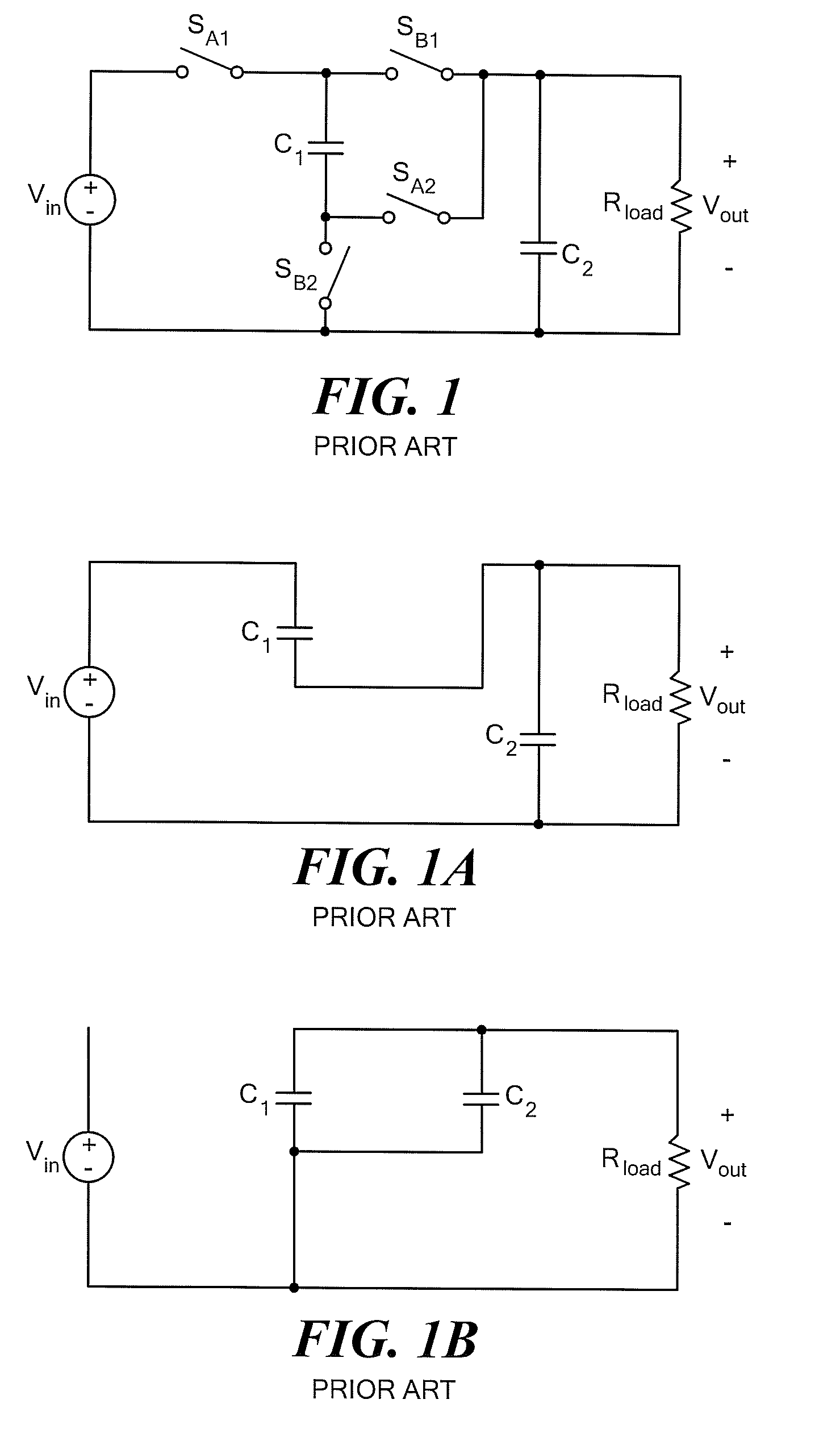
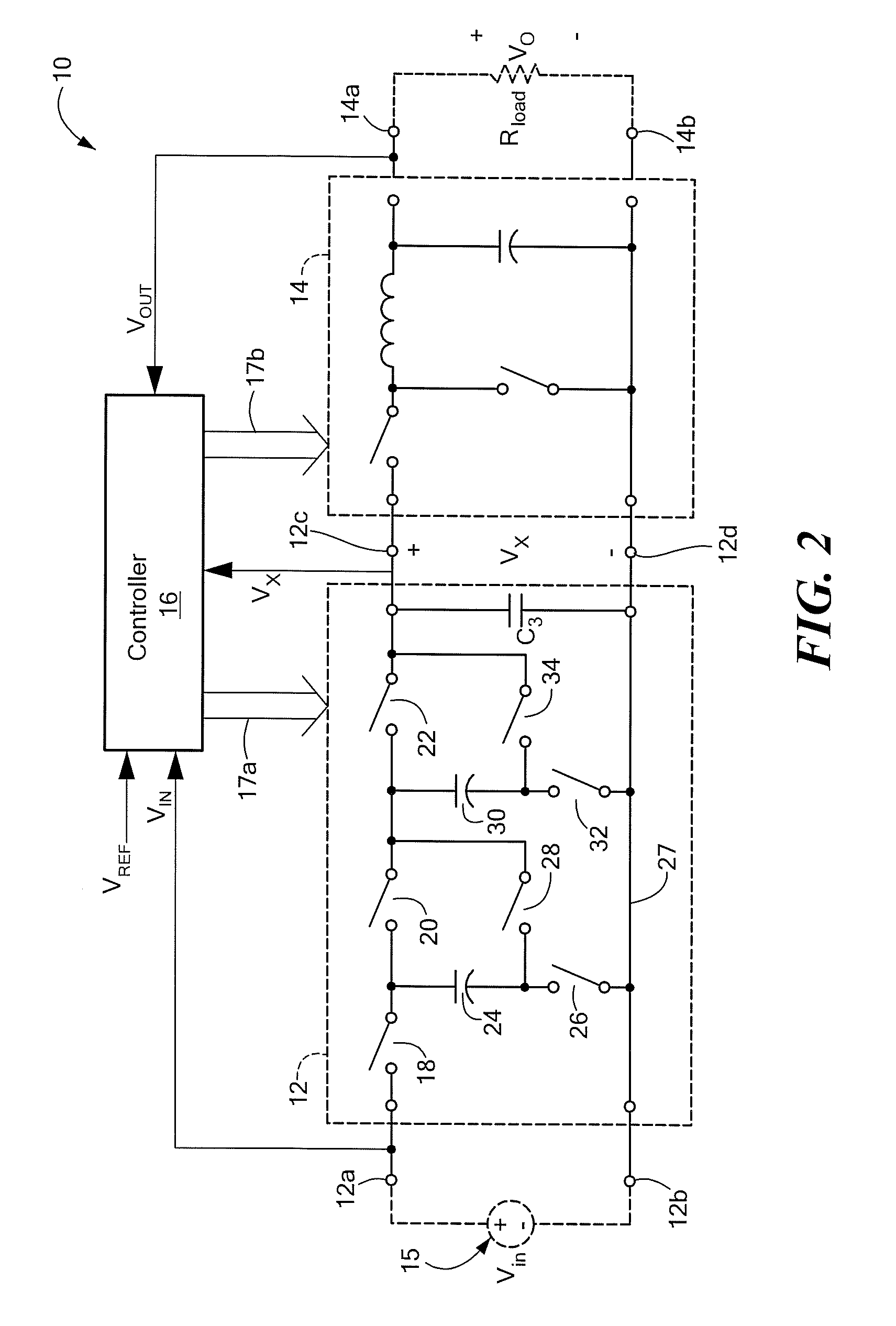
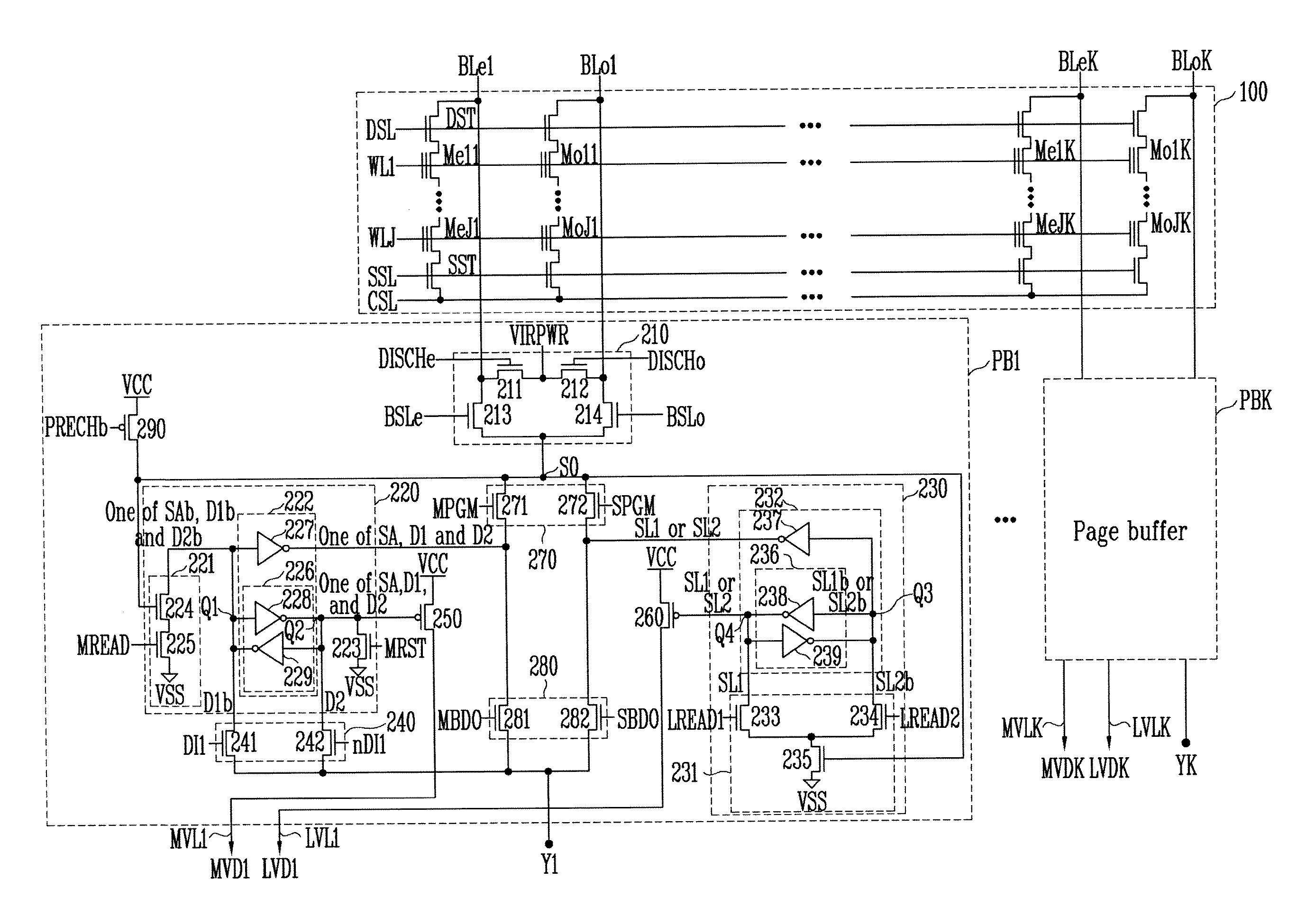
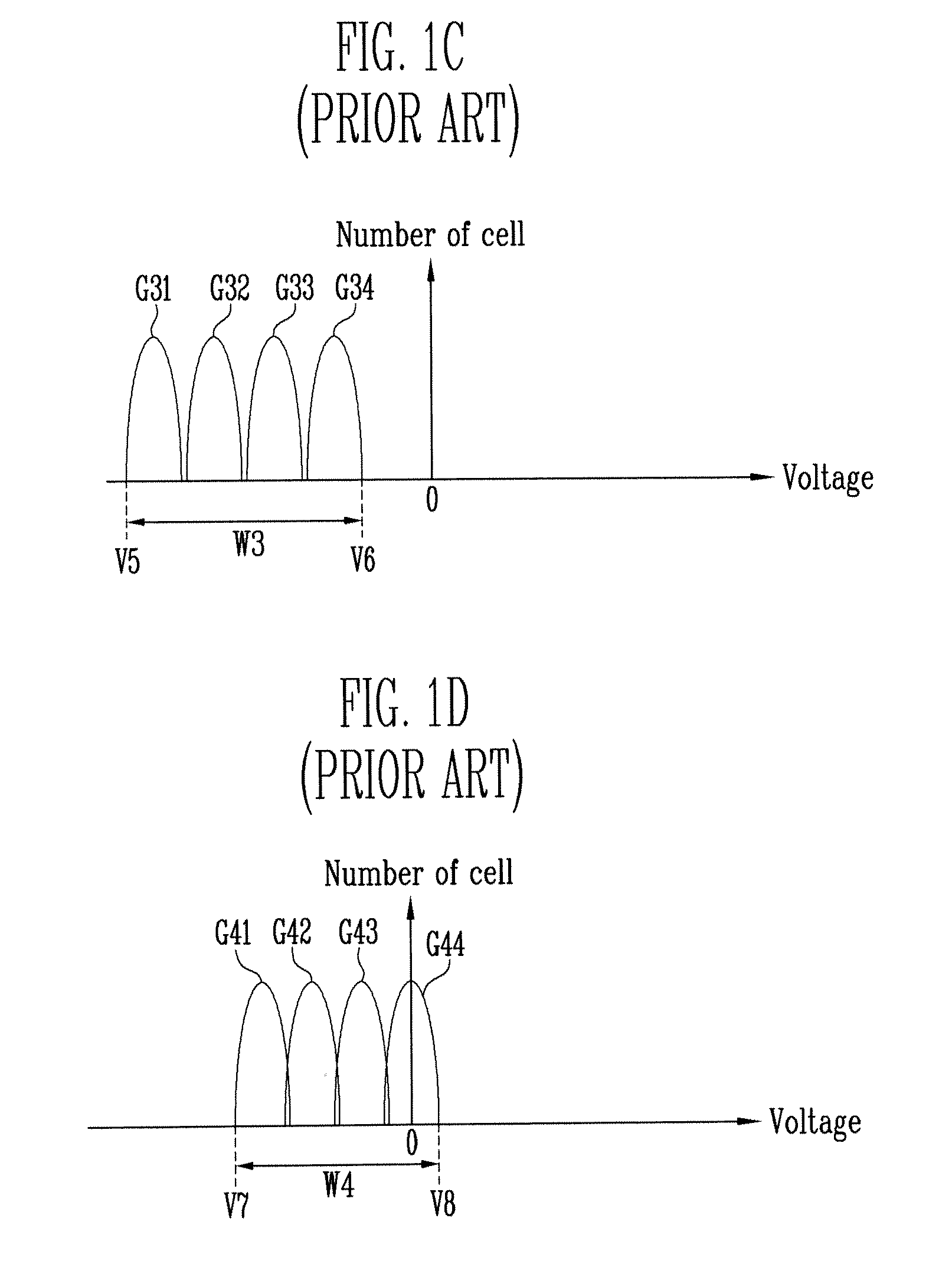
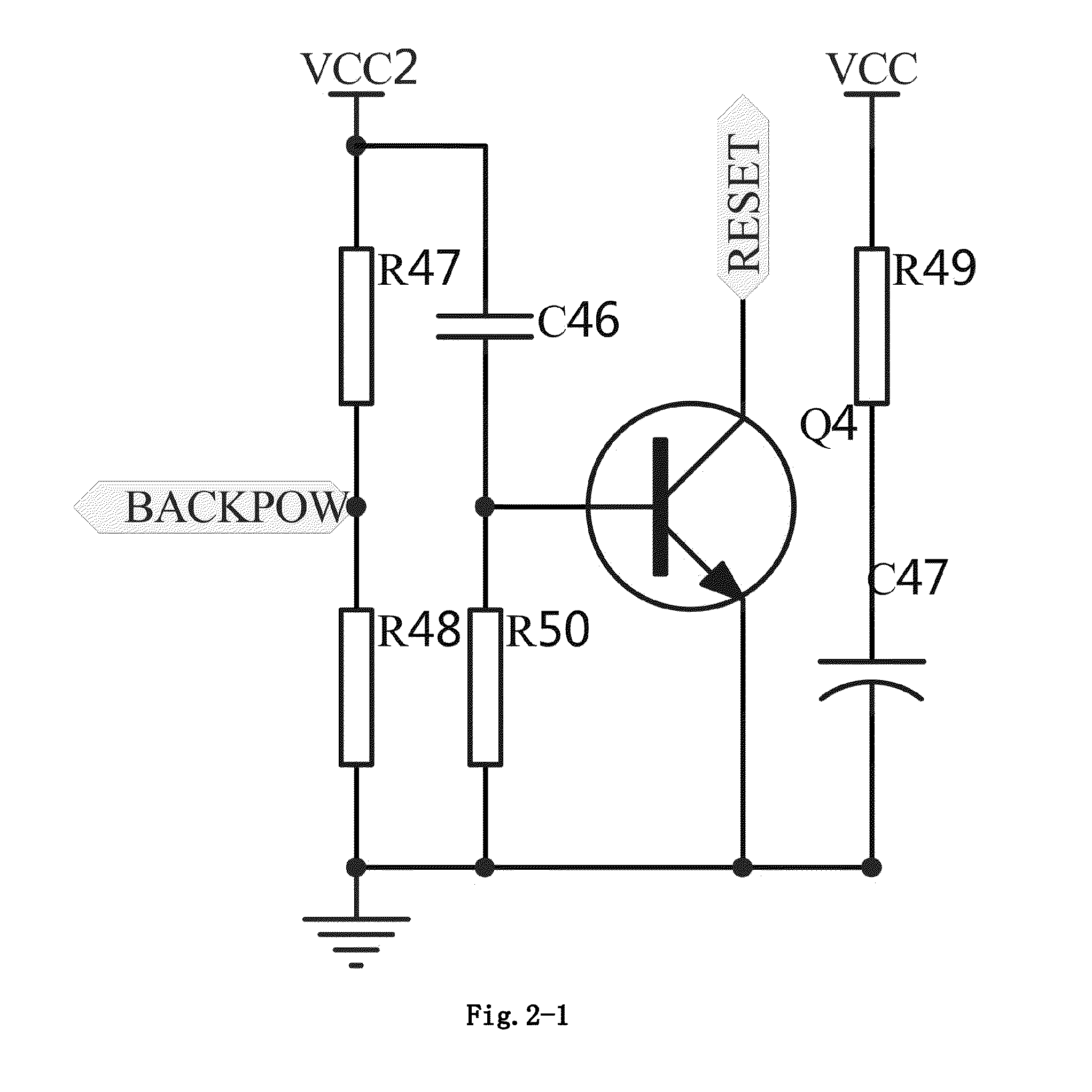
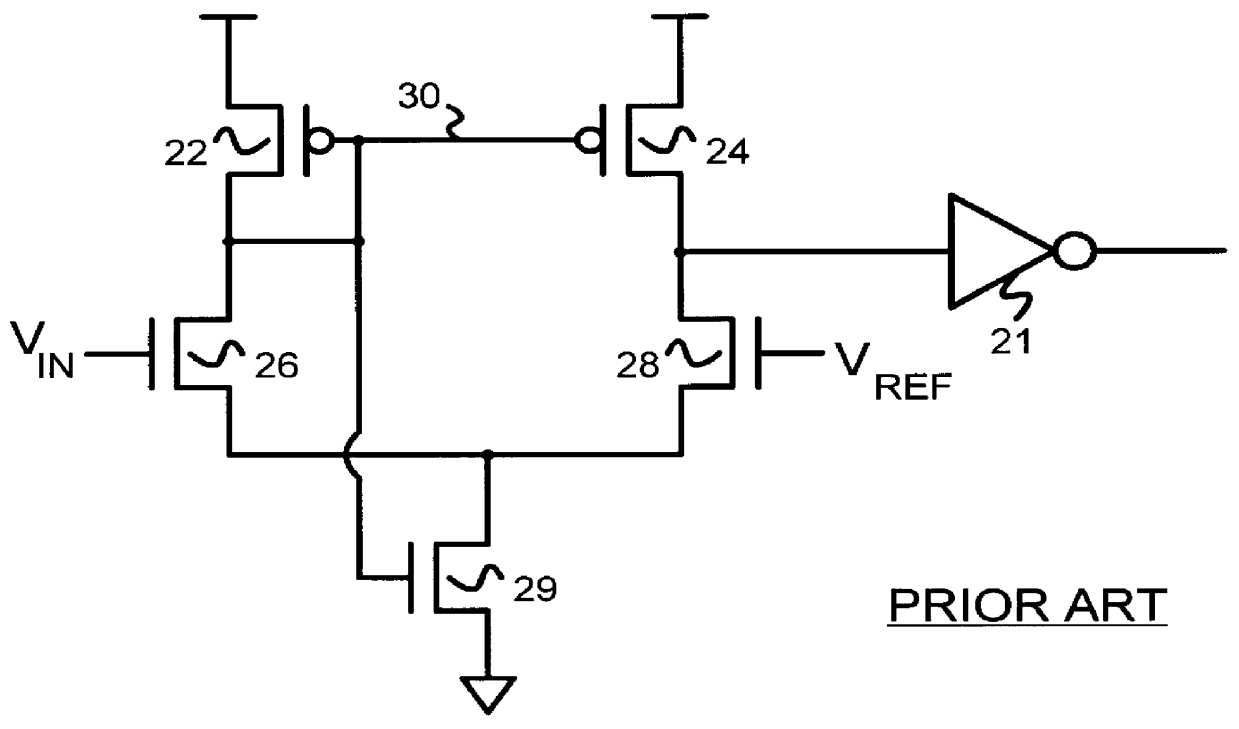
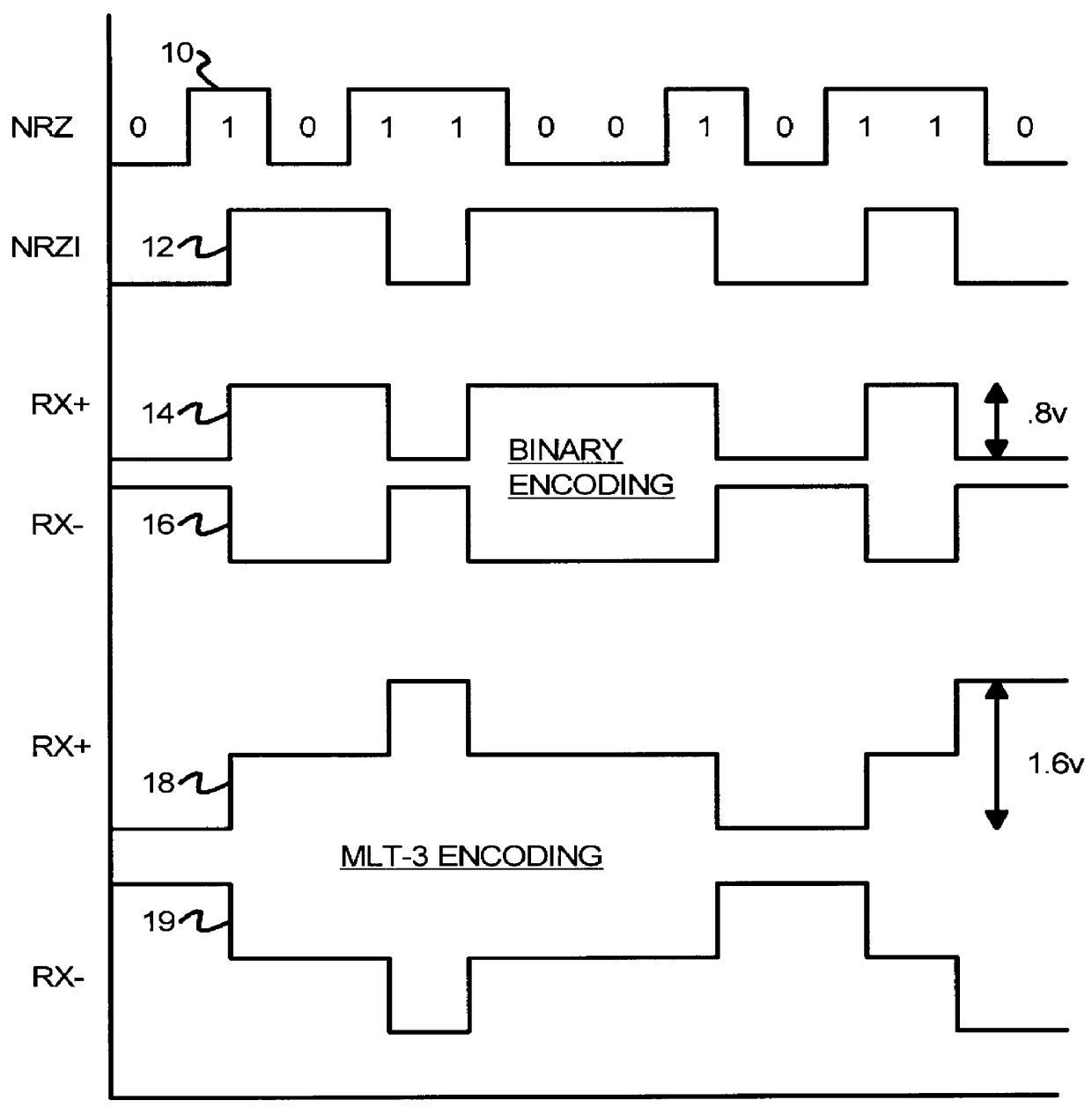
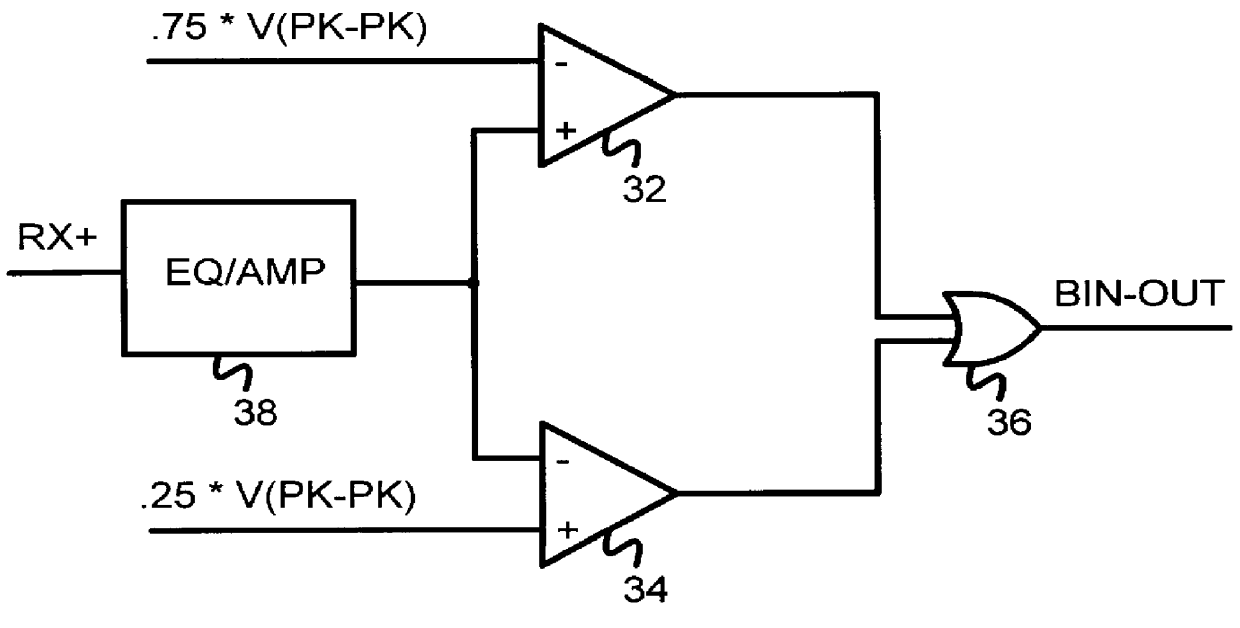
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5960 results about "Voltage range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
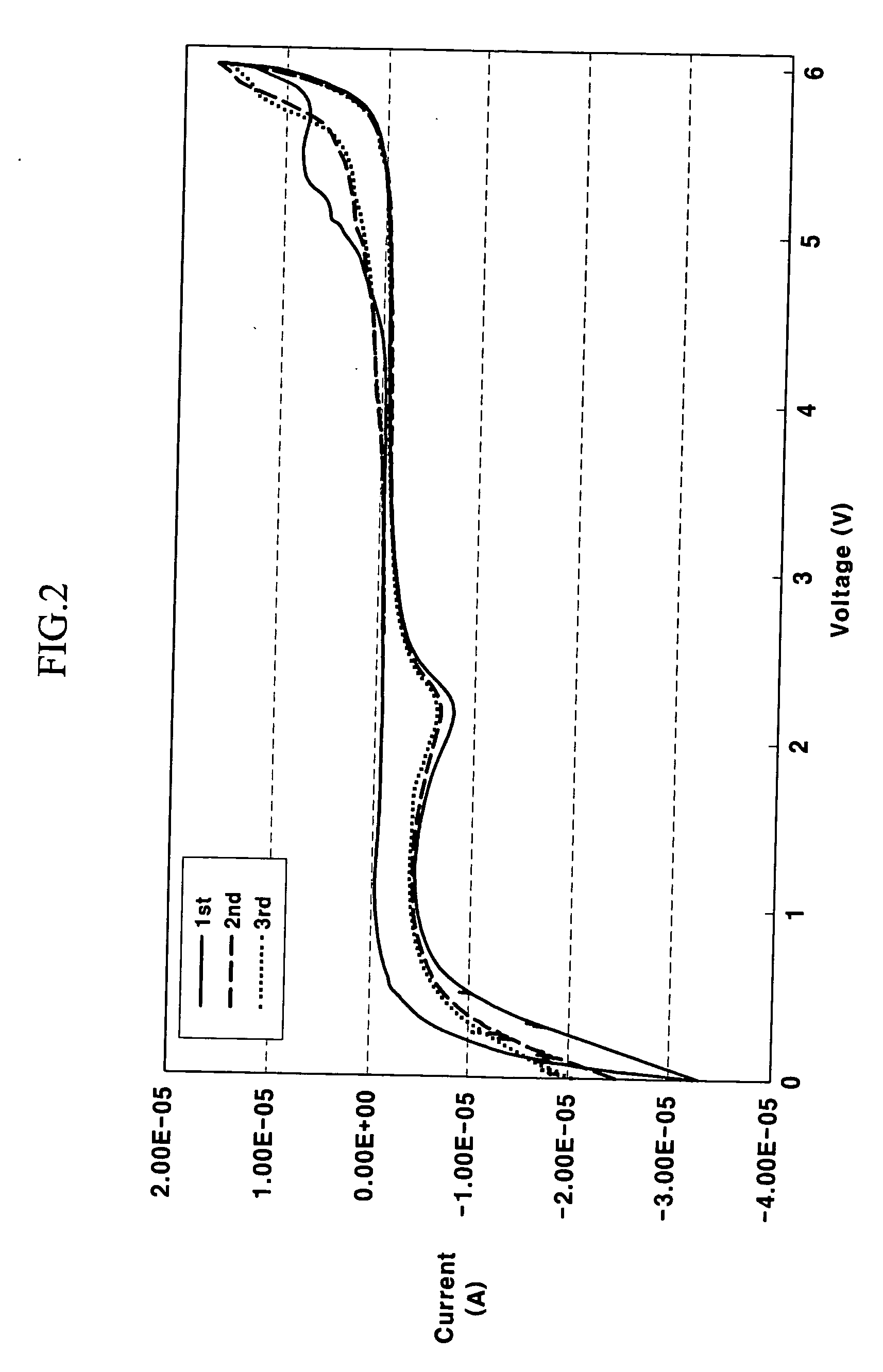
The voltage range can be measured easily with a voltmeter. All you have to do is set the meter to a maximum value above 12-15 volts (a 25 or 50-volt range should be enough), and touch the positive cable of the voltmeter to the positive terminal of the battery, and the negative cable of the meter to the negative terminal.
