Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1694 results about "Electron source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
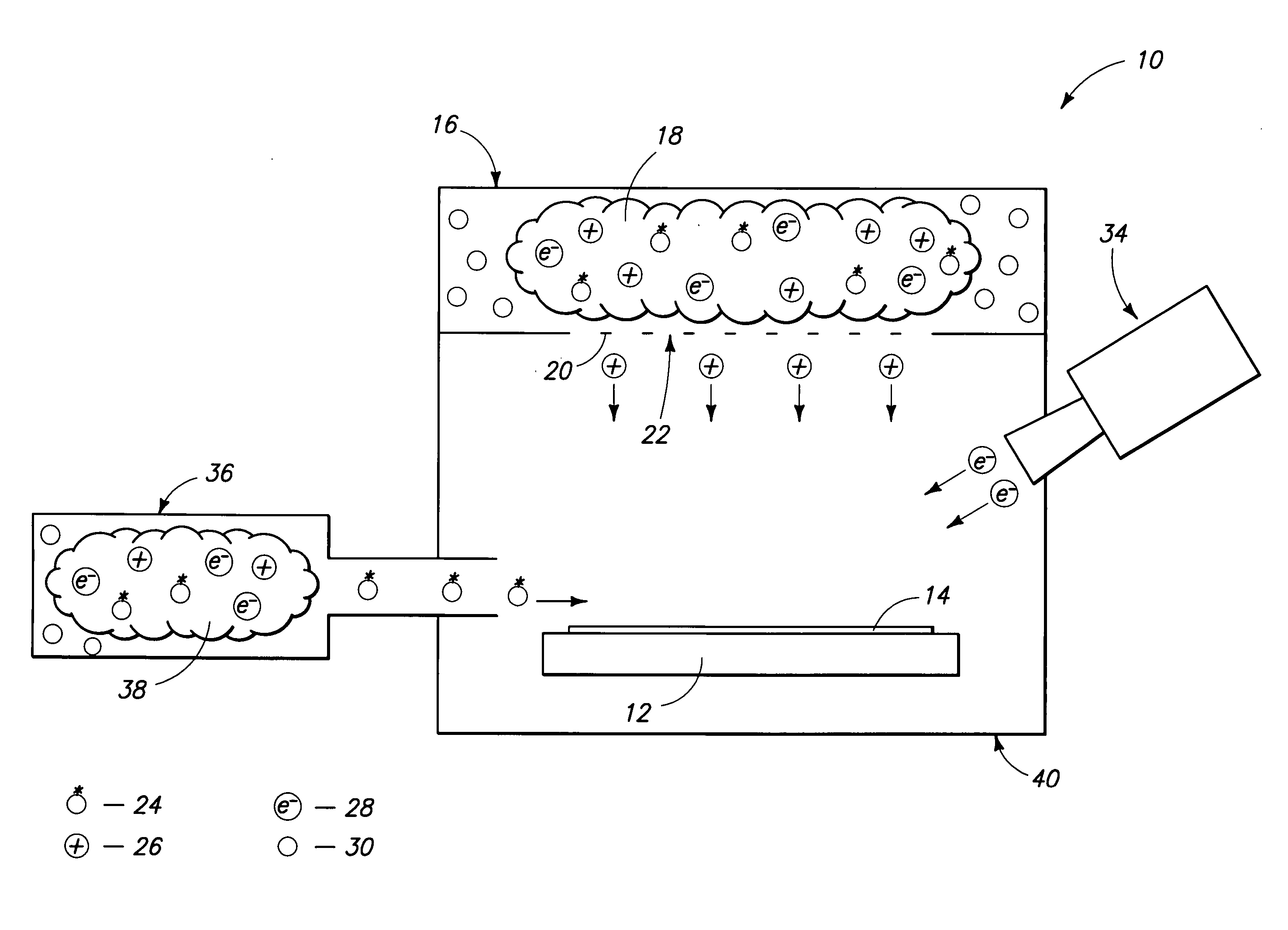
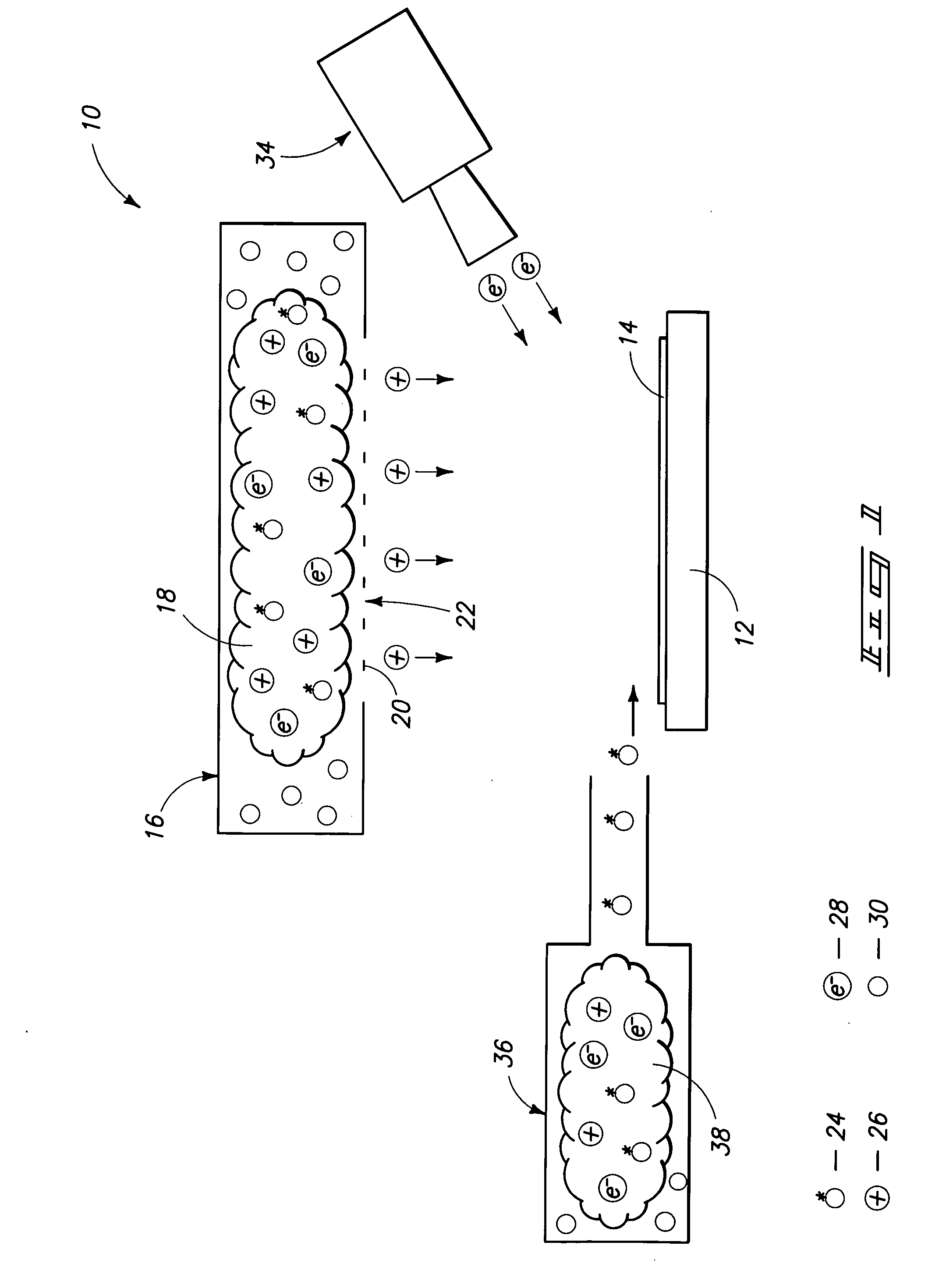
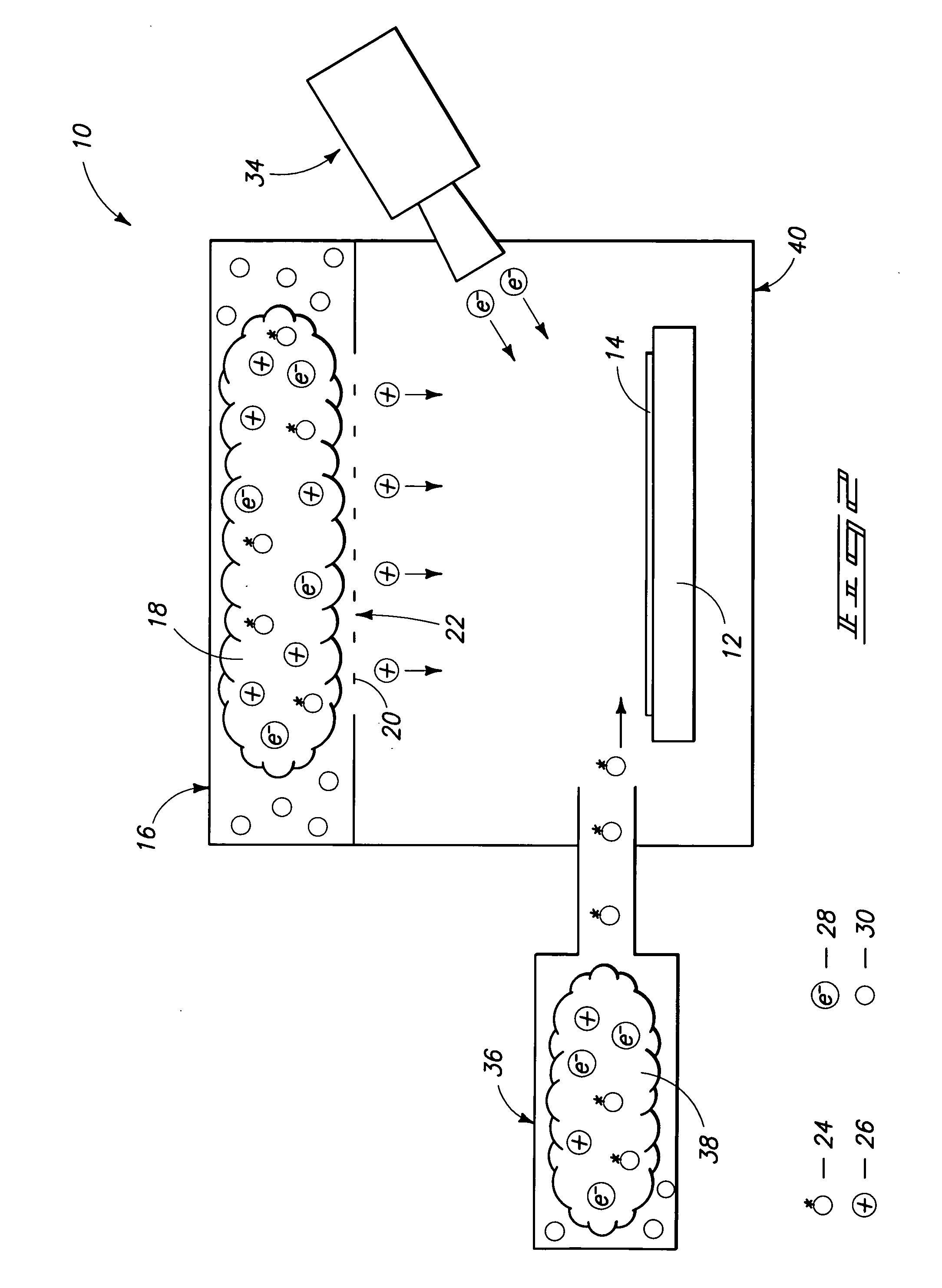
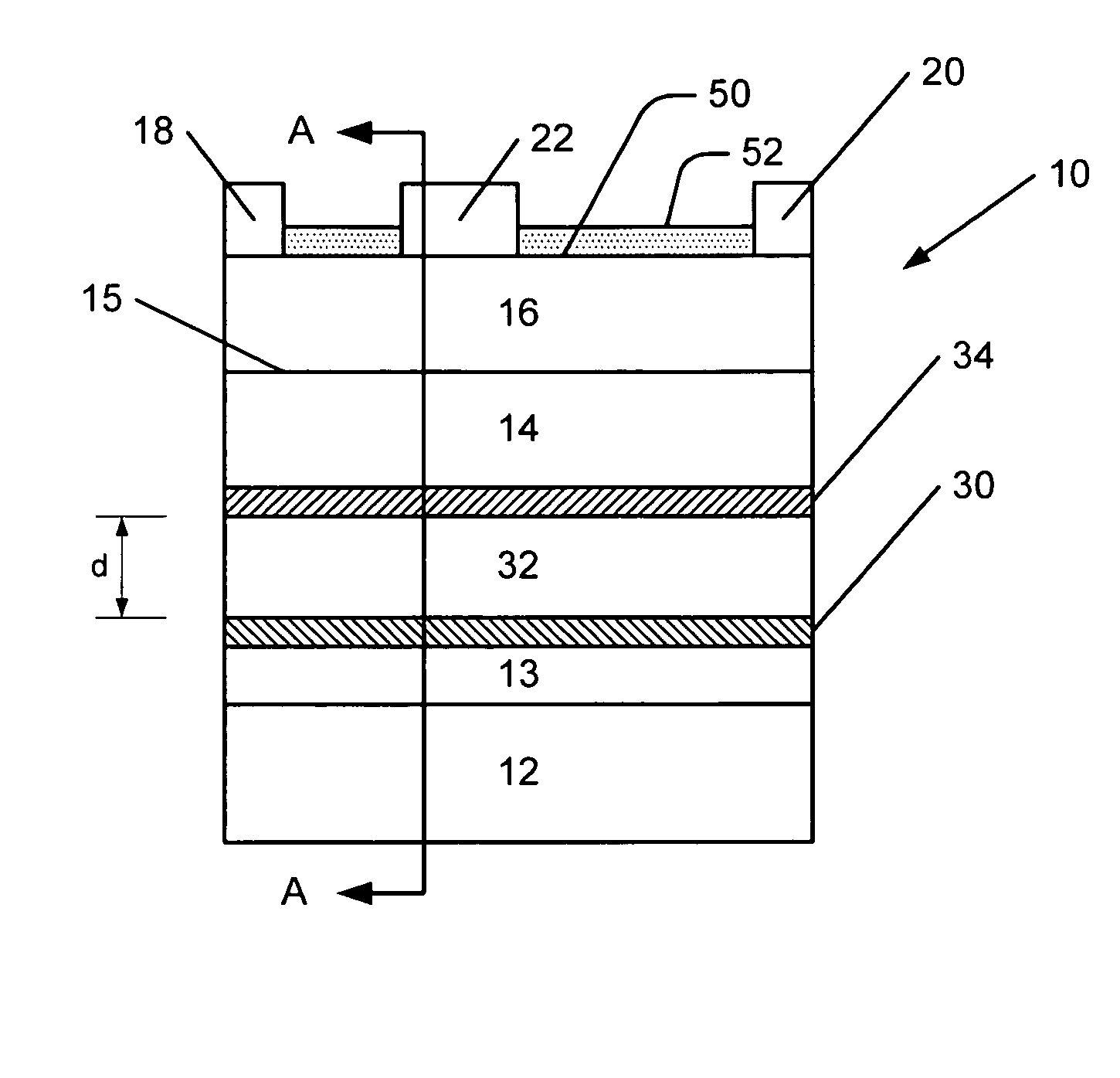
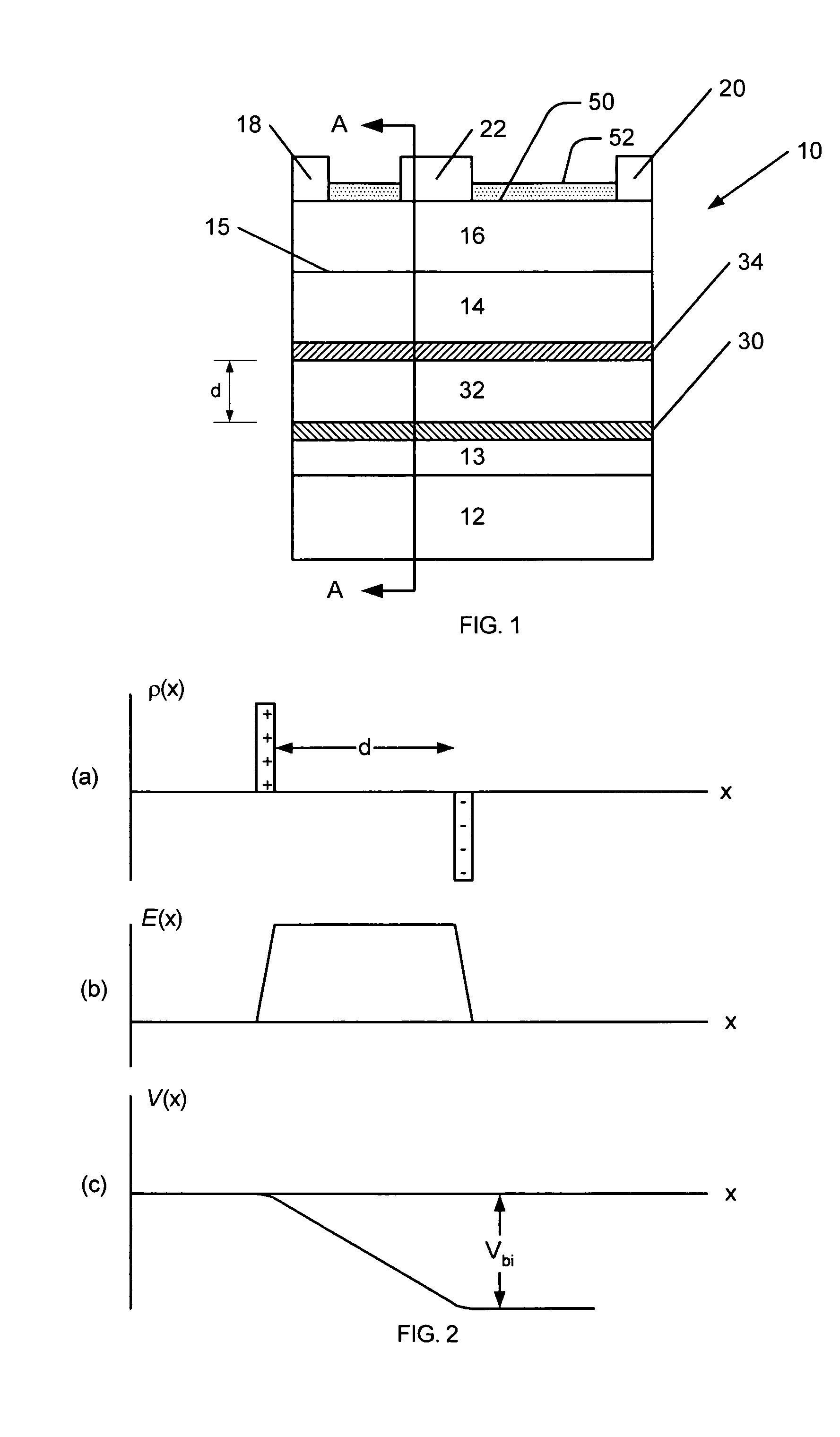
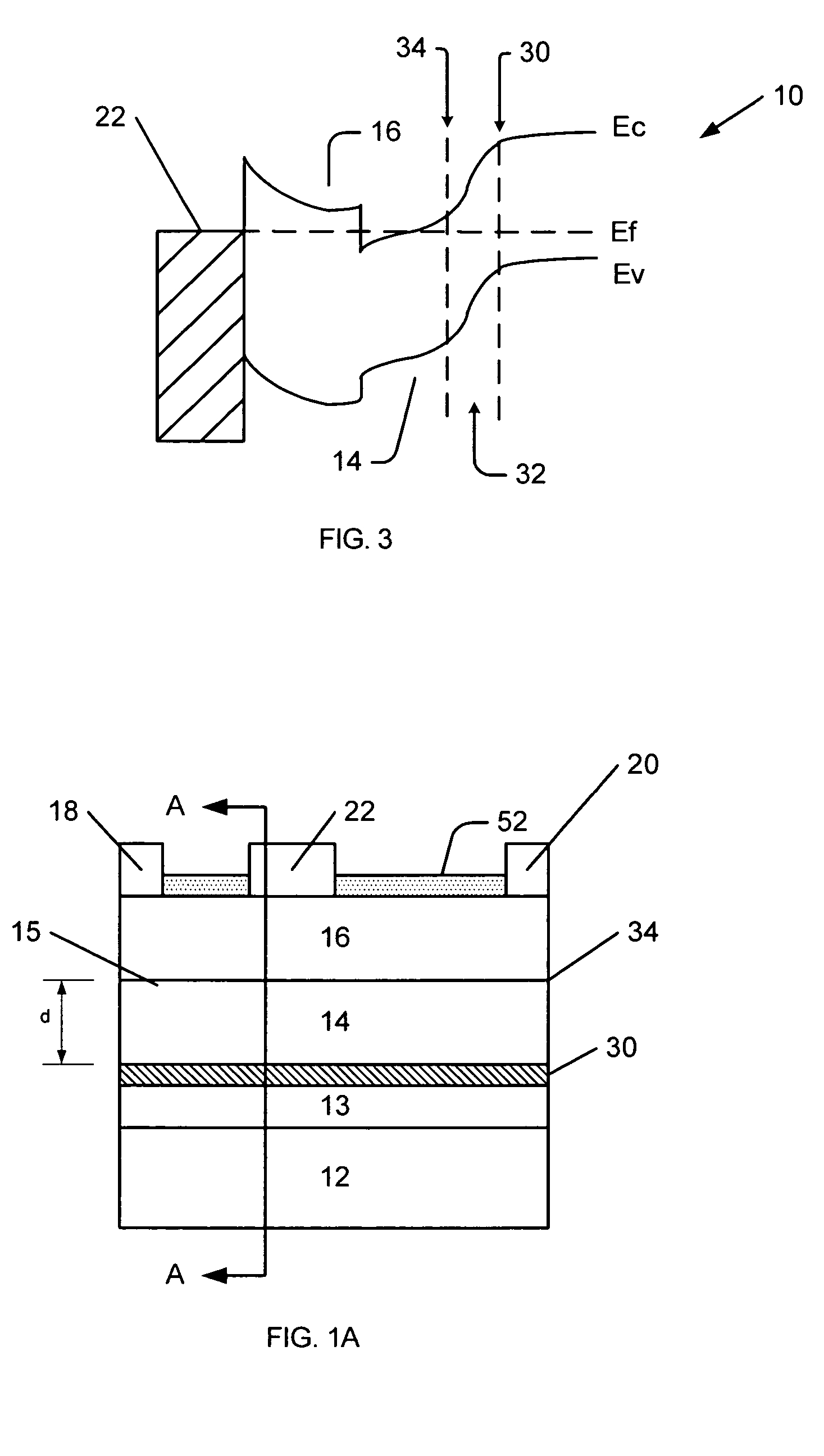
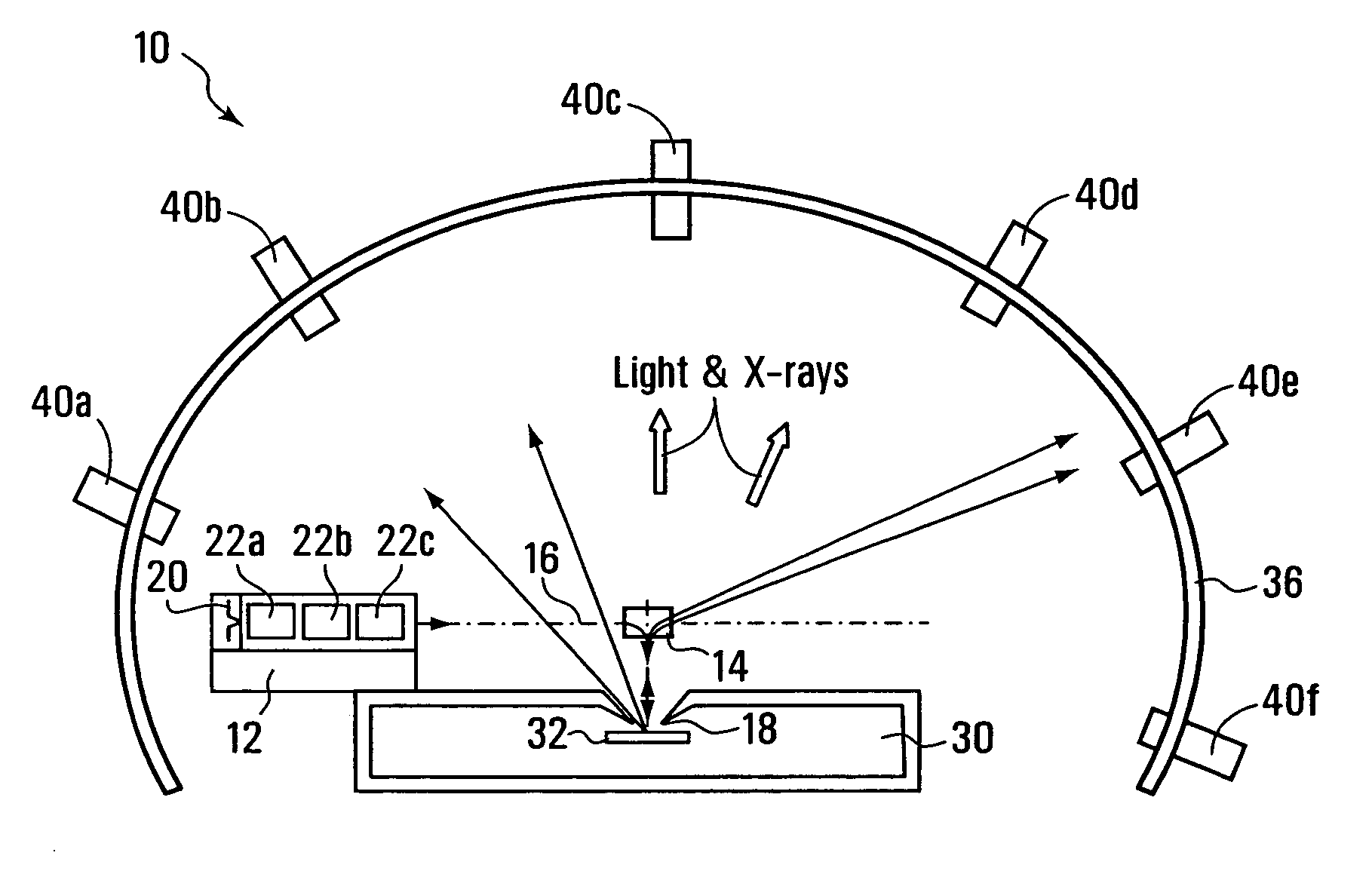
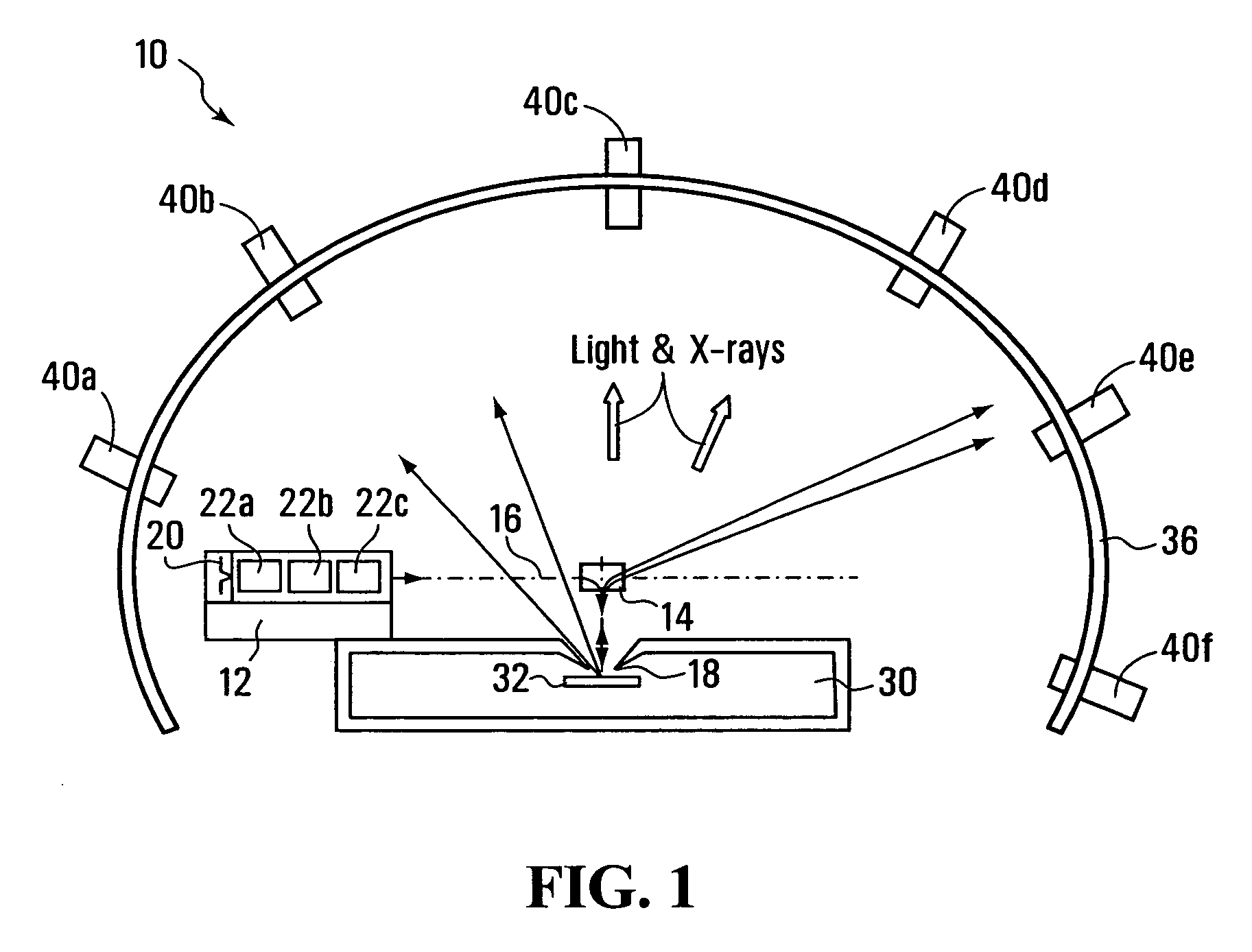
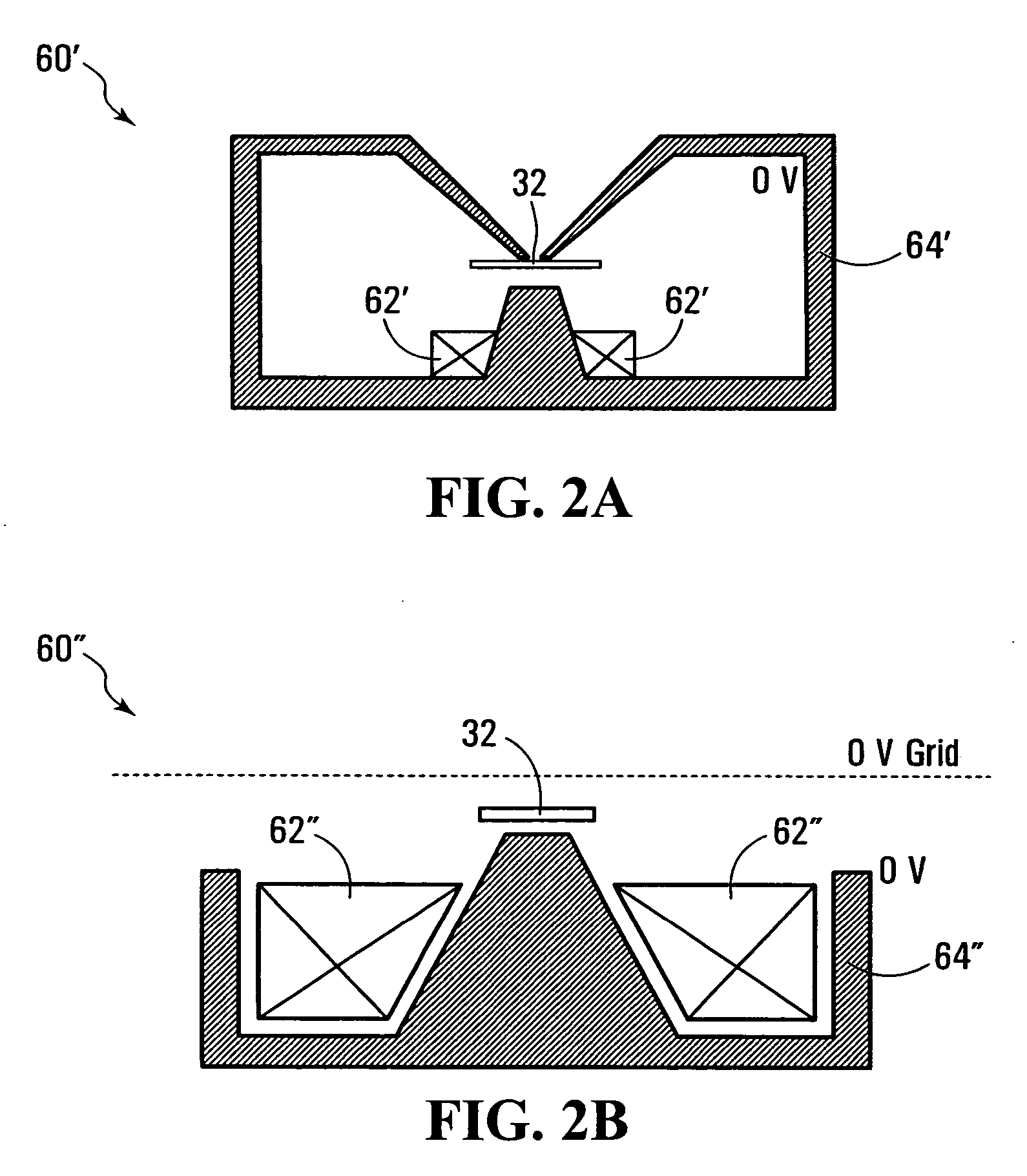
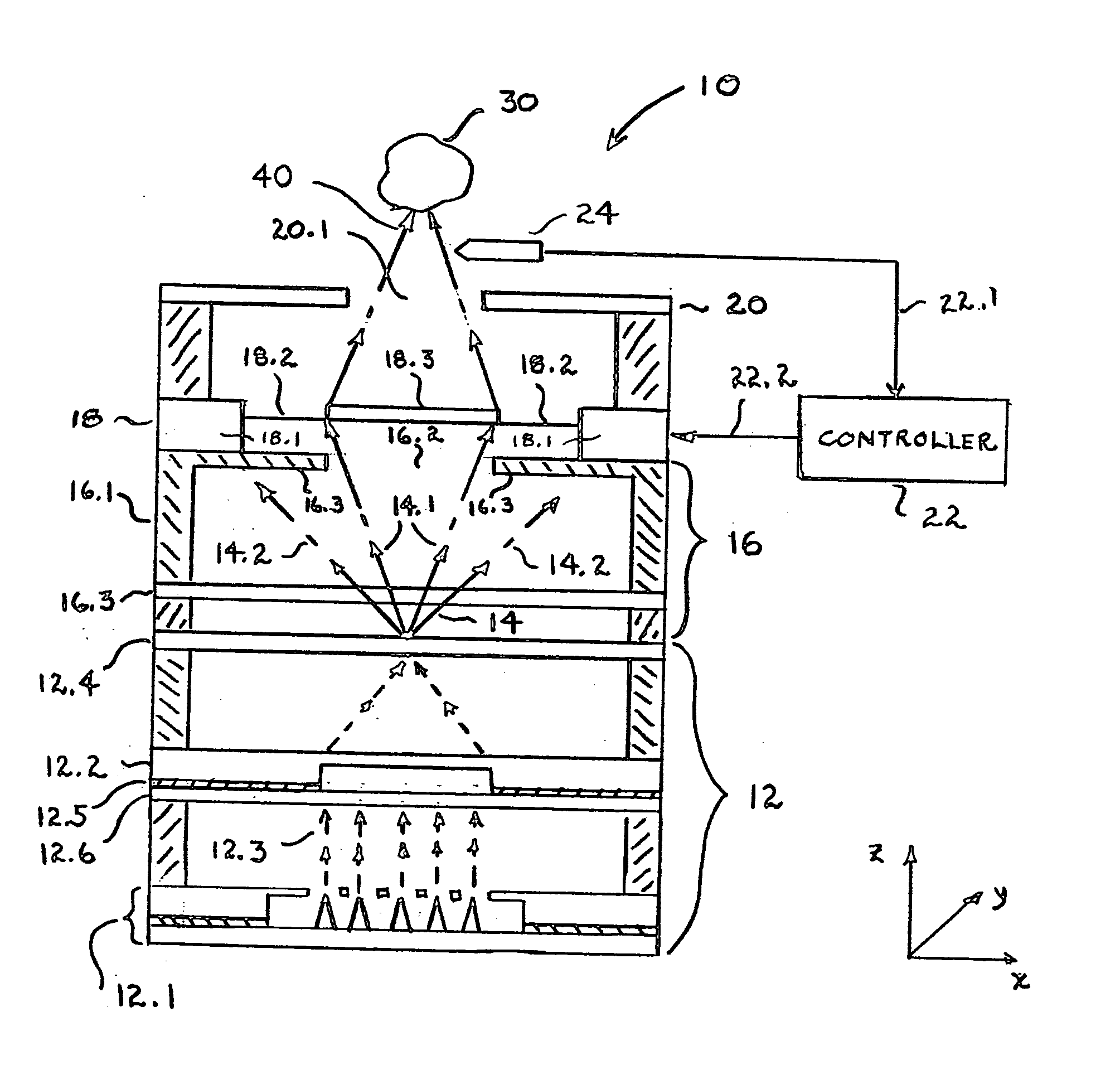
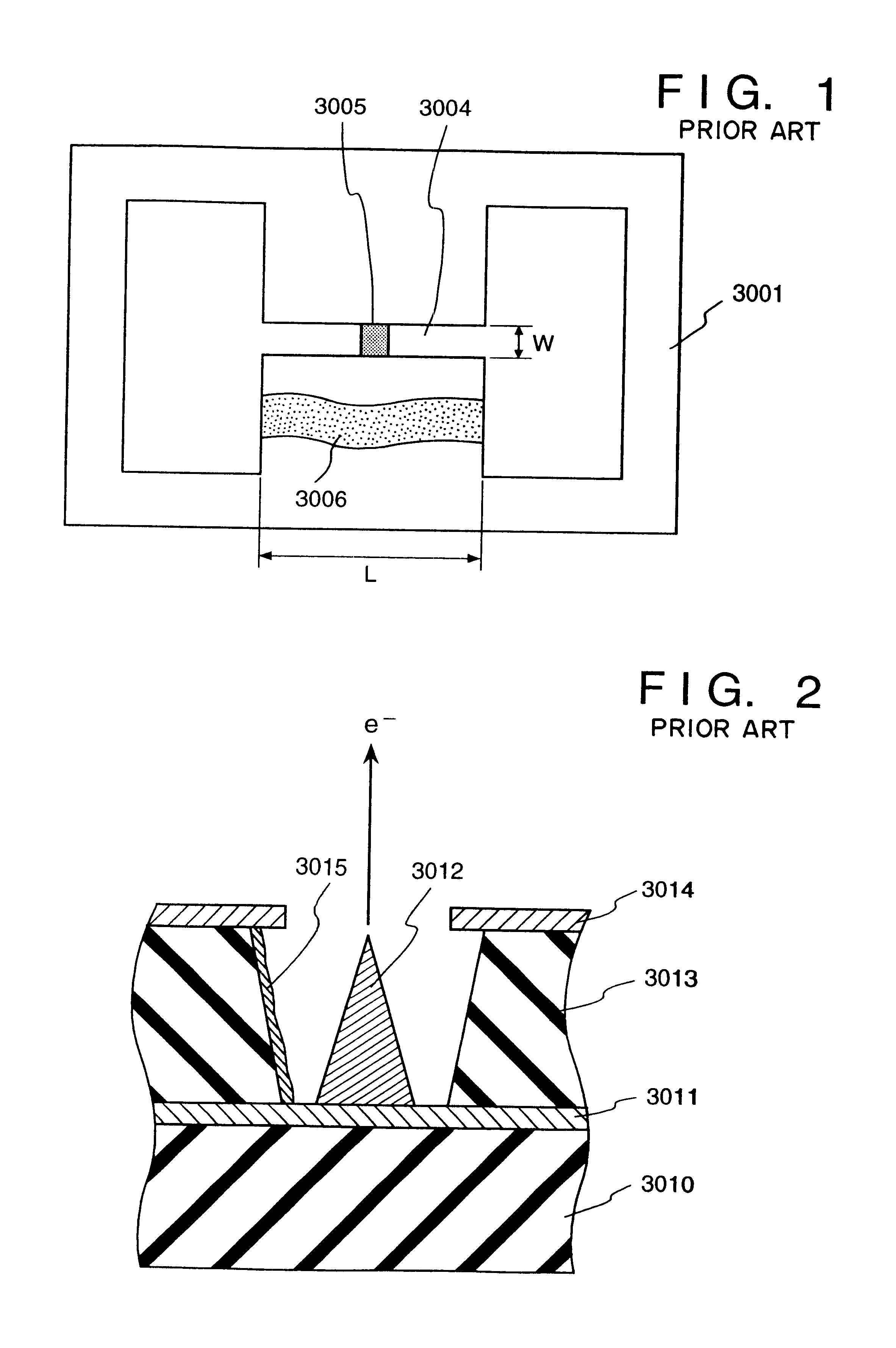
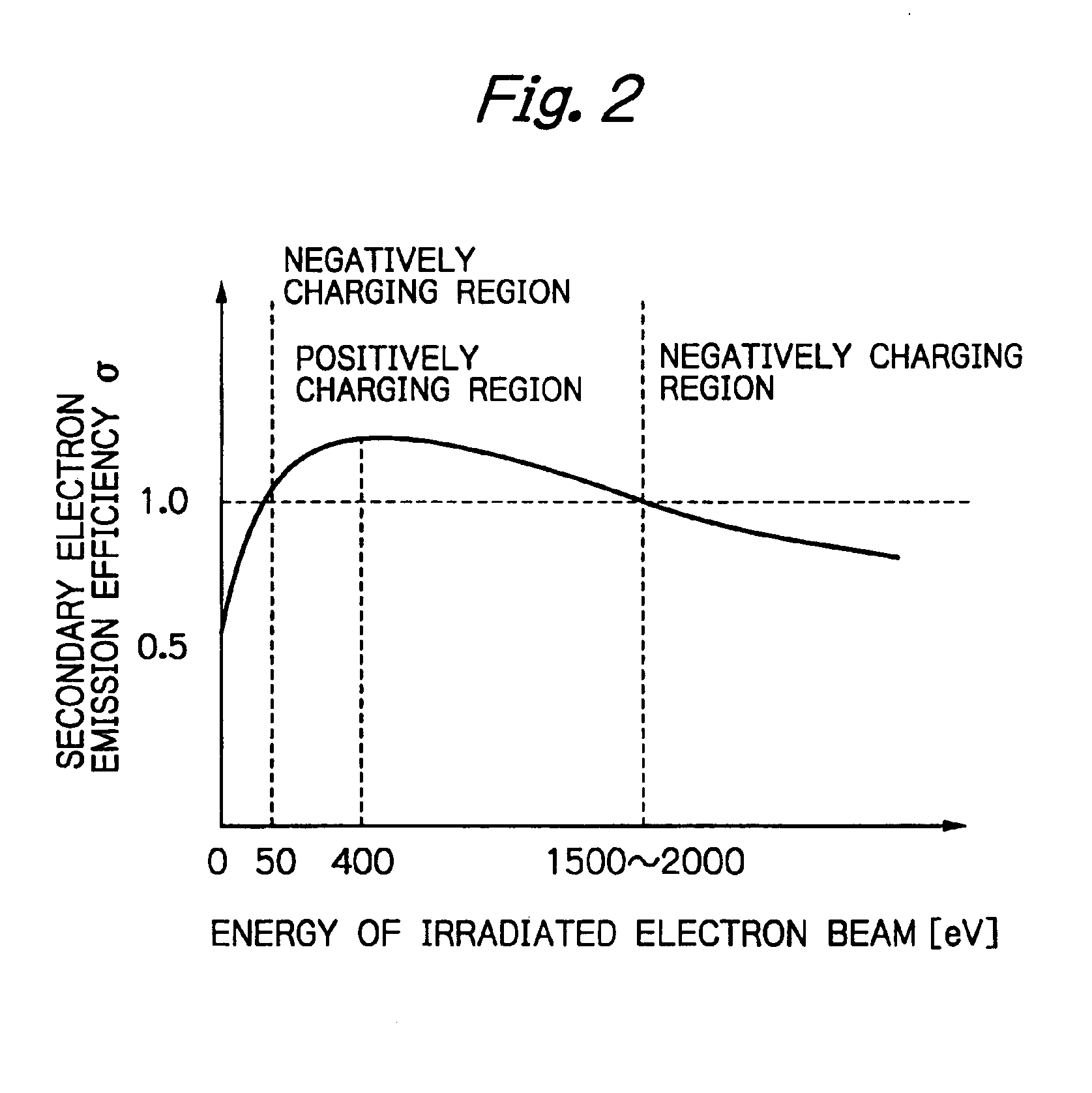
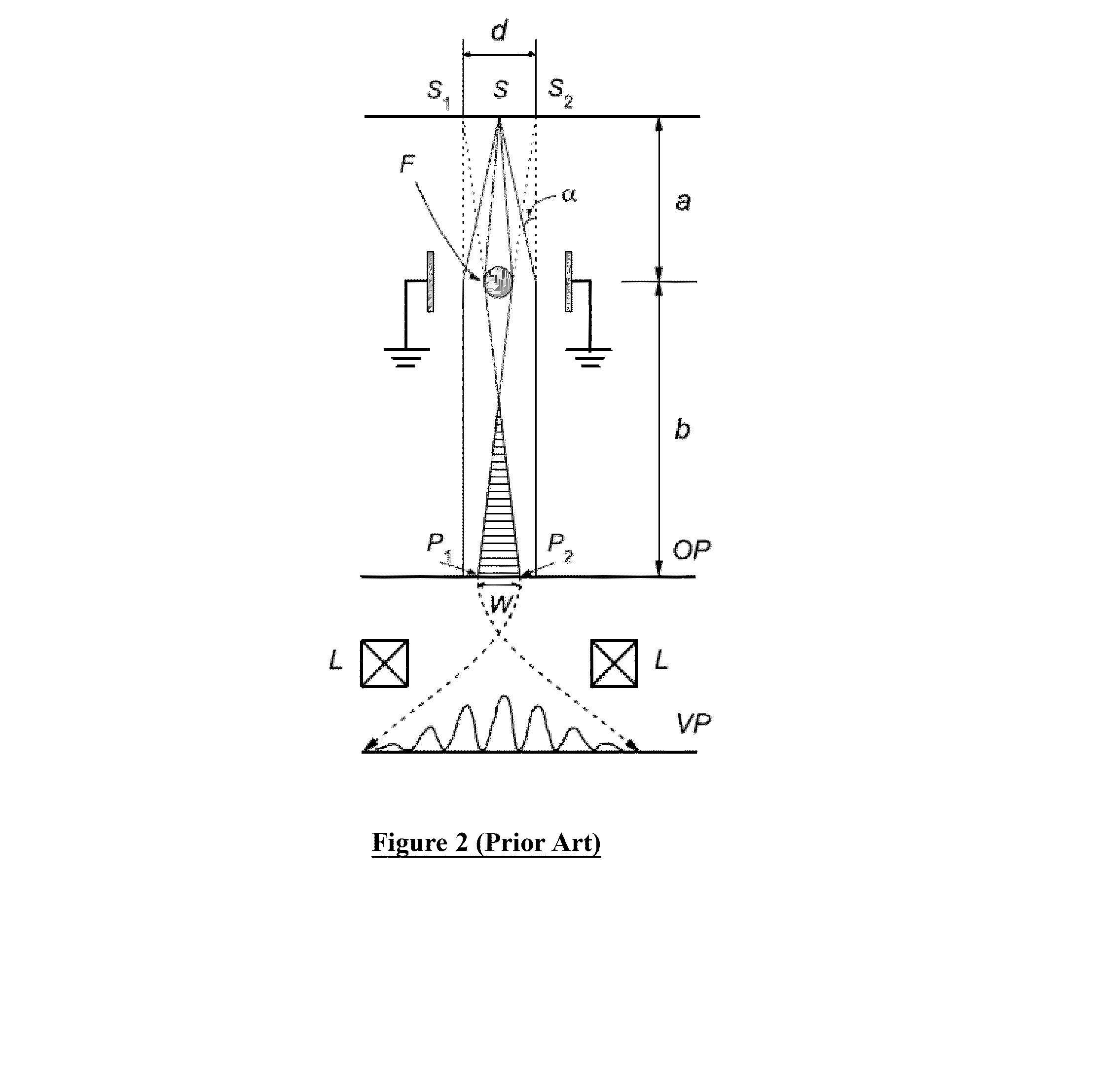
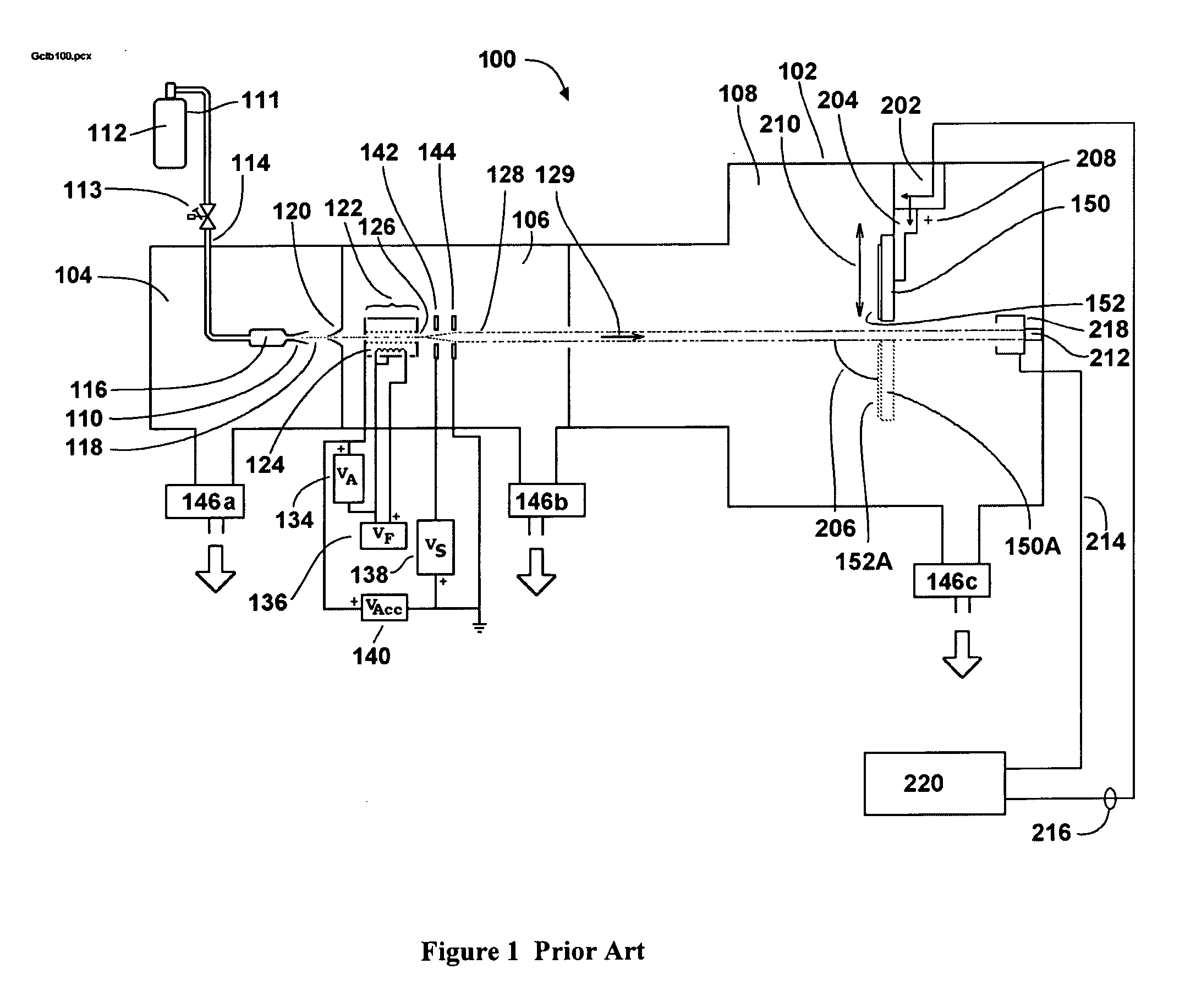
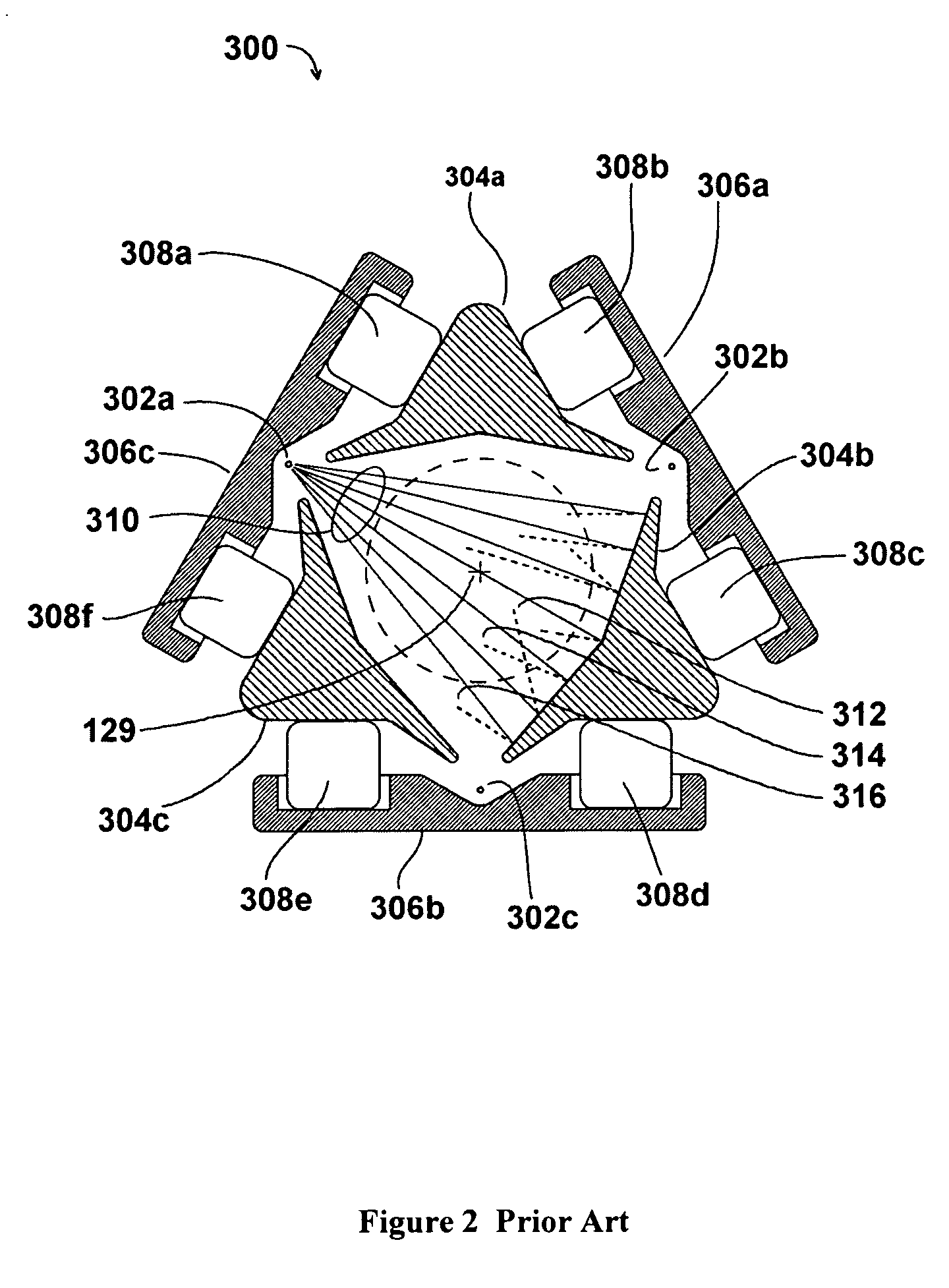
Electron Source. Electrons are produced at the source by thermionic heating. These electrons are then accelerated to a voltage between 1-40 kV and condensed into a narrow beam which is used for imaging and analysis. There are 3 commonly used types of electrons sources: Tungsten filament.
Field emission electron source
InactiveUS6057637AStable and reproducible current-voltage characteristicStraightforward and commercially feasibleElectric discharge tubesLayered productsElectron currentElectron source
