Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
406 results about "Junction diodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
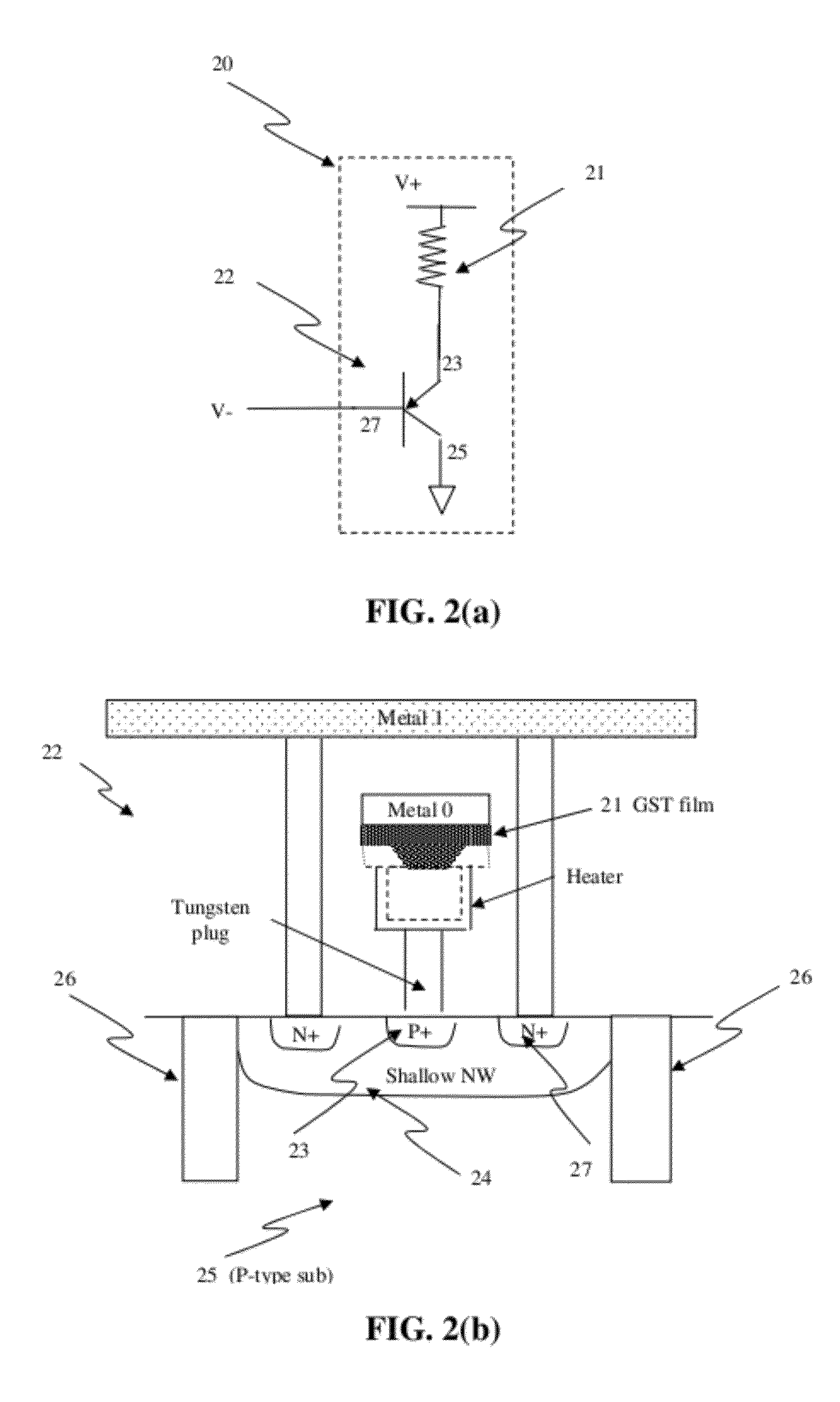
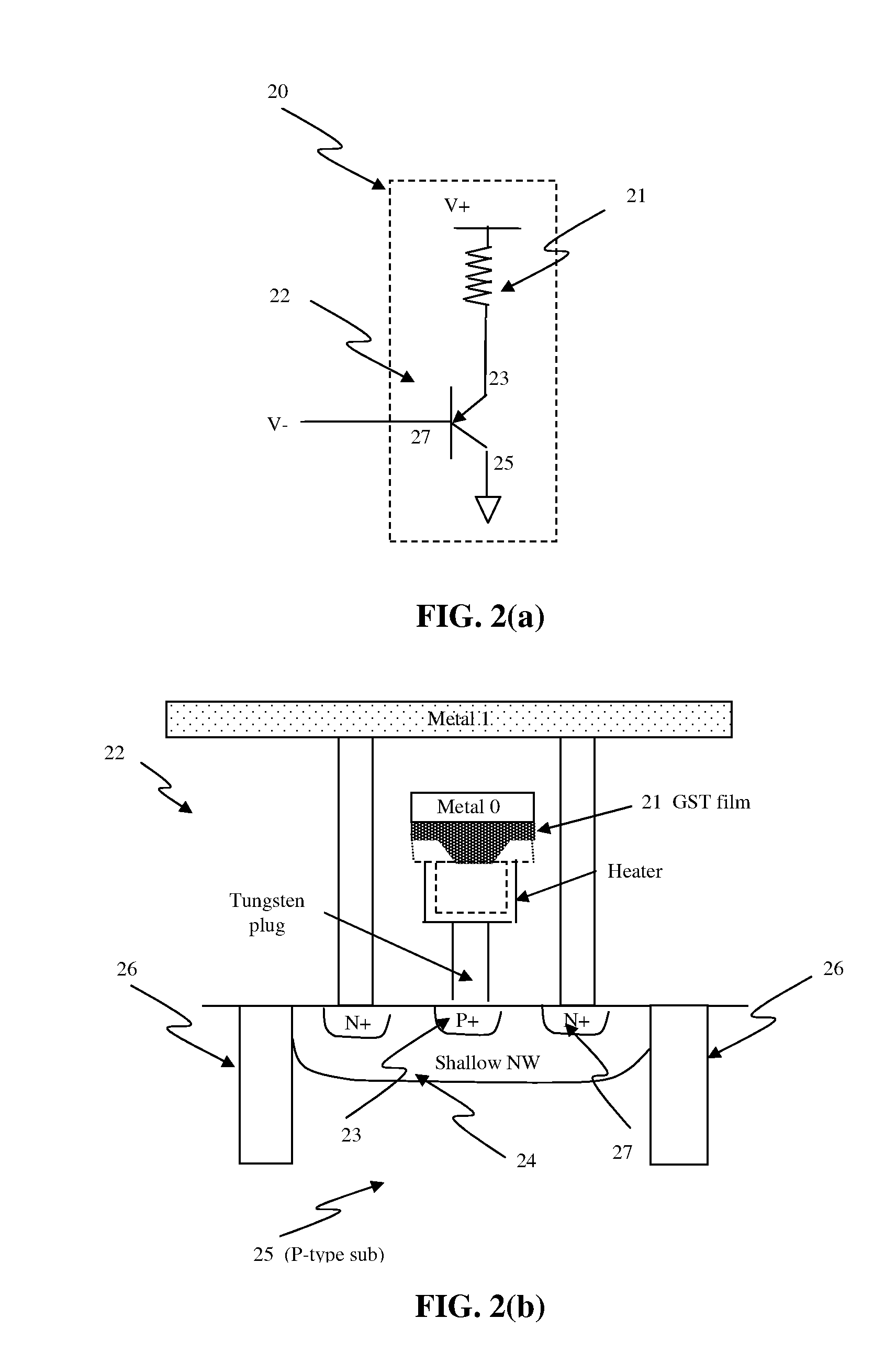
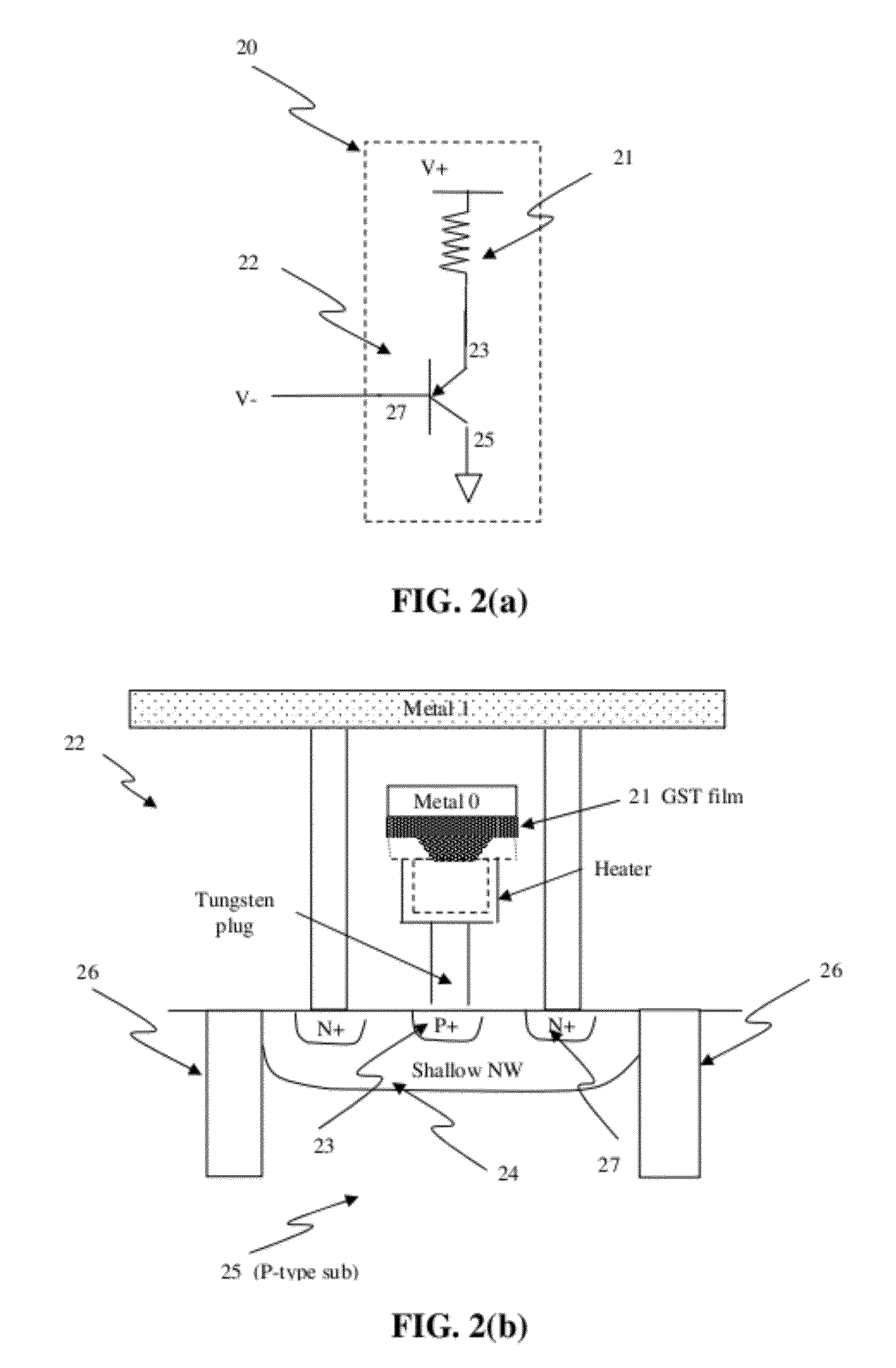
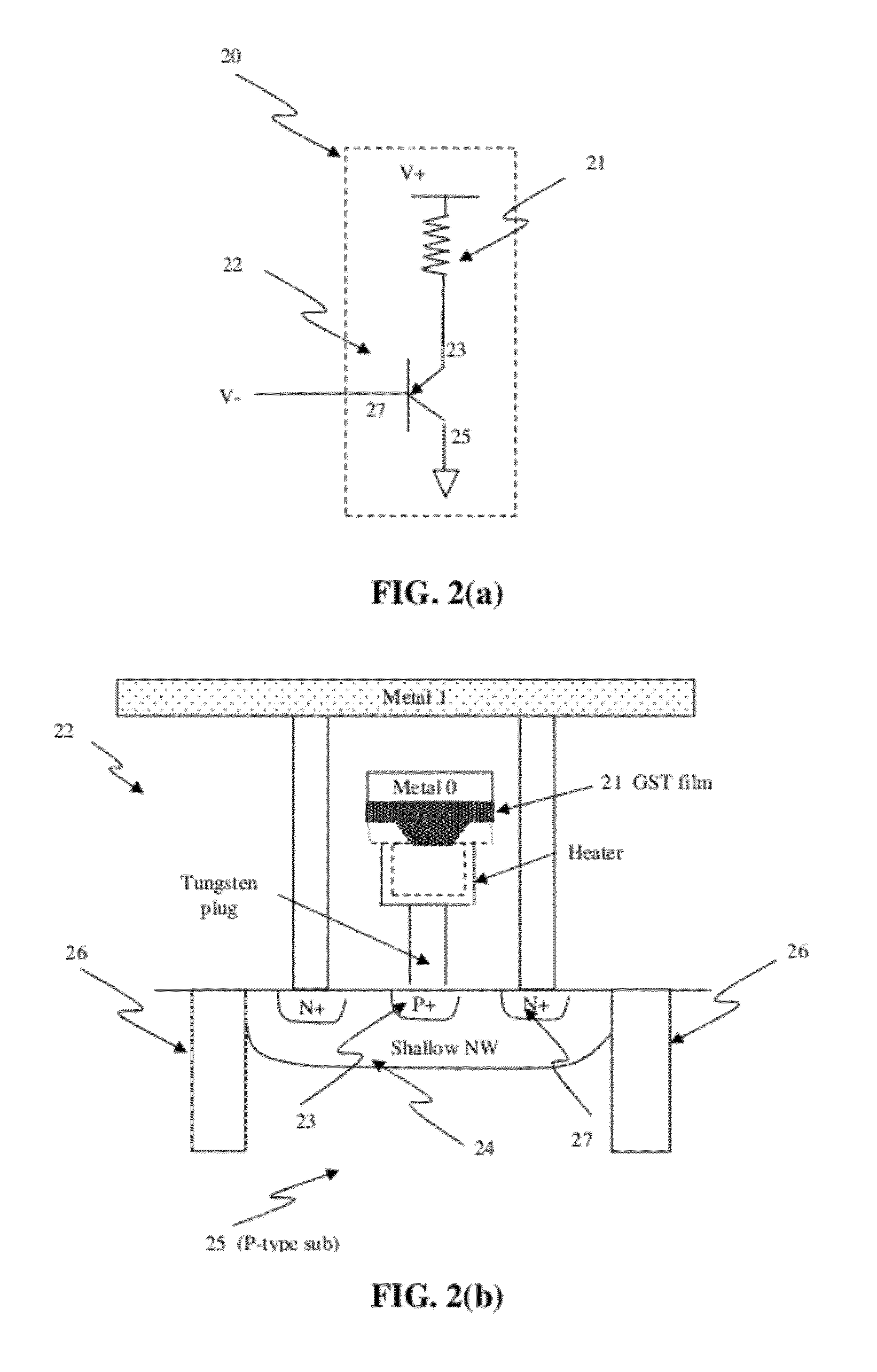
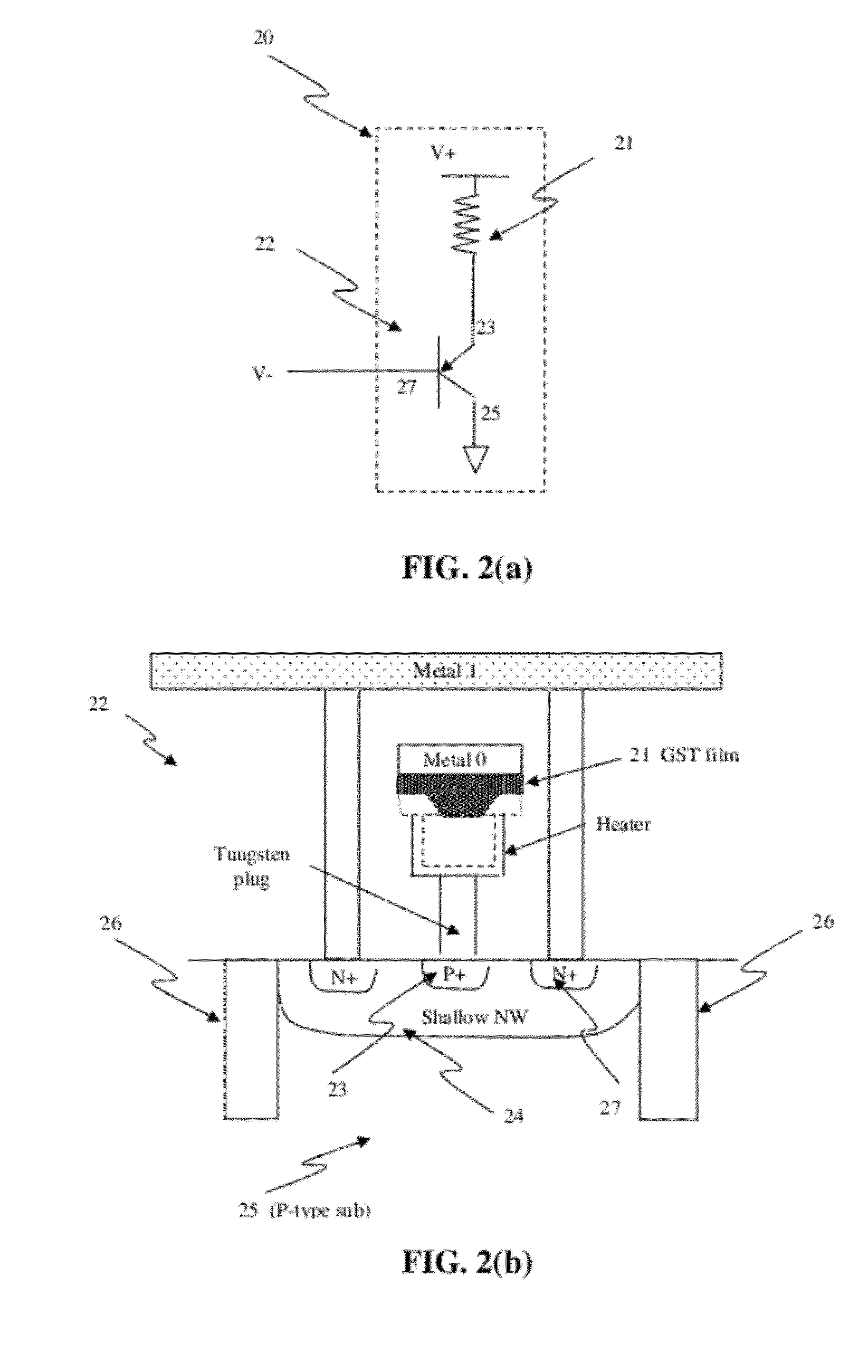
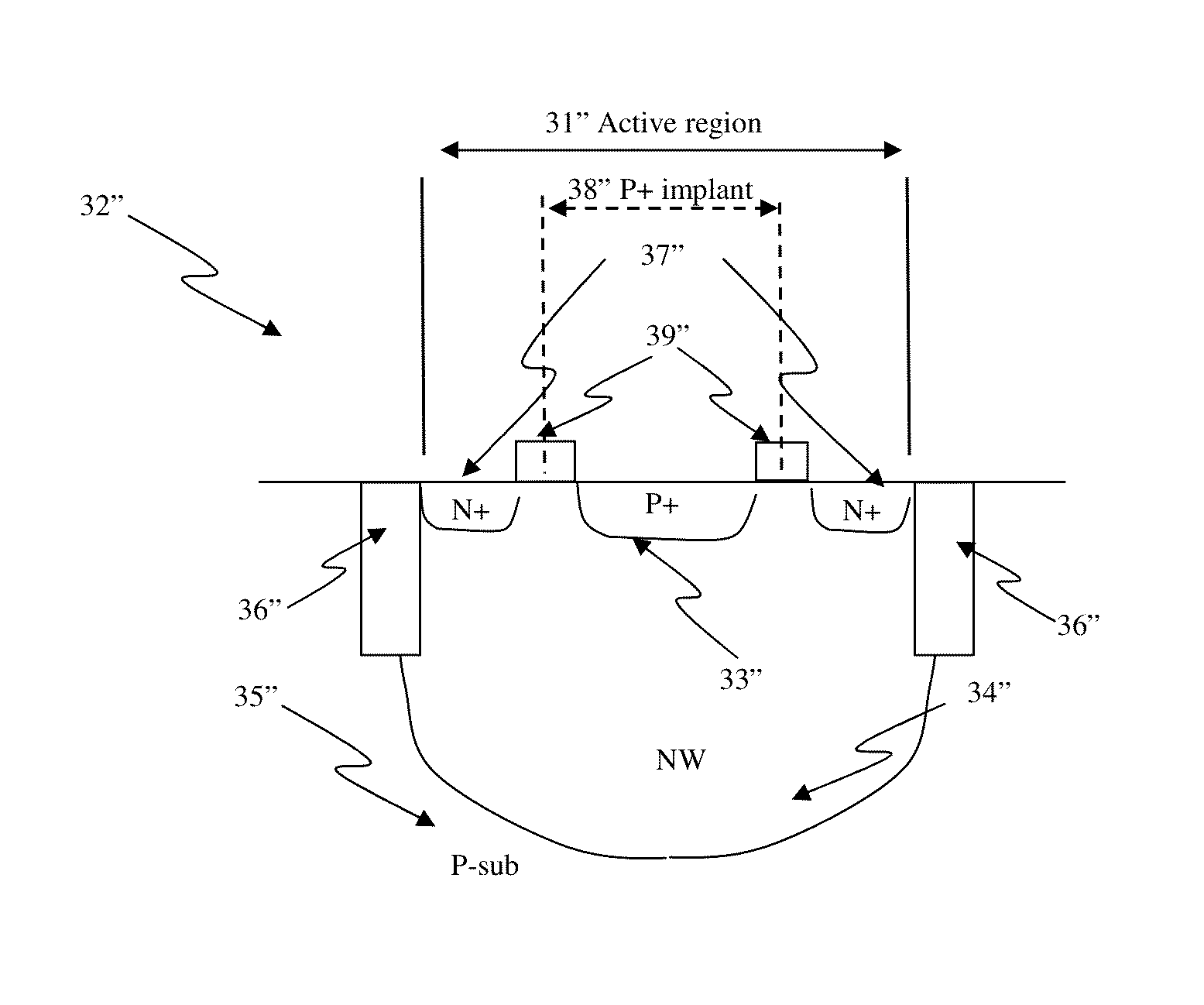
Circuit and system of using finfet for building programmable resistive devices
ActiveUS20130148409A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHemt circuitsEngineering
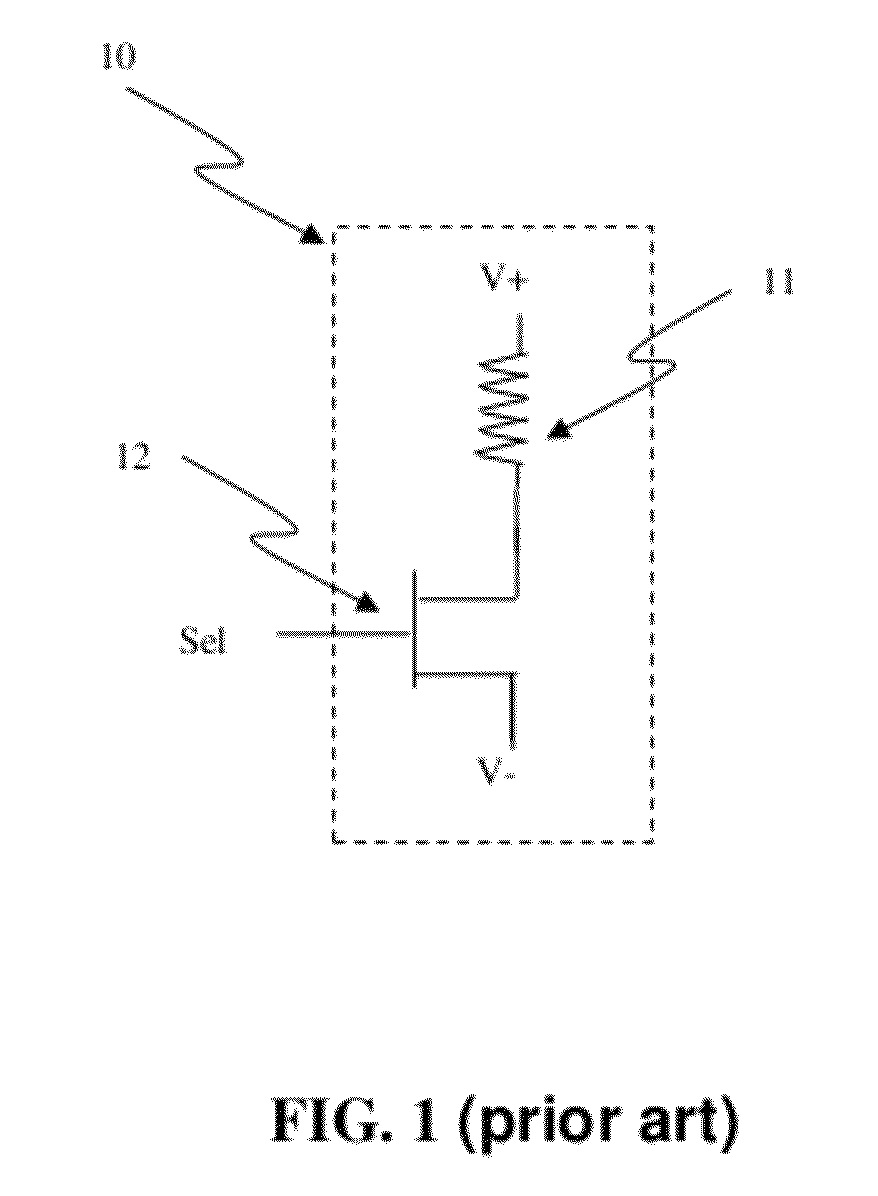
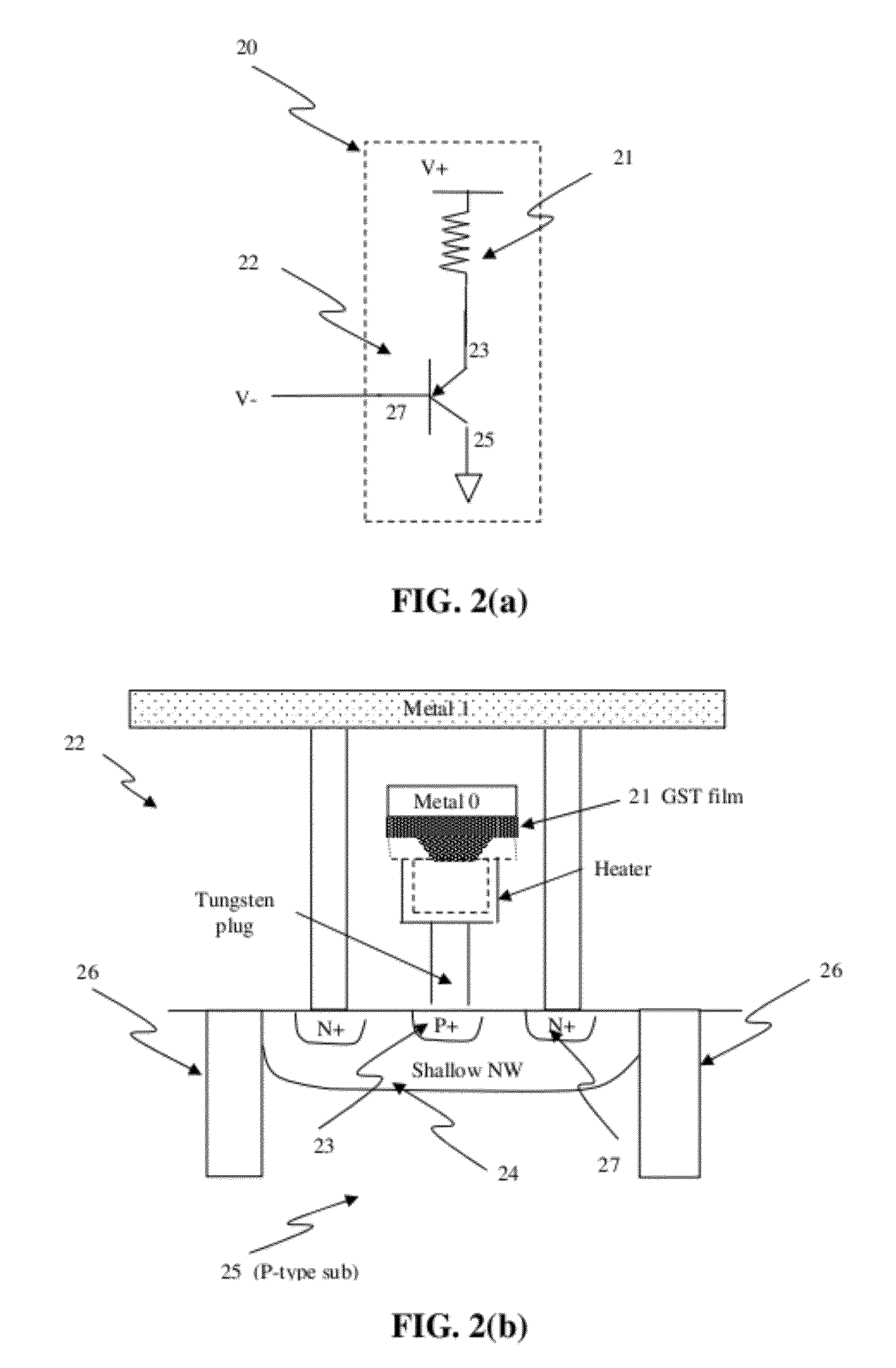
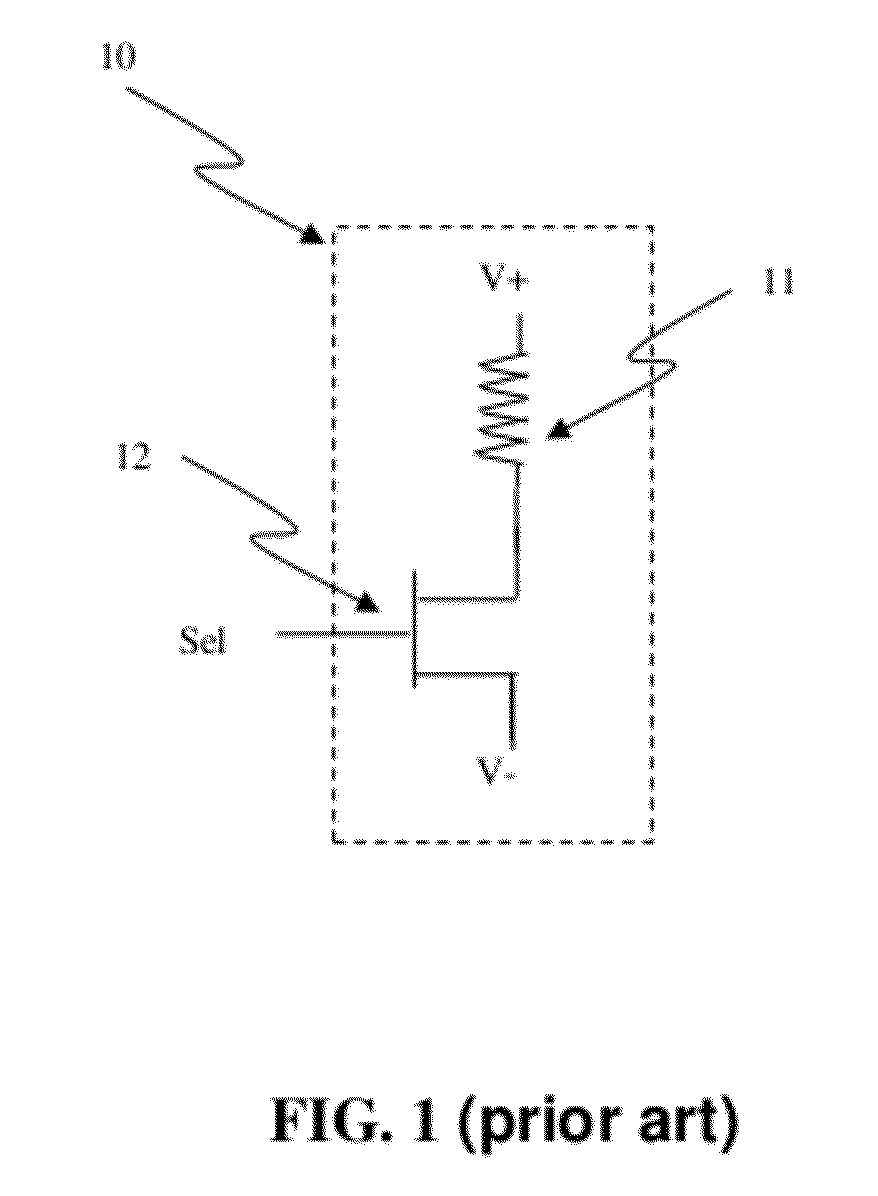
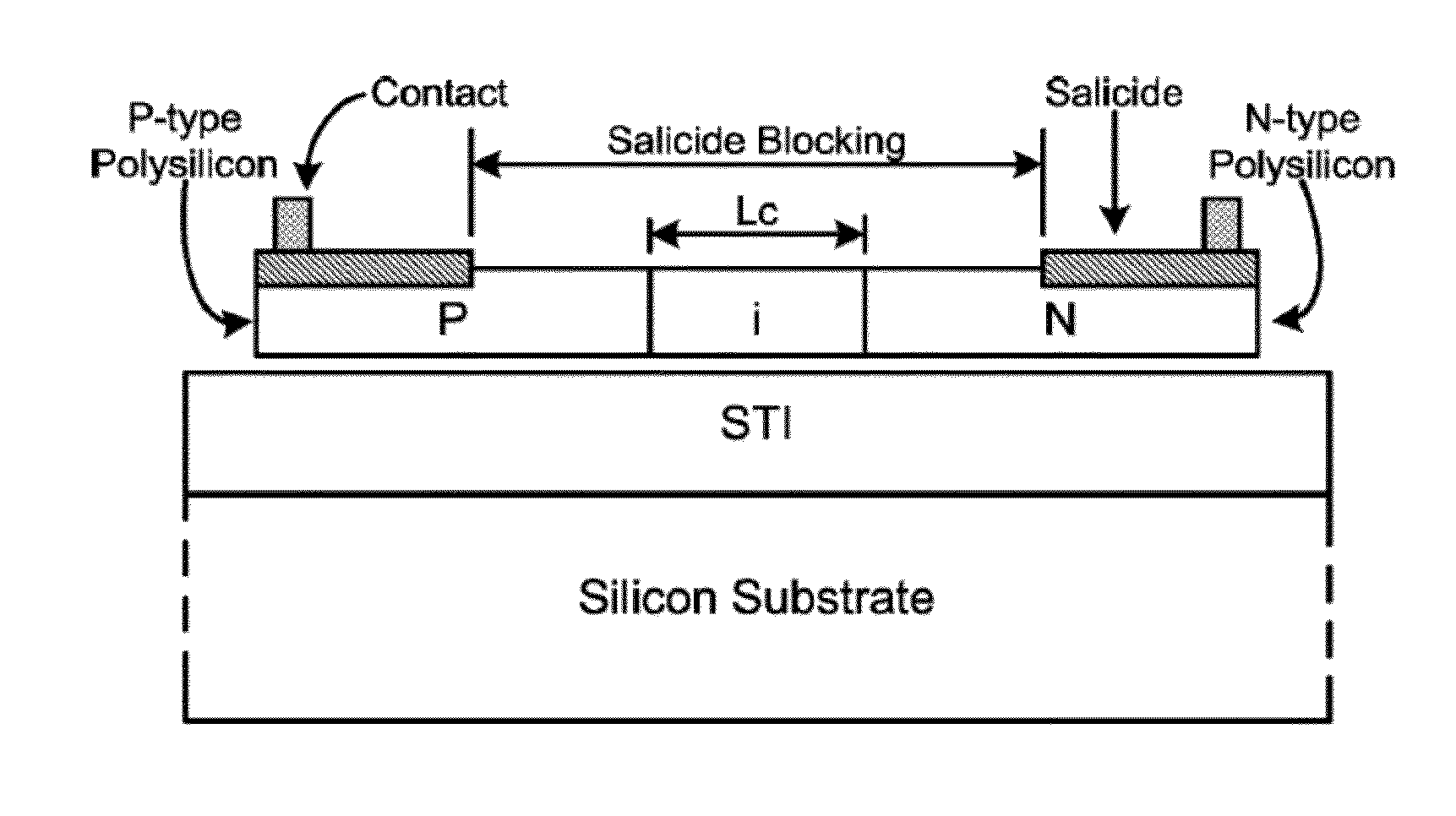
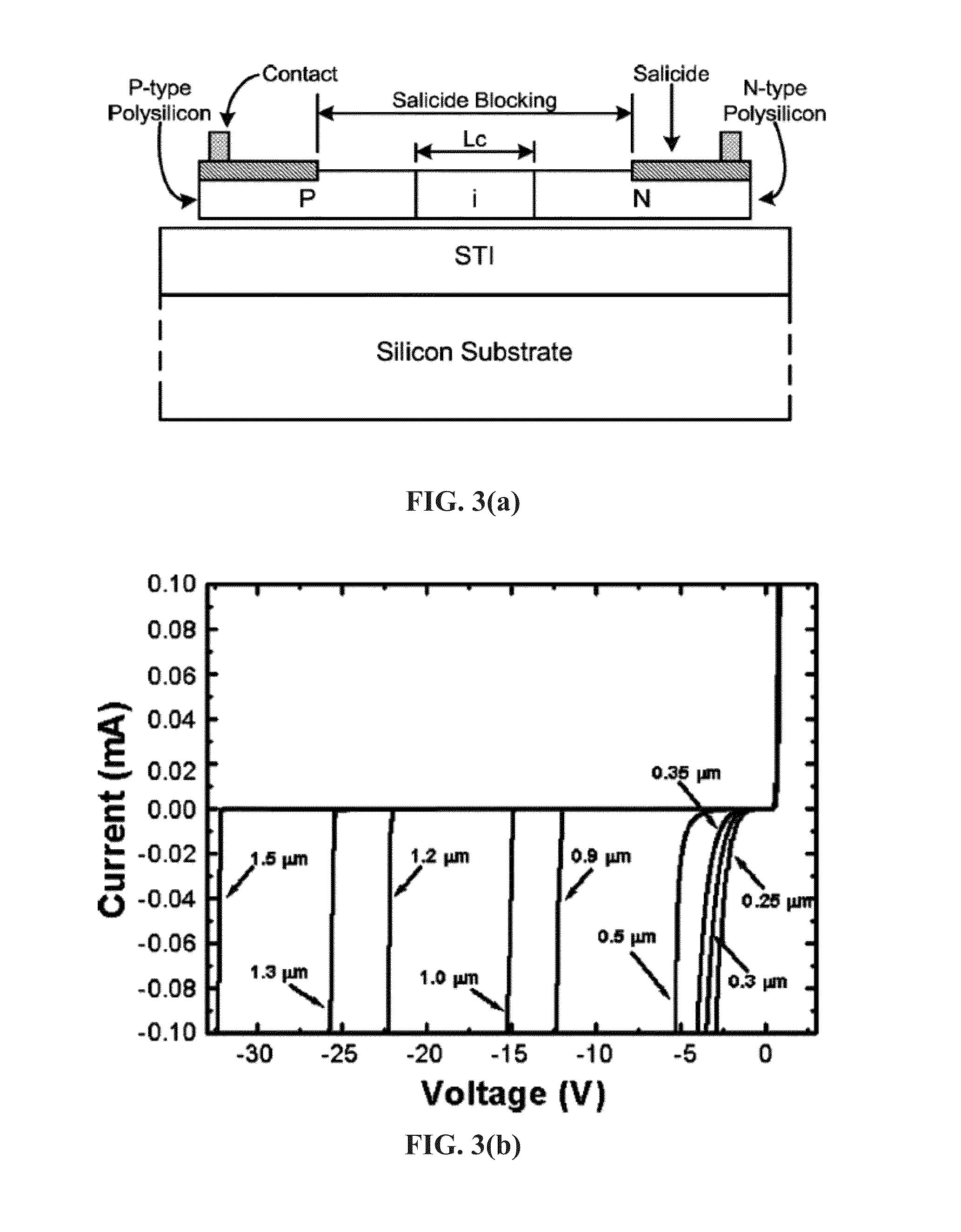
Junction diodes or MOS devices fabricated in standard FinFET technologies can be used as program selectors or One-Time Programmable (OTP) element in a programmable resistive device, such as interconnect fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCRAM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The MOS or diode can be built on at least one fin structure or at least one active region that has at least one first active region and a second active region. The first and the second active regions can be isolated by a dummy MOS gate or silicide block layer (SBL) to construct a diode.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
High-density nonvolatile memory array fabricated at low temperature comprising semiconductor diodes
InactiveUS20060249753A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorAlloy
A memory cell is described suitable for use in a high-density monolithic three dimensional memory array. In preferred embodiments of the memory cell, a semiconductor junction diode formed of germanium or a germanium alloy which can be crystallized at relatively low temperature is formed disposed between conductors. The use of a low-temperature material allows the conductors to be formed of copper or aluminum, both low-resistivity materials that provide adequate current at very small feature size, allowing for a highly dense stacked array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080105878A1Avoid makingPrevent crashSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor storage devicesEngineering
A nonvolatile semiconductor storage device is provided in which memory cells comprising PN junction diodes having satisfactory rectifying characteristics are arranged in three dimensions. The semiconductor storage device includes: a first wire which extends in one direction; a second wire which extends in a direction intersecting the first wire; and a memory cell which is positioned at a portion of intersection of the first wire with the second wire between the first wire and the second wire, the memory cell comprising a storage element and a PN junction diode connected thereto, positioned on a side of the second wire used in selecting the memory cell, and a P-type semiconductor forming the PN junction diode forms a portion of the second wire, wherein a plurality of structures, each structure comprising the first wire, the second wire, and the memory cell is provided three-dimensionally.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Electret condensor microphone preamplifier that is insensitive to leakage currents at the input
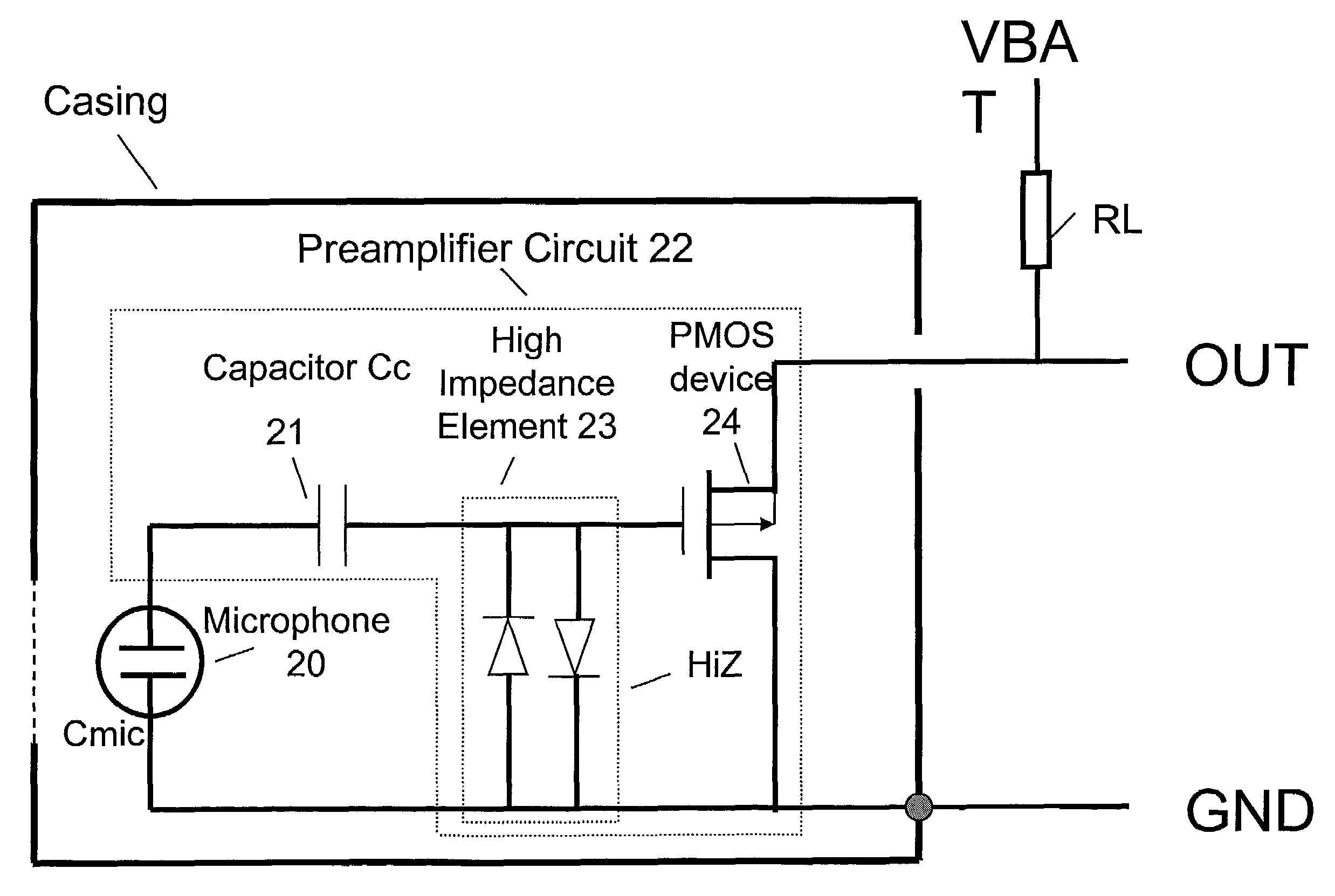
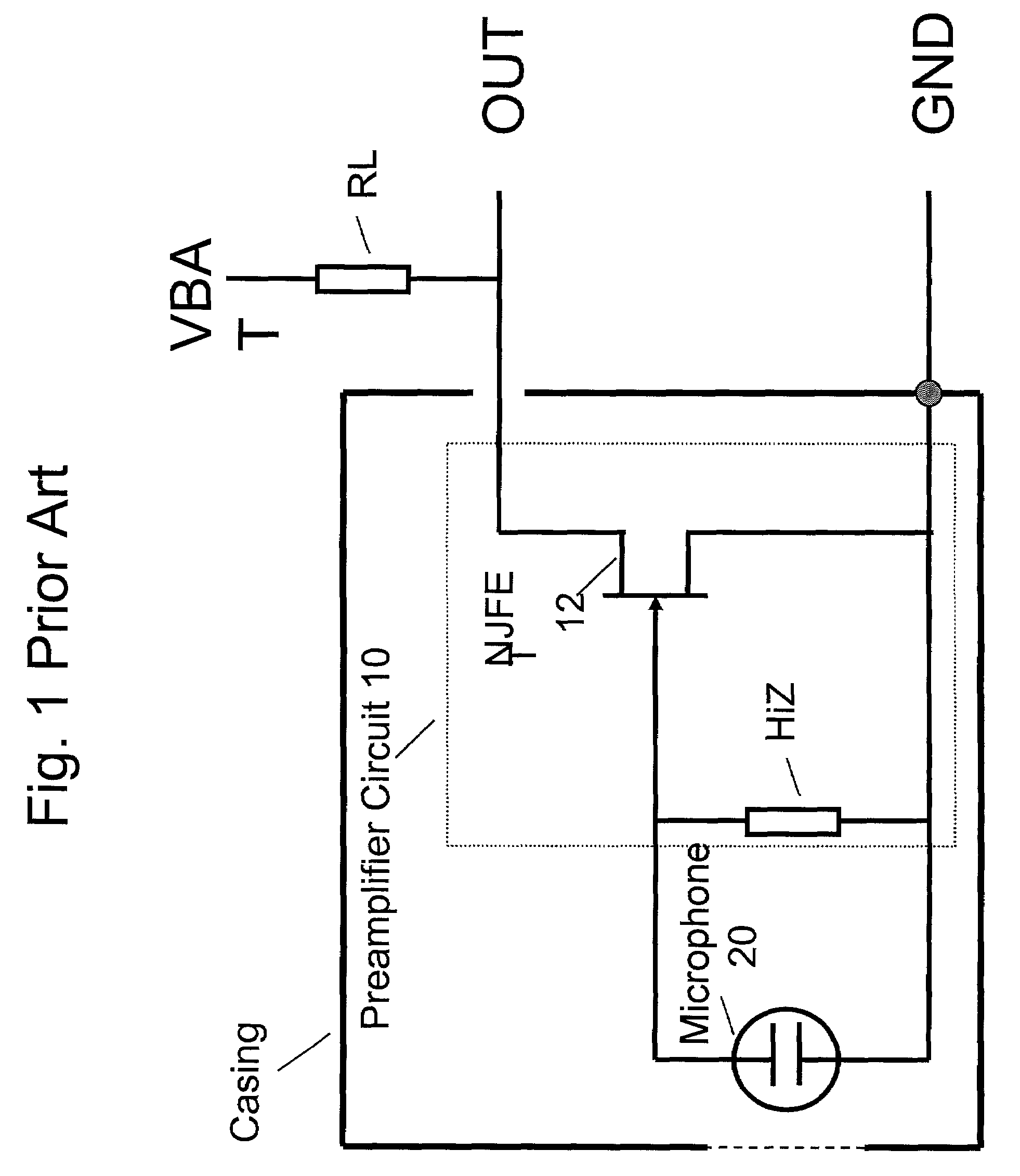
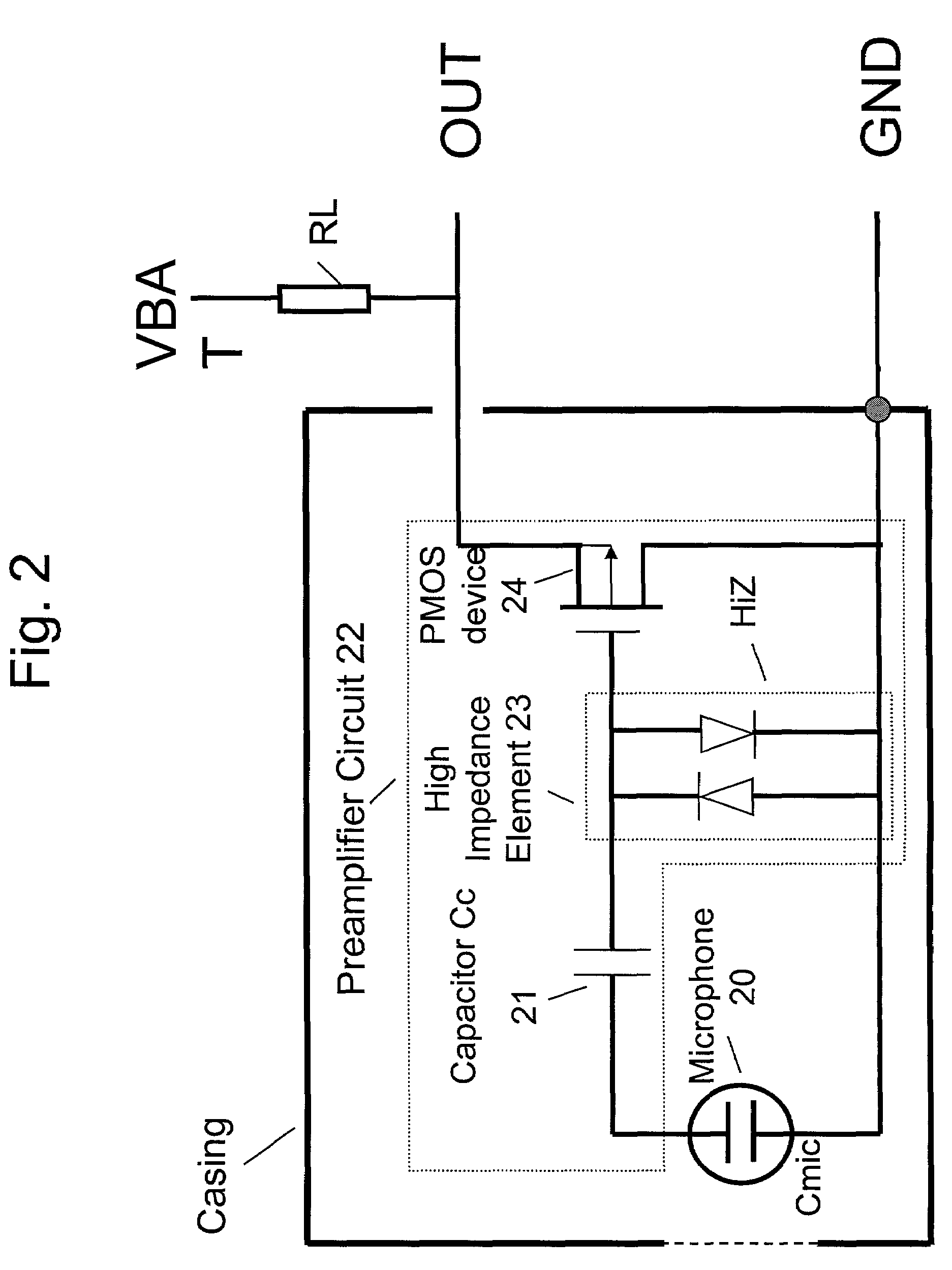
