Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1649results about "Gated amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
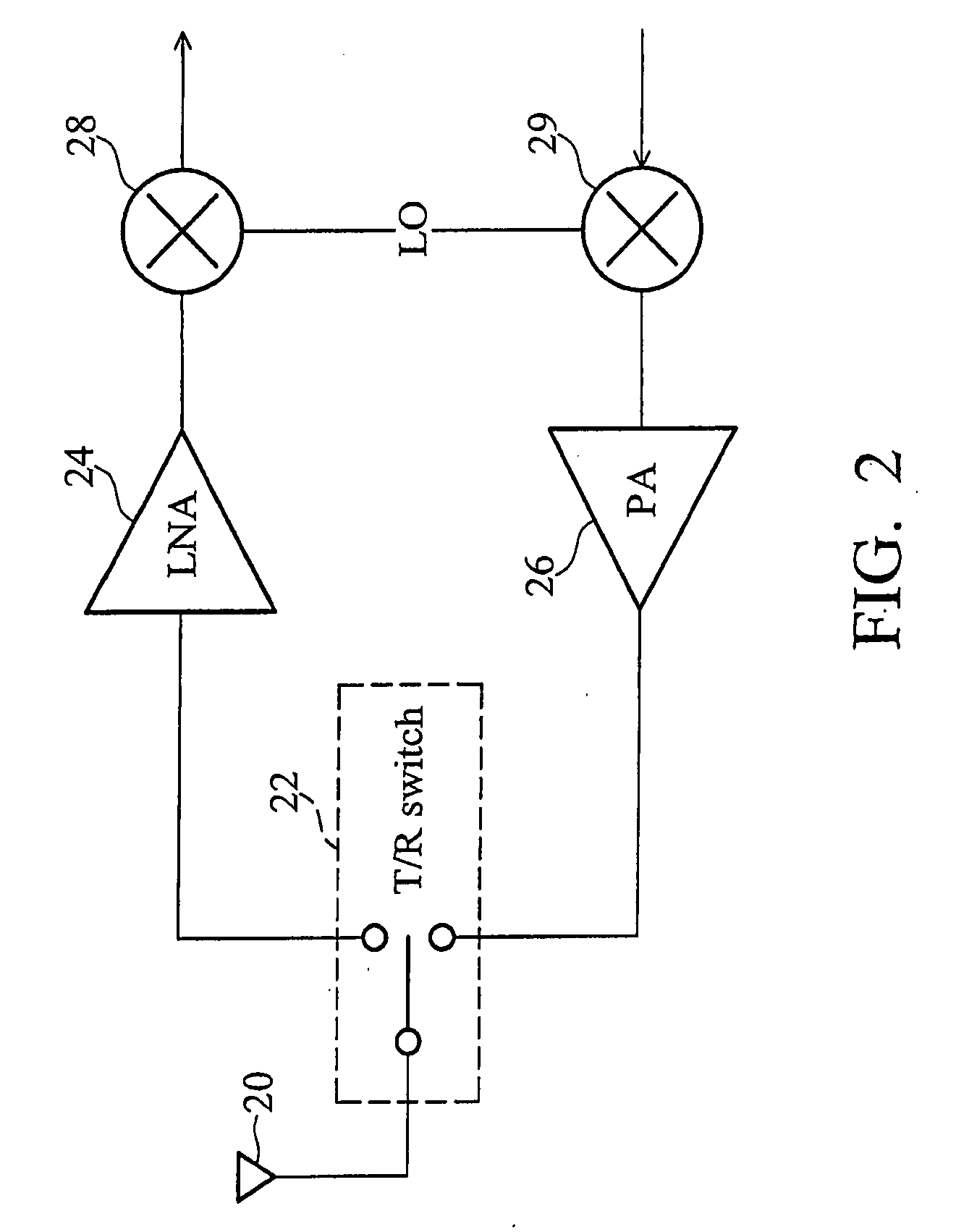
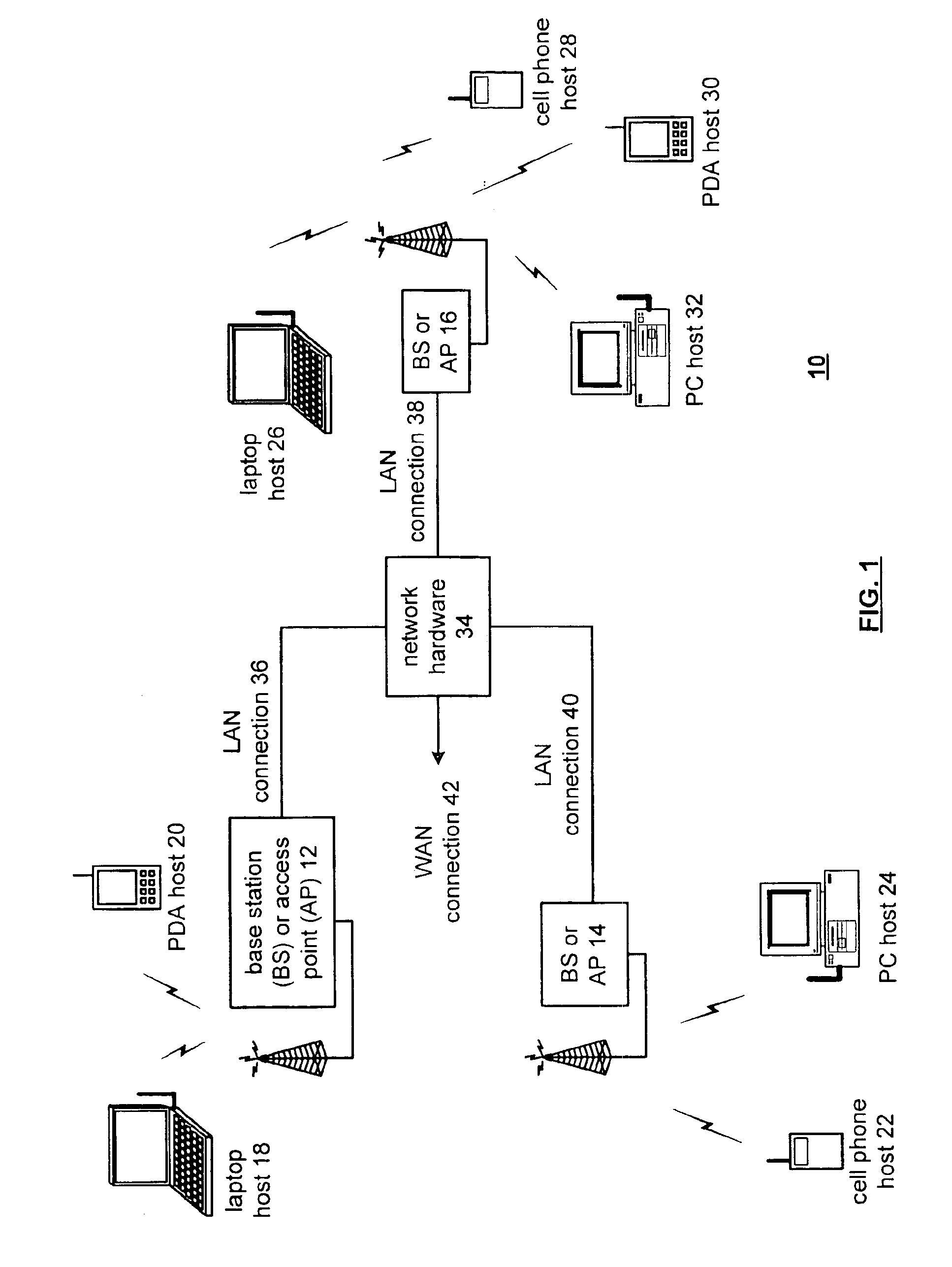
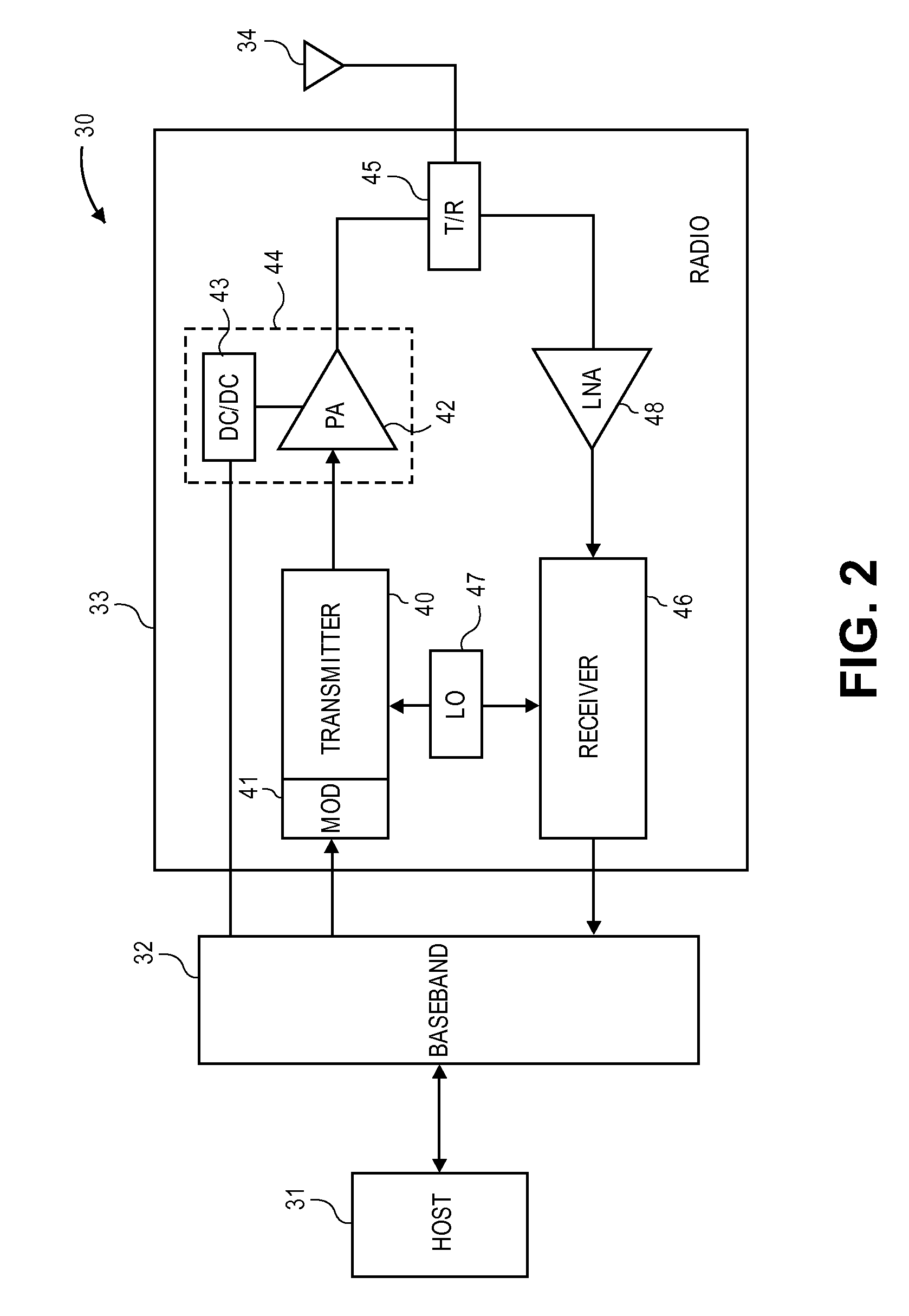
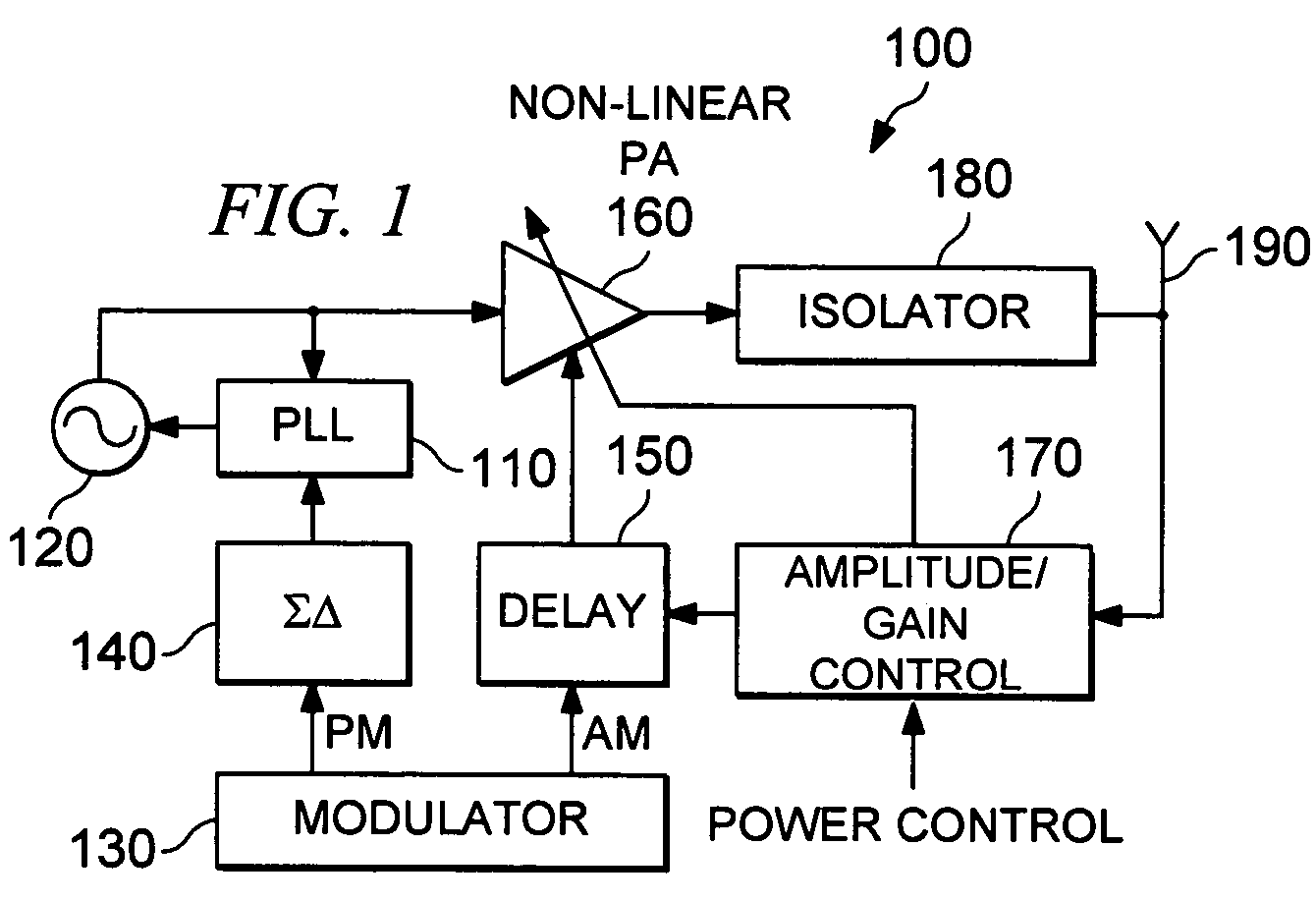
Transmit/receive switch
ActiveUS20090036065A1Reduce noiseMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasEngineeringImpedance matching
A radio frequency (RF) transmit / receive switch. The transmit / receive switch comprises an impedance matching circuit and a voltage scaling circuit. The impedance matching circuit matches an incoming RF signal to a low noise amplifier and an outgoing RF signal from a power amplifier. The voltage scaling circuit, coupled to the impedance matching circuit, the power amplifier, and the low noise amplifier, attenuates the outgoing RF signal to a scaled signal within a breakdown voltage of a transistor device in the low noise amplifier during transmission of the outgoing RF signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK USA INC
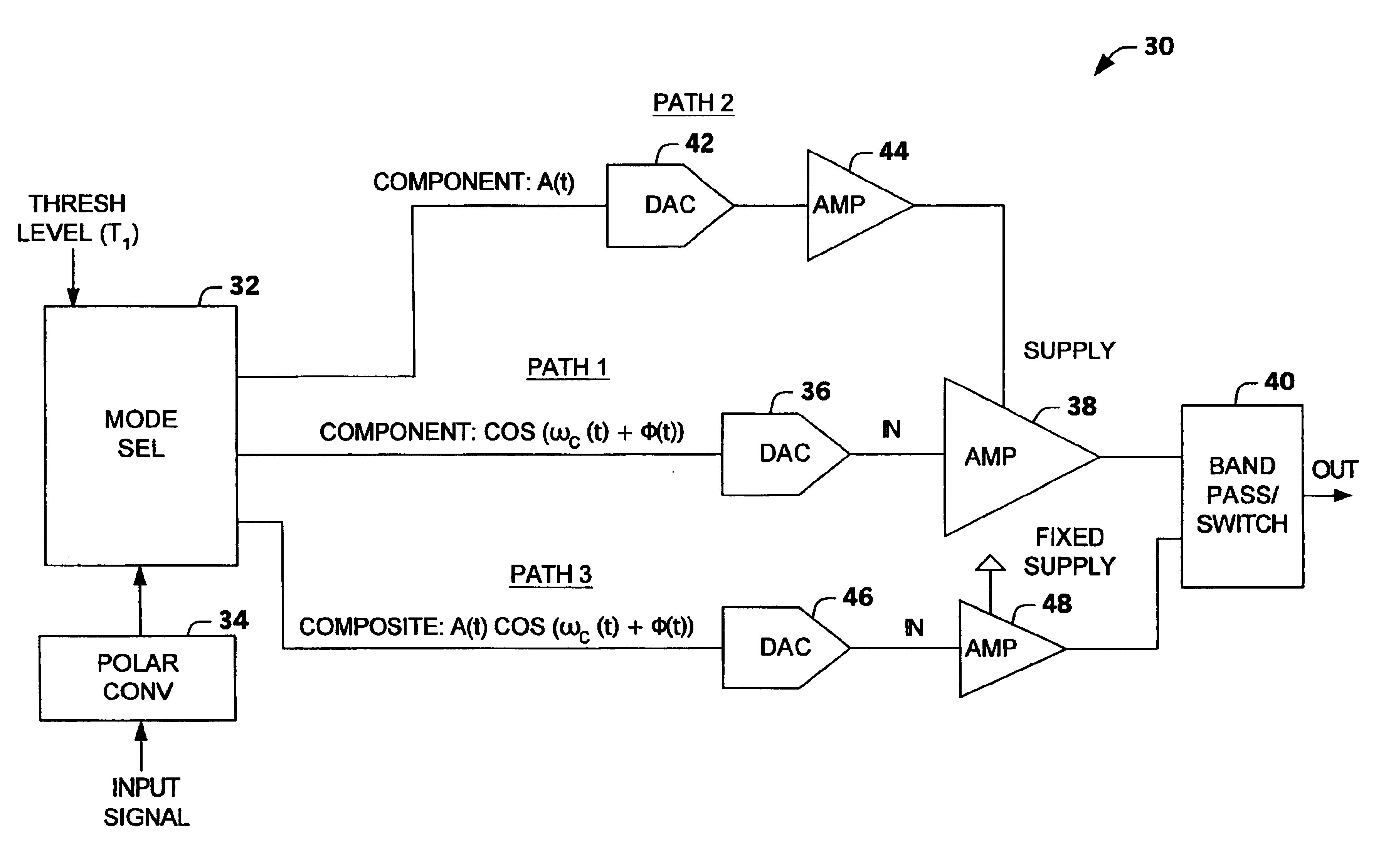
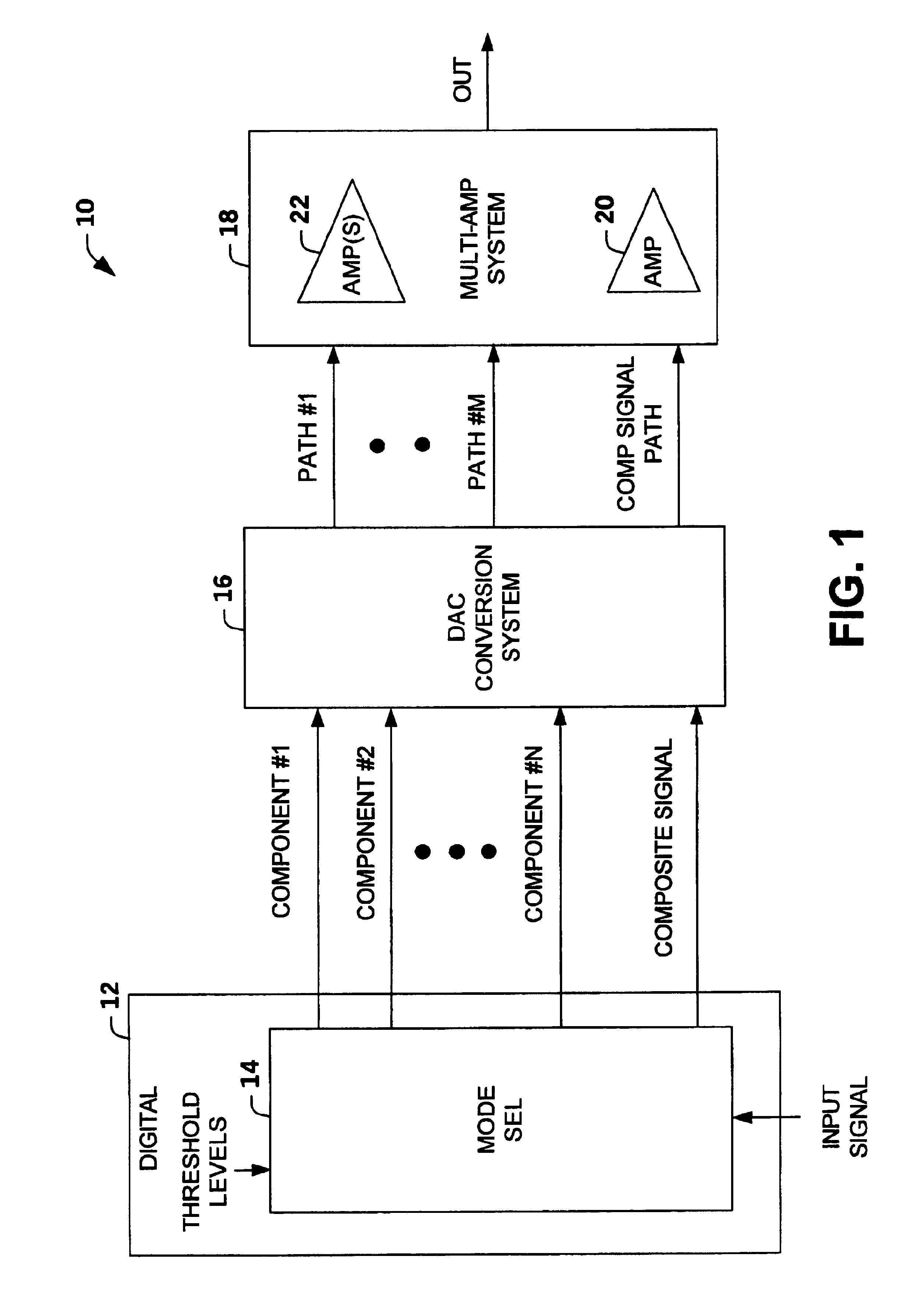
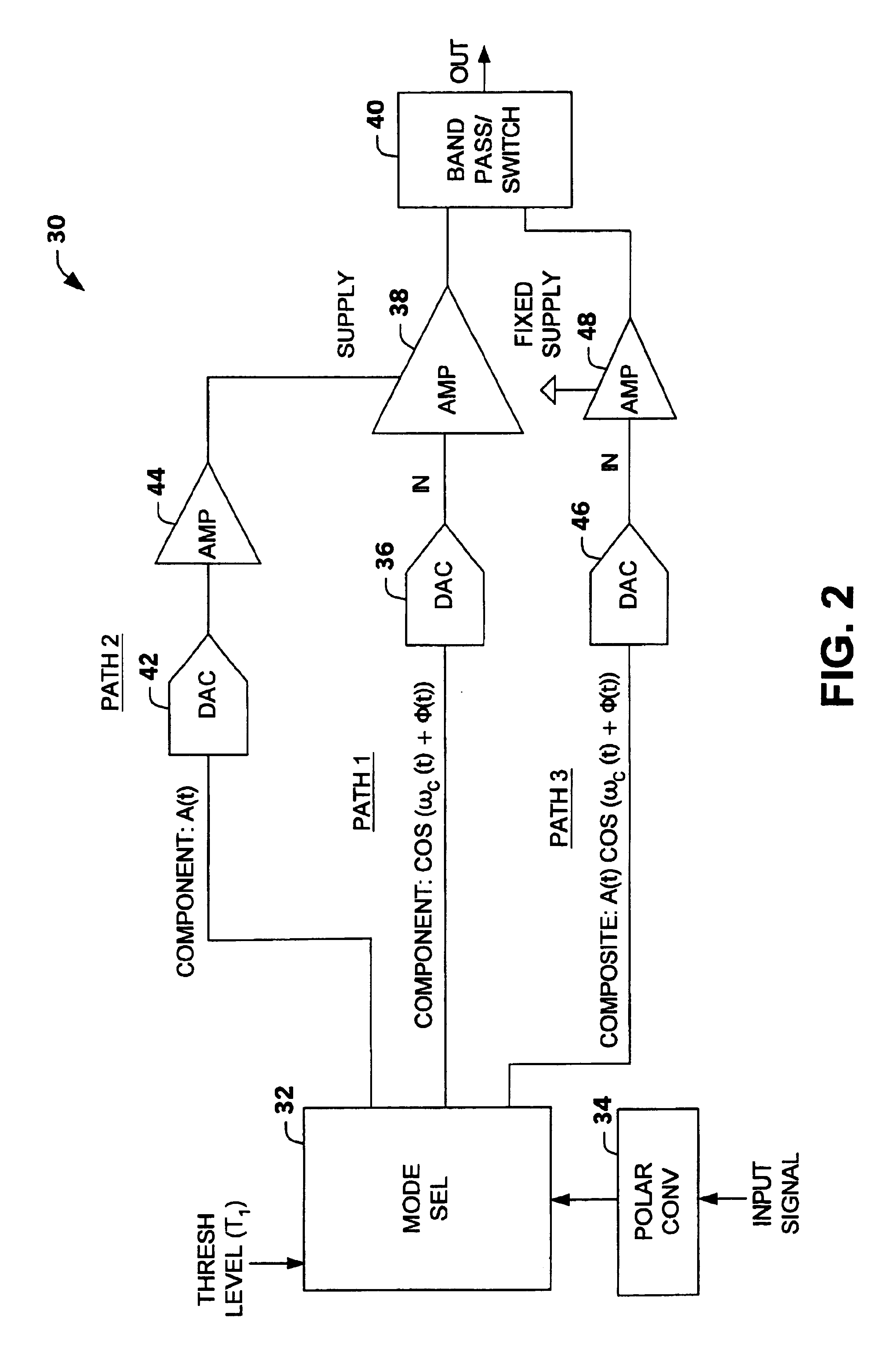
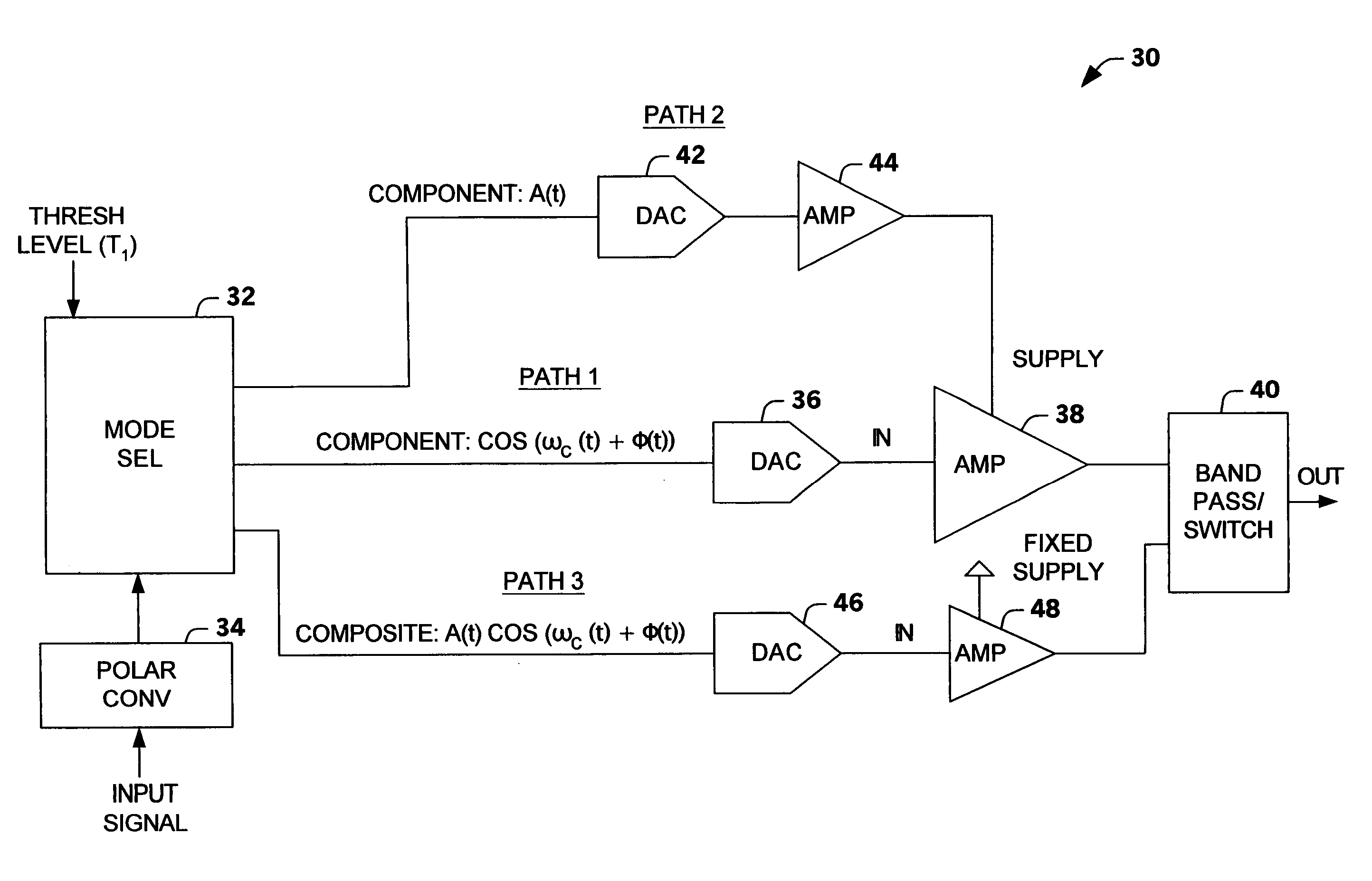
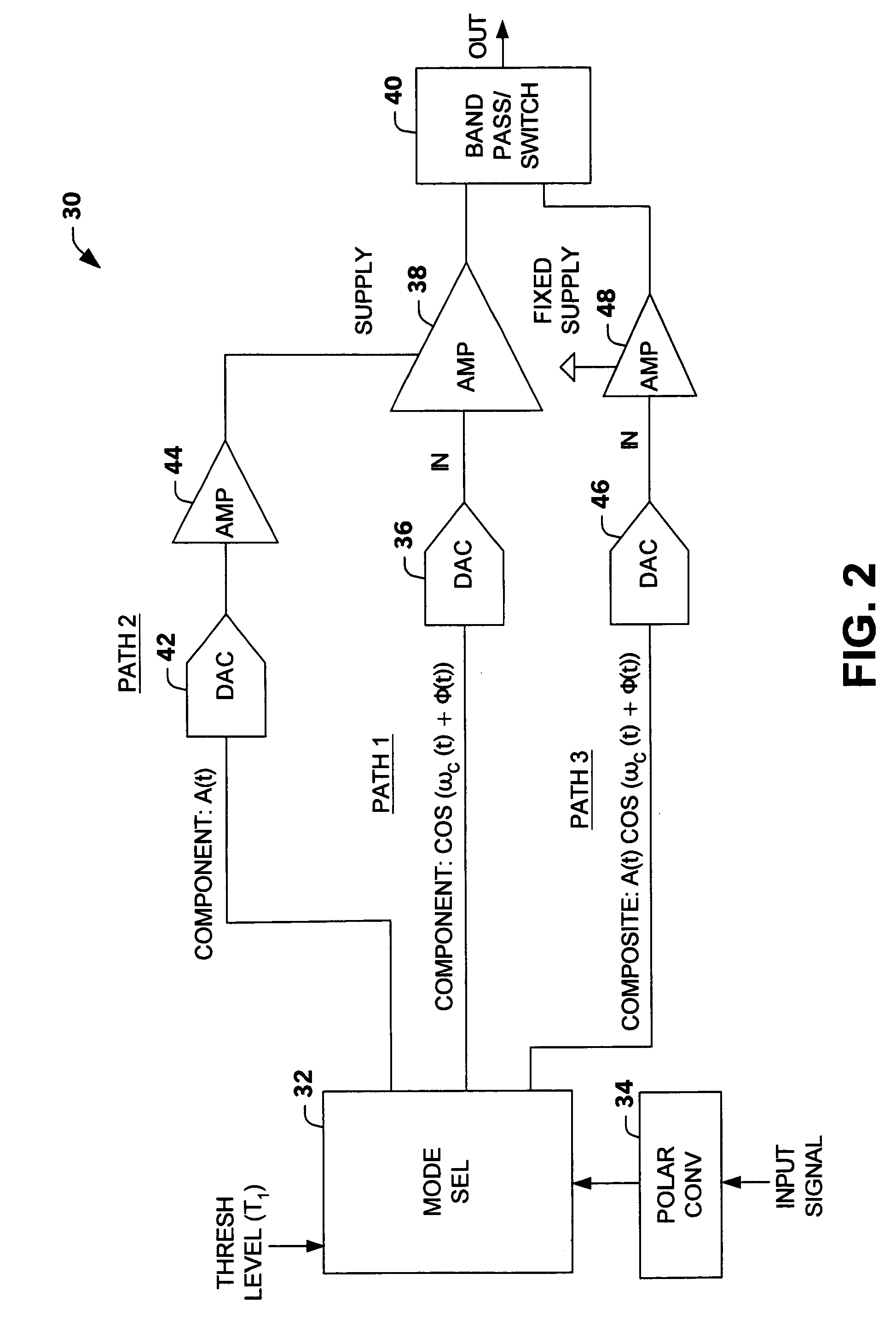
Multi-mode multi-amplifier architecture
InactiveUS6853244B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplification architecture or system is provided having a multiple amplifier system that switches modes of operation between operation in a component mode and a composite mode based on a characteristic of an input signal relative to a threshold level. In the component mode, the components of the input signal are employed to different terminals of the multiple amplifier system that provide a reconstructed amplified representation of the input signal. In the composite mode, the input signal is amplified to provide an amplified representation of the input signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
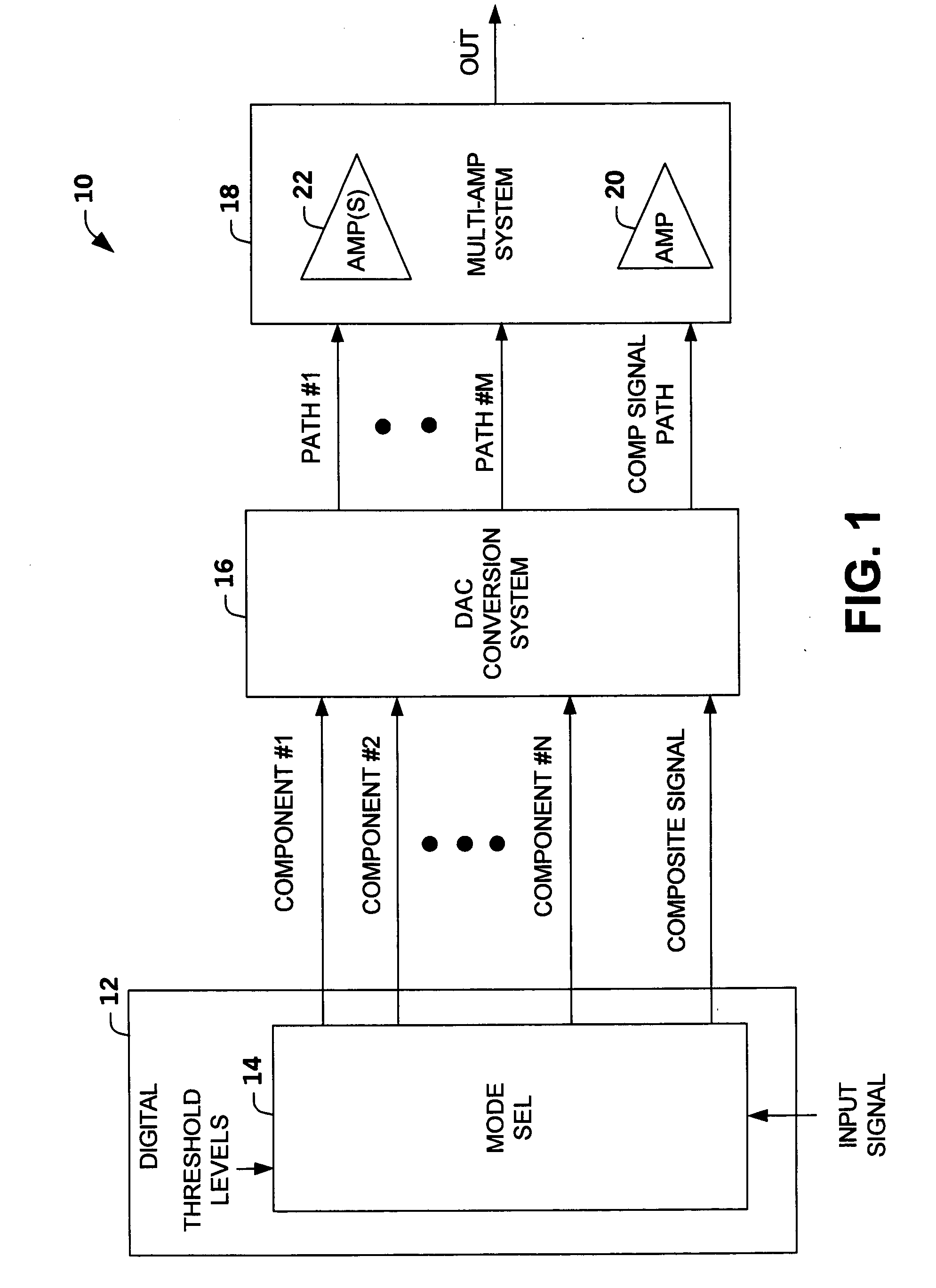
Multi-mode multi-amplifier architecture
InactiveUS20040263246A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplification architecture or system is provided having a multiple amplifier system that switches modes of operation between operation in a component mode and a composite mode based on a characteristic of an input signal relative to a threshold level. In the component mode, the components of the input signal are employed to different terminals of the multiple amplifier system that provide a reconstructed amplified representation of the input signal. In the composite mode, the input signal is amplified to provide an amplified representation of the input signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
