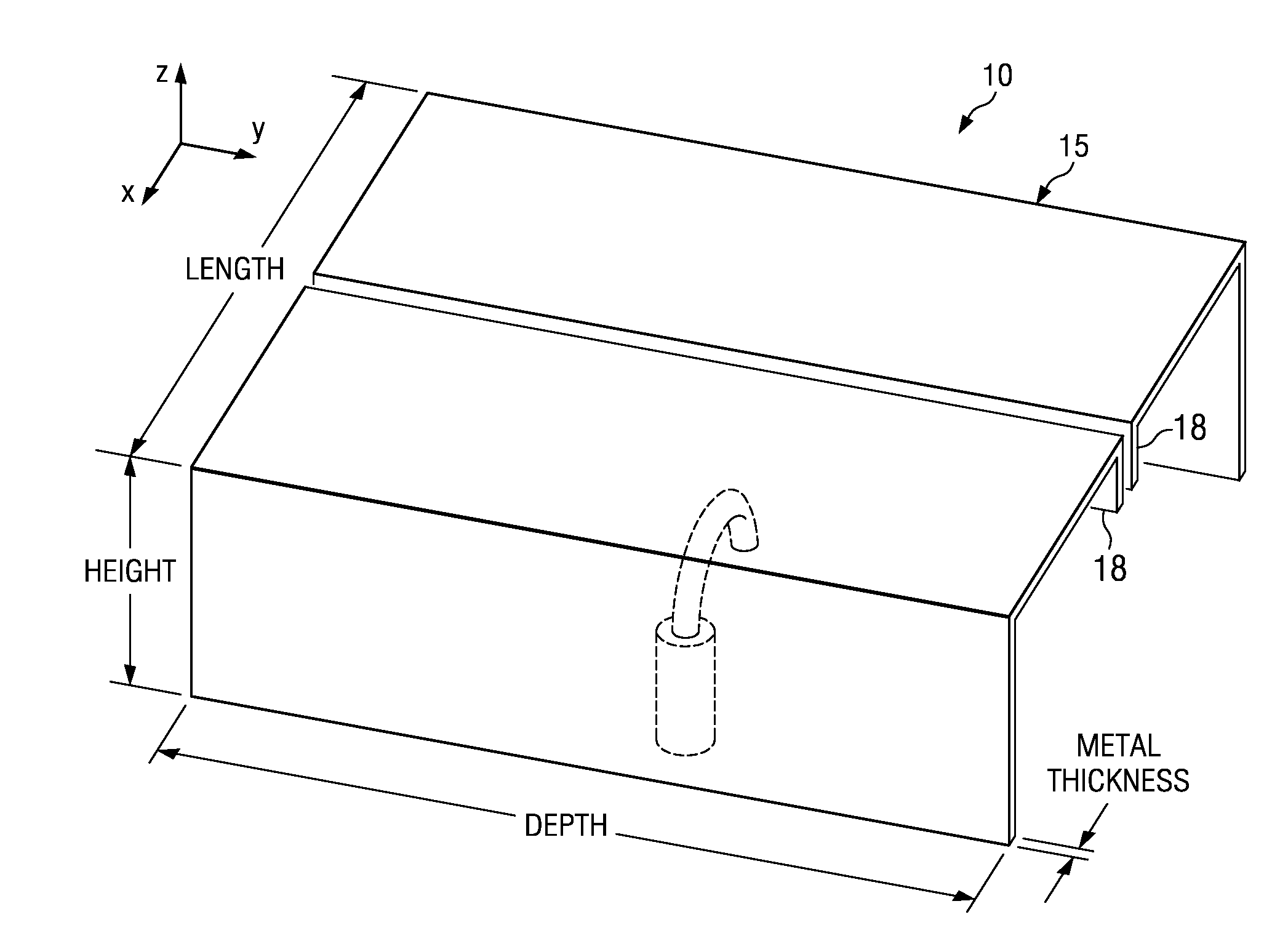
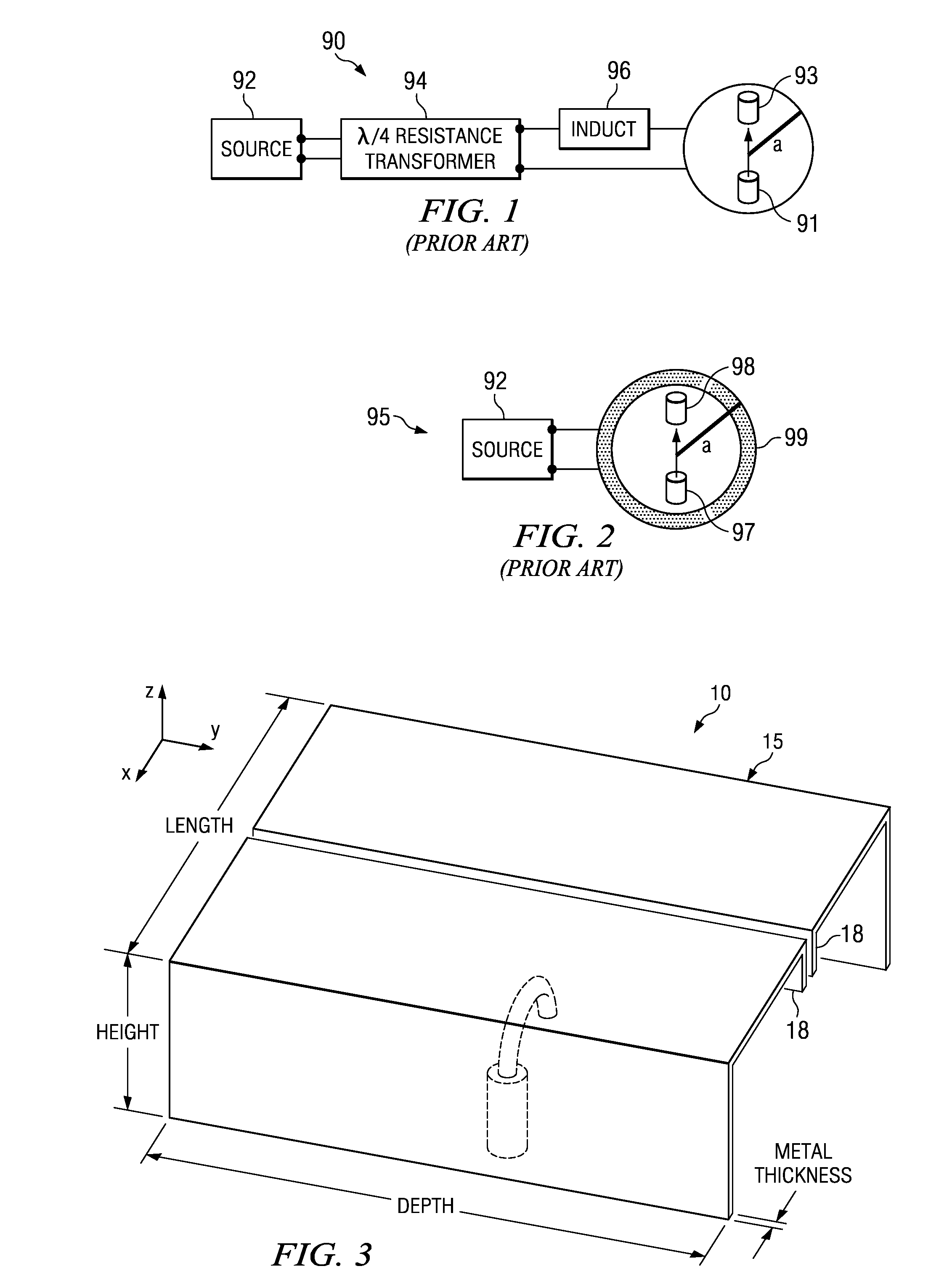
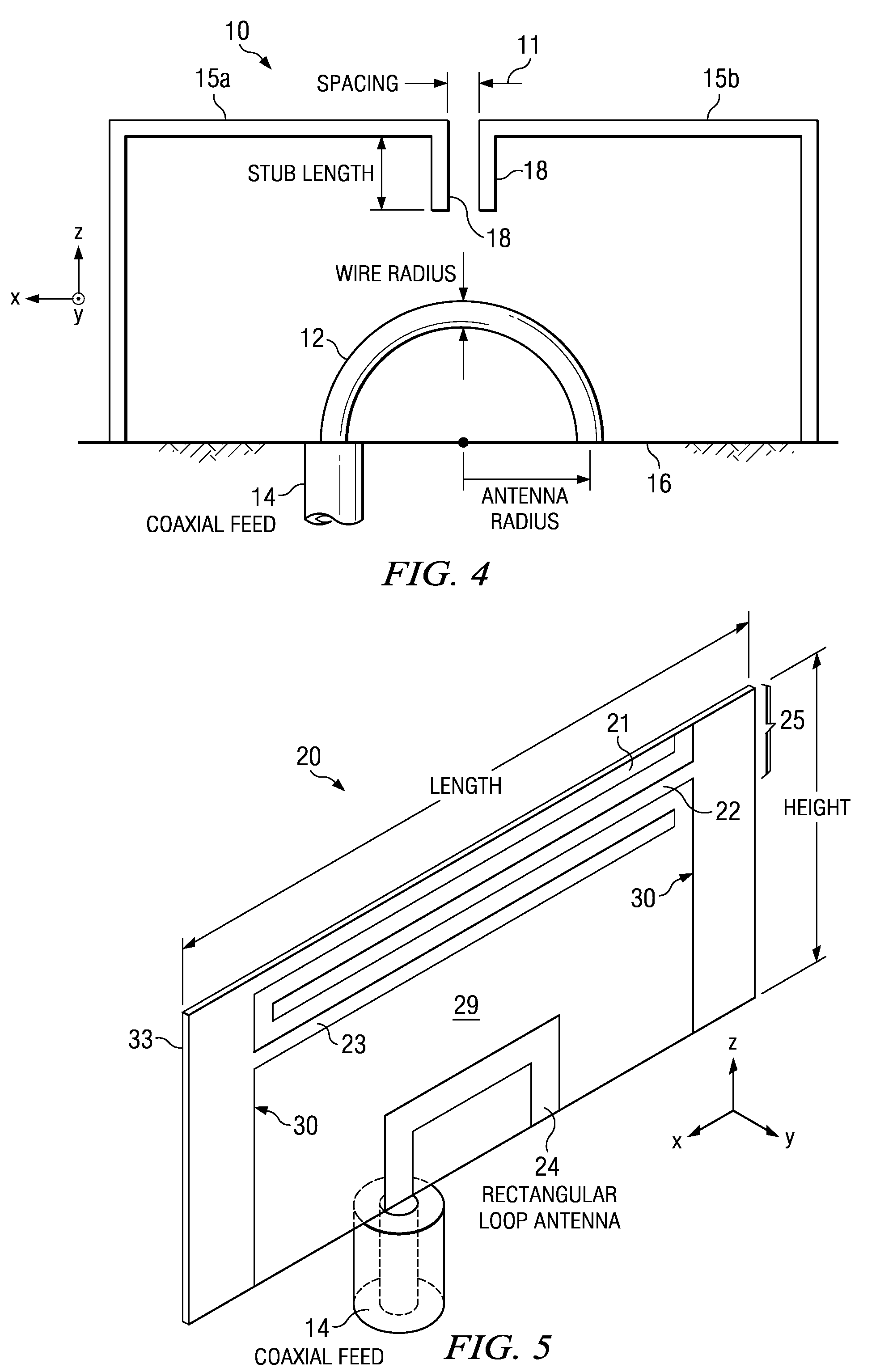
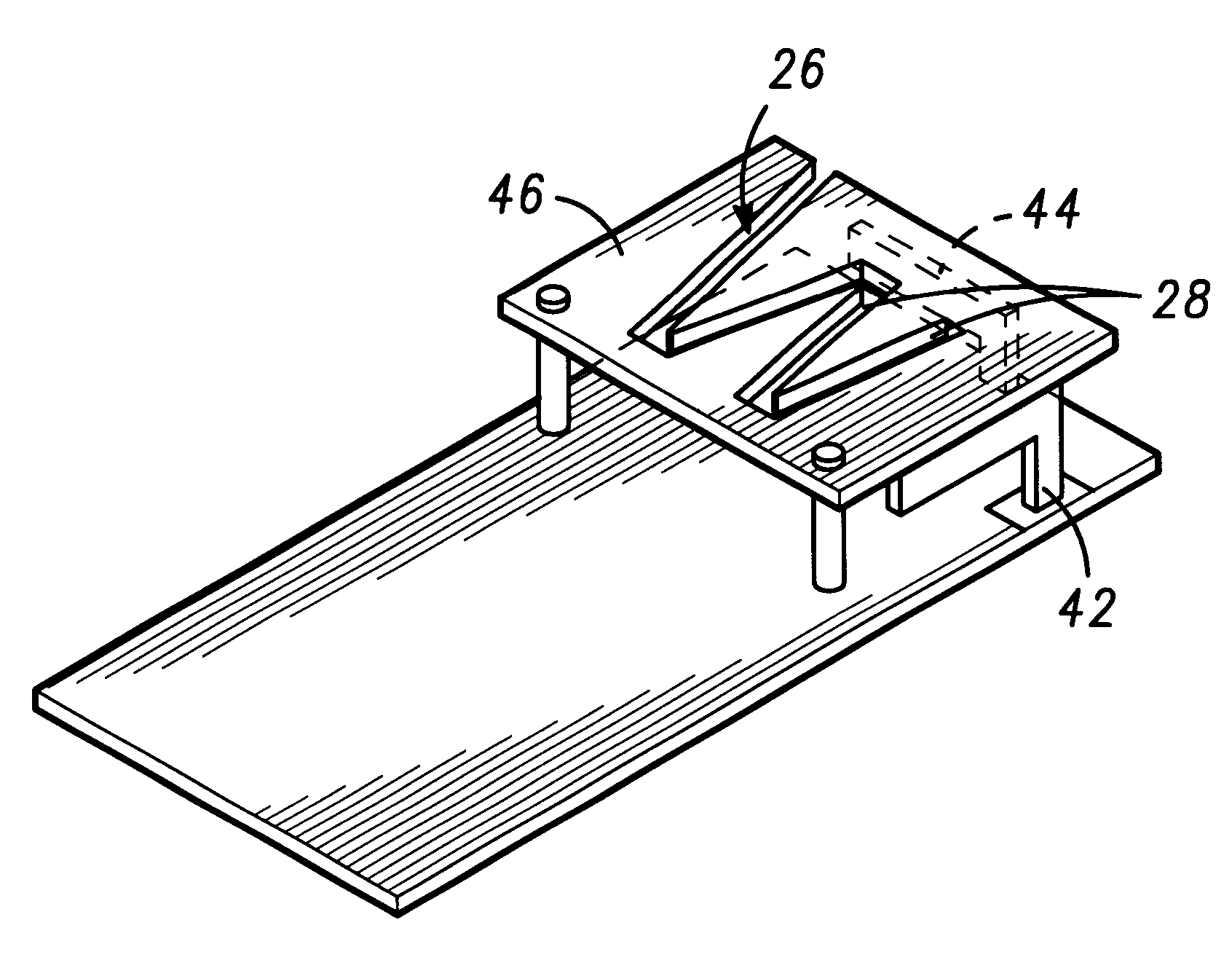
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2483 results about "Input impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The input impedance of an electrical network is the measure of the opposition to current (impedance), both static (resistance) and dynamic (reactance), into the load network that is external to the electrical source. The input admittance (1/impedance) is a measure of the load's propensity to draw current. The source network is the portion of the network that transmits power, and the load network is the portion of the network that consumes power.
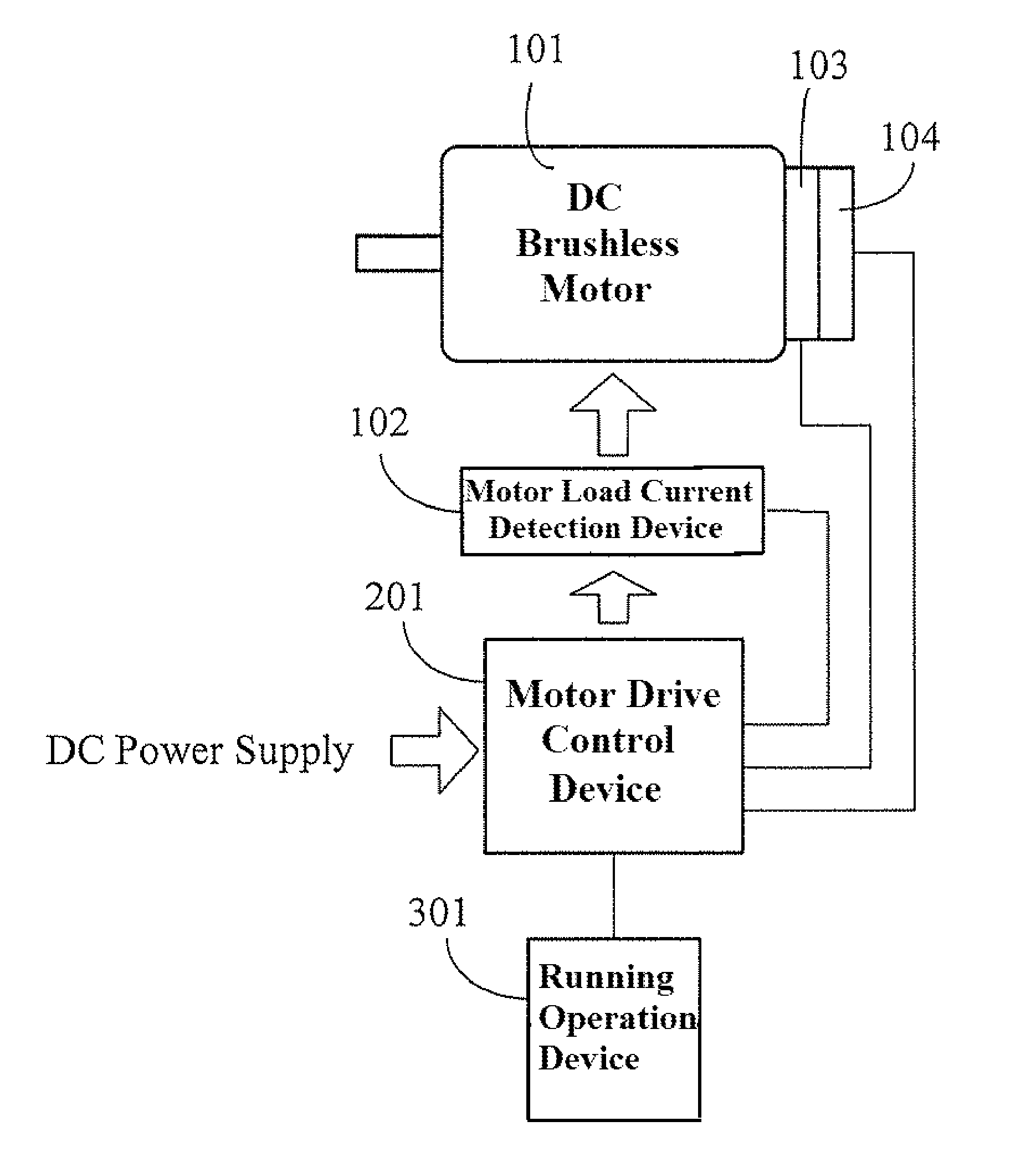
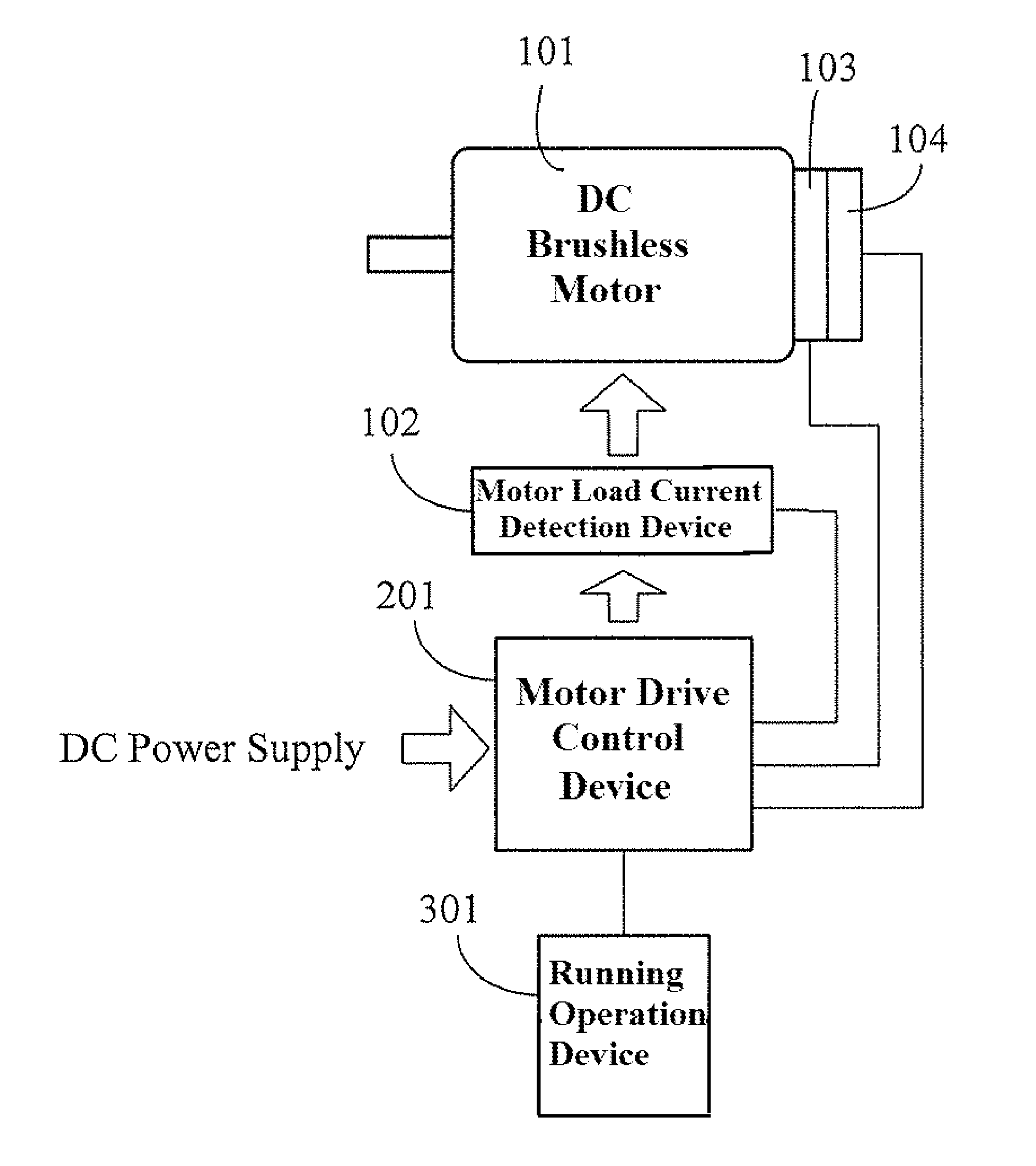
DC brushless motor drive circuit with speed variable-voltage
ActiveUS8288984B2Increase inputOvercome increased inductive impedanceTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersBrushless motorsMotor drive
For the present invention, under various running speeds statuses, the voltage supplied to the DC brushless motor is relatively increased or decreased on the basis of the internal setting of the motor drive control device according to the increased or decreased rotational output speed, so as to prevent the shortcoming of too much variation of the input impedance caused by the inductive reactance of the winding accordingly changed when the speed of the DC brushless motor is changed, specifically, to prevent the shortcoming of unable producing required torque resulting from the increased inductive reactance caused by increasing the rotational speed which makes the current value become too low when input by the original working voltage.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
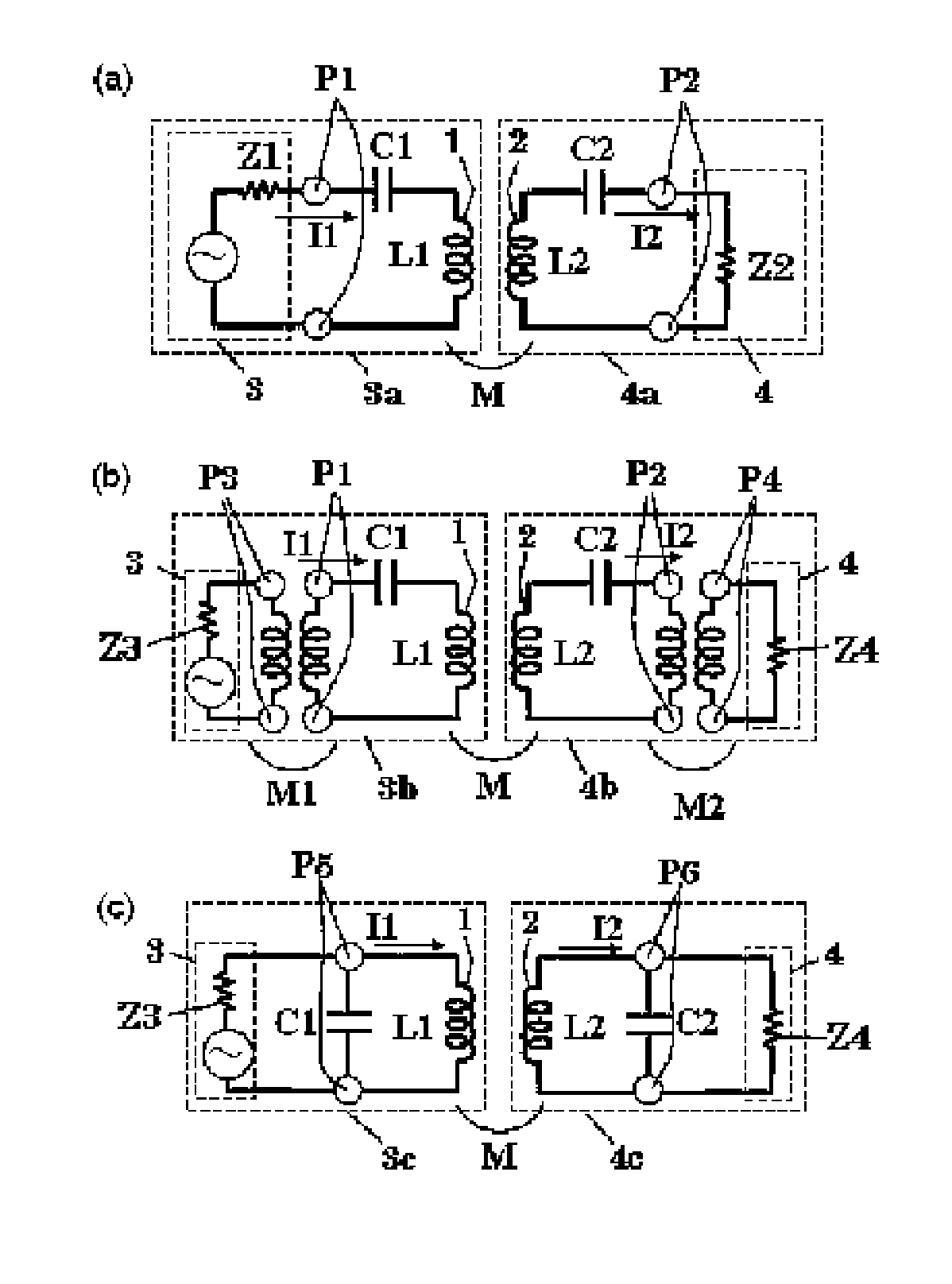
Induced power transmission circuit
ActiveUS20100213770A1Efficient transferEasy to calculateMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionLoad circuit
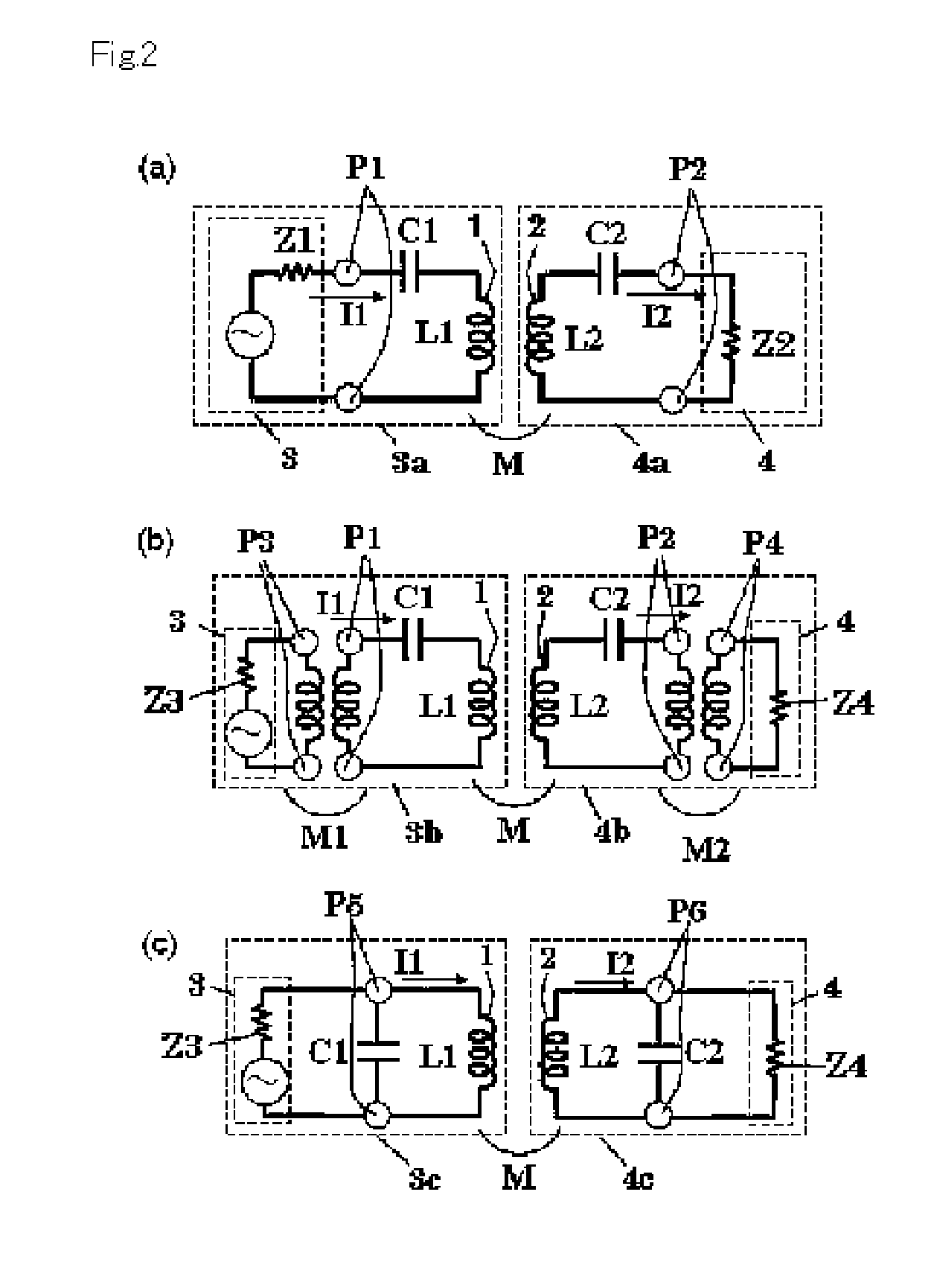
To provide an induced power transmission circuit that transmits, from a transmission antenna (1) connected to a power supply circuit, an AC power having an angular frequency ω to a spaced reception antenna (2) with an excellent efficiency, thereby transmitting it to a load circuit. The induced power transmission circuit comprises a circuit the two ends of which are coupled by a capacitor (C1) and in which the power supply circuit is connected in series to a midway port (1) (P1) of the transmission antenna (1) having an effective self-inductance L1; and a circuit the two ends of which are coupled by a capacitor (C2) and in which the load circuit is connected in series to a midway port (2) (P2) of the reception antenna (2) having an effective self-inductance L2; wherein for a coupling coefficient k of the electromagnetic induction between the antennas and for a phase angle β having an arbitrary value, the angular frequency ω is set to the square root of the reciprocal of a value of L2×C2×(1+k*cos (β)), the output impedance of the power supply circuit is set to approximately kωL1*sin (β), and the input impedance of the load circuit is set to approximately kωL2*sin (β). There is also provided an impedance converting circuit that converts the circuit impedances.
