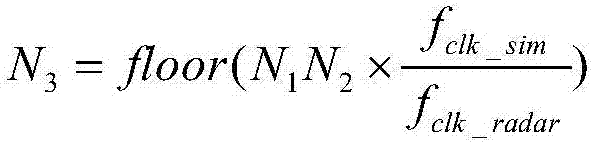Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Nominal frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nominal Frequency. The desired center frequency of a crystal or oscillator. The midpoint in the pass band, or the arithmetic mean between high and low cut off frequencies of the filter.
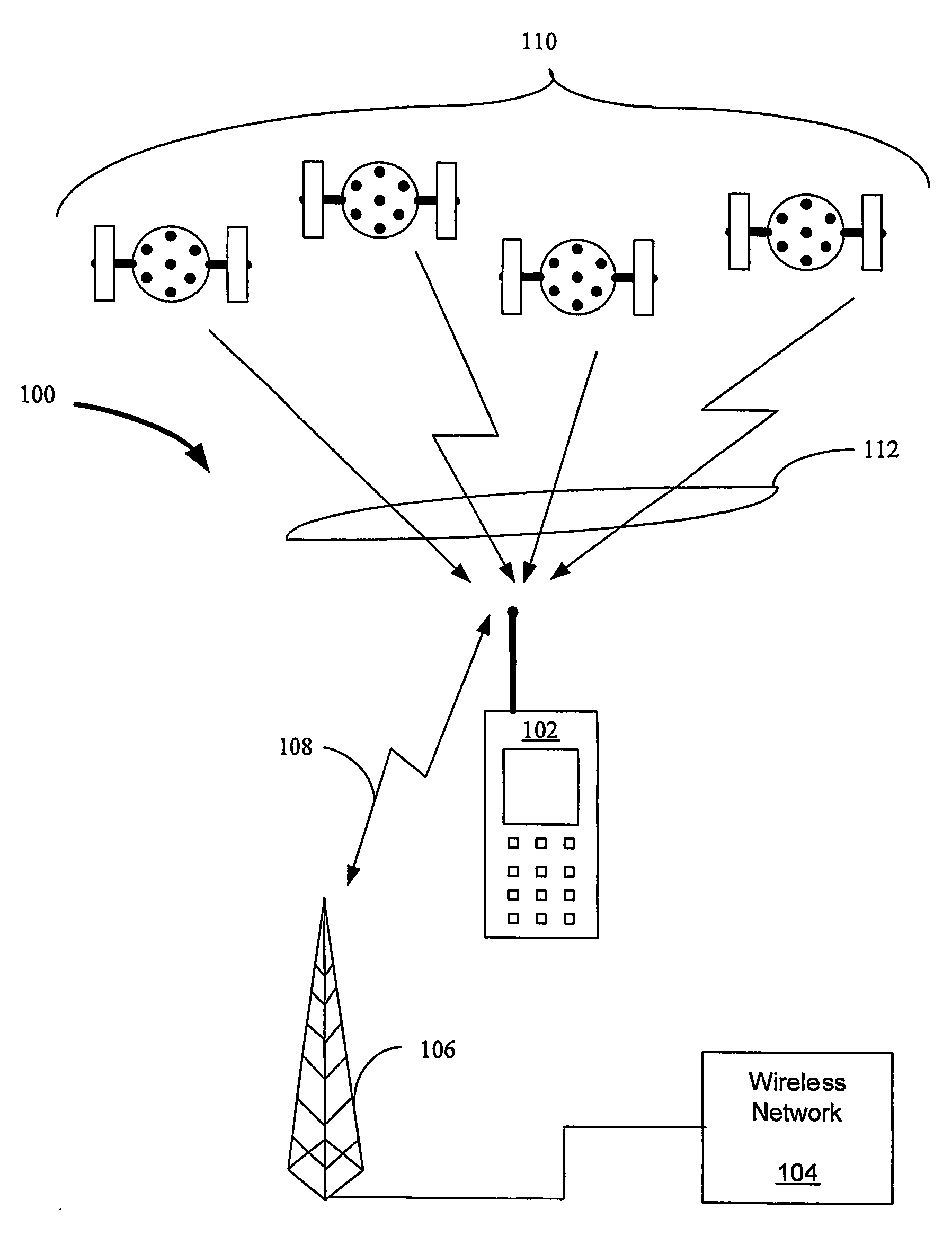
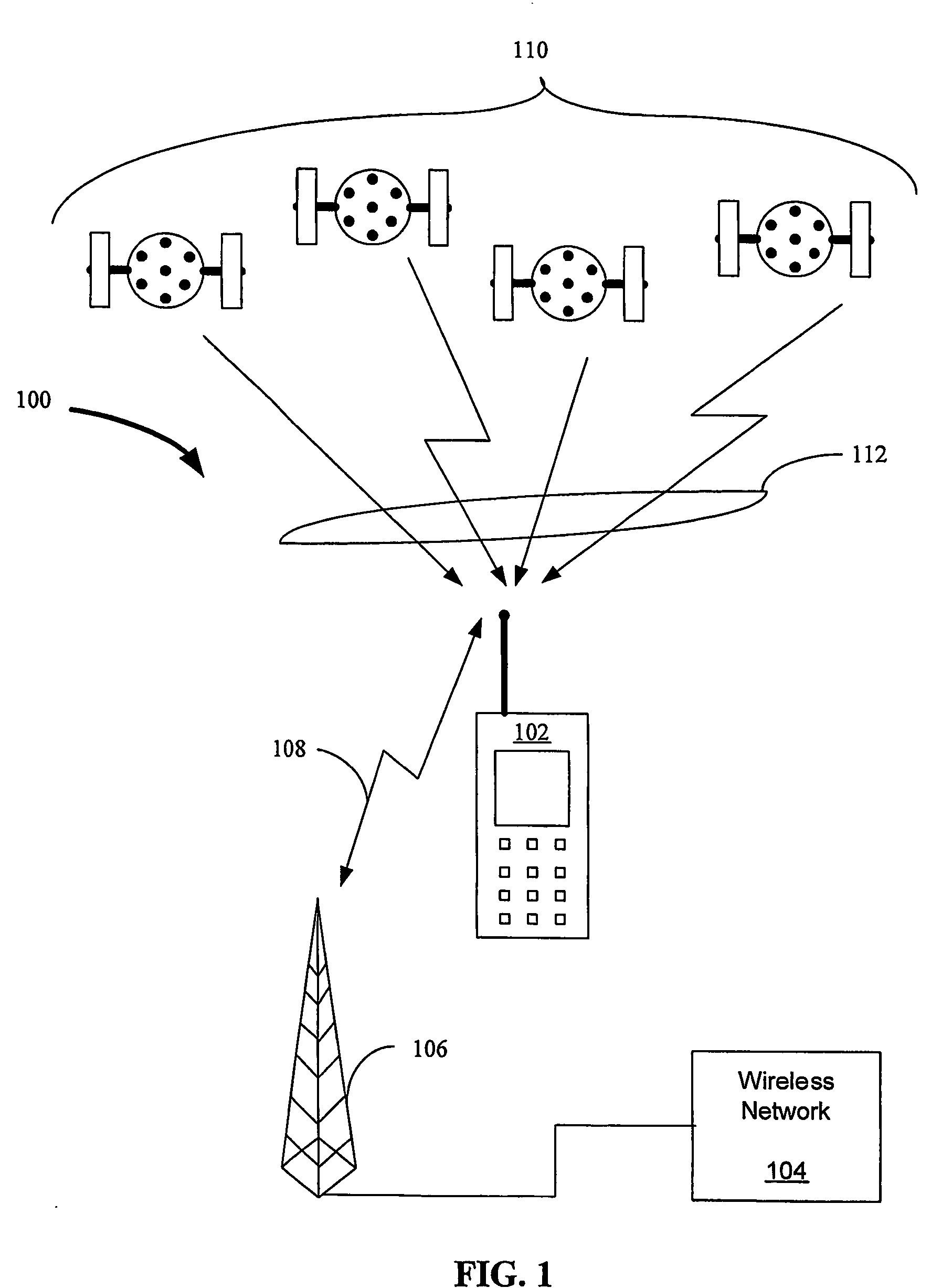
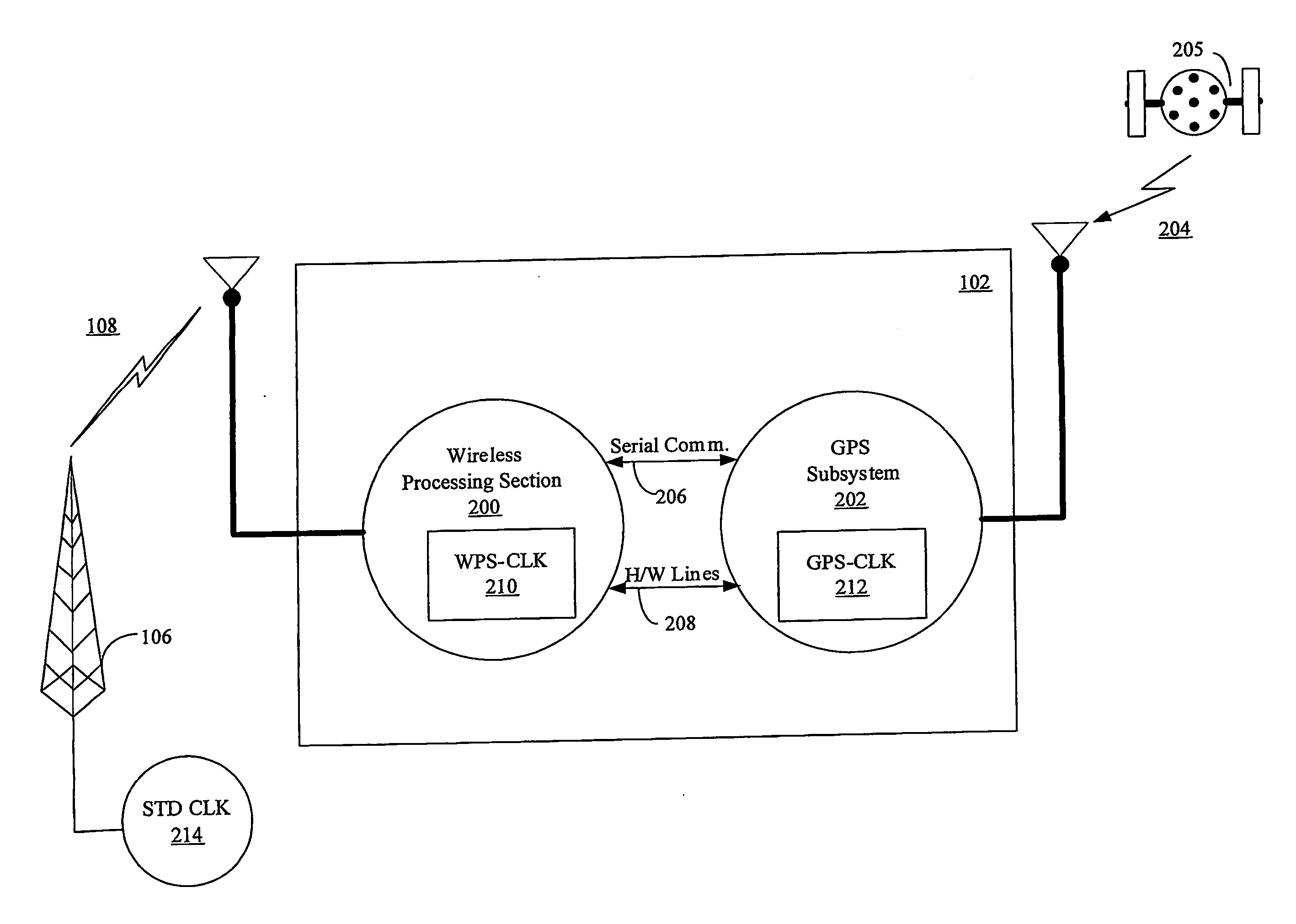
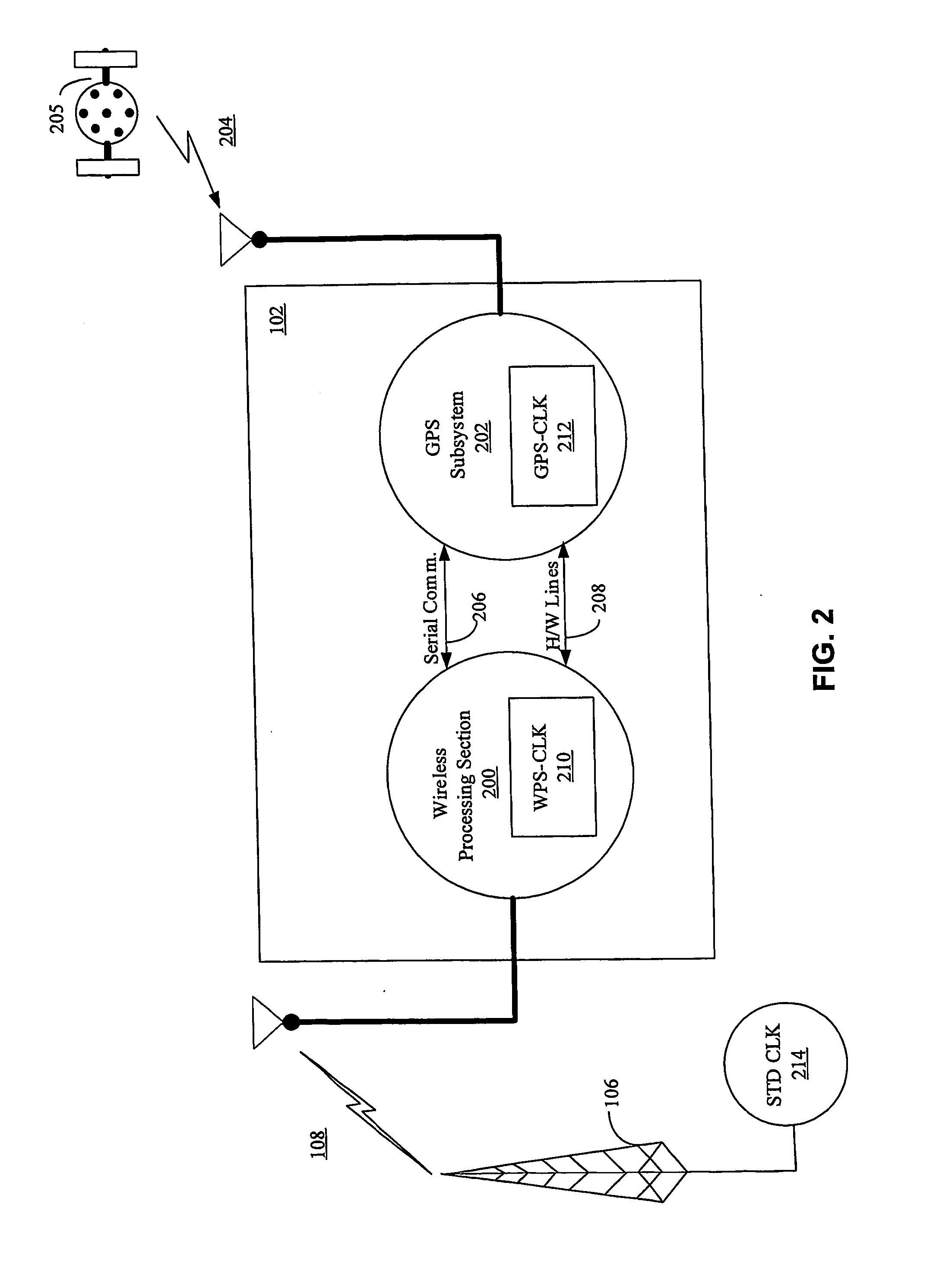
Aiding in a satellite positioning system
InactiveUS7236883B2Broadcast transmission systemsPosition fixationWireless mesh networkNetwork clock
The invention relates to an aided Global Positioning System (GPS) subsystem within a wireless device. The wireless device includes a wireless processing section capable of receiving signals from a wireless network and a GPS subsystem having a radio frequency (RF) front-end capable of receiving a GPS satellite signal. The wireless processing section of the wireless device receives an external clock and determines the offset between the clock in the wireless processing section and that of the external clock. The GPS subsystem then receives the offset information from the wireless processing section, information related to the nominal frequency of the wireless processing section clock and the wireless processing section clock. Using this information and the GPS clock in the GPS subsystem, the GPS subsystem determines an acquiring signal, which is related to a frequency offset between the GPS clock and the network clock. The GPS subsystem then acquires GPS satellite signals in an acquiring unit though the use of the acquiring signal.