Battery pack, electronic appliance, and method of detecting remaining amount of battery
InactiveUS8359174B2Accurate detectionCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingPower flowCharge current
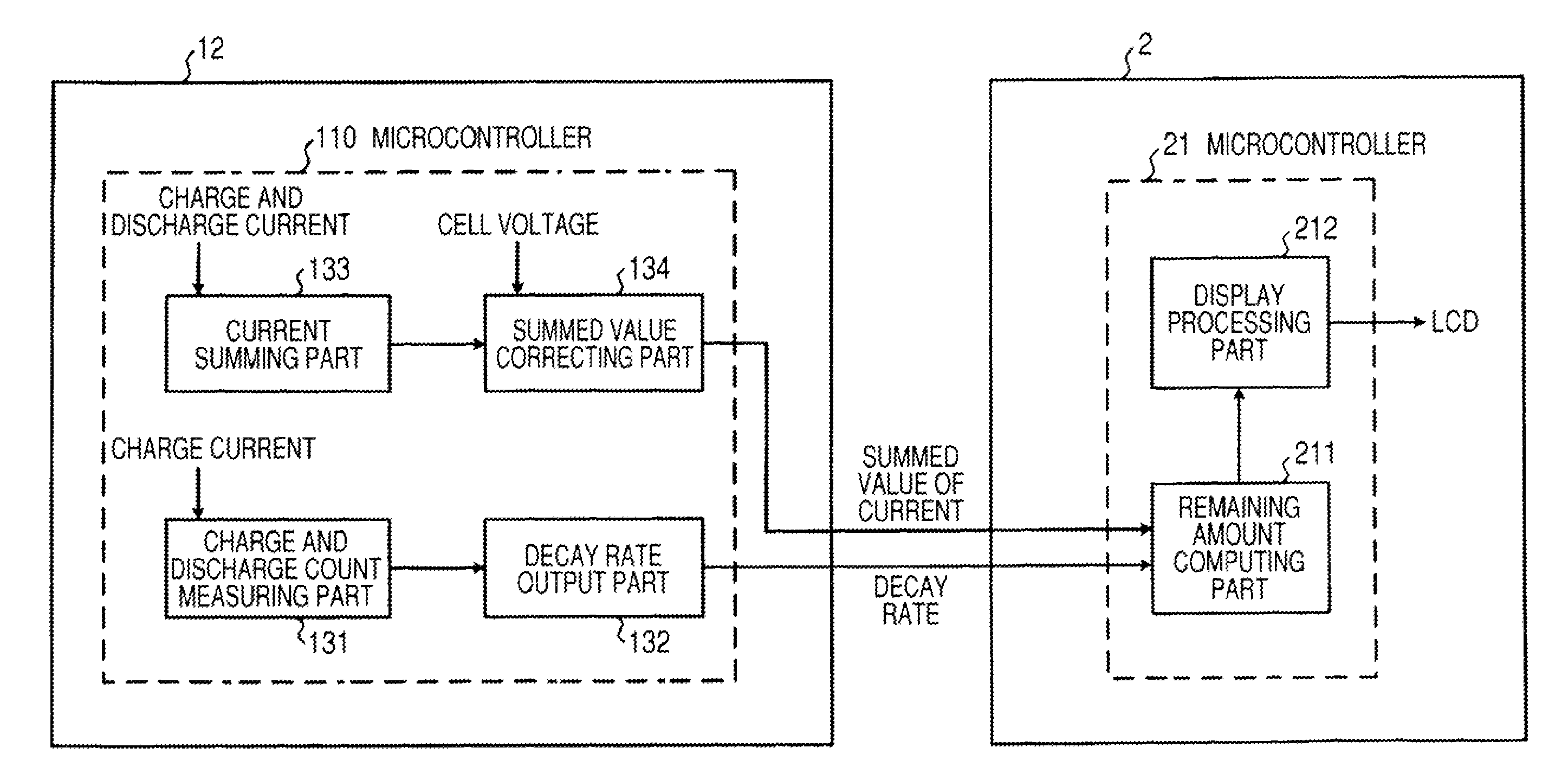
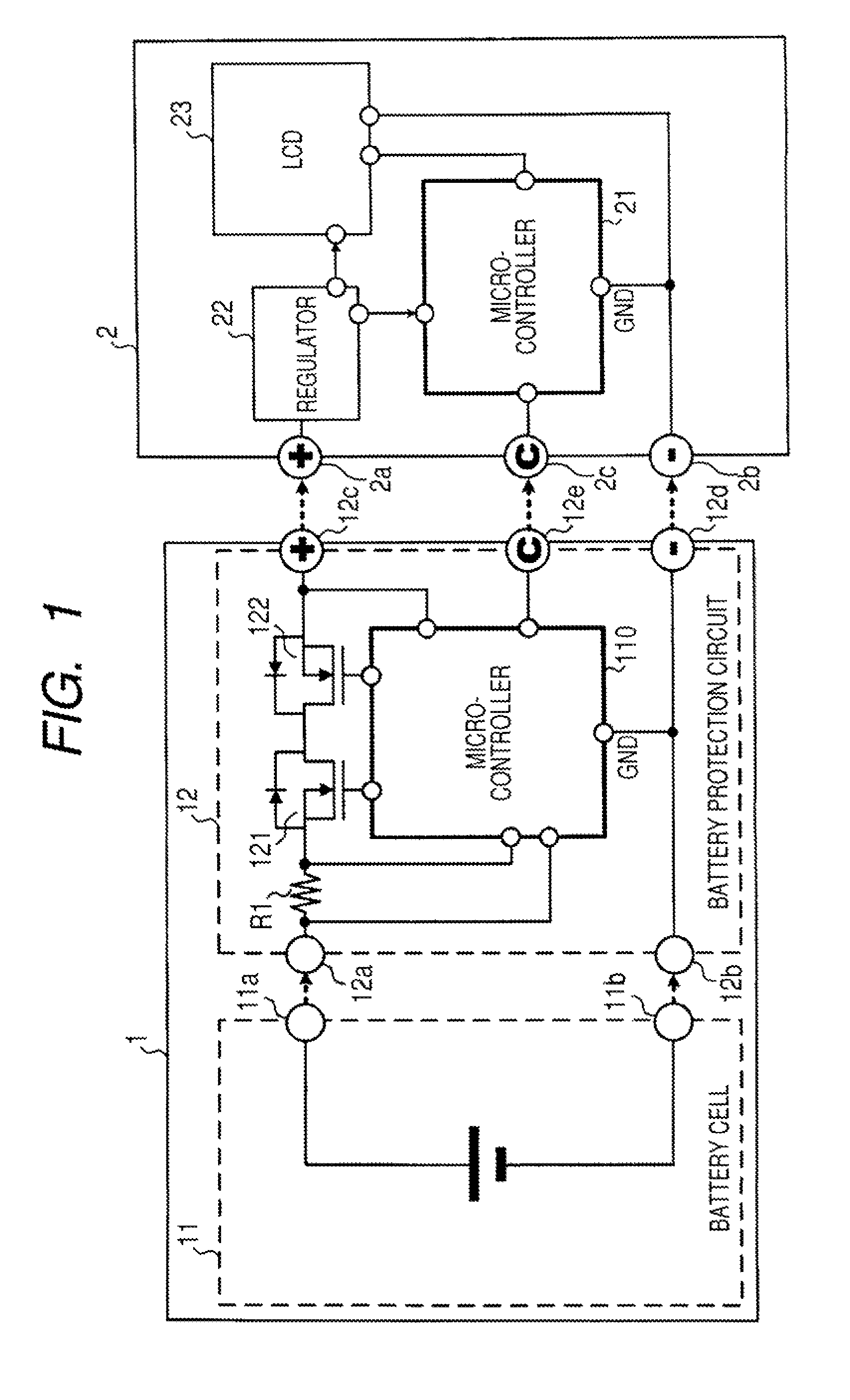
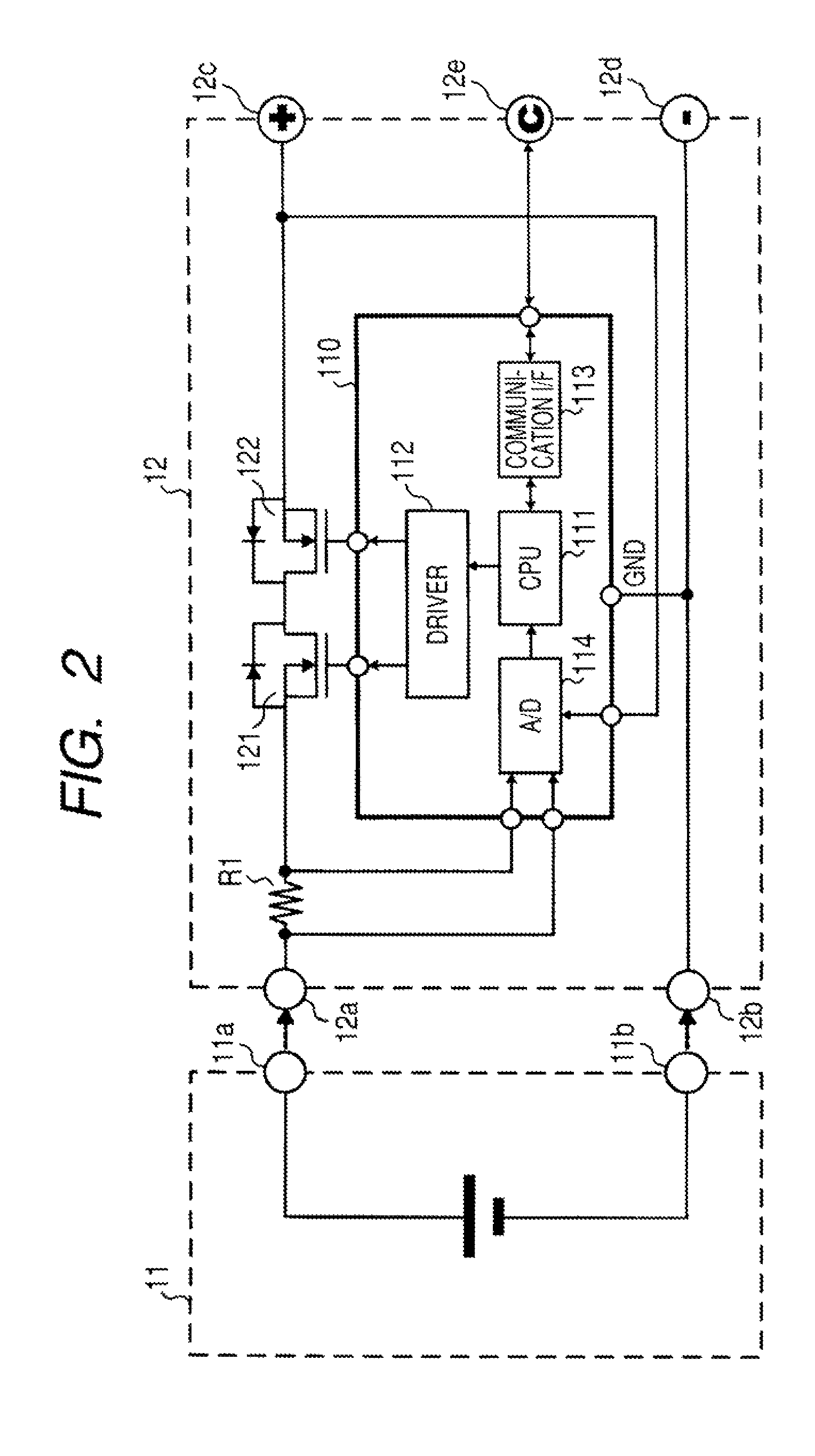
A battery pack has a charge and discharge count measuring part (131) configured to measure the number of times of charges and discharges of a secondary battery based on the summed value of the charge current for the secondary battery, and a decay rate output part (132) configured to compute a decay rate that indicates a degree of decay of the secondary battery based on the number of times of charges and discharges measured by the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) and to output it to a device being a discharge load. For example, the charge and discharge count measuring part (131) repeatedly sums the detected values of the charge current to a predetermined threshold, and counts up the number of times of charges and discharges every time when the summed value reaches the threshold. Accordingly, even though charges and discharges are repeated at finer steps in a relatively narrow voltage range, the number of times of charges and discharges can be counted accurately, and the computing accuracy of the decay rate is improved. In the battery pack in which the secondary battery is accommodated, parameters for detecting the remaining amount of the battery are detected more accurately.
Owner:SONY CORP
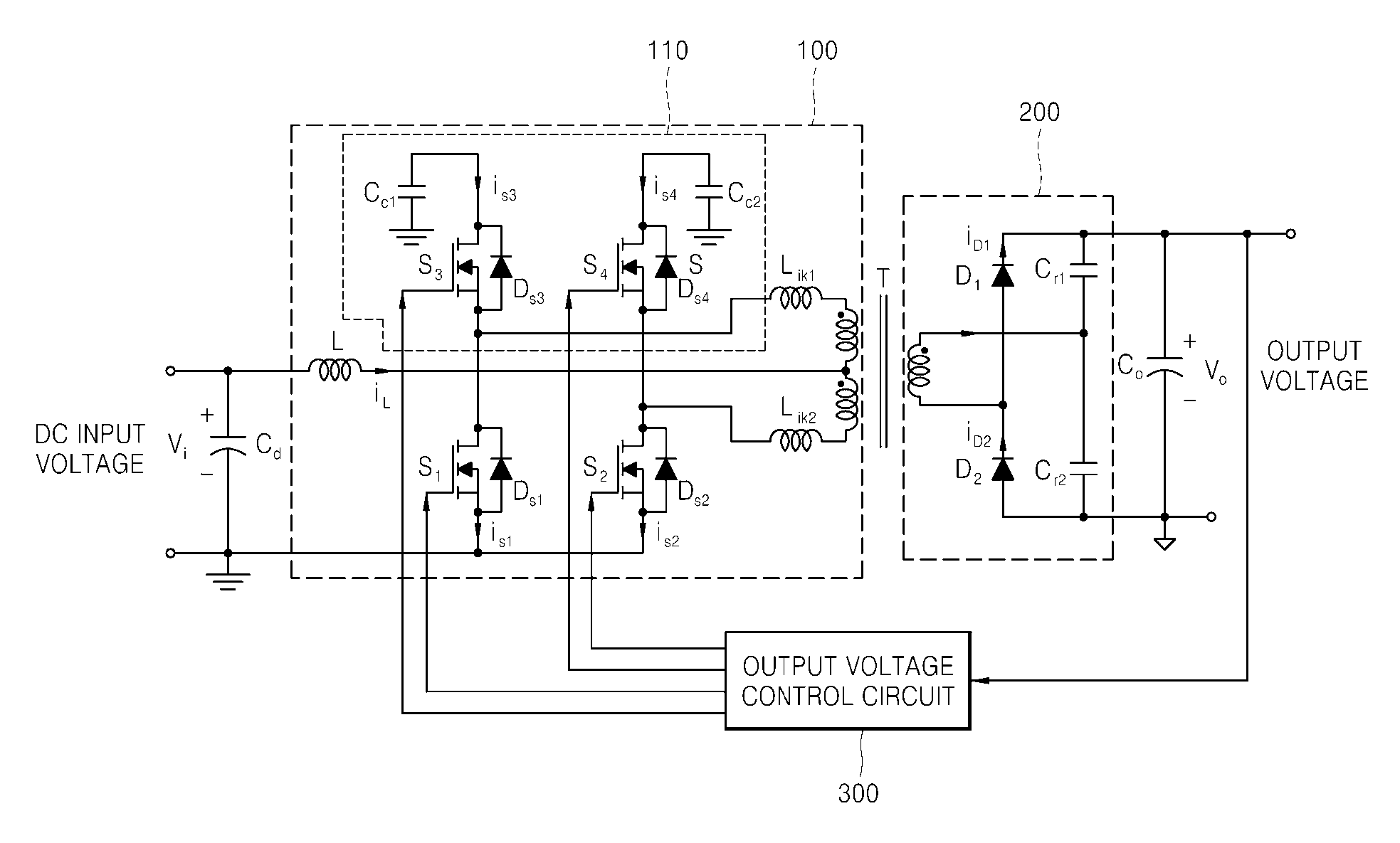
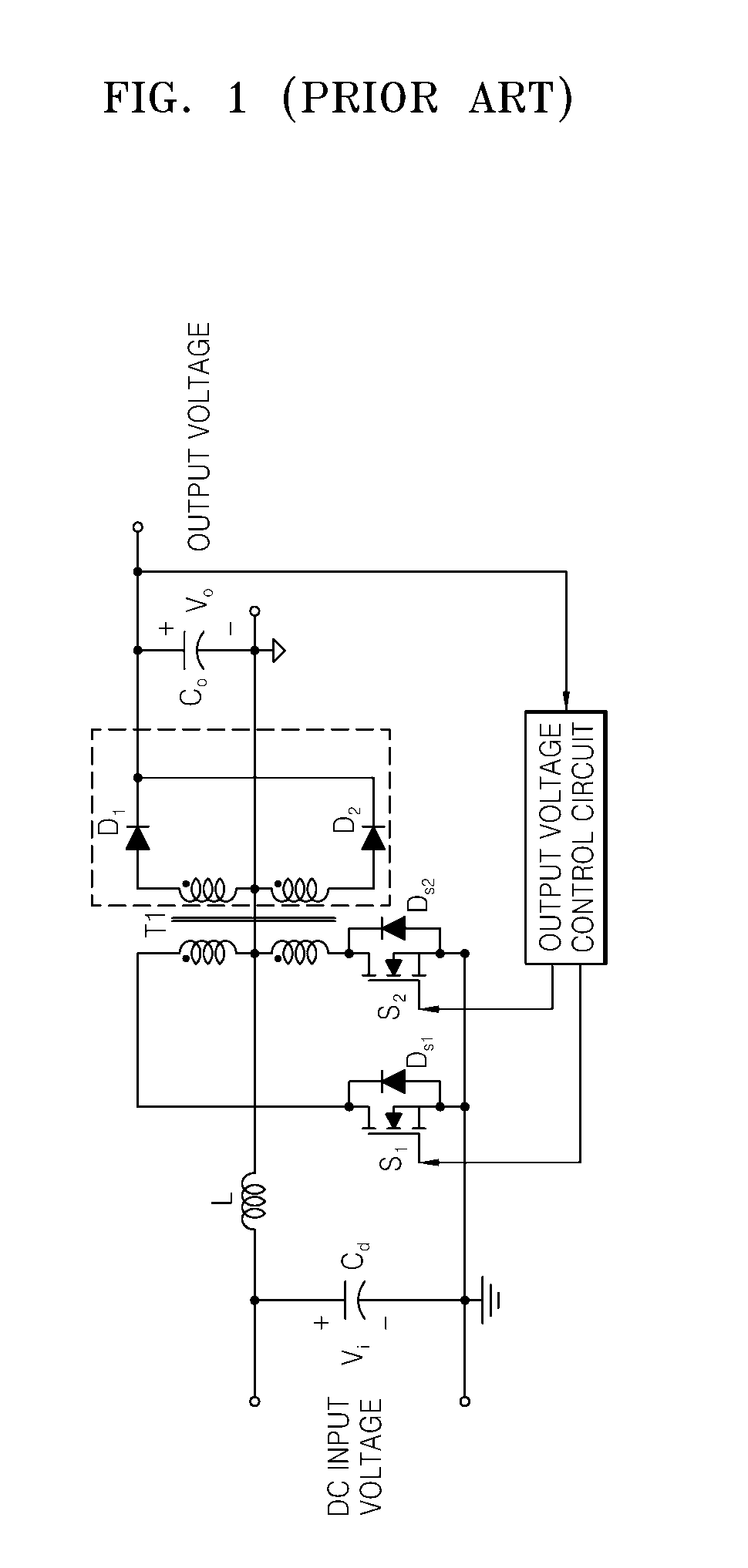
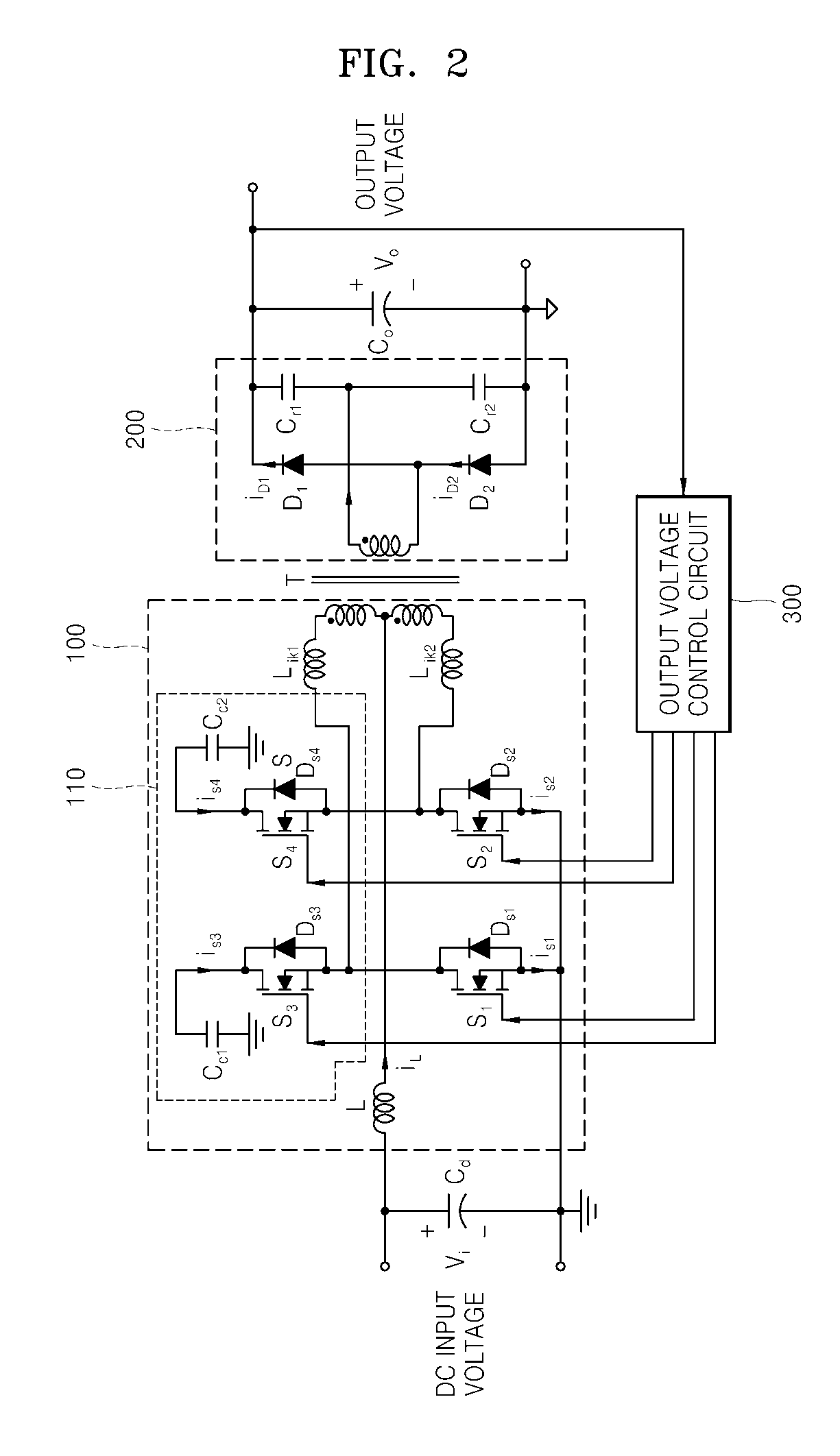
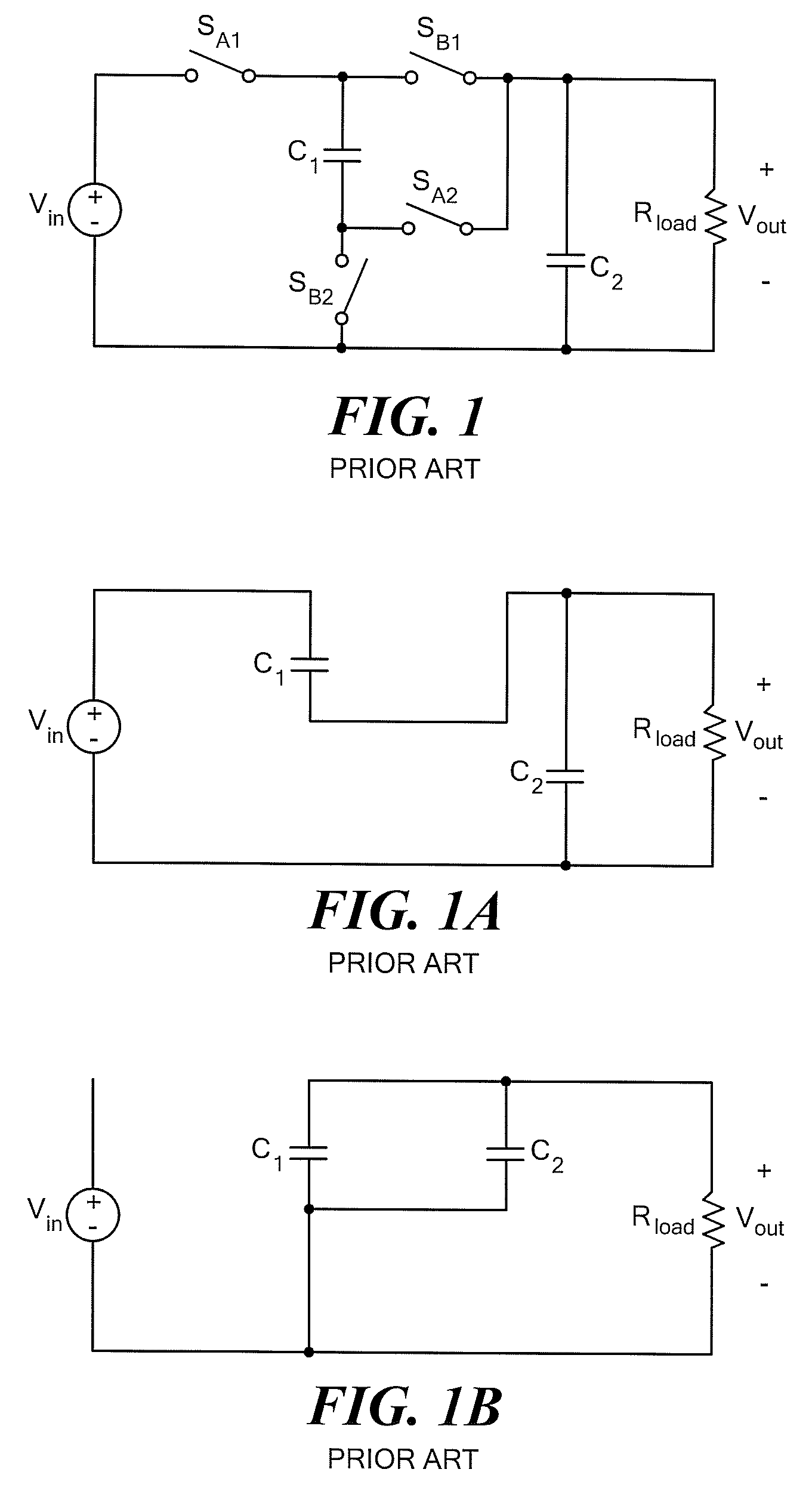
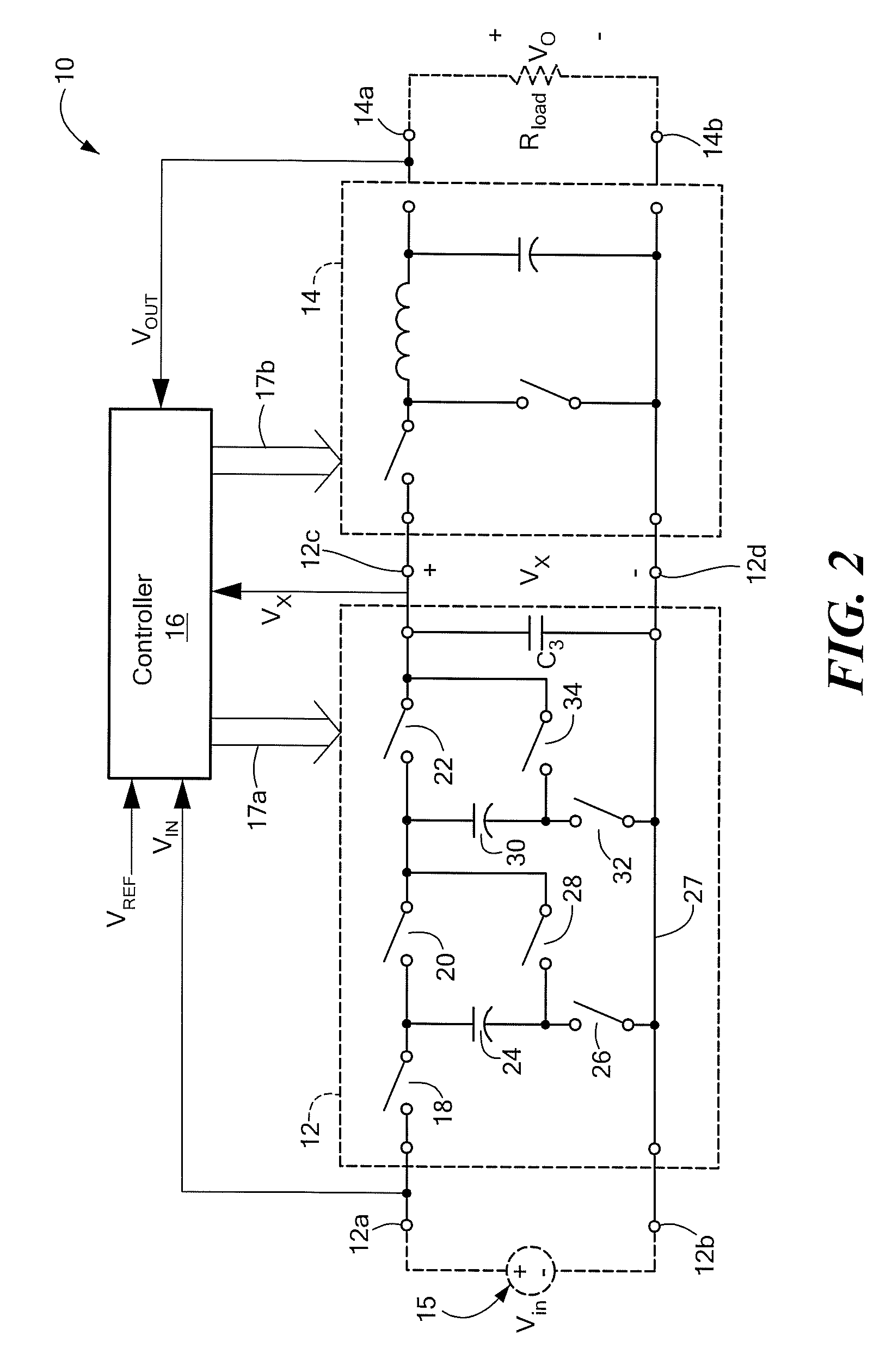
Power Converter with Capacitive Energy Transfer and Fast Dynamic Response
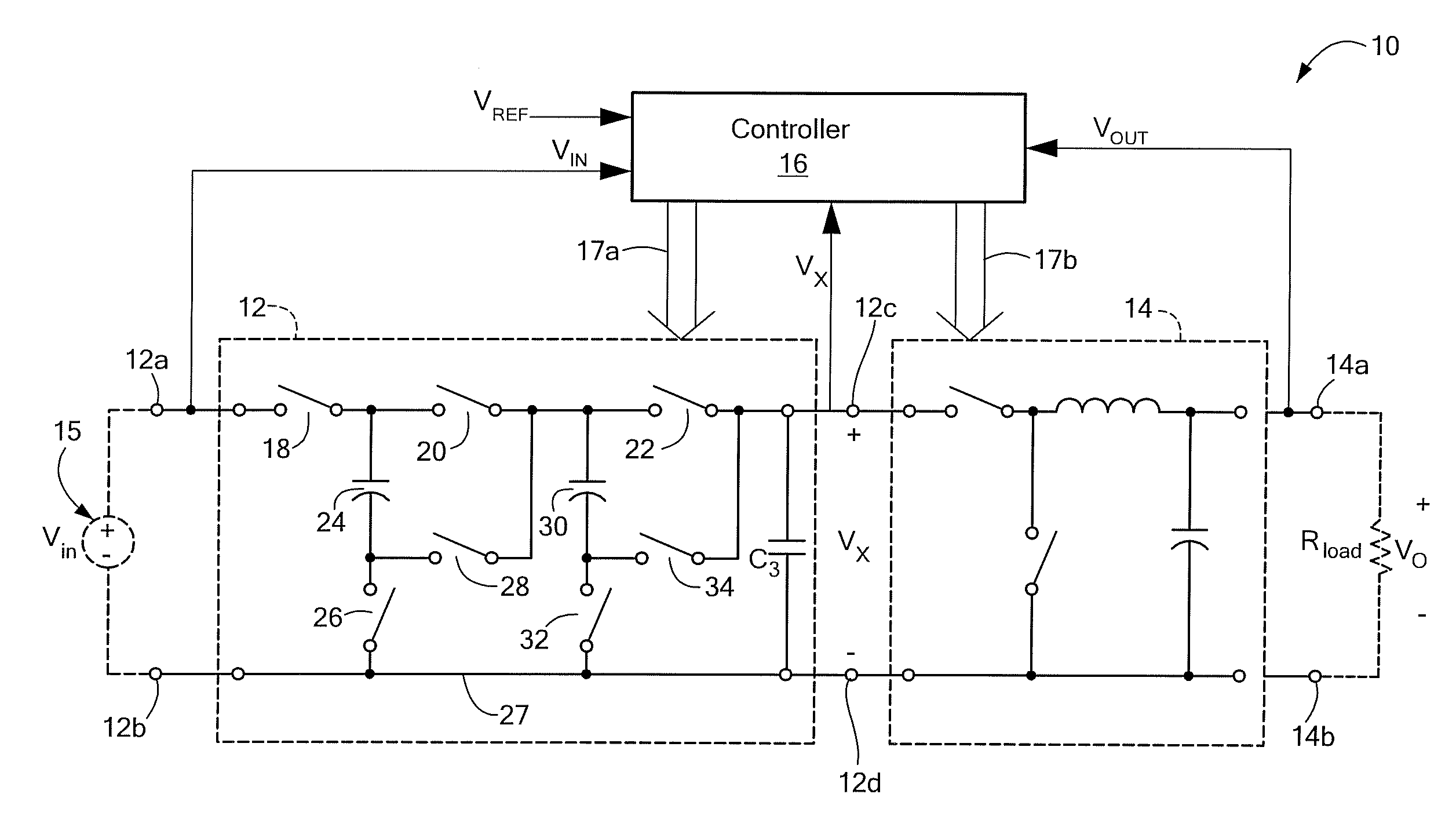
ActiveUS20090278520A1High power density power conversionImprove power densityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEnergy transferVoltage range
A converter circuit and related technique for providing high power density power conversion includes a reconfigurable switched capacitor transformation stage coupled to a magnetic converter (or regulation) stage. The circuits and techniques achieve high performance over a wide input voltage range or a wide output voltage range. The converter can be used, for example, to power logic devices in portable battery operated devices.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
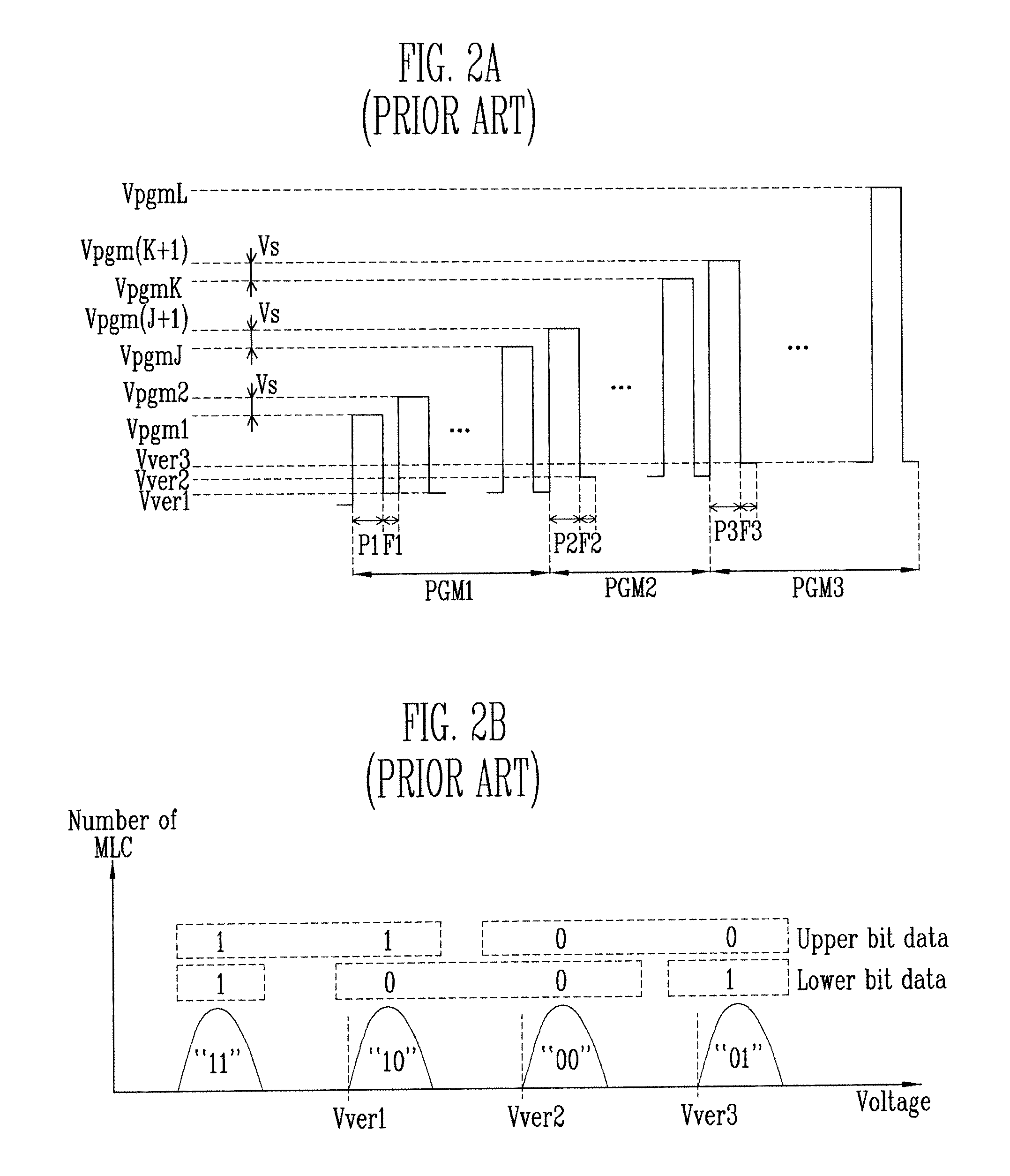
Erase and Program Method of Flash Memory Device for Increasing Program Speed of Flash Memory Device
ActiveUS20070058446A1Fail occurrence ratioImproved Threshold Voltage DistributionRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage rangeThreshold voltage
The present invention relates to erase and program methods of a flash memory device including MLCs for increasing the program speed. In the erase method according to the present invention, MLCs are pre-programmed so that a voltage range in which threshold voltages of MLCs are distributed can be reduced. Therefore, a fail occurrence ratio can be reduced when erasing MLCs, the threshold voltage distribution of MLCs can be improved and an overall program time can be shortened in a subsequent program operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
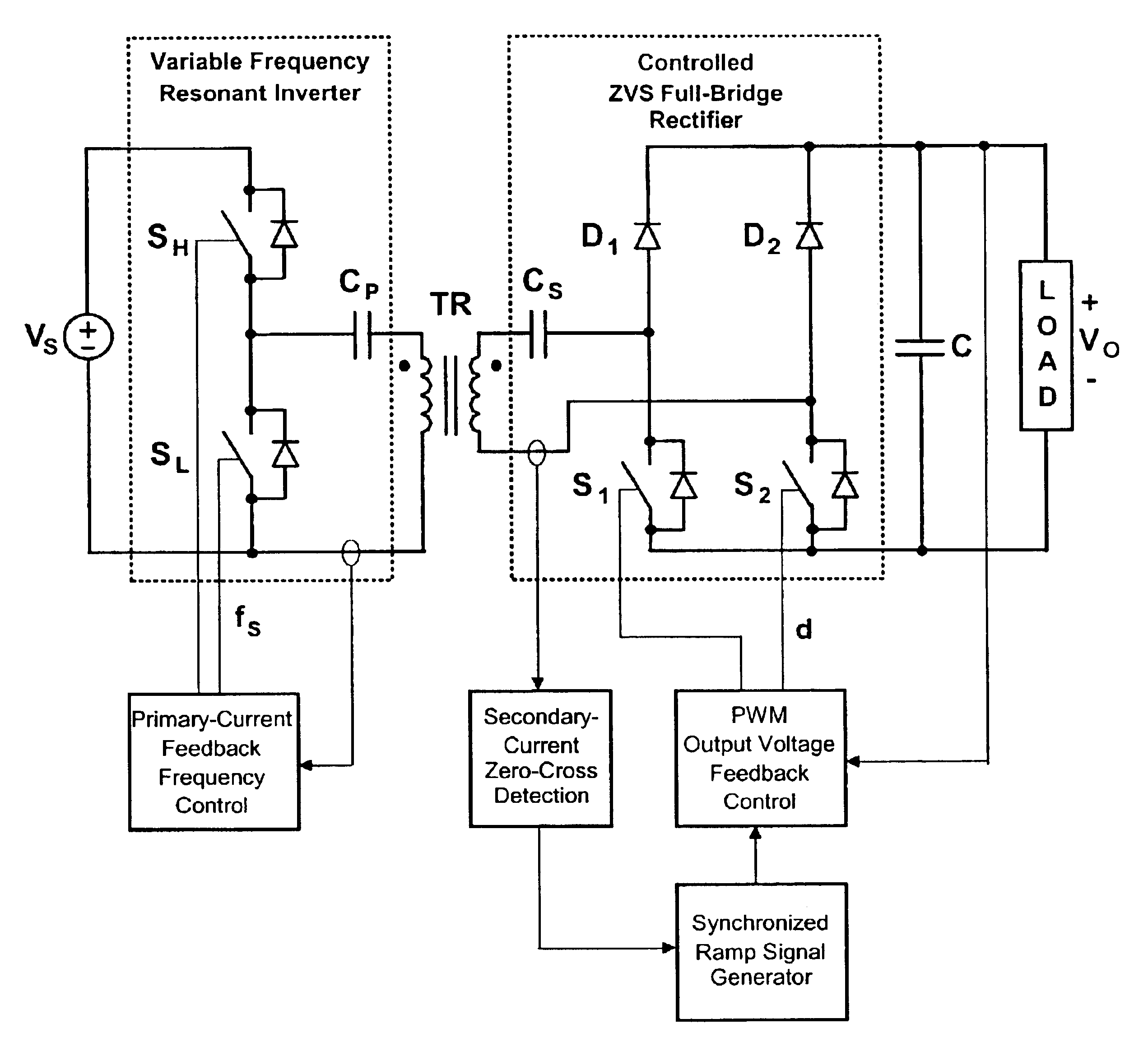
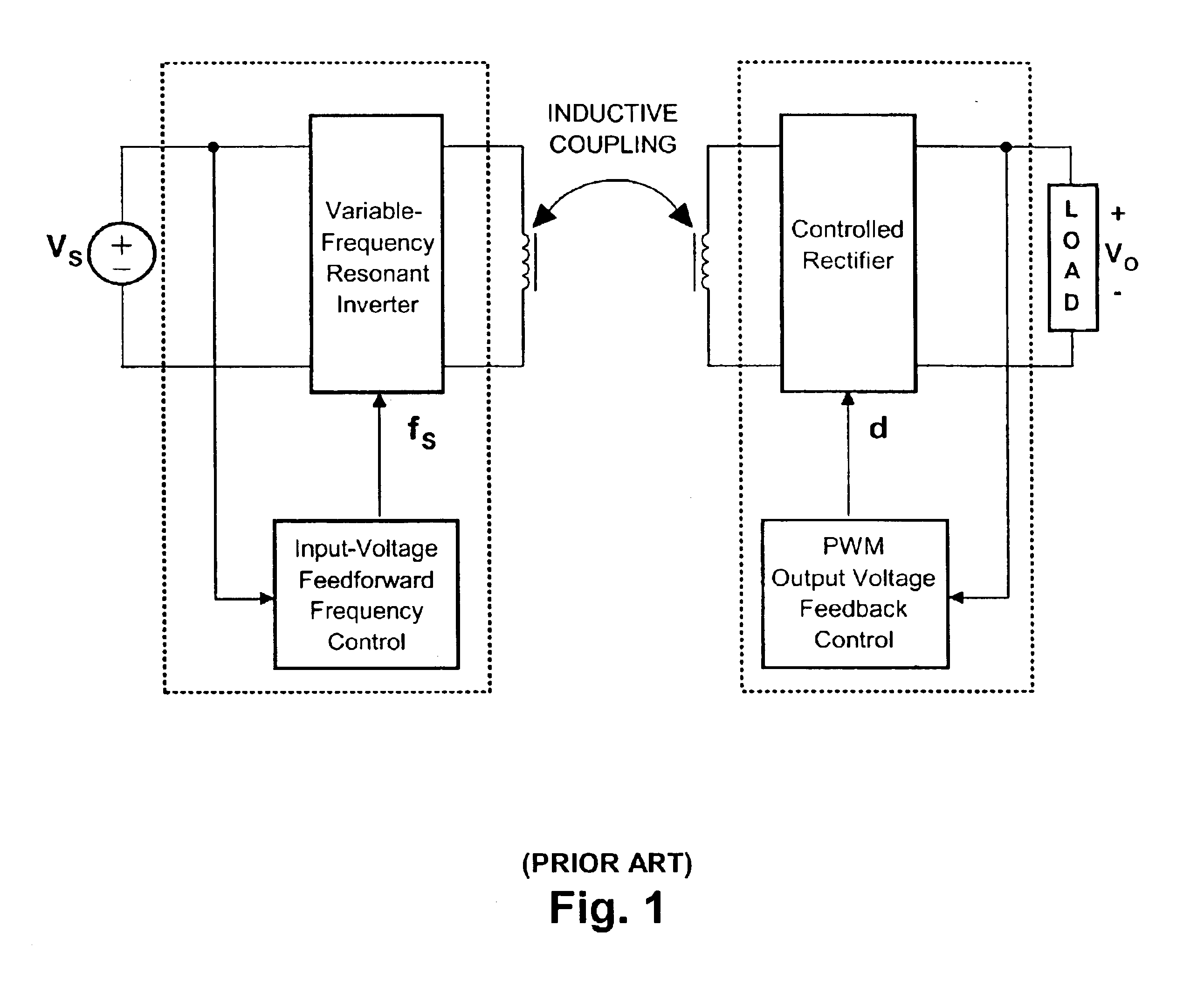
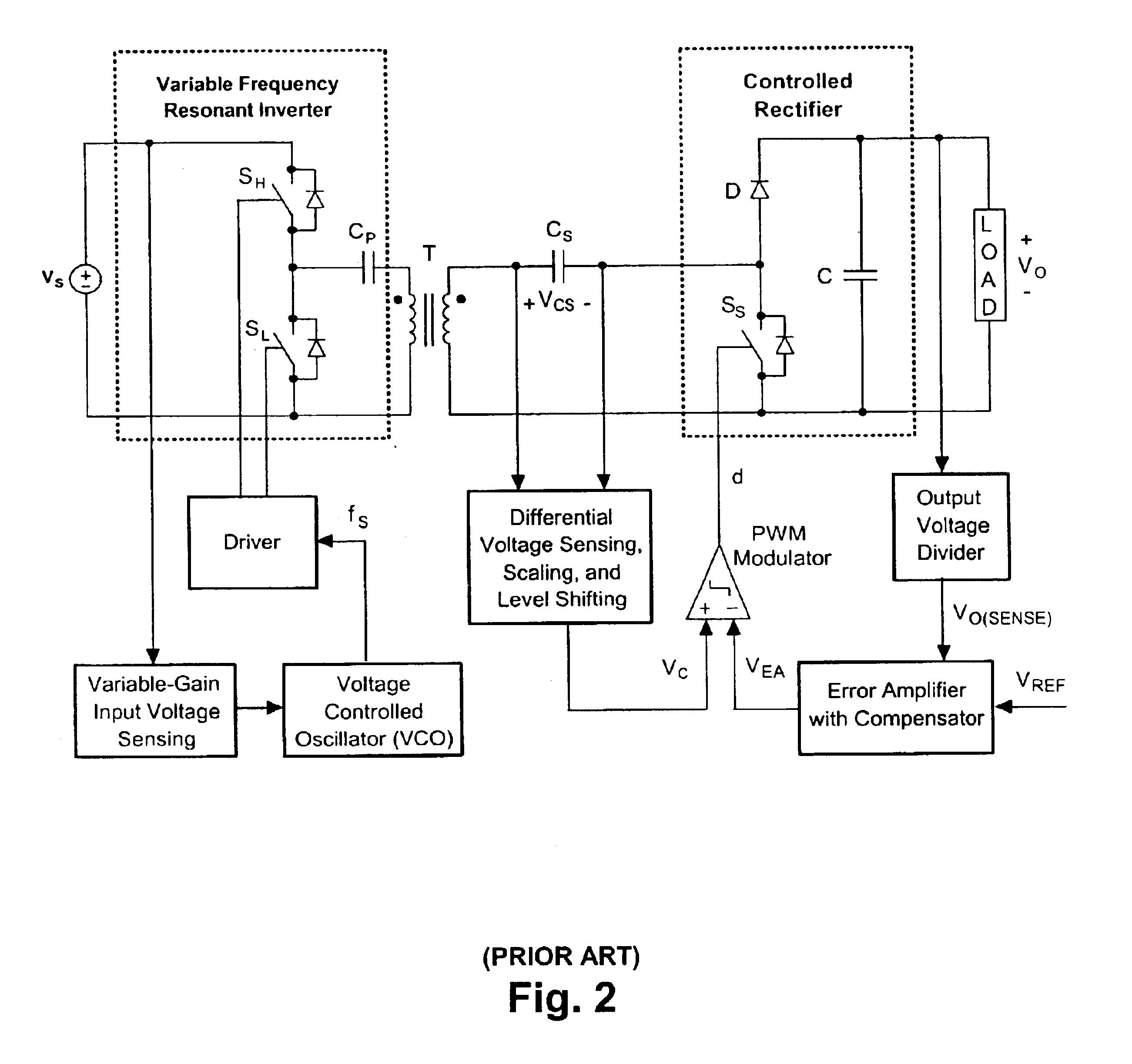
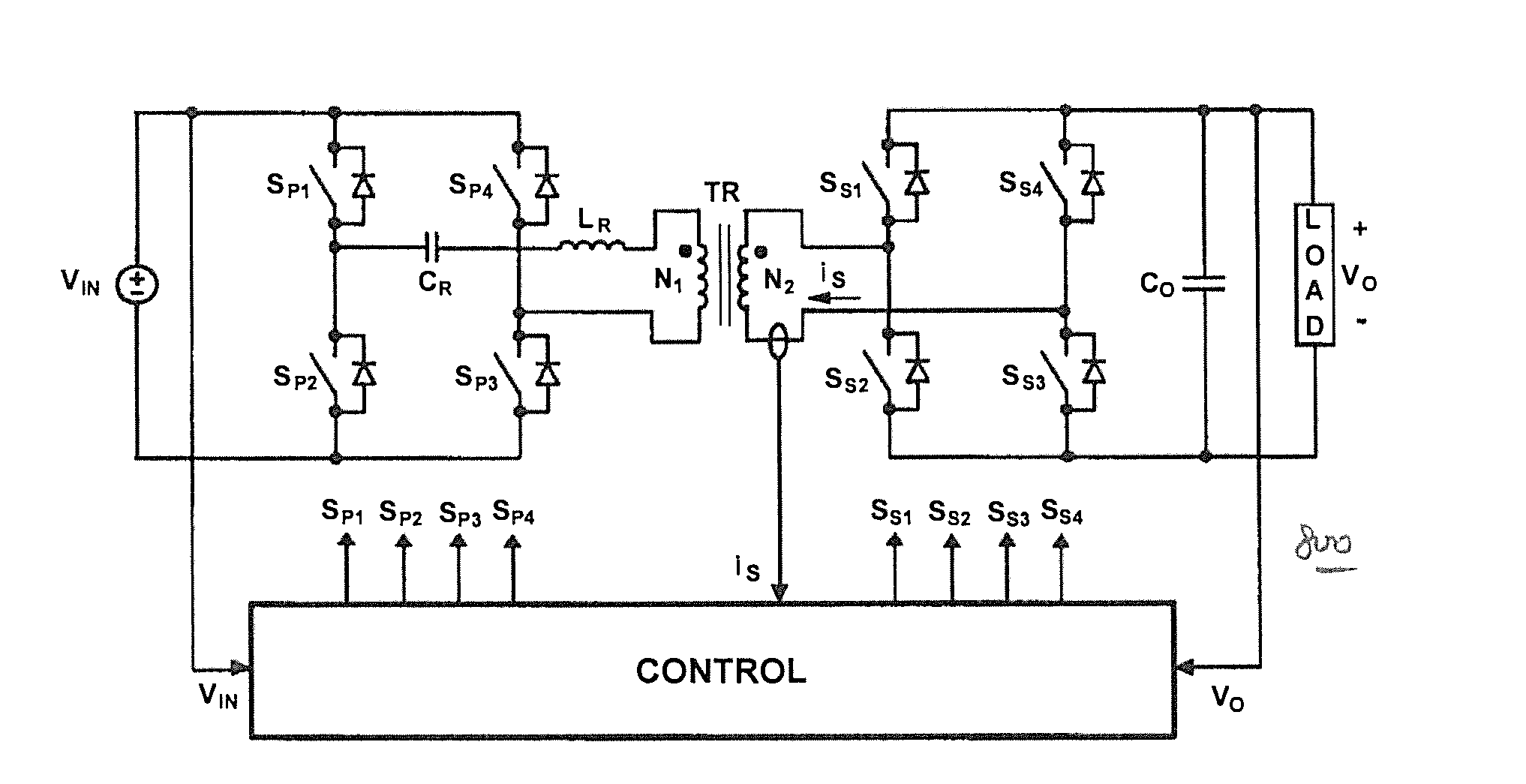
Contactless electrical energy transmission system having a primary side current feedback control and soft-switched secondary side rectifier
ActiveUS6934167B2Energy can transferEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching frequencyEngineering