Owner:KIKUCHI HIDEO
Energy conversion apparatus
InactiveUS20140159667A1Maximize energy conversion efficiencyMaximize efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric powerInput impedanceEngineering
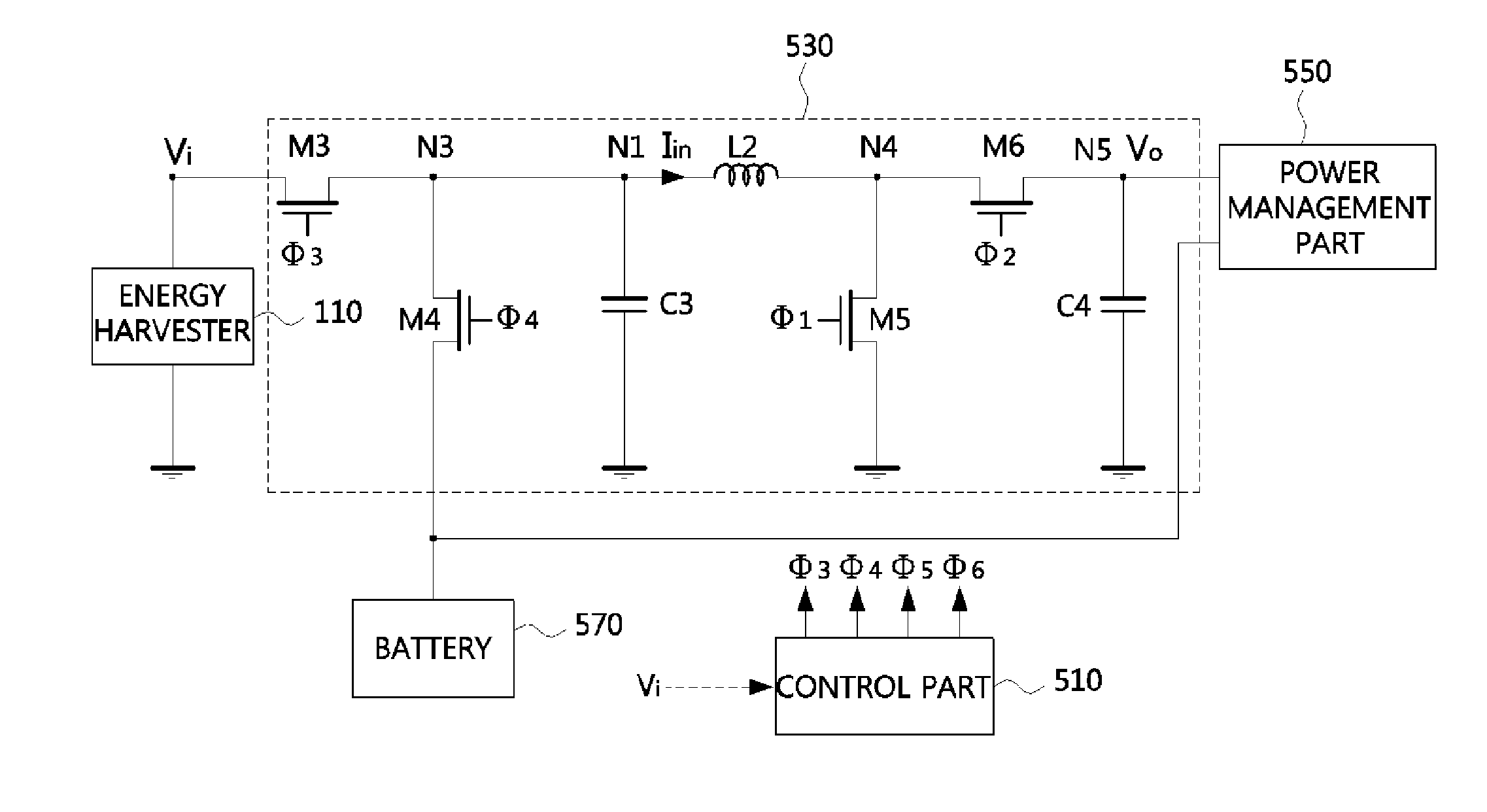
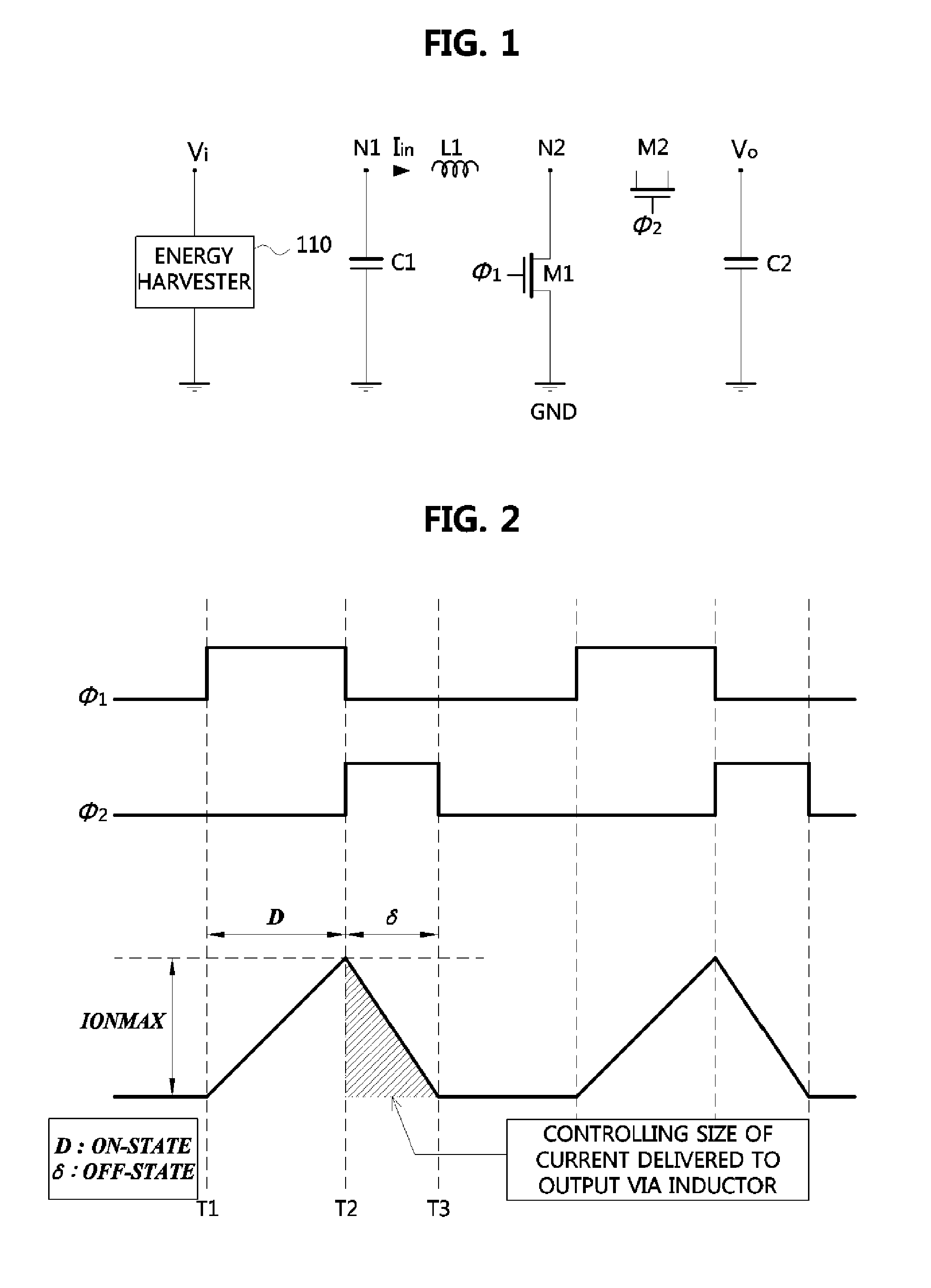
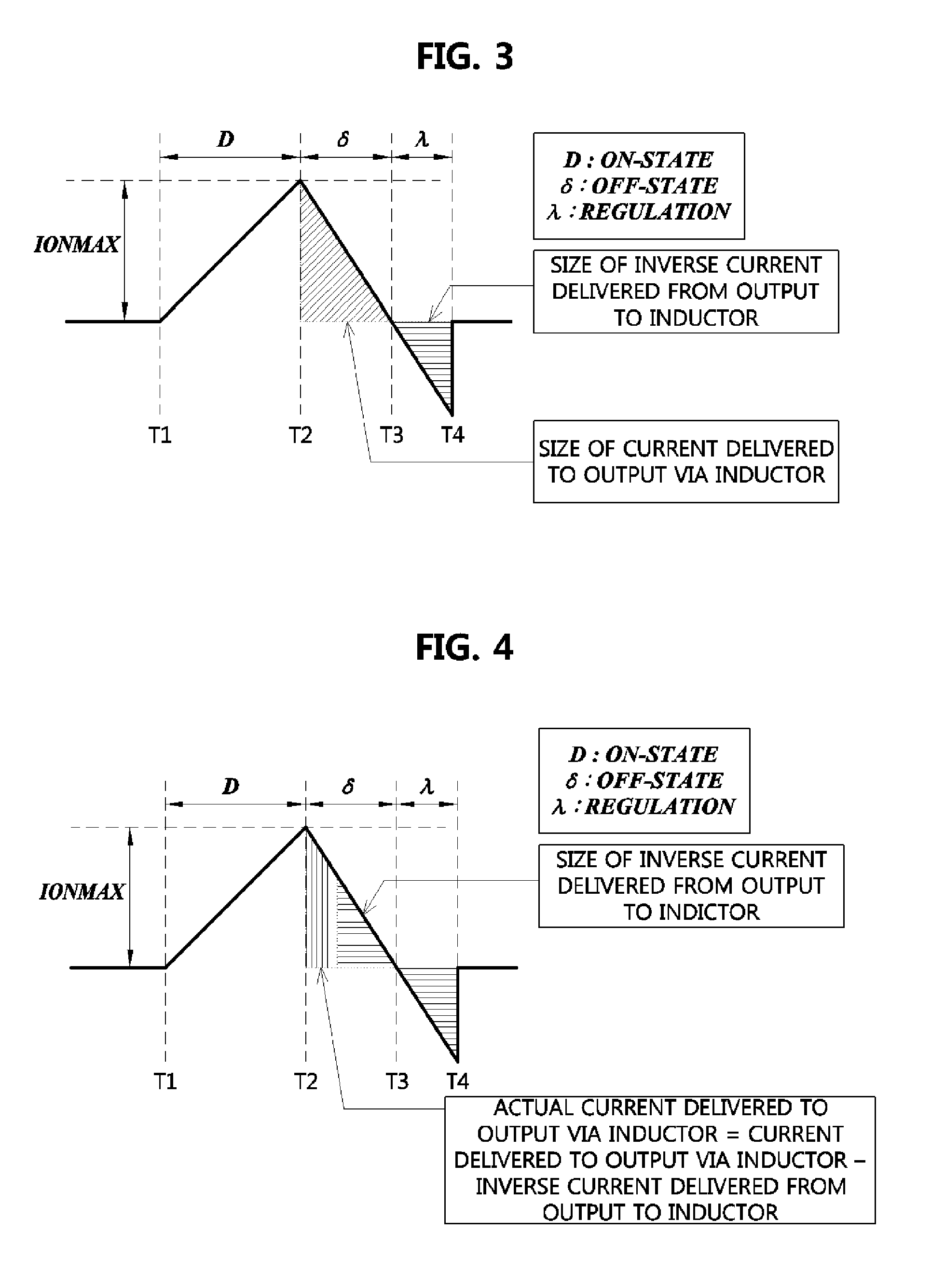
Disclosed is an energy conversion apparatus. An energy conversion apparatus may comprise a control part controlling a length of a first time duration in which input current is inputted and accumulated, a length of a second time duration in which the accumulated current is provided to a load, and a length of a third time duration in which inverse current flows; and a DC-to-DC converter including an inductor, a output capacitor, and at least one switching element, wherein the input current is accumulated during the first time duration by switching the at least one switching element according to a control of the control part so as to perform input impedance matching, and the DC-to-DC convert provides a current corresponding to a difference between the accumulated current provided during the second time duration and the inverse current flowing from the output capacitor during the third time duration to the load.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
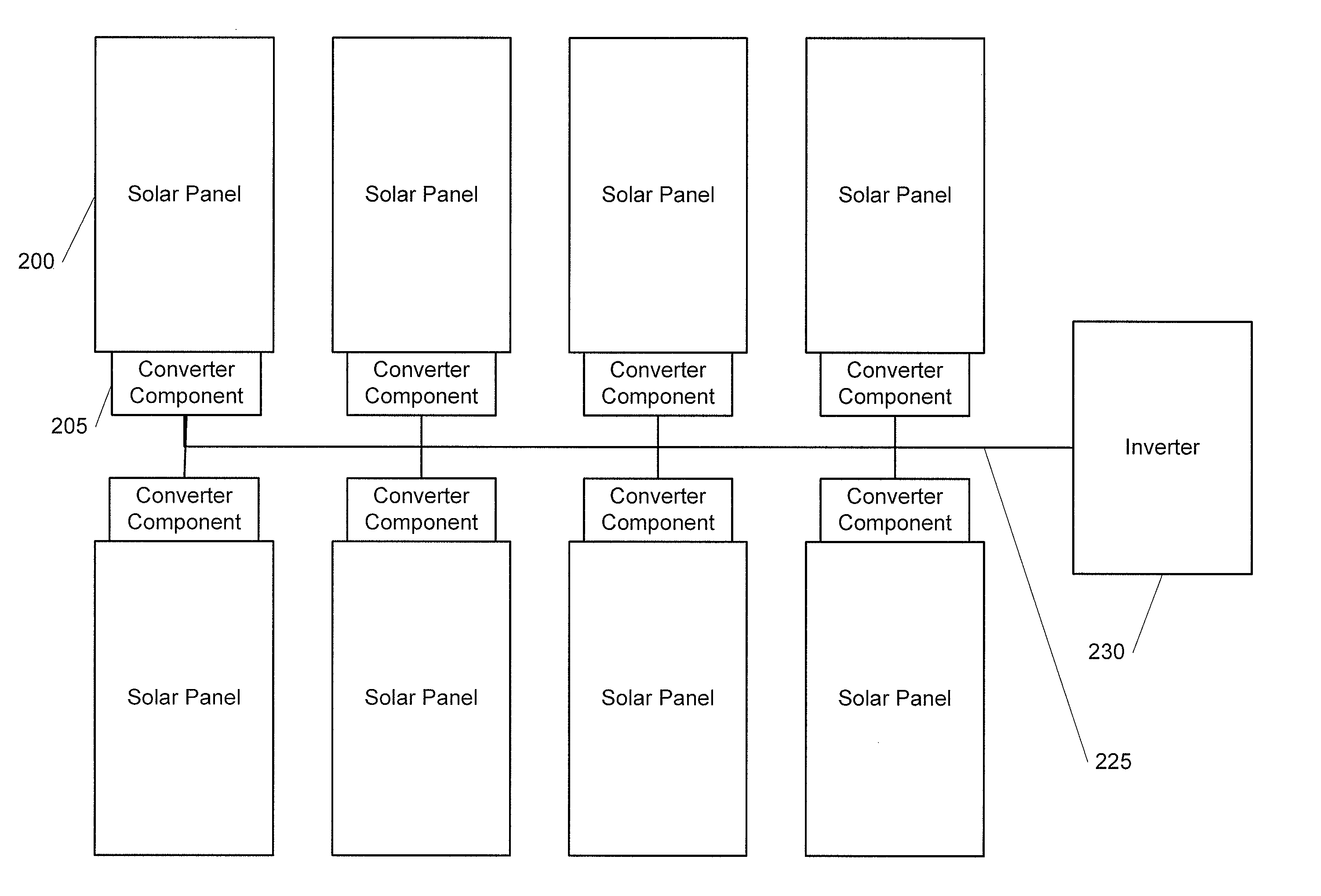
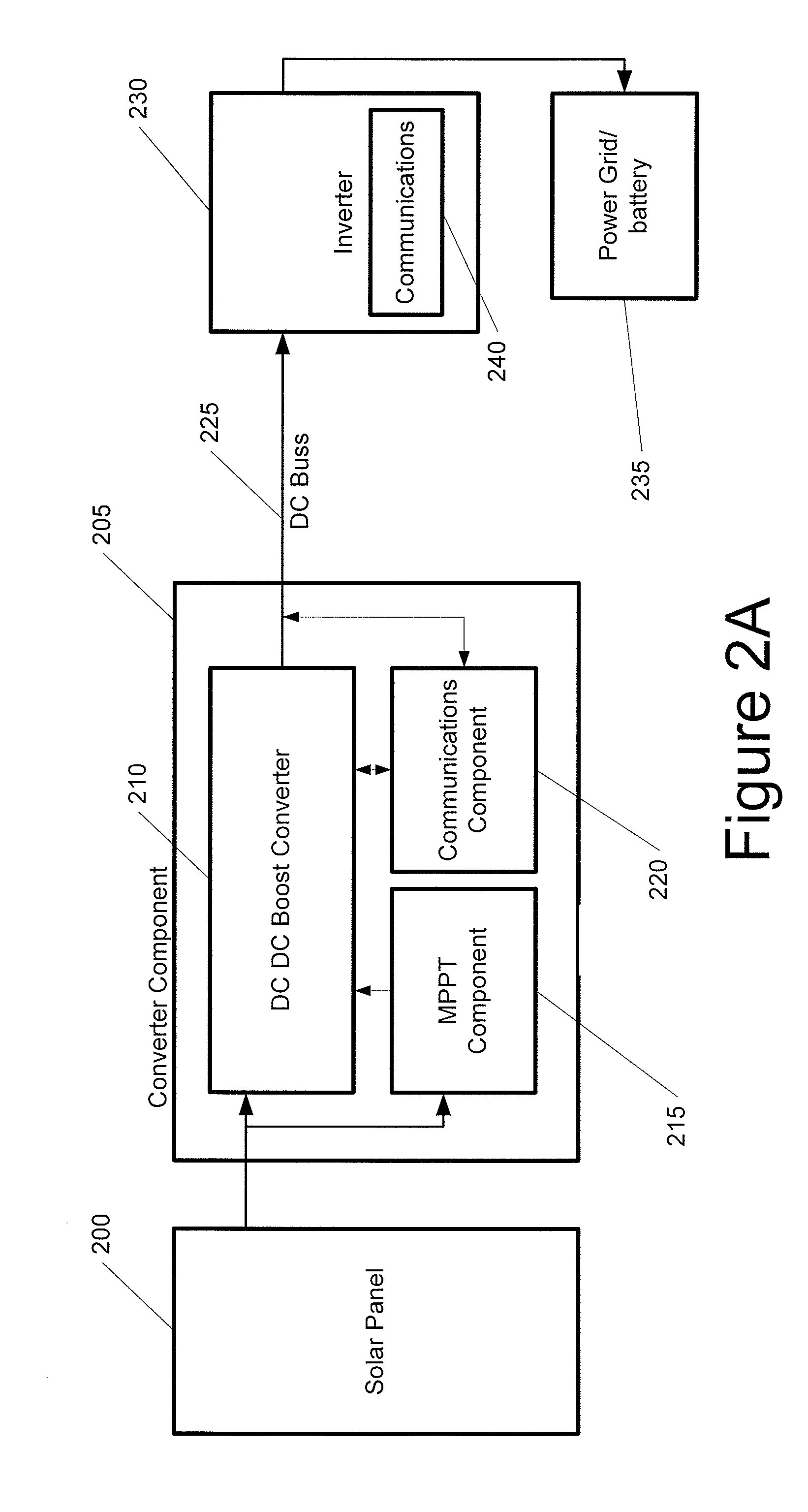
Advanced Renewable Energy Harvesting
InactiveUS20090160258A1Power maximizationMinimize transmission wire lossBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransverterInput impedance
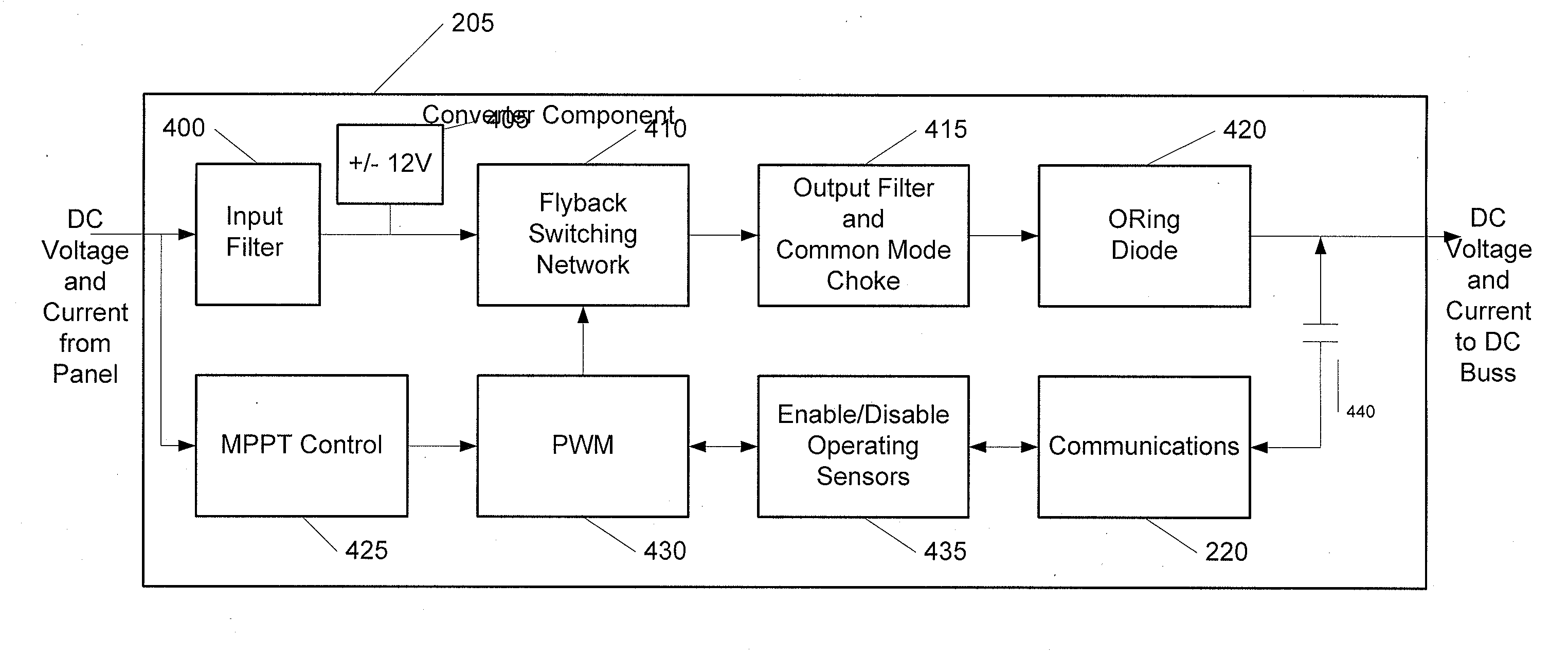
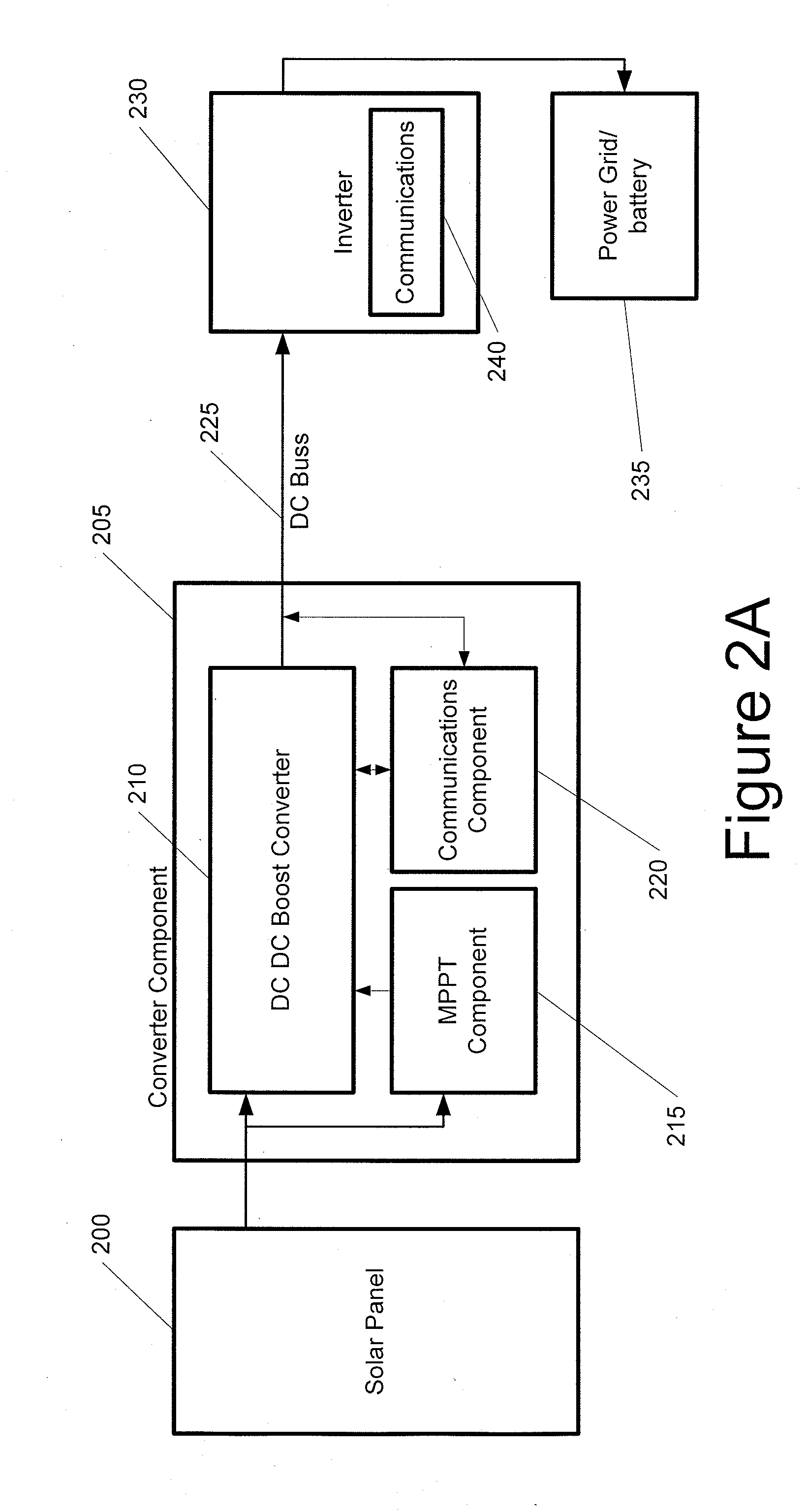
The power of DC electrical sources is combined onto a DC buss, such that each source behaves independently from any other source attached to the buss. In one embodiment, a converter module is attached to each of a plurality of solar photovoltaic panels and its output is attached in a parallel manner to a common buss that forms the input to a DC AC inverter. The converter module includes a Maximum Power Point Tracking component that matches the output impedance of the panels to the input impedance of the converter module. The converter also includes a communication component that provides parametric data and identification to a central inverter. Data generated by each converter module is transmitted over the power line or by wireless means and is collected at the inverter and forwarded to a data collection and reporting system.
Owner:EIQ ENERGY INC
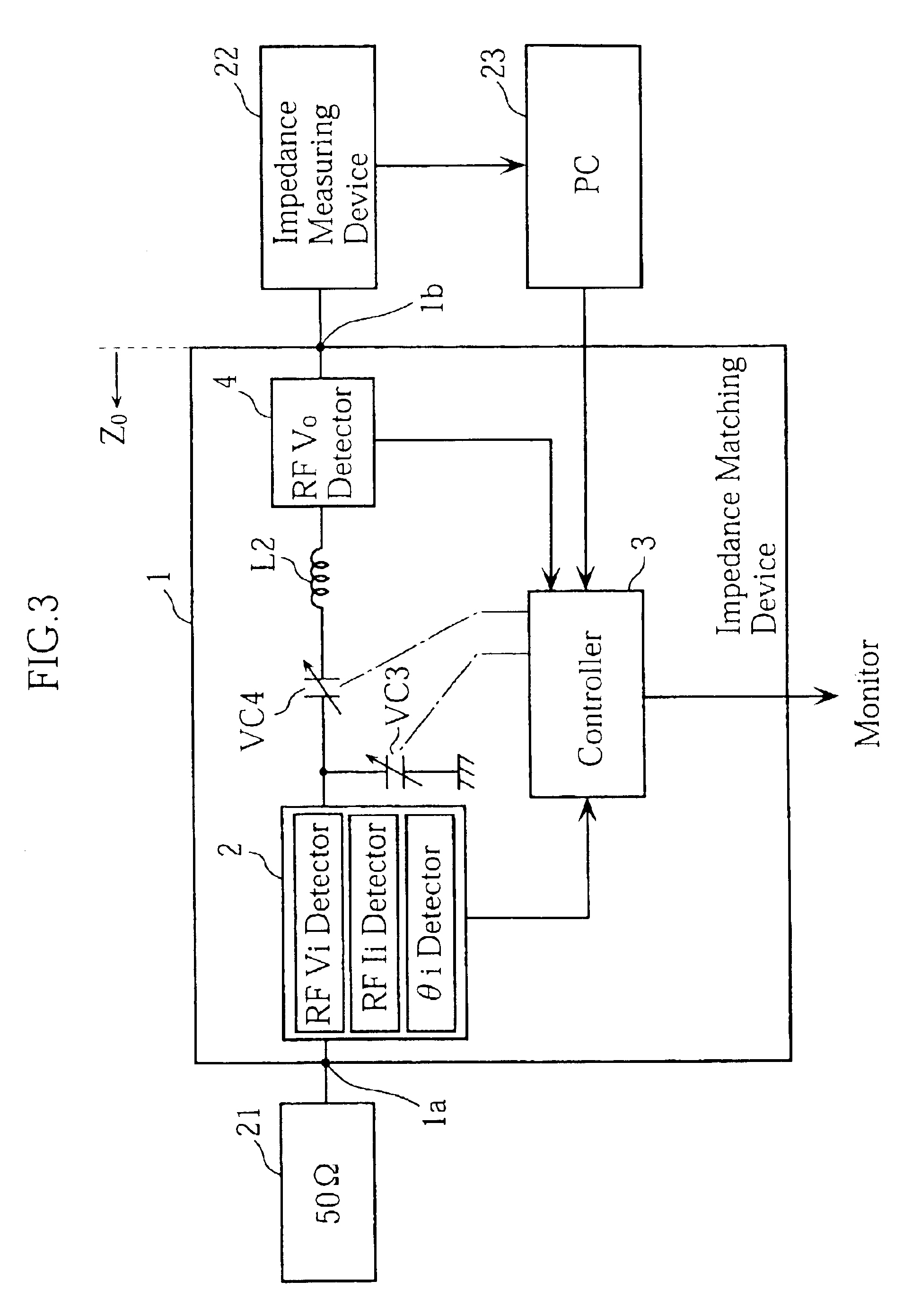
Impedance matching device provided with reactance-impedance table
InactiveUS6946847B2Accurate analysisImpedence matching networksMultiple-port networksCapacitanceElectricity
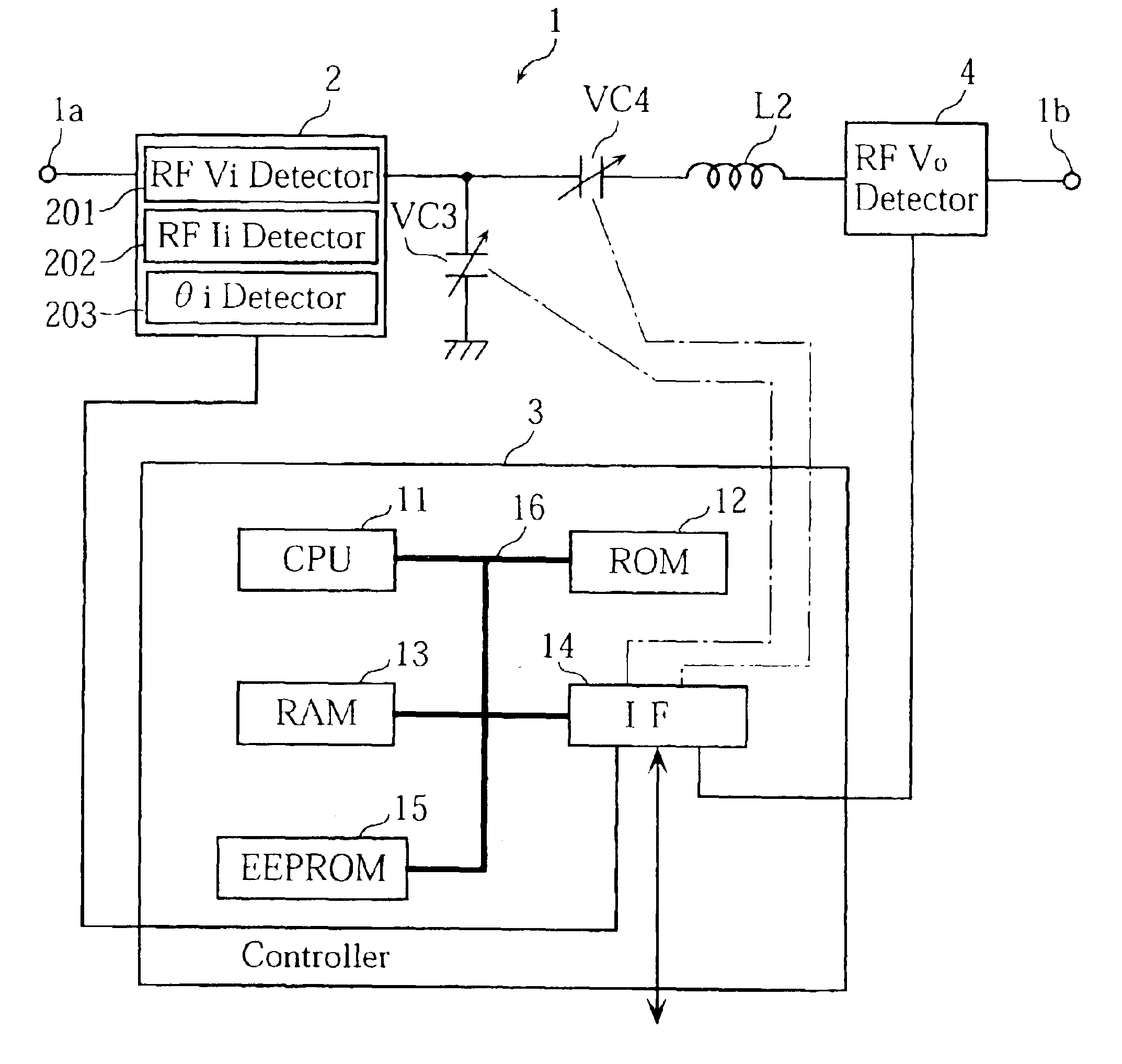
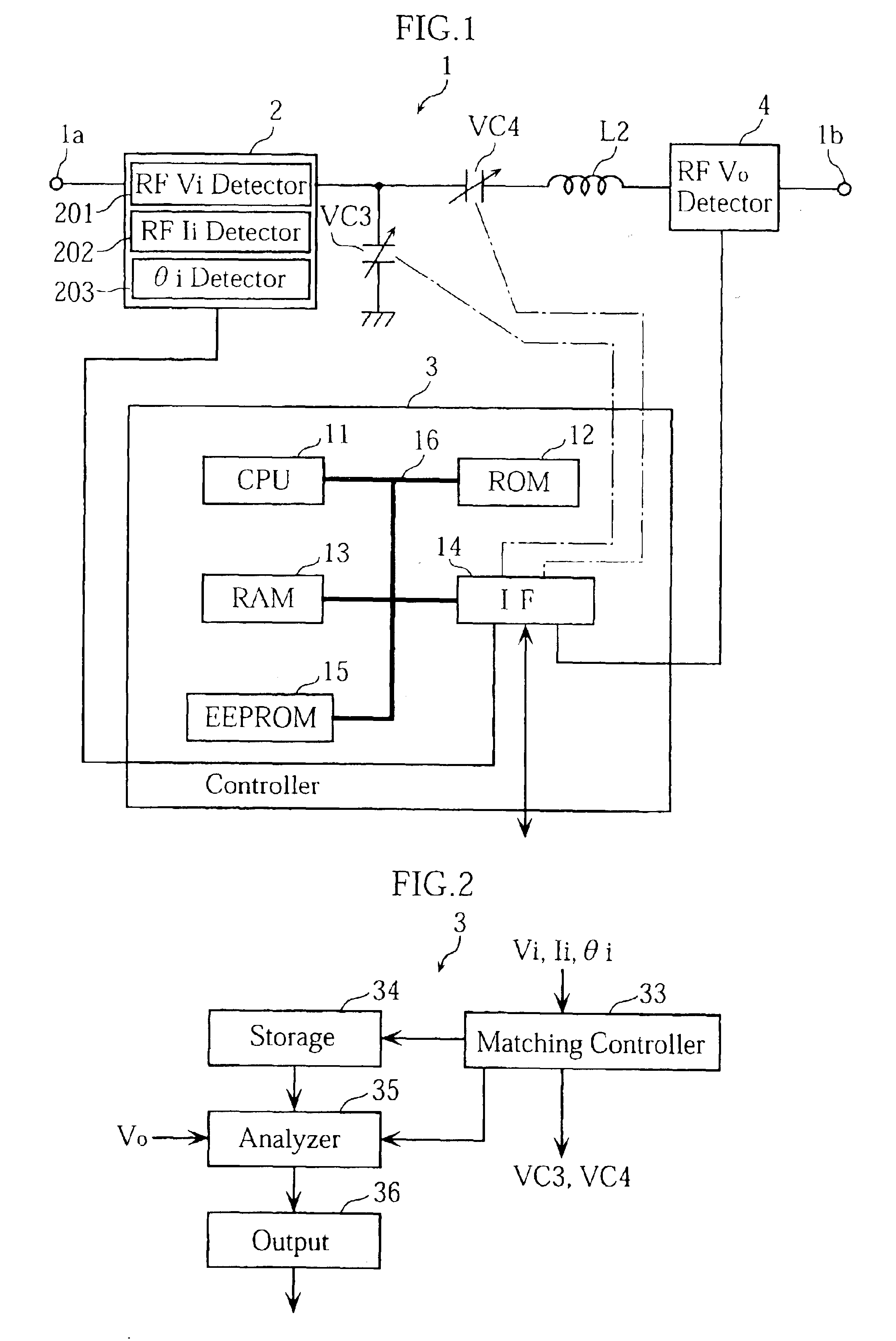
An impedance matching device is provided, for which the electric characteristics at an output terminal are accurately analyzed. The matching device is provided with an input detector for detecting RF voltage and current at the input terminal, and an output detector for detecting RF voltage outputted from the output terminal. The matching device also includes a controller for achieving impedance matching between a high frequency power source connected to the input terminal and a load connected to the output terminal. The impedance matching is performed by adjusting variable capacitors based on the detection data supplied from the input detector. When the impedance of the power source is matched to that of the load, the controller calculates the output impedance, RF voltage and RF current at the output terminal, based on the adjusted capacitances of the capacitors, a pre-obtained reactance-impedance data and the detection data supplied from the output detector.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Advanced renewable energy harvesting
InactiveUS8138631B2Power maximizationEfficiently invertingBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransverterInput impedance
The power of DC electrical sources is combined onto a DC buss, such that each source behaves independently from any other source attached to the buss. In one embodiment, a converter module is attached to each of a plurality of solar photovoltaic panels and its output is attached in a parallel manner to a common buss that forms the input to a DC AC inverter. The converter module includes a Maximum Power Point Tracking component that matches the output impedance of the panels to the input impedance of the converter module. The converter also includes a communication component that provides parametric data and identification to a central inverter. Data generated by each converter module is transmitted over the power line or by wireless means and is collected at the inverter and forwarded to a data collection and reporting system.
