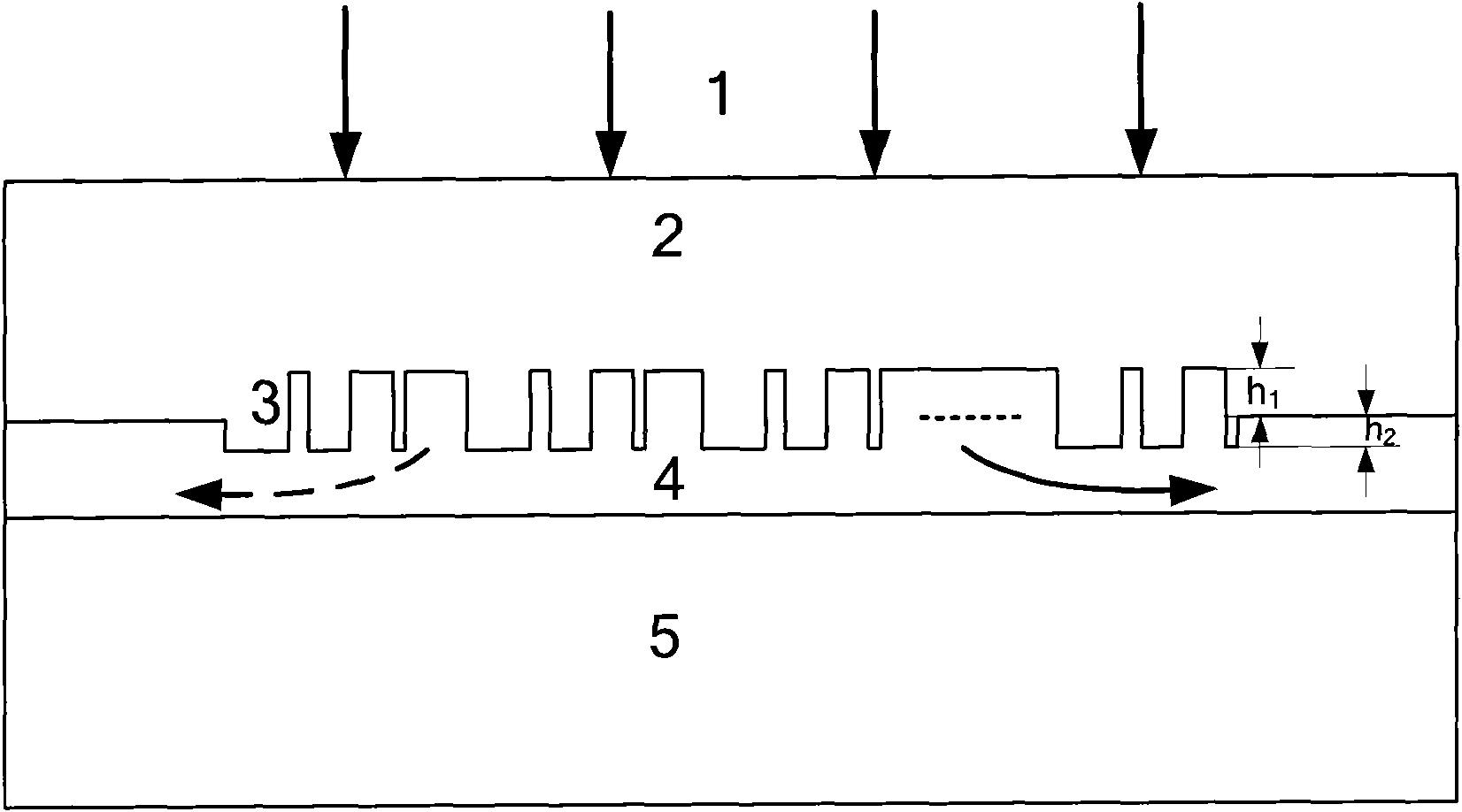
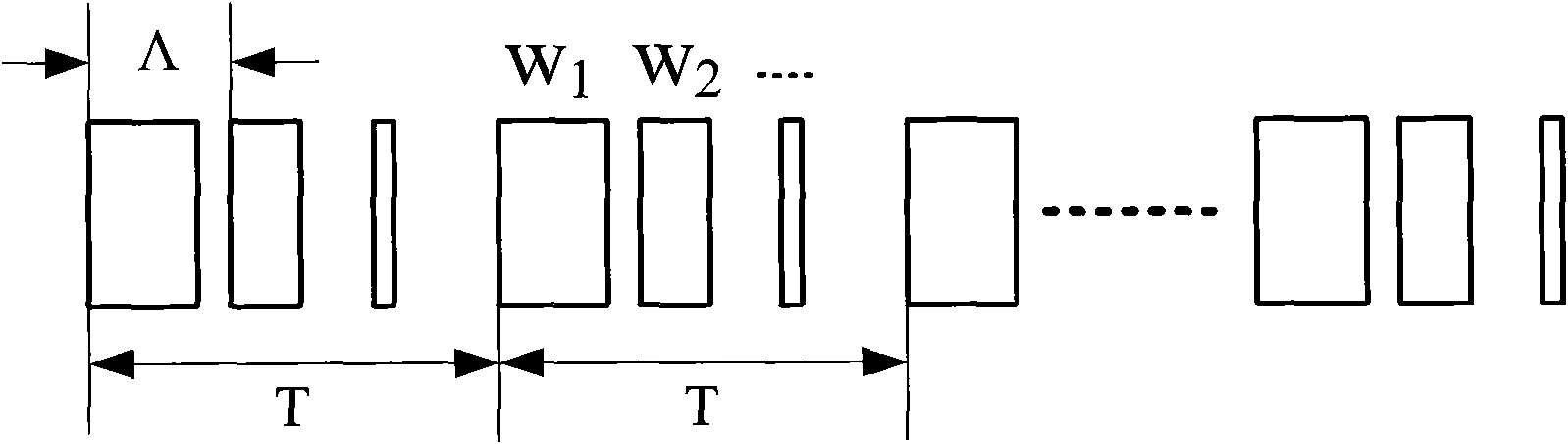
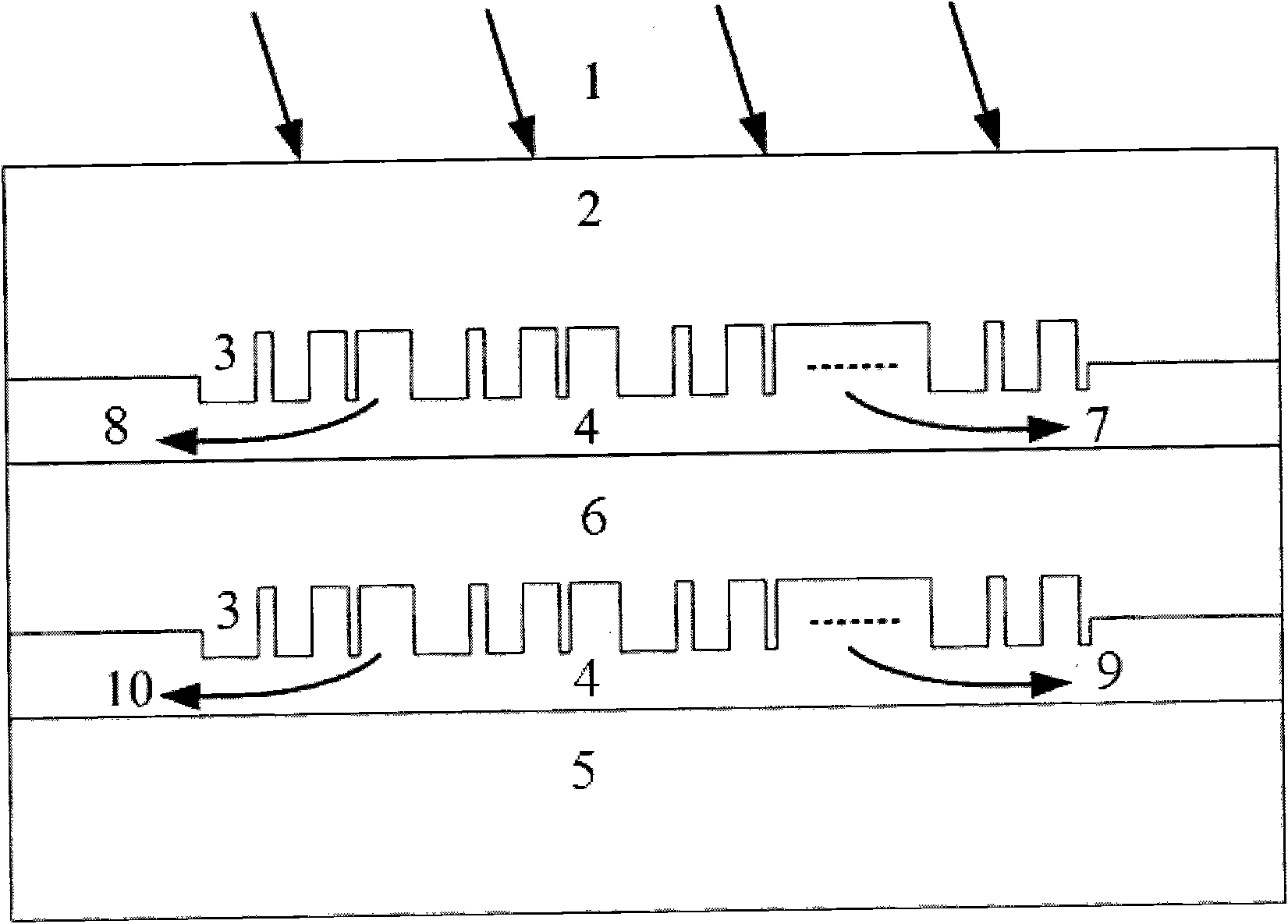
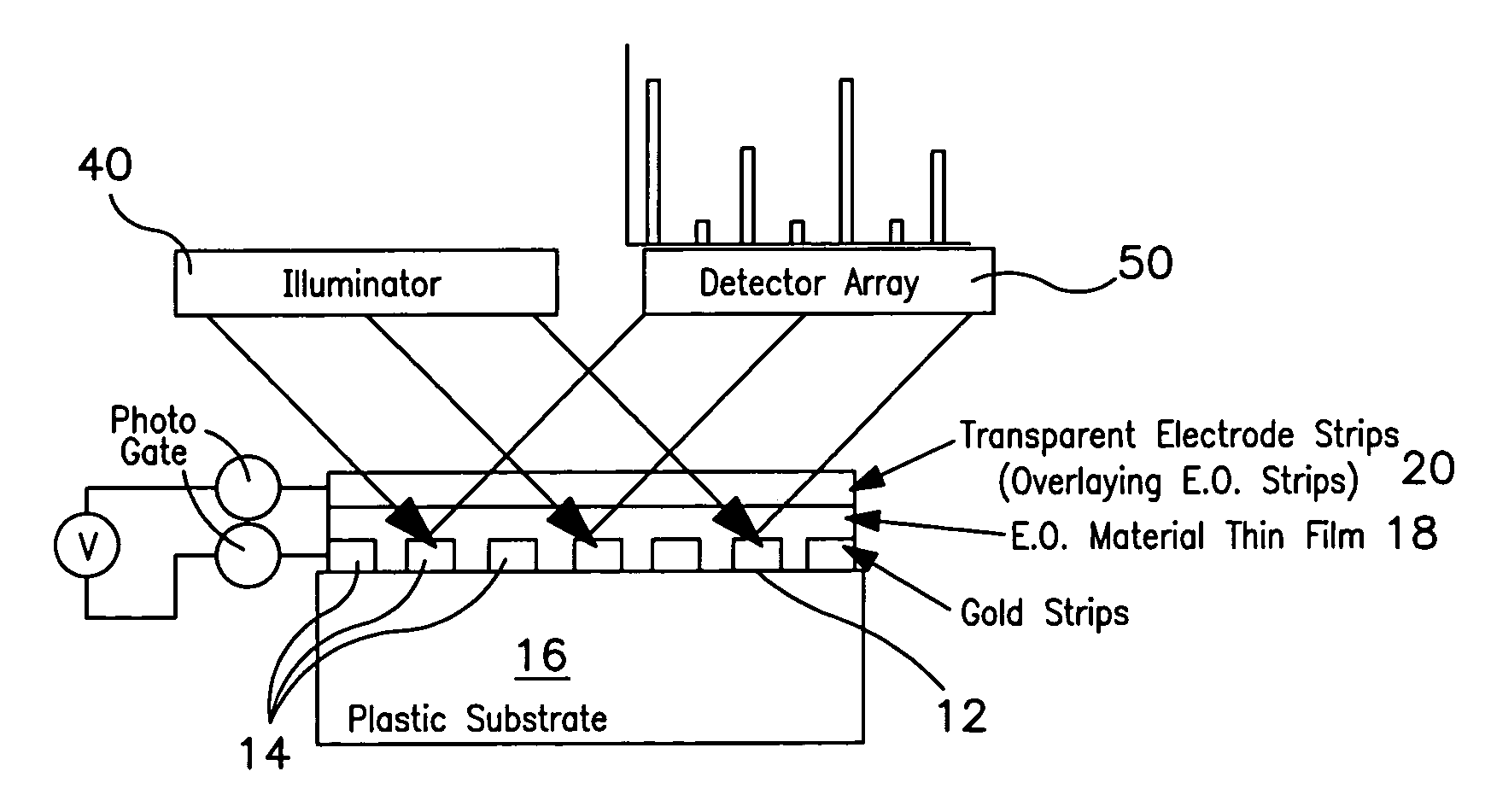
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
320 results about "Grating coupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
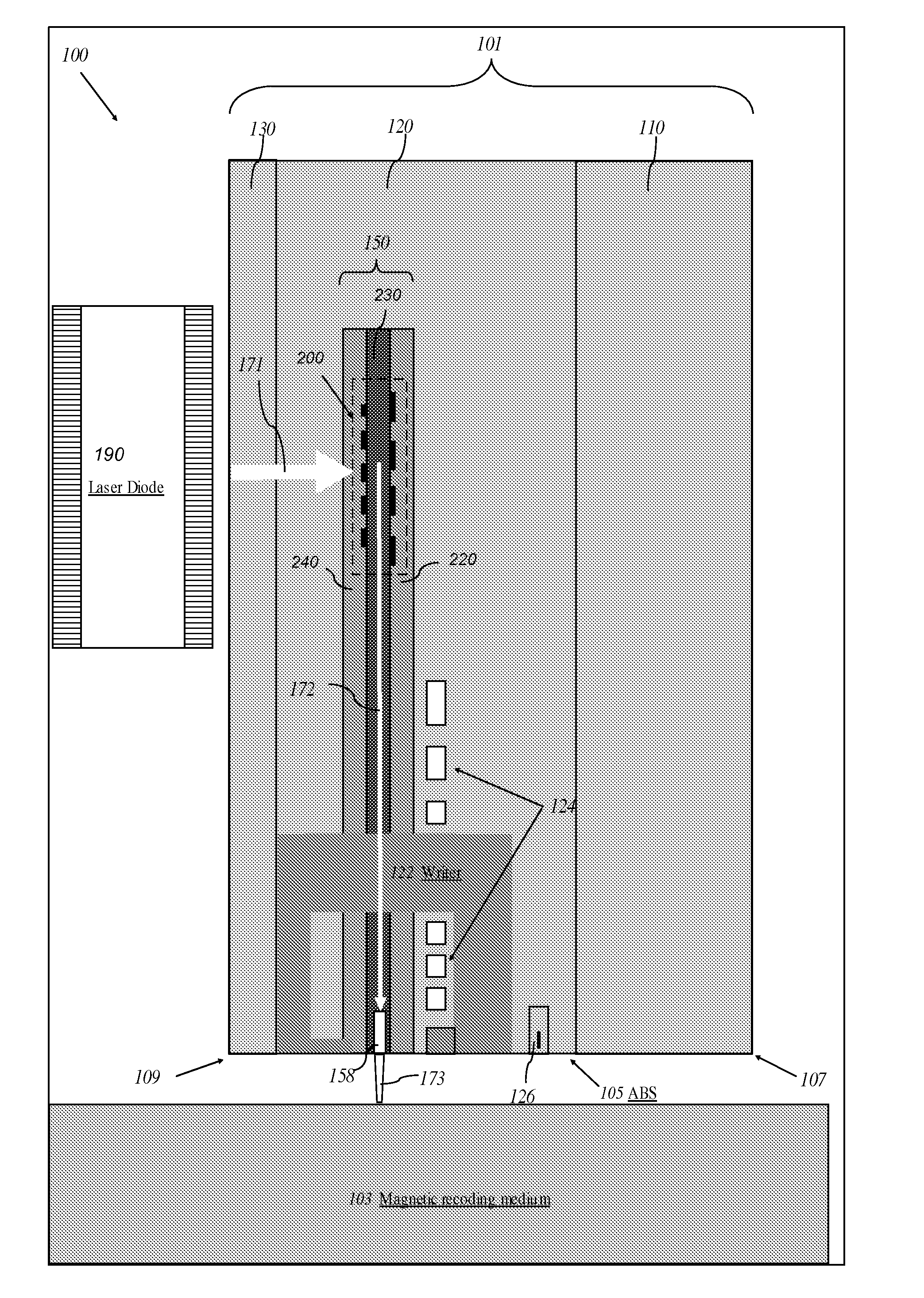
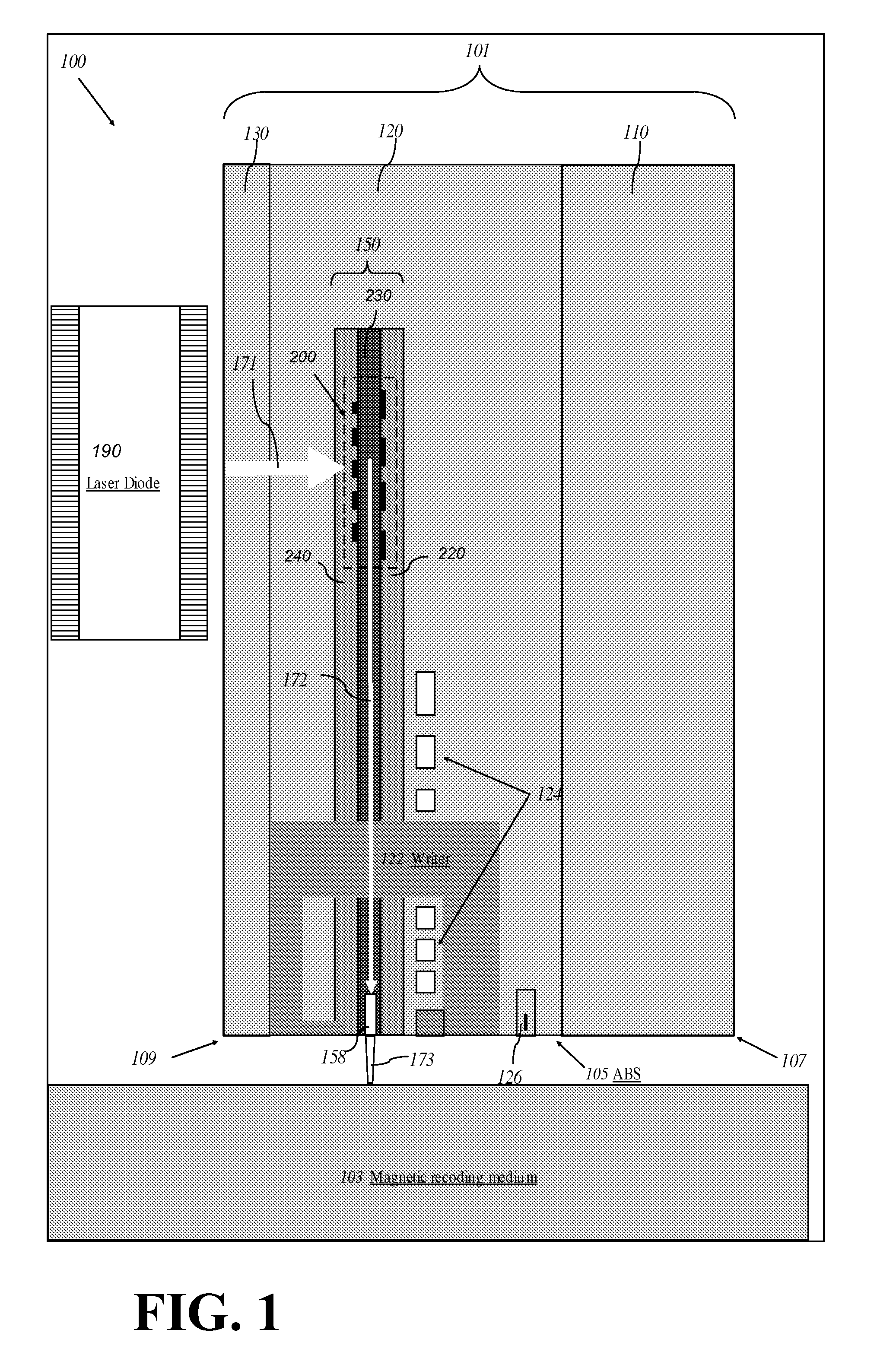
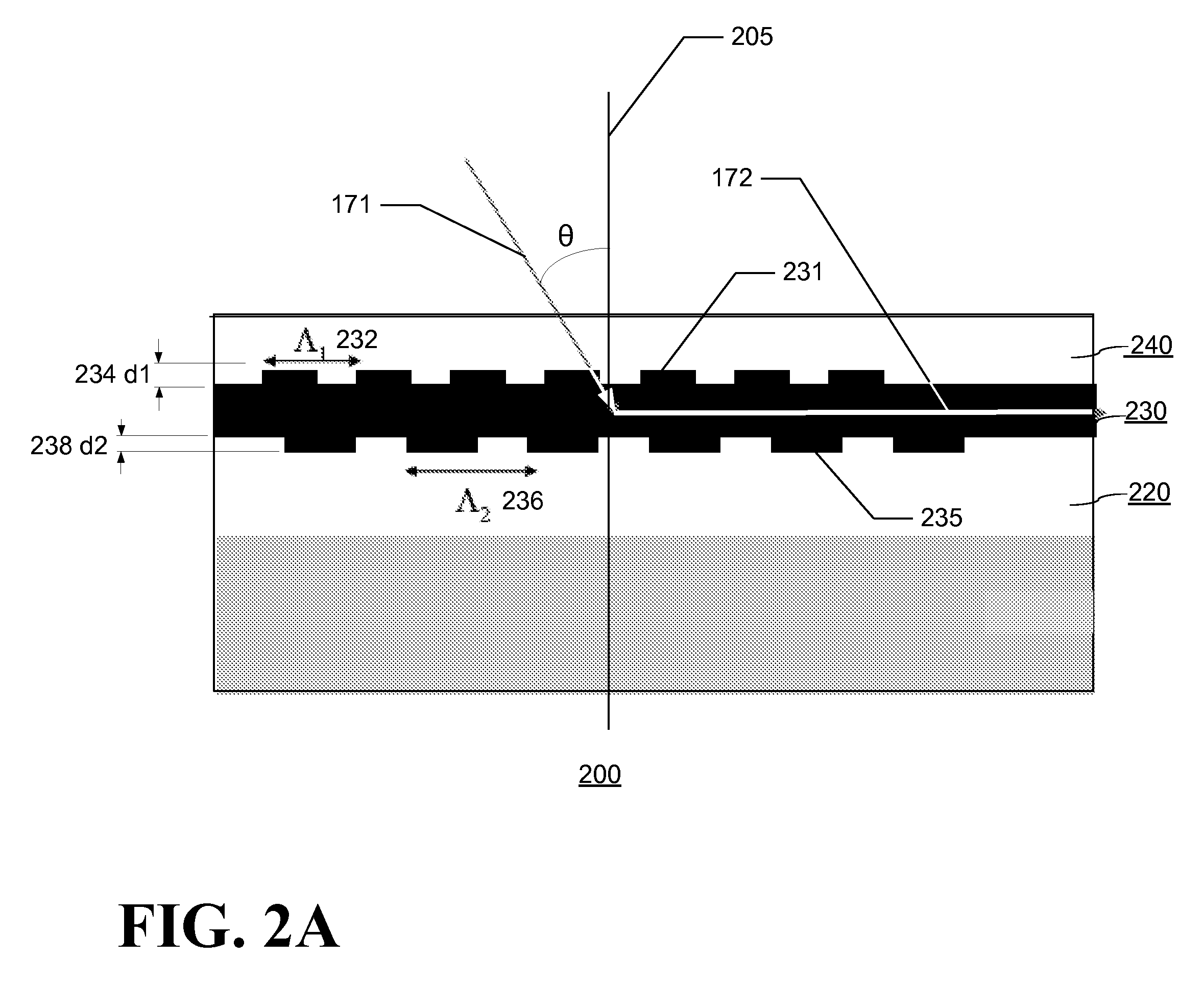
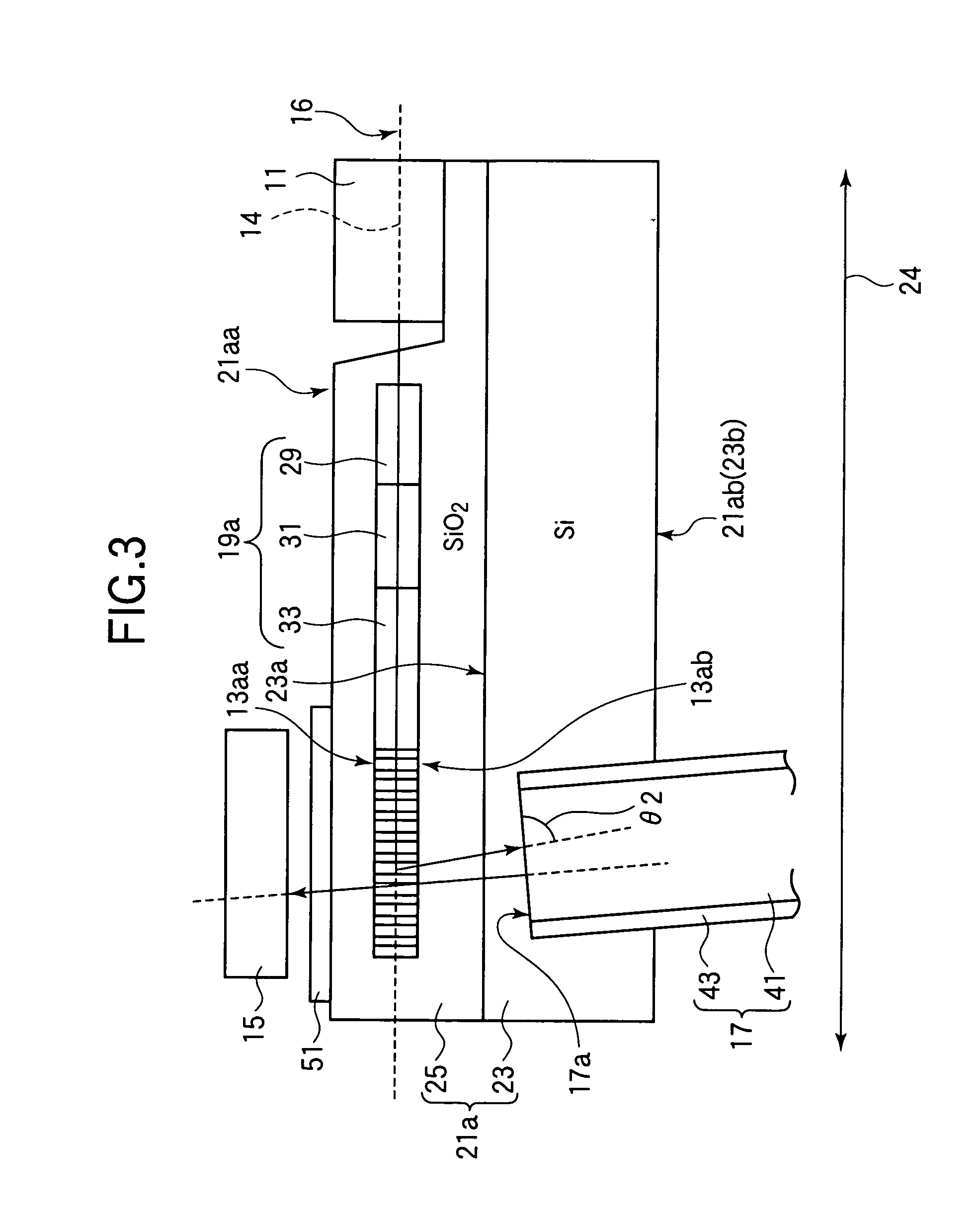
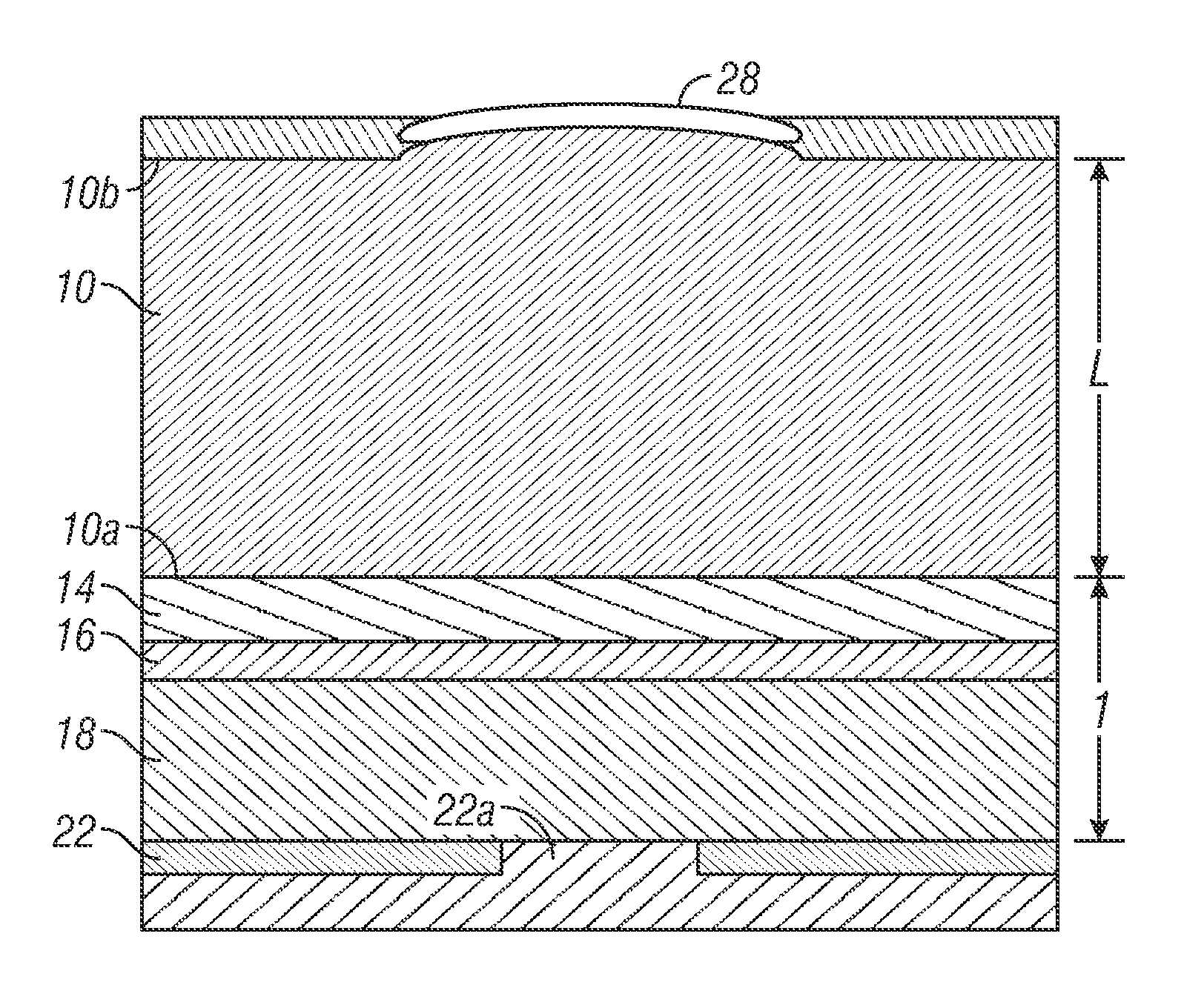
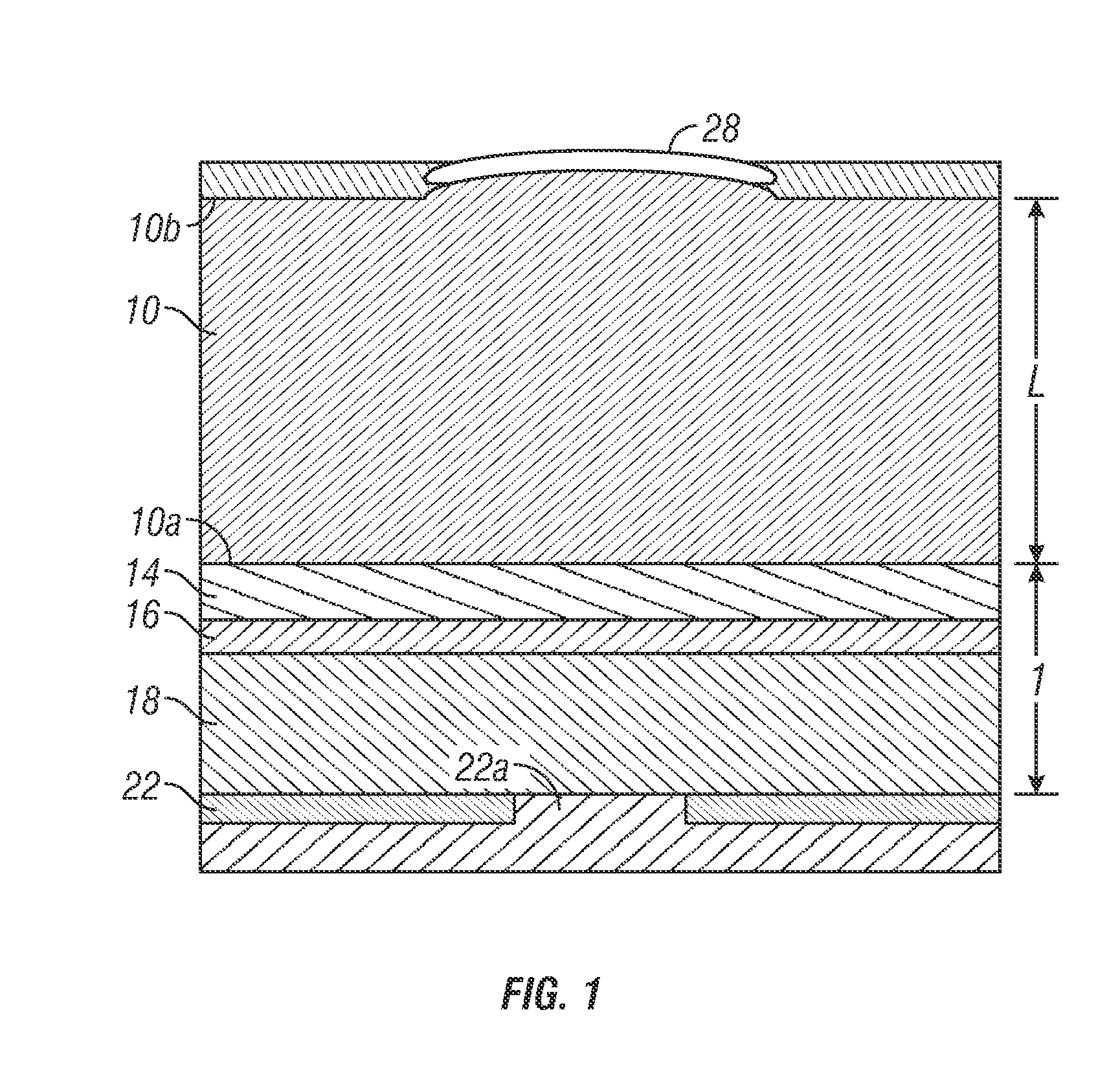
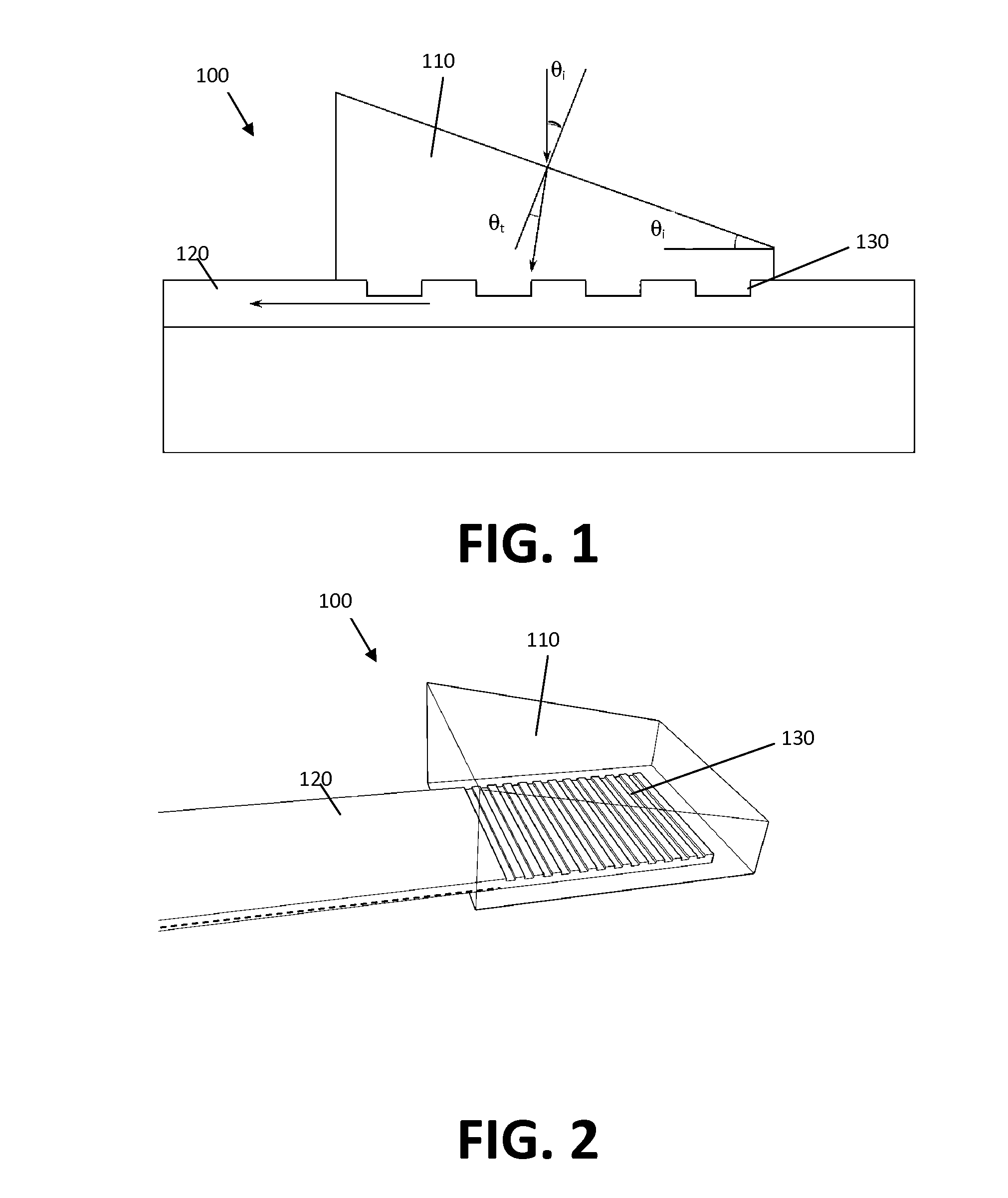
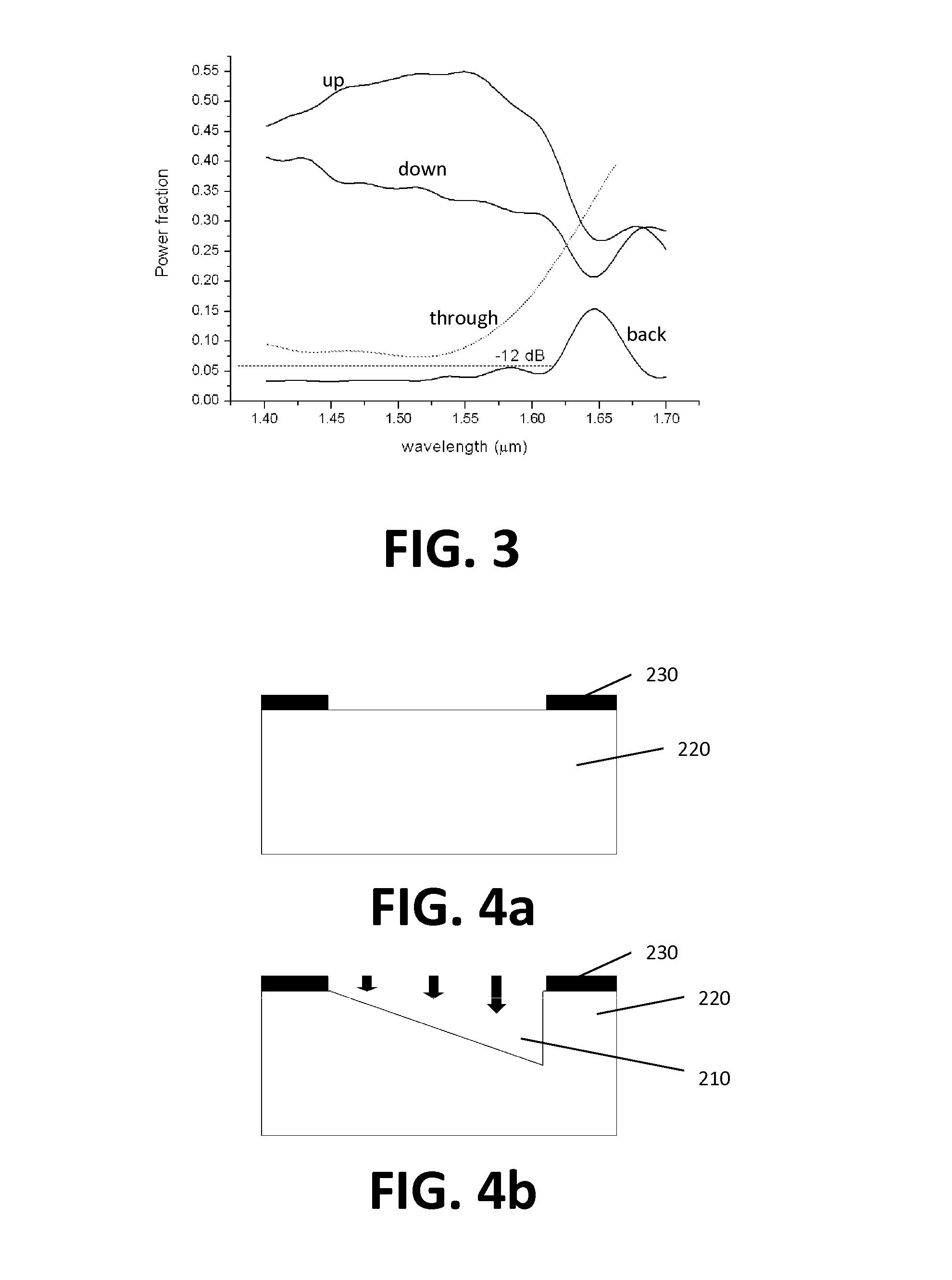
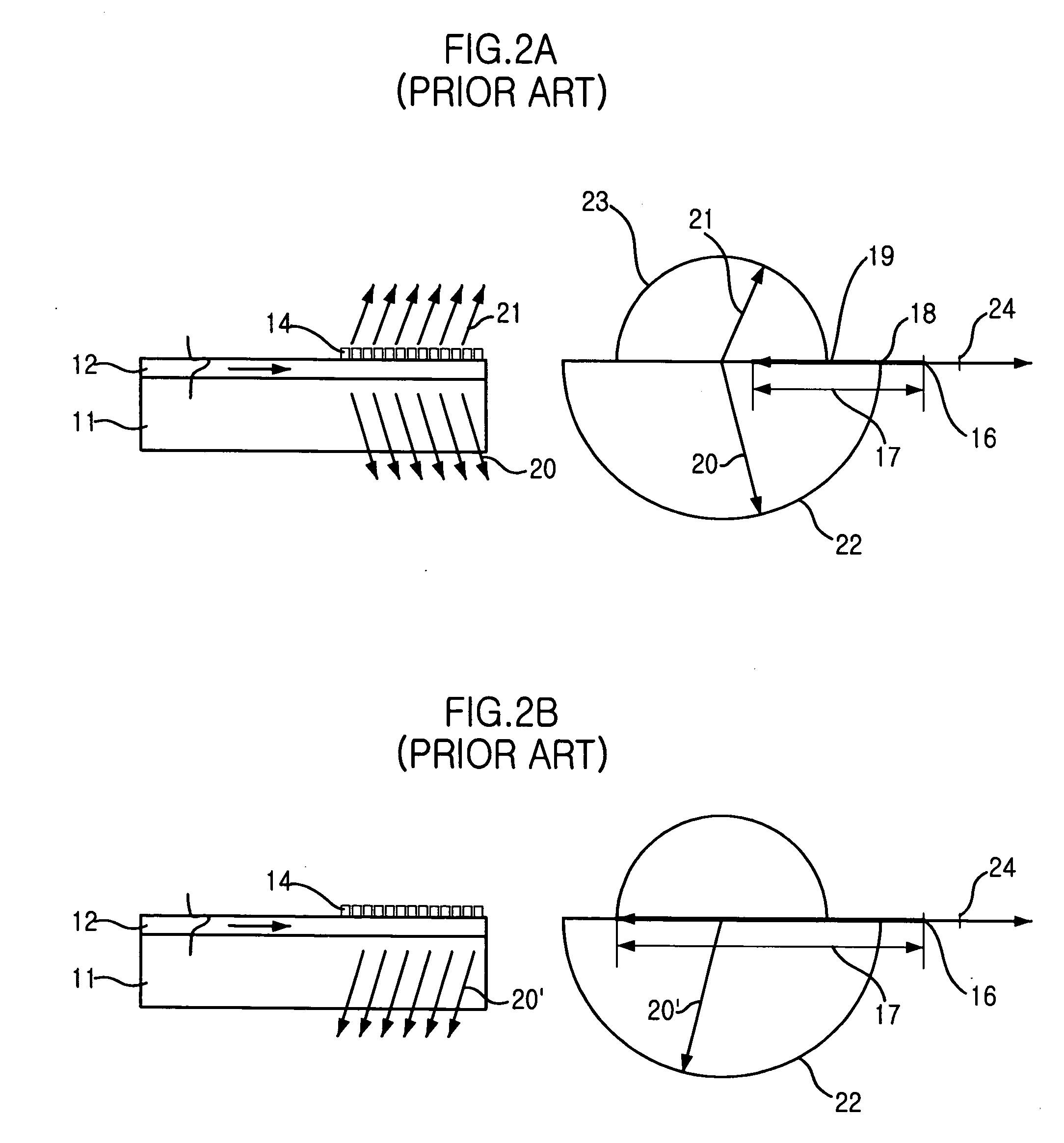
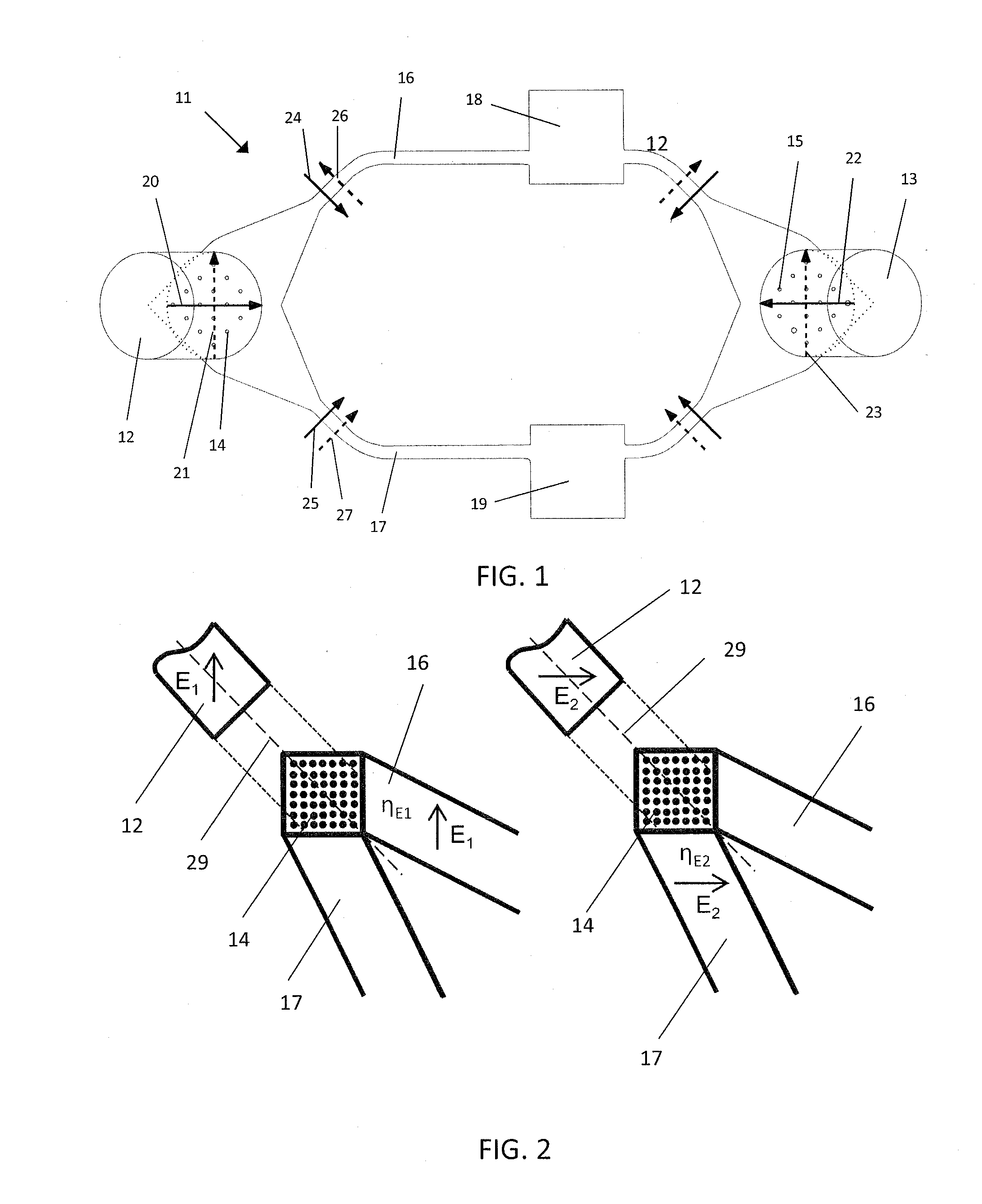
High efficiency grating coupling for light delivery in EAMR
ActiveUS8200054B1Maximise couplingCoupling efficiency is improvedRecord information storageMagnetic recordingGratingLight delivery
A magnetic head comprising a waveguide coupler for coupling incident electromagnetic (EM) radiation into a waveguide is disclosed. The waveguide coupler includes a bottom clad layer and a waveguide core layer formed above the bottom clad layer. An interface between the bottom clad layer and the waveguide core layer includes a first grating having a first period and a first etch depth, which are configured to couple a first portion of the incident EM radiation into the waveguide core layer. The waveguide coupler can further comprise a top clad layer formed above the waveguide core layer. An interface between the waveguide core layer and the top clad layer includes a second grating having a second period and a second etch depth. The second period and the second etch depth are configured to couple a second portion of the incident EM radiation into the waveguide core layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
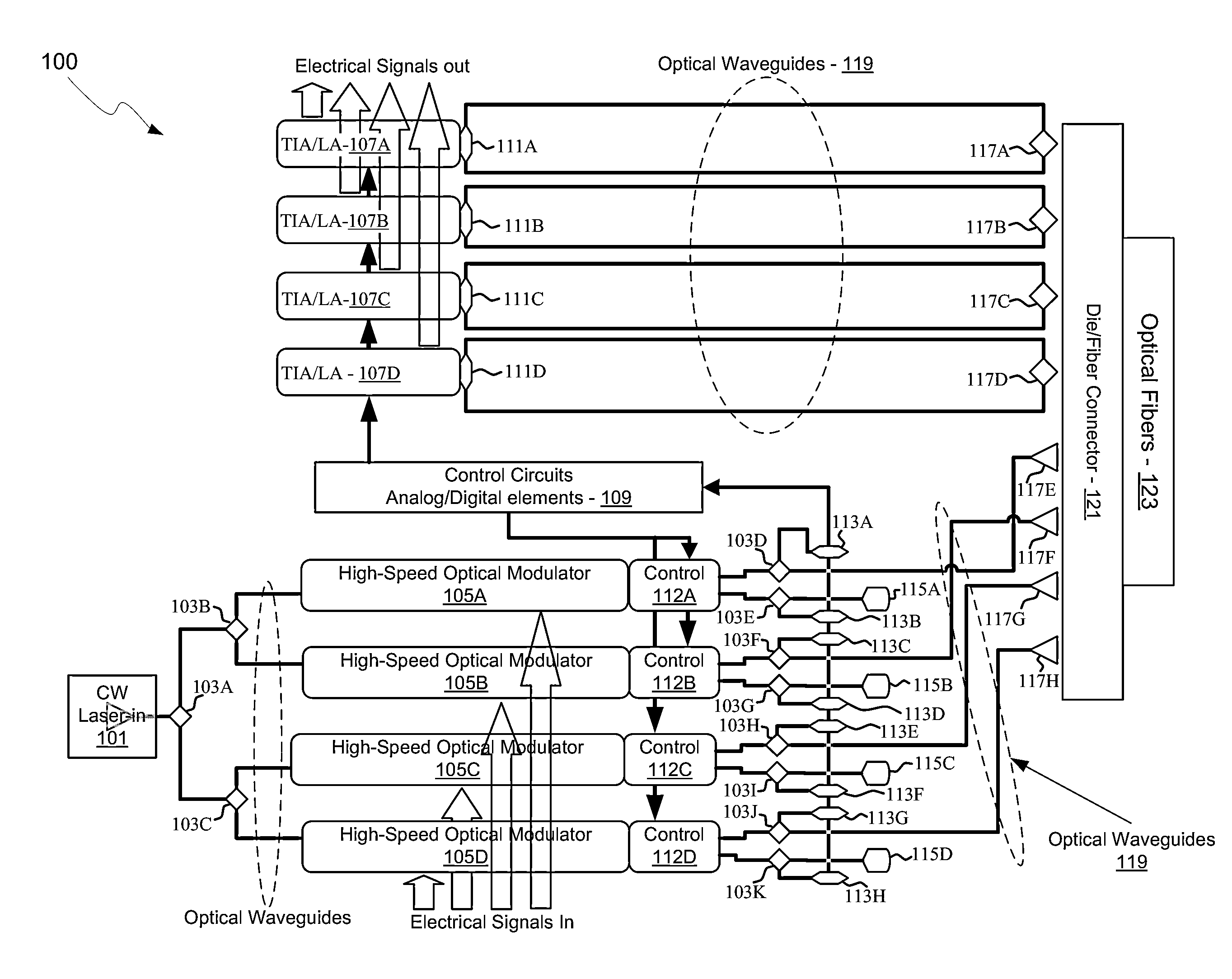
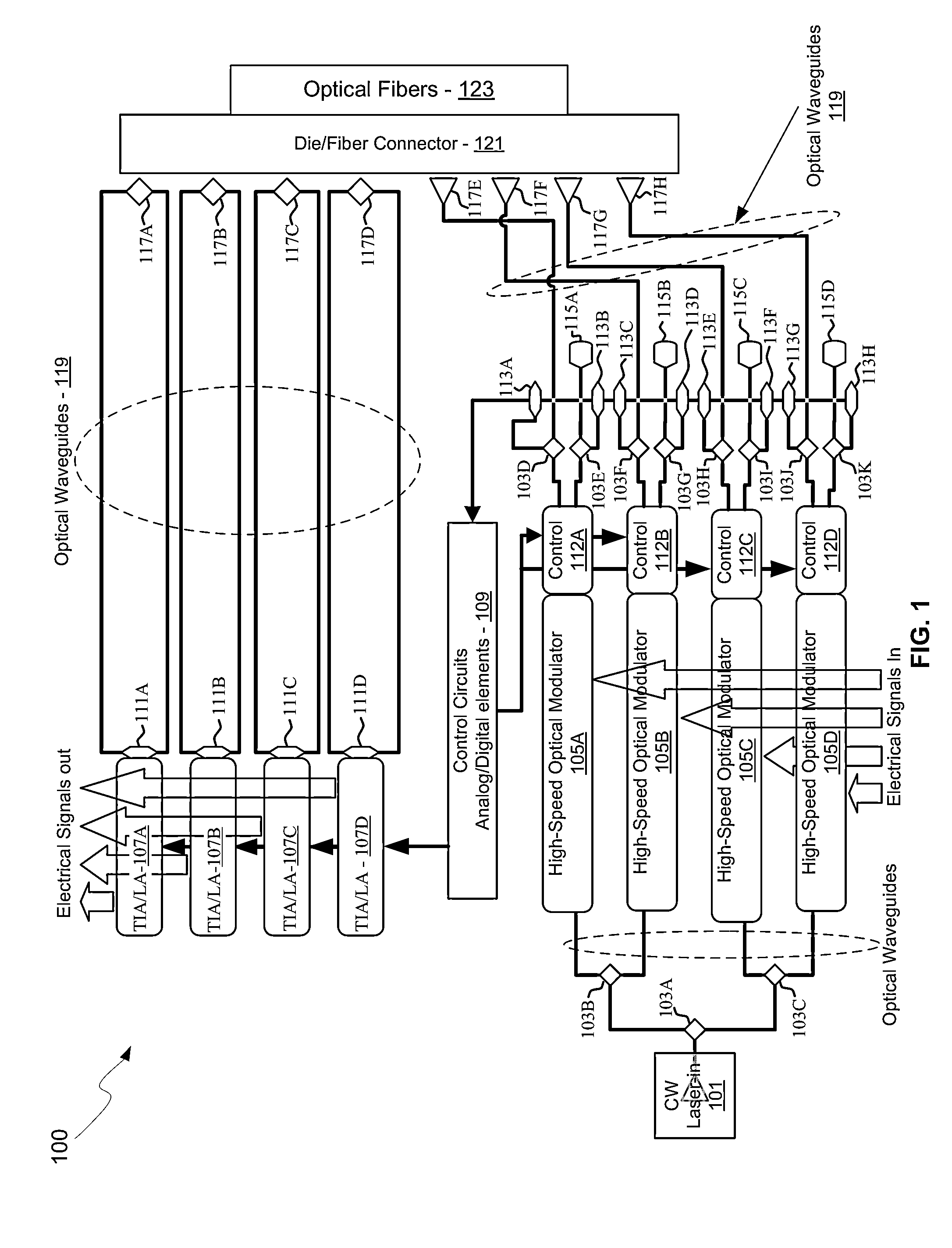
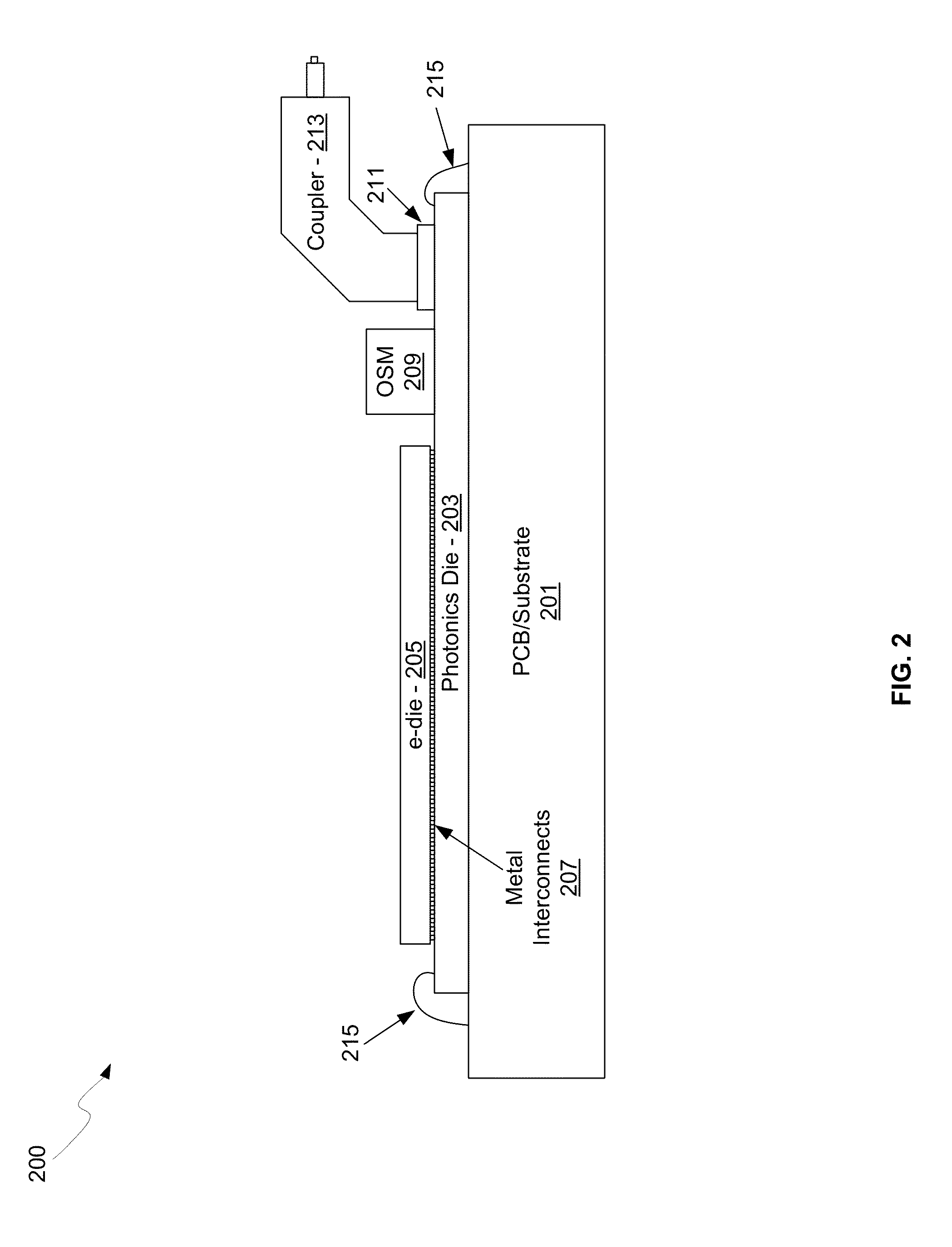
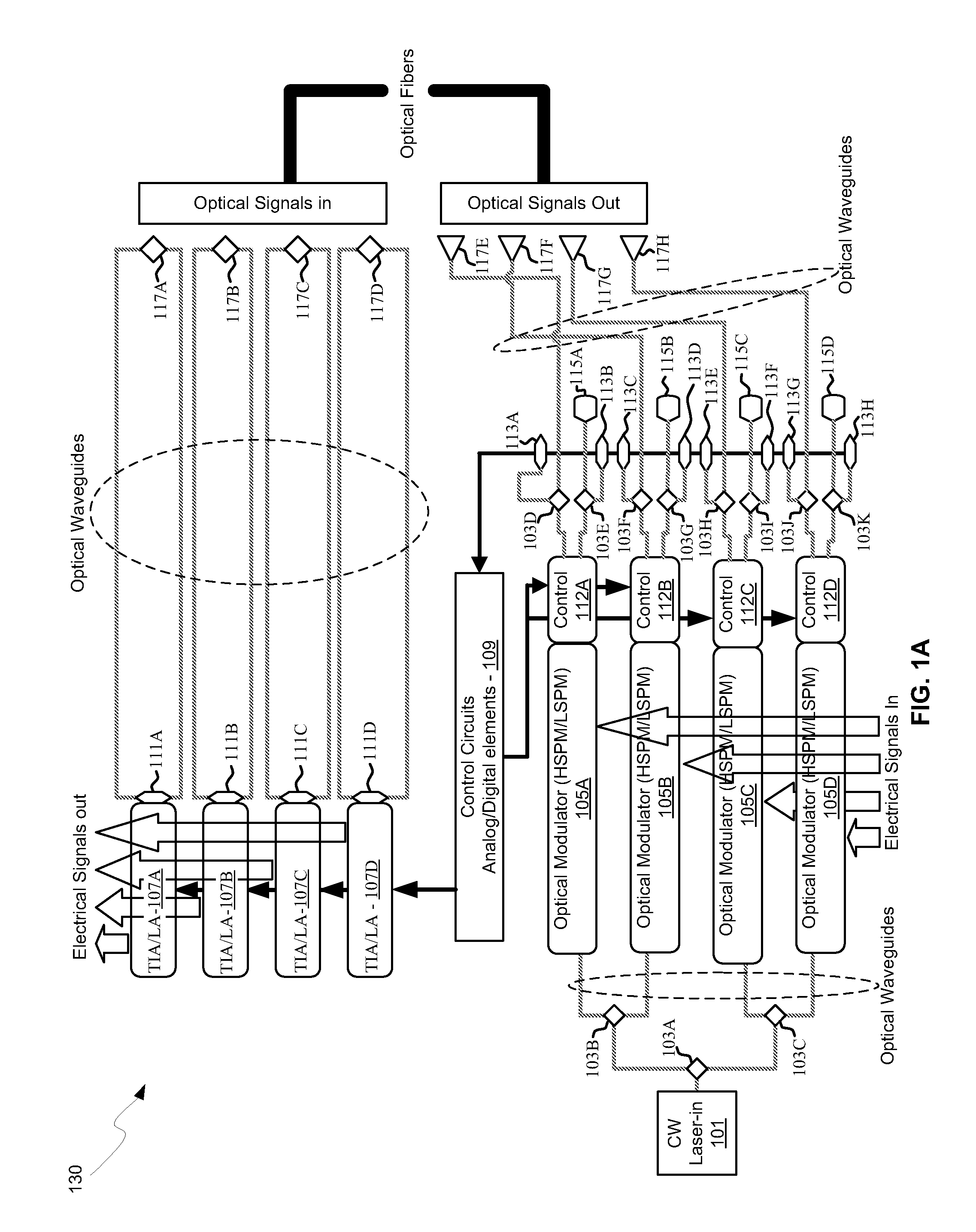
Method and system for an optical coupler for silicon photonics devices
