Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Polariton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, polaritons /pəˈlærɪtɒnz, poʊ-/ are quasiparticles resulting from strong coupling of electromagnetic waves with an electric or magnetic dipole-carrying excitation. They are an expression of the common quantum phenomenon known as level repulsion, also known as the avoided crossing principle. Polaritons describe the crossing of the dispersion of light with any interacting resonance. To this extent polaritons can also be thought as the new normal modes of a given material or structure arising from the strong coupling of the bare modes, which are the photon and the dipolar oscillation. The polariton is a bosonic quasiparticle, and should not be confused with the polaron (a fermionic one), which is an electron plus an attached phonon cloud.
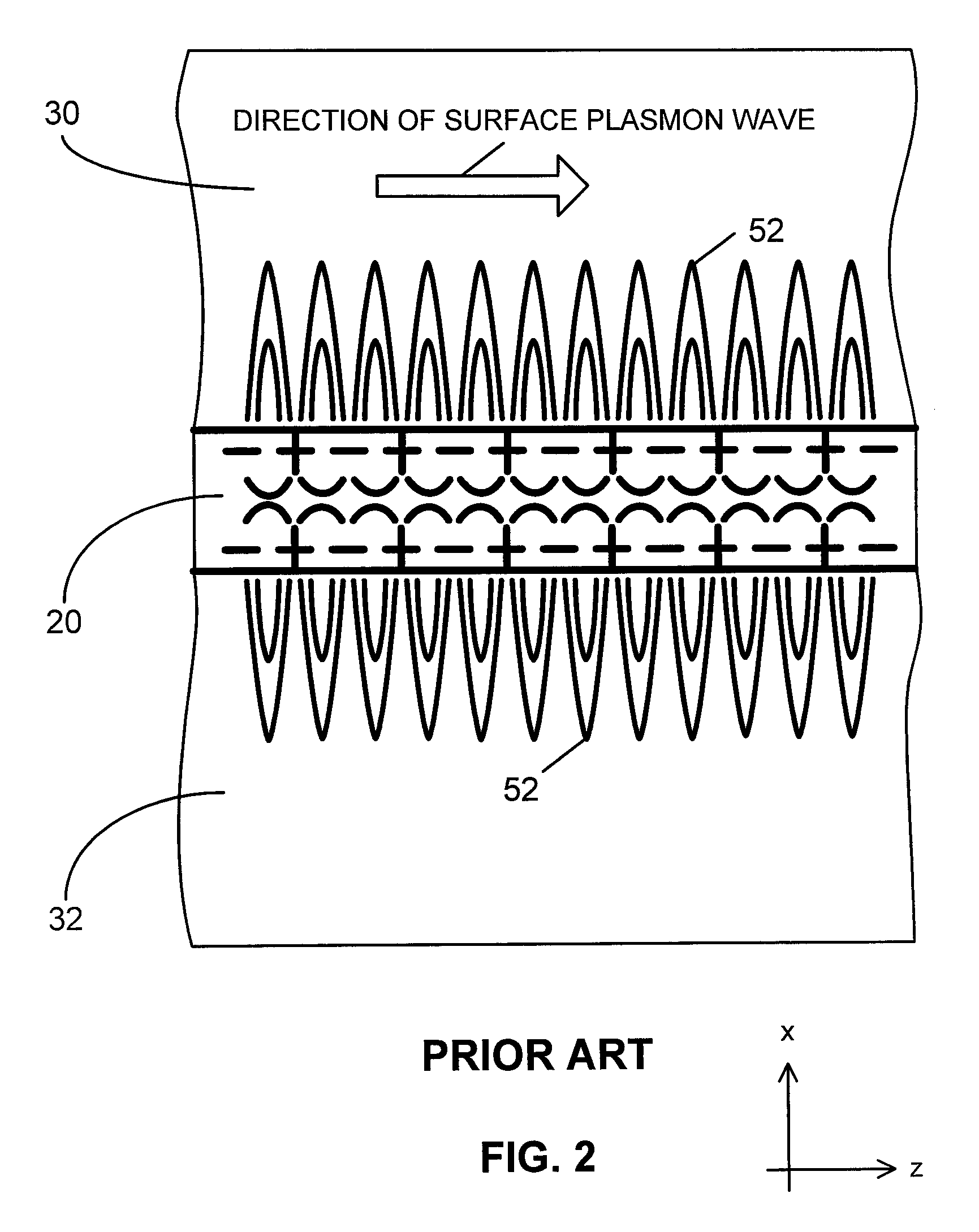
Thermo-optic plasmon-polariton devices
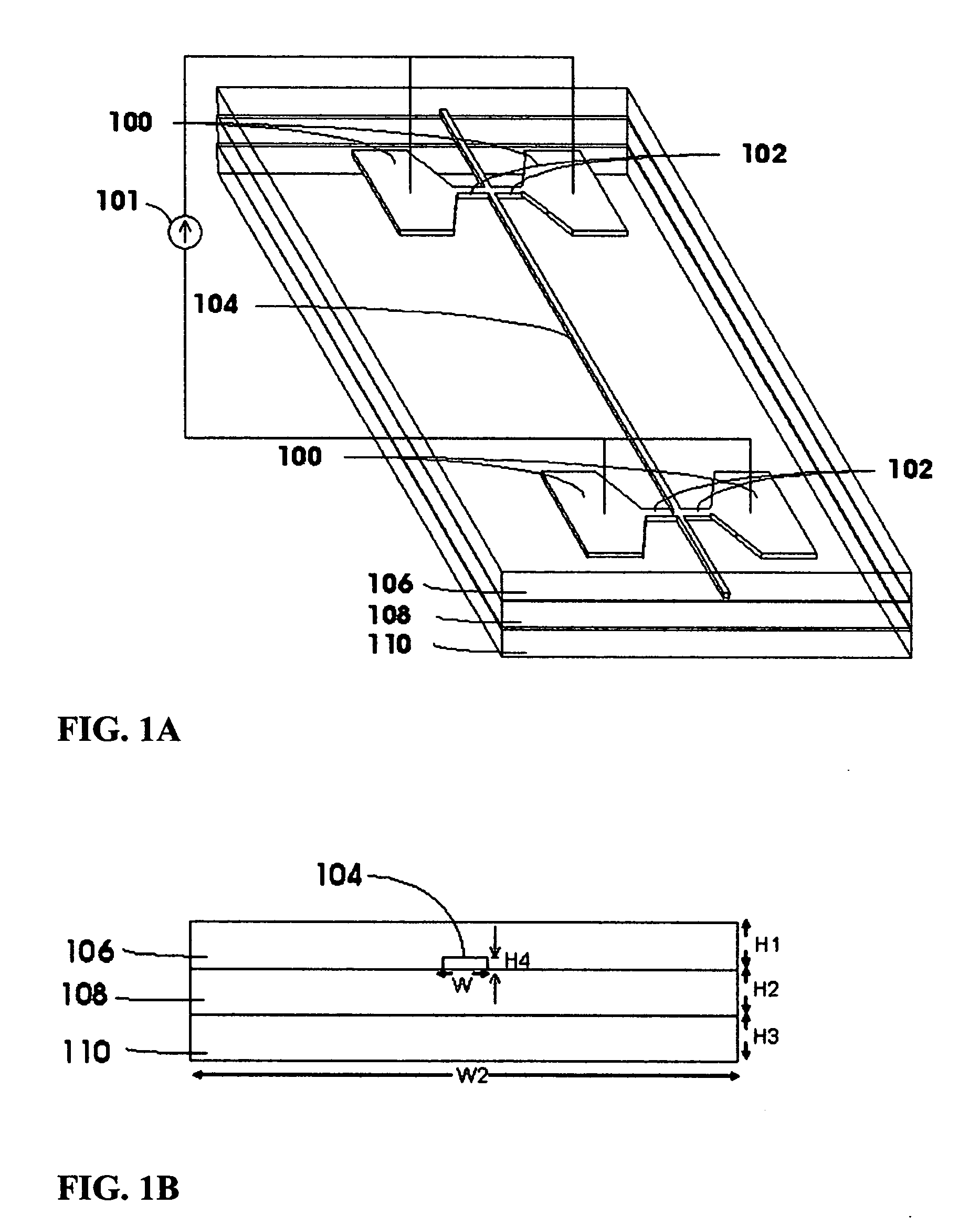
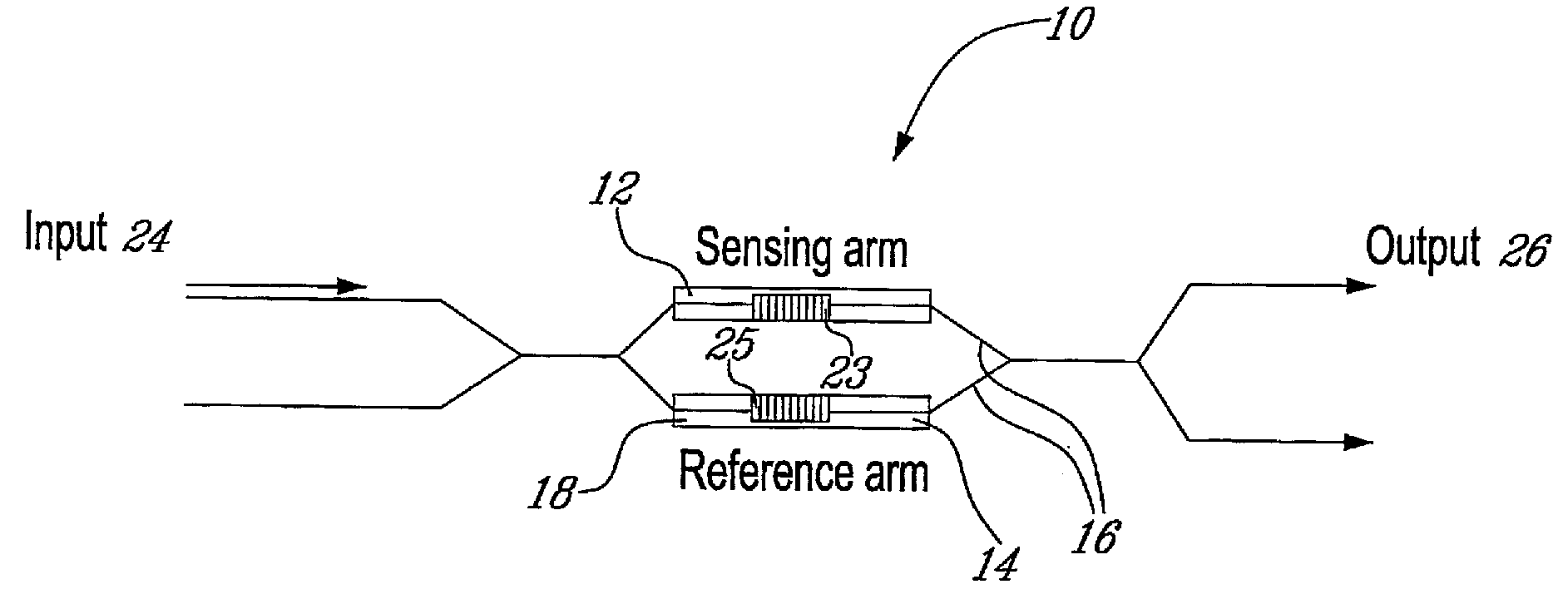
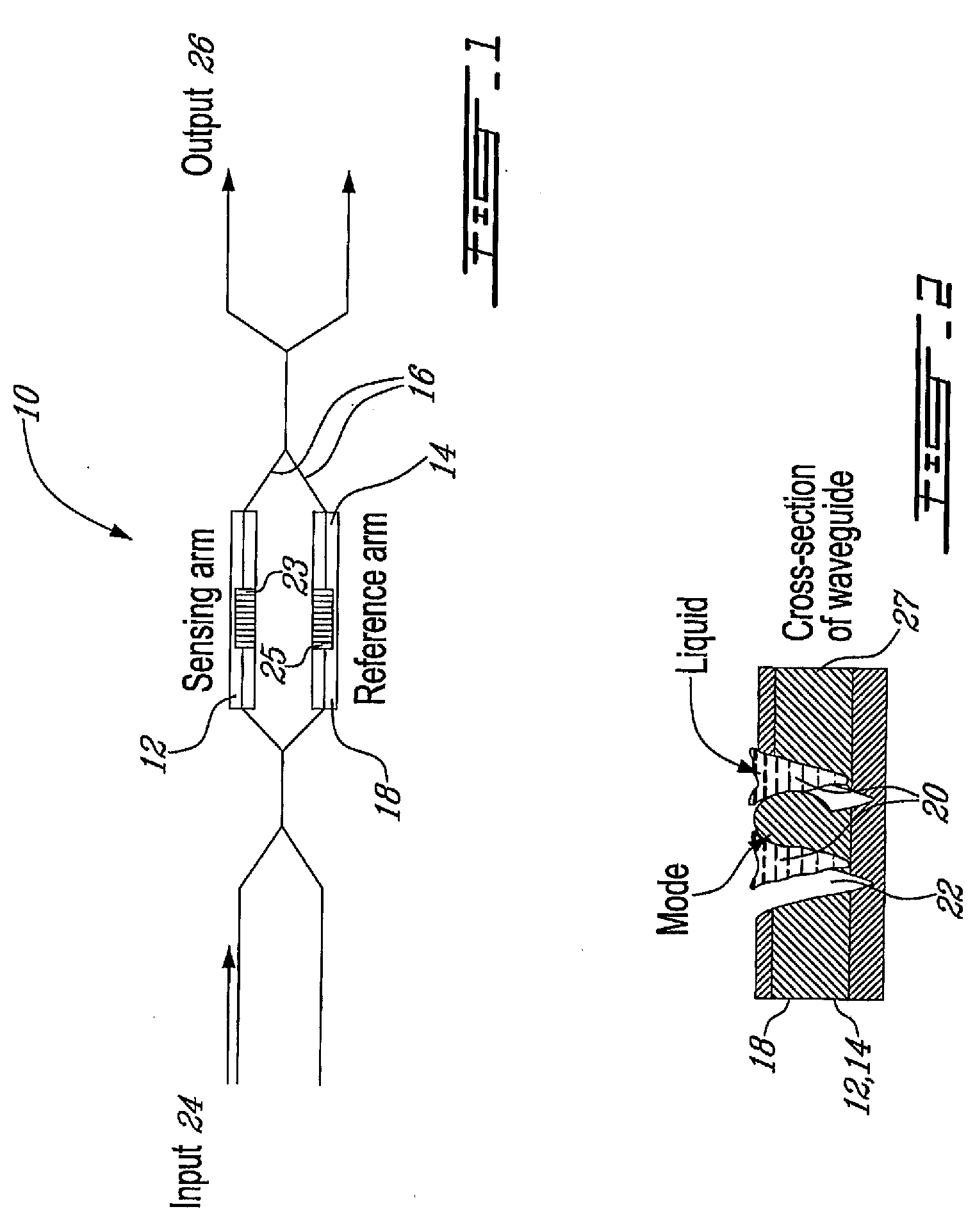
A waveguide structure comprises a thin strip of material having a relatively high free charge carrier density surrounded by material having a relatively low free charge carrier density. The width and thickness of the strip are dimensioned such that optical radiation having a wavelength in a predetermined range couples to the strip and propagates along its length as a plasmon-polariton wave. The device includes a waveguide heater for passing a current through the strip to heat it and the surrounding material, so as to vary propagation of the optical radiation, or means for monitoring propagation of the optical radiation to determine a change in temperature of the strip. Some embodiments provide both heating of the strip and monitoring of its temperature.
Owner:SPECTALIS
Multiplexed Olfactory Receptor-Based Microsurface Plasmon Polariton Detector
InactiveUS20120021932A1Reducing agentEasy to measureMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesG protein-coupled receptorSurface plasmon