Owner:CSR PLC
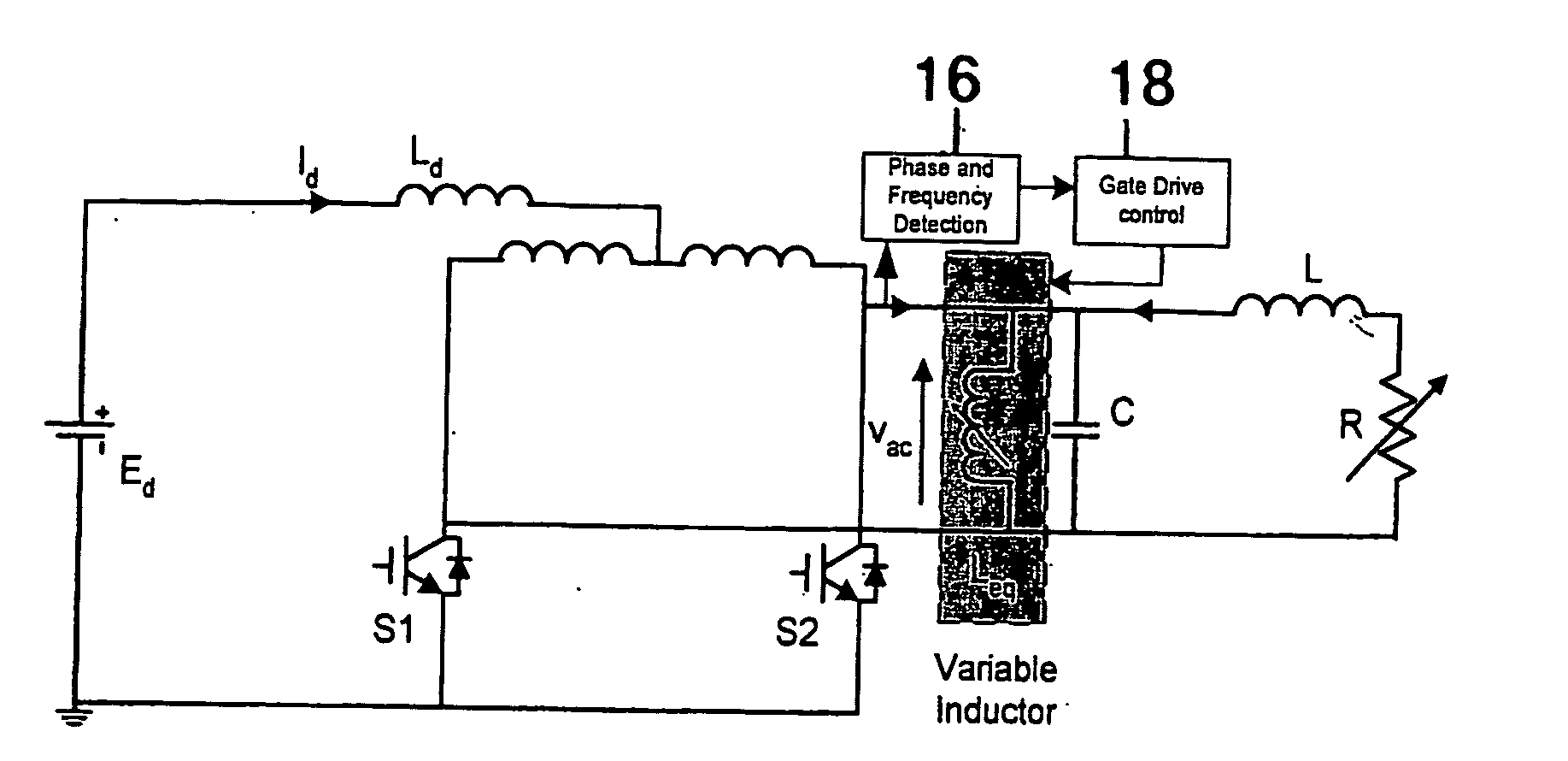
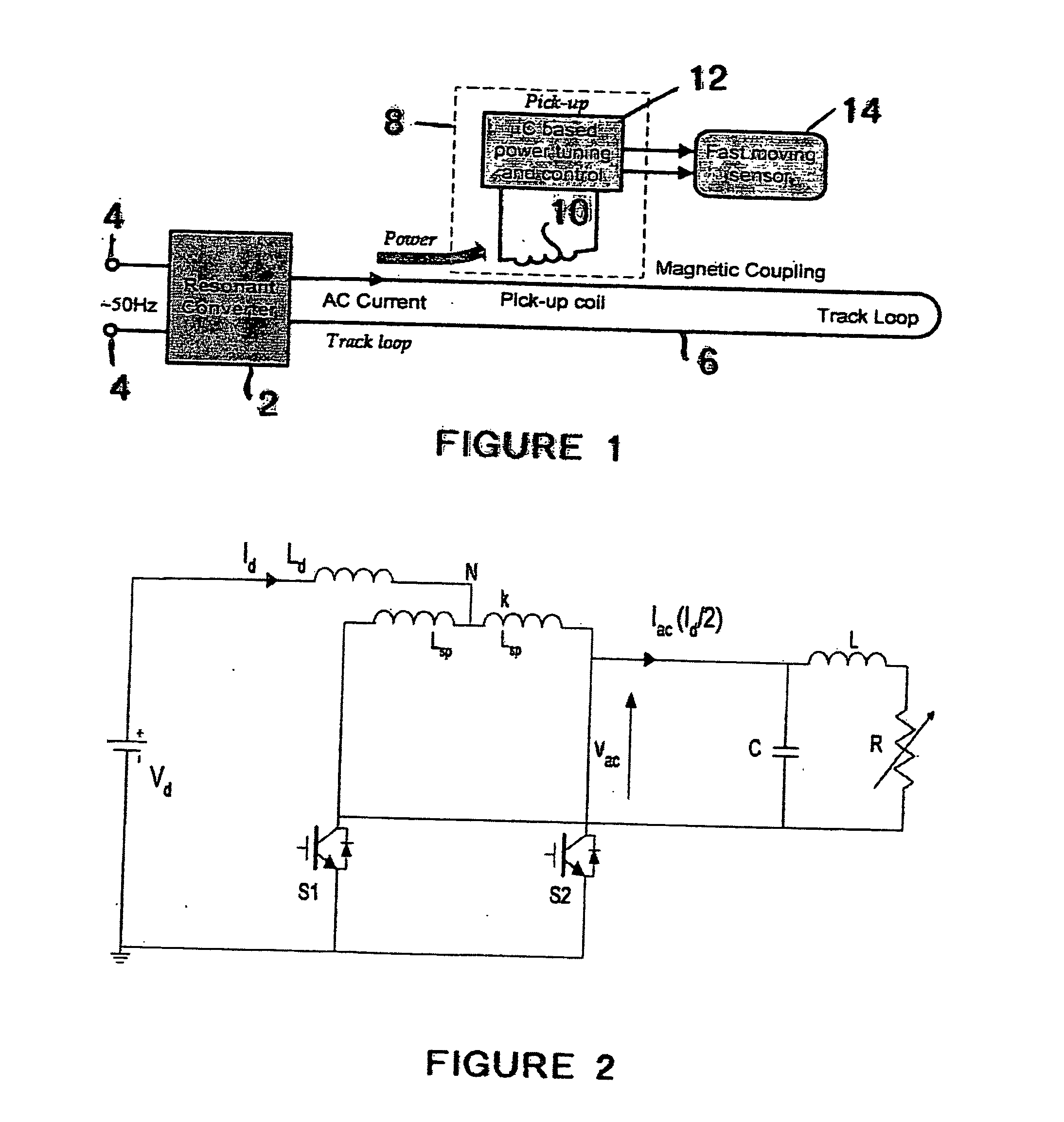
Frequency Controller Resonant Converter
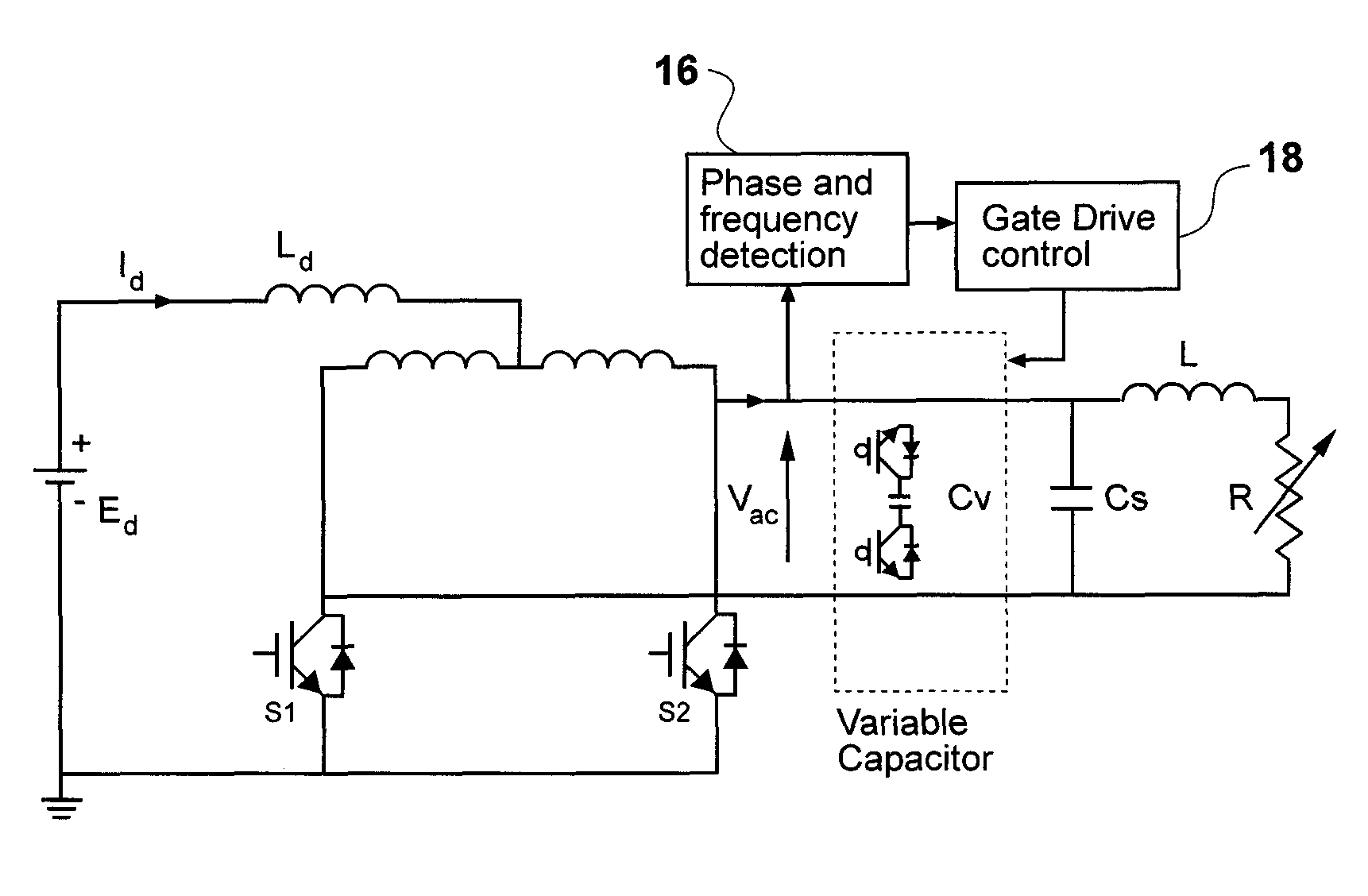
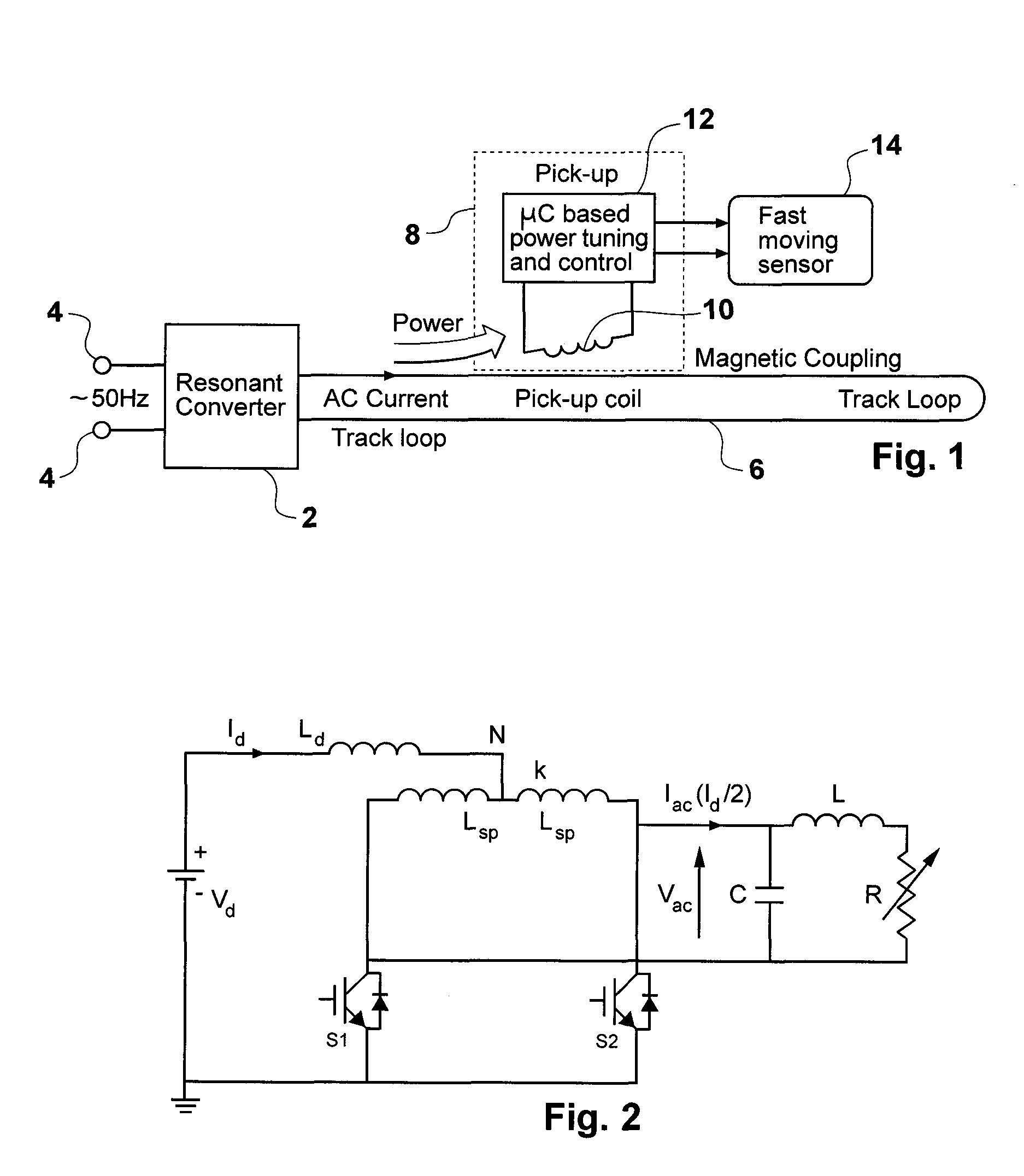
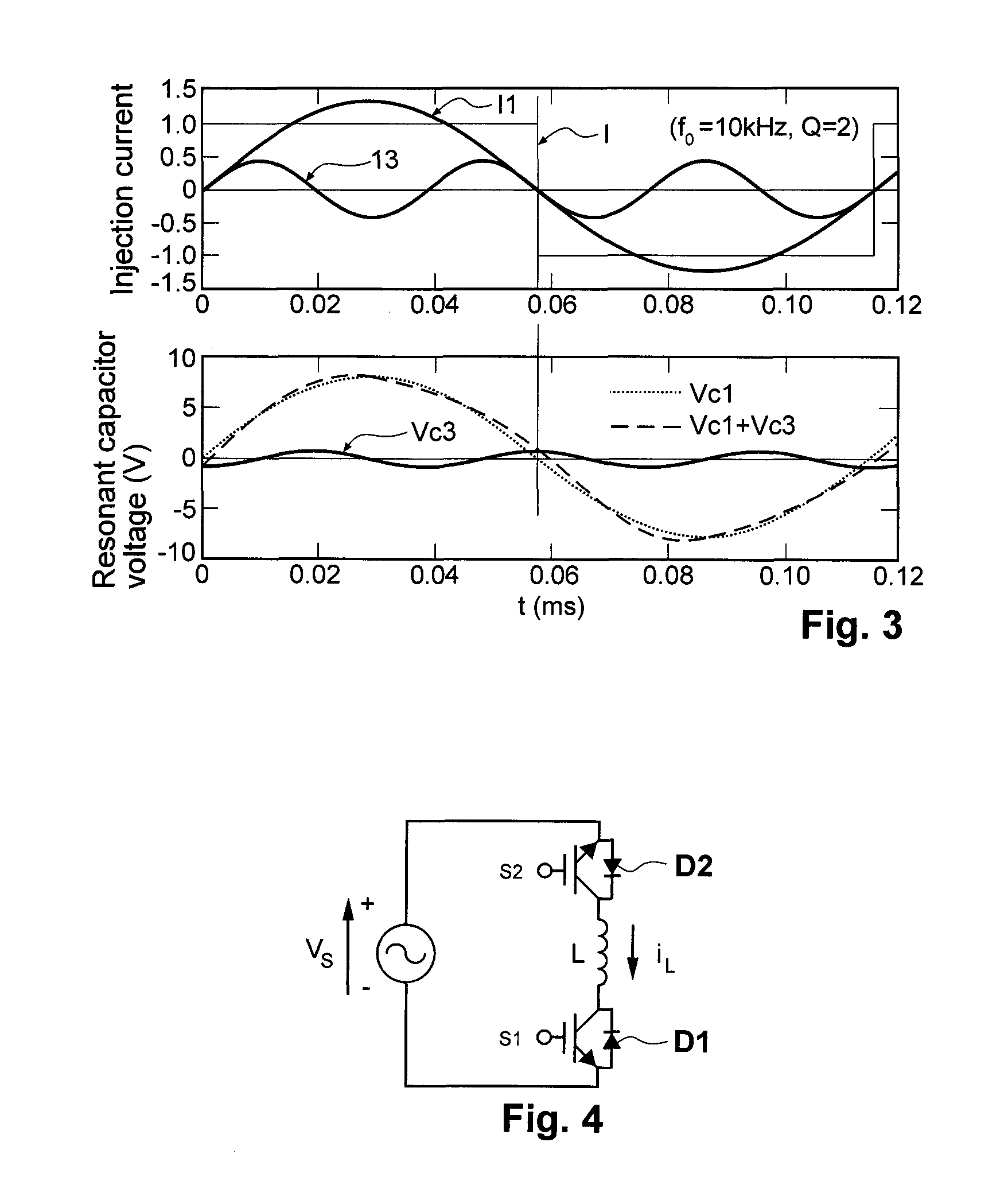
ActiveUS20080211478A1Overcome disadvantagesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectricityCapacitance
A resonant converter is provided which may be used for supplying power to the primary conductive path of an inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) system. The converter includes a variable reactive element in the resonant circuit which may be controlled to vary the effective inductance or capacitance of the reactive element. The frequency of the converter is stabilised to a nominal value by sensing the frequency of the converter resonant circuit, comparing the sensed frequency with a nominal frequency and varying the effective inductance or capacitance of the variable reactive element to adjust the converter frequency toward the nominal frequency.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
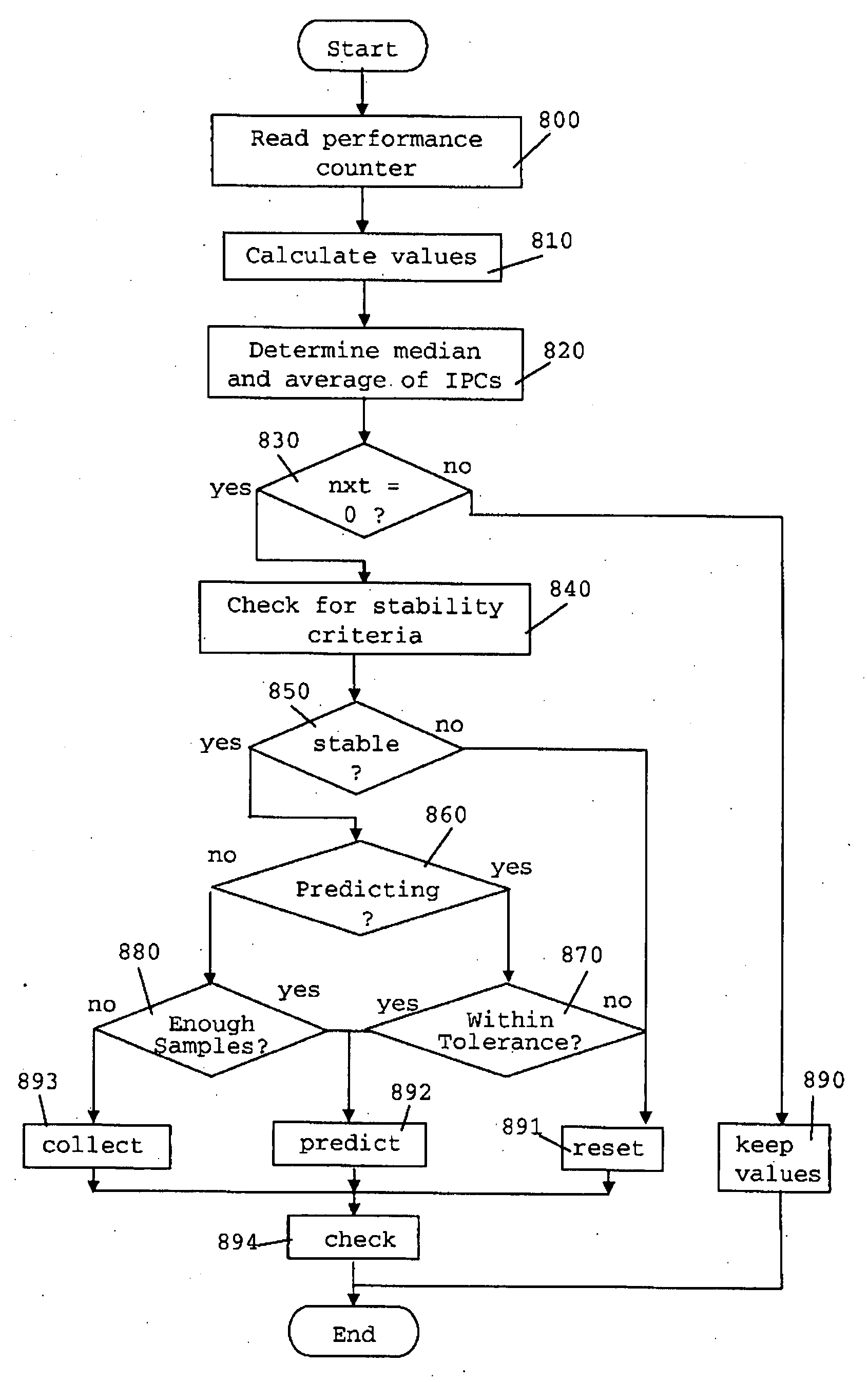
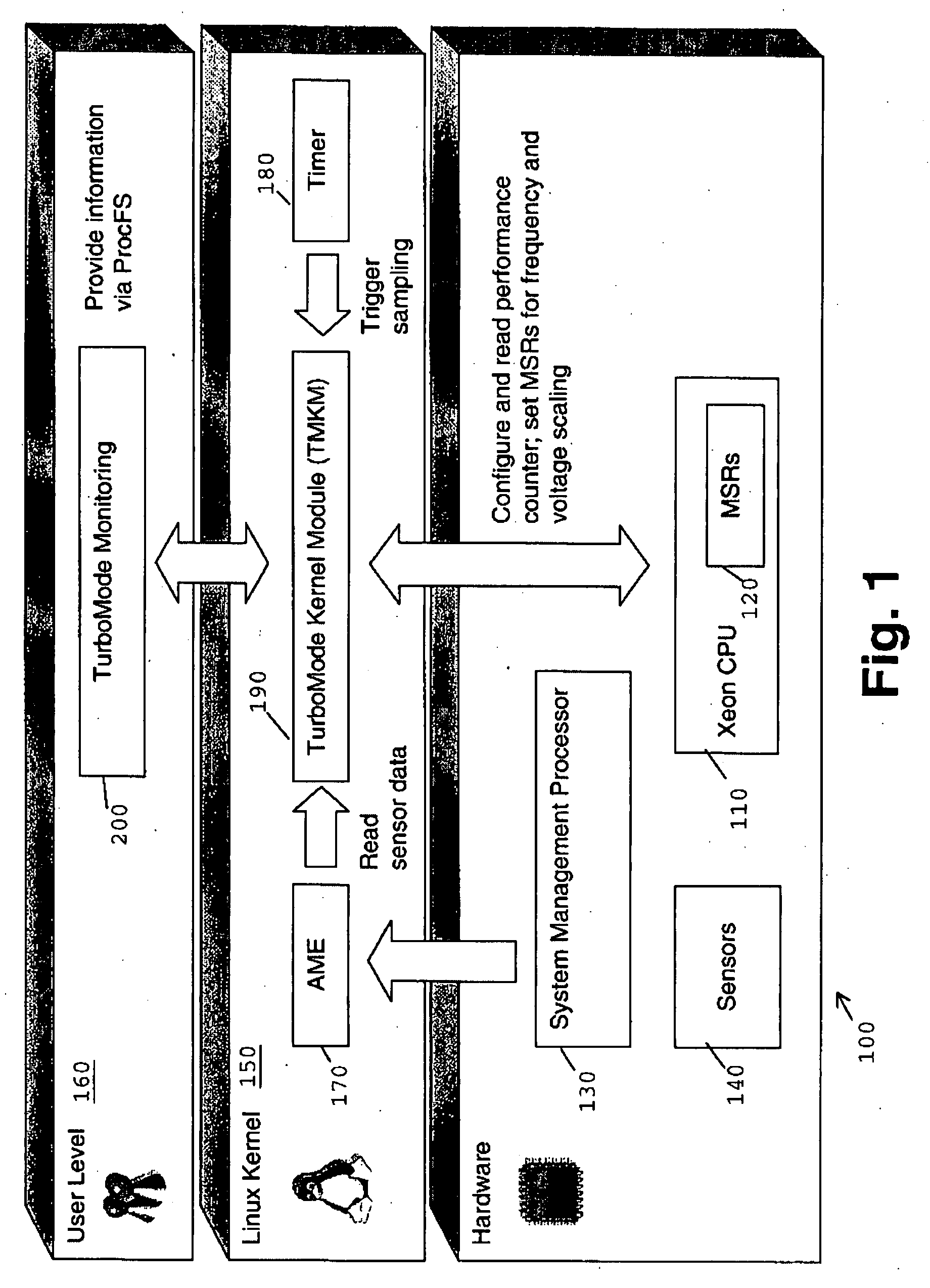
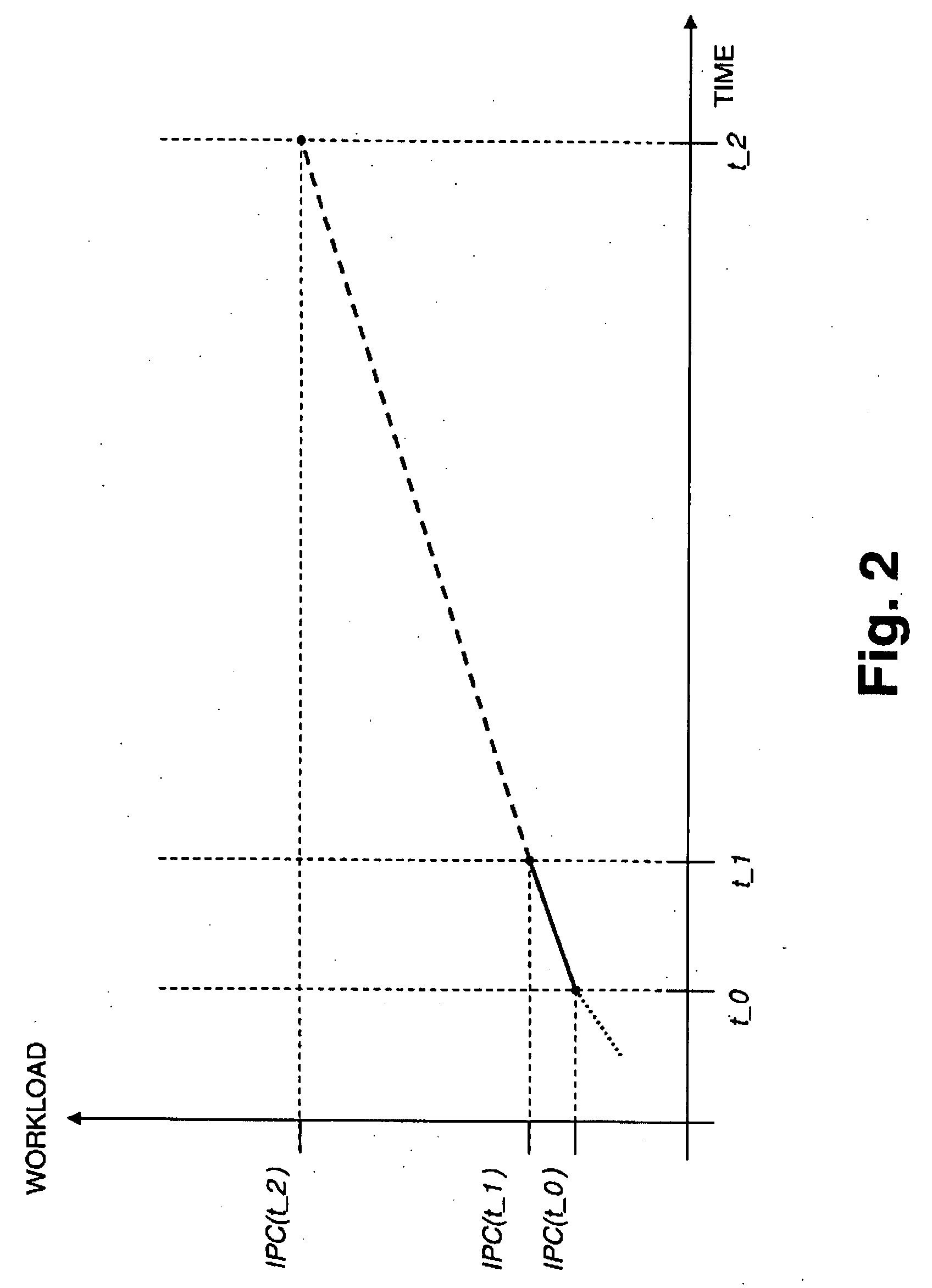
Method for Autonomous Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling of Microprocessors
ActiveUS20080098254A1Improve performanceSave energyEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:IBM CORP
Variable reactive element in a resonant converter circuit
ActiveUS8050068B2Overcome disadvantagesEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceFrequency stabilization