Owner:EIQ ENERGY INC
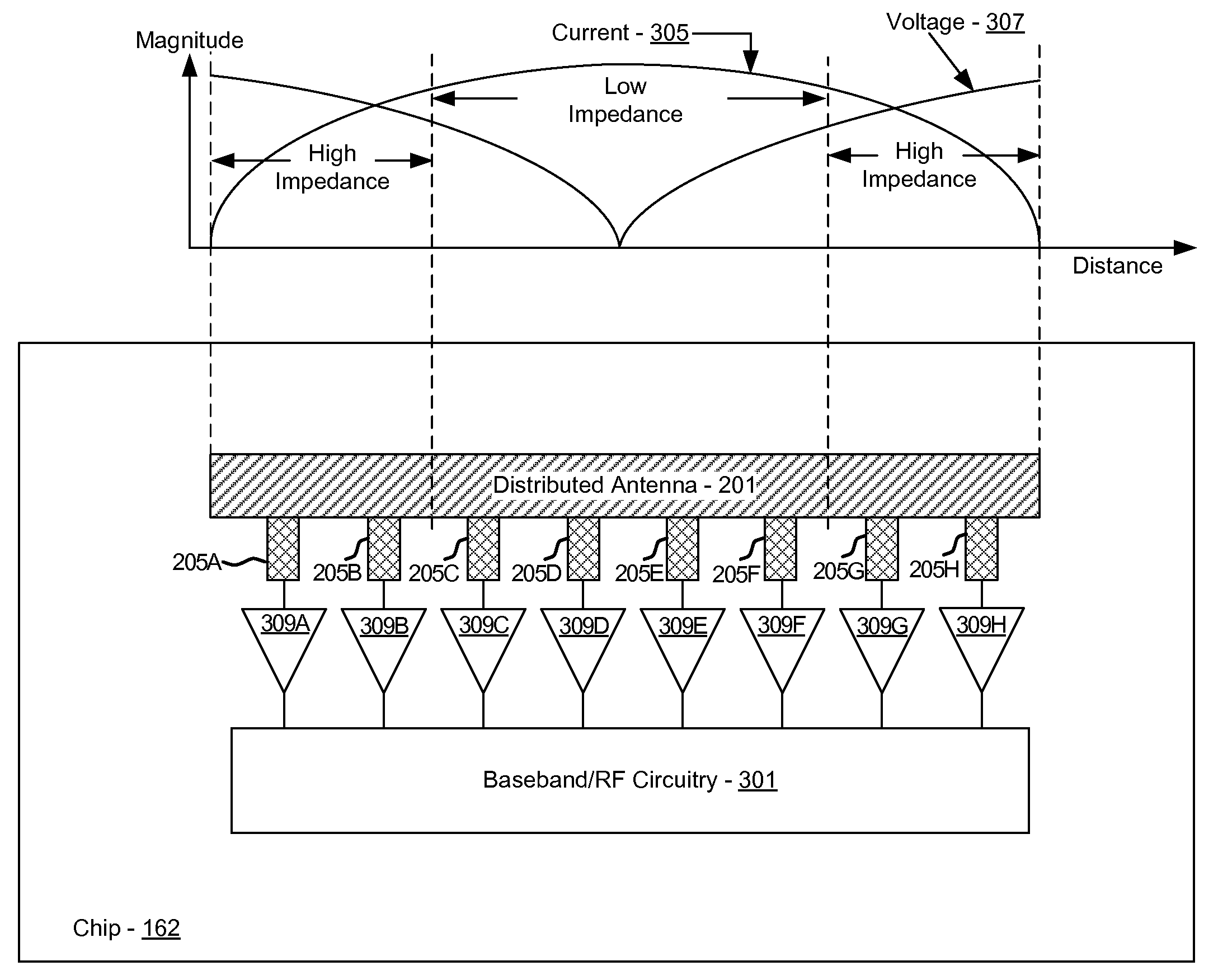
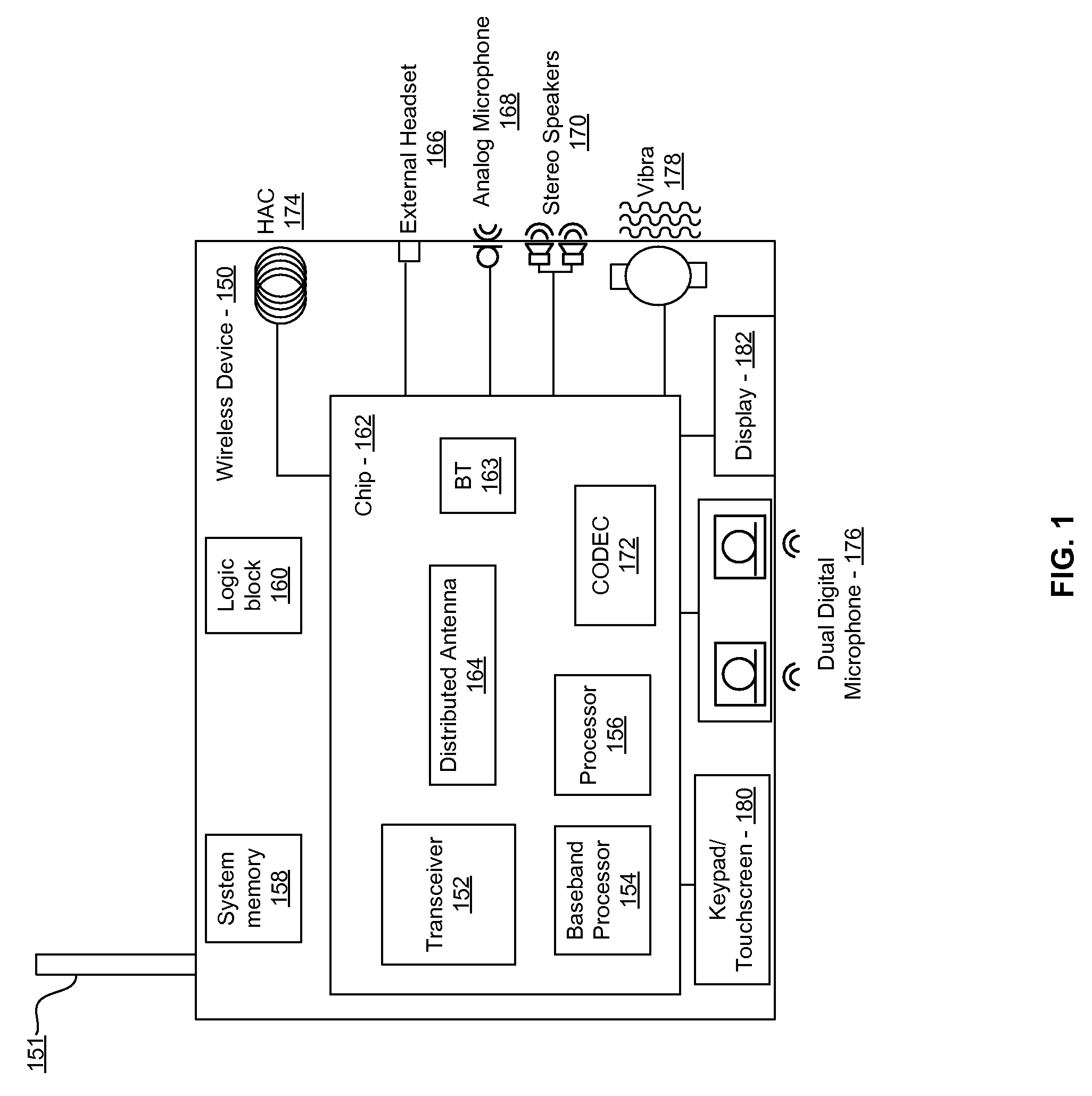
Method and system for receiving signals via multi-port distributed antenna
Methods and systems for receiving signals via a multi-port distributed antenna are disclosed and may include selectively enabling one or more low noise amplifiers (LNAs) coupled to the antenna. The selective enabling may be based on a desired gain level applied to a signal received from the antenna. The LNAs may be coupled to ports on the antenna based on an input impedance of the LNAs and an impedance of the ports. Each of the LNAs may be configured for optimum linearity in different gain ranges, which may be proportional to the input impedance of the LNAs. The antenna may be integrated on a chip with the LNAs, or may be located external to the chip. The antenna may include a microstrip antenna. The LNAs may include variable gain and may be enabled utilizing a processor. Linearity on demand may be enabled via the selective enabling of the LNAs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
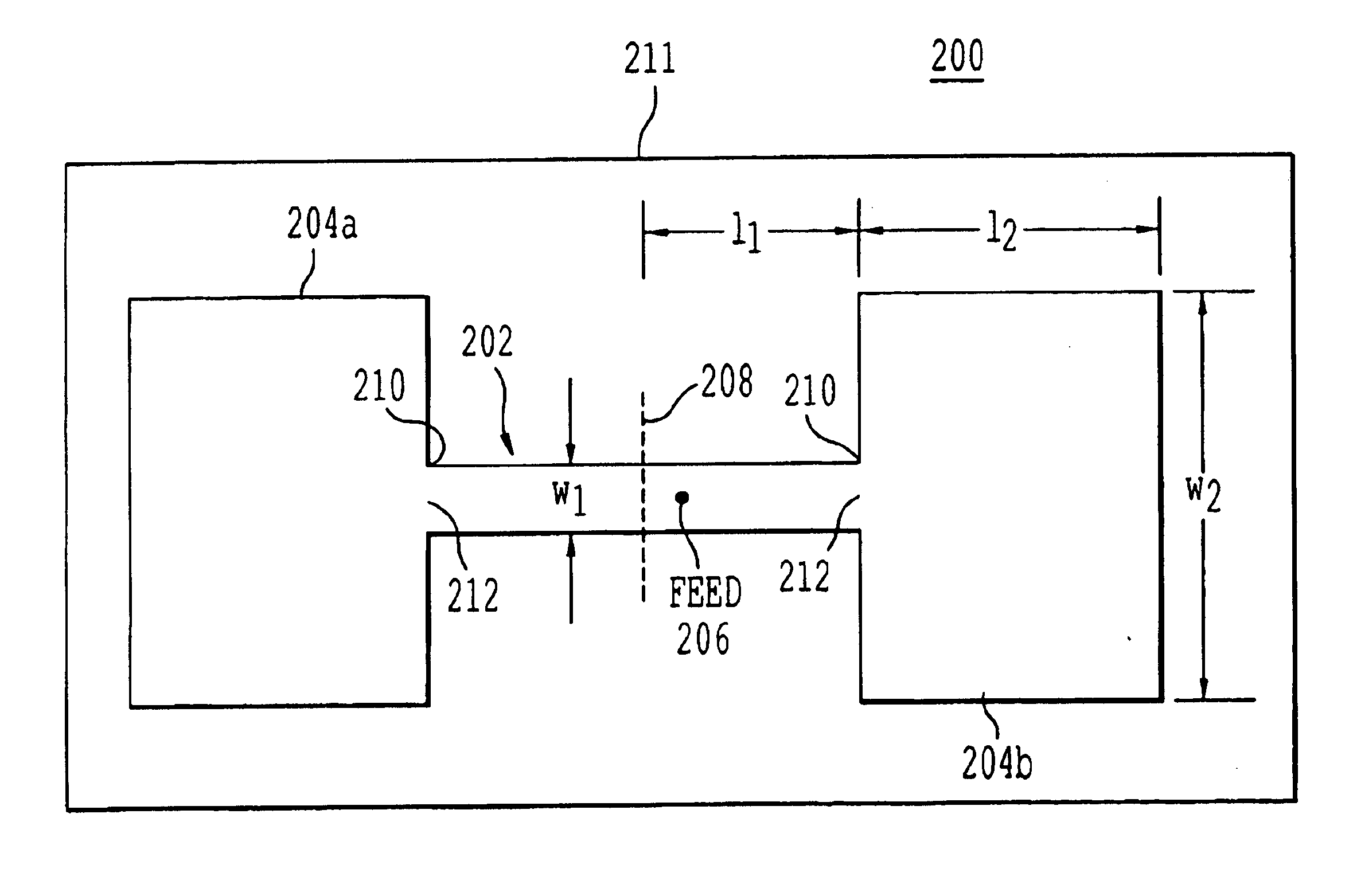
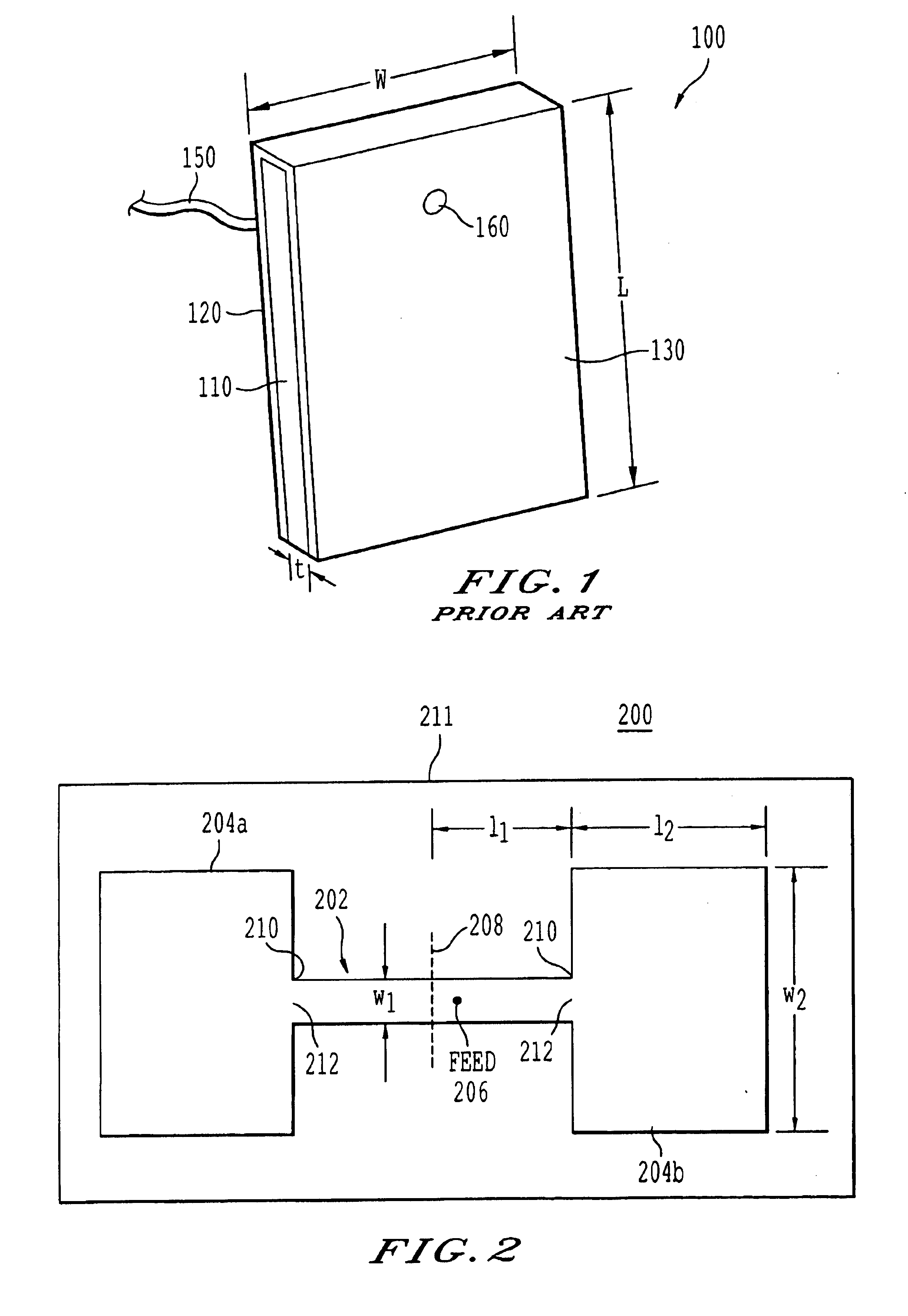
Microstrip antenna employing width discontinuities
InactiveUS6839028B2Increase in sizeReduce antenna sizeParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsInput impedanceEngineering
An apparatus and method to reduce the size of a microstrip antenna without sacrificing antenna efficiency too much are described. The antenna structure includes discontinuity of strip width in the middle of the antenna patch to reduce the size of the antenna at a given resonant frequency. The antenna structure further includes a plurality of patches of differing widths connected to each other at junctions. The junctions are placed symmetrically to ensure maximum radiation at the boresight and also to further reduce cross-polarization levels. A coaxial feed is connected at a predetermined location near the center of a patch, having a narrower width, in order to match the input impedance of the antenna to the coaxial feed.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
Package filter and combiner network
InactiveUS7283793B1Improve powerImprove efficiencyOne-port networksTransmissionPhase shiftedTransceiver
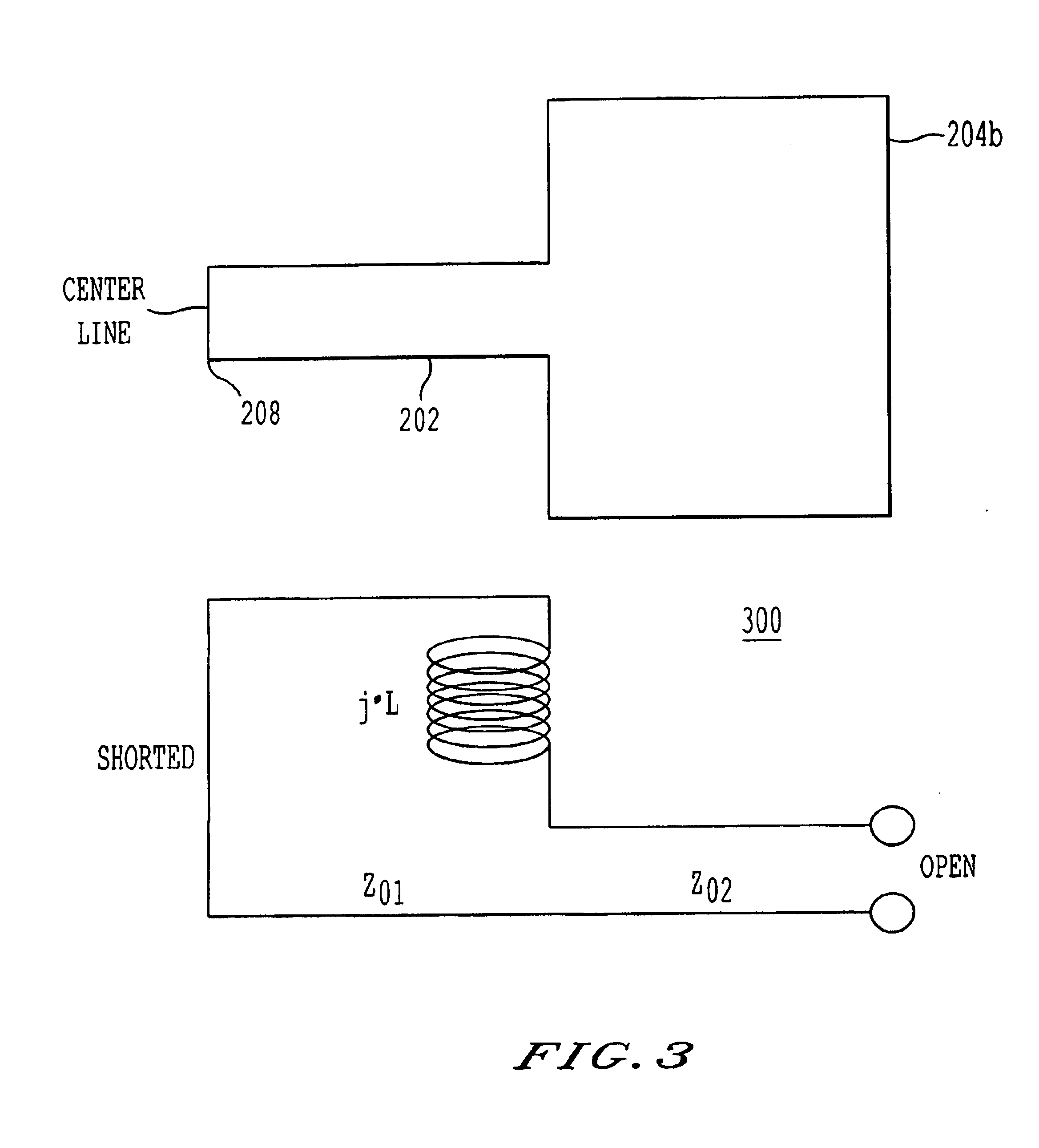
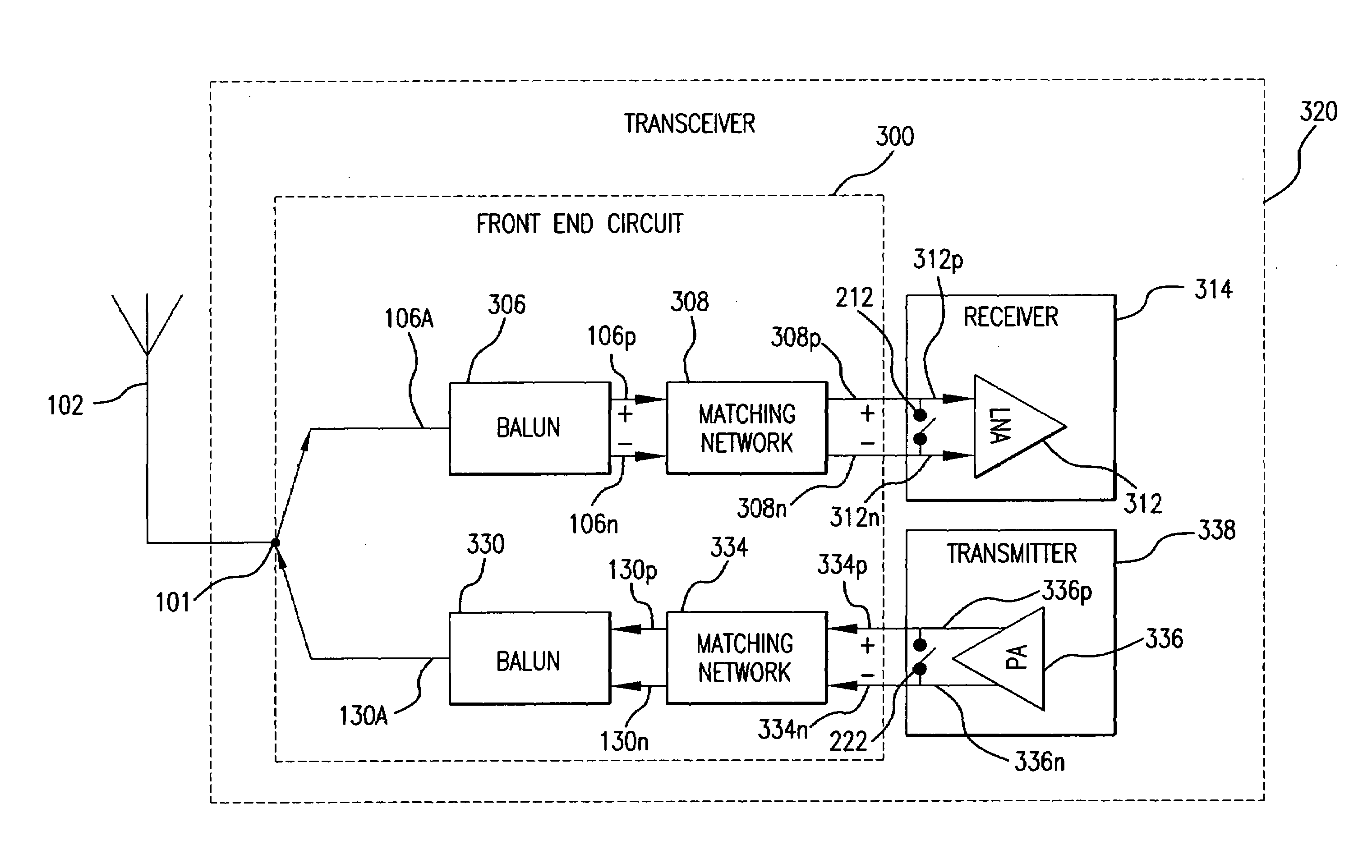
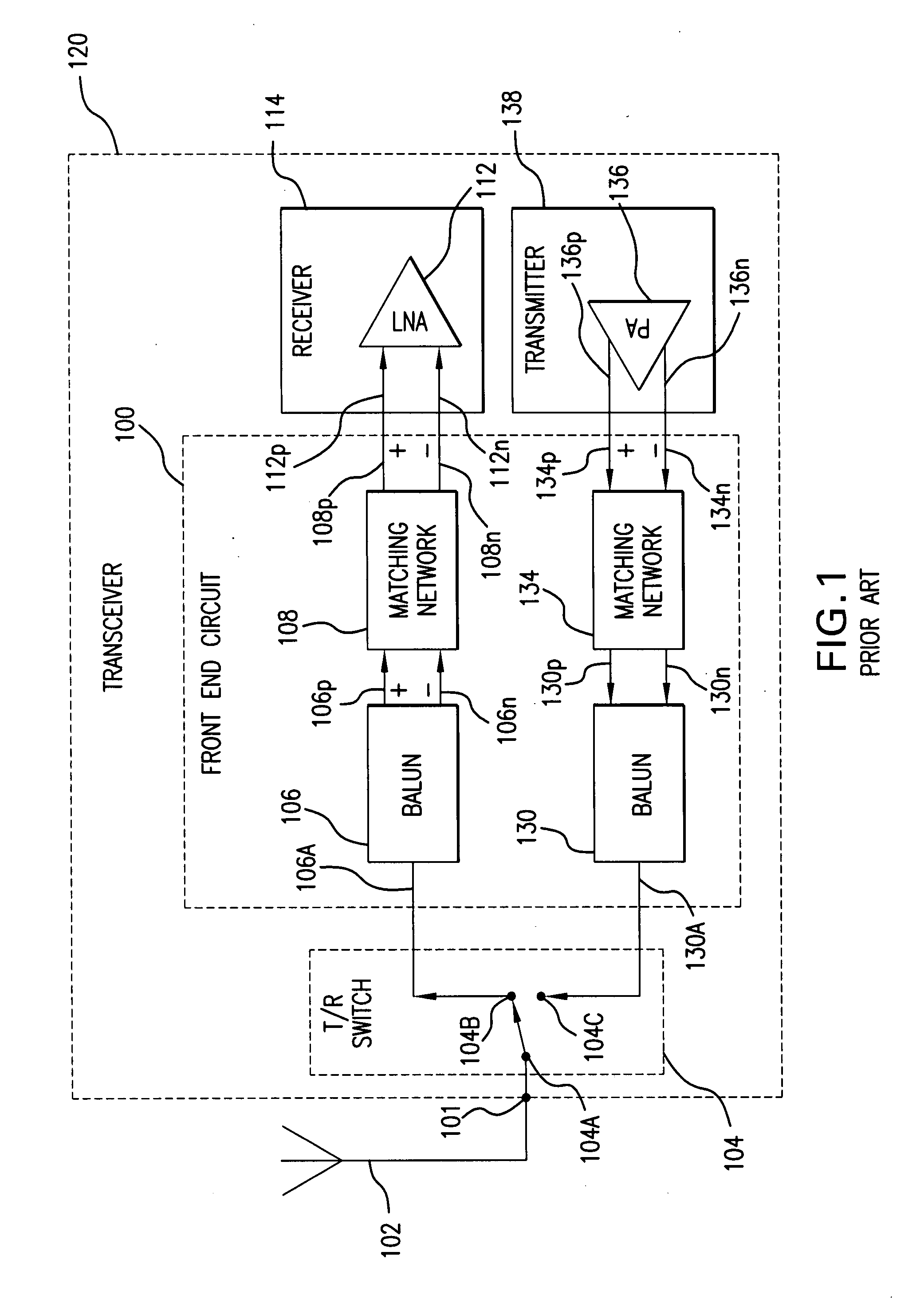
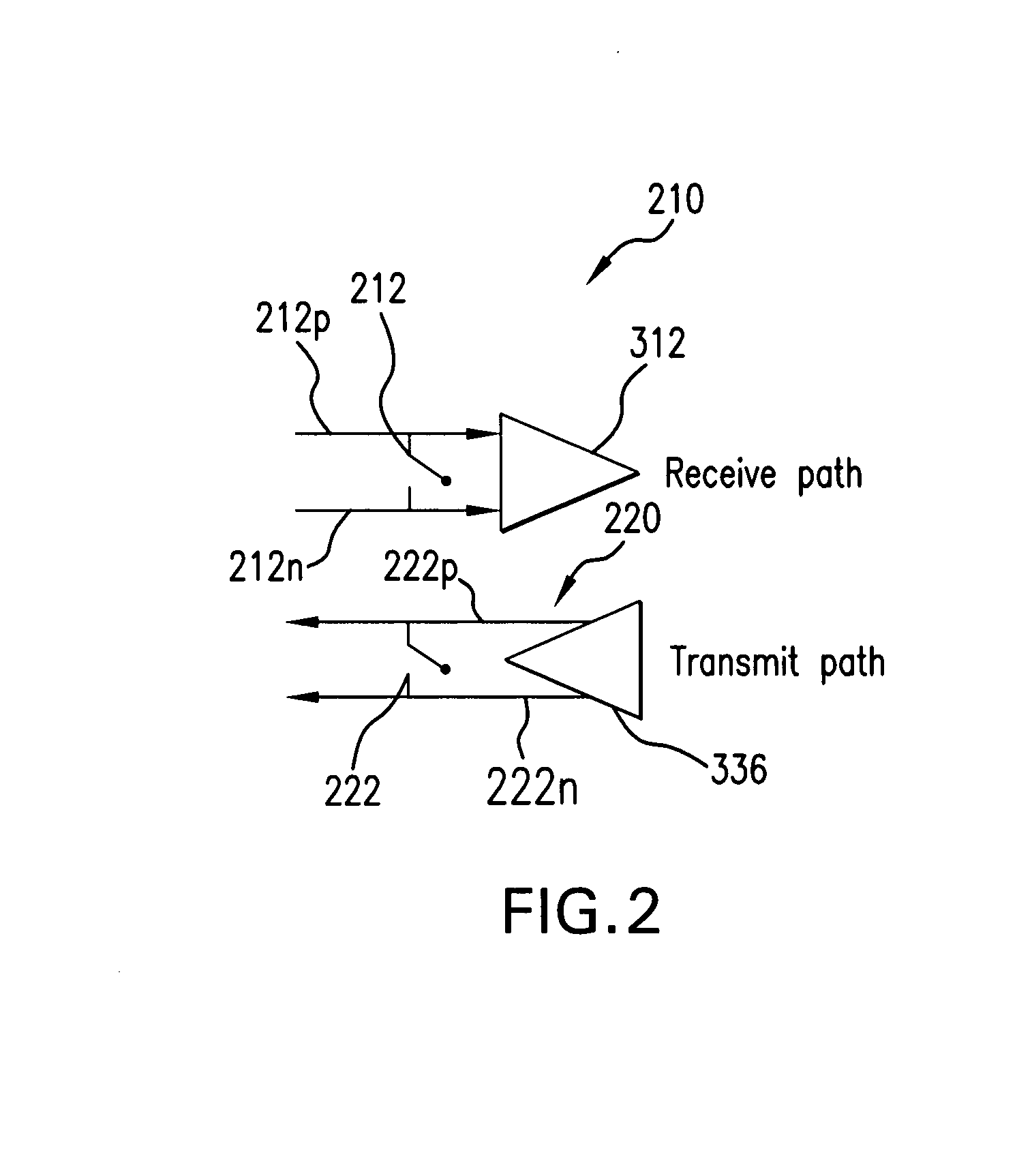
A transceiver front end circuit includes an antenna terminal capable of being coupled to an antenna. A first balun circuit has a single input that is coupled to the antenna terminal, and a pair of balanced outputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced receiver inputs. The first balun circuit matches an input impedance of the pair of balanced receiver inputs and substantially phase shifts the input reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced receiver inputs by about 180-degrees. A second balun circuit has a single output coupled to the antenna terminal and a pair of balanced inputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced transmitter outputs. The second balun circuit matches an output impedance of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs and substantially phase shifts the output reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs by about 180-degrees. The first balun circuit and the second balun circuit can be contained within a single package. A first shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of receiver inputs. A second shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of transmitter outputs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
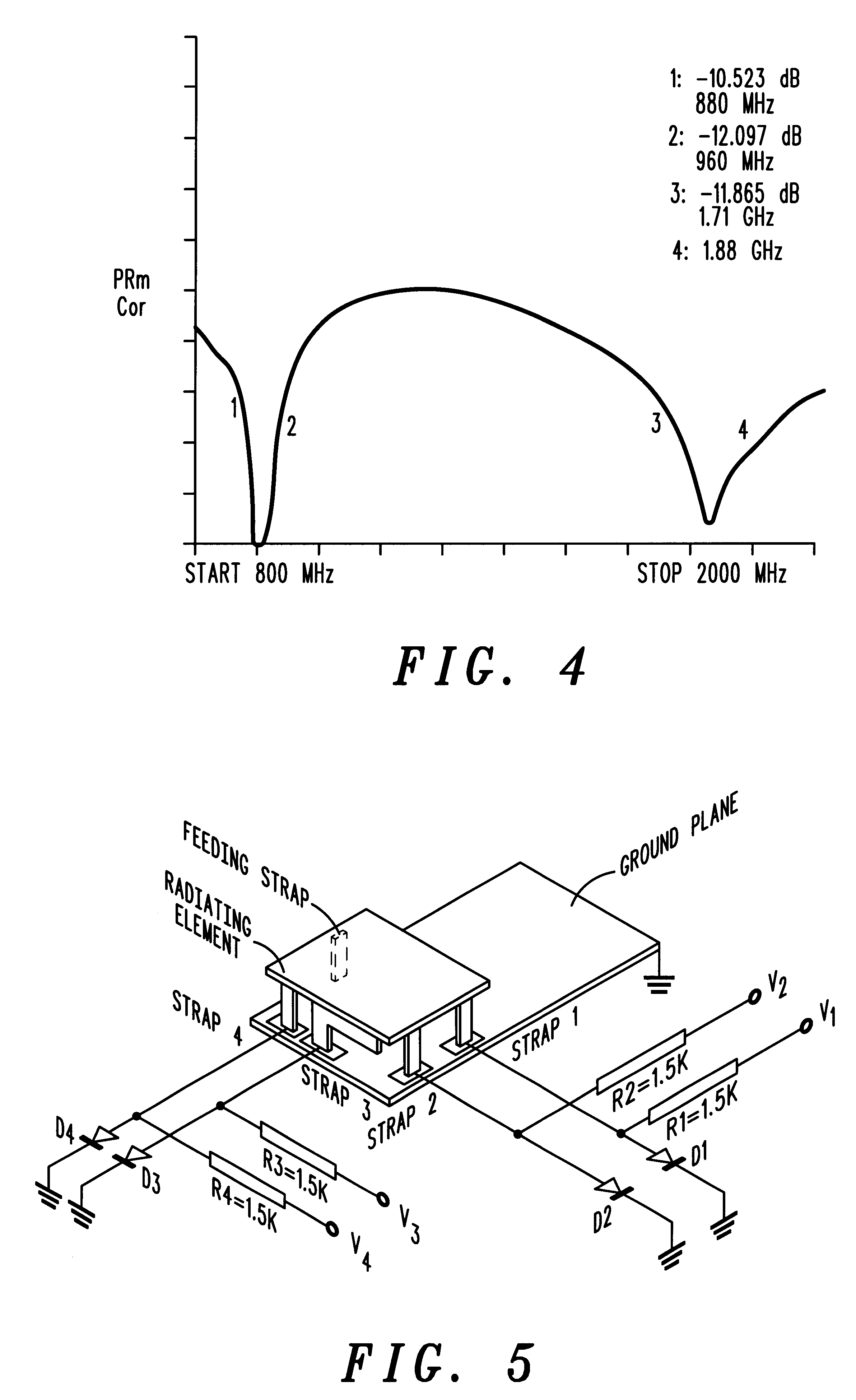
Efficient metamaterial-inspired electrically-small antenna
InactiveUS20090140946A1Effective radiationImprove radiation efficiencyLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntennas earthing switches associationElectricityInput impedance
Planar (two-dimensional) and volumetric (three-dimensional), metamaterial-inspired, efficient electrically-small antennas. The electric-based and magnetic-based antenna systems are shown to be naturally matched to a source and are linearly scalable to a wide range of frequencies. The systems include a radiating element that is fed by the source through a finite ground plane via a feedline and an electrically-small, one-unit cell made of a metamaterial that is adapted to match the input impedance of the antenna.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Internal multi-band antennas for mobile communications
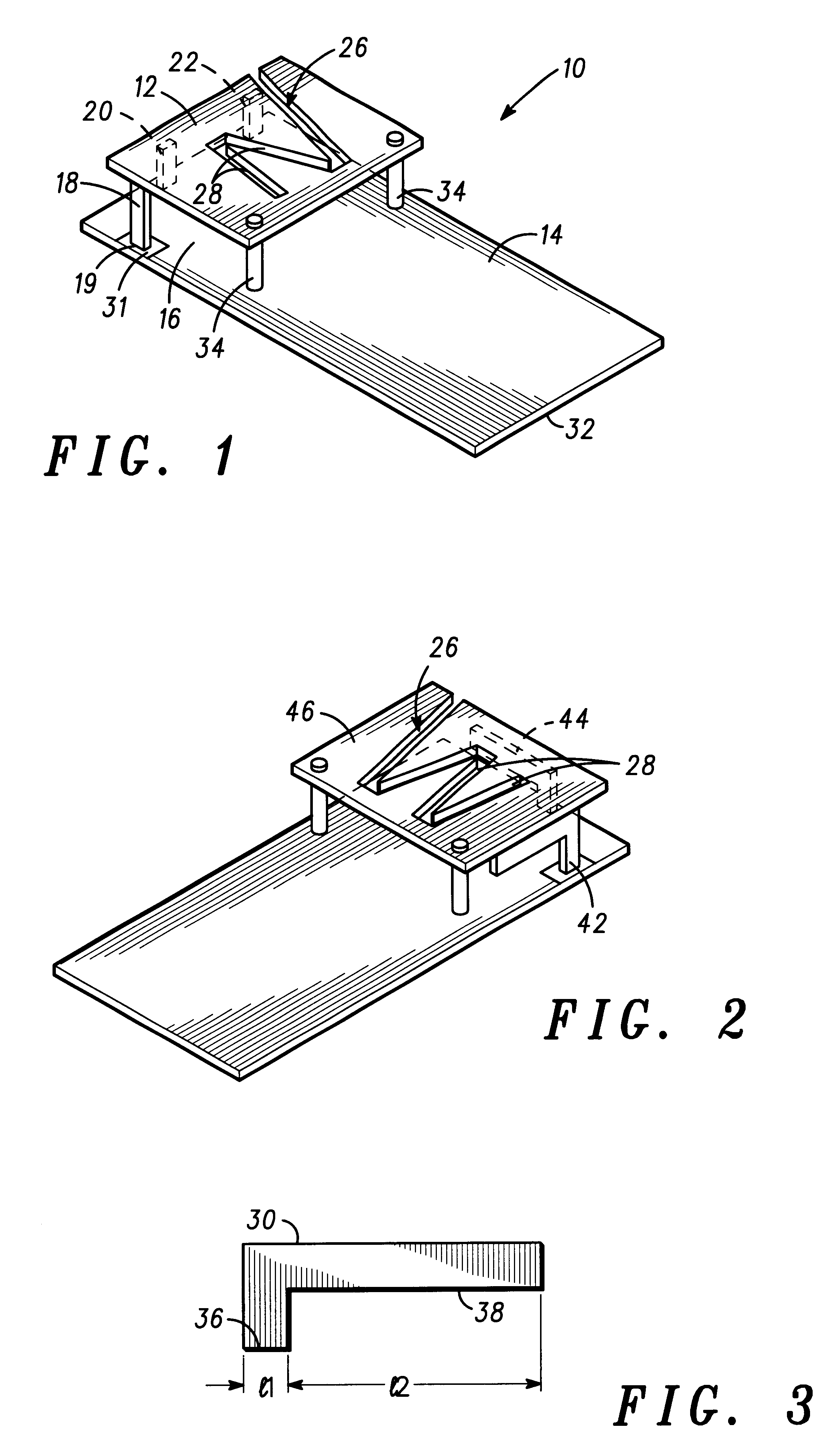
An internal multi-band antenna (10) for a mobile communication devices having a planar radiating element (12) and a ground plane conductor (14) disposed substantially parallel thereto with a dielectric (16) such as air or a substrate therebetween. The radiating element (12) includes at a feed point, for example, a feeding strap (18), which may have an L-shape. One or more shorting straps (20,22) are selectively connected between the radiating element (12) and the ground conductor (14), positioned relative to the feed point for tuning the input impedance at the feed point, and for tuning the resonant frequency of the planar radiating element (12). The radiating element includes an angled slot (26) having at least three slot sections, for example, N, M, W shapes and the like, mutually coupled at a second resonant frequency to increase resonant frequency bandwidth. The feeding strap (18) and one or more shorting straps may be provided as inverted L straps (30) for a series LC impedance.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
