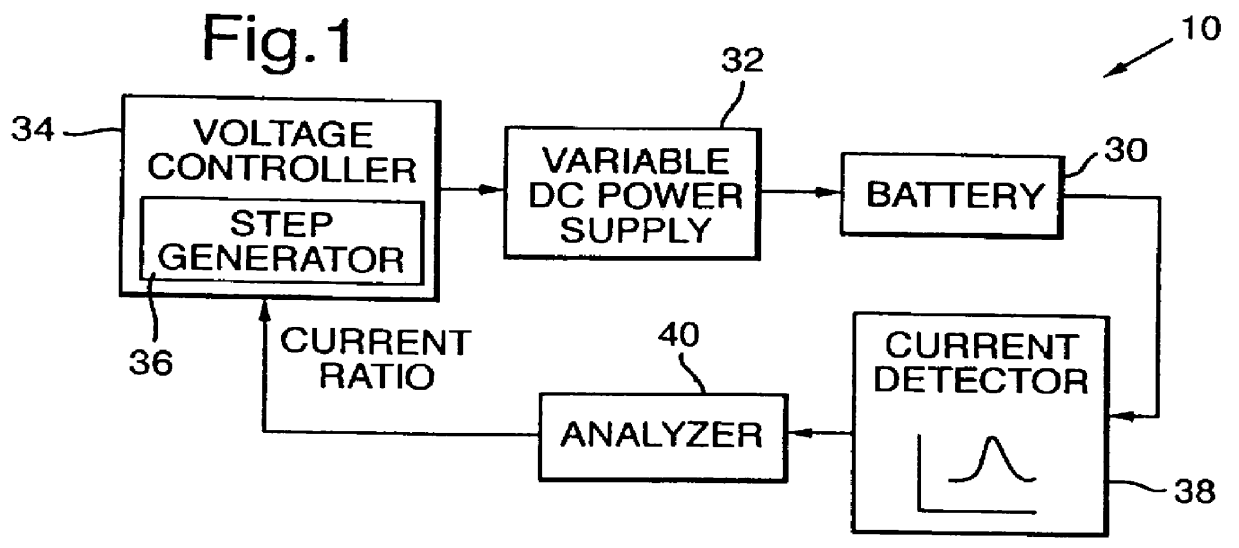
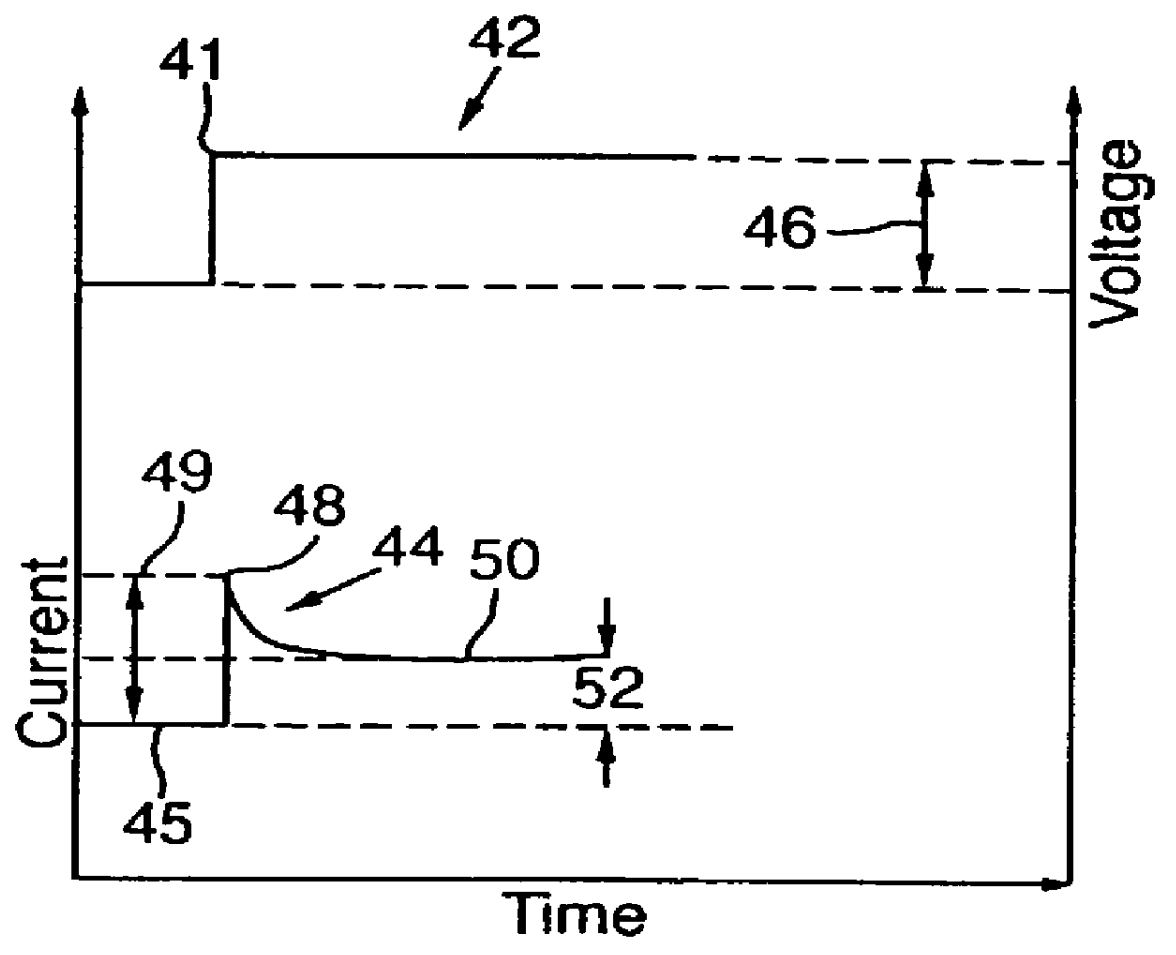
Method and apparatus for charging batteries
InactiveUS6037751AEfficient chargingLow charge acceptanceBatteries circuit arrangementsLead-acid accumulatorsCharge currentCurrent voltage
A method and apparatus for efficiently charging lead-acid batteries applies small voltage steps to probe the charging efficiency of a battery being charged. The application of a voltage step causes the current to change from a base current to a surge current immediately after the voltage step, and to decay asymptotically to a plateau current after the surge current. A current ratio, defined as the difference between the plateau current and the base current divided by the difference between the surge current and the base current, is used as an indicator of the charging efficiency. The output voltage of the power supply charging the battery is then adjusted according to the measured current ratio. A current-voltage slope, defined as the difference between the plateau current and the base current divided by the magnitude of the voltage step, may also be used as an indicator of the charging efficiency for controlling the charging process. Alternatively, in a current-controlled charging process, small current steps are used to probe the charging efficiency. For a current step, the induced voltage changes are measured, and a transient-plateau voltage ratio is calculated. The charging current is then adjusted according to the calculated voltage ratio.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
Floor covering and inductive power system
InactiveUS20100314946A1Improving magnetic couplingPrevent short-circuitingRoof covering using slabs/sheetsBatteries circuit arrangementsCharge currentEngineering
The invention relates to a floor covering (100) comprising: a plurality of coils (110), each coil (110) being operable to supply inductive energy to a power receiver circuit (200); wherein the plurality of coils comprises a transmitter area occupying the largest area of the floor covering (100); and a charging current through the coils is operable to generate said inductive energy.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Battery Chargers and Methods for Extended Battery Life
InactiveUS20070024246A1Easy to optimizeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCharge currentBattery cell
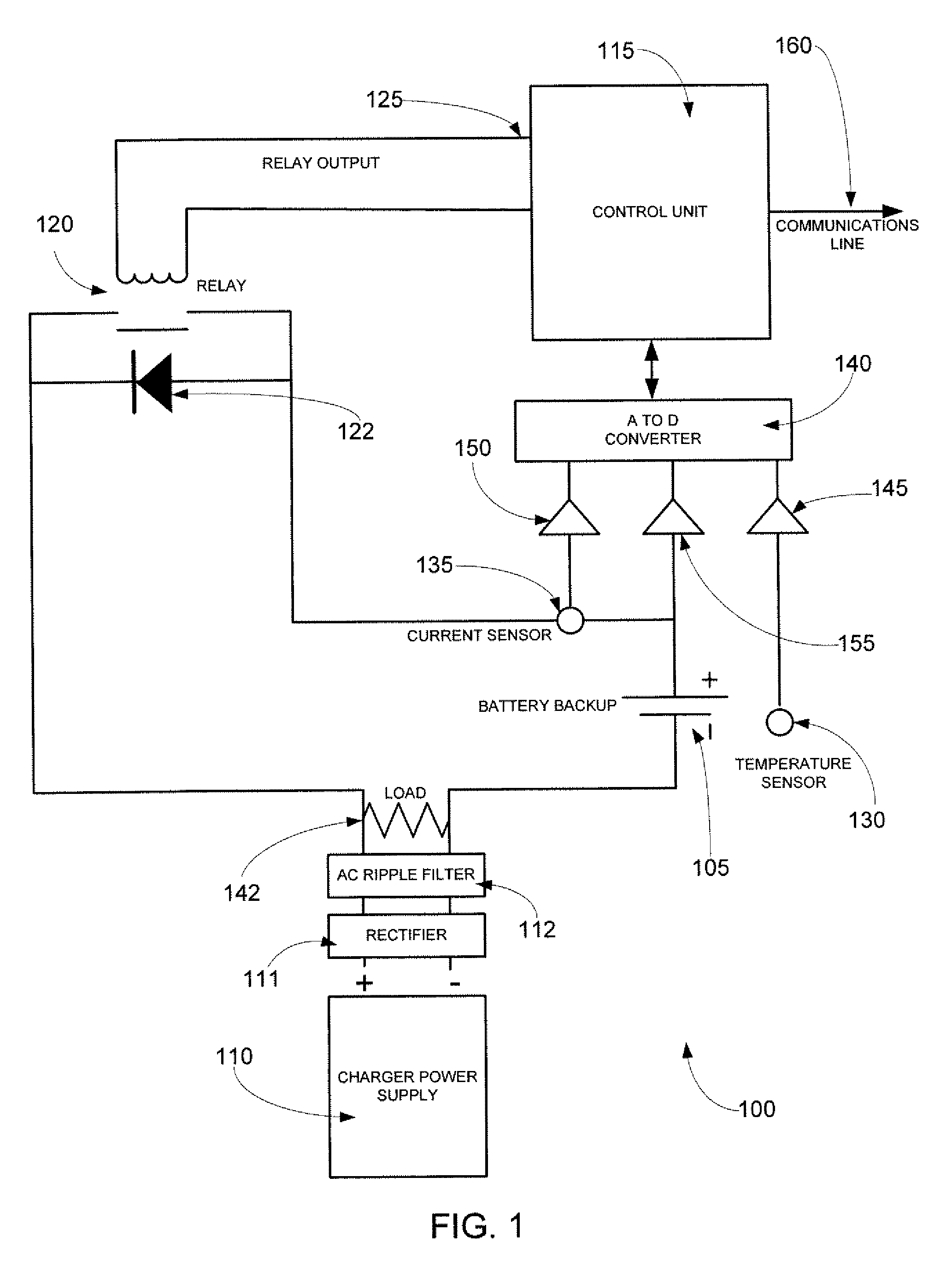
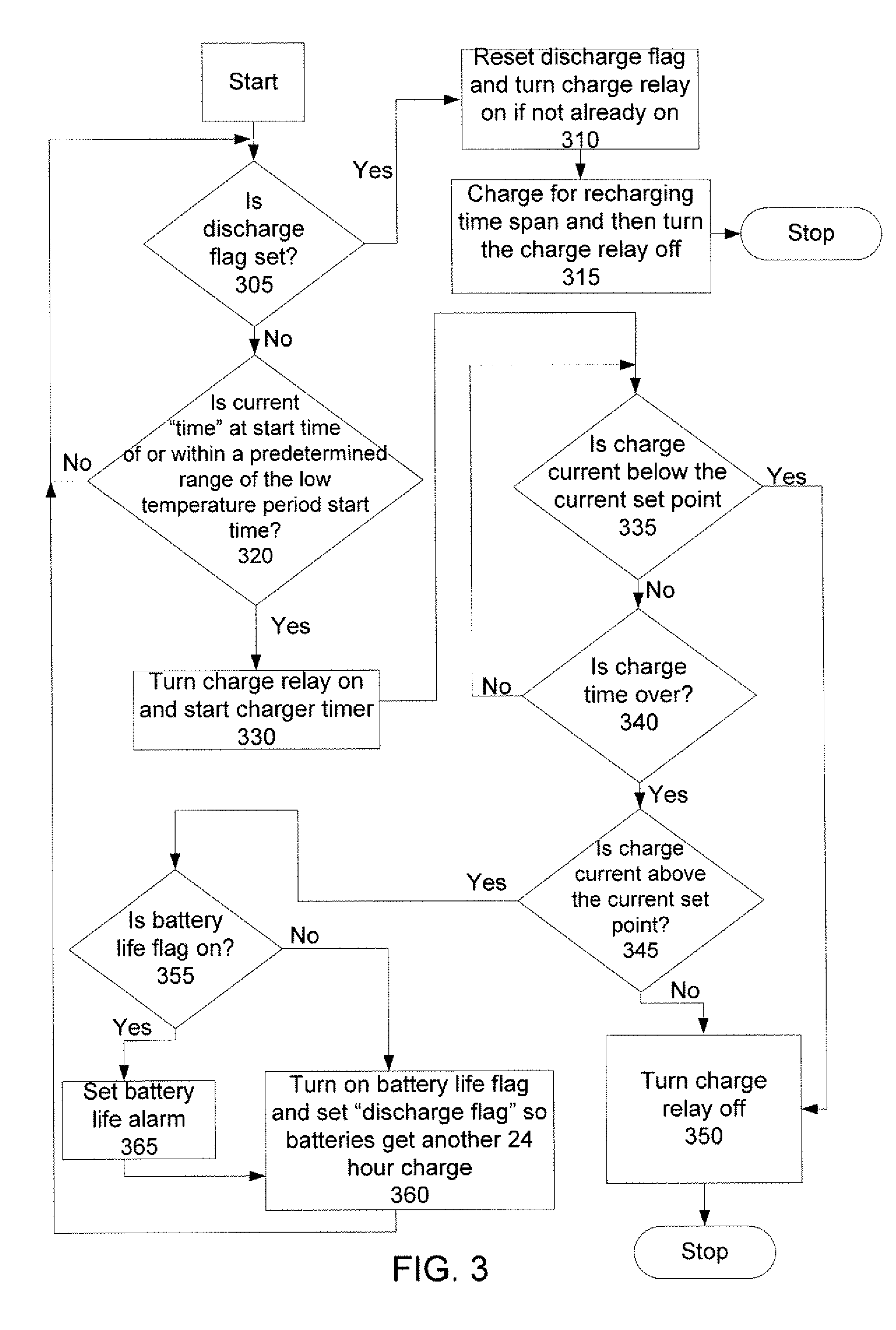
A battery charger that includes a relay, a control unit, and a temperature sensor. The relay controls the flow of an electrical charge current from a power supply to one or more batteries. The temperature sensor continuously measures the ambient temperature of the one or more batteries and communicates the temperature measurements to the control unit. The control unit control the actuation of the relay. The control unit receives the temperature measurements from the temperature sensor, determines a charging time period for the one or more batteries, and selectively actuates the relay for the charging time period. The charging time period has a predetermined duration and represents a coolest time period within a monitoring period of the control unit.
Owner:FLAUGHER DAVID J
High efficiency light source with integrated ballast
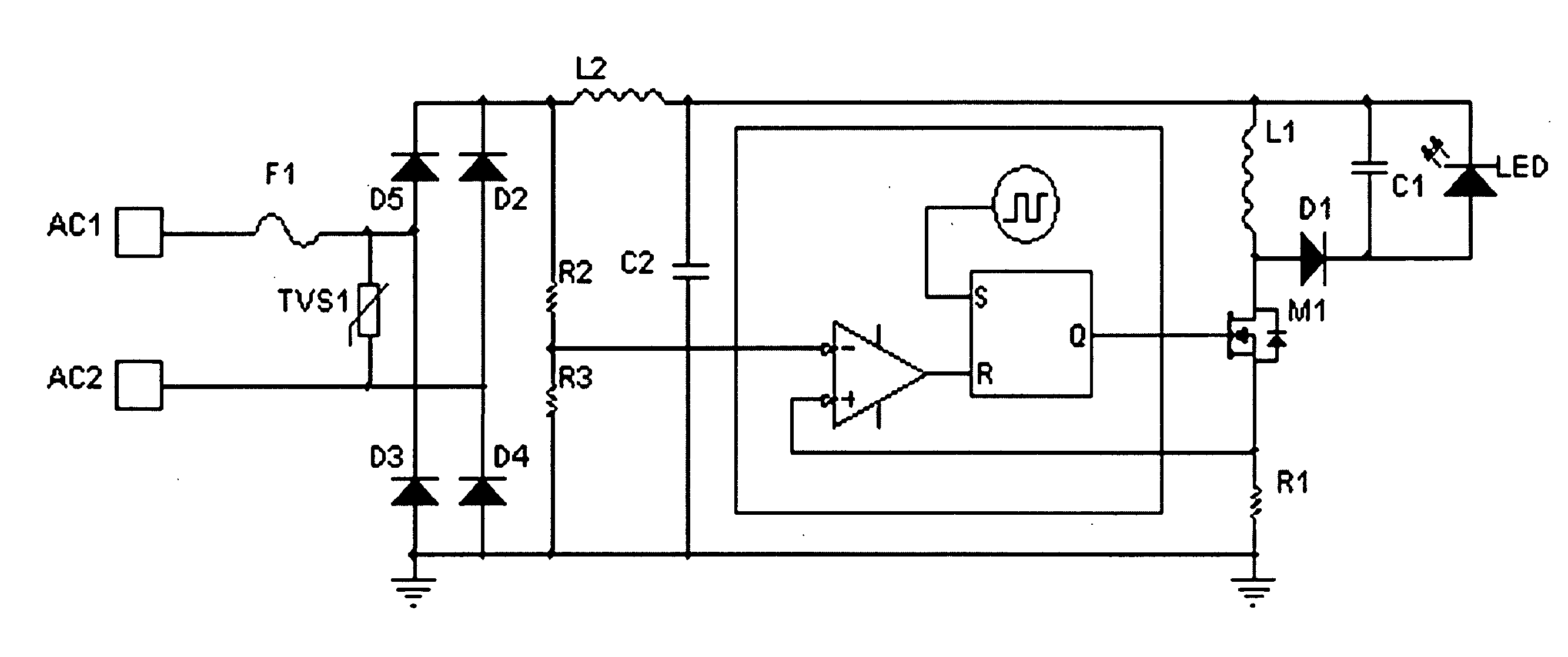
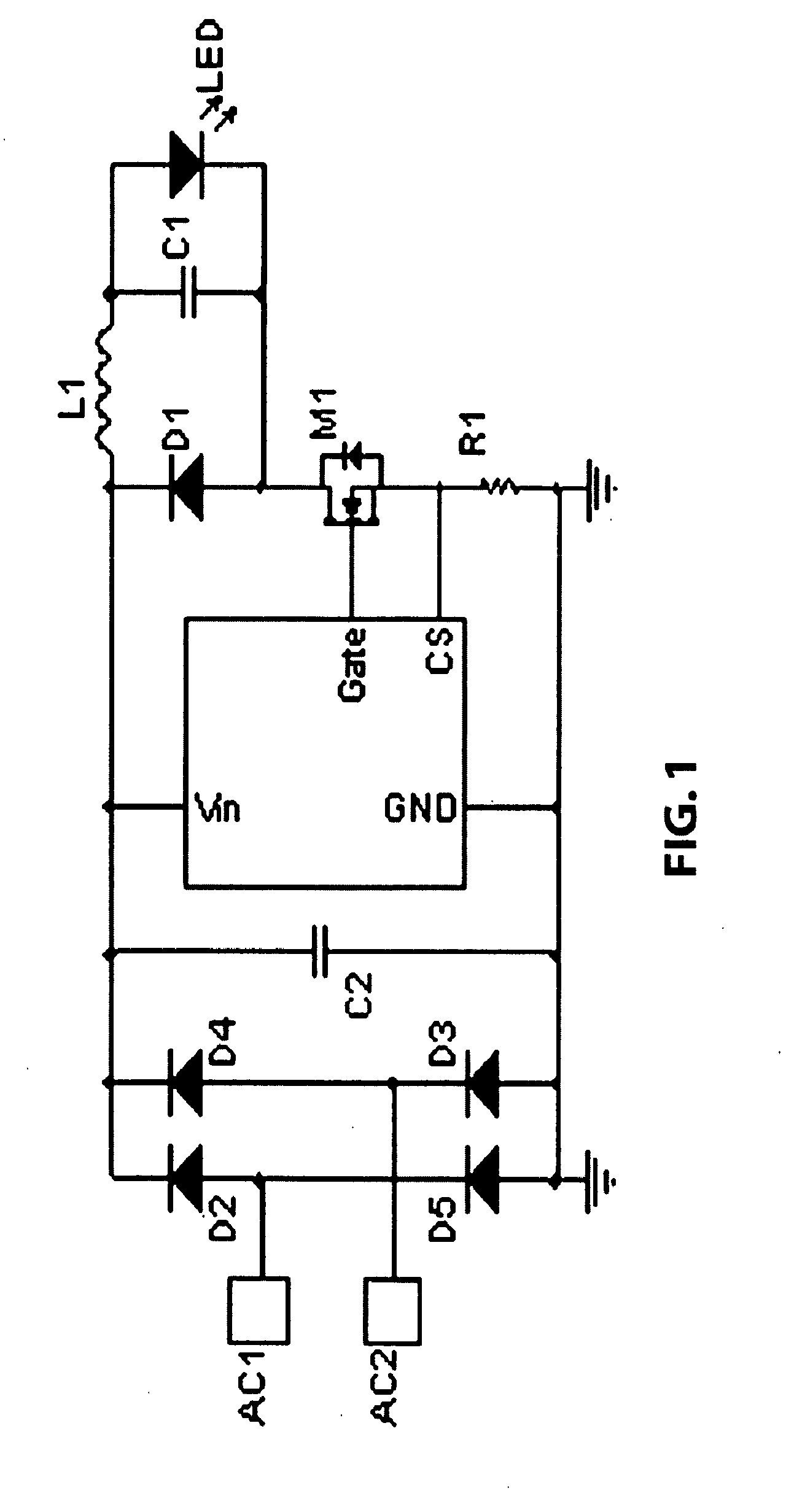
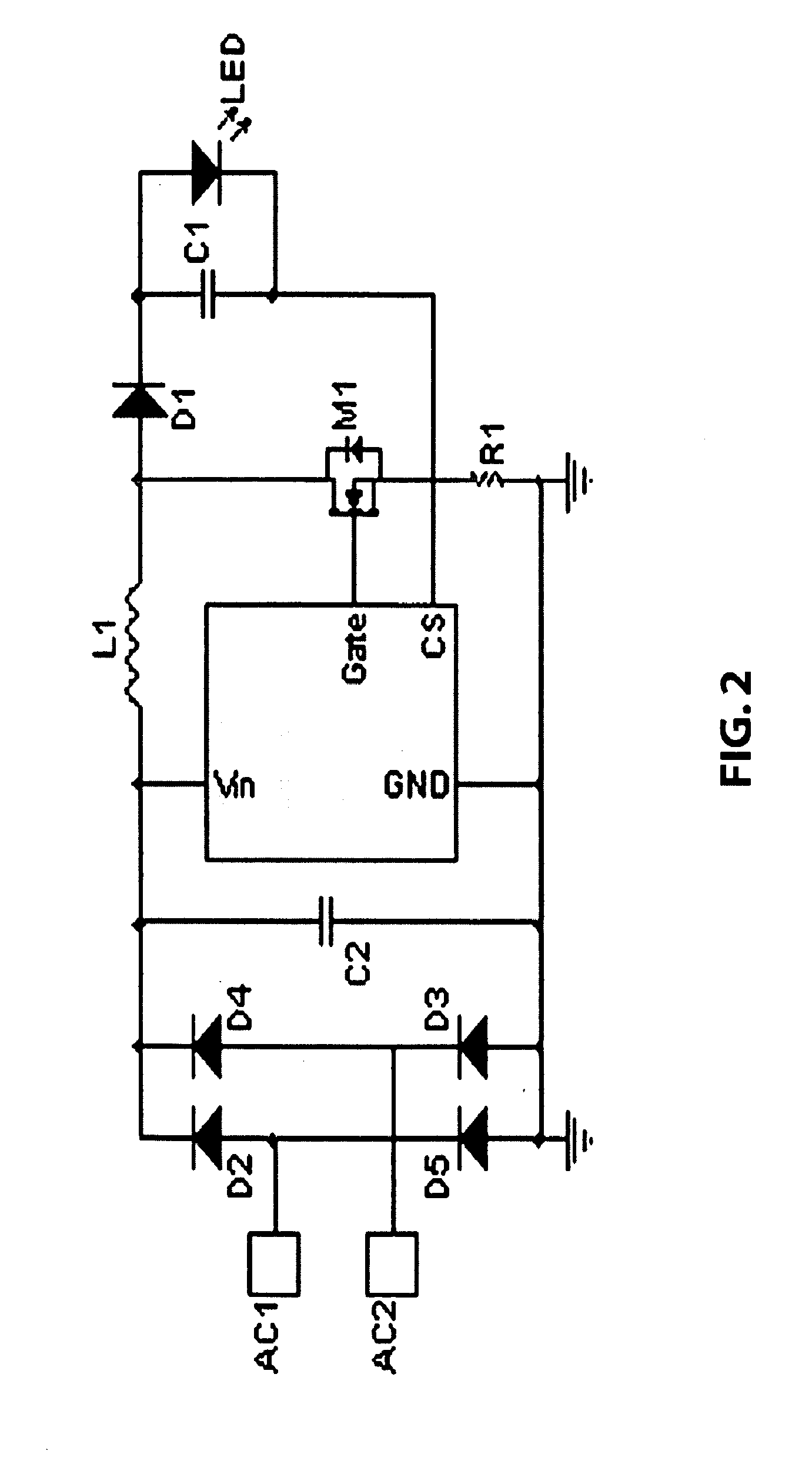
InactiveUS20100207536A1Improve circuit efficiencyImproving driver efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFrequency spectrumCharge current
