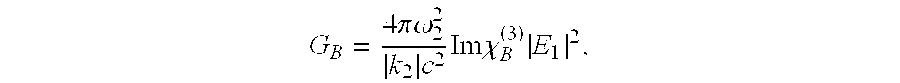Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Minimizing volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
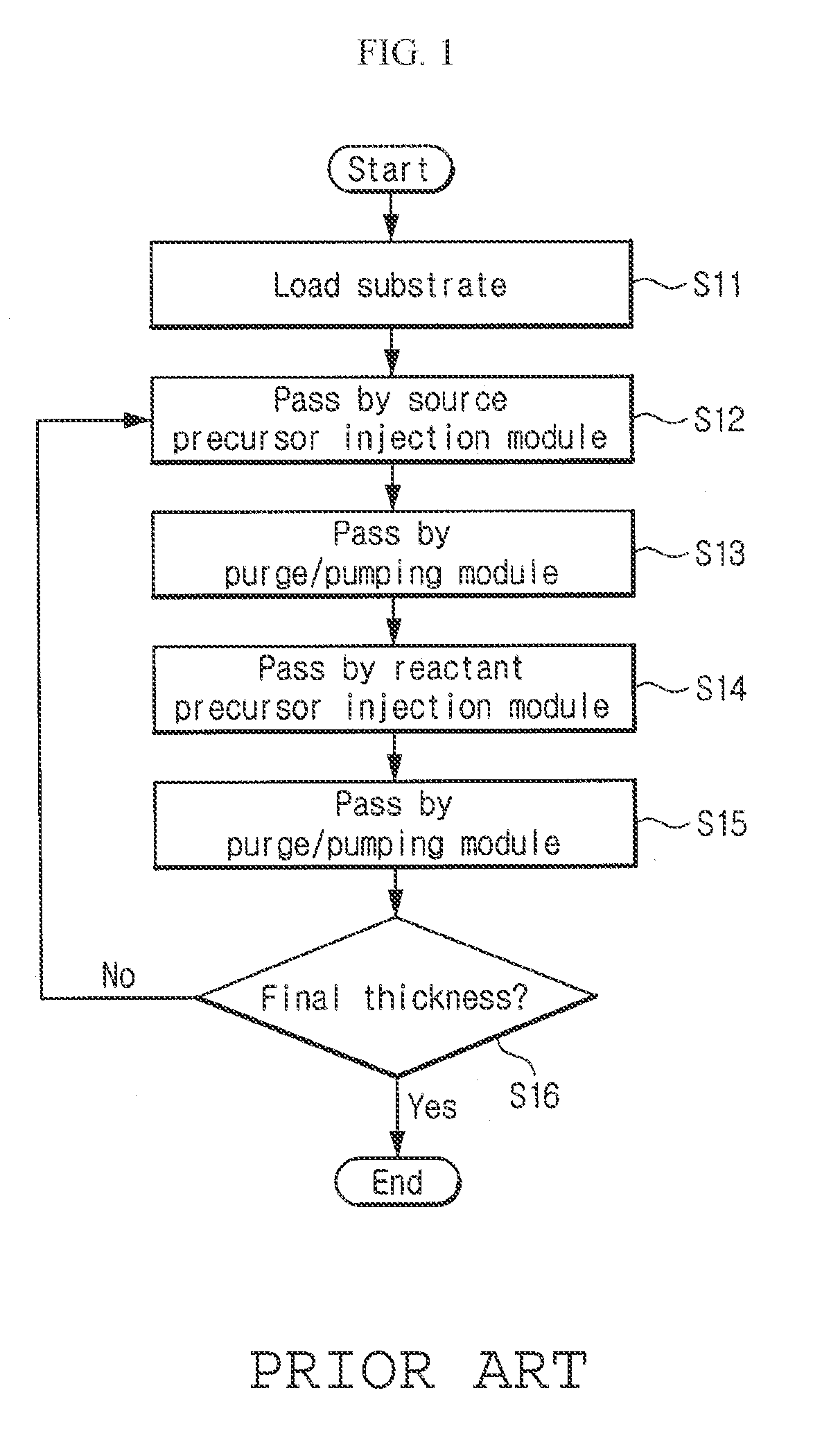
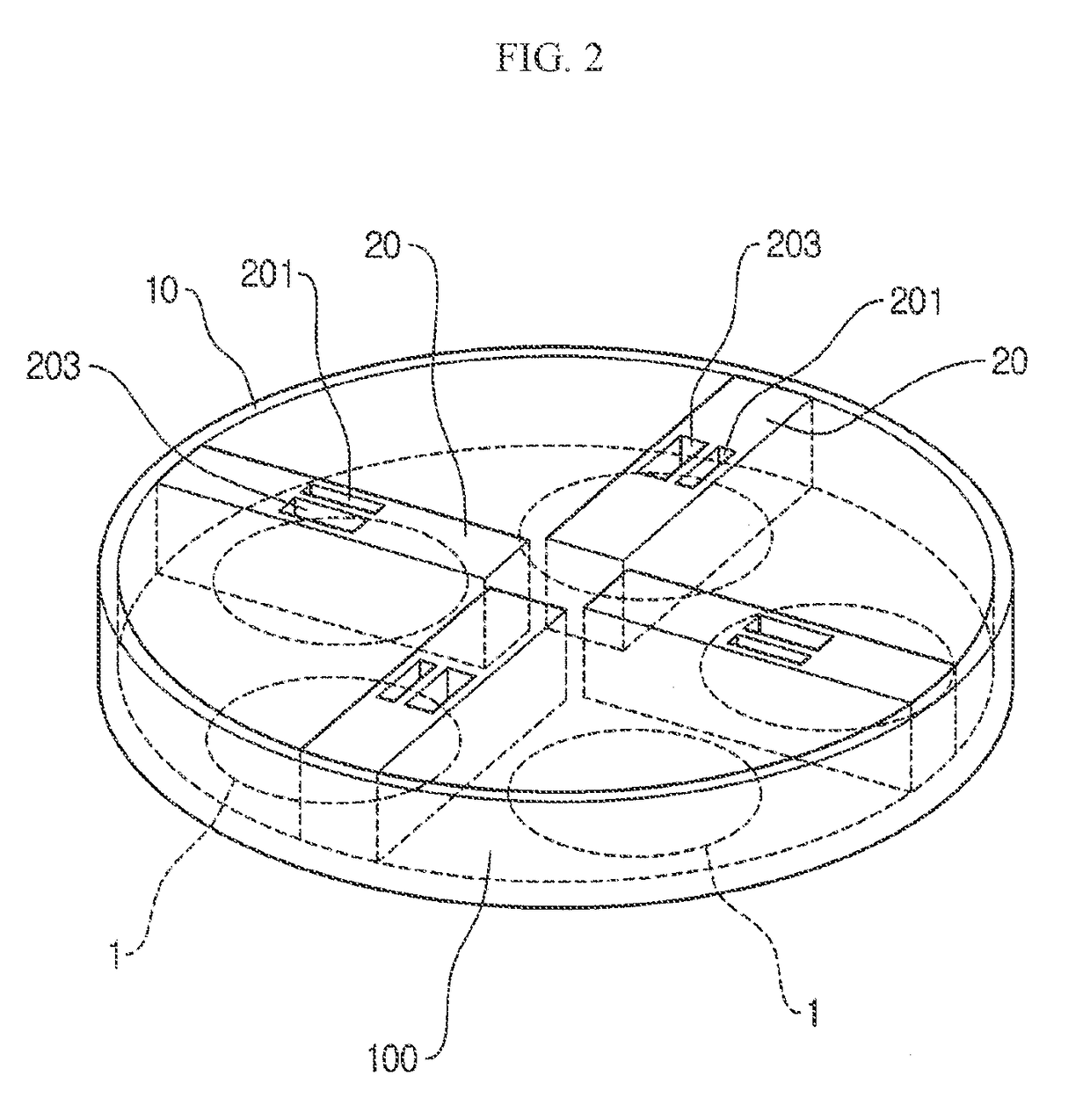
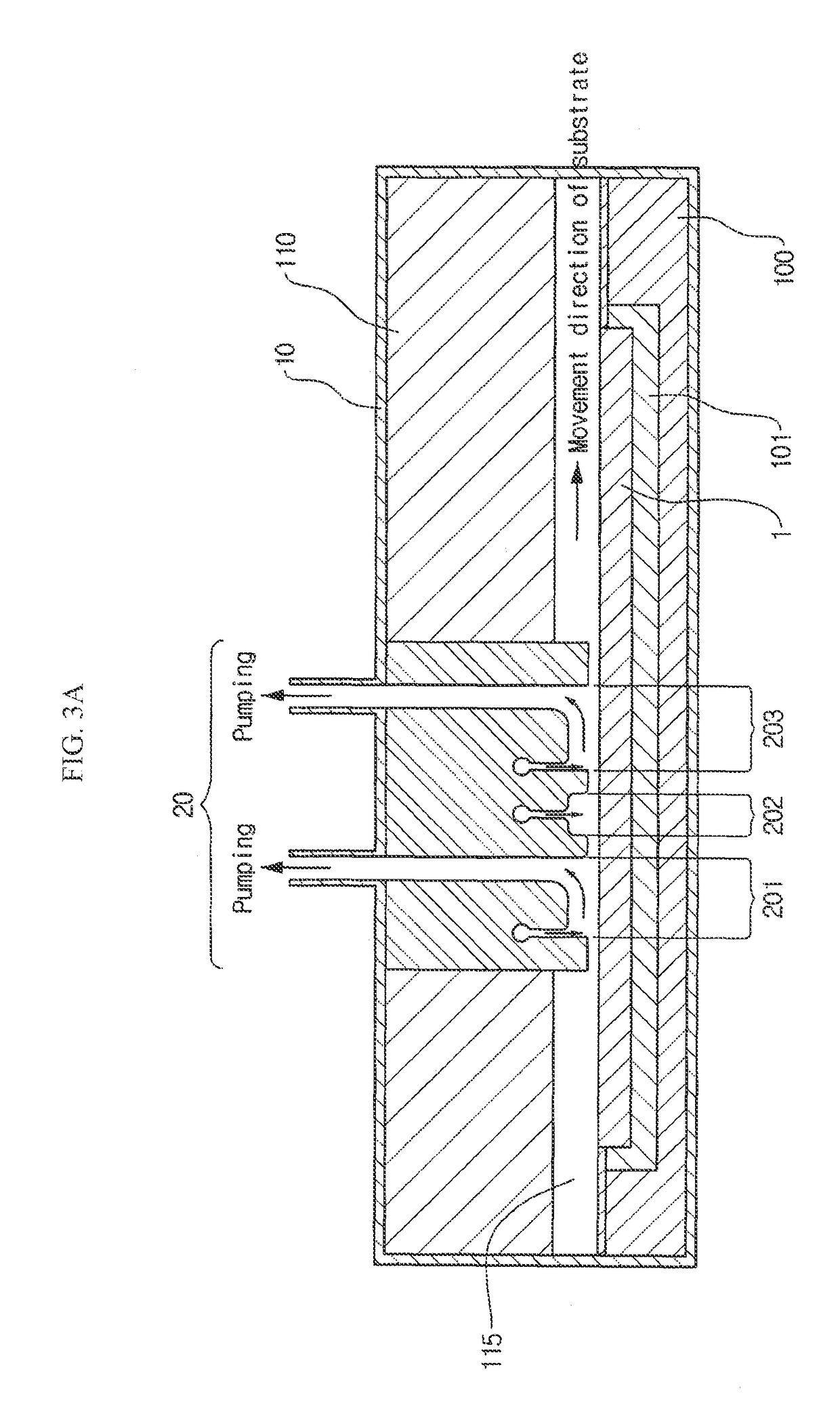
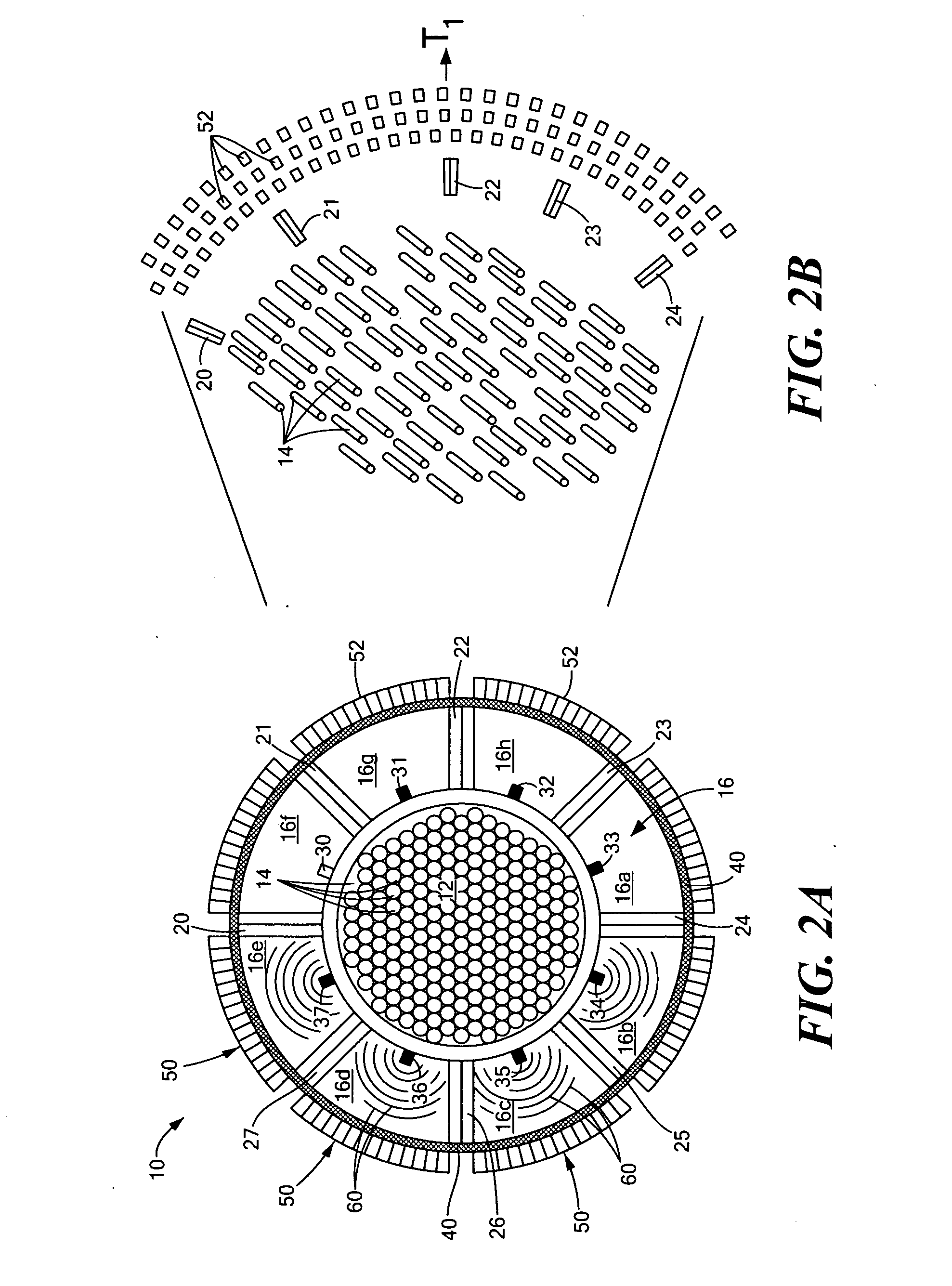
Vapor deposition reactor for forming thin film
InactiveUS8470718B2Improve area efficiencyArea minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringRelative motion
A vapor deposition reactor includes a chamber filled with a first material, and at least one reaction module in the chamber. The reaction module may be configured to make a substrate pass the reaction module through a relative motion between the substrate and the reaction module. The reaction module may include an injection unit for injecting a second material to the substrate. A method for forming thin film includes positioning a substrate in a chamber, filling a first material in the chamber, moving the substrate relative to a reaction module in the chamber, and injecting a second material to the substrate while the substrate passes the reaction module.
Owner:VEECO ALD
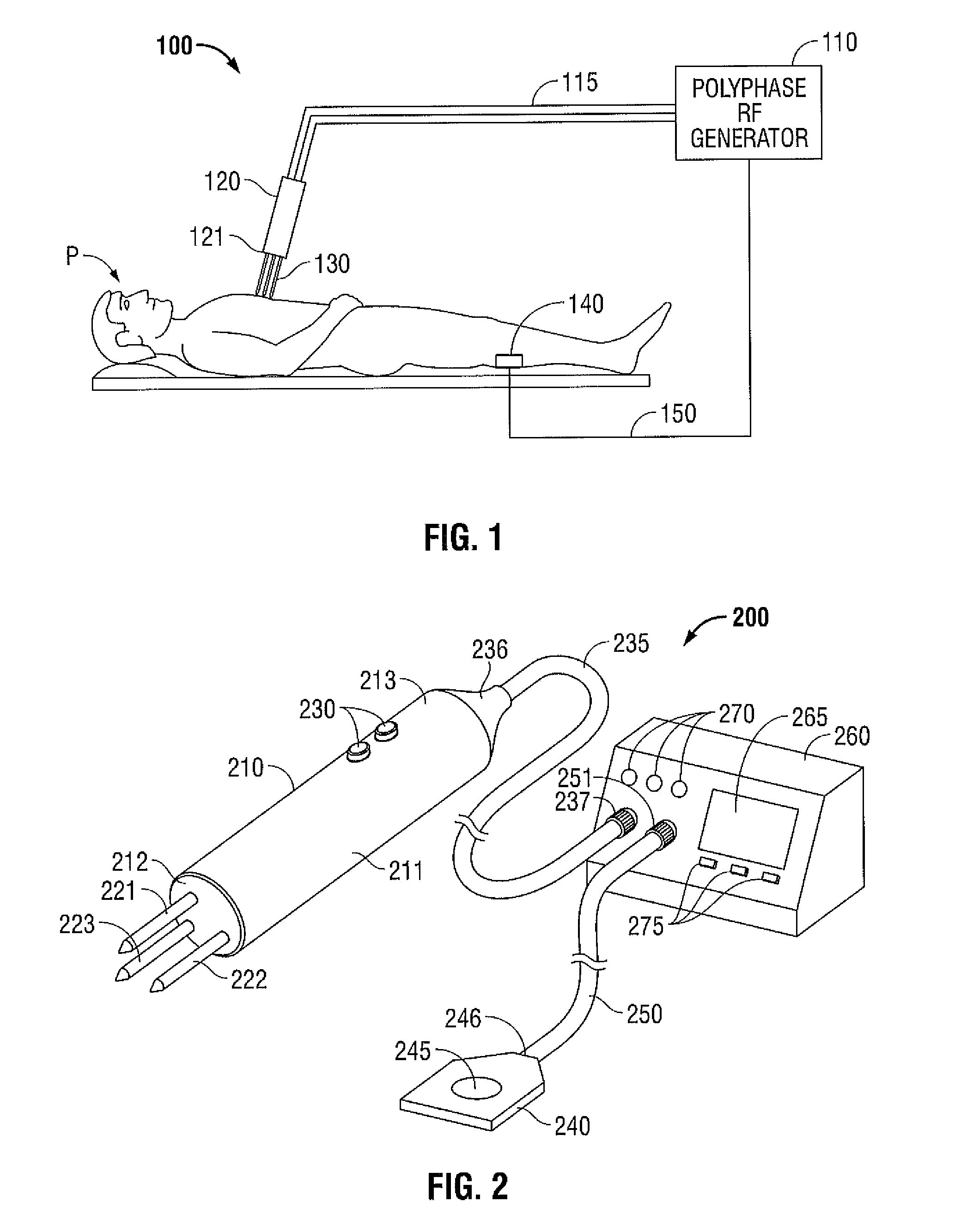
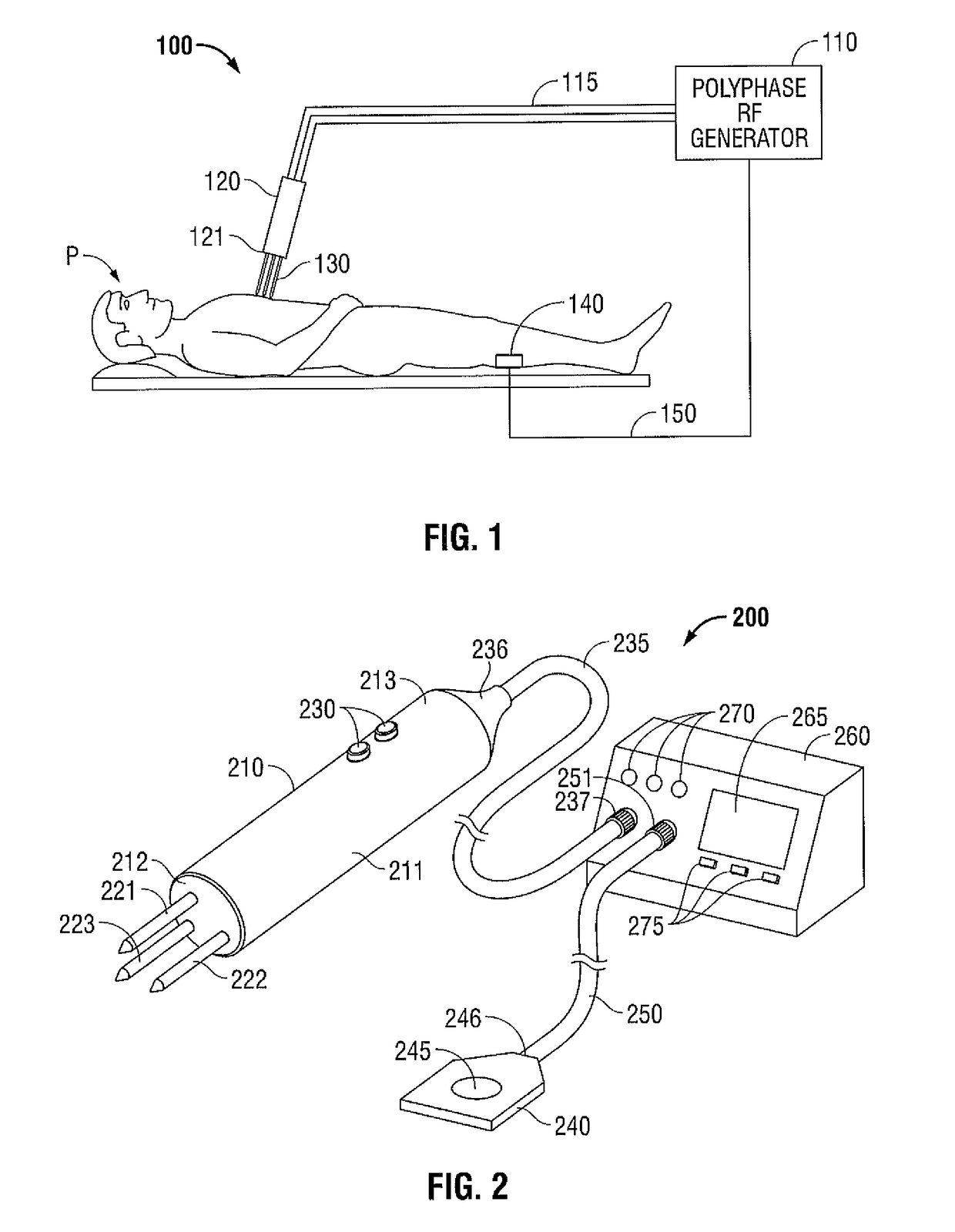
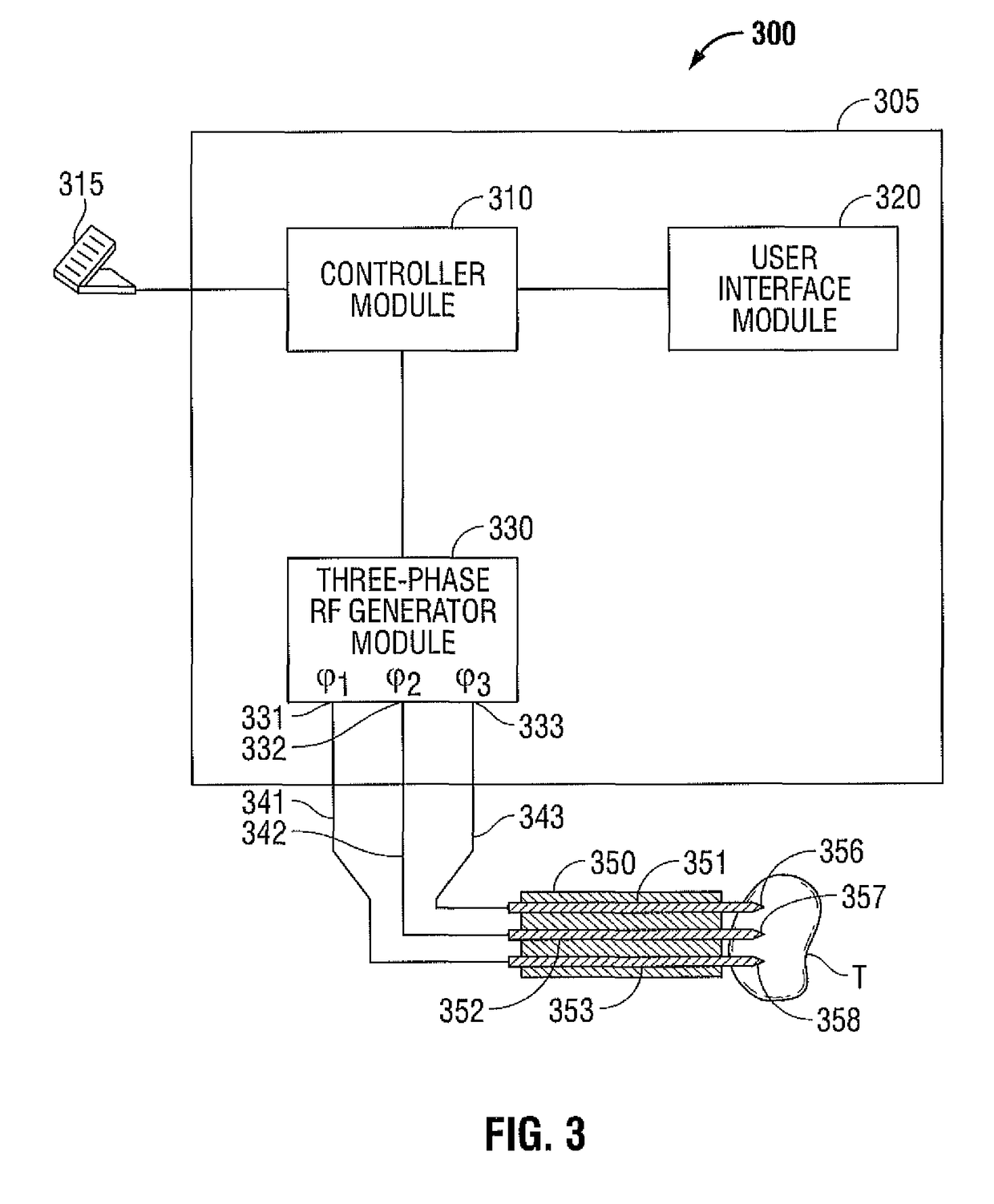
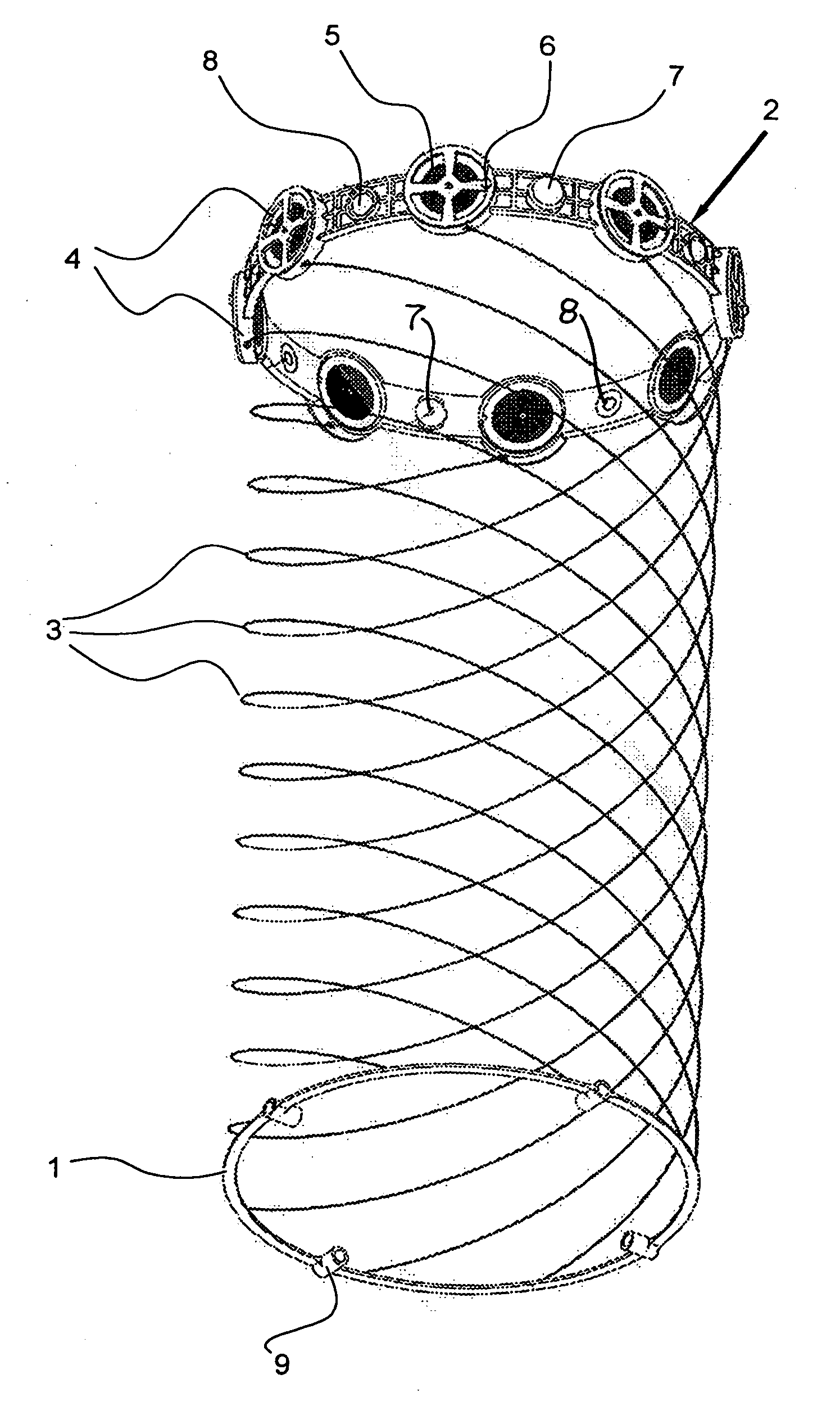
Polyphase Electrosurgical System and Method
ActiveUS20100030210A1Area minimizationMinimizing volumeSurgical instruments for heatingUser inputThree-phase
A polyphase electrosurgical system and method are provided. In embodiments, a radiofrequency generator having the capability of delivering a plurality of independent electrosurgical signals is disclosed. An electrosurgical instrument having an array of electrodes that correspond to the plurality of signals may be used to deliver the electrosurgical signals to tissue. In embodiments, three RF signals having a phase offset of about 120° therebetween, i.e., a three-phase configuration, may be used to achieve a balanced delivery of electrosurgical energy, which may lead to increased rates of energy delivery, improved control of tissue ablation regions, and improved operative outcomes. The phase, amplitude, and / or frequency of each signal may be independently variable in response to user inputs and / or biological parameters such as tissue impedance or return electrode current.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