InactiveUS7110560B2Reduce input leakage currentAvoid leakage currentLow frequency amplifiersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOperating point
A preamplifier having extremely high input impedance amplifies the electrical signal output from an electret condenser microphone (ECM) without suffering from the effects of a DC leakage current at the input. The preamplifier circuit includes a pair of cross-coupled PN junction diodes setting the input impedance, a PMOS device, and a load resistor configured similarly to a conventional preamplifier. A capacitor is placed between the input and the cross-coupled diodes such that a DC path no longer exists to bias the cross-coupled diodes. Therefore, leakage currents are prevented from upsetting the DC operating point of the preamplifier and biasing the cross-coupled diodes. Consequently, small signal gain distortion, excessive demodulation products and increased noise can be avoided.
Owner:SONION
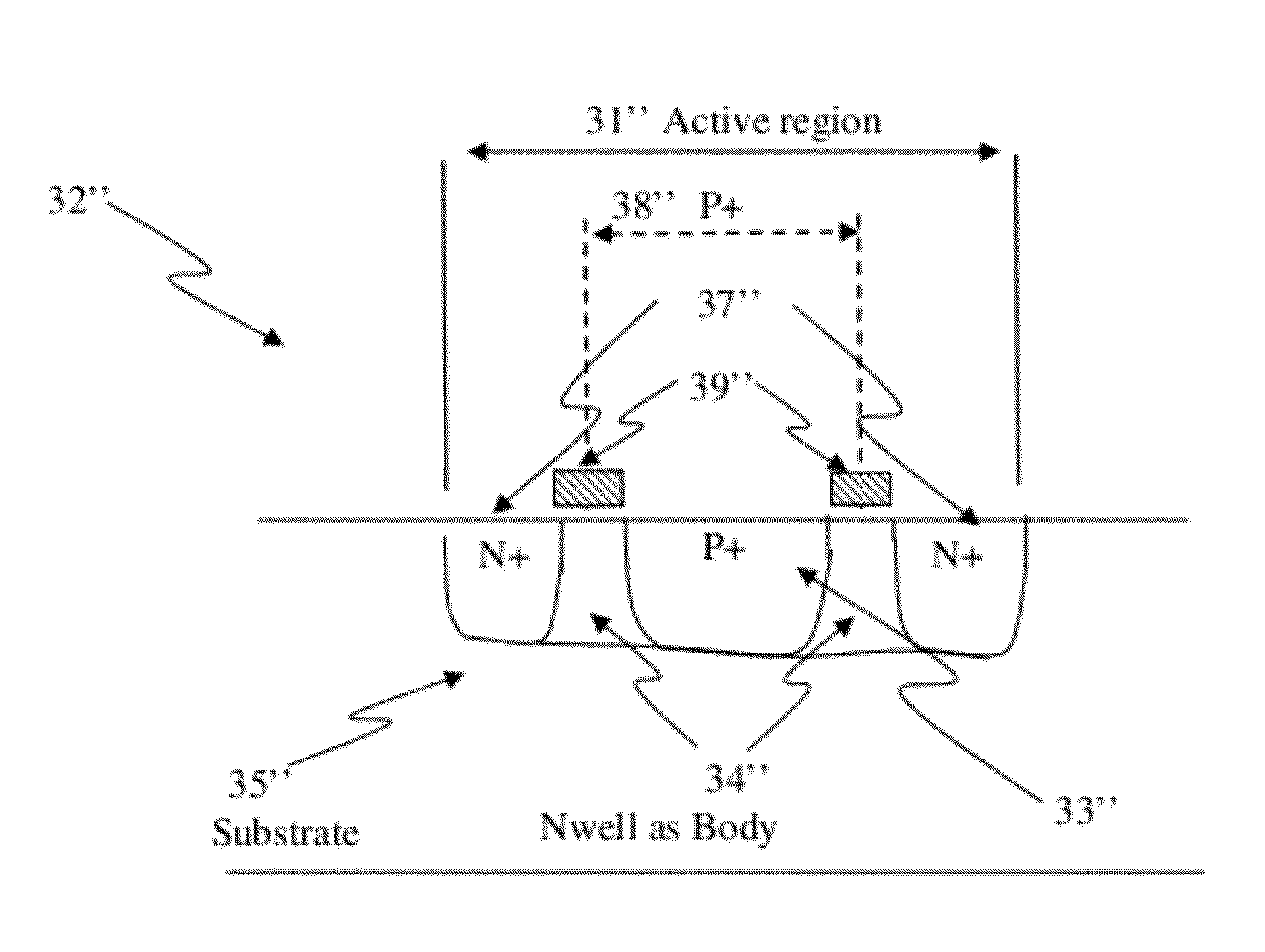
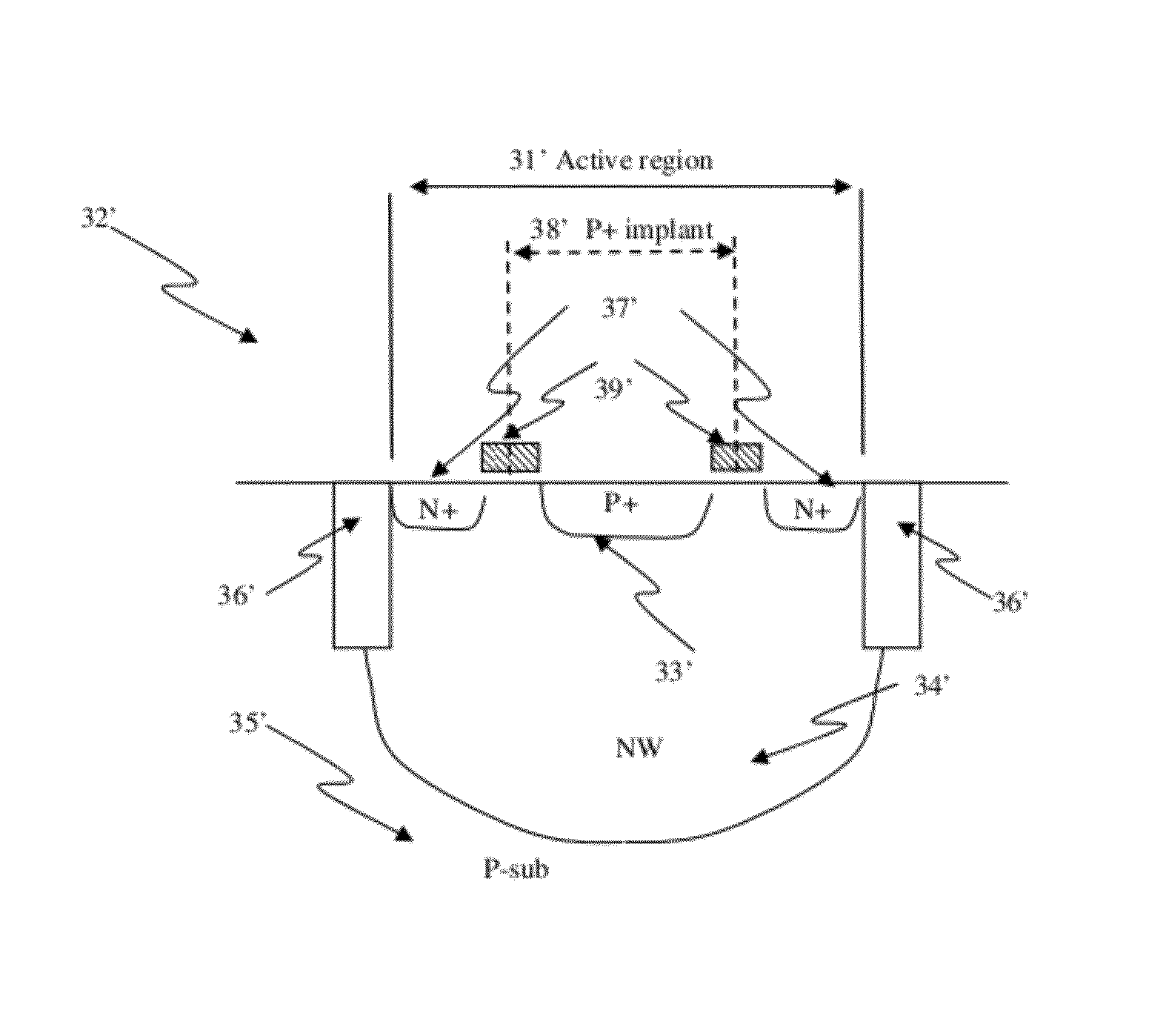
Memory devices using a plurality of diodes as program selectors for memory cells
At least one junction diode fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for the memory cells that can be programmed based on the directions of current flow. These memory cells are MRAM, RRAM, CBRAM, or other memory cells that have a resistive element coupled to the P terminal of the first diode and to the N terminal of a second diode. The diodes can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diodes. By applying a high voltage to a resistive element and switching the N terminal of the first diode to a low voltage while disabling the second diode, a current flows through the memory cell can change the resistance into one state. Similarly, by applying a low voltage to a resistive element and switching the P terminal of the second diode to a high voltage while disabling the first diode, a current flows through the memory cell can change the resistance into another state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in an N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI isolations.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and Method of a Memory Compiler Based on Subtraction Approach
ActiveUS20120209888A1Digital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDatasheetParallel computing
A memory compiler to generate a set of memories is based on a subtraction approach from a set of templates (memory templates), including at least one layout database and auxiliary design databases, by software. The software can be based on general-purpose programming language or a layout-specific language. The compiled memories can be generated by reducing the memory array sizes in row and / or column directions by moving, deleting, adding, sizing, or stretching the layout objects, and disabling the high order addresses, etc. from the memory template by software. The new auxiliary design databases, such as layout phantom, behavior model, synthesis view, placement-and-routing view or datasheet, can also be generated by modifying some parameters from the memory template by software. One-time programmable memory using junction diode, polysilicon diode, or isolated active-region diode as program selector in a cell can be generated accordingly.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using a junction diode as program selector for resistive devices
