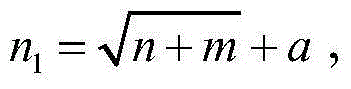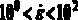Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
924 results about "Strain rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strain rate is the change in strain (deformation) of a material with respect to time. The strain rate at some point within the material measures the rate at which the distances of adjacent parcels of the material change with time in the neighborhood of that point. It comprises both the rate at which the material is expanding or shrinking (expansion rate), and also the rate at which it is being deformed by progressive shearing without changing its volume (shear rate). It is zero if these distances do not change, as happens when all particles in some region are moving with the same velocity (same speed and direction) and/or rotating with the same angular velocity, as if that part of the medium were a rigid body.
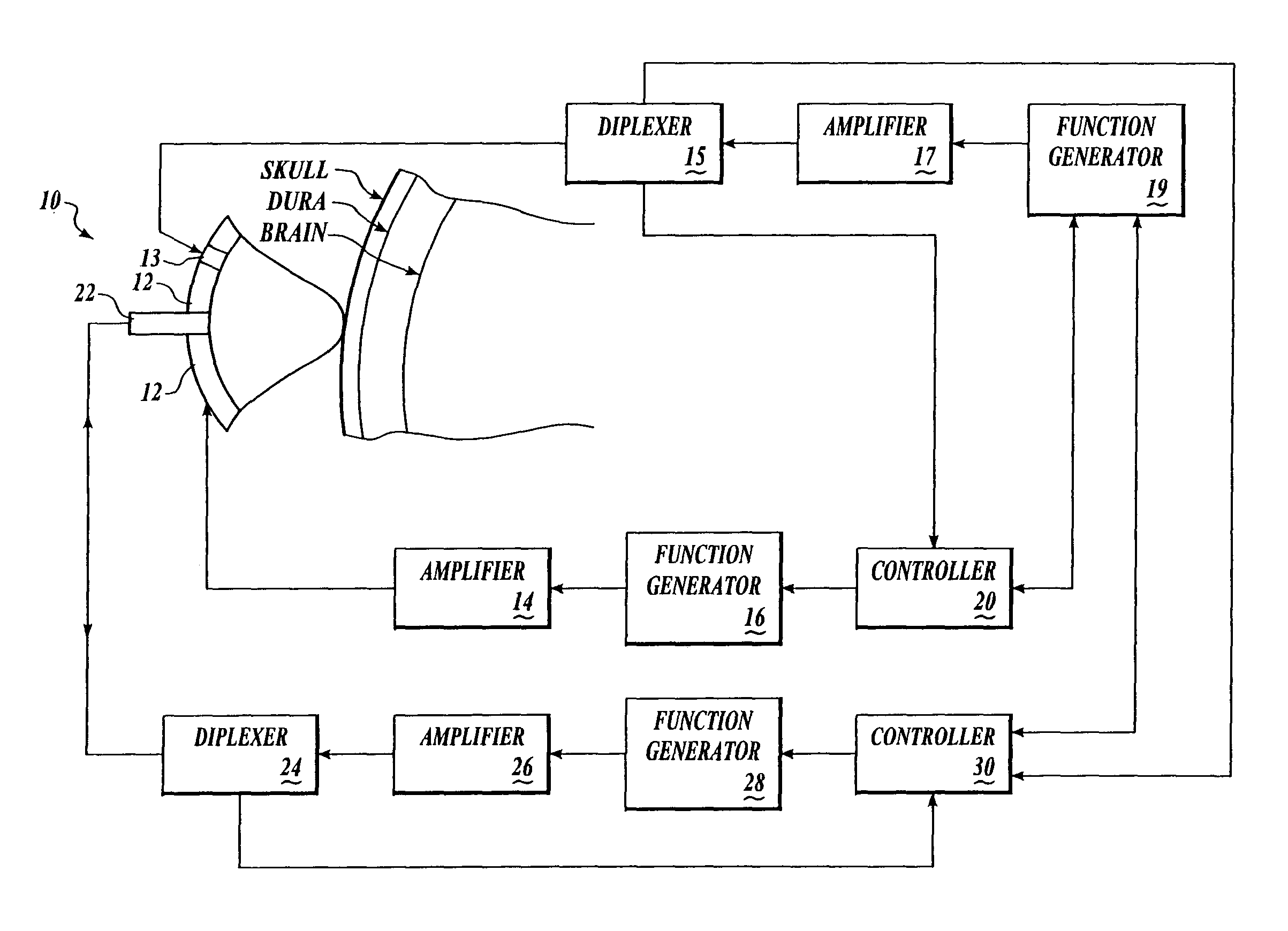
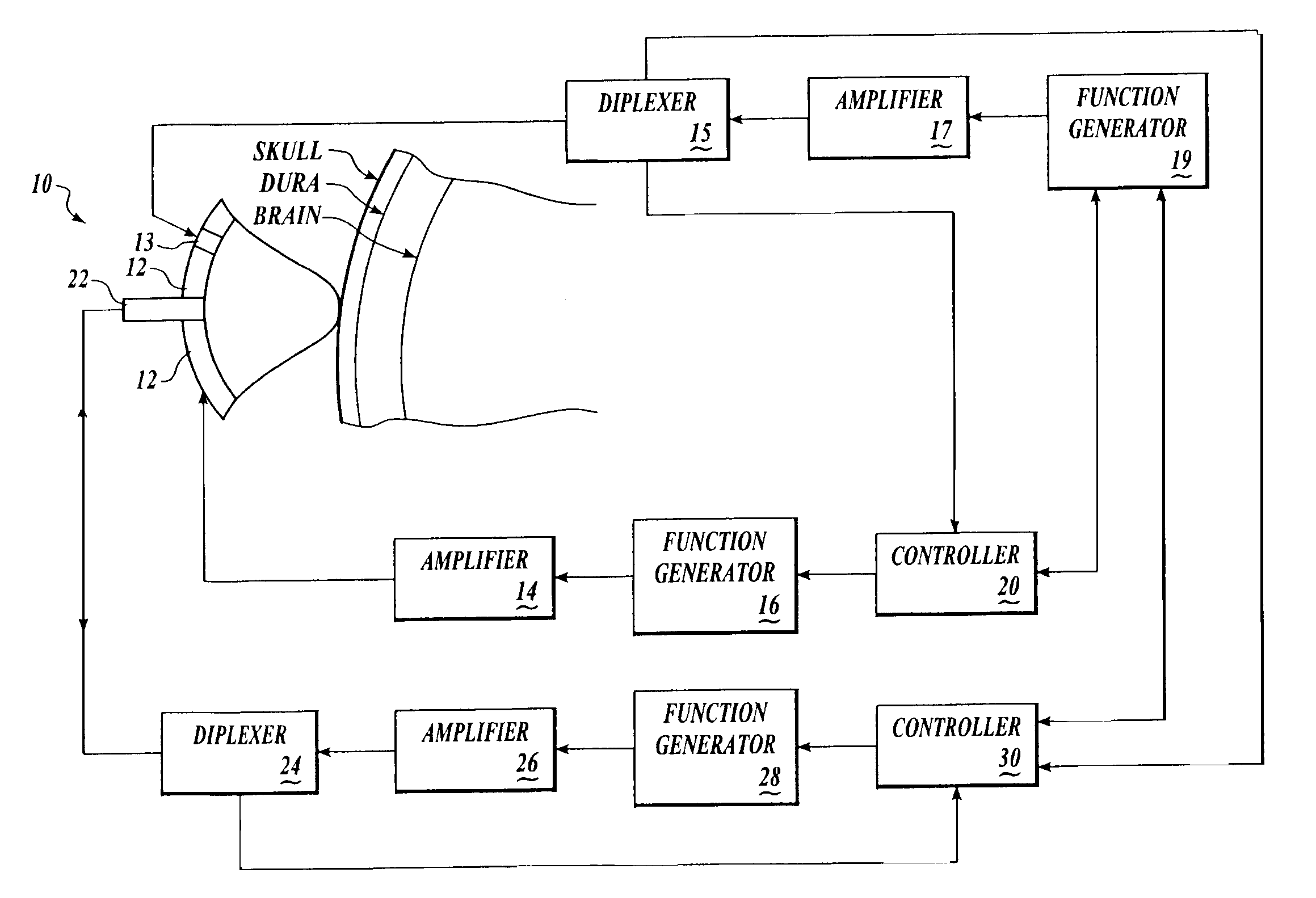
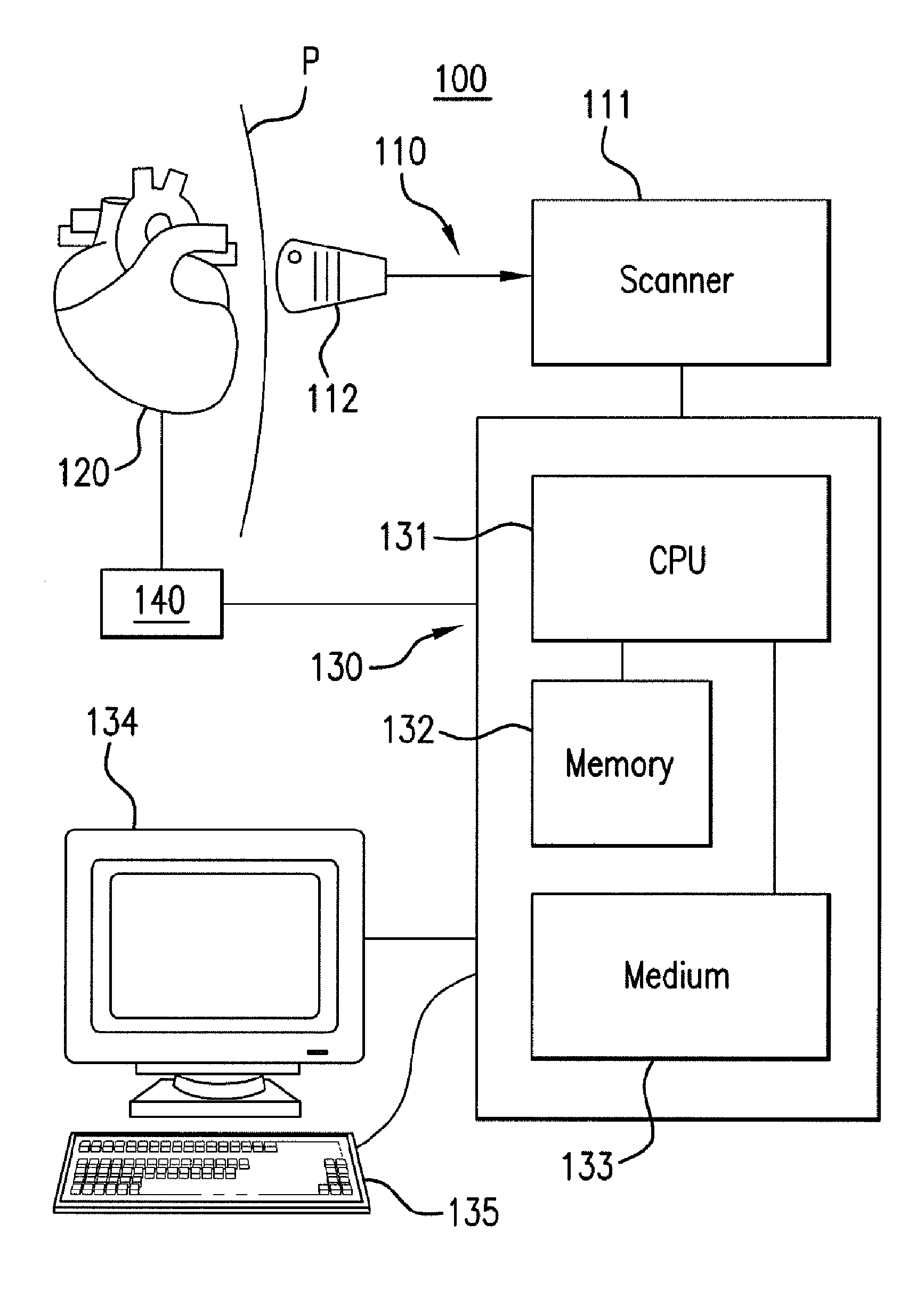
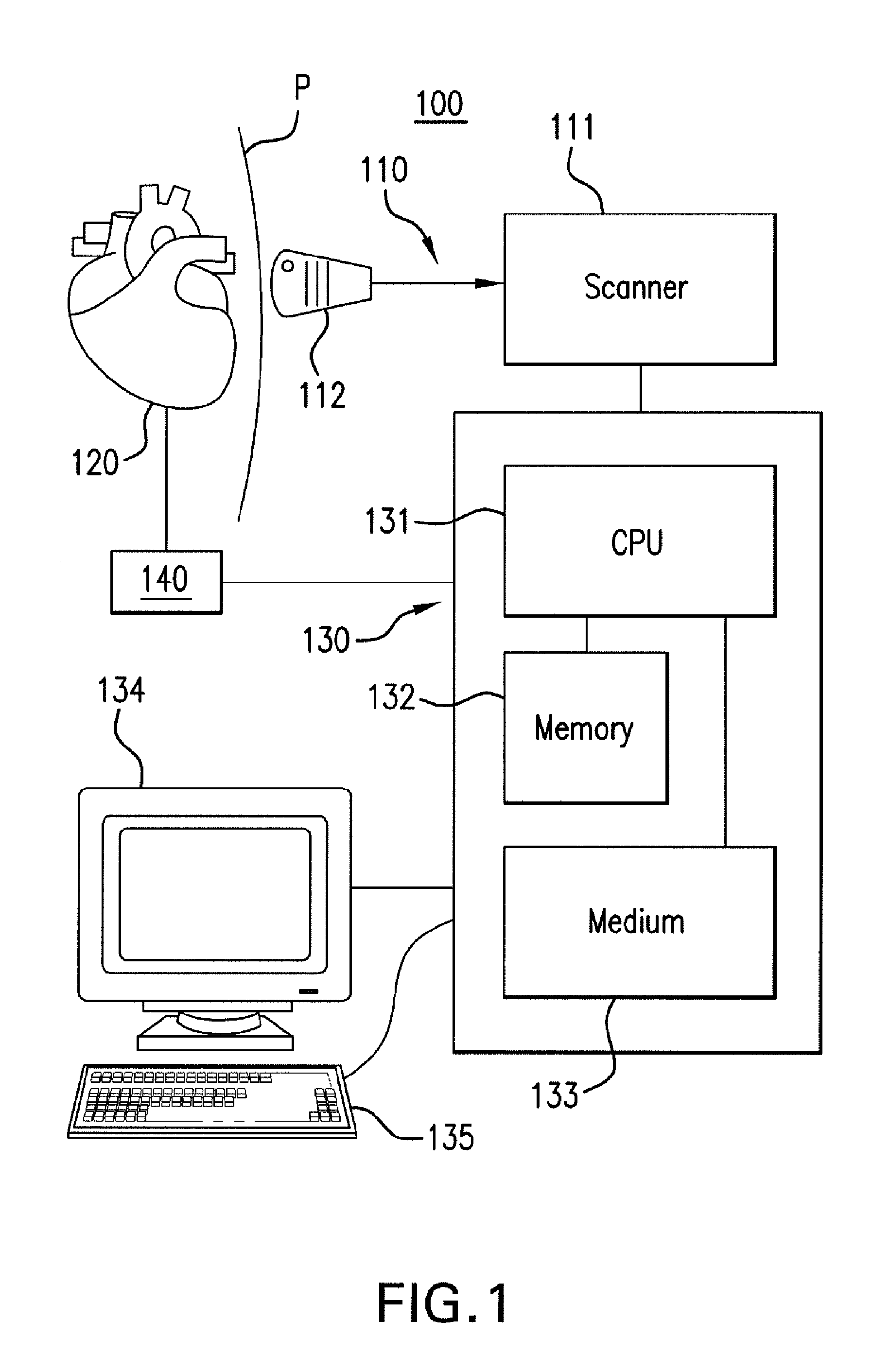
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
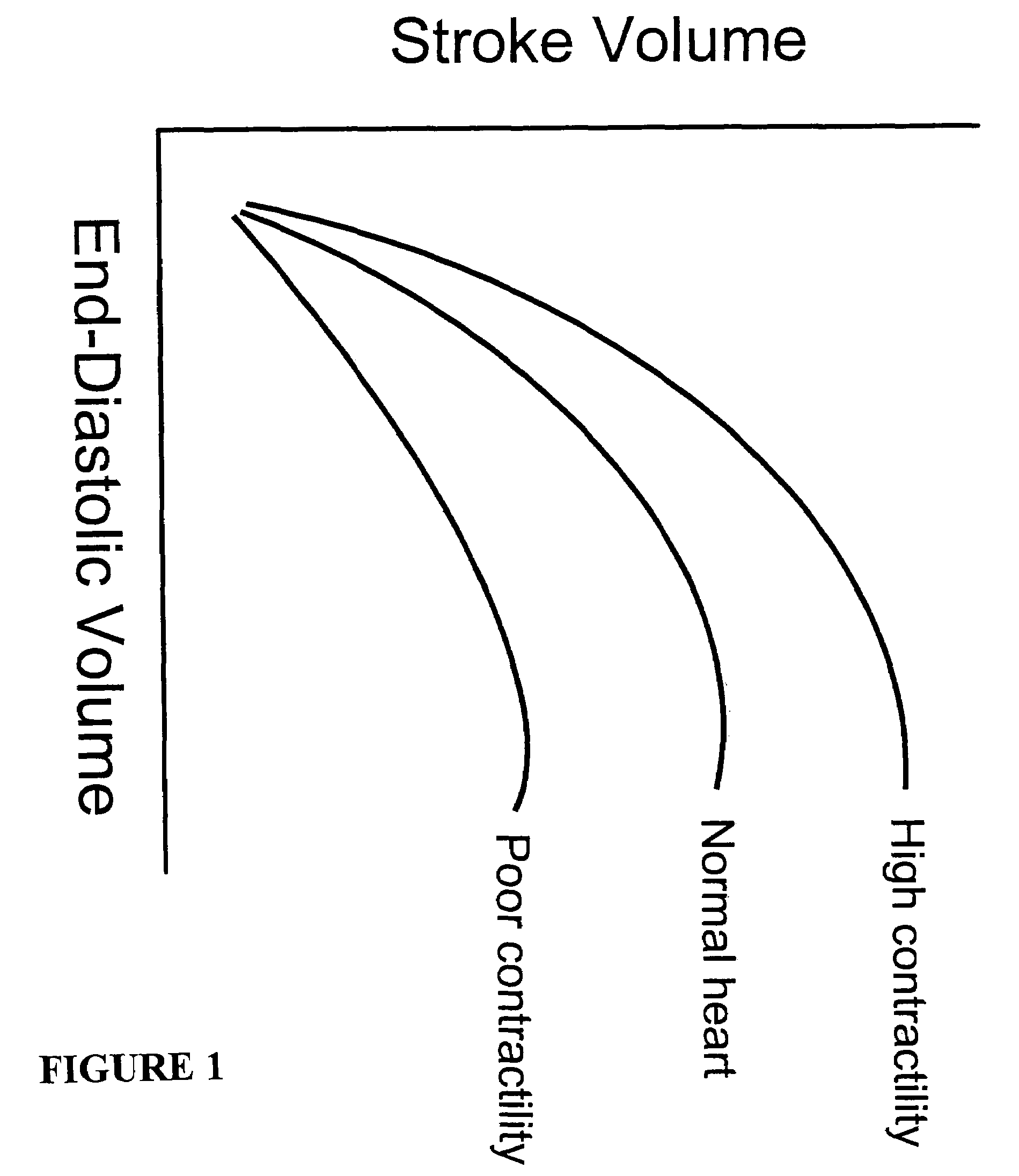
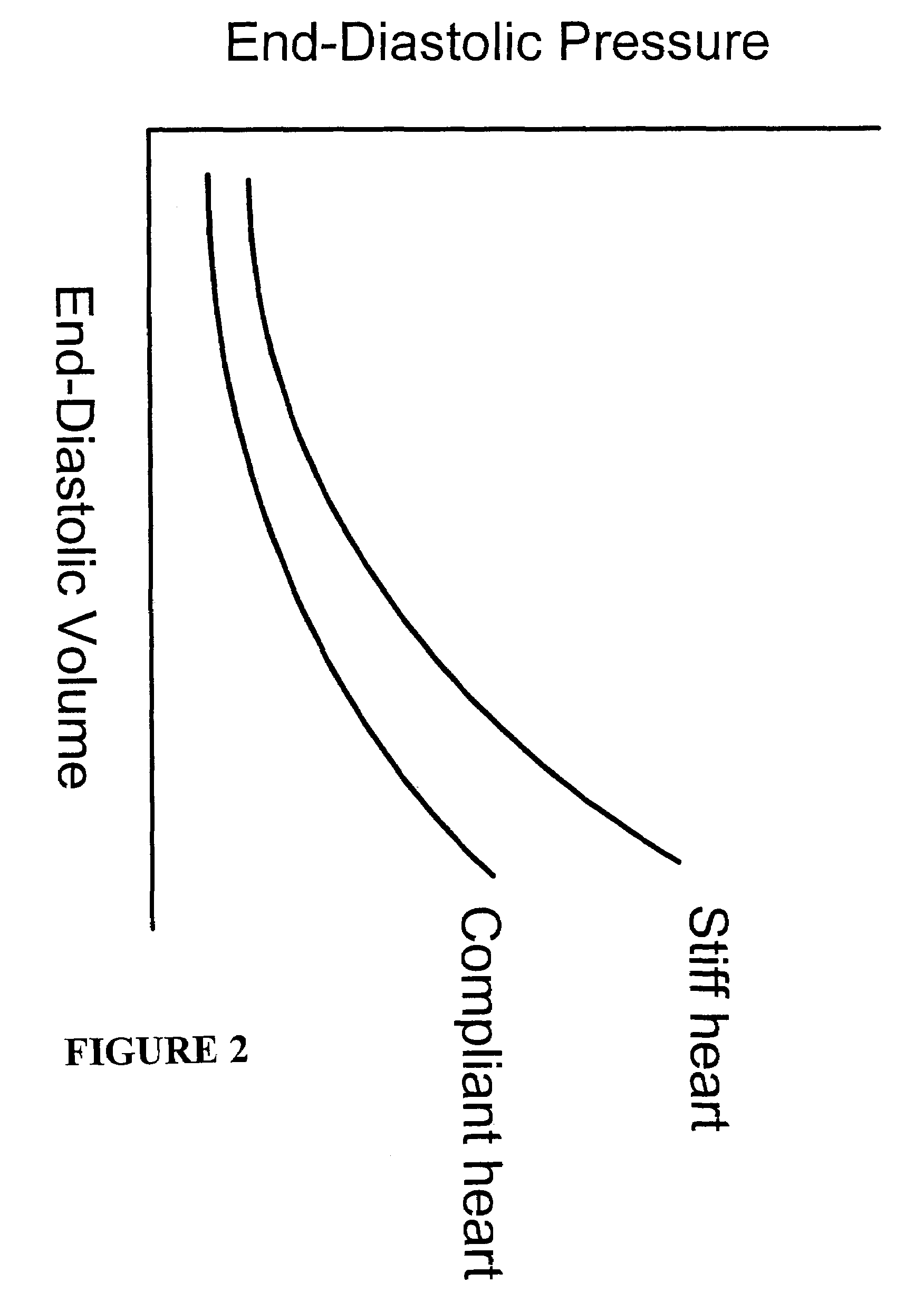
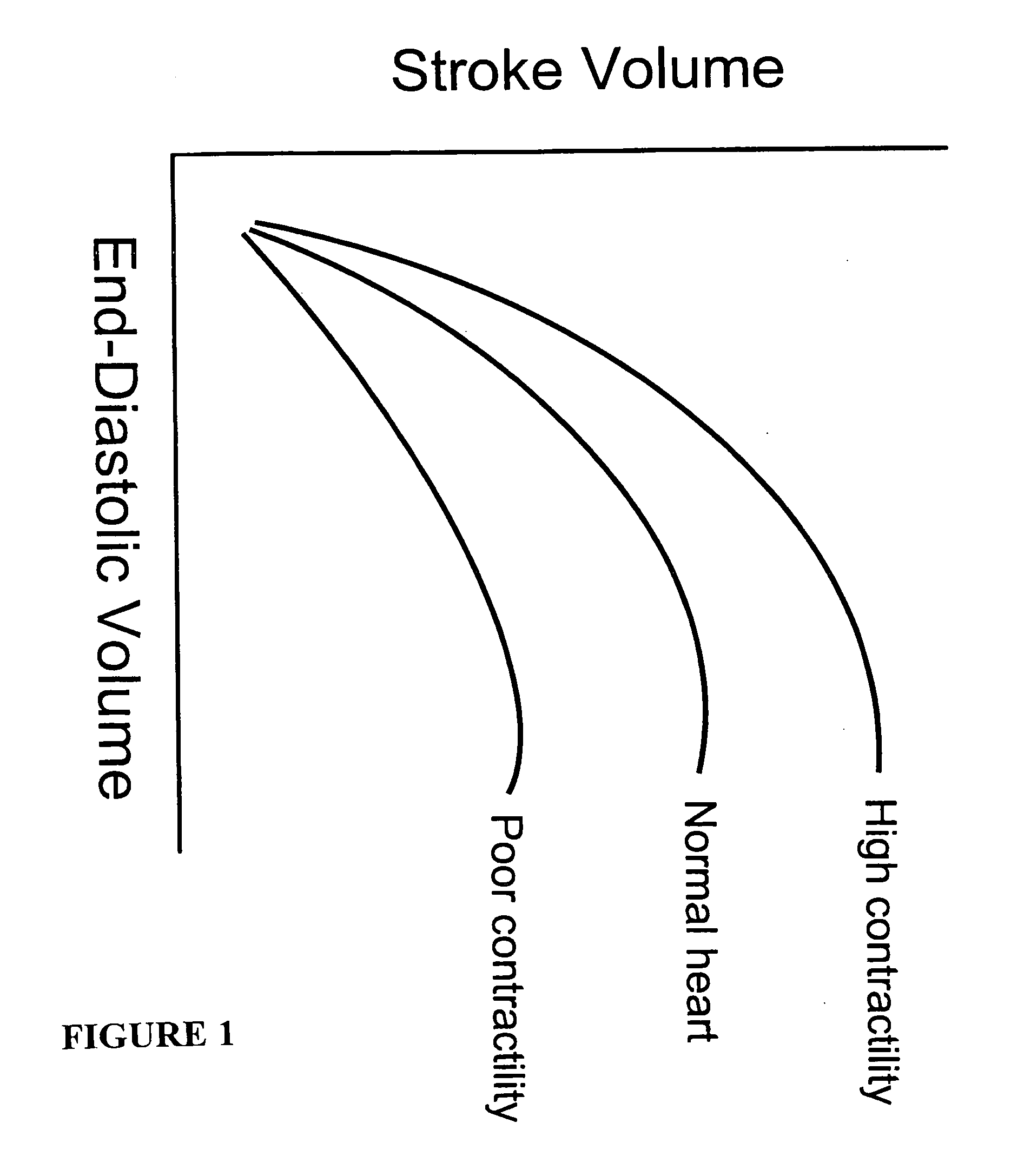
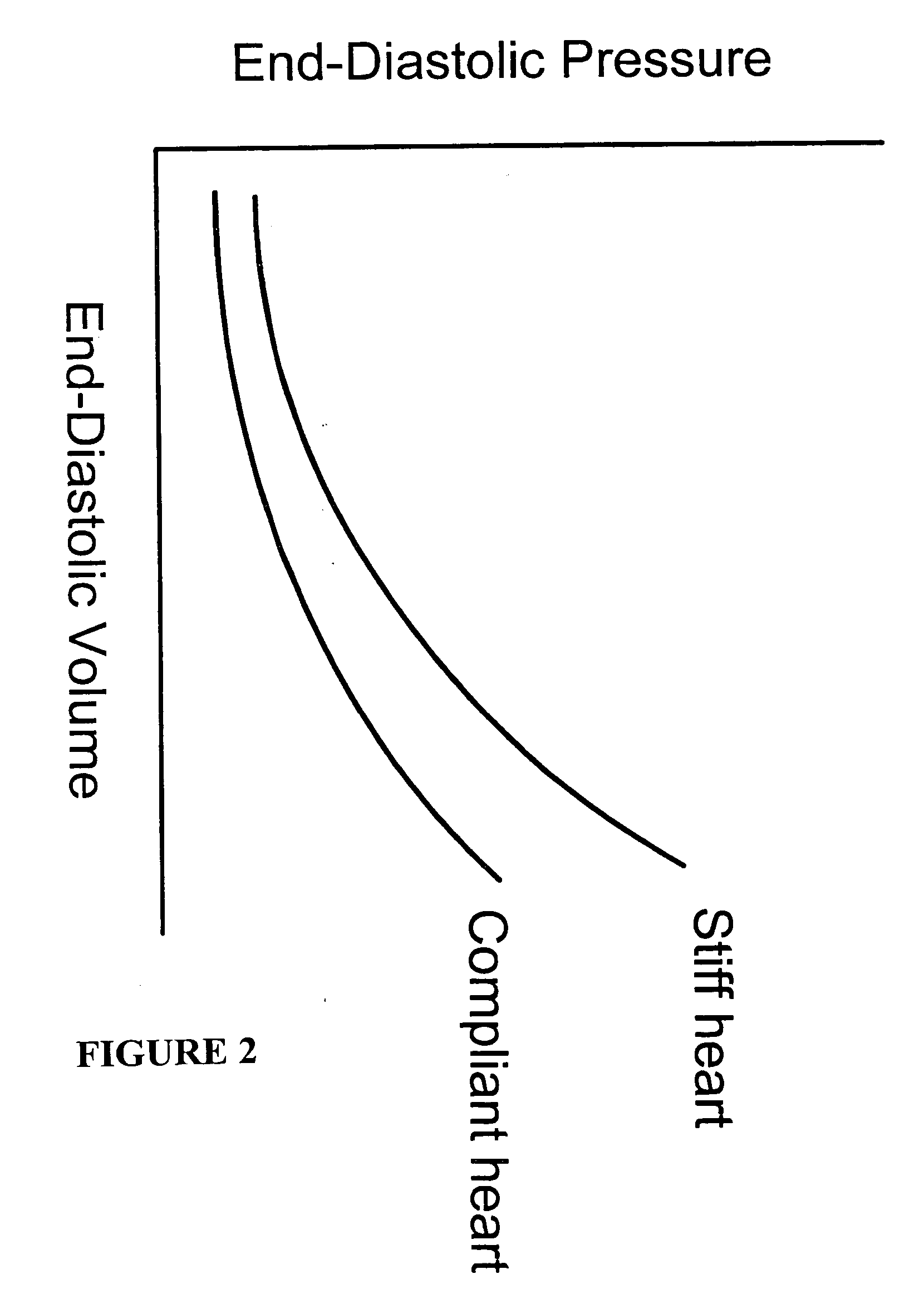
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
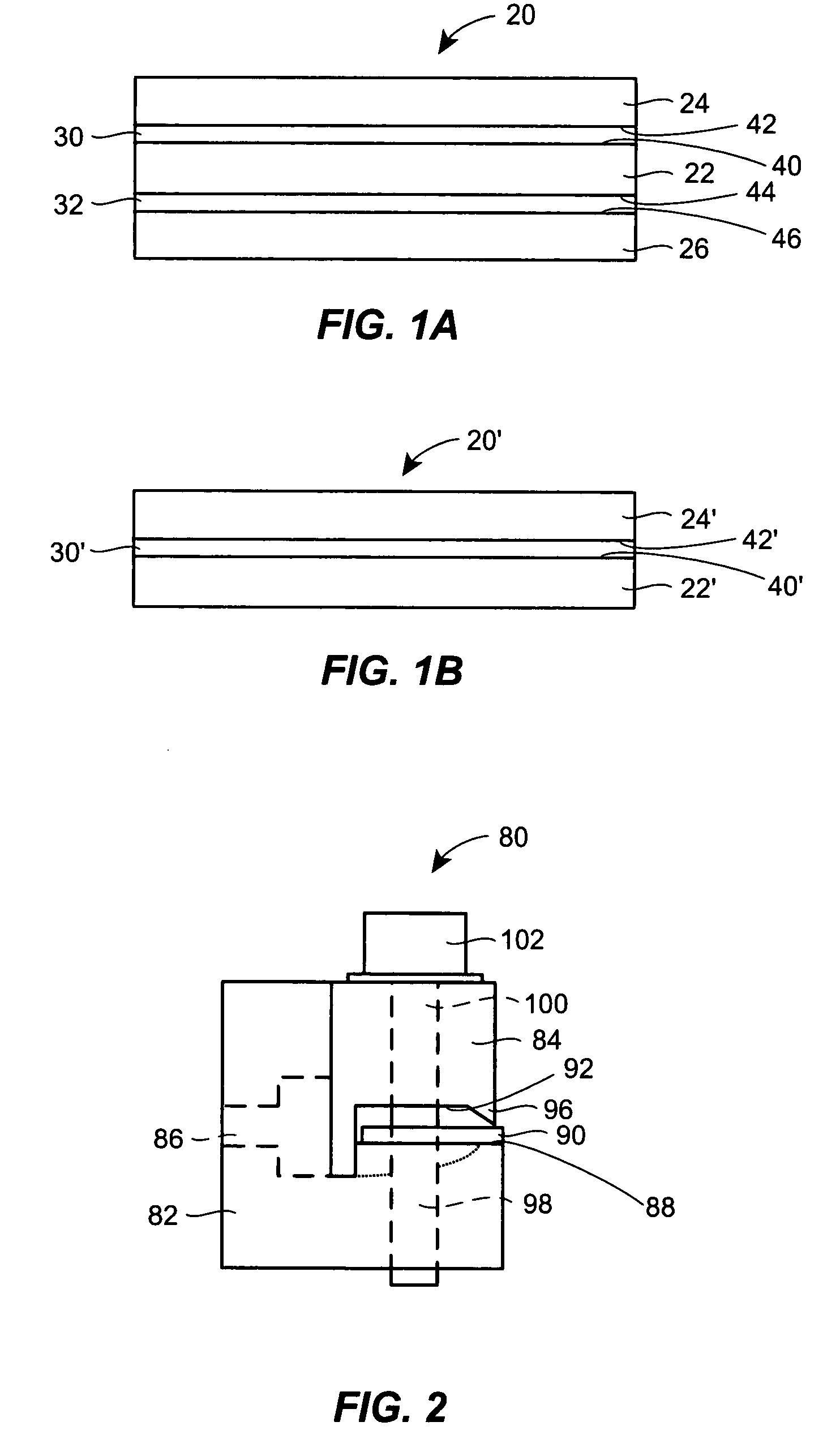
Stretch laminate, method of making, and absorbent article
A stretch laminate includes a first layer including an elastomer film, the first layer having a surface, and a second layer including a nonwoven material, the second layer having a basis weight of less than about 25 gsm and a surface that is attached to the surface of the first layer. The elastomer film has a strength of an engineering tensile strength, at an engineering strain rate of about 600 / s, of at least one of about greater than about 14 MPa for a plain specimen or about greater than about 7 MPa for a notched specimen. A method of making the stretch laminate and an absorbent article having at least one region defined by the stretch laminate are also provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method and Apparatus for Incrementally Stretching a Web
ActiveUS20080224351A1Increase path lengthIncrease line speedDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsConfectioneryEngineeringBiological activation
A method and apparatus is provided which uses activation members for incrementally stretching a web at a low strain rate. The activation members include an activation belt and a single activation member wherein the activation belt and single activation member comprise a plurality of teeth and grooves that complement and engage one another at a depth of engagement in a deformation zone. The depth of engagement can be controlled to increase linearly over at least a portion of the deformation zone such that a web interposed between the activation belt and the single activation member in the deformation zone is incrementally stretched at a low rate of strain.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
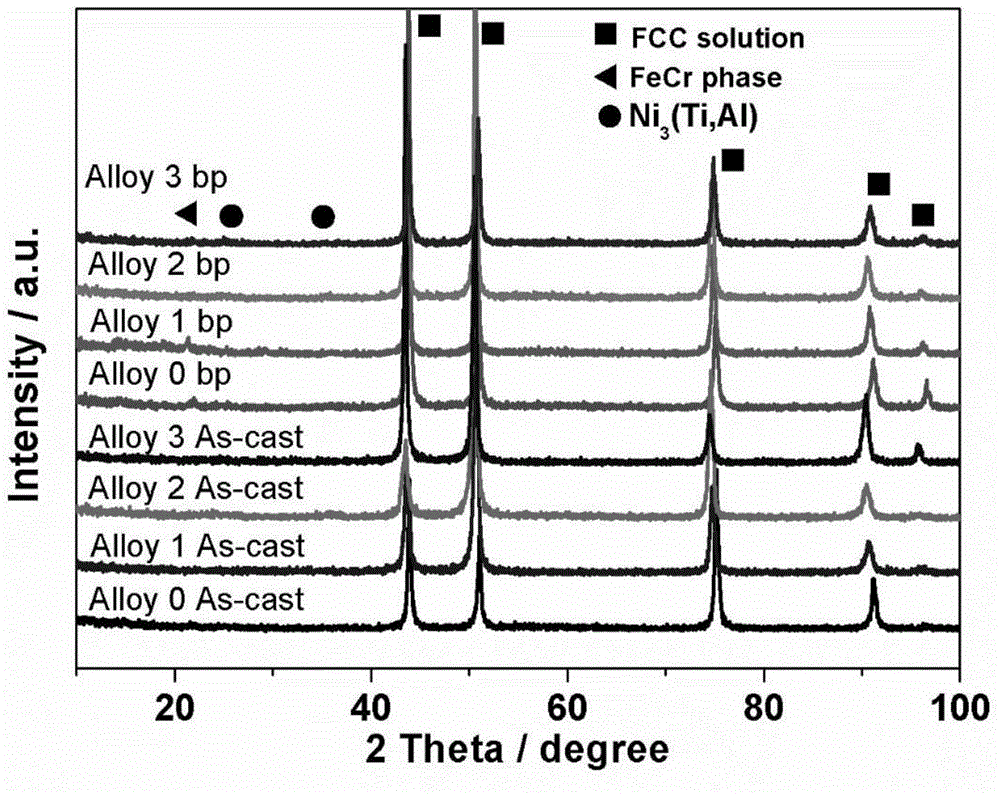
High-entropy alloy with dispersion nano-sized precipitate strengthening effect and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104694808AWide range of ingredientsControl mechanical propertiesElectric arc furnaceHigh entropy alloys