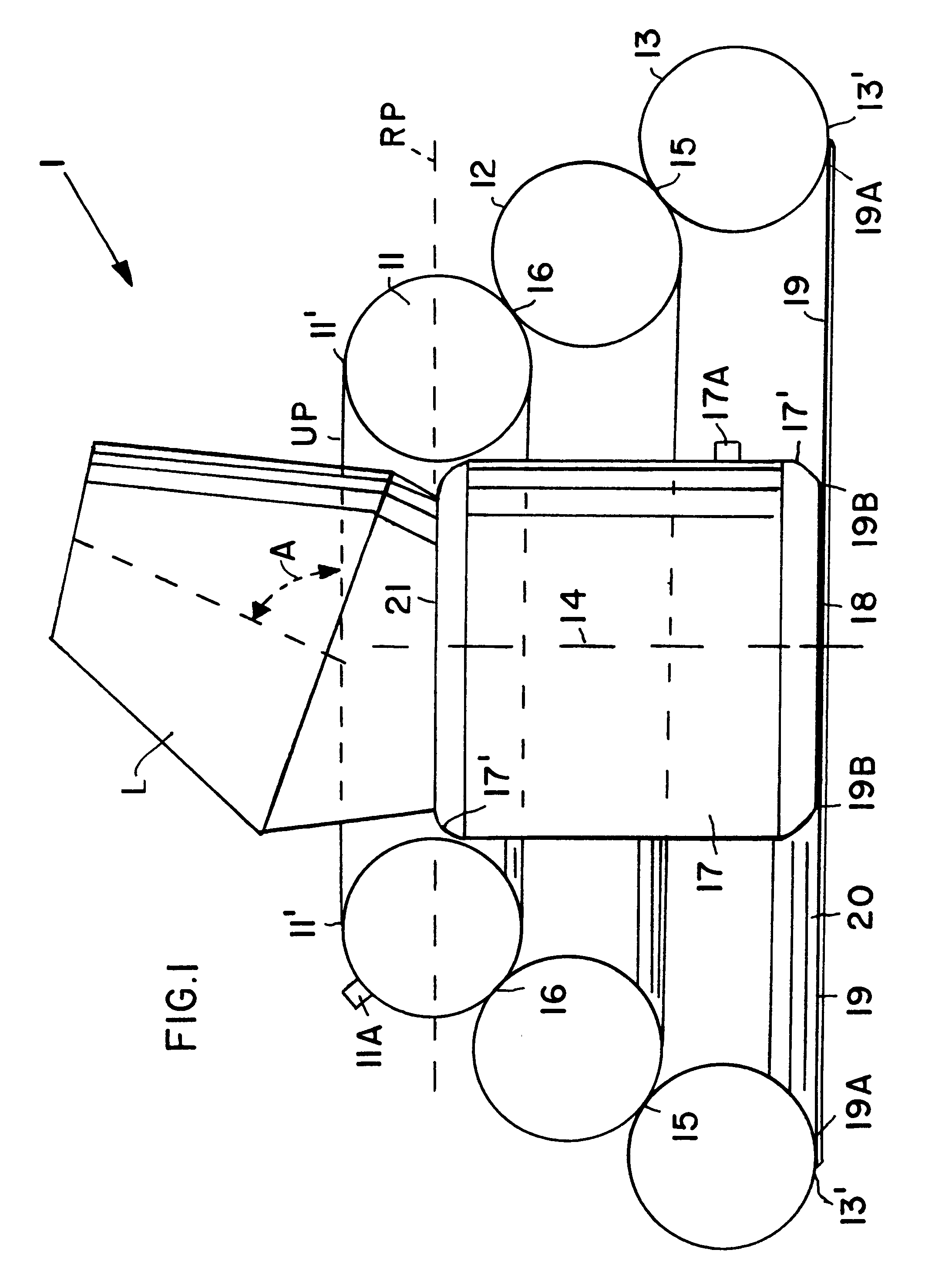
Airbag payload landing system for damping landing impact forces on a flying payload
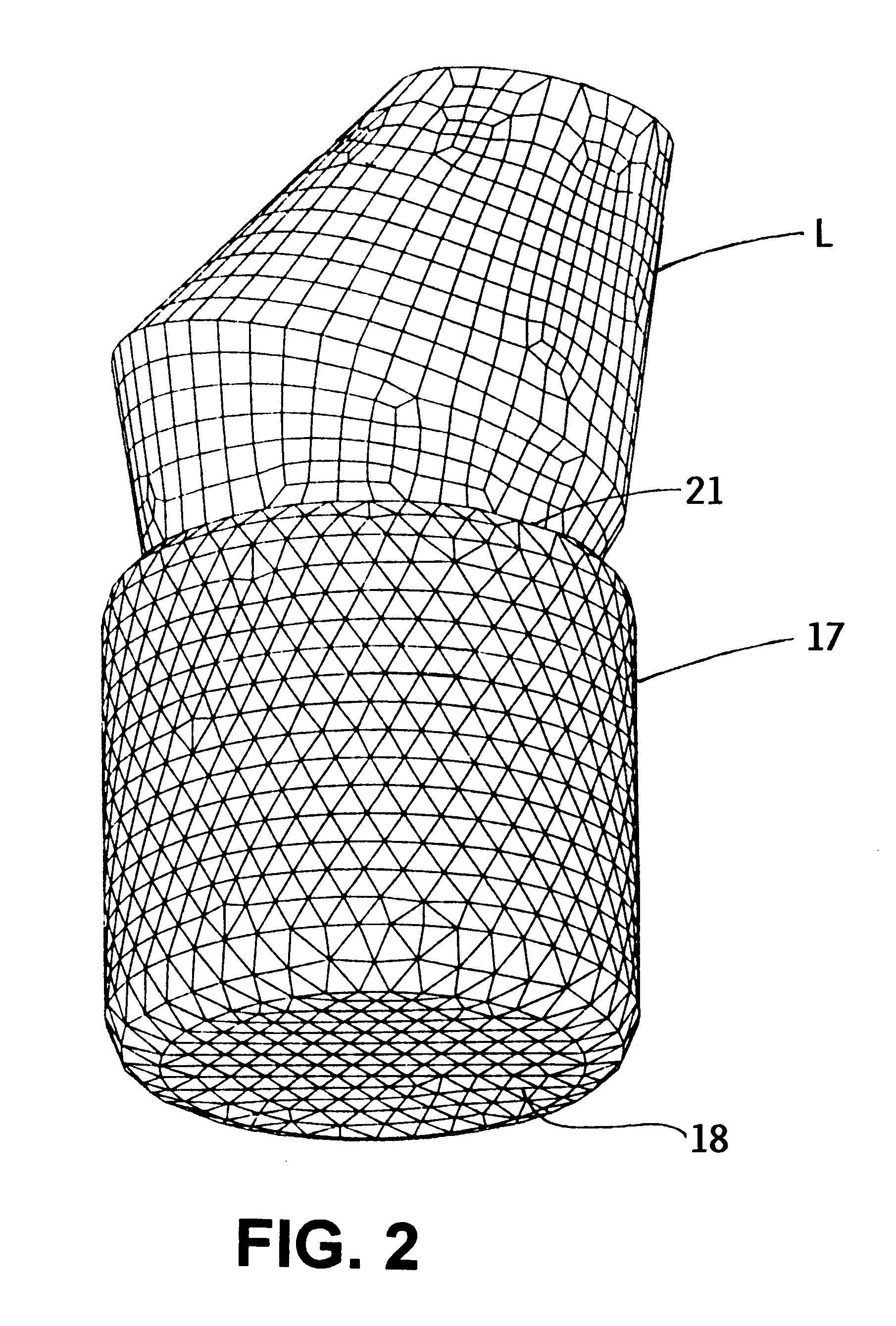
InactiveUS6237875B1Easy constructionMinimize packing volumeFloatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAirbagPayload
An airbag configuration for braking the landing impact of flying payloads has a central airbag (17) and at least one torus ring (11, 12, 13) surrounding the central airbag. A payload (L) is attachable on the central airbag (17). A stabilizing device (19) is provided which extends from the lowermost portion of the at least one torus ring (11, 12, 13) to the central airbag (17). The central airbag provides primarily vertical braking of the landing impact while the torus ring provides primarily horizontal braking of the landing impact.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Washing machine
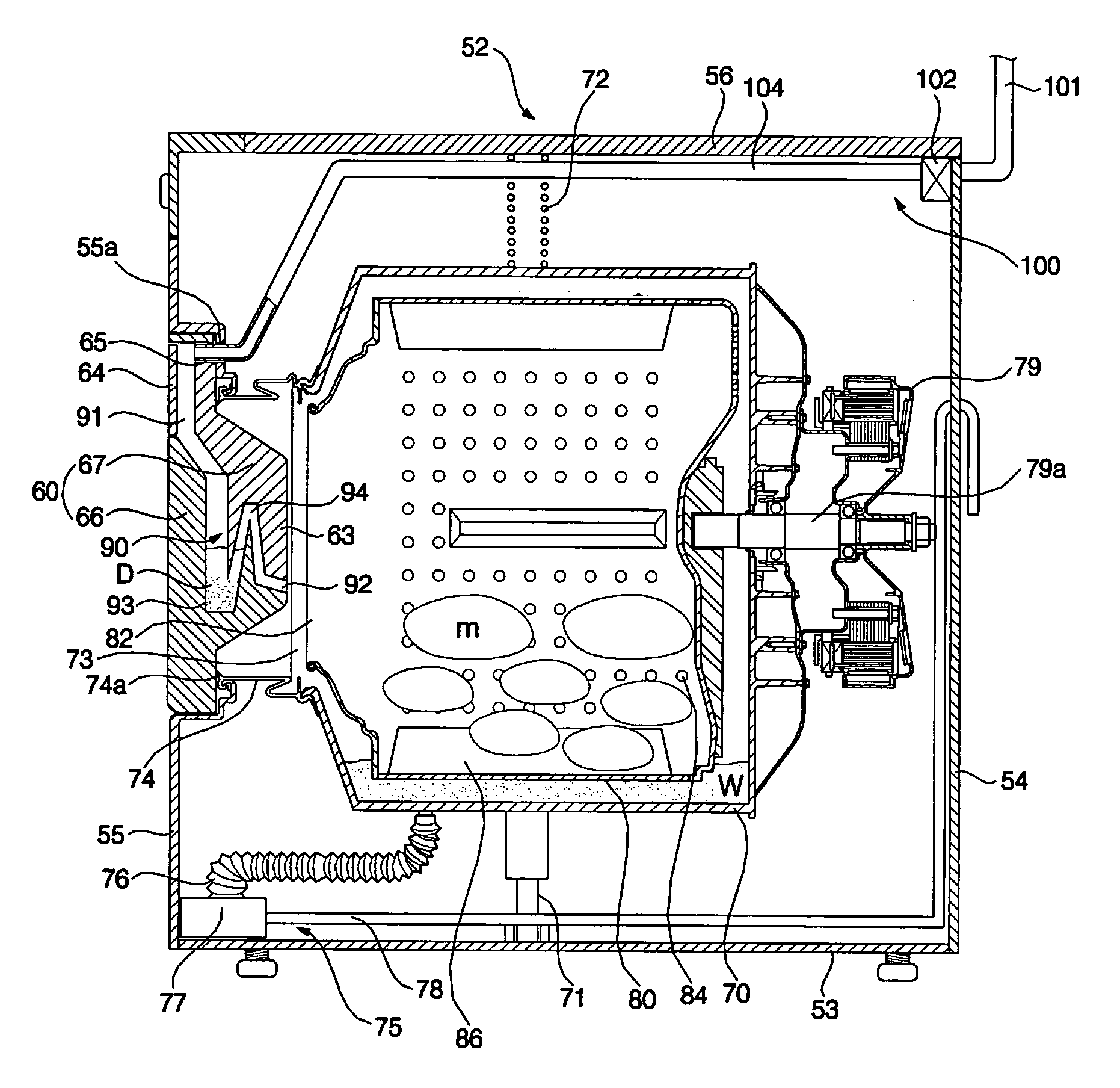
InactiveUS20060053842A1Lower the volumeMinimize the numberOther washing machinesTextiles and paperInterior spaceEngineering
Disclosed herein is a washing machine which has a detergent supply part formed in a door. The detergent supply part is formed in the door and has a function of containing detergent and supplying detergent into a tub through the door. The washing machine has an advantage of considerable space saving compared with the washing machine having the detergent supply part formed in an inner space thereof, thereby minimizing the volume and the number of components of the washing machine.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
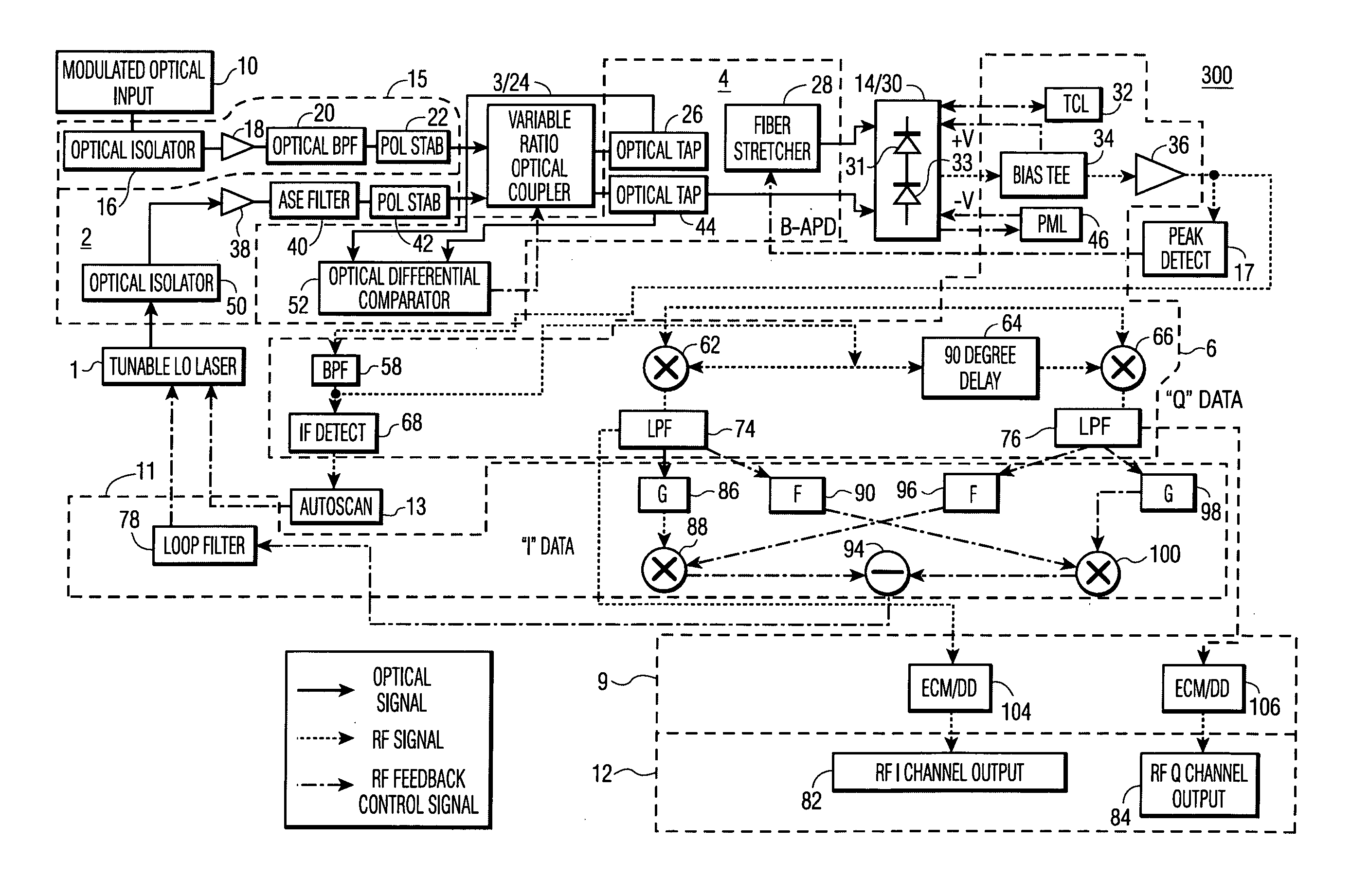
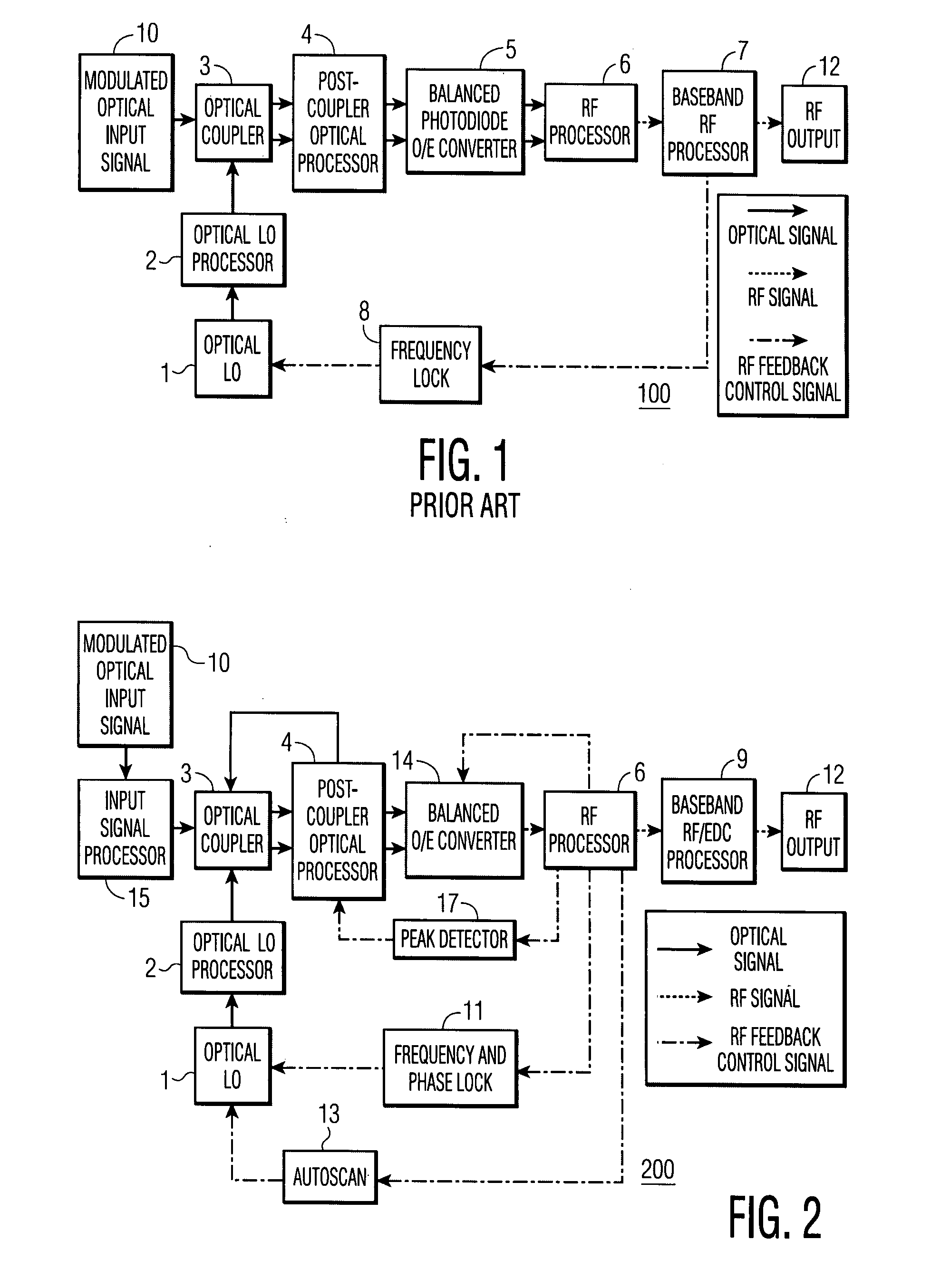
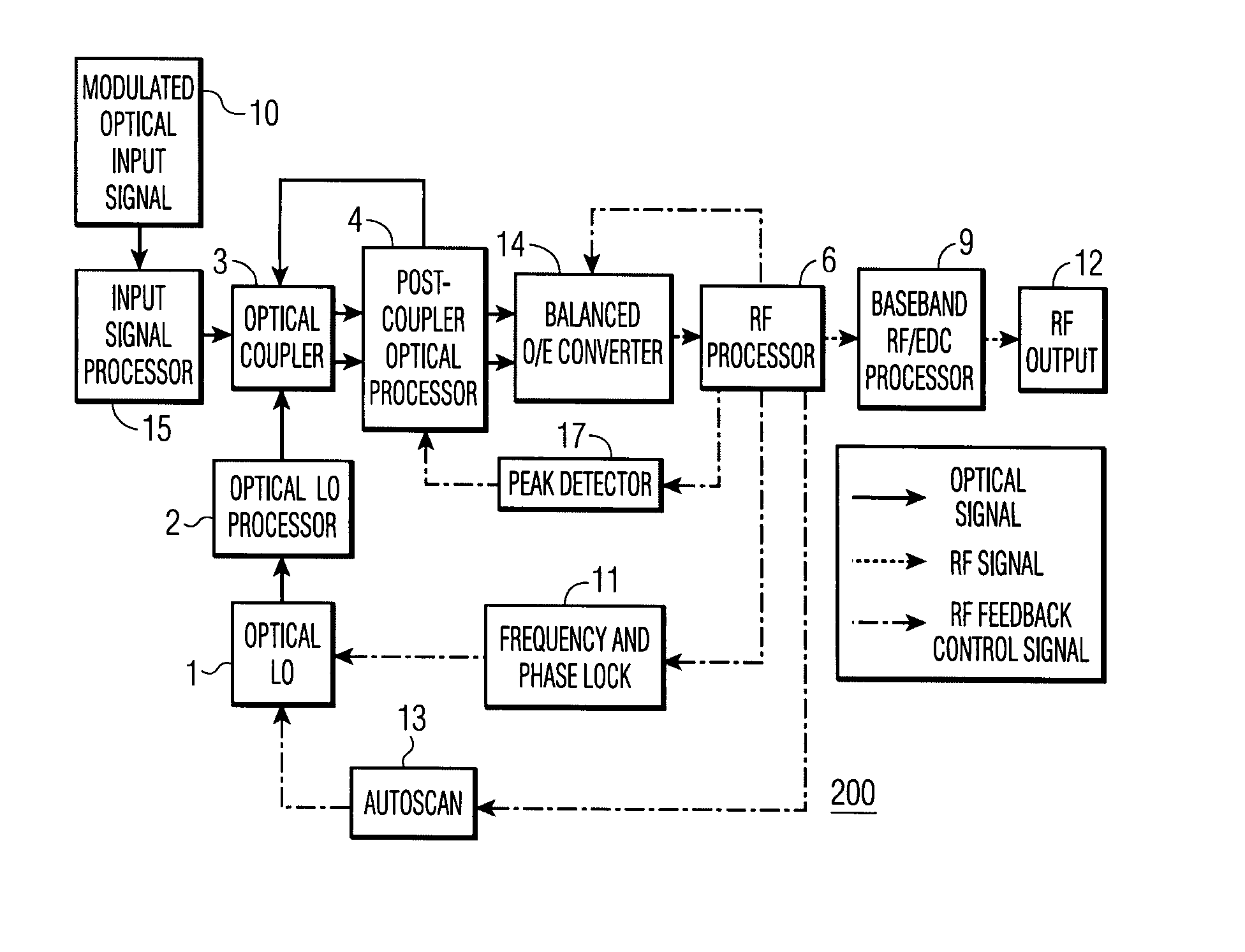
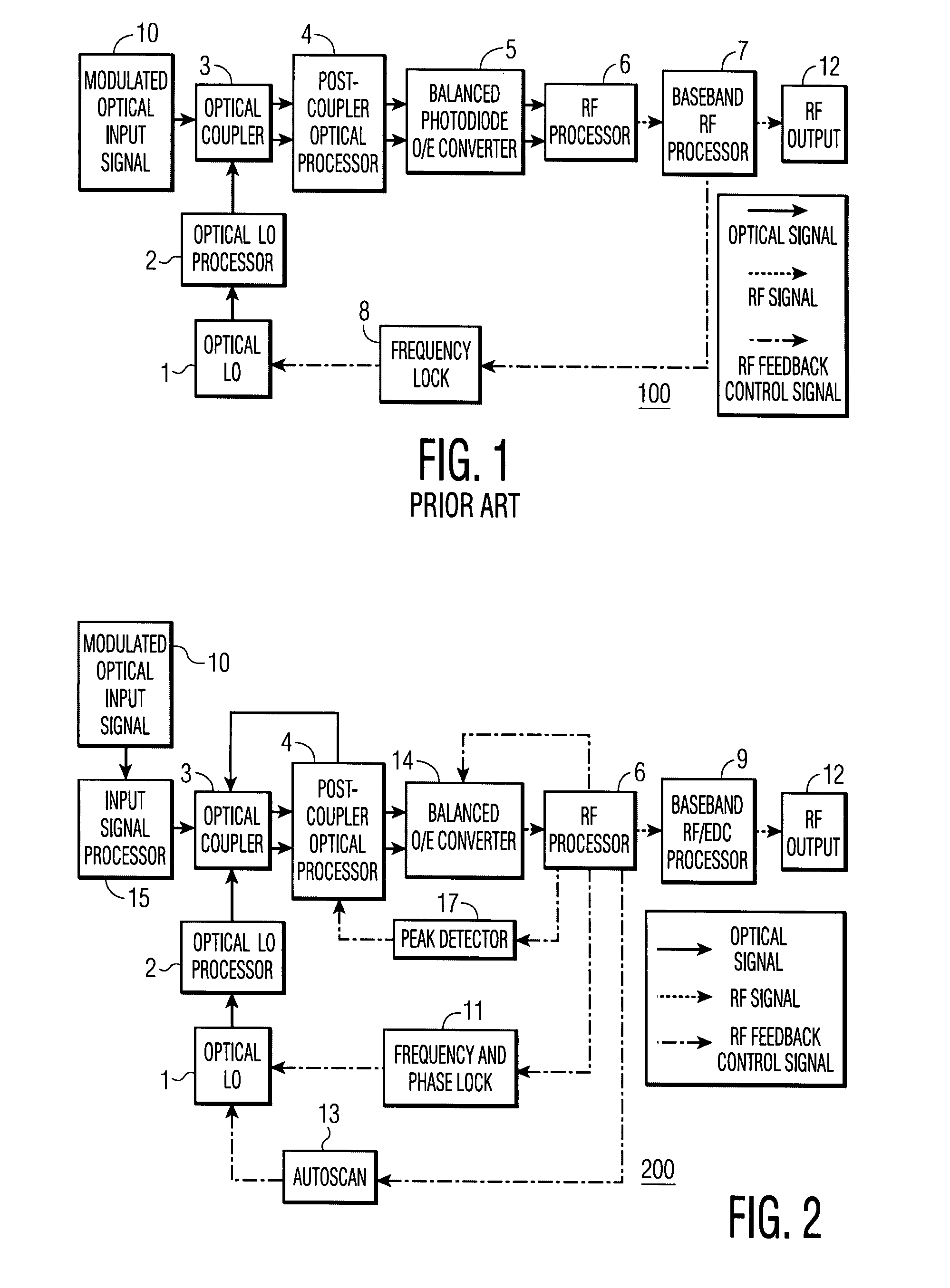
Feedback-controlled coherent optical receiver with electrical compensation/equalization
ActiveUS20080038001A1Low costImprove reliabilityElectromagnetic receiversElectromagnetic transceiversEqualizationFeedback control
An optical coherent receiver in one embodiment has a heterodyne configuration, and in another embodiment has a homodyne configuration, in each configuration employs multiple feedback signaling and analog / digital processing to optimize response to a modulated optical input signal, the provision of both individual RF I and RF Q channel outputs.
