Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
152 results about "Tissue impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
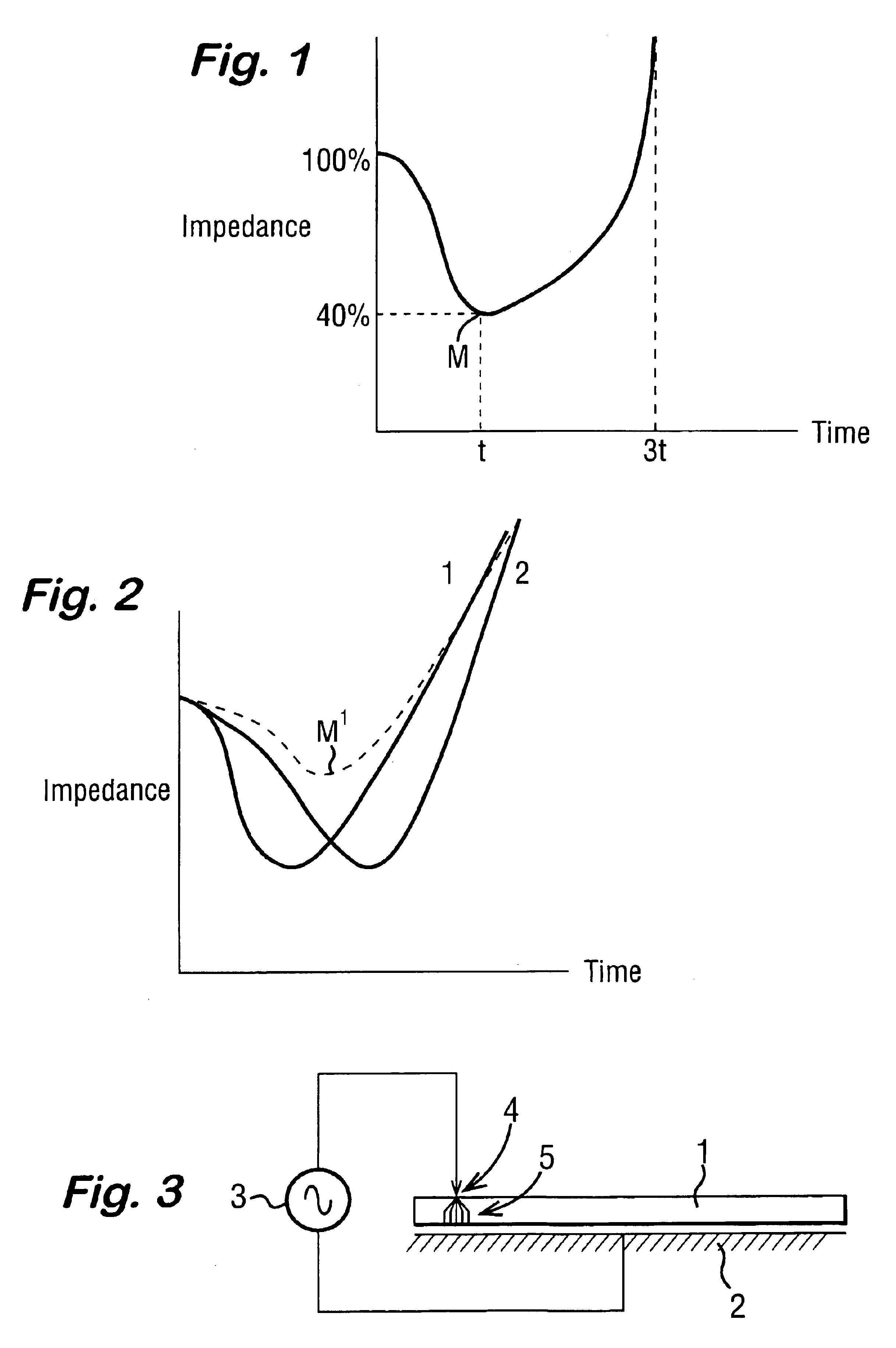
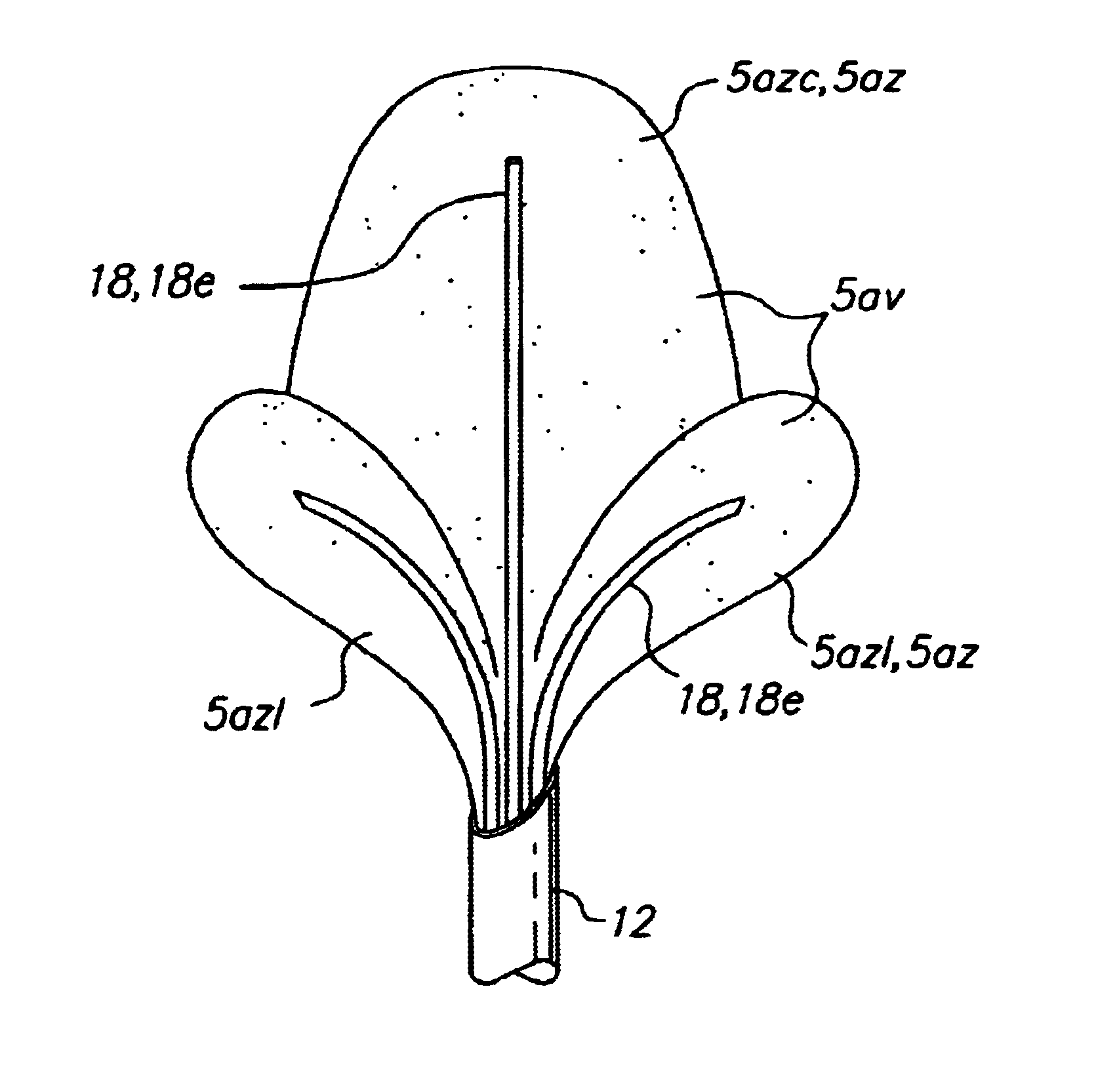
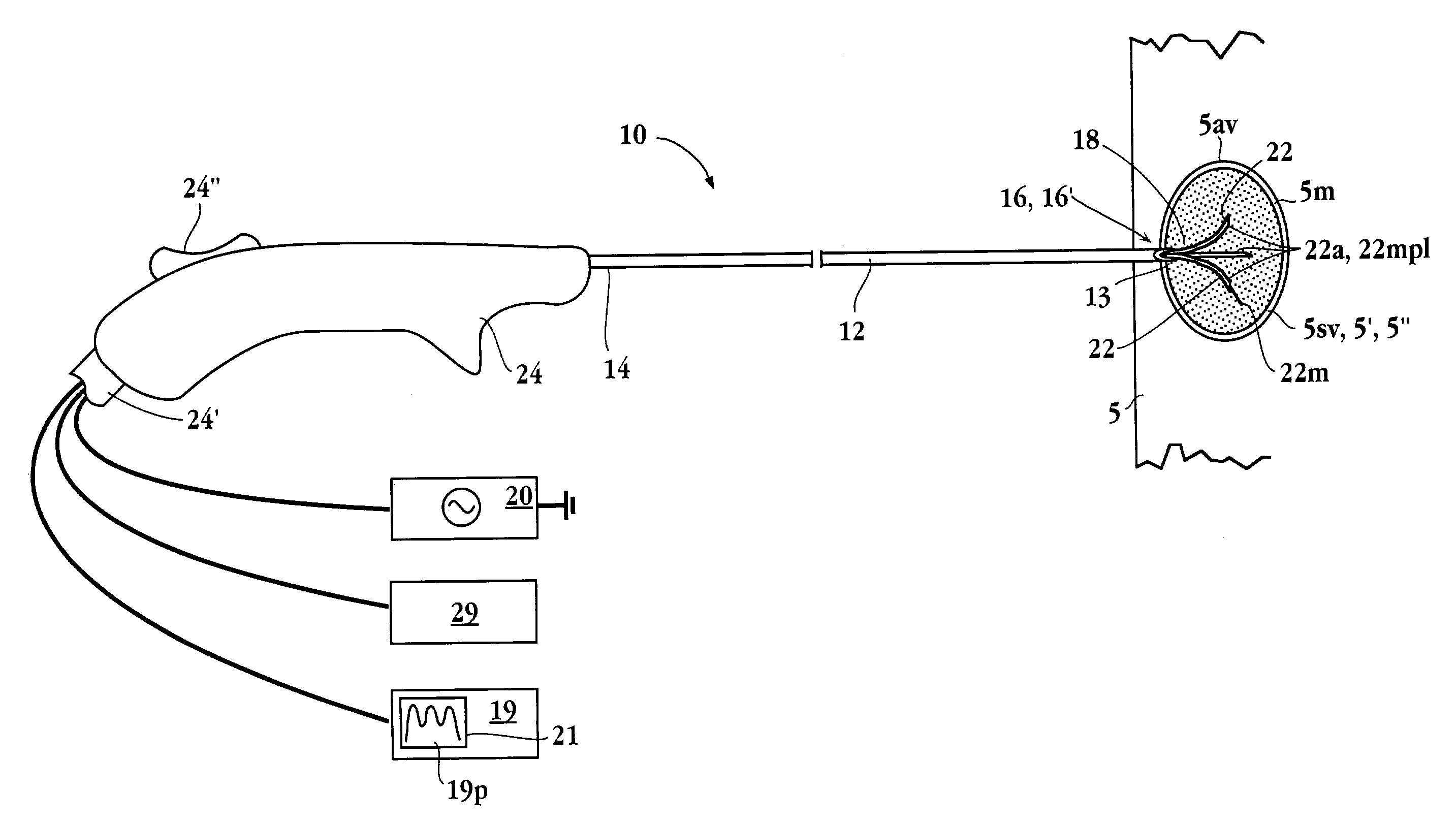
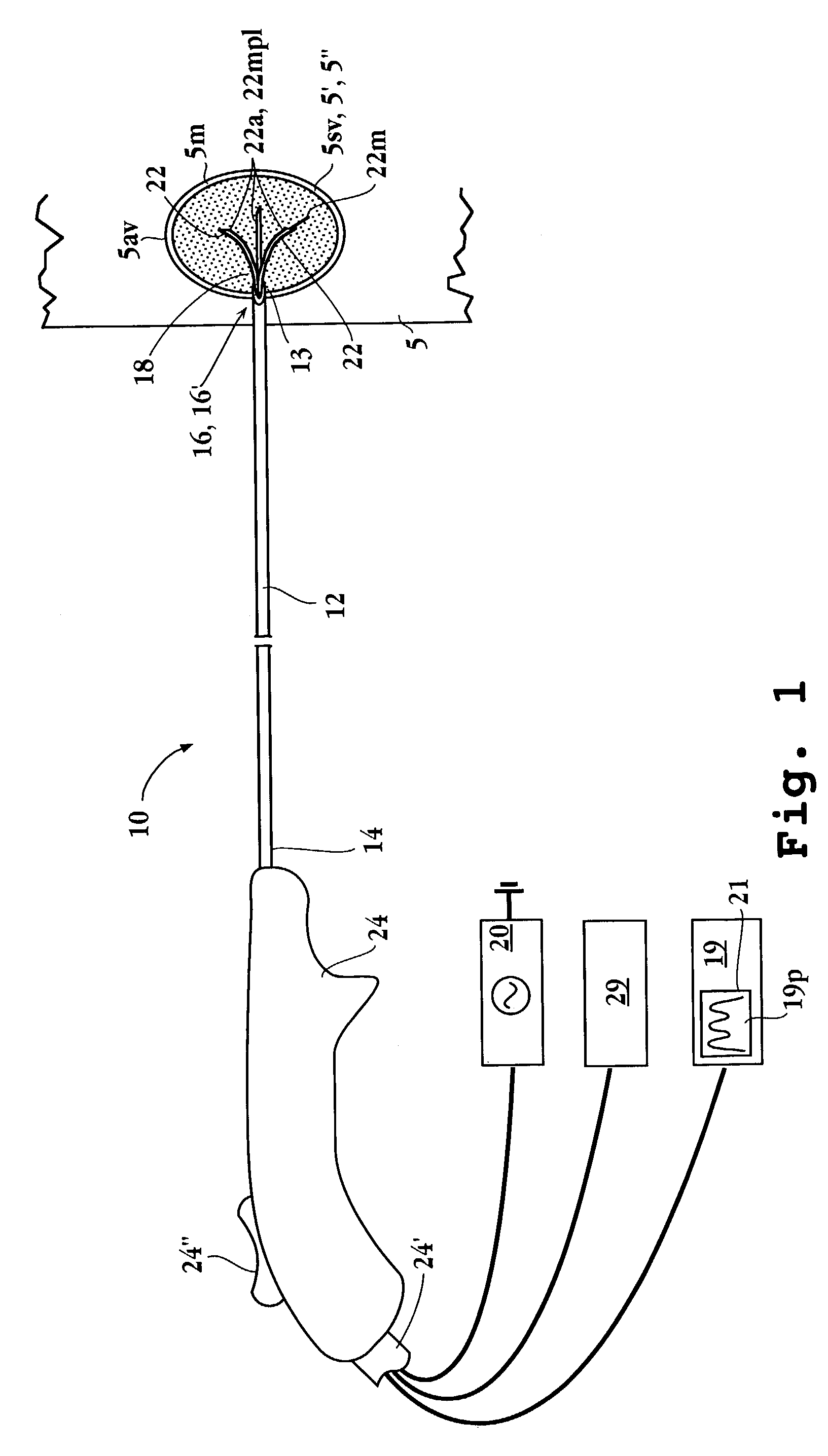
Electrical impedance is a measurement of how electricity travels though a given material. Every tissue has different electrical impedance determined by its molecular composition. Some materials have high electrical impedance while others have low electrical impedance.
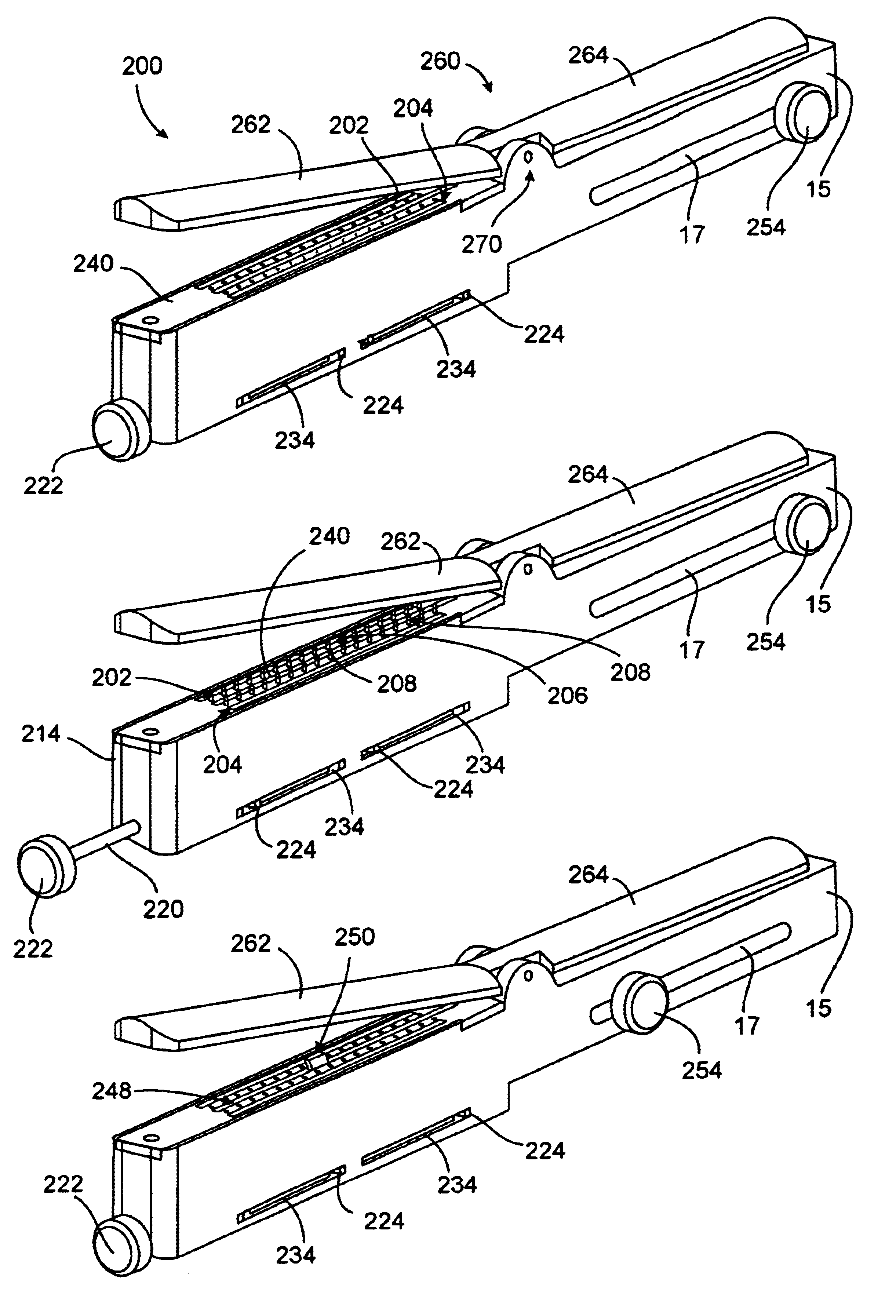
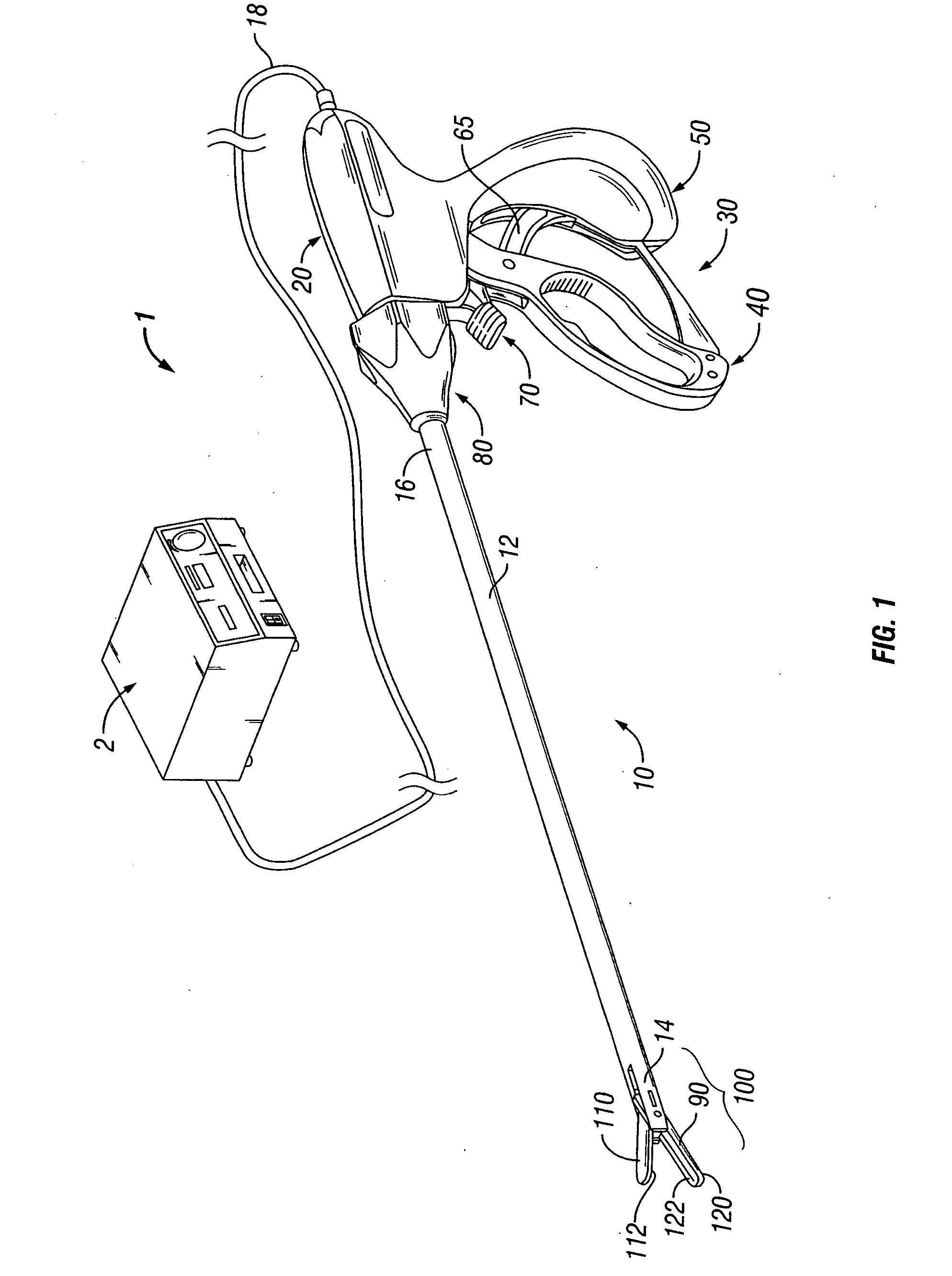
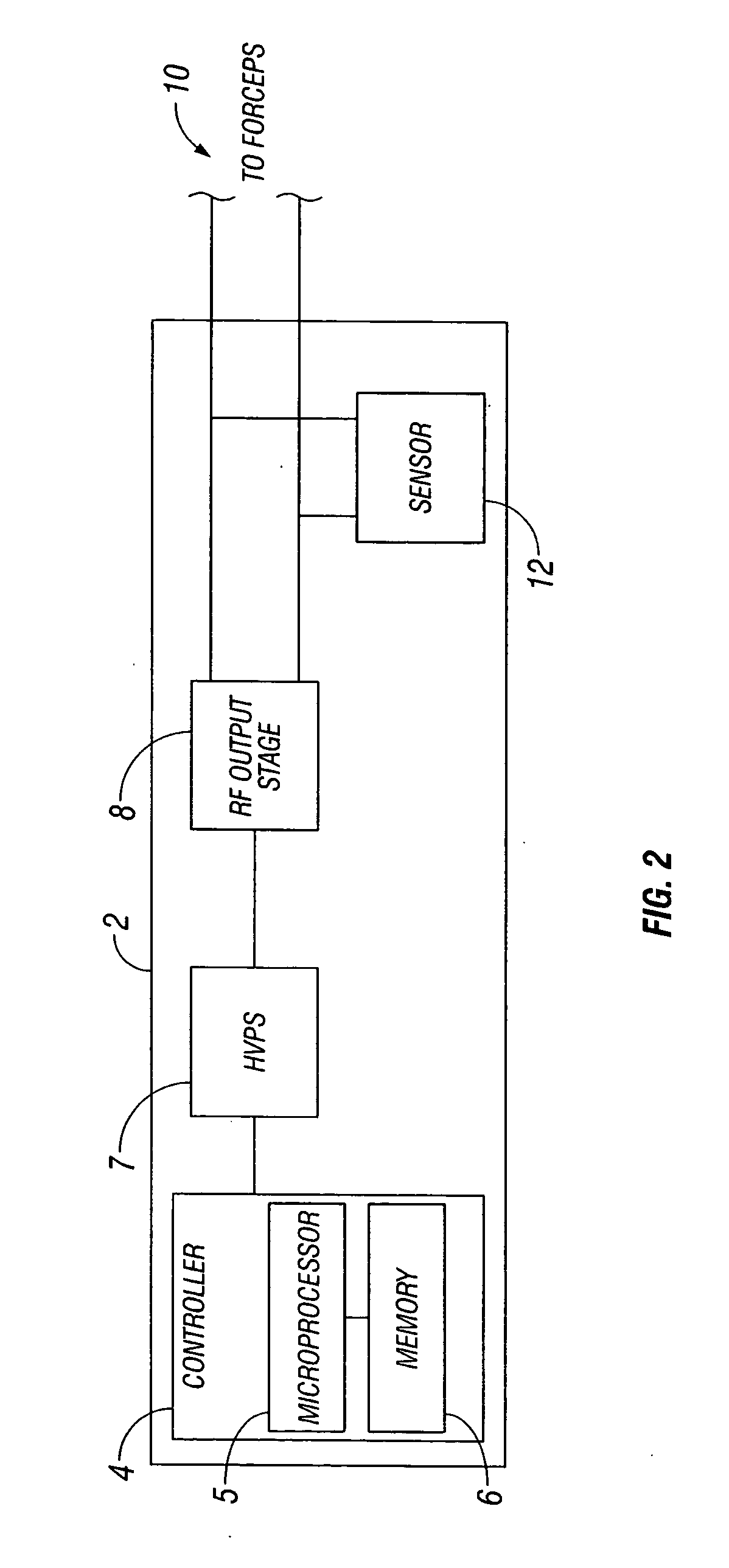
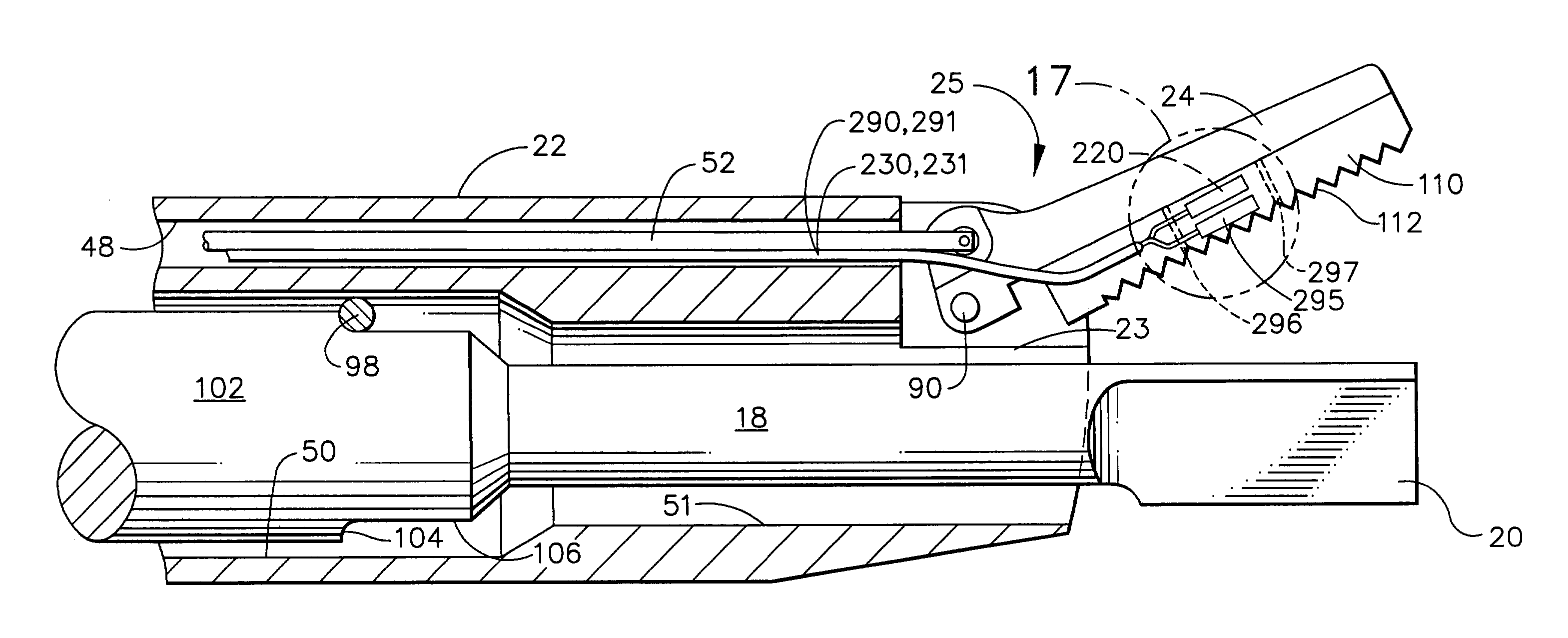
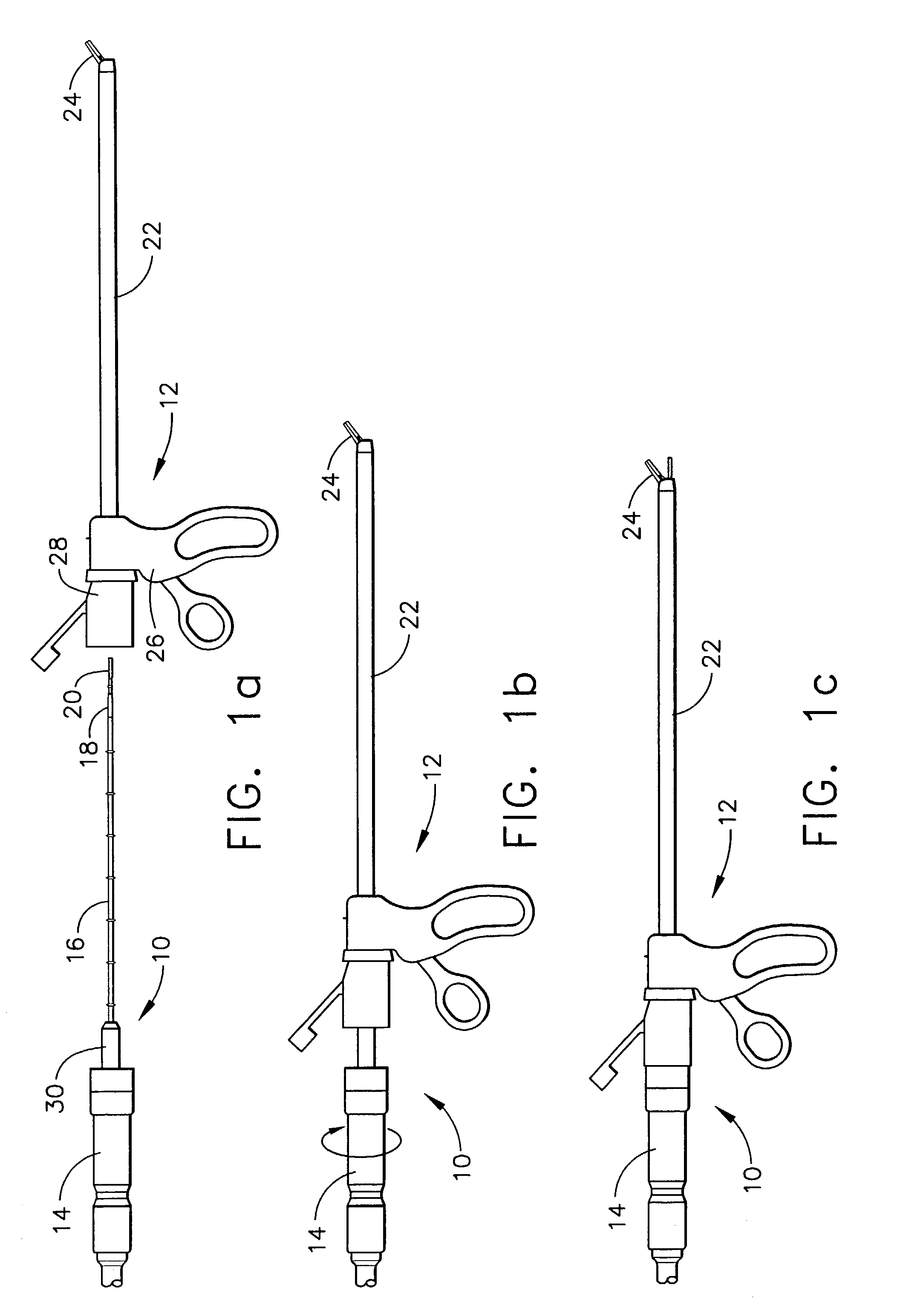
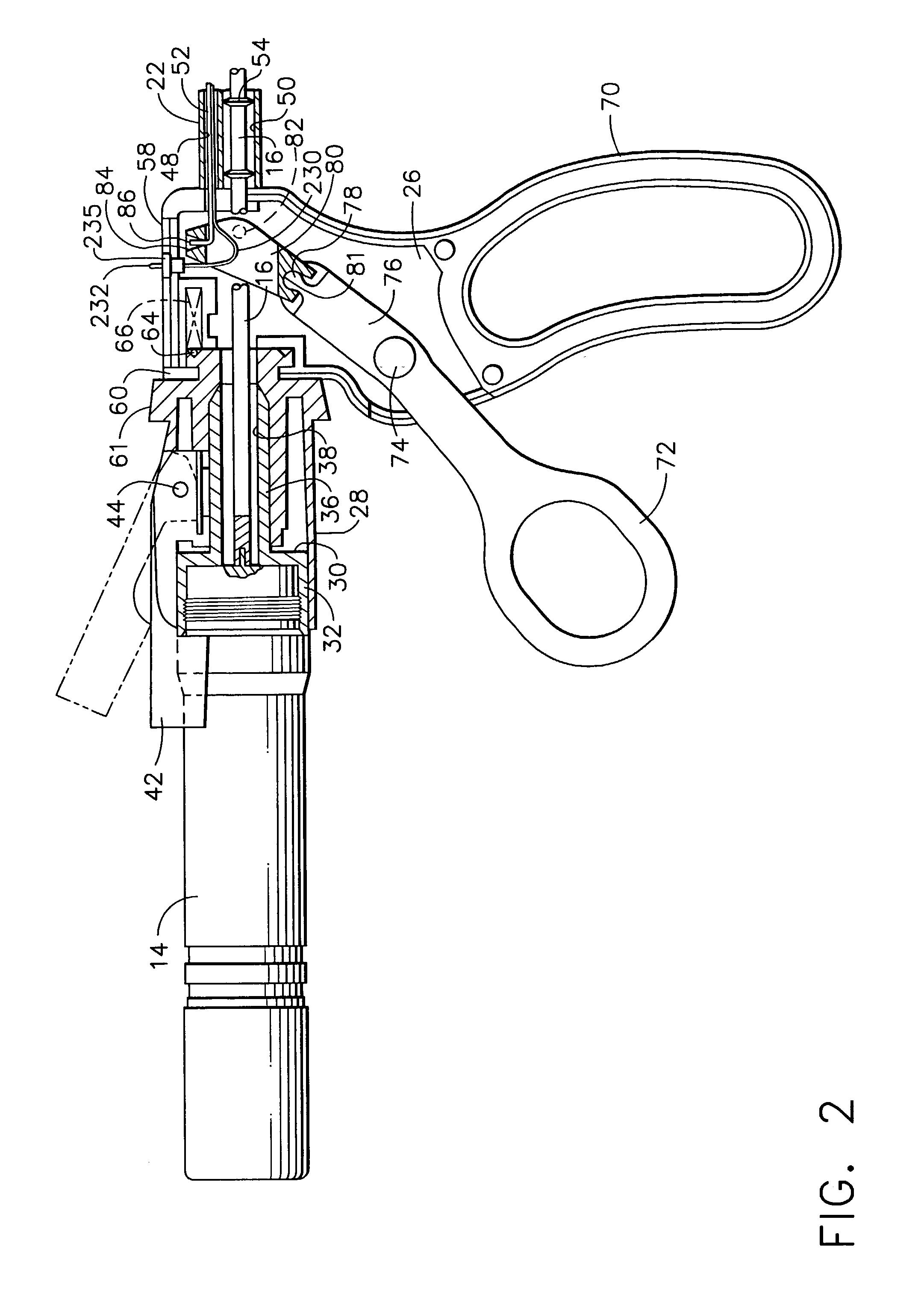
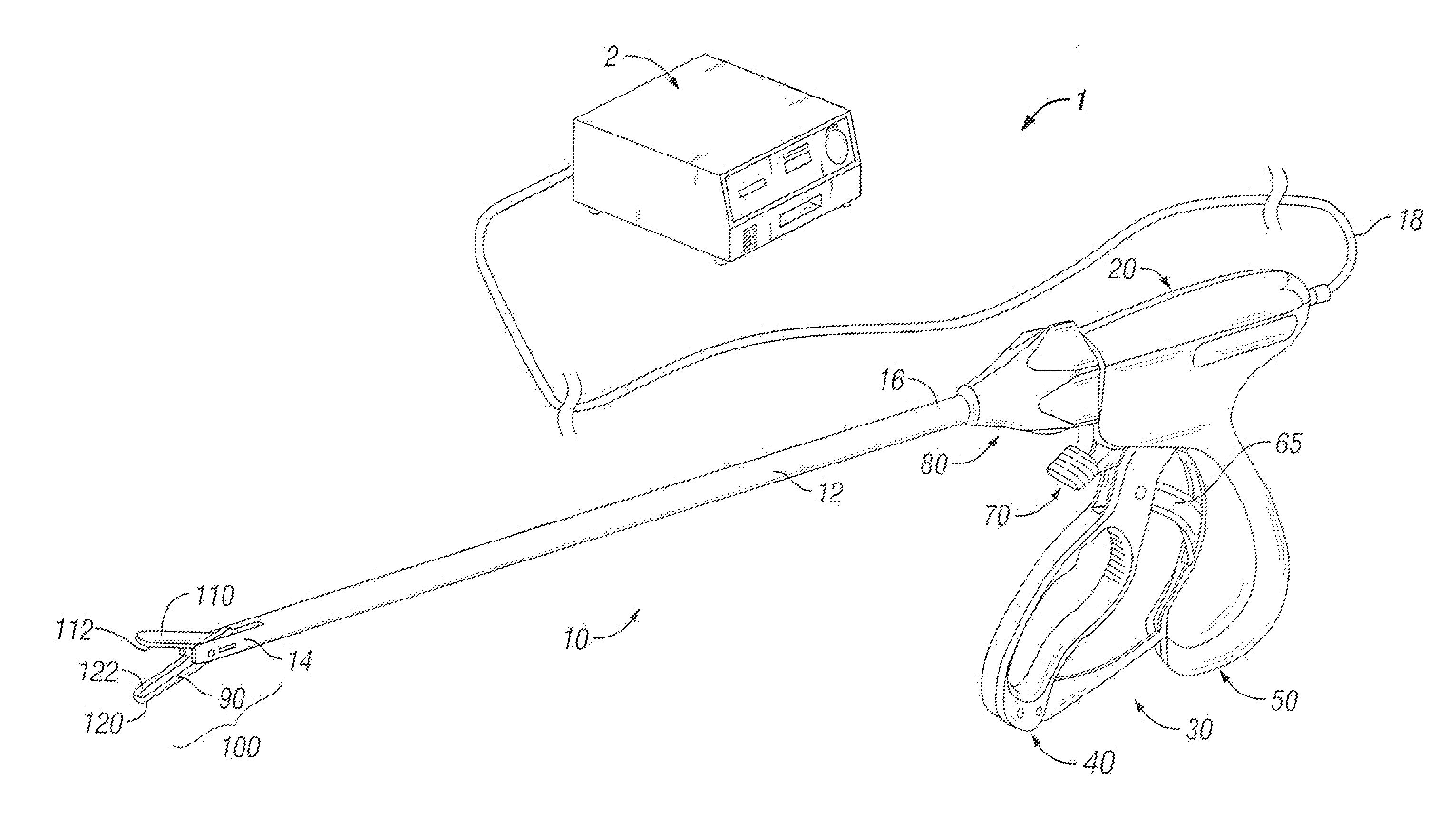
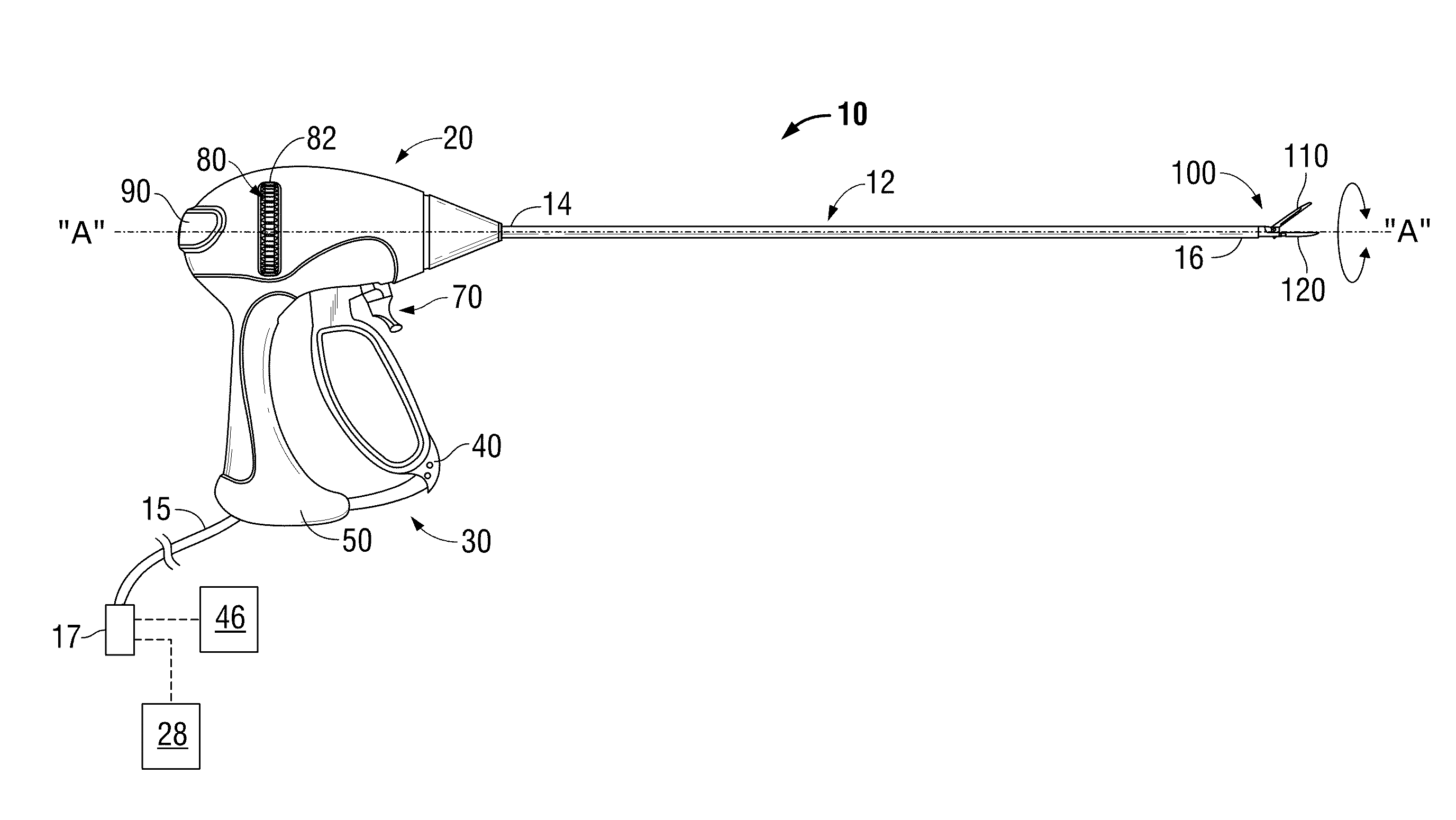
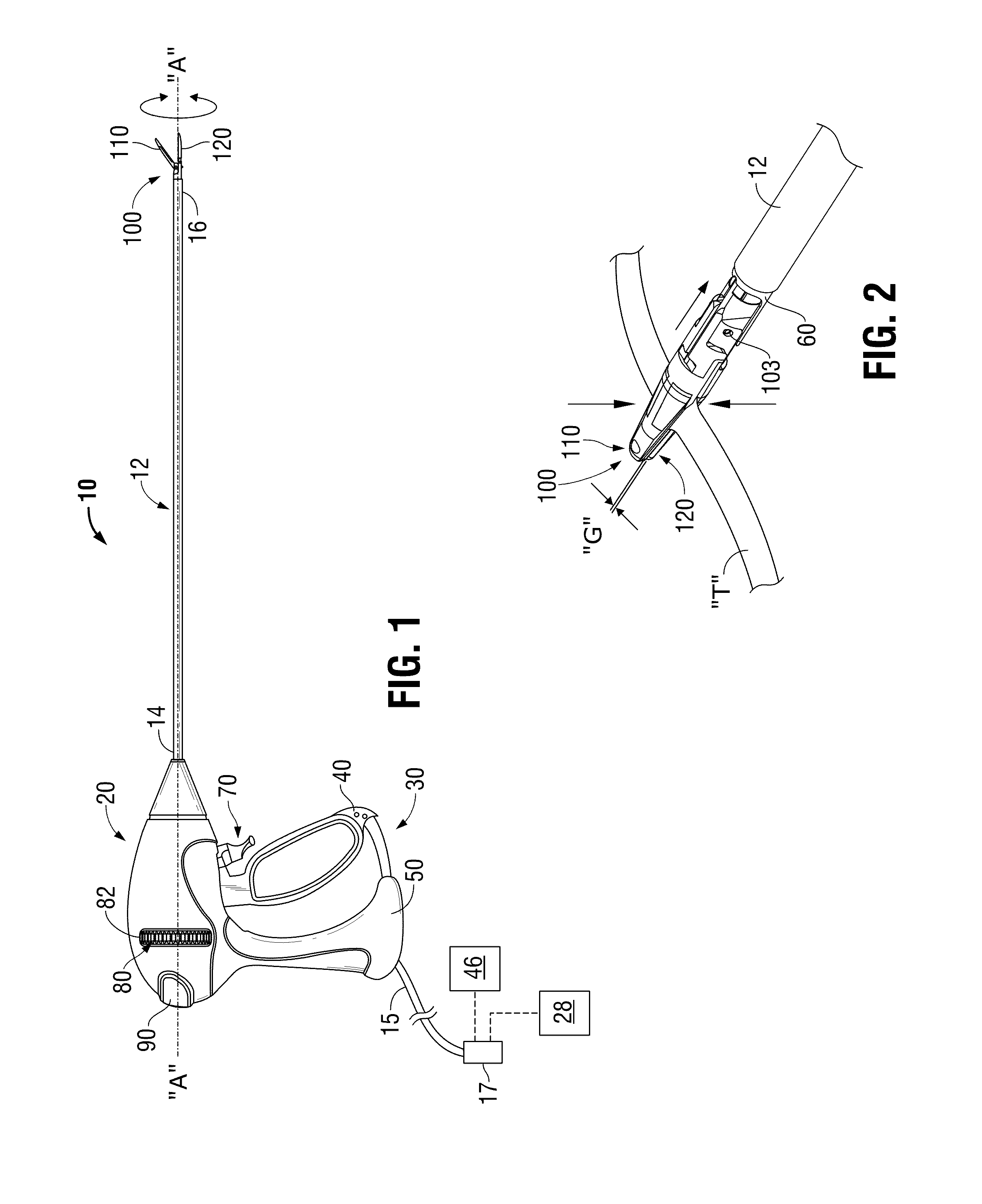
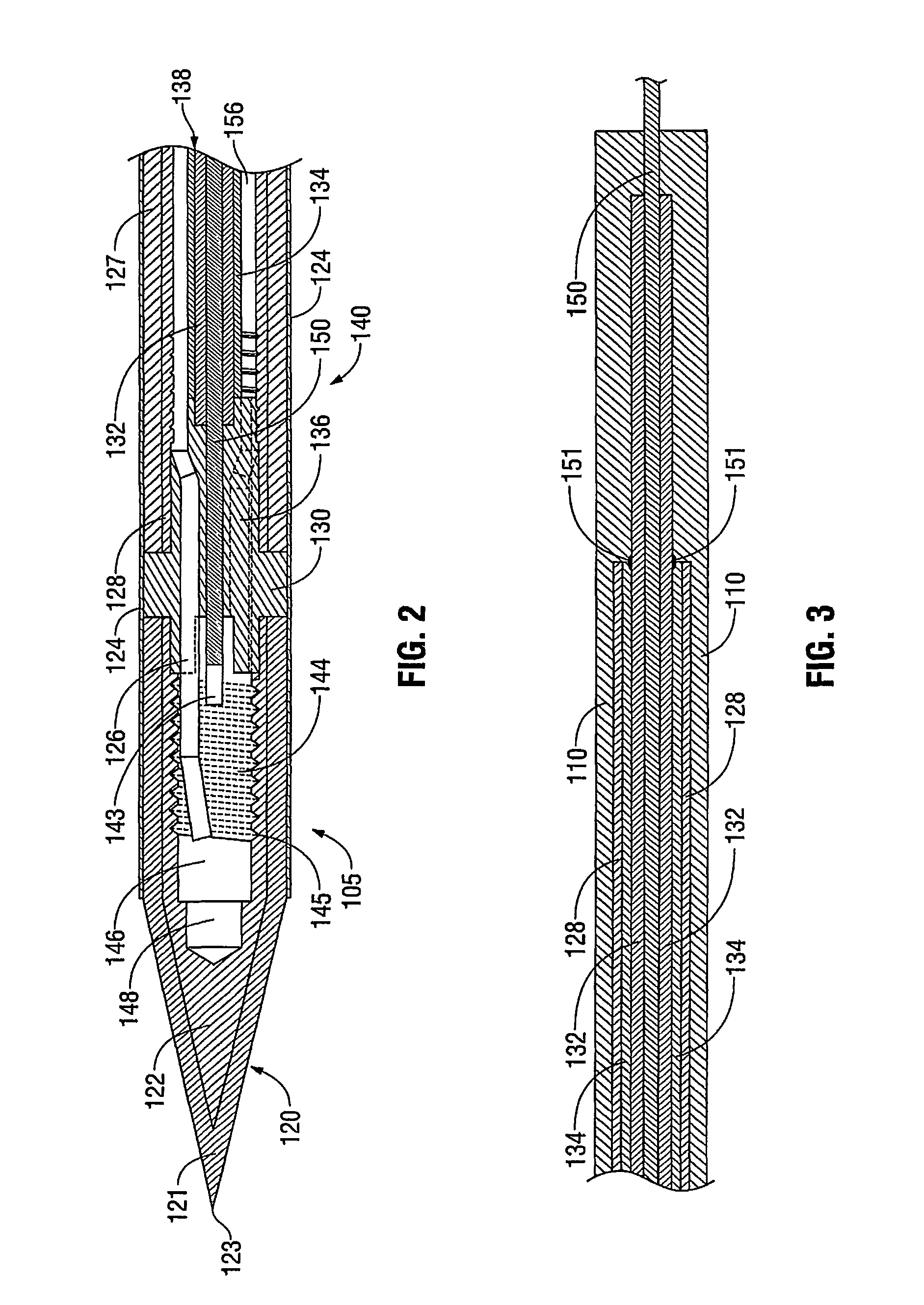
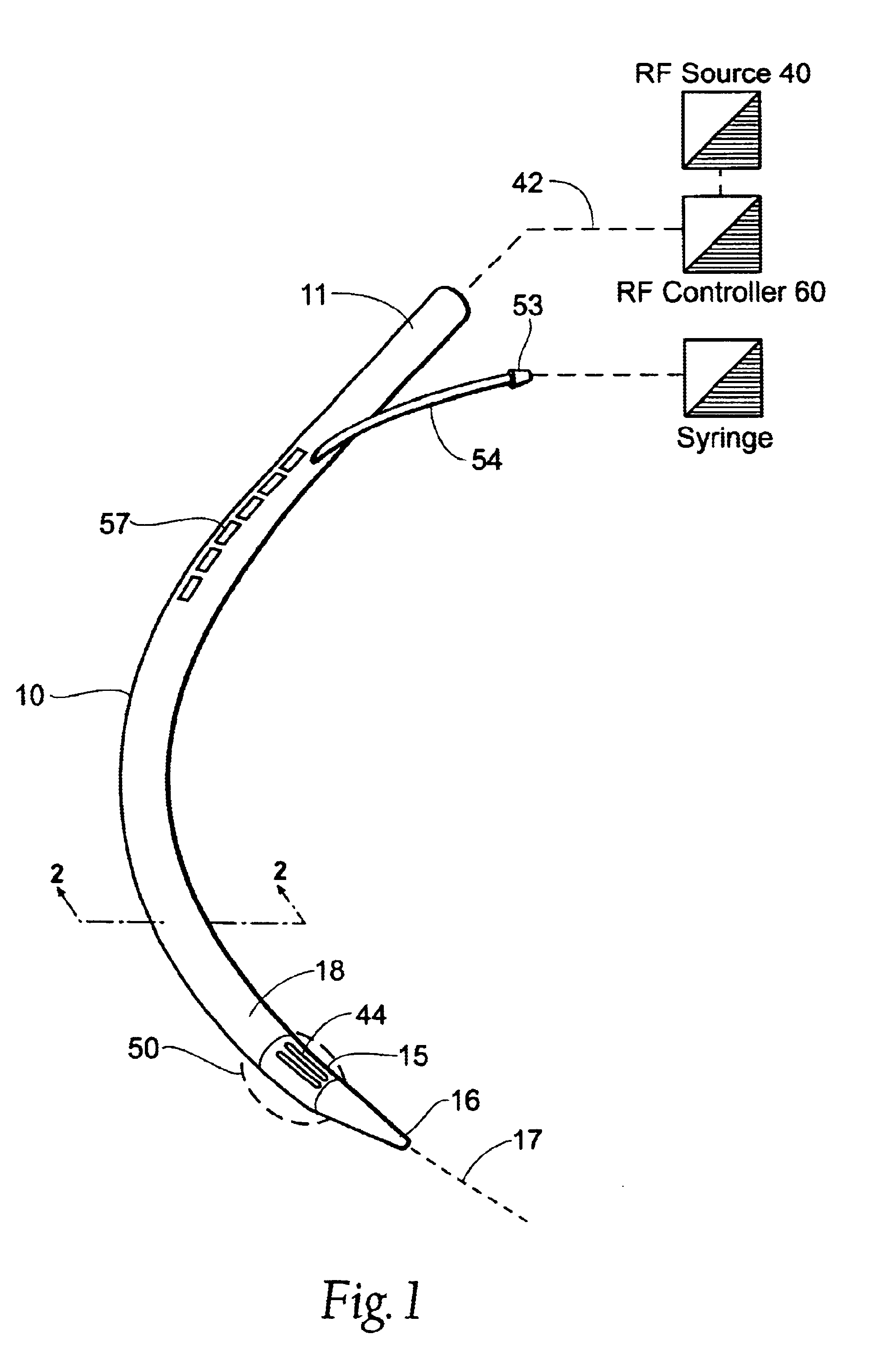
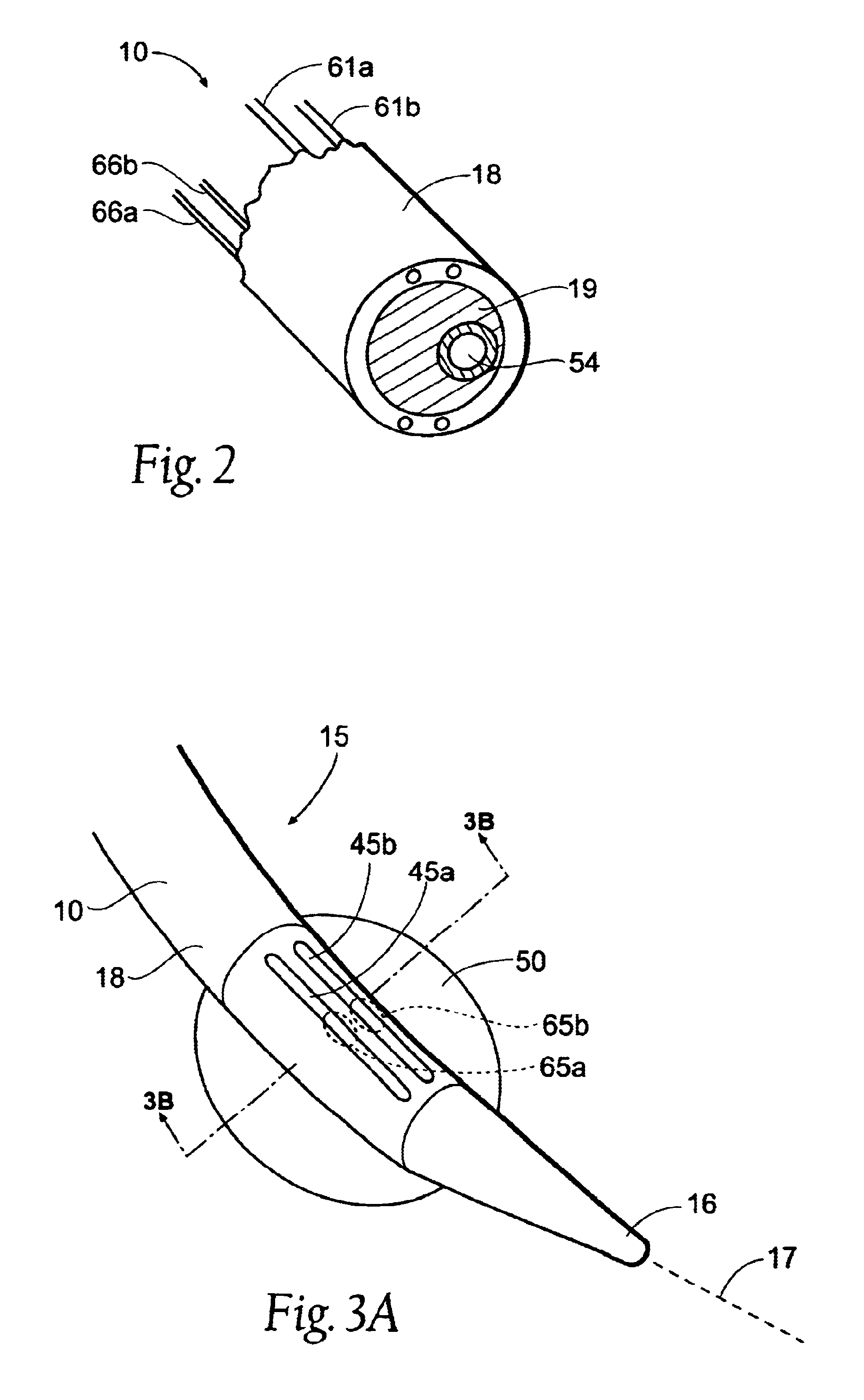
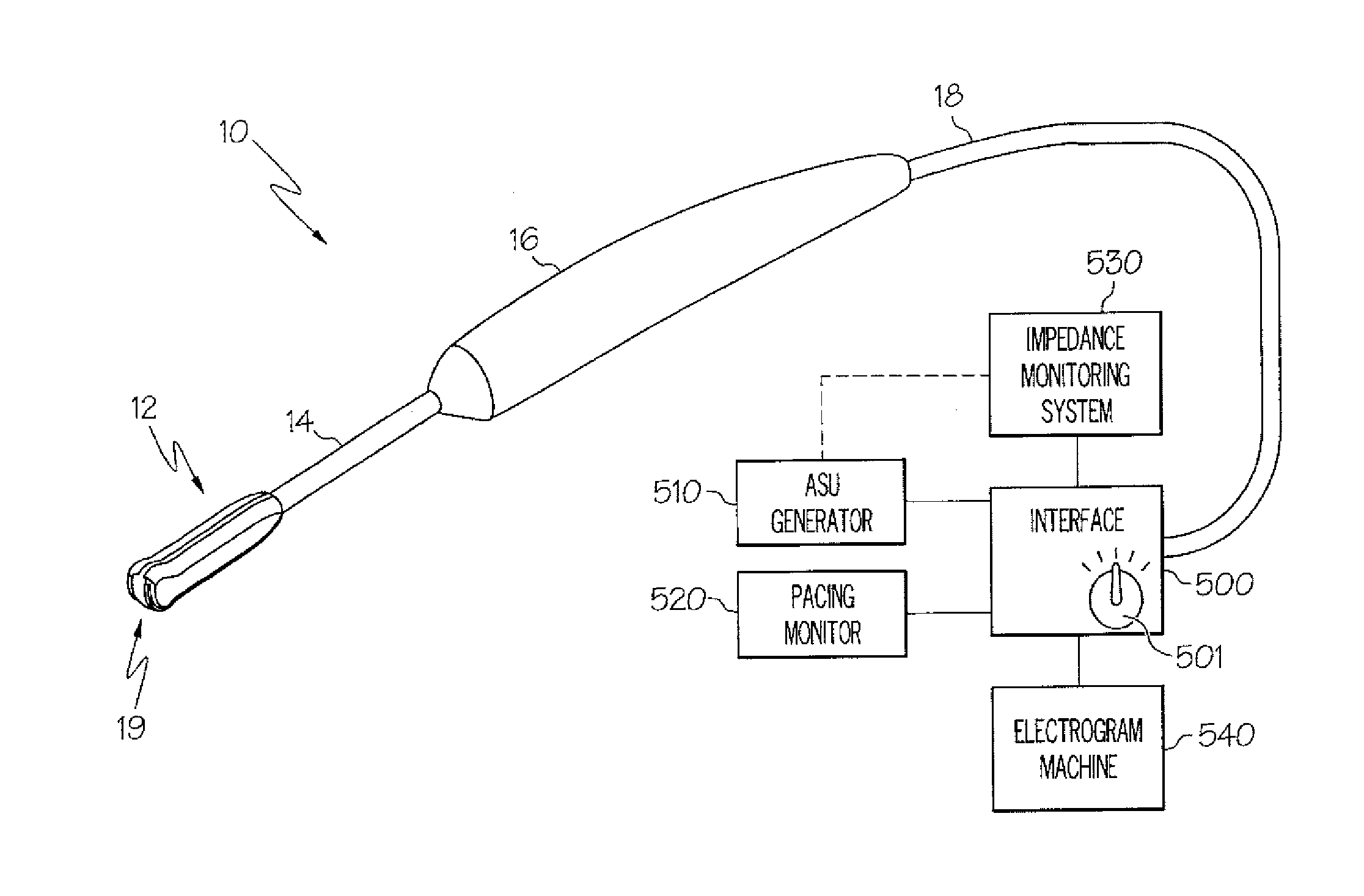
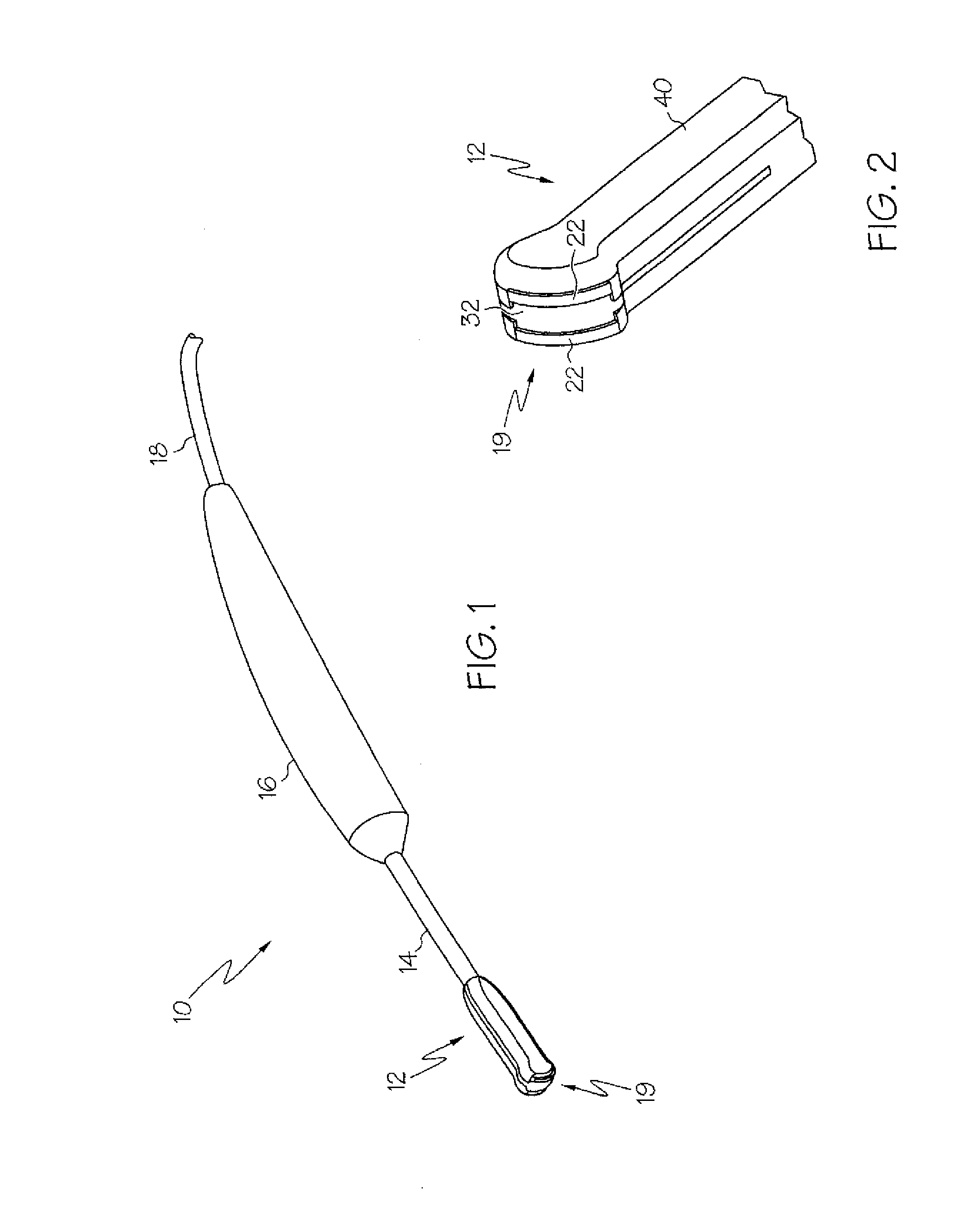
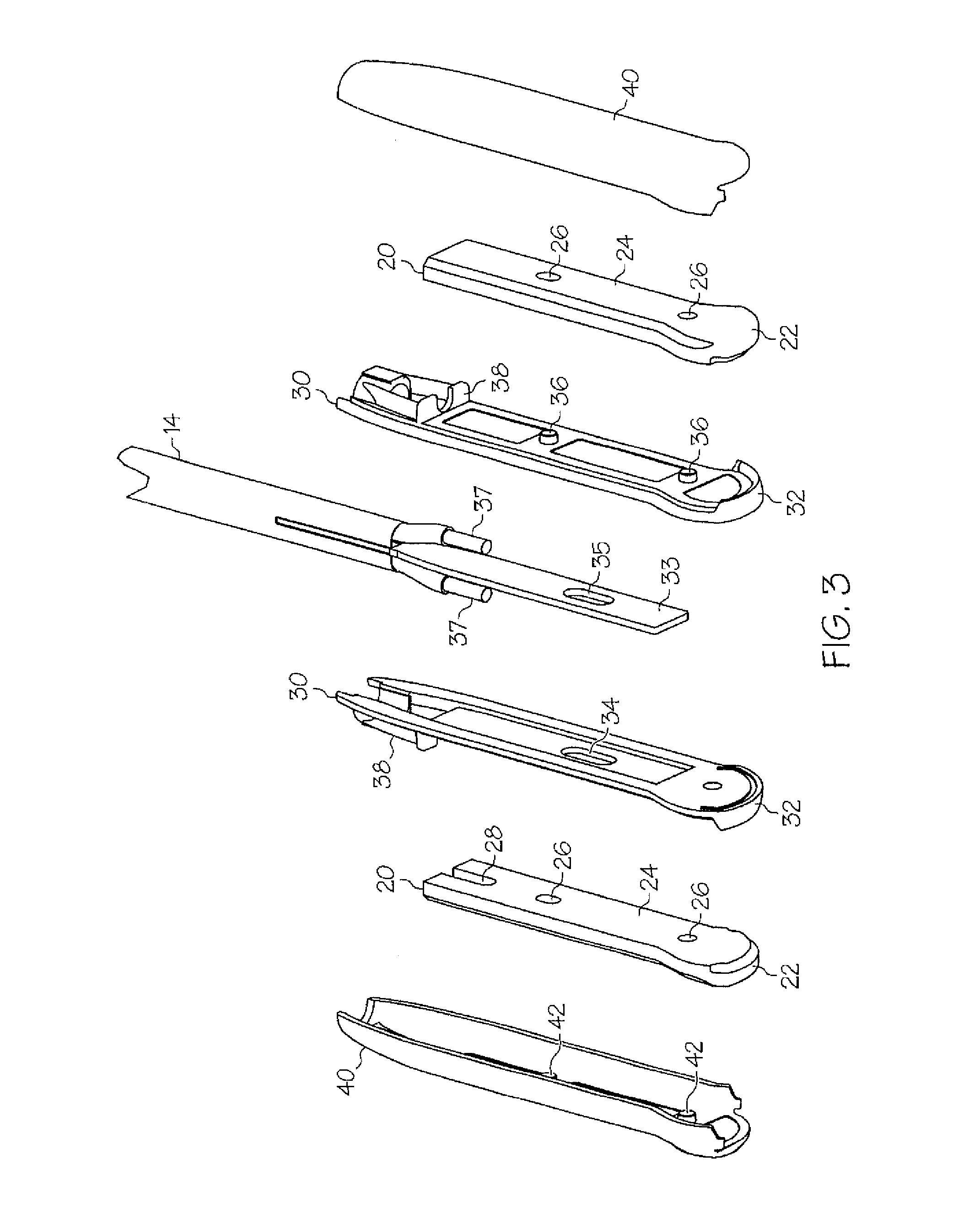
Method and system for heating tissue with a bipolar instrument
InactiveUS6682527B2Improving impedanceAvoid creatingSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringTherapeutic Area
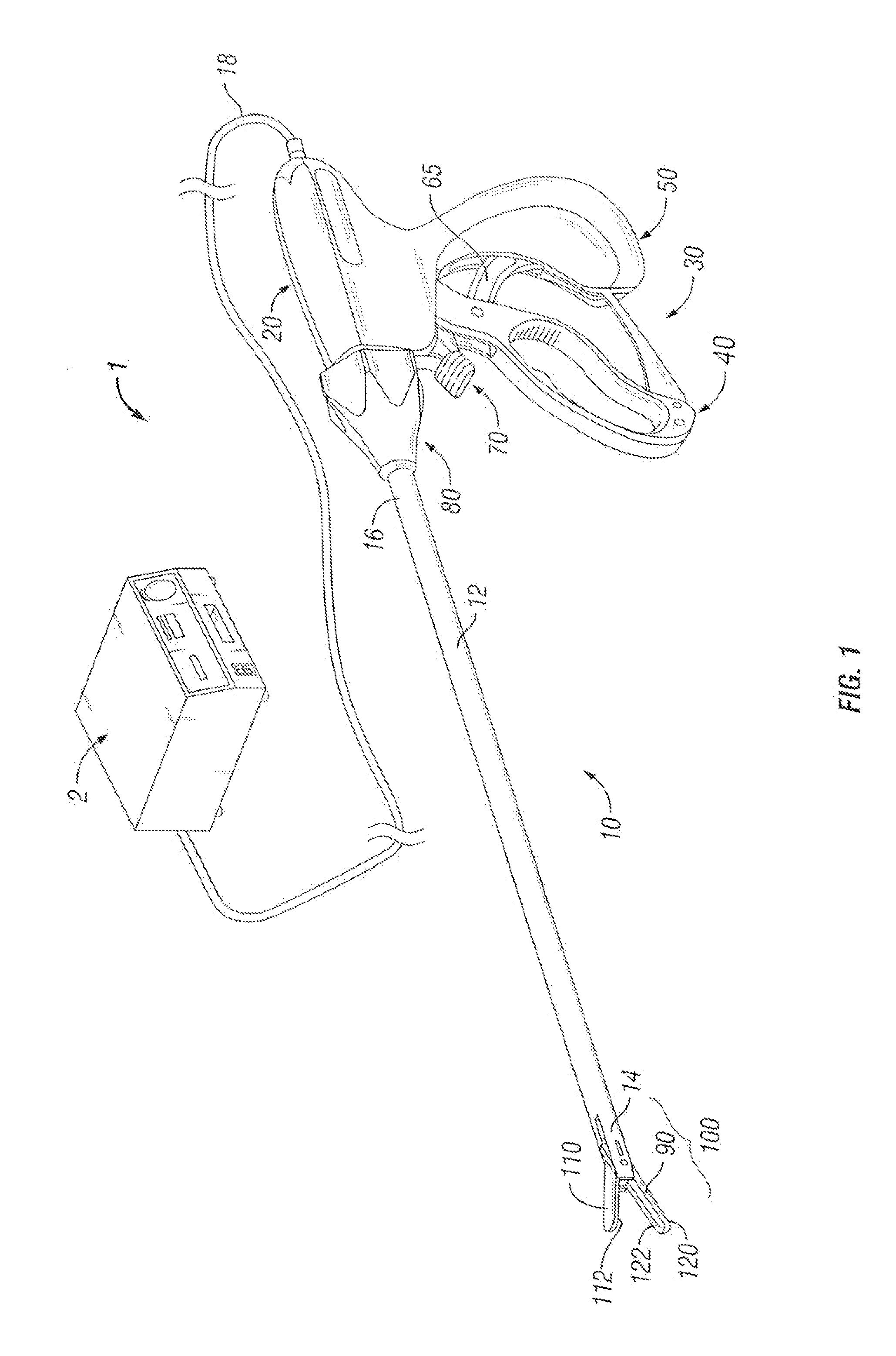
Methods for heating tissue completely, thoroughly, and uniformly comprise delivering radio frequency energy through a bipolar surgical instrument having first and second jaws with first and second electrode members within the treatment region. Tissue is grasped between the first and second jaws of the bipolar instrument. The electrode members are energized at a power level to deliver electrical energy to and heat tissue between the first and second electrode members. The power level is increased at a predetermined rate from an initial level. The initial level and predetermined rate are selected to avoid creating a vapor layer and to permit an impedance increase to occur as a result of complete tissue desiccation. A tissue impedance may also be measured and compared to a preset impedance limit for terminating the power delivery when the measured impedance exceeds the impedance limit.
Owner:PERFECT SURGICAL TECHN
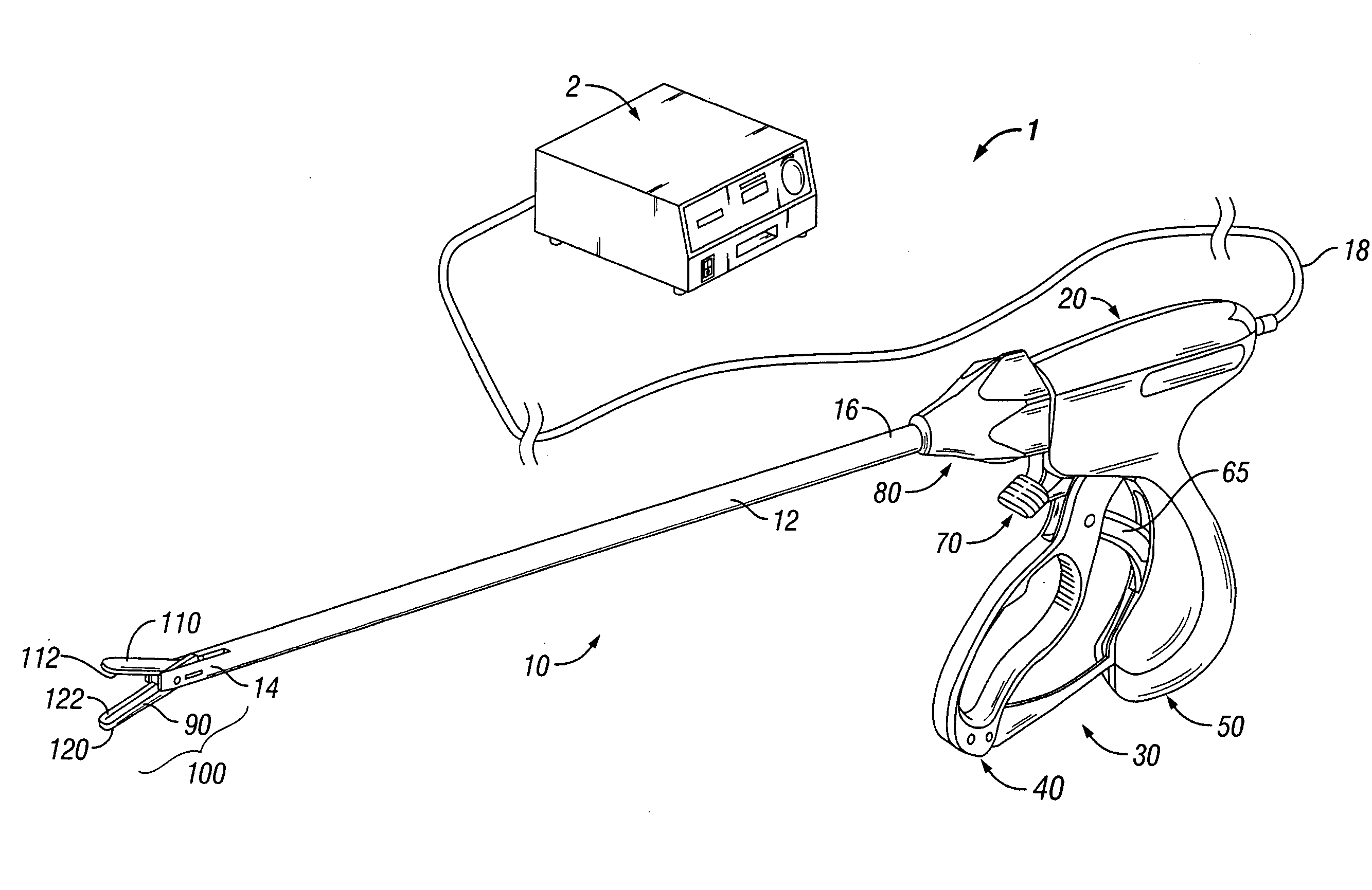
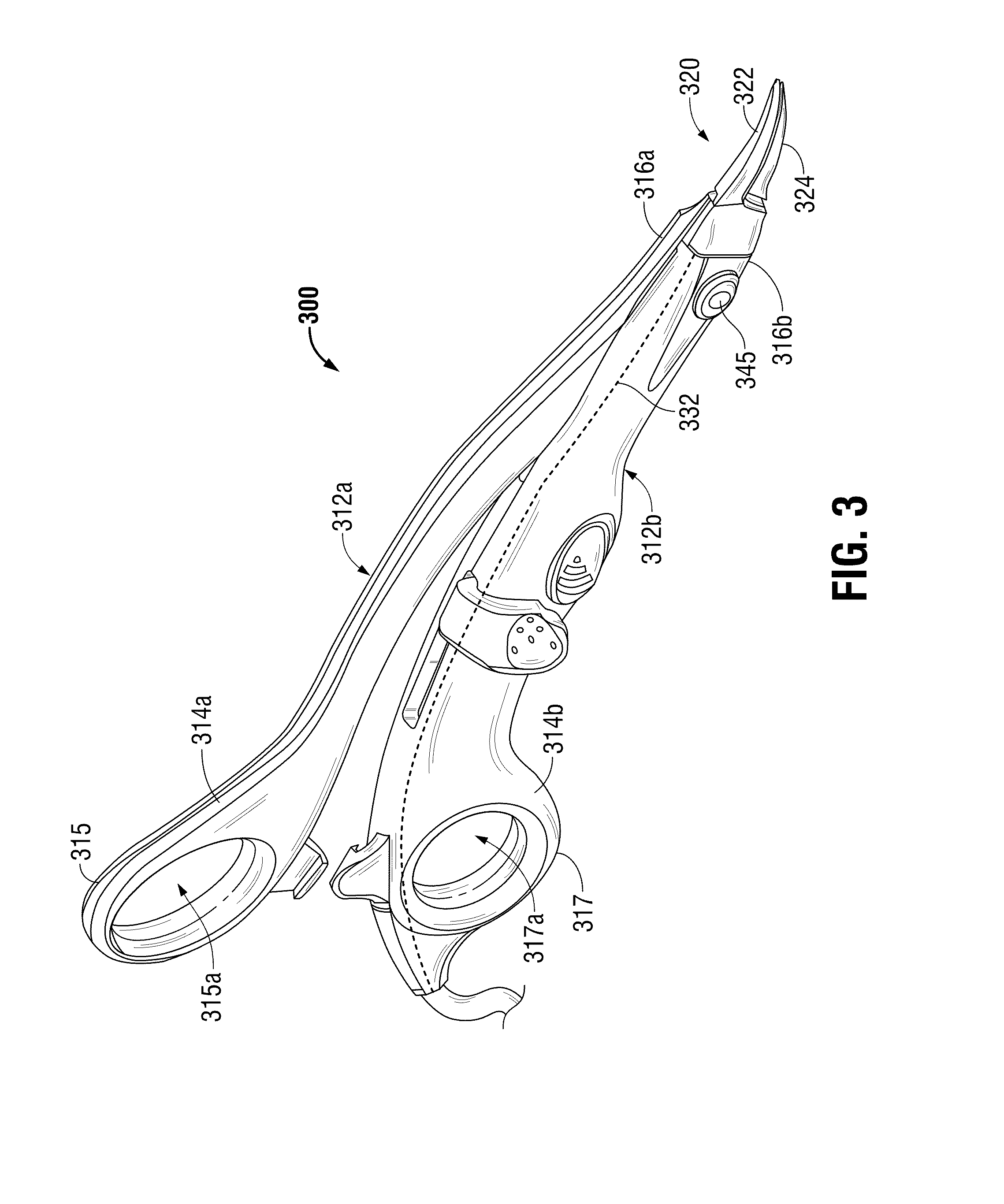
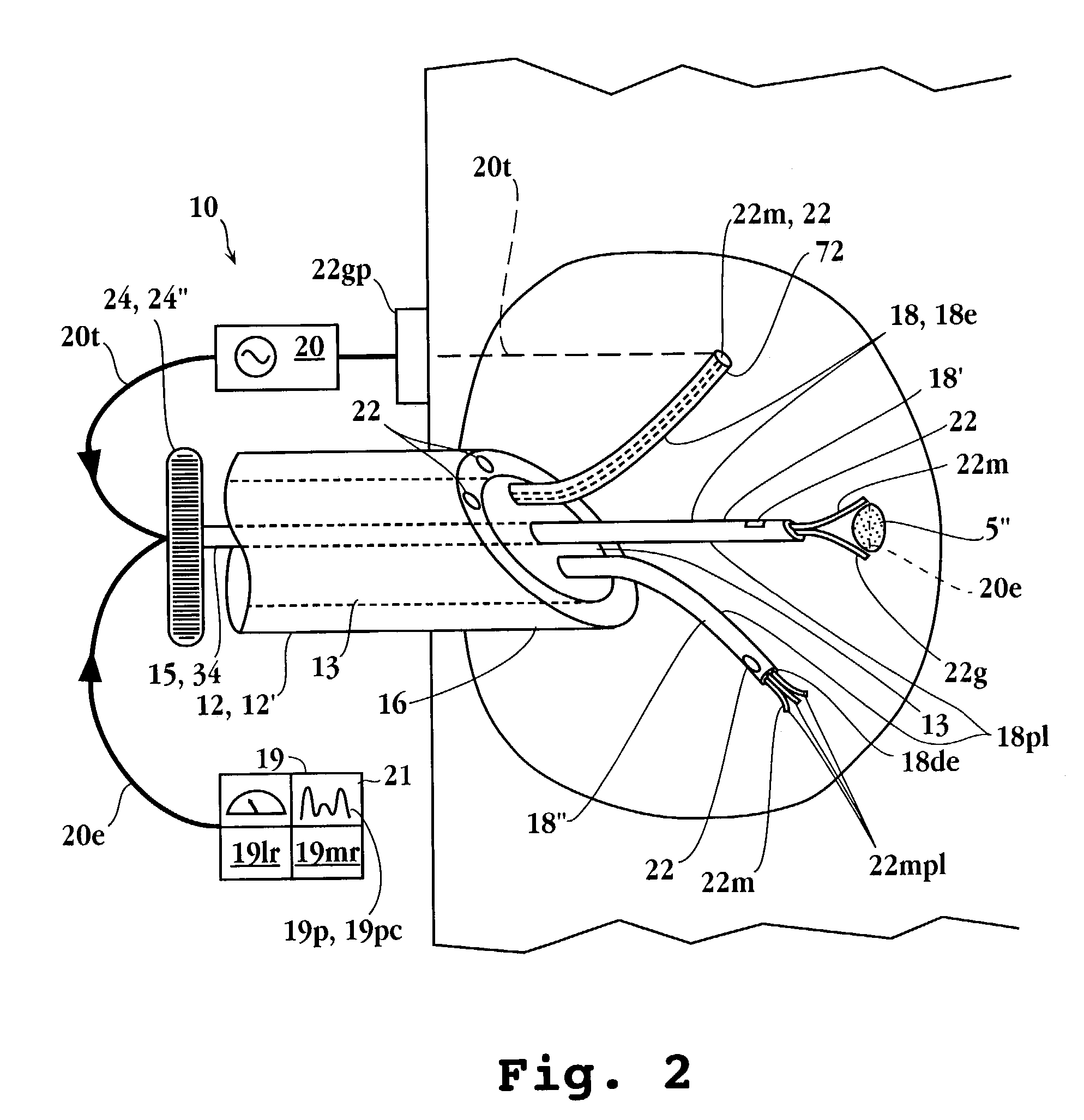
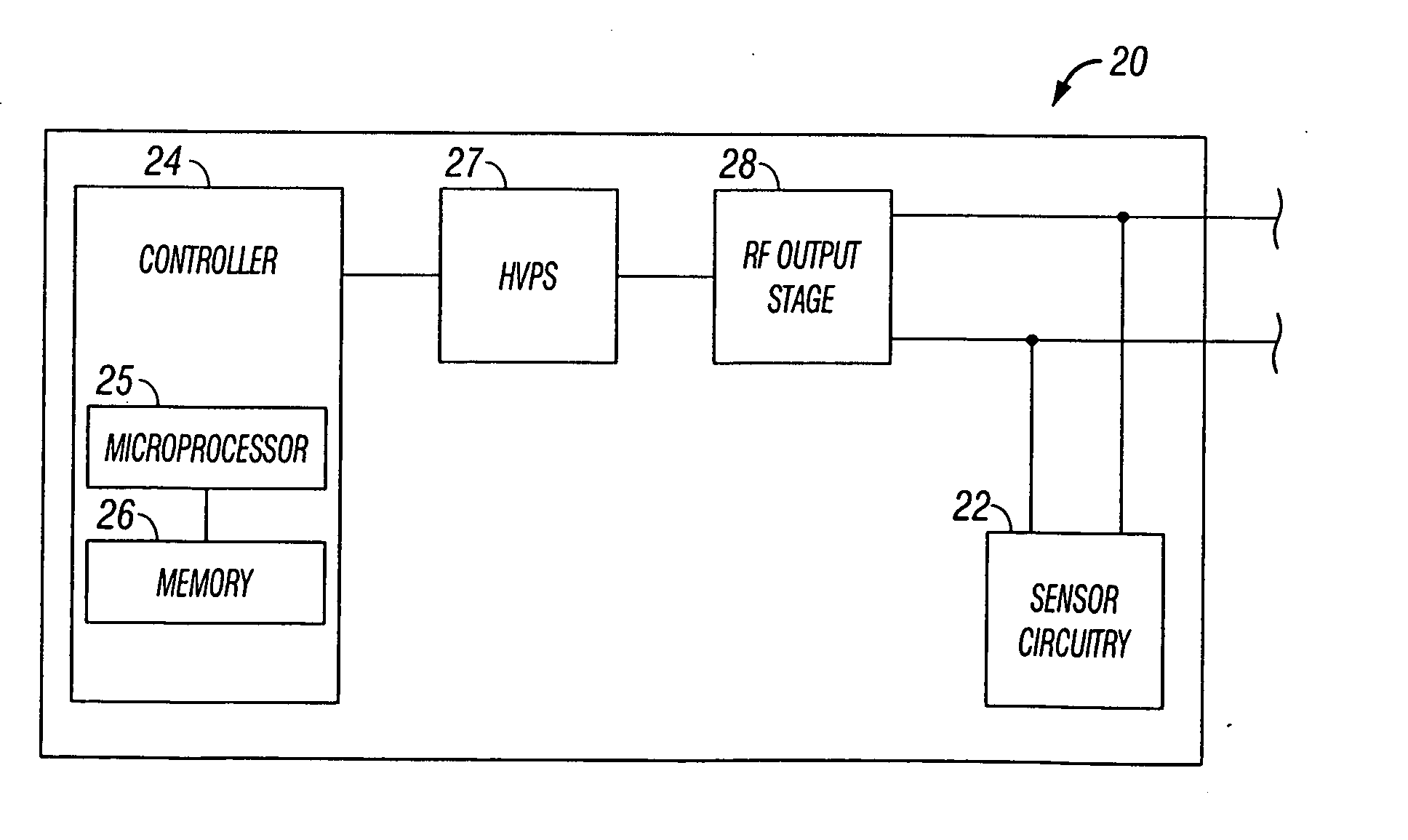
System and method for tissue sealing
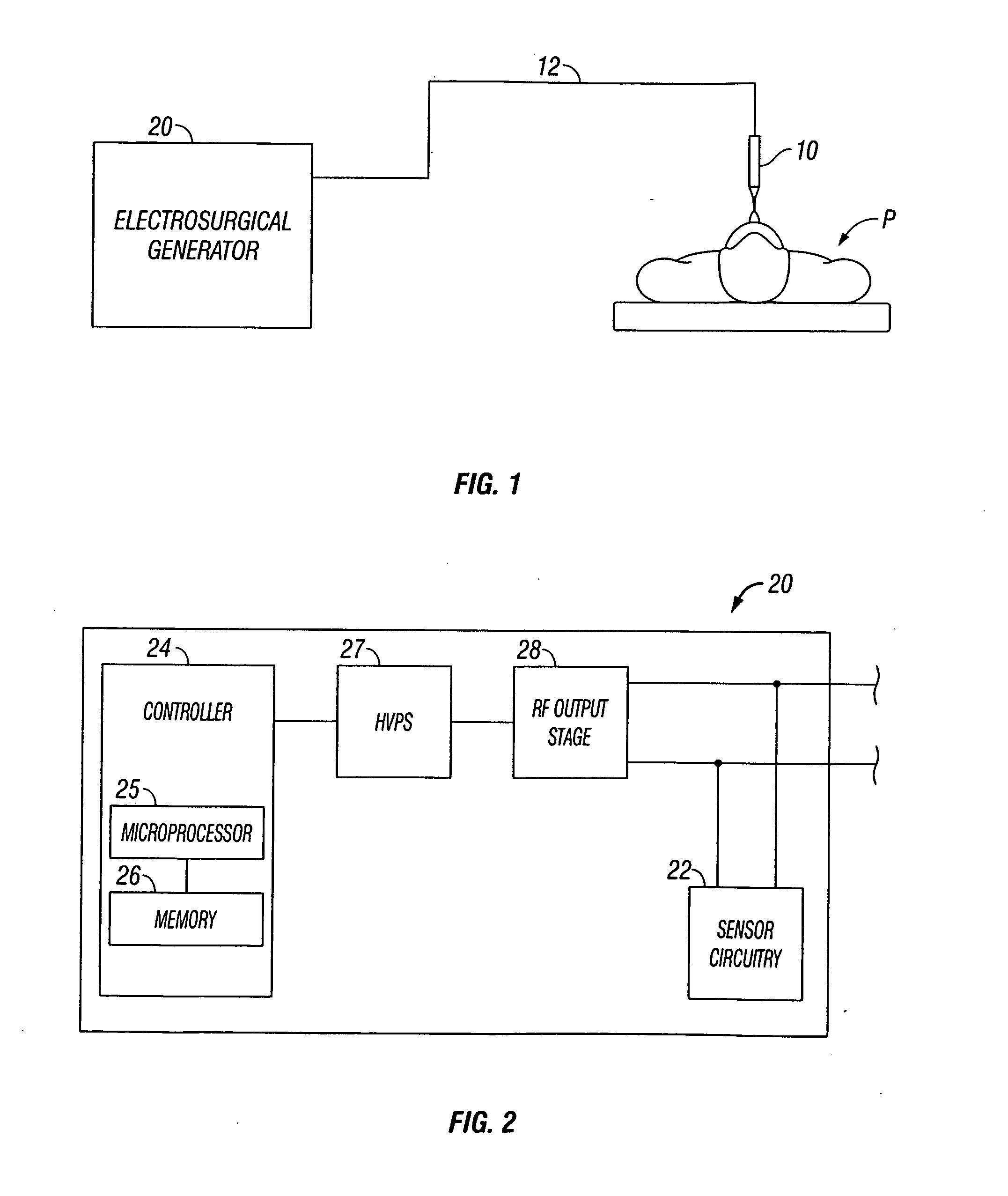
An electrosurgical bipolar forceps for sealing is disclosed. The forceps includes one or more shaft members having an end effector assembly disposed at the distal end. The end effector assembly includes two jaw members movable from a first position to a closed position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue at constant pressure. Each of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive sealing plate connected to a first energy source which communicates electrosurgical energy through the tissue held therebetween. The electrosurgical energy is communicated at constant voltage. The electrically conductive sealing plates are operably connected to sensor circuitry which is configured to measure initial tissue impedance and transmit an initial impedance value to a controller. The controller determines the constant pressure and the constant voltage to be applied to the tissue based on the initial impedance value.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Feedback control in an ultrasonic surgical instrument for improved tissue effects