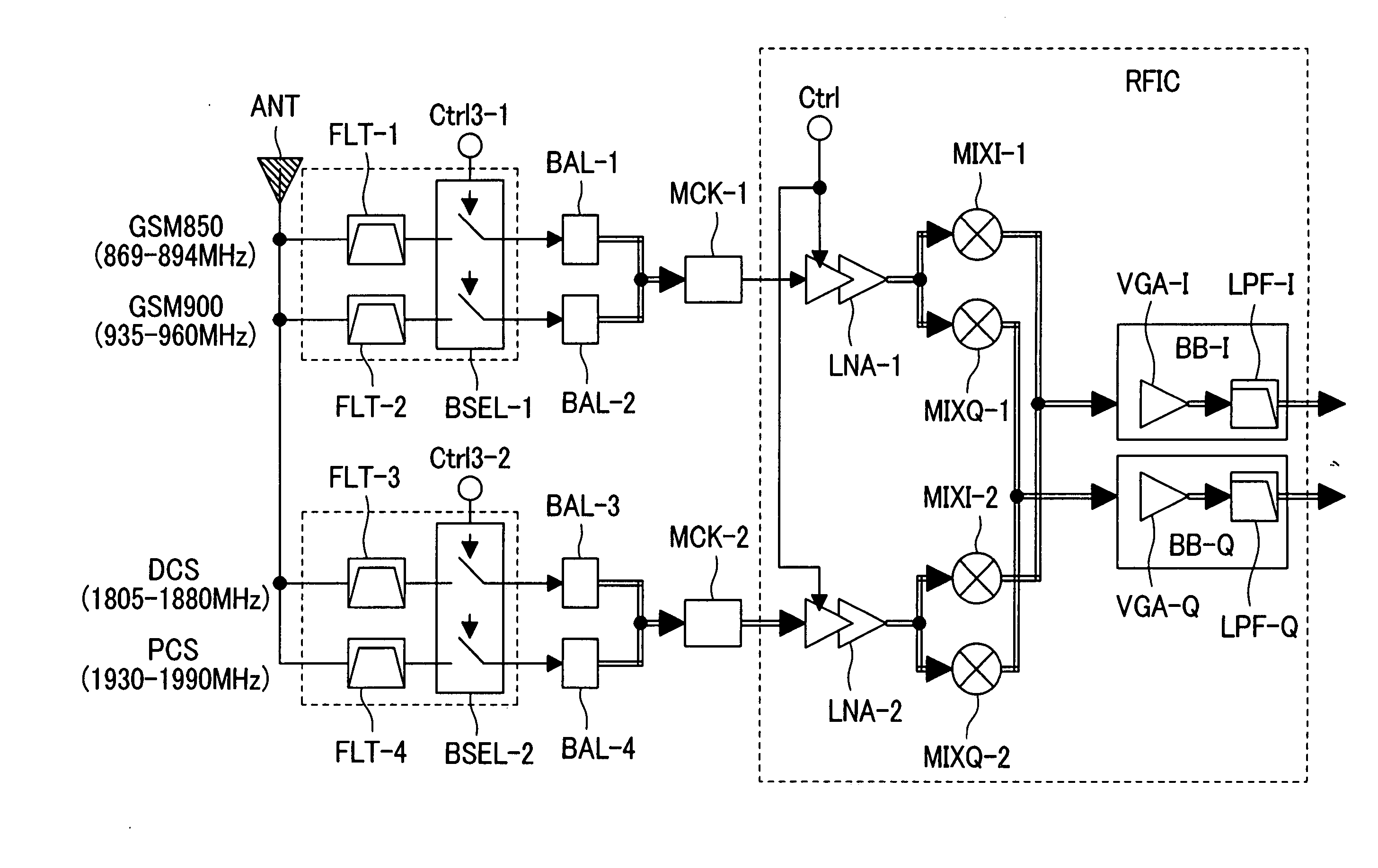
Multi-band low noise amplifier, multi-band low noise amplifier module, wireless integrated circuit and multi-band RF module
InactiveUS20060189286A1Small sizeSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A multi-band radio module for selectively supplying received signals in a plurality of frequency bands to a low noise amplifier via an input impedance matching circuit by switching over the operation mode of the low noise amplifier is comprised of: a pre-stage amplification unit including a plurality of fundamental amplifiers connected to one another in parallel, the fundamental amplifiers sharing a load impedance connected to a source voltage and a grounded degeneration impedance and having input signal lines commonly connected to an input impedance matching circuit; a post-stage amplifier to which the output signals of the plurality of fundamental amplifiers are commonly inputted; and a bias control unit for selectively turning on the fundamental amplifiers, wherein the input impedance of the low noise amplifier is selectively optimized for the matching circuit depending on the RF band to be received.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Antenna device and method for transmitting and receiving radio waves
InactiveUS6980782B1Easy to manufactureEasy to installResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsResonanceInput impedance
An antenna device for transmitting and receiving radio frequency waves, installable in a communication device includes an antenna structure switchable between antenna configuration states. Each state is distinguished by a set of radiation parameters, such as resonance frequency, input impedance, bandwidth, radiation pattern, gain, polarization, and near-field pattern. A switching device selectively switches the structure between the states. The antenna device includes a first receiver which receives a first measured operation parameter indicative of quality of transmission of radio frequency waves by the antenna structure, and a second receiver which receives a second measured operation parameter indicative of quality of reception of radio frequency waves by the structure. The antenna device includes a controller which controls the switching device, and selective switching of the antenna structure between the states, based on the first and second measured operation parameters, to improved transmission and / or reception quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
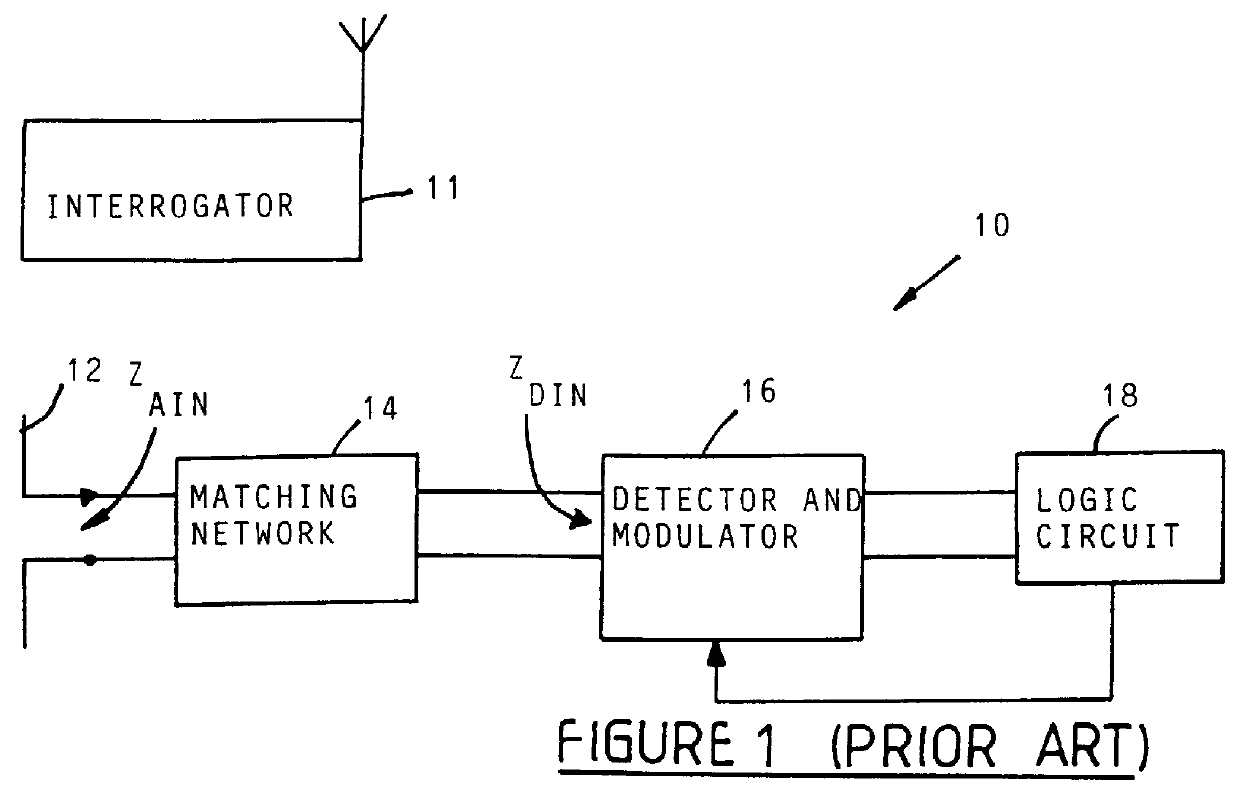
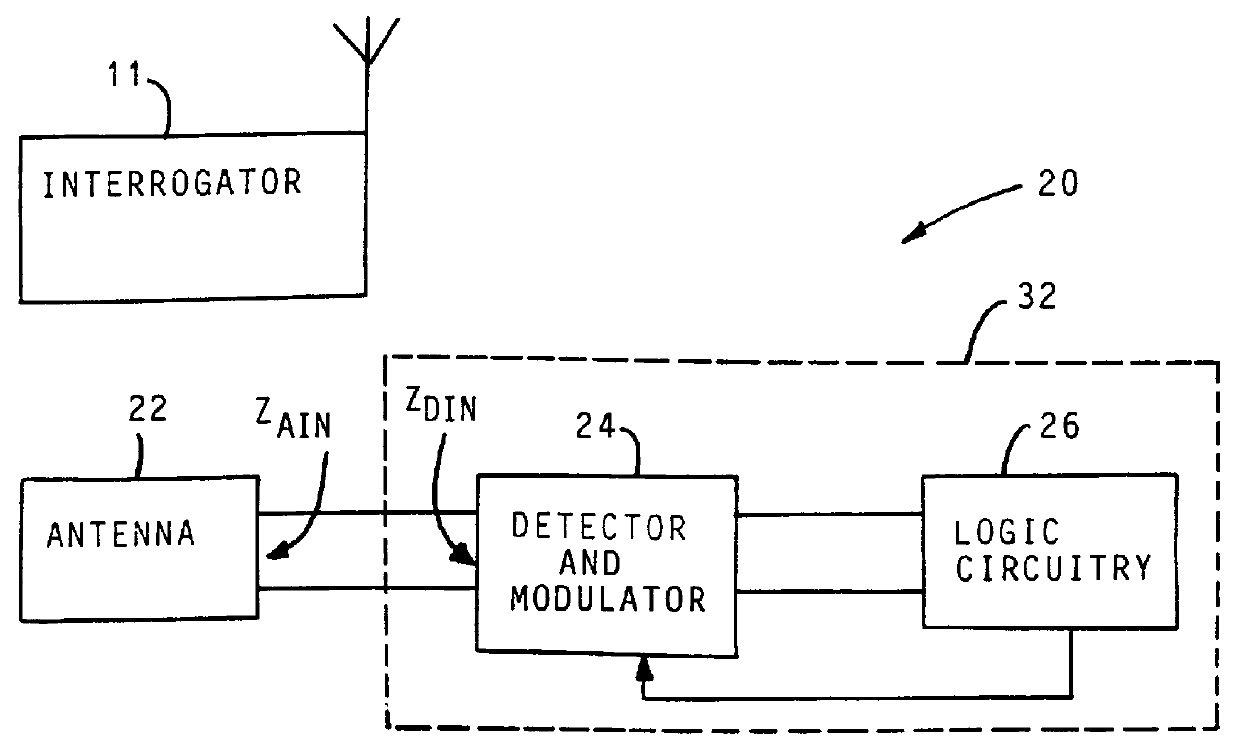
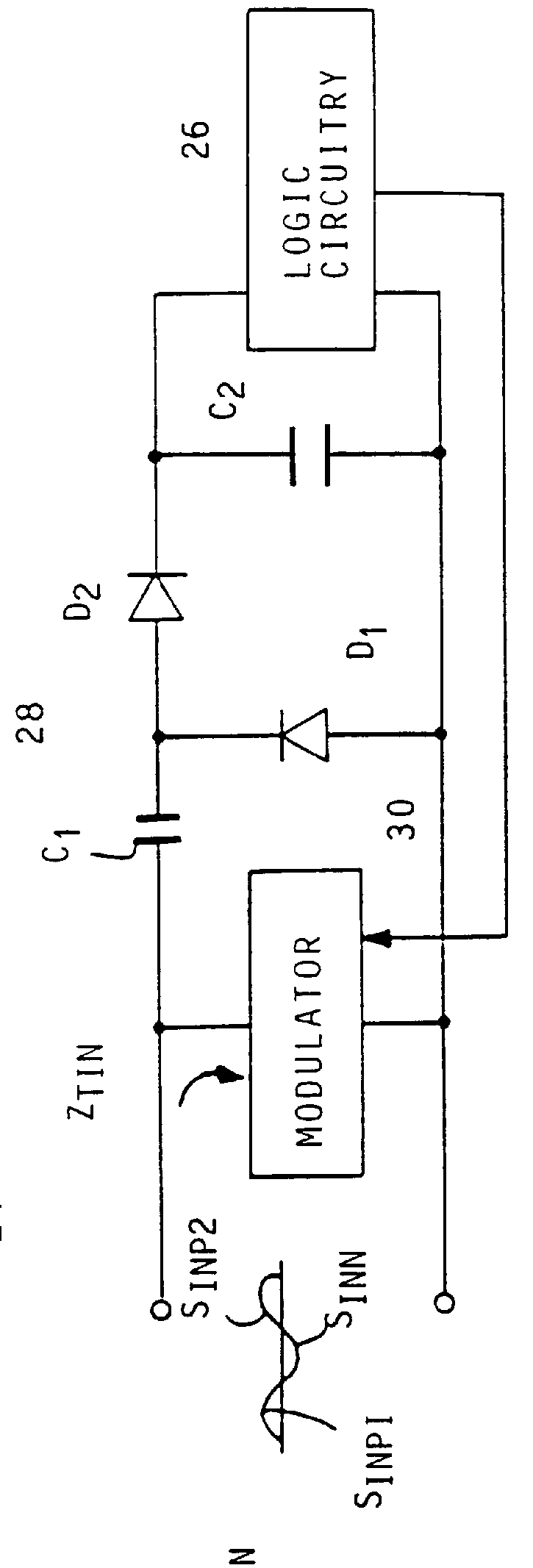
High impedance transponder with improved backscatter modulator for electronic identification system
InactiveUS6054925ATransmissionRecord carriers used with machinesElectronic identificationInput impedance
A transponder 20 for an electronic identification system transponder is characterized in that it presents a high input impedance (>400 OMEGA ) at an input thereof which is directly connected to an antenna 22 with a matched high input impedance. The transponder is aimed at improving the voltage recovered on capacitor C2 from an interrogation signal and thus the operational range of the system. The modulator 30 of the transponder is arranged to backscatter modulate the interrogation signal at a modulation depth of less than 80%, preferably in the order of 30%. This also results in an improvement of the operational range of the system.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
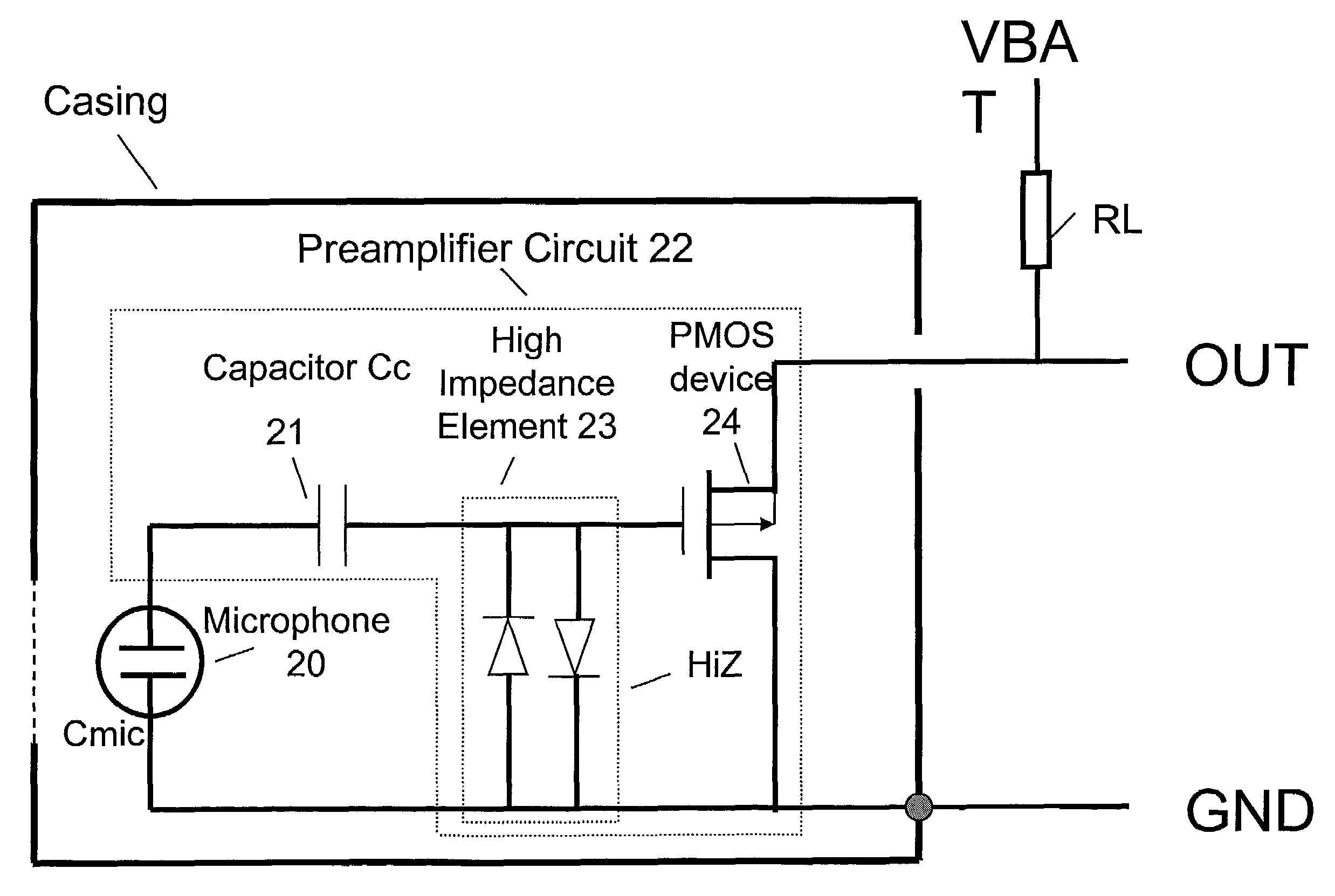
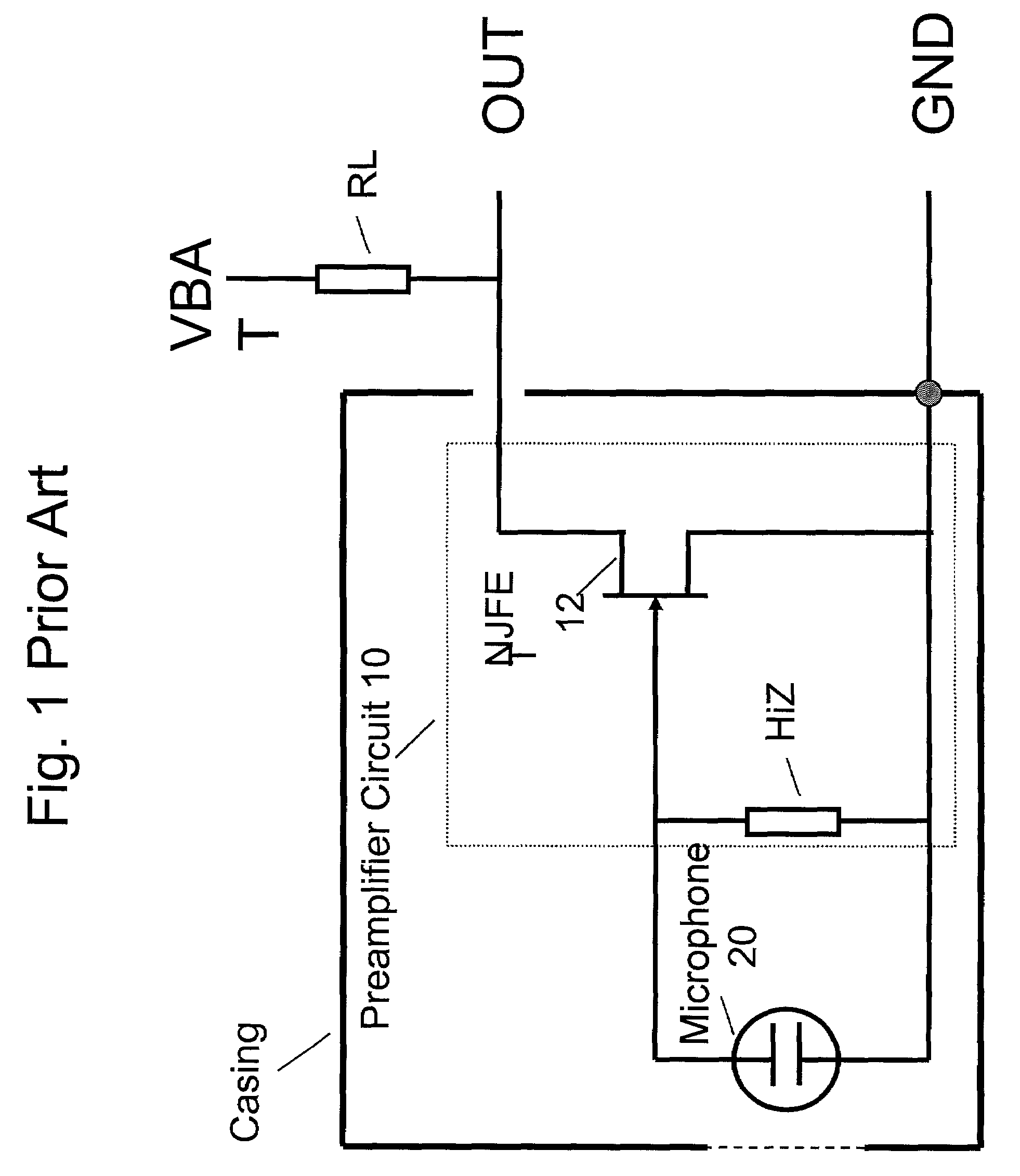
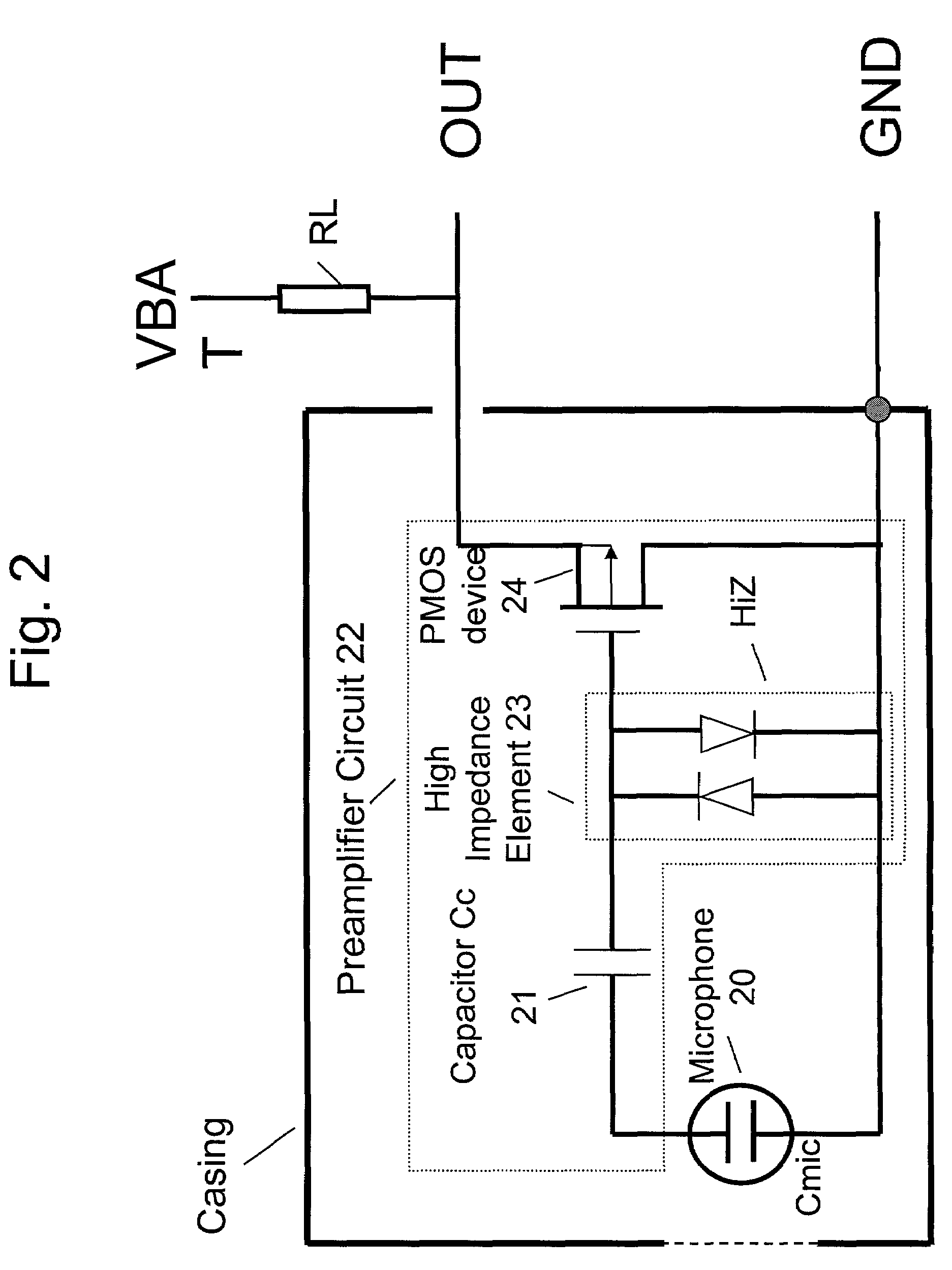
Electret condensor microphone preamplifier that is insensitive to leakage currents at the input
InactiveUS7110560B2Reduce input leakage currentAvoid leakage currentLow frequency amplifiersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOperating point
A preamplifier having extremely high input impedance amplifies the electrical signal output from an electret condenser microphone (ECM) without suffering from the effects of a DC leakage current at the input. The preamplifier circuit includes a pair of cross-coupled PN junction diodes setting the input impedance, a PMOS device, and a load resistor configured similarly to a conventional preamplifier. A capacitor is placed between the input and the cross-coupled diodes such that a DC path no longer exists to bias the cross-coupled diodes. Therefore, leakage currents are prevented from upsetting the DC operating point of the preamplifier and biasing the cross-coupled diodes. Consequently, small signal gain distortion, excessive demodulation products and increased noise can be avoided.