Owner:DISCOVERY SEMICON
Self-charging organic electroluminescent display device
InactiveUS20050023975A1Effectively charging functionMassive costDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical batteryPhotoelectric conversion
A self-charging organic electroluminescent display is disclosed. A solar cell and an organic electroluminescent device are installed on a same substrate or different substrates. Using the photoelectric conversion property of the solar cell, the solar energy is converted into electrical energy and stored in a battery. Therefore, the electrical energy converted from the solar energy can be provided for the organic electroluminescent device to emit light, forming a self-charging organic electroluminescent display module.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
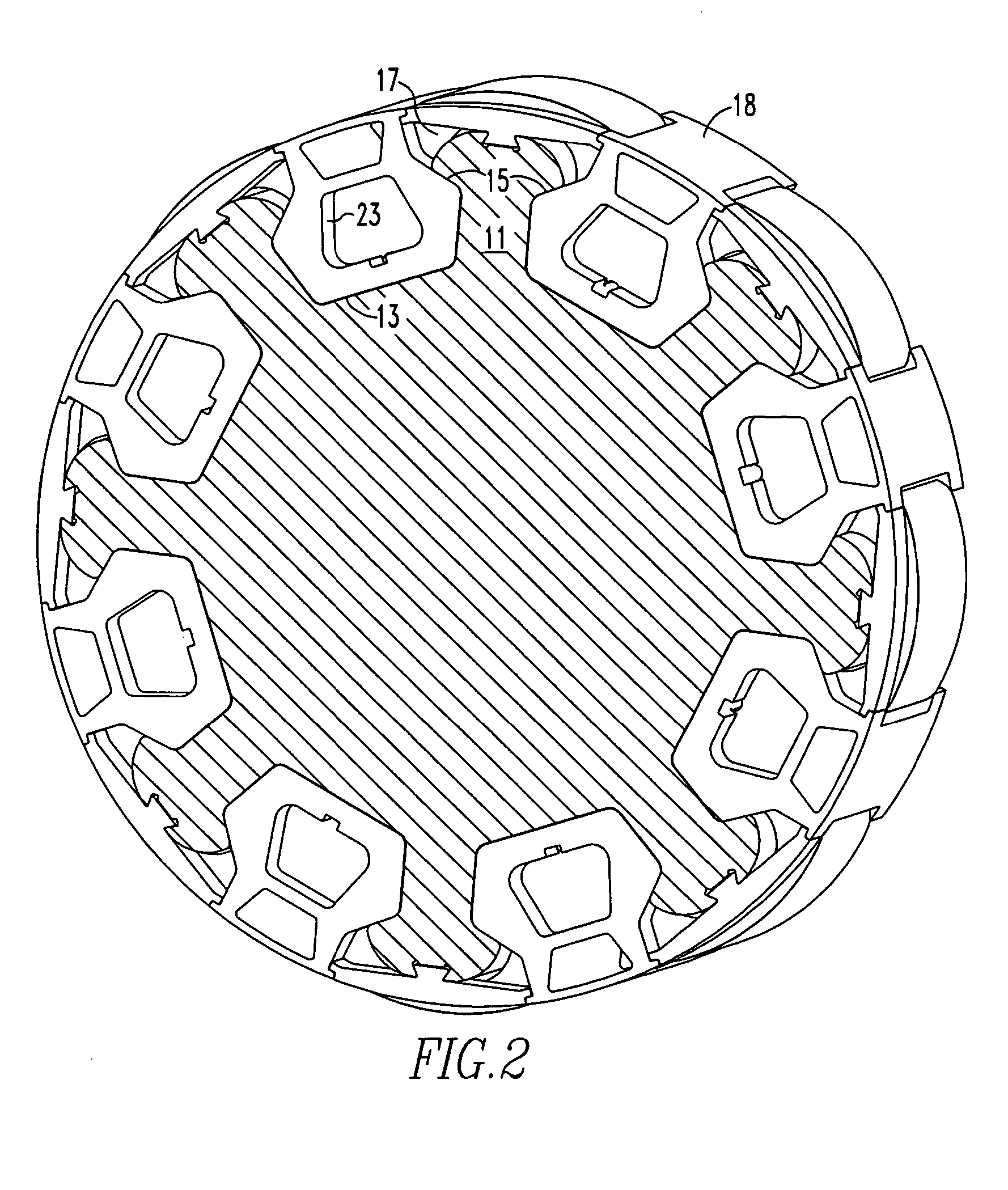
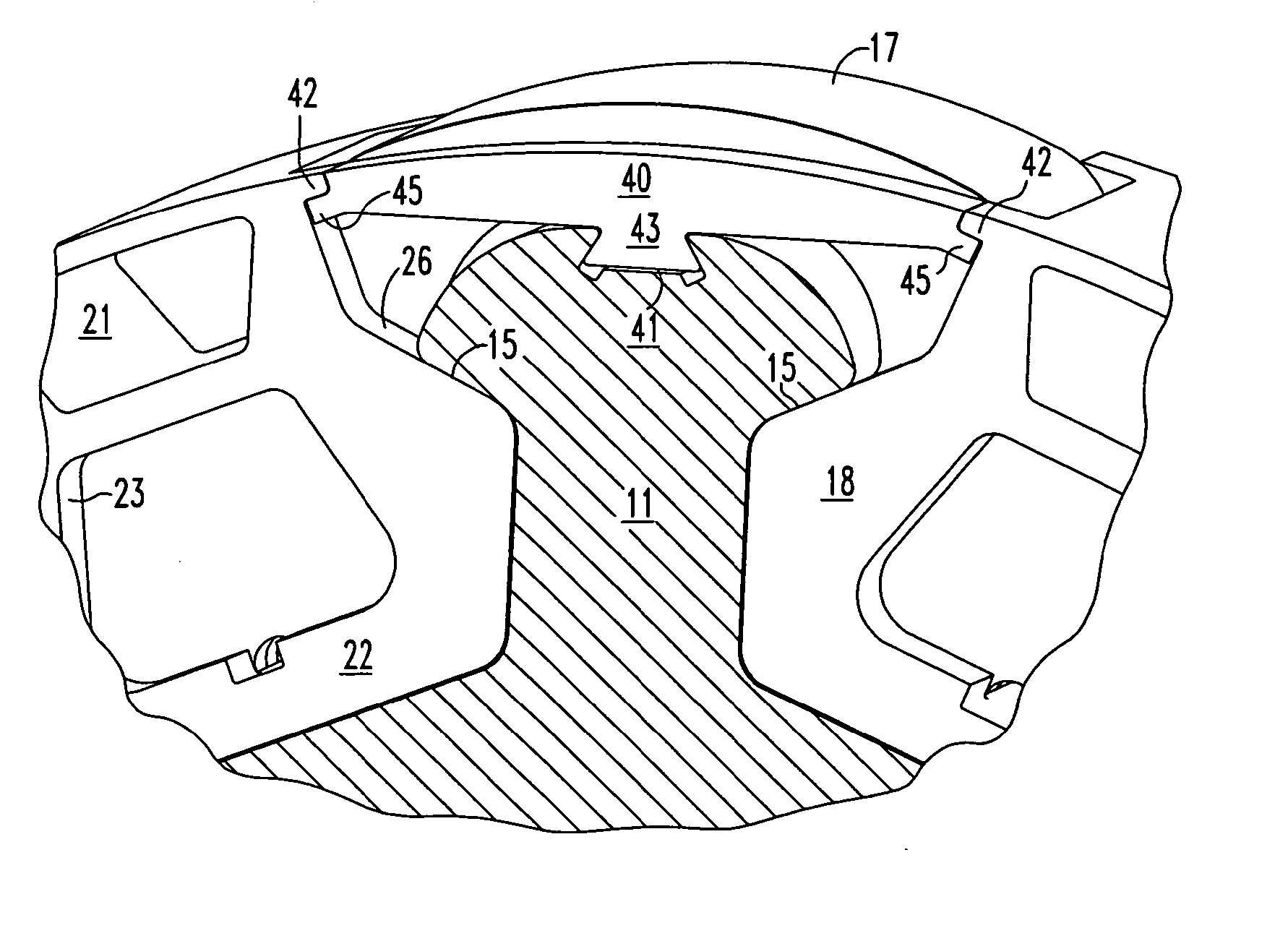
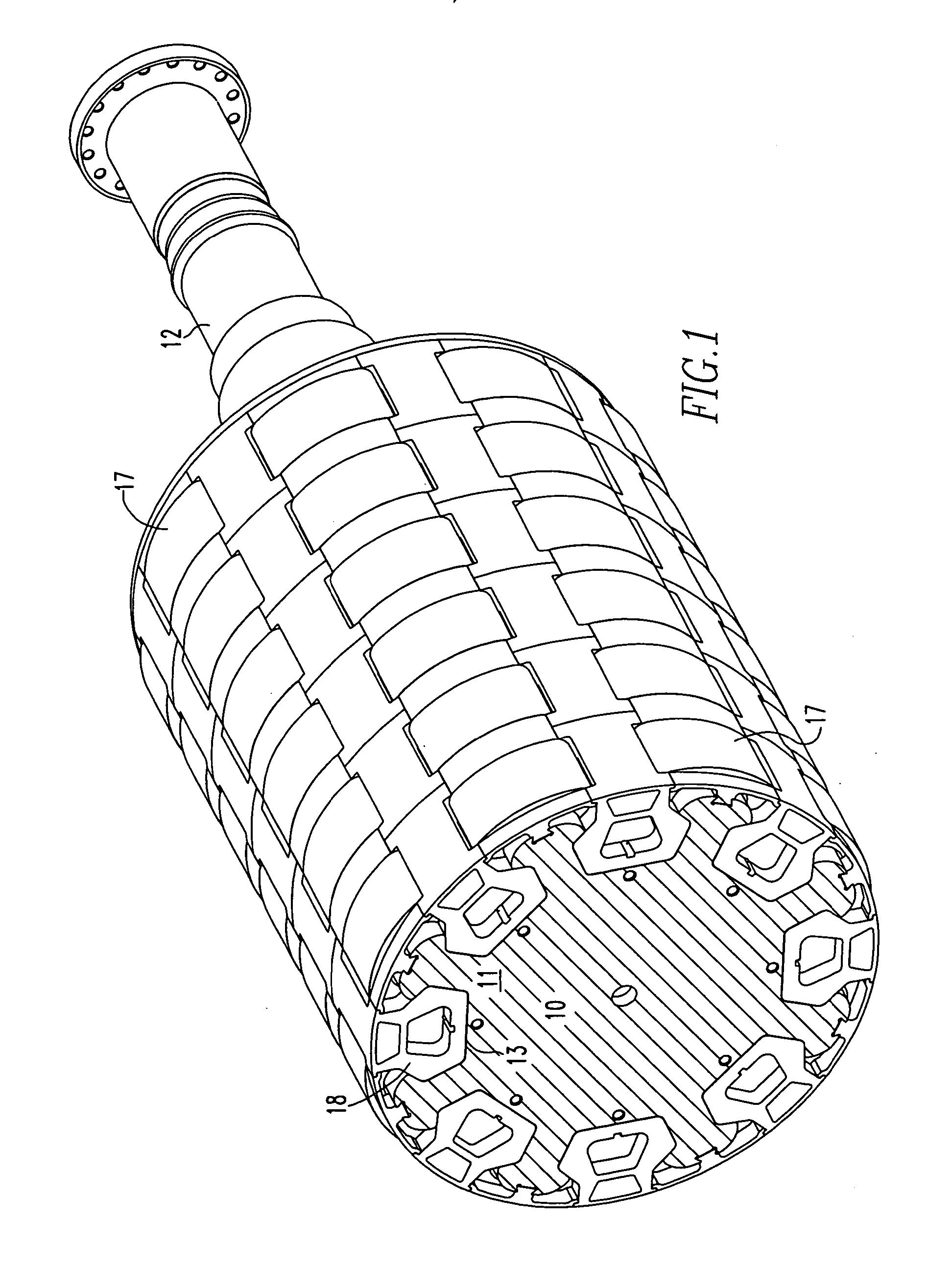
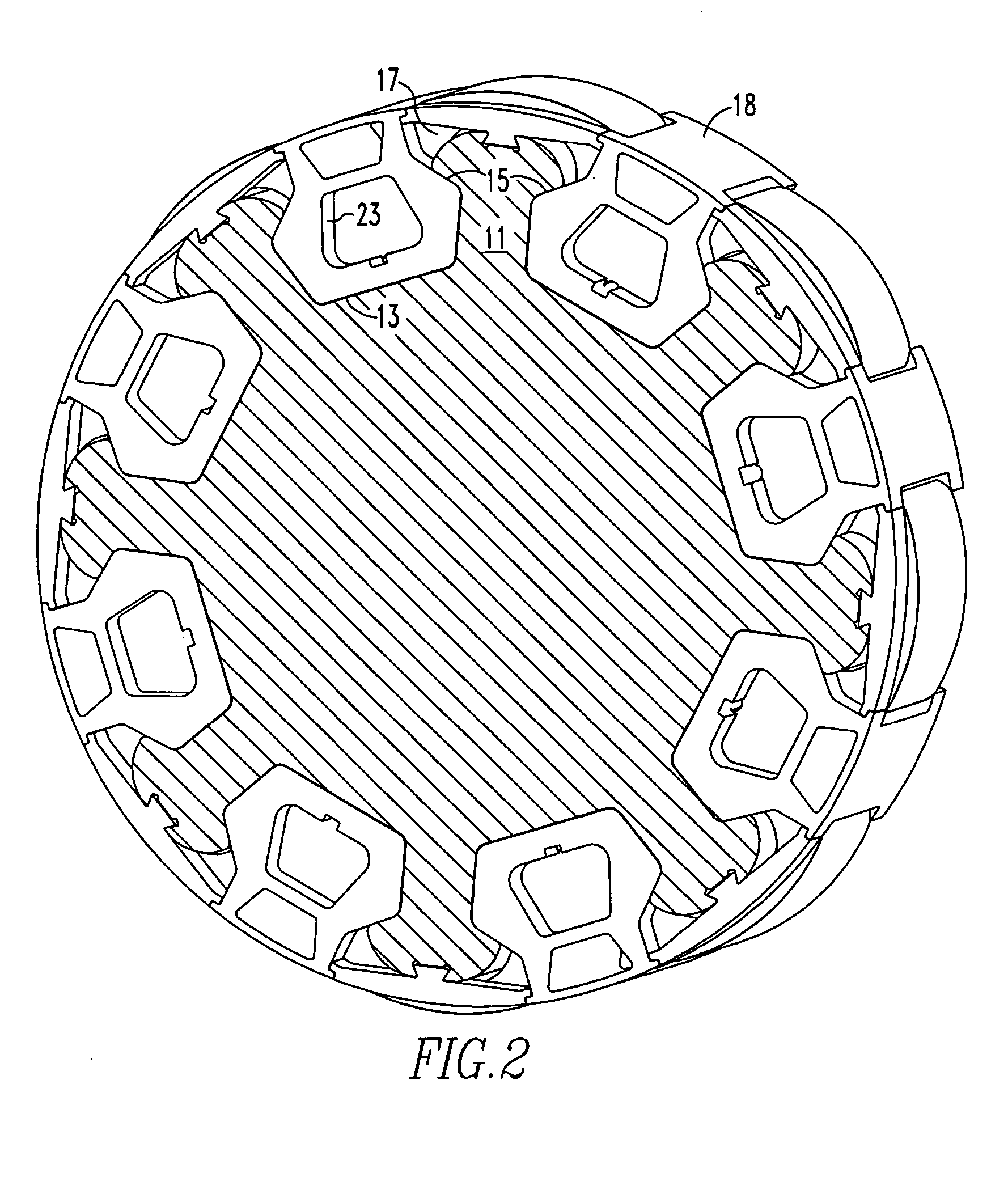
Aerodynamic insert for high speed permanent magnet motor
InactiveUS7466054B2Minimizing volumeMinimizing weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsSupports/enclosures/casingsPermanent magnet rotorPermanent magnet motor
An insert comprising a lightweight structure configured for filling the gaps between axially spaced C-shaped lamination stacks and circumferentially spaced non-magnetic cradles on a permanent magnet rotor. The insert is secured to a rib by a dovetail tongue that fits within a dovetail groove provided along the length of each rib. The insert engages the adjacent cradles and has a circumferential surface that has the same radius of curvature as the top surface of the cradles.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
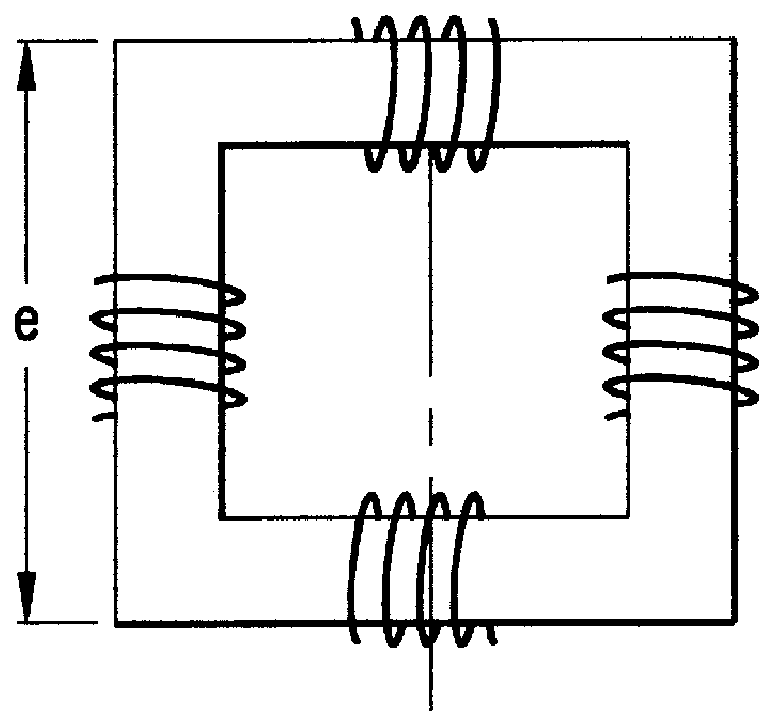
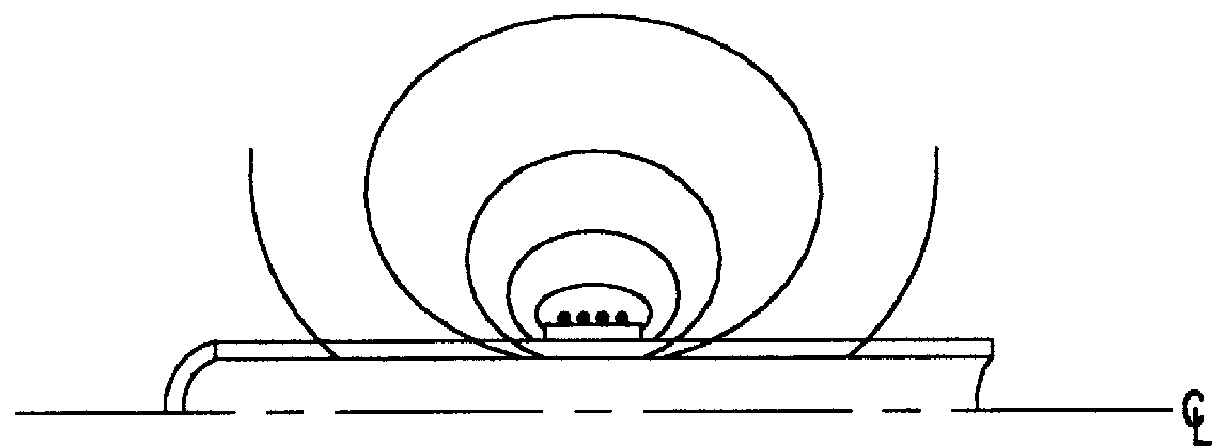
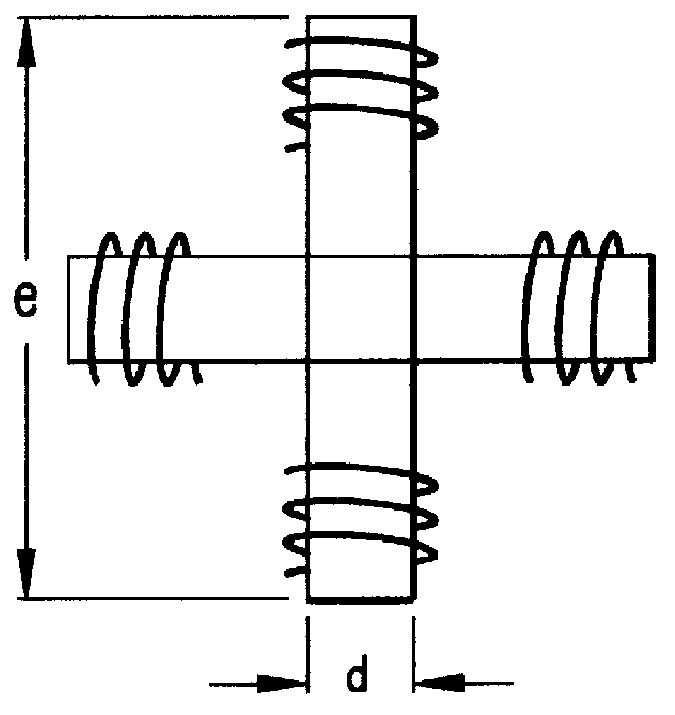
Ferrite crossed-loop antenna of optimal geometry and construction and method of forming same
InactiveUS6014111AMinimizing volume and weightMinimizing volumeLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna detailsMagnetic coreThin walled
A novel loop antenna containing a thin-walled ferrite box or other hollow; magnetic core structure of high permeability (considerably greater than 100), particularly useful for crossed loop antennas, and of optimal geometry and configuration for minimum volume, weight and space.
Owner:MEGAPULSE
Feedback-controlled coherent optical receiver with electrical compensation/equalization
ActiveUS7406269B2Improve reliabilityLow costElectromagnetic receiversElectromagnetic transceiversEqualizationFeedback control
An optical coherent receiver in one embodiment has a heterodyne configuration, and in another embodiment has a homodyne configuration, in each configuration employs multiple feedback signaling and analog / digital processing to optimize response to a modulated optical input signal, the provision of both individual RF I and RF Q channel outputs.
Owner:DISCOVERY SEMICON
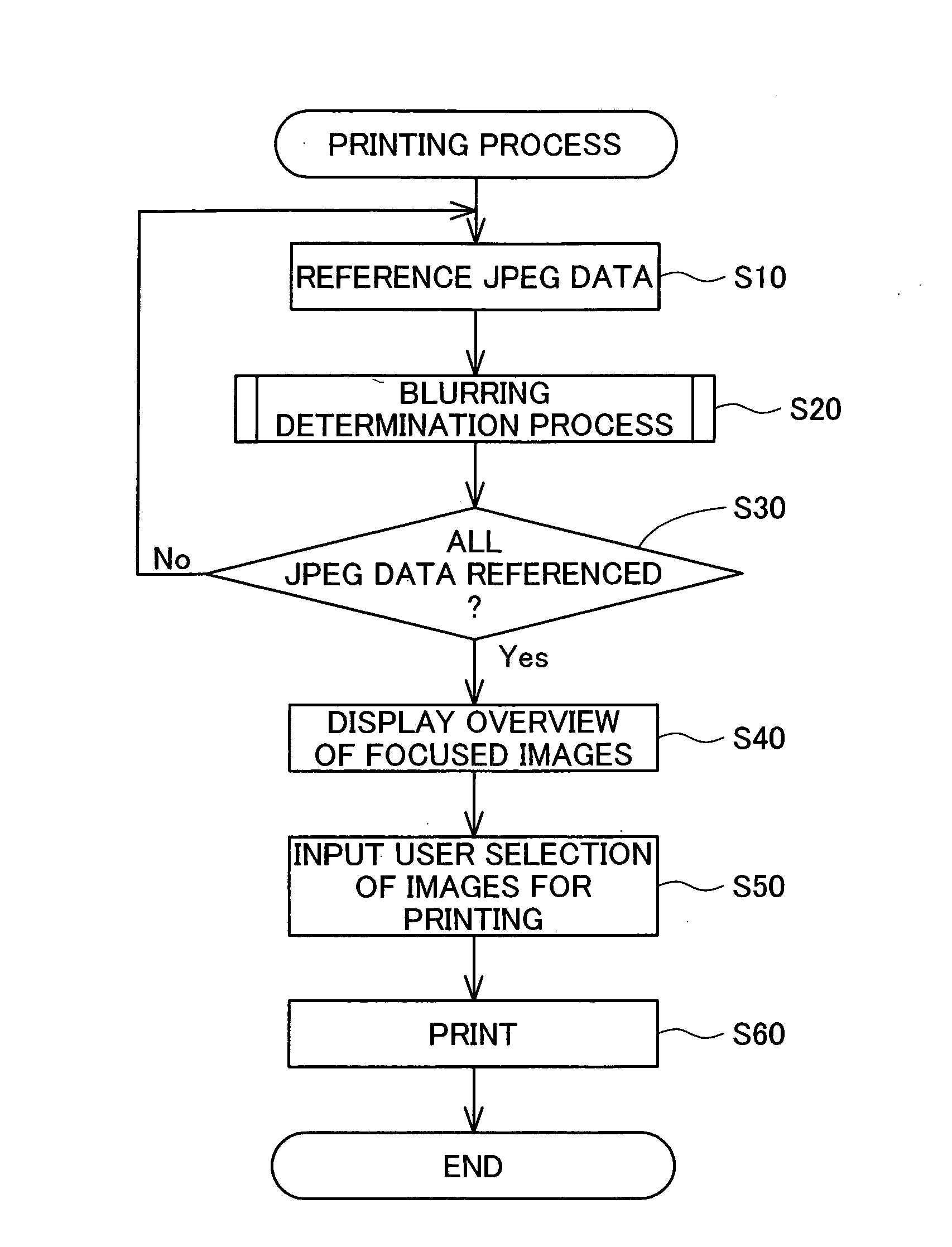
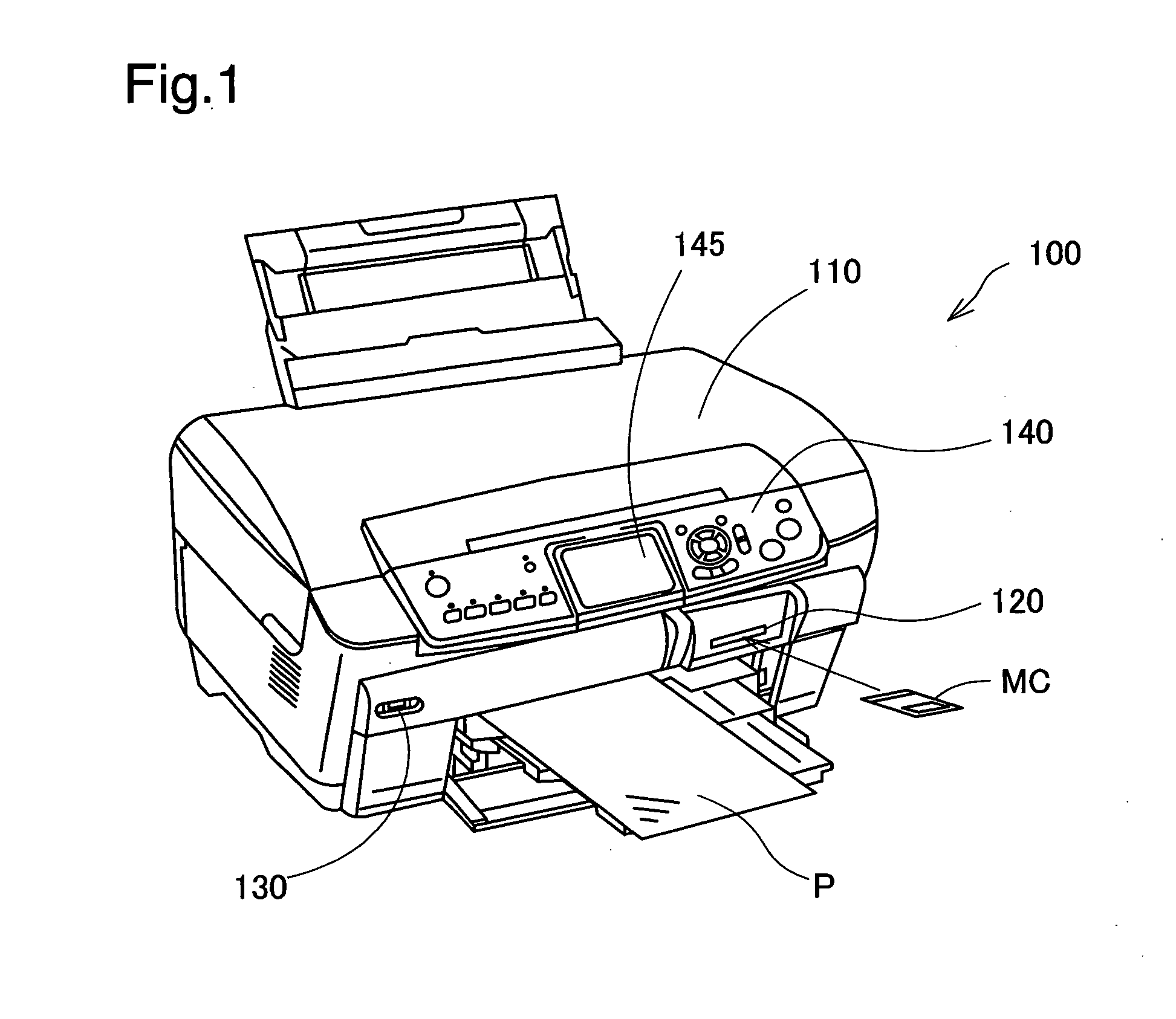
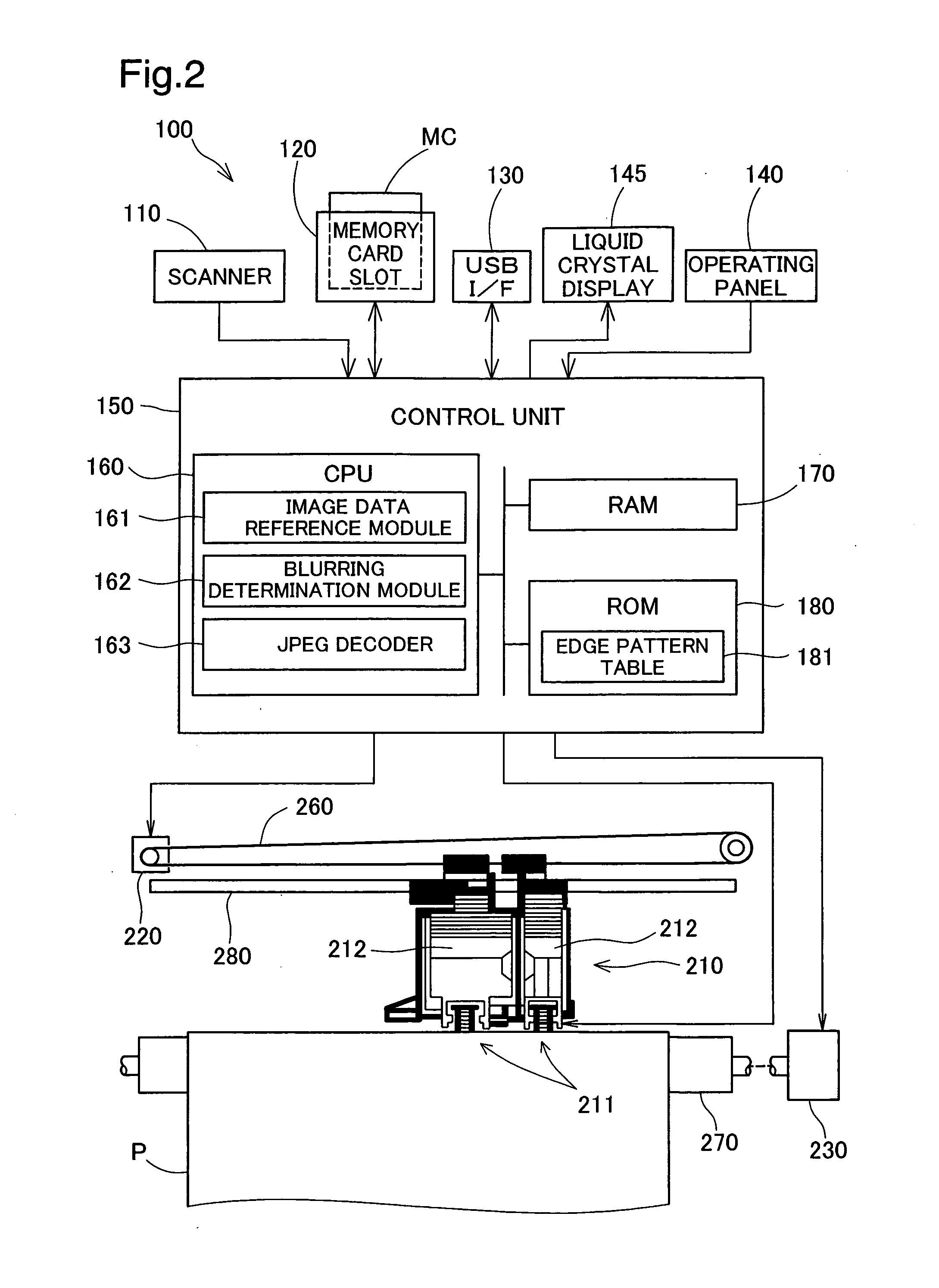
Blurring determination device, blurring determination method and printing apparatus
InactiveUS20080137982A1Detect blurringMinimizing burdenImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionReference image
The blurring determination device references image data in which are recorded coefficients that are obtained when pixel values forming the image in the spatial domain are converted to the frequency domain, and detects edges oriented in two or more directions, from among the image data, by comparing a series of the coefficients in each of the directions with various types of basic edge patterns whereby typical gradient patterns of the changes in pixel values are represented by values corresponding the coefficients. The representative values of the width of the detected edges is determined in each of the directions, and the image data is determined to not be blurred when the representative values meet the condition of being at or below a certain threshold.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Wall mountable acoustic assembly for indoor rooms
ActiveUS7565951B1Minimizes shipping weight and volumeMinimizing volumeCeilingsStaplesDiffusion chamberPANEL.FUNCTION
An acoustic assembly including a thin sound absorbing panel supported by foldable mounting brackets is adapted to be mounted upon the walls of an indoor listening enclosure. The space behind the panel functions as an acoustic diffusion chamber which augments the acoustic performance of the panel. A number of such assemblies are employed in a manner such that the panels are offset from the wall and downwardly angled.
