Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183 results about "Tissue characterization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
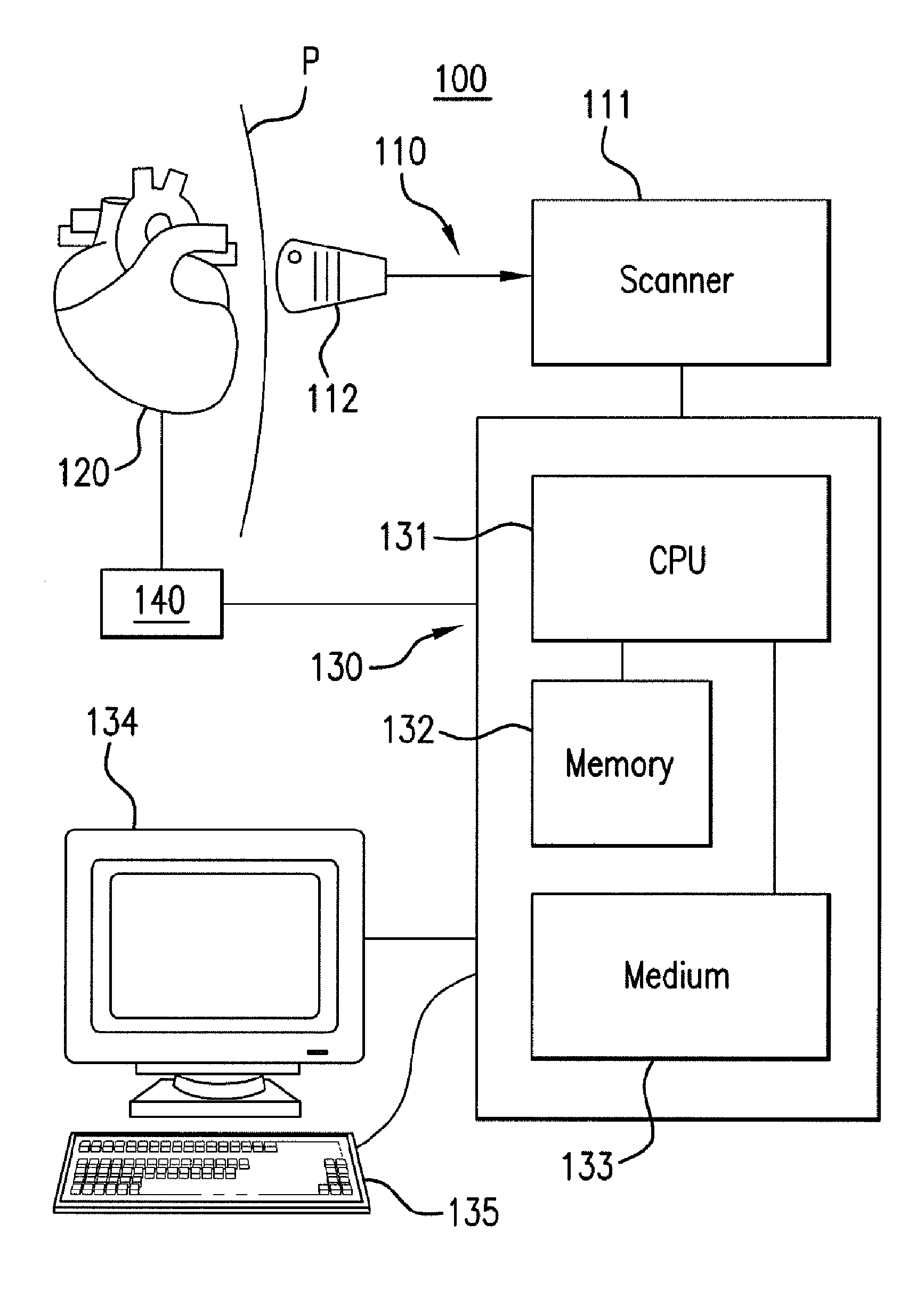
Use the Tissue Characterization module to assess the extent and regional distribution of injury (scar, edema, inflammation) to the heart.
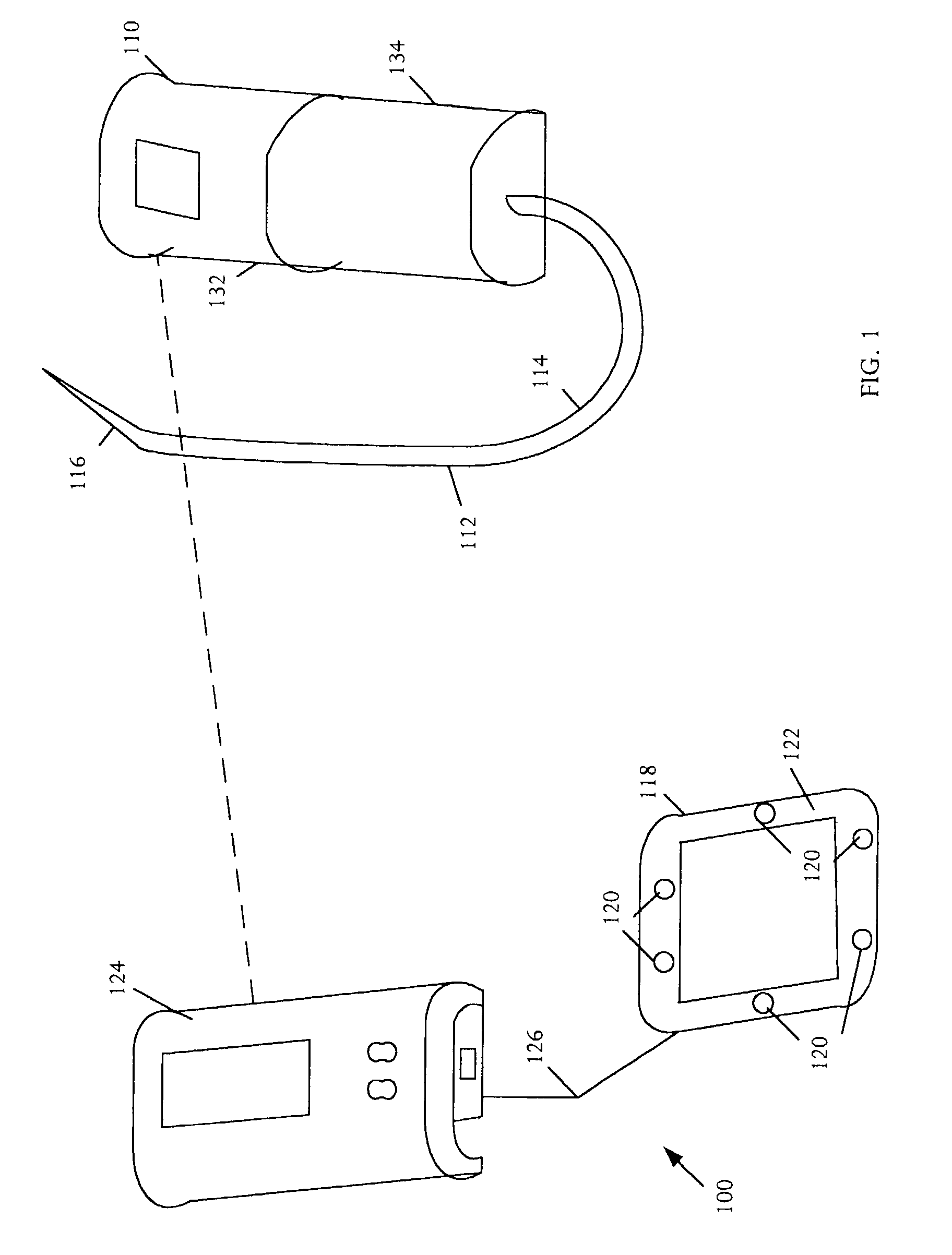
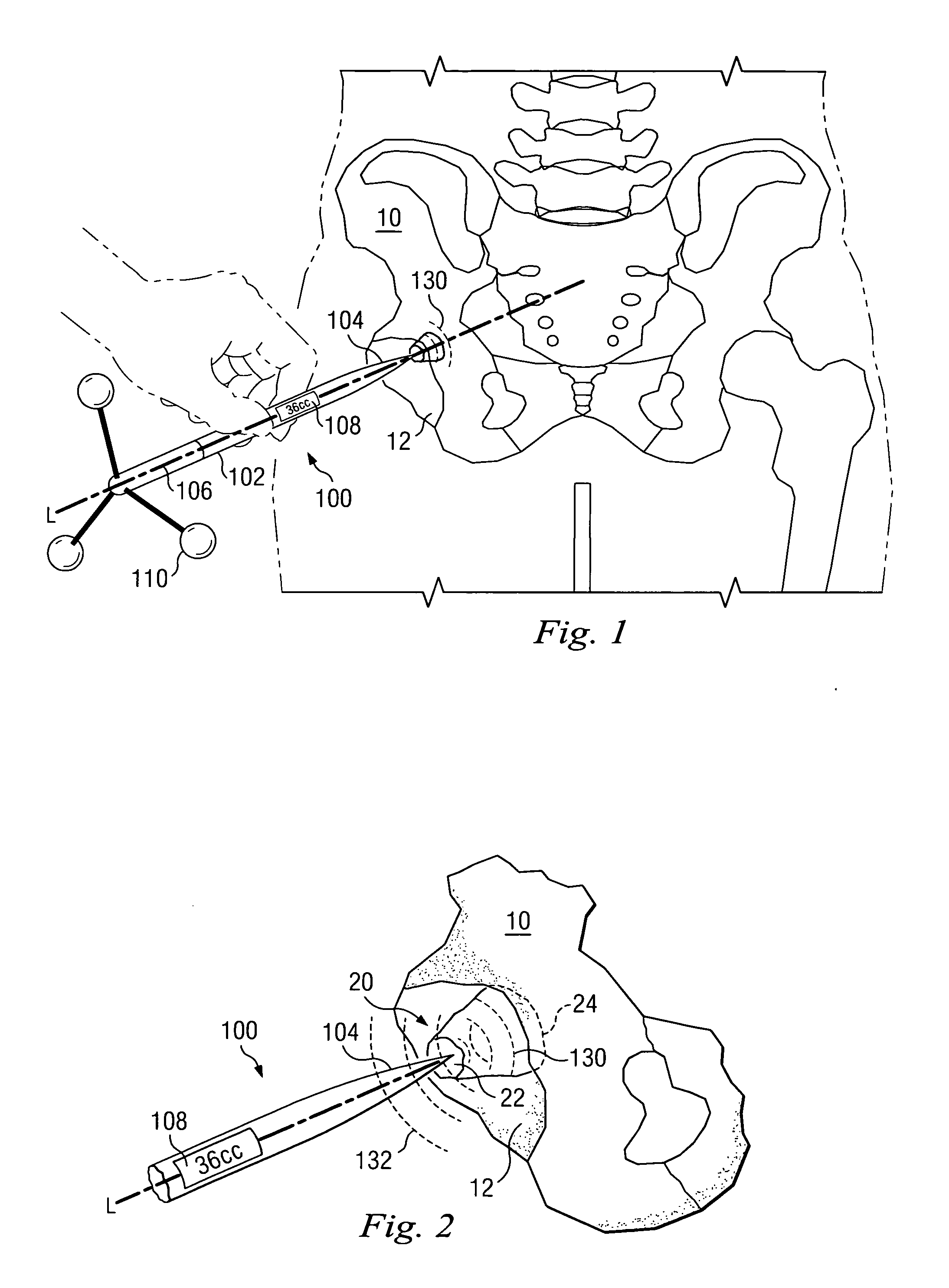
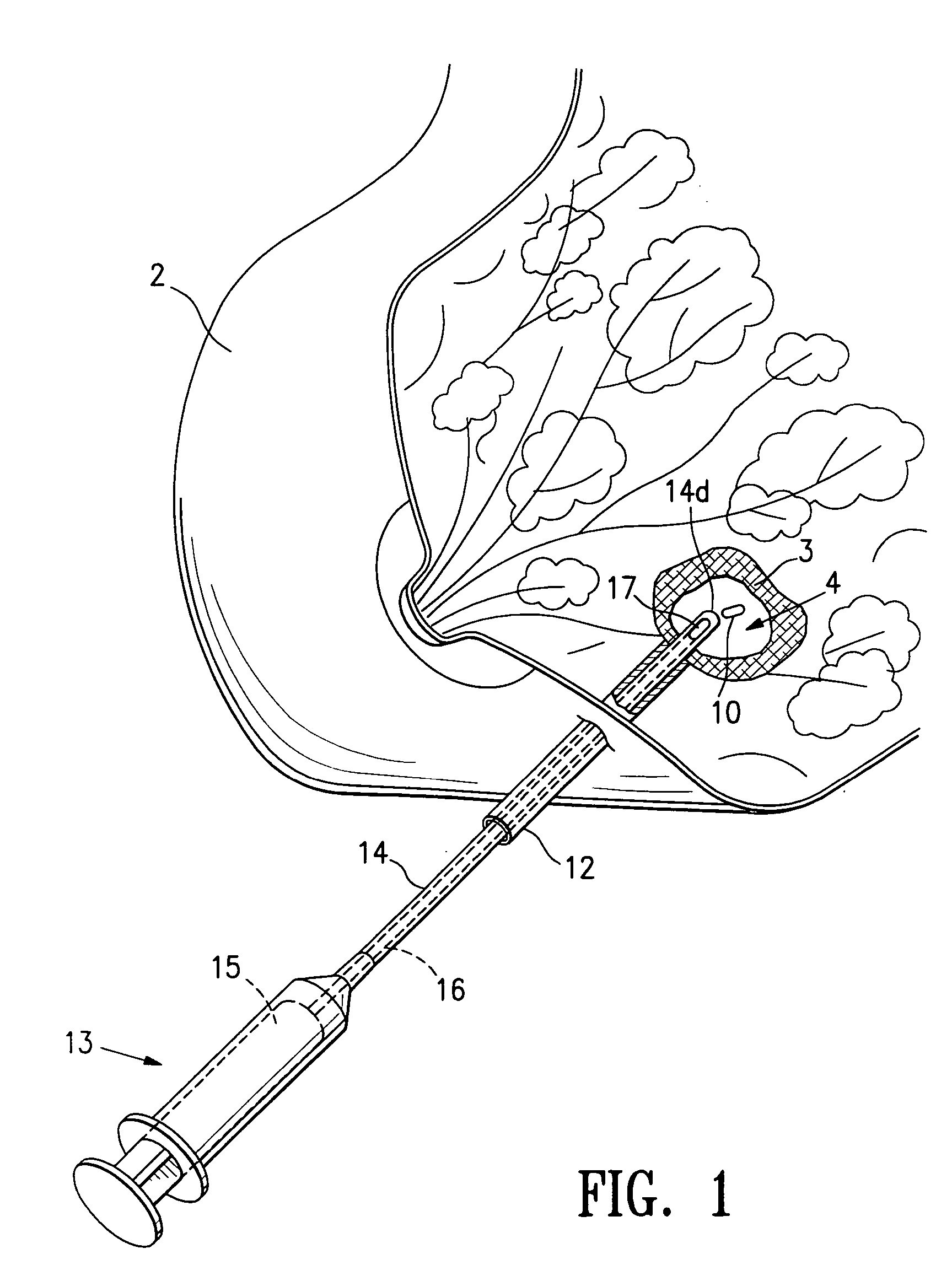
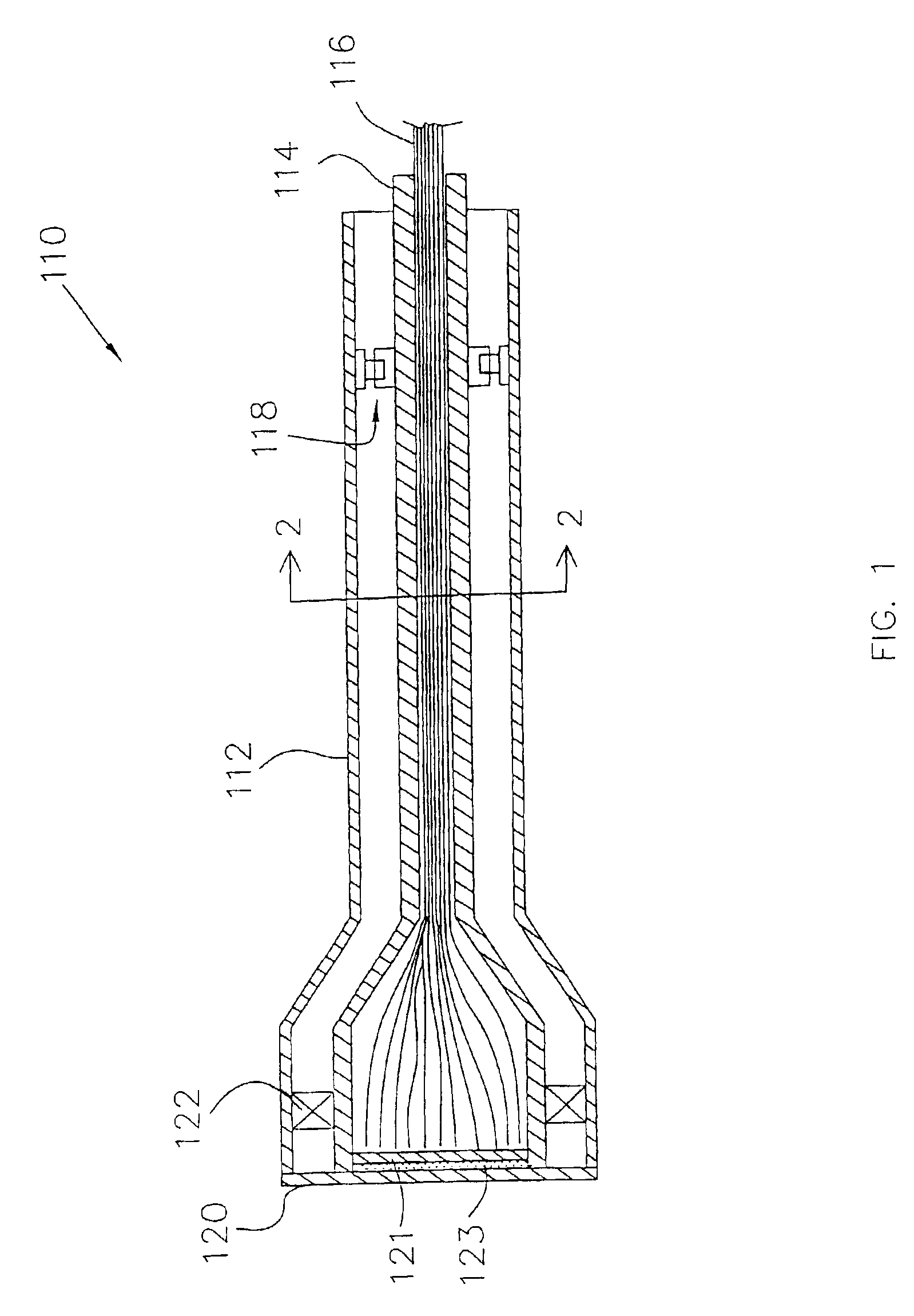
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS6993375B2Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
Owner:SENORX
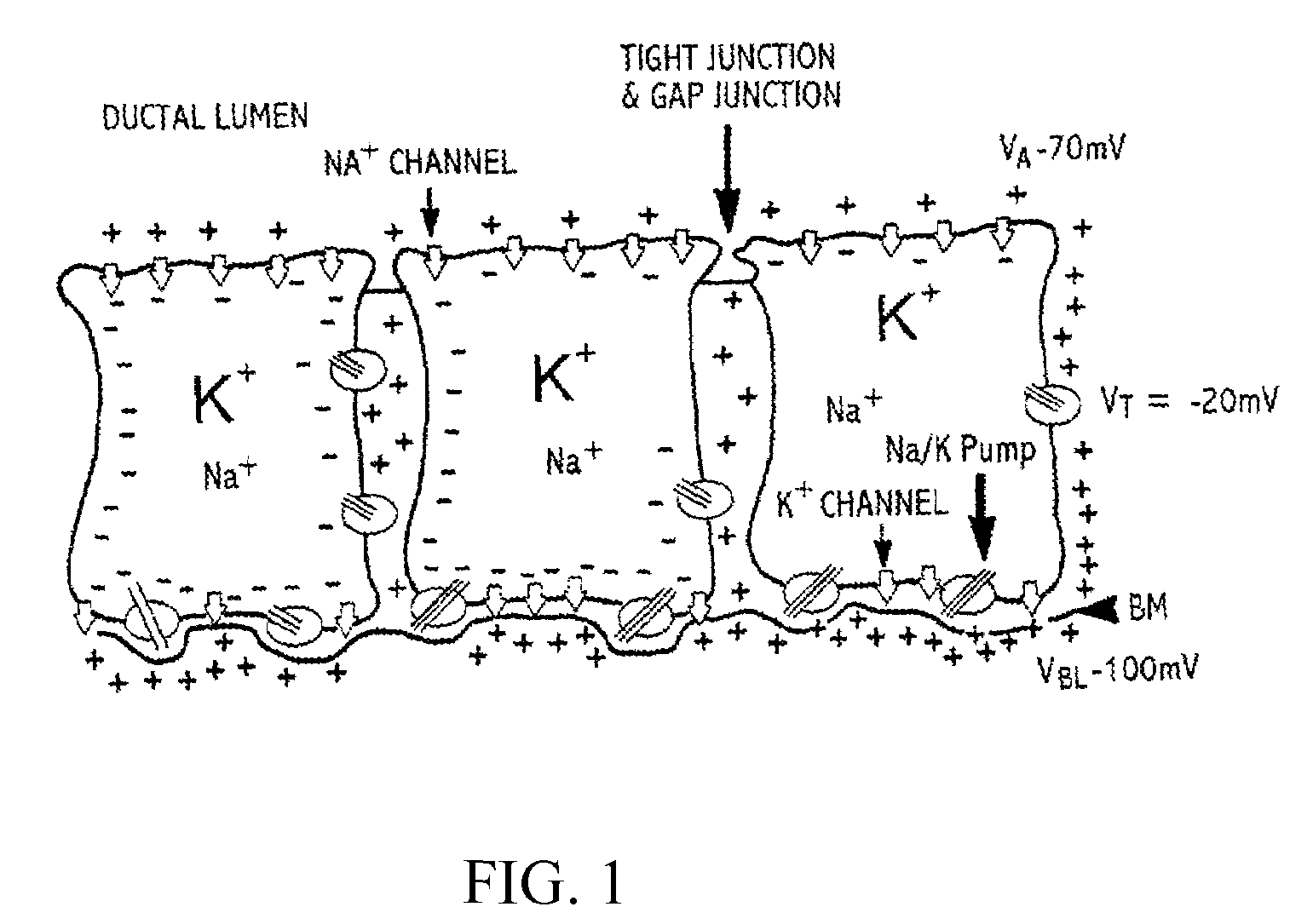
Conductivity reconstruction based on inverse finite element measurements in a tissue monitoring system
InactiveUS7169107B2Low and high conductivityReduce conductivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical devicesElectrical impedance tomographyEngineering
An impedance model of tissue is useful for describing conductivity reconstruction in tissue. Techniques for determining and mapping conductivity distribution in tissue supply useful information of anatomical and physiological status in various medical applications. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) techniques are highly suitable for analyzing conductivity distribution. Electrical characteristics of tissue include resistive elements and capacitive elements. EIT techniques involve passing a low frequency current through the body to monitor various anatomical and physiological characteristics. The system can interrogate at multiple frequencies to map impedance. Analytical techniques involve forward and inverse solutions to boundary value analysis to tissue characteristics.
Owner:INOTECH MEDICAL SYST
Tissue characterization based on impedance images and on impedance measurements
InactiveUS7141019B2Improved and uniform and repeatable contactMinimal operator expertiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDisplay deviceTissues types
Apparatus for aiding in the identification of tissue type for an anomalous tissue in an impedance image comprising a first device providing a polychromic immitance map of a portion of the body; a second devise determining a plurality of polychromic measures from one or both of a portion of the body; and a display which displays an indication based on the plurality of polychromic measures.
