Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2816 results about "Voltage divider" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
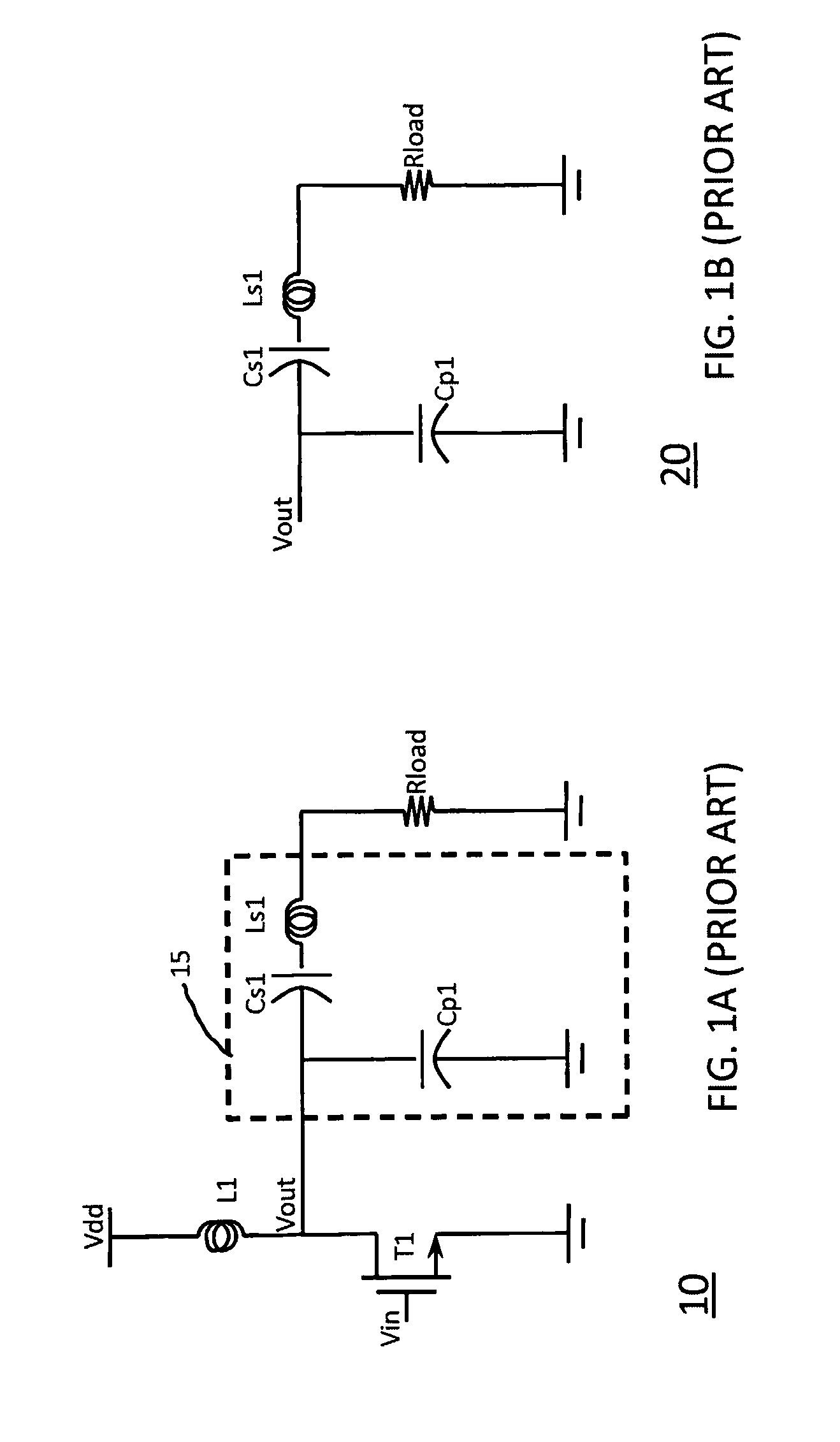
In electronics, a voltage divider (also known as a potential divider) is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage (Vₒᵤₜ) that is a fraction of its input voltage (Vᵢₙ). Voltage division is the result of distributing the input voltage among the components of the divider. A simple example of a voltage divider is two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied across the resistor pair and the output voltage emerging from the connection between them.
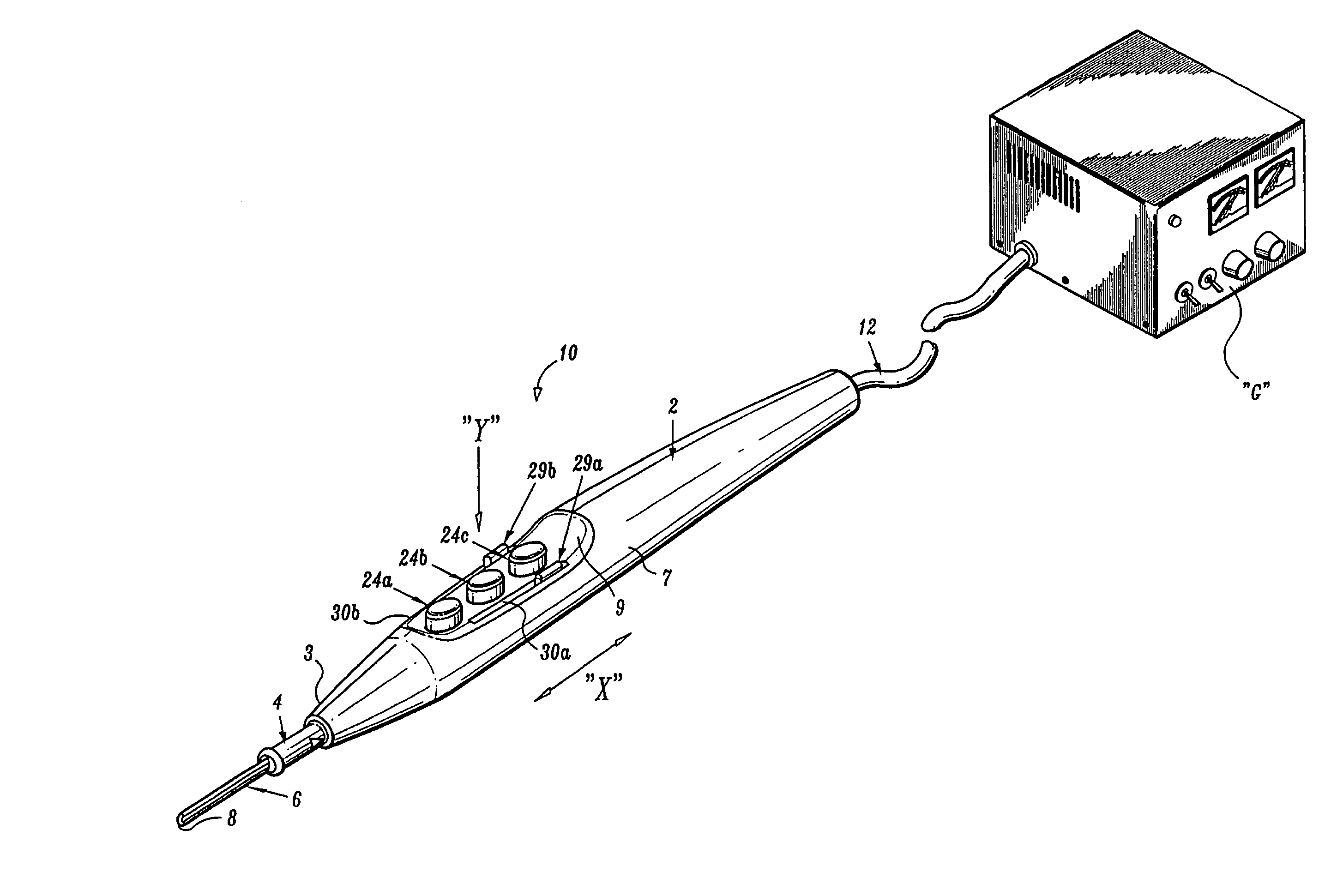
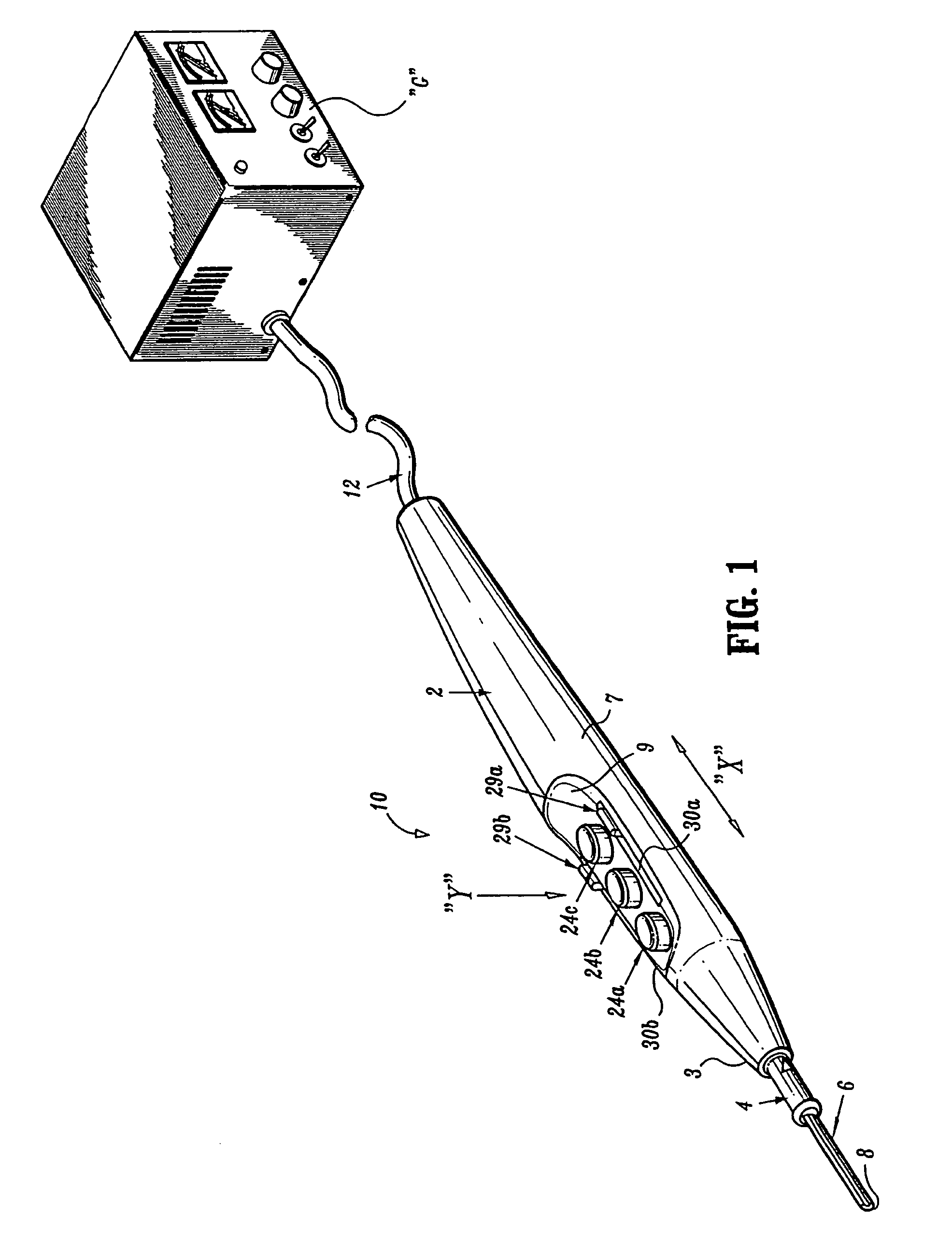
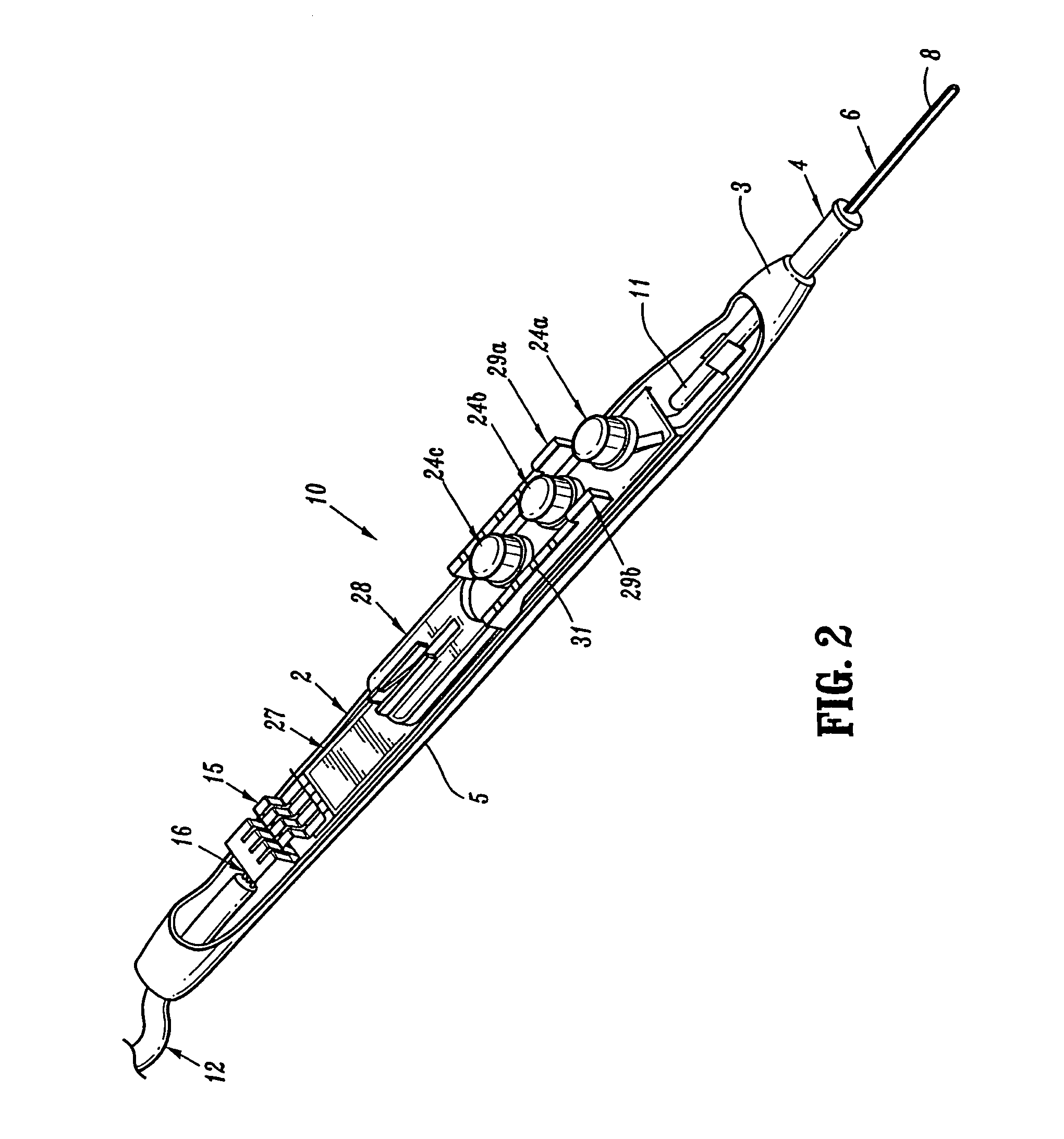
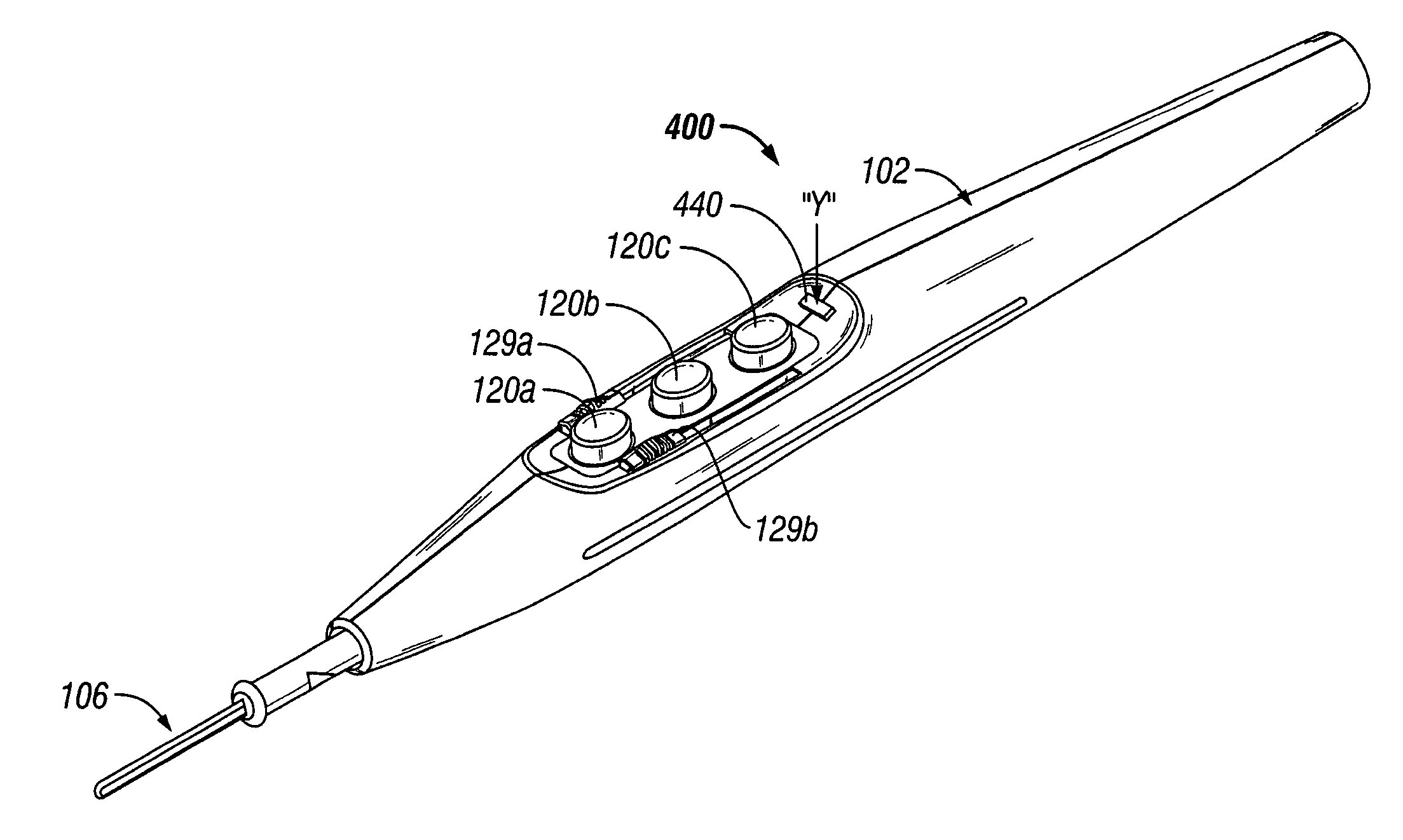
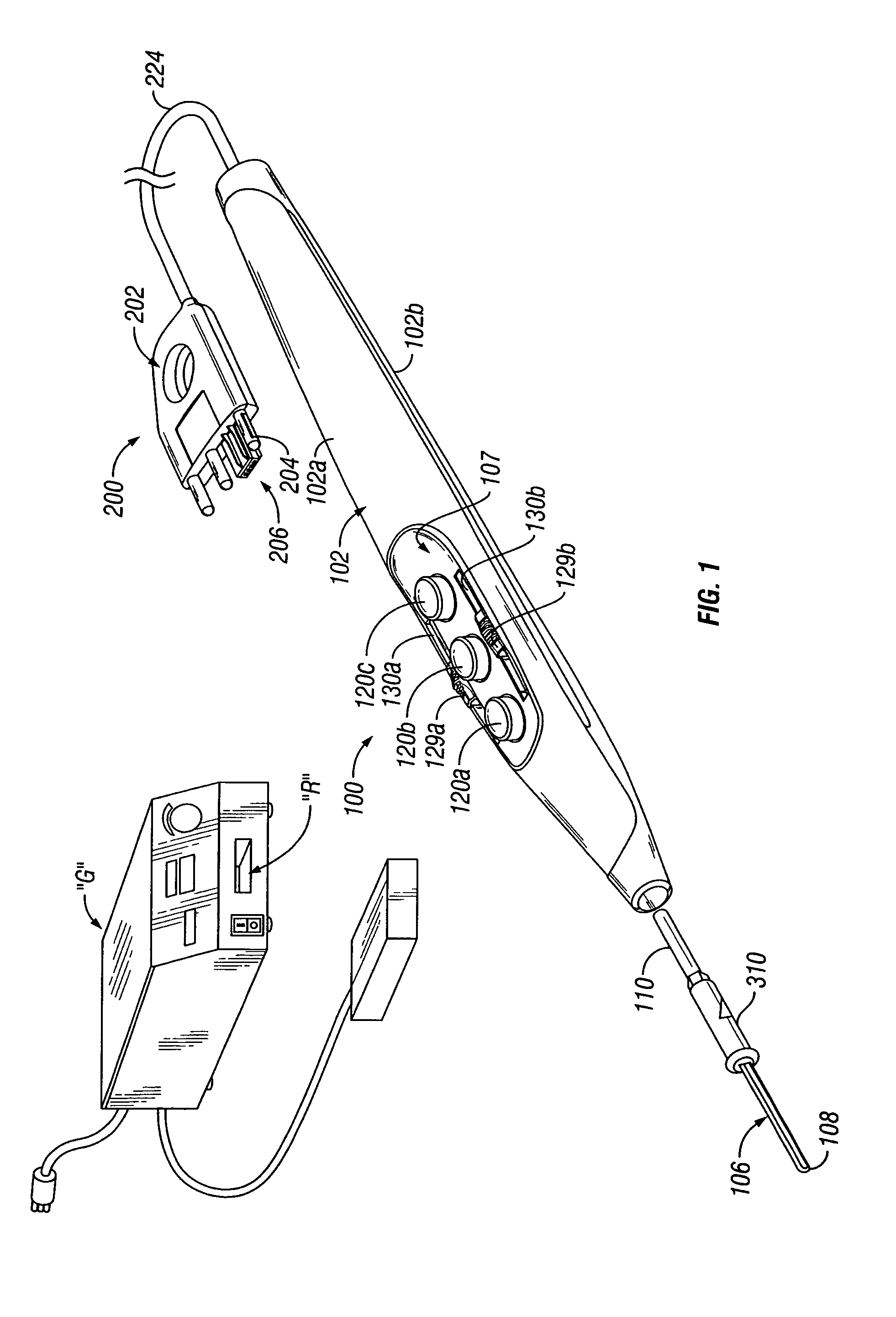
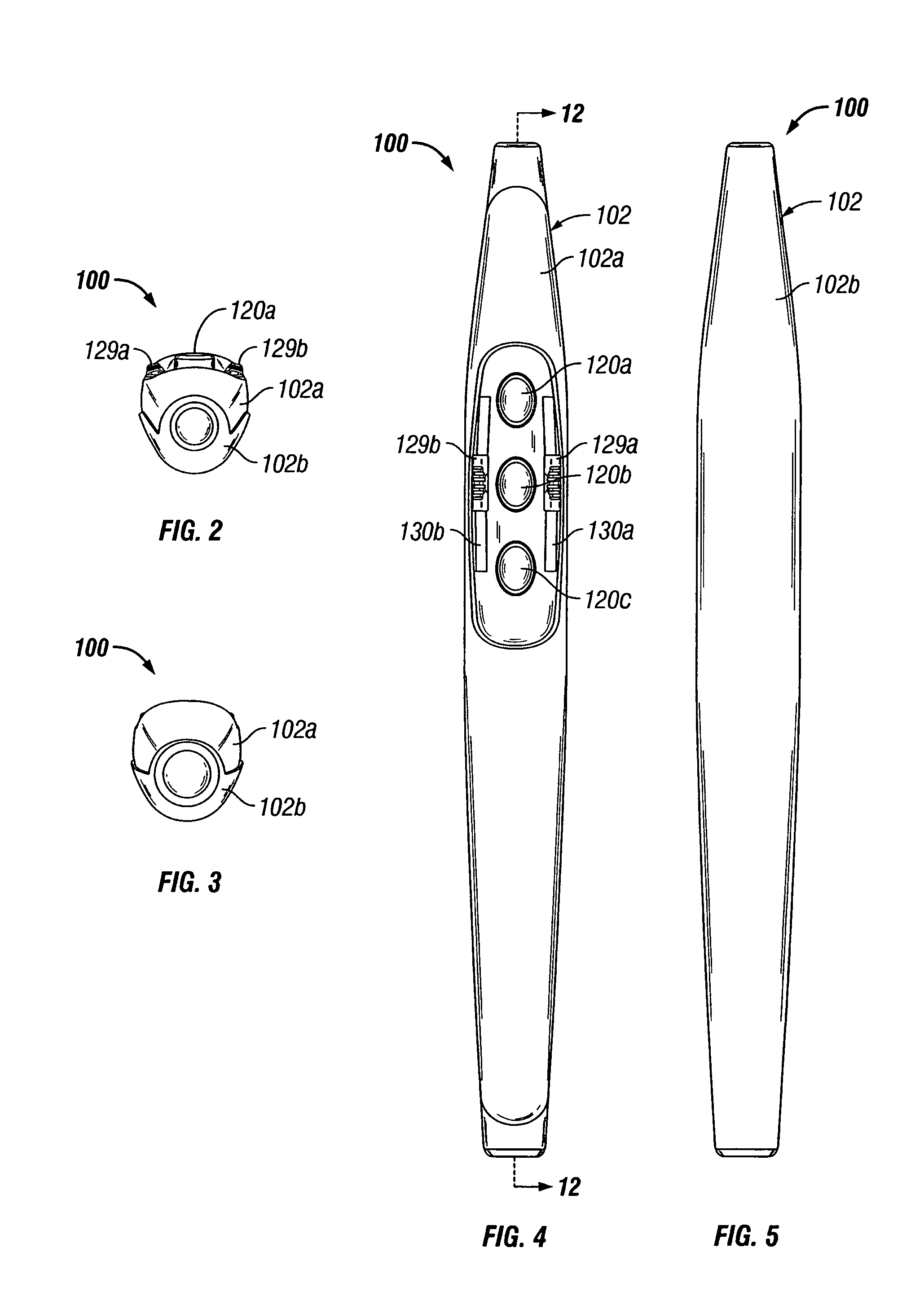
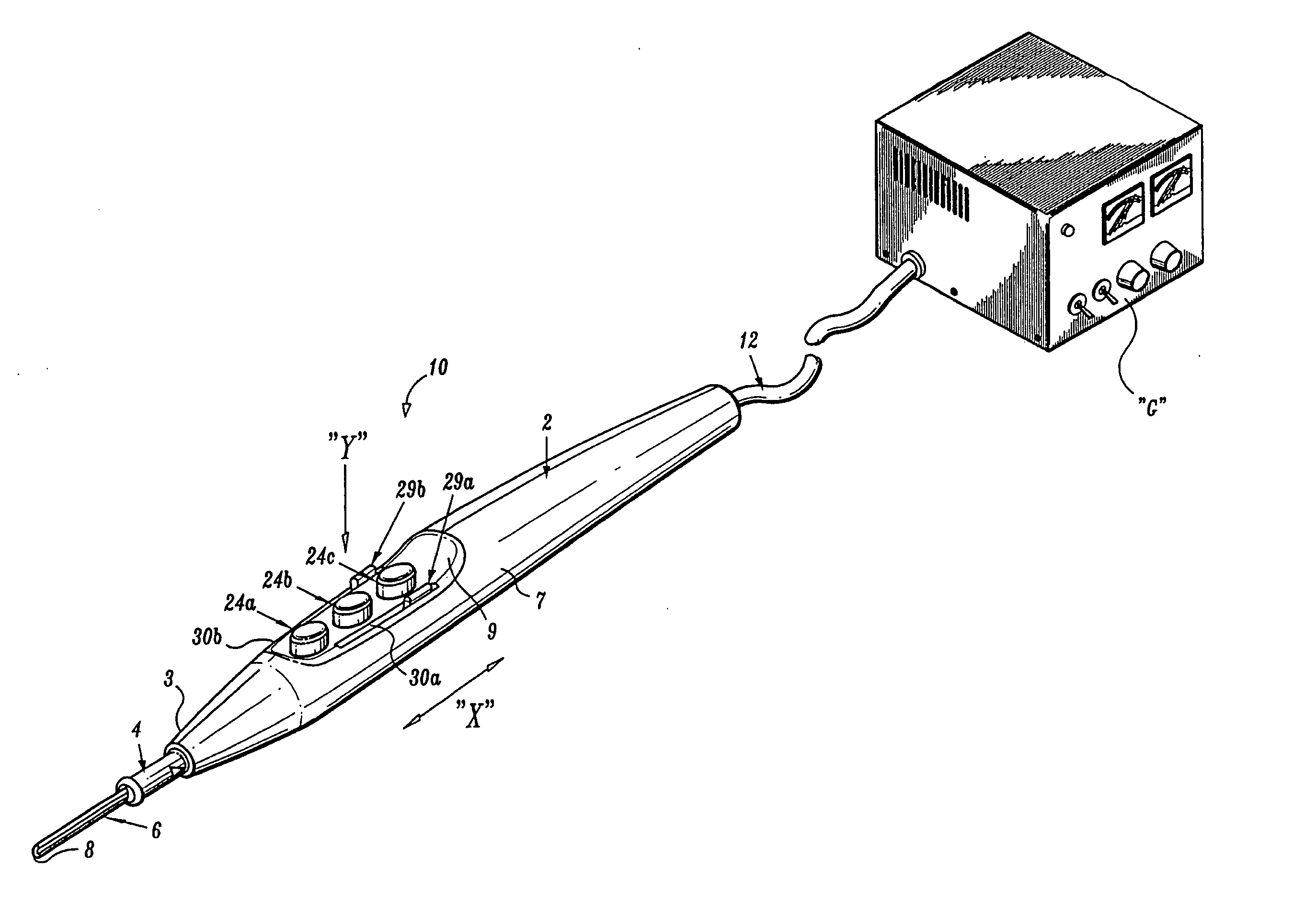
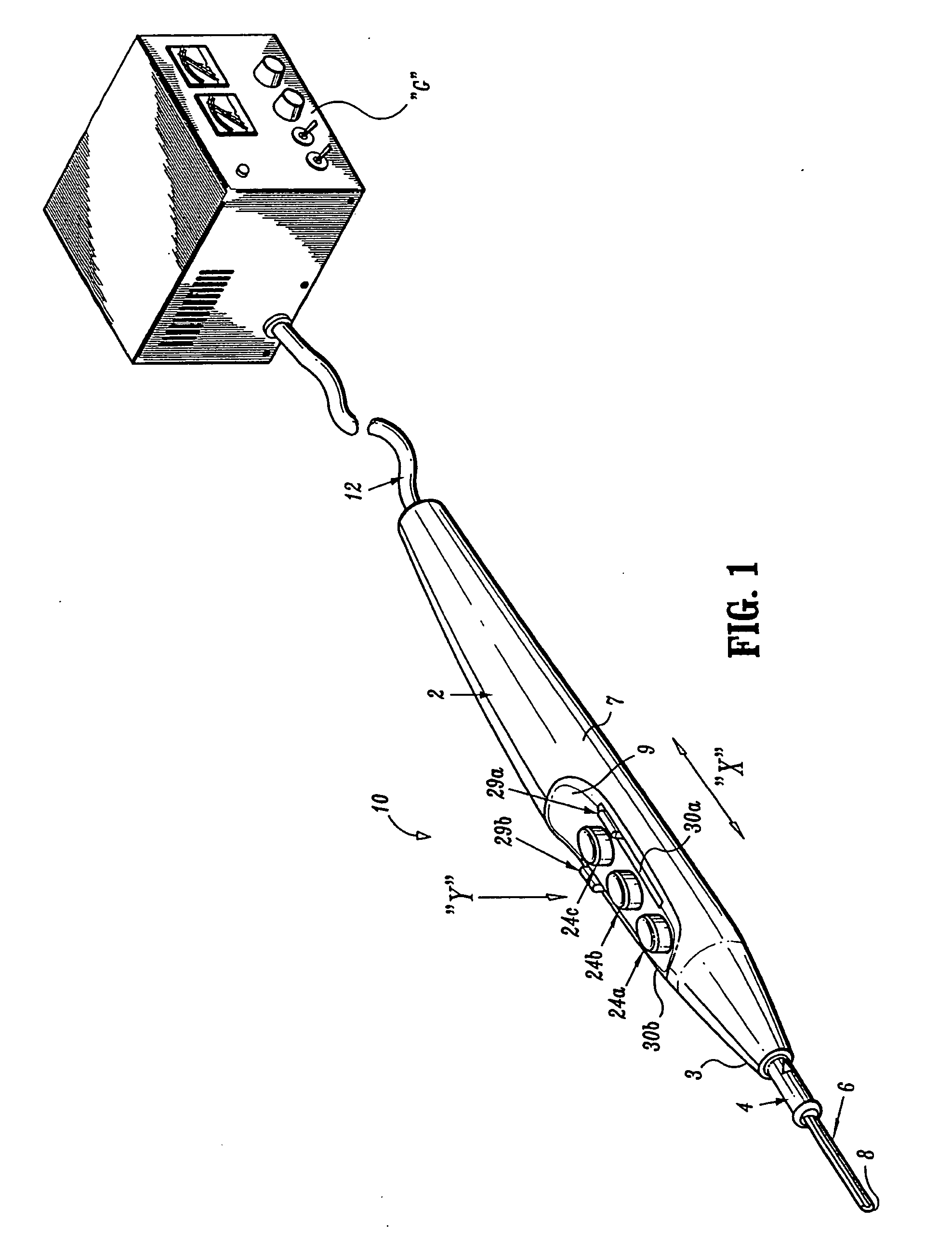
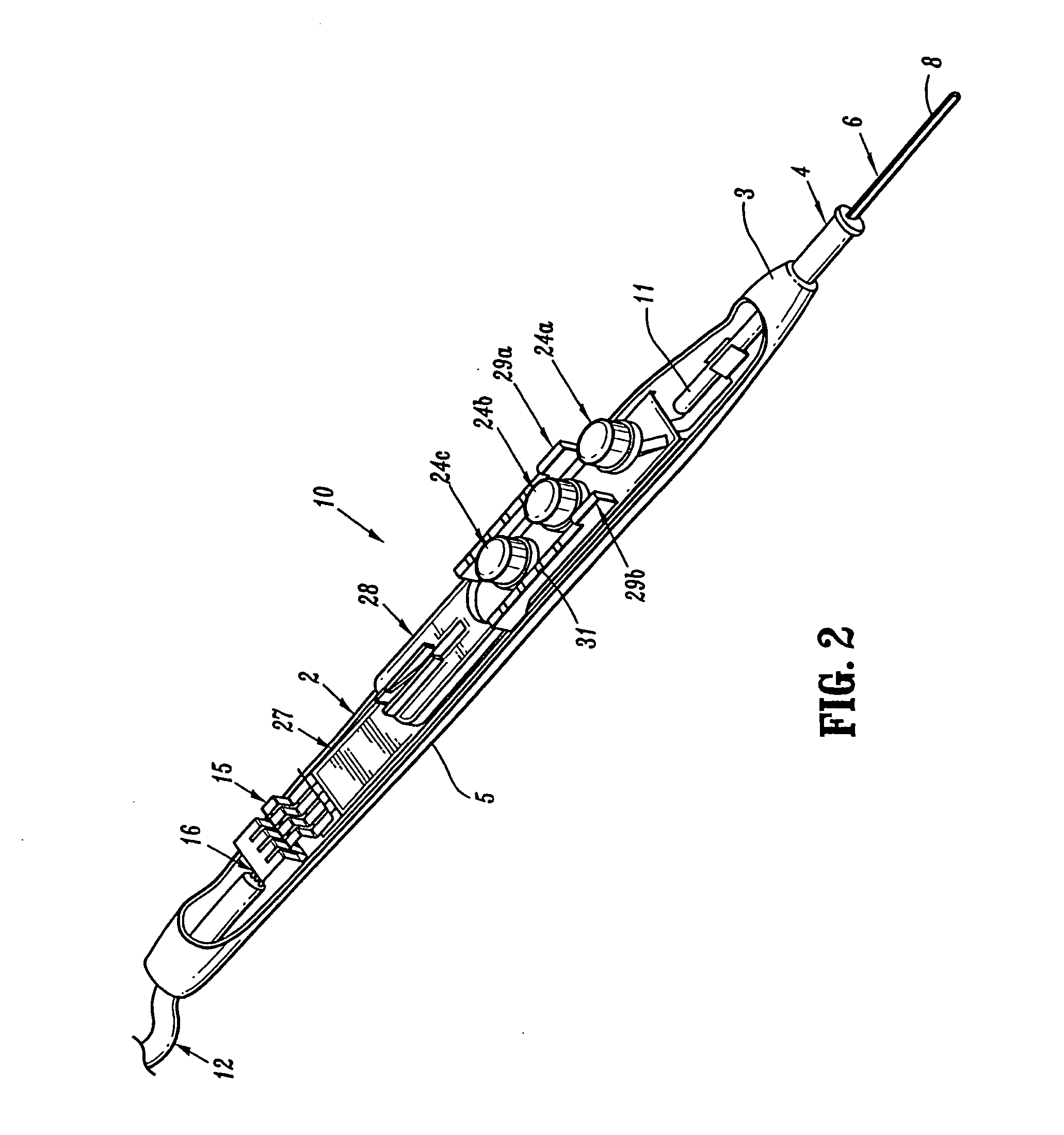
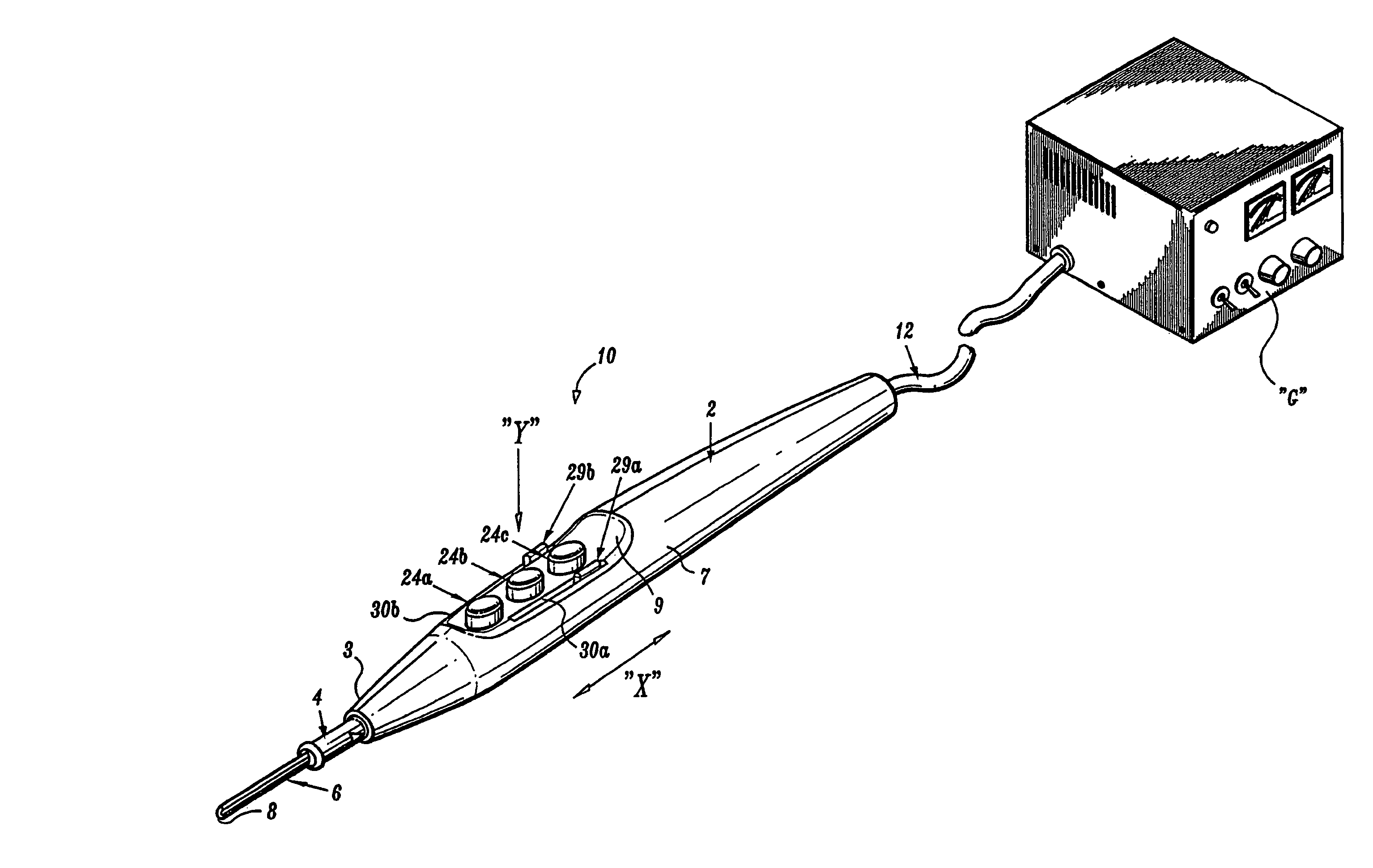
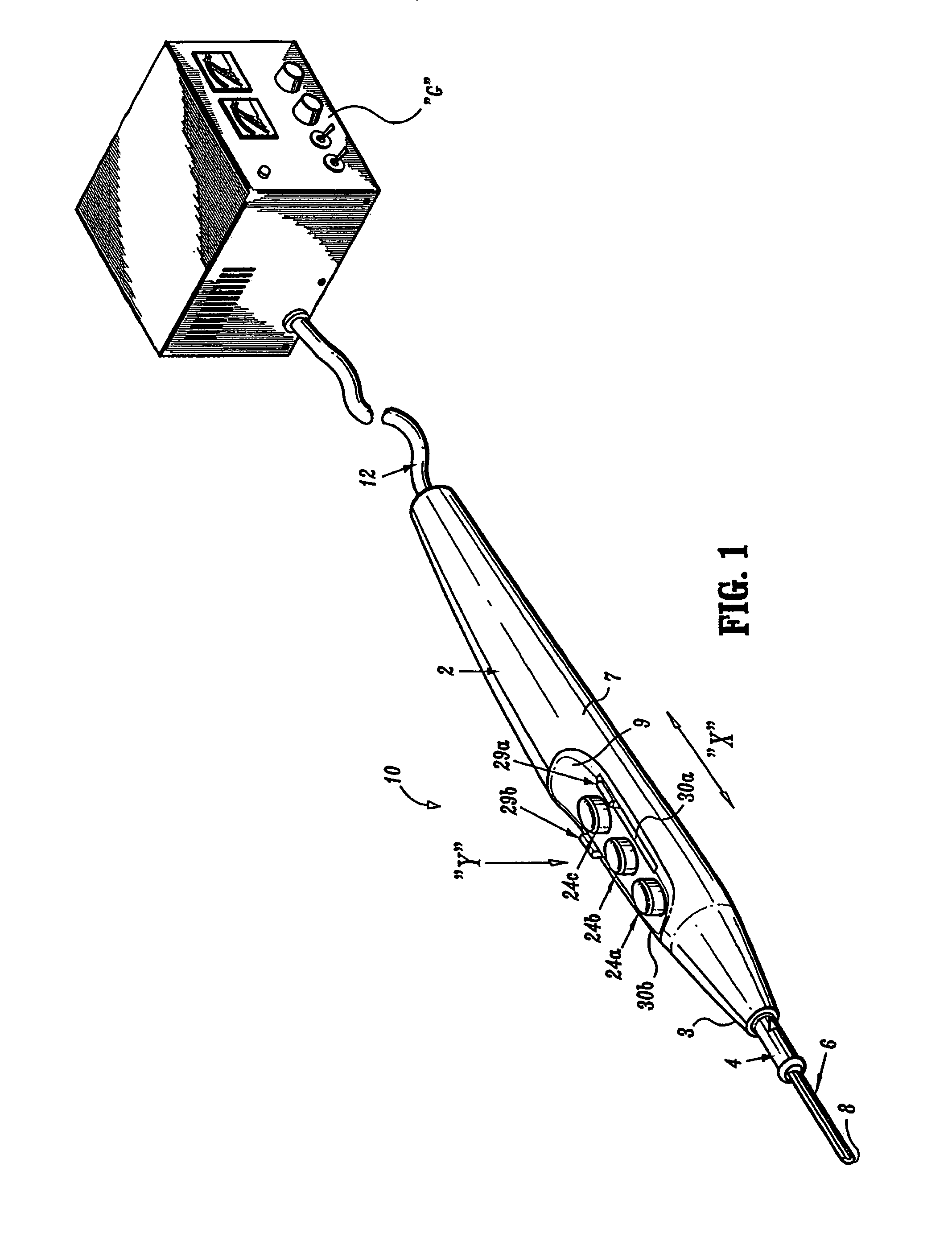
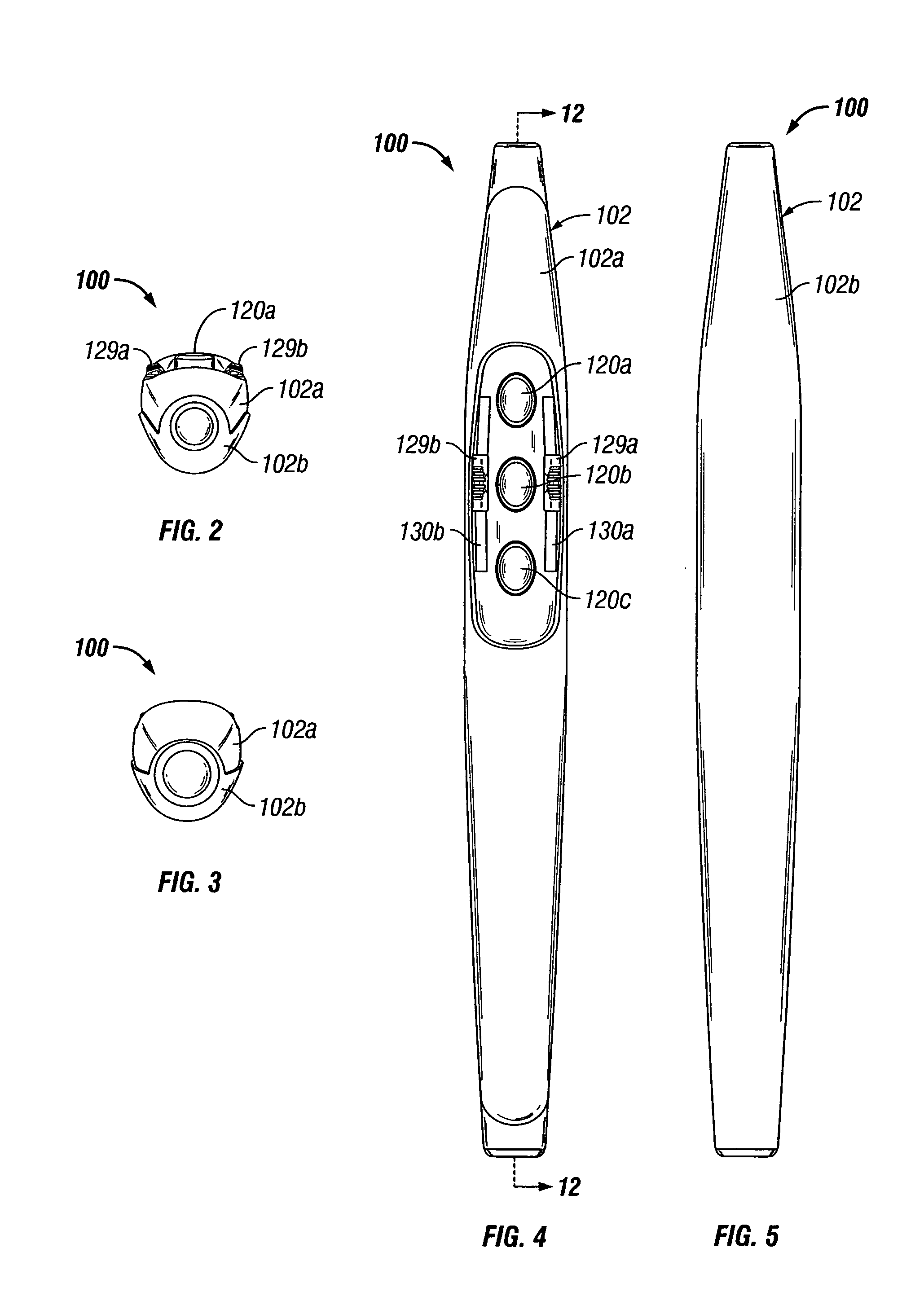
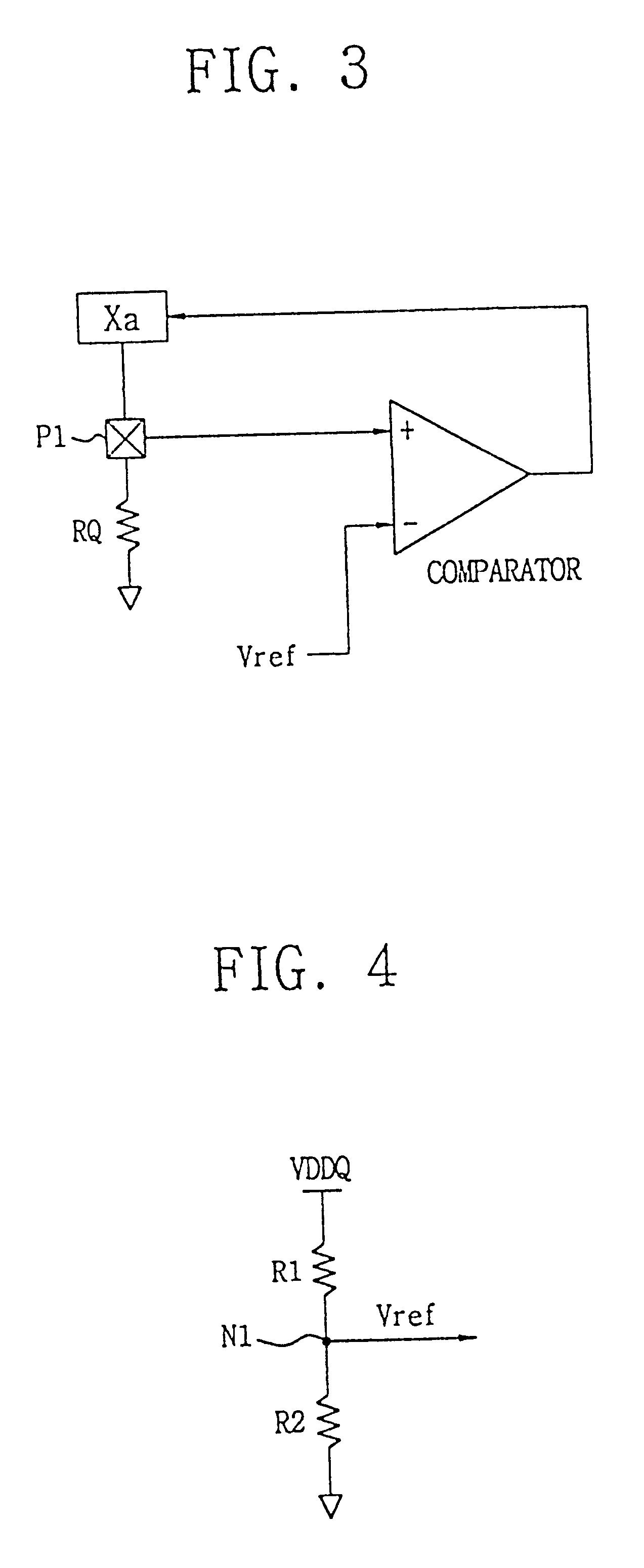
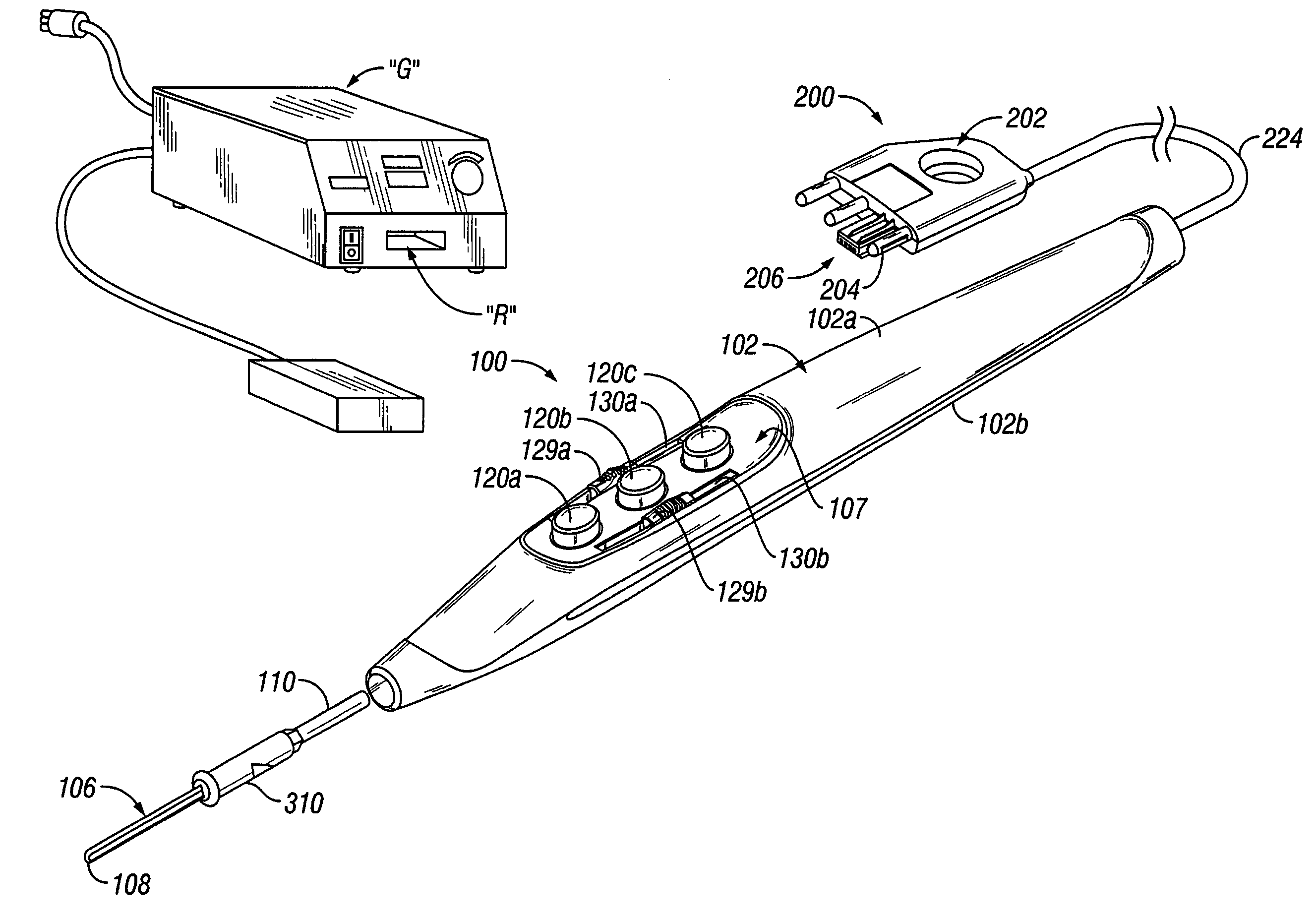
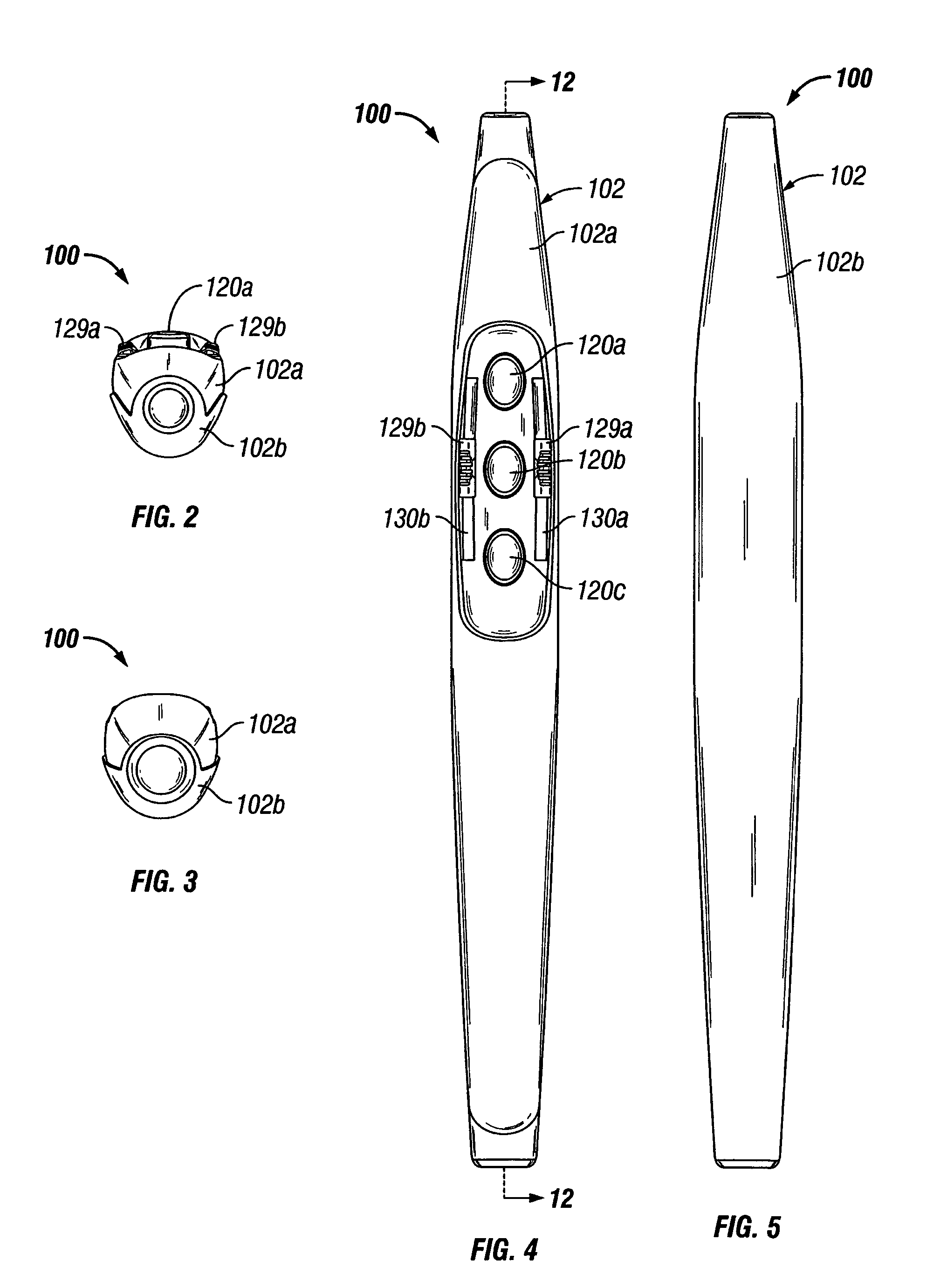
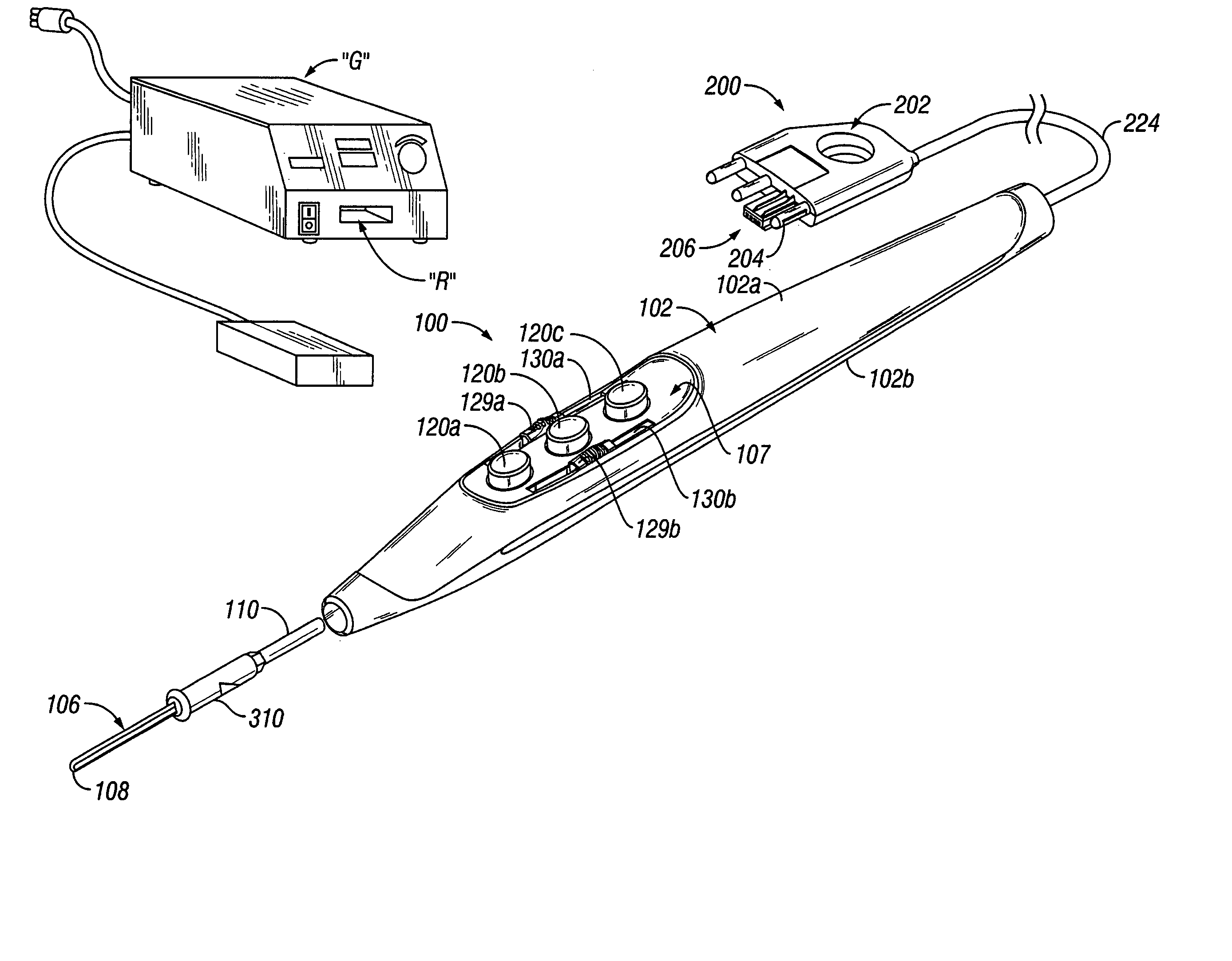
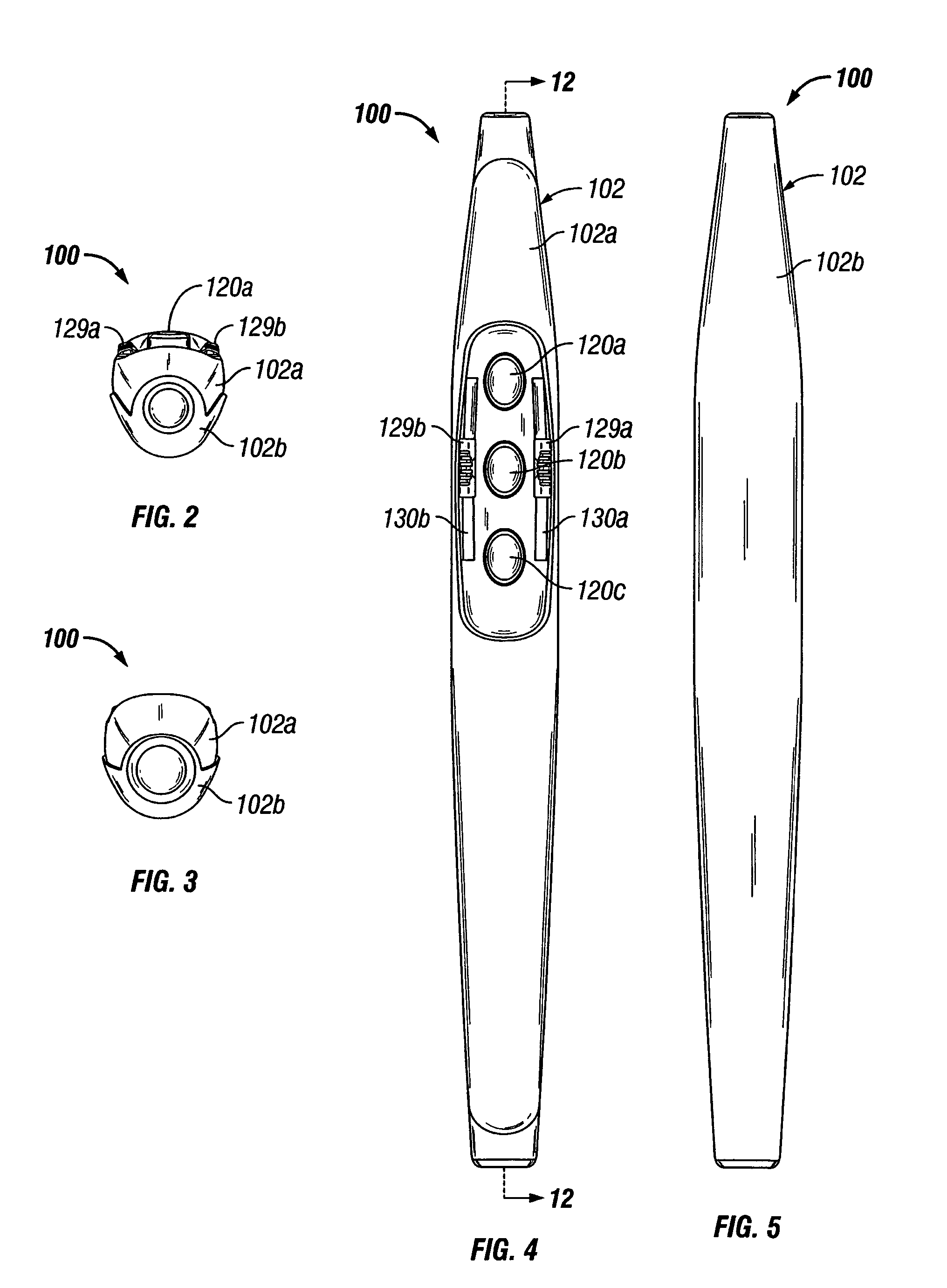
Electrosurgical pencil with improved controls
An electrosurgical pencil is provided which includes an elongated housing, an electrocautery blade supported within the housing and extending distally from the housing. The electrocautery blade is connected to a source of electrosurgical energy. The pencil also includes at least one activation switch supported on the housing which is configured and adapted to complete a control loop extending from the source of electrosurgical energy. At least one voltage divider network is also supported on the housing and is electrically connected to the source of electrosurgical energy.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