The present invention relates to regulated power supplies or ballasts integrated with an LED light source. The invention provides a power factor correction scheme producing a greater circuit power factor and improved frequency spectrum characteristics, in which a voltage corresponding to the instantaneous inductor current is sampled and compared to a scaled sample of the rectified input AC line voltage. The line voltage sample modulates the inductor peak charge current in the envelope of the rectified AC voltage waveform. This drives the LED output voltage at a frequency of twice the input line voltage frequency, such that no flicker is perceived in the light output because the persistence in LED phosphor assists in averaging the flux output.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Phototherapeutic treatment methods and apparatus
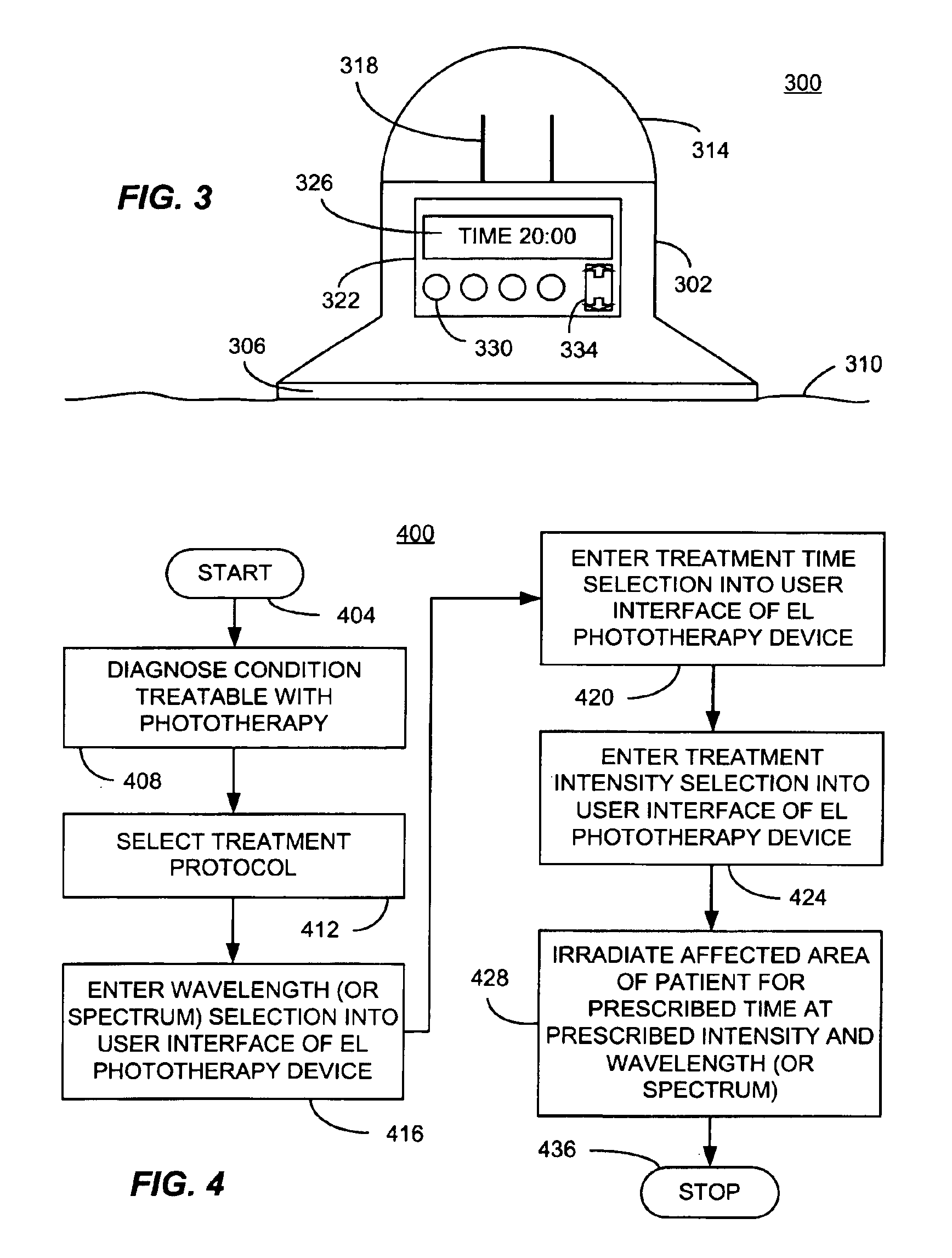
A thin film electroluminescent (TFEL) phototherapy device based on high field electroluminescence (HFEL) or from organic light emitting devices (OLED), consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention has a battery and a charging circuit coupled to the battery, so that when connected to a source of current acts to charge the battery. A TFEL panel produces light when voltage from the power source (battery or AC source) is applied. A processor such as a microprocessor is used to control the application of voltage from the power source to the TFEL panel under control of a control program. A housing is used to contain the battery, the charging circuit and the processor and carry the TFEL panel on an outer surface thereof. In one embodiment, the housing incorporates a removable cover that uncovers a household electrical plug useful for supplying charging current to the charger. In use, a method of carrying out phototherapy, consistent with certain embodiments of the invention involves diagnosing a condition of an affected area of tissue that can be treated with phototherapy. A treatment protocol is determined including, for example, a treatment light intensity, a treatment time, a light modulation characteristic and a treatment light wavelength suitable for treating the condition. The affected area is then irradiated with light from the TFEL panel in accord with the treatment protocol.
Owner:INT TECH CENT
Method and apparatus for welding with battery power
A method and apparatus provides welding-type power and preferably includes a removable battery or other energy storage device, a converter connected to the battery, and a controller. The controller may have a CV and / or a CSC and / or an AC weld control module, and / or an ac auxiliary control module. The converter is a boost converter, a buck converter, a cuk converter, a forward converter, an inverter, a bridge converter, and / or a resonant converter. The controller may include a battery charging control module, and may have one or more charging schedules, and / or data for stored charge, thermal information, expected life of the battery, maximum amp-hour charge for the battery, maximum charging current and / or feedback. The battery charging schedules may include at least 3 phases, such as a phase of increasing voltage and a phase of decreasing current, a substantially constant power phase. The controller can wirelessly provide data to a display or pda. A generator may provide power to the battery, charger, and / or the weld. It can include a vehicle and use its dc power system.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