The invention discloses high-entropy alloy with the dispersion nano-sized precipitate strengthening effect and a preparing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of removing oxidized skin of a metal material, and then conducting weighing and burdening accurately according to a ratio; conducing smelting in an electric-arc furnace in an argon shield atmosphere of titanium absorbed oxygen to obtain an initial high-entropy alloy ingot, and conducting cold rolling, wherein rolling reduction is 20-50%; placing the ingot in a heat treatment furnace with a temperature ranging from 900 DEG C to 1000 DEG C for heat preservation for 0.5-2 hours, and conducting quenching; placing the ingot in a heat treatment furnace with a temperature ranging from 700 DEG C to 800 DEG C for heat preservation for 2-18 hours, and conducting quenching. By means of precipitation strength, on the premise that high plasticity is kept, yield strength and tensile strength are improved greatly. The room-temperature tensile strength of (FeCoNiCr)94Ti2Al4 in the final state reaches 1094 MPa, plastic elongation is 35%, work hardening effect is remarkable, comprehensive room-temperature mechanical property is prominent, high-temperature tensile strength can reach 400 MPa at the temperature of 800 DEG C and strain rate of 10<-3>, steady creep rate is smaller than or equal to 10<-8> under the stress of 100 MPa and at the temperature of 750 DEG C, and high-temperature tensile strength and creep mechanical property are excellent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
System and method for performing impact loading on micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property
InactiveCN102135480ASolve the study of dynamic mechanical properties at high strain ratesLaunch fastStrength propertiesFerroelectric thin filmsStress–strain curve
The invention relates to a system and a method for performing impact loading on a micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property. The method comprises the following steps of: instantly accelerating a bullet by using an electromagnetic pulse launch technology and launching the bullet at high speed; transmitting a stretching stress wave generated by collision of the bullet to the micro test piece by using a separated Hopkinson bar technology so as to generate the impact loading on the micro test piece; recording strain data of an input bar and an output bar, and acquiring an enlarged surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece; analyzing and obtaining a stress strain curve of the micro test piece subjected to the impact loading having different strain rates; and analyzing the surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece and obtaining a distribution of a bidimensional displacement field and a strain field during dynamic impact loading of the micro test piece. By the system and the method, the problem of research on the dynamic mechanical property of a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and membrane materials such as piezoelectric thin films, ferroelectric thin films and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
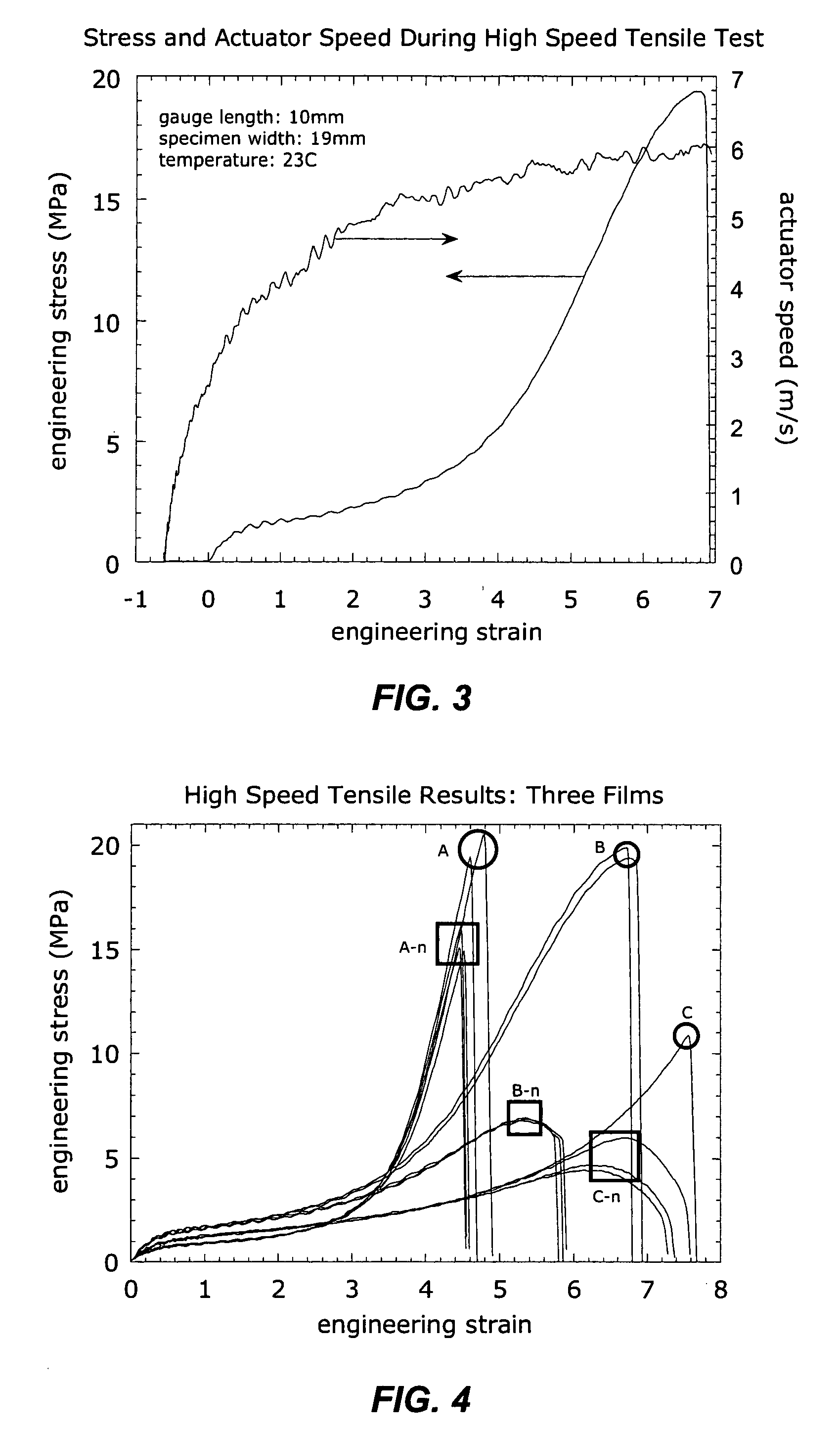
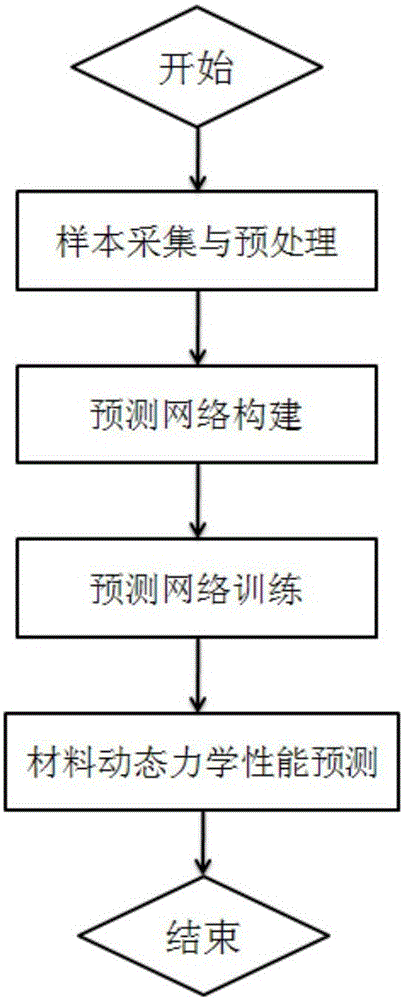
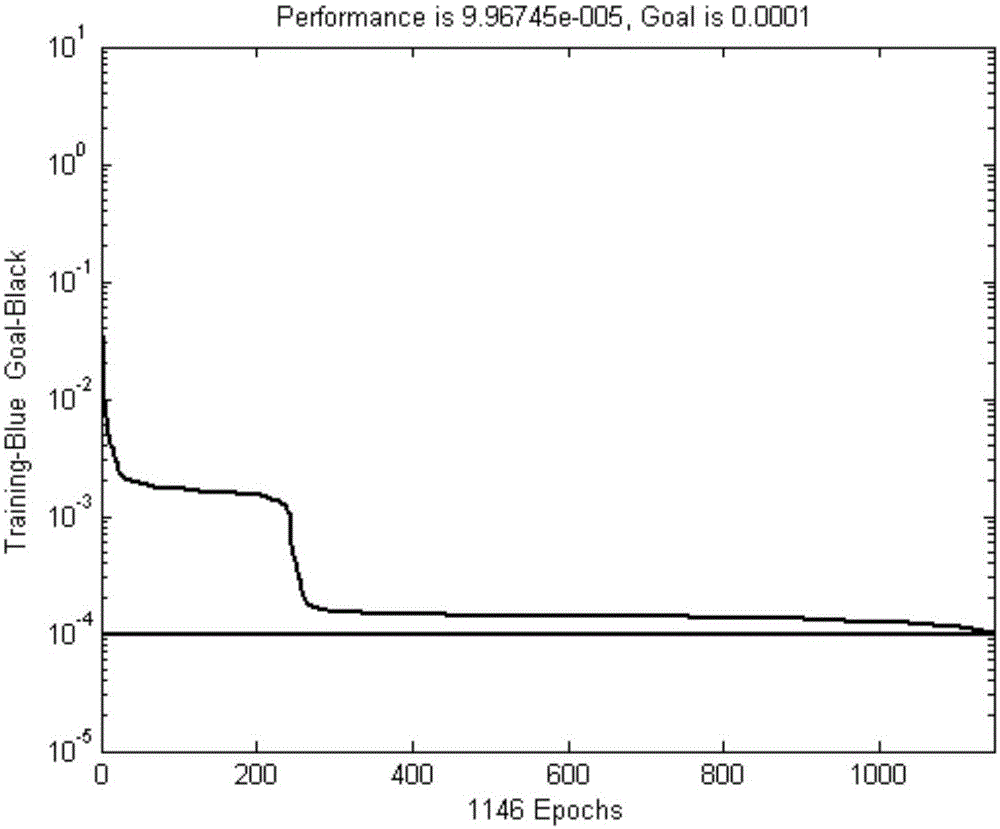
Method for predicting dynamic mechanical property of material based on BP artificial neural network
ActiveCN105095962AImprove simulation accuracyAccurate and fast dynamic mechanical propertiesBiological neural network modelsHidden layerFlow curve
The invention relates to a method for predicting the dynamic mechanical property of a material based on a BP artificial neural network, aims at achieving the prediction of the dynamic mechanical property of the material through the BP artificial neural network, and belongs to the testing field of the dynamic mechanical property of the material. The principle of the method comprises the steps: collecting stress-strain data through employing a high-speed tensile test method, and obtaining a training sample set after normalization preprocessing; building a BP artificial neural network model through designing an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, and selecting a proper transfer function, a training function, and a learning function; carrying out the iterative training of the BP artificial neural network through employing the training sample set, and obtaining an optimal prediction network. The above prediction method can be used for the prediction of the dynamic mechanical property of the material, can achieve the quick prediction of a flow curve of the material at different strain rates in a short time, and can provide enough sample data for automobile safety simulation.