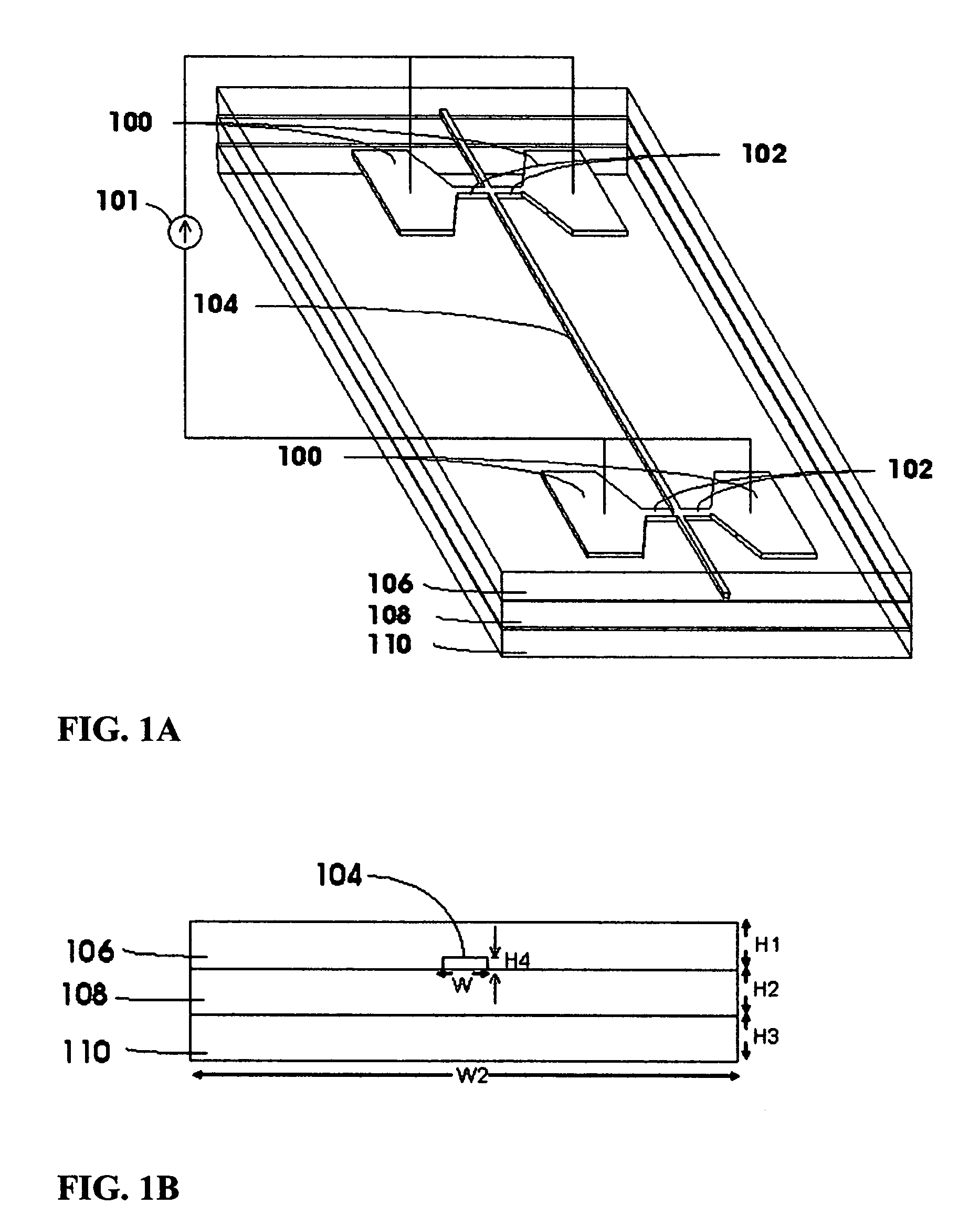
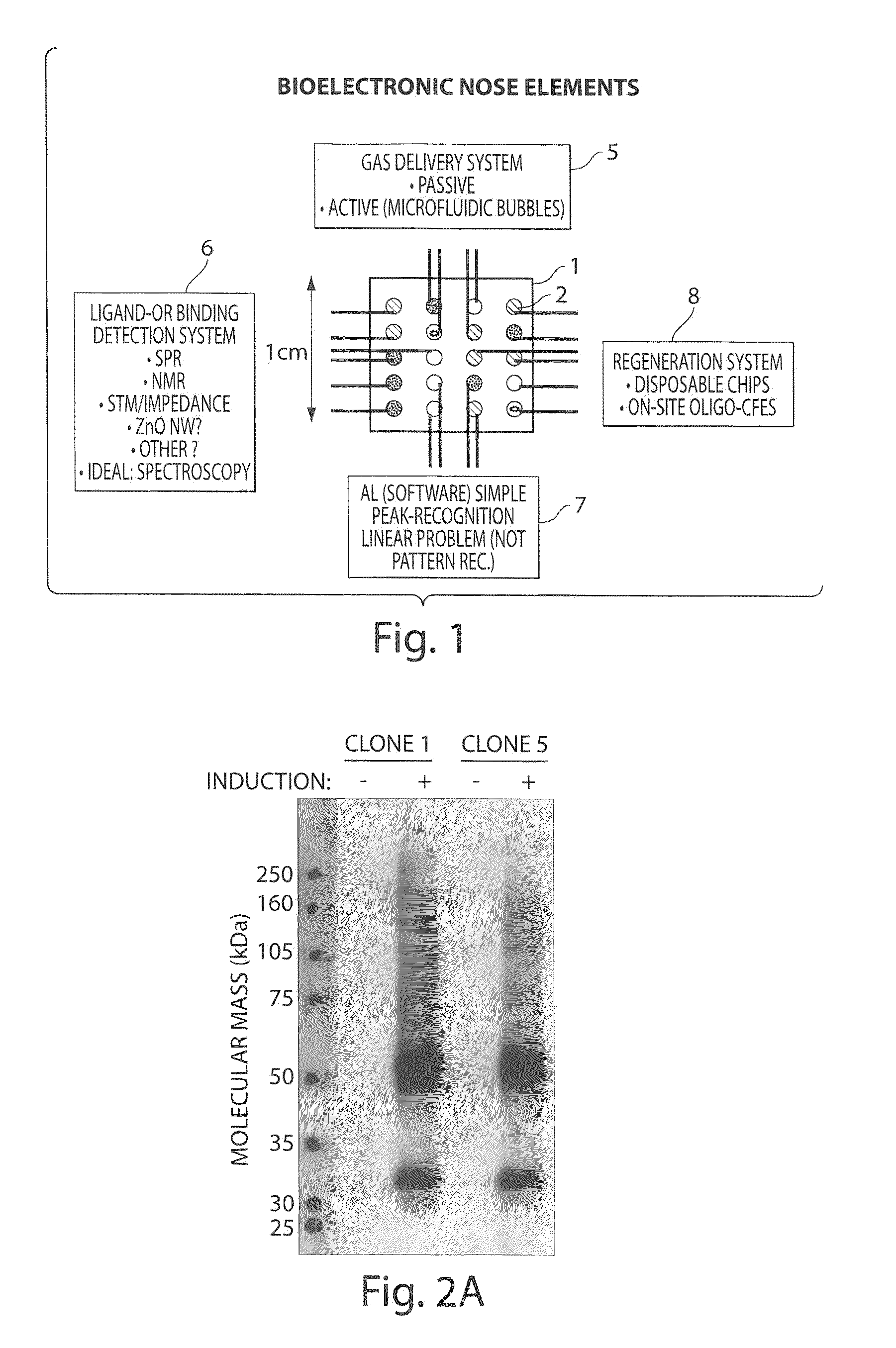
The invention provides a bio-sensing nanodevice comprising: a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor on a support, a real time receptor-ligand binding detection method, a test composition delivery system and a test composition recognition program. The G-protein coupled receptor can be stabilized using surfactant peptide. The nanodevice provides a greater surface area for better precision and sensitivity to odorant detection. The invention further provides a microfluidic chip containing a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor immobilized on a support, and arranged in at least two dimensional microarray system. The invention also provides a method of delivering odorant comprising the step of manipulating the bubbles in complex microfluidic networks wherein the bubbles travel in a microfluidic channel carrying a variety of gas samples to a precise location on a chip. The invention further provides method of fabricating hOR17-4 olfactory receptor.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Thermo-optic plasmon-polariton devices
A waveguide structure comprises a thin strip of material having a relatively high free charge carrier density surrounded by material having a relatively low free charge carrier density. The width and thickness of the strip are dimensioned such that optical radiation having a wavelength in a predetermined range couples to the strip and propagates along its length as a plasmon-polariton wave. The device includes a waveguide heater for passing a current through the strip to heat it and the surrounding material, so as to vary propagation of the optical radiation, or means for monitoring propagation of the optical radiation to determine a change in temperature of the strip. Some embodiments provide both heating of the strip and monitoring of its temperature.