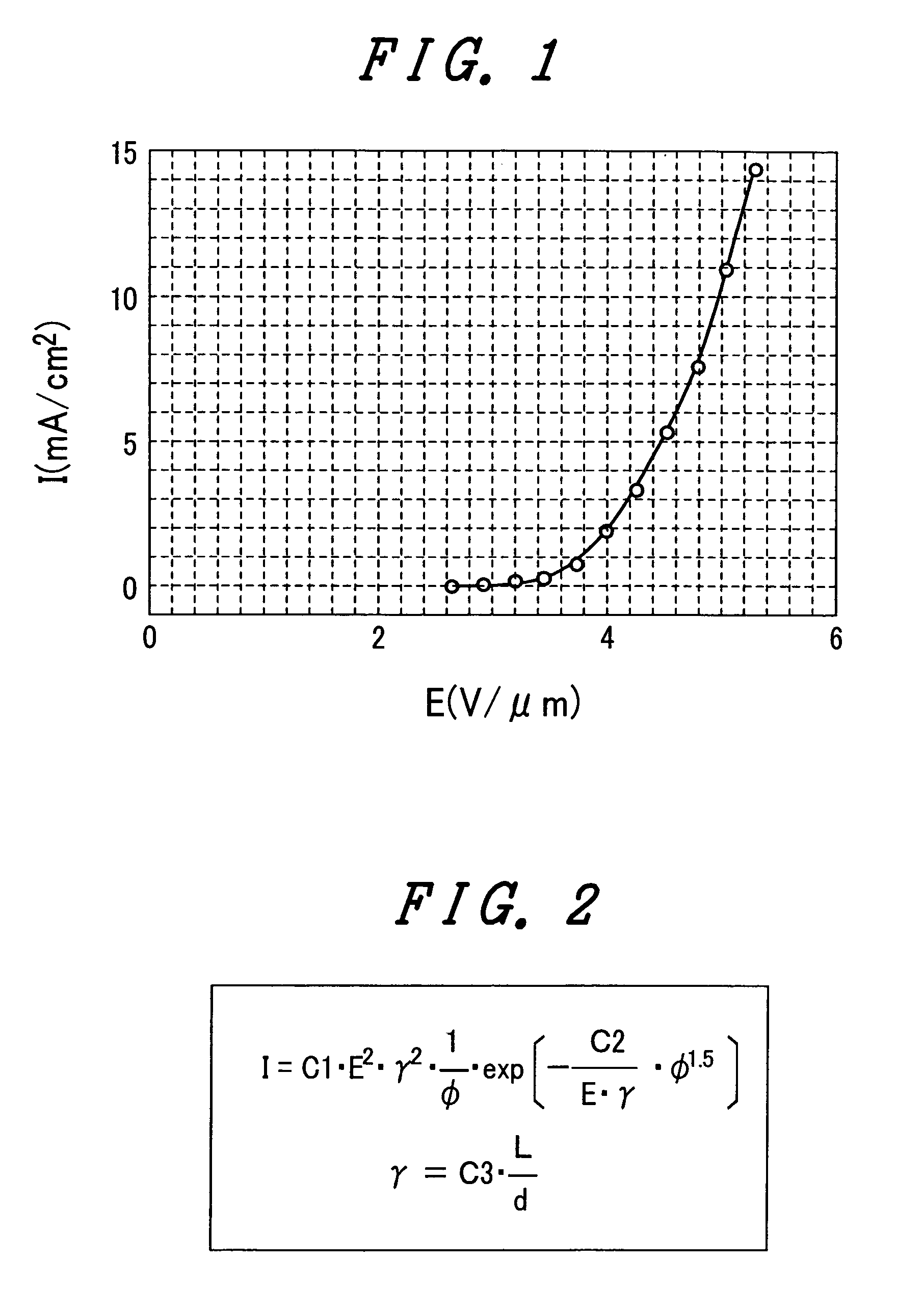
A novel field emitter material, field emission electron source, and commercially feasible fabrication method is described. The inventive field emission electron source produces reliable electron currents of up to 400 mA / cm2 at 200 volts. The emitter is robust and the current it produces is not sensitive to variability of vacuum or the distance between the emitter tip and the cathode. The novel emitter has a sharp turn-on near 100 volts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electron beam exciter for use in chemical analysis in processing systems
ActiveUS20100032587A1Disparity will become so greatHigh electron energyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesRadiation therapyElectron sourceFluorescence
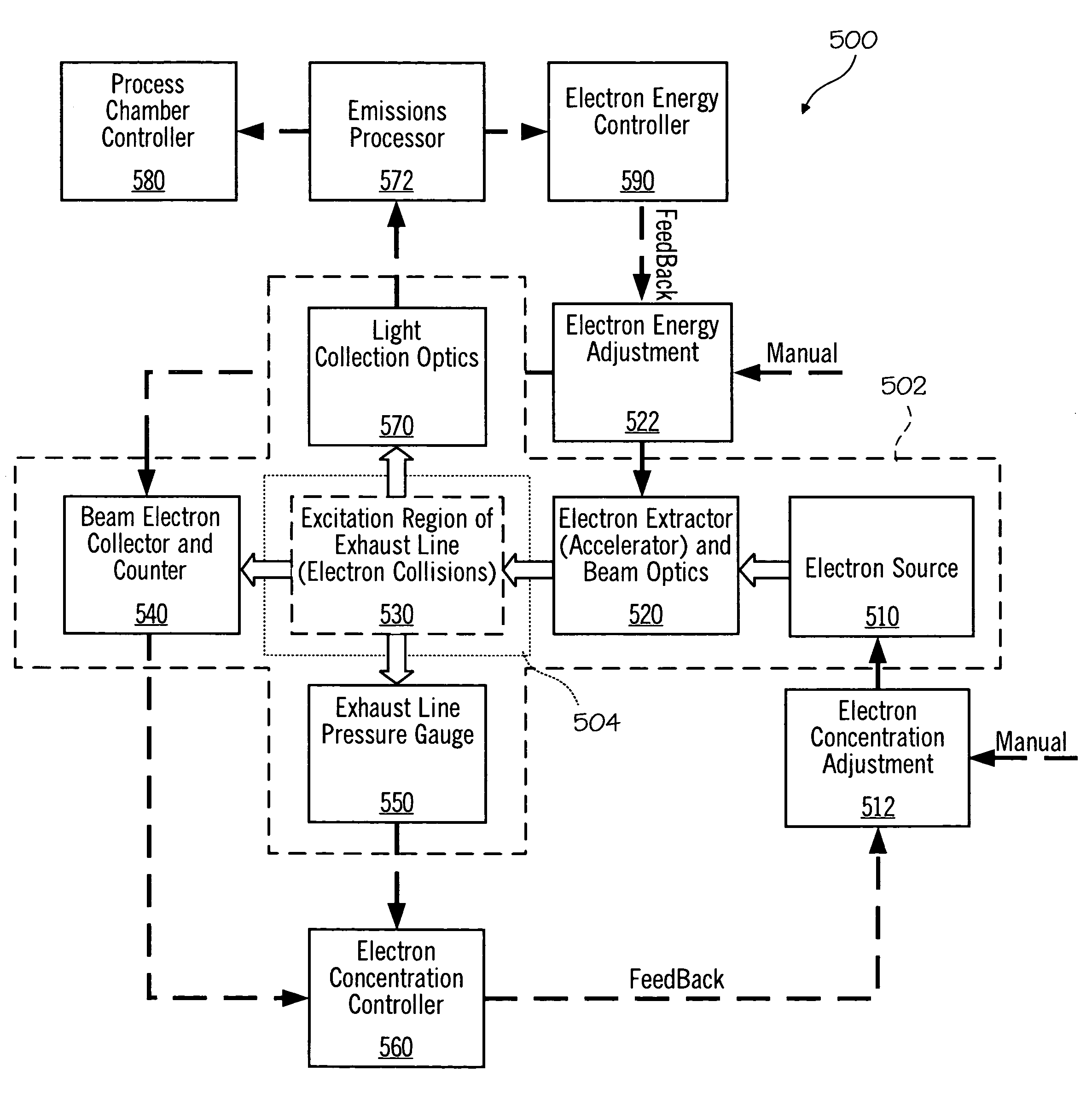
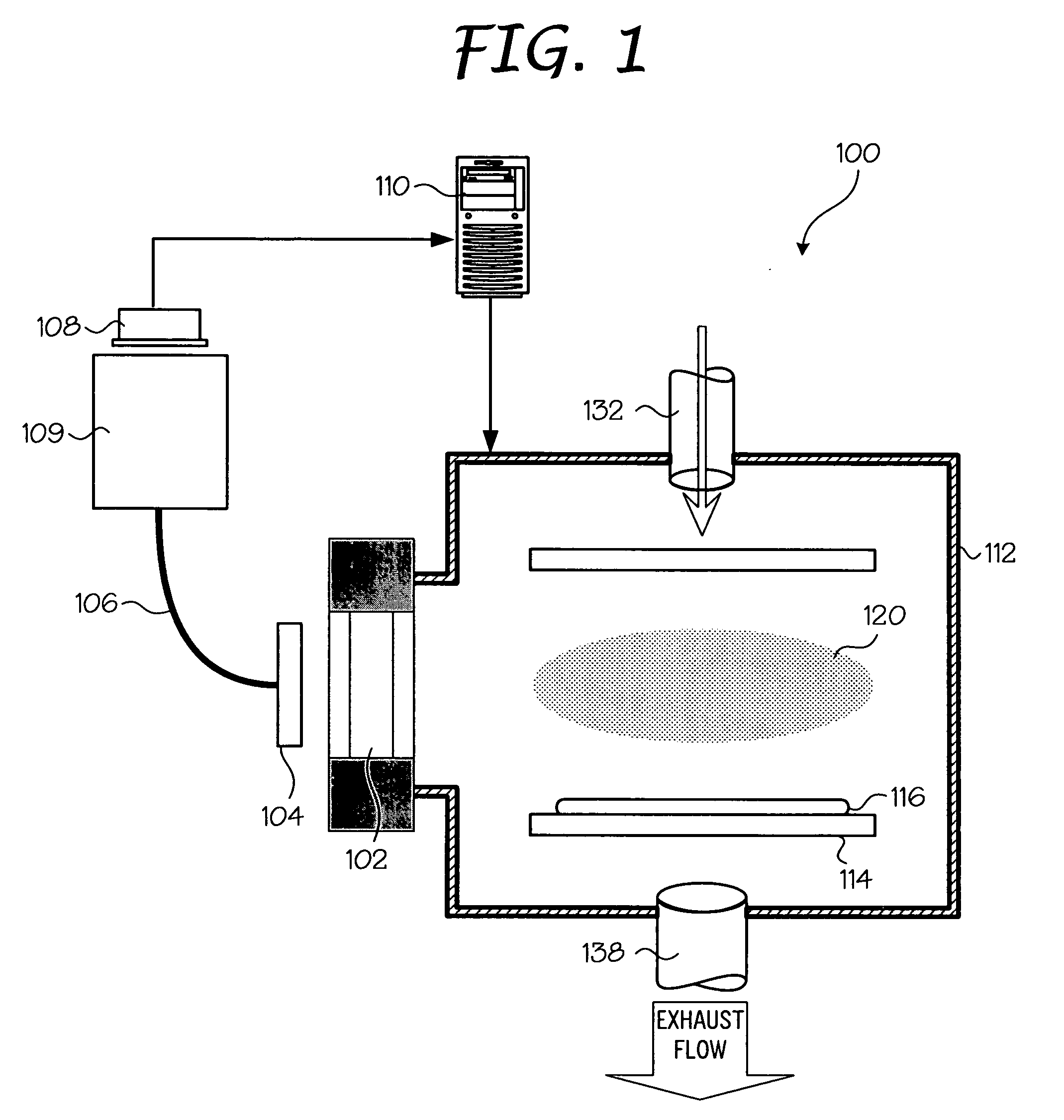
The present invention is directed to a gas line electron beam exciter, gas line electron beam excitation system and method for exciting a gas using an electron beam exciter. The electron beam exciter generally comprises a variable density electron source for generating a cloud of electrons in an electron chamber and a variable energy electron extractor for accelerating electrons from the electron chamber as an electron beam and into an effluent stream for fluorescing species in the effluent. The electron density of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting the excitation power applied to the variable density electron source. The electrons in the electron chamber reside at a reference electrical potential of the chamber, typically near ground electrical potential. The electron energy of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting an electrical potential across the variable energy electron extractor, which energizes the electrons through an extraction hole of the chamber and toward the extractor. The greater the difference in the electrical potential between the electron extractor and the electron source, the higher the energy imparted to the electrons in the electron beam. The excitation power applied to the electron source can be adjusted independently from the electron energy of the electron beam, thereby altering the electron density of the electron beam without changing the energy level of the electrons of the electron beam.