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE ENG RES INST
Semiconductor power module
ActiveUS20070246833A1Temperature cycle life is improvedImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsCrazingEngineering
Use of Pb-free solder has become essential due to the environmental problem. A power module is formed by soldering substrates with large areas. It is known that in Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu which hardly creeps and deforms with respect to large deformation followed by warpage of the substrate, life is significantly shortened with respect to the temperature cycle test, and the conventional module structure is in the situation having difficulty in securing high reliability. Thus, the present invention has an object to select compositions from which increase in life can be expected at a low strain rate. In Sn solder, by doping In by 3 to 7% and Ag by 2 to 4.5%, the effect of delaying crack development at a low strain rate is found out, and as a representative composition stable at a high temperature, Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu-5In is selected. Further, for enhancement of reliability, a method for partially coating a solder end portion with a resin is shown.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
Stretching and compression stress wave generator based on electromagnetic force and experimental method
ActiveCN103994922AEasy to controlGood repeatabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAudio power amplifierExperimental methods
The invention provides a stretching and compression stress wave generator based on electromagnetic force and an experimental method. The stress wave generator is such structured that a capacitor charger is connected with a loading gun. A main coil, an insulating layer and a secondary coil all sleeve the locating shaft of a tapered amplifier. A power supply system is employed to provide the main coil of the loading gun with instant strong current, so strong eletromagnetic repulsion is generated between the main coil and the secondary coil; and the eletromagnetic repulsion is converted into stress waves which are amplified by the tapered amplifier and then output to a Hopkinson bar. The stretching and compression stress wave generator has a simple structure and strong controllability, can realize a strain rate and a strain scope which cannot be reached by a traditional disconnect-type Hopkinson bar, allows Hopkinson bar experimental techniques to be standardized, realizes integration of experimental apparatuses of a pull bar and a pressure bar and reduces complexity and occupied space of equipment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
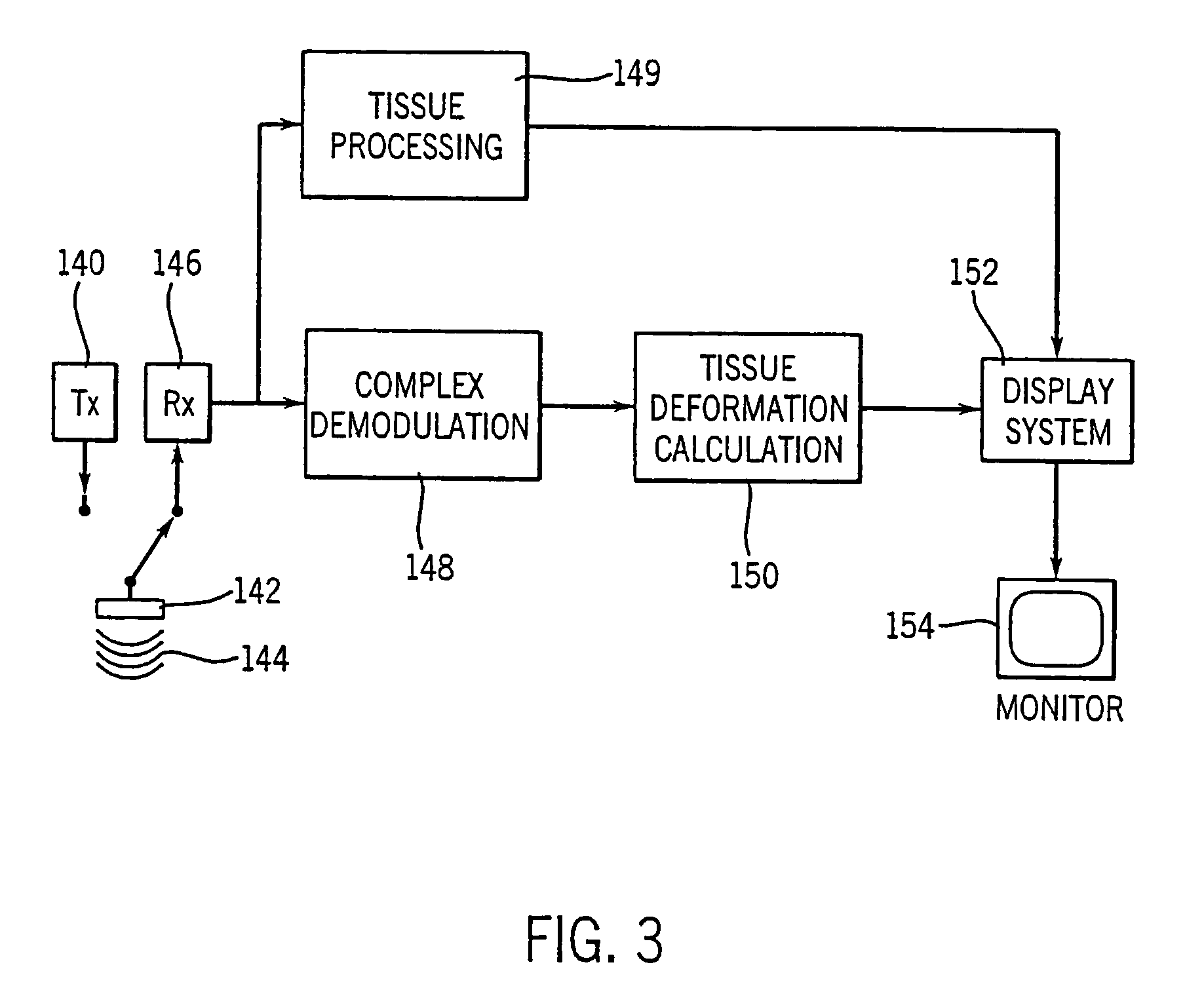
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7077807B2Reduce impactReduce aliasingElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
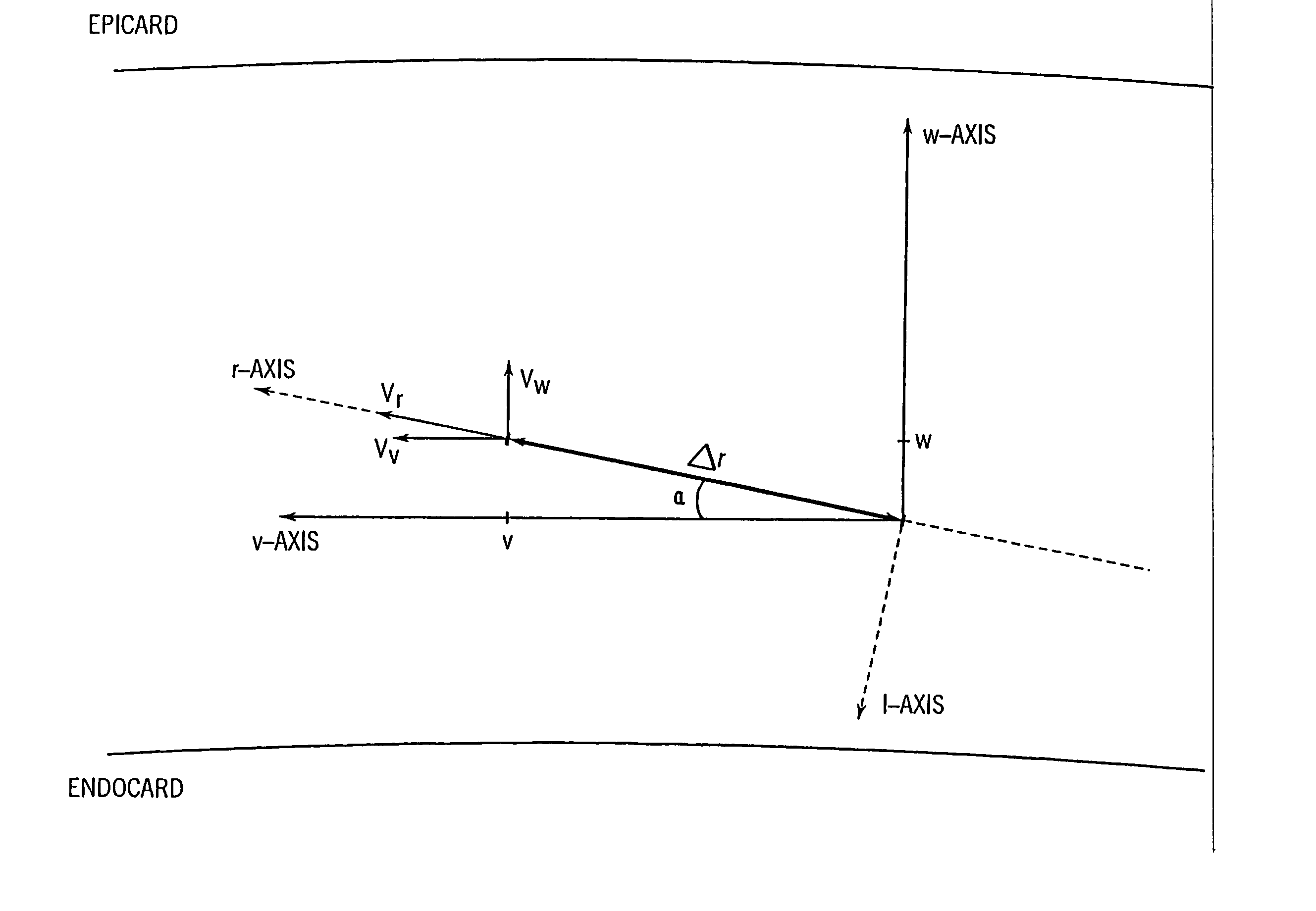
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. A method to estimate a strain rate in any direction, not necessarily along the ultrasound beam, based on tissue velocity data from a small region of interest around a sample volume is disclosed. Quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle.