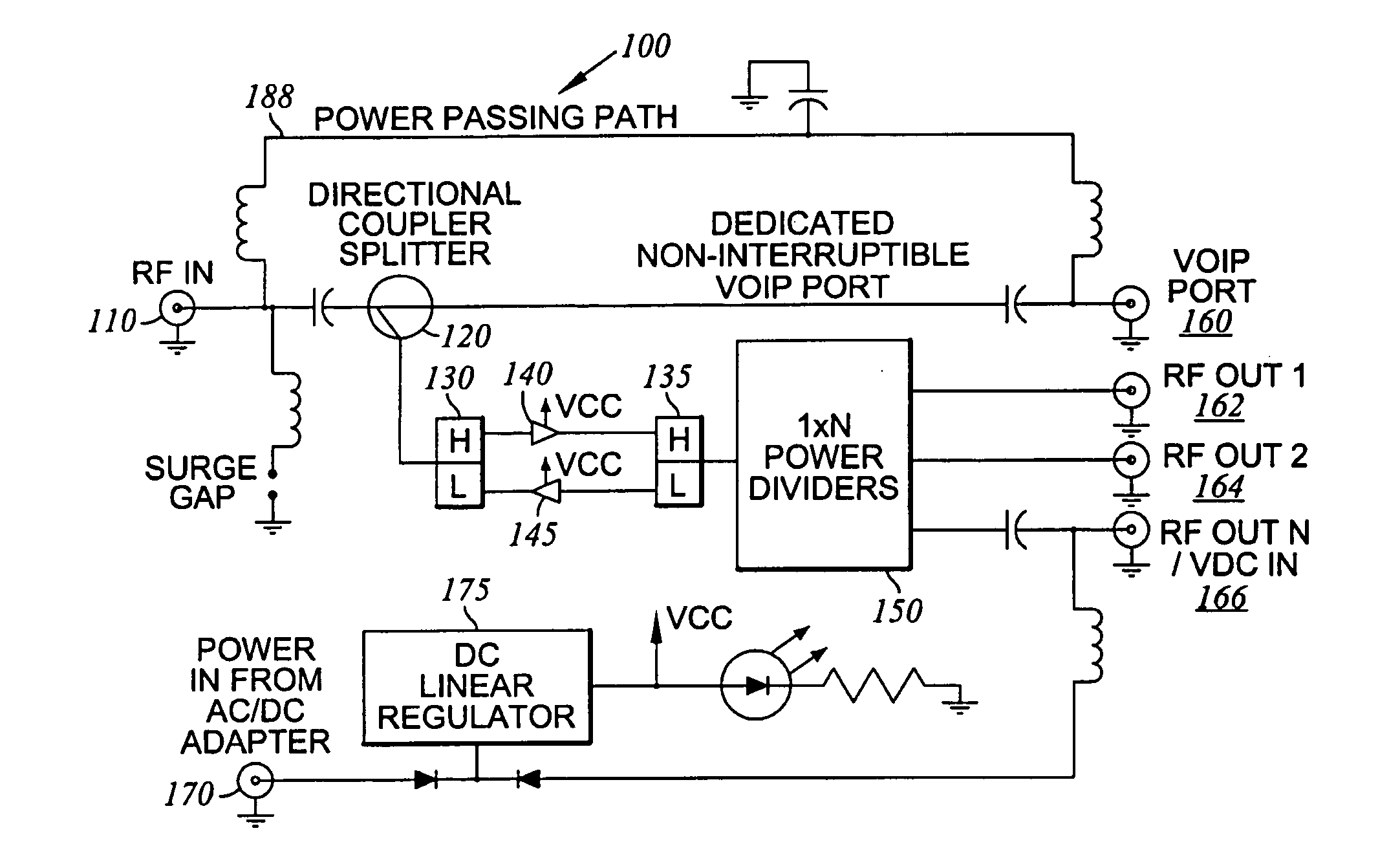
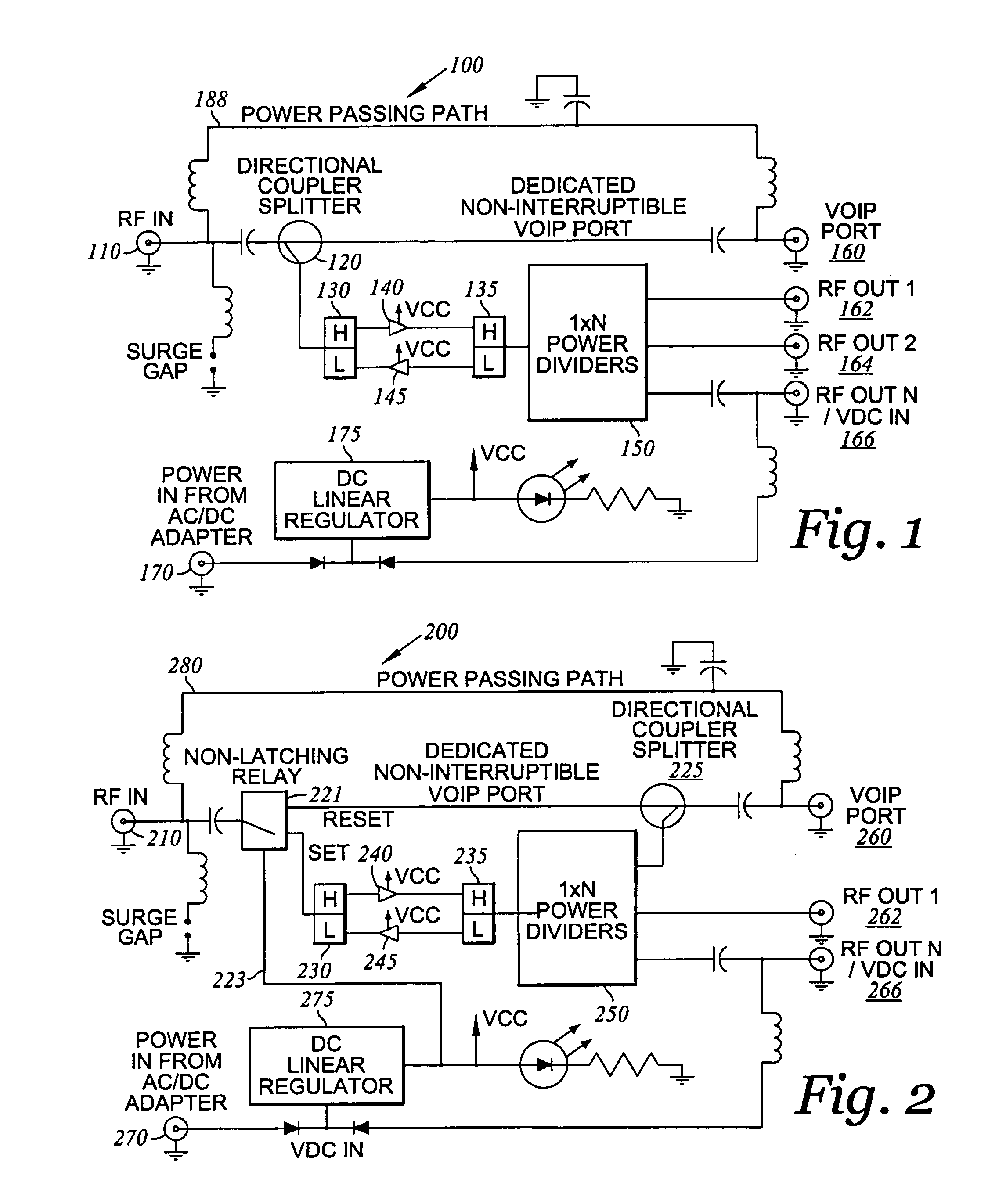
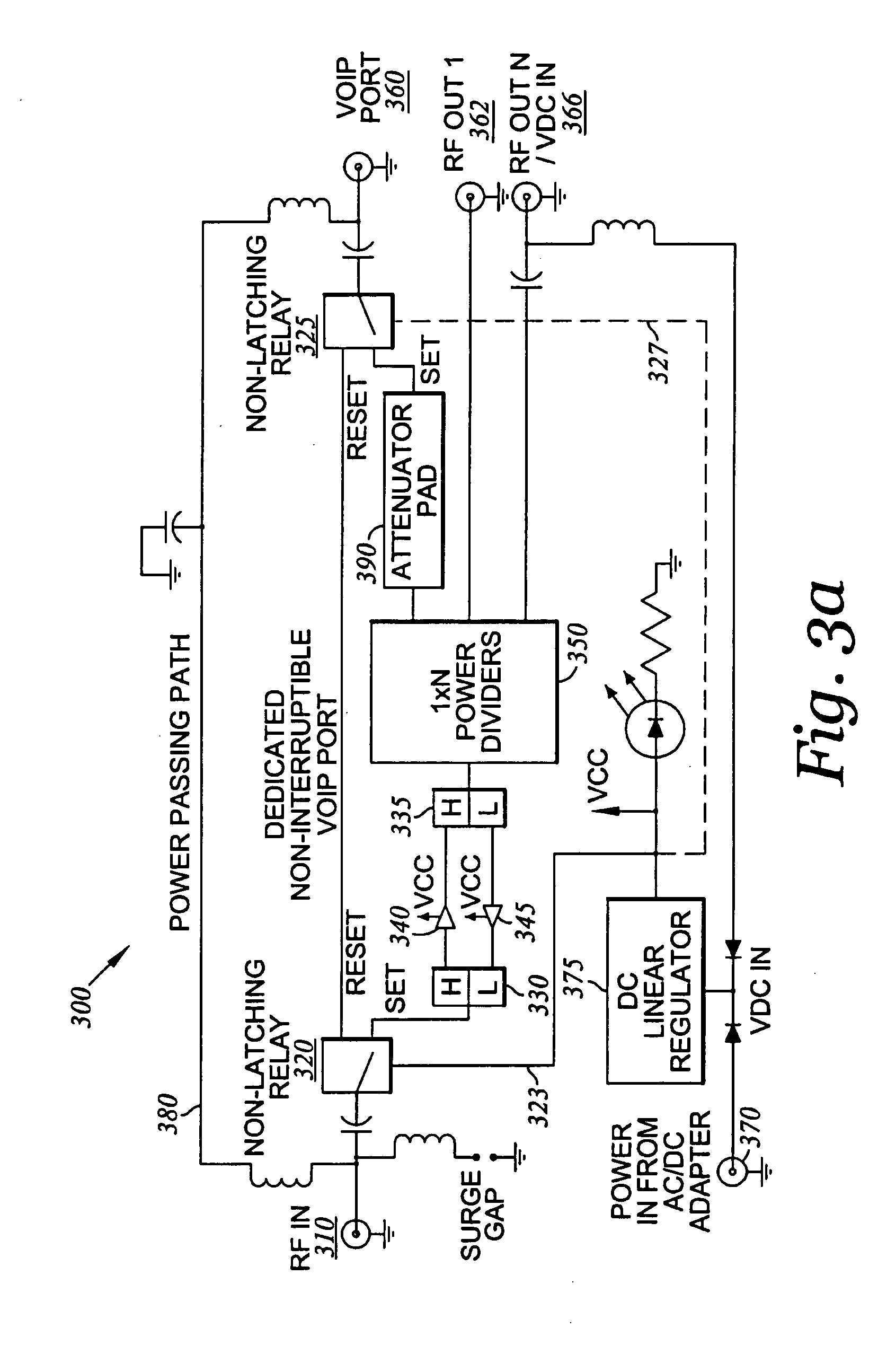
Bi-directional amplifier with non-interruptible port
InactiveUS20060205442A1Facilitate communicationGated amplifiersTwo-way amplifiersAudio power amplifierService provision
A bi-directional RF signal amplifier can be provided with a non-interruptible communication path for maintaining communication between an input and output port in the event of power failure. The amplifier may receive RF signals from a service provider or any other appropriate signal source through an input port. In residential applications, the amplifier may receive a composite RF signal comprising information for telephone, cable television (CATV), Internet, VoIP, and / or data communication from a service provider. The amplifier may increase the signal to a more useful level of approximately 20 dBmV / carrier and pass the amplified signal to one or more devices in communication with the amplifier through various output ports. In the event of power failure, a signal may still be passed through the non-interruptible communication path between the service provider and the communication device.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
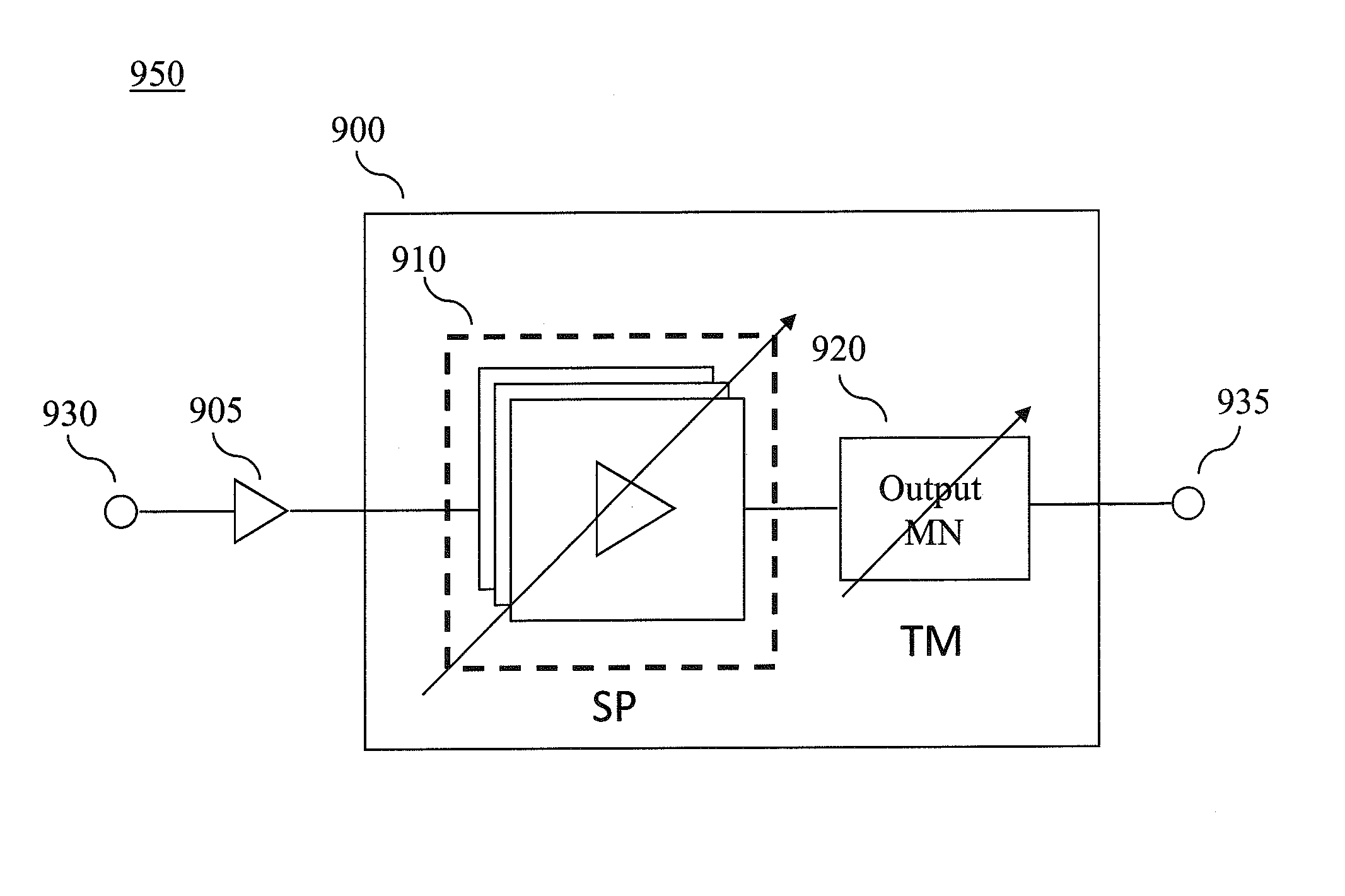
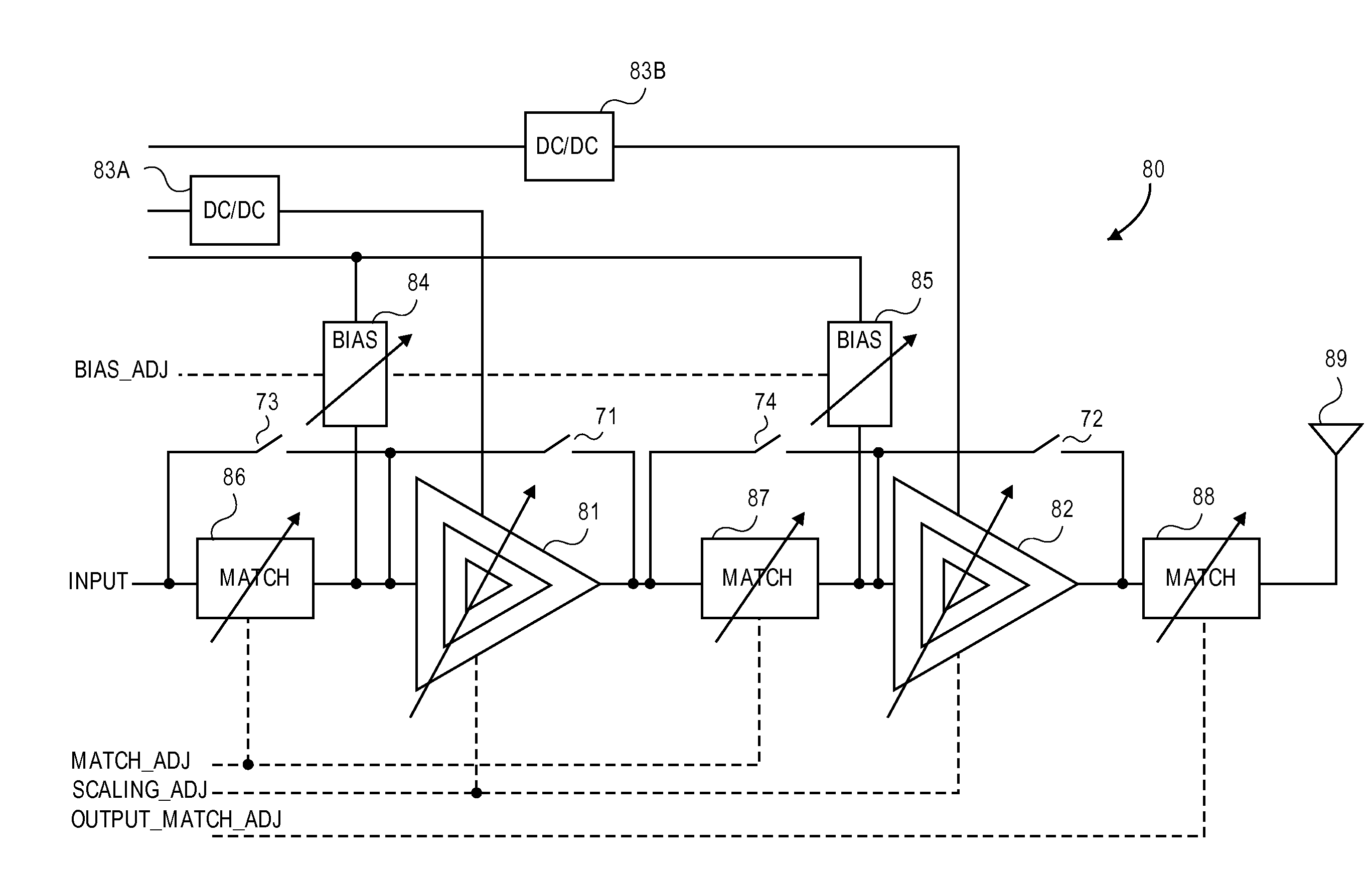
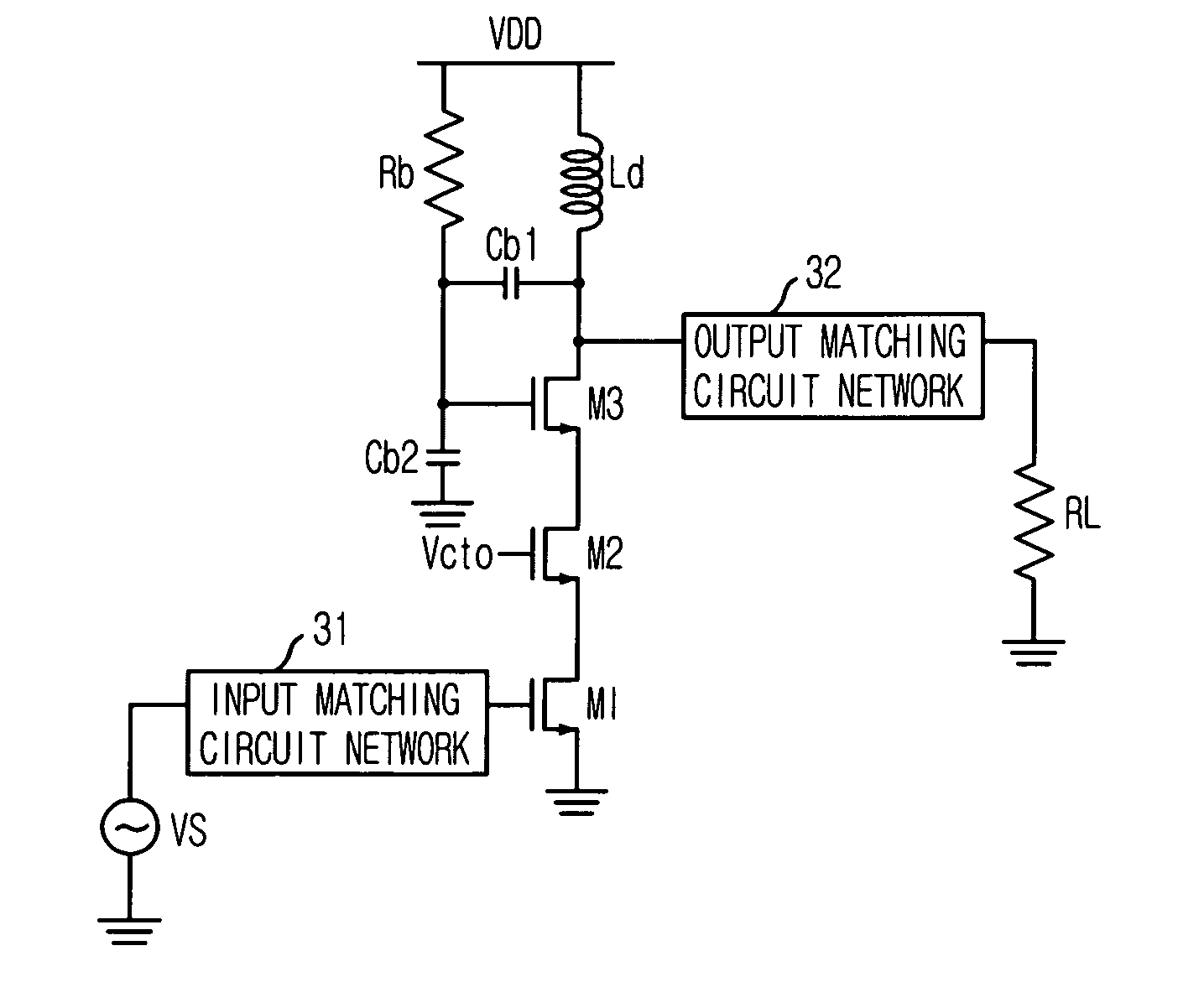
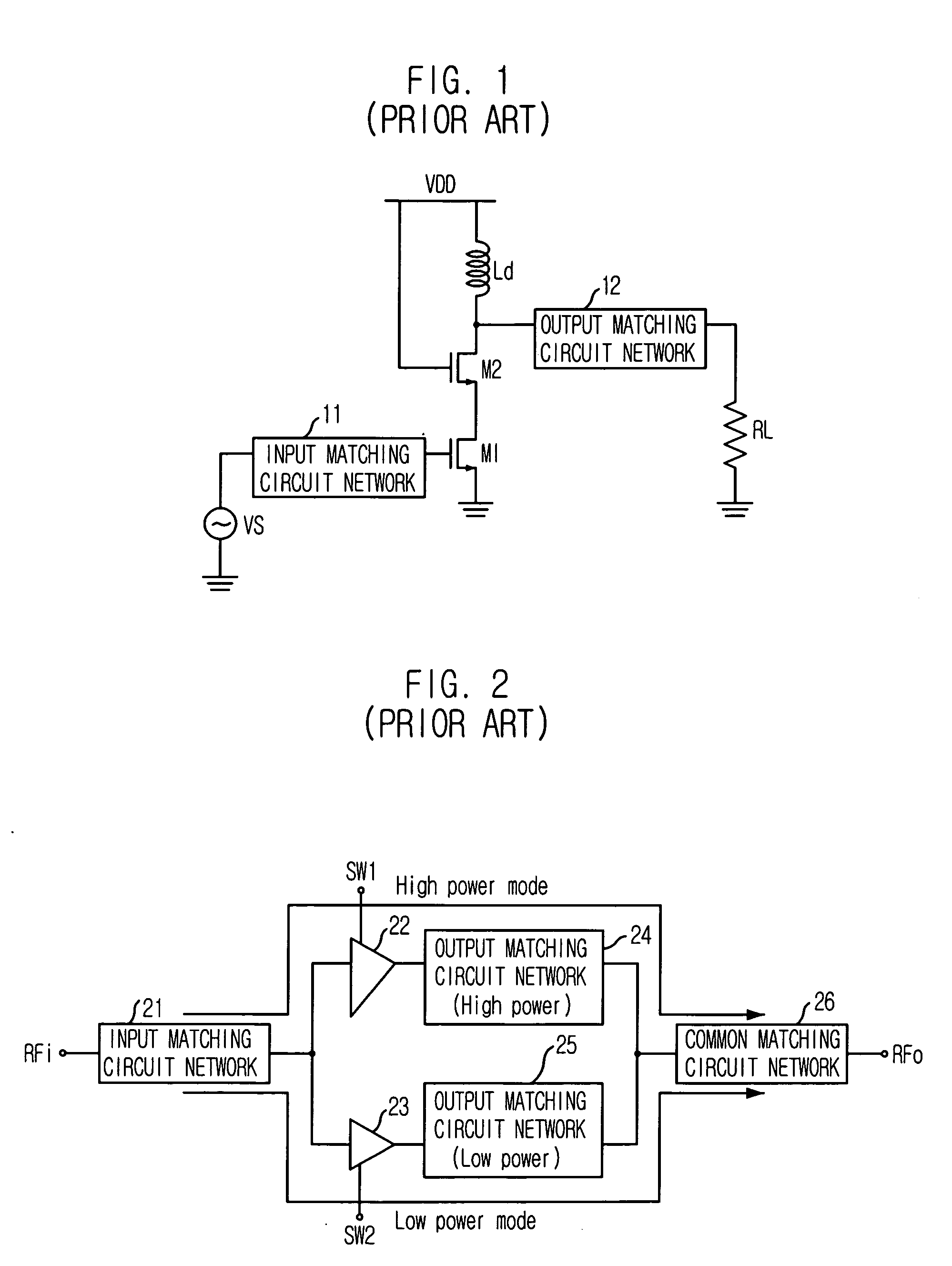
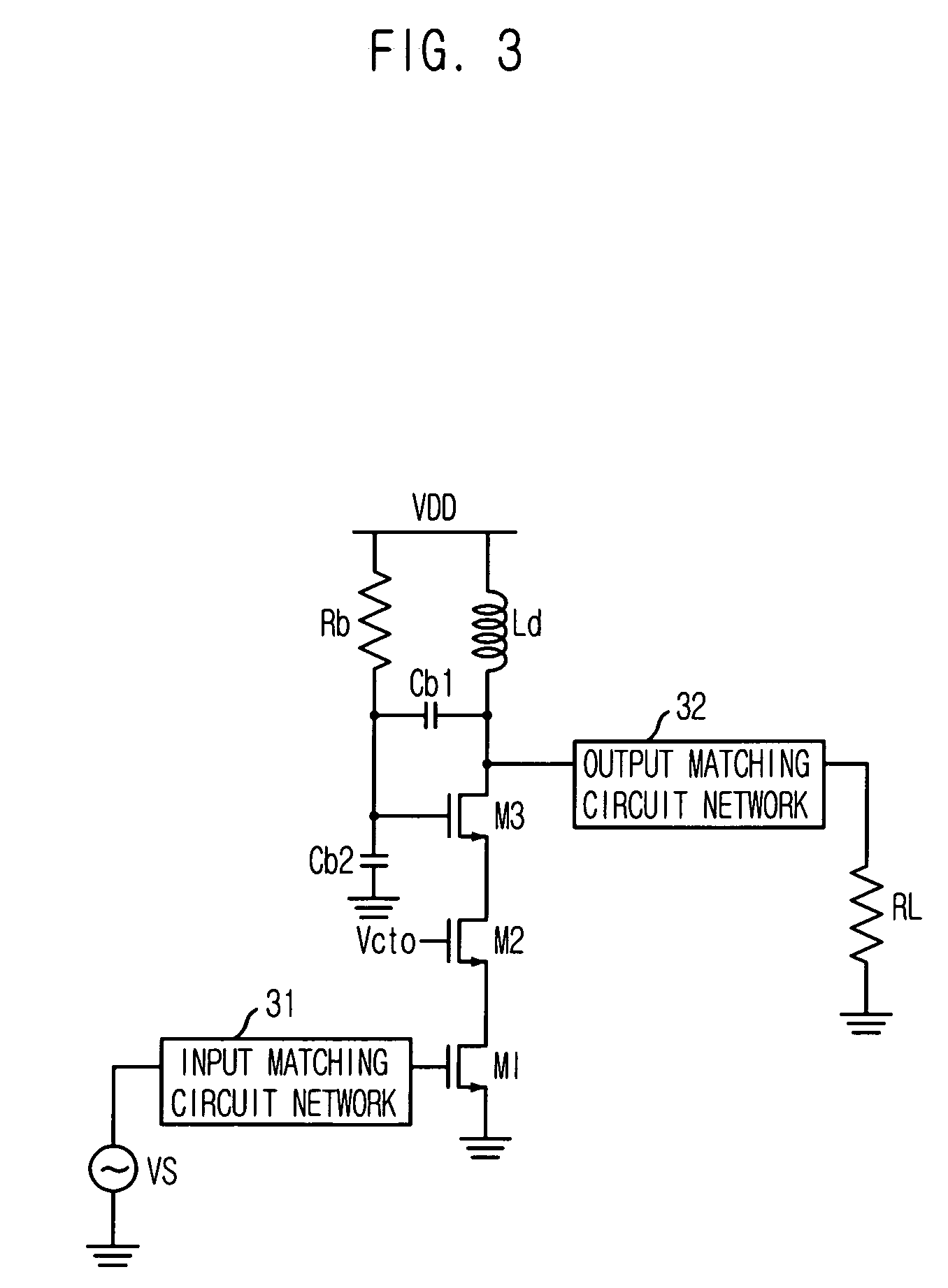
Scalable Periphery Tunable Matching Power Amplifier
A scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is presented. Varying power levels can be accommodated by selectively activating or deactivating unit cells of which the scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is comprised. Tunable matching allows individual unit cells to see a constant output impedance, reducing need for transforming a low impedance up to a system impedance and attendant power loss. The scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier can also be tuned for different operating conditions such as different frequencies of operation or different modes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
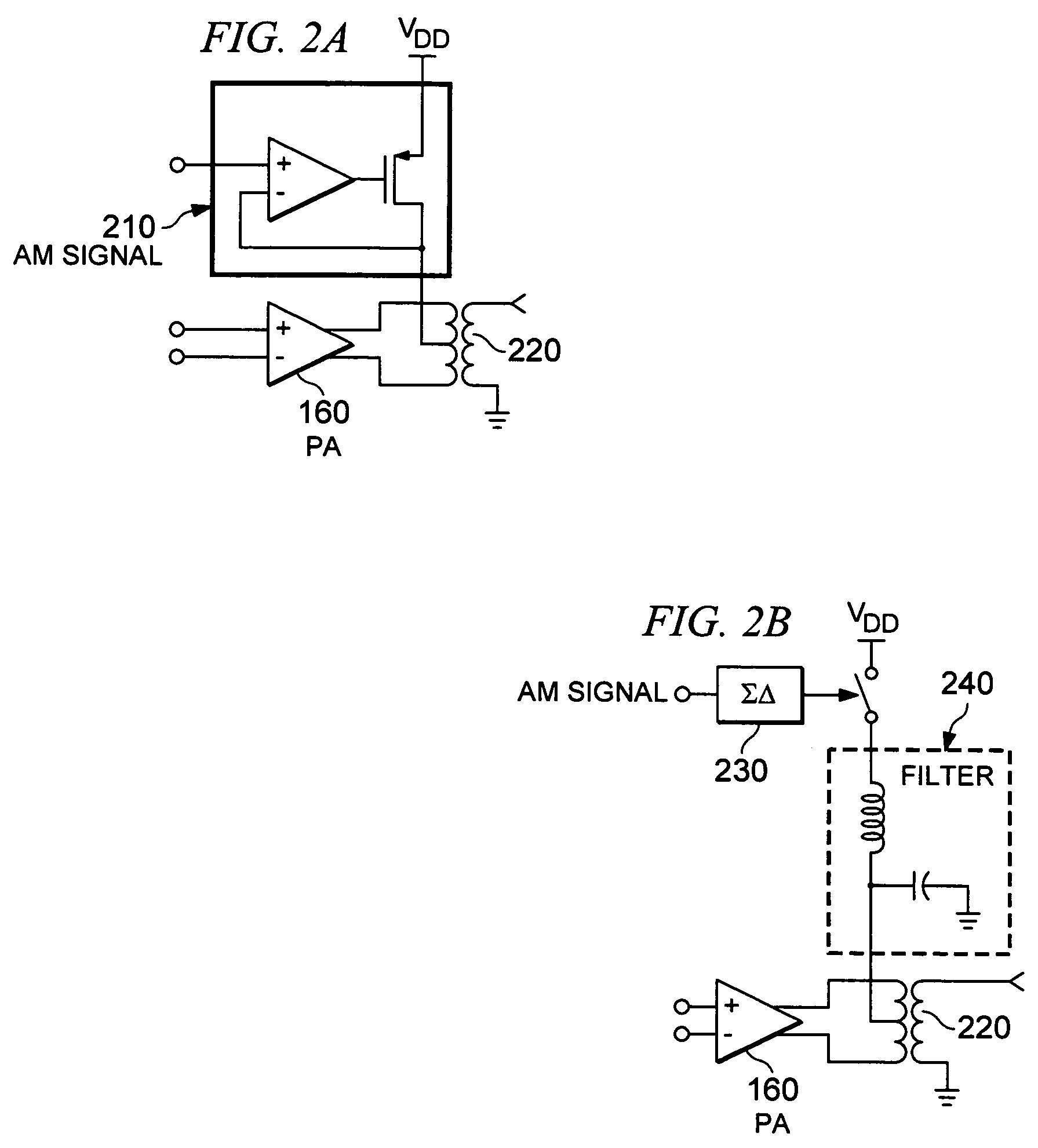
Efficient class-G amplifier with wide output voltage swing
InactiveUS6838942B1Reduce noiseImprove efficiencyGated amplifiersPower amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
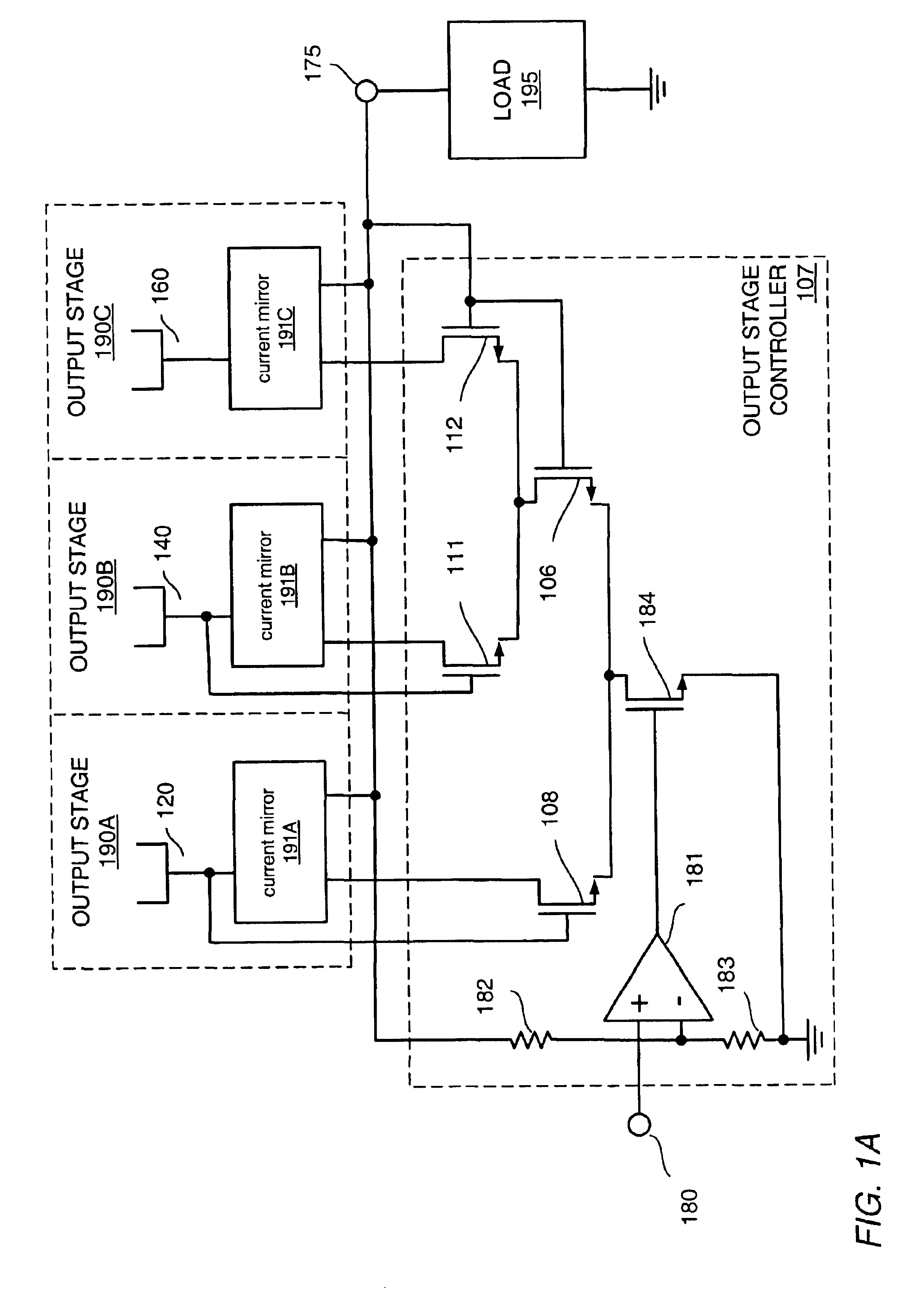