Owner:TRANSSCAN MEDICAL
Quantitative methods for obtaining tissue characteristics from optical coherence tomography images
InactiveUS20090306520A1Improve tissue type classificationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationLight beam
A method and apparatus for determining properties of a tissue or tissues imaged by optical coherence tomography (OCT). In one embodiment the backscatter and attenuation of the OCT optical beam is measured and based on these measurements and indicium such as color is assigned for each portion of the image corresponding to the specific value of the backscatter and attenuation for that portion. The image is then displayed with the indicia and a user can then determine the tissue characteristics. In an alternative embodiment the tissue characteristics is classified automatically by a program given the combination of backscatter and attenuation values.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
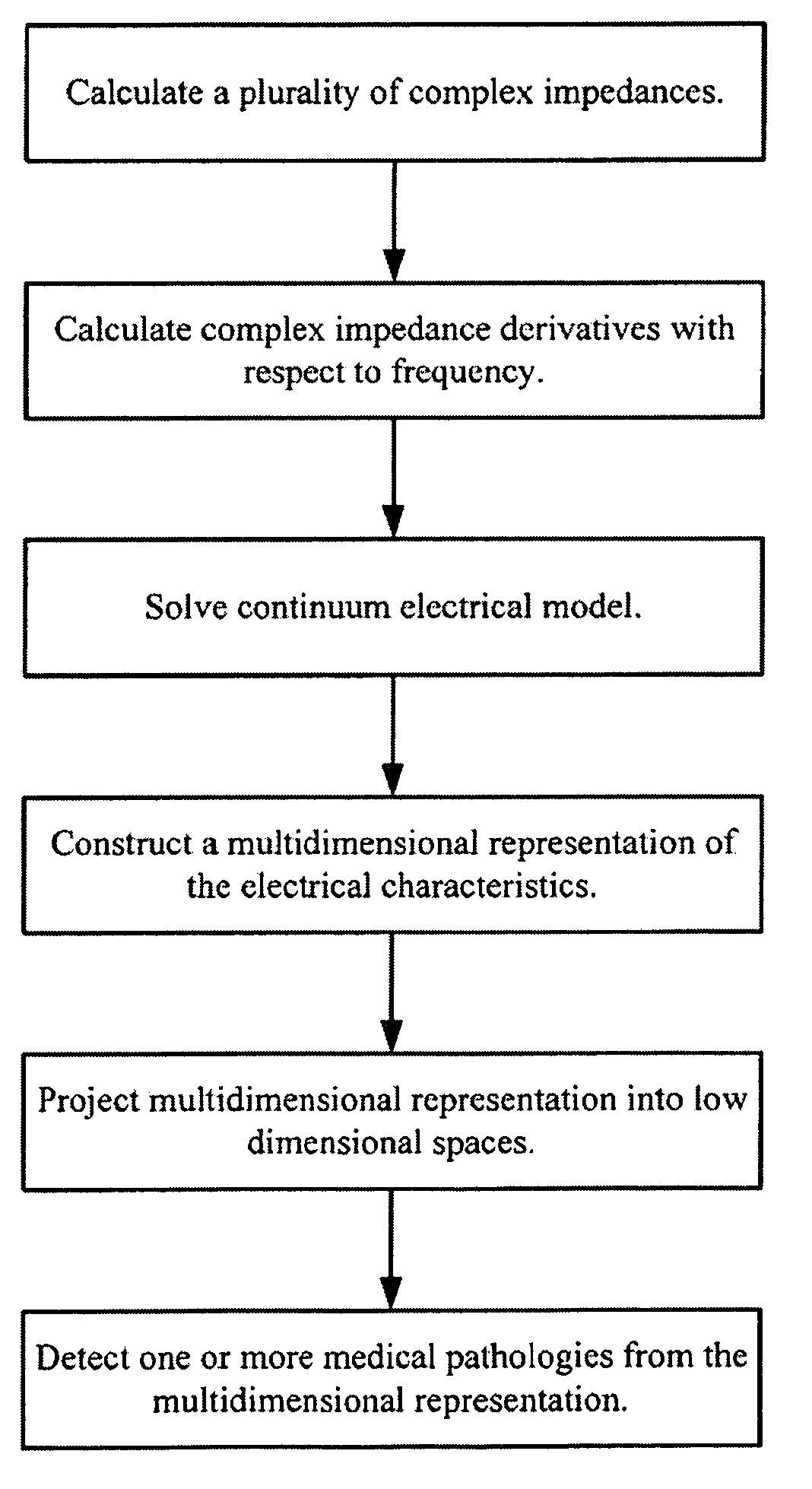
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
A method and apparatus that use complex impedance measurements of tissue in human or animal bodies for the detection and characterization of medical pathologies is disclosed. An analysis of the complex impedance measurements is performed by a trained evaluation system that uses a nonlinear continuum model to analyze the resistive, capacitive, and inductive measurements collected from a plurality of sensing electrodes. The analysis of the impedance measurements results in the construction of a multidimensional space that defines the tissue characteristics, which the trained evaluation system uses to detect and characterize pathologies. The method and apparatus are sufficiently general to be applied to various types of human and animal tissues for the analysis of various types of medical pathologies.