Owner:VERITY INSTR +1
Cylindrical electron beam generating/triggering device and method for generation of electrons
ActiveUS7122949B2Intensity controllableLong lastingDischarge tube electron gunsSolid cathode detailsDielectricElectron source
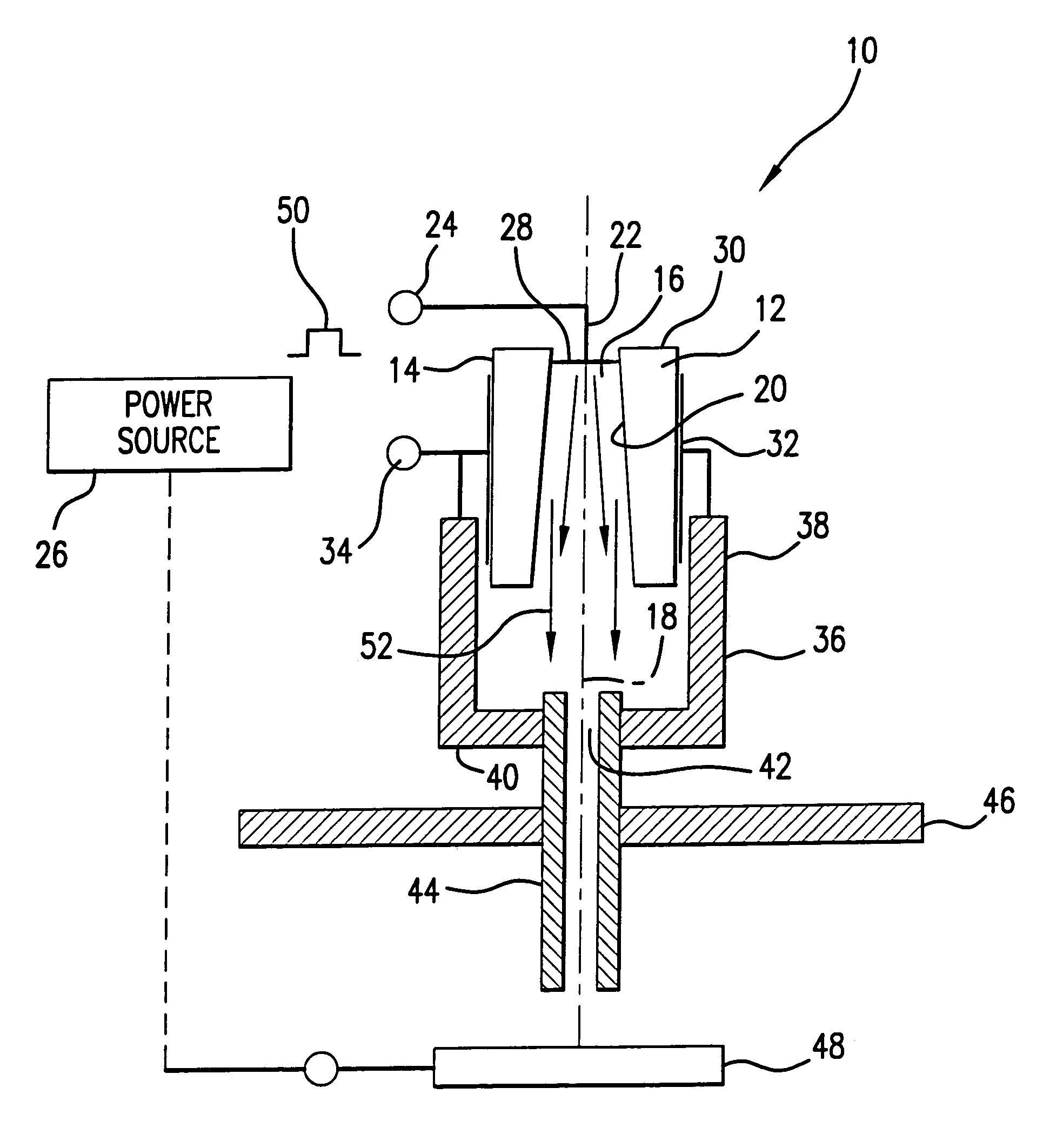
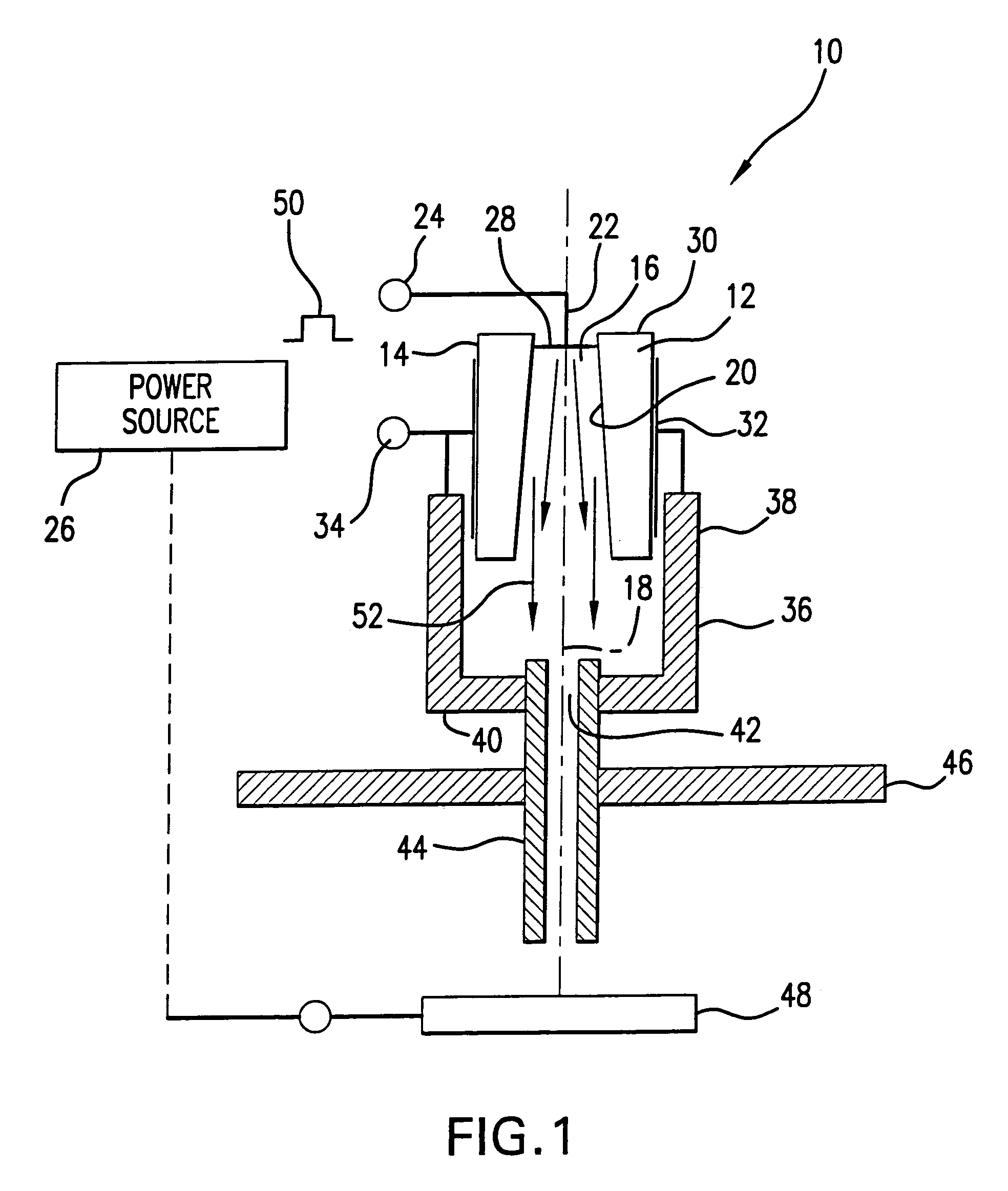
A surface discharge device performing functions of a trigger and electron beam generator includes a cylinder shaped member formed from a dielectric material with dielectric constant ε>100, in which a central opening is formed having a conical or cylindrical shape. An internal electrode is electrically coupled to the internal surface of the cylinder shaped member. An external electrode covers the external surface of the cylinder shaped member. A triggering pulse is applied between the external and internal electrodes to generate emission of electrons in the central opening and formation of the conducting plasma to ignite the device and serve as a source of electrons for generating an electron beam. The conducting plasma charges a capacitor formed by the cylinder shaped dielectric member and the external electrode. The cylinder shaped member is positioned in a hollow cathode having a central bore hole in the bottom. An anode is positioned remotely from the cathode and an electric field exists dynamically in space between the cathode and anode for at least a portion of the duration of the triggering pulse.
Owner:NEOCERA
Plasma processing apparatuses and methods
InactiveUS20060260750A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaElectron source
A plasma processing apparatus and method includes a processing chamber having a substrate support and at least two separate and independently controlled devices selected from the following three devices: a first plasma generator, a second plasma generator, and an electron source. The first plasma generator directs plasma-generated cations toward the substrate support. The second plasma generator directs plasma-generated reactive neutral species toward the substrate support. The electron source directs electrons toward the substrate support. The first chamber may be separated from the substrate by an ion filter and the method may include directing predominately cations, rather than electrons, through the filter to the substrate. Along with the step of generating a remote plasma, the method may also includes directing predominately reactive neutral species, rather than ions and electrons, to the substrate. The apparatus or method may reduce structural charging on the substrate.
Owner:RUEGER NEAL R
Nitride heterojunction transistors having charge-transfer induced energy barriers and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050173728A1Affect performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionElectron source
A nitride-based field effect transistor includes a substrate, a channel layer comprising InAlGaN formed on the substrate, source and drain ohmic contacts in electrical communication with the channel layer, and a gate contact formed on the channel layer. At least one energy barrier opposes movement of carriers away from the channel layer. The energy barrier may comprise an electron source layer in proximity with a hole source layer which generate an associated electric field directed away from the channel. An energy barrier according to some embodiments may provide a built-in potential barrier in excess of about 0.5 eV. Method embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CREE INC
Method and apparatus for generating electron beams
InactiveUS20130300286A1Quick controlEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrode and associated part arrangementsPlasma electronElectron source
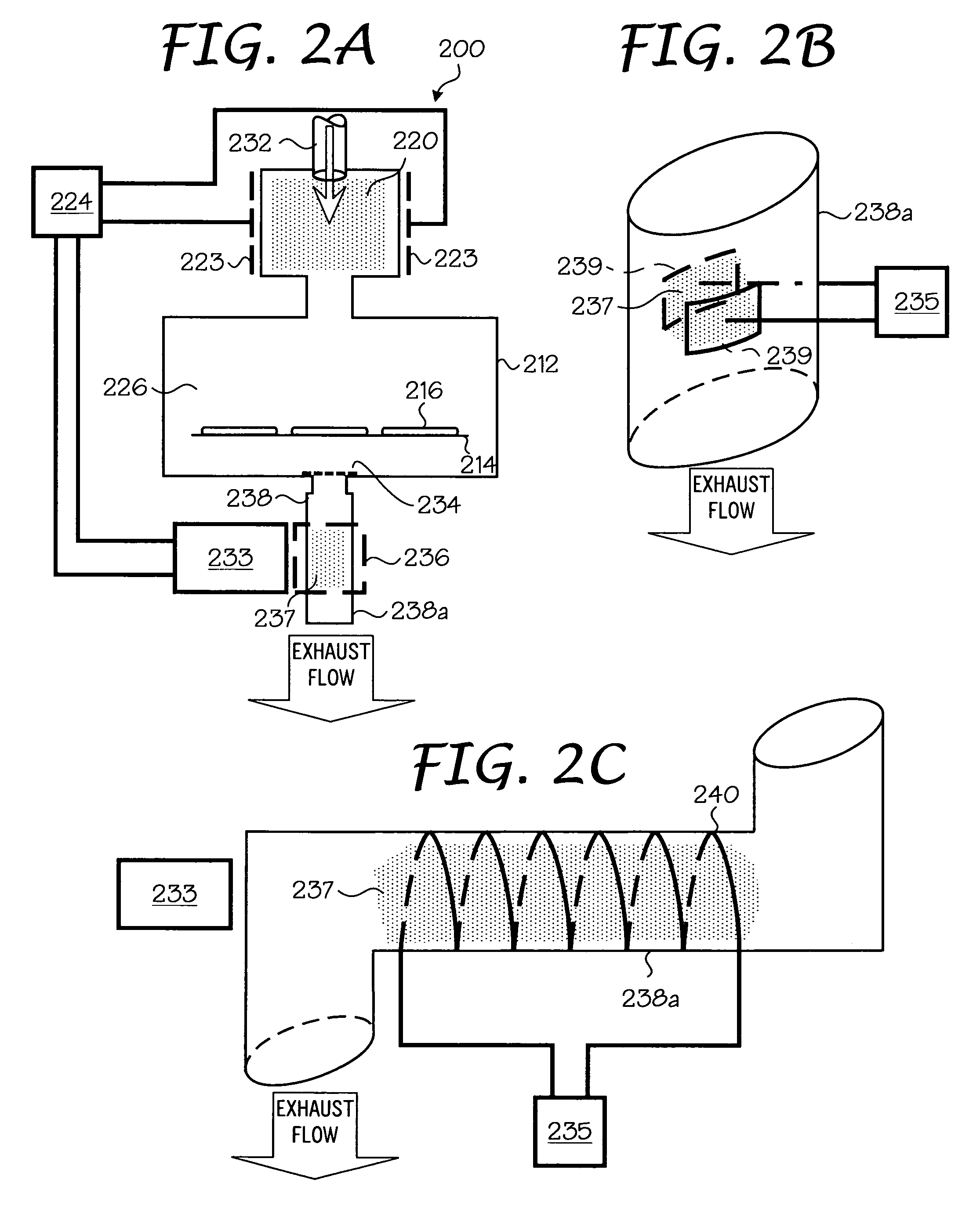
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to a plasma electron source apparatus. The apparatus comprises a cathode discharge chamber in which a plasma is generated, an exit hole provided in said cathode discharge chamber from which electrons from the plasma are extracted by an accelerating field provided between said cathode discharge chamber and an anode, at least one plasma confinement device, and a switching mechanism for switching the at least one plasma confinement device between a first value allowing for electron extraction from the plasma and a second value prohibiting electron extraction from the plasma. Associated methods are also provided.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Large-area individually addressable multi-beam x-ray system and method of forming same
A structure to generate x-rays has a plurality of stationary and individually electrically addressable field emissive electron sources with a substrate composed of a field emissive material, such as carbon nanotubes. Electrically switching the field emissive electron sources at a predetermined frequency field emits electrons in a programmable sequence toward an incidence point on a target. The generated x-rays correspond in frequency and in position to that of the field emissive electron source. The large-area target and array or matrix of emitters can image objects from different positions and / or angles without moving the object or the structure and can produce a three dimensional image. The x-ray system is suitable for a variety of applications including industrial inspection / quality control, analytical instrumentation, security systems such as airport security inspection systems, and medical imaging, such as computed tomography.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Multi-beam multi-column electron beam inspection system
InactiveUS6844550B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSystems designData stream
A multi-column electron beam inspection system is disclosed herein. The system is designed for electron beam inspection of semiconductor wafers with throughput high enough for in-line use. The system includes field emission electron sources, electrostatic electron optical columns, a wafer stage with six degrees of freedom of movement, and image storage and processing systems capable of handling multiple simultaneous image data streams. Each electron optical column is enhanced with an electron gun with redundant field emission sources, a voltage contrast plate to allow voltage contrast imaging of wafers, and an electron optical design for high efficiency secondary electron collection.
Owner:MULTIBEAM CORP
Field emitter based electron source with minimized beam emittance growth
InactiveUS7801277B2Low voltage extractionMinimal emittance growthCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingElectrode and associated part arrangementsEmissivityElectron source
A system and method for limiting emittance growth in an electron beam is disclosed. The system includes an emitter element configured to generate an electron beam and an extraction electrode positioned adjacent to the emitter element to extract the electron beam out therefrom, the extraction electrode including an opening therethrough. The system also includes a meshed grid disposed in the opening of the extraction electrode to enhance intensity and uniformity of an electric field at a surface of the emitter element and an emittance compensation electrode (ECE) positioned adjacent to the meshed grid on the side of the meshed grid opposite that of the emitter element and configured to control emittance growth of the electron beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nitride heterojunction transistors having charge-transfer induced energy barriers and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7170111B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionElectron source
A nitride-based field effect transistor includes a substrate, a channel layer comprising InAlGaN formed on the substrate, source and drain ohmic contacts in electrical communication with the channel layer, and a gate contact formed on the channel layer. At least one energy barrier opposes movement of carriers away from the channel layer. The energy barrier may comprise an electron source layer in proximity with a hole source layer which generate an associated electric field directed away from the channel. An energy barrier according to some embodiments may provide a built-in potential barrier in excess of about 0.5 eV. Method embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
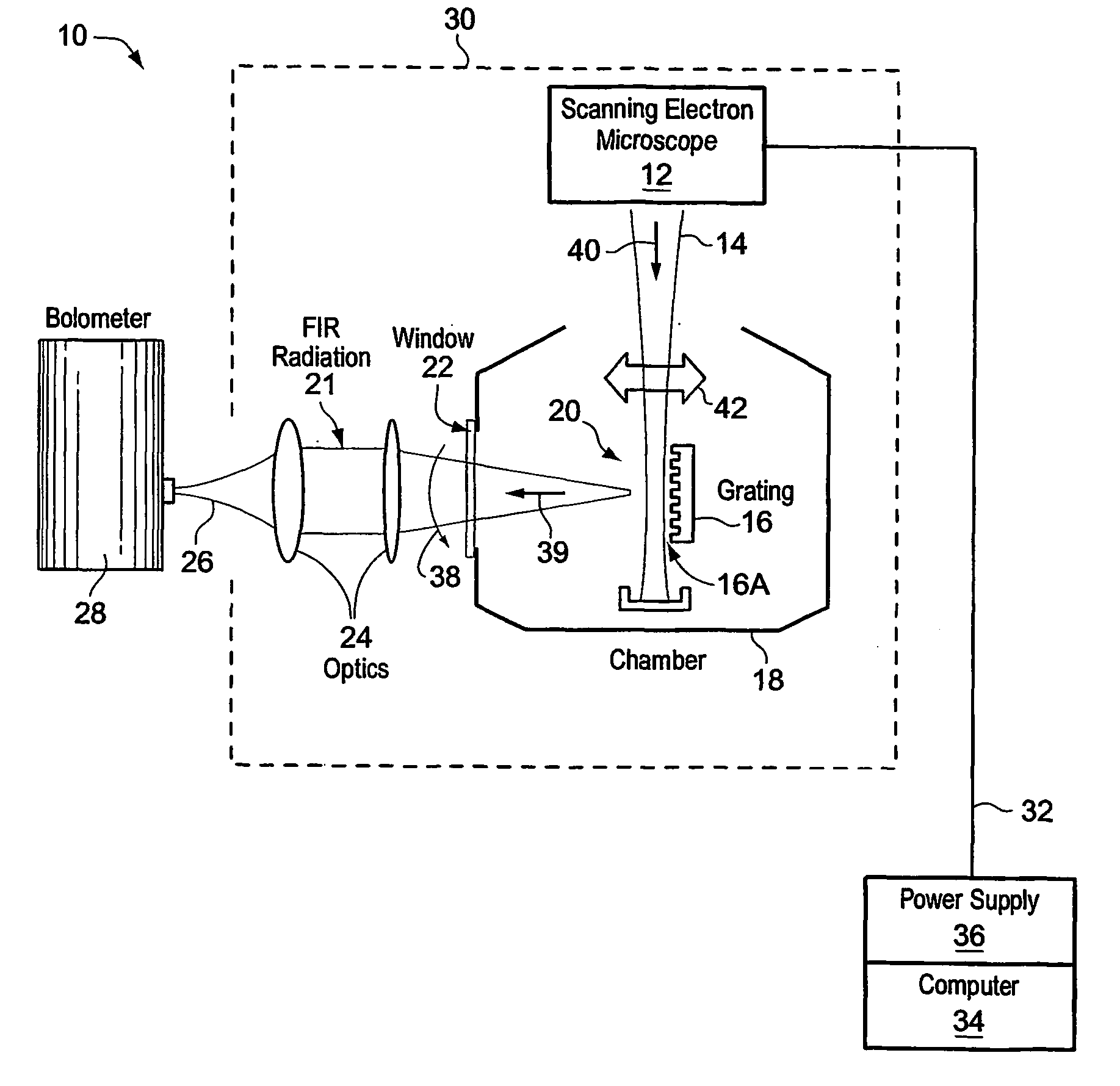
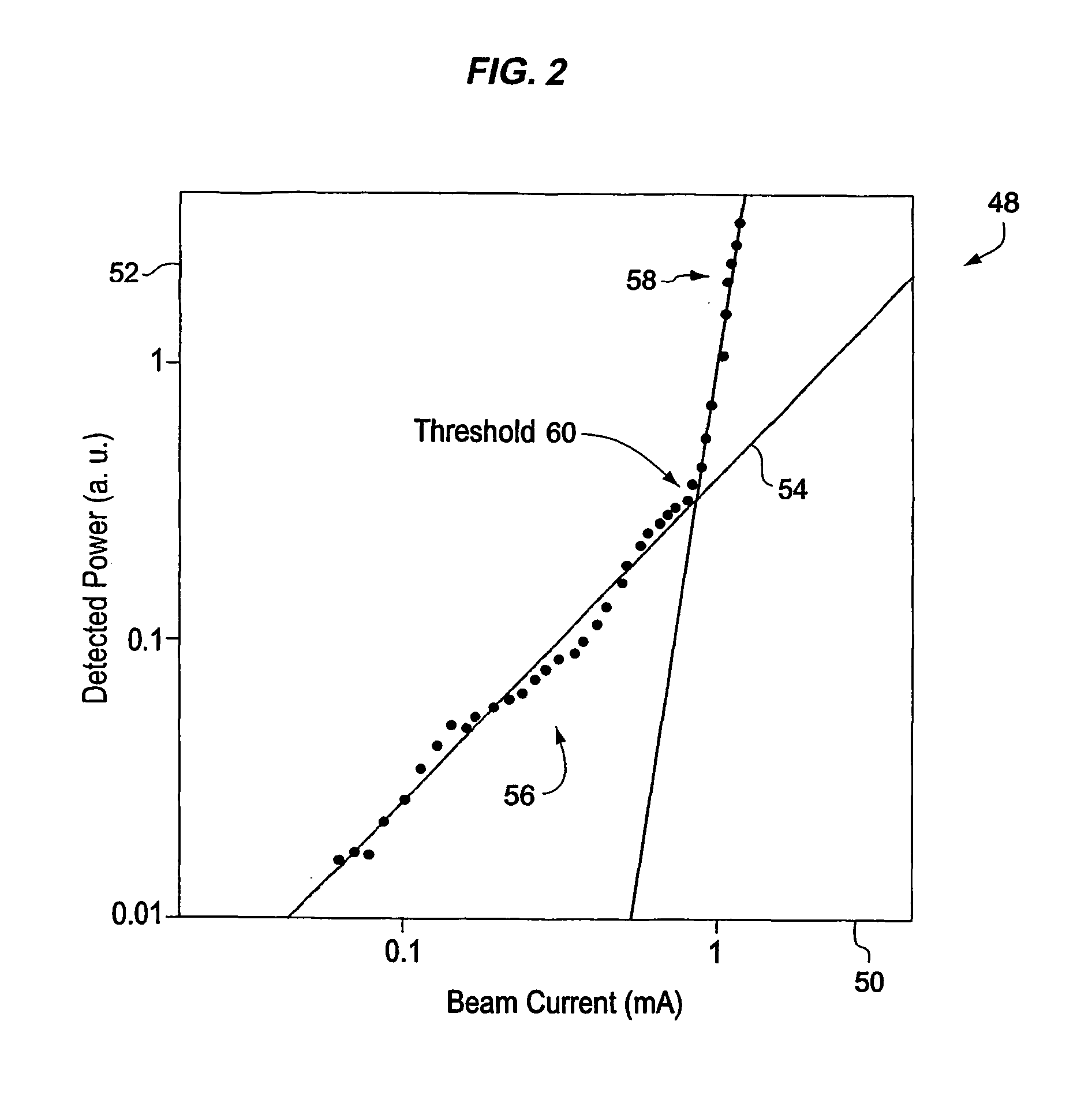
Scanning electron microscope
ActiveUS20060060782A1Improve transport efficiencyImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAngle of incidenceElectron source
In a scanning electron microscope, an emitted primary electron beam is diverted by an angle of at least about 45 degrees prior to incidence with a specimen. The beam may be bent by a magnetic separator. The separator may also serve to deflect secondary electron and back scattered electrons. As the angle of emissions and reflections from the specimen is close to the angle of incidence, bending the primary electron beam prior to incidence, allows the electron source to be located so as not to obstruct the travel of emissions and reflections to suitable detectors.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Focusable and steerable micro-miniature x-ray apparatus
ActiveUS20050105690A1Inexpensive to fabricateUse disposableX-ray tube windowsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayEngineering
A micro-miniature x-ray apparatus comprises: a first chip subassembly including a source of x-rays including both Bremsstrahlung photons and characteristic x-rays; a second chip subassembly including a filter for transmitting the characteristic x-rays and blocking the Bremsstrahlung photons; a third chip subassembly including a movable element for focusing or collimating the transmitted characteristic x-rays into a beam and means for controlling the position of the focusing element. In one embodiment, the controlling means include a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS). In another embodiment, the position of the movable element determines how the x-ray beam is steered to the focal area. In still another embodiment, the x-ray source includes a field emitter electron source and a target responsive to the electrons for generating x-rays. In this case, the x-ray beam is also steered by selectively energizing the anode segments. In yet another embodiment, the movable element includes a Fresnel zone plate; in still another embodiment it includes an array of poly-capillaries. Advantageously, our x-ray source, including its focusing, collimating and steering components, can be fabricated small enough to be mounted at the end of a catheter. In addition, in some embodiments it can also fabricated sufficiently inexpensively to be disposable after each use.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Non-dispersive charged particle energy analyzer
InactiveUS20050045832A1Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersElectron sourceEnergy analyser
An electron energy analyzer including a curved electrostatic low-pass reflector and a high-pass electrostatic transmissive filter. The reflector comprises a curved grid, preferably ellipsoidal, and an absorber electrode placed in back of the curved grid with respect to the electron source and biased negatively to the curved grid to act as a reflective low-pass filter and a collimating optics for the reflected beam. The transmissive filter includes first and second flat grids extending across the collimated reflected beam. The second grid on the side of the first grid opposite the curved grid is biased negatively to the first grid and the absorber electrode. A field free region is created by applying the same bias to the curved grid, the first grid, and chamber sidewall sleeve. An electron detector detects all electrons passed by the second grid in an energy band in the overlap of the high-pass and low-pass bands.