Methods and systems for an optical coupler for photonics devices are disclosed and may include a photonics transceiver comprising a silicon photonics die, an optical source module, and a fiber connector for receiving optical fibers and including a die coupler and an optical coupling element. The die coupler may be bonded to a top surface of the photonics die and aligned above an array of grating couplers. The optical coupling element may be attached to the die coupler and the electronics die and the source module may be bonded to the top surface of the photonics die. A continuous wave (CW) optical signal may be received in the photonics die from the optical source module. Modulated optical signals may be received in the photonics die from optical fibers coupled to the fiber connector.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical Transceiver module
InactiveUS20100092128A1Small sizeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsGrating
An optical transceiver module includes a semiconductor laser that emits light along a first optical axis. A grating coupler, located in a plane including the first optical axis, diffracts the emitted light out of the plane and into an external optical system. A photodetector receives incoming light from the external optical system on a second optical axis that passes through the grating coupler at an angle to the plane. The photodetector can be placed parallel to the plane, directly above or below the grating coupler, to create an extremely compact optical transceiver module.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
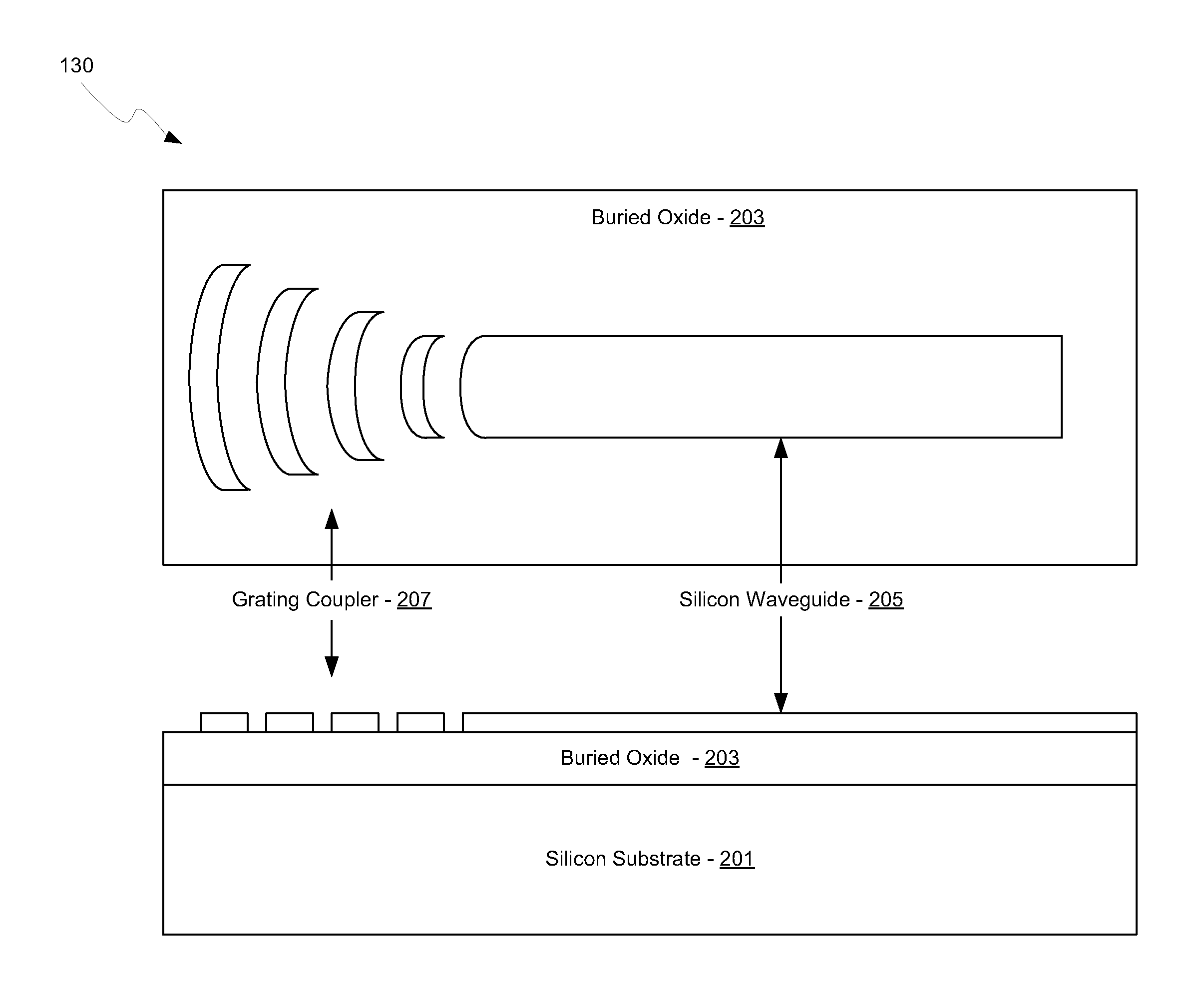
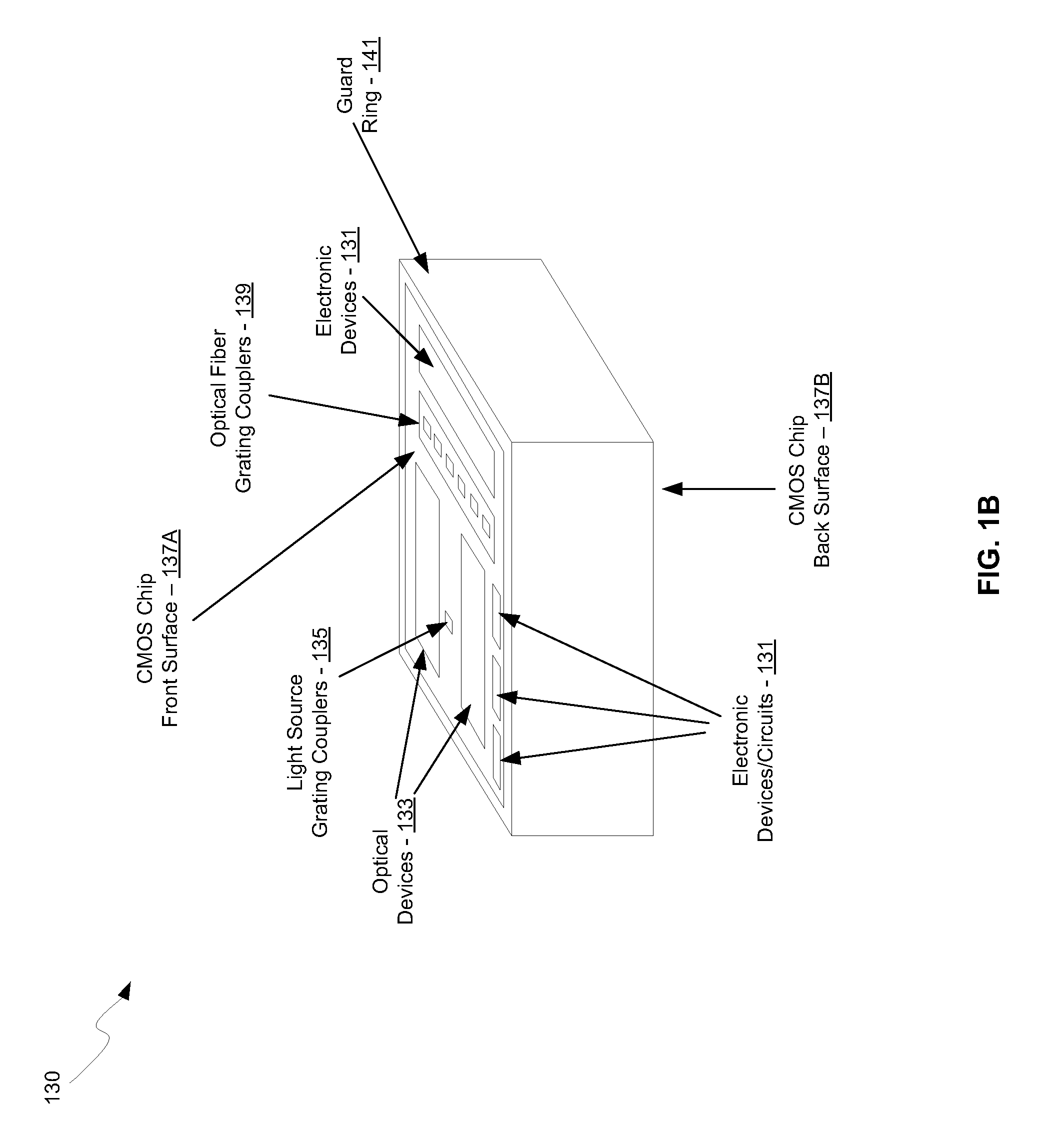
Method and System For Coupling Optical Signals Into Silicon Optoelectronic Chips
ActiveUS20100111473A1PhotometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingGrating coupling
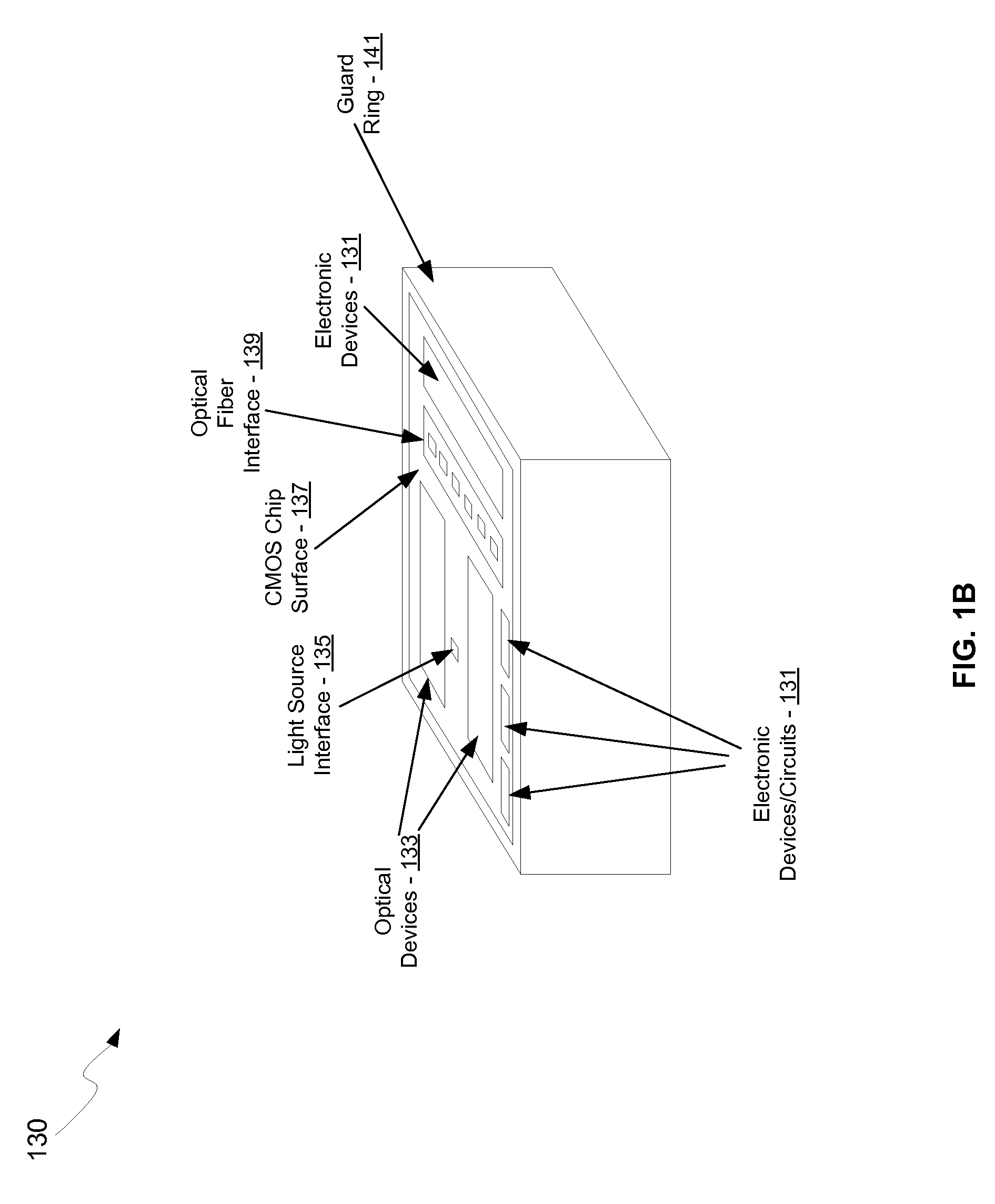
A method and system for coupling optical signals into silicon optoelectronic chips are disclosed and may include coupling one or more optical signals into a back surface of a CMOS photonic chip comprising photonic, electronic, and optoelectronic devices. The devices may be integrated in a front surface of the chip and one or more grating couplers may receive the optical signals in the front surface of the chip. The optical signals may be coupled into the back surface