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
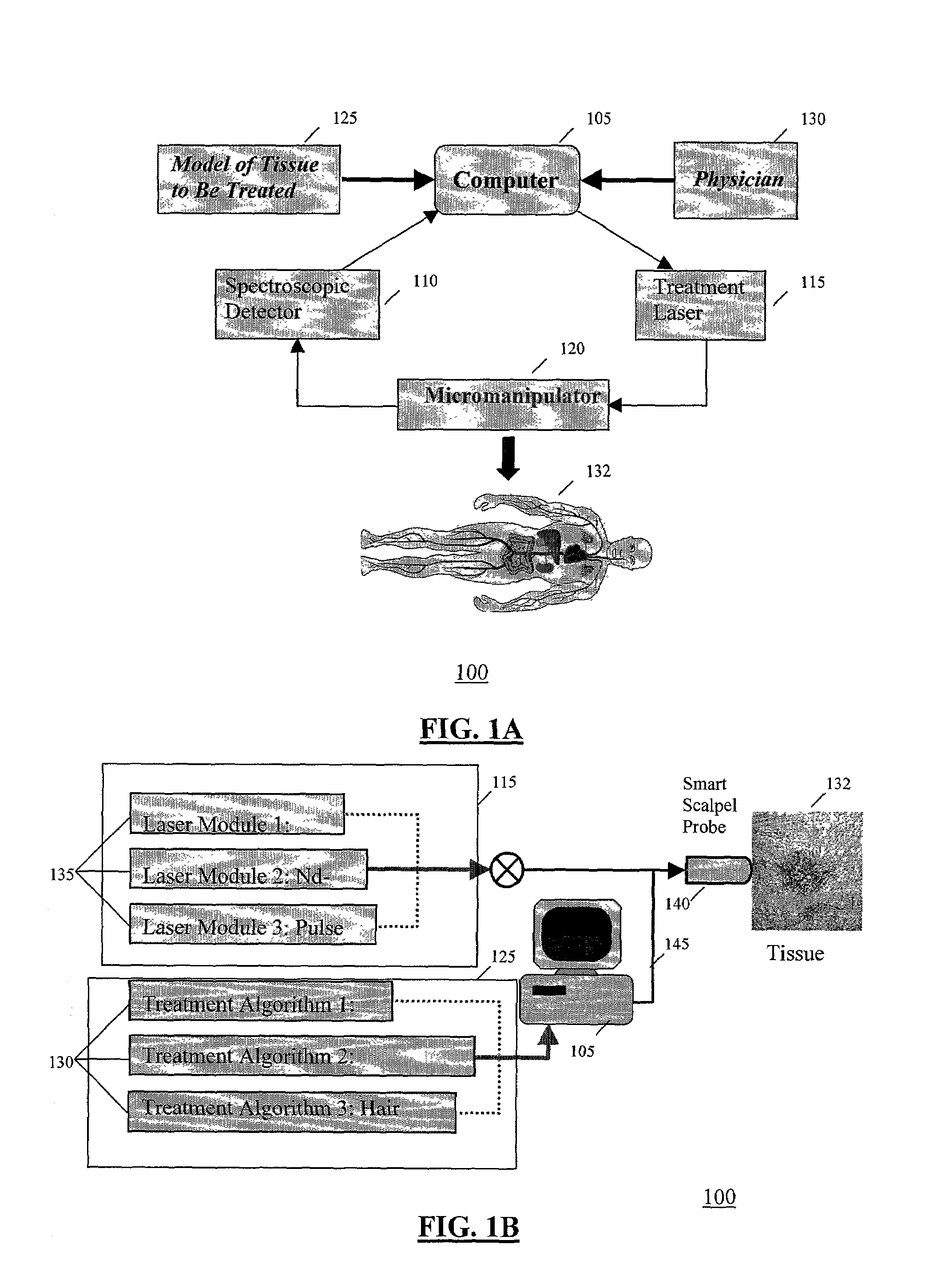
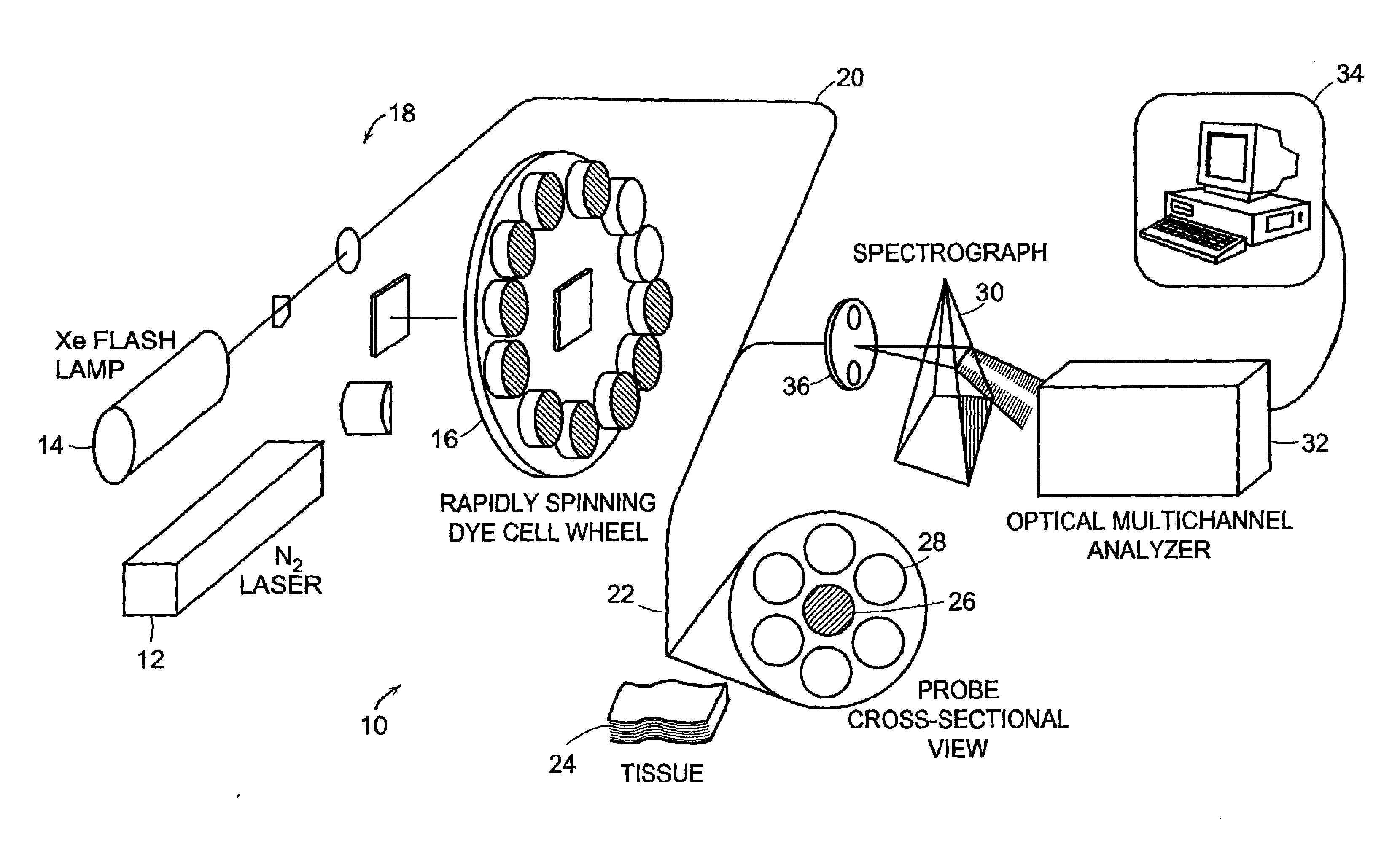
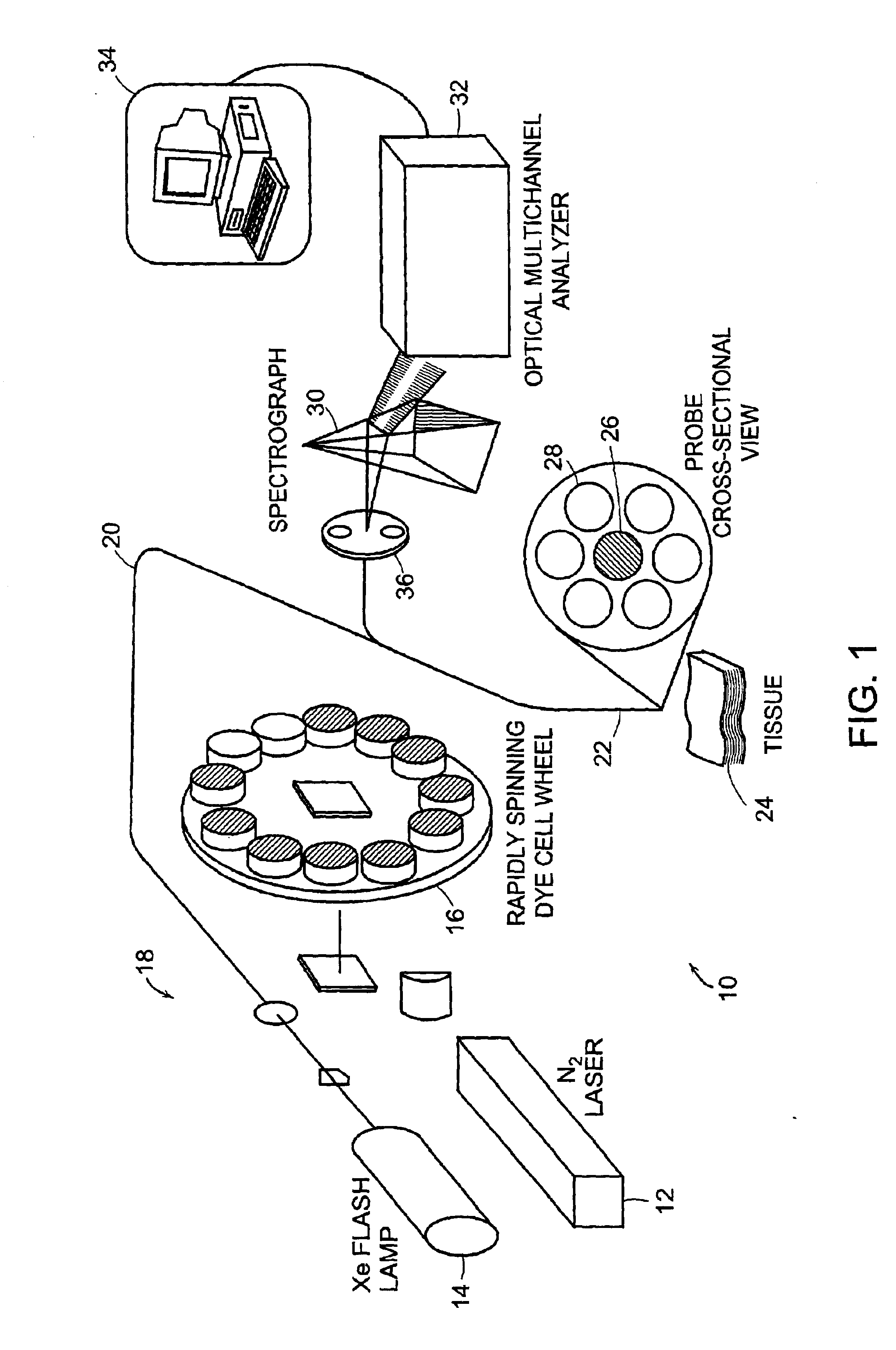
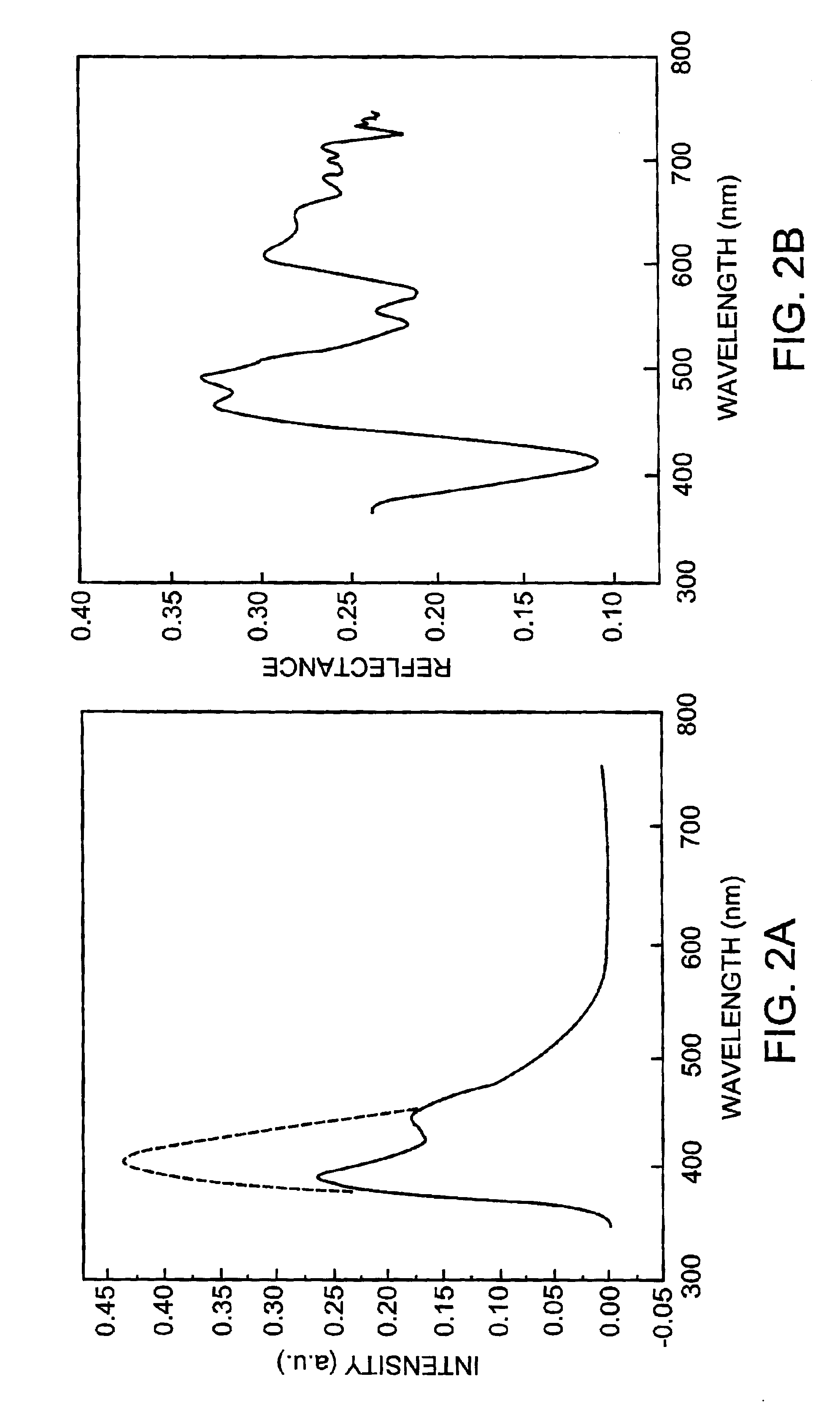
Apparatus and method for laser treatment with spectroscopic feedback
InactiveUS7217266B2Easy to modifyEasy programmingDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using lightTissue characterizationTreatment use
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
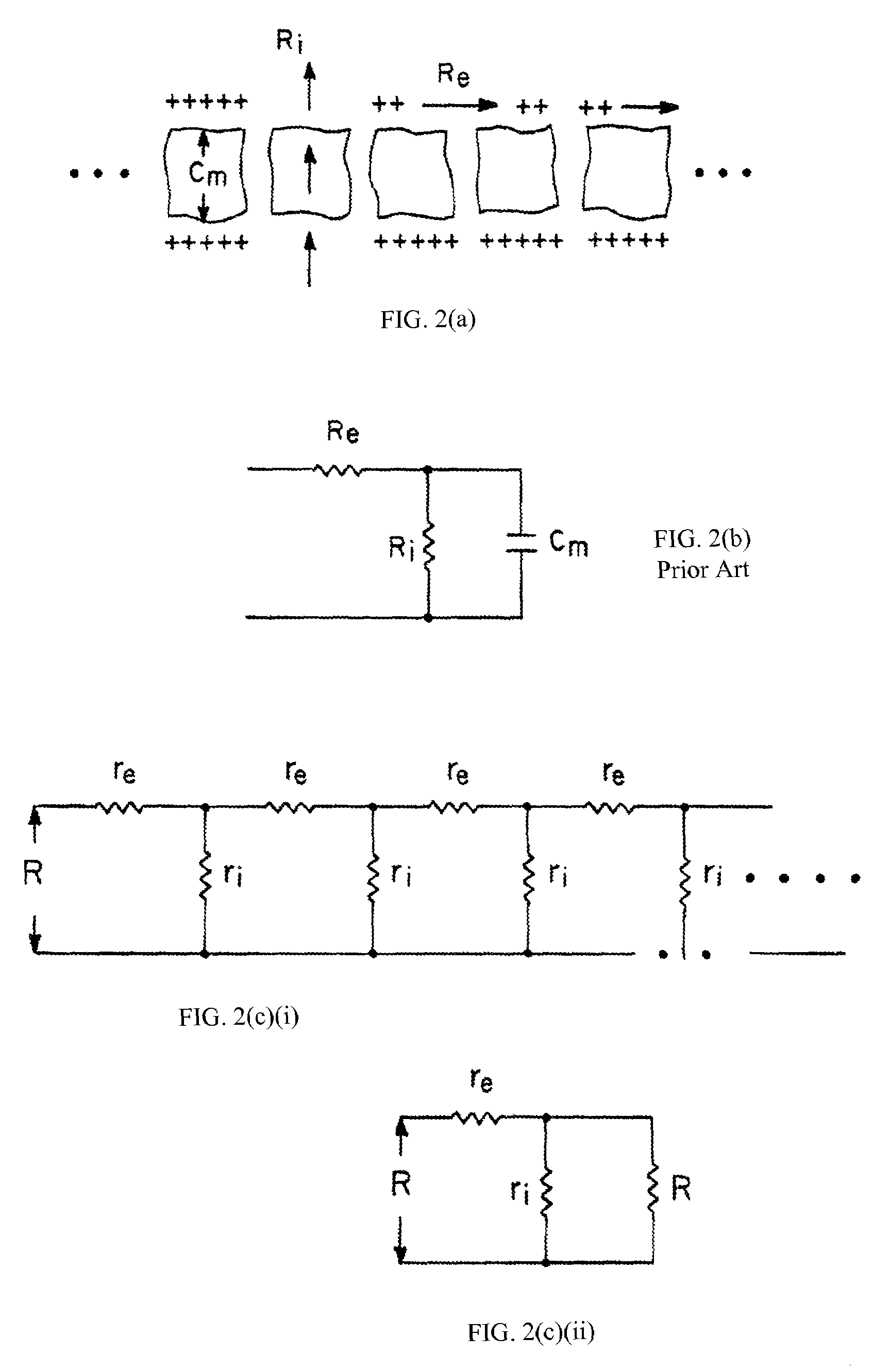
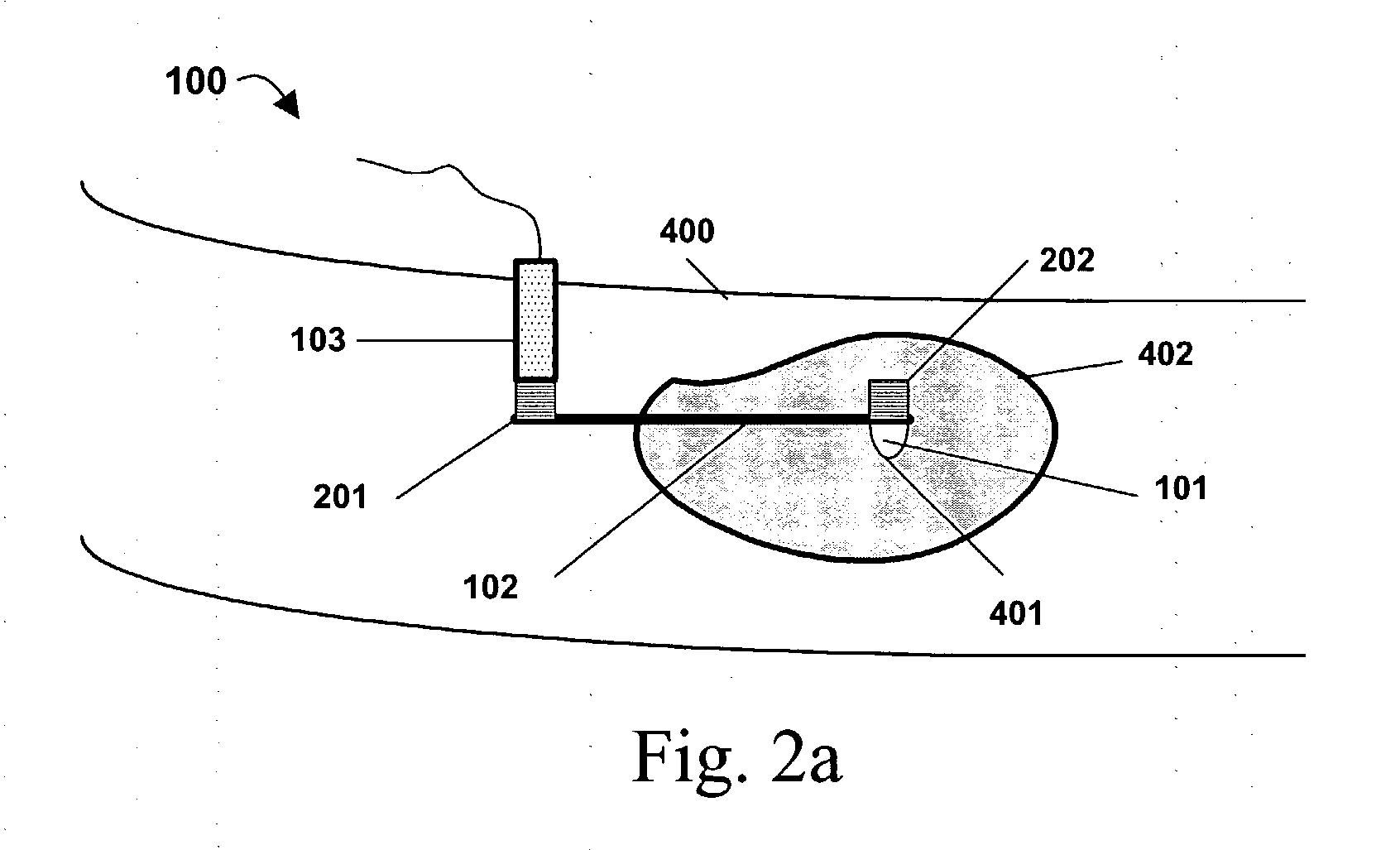
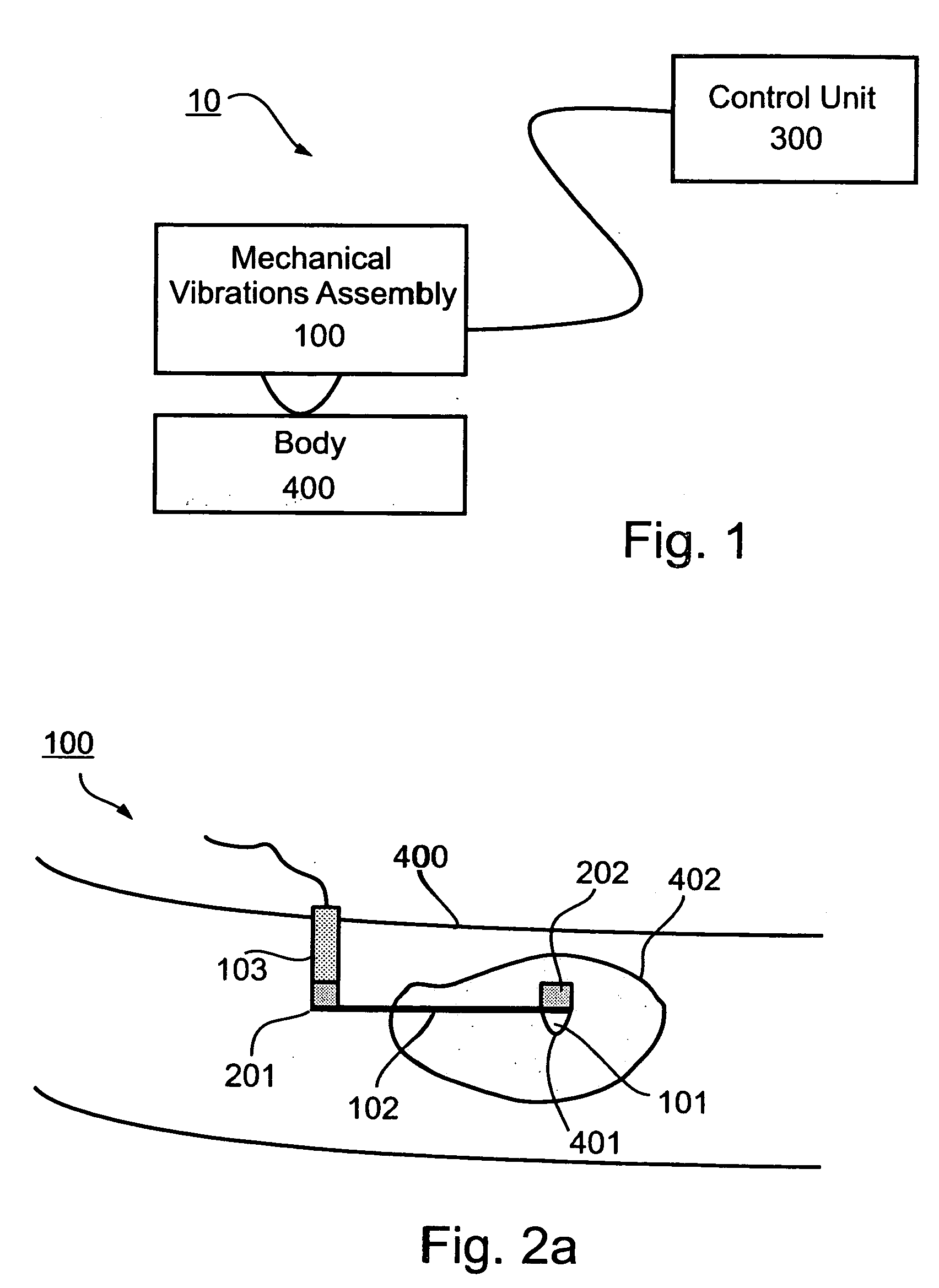
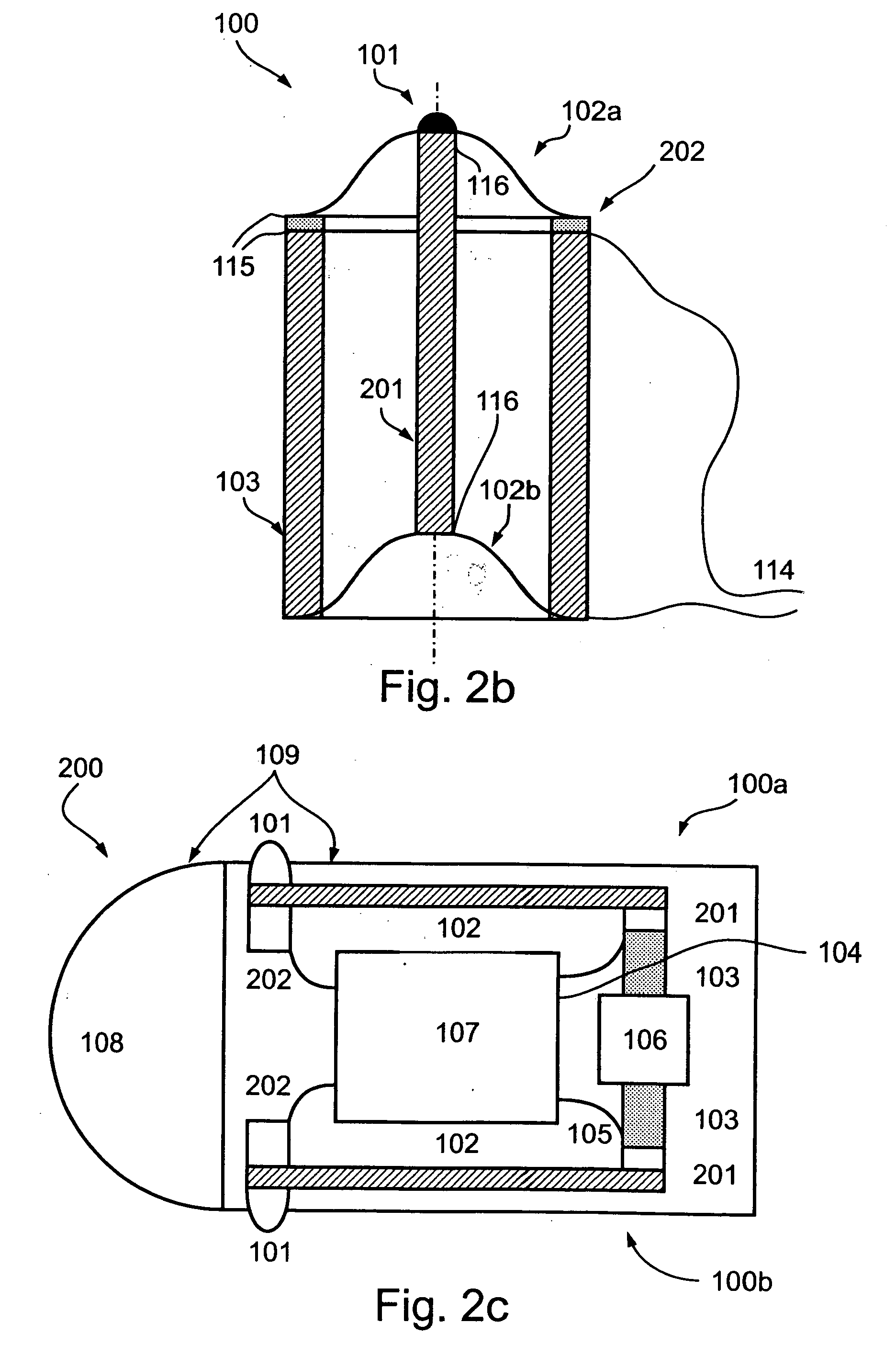
Method, system and device for tissue characterization
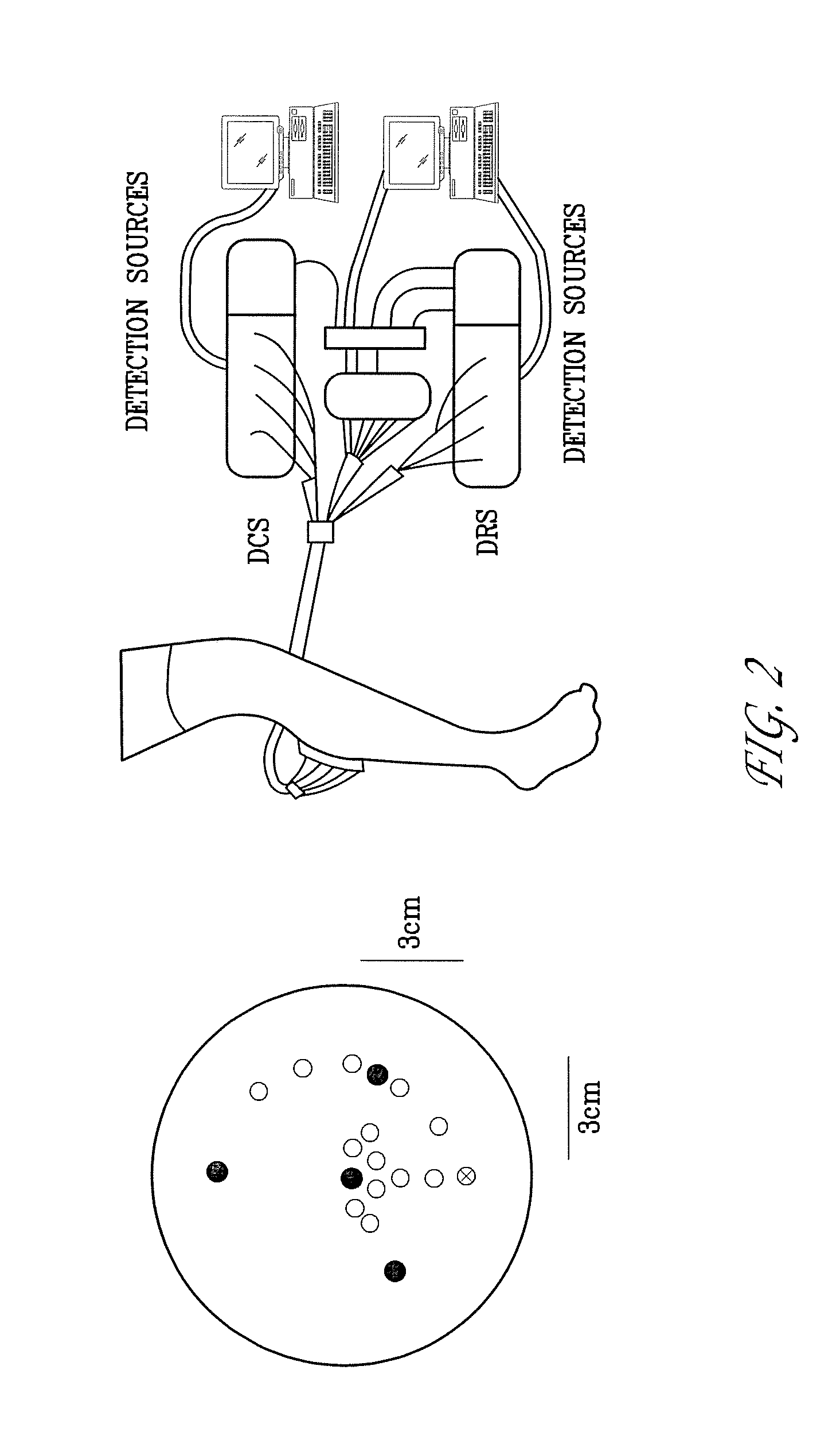
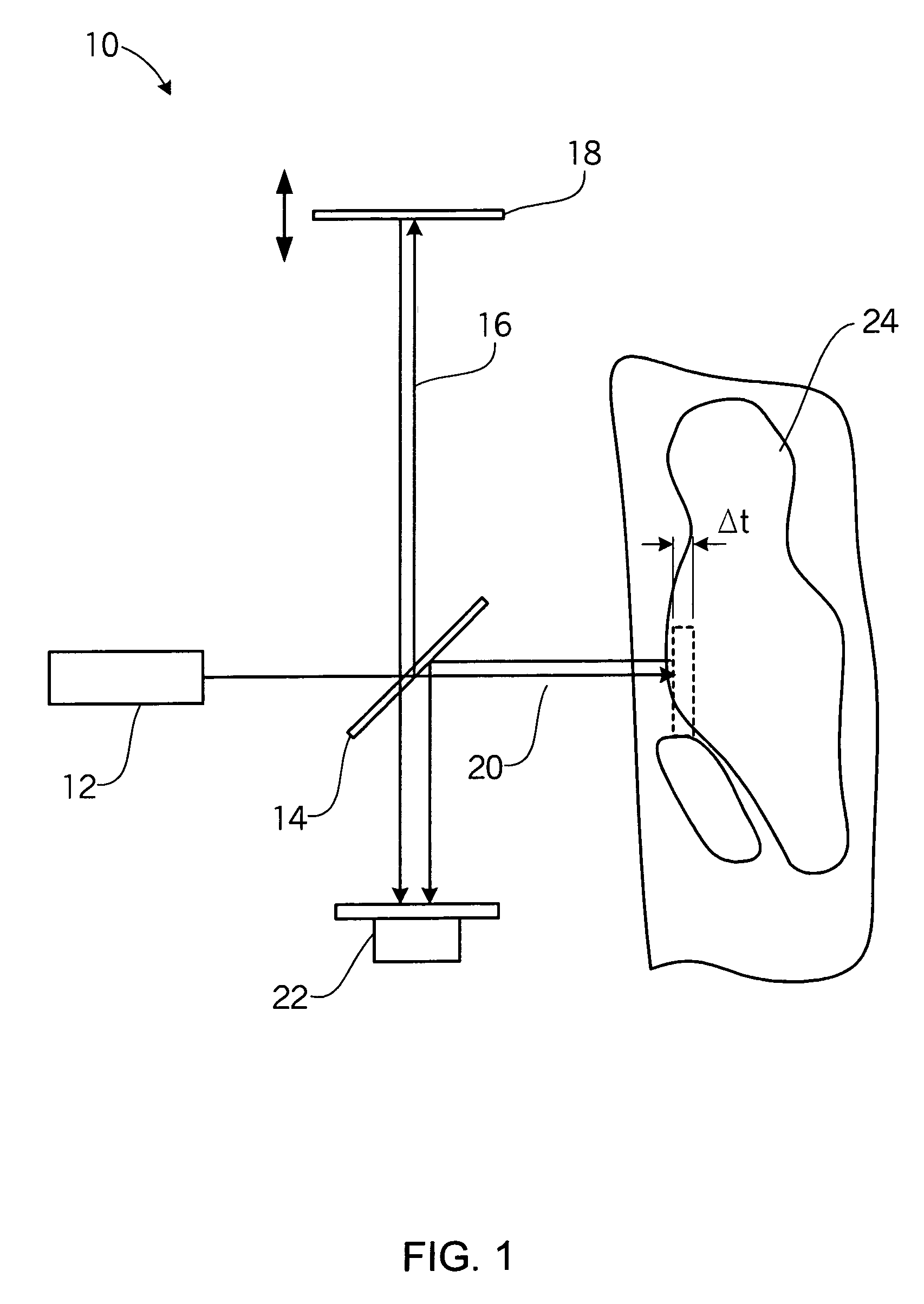
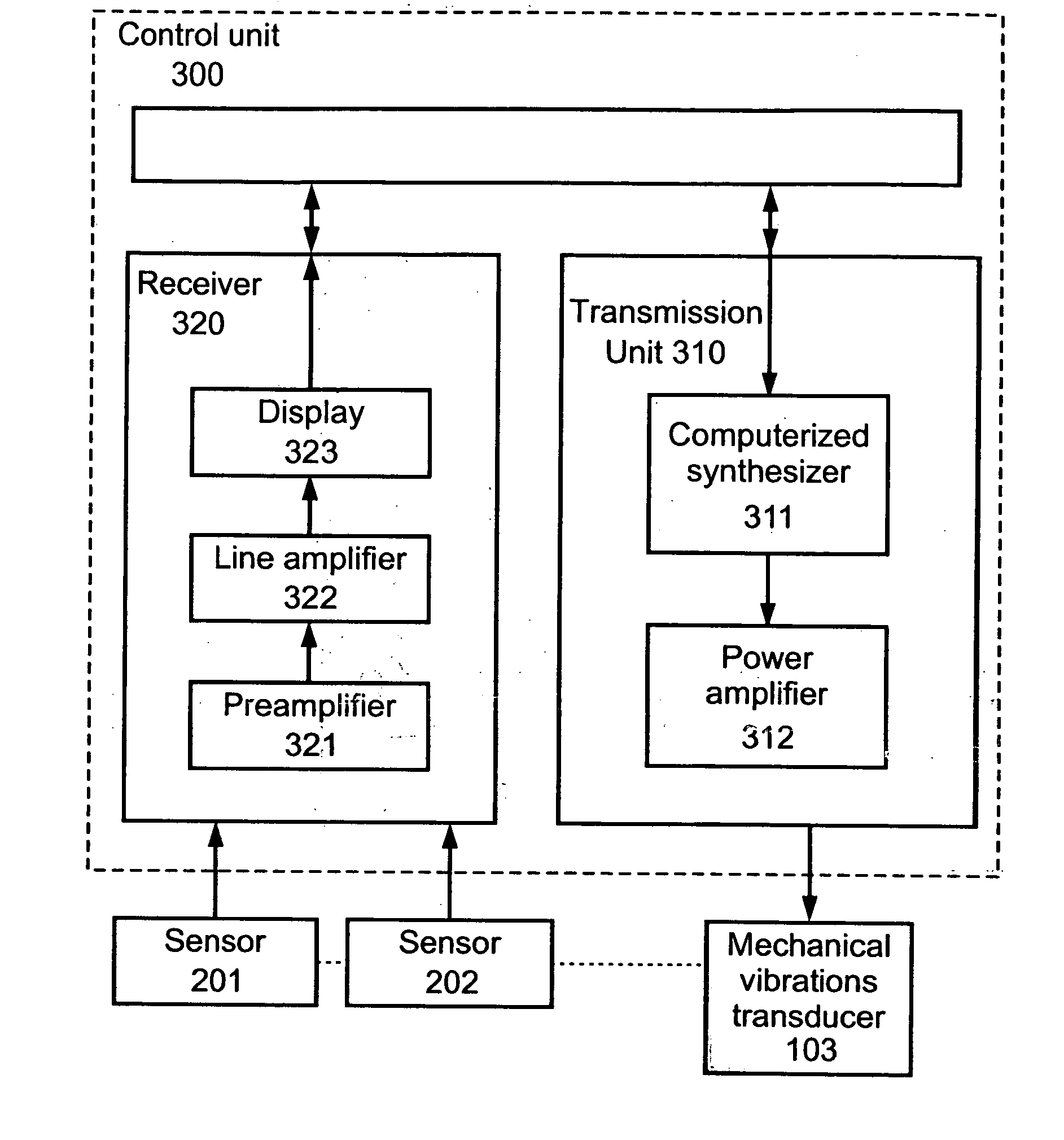
InactiveUS20030220556A1Increase dynamical interactionEnhanced interactionDiagnostics using vibrationsSurgeryTissue characterizationEngineering
A method of characterizing a tissue present in a predetermined location of a body of a subject, the method comprising: generating mechanical vibrations at a position adjacent to the predetermined location, the mechanical vibrations are at a frequency ranging from 10 Hz to 10 kHz; scanning the frequency of the mechanical vibrations; and measuring a frequency response spectrum from the predetermined location, thereby characterizing the tissue.