Owner:SPECTALIS
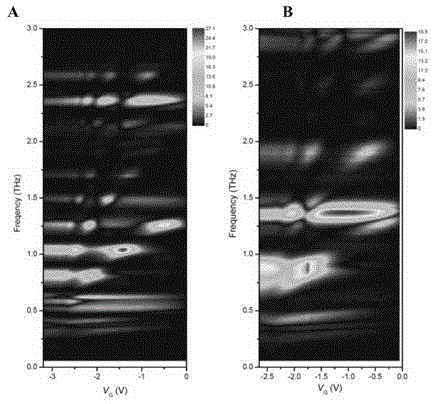
Terahertz light source chip and manufacturing method thereof, terahertz light source device and manufacturing method thereof, and terahertz light source module and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104466617AAvoid frequencyAvoid temperatureSolid masersSemiconductor devicesGratingWorking temperature
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Sensors
A gas sensor for hydrogen or other gases, especially flammable or explosive gases, has a plasmon-polariton waveguide comprising a metal strip on a membrane supported by a substrate in an environment in which the gas is to be introduced, and coupling means for coupling optical radiation into and out of the plasmon-polariton waveguide such that the optical radiation propagates therealong as a plasmon-polariton wave. The metal strip comprises by a chemical transducer (e.g. Pd or PdNi), the arrangement being such that exposure of the metal strip or coating to the gas to be monitored causes a change in the propagation characteristics of the plasmon-polariton wave and hence the optical radiation coupled out of the plasmon-polariton waveguide.
Owner:SPECTALIS
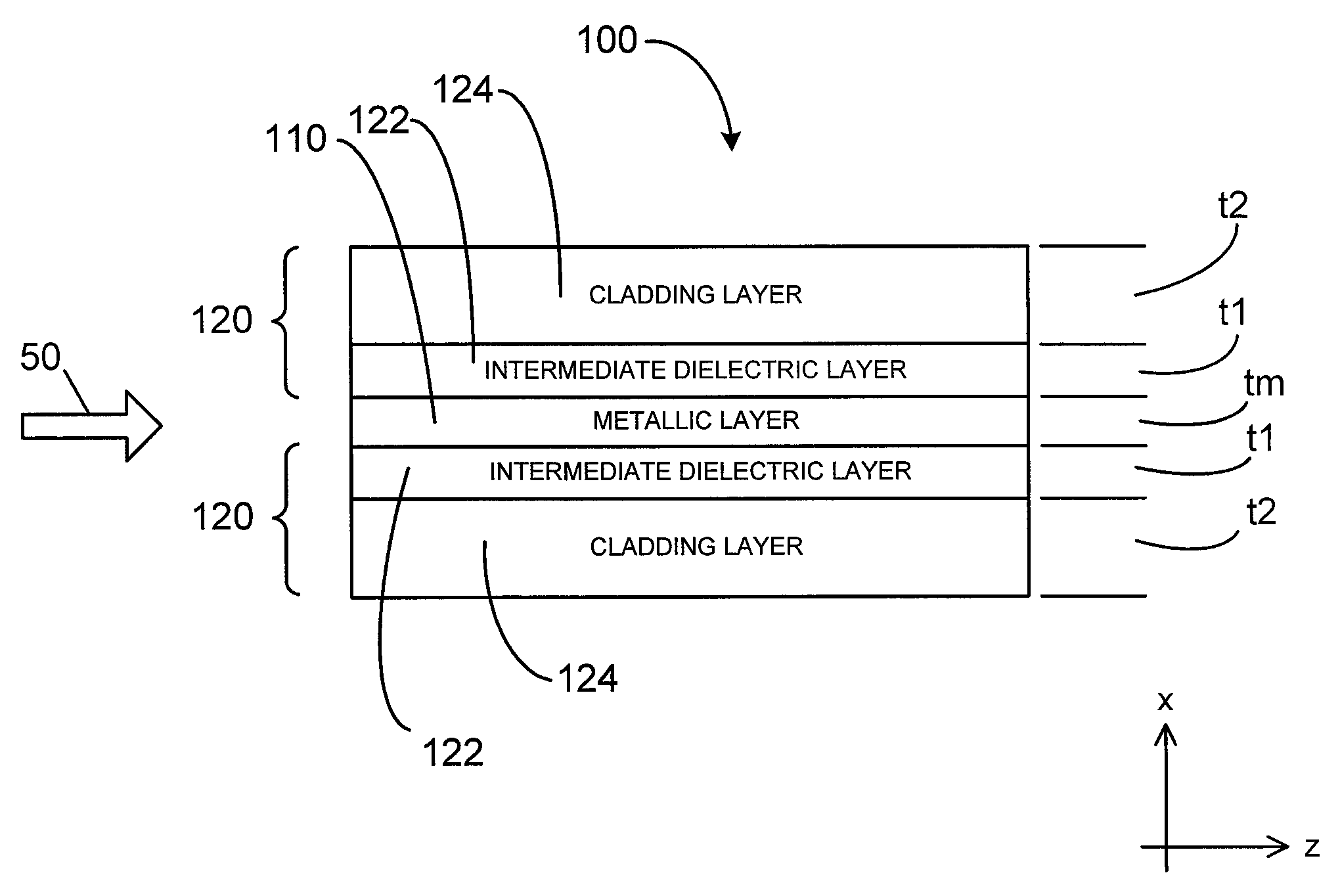
Waveguides for ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton propagation
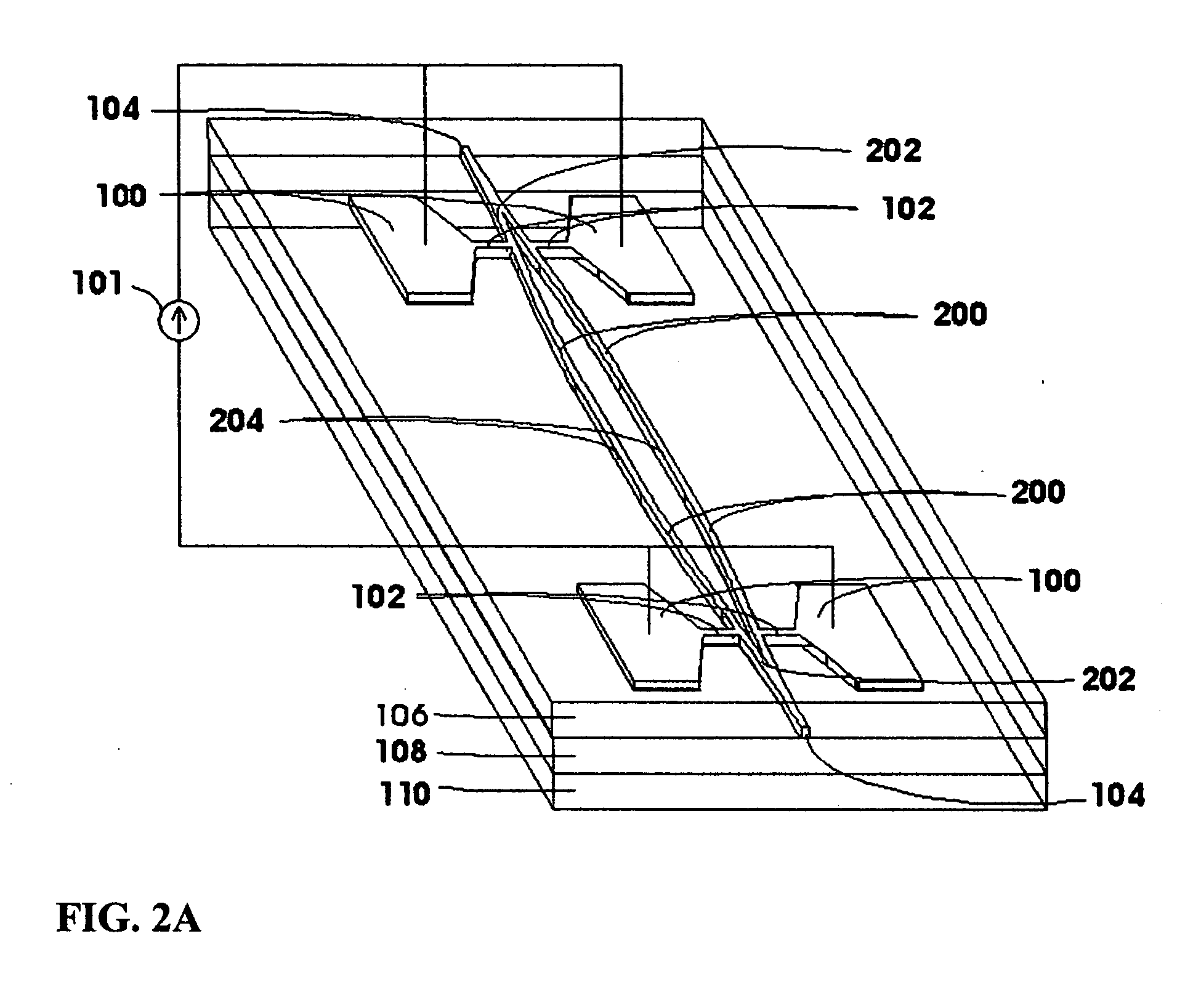
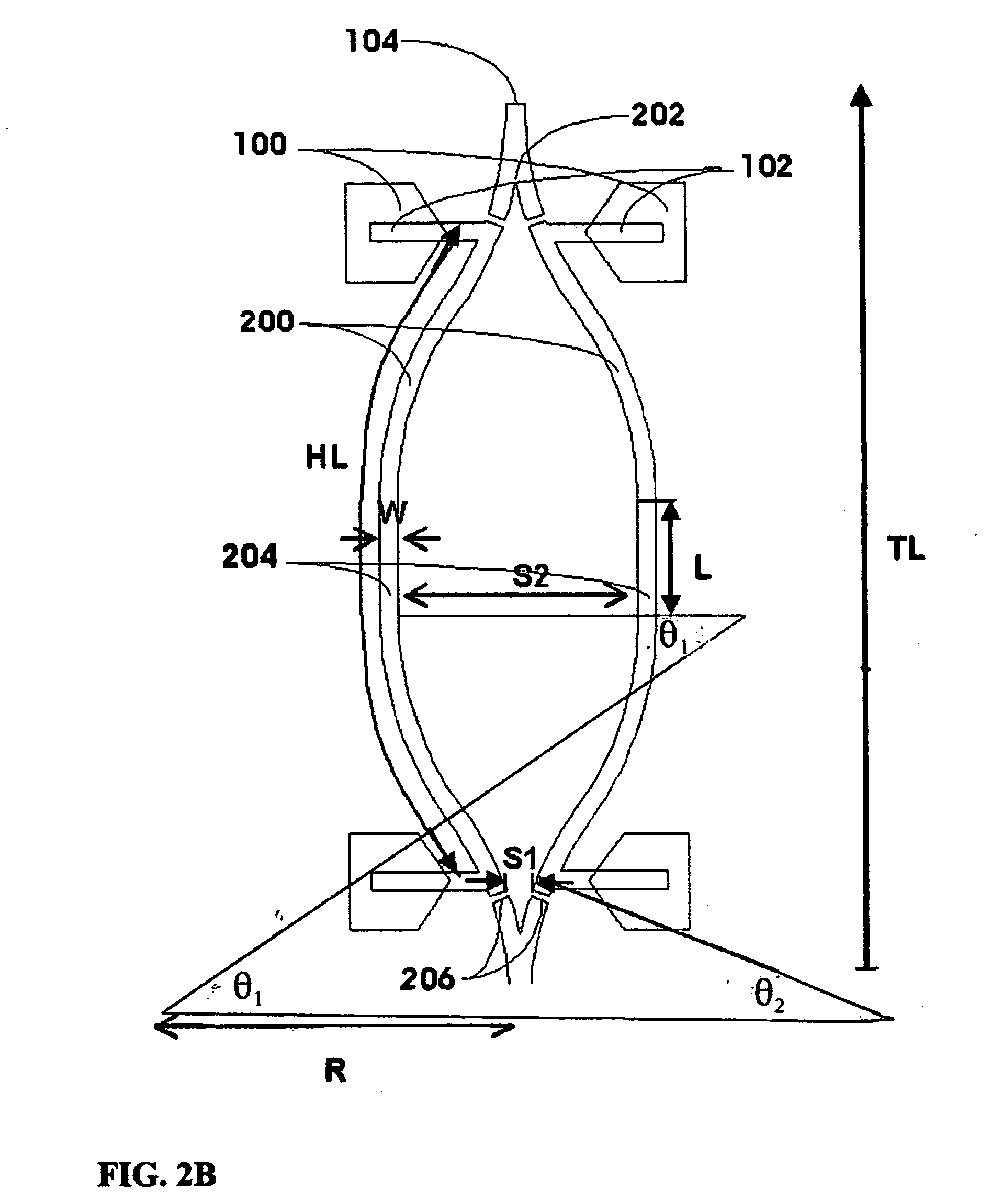
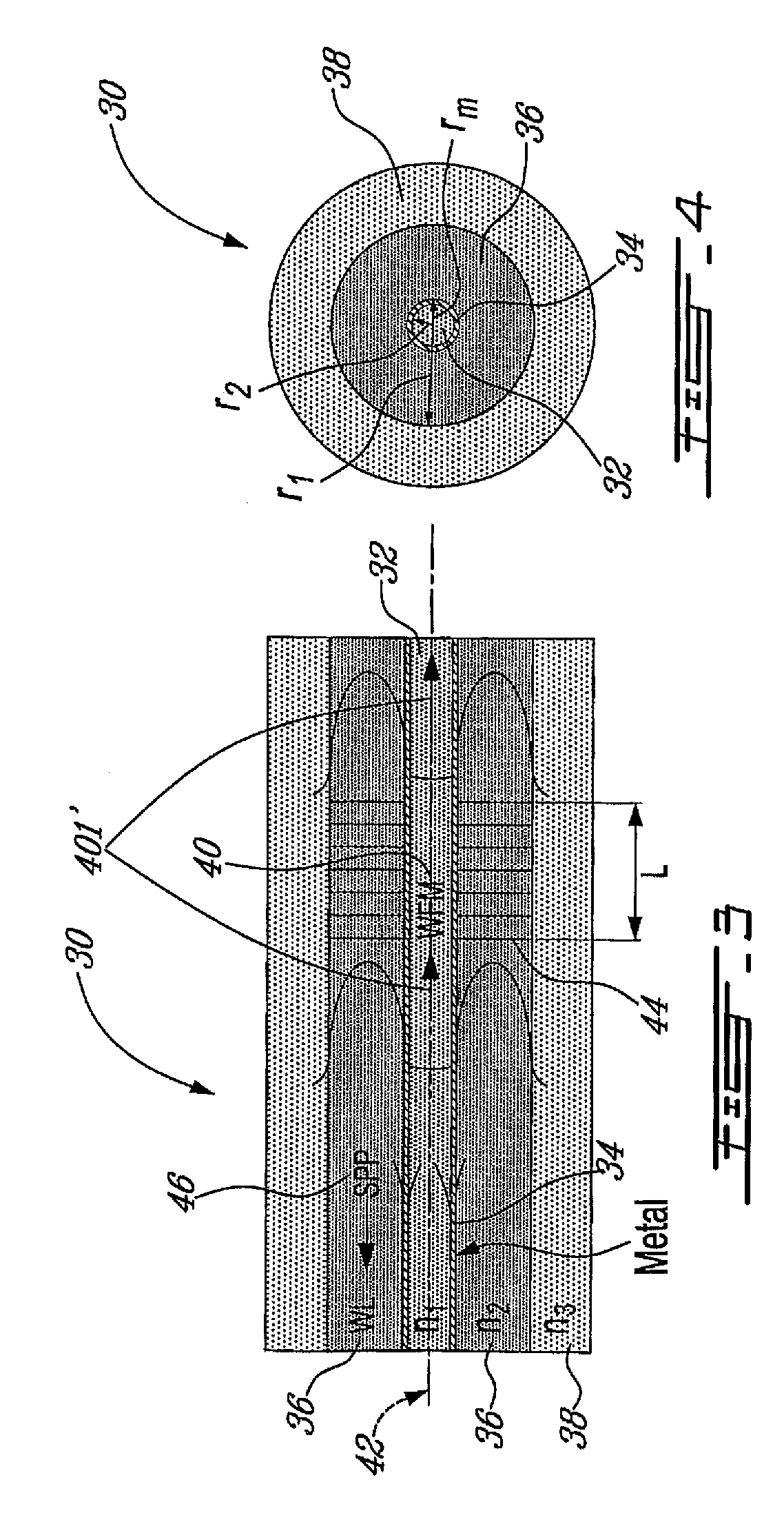
The disclosure relates to surface plasmon-polariton waveguides, which can guide ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves. The attenuation of an ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves is much lower than the attenuation of the conventional long range surface plasmon-polariton waves guided with the same kind of metal film or metal strip at the same plasmon-polariton frequency. An exemplary ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waveguide disclosed in this disclosure comprises a metal layer, such as a metal film or finite width metal strip, intermediate dielectric layers adjacent to the metal layer, and outer cladding dielectric material. The intermediate dielectric layers redistribute the electromagnetic energy distribution of the surface plasmon-polariton waves so that less of the energy propagates in