A resonant converter is provided which may be used for supplying power to the primary conductive path of an inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) system. The converter includes a variable reactive element in the resonant circuit which may be controlled to vary the effective inductance or capacitance of the reactive element. The frequency of the converter is stabilised to a nominal value by sensing the frequency of the converter resonant circuit, comparing the sensed frequency with a nominal frequency and varying the effective inductance or capacitance of the variable reactive element to adjust the converter frequency toward the nominal frequency.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
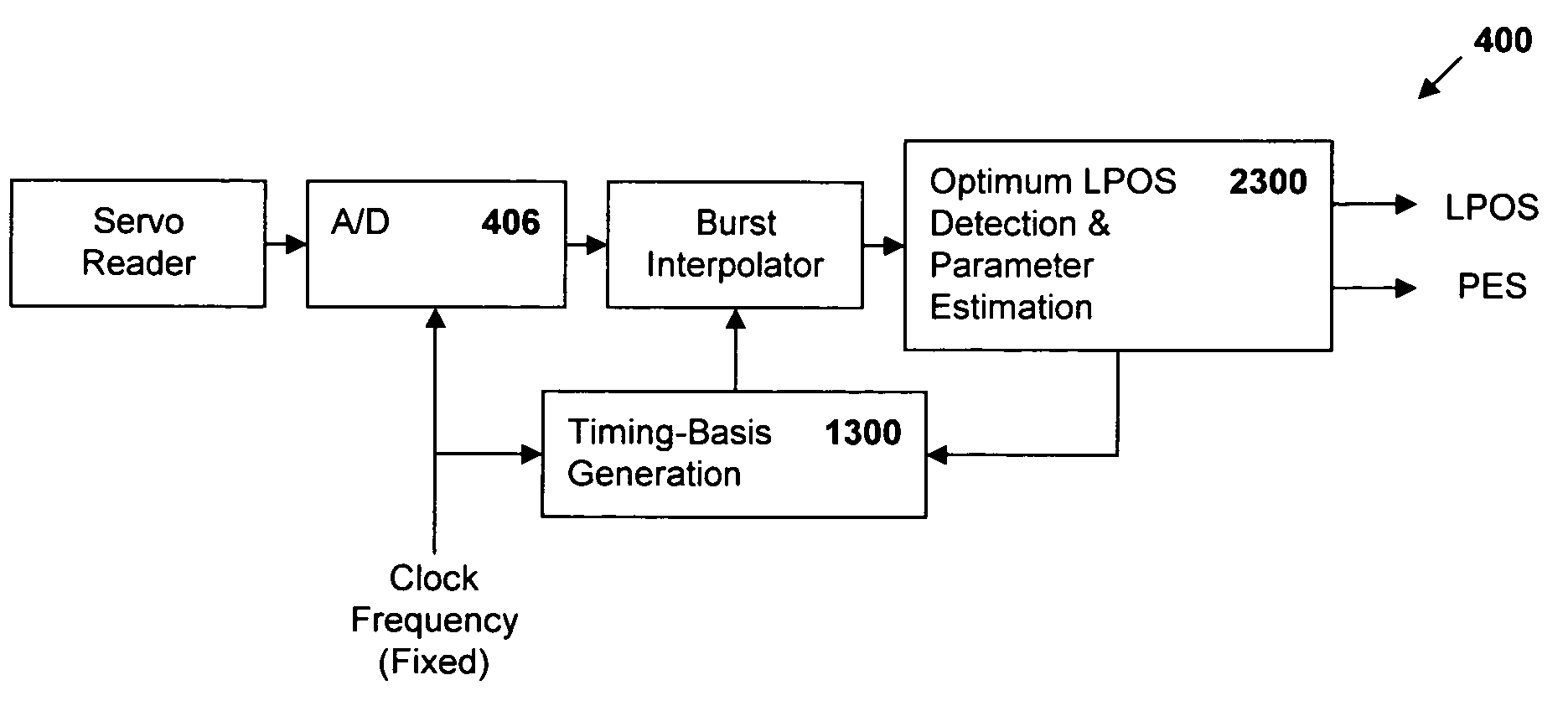
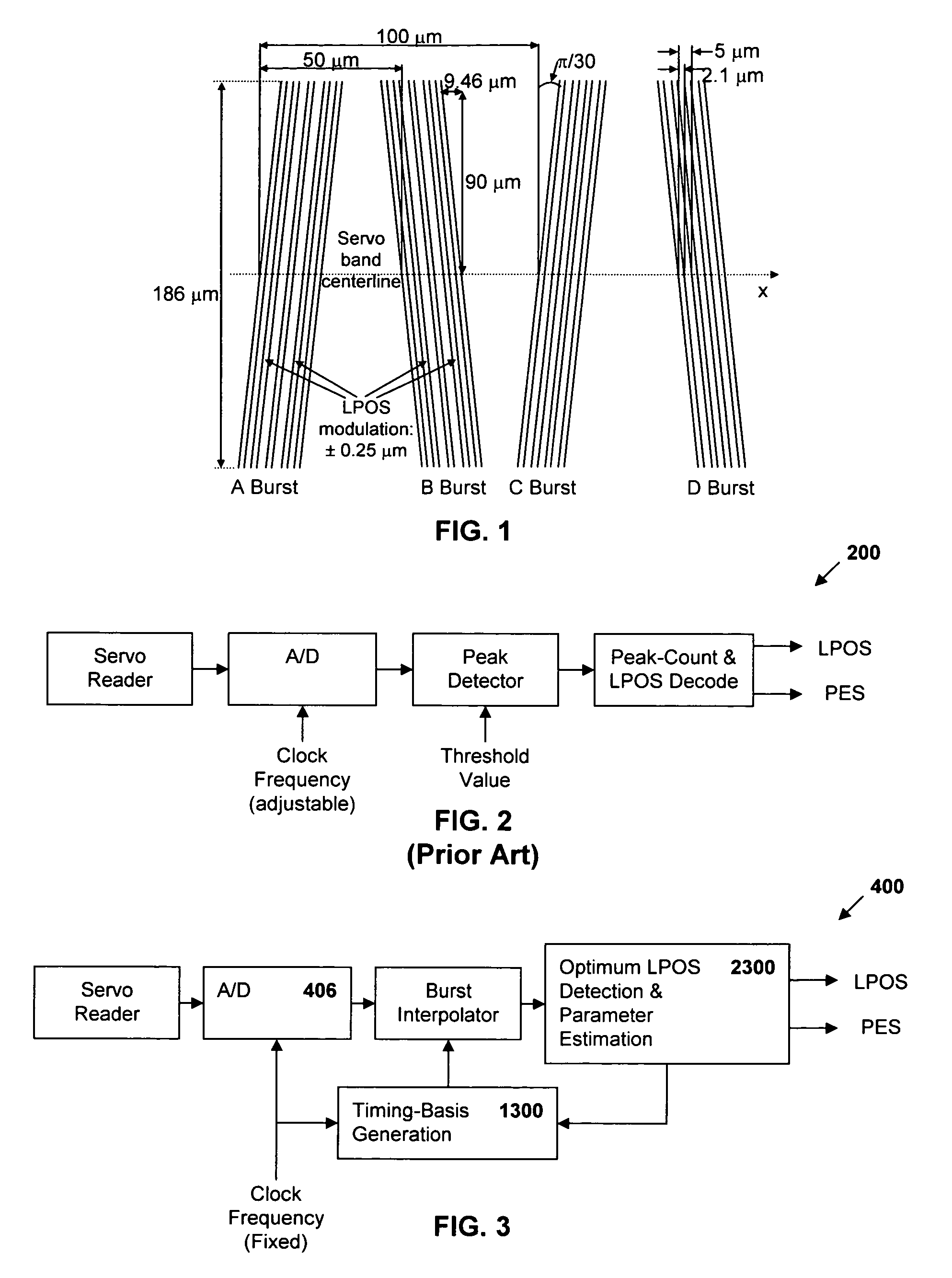
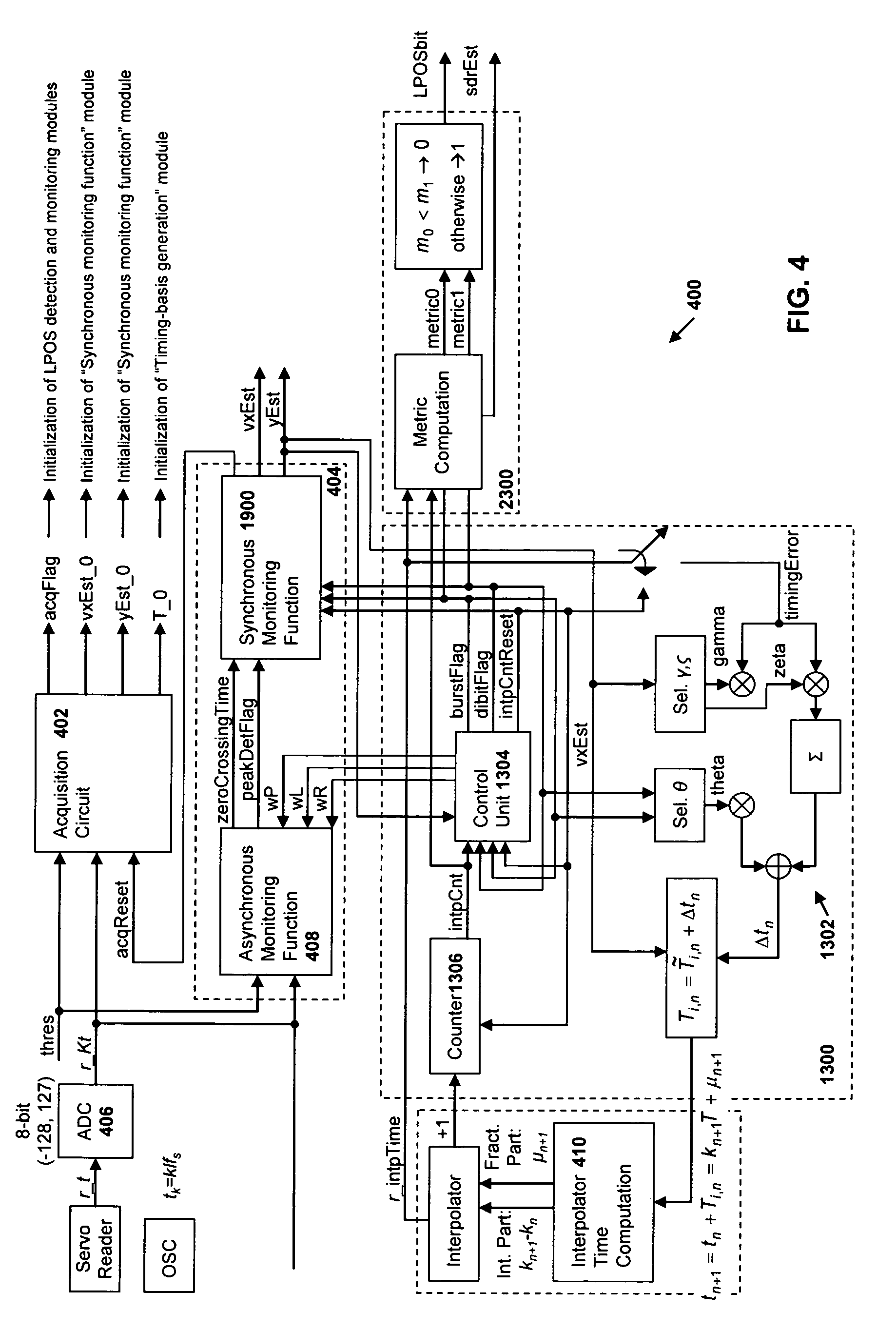
Synchronous servo channel for longitudinal position detection and position error signal generation in tape drive systems
InactiveUS7245450B1Improve reliabilityFilamentary/web record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesTape speedUnit of length
A fully synchronous longitudinal position (LPOS) detection system is provided for improving the reliability of servo channels in tape systems. The system is based on the interpolation of the servo channel output signal, which is sampled by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) at a fixed sampling rate, using a clock at a nominal frequency, so that interpolated signal samples are obtained at a predetermined fixed rate, independent of tape velocity. This predetermined fixed rate is defined in terms of samples per unit of length, as opposed to samples per unit of time, which is the measure of the ADC sampling rate. The resolution with which the servo channel signal is obtained at the interpolator output is thus determined by the step interpolation distance.