of the chip via one or more optical fibers and / or optical source assemblies. The optical signals may be coupled to the grating couplers via a light path etched in the chip, which may be refilled with silicon dioxide. The chip may be flip-chip bonded to a packaging substrate. Optical signals may be reflected back to the grating couplers via metal reflectors, which may be integrated in dielectric layers on the chip.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Grating coupler and application thereof in polarization and wave length beam splitting
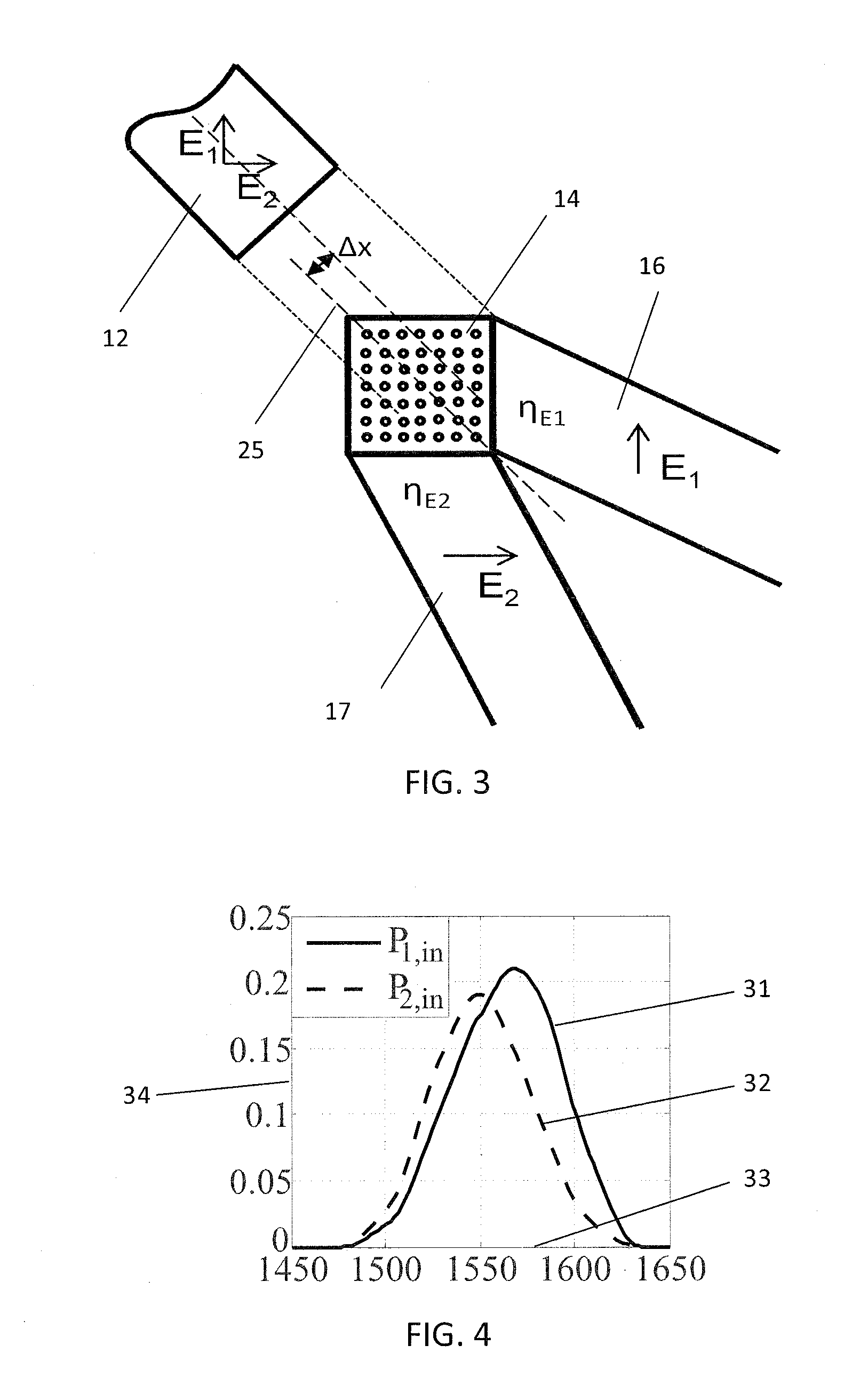
ActiveCN101556356AImprove coupling efficiencyAchieve full vertical couplingDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesGratingBlazed grating
The invention discloses a grating coupler, which sequentially comprises an upper cladding, a grating layer, a wave guide layer and a lower cladding from top to bottom. The grating layer adopts a binary blazed grating that is a one-dimension binary blazed grating or a two-dimension binary blazed grating. The binary blazed grating coupler provided by the invention can obtain high coupling efficiency and realize complete vertical coupling; besides, the preparation is easy. By adjusting a grating parameter, the grating coupler realizes that incident light is respectively coupled in different wave guides according to different polarization states or wave lengths, thus offering effective ways for polarization beam splitting, wavelength division multiplex, etc.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Electro-optic array interface
InactiveUS6982819B2Exquisite sensitivity of SPRCladded optical fibreNanoopticsAngle of incidenceRefractive index
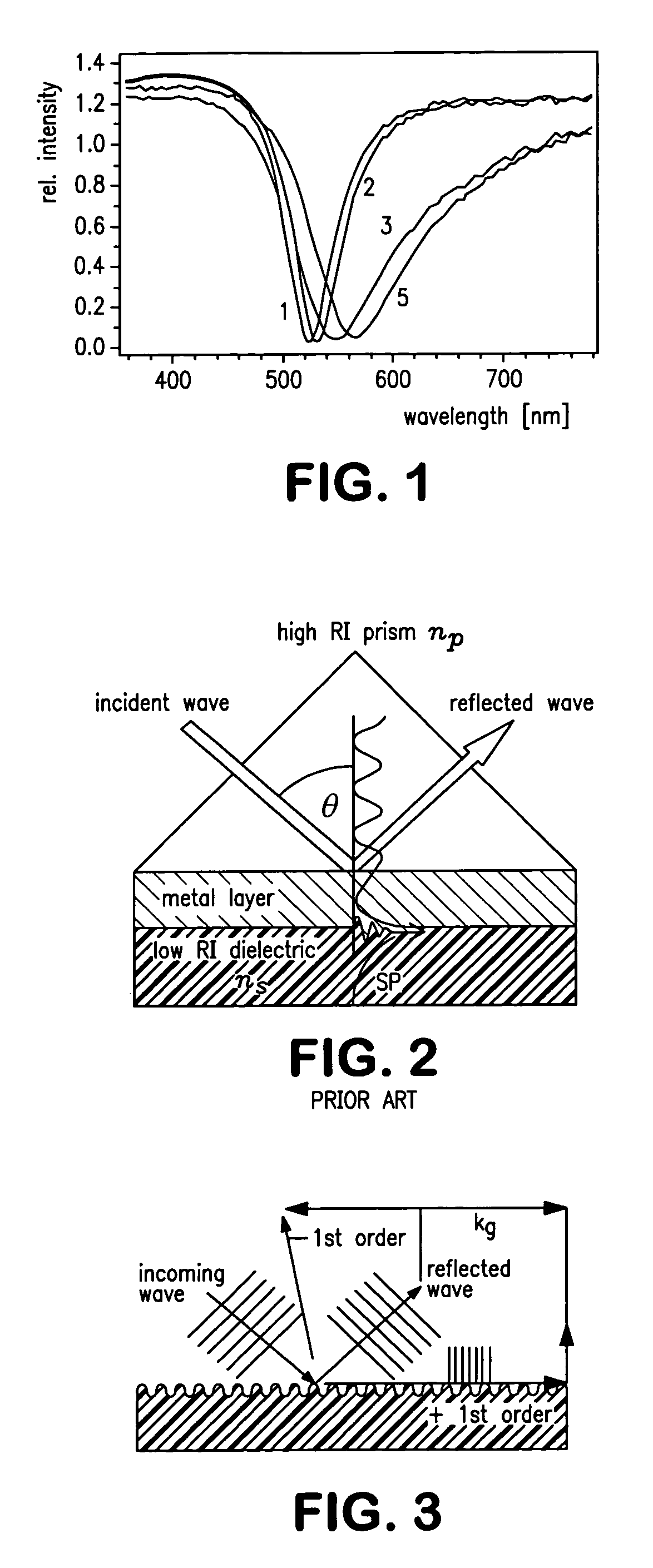
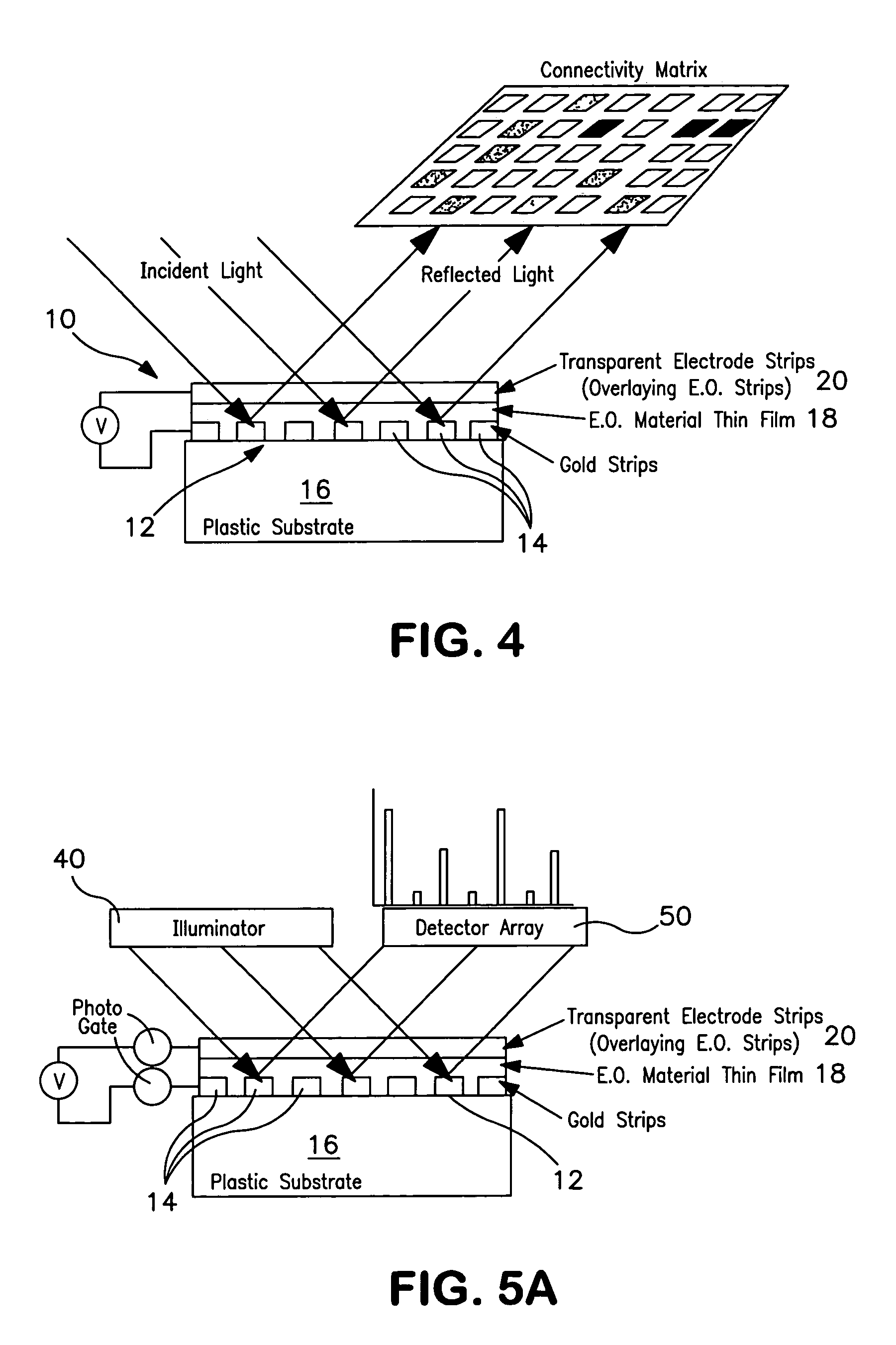
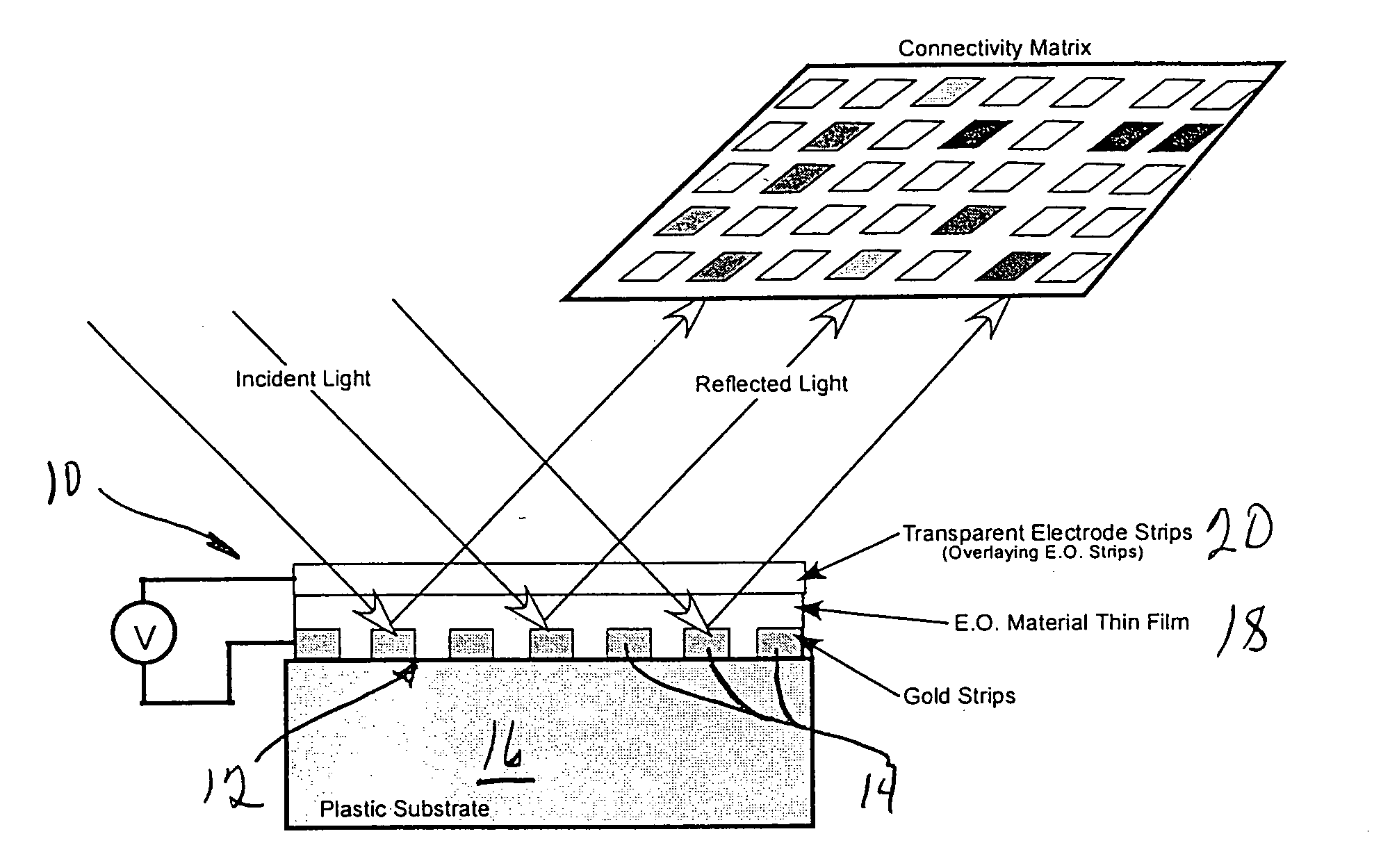
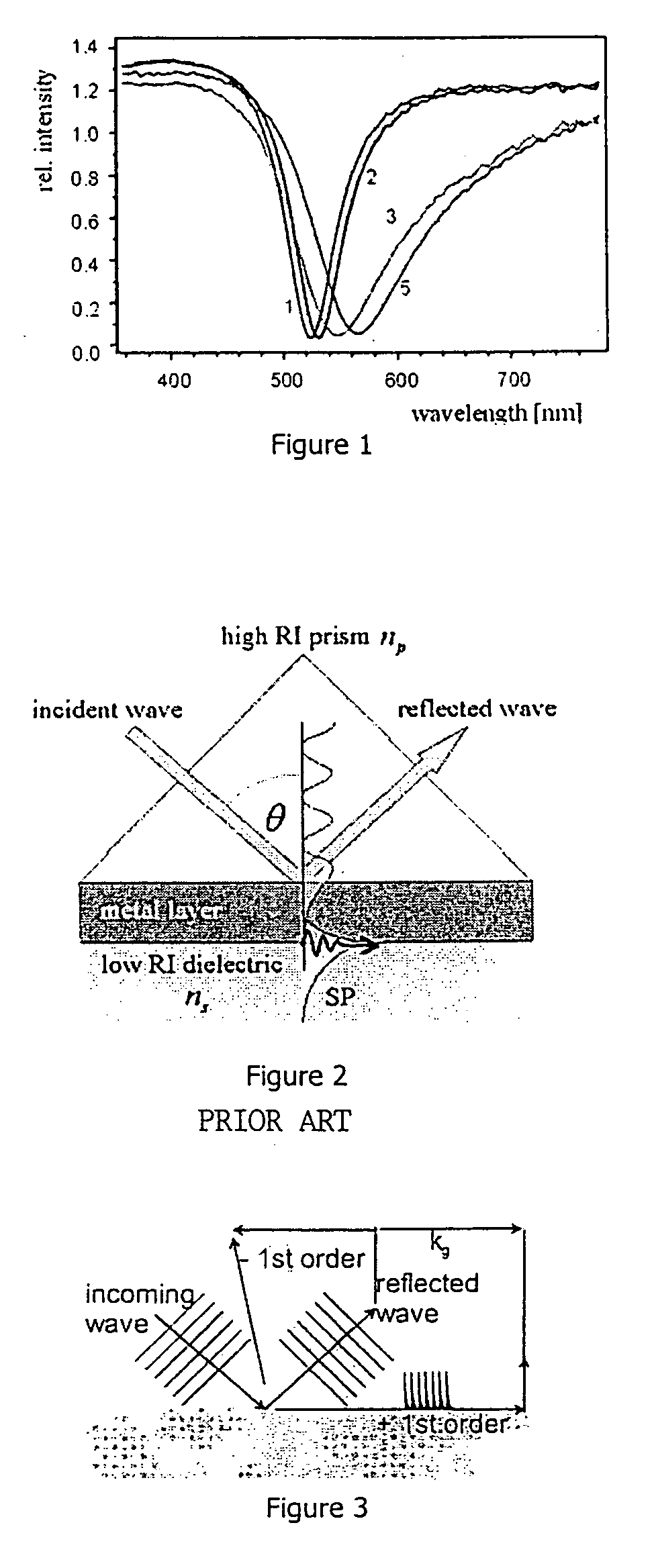
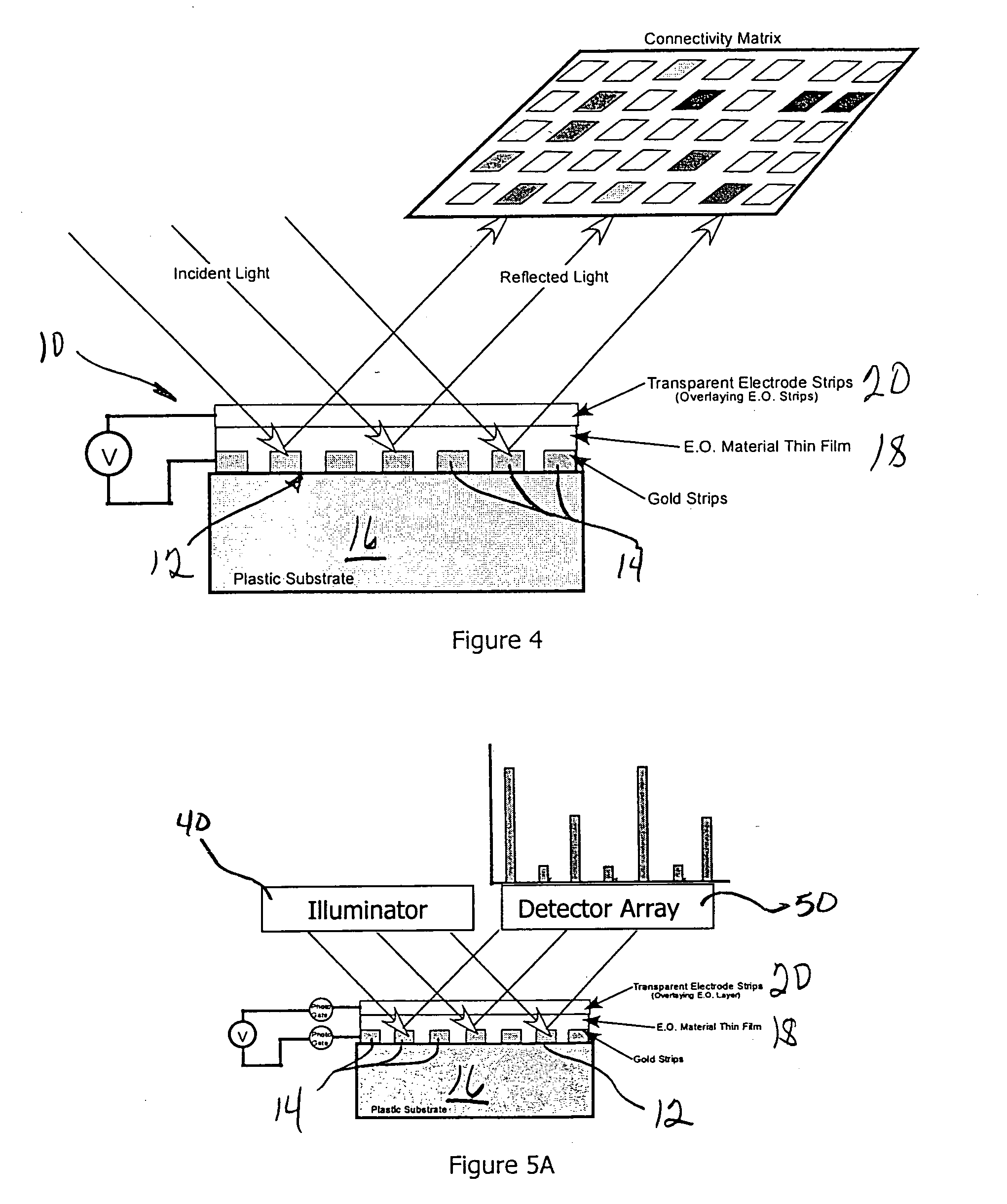
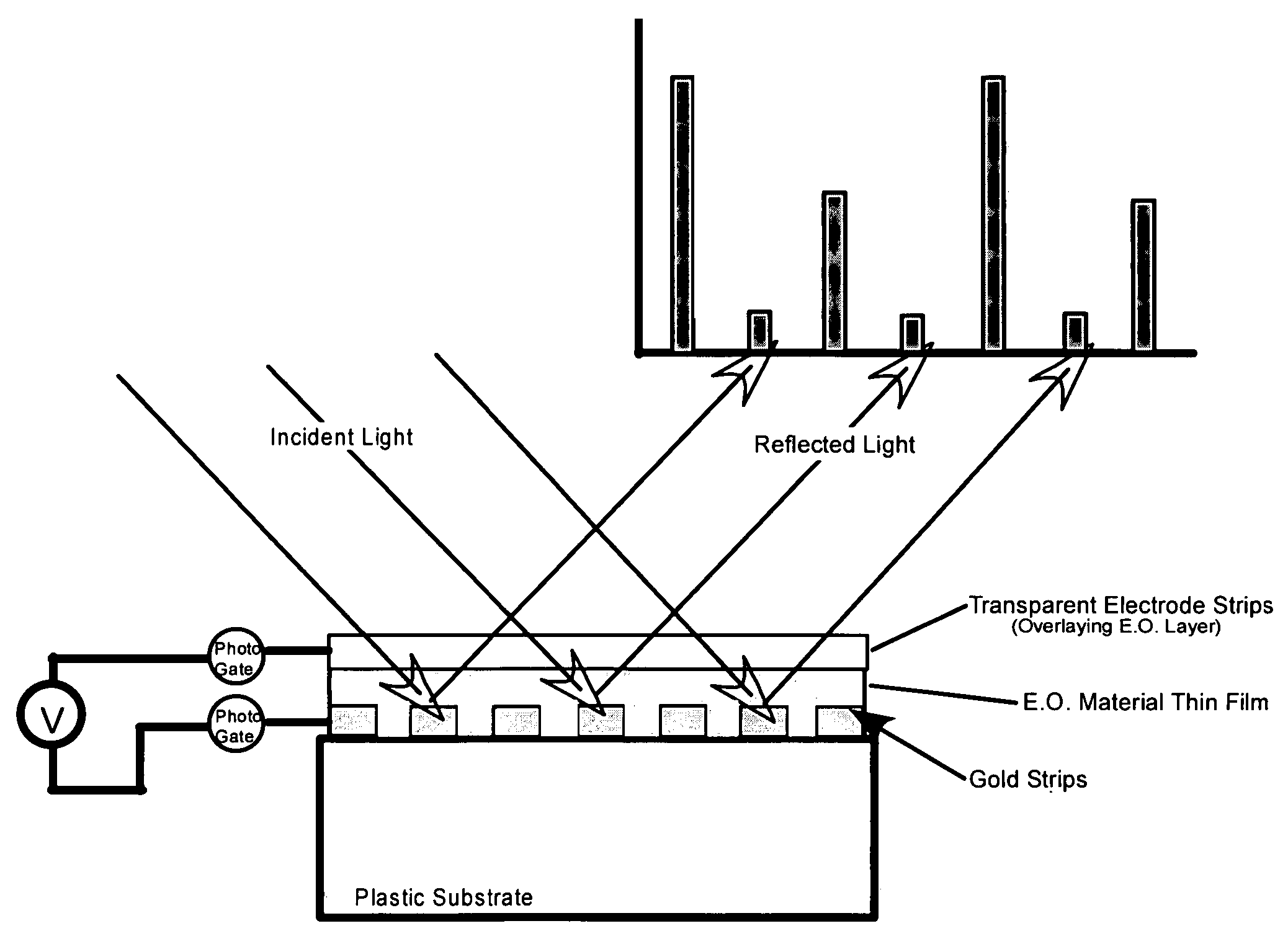
A grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator is disclosed. A electro-optic polymer dielectric is deposited on the metallic surface of a diffraction grating to provide a metal / dielectric interface. A surface plasmon will propagate at the metal / dielectric interface in a resonant condition, e.g., when the metal surface is illuminated by transverse magnetic (TM) polarized light of the appropriate wavelength, angle of incidence and phase velocity. In the present invention, phase velocity is controlled by the diffraction grating. A transparent electrode deposited on the electro-optic layer allows an electrical potential to be applied across the electro-optic polymer. The applied electrical potential (voltage) changes the index of refraction of the electro-optic polymer, thereby disrupting the resonant condition to produce an optically detectable change in reflectance of incident light from the metal layer. The disclosed grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator may be configured as an electronically or optically addressable array.
Owner:CIENCIA
Hybrid silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling
A silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling comprises wafer bonding an active III-V semiconductor material above a grating coupler made on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer. This bonding does not require any alignment, since all silicon processing can be done before bonding, and all III-V processing can be done after bonding. The grating coupler acts to couple the vertically emitted light from the hybrid vertical cavity into a silicon waveguide formed on an SOI wafer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Use of waveguide grating couplers in an optical mux/demux system
A group of waveguide grating couplers is disposed on a semiconductor substrate. The grating couplers are all within a spot illuminated on the substrate by a light from an optical fiber. The light propagating in the fiber is wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) and consists of several channels. Within the group of grating couplers, at least one grating coupler is designed to be tuned to each of the channels. The group of grating couplers demultiplexes the channels propagating in the fiber. A group of waveguide grating couplers can also be used to multiplex several channels of light into an optical fiber. Single mode and multimode fiber can be used to carry the multiplexed channels of light in an optical multiplexing and demultiplexing system.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Light source packaging structure, and positioning and coupling method thereof
