Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
718 results about "Electron energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
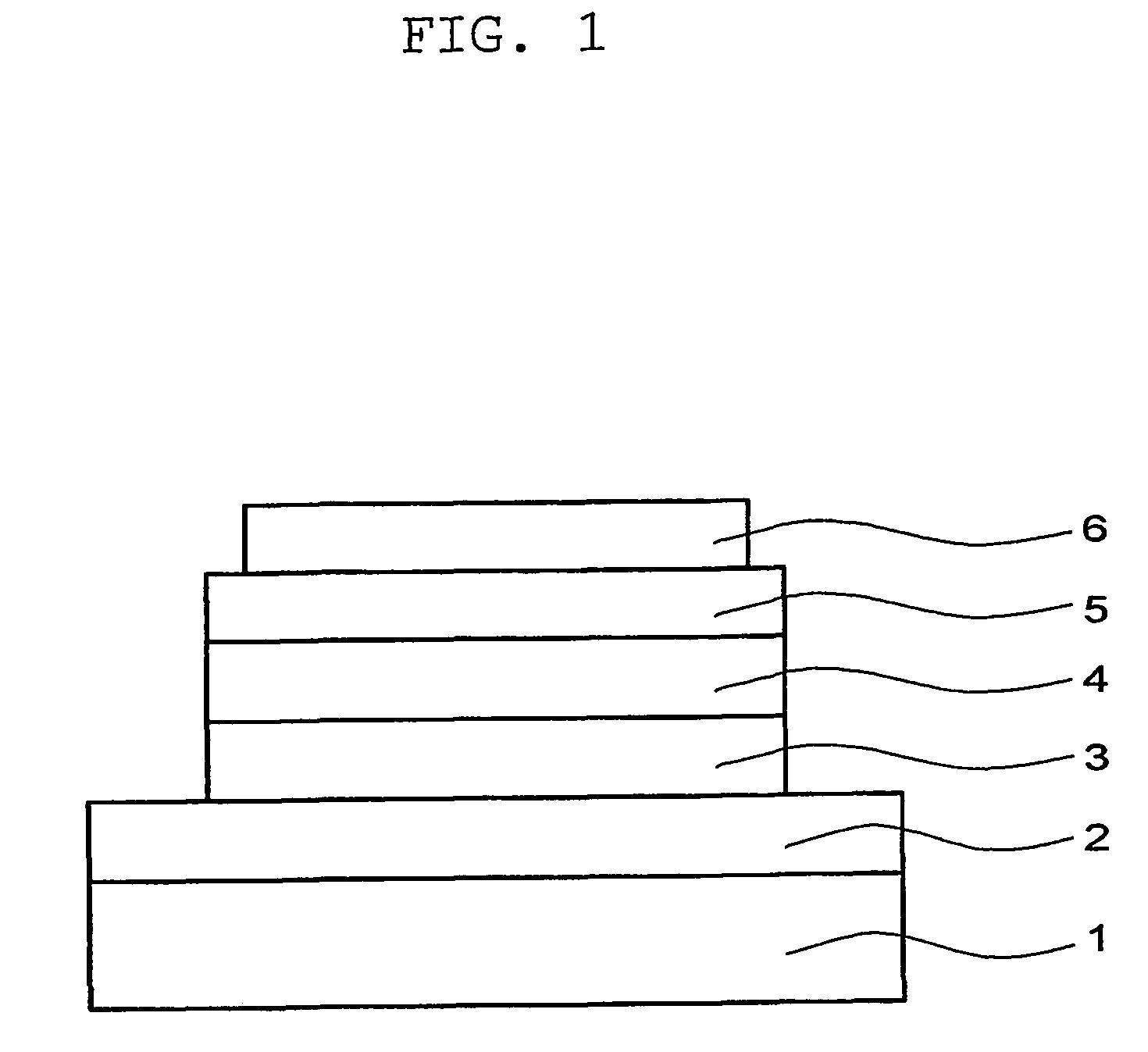
Light emitting material and organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS7396598B2High efficiency of light emissionKeep energy smallDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsFluorescenceTriplet state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
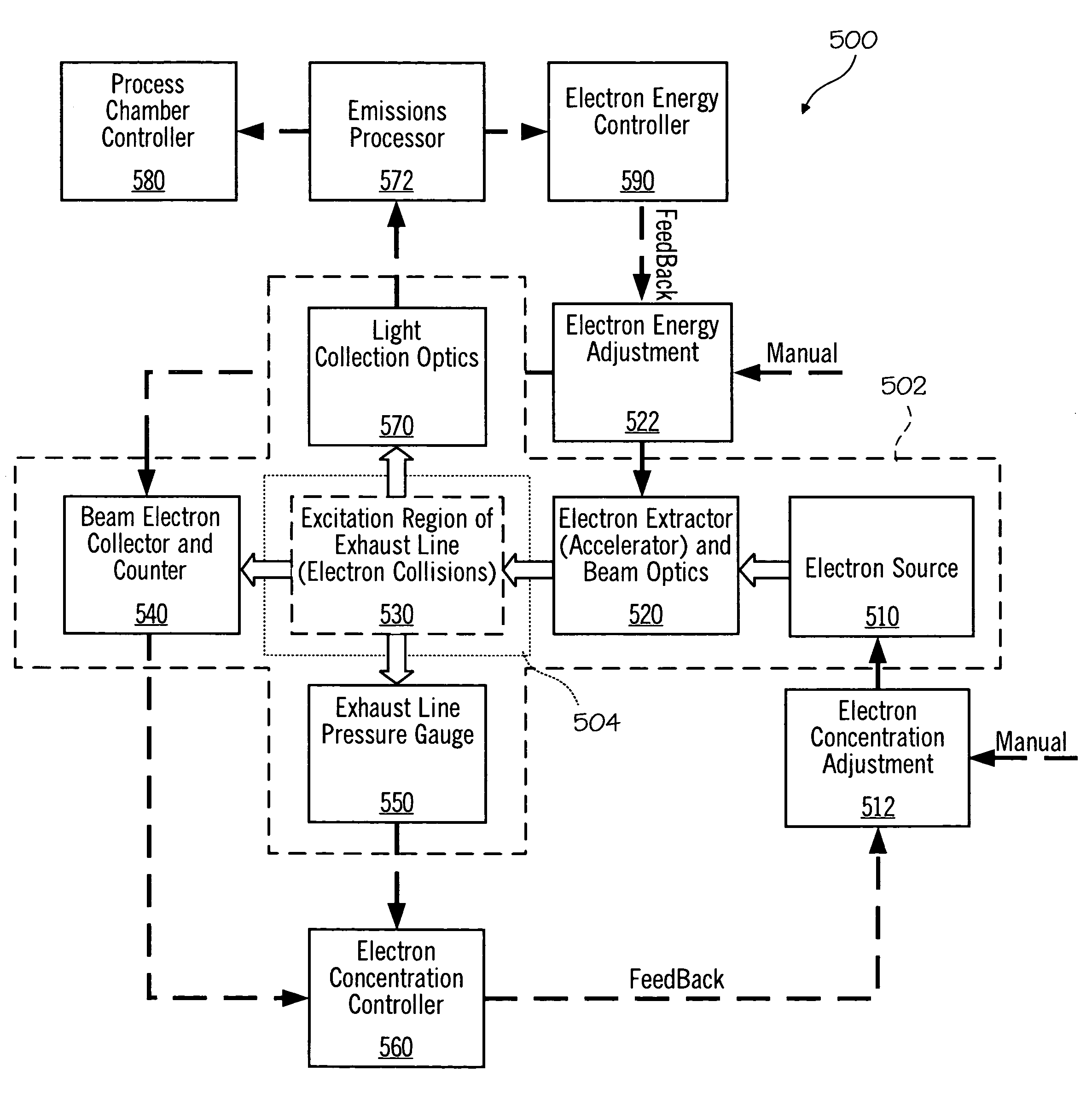
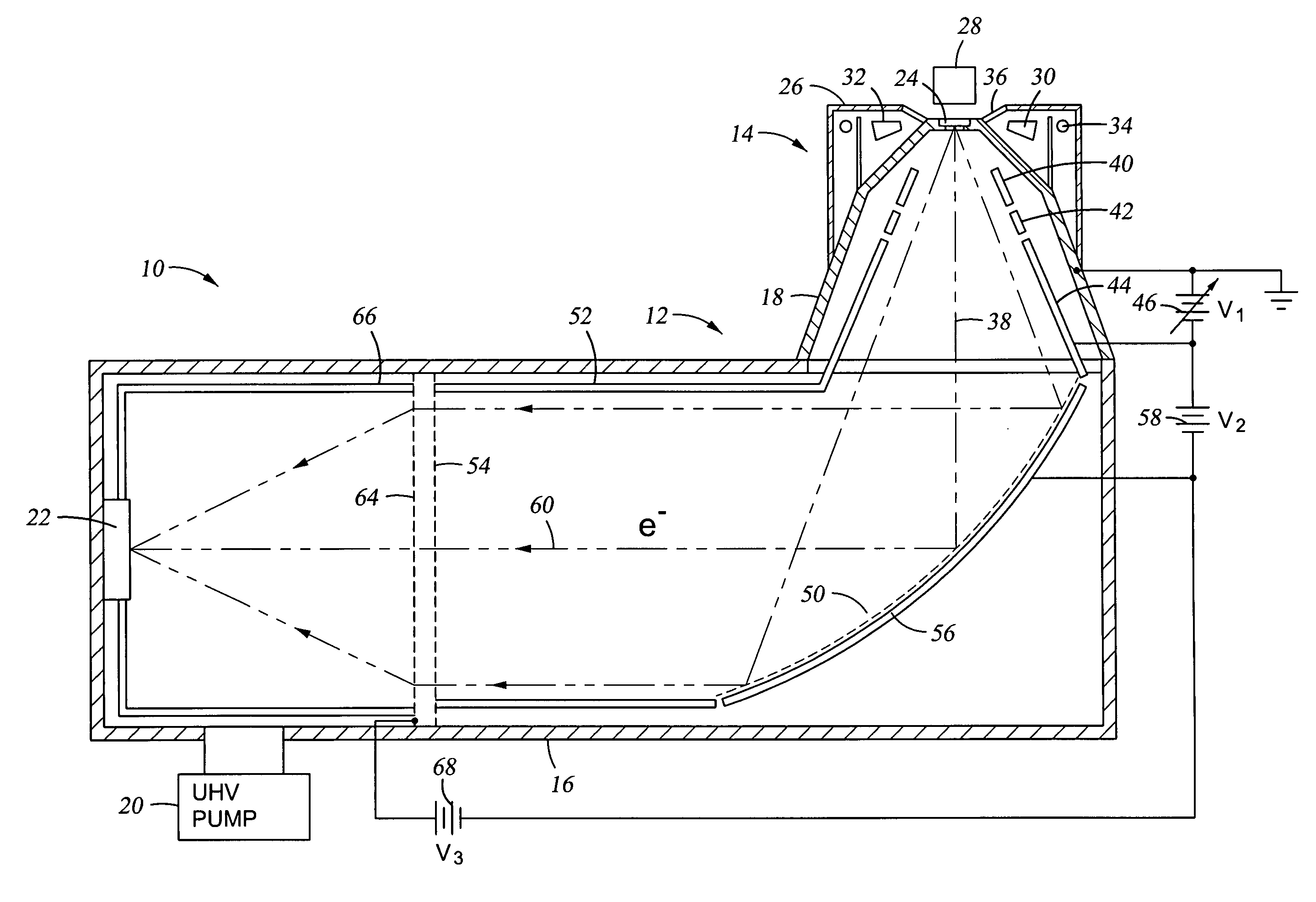
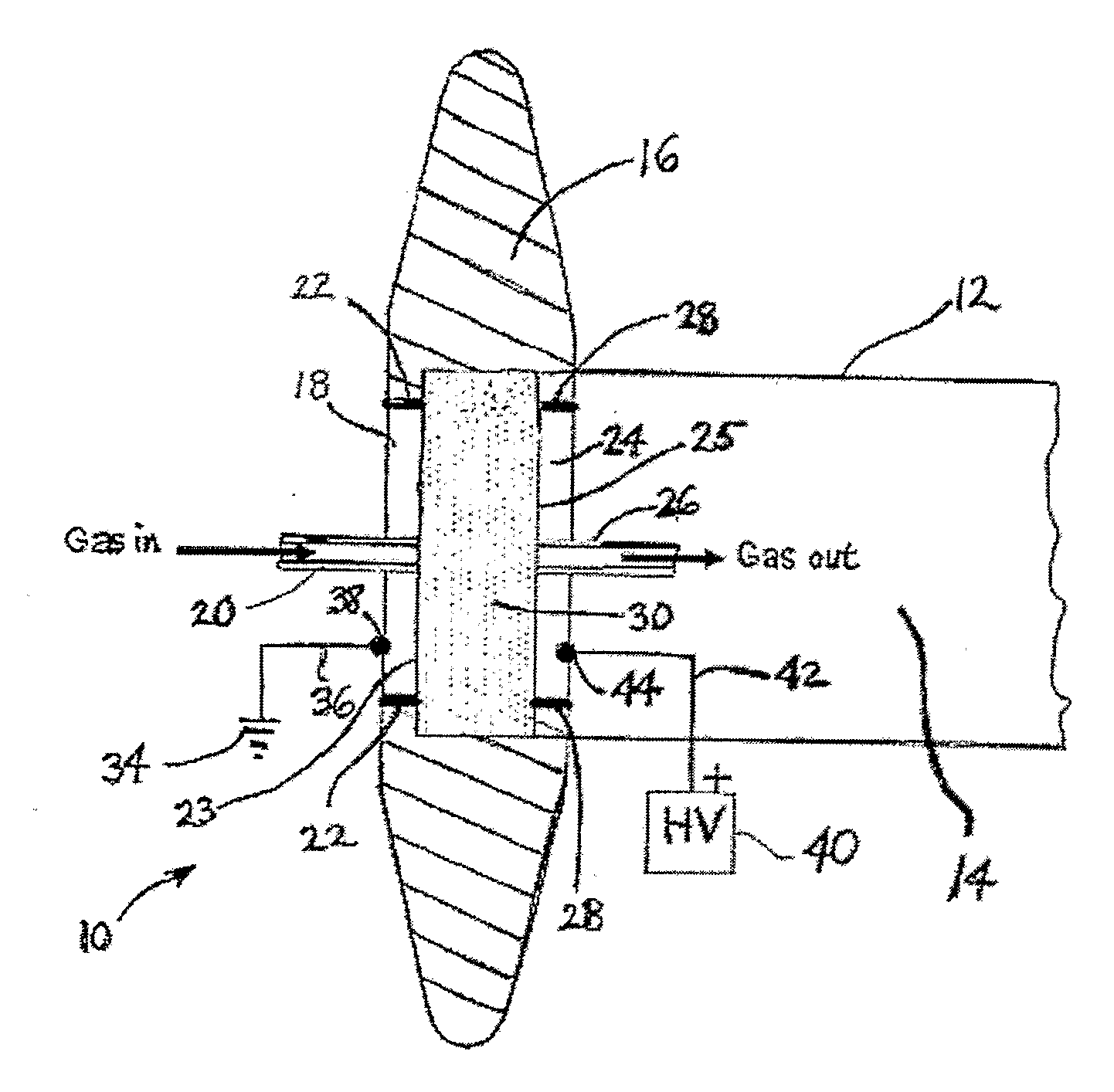
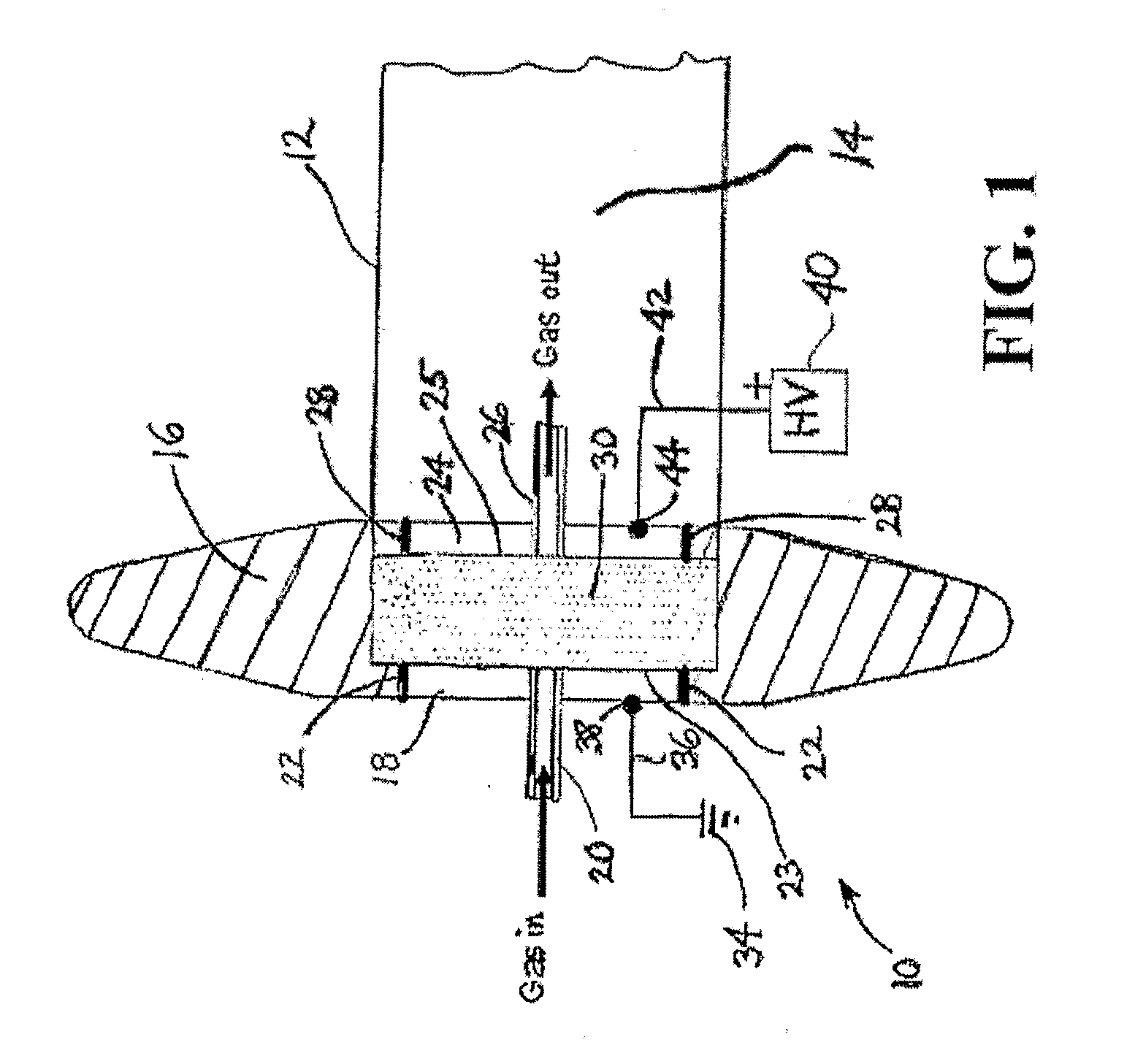
Electron beam exciter for use in chemical analysis in processing systems
ActiveUS20100032587A1Disparity will become so greatHigh electron energyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesRadiation therapyElectron sourceFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a gas line electron beam exciter, gas line electron beam excitation system and method for exciting a gas using an electron beam exciter. The electron beam exciter generally comprises a variable density electron source for generating a cloud of electrons in an electron chamber and a variable energy electron extractor for accelerating electrons from the electron chamber as an electron beam and into an effluent stream for fluorescing species in the effluent. The electron density of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting the excitation power applied to the variable density electron source. The electrons in the electron chamber reside at a reference electrical potential of the chamber, typically near ground electrical potential. The electron energy of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting an electrical potential across the variable energy electron extractor, which energizes the electrons through an extraction hole of the chamber and toward the extractor. The greater the difference in the electrical potential between the electron extractor and the electron source, the higher the energy imparted to the electrons in the electron beam. The excitation power applied to the electron source can be adjusted independently from the electron energy of the electron beam, thereby altering the electron density of the electron beam without changing the energy level of the electrons of the electron beam.