the metal layer. Therefore, the attenuation of the surface plasmon-polariton wave is reduced. The propagation distance of the ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton wave can be designed to a desired value by adjusting the thickness and the material property of the intermediate dielectric layers and other parameters related to the waveguide.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Planar integrated circuit including a plasmon waveguide-fed Schottky barrier detector and transistors connected therewith
InactiveUS7170142B2Easy to controlHigh precisionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPlasmonic waveguideSchottky barrier
A planar integrated circuit includes a semiconductor substrate having a substrate surface and a trench in the substrate, a waveguide medium in the trench having a top surface and a light propagation axis, the trench having a sufficient depth for the waveguide medium to be at or below said substrate surface, and at least one Schottky barrier electrode formed on the top surface of said waveguide medium and defining a Schottky barrier detector consisting of the electrode and the portion of the waveguide medium underlying the Schottky barrier electrode, at least the underlying portion of the waveguide medium being a semiconductor and defining an electrode-semiconductor interface parallel to the light propagation axis so that light of a predetermined wavelength from said waveguide medium propagates along the interface as a plasmon-polariton wave.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
External-cavity lasers
InactiveUS7151789B2Small sizeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionExternal cavity laserLength wave
An external-cavity laser, suitable for producing a coherent and highly-polarized optical emission, particularly at communication wavelengths, is enabled by a novel wavelength selective element based on a waveguide technology that supports a long-range plasmons polariton mode. These external-cavity lasers leverage the inherent properties of the novel wavelength selective elements, which are materials agnostic, providing easier means for tunability, laser stability, and low cost of fabrication, high output power and a highly polarized output. Tunable versions are also disclosed.