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
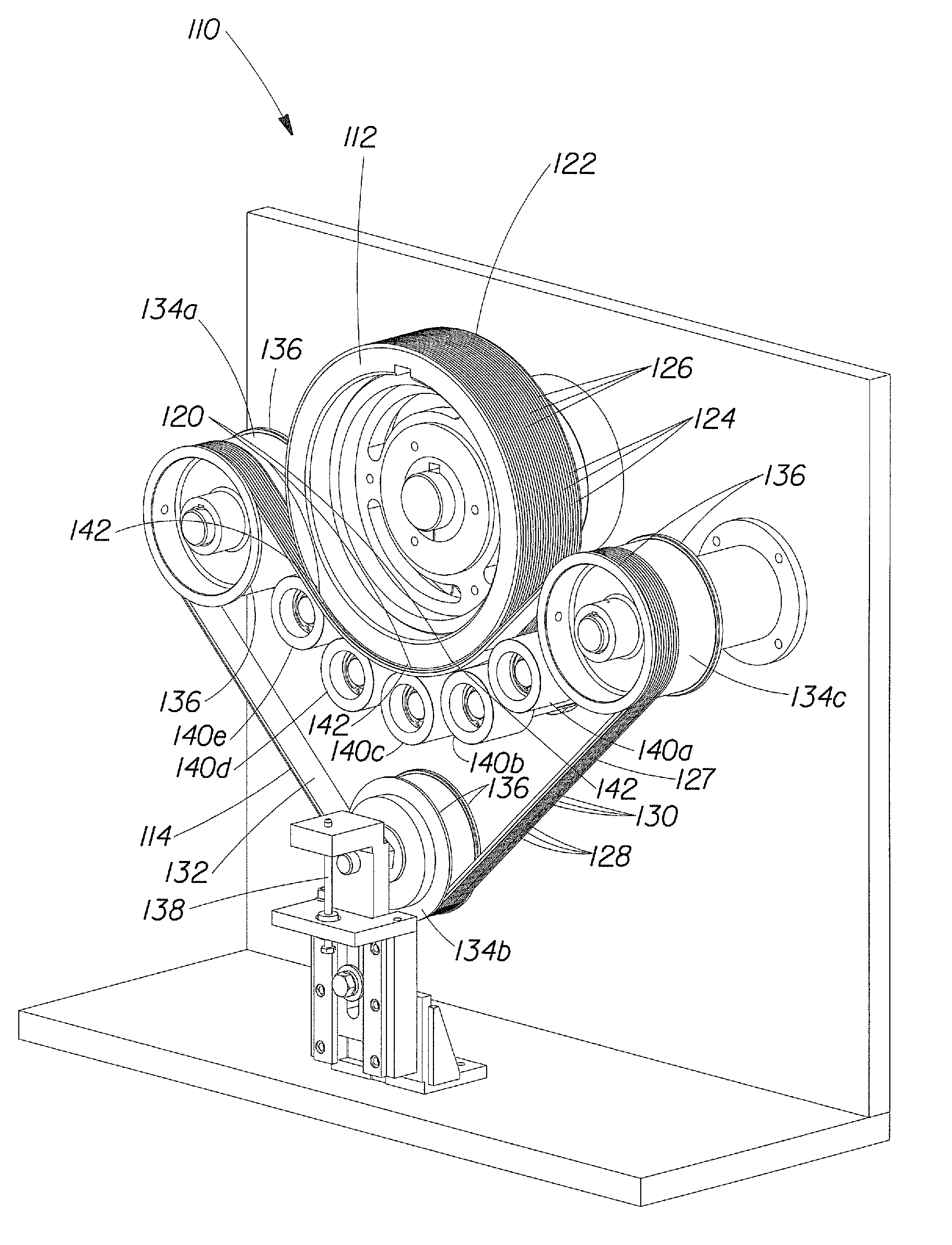
Six-dimensional force sensor
InactiveCN101672705ARealize overload protectionIncrease stiffnessForce measurementElastomerElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to a six-dimensional force sensor which comprises a sensor elastomer and resistance strain gages, wherein the sensor elastomer comprises a cylindrical shell and a crossed elasticbeam; the crossed elastic beam is positioned in the center in the shell and comprises a strain beam (1) and a loading platform (3); an upper base (6) and a lower base (10) are respectively positionedat both ends of the shell; force transmission columns (7) are positioned in the middle of the shell and connected with an upper elastic beam (4) and a lower elastic beam (8); a flexible beam (2) is positioned between the force transmission columns, and the inner side of the flexible beam (2) is connected with the strain beam. A sensor force sensing element comprises the upper elastic beam, the lower elastic beam and the strain beam, and 28 resistance strain gages are attached to the proper position on the force sensing element, wherein 24 strain gages form six groups of full-bridge detectingcircuits for realizing the acquisition of six-dimensional force information, and other four strain gages are reserved. The invention has the characteristics of compact structure, large rigidity, lessdimensional coupling, high precision and good dynamic performance and can be used for the research of an intelligent robot, automated detection and control, bionic motion analysis and sports research.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
InactiveUS20050124892A1Reduce internal pressureBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
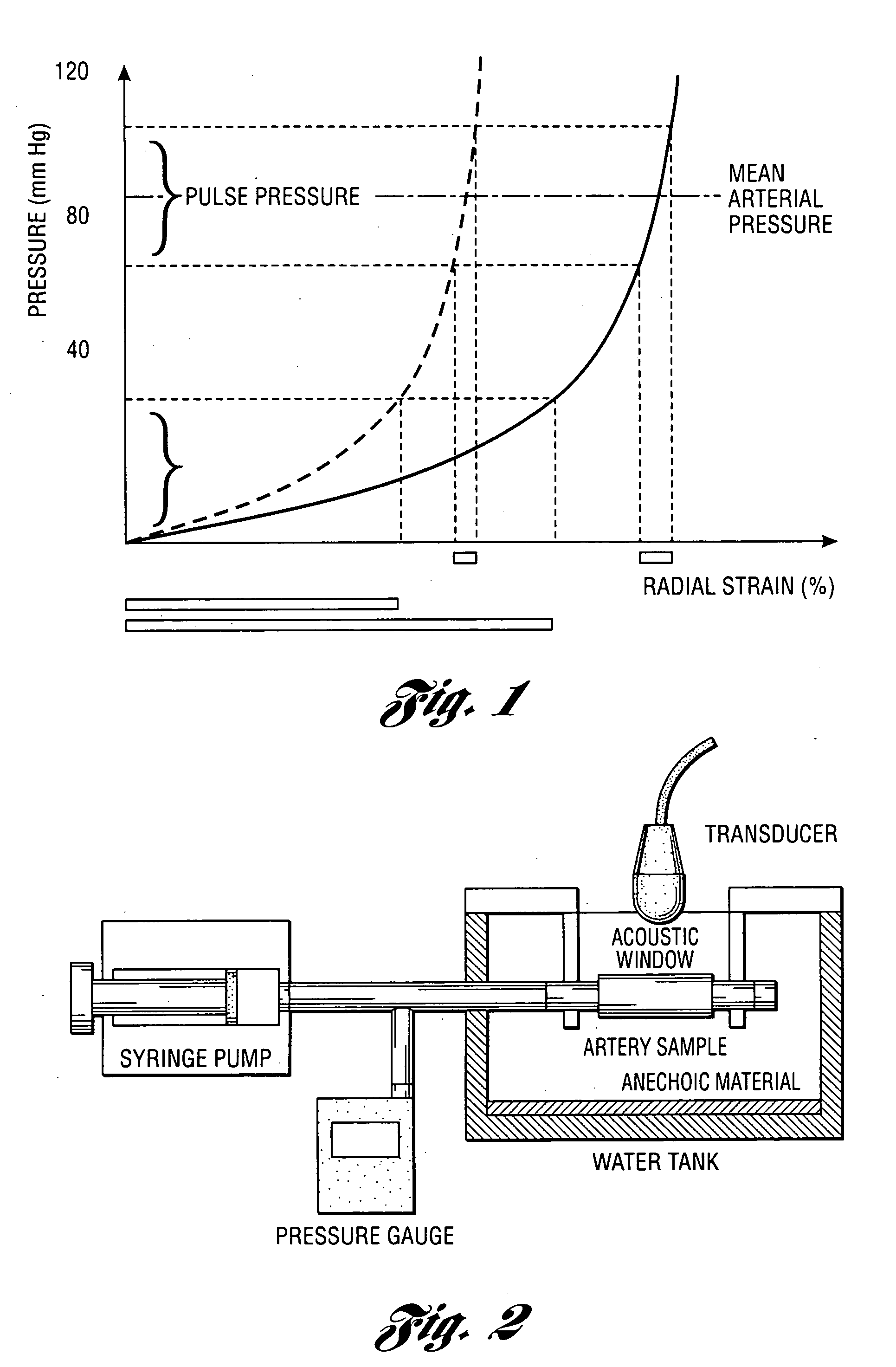
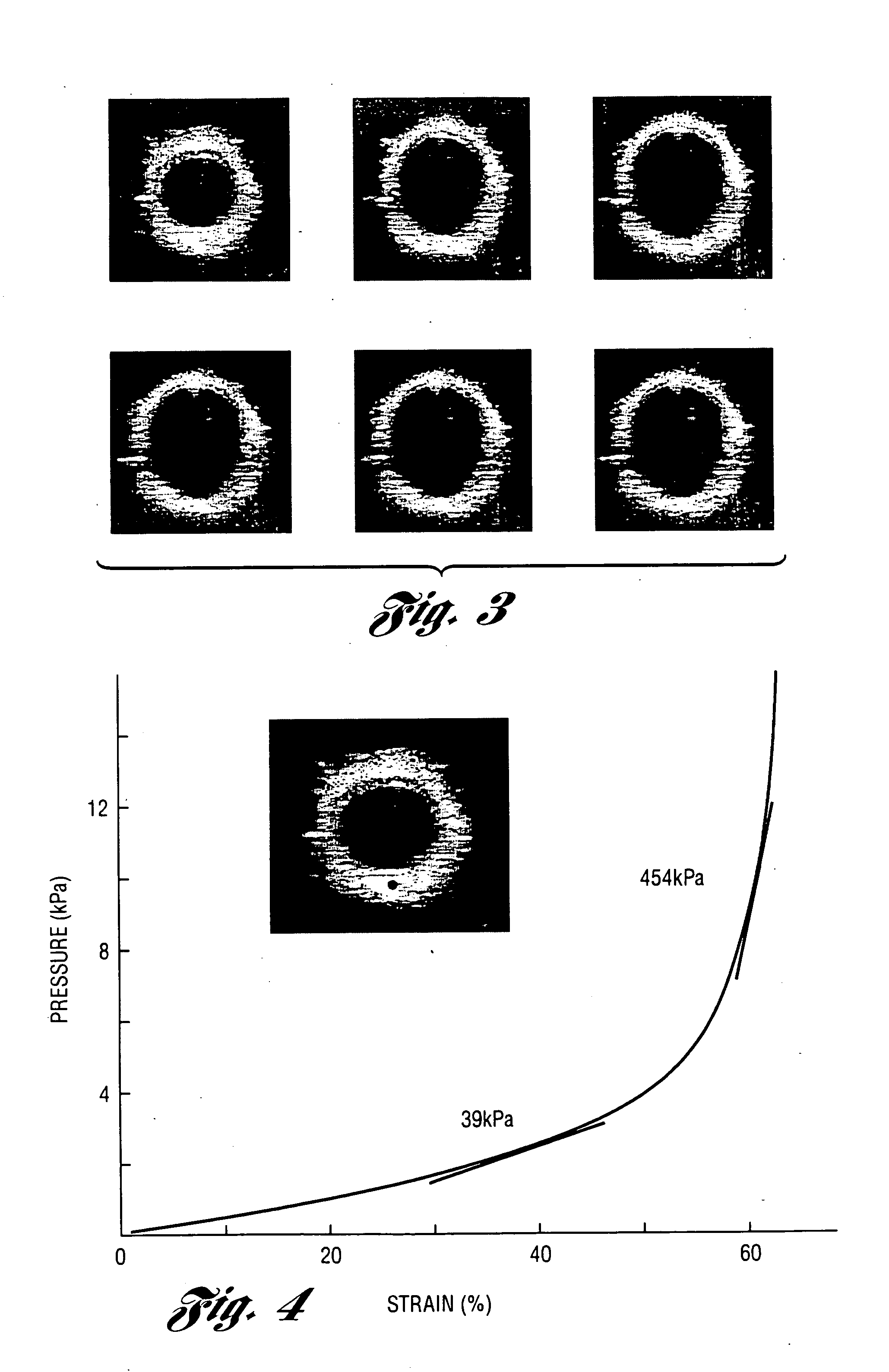
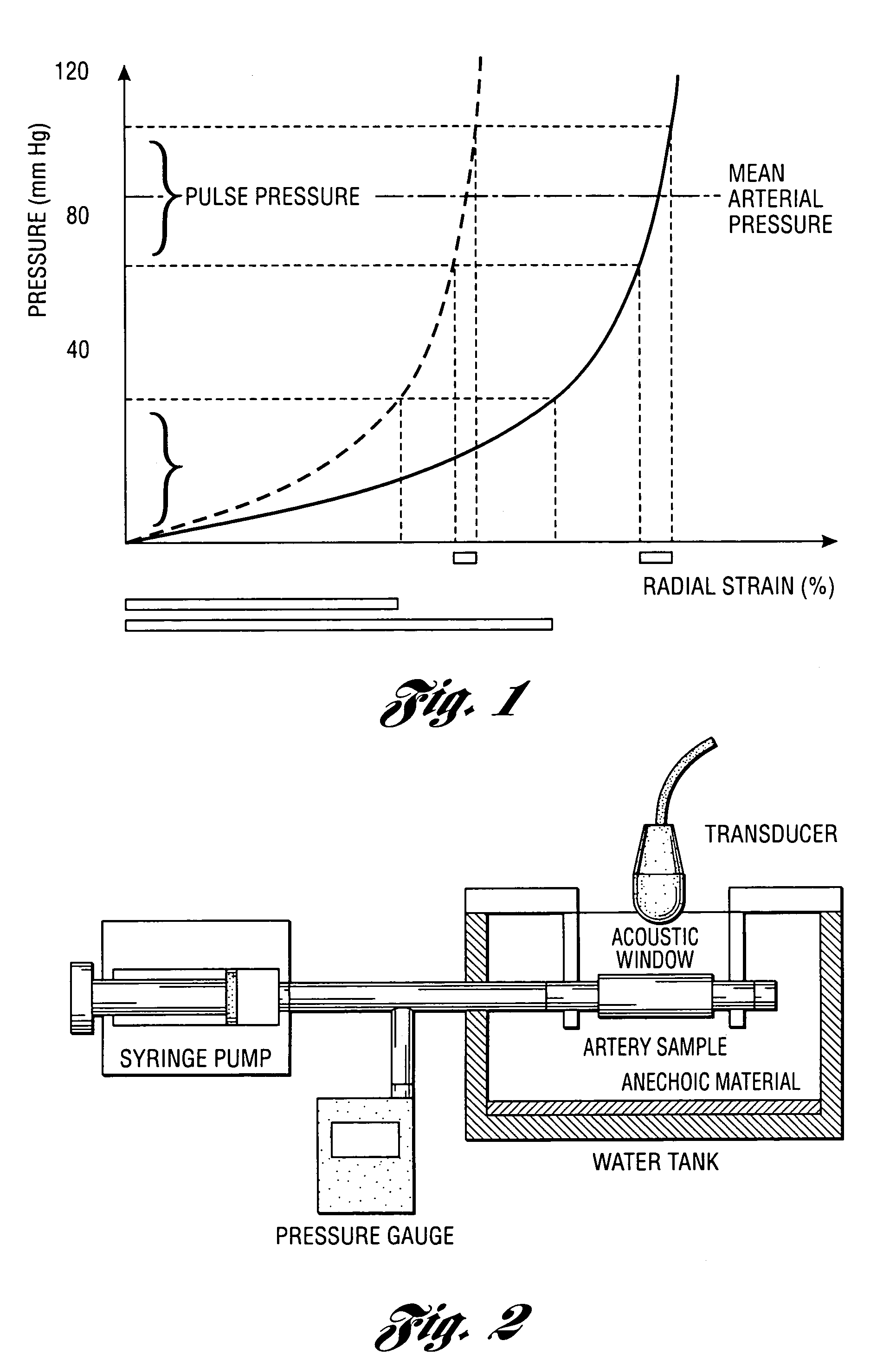
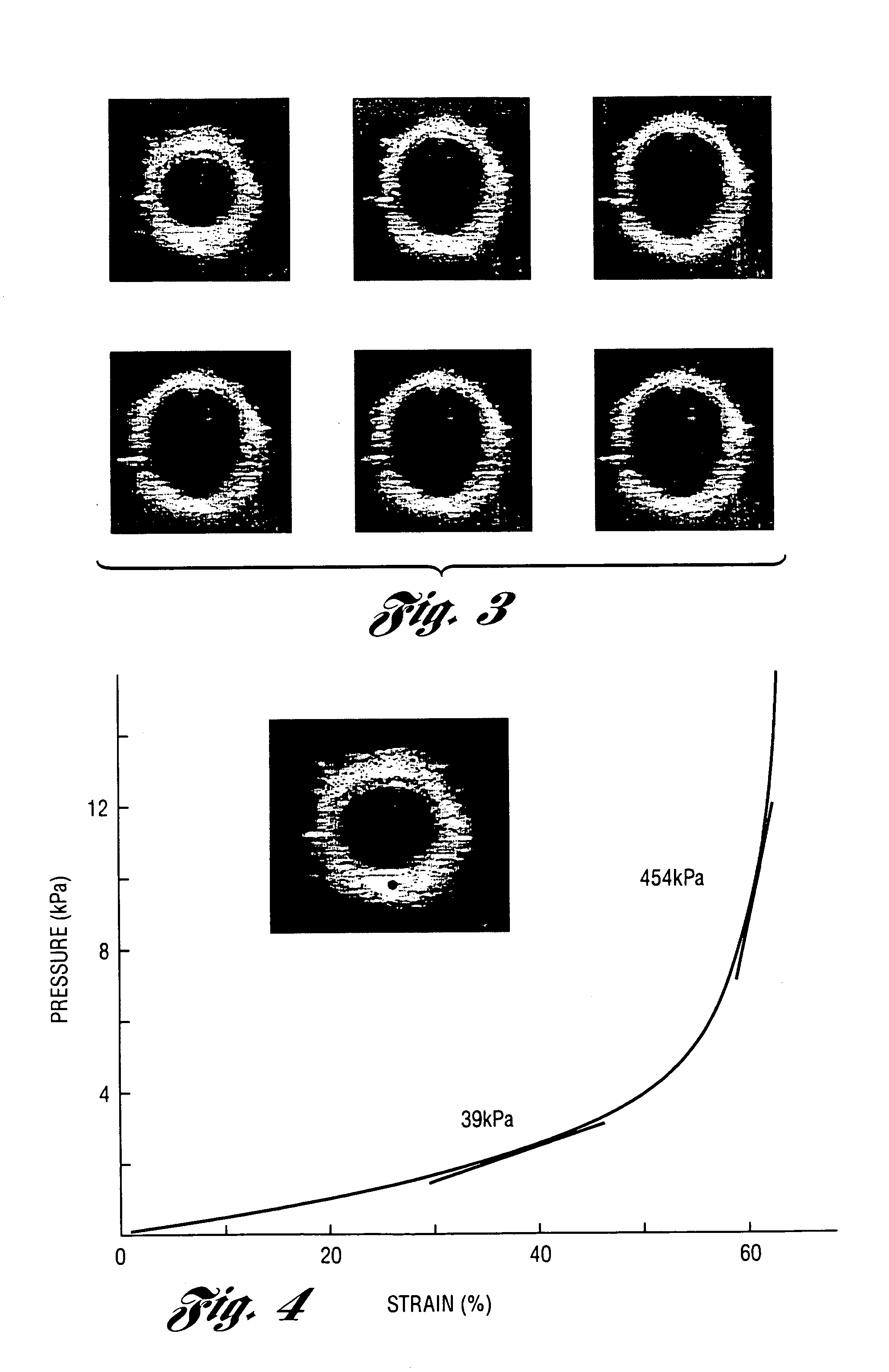
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Single sided stretch bonded laminates, and methods of making same
InactiveUS20050170729A1Short opening timeSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationInter layerPolyolefin
An elastic laminate capable of being rolled for storage and unwound from a roll when needed for use, includes an elastic layer of an array of continuous filament strands with meltblown deposited on the continuous filament strands, and a facing layer bonded to only one side of the elastic layer. The meltblown layer may include an elastic polyolefin-based meltblown polymer having a degree of crystallinity between about 3% and about 40%. The laminate suitably has an inter-layer peel strength of less than about 70 grams per 3 inches cross-directional width at a strain rate of 300 mm / min. Alternatively or additionally, the continuous filament strands and / or the facing layer may include an elastic polyolefin-based meltblown polymer having a degree of crystallinity between about 3% and about 40%. In certain embodiments, the elastic laminate may include an extensible facing layer bonded to an elastic or semi-elastic film layer having a basis weight of about 50 gsm or less, wherein the facing layer includes an elastic polyolefin-based polymer having a degree of crystallinity between about 3% and about 40%.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Production method of low-alloy complex-phase (Q and P) steel
InactiveCN101775470AImprove plasticityHigh strengthTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsRoom temperatureManganese
The invention discloses a production method of low-alloy complex-phase (Q and P) steel. In the method, low-carbon manganese silicon steel or low-carbon manganese silicon aluminium steel is used as raw materials, and the method comprises the following steps of: heating a steel blank to 1100-1250 DEG C; keeping the temperature for 5-120 minutes, and then cooling to 1000-1100 DEG C at the speed of 5-20 DEG C / s; then roughly rolling at the strain rate of 1-50 s<-1>; then cooling to a temperature ranging from T1 to T2 at the speed of 5-50 DEG C / s, wherein T1=A3-(A3-30) DEG C, and T2=Ar3-(Ar3+10) DEG C; then finely rolling at the strain rate of 1-50 s<-1>; after the fine rolling, cooling to the temperature ranging from T3 to T4 at the speed of 40-100 DEG C / s, wherein T3 is lower than a Ms point, and T4 is higher than a Mf point; then heating to 250-450 DEG C; keeping the temperature unchanged for 3-30 minutes, and then cooling to room temperature. Experiences prove that the low-alloy complex-phase (Q and P) steel produced by using the method has higher strength, good plasticity and comprehensive mechanical property better than that of the conventional complex-phase (Q and P) steel.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
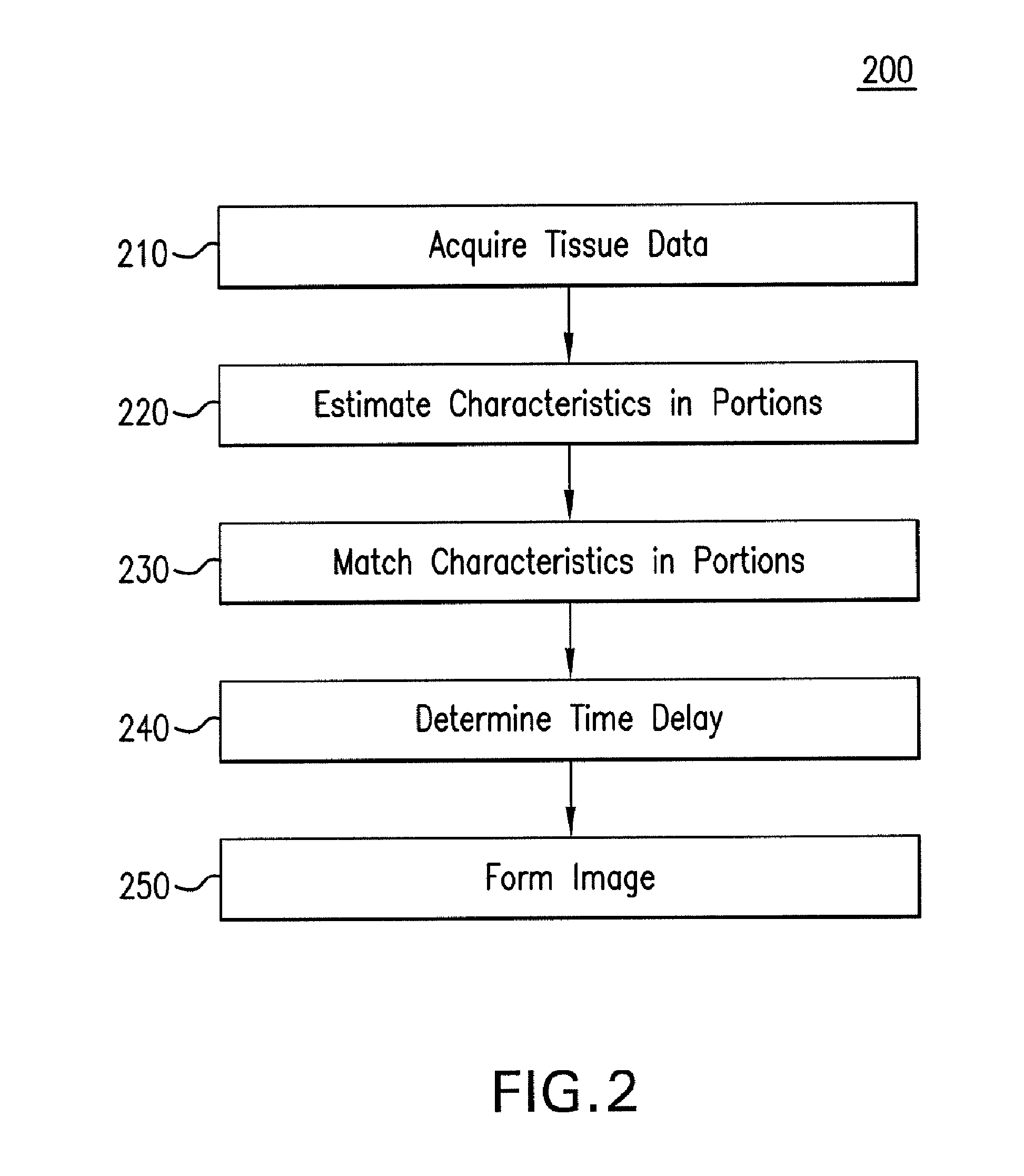
Systems And Methods For Matching And Imaging Tissue Characteristics
