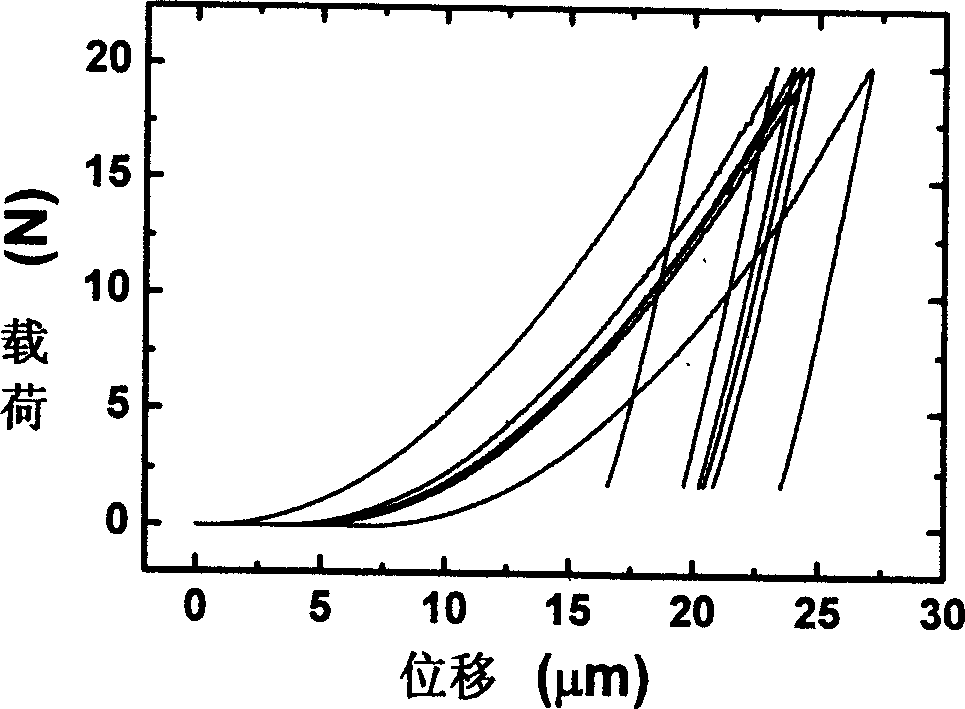
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1041 results about "Materials testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Materials testing is a well-established technique used to determine the physical and mechanical properties of raw materials and components from a human hair to steel, composite materials and ceramics.
Material flowing deformation disturbed effect testing system and testing method thereof
InactiveCN1948945ASimple structureEvenly loadedFlow propertiesMaterial strength using single impulsive forceMaterials testingAxial pressure
The invention discloses material fluid deformation disturbance effect experimental system and method. It includes dead load loading system realized by loading system, crankshaft force enlarging device, and force transmission connecting rod, disturbance loading system realized by impact and blasting disturbance loading devices, confining pressure loading system realized by tri-axial pressure tank includes closed box set ring capsule. The material fluid deformation disturbance effect experimental system can realize uniaxial and tri-axial fluid deformation experiences, uniaxial and tri-axial fluid deformation disturbance experiments for the testing specimen. It has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, precise testing, suiting for various materials testing specimen to do fluid deformation disturbance experiment, especially for rock testing specimen.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Methods and instruments for materials testing
ActiveUS20090056427A1Improve abilitiesIncreases ease and speedDiagnostics using pressureSurgeryMaterials testingHand held
Methods and instruments for characterizing a material, such as the properties of bone in a living human subject, using a test probe constructed for insertion into the material and a reference probe aligned with the test probe in a housing. The housing is hand held or placed so that the reference probe contacts the surface of the material under pressure applied either by hand or by the weight of the housing. The test probe is inserted into the material to indent the material while maintaining the reference probe substantially under the hand pressure or weight of the housing allowing evaluation of a property of the material related to indentation of the material by the probe. Force can be generated by a voice coil in a magnet structure to the end of which the test probe is connected and supported in the magnet structure by a flexure, opposing flexures, a linear translation stage, or a linear bearing. Optionally, a measurement unit containing the test probe and reference probe is connected to a base unit with a wireless connection, allowing in the field material testing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
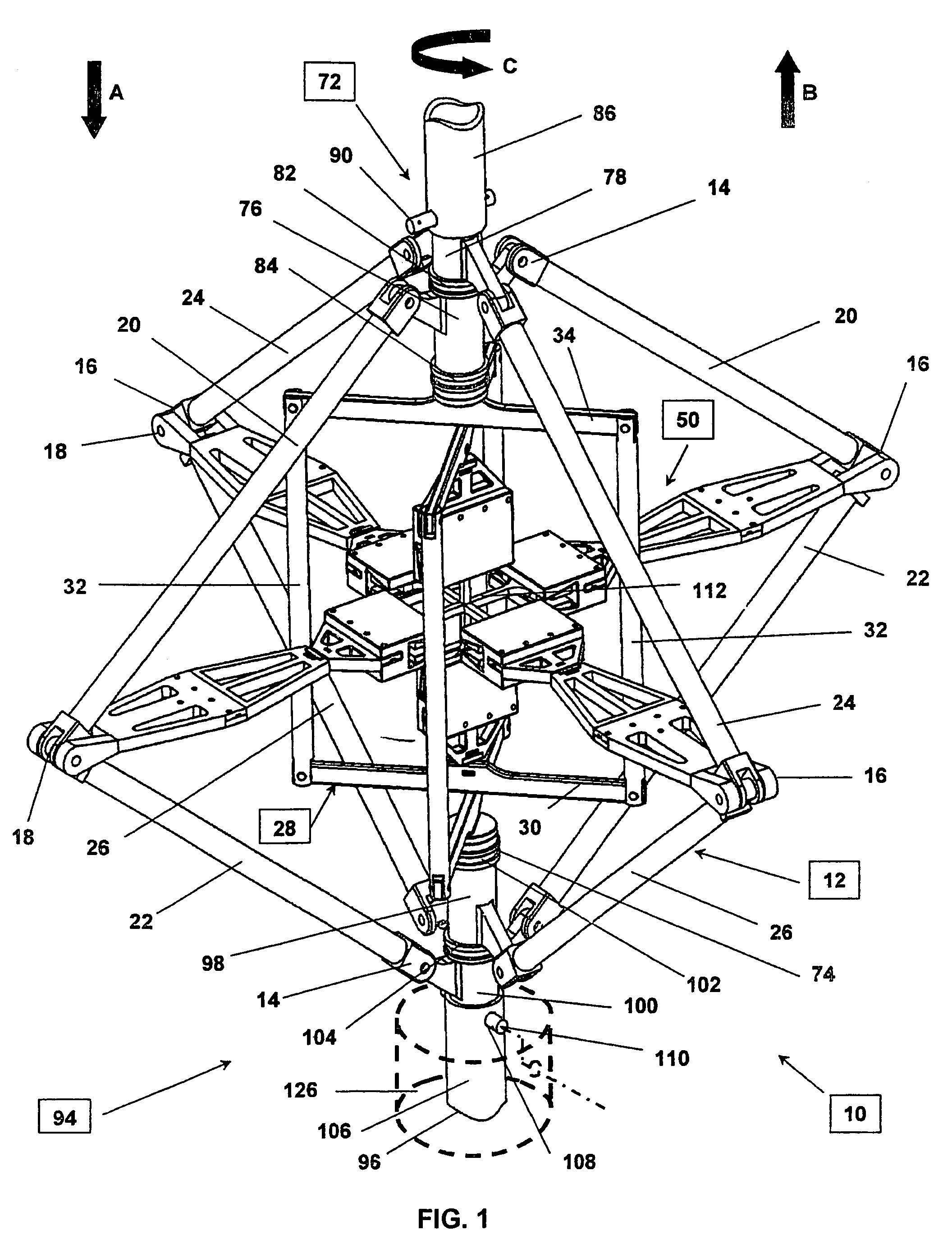
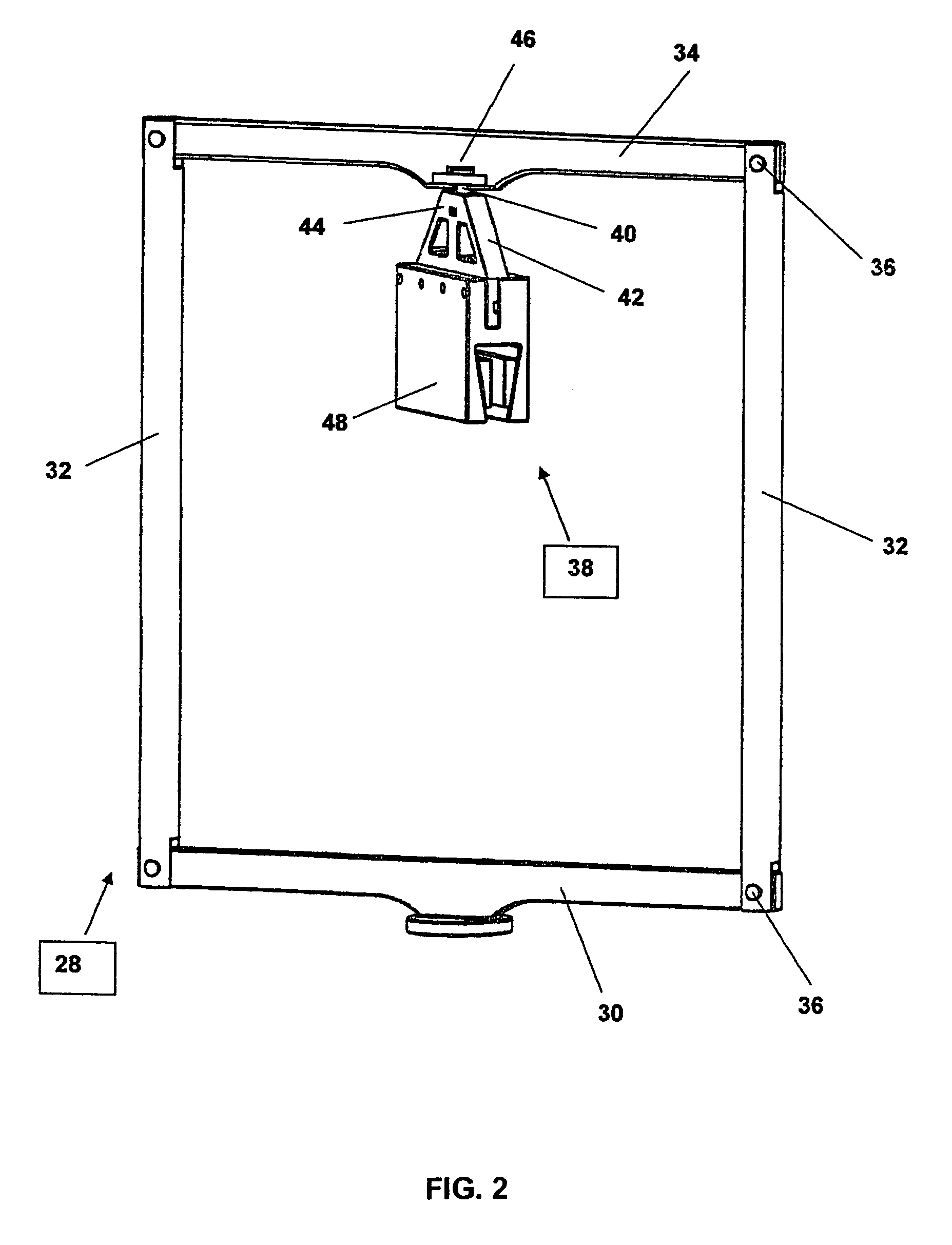
Triaxial tension compression, shear testing apparatus
InactiveUS7051600B1Facilitate triaxial testingCost-effectiveForce measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesIn planeTension compression
A triaxial testing system of material properties having top and bottom joint assemblies that rotate about and move along a longitudinal axis in response to forces imparted by a testing machine. The joint assemblies are connected together by horizontal and vertical linkage assemblies. The horizontal and vertical linkage assemblies are connected to horizontal and vertical loading and clamping assemblies to thereby transfer in-plane and multi-axial loads from the testing machine and the joint assemblies to a material test specimen. The test specimen is rigidly clamped to the horizontal and vertical clamping assemblies. The bases and ends of the test specimen are shaped for clamping and axial loading. Rigid plates may be disposed over ends of composite test specimens for spatially stabilizing such specimens during testing. The test specimens may include devices to measure and record the axial and shear loads, displacement and strains imparted to the specimens during testing.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Location loading material testing machine
InactiveCN101881710ASimple structureCompact structureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTension compressionTorsion test