A contactless electrical energy transmission system includes a transformer having a primary winding that is coupled to a power source through a primary resonant circuit and a secondary winding that is coupled to a load through a secondary resonant circuit. The primary and secondary resonant circuits are inductively coupled to each other. A primary control circuit detects current changes through the primary resonant circuit to control the switching frequency of a controllable switching device for maintaining a substantially constant energy transfer between the primary winding and secondary winding in response to at least one of a power source voltage change and a load change. As a result, excessive circulating energy of the CEET system is minimized providing a tight regulation of the output voltage over the entire load and input voltage ranges without any feedback connection between the primary side and the secondary side.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Active-clamp current-source push-pull dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20070247877A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePush pull
Provided is a current-source push-pull DC-DC converter using an active clamp circuit for reusing energy of leakage inductances by not only diodes on a secondary side of a transformer being zero-current switched using a series-resonant full-wave rectifier, but also the active clamp circuit on a primary side of the transformer, which provides a discharge path of the energy stored in the leakage inductances, increases power conversion efficiency even for a wide input voltage range and reduces a switch voltage stress as compared to a conventional current-source push-pull circuit by operating even for a duty ratio below 0.5 by flowing a current of an input inductor through capacitors of the active clamp circuit when both main switches are off.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
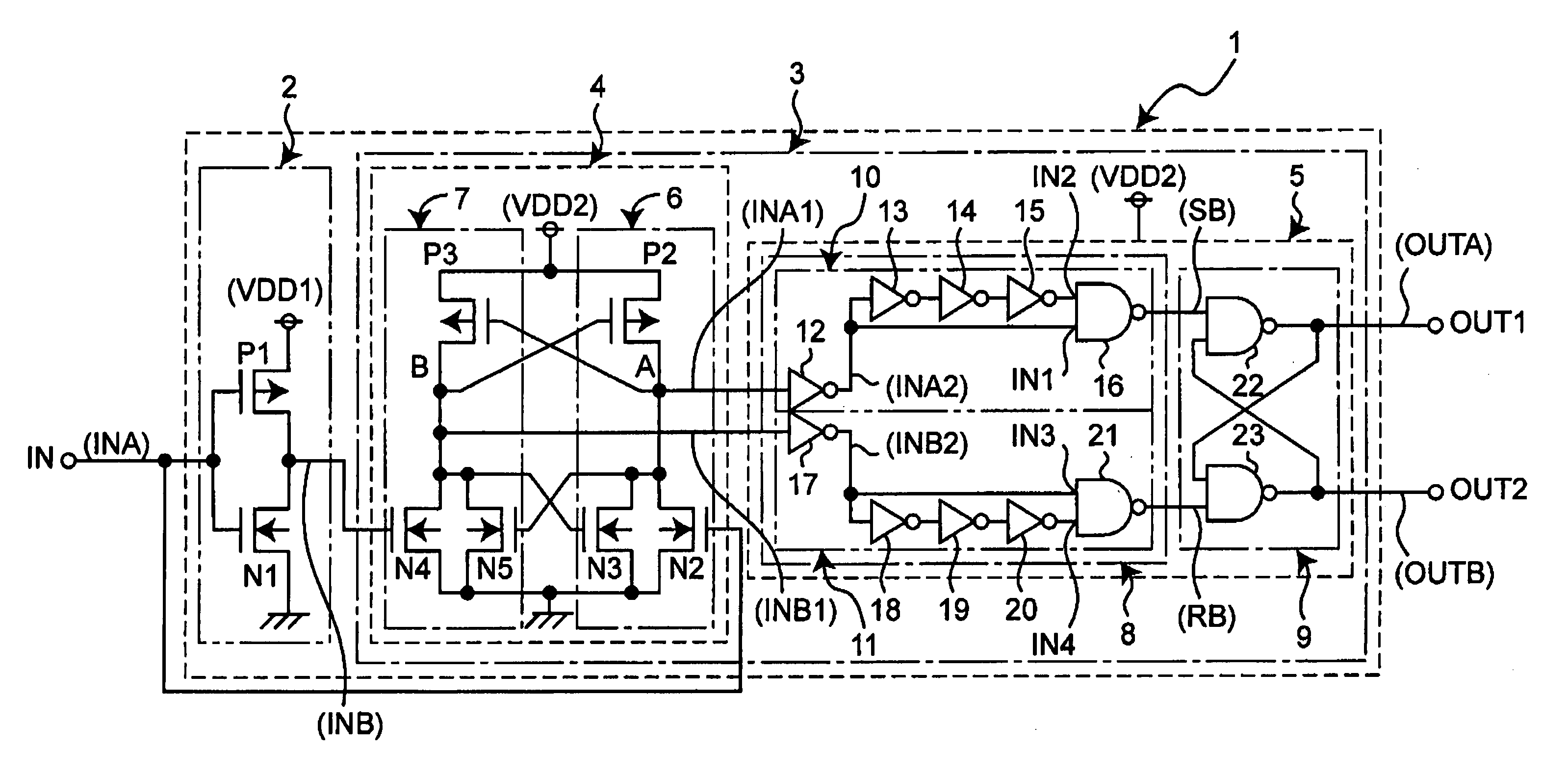
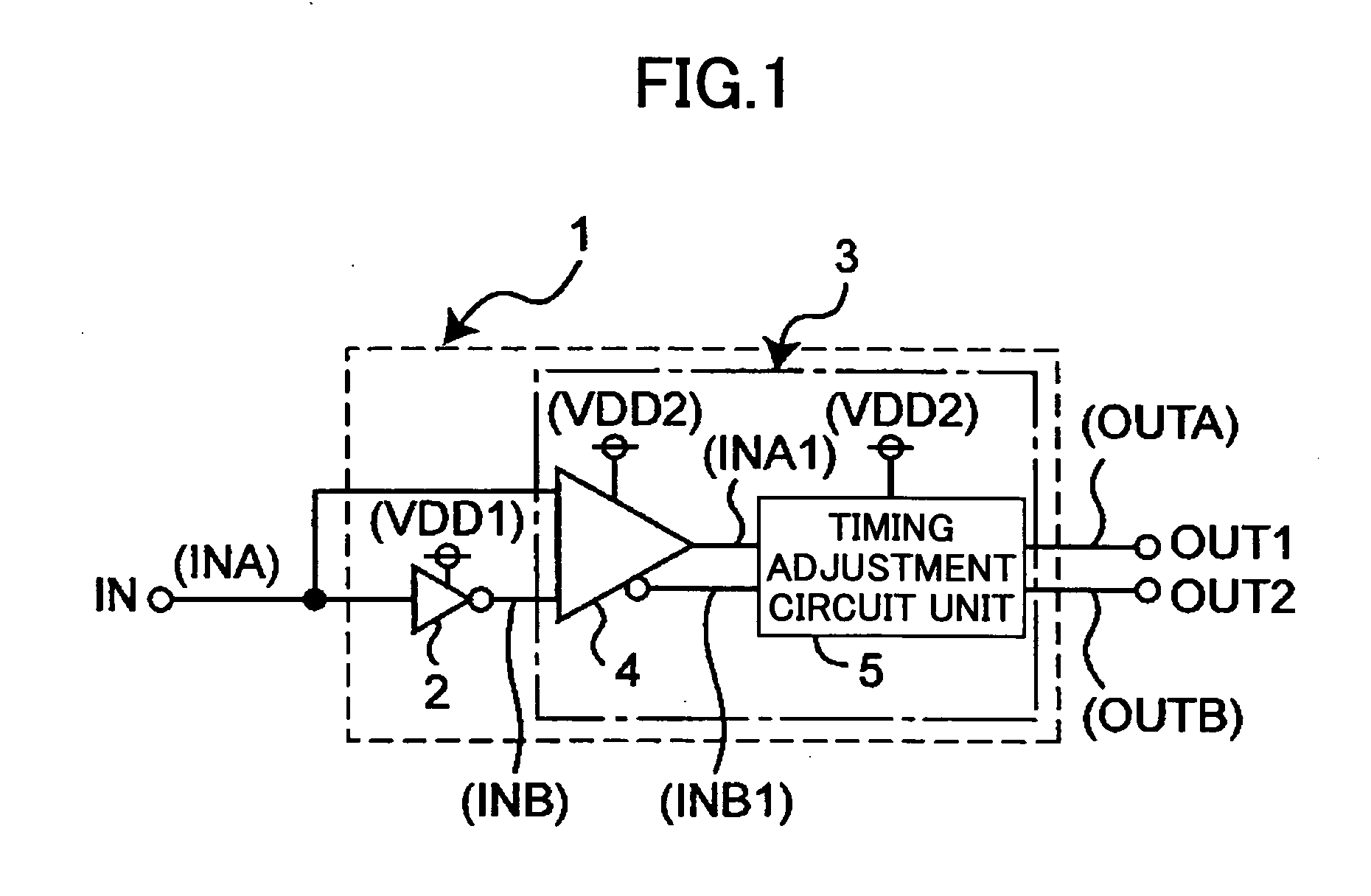
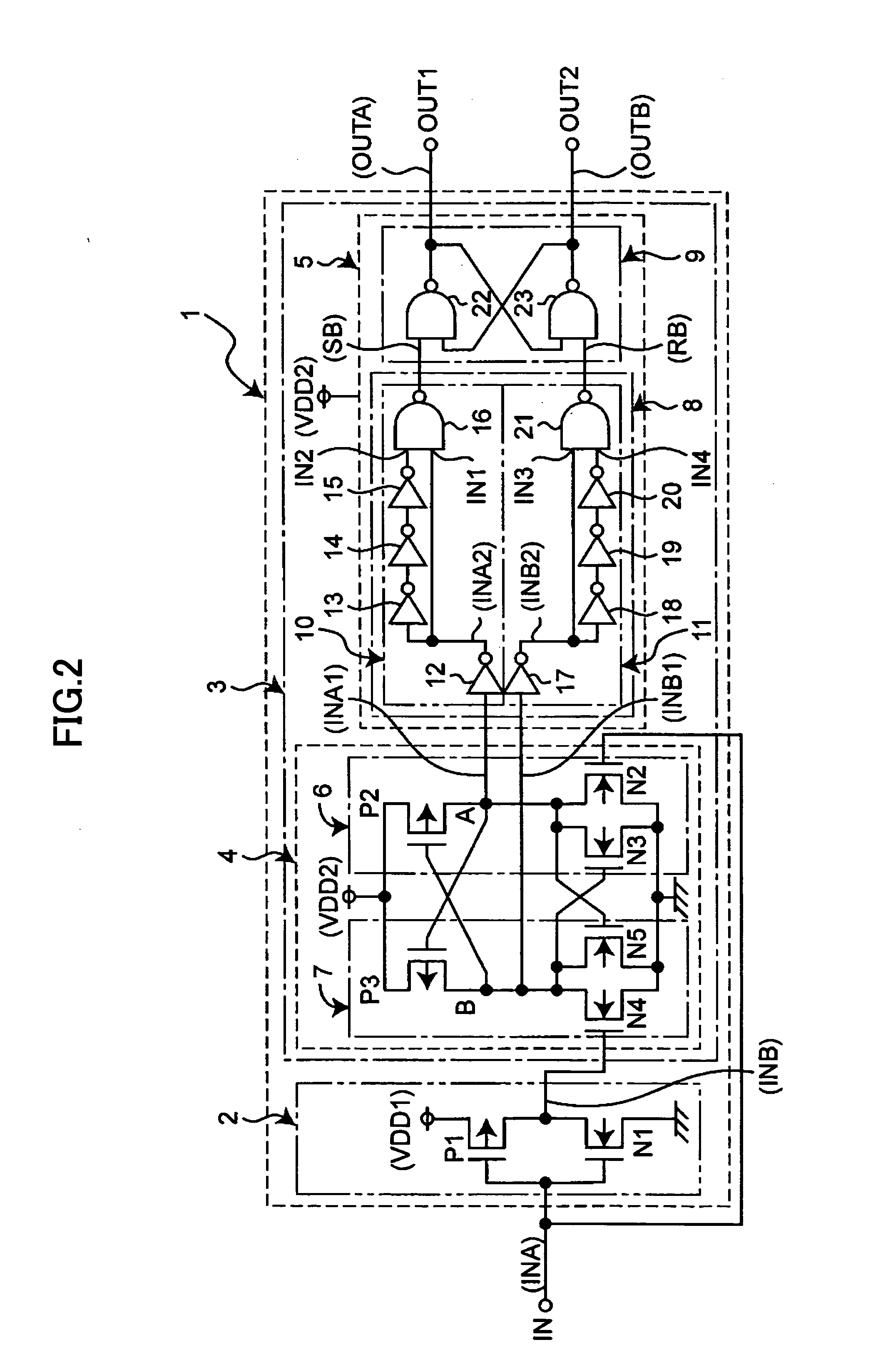
Level shift circuit having timing adjustment circuit for maintaining duty ratio
InactiveUS20060066349A1Accurate operationReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingEngineeringVoltage range
A level shift circuit for shifting levels of a pair of binary input signals having a first voltage range to produce a pair of binary output signals having a second voltage range includes a first circuit to shift a level of a first one of the binary input signals thereby to produce a first signal having the second voltage range, a second circuit to shift a level of a second one of the binary input signals thereby to produce a second signal having the second voltage range, and a timing adjustment circuit to produce the binary output signals by adjusting a pulse width thereof in response to the first and second signals such that the pulse width is equal to a time interval from when one of the first and second circuits stops level shift operation to when another one of the first and second circuits stops level shift operation.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
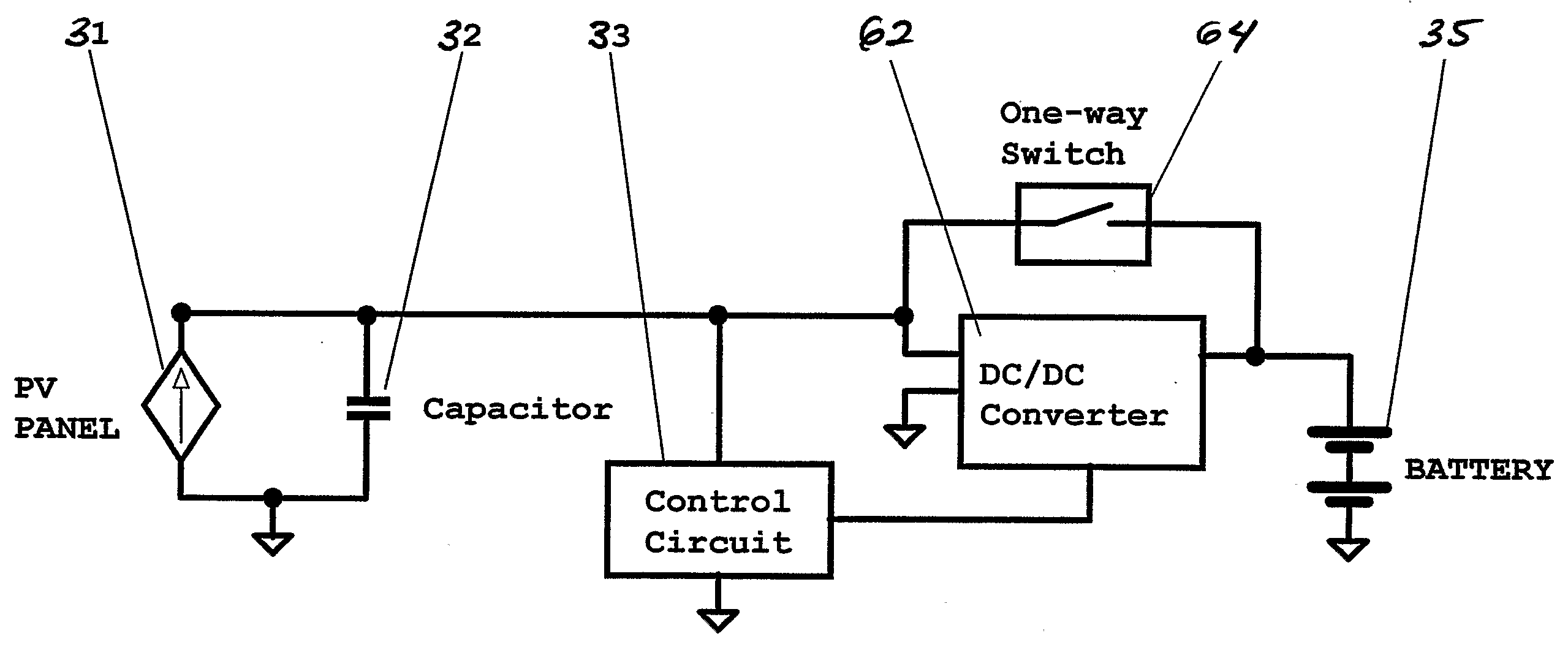
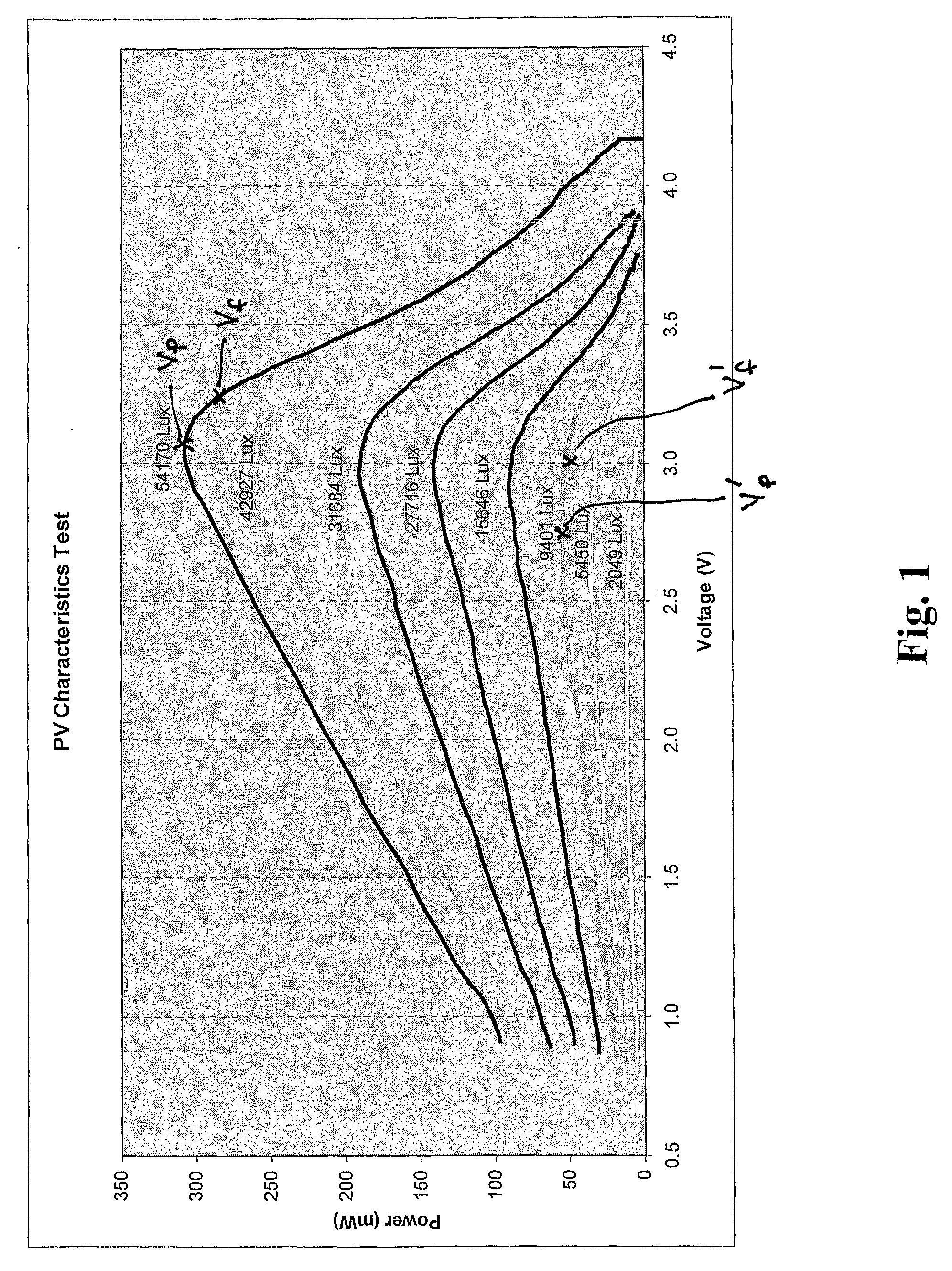
Photovoltaic Power Output-Utilizing Device
InactiveUS20080224652A1Increase discharge voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaicsPeak valueEngineering
Briefly described, the invention provides a photovoltaic assembly power output utilizing device which partially charges a capacitor assembly. This capacitor assembly is then partially discharged by a DC / DC power converter in different ranges of voltages in which the power output from the photovoltaic assembly peaks for different light intensities.