Owner:BRYSON III CHARLES E
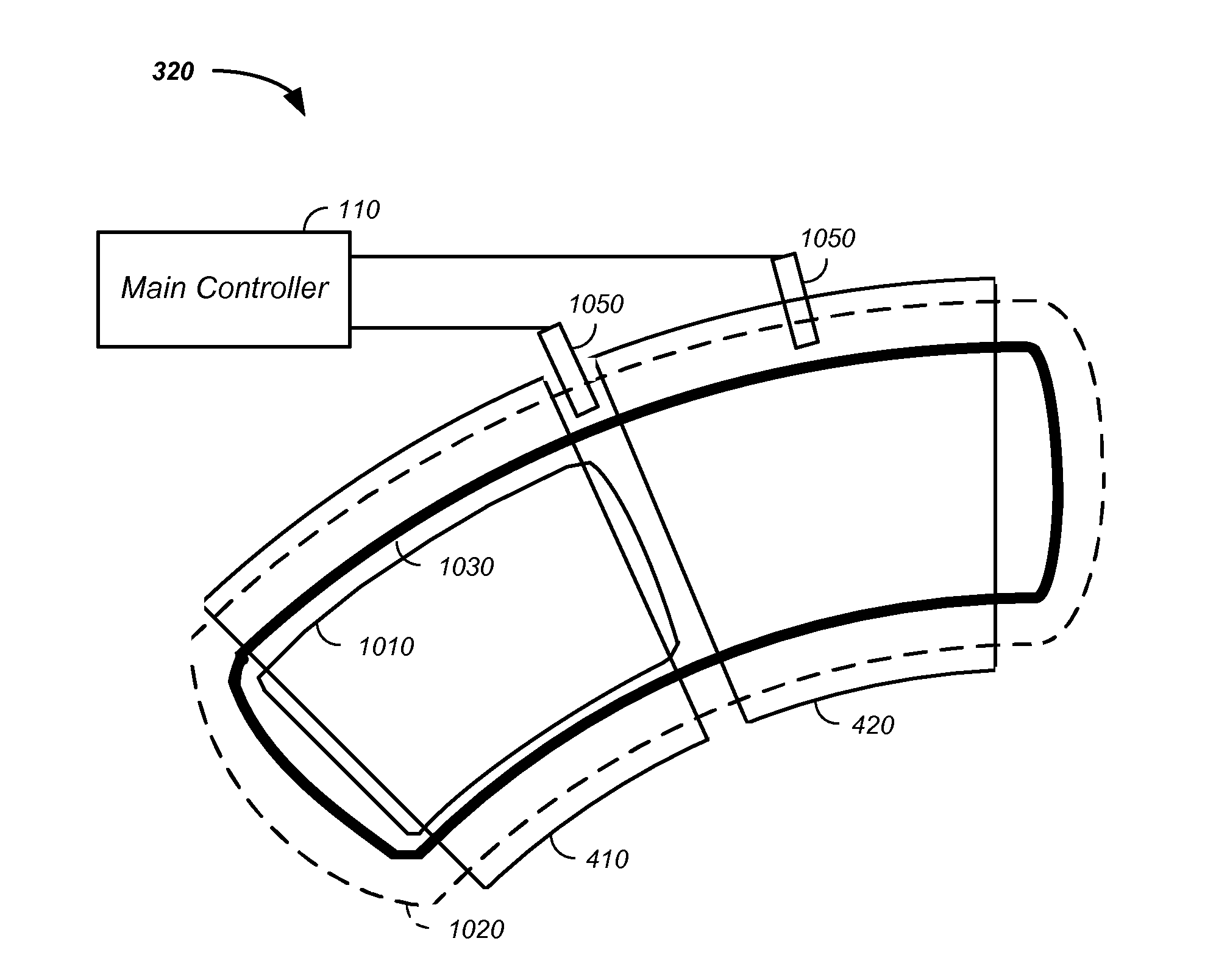
X-ray tomography method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS20120209109A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectron sourceX-ray
The invention comprises an X-ray tomography method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. In various embodiments, 3-D images are generated from a series of 2-D X-rays images; the X-ray source and detector are stationary while the patient rotates; the 2-D X-ray images are generated using an X-ray source proximate a charged particle beam in a charged particle cancer therapy system; and the X-ray tomography system uses an electron source having a geometry that enhances an electron source lifetime, where the electron source is used in generation of X-rays. The X-ray tomography system is optionally used in conjunction with systems used to both move and constrain movement of the patient, such as semi-vertical, sitting, or laying positioning systems. The X-ray images are optionally used in control of a charged particle cancer therapy system.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
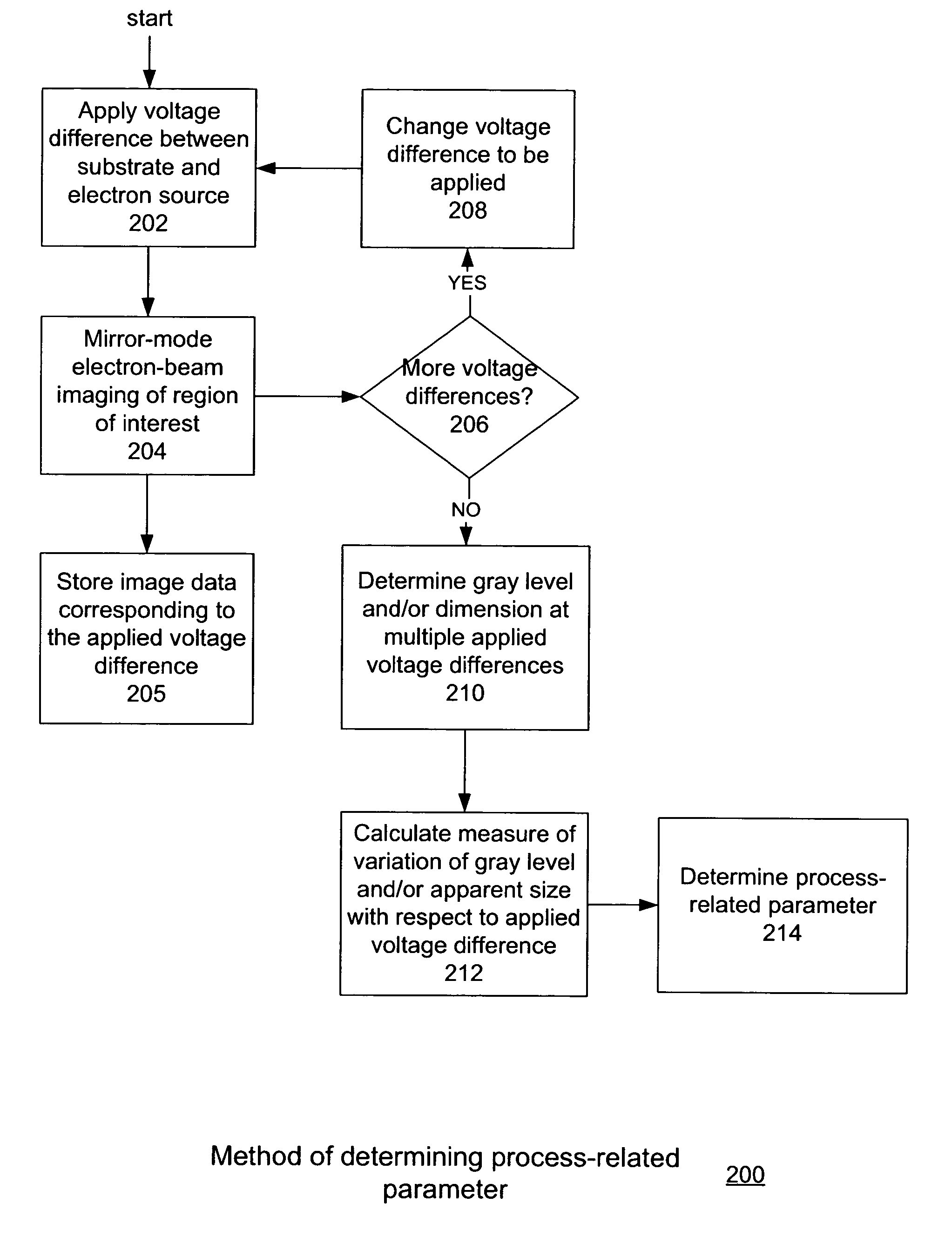
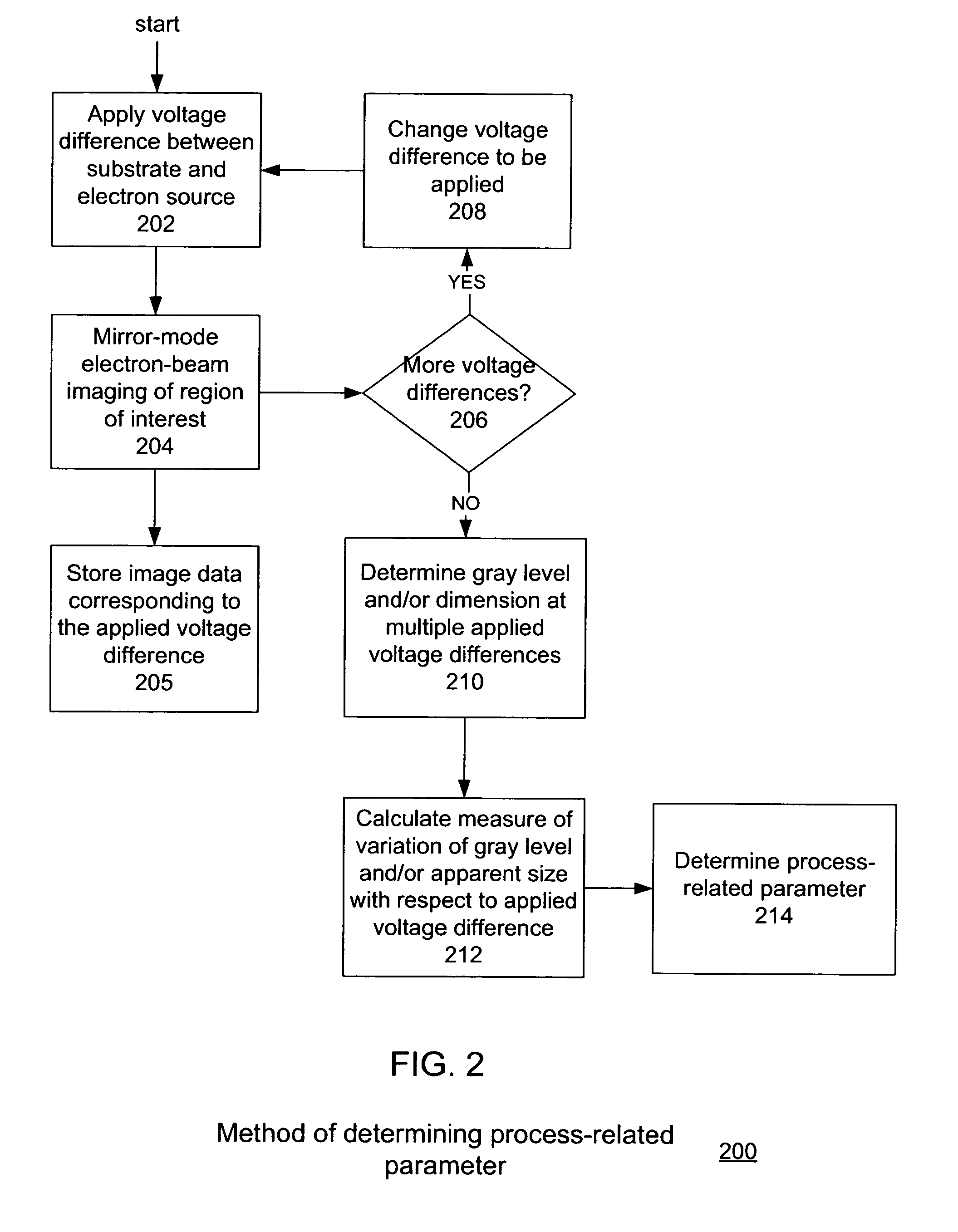
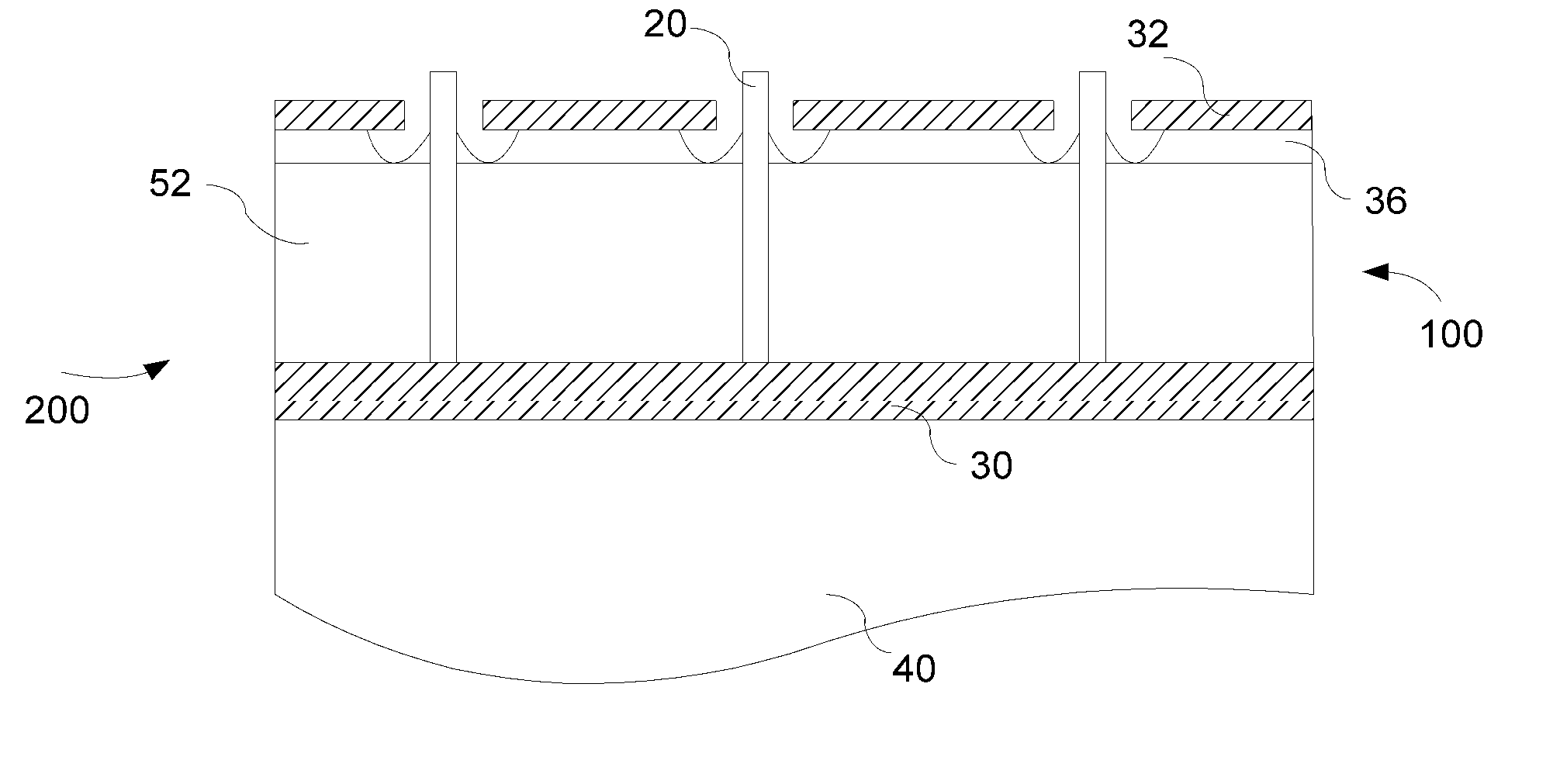
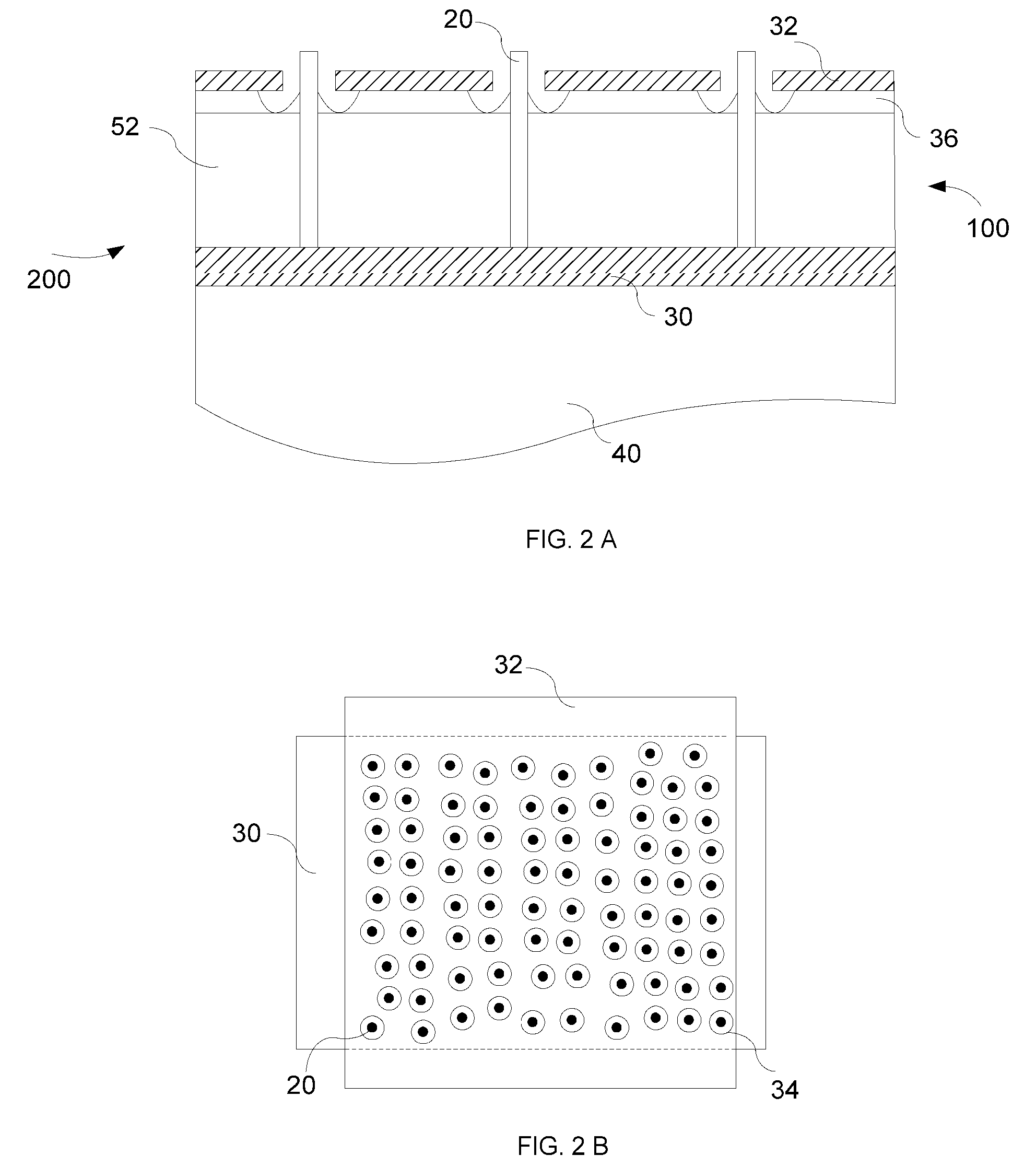
Electrical process monitoring using mirror-mode electron microscopy
ActiveUS7514681B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceImaging data
One embodiment relates to a method of inspecting a substrate using electrons. Mirror-mode electron-beam imaging is performed on a region of the substrate at multiple voltage differences between an electron source and a substrate, and image data is stored corresponding to the multiple voltage differences. A calculation is made of a measure of variation of an imaged aspect of a feature in the region with respect to the voltage difference between the electron source and the substrate. Other embodiments and features are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Low voltage electron source with self aligned gate apertures, fabrication method thereof, and luminous display using the electron source
InactiveUS20050127351A1Narrow diameterHigh densityNanoinformaticsThermionic cathodesHigh current densityHigh energy
An electron source include a first cathode electrode disposed over a substrate and terminated to provide electrons; an emitter layer disposed over the cathode electrode and formed from one or plurality vertically aligned and mono-dispersed nano-structures that are truncated to the same length, embedded in a solid matrix and protruding above the surface for emitting electrons; an insulator disposed over the emitter layer and having one or plurality of apertures, each is self-aligned with and exposes one nano-structure in the emitter layer; and a second gate electrode disposed over the insulator, having one or plurality of apertures self-aligned with the apertures in the insulator and terminated to extract electrons from the exposed nano-structures through the apertures. The gate aperture is substantially less than one micrometer and the gated nano-structures can have a density on the order of 108 / cm2. Such an electron source can be modulated with an extra low voltage, emits electrons with high current density and high uniformity, and operates with high energy-efficiency and long lifetime.