Owner:SONION
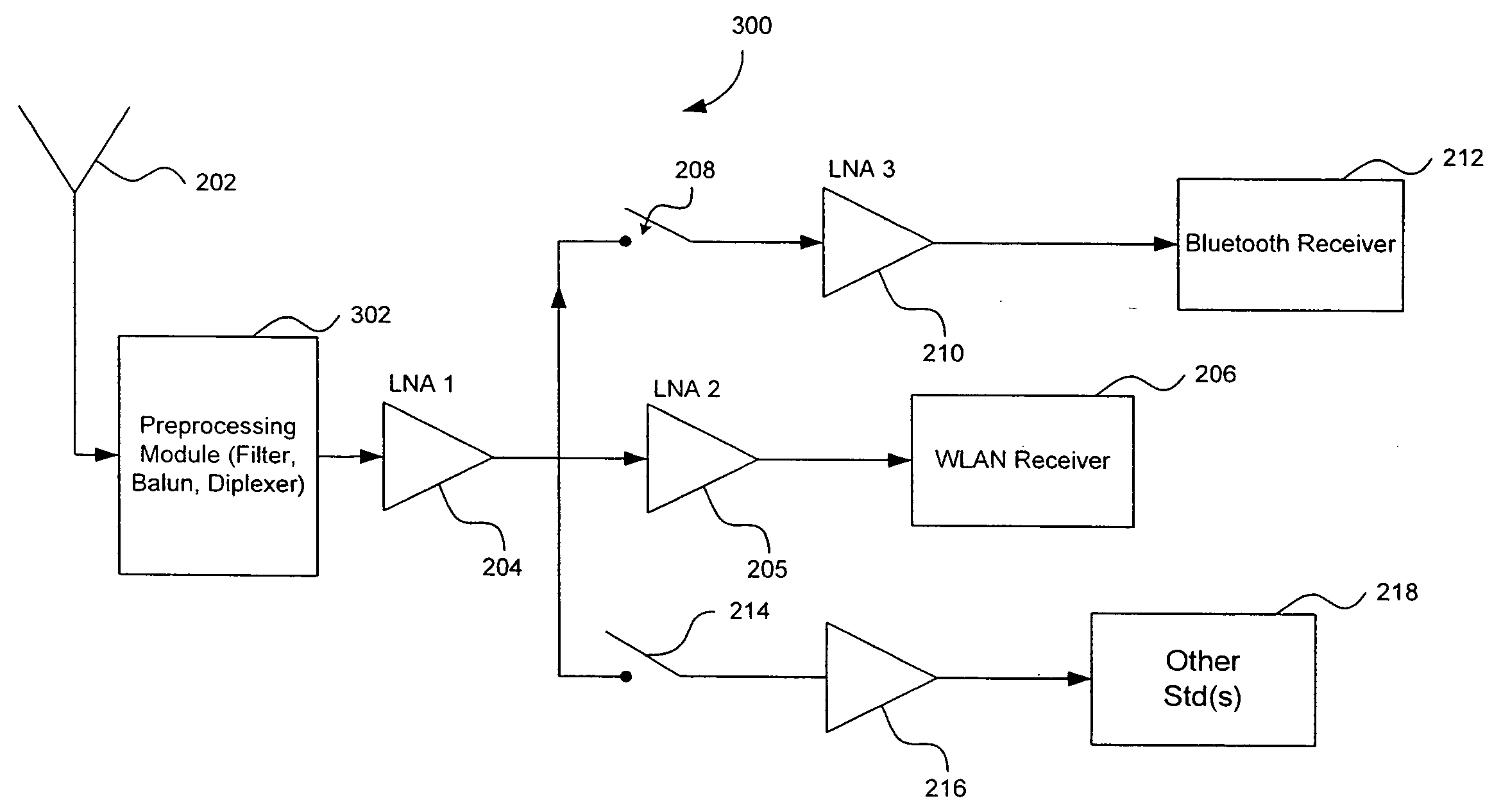
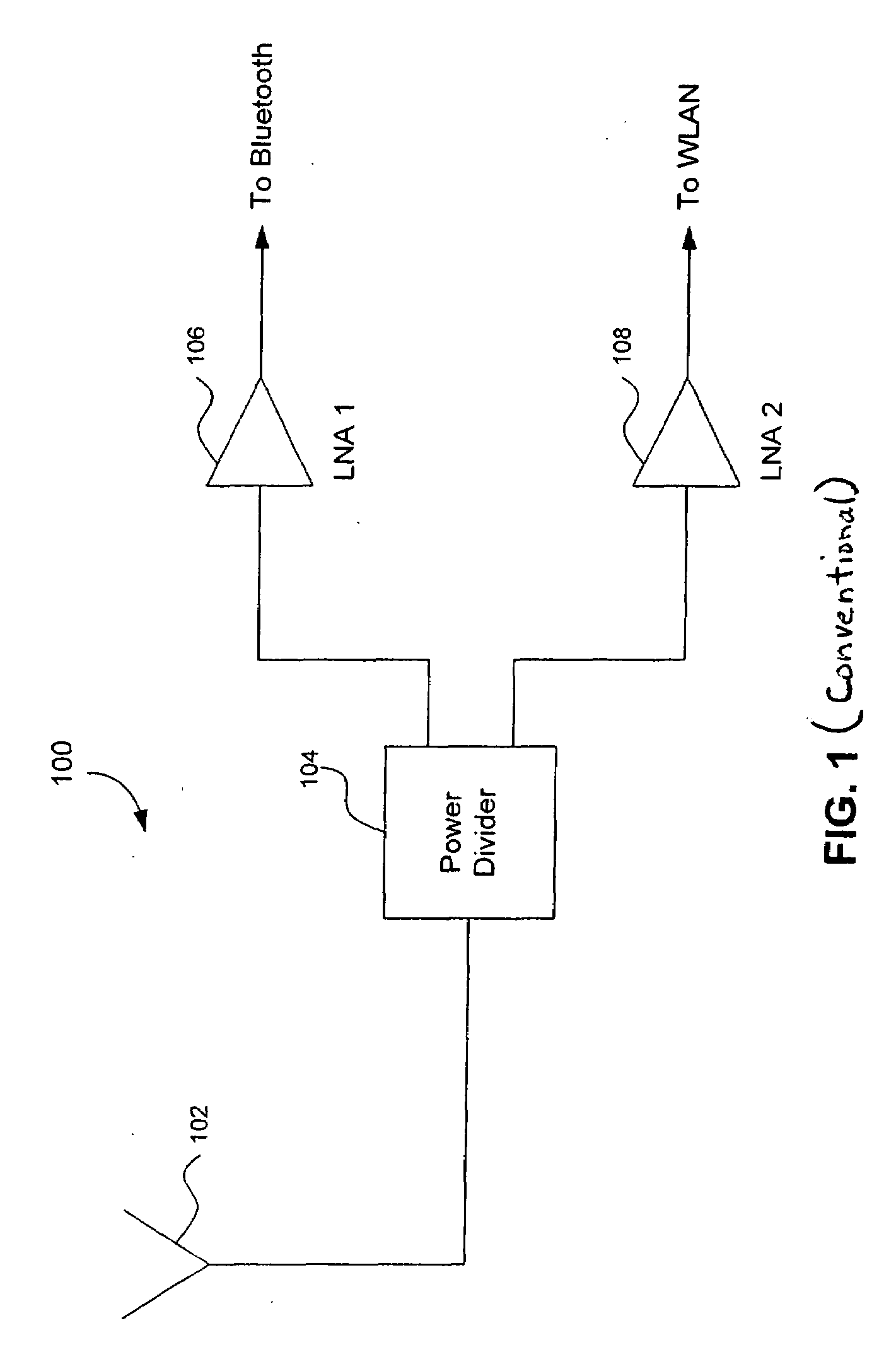
Radio Receiver with shared low noise amplifier for multi-standard operation in a single antenna system with loft isolation and flexible gain control
ActiveUS20070207752A1Improve reverse isolationReduce noiseSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentAudio power amplifierRadio reception
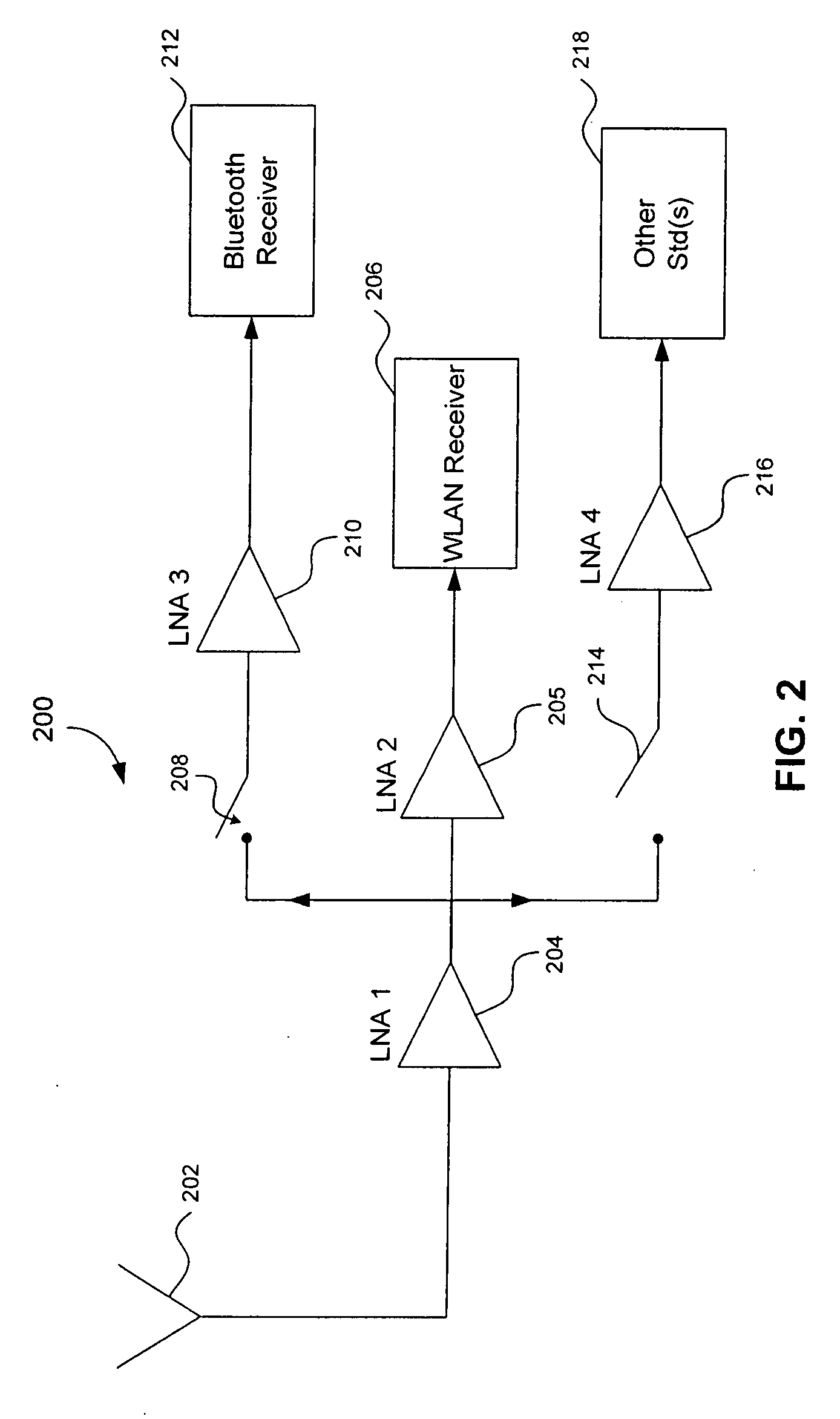
A radio receiver is described that processes multiple wireless standards using a single antenna according to embodiments of the invention. The radio receiver includes a single antenna, and a low noise amplifier that is connected to the antenna, without an intervening power divider or power splitter. The output of the low noise amplifier feeds multiple wireless receivers in a parallel arrangement that are operating according to different communications standards, including for example a Bluetooth and a WLAN 802.11. Additional wireless standards and their corresponding receivers could be added as well. The input impedance of the low noise amplifier defines the impedance seen by the antenna, regardless of which operational standard is actually in use. Each signal path includes an additional low noise amplifier having a gain that can be customized for the particular signal path and receiver in use, and which also improves the reverse isolation between signal paths. Further, a switch can be added to one or more of the signal paths so as to further improve isolation when a particular path is not being used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low noise and high gain low noise amplifier
ActiveUS20060097786A1Low NFIncrease power gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
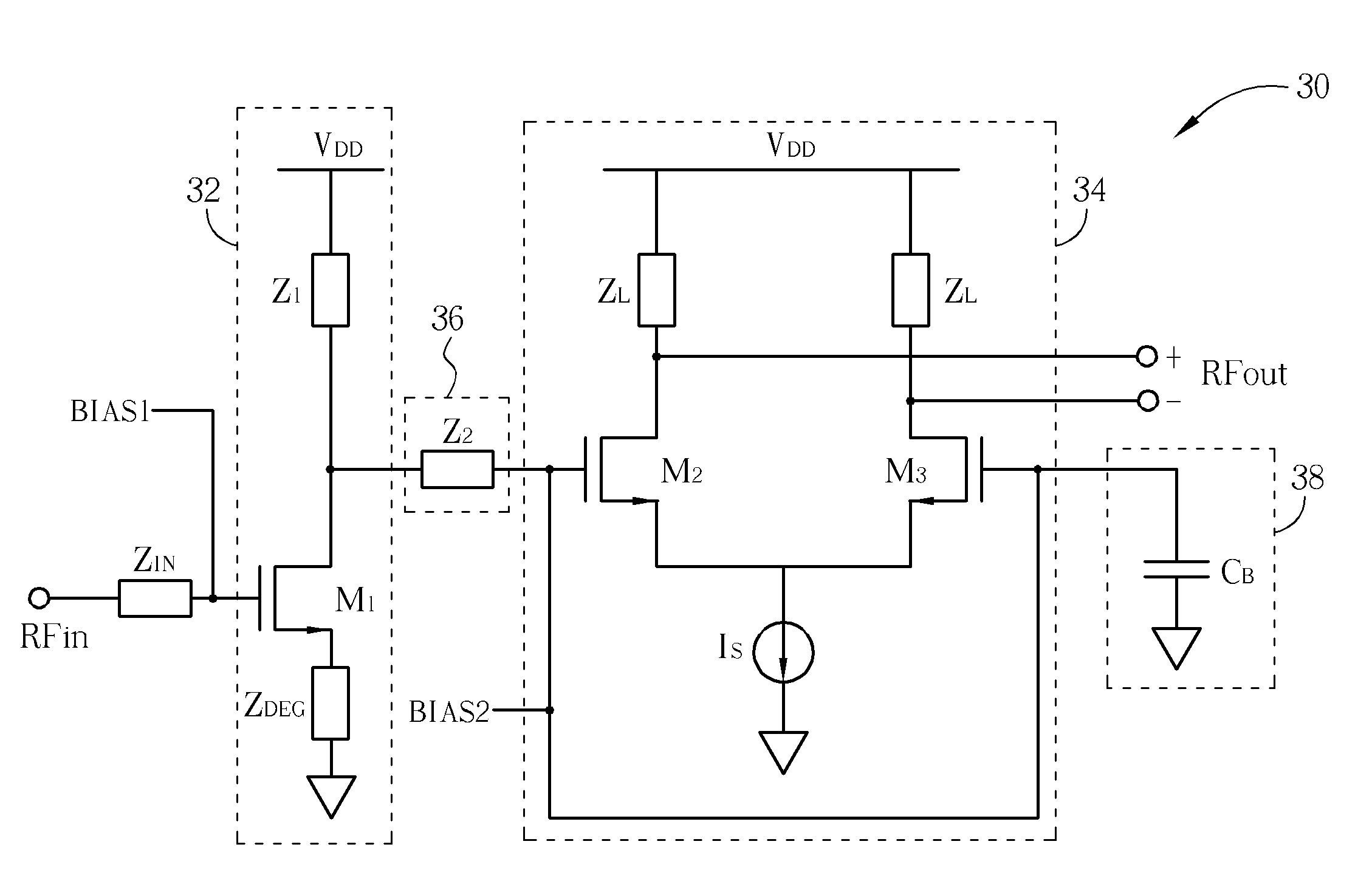
A high-gain and low-noise low noise amplifier (LNA) includes a differential amplifier, a pre-amplifier and an impedance matching network. The differential amplifier includes a first input end and a second input end coupled to a grounded impedance. The pre-amplifier includes an input end and an output end. The impedance matching network is coupled between the first input end of the differential amplifier and the output end of the pre-amplifier for matching an input impedance of the differential amplifier with an output impedance of the pre-amplifier. The present invention provides a LNA structure with low noise, high gain and easy design.
Owner:RICHWAVE TECH CORP
Neural Measurement
ActiveUS20170049345A1Easy to solveInhibition of charge injectionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesInput impedanceEngineering
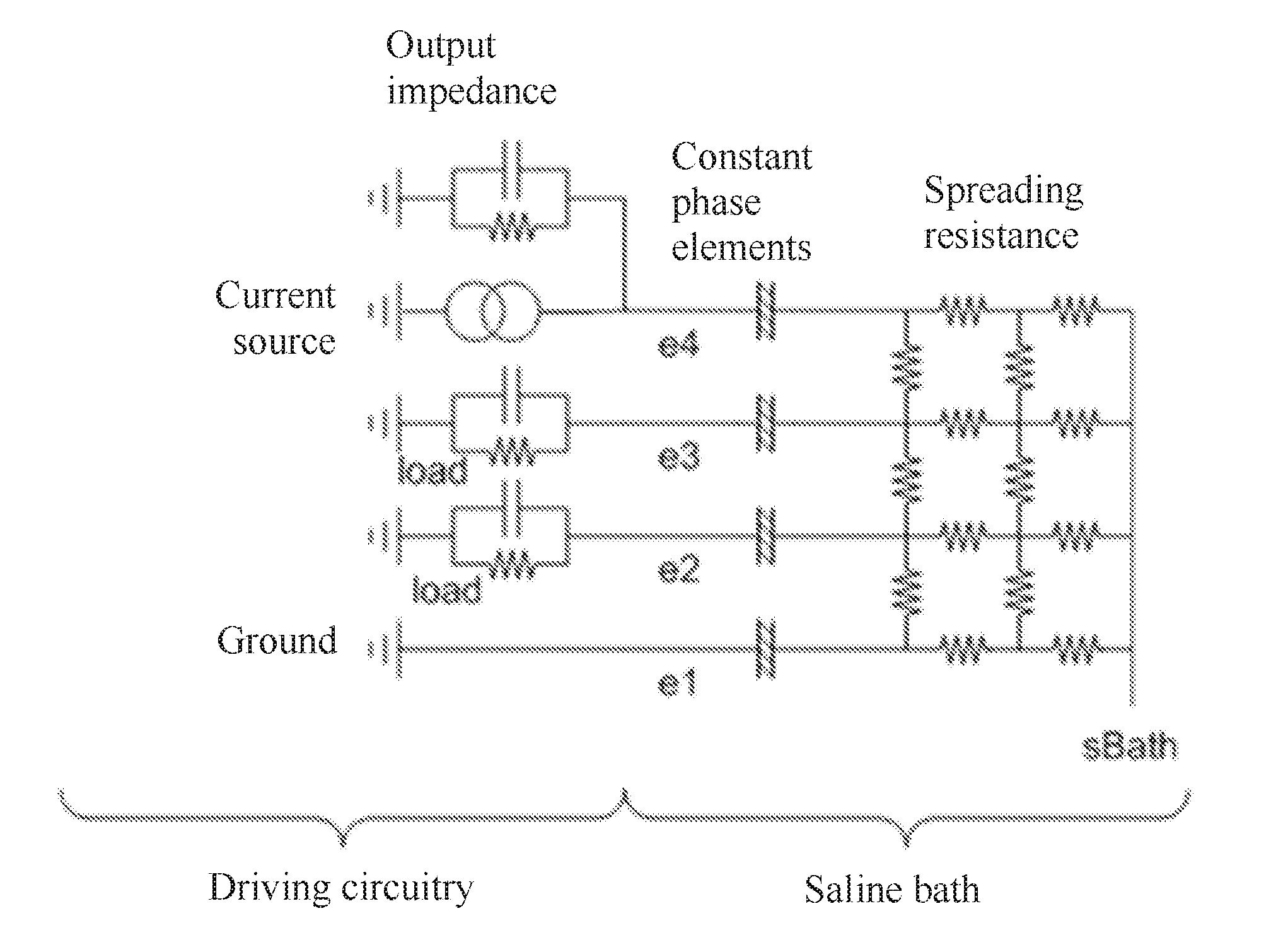
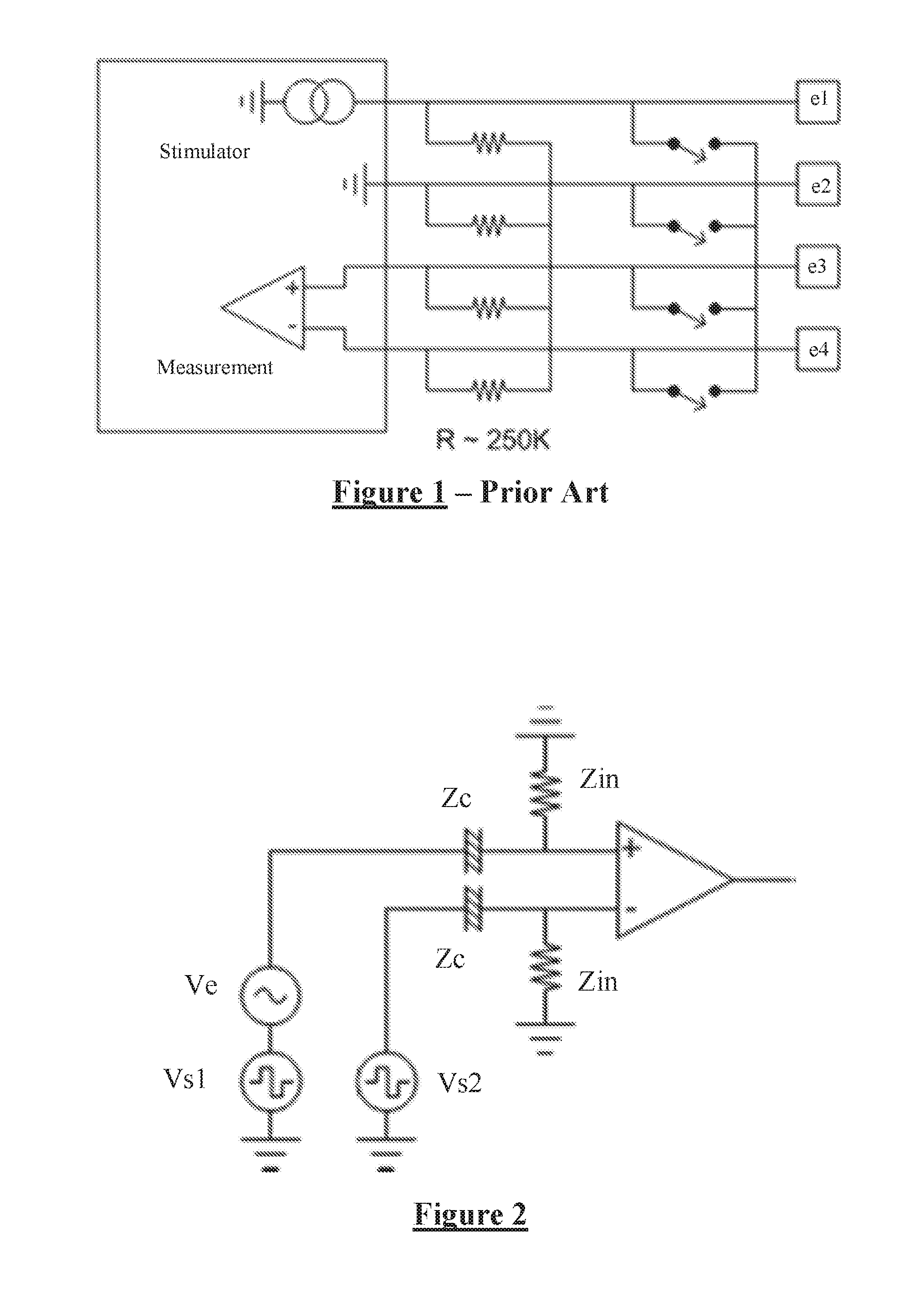
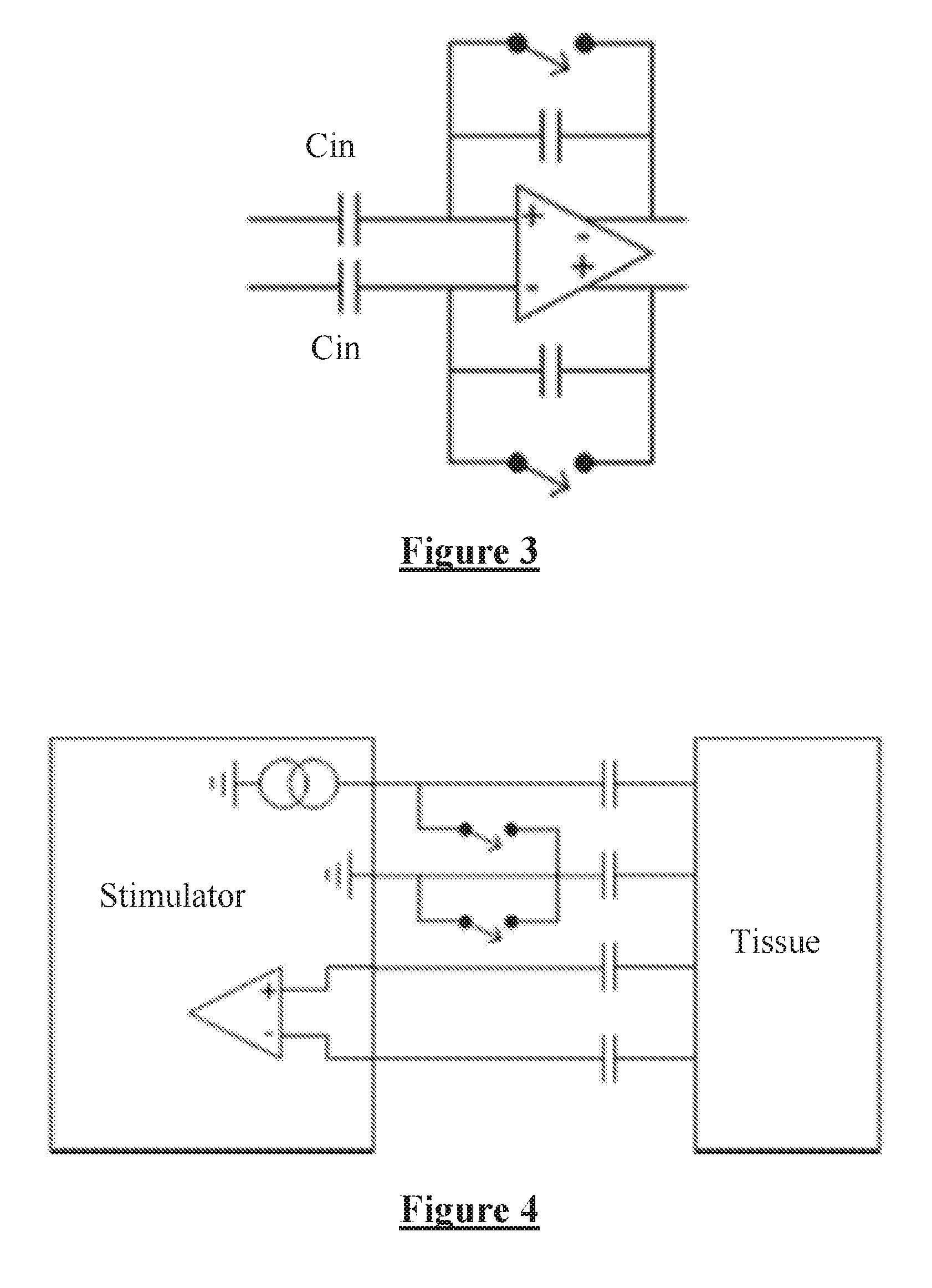
Measuring a neural response to a stimulus comprises applying an electrical stimulus, then imposing a delay during which the stimulus electrodes are open circuited. During the delay, a neural response signal present at sense electrodes is measured with a measurement amplifier, while ensuring that an impedance between the sense electrodes is sufficiently large that a voltage arising on the sense electrode tissue interface in response to the stimulus is constrained to a level which permits assessment of the neural response voltage seen at the sense electrode. For example the input impedance to the measurement amplifier (ZIN) can beZIN>ZC(VS1-VS2)VE,where ZC is the sense electrode(s) constant phase element impedance, Vs1−Vs2 is the differential voltage arising on the sense electrode tissue interface, and VE is the neural response voltage seen at the sense electrode.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
In-vivo interstitial antennas
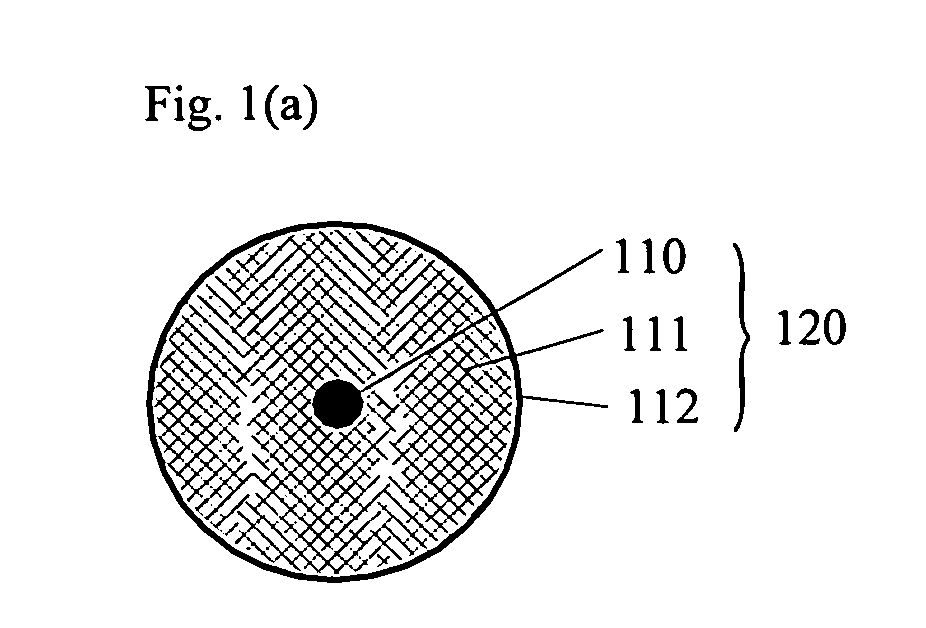
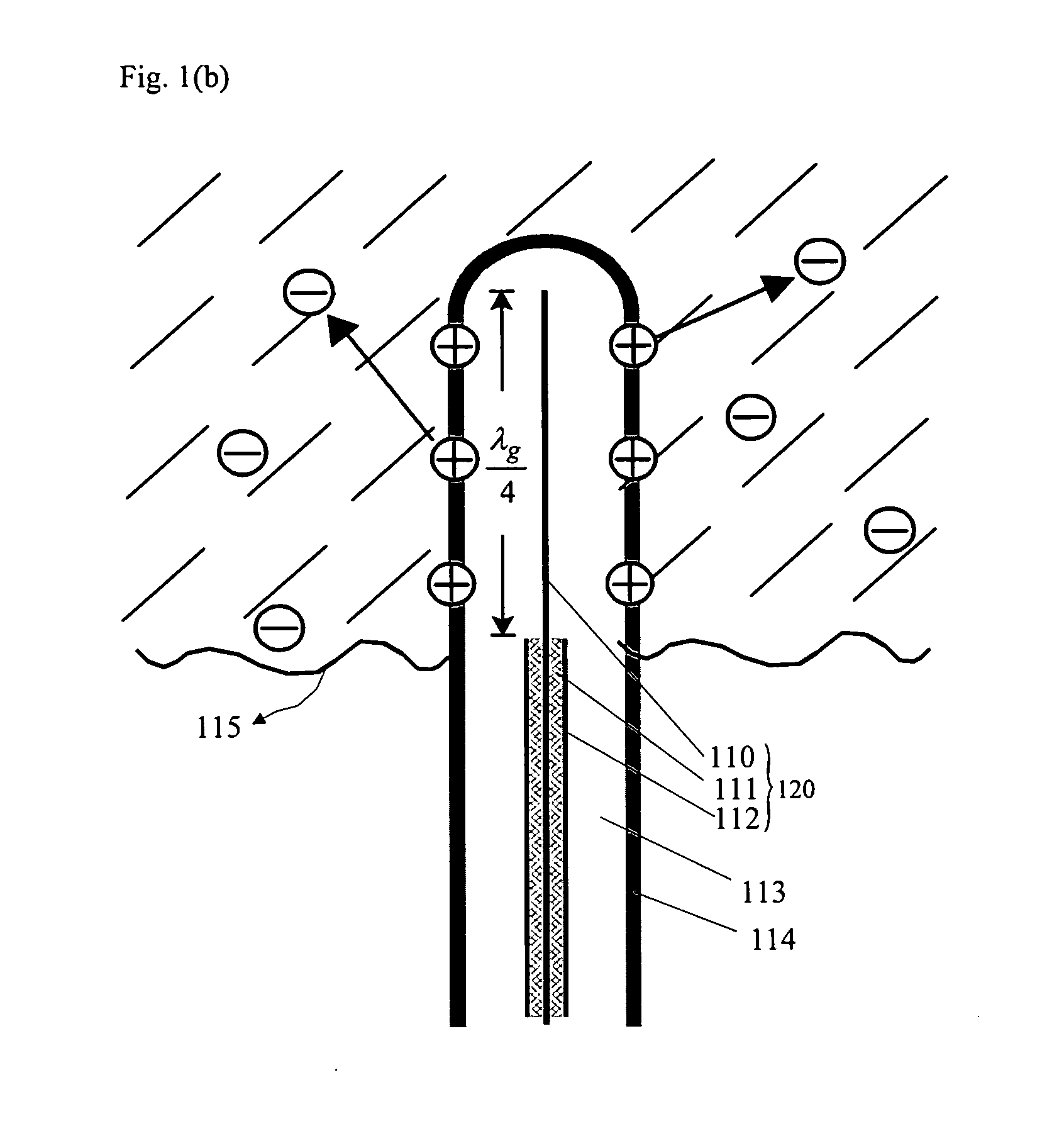
InactiveUS20070142829A1Improve matchHigh thermal efficiencyElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingAbnormal tissue growthElectrical conductor
Disclosed are in-vivo interstitial antennas (IVIAs) for thermal treatment and deactivation of tumors by means of microwaves. An IVIA comprises a microwave monopole antenna (MMA) and a medical catheter, and the MMA is inserted into the medical catheter to form the IVIA. The MMA comprises coaxial cable and three types of capacitors. The coaxial cable consists of first and second conductors and a first insulator, and only the first conductor extends less than a quarter wavelength. The first capacitor is located around the end of the extended first conductor and includes the second insulator and the third conductor. The second and third capacitors are located between the first capacitor and the apertures of the MMAs and have about same function. Because of arbitrarily changed input impedance of the first capacitor, almost perfect matching can be achieved and desirable temperature distributions can be obtained due to the second and third capacitors.