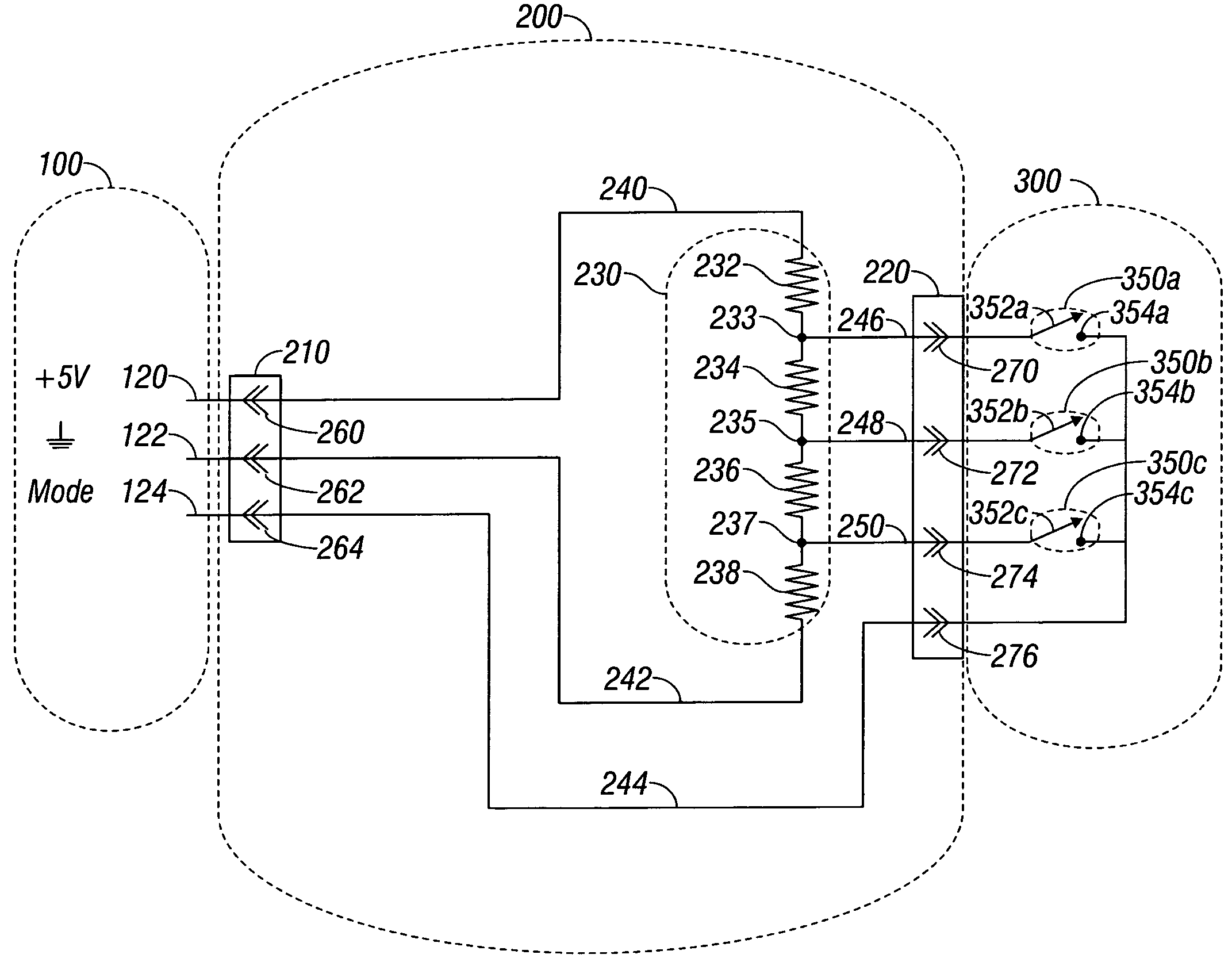
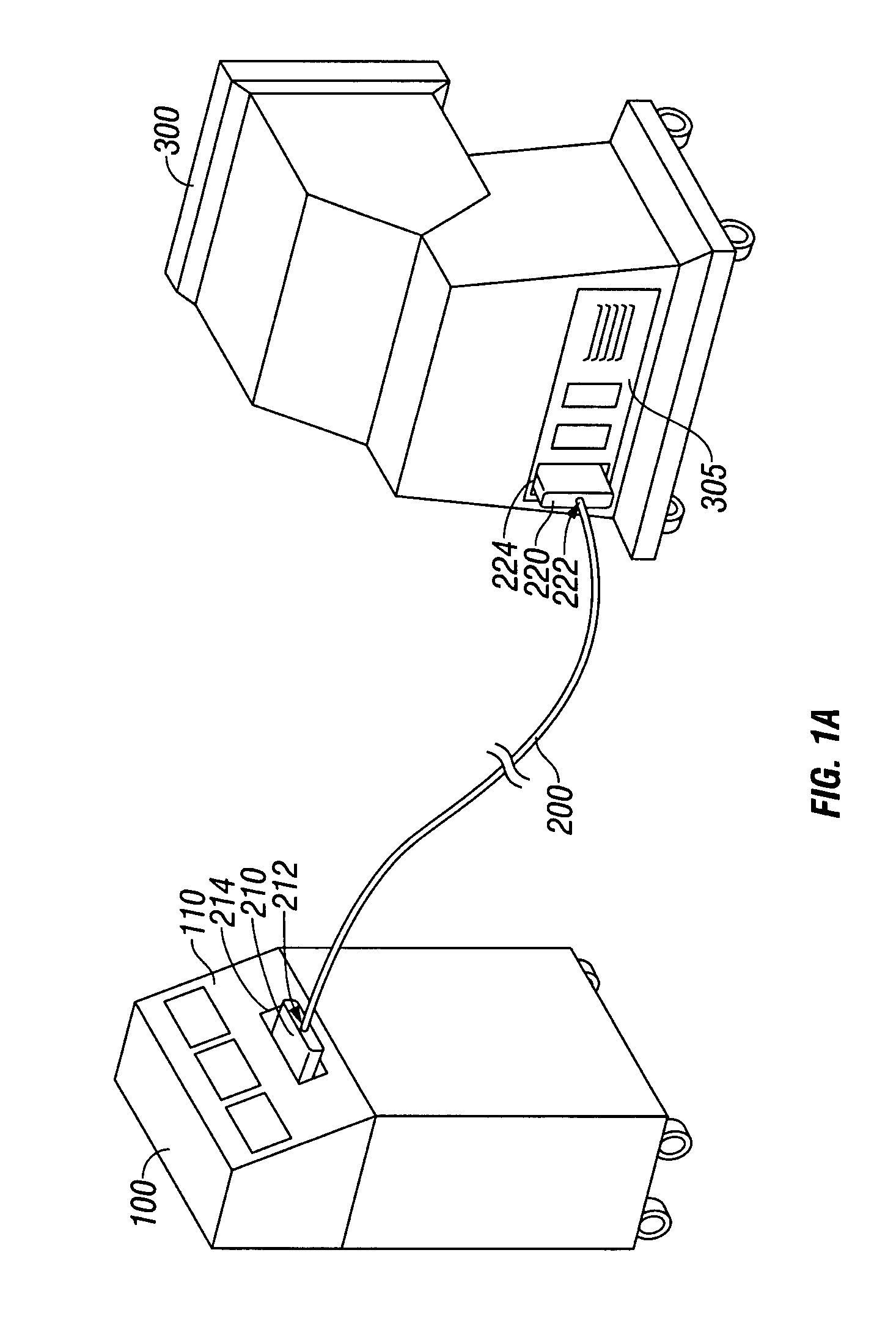
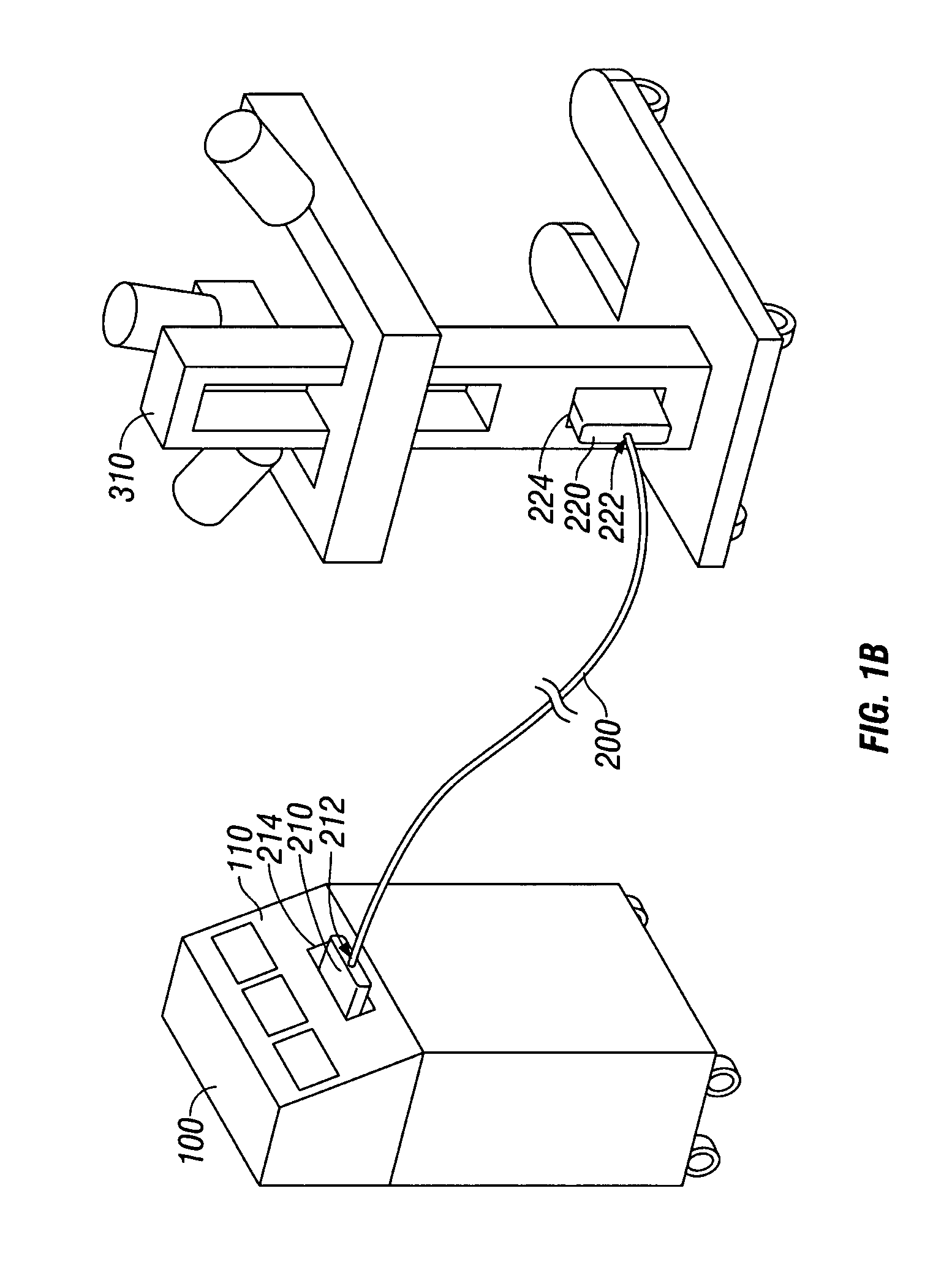
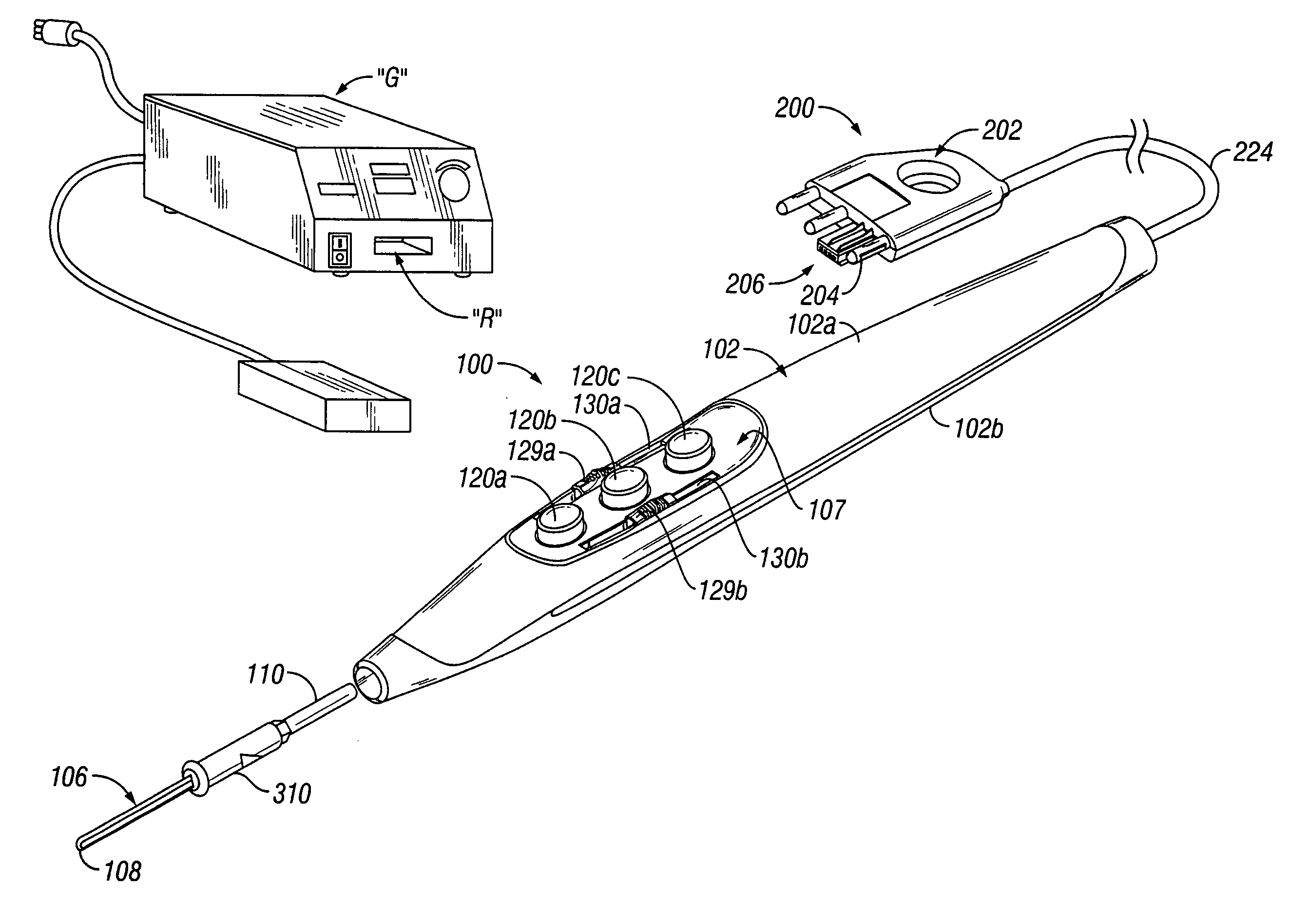
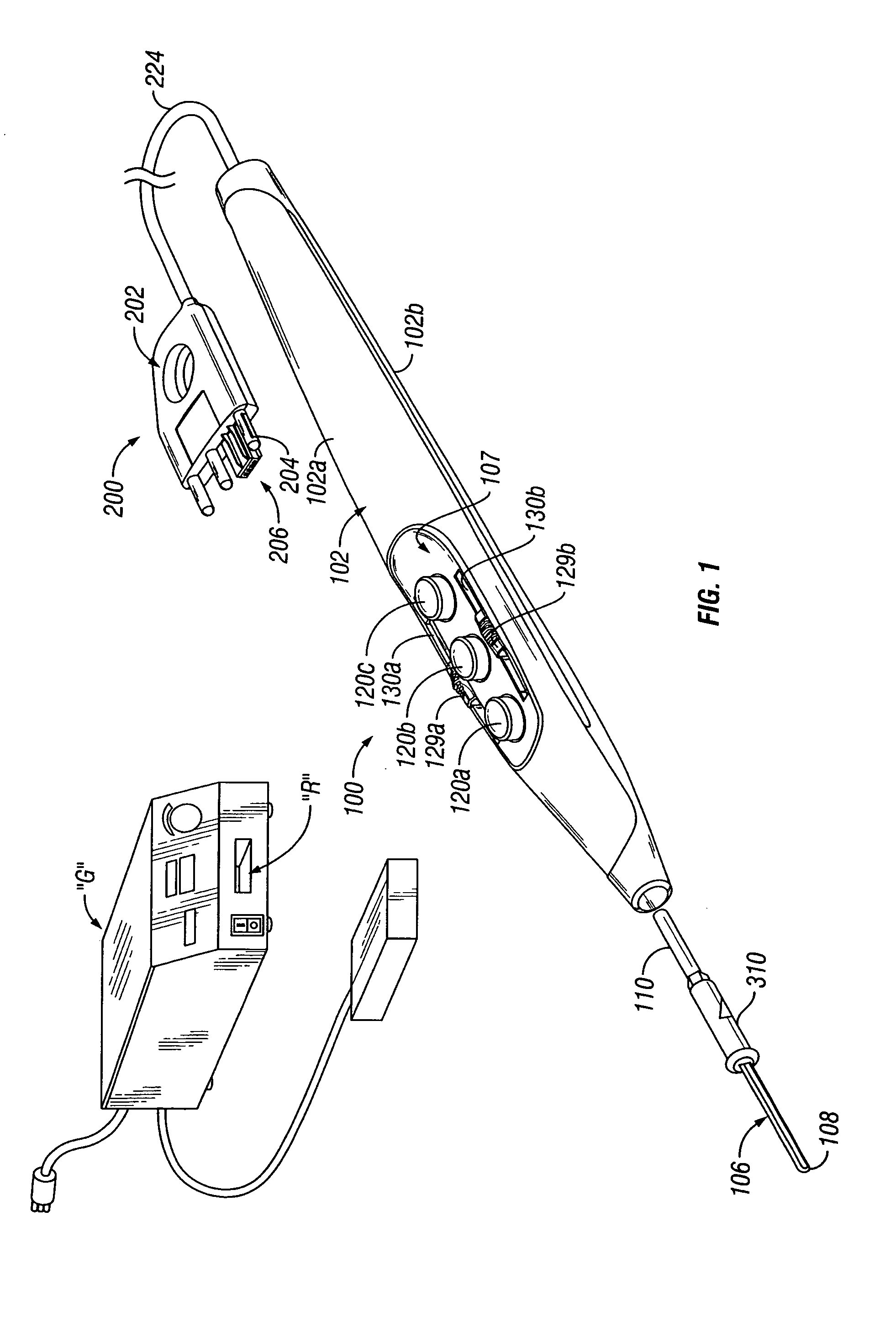
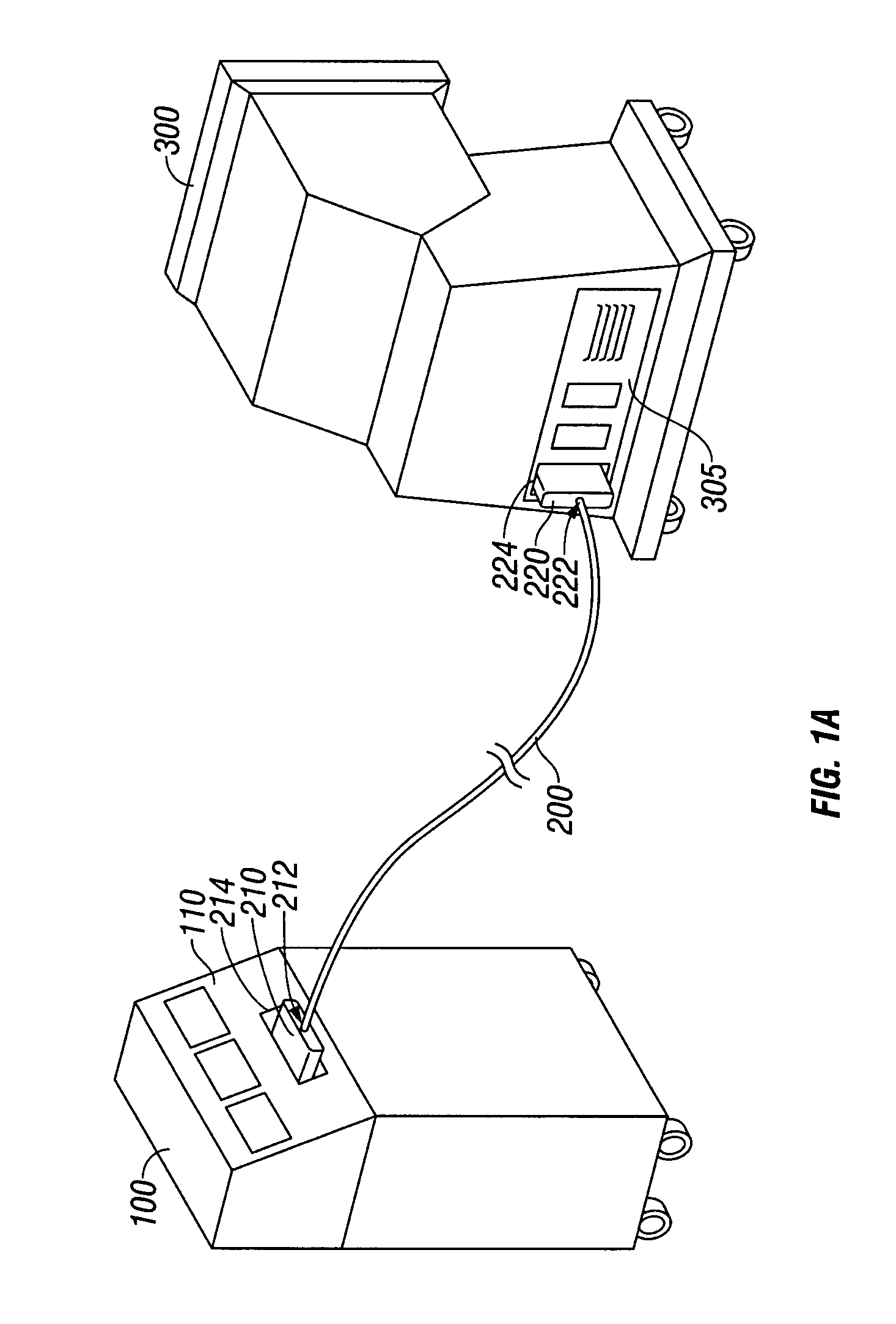
Connection cable and method for activating a voltage-controlled generator
ActiveUS7834484B2Batteries circuit arrangementsIncorrect coupling preventionSurgical operationElectrosurgery
A connection cable is disclosed for controlling a voltage-controlled generator such as an electrosurgery generator from a controlling device such as a robotic surgery system. The cable includes a first connector adapted to connect to a voltage-controlled generator and a second connector adapted to connect to a controlling device. Within the cable is a voltage divider interdisposed between the first connector and the second connector. The voltage divider is configured to divide a reference voltage provided by the voltage-controlled generator into at least one control voltage which is selectable by the controlling device. The cable additionally includes a plurality of electrical wires which operatively connect the first connector, the second connector and the voltage divider. During robotic electrosurgery, said operating parameters can be actuated by a surgeon operating at the robotic surgical system console, which causes a corresponding control voltage to be switched to a control voltage input on an electrosurgery generator, which, in turn, generates a corresponding electrosurgical signal in response thereto.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Electrosurgical pencil with advanced ES controls