The invention relates to a location loading material testing machine which belongs to the technical field of material test. The location loading material testing machine is characterized in a location loading system; a support stand and a loading support part of the location loading system are respectively positioned at both ends of a fixing base; the loading support part comprises a location loading stand, a flange shaft, an overrunning clutch, a rolling bearing, a groove-shaped nut and two sliding blocks; three guide grooves are arranged on the location loading stand; the sliding blocks are respectively positioned in two keyways of the right external diameter of the groove-shaped nut; the overrunning clutch and the rolling bearing are fixed in the location loading stand in parallel; one end of the flange shaft is fixed by a hexagon nut through threads, and the other end is connected with the groove-shaped nut by threads; the left side of the groove-shaped nut is provided with a groove-shaped cavity; two through holes which are distributed left and right are radially arranged in the groove-shaped cavity; and the positions of the two through holes correspond to the first guide groove and the second guide groove on a loading support stand. The invention can realize a series of tension and compression tests and torsion tests by applying the guide grooves in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction of a location tension-compression-torsion loading stand.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
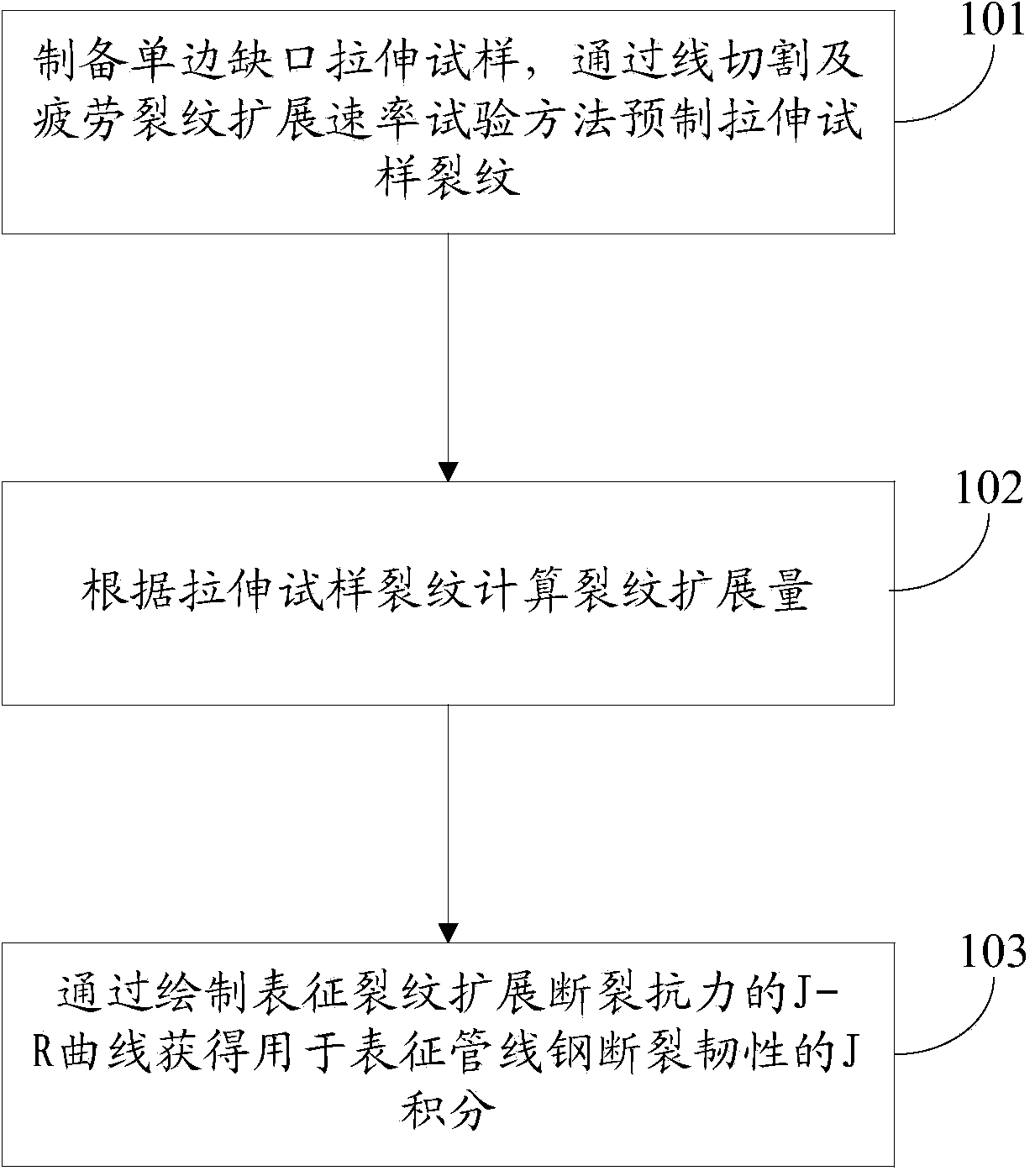
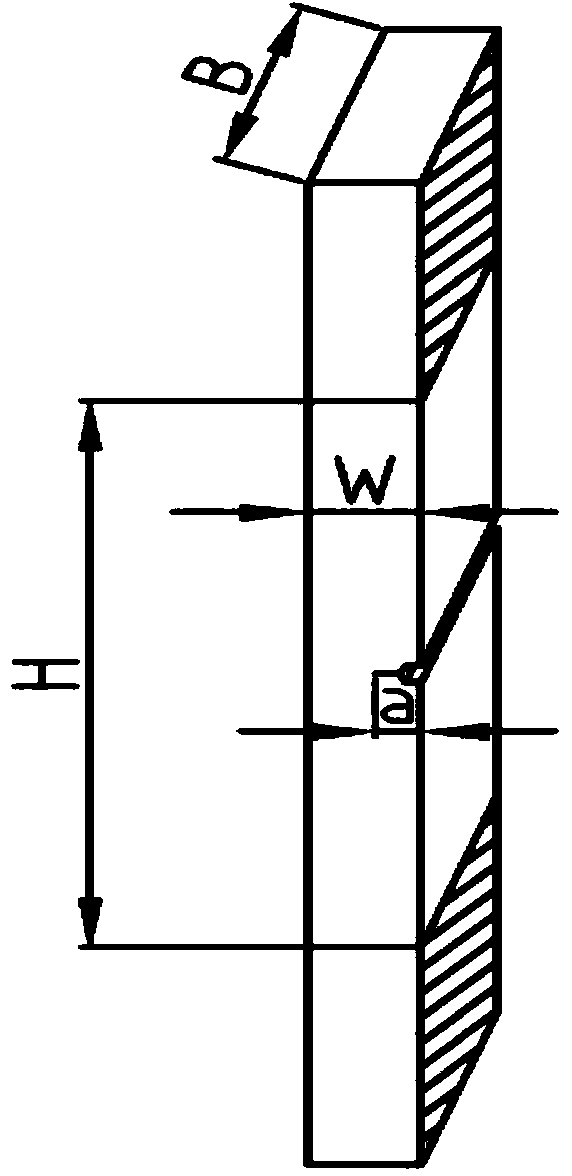
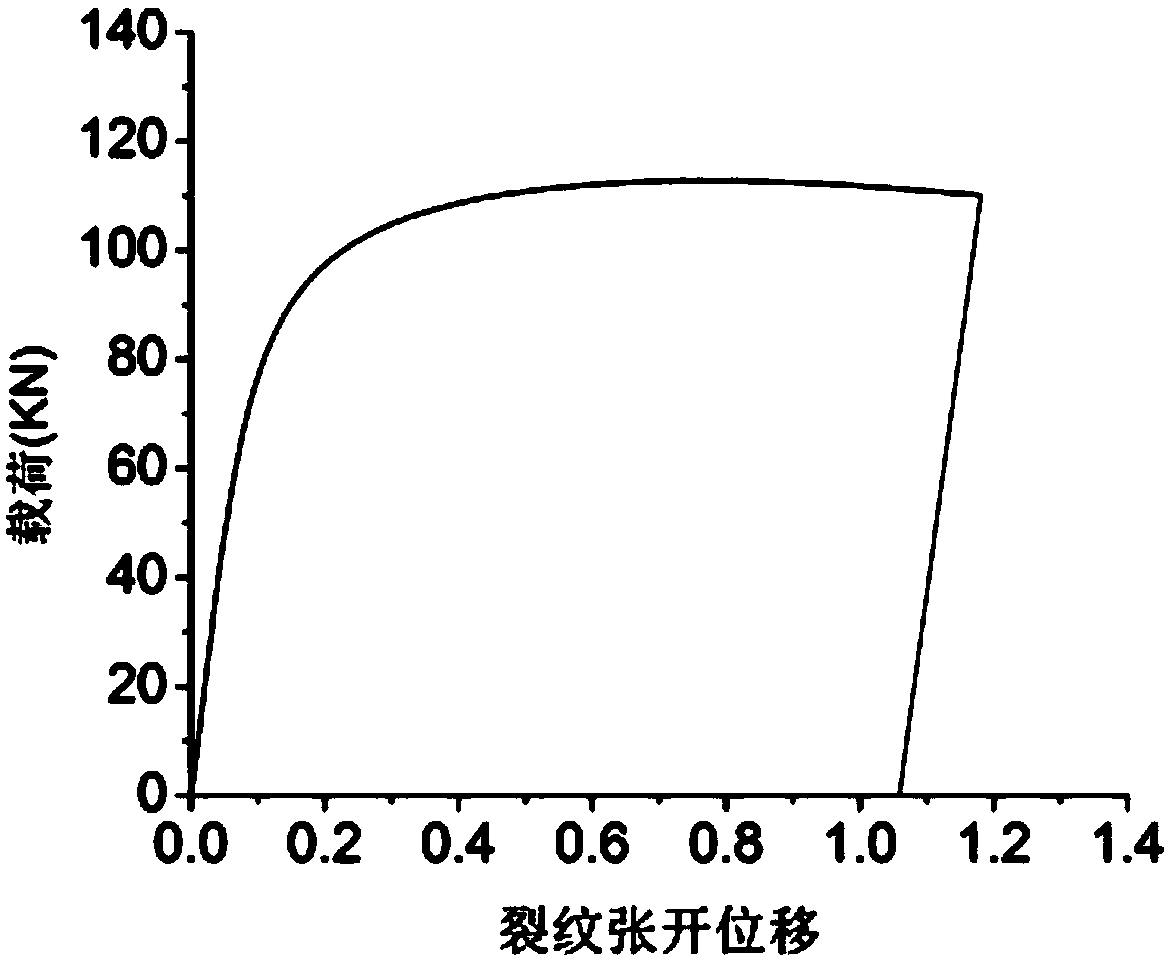
Method for measuring fracture toughness of pipeline steel by using unilateral notched tensile test
ActiveCN103604694AAvoid wastingReasonable fracture toughness valueMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCrack resistanceStress intensity factor
The invention discloses a method for measuring fracture toughness of pipeline steel by using a unilateral notched tensile test. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of preparing a unilateral notched tensile test sample; prefabricating a tensile sample crack by wire-electrode cutting and fatigue crack growth rate test method; calculating crack growth amount according to the tensile sample cracks; and acquiring J integration and stress intensity factor K for characterizing the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel by drawing a J-R curve for characterizing crack resistance of the crack growth. The method measures the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel by using tensile samples (SENT samples), overcomes the defects that the scope of measurement results of tensile samples (SENT samples) by a conventional technology is so small that the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel can not be evaluated; the crack toughness value of the tensile samples (SENT samples) can be more reasonable; waste of test for pipeline steel materials can be prevented; and the method has the advantages of high measurement accuracy.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
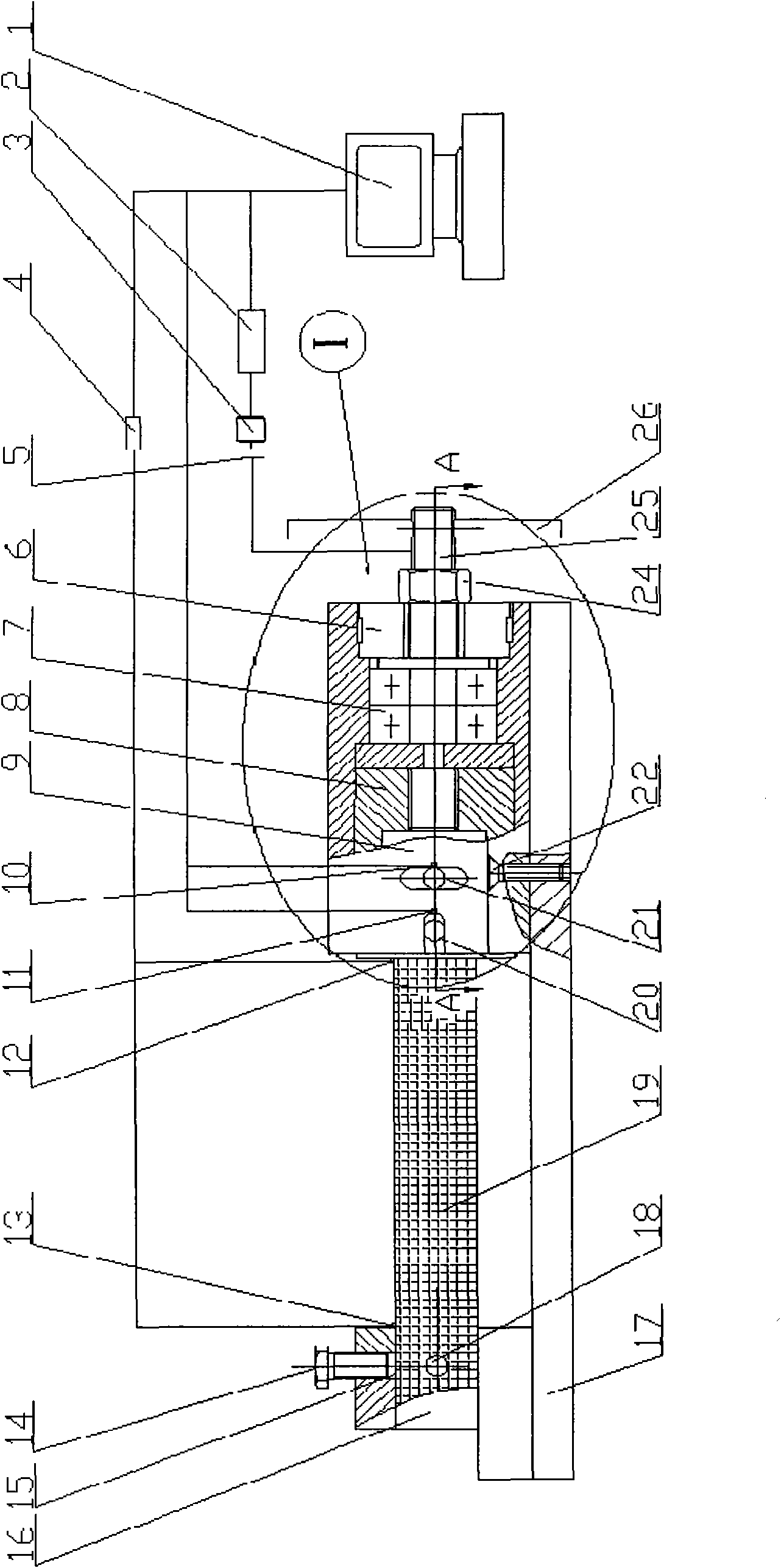
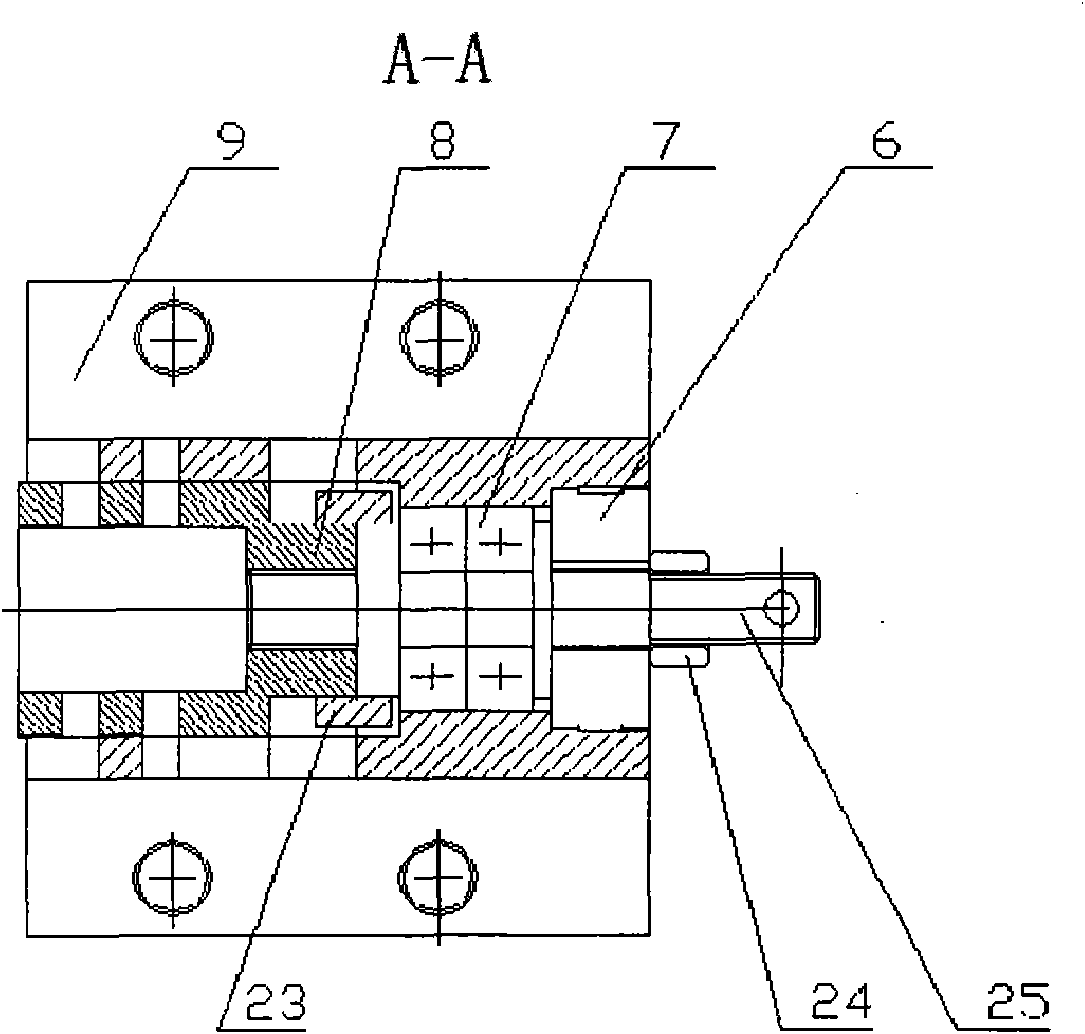
True stress-true strain computation model and test system
InactiveCN101319977AAccurate performance characteristics of mechanical behaviorExpress mechanical behavior characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsStrength propertiesVisual technologySoftware system
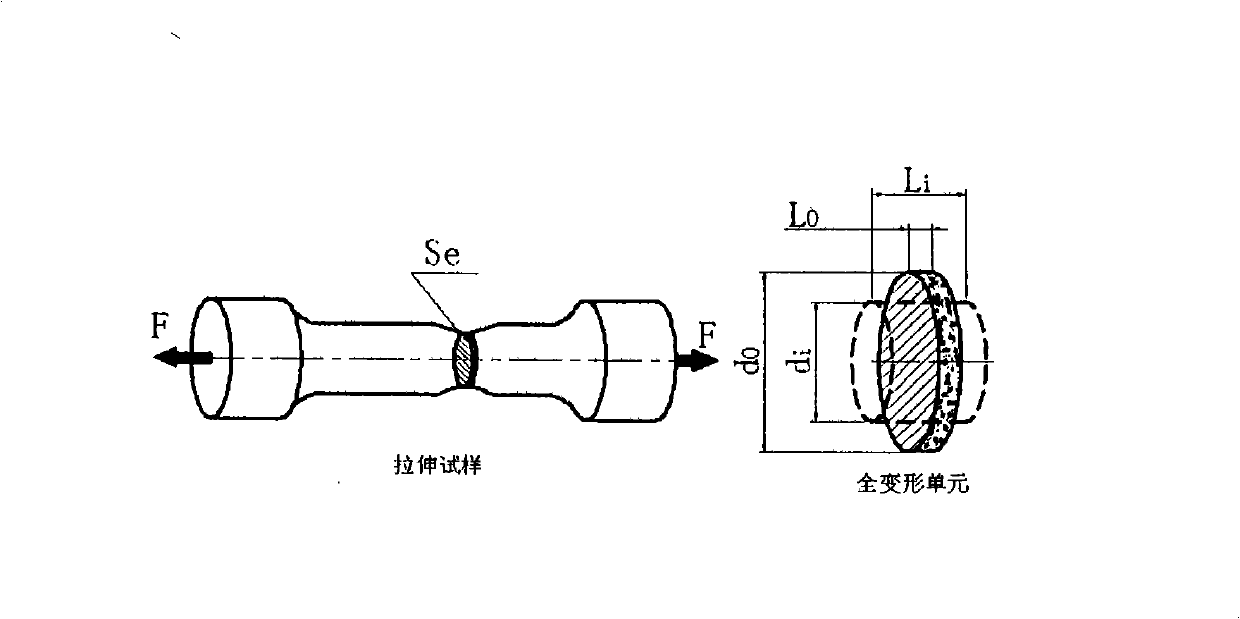
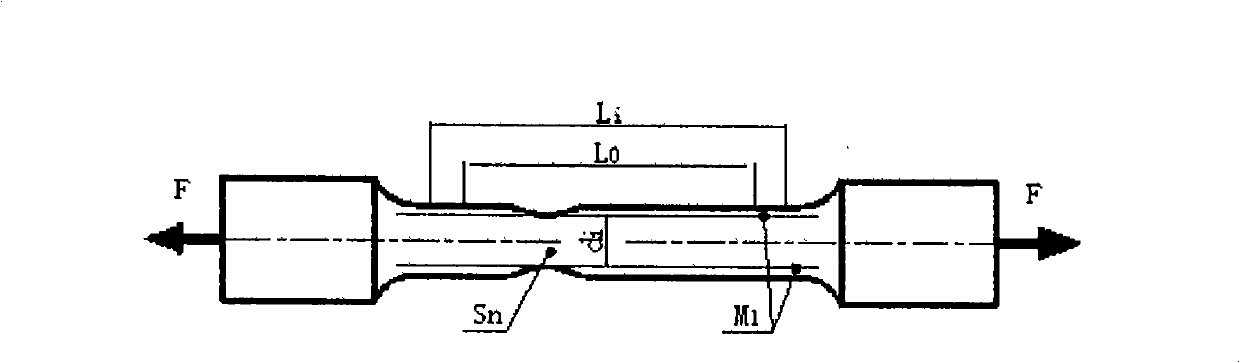
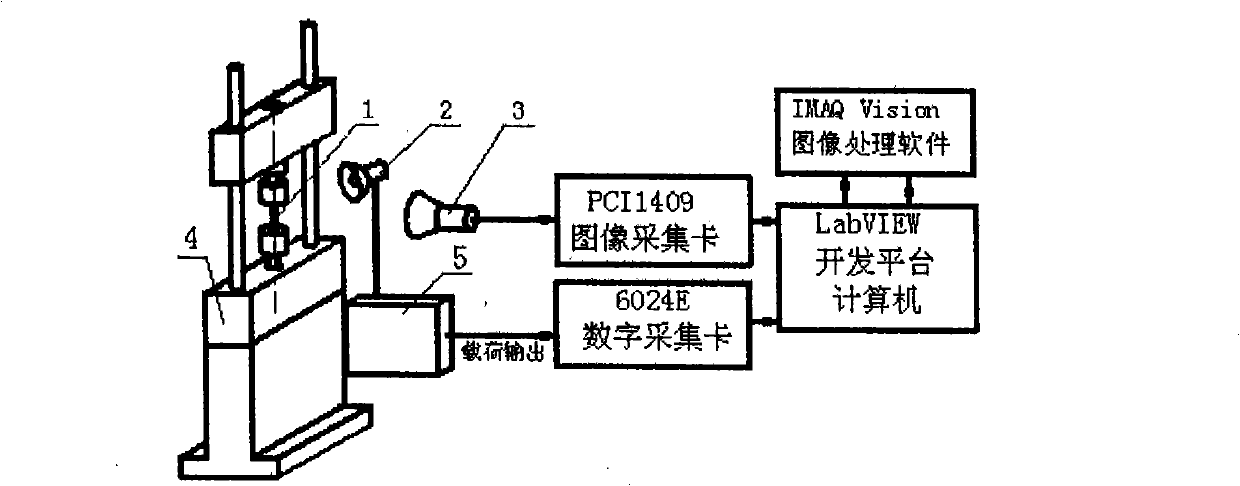
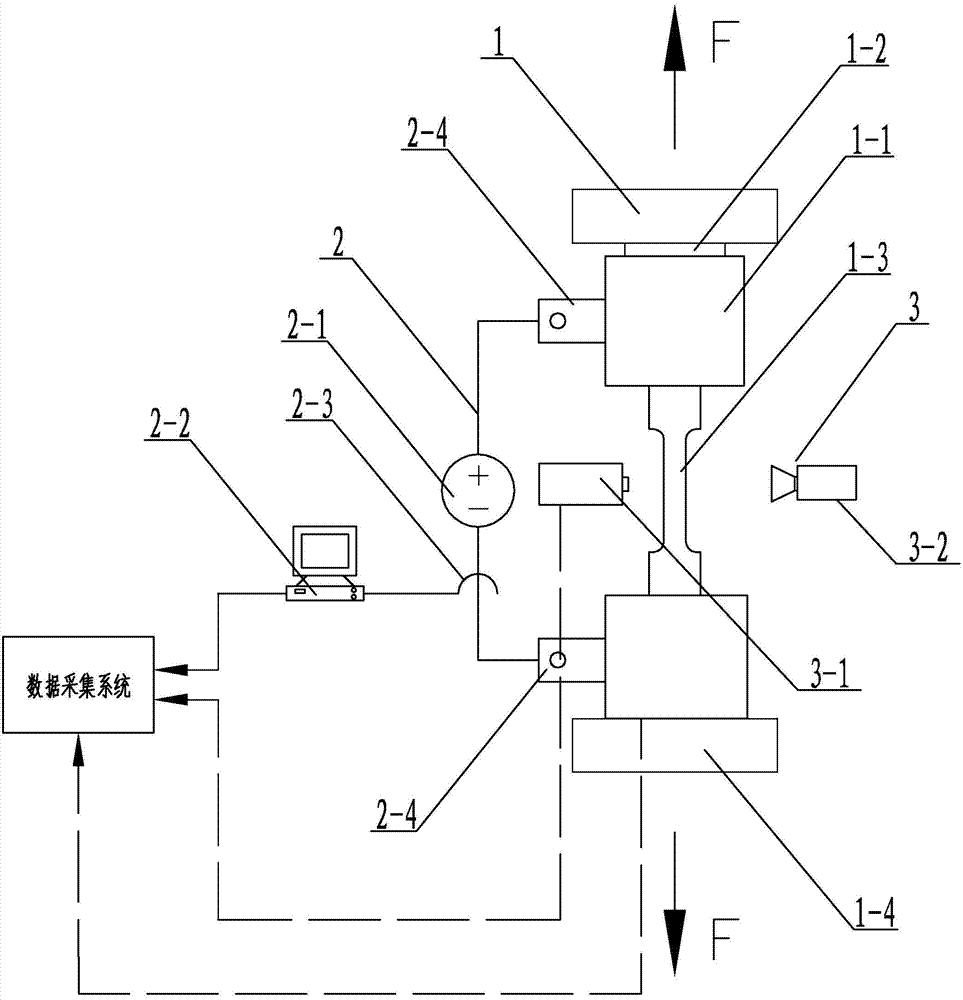
The invention researches the substantive characteristics of material deformation to aim at the practical problem of measuring real stress-real strain and discloses a real stress-real strain calculating model and a practical testing system: 1, based on the analysis on the deformation of a tension specimen, taking a unit body the special part of which is provided with characteristics as the object for the stress-strain analysis, building a unique full-deformation unit model, firstly solving the theory analysis problem of real stress-real strain, establishing a theory foundation and building a novel real stress-real strain calculating formula: Sigma i is equal to 4Fi / Pi d<2>I and Epsilon is equal to (d<2>0 / d<2>i) minus 1; 2, adopting a machine visual technology and an image processing method to develop a practical software system and a practical hardware system that are compatible with the machine visual technology and the image processing method, and realizing the direct non-contact real stress-real strain measuring in real meaning; 3, the testing system includes a light source (1), CCD camera (2), an image acquisition card (3), a data acquisition card (4) and a material testing machine (5); 4,the software includes image capturing program, load data acquisition program and comprehensive calculation analysis program.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Test method for J-R resistance curve of high-toughness material