Owner:VESPRO
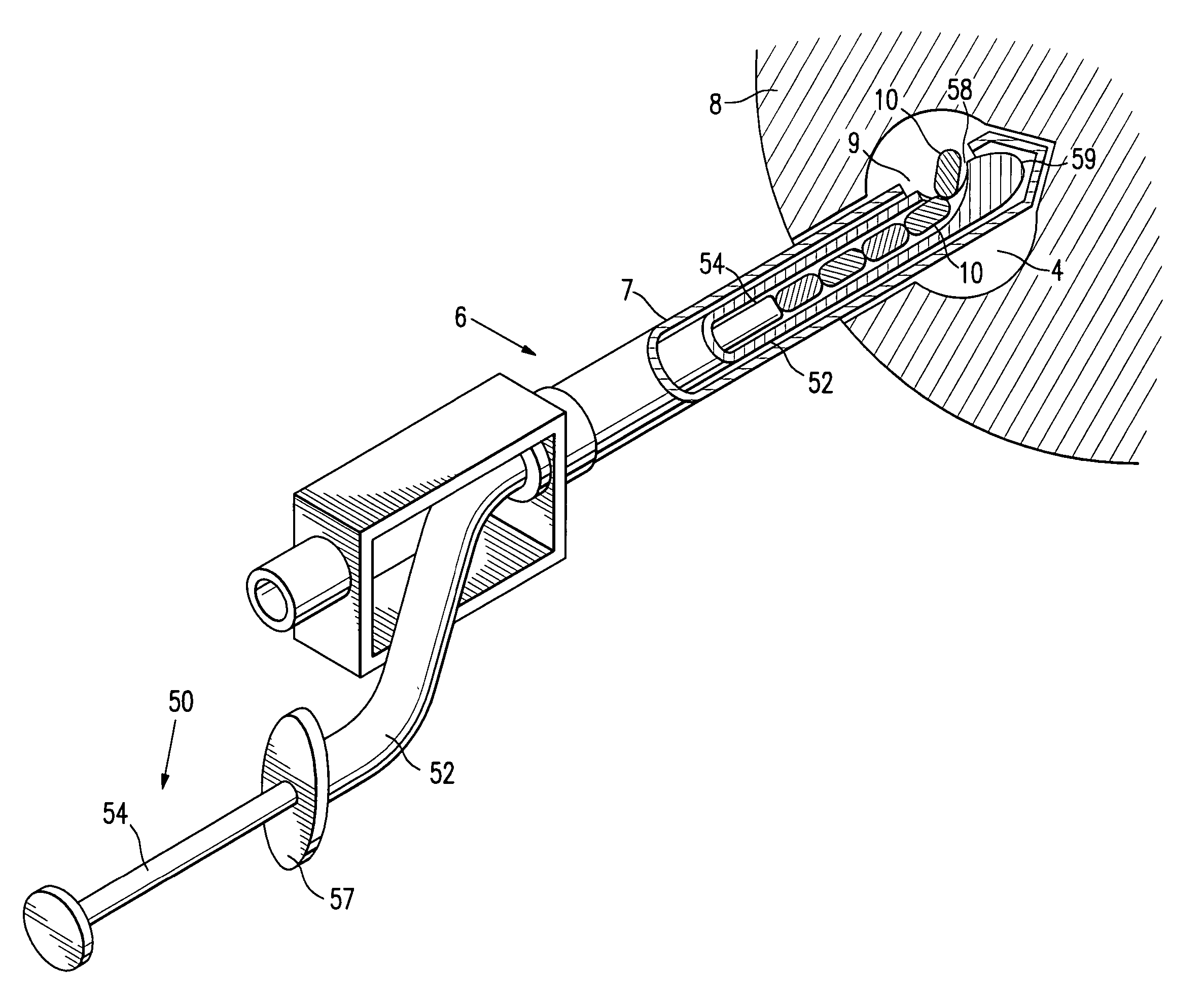
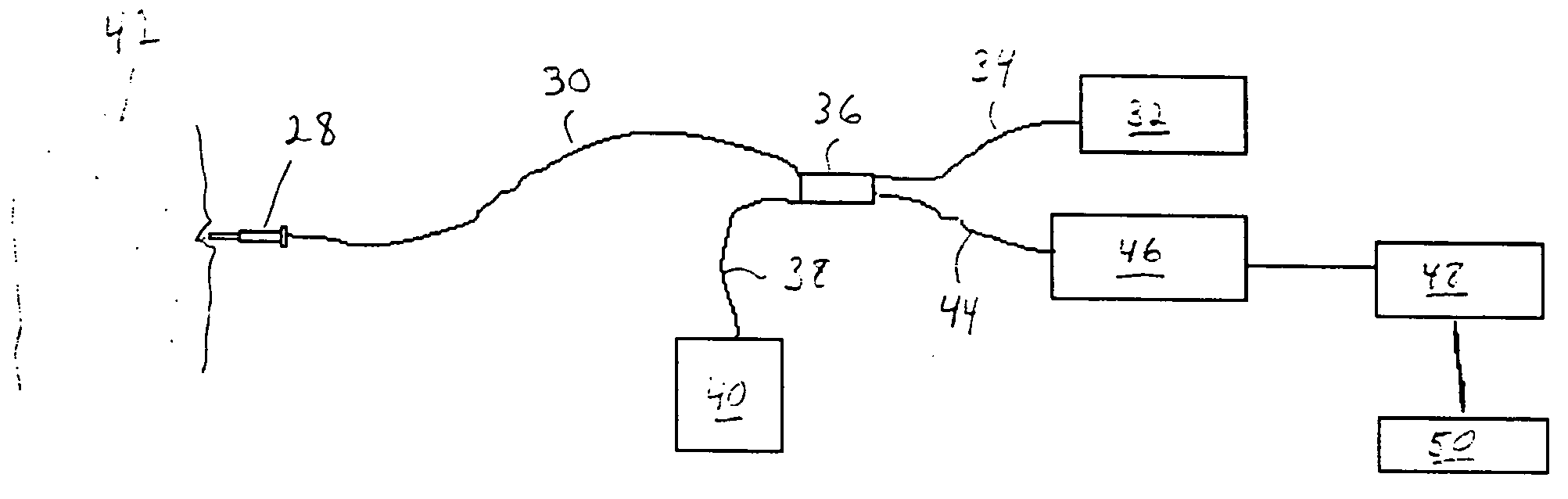
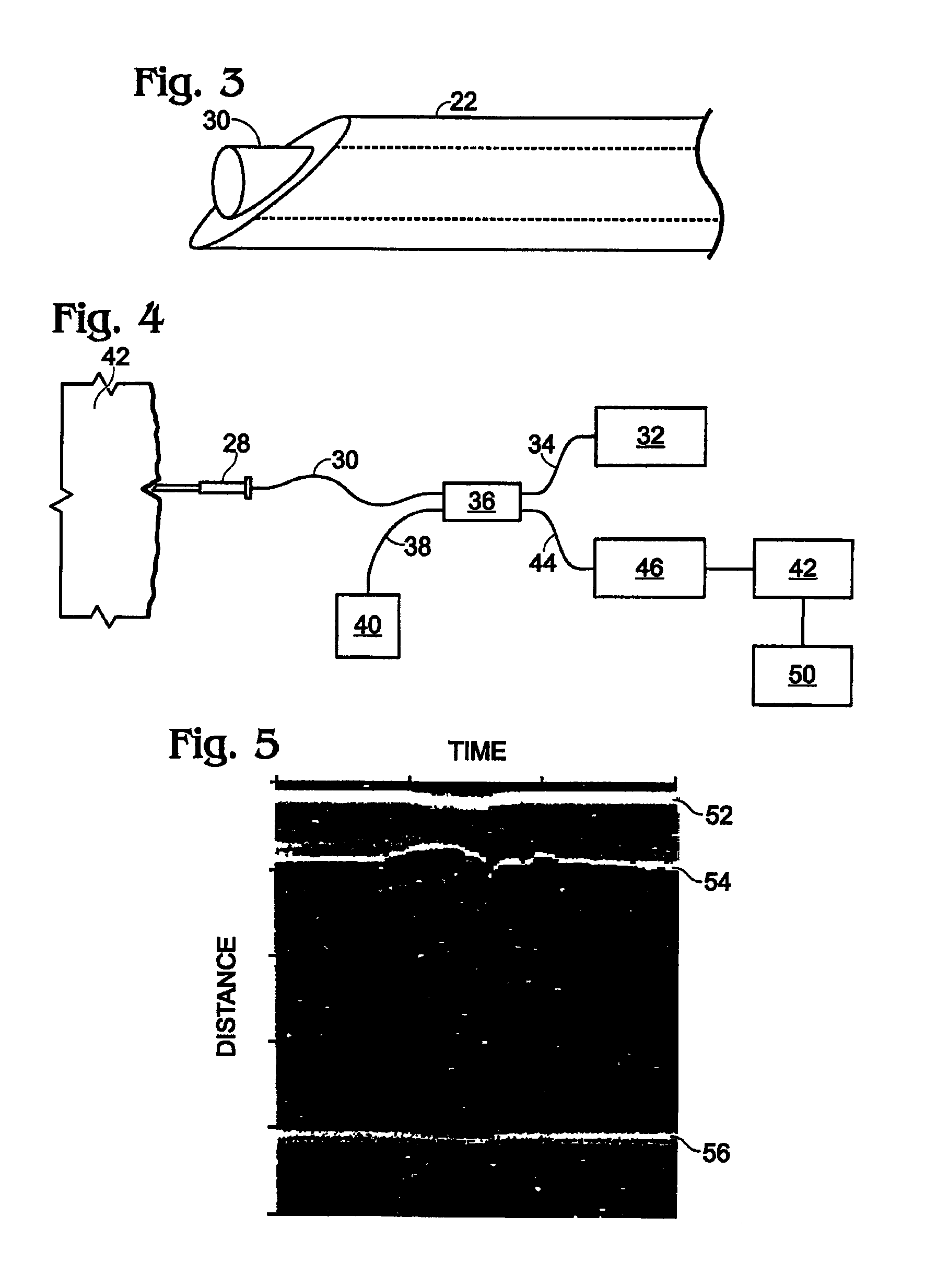
Tissue structure identification in advance of instrument
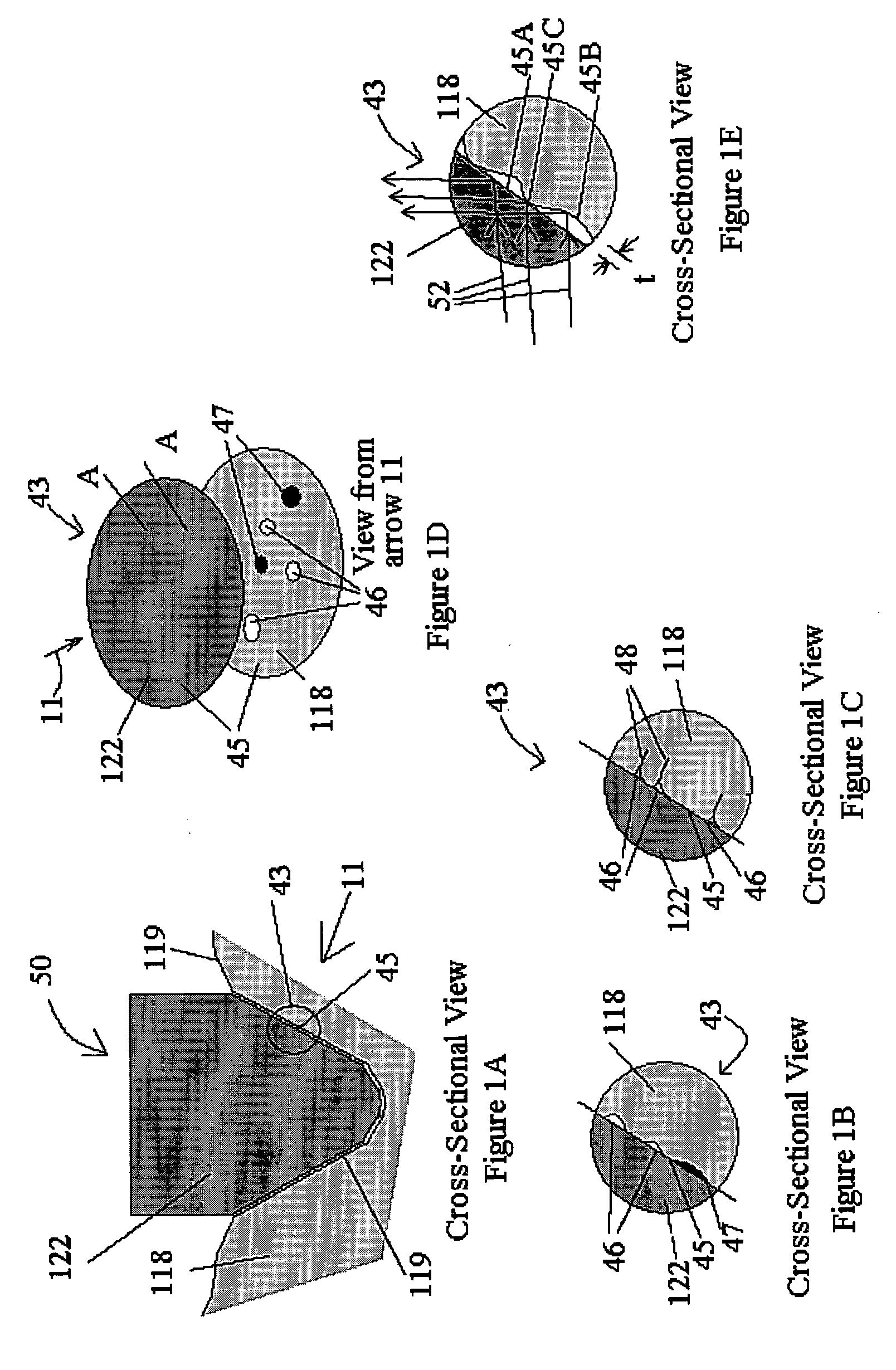
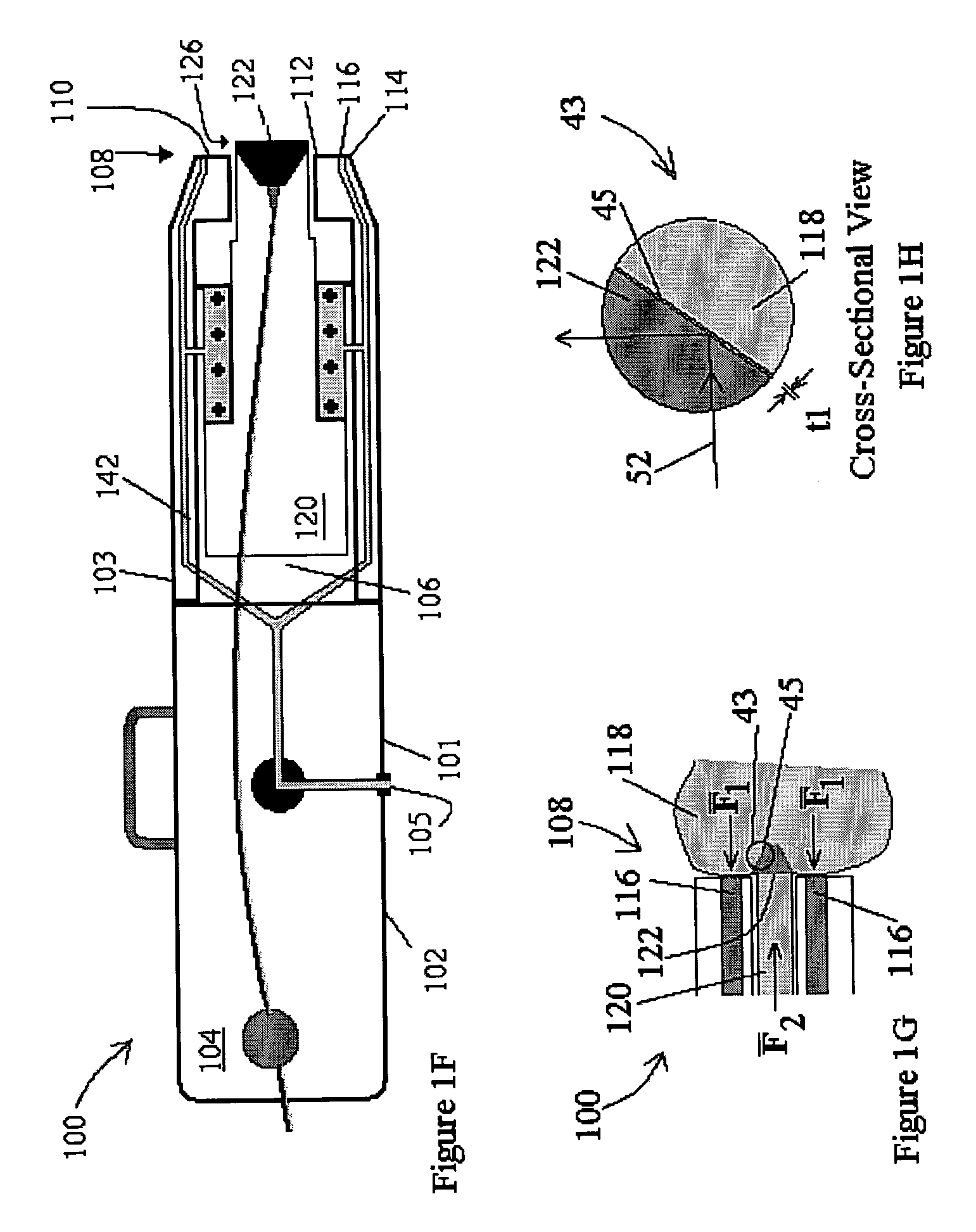
InactiveUS20050027199A1Increase contentIncision instrumentsSurgical needlesFiberTissue characterization
A method and apparatus for identifying tissue structures in advance of a mechanical medical instrument during a medical procedure. A mechanical tissue penetrating medical instrument (22) has a distal end for penetrating tissue in a penetrating direction. An optical wavefront analysis system (32-50) provides light to illuminate tissue ahead of the medical instrument and receives light returned by tissue ahead of the medical instrument. An optical fiber (30) is coupled at a proximal end to the wavefront analysis system and attached at a distal end to the medical instrument proximate the distal end of the medical instrument. The distal end of the fiber has an illumination pattern directed substantially in the penetrating direction for illuminating the tissue ahead of the medical instrument and receiving light returned therefrom. The wavefront analysis system provides information about the distance from the distal end of the medical instrument to tissue features ahead of the medical instrument.
Owner:CLARKE DANA S
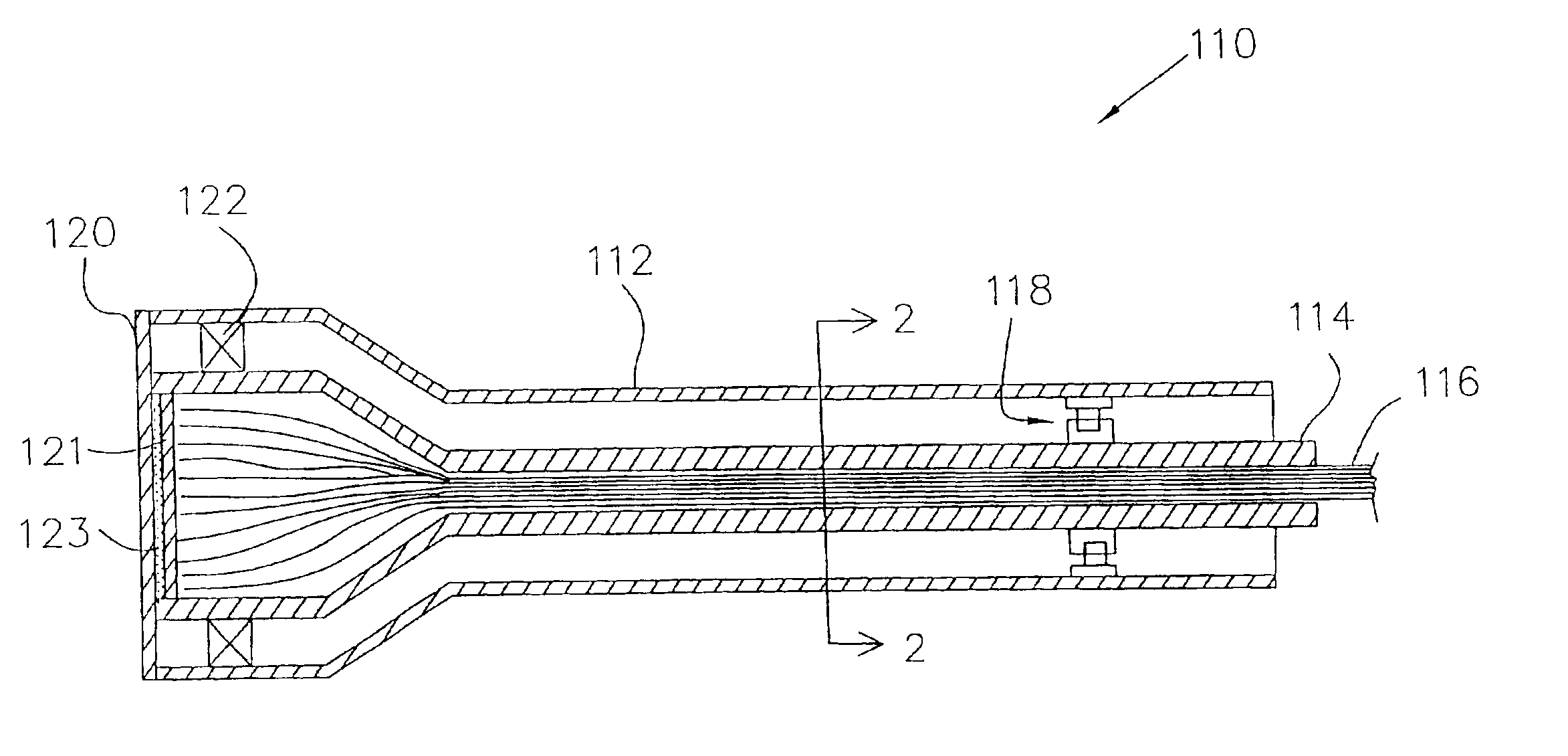
Rotational intravascular ultrasound probe with an active spinning element
ActiveUS20100234736A1Improve image qualityAccurate diagnosis of medicalCatheterInfrasonic diagnosticsManufacturing cost reductionSonification
An intravascular ultrasound probe is disclosed, incorporating features for utilizing an advanced transducer technology on a rotating transducer shaft. In particular, the probe accommodates the transmission of the multitude of signals across the boundary between the rotary and stationary components of the probe required to support an advanced transducer technology. These advanced transducer technologies offer the potential for increased bandwidth, improved beam profiles, better signal to noise ratio, reduced manufacturing costs, advanced tissue characterization algorithms, and other desirable features. Furthermore, the inclusion of electronic components on the spinning side of the probe can be highly advantageous in terms of preserving maximum signal to noise ratio and signal fidelity, along with other performance benefits.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Tissue structure identification in advance of instrument
A method and apparatus for identifying tissue structures in advance of a mechanical medical instrument during a medical procedure. A mechanical tissue penetrating medical instrument (22) has a distal end for penetrating tissue in a penetrating direction. An optical wavefront analysis system (32-50) provides light to illuminate tissue ahead of the medical instrument and receives light returned by tissue ahead of the medical instrument. An optical fiber (30) is coupled at a proximal end to the wavefront analysis system and attached at a distal end to the medical instrument proximate the distal end of the medical instrument. The distal end of the fiber has an illumination pattern directed substantially in the penetrating direction for illuminating the tissue ahead of the medical instrument and receiving light returned therefrom. The wavefront analysis system provides information about the distance from the distal end of the medical instrument to tissue features ahead of the medical instrument.