A temperature monitoring device and / or method which control the tissue temperature at the end-effector of a therapeutic ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument as the tissue is being heated with ultrasonic vibrations from the end-effector. One or more temperature sensors are located at the end-effector, preferably on a clamping member. The temperature sensors measure the temperature of the tissue engaged by the end-effector either directly or indirectly. An alternate method and apparatus provides an electrical tissue impedance measure in combination with an ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument to provide active feedback control of an ultrasonic generator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrosurgical system
InactiveUS6893435B2Sufficient powerImproving impedanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringRadio frequency
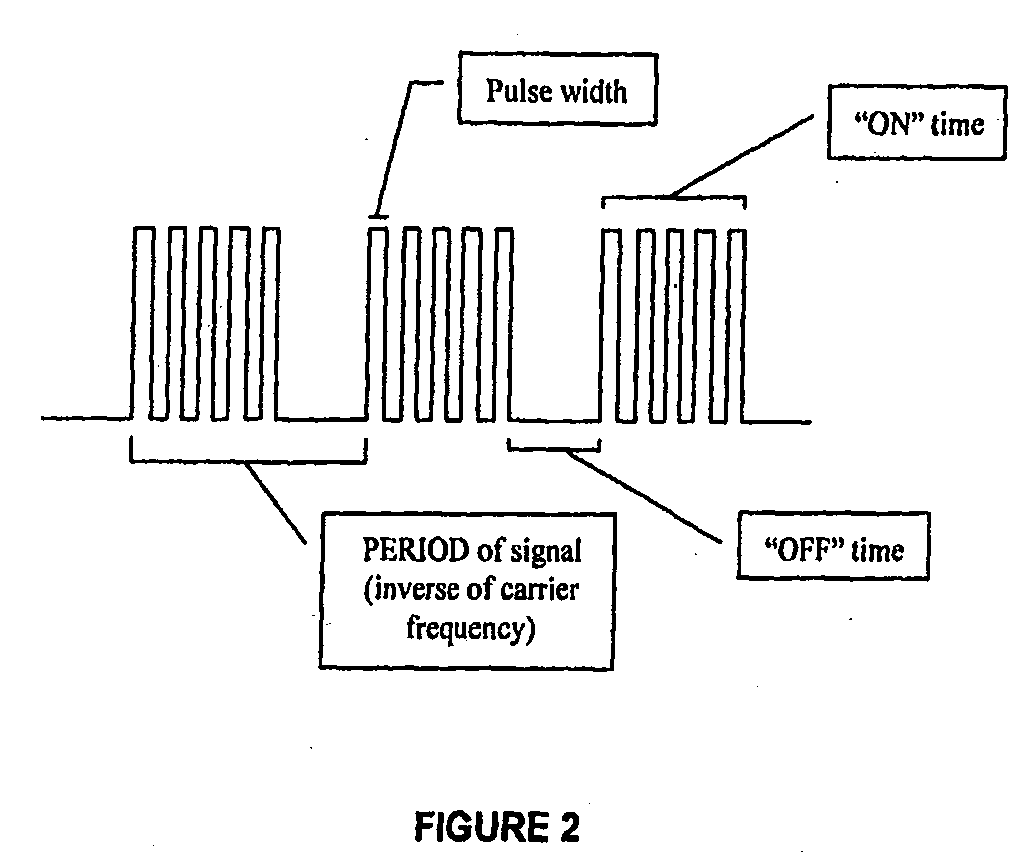
An electrosurgical system has an electrosurgical generator and a bipolar electrosurgical instrument, the generator being arranged to perform a treatment cycle in which radio frequency energy is delivered to the instrument as an amplitude-modulated radio frequency power signal in the form of a succession of pulses characterized by periods of a least 100 milliseconds between successive pulses and by a predetermined pulse mark-to-space ratio. Energy delivery between pulses is substantially zero and the mark-to-space ratio is typically 1:4 or less. Each burst is of sufficiently high power to form vapor bubbles within tissue being treated and the time between successive pulses is sufficiently long to permit condensation of the vapor. The treatment cycles may each include an initial period and a subsequent period, the pulse duty cycle being increased or energy being delivered continuously in the subsequent period in order that tissue coagulation can be achieved quickly despite increasing tissue impedance.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
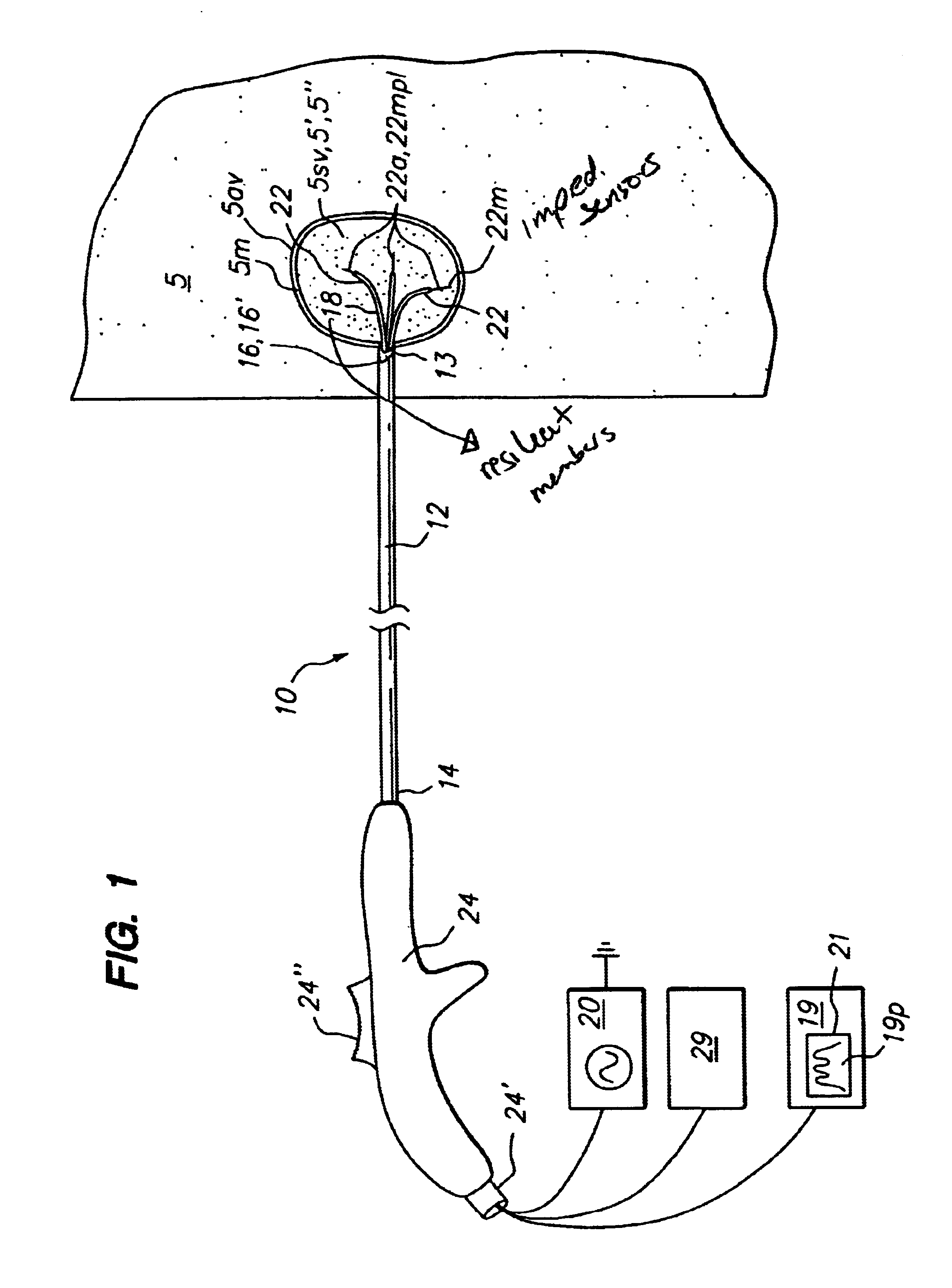
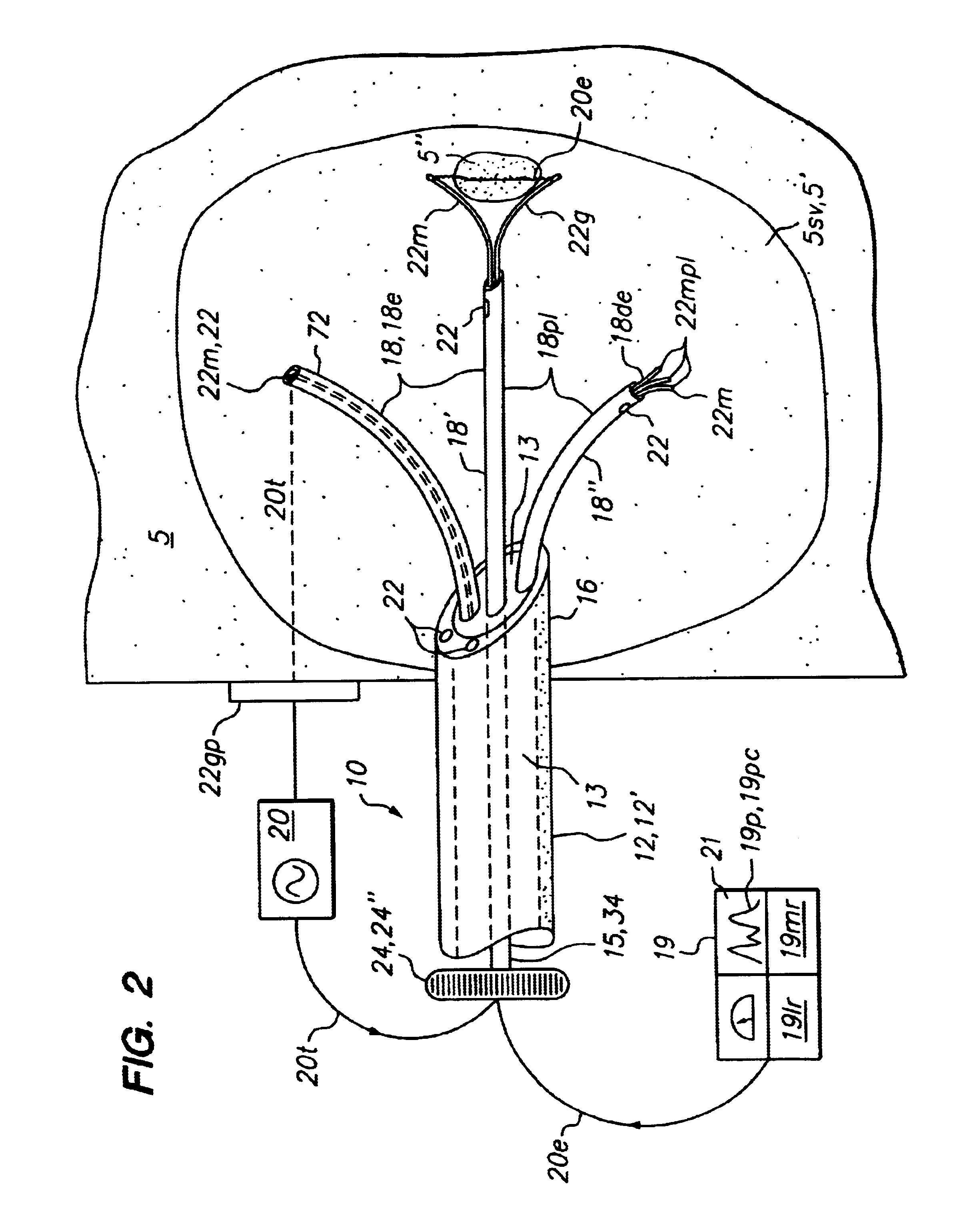
Method for detecting and treating tumors using localized impedance measurement
InactiveUS6962587B2Precise positioningEasy to monitorSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringAbnormal tissue growthEngineering
An embodiment of the invention provides a method for detecting and treating a tumor using tissue localized volumetric impedance measurement. The method includes providing an impedance measurement apparatus having a plurality of resilient members deployable with curvature and configured to sample tissue impedance through a plurality of conductive pathways. The apparatus is configured to be coupled to at least one of an energy delivery device, a power supply, a switching device or logic resources. The apparatus is then positioned at a selected tissue site and the impedance array deployed to define a sample volume. The impedance array is then utilized to make impedance measurements through a plurality of conductive pathways. Information from the impedance measurements is then utilized to determine a tissue condition of the sample volume. Energy is then delivered from the energy delivery device to ablate or necrose at least a portion of the tumor.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
System and method for tissue sealing
InactiveUS20090292283A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingActuatorBipolar forceps