ActiveCN102353595AAvoid restrictionsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMaterials testingLarge deformation
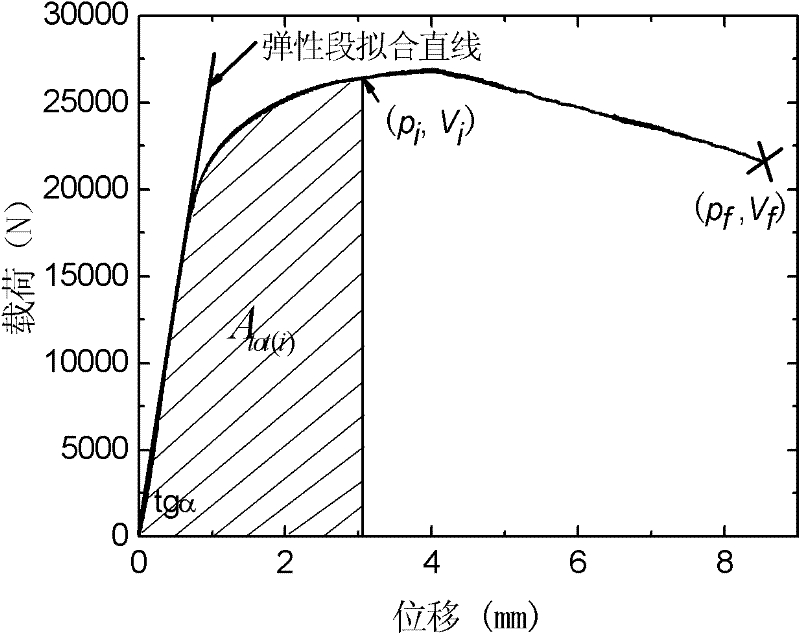
The invention relates to a test method for a J-R resistance curve of a high-toughness material. The method comprises the steps of sample processing, three point bending test, determination of crack length, calculation of J-integration at every load, establishment of a difference function, recursive calculation of crack length and p-V data pairs and construction of the J-R resistance curve. According to the invention, an extensometer is not employed for testing opening displacement and unloading flexibility of a crack mouth; instead, a testing machine is used for direct acquisition of deformation of a three point bending sample and a load-displacement curve in the whole process of fracture; then, the J-R resistance curve of the material is obtained through a series of calculation; therefore, the problem of restriction of testing apparatuses caused by large deformation of a sample in the testing of high-toughness materials is overcome, a J-R resistance curve in the situation of expandedlong size crack is measured, and the test method is applicable to measuring of J-R resistance curves of samples at different temperature and with different dimension.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Corrosion fatigue test apparatus with high temperature and high pressure circulating water
ActiveCN102346114ATemperature controlControl pressureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue loadingWater storage tank
The invention belongs to the field of material testing, specifically to a corrosion fatigue test apparatus with high temperature and high pressure circulating water. With the present invention, the problems of the complex structure and the cumbersome use and maintenance in the prior art are solved. The apparatus is provided with a high temperature and high pressure circulating water system, an autoclave and a fatigue machine. The high temperature and high pressure circulating water system is communicated with the autoclave. A test sample is placed in the autoclave, and is connected with a loading part of the fatigue machine. The high temperature and high pressure circulating water system comprises a water storage tank, a circulation pump, a high pressure pump, a buffer tank, a heat exchanger, a preheater, a condenser, a back pressure valve and an ion exchange resin. An inlet of the autoclave is connected with the heat exchanger through a pipeline. The pipeline is provided with the preheater. An outlet of the autoclave is connected with the heat exchanger through the pipeline. The high temperature and high pressure circulating water system is provided for providing high temperatureand high pressure water required by the test. The fatigue machine is provided for performing fatigue loading for the test sample in the autoclave. A control system controls the high temperature and high pressure circulating water system and the fatigue machine.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for material testing, material suitable for such testing and method for producing such material
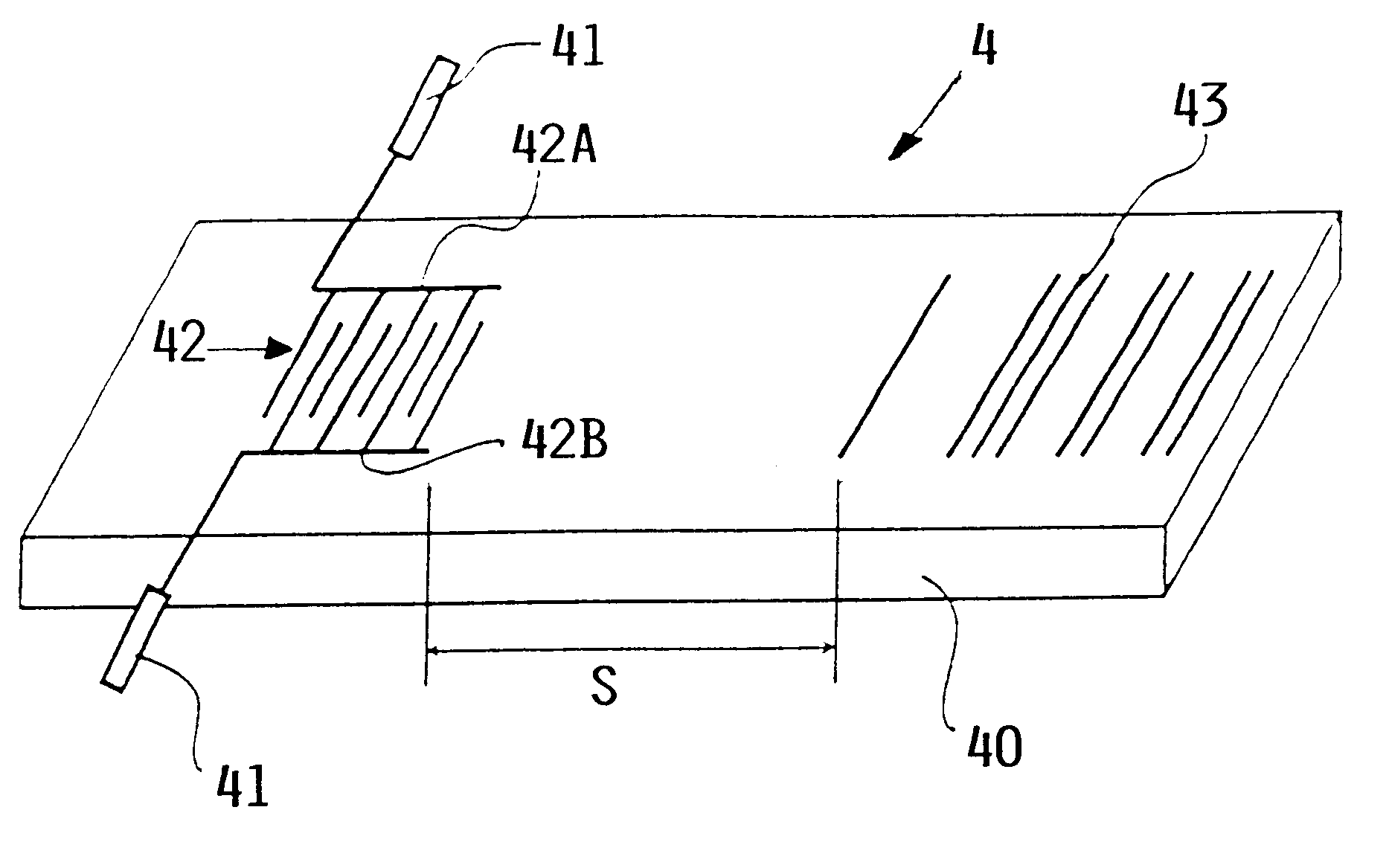
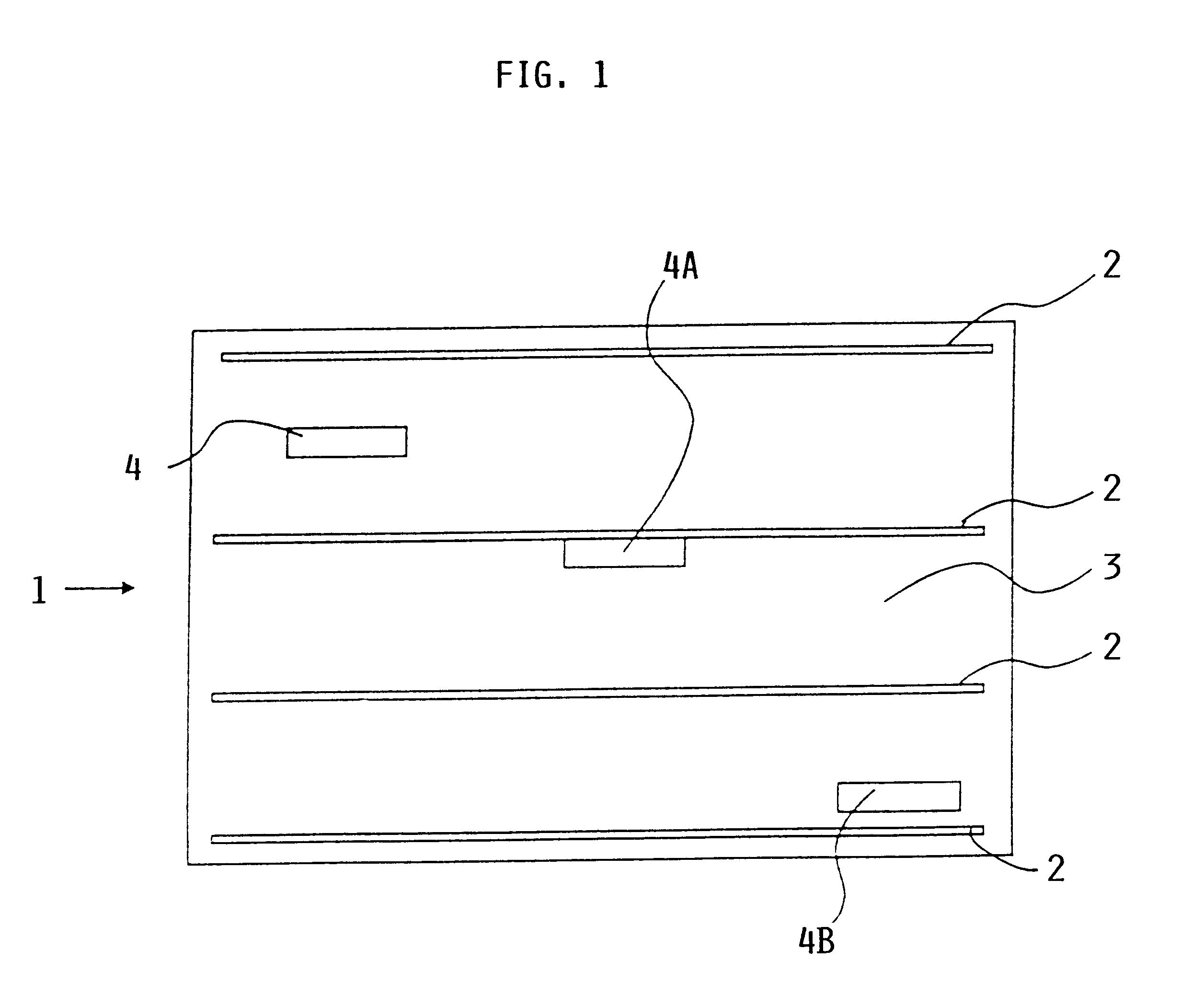
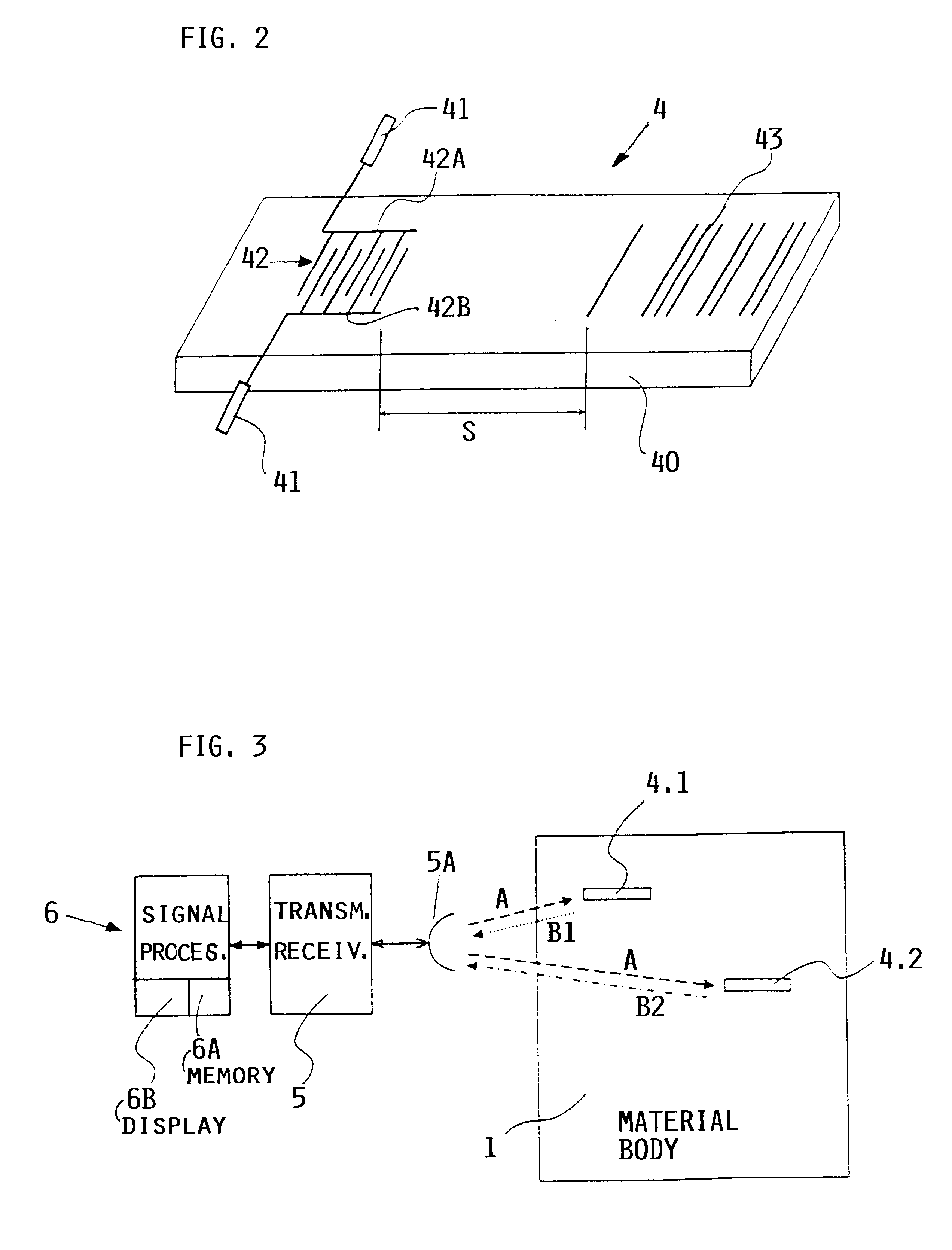
InactiveUS6260415B1Easy to testEasy assessment processAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationMaterial under testSurface acoustic wave
A material, such as a fiber composite material, has embedded inside at least one, preferably more, surface acoustic wave filters of piezoelectric material for receiving testing energy in a wireless manner and for retransmitting a material quality signal in a wireless manner which is evaluated in a system that has a wireless transmitter for sending testing energy into a material and a wireless receiver for receiving the material quality signal which is then processed and evaluated by a respective processor of the testing system. An output of the processor provides information regarding the nature and quality of the material tested and of the presence and location of any material faults that may be displayed on display screen.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Device for testing performance of low-temperature vacuum multilayer heat-insulation material based on thermal protection