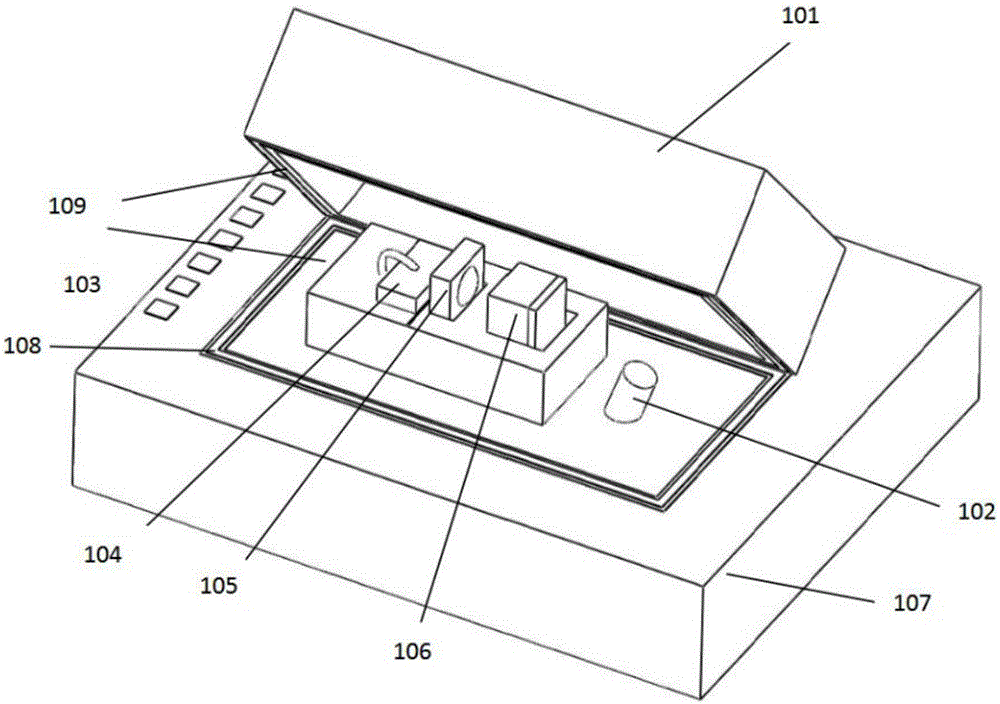
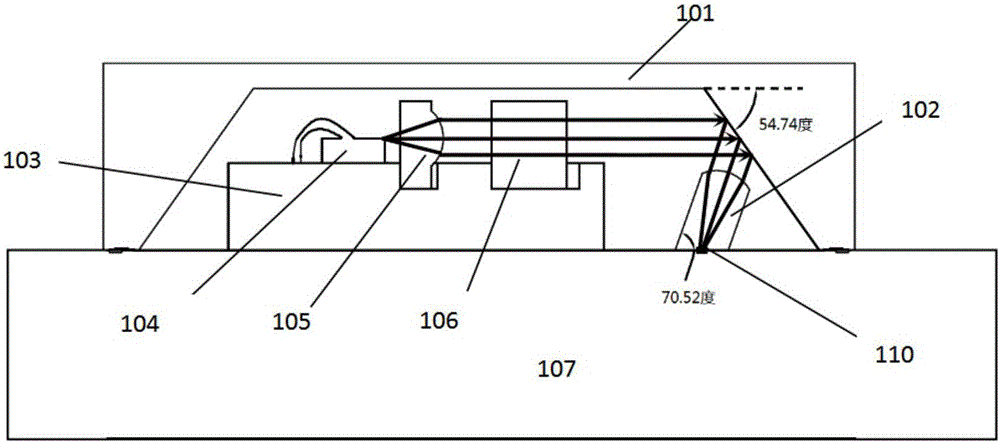
ActiveCN106019496AExtended service lifeInsulate from moistureCoupling light guidesPosition toleranceGrating
The invention provides a light source packaging structure, and a positioning and coupling method thereof. The light source packaging structure comprises a sealing box cover (101), a C lens (102), a silicon based heat sink (103), a laser chip (104), an isolator assembly (106), and a silicon light chip (107). The laser chip (104), a collimating lens (105), and the isolator assembly (106) are sequentially disposed on the silicon based heat sink (103). The C lens (102) is aligned with the grating coupler (110) of the silicon light chip (107) in a fixed and coupled manner. The sealed box cover (101) is provided with an inclined inner wall used to reflect light emitted by the laser chip (104) to the C lens, and the lower surface of the C lens (102) is provided with a polishing surface matched with the incident angle of the reflected light. The side of the C lens (102) inclined toward the direction away from the silicon based heat sink (103), and the optical axis of the C lens (102) is consistent with the transmission direction of the light, and the main light is superposed with the optical axis. A coupling structure is compact, and position tolerance is large.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Grating coupler for inter-chip optical coupling
ActiveUS20150260913A1Reduce layeringReduce absorptionLaser optical resonator constructionCoupling light guidesGratingGrating coupling
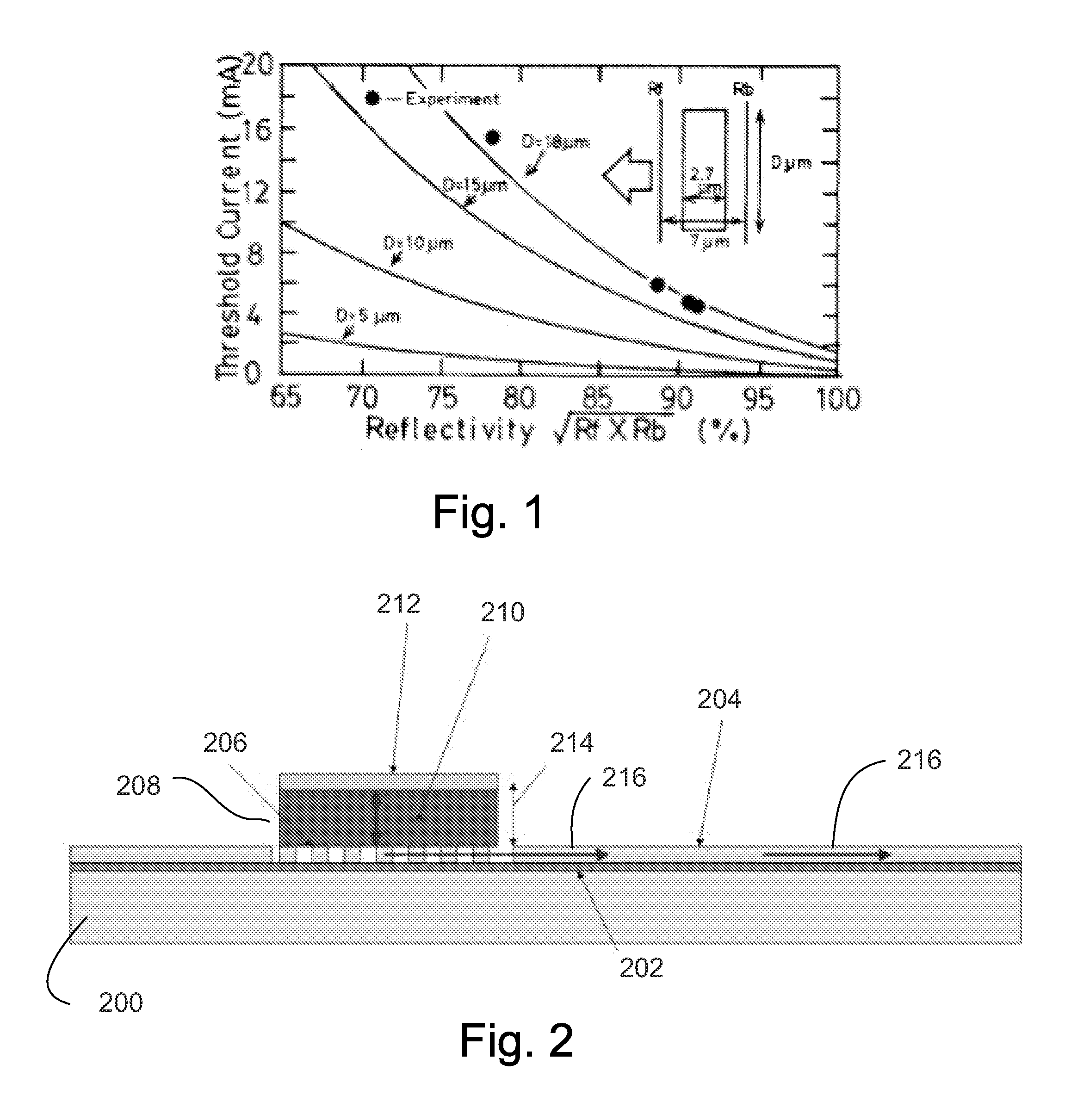
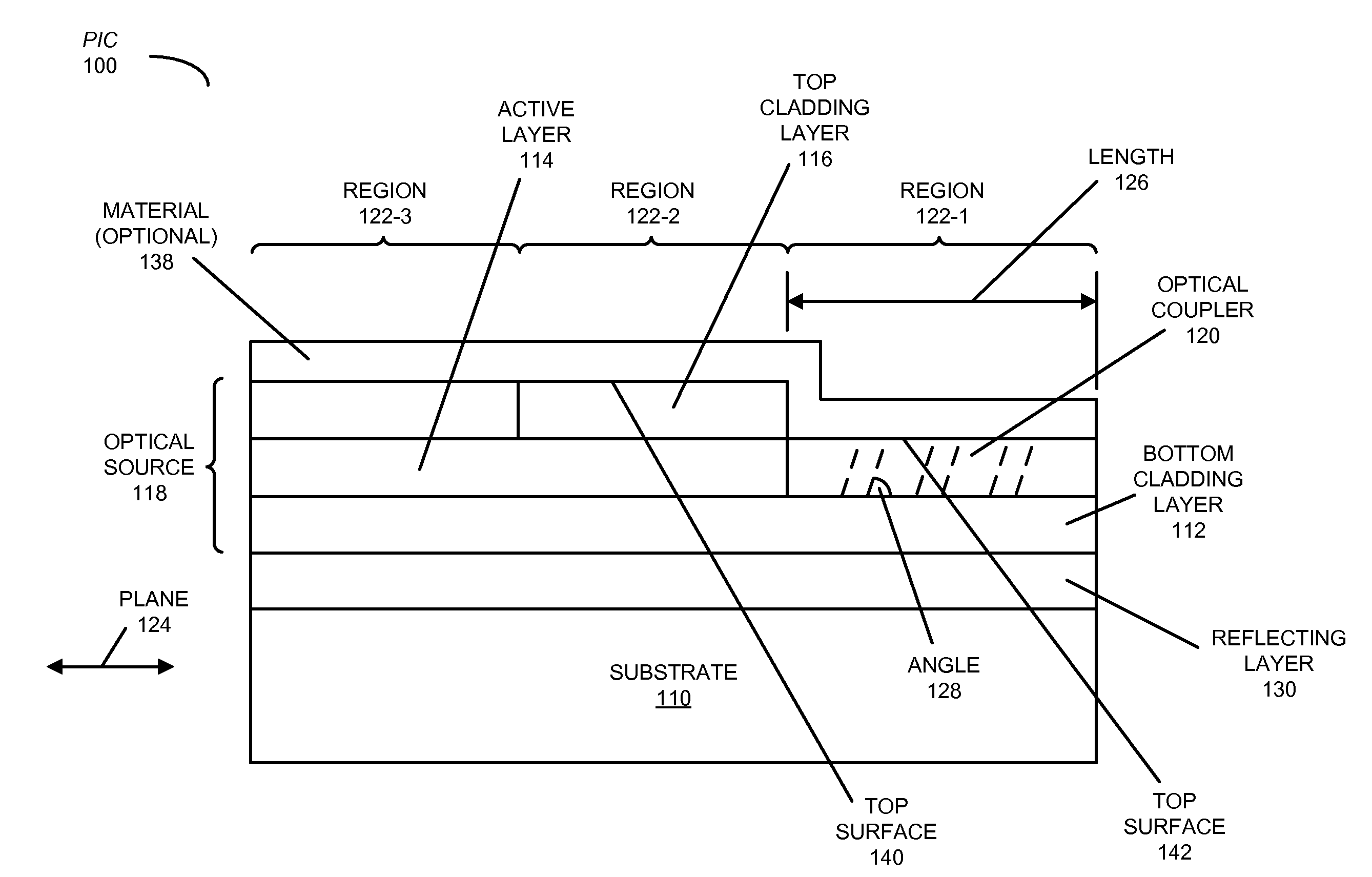
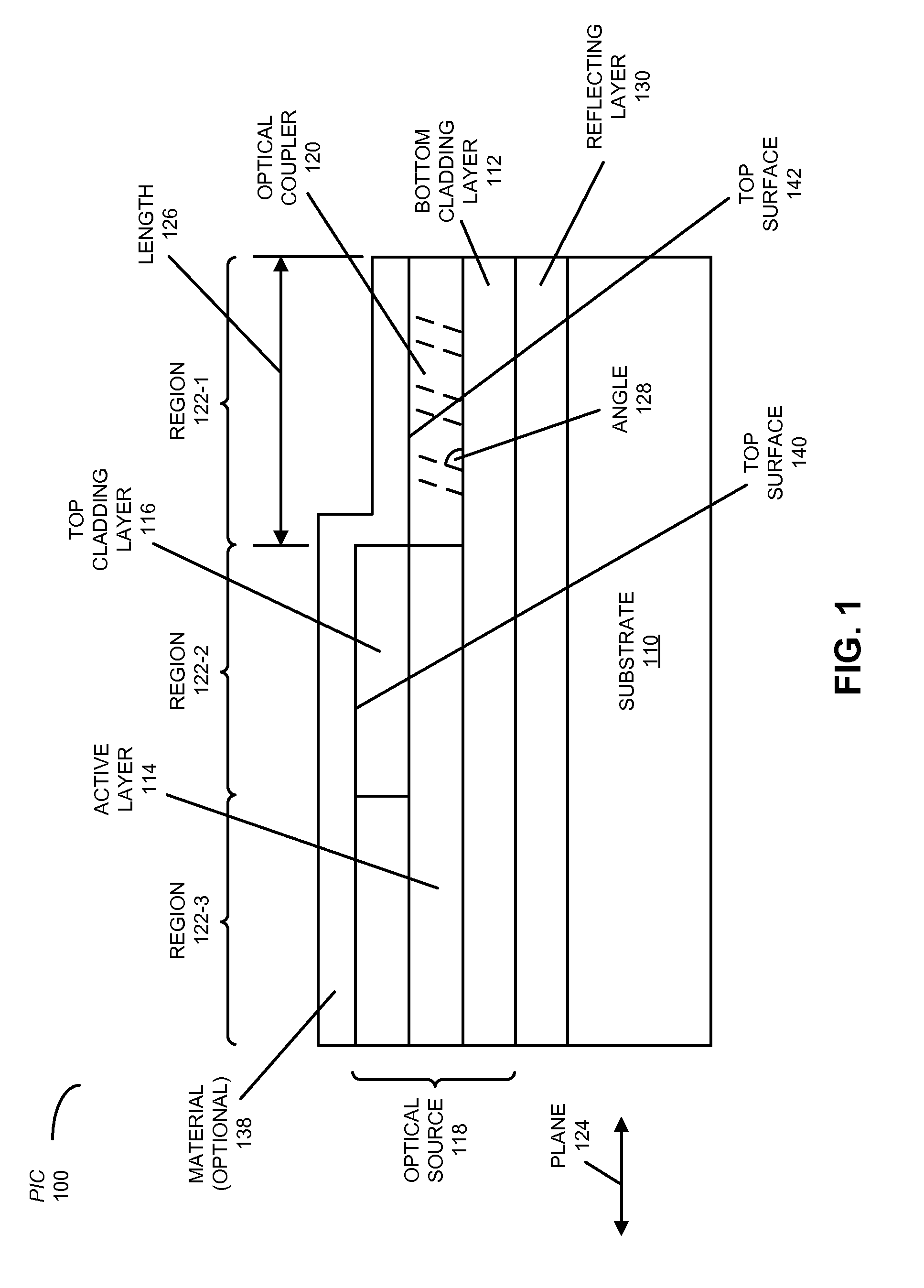
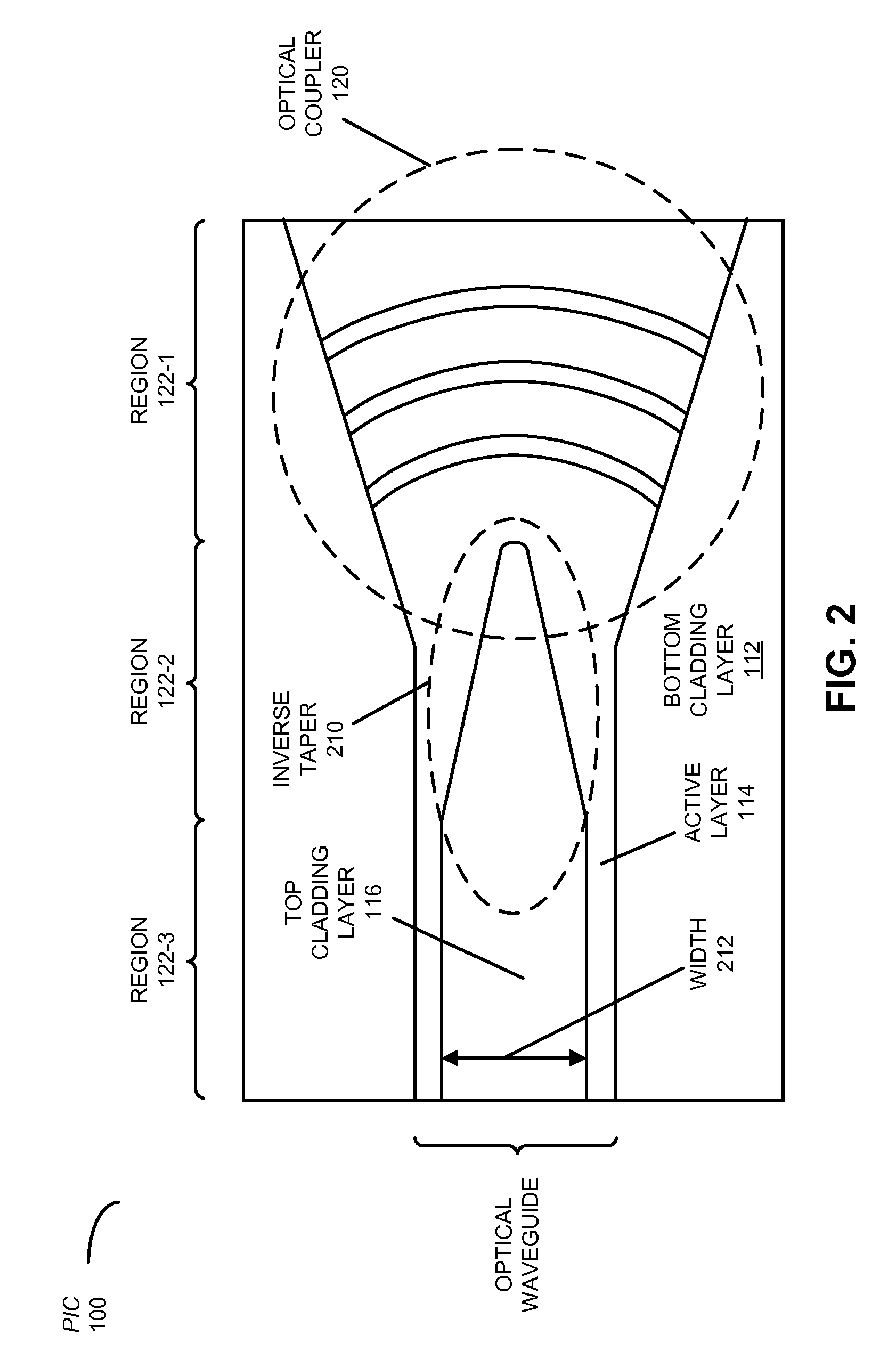