An electrosurgical system is provided that includes an electrosurgical generator; and an electrosurgical pencil selectively connectable to the electrosurgical generator. The electrosurgical pencil includes an elongated housing; at least one electrocautery end effector removably supportable within the housing and extending distally from the housing, the electrocautery end effector being connected to the electrosurgical generator; and at least one voltage divider network supported on the housing. The at least one voltage divider network is electrically connected to the electrosurgical generator and controls at least one of the intensity of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil and the mode of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil. The voltage divider network generates a plurality of characteristic voltages which are measurable by the electrosurgical generator and which electrosurgical generator in turn transmits a corresponding waveform duty cycle at a particular intensity to the electrocautery end effector of the electrosurgical pencil.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
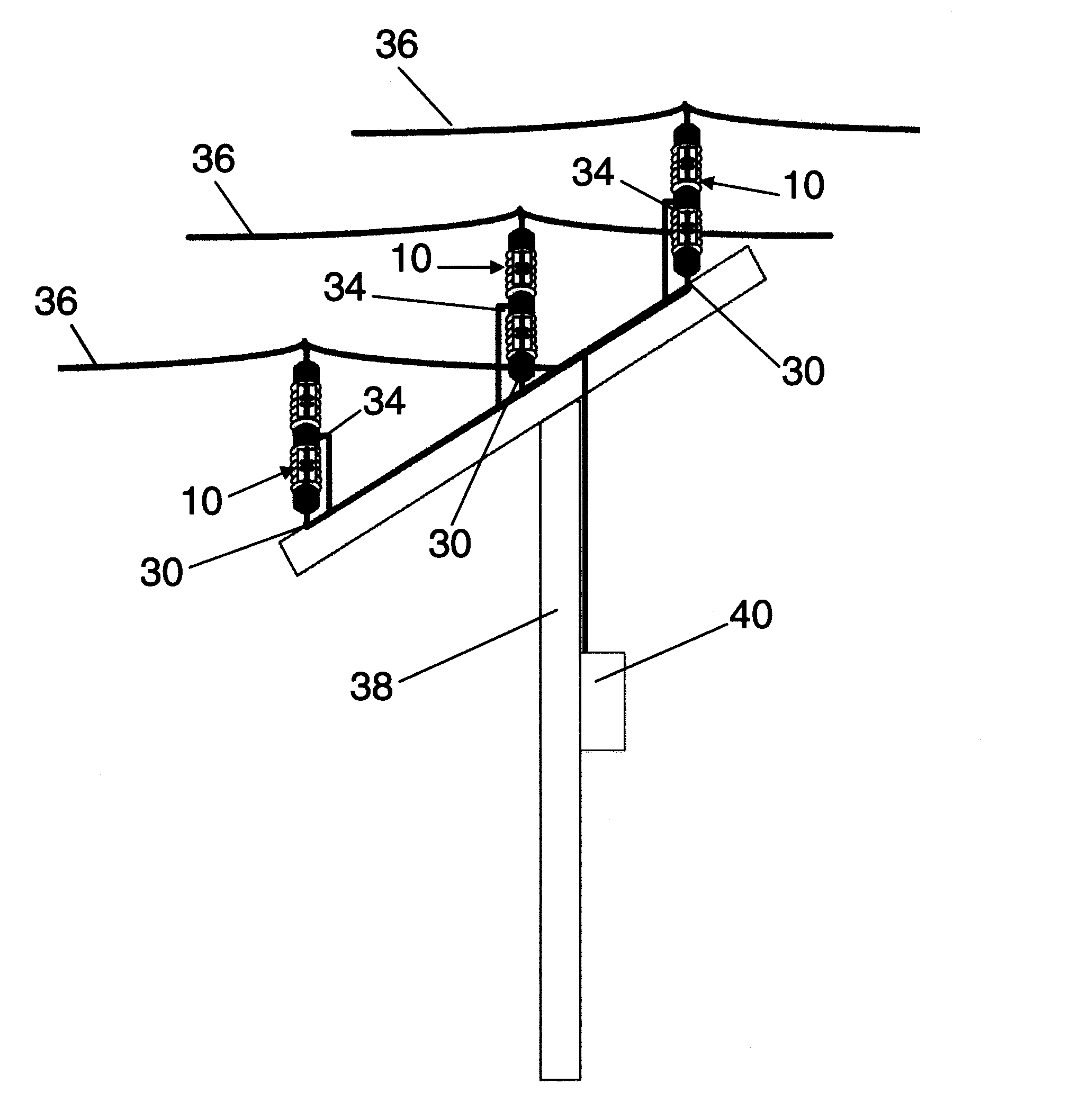
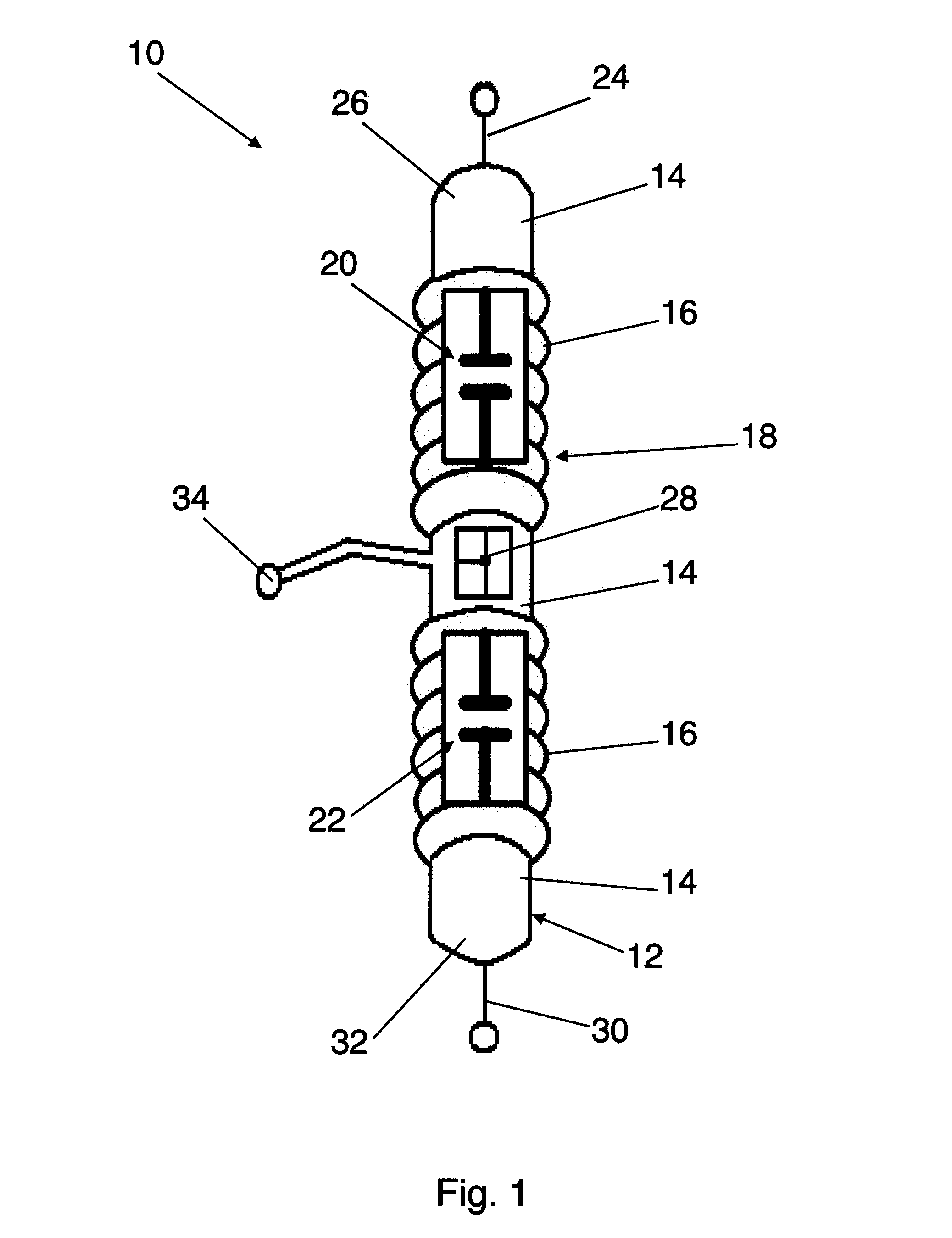
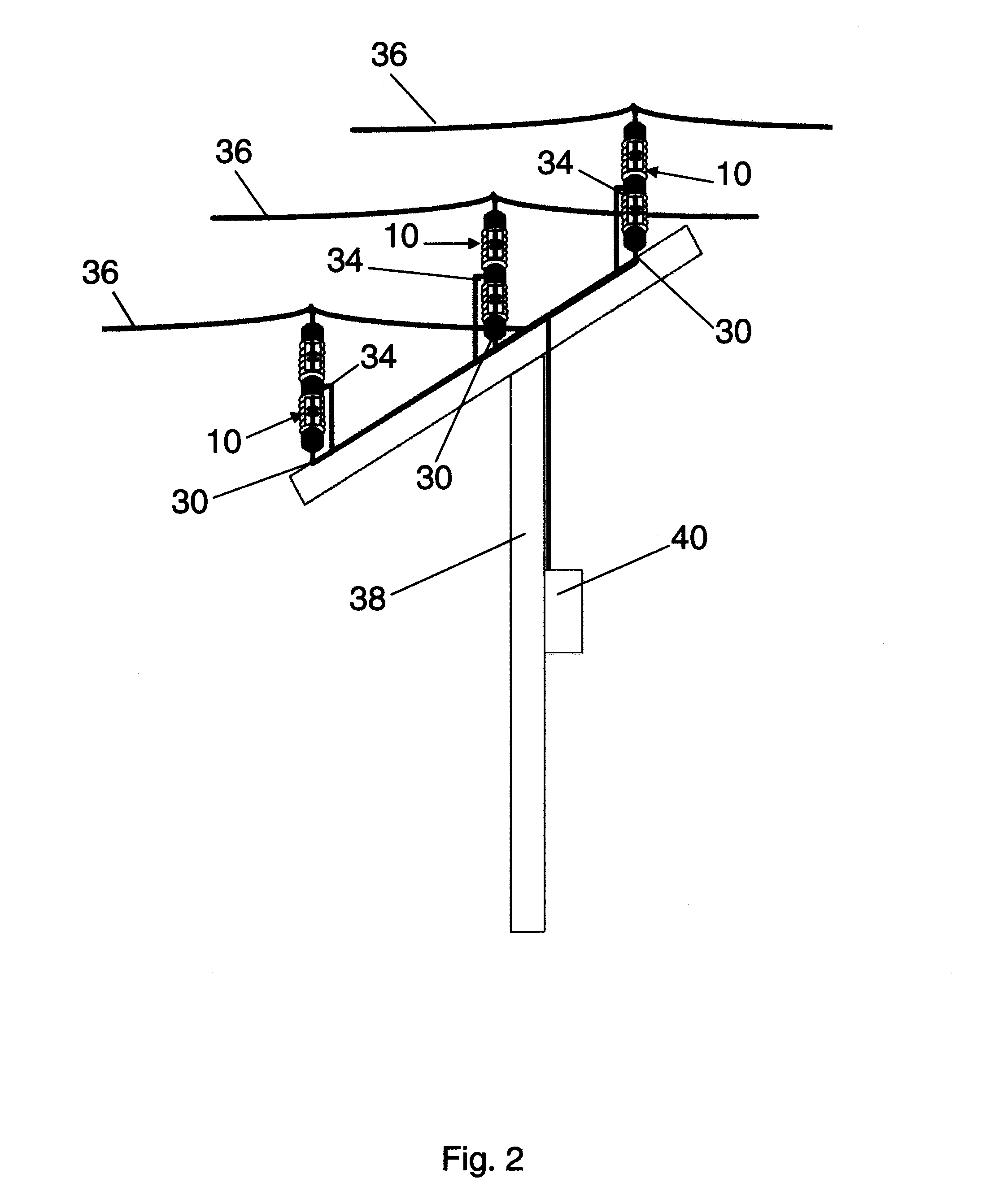
Insulator integrated power supply
ActiveUS8964433B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protection for supplying operative powerElectricityPower cable
A power scavenging device attaches to an overhead power cable and a support pole. The power scavenging device includes a non-conducting outer body and a first capacitor and a second capacitor that are connected in series forming a voltage divider. A voltage source converter is electrically connected to the output of the power scavenging device. The voltage source converter outputs a regulated power.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
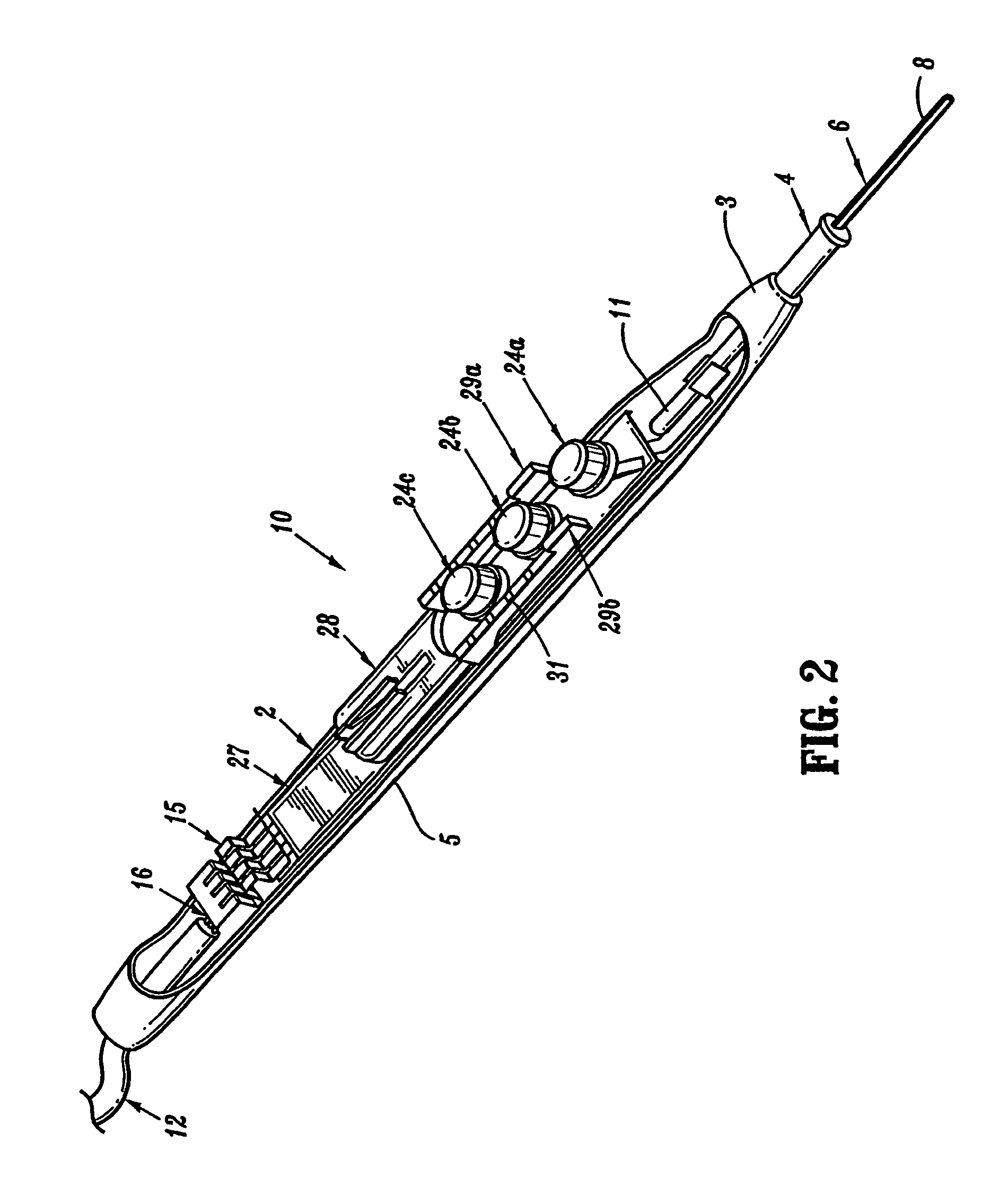
Electrosurgical pencil with improved controls