Systems and methods for matching a characteristic of multiple sectors of a moving tissue to verify an overlap thereof are disclosed herein. In an exemplary method, tissue data for at least a first sector and a second sector of a moving tissue is acquired. A characteristic of at least a portion of the first and second sectors is estimated from the acquired tissue data, and the estimated characteristics are matched to verify whether a portion of the first sector overlaps with a portion of the second sector. Estimating can include estimating a displacement such as an axial displacement and / or lateral displacements. Estimating can further include estimating a strain, a velocity, a strain rate and / or a stiffness or equivalent.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Microcomputer-controlled electro-hydraulic servo rock tri-axial dynamic shear-seepage coupling multifunctional test method
ActiveCN107748110AOvercoming direct shear-seepageEasy to disassembleMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesAxial pressureData acquisition
A microcomputer-controlled electro-hydraulic servo rock tri-axial dynamic shear-seepage coupling multifunctional test method belongs to the technical fields of rock mechanics and engineering technology and is characterized in that a test apparatus is composed of a loading system, a sealing system, a multiphase fluid injection system, an acoustic emission monitoring system, a deformation monitoringsystem and a data collection system. The test method not only solves technical problems that a tri-axial pressure chamber cannot be used for performing large displacement shear-seepage coupling of rocks under high confining pressure and high seepage pressure, and also can achieve various extended functions on the basis of the technology. The apparatus can achieve servo control loading of force, displacement and strain rate in shear direction and injection seepage of a multiphase fluid during dynamic shear. In addition, the apparatus is equipped with a temperature control system for performingconstant temperature control to the tri-axial pressure chamber at 0-200 DEG C; therefore, a series of extended experiments of dynamic shear-seepage coupling features of rocks under effect of temperature can be carried out.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Foamable Thermoplastic Reactor Blends and Foam Article Therefrom
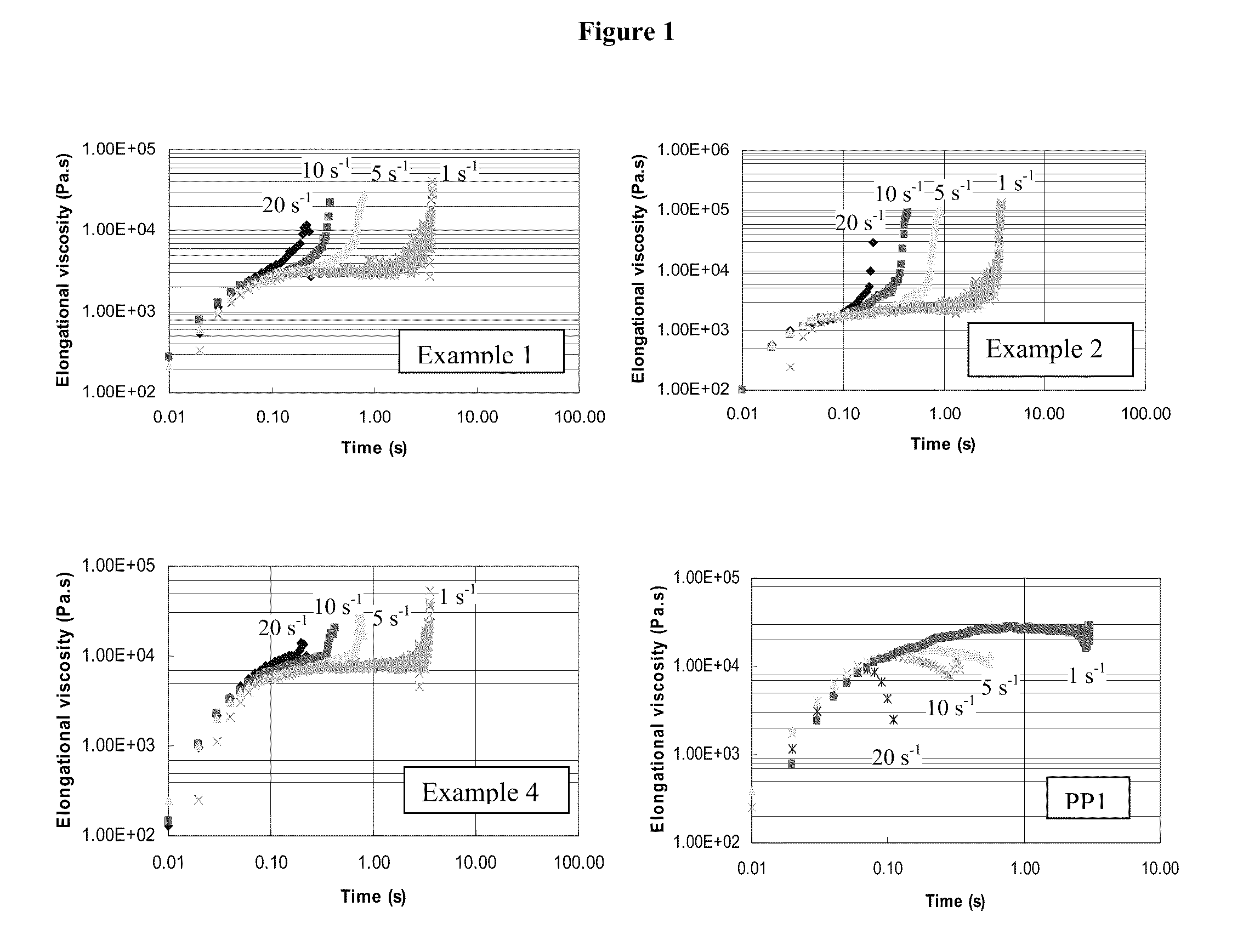
This invention relates to a foamable blend comprising an in-reactor polymer blend comprising: (a) a first propylene polymer component comprising 90 to 100 wt % propylene and from 0 to less than 10 wt % comonomer, said first propylene component having a Tm of 120° C. or more; and (b) a second propylene polymer component comprising from 30 to 90 wt % propylene and 70 to 10 wt % comonomer, said second propylene polymer having an Mw of 30,000 g / mol or more, and said second propylene-containing polymer having a crystallinity different by at least 5% from the first polymer, wherein the polymer blend, prior to combination with a foaming agent, has: (i) a Tm of at least 120° C.; (ii) a MFR of 10 dg / min or more; (iii) a tensile strength of at least 8 MPa; (iv) an elongation at break of at least 200%, and (v) a ratio of elongational viscosity at break to linear viscosity of 5 or more when the elongational viscosity is measured at a strain rate of 1 sec−1 and temperature of 180° C.; and where when the blend is foamed with a foaming agent, the foamed article has a density of 800 kg / m3 or less.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
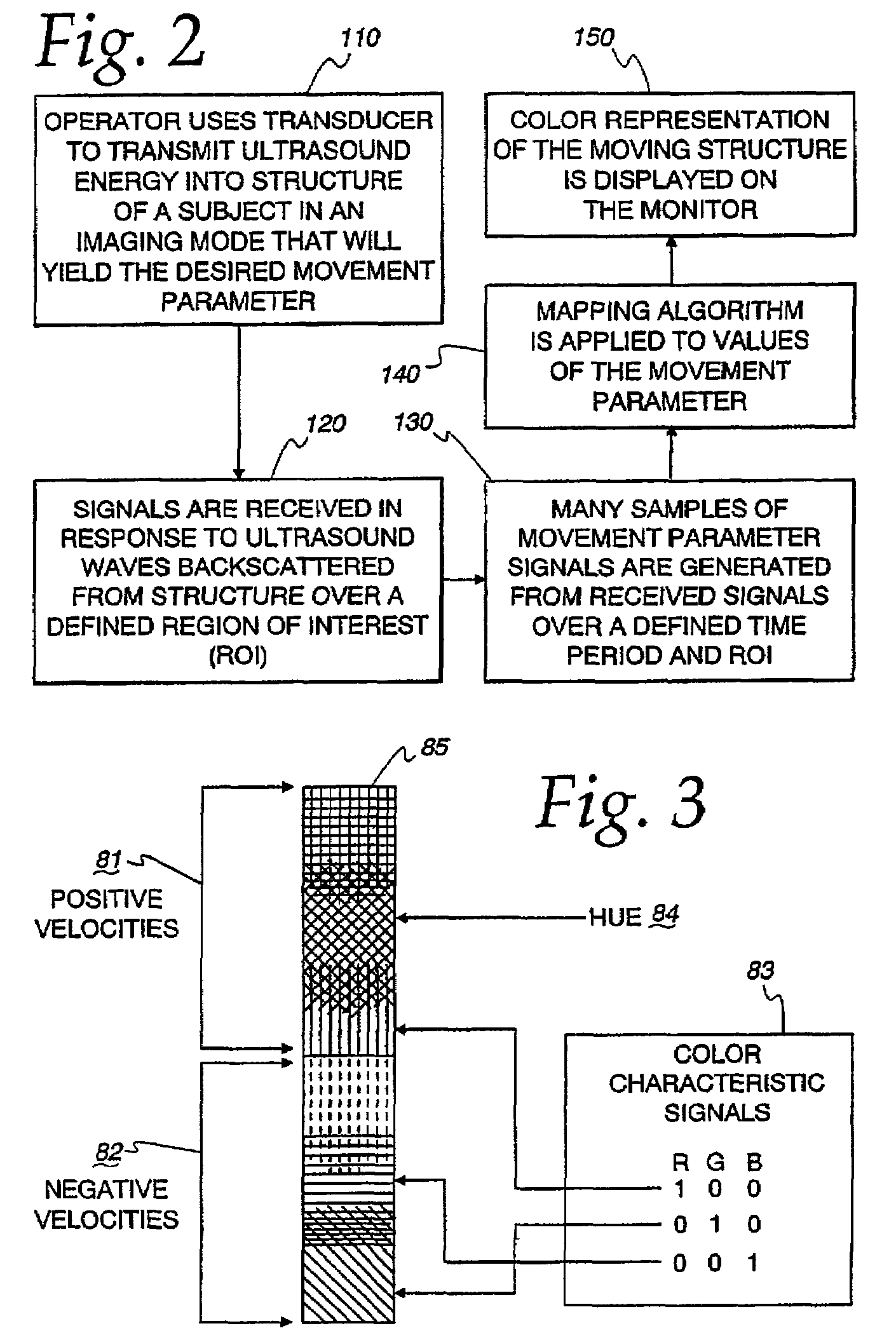
Ultrasound color characteristic mapping
ActiveUS7245746B2Improve visualizationEasily visualizedElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionCardiac wallMotion parameter
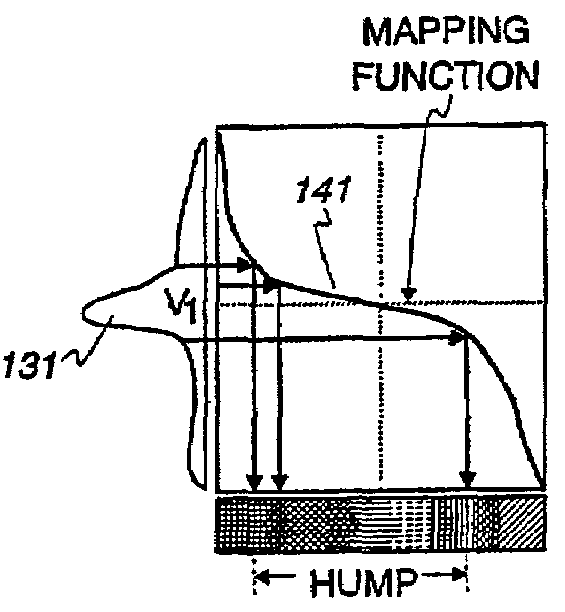
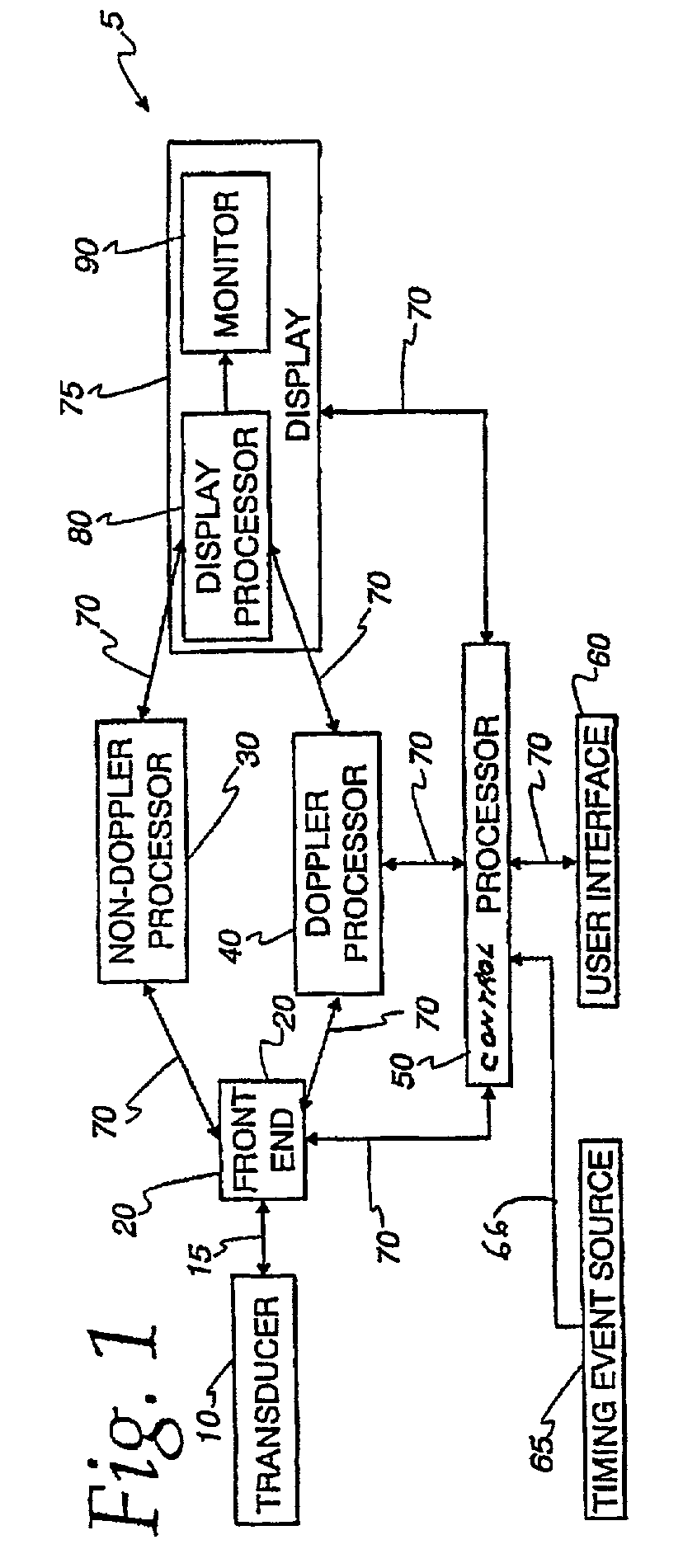
An ultrasound machine is disclosed that displays a color representation of moving structure, such as a cardiac wall tissue, within a region of interest on a monitor. The color representation is generated by displaying at least one color characteristic corresponding to a movement parameter of the structure, such as velocity or strain rate. The movement parameter is mapped to the color characteristic by apparatus comprising a front-end that generates received signals in response to ultrasound waves. A Doppler processor generates a set of parameter signals representing values of the movement parameter within the structure. A control processor adaptively generates a mapping function based on the distribution of the parameter signals to map the parameter signals to a set of color characteristic signals. A display processor applies the mapped values of the color characteristic legend to the values of the movement parameter representing the moving structure, to display a color representation on the monitor in response to the mapping function.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
High plastic-strain ratio galvanized steel sheet and production method
InactiveCN101255529ALower recrystallization temperaturePromotes secondary phase formationHot-dipping/immersion processesMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionSheet steel