Various embodiments of methods and apparatus for an amplifier with wide output voltage swing are disclosed. The amplifier may include multiple output stages, each associated with a distinct supply voltage. Each output stage may contribute current to the output of the amplifier over a range of amplifier output voltages and these ranges may overlap. Each output stage may contribute current until the amplifier output voltage reaches the supply voltage associated with that output stage. The amplifier output may be as great as the largest supply voltage minus a drop equal to Rdson for an output transistor multiplied by the output current. In a CMOS implementation, this voltage drop may be approximately 0.15V. When the amplifier output voltage is close to the supply voltage associated with an output stage, both that output stage and the output stage associated with the next highest supply voltage may contribute to the amplifier output.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
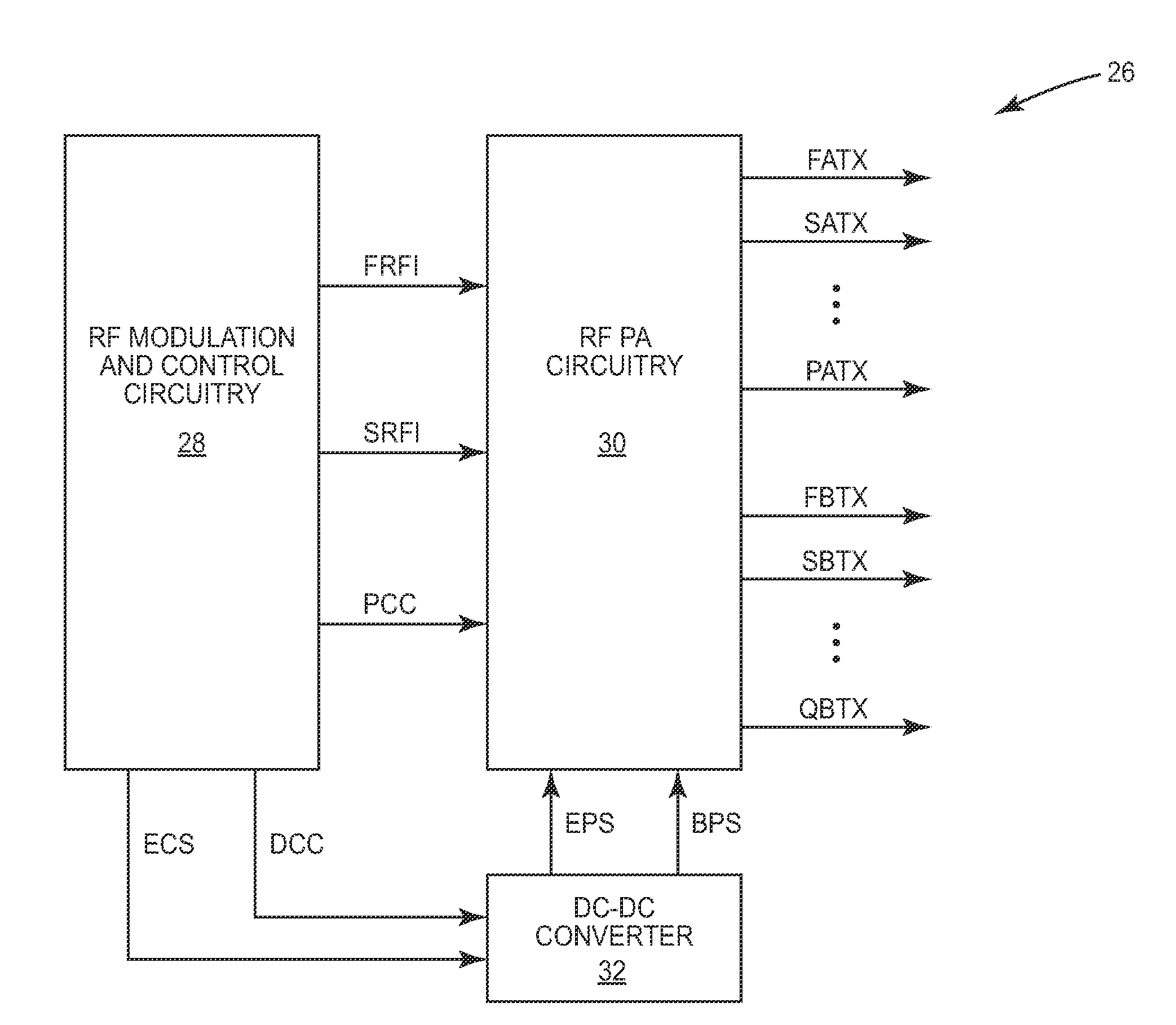
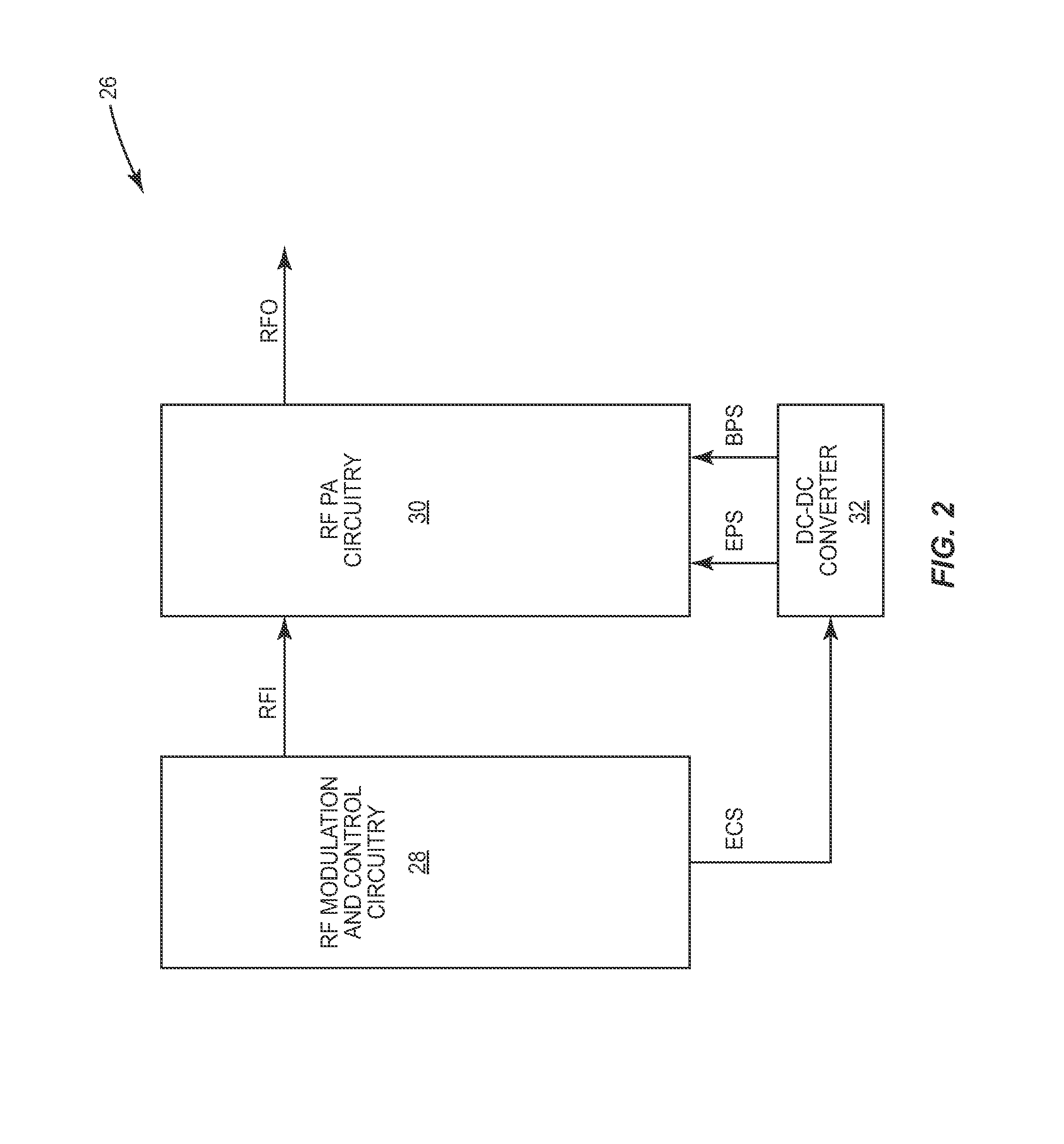
Pa envelope power supply undershoot compensation
ActiveUS20120299647A1Prevent undershootHigh frequency amplifiersGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier (PA) envelope power supply, which provides an envelope power supply signal to radio frequency (RF) PA circuitry, and a process to prevent undershoot of the PA envelope power supply is disclosed. The process includes determining if an envelope control signal to the PA envelope power supply has a step change from a high magnitude to a low magnitude that exceeds a step change limit. Such a step change may cause undershoot of the PA envelope power supply. As such, if the step change exceeds the step change limit, the envelope control signal is modified to use an intermediate magnitude for period of time. Otherwise, if the step change does not exceed the step change limit, the envelope control signal is not modified.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Low power consumption adaptive power amplifier
ActiveUS7170341B2Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierEngineering
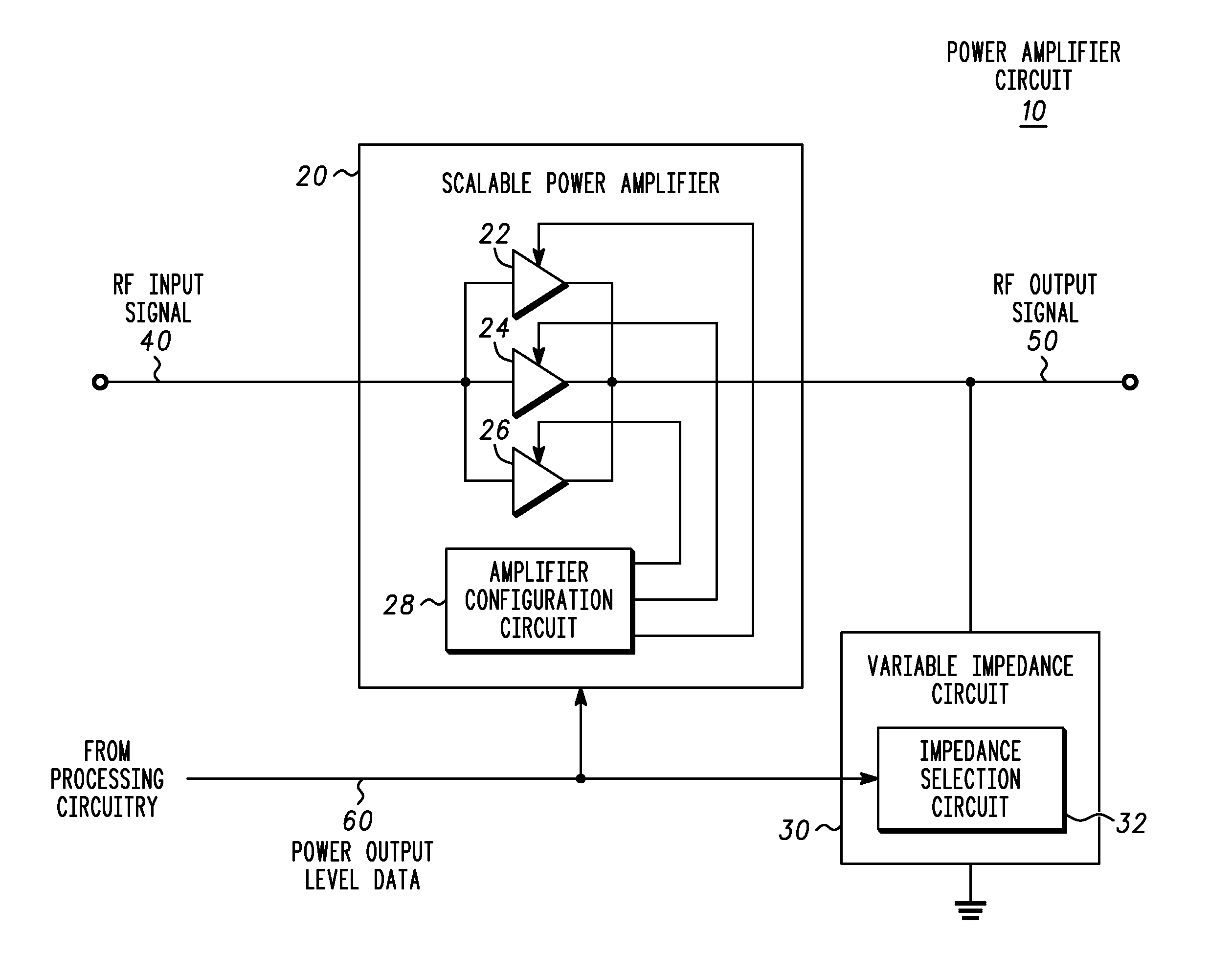
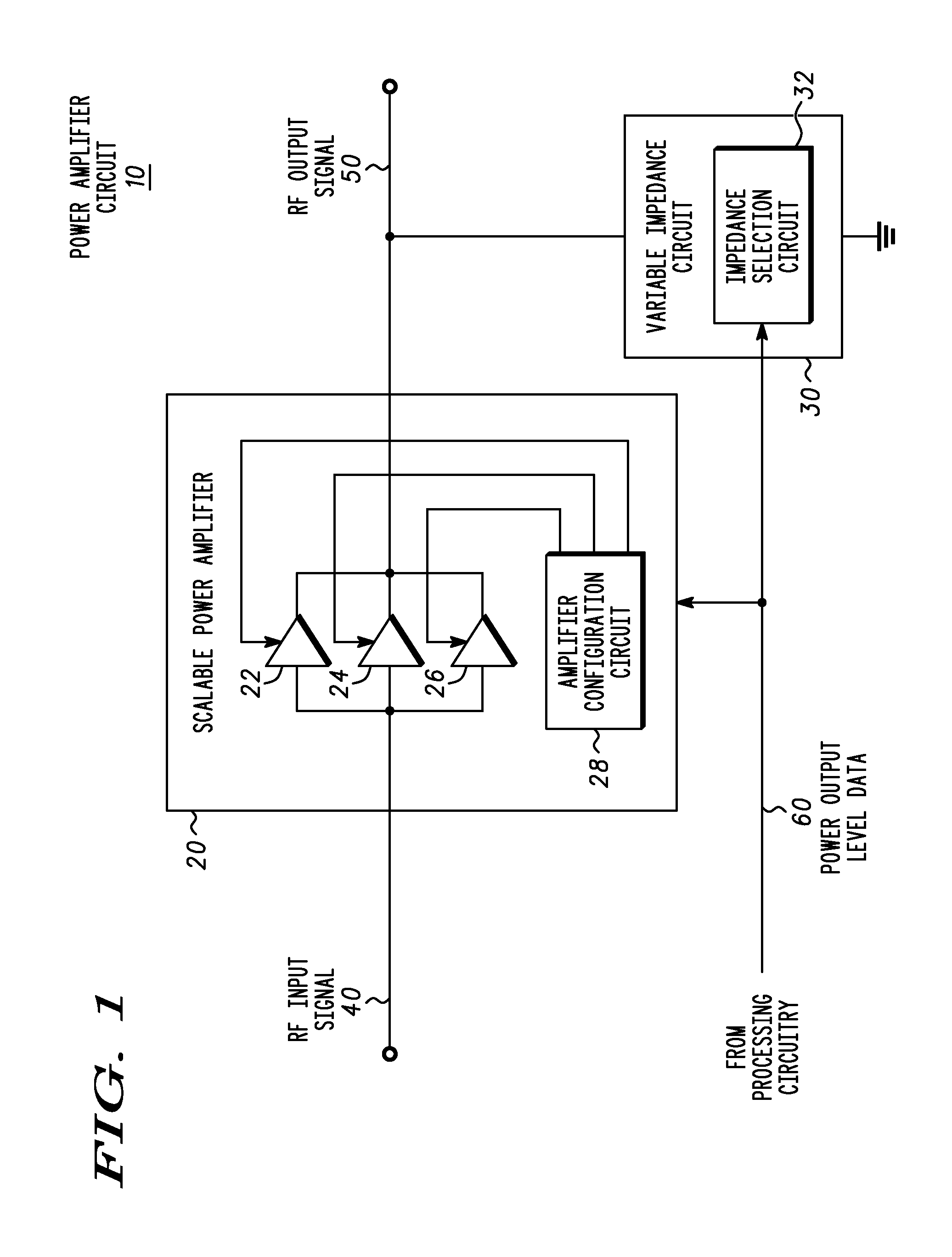
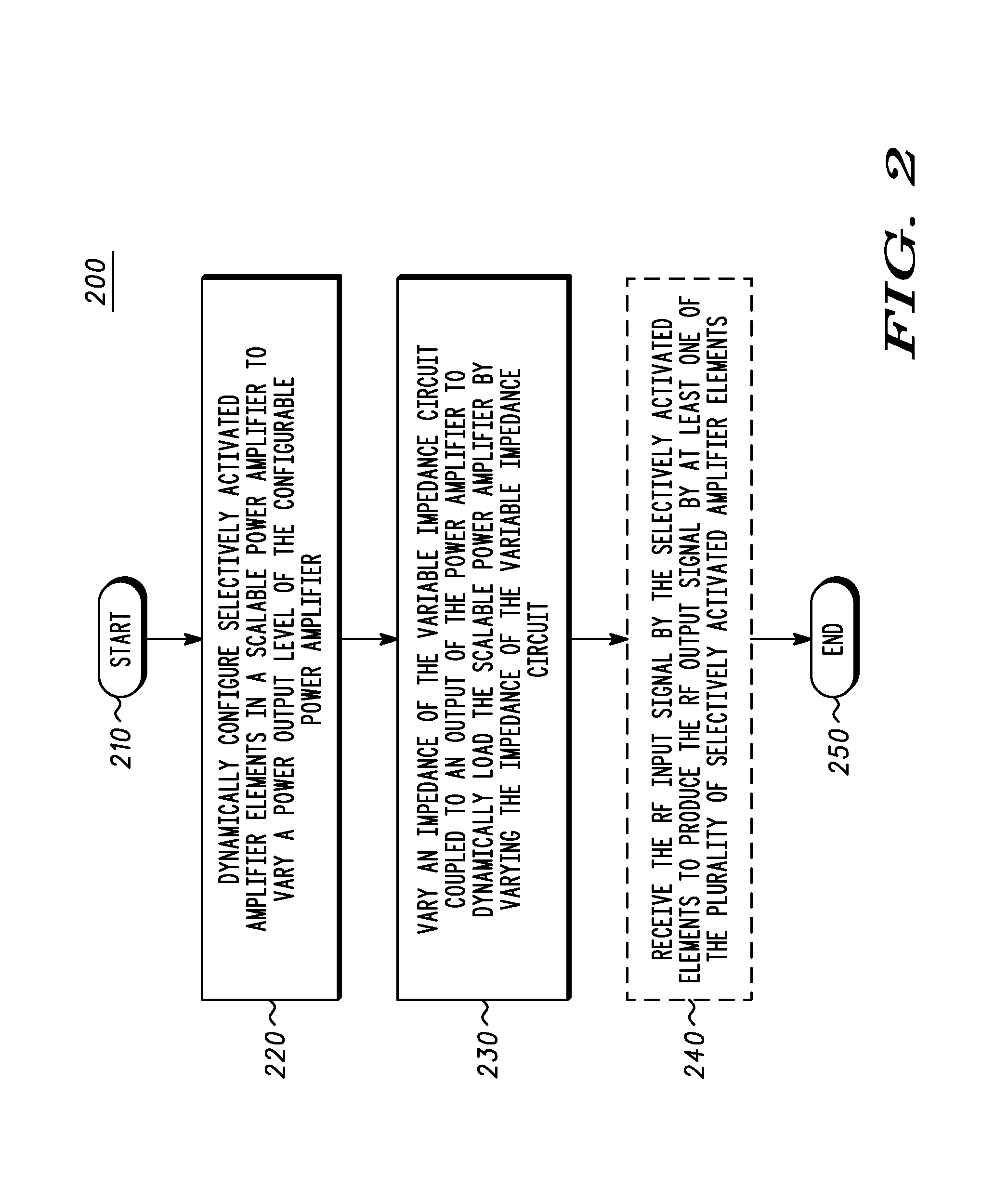
A power amplification circuit (10) includes a scalable power amplifier (20) to produce an RF output signal (50) at an output of the power amplification circuit (10), and a variable impedance circuit (30) coupled to the output of the power amplification circuit (10). The scalable power amplifier (20) includes a plurality of selectively activated amplifier elements (22), (24), (26) to produce the RF output signal (50) in accordance with a desired RF output signal power level. The power amplification circuit (10) selectively activates individual amplifier elements by, for example reducing power or increasing power to at least one amplifier element. The variable impedance circuit (30) varies an impedance of the variable impedance circuit (30) to dynamically load the output of the scalable power amplifier (20).