Owner:SPECTALIS
Light-emitting device and display device with use of light-emitting device
ActiveCN105374918AAchieving Nanoscale PolarizationSimple structureLiquid crystal compositionsMaterial nanotechnologyDisplay deviceNanoscopic scale
The present invention relates to a light-emitting device which comprises an insulating transparent substrate and a light-emitting material layer arranged at the surface of an insulating transparent substrate. The light-emitting device further comprises a metal metamaterial layer arranged between the insulating transparent substrate and the light-emitting material layer. The metal metamaterial layer comprises multiple metamaterial units in periodical arrangement. Through the plasmon polariton field of the metamaterial, the operation of electromagnetic wave properties is realized in a nanometer scale, the nanoscale polarization polarizing of the light emitted by the light-emitting device can be realized, and thus polarized light is directly emitted. A display device with the use of the light-emitting device does not need a special polarizing element, and the structure is simple.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Dual-frequency terahertz band-pass filter
InactiveCN104201443AImprove reliabilityEasy to integrateWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceMicro structure
The invention relates to a dual-frequency terahertz band-pass filter, in particular to the design and production of the dual-frequency terahertz band-pass filter with a semi-insulating gallium arsenide based hollow surface and a complementary split ring resonator, and relates to the terahertz technology and the technical field of semiconductor micromachining. The dual-frequency terahertz band-pass filter utilizing the working principle of the complementary split ring resonator achieves surface plasma polariton resonance through the adjustment on the inner diameter, outer diameter, opening width and periodic structure of the C-SRR (split ring resonator) and obtains low-frequency and high-frequency resonance in two abnormal transmission enhancement modes of inductance-capacitance (LC) resonance. The energy conversion between two resonance frequencies is achieved through the electromagnetic interaction of the two resonances, so that the terahertz reaching the same transmission strength at two bands can be output. The dual-frequency terahertz band-pass filter takes advantage of an existing semiconductor micromachining process and is simple in production process, easy to operate and capable of accurately controlling a micro-structure machining area of the complementary split ring resonator and greatly reducing production costs.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Schottky barrier photodetectors
InactiveUS20040173865A1Overcome disadvantagesReduce disadvantagesCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical radiationSchottky barrier
A Schottky barrier photodetector comprises a waveguide structure formed by a thin strip of material having a relatively high free charge carrier density, for example a conductor or certain classes of highly-doped semiconductor, surrounded by material having a relatively low free charge carrier density, the material on at least one side of the strip comprising a semiconductor, the strip having finite width and thickness with dimensions such that optical radiation couples to the strip and propagates along the length of the strip as a plasmon-polariton wave, light for detection being coupled to one end of the strip to propagate along the strip as said plasmon-polariton wave, ohmic contact means applied to the semiconductor material and at least one electrode means connected to the strip for applying bias to the Schottky barrier and extracting a photodetector current corresponding to the light applied to the photodetector. Where the strip of material is a flat, thin strip, the device will be polarisation dependent. Substantially polarisation-independent operation maybe achieved by using a strip whose width is of the same order as its thickness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Electro-optic modulators
A low loss, low drive voltage plasmon-polariton electro-optic modulator based on mode cutoff comprises a waveguide structure formed by a thin metallic strip surrounded by material having a relatively low free charge carrier density. The metallic strip has finite width and thickness with dimensions such that optical radiation having a wavelength in a predetermined range couples to the metallic strip and propagates along the length of the metallic strip as a plasmon-polariton wave. The surrounding material comprises two distinct portions with the metallic strip extending between them. The modulator comprises means for varying an electric field applied to at least one portion so as to vary the value of the electromagnetic property and thereby the propagation characteristics of the plasmon-polariton wave.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Waveguides for Ultra-Long Range Surface Plasmon-Polariton Propagation
The disclosure relates to surface plasmon-polariton waveguides, which can guide ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves. The attenuation of an ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves is much lower than the attenuation of the conventional long range surface plasmon-polariton waves guided with the same kind of metal film or metal strip at the same plasmon-polariton frequency. An exemplary ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waveguide disclosed in this disclosure comprises a metal layer, such as a metal film or finite width metal strip, intermediate dielectric layers adjacent to the metal layer, and outer cladding dielectric material. The intermediate dielectric layers redistribute the electromagnetic energy distribution of the surface plasmon-polariton waves so that less of the energy propagates in the metal layer. Therefore, the attenuation of the surface plasmon-polariton wave is reduced. The propagation distance of the ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton wave can be designed to a desired value by adjusting the thickness and the material property of the intermediate dielectric layers and other parameters related to the waveguide.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Directional coupler on basis of spoof surface plasmon polariton
InactiveCN102856622AImprove working bandwidthReduce transmission lossCoupling devicesCouplingEngineering
The invention discloses a directional coupler on the basis of the spoof surface plasmon polariton, which comprises an input end, an isolation end, a coupling end, a through end and a coupling section. The input end, the isolation end, the coupling end, the through end and the coupling section all consist of planar plasmon polariton waveguides; each planar plasmon polariton waveguide consists of metal units which are periodically arranged; grooves vertical to the length directions of the planar plasmon polariton waveguides are arranged on the metal units; and the grooves are all positioned at the same sides of the planar plasmon polariton waveguides. When electromagnetic waves are excited from the input end, surface waves can be formed on the surface of a device by the incidence electromagnetic waves; and after being coupled by a middle coupling section, the electromagnetic waves with different wavelengths can be output at the through end and the coupling end according to different ratios. The electromagnetic waves with different wavelengths in a specific frequency band can be output at different ports and can work in a random frequency band by amplifying or reducing the size in equal proportion, and thus, the directional coupler has high application value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multiplexed Olfactory Receptor-Based Microsurface Plasmon Polariton Detector
InactiveUS20140364330A1Easy to measureImprove signal-to-noise ratioMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesG protein-coupled receptorNanodevice
The invention provides a bio-sensing nanodevice comprising: a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor on a support, a real time receptor-ligand binding detection method, a test composition delivery system and a test composition recognition program. The G-protein coupled receptor can be stabilized using surfactant peptide. The nanodevice provides a greater surface area for better precision and sensitivity to odorant detection. The invention further provides a microfluidic chip containing a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor immobilized on a support, and arranged in at least two dimensional microarray system. The invention also provides a method of delivering odorant comprising the step of manipulating the bubbles in complex microfluidic networks wherein the bubbles travel in a microfluidic channel carrying a variety of gas samples to a precise location on a chip. The invention further provides method of fabricating hOR17-4 olfactory receptor.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Submicron surface plasmon polariton beam splitter based on composite cavity structure
InactiveCN103116226AEasy to adjustReduce horizontal sizeNon-linear opticsResonant cavityBeam splitter
The invention discloses a submicron surface plasmon polariton beam splitter based on a composite cavity structure. The surface plasmon polariton beam splitter comprises a metal thin film. A nanometer suture which can penetrate through an upper surface and a lower surface of the metal thin film are arranged on the metal thin film. A nanometer groove is formed on one side of the nanometer suture to form an asymmetric nanometer monolete suture. A metal-medium-metal metal injection molding (MIM) vertical cavity is integrated below the nanometer groove. On an operating wavelength of the beam splitter, a function point (FP) resonant cavity and the MIM vertical cavity are used for nearly manipulating surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) independently, wherein the FP resonant cavity is formed in the upper half portion of the asymmetric nanometer monolete suture and the MIM vertical cavity is integrated in the FP resonant cavity. Therefore, the submicron surface plasmon polariton beam splitter based on the composite cavity structure has the advantages that SPPs beam splitting can be achieved. The greater advantage is that beam splitting wavelength can be allowed and convenient to adjust. Meanwhile, transverse size can not be increased, and the integrated height can be increased. In a high integration density plasmon polariton return circuit, the submicron surface plasmon polariton beam splitter based on the composite cavity structure has a potential application. The submicron surface plasmon polariton beam splitter based on the composite cavity structure is simple in structure, good in beam splitting performance, high in extinction ratio and capable of providing a design thought for other surface plasmon polariton function components.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