Owner:TOLT ZHIDAN LI
Ionizer and method for gas-cluster ion-beam formation
ActiveUS7173252B2Improve efficiencyImprove throughputParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPlasma electronElectron source
An ionizer for forming a gas-cluster ion beam is disclosed including inlet and outlet ends partially defining an ionization region traversed by a gas-cluster jet and one or more plasma electron source(s) for providing electrons to the ionizing region for ionizing at least a portion of the gas-clusters to form a gas-cluster ion beam. One or more sets of substantially linear rod electrodes may be disposed substantially parallel to and in one or more corresponding partial, substantially cylindrical pattern(s) about the gas-cluster jet axis, wherein some sets are arranged in substantially concentric patterns with differing radii. In certain embodiments, the ionizer includes one or more substantially linear thermionic filaments disposed substantially parallel to the gas-cluster jet axis, heating means, electrical biasing means to judiciously bias sets of the linear rod electrodes with respect to the thermionic filaments to achieve electron repulsion.
Owner:TEL EPION
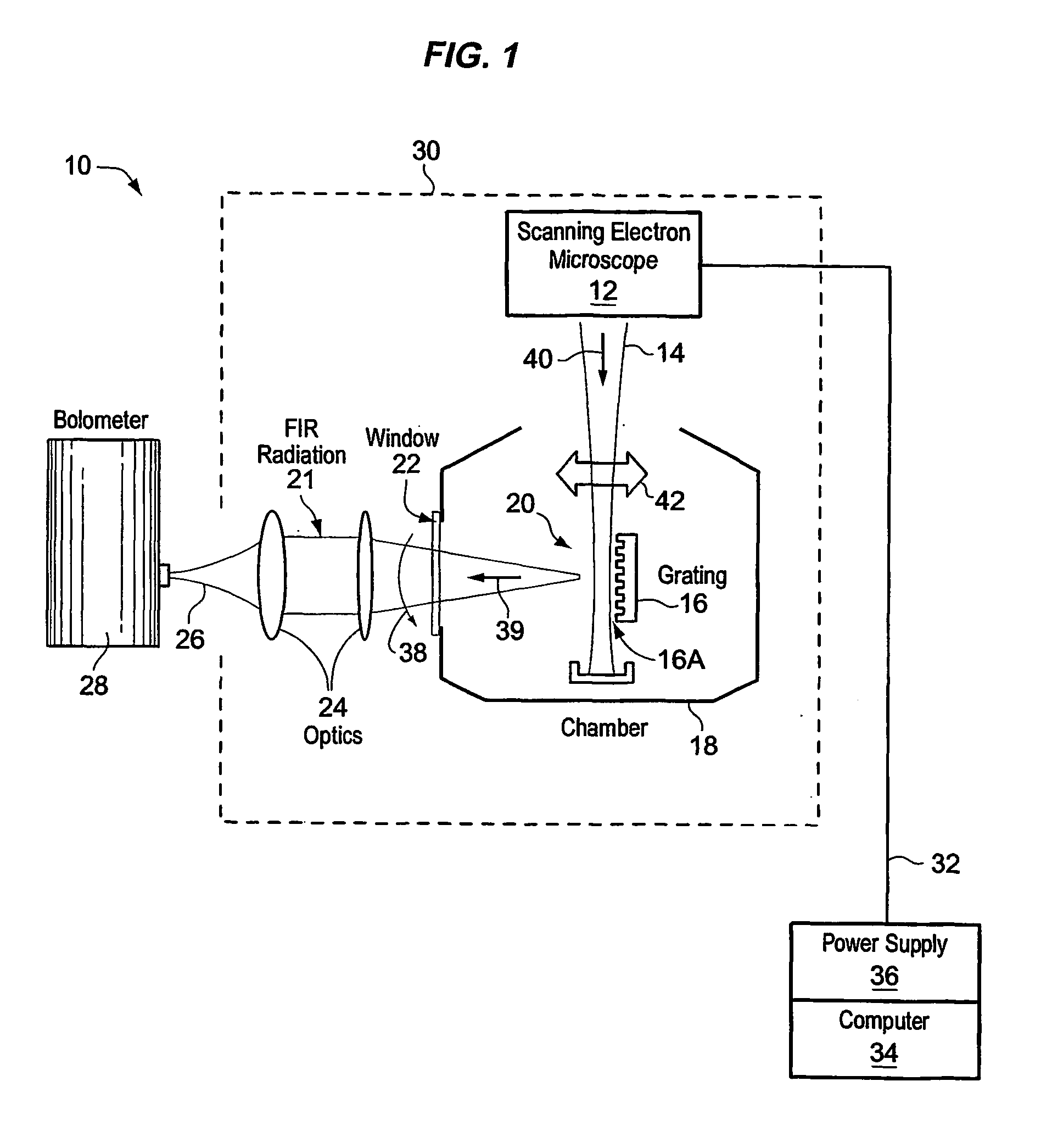
Free electron laser, and associated components and methods
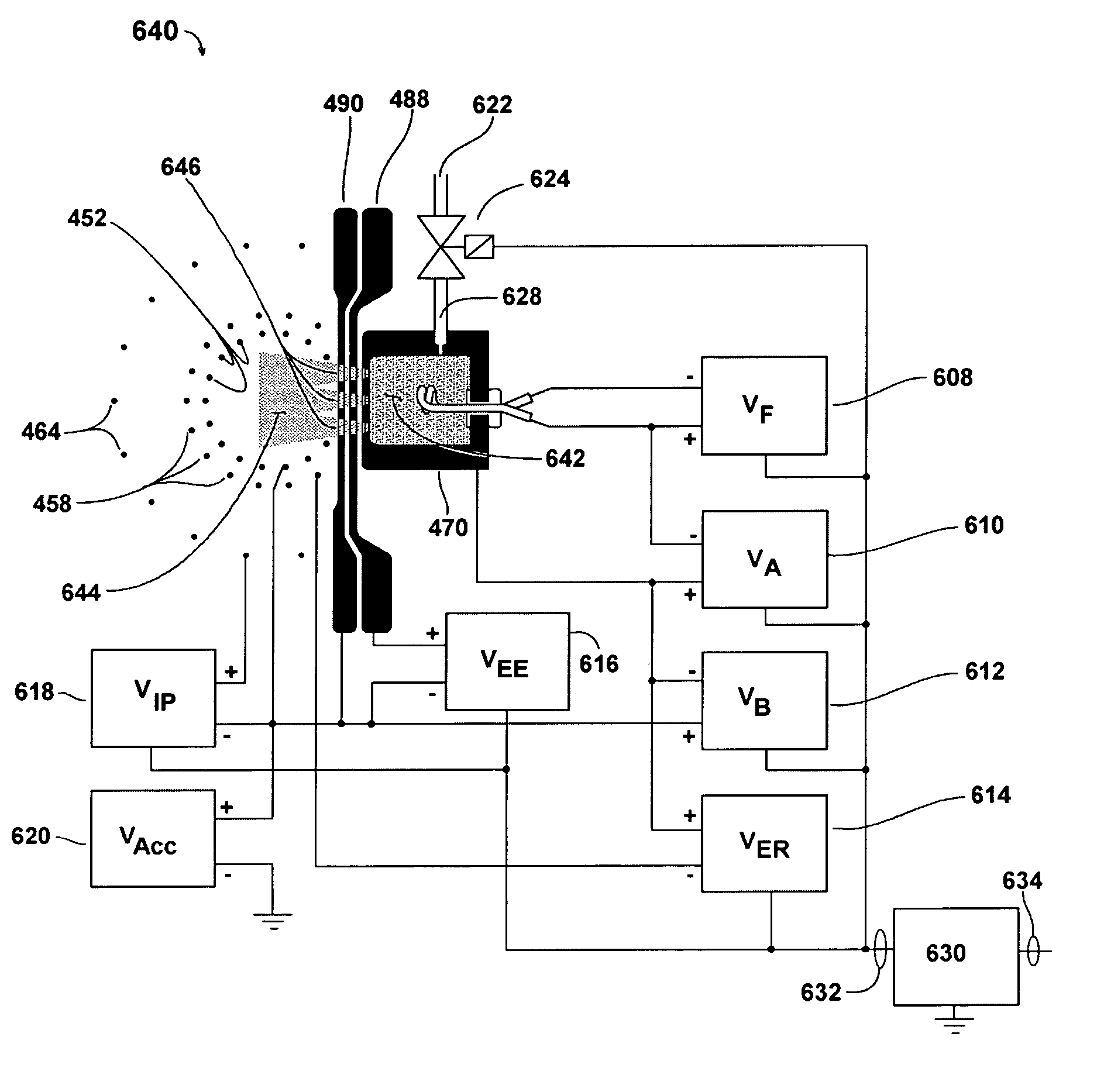
A system generates FIR laser radiation. An electron source generates an electron beam. A grating horn interacts with the electron beam to produce the FIR laser radiation. The grating horn may comprise a flat base and a pair of grating elements attached to the base, each of the grating elements being ruled with a grating period, the grating elements oriented in phase and in substantial symmetry about a normal to the flat base.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
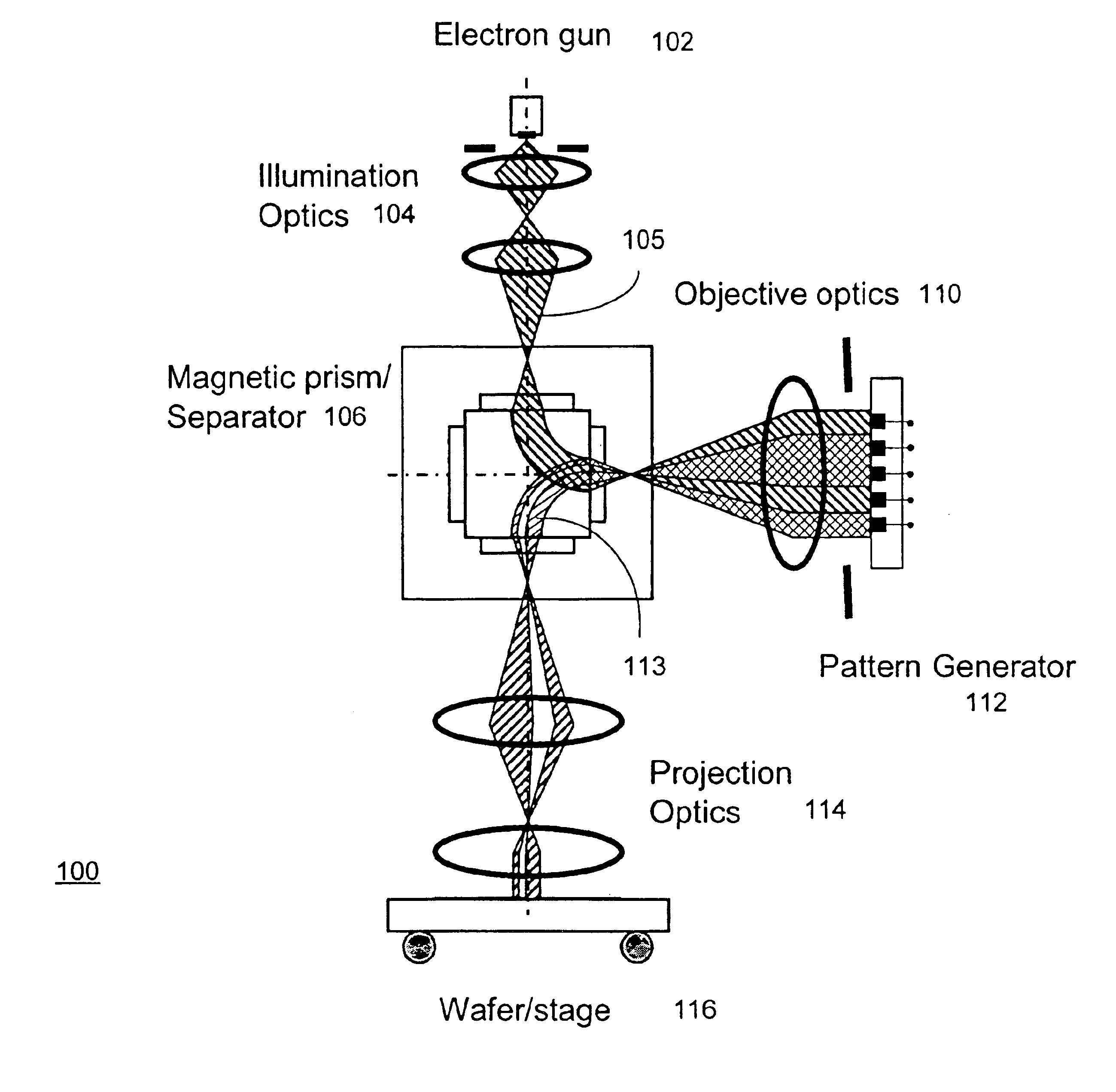
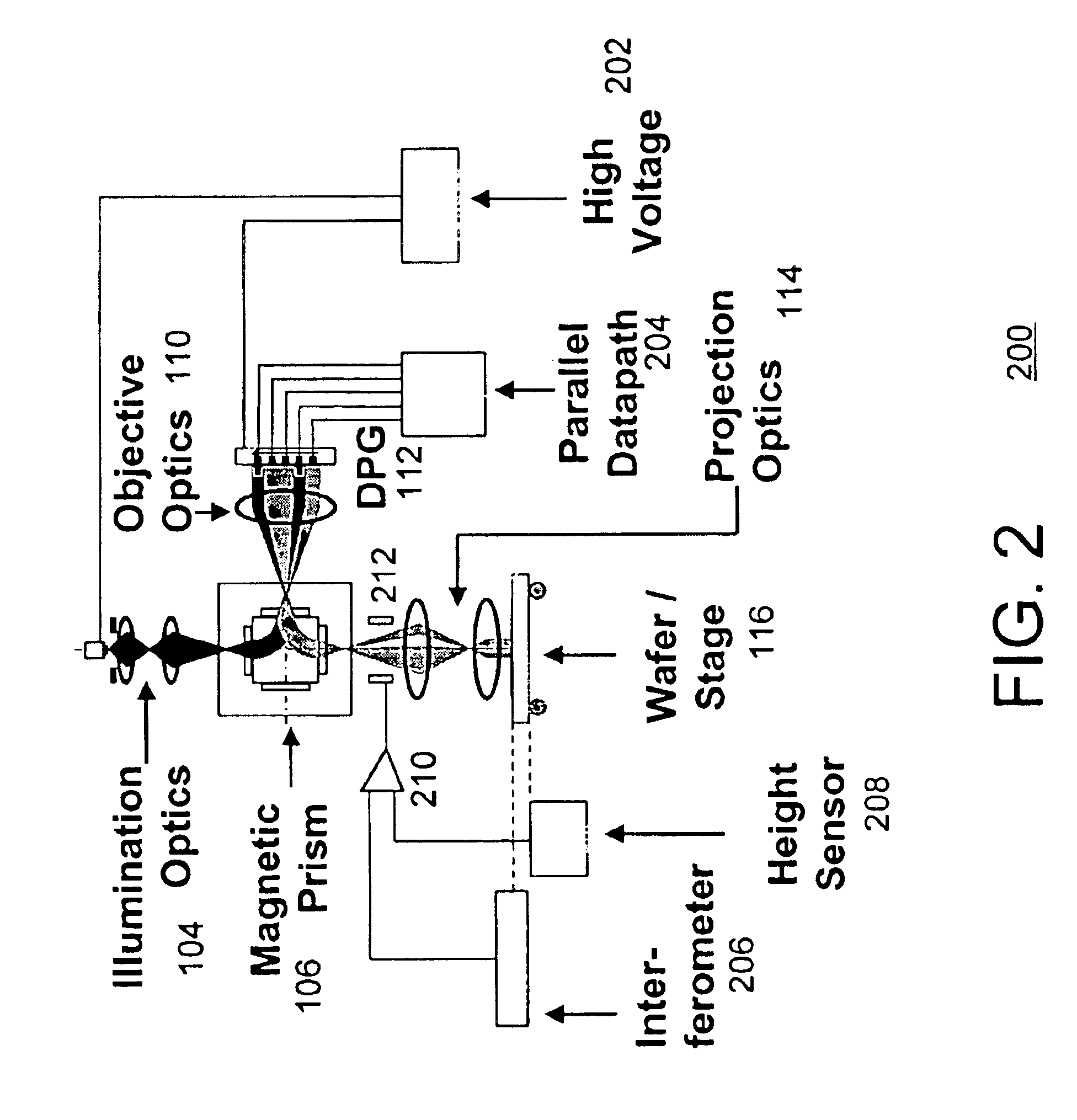
Maskless reflection electron beam projection lithography
One embodiment disclosed relates to an apparatus for reflection electron beam lithography. An electron source is configured to emit electrons. The electrons are reflected to a target substrate by portions of an electron-opaque patterned structure having a lower voltage level and are absorbed by portions of the structure having a higher voltage level. Another embodiment relates to a novel method of electron beam lithography. An incident electron beam is formed and directed to an opaque patterned structure. Electrons are reflected from portions of the structure having a lower voltage level applied thereto and are absorbed by portions of the structure having a higher voltage level applied thereto. The reflected electrons are directed towards a target substrate to form an image and expose a lithographic pattern.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus of Plural Charged-Particle Beams
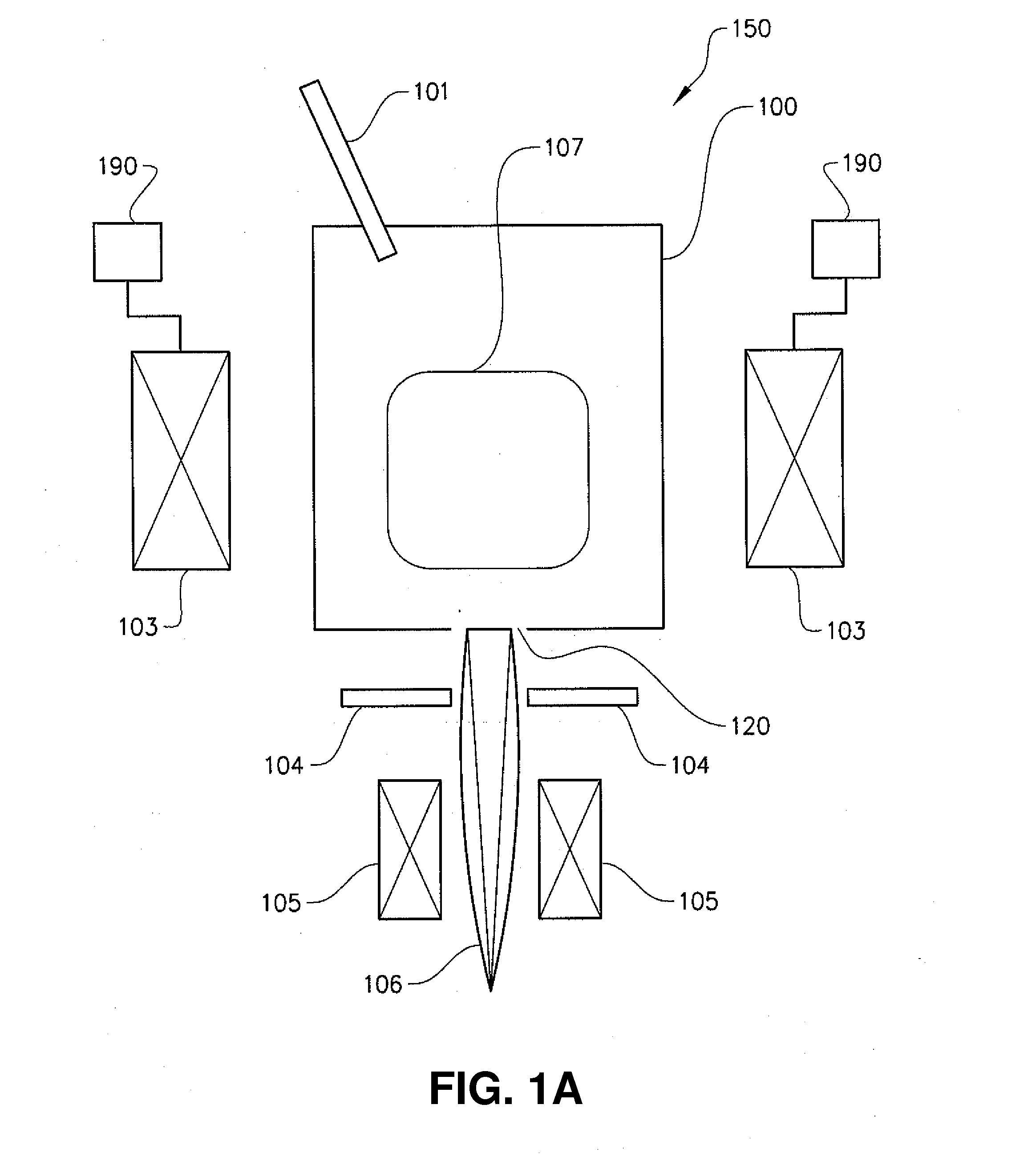
ActiveUS20170025241A1High resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSingle electronElectron source
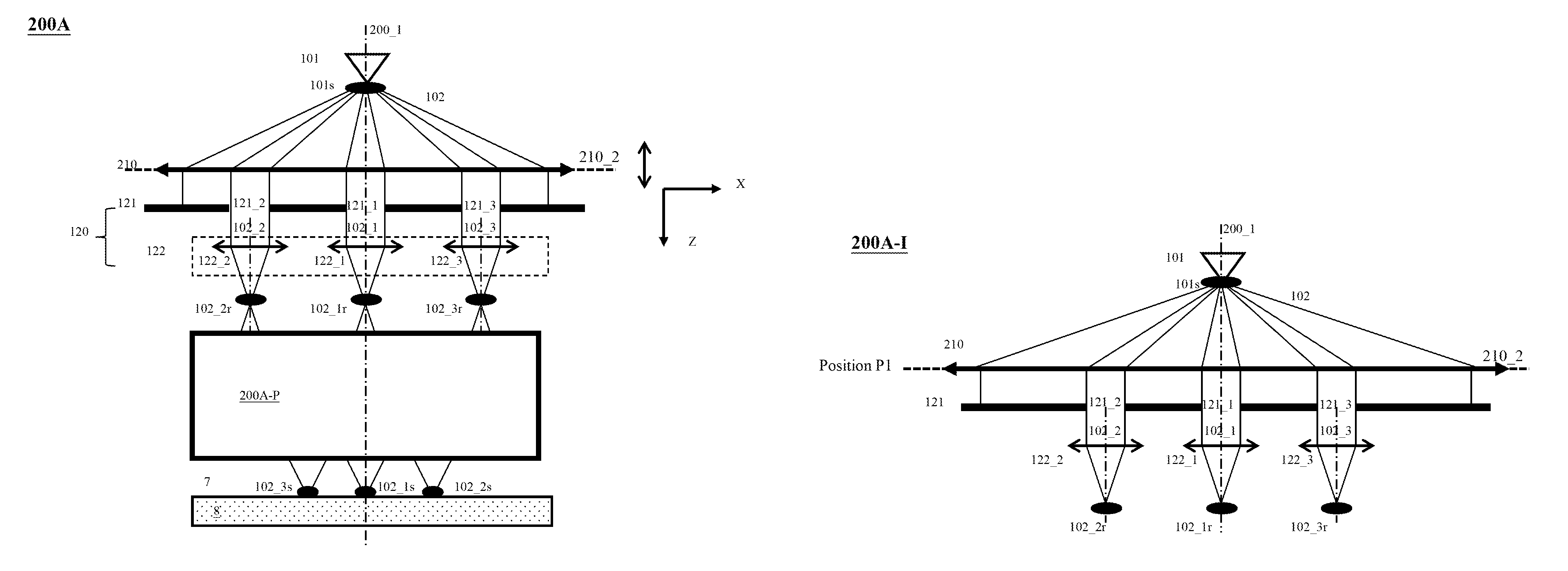
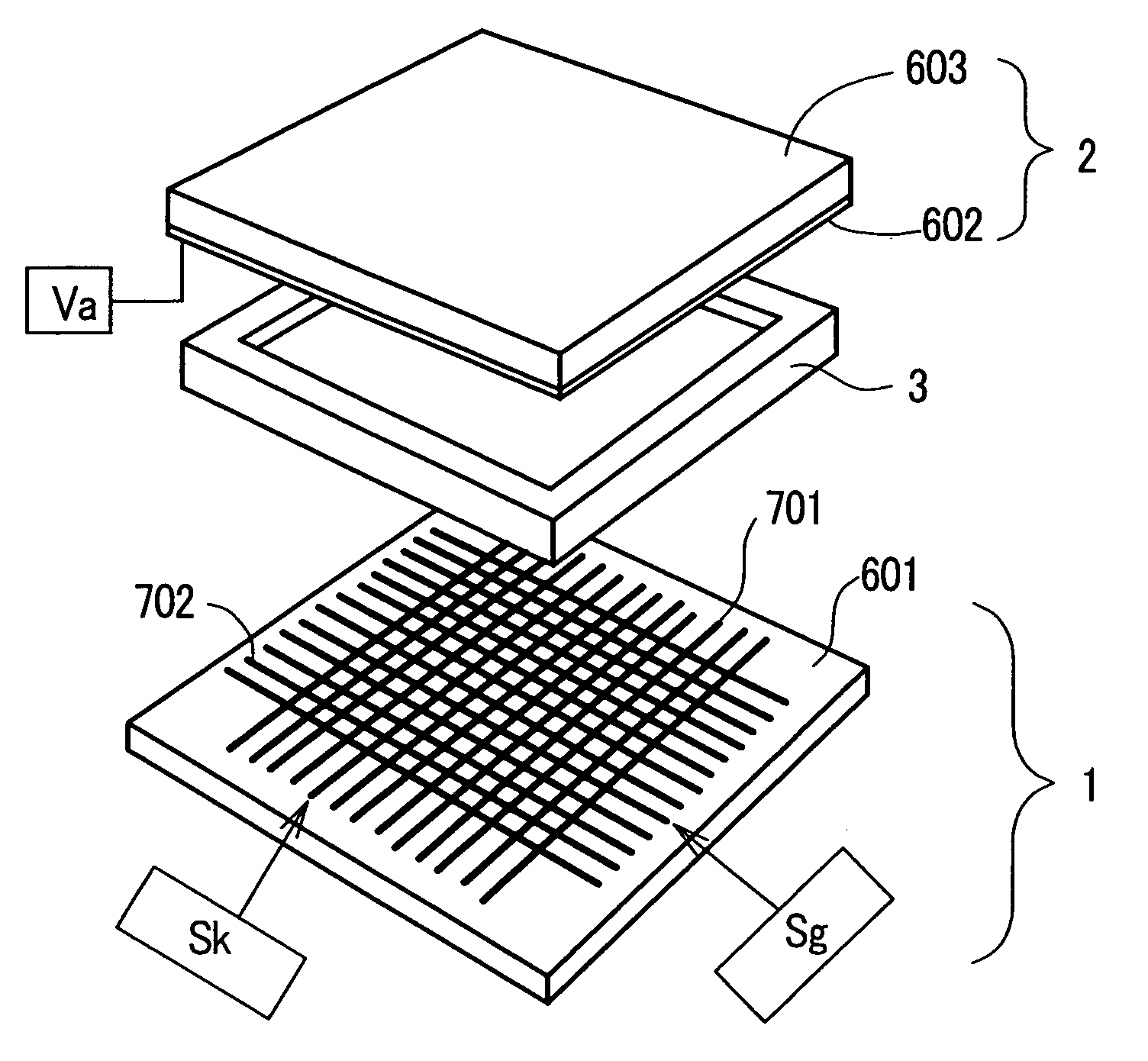
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with high resolution and high throughput and in flexibly varying observing conditions is proposed. The apparatus uses a movable collimating lens to flexibly vary the currents of the plural probe spots without influencing the intervals thereof, a new source-conversion unit to form the plural images of the single electron source and compensate off-axis aberrations of the plural probe spots with respect to observing conditions, and a pre-beamlet-forming means to reduce the strong Coulomb effect due to the primary-electron beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Image formation apparatus
InactiveUS6879096B1High display-quality configurationSatisfies requirementTelevision system detailsCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionEquipotential surfaceElectron source
An image formation apparatus is disclosed which includes, within an enclosure configured by a pair of substrates placed face to face and an external frame placed between the substrates, an electron source placed on one of the pair of substrates, an image formation material placed on the other substrate, and spacers placed between the substrates, characterized in that the spacers and the external frame is conductive and device is provided for electrically connecting the spacers and the external frame so that the equipotential surfaces between the spacers and the external frame are quasi-parallel when driven.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus
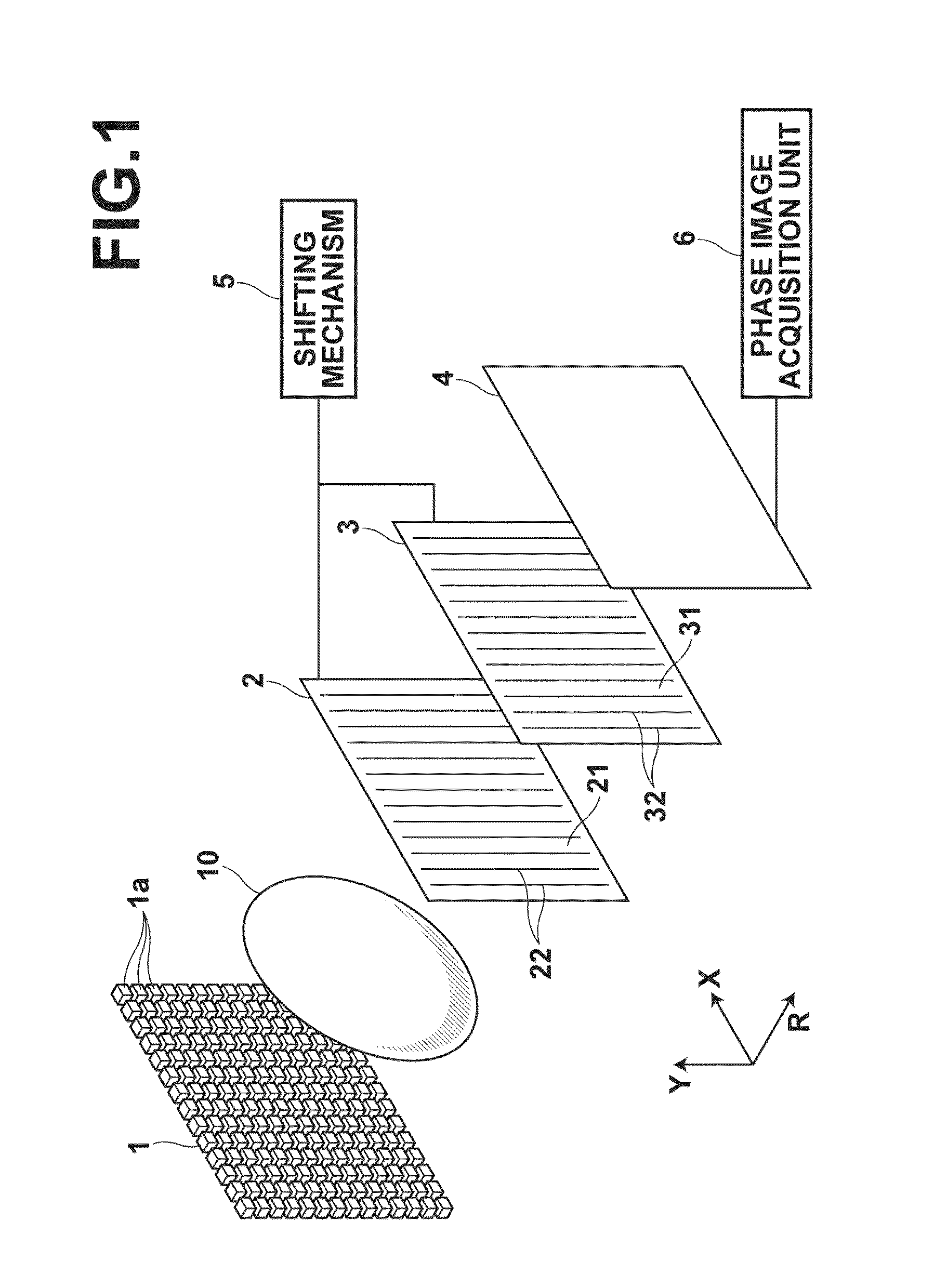
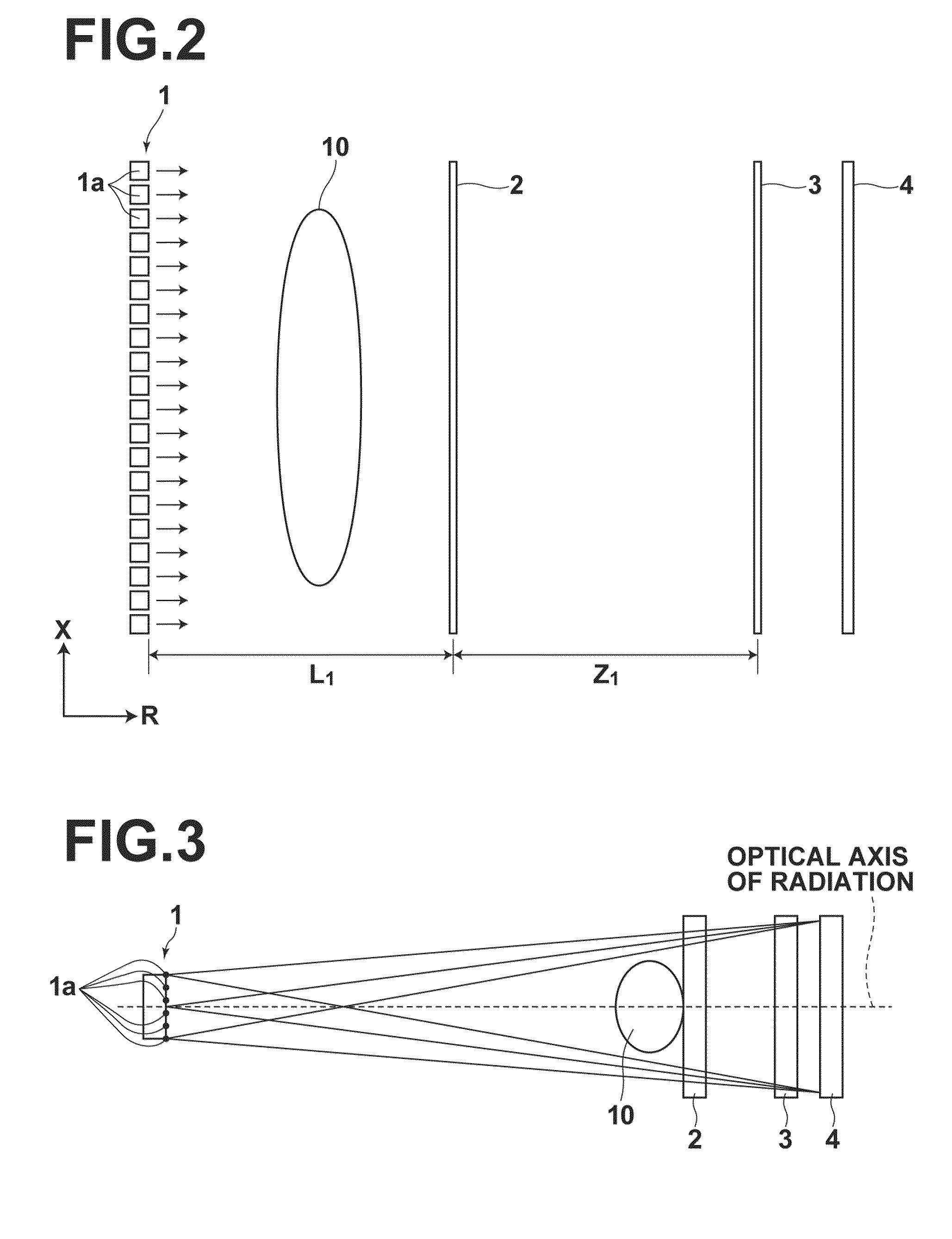