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Sound Generating Device with Removable Memory
A sound generating device for transforming an object into a loudspeaker is includes an exciter module adapted for receiving audio signals stored on a portable micro-memory card or the like and a mounting device connected to the exciter module for removably connecting the exciter module to an object such that the object is transformed into a loudspeaker when the exciter module is energized by the audio signals.
Owner:TUNEBUG
Power amplifier and radio wave transmitter having the same
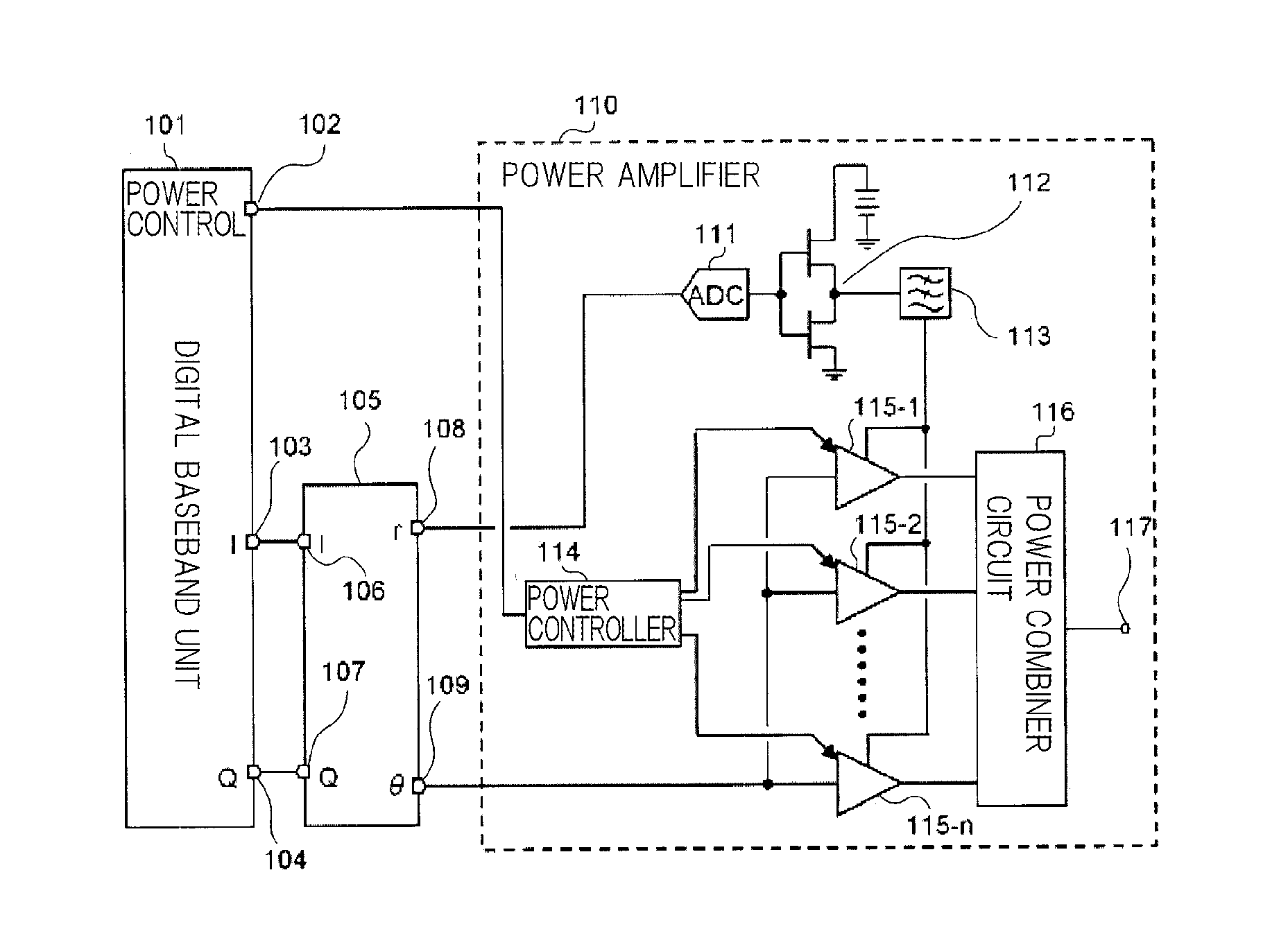
ActiveUS20100266066A1Eliminate high frequency noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsPower controllerHigh frequency power
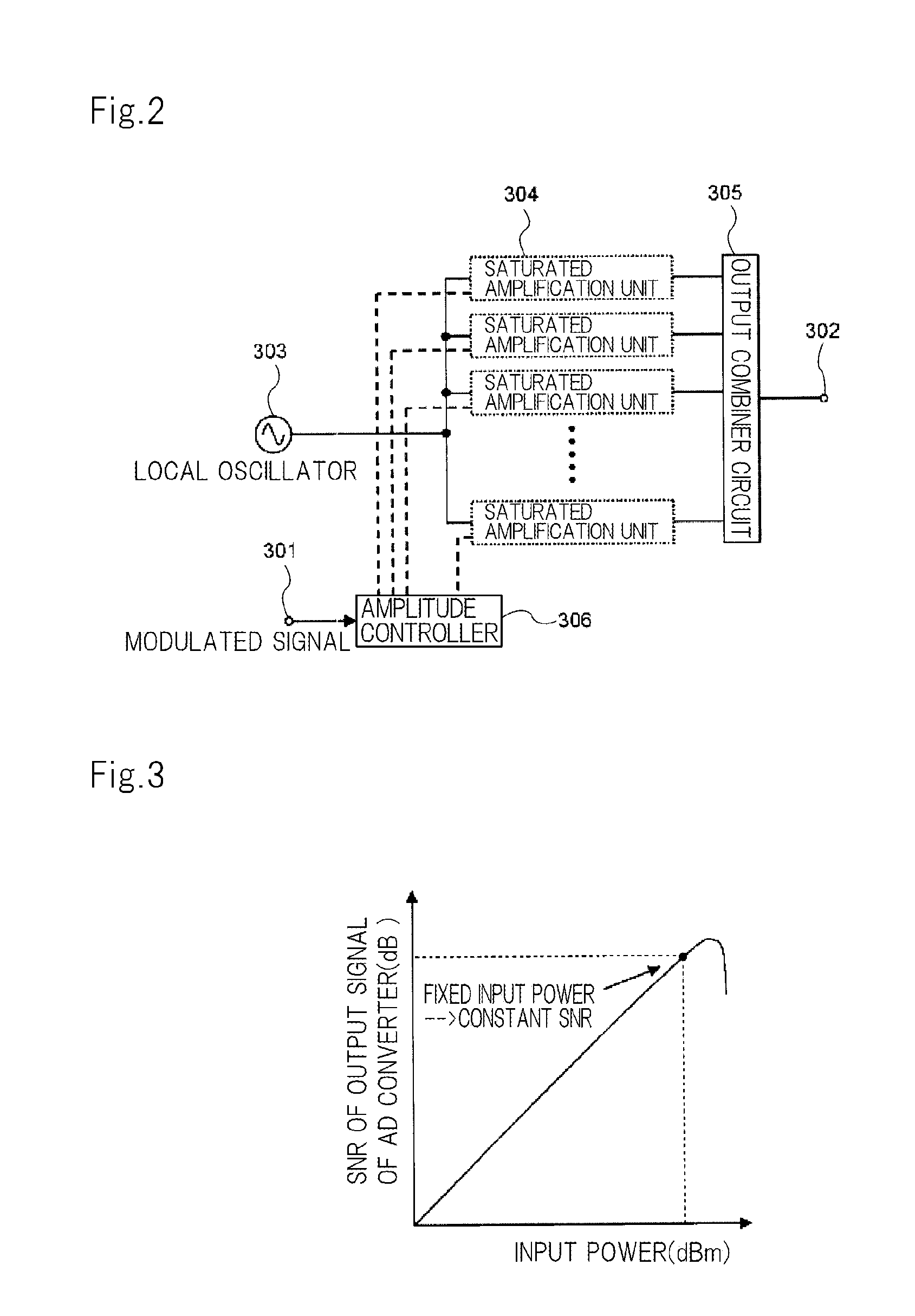
A power amplifier (10) comprises: an A / D converter (11) for converting, to a time discrete signal, an envelope signal included in a high-frequency modulated signal and including only an amplitude modulated component of the high-frequency modulated signal; a switching amplifier (12) for amplifying the output signal of the A / D converter (11); a low-pass filter (13) for removing high frequency noise from the output signal of the switching amplifier (12); a plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n) for receiving the output signal of the low-pass filter (13) as a power supply and for amplifying a carrier signal included in the high-frequency modulated signal; and a power controller (14) for adjusting the average power of the output signal of the power amplifier (10) by controlling the total gains of the plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n).
Owner:NEC CORP
Output voltage amplifier and driving device of liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS20100231577A1Accurate feedback voltageAvoid heatGated amplifiersCathode-ray tube indicatorsAudio power amplifierLiquid-crystal display
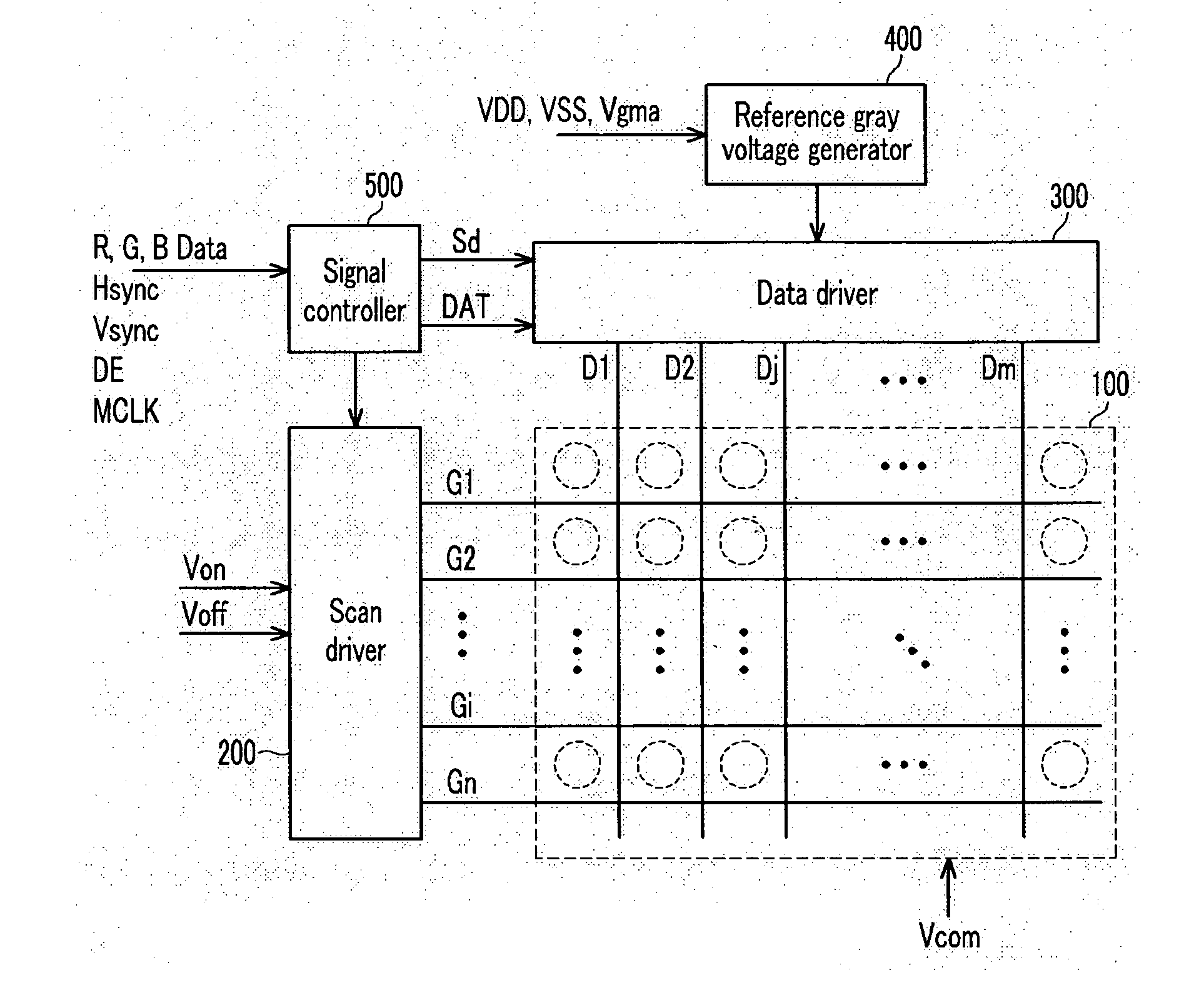
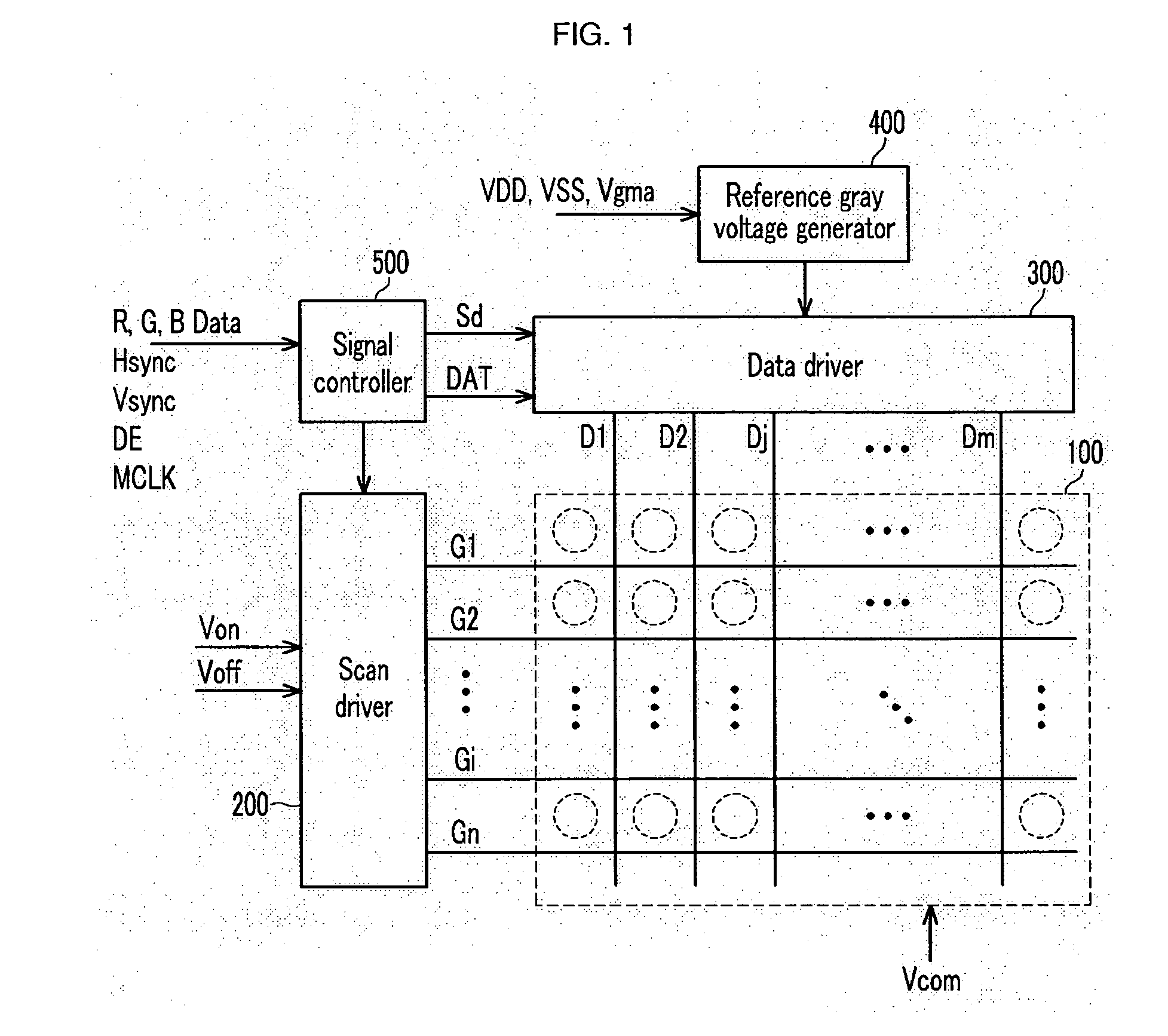
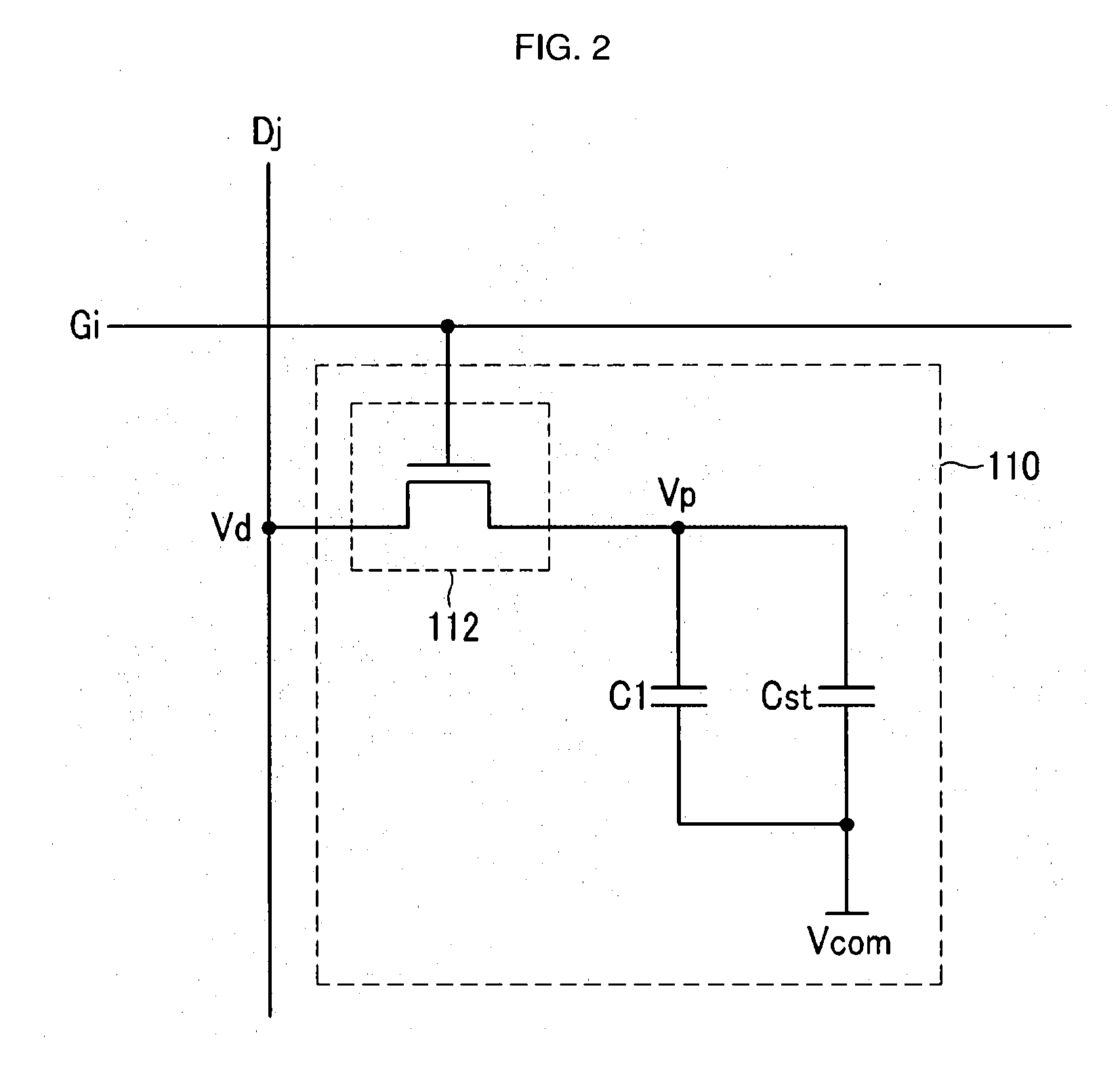
An output voltage amplifier, and a driving device of a liquid crystal display using the same are disclosed. The output voltage amplifier includes: an amplifying unit to generate first and second signals corresponding to a gray voltage input to a first input terminal and a feedback signal input to a second input terminal, and to output a first voltage by using first and second switches driven to be on or off according to the first and second signals; an output unit to apply the first and second data signals to the first and second pixels by using third and fourth switches turned on or off according to the first and second signals; and a feedback circuit unit to selectively supply one of the first voltage and the first and second data signals to the second input terminal. Heating characteristics and a slew rate can be improved.
Owner:MC TECH CO LTD
Direct current (DC)-dc converter having a multi-stage output filter
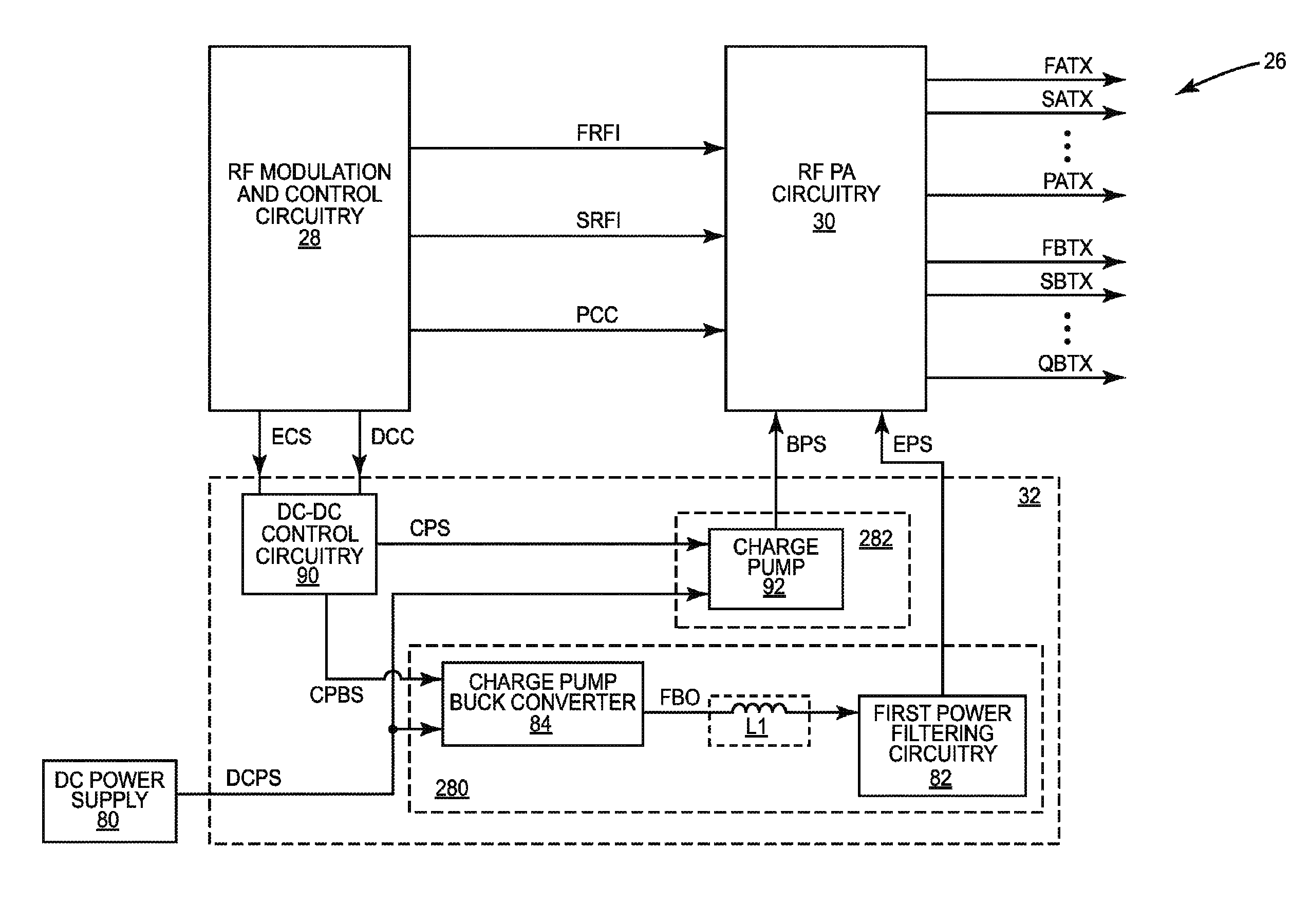
ActiveUS20130271221A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceDc dc converter
A direct current (DC)-DC converter that includes a first switching converter and a multi-stage filter is disclosed. The multi-stage filter includes at least a first inductance (L) capacitance (C) filter and a second LC filter coupled in series between the first switching converter and a DC-DC converter output. The first LC filter has a first LC time constant and the second LC filter has a second LC time constant, which is less than the first LC time constant. The first switching converter and the multi-stage filter form a feedback loop, which is used to regulate the first switching power supply output signal based on the setpoint. The first LC filter includes a first capacitive element having a first self-resonant frequency, which is about equal to a first notch frequency of the multi-stage filter.