Owner:VERITY INSTR +1
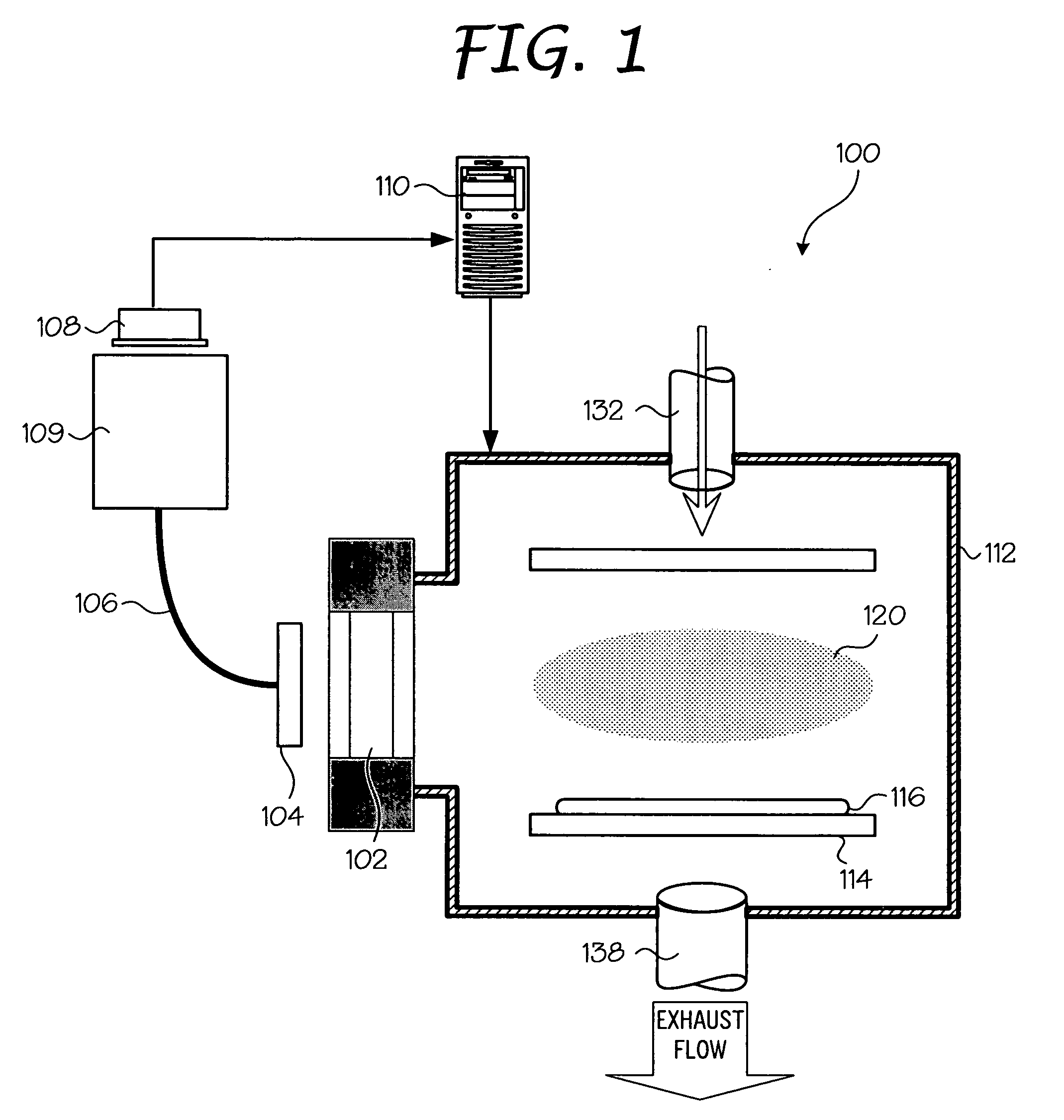
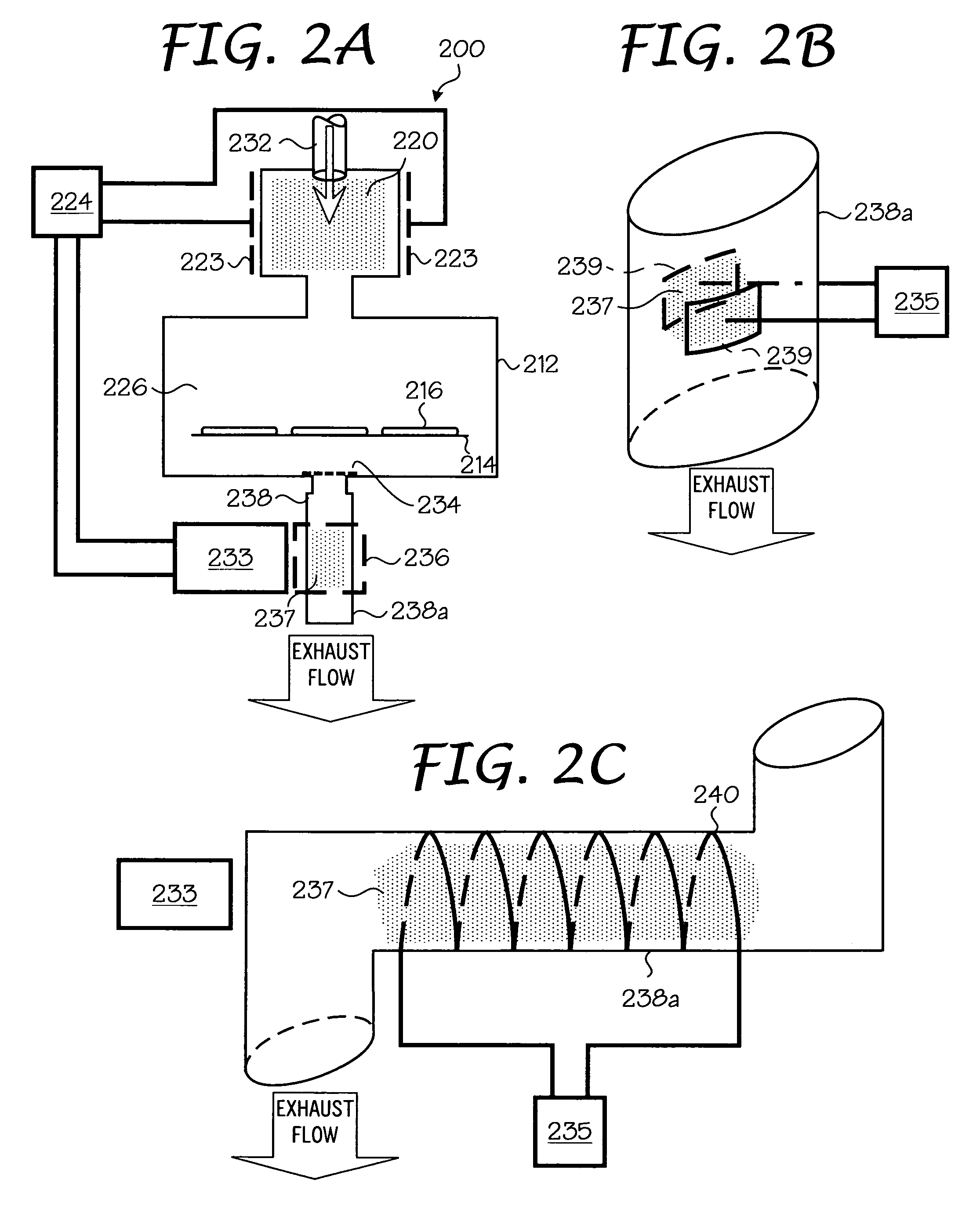
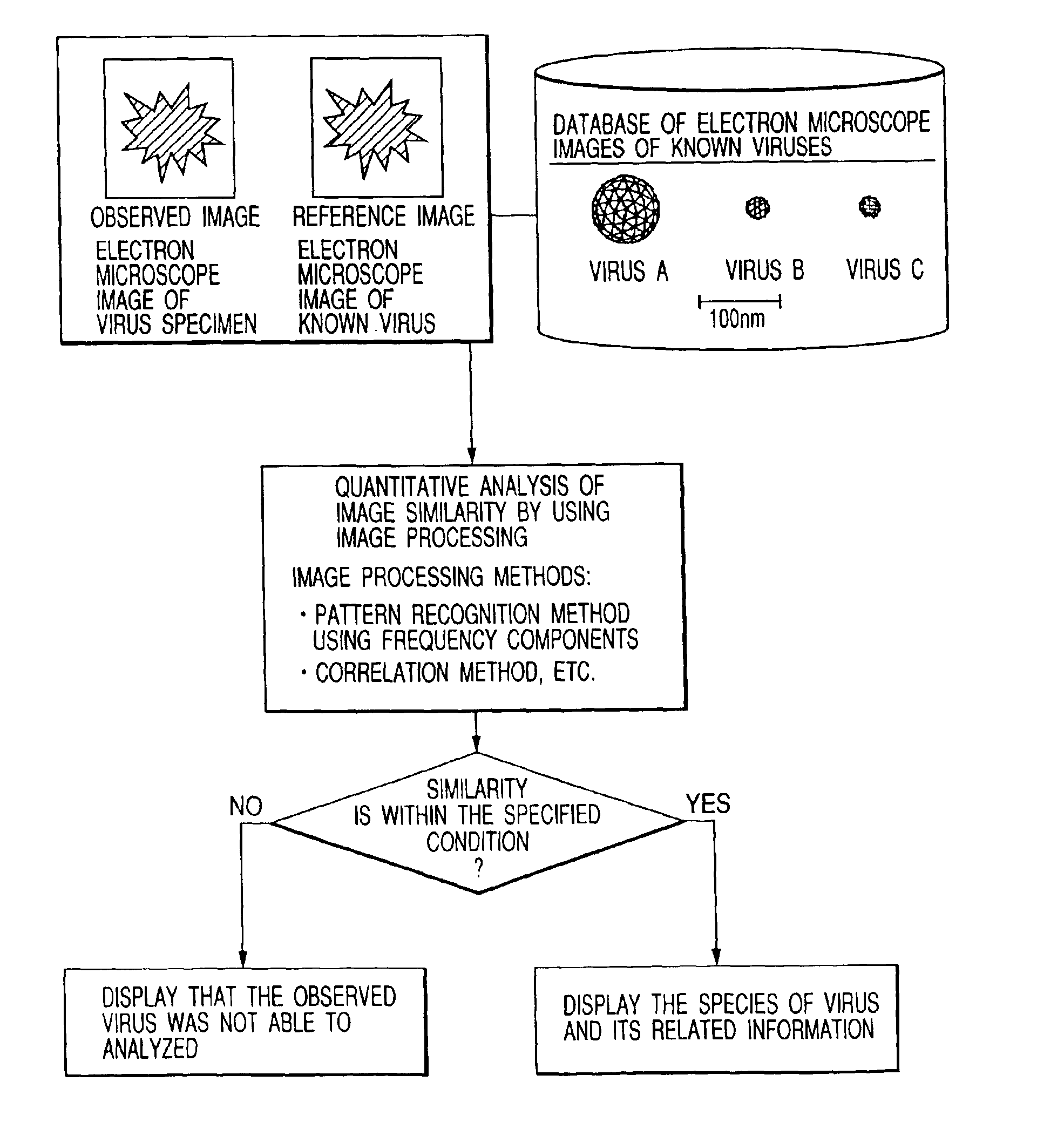
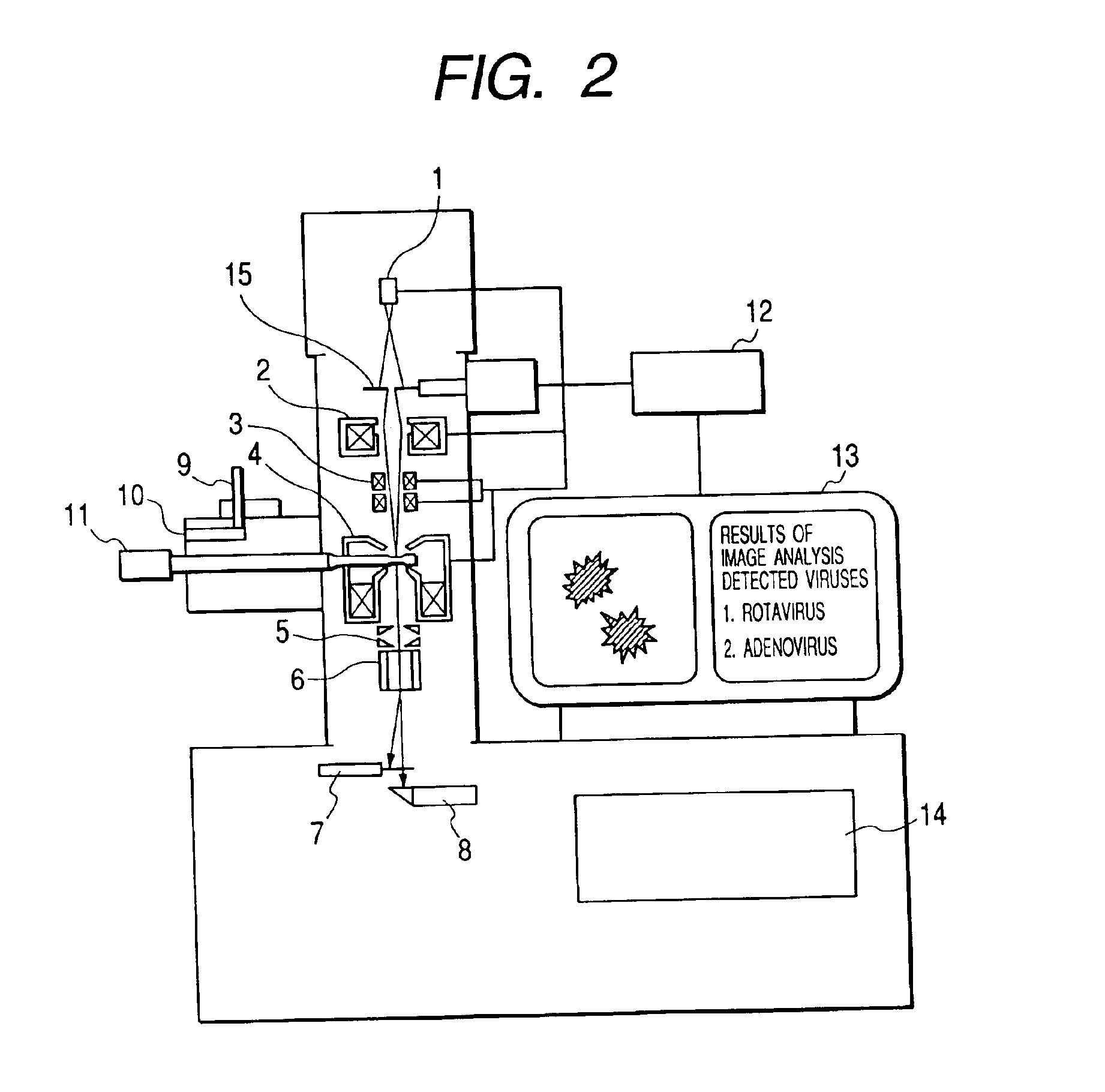
Bio electron microscope and observation method of specimen
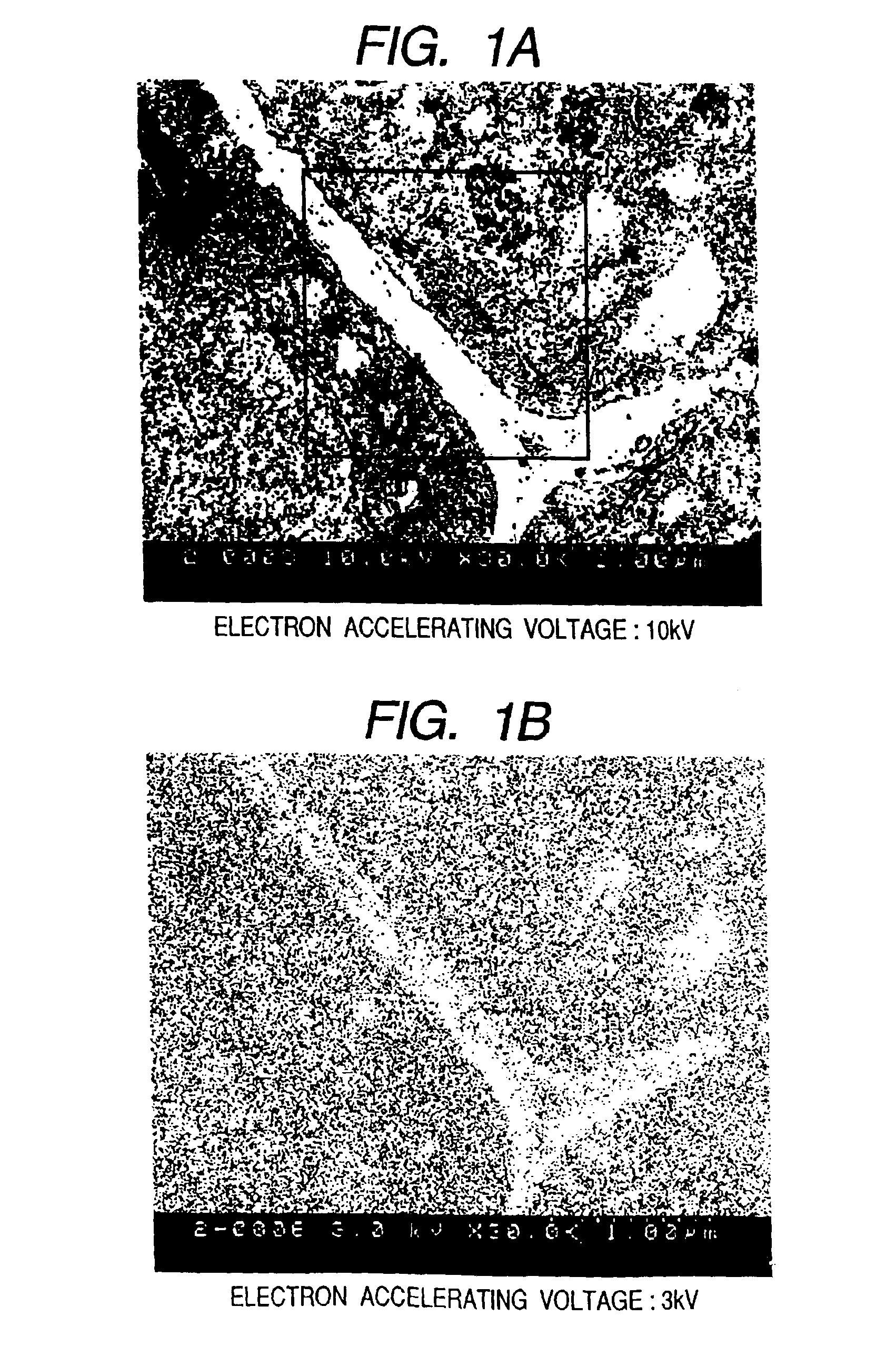
InactiveUS6875984B2Reduce harmHigh-accuracy image analysisEnergy spectrometersPreparing sample for investigationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
A bio electron microscope and an observation method which can observe a bio specimen by low damage and high contrast to perform high-accuracy image analysis, and conduct high-throughput specimen preparation. 1) A specimen is observed at an accelerating voltage 1.2 to 4.2 times a critical electron accelerating voltage possible to transmit a specimen obtained under predetermined conditions. 2) An electron energy filter of small and simplified construction is provided between the specimen and an electron detector for imaging by the electron beam in a specified energy region of the electron beams transmitting the specimen. 3) Similarity between an observed image such as virus or protein in the specimen and a reference image such as known virus or protein is subjected to quantitative analysis by image processing. 4) A preparation protocol of the bio specimen is made into a chip using an MEMS technique, which is then mounted on a specimen stage part of an electron microscope to conduct specimen introduction, preparation and transfer onto a specimen holder.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
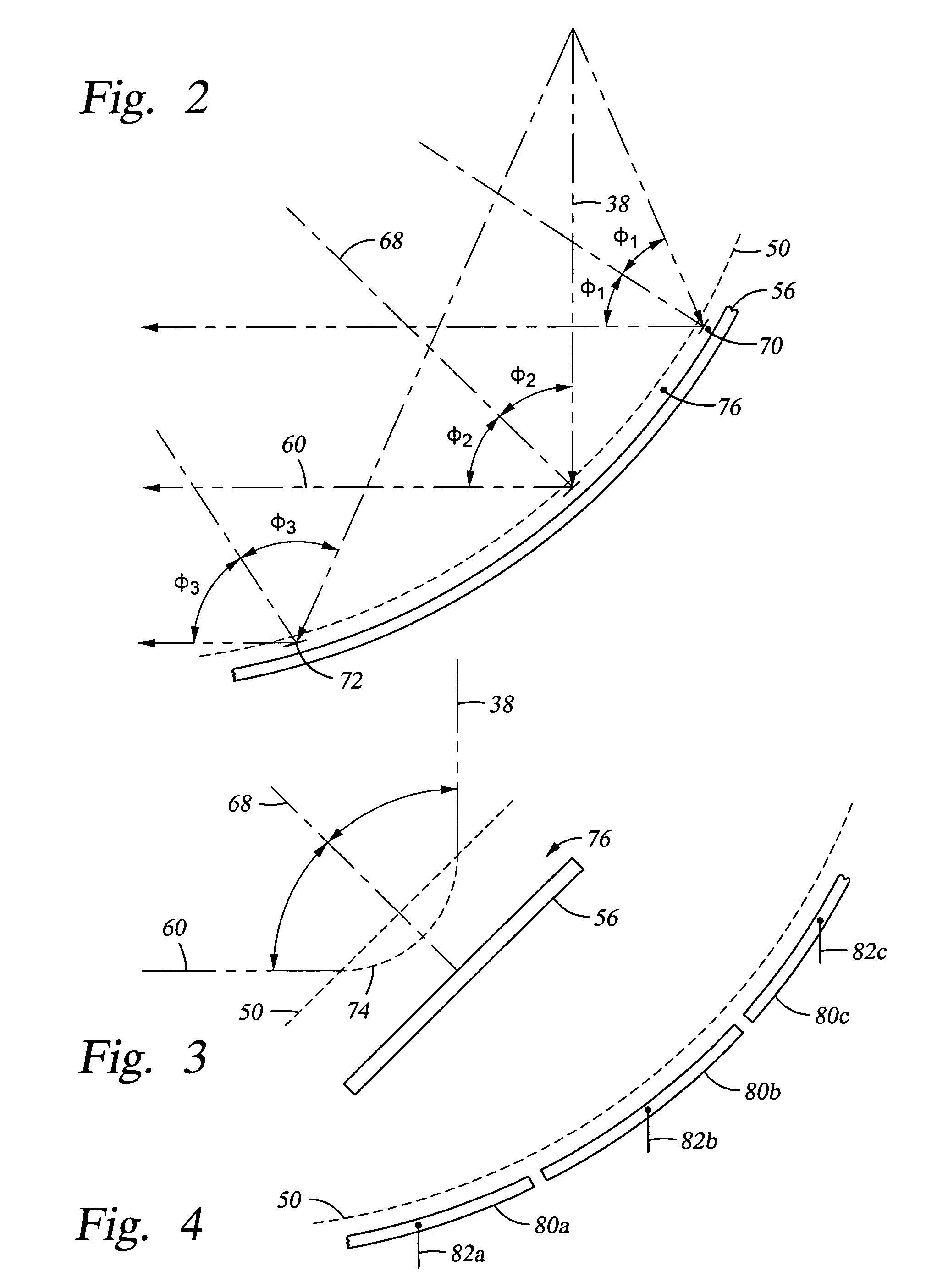
Non-dispersive charged particle energy analyzer
InactiveUS20050045832A1Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersElectron sourceEnergy analyser
An electron energy analyzer including a curved electrostatic low-pass reflector and a high-pass electrostatic transmissive filter. The reflector comprises a curved grid, preferably ellipsoidal, and an absorber electrode placed in back of the curved grid with respect to the electron source and biased negatively to the curved grid to act as a reflective low-pass filter and a collimating optics for the reflected beam. The transmissive filter includes first and second flat grids extending across the collimated reflected beam. The second grid on the side of the first grid opposite the curved grid is biased negatively to the first grid and the absorber electrode. A field free region is created by applying the same bias to the curved grid, the first grid, and chamber sidewall sleeve. An electron detector detects all electrons passed by the second grid in an energy band in the overlap of the high-pass and low-pass bands.