An electrosurgical pencil is provided which includes an elongated housing, an electrocautery blade supported within the housing and extending distally from the housing. The electrocautery blade is connected to a source of electrosurgical energy. The pencil also includes at least one activation switch supported on the housing which is configured and adapted to complete a control loop extending from the source of electrosurgical energy. At least one voltage divider network is also supported on the housing and is electrically connected to the source of electrosurgical energy.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electrosurgical pencil with improved controls
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electrosurgical pencil with advanced es controls
An electrosurgical system is provided that includes an electrosurgical generator; and an electrosurgical pencil selectively connectable to the electrosurgical generator. The electrosurgical pencil includes an elongated housing; at least one electrocautery end effector removably supportable within the housing and extending distally from the housing, the electrocautery end effector being connected to the electrosurgical generator; and at least one voltage divider network supported on the housing. The at least one voltage divider network is electrically connected to the electrosurgical generator and controls at least one of the intensity of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil and the mode of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil. The voltage divider network generates a plurality of characteristic voltages which are measurable by the electrosurgical generator and which electrosurgical generator in turn transmits a corresponding waveform duty cycle at a particular intensity to the electrocautery end effector of the electrosurgical pencil.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
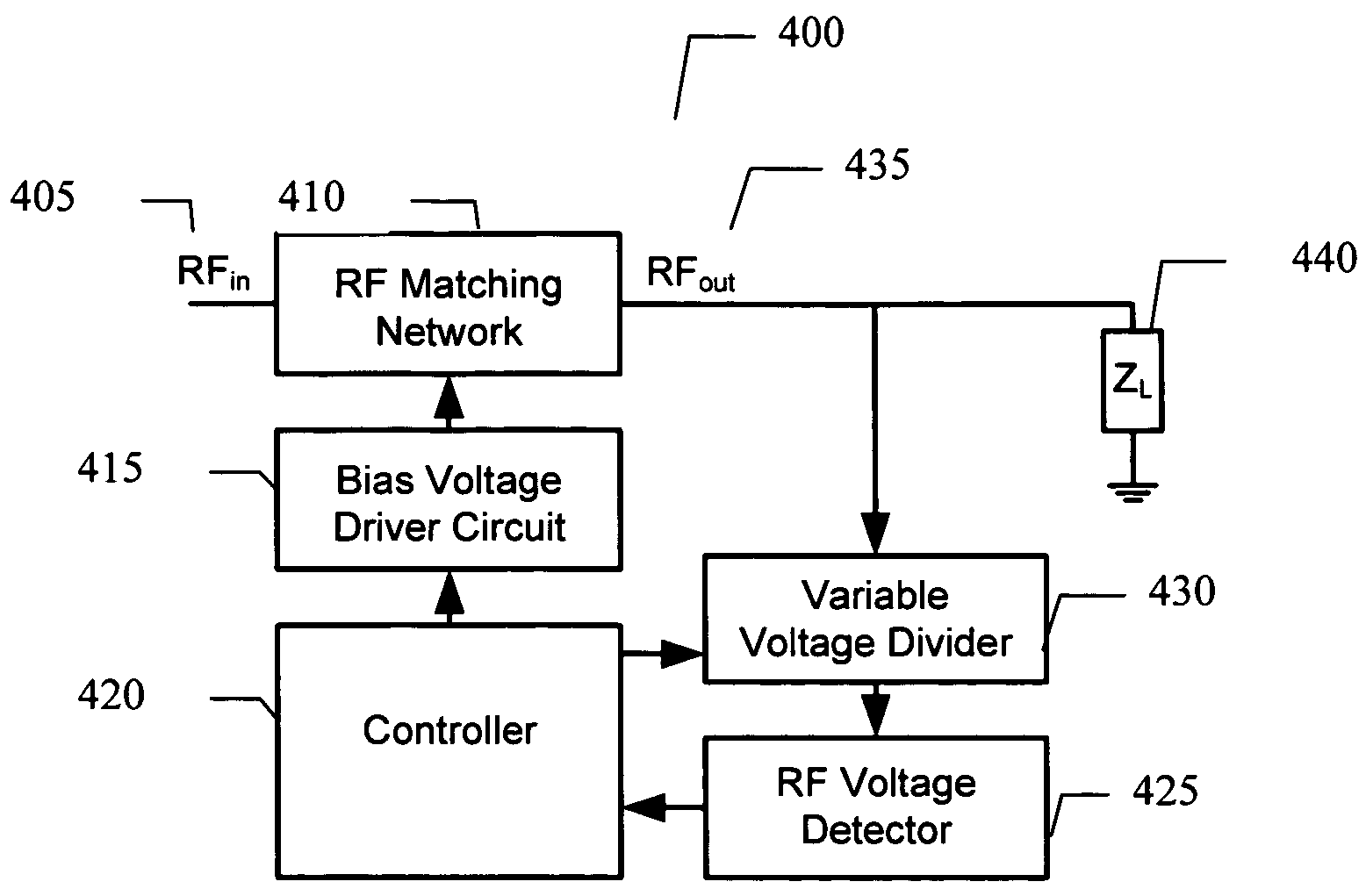
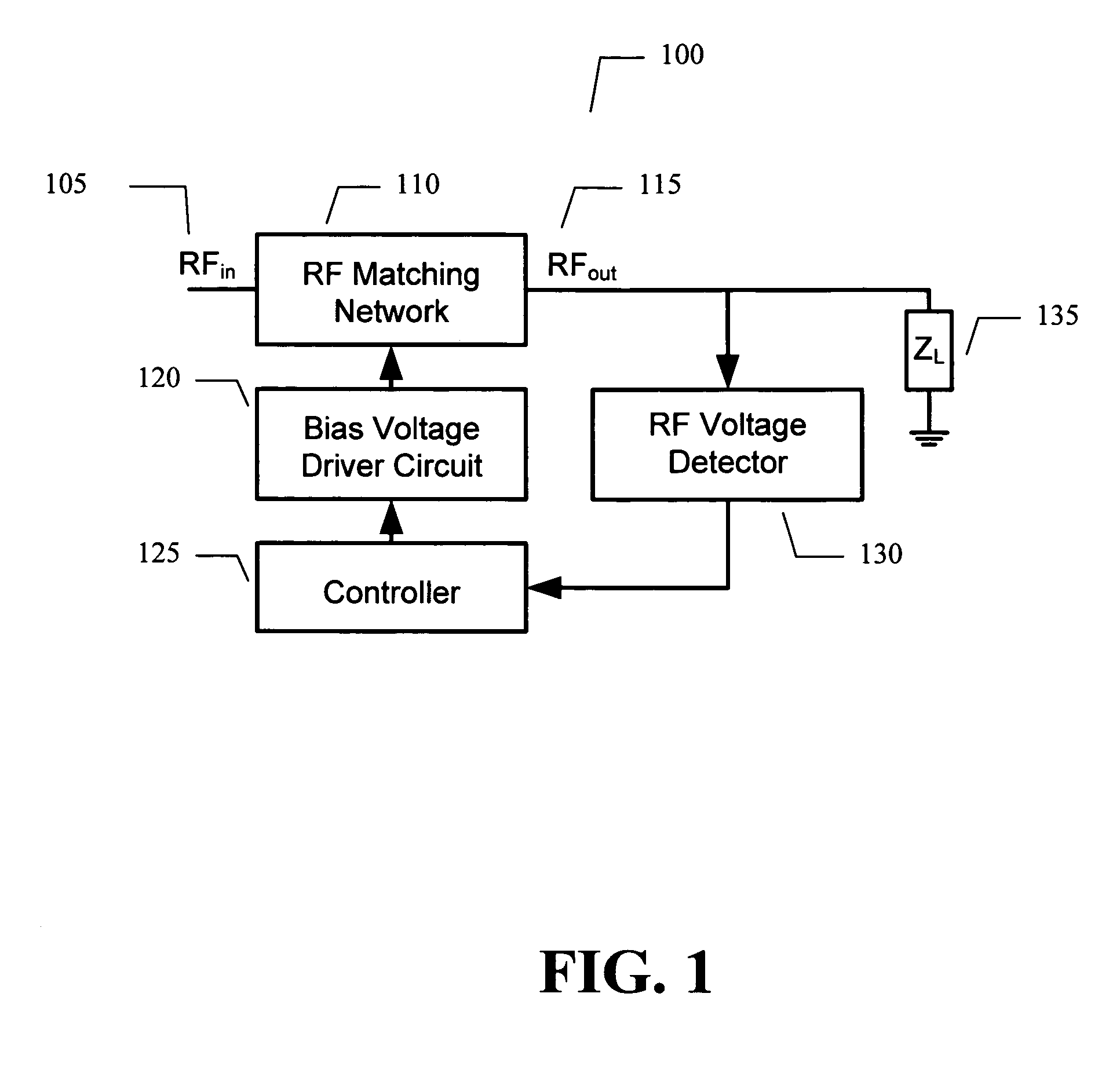
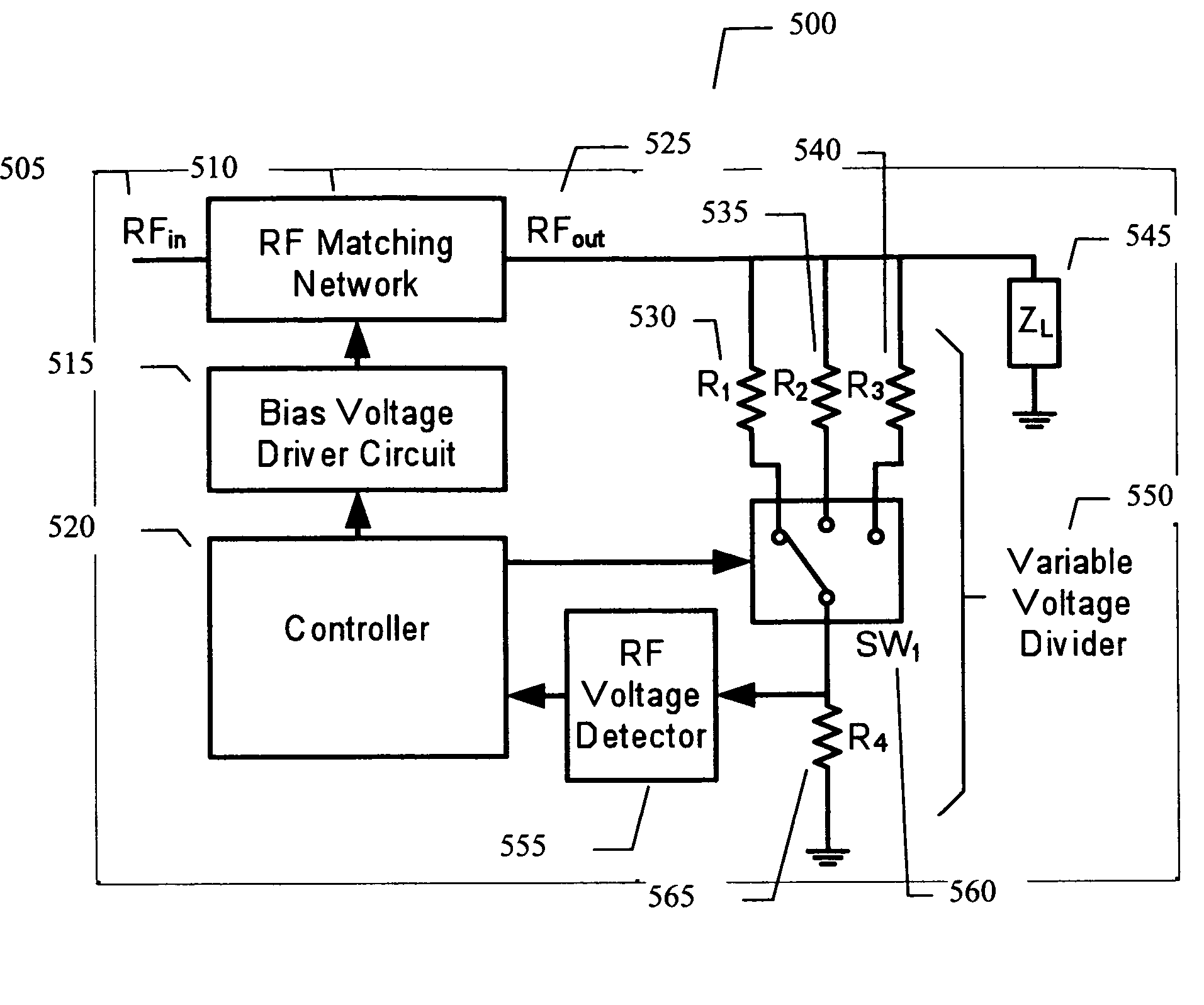
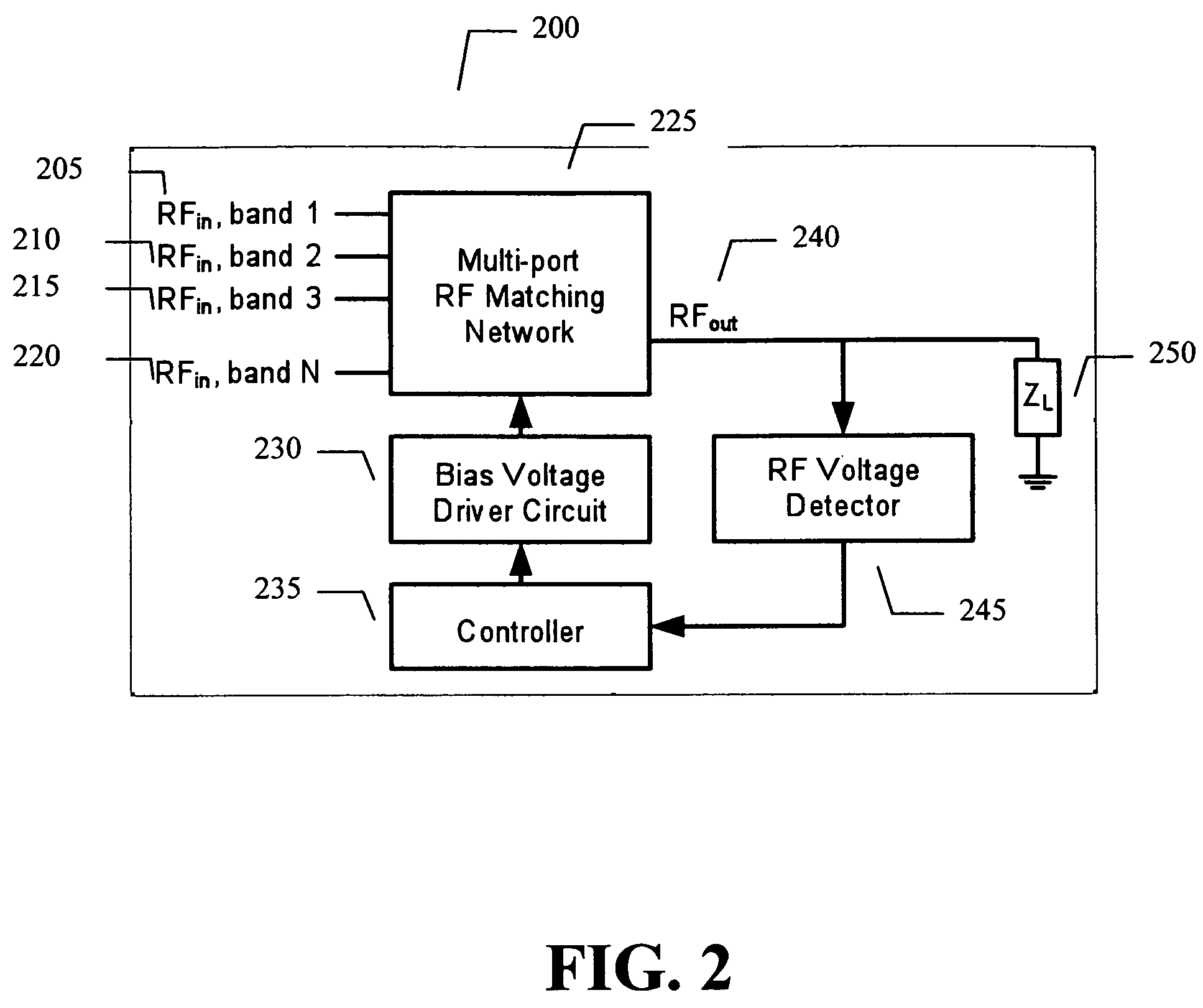
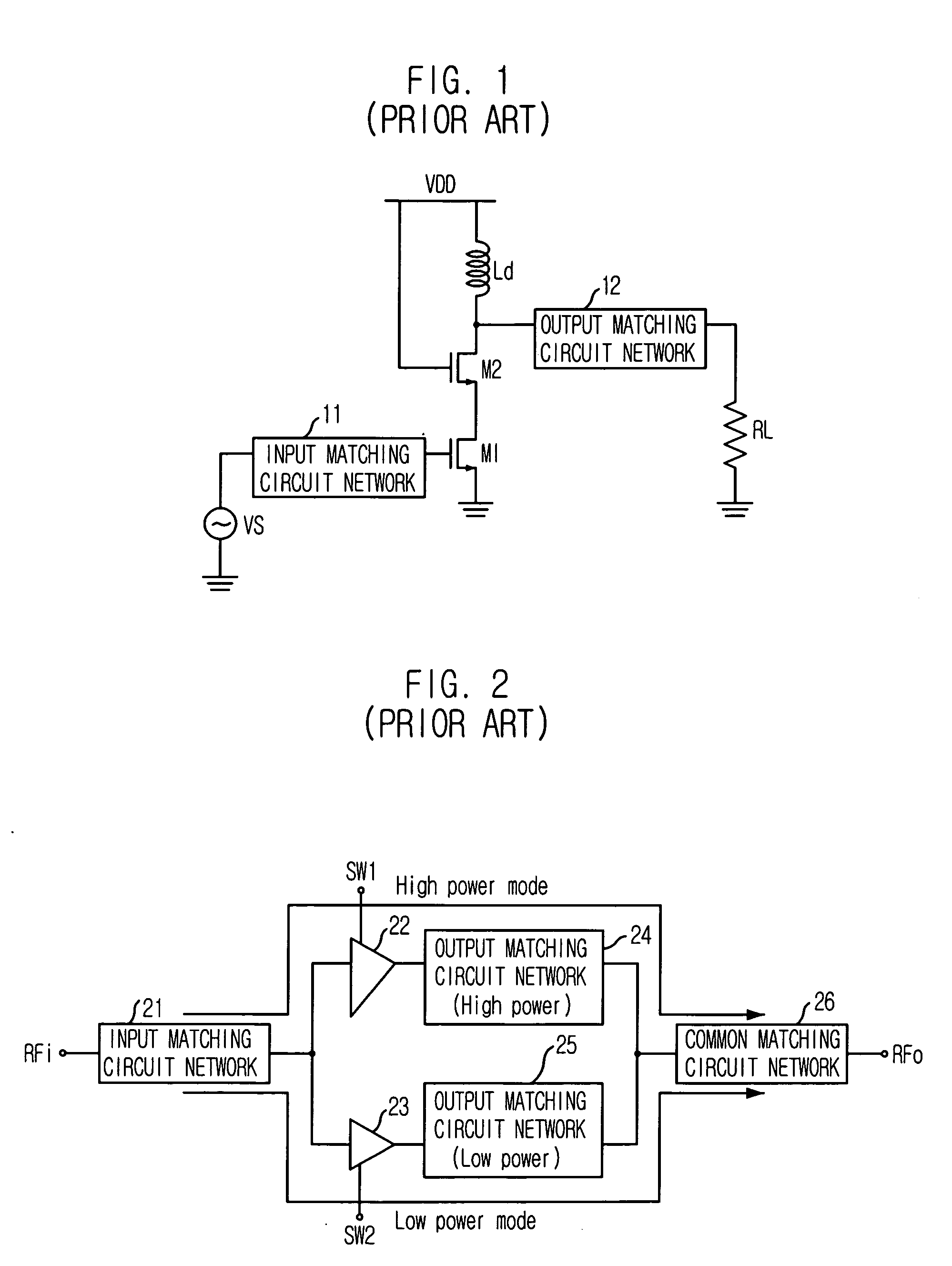
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7535312B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasImpedance matchingEngineering