Owner:PERDUE JOAB JAY
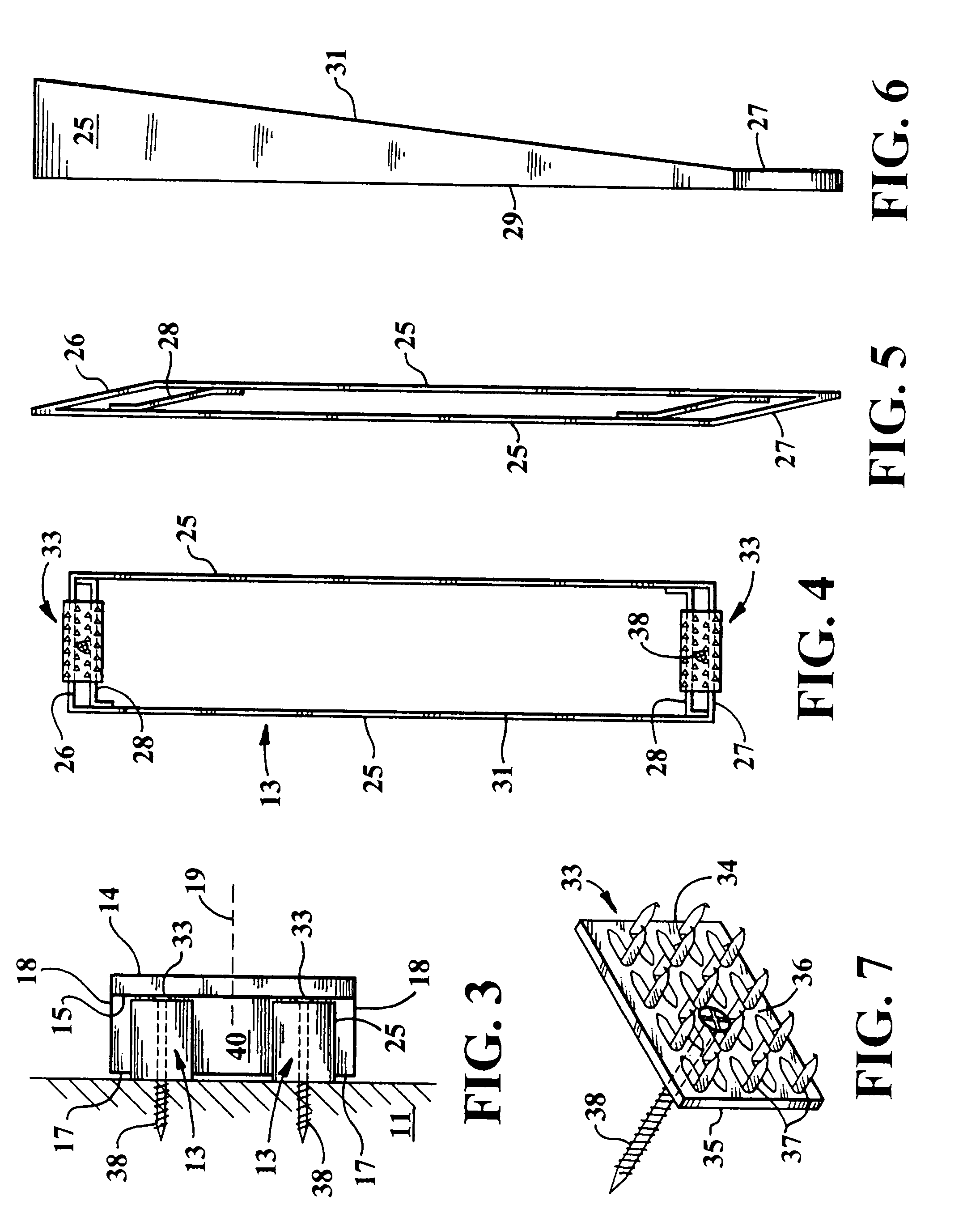
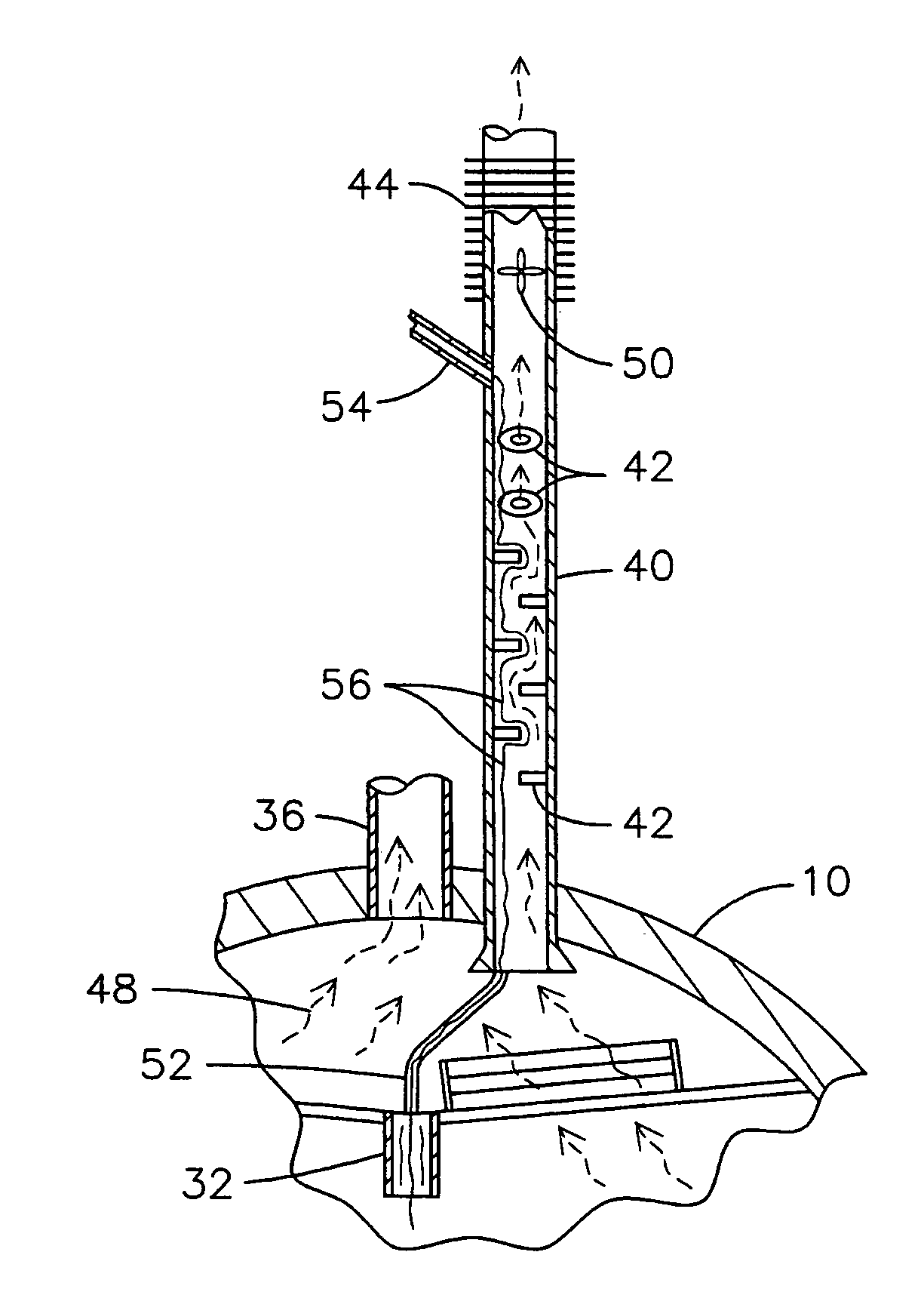
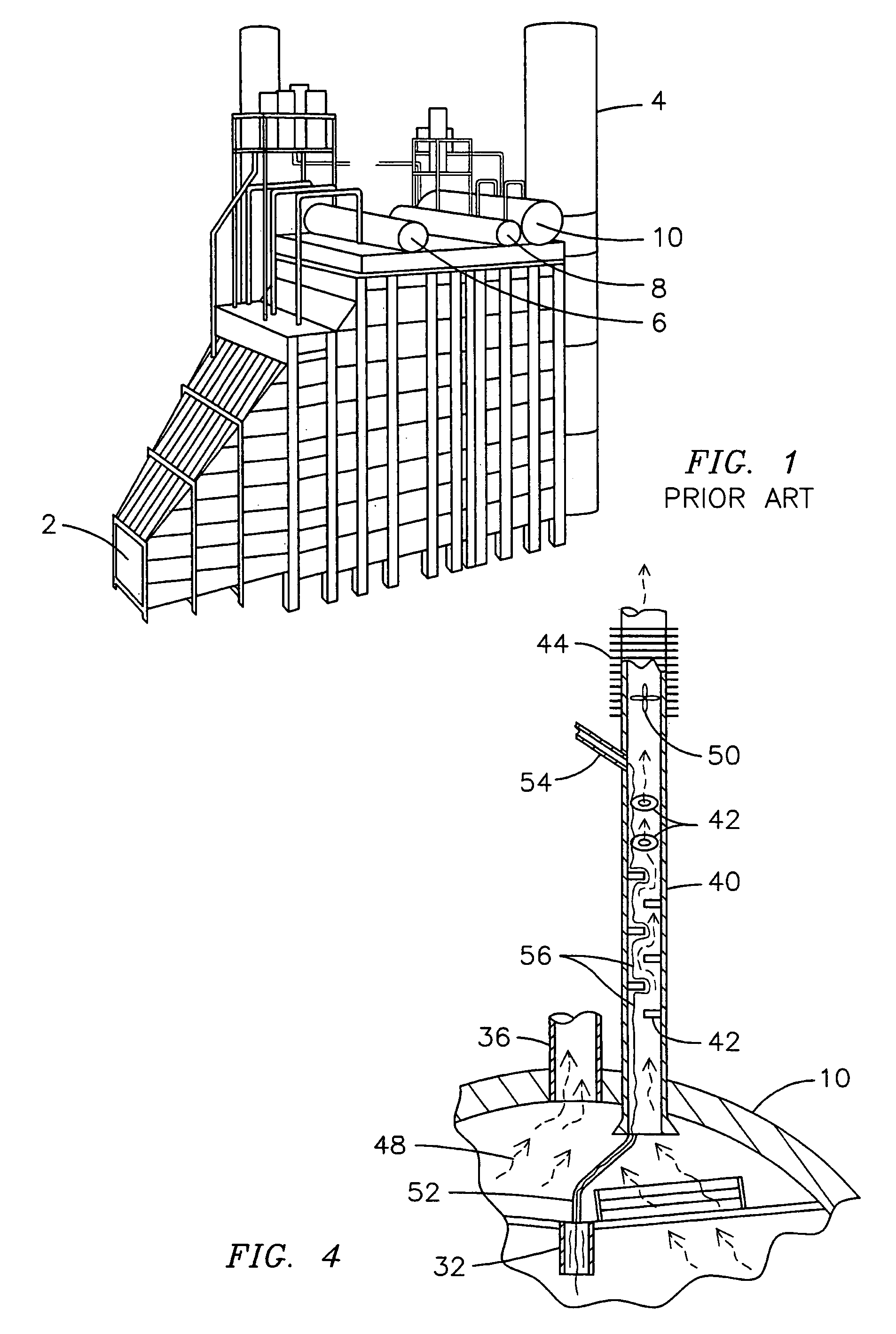
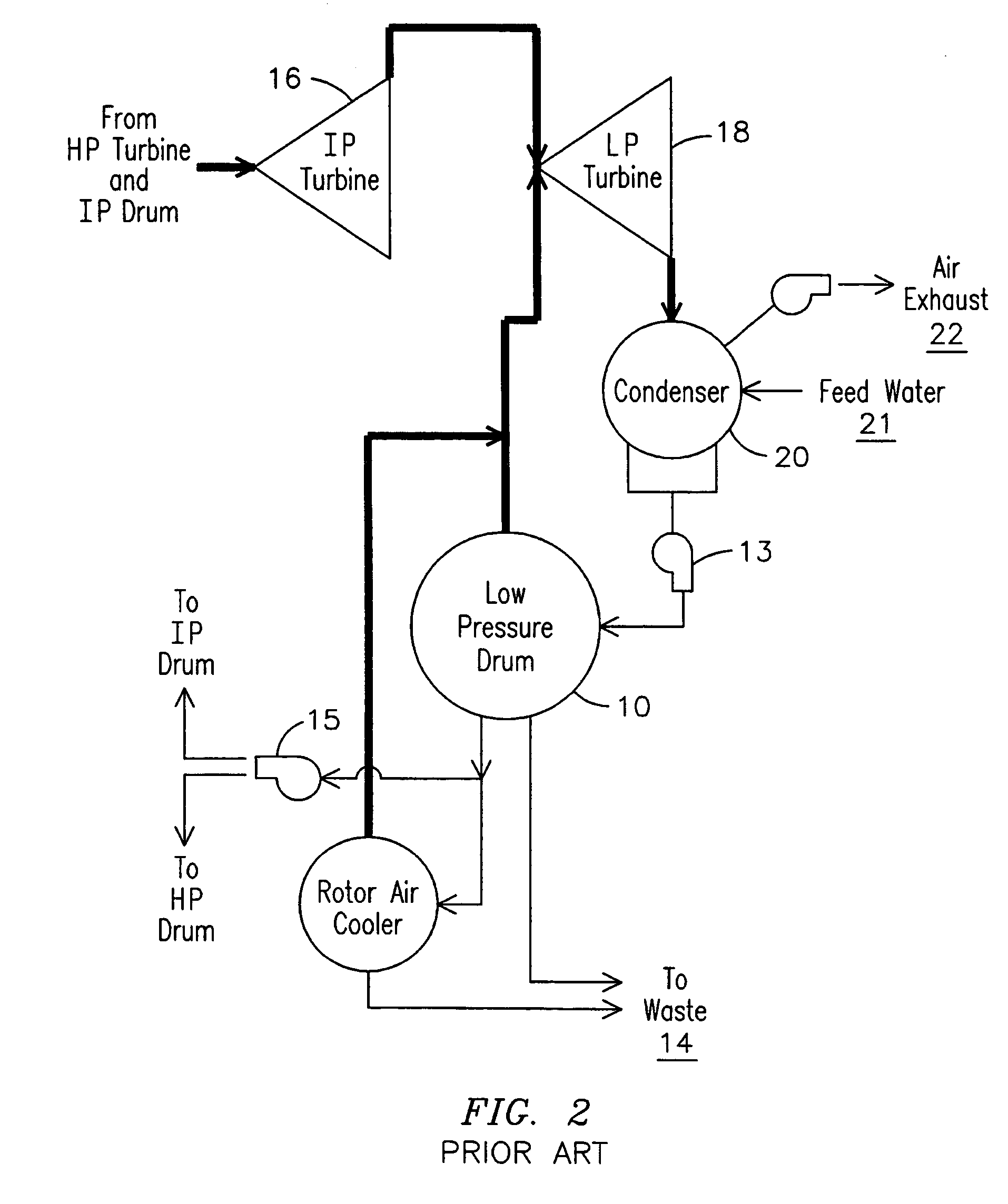
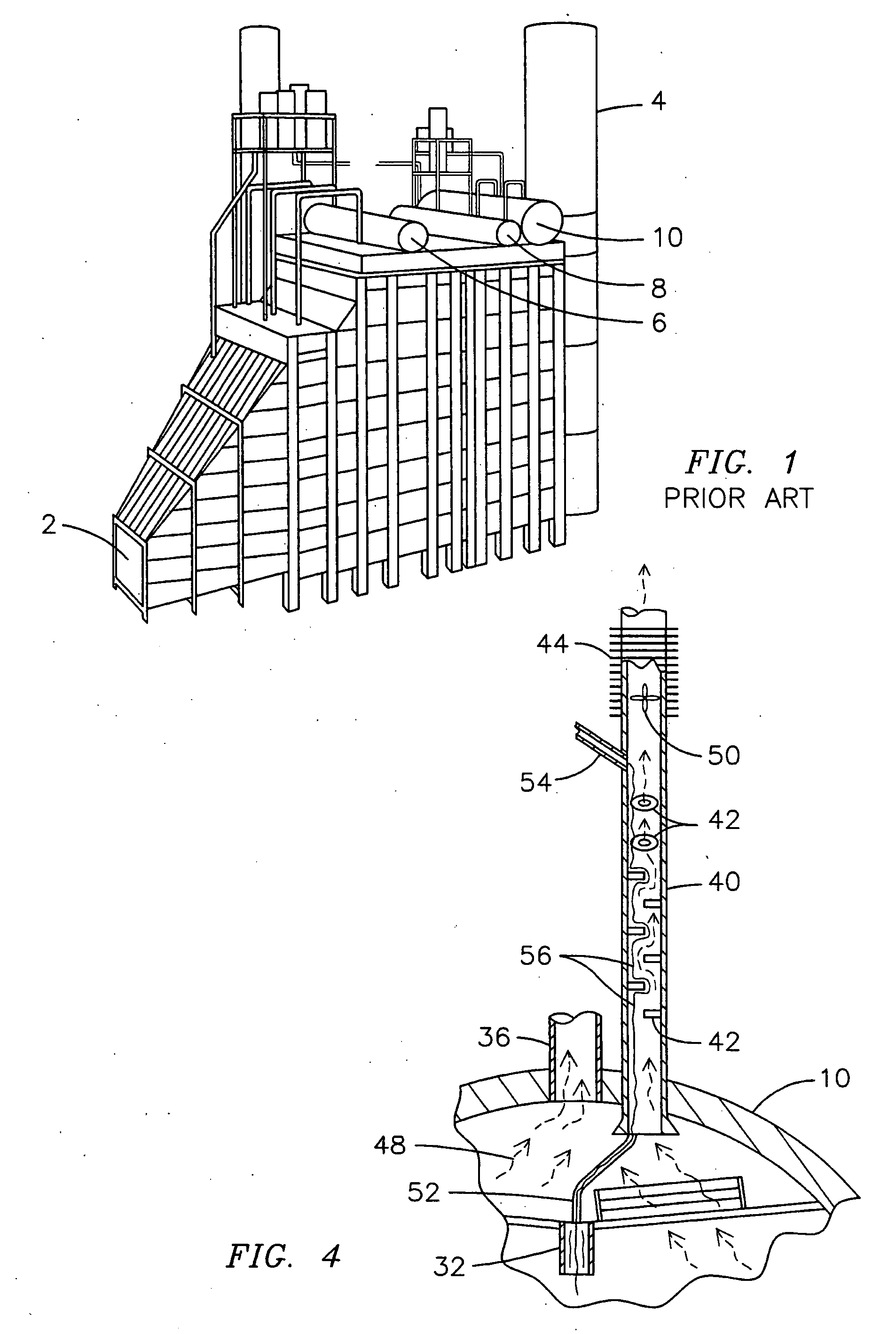
Condensing deaerating vent line for steam generating systems
InactiveUS7306653B2Efficient ventingMinimizing of amountUsing liquid separation agentThermal energyHigh concentration
The present invention comprises an apparatus and method for efficiently venting impurities from a heat recovery steam generator system by concentrating the impurities in a condensing deaerating vent line 40 and then venting a proportionately small amount of steam with a proportionately high concentration of impurities. The condensing deaerating vent line 40 is attached to a low pressure drum 10, and feed water 54 may be added to the upper portion of the condensing deaerating vent line 40 to improve condensation and conserve thermal energy.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
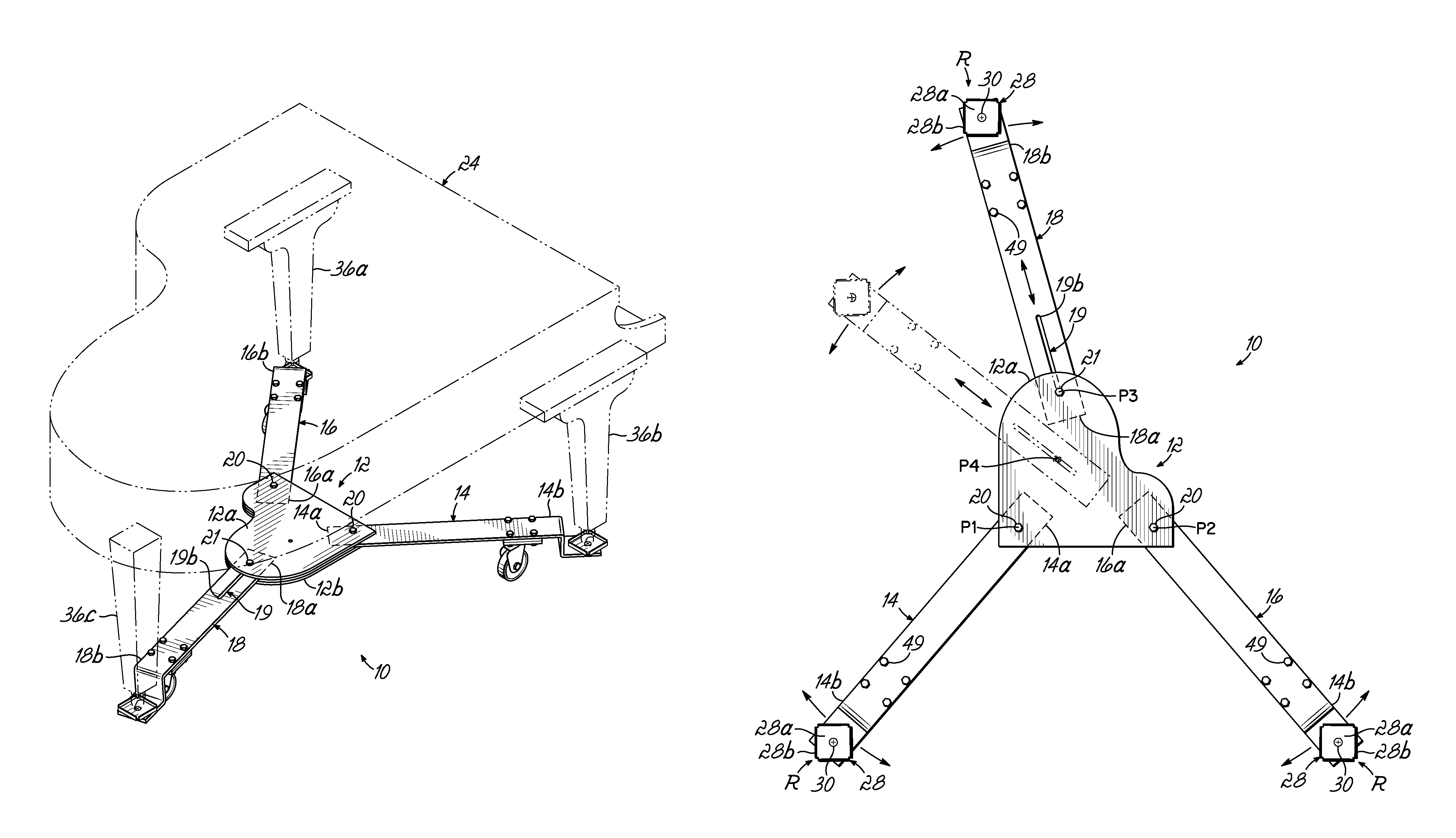
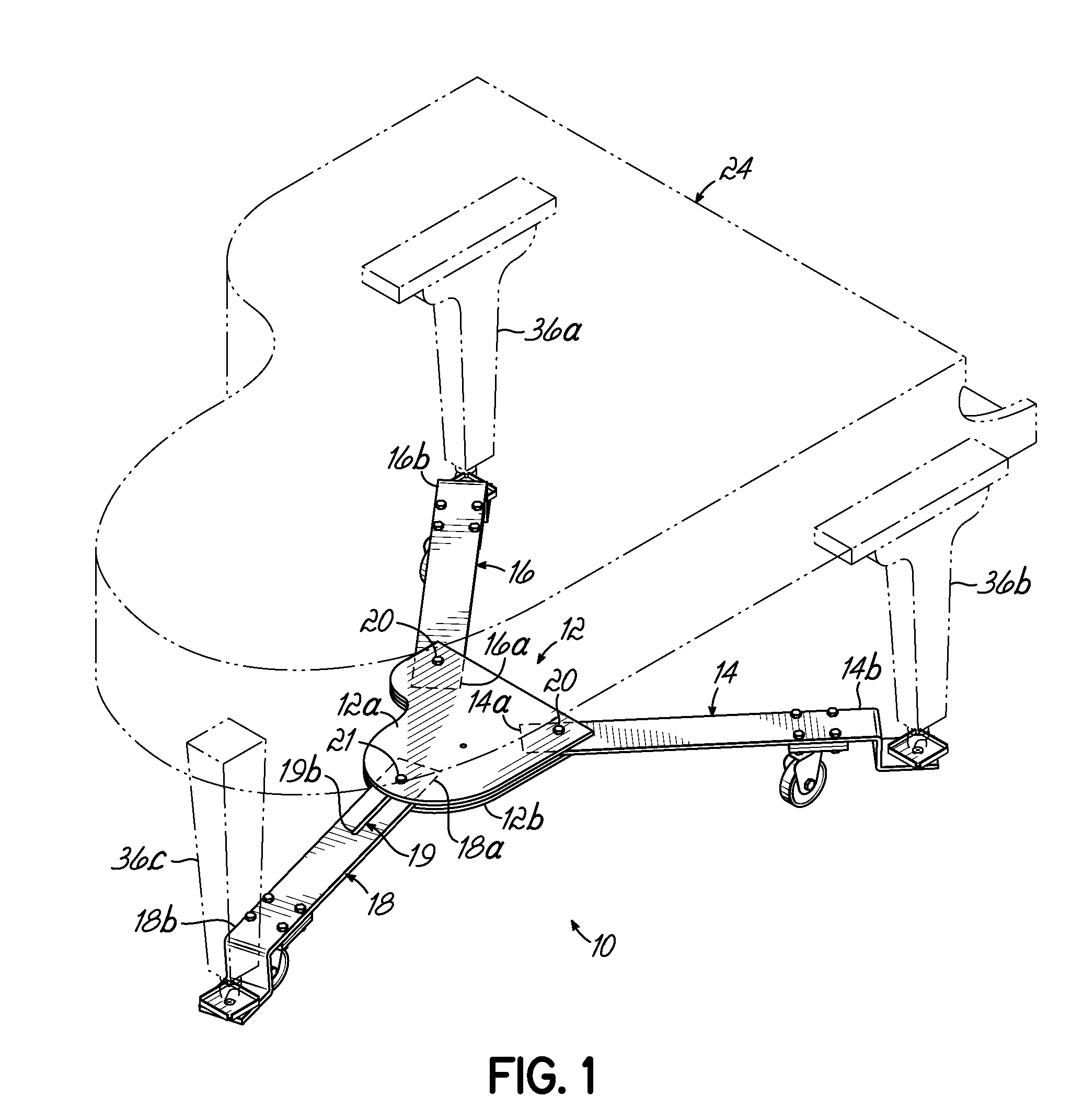
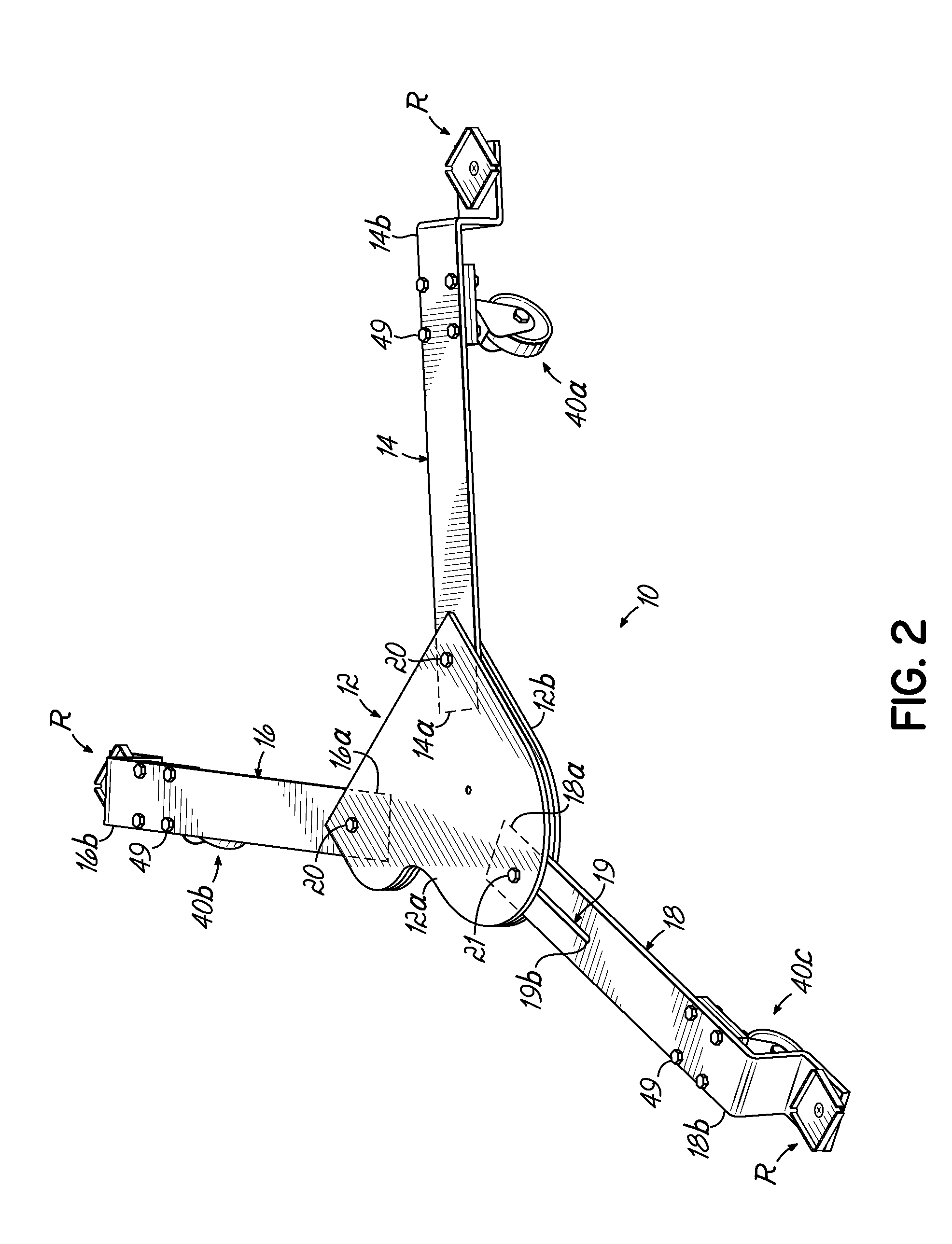
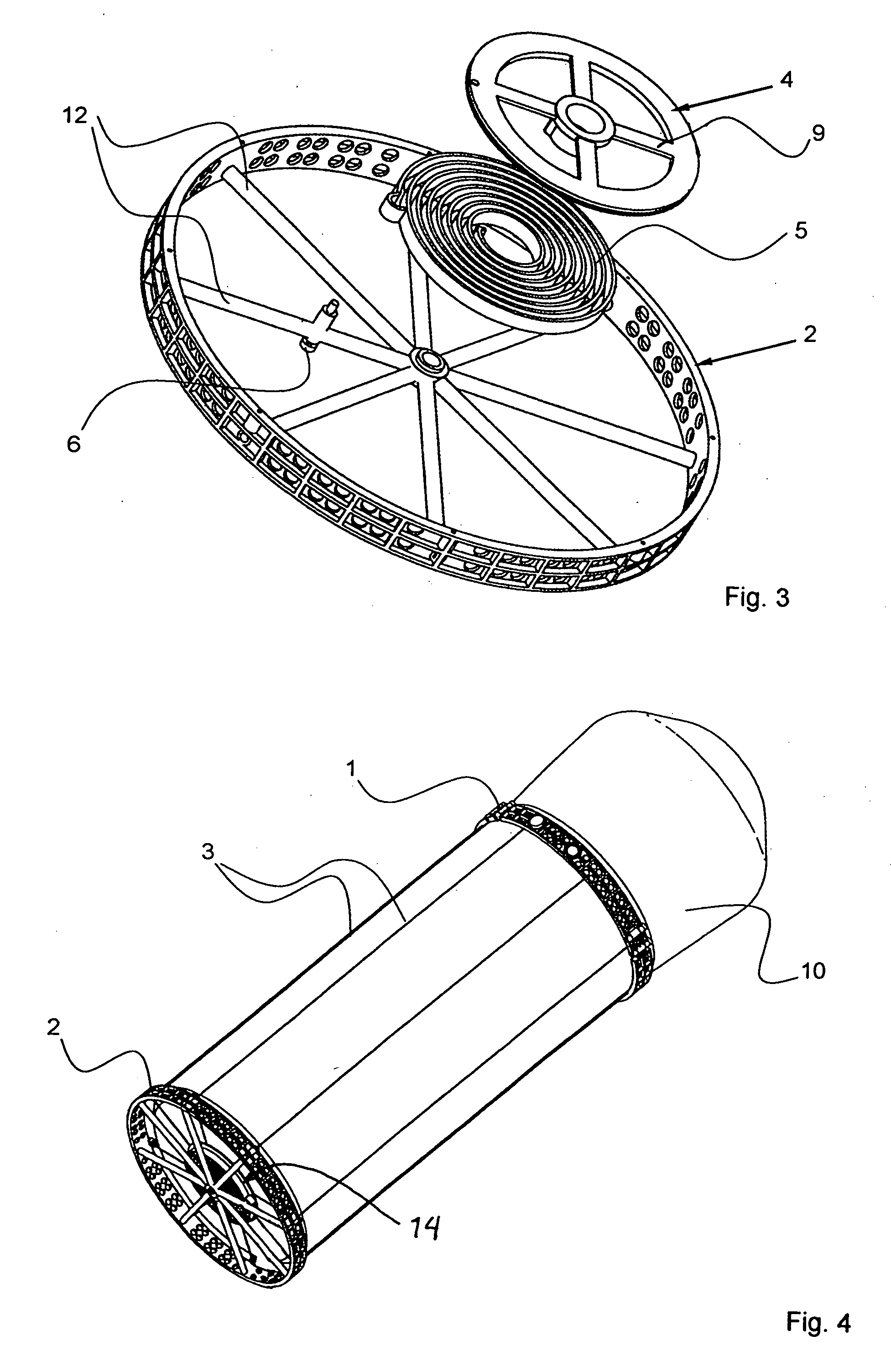
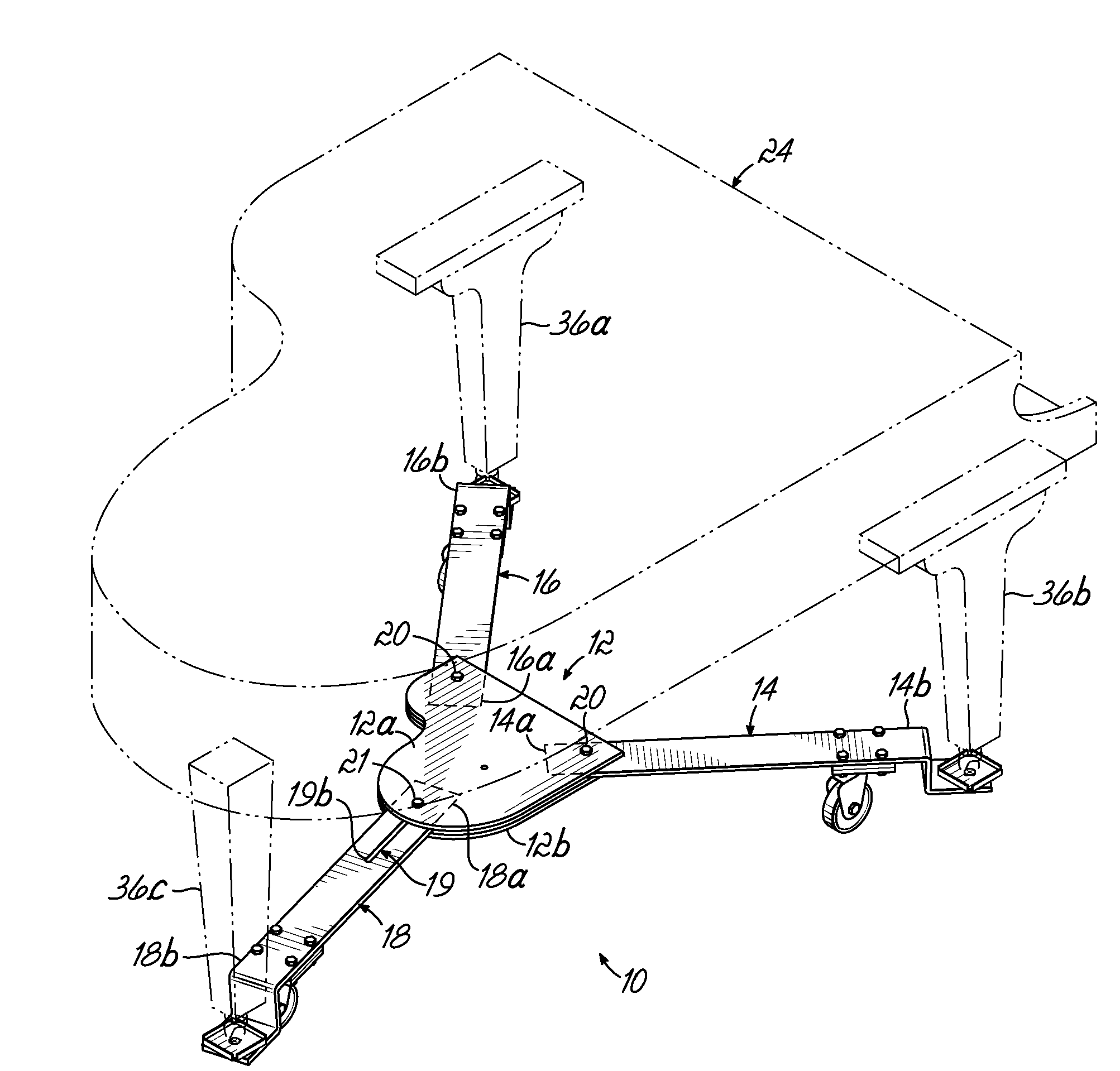
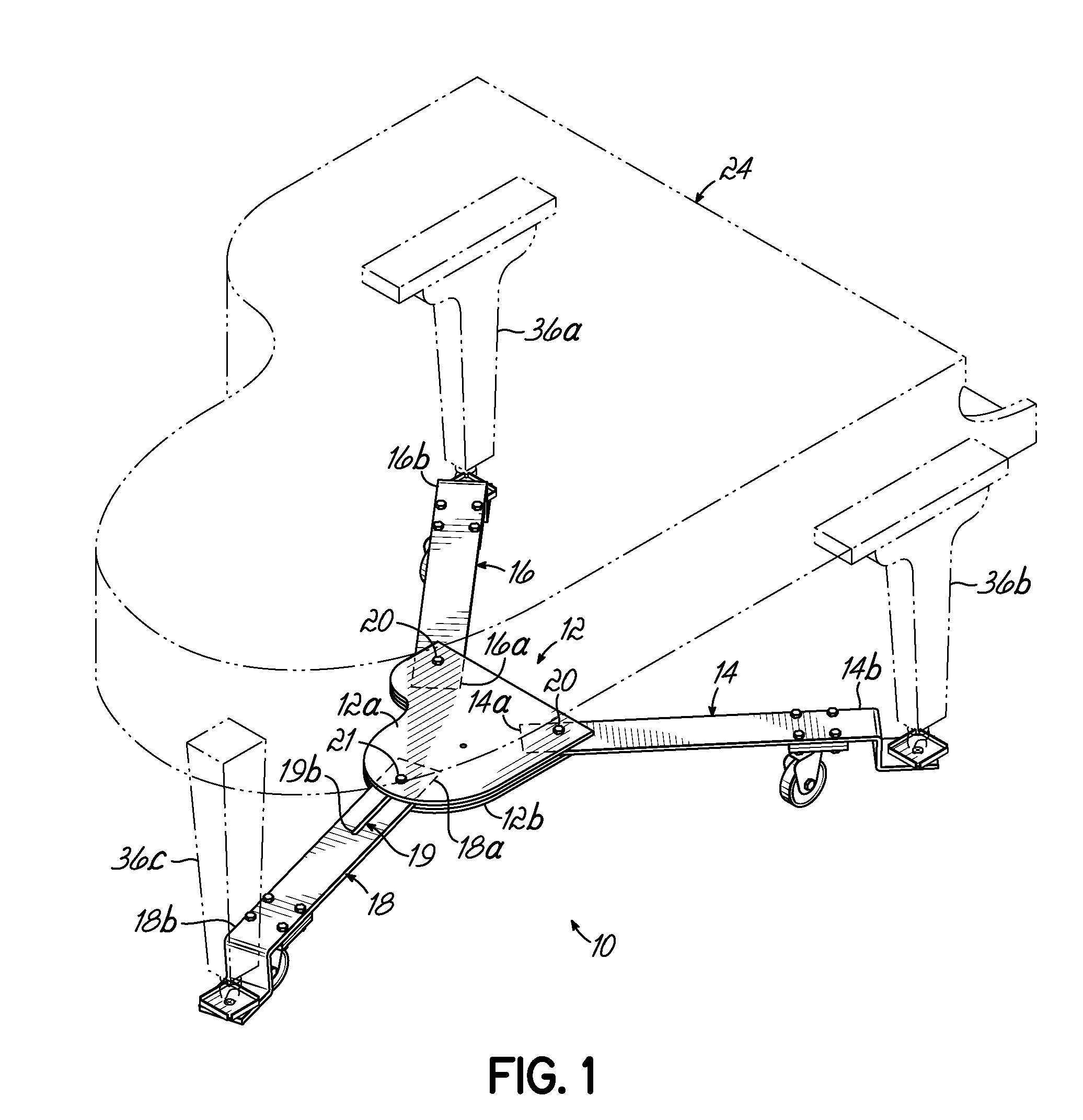
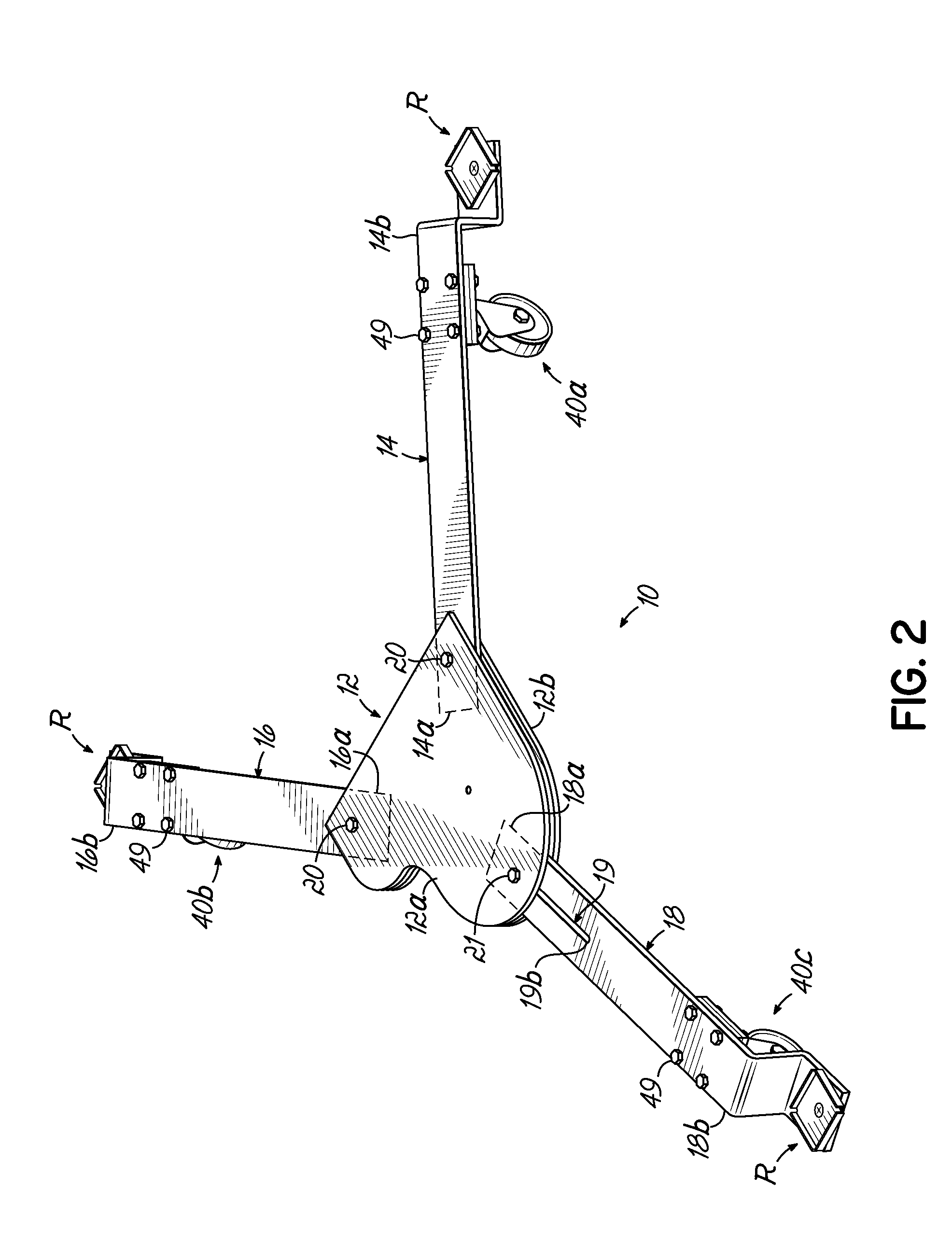
Piano dolly
InactiveUS7988161B2Minimize the numberMinimize timeCarriage/perambulator accessoriesSledgesPianoEngineering
A dolly on which a grand piano can be mounted to facilitate movement thereof over a surface from one location to another, which includes a central hub shaped in the form of a miniature grand piano, two fixed length arms of equal length pivotally connected to the front of the hub at opposite corners thereof, and a fixed length rear arm having a longitudinal slot which is pivotally connected to the rear of the hub at selectively adjustable positions along the length of the slot to accommodate grand pianos having a range of different lengths.
Owner:GRK MFG
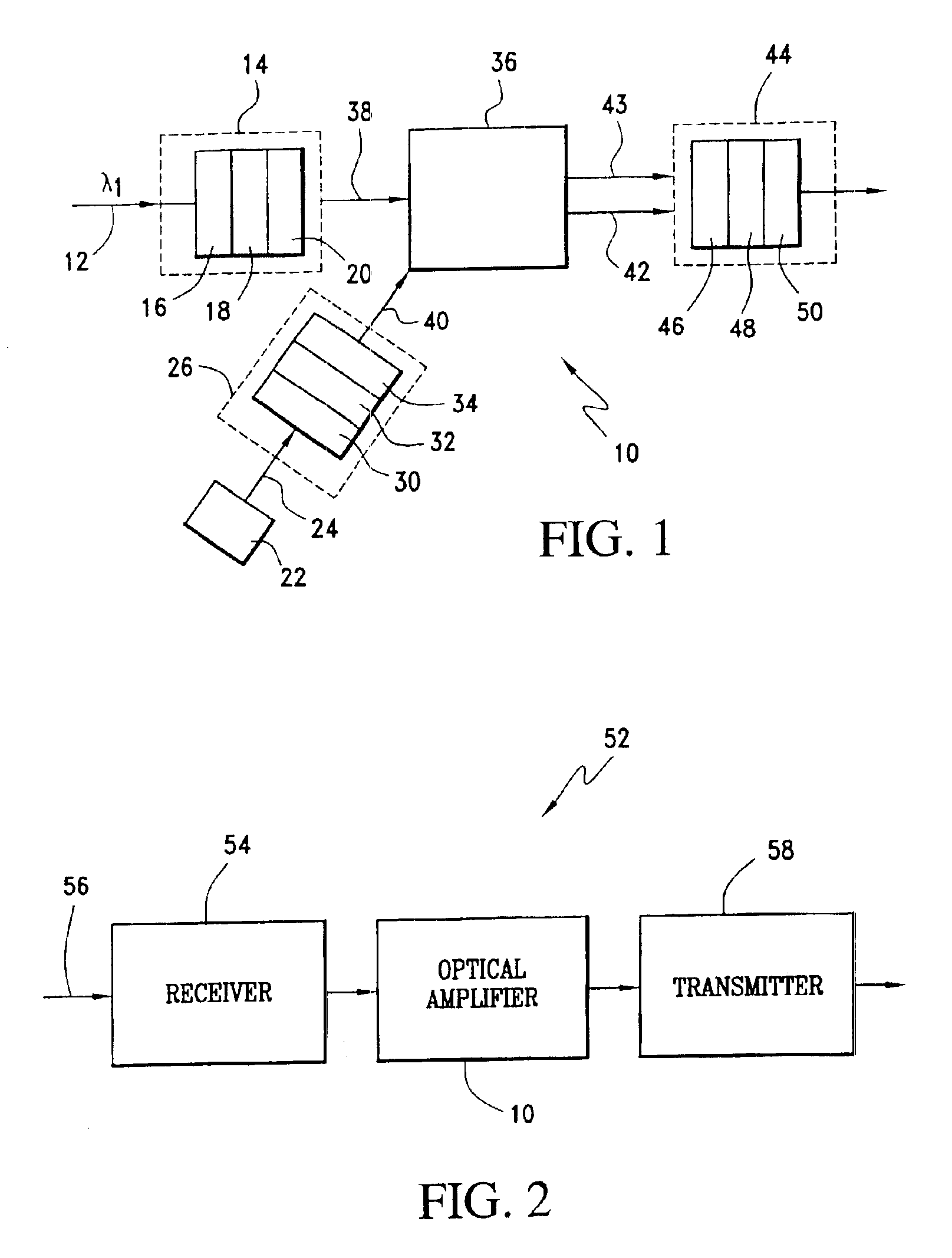
Stimulated brillouin scattering optical amplifier
ActiveUS6891660B2Avoid spreadingLess energy lossLaser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical interactionLight beam
The stimulated Brillouin scattering optical amplifier includes a first control optics assembly, a driver element, a second control optics assembly, a Brillouin active medium, and egressing optics. The first control optics assembly receives an incoming laser beam and adjusts that incoming laser beam in accordance with first desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A driver element produces a driver laser beam. A second control optics assembly receives the driver laser beam and adjusts that driver laser beam in accordance with second desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A Brillouin active medium receives an output from the first control optics assembly and an output from the second control optics assembly. The Brillouin active medium provides a non-linear optical interaction between the outputs such that the incoming laser beam is amplified producing an amplified Brillouin active medium output laser beam and a depleted driver laser beam. Egressing optics receives the amplified Brillouin active medium output laser beam and the depleted driver laser beam. The egressing optics controllably transmits the amplified Brillouin active medium output laser beam in accordance with third desired wavelength, polarization, and beam propagation parameters and prevents transmission of the depleted driver laser beam. The output of the egressing optics includes an amplified egressing optics output laser beam.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Kinetic energy rod warhead with blast fragmentation
InactiveUS20120186482A1Improve versatilityIncrease lethalityAmmunition projectilesProjectilesEngineeringProjectile
A hybrid kinetic energy rod warhead includes a projectile core including a plurality of projectiles, explosive segments about the projectile core, and isolators between the explosive segments. There is an initiator for each explosive segment and a shell about the explosive segments. A deployable casing including multiple fragment members is attached to the shell, and there is a housing about the deployable casing.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