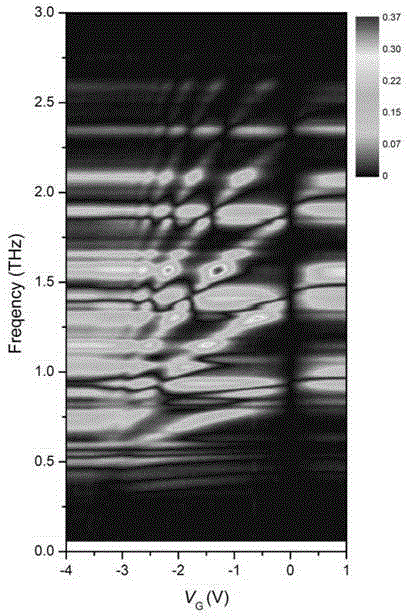
Terahertz modulator based on low-dimension electron plasma waves and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105204190AImprove modulation efficiencyEfficient modulationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsResonant cavityGrating
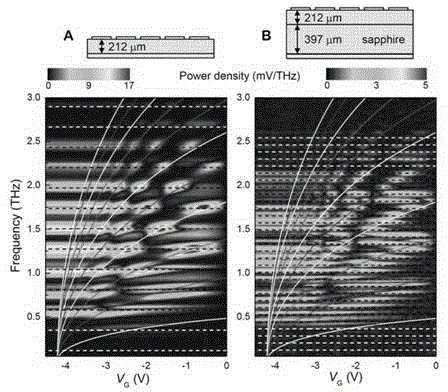
The invention provides a terahertz modulator based on low-dimension electron plasma waves, a manufacturing method thereof and a high-speed modulation method. The terahertz modulator comprises a plasmon and a resonant cavity. The resonance absorption mechanism is caused by electronic collective oscillation (plasma waves, namely Plasmon). In order to increase the coupling strength of the plasma waves and the plasmon, a GaN / AlGaN high-electronic-mobility transistor structure with a raster grid is integrated in a terahertz Fabry-Perot resonant cavity, plasmon polariton is formed through strong coupling of the plasmon and the resonant cavity mode. By means of the strong coupling effect, the transmission coefficient of the resonant cavity mode is the maximum at the resonance point, resonance conditions of the plasmon and the resonant cavity mode are adjusted and controlled by changing the raster pressure, and efficient and high-speed modulation for terahertz waves is achieved. The working principle and the achieving technology of the device are introduced in detail, and a good solution is provided for relevant applications.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
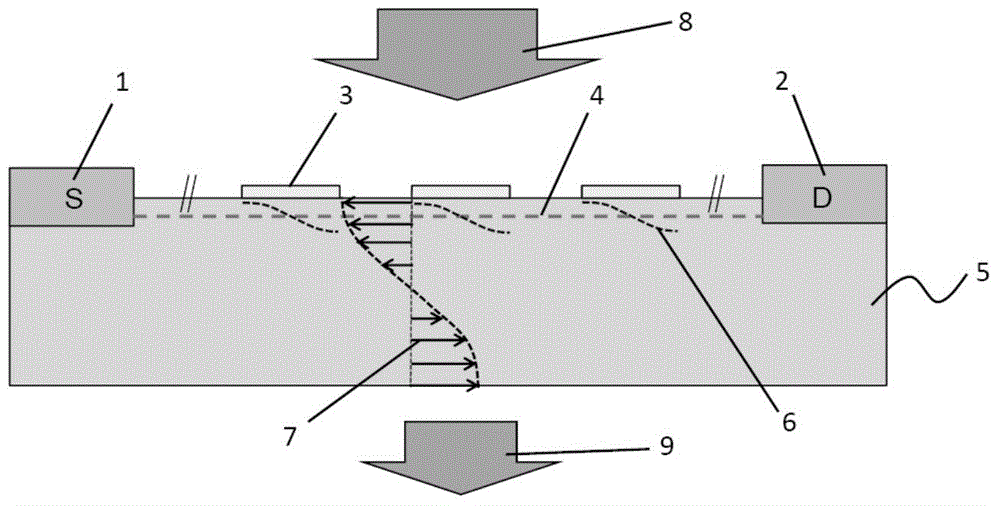
Near infrared photoelectric detector with enhancement based on utilization of indium tin oxide nanoparticles
InactiveCN102522438AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyHigh sensitivitySemiconductor devicesIndiumNanoparticle
The invention, which belongs to the infrared detector field, particularly relates to a near infrared photoelectric detector with enhancement based on utilization of indium tin oxide nanoparticles. The near infrared photoelectric detector successively comprises transparent glass (1) with high infrared transmissivity, a transparent electrode (2), a photoelectric conversion material (3), indium tin oxide nanoparticles (4), and a back electrode (5) from top to bottom. After incident infrared radiation passes through the transparent glass (1), the transparent electrode (2), and the photoelectric conversion material (3), a portion of the infrared radiation is localized at the surfaces of the indium tin oxide nanoparticles (4), scattering is generated and a surface plasma polariton transmission mode is formed, so that an effective transmission distance of the incident electromagnetic wave in the photoelectric conversion material (3) can be increased. According to the invention, the near infrared photoelectric detector with enhancement based on utilization of indium tin oxide nanoparticles has advantages of diversity of a preparation technology, low manufacturing cost, adjustable enhancement resonant position and high sensitivity and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Super-diffraction nano-optical probe
InactiveCN103149805AAchieving super-resolution lithographyEasy to compressPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusDielectricLight spot
The invention relates to a super-diffraction nano-optical probe. Specifically, a metal outer cladding is plated on the outer surface of conical medium core, and a multilayer film is deposited on the surface of a conical needle tip. The multilayer film is composed of dielectric films and metal film layers that are arranged alternately. Vertically incident light on the surfaces of the dielectric films can excite surface plasmon polaritons on interfaces of the metal films and the dielectric films. When the urface plasmon polaritons spread to the conical needle tip along the interfaces, a local enhancement effect can be achieved, and further, modification, compression and transmission enhancement on local enhanced light spots can be carried out through optical anisotropy of the multilayer film on the surface of the conical needle tip. According to the same principle, the invention also includes a design of a bow-tie structure with the multilayer film material deposited on its surface. The bow-tie structure is characterized in that the multilayer film material is deposited on its lower surface. According to the invention, the transmitted light intensity can also be changed by adjusting the thickness ratio of metal media in the multilayer film. Also, the probe has a simple structure, and can be applied to lithography very conveniently to improve lithographic resolution.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intermediate infrared graphene plasmon polariton biochemical sensor
ActiveCN106596449AImproved vibration absorption performanceHigh sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredGrating
The invention discloses an intermediate infrared graphene plasmon polariton biochemical sensor. The intermediate infrared graphene plasmon polariton biochemical sensor comprises an intermediate infrared broad band optical source, a first intermediate infrared lens, a graphene plasmon polariton sensing unit and a second intermediate infrared lens; the graphene plasmon polariton sensing unit comprises a doped silicon substrate, a first grating coupling area, a second grating coupling area, a sensing area, and a graphene layer, wherein the graphene layer covers the first grating coupling area, the second grating coupling area and the sensing area; an intermediate infrared light wave emitted by the broad band optical source is focused in the first grating coupling area through the first intermediate infrared lens so as to be coupled with a graphene plasmon polariton, the produced intermediate infrared graphene plasmon polariton reaches the sensing area through the graphene layer, repeatedly reacts with a biological sample in the sensing area, reaches the second grating coupling area through the graphene layer, is scattered to the far field, and is focused to a fourier infrared spectrometer through the second intermediate infrared lens to implement spectral measurement and analysis. The intermediate infrared graphene plasmon polariton repeatedly reacts with the biological sample in the sensing area, and the detection sensitivity of biomolecules is improved.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Schottky barrier photodetectors
InactiveUS7026701B2Improve efficiencyCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical radiationSchottky barrier
A Schottky barrier photodetector comprises a waveguide structure formed by a thin strip of material having a relatively high free charge carrier density, for example a conductor or certain classes of highly-doped semiconductor, surrounded by material having a relatively low free charge carrier density, the material on at least one side of the strip comprising a semiconductor, the strip having finite width and thickness with dimensions such that optical radiation couples to the strip and propagates along the length of the strip as a plasmon-polariton wave, light for detection being coupled to one end of the strip to propagate along the strip as said plasmon-polariton wave, ohmic contact means applied to the semiconductor material and at least one electrode means connected to the strip for applying bias to the Schottky barrier and extracting a photodetector current corresponding to the light applied to the photodetector. Where the strip of material is a flat, thin strip, the device will be polarisation dependent. Substantially polarisation-independent operation maybe achieved by using a strip whose width is of the same order as its thickness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Method for producing rod-shaped and branched metallic nano-structures by polyol compounds
InactiveUS20110088511A1Accelerates major axis growthMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNano structuringFluorescence
The various embodiments herein provide method of producing a rod-shape and branched metal nano-structures with polyol compounds as a reducing agent. The metal nano-structures are produced in a closed chamber of microwave system with variable irradiation power at a designed temperature. The metal nano-structures produced exhibits localized plasmon-polariton resonance, exhibit spectral resonance positions at microwave or radio frequencies and exhibit multiple spectral resonance peak at microwave or radio frequencies. The metal nano-structures produced are suitable as a coating composition material, a coating, a film, a wiring material, an electrode material, a catalyst, a colorant, a cosmetic, a near-infrared absorber, an anti-counterfeit ink and an electromagnetic shielding material, a surface enhanced fluorescent sensor, a biomarker and a nano-waveguide.
Owner:JALALEDIN GHANAVI +1
Organic polariton laser
ActiveUS20050195874A1Laser using scattering effectsLaser active region structureOrganic laserIntegrated devices
The present invention relates to organic lasers. More specifically, the present invention is directed to an organic laser that provides a self-stimulated source of coherent radiation originating from organic microcavity polaritons. The organic polariton laser of the present invention comprises a substrate, a resonant microcavity comprising an organic polariton emission layer; and an optical pump. In preferred embodiments the optical pump is a microcavity OLED allowing for the fabrication of a self-contained or integrated device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
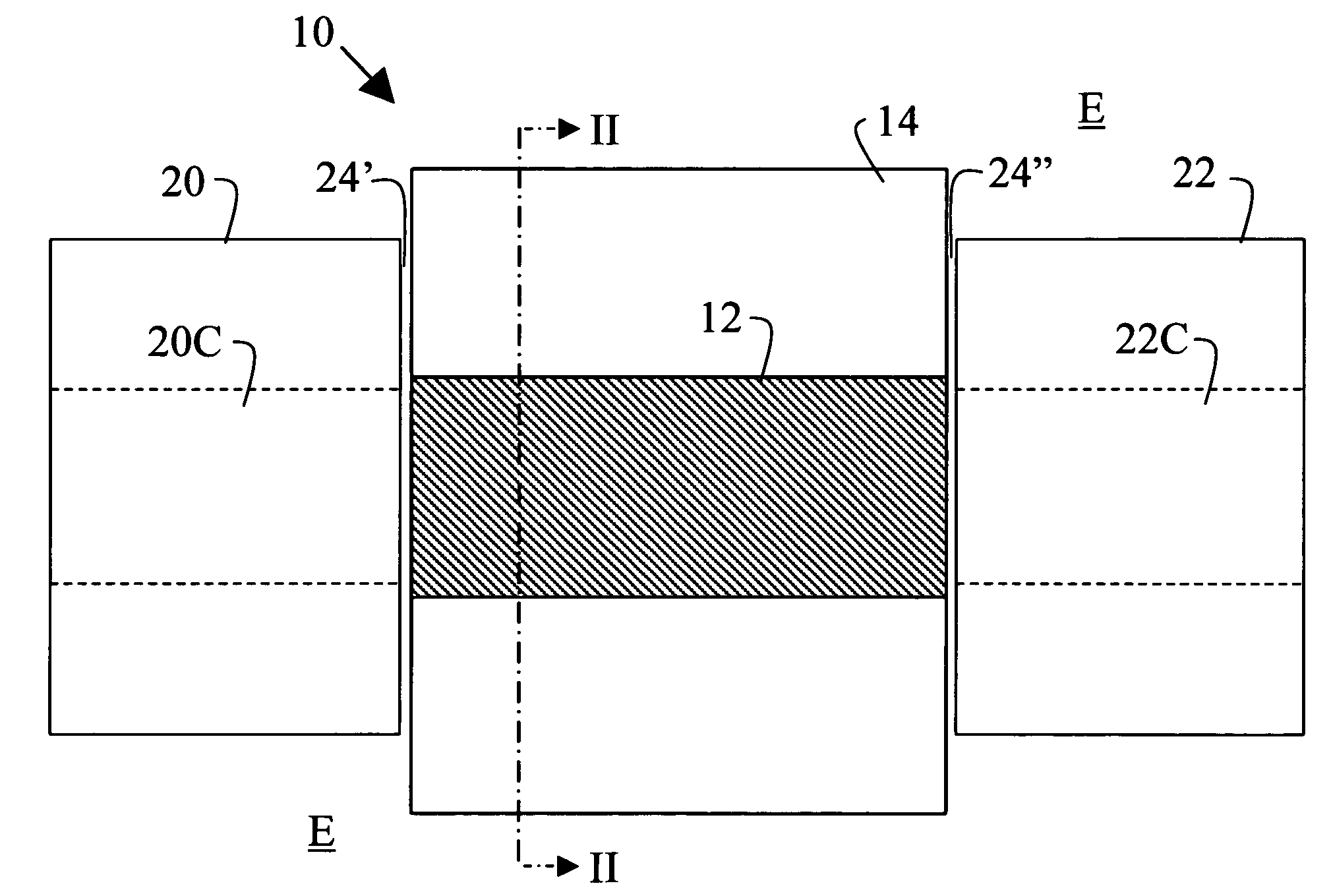
Optical Device Comprising a Waveguide Structure
InactiveUS20090136190A1Increased free carrier densityMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsOptical radiationLength wave
An optical device has a waveguide structure comprising a thin strip (12) having finite width and thickness of material having a relatively high free charge carrier density supported by a membrane (14) having a predetermined thickness of material that has a relatively low free charge carrier density. The dimensions of the width and thickness of the strip and the thickness of the supporting membrane are such that, when the waveguide structure is surrounded at least partially by an environment (E) having a low free charge carrier density, optical radiation having a wavelength in a predetermined range couples to the waveguide structure and propagates along the length thereof as a plasmon-polariton wave that permeates at least part of the environment (E).