ActiveUS20120044746A1Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
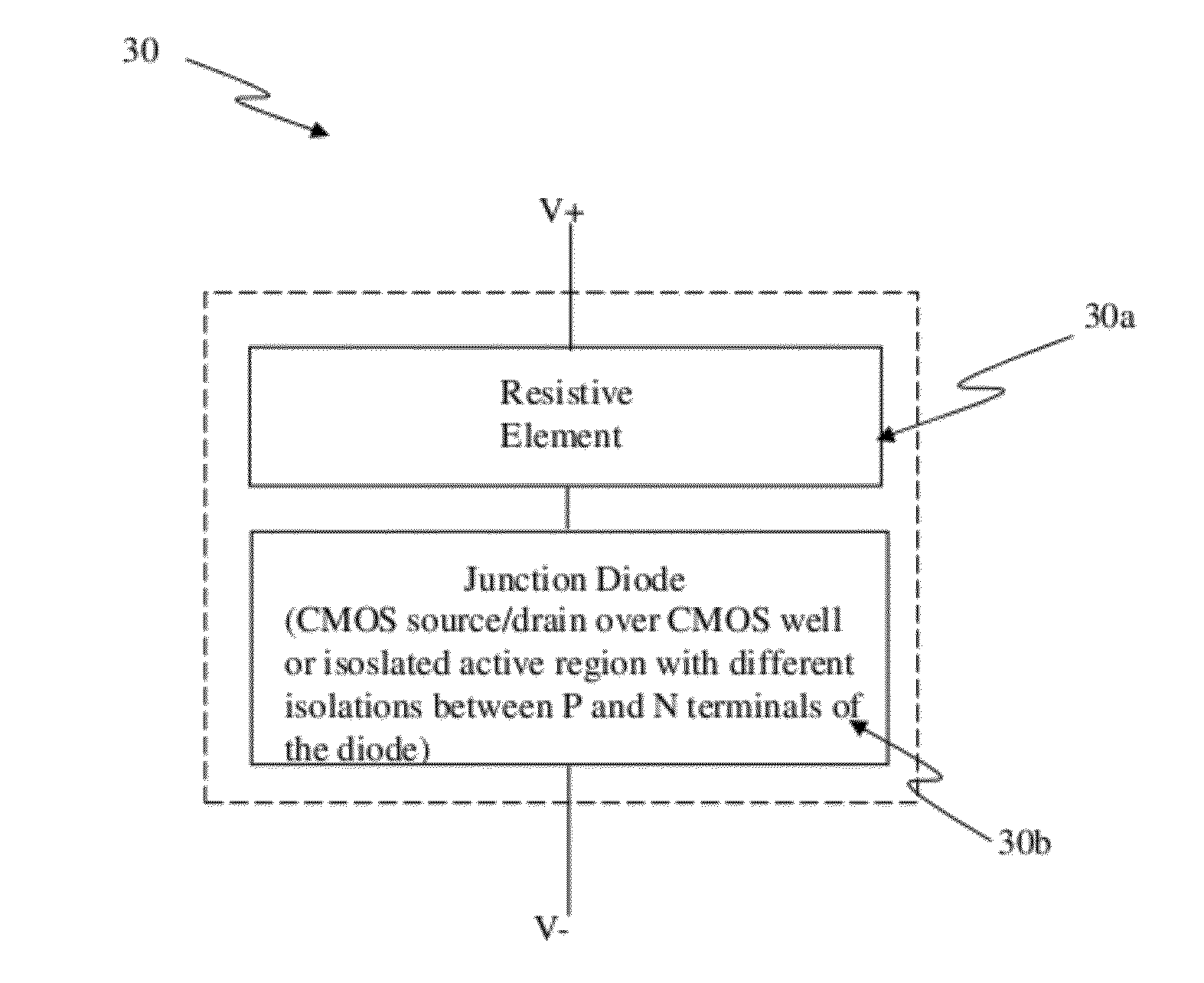
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic technologies can be used as program selectors for a programmable resistive device, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for proper duration of time, a current flows through a resistive element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal can be connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20090261314A1Highly integratedInexpensive to fabricateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
Provided are a non-volatile memory device that may be configured in a stacked structure and may be more easily highly integrated, and a method of fabricating the non-volatile memory device. At least one first electrode and at least one second electrode are provided. The at least one second electrode may cross the at least one first electrode. At least one data storage layer may be at an intersection between the at least one first electrode and the at least one second electrode. Any one of the at least one first electrode and the at least one second electrode may include at least one junction diode connected to the at least one data storage layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
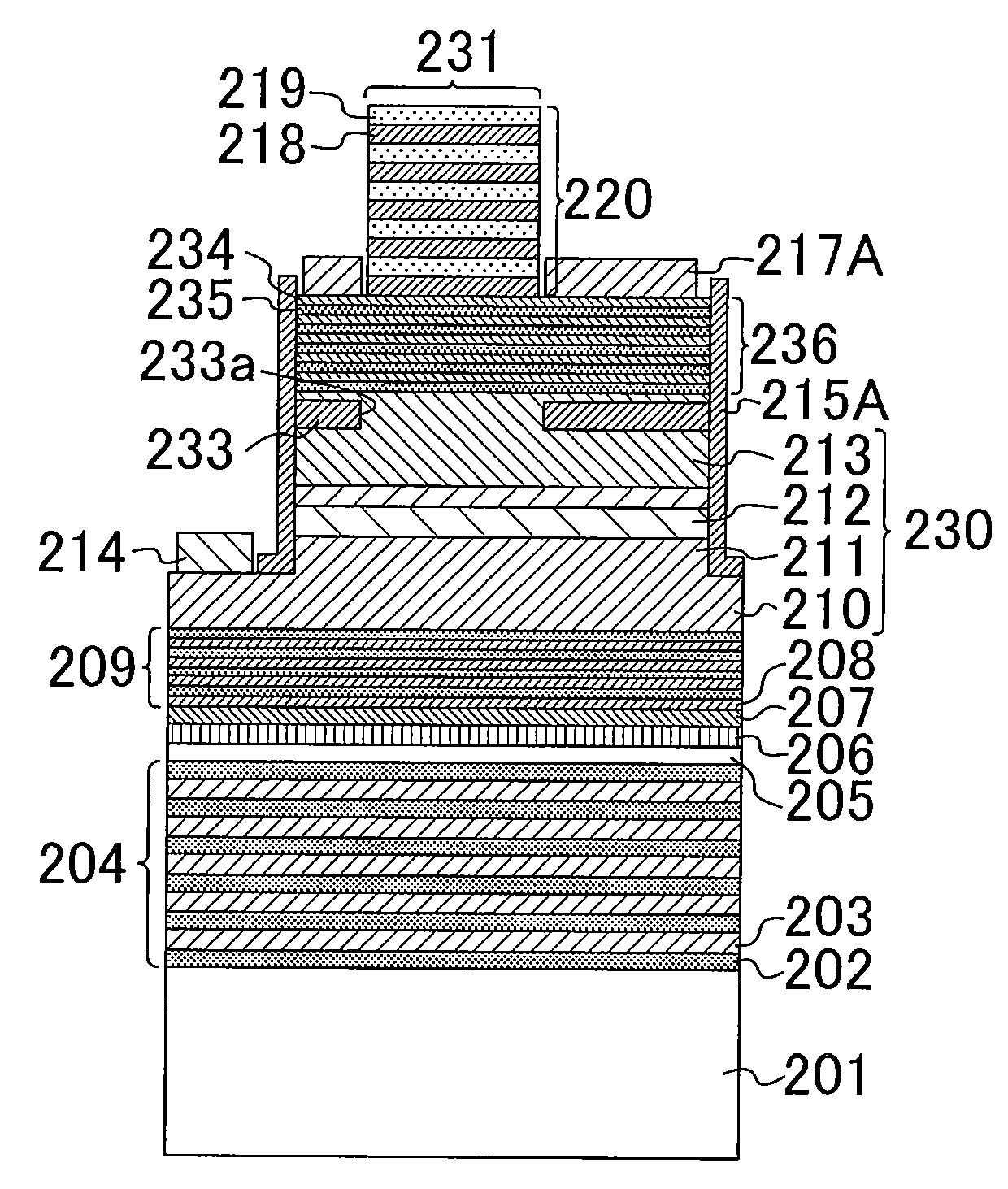
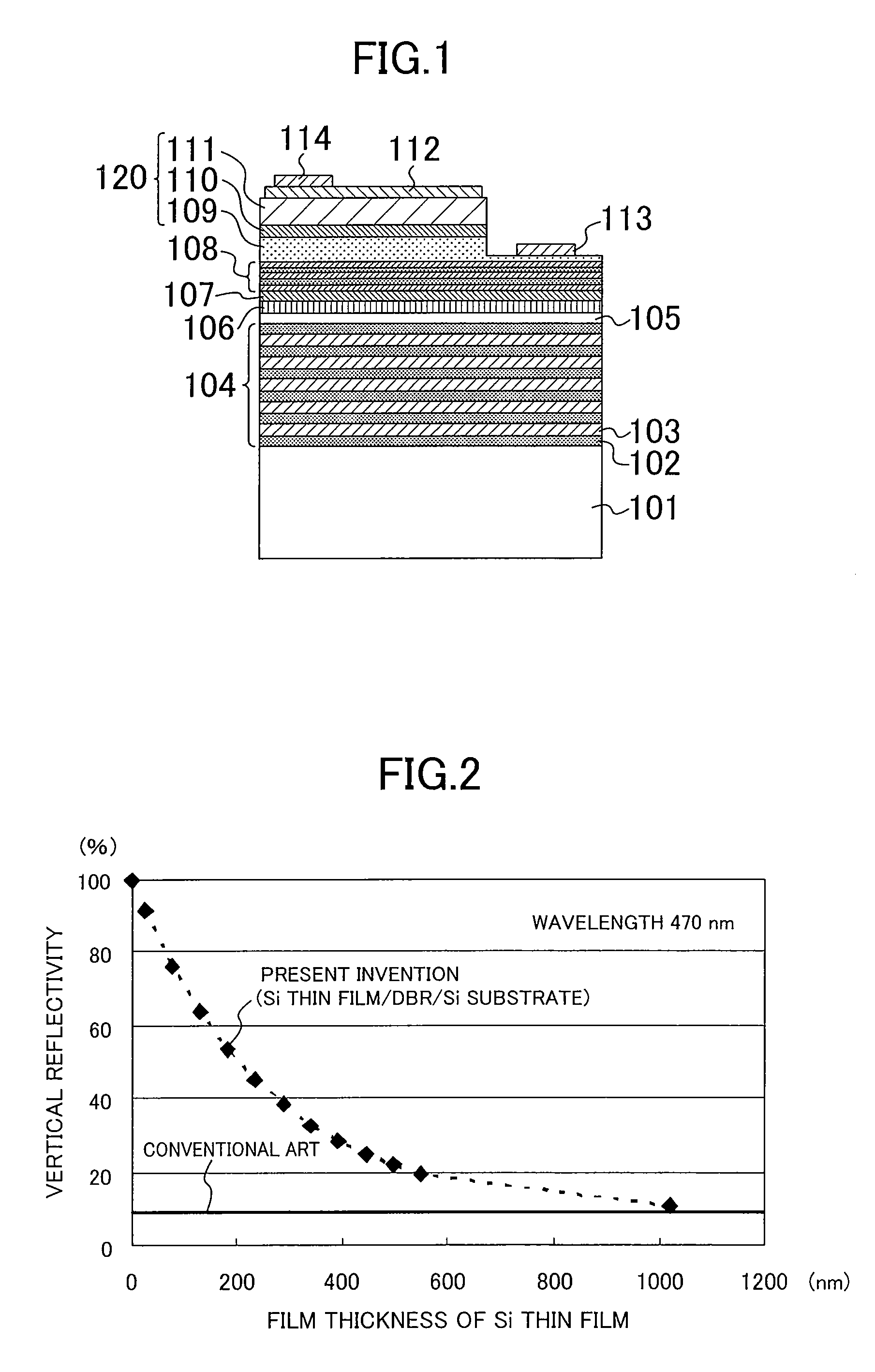
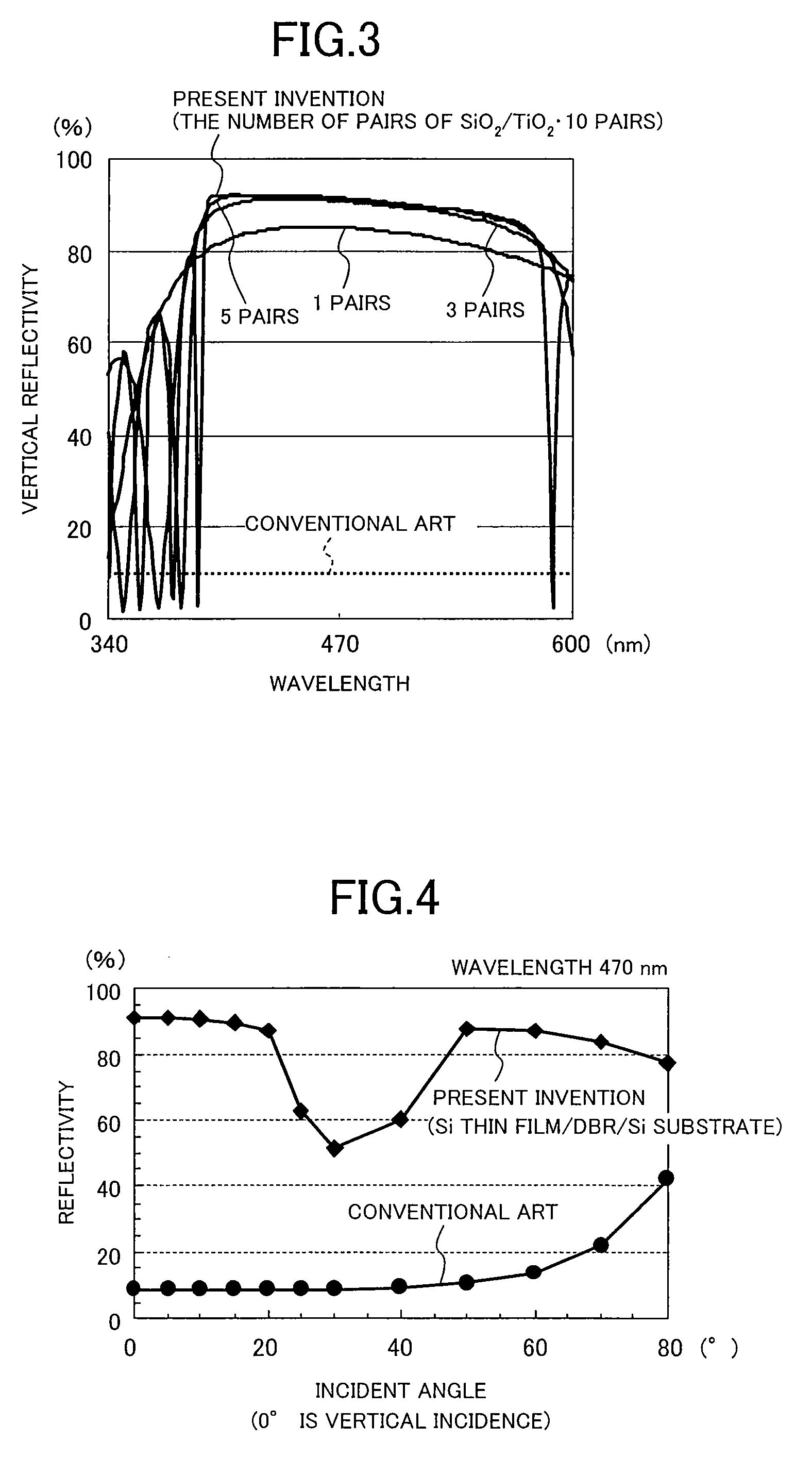
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080179605A1Reduce absorptionLight extraction efficiency of lightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricSingle crystal
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device includes: a dielectric layered film over a substrate, the dielectric layered film being formed by stacking a plurality of dielectric films having different compositions; a semiconductor thin film formed of a single crystal over the dielectric layered film; and a pn junction diode structure over the semiconductor thin film, the pn junction diode structure being formed of a nitride semiconductor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS8488359B2Low costSmall sizeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCMOSMetal alloy
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and System of Using Junction Diode as Program Selector for One-Time Programmable Devices
ActiveUS20120224406A1Small cell sizeLow costMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Reversible resistive memory using diodes formed in CMOS processes as program selectors
ActiveUS20120044747A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for reversible resistive memory cells that can be programmed based on magnitude, duration, voltage-limit, or current-limit of a supply voltage or current. These cells are PCM, RRAM, CBRAM, or other memory cells that have a reversible resistive element coupled to a diode. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. The memory cells can be used to construct a two-dimensional memory array with the N terminals of the diodes in a row connected as a wordline and the reversible resistive elements in a column connected as a bitline. By applying a voltage or a current to a selected bitline and to a selected wordline to turn on the diode, a selected cell can be programmed into different states reversibly based on magnitude, duration, voltage-limit, or current-limit. The data in the reversible resistive memory can also be read by turning on a selected wordline to couple a selected bitline to a sense amplifier. The wordlines may have high-resistivity local wordlines coupled to low-resistive global wordlines through conductive contact(s) or via(s).