InactiveUS20100246765A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedLow costRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGratingElectron source
A radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus, including a radiation emission unit having a plurality of electron sources for emitting electron beams, and a target for emitting radiation through collision of electron beam emitted from each electron source, a first grating in which grating structures for diffracting radiation are disposed periodically, a second grating in which grating structures for transmitting and shielding radiation are disposed periodically, and a radiation image detector for detecting radiation transmitted through the second grating, in which the first and second gratings are disposed in an optical axis direction of the radiation so as to be able to substantially superimpose each image of the first grating formed based on radiation corresponding to each electron source on a surface of the second grating, and the radiation corresponding to each electron source forms each phase image of the same subject on the radiation image detector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electron-beam generating device having a plurality of cold cathode elements, method of driving said device and image forming apparatus applying same
A method and apparatus for driving an electron source in which a high-quality image display is presented by correcting a non-uniform effective current distribution caused in cold cathode elements by leakage current. A digital video signal enters a shift register where a serial-to-parallel conversion is made for each line of an image based upon a shift clock signal. One line of the image data that has been subjected to the serial-to-parallel conversion is latched in a latch circuit and then applied to a voltage modulating circuit. The latter voltage-modulates the input data and sends the modulated signal to a voltage / current converting circuit. The latter converts the voltage quantity to a current quantity, which is applied to each of the cold cathode elements of a display panel through respective column terminals. A voltage V1 is applied to the selected row wire, and a voltage V2 (V2<> V1) is applied to all other row wires, for controlling the leakage current.
Owner:CANON KK
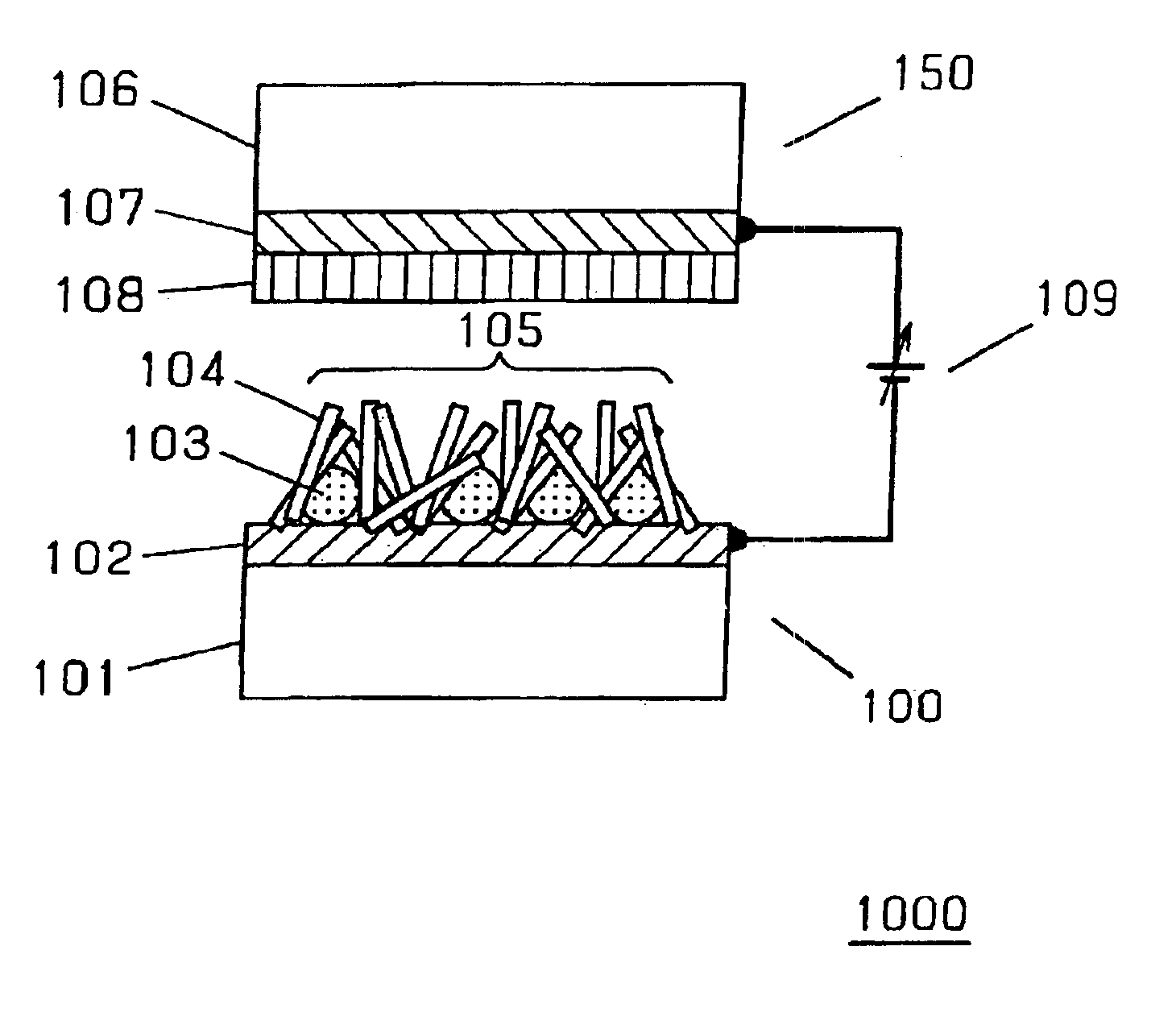
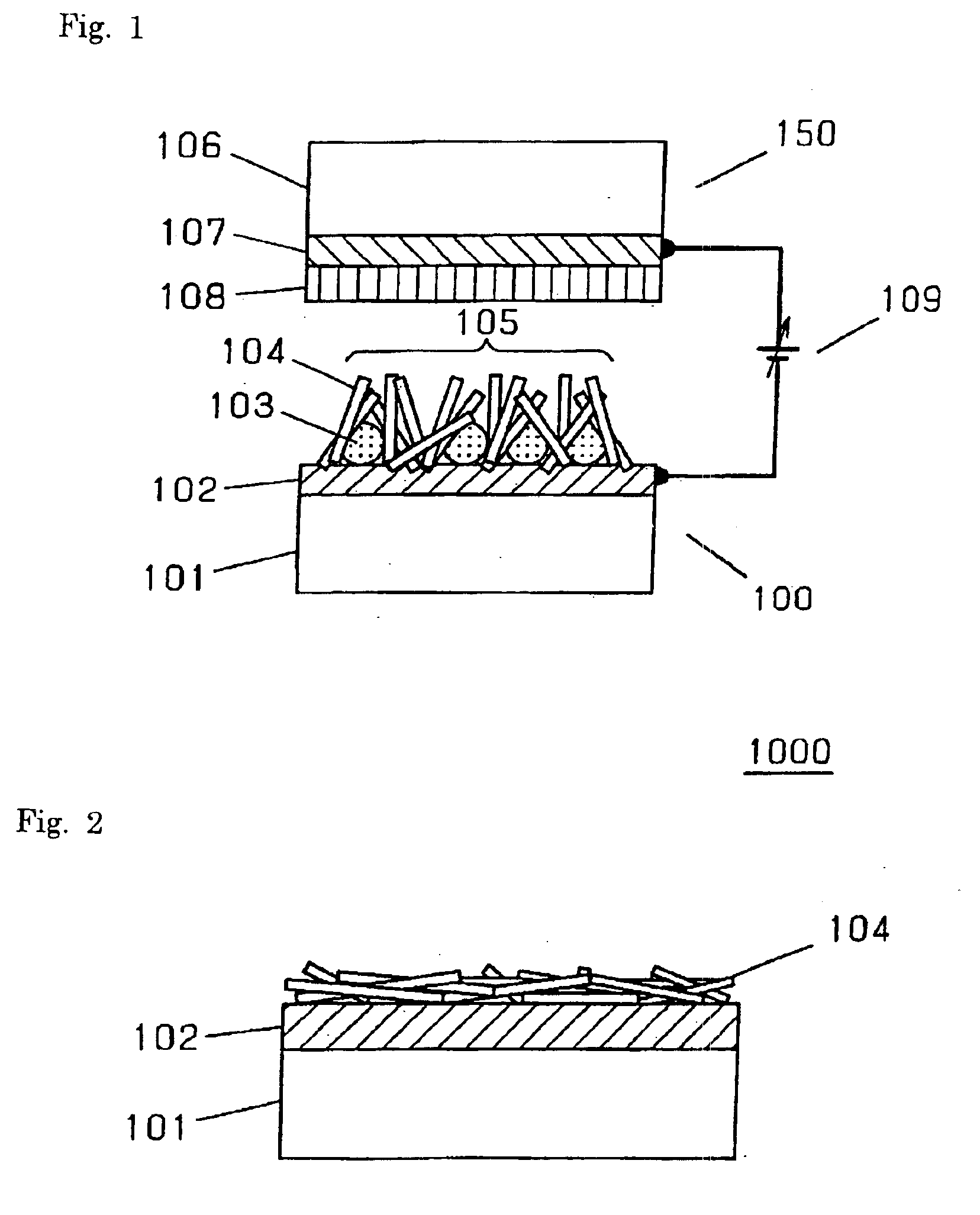
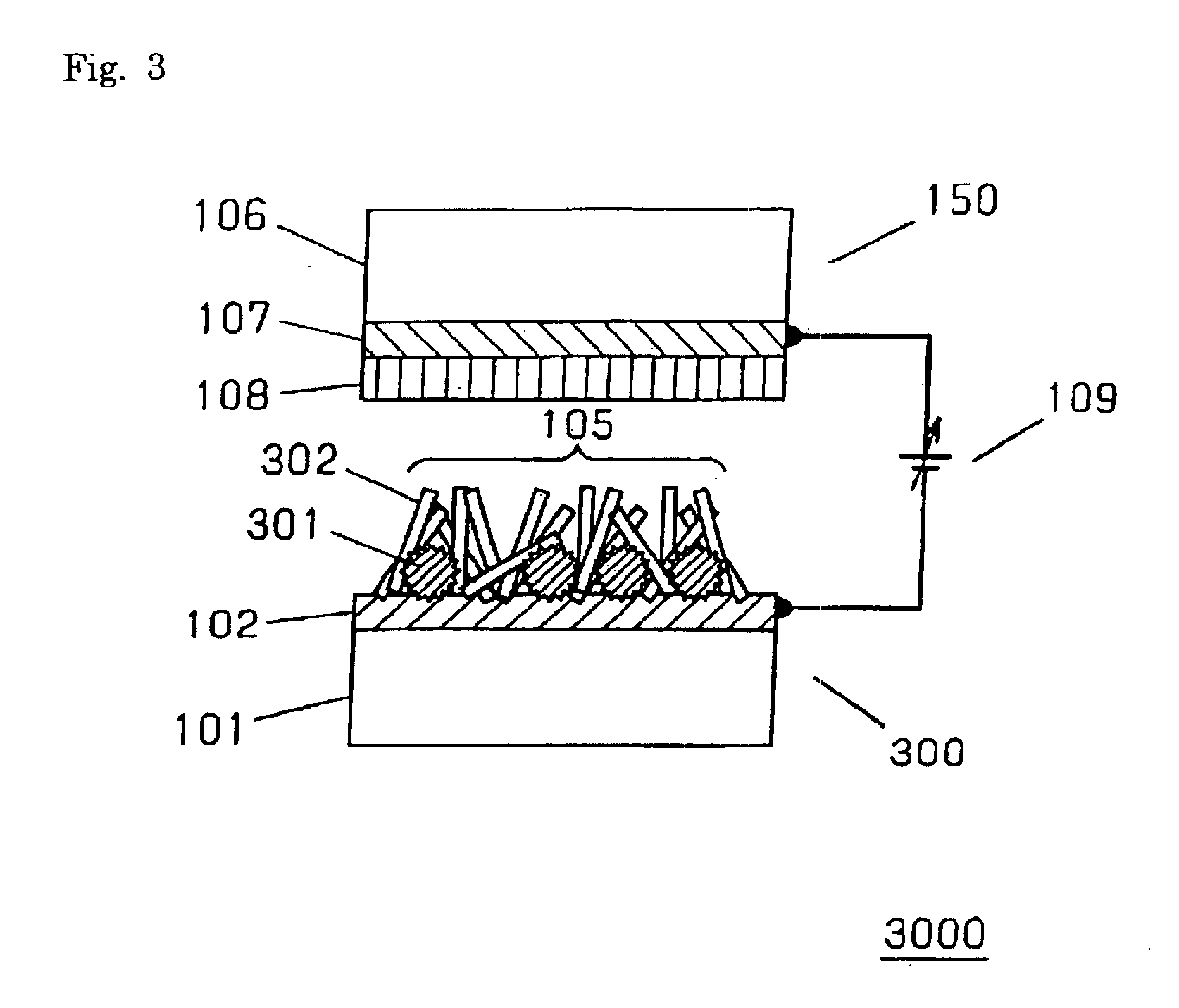
Emissive flat panel display having electron sources with high current density and low electric field strength
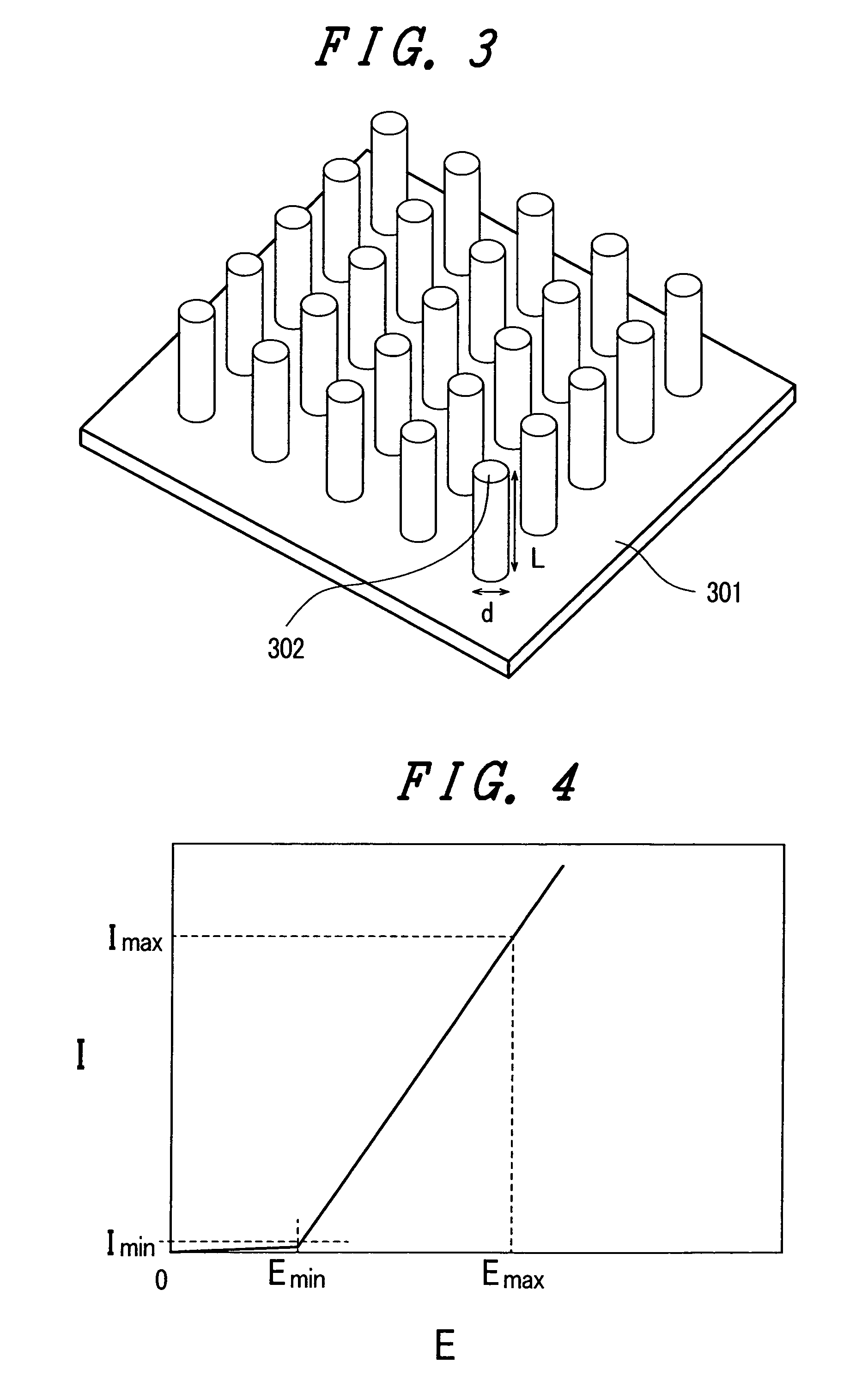
InactiveUS7196463B2Reduce voltageNo coarsenessDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsHigh current densityLow voltage
The present invention provides an emissive flat panel display device which is capable of performing a gate operation at a relatively low voltage of several V to several tens V using gate electrodes. In the emissive flat panel display device which includes a back panel which is constituted of a back substrate on which cathode electrodes having electron sources formed of carbon nanotubes and gate electrodes are formed, a face panel which forms phosphors and anode electrodes thereon, and a sealing frame which seals the back panel and the face panel, the difference between an electric field strength Emax for allowing the electron sources to obtain the required maximum emission current density and an electric field strength Emin which becomes the minimum emission current density is set to 1V / μm or less, and preferably 0.5V / μm or less.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Electron beam apparatus and device manufacturing method using same
InactiveUS6909092B2Reduce image distortionLess aberrationThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron sourceImaging processing
A defect inspecting apparatus is provided for generating a less distorted test image to reliably observe a surface of a sample for detecting defects thereon. The defect detecting apparatus comprises a primary electron beam source for irradiating a sample, electrostatic lenses for focusing secondary electrons emitted from the surface of the sample irradiated with the primary electron beam, a detector for detecting the secondary electrons, and an image processing unit for processing a signal from the detector. Further, a second electron source may be provided for emitting an electron beam irradiated to the sample, wherein the sample may be irradiated with the electron beam from the second electron source before it is irradiated with the primary electron beam from the first electron source for observing the sample. A device manufacturing method is also provided for inspecting devices under processing with high throughput using the defect detecting apparatus.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Thermionic electron source