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) that includes an optical source that provides an optical signal having a wavelength is described. This optical source includes a reflecting layer, a bottom cladding layer, an active layer (such as a III-V semiconductor) having a bandgap wavelength that exceeds that of silicon, and a top cladding layer. Moreover, an optical coupler (such as a grating coupler) that couples the optical signal out of a plane of the active layer is included in a region of the active layer. In this region, the top cladding layer is absent. Furthermore, in an adjacent region, the top cladding layer includes an inverse taper so that the top cladding layer is tapered down from a width distal from the region. In conjunction with the optical coupler, the inverse taper may facilitate low-loss optical coupling of the optical signal between the PIC and another PIC.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
3D photonic integration with light coupling elements
InactiveCN107111060AEasy to integrateLaser detailsCoupling light guidesPhotodetectorIntegrated electronics
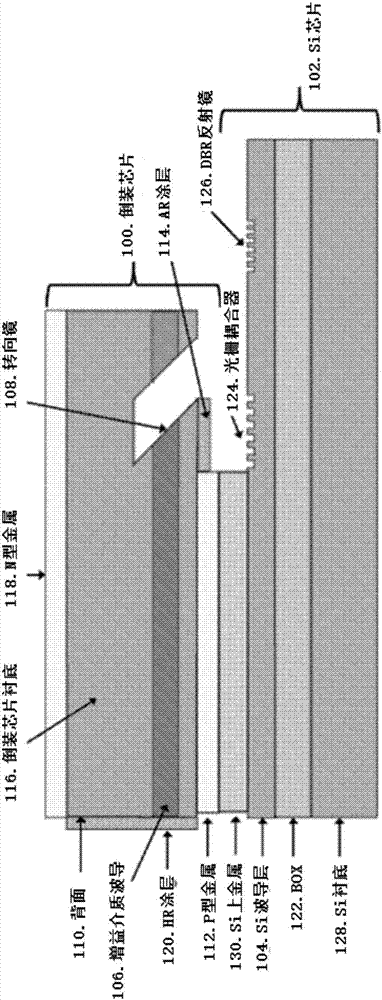
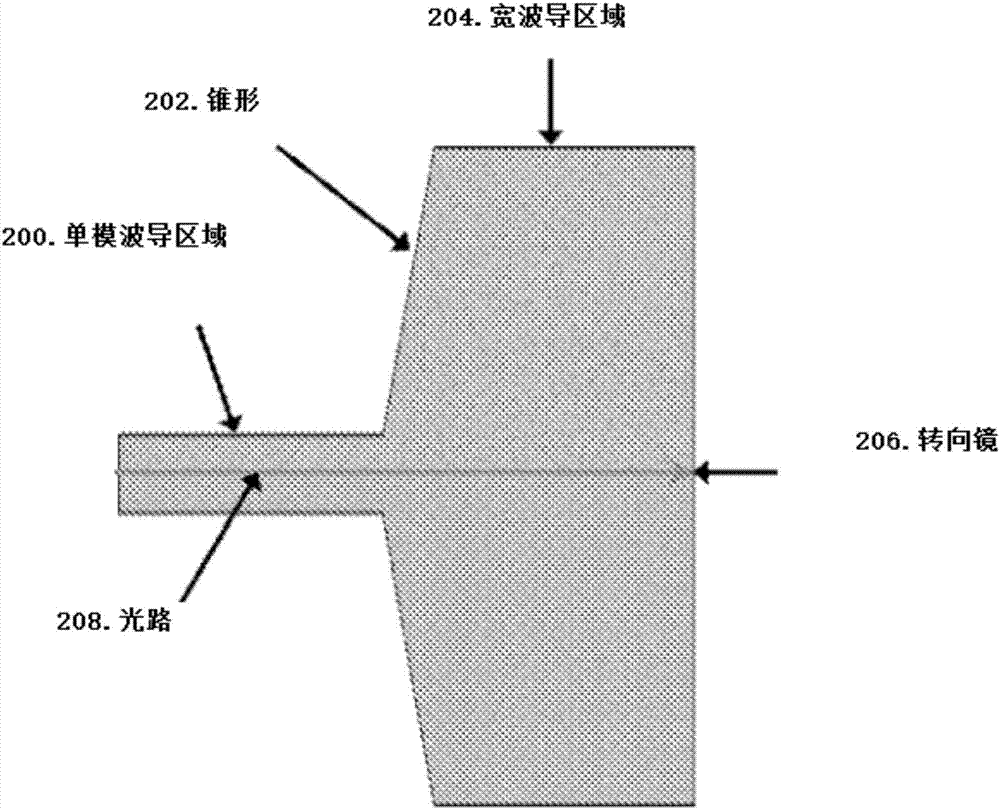
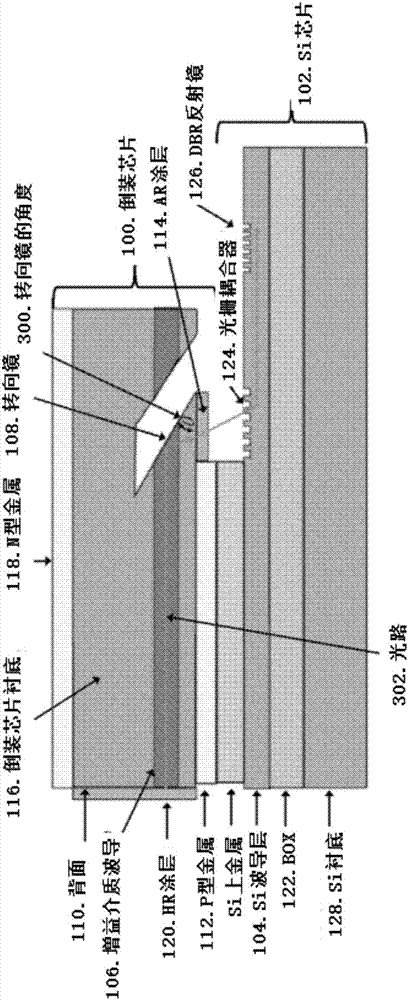
Methods for realizing integrated lasers and photonic integrated circuits on complimentary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible silicon (Si) photonic chips, potentially containing integrated electronics, are disclosed. The integration techniques rely on light coupling with integrated light coupling elements such as turning mirrors, lenses, and surface grating couplers. Light is coupled from between two or more substrates using the light coupling elements. The technique can realize integrated lasers on Si where a gain flip chip (the second substrate) is bonded to a Si chip (the first substrate) and light is coupled between a waveguide in the gain flip chip to a Si waveguide by way of a turning mirror or grating coupler in the flip chip and a grating coupler in the Si chip. Integrated lenses and other elements such as spot-size converters can also be incorporated to alter the mode from the gain flip chip to enhance the coupling efficiency to the Si chip. The light coupling integration technique also allows for the integration of other components such as modulators, amplifiers, and photodetectors. These components can be waveguide-based or non-waveguide based, that is to say, surface emitting or illuminating.