System and method for inductively transferring ac power and self alignment between a vehicle and a recharging station
InactiveUS20110204845A1Reducing induced noiseImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectrical batteryTransformer
A method and apparatus for hands free inductive charging of batteries for an electric vehicle is characterized by the use of a transformer having a primary coil connected with a charging station and a secondary coil connected with a vehicle. More particularly, the when the vehicle is parked adjacent to the charging station, the primary coil is displaced via a self alignment mechanism to position the primary coil adjacent to the secondary coil to maximize the inductive transfer of charging current to the secondary coil. The self alignment mechanism preferably utilizes feedback signals from the secondary coil to automatically displace the primary coil in three directions to position the primary coil for maximum efficiency of the transformer.
Owner:PLUGLESS POWER INC
Battery charger and method of charging a battery
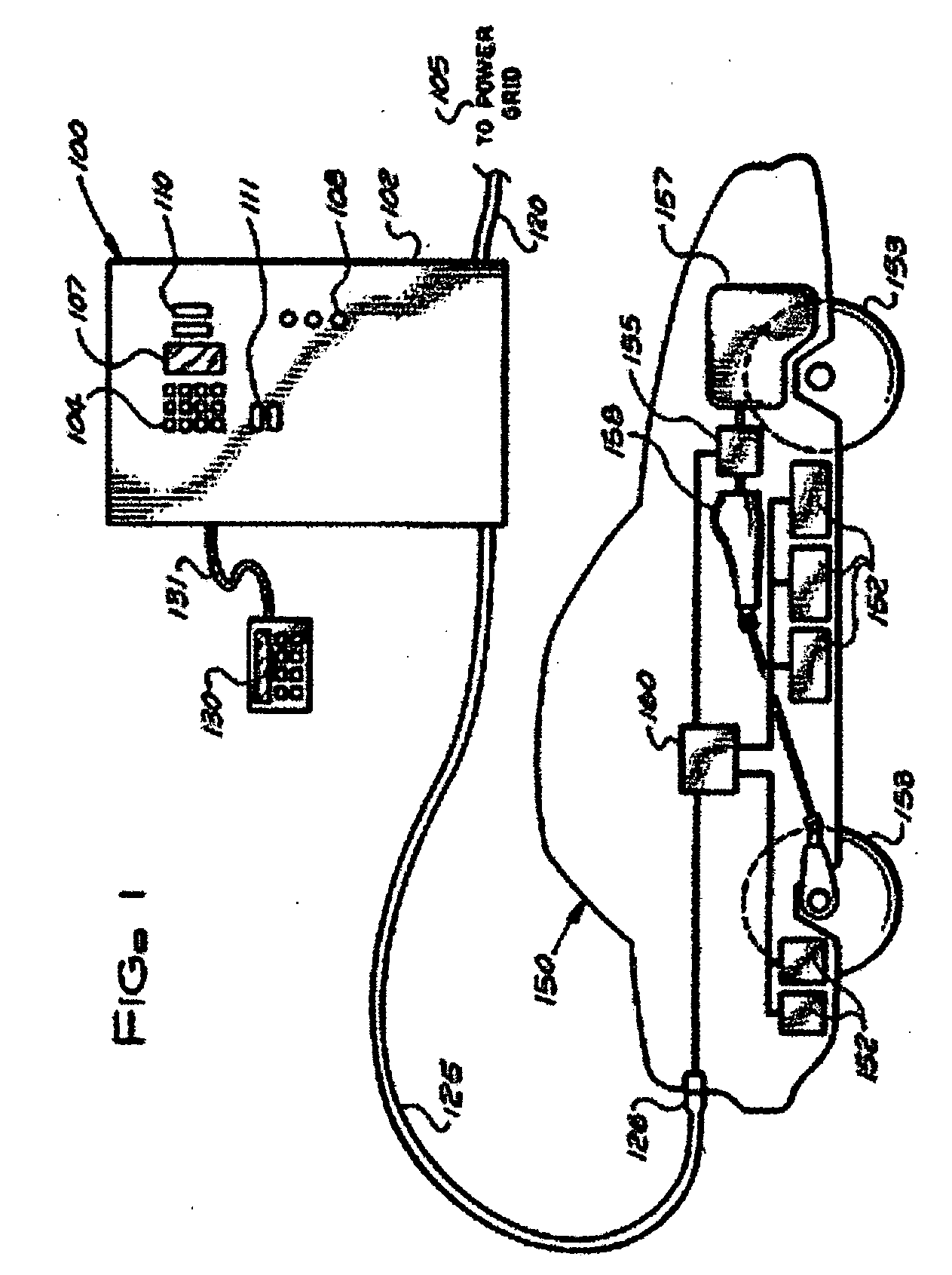
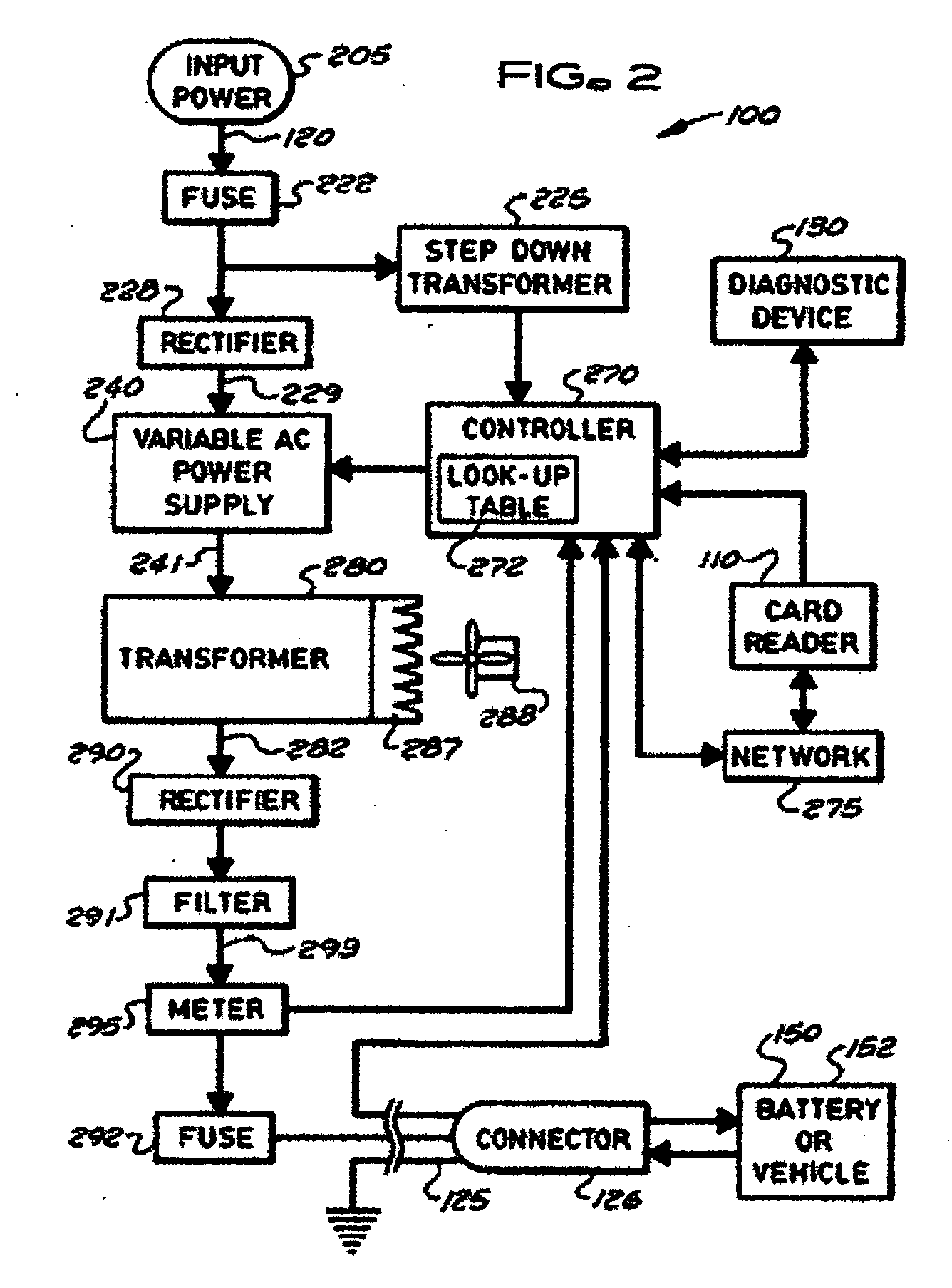
InactiveUS6963186B2Quickly and conveniently chargeSmall sizeCircuit monitoring/indicationSecondary cells charging/dischargingOn boardCopper foil
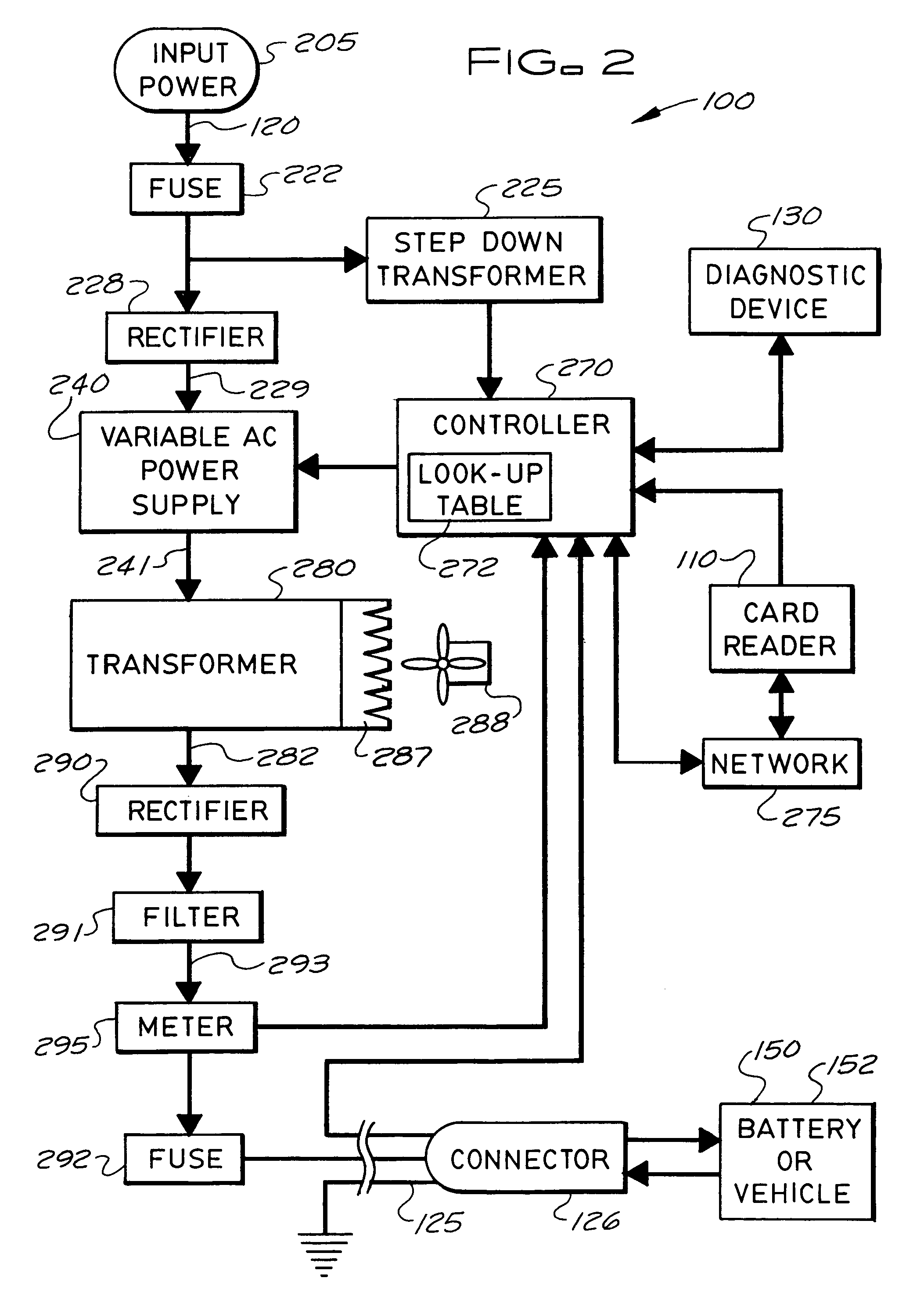
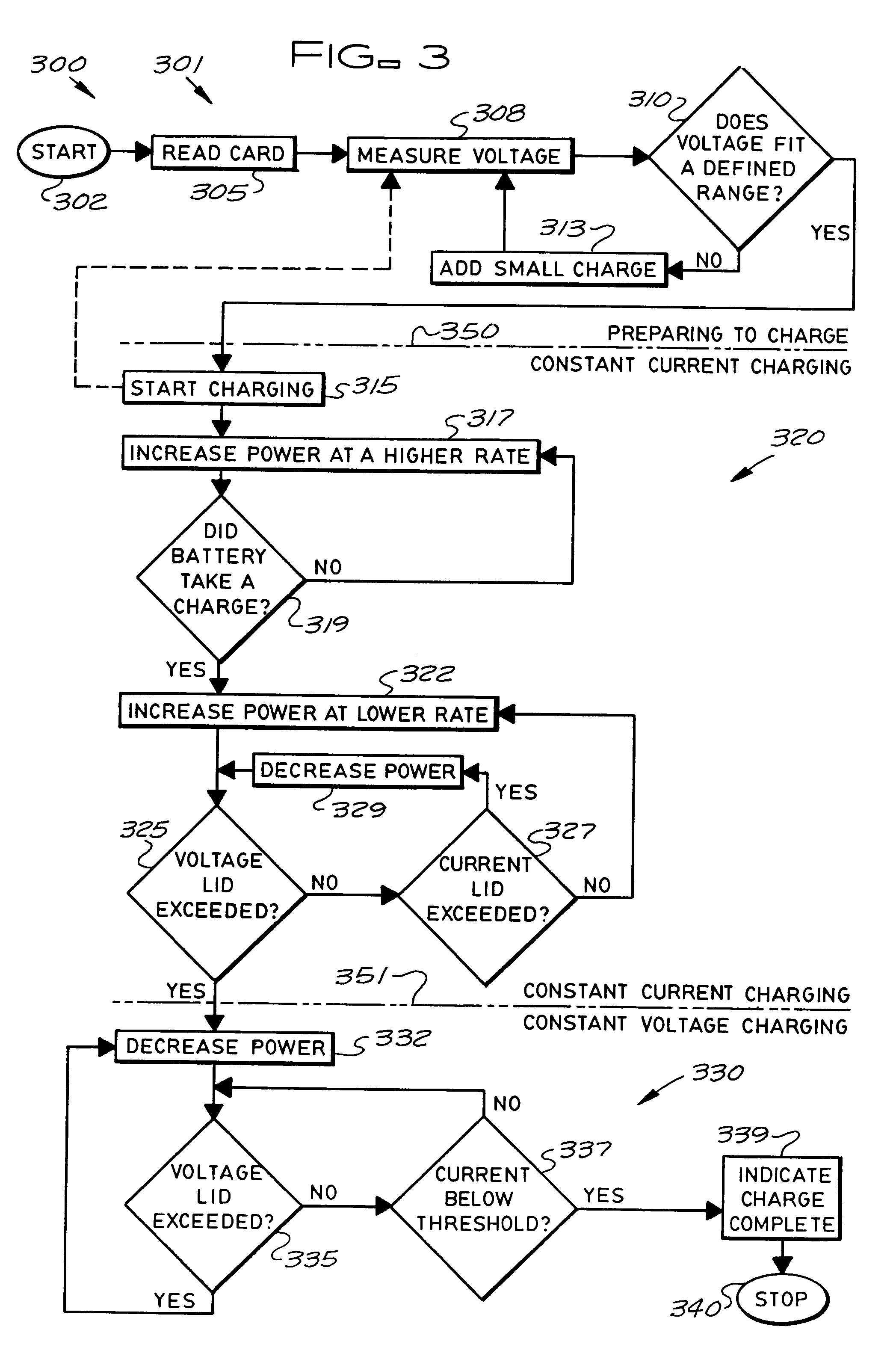
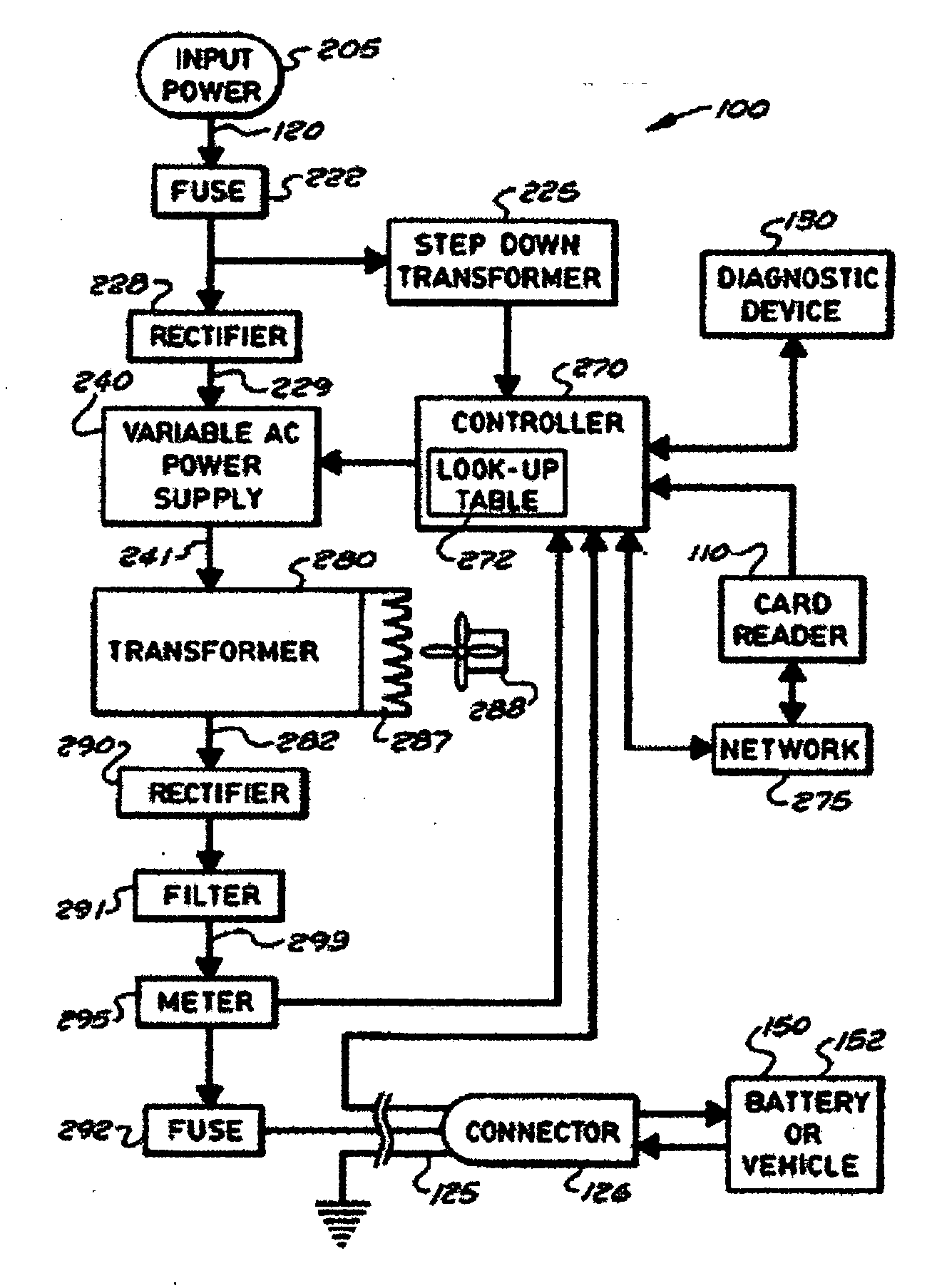
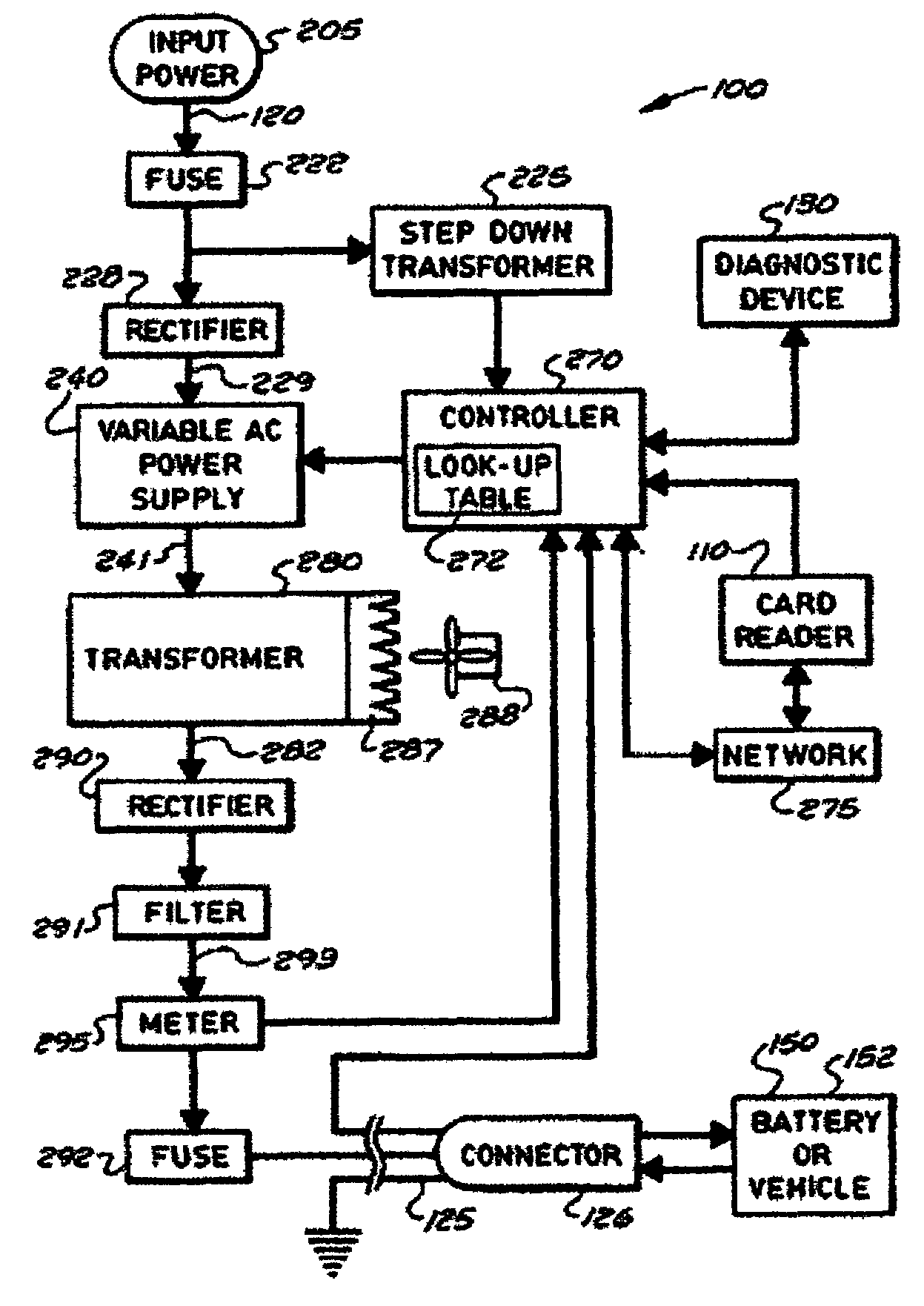
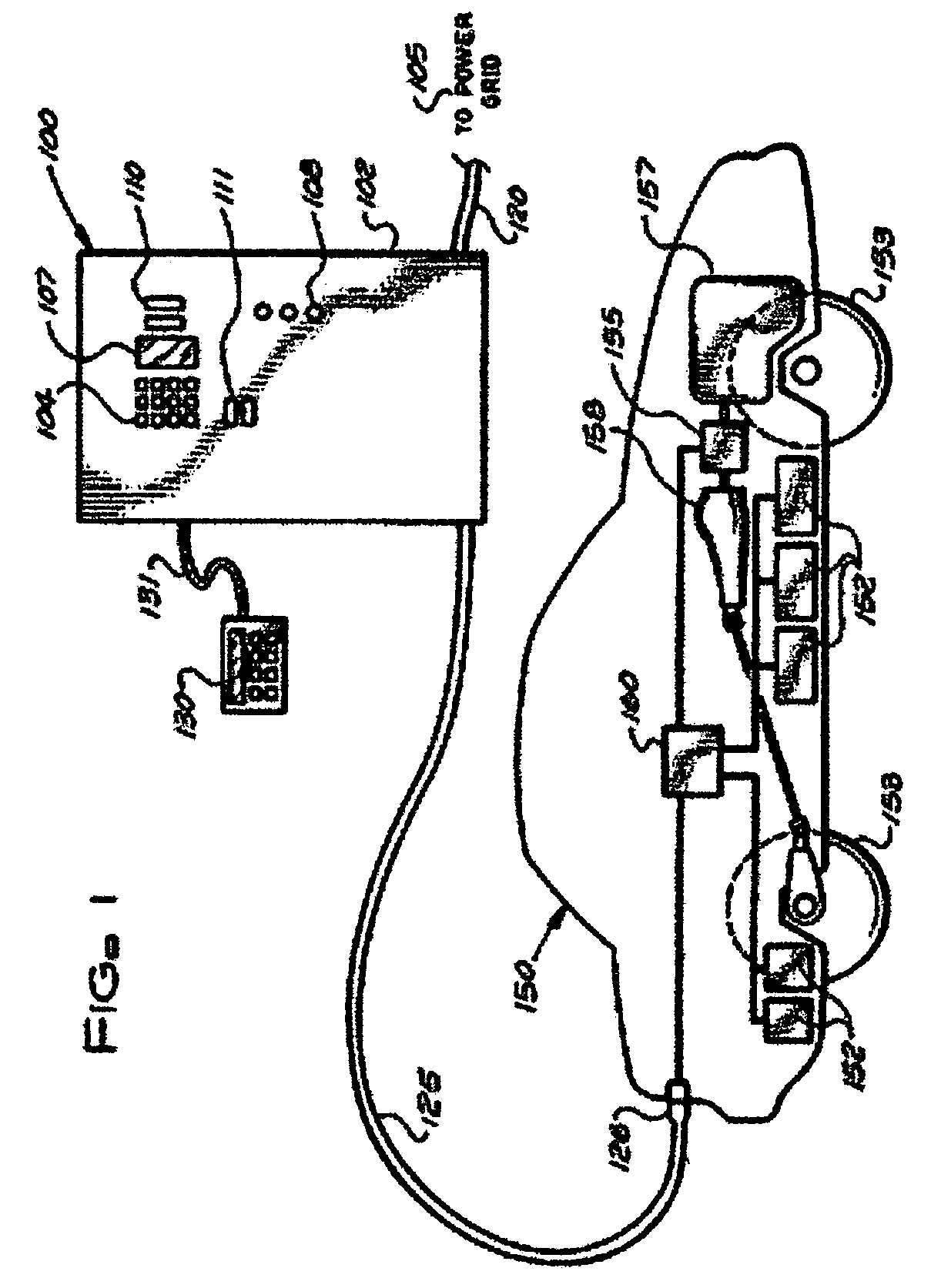
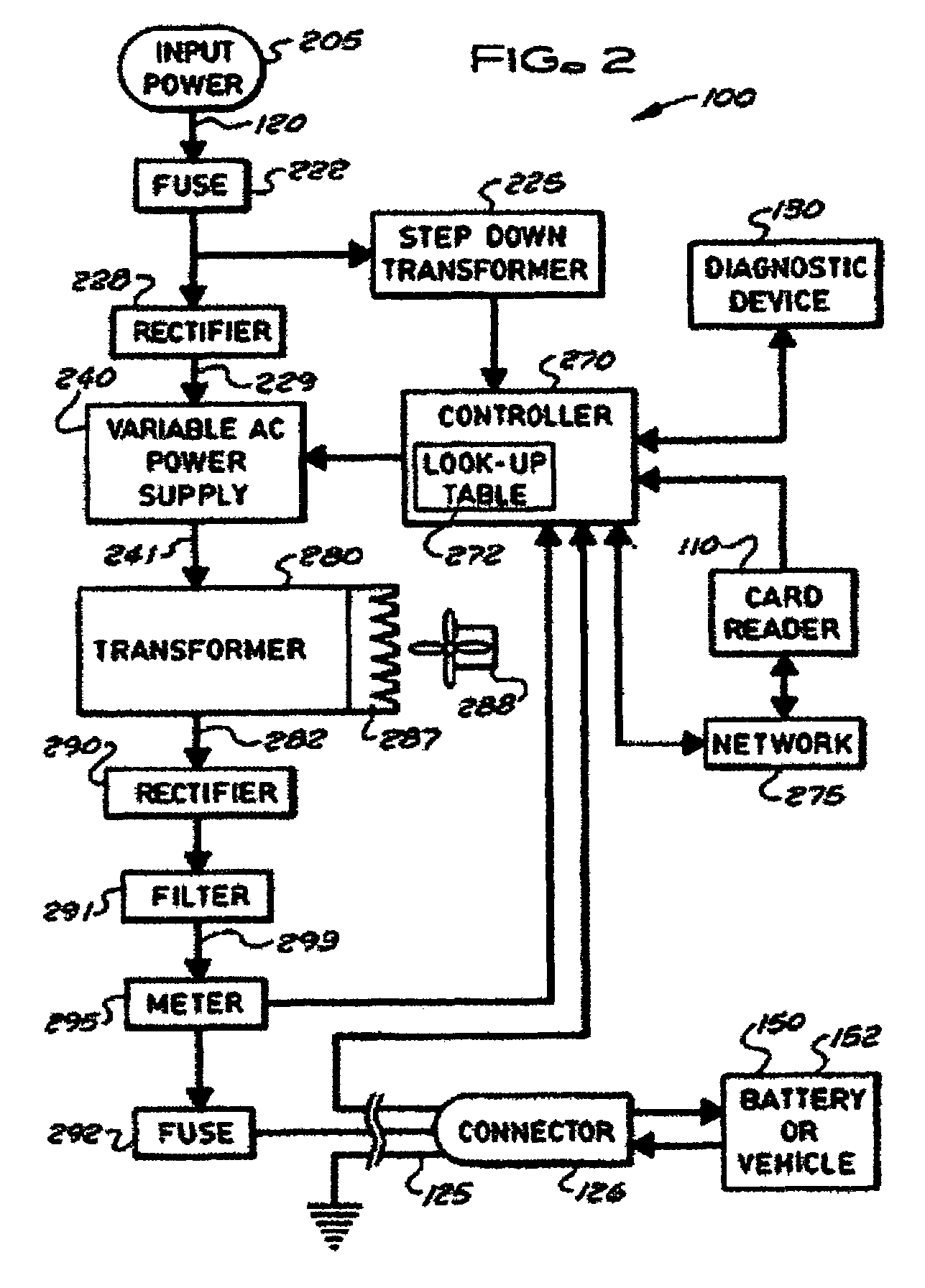
Stationary and on-board battery chargers, methods of charging batteries, electric-vehicle chargers, and vehicles with chargers, including electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. Chargers may automatically charge at the correct battery voltage for various types of batteries. Chargers have variable AC power supplies controlled by digital controllers, isolation transformers, and rectifiers. Transformers may be foil-type, and may have copper foil. Power supplies may be variable-frequency generators and the controllers may control the frequency. Electric vehicle chargers may have card readers, and vehicles may have batteries and a charger. Methods of charging include identifying the battery type and gradually increasing the charging at different rates of increase while monitoring charging voltage, charging current, or both, until a current lid is reached. Charging may occur at constant current and then at constant voltage.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Battery pack having memory
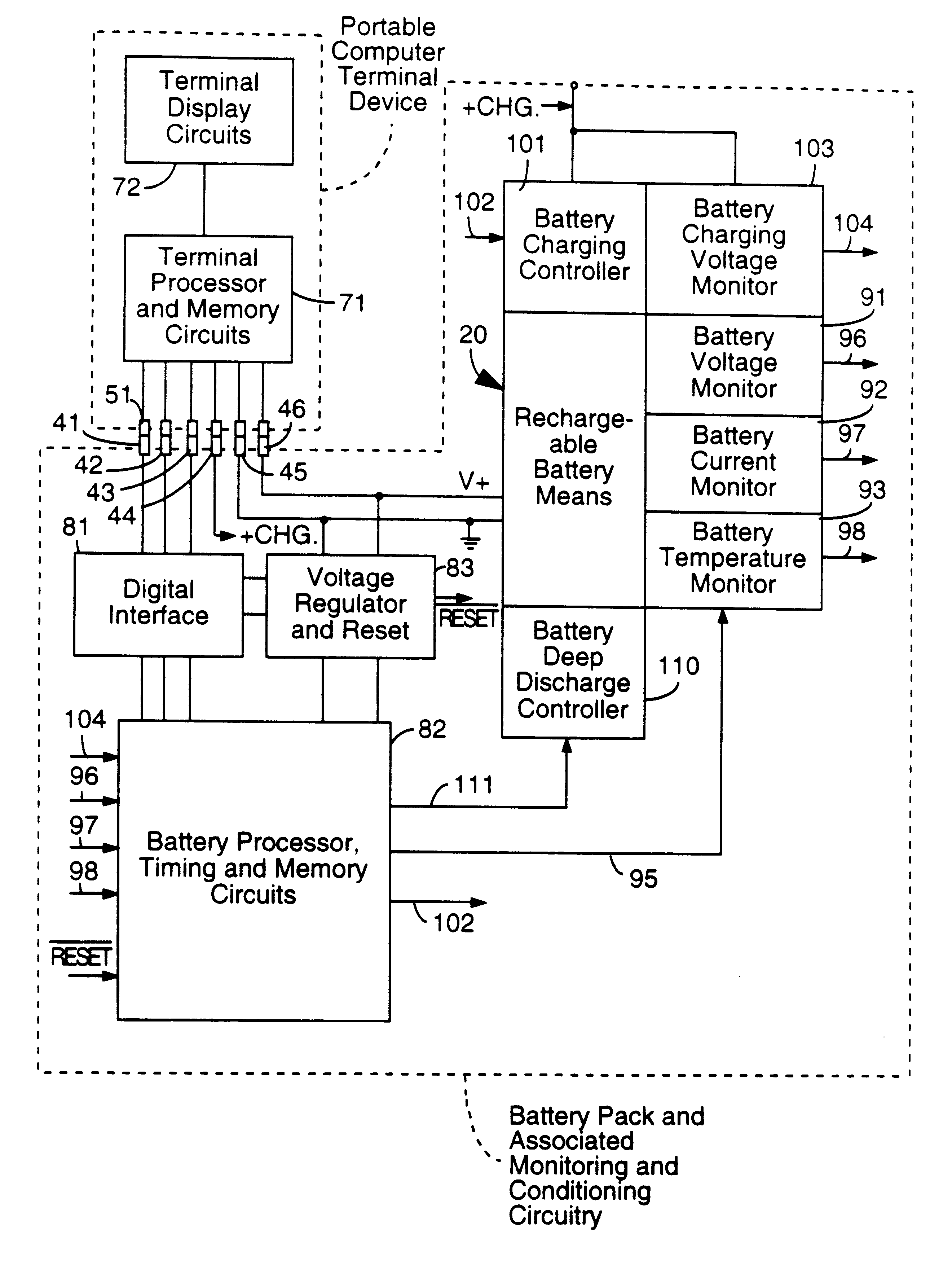
InactiveUS6271643B1Decreasing the turn on potentialWide flexibilityCircuit monitoring/indicationVolume/mass flow measurementCharge currentElectrical battery
In an exemplary embodiment, a method of charging a battery includes supplying a charging current to the battery and measuring one or more battery parameters. The battery parameters may be, for example, temperature, voltage and / or charging current. The battery parameter measured is used to determine a charging current set point. The set point may be selected from a number of different set points stored in memory, where each set point corresponds to a respective battery parameter range. If the charging current being supplied to the battery is different from the charging current set point determined the charging current is adjusted to match the set point. This process is repeated for each of a plurality of time periods (e.g., sampling periods) during charging of the battery.