Owner:ECOSOL SOLAR TECH USA
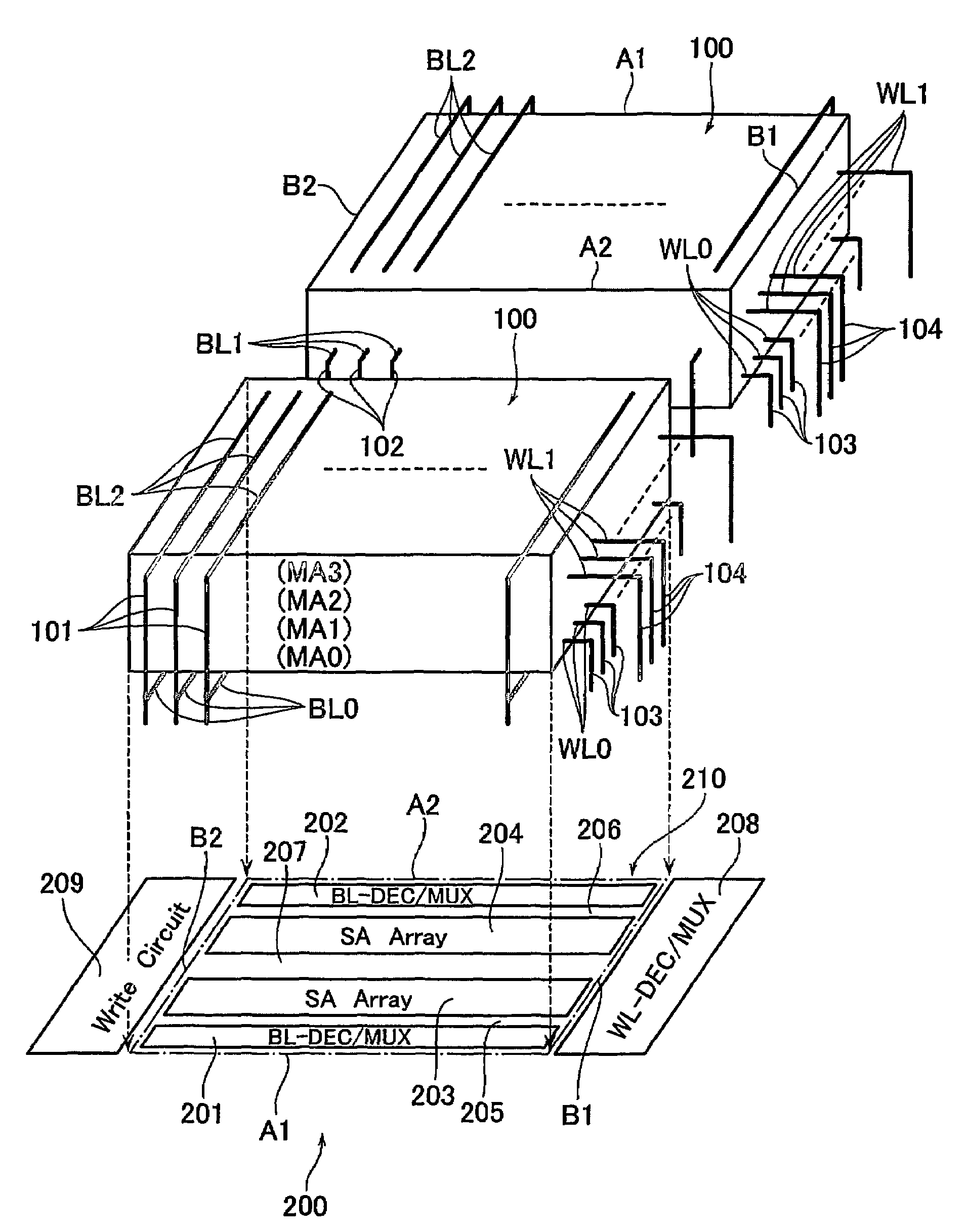
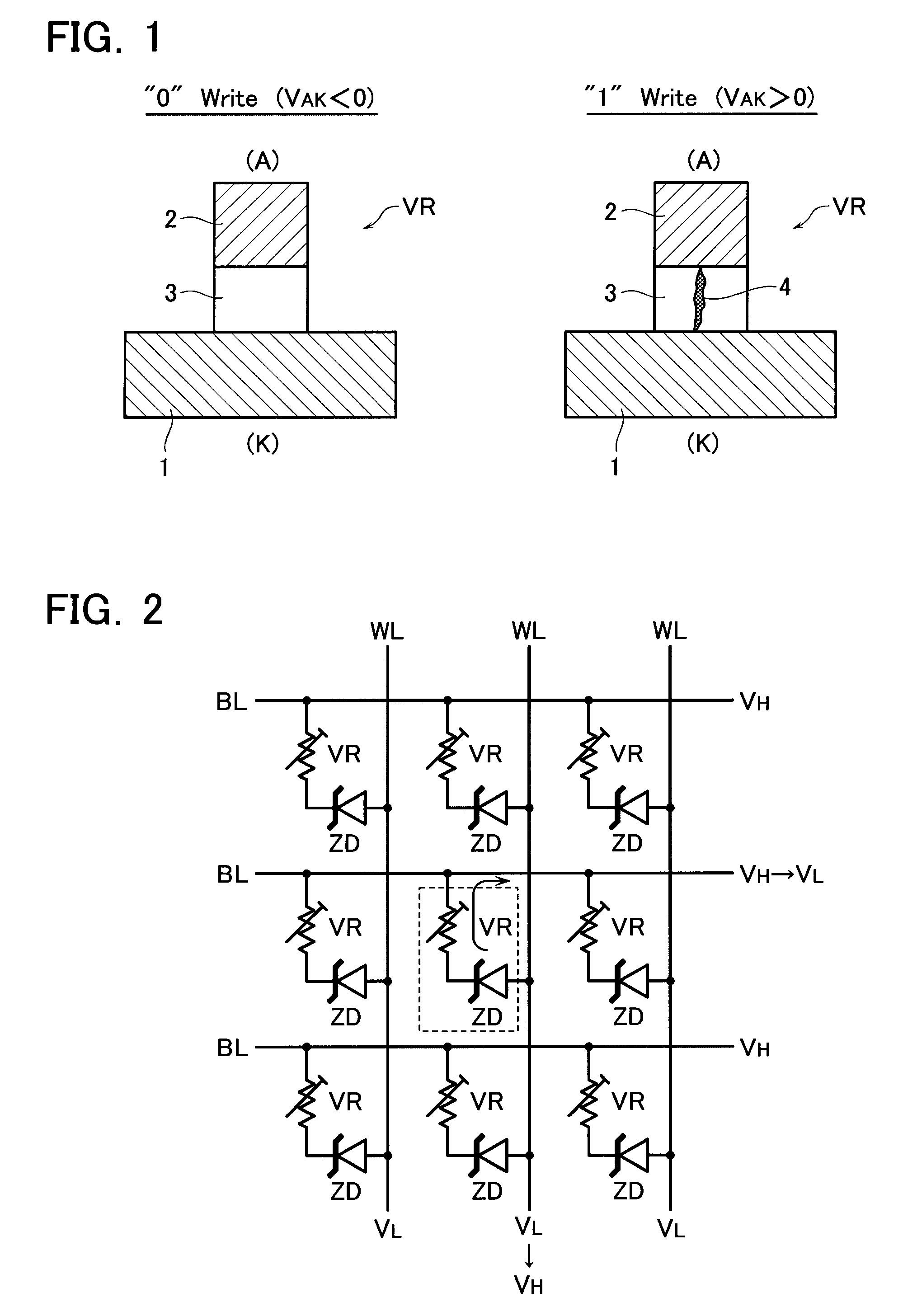
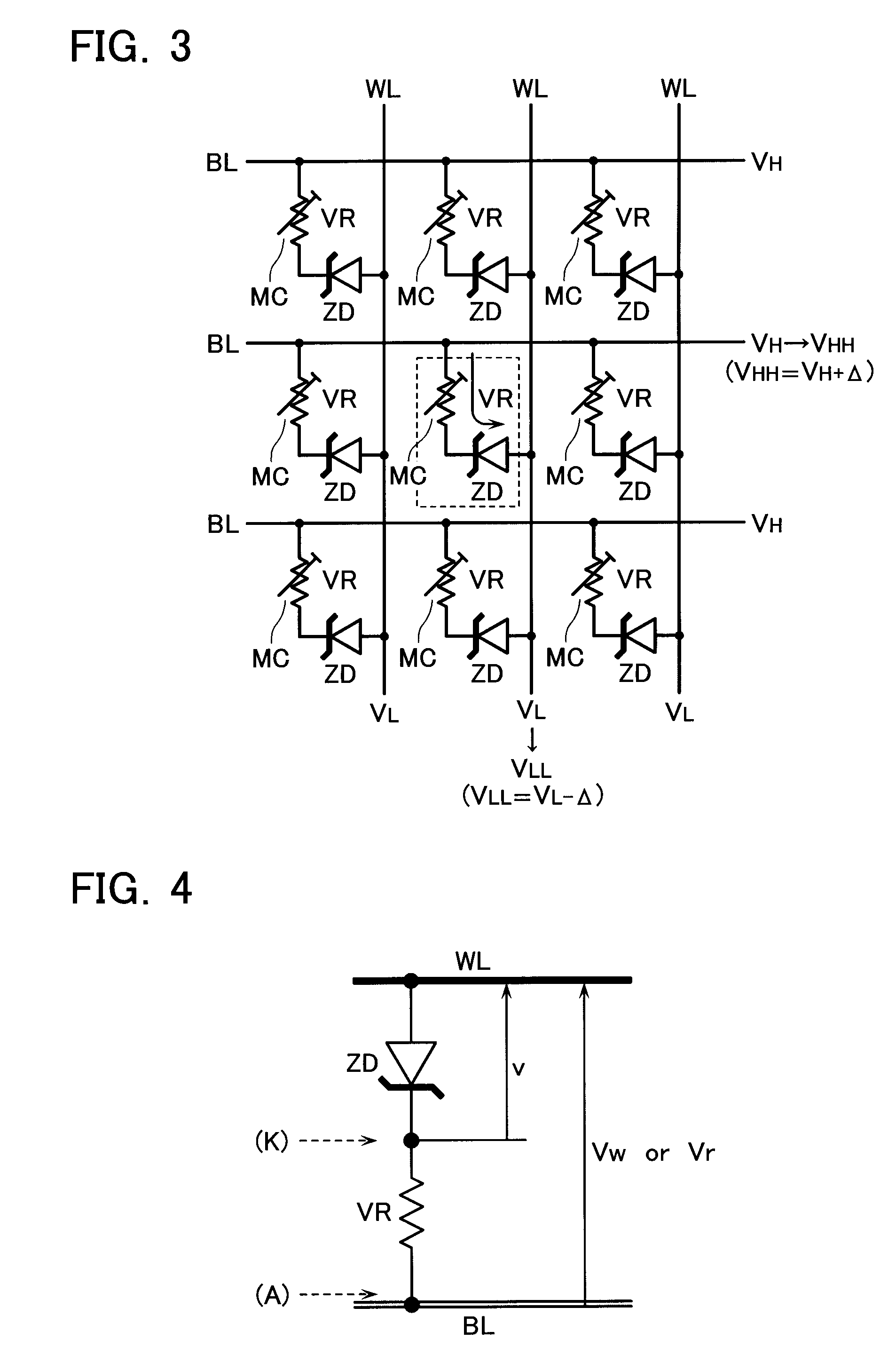
Three-dimensional programmable resistance memory device with a read/write circuit stacked under a memory cell array
A programmable resistance memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, at least one cell array, in which memory cells are arranged and formed above the semiconductor substrate. Each of the memory cells has a stack structure of a programmable resistance element and an access element, the programmable resistance element storing a high resistance state or a low resistance state based on the polarity of voltage application in a non-volatile manner. The access element has a resistance value in an off-state in a certain voltage range that is ten time or more as high as that in a select state. A read / write circuit is formed on the semiconductor substrate and underlying the cell array for data reading and data writing in communication with the cell array.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
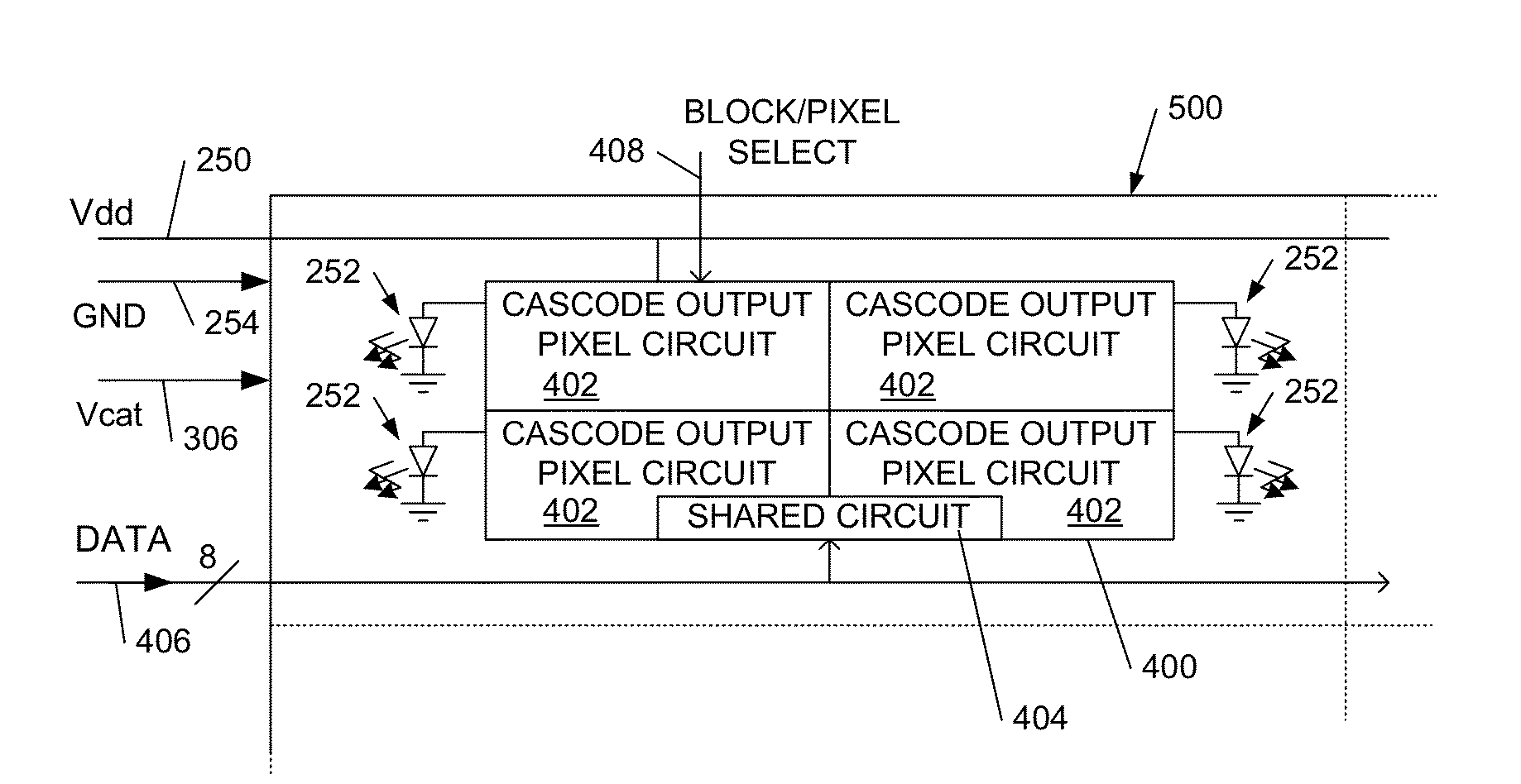
OLED Display Driver Circuits and Techniques
InactiveUS20130088416A1Reduce silicon areaLow costStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDriver circuitEngineering
We describe a method of driving an OLED display. The OLED display comprises a plurality of pixel driver circuits on chiplets, each pixel driver circuit comprising an output transistor for driving a first connection of an associated OLED pixel. A cascode transistor on the chiplet is coupled between the output transistor and the first connection of said associated OLED pixel. A power supply is provided to the chiplet, defining a chiplet voltage range. A second connection of the associated OLED pixel is connected to an OLED voltage outside said chiplet voltage range. The OLED pixel is then driven using the pixel driver circuit on the chiplet over an OLED voltage range greater than said chiplet voltage range. In some preferred embodiments a drain connection of the cascode transistor is set at a voltage below a ground or negative (Vss) power supply to a chiplet.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
Power converter with capacitive energy transfer and fast dynamic response
ActiveUS8212541B2Improve performanceIncrease conversionsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceConverters
A converter circuit and related technique for providing high power density power conversion includes a reconfigurable switched capacitor transformation stage coupled to a magnetic converter (or regulation) stage. The circuits and techniques achieve high performance over a wide input voltage range or a wide output voltage range. The converter can be used, for example, to power logic devices in portable battery operated devices.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
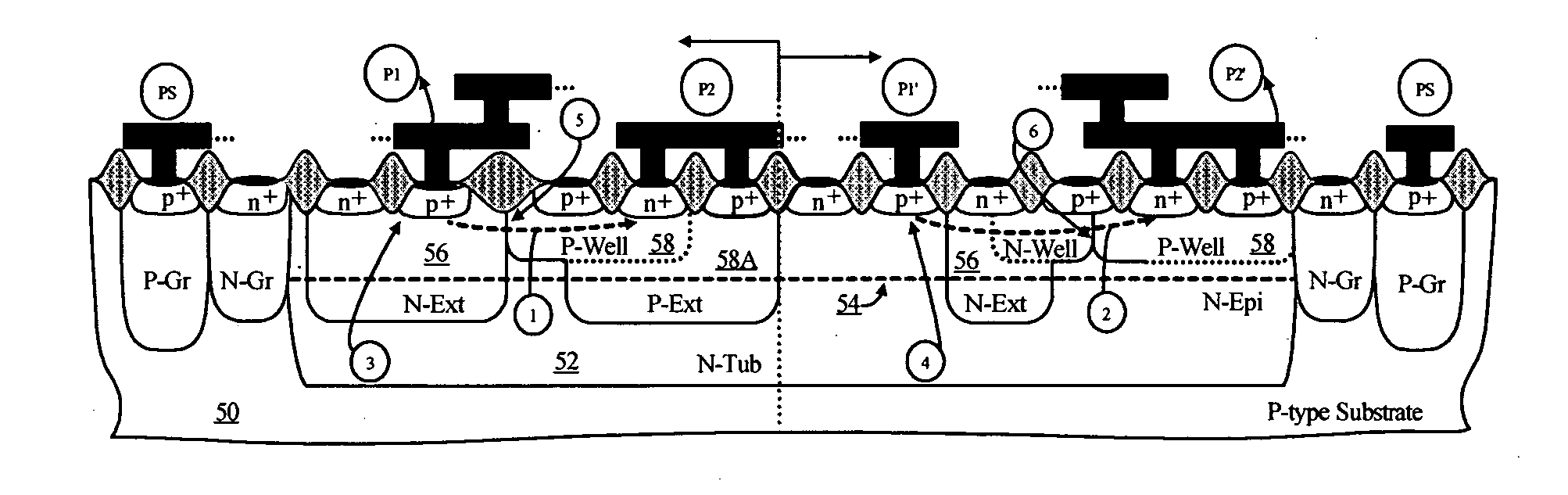
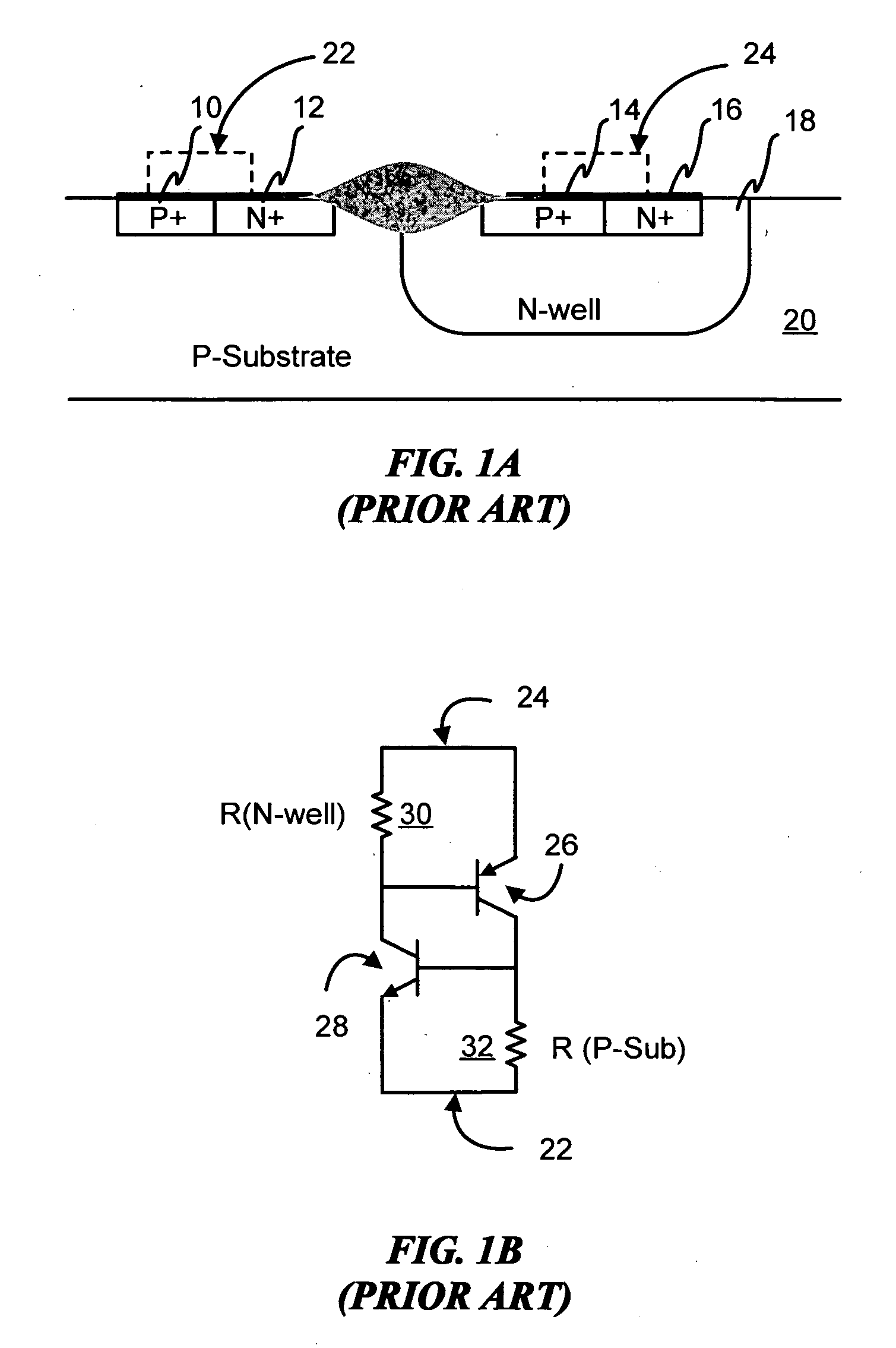
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger- and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal CMOS/BiCMOS integrated circuits
InactiveUS20070007545A1Impaired immunityHigh protection levelTransistorThyristorNon symmetricTransmission-line pulse
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1-N2-P2-N1 / / N1-P3-N3-P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2 standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC +1
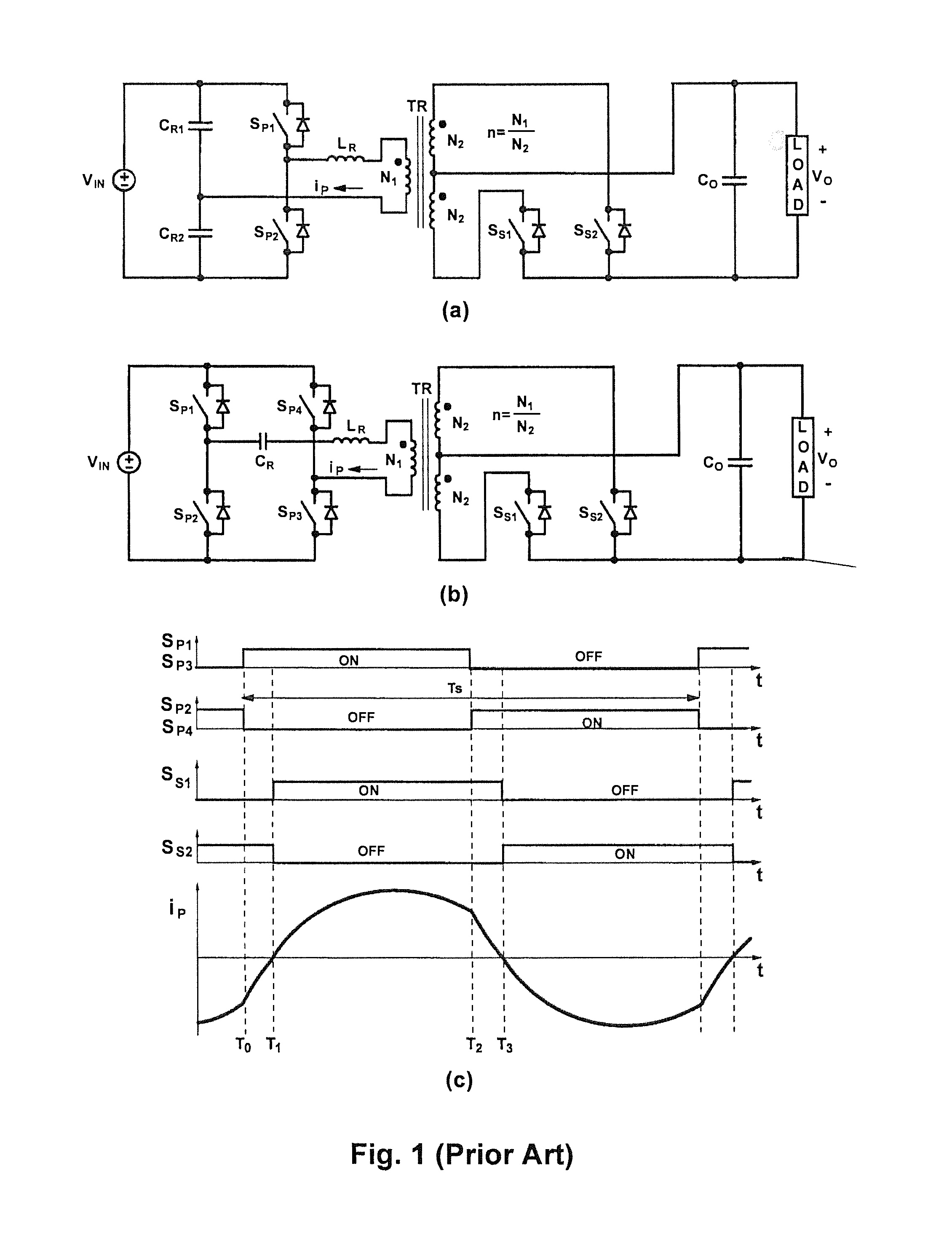
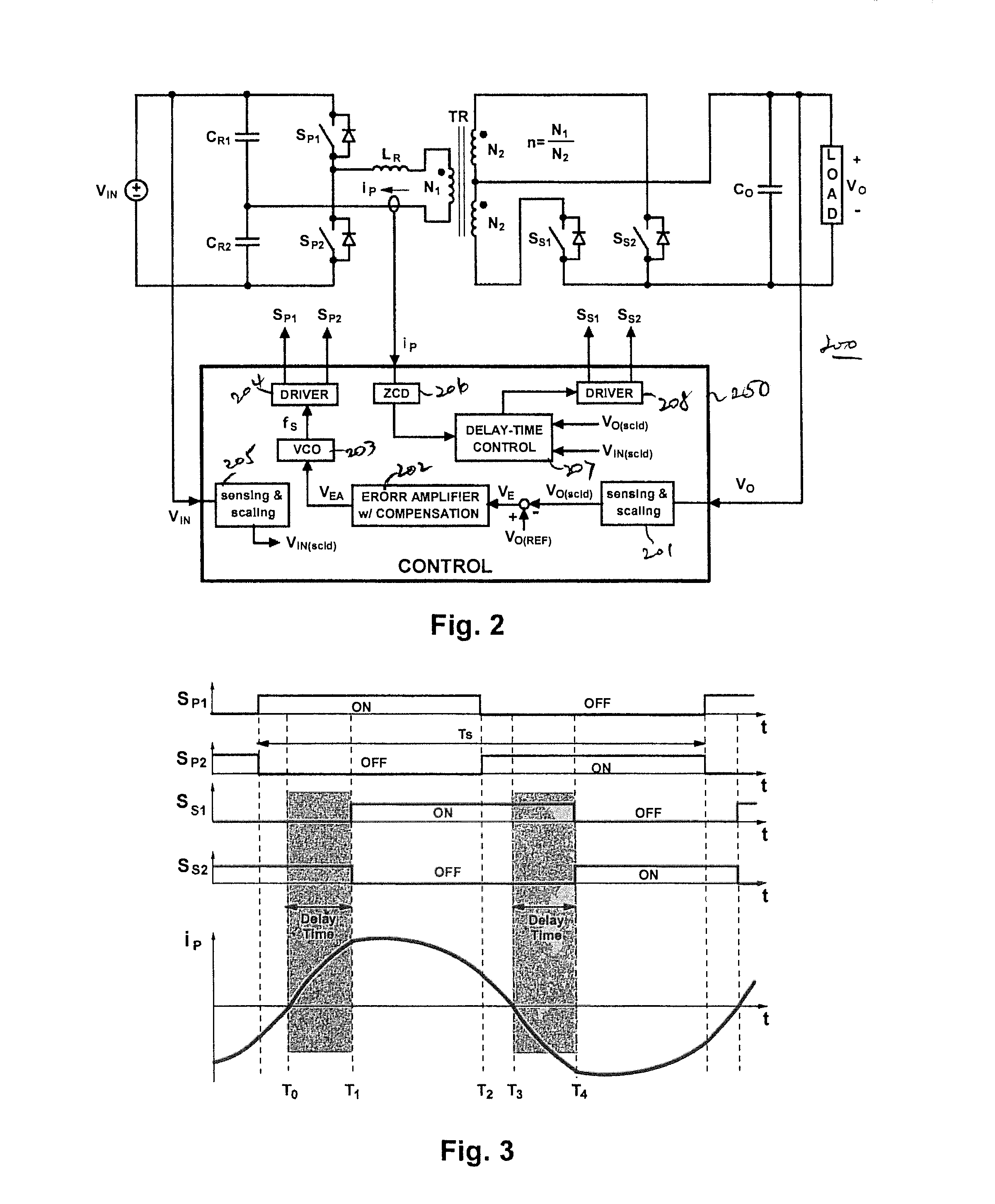
Resonant converters and control methods thereof
ActiveUS20150229225A1Improve performanceReducing switching-frequency rangeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTime delaysEngineering
Control methods for resonant converters offer improved performance in resonant converters that operate with a wide input-voltage range or a wide output-voltage range (or both) by substantially reducing the switching-frequency range. Reduction in the switching frequency range is achieved by controlling the output voltage with a combination of variable-frequency control and time-delay control. Variable-frequency control may be used to control the primary switches of an isolated resonant converter, while delay-time control may be used to control secondary-side rectifier switches provided in place of diode rectifiers. The secondary-side control may be implemented by sensing the secondary current or the primary current (or both) and by delaying the turning-off of the corresponding secondary switch with respect to the zero crossings in the secondary current or the primary current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Power Converter Circuitry
ActiveUS20100020576A1Avoid flowInhibit currentEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionPower gridPhotovoltaic generator