ActiveUS20090153012A1Increase kinetic energyControl electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectron sourceAtomic physics
A thermionic electron source includes a substrate, at least two electrodes, and a thermionic emitter. The electrodes are electrically connected to the thermionic emitter. The thermionic emitter has a film structure. Wherein there a space is defined between the thermionic emitter and the substrate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
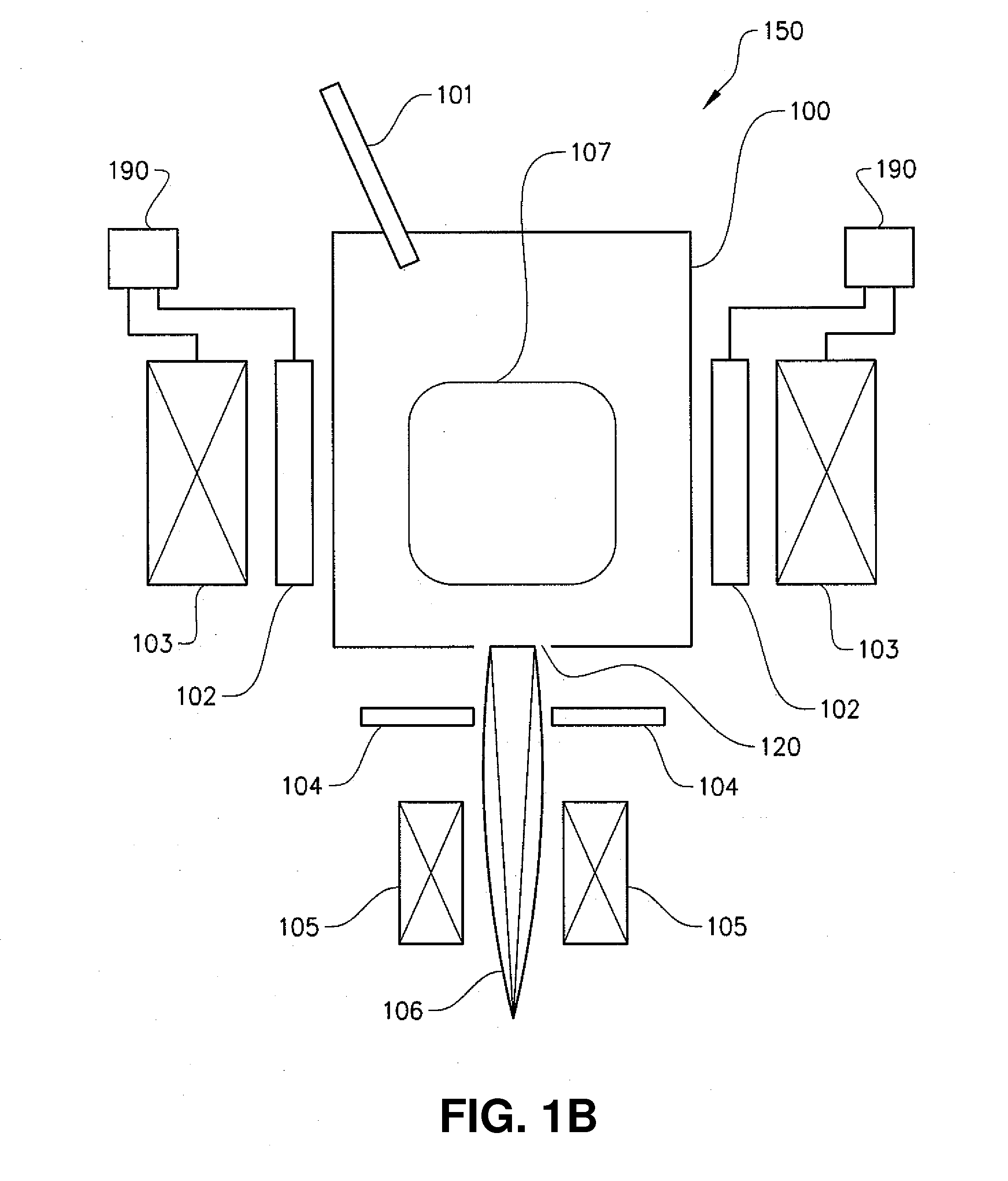
Apparatus of Plural Charged-Particle Beams
ActiveUS20160268096A1High resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSingle electronElectron source
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with high resolution and high throughput is proposed. In the apparatus, a source-conversion unit changes a single electron source into a virtual multi-source array, a primary projection imaging system projects the array to form plural probe spots on the sample, and a condenser lens adjusts the currents of the plural probe spots. In the source-conversion unit, the image-forming means is on the upstream of the beamlet-limit means, and thereby generating less scattered electrons. The image-forming means not only forms the virtual multi-source array, but also compensates the off-axis aberrations of the plurality of probe spots.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Electron-emitting element and electron source, field emission image display device, and fluorescent lamp utilizing the same and methods of fabricating the same
Disclosed are an electron-emitting element having a large operating current at a low operating voltage and excellent operation stability, and an electron source, an image display device and the like utilizing such an electron-emitting element, and further a method of fabricating such an element with few process steps at low cost. A cold cathode member is configured utilizing hybrid particle of a first particle serving to emit electrons into the space and a second particle being in the vicinity of the first particle and serving to control the position of the first particle. In this configuration, it is preferable that the first particle have a higher electron emission efficiency than the second particle and that the second particle be conductive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ionizer and method for gas-cluster ion-beam formation
ActiveUS20060097185A1Improve efficiencyImprove throughputMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesPlasma electronElectron source
An ionizer for forming a gas-cluster ion beam is disclosed including inlet and outlet ends partially defining an ionization region traversed by a gas-cluster jet and one or more plasma electron source(s) for providing electrons to the ionizing region for ionizing at least a portion of the gas-clusters to form a gas-cluster ion beam. One or more sets of substantially linear rod electrodes may be disposed substantially parallel to and in one or more corresponding partial, substantially cylindrical pattern(s) about the gas-cluster jet axis, wherein some sets are arranged in substantially concentric patterns with differing radii. In certain embodiments, the ionizer includes one or more substantially linear thermionic filaments disposed substantially parallel to the gas-cluster jet axis, heating means, electrical biasing means to judiciously bias sets of the linear rod electrodes with respect to the thermionic filaments to achieve electron repulsion.
Owner:TEL EPION
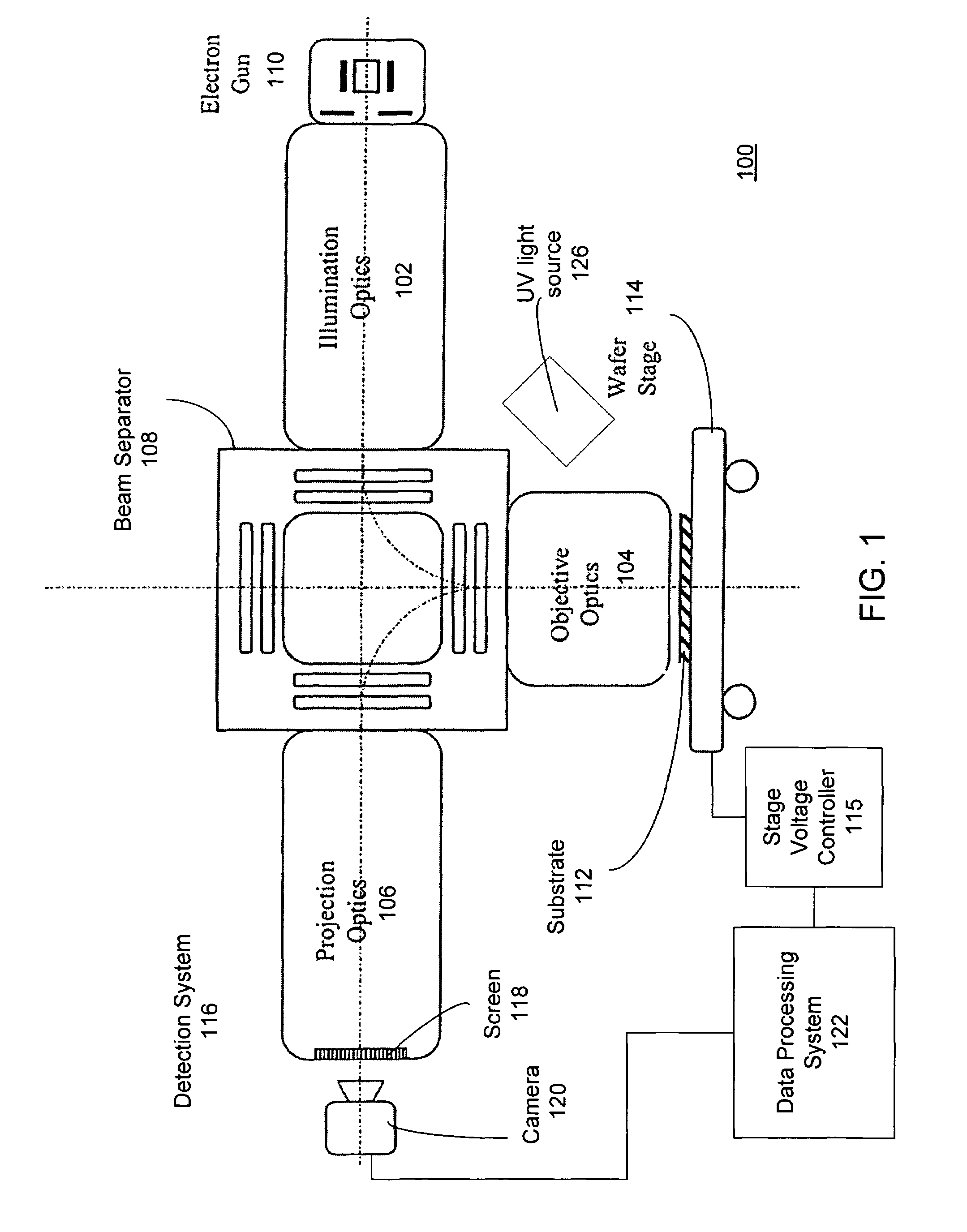
Testing apparatus using charged particles and device manufacturing method using the testing apparatus
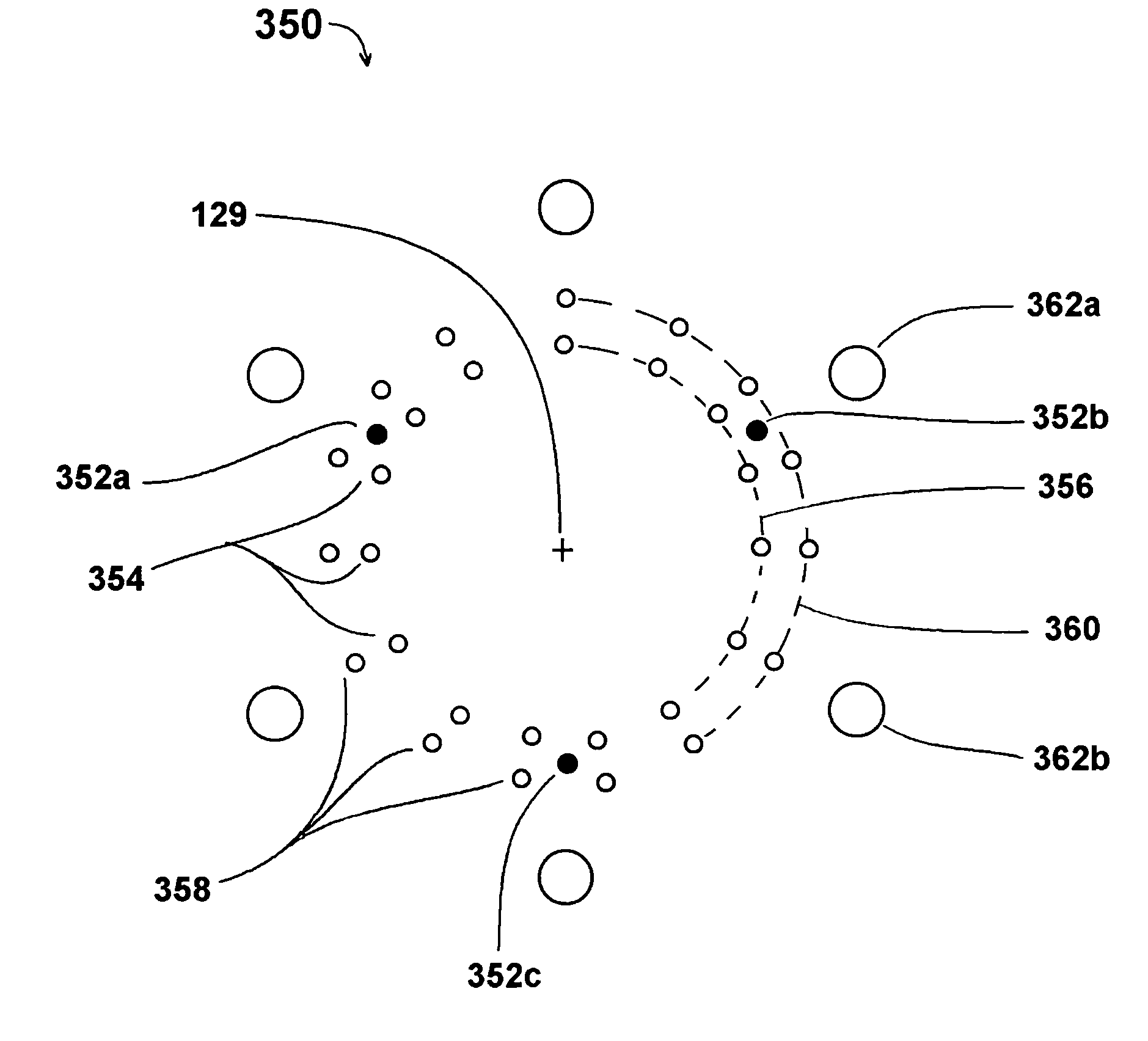
InactiveCN1820346AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementProduction rateElectron source
The invention provides a method for further increasing an inspection speed, i.e. increasing the productivity of the inspection device in an SEM manner. The inspection device which inspects the surface of a substrate images in the direction of a sample W with expected times to form crossover after an electron generated from an electron source (25*1) forms crossover. When allowing the crossover to pass through, an electron as noise is removed from an opening, the crossover is set to be expected times and adjusted to be parallel electron beams to irradiate a substrate with a desired sectional shape. The electron beam is adjusted so as to keep unevenness in electron beam illumination intensity to up to 10%. Electrons emitted from the sample W are detected by a detector (25*11).
Owner:EBARA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com