An electrosurgical bipolar forceps for sealing is disclosed. The forceps includes one or more shaft members having an end effector assembly disposed at the distal end. The end effector assembly includes two jaw members movable from a first position to a closed position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue at constant pressure. Each of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive sealing plate connected to a first energy source which communicates electrosurgical energy through the tissue held therebetween. The electrosurgical energy is communicated at constant voltage. The electrically conductive sealing plates are operably connected to sensor circuitry which is configured to measure initial tissue impedance and transmit an initial impedance value to a controller. The controller determines the constant pressure and the constant voltage to be applied to the tissue based on the initial impedance value.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
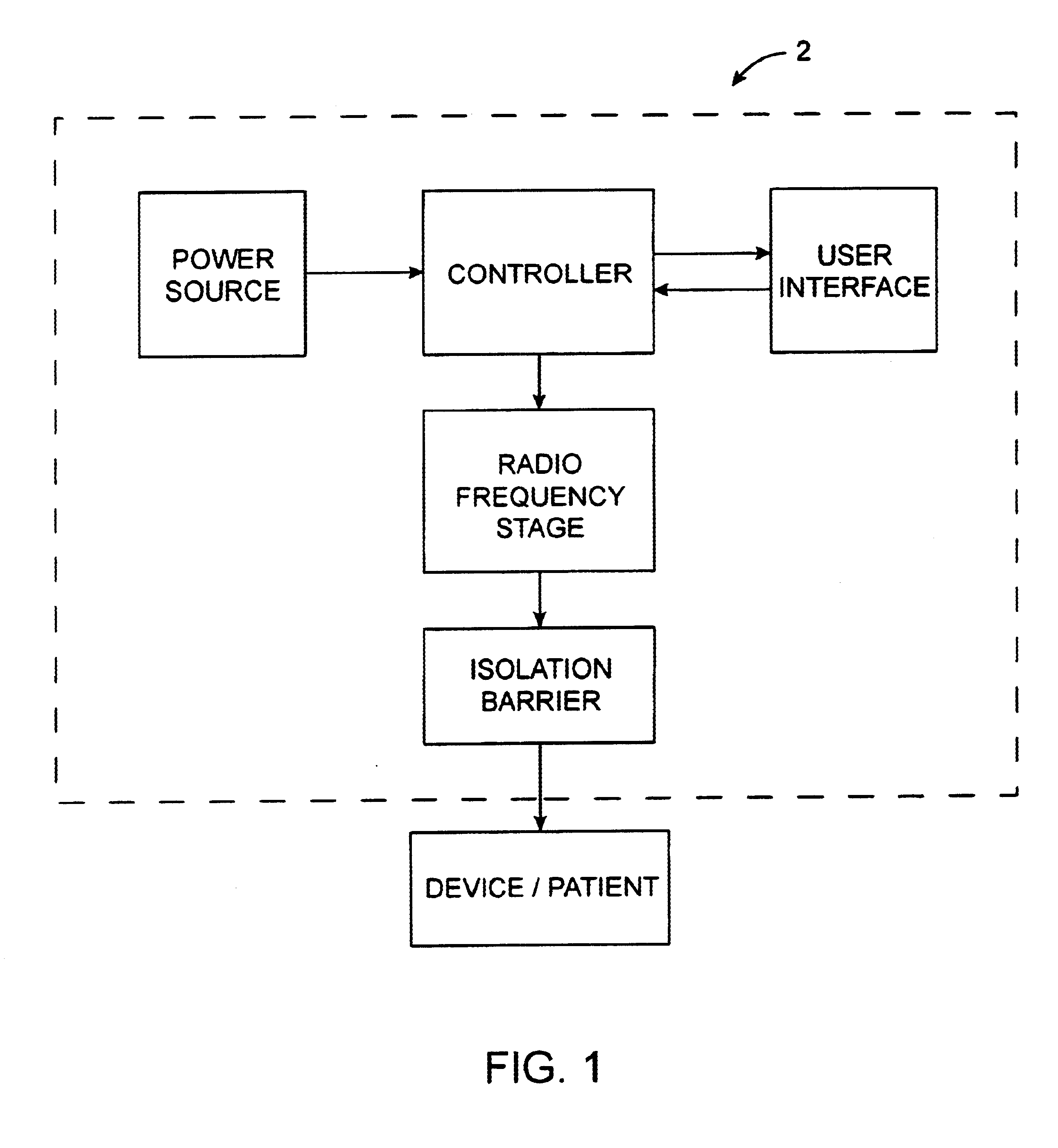
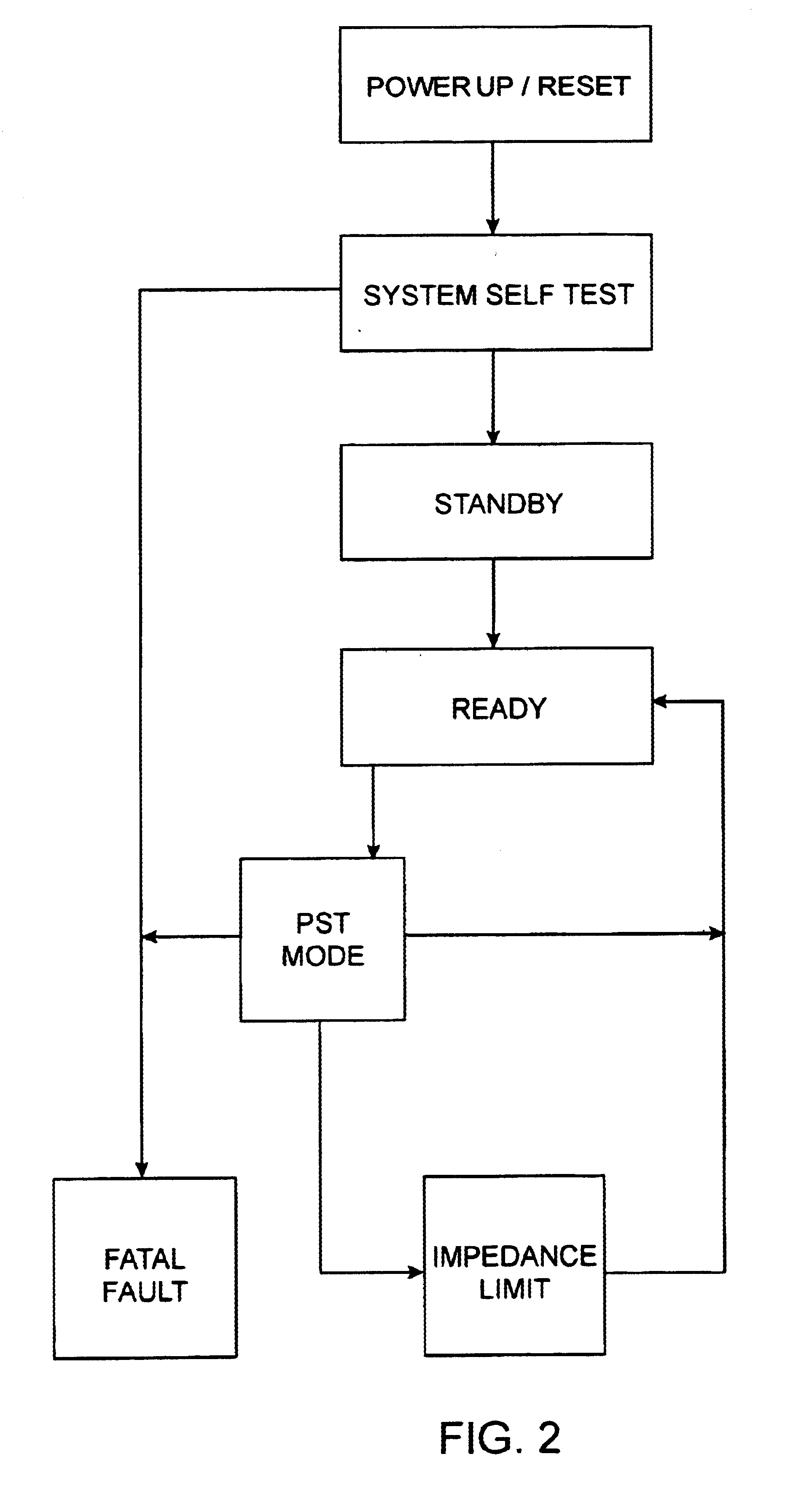
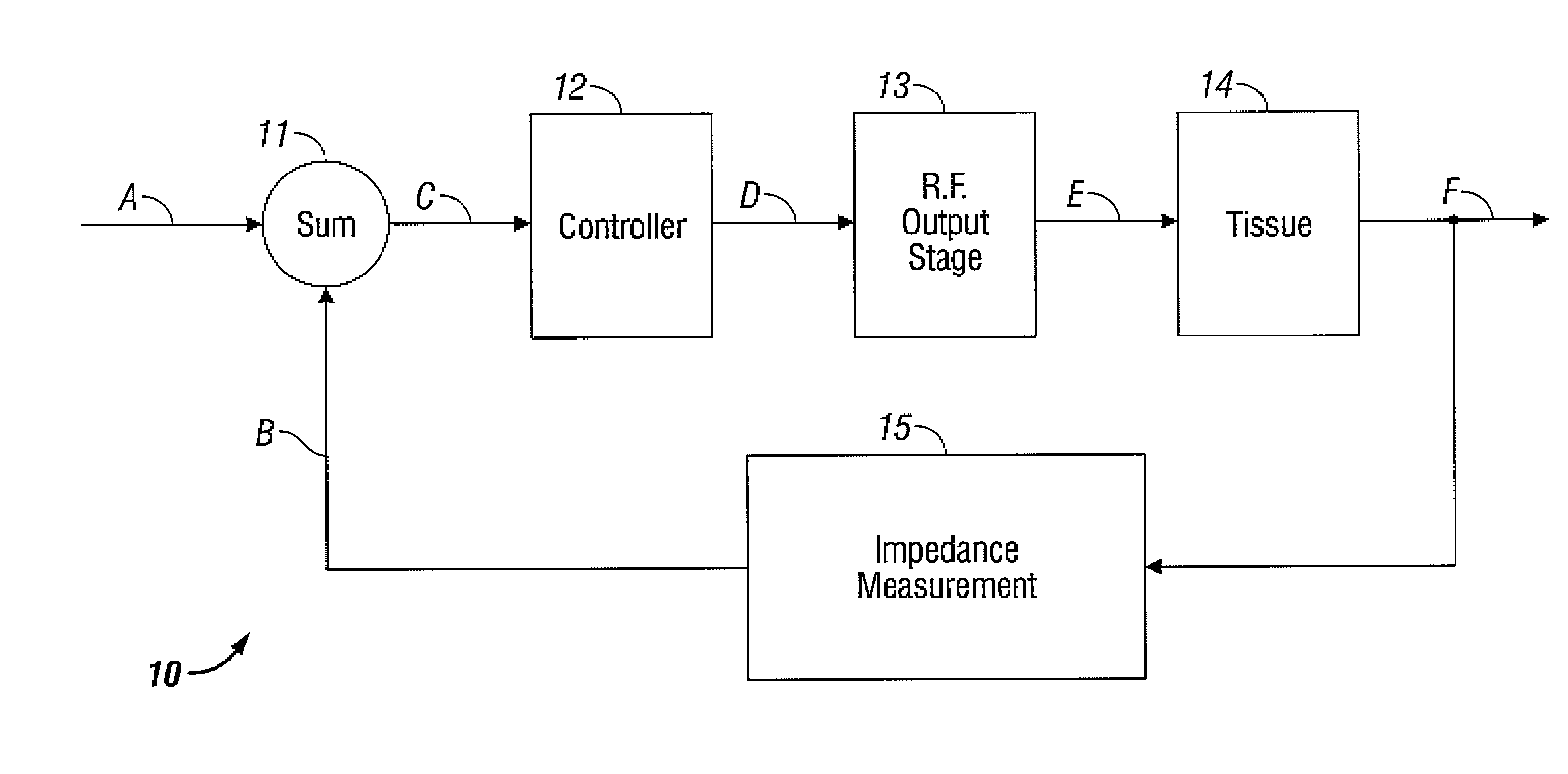
Electrosurgical generator with adaptive power control
InactiveUSRE40388E1Lower Level RequirementsImproved tissue sealing characteristicPulse automatic controlSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyVessel sealing
An electrosurgical generator has an output power control system that causes the impedance of tissue to rise and fall in a cyclic pattern until the tissue is desiccated. The advantage of the power control system is that thermal spread and charring are reduced. In addition, the power control system offers improved performance for electrosurgical vessel sealing and tissue welding. The output power is applied cyclically by a control system with tissue impedance feedback. The impedance of the tissue follows the cyclic pattern of the output power several times, depending on the state of the tissue, until the tissue becomes fully desiccated. High power is applied to cause the tissue to reach a high impedance, and then the power is reduced to allow the impedance to fall. Thermal energy is allowed to dissipate during the low power cycle. The control system is adaptive to tissue in the sense that output power is modulated in response to the impedance of the tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
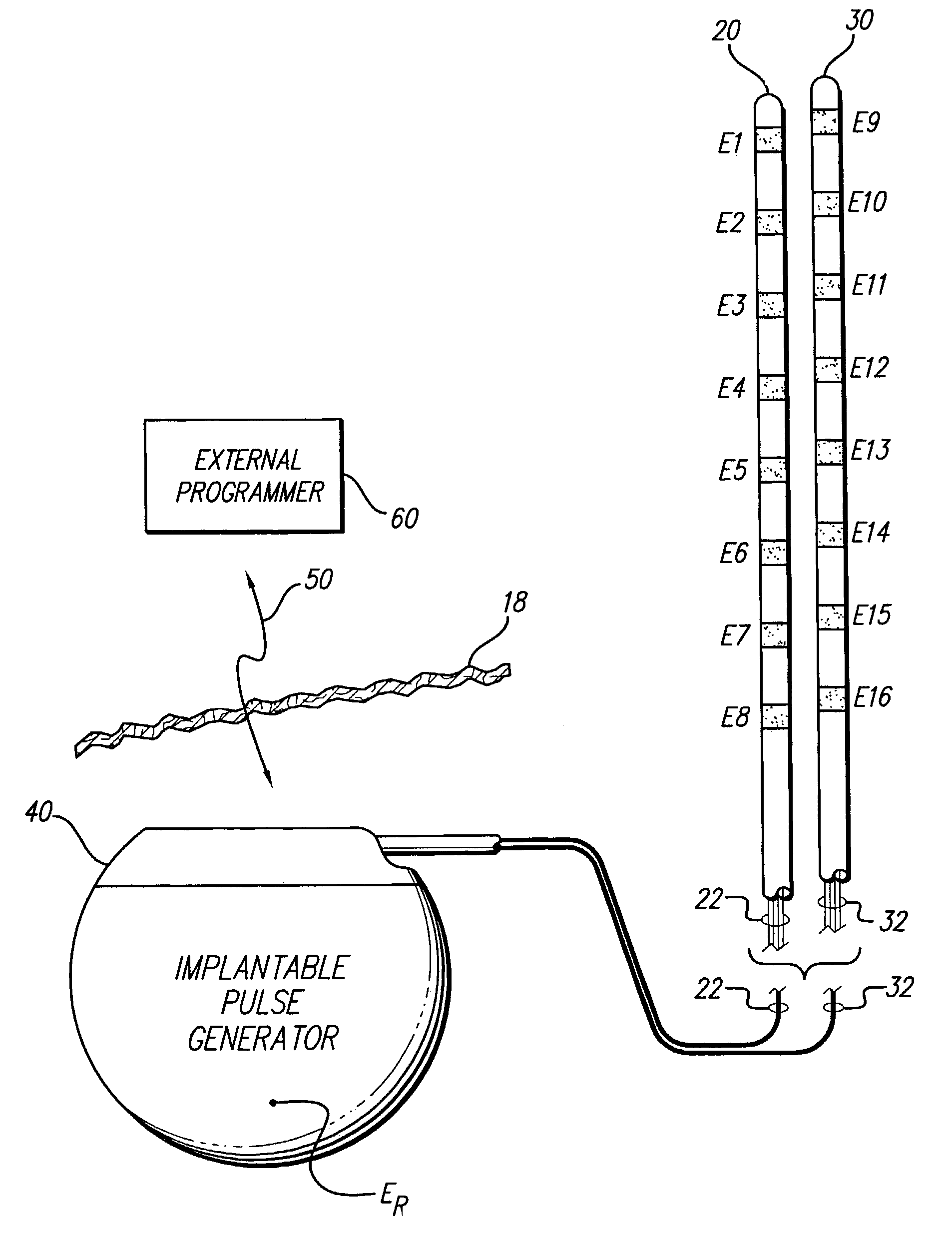
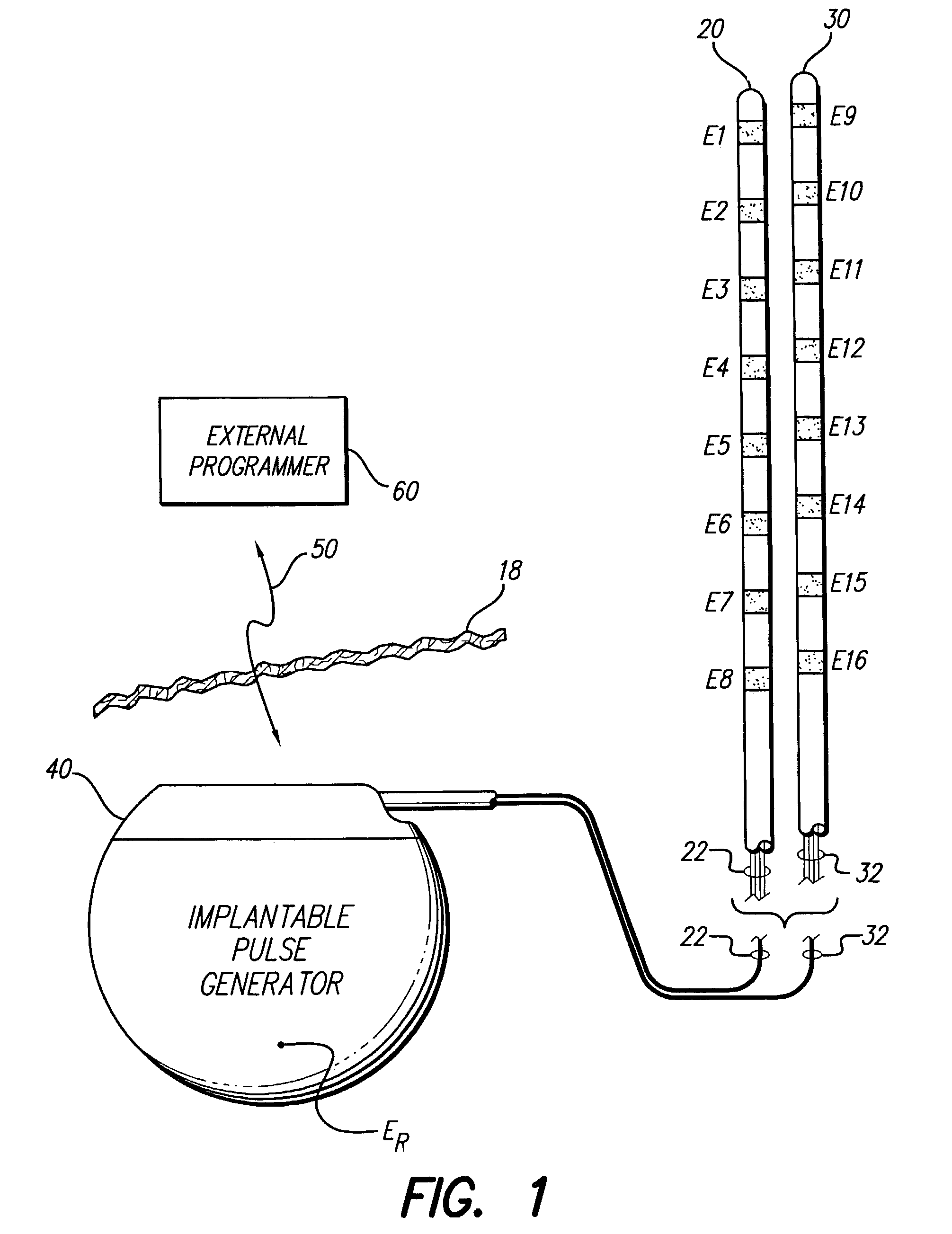
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Temperature-sensing electrically-conductive tissue-contacting plate configured for use in an electrosurgical jaw member, electrosurgical system including same, and methods of controlling vessel sealing using same
ActiveUS20150223868A1Readily integrated into manufacturing processSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectricityVessel sealing
An electrosurgical system includes an electrosurgical instrument, an electrosurgical power generating source, and a controller. The electrosurgical instrument includes a shaft extending from a housing. The shaft includes a distal end configured to support an end-effector assembly. The end-effector assembly includes opposing jaw members movably mounted with respect to one another and moveable from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to at least one subsequent position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. At least one of the jaw members includes a temperature-sensing electrically-conductive tissue-contacting plate defining a bottom surface. One or more temperature sensors are coupled to the bottom surface. The controller is configured to control one or more operating parameters associated with the electrosurgical power generating source based on one or more signals indicative of a tissue impedance value and indicative of a temperature sensed by the one or more temperature sensors.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electrosurgical Generator With Adaptive Power Control
InactiveUS20080281315A1Pulse automatic controlSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyVessel sealing