Owner:CLARKE DANA S
Endoscopic System for In-Vivo Procedures
An endoscopic system for in-vivo tissue characterization, using a nonirradiative electromagnetic sensor, is described. The endoscopic system is further configured to employ several follow-up procedures, for example, biopsy sampling, localized surgery, dispensing a medicament, and the like, so that on the whole, the endoscopic system provides for the early detection of cancerous and pre-cancerous tissue, in vivo, and for the application of immediate follow-up procedures to any such tissue.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
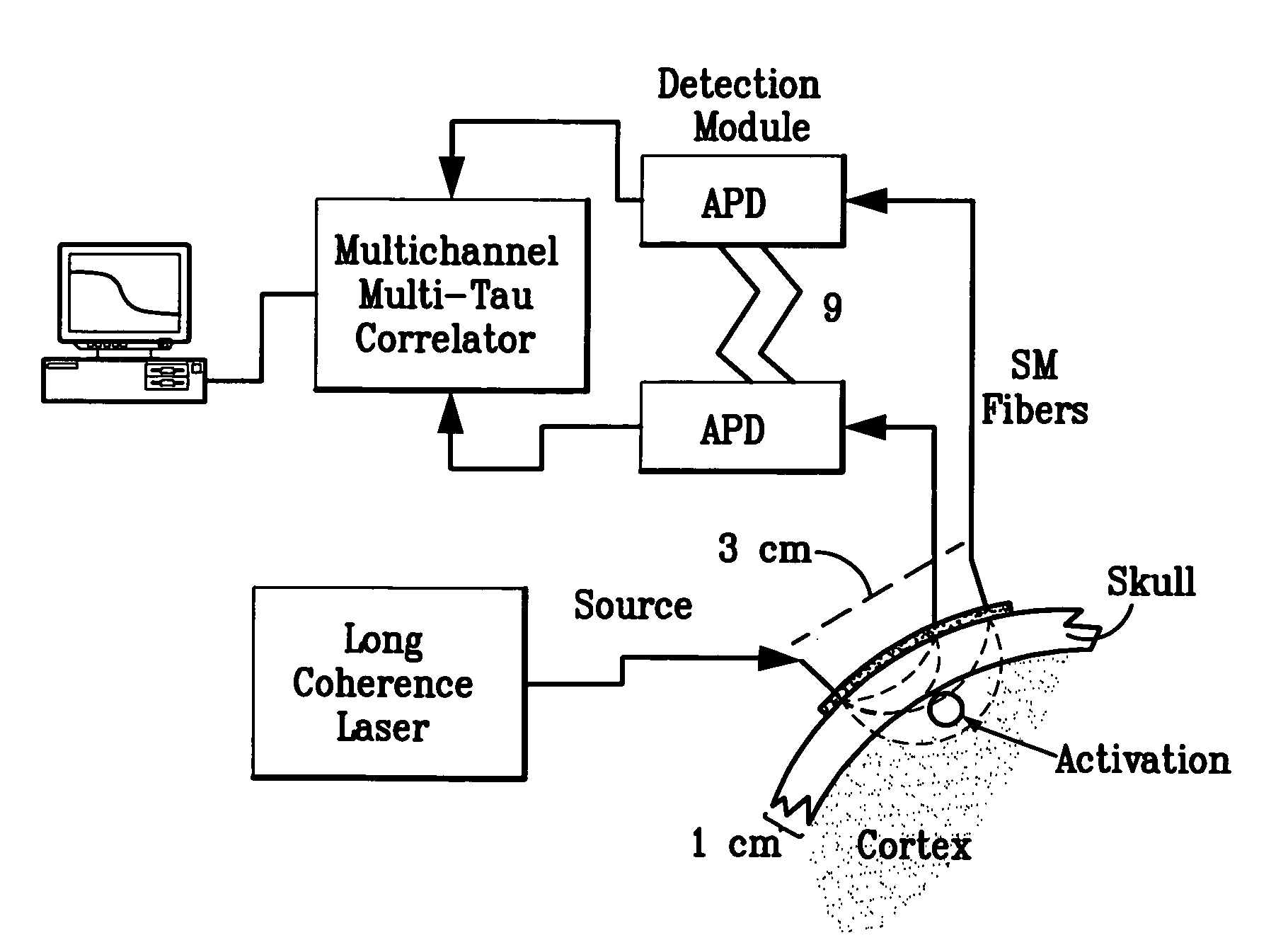
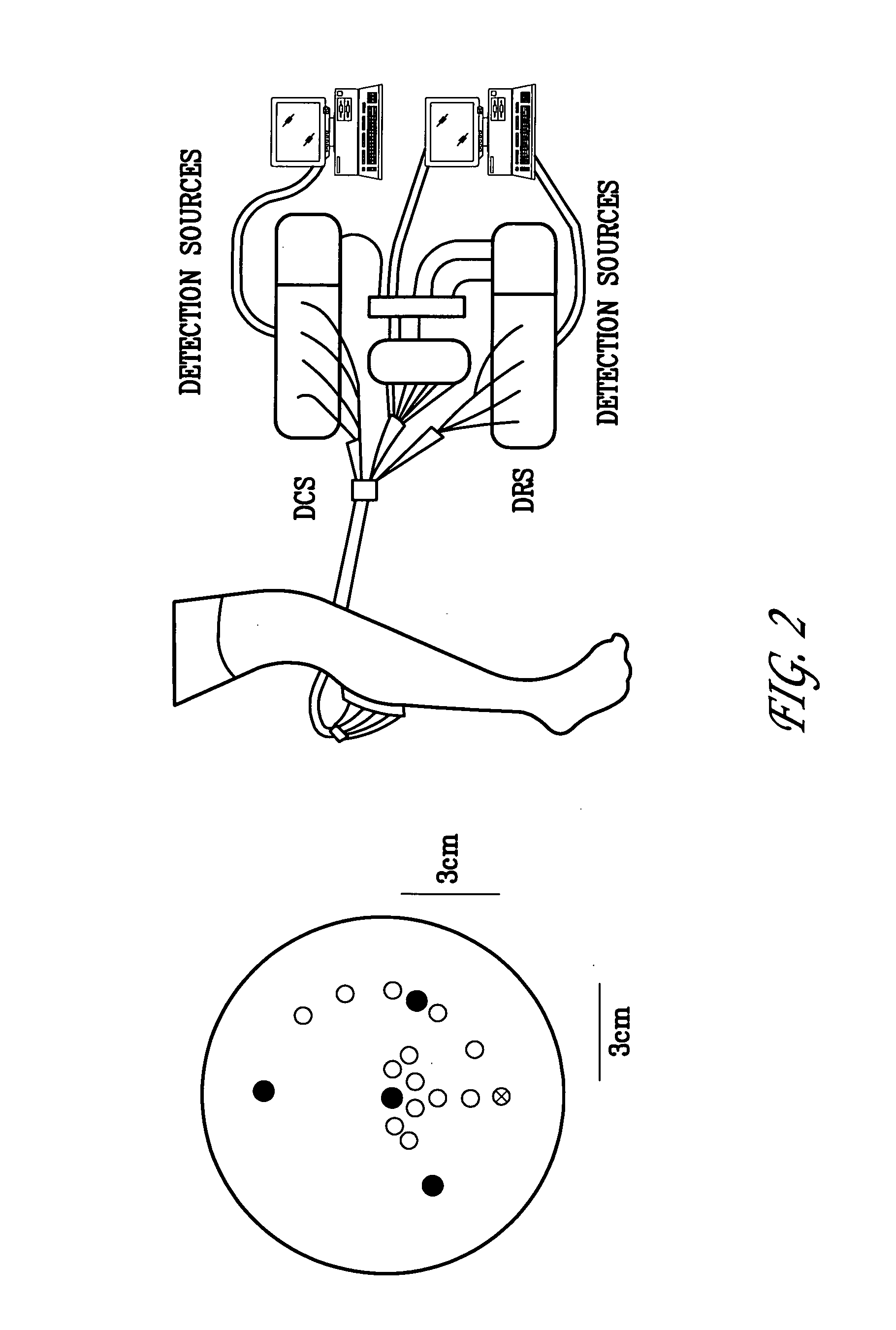
Optical measurement of tissue blood flow, hemodynamics and oxygenation
ActiveUS20060063995A1Promote blood flowDiagnostics using lightCatheterBlood flowOptical measurements
An embodiment of the invention includes a device, system and method for determining the characteristics of deep tissue. The novel method includes measuring blood flow rate and oxygenation characteristics of the tissue, and determining oxygen metabolism of the tissue as a function of the measure blood flow rate and measure oxygenation. The blow flow rate characteristics are measured as a function of light fluctuations caused by the tissue, while the oxygenation characteristics are measured as a function of transmission of light through the tissue with respect to the wavelength of light. The tissue may be layered tissue, for example, a portion of a brain. The tissue characteristics may be measured during times of varying levels of exercise intensity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Surgical instrument to assess tissue characteristics
A surgical instrument for assessing tissue characteristics such as tissue density and volume is disclosed. The surgical instrument is hand-held and includes transducers adapted for emitting and / or receiving acoustic signals. The surgical instrument utilizes pulse-echo to determine tissue characteristics. The surgical instrument may be utilized to determine such things as the size of a lesion and whether the lesion has been completely removed or filled with graft material.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Optical measurement of tissue blood flow, hemodynamics and oxygenation
An embodiment of the invention includes a device, system and method for determining the characteristics of deep tissue. The novel method includes measuring blood flow rate and oxygenation characteristics of the tissue, and determining oxygen metabolism of the tissue as a function of the measure blood flow rate and measure oxygenation. The blood flow rate characteristics are measured as a function of light fluctuations caused by the tissue, while the oxygenation characteristics are measured as a function of transmission of light through the tissue with respect to the wavelength of light. The tissue may be layered tissue, for example, a portion of a brain. The tissue characteristics may be measured during times of varying levels of exercise intensity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Device for tissue characterization
InactiveUS7242832B2Keep the flowMaintain normal flowPhase-affecting property measurementsSurgeryDistal portionTissue characterization
Owner:MEDEIKON
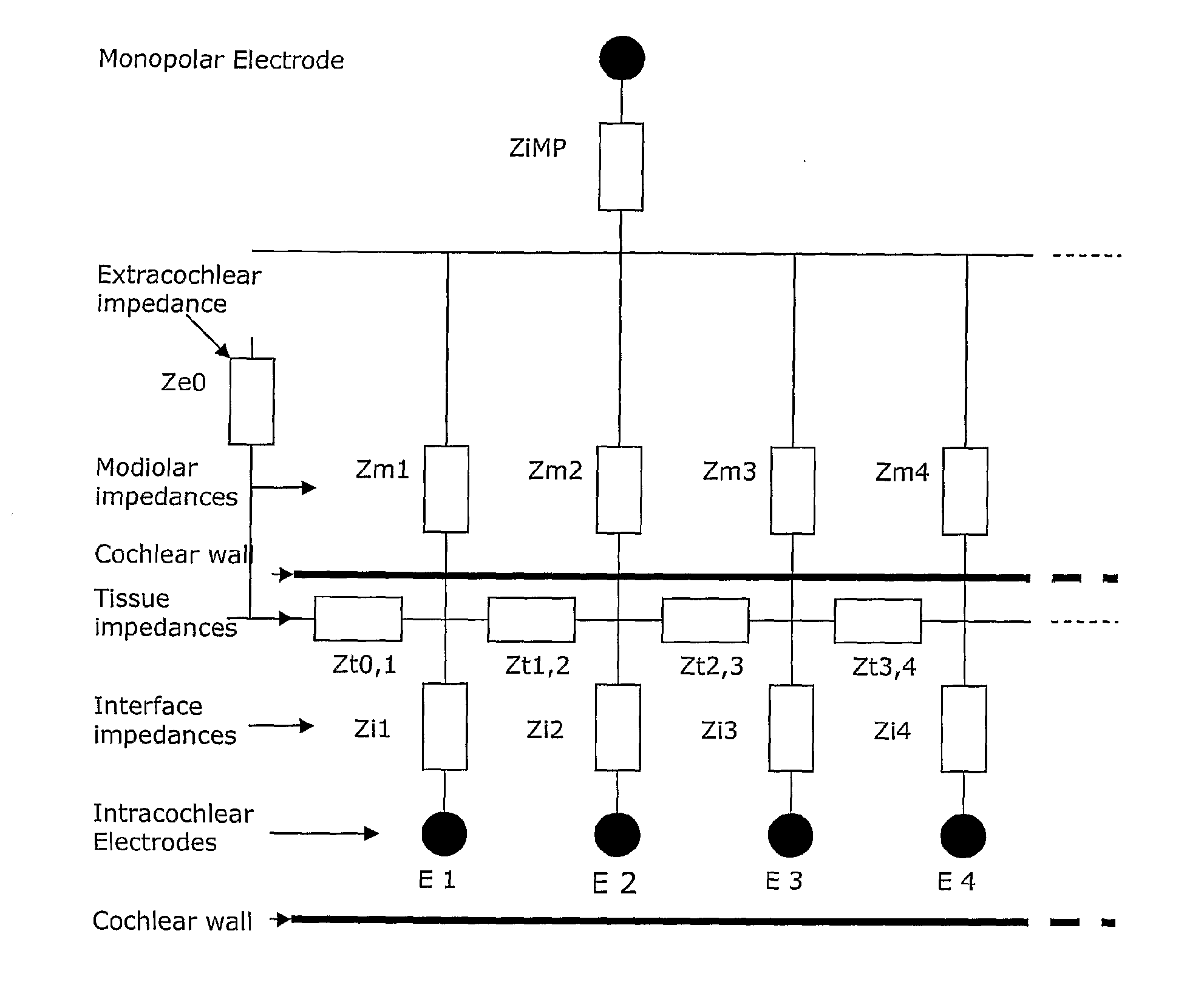
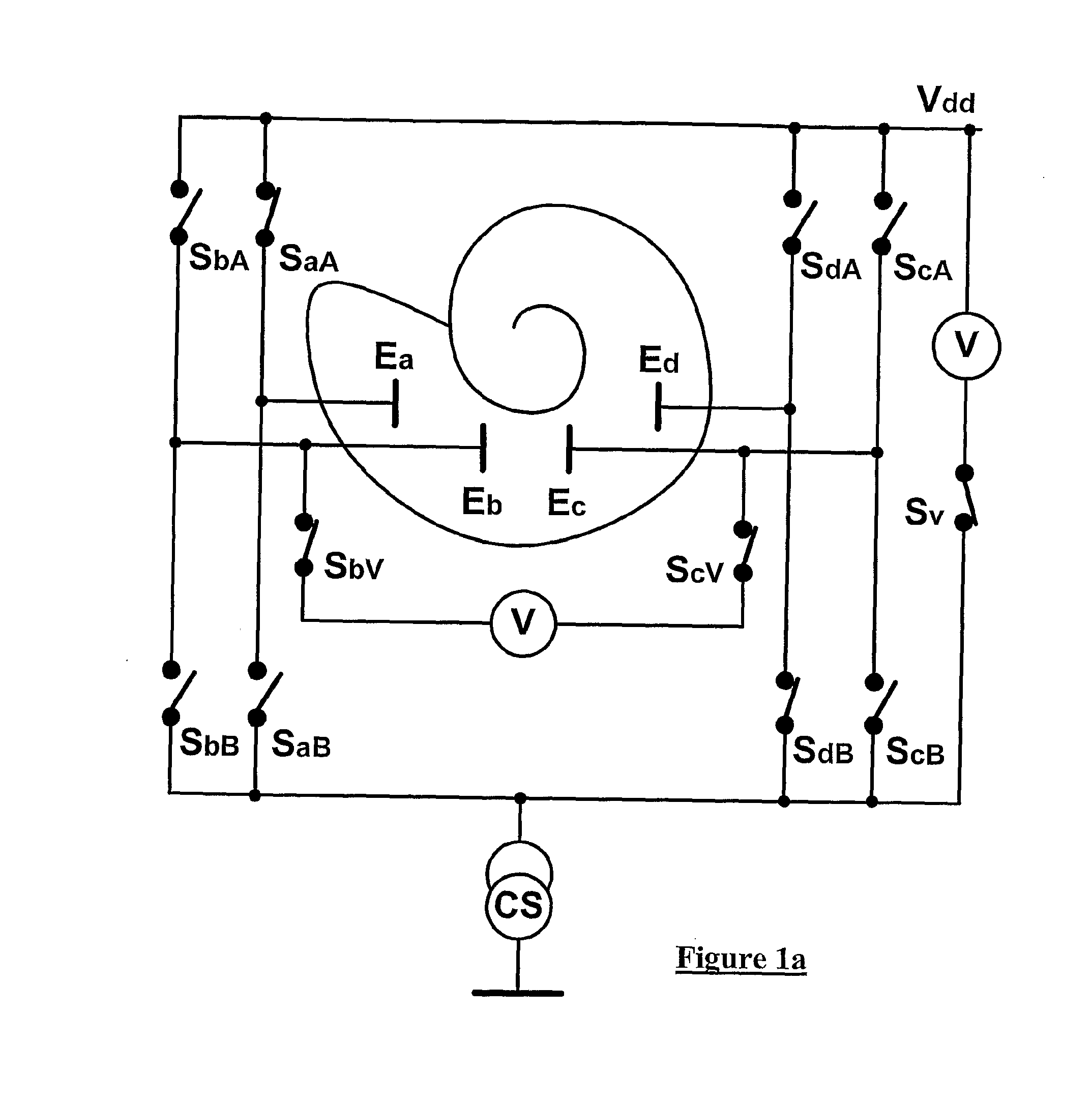
Method and device for intracochlea impedance measurement
ActiveUS20110087085A1Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMonopolar stimulationTissue characterization
This method of determining an intracochlea tissue impedance comprises using at least two stimulating electrodes to apply an electrical stimulus to intracochlea tissue. A voltage caused by the stimulus is measured between two measuring electrodes distinct from the stimulating electrodes. From the voltage a stimulus-response characteristic of tissue between the two measuring electrodes is determined. This allows the tissue / electrode interface impedance and potential and the tissue impedance and potential to be uniquely determined. In turn, modiolus currents can be estimated in monopolar stimulation mode. Also provided is automated initiation of re-mapping of the device when tissue characteristics change
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
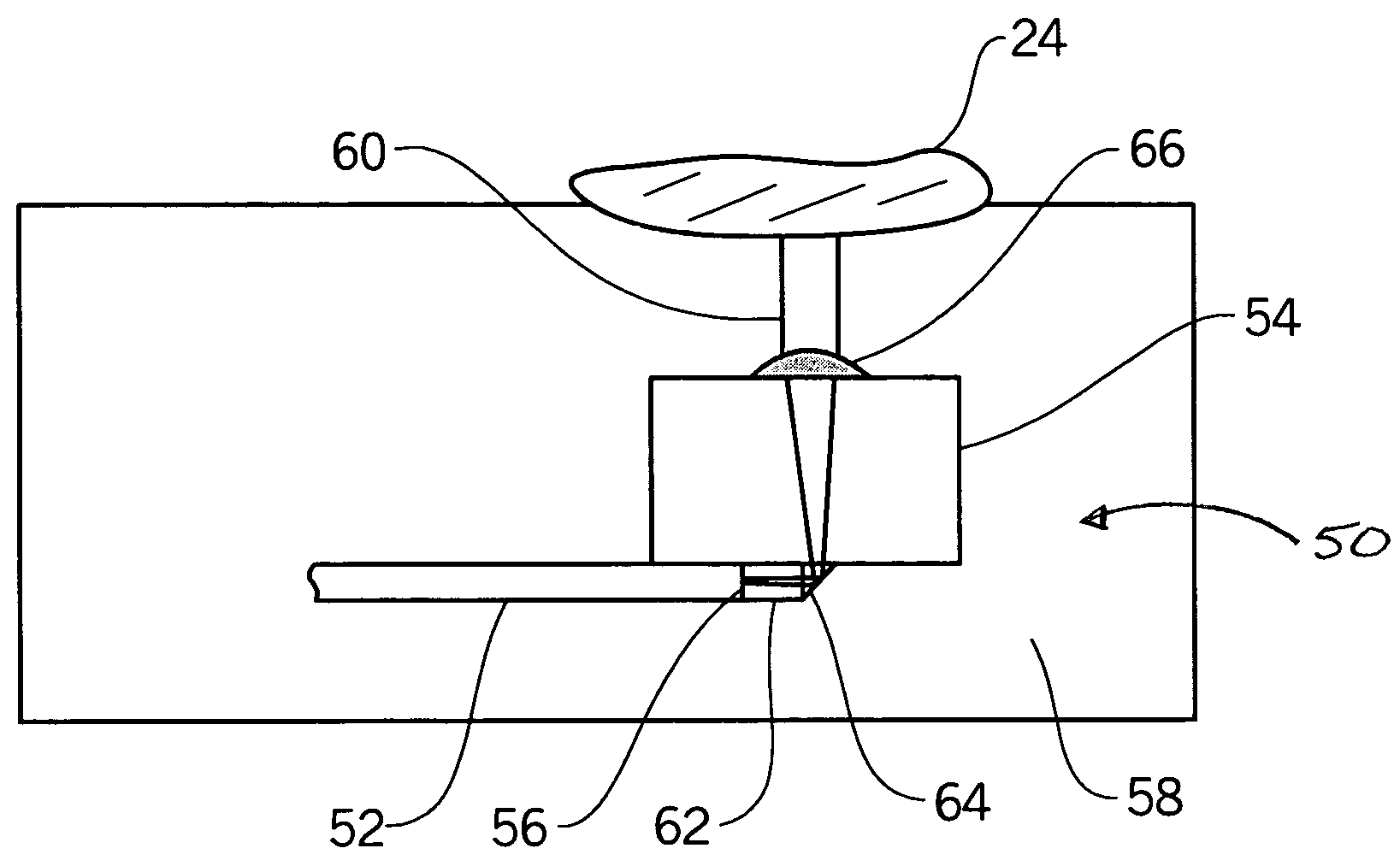
Tissue-characterization probe with effective sensor-to-tissue contact
ActiveUS20070032747A1Improve sensing accuracyEffective contactDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationAcute angleMinicomputer
The present invention relates to a device for tissue-characterization, designed for effective sensor-to-tissue contact. The device includes an element, having a rigid surface of a linear cross-section, on which at least one sensor is arranged, and a mechanism for applying a force to a soft tissue, the line of force being at an acute angle with the rigid surface, for stretching or stretching and pushing the soft tissue against the rigid surface, thus achieving effective contact between the tissue and the at least one sensor. In consequence, the accuracy of the sensing is improved. In accordance with another embodiment, a plurality of sensors is employed, arranged along a curved element, for providing three-dimensional information regarding the tissue, for example, by small-scale computerized tomography.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
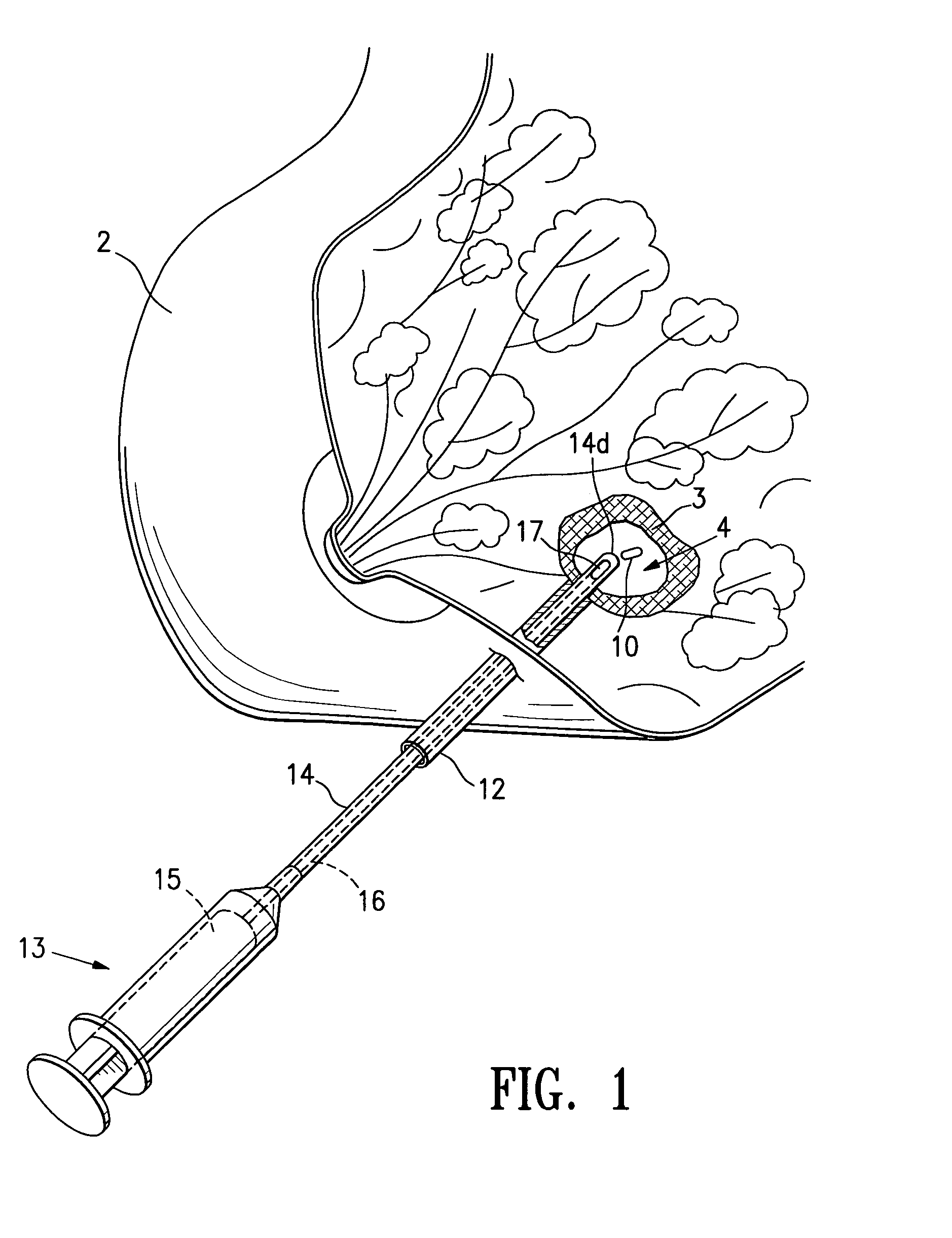
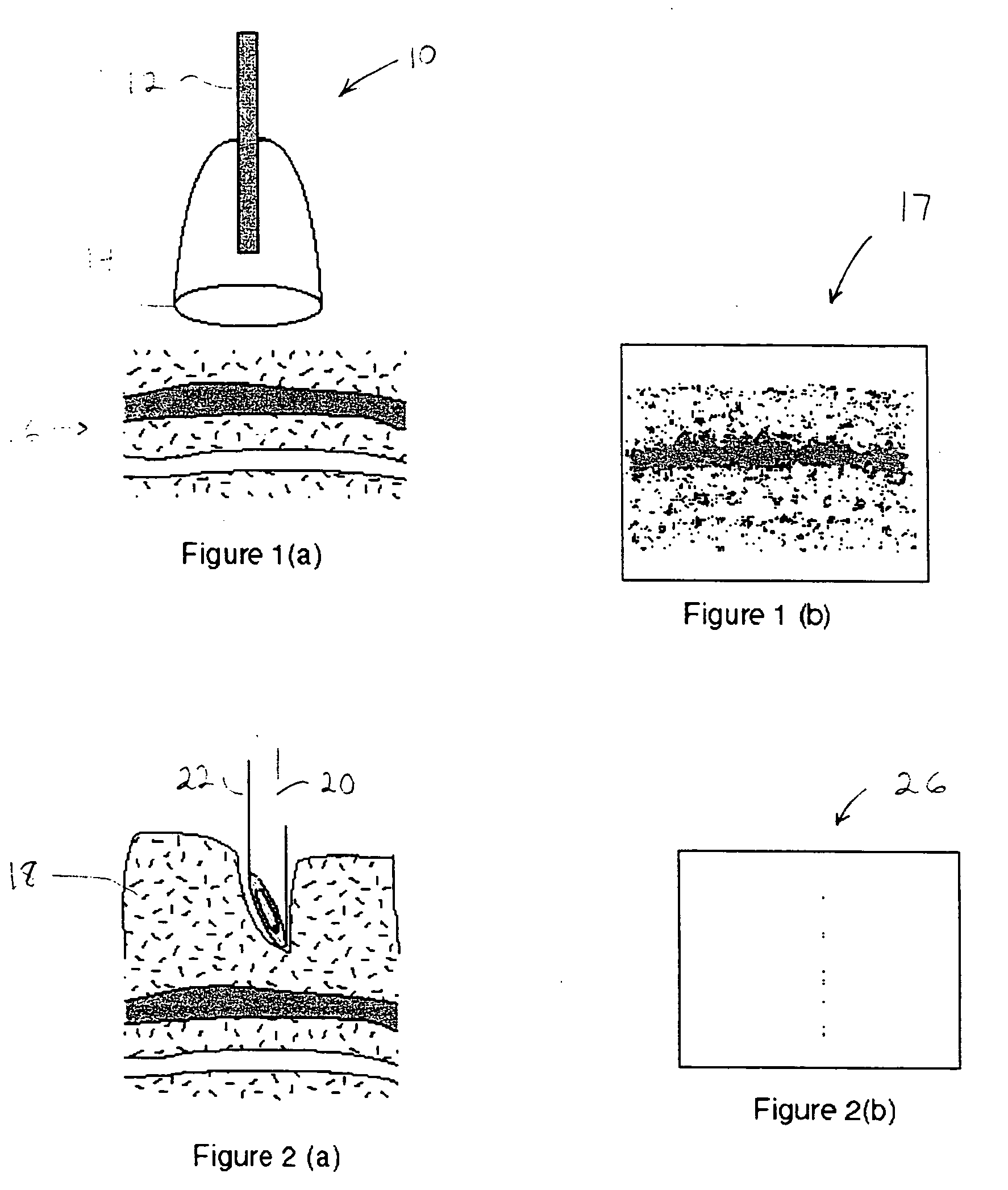
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20050063908A1Small volumeImprove reflectivityLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
The invention is directed biopsy site markers and methods of marking a biopsy site, so that the location of the biopsy cavity is readily visible by conventional imaging methods, particularly by ultrasonic imaging. The biopsy site markers of the invention have high ultrasound reflectivity, presenting a substantial acoustic signature from a small marker, so as to avoid obscuring diagnostic tissue features in subsequent imaging studies, and can be readily distinguished from biological features. The several disclosed embodiments of the biopsy site marker of the invention have a high contrast of acoustic impedance as placed in a tissue site, so as to efficiently reflect and scatter ultrasonic energy, and preferably include gas-filled internal pores. The markers may have a non-uniform surface contour to enhance the acoustic signature. The markers have a characteristic form which is recognizably artificial during medical imaging. The biopsy site marker may be accurately fixed to the biopsy site so as to resist migration from the biopsy cavity when a placement instrument is withdrawn, and when the marked tissue is subsequently moved or manipulated.