Owner:BRYSON III CHARLES E
Free electron laser
A free electron laser is disclosed. The free electron laser separates pulse bunching at a first electron energy from light generation stage at a second electron energy. A first wiggler pulse bunches the electrons and a second wiggler generates light. The first wiggler may be an optical buncher with an injected seed wave, and the second wiggler can be a magnetic wiggler, optical wiggler, resonant transition radiator, parametric radiation radiator, Cerenkov radiation radiator or a Smith-Purcell radiation radiator. The disclosed free electron laser is particularly useful for lithography applications at an extreme ultraviolet wavelength range near 13.5 nm.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical semiconductor device with multiple quantum well structure
InactiveUS7106090B2Improve quantum efficiencyEnhanced nucleationLaser detailsElectronic circuit testingQuantumNitride semiconductors
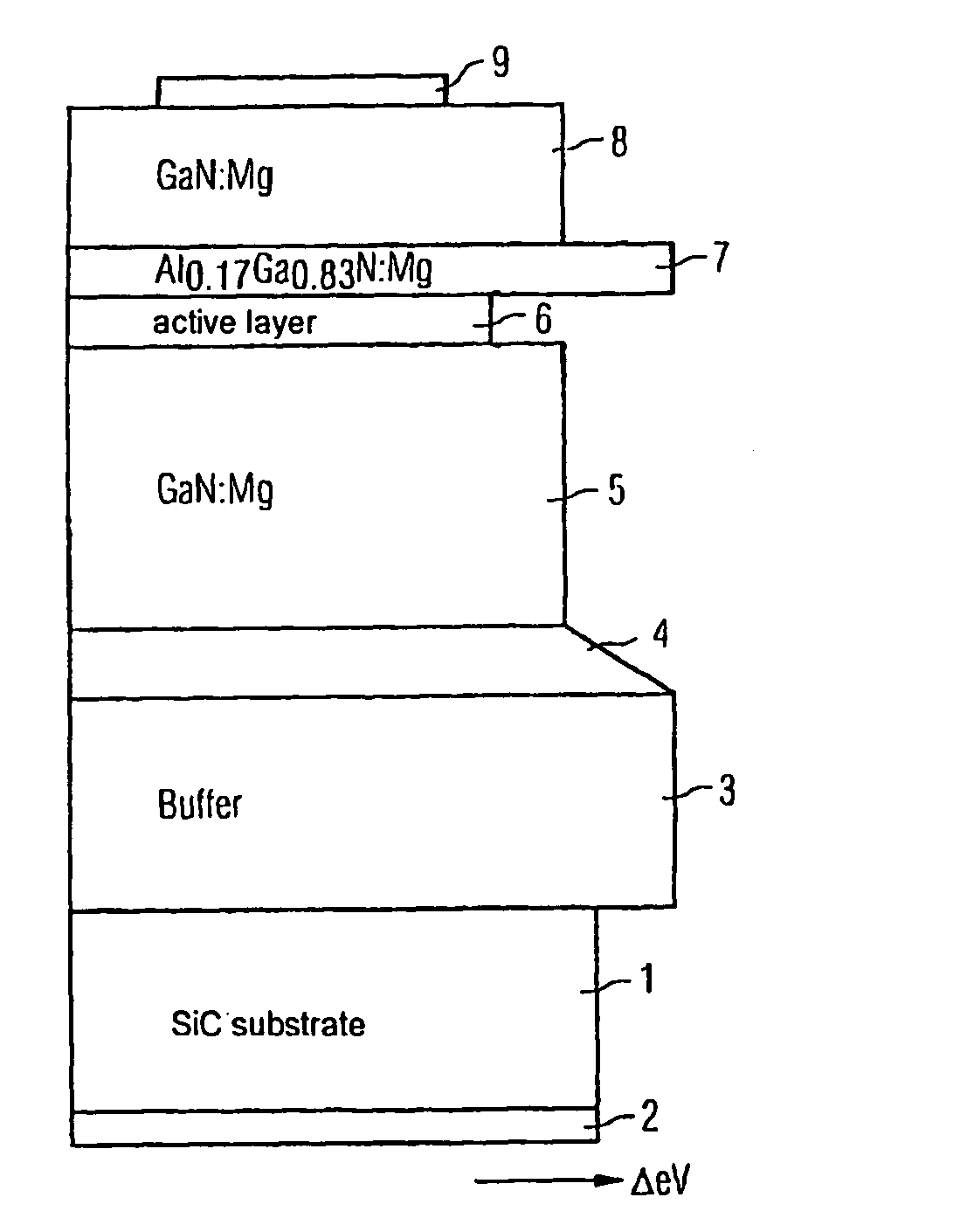
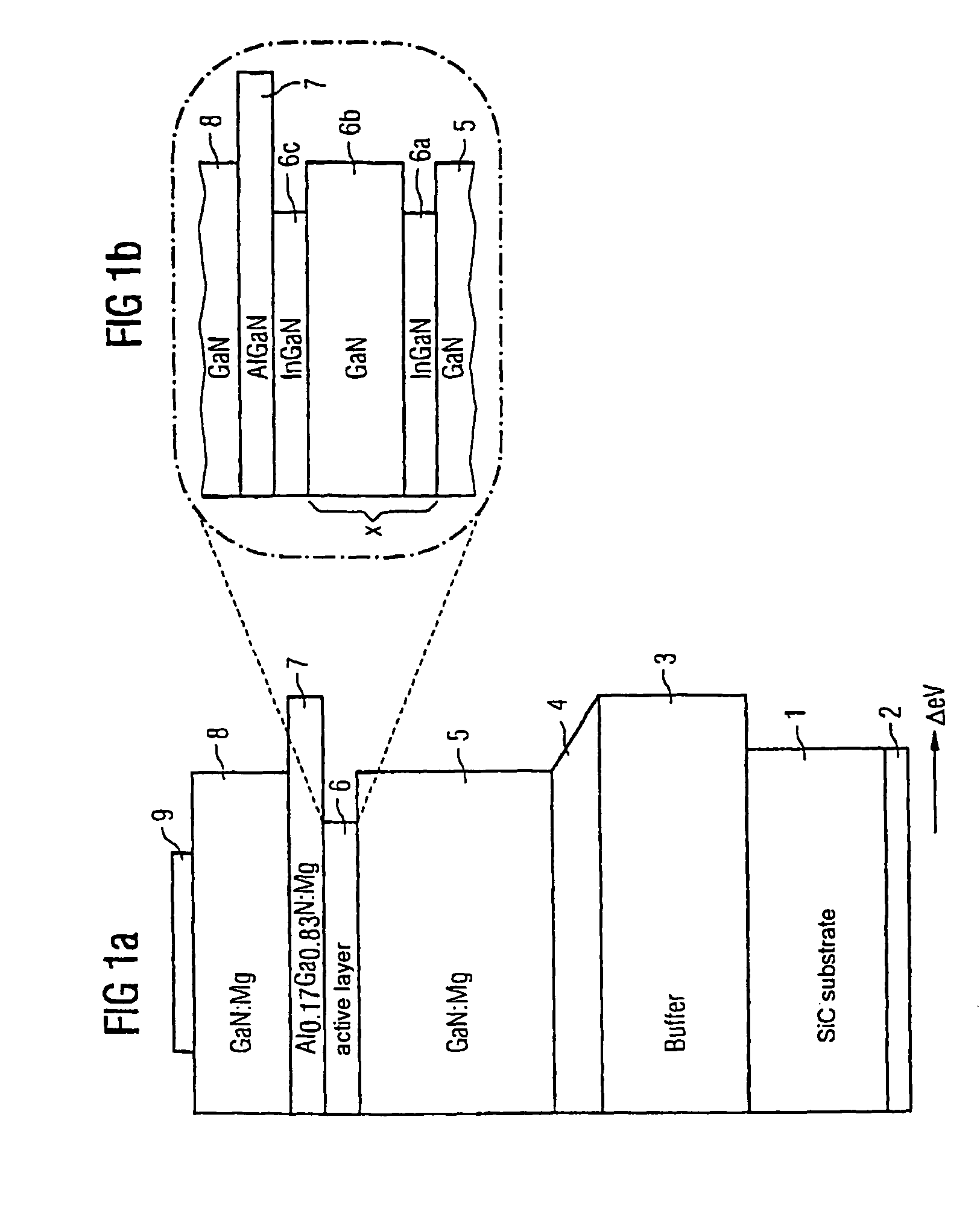
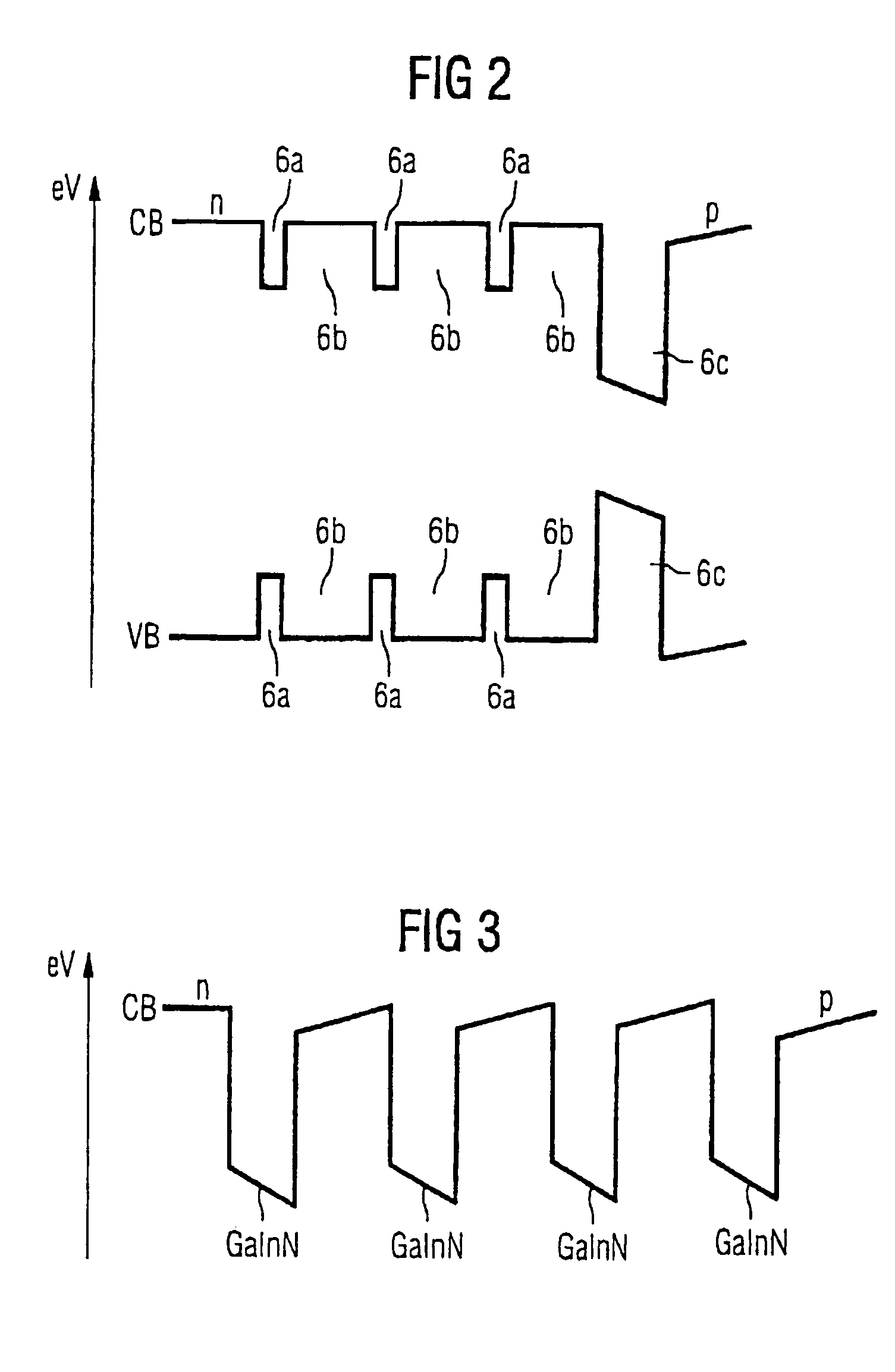
An optical semiconductor device with a multiple quantum well structure, in which well layers and barrier layers comprising various types of semiconductor layers are alternately layered, in which device well layers (6a) of a first composition based on a nitride semiconductor material with a first electron energy and barrier layers (6b) of a second composition of a nitride semiconductor material with electron energy which is higher in comparison with the first electron energy are provided, followed, seen in the direction of growth, by a radiation-active quantum well layer (6c), for which the essentially non-radiating well layers (6a) and the barrier layers (6b) arranged in front form a superlattice.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Embedded NV-center diamond based magnetic field metering device
ActiveCN105158709AReduce probe sizeIncrease polarizabilityMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesPhase shiftedImage resolution
The invention relates to an embedded NV-center diamond based magnetic field metering device. A nanometer diamond particle with a negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy(NV)-center is adopted as a sensitive element. Phase-shift micro-nano FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) is adopted to be a sample cavity. Laser and microwave are utilized for controlling NV-center electronic energy level and magnetic field metering is realized through detecting the fluorescent intensity of the NV-center. The device provided by the invention has comparatively high spatial resolution and comparatively good stability and also has advantages of being small in size, low in cost and being compatible to room temperature operation. The device can perform metering on the surface of a to-be-meter object or in micro holes or gaps and is a magnetic field metering device based on solid atom spin. The device can be used for satisfying requirements for weak magnetic field metering with low cost and high spatial resolution in different field in the future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ionization device for aerosol mass spectrometer and method of ionization
ActiveUS20050178975A1Efficient methodTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansEnergy controlVoltage source
The ionization device of the present invention is intended for use in conjunction with an aerosol TOF MS operating in a continuous mode and is capable of ionizing particulated substances in a wide range of particle masses. In the illustrated embodiment, the ionization unit consists of three coaxial cylindrical bodies having a three aligned longitudinal slits for directing electron beams from externally located electron gun onto the axially arranged flow of droplets. The cylindrical bodies are connected to voltage sources so that the external cylindrical body functions as an anode that extracts electrons from the current-heated filament. The central cylindrical body, in combination with the aforementioned anode, serves as an electron-energy control member for precisely controlling and selecting the energy of electrons that reach the flow of particles, while the inner cylindrical body functions as a decelerating member that can be used for adjusting energy of electrons which reached the flow of particles. The heated filament of each electron gun, which is used as a source of electrons, is inclined with respect to the aforementioned longitudinal axis whereby modulation applied to the elongated outer electrode of the electron gun provides different ionization conditions for specific particles of predetermined masses for analysis of which the aerosol TOF MS is tuned.