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Tissue impedance measurement using a secondary frequency
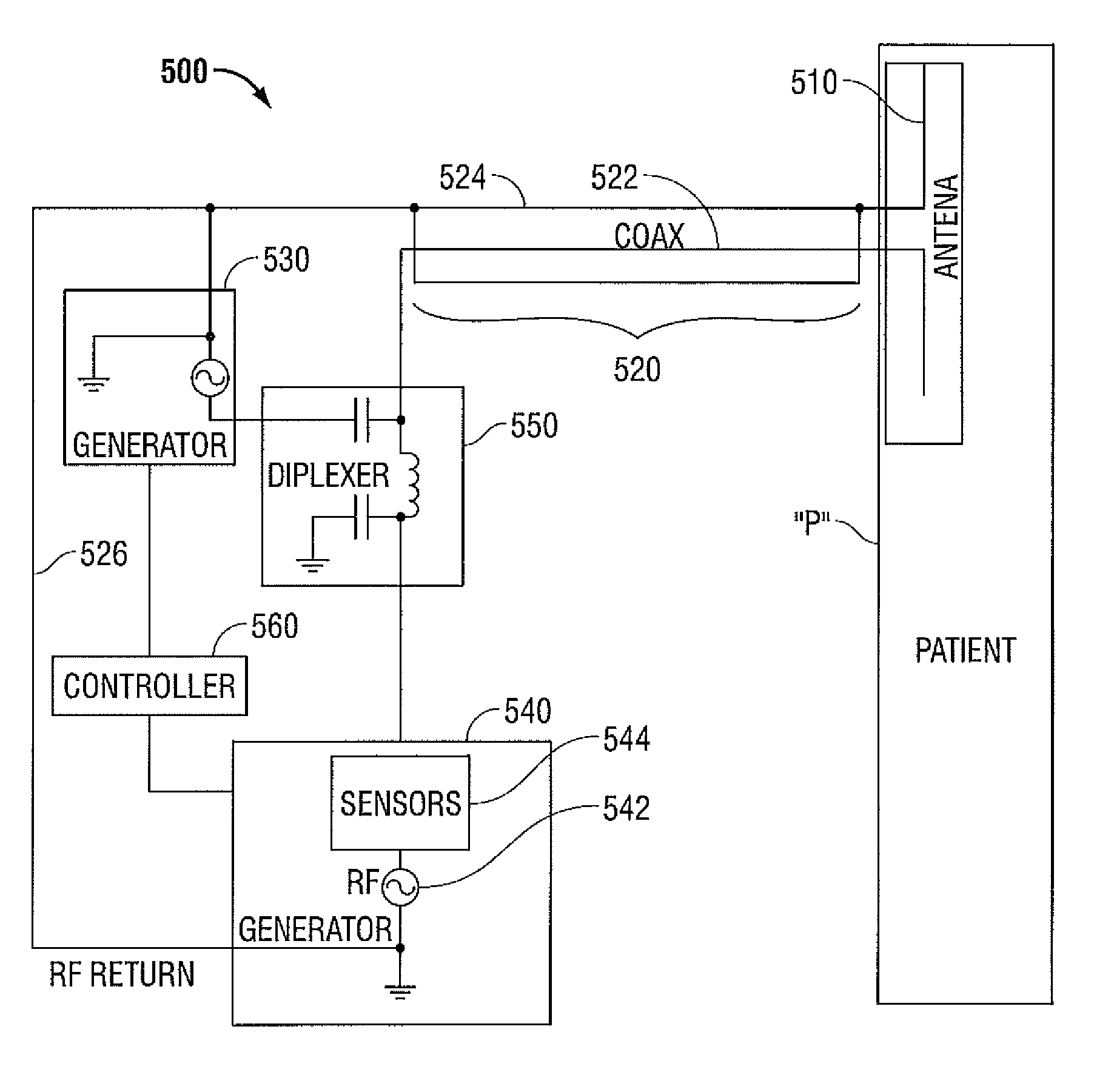
A microwave ablation system includes a generator including a first energy source, a second energy source and a diplexer, the diplexer multiplexes a first energy from the first energy source and a second energy from the second energy source. The system also includes a cable including a center conductor and an outer sheath where the multiplexed energy is transmitted through the center conductor. In addition an antenna is provided that is operable to receive the multiplexed energy from the center conductor and to deliver the multiplexed energy to a region of tissue. The outer sheath acts as a return path of the second energy to the second energy source. A sensor is also provided that measures at least one parameter of the second energy generated by the second energy source and the second energy returned from the region of tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
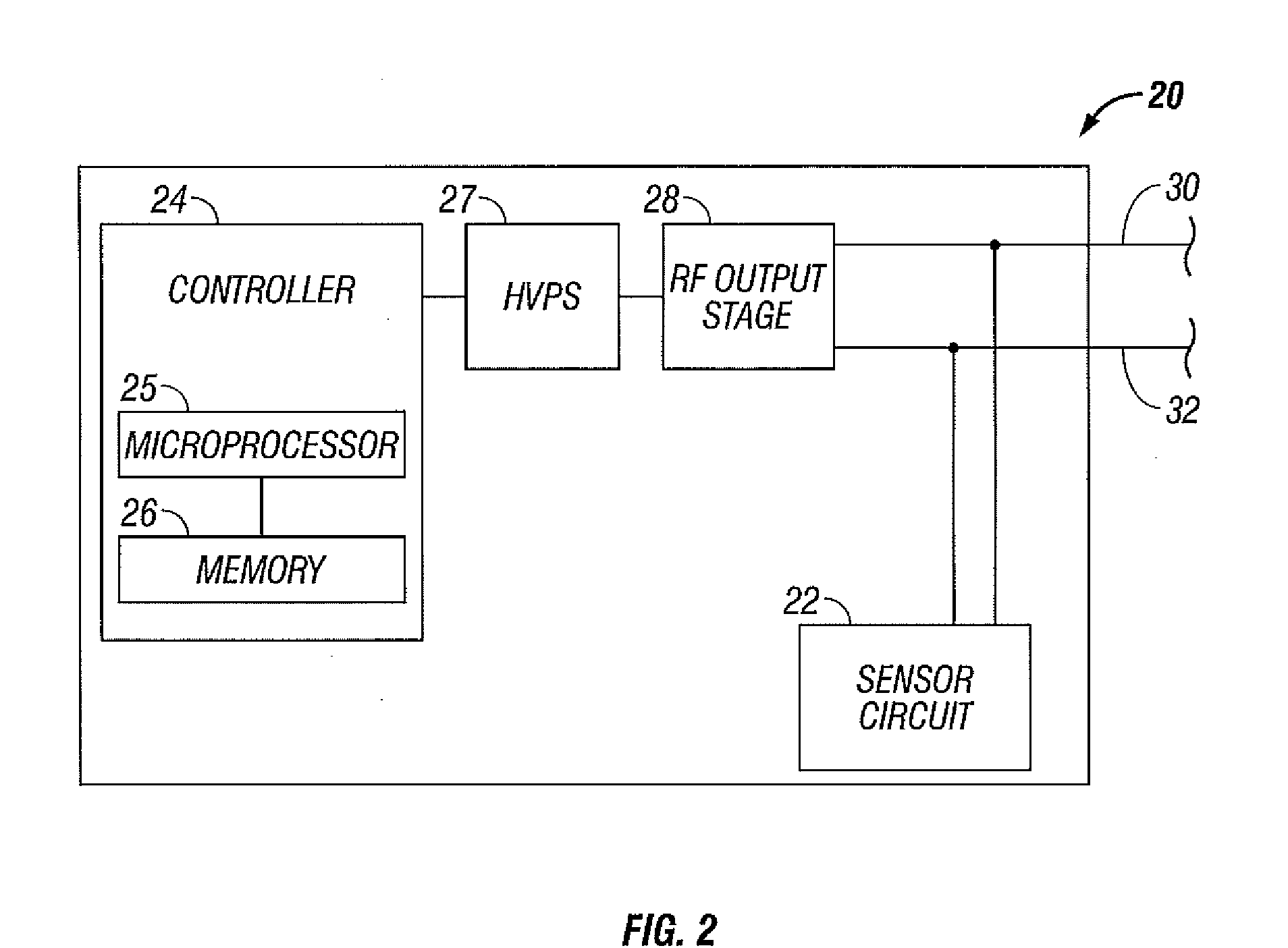
Arc Generation in a Fluid Medium
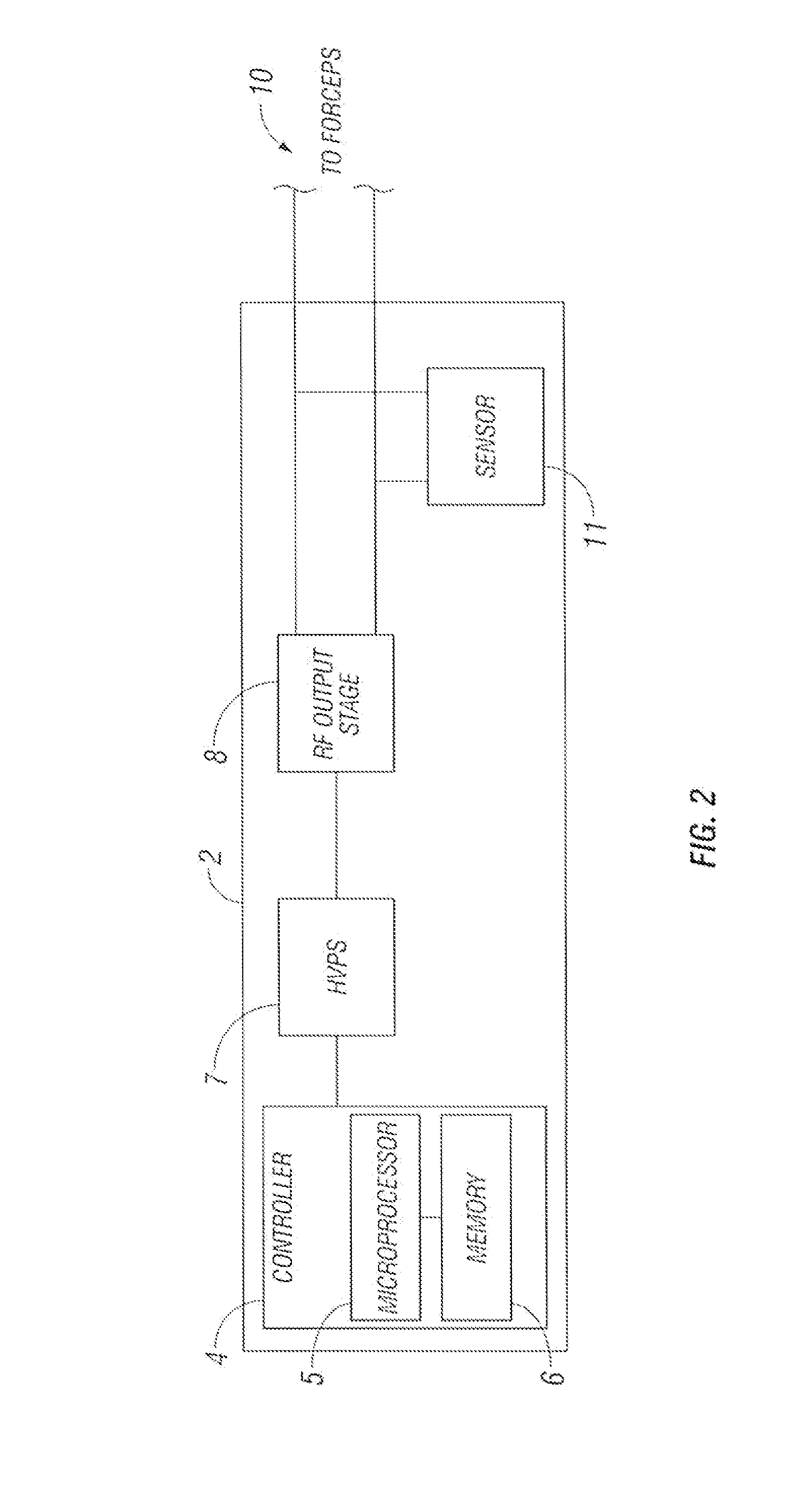
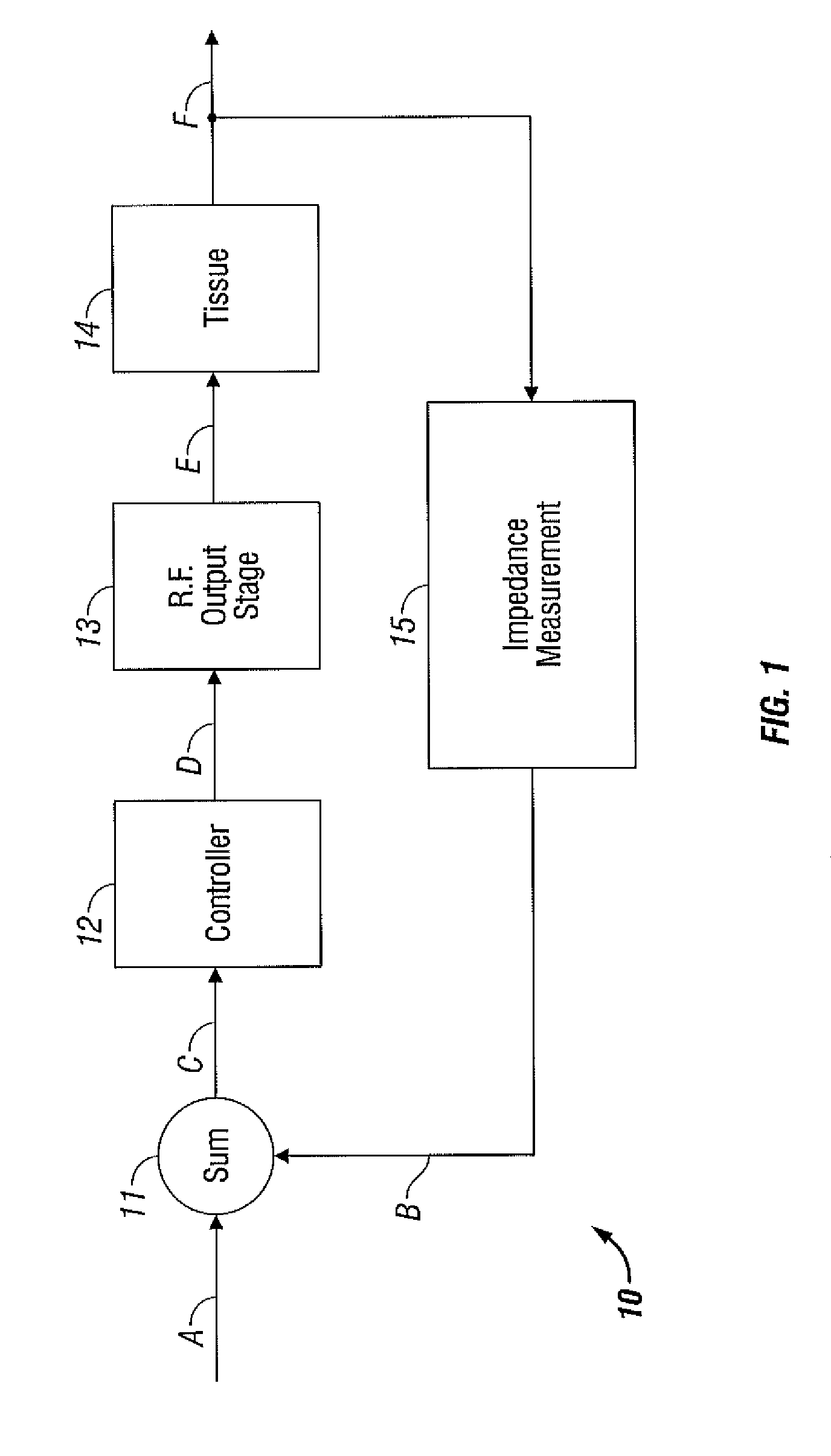
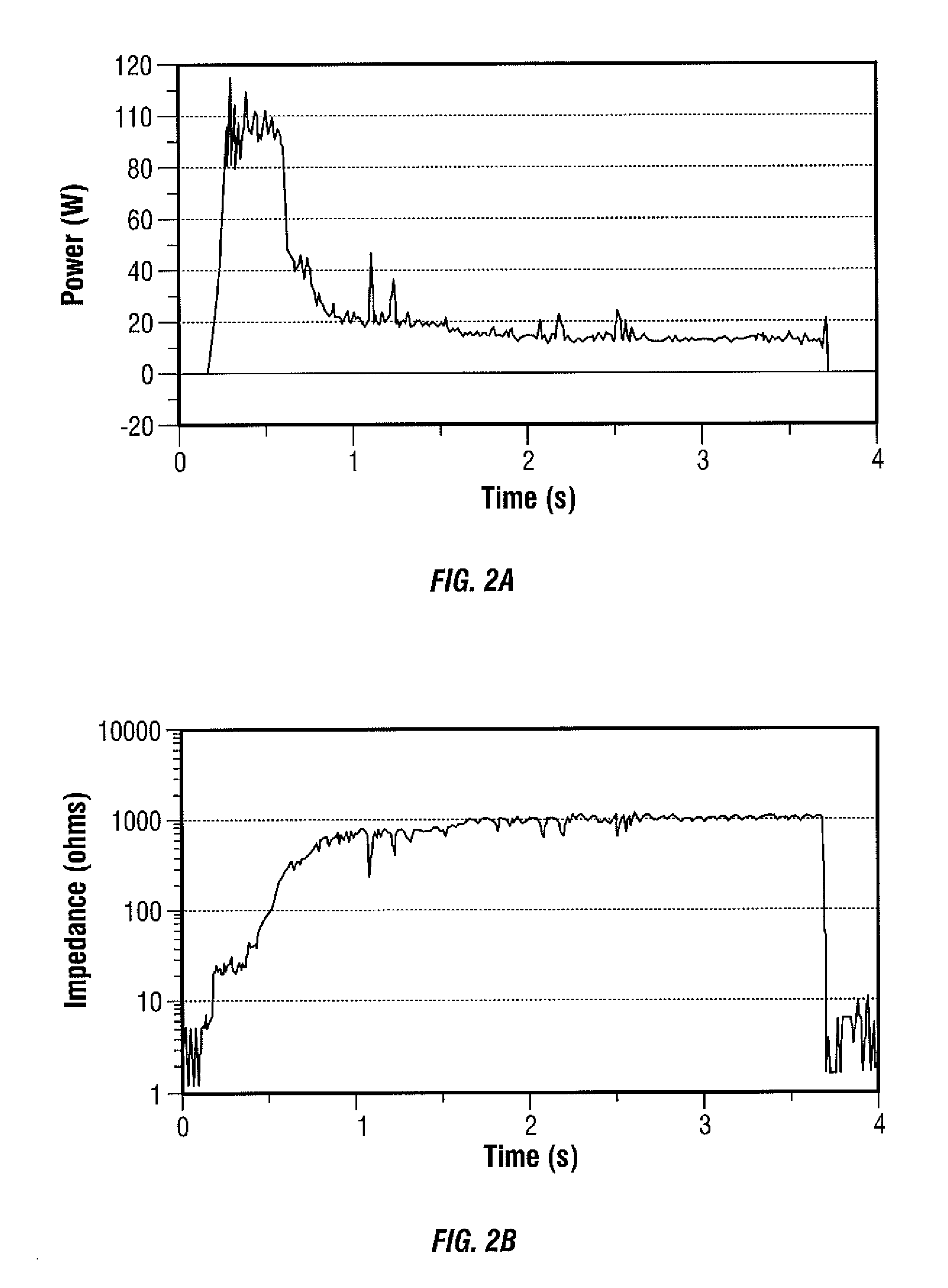
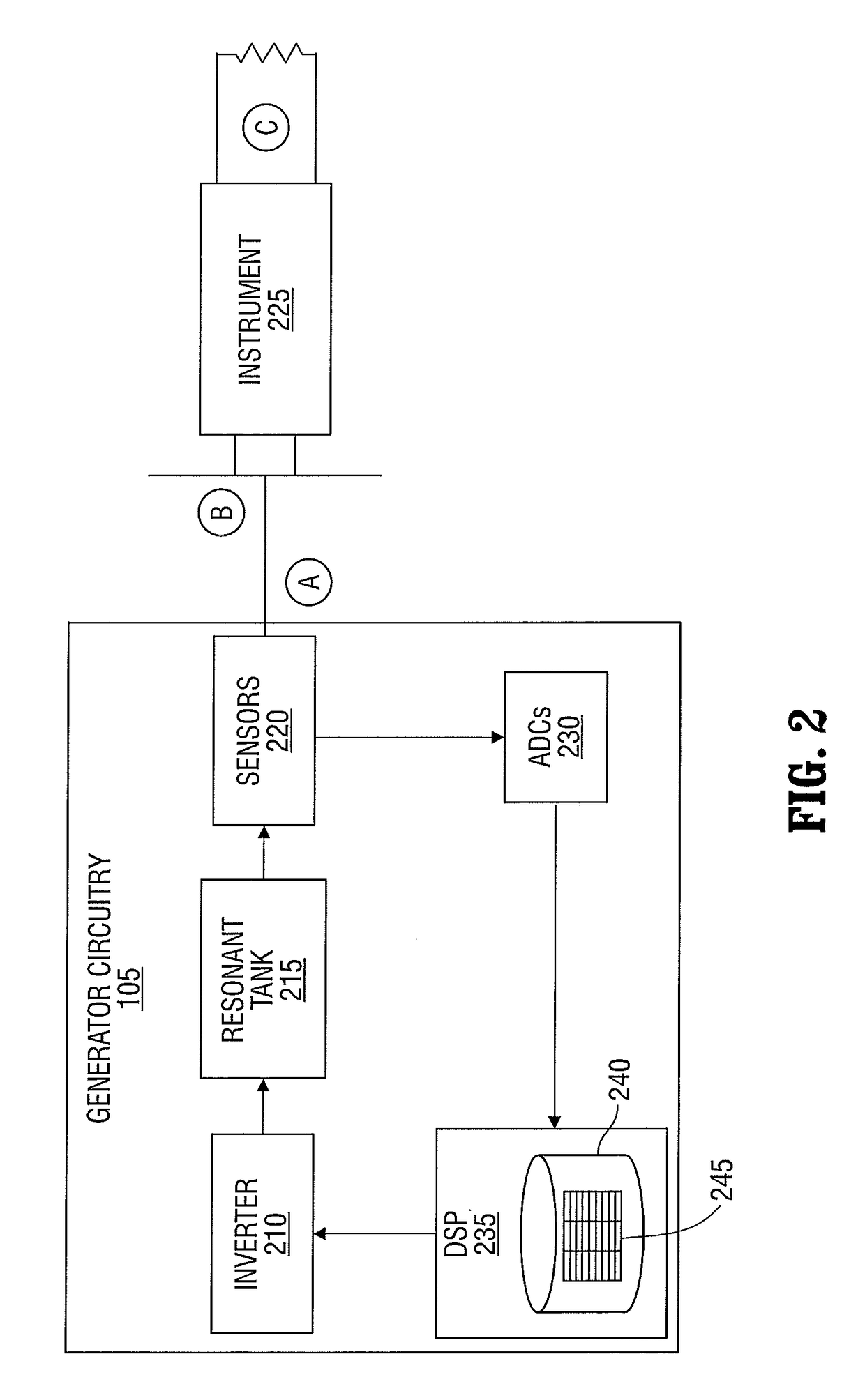
An electrosurgical generator is disclosed. The generator includes a radio frequency output stage configured to generate a frequency waveform to an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument when the active electrode is disposed in a fluid medium. The generator also includes a sensor circuit configured to measure tissue impedance and a controller configured to increase power of the radio frequency waveform to a predetermined electrical arcing level in response to the tissue impedance being within an open circuit impedance range and tissue contact impedance range. The controller is further configured to lower the power of the radio frequency waveform to a lower level when the tissue impedance is outside the open circuit impedance range and the tissue contact impedance range.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
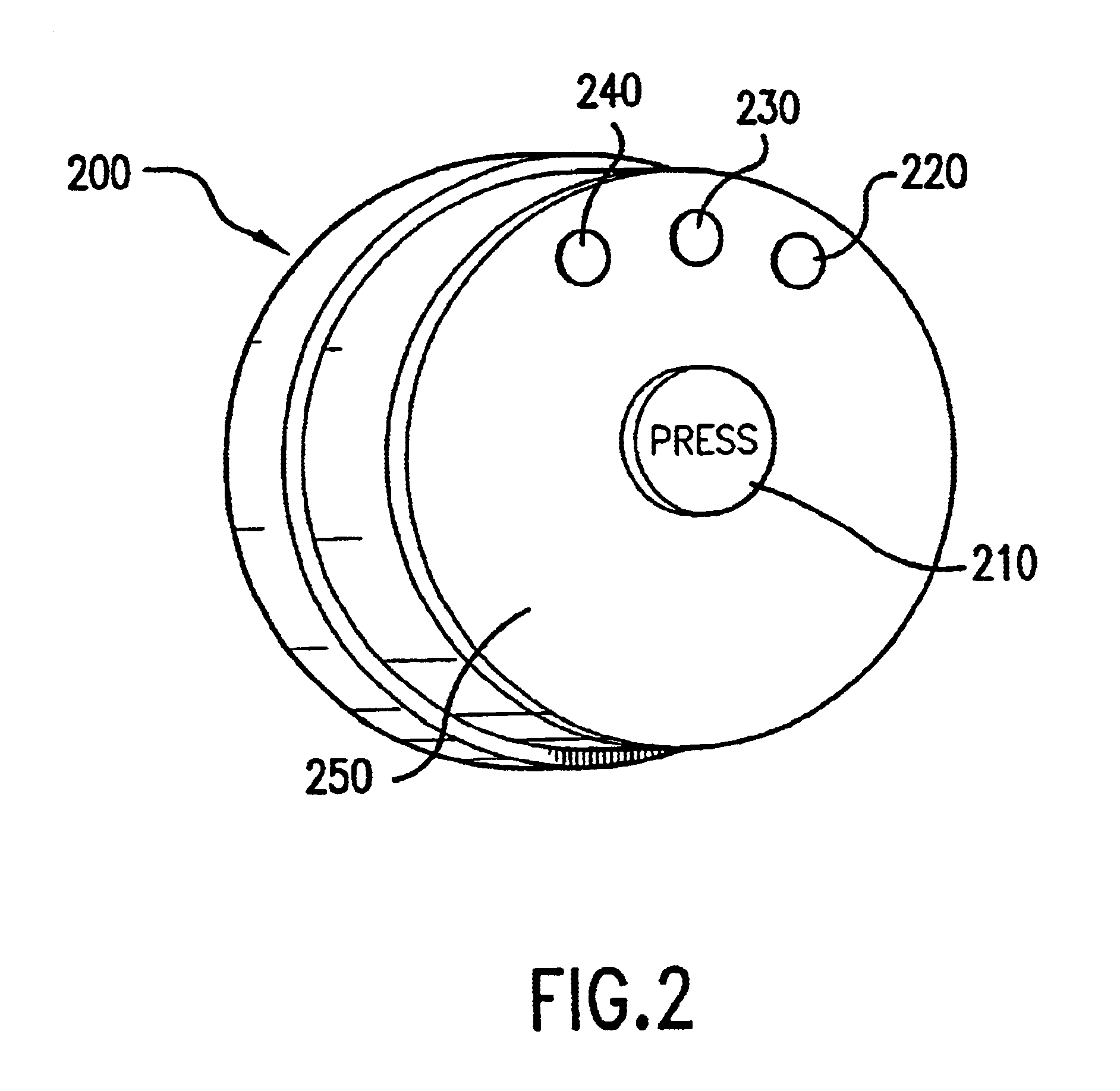
Nerve Stimulation Patches And Methods For Stimulating Selected Nerves
ActiveUS20090132018A1Improve efficiencyLess battery powerPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufacturePulse envelopeCarrier signal
A selective nerve stimulation patch includes a substrate having a top surface and a bottom surface, integrated components overlying the top surface of the substrate and being electrically interconnected with one another for generating at least one nerve stimulating signal, electrodes integrated into the substrate and exposed at the bottom surface thereof for applying the at least one nerve stimulating signal to a target nerve, a waterproof, breathable cover overlying the substrate and the integrated components, and a support flange surrounding the substrate and coupling the cover and the substrate together. The support flange has a top surface that slopes downwardly toward an outer perimeter thereof, and at least a portion of the cover conforms to the sloping top surface of the support flange. In one embodiment, the patch generates a high frequency waveform with properties such as amplitude, frequency and the like chosen so as to overcome tissue impedance and the stimulation threshold of the target nerve. The modulated waveform is the waveform obtained by modulating the carrier waveform by a pulse envelope.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Surgical instruments for treating gastro-esophageal reflux
InactiveUS6740082B2Augment objectInexpensive and disposableElectrotherapyEndoscopesSensor arrayFiber