Owner:BERINI PIERRE SIMON JOSEPH +2
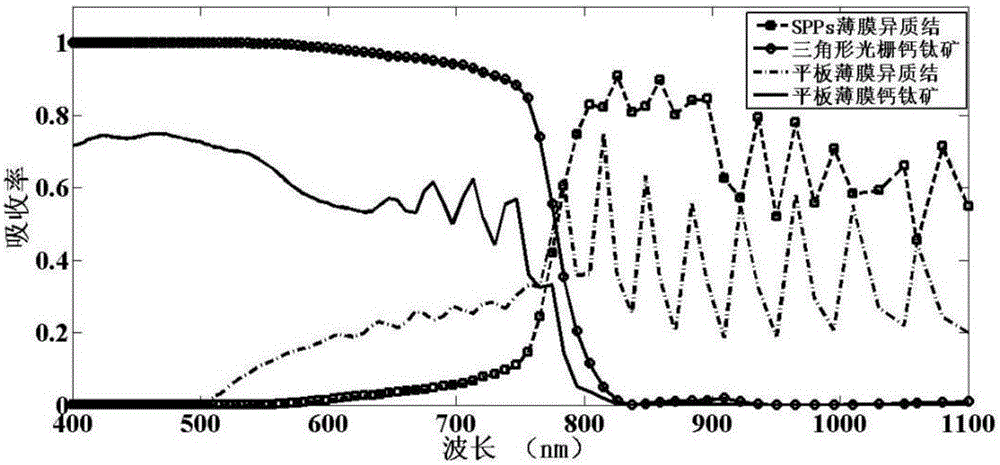
SPPs (Surface Plasma Polaritons) thin film heterojunction and perovskite laminated solar cell and preparation method of solar cell
ActiveCN106299131AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyReduce usageFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionGrating
The invention discloses an SPPs (Surface Plasma Polaritons) thin film heterojunction and perovskite laminated solar cell and a preparation method of the solar cell. The solar cell comprises an aluminum electrode, an SPPs thin film heterojunction solar cell, an ITO connection layer, a triangular grating perovskite cell and a metal grid line electrode from bottom to top. The preparation method of the solar cell comprises the following steps: 1, preparing the SPPs thin film heterojunction solar cell; 2, preparing the ITO connection layer on a front surface of the SPPs thin film heterojunction cell by a magnetron sputtering coating system; 3, preparing the triangular grating perovskite cell; and 4, preparing the metal grid line electrode by a silk-screen printing method. The prepared solar cell first utilizes a perovskite top cell to absorb short-wavelength sunlight, and then utilizes a thin film heterojunction bottom cell to absorb long-wavelength sunlight, so as to form a reasonable laminated thin film cell structure, the spectral absorption range of the thin film cell is effectively expanded, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
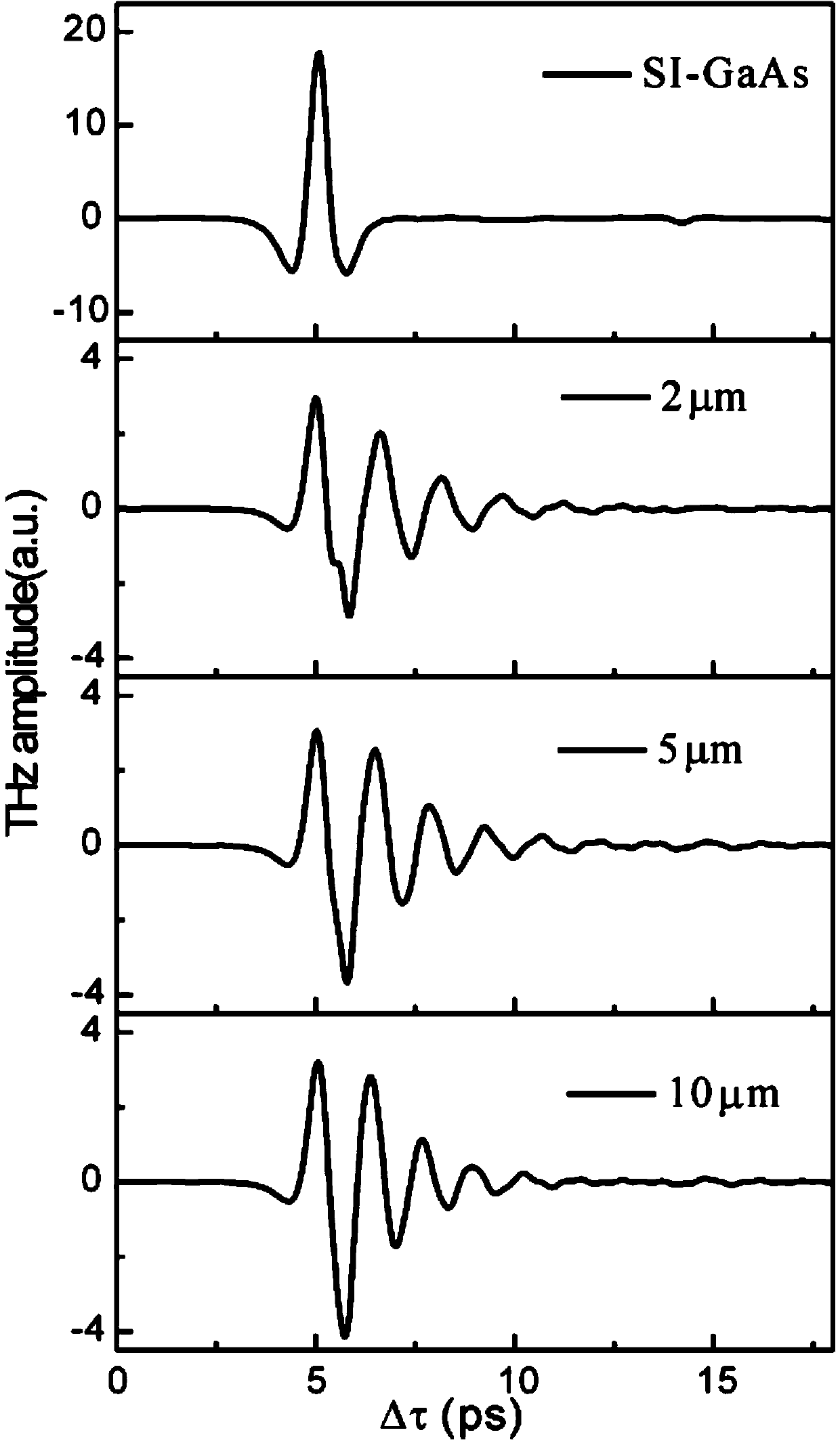
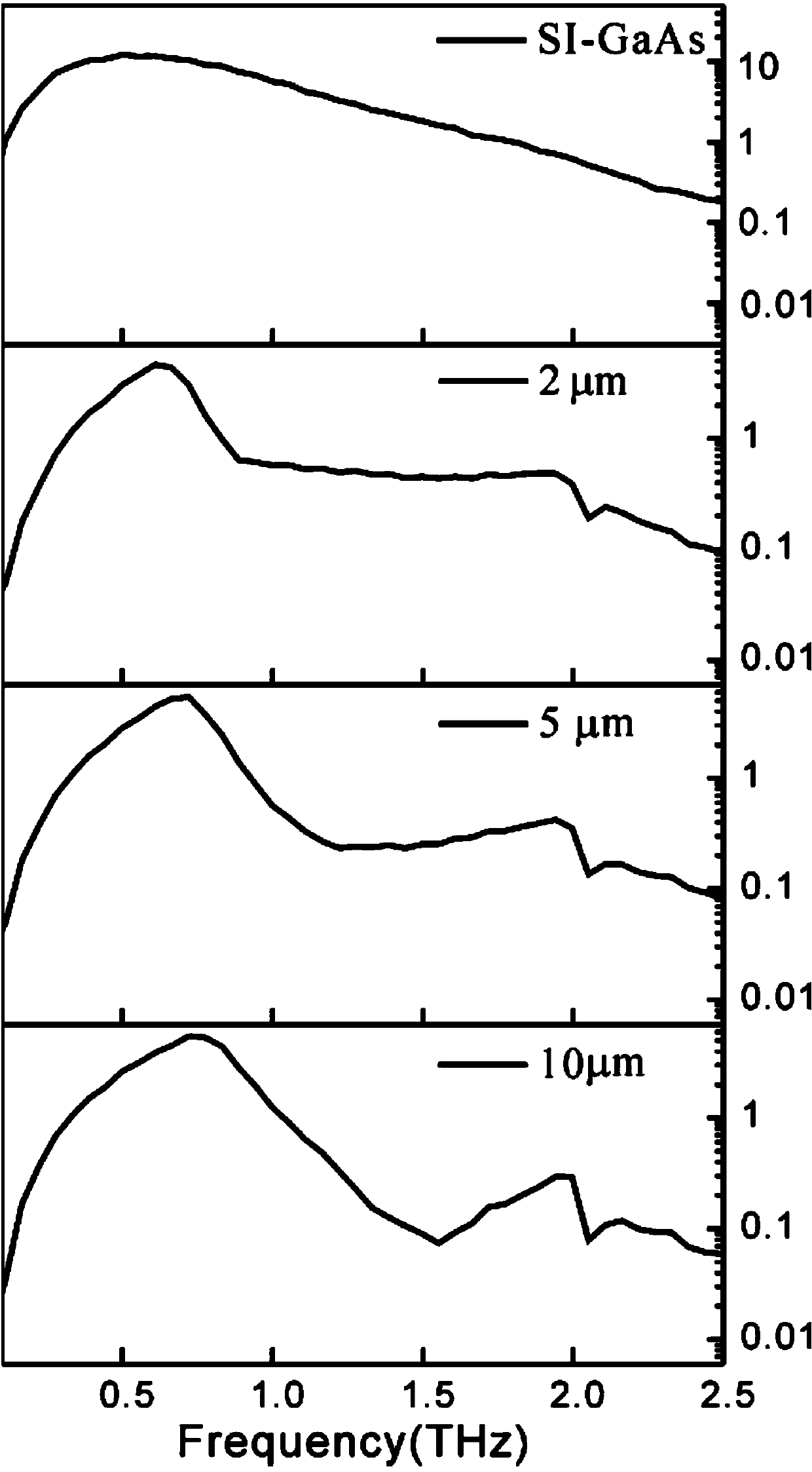
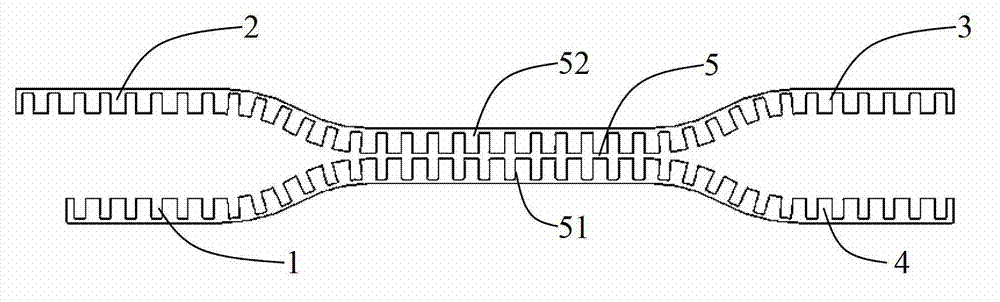
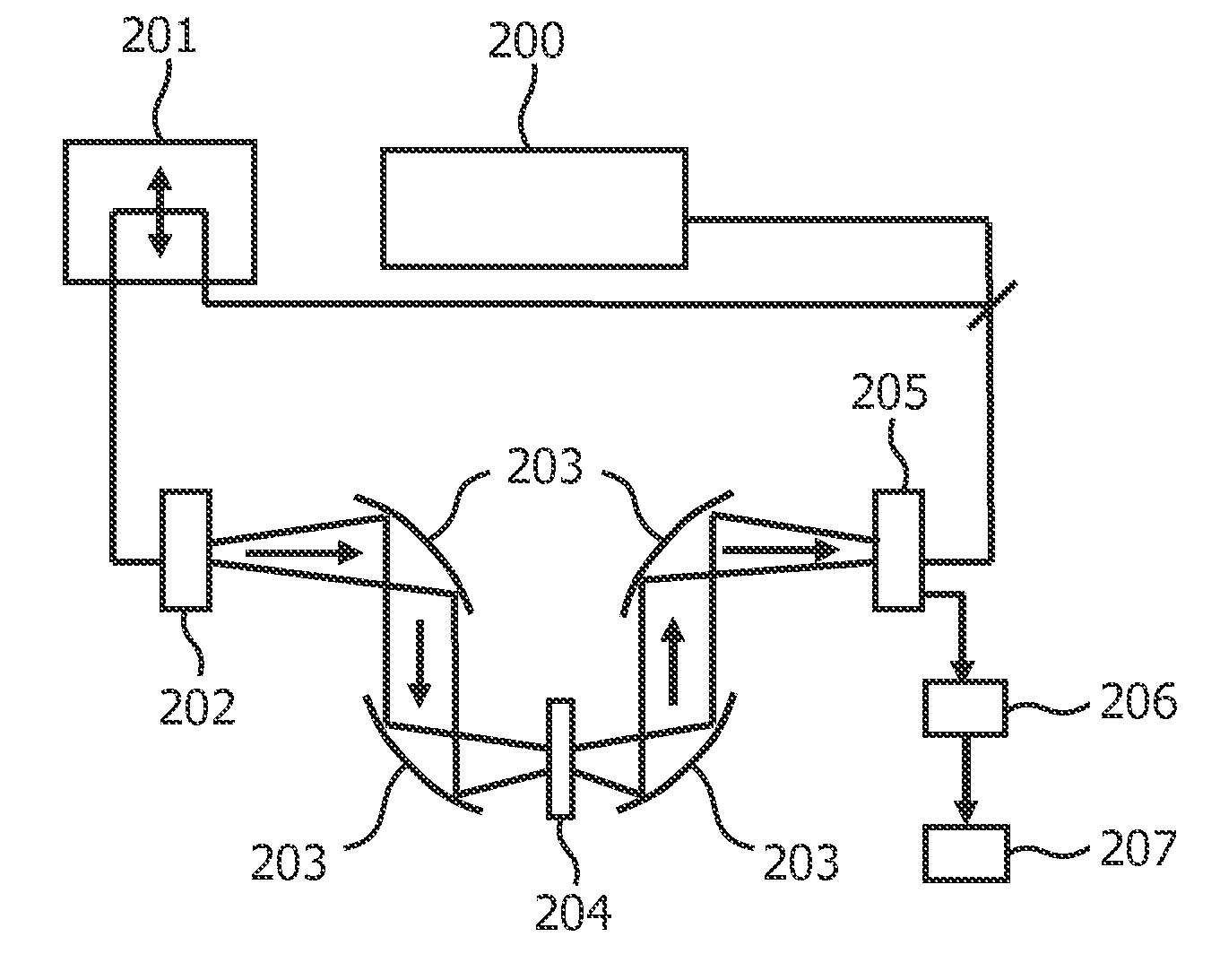
Device for analyzing a sample using radiation in the terahertz frequency range
InactiveUS20120305772A1High sensitivityLow-cost commercialSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSignal generatorNonlinear transmission line
A device for analyzing a sample using radiation in the terahertz frequency range is provided. The device comprises a transmitter (3) comprising a THz signal generator (5, 6, 7; 51) for generating an electromagnetic THz signal, the THz signal generator comprising a nonlinear transmission line (7; 52). The device further comprises a surface plasmon polariton generating unit (8) adapted to convert the THz signal into a surface plasmon polariton. The transmitter (3) and the surface plamon polariton generating unit (8) are either integrated on one common substrate or on two separate substrates.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
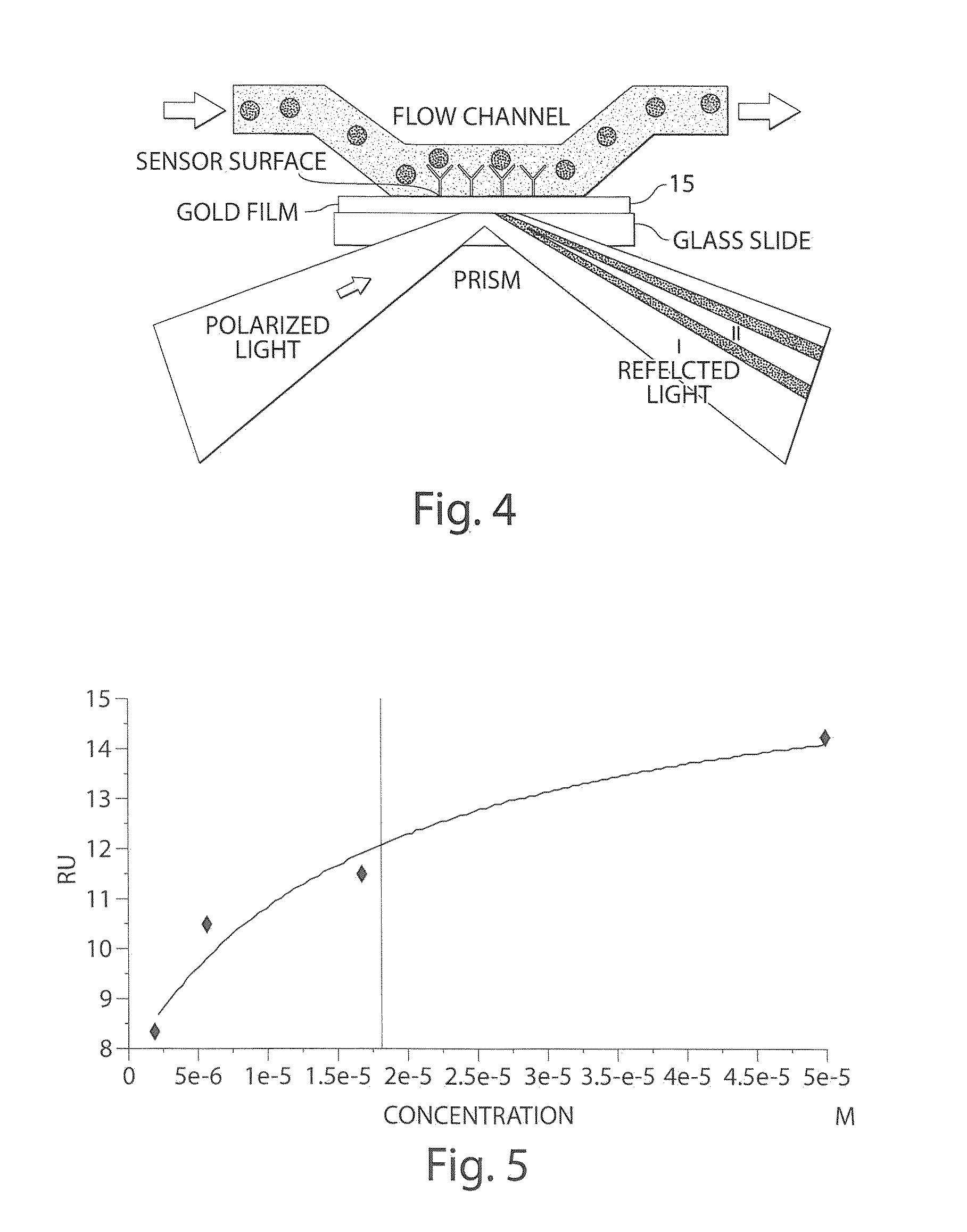
Plasmon-polariton refractive-index fiber bio-sensor with fiber Bragg grating
An optical waveguide sensing method and device in which a waveguide layer receives an optical signal and propagates the optical signal in accordance with a predetermined optical waveguide propagation mode. A testing medium surface in communication with the waveguide layer is responsive to a testing medium for modifying at least one characteristic of the propagated optical signal in relation to a given parameter of the testing medium. In this manner, the modified characteristic of the propagated optical signal can be measured in view of determining the given parameter of the testing medium.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
Ultra-fast detection structure for metal micro Nano supersrtucture surface plasma polariton