The invention discloses a device for testing performance of a low-temperature vacuum multilayer heat-insulation material based on thermal protection. The device comprises a vacuum outer cover, a blind plate end cover flange, an upper protective cavity, a testing cavity, a lower protective cavity, a back pressure stabilizing device, a controllable electric heating system, a temperature and flow-rate sensing system, a liquid nitrogen filling system, a data collecting-processing system and a vacuum pumping system, wherein the upper protective cavity and the lower protective cavity are used for insulating heat leakage in the vertical direction and connected with the blind plate end cover flange of the vacuum outer cover through thin-wall steel tubes; the testing cavity is connected with the blind plate end cover flange through the same thin-wall steel tube structure as the protective cavities. An insulating material testing sample of the device can be replaced at will, the temperature distribution inside the insulating material and the evaporation rate of stored liquid under different thermal boundary temperature conditions can be measured, and the heat leakage percentage and the material apparent thermal conductivity can be further obtained by the evaporation rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for quantitatively measuring inhomogeneous deformation of nano-crystal material
InactiveCN101526453ALow costMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansStress–strain curveEngineering
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively measuring the inhomogeneous deformation of a nano-crystal material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly processing the measured nano-crystal material into a stretching sample, selecting a marking area on the stretching sample and marking the stretching sample; secondly, putting the stretching sample into a mechanics testing machine, and loading the stretching sample under the condition that the quasistatic strain rate of a displacement control mode at room temperature is 10<-4>s<-1>; obtaining data and displaying a stress strain curve by a material testing system of the mechanics testing machine, adopting a digital camera to acquire the image on the surface of the sample at the same time of loading, and recording the image by connecting the digital camera with a computer; and finally, carrying out digital image processing on the image acquired by the digital camera in the process of stretching to obtain the surface displacement and a stain field image of the tested image in the process of stretching. The method measures the cause of formation of a shear zone in a simple mode with low cost, so the method can have wide application prospect in the fields of modern mechanics, microelectronic technology, ultraprecise processing technology, nanometer technology, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
High density storage of excited positronium using photonic bandgap traps
A device is provided that can capture and store electrically neutral excited species of antimatter or exotic matter (a mixture of antimatter and ordinary matter), in particular, excited positronium (Ps*). The antimatter trap comprises a three-dimensional or two-dimensional photonic bandgap (PBG) structure containing at least one cavity therein. The species are stored in the cavity or in an array of cavities. The PBG structure blocks premature annihilation of the excited species by preventing decays to the ground state and by blocking the pickoff process. A Bose-Einstein Condensate form of Ps* can be used to increase the storage density. The long lifetime and high storage density achievable in this device offer utility in several fields, including medicine, materials testing, rocket motors, high power / high energy density storage, gamma-ray lasers, and as an ignition device for initiating nuclear fusion reactions in power plant reactors or hybrid rocket propulsion systems.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Metallic nanostructures self-assembly, and testing methods
The invention provides method for metallic nanonstructures self-assembly methods and materials testing. Preferred embodiment methods permit for the formation of individual nanonstructures and arrays of nanostructrues. The nanostructures formed can have a metal alloy crystal structure. Example structures include slender wires, rectangular bars, or plate-like structures. Tips can be shaped, single layer and multiple layer coatings can be formed, tips can be functionalized, molecules can be adhered, and many testing methods are enabled.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Temperature controllable PEA space charge test device