Instruments for thermally-mediated treatment of a patient's lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to induce an injury healing response to thereby populate the extracellular compartment of walls of the LES with collagen matrices to altere the biomechanics of the LES to provide an increased intra-esophageal pressure for preventing acid reflux. A preferred embodiment is a bougie-type device for trans-esophageal introduction that carries conductive electrodes for delivering Rf energy to walls of the LES (i) to induce the injury healing response or (ii) to "model" collagenous tissues of the LES by shrinking collagen fibers therein. Typically, an Rf source is connected to at least one conductive electrode that may be operated in a mono-polar or bi-polar fashion. A sensor array of individual sensors is provided in the working end. A computer controller is provided, which together with feedback circuitry, is capable of full process monitoring and control of: (i) power delivery; (ii) parameters of a selected therapeutic cycle, (iii) mono-polar or bi-polar energy delivery, and (iv) multiplexing of current flow between various paired electrodes. The controller can determine when the treatment is completed based on time, temperature, tissue impedance or any combination thereof.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Method and apparatus to measure bioelectric impedance of patient tissue
ActiveUS8412317B2Minimizing memory resourceReduce gainElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsDriving currentPower flow
A device to measure tissue impedance comprises drive circuitry coupled to calibration circuitry, such that a calibration signal from the calibration circuitry corresponds to the current delivered through the tissue. Measurement circuitry can be coupled to measurement electrodes and the calibration circuitry, such that the tissue impedance can be determined in response to the measured calibration signal from the calibration circuitry and the measured tissue impedance signal from the measurement electrodes. Processor circuitry comprising a tangible medium can be configured to determine a complex tissue impedance in response to the calibration signal and the tissue impedance signal. The processor can be configured to select a frequency for the drive current, and the amount of drive current at increased frequencies may exceed a safety threshold for the drive current at lower frequencies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Method and apparatus for determining local tissue impedance for positioning of a needle
InactiveUS20090036794A1Eliminate impedanceGood distinctionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTissues typesSubcutaneous tissue
The invention relates to apparatus and methods for measuring local tissue impedance for subcutaneous tissue surrounding a needle tip inserted into a subject, impedance spectra and / or complex impedance values are determined. The invention applies a monopolar impedance measuring setup with a needle, a current-carrying electrode, an optional reference electrode. The setup is configured to eliminate contributions from the current-carrying electrode in order to measure local impedance of tissue in the close neighbourhood of the needle tip instead of an averaged value over the volume or current path between the needle and the electrode(s). The determined impedance can be correlated with either a tissue type or state, or with a position of the needle tip in the subject, and can thereby provide an insertion history to the operator in the form of impedance or corresponding tissue type as a function of insertion depth or time.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