Owner:BIOND PHOTONICS
Optical grating coupler and optical signal coupling method
InactiveCN103777282AImprove working bandwidthSimple structureCoupling light guidesTime domainGrating
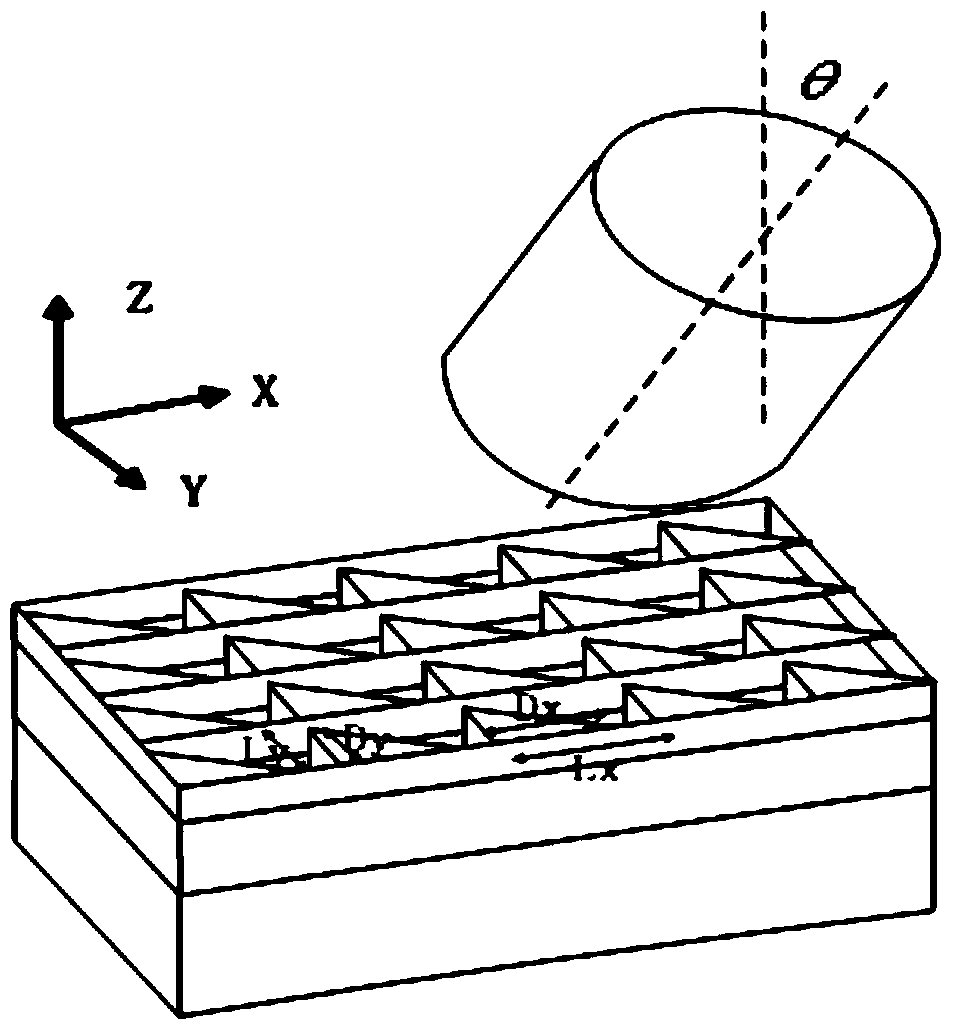
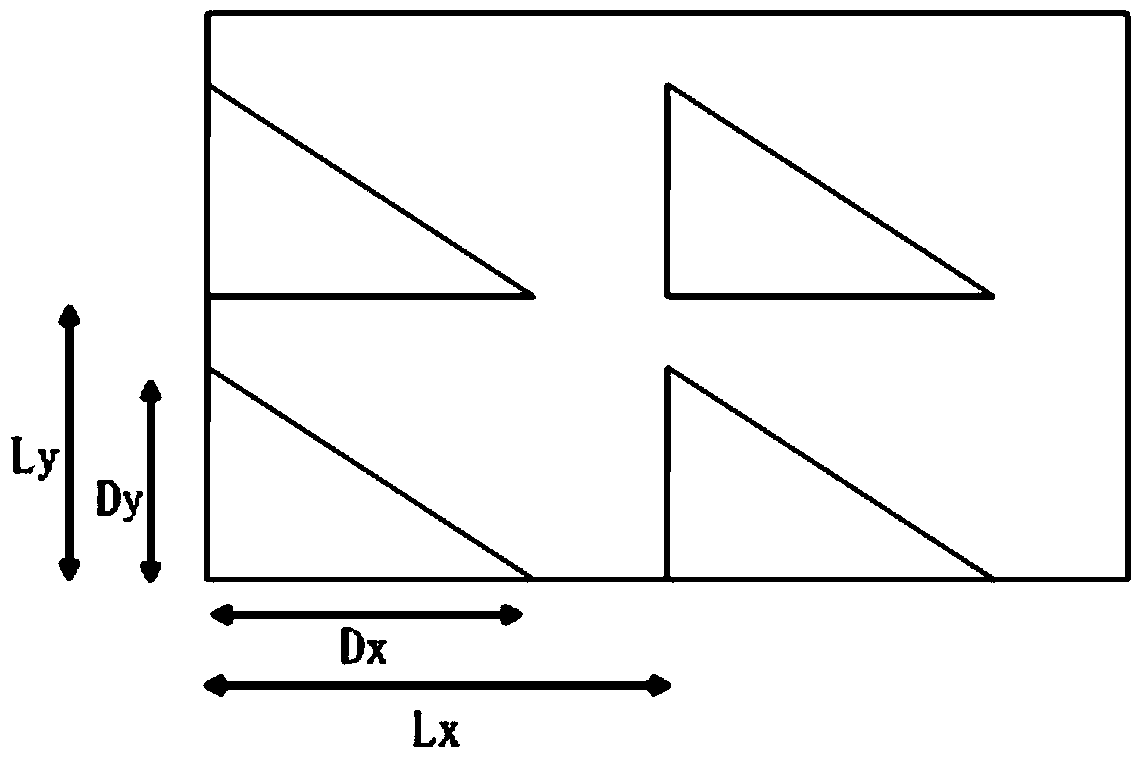
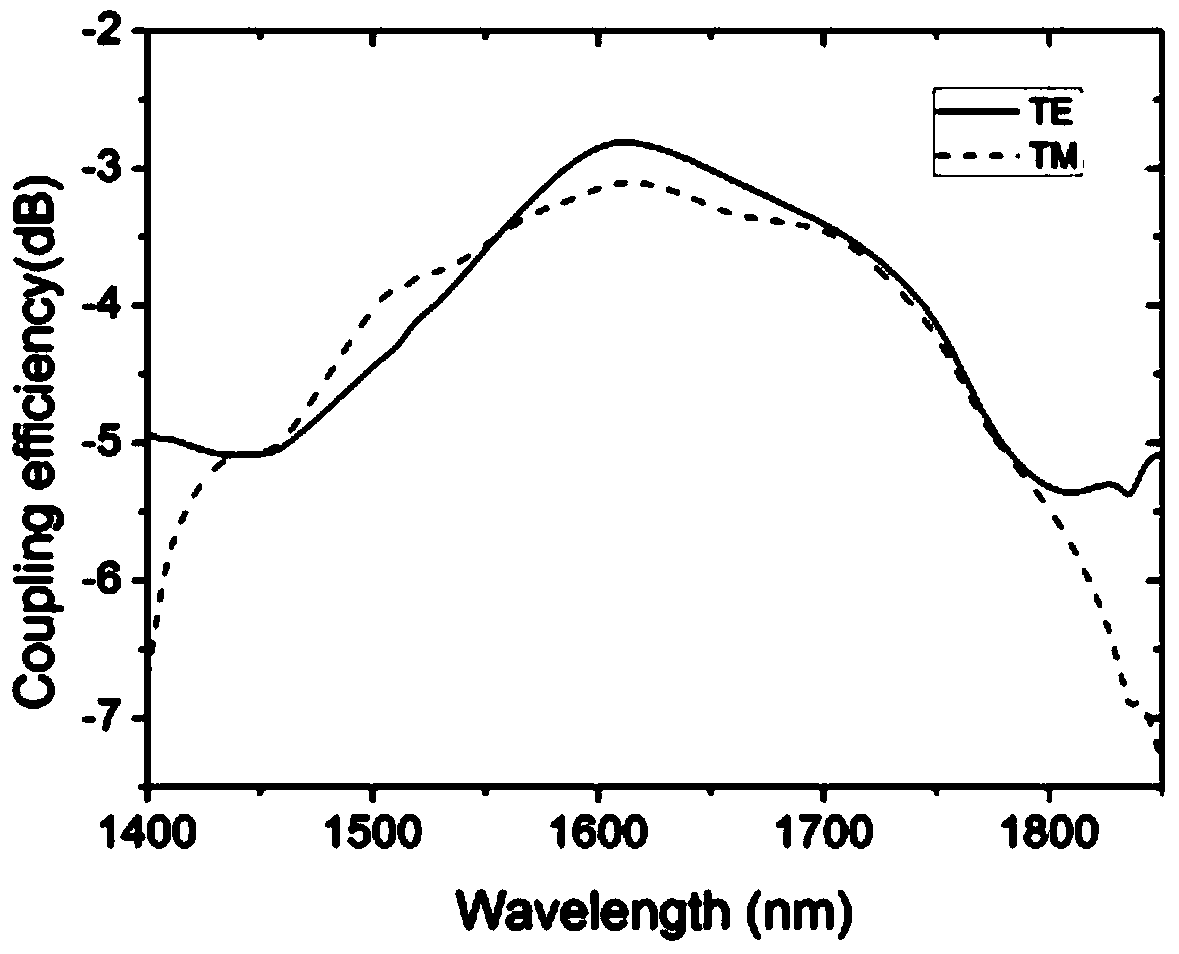
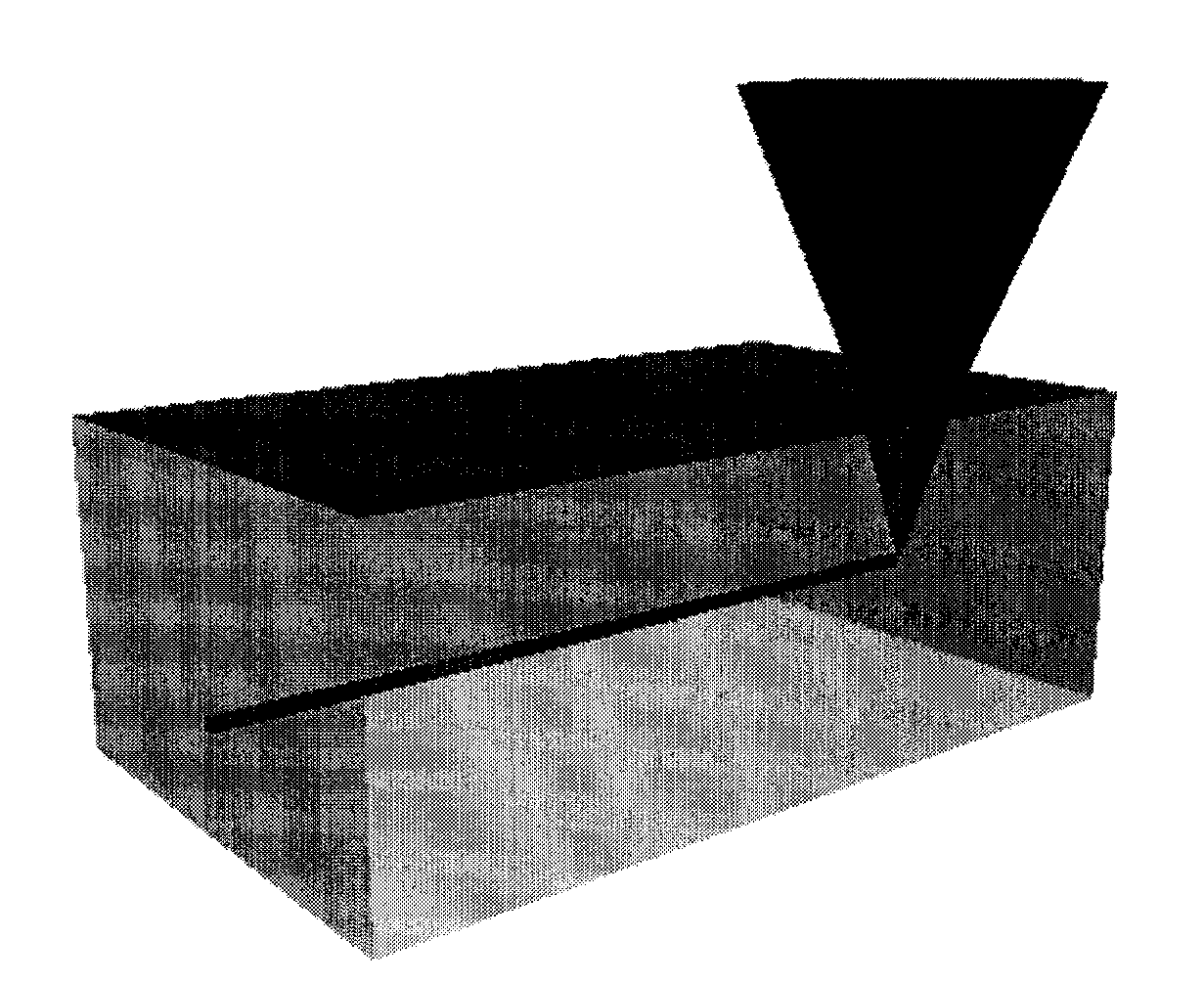
The invention relates to the technical field of optical communication and discloses an optical grating coupler and an optical signal coupling method. The optical grating coupler comprises a top silicon layer, a base silicon layer and a silicon dioxide layer, wherein the silicon dioxide layer is arranged on the upper surface of the base silicon layer, the top silicon layer is disposed on the upper surface of the silicon dioxide layer, the top silicon layer is of a structure formed by ranking at least two right triangles in the direction perpendicular to the light transmission direction, and received optical fibers face toward the rank structure of the right triangles. According to the optical grating coupler and the optical signal coupling method, through application of triangular optical gratings, work bandwidth of the optical grating coupler is increased, and applicability of the optical grating coupler is improved; besides, simulating calculation is performed through a three-dimensional time domain finite difference method so that TE and TM light coupling efficiencies are the same, optical grating structural parameters are determined, polarization insensitivity is achieved; the optical grating coupler has the advantages of being simple in structure, wide in work bandwidth, low in polarization loss and high in coupling efficiency.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical devices and digital laser method for writing waveguides, gratings, and integrated optical circuits
ActiveUS20090304331A1Short timeChange the refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical articlesGrating couplingLaser fabrication
The invention relates to devices having periodic refractive index modulation structures and fabrication methods for the devices using a laser means. By focusing a pulsed laser beam into a transparent material substrate, a path of laser modified volumes can be formed with modified refractive index compared with the unprocessed material. By selecting appropriate laser parameters and relative scan speed, the laser modified path defines an optical waveguide. Separation distance of the individual modified volumes define a periodic modification pattern along the waveguide path, so that the waveguide structures also exhibit grating responses, for example, as spectral filters, Bragg reflectors, grating couplers, grating sensors, or other devices. This method of direct laser fabrication enables one-step fabrication and integration of periodic or aperiodic refractive-index modulation devices together with optical waveguiding properties to enable low-cost, multifunctional I D, 2D or 3D optical circuit fabrication for simple and complex applications.
Owner:HERMAN +1
Test systems and methods for chips in wafer scale photonic systems
ActiveUS20170082799A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptical waveguide light guideGratingPhotonic Chip
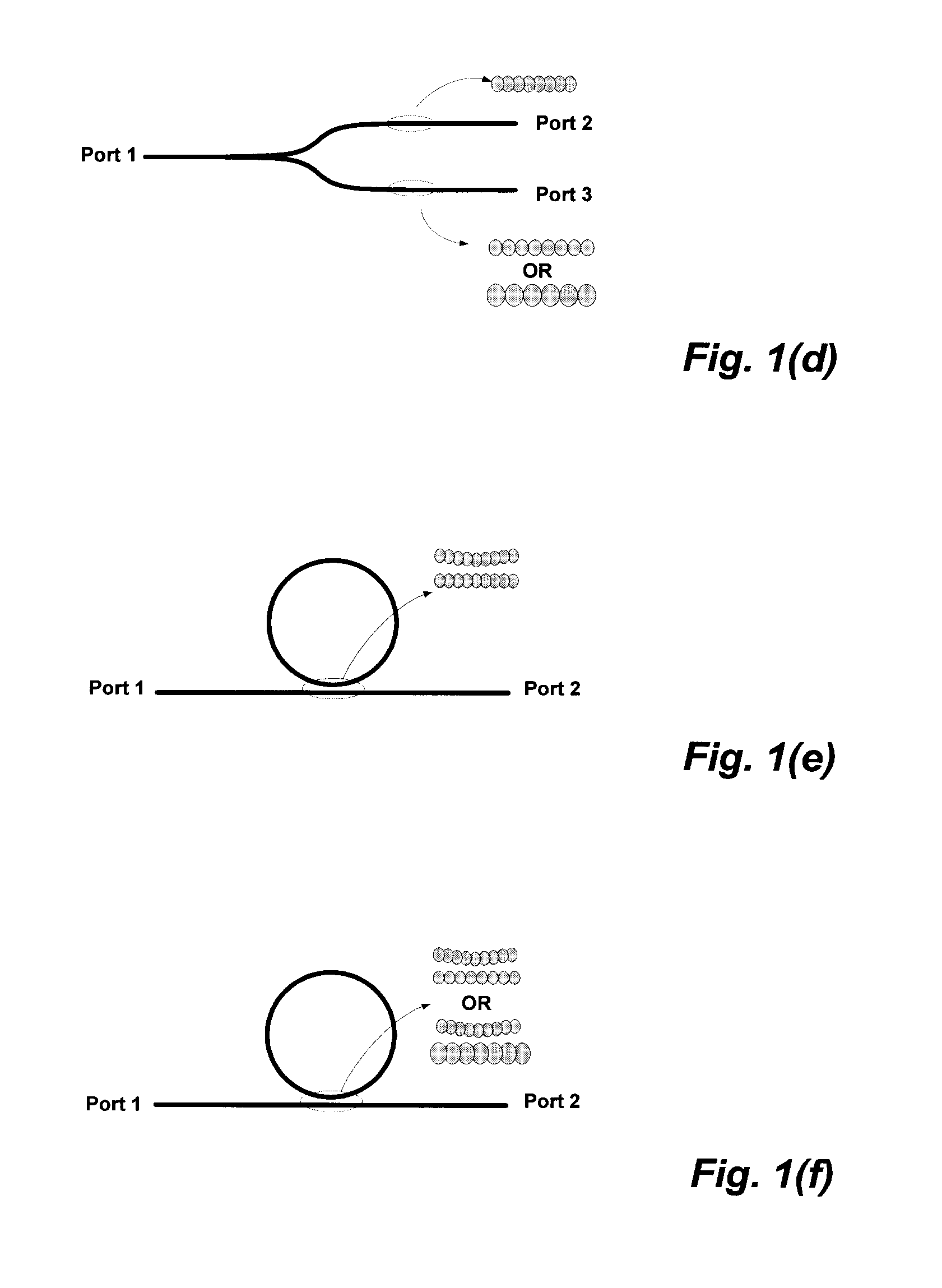
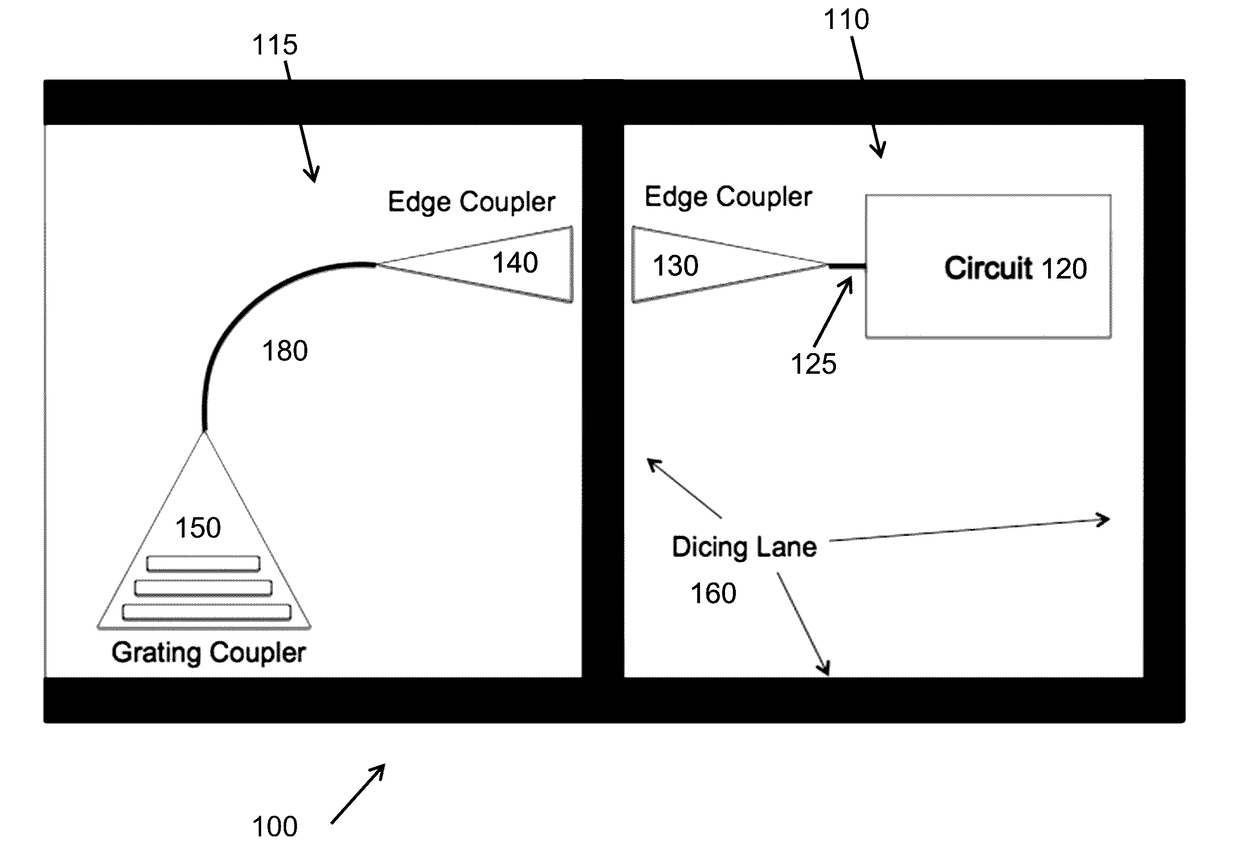
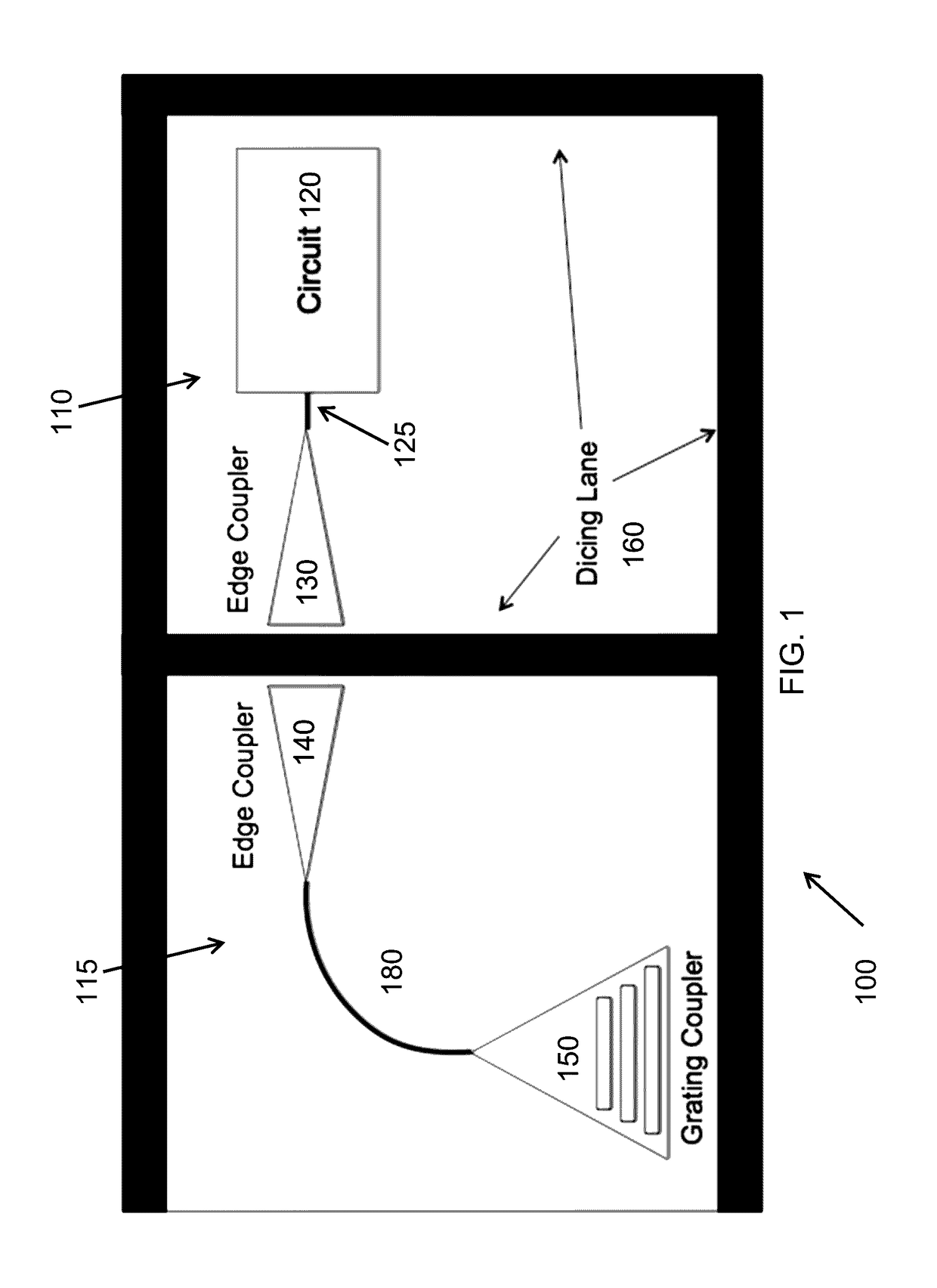
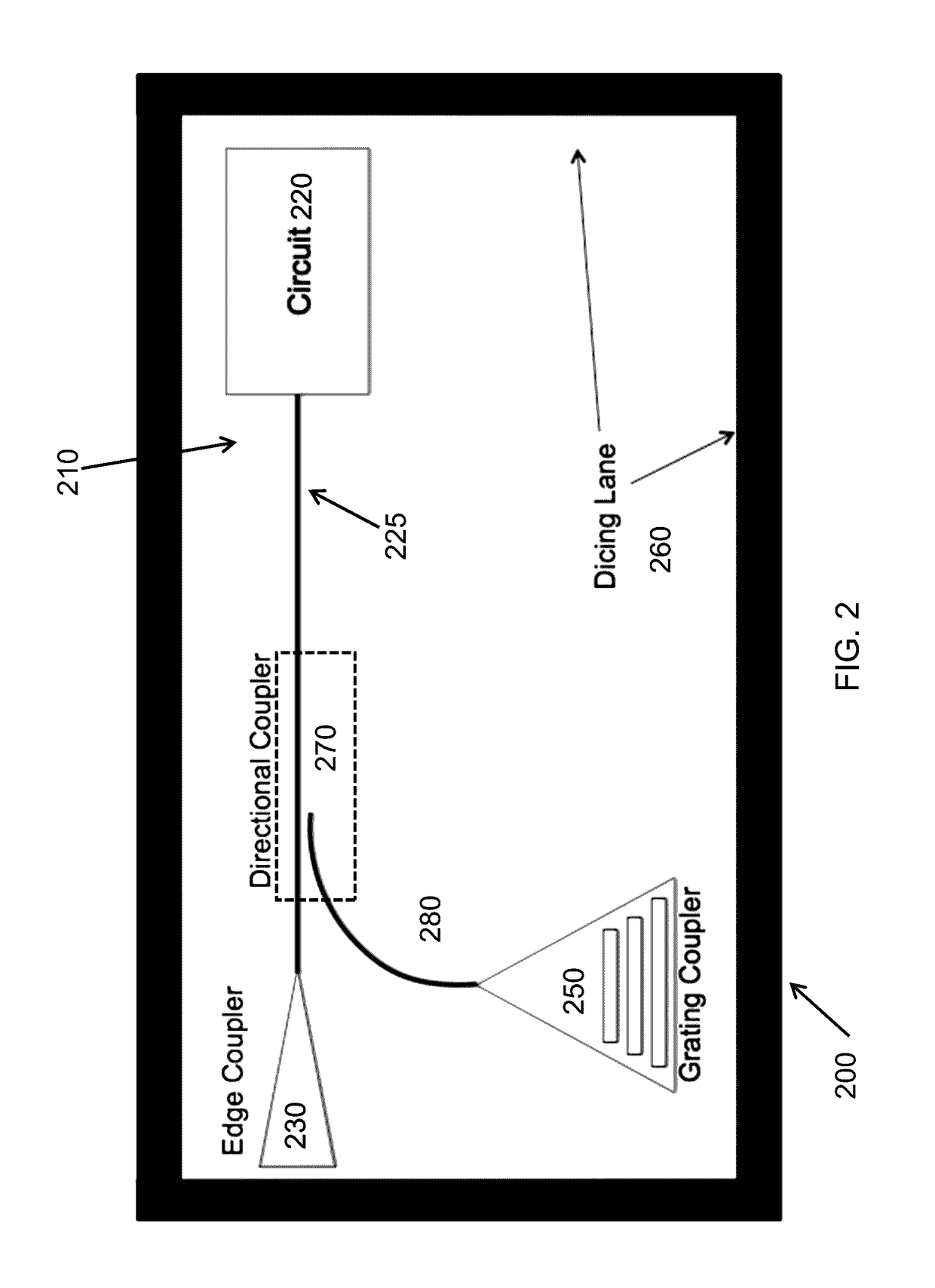
A qualification apparatus for a photonic chip on a wafer that leaves undisturbed an edge coupler that provides an operating port for the photonic devices or circuits on the chip during normal operation in order to not introduce extra loss in the optical path of the final circuit. The qualification apparatus provides an optical path that is angled with regard to the surface of the chip, for example by using a grating coupler. The qualification apparatus can be removed after the chip is qualified. Optionally, the qualification apparatus can be left in communication with the chip and optionally employed as an input port for the chip after the chip has been separated from other chips on a common substrate.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