Owner:SENORX
Apparatus and method for determining tissue characteristics
InactiveUS6870620B2Reduce and eliminate cross-talkHigh resolutionDiagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesTissue characterizationTarget tissue
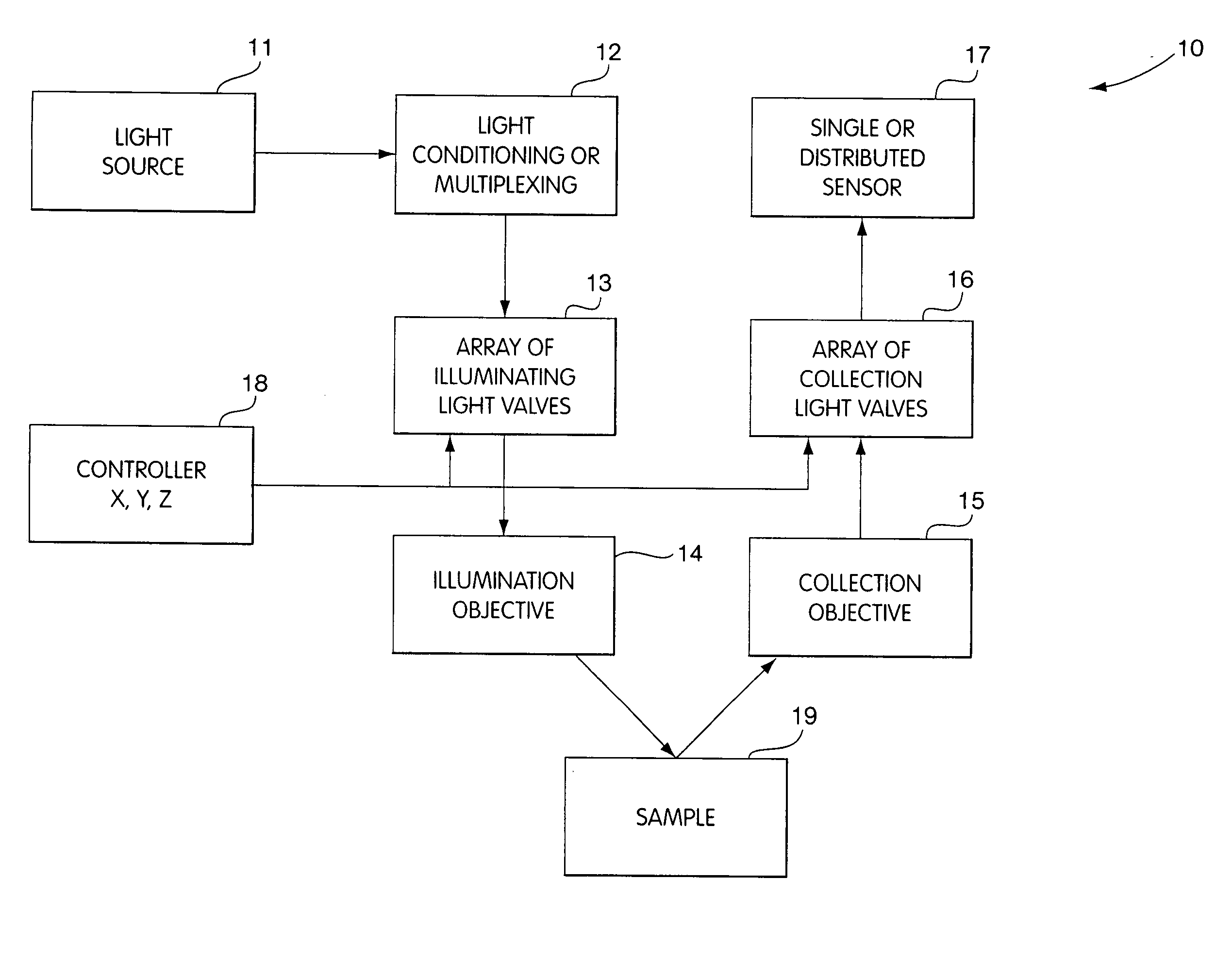
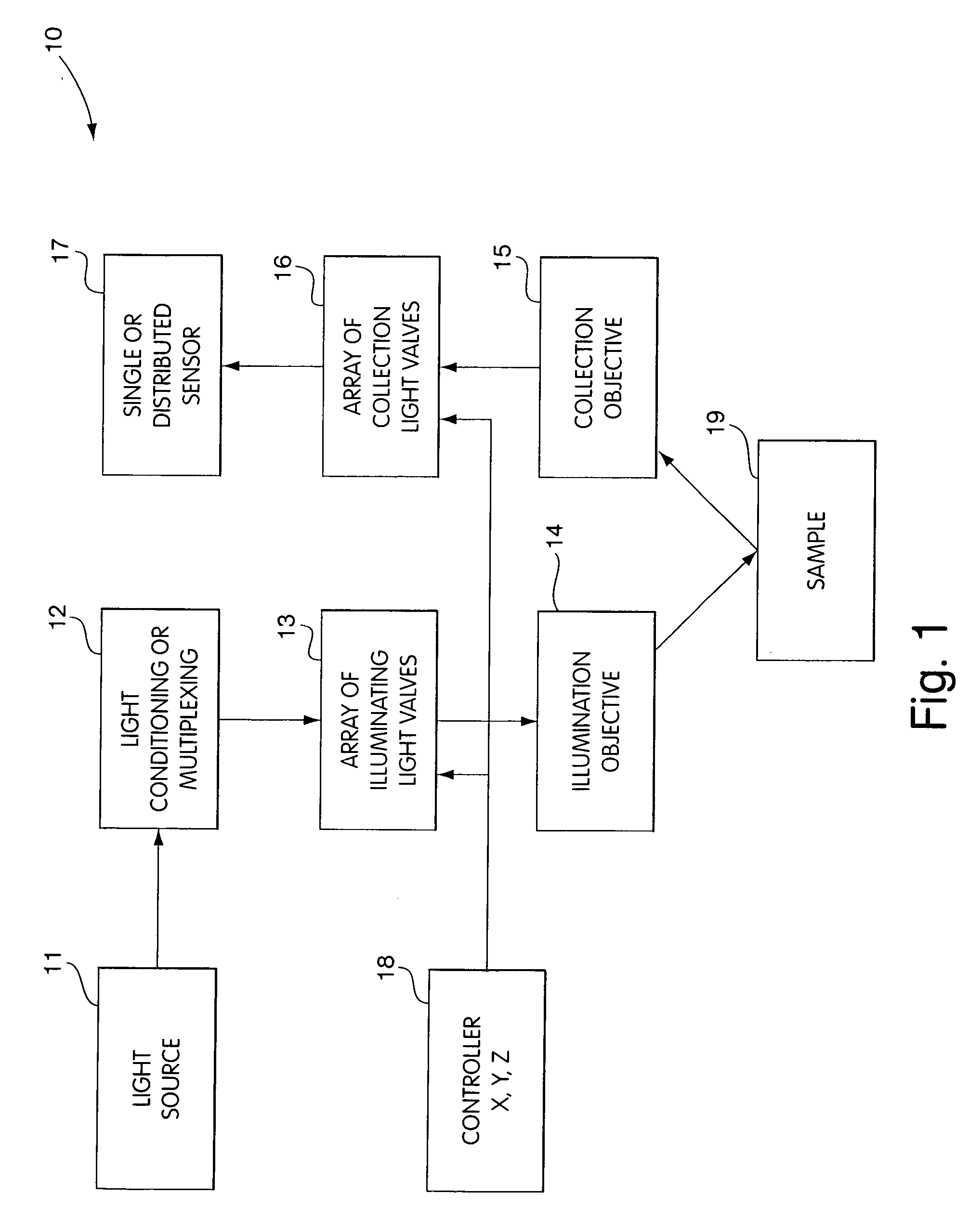
An apparatus embodying the invention includes a probe head with an interrogation surface that is intended to be positioned adjacent or pushed into contact with a target material or tissue. The probe head is constructed to have a plurality of interrogation devices arranged across the face of the interrogation surface. The probe head is also constructed so that the interrogation device can conform to a non-uniform or non-planar surface of the target tissue. In some embodiments, the interrogation surface may have a particular shape that conforms to the shape of a target material. In other embodiments, one or more portions of the interrogation surface could be movable with respect to the remaining portions so that the interrogation surface could be movable with respect to remaining portions so that the interrogation surface can thereby conform to a non-uniform surface. In still other embodiments, a plurality of separately moveable interrogation devices can be arranged across the interrogation surface. During a measurement process, the interrogation surface would be pressed into contact with the non-uniform surface to cause individual ones of the interrogation devices to move, thereby causing the probe head to conform to the non-uniform surface.
Owner:SPECTRX
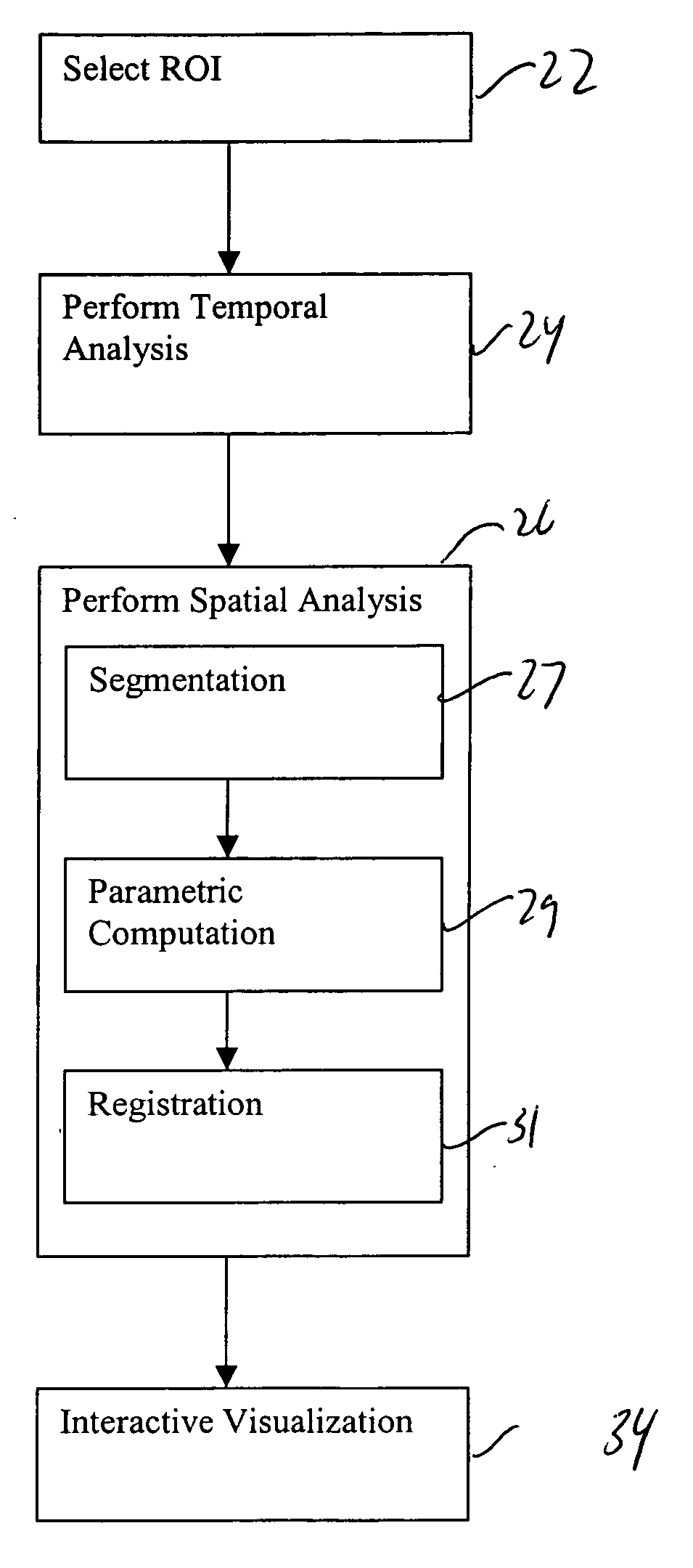
Computer-aided detection system utilizing temporal analysis as a precursor to spatial analysis
ActiveUS20070165920A1Improve analysisImprove interpretabilityImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsSpatial analysis
A computer-aided detection system for evaluating tissue based on a series of timed images acquired both before and after a contrast agent is administered performs a temporal analysis of the tissue and then a spatial analysis in which the tissue is categorized. After the temporal and spatial analysis is performed, the results can be displayed. The displayed results can include both tissue characterization results, underlying curves used to determine the characterization, and confidence data regarding how good the characterization is expected to be. The confidence data can be provided, for example, by using variations in color schemes, displaying numerical confidence levels, or providing graphical features such as piecewise linear models.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
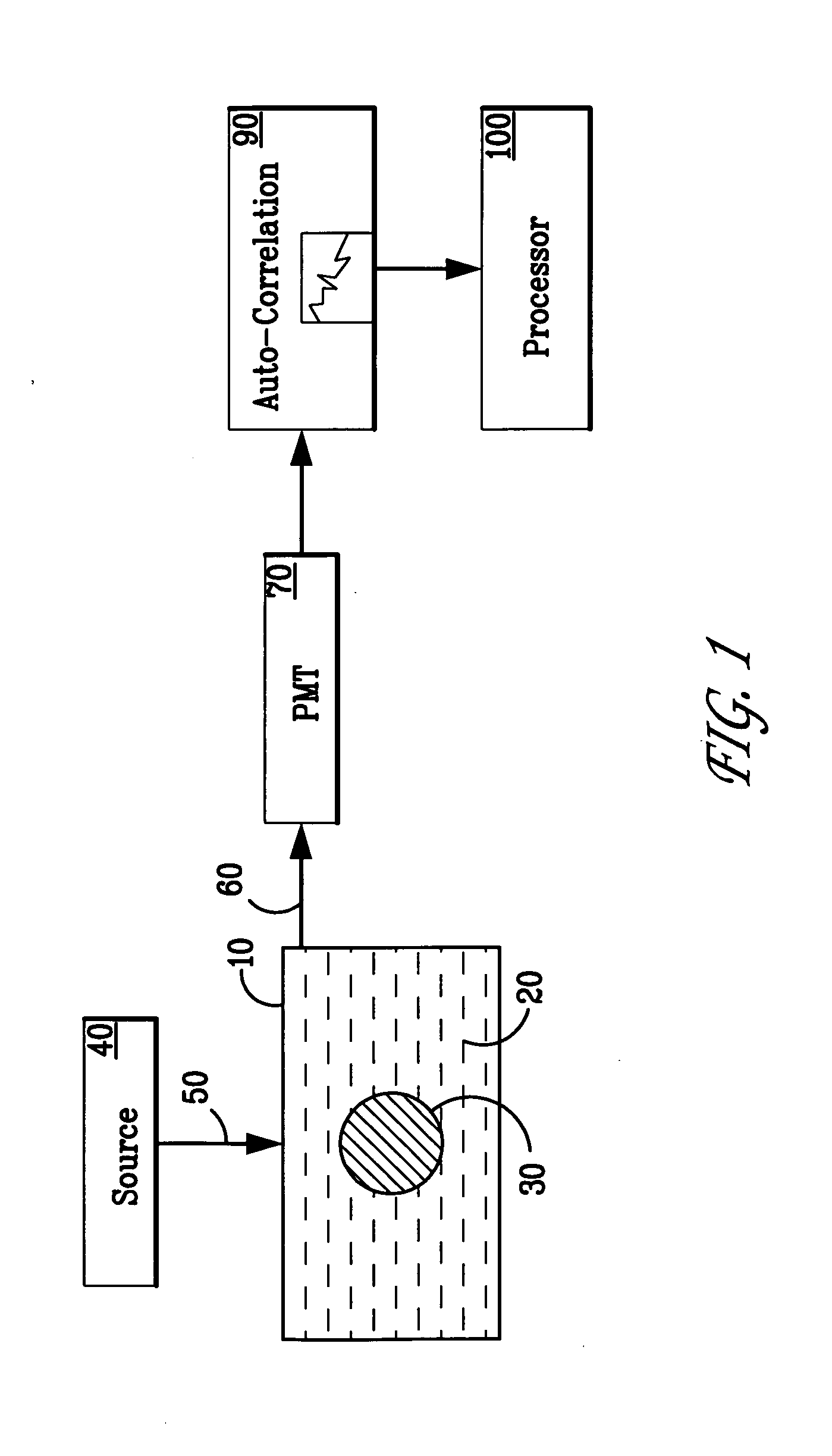
Analysis of volume elements for tissue characterization
InactiveUS20060052709A1Accurate scoreSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyTissue characterizationElectromagnetic radiation
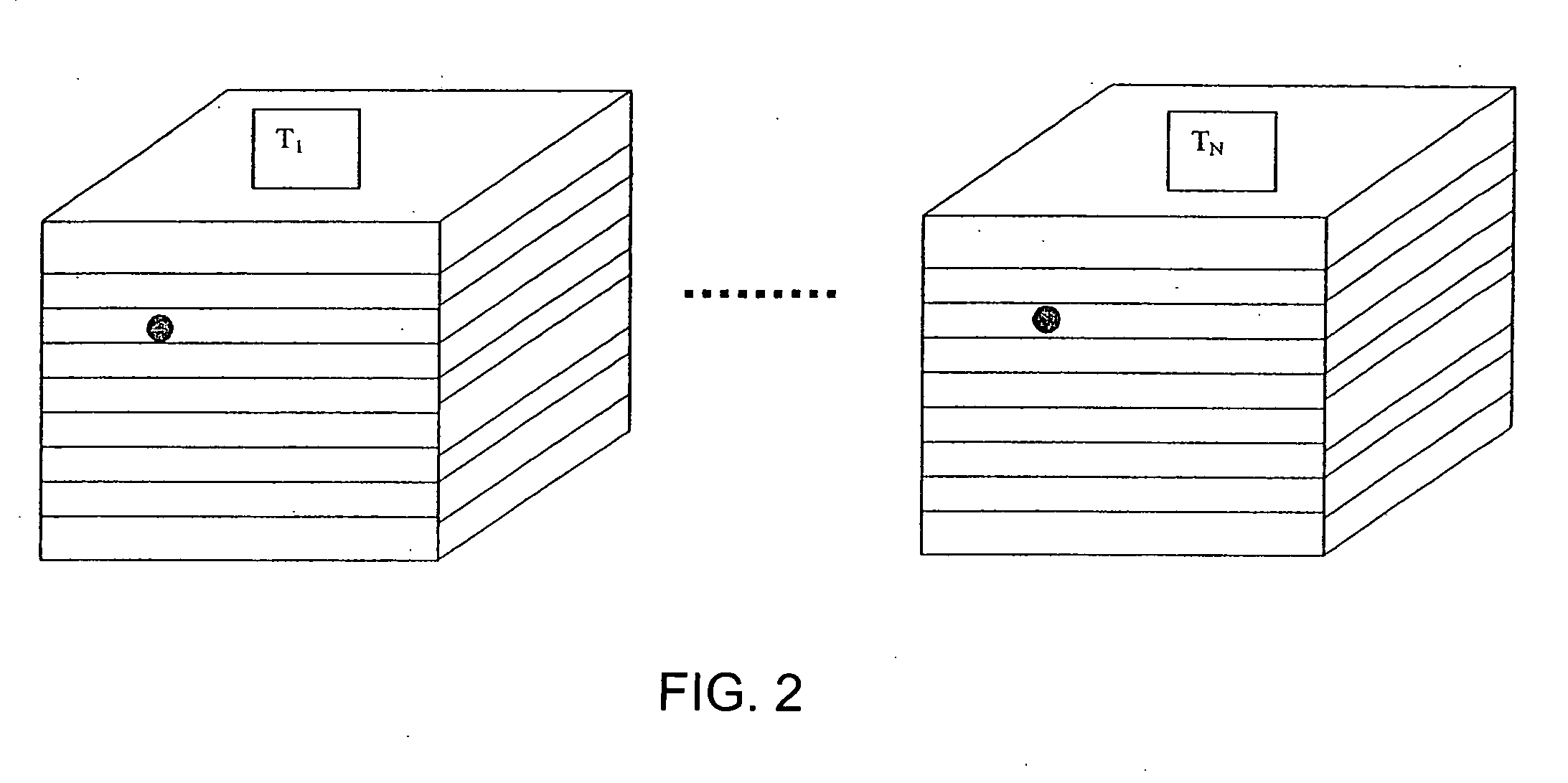
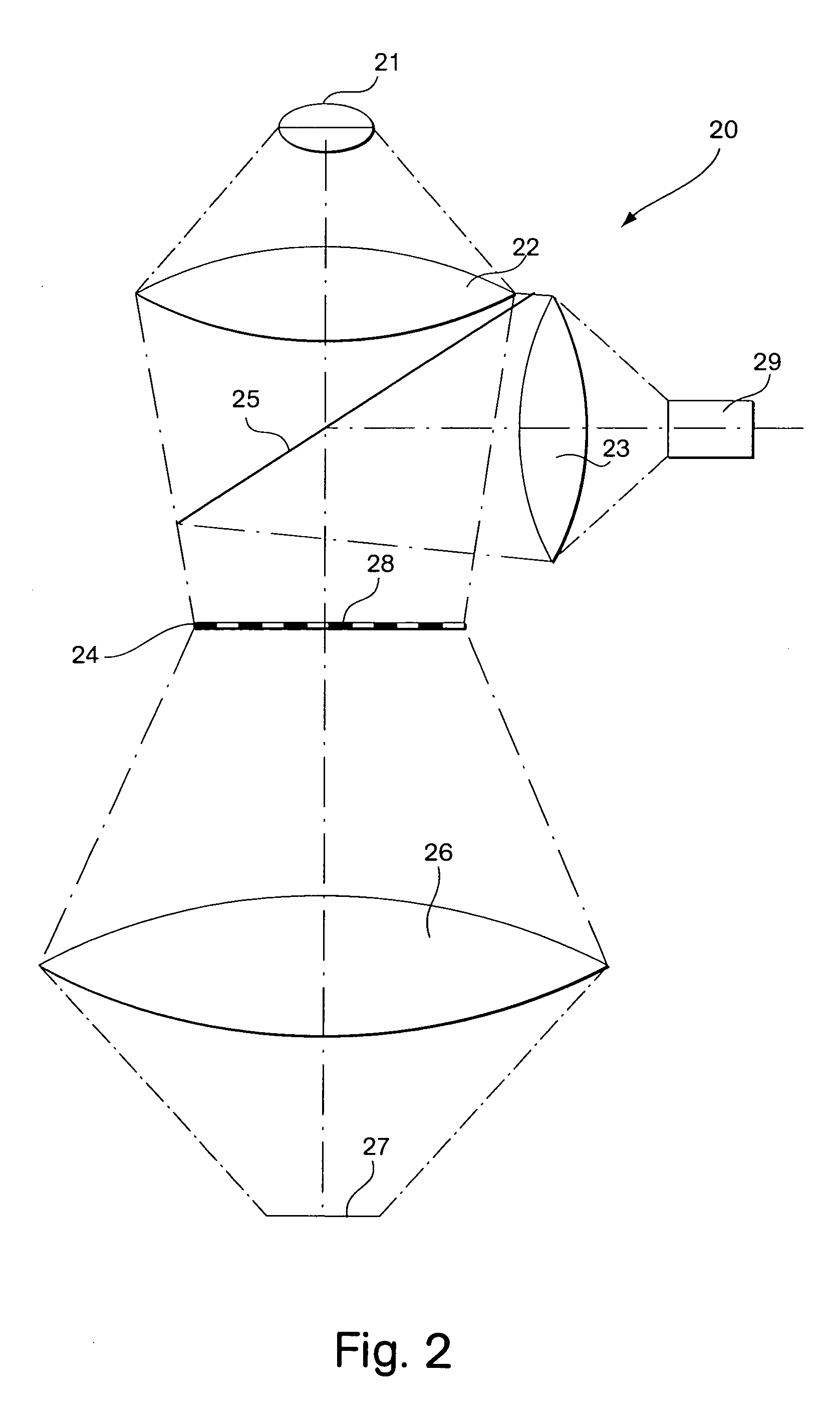
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining a characteristic of a sample of a material by the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with the sample. The apparatus includes a source of electromagnetic radiation, an optical assembly and a detector. The optical assembly sequentially illuminates a plurality of volume elements in the sample with an intensity distribution in the sample that drops off substantially monotonically from a first region in a first optical path and collects electromagnetic radiation emanating from each of the volume elements. The optical assembly collects the electromagnetic radiation emanating from each of the volume elements with a collected distribution that drops off substantially monotonically from a second region in a second optical path. The first and second regions at least partially overlap in each of the volume elements. The detector detects the collected electromagnetic radiation emanating from each of the sequentially illuminated volume elements to produce responses representative of the characteristic in each of the volume elements.