A power converter circuitry for converting a DC voltage generated by a generator with varying output power in the mean voltage range into an alternating voltage for feeding into a grid, with several series-connected power converters, which are connected in parallel with said generator, as well as with a controllable bridging switch for each power converter, said bridging switch lying in a direct voltage intermediate circuit and bridging the respective power converter in the closed condition, is intended to be used for a photovoltaic generator. This is achieved in that a resistance chopper is connected between each power converter and the generator, no input diode being provided in the current path from the generator to the power converter, and that each bridging switch is connected in parallel with the resistance chopper in the direct voltage intermediate circuit.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Efficient class-G amplifier with wide output voltage swing
InactiveUS6838942B1Reduce noiseImprove efficiencyGated amplifiersPower amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
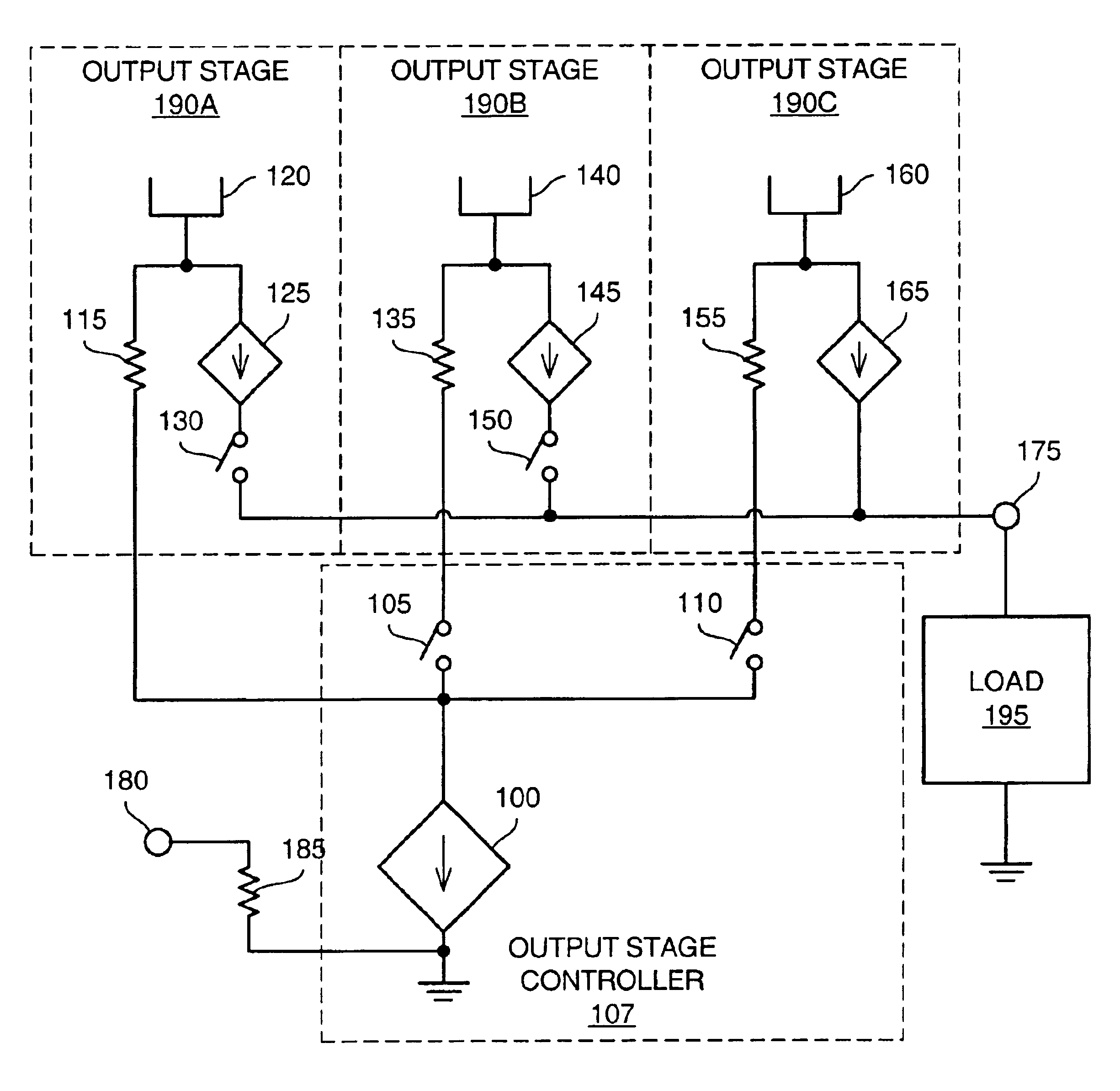
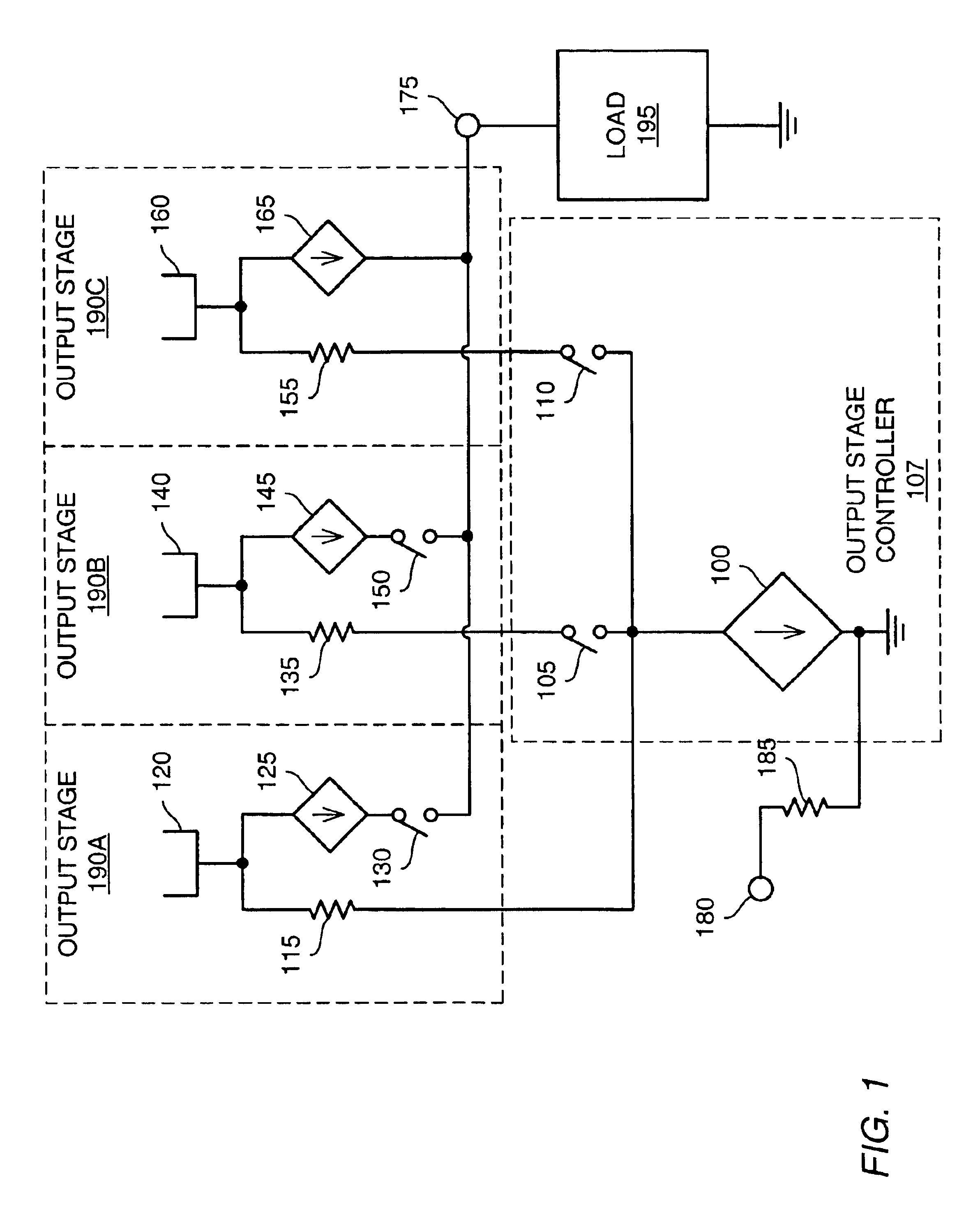
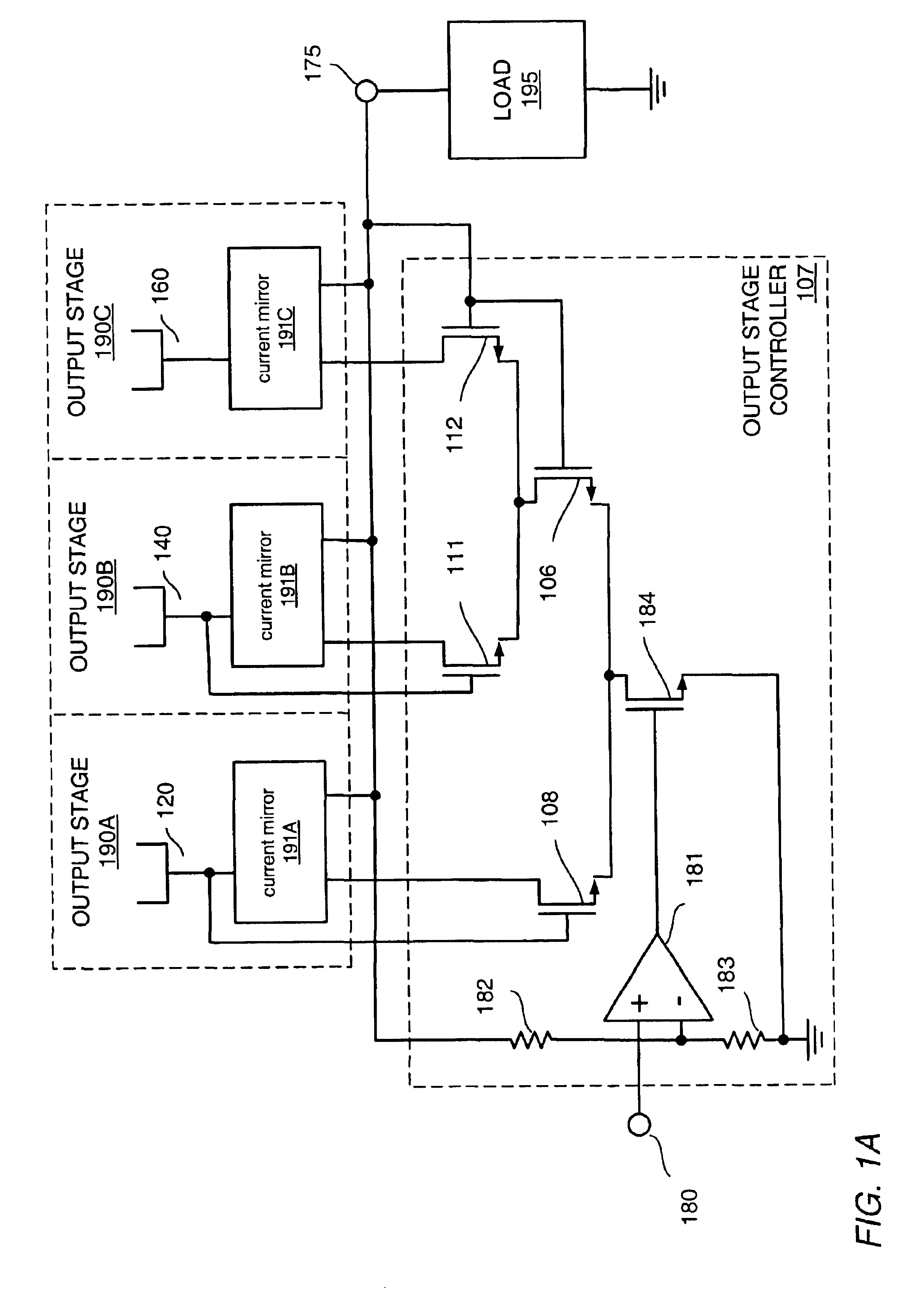
Various embodiments of methods and apparatus for an amplifier with wide output voltage swing are disclosed. The amplifier may include multiple output stages, each associated with a distinct supply voltage. Each output stage may contribute current to the output of the amplifier over a range of amplifier output voltages and these ranges may overlap. Each output stage may contribute current until the amplifier output voltage reaches the supply voltage associated with that output stage. The amplifier output may be as great as the largest supply voltage minus a drop equal to Rdson for an output transistor multiplied by the output current. In a CMOS implementation, this voltage drop may be approximately 0.15V. When the amplifier output voltage is close to the supply voltage associated with an output stage, both that output stage and the output stage associated with the next highest supply voltage may contribute to the amplifier output.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
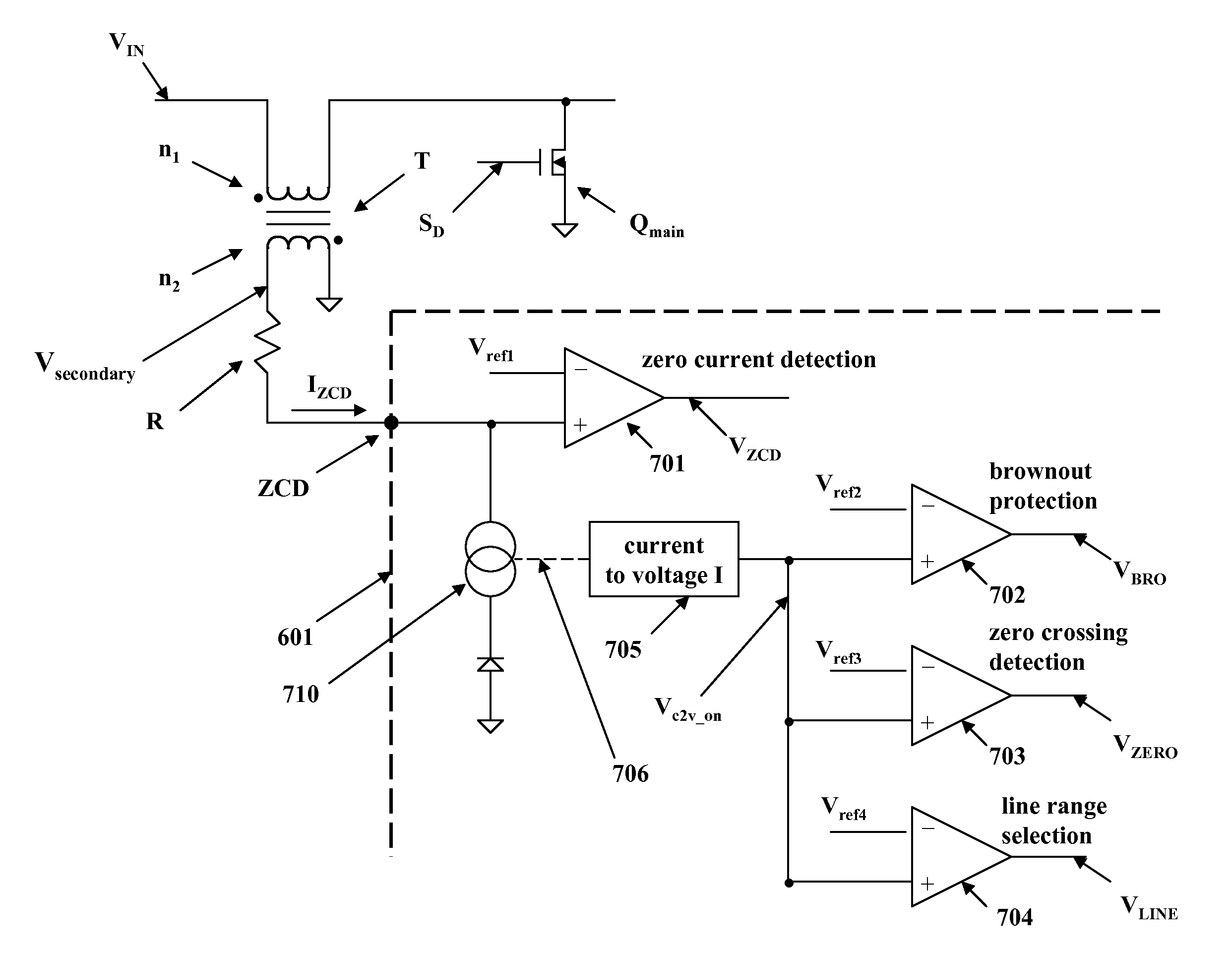
Utilization of a multifunctional pin combining voltage sensing and zero current detection to control a switched-mode power converter
InactiveUS8670255B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionOvervoltagePower flow
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Fabrication of semiconductor structure having N-channel channel-junction field-effect transistor
ActiveUS7595243B1Performance characteristicHigh electron mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor technology combines a normally off n-channel channel-junction insulated-gate field-effect transistor (“IGFET”) (104) and an n-channel surface-channel IGFET (100 or 160) to reduce low-frequency 1 / f noise. The channel-junction IGFET is normally fabricated to be of materially greater gate dielectric thickness than the surface-channel IGFET so as to operate across a greater voltage range than the surface-channel IGFET. A p-channel surface-channel IGFET (102 or 162), which is typically fabricated to be of approximately the same gate-dielectric thickness as the n-channel surface-channel IGFET, is preferably combined with the two n-channel IGFETs to produce a complementary-IGFET structure. A further p-channel IGFET (106, 180, 184, or 192), which is typically fabricated to be of approximately the same gate dielectric thickness as the n-channel channel-junction IGFET, is also preferably included. The further p-channel IGFET can be a surface-channel or channel-junction device.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
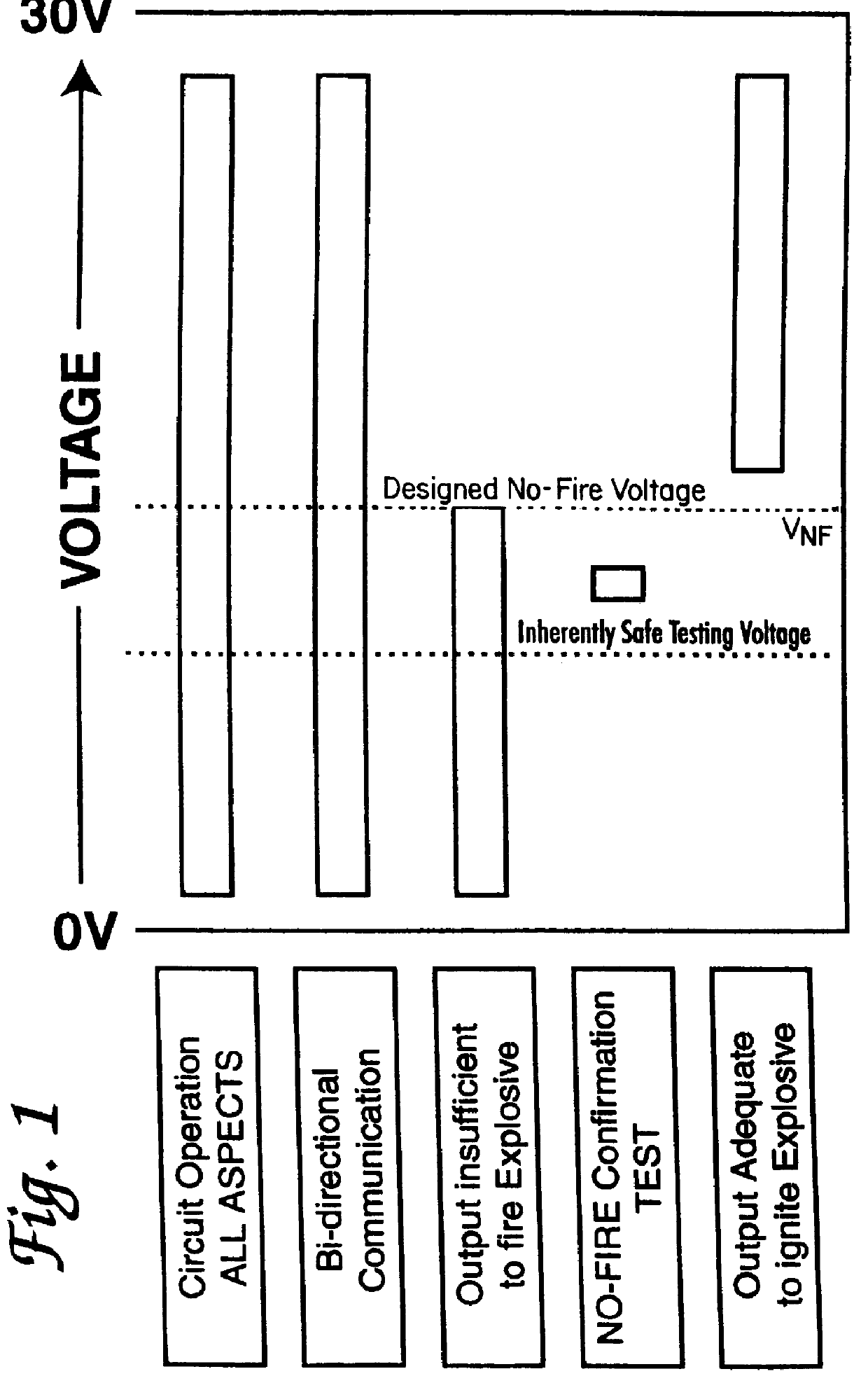
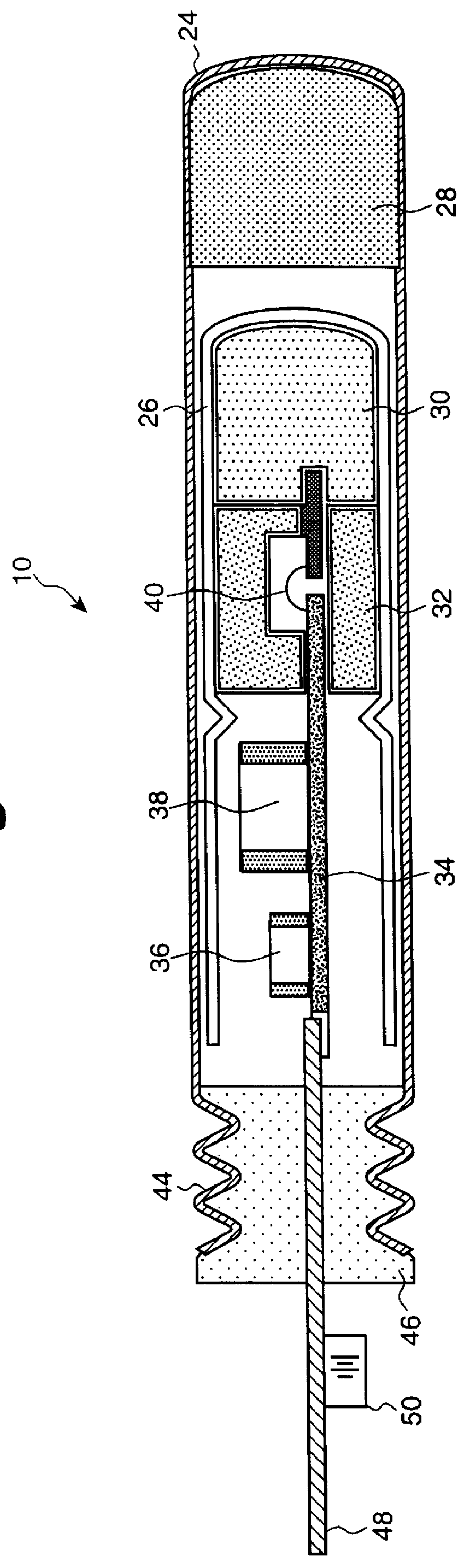
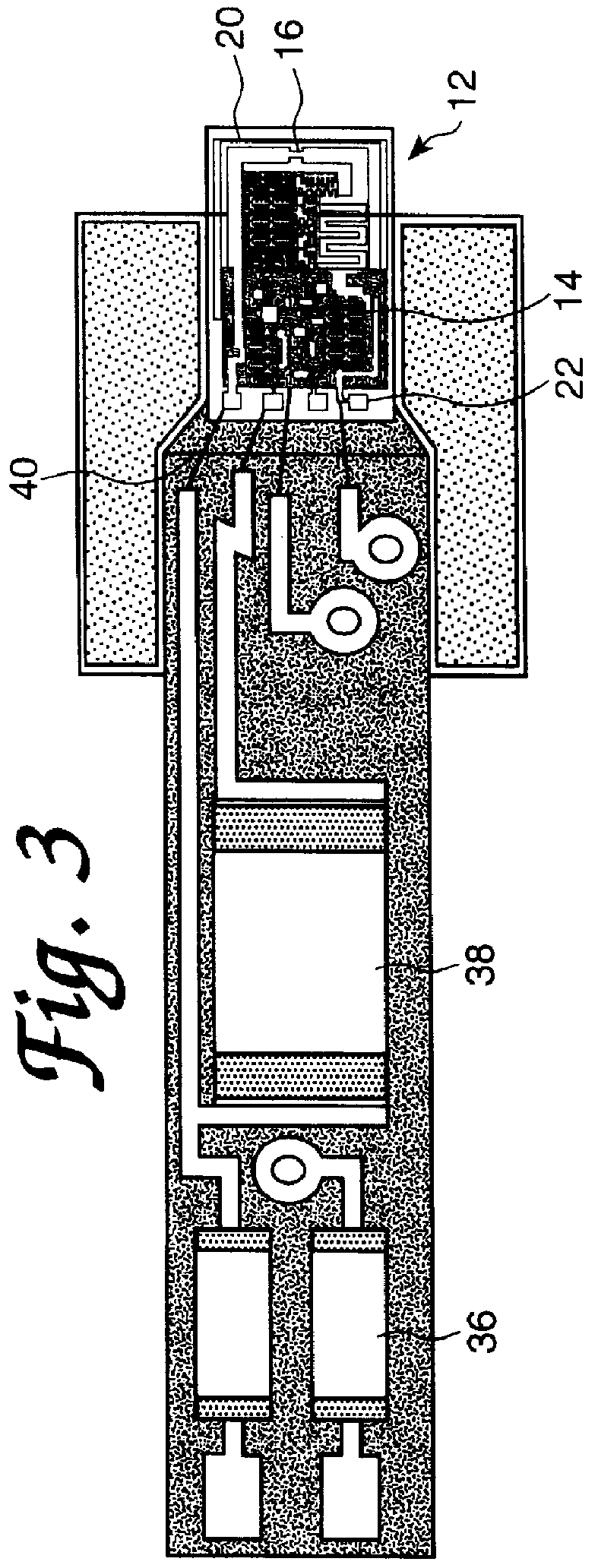
Electronic explosives initiating device
InactiveUS6085659AInherent flexibilityPosition information can be generated with easeIncandescent ignitionBlasting cartridgesVoltageExplosive Agents
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 02987 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 10, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 10, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 4, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 21067 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 12, 1997An electronic explosives initiating device which includes a firing element which has a designed no-fire voltage and an operating circuit which operates at any voltage in a range of voltages which straddles the designed no-fire voltage.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
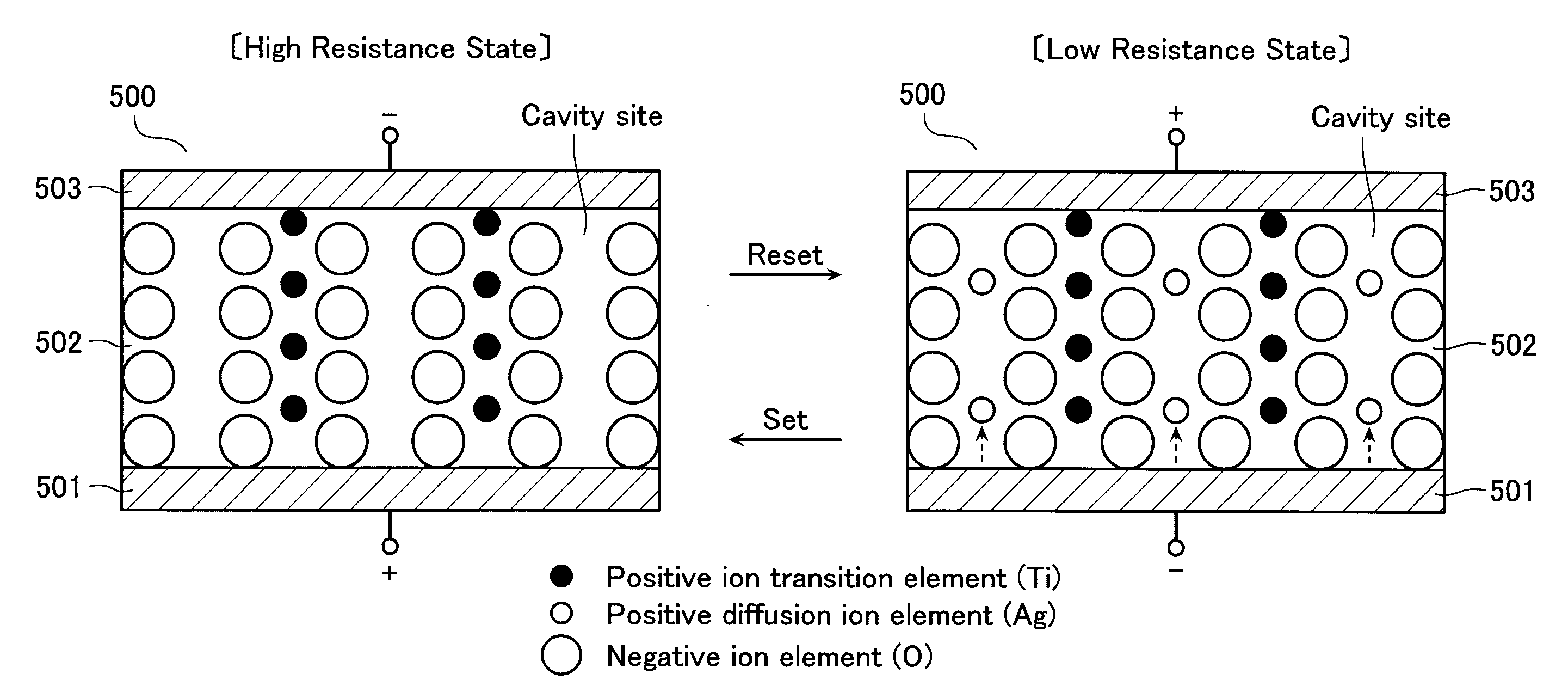
Resistance change memory device having a variable resistance element with a recording layer electrode served as a cation source in a write or erase mode