Owner:QORVO US INC
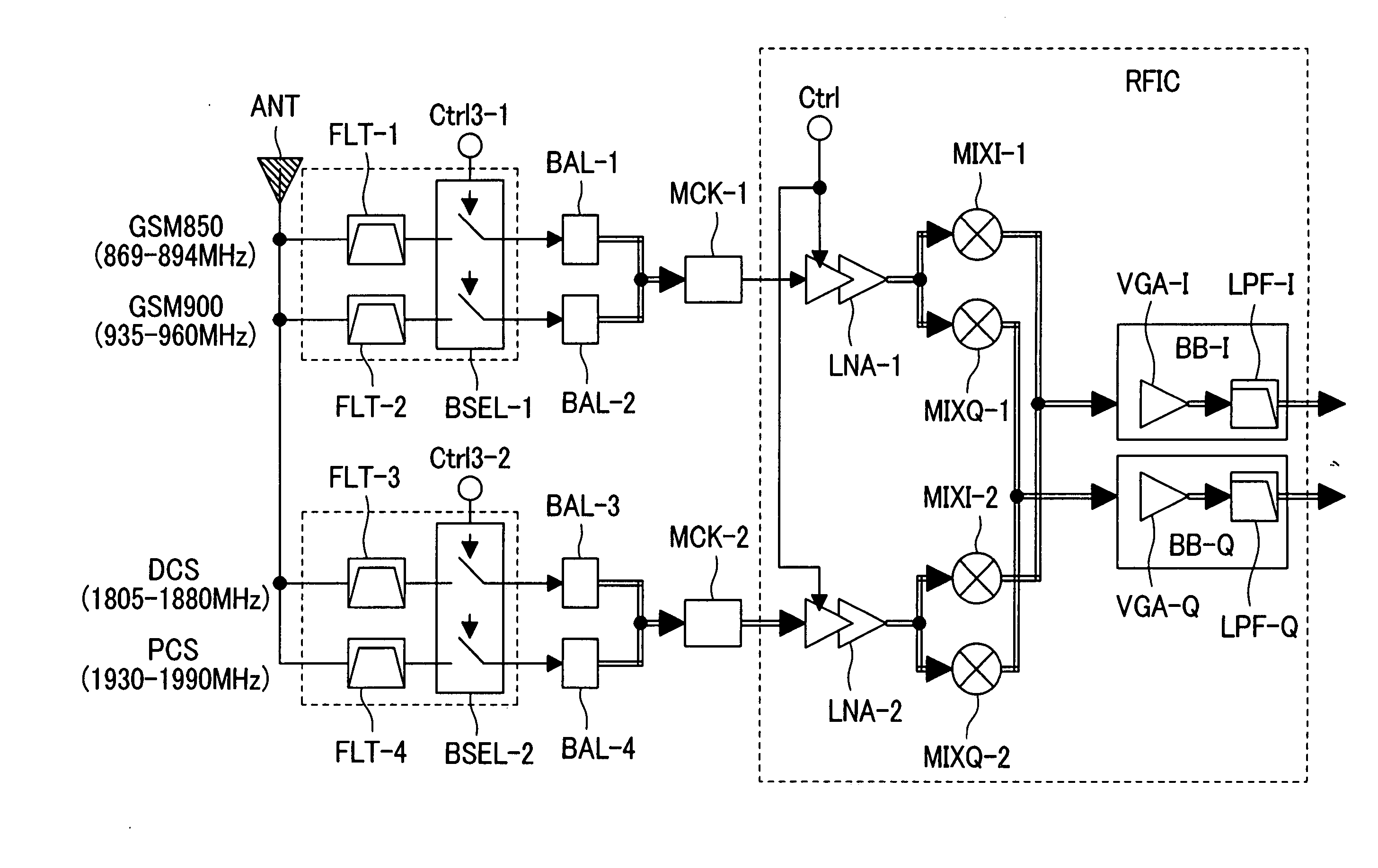
Radio frequency integrated circuit having an antenna diversity structure
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
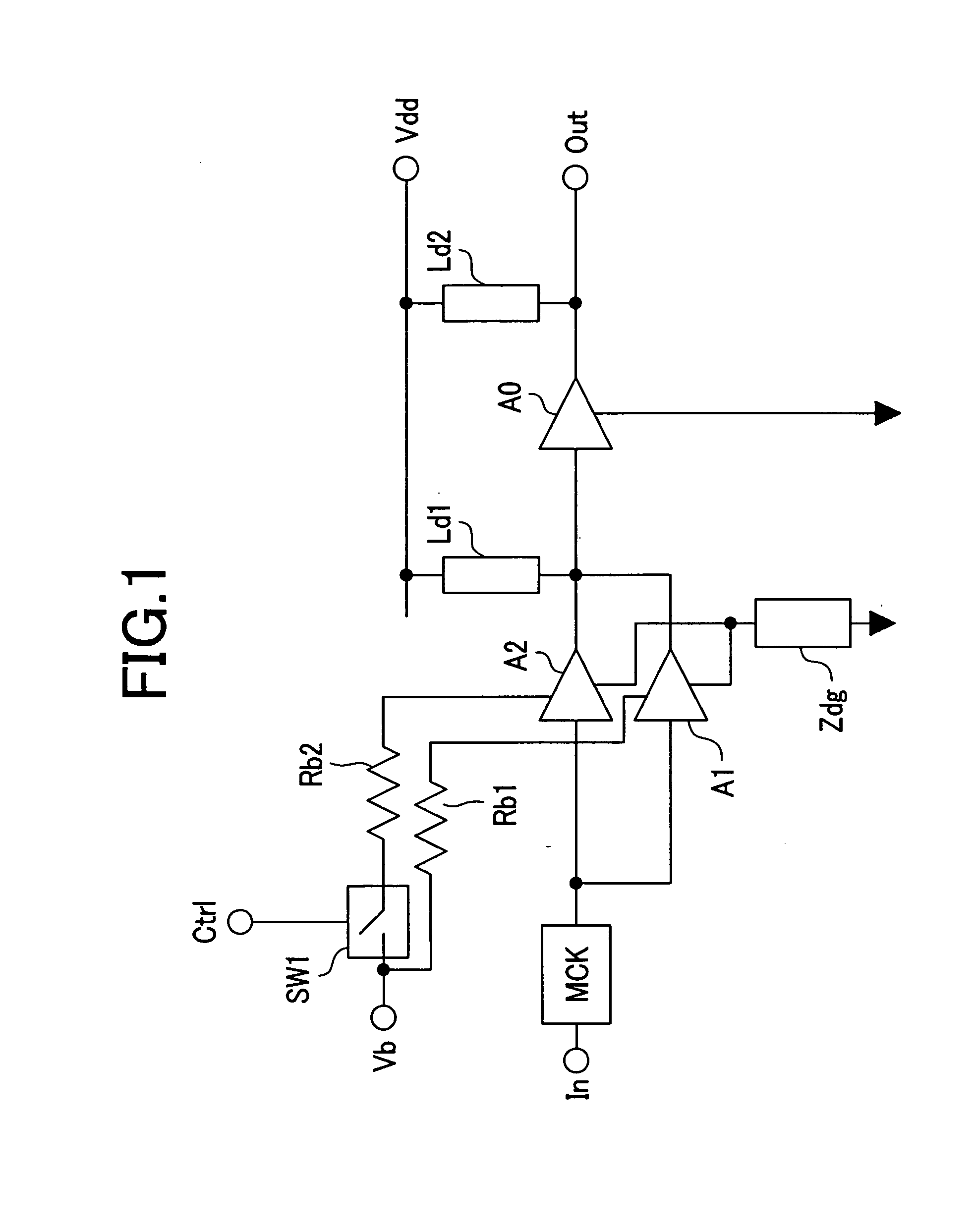
Triple cascode power amplifier of inner parallel configuration with dynamic gate bias technique
InactiveUS20060119435A1Easily embodiedIncrease output powerGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCascode
Provided is a power amplifier which fits to a deep-submicron technology in radio frequency wireless communication. The power amplifier includes a cascode including a first transistor which receives and amplifies an input signal, and a second transistor which is connected to the first transistor in series and operated by a DC bias voltage; a third transistor which is connected between the cascode and an output end, operated by a dynamic gate bias and outputting a signal; and a voltage divider which includes first and second capacitors that are connected between the output end, i.e. a drain of the third transistor, and a ground in series, and provides the dynamic bias to a gate of the third transistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
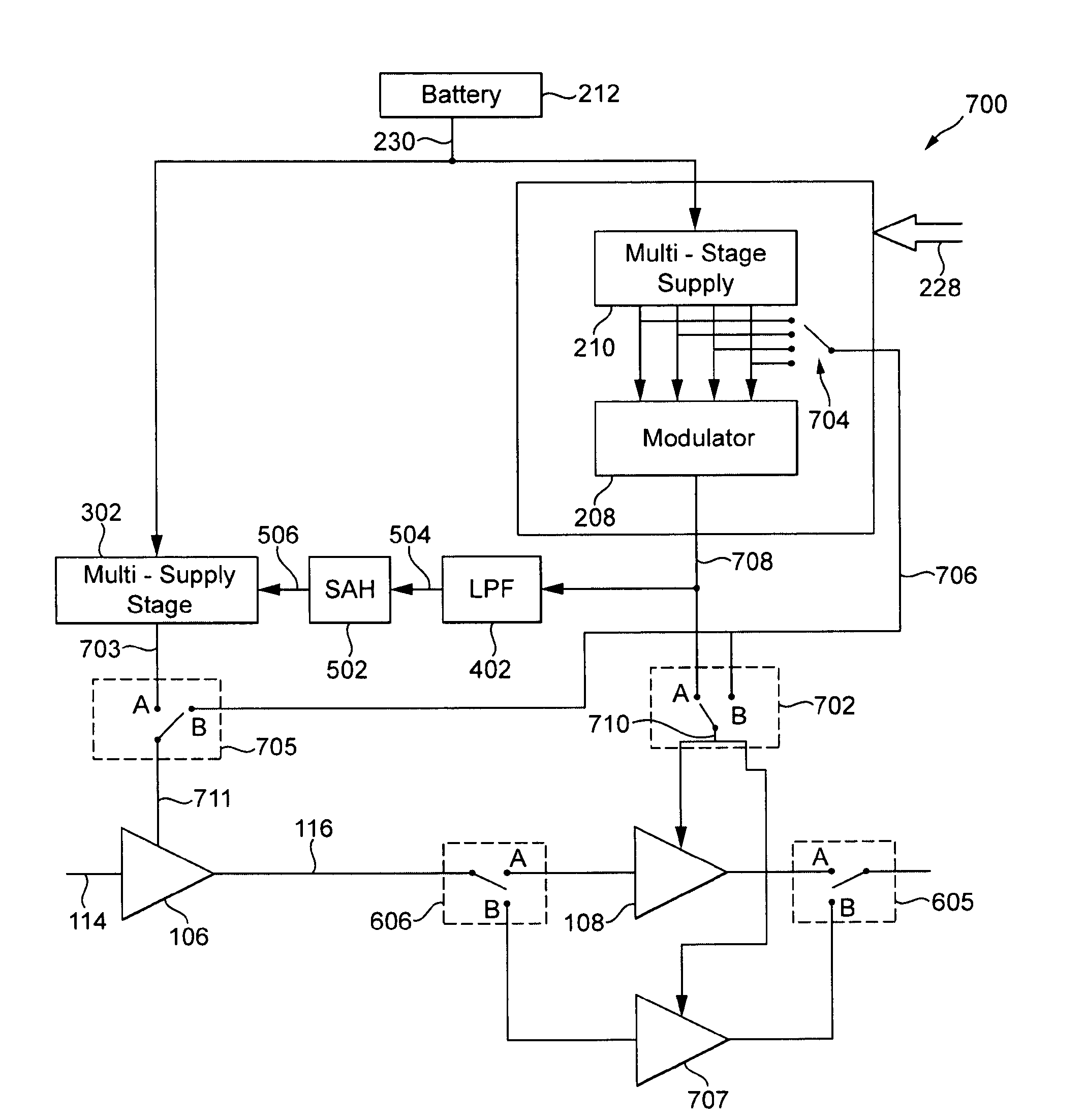
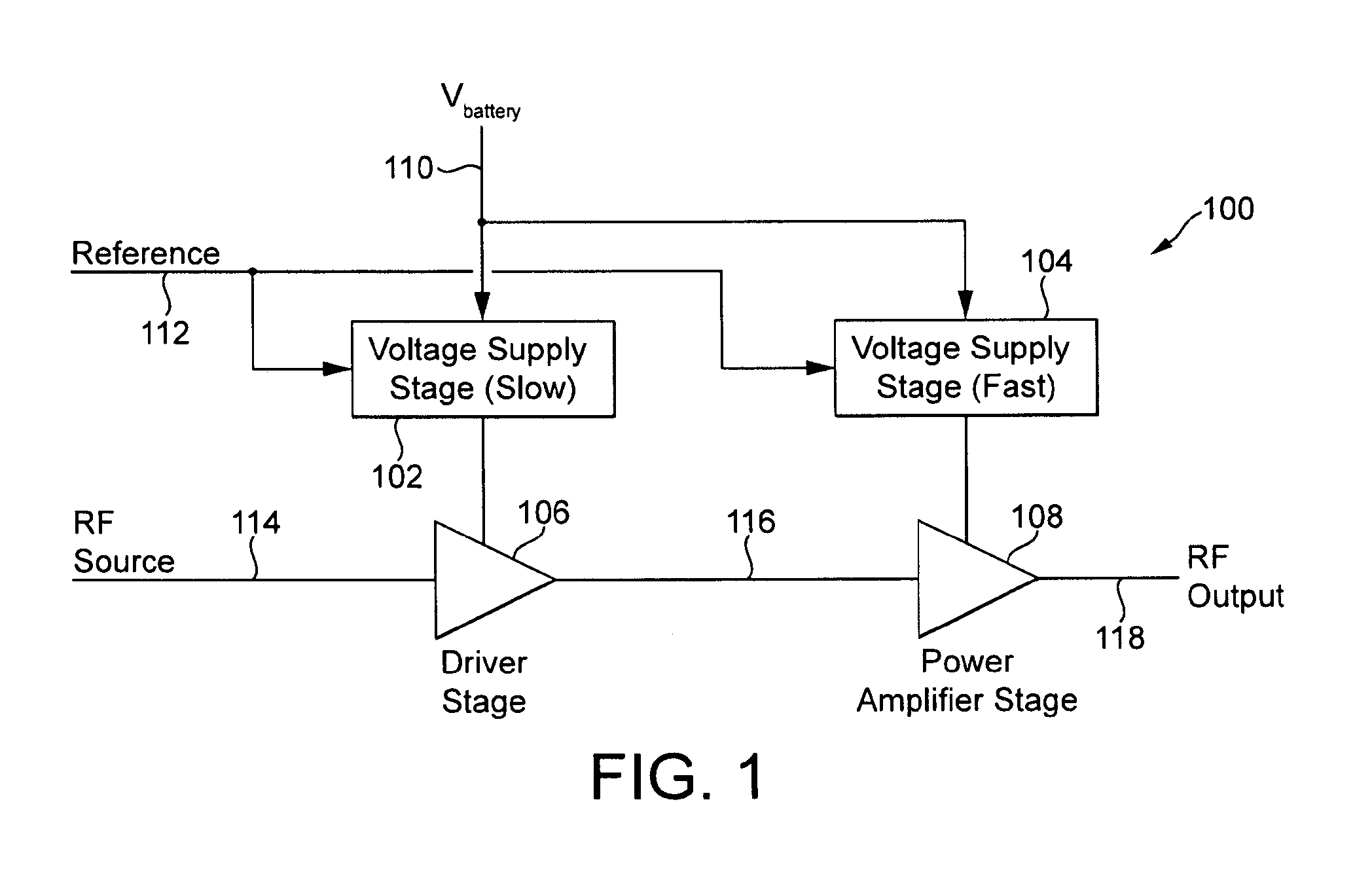
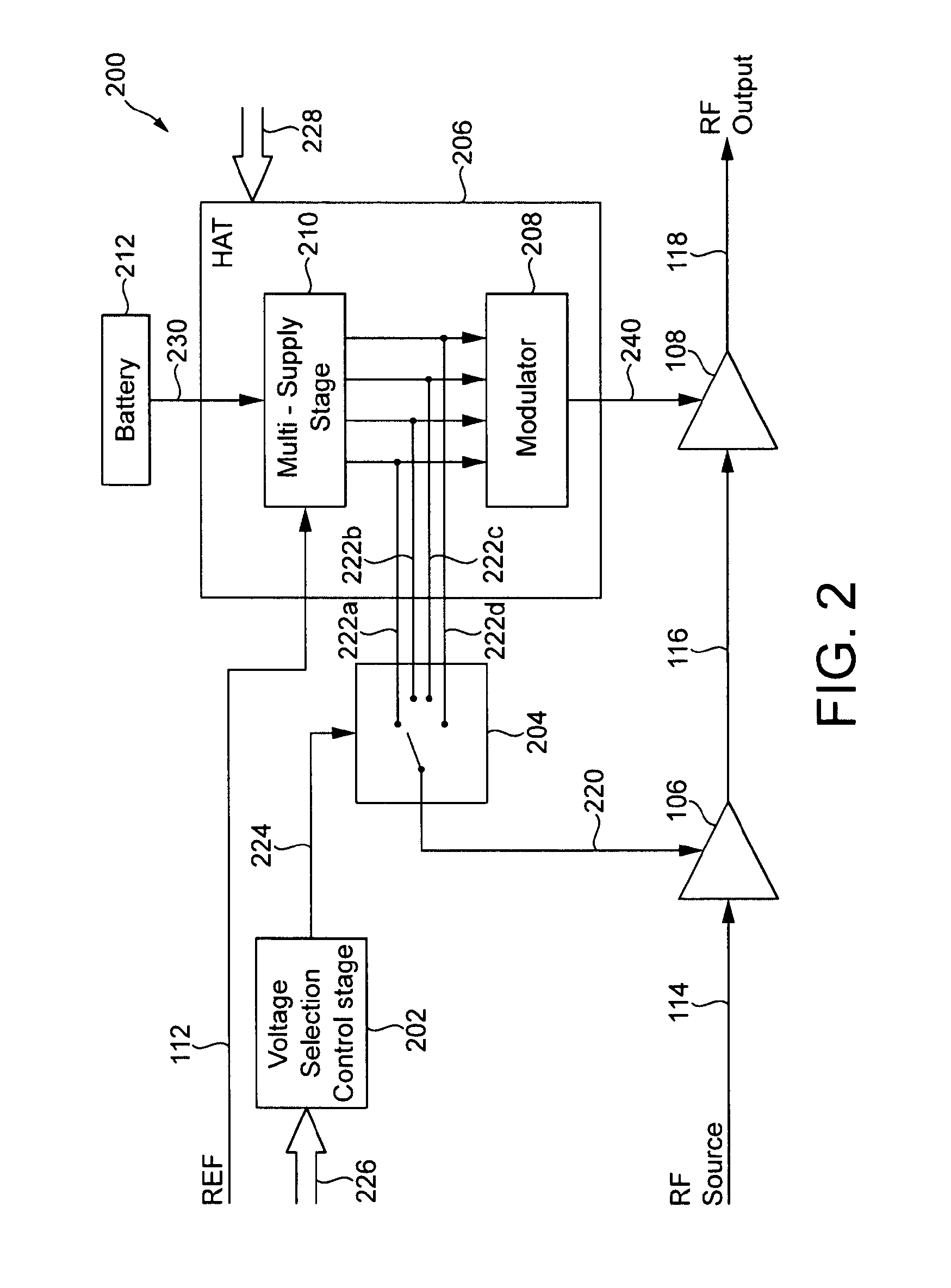
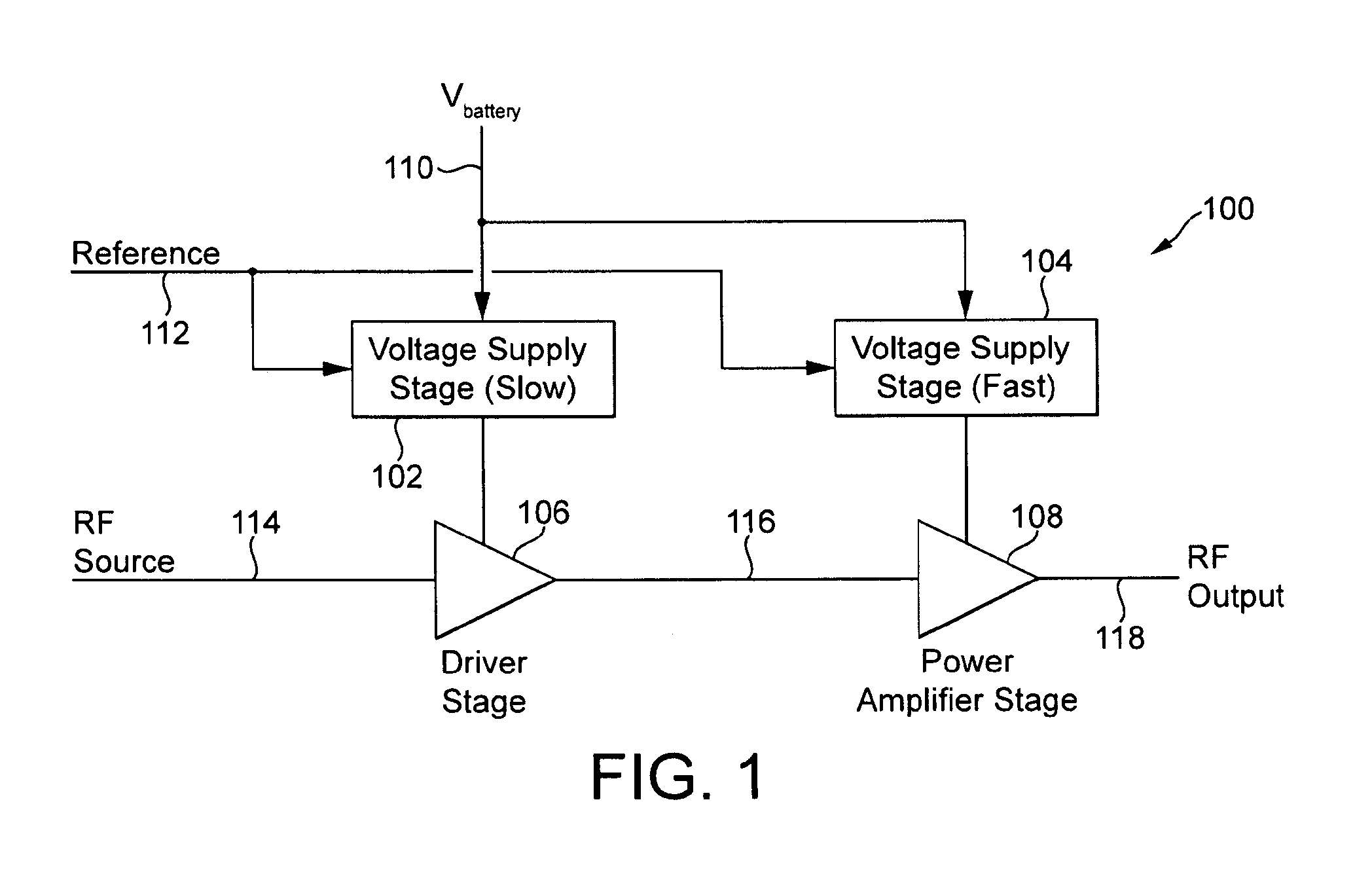
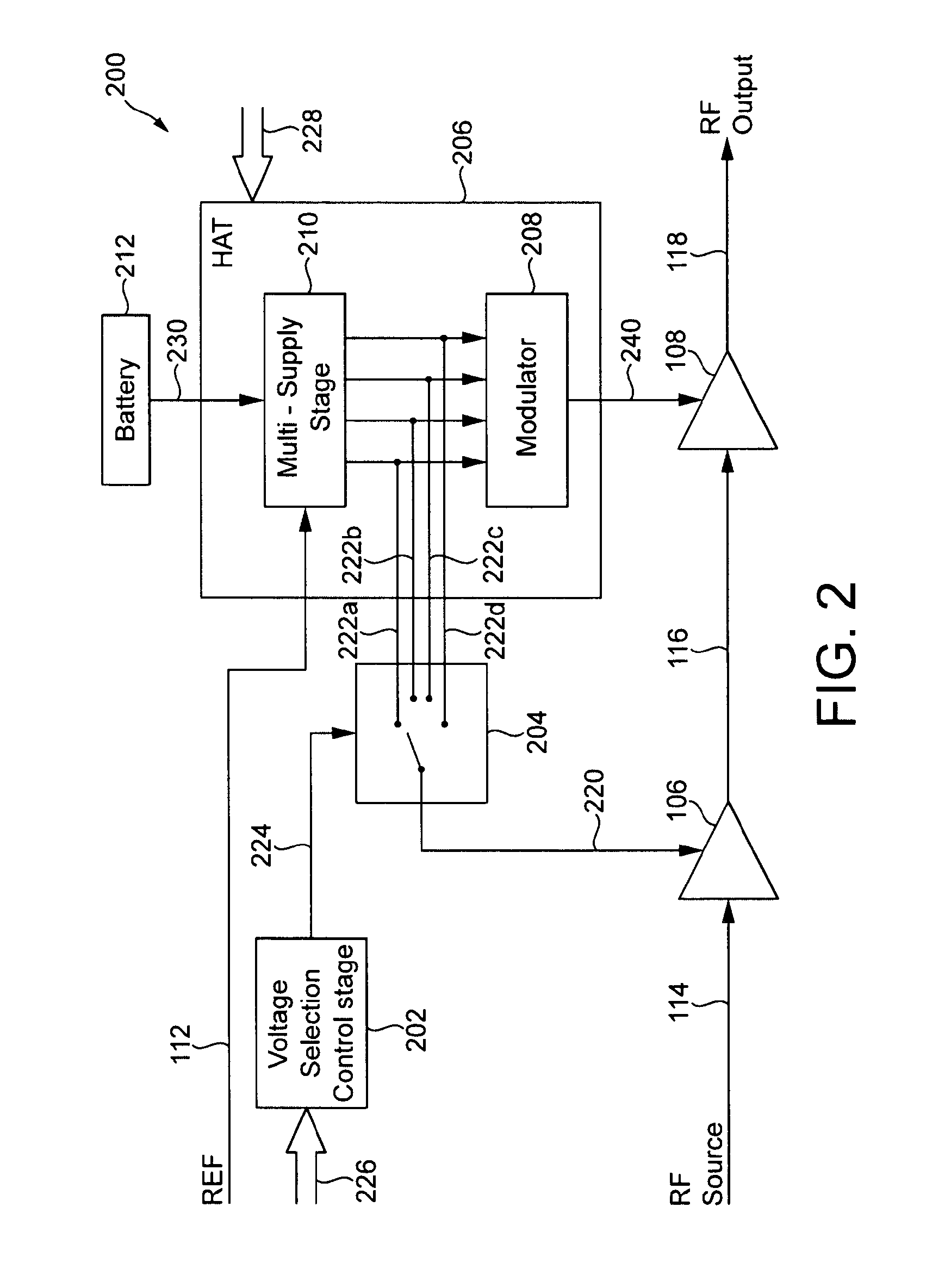
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
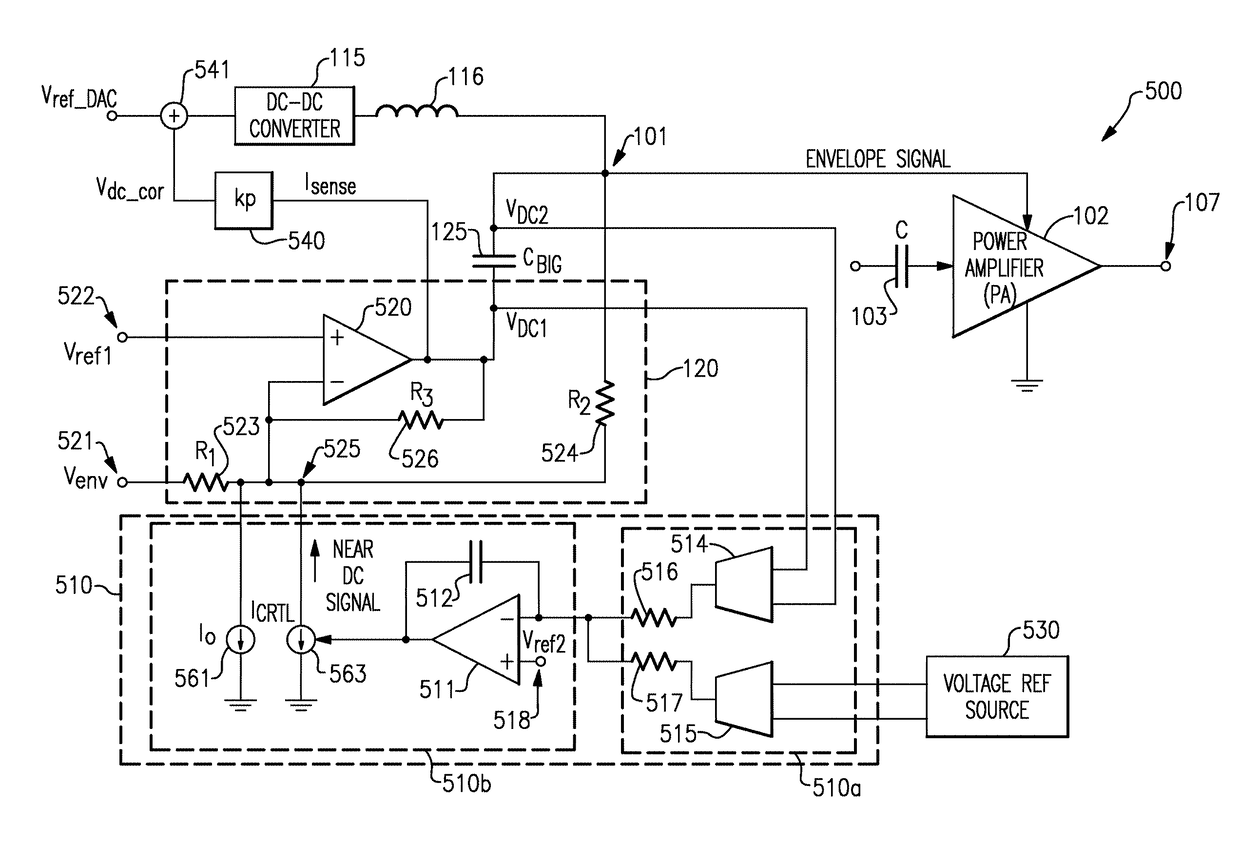
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
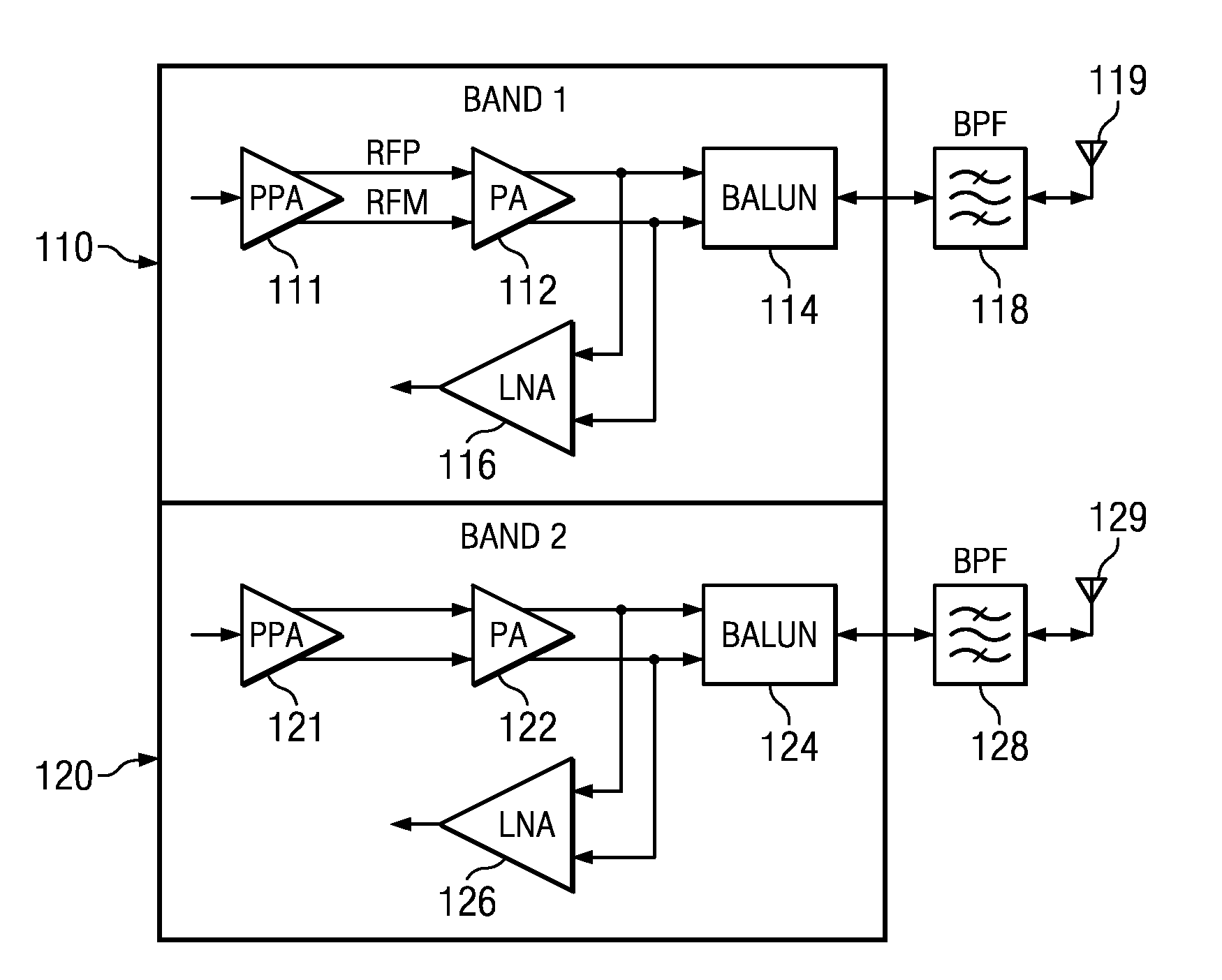
Multi-band low noise amplifier, multi-band low noise amplifier module, wireless integrated circuit and multi-band RF module
InactiveUS20060189286A1Small sizeSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A multi-band radio module for selectively supplying received signals in a plurality of frequency bands to a low noise amplifier via an input impedance matching circuit by switching over the operation mode of the low noise amplifier is comprised of: a pre-stage amplification unit including a plurality of fundamental amplifiers connected to one another in parallel, the fundamental amplifiers sharing a load impedance connected to a source voltage and a grounded degeneration impedance and having input signal lines commonly connected to an input impedance matching circuit; a post-stage amplifier to which the output signals of the plurality of fundamental amplifiers are commonly inputted; and a bias control unit for selectively turning on the fundamental amplifiers, wherein the input impedance of the low noise amplifier is selectively optimized for the matching circuit depending on the RF band to be received.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
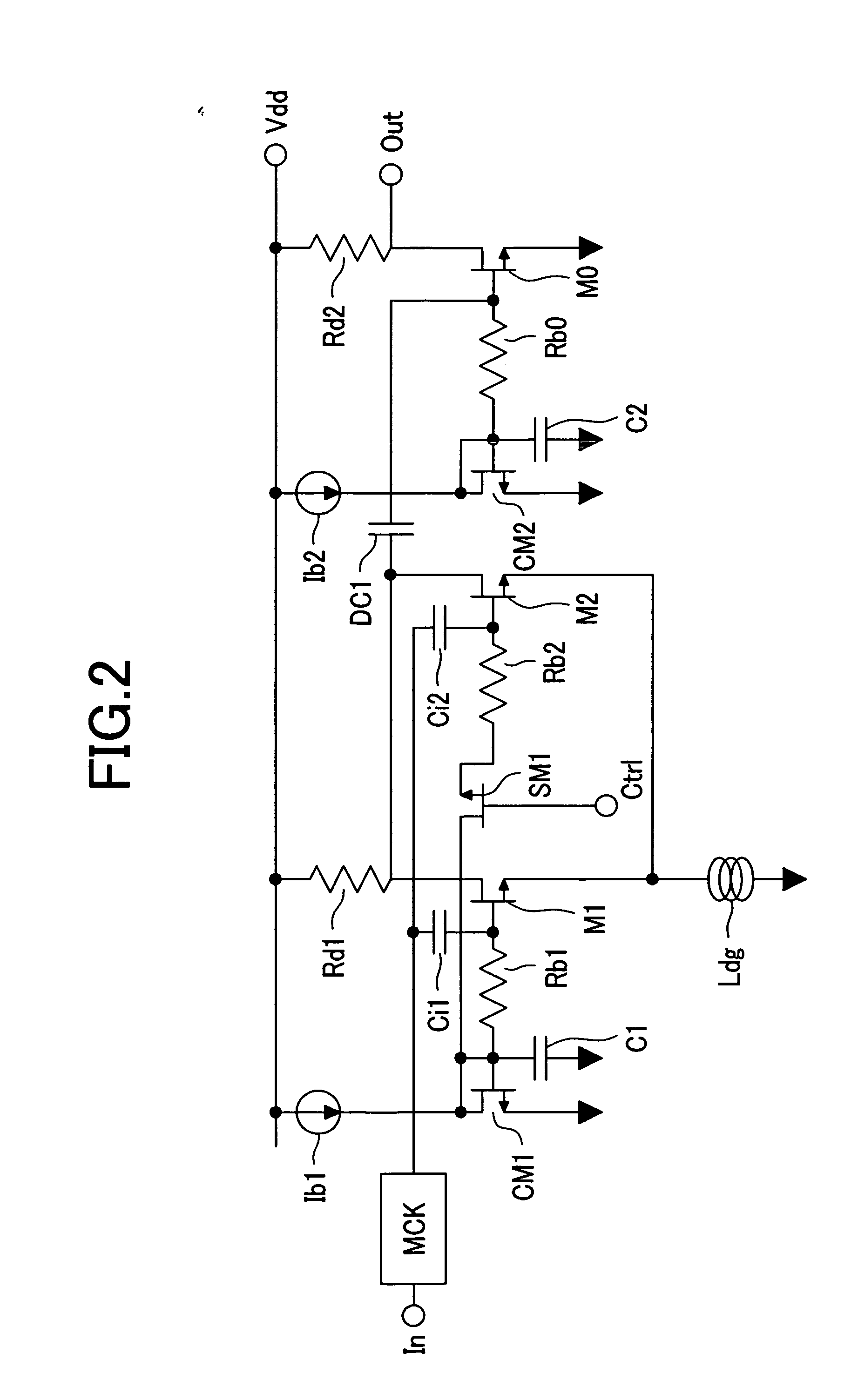
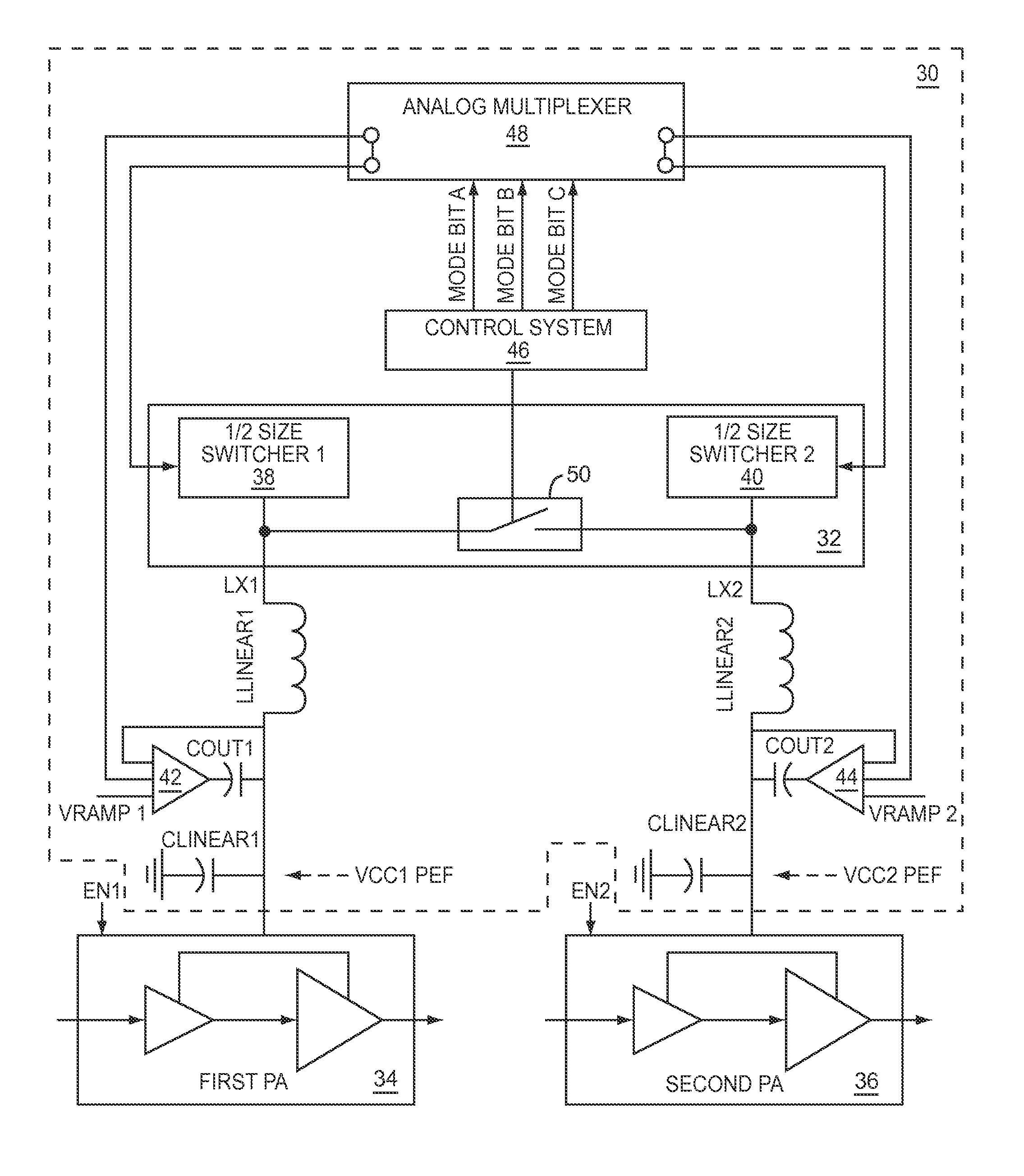
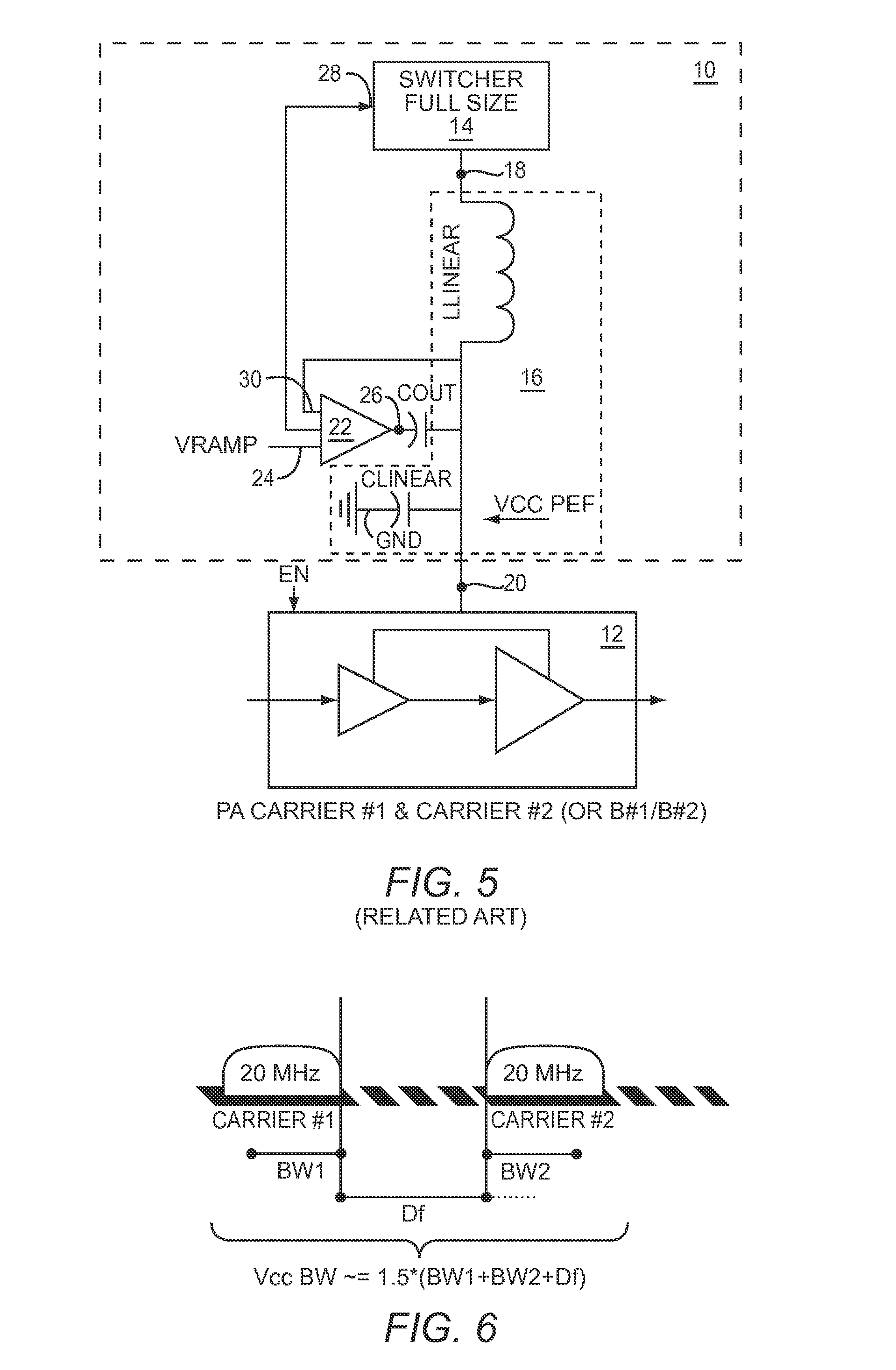
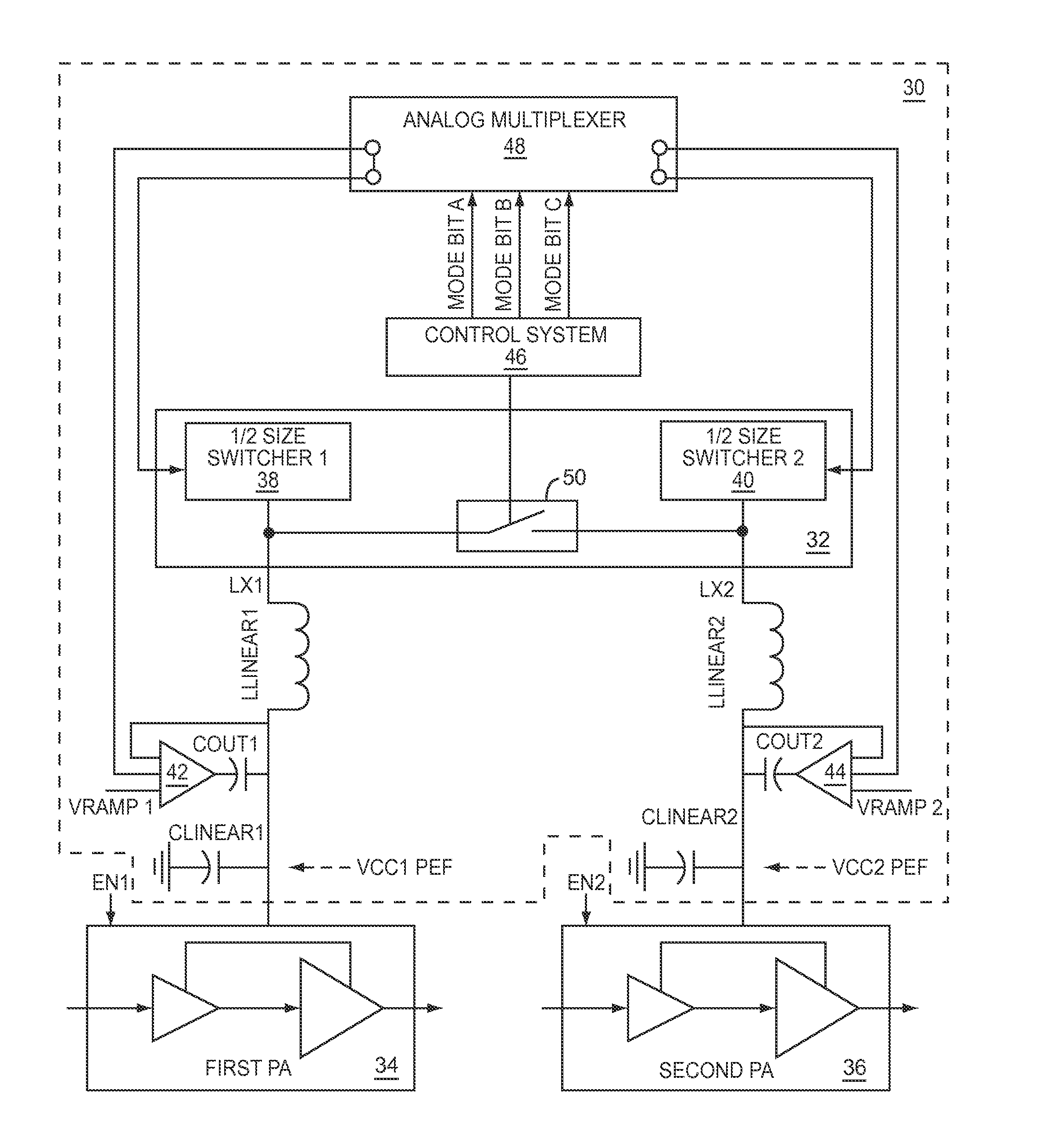
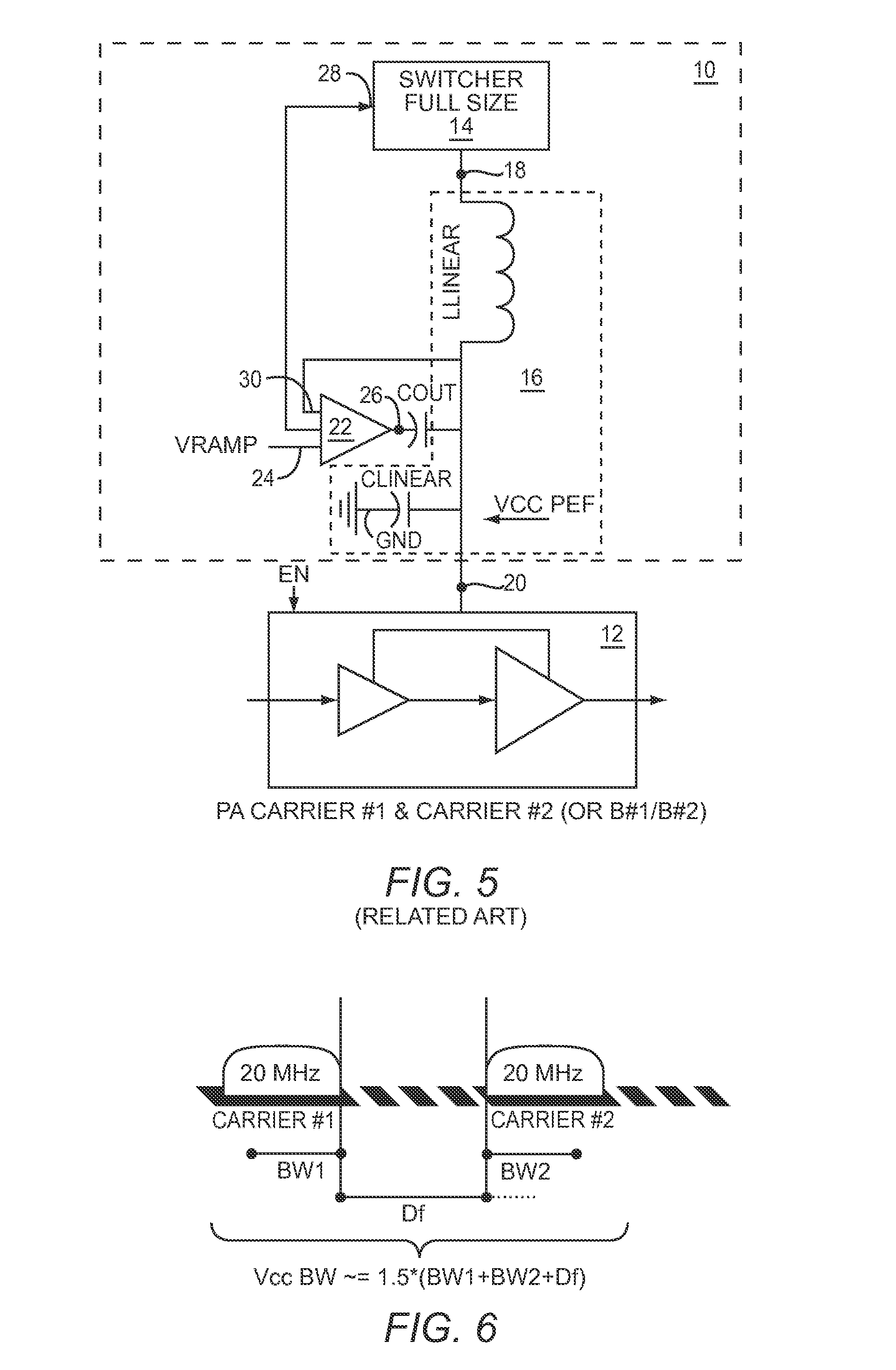
Power management system for multi-carriers transmitter