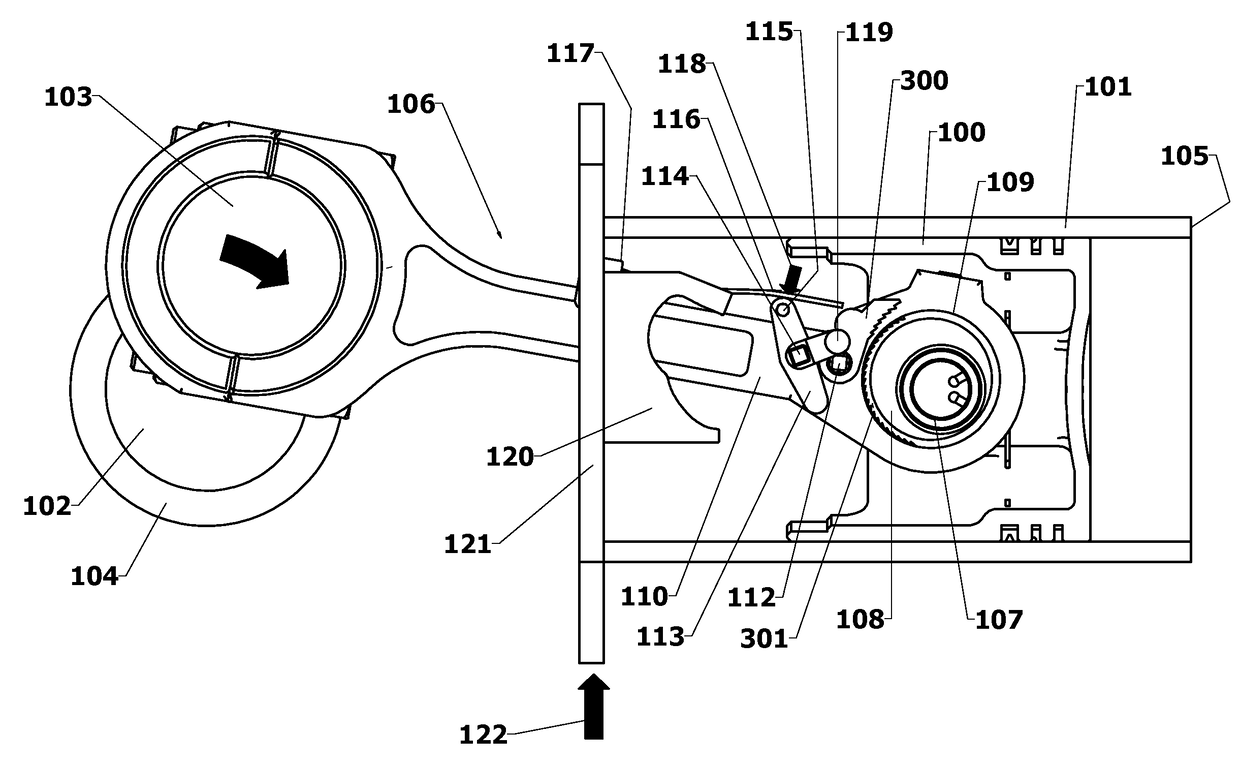
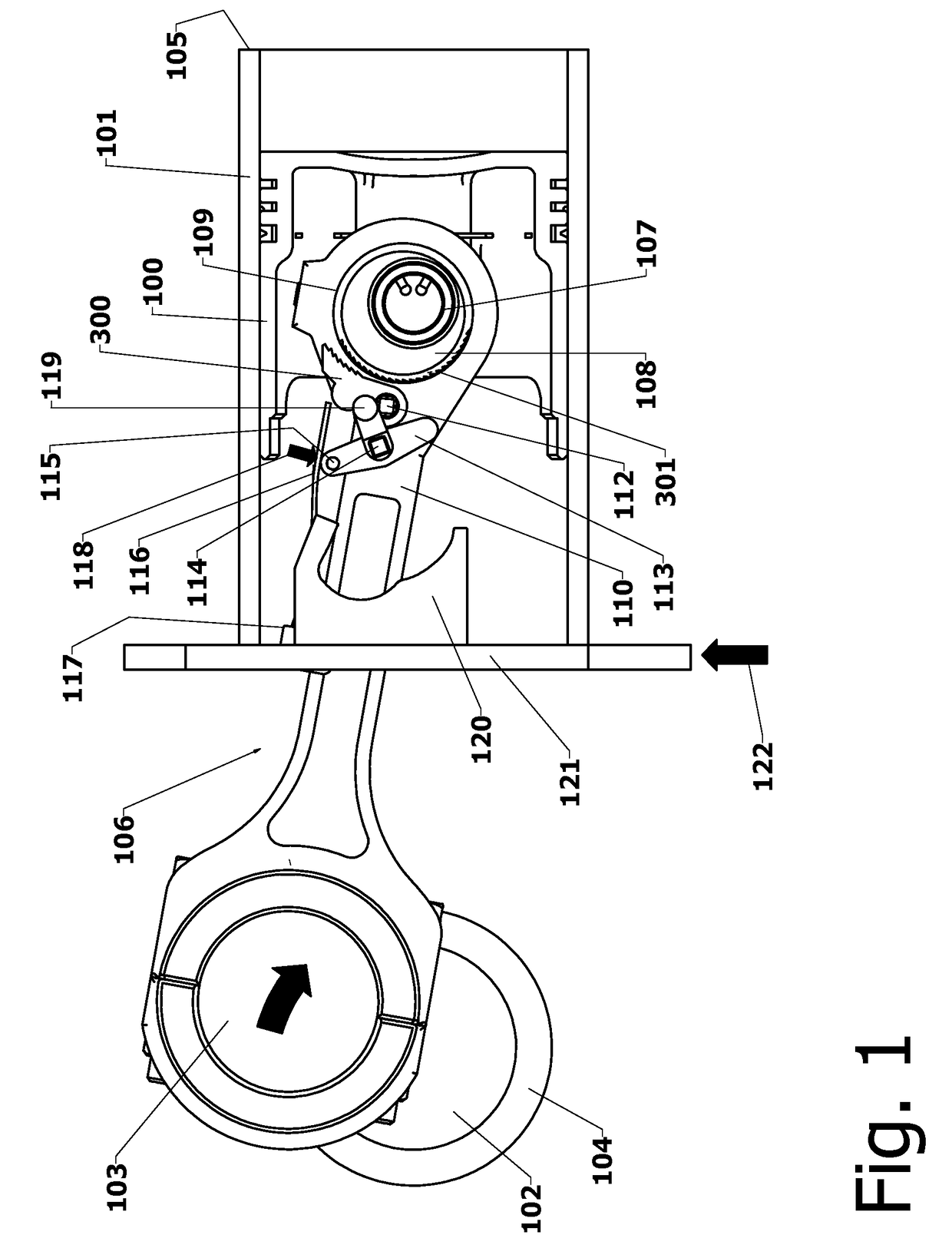
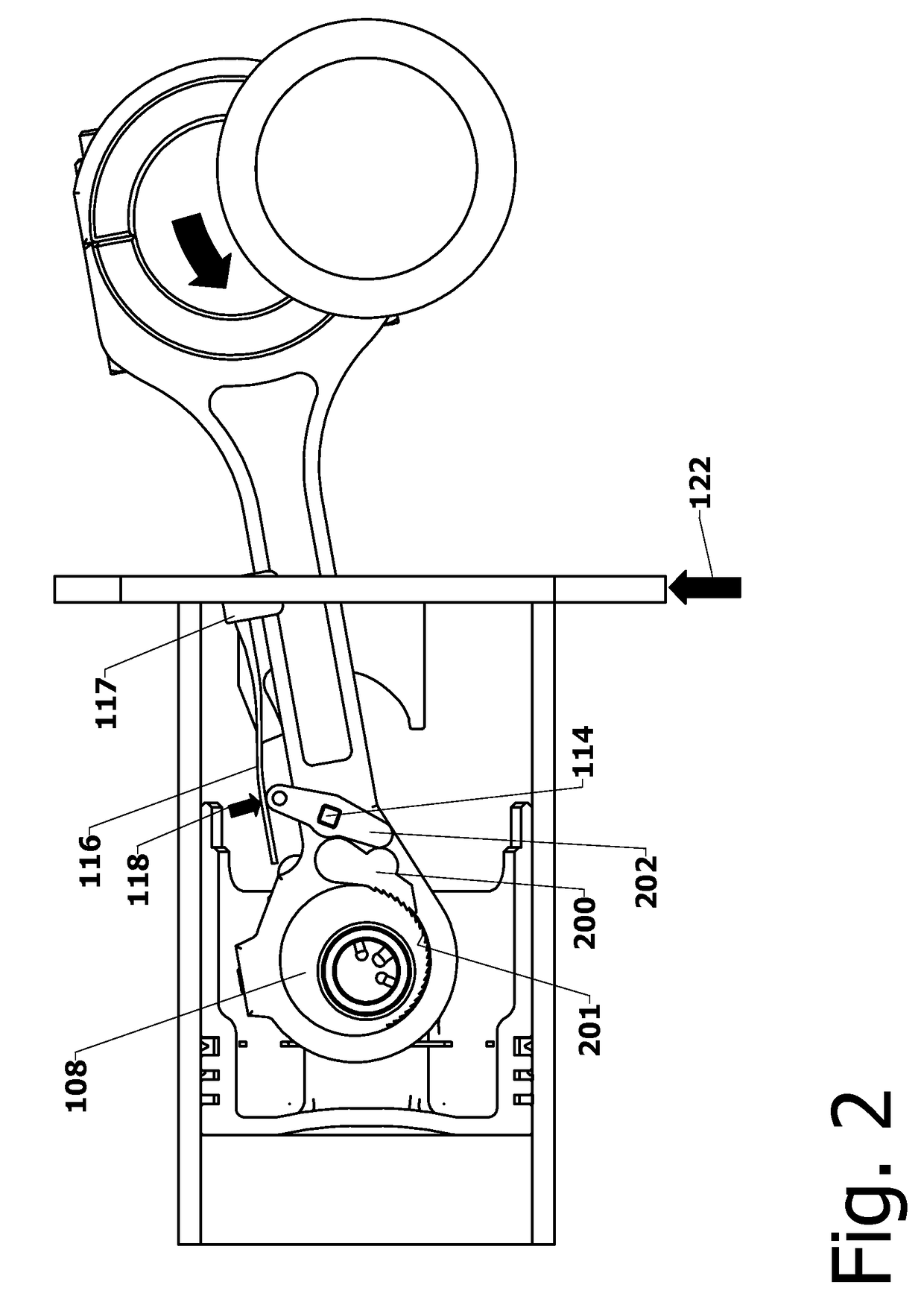
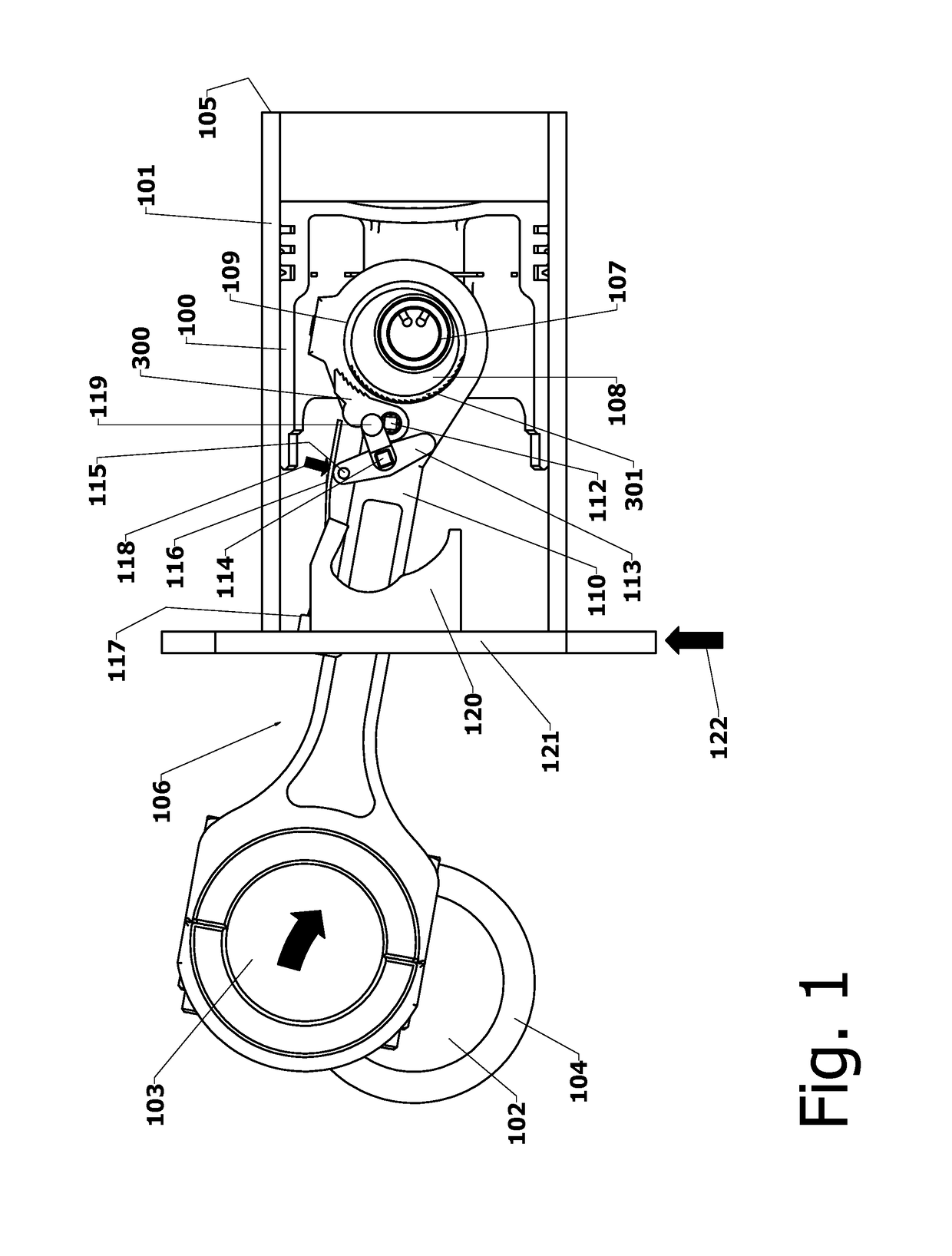
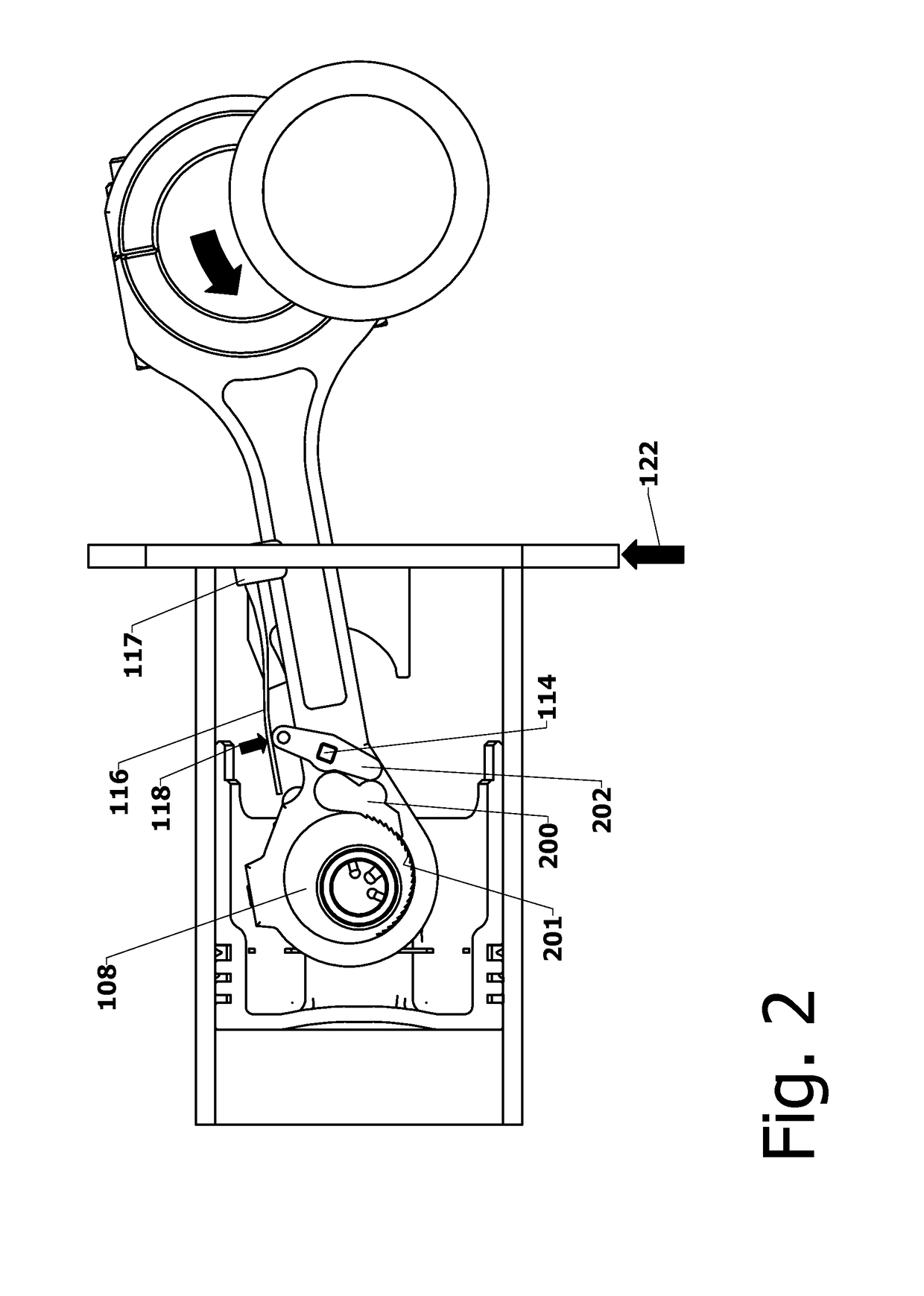
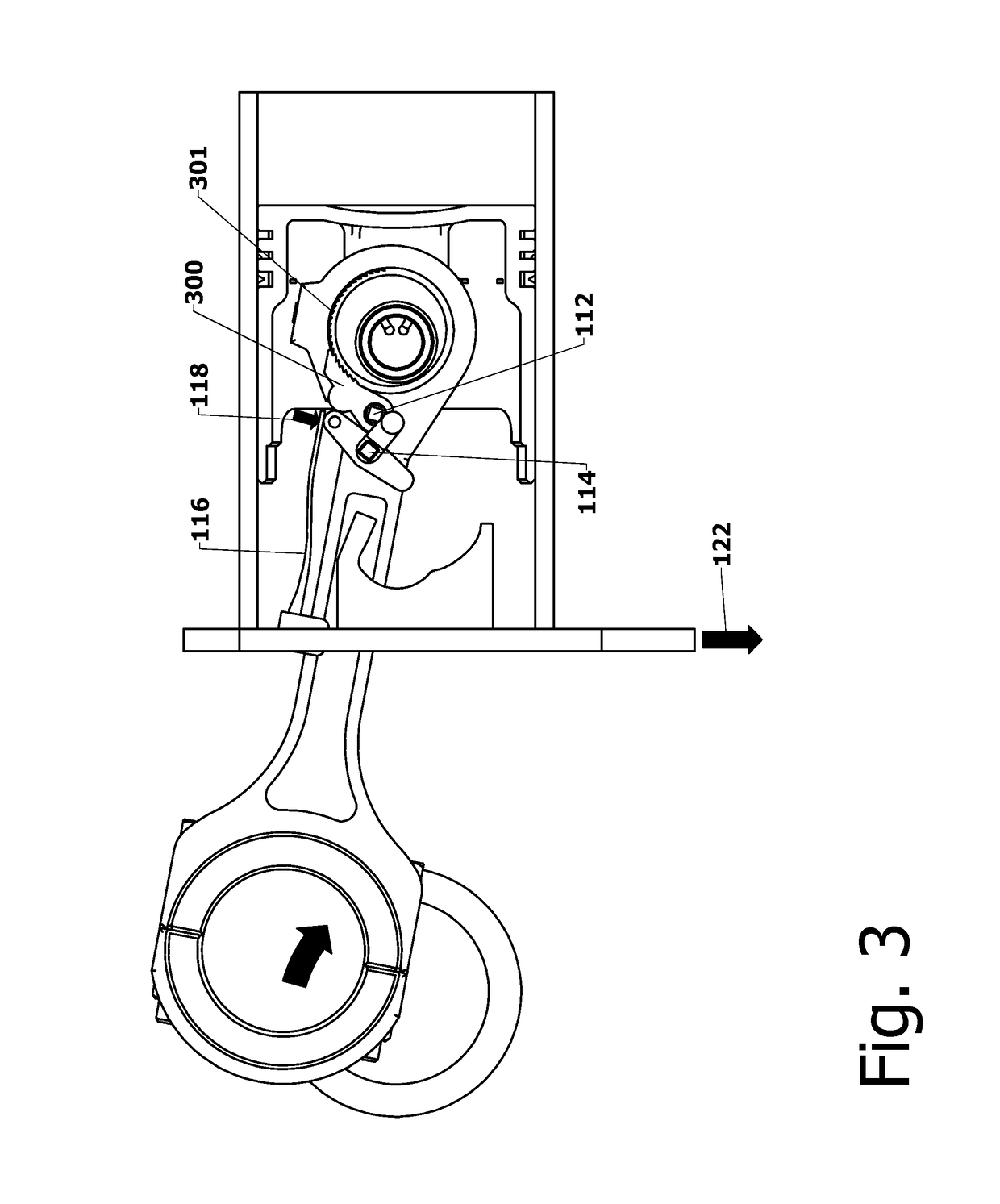
Variable Compression Connecting Rod
The present invention is directed to improved designs and methods for improving engine fuel efficiency by providing two-stage engine variable compression in running engines using connecting rod force reversals to rotate eccentric bushings to change the connecting rod length. Compression ratio changes are initiated by shifting a block-mounted cam such that it engages and flips a bi-stable toggle on the connecting rod. The clutch mechanism latches the eccentric at the eccentric rotation end point, whereupon the connecting rod acts as a rigid rod. The invention includes novel configurations of the lubricated journal bearing between the connecting rod and the eccentric that modify the squeeze film bearing effects and resulting friction. These configurations reduce the peak eccentric torque carried by the clutch mechanism while facilitating eccentric rotation at lower torque.
Owner:MEACHAM G B KIRBY
Electric catalytic oxidizer
ActiveUS8038957B1Minimizing energy useMinimizing structural massCombination devicesPhysical/chemical process catalystsParticulatesHydrocarbon
A containment vessel having a spiral plate heat exchanger, a central catalyst chamber packed with particulate catalyst, a central heater, a plenum providing conductive flow access for a hydrocarbon-air mixture to and from the containment vessel interior, and essential flow pathways interconnecting the plenum section, heat exchanger, catalyst chamber and central heater. The spiral plate heat exchanger, catalyst chamber, and heater assembly occupy successively smaller annular regions within the containment vessel.
Owner:THE MARITAL TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER ARTICLE FOURTH OF THE JAMES M CLEARY JR TRUST +1
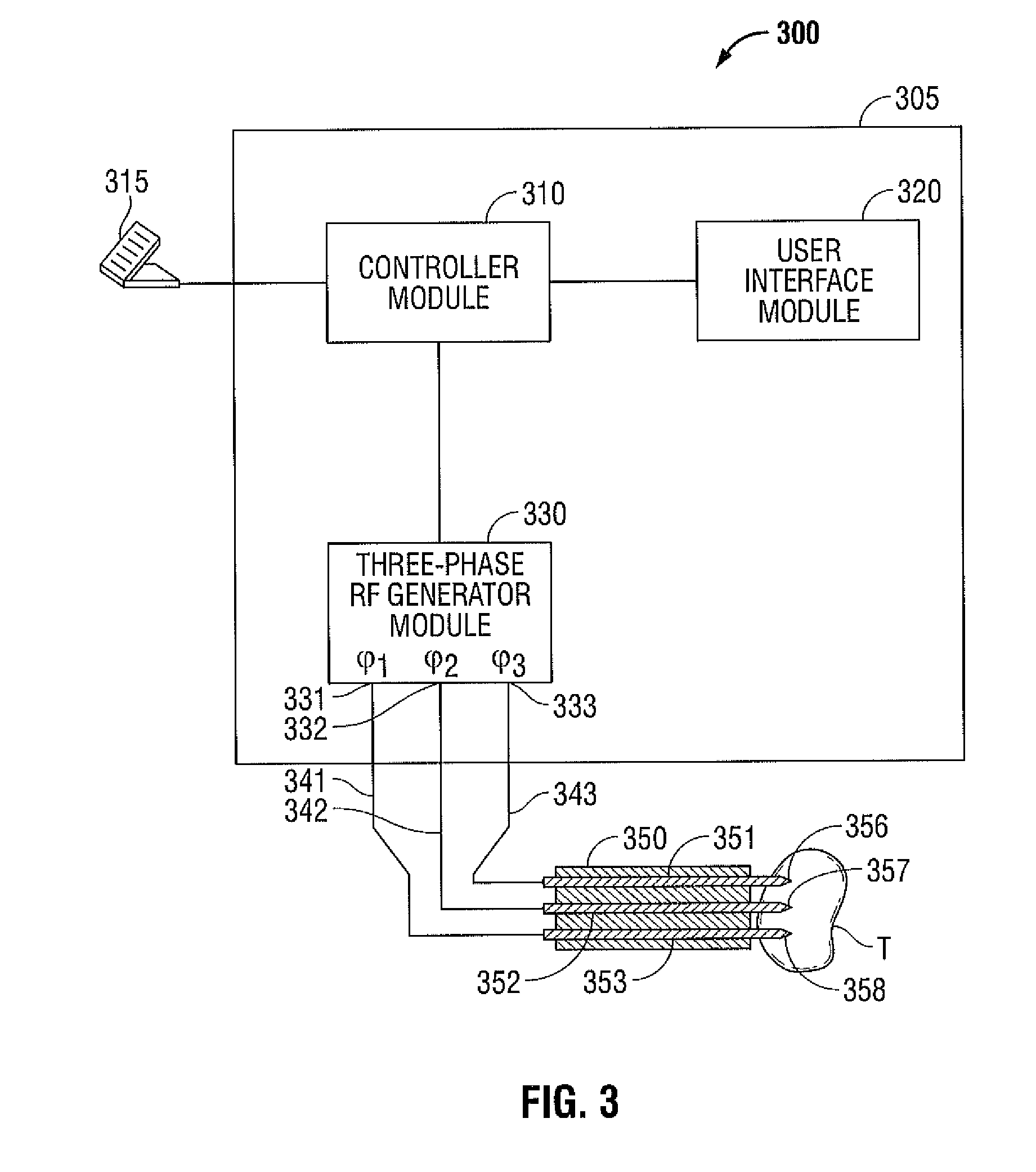
Polyphase electrosurgical system and method
ActiveUS9700366B2Area minimizationMinimizing volumeSurgical instruments for heatingUser inputThree-phase
A polyphase electrosurgical system and method are provided. In embodiments, a radiofrequency generator having the capability of delivering a plurality of independent electrosurgical signals is disclosed. An electrosurgical instrument having an array of electrodes that correspond to the plurality of signals may be used to deliver the electrosurgical signals to tissue. In embodiments, three RF signals having a phase offset of about 120° therebetween, i.e., a three-phase configuration, may be used to achieve a balanced delivery of electrosurgical energy, which may lead to increased rates of energy delivery, improved control of tissue ablation regions, and improved operative outcomes. The phase, amplitude, and / or frequency of each signal may be independently variable in response to user inputs and / or biological parameters such as tissue impedance or return electrode current.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
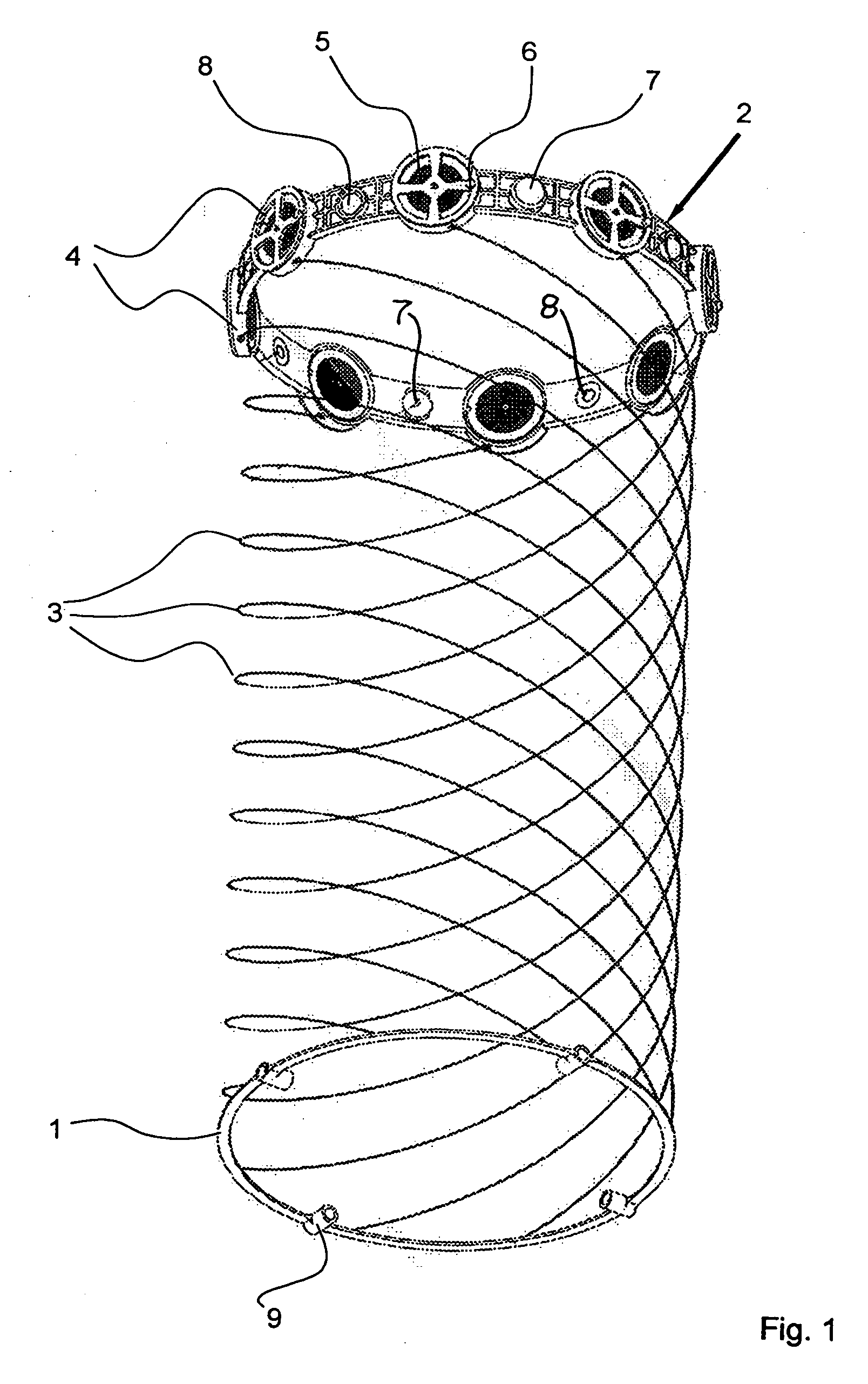
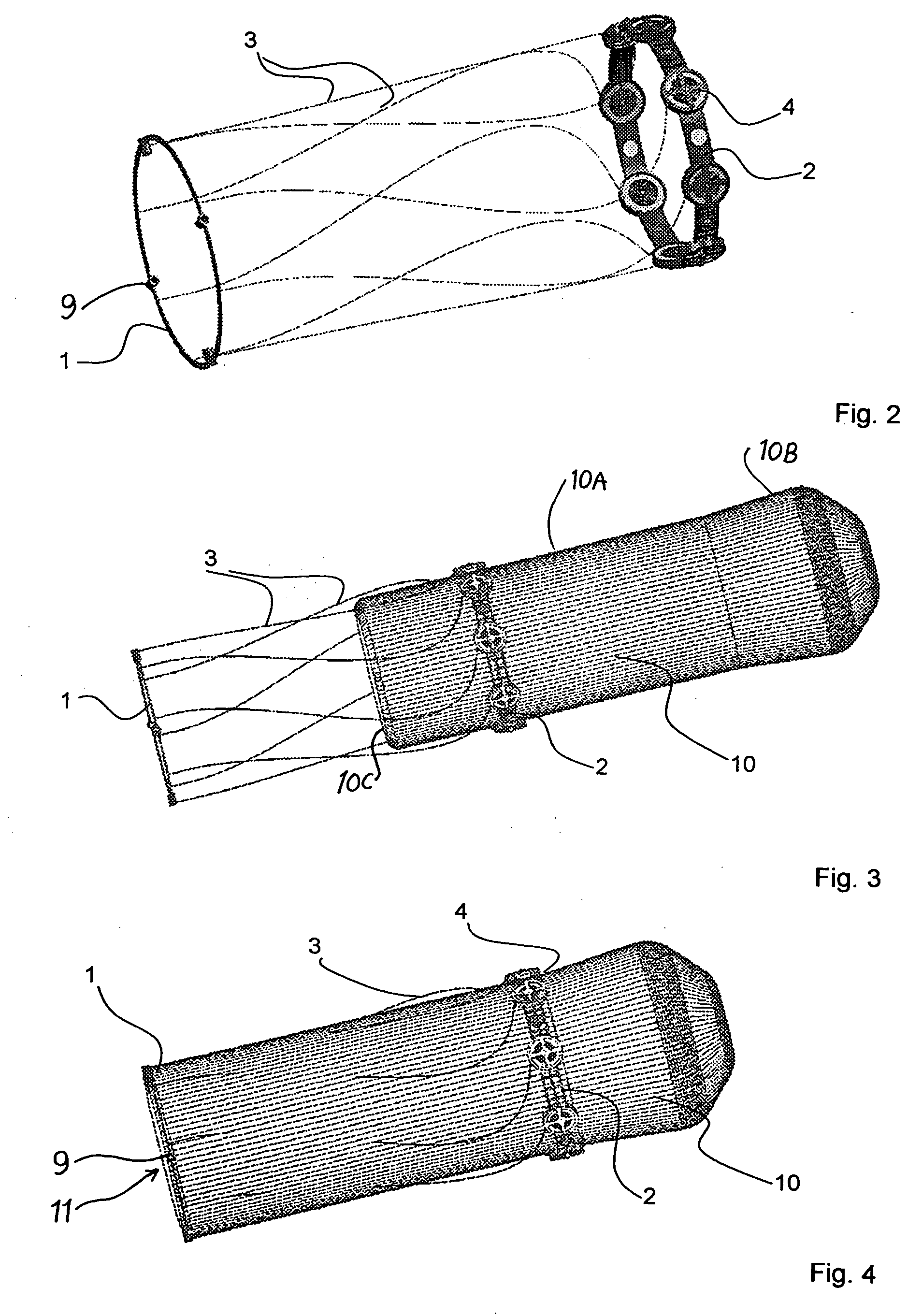
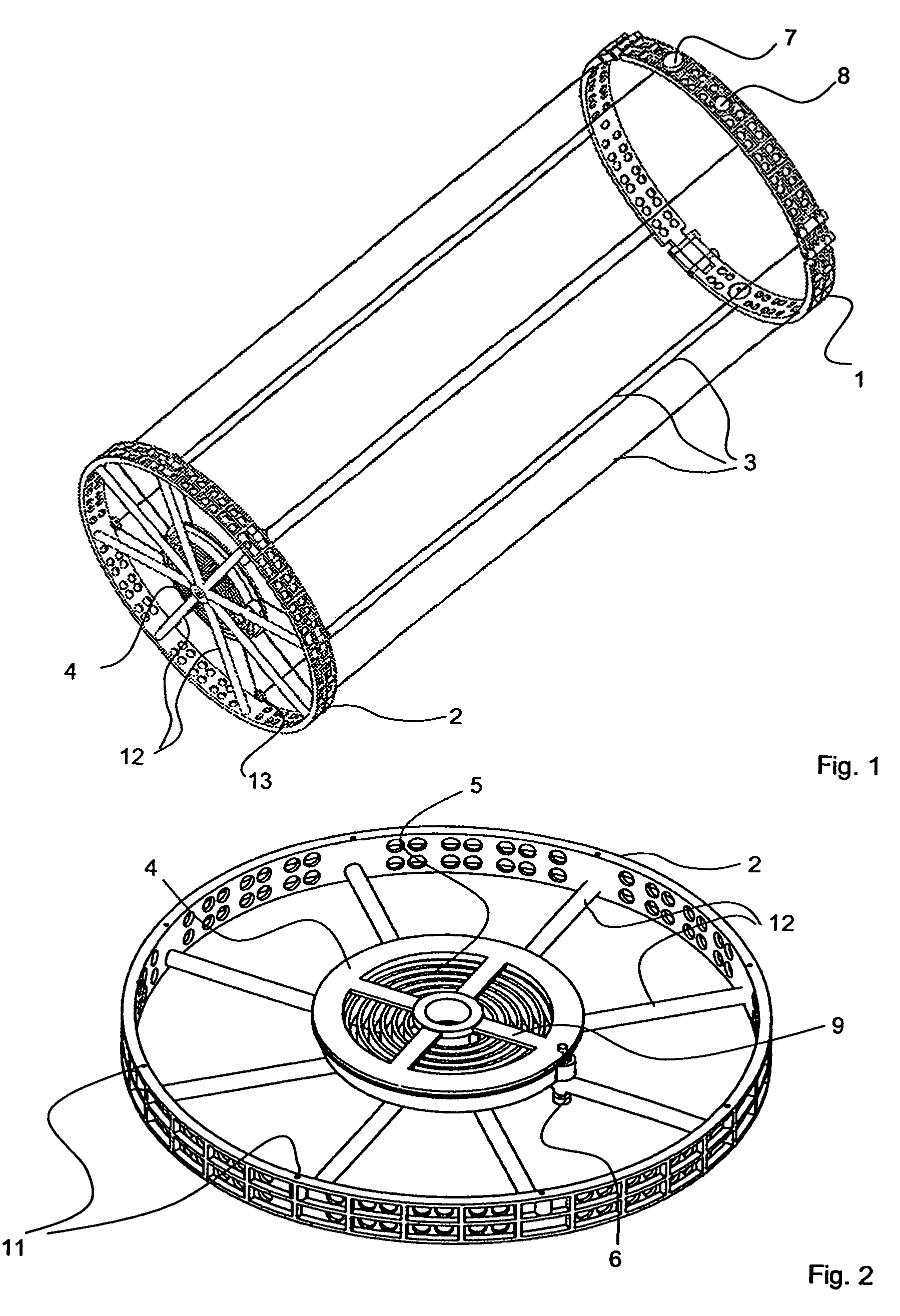
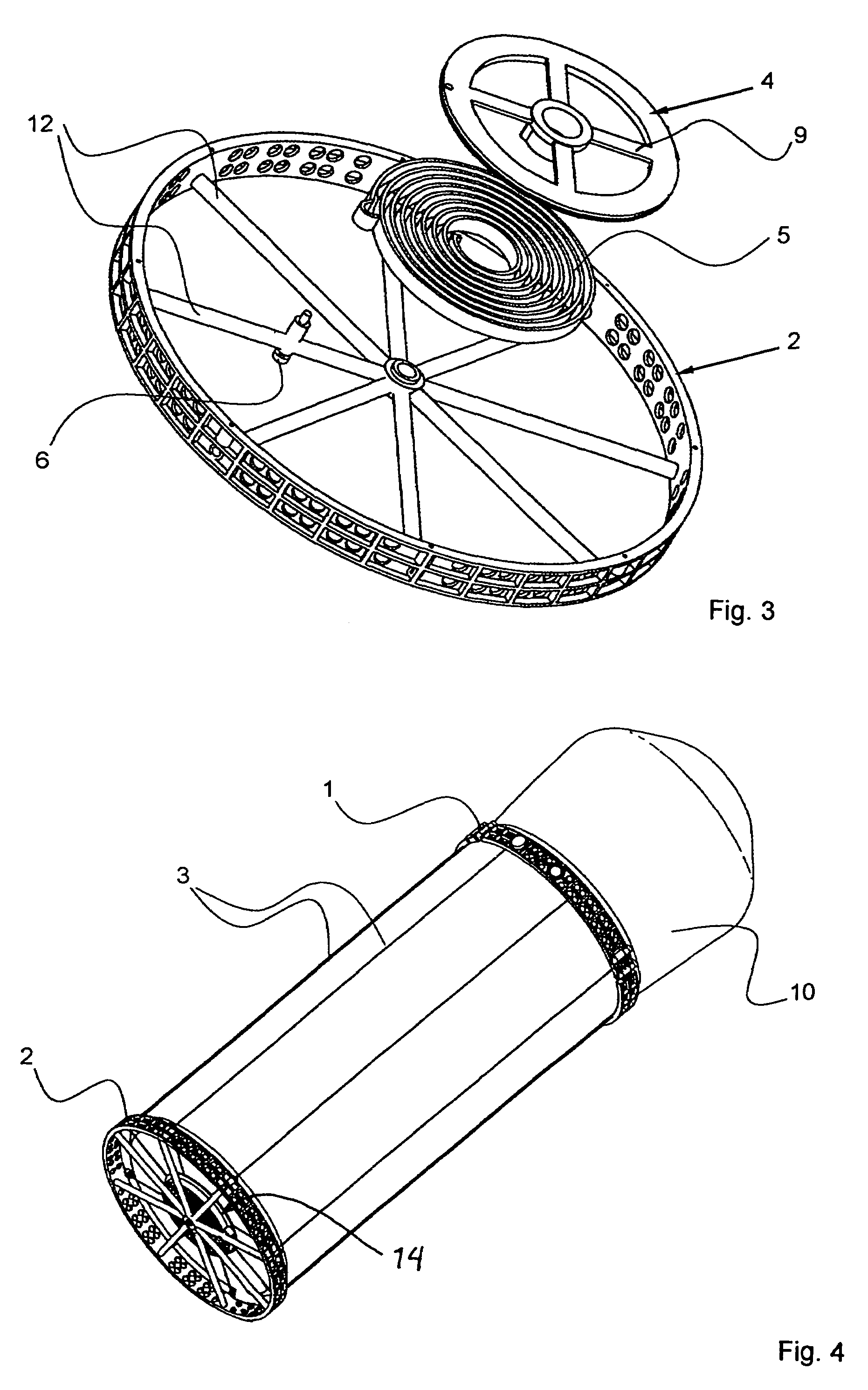
Apparatus with helical tension cables for ejecting a spin-stabilized body from a spacecraft
InactiveUS20060138283A1Considerable safety riskMinimizing volumeCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsEngineeringConductor Coil