A resistance change memory device including: a semiconductor substrate; at least one cell array formed above the semiconductor substrate to have a stack structure of a variable resistance element and an access element, the variable resistance element storing a high resistance state or a low resistance state in a non-volatile manner, the access element having such an off-state resistance value in a certain voltage range that is ten times or more as high as that in a select state; and a read / write circuit formed on the semiconductor substrate, wherein the variable resistance element includes: a recording layer formed of a composite compound containing at least one transition element and a cavity site for housing a cation ion; and electrodes formed on the opposite sides of the recording layer, one of the electrodes serving as a cation source in a write or erase mode for supplying a cation to the recording layer to be housed in the cavity site.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Method of refreshing an electrically erasable and programmable non-volatile memory
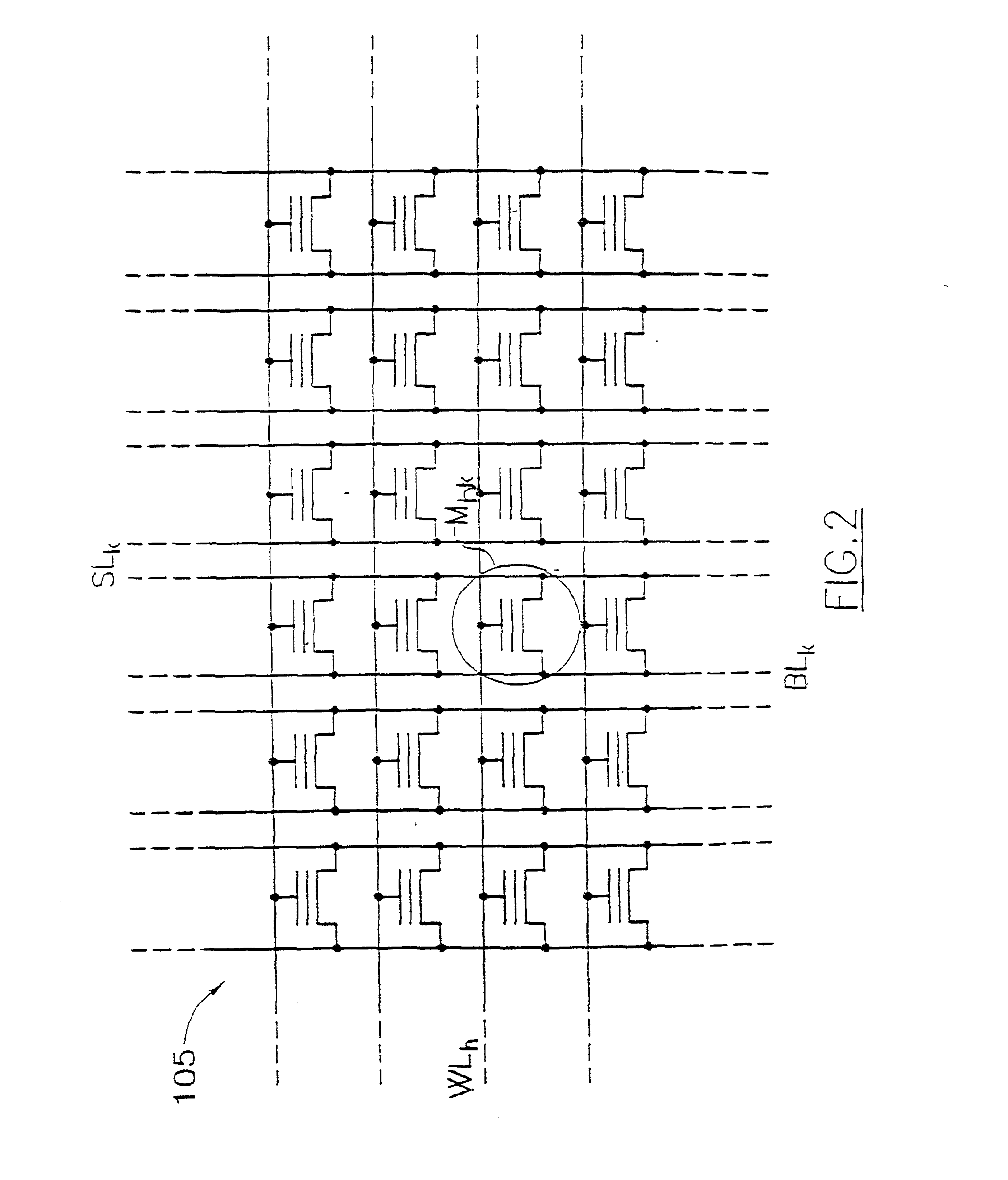
A method (1110a;1110b) of refreshing an electrically erasable and programmable non-volatile memory (100) having a plurality of memory cells (Mhk) is proposed. The method includes the steps of: verifying (1106-1114; 1152-1162) whether a memory cell has drifted from a correct condition (i.e., a predetermined voltage and / or voltage range), and individually restoring (1116-1130) the correct condition of the memory cell if the result of the verification is positive.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
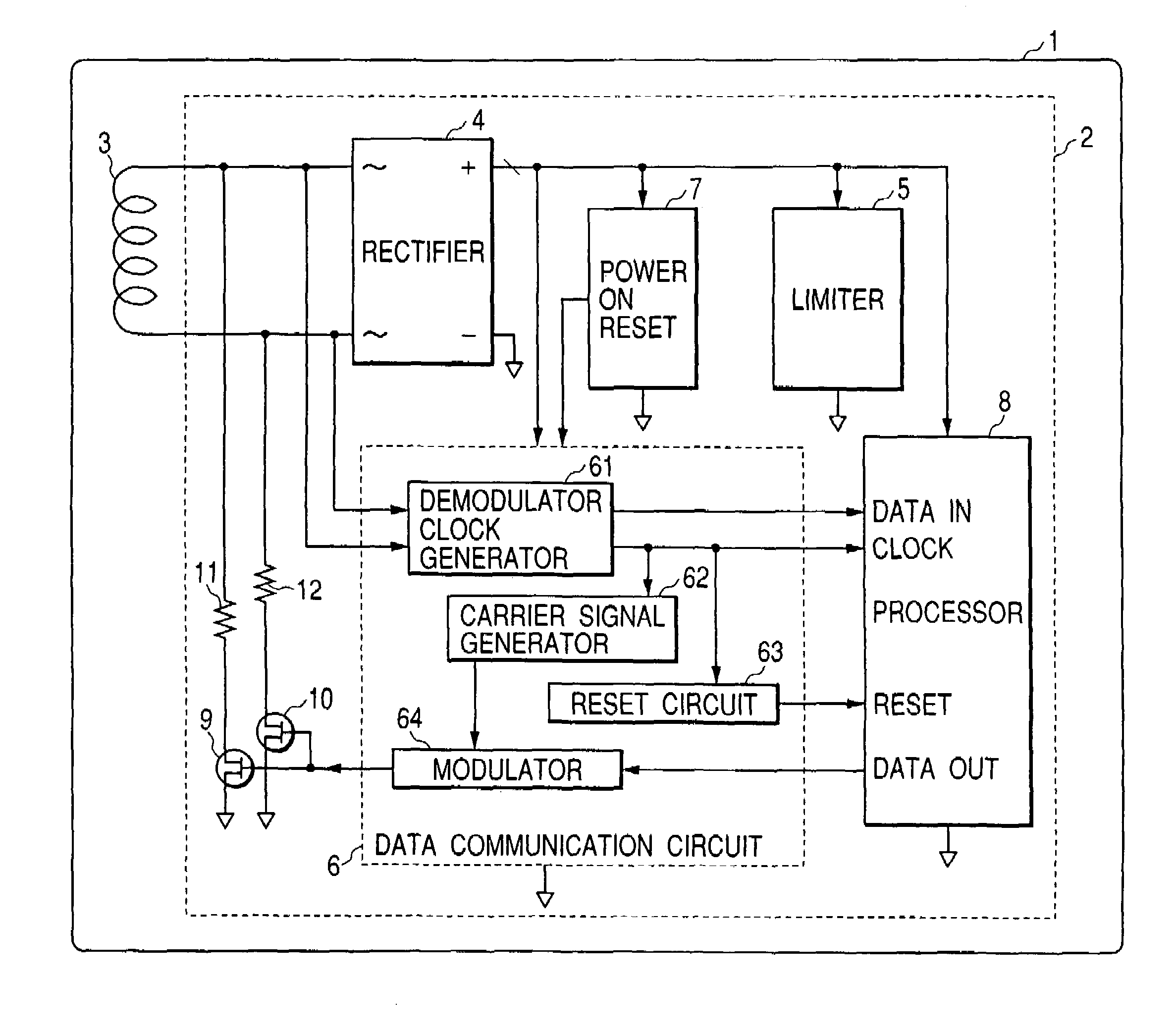
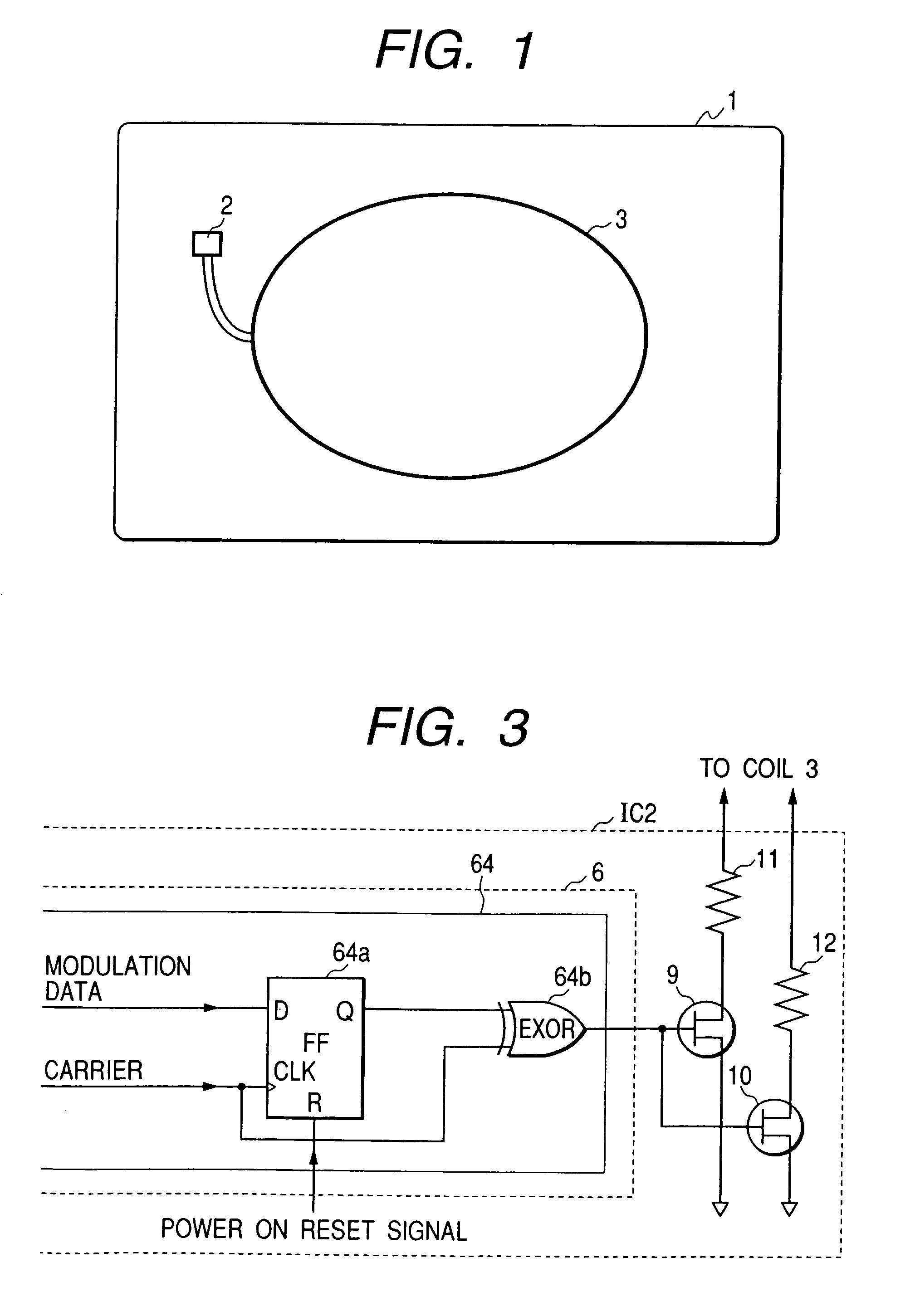
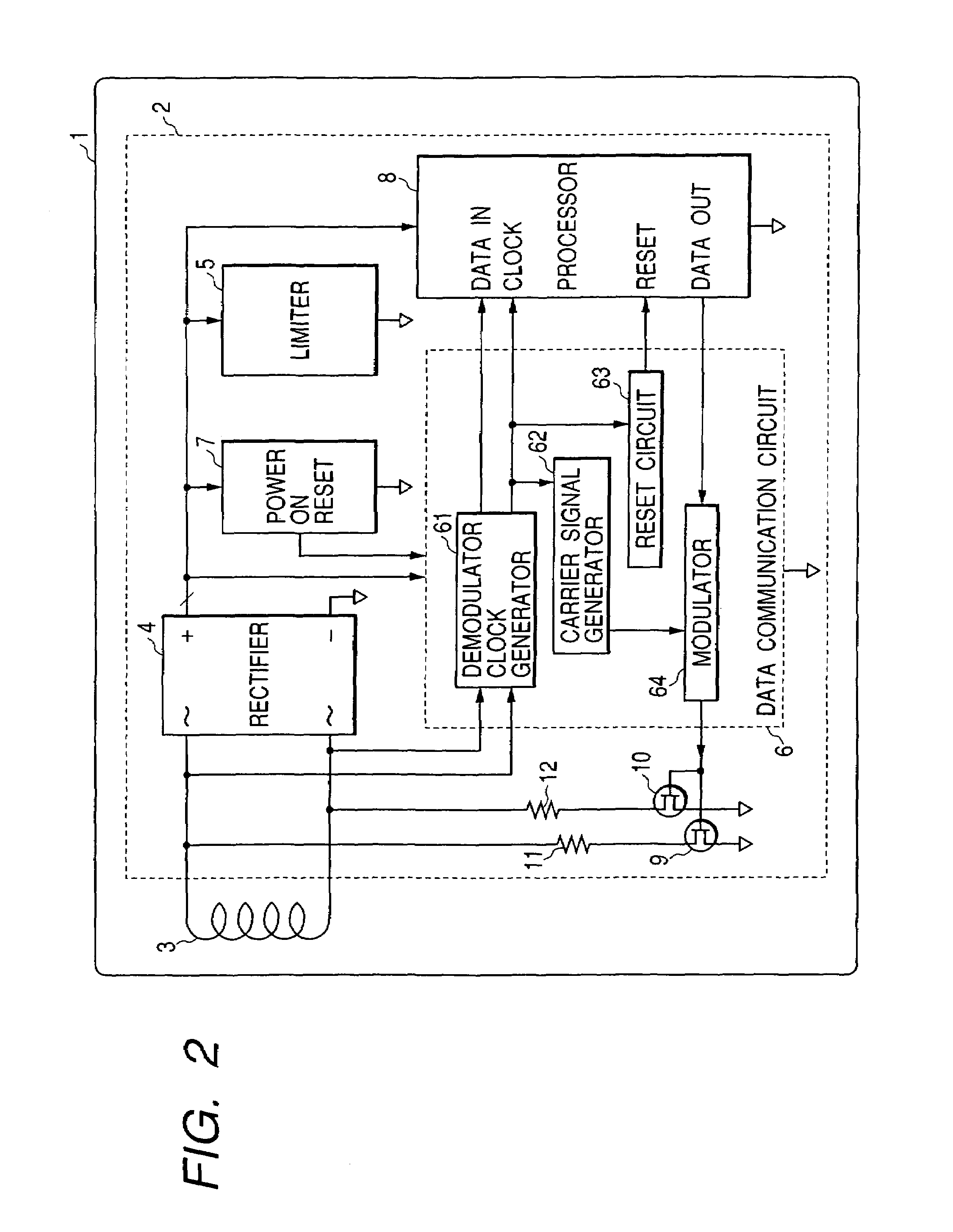
RFID (radio frequency identification) and IC card
InactiveUS6972662B1Reduce voltage marginVariation width of a power supply voltage of the IC is rather largeOther printing matterData resettingEngineeringVoltage range
An RFID which provides a wide working voltage range and general versatility at low cost, without the need for changing its internal circuit design due to external factors. In the RFID, there is provided an arrangement that a low impedance state is given when its internal data communication circuit is in a reset state.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Highly efficient series string LED driver with individual LED control
ActiveUS7649326B2Increase brightnessStable changeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalField-effect transistor
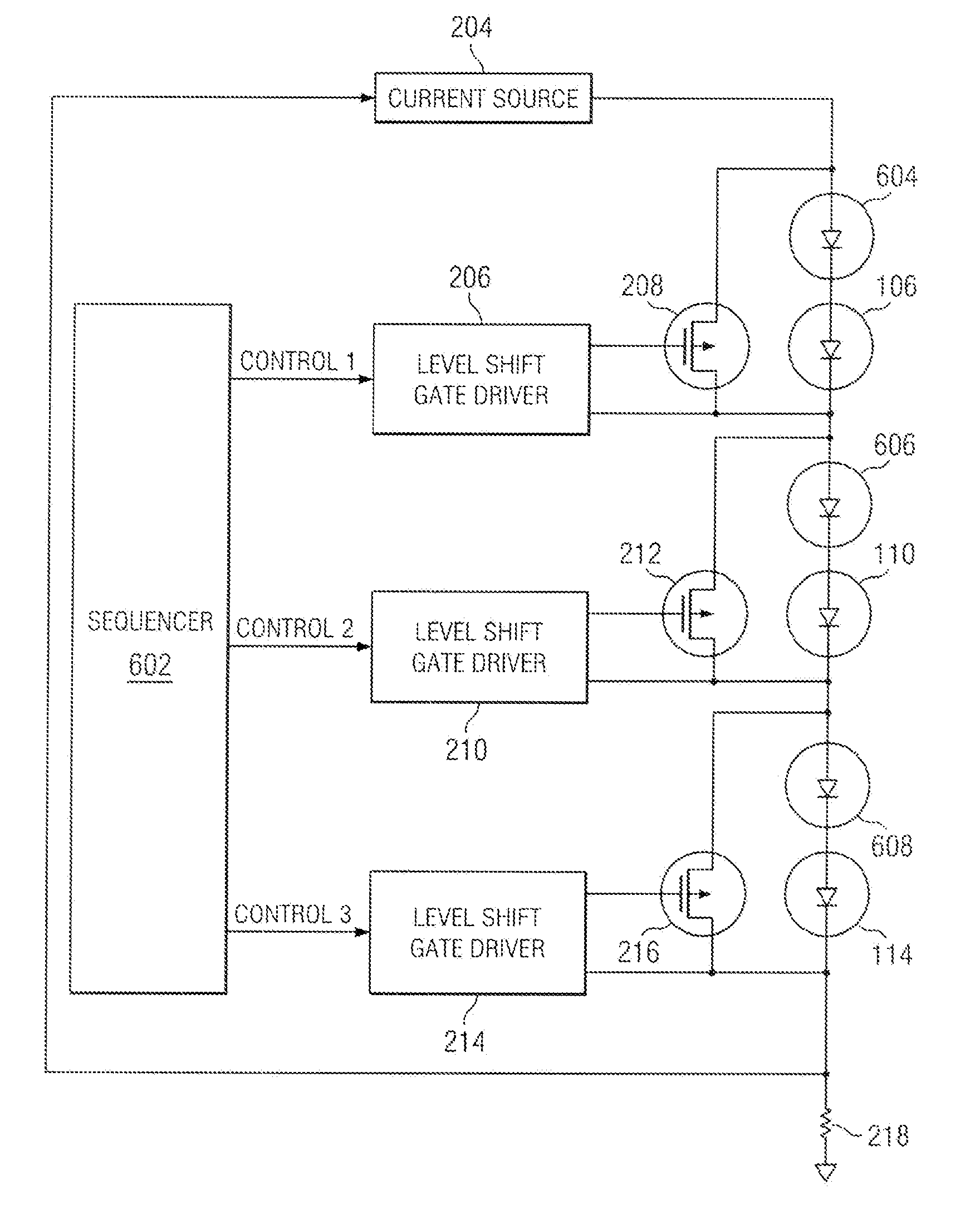
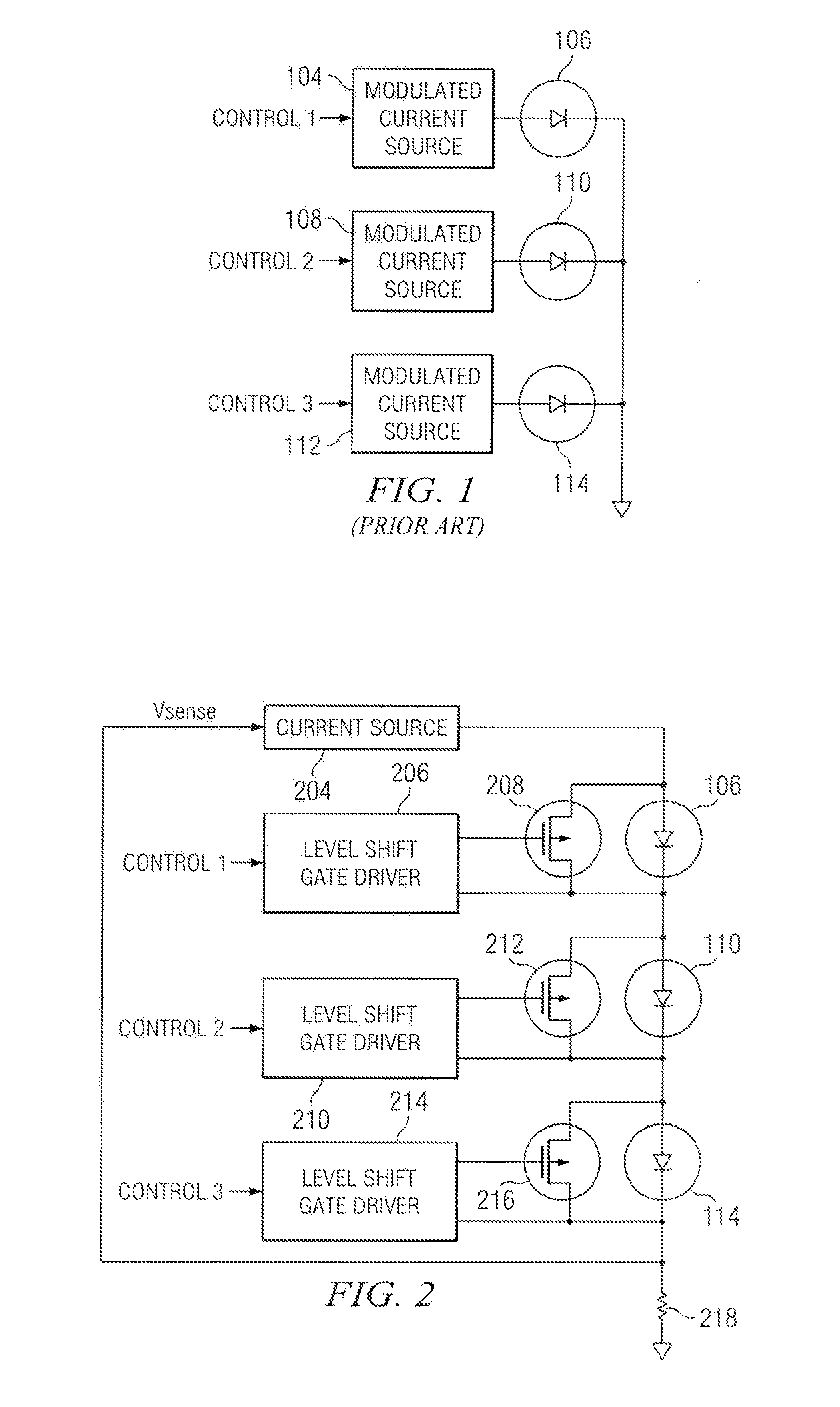
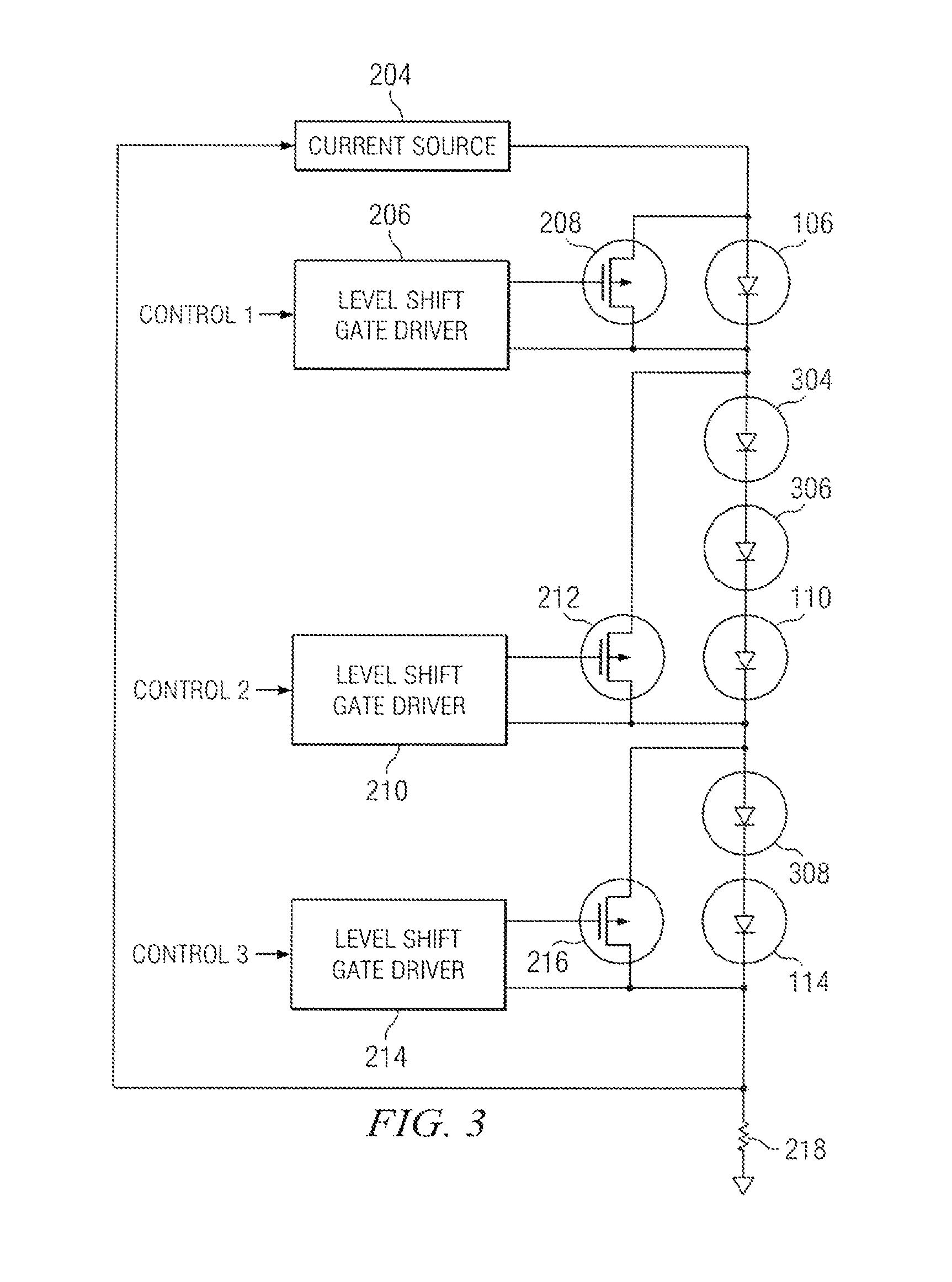
A current source generates, with high efficiency, a current that is substantially constant over a wide range of output voltages. This current is injected into the first end of a series-connected string of LEDs, with the second end of the string connected through a resistor to ground. The voltage developed across this resistor, which is a measure of current flow in the series string, is fed back to the current source, wherein feedback maintains nearly constant current output over a wide range of output voltages. A field effect transistor (FET) is placed in parallel with each LED in the string. A level shift gate driver couples a pulse width modulated control signal to the gate of each FET. With the FET being coupled across a particular LED, the LED can be bypassed when the FET is actuated or receive current when the FET is deactuated. By modulating the duty cycle of each FET, the brightness of each associated LED may be varied smoothly over its full range.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High efficiency constant current LED driver
InactiveUS20110080102A1Improve efficiencyLarge gainEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesFull bridgeEngineering
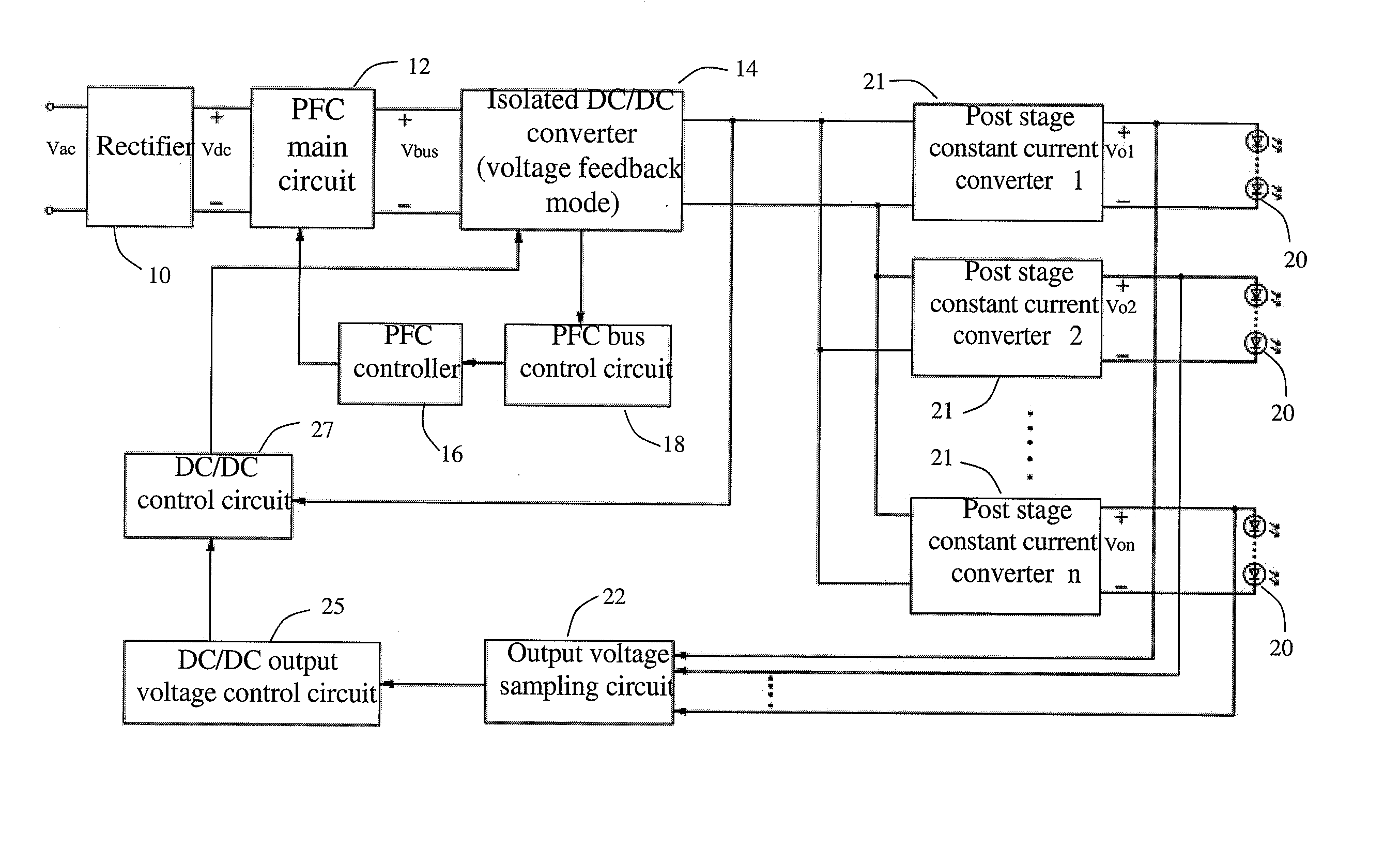
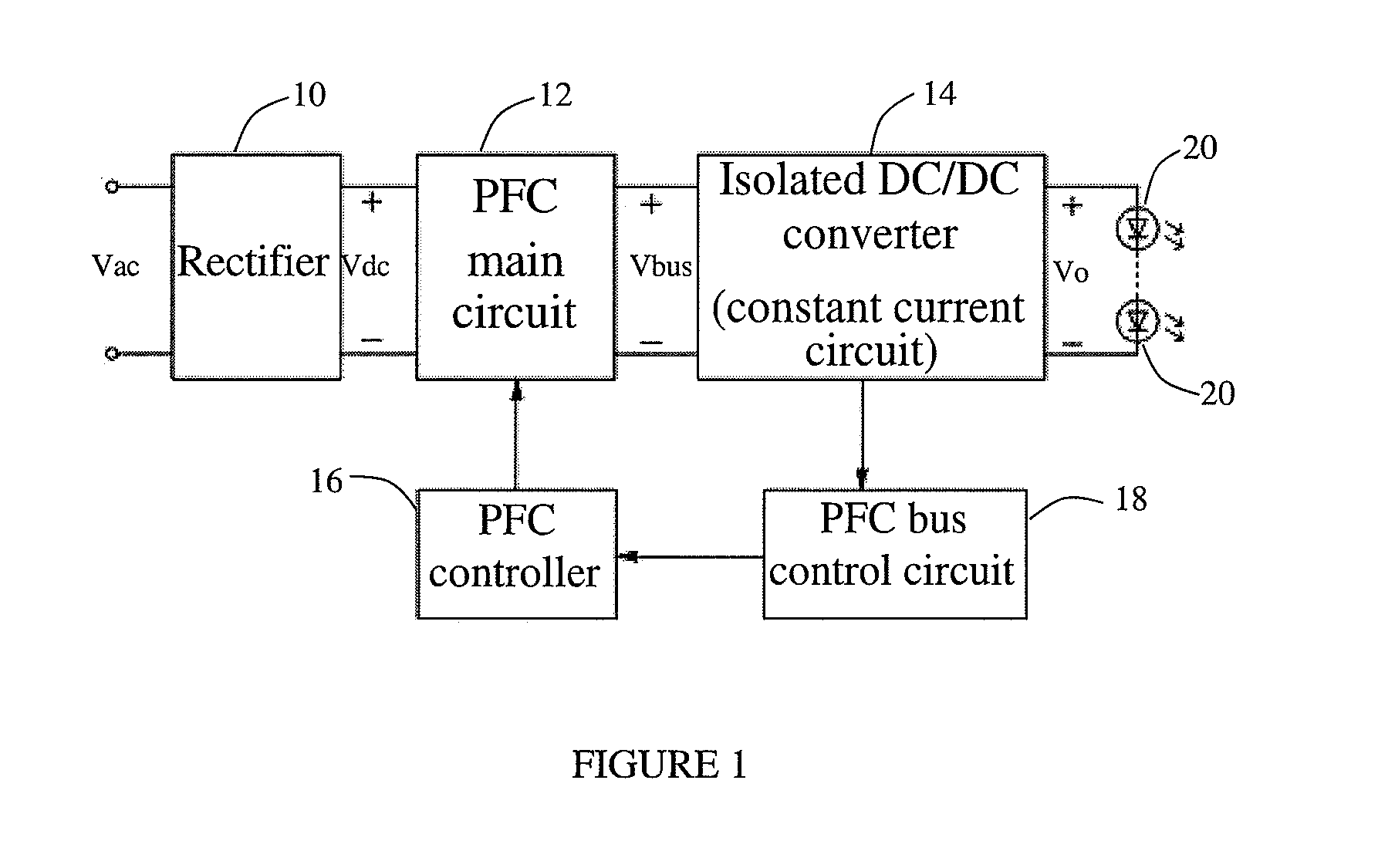
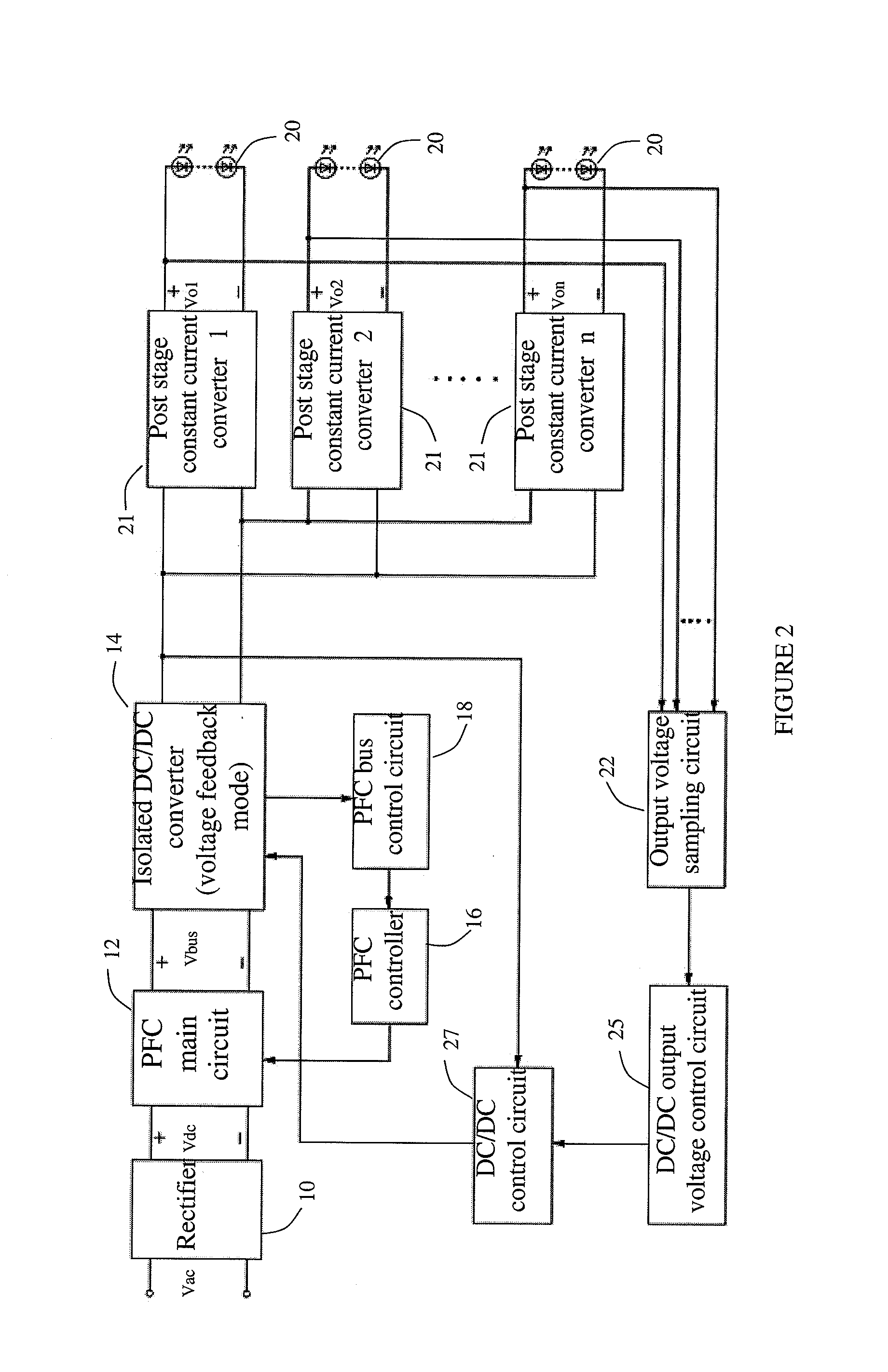
The present invention discloses a high efficiency constant current LED driver, which comprises a rectification bridge, a PFC main circuit, an isolated DC / DC converter, a PFC controller and a PFC bus control circuit. Since the input voltage is an intermediate PFC bus voltage, which varies with the output voltage of the DC / DC converter. When the isolated DC / DC converter is an LLC resonant circuit, the operating frequency of the LLC circuit is close to the resonant frequency within a wide output voltage range. Thus, the gain range and the operating frequency is narrow, and can enable the constant current module to work with a high efficiency at a wide output voltage range. When the isolated DC / DC converter is a symmetric half bridge, or an asymmetric half bridge or a full bridge circuit, the duty cycle of DC / DC circuit is close to 50% within a wide output voltage range. Thus, the changing range of the duty cycle of the DC / DC converter will be narrow and can improve the efficiency dramatically.
