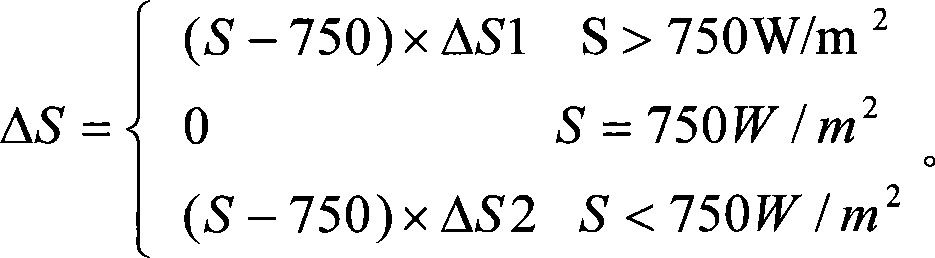Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1531 results about "Operational stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stability operations generally place the military in direct, prolonged contact with civilian populations and generally involve the intentional restructuring or resetting of the civilian population’s relationship with their government.
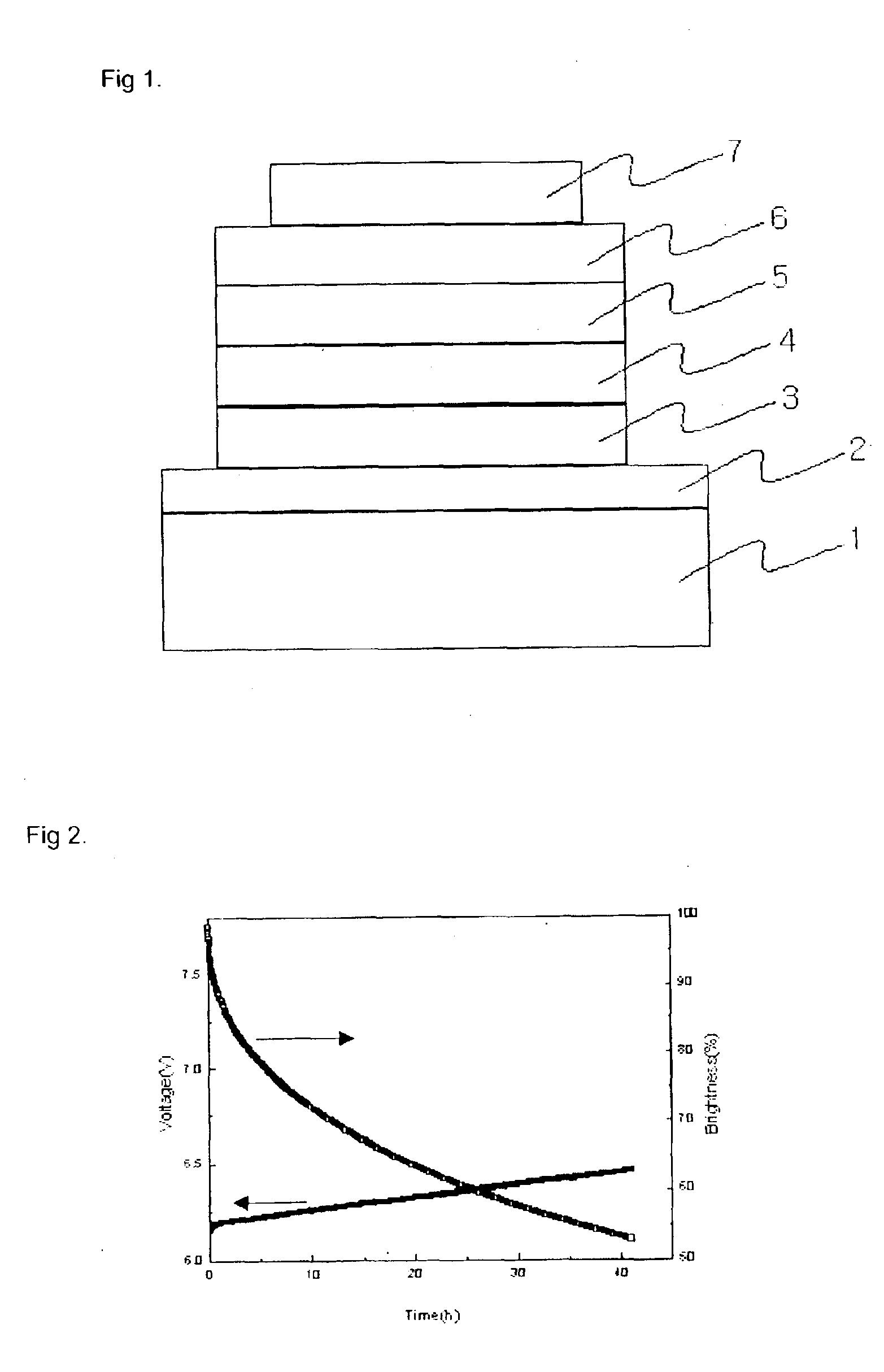
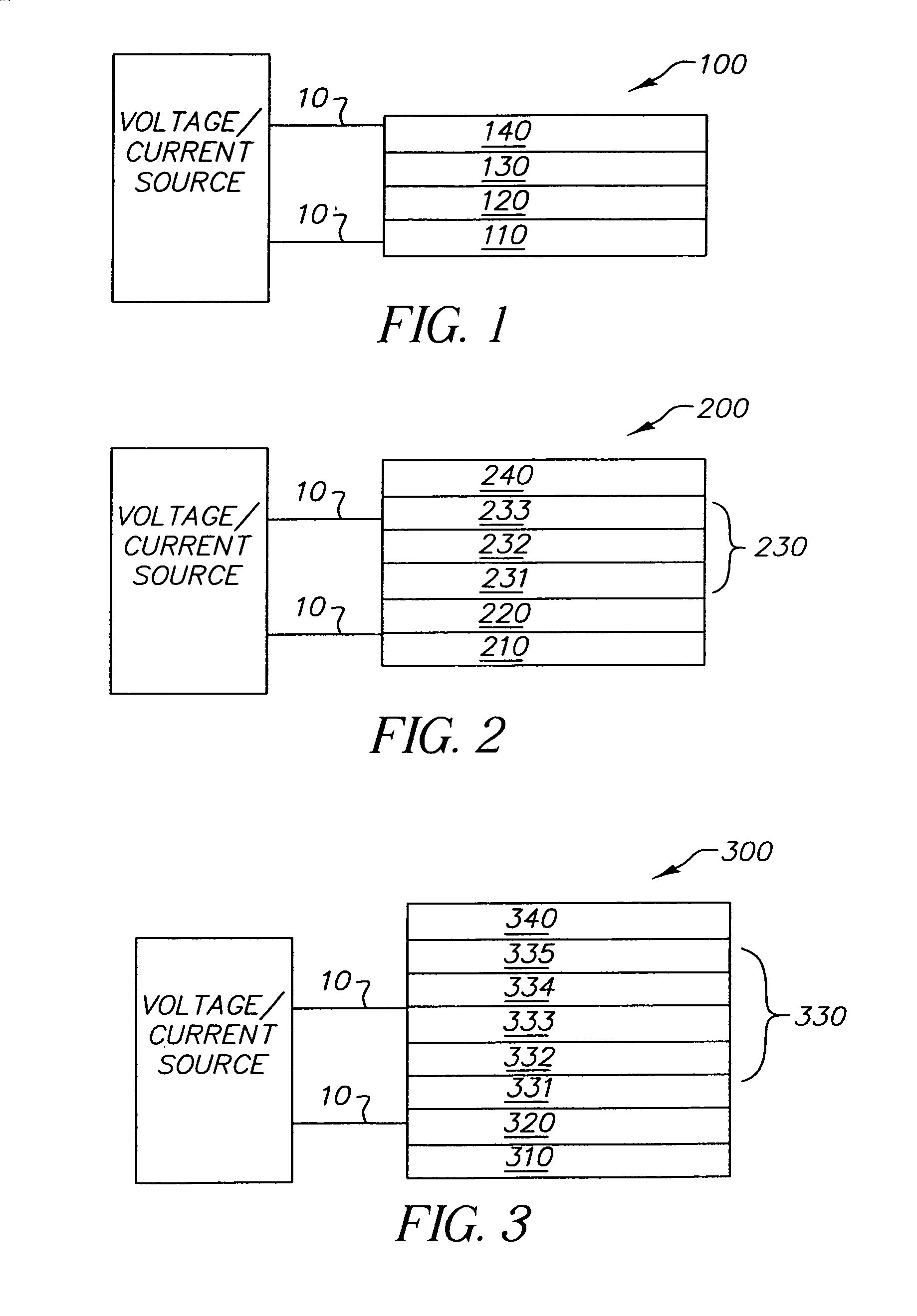
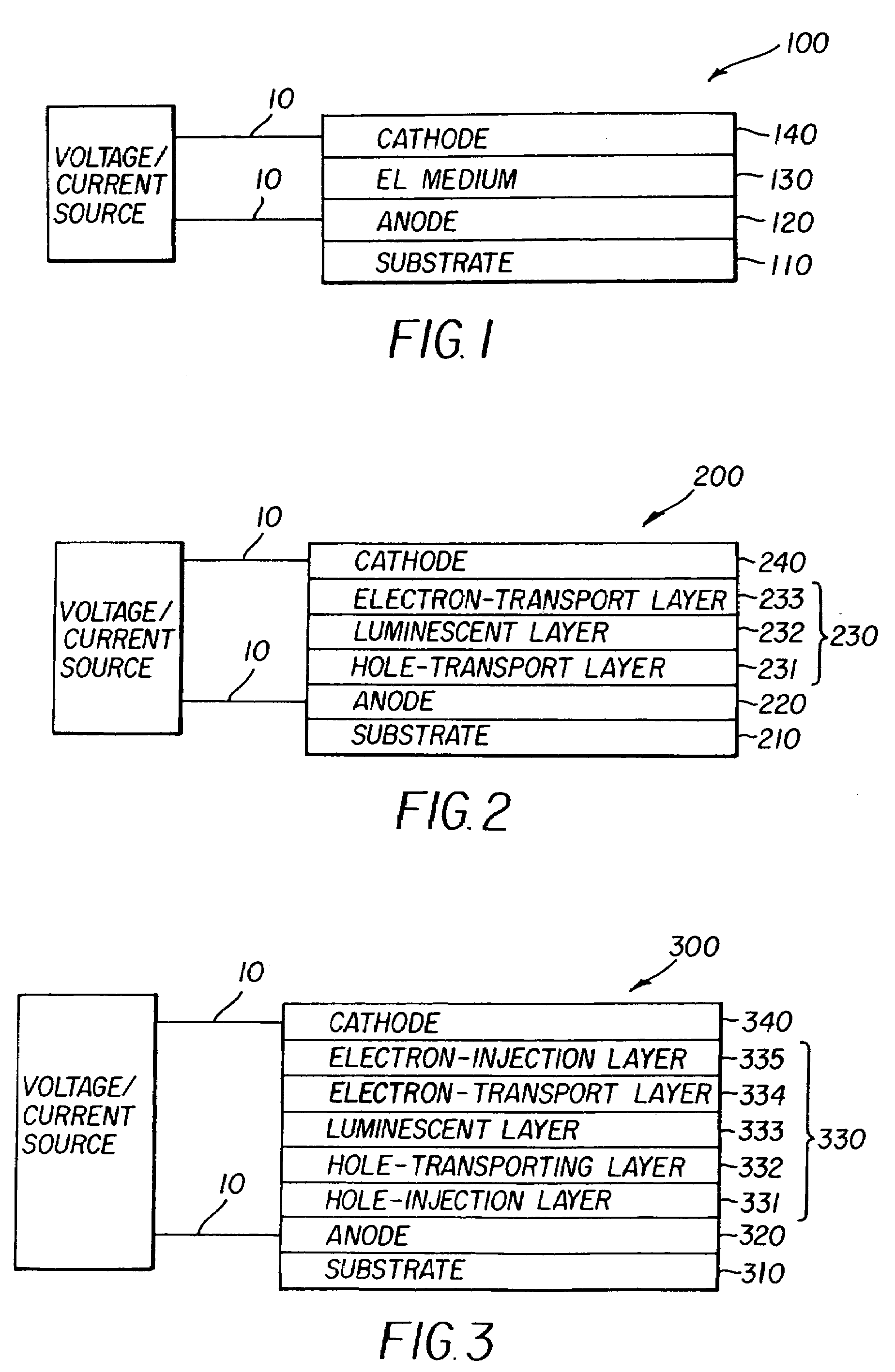
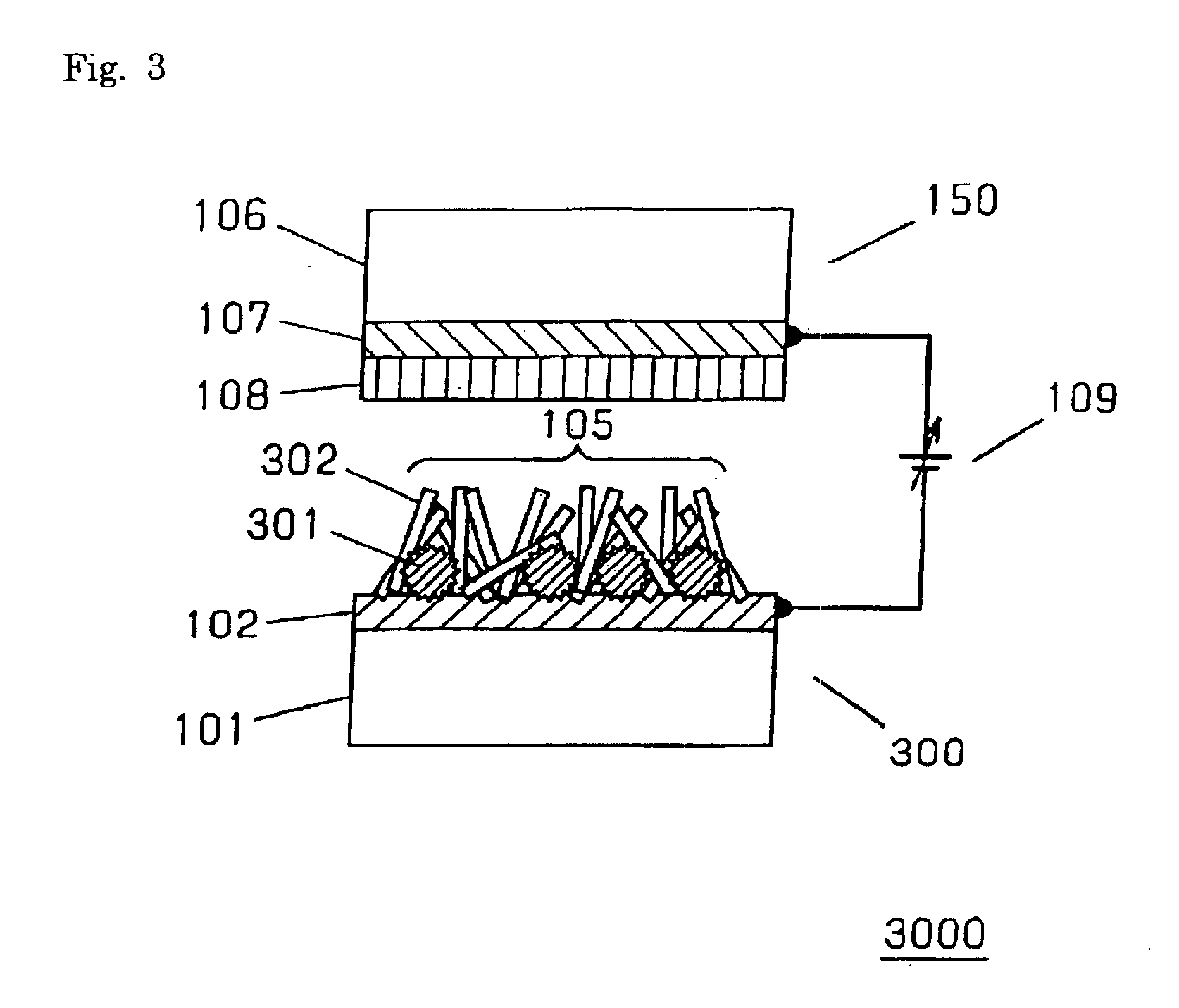
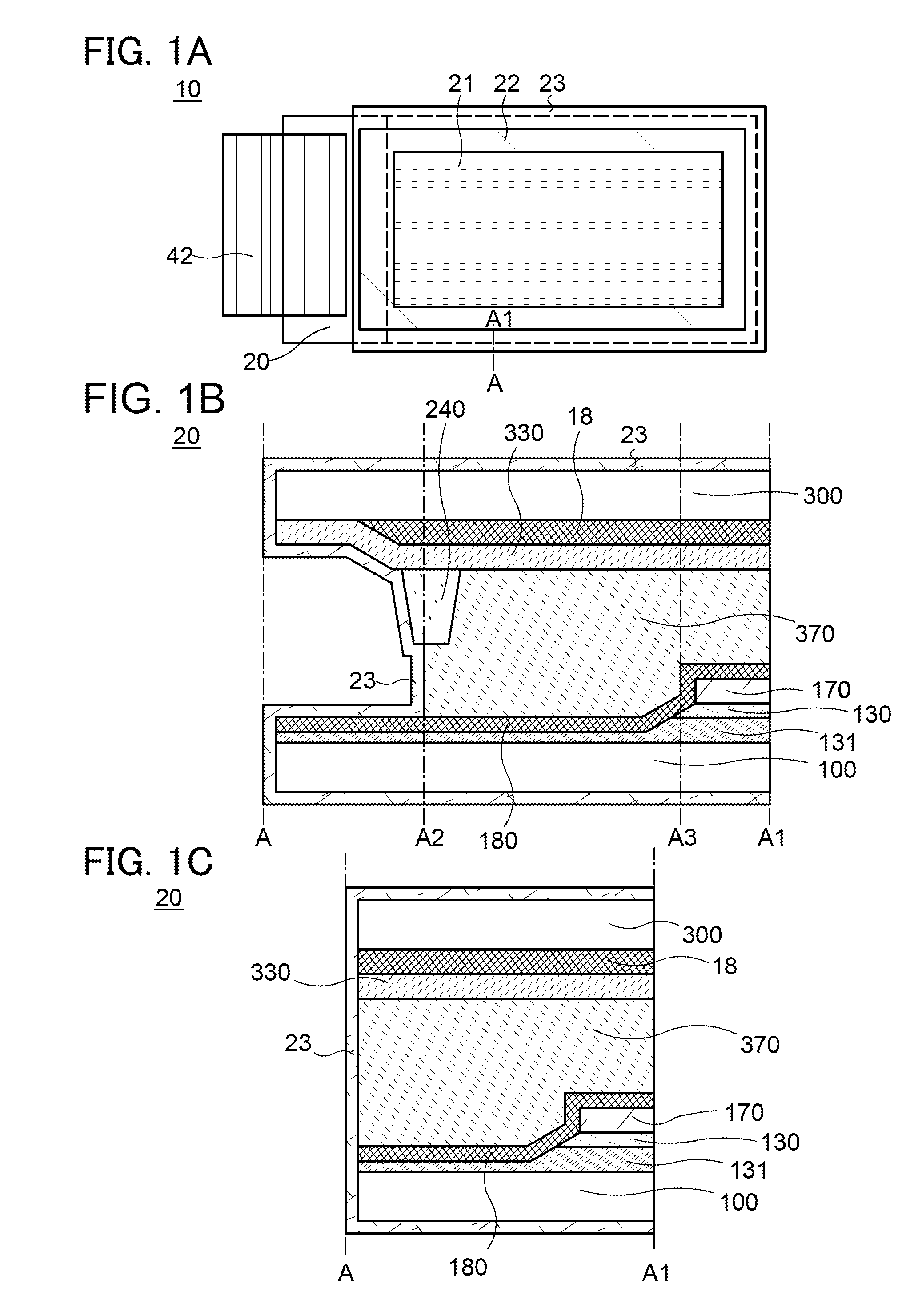
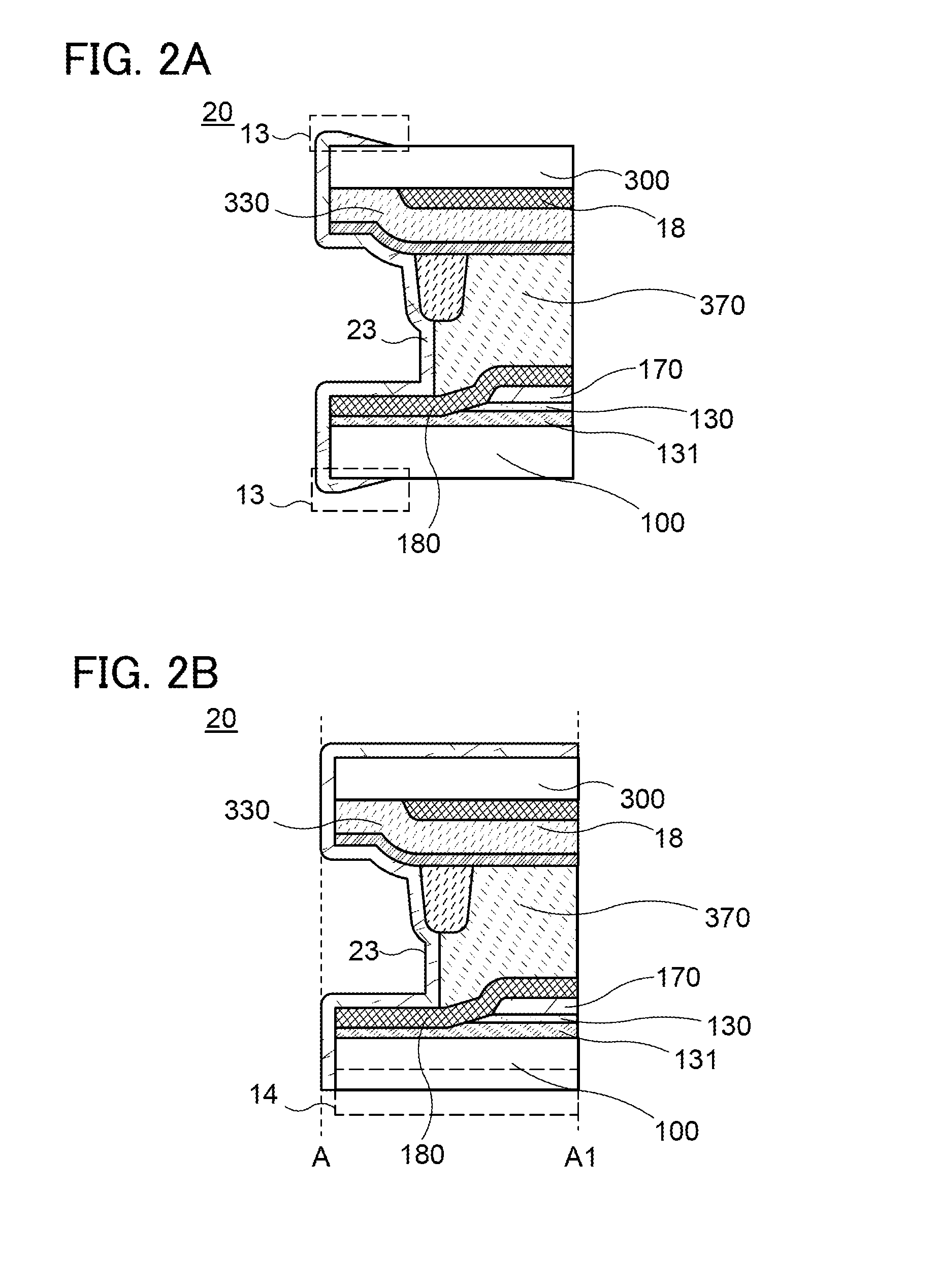
Material for transporting electrons and organic electroluminescent display using the same
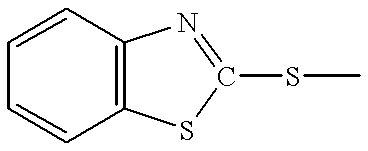
InactiveUS6878469B2Improve the display effectImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensAnthraceneElectron injection
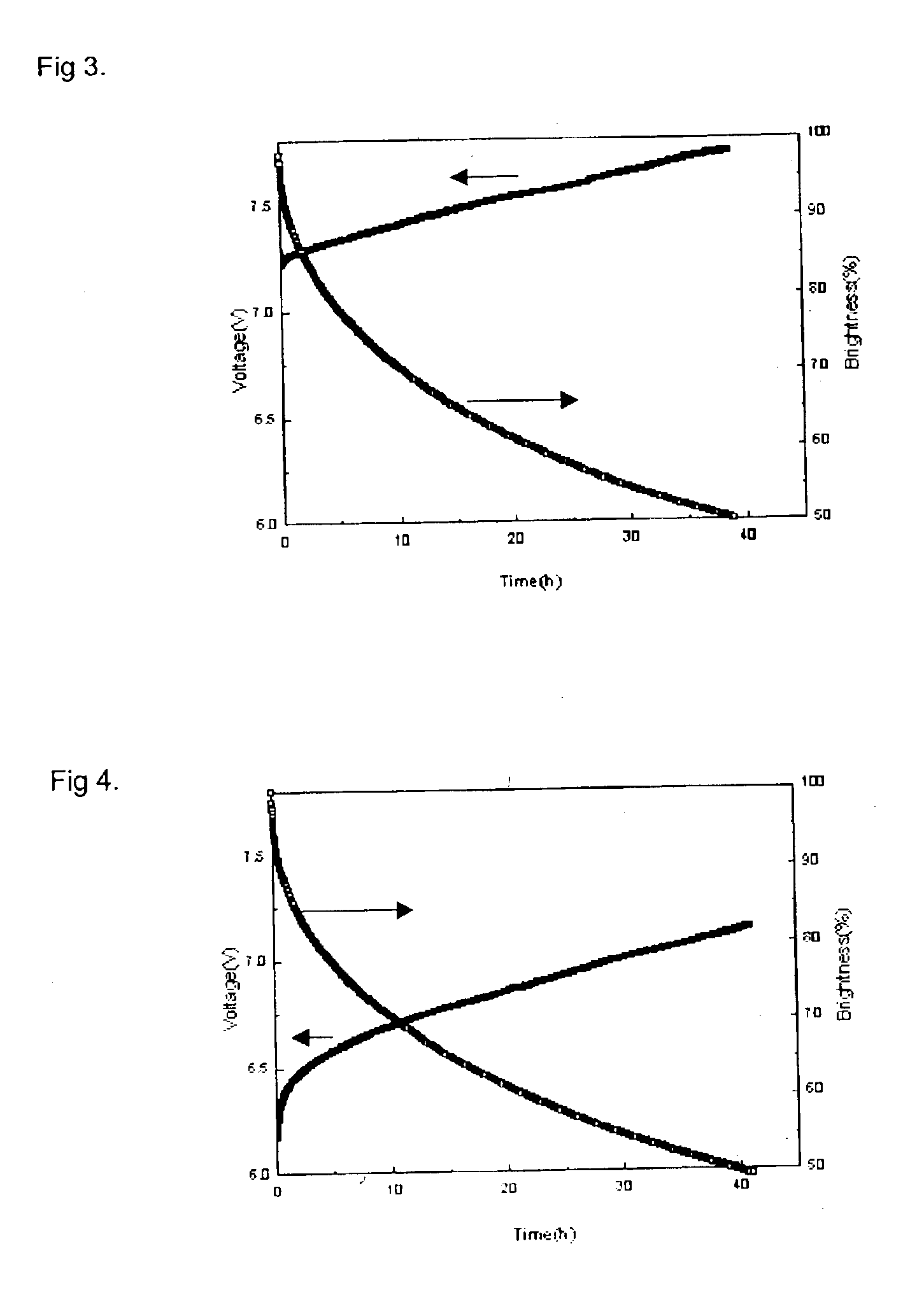
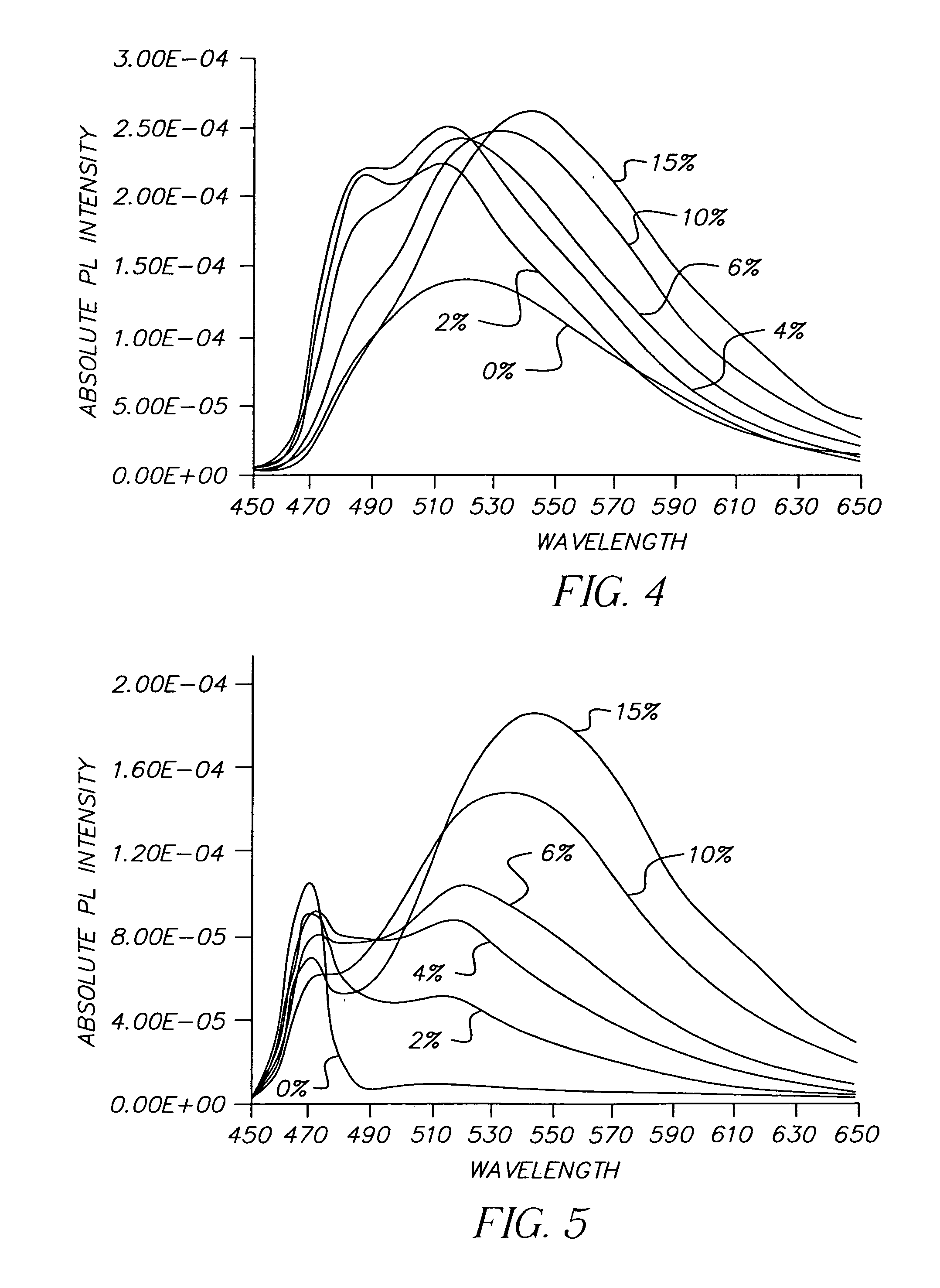
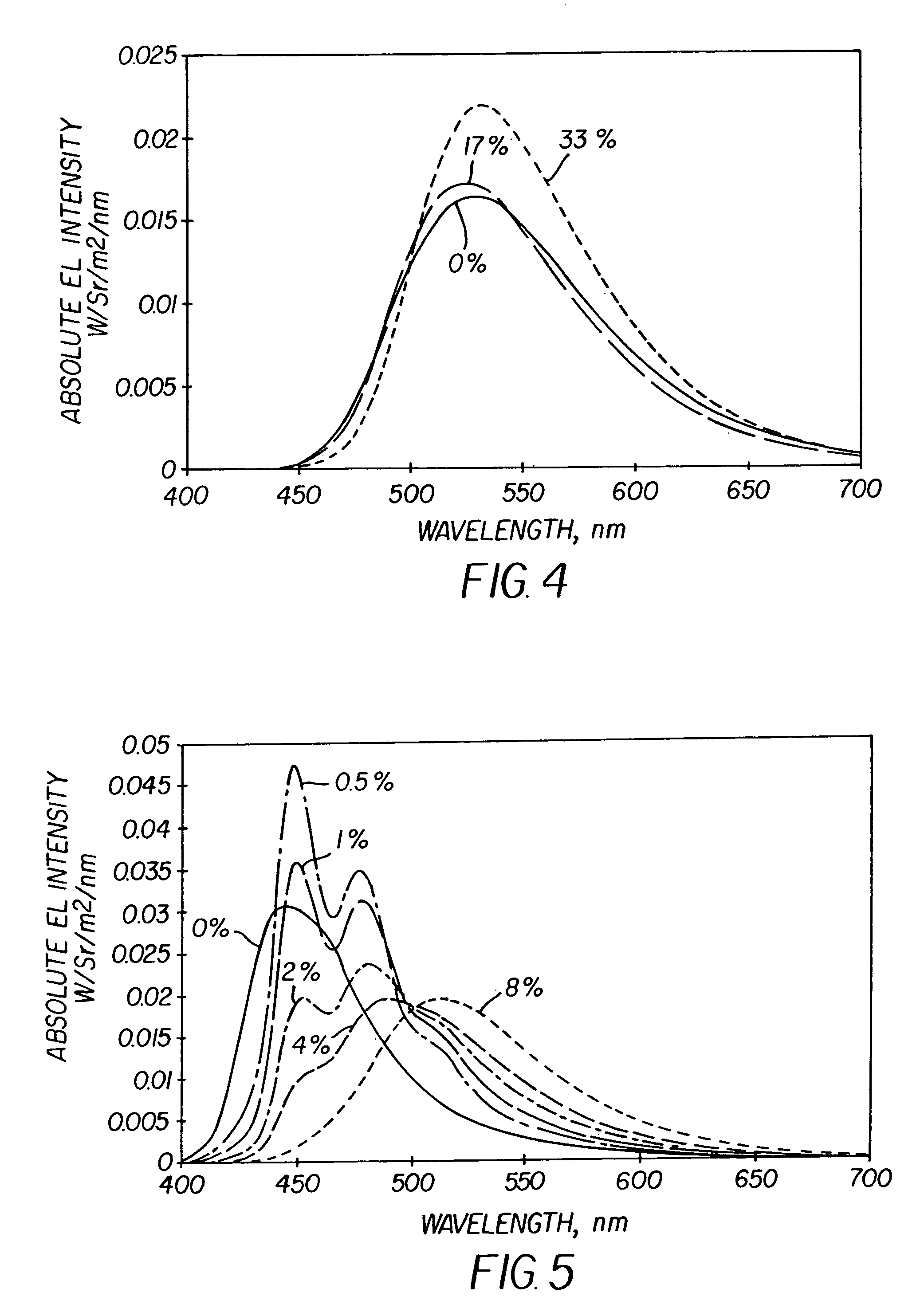
Novel materials for electron injection / transportation and emitting layers can greatly improve the stability of an organic electroluminescent display. Electroluminescent displays incorporating these materials produce blue light at low voltage levels. These novel organic materials include compounds in which 1 to 2 imidazole functional groups are introduced in the 2 or 2,6-site of 9,10 substituted anthracene. An organic electroluminescent display with an organic compound layer of these materials has high efficiency, thermal stability, operationally stability and maintains driving voltage before and after operation.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Organic light-emitting diode devices with improved operational stability
InactiveUS7183010B2High operational stabilityReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantOrganic light emitting device
An organic light-emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a luminescent layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the luminescent layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the luminescent layer is selected to include a solid organic material comprising a mixture of at least two components, one of which is capable of forming both monomer state and an aggregate state.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Aggregate organic light emitting diode devices with improved operational stability
ActiveUS7175922B2Long lastingHigh operational stabilityOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantPerylene
An organic light emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a luminescent layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the luminescent layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the luminescent layer is selected to include a solid organic material comprising a mixture of at least two components, one of which contains at least one perylene carbocyclic ring structure or at least one mono-aza-perylene or poly-aza-perylene ring structure and is capable of forming both monomer state and an aggregate state.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Aggregate organic light emitting diode devices with improved operational stability
ActiveUS20050106415A1Long lastingHigh operational stabilityOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantPerylene
An organic light emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a luminescent layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the luminescent layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the luminescent layer is selected to include a solid organic material comprising a mixture of at least two components, one of which contains at least one perylene carbocyclic ring structure or at least one mono-aza-perylene or poly-aza-perylene ring structure and is capable of forming both monomer state and an aggregate state.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Apparatus for detecting driver's mental state and method for detecting mental state
InactiveUS20090209829A1Improve detection reliabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMental stateDriver/operator