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements, a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides bias voltage or bias current to the RF matching network, and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
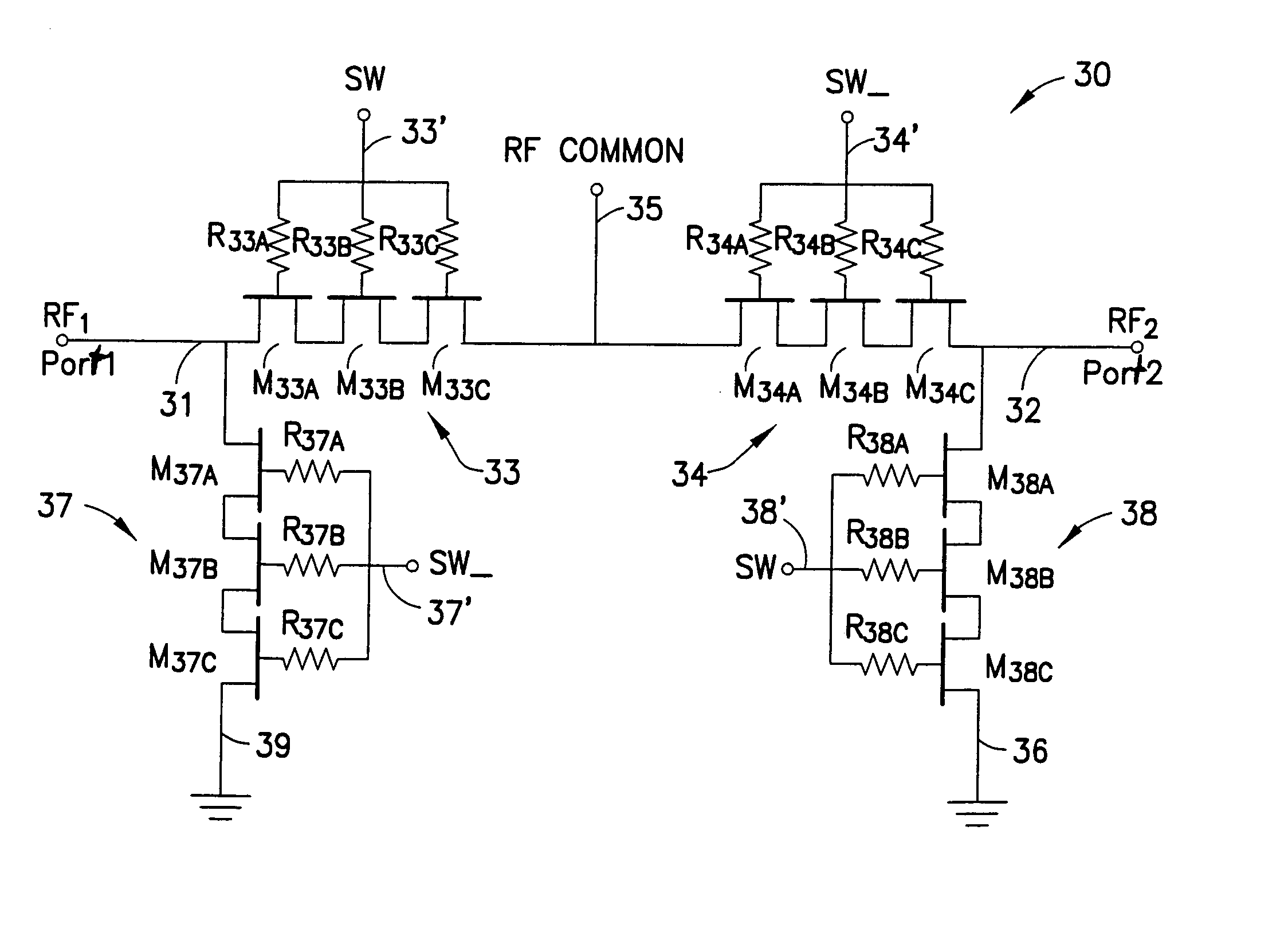
InactiveUS7123898B2Easy to switchImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETDigital control
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
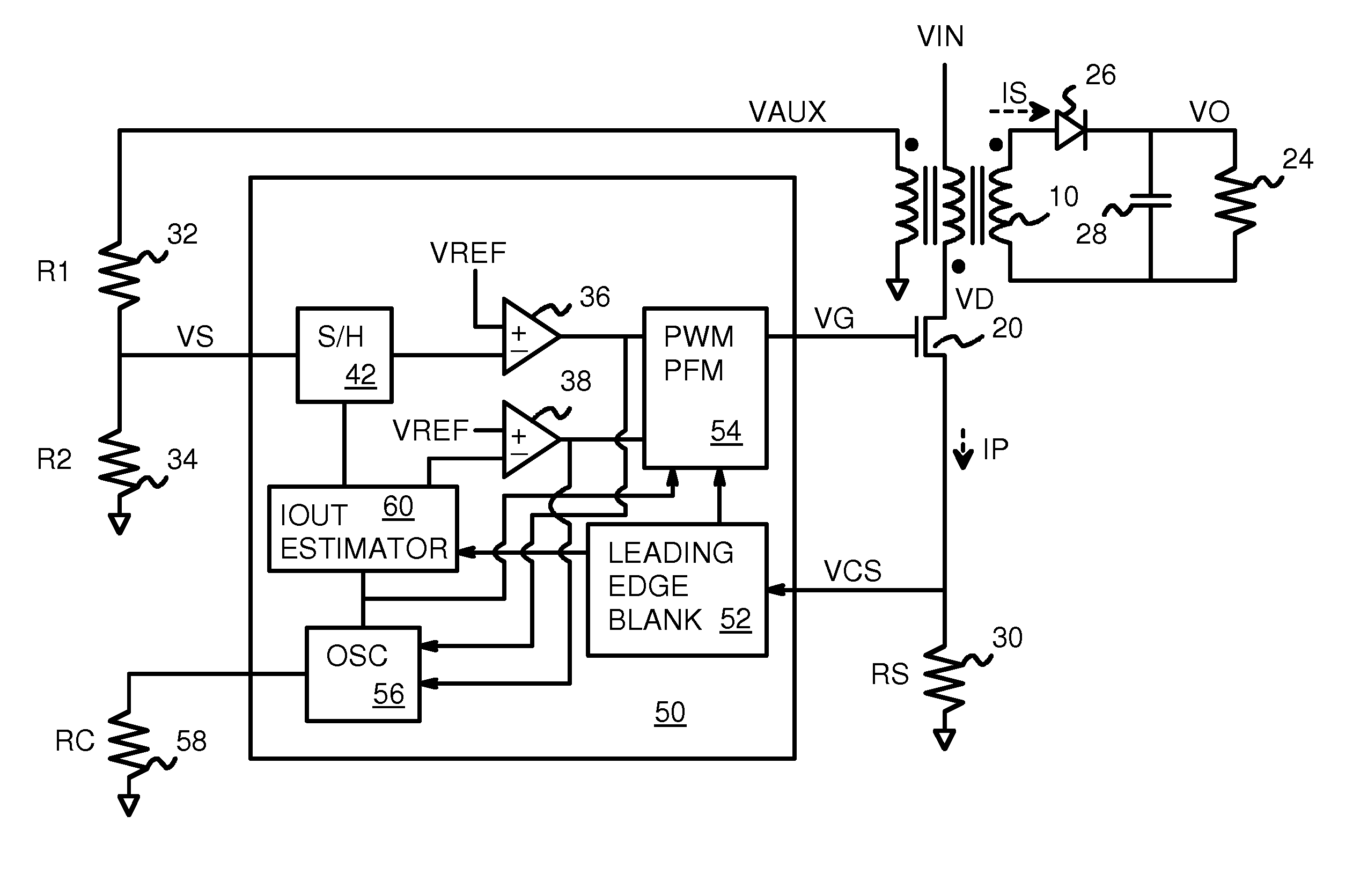
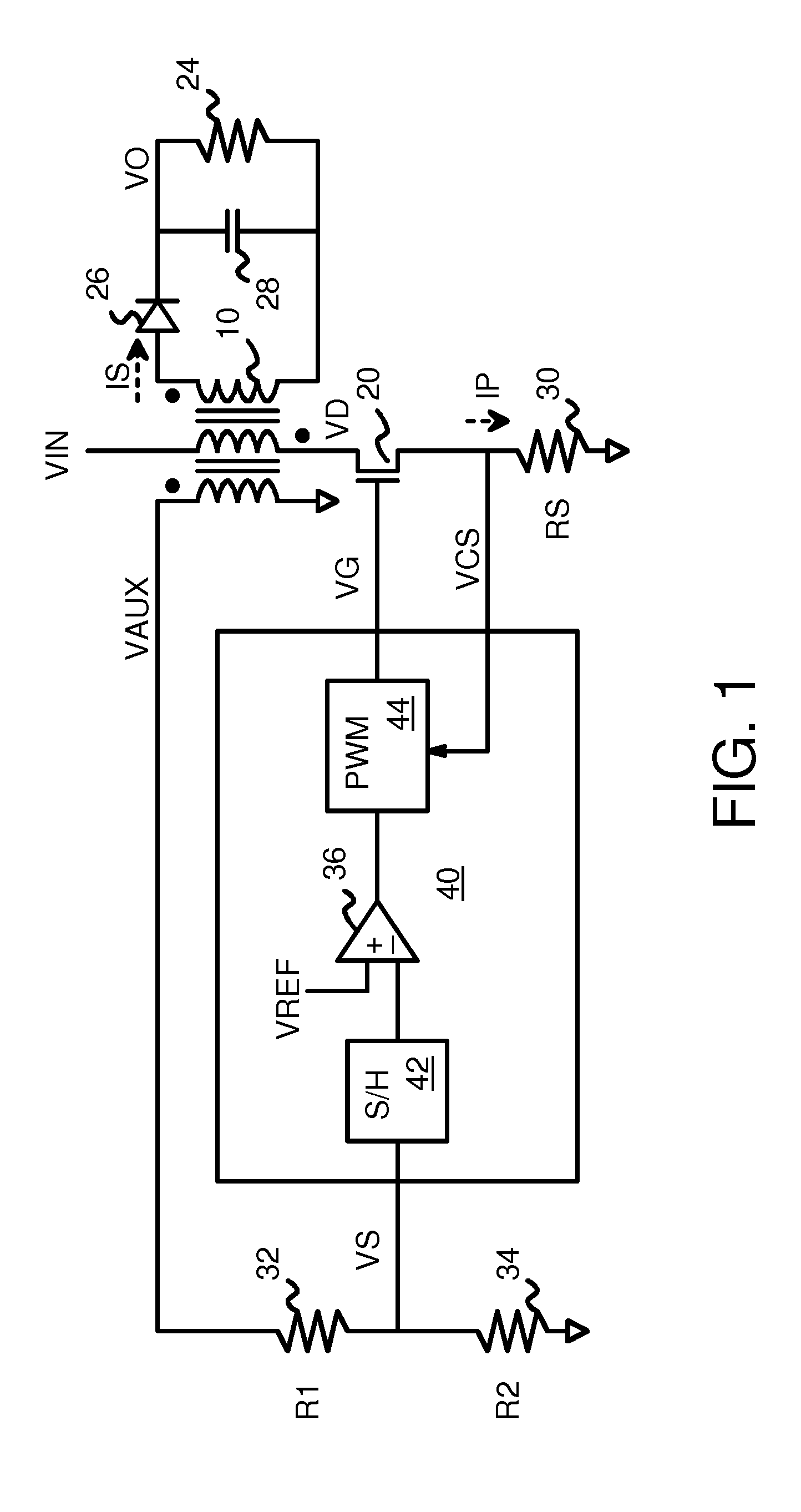
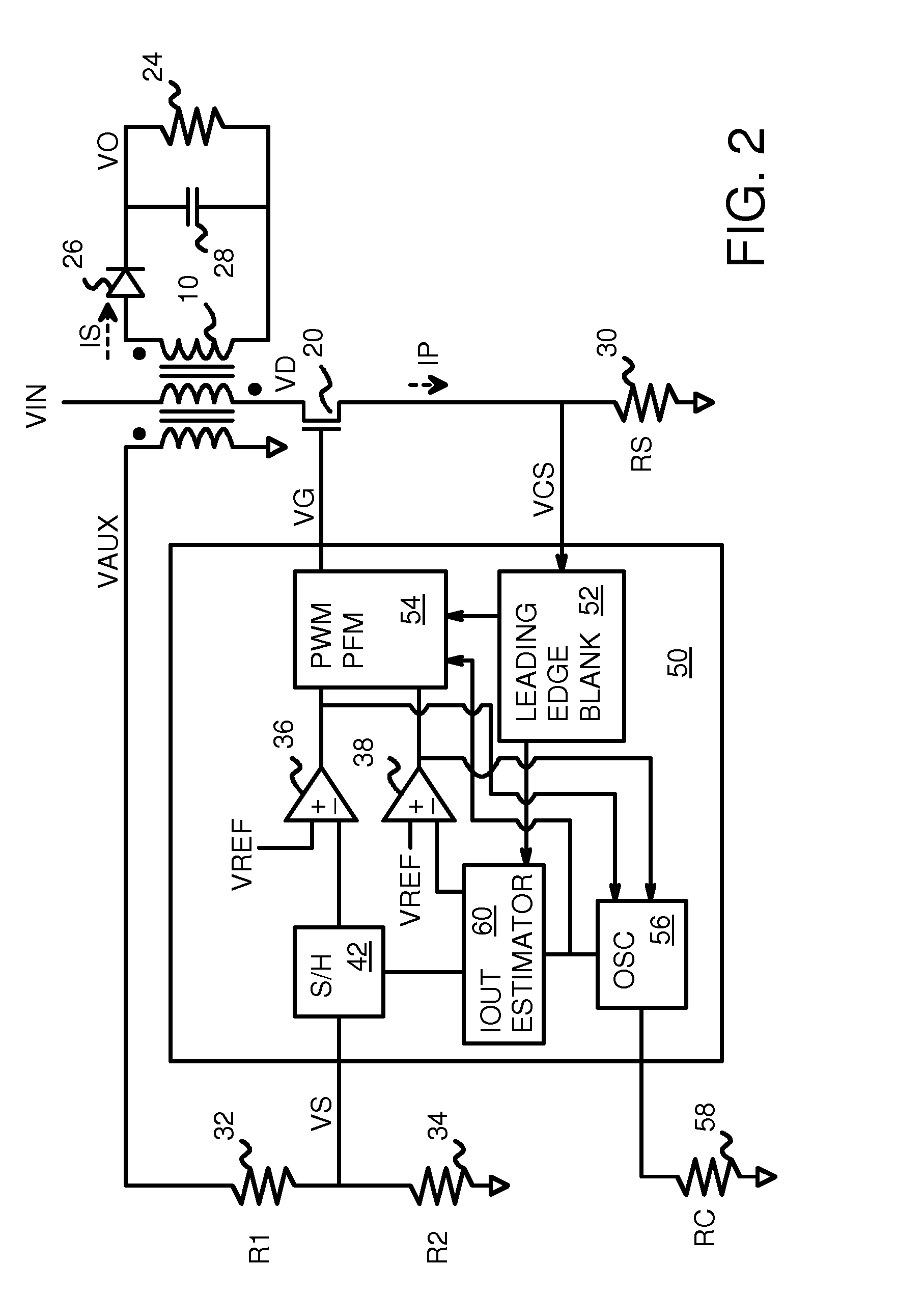
Output Current Estimation for an Isolated Flyback Converter With Variable Switching Frequency Control and Duty Cycle Adjustment for Both PWM and PFM Modes
InactiveUS20130294118A1Dc-dc conversionDifferential amplifiersTransformerSwitching frequency control
A fly-back power converter has a current-estimating control loop that senses the primary output current in a transformer to control the secondary output. A primary-side control circuit switches primary current through the transformer on and off. A discharge time when a secondary current through an auxiliary winding of the transformer is flowing is generated by sampling a voltage divider on an auxiliary loop for a knee-point. A normalized duty cycle is calculated by multiplying the discharge time by a current that is proportional to the switching frequency and comparing to a sawtooth signal having the switching frequency. The peak of a primary-side voltage is sensed from the primary current loop and converted to a current and multiplied by the normalized duty cycle to generate an estimated current. An error amp compares the estimated current to a reference to adjust the oscillator frequency and peak current to control primary switching.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
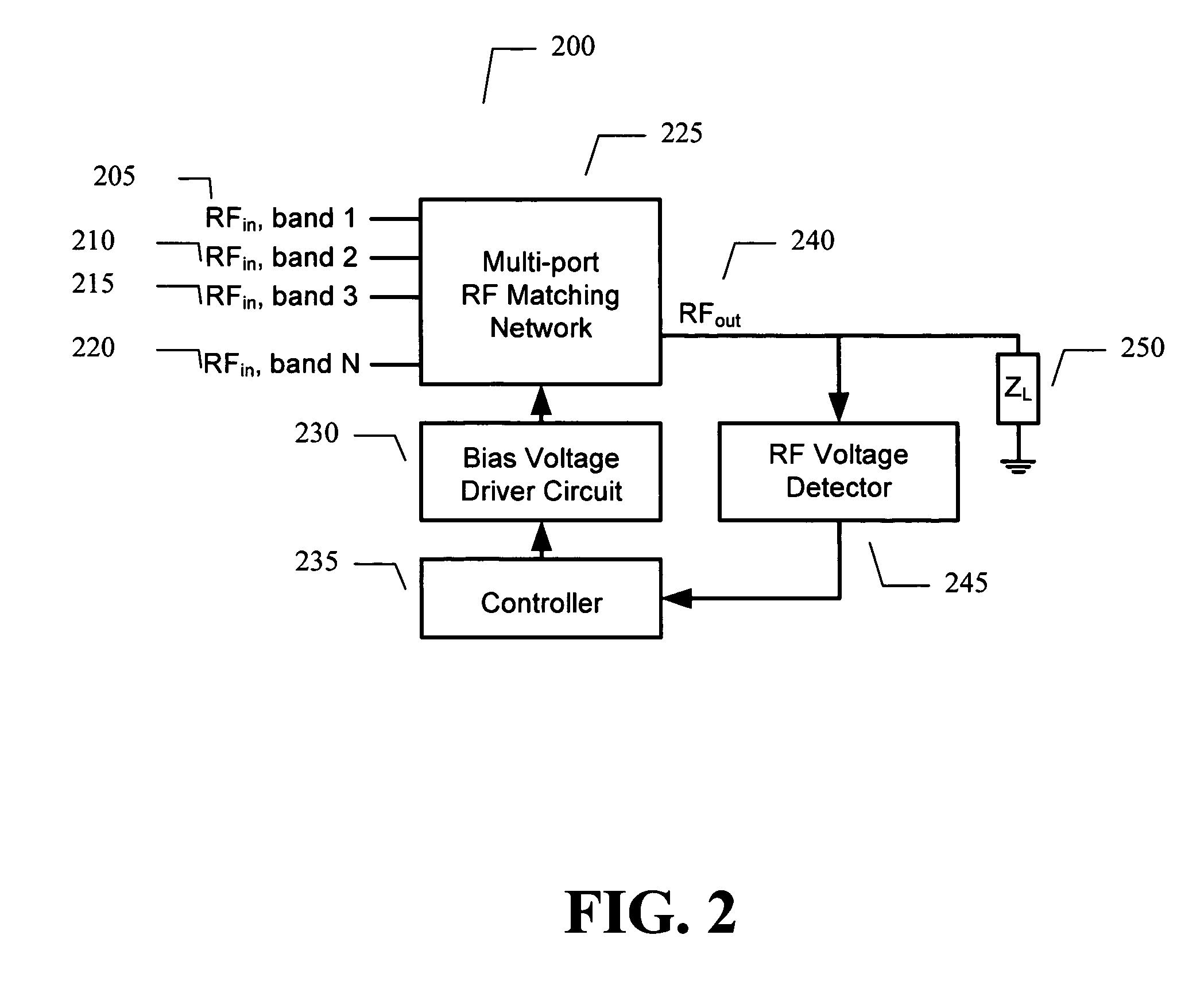