Apparatus for detecting and treating tumors using localized impedance measurement
InactiveUS7419487B2Precise positioningEasy to monitorSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringAbnormal tissue growthImpedance sensor
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
System and method for controlling tissue heating rate prior to cellular vaporization
InactiveUS20070282320A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for coolingElectricityTissue heating
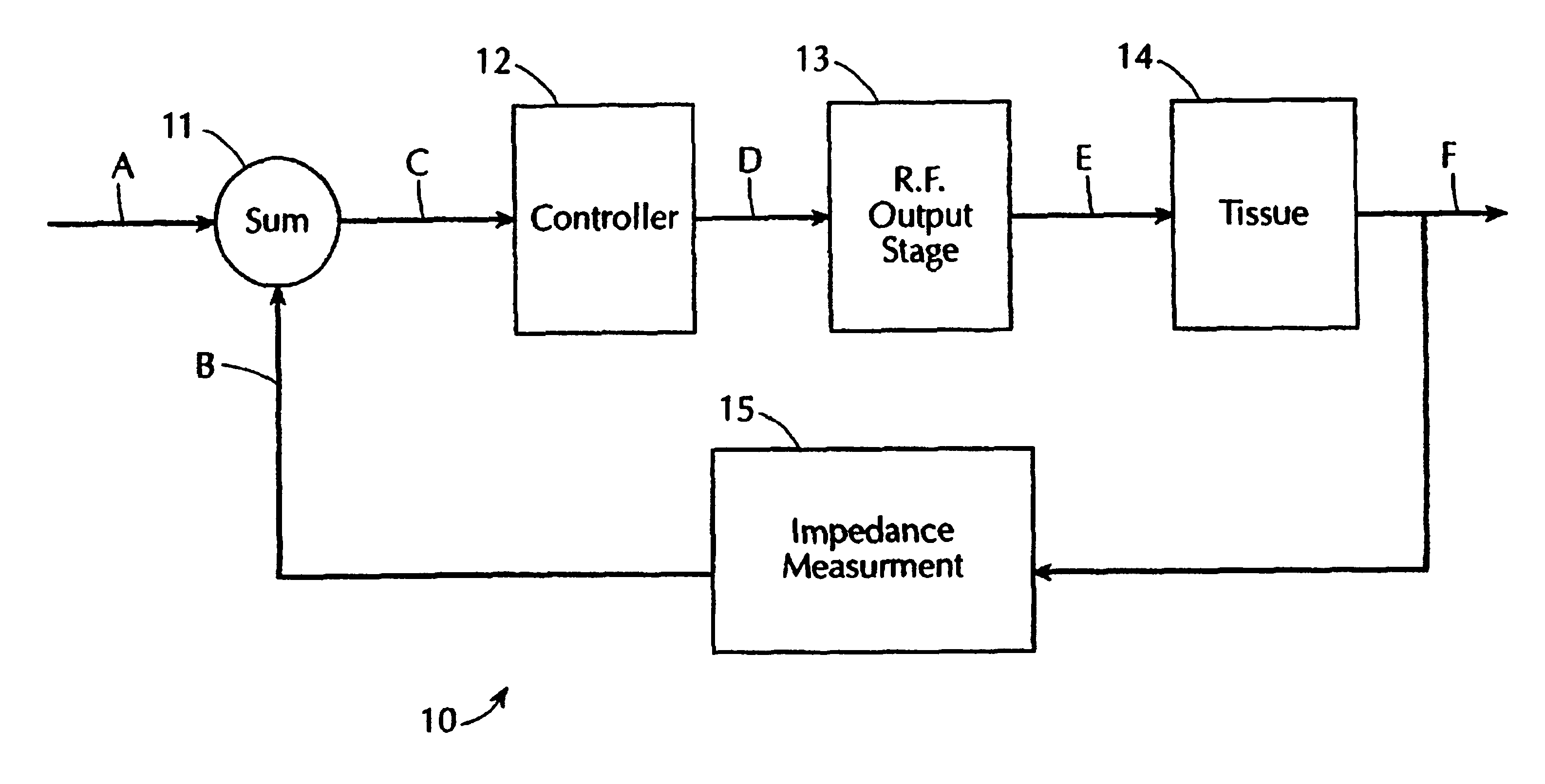
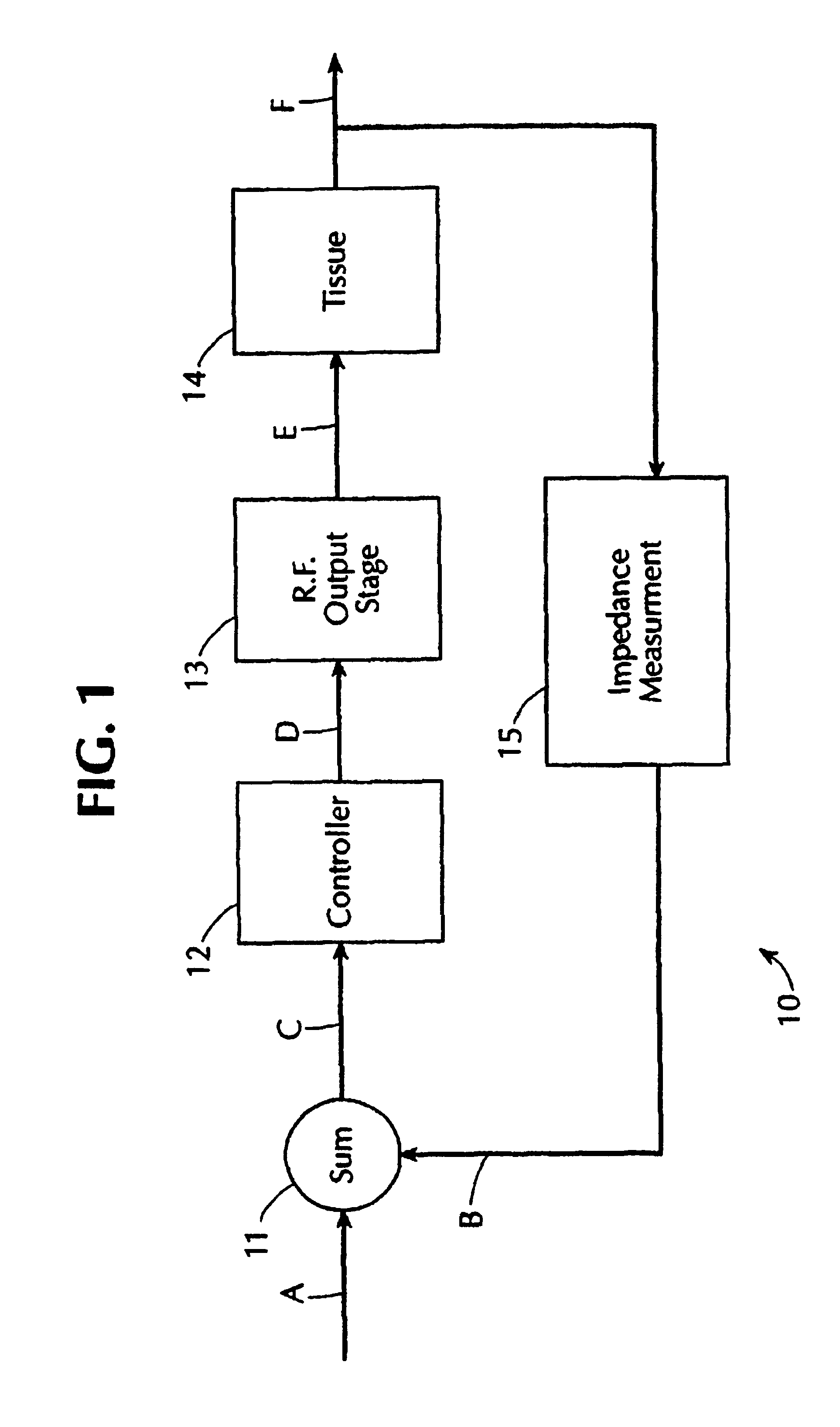
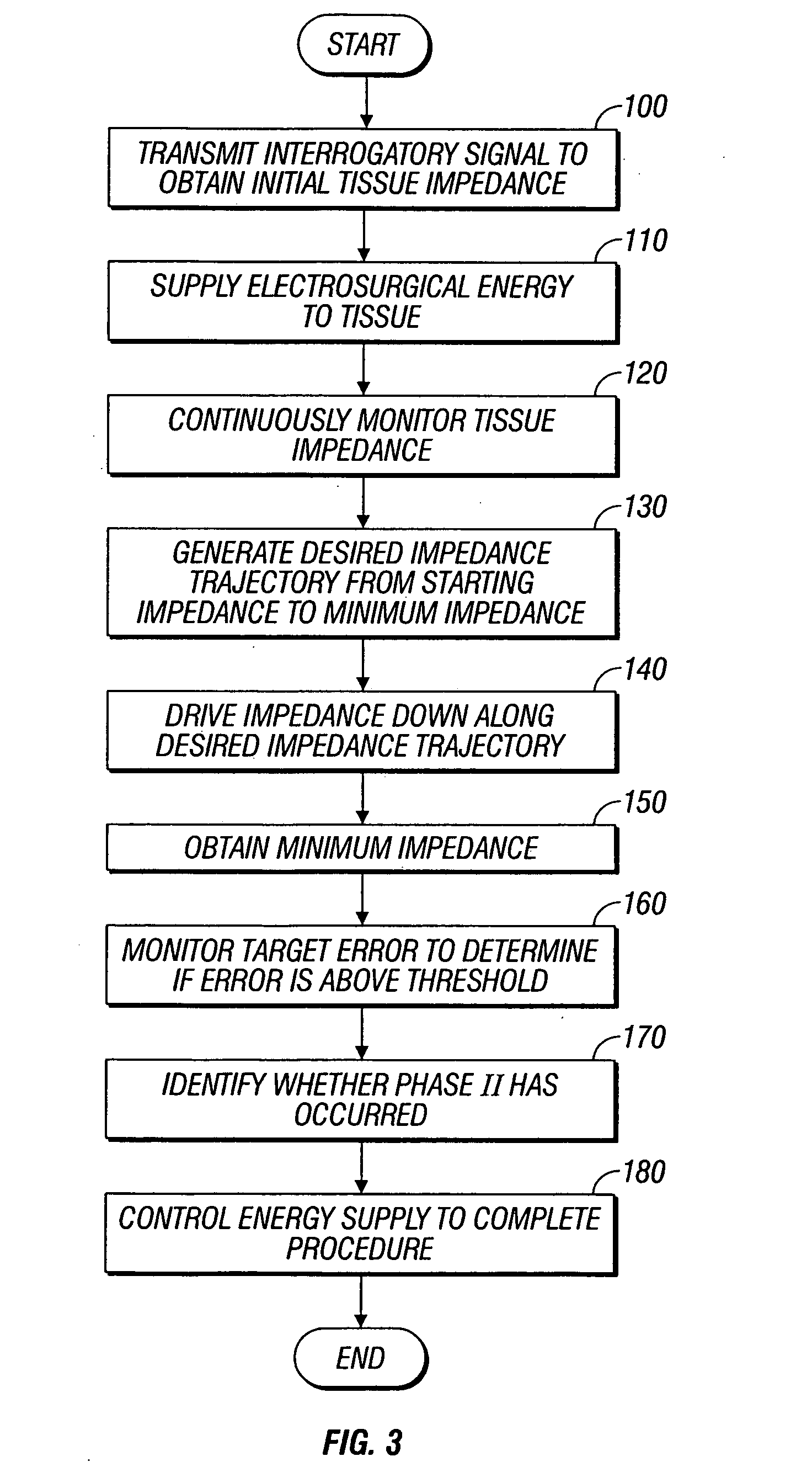
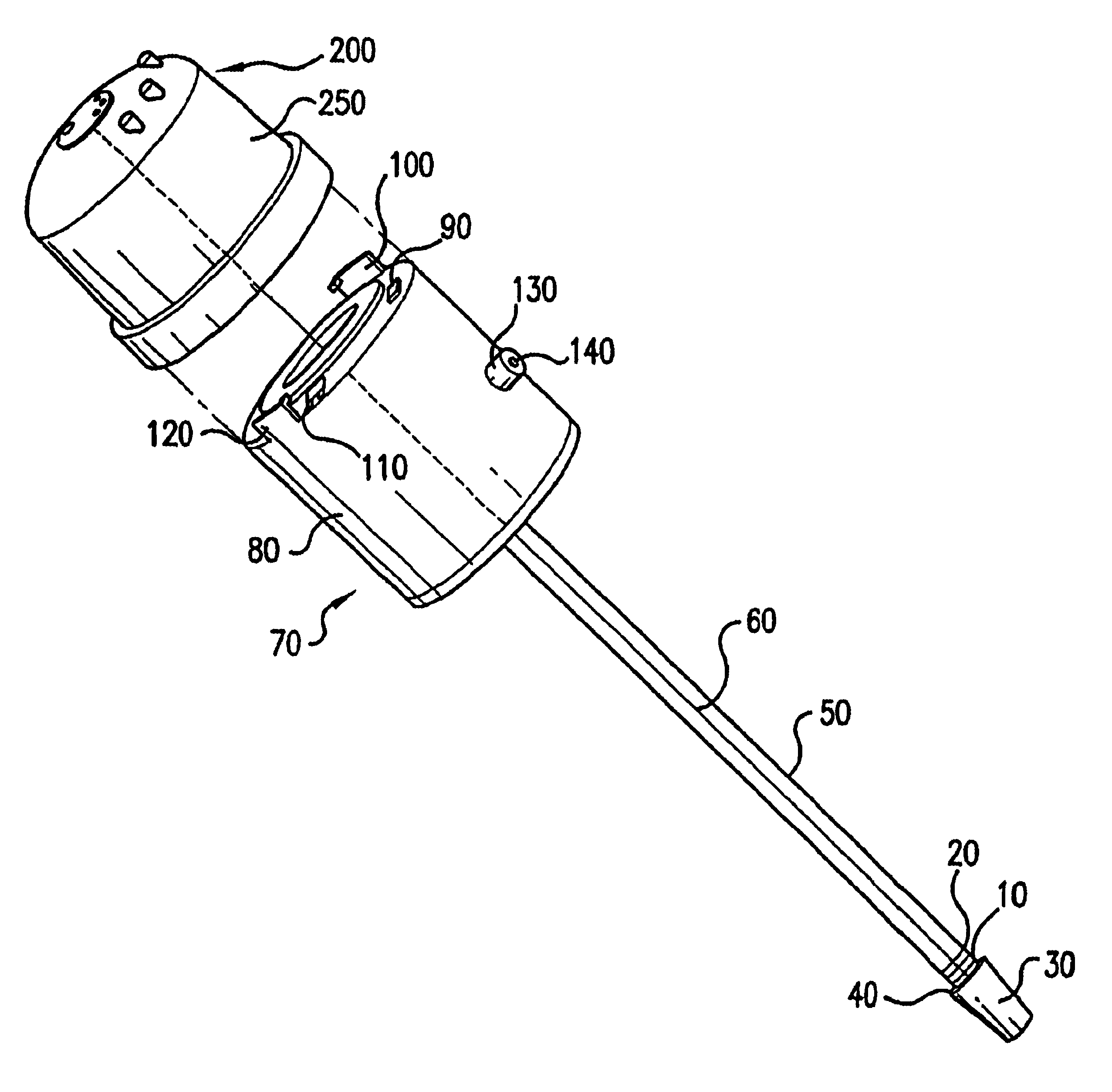
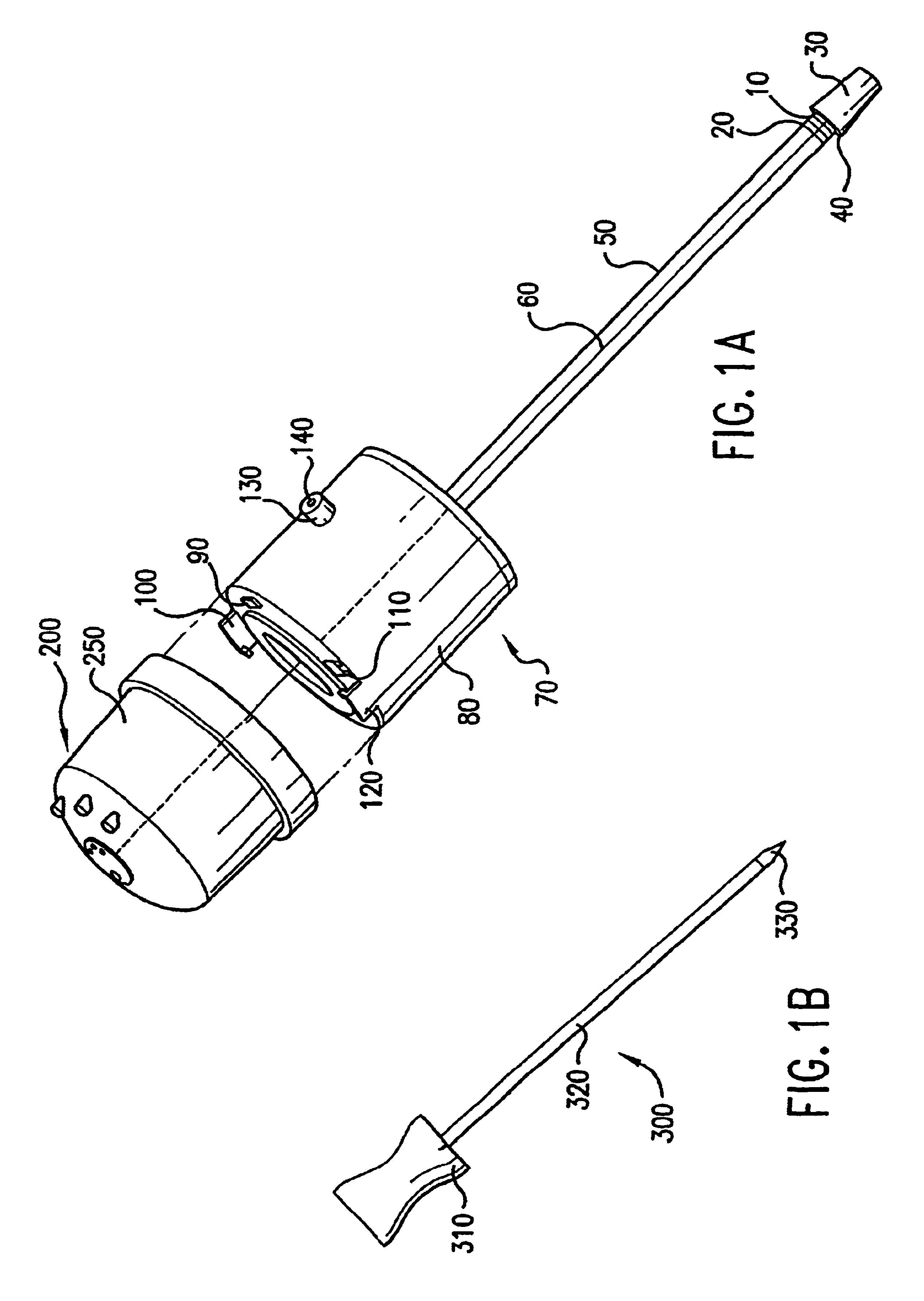
A system and method for performing electrosurgical procedures are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator adapted to supply energy at an output level to tissue and to transmit an interrogatory signal to obtain initial tissue impedance to derive a starting impedance value. The electrosurgical generator includes a microprocessor adapted to generate a desired impedance trajectory as a function of either of the initial tissue impedance or the starting impedance value. The desired impedance trajectory includes a plurality of target impedance values. The electrosurgical generator is further adapted to drive tissue impedance along the desired impedance trajectory by adjusting the output level to match tissue impedance to a corresponding target impedance value. The system also includes an electrosurgical instrument including at least one active electrode adapted to apply electrosurgical energy to tissue.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Systems and methods for reducing post-surgical complications
InactiveUS6645198B1Easy to holdLimit depth of insertionDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical incisionAbdominal wall
The present invention provides systems and methods for applying RF energy to injured tissue, particularly the peritoneum, in order to prevent harmful post-surgical adhesions. One aspect of the invention is RF energy delivery systems employing trocars, which are designed for use in laparotomies and laparoscopies. Another aspect of the invention is an RF delivery system comprising a surgical sheet with one or more electrodes for delivering the RF energy to the injured tissue resulting from conventional surgical incisions into the abdominal wall. Additionally, another aspect of the invention provides methods for controlling the treatment dosage of RF heat to the injured tissue using parameters such as treatment time, change in tissue temperature, and change in tissue impedance.
Owner:NTERO SURGICAL
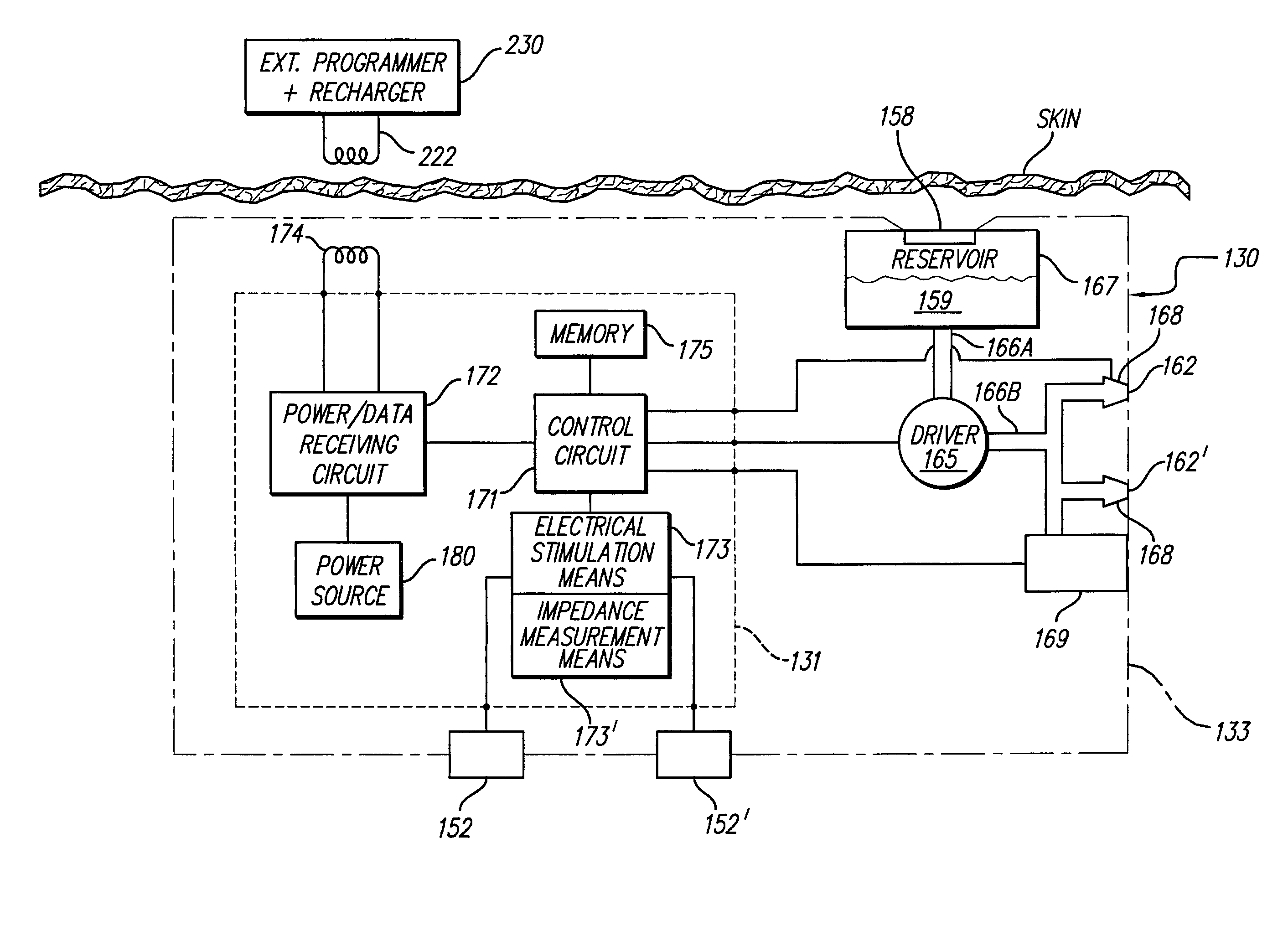
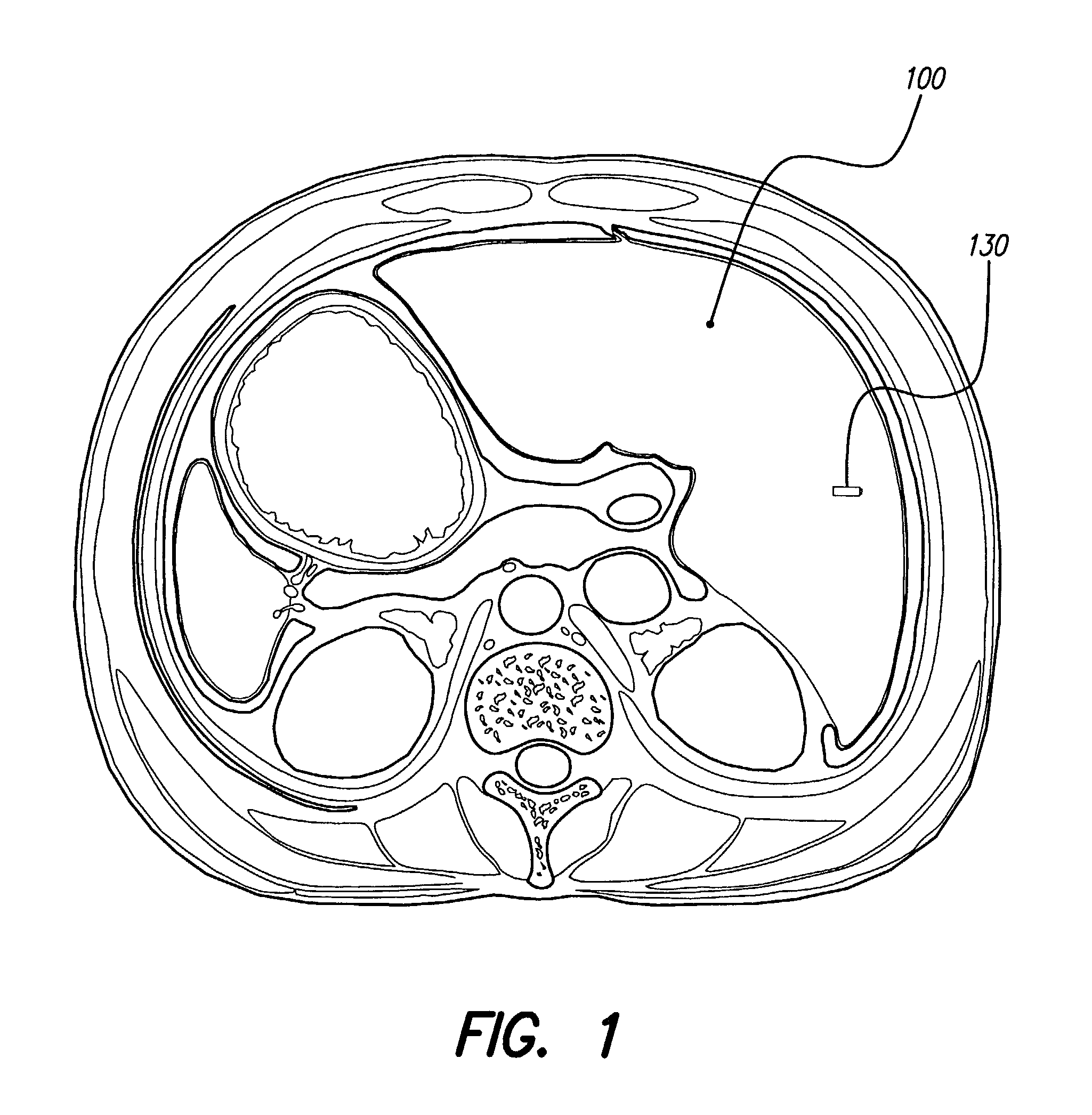
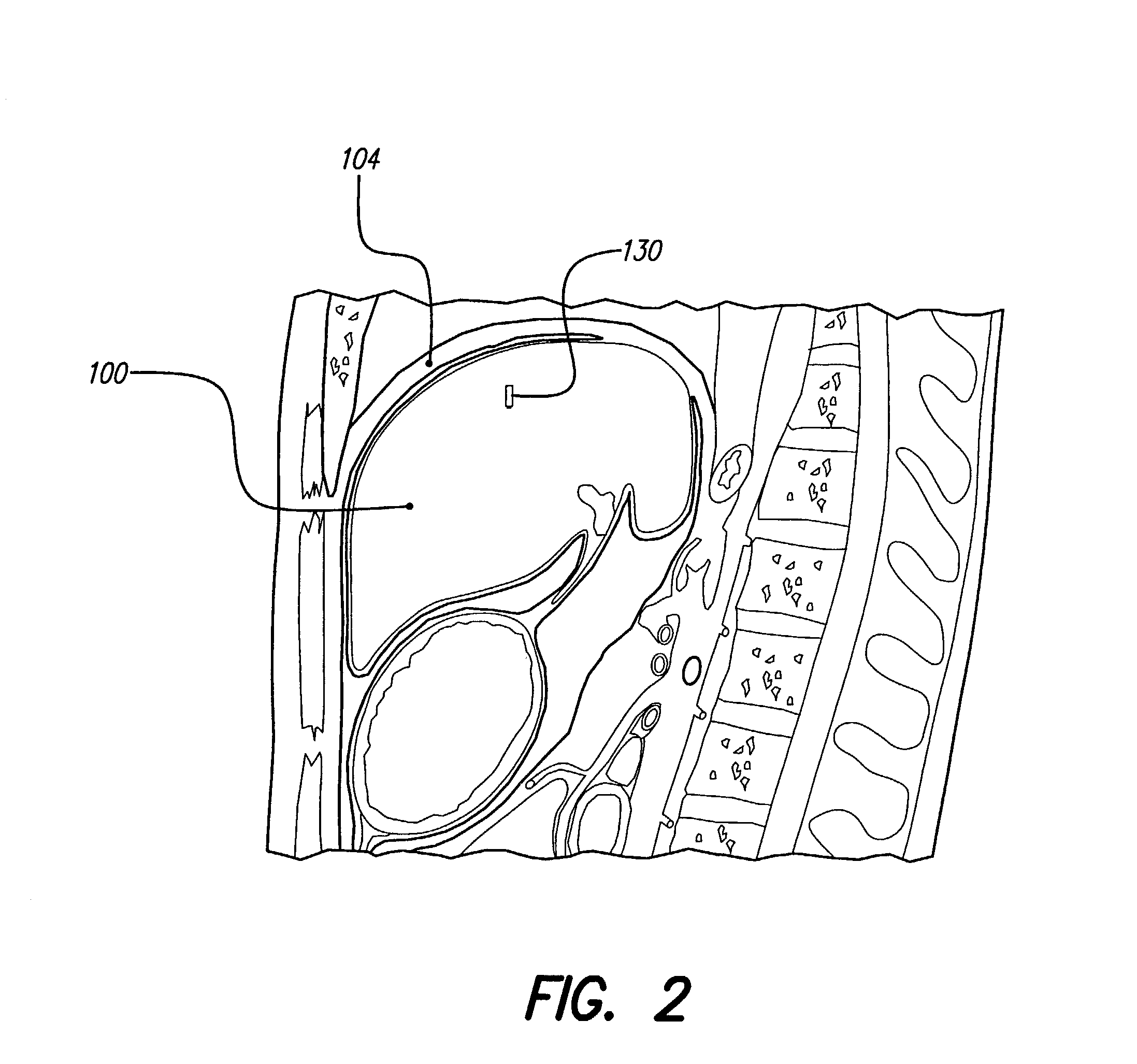
Monitoring, preventing, and treating rejection of transplanted organs
An implantable system control unit (SCU) includes means for measuring tissue impedance or other condition to determine allograft health, in order to predict or detect allograft rejection. The SCU also includes at least two electrodes coupled to means for delivering electrical stimulation to a patient within whom the device is implanted, and may also include a reservoir for holding one or more drugs and a driver means for delivering the drug(s) to the patient. In certain embodiments, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters. Alternatively, this sensory “SCU” sounds an alarm, communicates an alarm to an external device, and / or is responsive to queries regarding sensed information, such as tissue impedance.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Ablation Device with Sensor