Owner:UNOVA
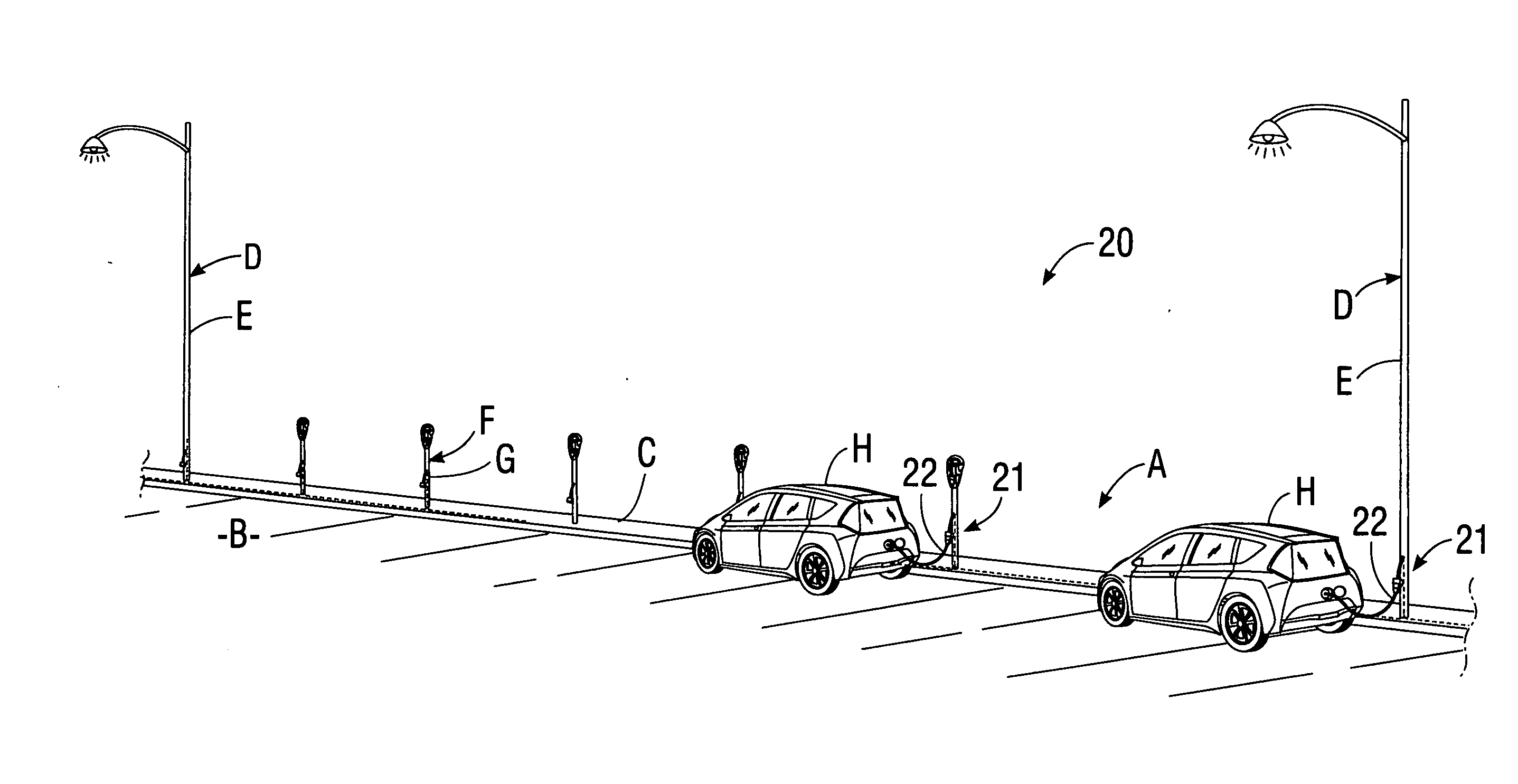
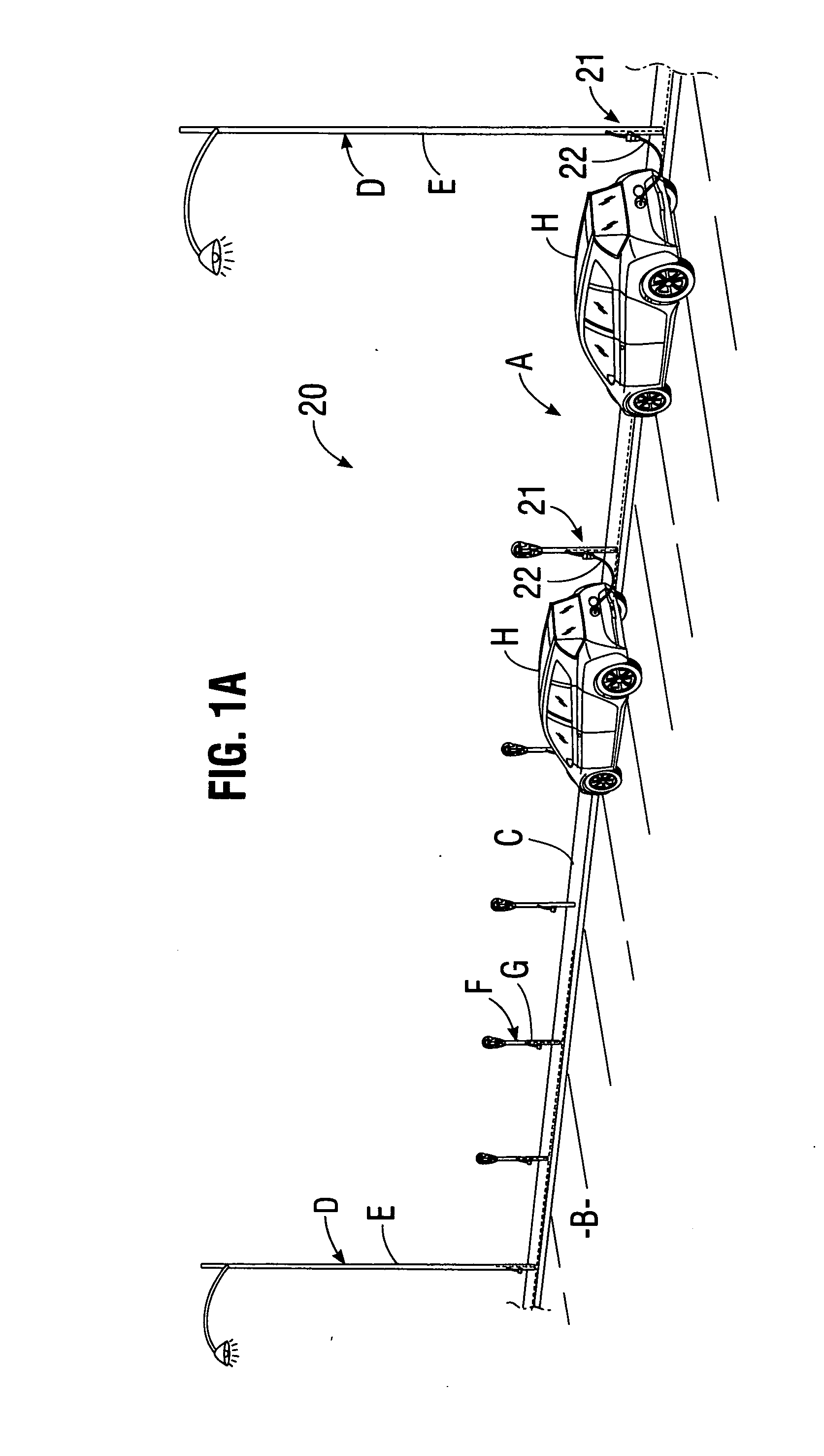
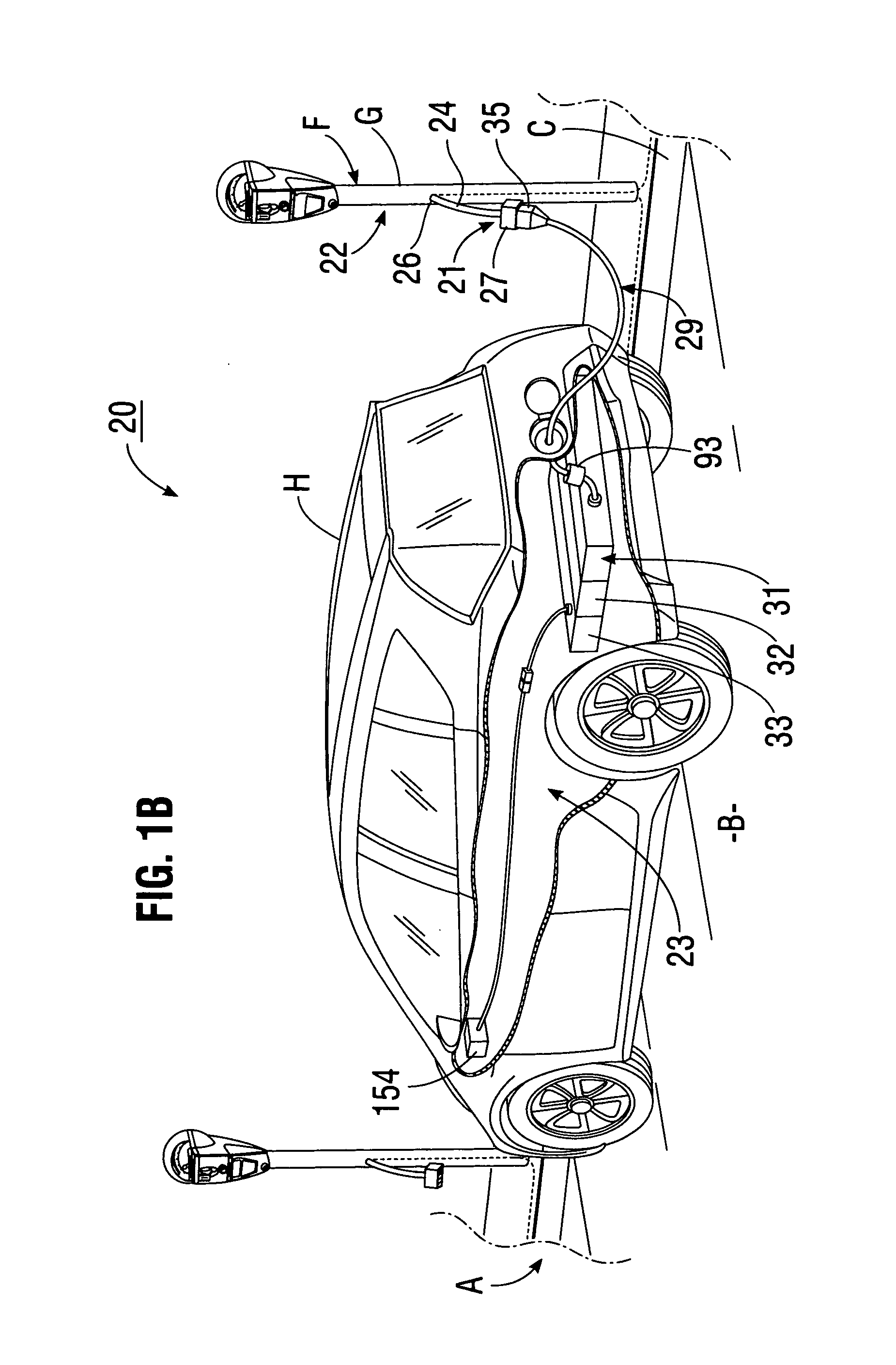
System for charging electric vehicle batteries from street lights and parking meters
InactiveUS20120229085A1Easy to modifyAvoid flowBatteries circuit arrangementsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingEngineeringCard reader
A system for charging batteries of electric vehicles from public fixtures such as street lights and parking meters includes modifying the fixture to convert it to a vehicle battery charging station using a power interface module having a novel keyed electrical power output receptacle connectable to power mains powering the fixture. The system includes a complementarily coded, keyed plug which must be inserted into the power output receptacle to access electrical power from the receptacle, the plug being located at the input end of vehicle charger cable terminated at output end thereof by a vehicle-mounted charge control system which will actuate a charging current contactor permitting charging current to flow from the receptacle to batteries within the vehicle only if a pre-paid charge authorization payment device, such as a magnetically or electronically encoded charge card is inserted into a charger station access enable device such as card reader mounted in the vehicle.
Owner:CHAPIN WILLIAM L MR
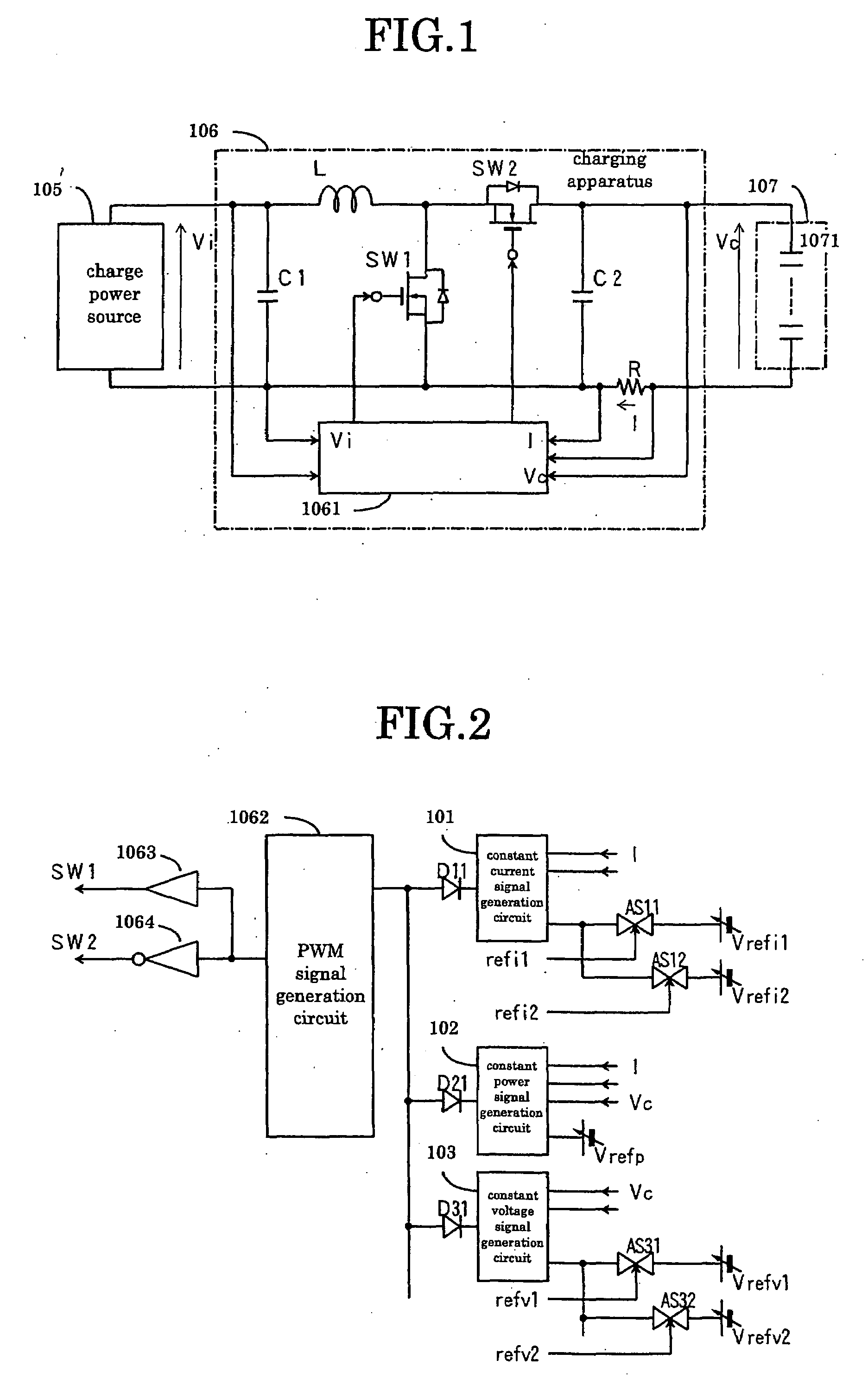
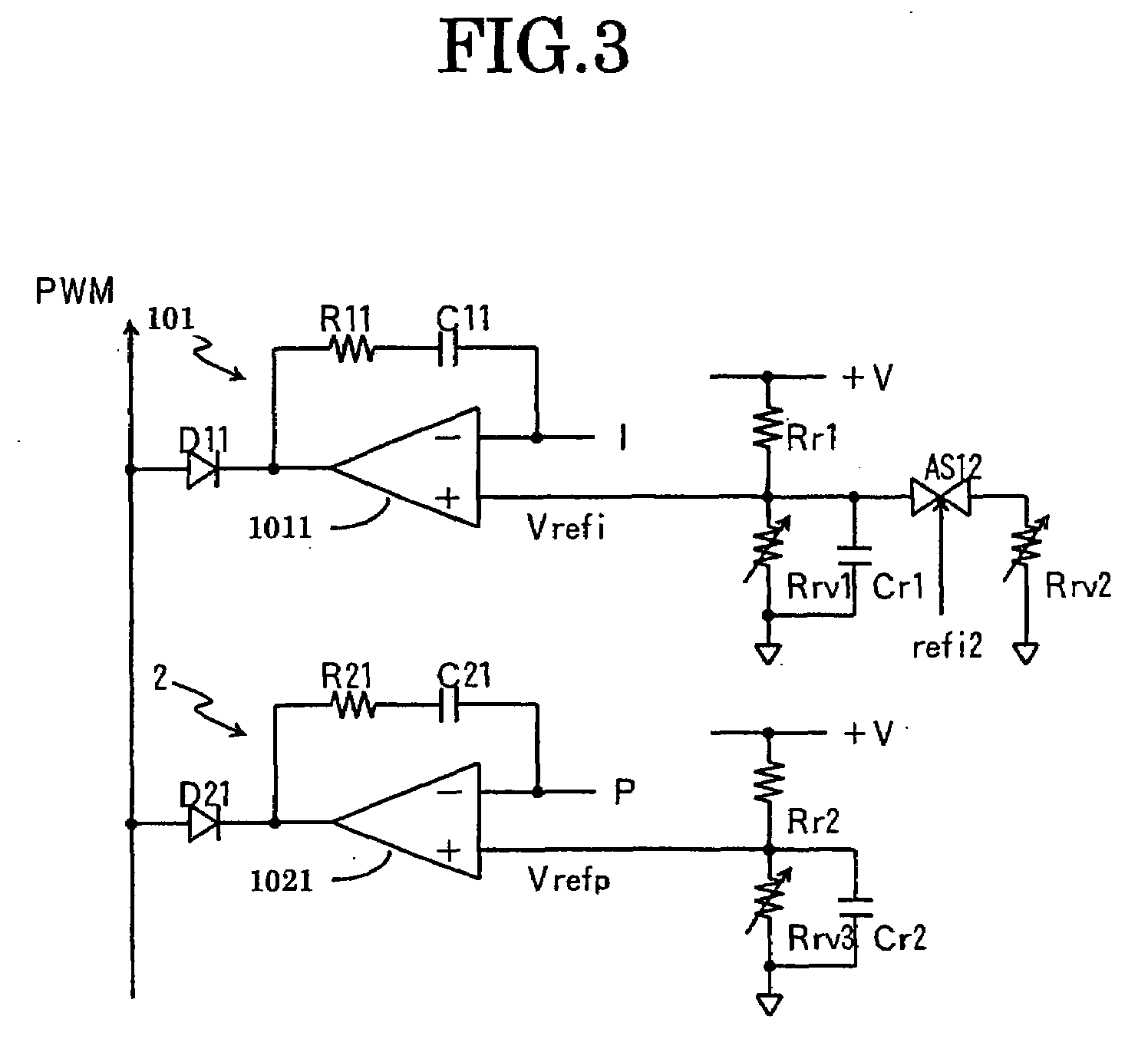
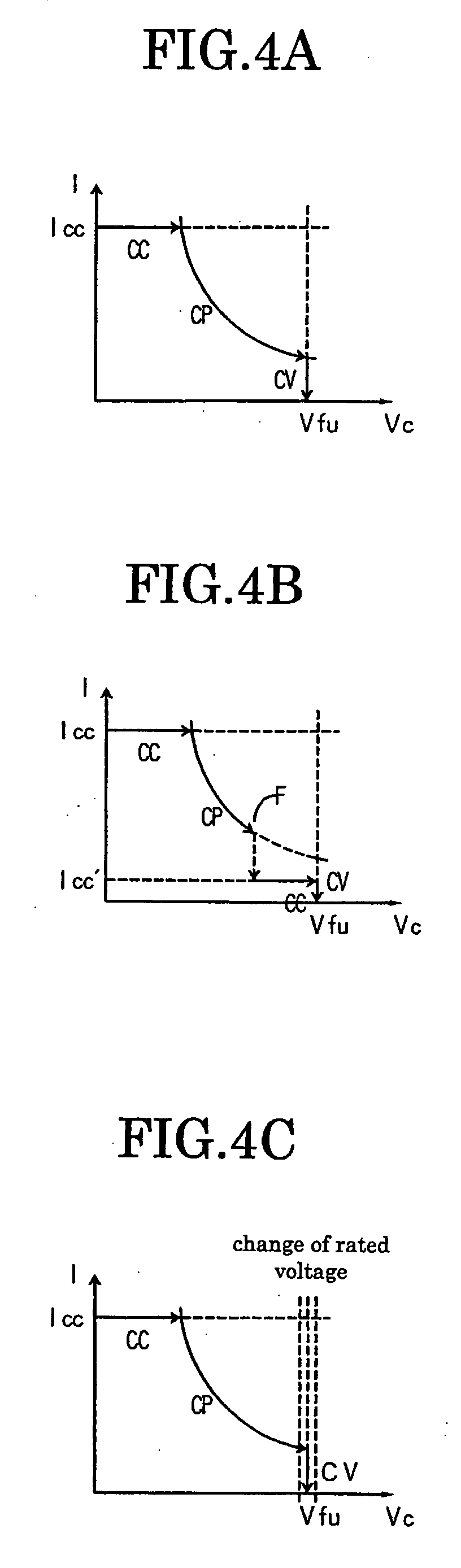
Charging apparatus for capacitor storage type power source and discharging apparatus for capacitor storage type power source
InactiveUS20070194759A1MinimizeImprove efficiencyCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerCharge currentVoltage reference
A charging apparatus for electrically charging a capacitor storage type power source comprises a switching circuit for turning on / off the charge current, a current detection circuit for detecting the charge current, a voltage detection circuit for detecting the voltage of power source, a constant current control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the current value, a power control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the current value, the voltage value-and a power reference value, a constant voltage control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the voltage value and a voltage reference value, an OR circuit for selecting one of the error amplifying signals and a control circuit for generating a pulse width modulation signal according to the error amplifying signal output from the OR circuit to turn on / off the switching circuit and control the charge current.
Owner:POWER SYST KK
Battery charger and method of charging a battery
InactiveUS20060028178A1Quickly and conveniently chargeSmall sizeBatteries circuit arrangementsPropulsion by batteries/cellsOn boardCopper foil
Stationary and on-board battery chargers, methods of charging batteries, electric-vehicle chargers, and vehicles with chargers, including electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. Chargers may automatically charge at the correct battery voltage for various types of batteries. Chargers have variable AC power supplies controlled by digital controllers, isolation transformers, and rectifiers. Transformers may be foil-type, and may have copper foil. Power supplies may be variable-frequency generators and the controllers may control the frequency. Use of the variable frequency generator supply facilitates reduced component size and weight and better battery charging performance. Electric vehicle chargers may have card readers, and vehicles may have batteries and a charger. Methods of charging include identifying the battery type and gradually increasing the charging at different rates of increase while monitoring charging voltage, charging current, or both, until a current lid is reached. Charging may occur at constant current and then at constant voltage.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Control arrangement for a resonant mode power converter
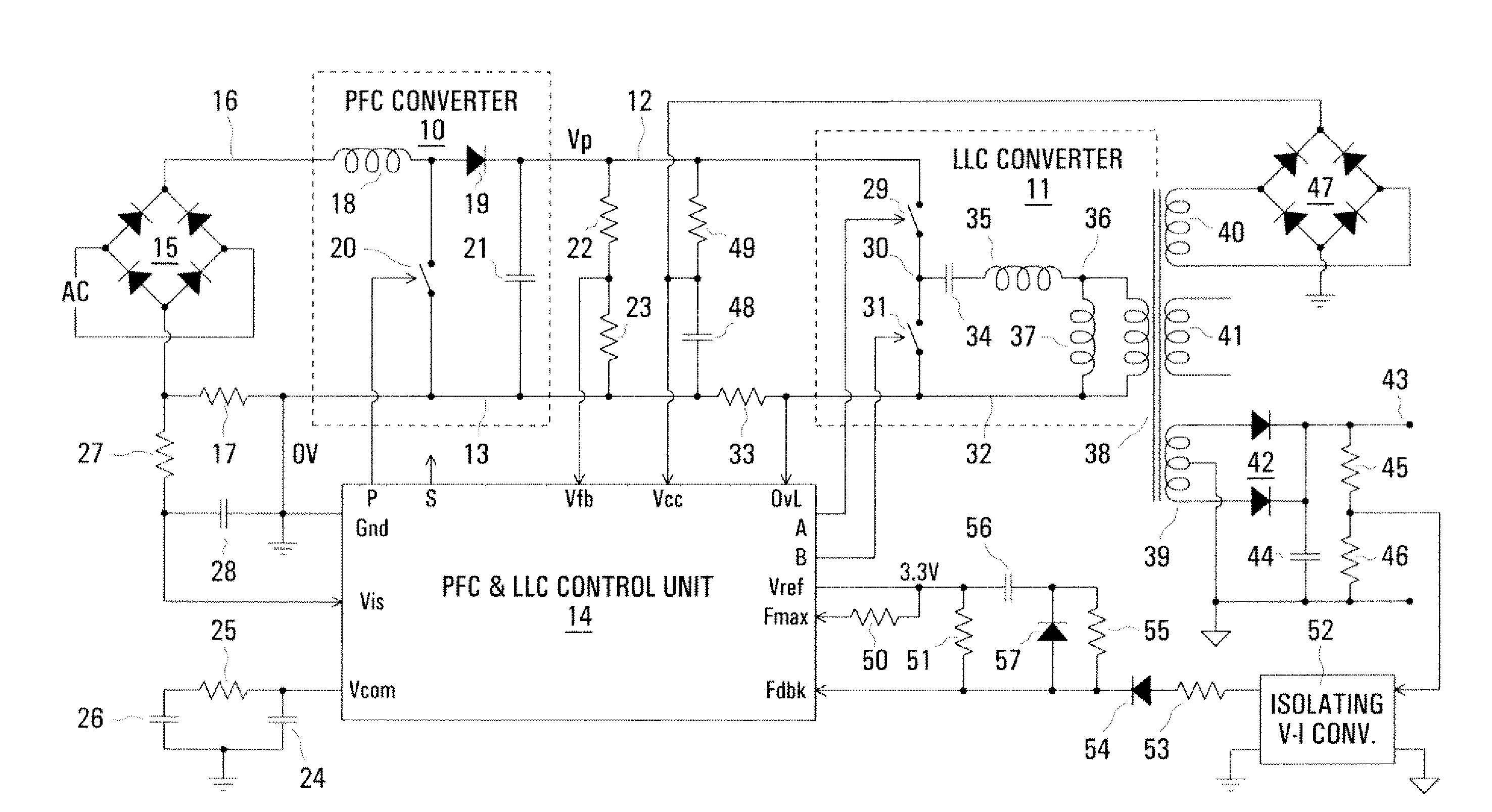
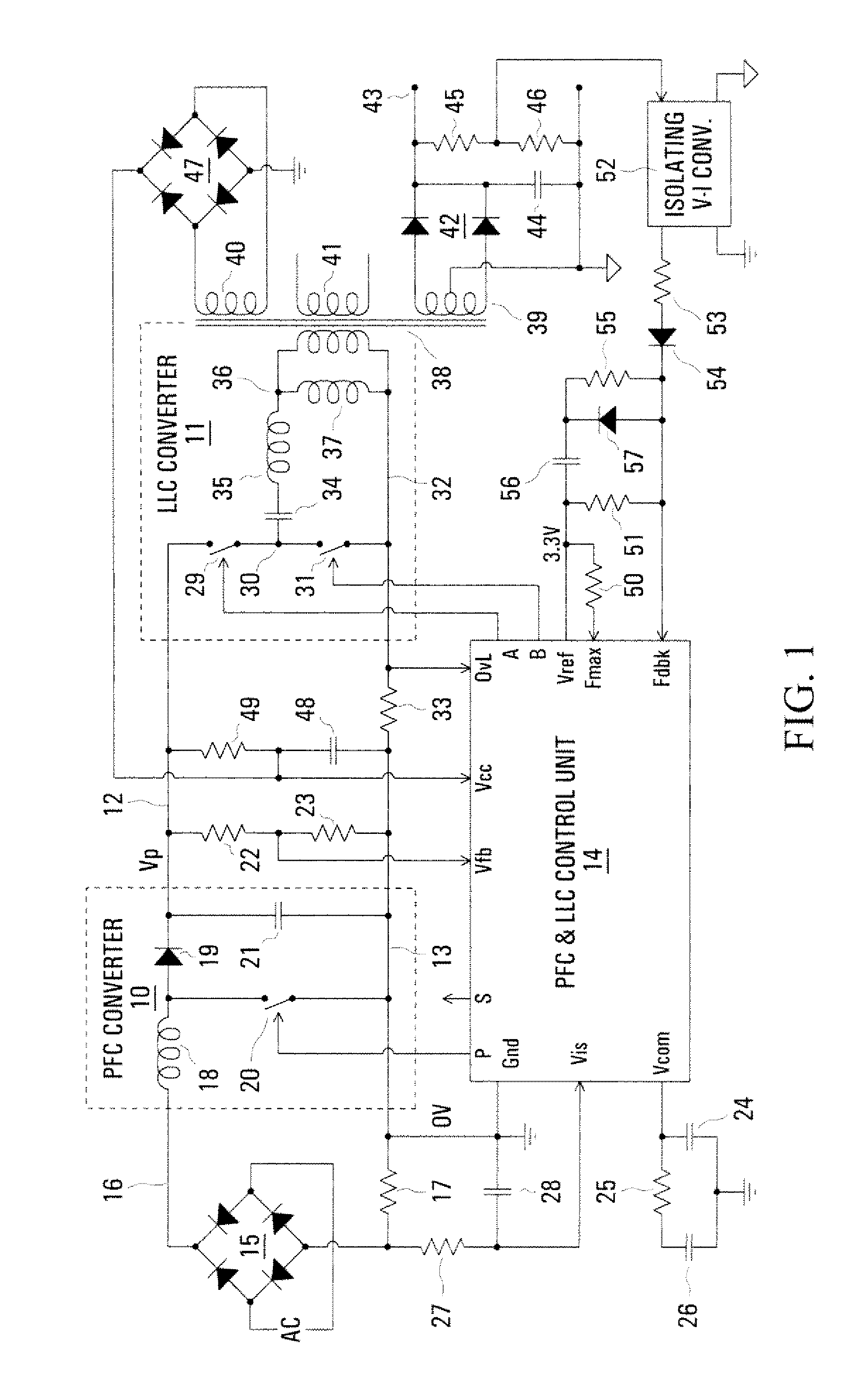
InactiveUS20080198638A1Minimize such dead timeMinimize timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCharge currentControl signal
The switching frequency of an LLC converter is controlled by a control unit to which a feedback circuit provides a first current dependent upon the output voltage of the converter. An oscillator circuit produces a sawtooth waveform at a frequency dependent upon the first current, up to a limit equal to a second current set by a resistor. Two complementary switch control signals are produced for controlling two switches of the converter for conduction in alternate cycles of the sawtooth waveform. A timer produces dead times between the two complementary switch control signals in dependence upon the second current. Another resistor provides a current constituting a minimum value of the first current, and a charging current of a capacitor in series with a resistor modifies the first current for soft starting of the converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Photovoltaic powered charging apparatus for implanted rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS7003353B1Prolong lifeAmount of timeElectrotherapyBatteries circuit arrangementsPower flowCharge current
A photovoltaic powered charging unit is mounted in a head covering, such as a cap or hat, for a patient who has an inductively chargeable medical device implanted in his head. The implanted device includes an implanted battery which powers the device. The photovoltaic cells provide continuous charging for the implanted battery and power for the implanted device when subjected to light. The charging unit includes a nonphotovoltaic cell that may be used to charge the implanted battery and power the implanted device in the absence of sufficient power from the photovoltaic cells. The cap has a sending coil located so that when the wearer dons the cap, the sending coil aligns with a receiving coil implanted in the patient's skull or brain. The implanted receiving coil is coupled to provide charging current to the implanted battery and power to the implanted device.