The invention belongs to the high voltage and insulation technical field, in particular relates to a temperature controllable PEA space charge test device. The test device is composed of an upper electrode, a lower electrode, a space charge collecting channel and a temperature control measuring unit. A groove-shaped lower electrode is inlaid in a lower electrode insulation clapboard, the lower electrode insulation clapboard is inlaid in a lower electrode clapboard, so as to form the lower electrode, a piezoelectric sensor is adhered on the lower surface of the groove-shaped lower electrode tocollect space charge, a voltage signal transmitted by a metal film coated organic glass column is displayed by an oscilloscope, the heating coil of the temperature control measuring unit is coated inthe outer side of the groove-shaped lower electrode to heat the groove-shape lower electrode, so as to provide a temperature field for a sample, a platinum resistor is inlaid in the bottom surface ofthe groove-shaped lower electrode to measure the temperature of the sample, and the platinum resistor is connected with a computer by virtue of a thermodetector. The invention can measure dielectric medium space charge under different temperature conditions, so that researching on dielectric medium space charge characteristic can be realized, thus being especially applicable to test and research of electrical insulating material.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Cellular, electron cooled storage ring system and method for fusion power generation
InactiveUS20110158369A1Large output levelSave energyNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorThermal energyFusion power
A cellular electron cooled storage ring system and method for achieving particle-fusion based energy, including a vacuum chamber to allow electron beam and ion beam merging and separation, cathodes to generate the electron beams, collectors to collect the electron beams, and magnetic field generation devices to guide the electrons and ions on their desired trajectories as well as contain neutralizing particles. By overlapping the electron and ion beams, thermal energy is transferred from the ion beams to the electron beams, which allows the invention to overcome particle losses due to resonances, scattering and heating of the ion beams. Advantageously, ions are accelerated to an energy that is near optimum for fusion reactions to occur, and uses electron energies that maintain this advantageous situation. Advantageously, the recirculation of ions that do not fuse or scatter at too large of an angle is allowed, giving such ions additional chances to participate in a desired fusion reaction. Advantageously, the invention allows for a continual addition of new ions to be added to the circulating ions already in the system. This combination of advantages results in a significant improvement in the predicted output power to input power ratio over previous particle fusion technologies. The invention will also enable improved yields of fast neutrons for materials testing.
Owner:LARSON DELBERT JOHN
Device and method for testing normal static characteristics of junction surface of high-strength bolt
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing normal static characteristics of a junction surface of a high-strength bolt. The device for testing the normal static characteristics of the junction surface of the high-strength bolt comprises a material testing machine, two screws, a lower test piece, an upper test piece, the high-strength bolt, a slotless locating support, a slotted locating support, an eddy current displacement sensor, a force sensor, a dynamic strain indicator, a modal testing system and a personal computer (PC) machine. The high-strength bolt penetrates through the upper test piece and the lower test piece in a vertical mode so that the upper test piece and the lower test piece are mutually attached to form the junction surface, and a strain gage is embedded in the high-strength bolt. The eddy current displacement sensor is used for measuring the normal displacement variable quantity of the junction surface. The upper test piece and the lower piece are respectively connected with the material testing machine through the two screws. The material testing machine carries the force sensor and exerts static tensile force on the upper test piece and the lower test piece along the longitudinal direction. The dynamic strain indicator for measuring the pretightening force and a strain signal of the high-strength bolt, the eddy current displacement sensor for measuring the normal displacement variable quantity of the junction surface, and the force sensor for measuring a static force signal output self-signals to the modal testing system, and then the signals are transmitted to the PC machine.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and Method for the Material Testing and/or Thickness Measurements of a Test Object That Contains at Least Fractions of Electrically Conductive and Ferromagnetic Material