Owner:MEDISPECTRA
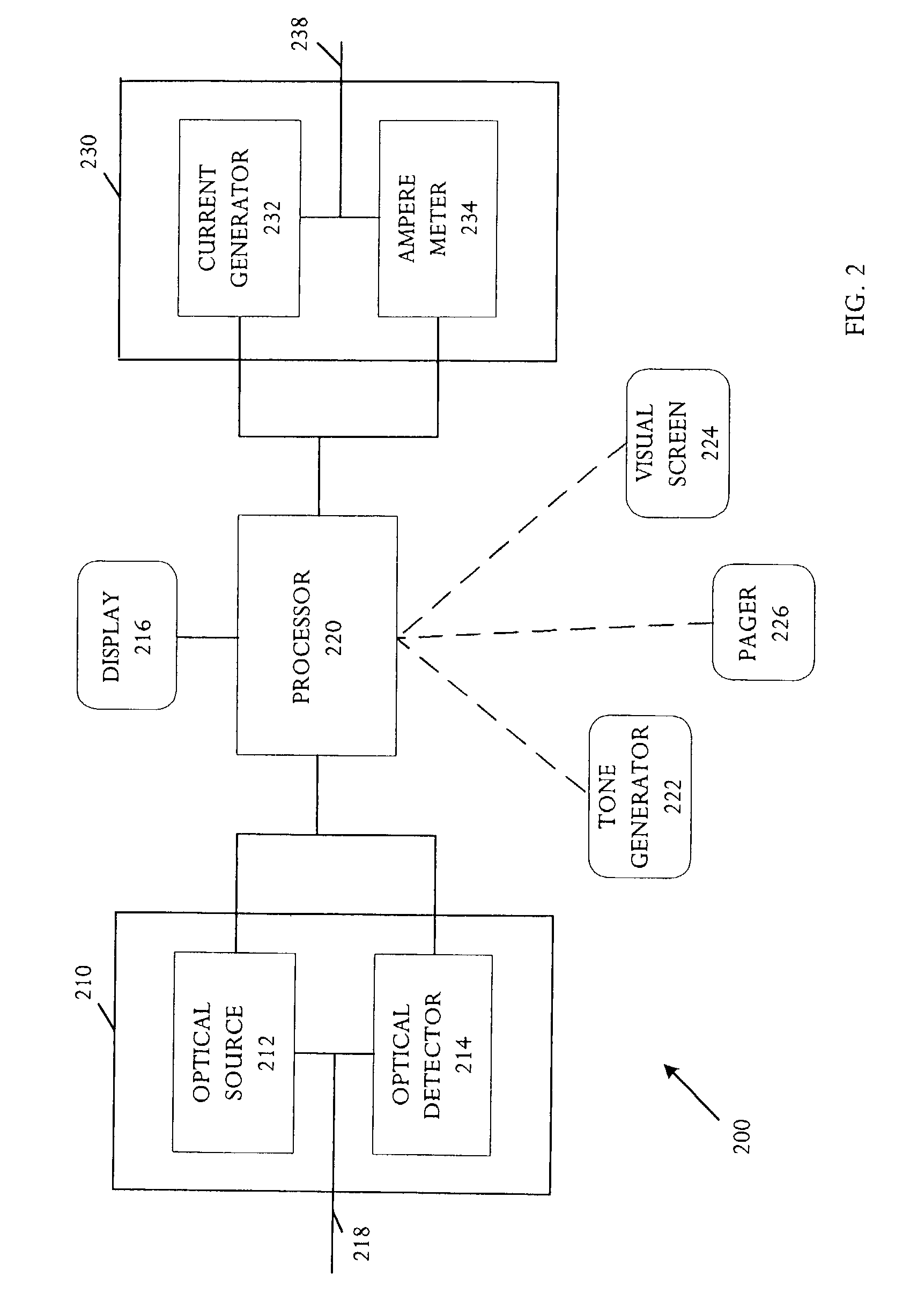
System and methods of fluorescence, reflectance and light scattering spectroscopy for measuring tissue characteristics
InactiveUS6912412B2High sensitivityImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightSurgeryDiseaseFluorescence
The present invention utilizes a plurality of spectroscopic systems and methods to measure characteristics of tissue useful in the diagnosis of disease. In a preferred embodiment, a combination of fluorescence, reflectance and light scattered spectra can be measured and processed to provide biochemical, architectural and morphological state of tissue. The methods and systems can be used particularly in the early detection of carcinoma within tissue in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
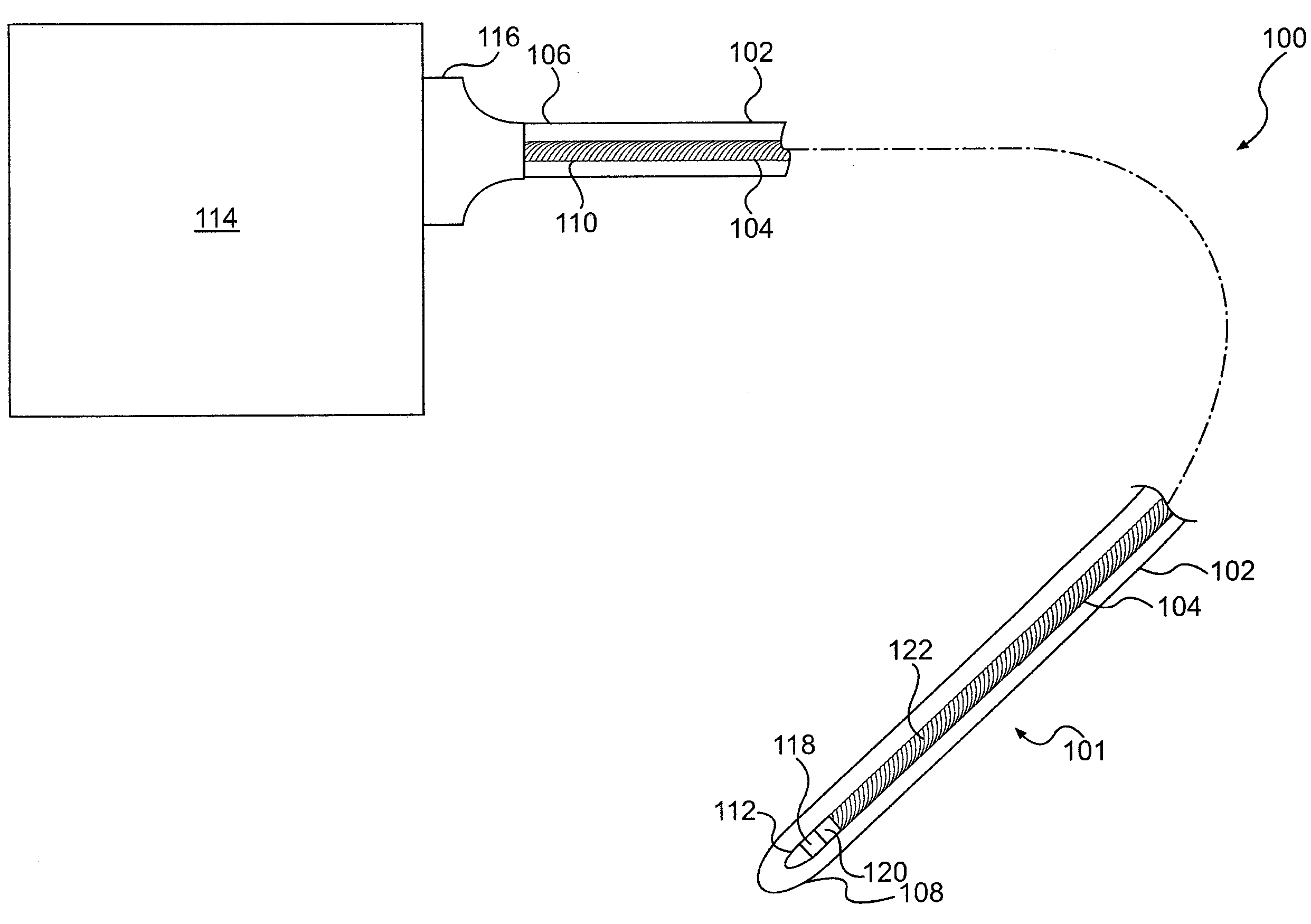
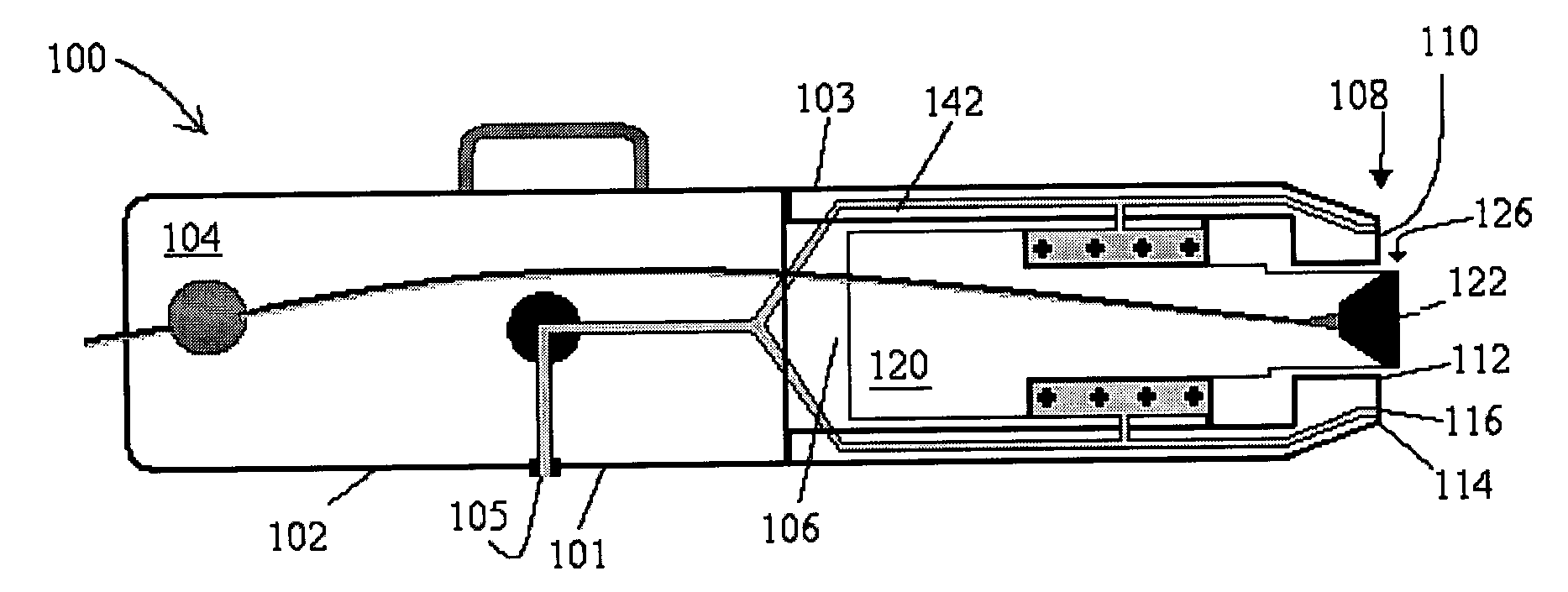
Device for forming an effective sensor-to-tissue contact
ActiveUS20070032739A1Effective contactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringTissue characterization
A device and method for tissue characterization are provided, the device comprising: a structure; a first mechanism, associated with said structure, configured for exerting a first force on a tissue, for fixing the tissue to said structure, so as to substantially immobilize the tissue; and a second mechanism, associated with said structure, configured for pressing a sensor against an external surface of the immobilized tissue, thereby exerting a second force on the immobilized tissue, wherein at least a component of said first force is in opposition to at least a component of said second force, forcing the immobilized tissue against said sensor, and forcing said sensor against the immobilized tissue, bringing about an effective contact between said sensor and the immobilized tissue.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
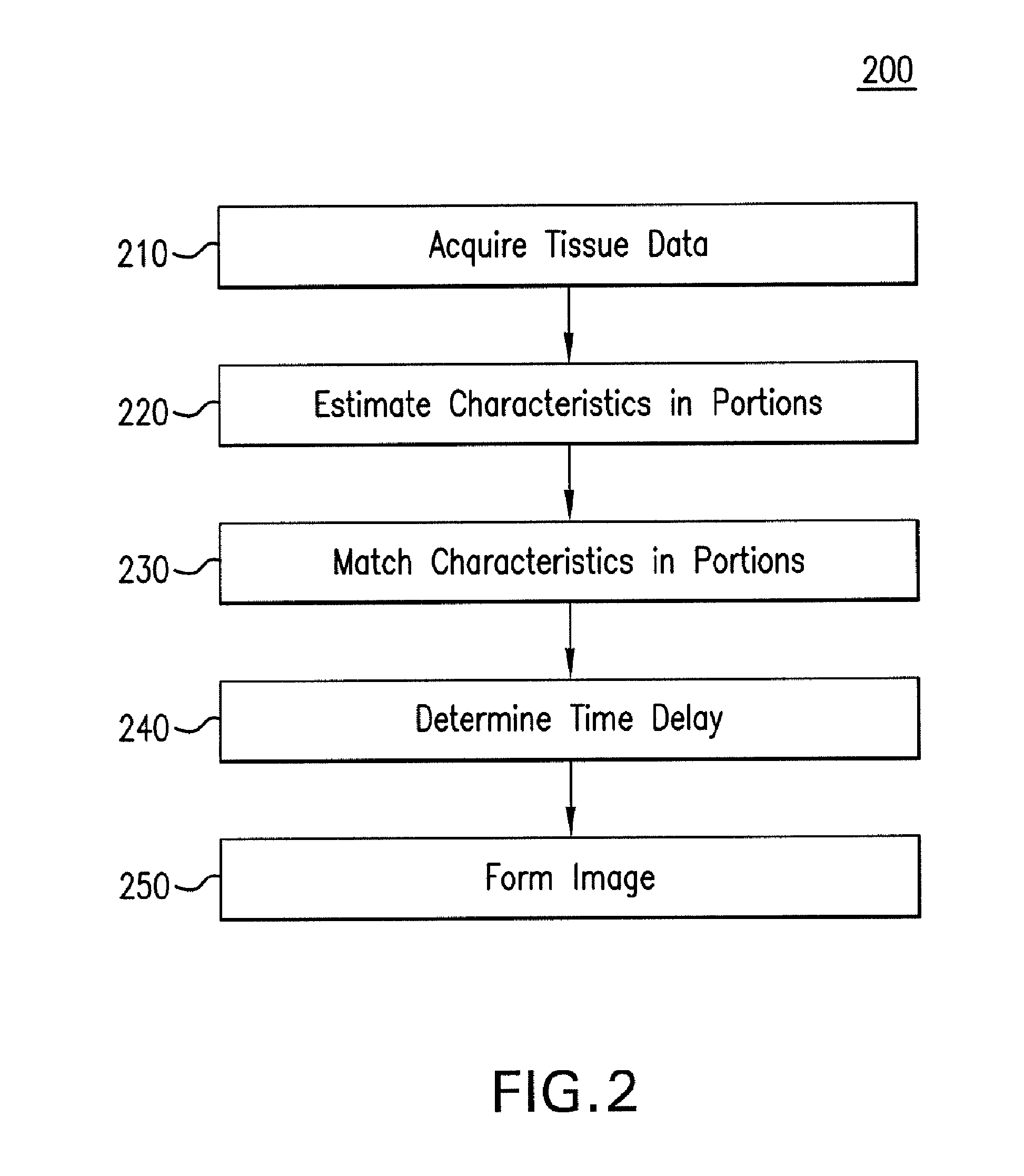
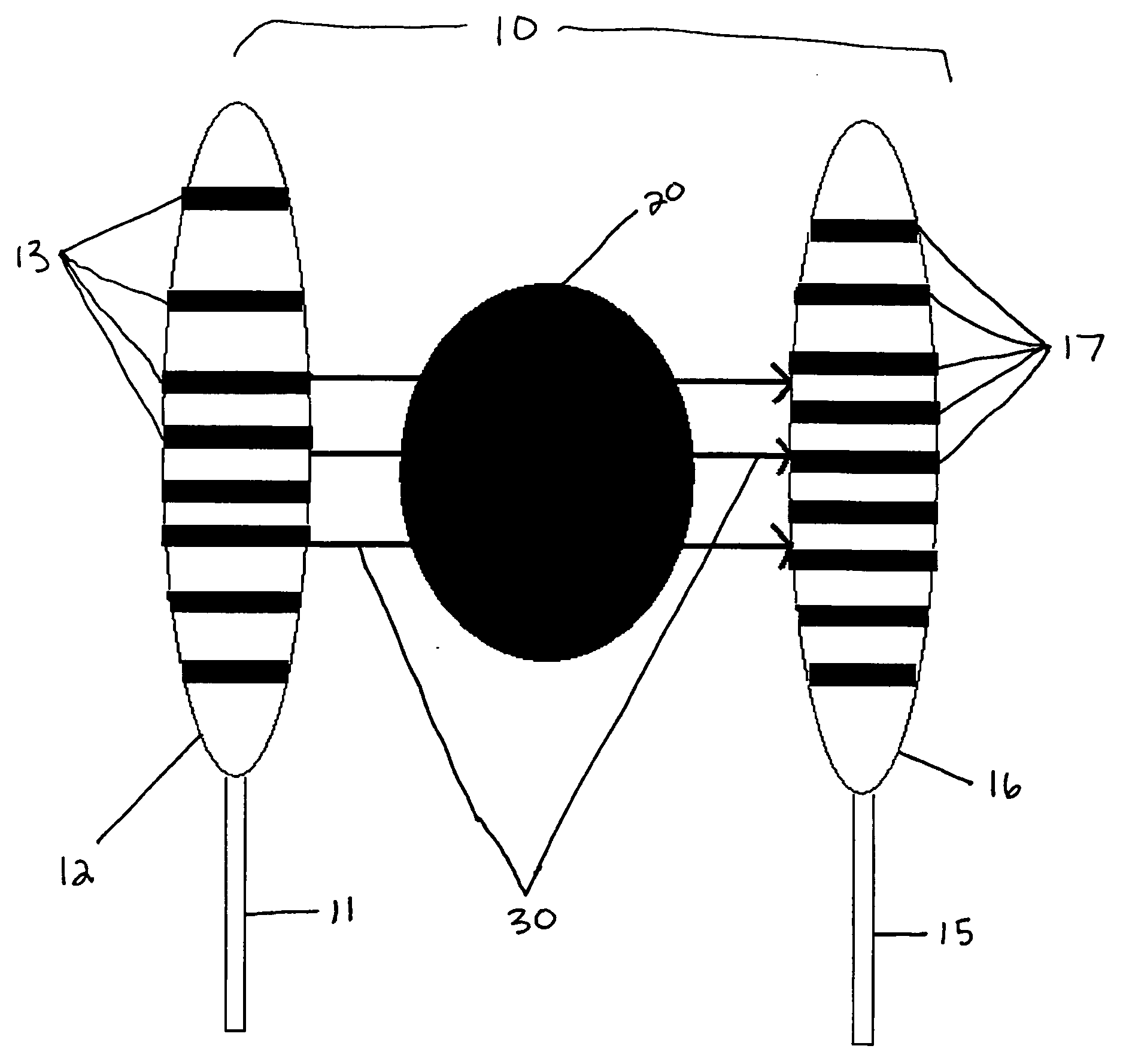
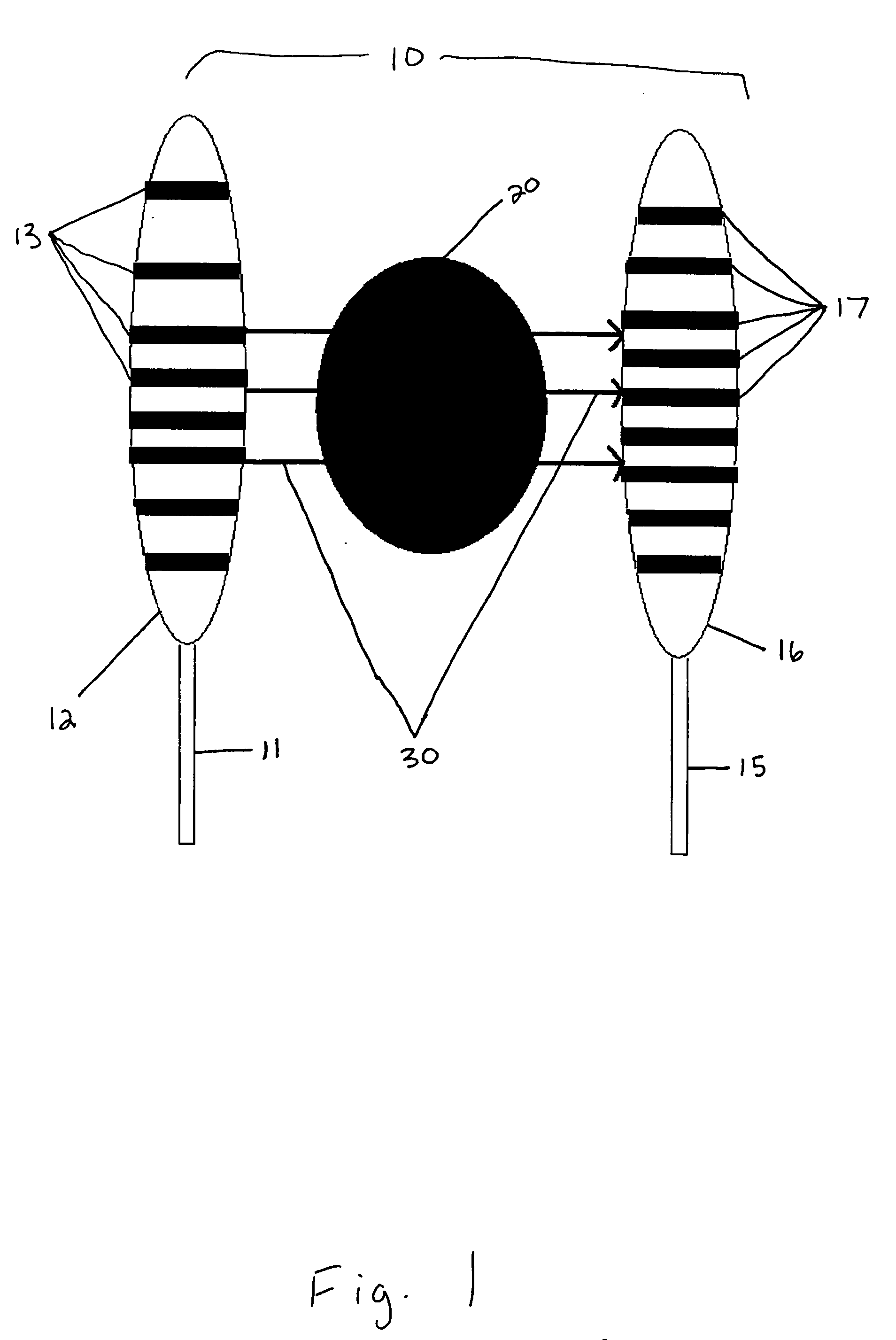
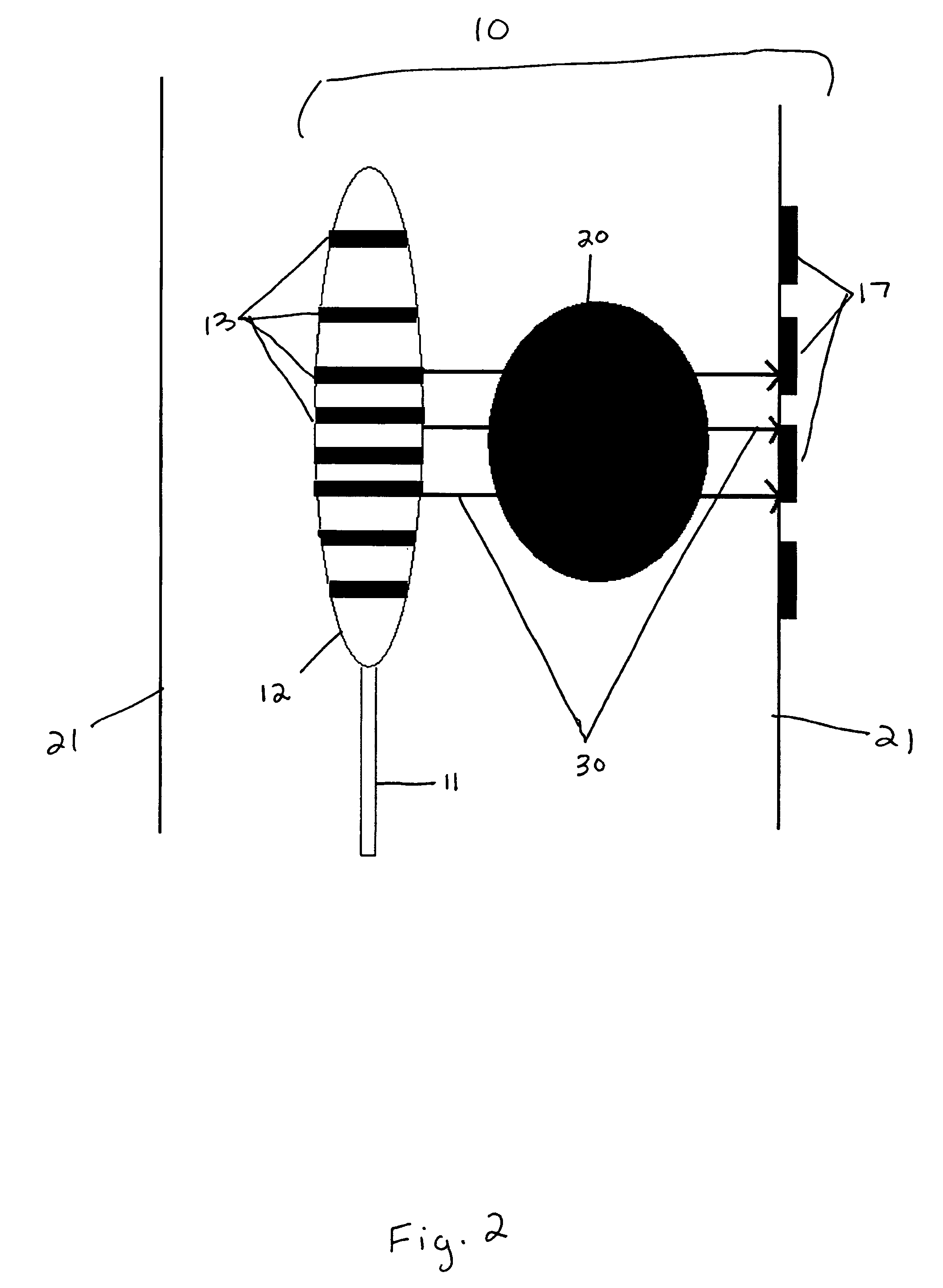
Systems And Methods For Matching And Imaging Tissue Characteristics
Systems and methods for matching a characteristic of multiple sectors of a moving tissue to verify an overlap thereof are disclosed herein. In an exemplary method, tissue data for at least a first sector and a second sector of a moving tissue is acquired. A characteristic of at least a portion of the first and second sectors is estimated from the acquired tissue data, and the estimated characteristics are matched to verify whether a portion of the first sector overlaps with a portion of the second sector. Estimating can include estimating a displacement such as an axial displacement and / or lateral displacements. Estimating can further include estimating a strain, a velocity, a strain rate and / or a stiffness or equivalent.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Clinical application of electrical impedance tomography to characterize tissue
InactiveUS20060004301A1CatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical impedance tomography
The present invention is a system for use in creating images of portions of human tissue inside the body by electrical impedance tomography. The system may comprise at least one flexible tube for insertion in the body in proximity to a targeted portion of human tissue in the body, an inflatable balloon removably attached to the distal end of the flexible tube, a first array of electrodes attached to the surface of the inflatable balloon for at least one of injecting current into the targeted portion of human tissue and receiving current that was injected into the targeted portion of human tissue, and a second array of electrodes for at least one of injecting current into the targeted portion of human tissue to the first array of electrodes and for receiving current from the first array of electrodes.