Owner:QUALLION
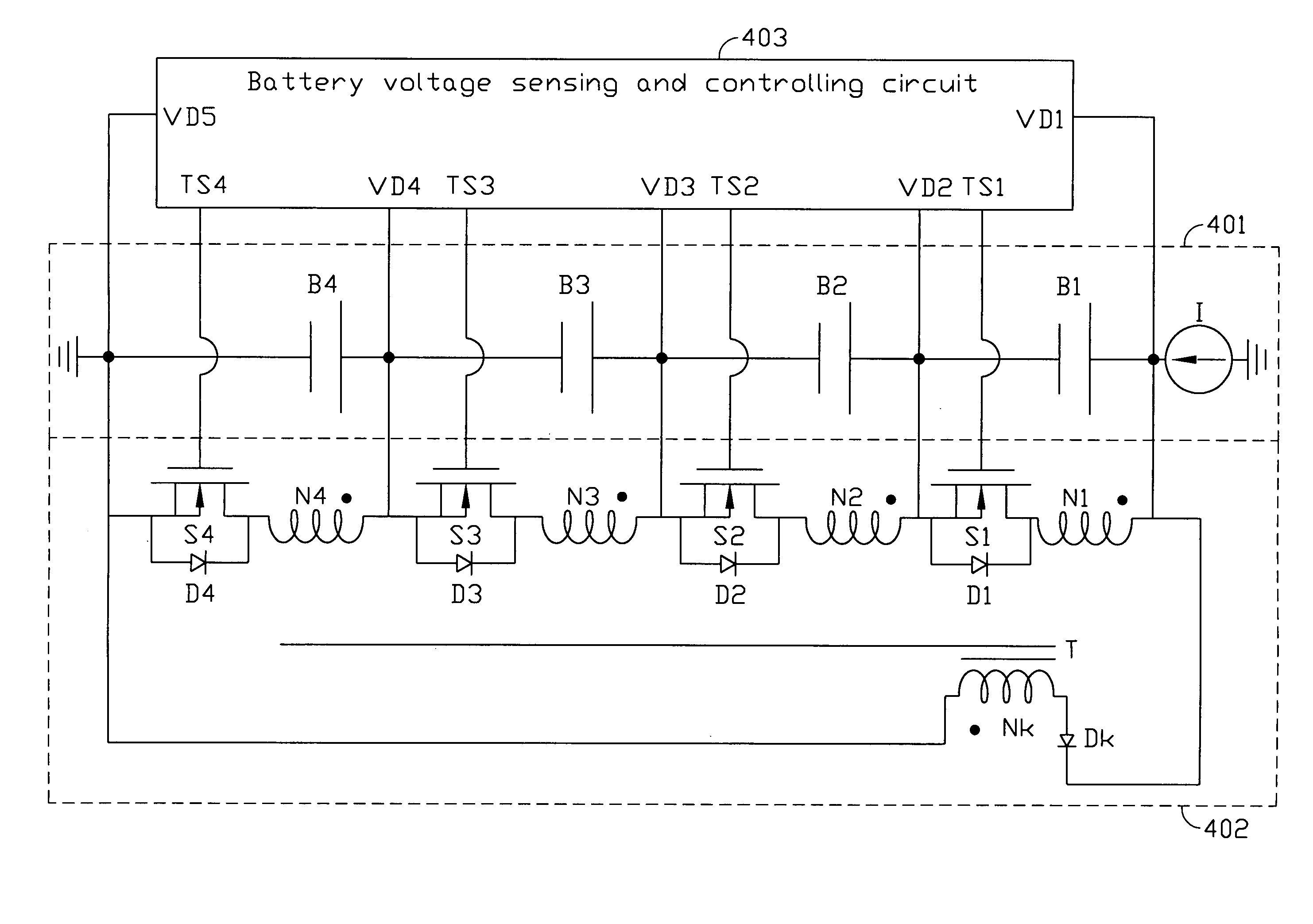
Equalizer for series of connected battery strings
InactiveUS20050140335A1Quick effectLower the volumeCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerCharge currentTransformer
A terminal voltage equalization circuit is used to equalize the terminal voltage of the series of connected battery strings so that each battery in the series of connected battery strings can be equally charged. When voltage of a certain battery in the battery string is higher than that of the other batteries, the battery voltage sensing and controlling circuit will output a high frequency signal to drive the switch devices to transit power from the high voltage batteries to the low voltage batteries by transformer. By the high switching switches, the charging currents through the batteries with high terminal voltages can be reduced, the charging currents through the batteries with low terminal voltages can be enhanced, and therefore the damages to the batteries due to overcharging can be avoided and speedy balance of the terminal voltages between each battery can be achieved.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Discharge prevention circuit and electronic equipment provided with the discharge prevention circuit
ActiveUS20060261751A1Consumes less energyDc network circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsCharge currentEngineering
A discharge prevention circuit and electronic equipment with the discharge prevention circuit are provided. The discharging prevention circuit includes a first power line, a second power line, a capacitor, a current detector and a switch. The first and second power lines directly or indirectly connect a power feed line to a load. The capacitor and the current detector are directly or indirectly connected in series between the first and second power lines. The switch is disposed in the first or second power line. The current detector detects at least charging current to the capacitor and discharging current from the capacitor. And if the current detector detects discharging current from the capacitor, the switch acts to stop current flow between the capacitor and the power feed line through the switch.
Owner:NEC CORP
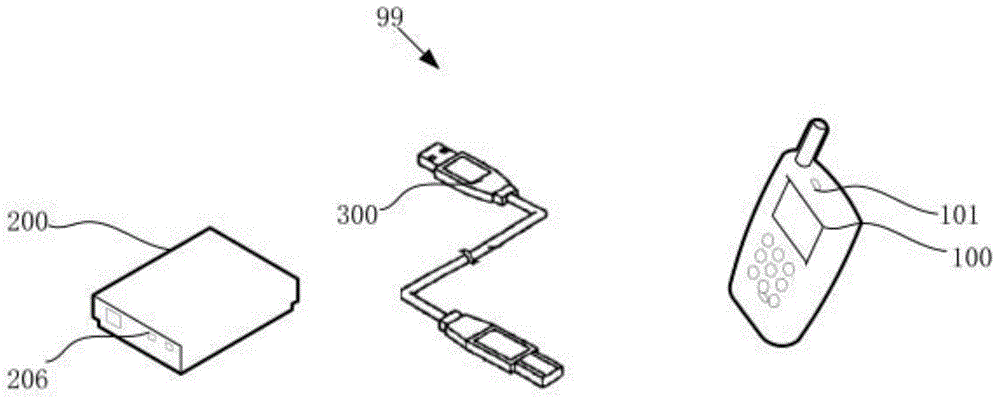
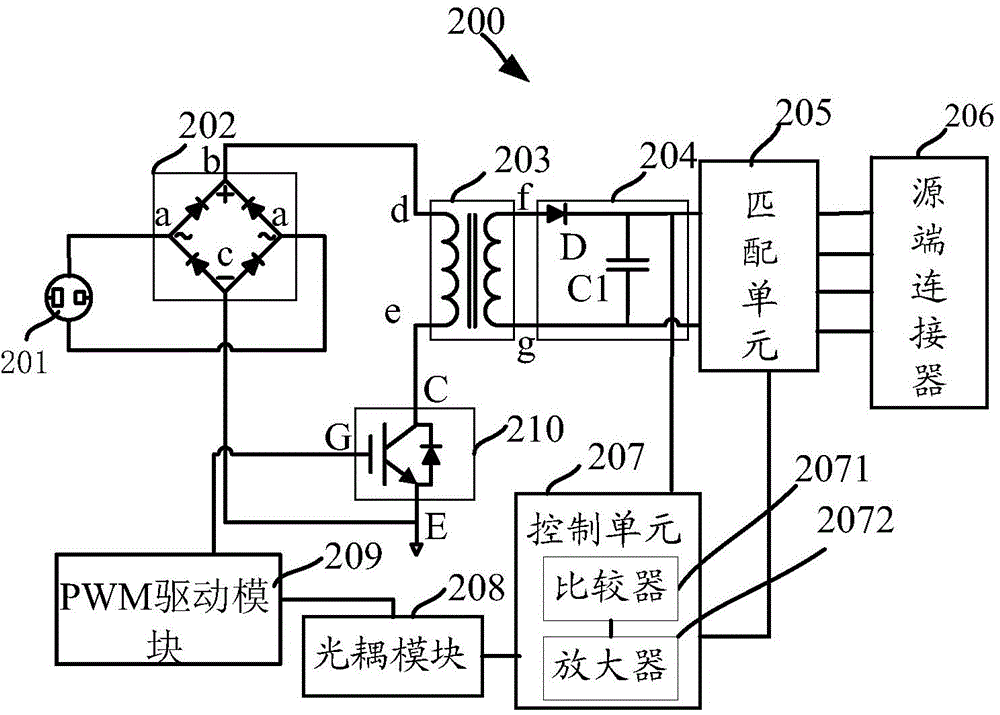
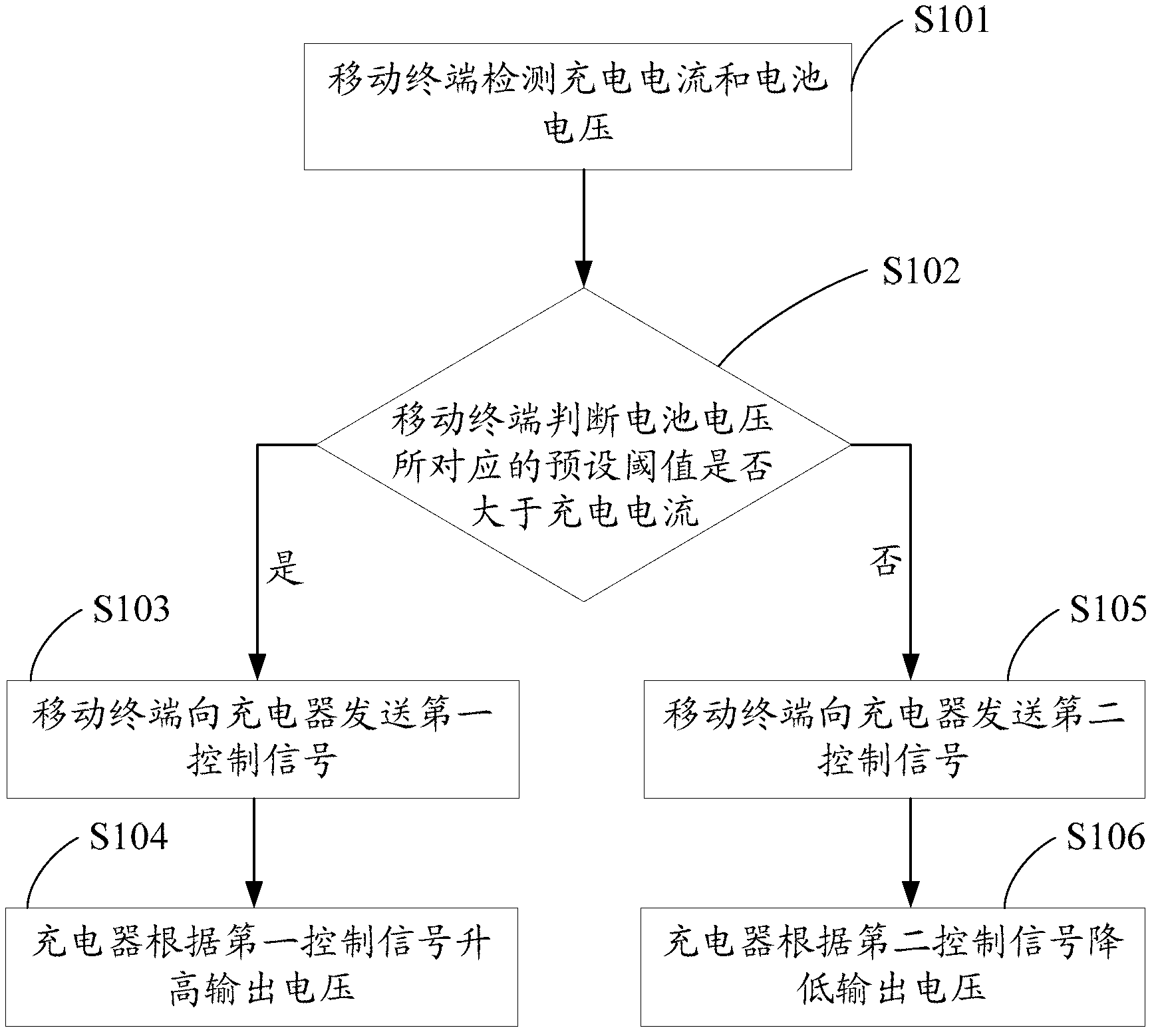
Adapter
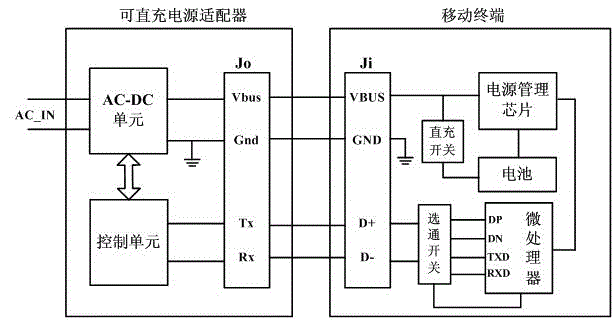
The invention discloses an adapter. A mobile terminal is charged through a data line, and a source end connector is used for receiving required charging voltage and required charging current from the mobile terminal. A control unit is used for obtaining the charging voltage and the charging current. The control unit is used for comparing the charging voltage and the charging current with the required charging voltage and the required charging current respectively, and a control signal is generated when the charging voltage and the charging current are different from the required charging voltage and the required charging current. A PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) driving module is used for adjusting an output pulse signal according to the control signal so as to control the start frequency of a switch unit and change a third alternating current, and thus the charging voltage and the charging current are adjusted to the required charging voltage and the required charging current. In the charging process of the adapter, the adapter outputs voltage and current matched with the required charging voltage and the required charging current of the mobile terminal, and thus the charging effect of the mobile terminal is better.