InactiveUS20140194864A1ElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingElectricityConduction time
An electrosurgical device having a distal tip for creating a lesion on tissue includes a first electrode and a second electrode that are parallel for the delivery of RF energy to tissue. A sensor electrode is provided parallel to and spaced away from the first electrode a different distance than the second electrode. When the sensor electrode and at least one of the first and second electrodes are in contact with tissue. The electrosurgical device can perform at least one of the following: ablating tissue, and sensing at least one selected from the group of voltage, tissue impedance, electrical conduction, conduction time, conduction velocity, and signal phase angle.
Owner:ATRICURE
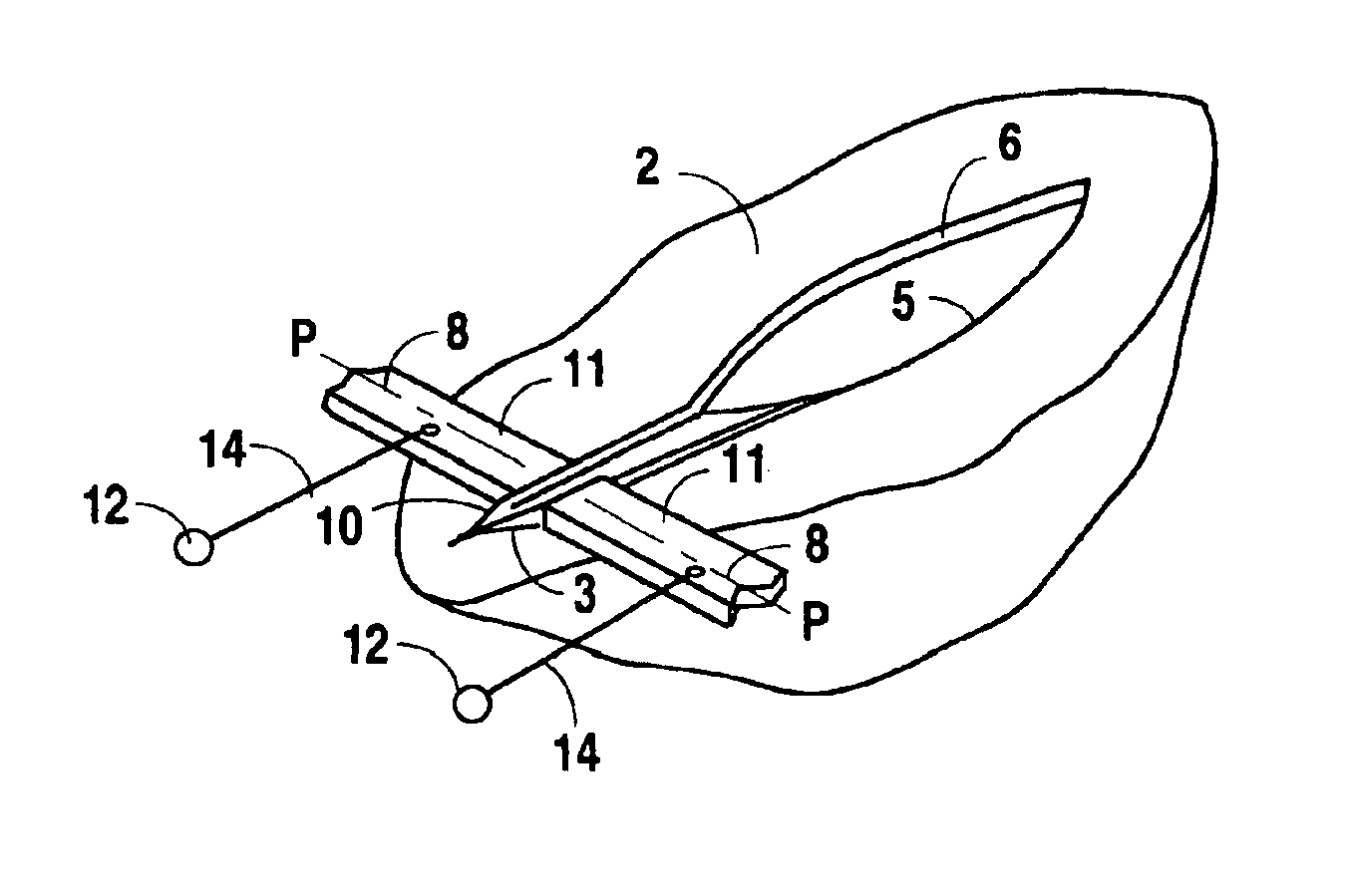
Bonding of soft biological tissues by passing high frequency electric current therethrough
InactiveUS7025764B2Avoid stickingAvoid burnsDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingForcepsEngineering
Technique for bonding soft biological tissue having an incision therein with forceps adapted to grip a portion of tissue on both sides of incision. Electrodes are secured to forceps for contracting the tissue portion. An electrical power source provides a high frequency electrical signal to electrodes to be passed through the tissue portion. The electrical power source is controlled to provide electrodes with one voltage signal during a first of two stages, wherein the voltage rises linearly, and another voltage signal during a second of the two stages, wherein the voltage is stabilized and modulated with a low frequency rectangular signal. A clamping means applies force with the forceps to compress the tissue at one or different levels during two time periods while the high frequency voltage is passed through the electrodes. The tissue impedance is measured as a function of time, with its minimal value being determined and stored.
Owner:BIOFUSE MEDICAL TECH +1
Methods and Apparatus for Electrical Stimulation of Tissues Using Signals that Minimize the Effects of Tissue Impedance
InactiveUS20090030476A1Optimization mechanismFunction increaseElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyElectricityMedicine
A tissue stimulation system that generates an electrical tissue stimulation signal configured to reduce tissue impedance and increase depth of signal penetration. The use of leads is dynamically controlled and altered between conducting biopotential voltages, conducting electrical tissue stimulation signals, and grounding, in response to a computational analysis of biopotential data acquired from a region of tissue to be stimulated.
Owner:HARGROVE JEFFREY B
Systems and methods for reducing post-surgical complications
InactiveUS6520185B1Reduce morbidityMinimizes and eliminates formationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSurgical incisionAbdominal wall
The present invention provides systems and methods for applying RF energy to injured tissue, particularly the peritoneum, in order to prevent harmful post-surgical adhesions. One aspect of the invention is RF energy delivery systems employing trocars, which are designed for use in laparotomies and laparoscopies. Another aspect of the invention is an RF delivery system comprising a surgical sheet with one or more electrodes for delivering the RF energy to the injured tissue resulting from conventional surgical incisions into the abdominal wall. Additionally, another aspect of the invention provides methods for controlling the treatment dosage of RF heat to the injured tissue using parameters such as treatment time, change in tissue temperature, and change in tissue impedance.