Owner:NANOMAT
High density plasma tool with adjustable uniformity and stochastic electron heating for reduced gas cracking
InactiveUS6262538B1Increase chanceDevoid of excess gas cracking effectsElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitanceEtching
VHF / UHF power having a frequency of about 40 MHz or higher is applied across generally radial elements of an antenna and the phase of a standing wave component of the voltage in the generally radial elements is adjusted to provide relatively uniform density of a high density plasma across an area of at least the size of a semiconductor wafer being processed. Capacitive coupling of power to the plasma enhances the hot tail distribution of electron energies which is associated with low levels of gas cracking and the production of radicals such as fluorine which are not material-selective in semiconductor processing operations such as oxide etching. Accordingly, material-selectivity of processes may be maintained while the high density plasma accelerates the process to significantly improve tool throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
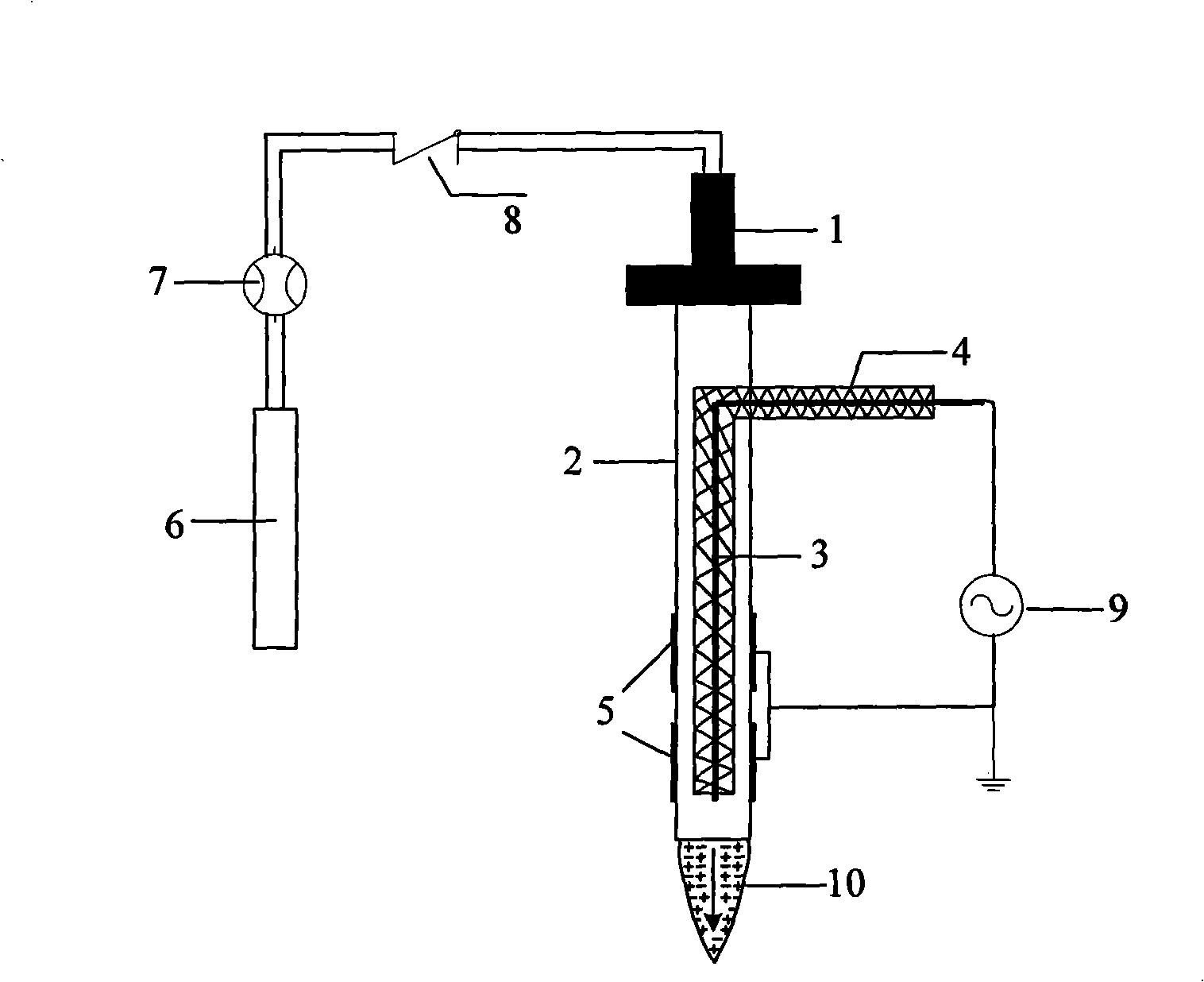
Jet apparatus capable of blocking discharging from generating low temperature plasma by atmos medium
InactiveCN101330794ASolve the problem of limited application rangeEasy to modifyPlasma techniquePlasma jetParallel plate
A jetting device for a low-temperature plasma generated by the atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge relates to the technical field of the application of gas discharge plasma. Inert gas and air are used as working gas; the plasma generated in a discharge area is blown out in the form of jet; the problem of limited application range caused by the narrow parallel-plate dielectric barrier discharge area and a high plasma macroscopic temperature can be solved. The device has the structural characteristics that a hollow pipe-shaped connector is connected with a hollow dielectric pipe; an electrode coated with insulation dielectric is fixed at the center of the dielectric pipe; an annular electrode is closely attached to the outer wall of the dielectric pipe; the working gas enters the dielectric pipe from a flow meter and a retaining valve through the connector; the plasma is blown out to form the plasma jetting. The jetting device has the advantages of low plasma macroscopic temperature, large electron energy, wide expanded range, low cost, low energy consumption and high reliability; furthermore, the jetting device can used in the fields of sterilization and disinfection, the surface modification of complex-shaped material, waste gas treatment, ozone synthesis, as well as the physical and chemical fields of the discharge light source plasma.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
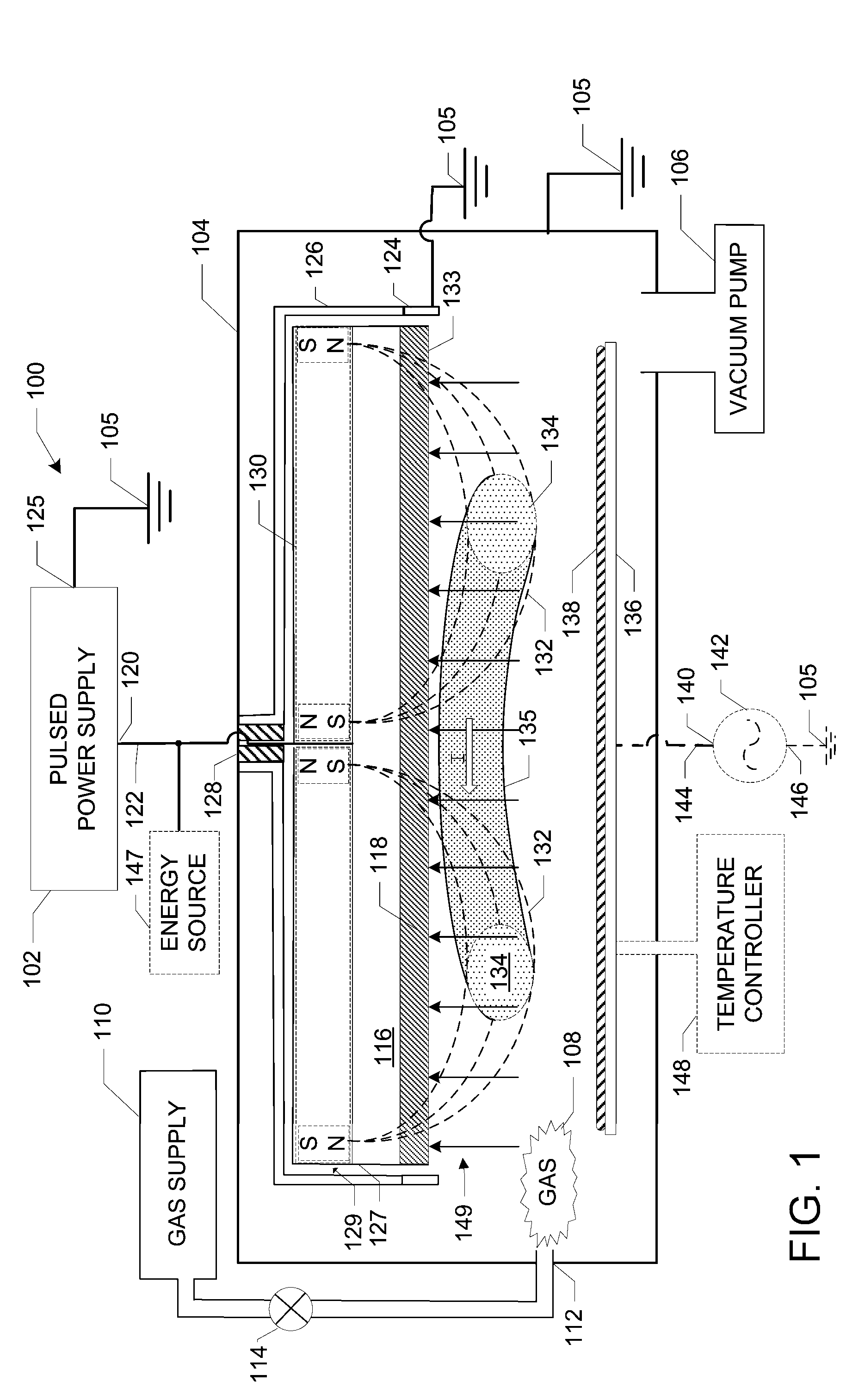
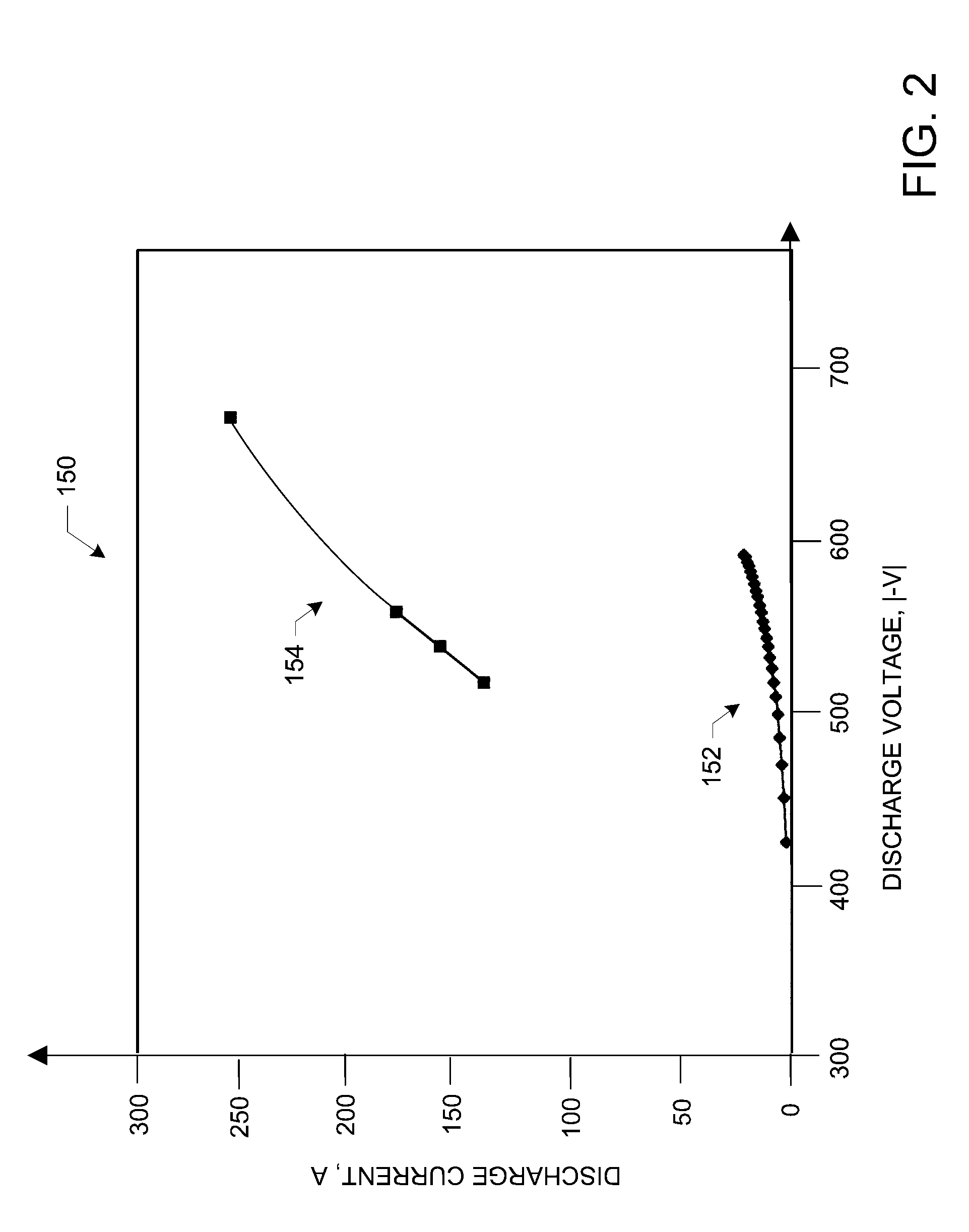
Methods and Apparatus for Generating Strongly-Ionized Plasmas with Ionizational Instabilities
Methods and apparatus for generating strongly-ionized plasmas are disclosed. A strongly-ionized plasma generator according to one embodiment includes a chamber for confining a feed gas. An anode and a cathode assembly are positioned inside the chamber. A pulsed power supply is electrically connected between the anode and the cathode assembly. The pulsed power supply generates a multi-stage voltage pulse that includes a low-power stage with a first peak voltage having a magnitude and a rise time that is sufficient to generate a weakly-ionized plasma from the feed gas. The multi-stage voltage pulse also includes a transient stage with a second peak voltage having a magnitude and a rise time that is sufficient to shift an electron energy distribution in the weakly-ionized plasma to higher energies that increase an ionization rate which results in a rapid increase in electron density and a formation of a strongly-ionized plasma.
Owner:ZOND
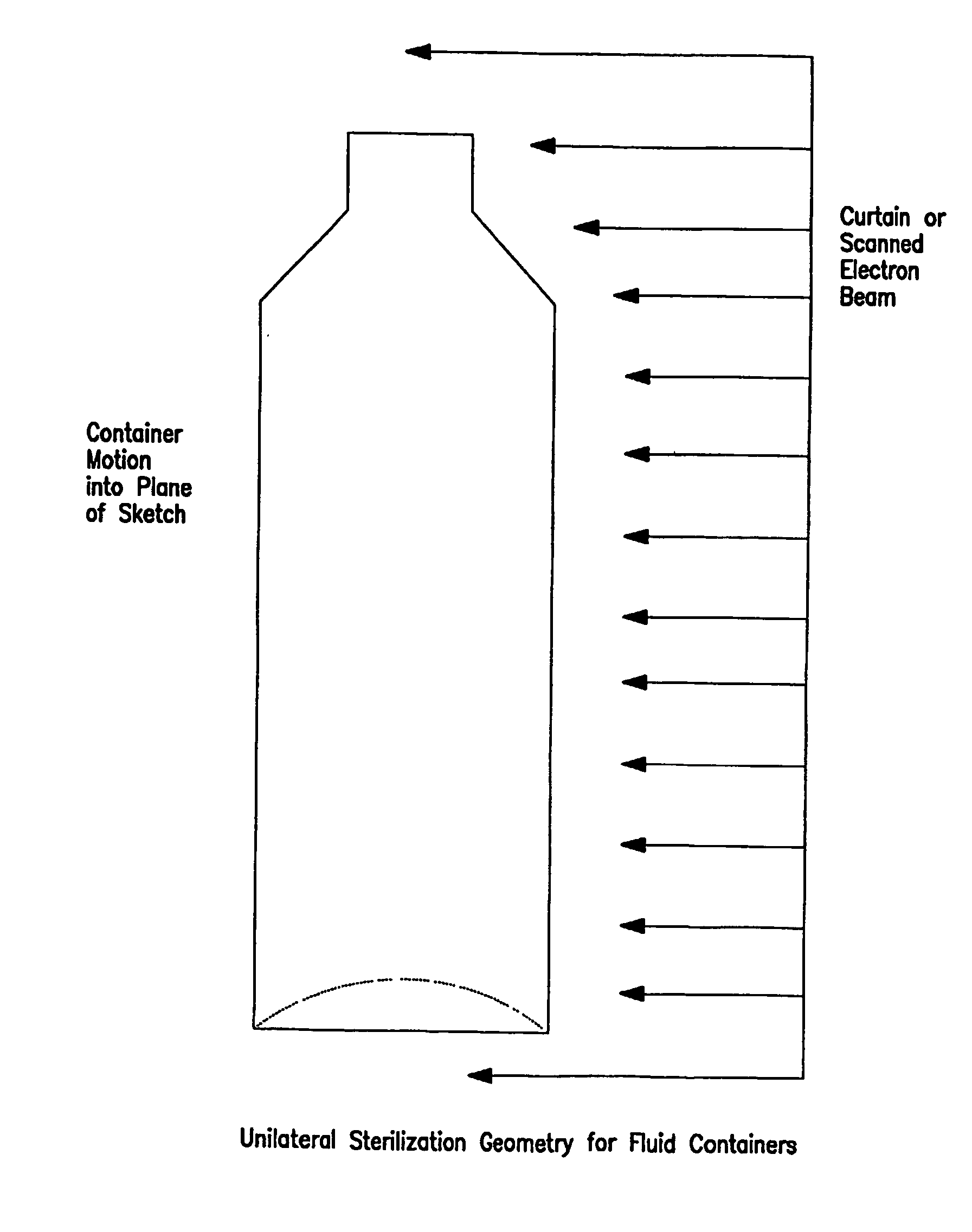
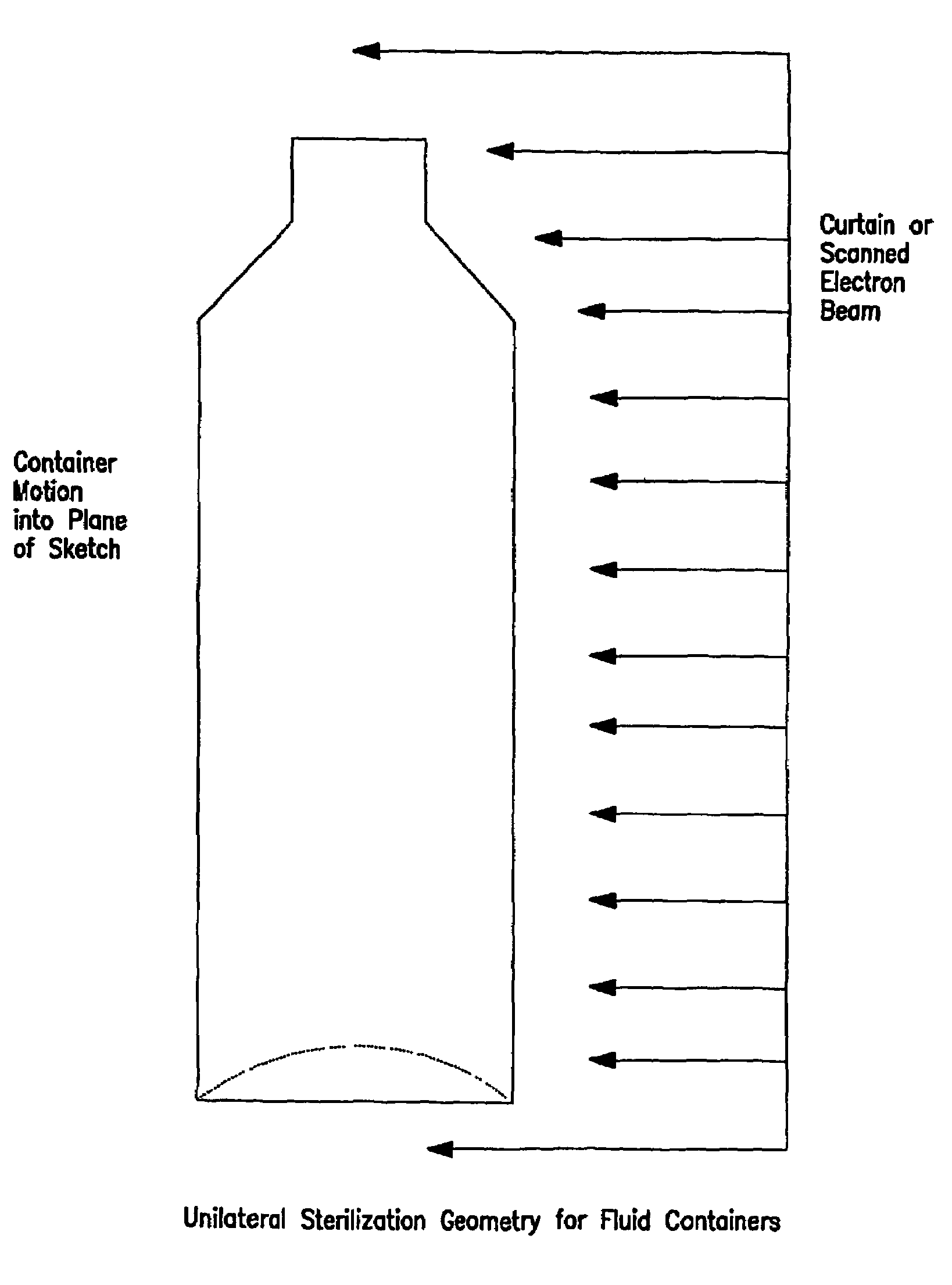
Process for electron sterilization of a container
InactiveUS20060192140A1Radiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsIrradiationElectron energy
Minimum electron energy is used for the sterilization of preformed containers in order to minimize the machinery size, cost and radiation shielding required for in-line use. The electron energy required is reduced by the use of one-sided (unilateral) irradiation wherein the dose delivered by the primary radiation to thicker portions of the containers is supplemented by the dose delivered by scattered electrons.