Owner:李昊
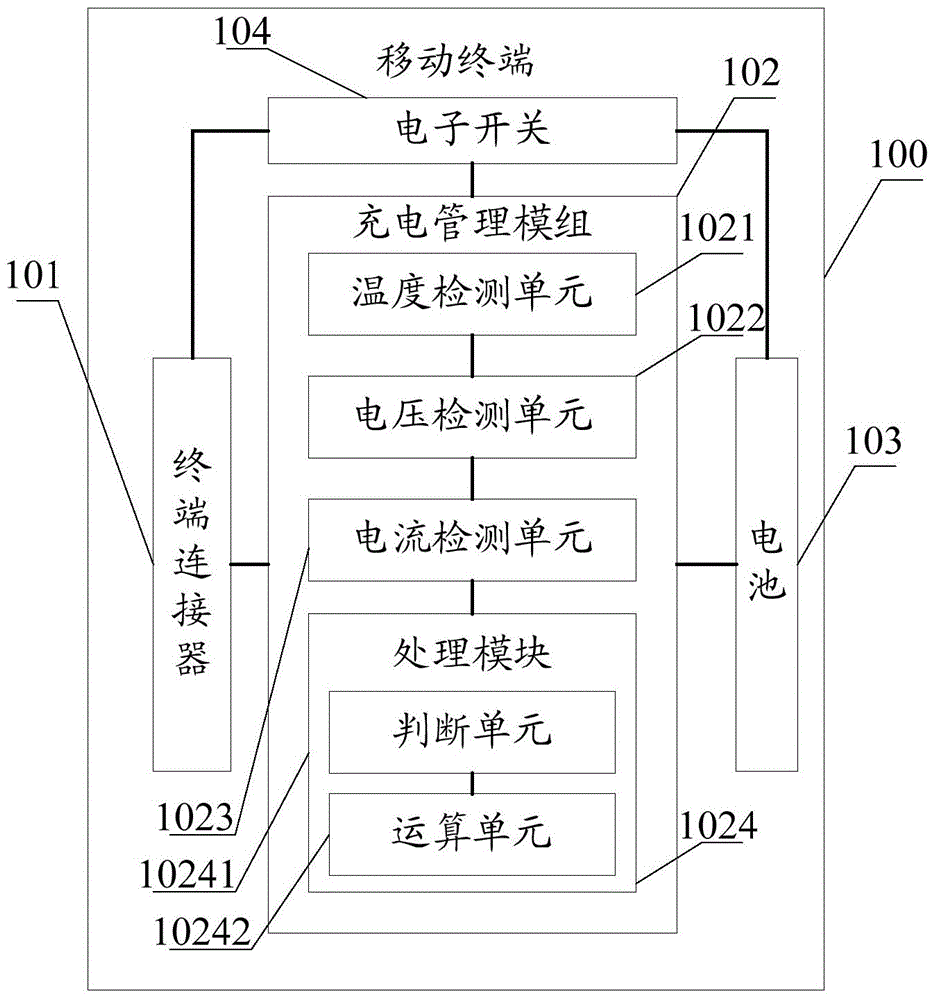
Charging method and charging system
ActiveCN103236568ANo lossReduce wasteBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingCharge currentControl signal
The invention discloses a charging method and a charging system. The charging method comprises the steps that a mobile terminal detects charging current and battery voltage, and sends a corresponding control signal to a charger according to the detected charge current and battery voltage, and the charger controls output voltage according to the corresponding control signal, so that the charge current can be adjusted. The optimal charge current can be matched according to the current battery voltage, so that the charging efficiency is maximized, and the quick and efficient charging is achieved. The charger directly controls the output voltage to adjust the magnitude of the charging current, so that charging heat due to the loss of electric energy is not caused, the charging safety is improved, and the energy waste is reduced.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
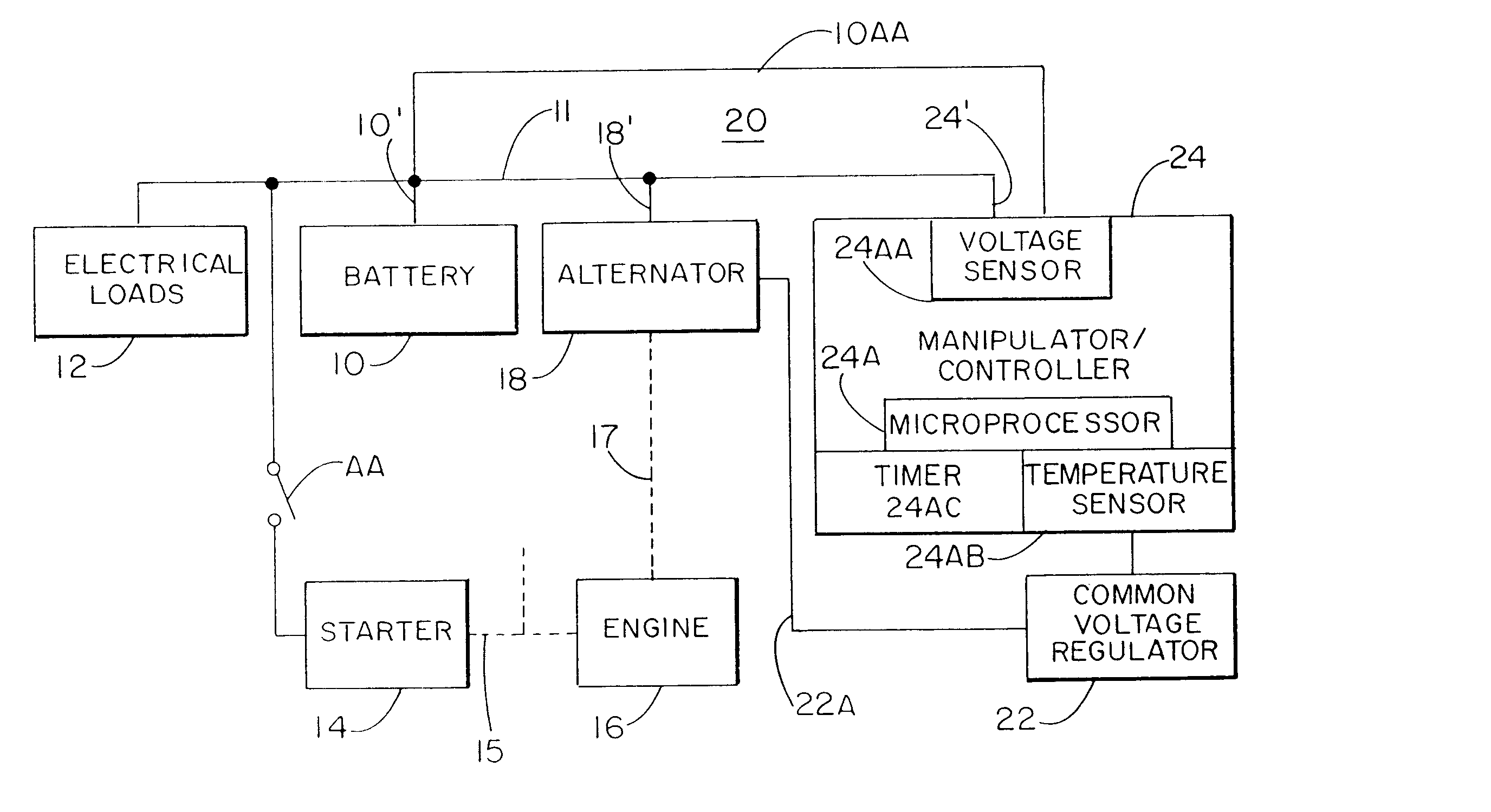
Battery charger apparatus
InactiveUS6515456B1Improve economyProlong lifeElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingBattery state of chargeAlternator
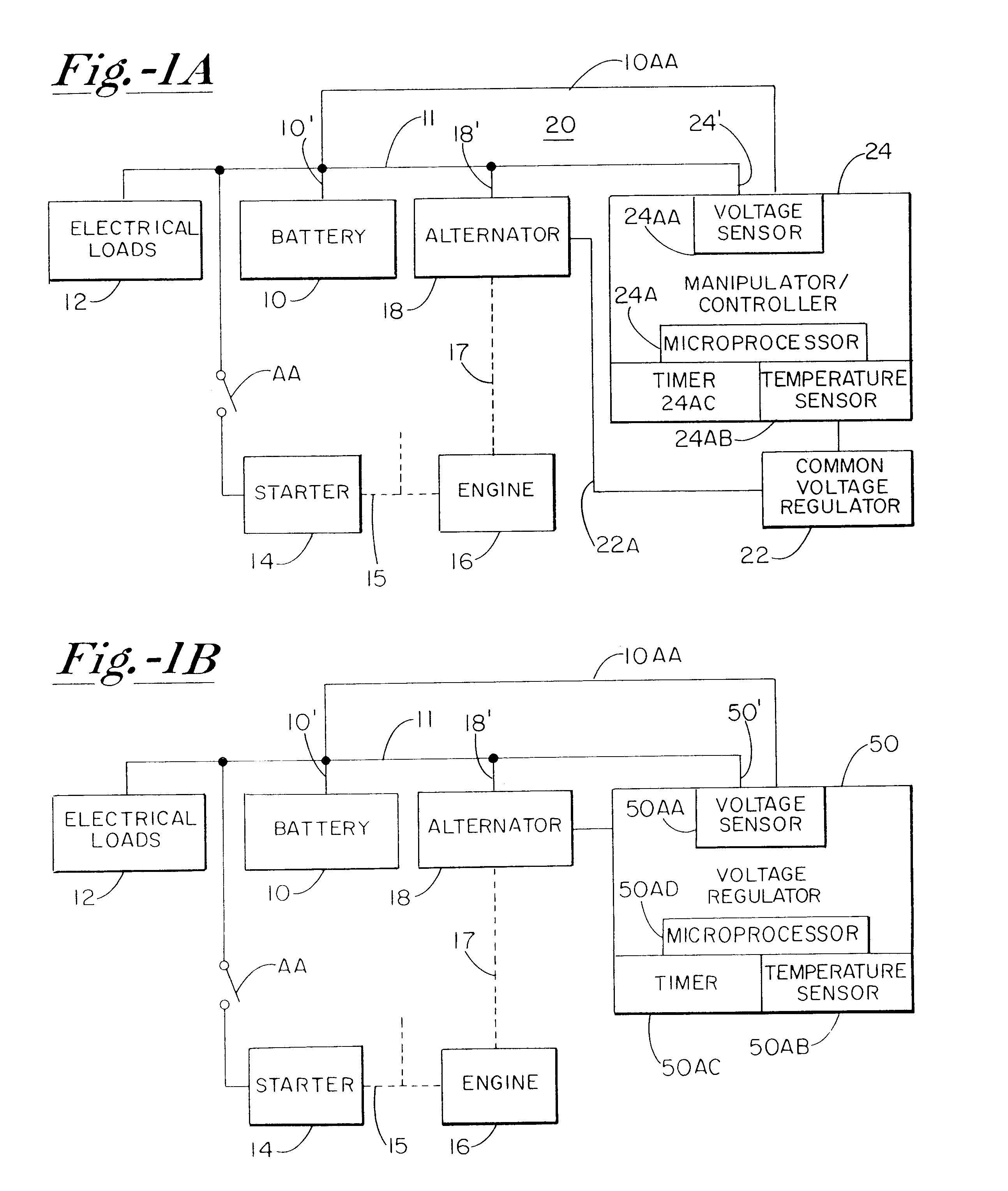
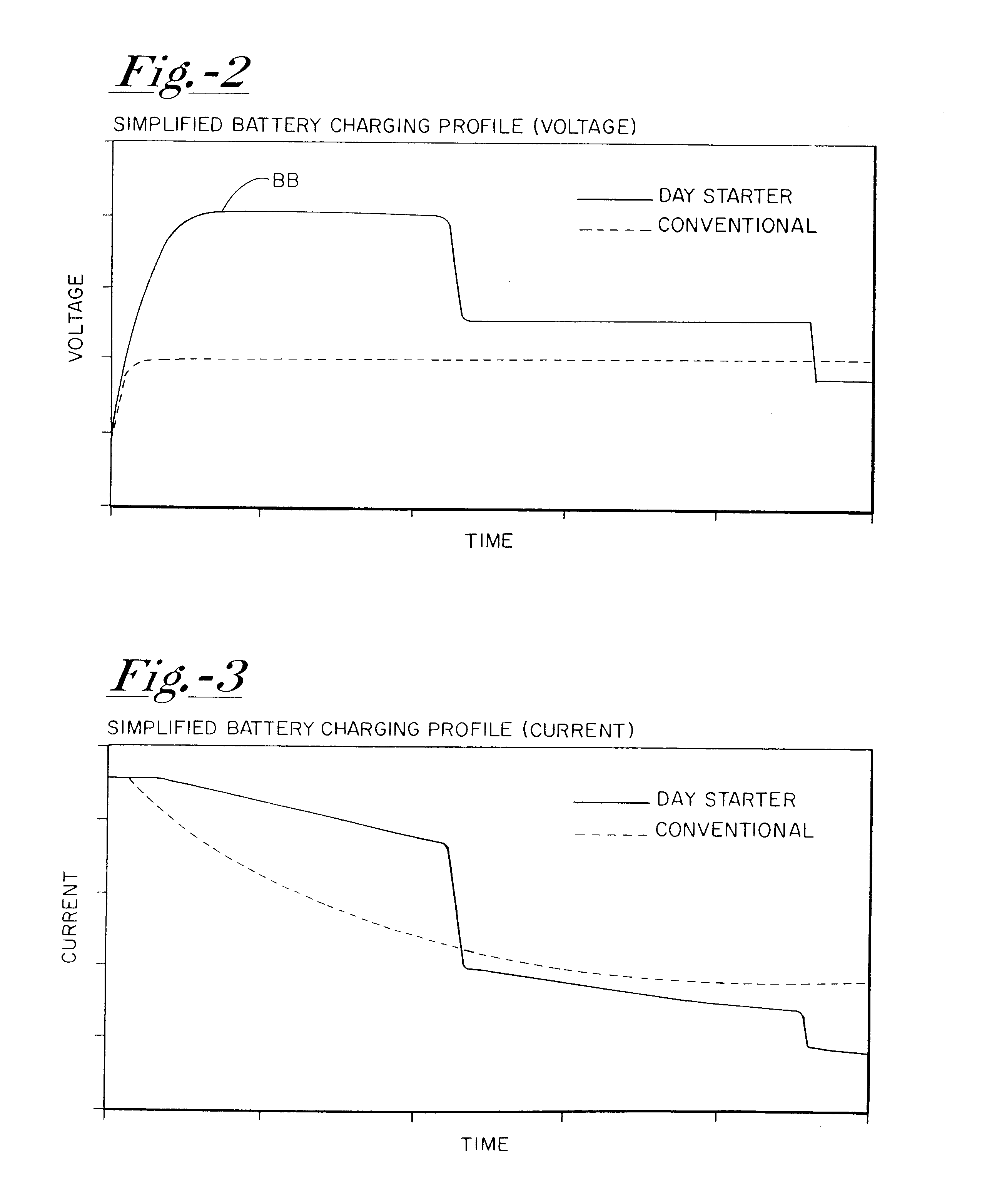
A system for actively controlling the charging profile of a battery uses a software-based alternator control unit to control the charging voltage. The system optimizes battery and alternator life. The system, on a dynamic basis, uses battery open-circuit voltage (OCV) to estimate battery state-of-charge (SOC). Also, the charging current of the battery is periodically estimated; this, after processing, provides an estimated SOC of the battery.
Owner:MIXON
Apparatus for transferring energy using power electronics and machine inductance and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20100096926A1Auxillary drivesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical conductorCharge current
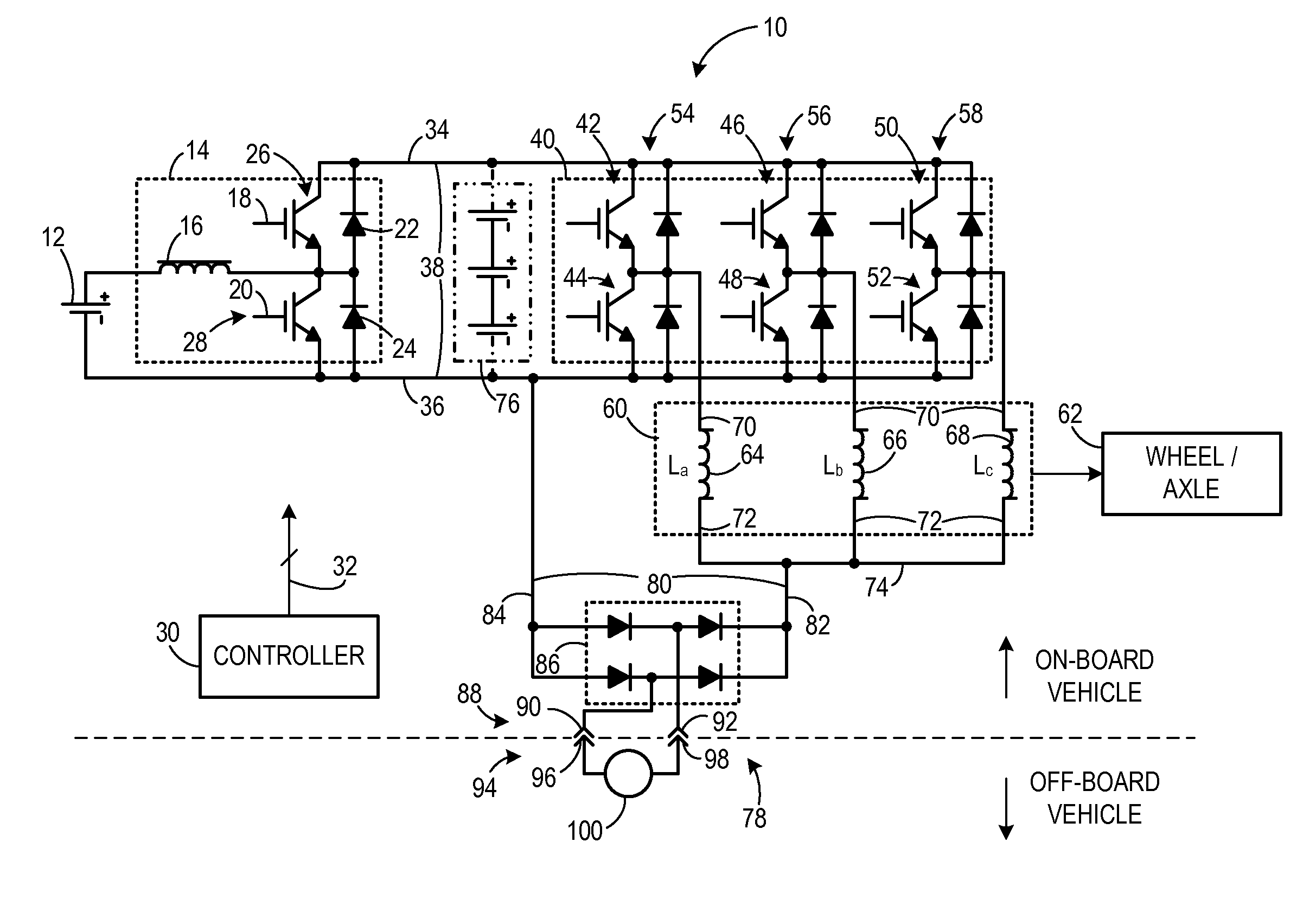
A traction inverter circuit includes a first energy storage device configured to output a DC voltage, a first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter coupled to the first energy storage device, and a first electromechanical device. The first electromechanical device includes a first plurality of conductors coupled to the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter, a second plurality of conductors coupled together, and a plurality of windings coupled between the first plurality of conductors and the second plurality of conductors. The traction converter circuit also includes a charge bus comprising a first conductor coupled to the second plurality of conductors of the first electromechanical device, the charge bus configured to transmit a charging current to or receive a charging current from the first electromechanical device to charge the first energy storage device via the first electromechanical device and the first bi-directional DC-to-AC voltage inverter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electric vehicle and vehicle charging system
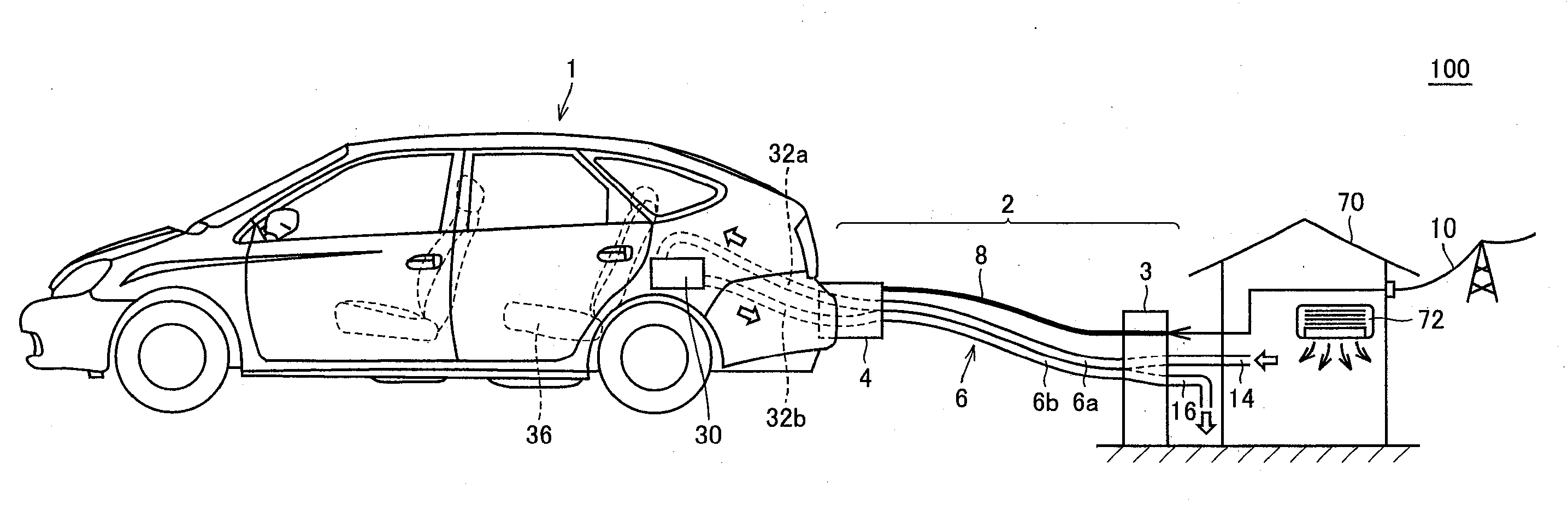
ActiveUS20100089669A1Maintain performancePassenger comfort is ensuredPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingPropulsion by batteries/cellsThermal energyElectrical resistance and conductance
When a current flows through a battery, a resistance loss proportional to the square of the current is produced by an internal resistance component of the current. In a case where the temperature of a heat capacity element is raised, a charging current is controlled such that prescribed thermal energy is provided to the heat capacity element by this resistance loss. Air is induced into a power supply unit through a vehicle compartment air exhaust duct. Then, the thermal energy stored in the heat capacity element is transferred to the air induced into the power supply unit. The air to which the thermal energy has been provided from the heat capacity element is blown out toward a vehicle compartment space by a fan.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