Owner:INVENTRONICS HANGZHOU
Thermostat with gfci
InactiveUS20100163635A1Quick checkFast handlingFluid heatersMechanical apparatusComputer moduleThermostat
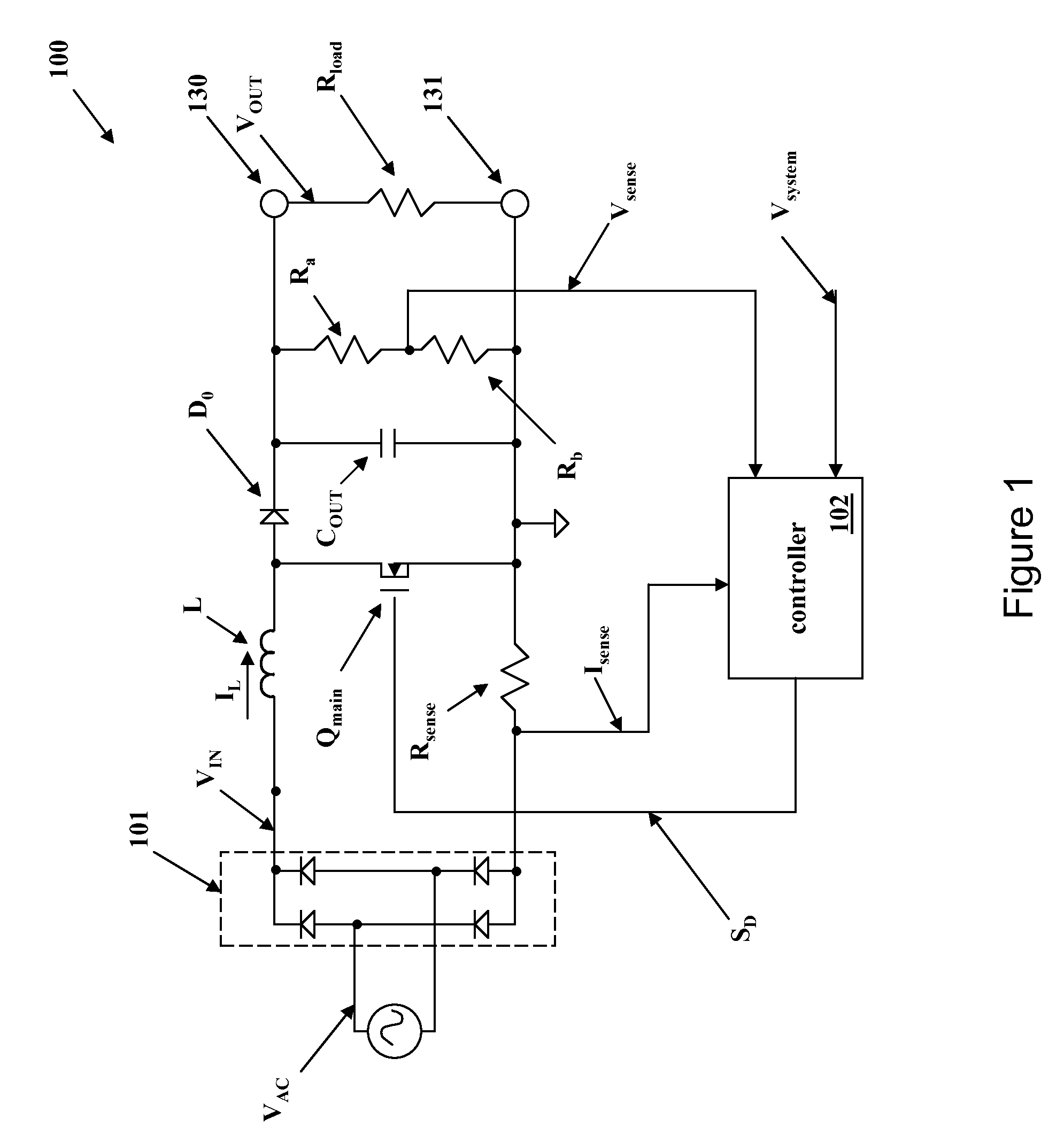
The present invention provides a thermostat with GFCI which includes control module, keyboard module, communication module and display module, and it further includes a leakage detection module, and the control module includes the temperature sensor, and the leakage detection module is connected with the control module, keyboard module and display module respectively. The control module is connected with the controlled device by the leakage detection module. The thermostat monitors current status of output circuit while adjusting the temperature of room, so that it can ensure the safety of the output circuit in use. If leakage occurs to the controlled device, the thermostat can cut off the power and stop power supplying at once, and the alarm light illuminates in the meantime. After manual reset, the alarm light goes out. It works with a wide input voltage range and makes the thermostat normally work at multistage voltage, and it can detect the leakage current accurately, and cut off power in time and report to the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI OKONOFF ELECTRIC
Self-biasing CMOS PECL receiver with wide common-mode range and multi-level-transmit to binary decoder
InactiveUS6049229AReduced Power RequirementsSimplify interconnect routingLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsThree levelEmitter-coupled logic
A pseudo-emitter-coupled-logic (PECL) receiver has a wide common-mode range. Two current-mirror CMOS differential amplifiers are used. One amplifier has n-channel differential transistors and a p-channel current mirror, while the second amplifier has p-channel differential transistors and an n-channel current mirror. When the input voltages approach power or ground, one type of differential transistor continues to operate even when the other type shuts off. The outputs of the two amplifiers are connected together and each amplifier receives the same differential input signals. The tail-current transistor is self-biased using the current-mirror's gate-bias. This self biasing of each amplifier eliminates the need for an additional voltage reference and allows each amplifier to adjust its biasing over a wide input-voltage range. Thus the common-mode input range is extended using self biasing and complementary amplifiers. The complementary self-biased comparators can be used for receiving binary or multi-level-transition (MLT) inputs by selecting different voltage references for threshold comparison. Using the same reference on both differential inputs eliminates a second reference for multi-level inputs having three levels. Thus binary and MLT inputs can be detected and decoded by the same decoder.
Owner:DIODES INC
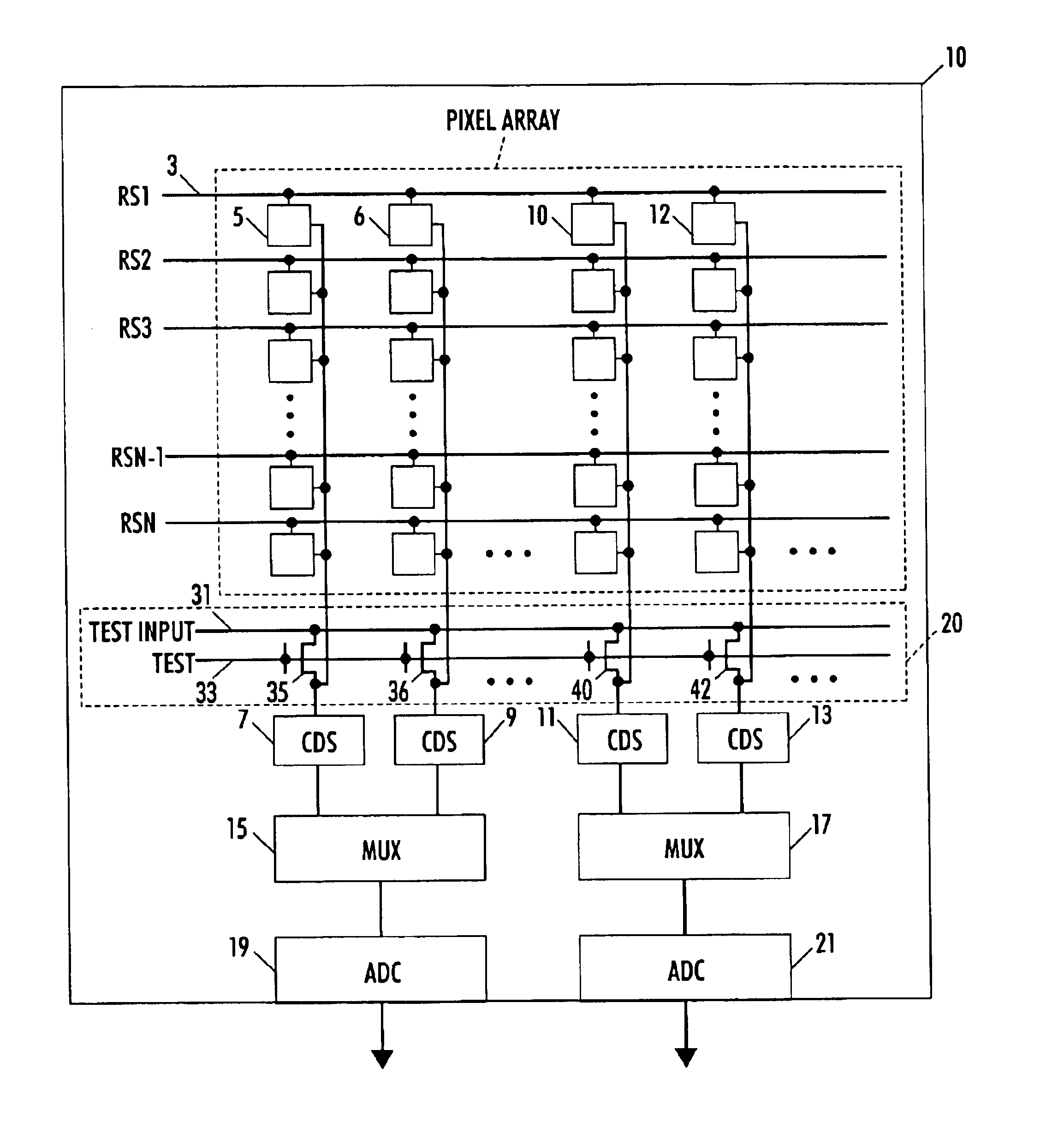
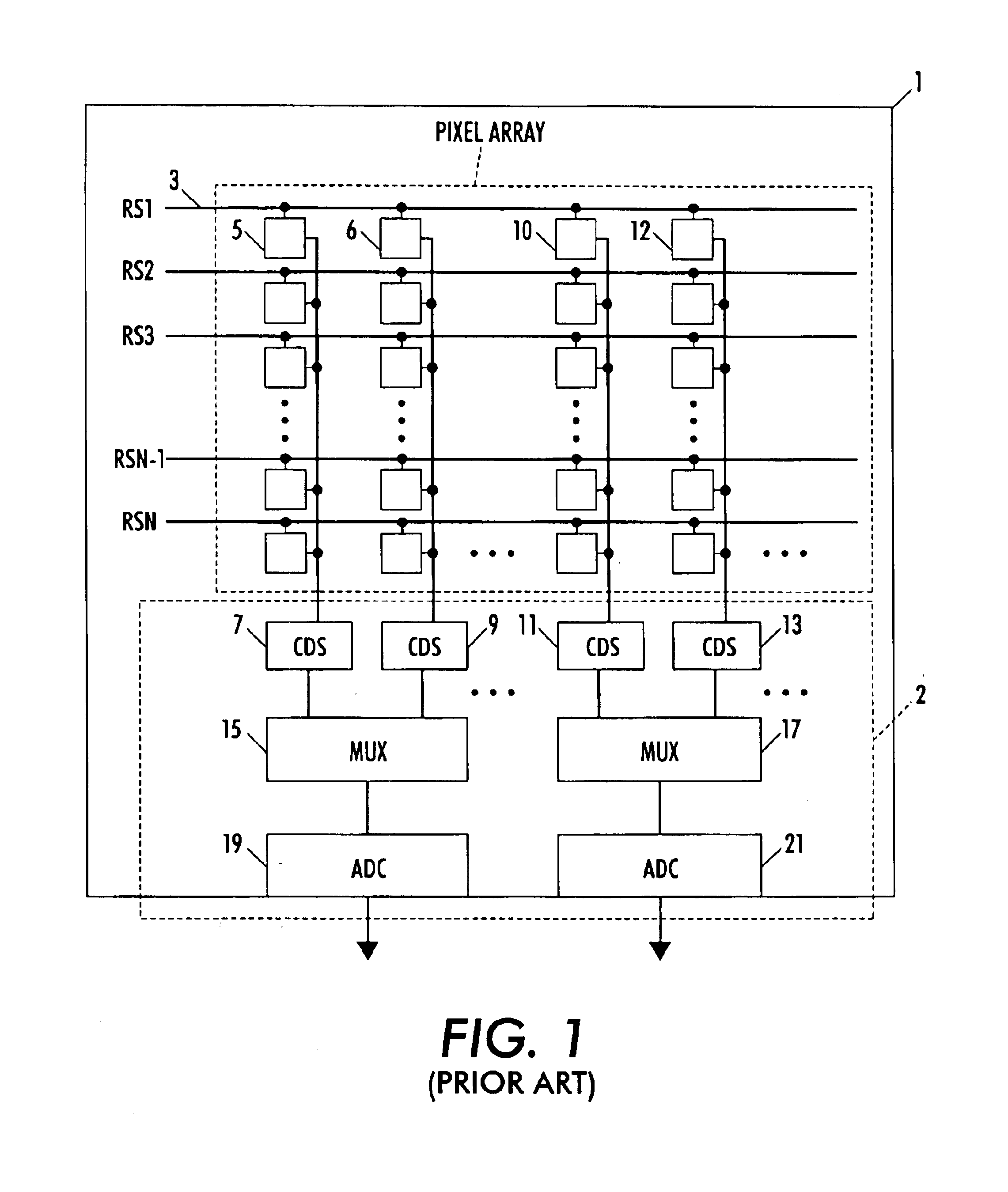
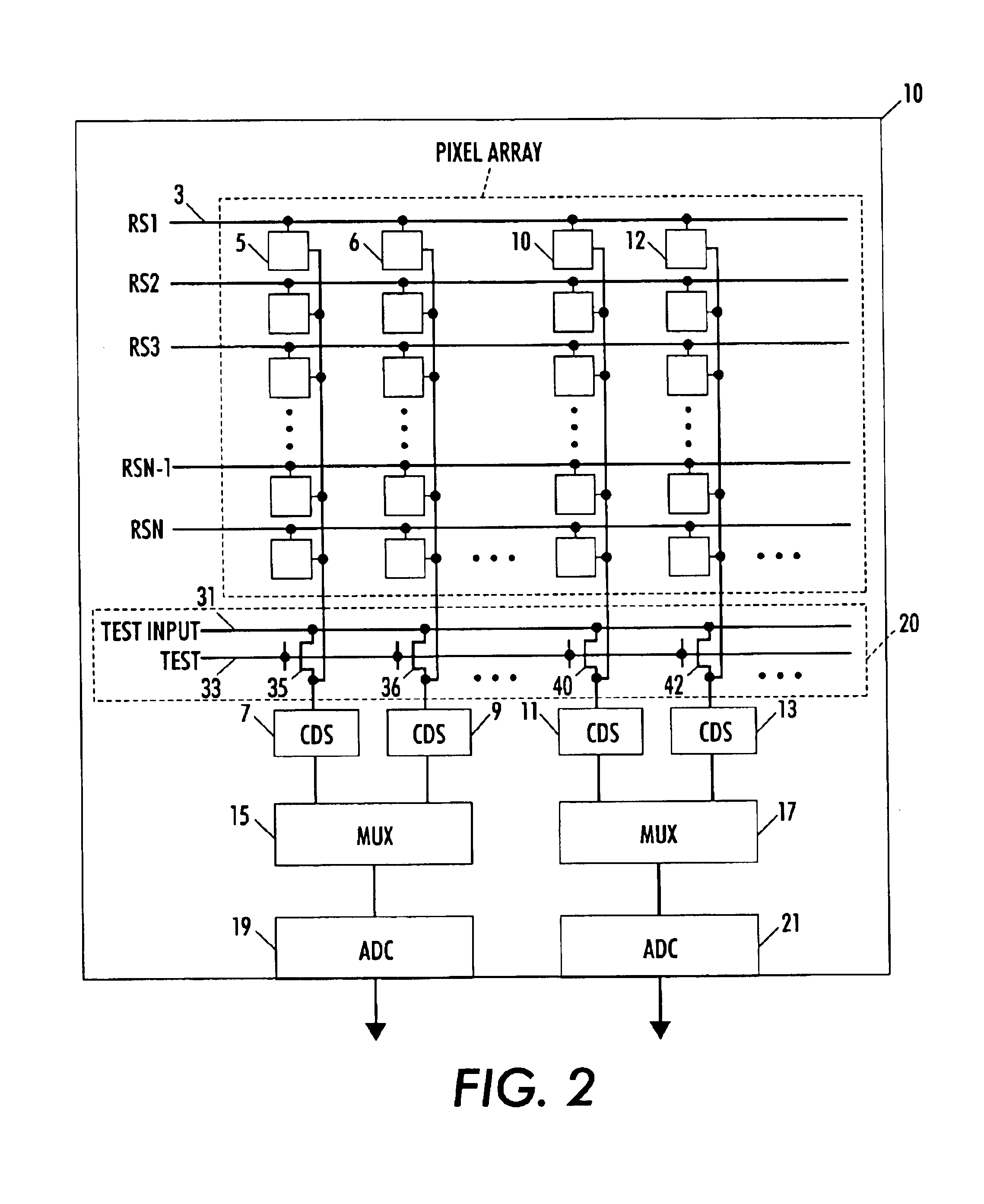
Circuit and method for cancellation of column pattern noise in CMOS imagers
ActiveUS6903670B1Corrects non-linearityCompensating for such errorTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
A circuit and method measure the output voltage of a CMOS pixel in a manner that substantially reduces all columnar pattern noise due to mismatches in the signal processing circuits including the correlated double sampling amplifiers and A / D converters. The circuit includes a test switch, operatively connected between a reference voltage source and a correlated double sampling amplifier, for applying a test voltage from the reference voltage source when the state of the test switch is ON to the correlated double sampling amplifier. The reference voltage source produces a voltage corresponding to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of a gain error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; a voltage corresponding to ground to enable the determination of an offset error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; and a plurality of analog voltages ranging from analog ground to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of non-linearity errors in the A / D converter.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
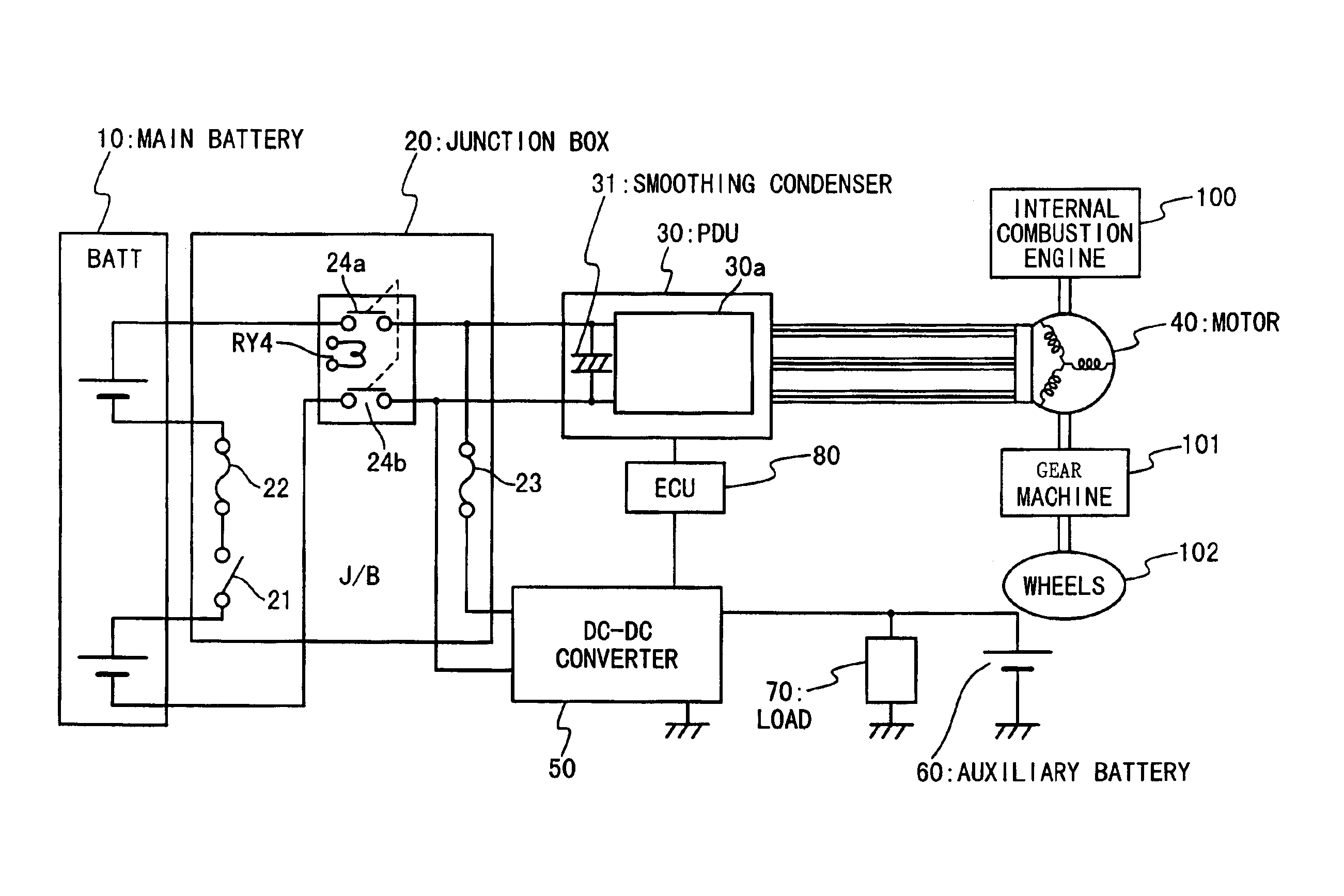
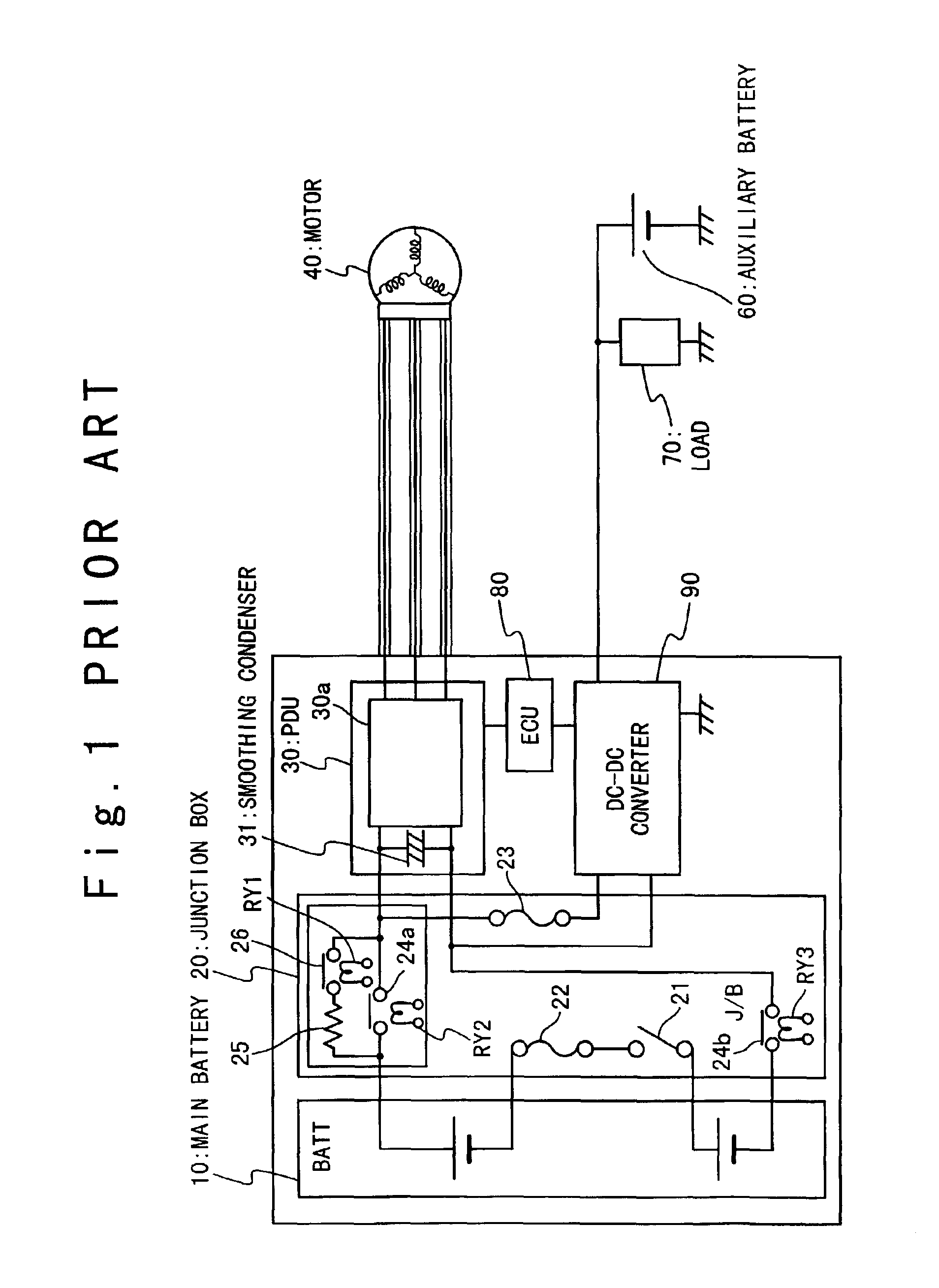
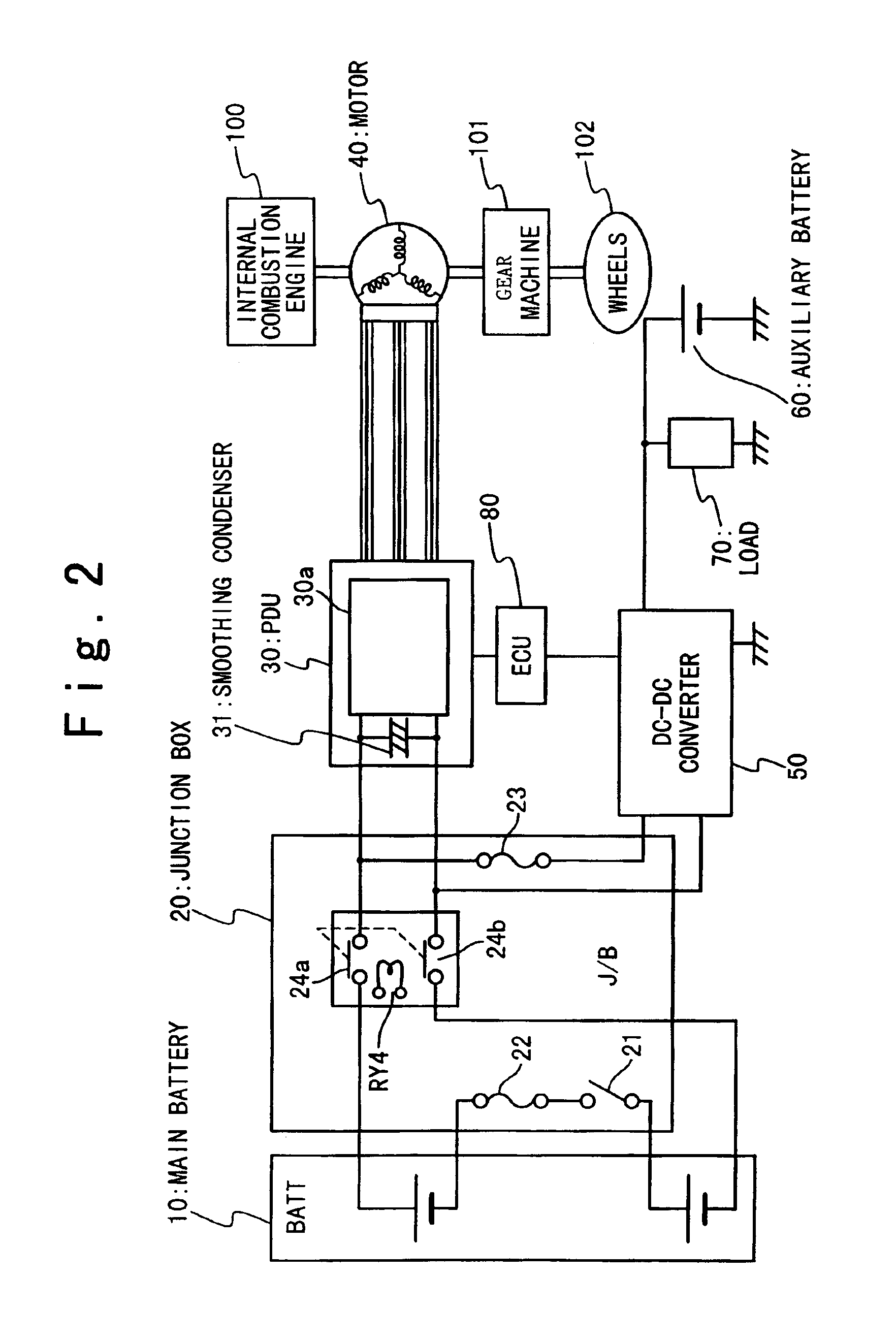
Power supply apparatus and electric vehicle using the same
InactiveUS6923279B2Simple circuit structureReduce supplyHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsPower inverterDc dc converter