Owner:ELECTRON PROCESSING SYST
E-Beam Enhanced Decoupled Source for Semiconductor Processing
ActiveUS20120258606A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron injectionDensity ratio
A semiconductor substrate processing system includes a processing chamber and a substrate support defined to support a substrate in the processing chamber. The system also includes a plasma chamber defined separate from the processing chamber. The plasma chamber is defined to generate a plasma. The system also includes a plurality of fluid transmission pathways fluidly connecting the plasma chamber to the processing chamber. The plurality of fluid transmission pathways are defined to supply reactive constituents of the plasma from the plasma chamber to the processing chamber. The system further includes an electron injection device for injecting electrons into the processing chamber to control an electron energy distribution within the processing chamber so as to in turn control an ion-to-radical density ratio within the processing chamber. In one embodiment, an electron beam source is defined to transmit an electron beam through the processing chamber above and across the substrate support.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
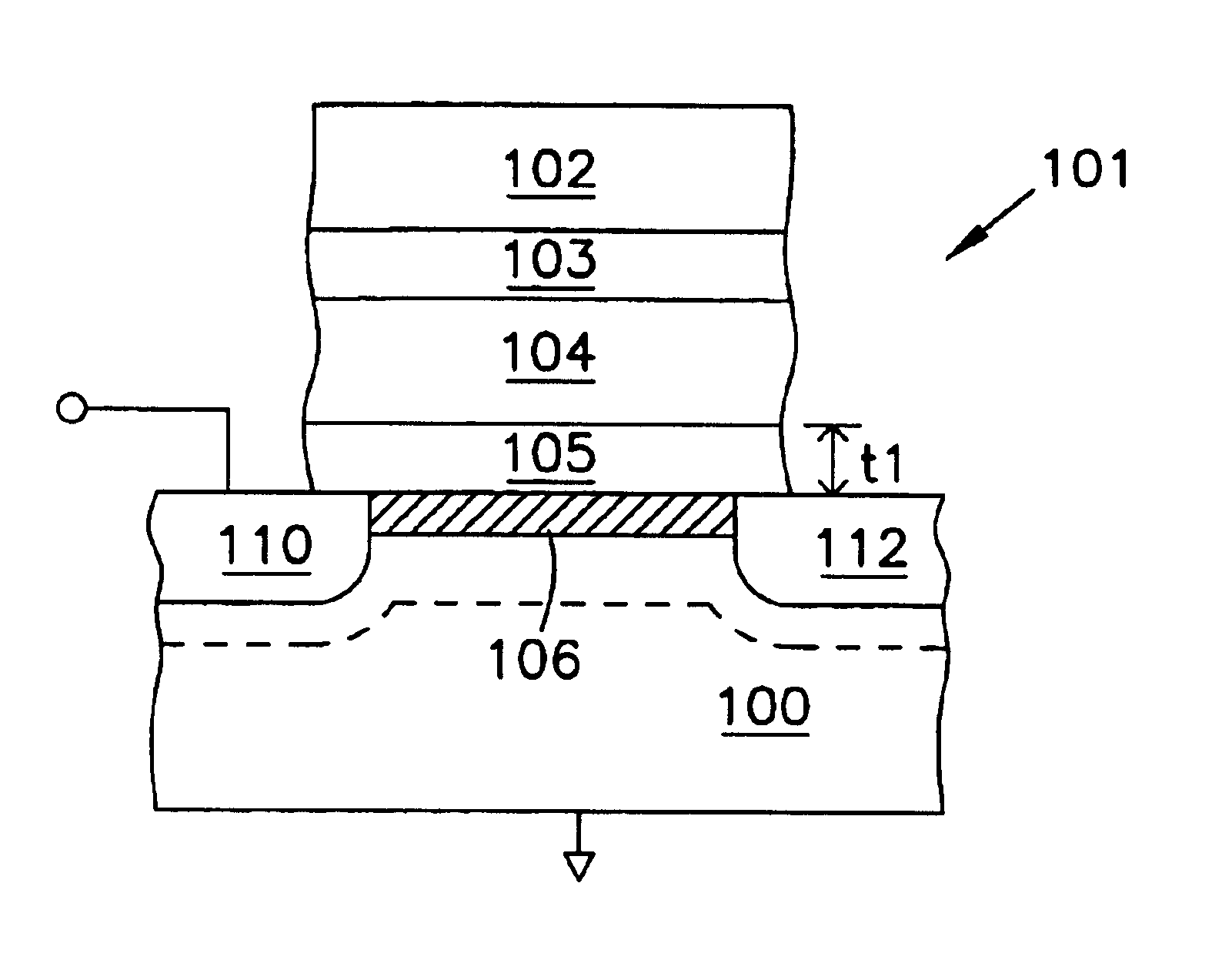
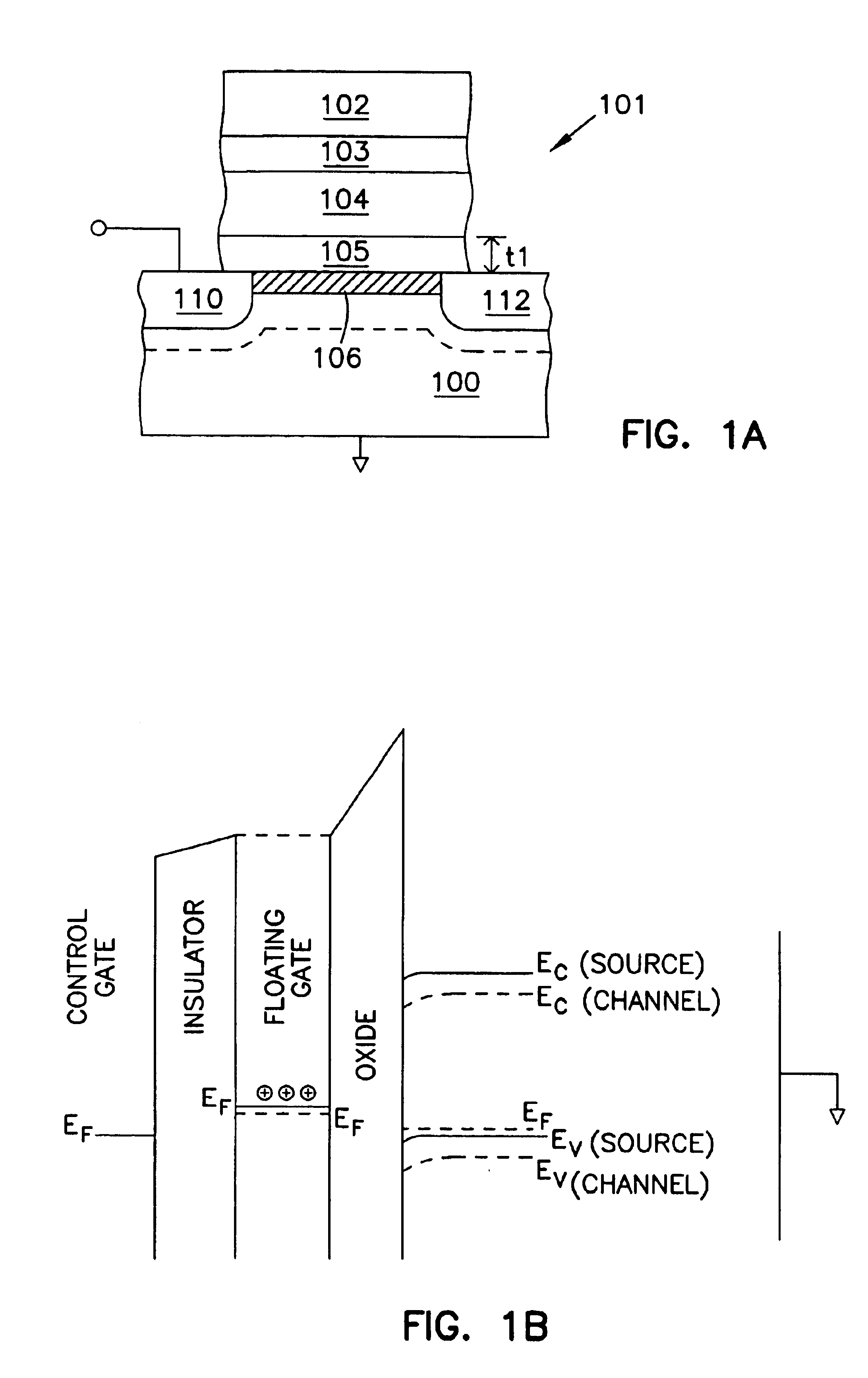
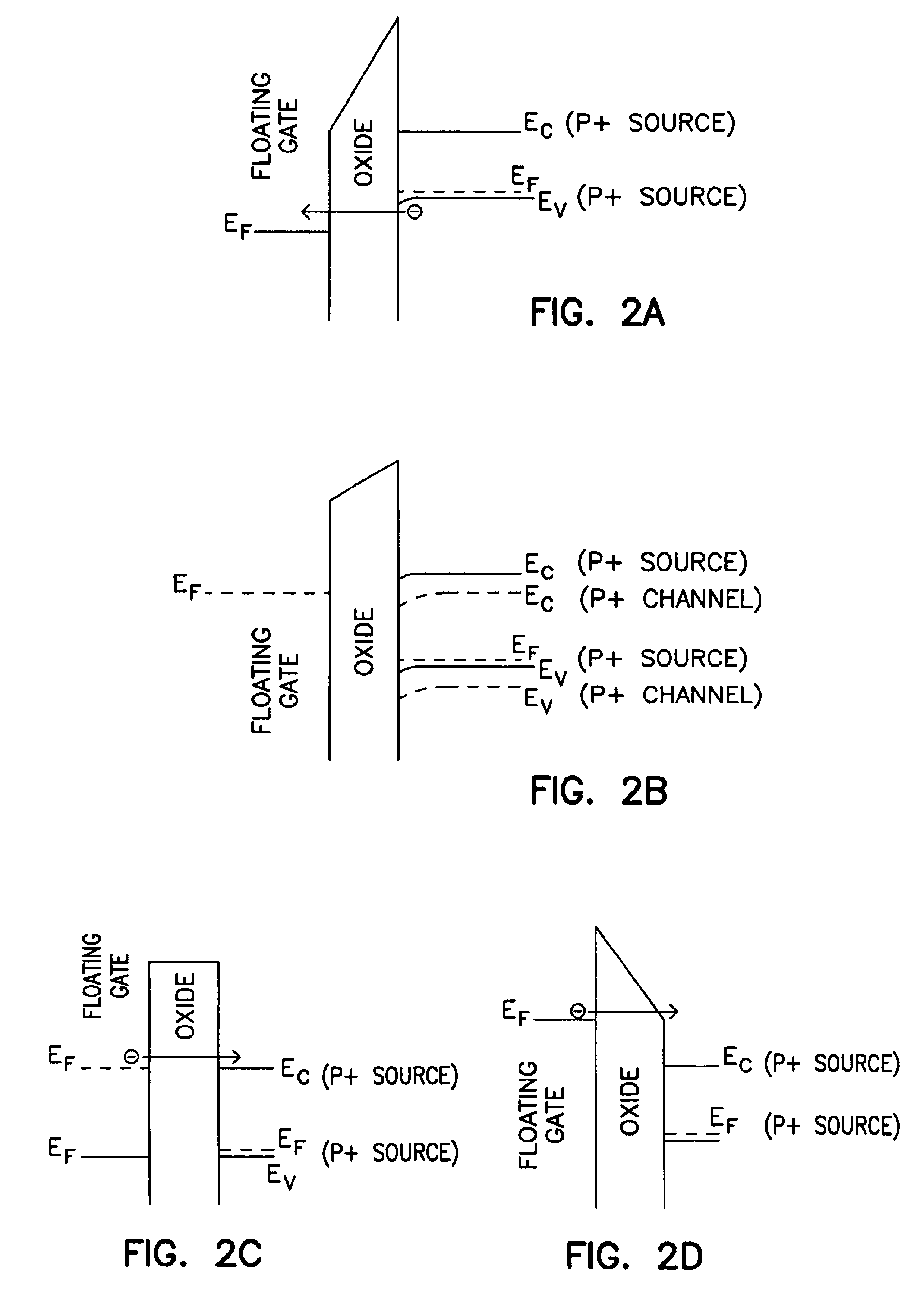
Static NVRAM with ultra thin tunnel oxides
Structures and methods involving non volatile depletion mode p-channel memory cells with an ultrathin tunnel oxide thicknesses, e.g. less than 50 Angstrom (Å), have been provided. Write and erase operations are performed by tunneling. The floating gate of the depletion mode p-channel memory cell is adapted to hold a fixed charge over a limited range of floating gate potentials or electron energies. There is a range potentials applied to the floating gate for which there are no final nor initial states in the silicon substrate or p+ source region. In this range of potentials there can be no charge leakage from the floating gate by tunneling or thermally assisted tunneling. The charge state of the floating gate will modulate the conductivity of the underlying transistor channel, with different stable and non-volatile charge states resulting in different conductivity states. Other aspects are also included.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Process for electron sterilization of a container
InactiveUS7145155B2Radiation applicationsElectrode and associated part arrangementsIrradiationRadiation shield
Minimum electron energy is used for the sterilization of preformed containers in order to minimize the machinery size, cost and radiation shielding required for in-line use. The electron energy required is reduced by the use of one-sided (unilateral) irradiation wherein the dose delivered by the primary radiation to thicker portions of the containers is supplemented by the dose delivered by scattered electrons.