Owner:IBM CORP
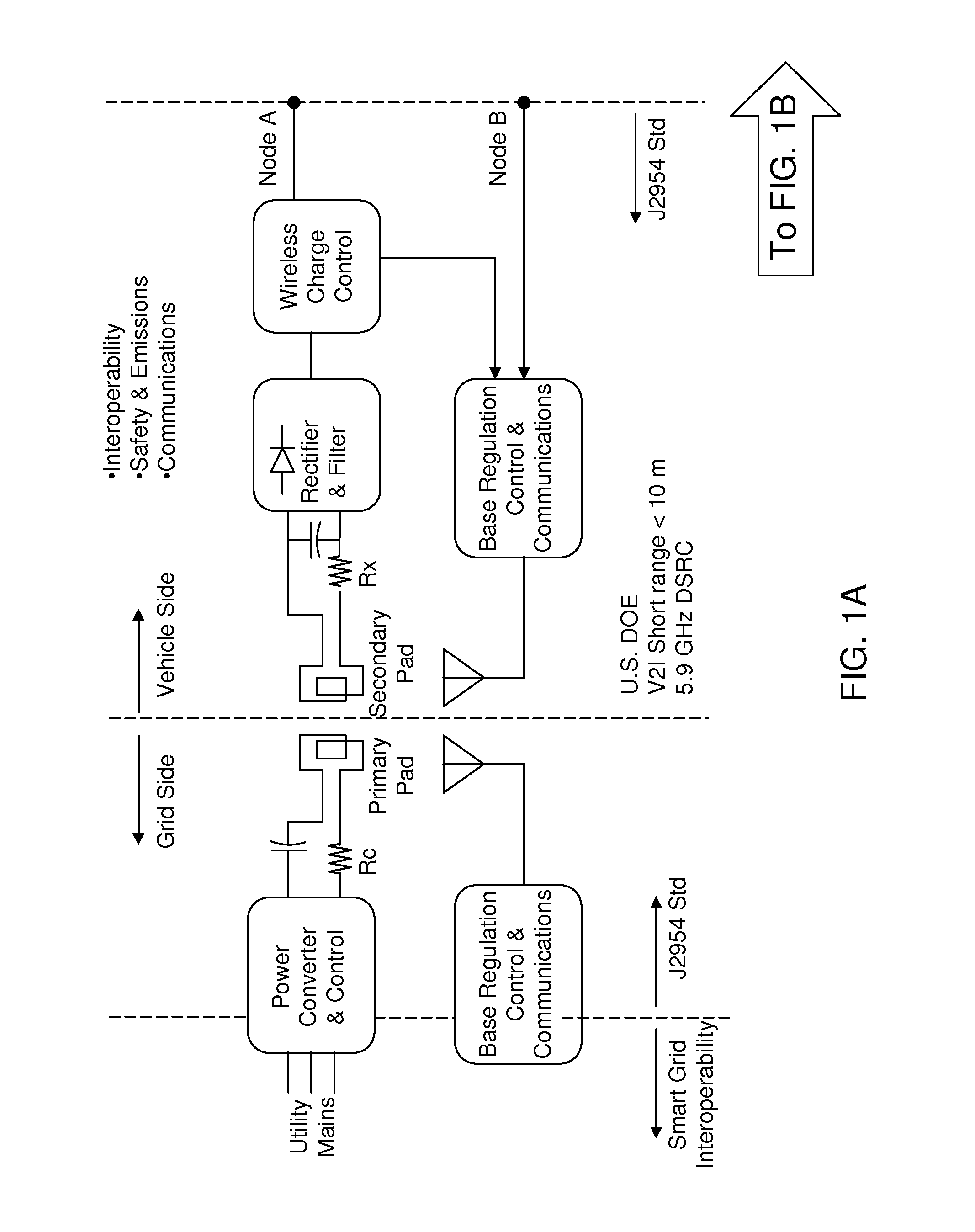
Regulation control and energy management scheme for wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20130020862A1Maximize power transfer efficiencyOptimal duty ratioBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionResonance
Power transfer rate at a charging facility can be maximized by employing a feedback scheme. The state of charge (SOC) and temperature of the regenerative energy storage system (RESS) pack of a vehicle is monitored to determine the load due to the RESS pack. An optimal frequency that cancels the imaginary component of the input impedance for the output signal from a grid converter is calculated from the load of the RESS pack, and a frequency offset f* is made to the nominal frequency f0 of the grid converter output based on the resonance frequency of a magnetically coupled circuit. The optimal frequency can maximize the efficiency of the power transfer. Further, an optimal grid converter duty ratio d* can be derived from the charge rate of the RESS pack. The grid converter duty ratio d* regulates wireless power transfer (WPT) power level.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
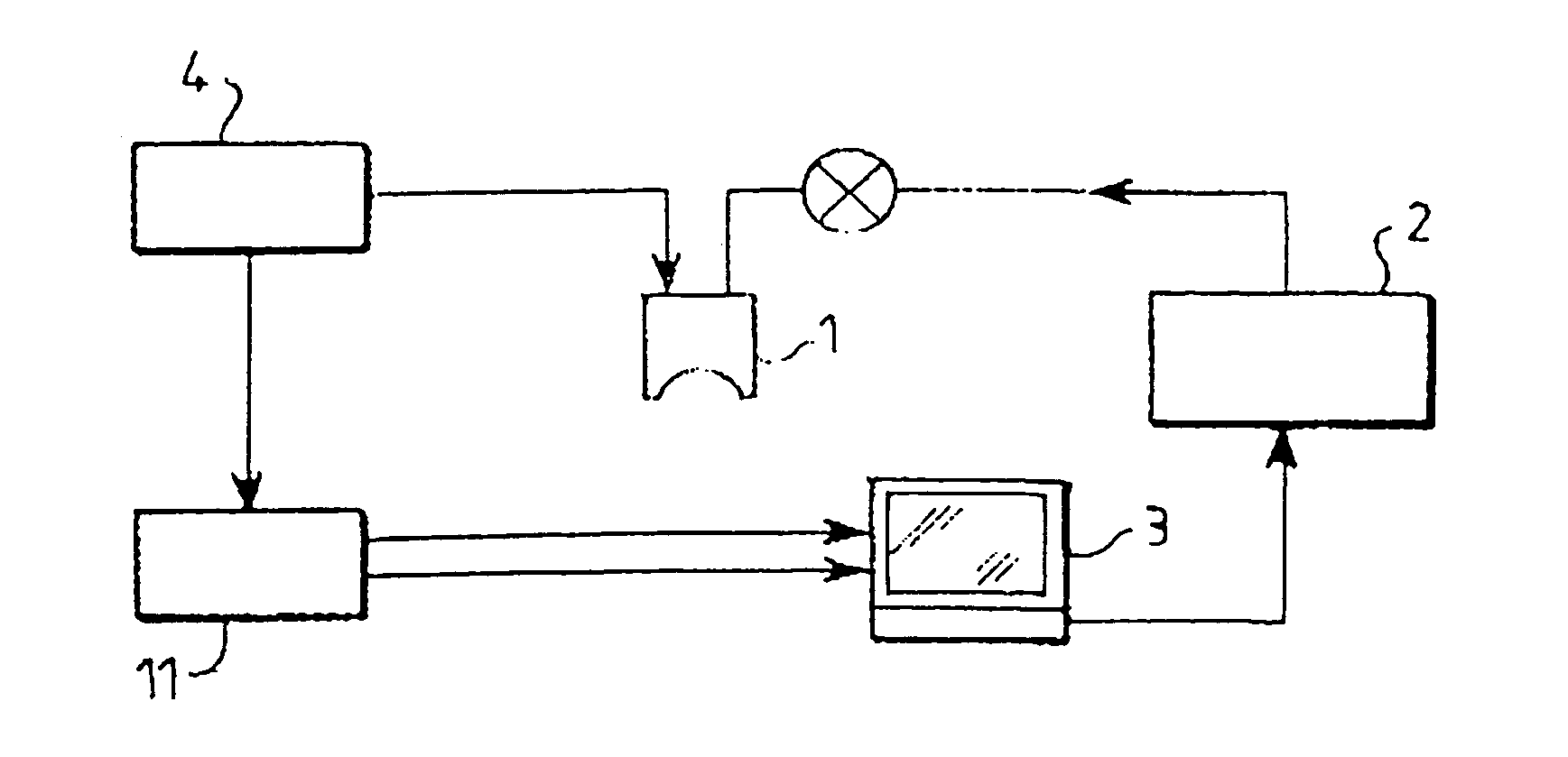
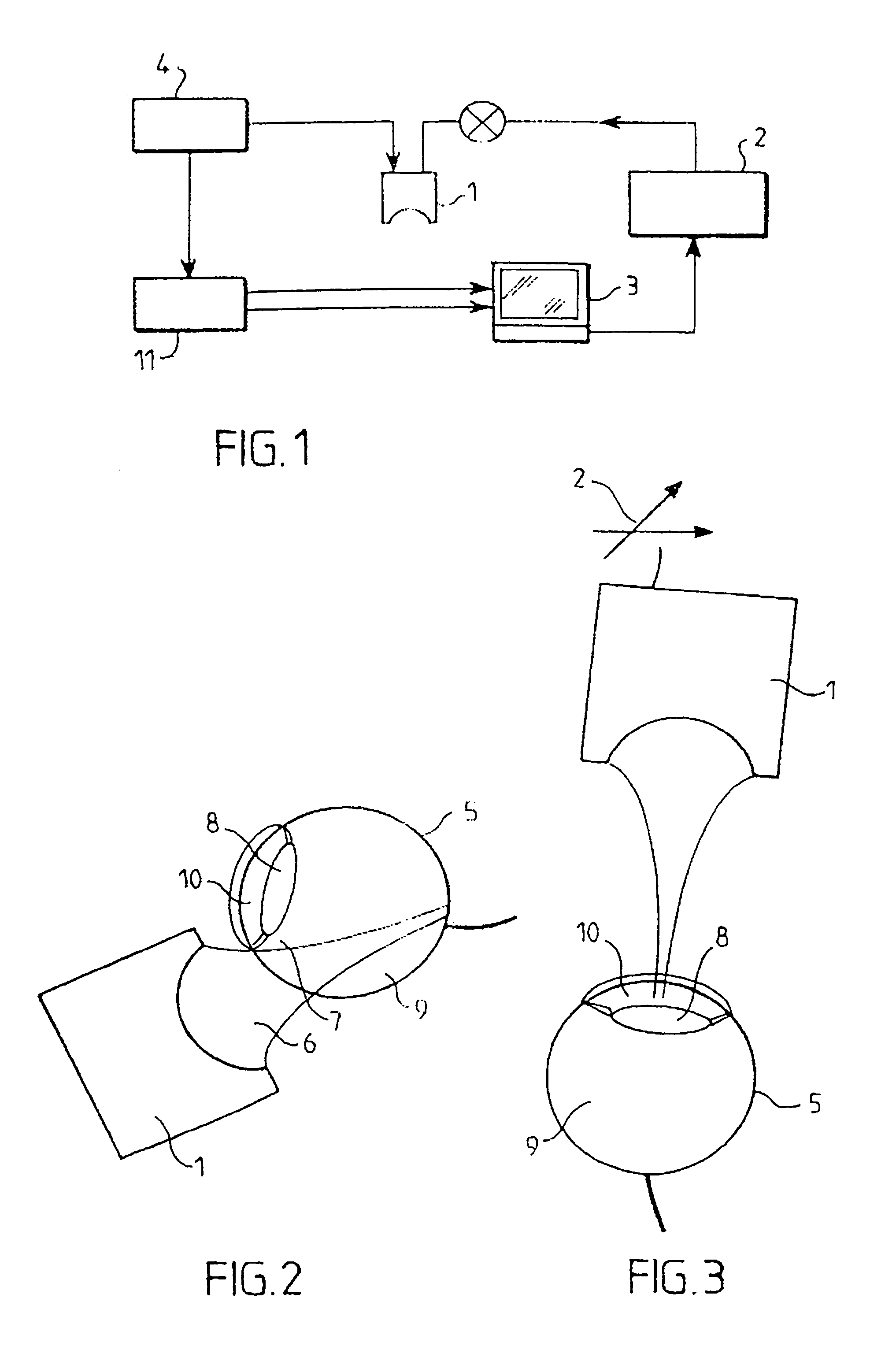
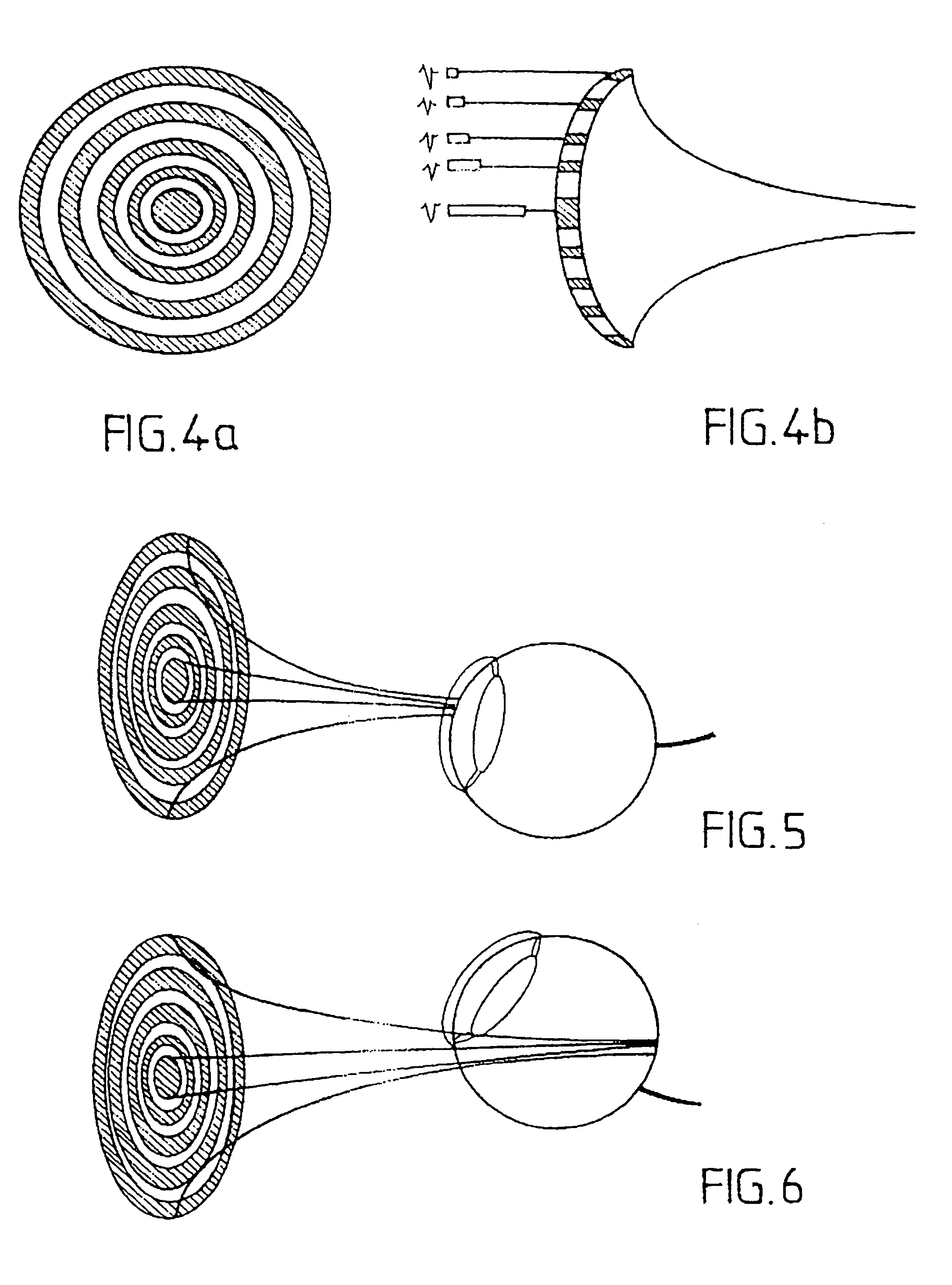
Method for exploring and displaying tissue of human or animal origin from a high frequency ultrasound probe
InactiveUS6949071B1Promote reproductionEasy to explainInfrasonic diagnosticsEye diagnosticsProximateUltrasonic transmission
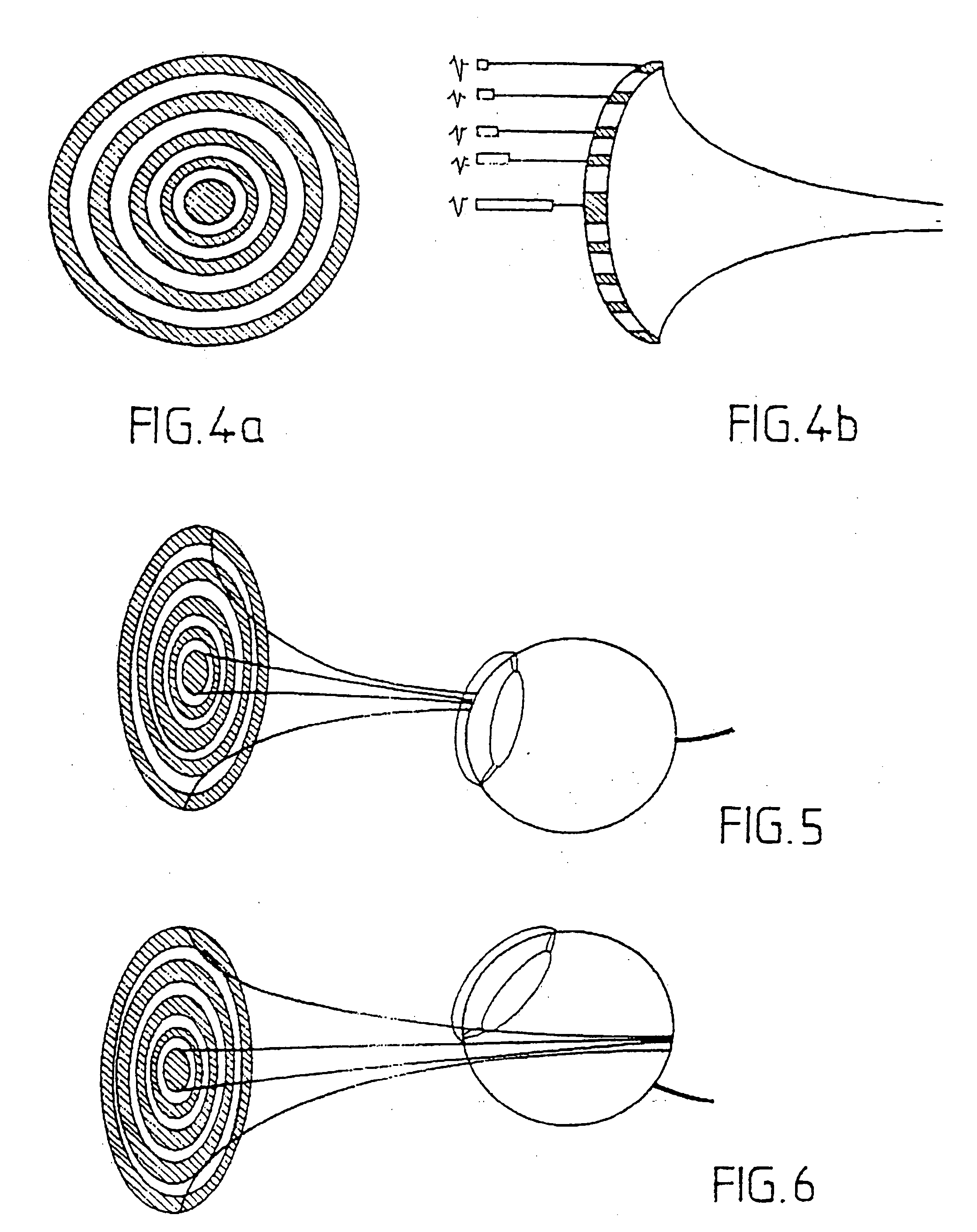
A method for displaying scanned ultrasound images of tissue employs an apparatus including an ultrasound probe mounted to a mechanical head. A three-dimensional positioning system mounts the head for positioning the probe in proximate orthogonal relation to the tissue. A computer controls the three-dimensional positioning system thereby moving the probe during a scan. The probe transmits high frequency ultrasound waves whose nominal frequency is included within the range from 30 to 100 MHz and with a large pass band, adapted to frequencies reflected by the tissue. The beams of ultrasound transmission are focused in a given zone of the tissue over a vertical penetration distance of between 20 and 30 mm. Reflected signals are acquired and processed for display.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Stator turn fault detection apparatus and method for induction machine