A power management system for a multi-carriers transmitter is disclosed. The power management system includes a first switcher having a control input and a power output, and a second switcher having a control input and a power output. Also included is a mode switch having a mode control input, wherein the mode switch is adapted to selectively couple the power output of the first switcher to the power output of the second switcher in response to a mode control signal received by the mode control input. Further included is a control system adapted to generate the mode control signal. The control system is coupled to the mode control input of the mode switch.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Power management system for multi-carriers transmitter
A power management system for a multi-carriers transmitter is disclosed. The power management system includes a first switcher having a control input and a power output, and a second switcher having a control input and a power output. Also included is a mode switch having a mode control input, wherein the mode switch is adapted to selectively couple the power output of the first switcher to the power output of the second switcher in response to a mode control signal received by the mode control input. Further included is a control system adapted to generate the mode control signal. The control system is coupled to the mode control input of the mode switch.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Mobile telephone apparatus
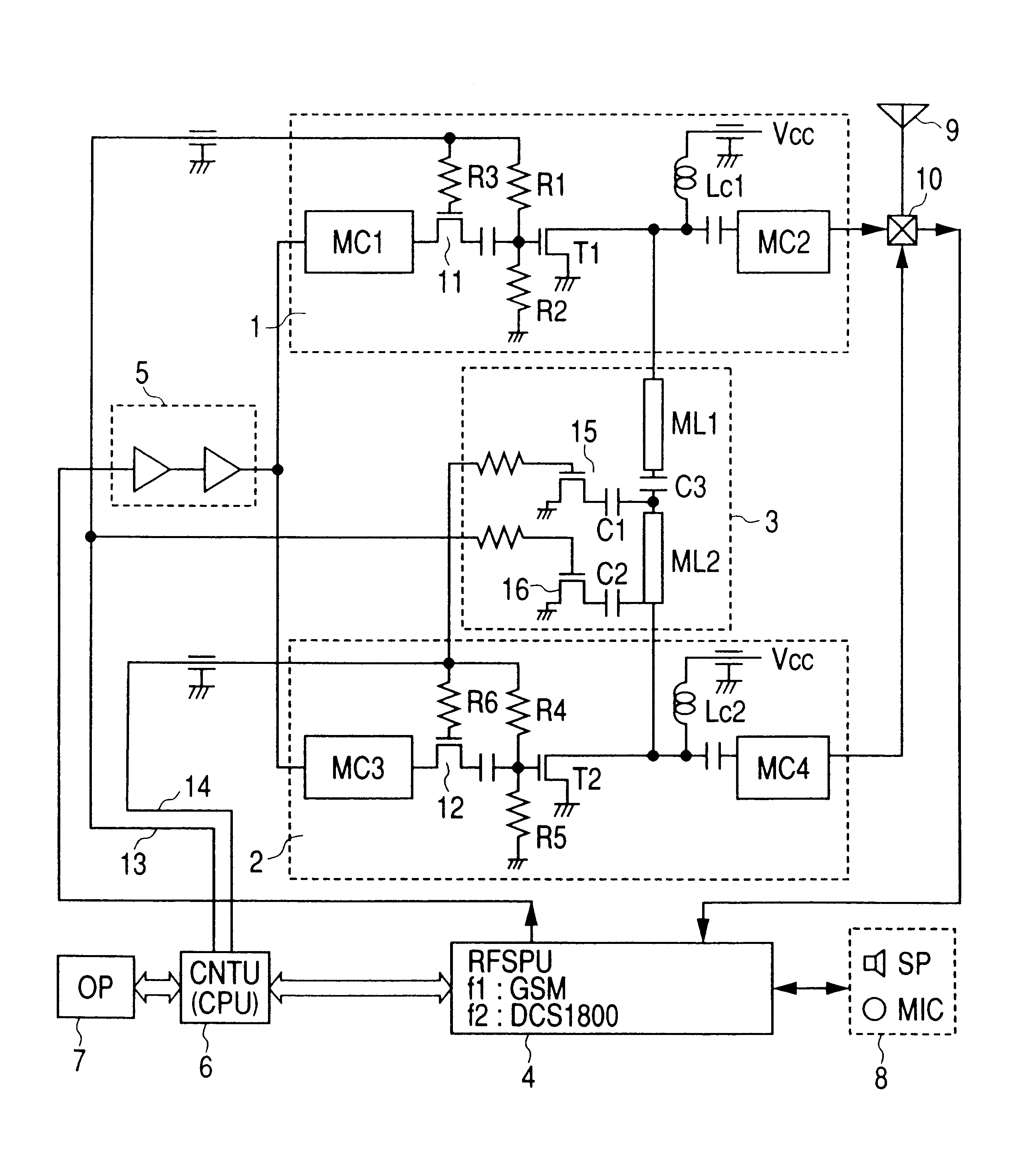
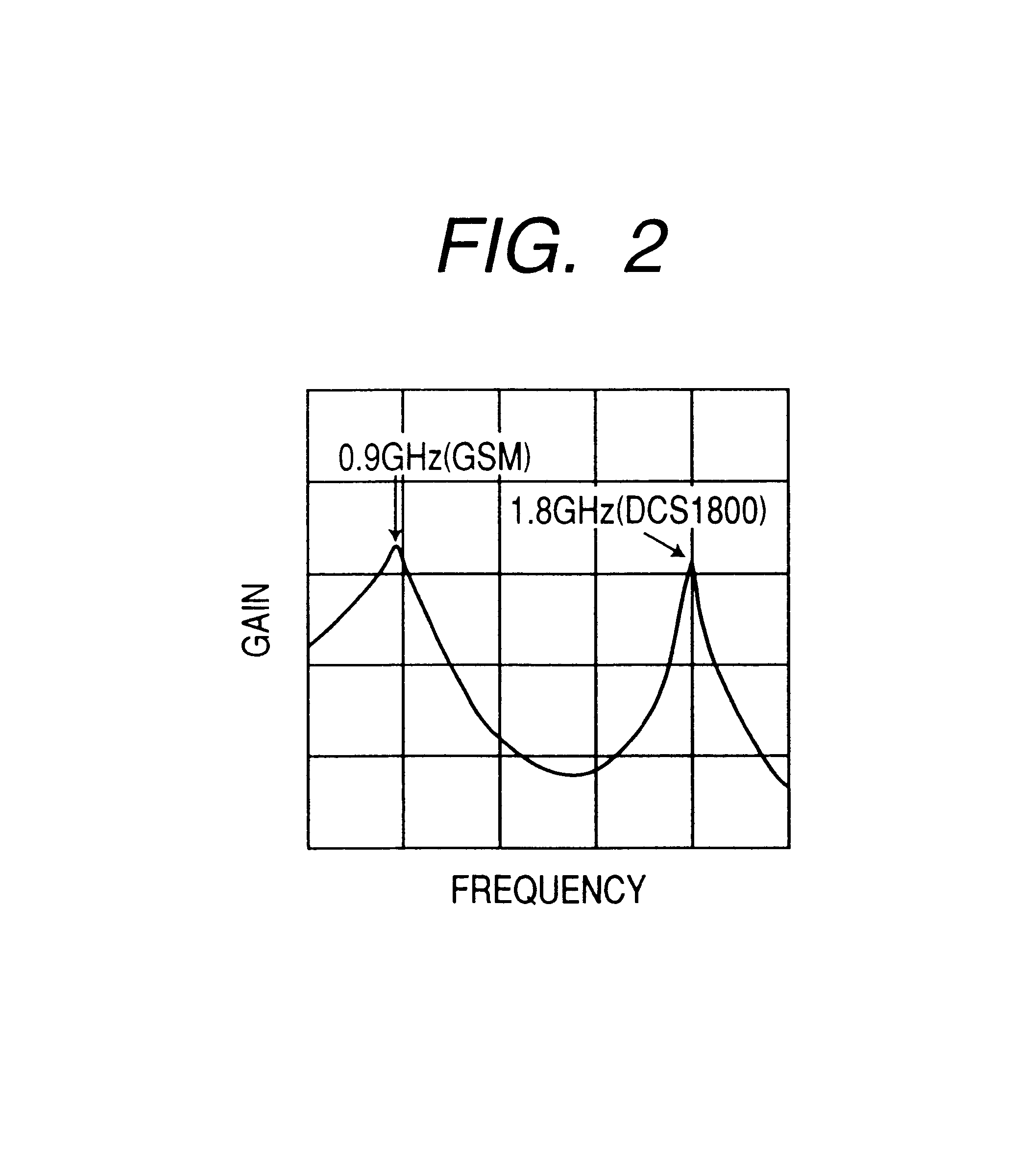
InactiveUS6865399B2Efficient outputMost efficientResonant long antennasGated amplifiersCommunications systemControl signal
In a mobile telephone apparatus corresponding to dual-band provided with an RF power module to operate in two kinds of different frequencies, a common harmonics control circuit is provided to the output circuit of such RF power module to realize higher efficiency in view of controlling respective harmonics power for both band frequencies. Moreover, a means for selectively setting the bias is also provided so that the maximum efficiency can be attained depending on the output power required with respective communication systems with the bias control signal output from the CPU of the control unit interlocking with selection of frequency of the mobile telephone apparatus body.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
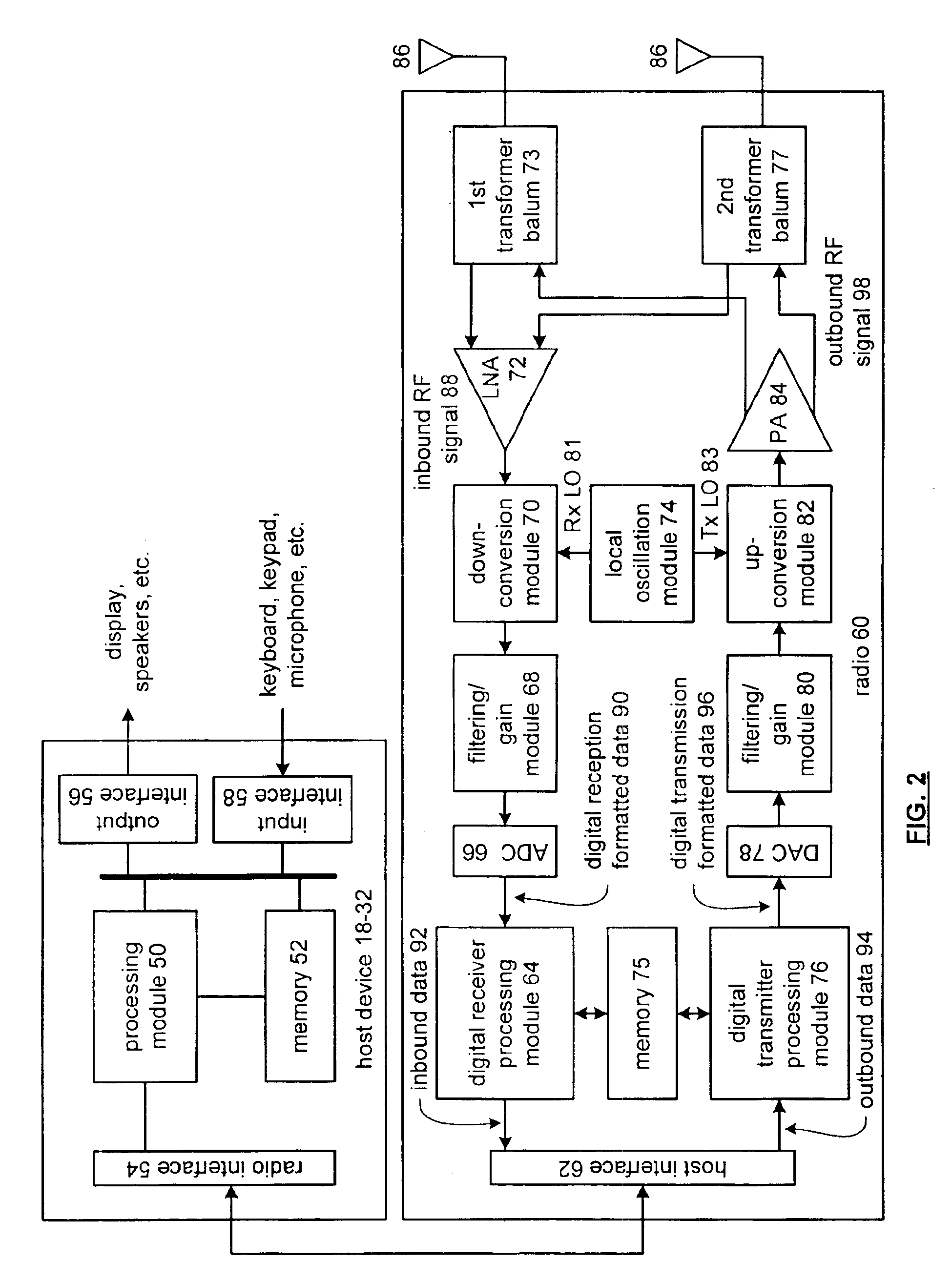
Circuits, processes, devices and systems for full integration of RF front end module including RF power amplifier
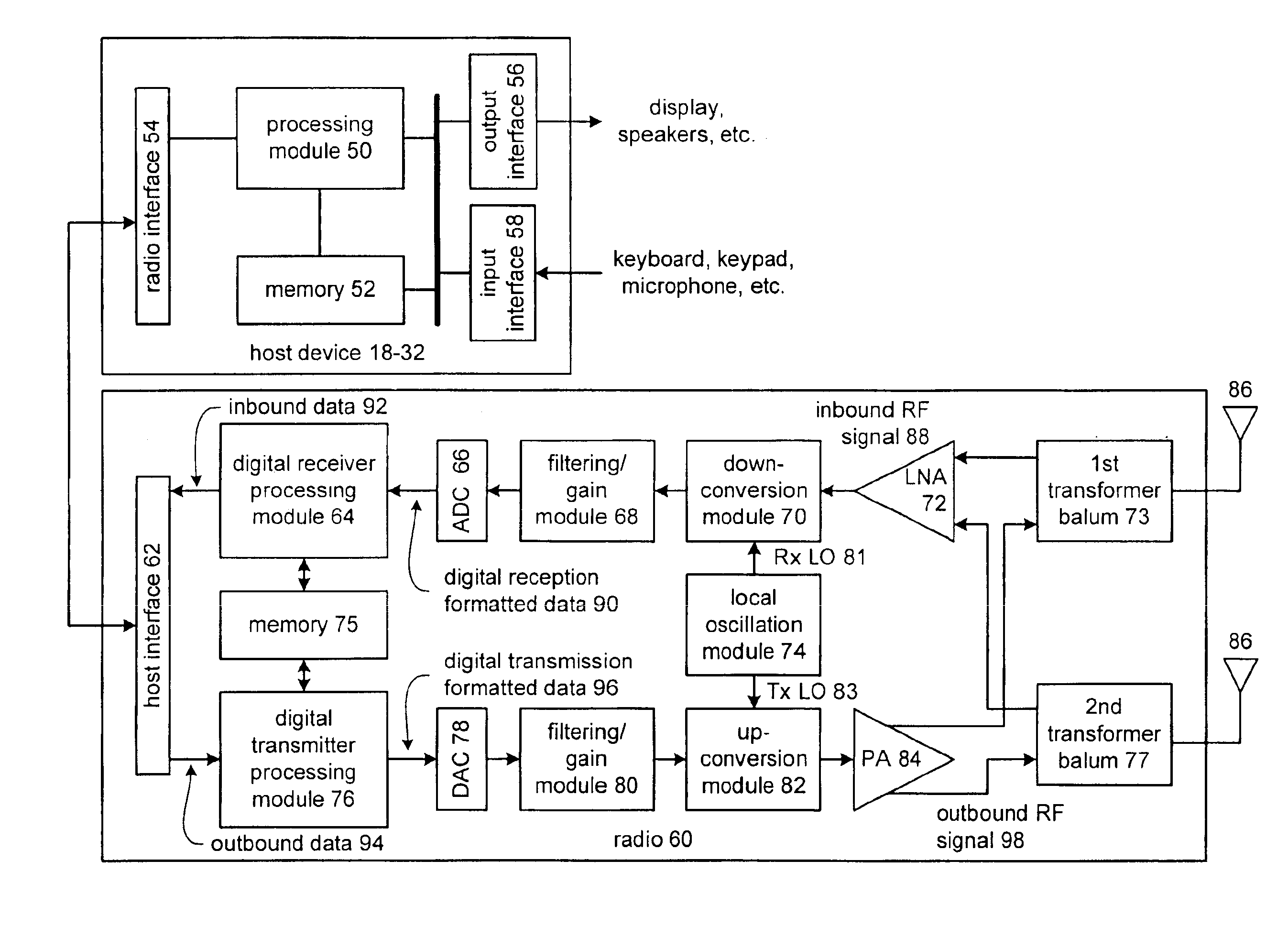
ActiveUS20090289721A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioGated amplifiersStatic storageRF front endAudio power amplifier
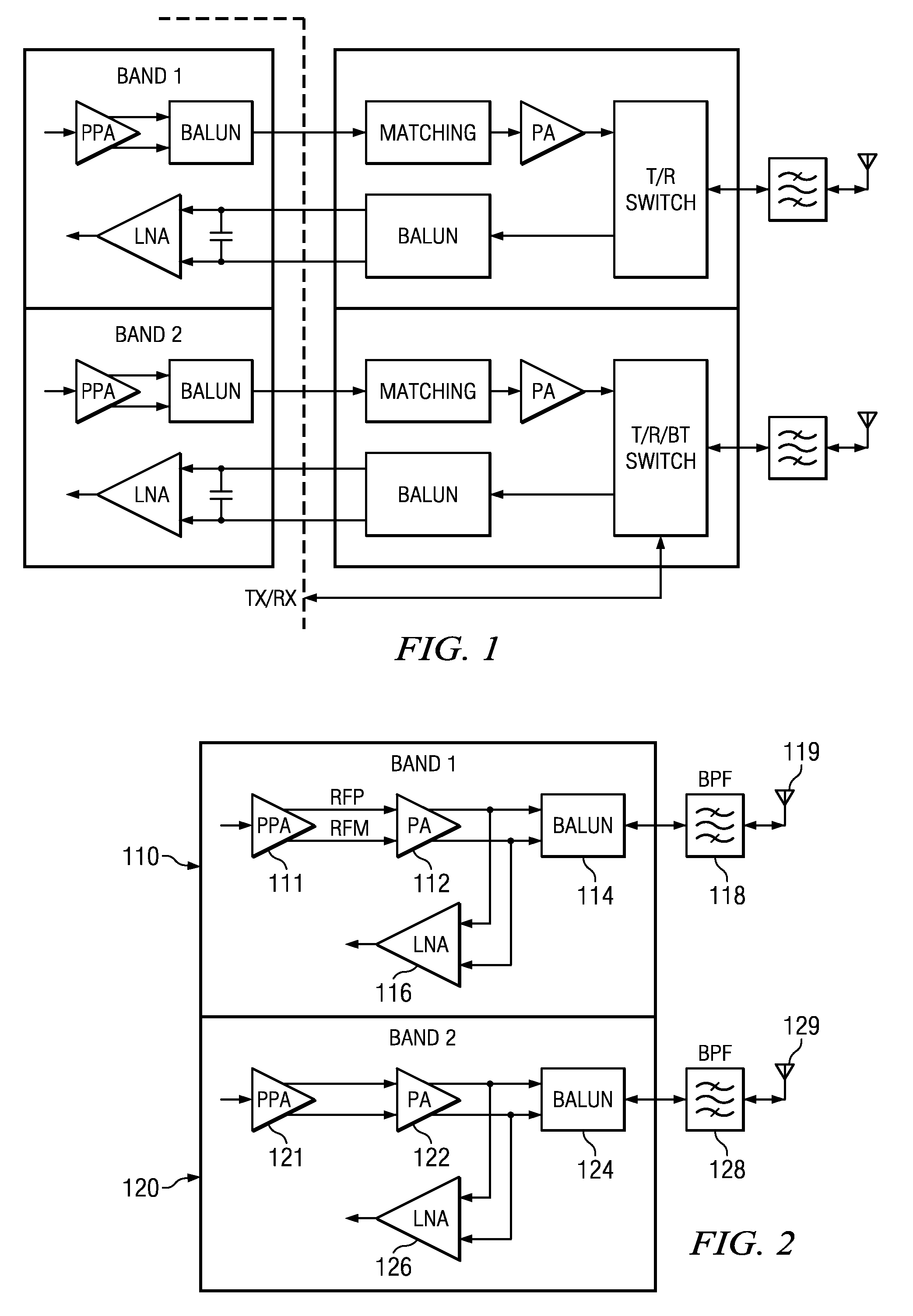
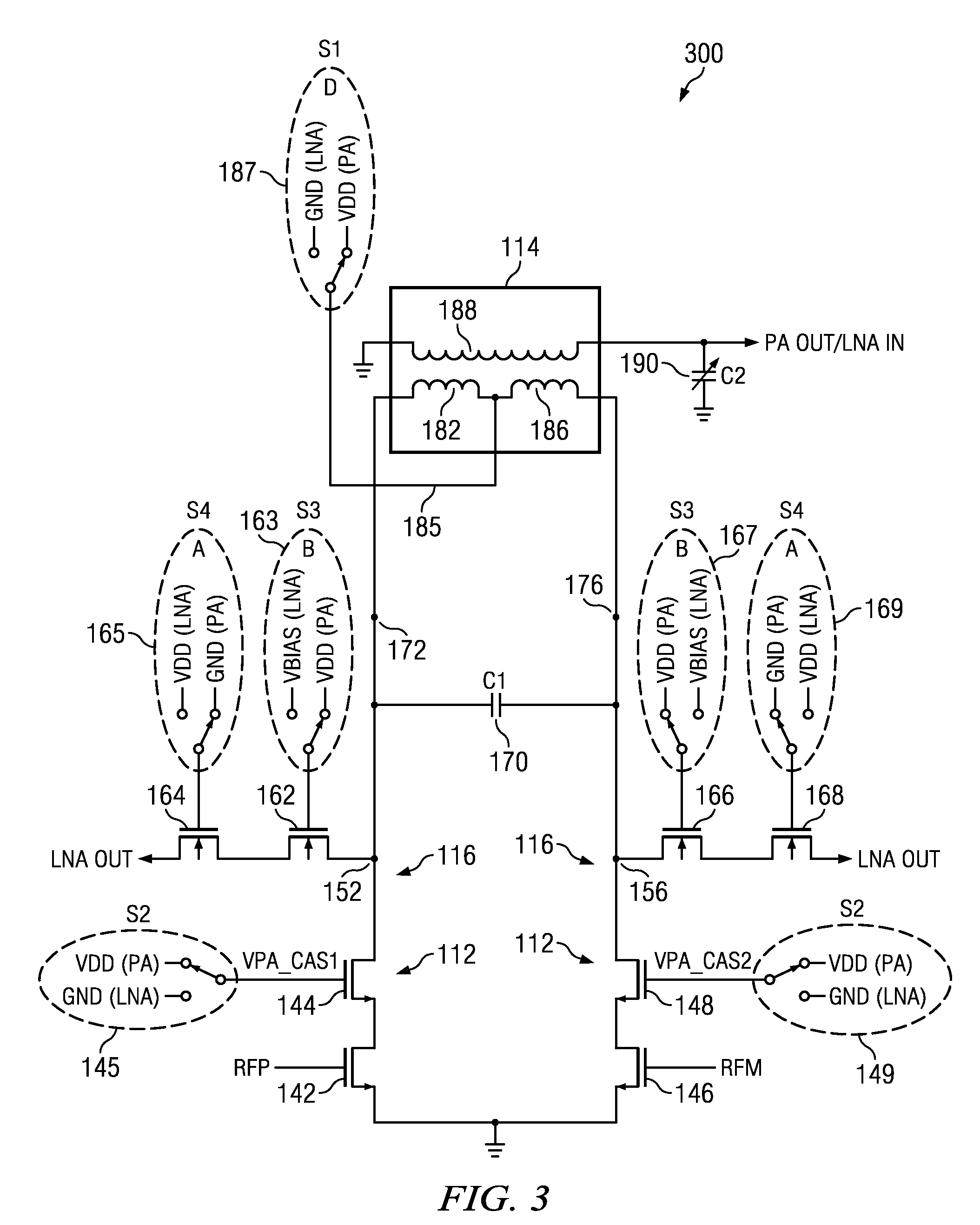
An electronic circuit comprising a transistor-based RF (radio frequency) power amplifier (112) having balanced outputs (172, 176), a transistor-based receiver RF amplifier (116) having balanced inputs (152, 156) ohmically connected to said balanced outputs (172, 176) respectively of said RF power amplifier (112), and a balun (114) having a primary (182, 186) and a secondary (188), said primary (182, 186) having primary connections and a supply connection (185) of said primary (182, 186) intermediate said primary connections and said