Owner:ELECTRON PROCESSING SYST
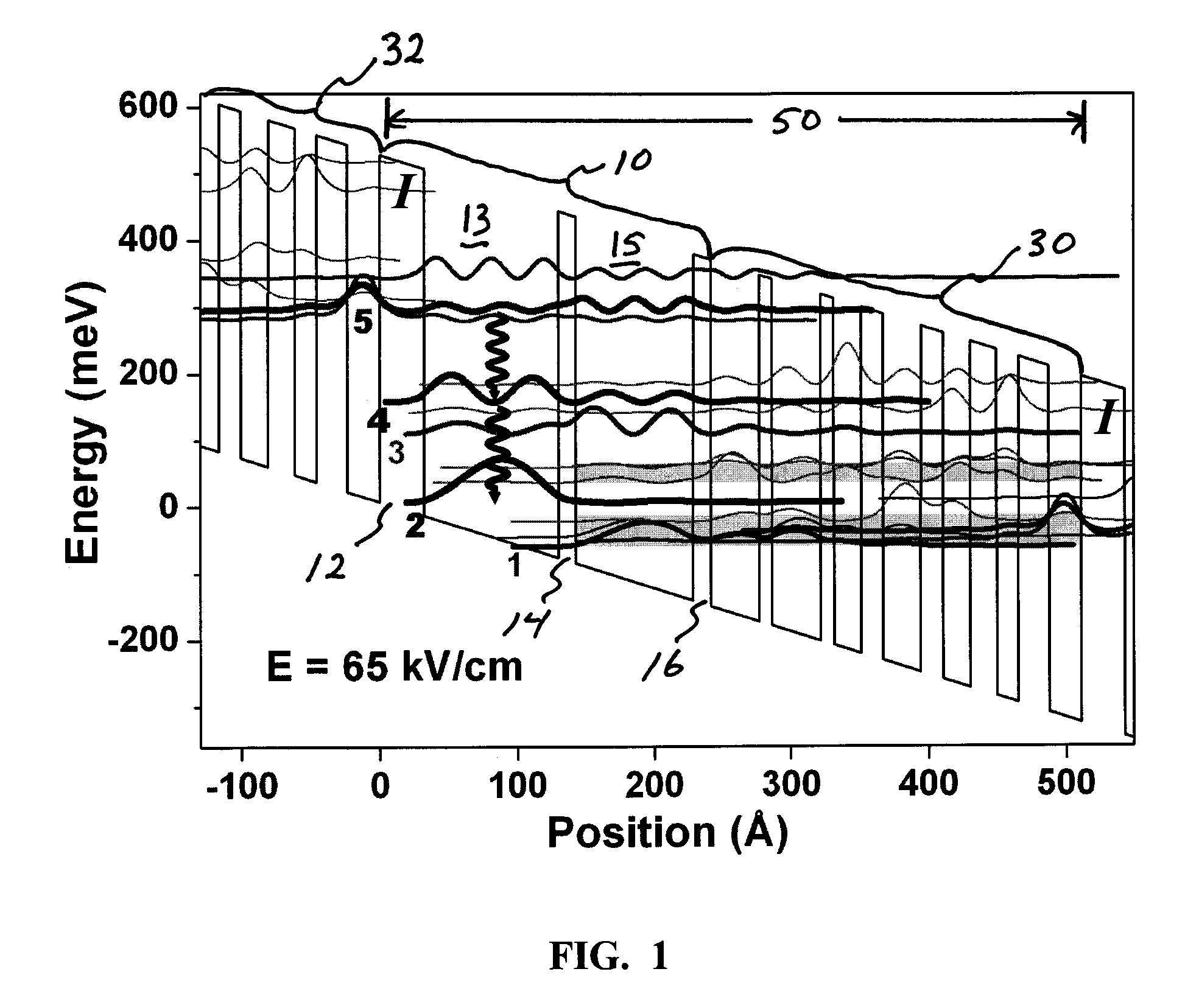
Excited state quantum cascade photon source
InactiveUS20080273565A1Lower level of energyLaser detailsLaser active region structureExcited stateQuantum well
A quantum cascade source, such as a QC laser, is provided comprising a plurality of repeat units each including an active region and an injector region. The active region includes at least two quantum wells that, in response to an applied electrical bias, provide a first, second, and third electron energy level, each resulting from a respective quantum well excited state. The first and second energy levels are configured so that an electron transition from the first energy level to the second energy level emits a photon of a selected wavelength. The second and third energy levels are configured so that an electron transition from the second energy level to the third energy level comprises a nonradiative transition to empty the second energy level sufficiently quickly to promote a population inversion between the first and second energy levels.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Quantum vacuum energy extraction
A system is disclosed for converting energy from the electromagnetic quantum vacuum available at any point in the universe to usable energy in the form of heat, electricity, mechanical energy or other forms of power. By suppressing electromagnetic quantum vacuum energy at appropriate frequencies a change may be effected in the electron energy levels which will result in the emission or release of energy. Mode suppression of electromagnetic quantum vacuum radiation is known to take place in Casimir cavities. A Casimir cavity refers to any region in which electromagnetic modes are suppressed or restricted. When atoms enter into suitable micro Casimir cavities a decrease in the orbital energies of electrons in atoms will thus occur. Such energy will be captured in the claimed devices. Upon emergence form such micro Casimir cavities the atoms will be re-energized by the ambient electromagnetic quantum vacuum. In this way energy is extracted locally and replenished globally from and by the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. This process may be repeated an unlimited number of times. This process is also consistent with the conservation of energy in that all usable energy does come at the expense of the energy content of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Similar effects may be produced by acting upon molecular bonds. Devices are described in which gas is recycled through a multiplicity of Casimir cavities. The disclosed devices are scalable in size and energy output for applications ranging from replacements for small batteries to power plant sized generators of electricity.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
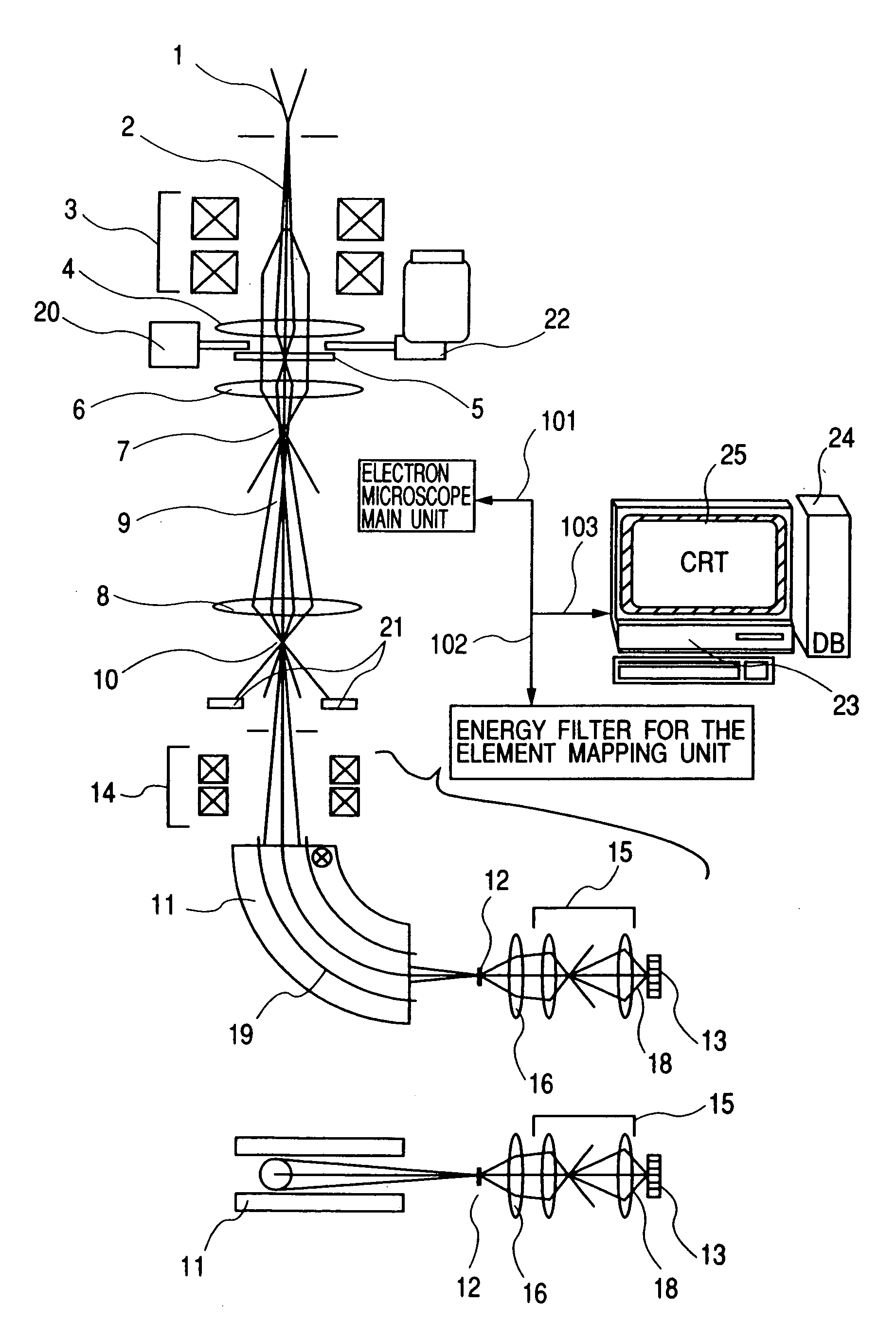
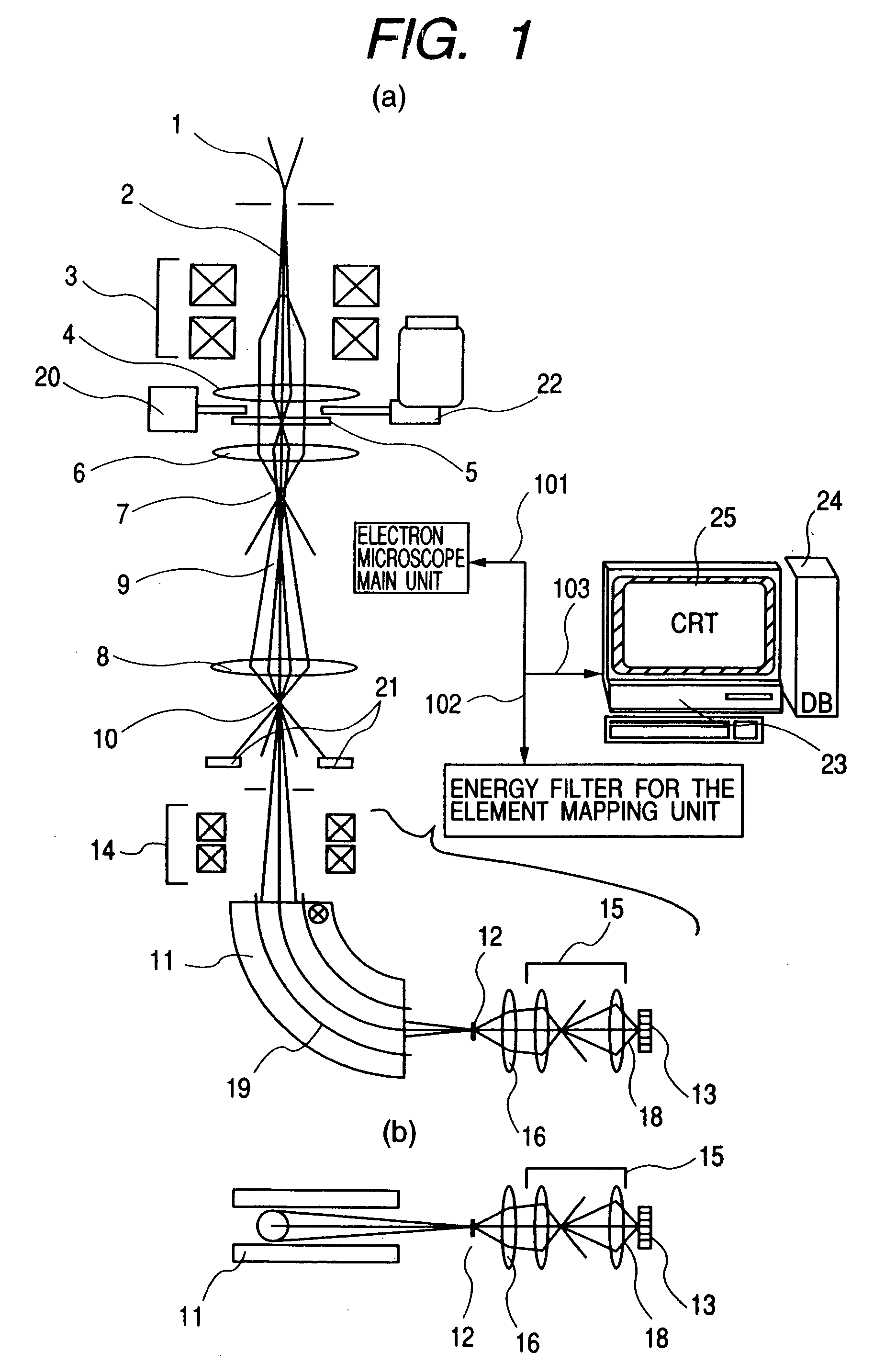
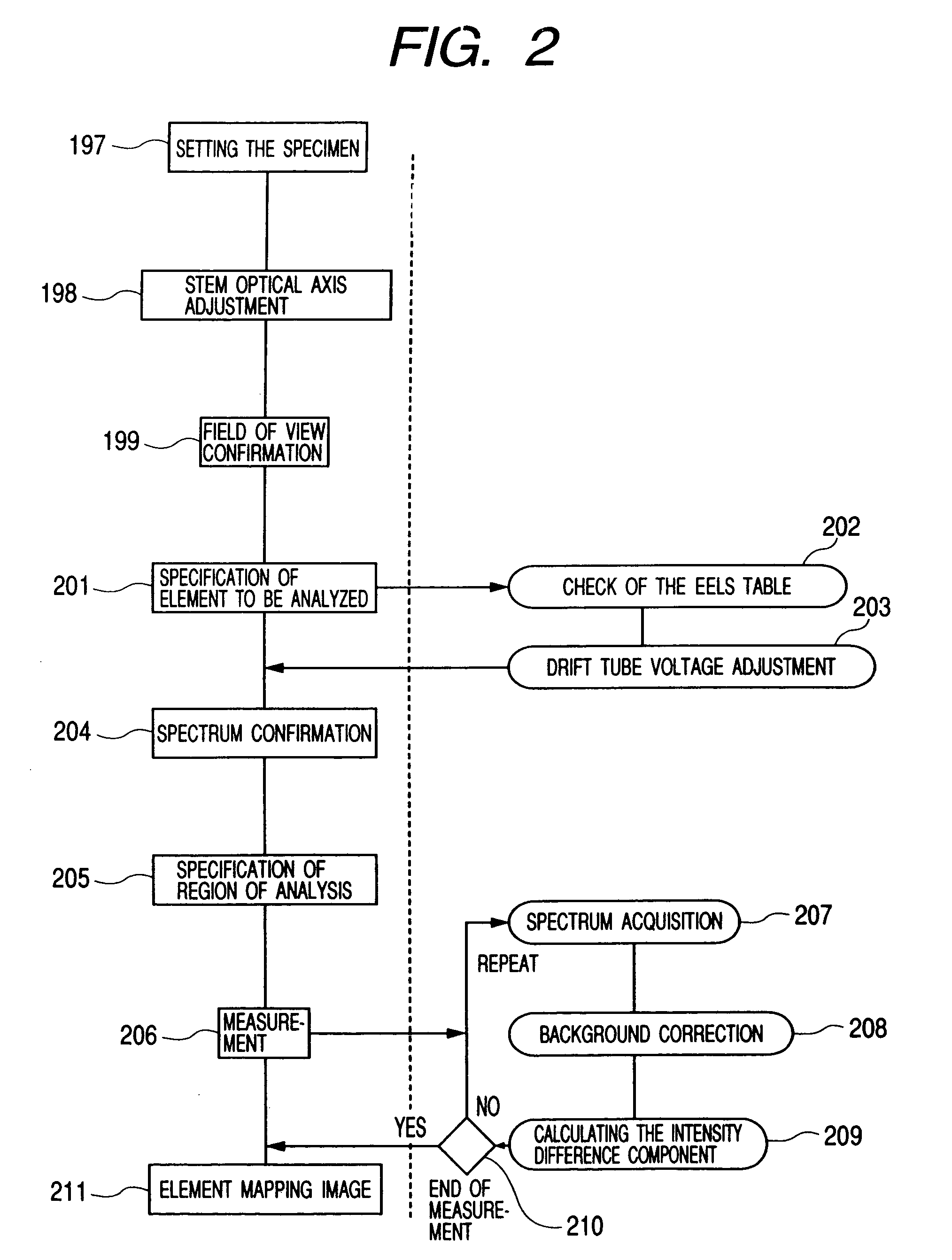
Element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method
InactiveUS20060011836A1Easy to operateHigh EELS spectrum energy stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeFrequency spectrum
There is provided an element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method that enable to acquire an element mapping image very easily. On the scanning transmission electron microscope, the electron beam transmitted through an object to be analyzed enters into the element mapping unit. The electron beam is analyzed of its energy into spectrum by an electron spectrometer and an electron energy loss spectrum is acquired. Because the acceleration voltage data for each element and window data for 2-window method, 3-window method or contrast tuning method are already stored in a database and accordingly the spectrum measurement is carried out immediately even when an element to be analyzed is changed to another, the operator can confirm a two-dimensional element distribution map immediately. Besides, because every electron beam that enters into an energy filter passes through the object point, aberration strain in the electron spectrometer can be minimized and higher energy stability can be achieved. As a result, drift of the electron energy loss spectrum acquired by analyzing the electron beam into spectrum can be minimized and element distribution with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Detector system for use with transmission electron microscope spectroscopy
ActiveUS8334512B2Improve performanceRapid and accurate informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectron spectroscopyElectron microscope
A detector system for a transmission electron microscope includes a first detector for recording a pattern and a second detector for recording a position of a feature of the pattern. The second detector is preferably a position sensitive detector that provides accurate, rapid position information that can be used as feedback to stabilize the position of the pattern on the first detector. In one embodiment, the first detector detects an electron energy loss electron spectrum, and the second detector, positioned behind the first detector and detecting electrons that pass through the first detector, detects the position of the zero-loss peak and adjusts the electron path to stabilize the position of the spectrum on the first detector.
Owner:FEI CO
Subsurface imaging using an electron beam
ActiveUS20060219953A1Sufficient energyAccurate locationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLight beamSubsurface imaging
A method of navigating or endpointing a microscopic structure by subsurface imaging using a beam of electrons having sufficient energy to penetrate the surface and produce a subsurface image. For endpointing, when the subsurface image become relatively clear at a known electron energy, a user knows that he is approaching the buried feature. For navigating, a subsurface image can be formed of fiducials or other features to determine the position of the beam on the device.