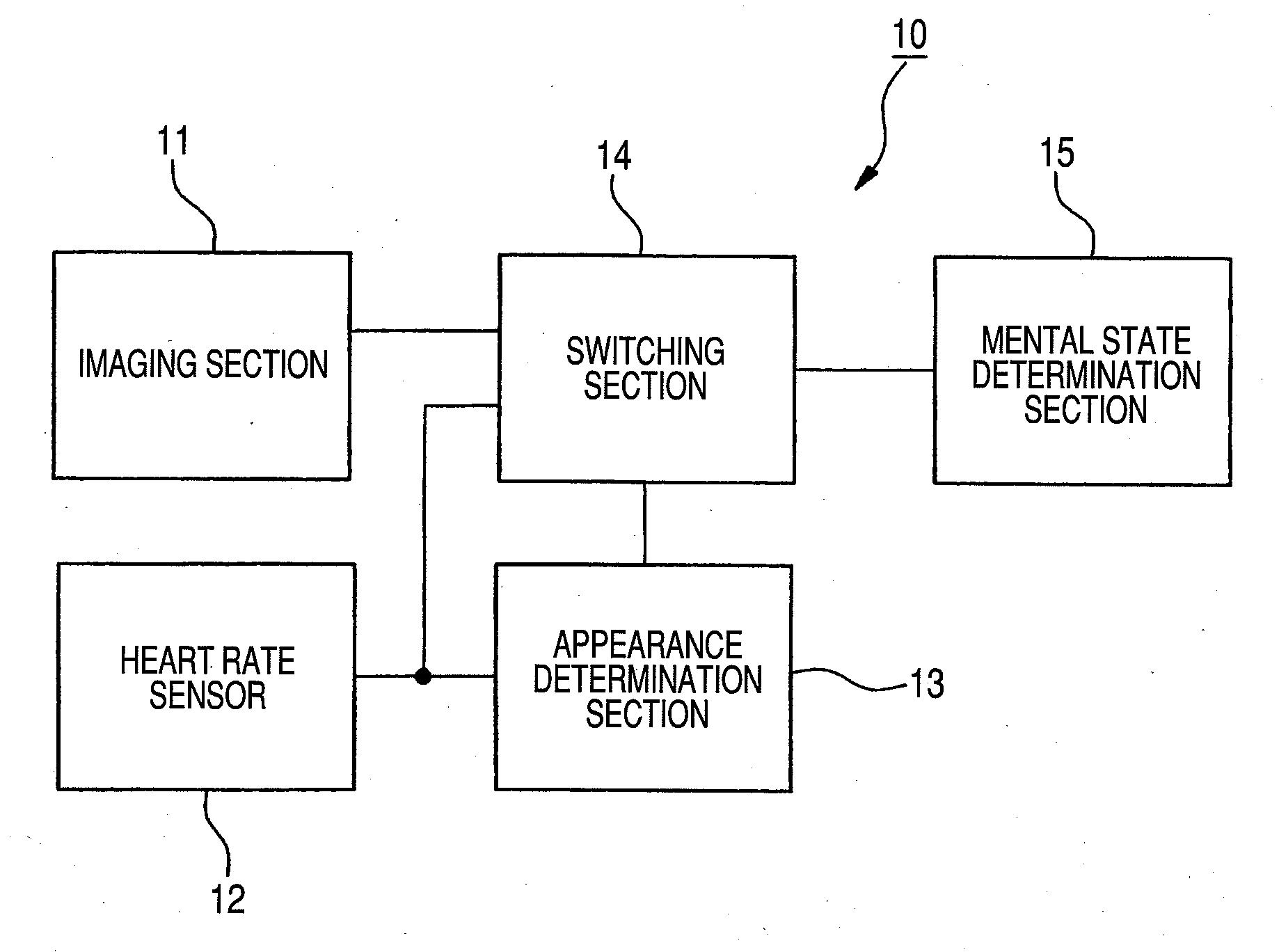
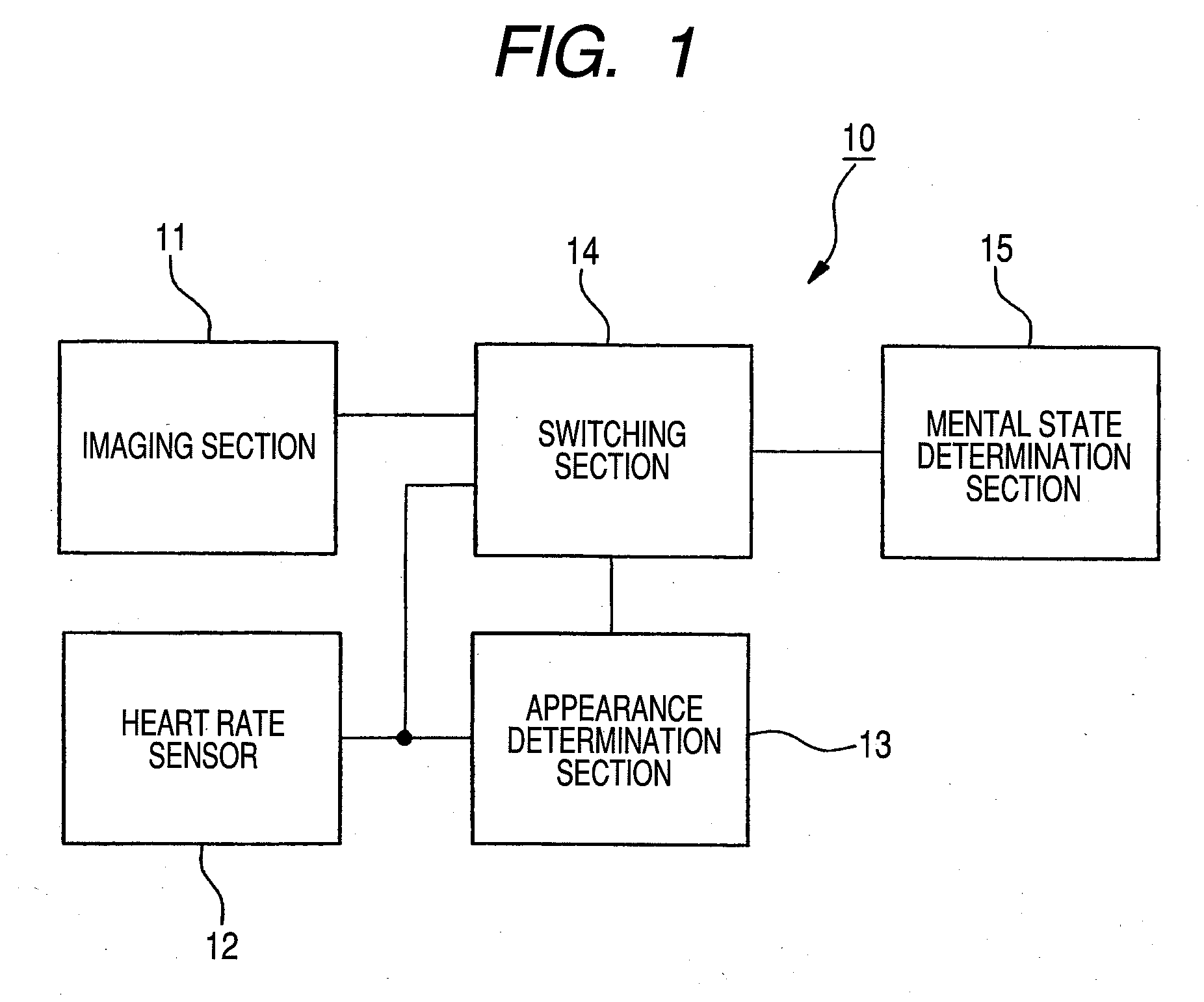
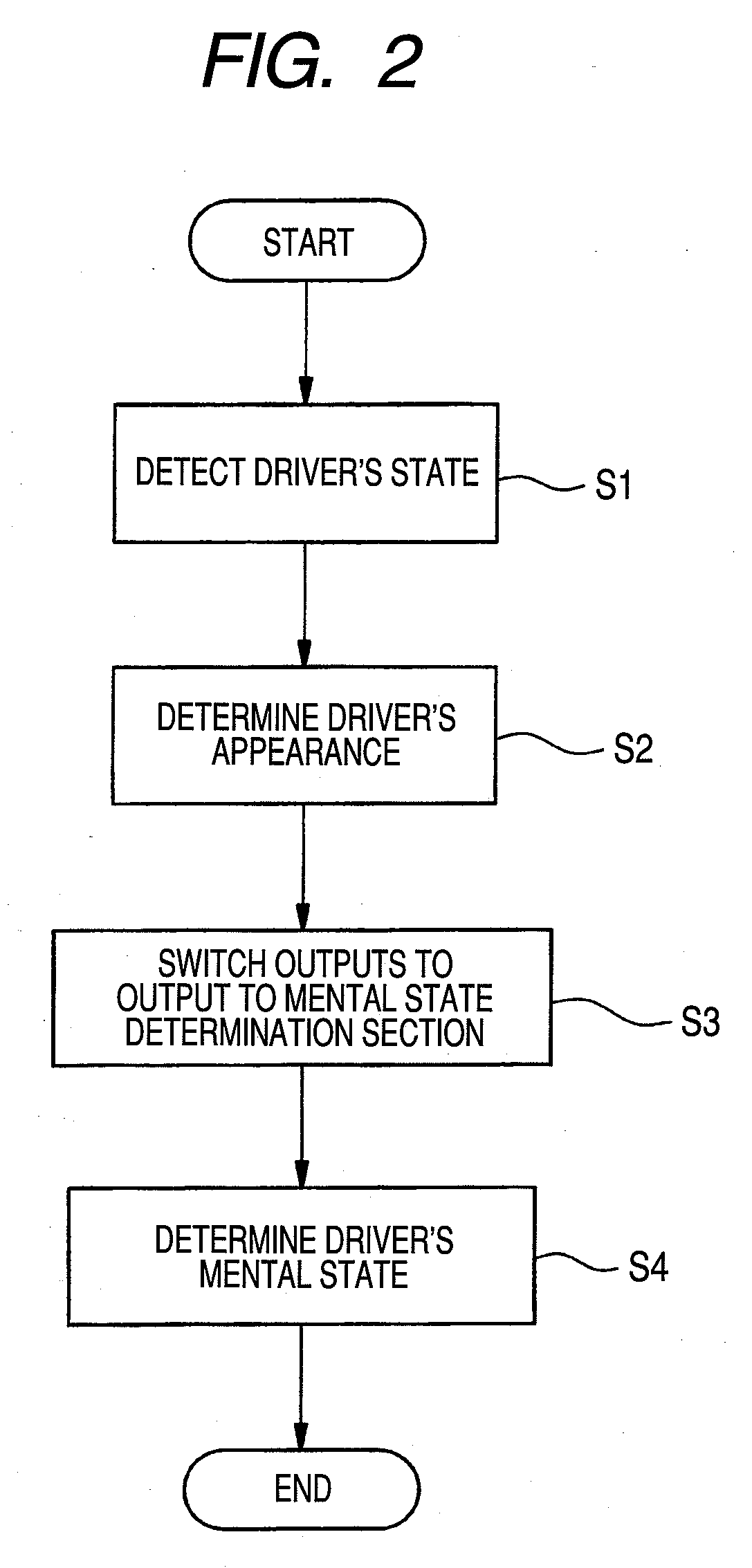
The reliability of detection of a driver's mental state in a vehicle in a driving state is enhanced without impairing operation stability of driving action of the vehicle.There are provided an imaging section 11 and a heart rate sensor 12 that serve as a plurality of detection means for detecting a driver's state; an appearance determination section 13 for determining a driver's appearance from detection results from the imaging section 11 and the heart rate sensor 12; and a mental state determination section 15 for determining a driver's mental state from the detection results from the imaging section 11 and the heart rate sensor 12. A switching section 14 switches the outputs from the imaging section 11 and the heart rate sensor 12 to an output from the mental state determination section 15 on the basis of a determination result from the appearance determination section 13.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
System and method for managing business performance
InactiveUS20060178973A1Improve performanceReduce usageFinanceCommerceVisibilityOperational stability
A preferred embodiment of the invention includes a method and system to achieve improved profitability, liquidity and operational stability of a used vehicle operation. In broad overview, one embodiment of the invention includes four main aspects including the establishment of departmental objectives as a predetermined metric, the integration of the most current market and inventory information into an existing business process, the assessment of strategic impact of each key decision at a transactional level by calculating a real time performance metric and comparing the real time performance metric to the predetermined baseline or target metric and providing visibility and accountability of all key decisions.
Owner:VAUTO
Electron-emitting element and electron source, field emission image display device, and fluorescent lamp utilizing the same and methods of fabricating the same
Disclosed are an electron-emitting element having a large operating current at a low operating voltage and excellent operation stability, and an electron source, an image display device and the like utilizing such an electron-emitting element, and further a method of fabricating such an element with few process steps at low cost. A cold cathode member is configured utilizing hybrid particle of a first particle serving to emit electrons into the space and a second particle being in the vicinity of the first particle and serving to control the position of the first particle. In this configuration, it is preferable that the first particle have a higher electron emission efficiency than the second particle and that the second particle be conductive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
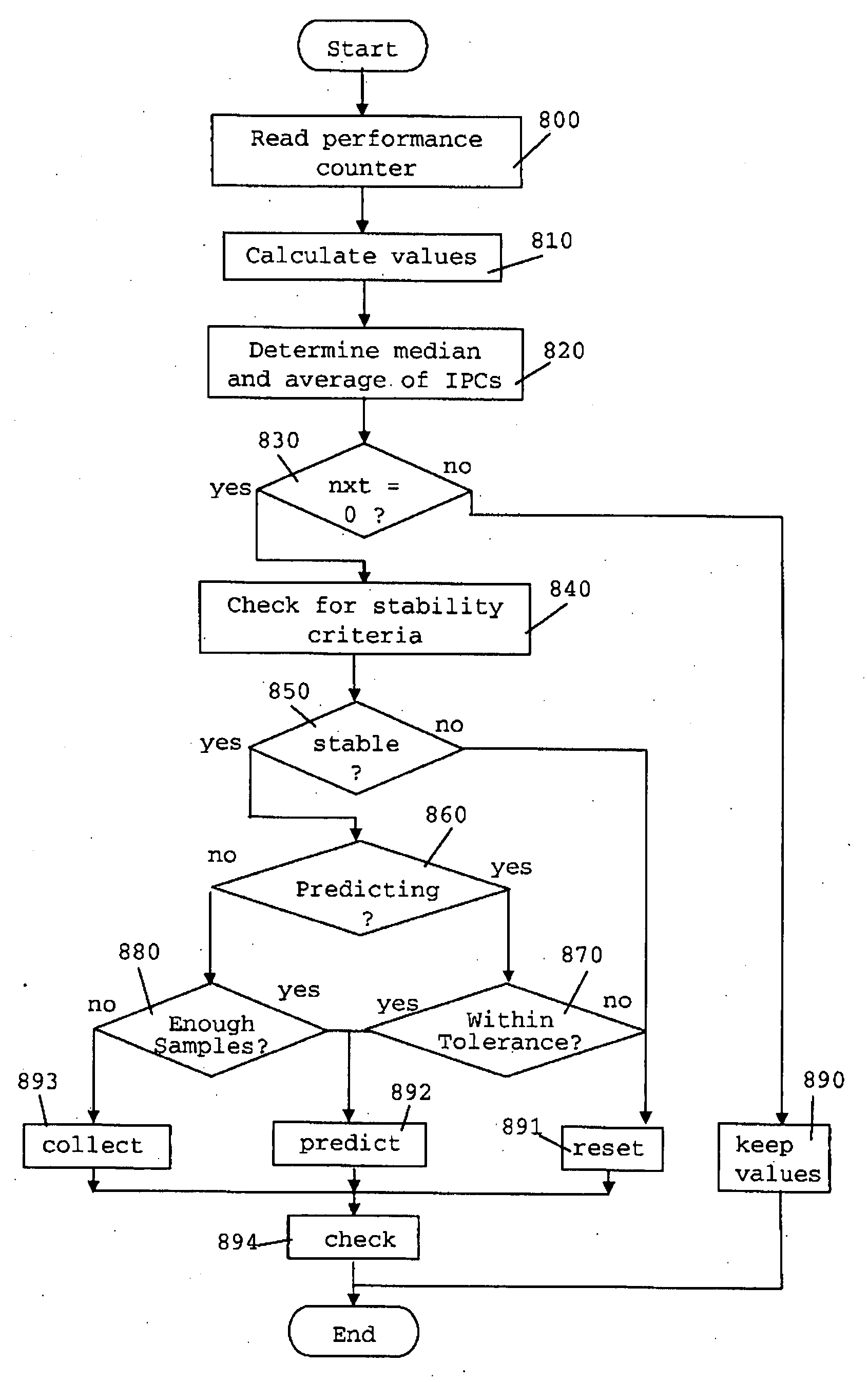
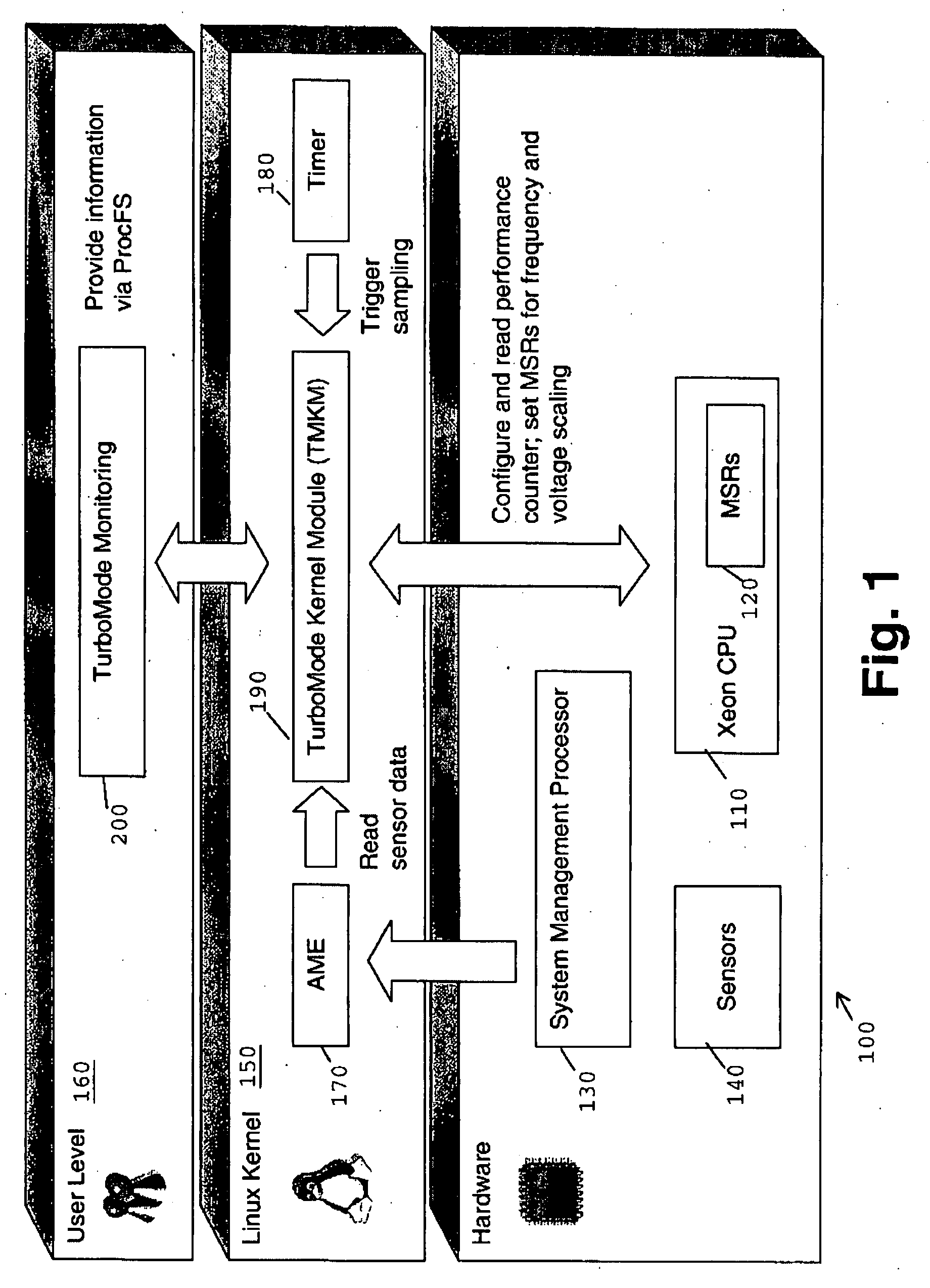
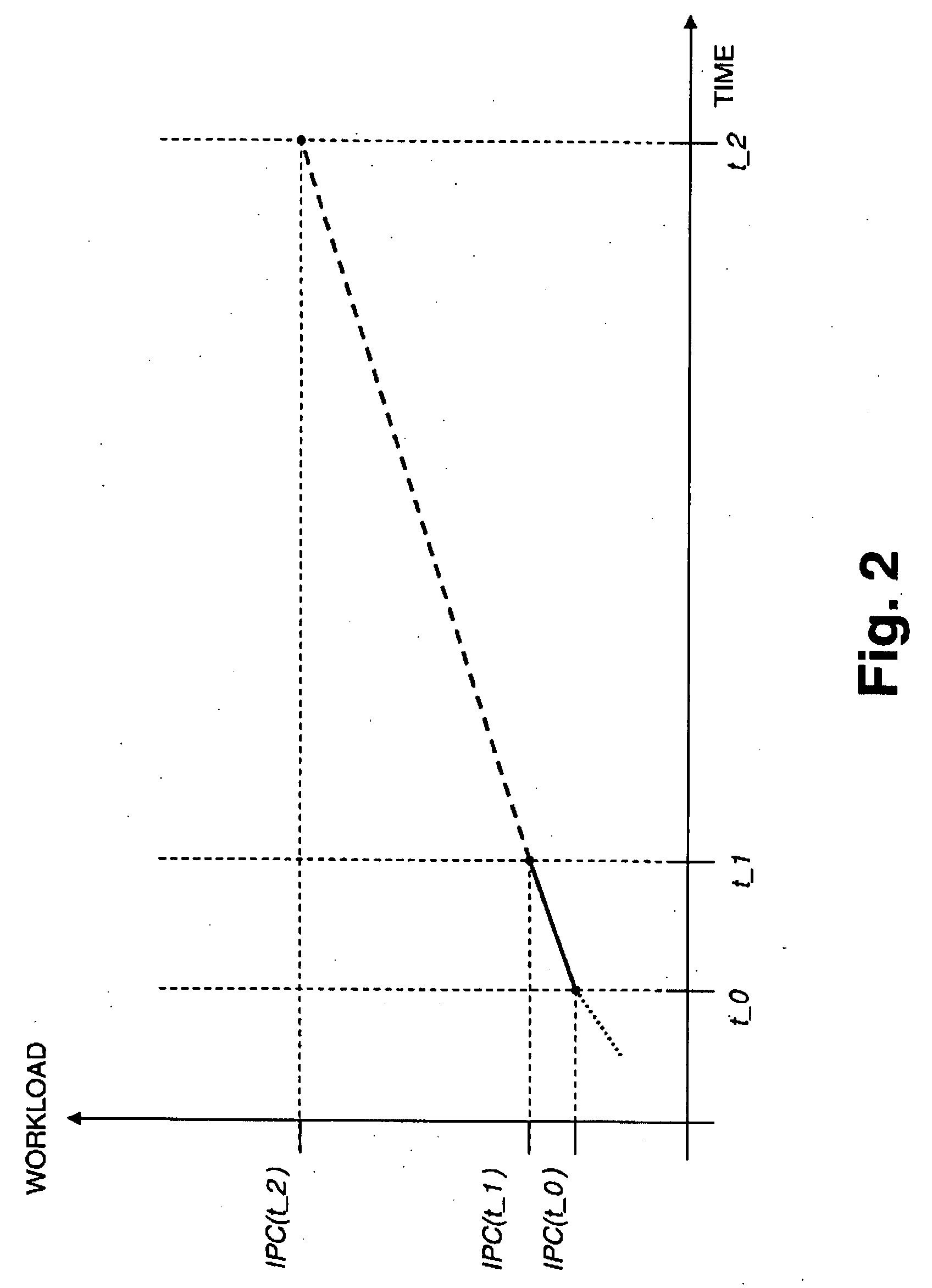
Method for Autonomous Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling of Microprocessors
ActiveUS20080098254A1Improve performanceSave energyEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless headset and control method thereof
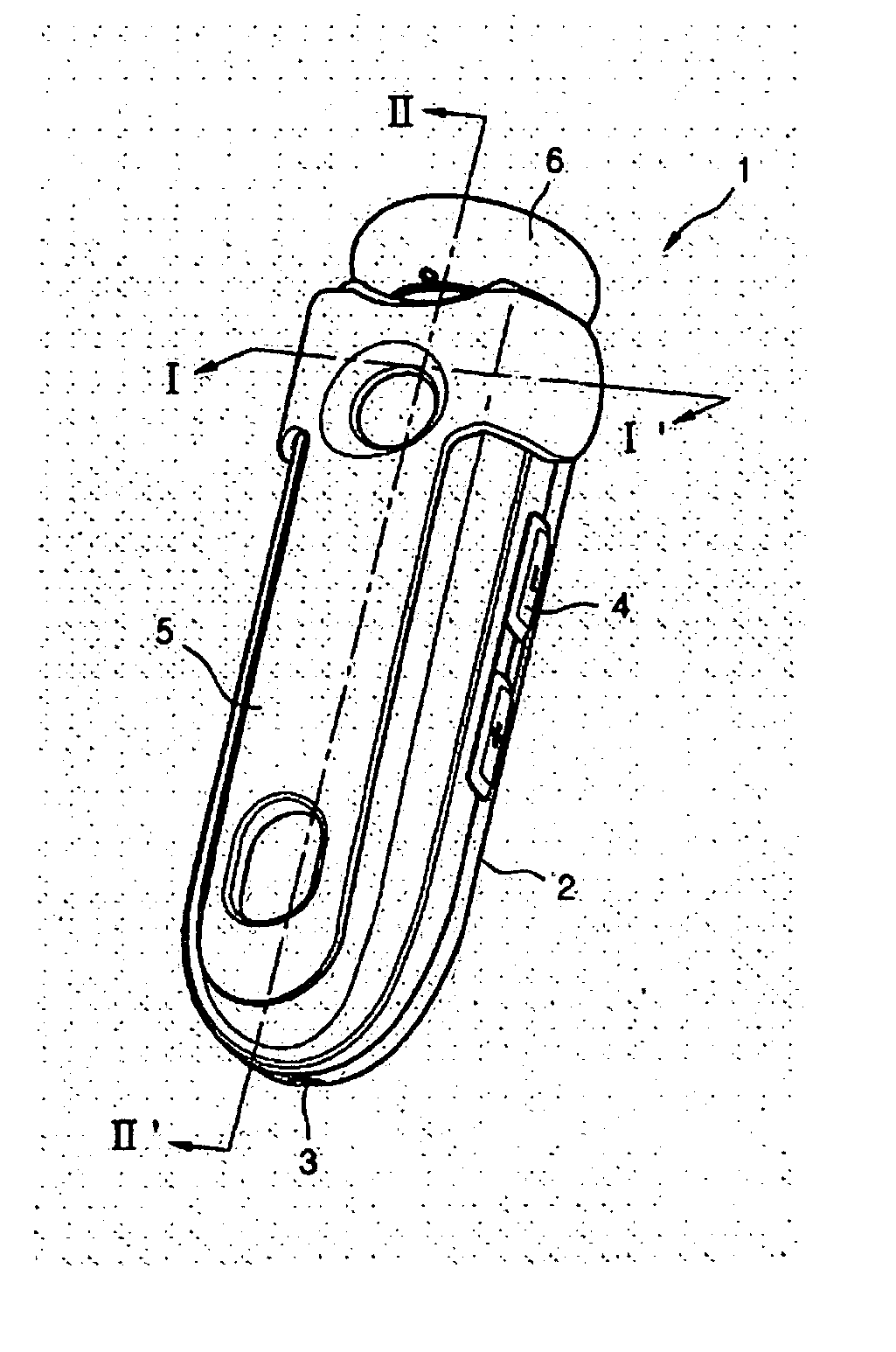
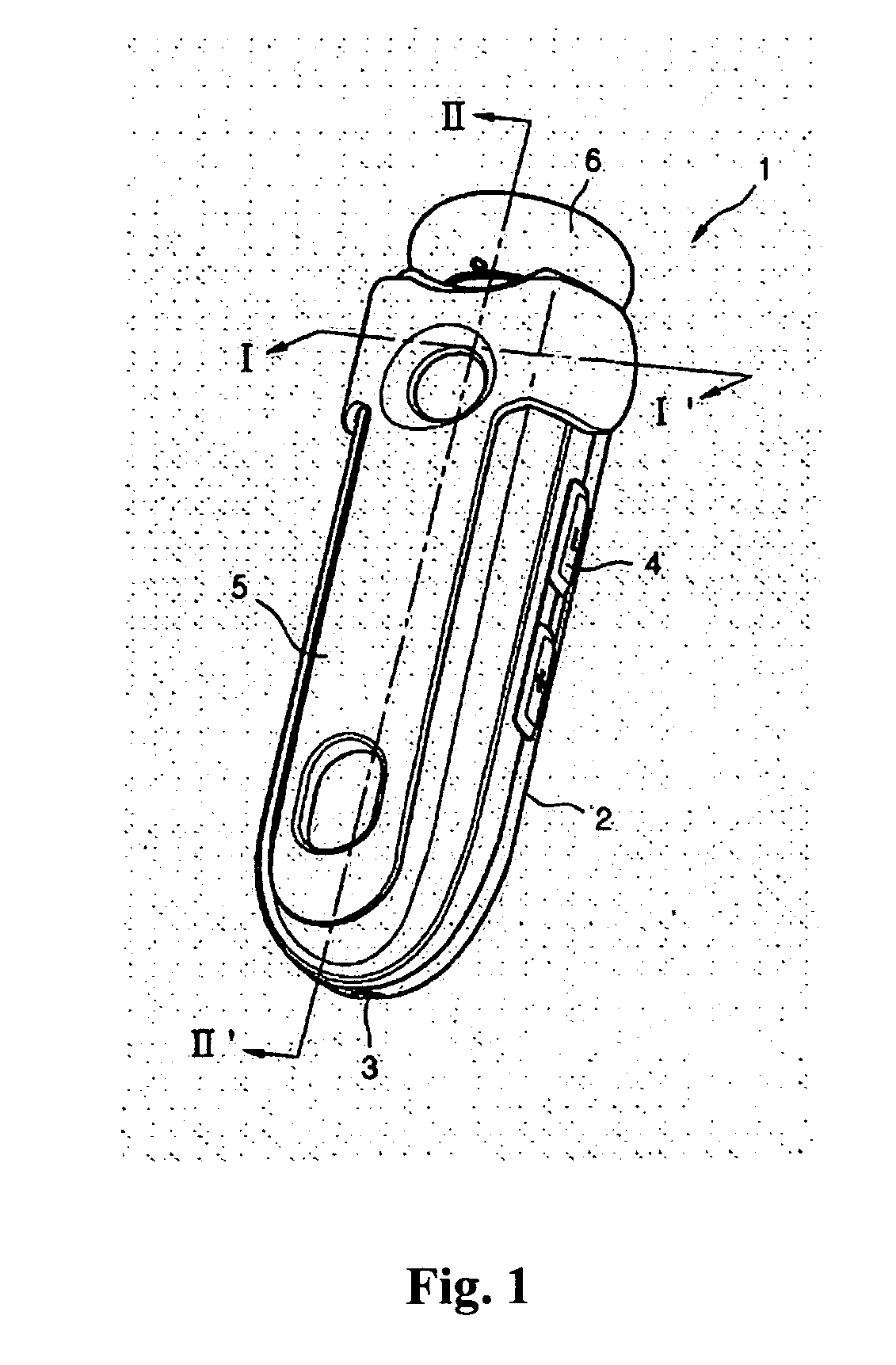
InactiveUS20070133836A1Operational stability can be improvedReduce manufacturing costTelephone set constructionsDeaf-aid setsEngineeringOperational stability
A foldable wireless headset is introduced comprising an elongated bar-shape main body, a hinged earphone attached at the proximal end of the main body, and an earphone position guidance for maintaining the earphone stationary at the selected position with respect to the main body either one of an extending position, retracting position and intermediate position. The wireless headset enhances operational stability, saves manufacturing costs, is easily carried, and is convenient to use. Also, the wireless headset can be automatically turned on and off in response to the extraction and retraction of the earphone.