Owner:KSN ENERGIES
Real-time optoacoustic monitoring with electophysiologic catheters
InactiveUS20080154257A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionCatheterSurgical instrument detailsRf ablationLesion progression
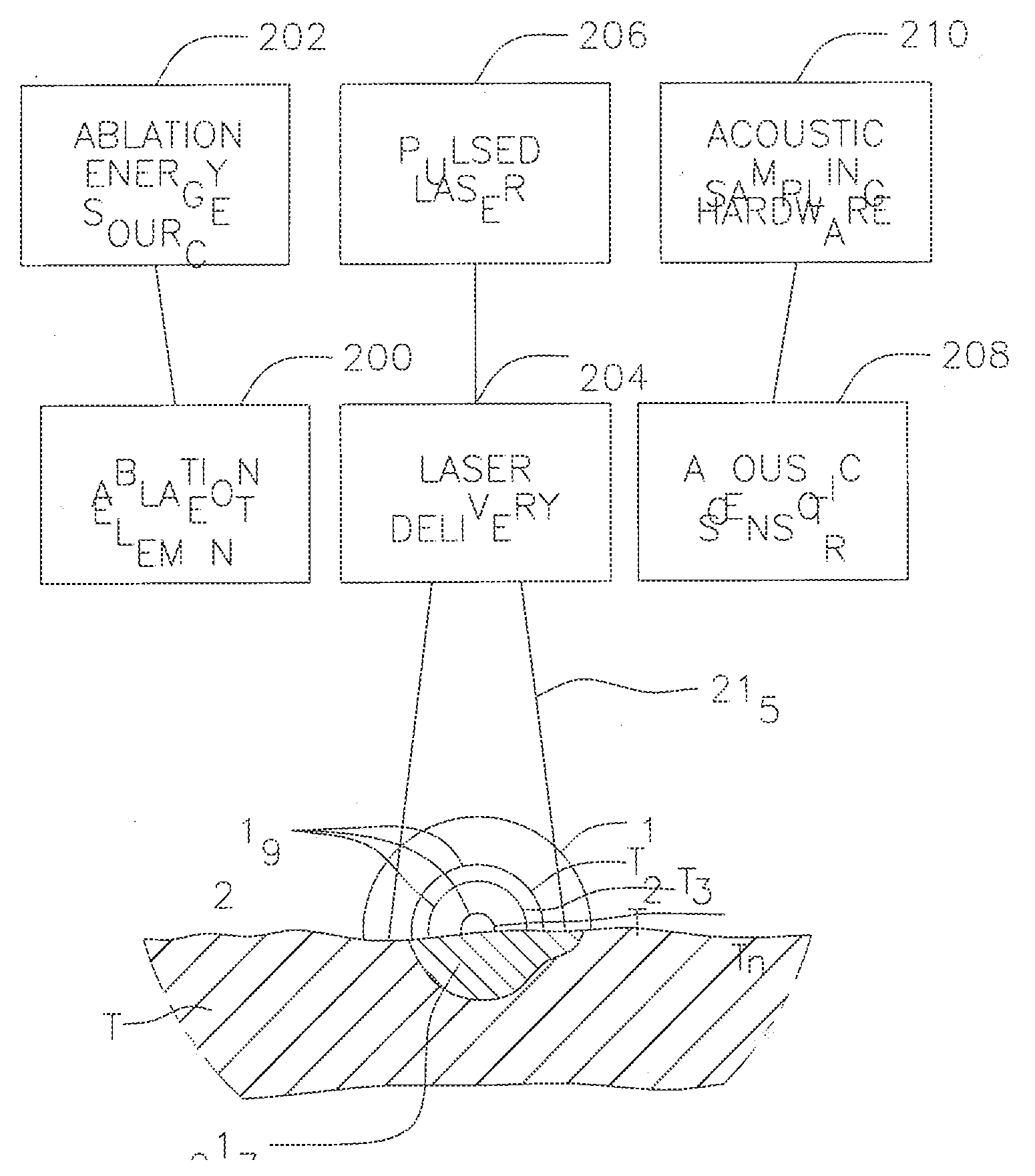
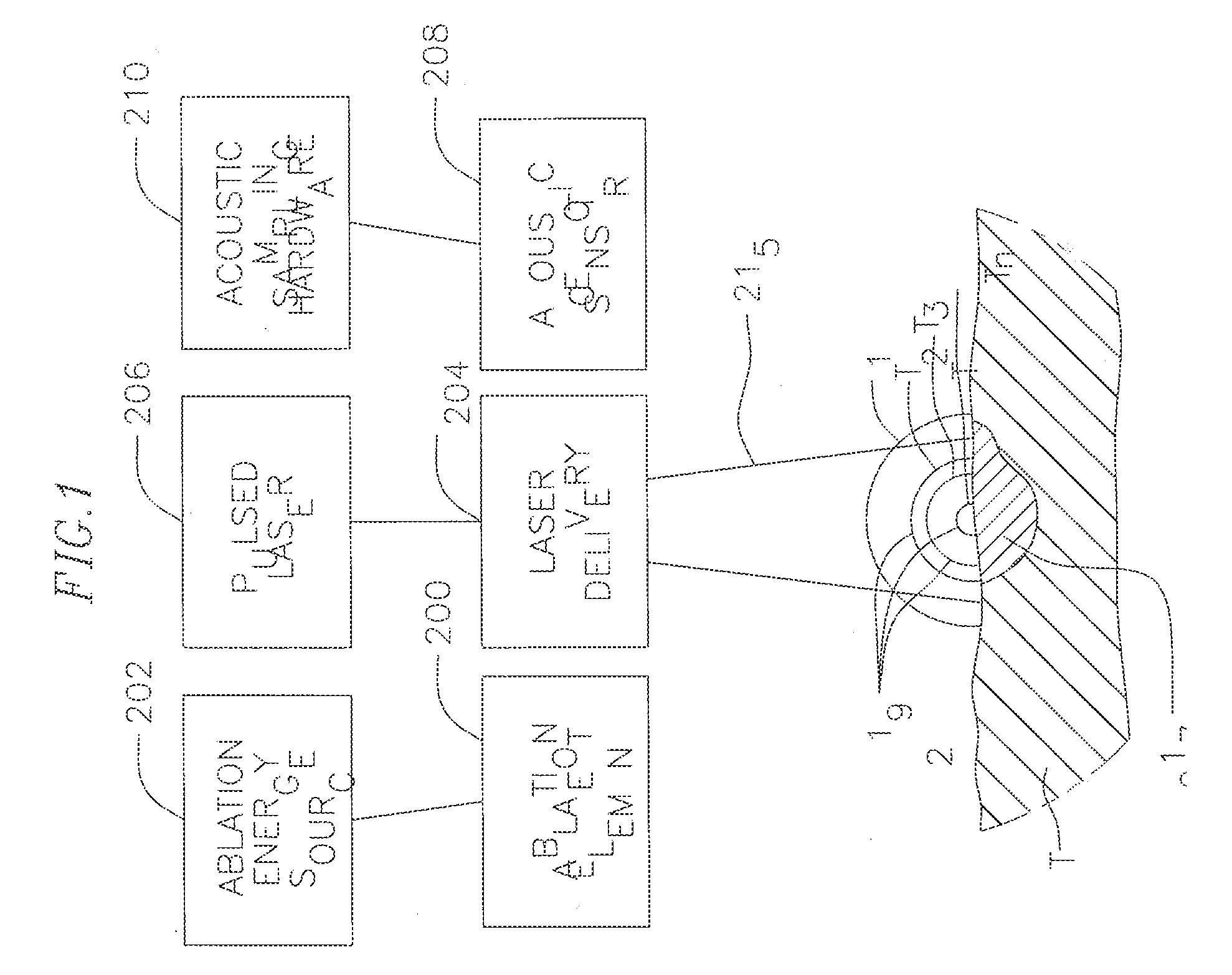
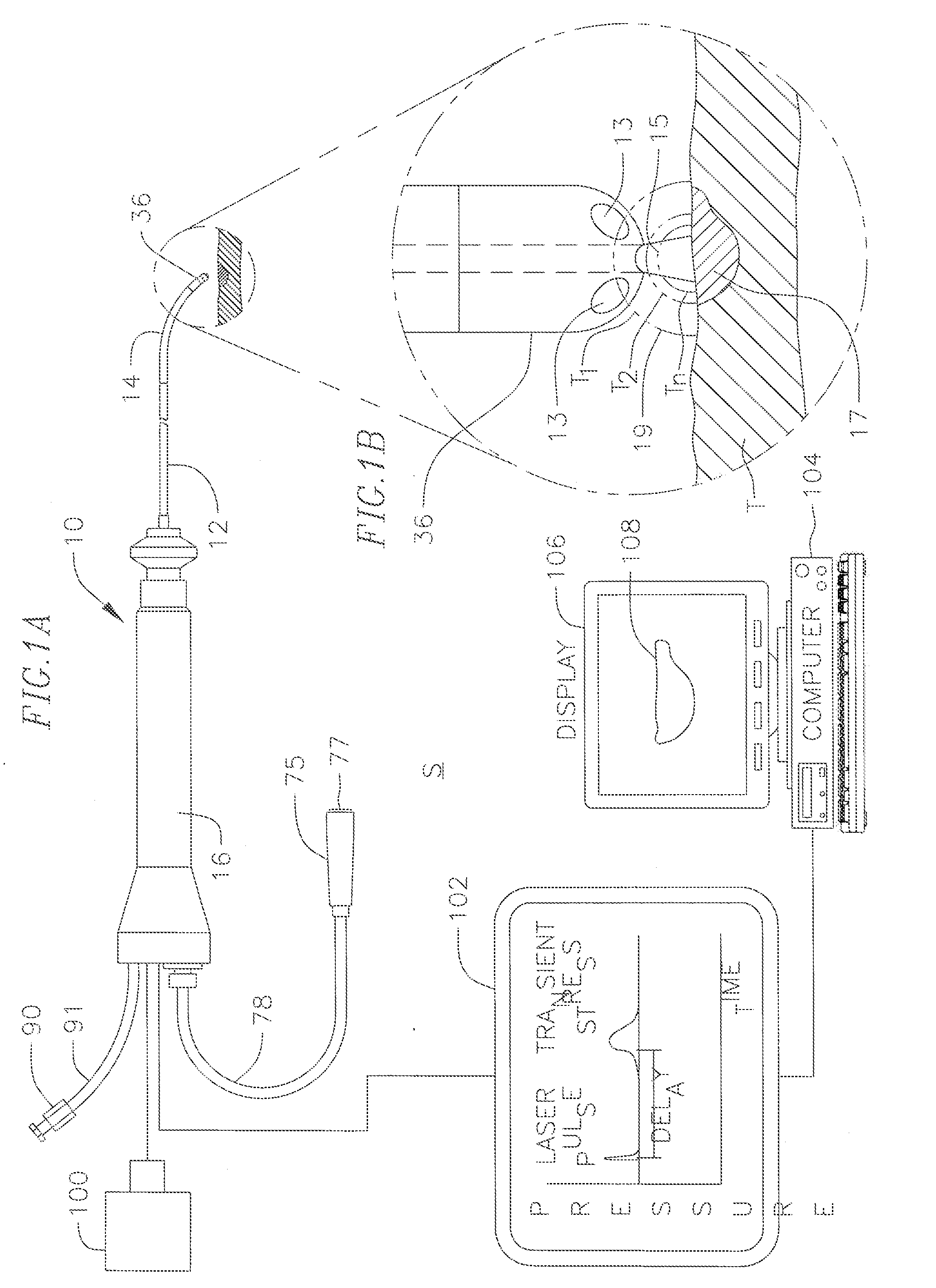
A system and method for opto-acoustic tissue and lesion assessment in real time on one or more of the following tissue characteristics: tissue thickness, lesion progression, lesion width, steam pop, and char formation, system includes an ablation element, laser delivery means, and an acoustic sensor. The invention involves irradiating tissue undergoing ablation treatment to create acoustic waves that have a temporal profile which can be recorded and analyzed by acoustic sampling hardware for reconstructing a cross-sectional aspect of the irradiated tissue. The ablation element (e.g., RF ablation), laser delivery means and acoustic sensor are configured to interact with a tissue surface from a common orientation; that is, these components are each generally facing the tissue surface such that the direction of irradiation and the direction of acoustic detection are generally opposite to each other, where the stress waves induced by the laser-induced heating of the tissue below the surface are reflected back to the tissue surface.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Method using three-dimensional mechanics and tissue specific imaging of blood vessels and plaques for detection
InactiveCN104398271ARealize three-dimensional mechanical property detectionRealize simultaneous measurementOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsVulnerable plaqueShear rate
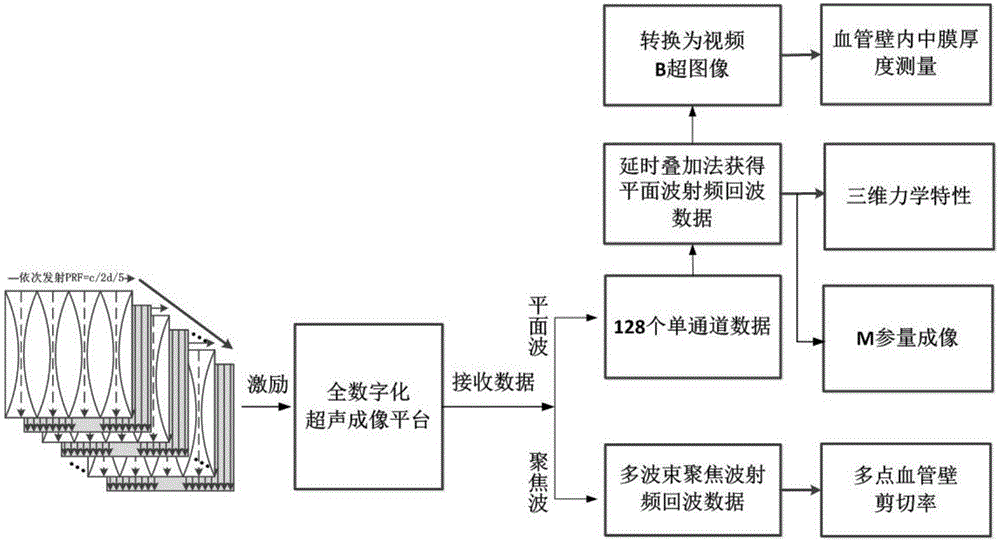
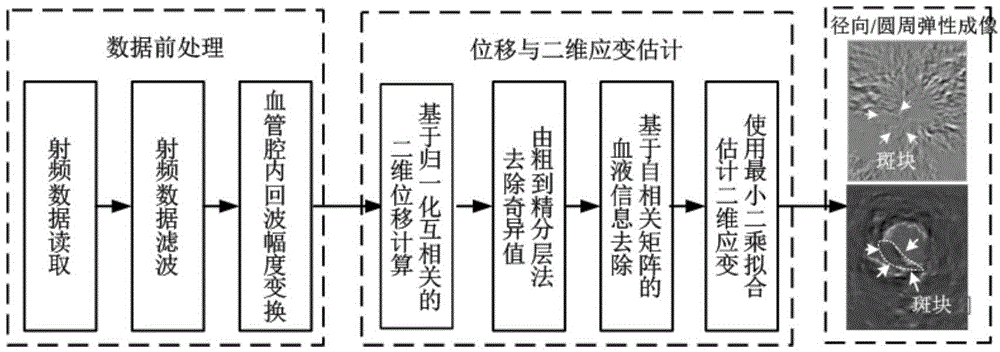
The invention relates to a method using three-dimensional mechanics characteristics and tissue specific imaging of blood vessels and plaques for detection. The method is on the basis of a multi-beam focus wave and superfast plane wave alternative transmitting sequence and can also be extended to a line-by-line scan imaging manner; the forms and the functions of the blood vessels and the plaques are evaluated and imaged respectively from the aspects of the radial-direction, circumferential and axial-direction three-dimensional mechanics characteristics, blood vessel wall shear rate, plaque form and tissue characterization, and the like; the new method which is provided for detection of the vulnerable plaques of a carotid artery is regarded as the improvement of the existing method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
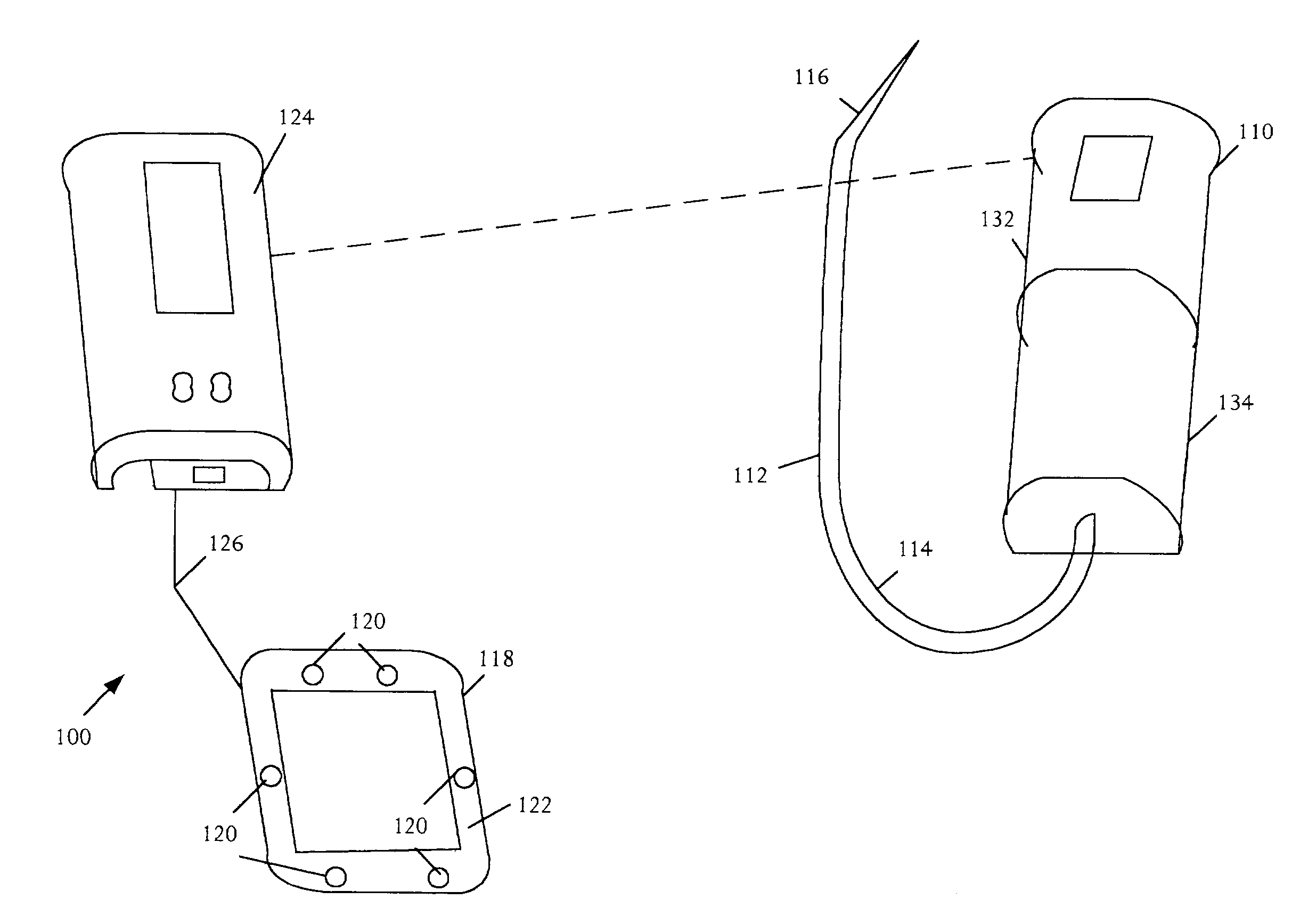
Probes, systems, and methods for examining tissue according to the dielectric properties thereof
InactiveUS20080021343A1Enhance the localized electrical fringe fieldsPerson identificationVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectrical conductorTissue characterization
The present invention relates to probes, systems, and methods for tissue characterization by its dielectric properties, wherein a physical feature of the probe is designed to define and delimit a tissue volume, at a tissue edge, where characterization takes place. Thus, the probe for tissue-edge characterization comprises: a first inner conductor, which comprises: proximal and distal ends, with respect to a tissue edge, along an x-axis; a first sharp edge, inherently associated with the proximal end; at least one feature, issuing from the first inner conductor, substantially at the proximal end, for forming at least one additional sharp edge, operative to enhance localized electrical fringe fields in the tissue, within a generally predefined tissue volume, at the tissue edge, the tissue volume being generally defined by physical parameters associated with the at least one feature; and a dielectric material, which encloses the conductor, in the y-z planes.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com