InactiveUS20090139335A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorMaterials testing
The invention relates to a device and a method for testing the material of a test object (4) which contains at least electrically conductive and ferromagnetic material fractions and has at least one engineered surface (5), by means of at least one electromagnetic ultrasonic transducer assembly (EMUS). Said assembly comprises a permanent or electromagnetic assembly (1) comprising at least two magnetic poles (N, S) of different magnetic polarity that face the engineered surface (5), in addition to an eddy current coil (2) that is placed in close proximity to the engineered surface (5) between the two magnetic poles (N, S) in indirect or direct relation to the engineered surface (5). The invention is characterized in that the eddy current coil (2) is configured and arranged in such a way that when said coil (2) is supplied with an alternating current, free ultrasonic waves that run essentially perpendicular to the engineered surface (5) are generated and propagate inside the test object (4).
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and device for synchronously testing tension, compression and split resilience moduli of pavement material
ActiveCN106706422AHigh precisionGuide engineering practice wellMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTest efficiencyElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a method and device for synchronously testing tension, compression and split resilience moduli of a pavement material. The method comprises the following steps: performing a split loading test on a test sample through an MTS multifunctional material testing system, and deducing computing formulae for the tension modulus and the compression modulus of the pavement material test sample during split loading; and respectively pasting resistance strain gages on horizontal radial and vertical radial centers in the front and back parts of the test sample, measuring the average tension strain and the average compression strain of the center positions of the test sample, measuring the horizontal radial deformation of the test sample through a displacement sensor, and substituting in the formulae to obtain the testing results of the split modulus, the tension modulus and the compression modulus of the material. According to the invention, the three moduli of the material can be simultaneously measured through a single test, thereby improving the modulus testing precision and test efficiency of the pavement material and lowering the indoor test and testing cost; and accurate design parameters can be provided for scientific design of a durable pavement considering the difference in the tension and compression moduli of the material.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Instrumented mold for use in material testing equipment for measurement of material properties
InactiveUS6622569B2Material strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterials testingMixed materials
A system and method for measuring forces and behavior of a material when subjected to an applied force in a contained vessel or mold in directions not aligned with the applied force. Materials which flow, including mixed materials with an aggregate and a mastic, can be tested within a material vessel or mold by applying a force to the material within the mold and, in addition to measuring resistance of the material to the applied force, resulting forces applied by the material to the mold walls, for example laterally relative to the applied force, are measured and are indicative of flow characteristics and load bearing performance, and shear strength of the material. In a specific testing device, a material testing mold for use with material testing equipment which applies forces to material within the mold, has a mold cavity formed by walls. At least one portion of the wall is configured to deflect or deform in response to material pressure created by a force applied to the material. Deflection or deformation of the mold wall is measured to provide an indication of force transfer load bearing properties and behavior of the material in the mold, which is indicative of real world performance.