Owner:FEI CO
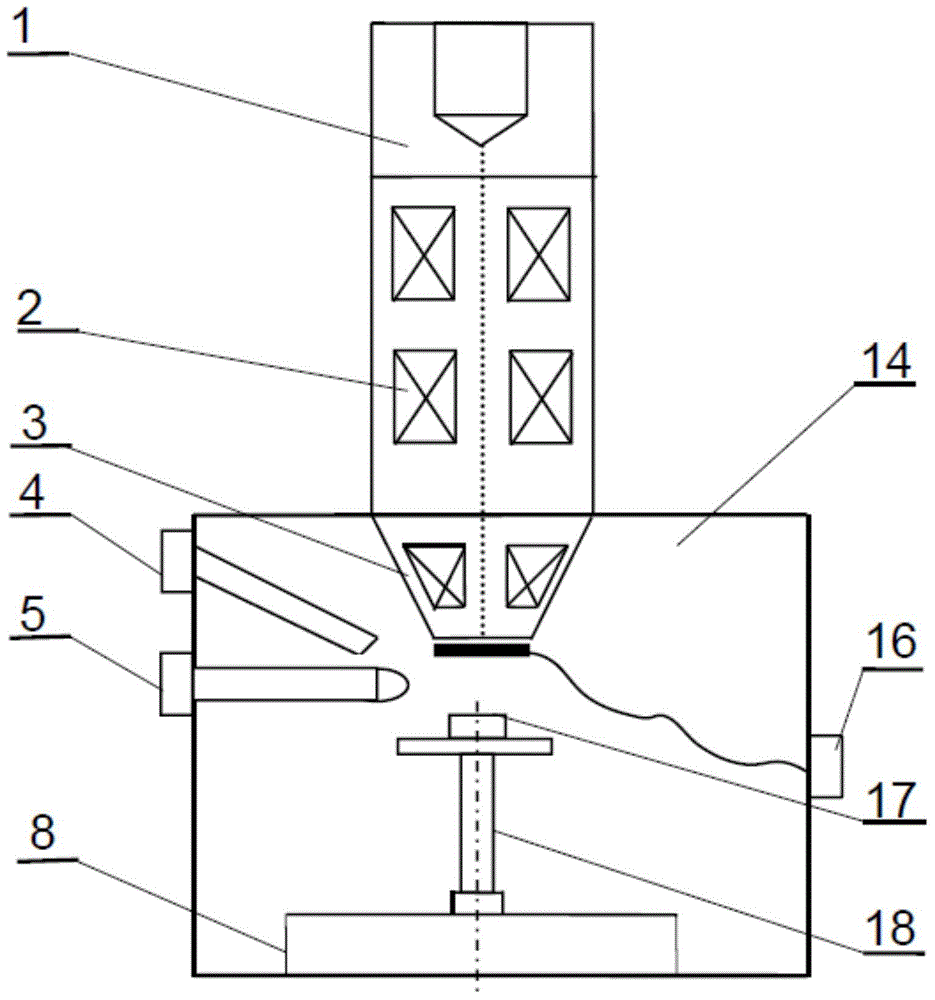
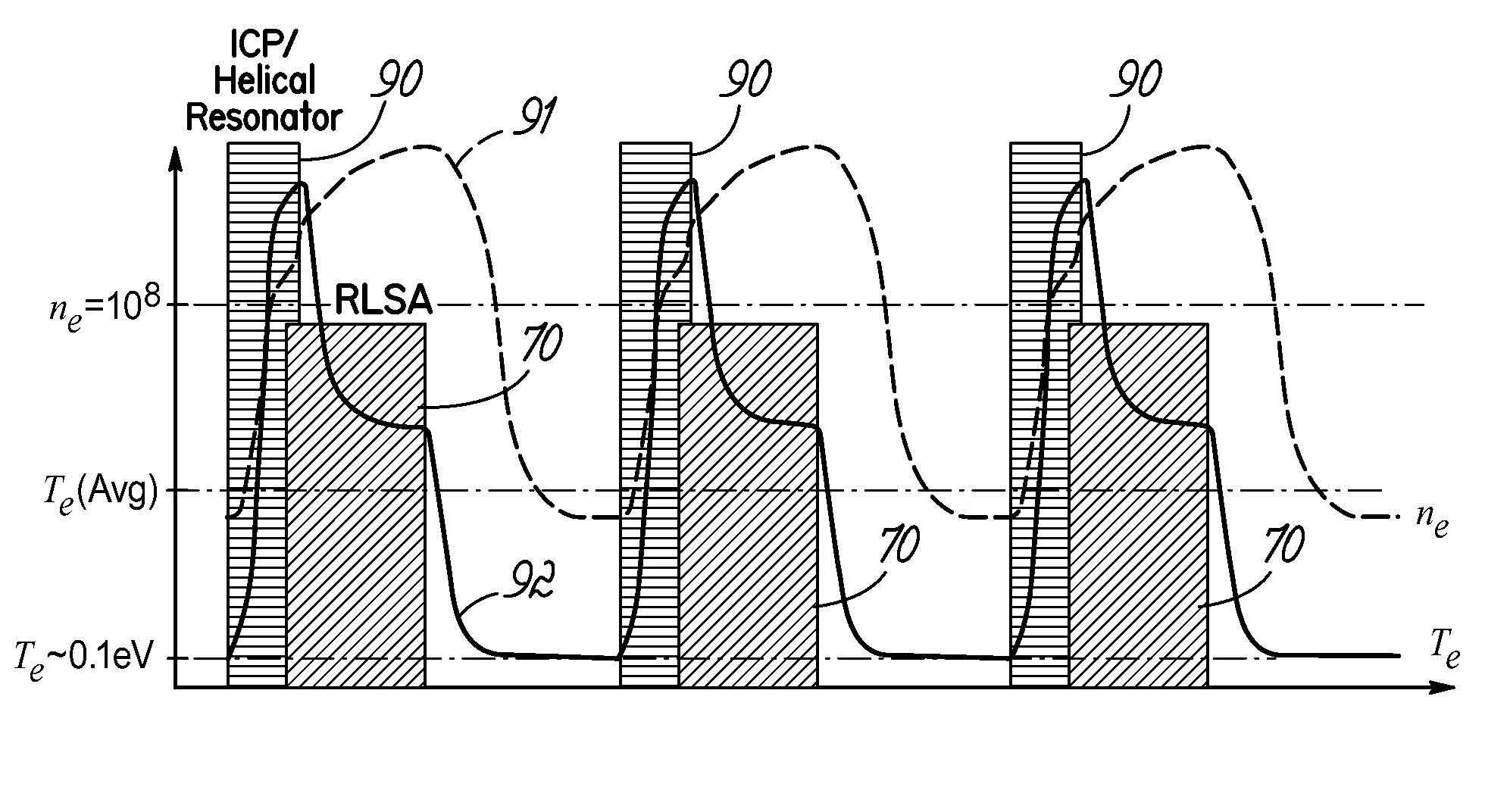
Low electron temperature, edge-density enhanced, surface wave plasma (SWP) processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130270997A1High degree of ionizationReduces temperature of electronElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceElectron temperature
A surface wave plasma (SWP) source couples microwave (MW) energy into a processing chamber through, for example, a radial line slot antenna, to result in a low mean electron energy (Te). An ICP source, is provided between the SWP source and the substrate and is energized at a low power, less than 100 watts for 300 mm wafers, for example, at about 25 watts. The ICP source couples energy through a peripheral electric dipole coil to reduce capacitive coupling.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
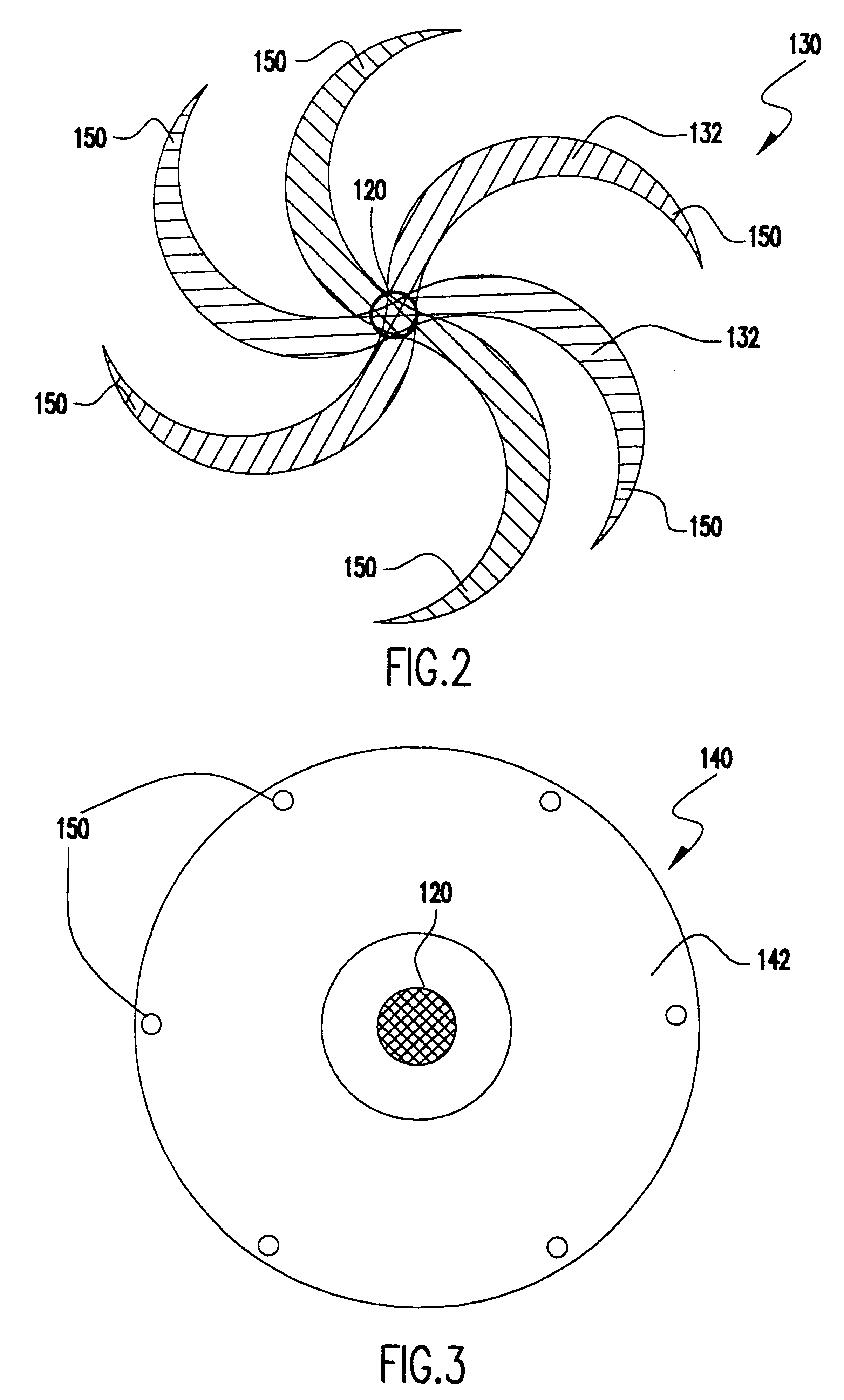
Cellular, electron cooled storage ring system and method for fusion power generation
InactiveUS20110158369A1Large output levelSave energyNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorThermal energyFusion power
A cellular electron cooled storage ring system and method for achieving particle-fusion based energy, including a vacuum chamber to allow electron beam and ion beam merging and separation, cathodes to generate the electron beams, collectors to collect the electron beams, and magnetic field generation devices to guide the electrons and ions on their desired trajectories as well as contain neutralizing particles. By overlapping the electron and ion beams, thermal energy is transferred from the ion beams to the electron beams, which allows the invention to overcome particle losses due to resonances, scattering and heating of the ion beams. Advantageously, ions are accelerated to an energy that is near optimum for fusion reactions to occur, and uses electron energies that maintain this advantageous situation. Advantageously, the recirculation of ions that do not fuse or scatter at too large of an angle is allowed, giving such ions additional chances to participate in a desired fusion reaction. Advantageously, the invention allows for a continual addition of new ions to be added to the circulating ions already in the system. This combination of advantages results in a significant improvement in the predicted output power to input power ratio over previous particle fusion technologies. The invention will also enable improved yields of fast neutrons for materials testing.
Owner:LARSON DELBERT JOHN
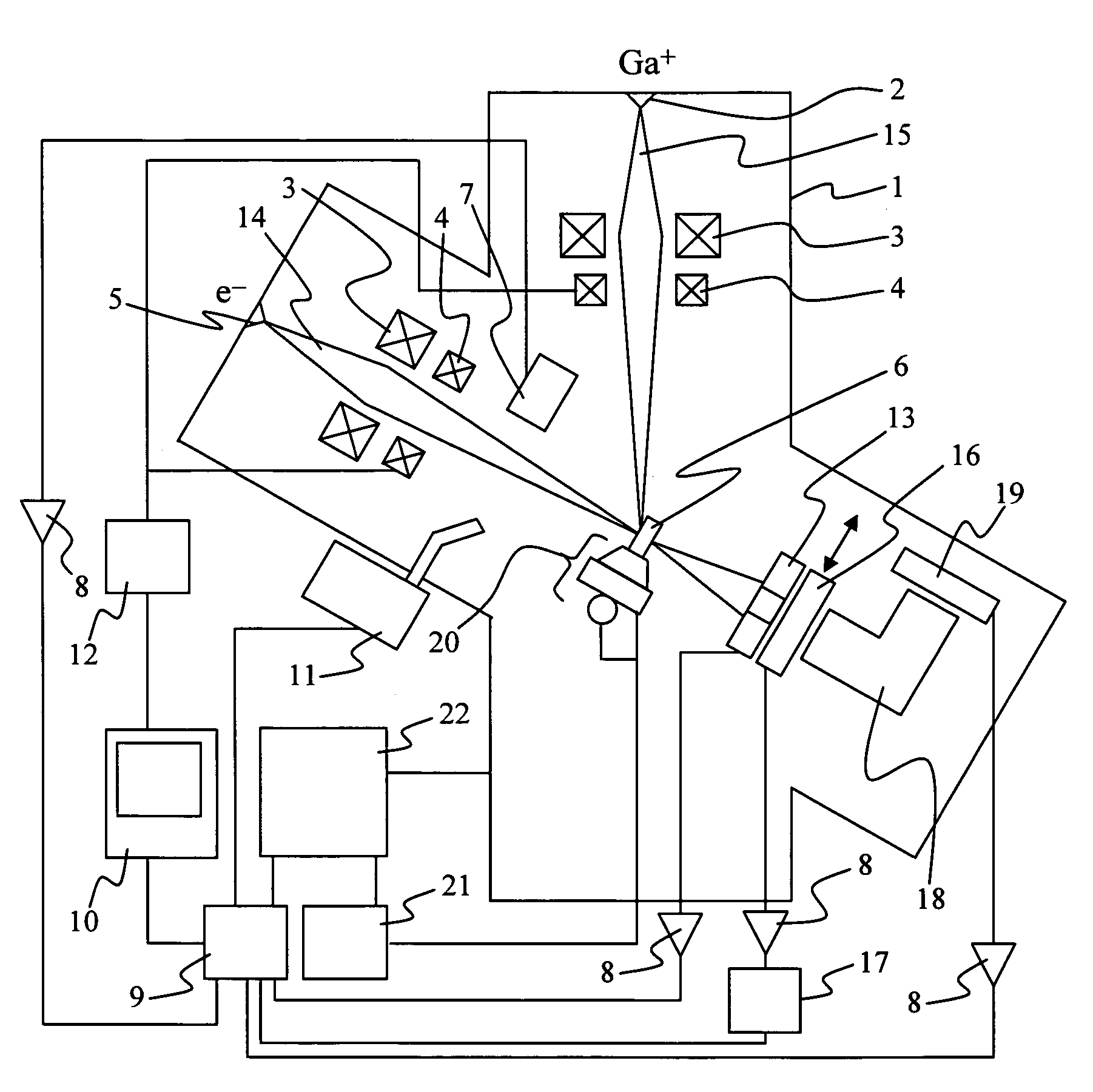
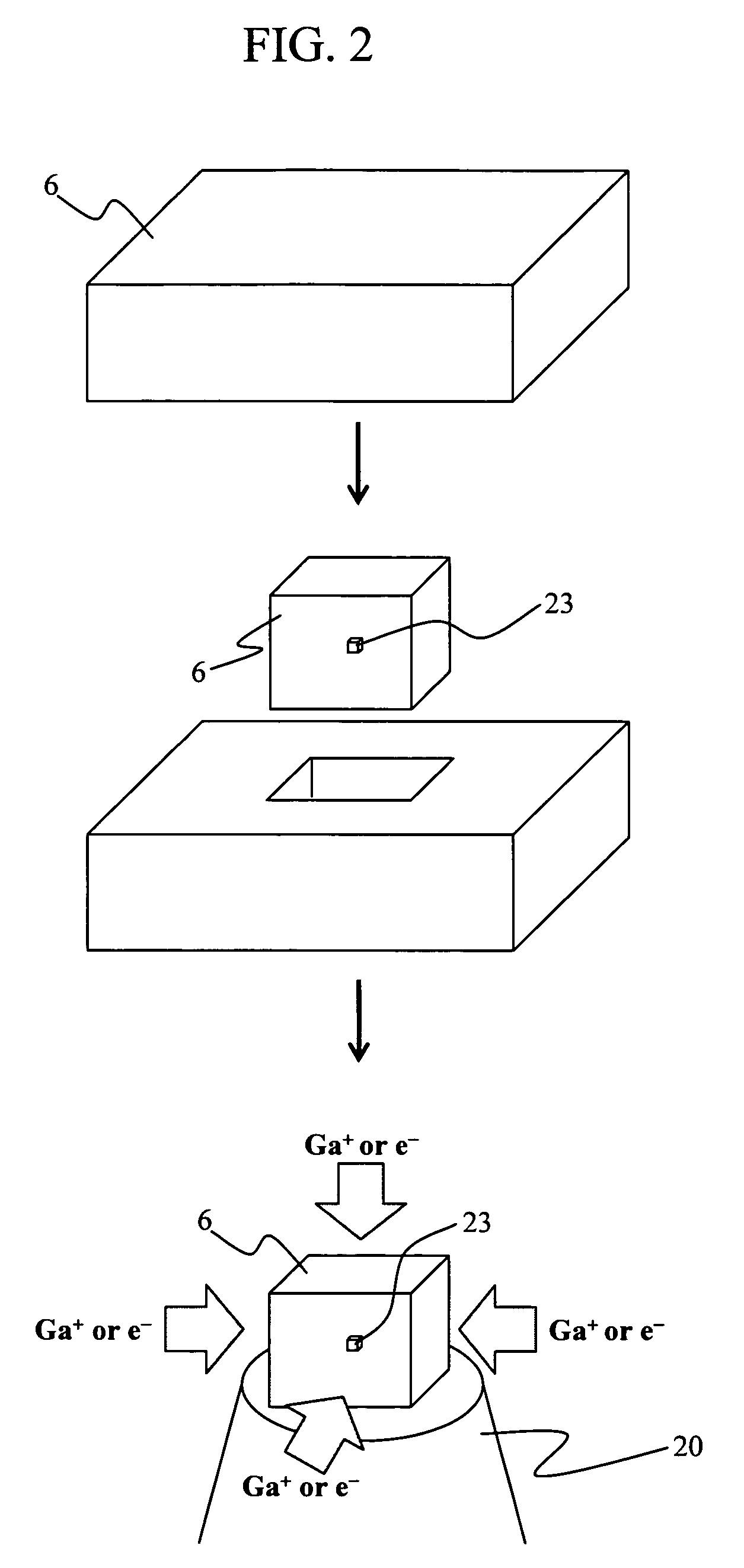
Focused ion beam system and a method of sample preparation and observation
InactiveUS7612337B2Accurate settingEasy to stackElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapySample rotationX-ray
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
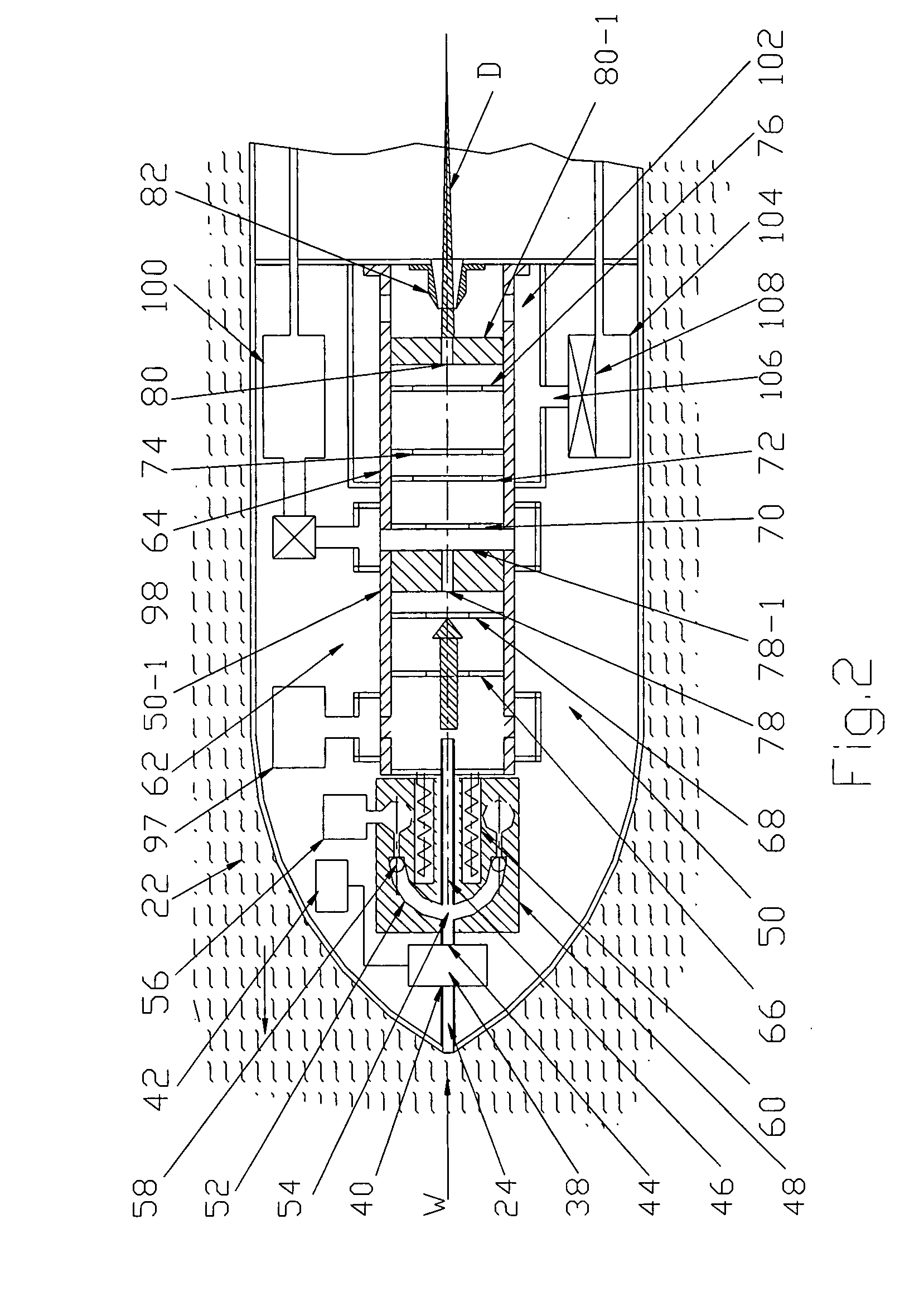
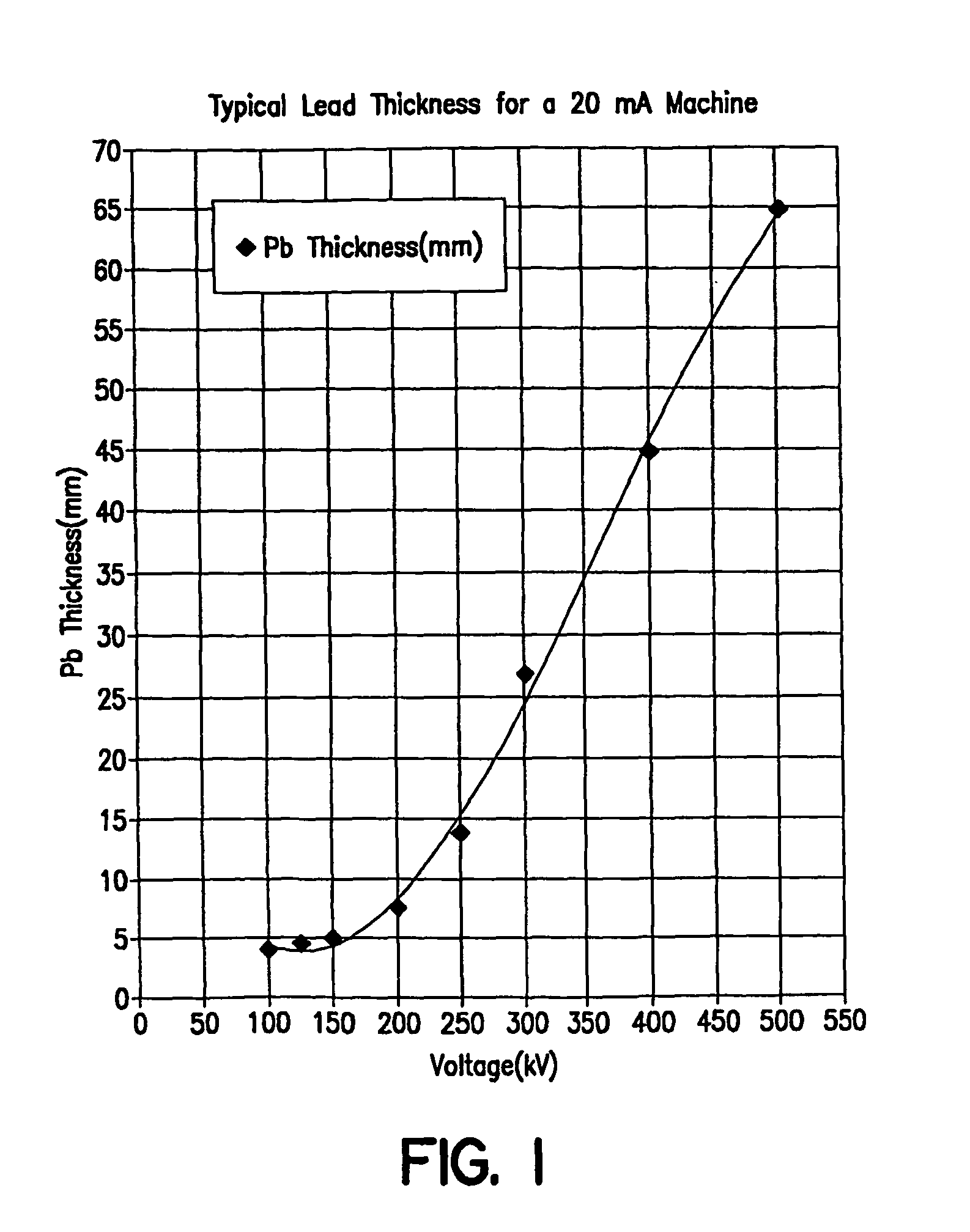
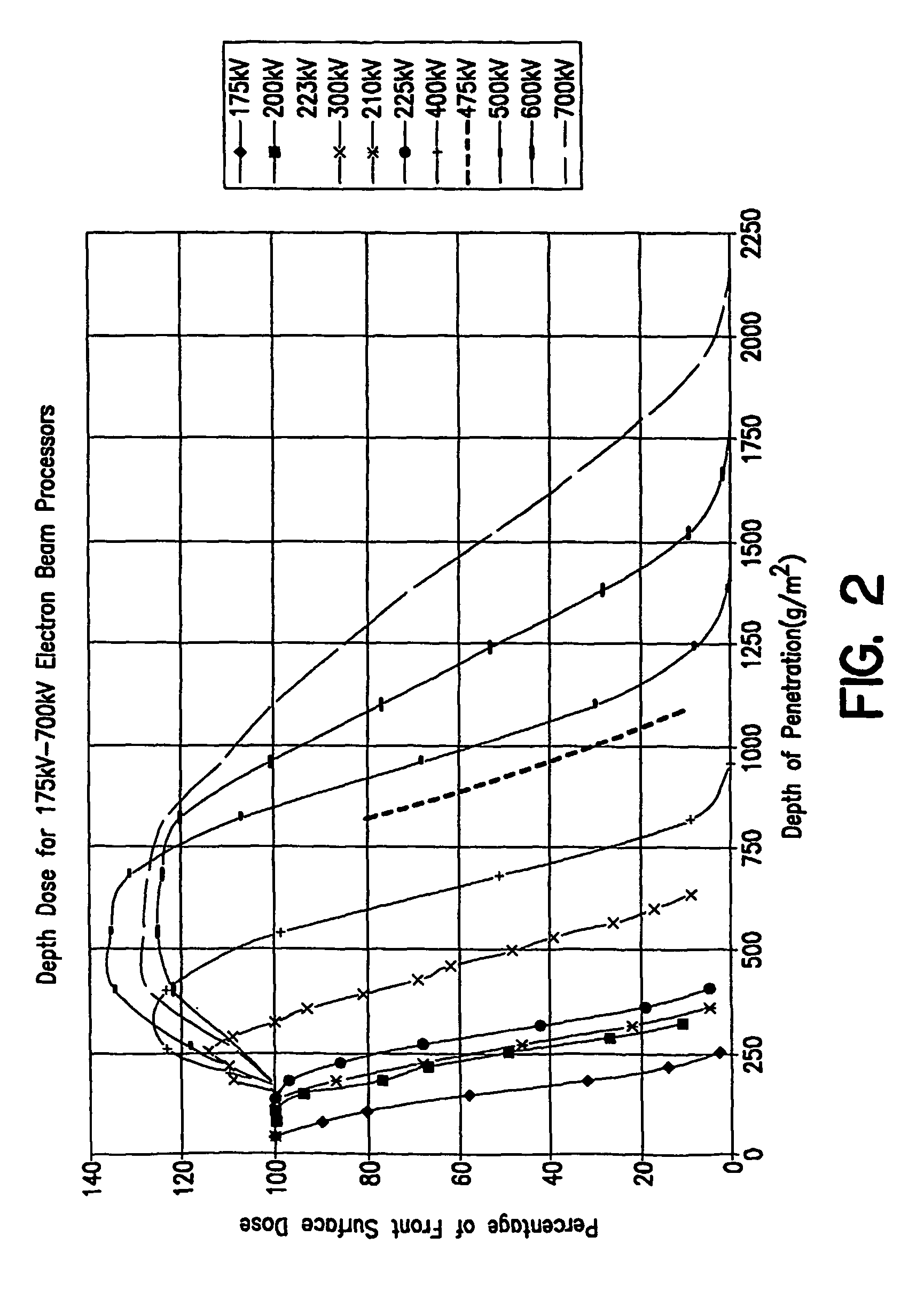
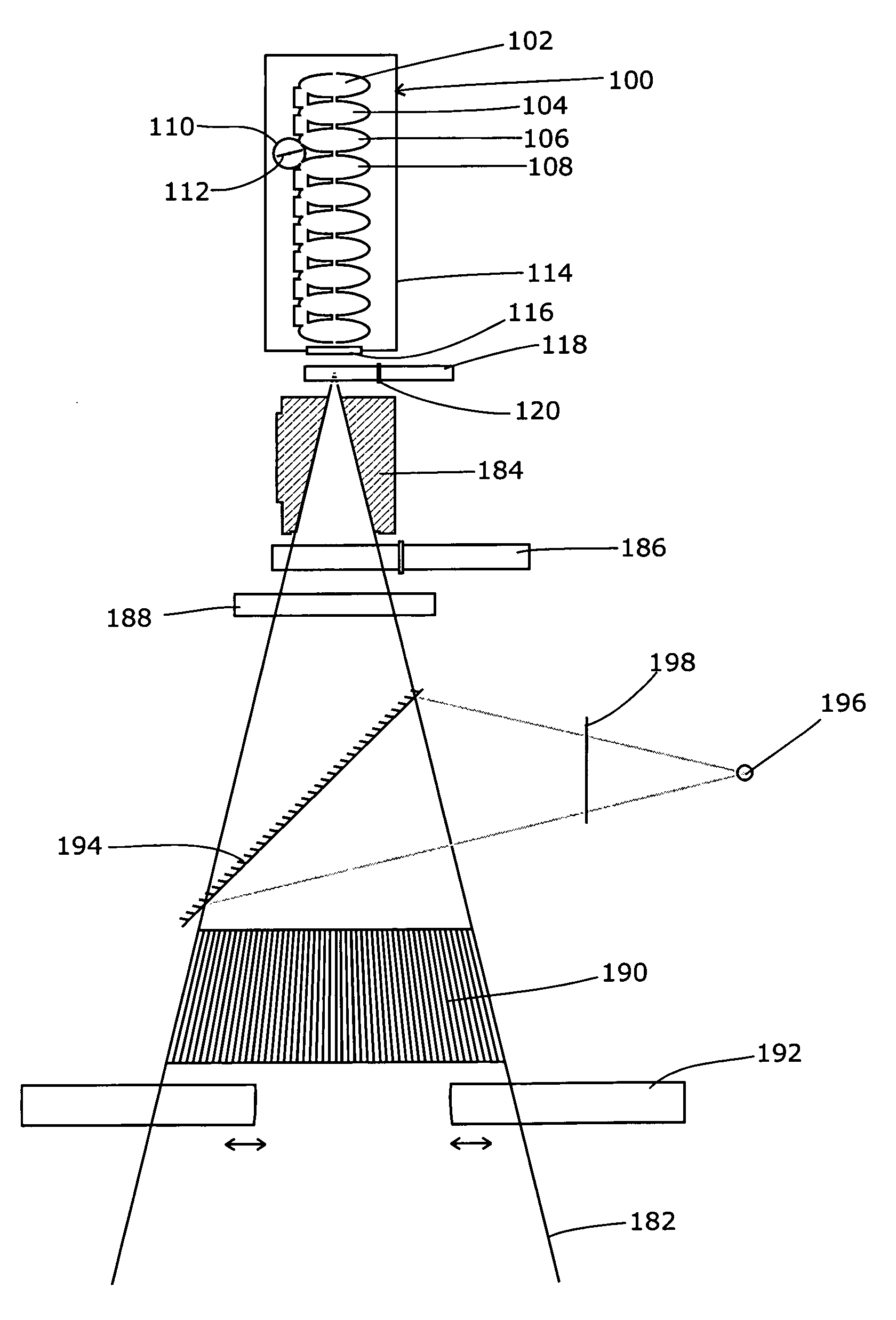
X-ray Apparatus
X-ray apparatus comprises a linear accelerator adapted to produce a beam of electrons at one of at least two selectable energies and being controlled to change the selected energy on a periodic basis, and a target to which the beam is directed thereby to produce a beam of x-radiation, the target being non-homogenous and being driven to move periodically in synchrony with the change of the selected energy. In this way, the target can move so that a different part is exposed to the electron beam when different pulses arrive. This enables the appropriate target material to be employed depending on the selected energy. The easiest form of periodic movement for the target is likely to be a rotational movement. The target can be immersed in a coolant fluid such as water. The linear accelerator can be of the type disclosed in WO2006 / 097697A1. The target preferably contains at least one exposed area of tungsten and / or at least one exposed area of carbon. These can be present as inhomogeneities in the material of which the target is composed, such as Carbon inserts in a Tungsten substrate (or vice versa), alternating segments of Carbon and Tungsten, Carbon and Tungsten inserts in a substrate of a third material, or arrangements involving other materials in addition to or instead of Carbon and / or Tungsten. Alternatively, the target can be of a homogenous material but have inhomogeneities in its thickness to cater for the different electron energies. The same concept can be applied to the filter. A detector can be provided, operating in synchrony with the energy variation. Such an x-ray apparatus can form a part of a radiotherapy apparatus, in which case the first selected energy can be a diagnostic energy and a second selected energy a therapeutic energy.
Owner:ELEKTA AB +1
Detector System for Use with Transmission Electron Microscope Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20120049060A1Improve performanceRapid and accurate informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectron spectroscopyElectron microscope