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Programmably reversible resistive device cells using CMOS logic processes
ActiveUS20120044753A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSCurrent limiting
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for reversible resistive devices, such as PCM, RRAM, CBRAM, or other memory cells. The reversible resistive devices have a reversible resistive element coupled to a diode. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a voltage or a current between a reversible resistive element and the N terminal of a diode, the reversible resistive device can be programmed into different states based on magnitude, duration, voltage-limit, or current-limit in a reversible manner. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044739A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal are connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using at least one junction diode as program selector for memories
ActiveUS20120044758A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
At least one junction diode fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for memory cells that can be programmed based on direction of current flow. These cells are MRAM, RRAM, CBRAM, or other memory cells that have a programmable resistive element coupled to a P terminal of a first diode and to an N terminal of a second diode. The diodes can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diodes. The memory cells can be used to construct a two-dimensional memory array with the N terminals of the first diodes and the P terminals of the second diodes in a row connected as wordline(s) and the resistive elements in a column connected as a bitline. By applying a high voltage to a selected bitline and a low voltage to a selected wordline to turn on the first diode while disabling the second diode, a selected cell can be programmed into one state. Similarly, by applying a low voltage to a selected bitline and a high voltage to a selected wordline to turn on the second diode while disabling the first diode, a selected cell can be programmed into another state. The data in the resistive memory cell can also be read by turning on a selected wordline to couple a selected bitline to a sense amplifier. The wordlines may have high-resistivity local wordlines coupled to low-resistivity global wordlines through conductive contact(s) or via(s).
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
One-time programmable memories using junction diodes as program selectors
ActiveUS20120044740A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to the diode. The OTP device can be used to construct a two-dimensional OTP memory with the N terminals of the diodes in a row connected as a wordline and the OTP elements in a column connected as a bitline. By applying a high voltage between a selected bitline and a selected wordline to turn on a diode in a selected cell for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The cell data in the OTP memory can also be read by turning on a selected wordline and to couple a selected bitline to a sense amplifier. The wordlines may have high-resistivity local wordlines coupled to low-resistivity global wordlines through conductive contact(s) or via(s).