An apparatus for ejecting a flying body such as a payload recovery container from a spacecraft includes a first ring to be releasably engaged with the flying body, a second ring to be secured to the spacecraft, and tension cables extending between and interconnecting the two rings. Cable winding devices mounted on at least one of the rings are spring-biased to wind-up the cables. The flying body is inserted through the open inner diameter of the second ring, and the first ring is separated from and rotated relative to the second ring, so that the cables extend helically along the outer circumference of the flying body. Holding and guide elements on the second ring hold and guide the flying body. When the holding elements are released, the cables are retracted by the cable winding devices, whereby the flying body is rotated and translationally ejected through the second ring.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
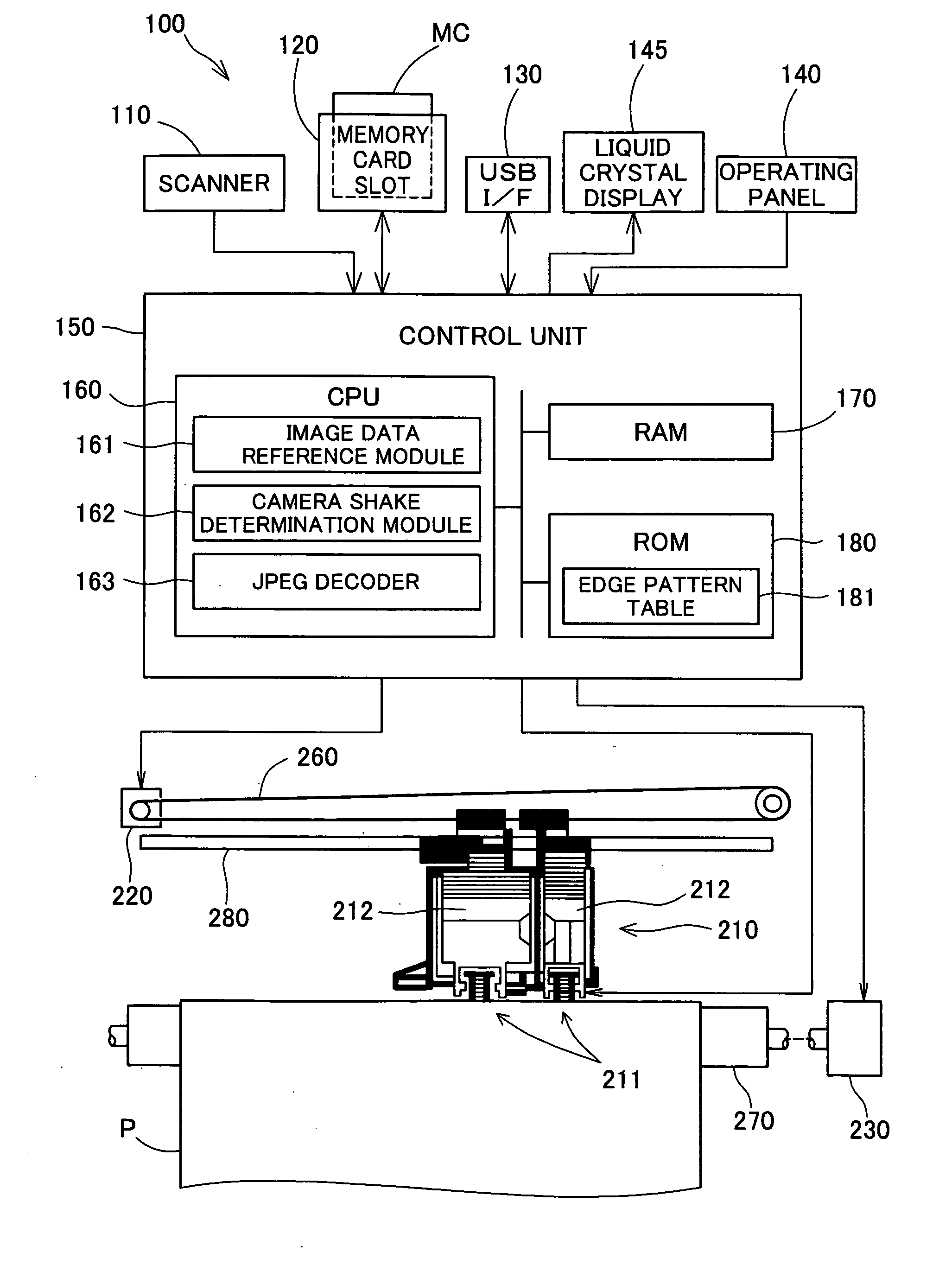
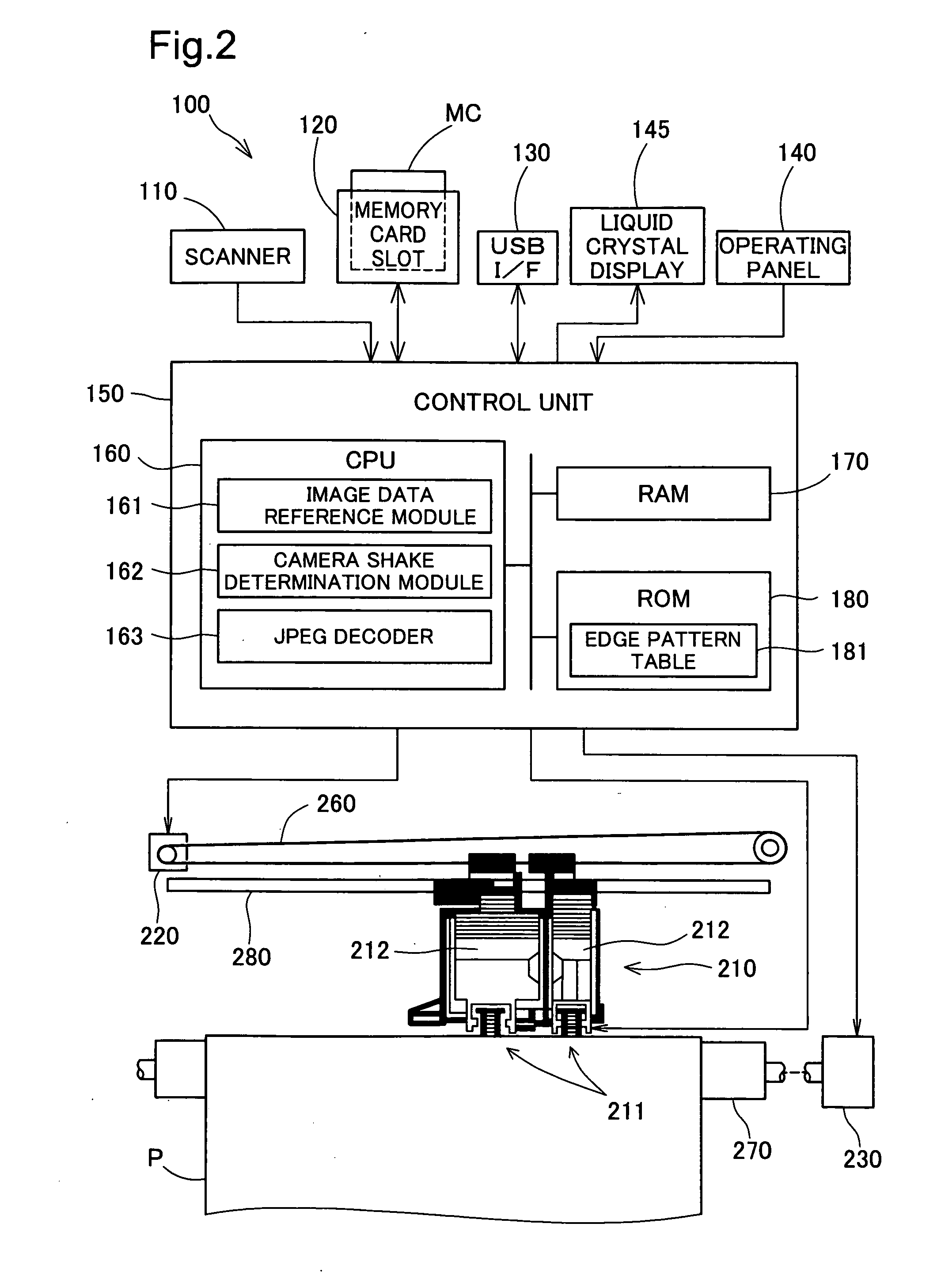
Camera shake determination device, printing apparatus and camera shake determination method
InactiveUS20080151309A1Detect blurringMinimizing burdenImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersComputer scienceImaging data
The device employs a plurality of coefficients recorded in image data to detect whether edges are included per block, and determines as the blur level the proportion of edges, among the detected edges, in which the edge width is over a certain threshold. The device also determines, per block, coordinates composed of a first coefficient value representing frequency components in a first direction in the blocks and a second coefficient value representing frequency components in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction, and calculates the extent of bias in the distribution of the coordinates as the ellipticity. The device determines whether or not blurring has been produced by camera shake in an image based on the relationship between the blur level and ellipticity which have thus been determined.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Aerodynamic insert for high speed permanent magnet motor
InactiveUS20070247013A1Minimizing volumeMinimizing weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsSupports/enclosures/casingsPermanent magnet rotorEngineering
An insert comprising a lightweight structure configured for filling the gaps between axially spaced C-shaped lamination stacks and circumferentially spaced non-magnetic cradles on a permanent magnet rotor. The insert is secured to a rib by a dovetail tongue that fits within a dovetail groove provided along the length of each rib. The insert engages the adjacent cradles and has a circumferential surface that has the same radius of curvature as the top surface of the cradles.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
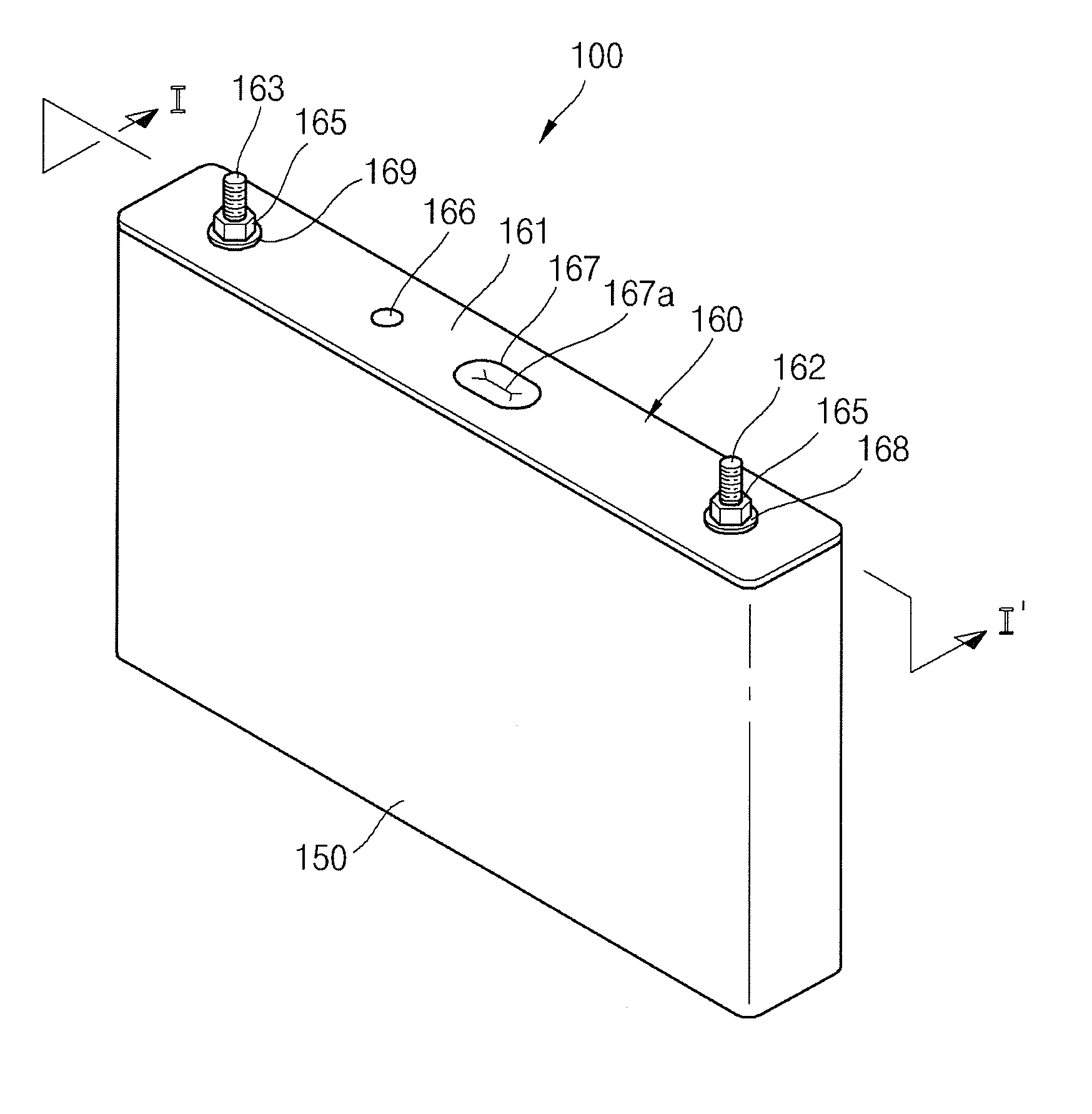
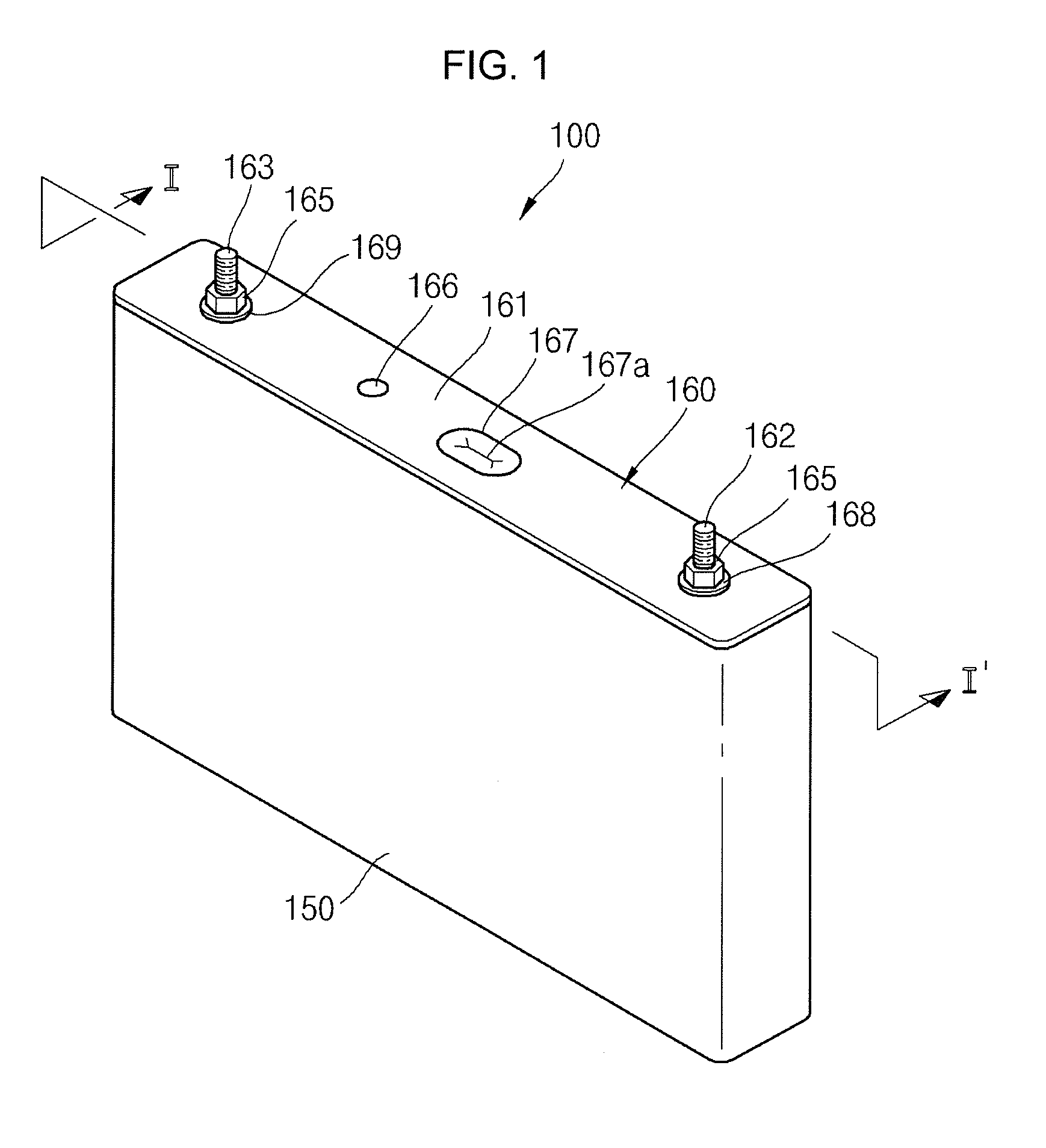
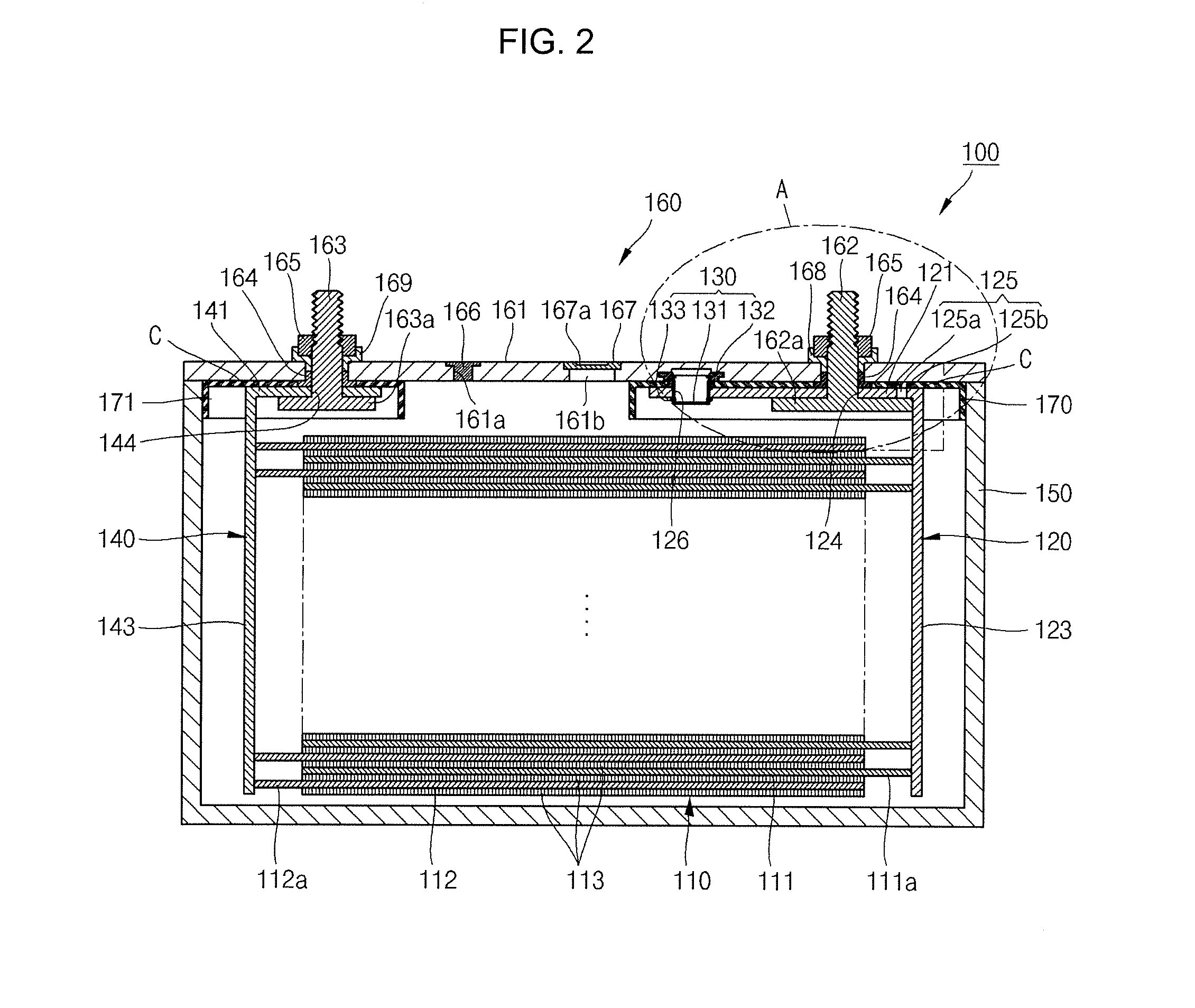
Secondary Battery
ActiveUS20120251852A1Minimizing weightMinimizing volumeFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsElectricityElectrical battery
A secondary battery includes an electrode assembly; a collecting plate electrically coupled to the electrode assembly and having a short circuit hole; a short circuit member comprising a metal can, wherein the metal can is in the short circuit hole; a case accommodating the electrode assembly and the collecting plate and having an opening; and a cap assembly comprising a cap plate sealing the opening of the case.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Stimulated polariton scattering optical amplifier
InactiveUS6924925B2Improve technical flexibilitySimple optical designLaser using scattering effectsPhysicsActive medium
The stimulated polariton scattering optical amplifier includes a first control optics assembly, a driver element, a second control optics assembly, a polariton active medium and egressing optics. The first control optics assembly receives an incoming laser beam and adjusts that incoming laser beam in accordance with first desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A driver element produces a driver laser beam. A second control optics assembly receives the driver laser beam and adjusts that driver laser beam in accordance with second desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A polariton active medium receives an output from the first control optics assembly and an output from the second