A system and method are provided for correction of parameters used in determination of stator turn faults of an induction motor. An embodiment may include determining a residual impedance and / or a residual voltage of the motor, and correcting a normalized cross-coupled impedance based on the residual impedance and residual voltage. Additional embodiments may include measuring an operating temperature of the motor and determining a negative sequence impedance of the motor based on the temperature. Another embodiment may include measuring voltages and currents of the motor and determining phasors for the voltages and currents using compensation for variations from a nominal frequency of the motor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for autonomous dynamic voltage and frequency scaling of microprocessors and computer system
ActiveCN101187831AImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
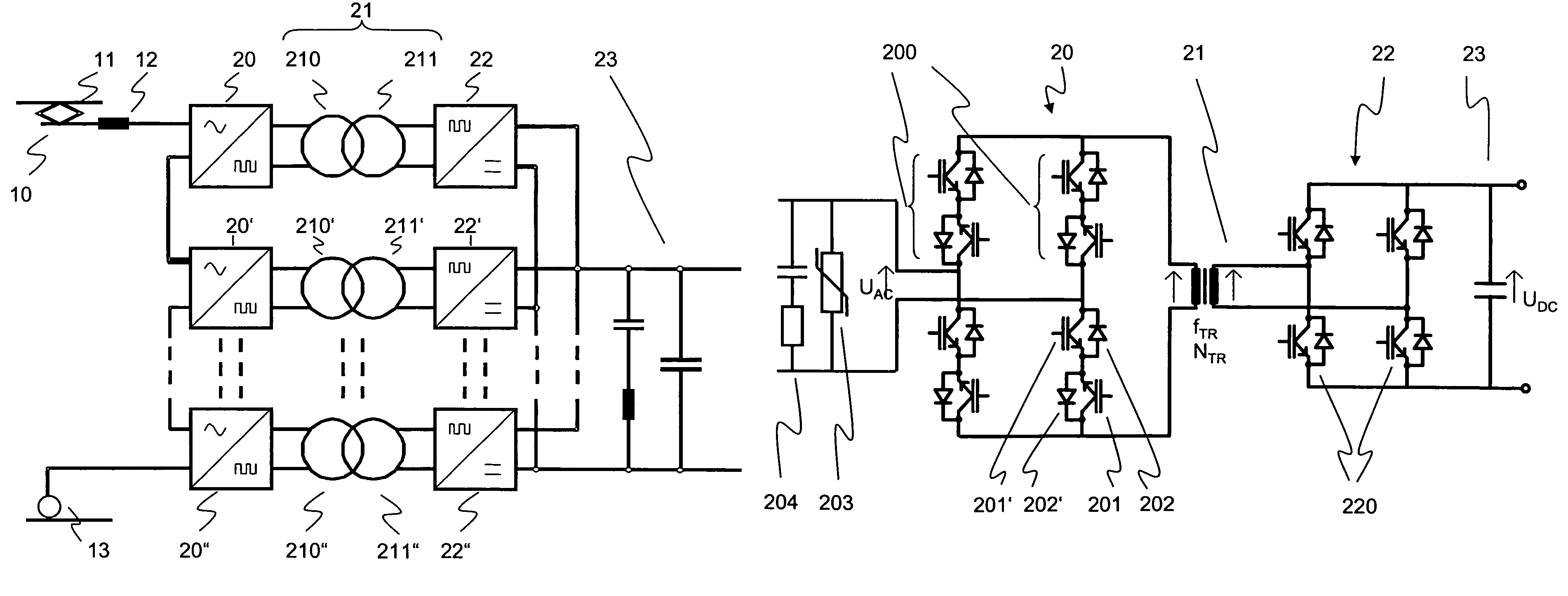
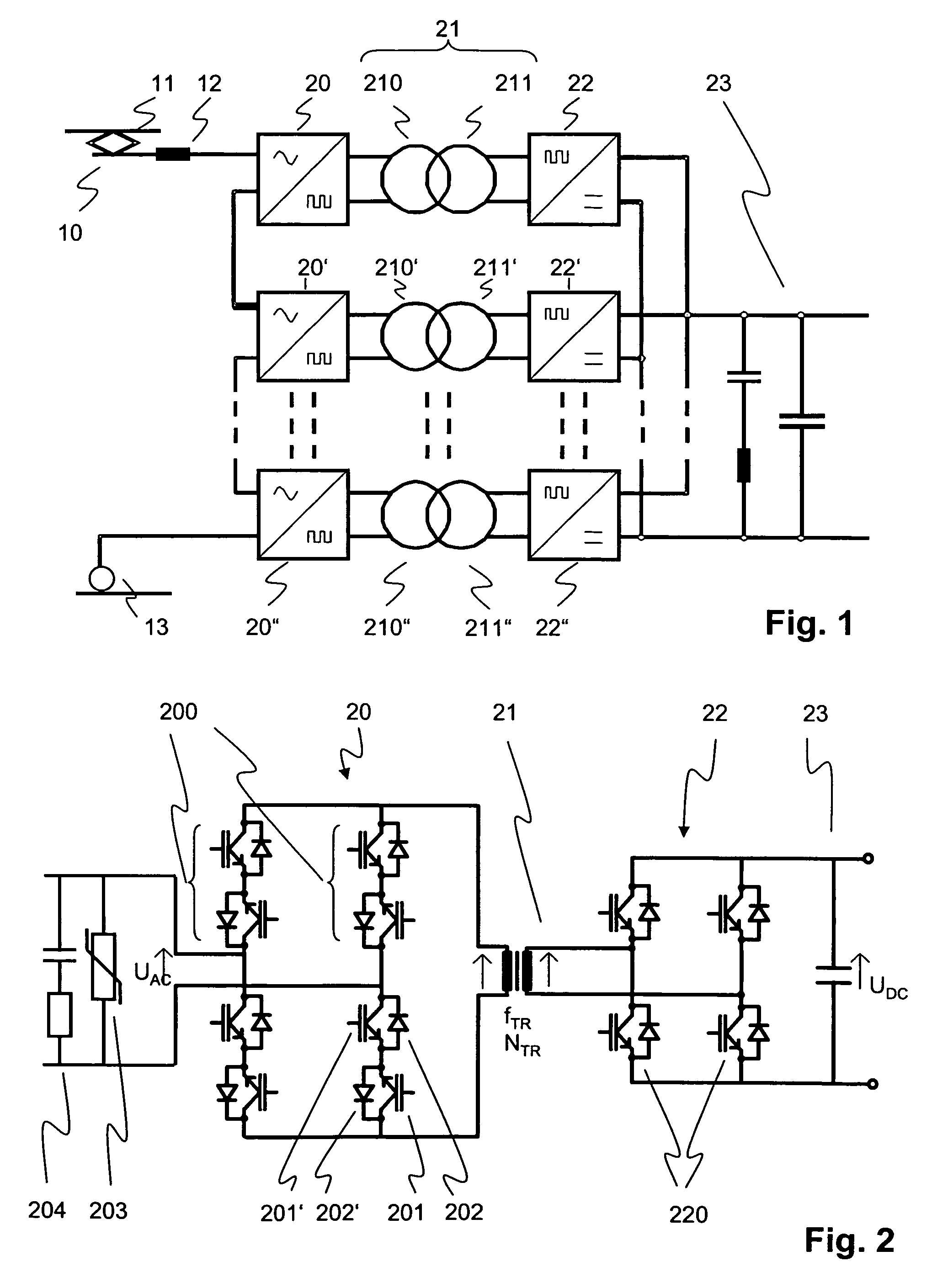
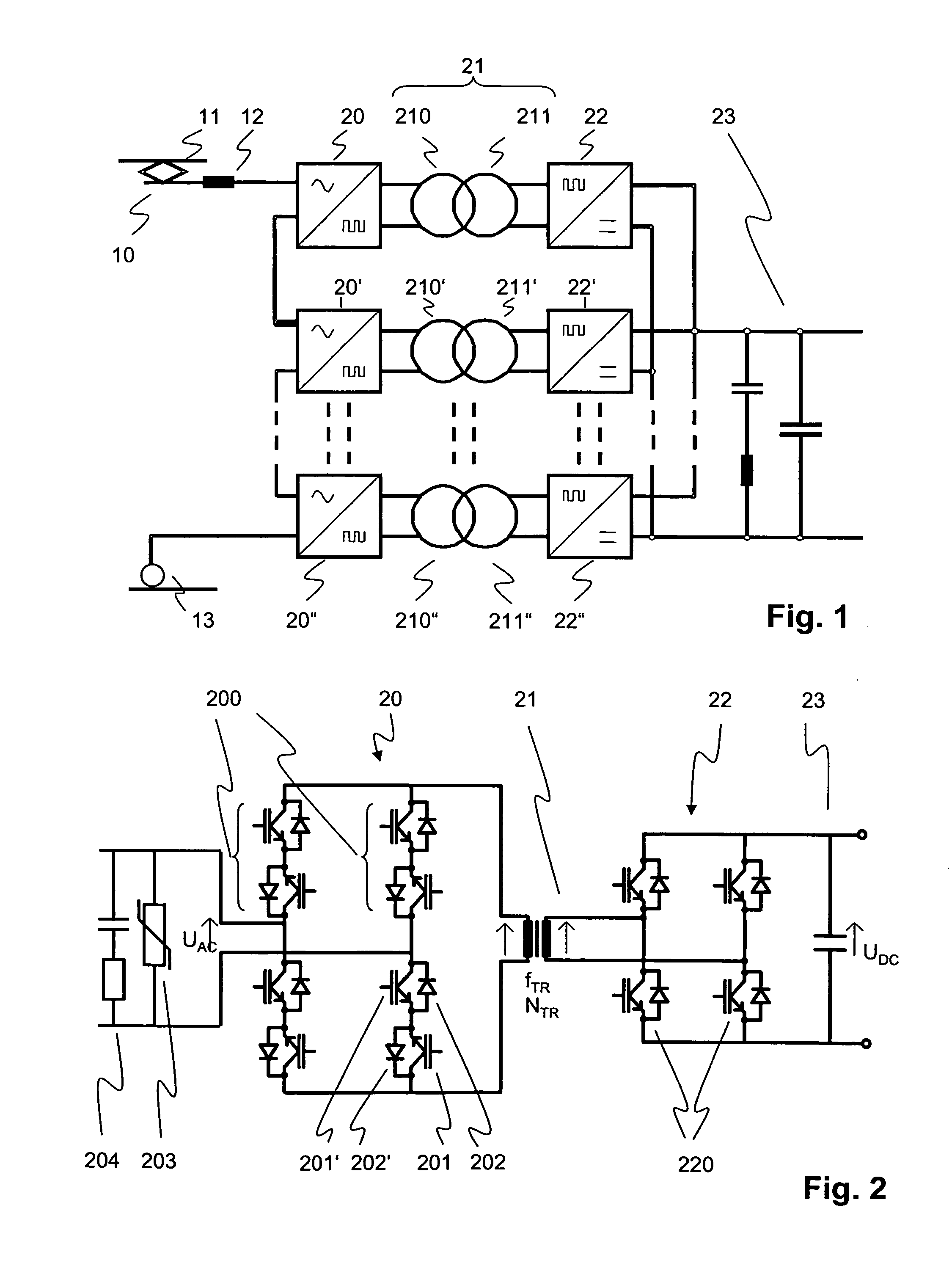
Multilevel AC/DC converter for traction applications
InactiveUS7558087B2Weight increaseImprove usabilityAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric power transfer ac networkSingle stageTraction transformer
A power supply system for railway traction applications including a multilevel AC / DC converter. The converter comprises a plurality of series-connected single-stage cycloconverters or direct AC frequency converters connected between an AC supply line and a traction transformer. The transformer is operable at a transformer nominal frequency below 3 kHz and above the AC line frequency. On the secondary side of the transformer, more than one parallel-connected secondary converter are provided and connected to a DC link. In case of failure of one of the secondary converters, the multilevel AC / DC converter may continue to operate with reduced power delivered by the remaining operating levels.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
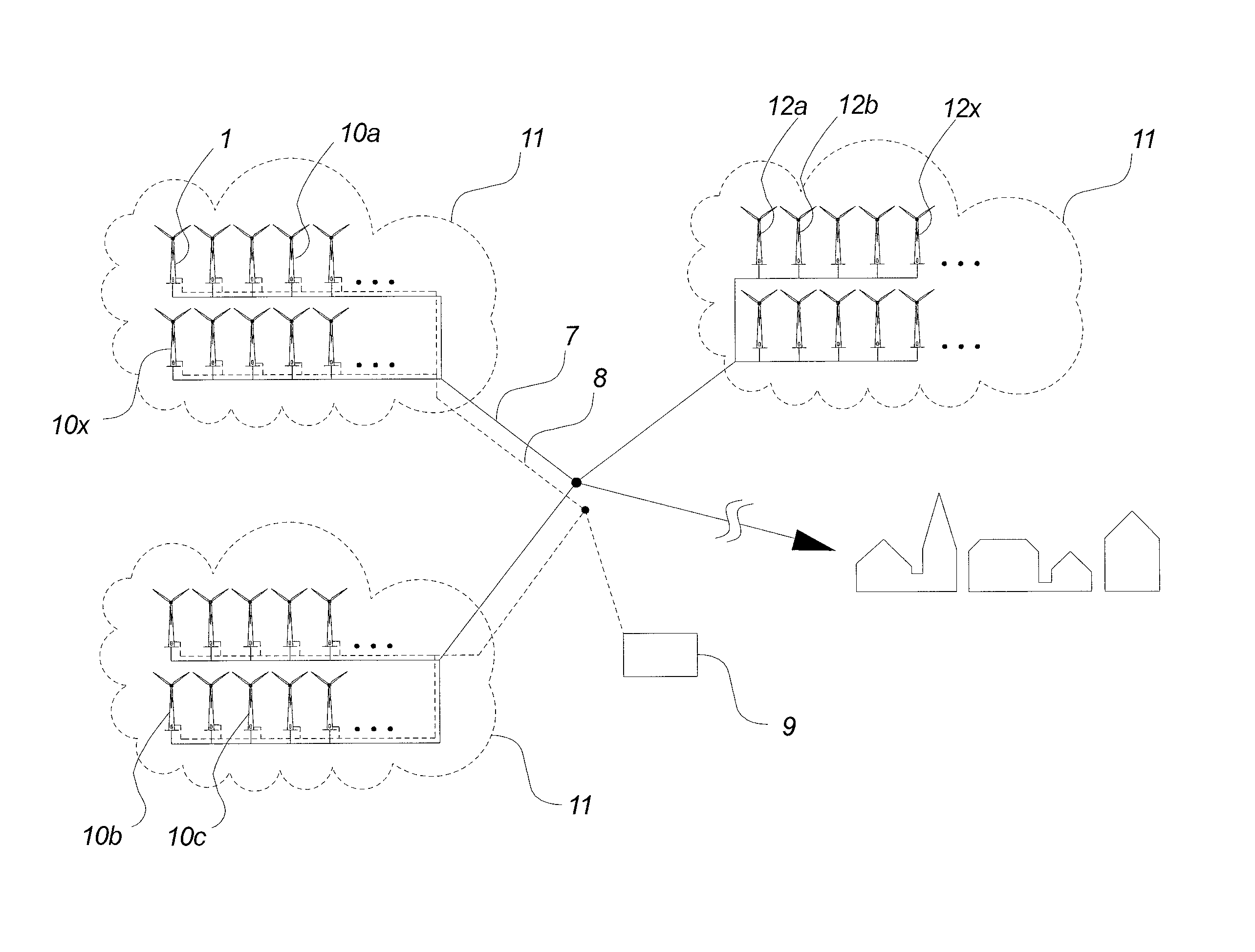
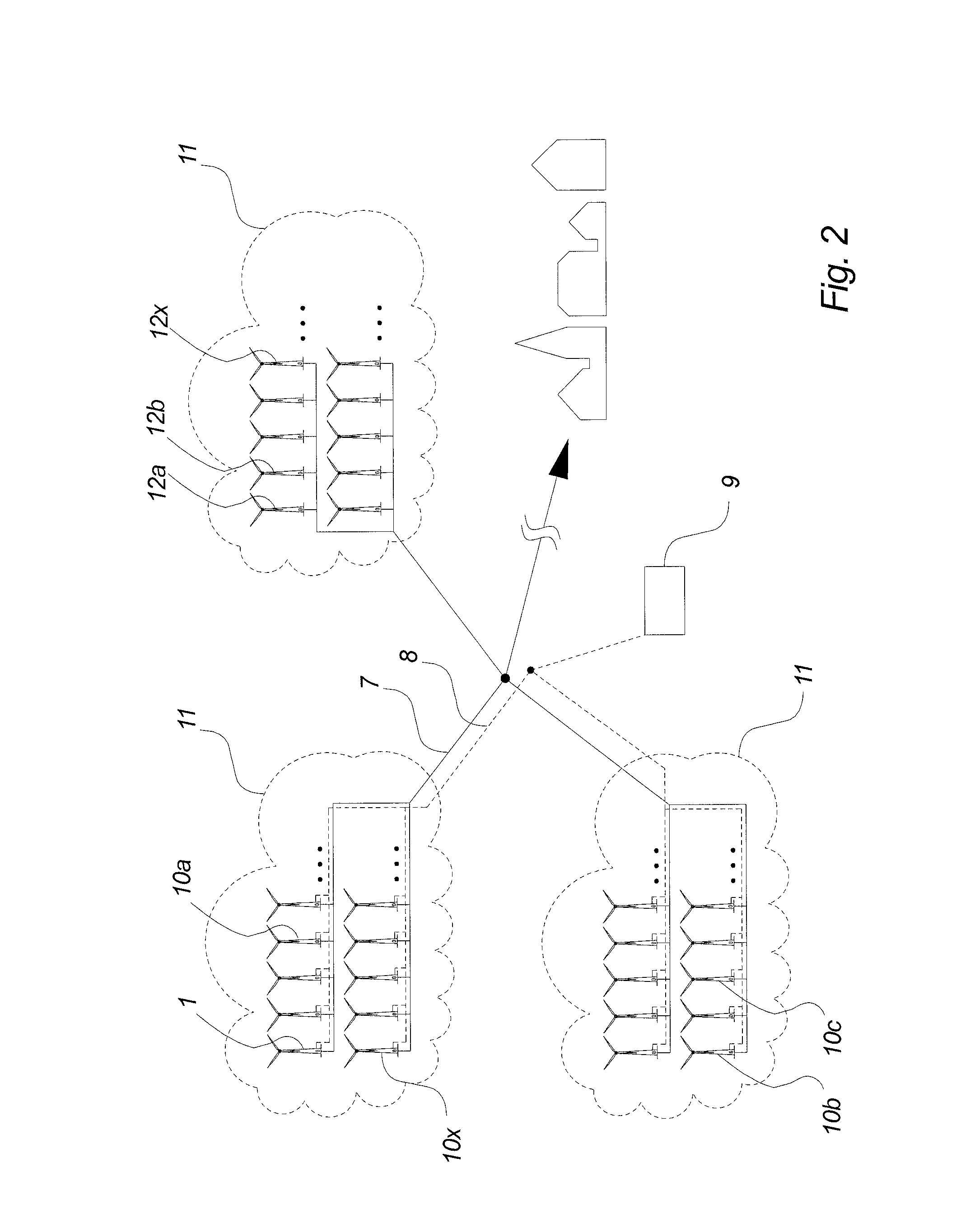
Method For Controlling A Cluster Of Wind Turbines Connected To A Utility Grid, Method For Planning The Strategy Of A Utility Grid Including A Wind Turbine Cluster Connected To The Grid And Wind Turbine Cluster
A method for controlling a cluster of wind turbines connected to a utility grid includes the steps of determining the frequency of the utility grid, detecting a frequency deviation in the utility grid, and disconnecting the wind turbines at different predefined frequency values above the nominal frequency value. A method for planning the strategy of a utility grid including a wind turbine cluster connected to the grid and a wind turbine cluster is also contemplated.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
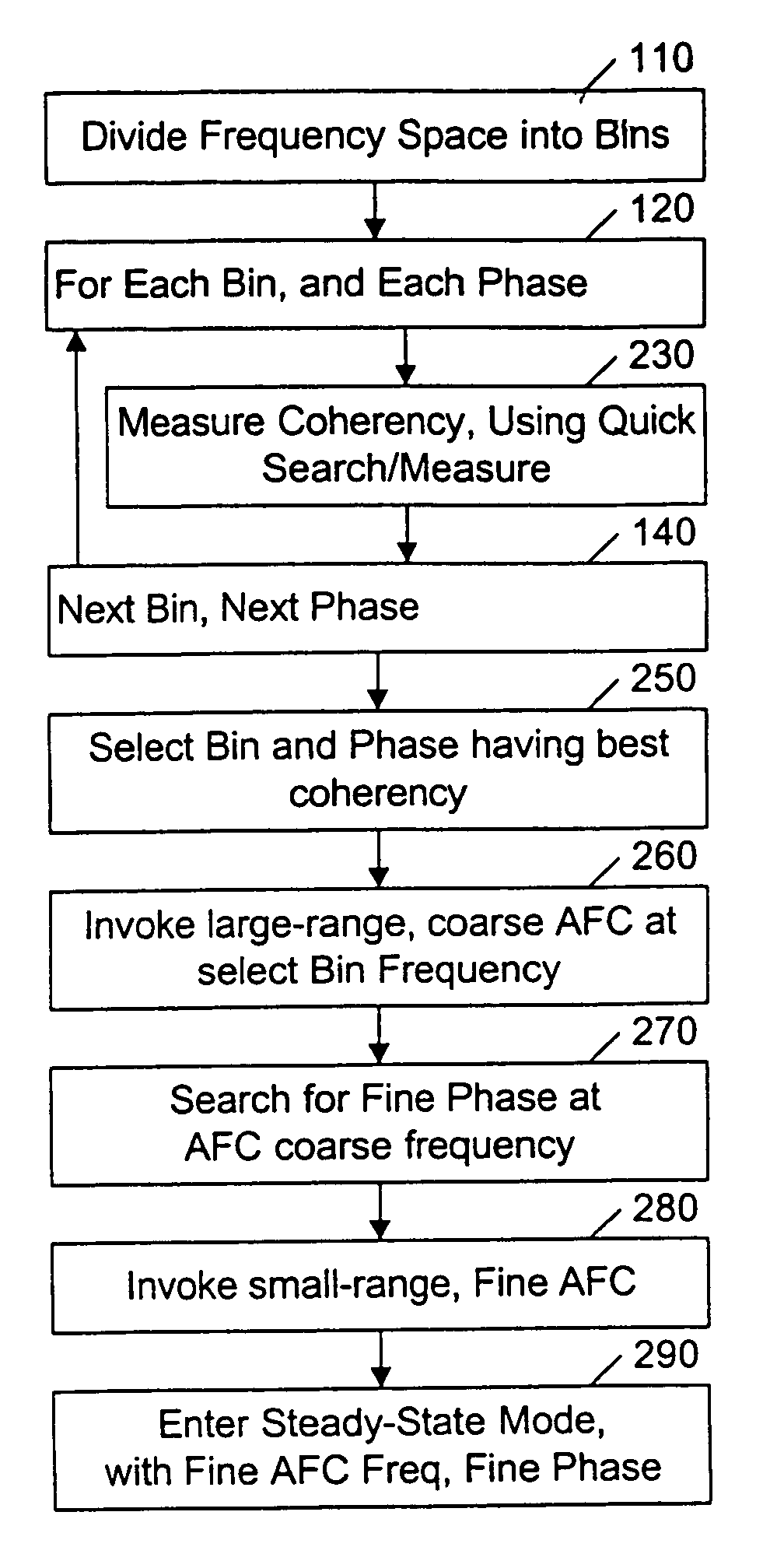
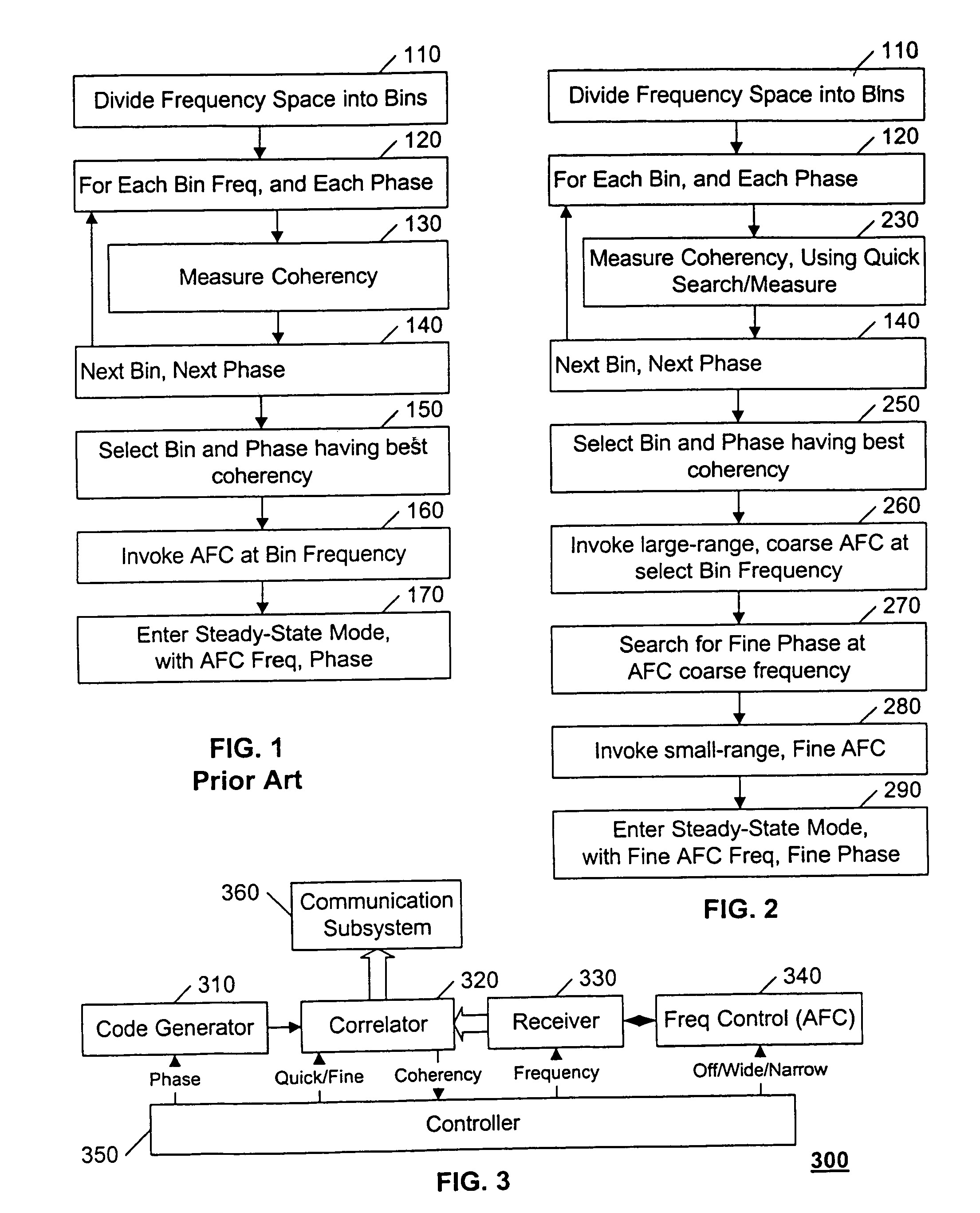
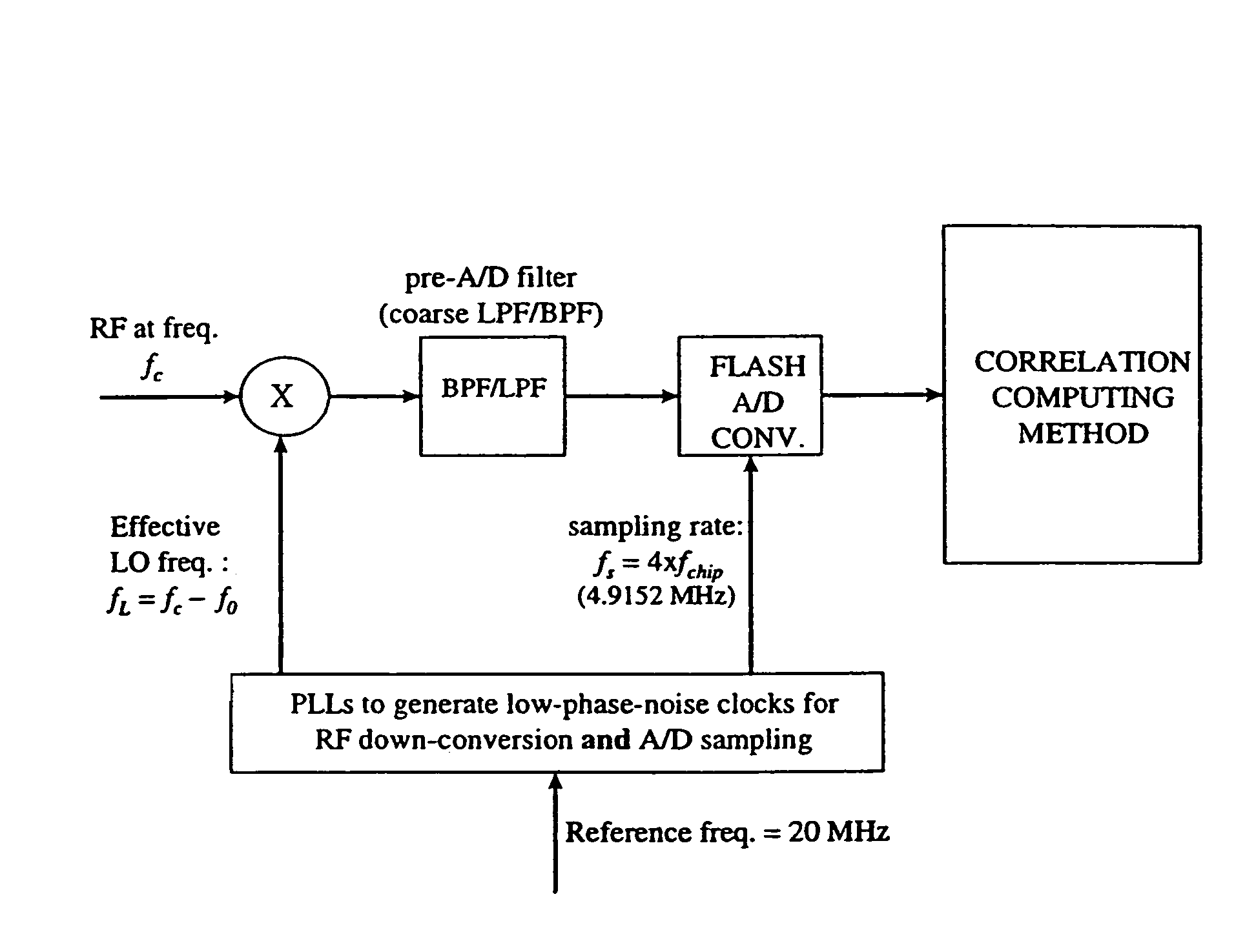
Iterative CDMA phase and frequency acquisition