A detector system for a transmission electron microscope includes a first detector for recording a pattern and a second detector for recording a position of a feature of the pattern. The second detector is preferably a position sensitive detector that provides accurate, rapid position information that can be used as feedback to stabilize the position of the pattern on the first detector. In one embodiment, the first detector detects an electron energy loss electron spectrum, and the second detector, positioned behind the first detector and detecting electrons that pass through the first detector, detects the position of the zero-loss peak and adjusts the electron path to stabilize the position of the spectrum on the first detector.
Owner:FEI CO
Delivery of Low Pressure Dopant Gas to a High Voltage Ion Source
InactiveUS20080220596A1Ionization suppressionReduce the impactMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDelivery systemHigh voltage
A system for delivery of low-pressure dopant gas to a high-voltage ion source in the doping of semiconductor substrates, in which undesired ionization of the gas is suppressed prior to entry into the high-voltage ion source, by modulating electron energy upstream of the high-voltage ion source so that electron acceleration effects are reduced to below a level supporting an electronic ionization cascade. The gas delivery system in a specific application includes a gas flow passage, a voltage generator electrically coupled with at least a portion of the gas flow passage to impose an electric field thereon, and an obstructive structure that is deployed to modulate acceleration length of electrons of the low-pressure gas in relation to ionization potential of the gas, to suppress ionization in the gas flow passage.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Device and method for transmission-scattering imaging of nanometer liquid sample in scanning electron microscope
ActiveCN104897700AImprove imaging resolutionHigh magnificationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionSpectroscopyScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses a device and a method for transmission-scattering imaging of a nanometer liquid sample in a scanning electron microscope, belongs to the technical field of electronic micro-analysis devices, and particularly relates to the technical field of reflection and transmission-scattering imaging of the nanometer liquid sample in the scanning electron microscope (SEM). The device and the method are characterized in that a transmission-scattering electronic detector (TSD) is mounted in a sample chamber of the SEM and 5-10 mm under a thin window of the nanometer liquid sample; under the condition that the incident electron energy is 15-30 keV, a transmission-scattering electron image with a resolution ratio of several nanometers, an amplification factor of 50-100000 times and high image contrast can be formed for several to 500 nanometers of nano-particles in a sealed liquid; the TSD is suitable for being mounted in various SEMs, and can be cooperatively used with a secondary electron detector (ETD), an energy disperse spectroscopy (EDS) and a cathode fluorescence spectrometer (CL) for observation of such nanometer-like materials as metal, semiconductors, inorganic matters, organic matters, composites and biological matters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device for obtaining the image and/or spectra of electron energy loss
ActiveUS7642513B2Maintain stabilityMaintain precisionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputer scienceImage capture
The inventive device for obtaining the electron energy loss image and / or spectra includes an image sensor, a control for at least two deflectors for alternately exposing at least two photosensitive parts of the image sensor, sensor reading means for generating the representative signal of an image captured by each photosensitive part of the image sensor, means for synchronizing the deflector and the reading means for successively controlling the exposition of the photosensitive part and the reading of the other photosensitive part for each photosensitive part and means for combining the two image parts in such a way that a spectrum is formed.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Low electron temperature microwave surface-wave plasma (SWP) processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS8968588B2High degree of ionizationImprove uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectron temperaturePlasma density
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
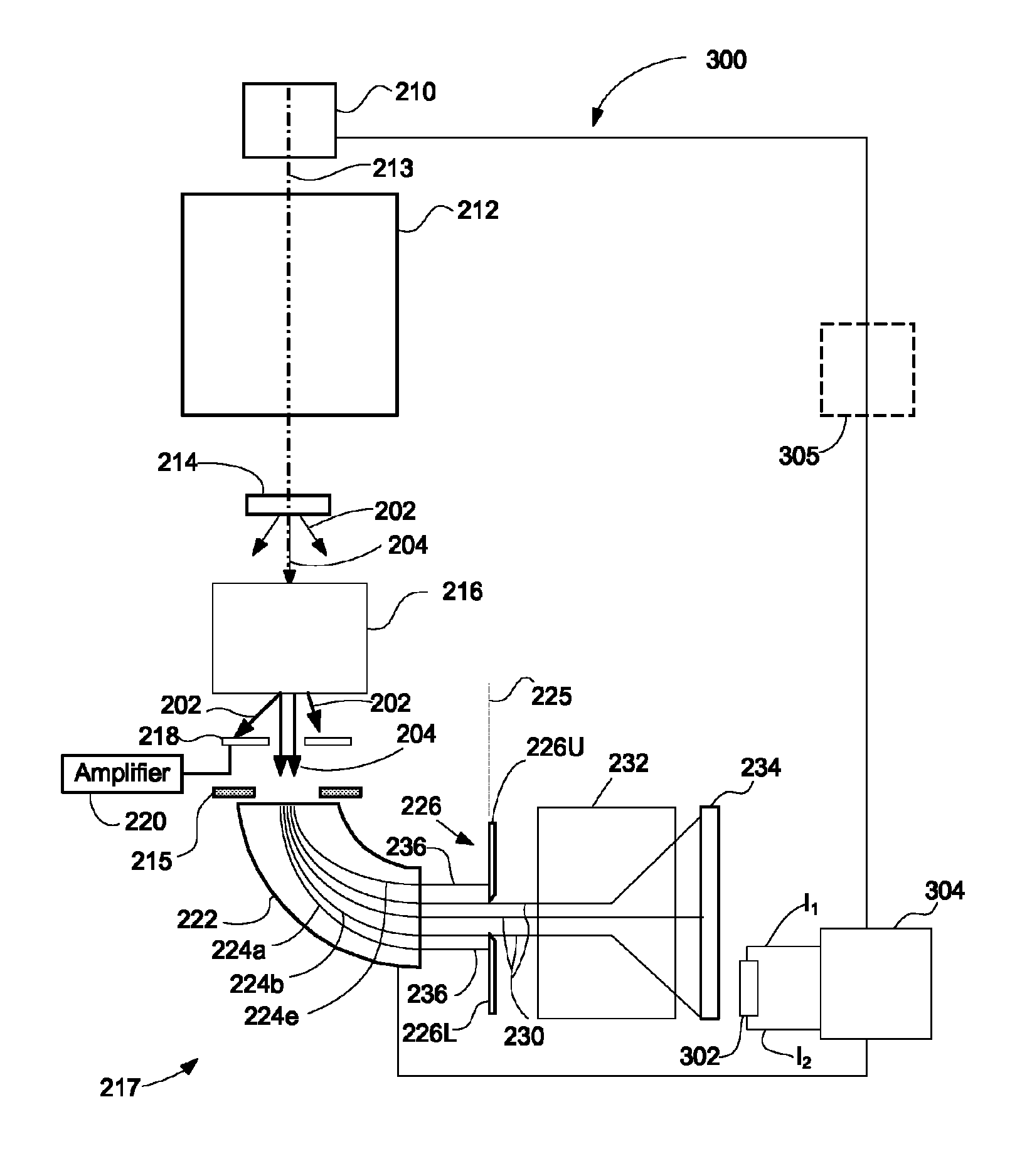
Multichannel Energy Analyzer for Charged Particles
InactiveUS20080290287A1High resolutionGuaranteed normal transmissionThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersElectricityEnergy analyser
The present invention provides charged particle energy deflectors, analyzers, devices, device components and methods for terminating charged particle systems and electrically isolating device components. One embodiment of the present invention provides a transparent field termination system for a cylindrical charged particle deflector that is capable of providing an electric field that closely approximates the substantially logarithmically varying electric field of the deflector. The present invention also provides multichannel charged particle analyzers and multichannel EEL spectrometers capable of measuring charged particle energy distributions, including electron energy distributions, with enhanced resolution and sensitivity compared to conventional analyzers.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com