The invention relates to a hot galvanizing sedan plate and the production method thereof, which solves the following problems: P and S in steel are difficult to control because of being lowly required; as to a horizontal Sendzimir hot galvanizing machine, the recrystallization temperature of a steel plate is slightly high, and the plastic strain ratio and extension are low. The high-plastic-strain-ratio galvanizing plate is composed of no more than 0.004% by weight of C, no more than 0.020% by weight of Si, 0.05% to 0.20% by weight of Mn, no more than 0.016% by weight of 0.016, no more than 0.015% by weight of S, 0.04% to 0.07% by weight of Ti, 0.02% to 0.06% by weight of Als, no more than 0.003% by weight of N, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurity. The production steps are as follows: smelting by hot metal desulphurization and secondary refining process; hot rolling; cold rolling with a total reduction of 80%; and galvanizing. The invention has the characteristics that the method is pure Ti processing; the control scopes of S and P are wide; the plastic strain ratio is r90 DEG C >=2.5, the extension A80mm is 45% to 50%; and the current process route and equipment is unchanged.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Method of controlling and refining final grain size in supersolvus heat treated nickel-base superalloys
InactiveUS20090000706A1High strain rateAvoiding necessity to forge superplasticallyHigh carbonHeat treated
A method of forming a component from a gamma prime precipitation-strengthened nickel-base superalloy. The method entails formulating the superalloy to have a sufficiently high carbon content and forging the superalloy at sufficiently high local strain rates so that, following a supersolvus heat treatment, the component is characterized by a fine and substantially uniform grain size distribution, preferably finer than ASTM 7 and more preferably in a range of about ASTM 8 to 10.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
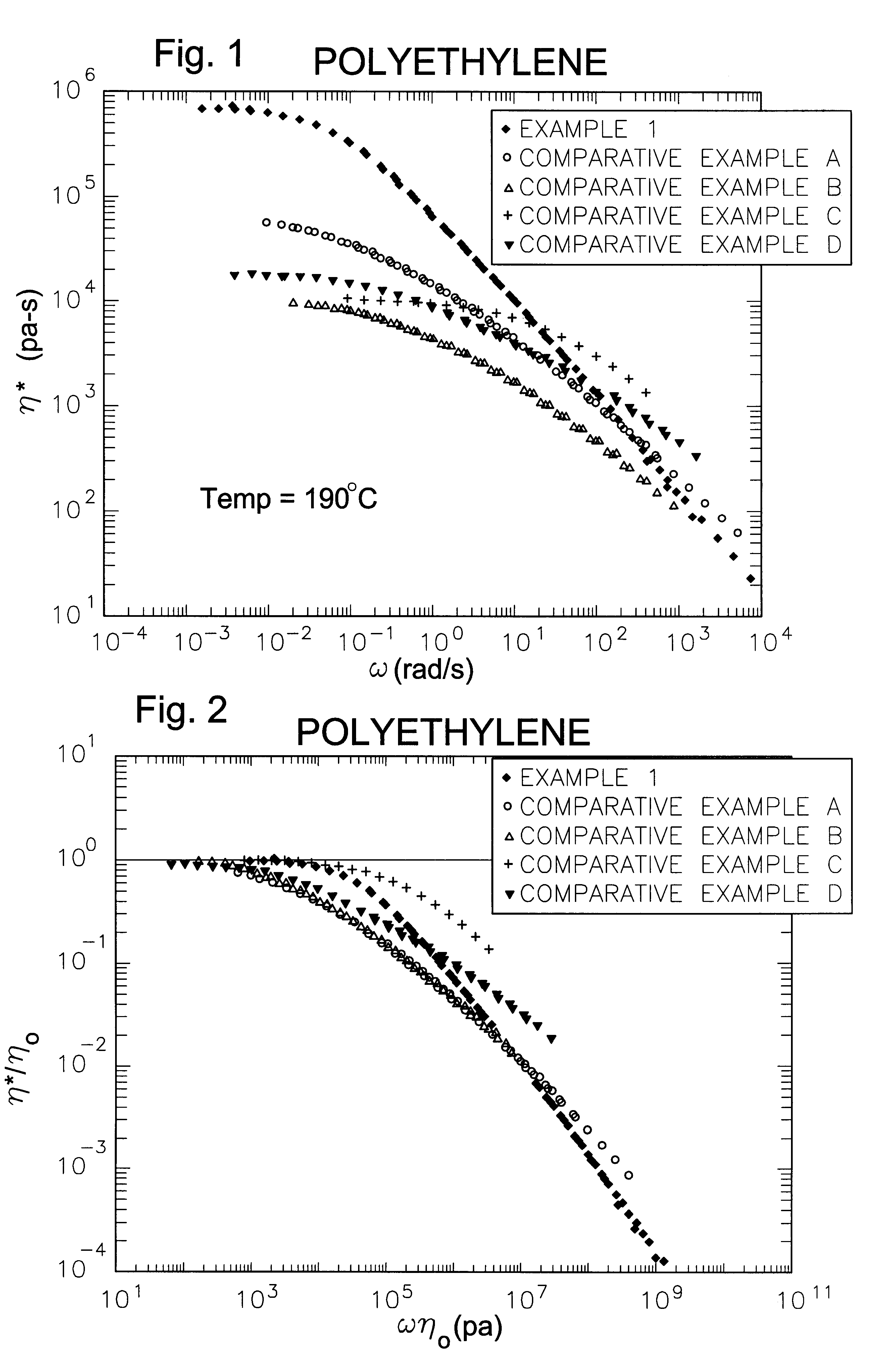
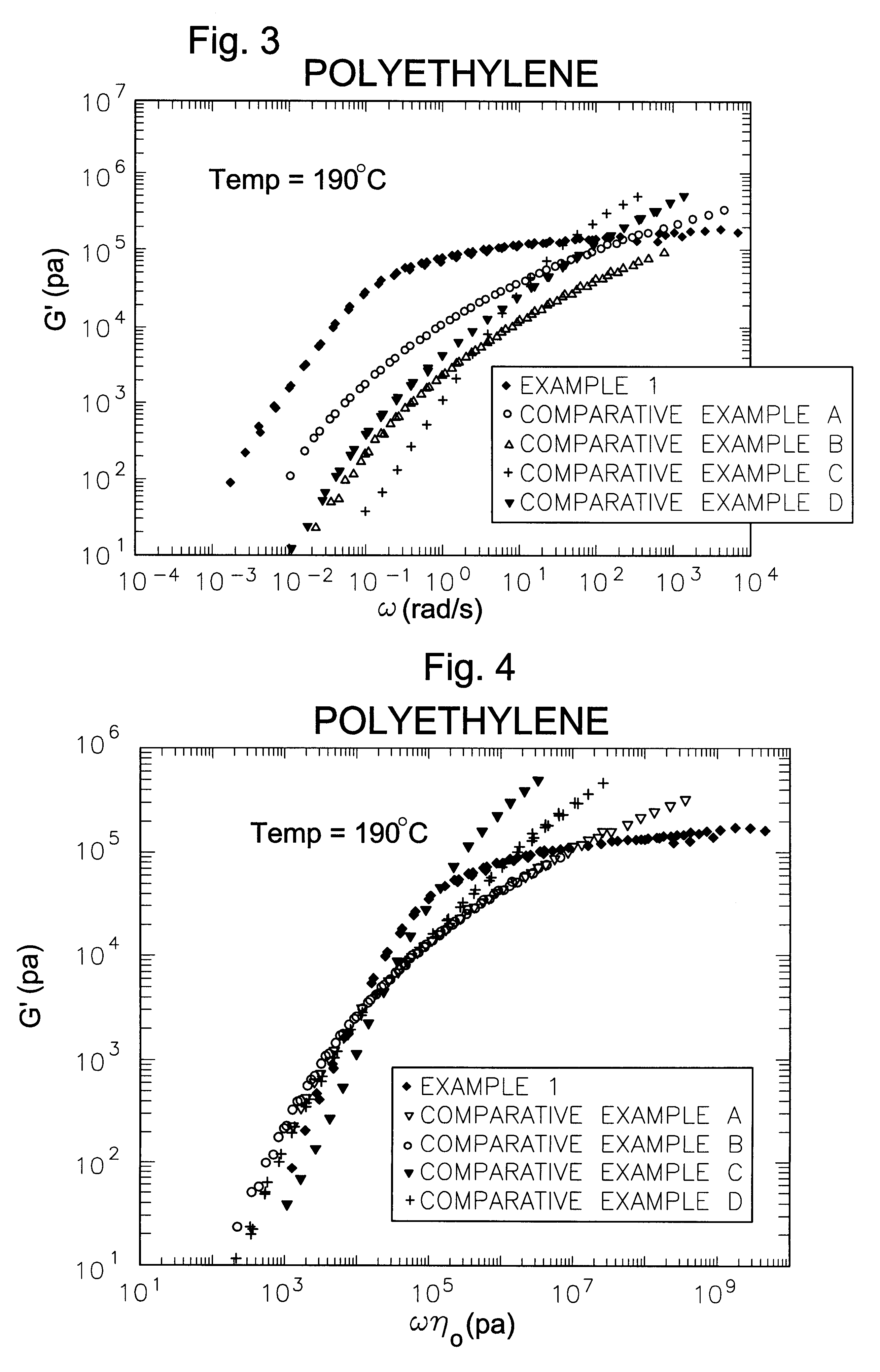
Processing olefin copolymers
The invention is directed to essentially saturated hydrocarbon polymer composition comprising essentially saturated hydrocarbon polymers having A) a backbone chain, B) a plurality of essentially hydrocarbyl sidechains connected to A), said sidechains each having a number-average molecular weight of from 2500 Daltons to 125,000 Daltons and a MWD by SEC of 1.0-3.5; and having A) a Newtonian limiting viscosity (eta0) at 190° C. at least 50% greater than that of a linear olefinic polymer of the same chemical composition and weight average molecular weight, preferably at least twice as great as that of said linear polymer, B) a ratio of the rubbery plateau modulus at 190° C. to that of a linear polymer of the same chemical composition less than 0.5, preferably <0.3, C) a ratio of the Newtonian limiting viscosity (eta0) to the absolute value of the complex viscosity in oscillatory shear (eta*)at 100 rad / sec at 190° C. of at least 5, and D) a ratio of the extensional viscosity measured at a strain rate of 1 sec-1, 190° C., and time=3 sec (i.e., a strain of 3) to that predicted by linear viscoelasticity at the same temperature and time of 2 or greater. Ethylene-butene prepared by anionic polymerization and hydrogenation illustrate and ethylene-hexene copolymers prepared by coordination polymerization illustrate the invention. The invention polymers exhibit improved processing characteristics in that the shear thinning behavior closely approaches that of ideal polymers and exhibit improved strain thickening.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Electromagnetic induction type Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar loading device and experimental method
ActiveCN105571961AStable incomingEasy to controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementCapacitanceExperimental methods
The invention discloses an electromagnetic induction type Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar loading device and an experimental method. An anode output line of a capacitance charger is connected with an anode line of a loading gun while a cathode output line of the capacitance charger is connected with a cathode line of the loading gun, and consequently both compressive stress waves and tensile stress waves can be generated, and application to loading of Hopkinson torsion and pressure bars is realized. Loading systems of the Hopkinson torsion and pressure bars can be arranged on the same device, the strain rate and the strain range which are beyond the reach of traditional split Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar experiments are realized to further realize technical standardization of the Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar experiments, integration of torsion and pressure bar experiment devices is realized, and accordingly equipment complexity and space occupancy are reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Non-resiliency body-contact protective helmet interface structure
InactiveUS20050166302A1Significant anti-injury impact deliverySpringsProtective equipmentElastomerBody contact
Shock-absorbing, load-cushioning interface structure for use inside, and in operative cooperation with, the shell of a helmet for operative interposition such a shell and the head of a wearer. This structure is characterized with features and performances including (a) compression-deformation-and-slow-return viscoelasticity, (b) non-springy (anti-rebound) during a return from deformation, (c) acceleration-rate(strain-rate)-sensitivity, and (d) a durometer associated with an ILD number which is no less than about 15-ILD.