InactiveUS7050485B2Improve acquisitionHigh frequency accuracyTransmissionFrequency determinationEngineering
A system and method is provided that searches for the frequency and phase of a CDMA transmission in an iterative manner. With its automatic frequency control (AFC) disabled, the receiving system performs a coarse search for the transmitter's CDMA phase at a nominal receiving frequency. When the coarse phase is obtained, the AFC is invoked with a large-range pull-in, to obtain an initial, coarse frequency that is likely to be closer to the transmitter's frequency than the initial nominal frequency. At this coarse frequency, the receiving system repeats its search for the transmitter's CDMA phase, starting at the previously determined coarse phase. Because this second phase determination is conducted in the presence of less frequency error, it provides for a more accurate phase determination. The AFC is again invoked, but with a small-range pull-in, to obtain a finer frequency determination. Because the finer frequency determination is conducted in the presence of less phase error, a substantial improvement in the accuracy and precision of the frequency determination can be achieved. To achieve this more accurate phase and frequency determination within the same time duration as a conventional acquisition process, the initial coarse phase determination is conducted using a rapid, albeit less accurate, process than the conventional phase determination.
Owner:NXP BV
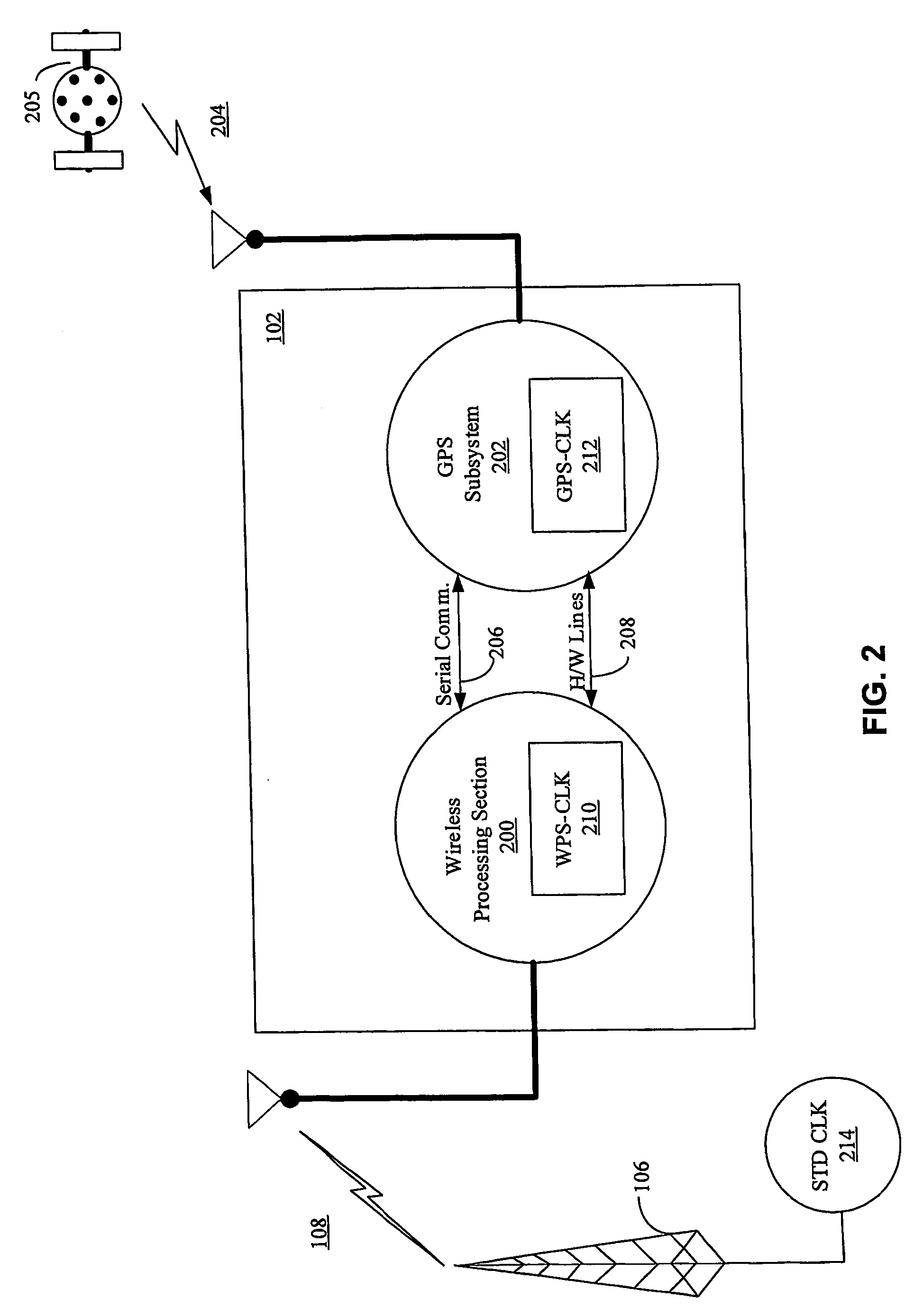
Aiding in a satellite positioning system
InactiveUS20060095206A1Instruments for road network navigationPosition fixationNetwork clockEngineering
The invention relates to an aided Global Positioning System (GPS) subsystem within a wireless device. The wireless device includes a wireless processing section capable of receiving signals from a wireless network and a GPS subsystem having a radio frequency (RF) front-end capable of receiving a GPS satellite signal. The wireless processing section of the wireless device receives an external clock and determines the offset between the clock in the wireless processing section and that of the external clock. The GPS subsystem then receives the offset information from the wireless processing section, information related to the nominal frequency of the wireless processing section clock and the wireless processing section clock. Using this information and the GPS clock in the GPS subsystem, the GPS subsystem determines an acquiring signal, which is related to a frequency offset between the GPS clock and the network clock. The GPS subsystem then acquires GPS satellite signals in an acquiring unit though the use of the acquiring signal.