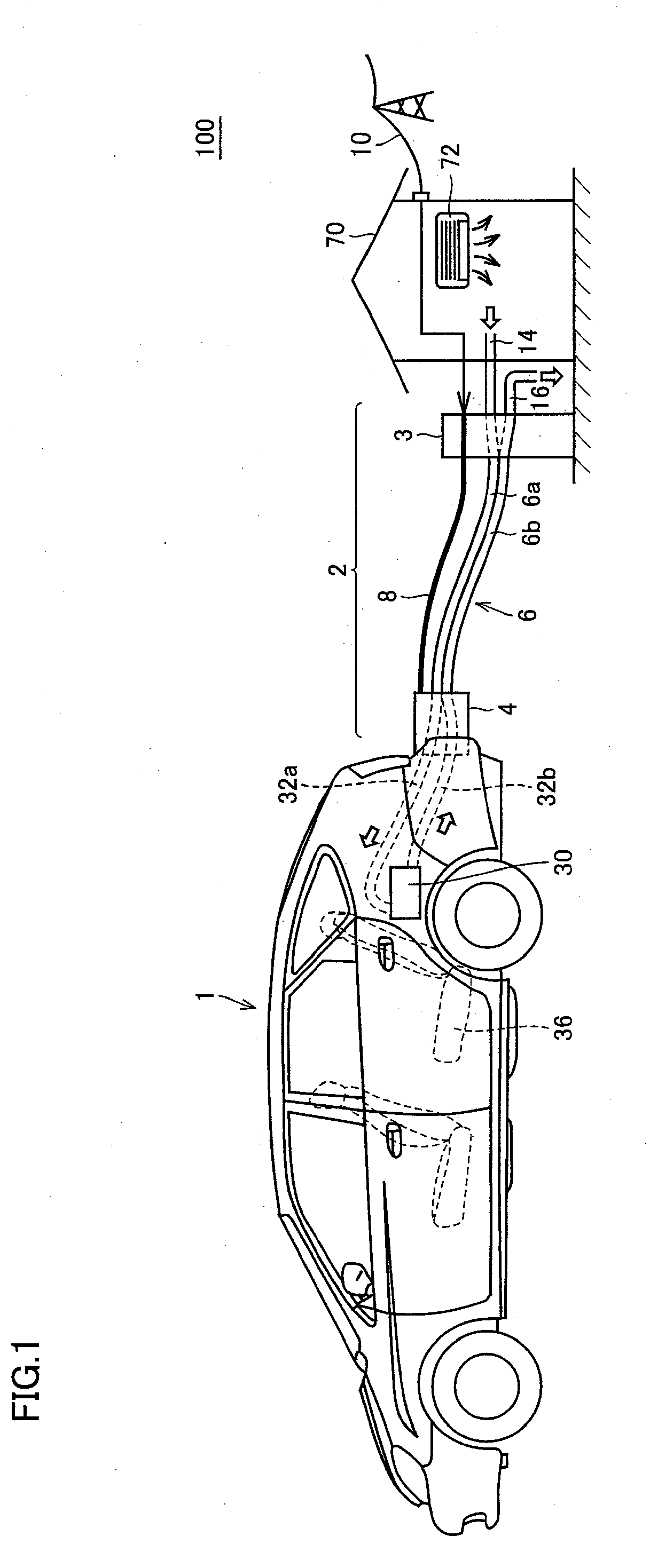
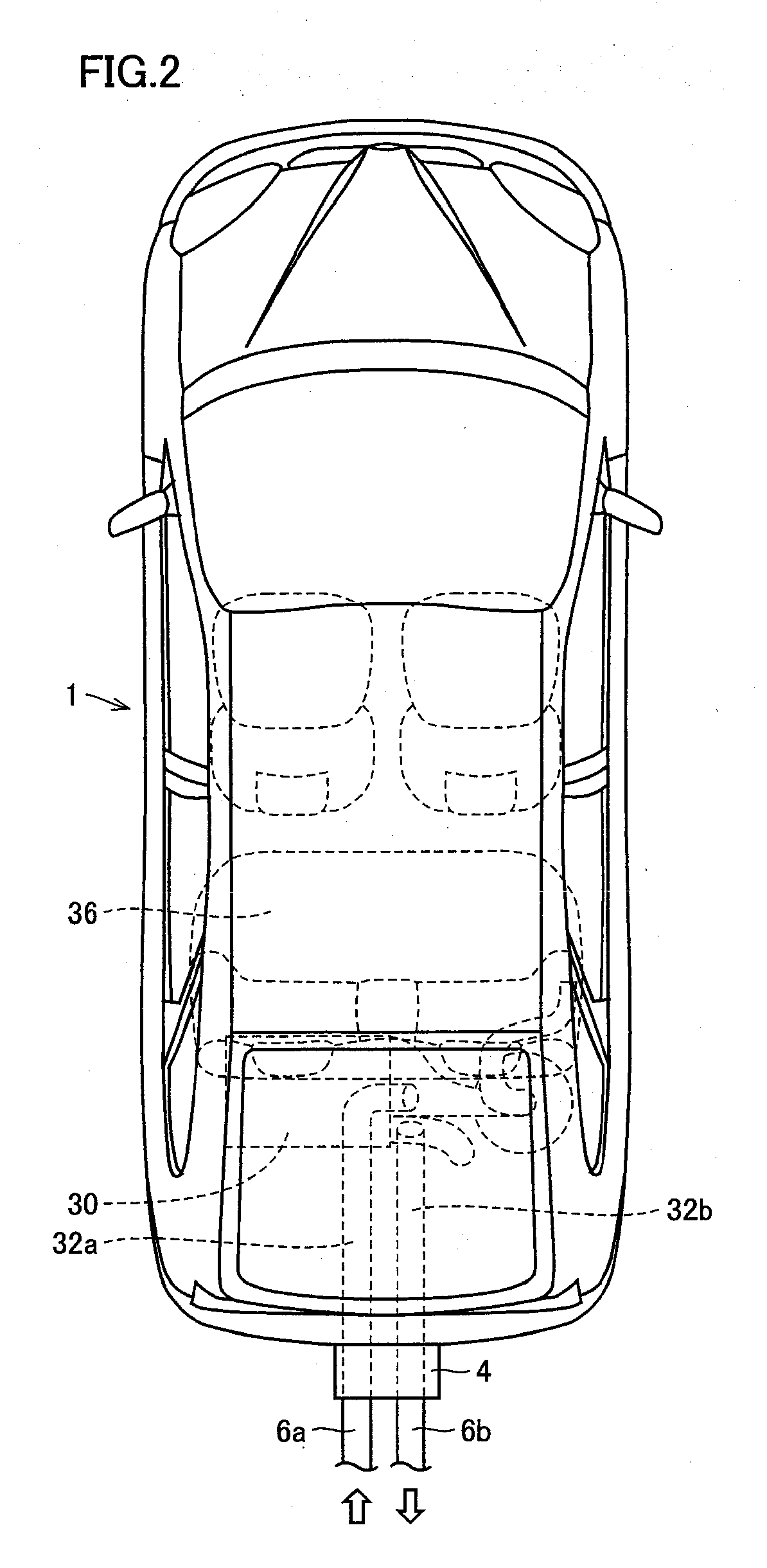
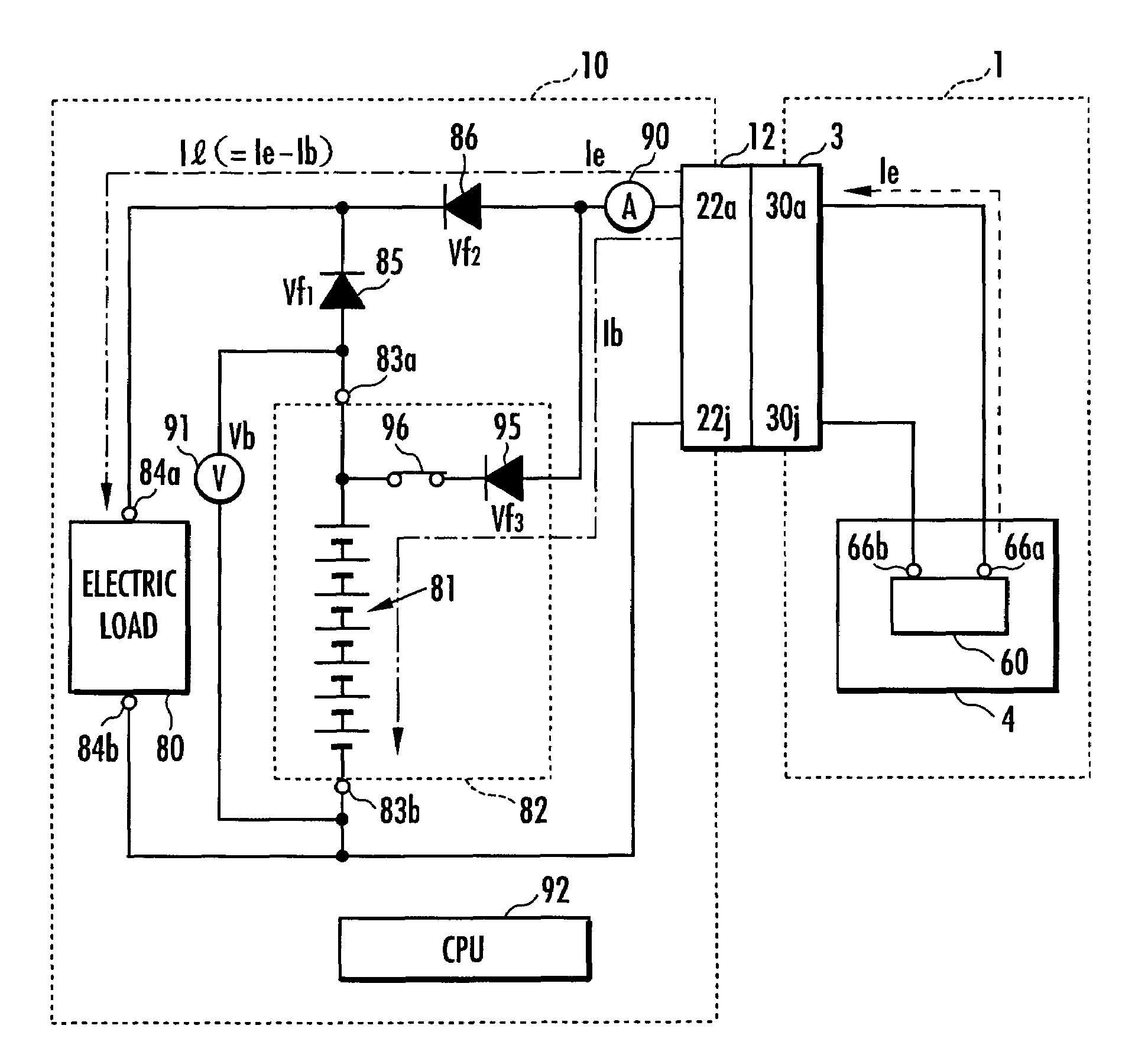
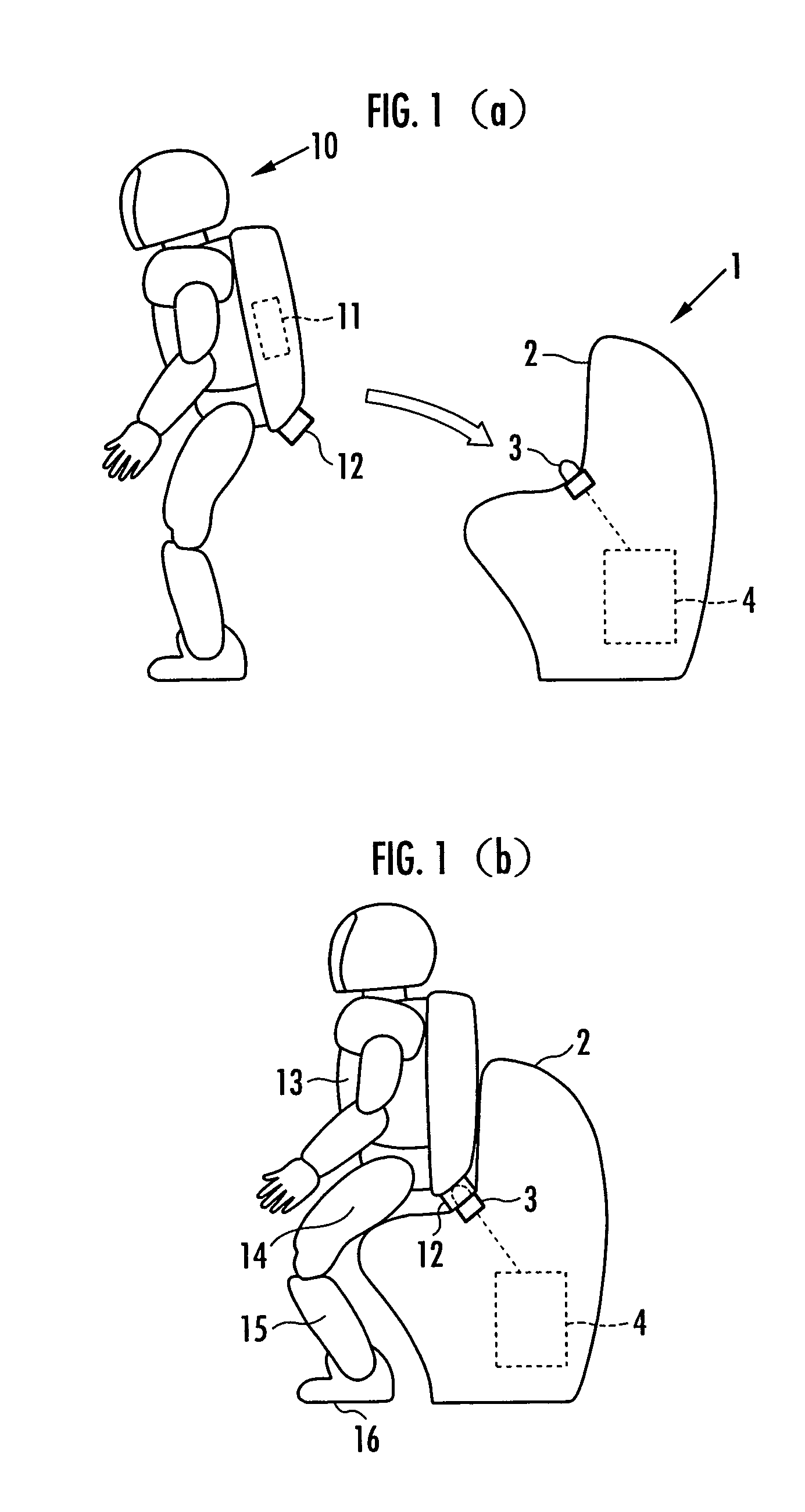
Charging system for legged walking robot
An inexpensive charging system with a simple construction can supply charging current to a battery of a legged walking robot while maintaining the supply of required current to an electric load of the legged walking robot by an external power source. The charging system includes a connection circuit having a first, a second diode, a third diode, and a circuit that brings various negative electrode and a negative input terminal of the electric load into conduction, and an output electric power controller that sets an output voltage of the external power source to be higher than a total voltage of a voltage across electrodes of the battery when the battery is fully charged and a forward voltage of the third diode, while setting a current of the external power source that can be output to be larger than a required current of the electric load.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
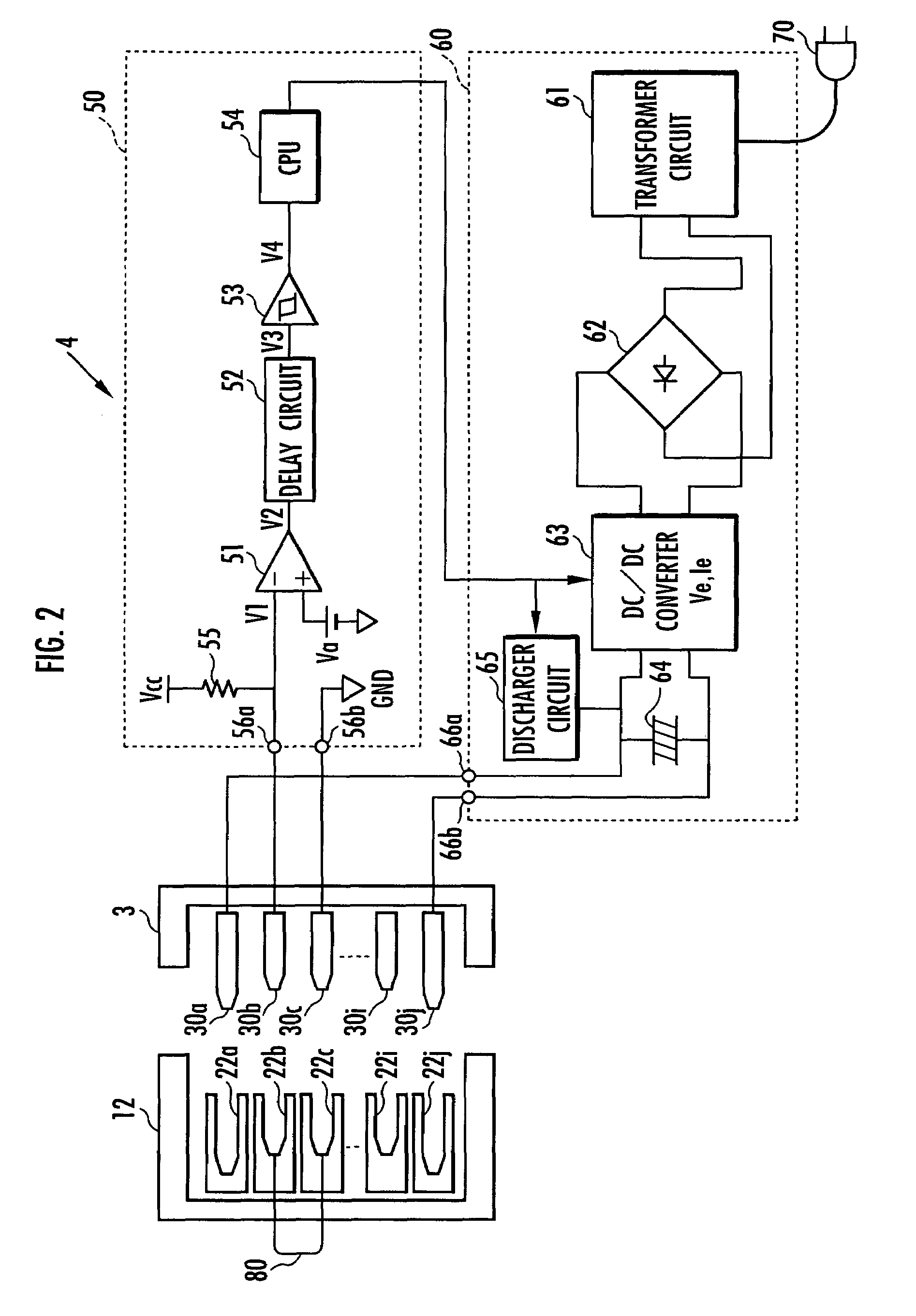
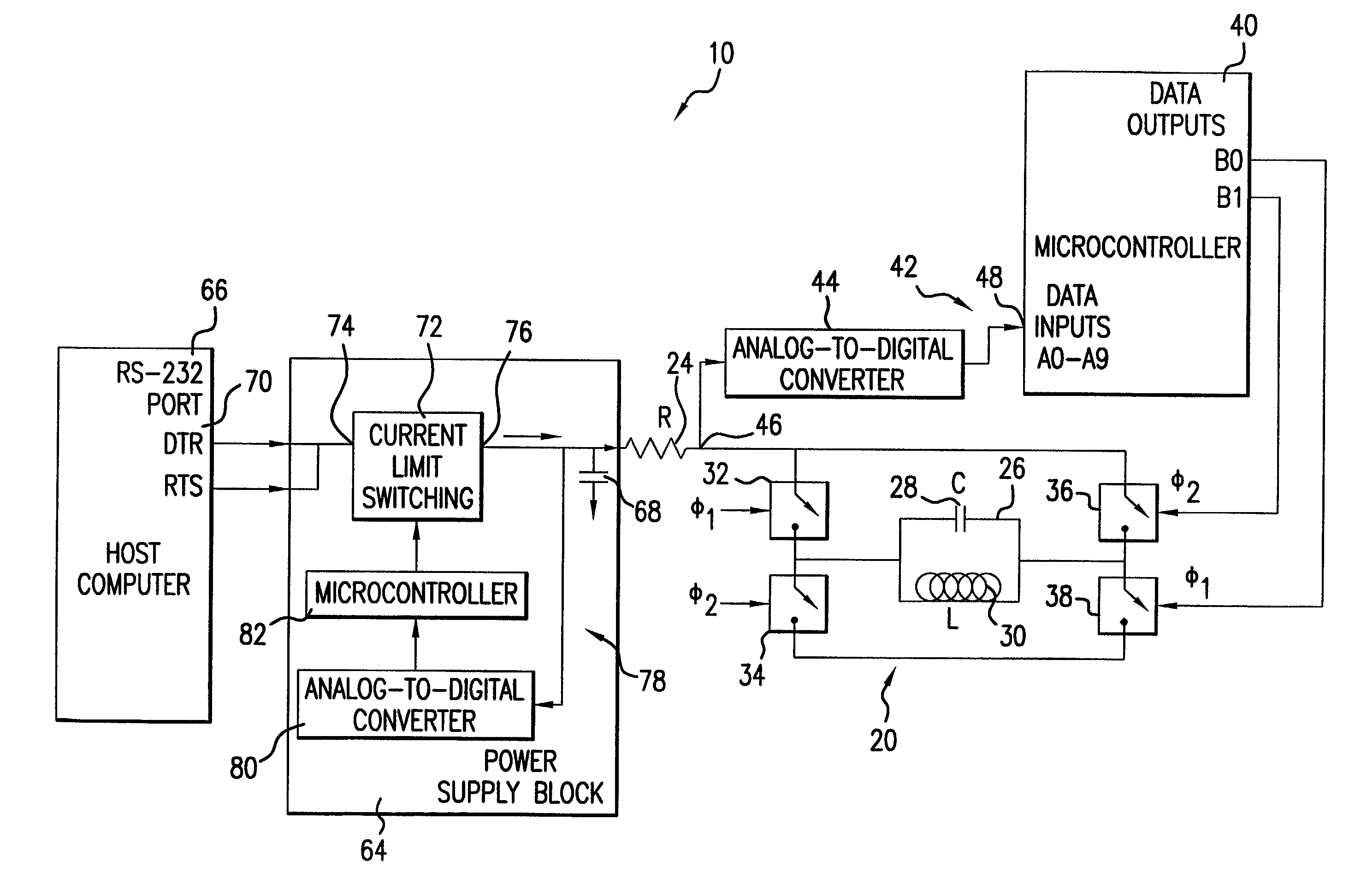
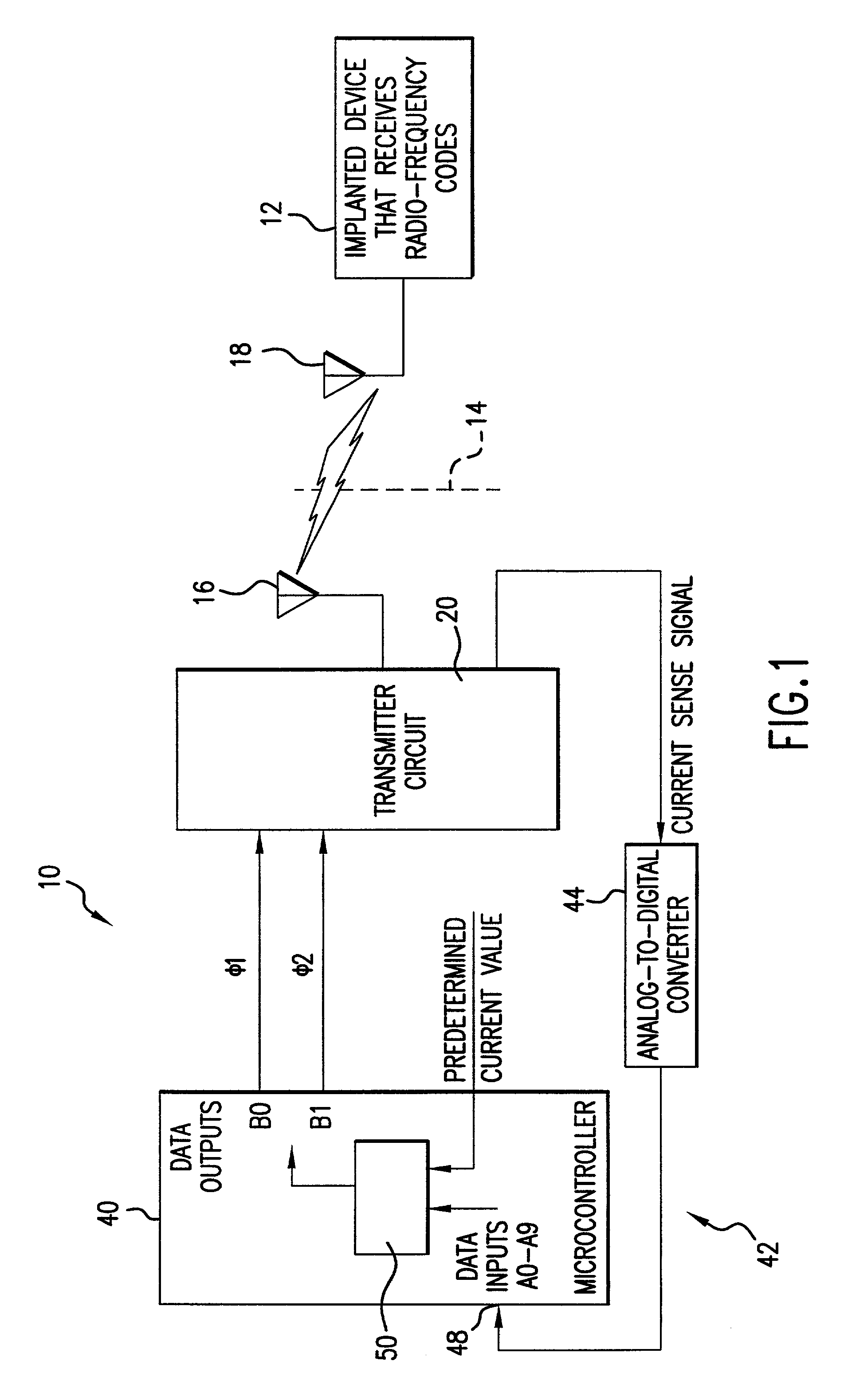
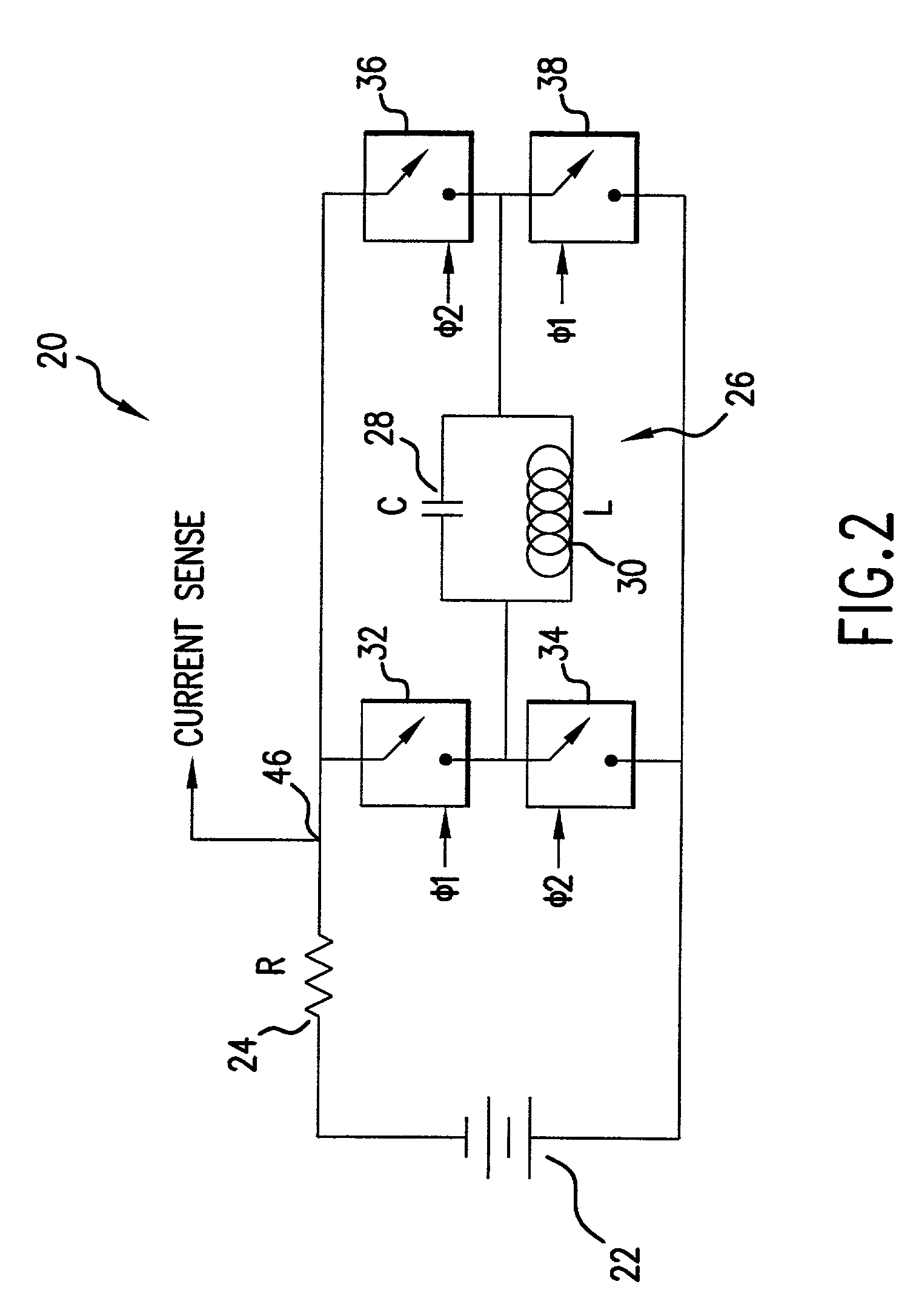
Transmitter system for wireless communication with implanted devices
ActiveUS7151914B2Low power operationCurrent consumptionResonant long antennasElectrotherapyMaximum levelFeedback circuits
A transmitter system for wireless communication with implanted medical devices includes a transmitter circuit having a resonant network the resonant frequency of which is adjusted by a feedback circuit in order to minimize the current drain from the power source and maximizing the power source life. The transmitter system may be powered by a power supply block which uses commonly available RS-232 signals of a host computer as a raw power source, combined with a high value storage capacitor to provide power for the wireless medical data programmer. A feedback circuit monitors the charging current as well as voltage impressed across the storage capacitor in order to maintain the charging current at maximum level during the charging time and in order to stop the charging once the full charge of the storage capacitor has been reached.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Battery charger and method of charging a battery
InactiveUS7411371B2Quickly and conveniently chargeReduced size and massBatteries circuit arrangementsPropulsion by batteries/cellsOn boardCopper foil
Stationary and on-board battery chargers, methods of charging batteries, electric-vehicle chargers, and vehicles with chargers, including electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. Chargers may automatically charge at the correct battery voltage for various types of batteries. Chargers have variable AC power supplies controlled by digital controllers, isolation transformers, and rectifiers. Transformers may be foil-type, and may have copper foil. Power supplies may be variable-frequency generators and the controllers may control the frequency. Use of the variable frequency generator supply facilitates reduced component size and weight and better battery charging performance. Electric vehicle chargers may have card readers, and vehicles may have batteries and a charger. Methods of charging include identifying the battery type and gradually increasing the charging at different rates of increase while monitoring charging voltage, charging current, or both, until a current lid is reached. Charging may occur at constant current and then at constant voltage.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
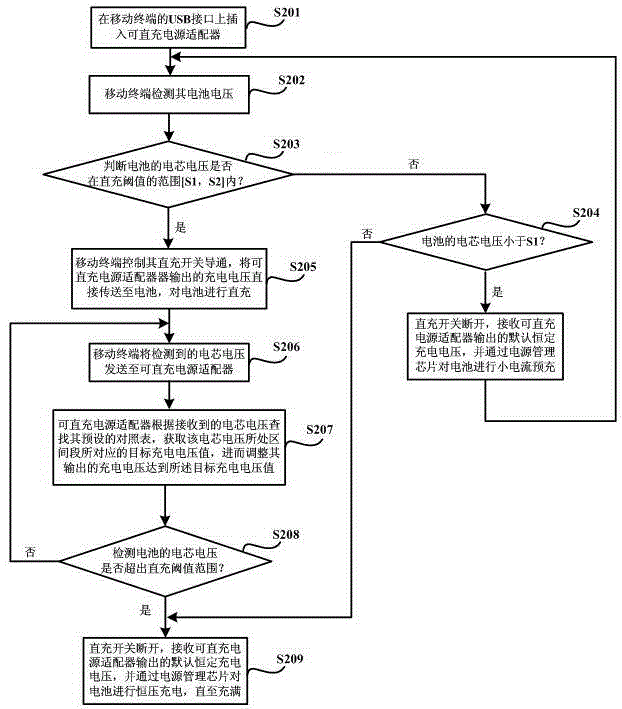
Fast-charging method, mobile terminal and power adapter capable of being charged directly