Owner:MJD INNOVATIONS
Device and method for testing looseness of rock under disturbance of strain rate in loading process of pendulum bob
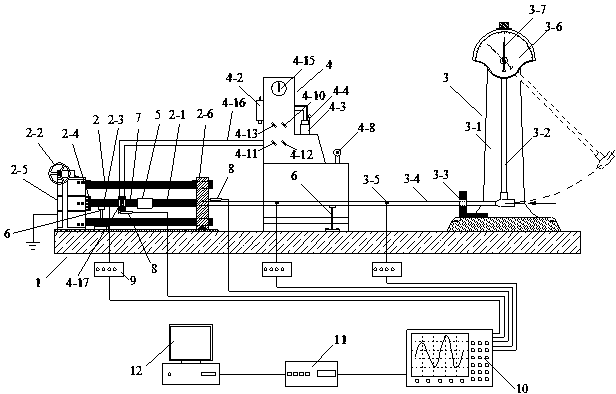
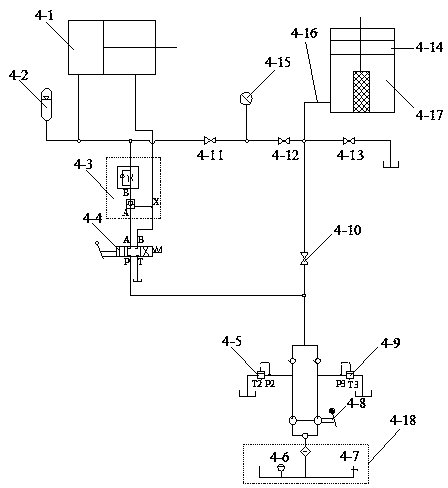
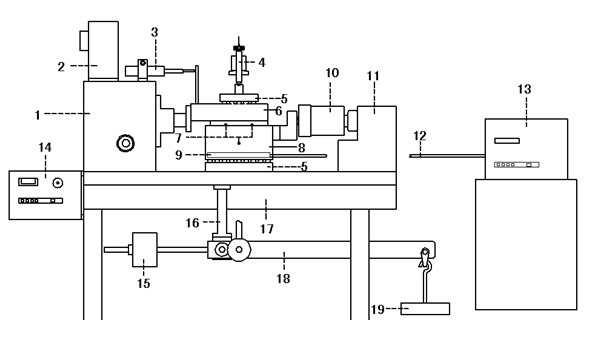
ActiveCN104181029AImplement relaxation testStress waves are easy to controlStrength propertiesStrain rateAxial pressure
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Frozen soil-structure direct shear apparatus and use method thereof
ActiveCN102252919AApplicable Mechanical PropertiesPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesEngineeringStrain rate
The invention discloses a frozen soil-structure direct shear apparatus and a use method thereof. The frozen soil-structure direct shear apparatus comprises a horizontal thruster, a stepping motor, a displacement sensor, a vertical pressure dowel bar, a horizontal ball guide rail, an upper shearing box, a thermocouple, a lower shearing box, a semiconductor refrigeration block, a load sensor, a horizontal end fixing device, a cooling liquid delivery pipe, a low temperature thermostatic bath, a strain rate controller, counterbalance weights, a lever end fixing device, a horizontal bearing platform, a lever and weights. The frozen soil-structure direct shear apparatus has the advantage of being suitable for the research on the mechanical characteristics of the contact surface of different materials at a low temperature. The apparatus can provide different normal stress and temperatures for the contact surface of the materials according to test requirements; and when the freeze condition of the contact surface of the different materials meets the corresponding requirements, a shear force is applied on the contact surface at a selected shear rate until the contact surface of the sample is subjected to damage, and the relation curve of the shear stress of the frozen soil-structure contact surface and the shear displacement is determined.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANKE PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Amorphous alloy thermoforming apparatus and technique
ActiveCN101468370APrevent crystallizationImprove processing efficiencyShaping toolsForging/hammering/pressing machinesNitrogen gasAmorphous metal
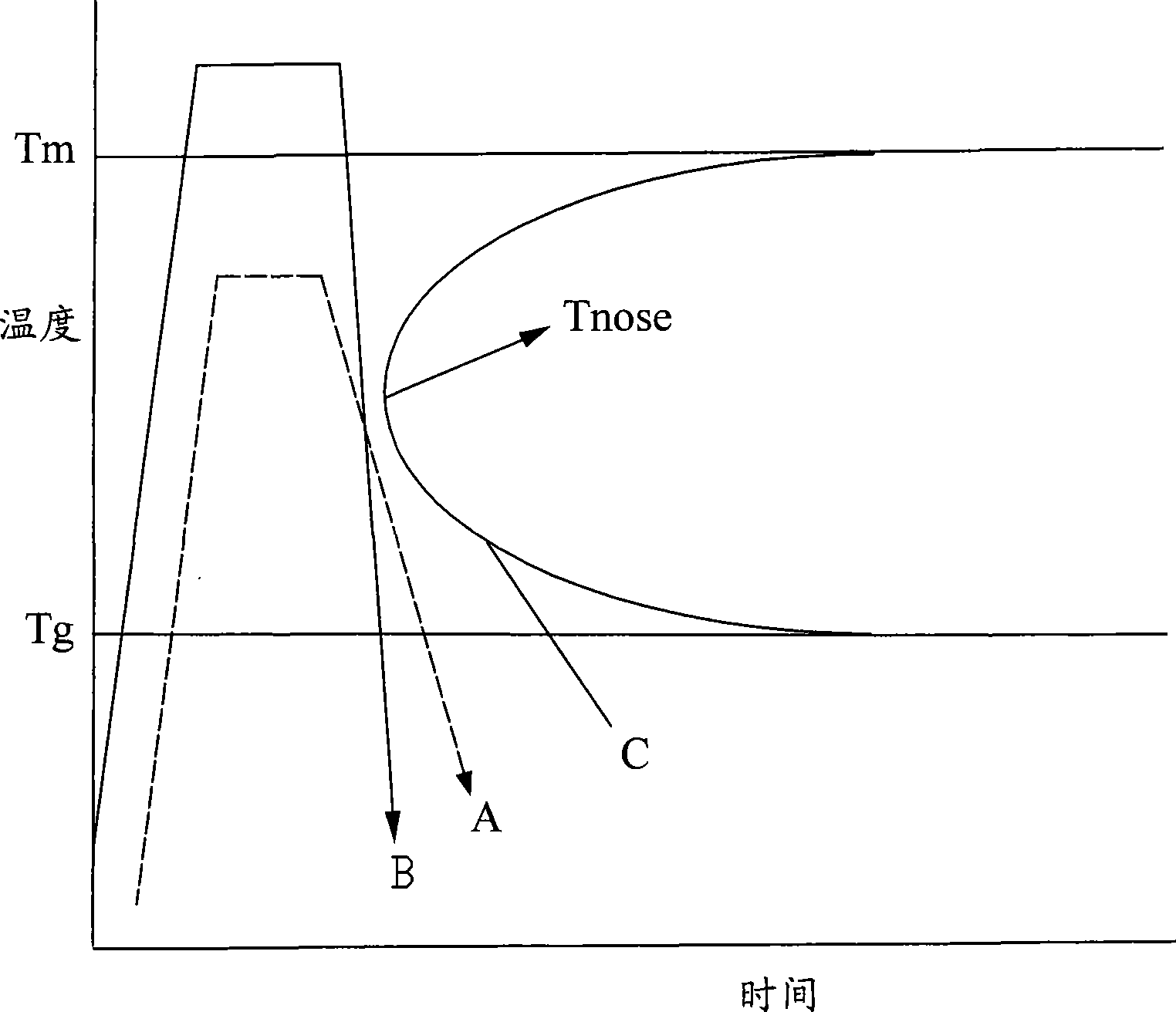
The invention provides a device and a process for the hot pressing and molding of an amorphous alloy. The device is provided with a vacuum, inert gas or nitrogen gas protective environment, and a mould set and an induction heating coil positioned in the environment; the mould set comprises an upper mould, a lower mould and a molding mould; the induction heating coil is at least wound in a peripheral space of the molding mould and is not contacted with the molding mould; and the process sequentially comprises the following steps in the vacuum, inert gas or nitrogen gas protective environment: blank placement, induction heating, hot pressing and molding, cooling, and mould extraction. By adopting an induction heating mode, the process can rapidly concentrate on heating a molded blank to Tg temperature above, and carry out the hot pressing and molding within the temperature range between Tg and Tm or the Tm temperature above; a molding strain rate can reach between 10 and 10S; and the process has high processing efficiency and can effectively prevent crystallization of the amorphous alloy in the molding process within shorter temperature rise time.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
In-situ high-frequency fatigue material mechanical test platform under scanning electron microscope based on stretching/compressing mode
ActiveCN102331370AGood structural compatibilityImprove compatibilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesControl cellEngineering