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
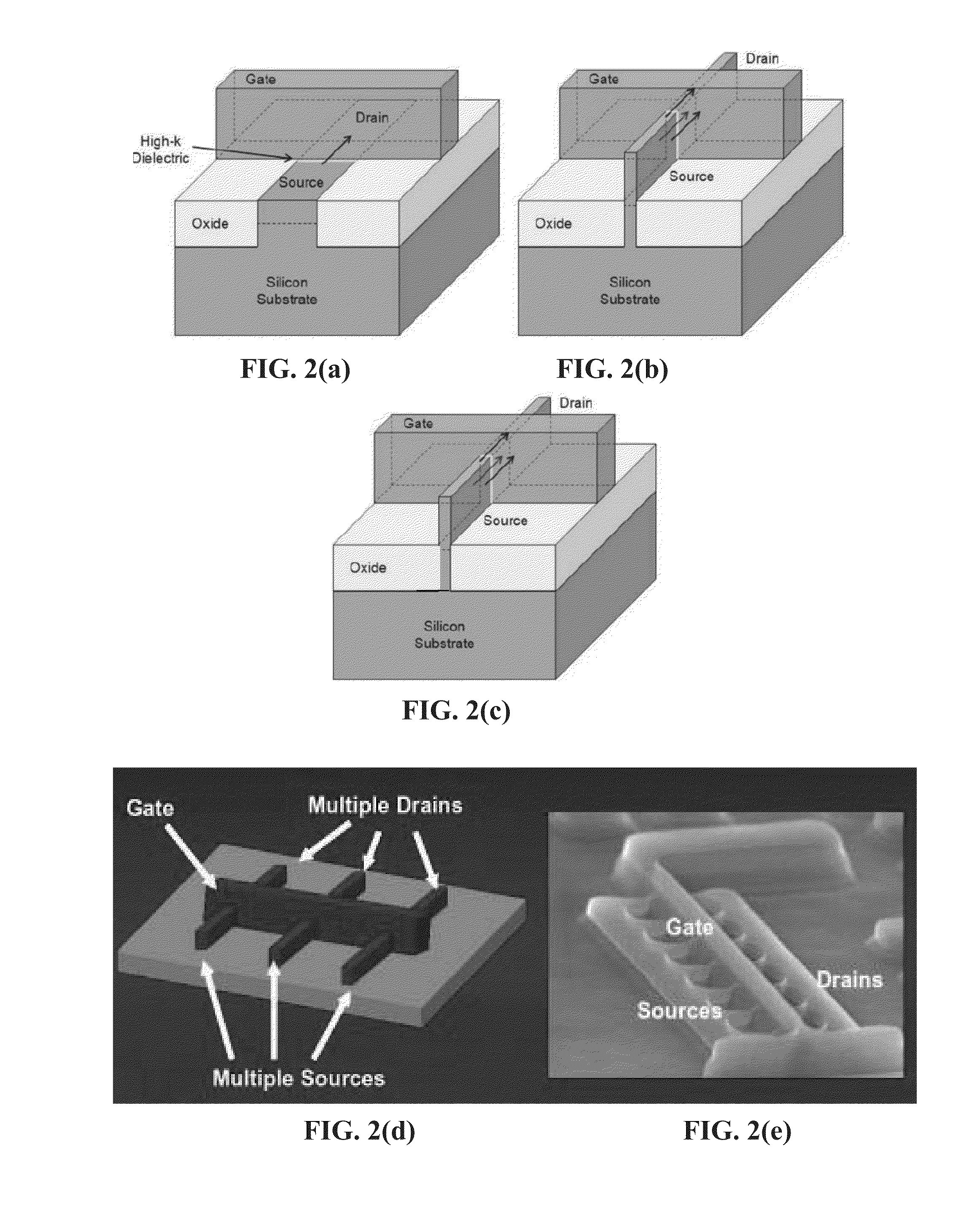
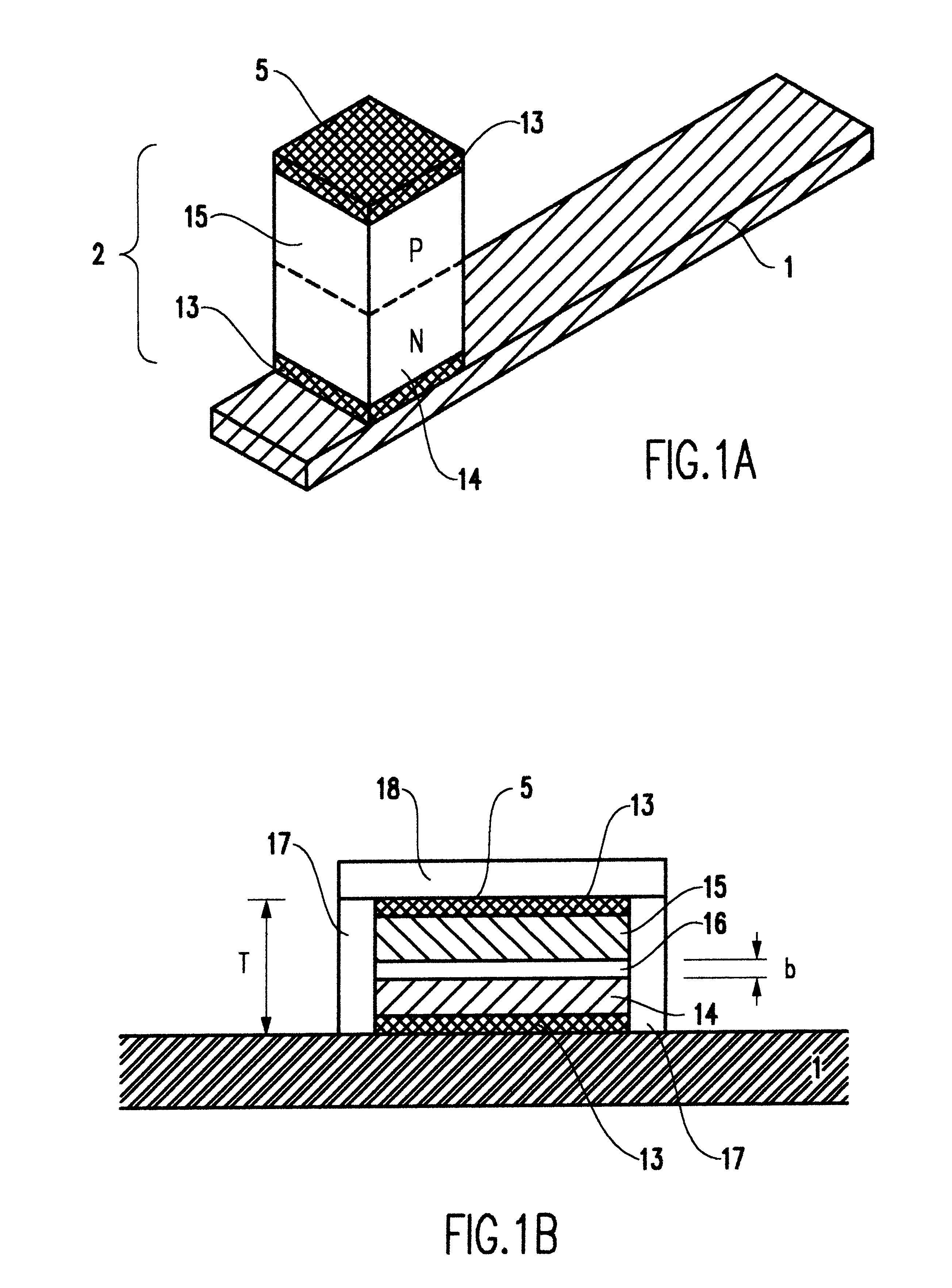
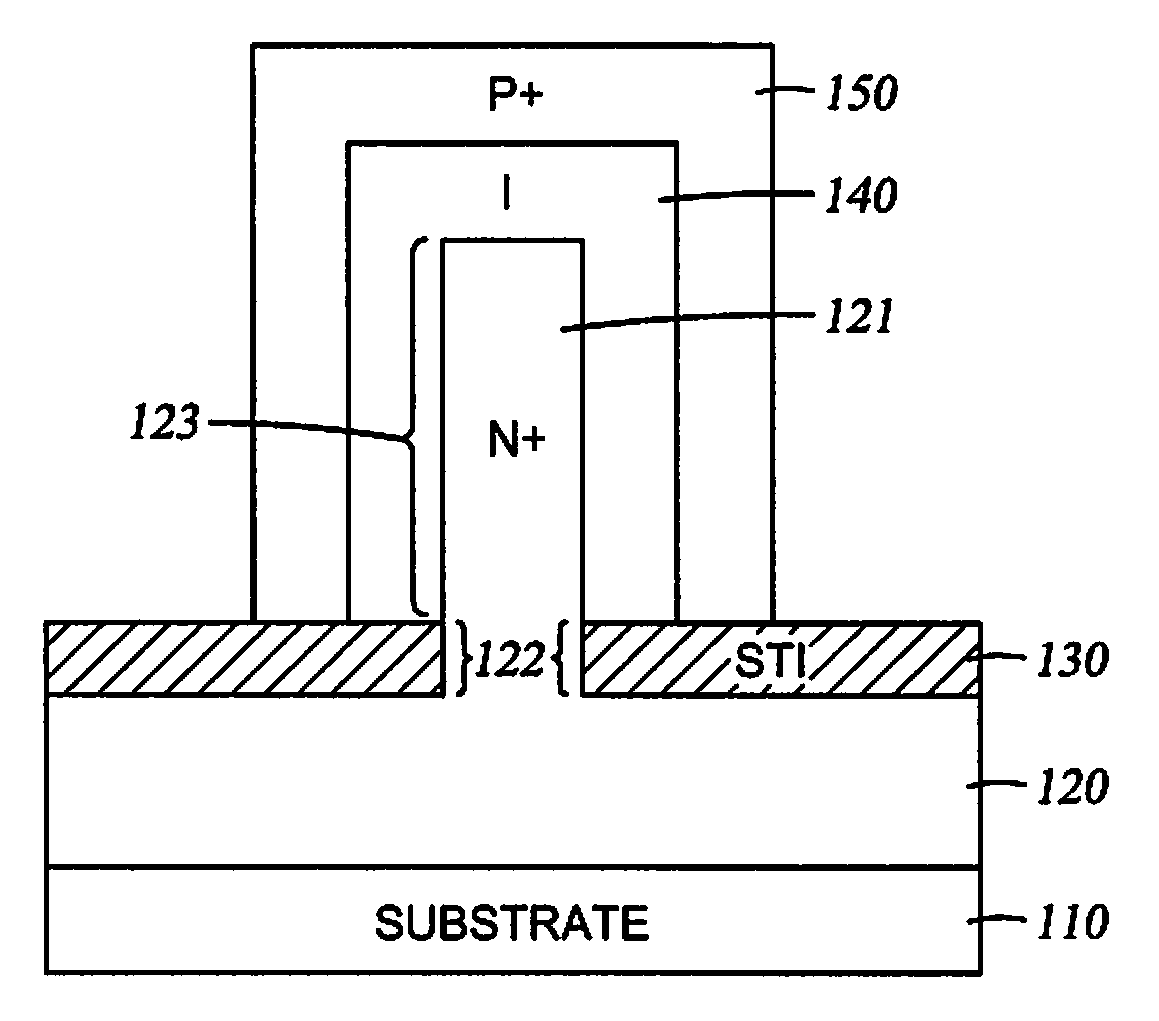
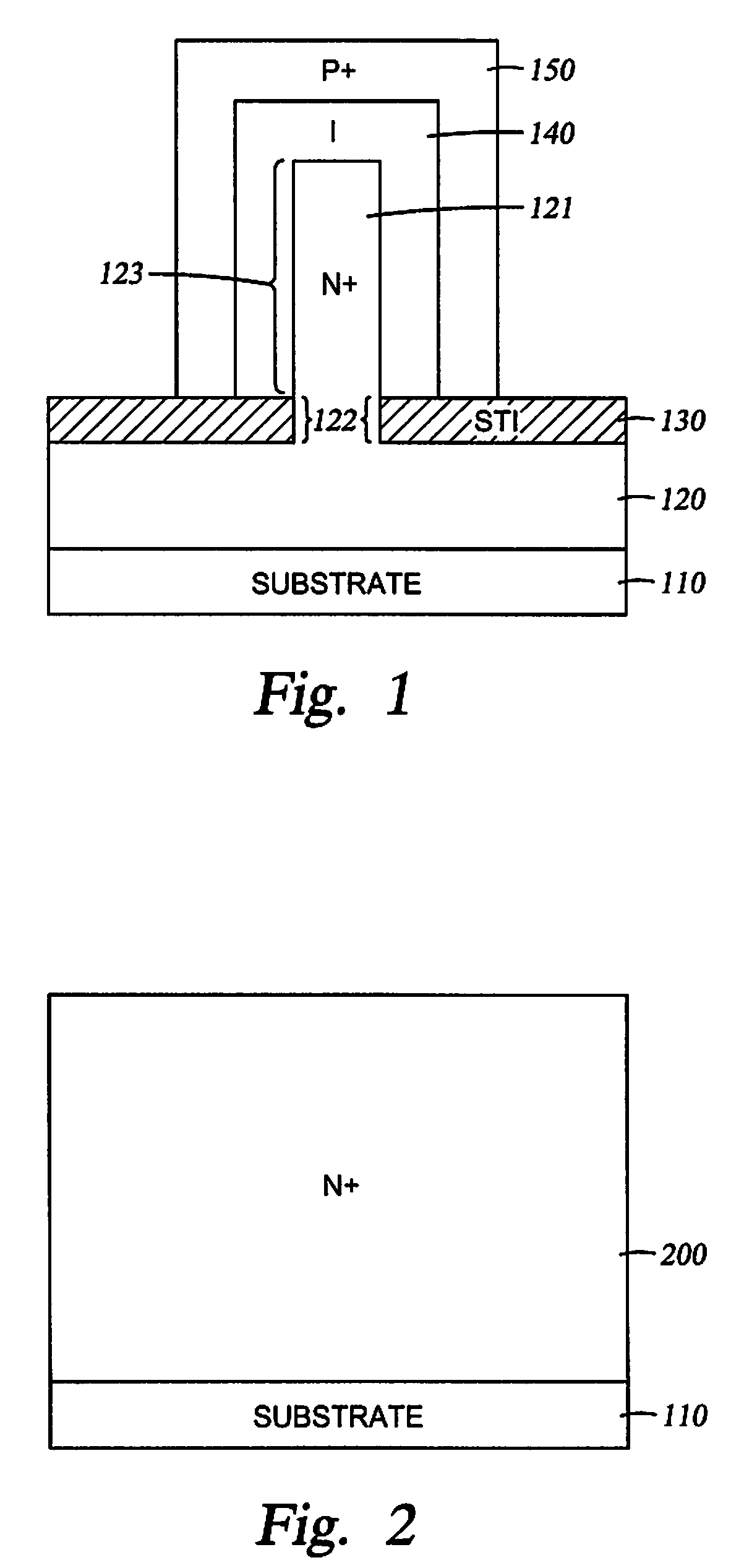
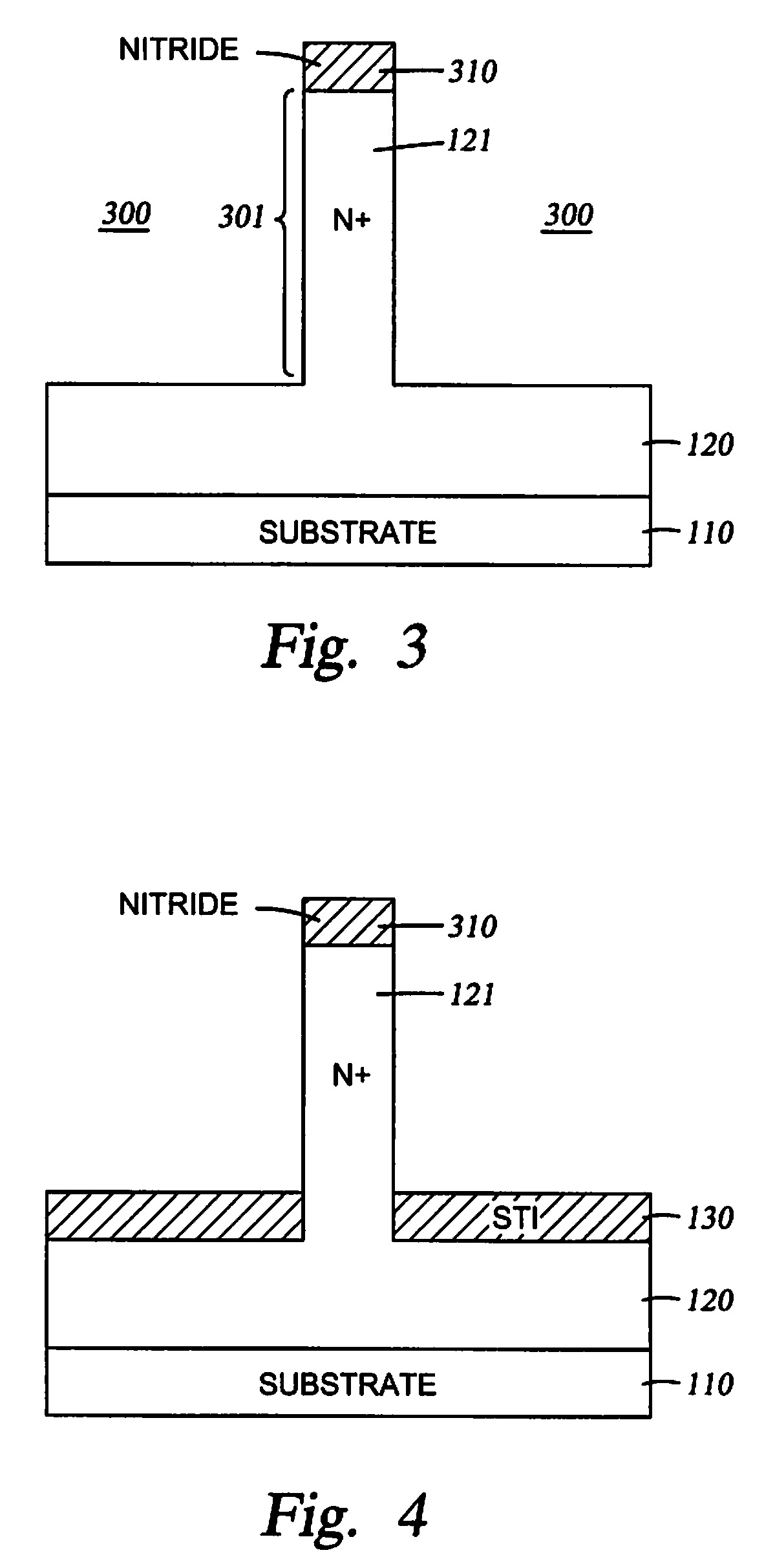
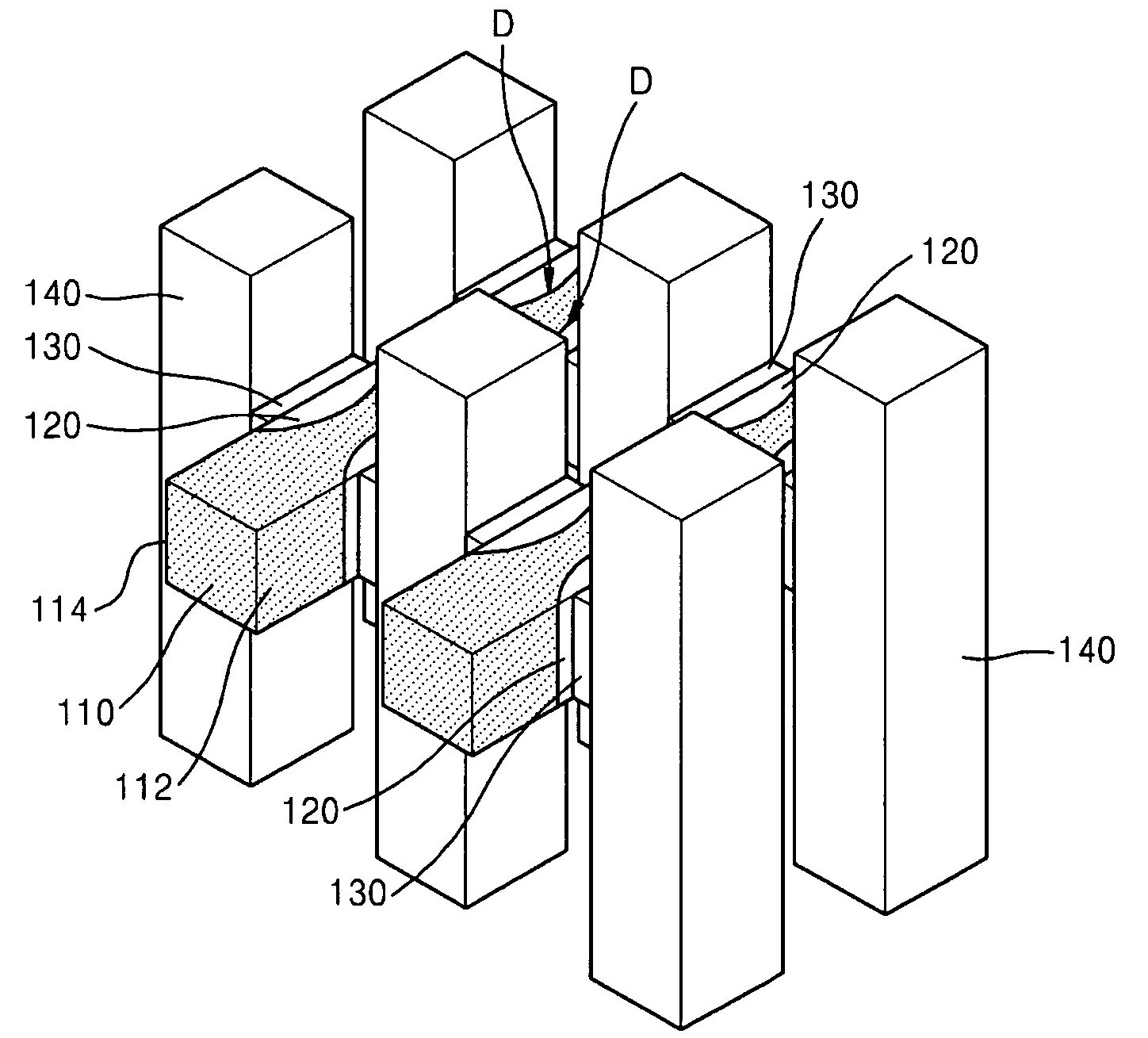
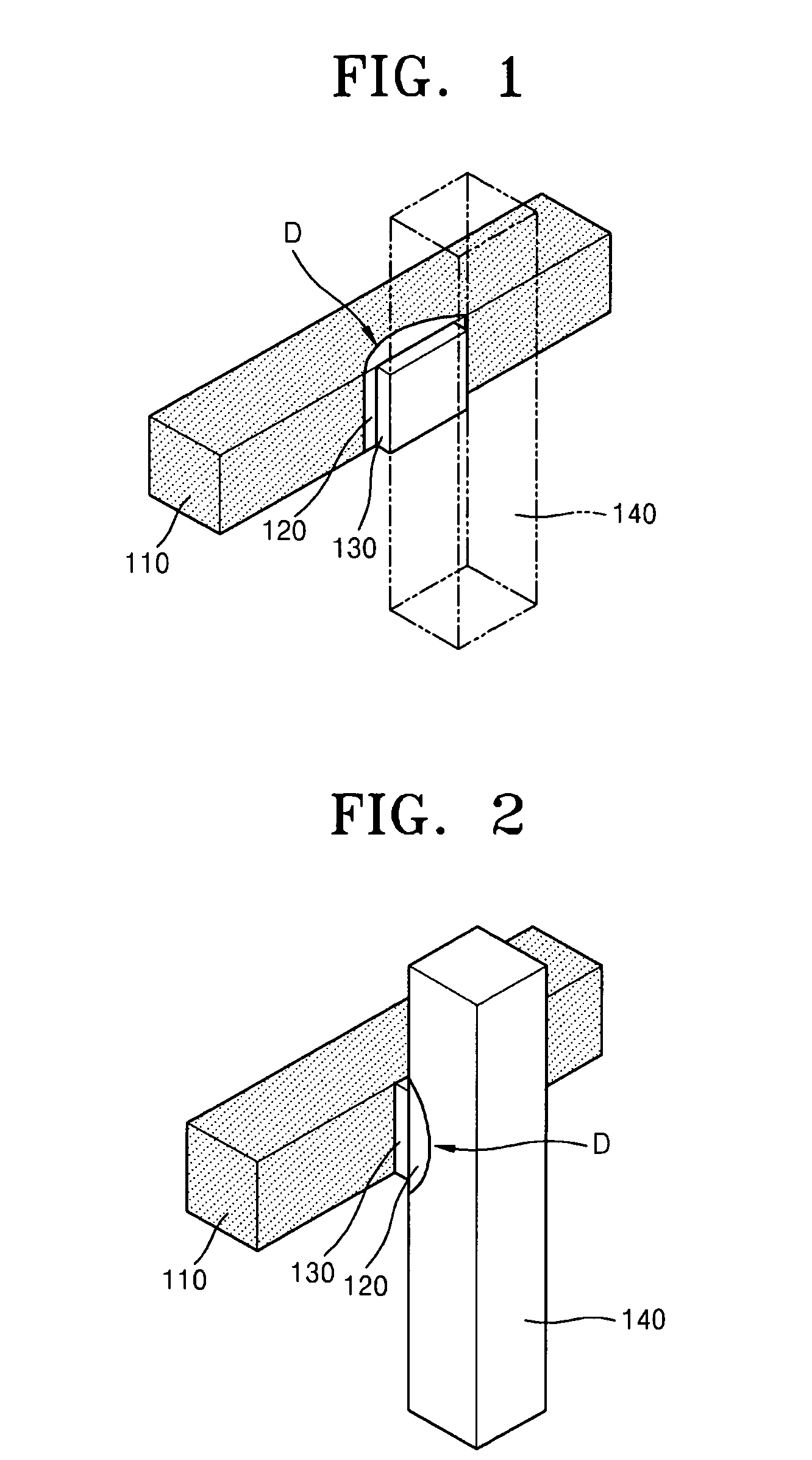
Fin PIN diode
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to the field of semiconductor devices, and more specifically to fin-based junction diodes. A portion of a doped semiconductor fin may protrude through a first doped layer. An intrinsic layer may be disposed on the protruding semiconductor fin. A second semiconductor layer may be disposed on the intrinsic layer, thereby forming a PIN diode compatible with FinFET technology and having increased junction area.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
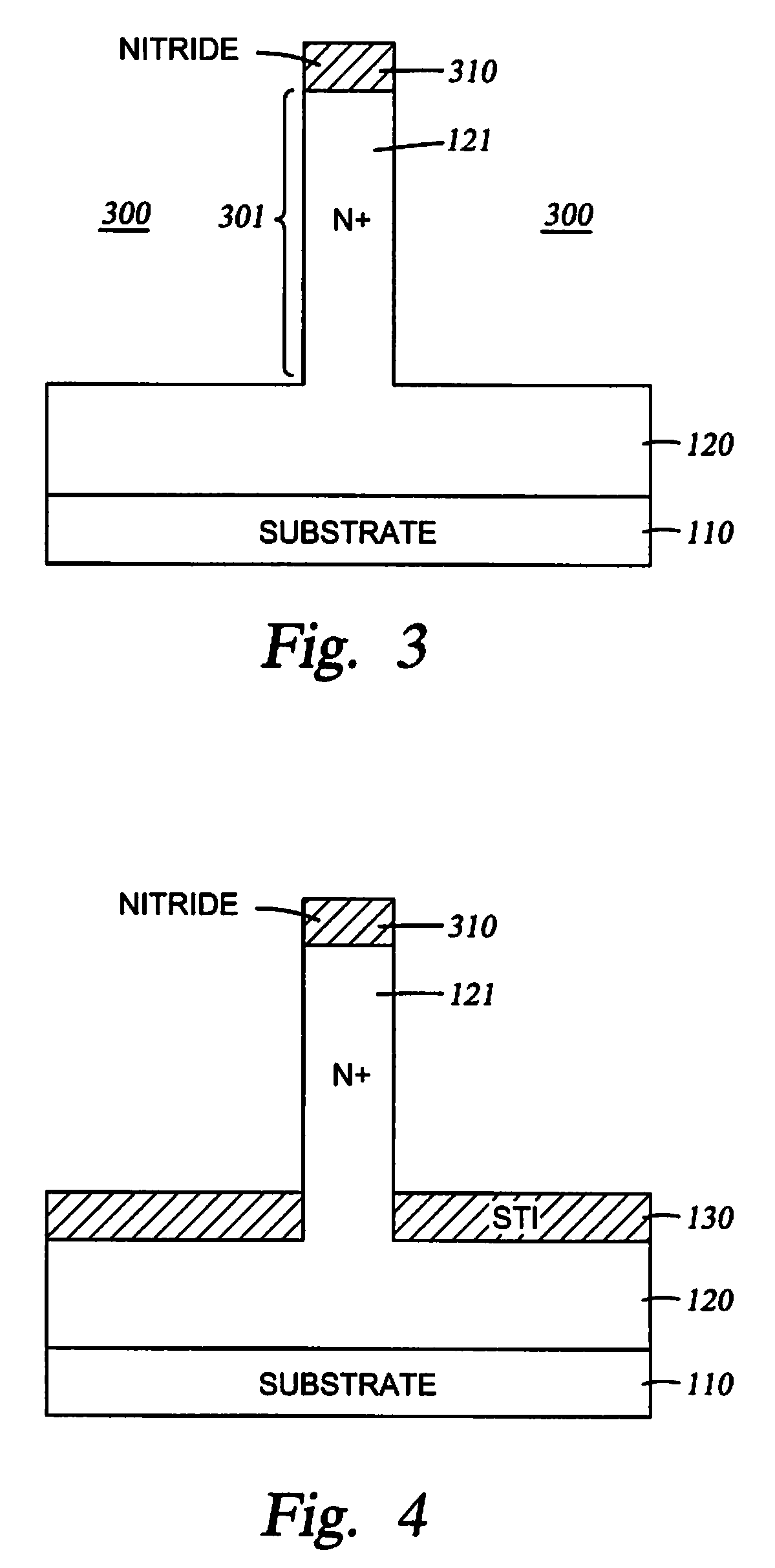
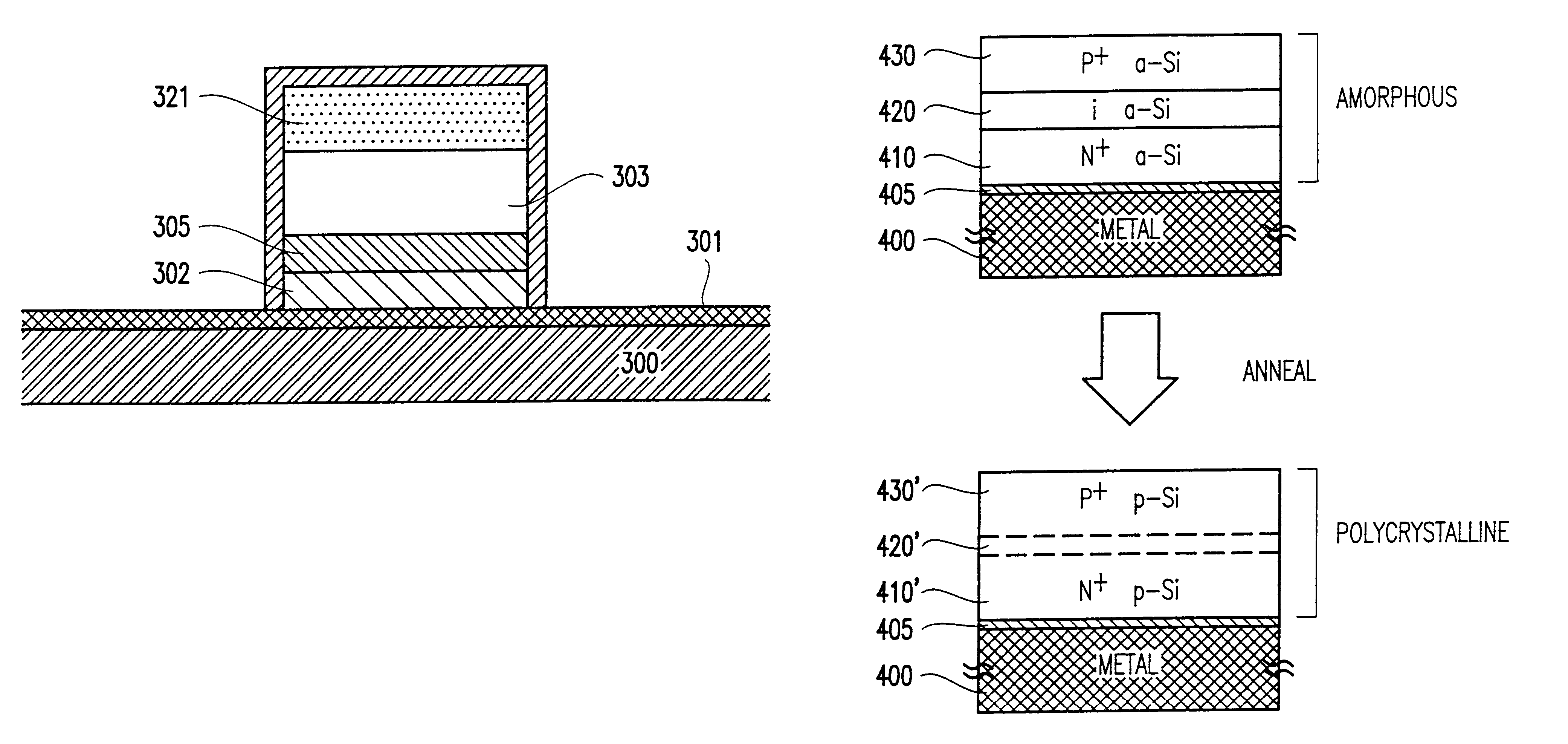
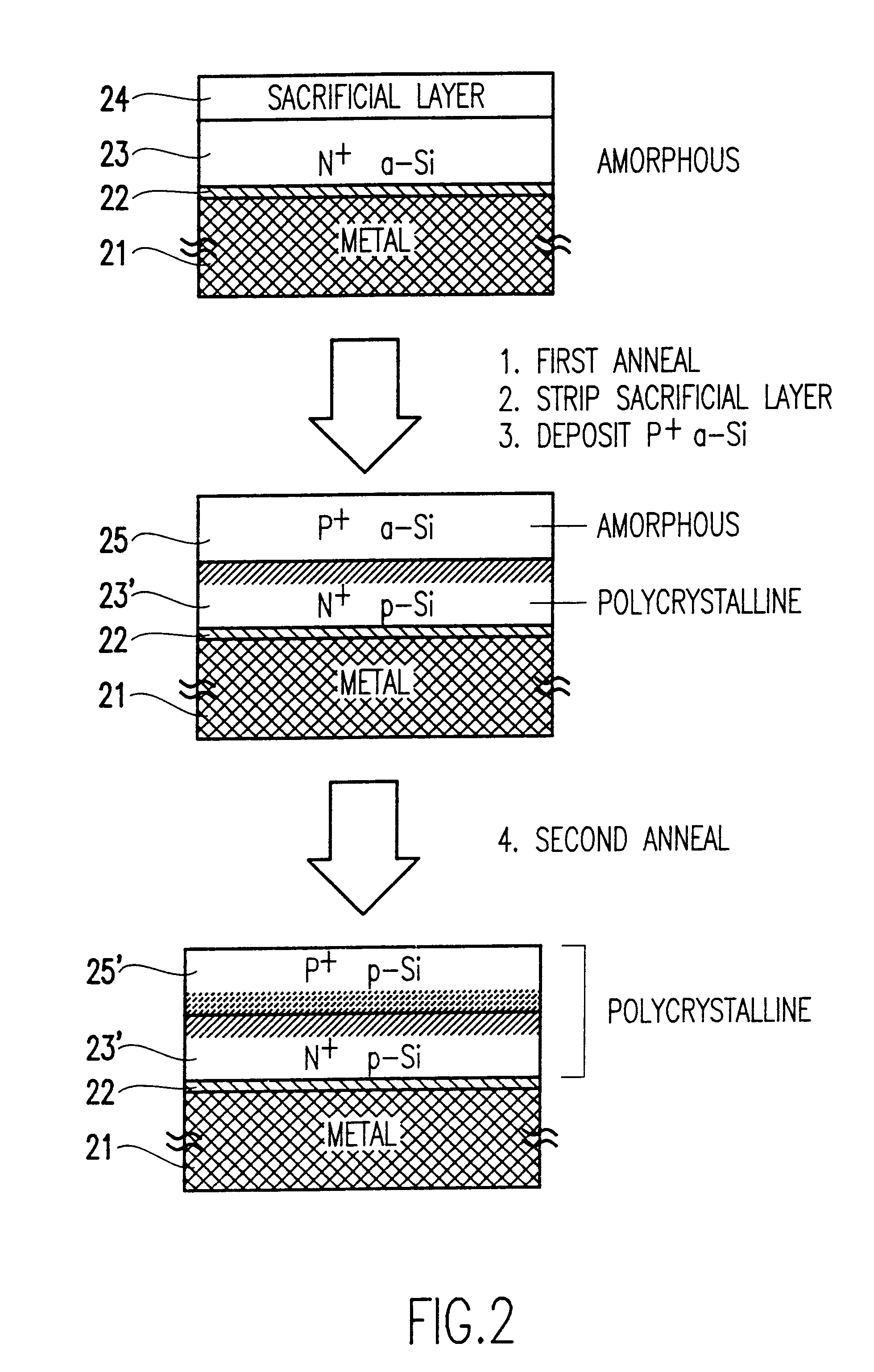
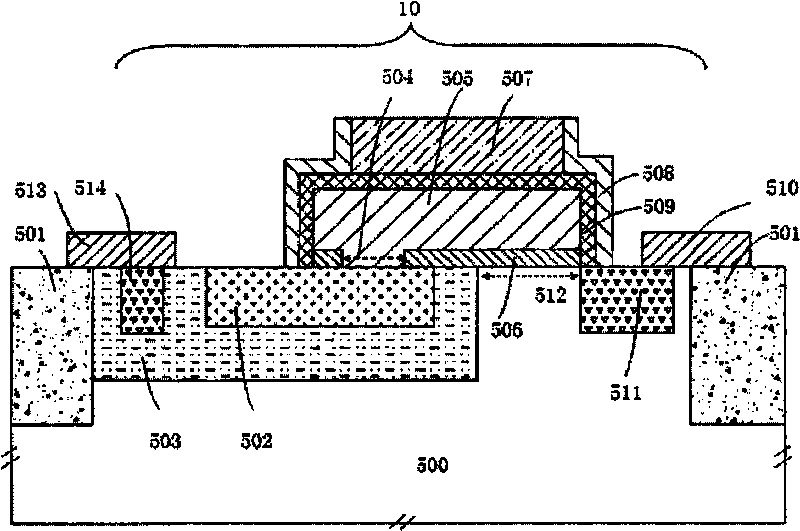
Semiconductor device having ultra-sharp P-N junction and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6180444B1Easy to makeReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor device such as a P-N or P-I-N junction diode, includes a first semiconductor layer having a first conductivity-type and being mounted over a metal address line, and a second semiconductor layer having a second conductivity-type and being mounted over the first semiconductor material. The diode preferably has a thickness of substantially no more than about 1 micron, and the diode includes a P-N junction confined to a thickness of less than about 0.1 micron. In the preferred embodiment the method comprises depositing a first semiconductor layer having a first conductivity type, depositing a second intrinsic layer, annealing to convert both layers to a polycrystalline layer, implanting ions of a second conductivity type into the second layer, and annealing to convert the second layer to a polycrystalline. The result is a diode having an ultra-sharp p-n junction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