Owner:SIMPLEBE +1
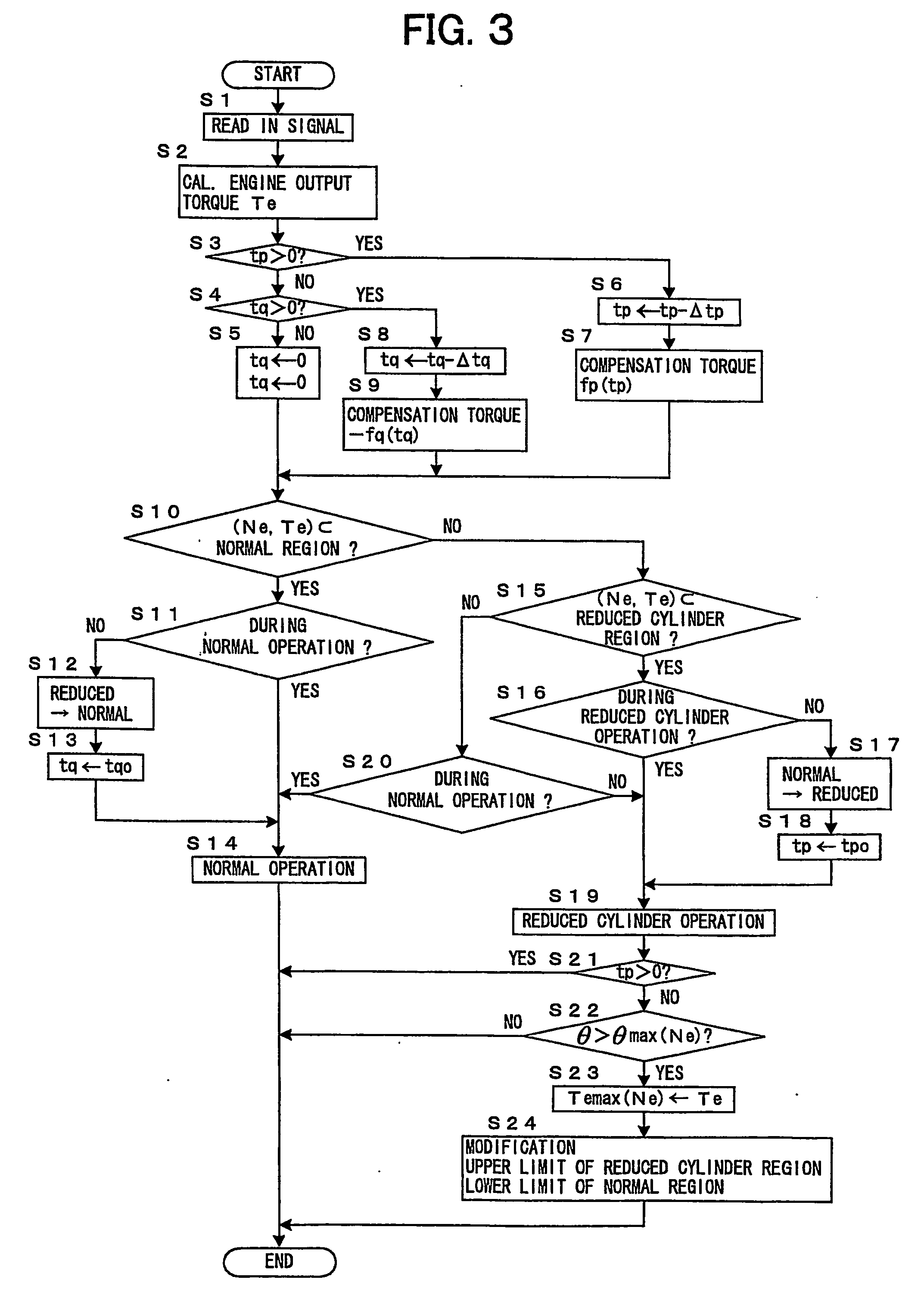
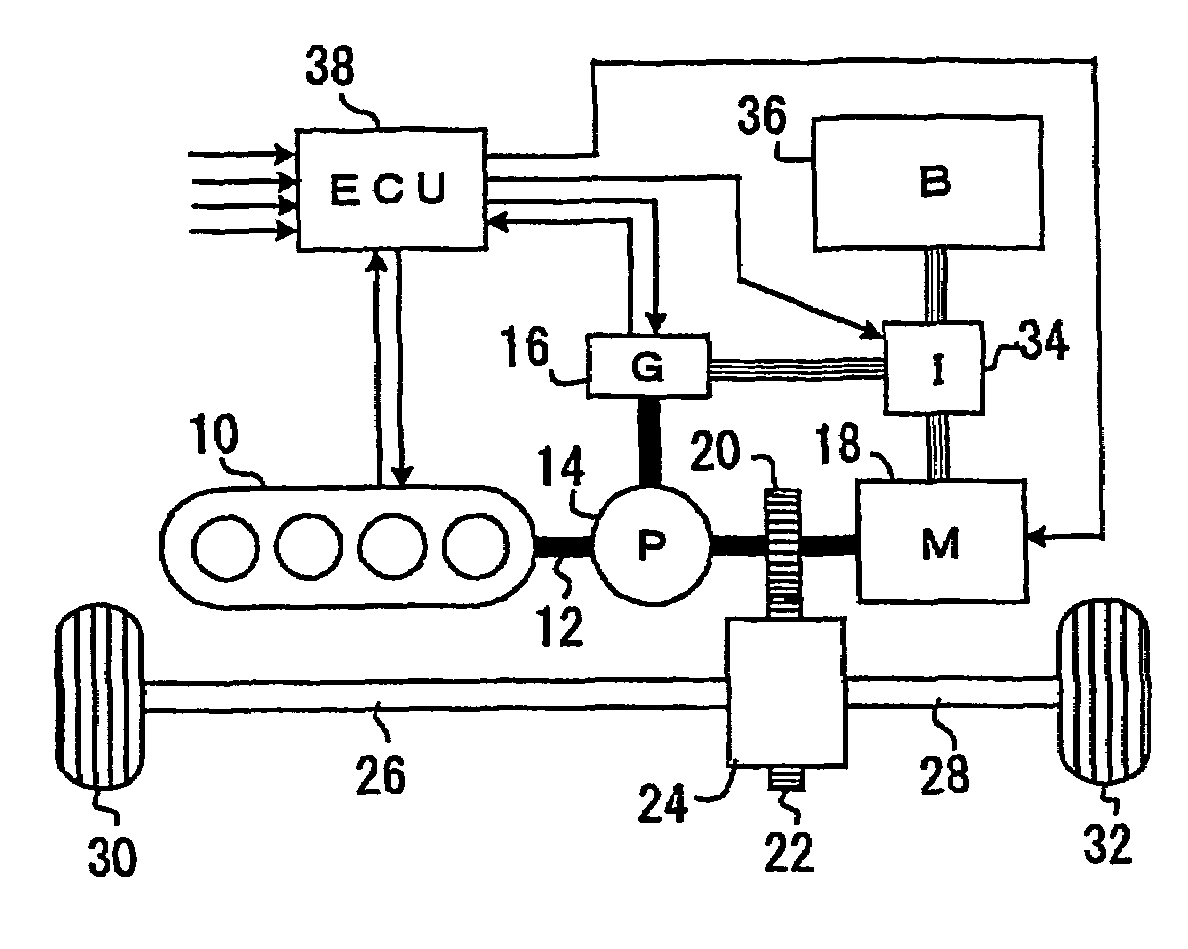
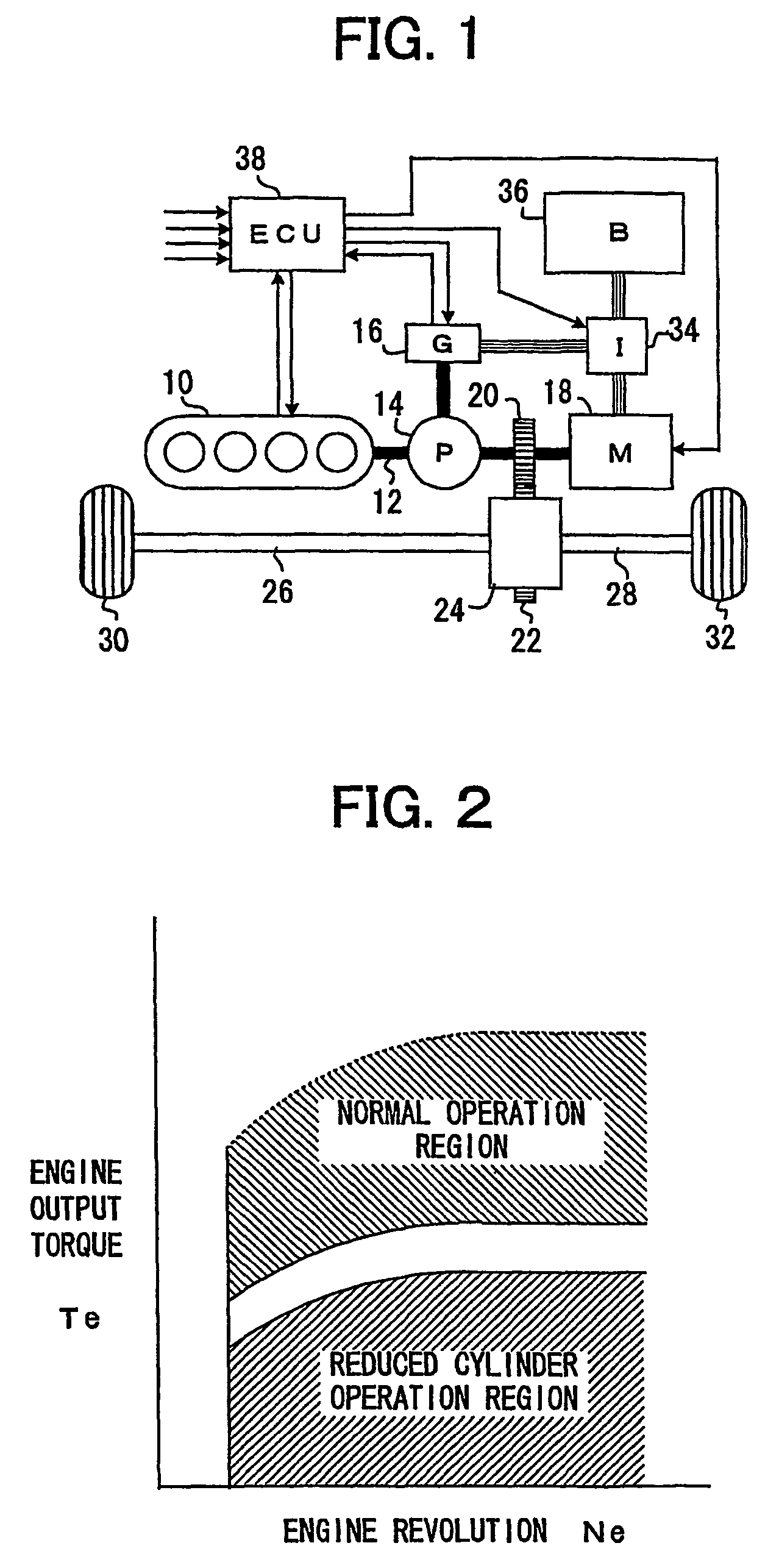
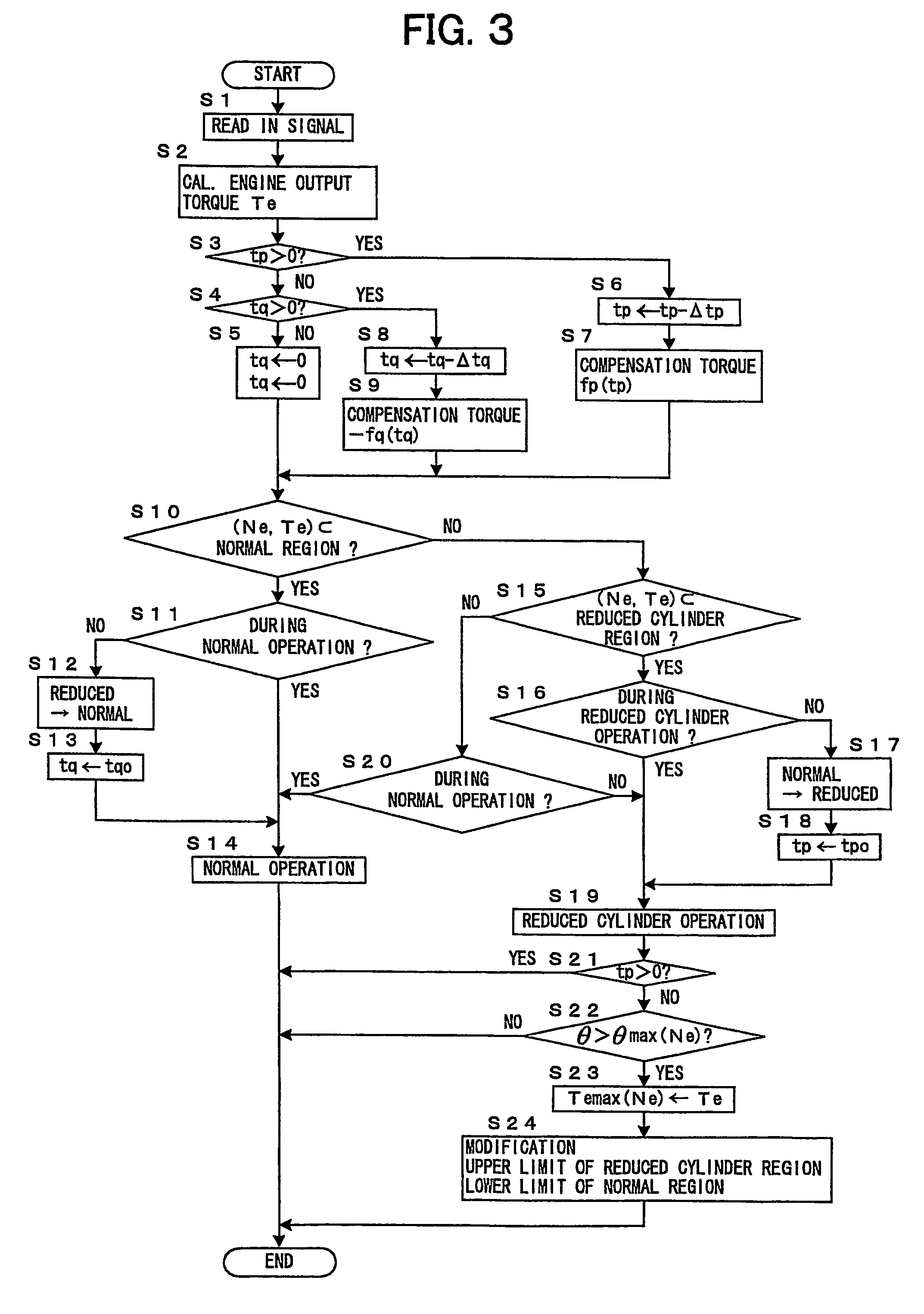
Control device of cylinder reducing operation of multi-cylinder engine
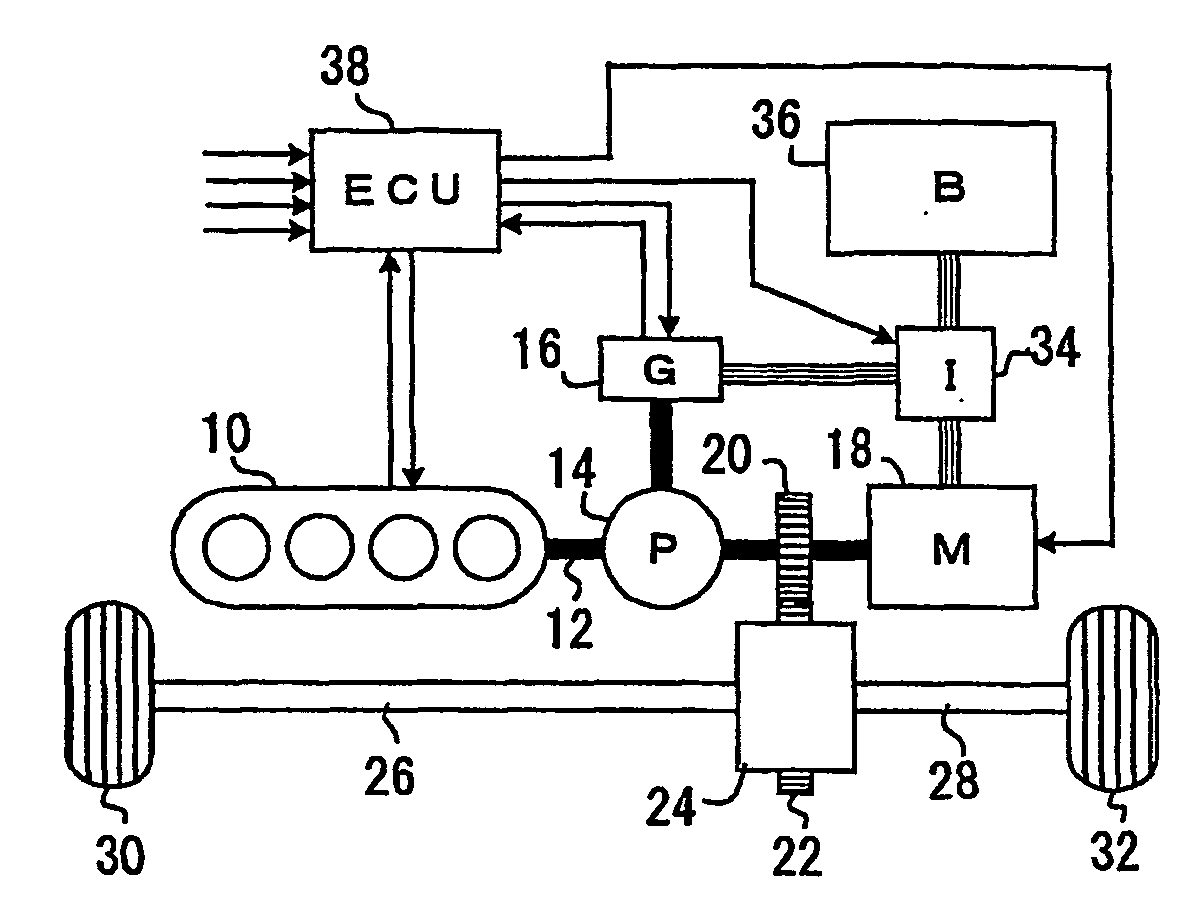
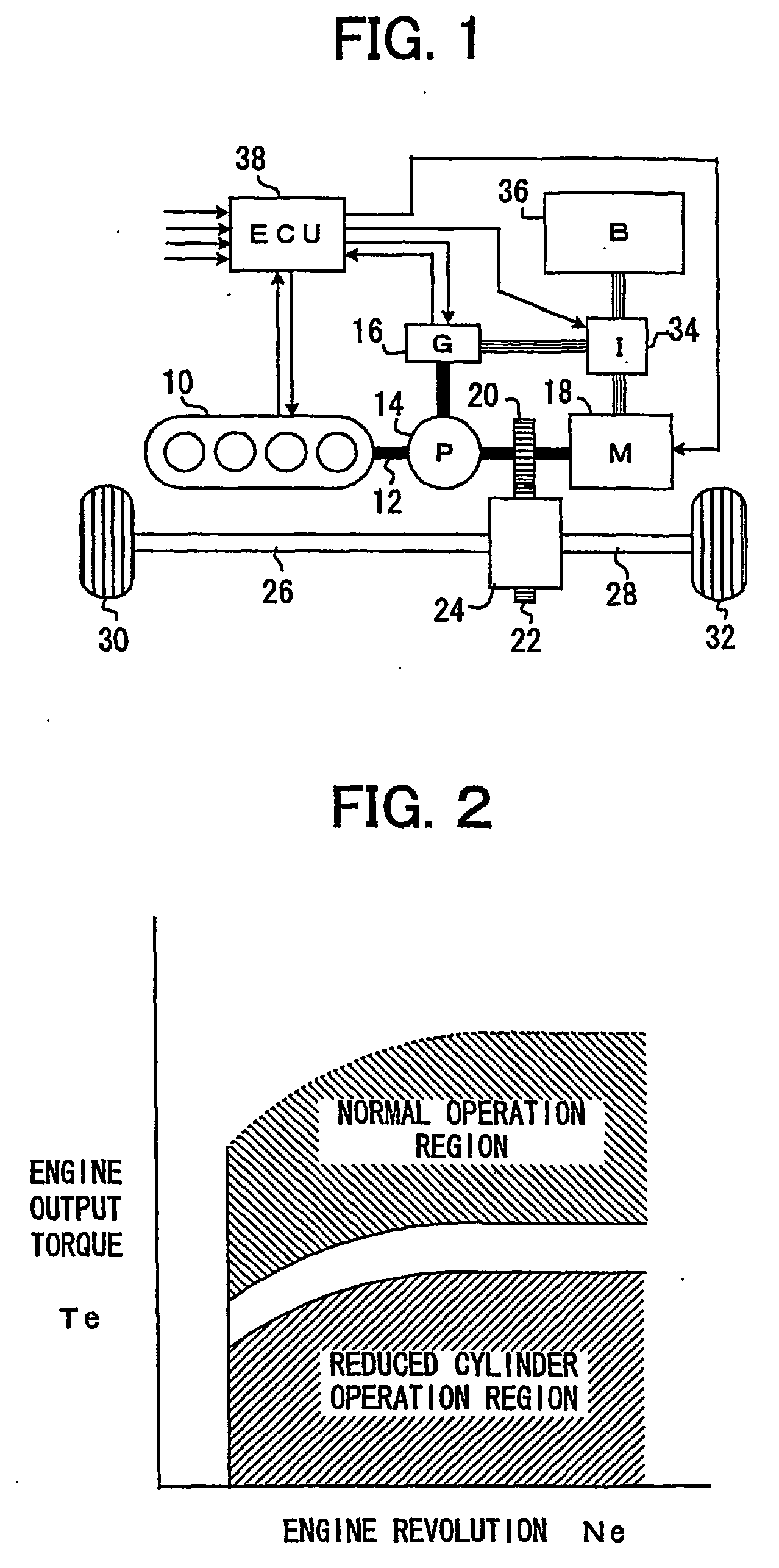
ActiveUS20070042861A1Reduce stepsEasy to controlHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlOperational stabilityVehicle control
A control device for cylinder reducing operation of a multi-cylinder engine for a vehicle controls the number of working cylinders in the engine more appropriately for fuel economy while ensuring the operational stability of the engine and comfortable drivability of the vehicle. The control device comprises a detector detecting engine output torque and judges if cylinder reducing operation is to be executed while referring to the engine output torque. Because of the detection of engine output torque, cylinder reducing operation will be executed as long as torque requested of the engine is available from the reduced number of working cylinders, thereby ensuring the generation of torque required in operating the engine while saving fuel as much as possible. Through a learning process, criteria for the judgment of execution of cylinder reducing operation are modified to be adapted for any variation of engine output performances.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
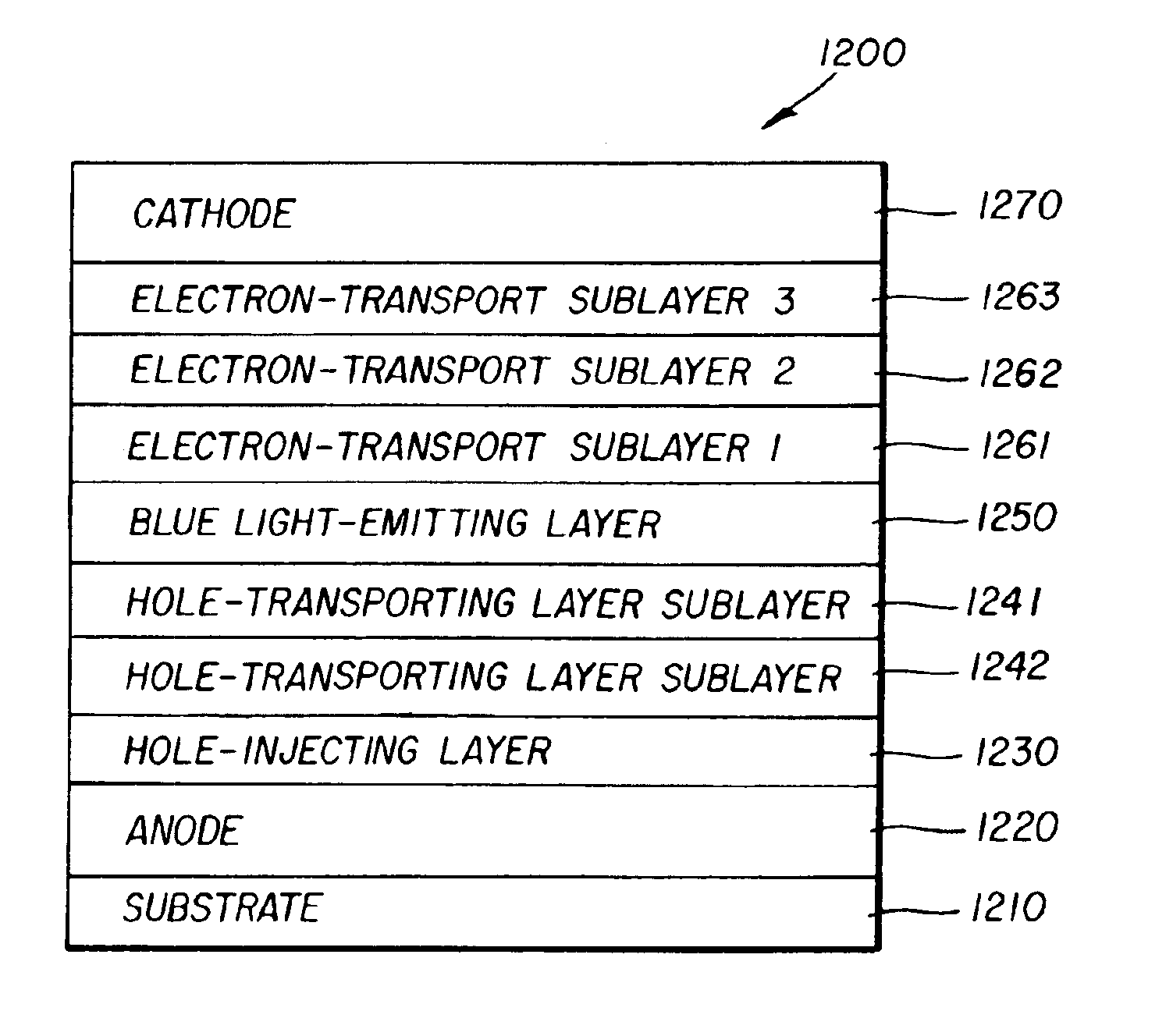
White light-emitting OLED device having a blue light-emitting layer doped with an electron-transporting or a hole-transporting material or both
InactiveUS6967062B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionElectron transporting layer
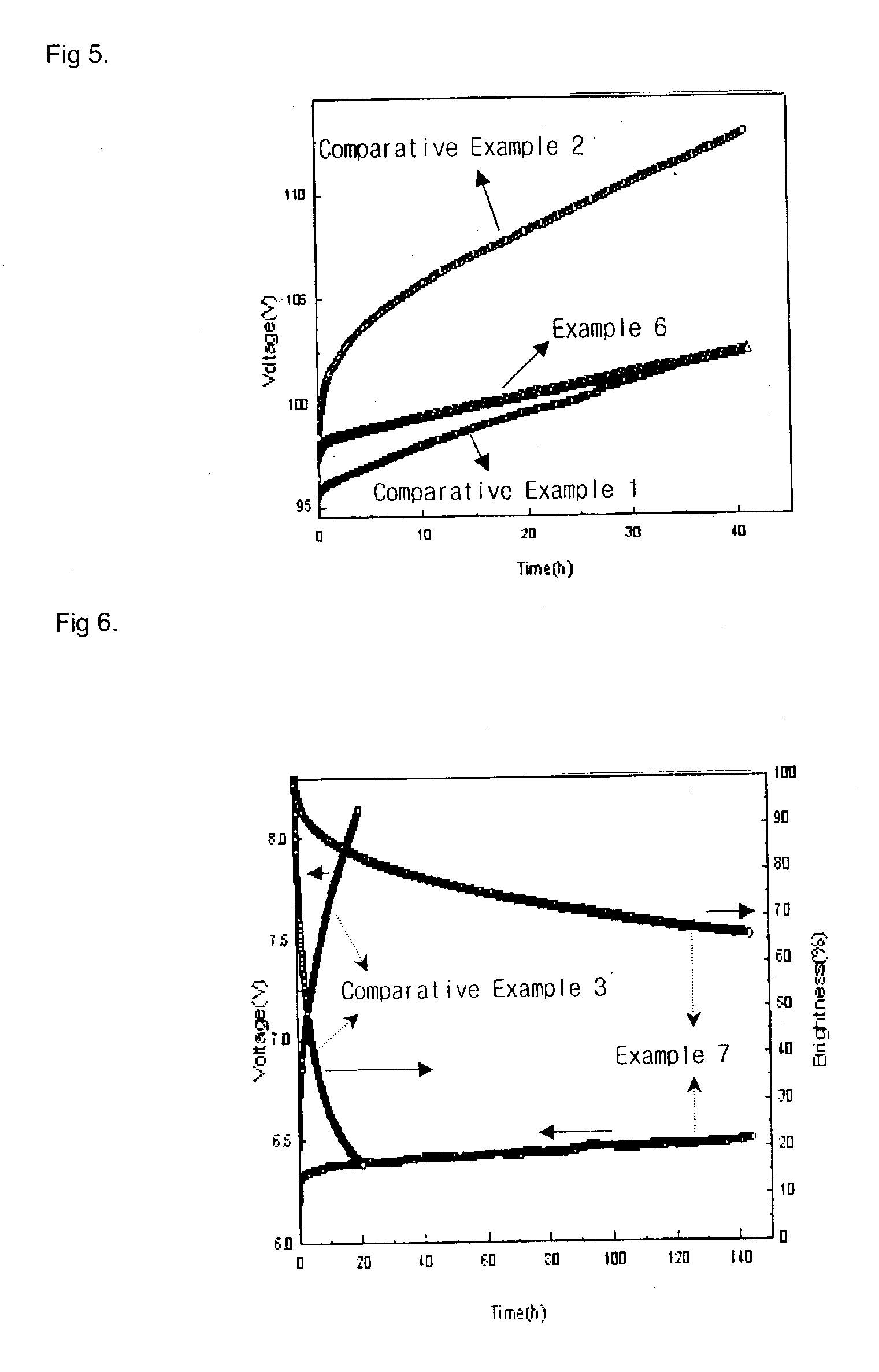
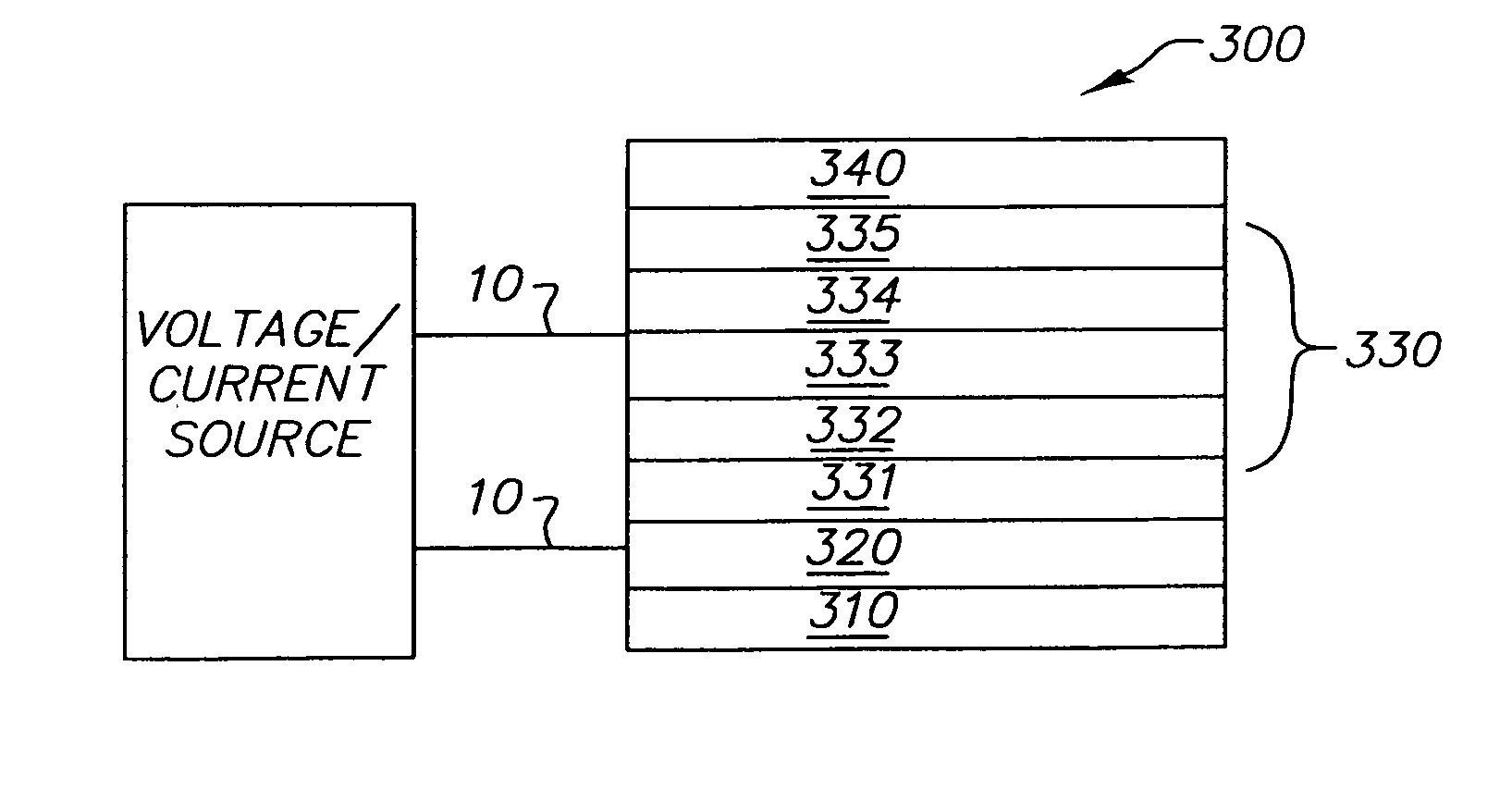
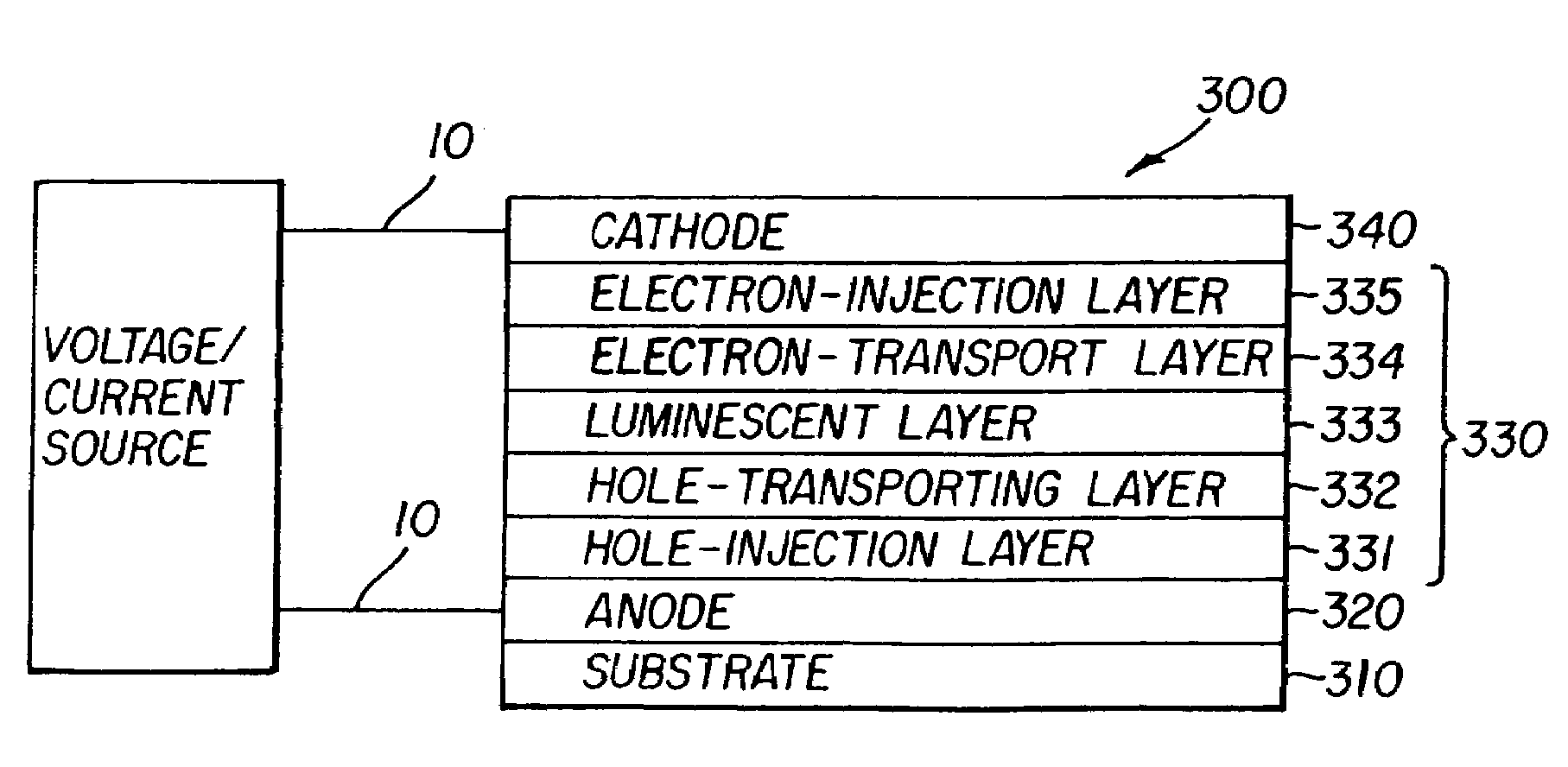
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device which produces substantially white light includes an anode; a hole-transporting layer disposed over the anode; and a blue light-emitting layer having a host doped with a blue light-emitting compound disposed directly on the hole-transporting layer and the blue light-emitting layer being doped with an electron-transporting or a hole-transporting material or both selected to improve efficiency and operational stability. The device also includes an electron-transporting layer disposed over the blue light-emitting layer; a cathode