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7852170B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksAntennas earthing switches associationElectrical resistance and conductanceNetwork connection
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements; a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides voltage or current bias to the RF matching network; a variable voltage divider connected to the voltage detector and implemented using a multi-pole RF switch to select one of a plurality of different resistance ratios to improve the dynamic range of the apparatus; and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Radio frequency Langmuir probe
InactiveUS7015703B2Reduce distortion problemsLow rateCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical conductorLangmuir probe
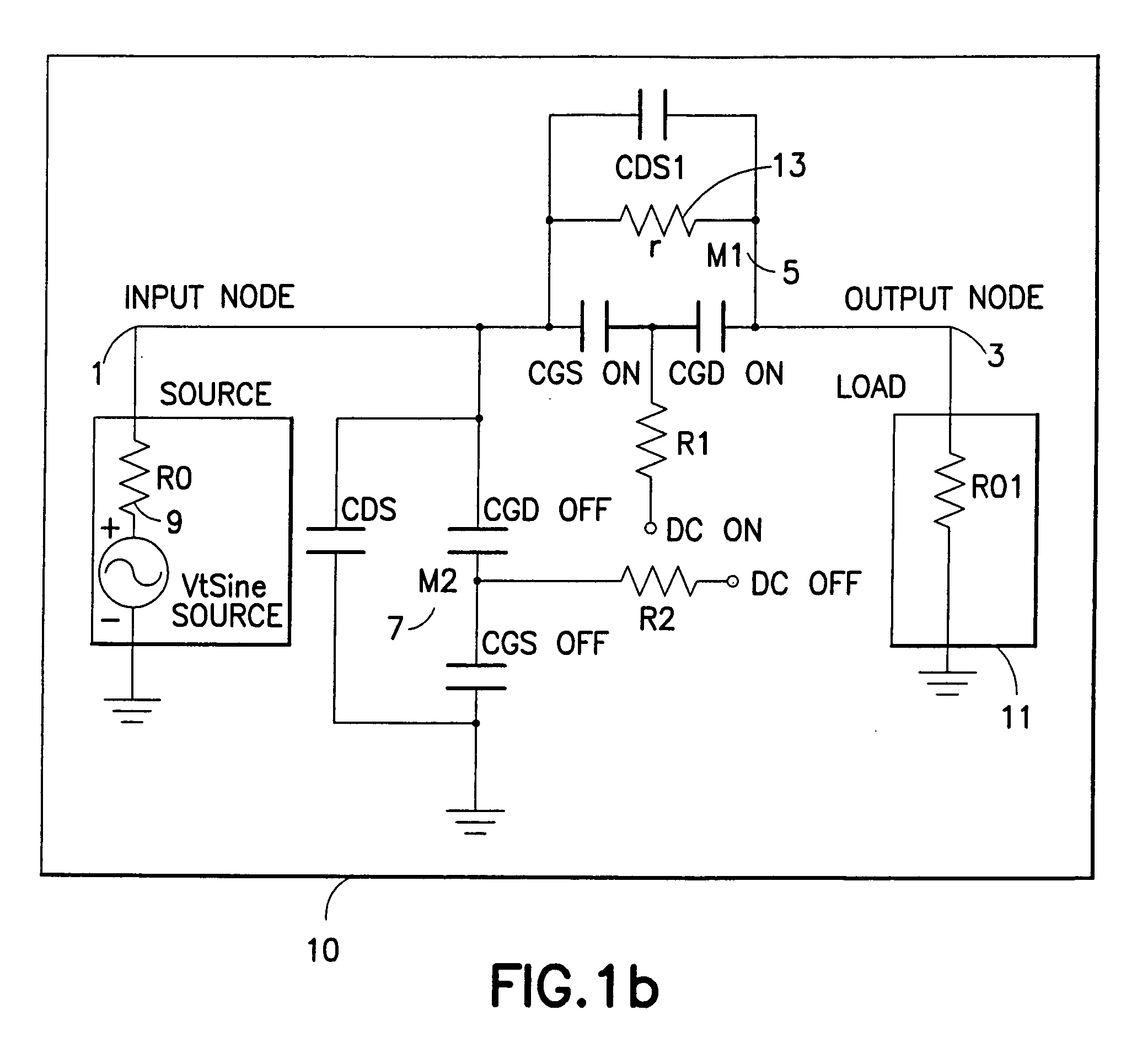
A Langmuir probe for measuring characteristics of a plasma driven by radio frequency (RF) power comprises an elongated conductor 10 having an exposed tip 1 for insertion into an RF plasma and an outer end 3 for connection to external measuring circuitry. In order to reduce distortion over a range of RF frequencies, the probe includes an RF voltage divider 11, 12, 13, 14 in series between the tip and outer end of the conductor.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Case flow system with adjustable lane dividers
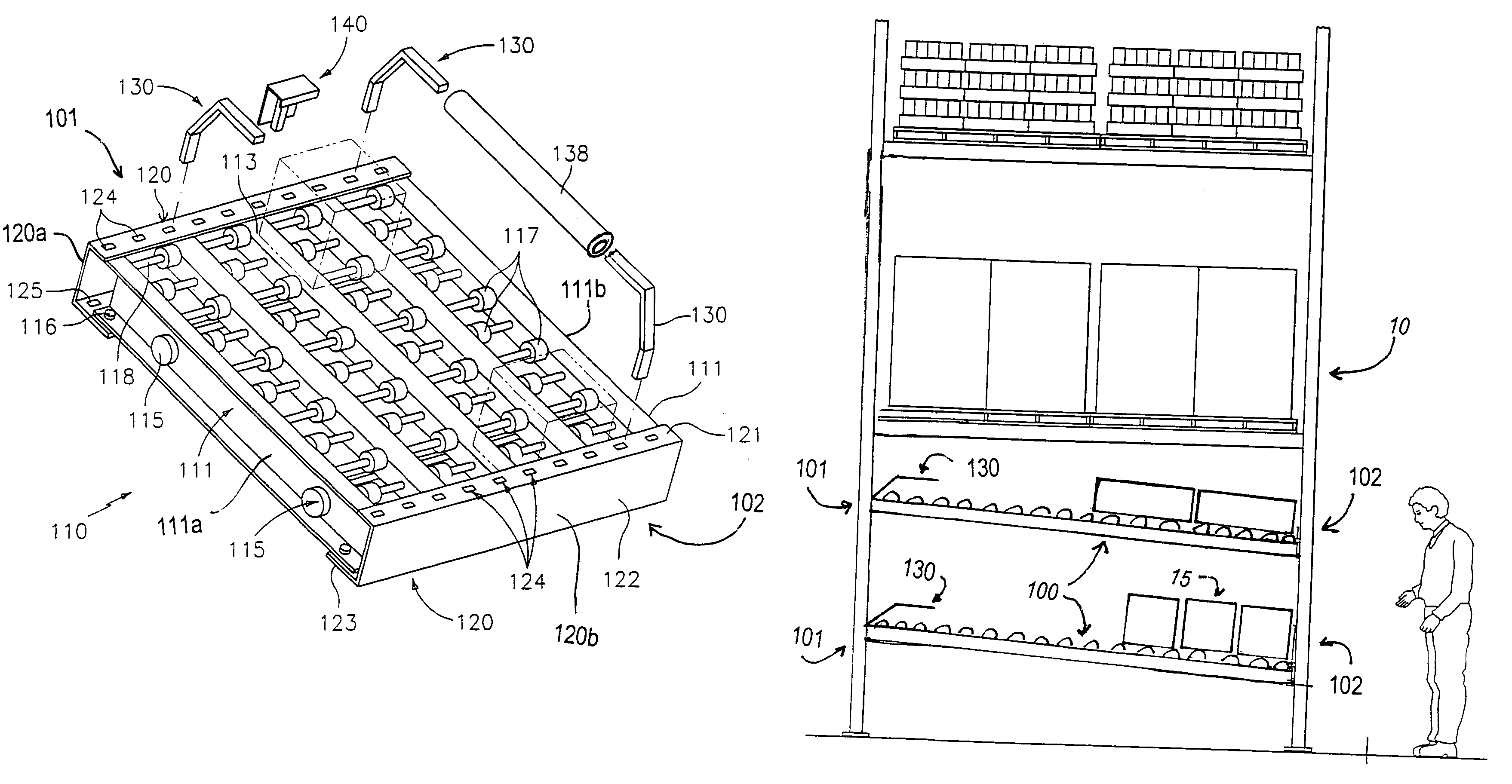
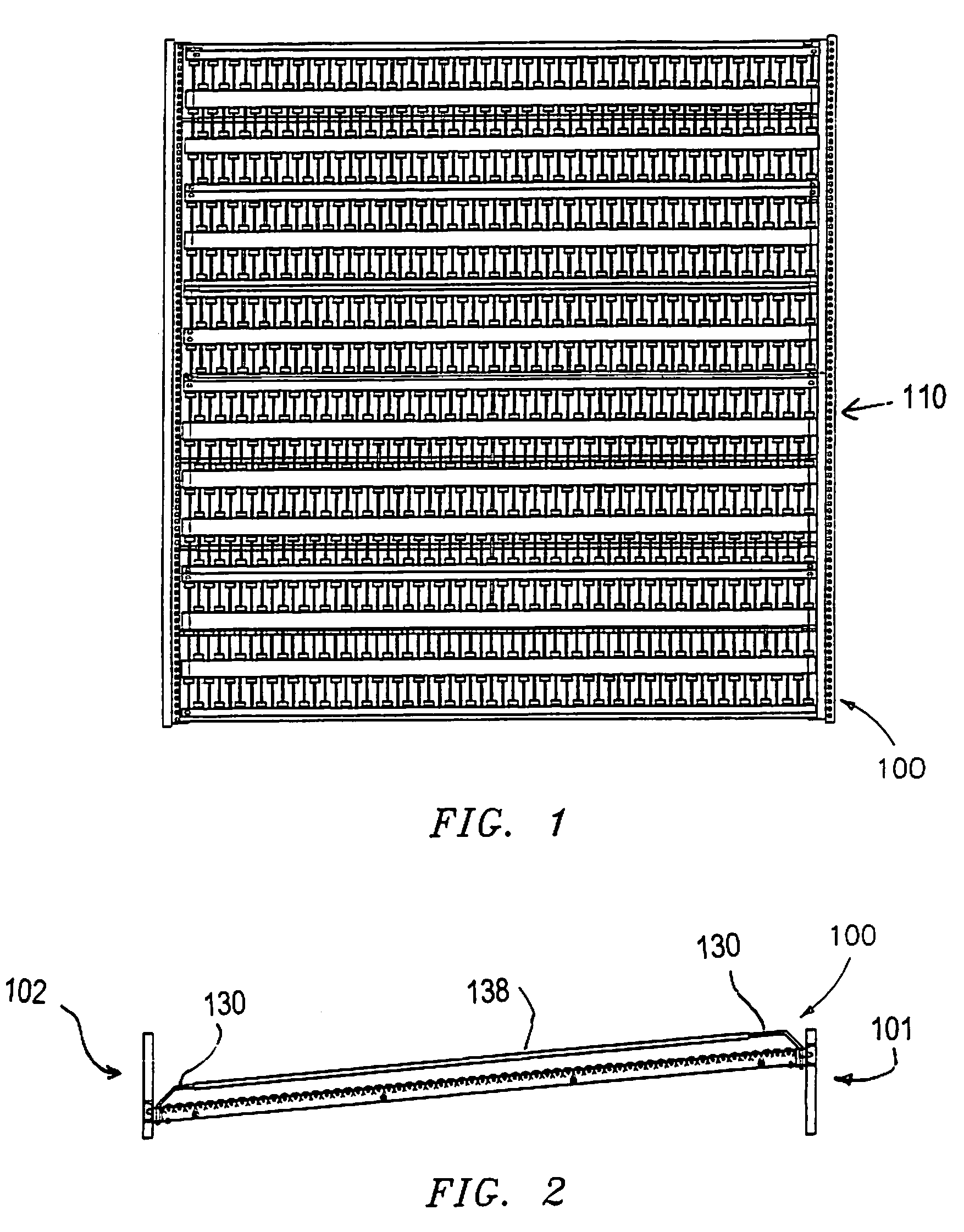
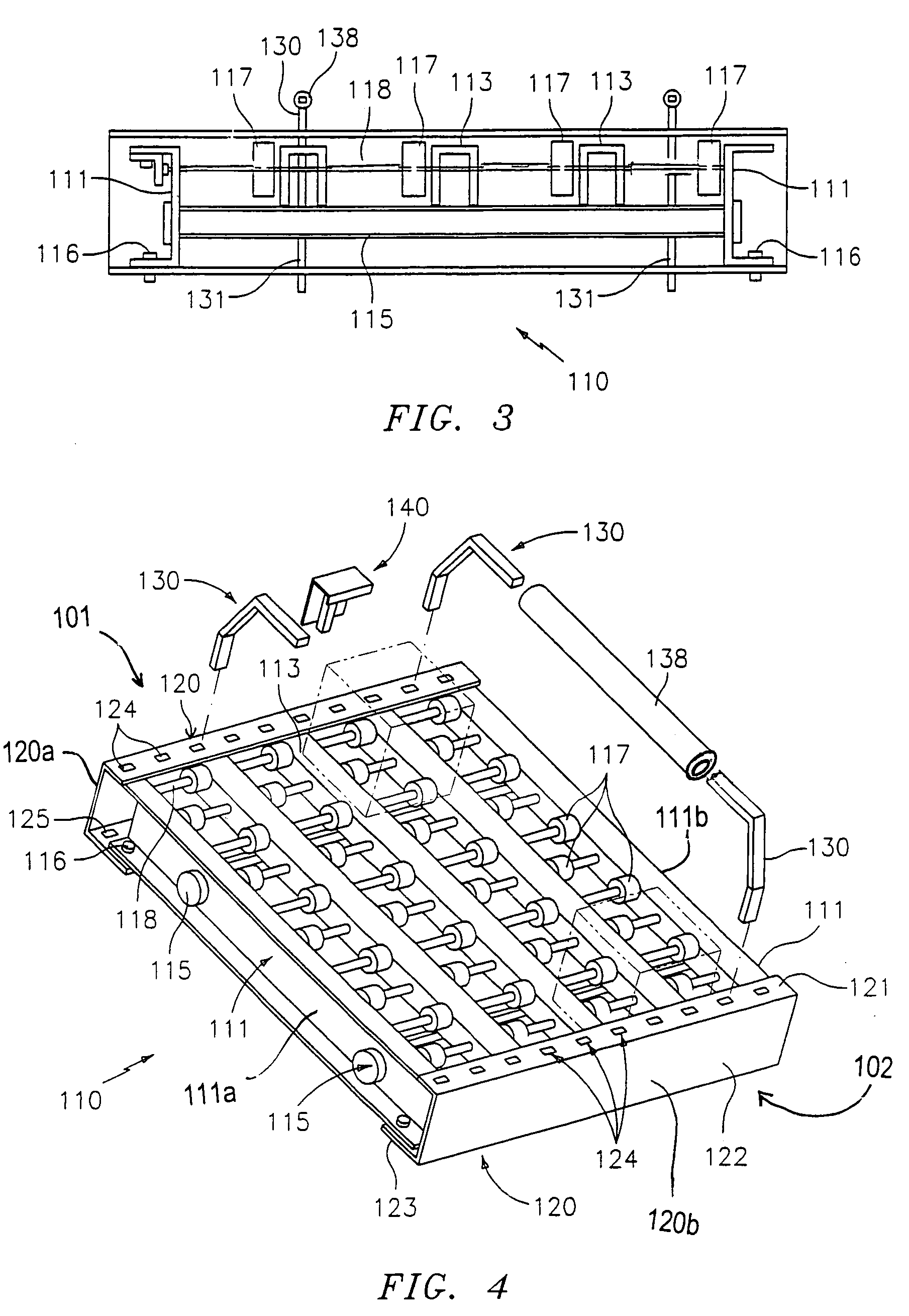
A case flow bed for the handling of merchandise. The case flow bed including (a) a loading end and, opposite thereto, an unloading end; (b) a roller bed positioned between the loading end and unloading end for supporting and permitting sliding movement of merchandise from the loading end to the unloading end; and (c) apertures associated with at least the loading end for removably receiving at least one lane divider in any of a plurality of laterally extending positions for delimiting lanes of travel for the sliding movement of the merchandise.