control optics assembly. The polariton active medium provides a non-linear optical interaction between the outputs such that the incoming laser beam is amplified, producing an amplified polariton active medium output laser beam and a depleted driver laser beam. Egressing optics receives the amplified polariton active medium output laser beam and the depleted driver laser beam. The egressing optics controllably transmits the amplified polariton active medium output laser beam in accordance with third desired wavelength, polarization, and beam propagation parameters and prevents transmission of the depleted driver laser beam. The output of the egressing optics includes an amplified egressing optics output laser beam.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
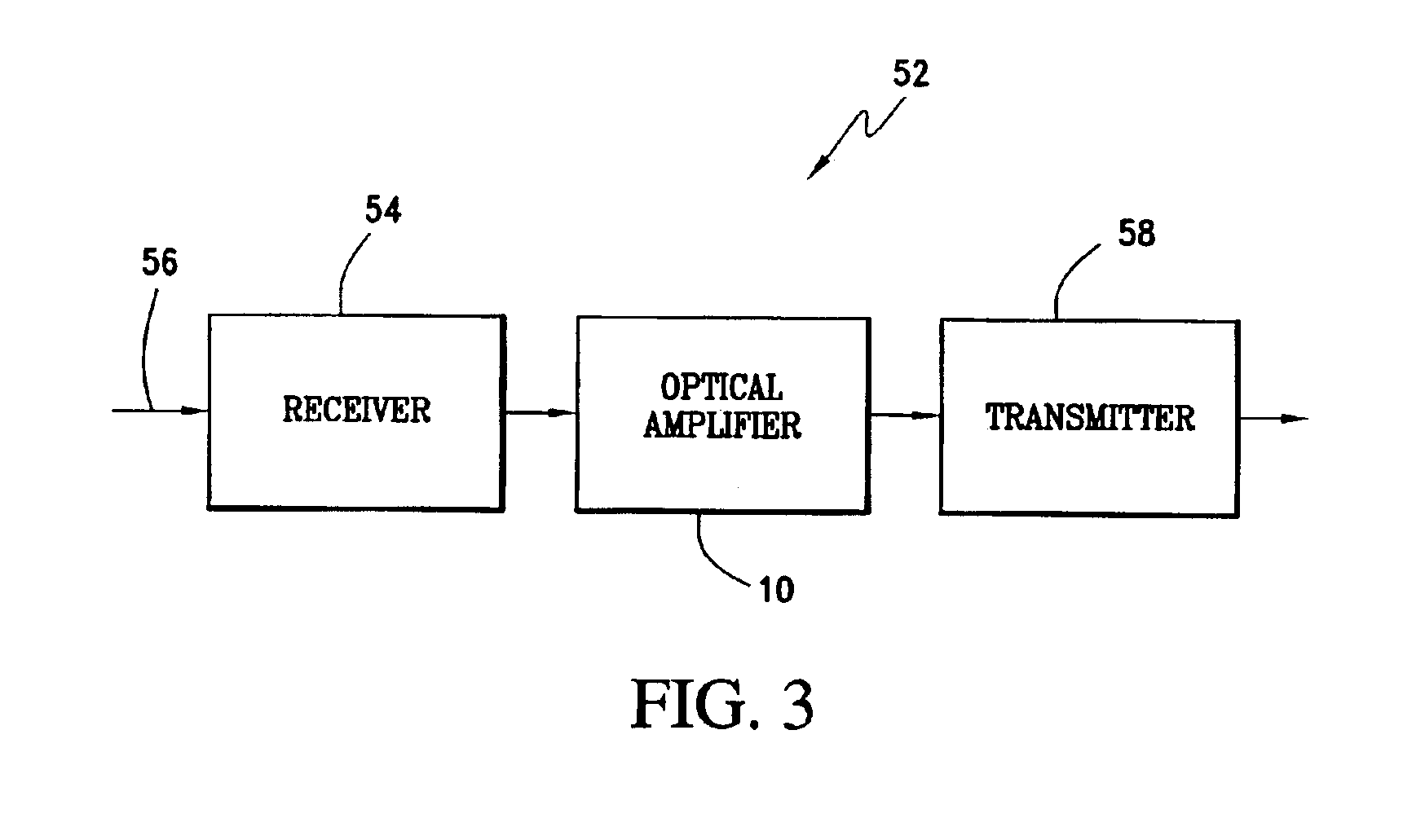
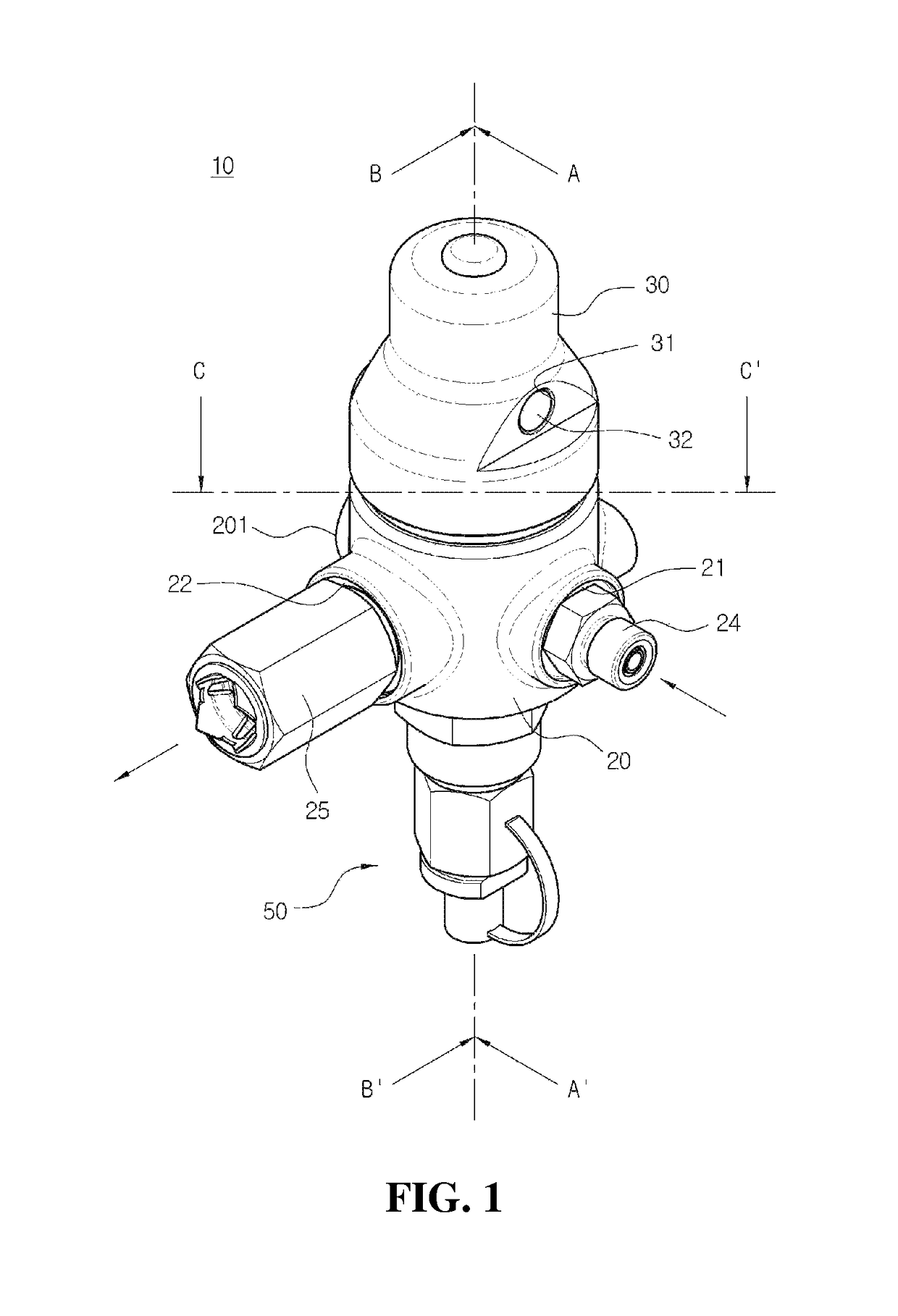
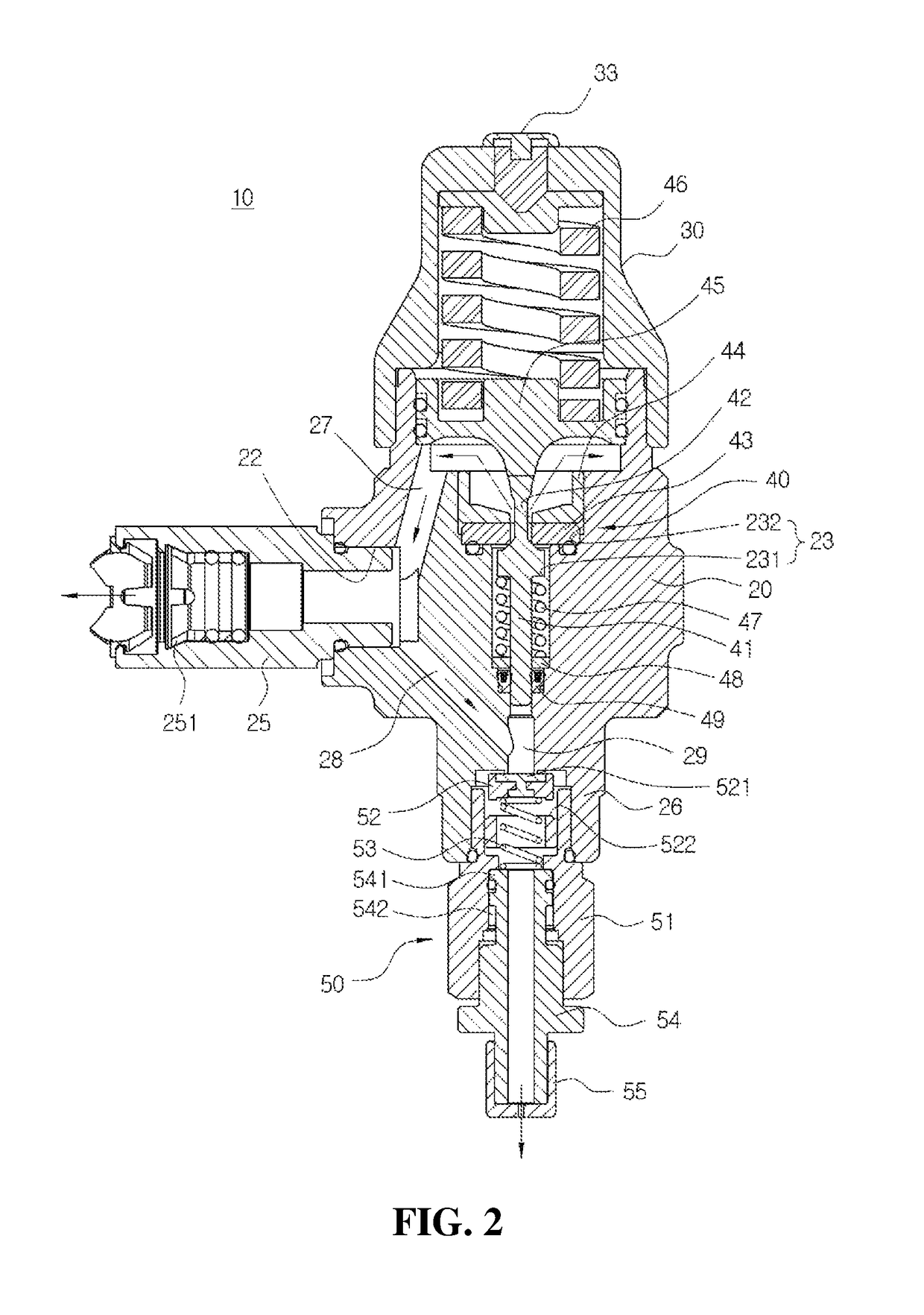
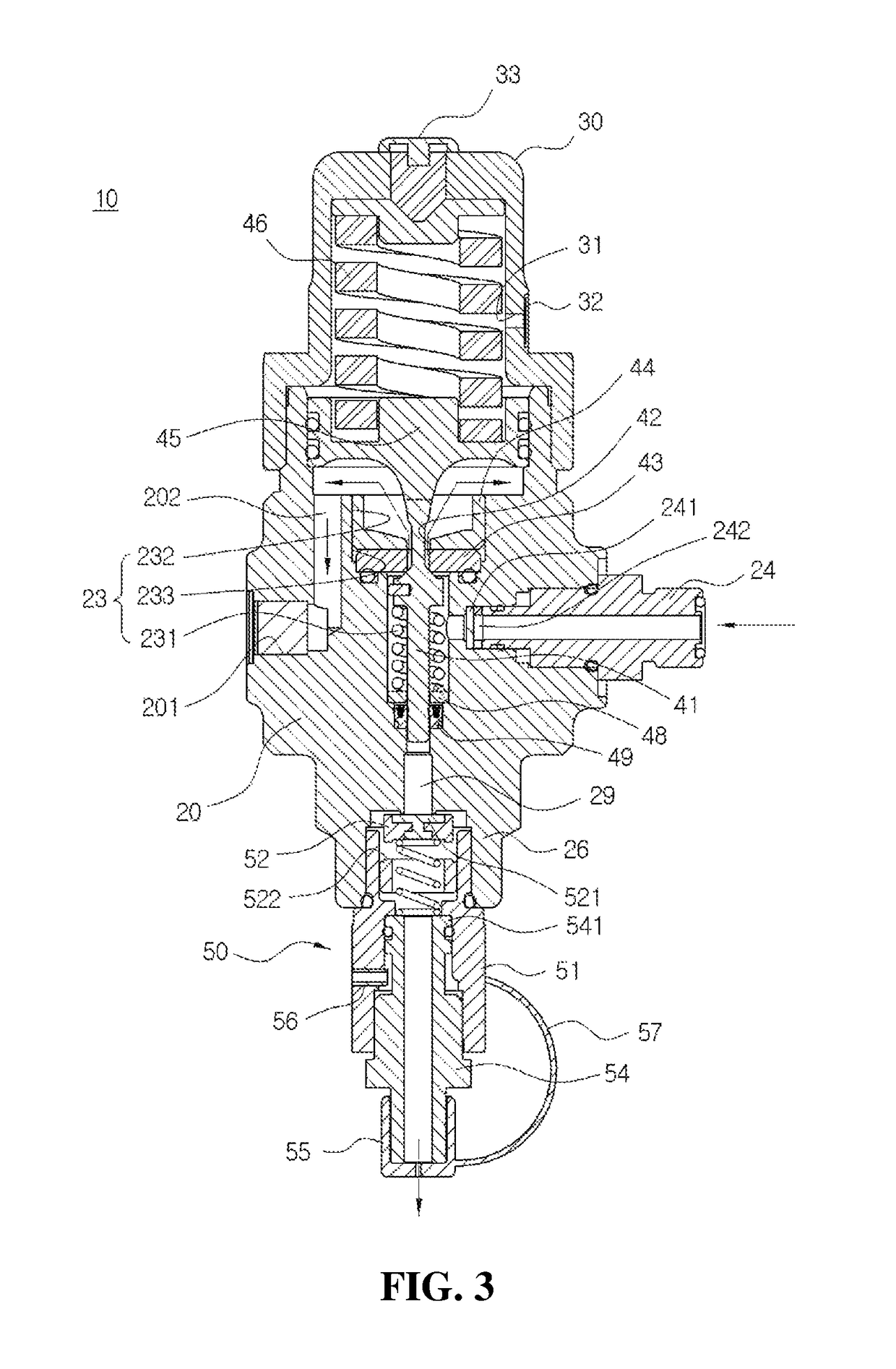
Safe valve for high pressure regulator
ActiveUS10167970B2Avoid separationEasy to reassembleOperating means/releasing devices for valvesReactant parameters controlEngineeringHigh pressure
Owner:MOTONIC
Double replacement cation neutralization of high alkalinity waste materials
InactiveUS20060051286A1Safe long-term storageAdd additional massAluminium compoundsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSolubilityManganese
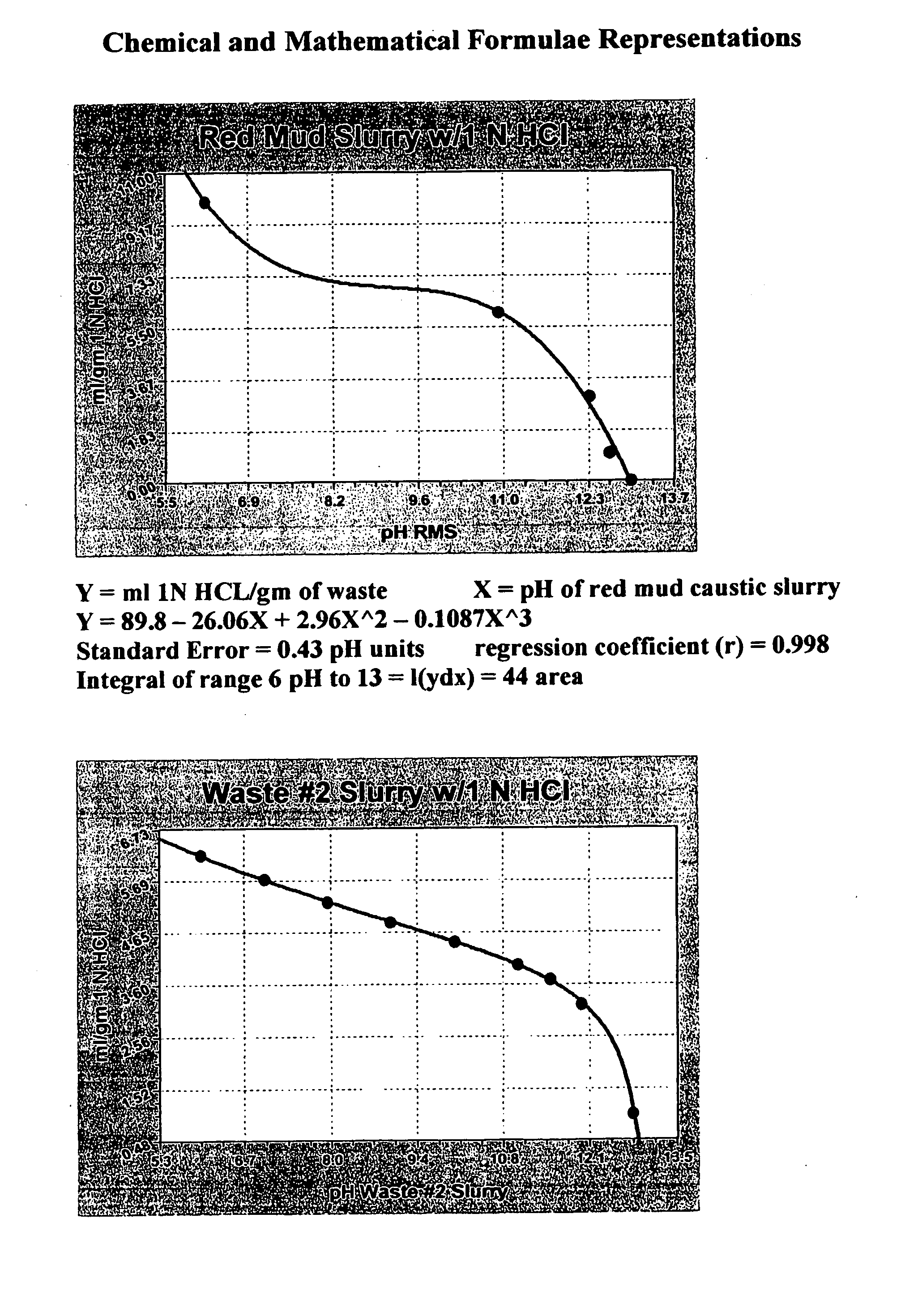
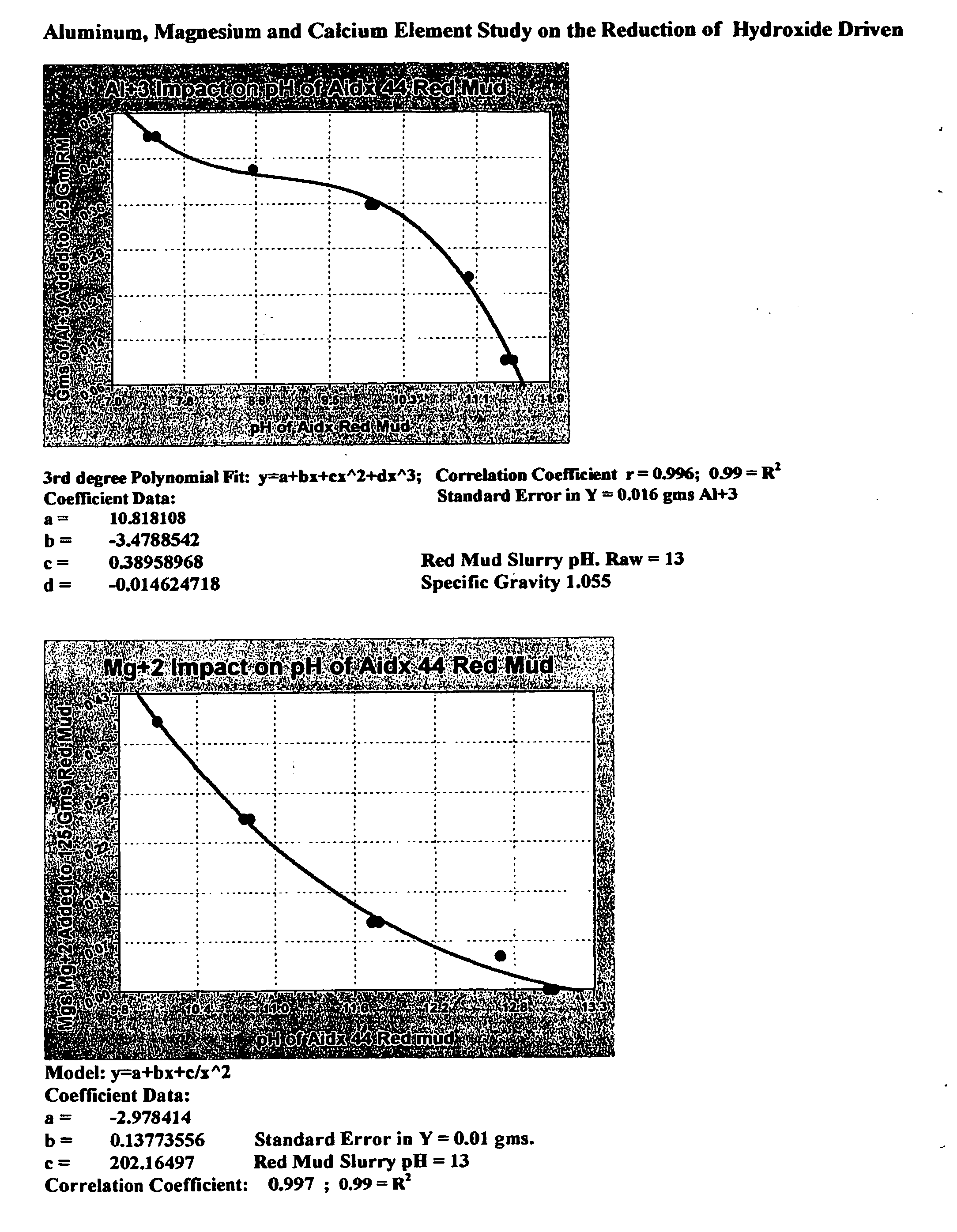
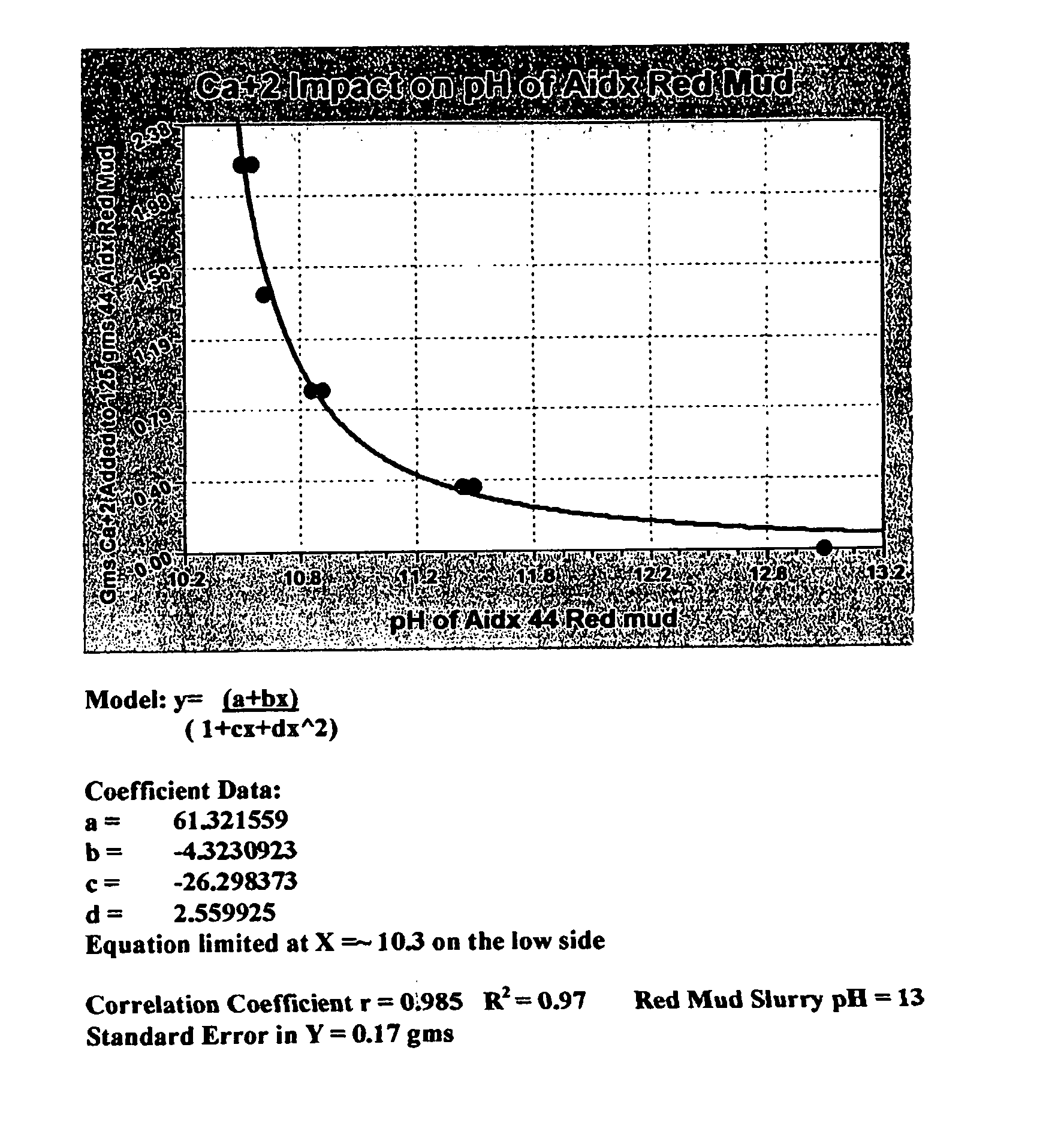
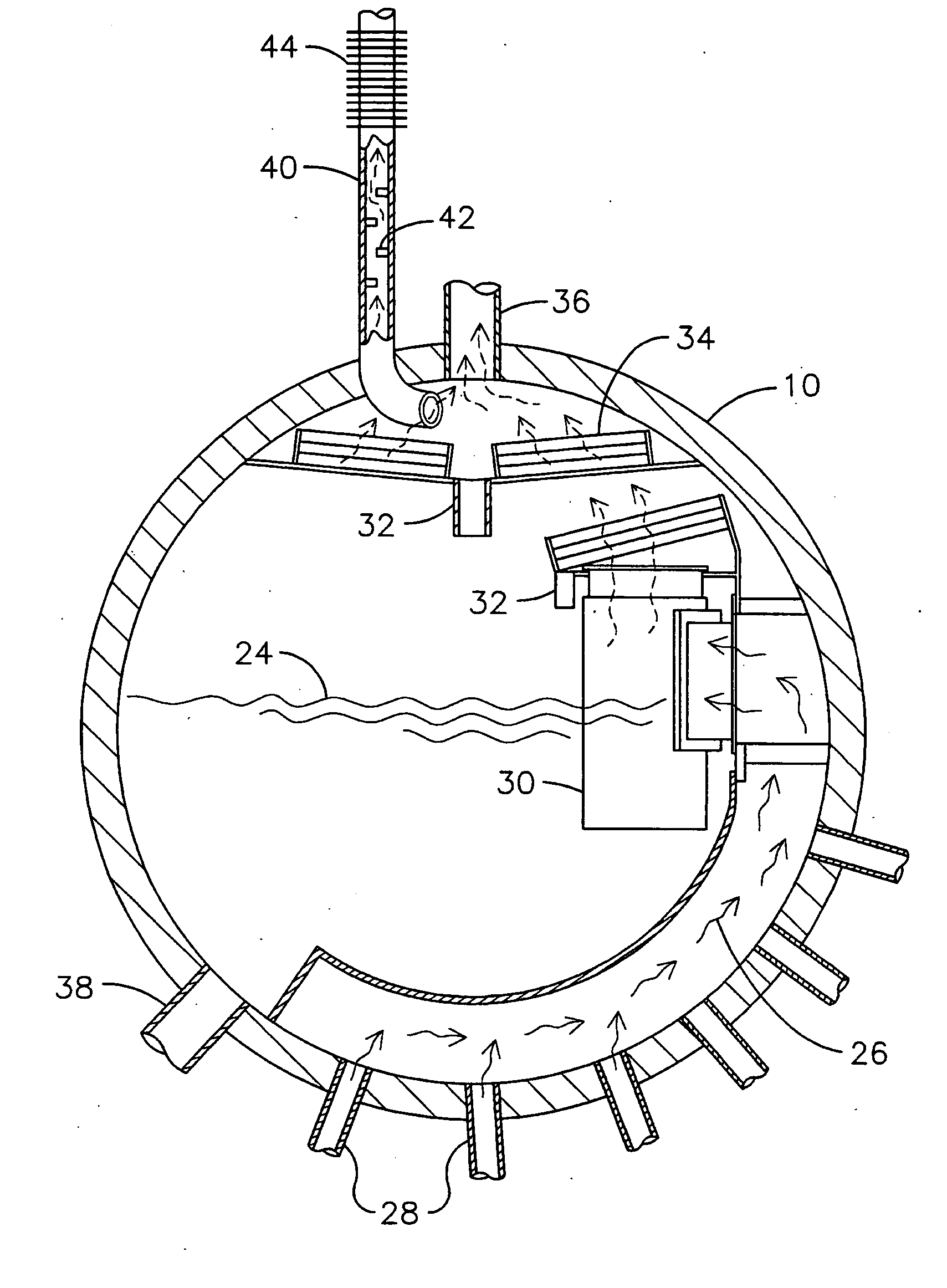
A method of treating hydroxide alkaline waste and by-products to render the material neutralized or reduced in pH from near 14 to a minimum lower limit of about 5.3 based on aluminum poly cation salts, rendering the waste or by-product stream suitable for ultimate disposal or reuse. The method comprises contacting together a mixture of moderate to high alkaline waste or by-product material with a pH in the range of 7.5-14, with sufficient water added or found within the alkaline material, with one or more poly cationic salts in the dry form taken from a group of salts containing tri-valent aluminum, tri-valent iron, di-valent calcium, di-valent magnesium, di-valent manganese, di-valent zinc, or any polyvalent cationic salt that is soluble in water to a minimum extent of 0.5 grams per 100 milliliters of water at near 0° Centigrade and 2 grams per 100 milliliters of water at near 100° Centigrade, in such a way to cause these materials to interact in a double replacement reaction to form a soluble salt reaction by-product and an insoluble hydroxide precipitate with water solubility characteristics, between 0° Centigrade and 100° Centigrade, equal to or exceeding that of CaS04*2H2O (gypsum) or approximately 0.20 grams per 100 milliliters of water. The added salts) may be dry or made up of a brine or dilute salt solution of the chosen salt or salts from the set of poly cation salts suitable to reduce hydroxide alkalinity in waste and by-product materials causing the pH to drop immediately upon thorough mixing of the poly cation salts and the waste / product materials, resulting in a treated waste / by-product stream / that is suitable for ultimate disposal or re-use.
Owner:BALDWIN N PHILIP JR +3
Condensing deaerating vent line for steam generating systems
InactiveUS20060086248A1Efficient ventingMinimizing of amountUsing liquid separation agentThermal energyHigh concentration
The present invention comprises an apparatus and method for efficiently venting impurities from a heat recovery steam generator system by concentrating the impurities in a condensing deaerating vent line 40 and then venting a proportionately small amount of steam with a proportionately high concentration of impurities. The condensing deaerating vent line 40 is attached to a low pressure drum 10, and feed water 54 may be added to the upper portion of the condensing deaerating vent line 40 to improve condensation and conserve thermal energy.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Apparatus with axis-parallel tension cables for ejecting a spin-stabilized body from a spacecraft