Owner:NTERO SURGICAL
Tissue treatment system and method for tissue perfusion using feedback control
A system, ablation probe, and method is provided for treating tissue, e.g., tissue having tumors. The treatment system is configured to automatically deliver infusaid to tissue when needed and comprises an ablation probe having an ablative element and at least one perfusion exit port. The system further comprises an ablation source operably coupled to the ablative element, and a pump assembly operably coupled to the perfusion exit port(s). The pump assembly is configured for pumping infusaid out through the perfusion exit port(s), preferably during the ablation process. The system further comprises a feedback device configured for controlling the amount of infusaid displaced by the pump assembly based on a sensed tissue parameter, e.g., tissue temperature or tissue impedance.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
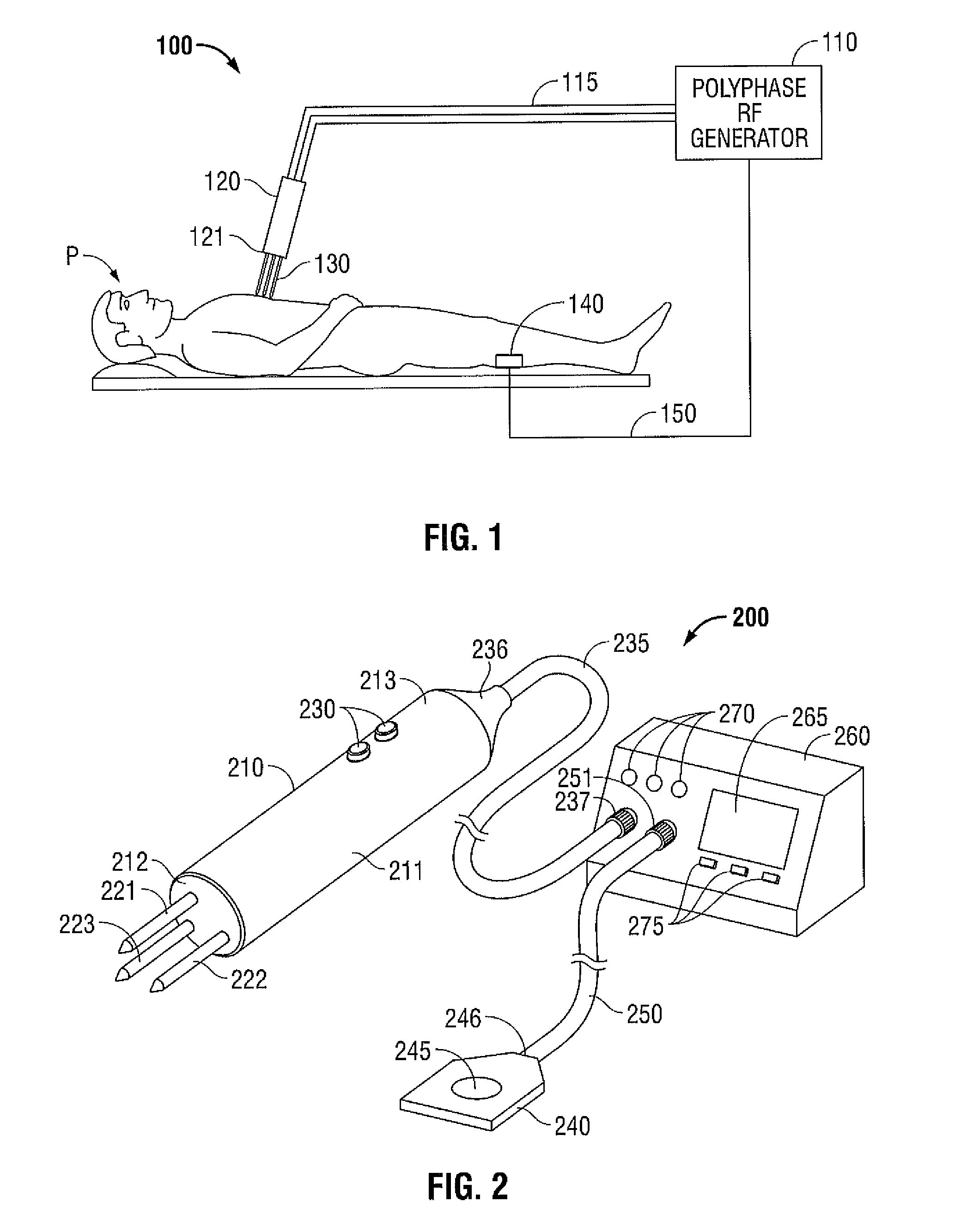
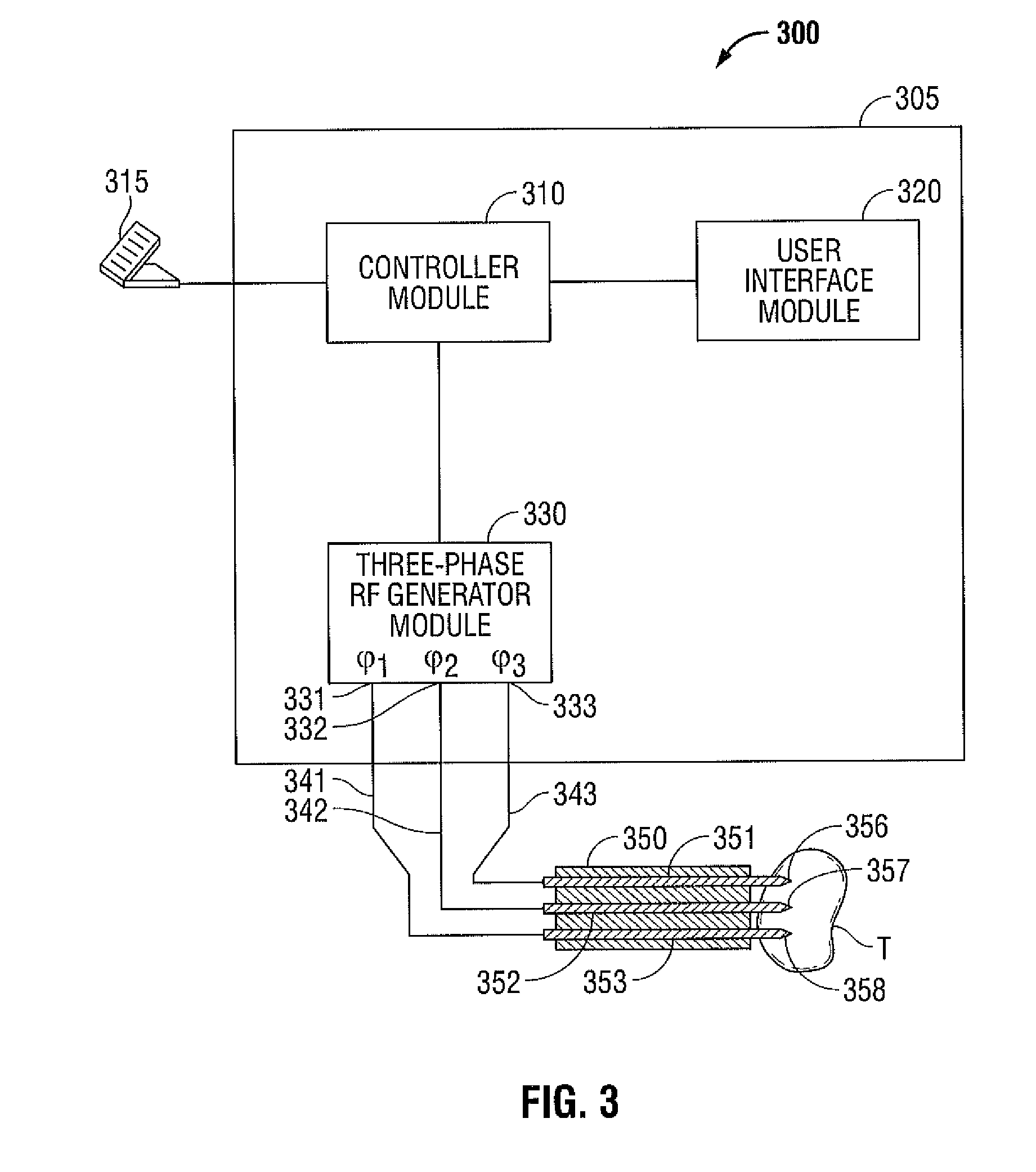
Polyphase Electrosurgical System and Method
ActiveUS20100030210A1Area minimizationMinimizing volumeSurgical instruments for heatingUser inputThree-phase
A polyphase electrosurgical system and method are provided. In embodiments, a radiofrequency generator having the capability of delivering a plurality of independent electrosurgical signals is disclosed. An electrosurgical instrument having an array of electrodes that correspond to the plurality of signals may be used to deliver the electrosurgical signals to tissue. In embodiments, three RF signals having a phase offset of about 120° therebetween, i.e., a three-phase configuration, may be used to achieve a balanced delivery of electrosurgical energy, which may lead to increased rates of energy delivery, improved control of tissue ablation regions, and improved operative outcomes. The phase, amplitude, and / or frequency of each signal may be independently variable in response to user inputs and / or biological parameters such as tissue impedance or return electrode current.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
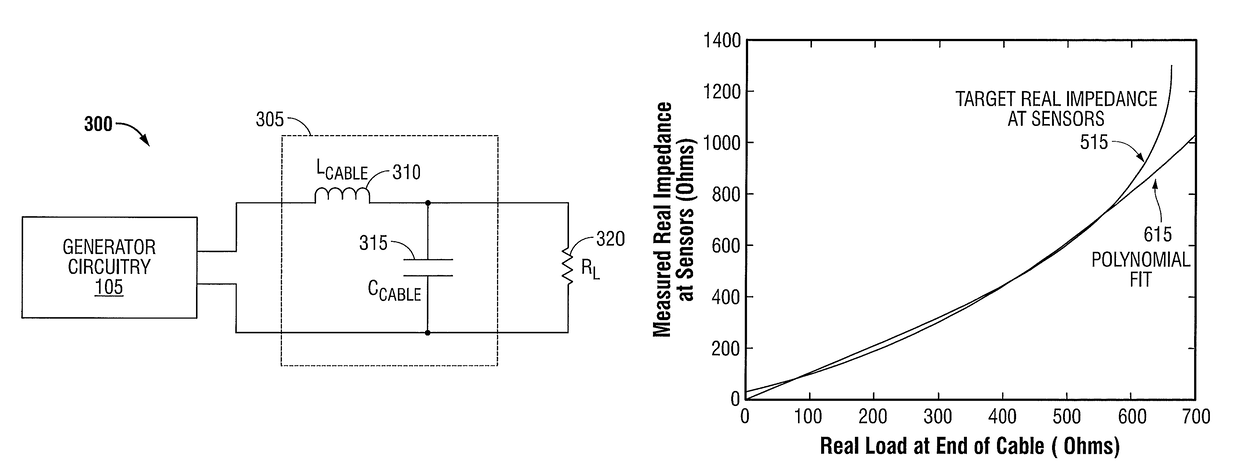
Systems and methods for measuring tissue impedance through an electrosurgical cable
ActiveUS9636165B2Reduce the amount requiredExact impedanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The electrosurgical systems and methods of the present disclosure include a tissue resistance measurement system that compensates for capacitive parasitics in a cable connecting an electrosurgical generator to and electrosurgical cable to estimate the real resistance of a tissue load. The electrosurgical generator includes an output stage coupled to an electrical energy source and generates electrosurgical energy. The electrosurgical generator includes a plurality of sensors sensing a voltage and current of the electrosurgical energy and a controller controlling the output stage. The controller includes a calculator that calculates a real part of an impedance based on the sensed voltage and current, an estimator that estimates a resistance of the tissue using a solution to a quadratic equation that is a function of the real part of the impedance, and a control signal generator configured to generate a control signal for the output stage based on the resistance of the tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Power level transitioning in a surgical instrument
An electrosurgical system and method are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator adapted to supply electrosurgical energy to tissue. The generator is further adapted to supply an electrosurgical signal at a variable power level. The generator includes sensor circuitry adapted to sense tissue impedance and / or an electrosurgical signal zero crossing. The generator also includes a controller, which may include a microprocessor, that is adapted to receive a tissue impedance signal and / or a waveform zero crossing signal. The controller is configured to monitor tissue impedance, and in response to a threshold value of impedance being reached, to cause a power level of the electrosurgical energy to transition from a first power level to a second power level. The slew rate of the power transition may be in accordance with a transition function, such as a cosine function. The power transition may additionally or alternatively be performed during, or correlated with, an electrosurgical signal zero crossing. The system also includes an electrosurgical instrument including at least one active electrode adapted to apply electrosurgical energy to tissue for treatment.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
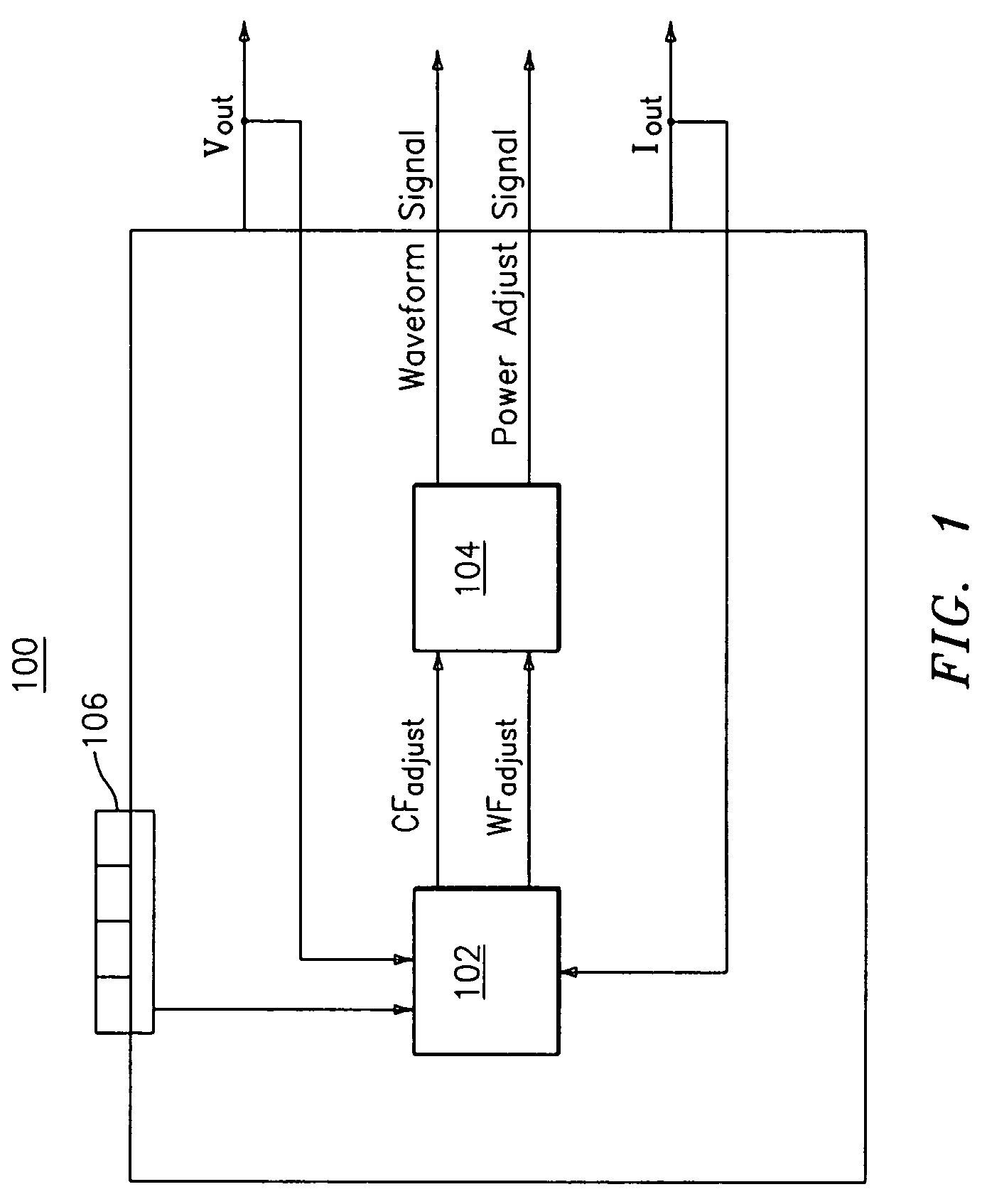
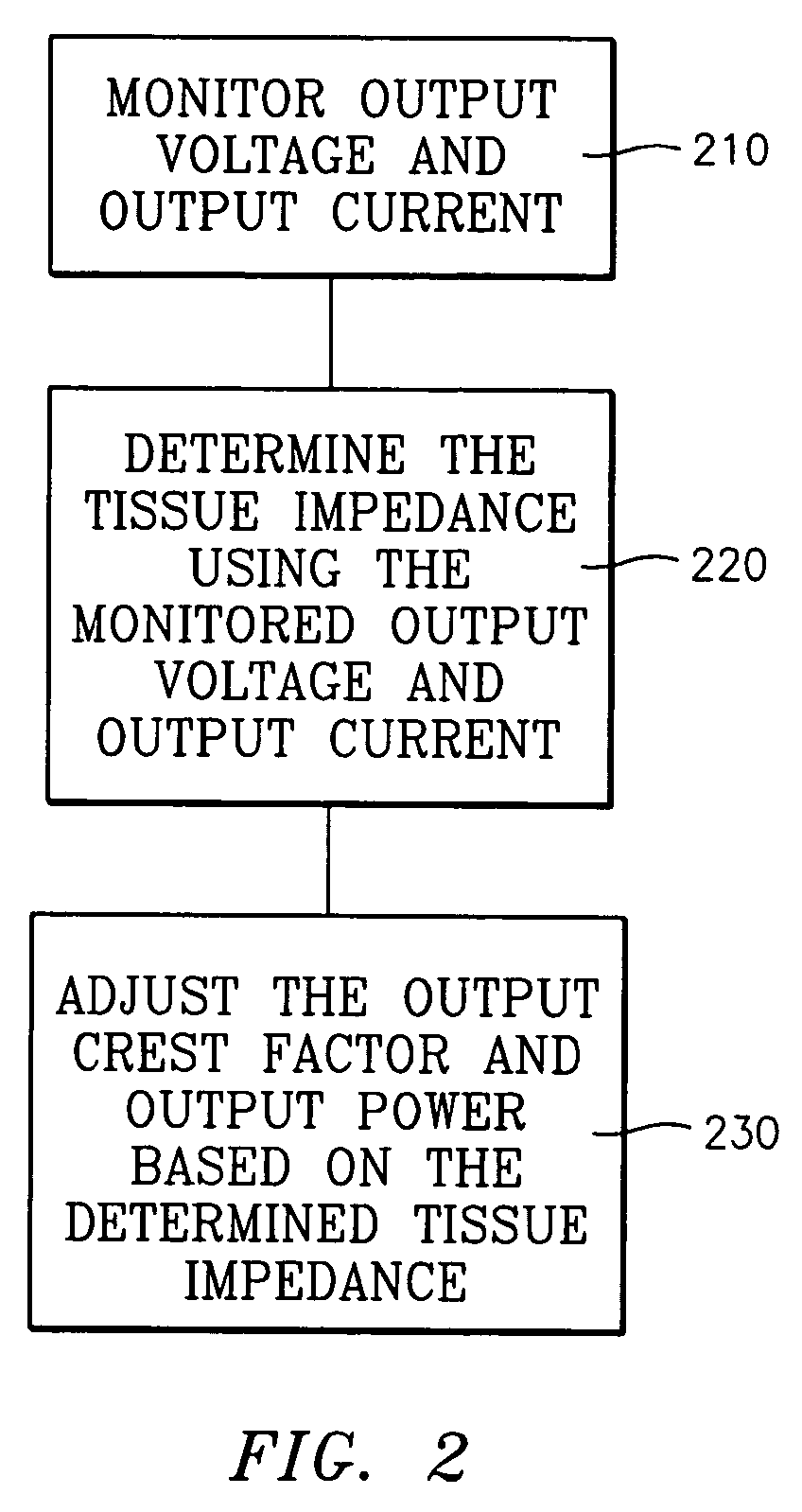
Variable output crest factor electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS7255694B2Range of effect and desirableSurgical effect and desirable surgical resultSurgical instruments for heatingElectrosurgeryEngineering
An electrosurgical generator is disclosed capable of controlling the output crest factor, as well as the output power of the electrosurgical generator across a range of tissue impedances during electrosurgery. The control occurs automatically, in real time and continuously during the duration of electrosurgical activation of the electrosurgical generator by varying both the output crest factor and output power based on the changing impedance of the tissue. The electrosurgical generator also includes controls for allowing a surgeon to manually select the appropriate crest factor value and power output value for a particular surgical procedure. By automatically adjusting the output crest factor and by giving the surgeon the ability to manually “tailor” the output crest factor across a range of tissue impedance, the electrosurgical generator enhances the ultimate surgical effect and desirable surgical results.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
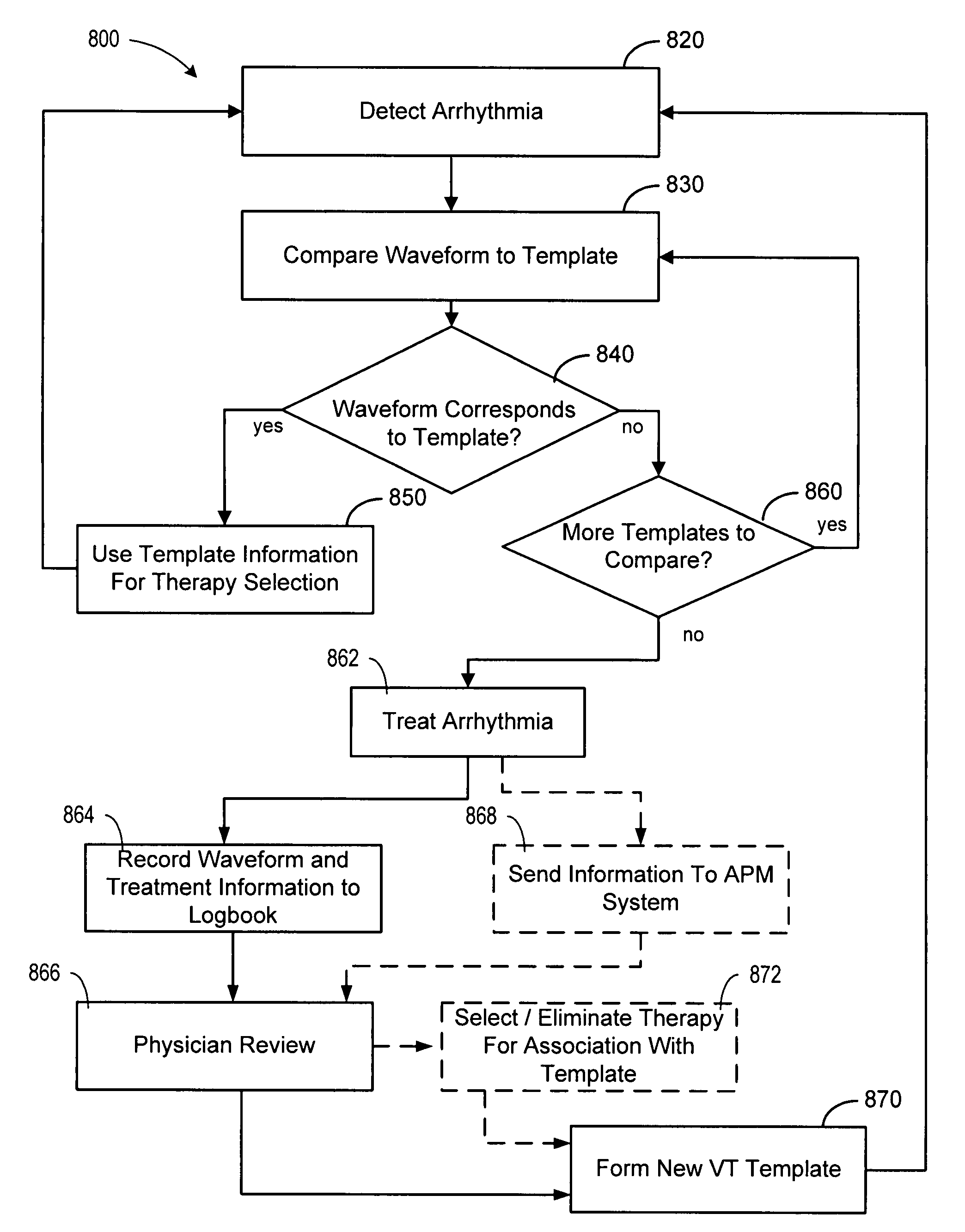
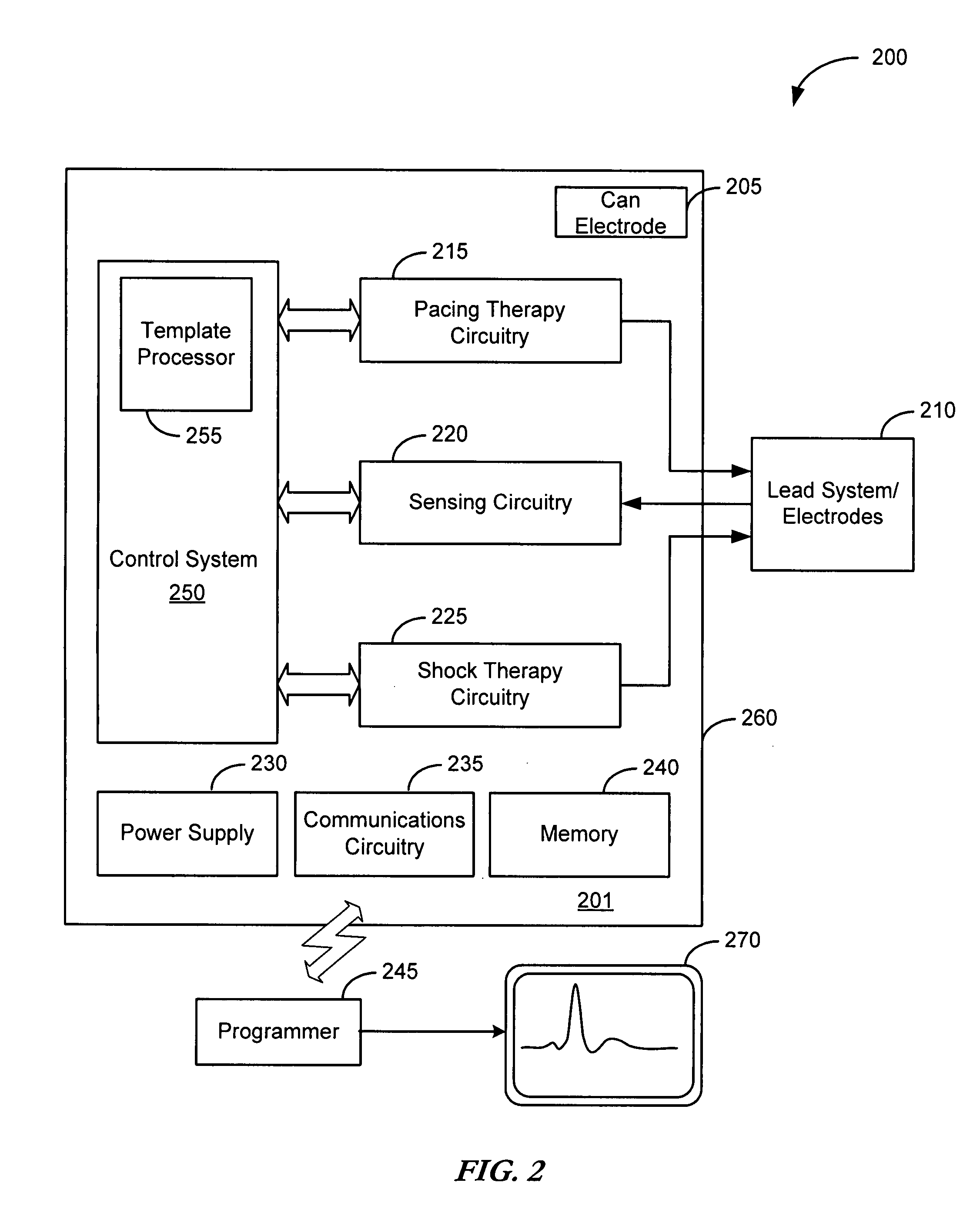
Cardiac tachyarrhythmia therapy selection based on patient response information
Cardiac treatment methods and devices providing templates representative of past tachyarrythmia events, each template associated with a therapy. A cardiac waveform is detected, and if it corresponds to a particular template associated with a previous therapy that was satisfactory in terminating a past event, the previous therapy is delivered again. If unsatisfactory, the previous therapy is eliminated as an option. If, for example, the previous therapy was an antitachycardia pacing therapy unsatisfactory in terminating the past tachyarrythmia event, delivery of the antitachycardia pacing therapy is eliminated as an option. Instead of ATP therapy, one or more of a cardioversion, defibrillation, or alternate anti-tachycardia pacing therapy may be associated with the particular template. Cardiac waveforms and templates may correspond in terms of one or more of morphology, timing, drug regimen, medication, neural activity, patient activity, hemodynamic status, cardiac tissue impedance, transthoracic impedance, or other information corresponding to the episode.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com