disposed over the electron-transporting layer; and the hole-transporting layer or electron-transporting layer, or both the hole-transporting layer and electron-transporting layer, being selectively doped with a compound which emits light in the yellow region of the spectrum which corresponds to an entire layer or a partial portion of a layer in contact with the blue light-emitting layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
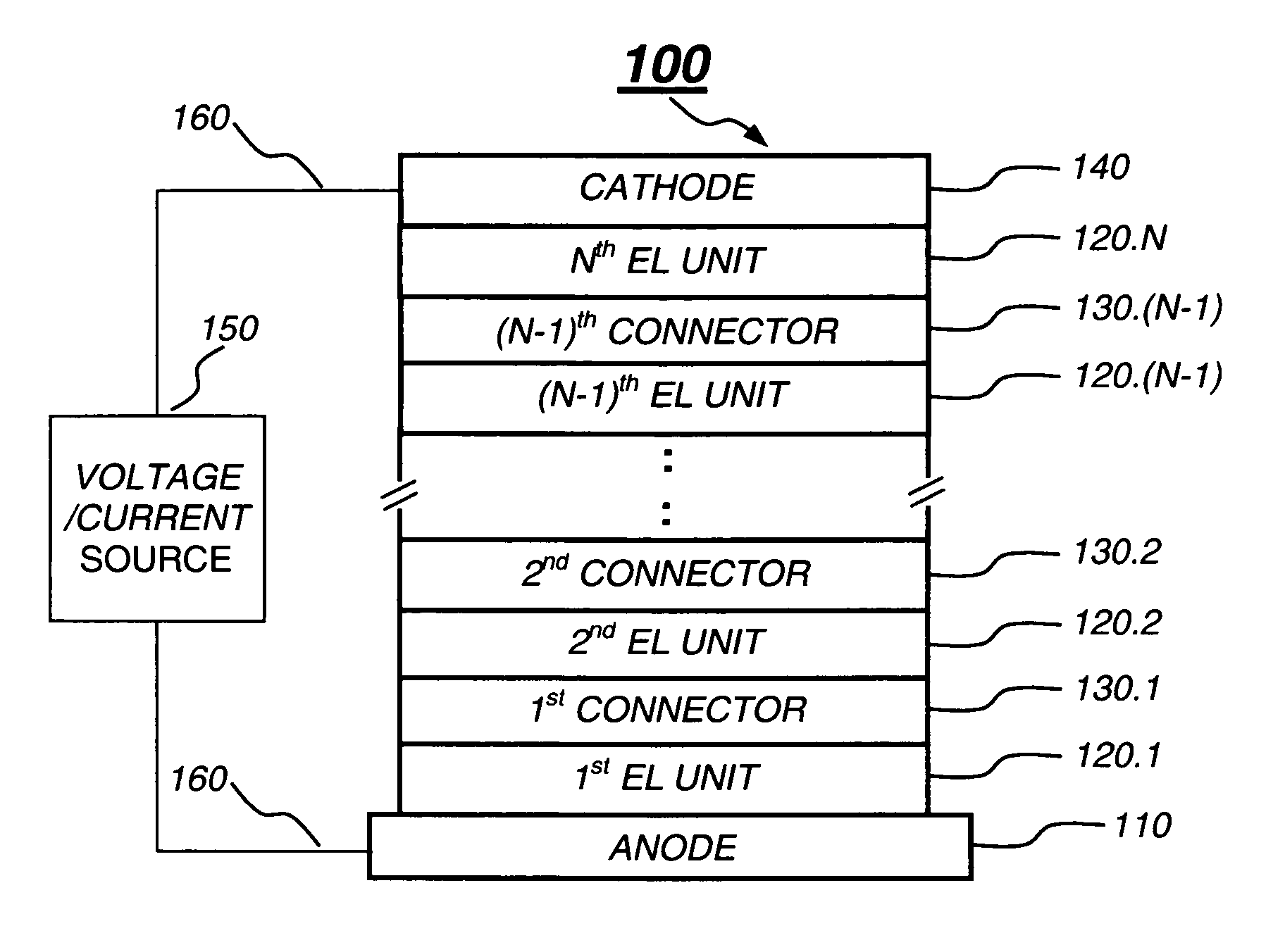
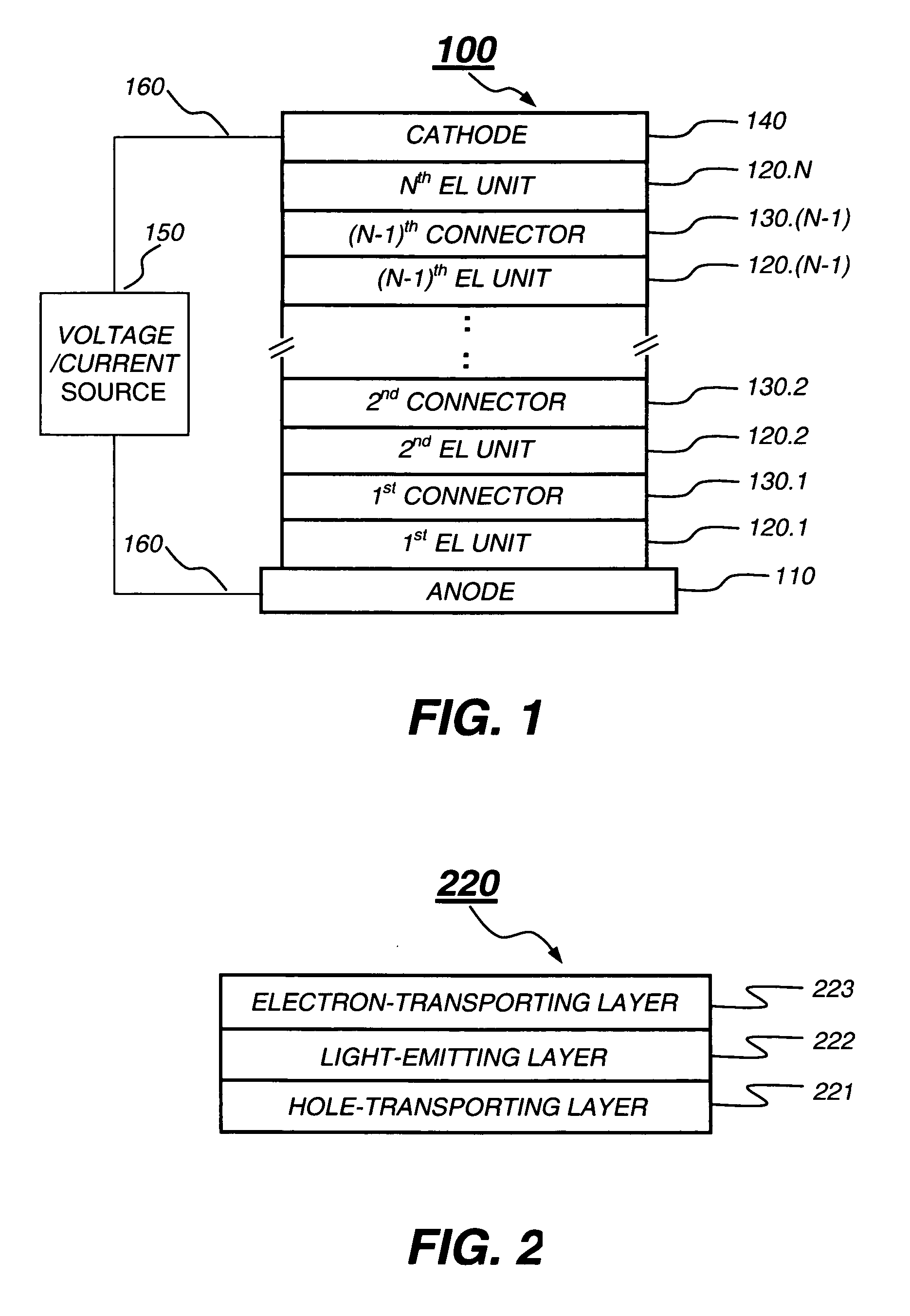
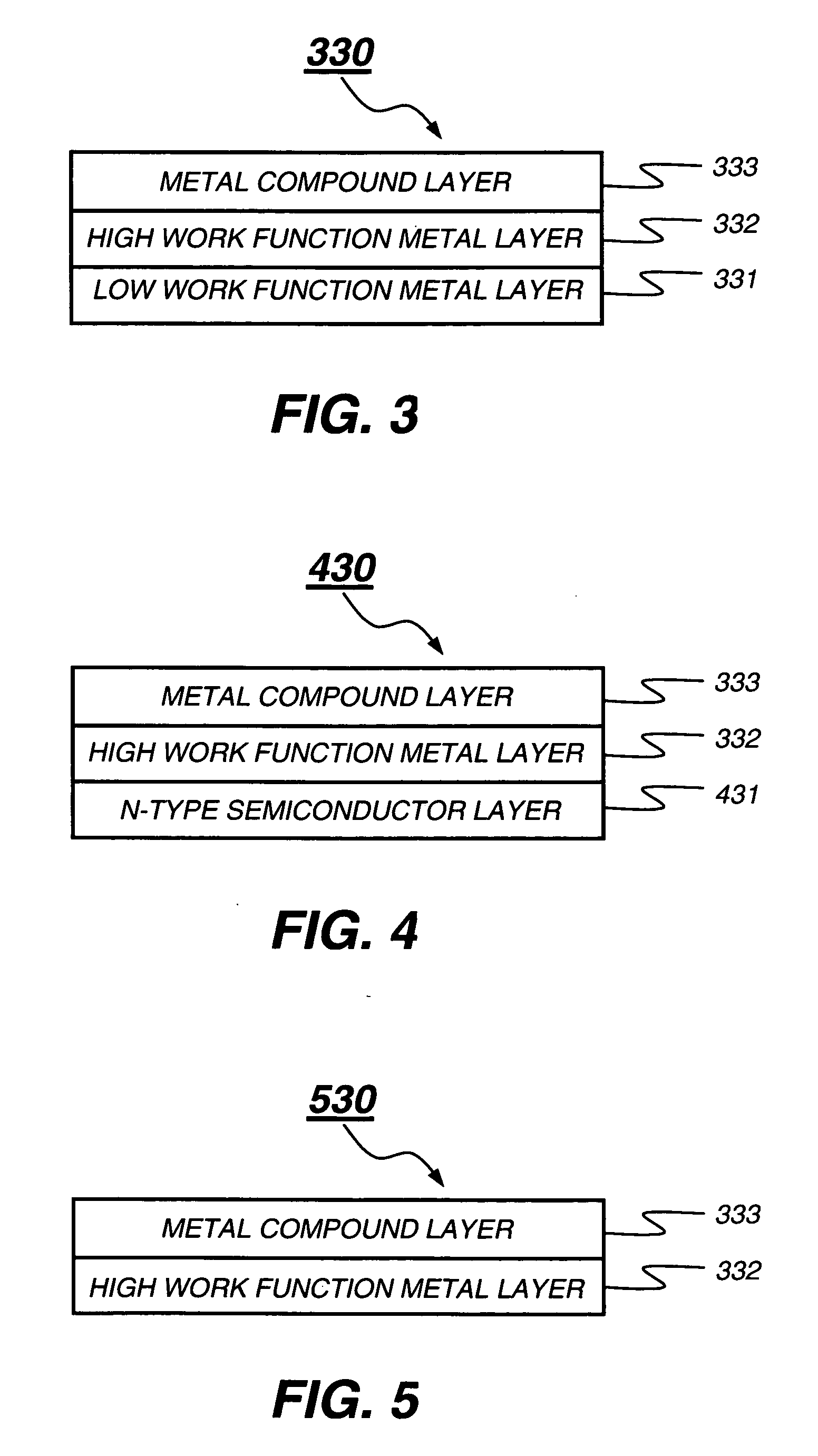
Tandem OLED having stable intermediate connectors
ActiveUS20050264174A1Highly functionalEasy to operateDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesWork functionOperational stability
A tandem OLED includes an anode, a cathode, and a plurality of organic electroluminescent units disposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein each organic electroluminescent unit includes at least one light-emitting layer, and an intermediate connector disposed between each adjacent organic electroluminescent unit, wherein the intermediate connector includes at least a high work function metal layer having a work function of no less than 4.0 eV and a metal compound layer, wherein the intermediate connector has a sheet resistance of higher than 100 kΩ per square, and wherein the high work function metal layer improves the operational stability of the OLED.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
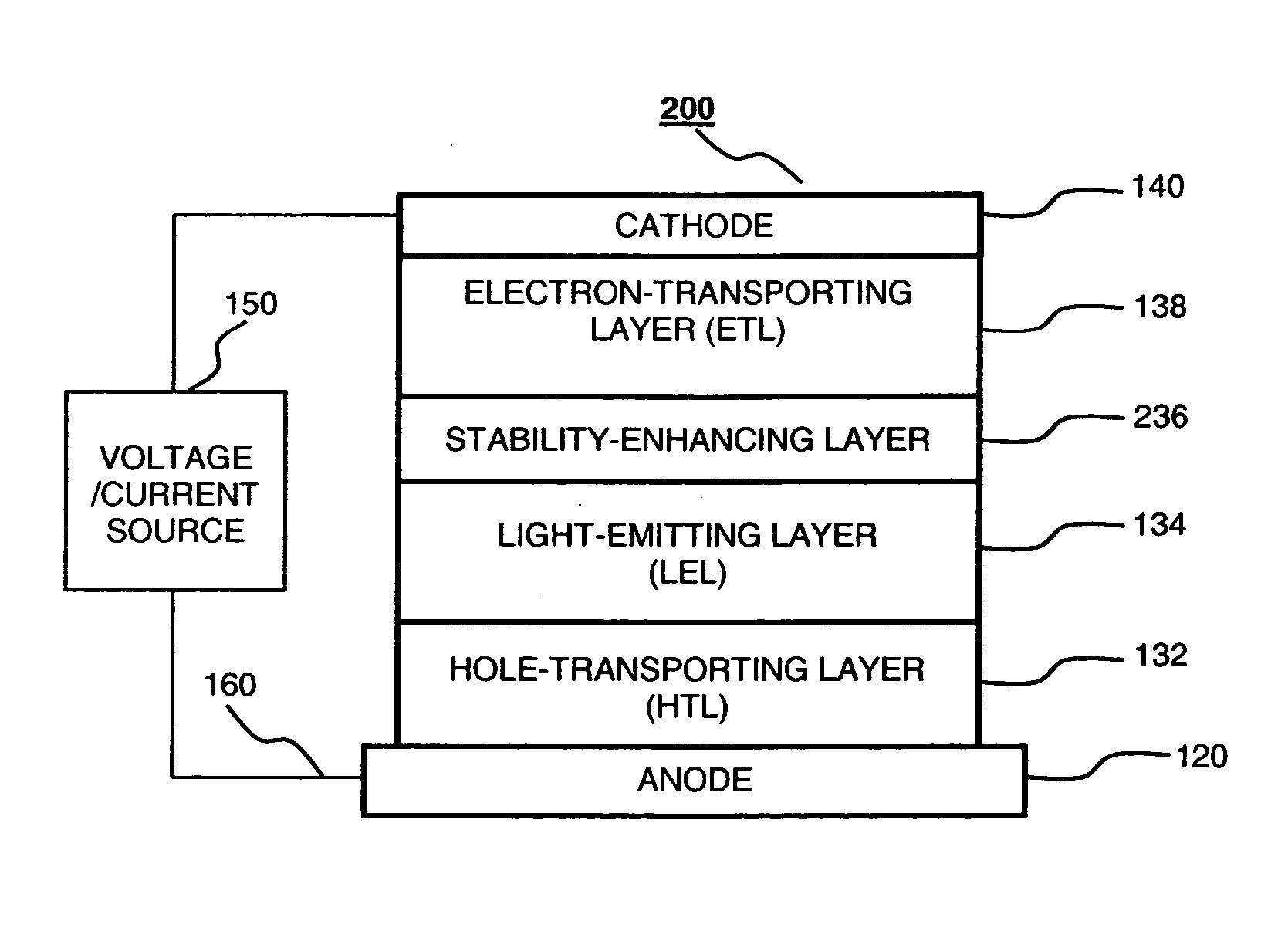
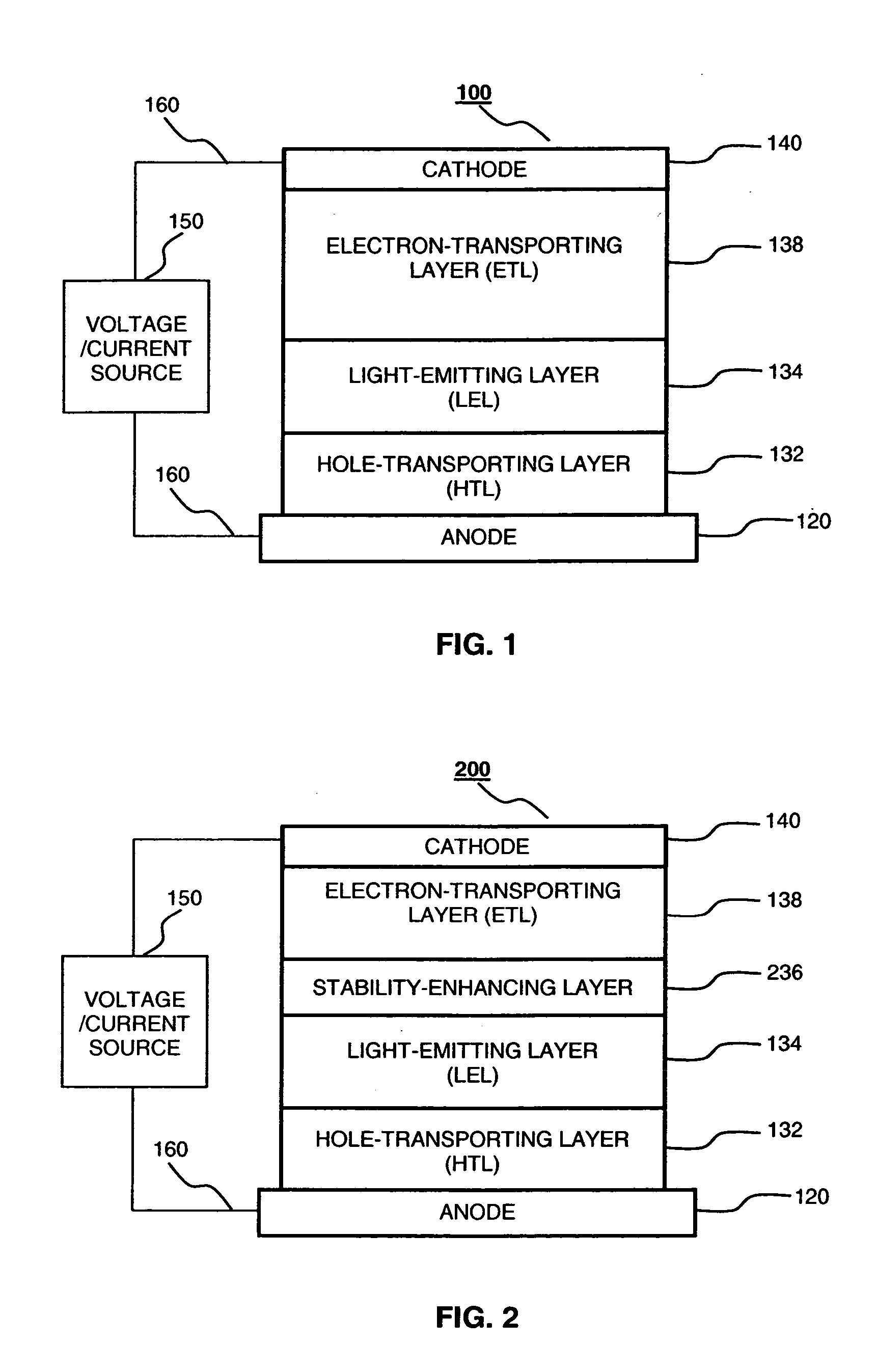
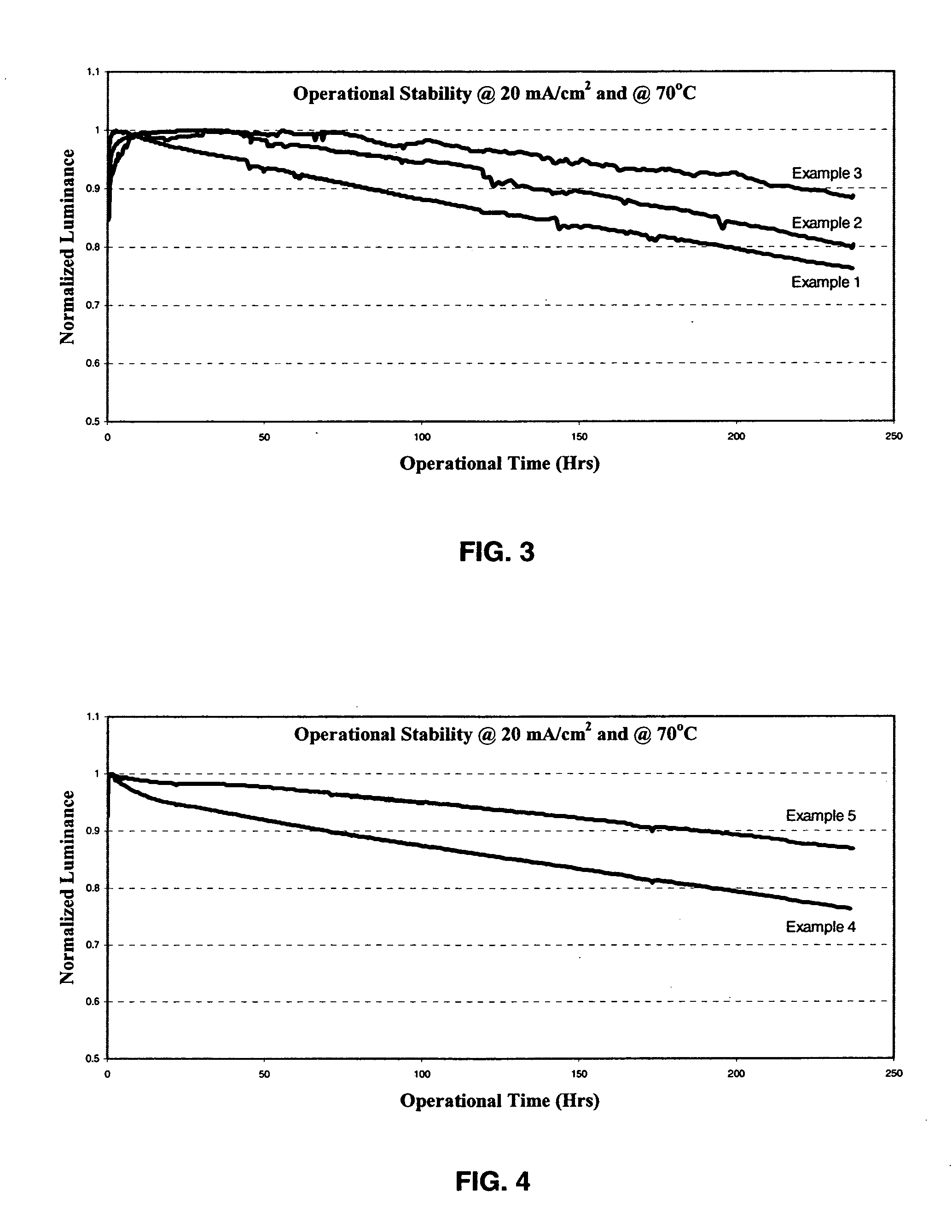
Organic electroluminescent devices having a stability-enhancing layer
ActiveUS20050104511A1Operational stability can be improvedGuaranteed uptimeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHole transport layerLight emitting device
An organic light-emitting device with enhanced operational stability comprising an anode; a hole-transporting layer disposed over the anode; a light-emitting layer disposed over the hole-transporting layer for producing light in response to hole-electron recombination, wherein the light-emitting layer includes at least one organic host material and one organic luminescent dopant material; a stability-enhancing layer disposed in contact with the light-emitting layer, wherein the stability-enhancing layer includes at least one organic host material and one inorganic dopant material; an electron-transporting layer disposed over the stability-enhancing layer; and a cathode disposed over the electron-transporting layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Control device of cylinder reducing operation of multi-cylinder engine