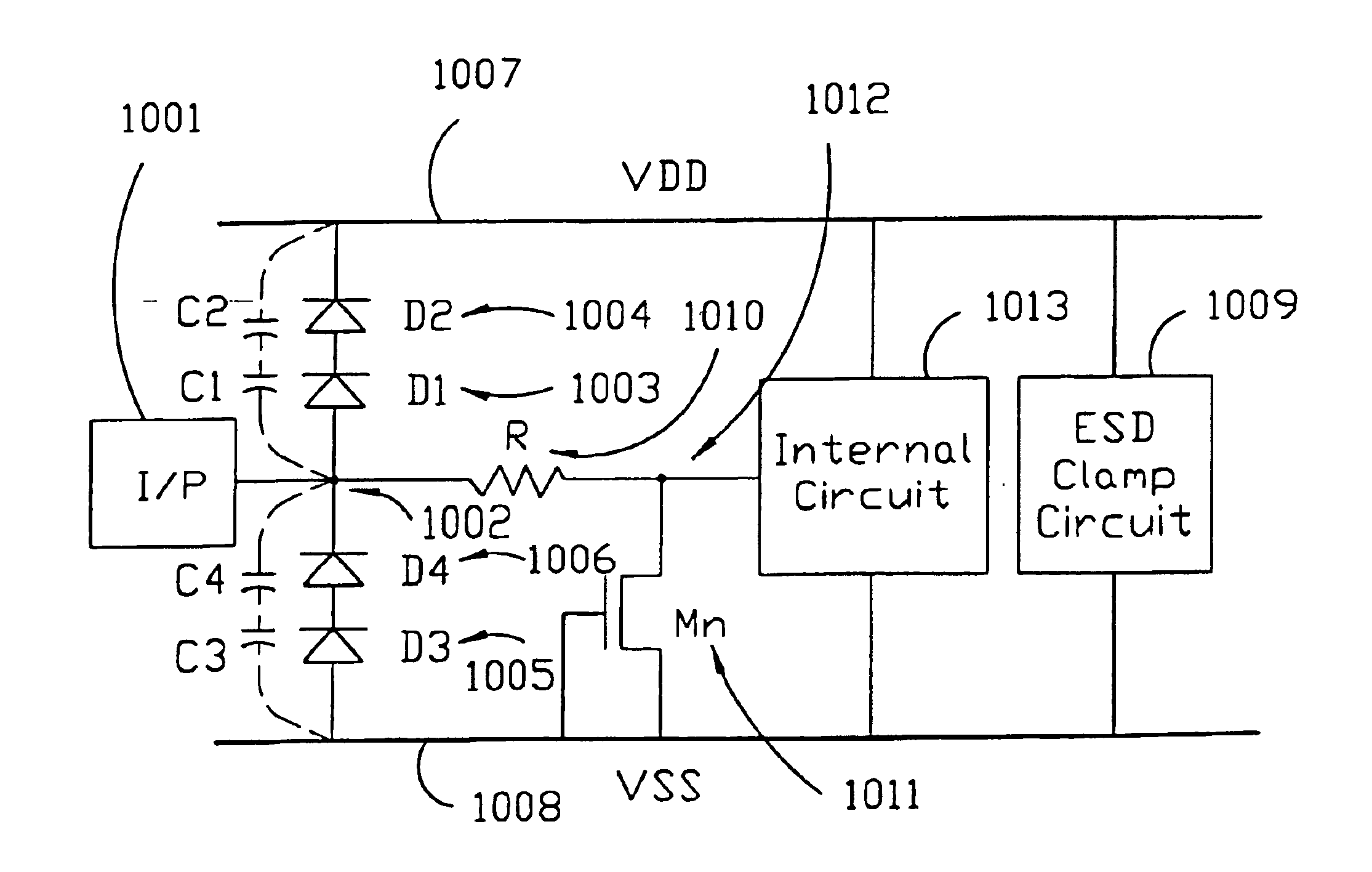
Structures and techniques for electro-static discharge (ESD) protection using ring structured diodes
InactiveUS20140131710A1High ESD immunityReduce input capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSEngineering
Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) protection using at least one ring-shape diode is disclosed. The ring-shape diode can be constructed from polysilicon, active region body on insulated substrate, or junction diode on silicon substrate. The diodes can have a first type of implant in an outer ring and a second type of implant in an inner ring to serve as two terminals of a diode coupled through contacts, vias, or metals. The two types of implant ring regions are separated with an isolation structure. The isolation can be LOCOS, STI, dummy gate, or silicide block layer (SBL). The ESD structure has at least a ring-shape diode with a first terminal coupled to an I / O pad and the second terminal coupled to a first supply voltage. The contours of the ring-shape diode can be circles, polygons, or other shapes. The ring-shape ESD structures can be multiple and be constructed in concentric manner.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Fin Pin Diode
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to the field of semiconductor devices, and more specifically to fin-based junction diodes. A portion of a doped semiconductor fin may protrude through a first doped layer. An intrinsic layer may be disposed on the protruding semiconductor fin. A second semiconductor layer may be disposed on the intrinsic layer, thereby forming a PIN diode compatible with FinFET technology and having increased junction area.