Owner:PINE INSTR +1
Catalytic testing device and method for its use in material testing
InactiveUS20030040116A1Quick and accurate decisionWide rangeSequential/parallel process reactionsTemperatue controlMaterials testingEngineering
A catalytic testing device comprising a reaction block comprising a set of reaction chambers, each chamber comprising a fluid inlet and outlet connected to an outgoing fluid duct connected to analysis means, fluid feed means capable of performing regulated dosing of flows of the fluid at the required pressure independently in each of the reaction chambers, automatic and dynamic pressure control means, capable of performing pressure regulation in each reaction chamber, which comprise a non-return valve in the outgoing fluid duct between the outlets of the reaction chambers and a common regulating tank that receives the outgoing fluid from the chambers, a pressure sensor provided in a first outlet duct and an automatic needle valve provided in a second outlet duct from the tank.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Improved method of impression testing function for material tester and improving device thereof
InactiveCN1752736AGreat advantageAvoid Displacement Measurement ErrorsInvestigating material hardnessMaterials testingContact type
The invented improved method includes the following steps: firstly, measuring loaded / unloaded displacement-loaded curve, then utilizing pressed depth measurement method to making data process so as to obtain hardness and modulus of the tested material. The improved equipment of the material testing machine also includes a sample table directly mounted on the base of material testing machine and a non-contact type displacement sensor mounted on the sample table of material testing machine.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for crack detection during heat and load testing
InactiveUS20110249115A1Possible to viewTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTest fixtureFeedback control
Material testing under variable heat and load while continuously monitoring crack formation is provided using an apparatus that permits thermal control somewhat uniformly over a conductive sample, while permitting a controlled load to be applied to the sample in tensional or flexural modes. Thermographic imaging of a sample in situ within a standard thermo-mechanical fatigue (TMF) test rig or other heat and load test apparatus is used to detect and monitor cracks as they form. A 360° sample view is possible. Image analysis software may identify, count and / or characterize cracks. Thermographic images may be analyzed to determine a sample temperature, e.g. for temperature feedback control. Essentially passive thermography is used with an inductive heating coil that surrounds at least 60% of a length of the sample, with at least two windings, the windings having thickness and pitch so that at least half the sample is in view.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Material low-temperature mechanics performance testing device using refrigerator as cold source
InactiveCN102854056AAccurate temperature controlSimple structureStrength propertiesMaterials testingTest sample
The invention discloses a material low-temperature mechanics performance testing device using a refrigerator as a cold source. The device comprises a vacuum heat preservation barrel, a test sample cavity, a heat radiation preventing barrel, an outer gas storage bag and the refrigerator, wherein the vacuum heat preservation barrel is placed on a base in a universal material testing machine; the test sample cavity is arranged in an internally-built temperature controller which is arranged in the heat preservation barrel; the test sample cavity covers the heat radiation preventing barrel which is positioned in the heat preservation barrel; helium is arranged in the outer gas storage bag which is communicated with the test sample cavity; a sample to be tested is rigidly connected with a mechanics support frame by a measuring clamp and moves up and down; the testing machine is provided with a mechanics and displacement sensor and supplies the mechanics power source for the test sample to be tested; the mechanics support frame transmits a mechanics signal and a displacement signal of the test sample to be tested to a mechanics sensor and a displacement sensor; the refrigerator is arranged in the heat preservation barrel; a cooling head is in contact with the test sample cavity by virtue of bridge connection; and cold energy is supplied to the test sample cavity. By utilizing the device, the refrigerator is used as the cold source, liquid helium or liquid nitrogen are not needed to be consumed, so that the material mechanics test of any of the temperature points in the temperature area of 4.2-300K can be realized; and moreover, the temperature is accurately controlled, and the device has a simple structure, and is easy to operate and high in efficiency.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for testing bonding shearing strength of structural adhesive interface
ActiveCN104132856AEasy to maintain stabilityPrevent twistingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesBond interfaceShear stress
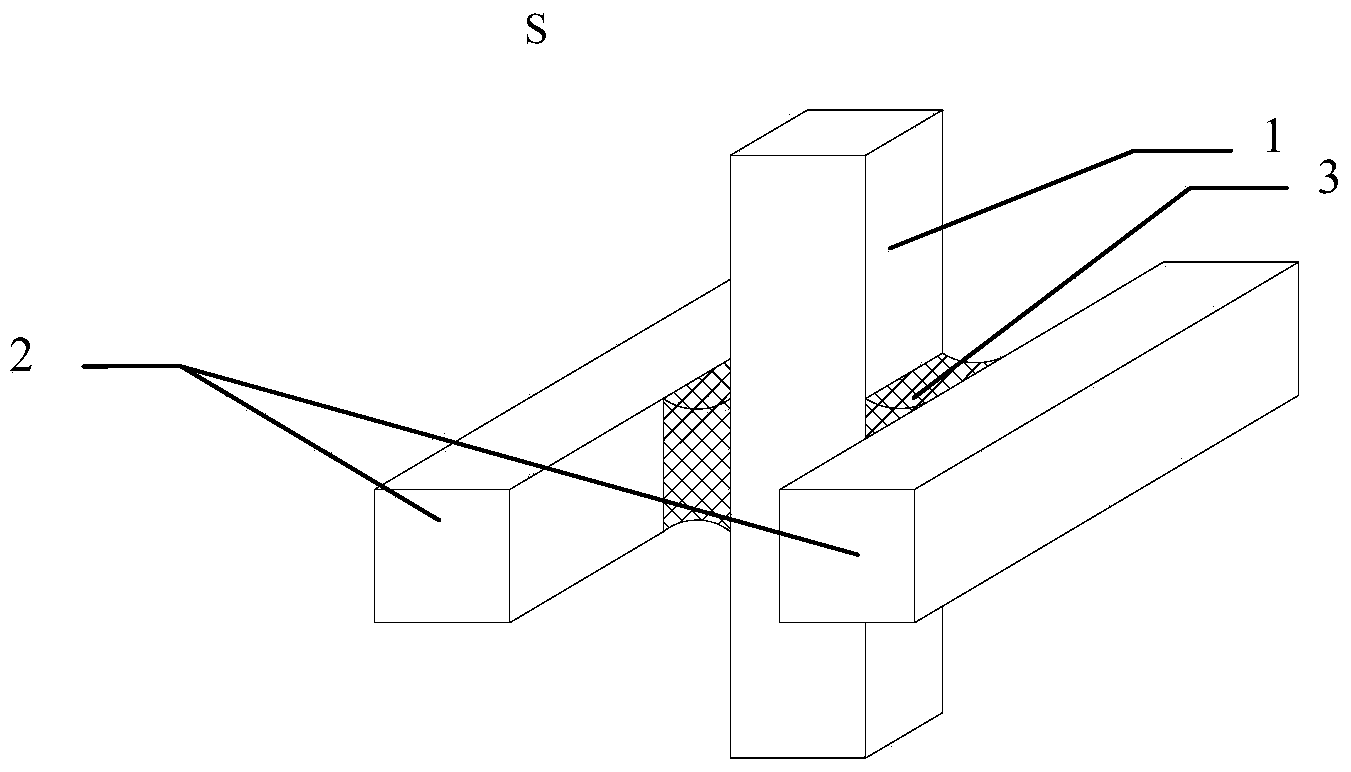
The invention relates to a device and method for testing bonding shearing strength of a structural adhesive interface. The device comprises a bonding base material testing piece and two bonded testing pieces, wherein the bonding base material testing piece and the two bonded testing pieces are bonded in a crisscross manner by using a structural adhesive, the two bonded testing pieces are mutually parallel and are located at two sides of the bonding base material testing piece, the respective centers of the two bonded testing pieces and the bonding base material testing piece are located on the same straight line, a compression load is applied to the bonding base material testing piece to ensure that shear stress can be generated on a bonding interface of two materials, and the bonding shearing strength of the interface is calculated through the shear stress generated during damaging. The device and the method for testing the bonding shearing strength of the structural adhesive interface are suitable for testing the bonding shearing strength of the interface among different materials with certain bonding layer thicknesses, and especially suitable for evaluating the bonding strength of the structural adhesive between glass of a curtain for doors and windows of a building and a metal base material.