ActiveUS7350499B2Guaranteed uptimeEasy to controlHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringOperational stability
A control device for cylinder reducing operation of a multi-cylinder engine for a vehicle controls the number of working cylinders in the engine more appropriately for fuel economy while ensuring the operational stability of the engine and comfortable drivability of the vehicle. The control device comprises a detector detecting engine output torque and judges if cylinder reducing operation is to be executed while referring to the engine output torque. Because of the detection of engine output torque, cylinder reducing operation will be executed as long as torque requested of the engine is available from the reduced number of working cylinders, thereby ensuring the generation of torque required in operating the engine while saving fuel as much as possible. Through a learning process, criteria for the judgment of execution of cylinder reducing operation are modified to be adapted for any variation of engine output performances.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
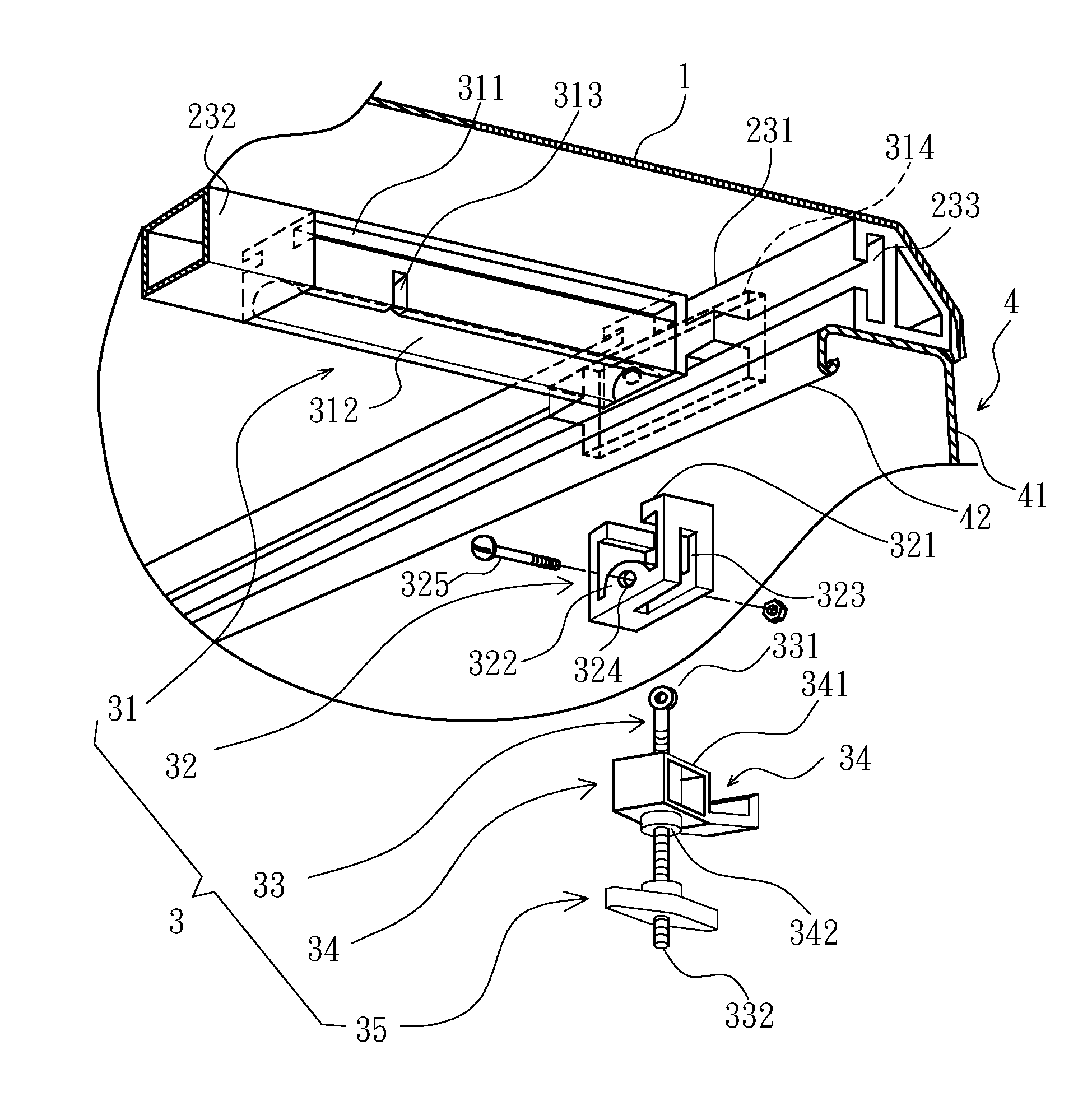
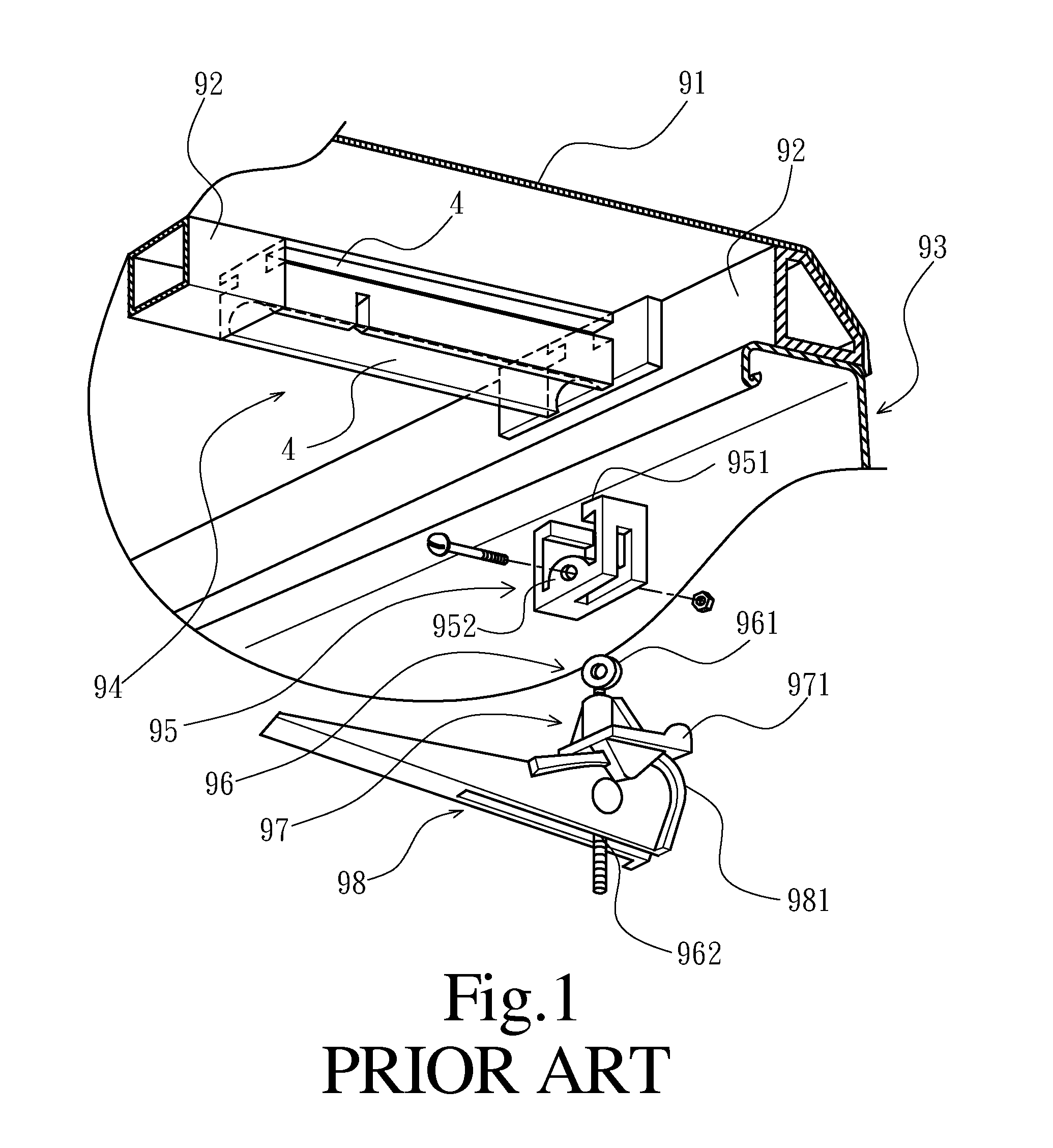
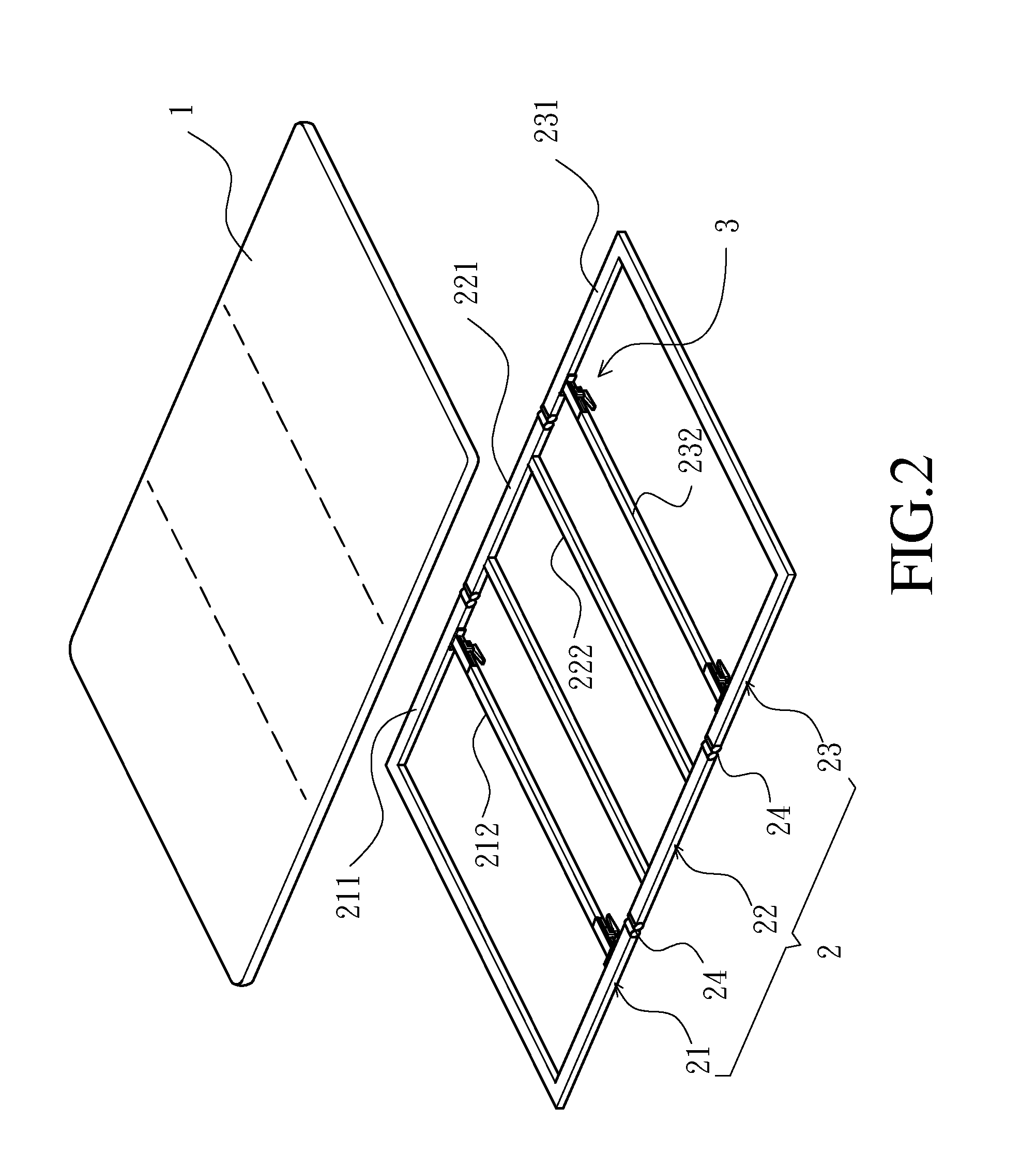
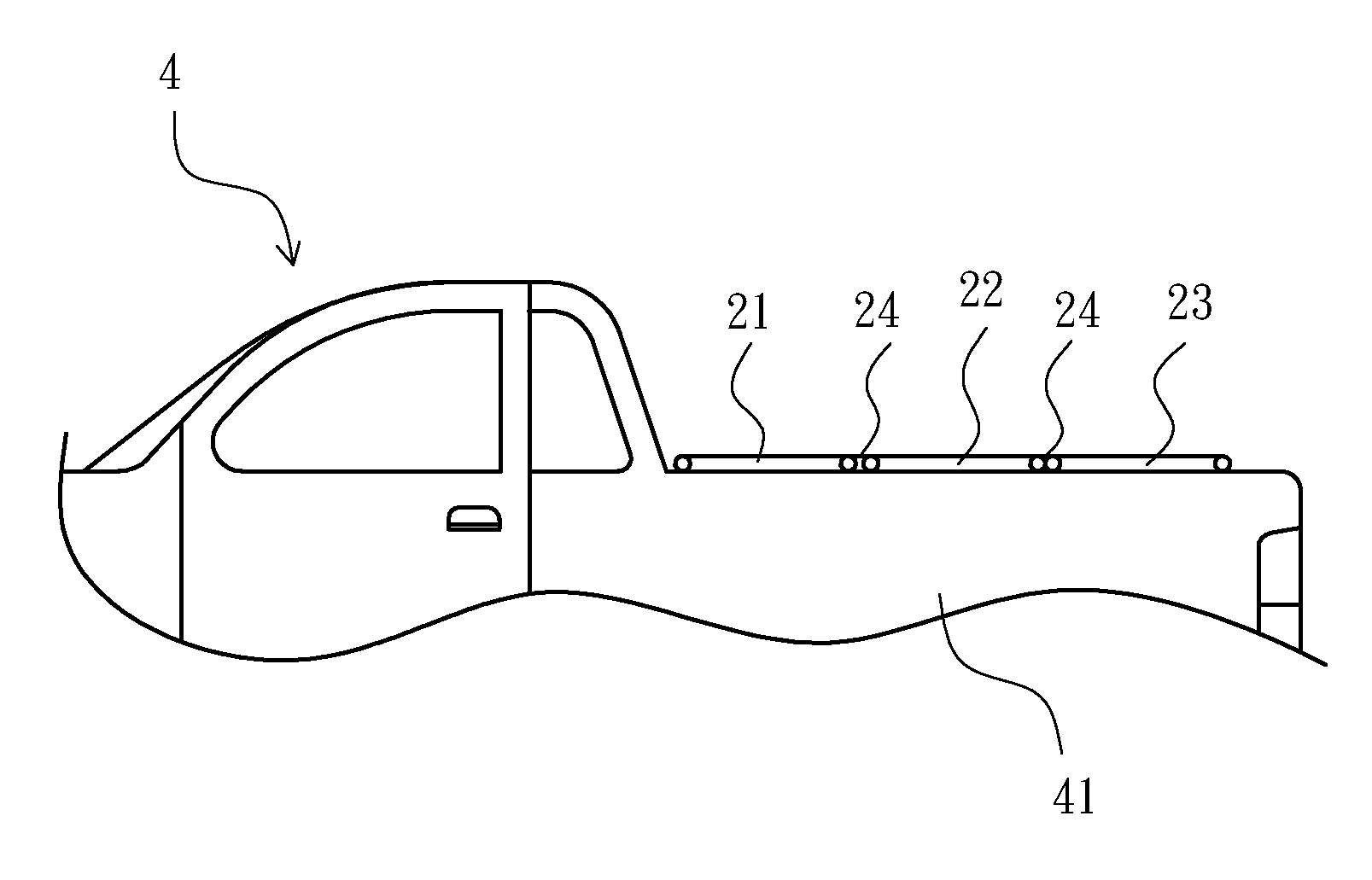
Clamp structure for tonneau cover of pick-up truck
ActiveUS20120274092A1Improve reliabilityImprove stabilityTransportation itemsRoofsPick-up truckPlastic materials
A clamp structure for a tonneau cover of a pick-up truck is disclosed and mounted to one frame section of a tonneau cover for releasably securing the frame section on a side wall of a cargo bed of the pick-up truck. The clamp structure has a composite grip element which has a metal grip body and a plastic sleeve. The metal grip body has an engaging portion to stably engage with the side wall of the pick-up truck. The plastic sleeve has a first abutment flange to smoothly abut against a turning handle, and a second abutment end facing a sliding block. Thus, the composite grip element can provide advantages of both of metal and plastic material, so that the operational stability and reliability of the clamp structure can be enhanced, and the lifetime thereof can be elongated.