In a power supply apparatus for a vehicle, an inverter circuit inputs a voltage from a first battery unit through switches. A smoothing condenser is provided between the first battery unit and the inverter circuit in parallel. A DC-DC converter is provided between the smoothing condenser and a second battery unit to voltage-convert electric energy stored in the first battery unit or the smoothing condenser to supply to the second battery unit, and to voltage-convert electric energy stored in the second battery unit to supply to the smoothing condenser. An electronic control unit controls the DC-DC converter before starting power supply to the inverter circuit, such that the switches are closed after the smoothing condenser is charged to a voltage within a predetermined permission voltage range from the voltage of the first battery unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
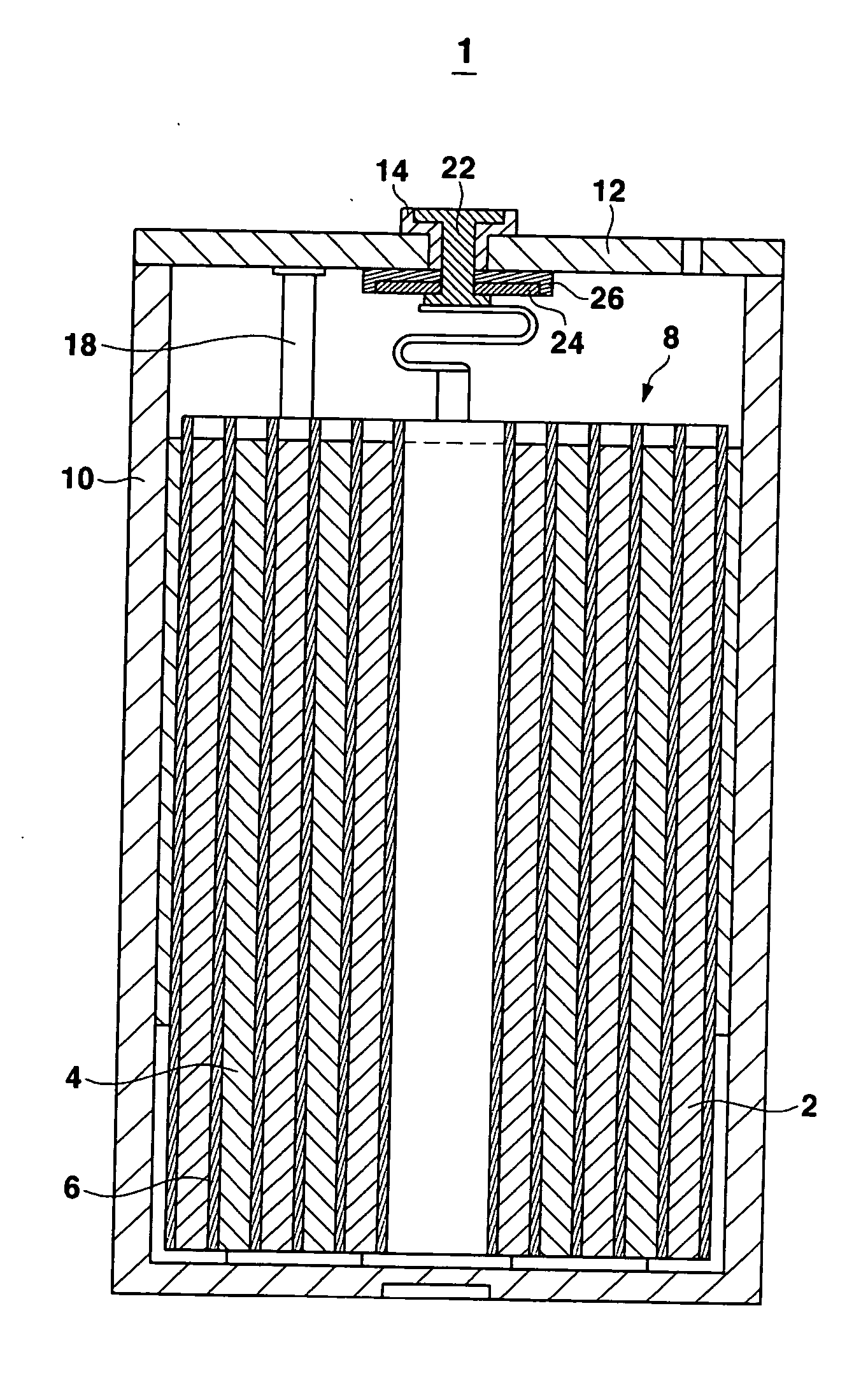
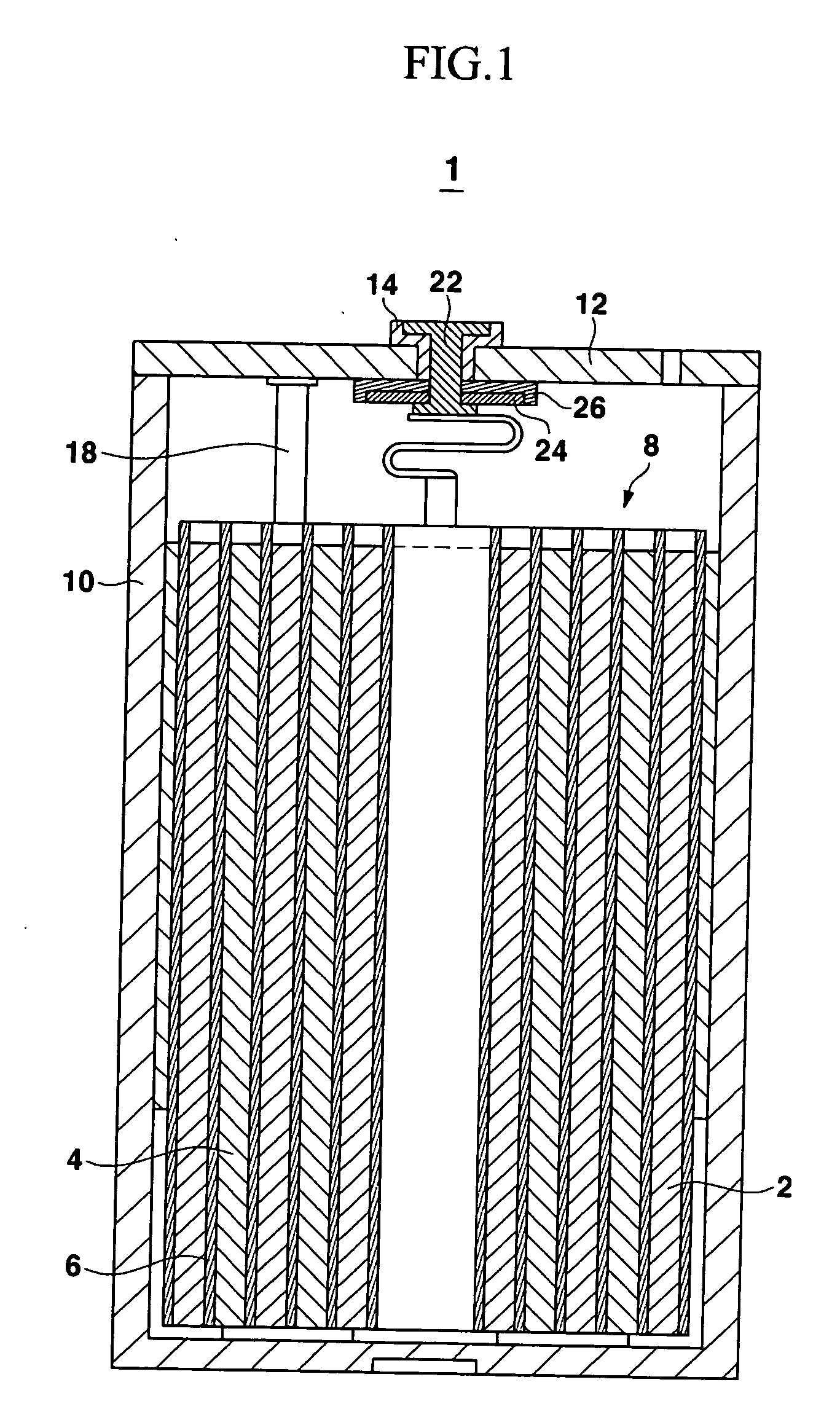
Electrolyte for a lithium battery and a lithium battery comprising the same
InactiveUS20060194118A1Improve battery safetyOrganic electrolyte cellsFurniture partsOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
The present invention relates to an electrolyte for a lithium battery and a lithium battery comprising the same. The electrolyte includes a non-aqueous organic solvent, a lithium salt, and a first additive capable of forming a chelating complex with a transition metal and which is stable at voltages ranging from about 2.5 to about 4.8 V.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
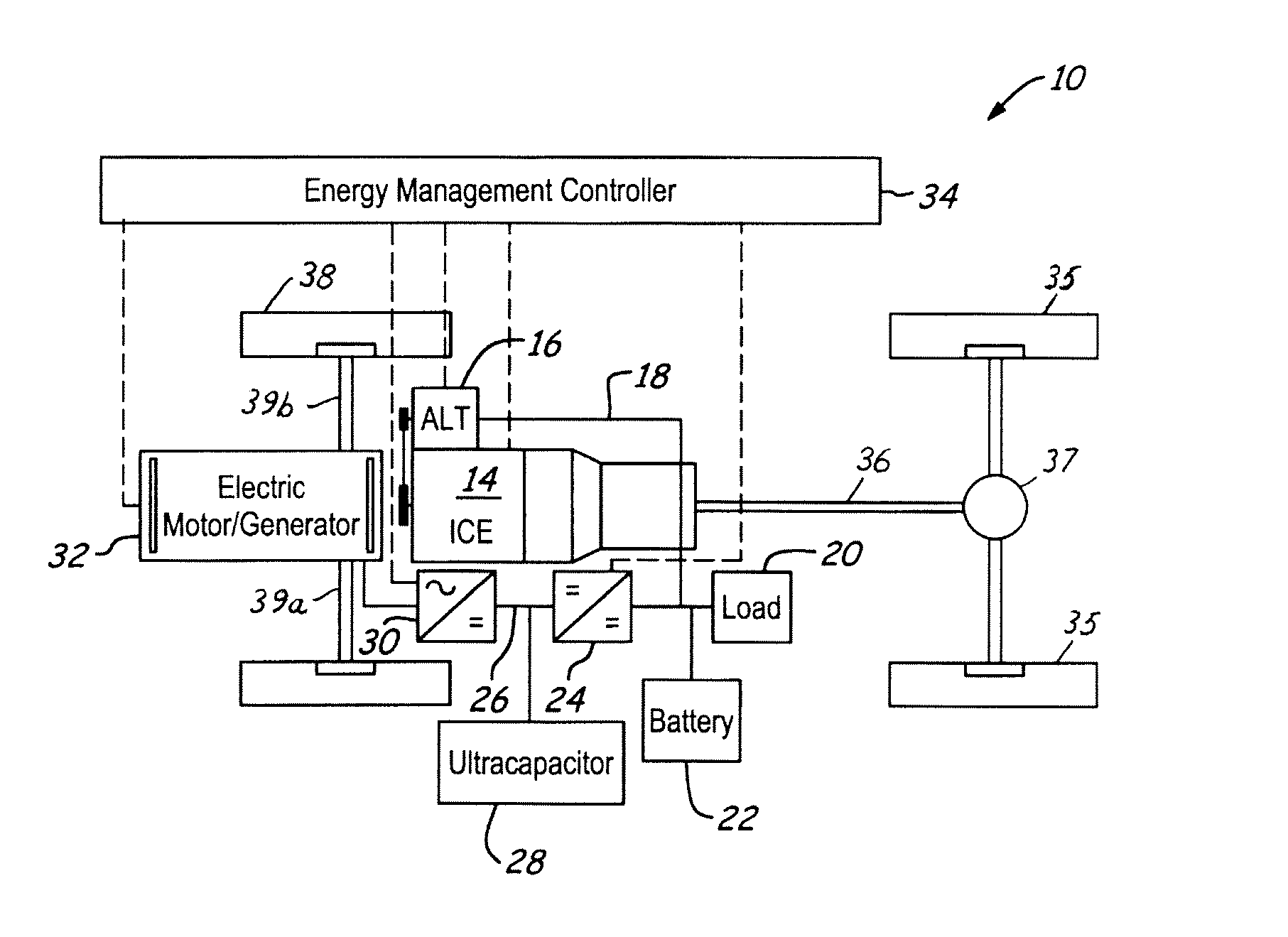
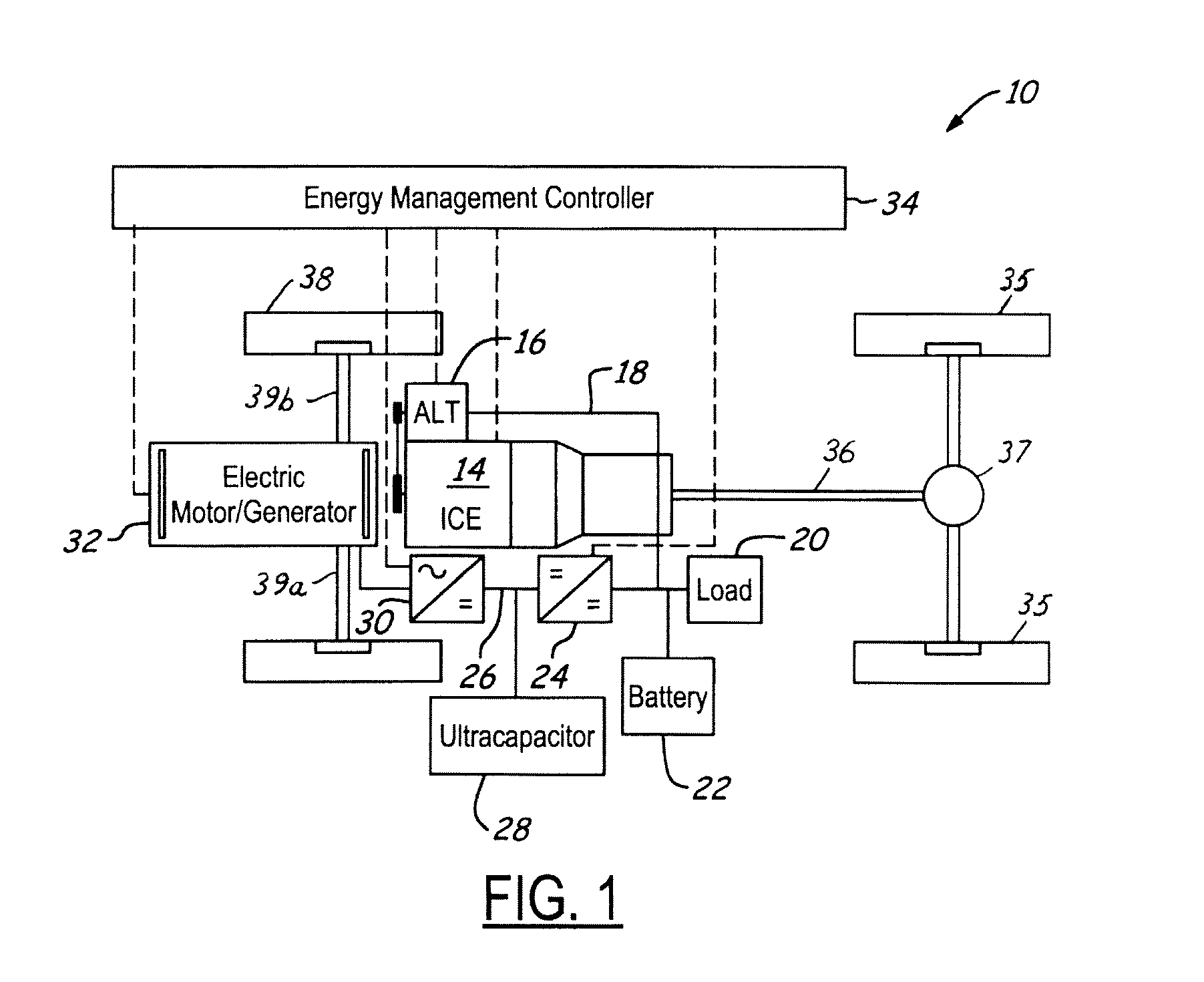
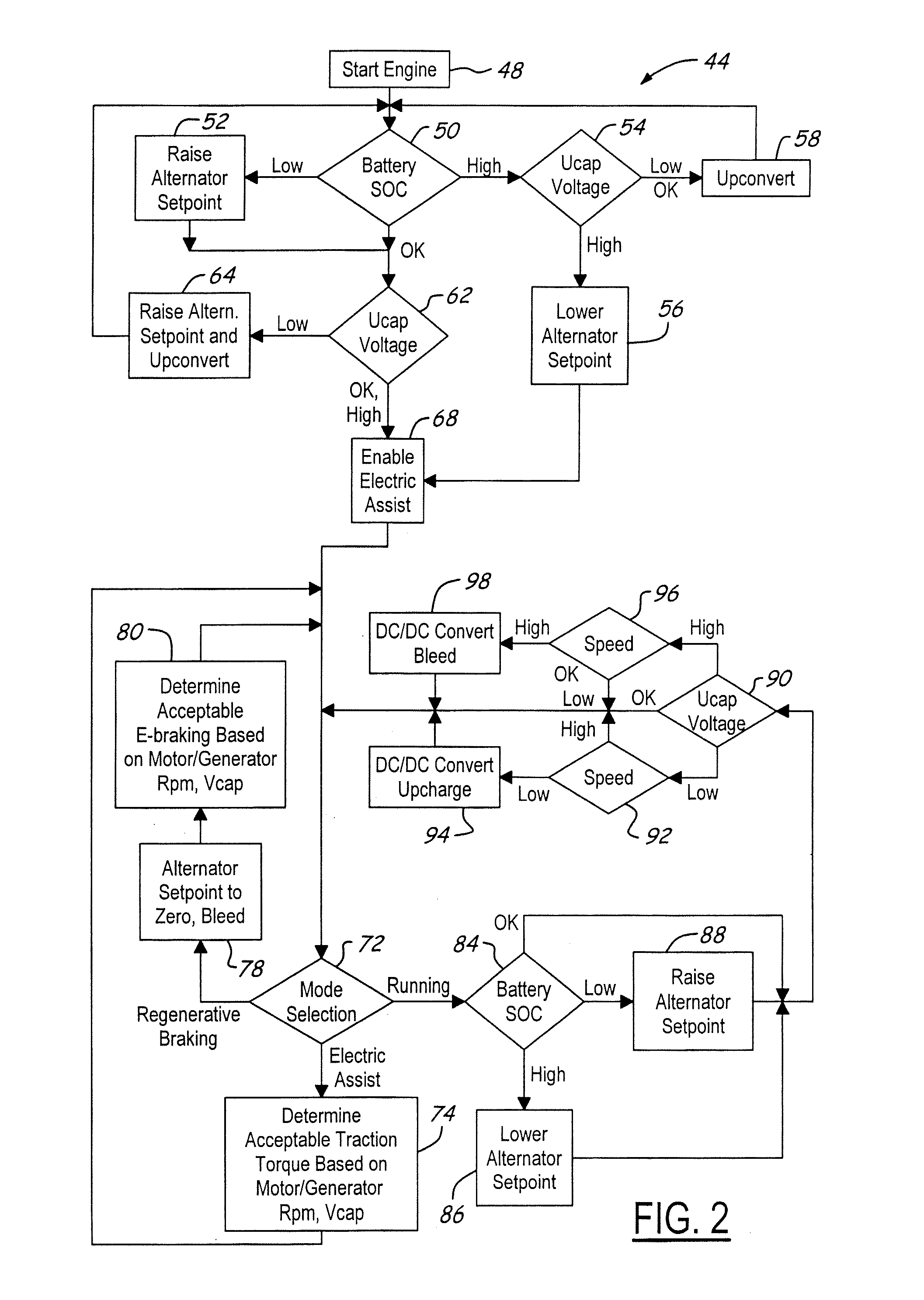
Stabilized electric distribution system for use with a vehicle having electric assist
A stabilized electric distribution system for use in a vehicle having electric assist. The system electrically couples an electric assist bus to an accessory load bus while protecting the first electrical bus from electric assist and regenerative braking induced voltage variations. An energy management controller selectively controls each of a electric motor / generator, a DC / DC converter, and an alternator to affect electric energy distribution within the system. Preferably, the electric energy distribution is controlled to maintain the first electrical bus voltage within a predefined voltage range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Semiconductor structure having n-channel channel-junction field-effect transistor
ActiveUS7176530B1Large noise reductionEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor technology combines a normally off n-channel channel-junction insulated-gate field-effect transistor (“IGFET”) (104) and an n-channel surface-channel IGFET (100 or 160) to reduce low-frequency 1 / f noise. The channel-junction IGFET is normally of materially greater gate dielectric thickness than the surface-channel IGFET so as to operate across a greater voltage range than the surface-channel IGFET. Alternatively or additionally, the channel-junction IGFET may conduct current through a field-induced surface channel. A p-channel surface-channel IGFET (102 or 162), which is typically of approximately the same gate-dielectric thickness as the n-channel surface-channel IGFET, is preferably combined with the two n-channel IGFETs to produce a complementary-IGFET structure. A further p-channel IGFET (106, 180, 184, or 192), which is typically of approximately the same gate dielectric thickness as the n-channel channel-junction IGFET, is also preferably included. The further p-channel IGFET can be a surface-channel or channel-junction device.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Programmable Light Display
ActiveUS20090051506A1Lower impedanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOperation modeEngineering
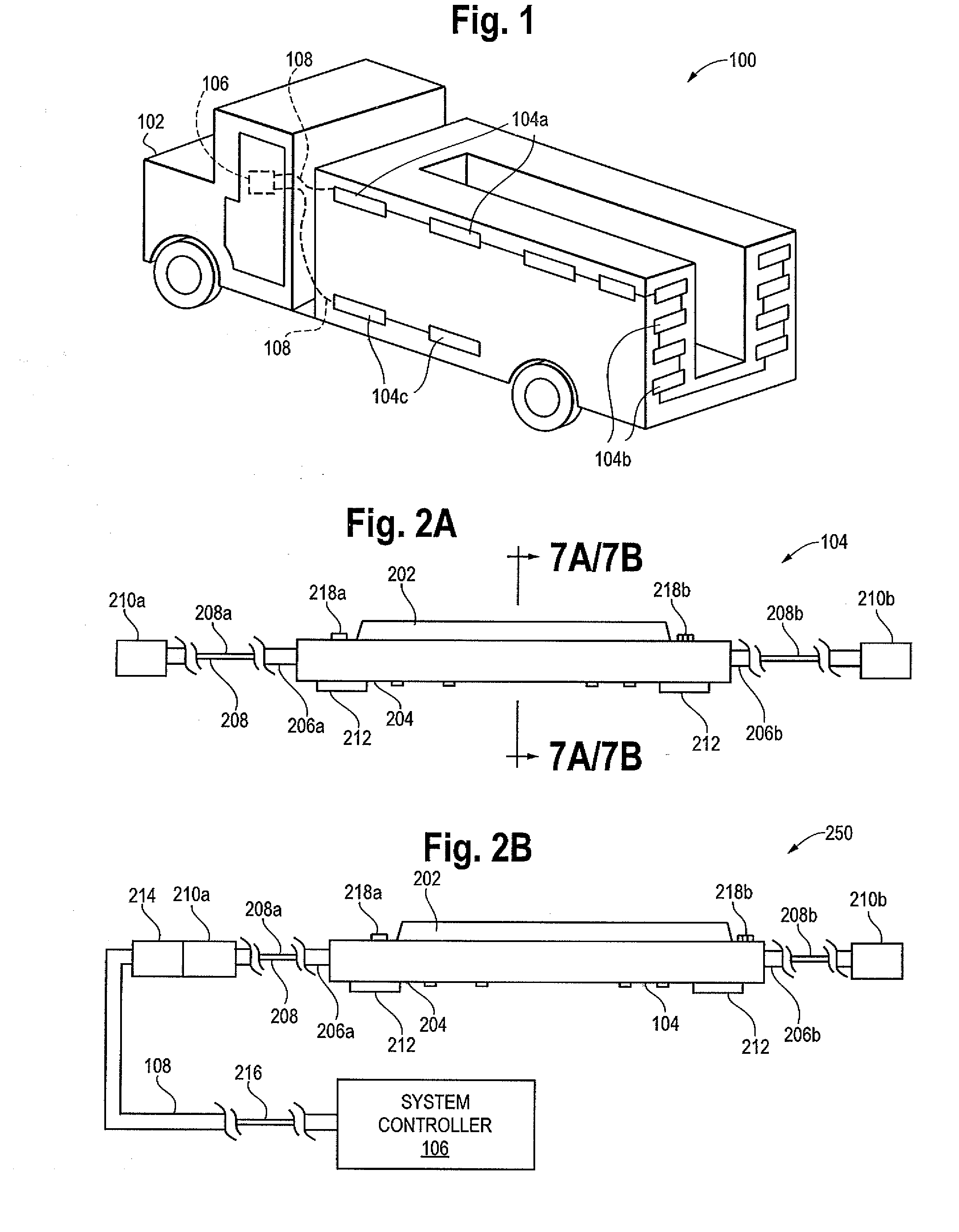
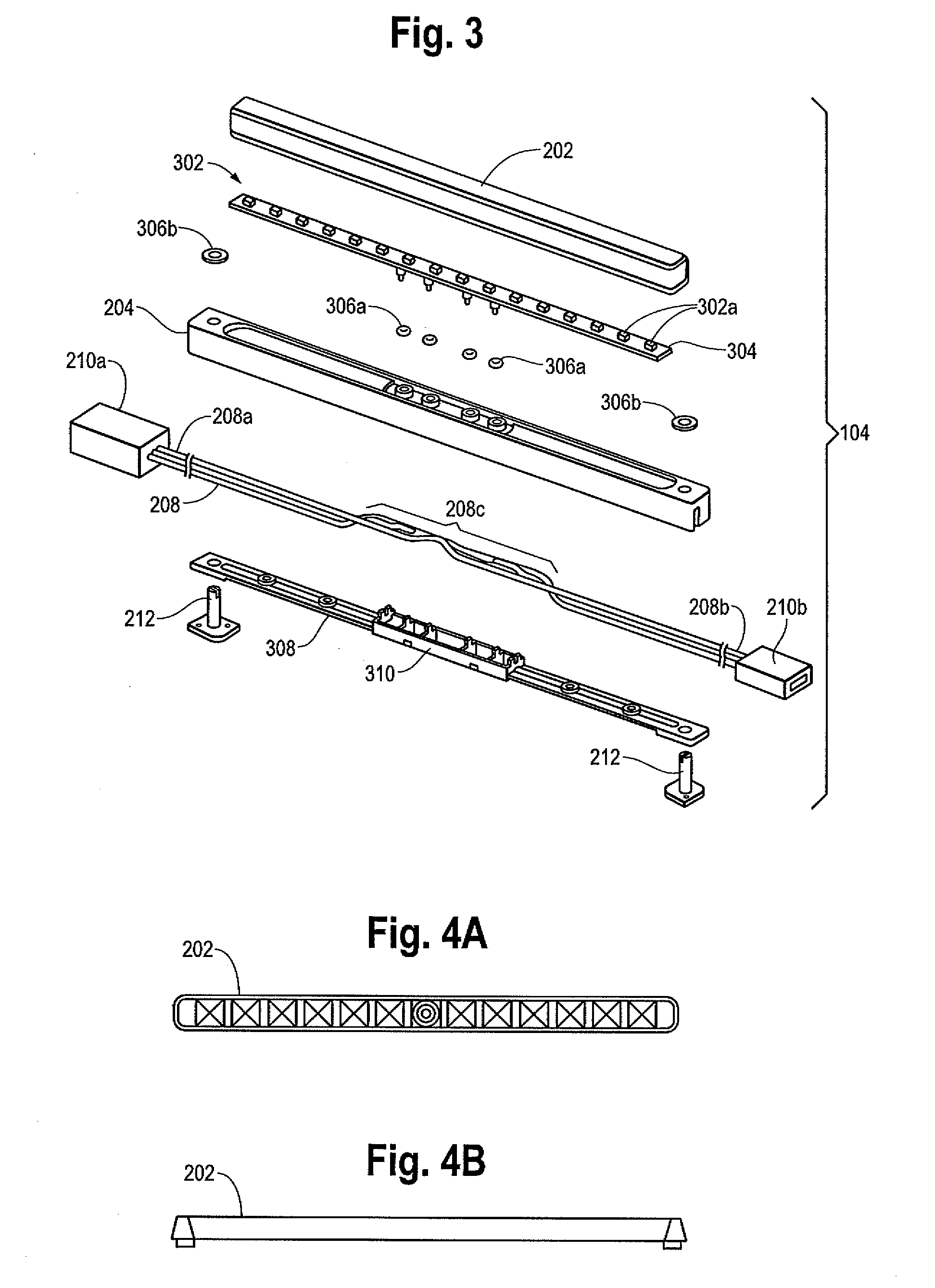
Programmable light assemblies that may function in various operating modes, such as to function as marker lights and / or emergency lights, or have other functions, are disclosed. The protocol and architecture of the light assemblies enables the associated light fixtures to provide a constant current output despite the presence of substantially large voltage ranges, and even when submerged in water. Alternative embodiments of the programmable light assemblies of the invention provide many other features as described herein.
Owner:SONOMA CIRCUITS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com