primary connections ohmically connected both to said balanced outputs (172, 176) of said RF power amplifier (112) respectively and to said balanced inputs (152, 156) of said receiver RF amplifier, thereby to switchlessly couple RF between the balun (114) and the RF power amplifier (112) and switchlessly couple RF between the balun (114) and the receiver RF amplifier (116). Other electronic circuits, processes, devices and systems are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Envelope tracking with low frequency loss correction
ActiveUS9831834B2Improve power efficiencyGated amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
DAC based switching power amplifier
InactiveUS7509102B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
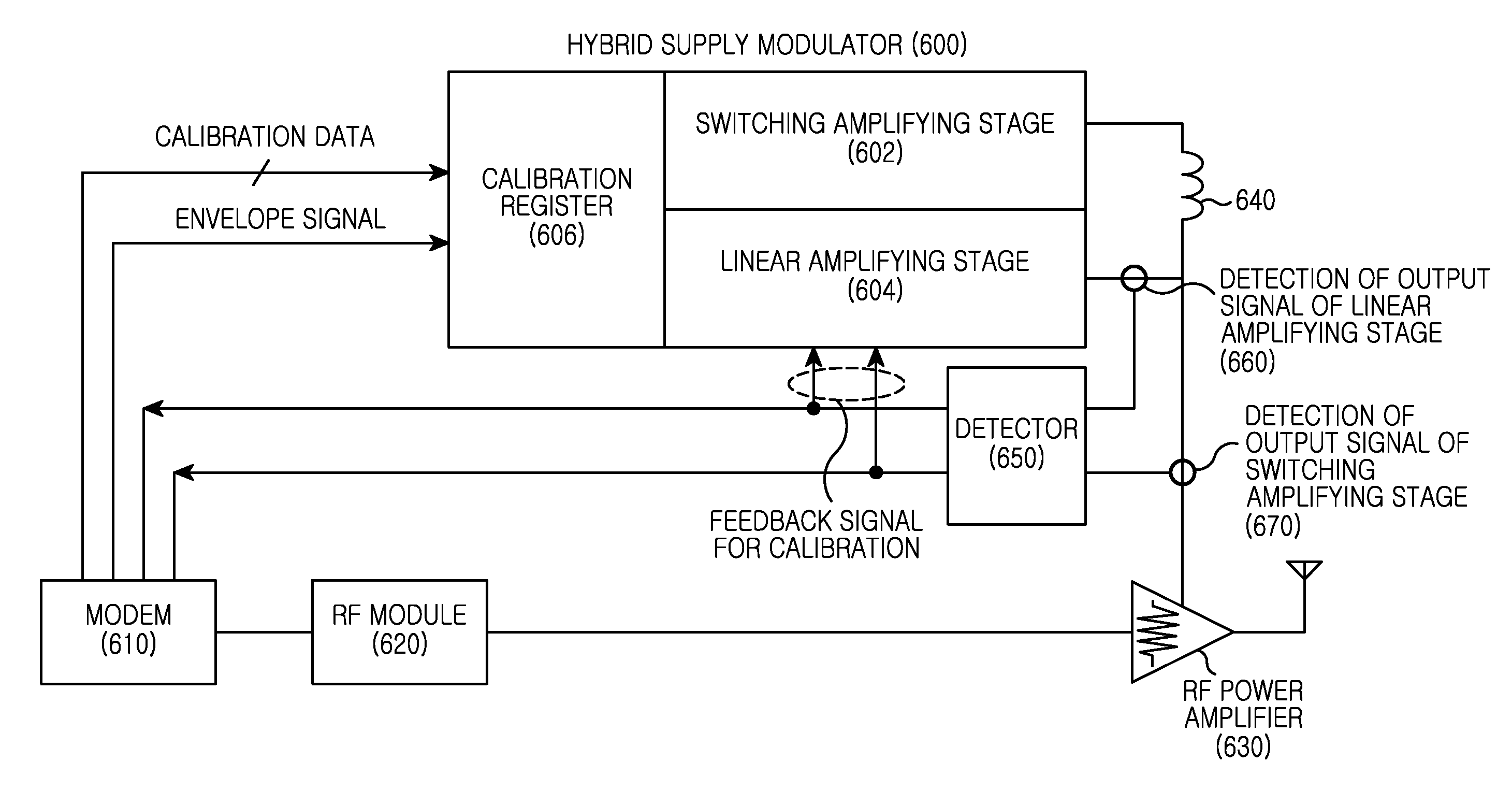
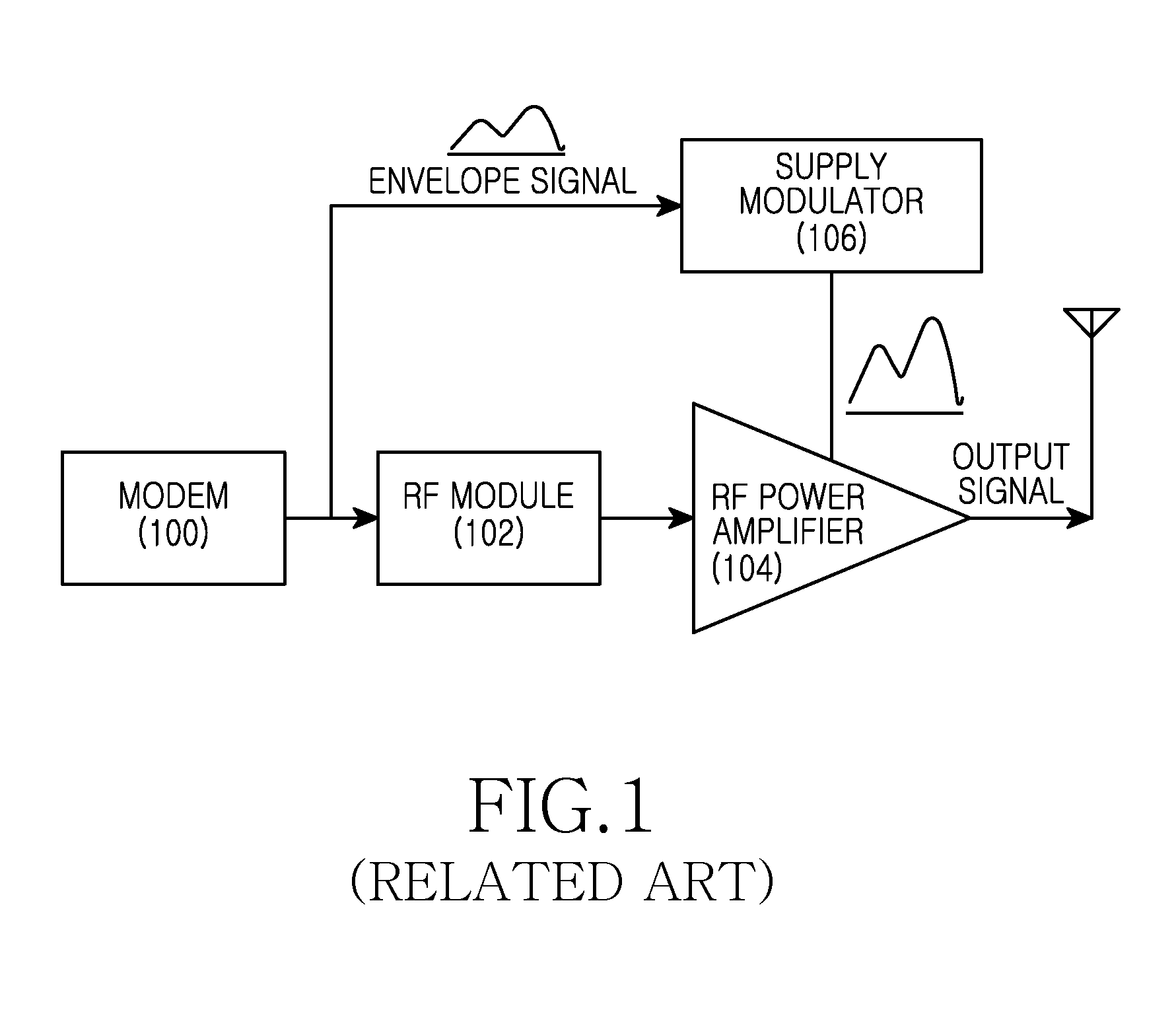
Apparatus and method for calibration of supply modulation in transmitter
ActiveUS20130094553A1Excellent characteristicsImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGated amplifiersModem deviceEngineering
A transmit apparatus having a supply modulator is provided. The apparatus includes a detector and the supply modulator. In the method, the detector detects an output signal of the supply modulator. Also, the supply modulator receives the detected output signal of the supply modulator from the detector and calibrates a modulation characteristic of the supply modulator. The transmit apparatus having a supply modulator includes a modulator / demodulator (modem) and the supply modulator. The modem provides a calibration signal for calibrating a modulation characteristic of the supply modulator, to the supply modulator. The supply modulator outputs a modulated signal in accordance with the calibrated modulation characteristic of the supply modulator based on the calibration signal from the modem.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient power amplification system
A system for efficient power amplification of an electromagnetic signal includes a switchplexer having at least two inputs and an output. The switchplexer may be configured to provide communication between a selected switchplexer input and the switchplexer output. The system also may include two or more amplifier stages, each having an input and an output, and one or more output matching circuits. Each of the output matching circuits may include an input in communication with one of the amplifier stage outputs, as well as an output in communication with one of the switchplexer inputs. A control unit may be configured to control selection of the selected switchplexer input and to selectively activate at least one of the amplifier stages.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
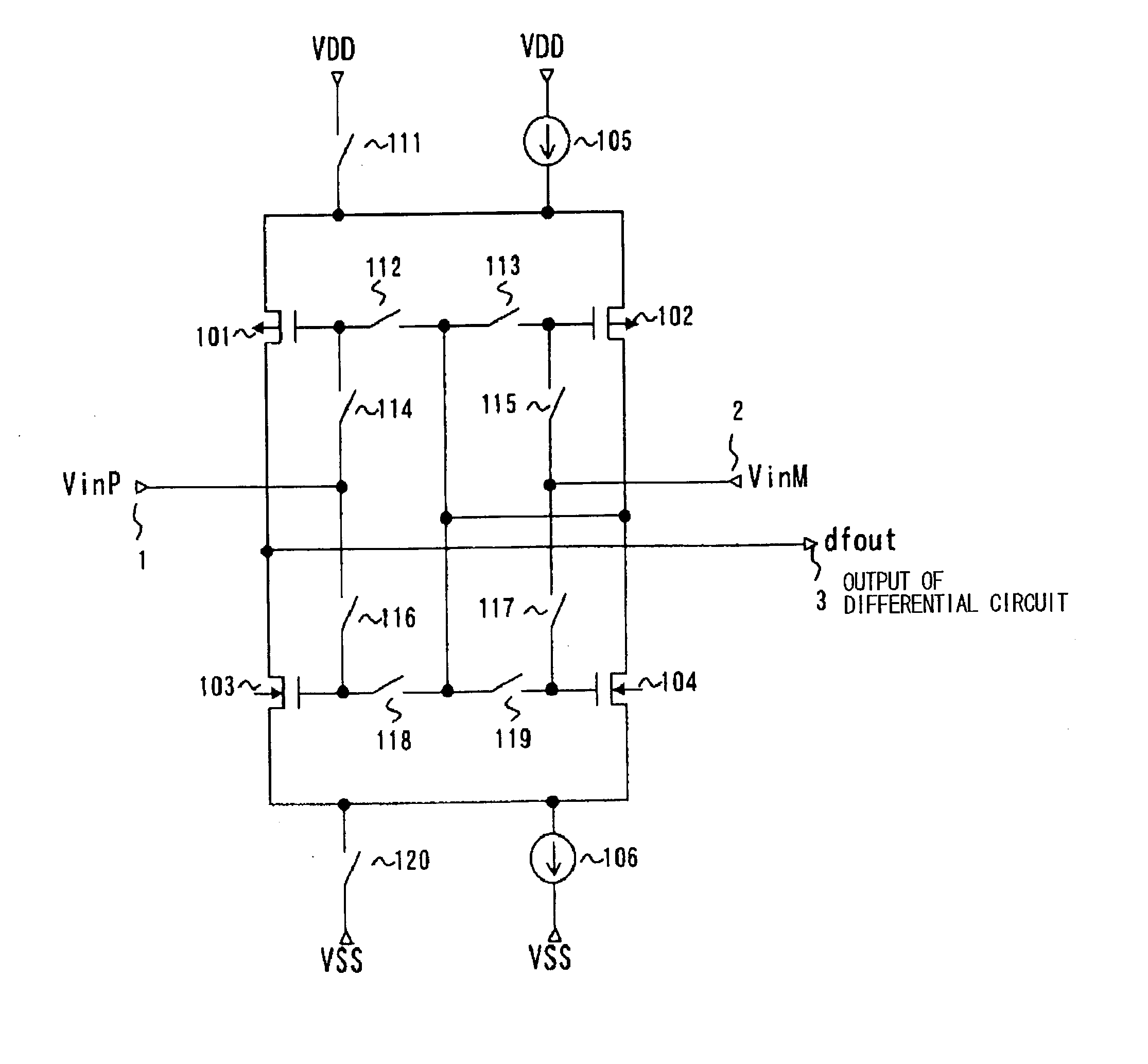
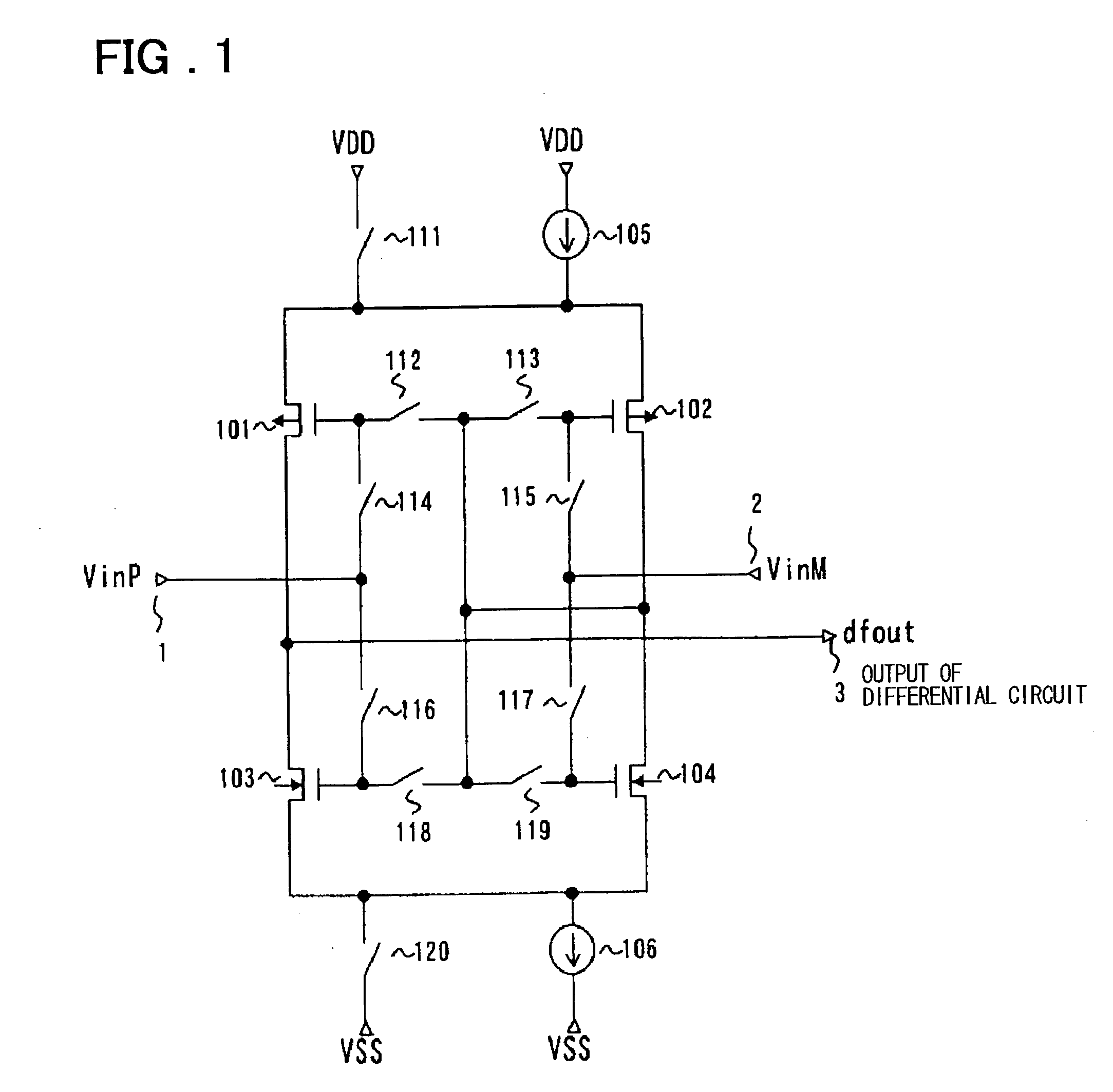
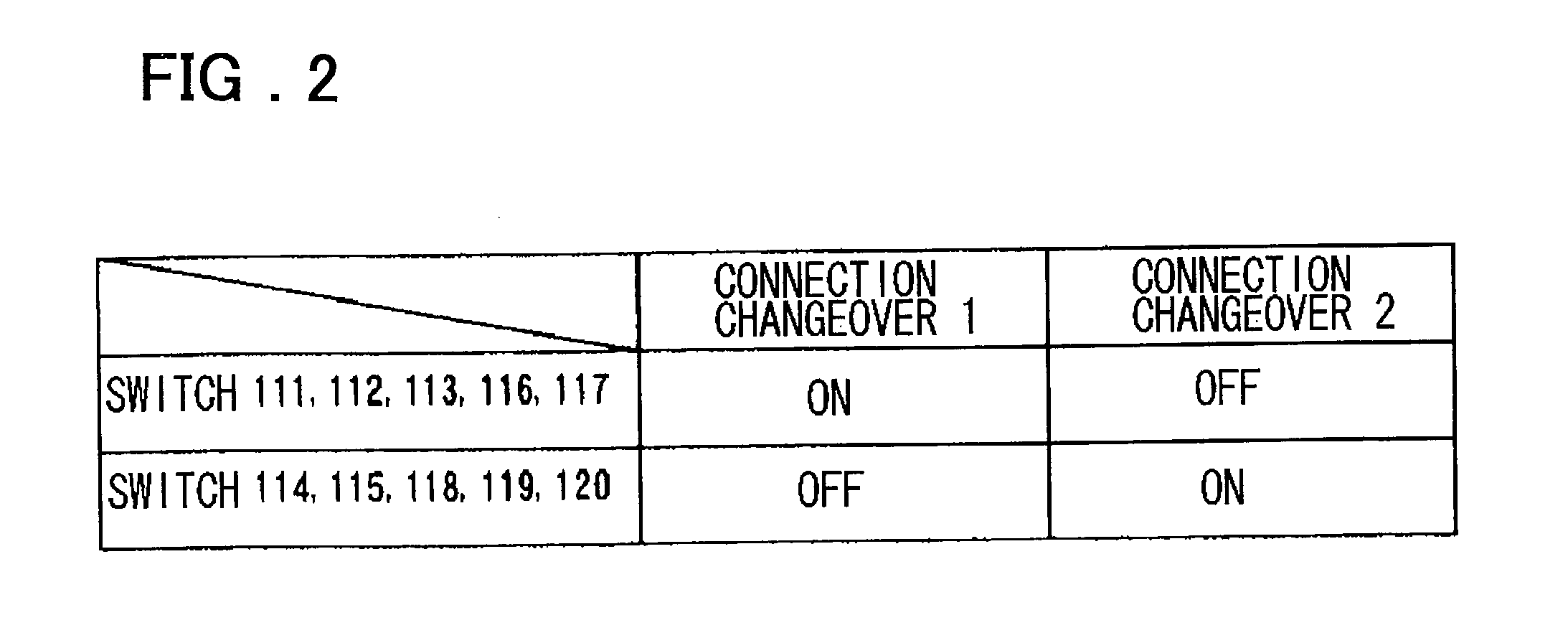
Differential circuit, amplifier circuit, driver circuit and display device using those circuits