Owner:CYC ENG
Touch switch
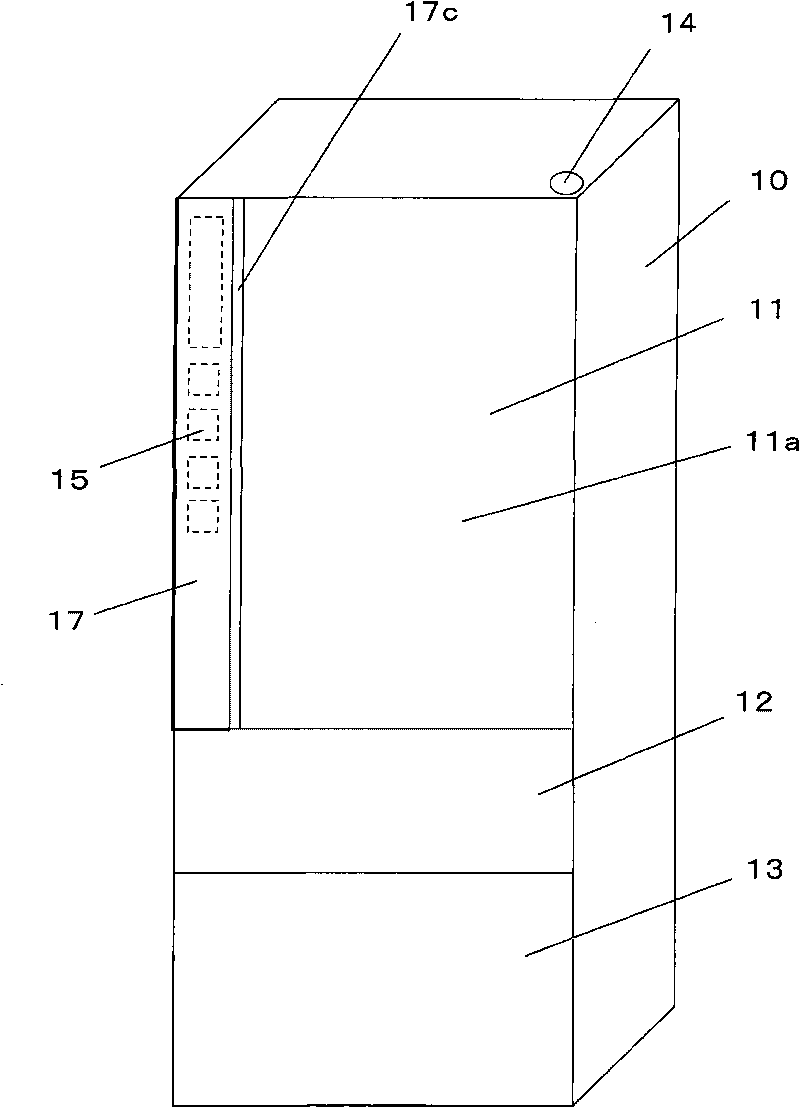
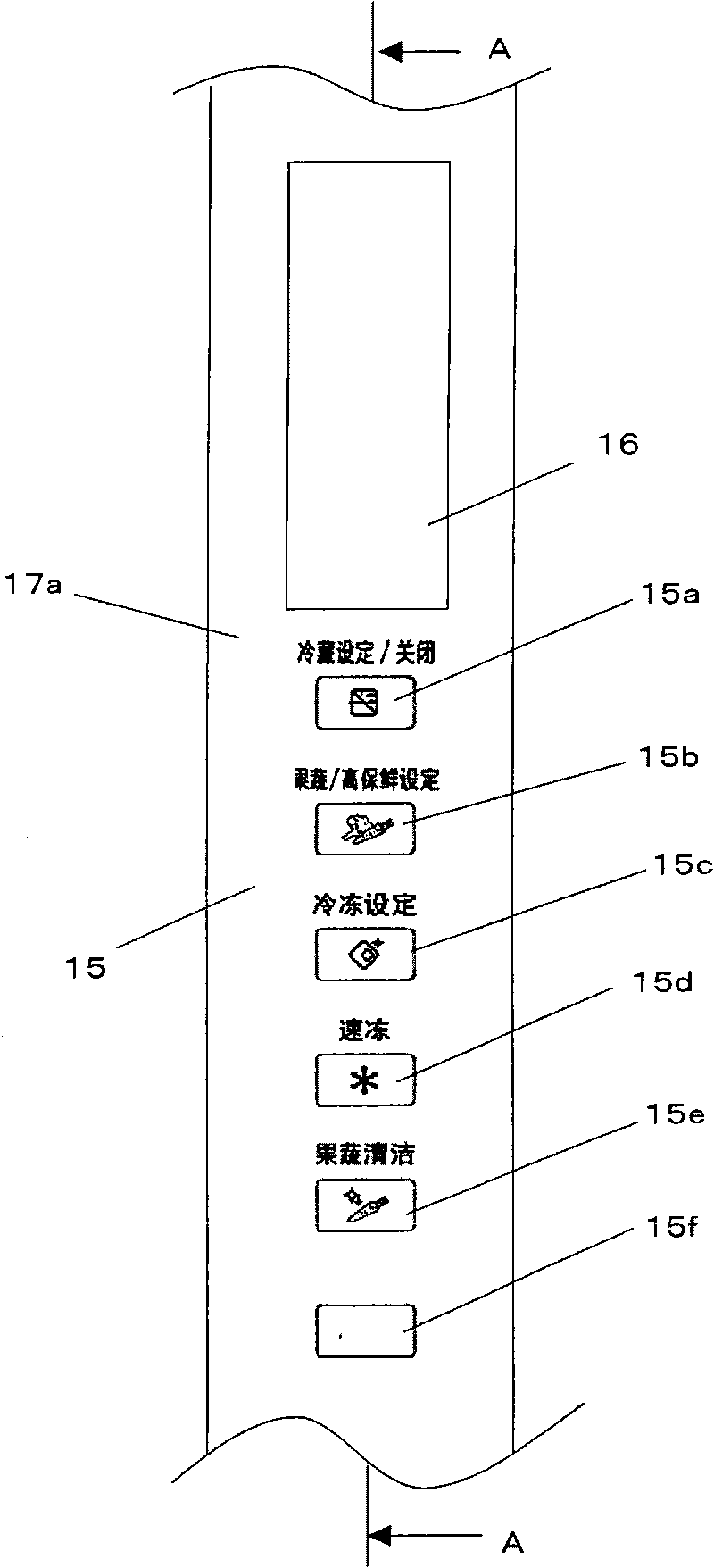
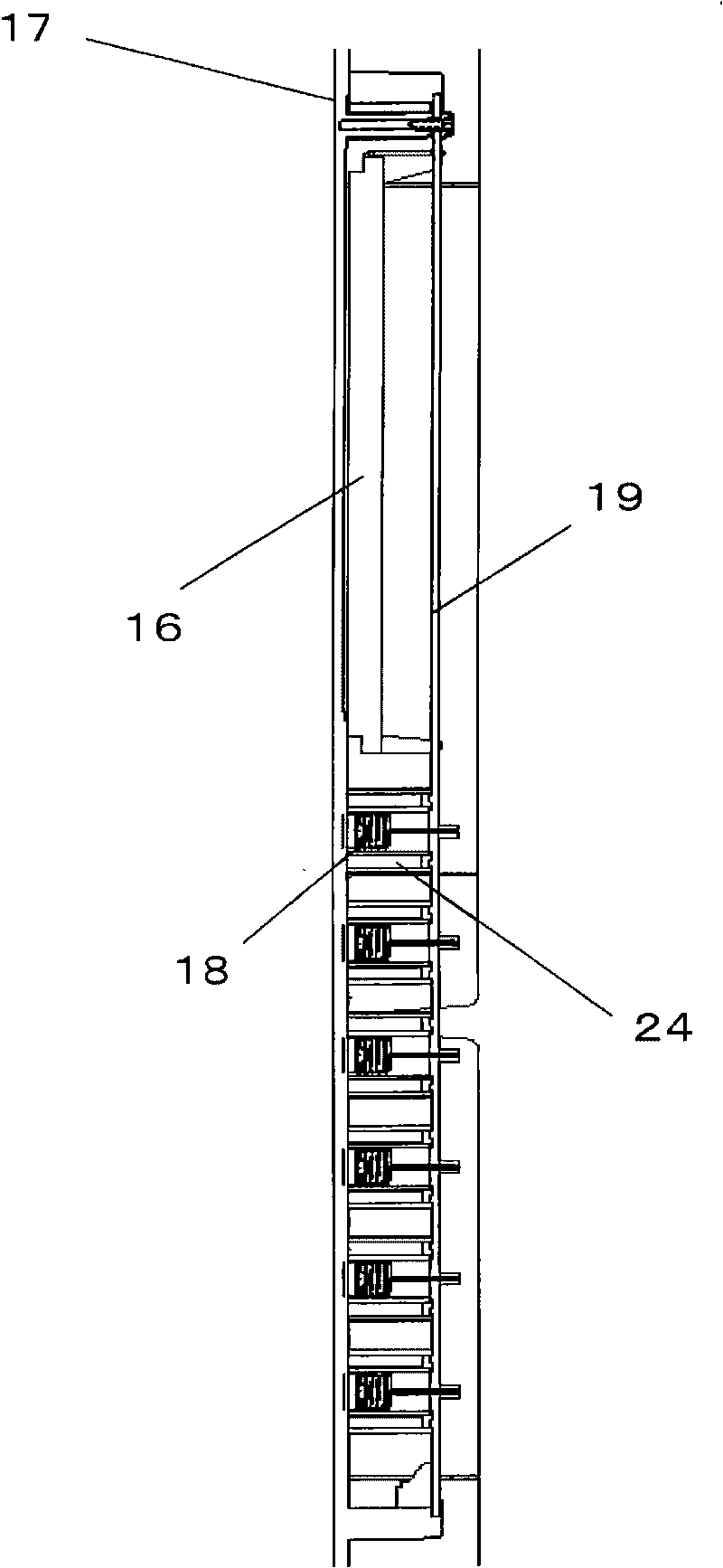
ActiveCN101741371AImprove reliabilityEasy to fixLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsEngineeringOperational stability
The invention provides a touch switch which can improve the operation stability and the reliability per se and also can ensure the operation convenience, the reliability and the appearance beauty of machinery equipment provided with the touch switch. The touch switch is internally provided with a box body (24) covering the periphery of an induction part (18), the induction part is connected with a connecting part (21) under a state that the upper surface (18a) of the induction part is higher than the upper surface (24c) of the box body, and the connecting part is an elastic part. After the box body is fixed on a printed substrate, the induction part after being connected with the connecting part is easy to be fixed on the printed substrate, and the difference of assembly operation also can be reduced. Because the induction part is arranged at the position protruding over the upper surface of the box body, tight attaching type fixation can be realized between a part arranged on the upper surface of the induction part and supplied for people to touch and the induction part, and the detection deviation of an electrostatic capacity can be lowered.
Owner:无锡松下冷机有限公司 +1
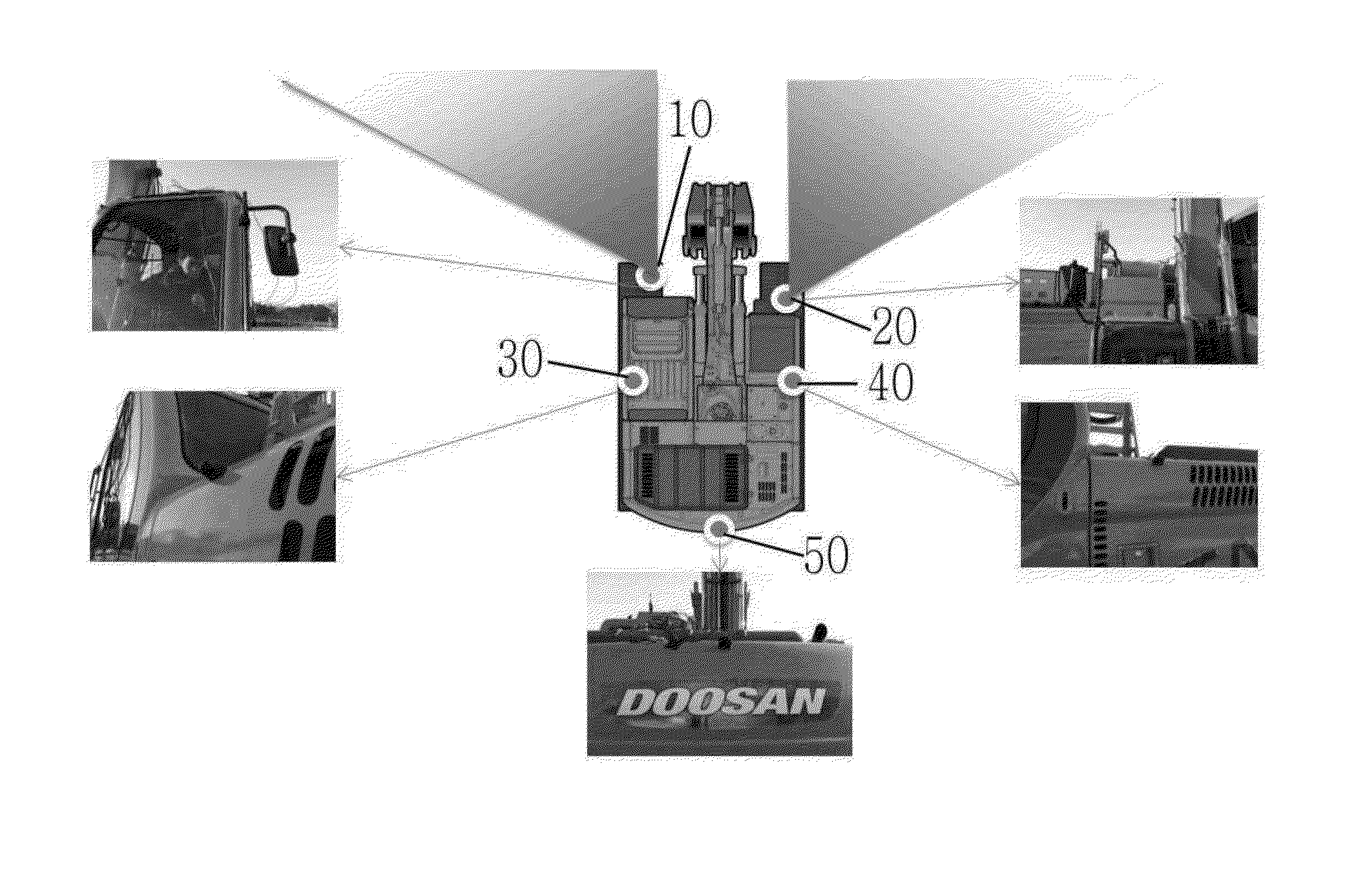
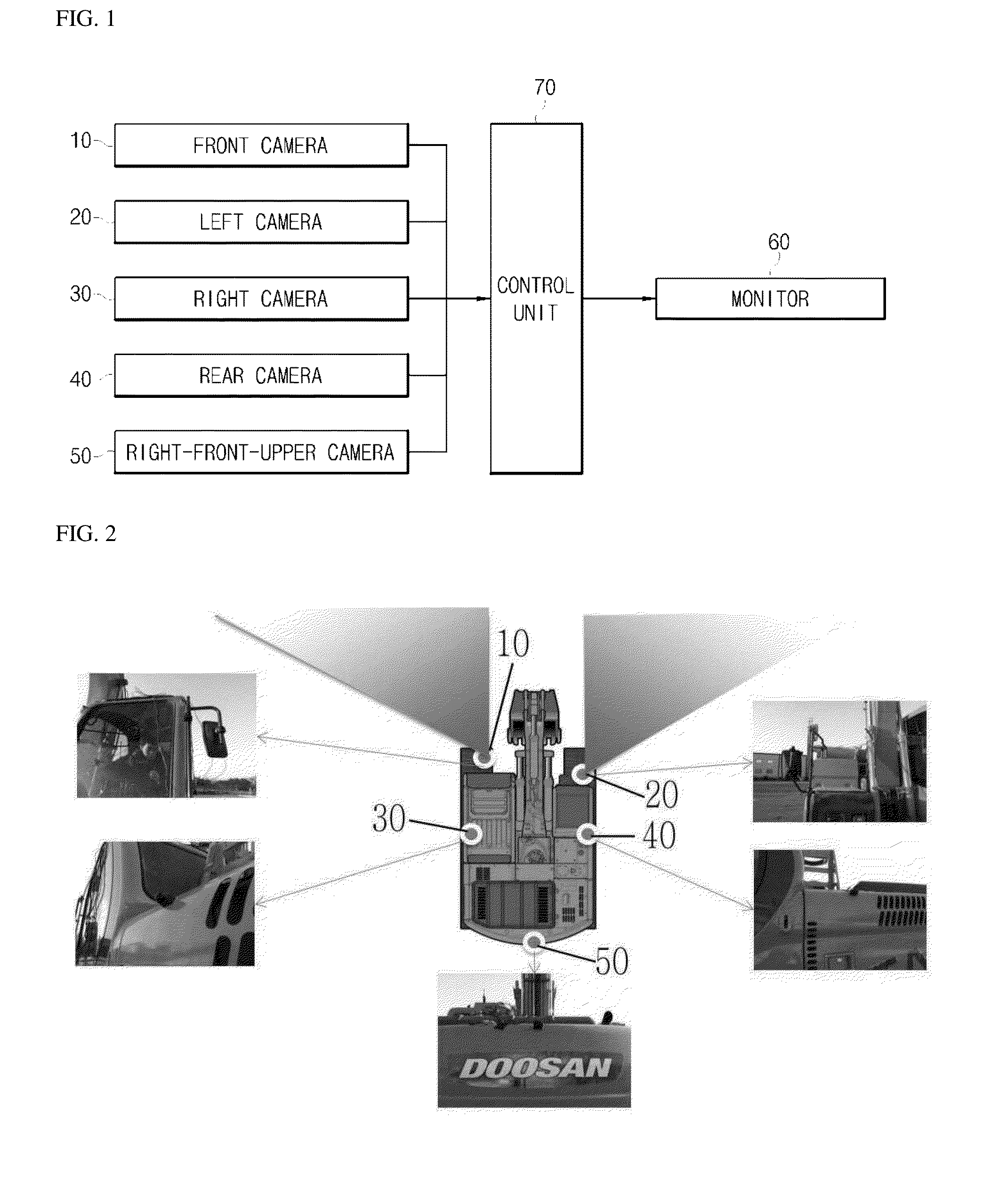
Operational stability enhancing device for construction machinery
InactiveUS20140118533A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityGeometric image transformationSoil-shifting machines/dredgersEngineeringOperational stability
According to the present invention, an operational stability enhancing device for construction machinery is provided. The operational stability enhancing device for construction machinery includes: a plurality of cameras configured to capture surrounding images of construction machinery; a plurality of sensors configured to detect an obstacle located in the surrounding area of the construction machinery; a monitor configured to display the surrounding images captured by the plurality of cameras; and a control unit configured to, in a case where a detected object is detected in a surrounding area of a moving path by the sensor, and the detected object is an avoidance processing target, display an image of the captured detected object on a monitor through screen conversion or change the image of the captured detected object so as to be easily recognized by an operator when the construction machines approaches the detected object.
Owner:DOOSAN INFRACORE CO LTD
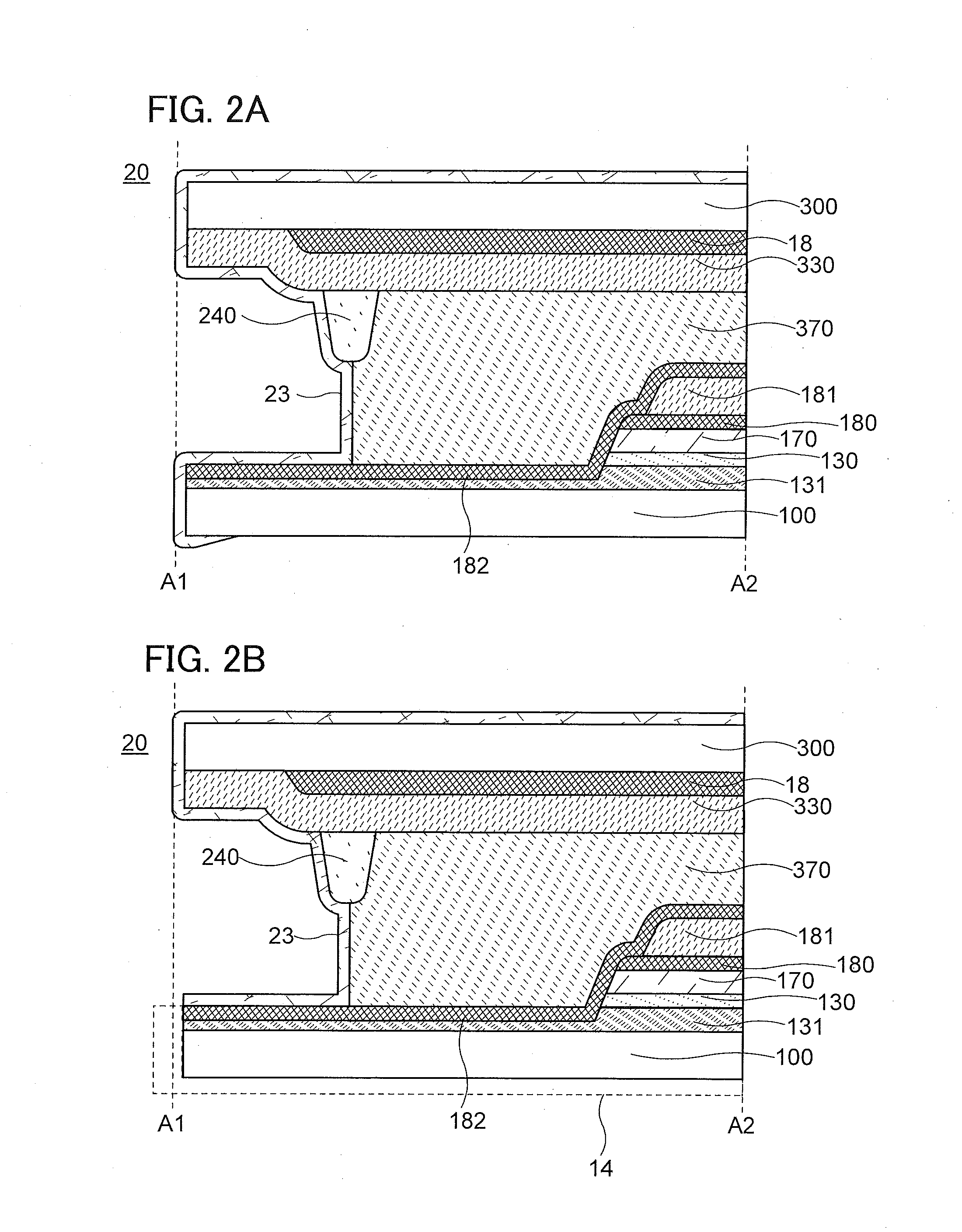
Display Device and Electronic Device
ActiveUS20160147109A1Improve reliabilityHigh operation stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTectorial membraneDisplay device
A display device including a peripheral circuit portion with high operation stability. The display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate. A first insulating layer is on a first plane of the first substrate, and a second insulating layer is on a first plane of the second substrate. An area of the first plane of the first substrate is the same as an area of the first plane of the second substrate. The first plane of the first substrate and the first plane of the second substrate face each other. A bonding layer is between the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer. A protection film is in contact with the first substrate, the first insulating layer, the bonding layer, the second insulating layer, and the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
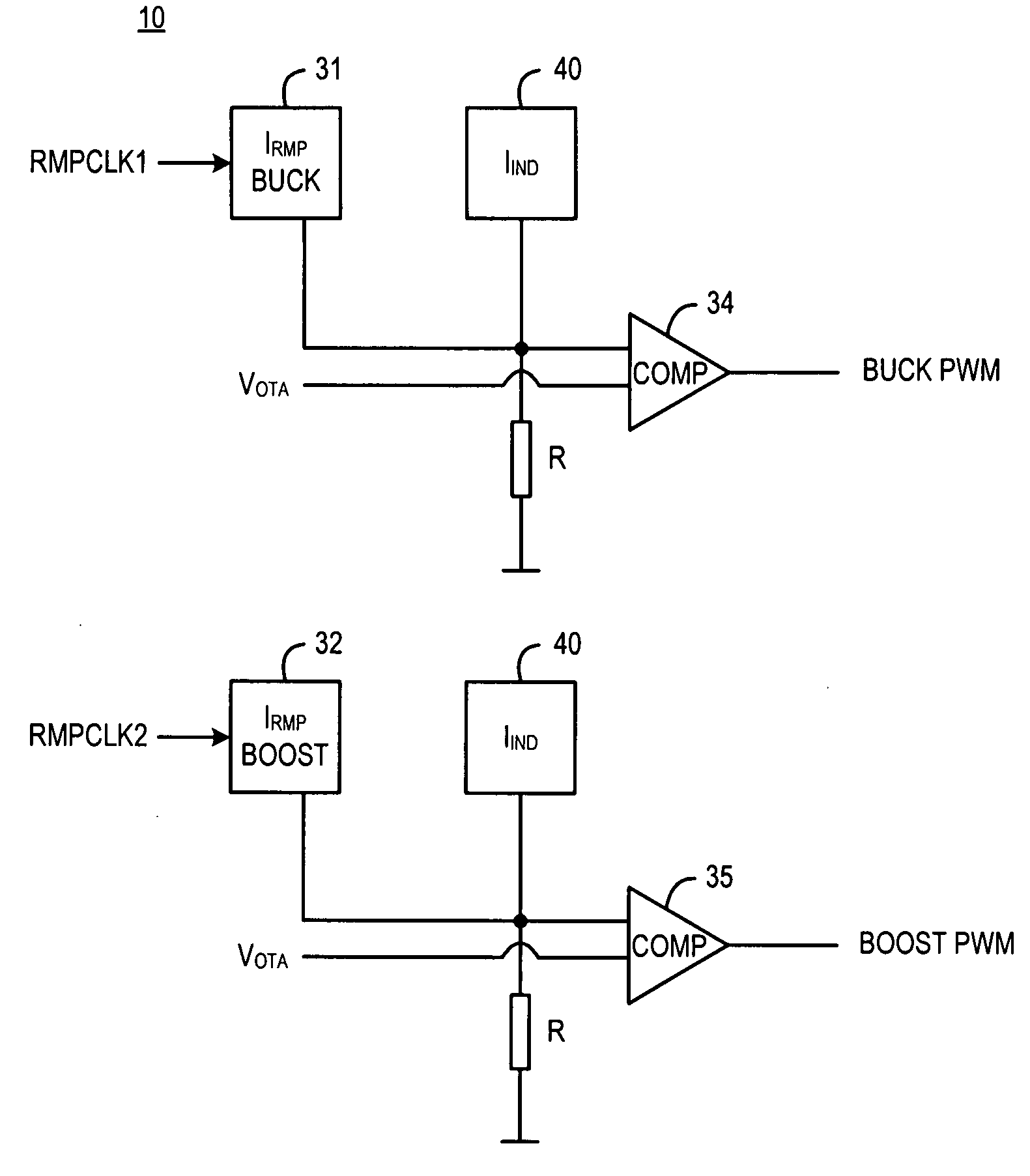
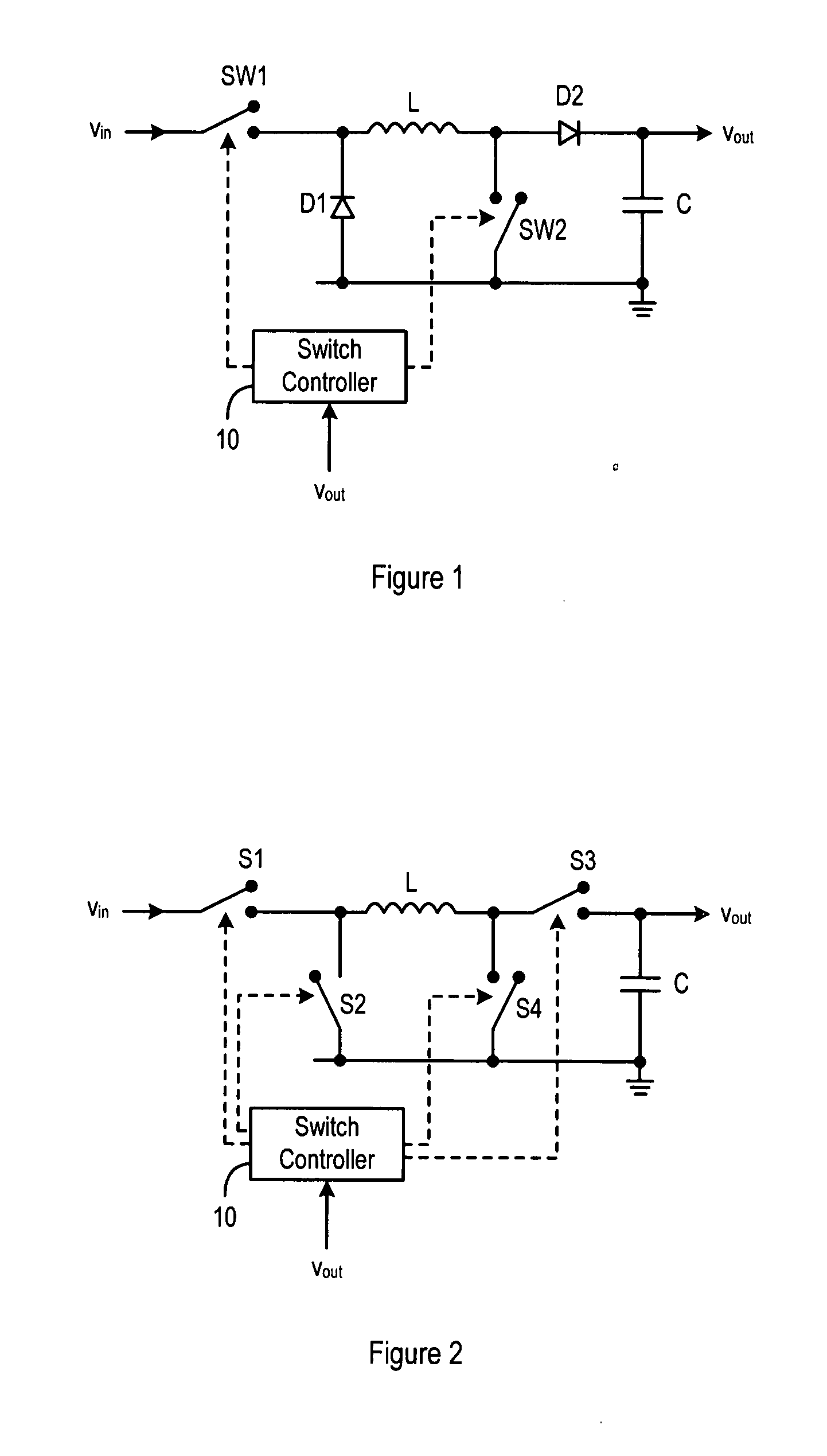
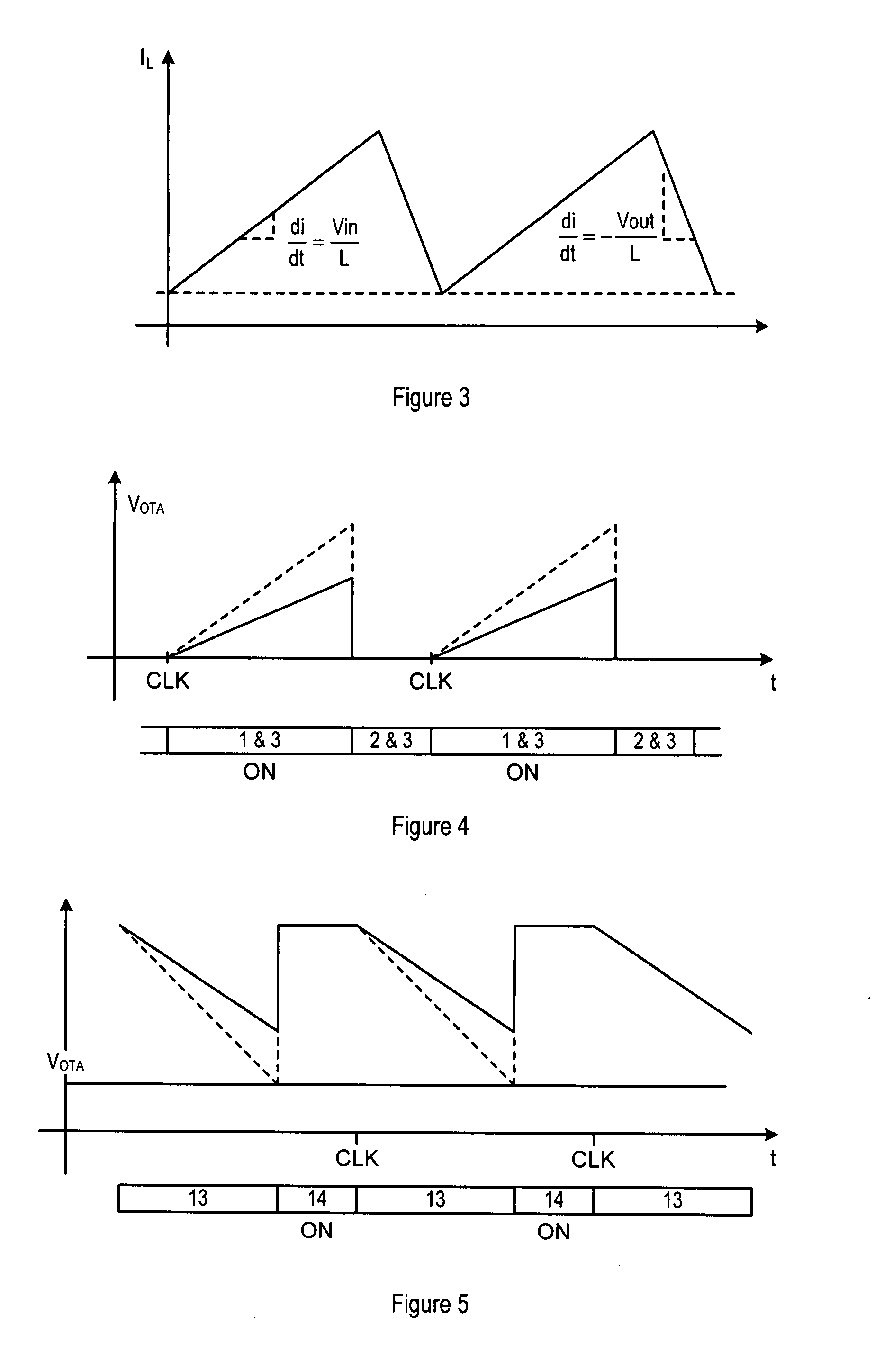
Buck-boost converter
ActiveUS20080303502A1Improve efficiencyEfficiency is not affectedDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationConstant frequencyCurrent sensor
A controller (10) for a constant frequency current-mode buck-boost converter, the converter including an inductor (L), a first switch (SW1, S1) connected between an input terminal (Vin) of the converter and one end of the inductor (L), a diode or a switch (D1, S2), connected between the first end of the inductor and ground, a second diode or switch (D2, S3) connected between a second end of the inductor and an output terminal (Vout) of the converter, and a second switch (SW2, S4) coupled between the other end of the inductor and ground. A current sensor is also present for sensing current in the first switch (SW1, S1) as a measure of the inductor (L) current. The controller (10) comprises a feedback circuit for deriving a feedback signal from the output terminal (Vout) and a waveform generator (31, 32) for generating buck and boost slope compensation ramps (RMP-BUCK, RMP-BOOST) used for improving stability of operation in both buck and boost operating modes of the converter. Control logic in the controller (10) generates drive signals during every clock period to repeatedly open and close the switches at individual duty cycles determined on the basis of the feedback signal, the sensed current signal and the slope compensation ramps. The buck and boost slope compensation ramps are mutually offset with respect to one another in time, for example by 50% of a clock cycle, and the control logic uses the sensed current signal only while the first switch (SW1, S1) is closed, thus avoiding the need for additional current sensing circuitry.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Low power stabilized voltage divider network