Owner:CSR PLC
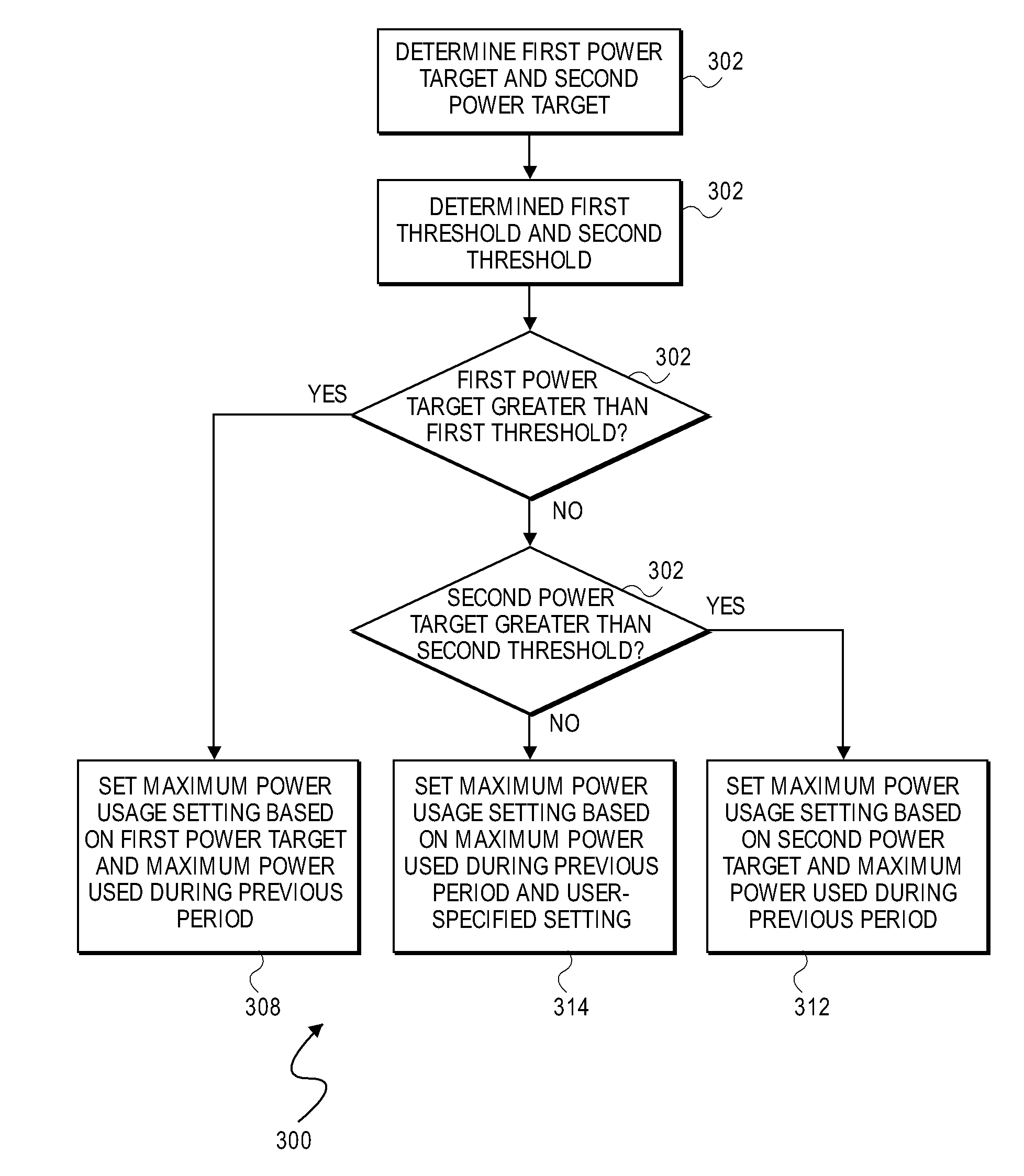
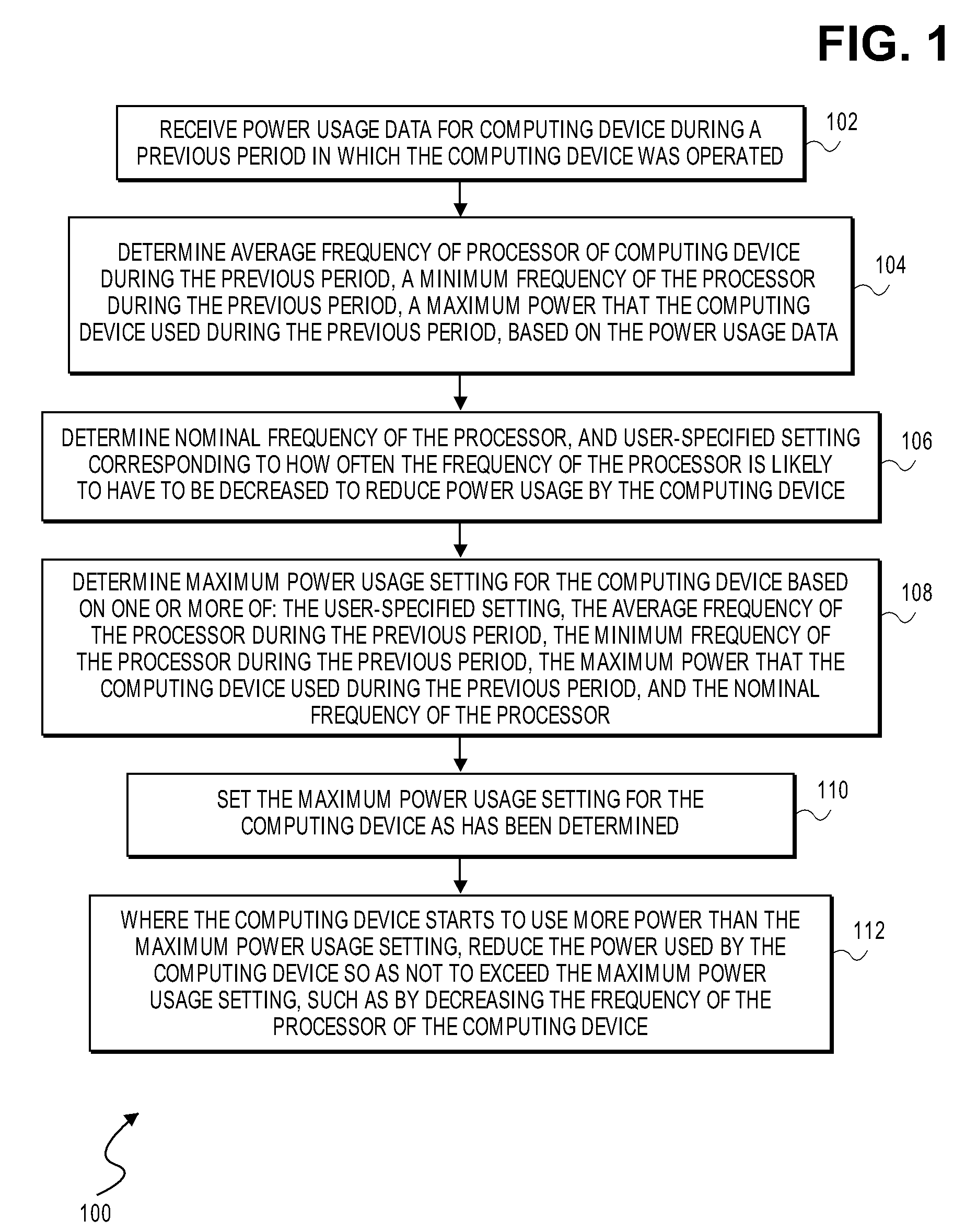
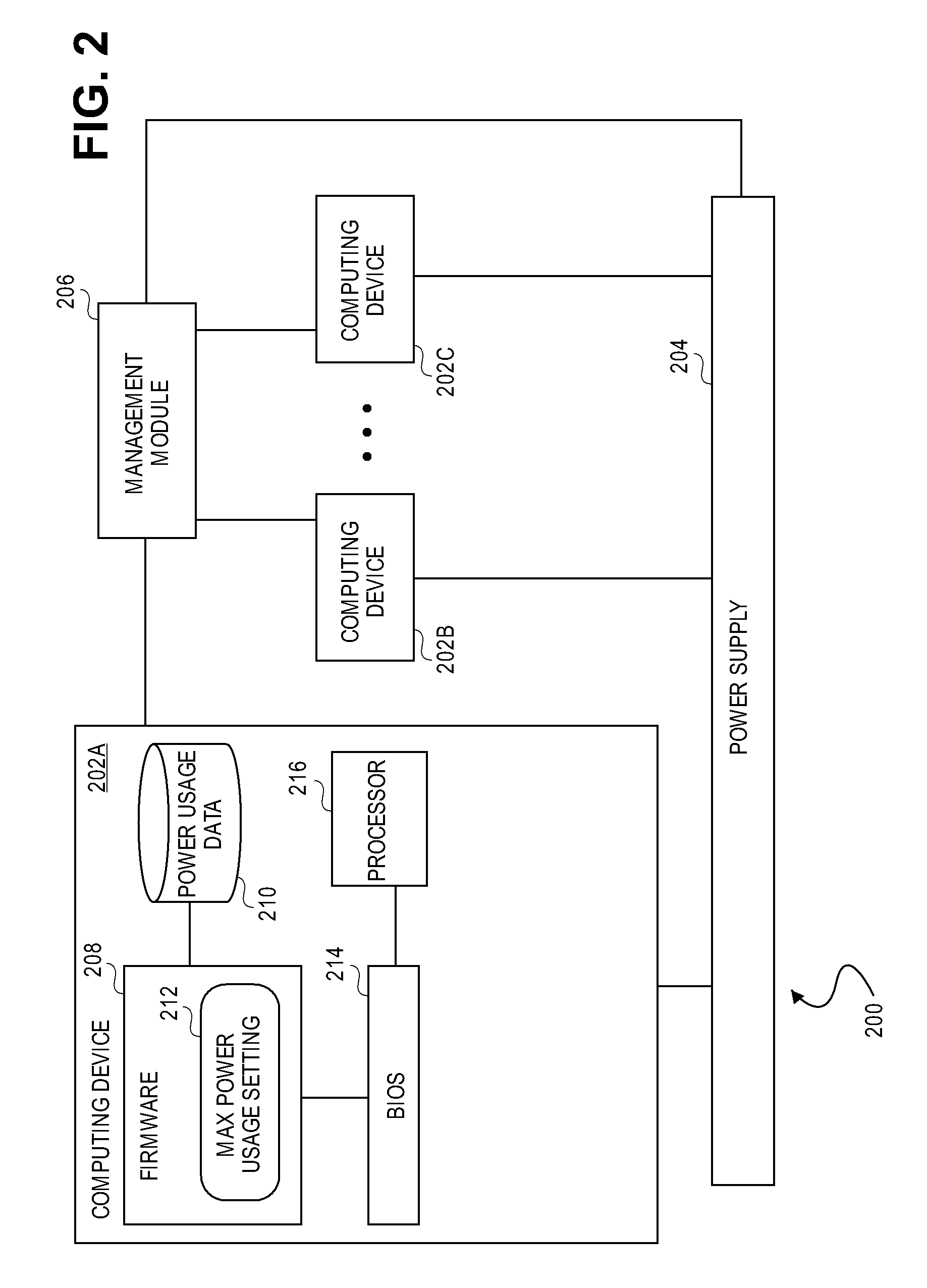
Maximum power usage setting for computing device
InactiveUS7783906B2Less powerReduce frequencyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementPower usageComputer science
A maximum power usage setting for a computing device is based on one or more of: a user-specified setting corresponding to how often a frequency of a processor of the computing device is likely to have to be decreased to reduce power usage by the computing device; an average frequency of the processor during a previous period in which the computing device was operated; a minimum frequency of the processor during the previous period; a maximum power that the computing device used during the previous period; and, a nominal frequency of the processor. When the computing device starts to use more power than the maximum power usage setting, the power used by the computing device is reduced so as not to exceed the setting, such as by decreasing the frequency at which the processor operates.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Ground Fault Detection
ActiveUS20090160454A1Change resistanceAvoid interferenceDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective arrangement detailsThree-phaseNominal frequency
The present invention relates to a ground fault detection arrangement for a synchronous three-phase electrical machine, and an electrical system comprising a ground fault detection arrangement and a synchronous three-phase electrical machine. The ground fault detection arrangement injects an off-nominal frequency voltage between a neutral point of the synchronous three-phase electrical machine and ground and measure resultant currents to detect a ground fault.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Multilevel AC/DC converter for traction applications
InactiveUS20080198637A1Improve usabilityWeight increaseAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric power transfer ac networkSingle stageTraction transformer
The present disclosure is concerned with a power supply system for railway traction applications including a multilevel AC / DC converter. The converter comprises a plurality of series-connected single-stage cycloconverters or direct AC frequency converters connected between an AC supply line and a traction transformer. The transformer is operable at a transformer nominal frequency below 3 kHz and above the AC line frequency. On the secondary side of the transformer, more than one parallel-connected secondary converter are provided and connected to a DC link. In case of failure of one of the secondary converters, the multilevel AC / DC converter may continue to operate with reduced power delivered by the remaining operating levels.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Method for autonomous dynamic voltage and frequency scaling of microprocessors
ActiveUS7840825B2Improve performanceSave energyEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Pilot tracking for synchronization using correlation between digital signal and locally generated version of PN signal
A method of tracking a pilot channel to discipline an oscillator includes: downconverting the RF signal to a low frequency that is of the order of, but greater than the chip rate; converting the signal into digital format; computing complex correlations between the received digital signal and local replicas of the PN codes; and establishing from the correlation values what is the nominal frequency error of the local oscillator. Correlation values between the digital signal {s(n)} and at least one locally generated version of I-channel and Q-channel PN signals {IPN(n)} and {QPN(n)} are averaged over multiple periods of the PN signals. Pilot signal tracking accuracy is improved, computational load is reduced without degradation in performance, and the technique is simple enough to be incorporated in an off-the-shelf FPGA.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
DC-DC regulator with switching frequency responsive to load
ActiveUS7208921B2Reduce switching frequencyDuty cycle decreasesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitching frequencyEngineering
A switch mode power supply in which the switching frequency is controlled by an oscillator having a nominal frequency, and having an error amplifier to provide an output signal which represents departure of the power supply output from a nominal value, and which functions by adjusting the frequency of the oscillator to a frequency which is higher or lower than the nominal frequency according to the value of the error amplifier output signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
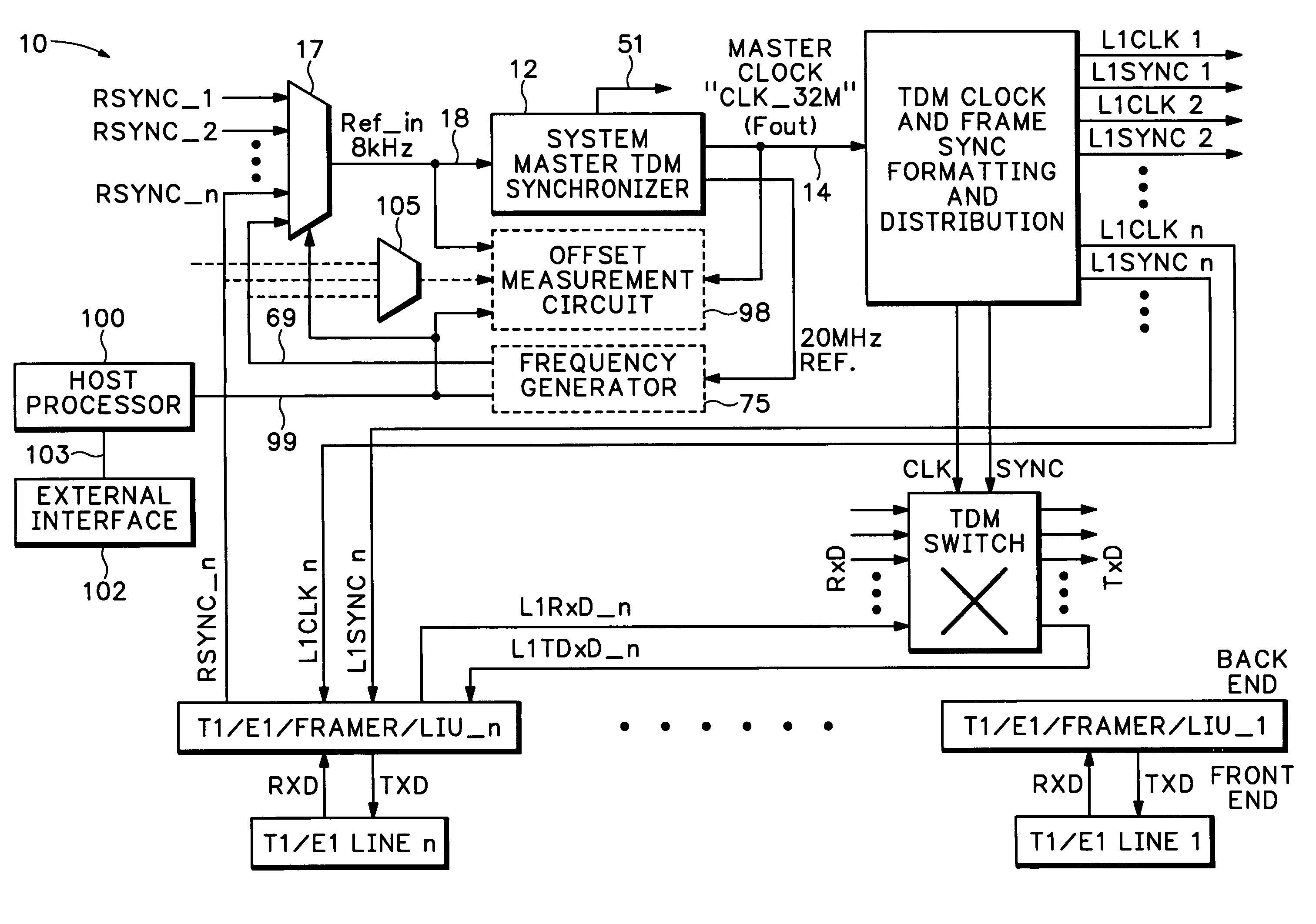
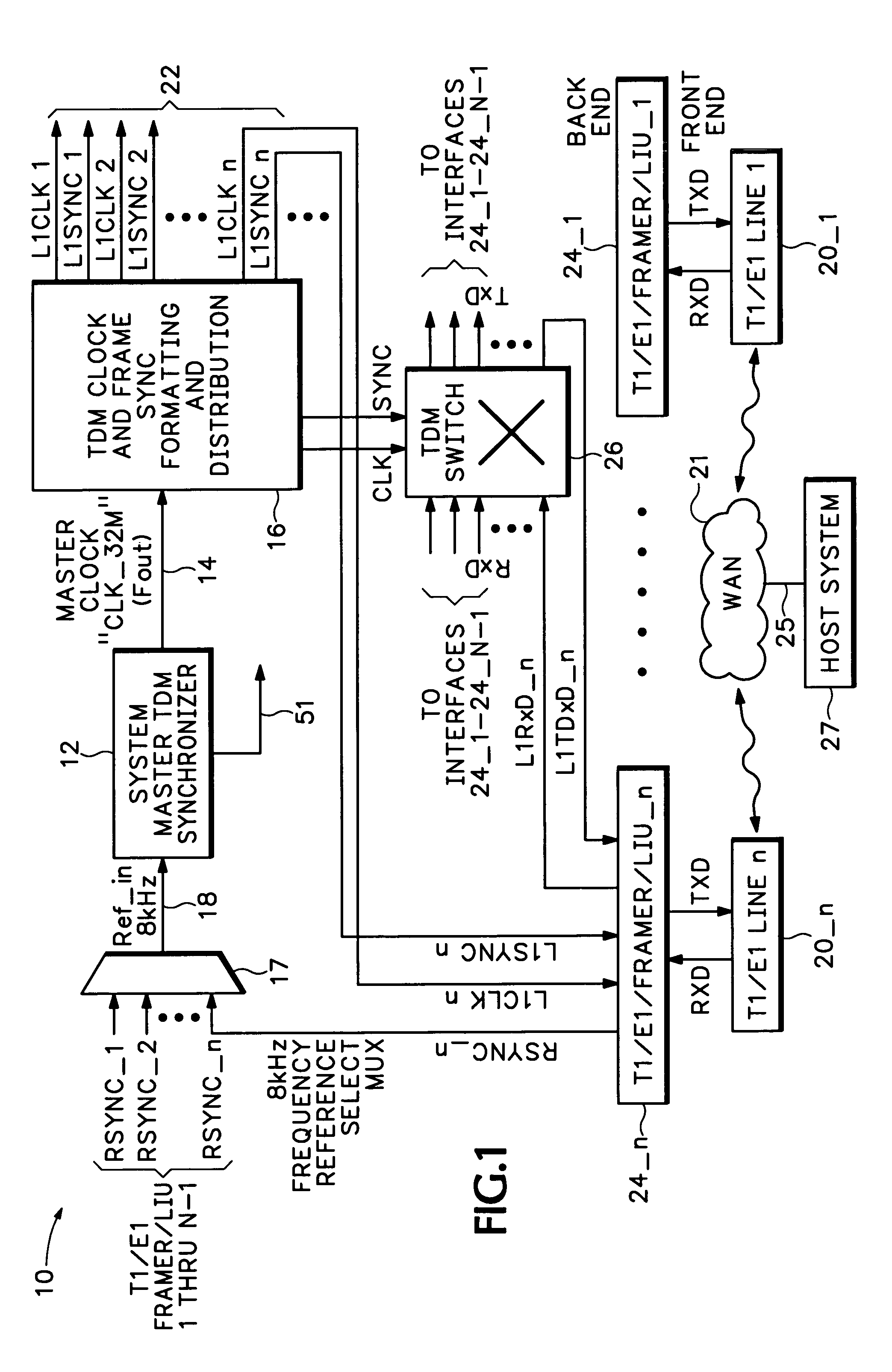
Method and apparatus for testing synchronization circuitry
InactiveUS6965224B1Efficiently indicatedCorrect operation testingPulse automatic controlEngineeringNominal frequency
A test circuit receives a reference signal having a reference frequency and generates a synchronizer input signal having a synchronizer input frequency for inputting into a synchronizer circuit. A frequency generator is configured to offset the synchronizer input frequency at selectable frequencies from a nominal frequency value. An offset measurement circuit is configured to compare the frequency offset for the synchronizer input frequency with the frequency offset of a synchronizer output signal.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for detecting and processing GPS signals
InactiveUS20050232338A1Highly integratedWeak signalModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityKaiman filterTime segment
A method acquires a location system signal where the location system signal includes a first data signal and a second data signal superimposed on the first data signal. The method includes generating an initial Doppler frequency offset value, the initial Doppler frequency offset representing a variance from a nominal frequency for the location system signal and a frequency of a received location system signal. The method also includes using the initial Doppler frequency offset value to generate a plurality of error signals, each error signal representing a difference between a sum of consecutive correlation values and a corresponding estimated ideal value. Each error signal corresponds to a different time offset and an associated time period in which the consecutive correlation values pertain. The second data signal has a bit edge that occurs during the time period of each of at least some of the sums of consecutive correlation values. A bit transition at the bit edge causes an increase in the error signal if the bit edge occurs during a time period associated with the error signal. The method also includes using a Kalman filter to generate a new initial Doppler frequency offset value, and generating new error signals.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for exploring and displaying tissues fo human or animal origin from a high frequency ultrasound probe
InactiveUS20050251043A1Promote reproductionEasy to explainInfrasonic diagnosticsEye diagnosticsProximateLight beam
A method for displaying scanned ultrasound images of tissue employs an apparatus including an ultrasound probe mounted to a mechanical head. A three-dimensional positioning system mounts the head for positioning the probe in proximate orthogonal relation to the tissue. A computer controls the three-dimensional positioning system thereby moving the probe during a scan. The probe transmits high frequency ultrasound waves whose nominal frequency is included within the range from 30 to 100 MHz and with a large pass band, adapted to frequencies reflected by the tissue. The beams of ultrasound transmission are focused in a given zone of the tissue over a vertical penetration distance of between 20 and 30 mm. Reflected signals are acquired and processed for display.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Measuring instantaneous signal dependent nonlinear distortion in response to varying frequency sinusoidal test signals
InactiveUS20050233702A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsNonlinear distortionFrequency spectrum
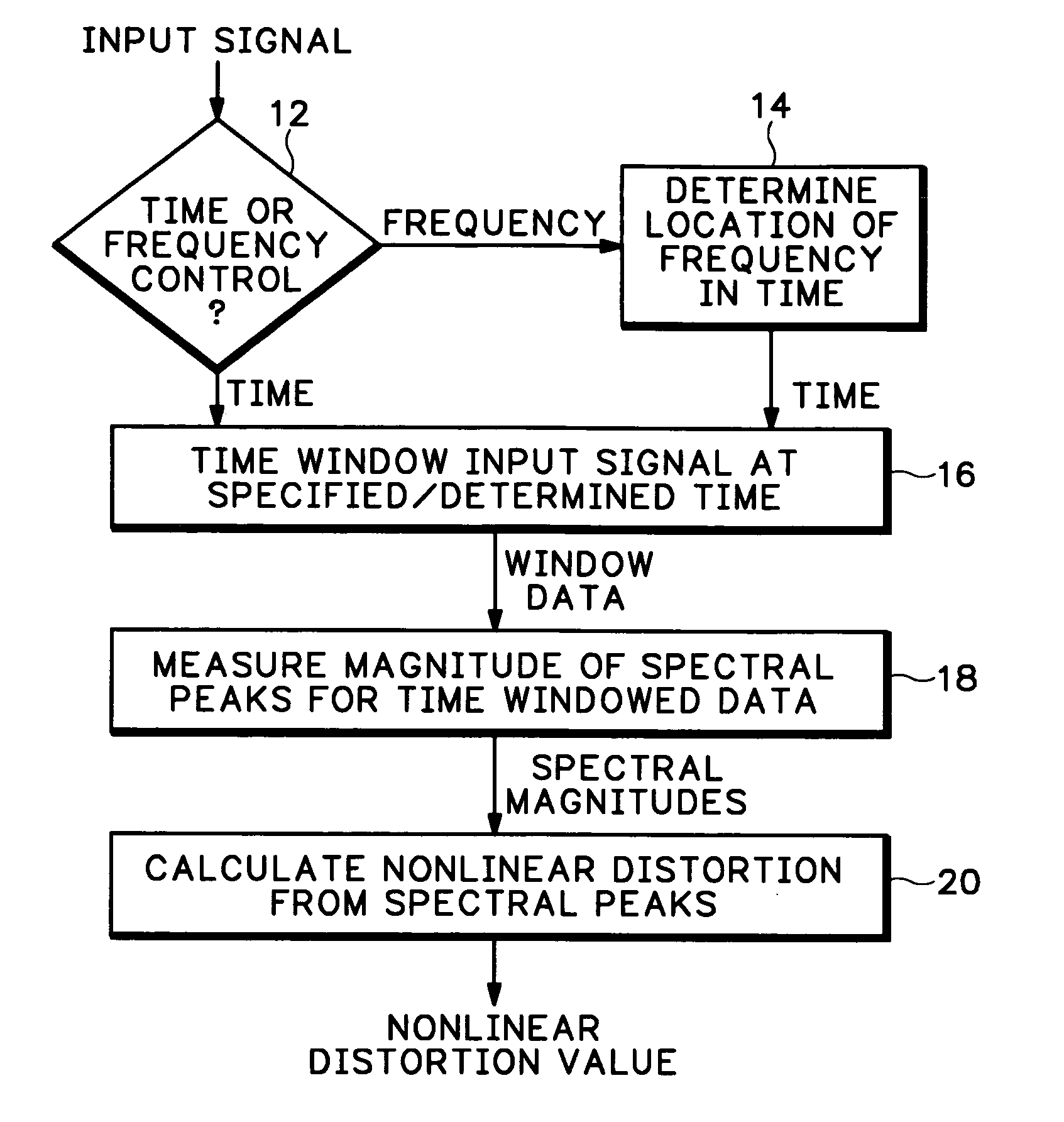
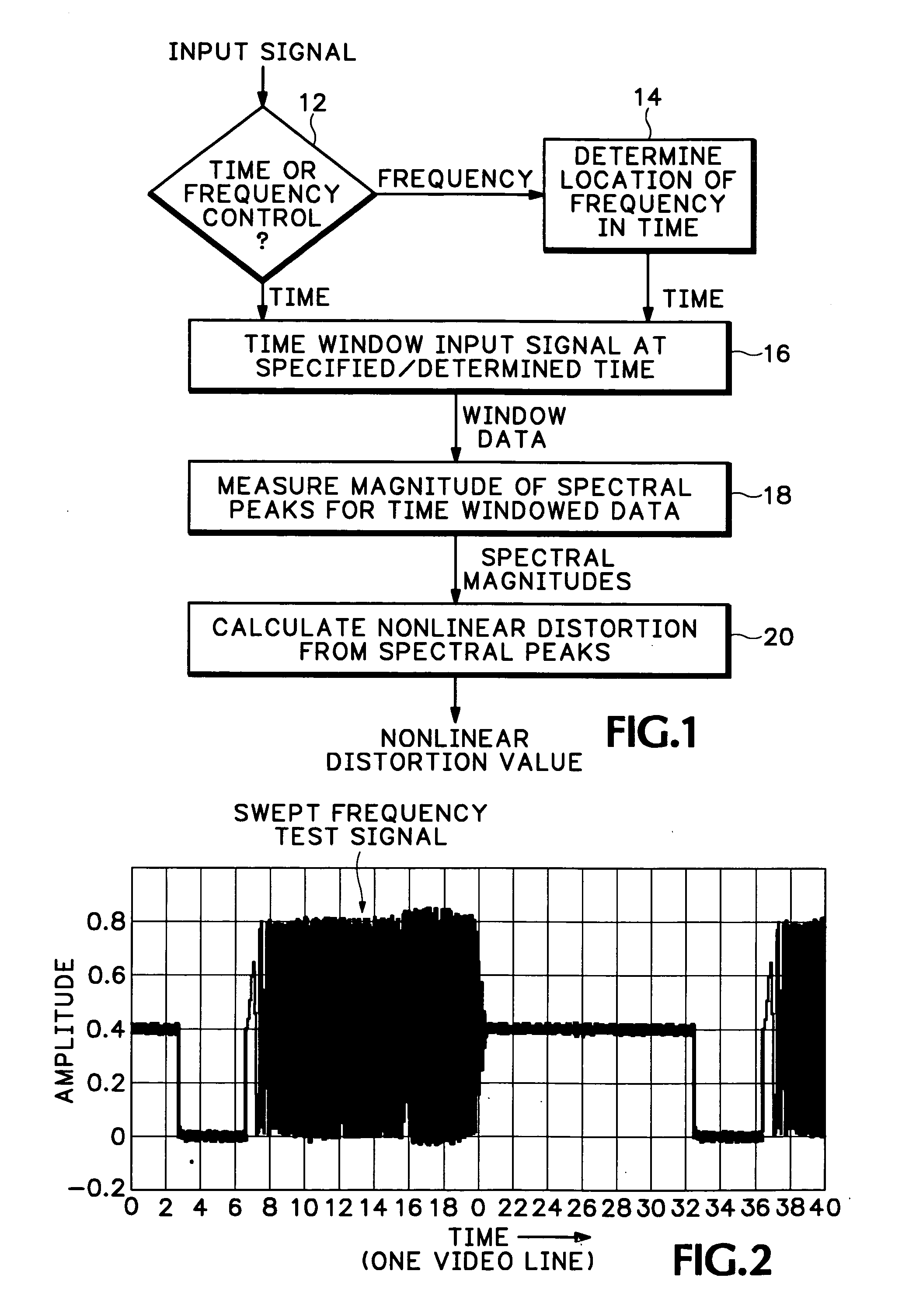