Owner:IBM CORP
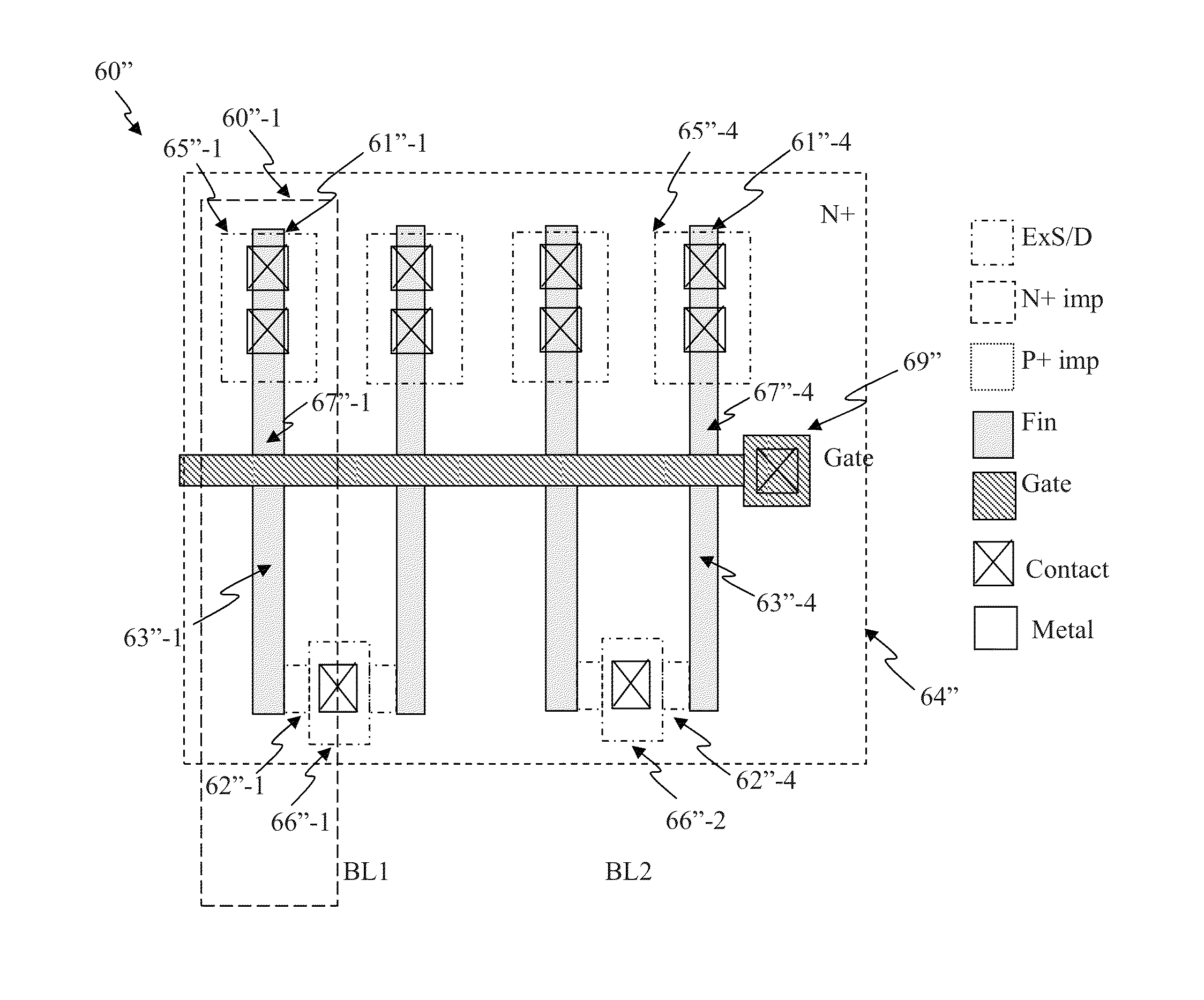
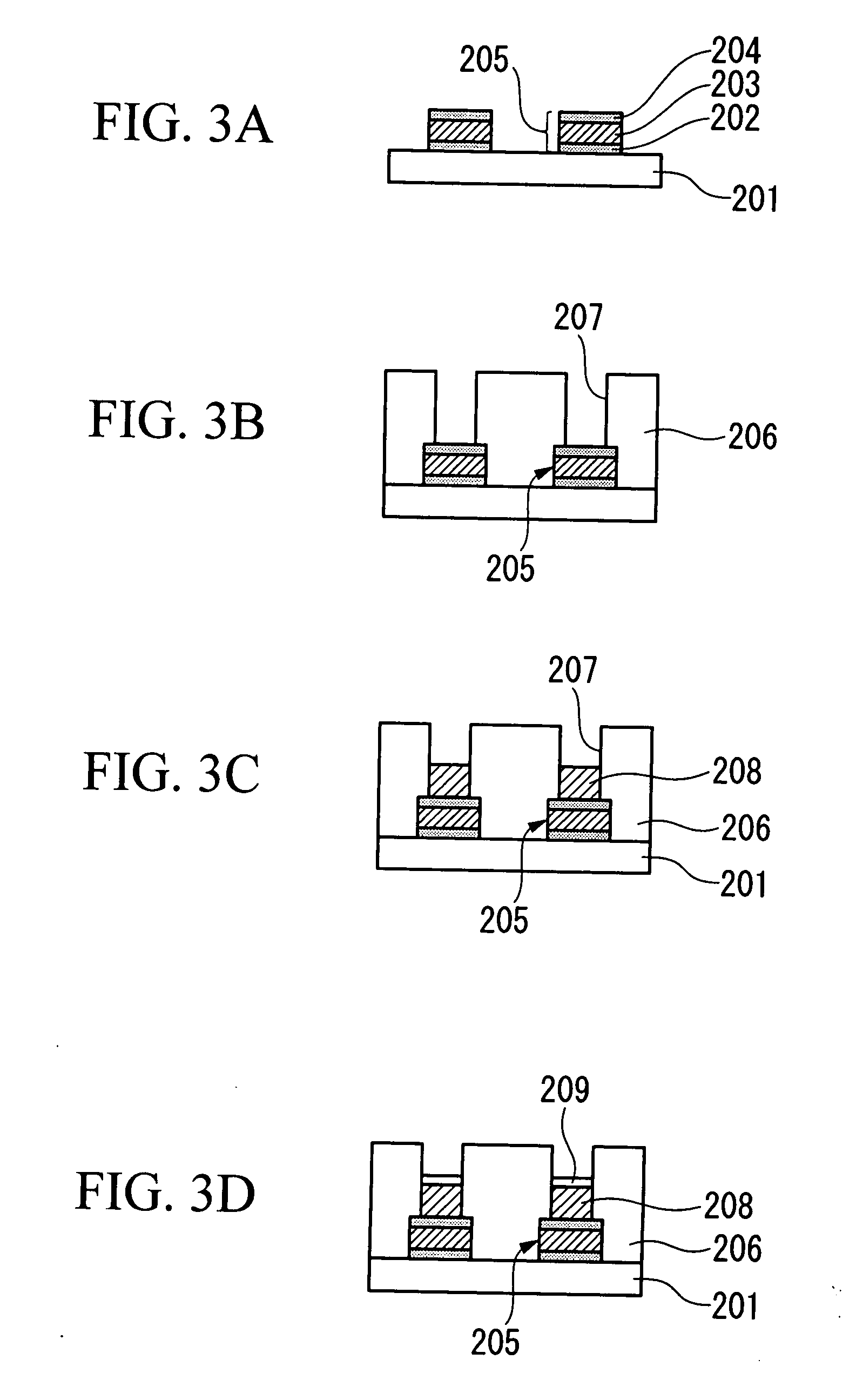
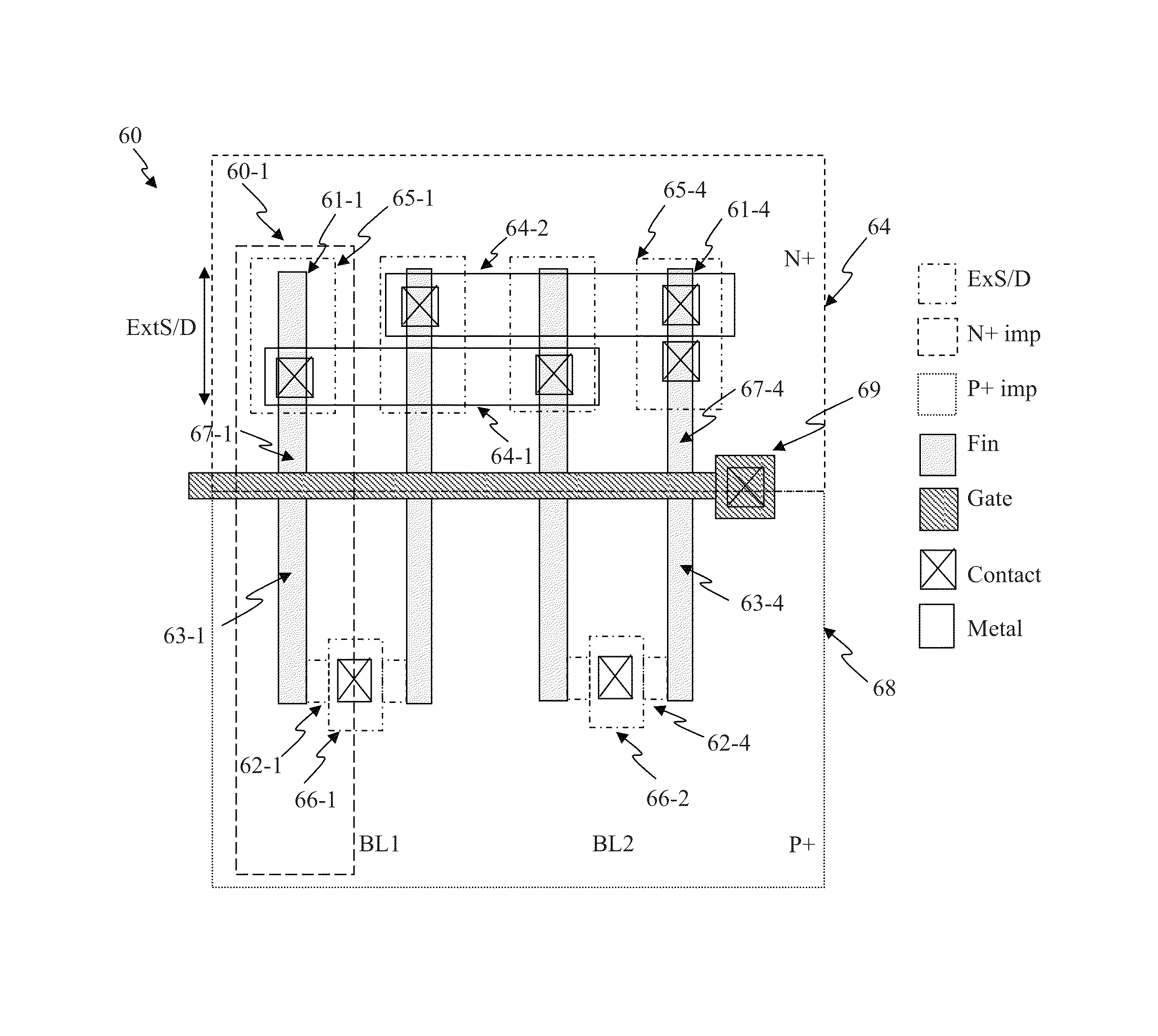
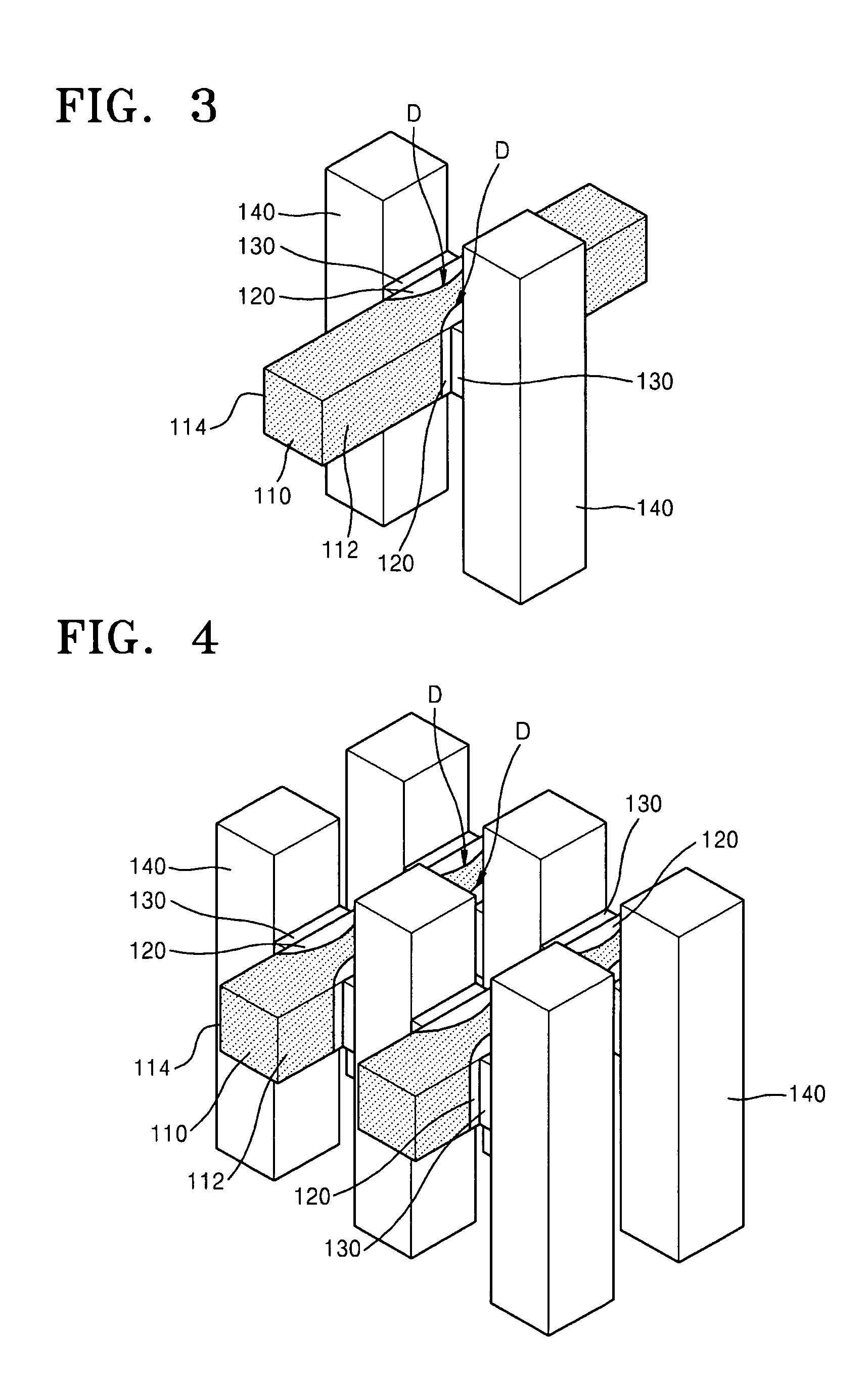
Circuit and system of using FinFET for building programmable resistive devices
Junction diodes or MOS devices fabricated in standard FinFET technologies can be used as program selectors or One-Time Programmable (OTP) element in a programmable resistive device, such as interconnect fuse, contact / via fuse, anti-fuse, or emerging nonvolatile memory such as MRAM, PCRAM, CBRAM, or RRAM. The MOS or diode can be built on at least one fin structure or at least one active region that has at least one first active region and a second active region. The first and the second active regions can be isolated by a dummy MOS gate or silicide block layer (SBL) to construct a diode.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
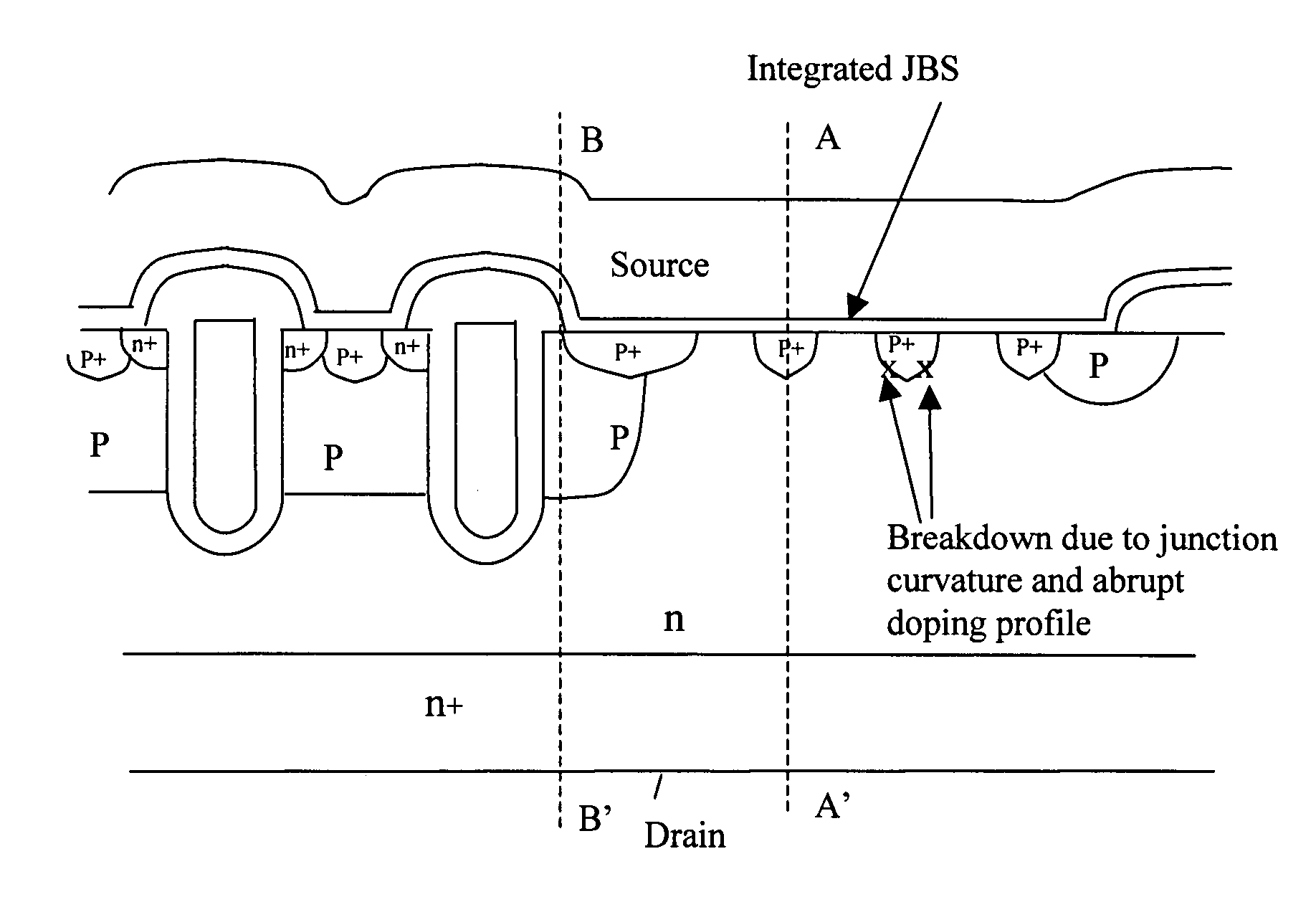
Planar SRFET using no additional masks and layout method
A semiconductor power device supported on a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type with a bottom layer functioning as a bottom electrode and an epitaxial layer overlying the bottom layer with a same conductivity type as the bottom layer. The semiconductor power device includes a plurality of FET cells and each cell further includes a body region of a second conductivity type extending from a top surface into the epitaxial layer. The body region encompasses a heavy body dopant region of second conductivity type. An insulated gate is disposed on the top surface of the epitaxial layer, overlapping a first portion of the body region. A barrier control layer is disposed on the top surface of the epitaxial layer next to the body region away from the insulated gate. A conductive layer overlies the top surface of the epitaxial layer covering a second portion of the body region and the heavy body dopant region extending over the barrier control layer forming a Schottky junction diode.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector and mos as read selector for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP cell can have a MOS in series with the OTP element as a read selector. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal-0, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector and MOS as read selector for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP cell can have a MOS in series with the OTP element as a read selector. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal-0, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
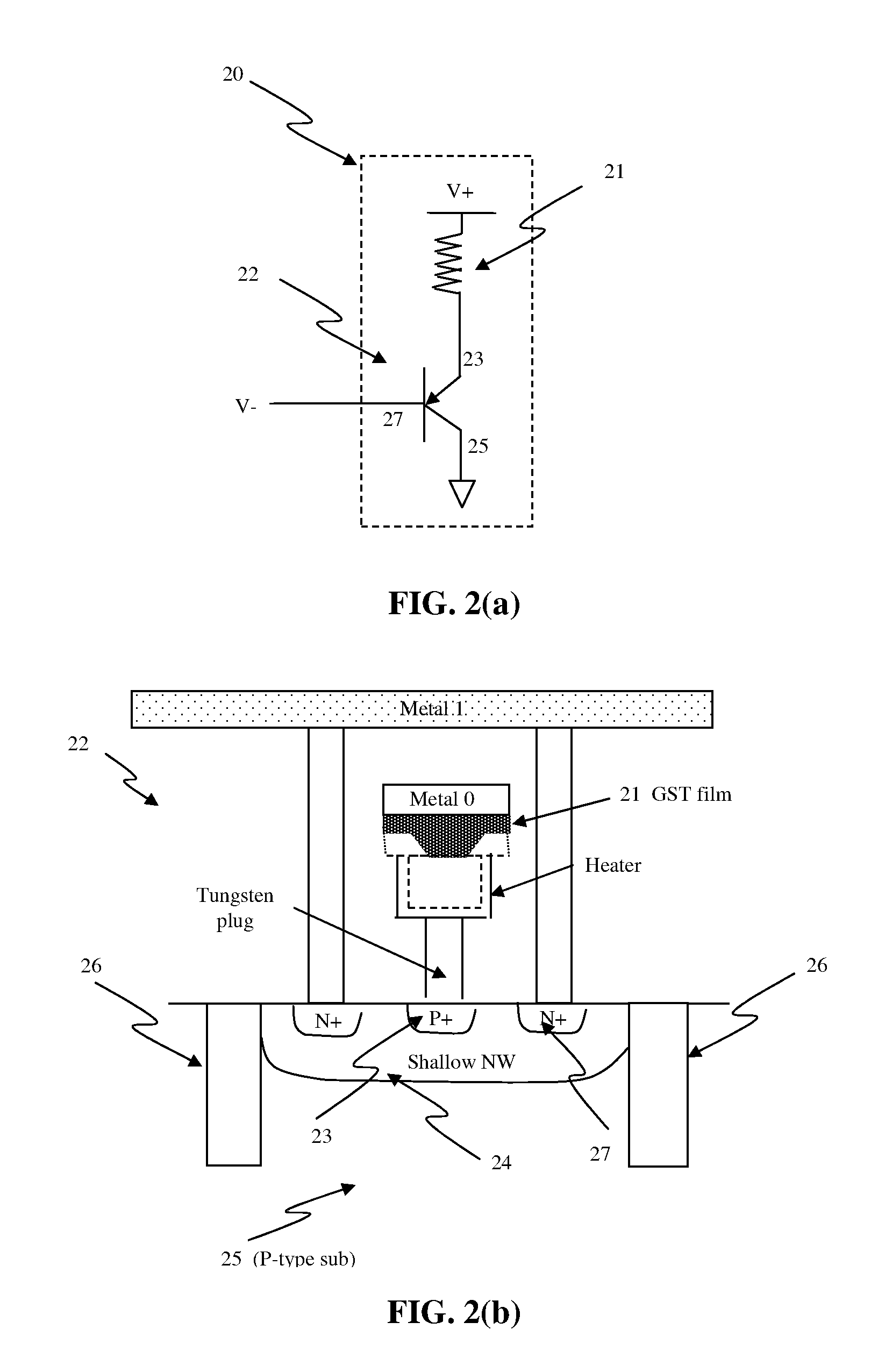
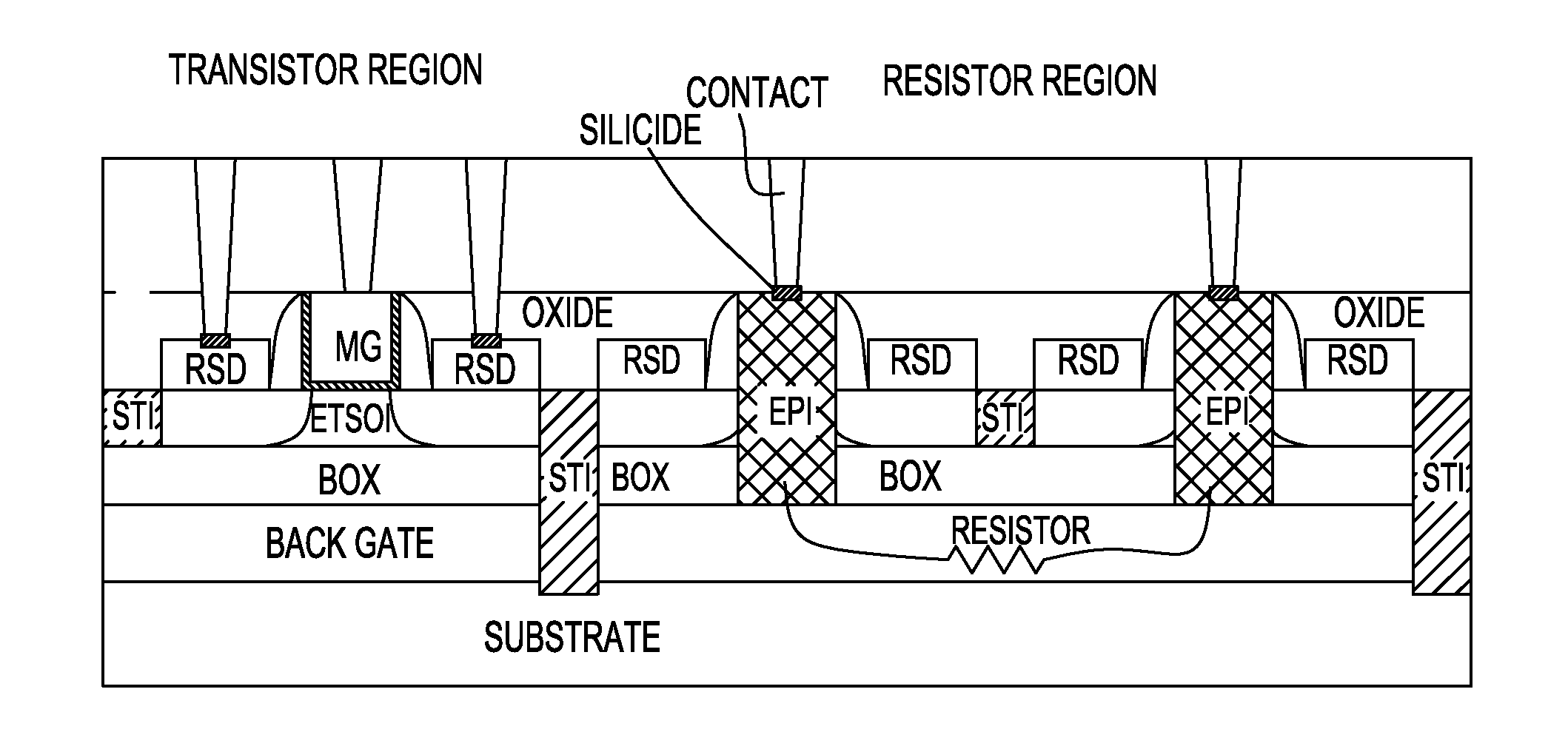
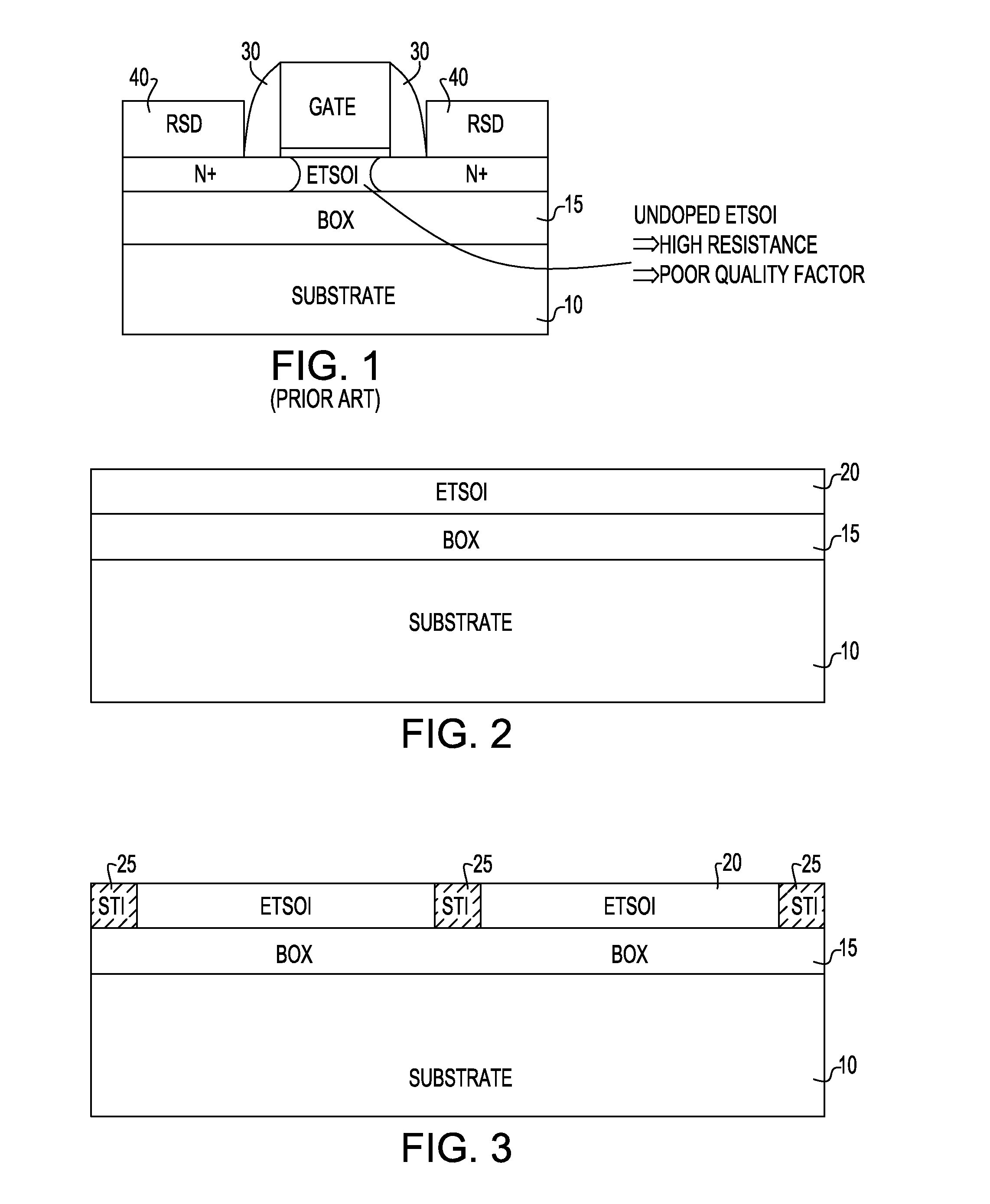
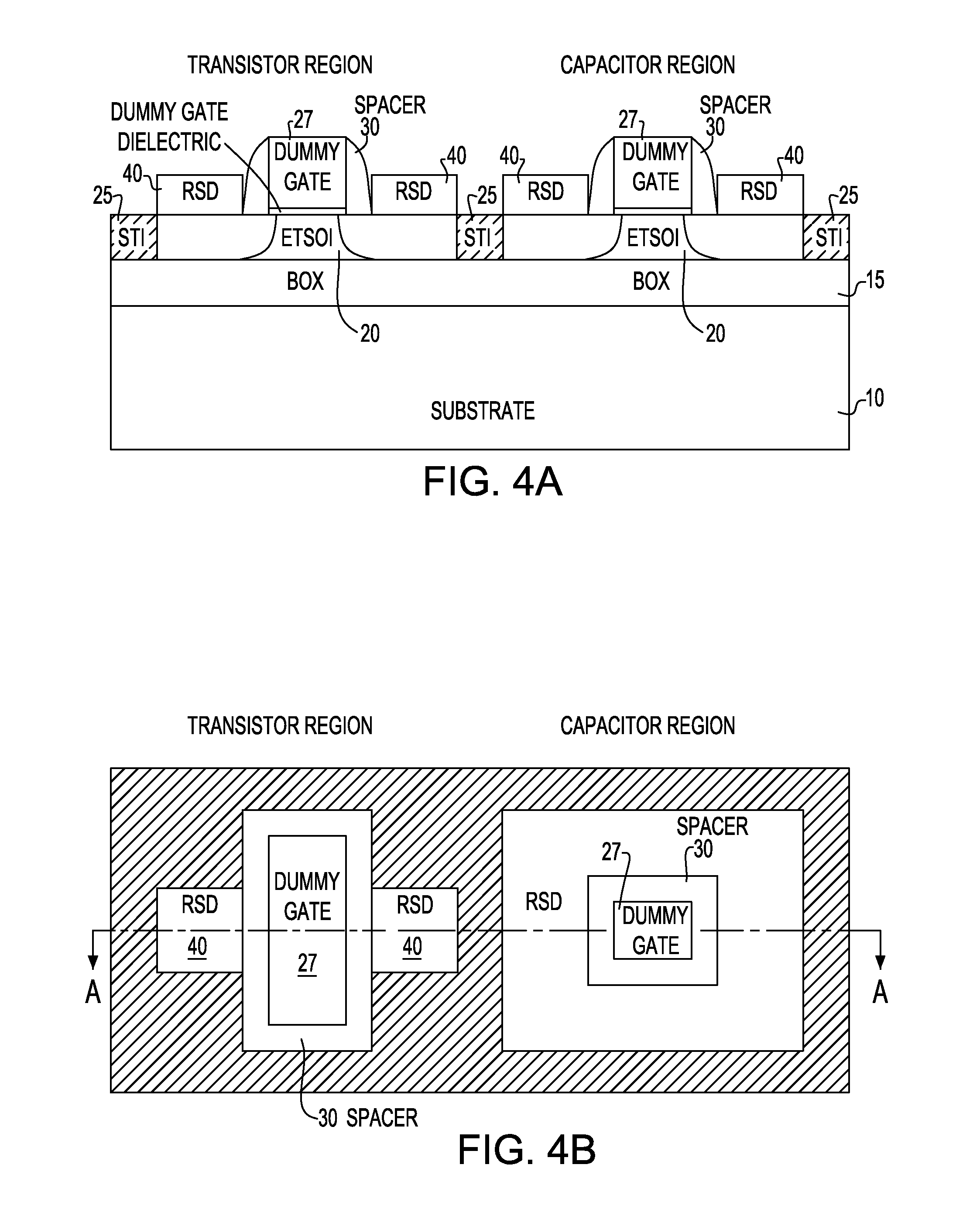
Method and Structure For Forming ETSOI Capacitors, Diodes, Resistors and Back Gate Contacts
An ETSOI transistor and a combination of capacitors, junction diodes, bank end contacts and resistors are respectively formed in a transistor and capacitor region thereof by etching through an ETSOI and BOX layers in a replacement gate HK / MG flow. The capacitor and other devices formation are compatible with an ETSOI replacement gate CMOS flow. A low resistance capacitor electrode makes it possible to obtain a high quality capacitor, and devices. The lack of topography during dummy gate patterning are achieved by lithography in combination accompanied with appropriate etch.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Ccircuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for metal fuses for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices. An OTP device can have at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. With a metal fuse is used by the OTP element, at least one contact and / or a plurality of vias can be built (possibly with use of one or more jumpers) in the program path to generate more Joule heat to assist with programming. The jumpers are conductive and can be formed of metal, metal gate, local interconnect, polymetal, etc. The metal fuse can also have an extended area that is longer than required by design rules for enhanced programmability. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
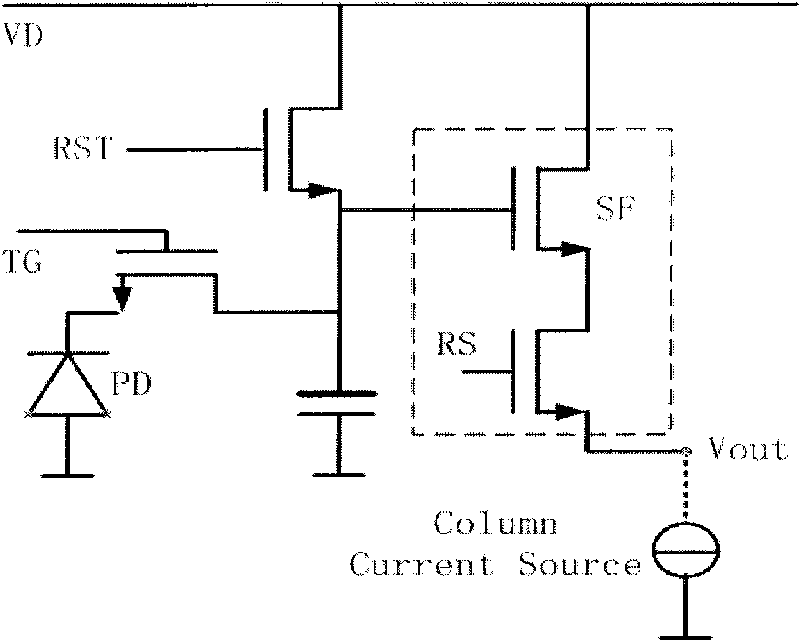
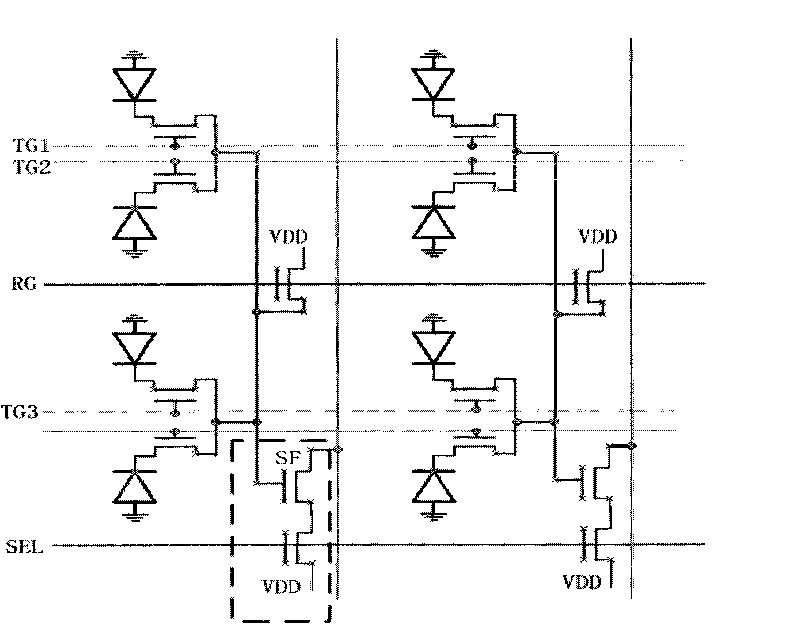
Semiconductor photosensitization device, production method and application thereof