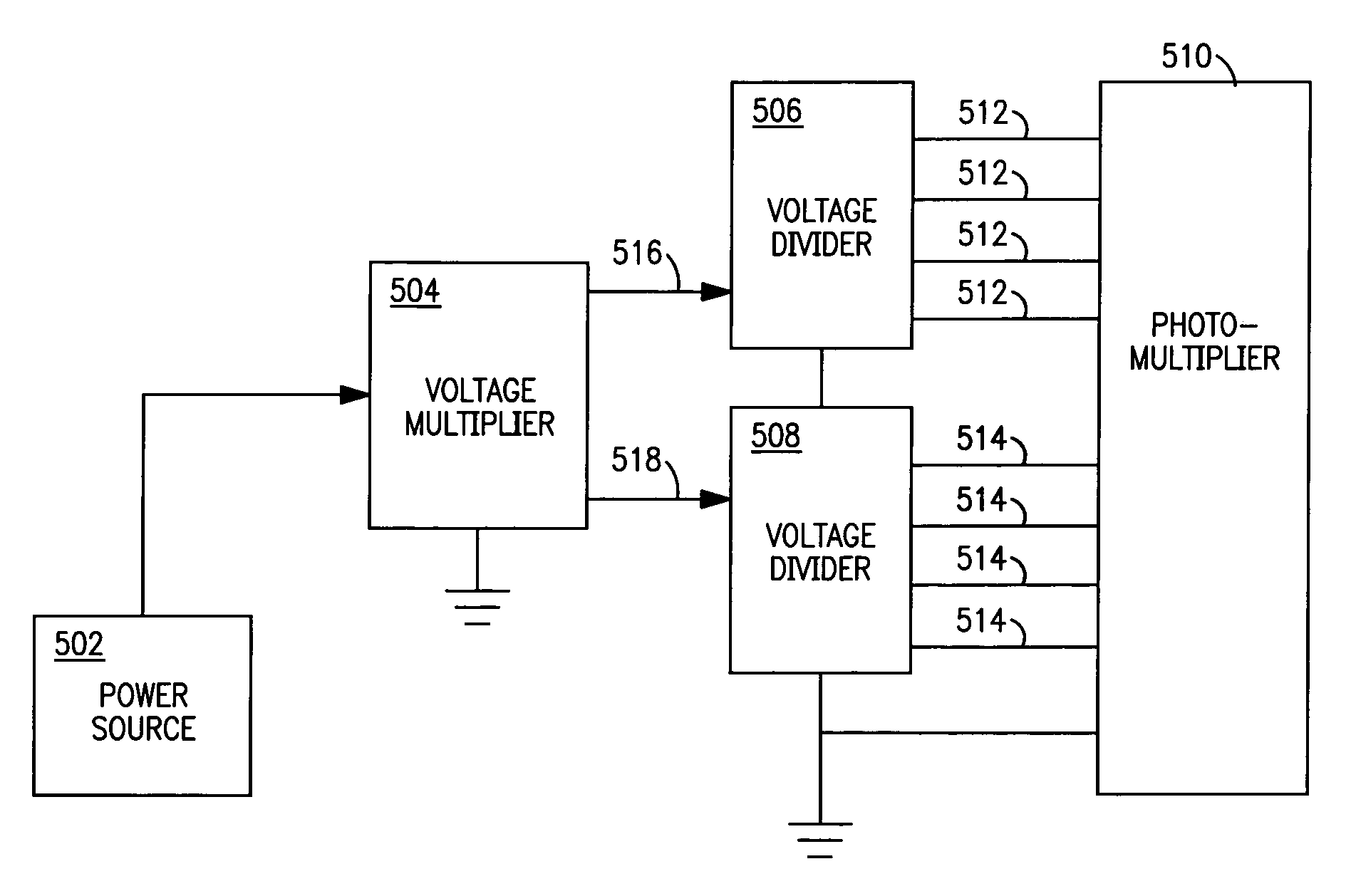
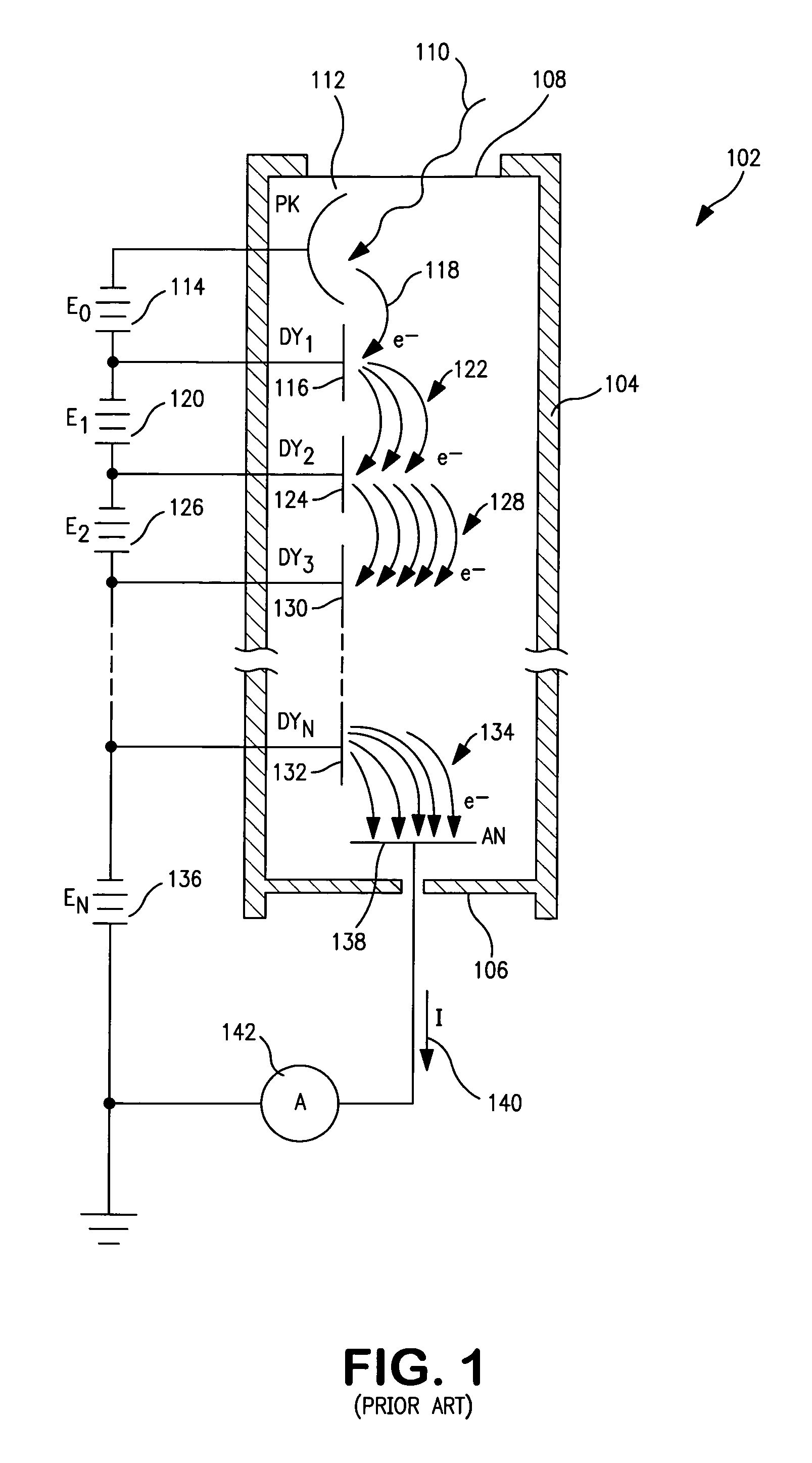
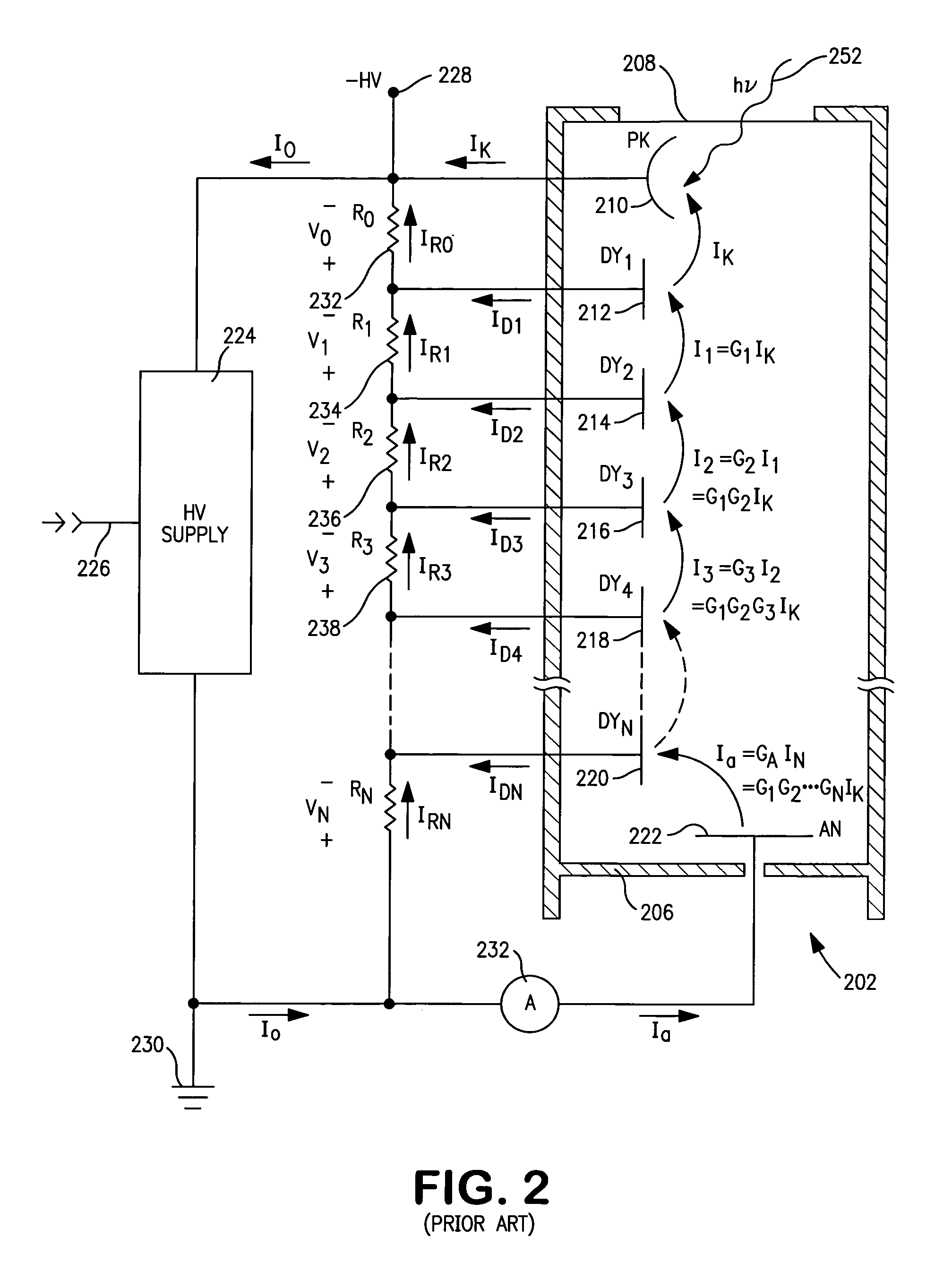
InactiveUS7005625B1Reduce the required powerReduce power consumptionMultiplier circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansVoltage multiplierPhotomultiplier
A voltage divider network in combination with a voltage multiplier circuit voltage biases the electrodes of a photomultiplier tubes or related device. The circuit exploits the several voltage levels produced at successive stages of a voltage multiplier circuit in order to optimize the voltage divider network with respect to power consumption, current draw from the power supply, operating stability, and linear operation of the photomultiplier tube.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
Susceptor device
ActiveUS20040065259A1Efficient solutionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlSusceptor
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Clamp structure for tonneau cover of pick-up truck
A clamp structure for a tonneau cover of a pick-up truck is disclosed and mounted to one frame section of a tonneau cover for releasably securing the frame section on a side wall of a cargo bed of the pick-up truck. The clamp structure has a composite grip element which has a metal grip body and a plastic sleeve. The metal grip body has an engaging portion to stably engage with the side wall of the pick-up truck. The plastic sleeve has a first abutment flange to smoothly abut against a turning handle, and a second abutment end facing a sliding block. Thus, the composite grip element can provide advantages of both of metal and plastic material, so that the operational stability and reliability of the clamp structure can be enhanced, and the lifetime thereof can be elongated.
Owner:CYC ENG
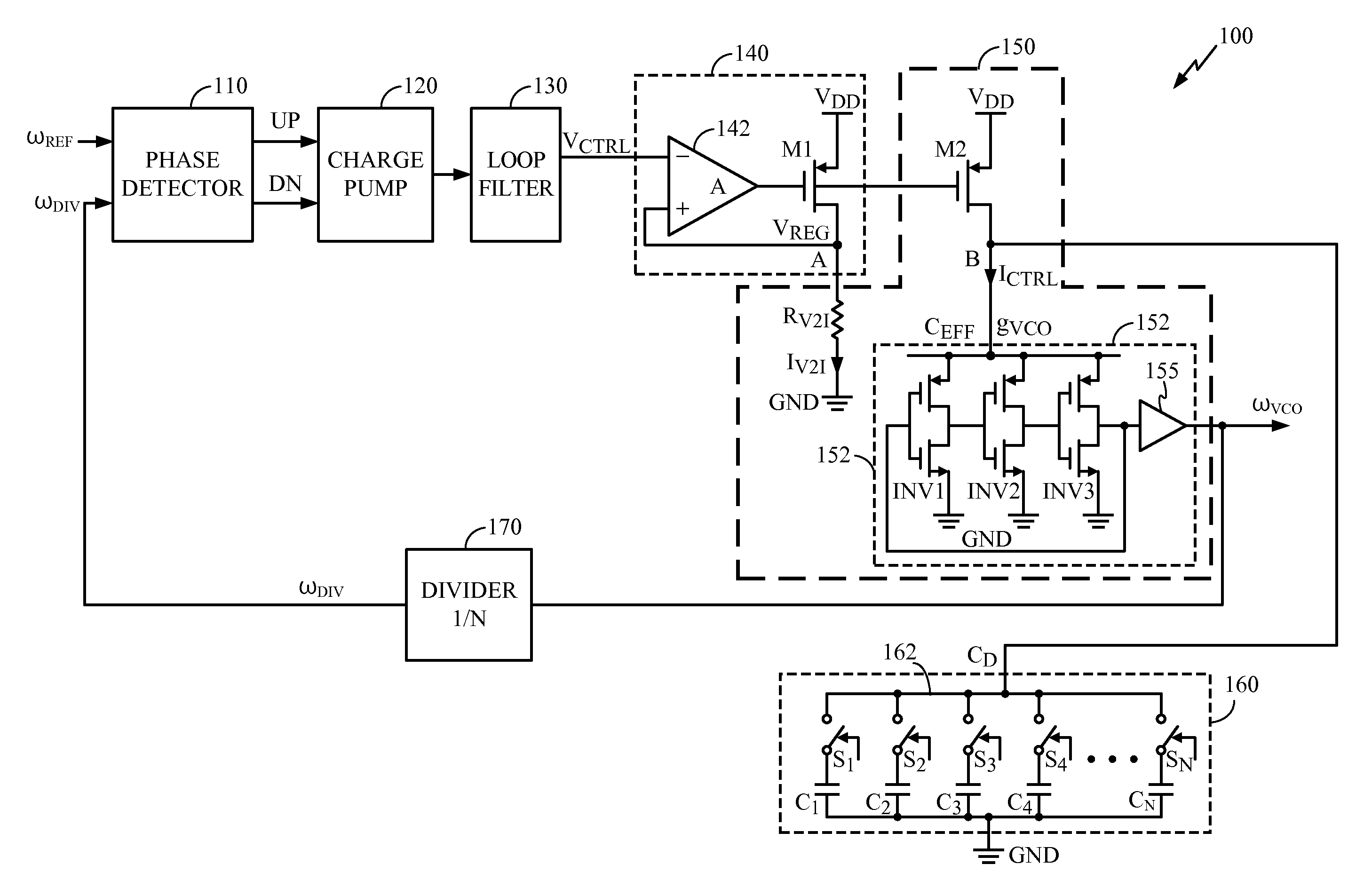
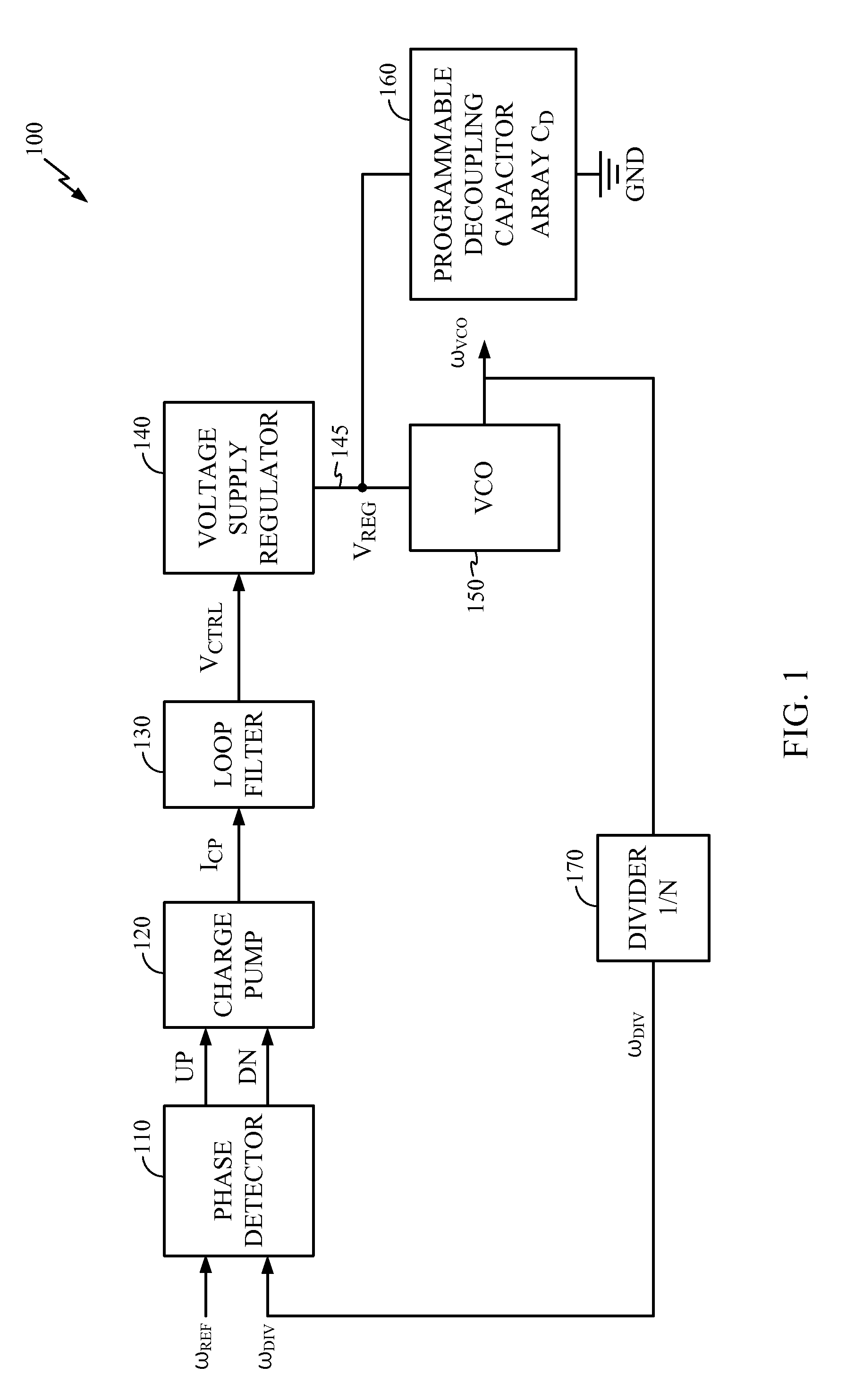
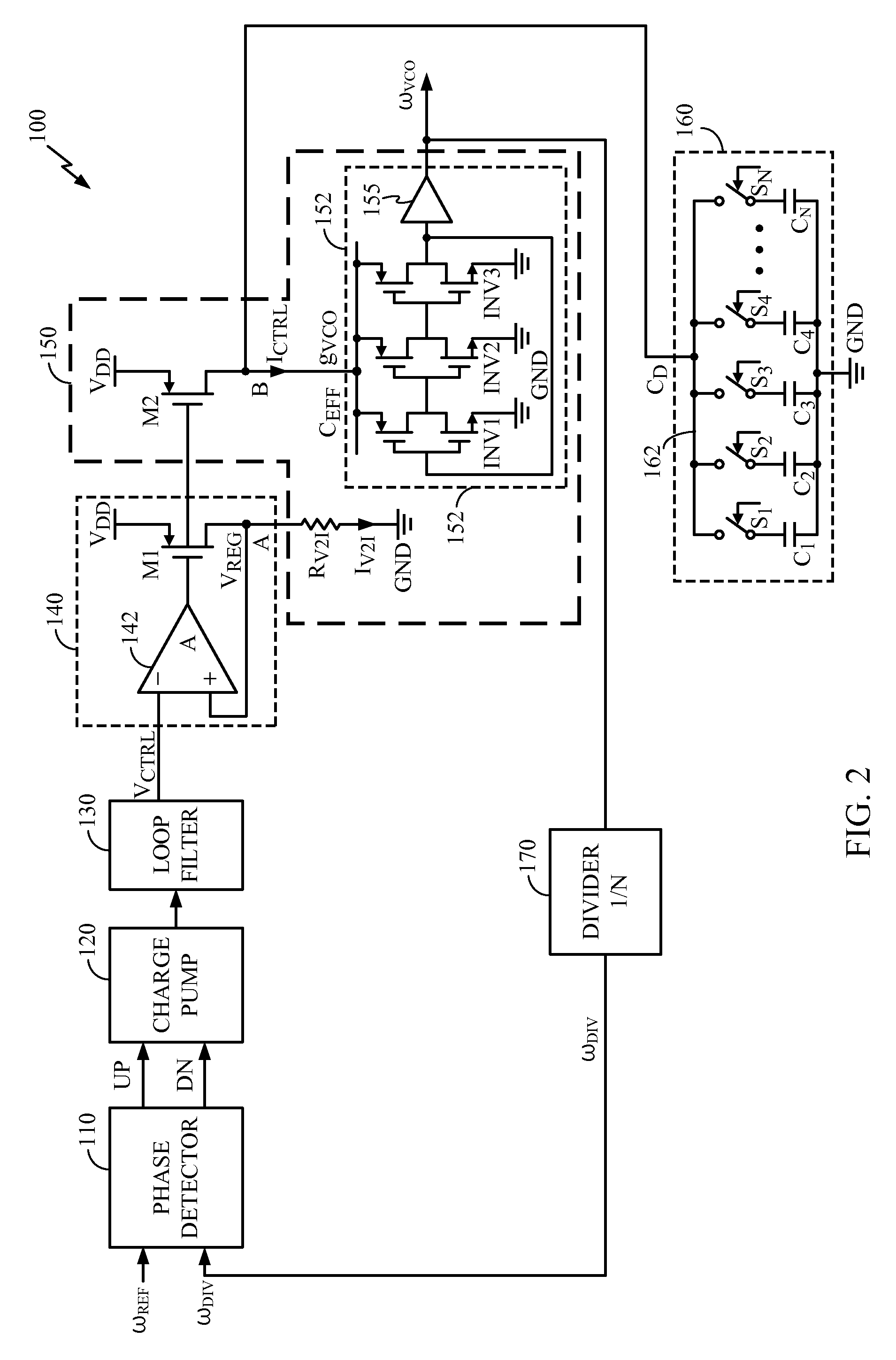
Supply-Regulated Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Method of Using
InactiveUS20100271140A1Maintaining PLL operational stabilityWide rangePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceOperational stability
A supply-regulated Phase-locked loop (PLL) is provided. The PLL comprises a supply-regulating loop, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), and a programmable decoupling capacitor array for the VCO. The capacitance of the VCO decoupling capacitor array is adjustable to be equal to N times CUNIT, where N is the current value of a multiplication factor of a divide-by-N circuit and CUNIT is a unit capacitance characterized for a processing technology chosen for fabricating the decoupling capacitor array. When the PLL switches from one frequency band to another, a higher-order pole introduced by the VCO decoupling capacitor tracks the PLL reference frequency, thus improving the PLL operational stability.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Stabilizer bushing
A cylindrical rubber elastic member for having a stabilizer bar inserted therein comprises an inner layer rubber with high sliding properties and an outer layer rubber provided outside of the inner layer rubber. Both the stability in operation and the riding comfort can be improved. Further, the rubber elastic member comprises a sliding surface made of a rubber with high sliding properties at the end face thereof. Frictional resistance can be lowered to prevent abnormal noise. A stabilizer bushing comprising a main body rubber portion of a sulfur-vulcanizable first rubber compound and a sliding rubber portion of a second rubber compound containing a sulfur-vulcanizable lubricant on the inner surface of the main body rubber portion, wherein the first rubber compound exhibits vulcanizability satisfying:and contains a crosslinking tackifier, t90 is a time to 90% vulcanization, t50 is a time to 50% vulcanization, and the vulcanizability is measured by a curastometer in accordance with JIS K 6300.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Display device, manufacturing method of display device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20160118416A1Low reliabilityUnstable circuit operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOperational stability
A display device in which a peripheral circuit portion has high operation stability is provided. The display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate. A first insulating layer is provided over a first surface of the first substrate. A second insulating layer is provided over a first surface of the second substrate. The first surface of the first substrate and the first surface of the second substrate face each other. An adhesive layer is provided between the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer. A protective film in contact with the first substrate, the first insulating layer, the adhesive layer, the second insulating layer, and the second substrate is formed in the vicinity of a peripheral portion of the first substrate and the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
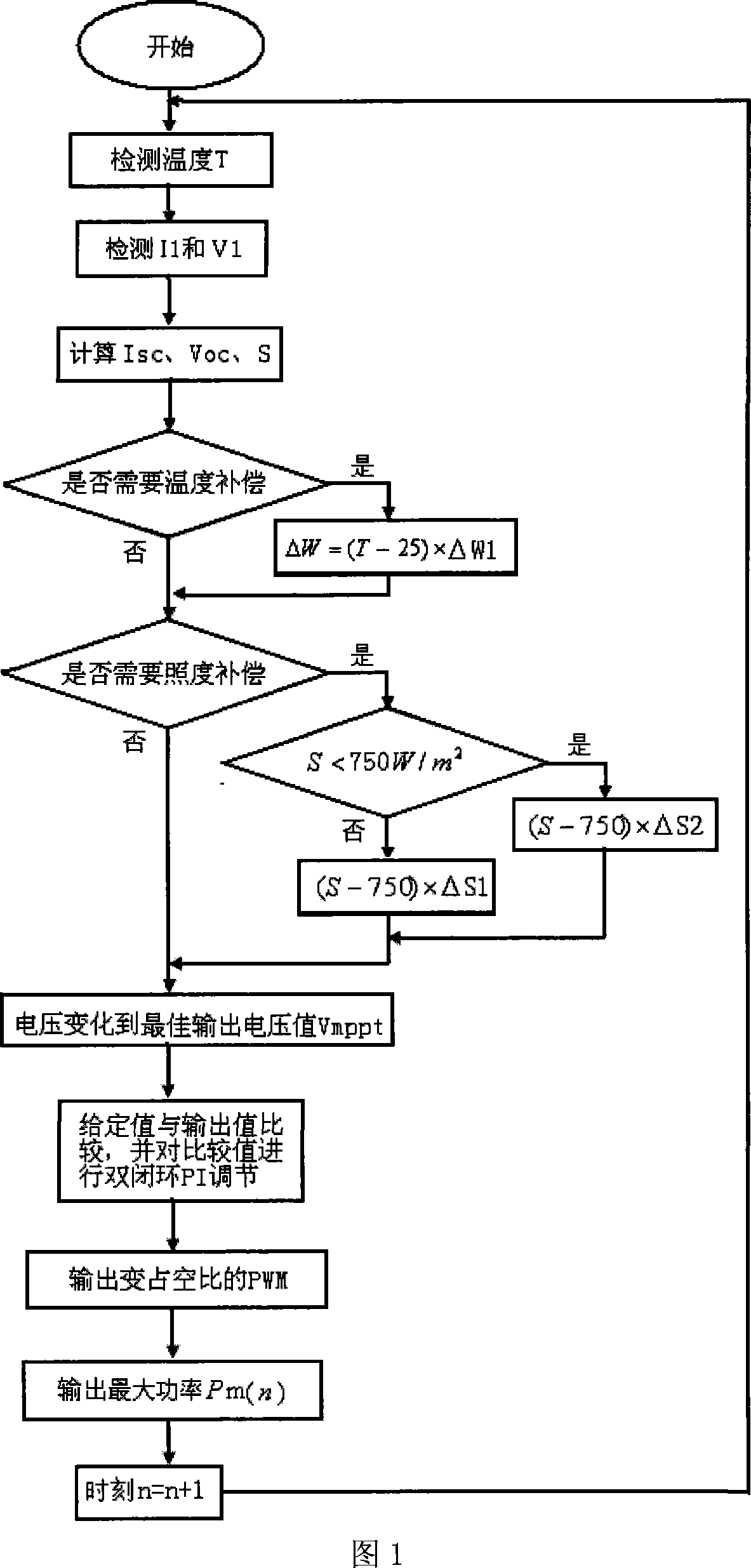
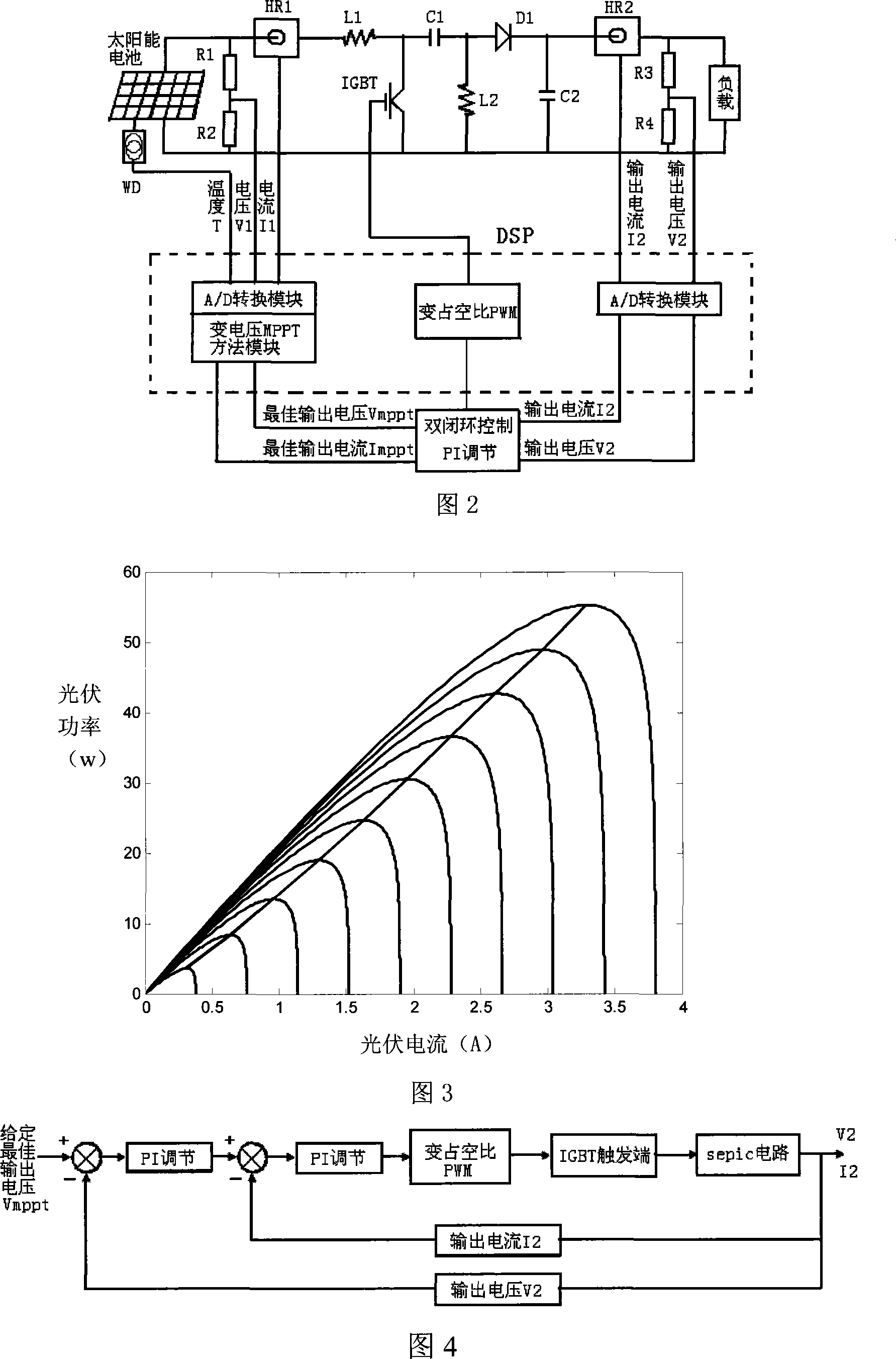
Voltage-variable photovoltaic system maximal power tracing control method adapting to weather status
InactiveCN101236446AMeet the needs of maximum power trackingImprove performancePhotovoltaic energy generationElectric variable regulationIlluminanceClosed loop