InactiveCN106684199AEffective generationEfficient collectionPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSemiconductor devicesMicro nanoPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention relates to the technical field of optics and micro Nano system, in particular to an ultra-fast detection structure for metal micro Nano superstructure surface plasma ploariton. The structure comprises Si base where a layer of silica is cultured. A lay of graphene film is provided on the layer of the silica and square shape metal Au is placed on the both sides of the graphene film and a layer of TiO is placed on the graphene film between the square shape metal Au. Globular metal Ag is provided on the layer of the TiO. A cover layer of the graphene film is provided on the globular metal Ag. A nanoscale gap is shown among the globular metal Ag. The invention solves the problems of being limited in sensitivity due to lack of photon-generated carriers brought by the photodetector made of the graphene and being low in transmission speed.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Plasmon-Polariton Refractive-Index Fiber Bio-Sensor with Fiber Bragg Grating
An optical waveguide sensing method and device in which a waveguide layer receives an optical signal and propagates the optical signal in accordance with a predetermined optical waveguide propagation mode. A testing medium surface in communication with the waveguide layer is responsive to a testing medium for modifying at least one characteristic of the propagated optical signal in relation to a given parameter of the testing medium. In this manner, the modified characteristic of the propagated optical signal can be measured in view of determining the given parameter of the testing medium.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
Symmetrical periodic groove leaky-wave antenna based on artificial surface plasmon polaritons
ActiveCN109742532AWorking frequency bandwidthImprove performanceRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCoplanar waveguideDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a symmetrical periodic groove leaky-wave antenna based on artificial surface plasmon polaritons, and relates to a leaky-wave antenna. A dielectric substrate is arranged; a metal structure covers the upper surface of the dielectric substrate; the metal structure comprises a trapezoidal coplanar waveguide transmission line feeding part, an artificial surface plasmon polariton gradual-change metal groove array part, a transition part and an artificial surface plasmon polariton periodic metal groove part; the trapezoidal coplanar waveguide transmission line feeding part ispositioned at one end of the dielectric substrate; the artificial surface plasmon polariton gradual-change metal groove array part is positioned in the middle of the dielectric substrate; the transition part is from the trapezoidal coplanar waveguide transmission line feeding part to the artificial surface plasmon polariton gradual-change metal groove array part; and the artificial surface plasmon polariton gradual-change metal groove array part is positioned at the tail end of the dielectric substrate. The working frequency band of the antenna is very wide; the corresponding working frequency band has relatively high gain and good directivity; and the symmetrical periodic groove leaky-wave antenna disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, simple and easy to manufacture, relatively small in size and good in performance, can be applied to actual working requirements, and has very important practical significance for application of the artificial surface plasmon polaritons in amicrowave frequency band.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com