Owner:POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
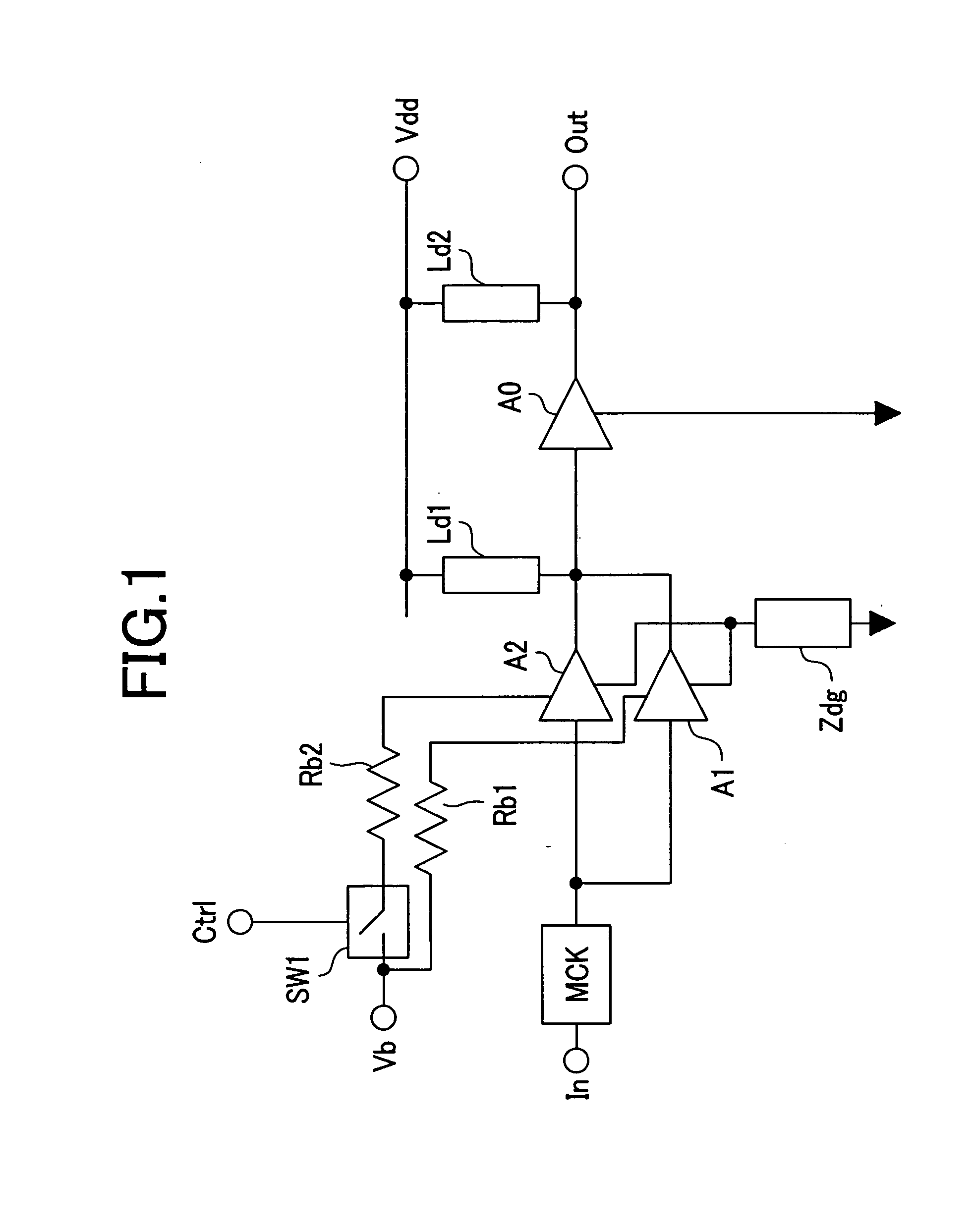
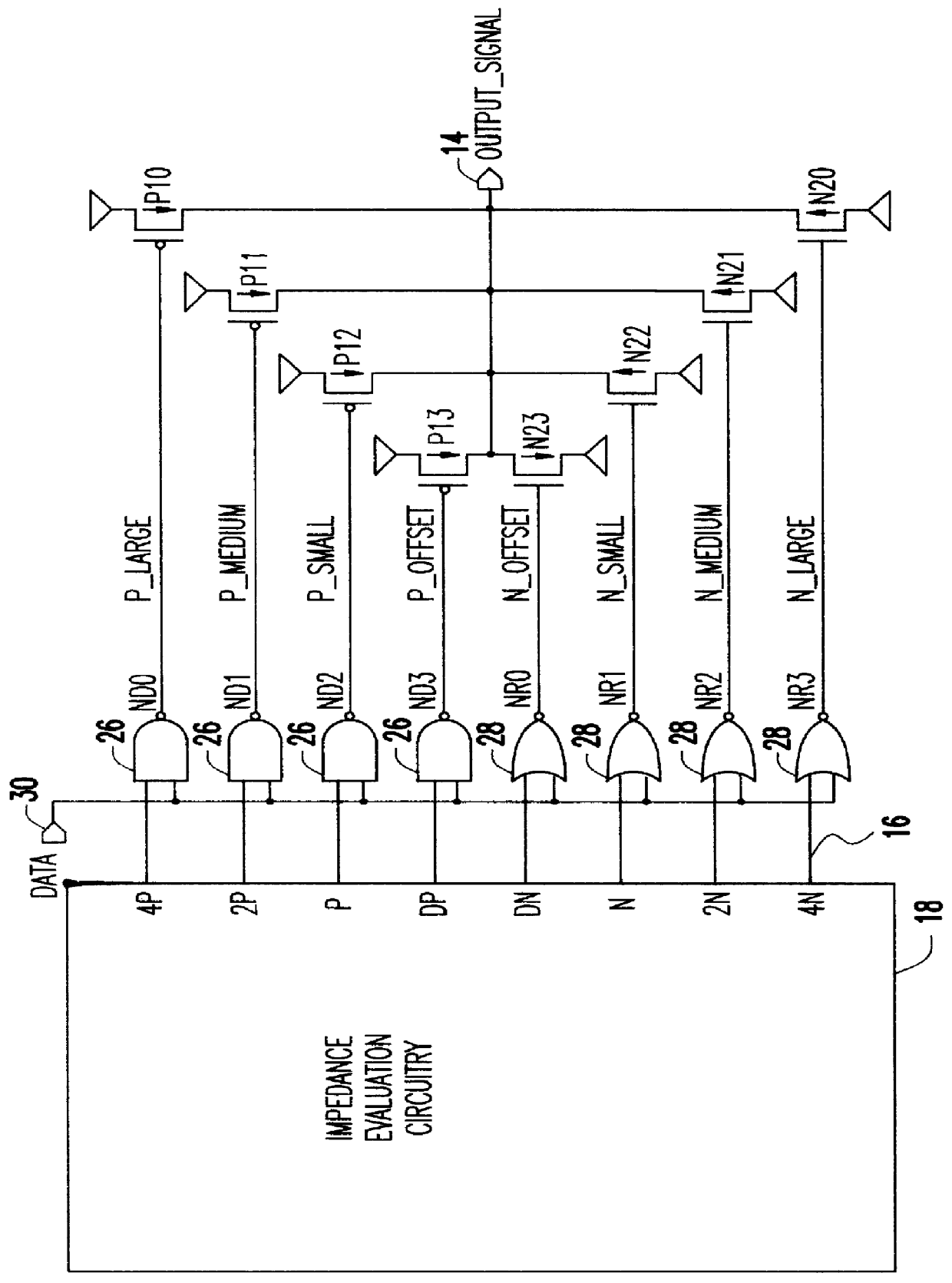
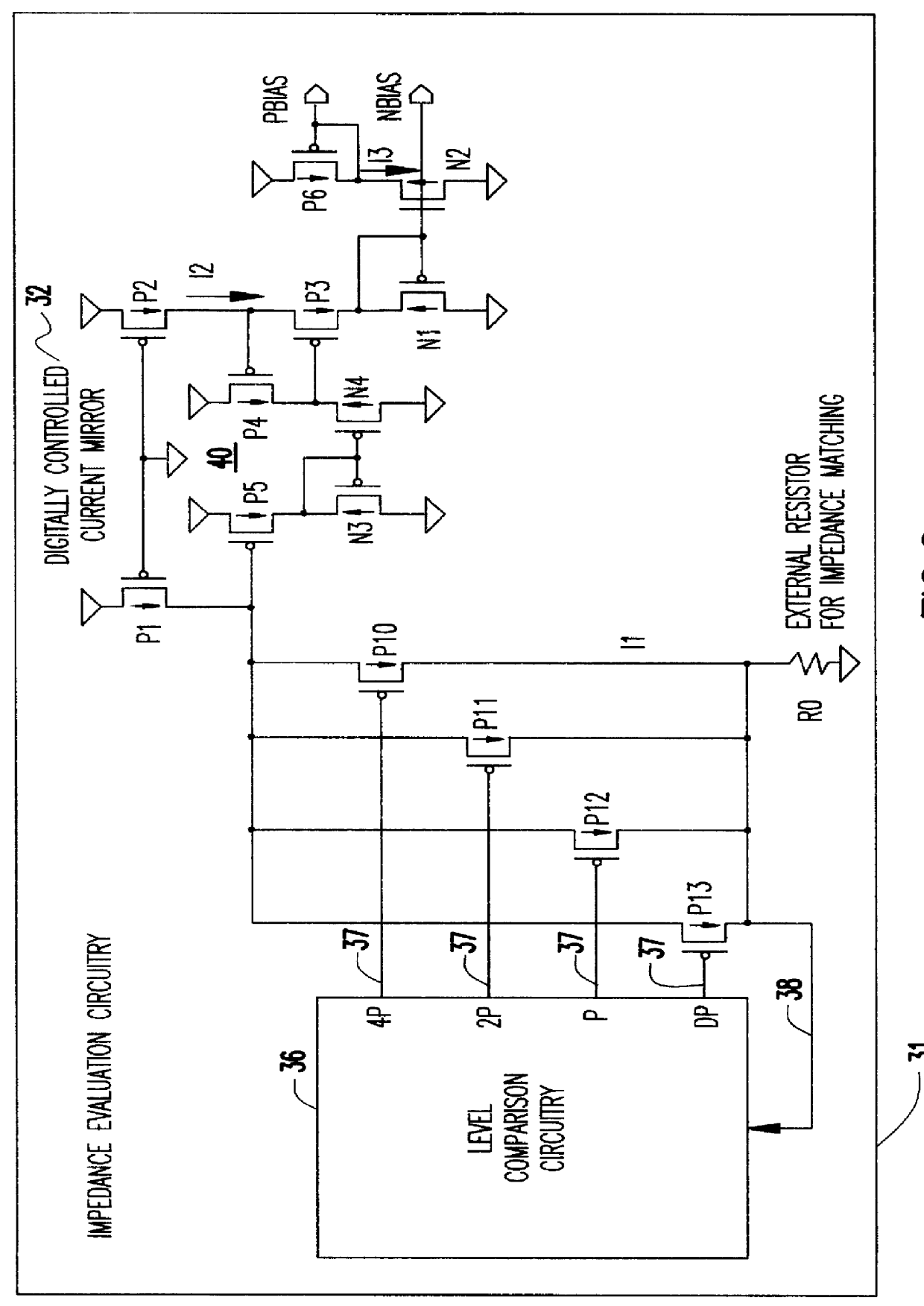
Variable impedance output driver circuit using analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance
InactiveUS6133749AInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
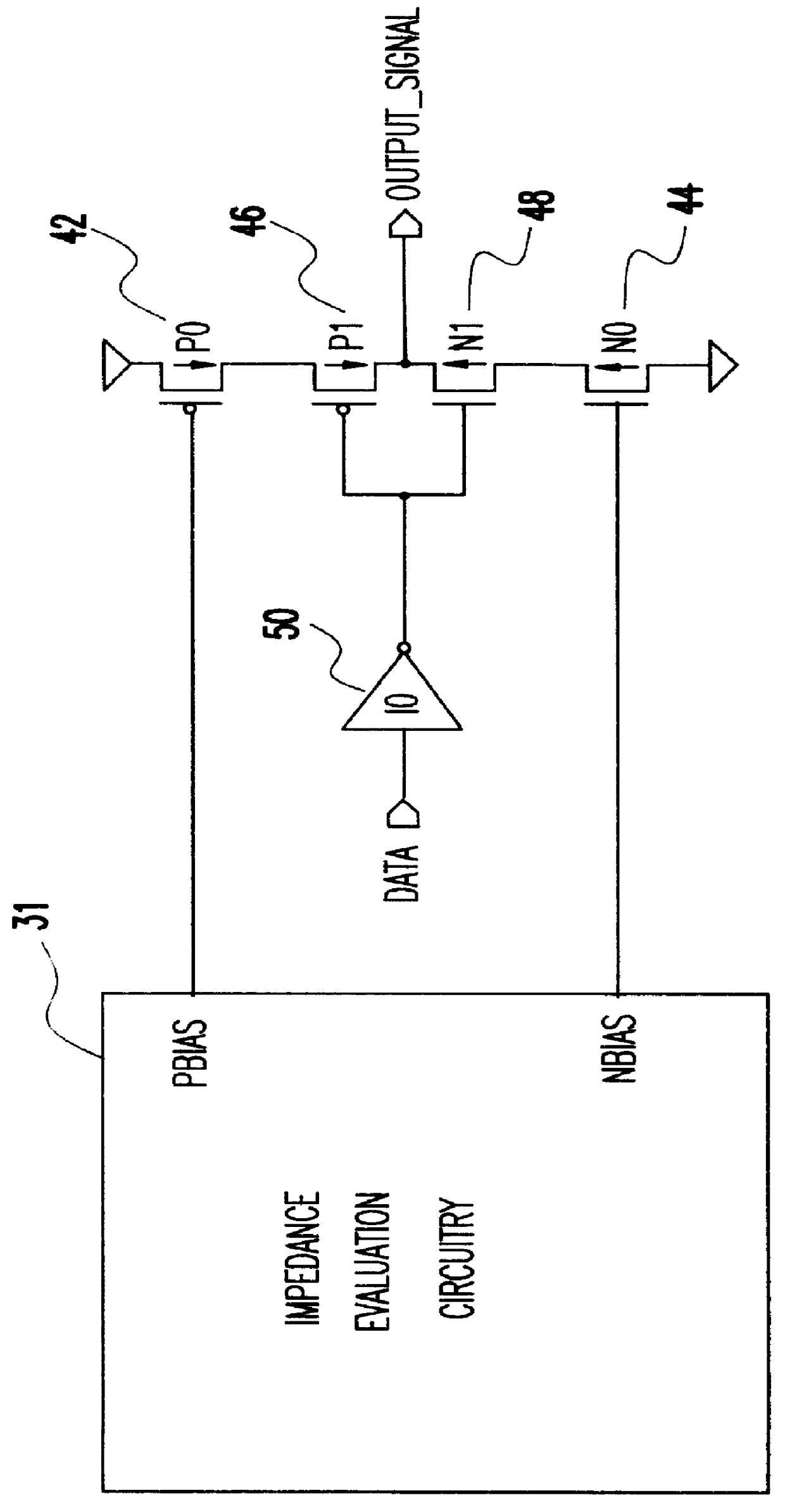
A programmable variable impedance output driver circuit uses analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance. A current mirror is used to obtain a measurement of an external resistance value for matching the impedance of a driven load. The mirrored current generates the voltage "NBIAS" when passed through the resistively connected NFET. Similarly, the current is again mirrored and passed through a resistively connected PFET resulting in the voltage "PBIAS". The analog bias voltages, NBIAS and PBIAS are used to vary the impedance of complementary FETs in an impedance matched driver for a high degree of dI / dt control. The driver provides a high degree of flexibility because its turn-on and turn-off characteristics do not depend on a combination of digital control signals connected directly to the driving FETs as in the prior art. Instead, the PBIAS and NBIAS signals provide analog controls which may be applied to single transistors whose impedance changes as PBIAS and NBIAS increase or decrease.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for controlling operation of an electrosurgical system
ActiveUS10172665B2Controlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingCapacitancePower flow
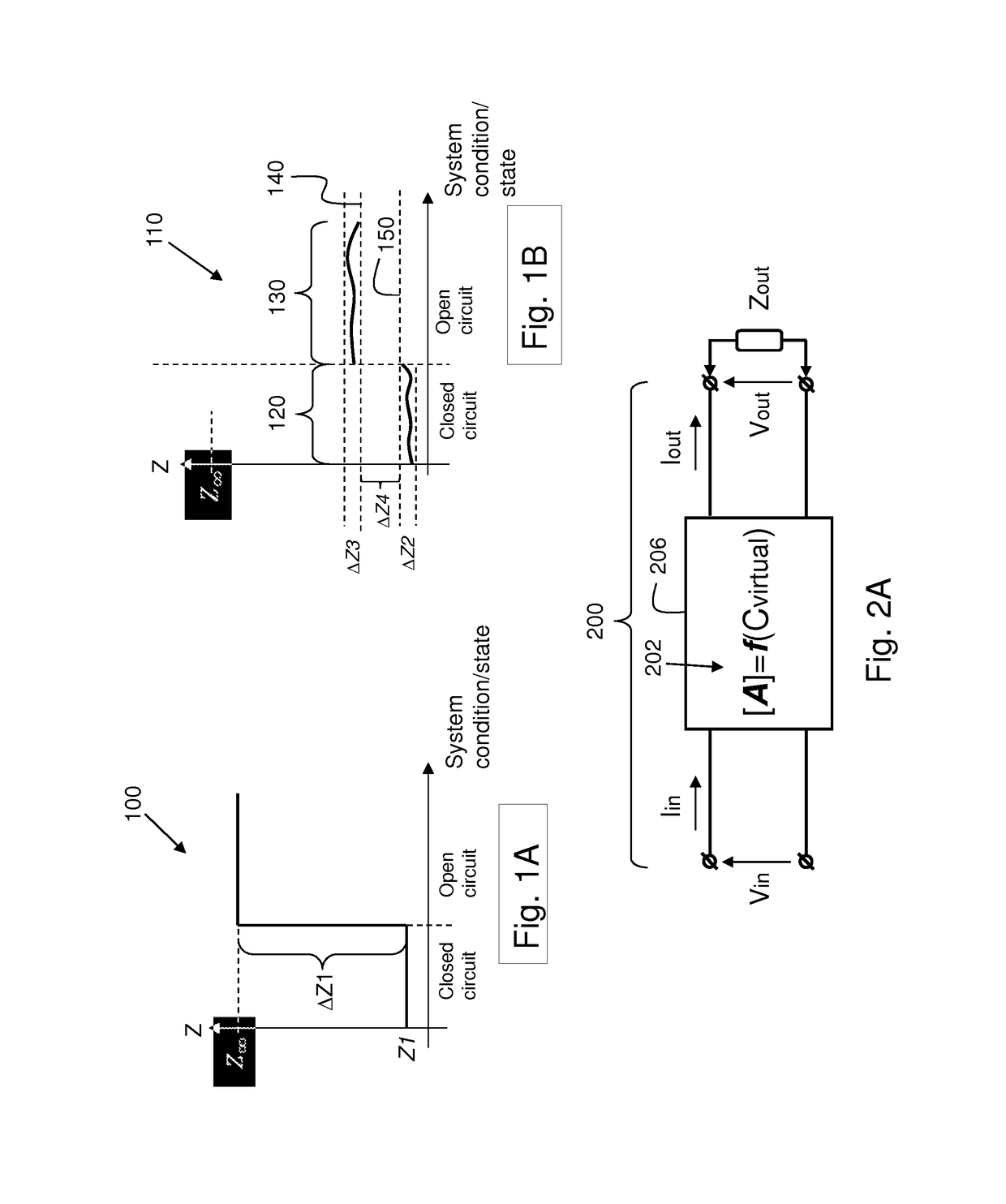
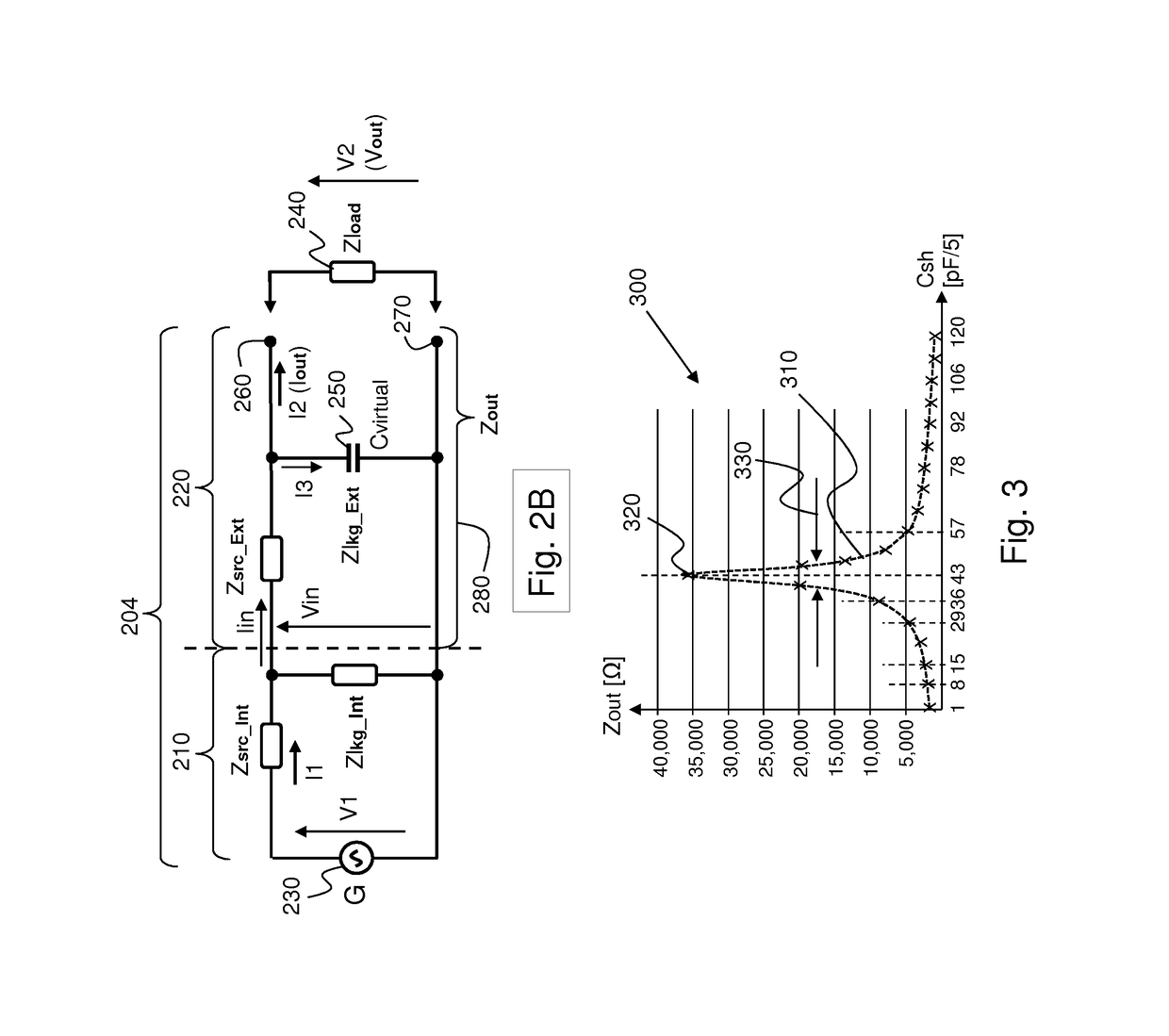
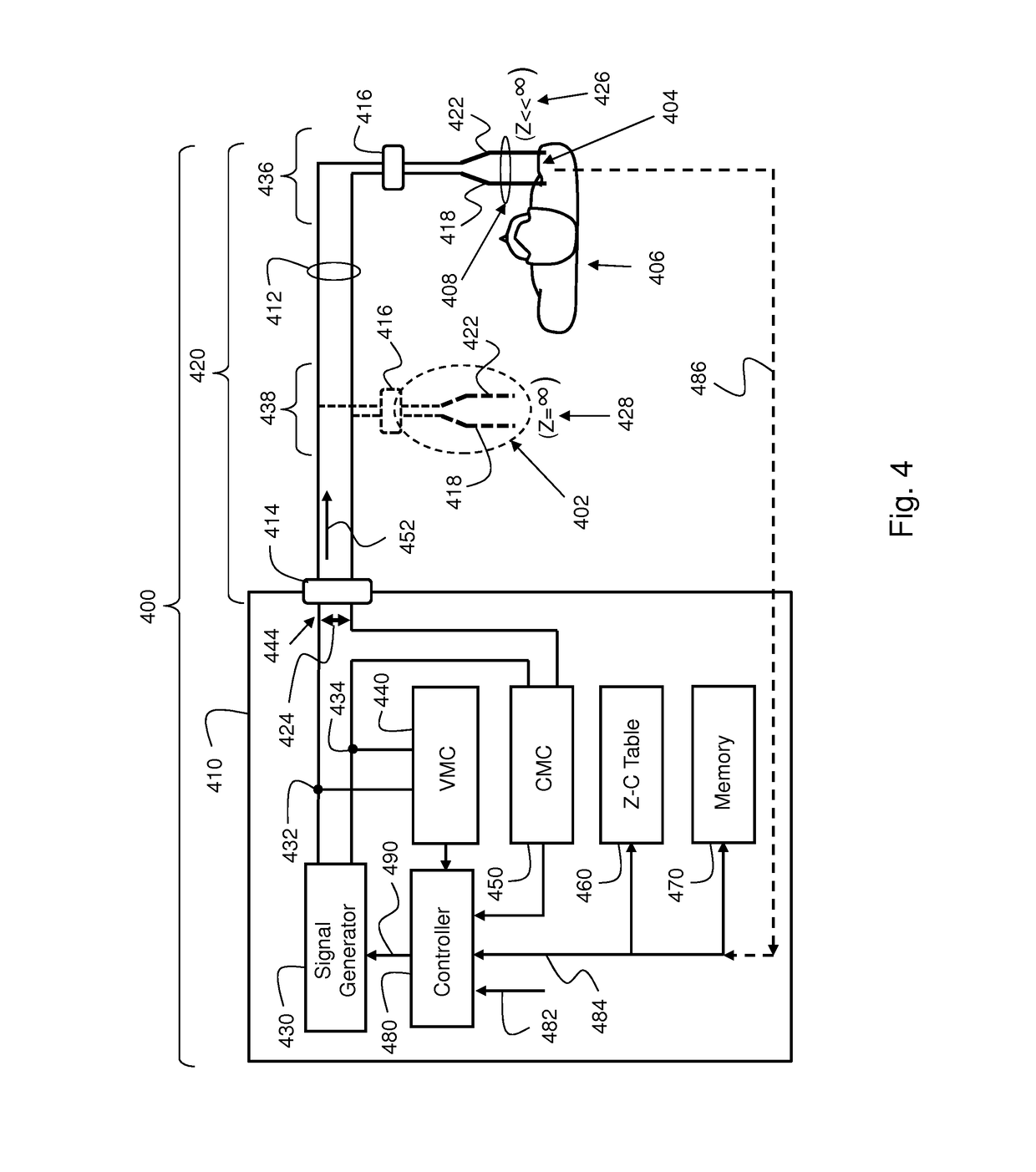
An electrosurgical system including or connected to an output circuitry comprising an electrosurgical device and an electrical cable is modelled during a cable interrogation phase using a transfer matrix in order to determine a leakage capacitance in the electrosurgical system. After the leakage capacitance is assigned or set to a virtual capacitor in the transfer matrix, an output parameter of the electrosurgical system, such as output voltage, output current, output impedance or output electrical power, may be determined by applying an actual input voltage to the output circuitry and measuring a resulting input current, and multiplying the input voltage and measured current by the transfer matrix.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Multi-mode input impedance matching for smart antennas and associated methods
InactiveUS7180464B2Antenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedInput impedanceSmart antenna
A smart antenna includes a ground plane, an active antenna element adjacent the ground plane and having a radio frequency (RF) input associated therewith, and passive antenna elements adjacent the ground plane. Impedance elements are connected to the ground plane and are selectively connectable to the passive antenna elements for antenna beam steering. Tuning elements are adjacent the passive antenna elements for tuning thereof so that an input impedance of the RF input of the active antenna element remains relatively constant during the antenna beam steering.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Biometric sensor and biometric method
InactiveUS20070010750A1Less invasiveEliminate riskElectrocardiographySensorsCapacitanceImpedance Converter
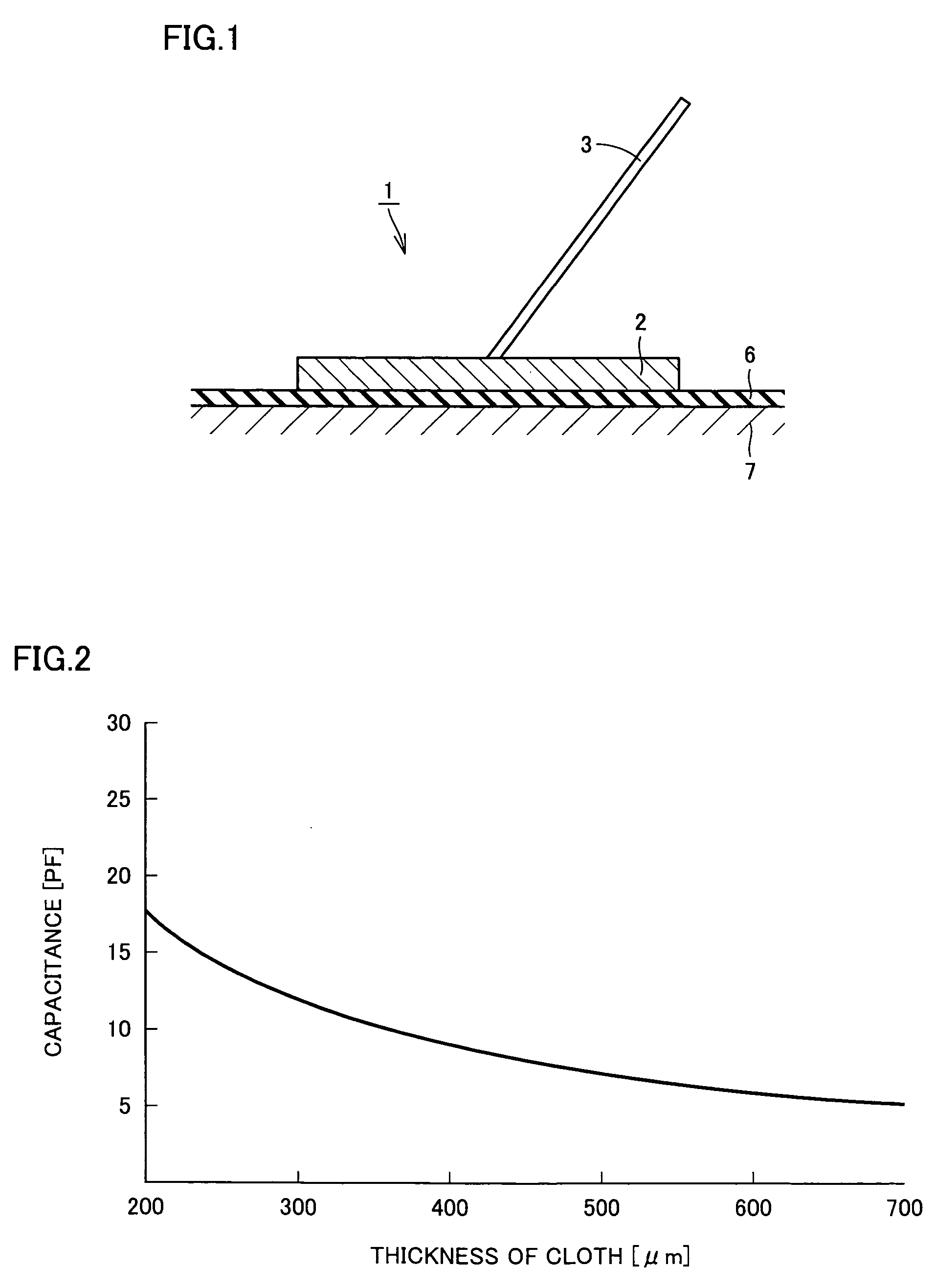
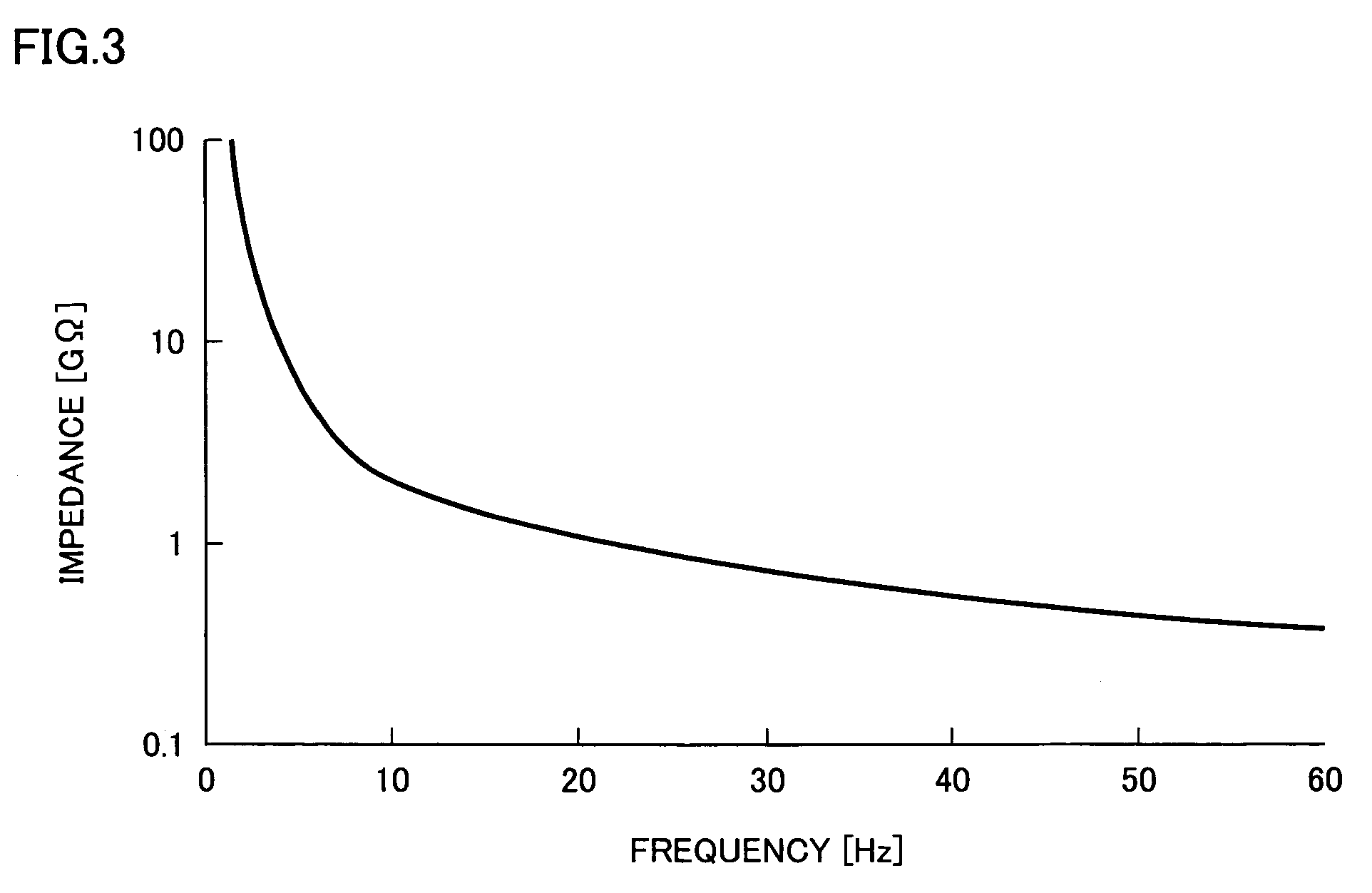
A living body measuring sensor (1) is made to contact a body surface of a measuring subject through capacitance coupling using a cloth (6) between a metal electrode (2) and the body surface as the capacitance, a living body electric signal is extracted from the metal electrode (2), and an elctrocardiographic waveform is outputted based on an output of the living body measuring sensor (1) using an impedance converter having a high input impedance and a low output impedance.