Owner:北京玻钢院检测中心有限公司
Testing device for current auxiliary type micro-stretching mechanical property of metal thin plate
ActiveCN104502203AImprove insulation performanceHigh withstand voltage breakdown indexMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesThin slabCopper electrode
The invention provides a testing device for a current auxiliary type micro-stretching mechanical property of a metal thin plate and relates to a mechanical property testing device. As no relative information can be referred at home and abroad at present, the problems of electrification and insulation of a micro-stretching clamp, a clamping form of a micro-test sample, control and acquisition of the temperature of the test sample, and current parameter acquisition are required to be solved. A force sensor is mounted at the lower part of a movable transverse beam of an all-purpose material testing machine; two sets of clamp bodies are symmetrically mounted on the all-purpose material testing machine; a micro-stretching test sample is mounted between the two sets of clamp bodies; the two ends of a pulse power supply are connected with the two sets of clamp bodies by purple copper electrodes; a digital storage type oscilloscope is connected with the pulse power supply through a Hall current probe; a loop is formed by the pulse power supply, the two purple copper electrodes, the two sets of clamp bodies and the micro-stretching test sample; and a thermal infrared imager and an industrial air blower are mounted on the two sides of the all-purpose material testing machine by brackets. The testing device is used for current auxiliary type micro-stretching mechanical property testing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
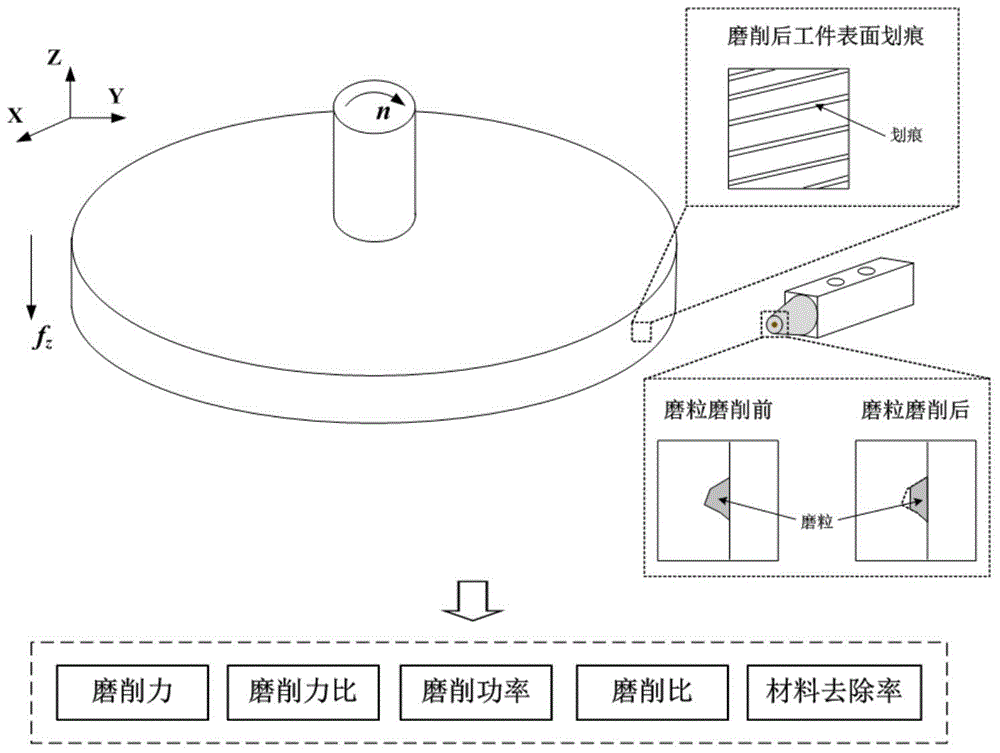
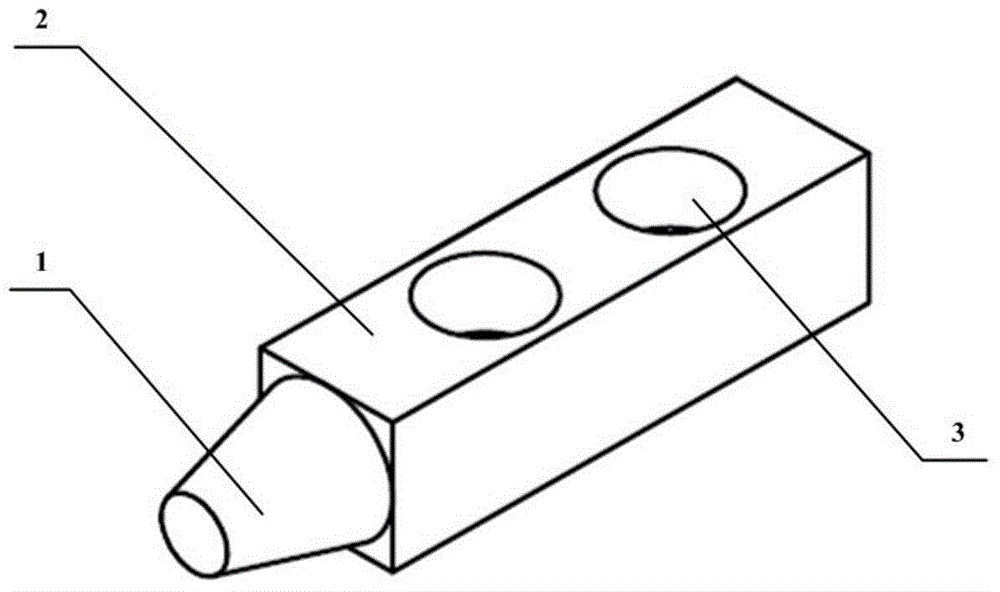
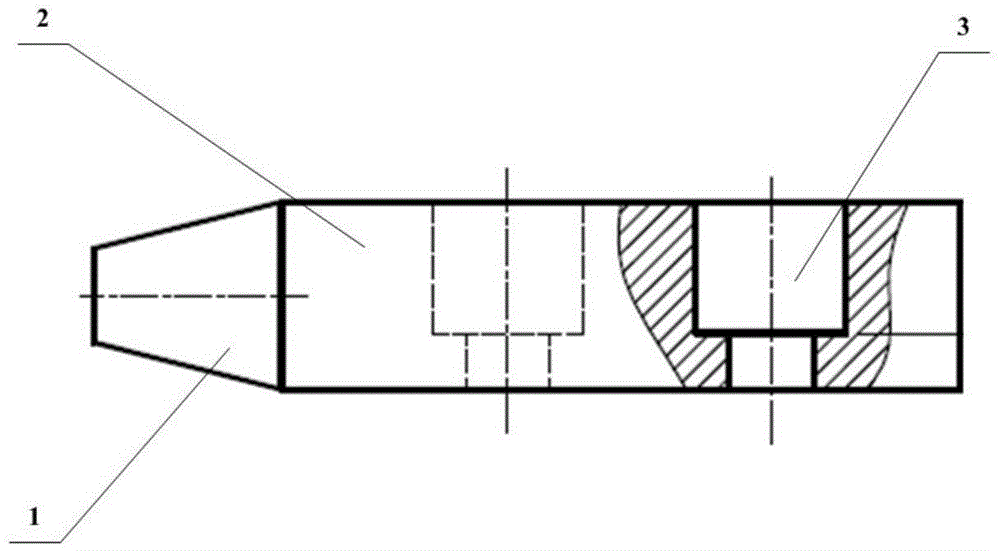
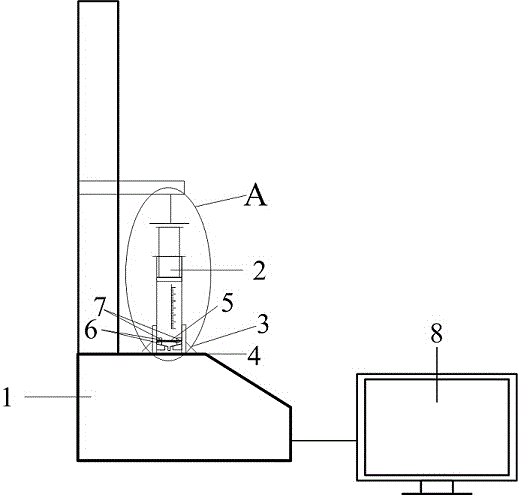
Grinding experiment method under single grain multi-level speed conditions
ActiveCN104568628AGuaranteed accuracySolve processing problemsInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceNumerical controlUltra high speed
The invention discloses a grinding experiment method under single grain multi-level speed conditions, relating to the technical fields of material testing and precision machining. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preparing a single grain tool, and acquiring the grain surface information by virtue of a microscope; mounting a disc-shaped workpiece on an electric spindle knife handle of a numerical control machine tool, grinding and polishing the workpiece so as to meet the cylindricity and roughness requirements; obtaining different cutting linear velocities by selecting the rotating speed of the electric spindle and the workpiece size, and fixing the single grain tool on a numerical control machine tool worktable; finishing tool setting by virtue of a precise dynamometer and an industrial camera, setting the numerical control parameters according to the test requirements, cutting, measuring the grains and the workpiece by using a microscope, and calculating the grinding ratio, grinding power and other powers by combining a force signal, thus analyzing the grinding mechanism under different process parameters. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the actual cutting action generated by the single grains and the workpieces under different speed conditions can be effectively simulated, particularly an experimental platform is provided for researching the generating mechanism on the grinding surface under high-speed or ultra-high-speed conditions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for testing permeability of porous material
ActiveCN105572013AEasy to operateHigh precisionPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityMaterials testing
The present invention discloses an apparatus and a method for testing permeability of a porous material, and belongs to the field of materials testing. According to Darcy's law, a test material is made into a cylinder / disk-shaped specimen, the cylinder / disk-shaped specimen is put into a syringe, hydraulic pressure is controlled by a material testing machine, and the permeability of the material can be obtained by testing and calculation of the speed of a liquid to pass through the material by. The method can be used as a method to test and characterize the porosity of the porous material and liquid permeability / penetrability. The testing technology is simple in operation and high in precision, is expected to promote as a testing technology for porosity characters of other porous materials, and has potential application value in material testing engineering filed.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Tensile test clamp for high-pressure hydrogen environment material testing machine
ActiveCN103674695ARealize automatic centeringEasy to installStrength propertiesMaterials testingHigh pressure hydrogen
The invention relates to material mechanical performance testing equipment, and aims to provide a tensile test clamp for a high-pressure hydrogen environment material testing machine. The clamp comprises an upper load transfer frame, a lower load transfer frame, an upper clamp arranged in the upper load transfer frame and a lower clamp arranged in the lower load transfer frame, wherein the upper clamp and the lower clamp respectively comprise a spherical cavity seat and a spherical hinge support seat; each spherical cavity seat is a cylinder with an opening formed in the center; a spherical mold cavity body is inward formed in one end of each cylinder; each spherical hinge support seat comprises a cylinder, a spherical coronal body and a convex part in sequence; the spherical cavity seats and the spherical hinge support seats are positioned in the corresponding load transfer frames; the cylinder of each spherical hinge support seat penetrates through an opening in the center of the spherical cavity seat and a central through hole in the corresponding load transfer frame in sequence and can move freely; the upper clamp and the lower clamp are symmetrical vertically. By utilizing the clamp disclosed by the invention, a sample installation process is rapid, simple and convenient; a sample can be automatically centered in the situations of parallel misalignment, deflection misalignment or mixed misalignment, and the test data accuracy is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Testing device and testing method for thermal performance of phase-change temperature regulation building material
ActiveCN101839873ATest the latent heat of phase changeTest RangeInvestigating phase/state changeMaterials testingEngineering
The invention relates to a testing device and testing method for the thermal performance of phase-change temperature regulation building material, belonging to the field of material testing. The testing device is formed by a heating device, an electronic balance, an incubator, a thermal resistance, a paperless recorder, a computer and the like in a connecting way. The testing method is that the principle that the released heat of hot water in an insulation system is equal to the sum of the heat absorbed by the phase-change material and the heat dissipated by the insulation system is used for testing the phase-change latent heat of the phase-change building material. The principle that the temperature of the phase-change material is kept within a certain temperature range in the process of phase change is used for testing the phase-change temperature of the phase-change building material. The invention has the advantages of simple testing device, low cost, simple and feasible testing method and high reliability, and can be used for testing the phase-change latent heat and the phase-change temperature of large-size phase-change temperature regulation building material.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYANYI ENG TECH DEV CENT
Minimally Invasive Systems and Methods for In Vivo Testing of Materials
InactiveUS20110052497A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMaterials testingBiological membrane
Implantable material testing devices and method of testing materials in an animals are provided. In one embodiment, a method of testing a material in an animal includes associating the material with a retention frame to form a testing device. The retention frame movable between a first shape suited for insertion through a deployment instrument and a second shape suited for retention in the animal. The testing device is inserted in the first shape into the deployment instrument and is driven through the deployment instrument into the animal. Once in the animal, the testing device is permitted to assume the second shape so that the testing device is retained in the animal for a testing period. The testing device is removed from the animal after the testing period is complete, and the material is analyzed. The material may be analyzed for biofilm formation, encrustation, or degradation. The animal also may be analyzed for infection or other reactions to the material. Tissue may be collected from the animal, and the tissue may be analyzed. The testing period may be between about 1 day and about 90 days.
Owner:TARIS BIOMEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com