A method of measuring instantaneous signal-dependent nonlinear distortion in a system under test in response to a test signal having a varying frequency sinusoidal component, such as a swept frequency signal or a multi-burst signal, uses a time window to locate a frequency of interest in the corresponding varying frequency component of a signal output from the system under test. Once the location of the frequency of interest is located in the output signal, a spectrum of the portion of the output signal within the time window is generated and the magnitudes of the spectral peaks, including the spectral peak for the frequency of interest or nominal frequency and all isolated peaks representing distortion frequencies, are measured. The amount of distortion is calculated as a ratio of the square-root of the sum of the magnitudes of the distortion frequencies to the magnitude of the nominal frequency.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Global position system (GPS) deception jamming method and system
ActiveCN102866406AReduce transmit powerImprove concealmentSatellite radio beaconingTransducerGps receiver
The invention discloses a global position system (GPS) deception jamming method and a GPS deception jamming system. The GPS deception jamming system comprises a GPS signal digital generating module and a radio frequency emitting part. A GPS deception jamming signal generating part is mainly composed of a field programmable gata array(FPGA) digital platform and used for generating a digital GPS jamming signal. The radio frequency emitting part includes a plurality of transducers, wherein the traducers are used for changing the digital GPS jamming signal to a nominal frequency of the GPS satellite signal and a plurality of frequencies up and down the nominal frequency of the GPS satellite signal, and emitting the radio frequency signal through an antenna; possibility of receiving signals by the GPS receiver is largely increased, the deception jamming can be realized for the GPS receiver with certain airspace. Compared with the traditional GPS jamming system, the emitting power of the jamming system is much smaller, and own safety can be guaranteed. Furthermore, the goal GPS receiver is positioned to a wrong position, and thus, the GPS losses a fighting effect.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
System and method for calibration and reproduction of audio signals based on auditory feedback
ActiveUS20160050507A1Increase sampling rateEliminate artifactsManually-operated gain controlSignal processingFrequency spectrumOutput device
Systems and methods are provided for testing an individual's hearing and correcting audio signals to compensate for the significant variance in each listener's sensitivity to various frequencies of the audible spectrum. An auditory calibration procedure includes identifying a first volume level as a minimum volume level at which nominal frequency tones are audible, a minimum frequency at which said first volume level is audible, a maximum frequency at which said first volume level is audible, and a minimum volume level at which a number of intervening sample frequencies are audible. A substantially parabolic correction curve is generated based on the minimum volume levels at the various sample frequencies. The correction curve is applied to modify real time audio signals generated upon execution of an audio file functionally linked to the processor, wherein the modified real time audio signals are provided to an audio output device.
Owner:EARIQ
Methods for searching for SAM patterns at multiple nominal frequencies
InactiveUS20050013030A1Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageDemodulationNominal frequency
Methods are provided for improving servo-demodulation robustness, especially when used with a disk having zone bit recorded servo wedges. A servo address mark (SAM) pattern is searched for, within a servo wedge, at a first nominal frequency useful for searching for the SAM pattern if the servo wedge is within a first zone. The SAM pattern is also searched for, within the same servo wedge, at a second nominal frequency useful for searching for the SAM pattern if the servo wedge is within the second zone. A determination of which one of two zones a head is reading, can then based at least in part on which nominal frequency was used to successfully detect the SAM pattern.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for providing reference frequency aiding among peers operating in a direct communication mode
InactiveUS20070026792A1Network traffic/resource managementFrequency diversityTelecommunicationsDirect communication
A mobile communication device (202) and peer mobile communication devices (204, 206) are capable of direct voice and data communication. The mobile communication device has a reference oscillator (104) which is used for generating operating frequencies, and is subject to frequency errors resulting from manufacturing tolerances, heat, and other error sources. The mobile communication device receives a frequency correction message (506) from a peer mobile communication device that has calibrated its reference oscillator. The frequency correction message contain offset information which is used by the mobile communication device to determine its offset (316) from a nominal frequency (302).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Clock source device based on GPS second pulse and control method thereof
InactiveCN101930211ASynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationNegative feedbackLoop control
The invention discloses a clock source device based on GPS second pulse and a control method thereof. A closed loop negative feedback control principle is adopted, and the output power of a voltage control x-tal crystal oscillator (VCXCO) is controlled at the nominal frequency thereof so as to satisfy the condition that multiple measuring systems can be used synchronously. Experiment results show that after the VCXCO is subjected to closed loop control, the cumulative errors can be controlled within a plurality of pulses.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
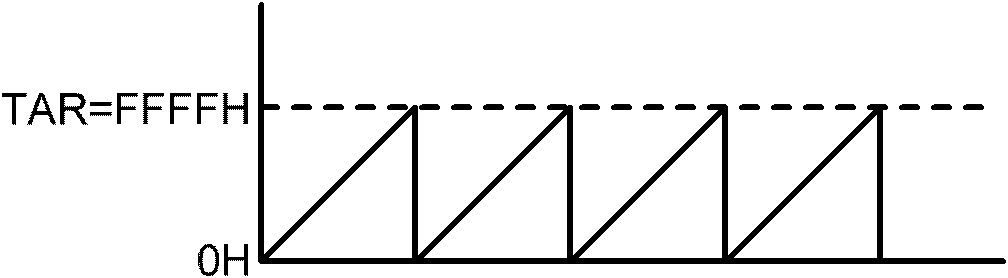
Coherent simulation method for radar echo Doppler frequency based on real-time frequency measurement
ActiveCN107271975AIncrease flexibilitySolve the problem of coherent simulation of institutional radar echoesWave based measurement systemsFrequency measurementsRadar
The invention provides a coherent simulation method for a radar echo Doppler frequency based on real-time frequency measurement. The specific process comprises the steps that step one, a simulator performs envelop extraction on transmitting signal pulses of a radar, and the simulator performs clock counting N3 by using a local clock in N2 radar transmitting pulse periods; step two, a corrected Doppler frequency simulation variable f'd is calculated, wherein f'd=fd*(N1N2 / N3)*(1 / [alpha]), fd represents the Doppler frequency corresponding to a simulated target, alpha represents a nominal frequency ratio of working clocks of the radar and the simulator, and N1N2 / N3 is a frequency correction coefficient; and step three, coherent simulation for the radar echo Doppler frequency is realized by using the Doppler frequency simulation variable f'd. Coherent simulation for the radar echo Doppler frequency can be realized quickly according to the method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Vibrating micro-mechanical sensor of angular velocity
ActiveUS20160334215A1Reduce decreaseOvercome disadvantagesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesLinear motionMomentum
A sensor structure and a method for operating a vibrating sensor of angular velocity comprising a rotor mass and two linearly moving masses is disclosed. The sensor structure and method comprises a rotor mass, two linearly moving masses, and two T-shaped levers each coupled with the two linearly moving masses and to the rotor mass. The T-shaped levers enable the rotor mass and the two linearly moving masses to be excited into an anti-phase primary mode, where the direction of angular momentum of the rotor mass is opposite to the direction of angular momenta of the linearly moving masses. Angular momenta of the rotor mass and the linearly moving masses cancel each other to a high extent, so that the total sum of angular momentum of the structure is very small. Nominal frequency of the anti-phase primary mode is distinctively low as compared to nominal frequencies of other possible primary modes, such as a parallel phase primary mode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com