Owner:GRACO CHILDRENS PROD INC
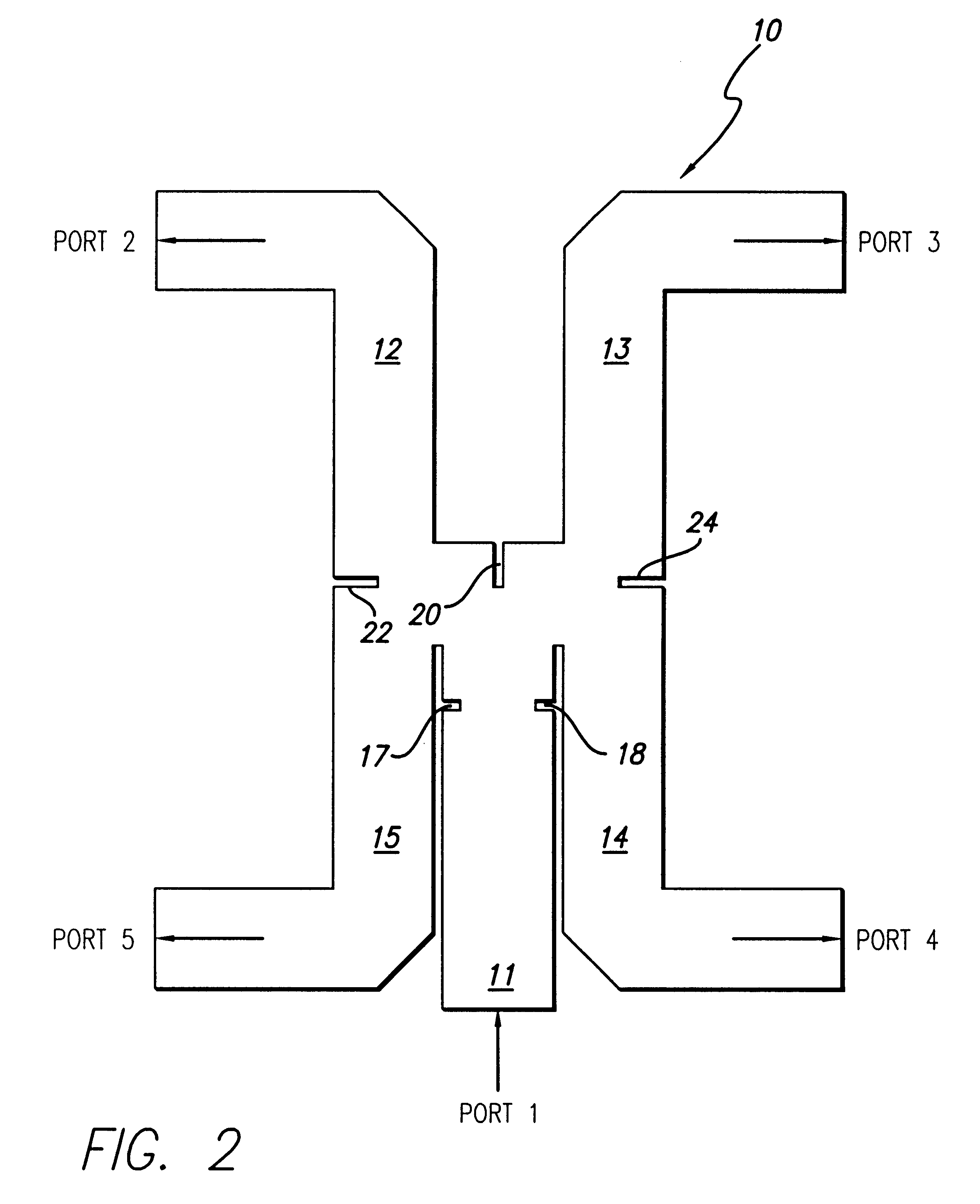
Compact four-way waveguide power divider
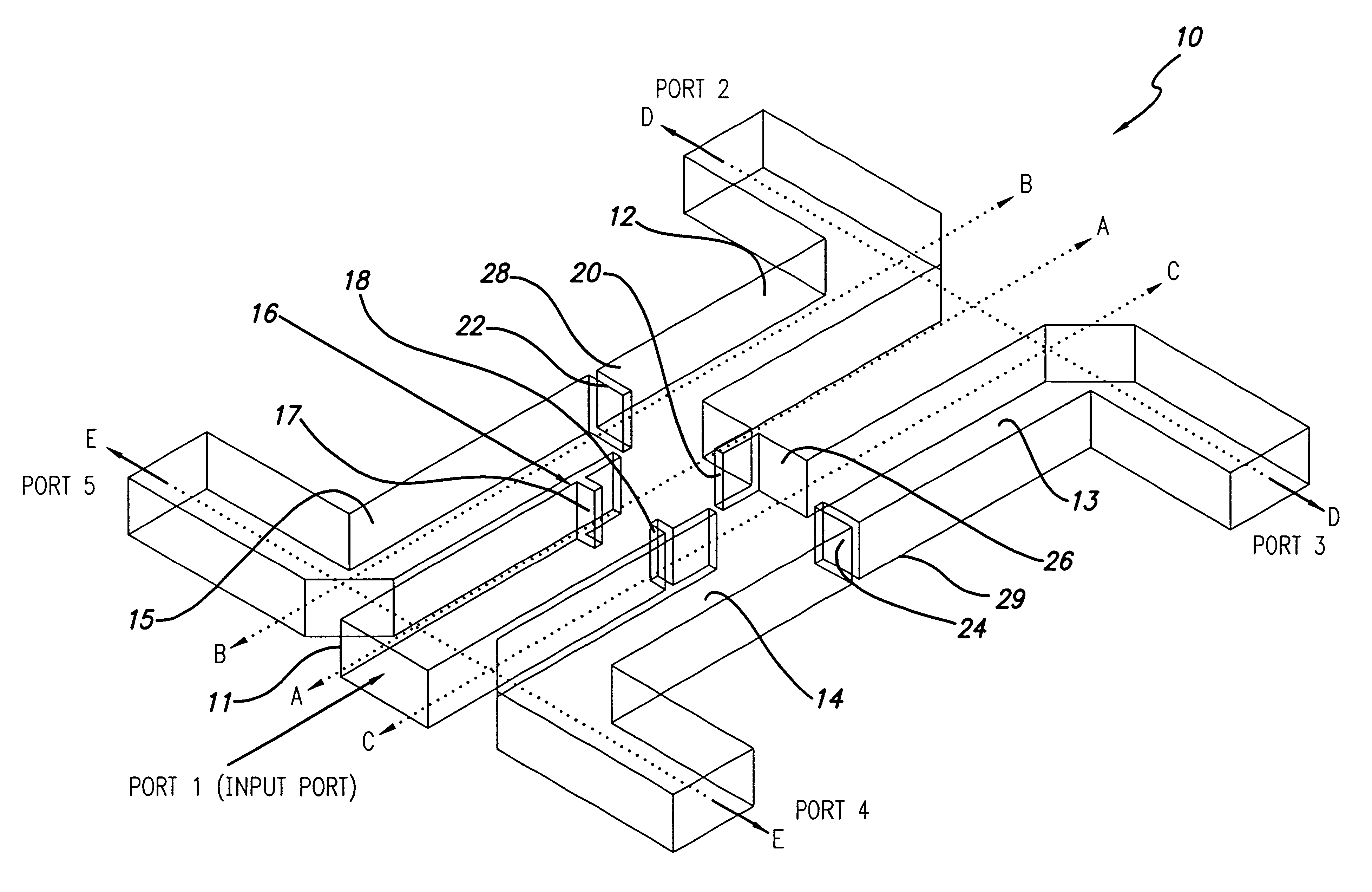
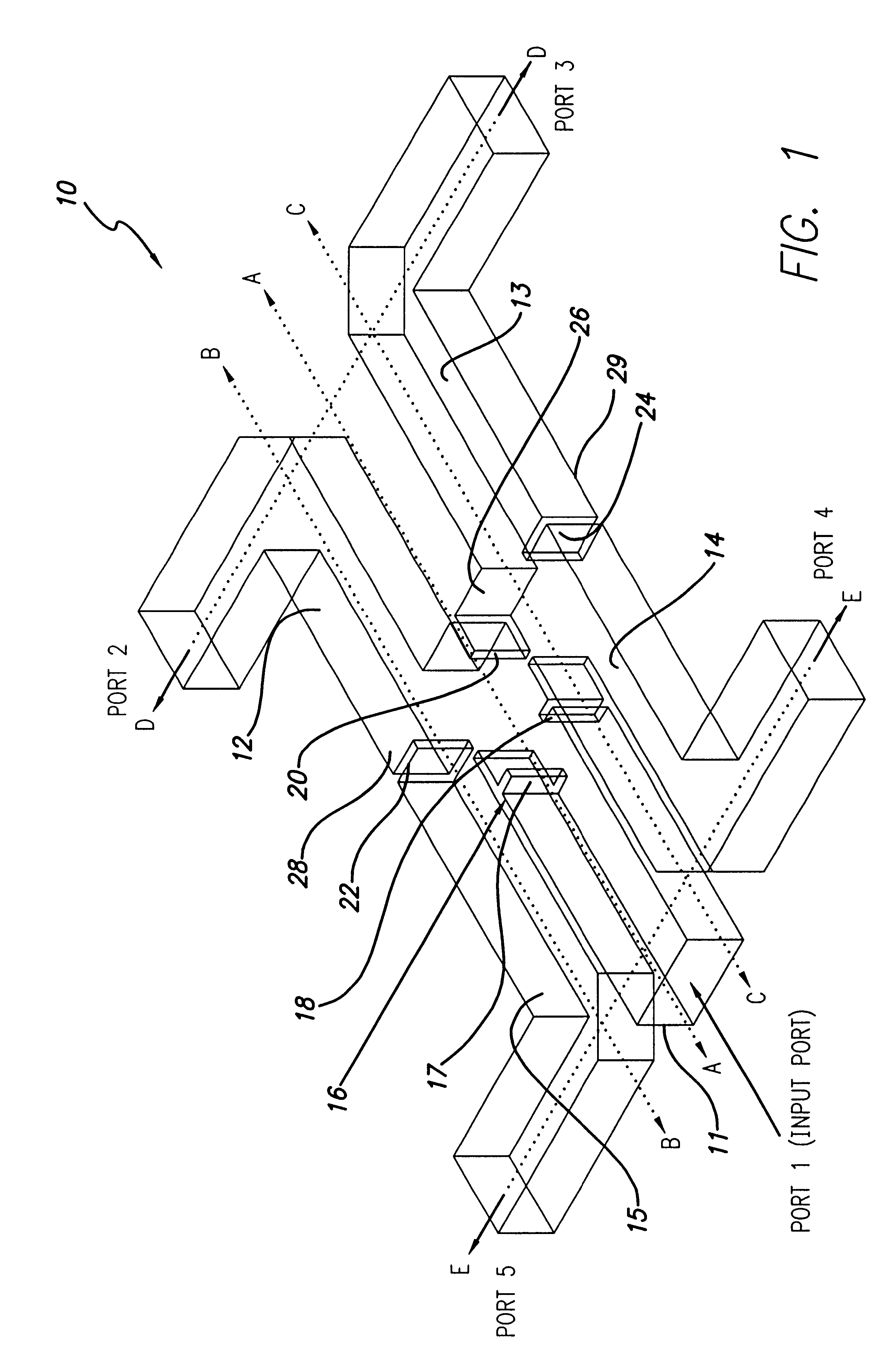
A compact four-way waveguide power divider (10). The inventive power divider (10) includes an input waveguide (11) that terminates at a junction with two adjacent waveguides on opposite sides of the input waveguide. On the opposite side of the junction is a conducting wall into which is built an inductive septum (20). The inductive septum (20) serves to partially match the input impedance of the structure. Second and third inductive septums (22 and 24) are also built into the output arms of the power divider (10). The purpose of the second and third septums (22 and 24) is twofold. In addition to partially matching the power divider's input impedance, the positions of the second and third septums (22 and 24) can be adjusted to equalize the power division between the output arms. Hence, the waves exiting the four output arms of the power divider have highly equalized amplitudes and phases. Further, the phases at the output ports are equalized by adjusting the lengths of the output arms. The use of offset inductive septums (22 and 24) in the output arms to achieve equalized power division allows the input and output waveguides to be placed in very close proximity, resulting in an extremely compact structure.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
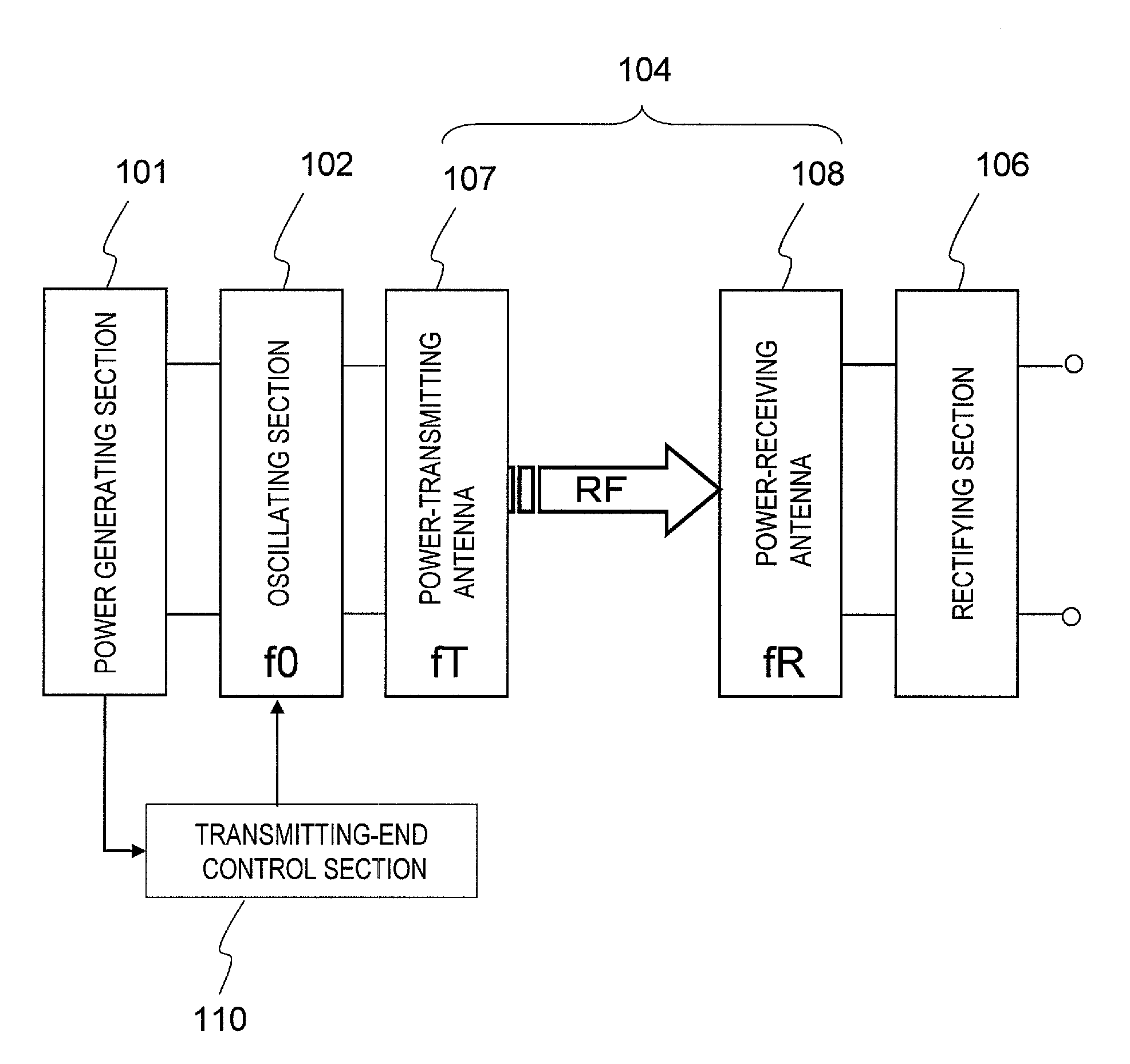
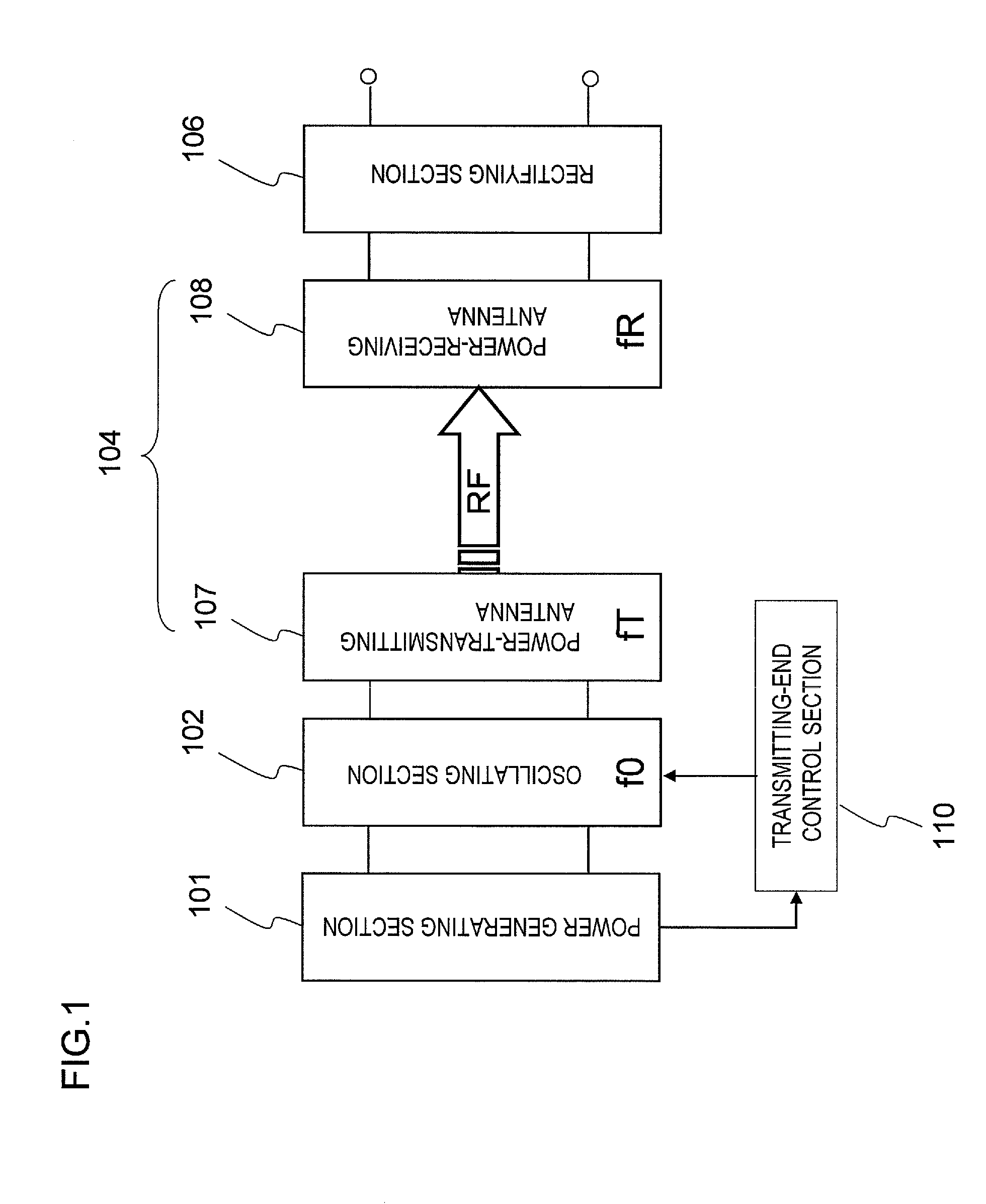
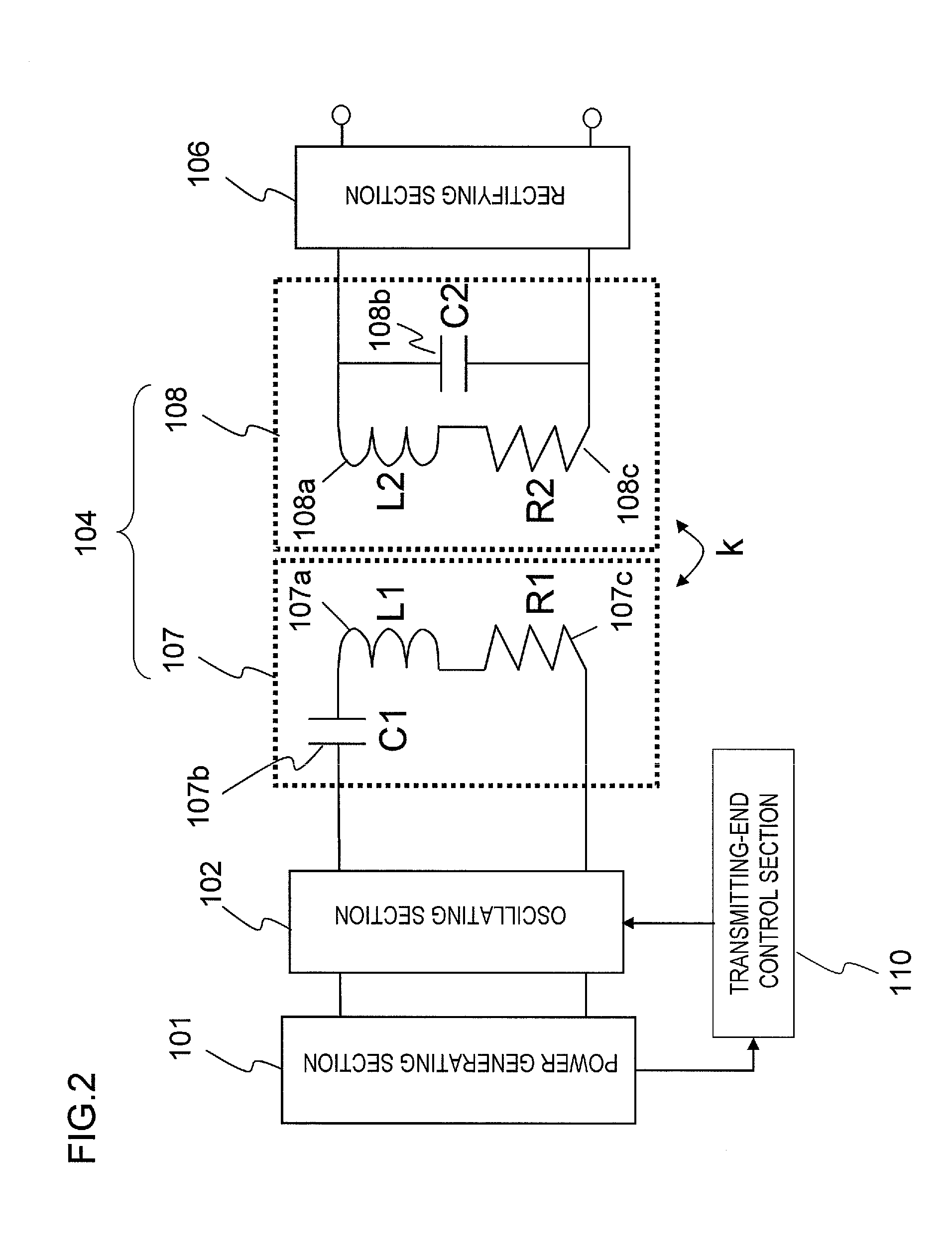
Power generating apparatus, power generating system, and wireless electric power transmission apparatus
ActiveUS20110266882A1Low costWork lessElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersElectric power transmissionInput impedance
A power generator includes: a power generating section 101 that outputs DC energy; an oscillating section 102 that converts the DC energy into RF energy with a frequency f0; a power-transmitting antenna 107 that transmits the RF energy; a power-receiving antenna 108 that receives at least a part of the RF energy that has been transmitted by the power-transmitting antenna 107; and a transmitting-end control section 110 that matches the input impedance of the oscillating section 102 to the output impedance of the power generating section 101 by changing the input impedance of the oscillating section 102 in accordance with a variation in the output impedance of the power generating section 101. The power-transmitting antenna 107 is a series resonant circuit, and the power-receiving antenna 108 is a parallel resonant circuit. And the resonant frequencies fT and fR of the power-transmitting and power-receiving antennas 107 and 108 are both set to be equal to the frequency f0 of the RF energy.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wireless power transmitter, wireless power receiver, and power transmission method of wireless power transmitting system
ActiveUS20130214612A1Controlling impedance of loadEfficient detectionNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionTransmitted power
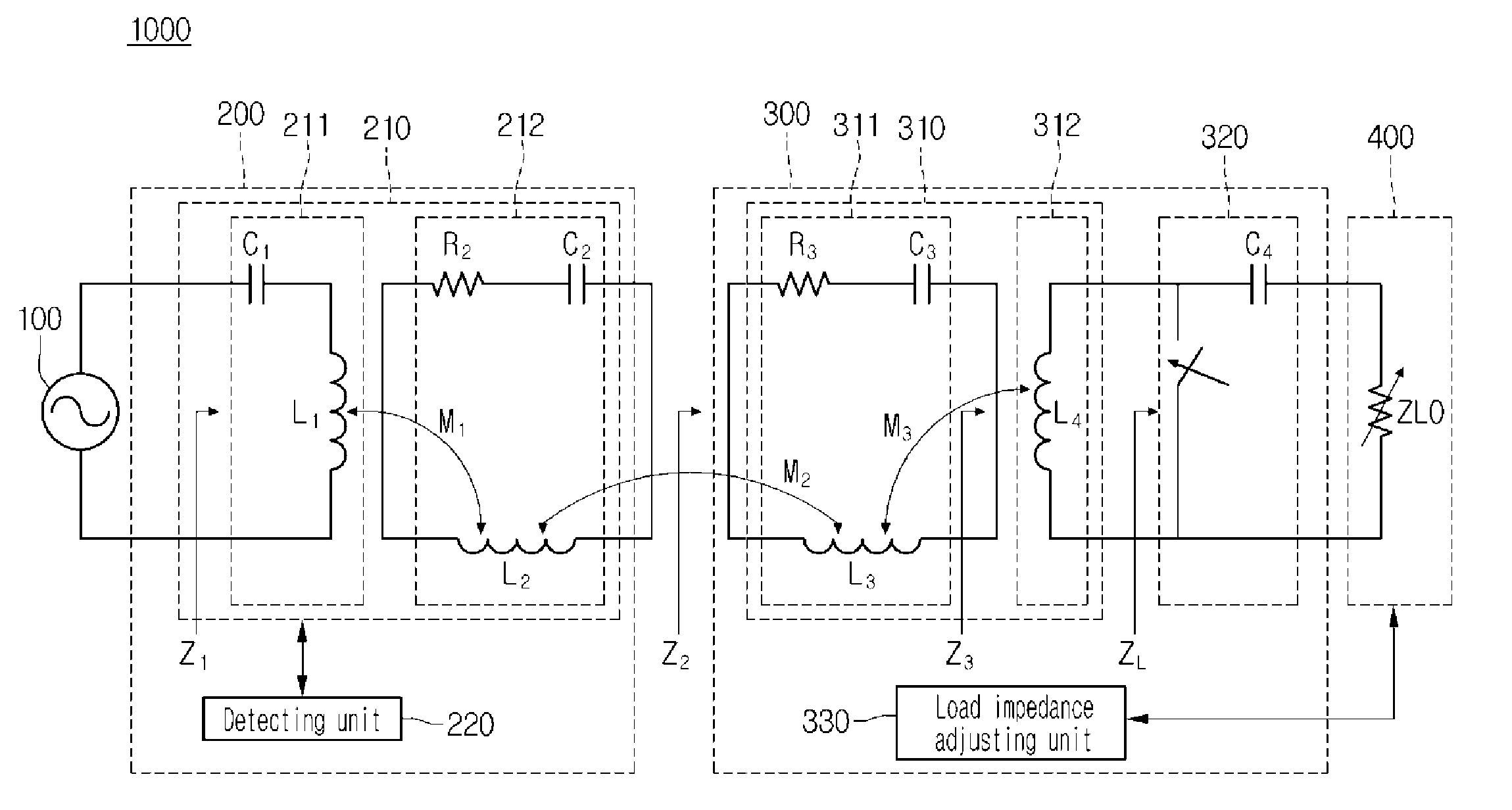
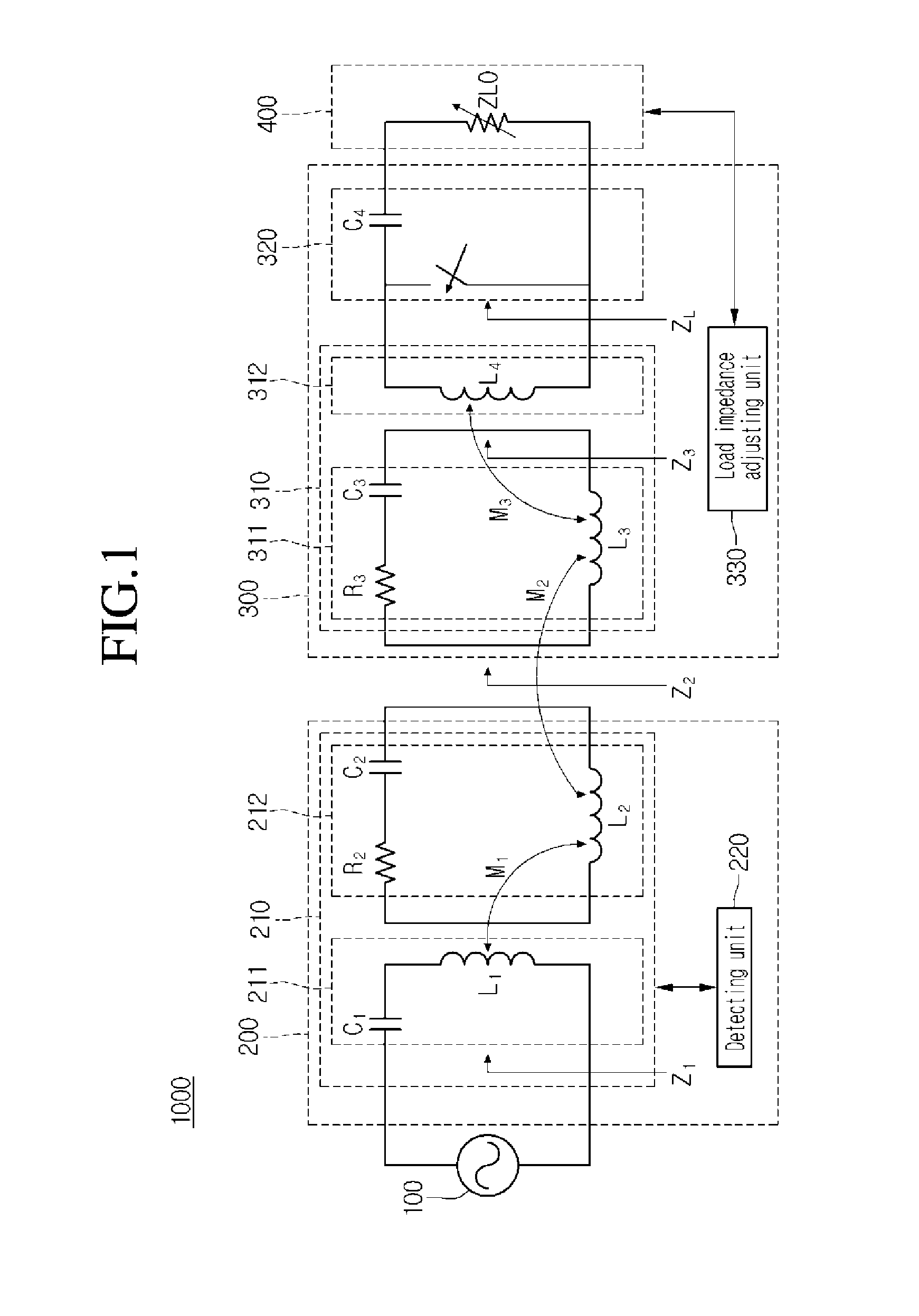
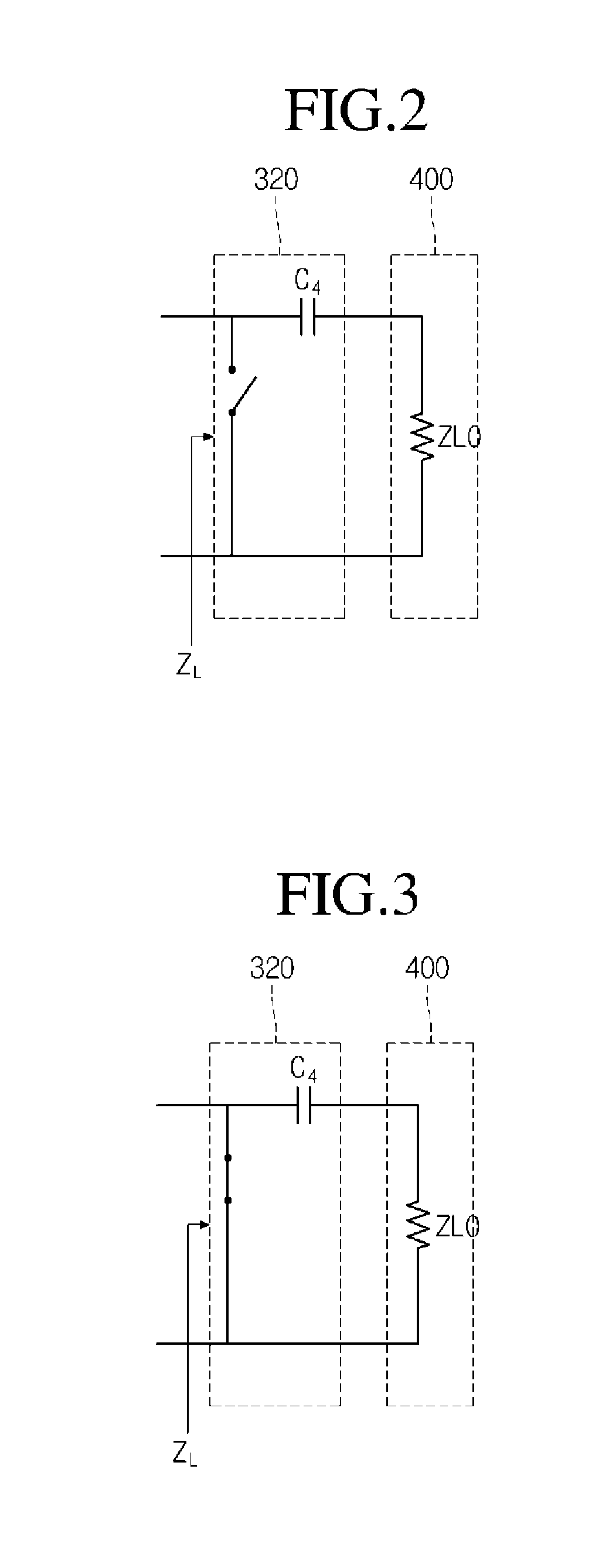
A wireless power transmitter for transmitting power to a wireless power receiver in a wireless scheme includes a transmitting coil configured to transmit power, which is supplied by a power source, to a receiving coil of the wireless power receiver using resonance; and a detecting unit configured to detect a coupling state between the transmitting coil and the receiving coil using an input impedance of the wireless power transmitter.