The invention relates to an in-situ high-frequency fatigue material mechanical test platform under a scanning electron microscope based on a stretching / compressing mode and belongs to the field of machinery and electronics. The test platform comprises a precise loading unit, a precise motion conversion unit, a load / displacement signal acquisition and control unit, a high-frequency driving unit and a test piece clamping and connecting unit. The test platform provided by the invention has the advantages that the structure is compact, the test precision is high, the strain rate and the test frequency are controllable, an in-situ high-frequency test based on the stretching / compressing mode can be performed on a three-dimensional test piece aiming at centimeter-scale or above in characteristicdimension under the condition of observation of various imaging instruments, the on-line monitoring can be carried out on the microcosmic deformation, damage and breaking process of a material under a fatigue stress, and a novel test method for revealing microcosmic deformation behaviors and a damage system of the material is provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods of and apparatus for pressure-ram-forming metal containers and the like
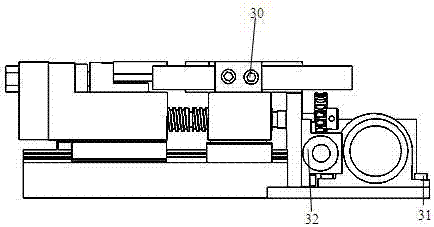
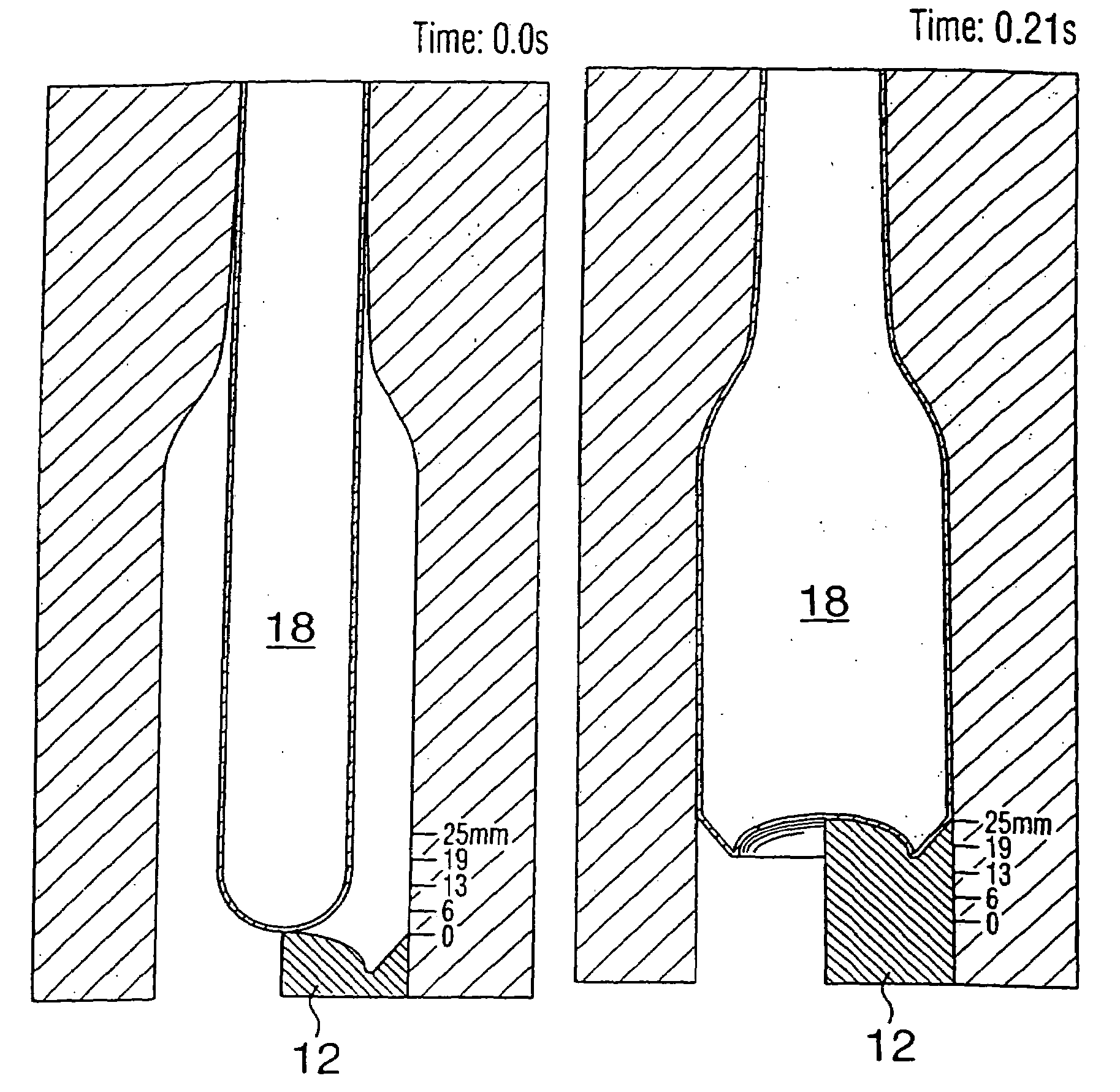
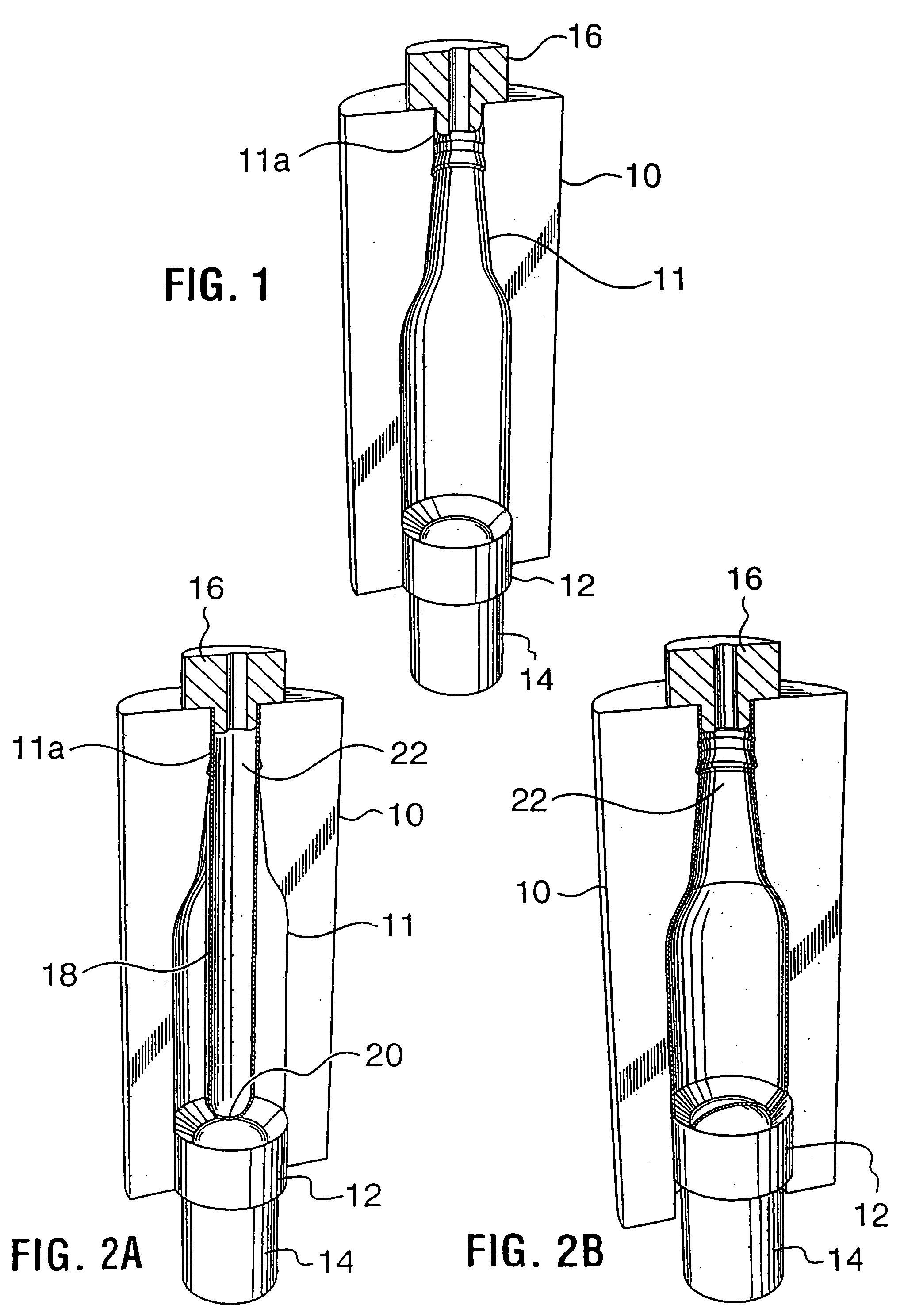
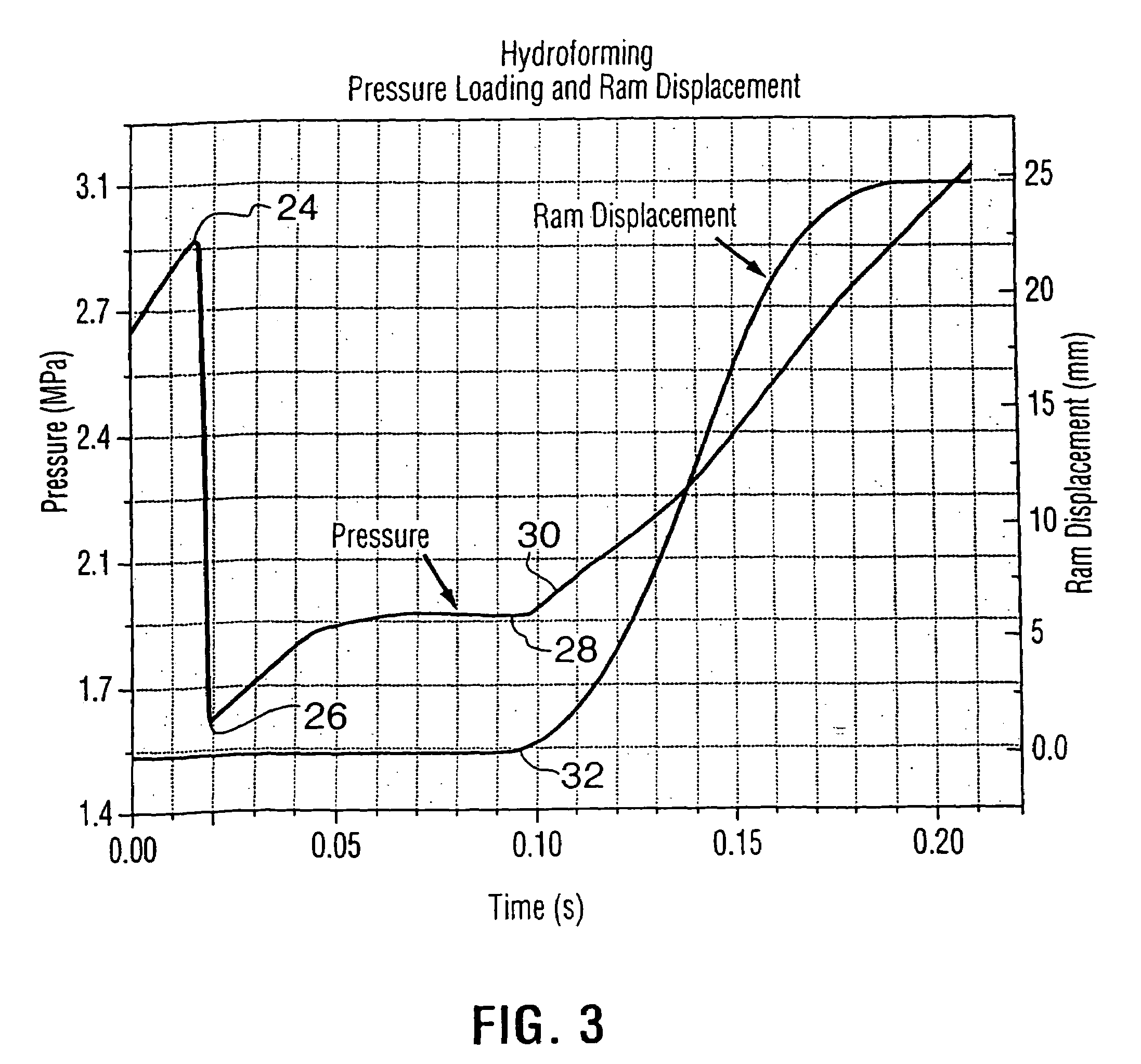
A method of forming a bottle-shaped or other contoured metal container by subjecting a hollow metal preform having a closed end to internal fluid pressure to cause the preform to expand against the wall of a die cavity defining the desired shape, and advancing a punch by means of a backing ram into the die cavity to displace and deform the closed end of the preform either before or after expansion begins but before it is complete. The pressure-subjecting step is performed by simultaneously subjecting the preform in the die cavity to independently controllable internal and external positive fluid pressures and varying the difference between them to control strain rate. Apparatus for performing the method includes a split die with plural split inserts disposed in tandem to define the die cavity wall and heaters respectively inserted within the preform and arranged to heat the backing ram.
Owner:MONTEBLLO PACKAGING A DIV OF GREAT PACIFIC ENTERPRISE INC
Machine Learning to Accelerate Alloy Design
PendingUS20200257933A1Tightly coupledEasy to predictChemical property predictionTurbinesPrior informationRegression analysis
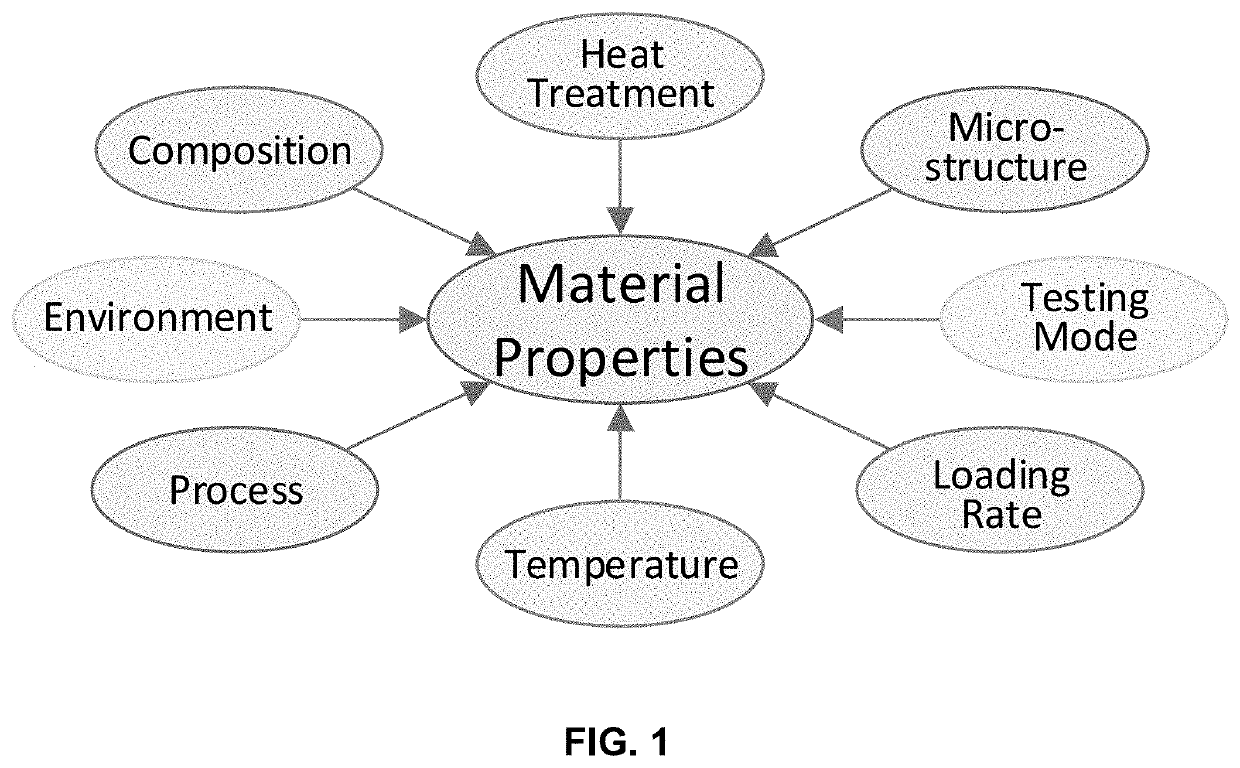
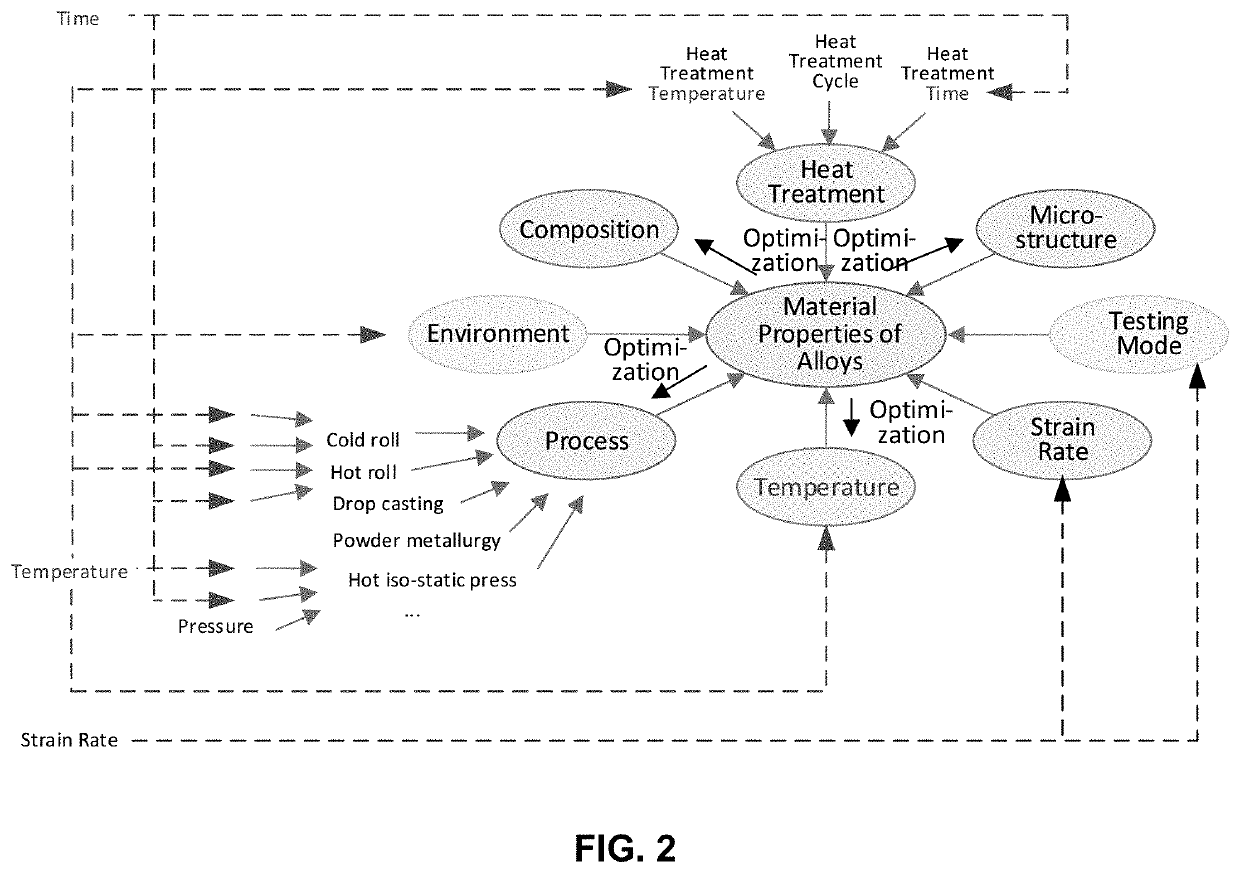
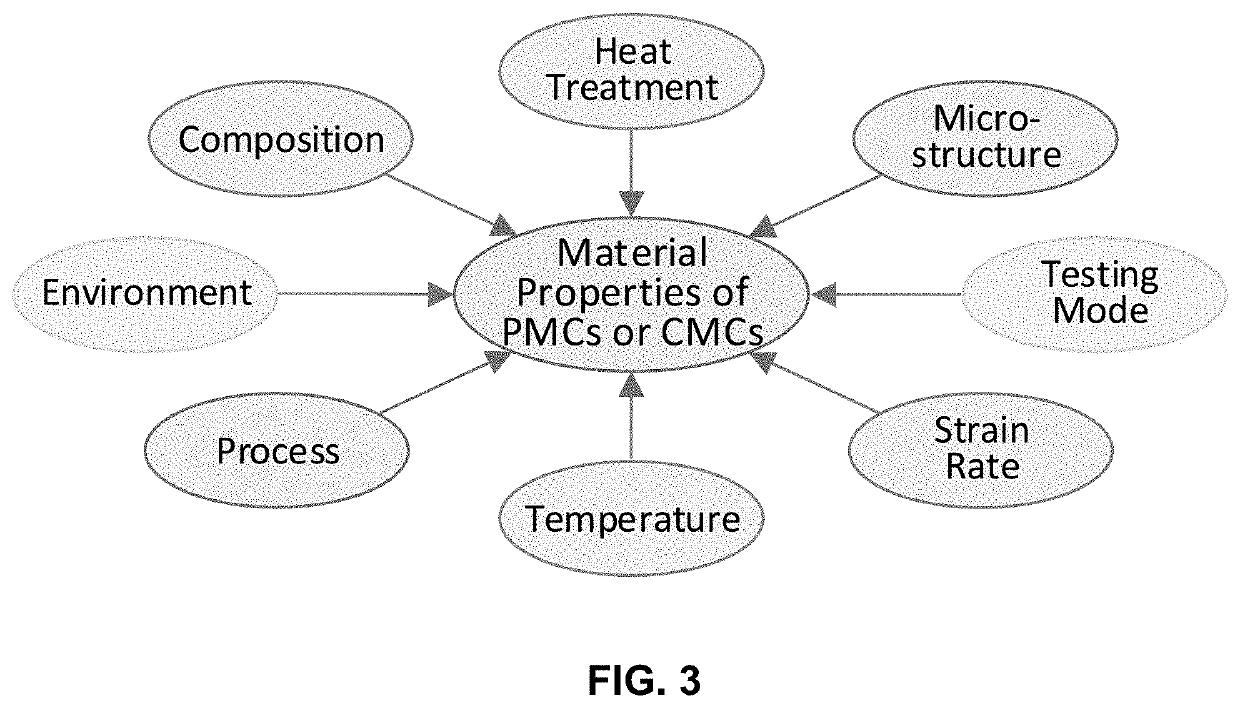
This invention presents an innovative framework for the application of machine learning for identification of alloys or composites with desired properties of interest. For each output property of interest, we identify the corresponding driving (input) factors. These input factors may include the material composition, heat treatment, process, microstructure, temperature, strain rate, environment or testing mode. Our framework assumes selection of optimization technique suitable for the application at hand and data available, starting with simple linear, or quadratic, regression analysis. We present a physics-based model for predicting the ultimate tensile strength, a model that accounts for physical dependencies, and factors in the underlying physics as a priori information. In case an artificial neural network is deemed suitable, we suggest employing custom kernel functions consistent with the underlying physics, for the purpose of attaining tighter coupling, better prediction, and extracting the most out of the—usually limited—input data available.
Owner:IMAGARS
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and method and system for determining health of a vascular structure
InactiveUS7318804B2Reduce internal pressureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cyclePhase sensitive
Methods and systems for measuring mechanical property of a vascular wall and a method and system for determining health of a vascular structure are provided wherein local deformation of a vessel wall resulting from physiologic pressures with altered transmural forces is measured. A non-invasive free-hand ultrasound scanning-procedure was performed to apply external force, comparable to the force generated in measuring a subject's blood pressure, to achieve higher strains by equalizing the internal arterial baseline pressure. When the applied pressure matched the internal baseline diastolic pressure, strain and strain rate increased by a factor of 10 over a cardiac cycle. Radial arterial strain was assessed in the vessel wall over the entire deformation procedure using a phase-sensitive, two-dimensional speckle-tracking algorithm. An elastic modulus reconstruction procedure was developed to estimate the non-linear elastic properties of the vascular wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com