Owner:FRAZIER INDAL
Adjustable over current protection circuit with low power loss
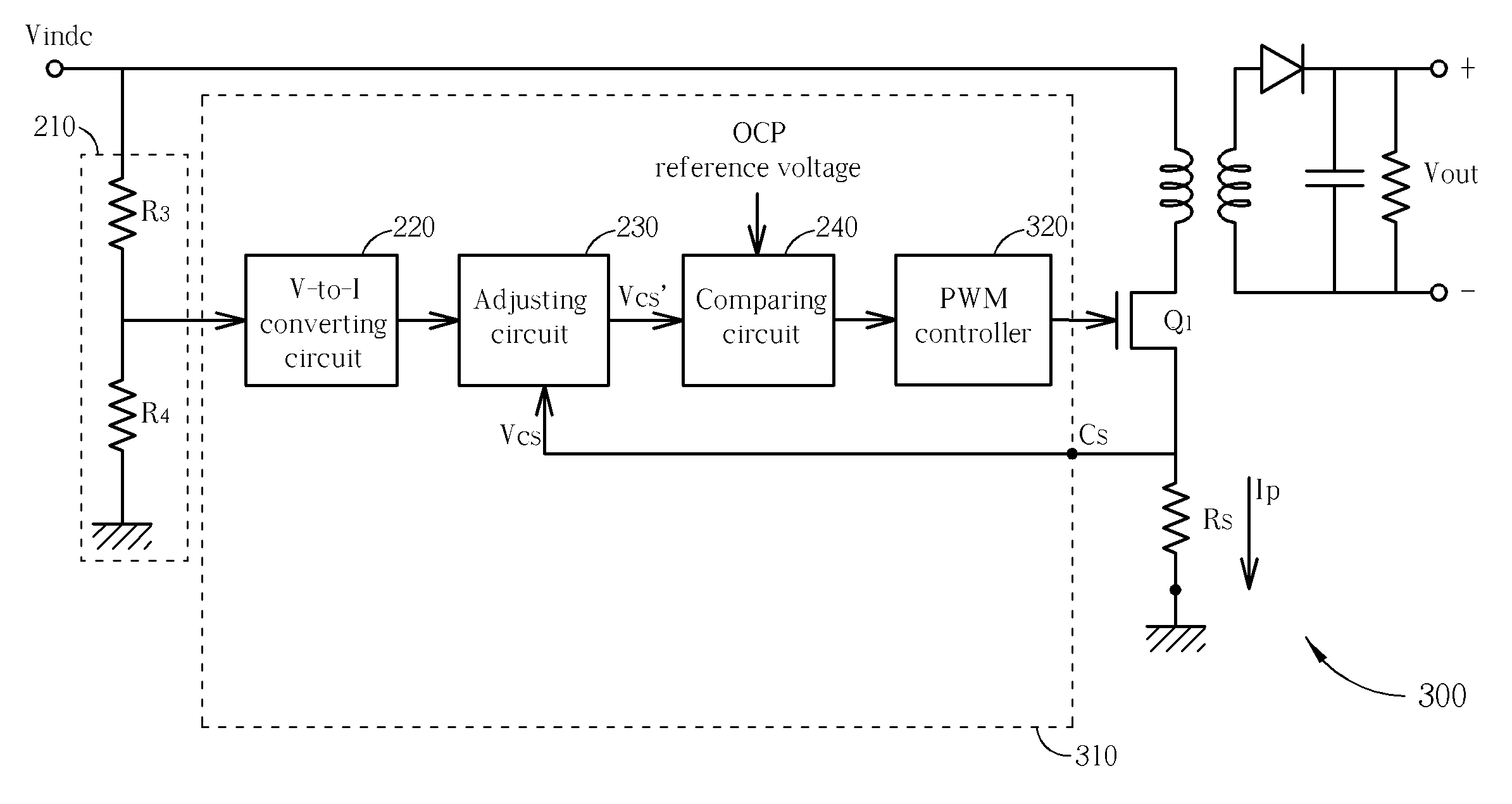
InactiveUS20080297963A1Reduce power consumptionParameter calibration/settingDc-dc conversionVoltage dividerElectrical current
Disclosed is an adjustable over current protection circuit which advances the timing of enabling an over current protection mechanism according to an input voltage, therefore the delay problem resulting from the non-instant response of the over current protection circuit is compensated with a low power loss. The over current protection circuit includes a voltage divider, a voltage-to-current converting circuit, an adjusting circuit and a comparing circuit. The voltage divider divides an input voltage to generate an adjusted input voltage, and the adjusted input voltage is converted into an adjusted input current by the voltage-to-current converting circuit. The adjusting circuit then adjusts a current sensing voltage according to the adjusted input current to generate an adjusted current sensing voltage. Finally, the comparing circuit compares the adjusted current sensing voltage with a predetermined over current protection reference voltage to selectively enable the over current protection mechanism according to a comparison result.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
Method and apparatus for signal reception using ground termination and/or non-ground termination
InactiveUS6856169B2Reliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsAbove groundInput selection
Receiving units with inputs that may be ground-terminated and with inputs that are selectively ground-terminated or non-ground terminated are enabled with signal level shifting and a termination mode selection input. In a first exemplary implementation, a receiving unit is capable of having ground-terminated inputs. However, common mode voltage of the signal that is input to decoding data recovery circuitry is above ground because the input signal may be level shifted in between the ground-terminated inputs and the decoding data recovery circuitry. In a second exemplary implementation, a mode selection is accomplished by switching a voltage divider into operation and bypassing a level shifter for a non-ground terminated mode. For a ground terminated mode, the voltage divider is switched out of operation and the level shifter is switched into operation for its signal output to be decoded. Pre-amplification may also be employed to improve signal strength.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
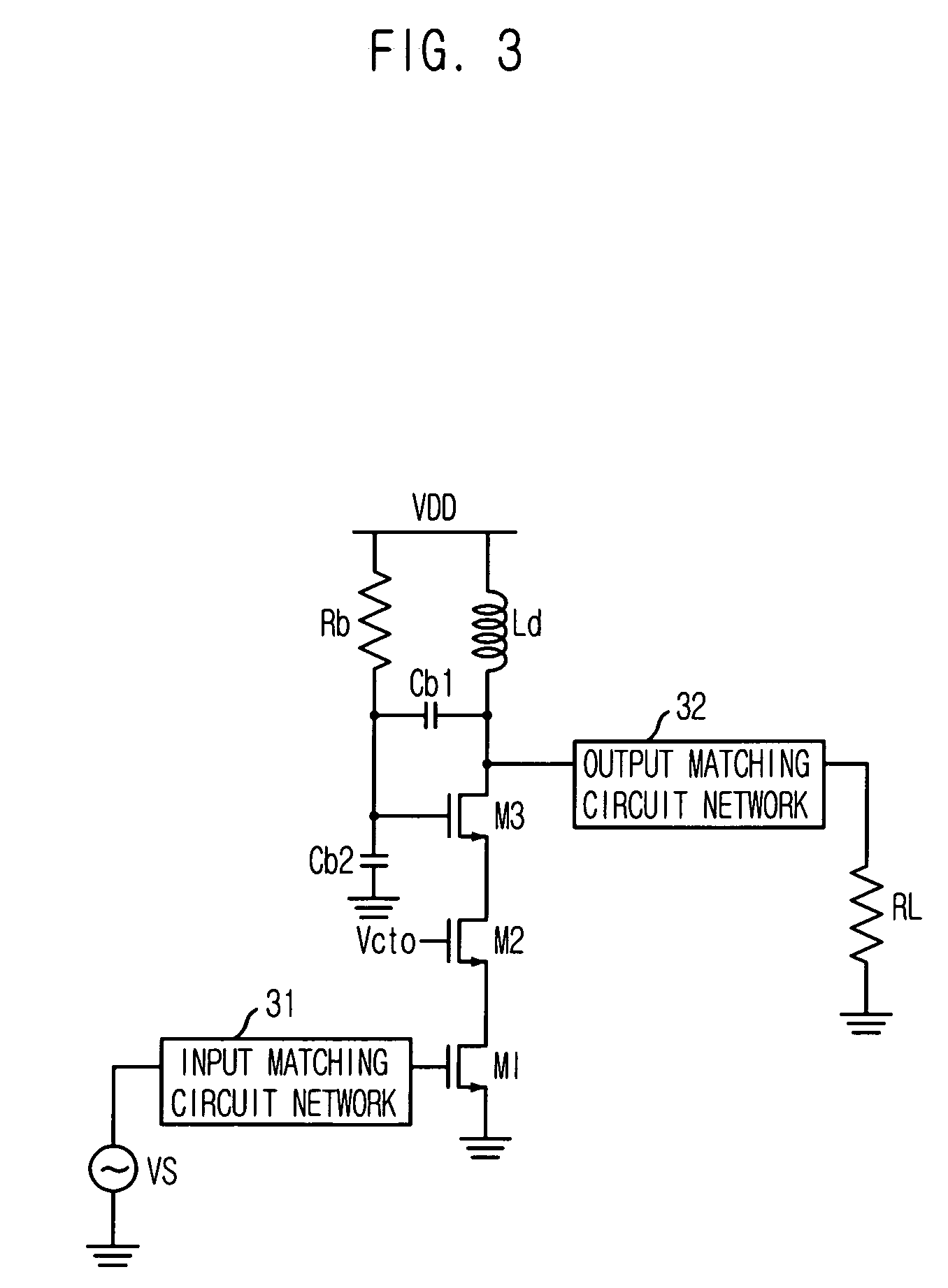
Triple cascode power amplifier of inner parallel configuration with dynamic gate bias technique
InactiveUS20060119435A1Easily embodiedIncrease output powerGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCascode
Provided is a power amplifier which fits to a deep-submicron technology in radio frequency wireless communication. The power amplifier includes a cascode including a first transistor which receives and amplifies an input signal, and a second transistor which is connected to the first transistor in series and operated by a DC bias voltage; a third transistor which is connected between the cascode and an output end, operated by a dynamic gate bias and outputting a signal; and a voltage divider which includes first and second capacitors that are connected between the output end, i.e. a drain of the third transistor, and a ground in series, and provides the dynamic bias to a gate of the third transistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
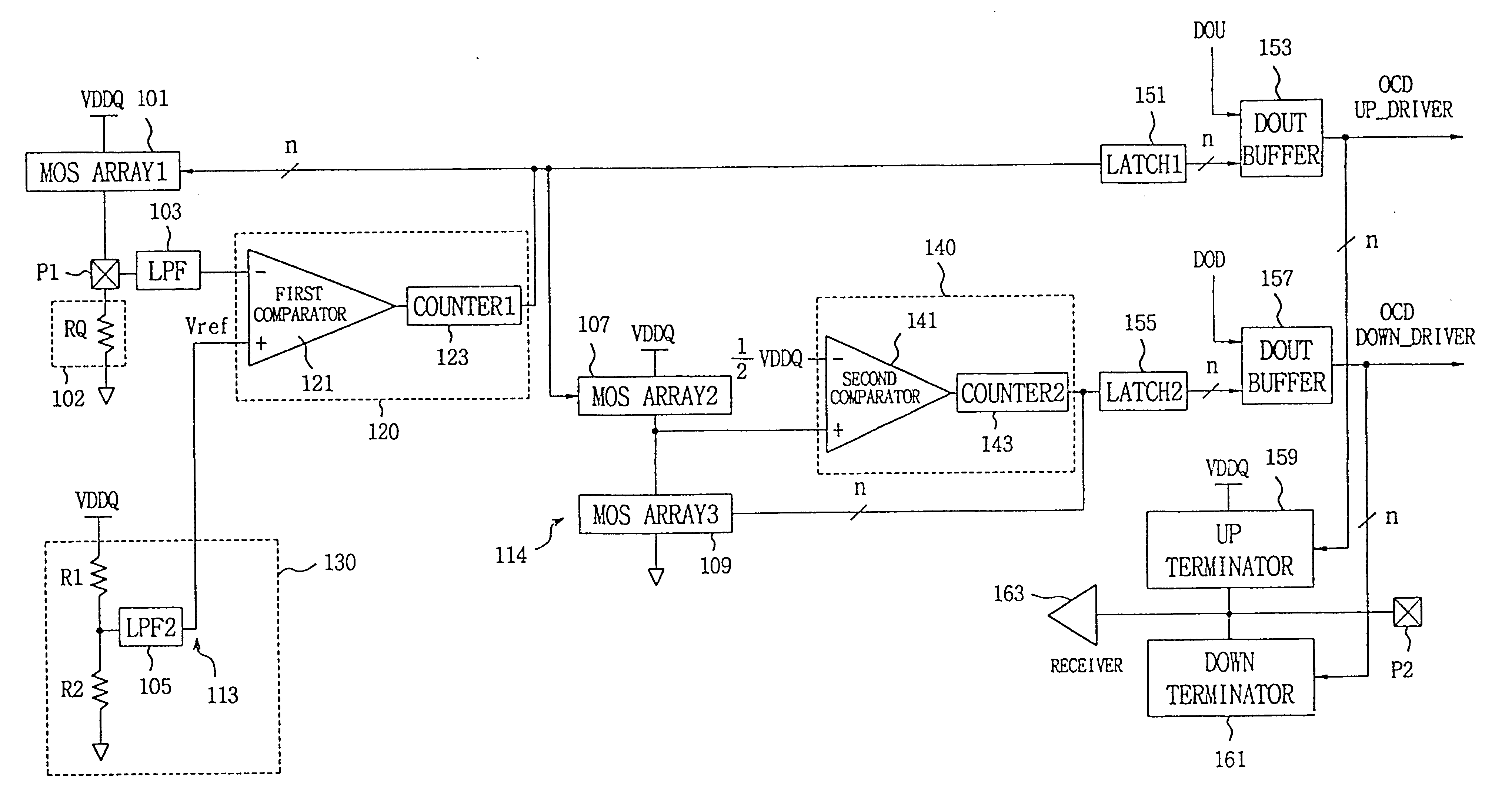
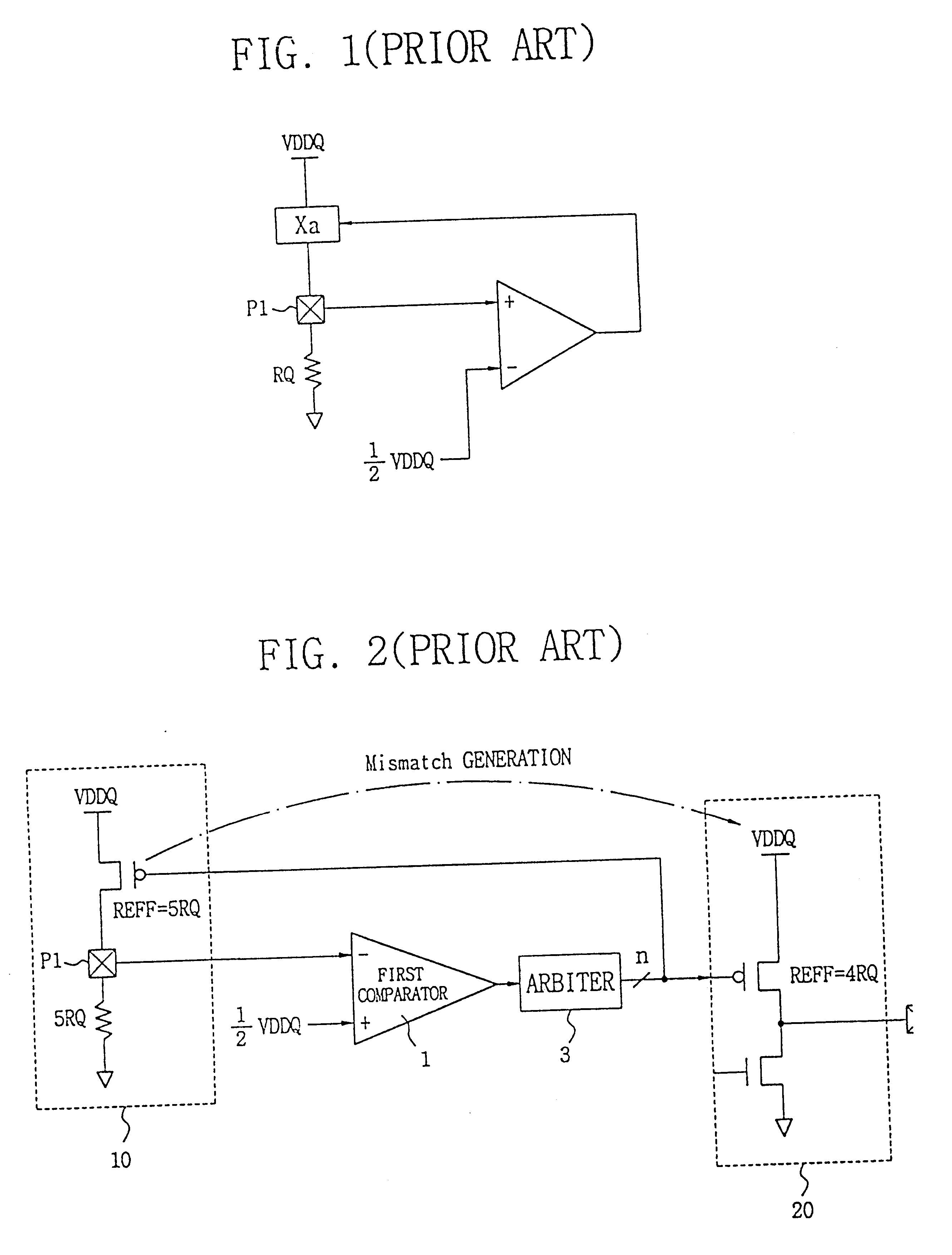
Programmable impedance control circuit
InactiveUS6525558B2Multiple-port networksImpedence matching networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
Disclosed is a programmable impedance control circuit, comprising a voltage divider, the voltage divider comprising an MOS array supplied with a first voltage and an external resistance having an external impedance equal to N times said external resistance. The voltage divider outputs a second voltage. A reference voltage generator is provided for generating a third voltage corresponding to N / (N+M) times said first voltage as a reference voltage for said second voltage, and wherein M times internal impedance is used for N times external impedance (N=M or N<> M).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrosurgical pencil with improved controls
An electrosurgical pencil is provided and includes an elongated housing having an electrocautery blade supported therein and extending distally from the housing. The electrocautery blade is connected to a source of electrosurgical energy. The pencil further includes a plurality of activation switches supported on the housing for activating electrocautery blade. Each activation switch is configured and adapted to selectively complete a control loop extending from the source of electrosurgical energy upon actuation thereof. In use, actuation of at least one of the plurality of activation switches produces a dividing with hemostatic effect at the electrocautery blade. The electrosurgical pencil further includes at least one voltage divider network supported on the housing. The at least one voltage divider network is electrically connected to the source of electrosurgical energy and controls the intensity of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Resistive touch panel using removable, tensioned top layer
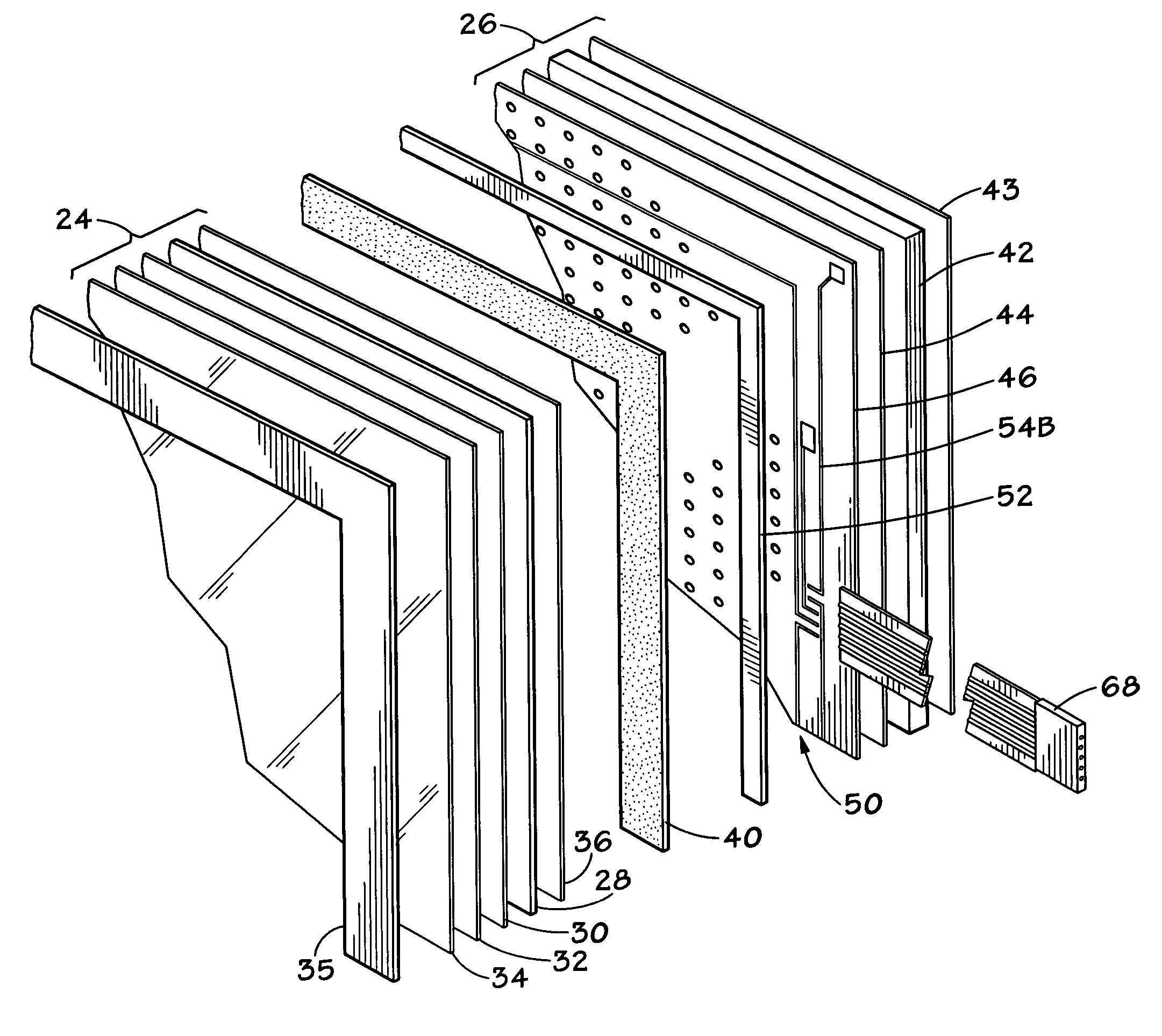
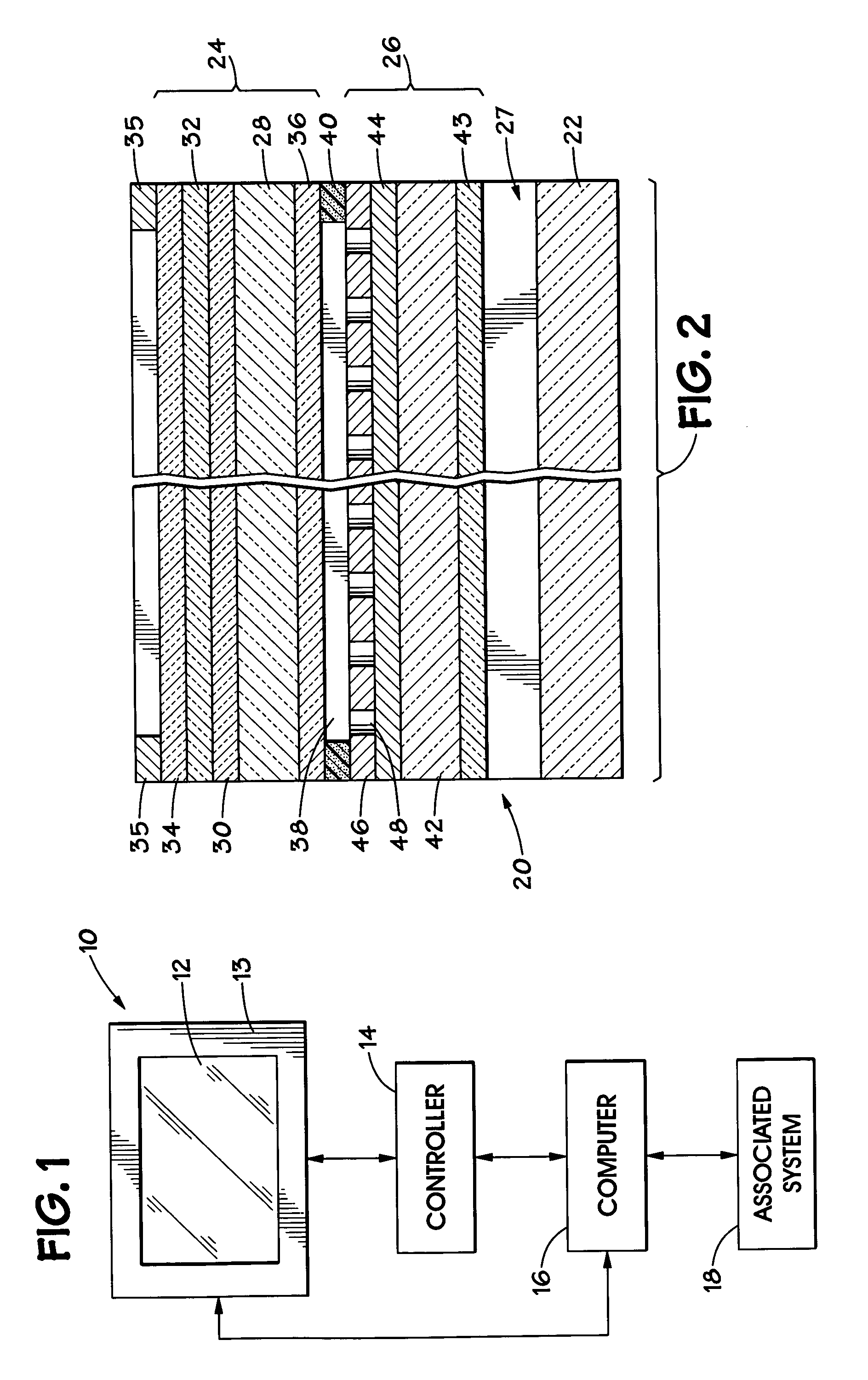
Sunlight can damage a conventional touch screen display and cause the display to be quite difficult to read. Furthermore, conventional touch screen displays are easily damaged, and, once damaged, the entire touch screen is replaced. To address these concerns, a touch panel includes anti-reflective coatings on the surfaces of the top plate and the base plate that are open to the air. These coatings substantially reduce reflections and make the touch screen easier to read in direct sunlight. In particular, the anti-reflective coating used on the upper surface of the base plate is dielectric in nature to reduce reflectivity even further. This dielectric coating includes openings to an underlying conductive layer so that an electrical contact is made when a user deflects the top plate into the base plate. Also, the top plate may be detachably coupled to the base plate, advantageously by double stick adhesive tape, so that only the top plate is replaced when damaged. In one embodiment, the top plate is placed in tension within a frame to prevent wrinkling. Furthermore, a resistive voltage divider may be fabricated on the base plate. The resistive voltage divider may include a substantially continuous strip of resistive material disposed on the conductive layer of the base plate, and a plurality of conductive traces disposed on the dielectric layer of the base plate and coupled to the resistive material in selected locations.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
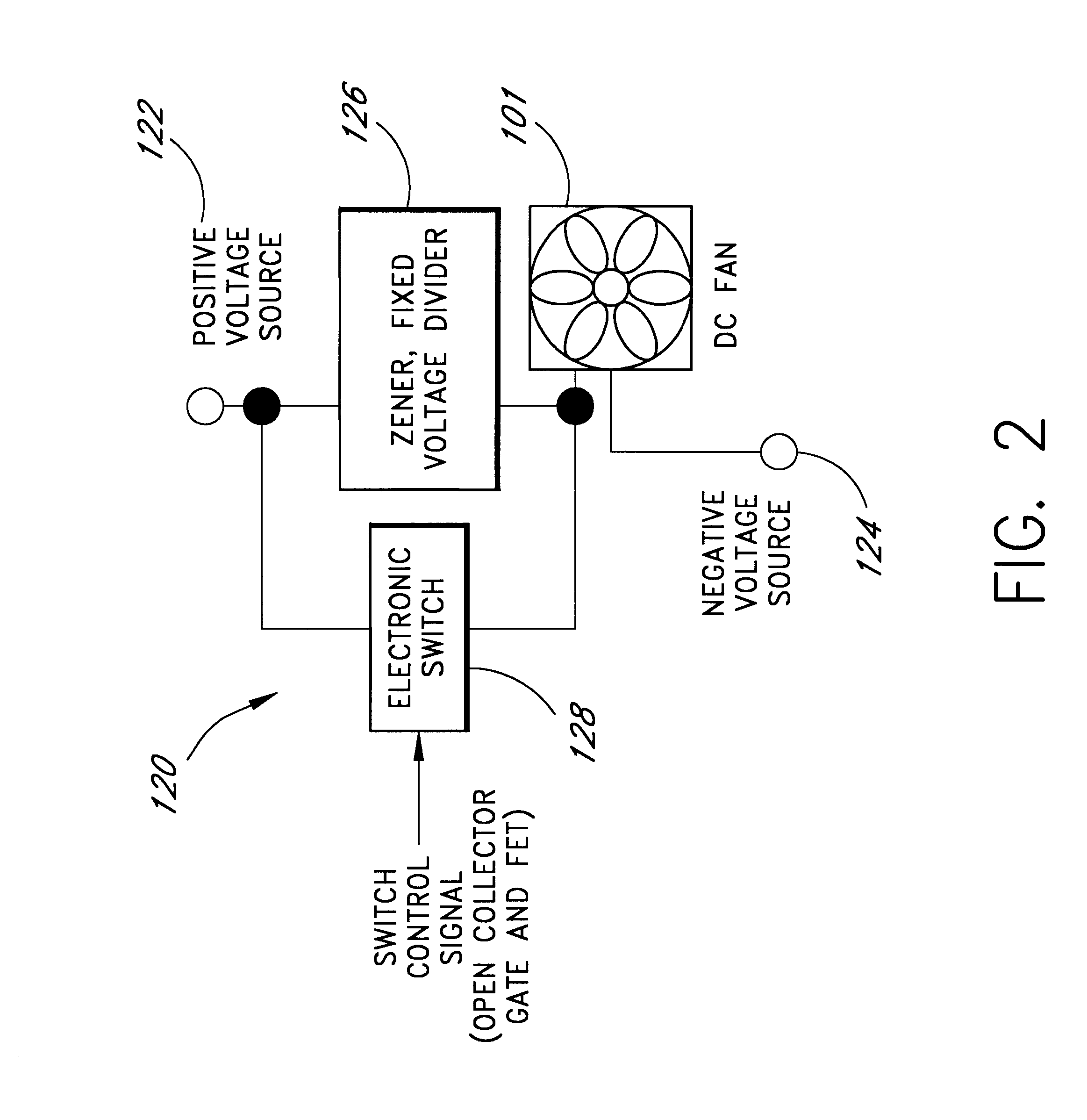
Computer fan speed control system
InactiveUS6247898B1Reduce stepsReduce voltageDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlSpeed control systemZener diode
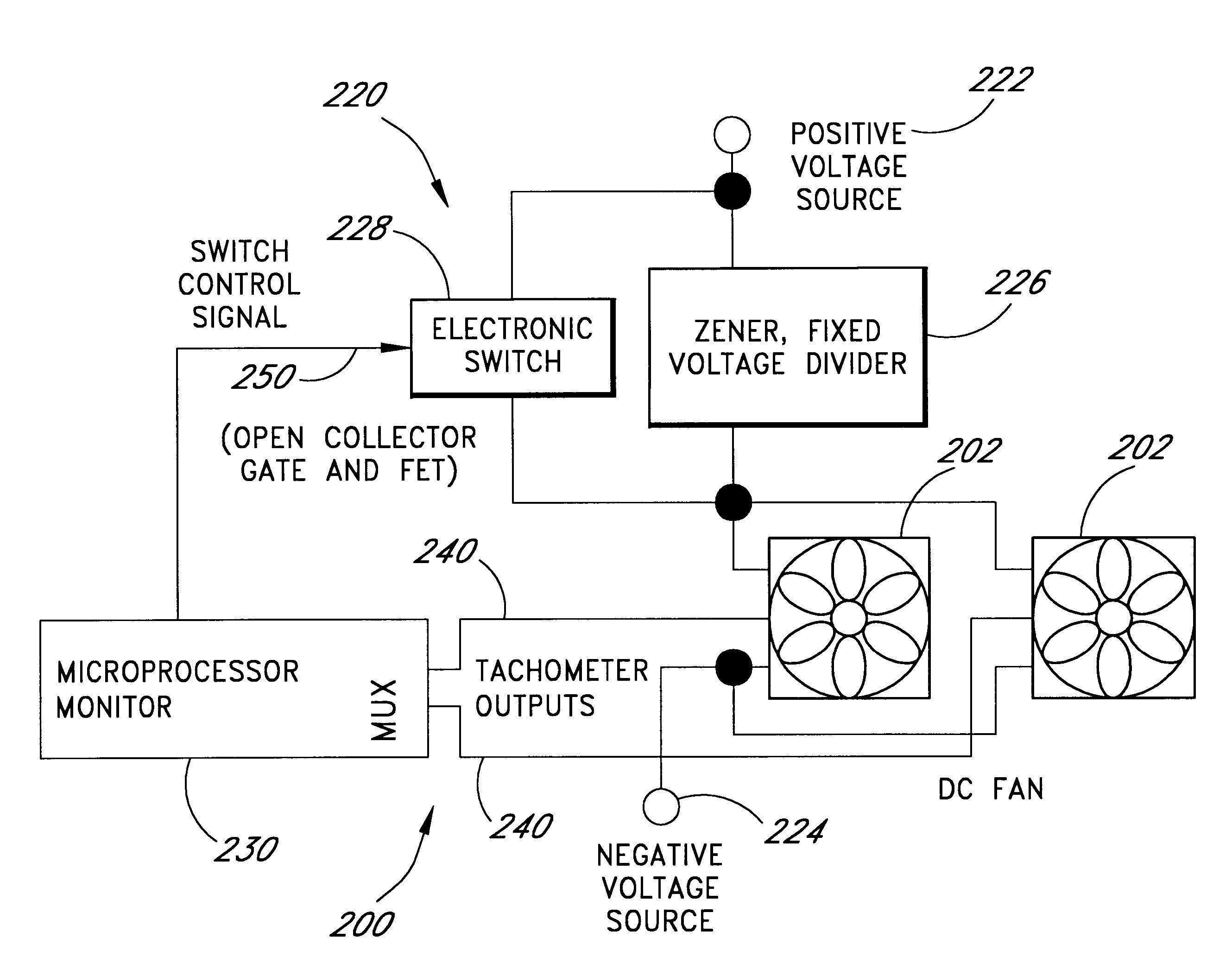
A cooling system for cooling components of a computer is provided. The cooling system includes a DC fan which operates at a speed which is substantially proportional to the voltage that is applied to the fan. A zener diode voltage divider is connected in series between a voltage source and a first input of the fan. The second input of the fan is connected to a reference voltage source. A switch is also connected in series between the voltage source and the first voltage input of the fan so as to be connected in parallel with the zener diode voltage divider. When the switch is in a first position, the voltage produced by the voltage source is applied directly to the fan allowing the fan to operate at a first speed. When the switch is in a second position, the voltage from the voltage source is applied to the first input of the fan through the zener diode such that the first input of the fan receives a second voltage that is less than the first voltage thereby causing the fan to operate at a second speed. The zener diode voltage divider is substantially current independent such that the voltage drop across the zener diode is substantially independent of the current that is drawn by the fan.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
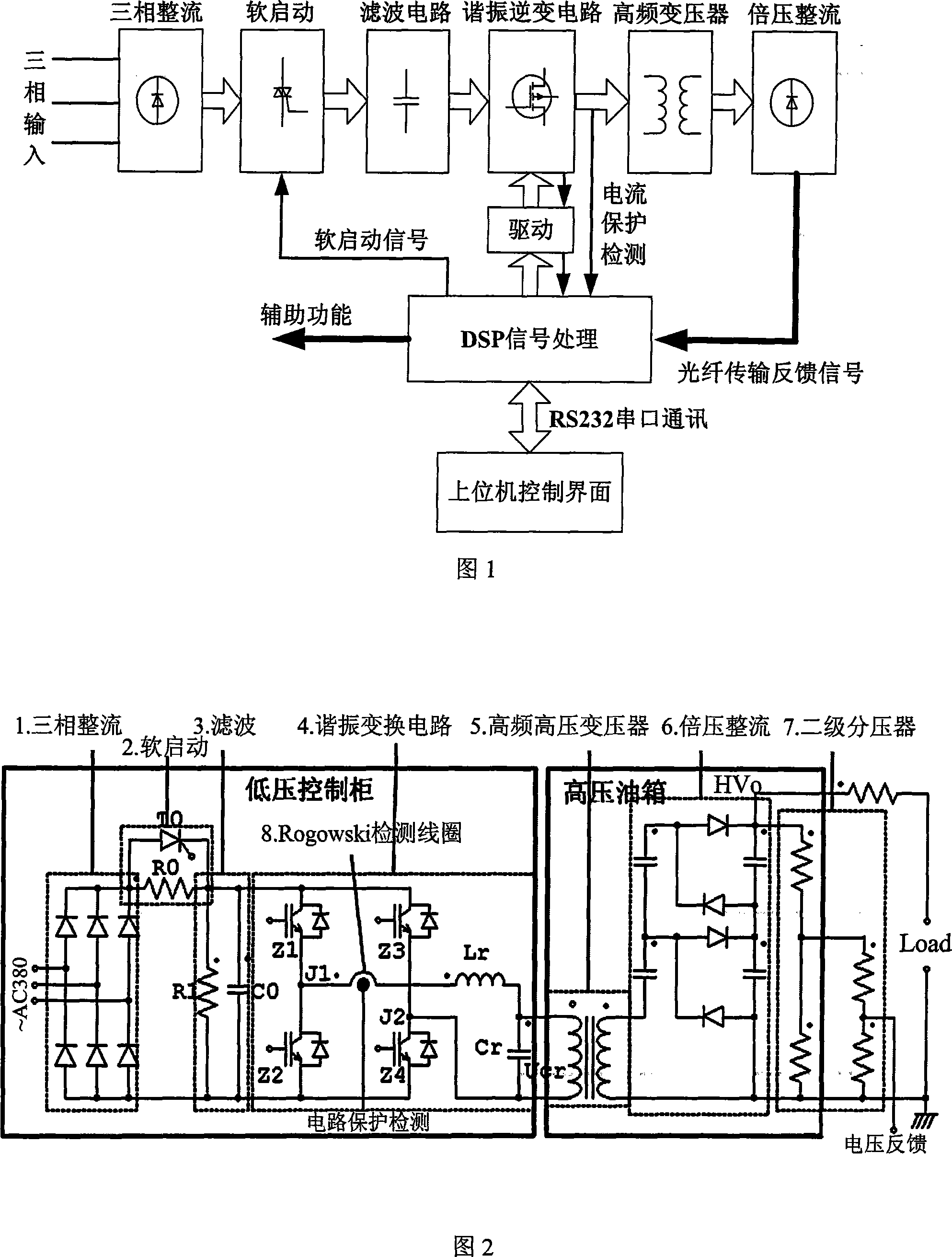
A digital high voltage DC power
InactiveCN101127484AReduce distractionsImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionBusbarPhase difference