Owner:SCRAMOGE TECH LTD
Electric potential sensor
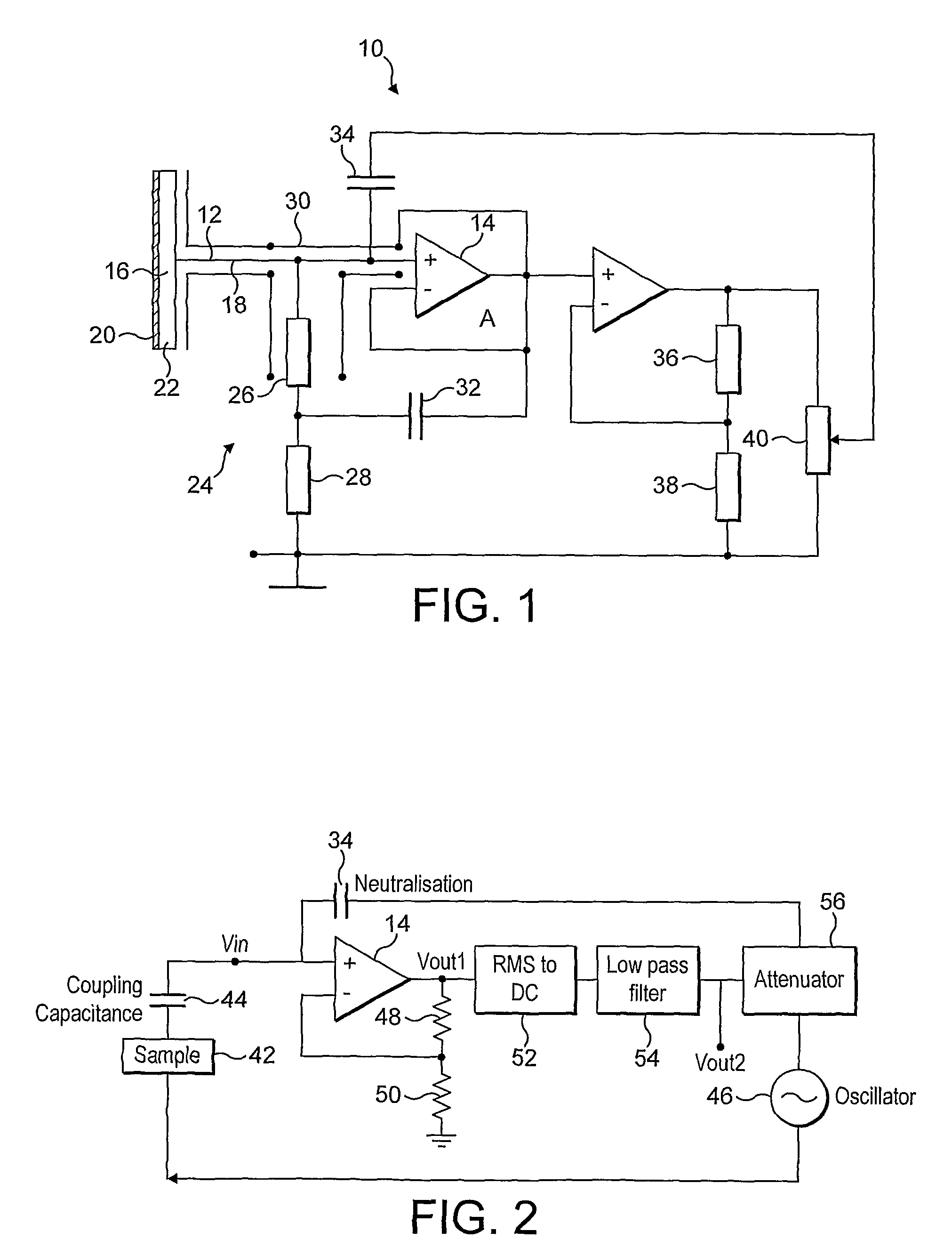
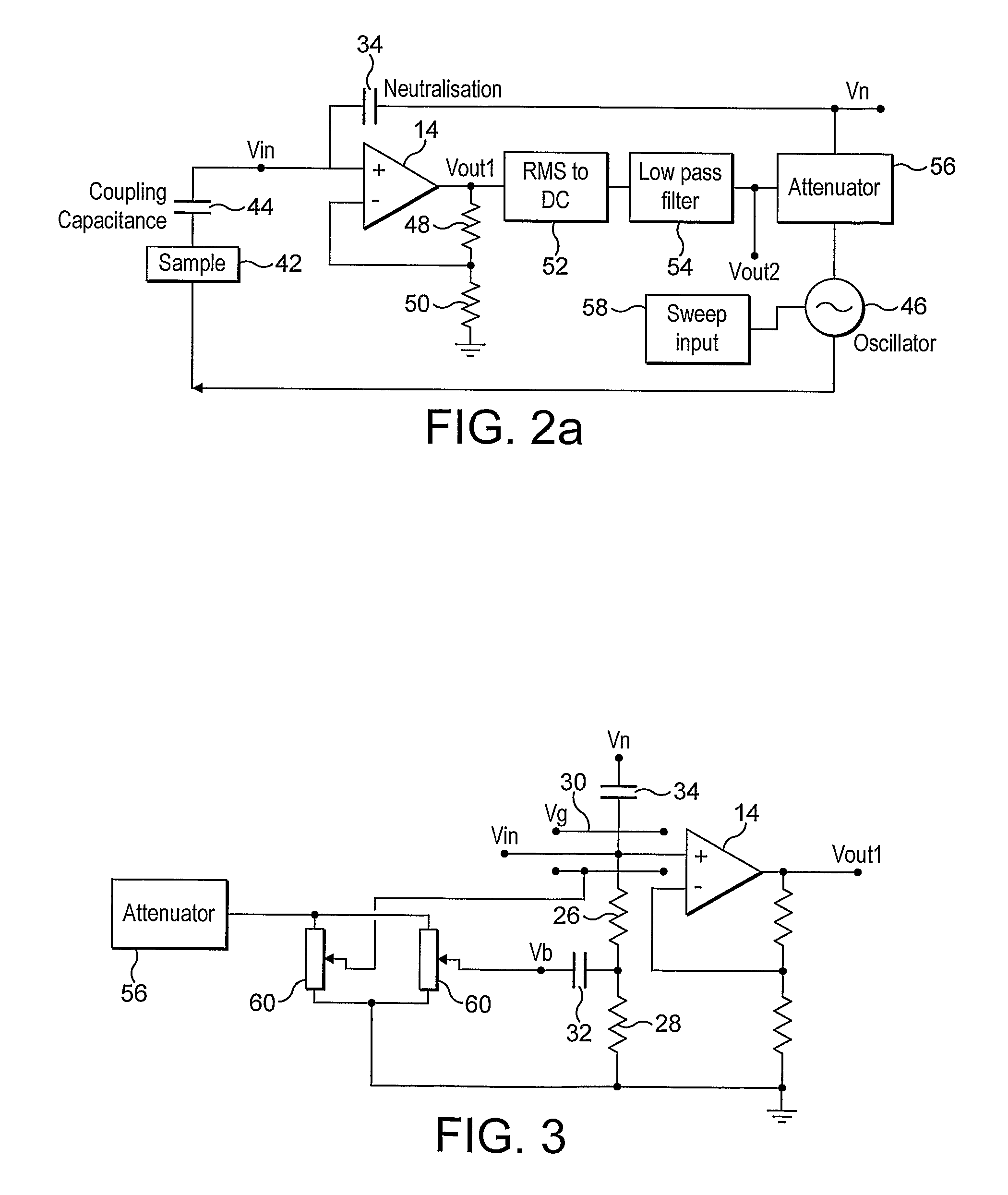
ActiveUS8054061B2Highly accurate signal measurementEnhanced signalElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Audio power amplifier
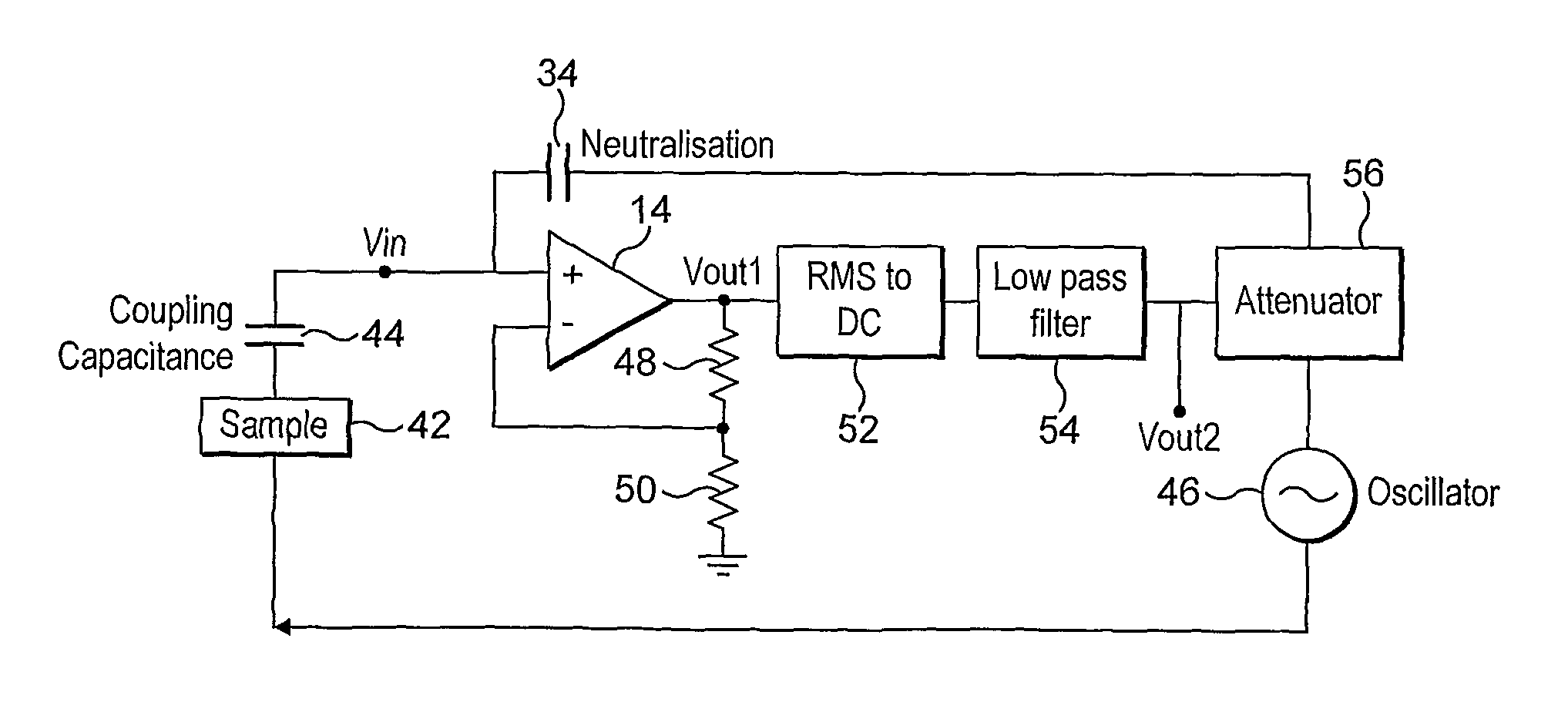
The invention provides an electric potential sensor including, at least one detection electrode arranged for capacitive coupling with a sample under test and for generating a measurement signal, and a sensor amplifier adapted to receive the measurement signal as input and to supply an amplified detection signal as output. An input impedance enhancing element provides a high input impedance to the sensor amplifier for increasing the sensitivity of the electrode to reduced electric potentials, and a feedback element applies a coherent feedback signal to the input of the sensor amplifier for enhancing the signal to noise ratio of the sensor.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SUSSEX
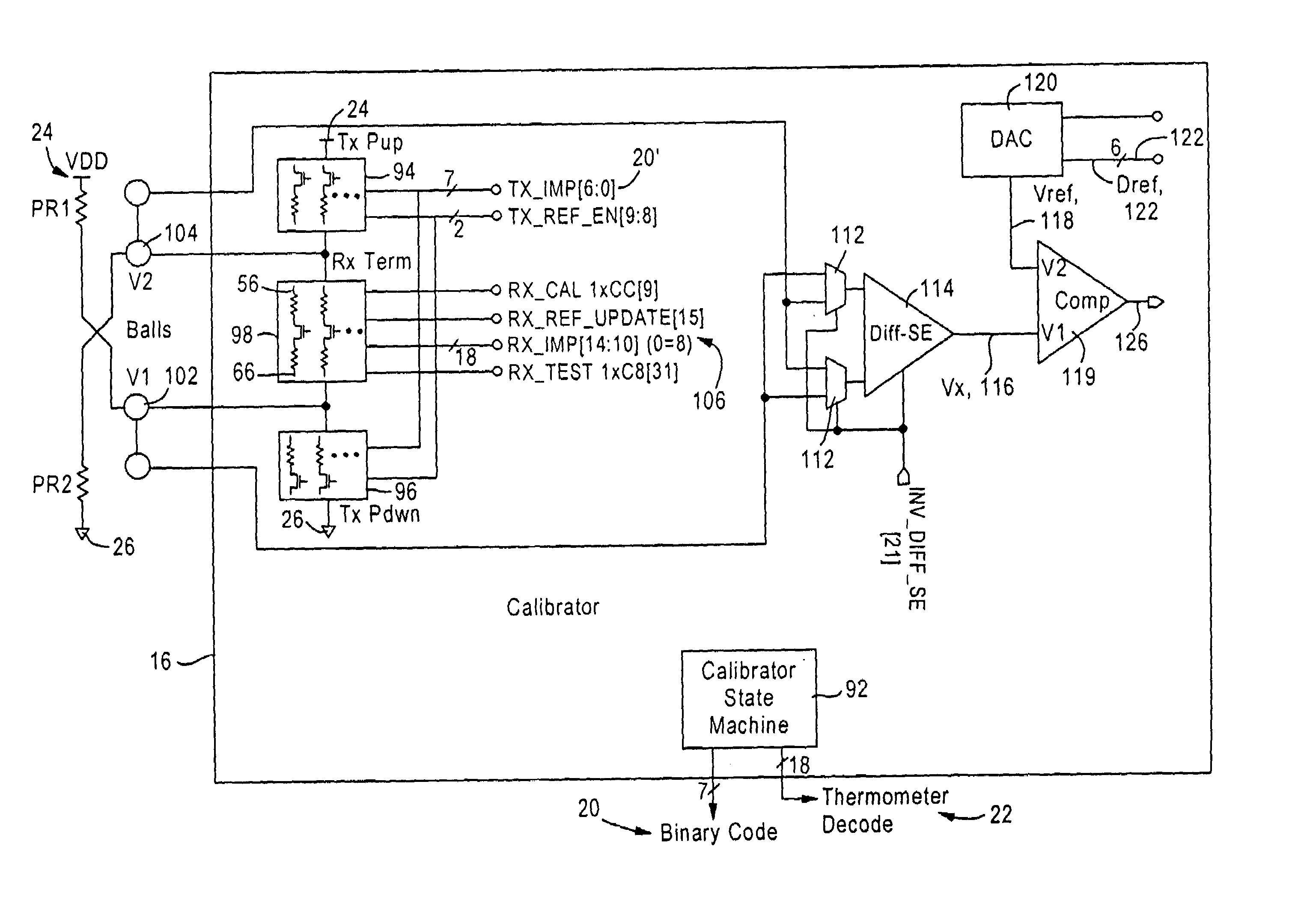
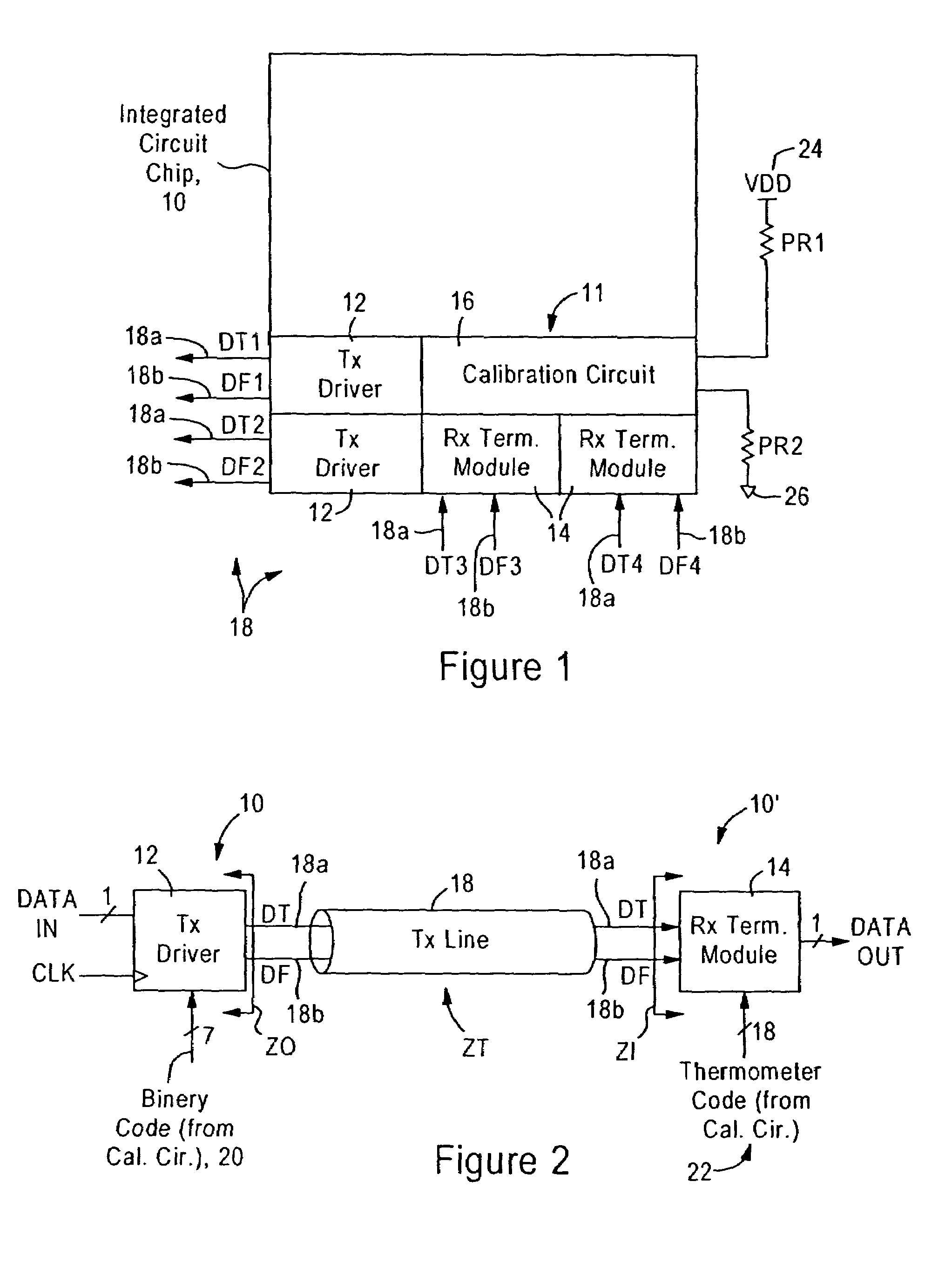
Voltage mode transceiver having programmable voltage swing and external reference-based calibration
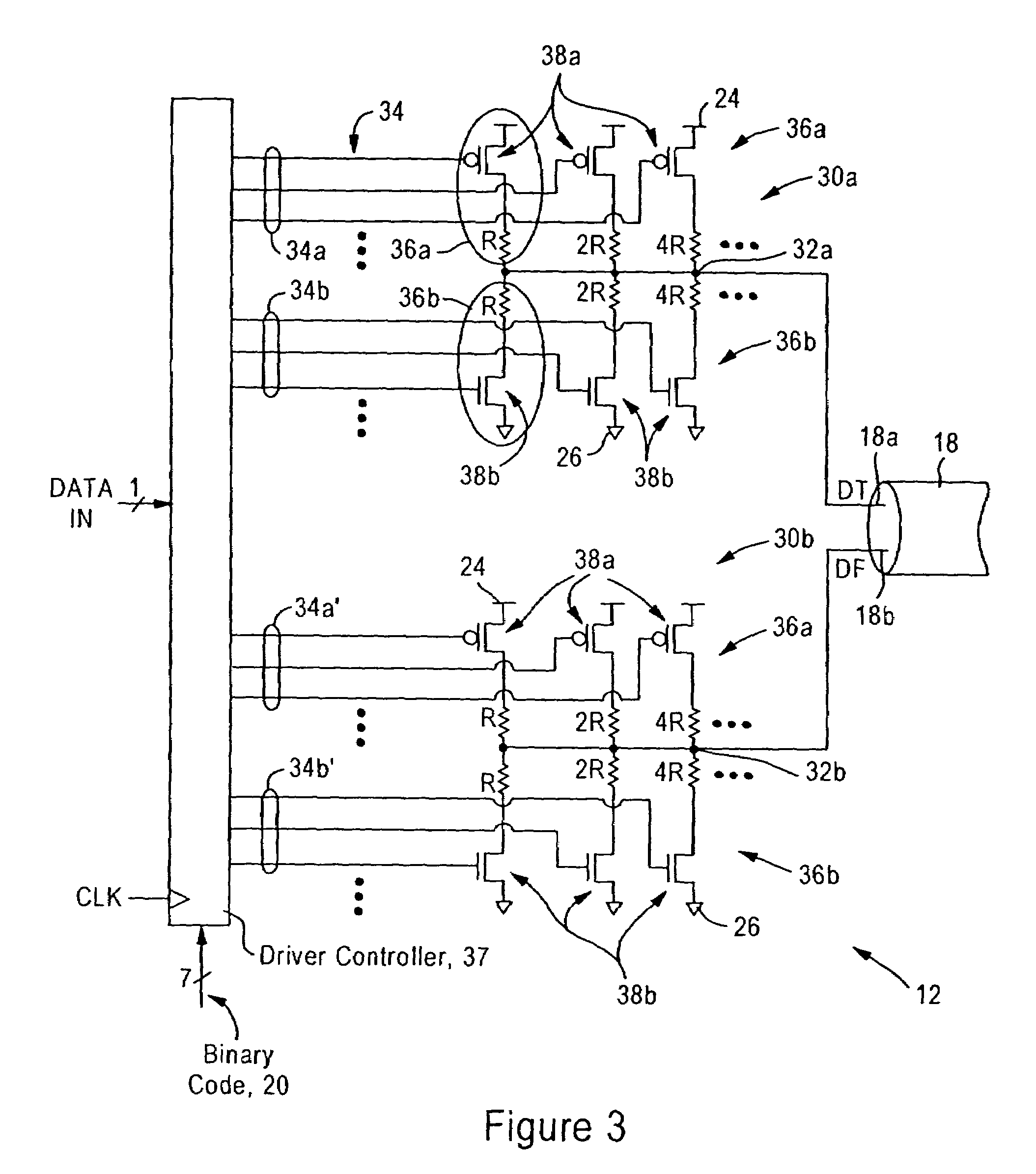
ActiveUS7135884B1Reduce input capacitanceImprove the level ofInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceInput impedance
An integrated device includes a voltage mode transmit driver for matching an output impedance to an output transmission line based on a binary code, an input termination module configured for matching an input impedance to an input transmission line based on an input impedance calibration value using thermometer-based decoding. The voltage mode transmit driver includes, for each differential output signal, a resistor network circuit having pull-up circuits and pull-down circuits for changing the voltage on the differential output signal, and having binary weighted resistance values relative to each other. The input termination module includes pull-up circuits and pull-down circuits having inverse hyperbolic resistance values relative to each other, and using thermometer-based decoding to ensure a linear change in input impedance during transitions in the input impedance calibration value. A calibration circuit generates the binary code and the input impedance calibration value based on replicas of the pull-up and pull-down circuits.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Single-port multi-resonator acoustic resonator device
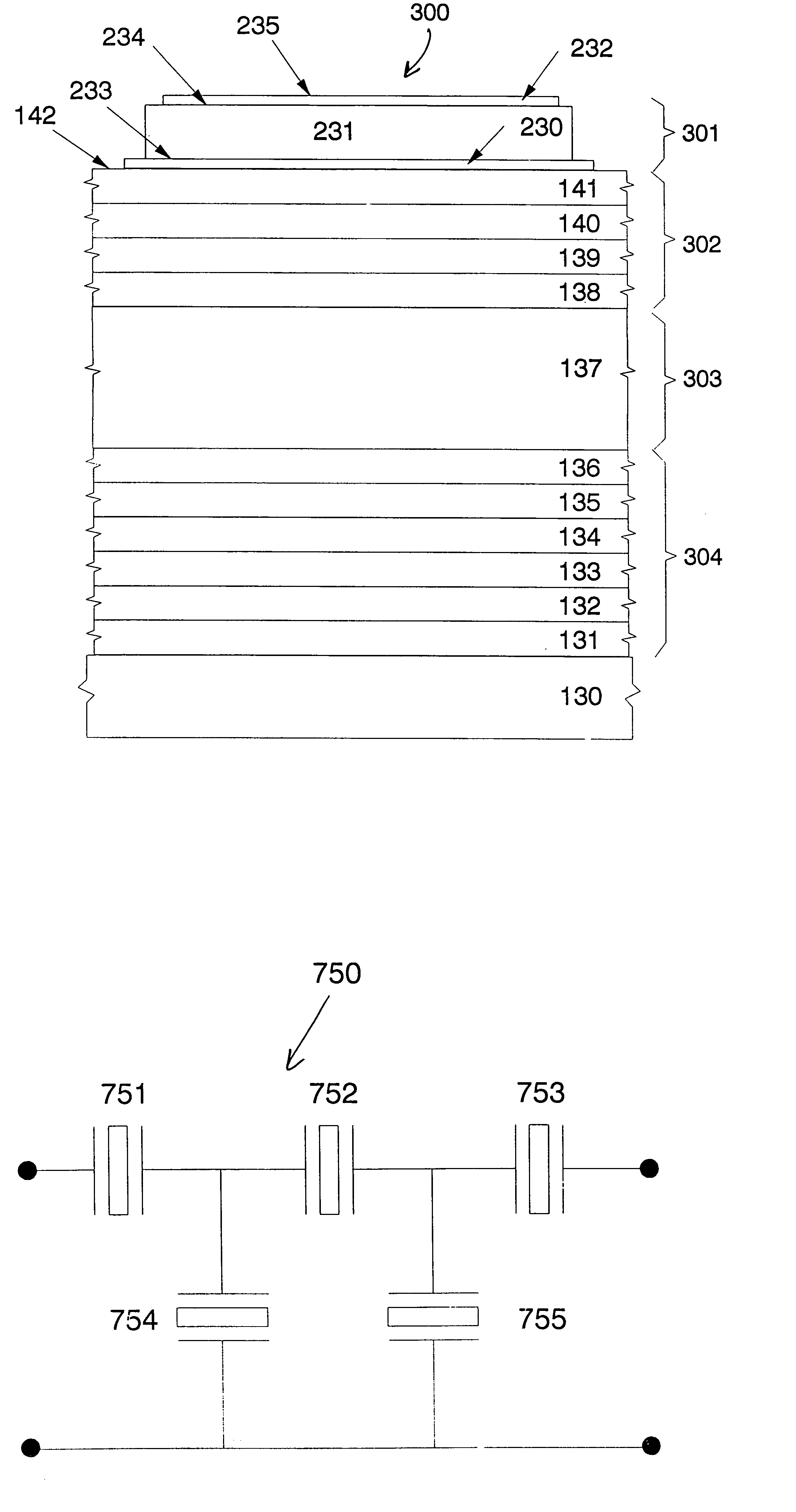
ActiveUS7138889B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksTransducerInput impedance
A single port multi-resonator acoustic resonator device (200, 300, 400, 490) possesses an input impedance that exhibits precisely designed electrical resonances. The device contains at least three parts: a transducer / resonator (201, 301, 401. 491) used both to interface to an external electrical circuit and to transform electrical energy into mechanical (i.e. acoustic) vibrations (and vice versa), and also function as a resonator; a mechanical (i.e. acoustic) resonator (203, 303, 460, 480) and an acoustic coupler (202, 302, 404, 494) that controls the acoustic interaction between the transducer / resonator and the mechanical resonator.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Regulation control and energy management scheme for wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20130020862A1Maximize power transfer efficiencyOptimal duty ratioBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionResonance
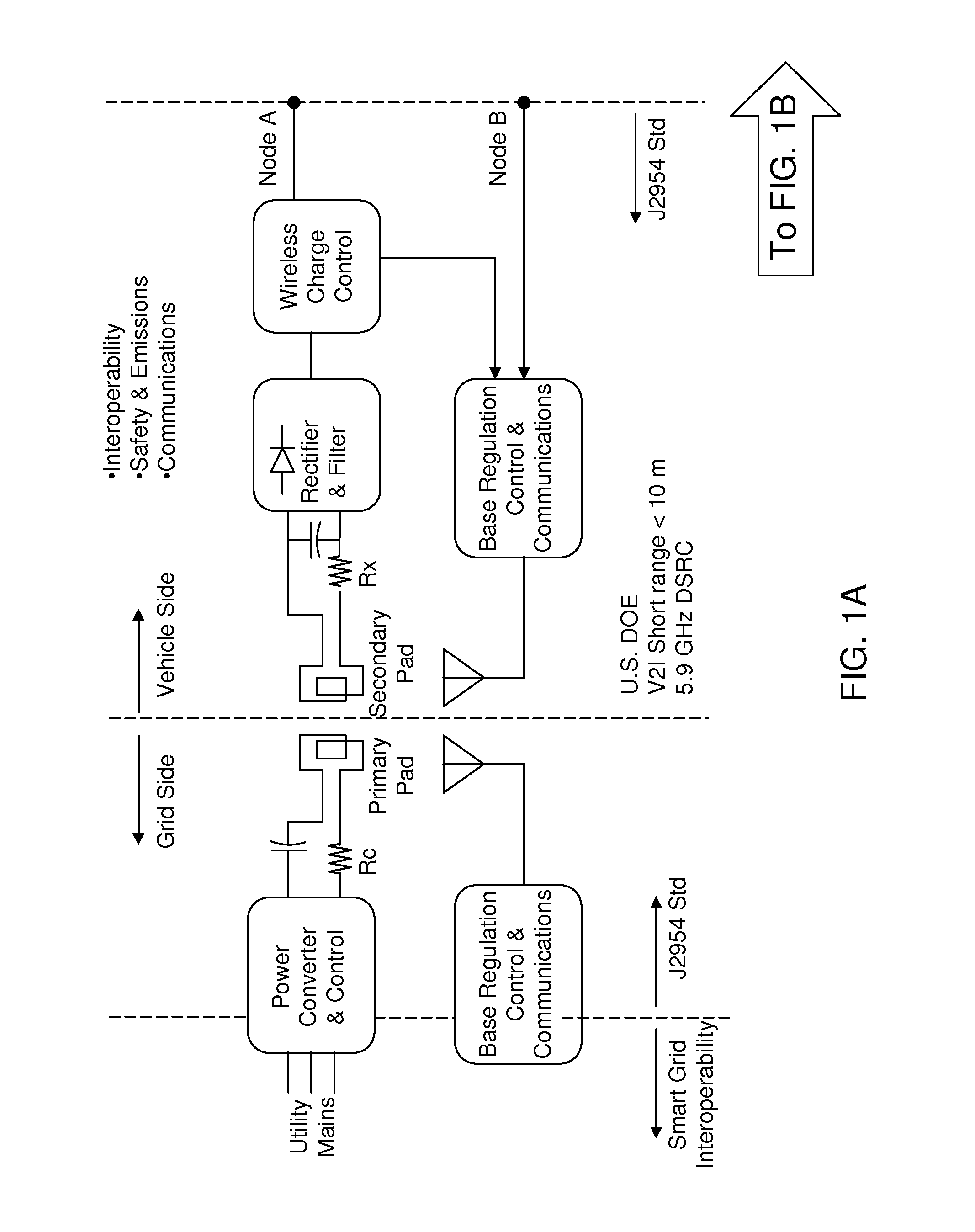
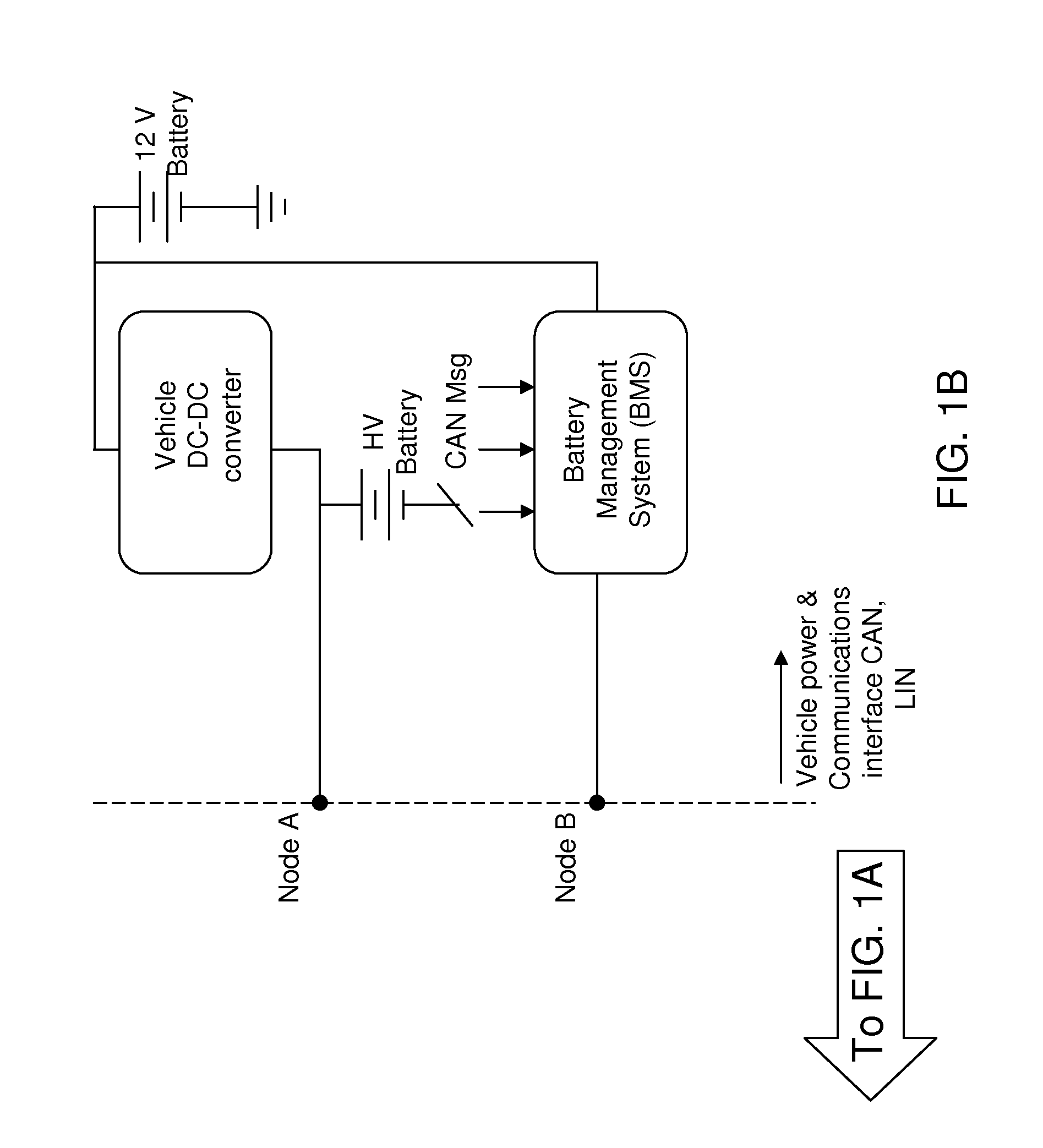
Power transfer rate at a charging facility can be maximized by employing a feedback scheme. The state of charge (SOC) and temperature of the regenerative energy storage system (RESS) pack of a vehicle is monitored to determine the load due to the RESS pack. An optimal frequency that cancels the imaginary component of the input impedance for the output signal from a grid converter is calculated from the load of the RESS pack, and a frequency offset f* is made to the nominal frequency f0 of the grid converter output based on the resonance frequency of a magnetically coupled circuit. The optimal frequency can maximize the efficiency of the power transfer. Further, an optimal grid converter duty ratio d* can be derived from the charge rate of the RESS pack. The grid converter duty ratio d* regulates wireless power transfer (WPT) power level.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com