ActiveCN104967201AShorten the time required for a single chargeFast chargingSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerCharge currentElectrical battery
The invention discloses a fast-charging method, a mobile terminal and a power adapter capable of being charged directly. The fast-charging method is provided based on the power adapter of which output voltage dynamic is adjustable. The voltage of the battery-core of a battery is divided into multiple sections, then a sectional-type constant-current charging way is adopted, the value of the charging voltage output through the power adapter is adjusted dynamically according to the located sections of the battery-core voltage of the battery inside the mobile terminal in the charging process, and the battery is charged directly through the charging voltage output through the power adapter, so that the charging current is improved greatly, thereby the charging speed of the battery is accelerated, the single-time charging time needed by the movable terminal is shortened, the influence of the situation that the mobile terminal needs to be charged frequently for a long time on daily use of a user is lowered, and the customer-using satisfaction degree in promoted to a large extent.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
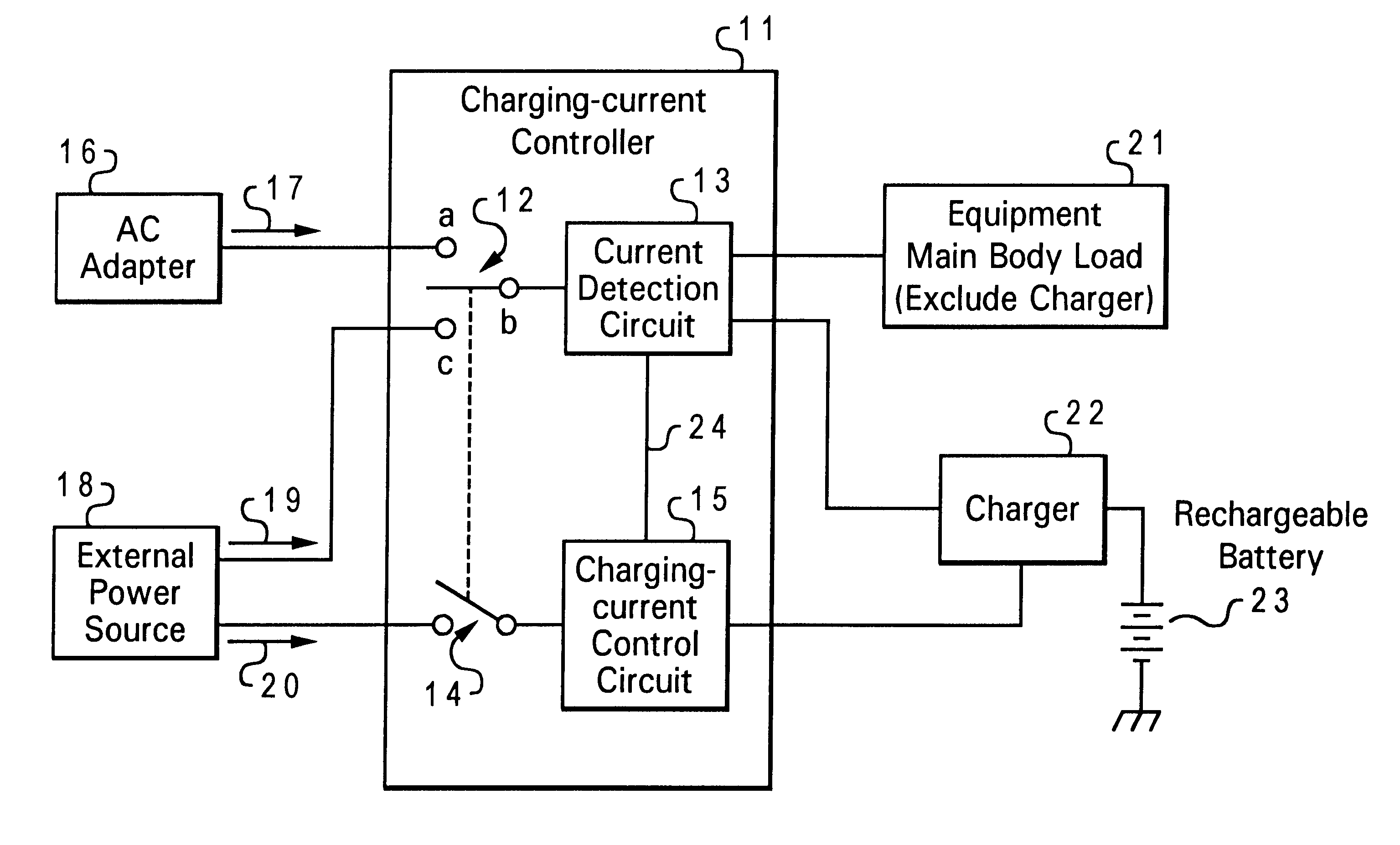
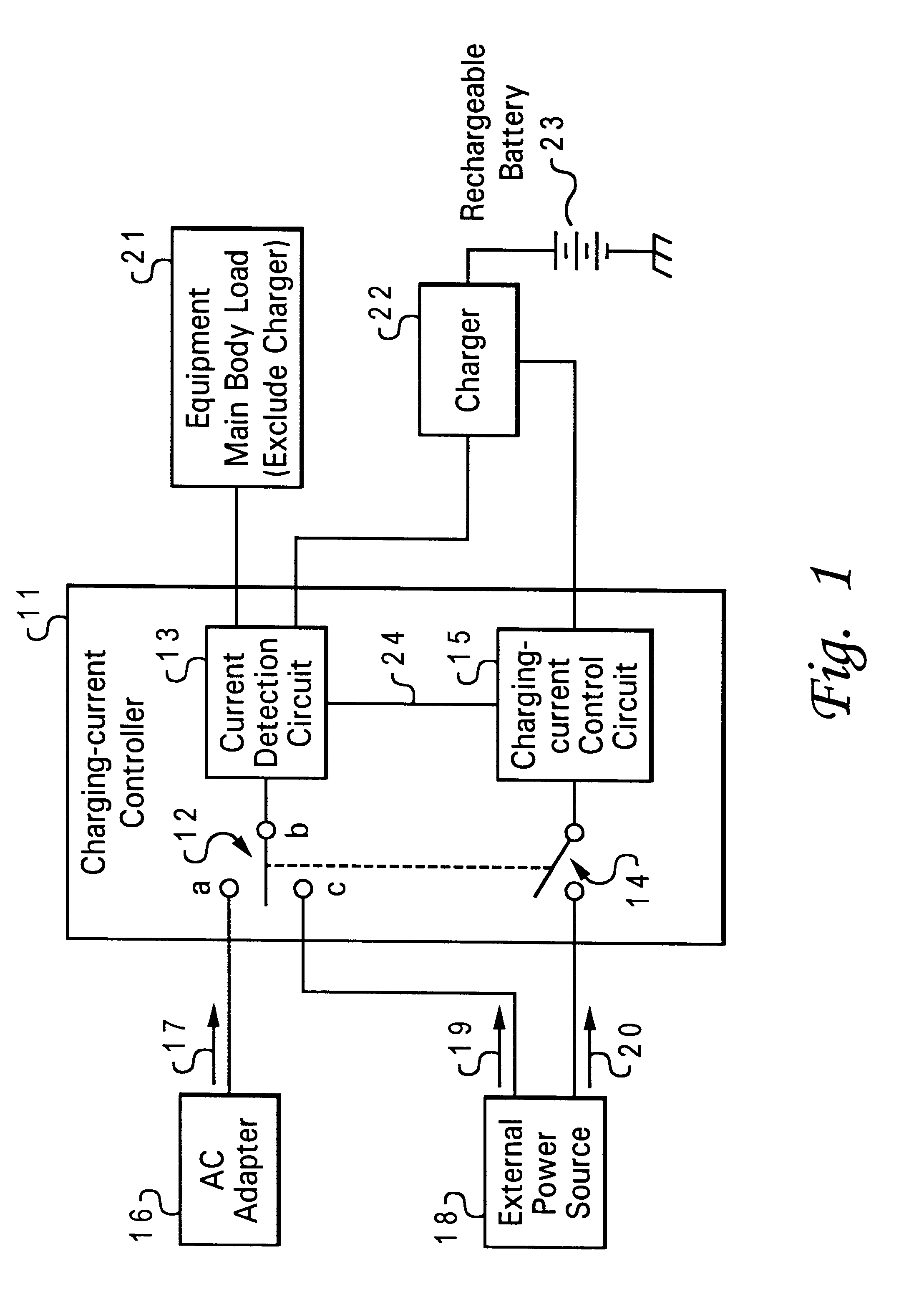
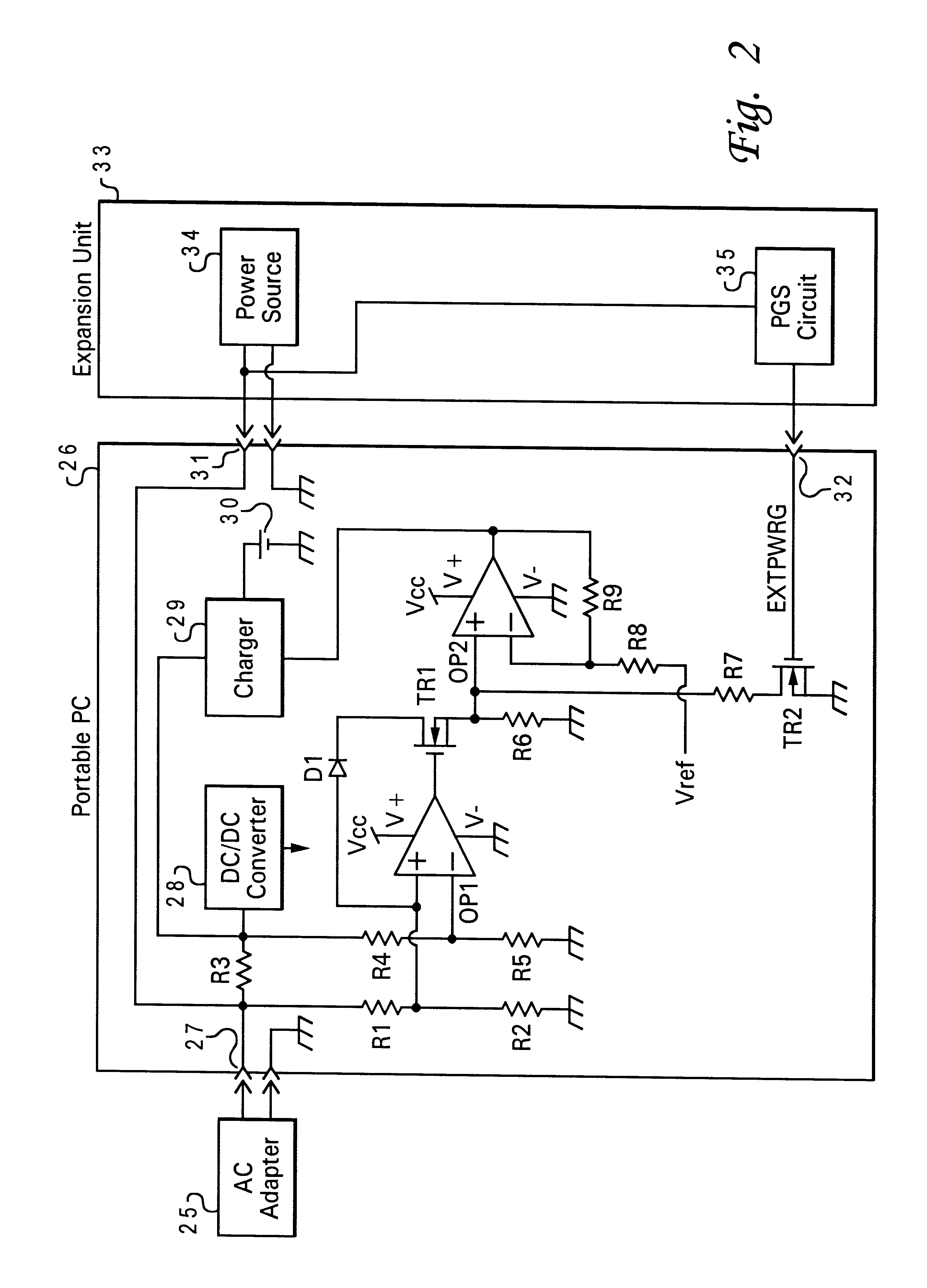
Method and apparatus for controlling battery charging current
A method and apparatus for controlling battery charging current selectively receive electrical power from either a first external power source or a second external power source and outputs part of the power source to a charger for charging a battery. A reference value supplying apparatus gives a first reference value equivalent to the output current capability of the first external power source when a charging-current controller is connected to the first external power source and gives a second reference value equivalent to the current capability of the second external power source when the charging-current controller is connected to the second external power source. A current detection circuit detects current that the charging-current controller receives from either the first external power source or the second external power source and a charging current control circuit controls a charging current in the charger so that the charging current does not exceed the first or second reference value detected by the current detection circuit.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Systems, apparatus and methods for battery charge management
ActiveUS20100052614A1Reduce the amount requiredEfficient and cost-effectiveCharge equalisation circuitElectrical testingMicrocontrollerThermal energy
Owner:ALTERNATIVE CURRENT LLC
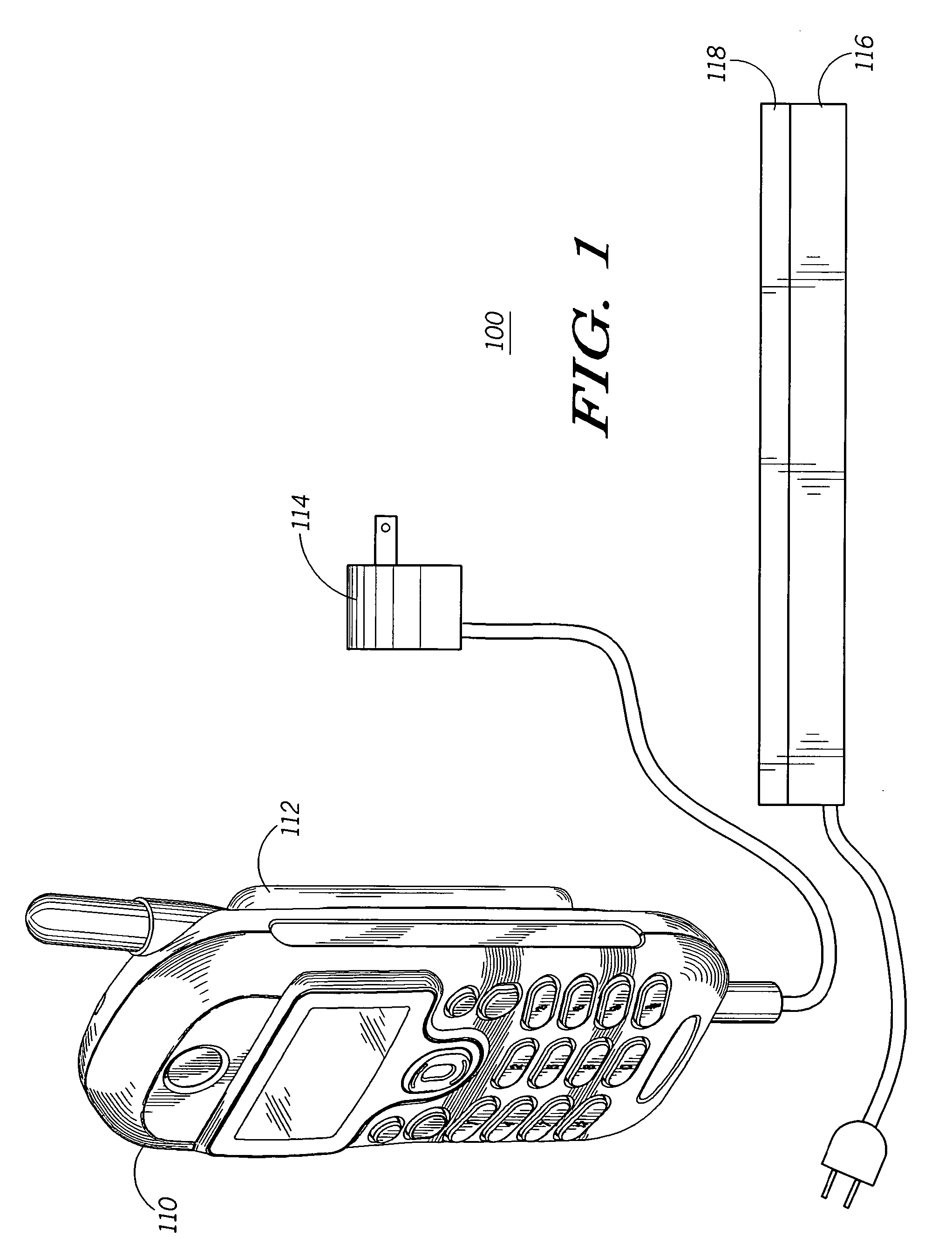
Method and system for selectively charging a battery
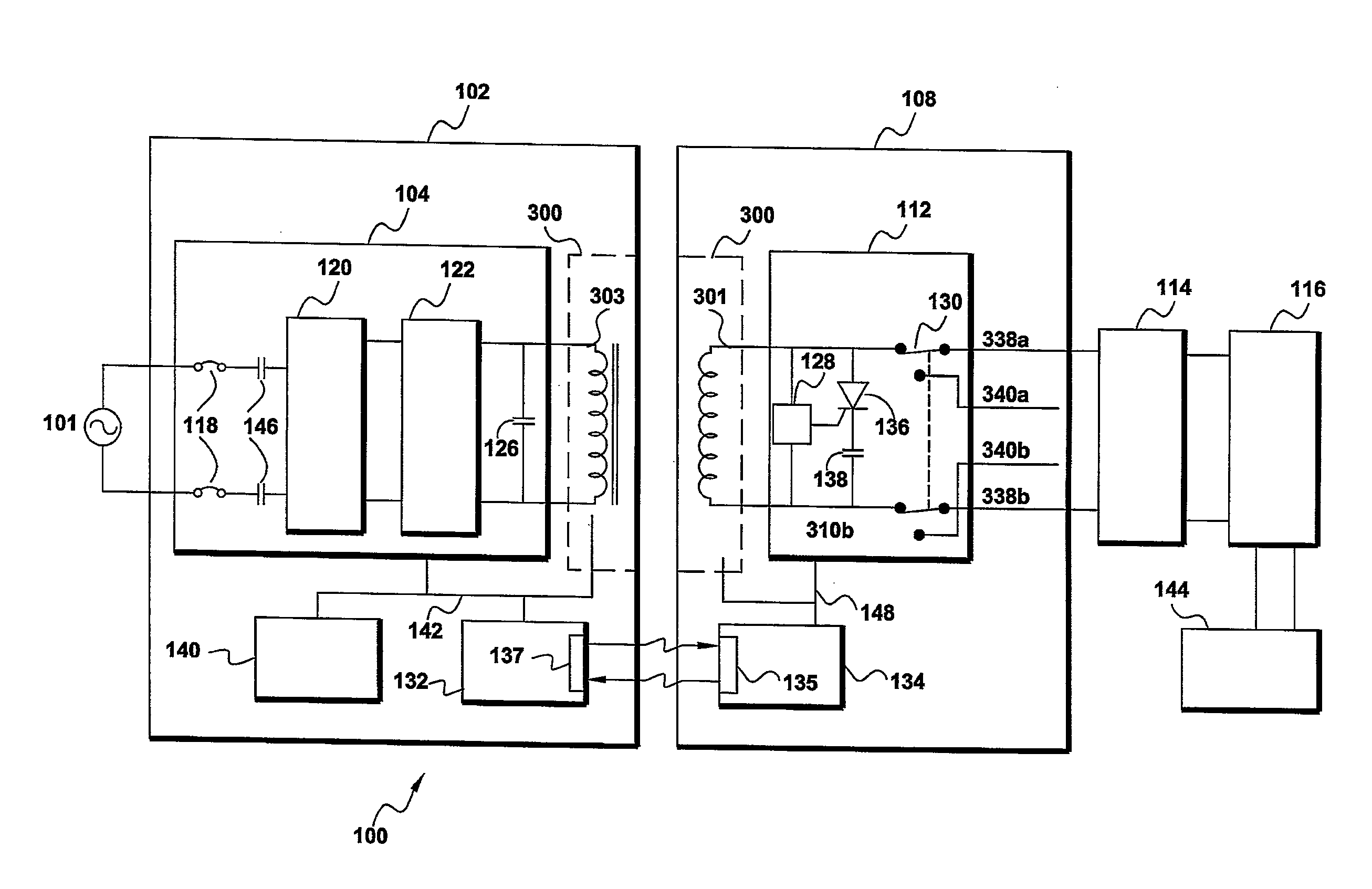
InactiveUS20060103355A1Maximizing available charging current parameterMinimize power consumptionElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingCharge currentCoupling
The invention concerns a method (300) and system (100) for selectively charging a battery (112). In one arrangement, the method can include the steps of coupling (311) the battery to a first power supply (114), coupling (311) the battery to a second power supply (116), determining (312) an available charging current parameter for the battery and selectively enabling (314) a charging circuit (120) for the first power supply and a charging circuit (122) for the second power supply based on the available charging current parameter of the battery. The selectively enabling process can be based on maximizing (316) an available charging current of the battery and minimizing (320) a power dissipation of the battery. As an example, the first power supply can be a hard-wired charger (114), and the second power supply can be a wireless charger (116).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com