The invention provides a maximum power tracking control method of a voltage variable photovoltaic system which adapts to weather conditions, belonging to the photovoltaic power generation technical field; firstly, three data of voltage, current outputted by a photovoltaic battery and temperature of a photovoltaic battery plate at a moment are collected by a collection circuit, and an open circuit voltage value and an illuminating value at the moment are worked out based on the collected data; secondly, an approximate optimum output voltage value is obtained by a real optimized voltage coefficient multiplying the open circuit voltage value, and the temperature and the illumination are compensated, which obtain a real optimum output voltage value, and further a real optimum output current value is obtained; thirdly, an output value of a load end is compared with the real optimum output voltage value and the real optimum output current value, and a maximum power output is realized based on the proportional plus integral control on a fluctuating chopper circuit and a double closed loop of the voltage and the current. The maximum power tracking control method of the voltage variable photovoltaic system improves the output power of a photovoltaic power generation system and simultaneously ensures the operational stability and reliability of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
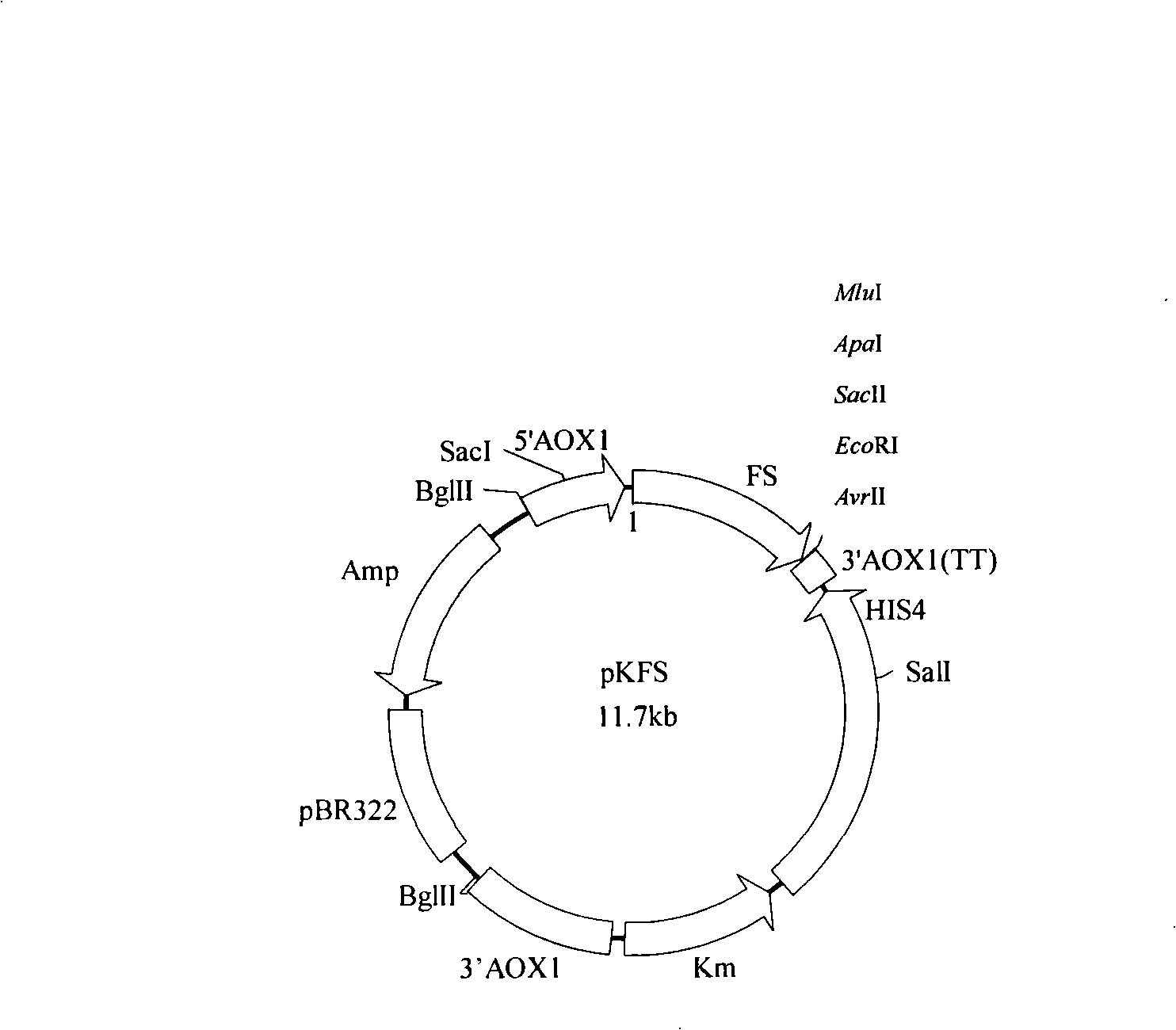
Process for synthesizing ethyl caproate by yeast display lipase synthesis
InactiveCN101285078AImprove operational stabilityHigh biosecurityFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologySurface display
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing ethyl caproate under the catalysis of yeast display lipase. The method comprises two steps, namely the production of full cellular zymin and the synthesis of ethyl caproate. The method comprises the following: a step of cloning the lipase gene into the Pichia yeast surface display vector pKFS to construct the Pichia yeast surface display expression vector pKFS-lipase which is transformed into the host bacteria of Pichia yeast through linearization, a yeast genetic engineering bacteria capable of displaying active pheron on the surface of the Pichia yeast being obtained through screening, and the engineering bacteria being fermented in a rocking bottle to obtain a thallus which is used to make the full cellular zymin after 24 hours of vacuum freeze drying; and then a step of adopting caproic acid and alcohol as raw material which is esterified at the action of the biocatalyst of yeast full cellular zymin with the lipase displayed on the surface to obtain the ethyl caproate product. The method is capable of collecting thalli centrifugally for reuse after the reaction with short reaction time, high yield and good operational stability, thereby greatly reducing production costs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
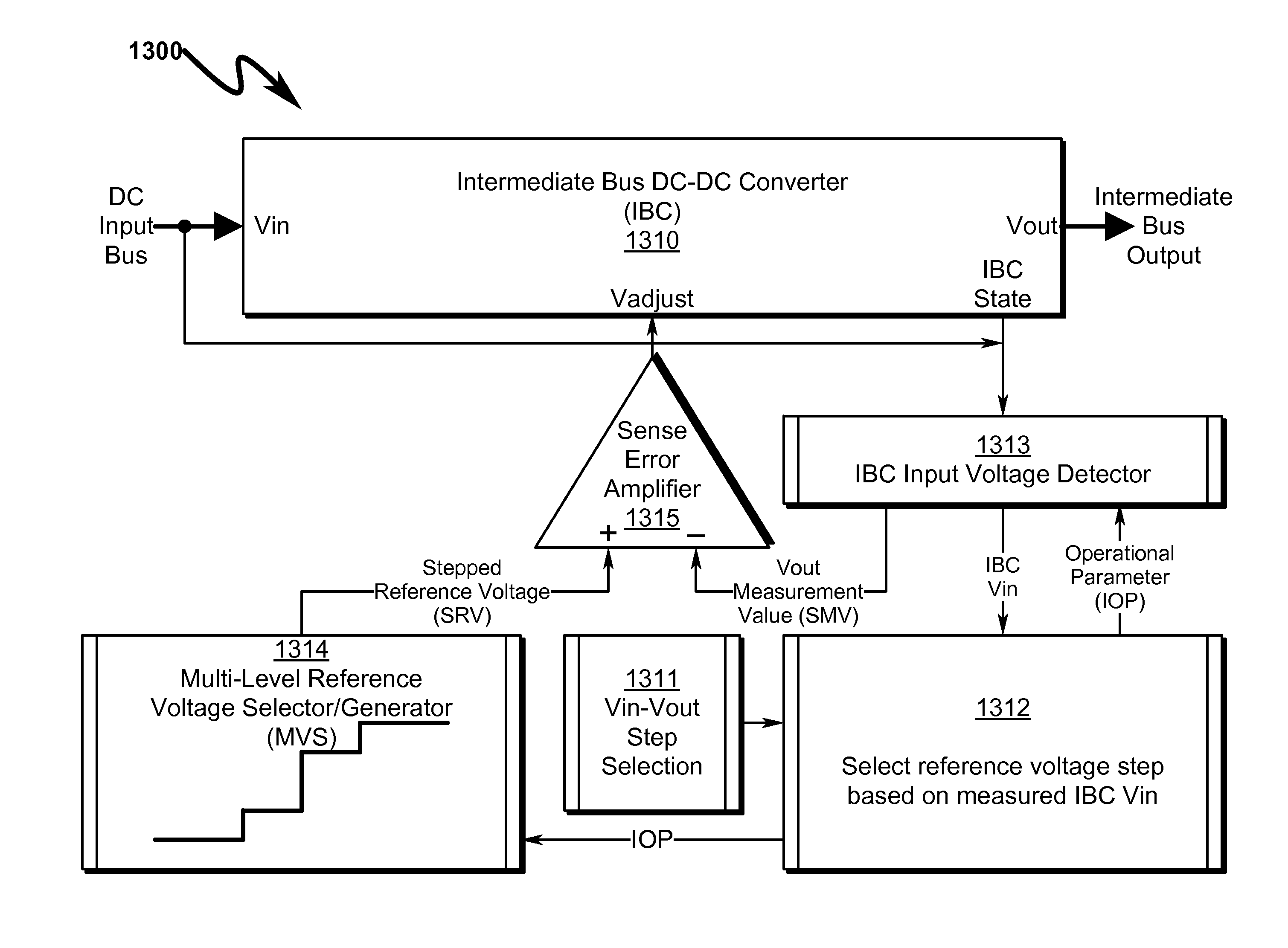
Multi-level voltage regulator system and method
ActiveUS20130335043A1Lower potentialGuaranteed uptimeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionHysteresisPoint of load
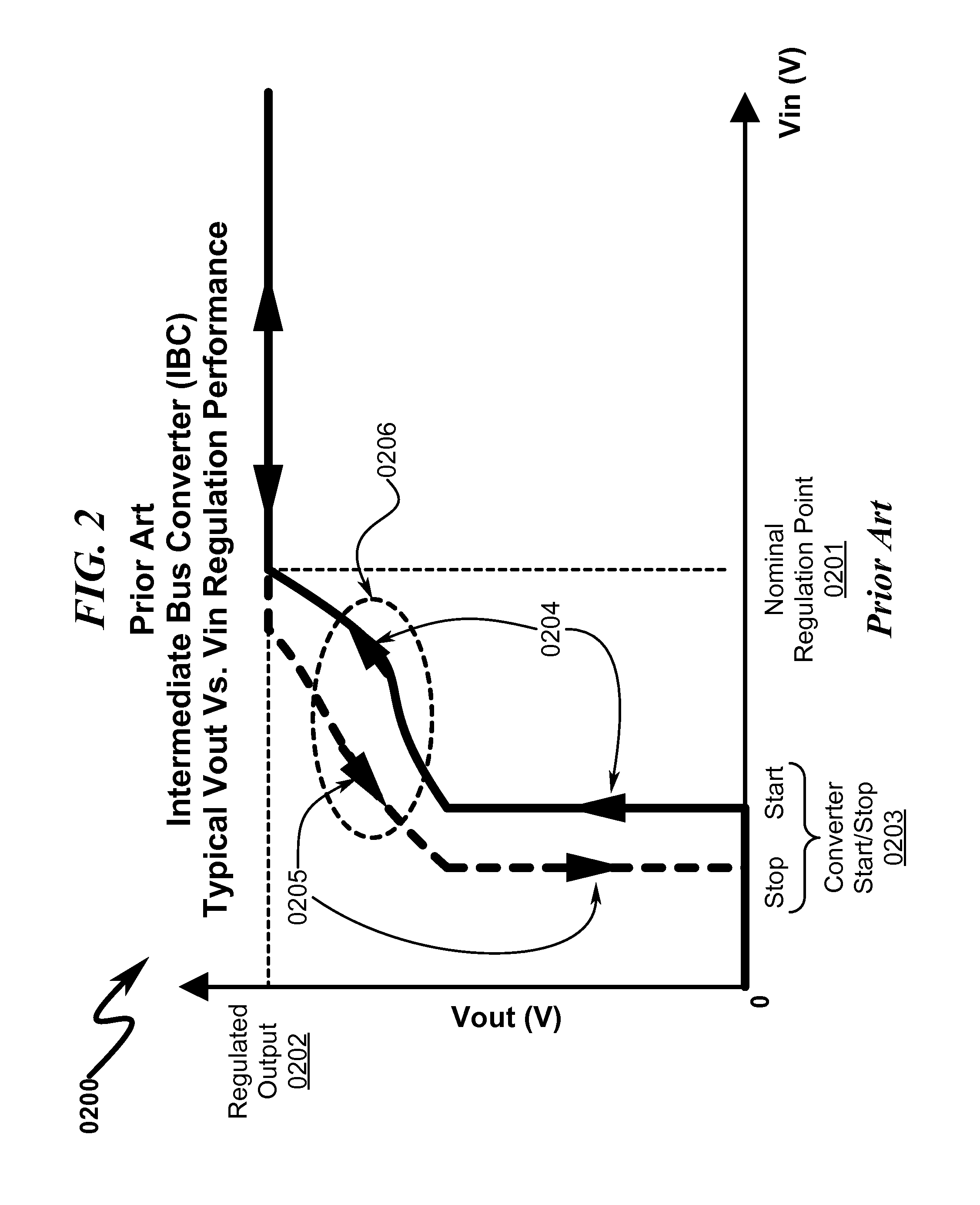
A multi-level voltage regulator system / method providing discrete regulation of a DC-DC intermediate bus converter (IBC) output voltage (Vout) is disclosed. The disclosed system / method allows IBC Vout to be regulated in discrete steps during periods where IBC input voltage (Vin) falls below nominal operating values. Rather than shutting down or degrading IBC Vout in an unpredictable non-linear fashion based on IBC input / loading, IBC Vout is regulated in fixed discrete steps, allowing IBC-connected point-of-load (POL) converters to obtain stable power input that is well-defined over IBC Vin. IBC operating parameters may define multi-dimensional operational state spaces of IBC Vout regulation that ensure optimum power flow to attached POLs while maintaining operational stability within the IBC regulator. Instabilities in IBC / POL performance across variations in IBC Vin, load transients, POL loading, and environmental variables may be prevented using Vin voltage step hysteresis.
Owner:TDK LAMBDA CORP
Three-phase fluidized bed reactor
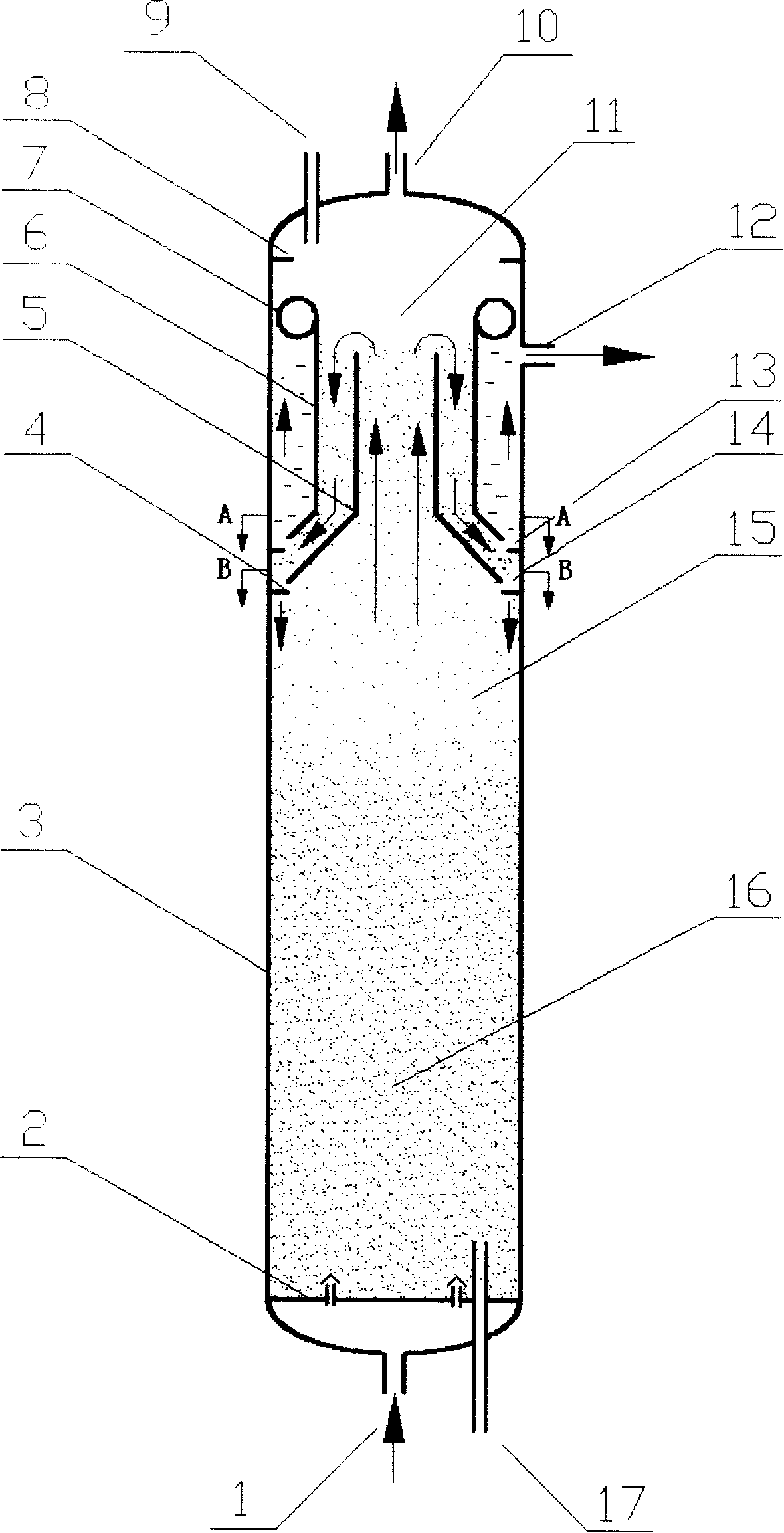
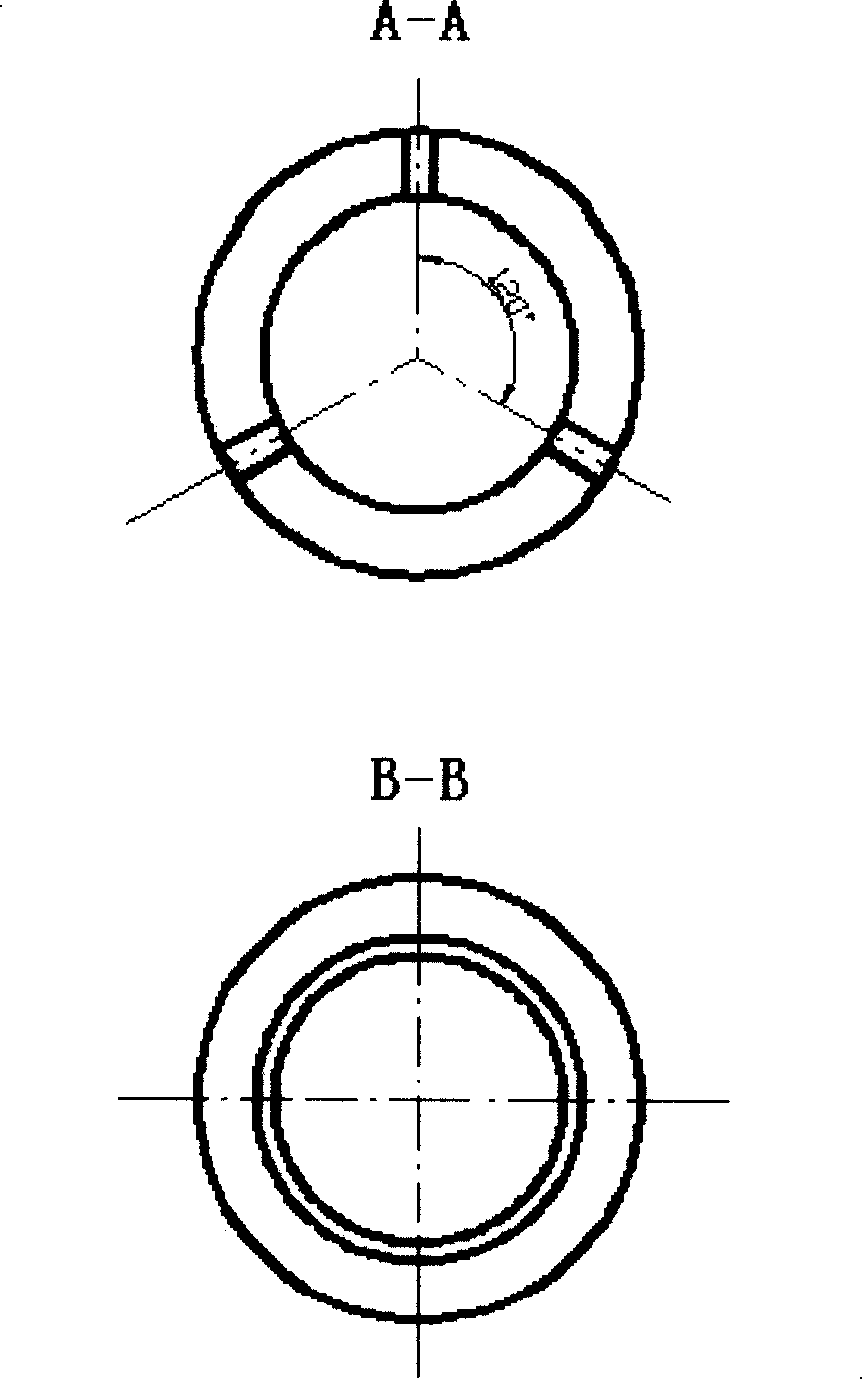
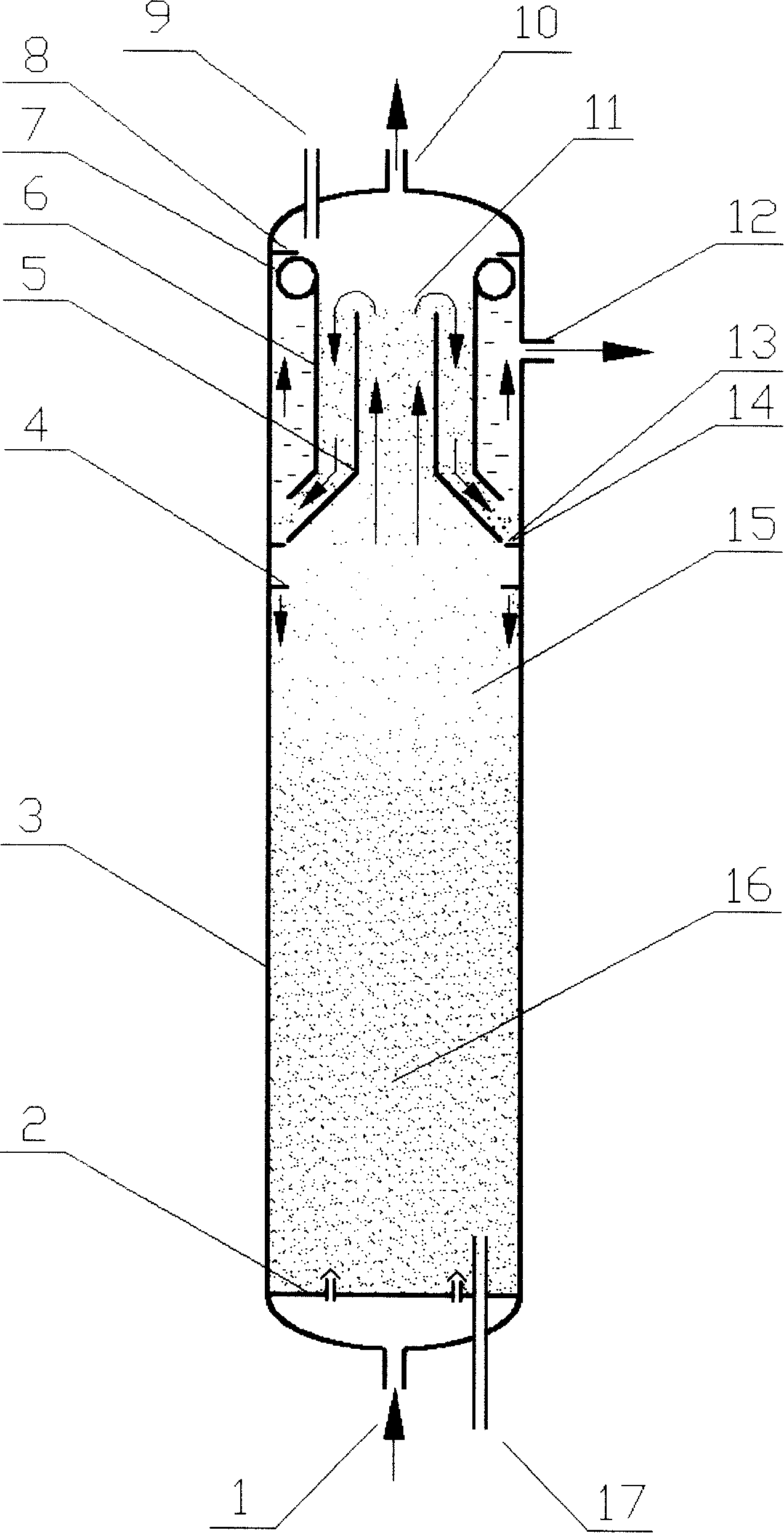
ActiveCN101172220AGreat operating flexibilityReduce carryoverChemical/physical processesLower limitChemical reaction
The invention discloses an improved three-phase fluidized layer reactor, which consists of a reactor casing body and a three-phase separator positioned at the inner upper part of the casing body, wherein, the three-phase separator is composed of the inner cylinders and outer cylinders of two concentric cylinders with different inner diameters, a float tube arranged on the outer cylinder, and the inner wall of the reactor casing body. An upper limiting apparatus and a lower limiting apparatus are arranged on the reactor casing body, and the three-phase separator is positioned between the upper limiting apparatus and the lower limiting apparatus. The reactor is mainly suitable for the chemical reaction of different kinds of liquid and gas substances under the circumstance of contacting with solid particles, and has the advantages of large catalyst inventory, high utilization rate of the reactor, and high stability of operation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for autonomous dynamic voltage and frequency scaling of microprocessors and computer system
ActiveCN101187831AImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com