ActiveUS20030160749A1Reduce power consumptionReducing amplitude difference deviationStatic indicating devicesGated amplifiersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A differential circuit and an amplifier circuit for reducing an amplitude difference deviation, performing a full-range drive, and consuming less power are disclosed. The circuit includes a first pair of p-type transistors and a second pair of n-type transistors. A first current source and a first switch are connected in parallel between the sources of the first pair of transistors, which are tied together, and a power supply VDD. A second current source and a second switch are connected in parallel between the sources of the second pair of transistors, which are tied together, and a power supply VSS. The circuit further includes connection changeover means that performs the changeover of first and second pairs between a differential pair that receives differential input voltages and a current mirror pair that is the load of the differential pair. When one of the two pairs is the differential pair, the other is the current mirror pair. In a differential amplifier circuit, there is provided an added transistor connected in parallel to a transistor, which is one transistor of a differential pair transistors, whose control terminal is a non-inverting input terminal. The added transistor has a control terminal for receiving a control voltage which is set so that, when an input voltage applied to the non-inverting input terminal is in a range in which the transistor whose control terminal is the non-inverting input terminal is turned off, the added transistor is turned on.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
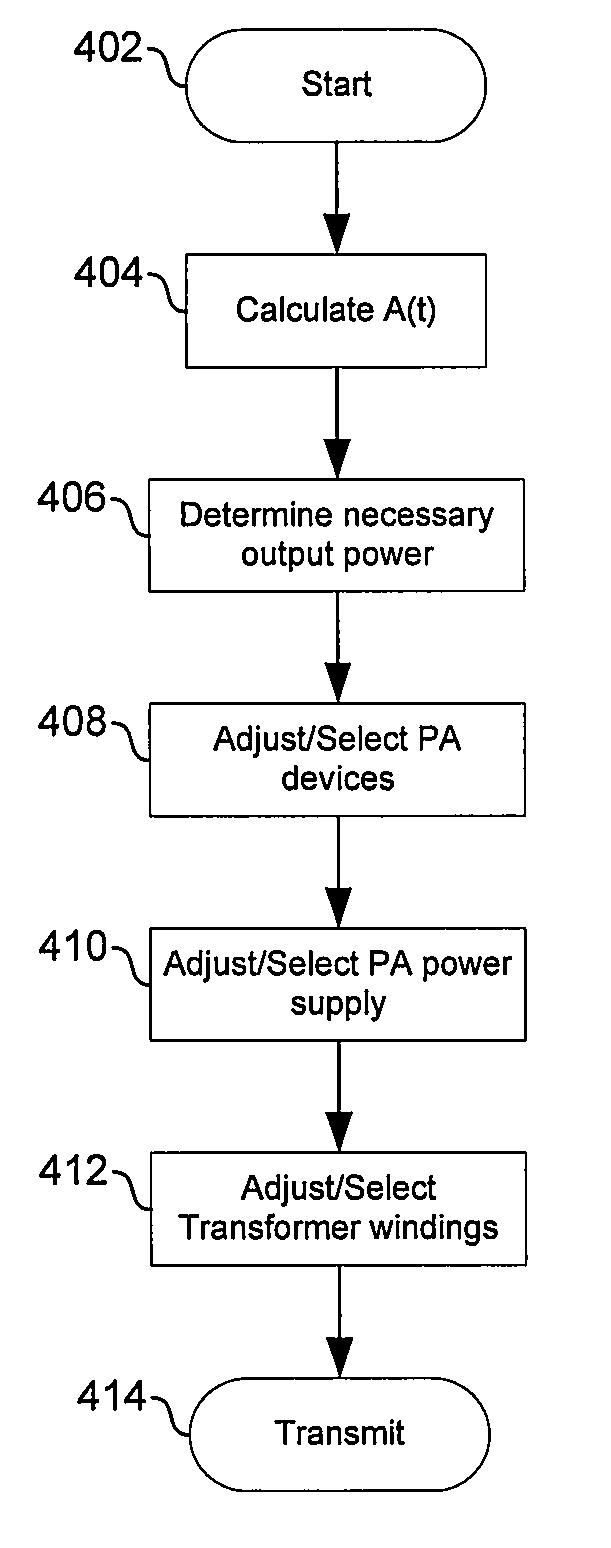
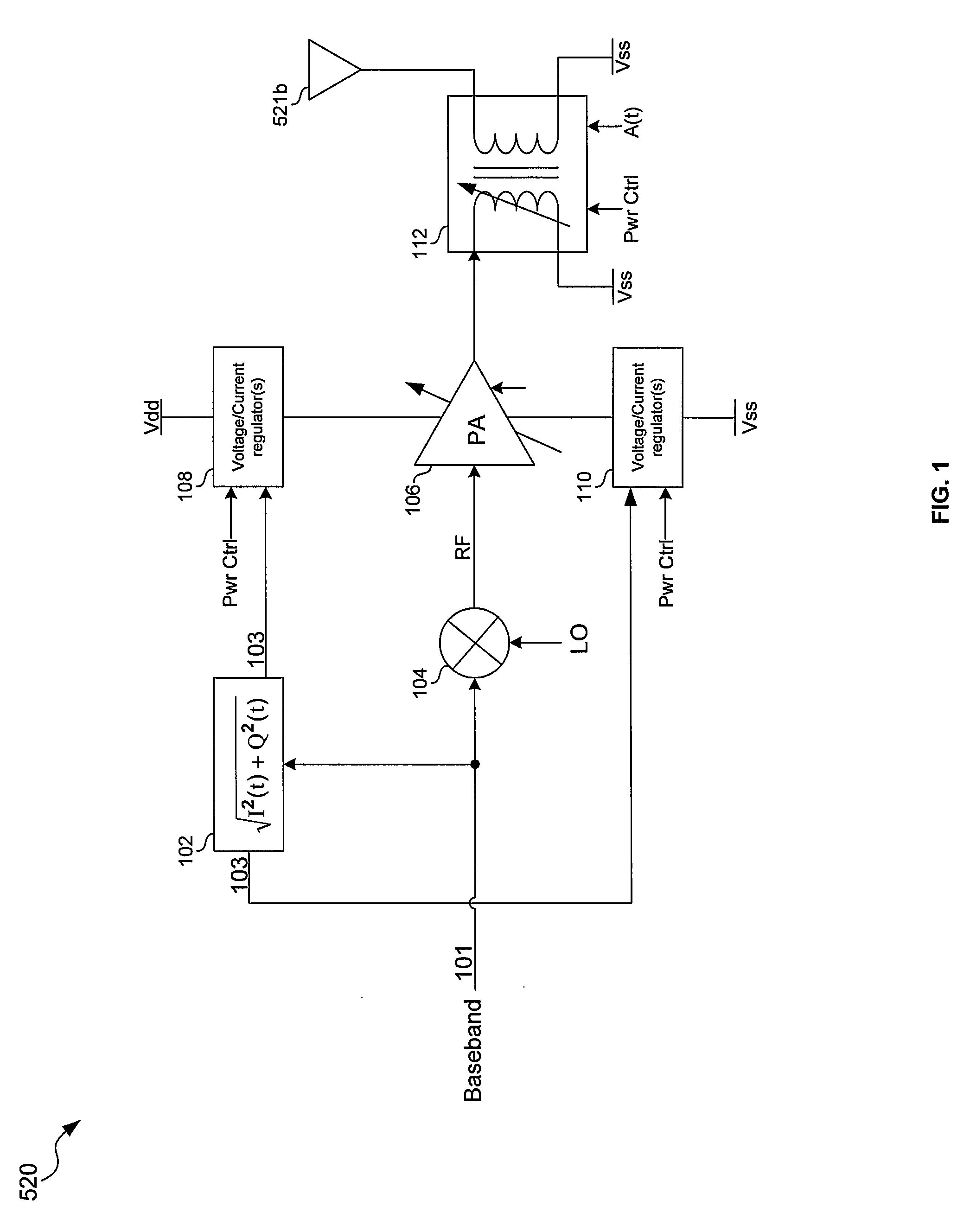
Method and system for scaling supply, device size, and load of a power amplifier
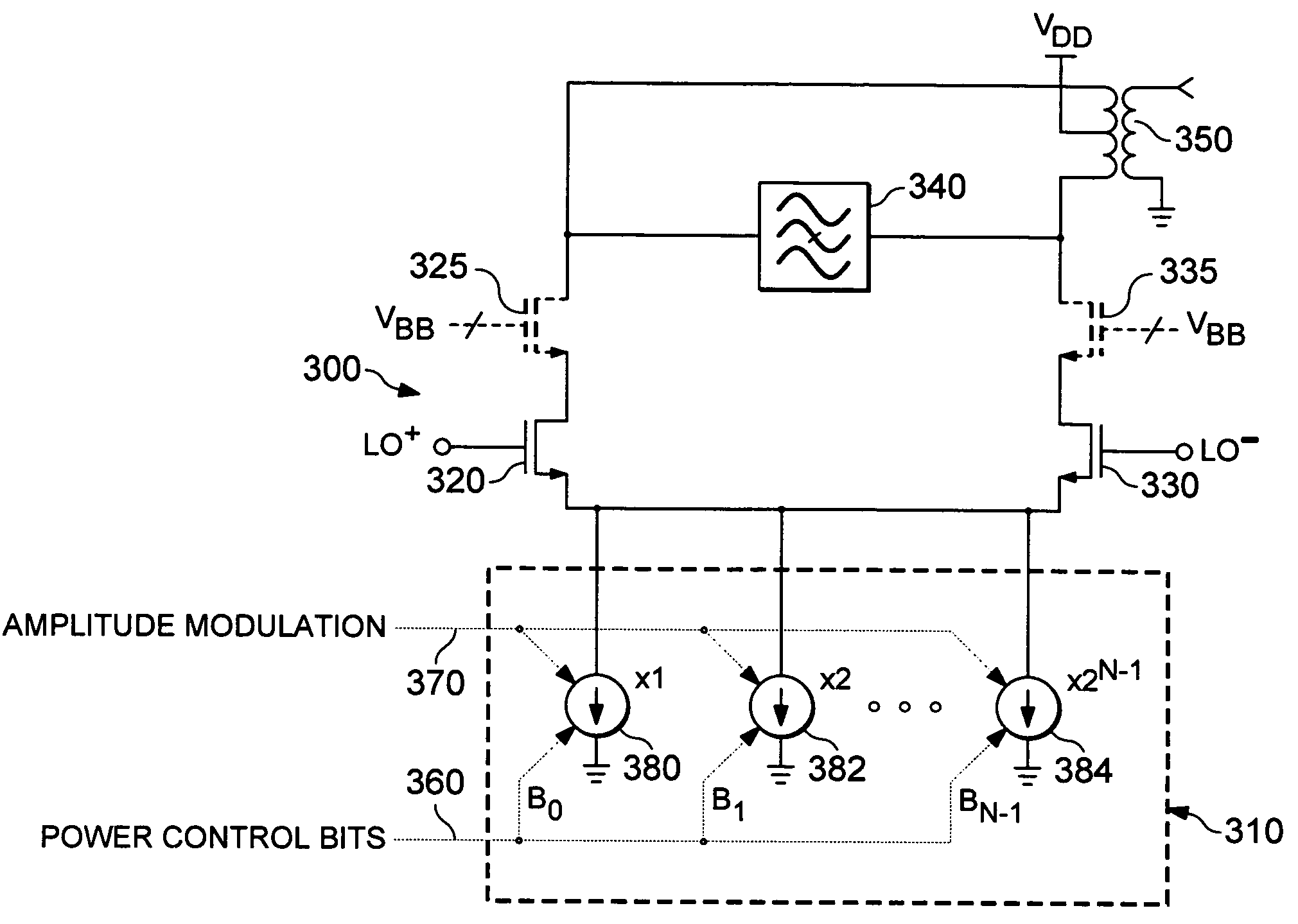
Aspects of a method and system for scaling supply, device size, and load of a power amplifier (PA) are provided. In this regard parameters of a PA, and a voltage, a current, and / or a load of the PA may be configured based on a determined amplitude of a baseband signal and based on a transmit power of the PA. In this regard, the PA may be configured by configuring device size of and / or selecting one or more transistors within the PA. The load may be a transformer and may be configured by adjusting a windings ratio. The PA may comprise one or more differential pairs. In this regard, device size of the differential pair(s) may be configured based on the determined amplitude of the baseband signal and based on a transmit power of the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Microcontroller having an on-chip high gain amplifier
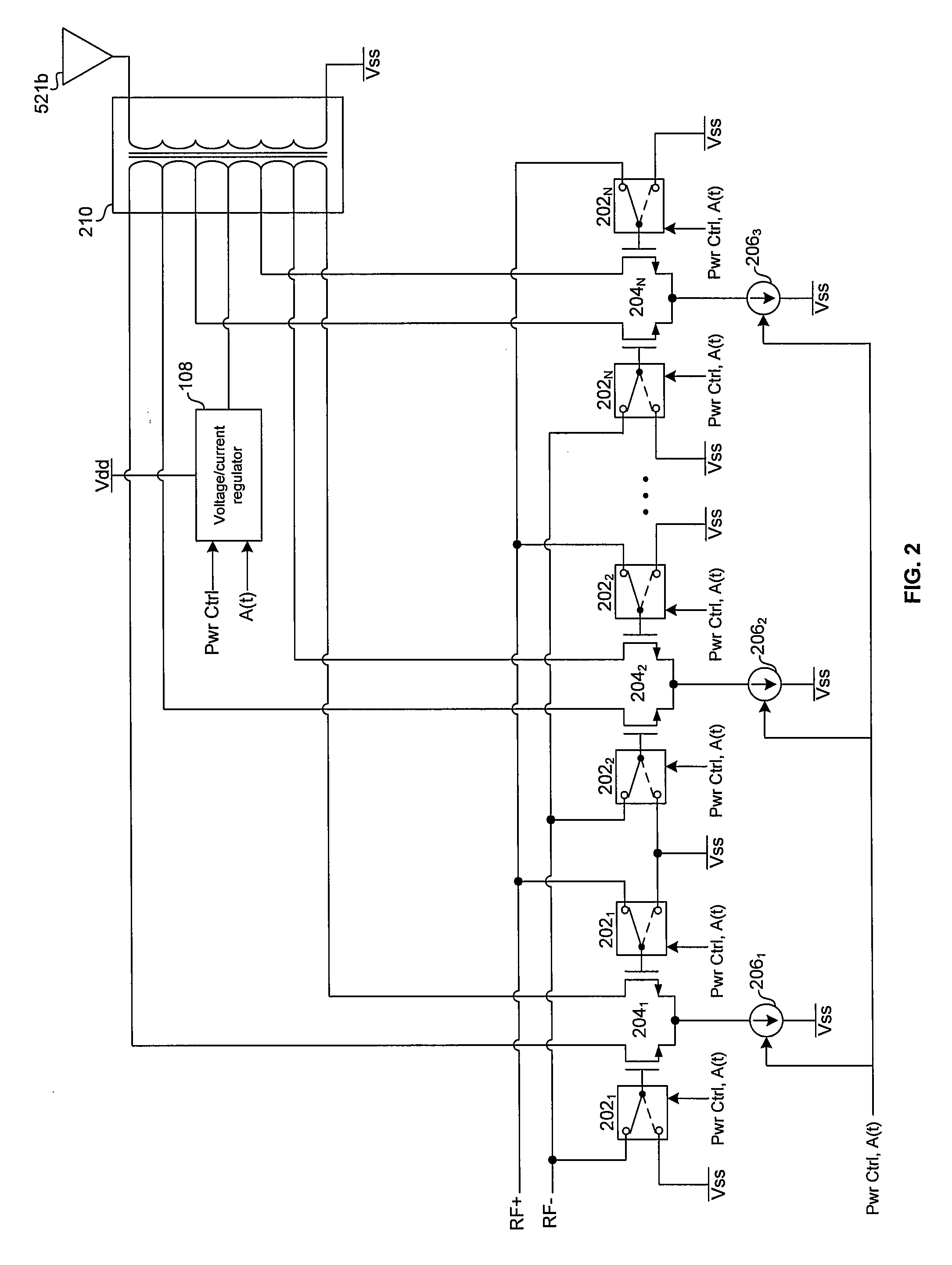
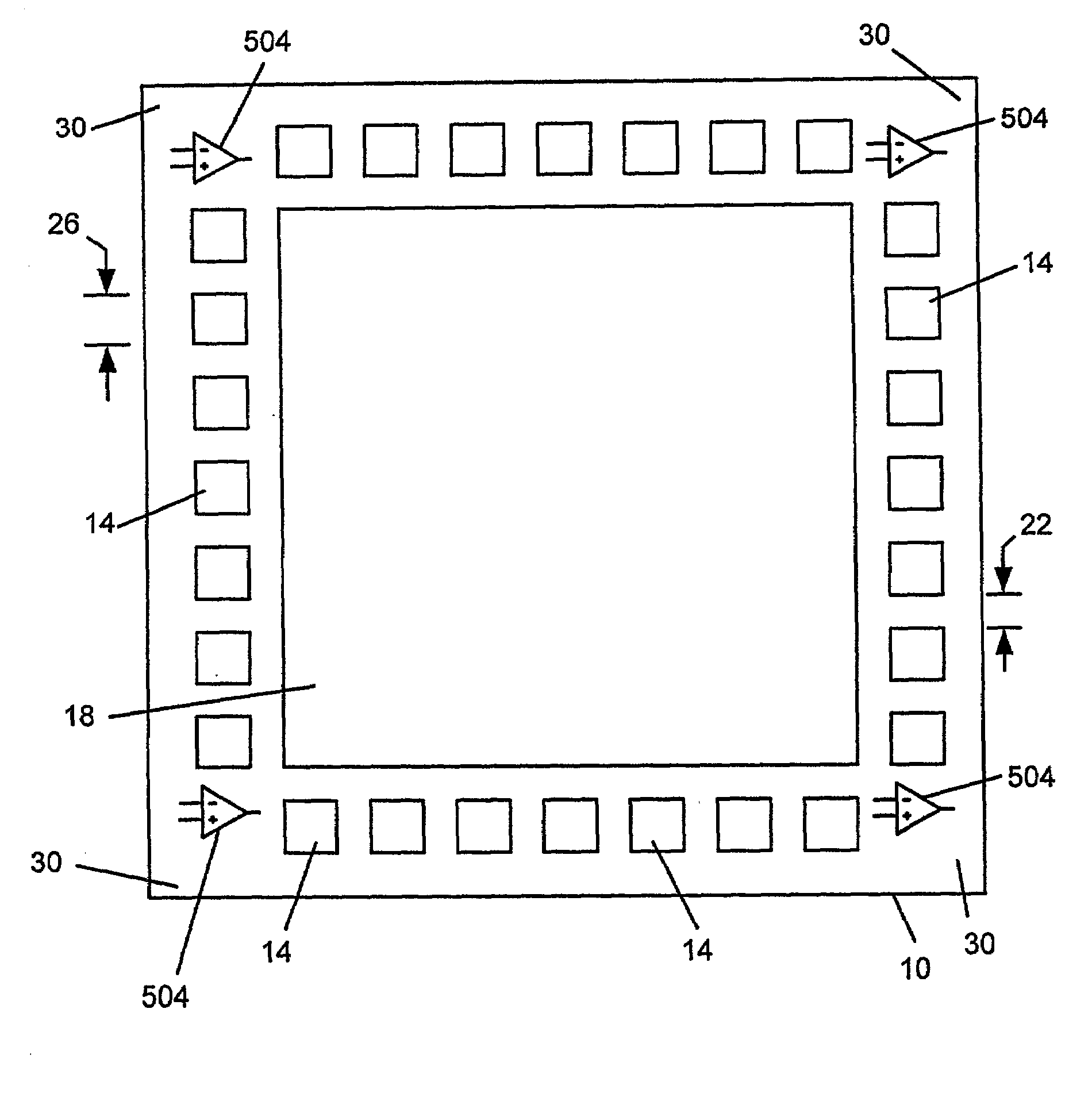
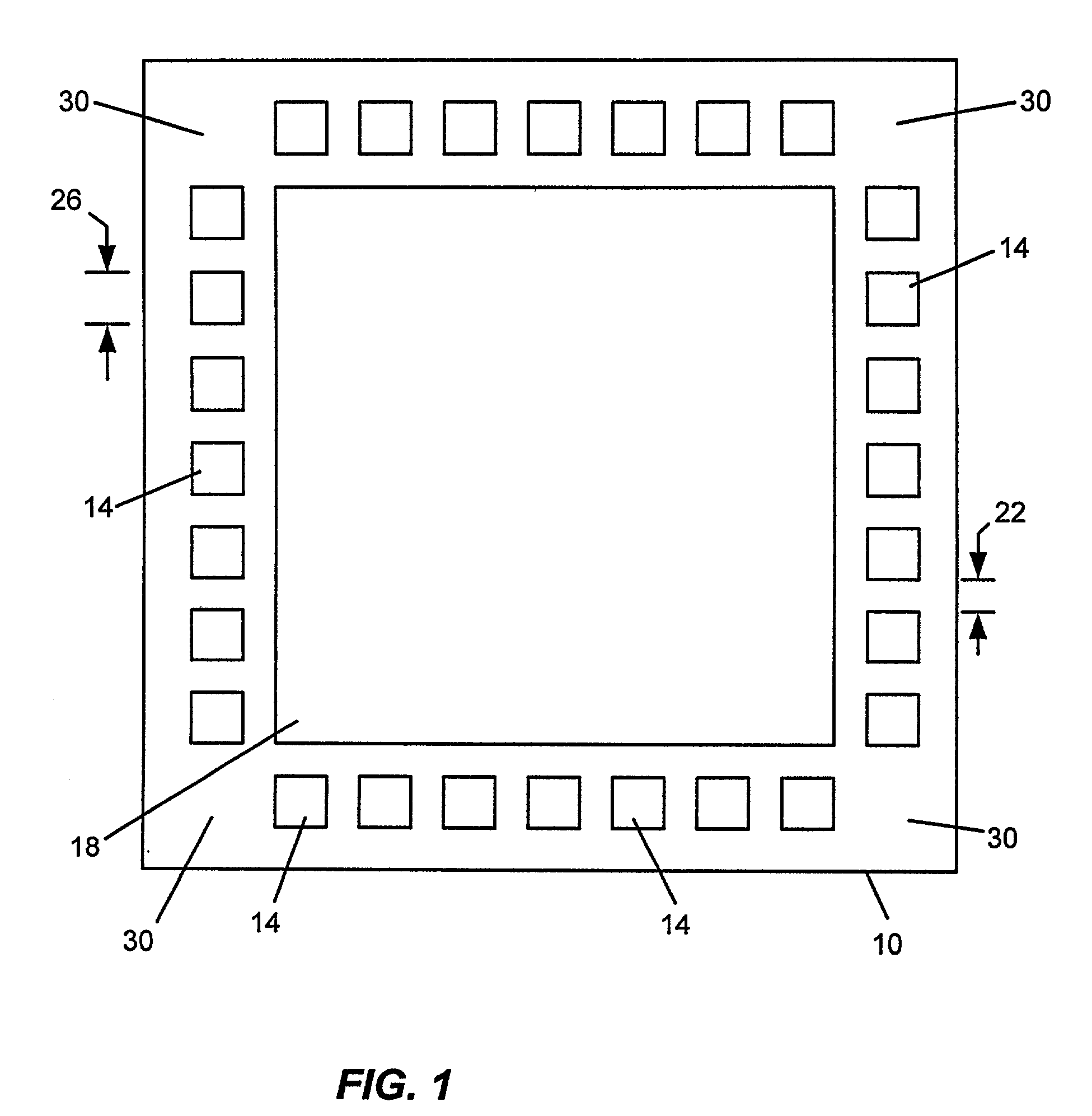
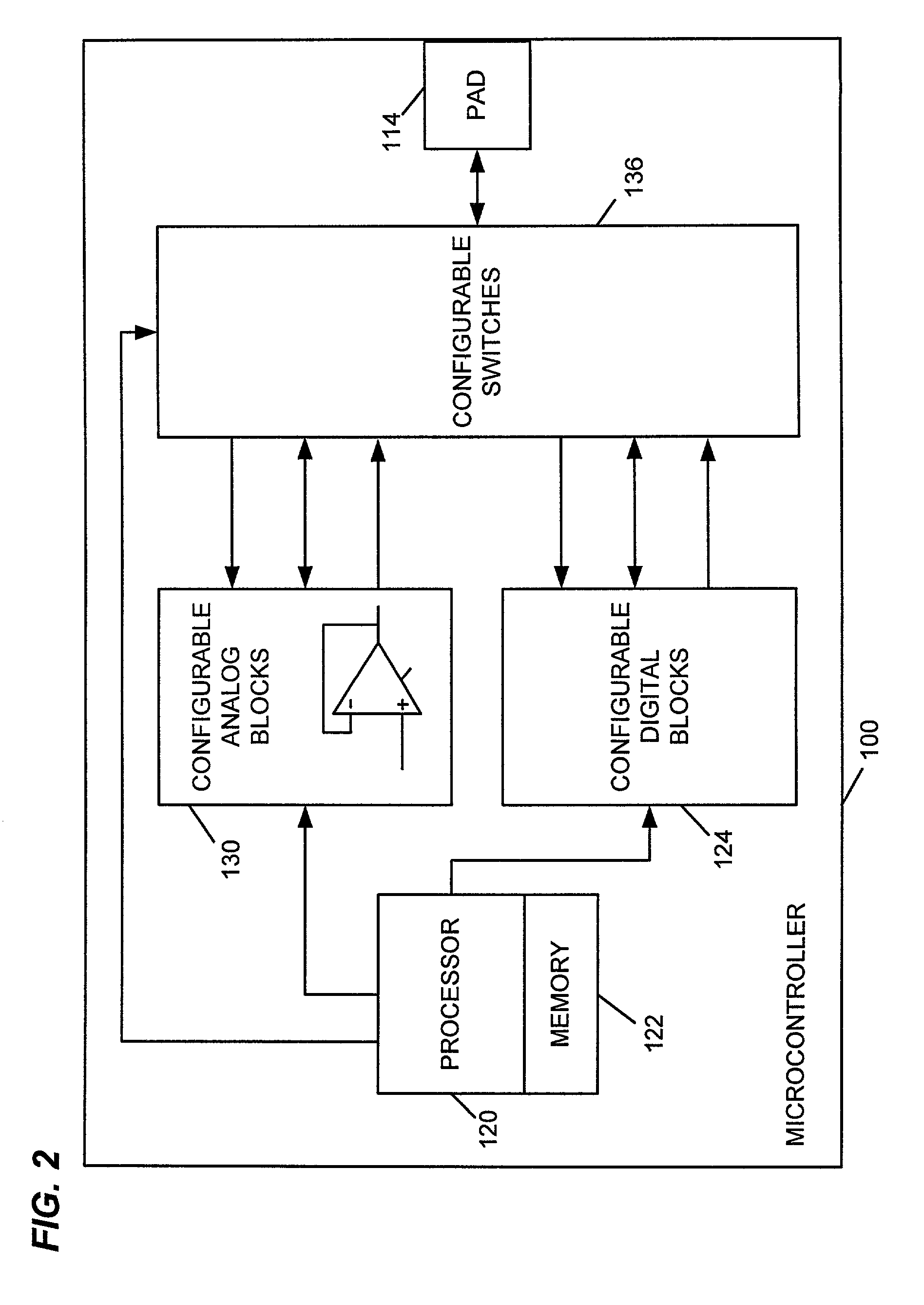
ActiveUS7149316B1Improve versatilityHigh gainGated amplifiersSolid-state devicesMicrocontrollerAudio power amplifier
A microcontroller includes a wide band, high gain amplifier on-chip capable of driving a 32 ohm speaker. The amplifier is controllable by the microcontroller processor to either enable or disable the amplifier and switch between multiple modes of power. In one embodiment, one or more such amplifiers are situated anywhere on the integrated circuit die including at the corners of the die.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com