ActiveCN101707202AReduce manufacturing costHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionPixel density
The invention discloses a semiconductor photosensitization device which comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode, a control grid, a floating grate region, a substrate, and a p-n node diode for connecting a floating gate region and a drain electrode. The floating grate region of the semiconductor photosensitization device is used for storing charges, and the floating grate potential of the semiconductor photosensitization device is related to light exposure intensity and time, thus, the invention can be used as a semiconductor photosensitization device. The invention also discloses production methods of the semiconductor photosensitization device and an image sensor, as well as an image sensor formed by arrays formed by the semiconductor photosensitization device. The semiconductor photosensitization device can simplify the design of a single pixel unit in a traditional image sensor and reduce the area occupied by the single pixel unit, thereby improving the pixel density of the image sensor, increasing the resolution of the image sensor and reducing the production cost of the image sensor.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7910909B2Highly integratedInexpensive to fabricateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
Provided are a non-volatile memory device that may be configured in a stacked structure and may be more easily highly integrated, and a method of fabricating the non-volatile memory device. At least one first electrode and at least one second electrode are provided. The at least one second electrode may cross the at least one first electrode. At least one data storage layer may be at an intersection between the at least one first electrode and the at least one second electrode. Any one of the at least one first electrode and the at least one second electrode may include at least one junction diode connected to the at least one data storage layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
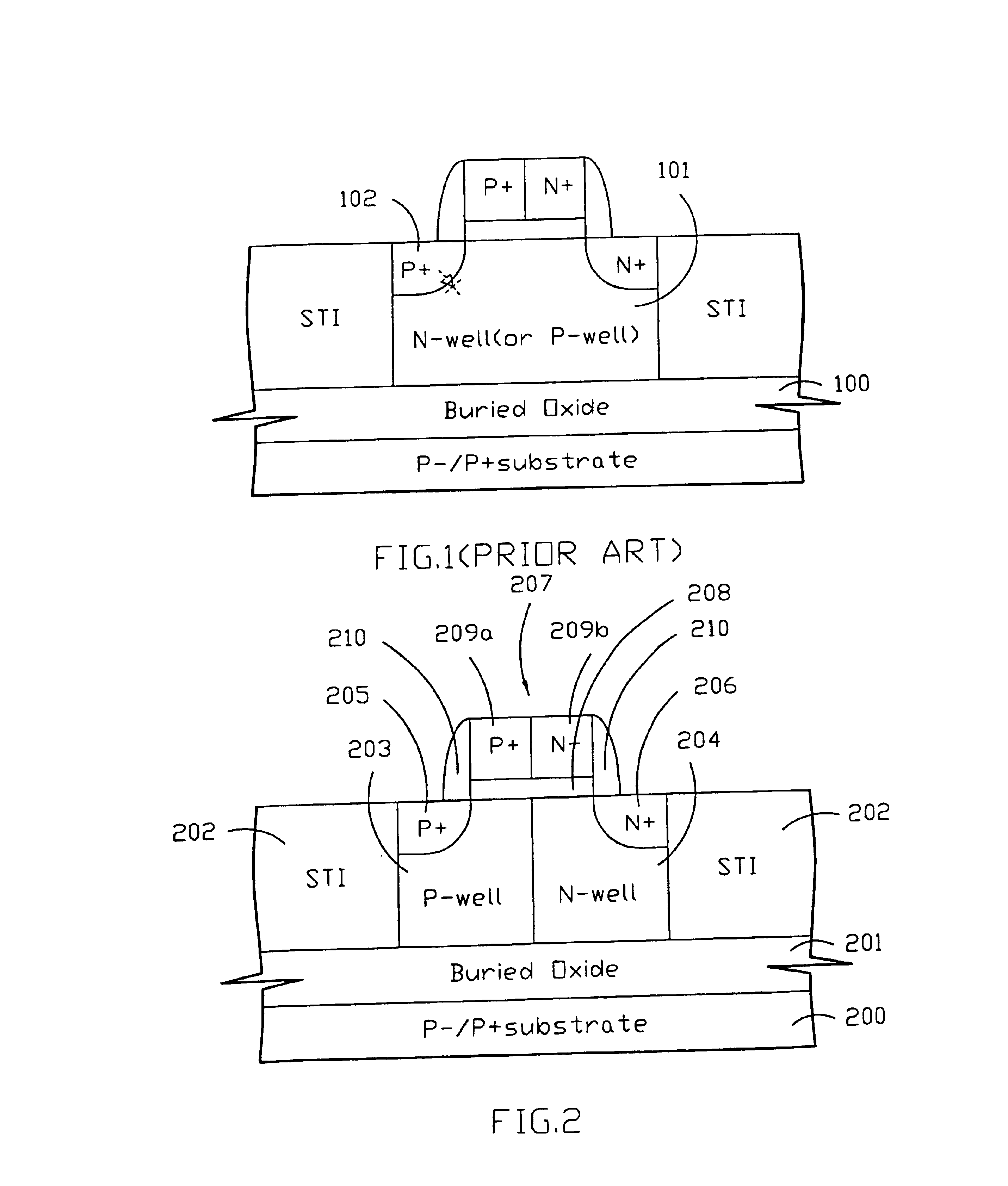
Silicon-on-insulator diodes and ESD protection circuits
InactiveUS6861680B2Reduce power densityHigh protection levelTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceSilicon on insulator
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) gated diode and non-gated junction diode are provided. The SOI gated diode has a PN junction at the middle region under the gate, which has more junction area than a normal diode. The SOI non-gated junction diode has a PN junction at the middle region thereof, and also has more junction area than a normal diode. The SOI diodes of the present invention improve the protection level offered for electrical overstress (EOS) / electrostatic discharge (ESD) due to the low power density and heating for providing more junction area than normal ones. The I / O ESD protection circuits, which comprise primary diodes, a first plurality of diodes, and a second plurality of diodes, all of which are formed of the present SOI diodes, could effectively discharge the current when there is an ESD event. And the ESD protection circuits, which comprise more primary diodes, could effectively reduce the parasitic input capacitance, so that they can be used in the RF circuits or HF circuits. The proposed gated diode and non-gated diode can be fully process-compatiable to general partially-depleted or fully-depleted silicon-on-insulator CMOS processes.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
One-time programmable devices using junction diode as program selector for electrical fuses with extended area
ActiveUS20150003143A1Small cell sizeLow costMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCMOSOne time programmable
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuses. At least one portion of the electrical fuse can have at least one extended area to accelerate programming. An extended area is an extension of the fuse element beyond contact or via longer than required by design rules. The extended area also has reduced or substantially no current flowing through. The program selector can be at least one MOS. The OTP device can have the at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com