InactiveUS20060138284A1Effective and simple and reliable and robust and safe driveConsiderable safety riskCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSpinsEngineering
An apparatus for ejecting a flying body (e.g. payload recovery container) from a spacecraft includes a first ring to be secured to the spacecraft, a cable winding device that is arranged on a second ring and that is releasably engageable with the flying body, and tension cables extending between the two rings. The cable winding device is spring-biased to wind-up the cables, which extend axis-parallel along the cylindrical outer shell of the flying body. Holding and guide elements on the first ring hold and guide the flying body. Catch elements on the cable winding device releasably engage receivers on the flying body. When the holding elements are released, the cables are retracted by the cable winding device, and the rotation of the cable winding device is transmitted to the flying body via the engaged catch elements and receivers. Thereby, the flying body is rotated and translationally ejected.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Piano dolly
InactiveUS20100176568A1Minimize the numberMinimize timeCarriage/perambulator accessoriesSledgesPianoEngineering
A dolly on which a grand piano can be mounted to facilitate movement thereof over a surface from one location to another, which includes a central hub shaped in the form of a miniature grand piano, two fixed length arms of equal length pivotally connected to the front of the hub at opposite corners thereof, and a fixed length rear arm having a longitudinal slot which is pivotally connected to the rear of the hub at selectively adjustable positions along the length of the slot to accommodate grand pianos having a range of different lengths.
Owner:GRK MFG
Variable compression connecting rod
InactiveUS10167776B2Reliable and consistent rod length shiftsMinimizing volumeConnecting rodsCranksFuel efficiencyCam
The present invention is directed to improved designs and methods for improving engine fuel efficiency by providing two-stage engine variable compression in running engines using connecting rod force reversals to rotate eccentric bushings to change the connecting rod length. Compression ratio changes are initiated by shifting a block-mounted cam such that it engages and flips a bi-stable toggle on the connecting rod. The clutch mechanism latches the eccentric at the eccentric rotation end point, whereupon the connecting rod acts as a rigid rod. The invention includes novel configurations of the lubricated journal bearing between the connecting rod and the eccentric that modify the squeeze film bearing effects and resulting friction. These configurations reduce the peak eccentric torque carried by the clutch mechanism while facilitating eccentric rotation at lower torque.
Owner:MEACHAM G B KIRBY
Apparatus with axis-parallel tension cables for ejecting a spin-stabilized body from a spacecraft
InactiveUS7445183B2Effective and simple and reliable and robust and safe driveConsiderable safety riskCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsElectric cablesSpacecraft
An apparatus for ejecting a flying body (e.g. payload recovery container) from a spacecraft includes a first ring to be secured to the spacecraft, a cable winding device that is arranged on a second ring and that is releasably engageable with the flying body, and tension cables extending between the two rings. The cable winding device is spring-biased to wind-up the cables, which extend axis-parallel along the cylindrical outer shell of the flying body. Holding and guide elements on the first ring hold and guide the flying body. Catch elements on the cable winding device releasably engage receivers on the flying body. When the holding elements are released, the cables are retracted by the cable winding device, and the rotation of the cable winding device is transmitted to the flying body via the engaged catch elements and receivers. Thereby, the flying body is rotated and translationally ejected.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com