The utility model relates to a digitized high voltage direct current power supply, and comprises a main power circuit, a digitized control circuit based on DSP and a control program of host computer based on PC, wherein the main power circuit comprises a three phase rectifying element [1], a soft start element [2], a filter element [3], a resonance inverting element [4], a high frequency and high voltage transformer [5], a doubling circuit [6] and a two-stage voltage divider [7]; the digitized control circuit based on DSP comprises an interface circuit of IPM drive signal, a high voltage feedback element, a resonance overcurrent protection element, a soft start circuit and a serial communication interface circuit. The voltage of power frequency electrical network is converted into DC voltage which is used as busbar voltage by three phase rectification, soft start and filter, and the busbar voltage is converted into 20KHz quasi-sine-wave by the resonance inverting element which is driven by a phase difference computed by the DSP according to feedback signal, and then 0-100Kv AC high voltage is output by the high frequency and high voltage transformer [5] and the doubling circuit [6]. The utility model adopts a host computer as a control device, and outputs the voltage via the control instructions of the DSP, therefore meets the requirements of voltage withstand test of insulation material.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrical circuit for delivering power to consumer electronic devices
InactiveUS20170099011A1Lower resistanceReduce conductionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLow voltageFull wave
An electrical circuit for providing electrical power for use in powering electronic devices, such as monitors, televisions, white goods, data centers, and telecom circuit boards, is described herein. The electrical circuit includes a voltage reduction circuit and a rectifier circuit for delivering input power signal to the voltage reduction circuit. The voltage reduction circuit is configured to receive an input power signal and generate an output power signal at a lower voltage level. The rectifier circuit includes a full wave bridge rectifier coupled to the electrical power source, a Zener based charging circuit coupled to the full wave bridge rectifier, a voltage divider coupled to the Zener based charging circuit and the full wave bridge rectifier, and an output terminal coupled to the full wave bridge rectifier, the Zener based charging circuit, and the voltage divider for delivering the input power signal to the voltage reduction circuit.
Owner:FREEMAN MICHAEL H FREE
Blister pack content usage monitoring
ActiveUS8960440B1Save battery powerExtended service lifeSmall article dispensingPharmaceutical containersElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage ratio
A system is provided for monitoring the removal of blister pack contents. An array of spatially-extended, electrically parallel breakable traces made from electrically resistive material is formed behind a corresponding array of blisters of a blister card. Then this array is connected in series with a reference resistor to form a voltage divider. All resistive traces are formed from the same materials in a single operation. Blister breakage is determined using changes in the ratio of the resistances of the array and the divider. A predictive algorithm is used to adjust the threshold resistance ratio change that signals blister breakage and voltage ratios are used to adjust for battery output changes over time. Breakage events and their time of occurrence are recorded in nonvolatile memory for later retrieval. Additional resistors can be used for activating the system and detecting tampering.
Owner:INTELLIGENT DEVICES SEZC
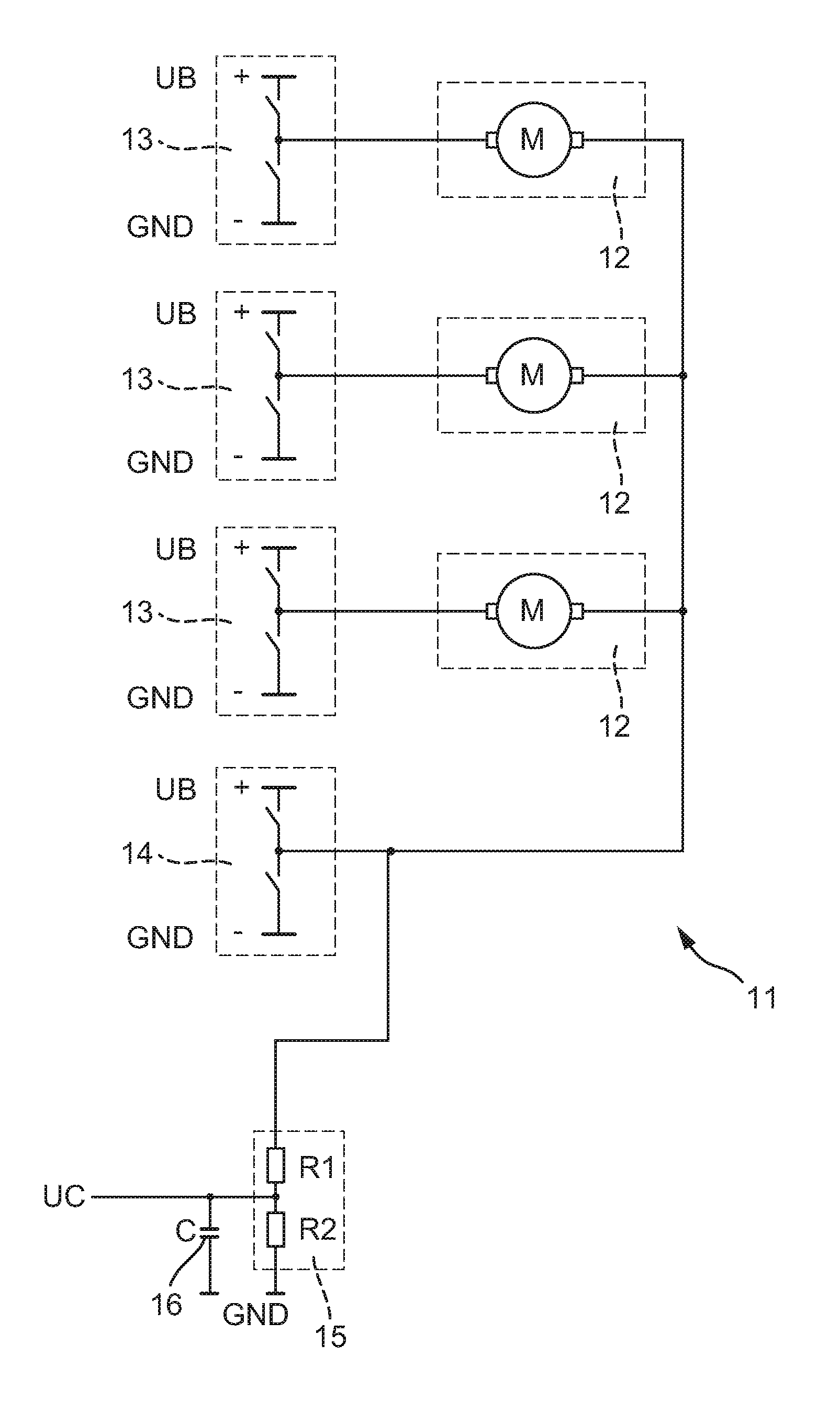
Fault detection of electric consumers in motor vehicles
ActiveUS8487633B2Simple and cost-effectiveLow costElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityVoltage divider
Fault detection of electric consumers in motor vehicles including at least one electric consumer switchably arranged between a first electric potential and a second electric potential. The electric consumer is switchably connected both to the first and to the second potential. A first switch is arranged between the first potential and the consumer and a second switch is arranged between the second potential and the consumer. The first and the second switch must be closed at the same time in order to operate the consumer. Fault detection is carried out when the device consuming the electricity is visibly off, in that a third electric potential is tapped at a voltage divider arranged parallel to the second switch. Fault detection is carried out by monitoring the third electric potential and the positions of the first and second switches.
Owner:SMR PATENTS S A R L
Current control circuit and method thereof for a power converter
InactiveUS20140119076A1Improve responsivenessImprove system stabilityAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage referenceEngineering
A power converter used in the current control circuit and control method, consisting of a converter, a voltage divider circuit, a current sampling circuit, a first gain circuit, a differential amplifier, a second gain circuit, a multiplier, a saw tooth wave generator, a modulation comparator, and a driver. The invention samples inductor current through the current sampling circuit and generates the current sense signal, then processes again. With the differential amplifier, it compares the feedback voltage from the voltage divider circuit with the reference voltage, and the results along a modulation comparator output a drive signal to control the duty cycle in order to avoid the generation of inrush current. The present invention avoids inrush current caused by the large drive signal and achieves a good response rate and better system stability.
Owner:LUXMILL ELECTRONICS
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS20050017789A1Improving RF switch isolationRaise the compression pointTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETEngineering
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Electrosurgical pencil with improved controls
An electrosurgical pencil is provided and includes an elongated housing having an electrocautery blade supported therein and extending distally from the housing. The electrocautery blade is connected to a source of electrosurgical energy. The pencil further includes a plurality of activation switches supported on the housing for activating electrocautery blade. Each activation switch is configured and adapted to selectively complete a control loop extending from the source of electrosurgical energy upon actuation thereof. In use, actuation of at least one of the plurality of activation switches produces a dividing with hemostatic effect at the electrocautery blade. The electrosurgical pencil further includes at least one voltage divider network supported on the housing. The at least one voltage divider network is electrically connected to the source of electrosurgical energy and controls the intensity of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
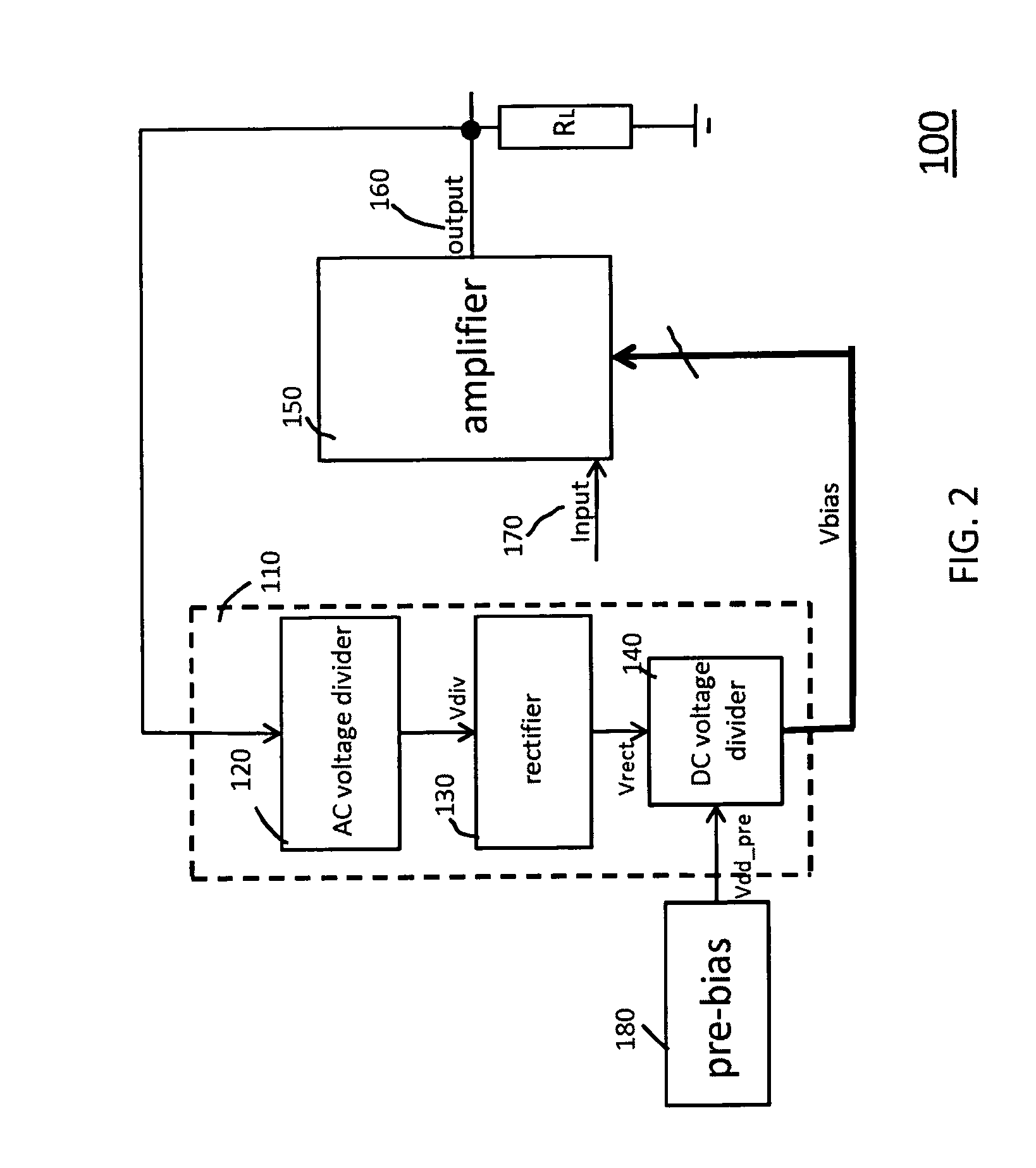
Biasing methods and devices for power amplifiers
ActiveUS8111104B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
Biasing methods and devices for power amplifiers are described. The described methods and devices use the power amplifier output voltage to generate bias voltages. The bias voltages are obtained using rectifiers and voltage dividers. The described biasing methods and devices can be used with class-E power amplifiers.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Gasinsulation combined electric device local discharge analog experimental apparatus and experimental method
The simulating experiment equipment for local discharge in gas insulated combined electric appliance consists of inducing pressure regulator, no-corona experiment transformer, no-local discharge protecting resistor, standard capacity voltage divider, GIS simulating experimental device, internal UHF antenna sensor and external UHF antenna sensor, microstrip line filtering amplifier, intelligent UHF multiplexer, wide band high speed ultrahigh capacirty digital storage oscilloscope and microcomputer. The simulating experiment equipment and method for local discharge in gas insulated combined electric appliance may be used for simulating various defaults inside GIS to obtain PD experiment data reflecting various kinds of insulation defaults and distinguish the PD modes of the insulation defaults in GIS, so that the present invention may be used widely in relevant theoretical analysis and application research.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Connection cable and method for activating a voltage-controlled generator
ActiveUS20090024120A1Batteries circuit arrangementsIncorrect coupling preventionSurgical operationElectrosurgery
A connection cable is disclosed for controlling a voltage-controlled generator such as an electrosurgery generator from a controlling device such as a robotic surgery system. The cable includes a first connector adapted to connect to a voltage-controlled generator and a second connector adapted to connect to a controlling device. Within the cable is a voltage divider interdisposed between the first connector and the second connector. The voltage divider is configured to divide a reference voltage provided by the voltage-controlled generator into at least one control voltage which is selectable by the controlling device. The cable additionally includes a plurality of electrical wires which operatively connect the first connector, the second connector and the voltage divider. During robotic electrosurgery, said operating parameters can be actuated by a surgeon operating at the robotic surgical system console, which causes a corresponding control voltage to be switched to a control voltage input on an electrosurgery generator, which, in turn, generates a corresponding electrosurgical signal in response thereto.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com