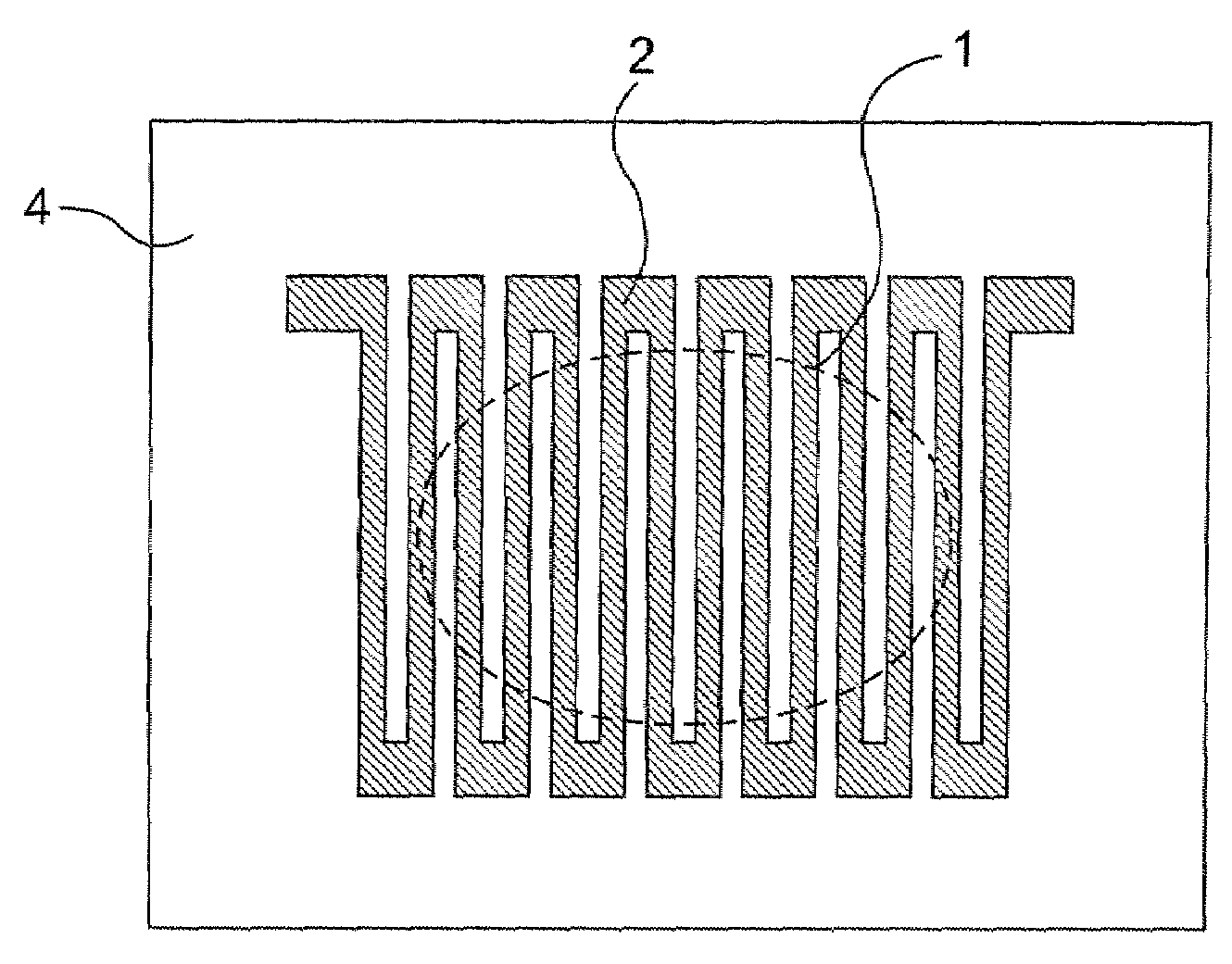
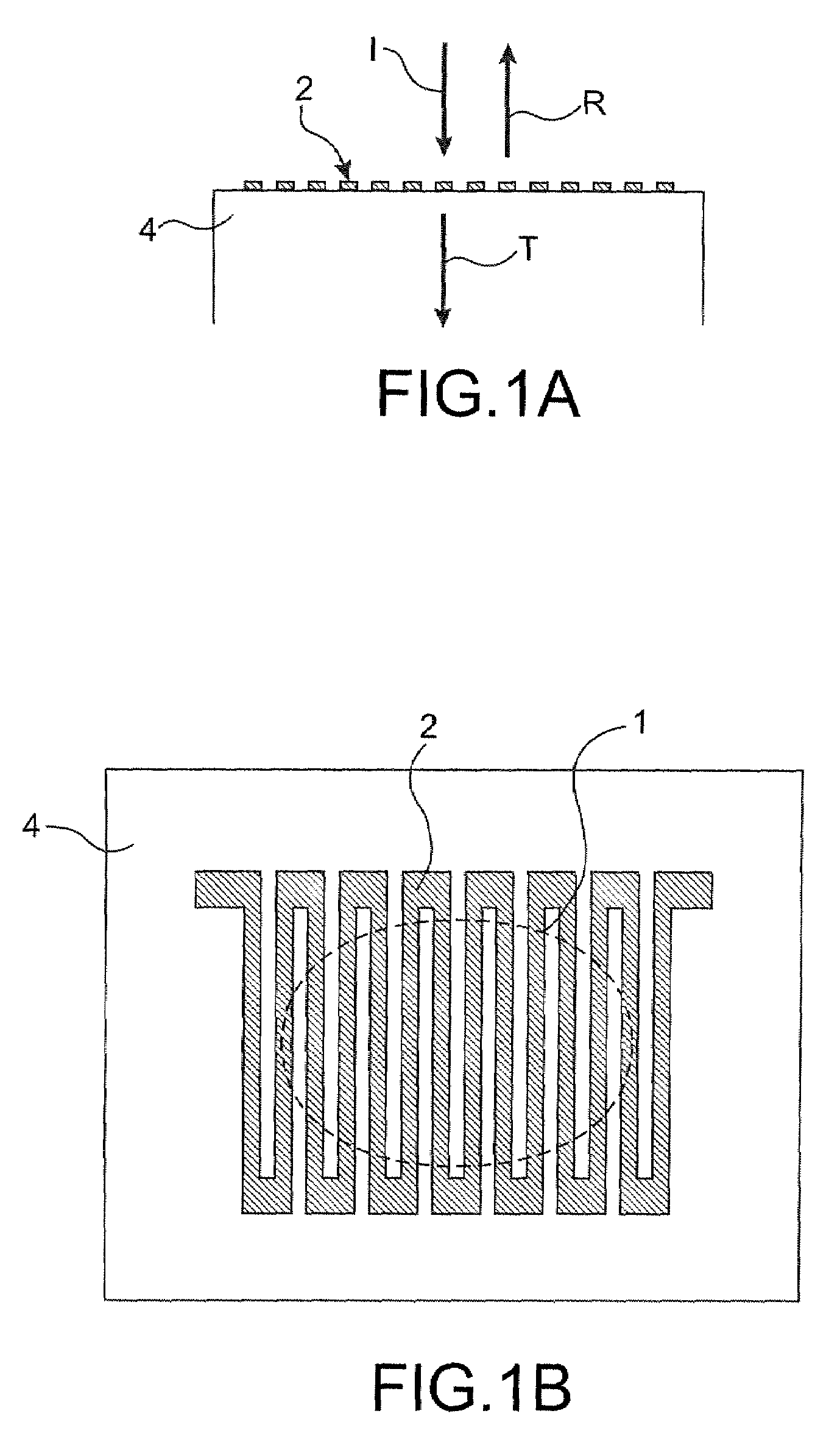
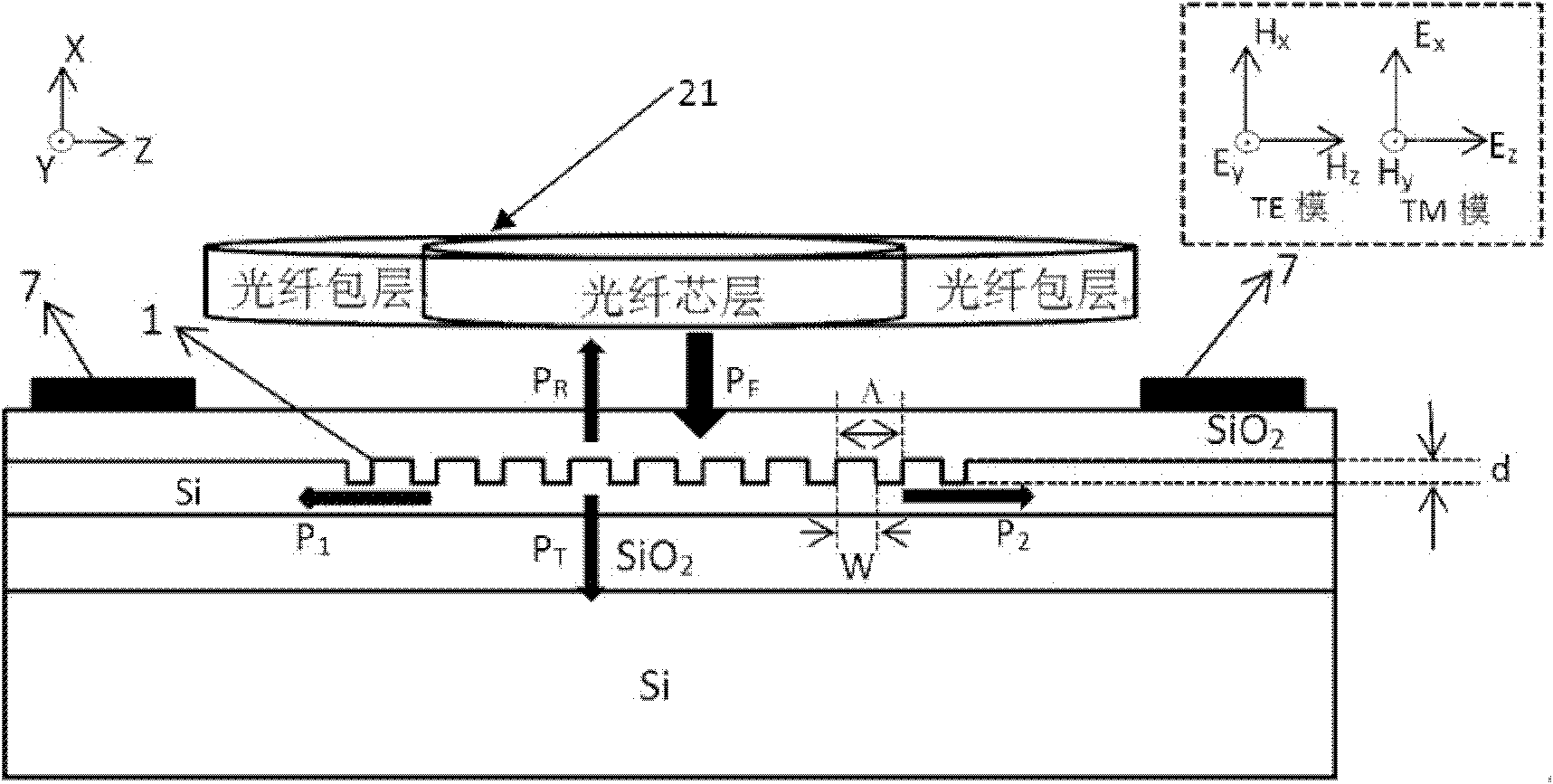
Grating coupler and coupling structure and packaging structure of grating coupler and optical fibers
The invention discloses a grating coupler, which comprises a silicon substrate layer (1) of a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, an optical waveguide structure and an optical coupling grating (5). The optical waveguide structure consists of a silicon dioxide intermediate layer (2) of the SOI substrate, a silicon top layer (3) of the SOI substrate and an upper cladding layer (4) from the bottom up. The optical coupling grating (5) is arranged on the silicon top layer (3) of the SOI substrate. An etched hole (6) is etched on the silicon substrate layer (1) of the SOI substrate. The invention additionally discloses a coupling structure of the grating coupler and optical fibers and a packaging structure for coupling of the grating coupler and the optical fibers. By using the grating coupler, the coupling structure and the packaging structure, the passive self-alignment and positioning of the optical coupling grating and the optical fibers can be realized.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN106291943AImprove coupling efficiencyReduce settingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsGratingRefractive index
The invention discloses a display panel and a display device. The display panel is characterized in that bright dipping direction and color can be selected through coupling of special modes in a waveguide layer by grating coupling structures; reflective index of a liquid crystal layer can be regulated after voltage exerted on the liquid crystal layer is regulated through an electrode structure by setting the refractive index to be (no, ne) through the grating coupling structures, and display gray level is controlled. Due to the selection action of the grating coupling structures on the bright dipping direction, near-to-eye display capable of being monocular focus can be favorably realized. Light rays can be effectively coupled out from the waveguide layer through the grating couple structures for a few grating periods which are generally short, so that the pixel size can be quite small and high definition display is favorably displayed. Due to selection action of the grating coupling structures on the bright dipping color, color films can be omitted, and all parts can be formed by transparent materials so as to achieve highly-transparent transparency display and virtual / augmented reality display.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Method and system for integrated power combiners
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Electro-optic array interface
InactiveUS20050248830A1Exquisite sensitivity of SPRCladded optical fibreNanoopticsAngle of incidenceRefractive index
A grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator is disclosed. A electro-optic polymer dielectric is deposited on the metallic surface of a diffraction grating to provide a metal / dielectric interface. A surface plasmon will propagate at the metal / dielectric interface in a resonant condition, e.g., when the metal surface is illuminated by transverse magnetic (TM) polarized light of the appropriate wavelength, angle of incidence and phase velocity. In the present invention, phase velocity is controlled by the diffraction grating. A transparent electrode deposited on the electro-optic layer allows an electrical potential to be applied across the electro-optic polymer. The applied electrical potential (voltage) changes the index of refraction of the electro-optic polymer, thereby disrupting the resonant condition to produce an optically detectable change in reflectance of incident light from the metal layer. The disclosed grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator may be configured as an electronically or optically addressable array.
Owner:CIENCIA
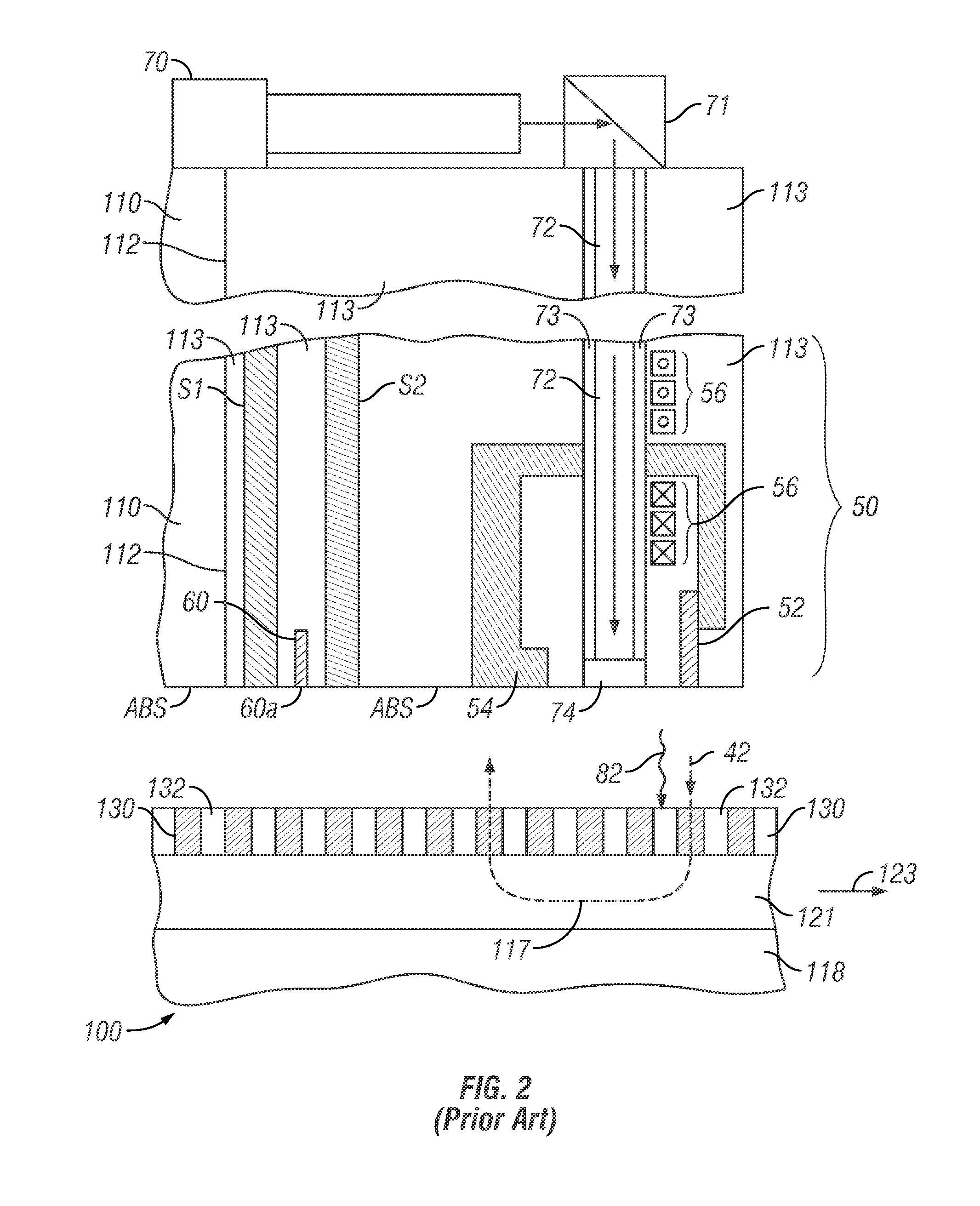
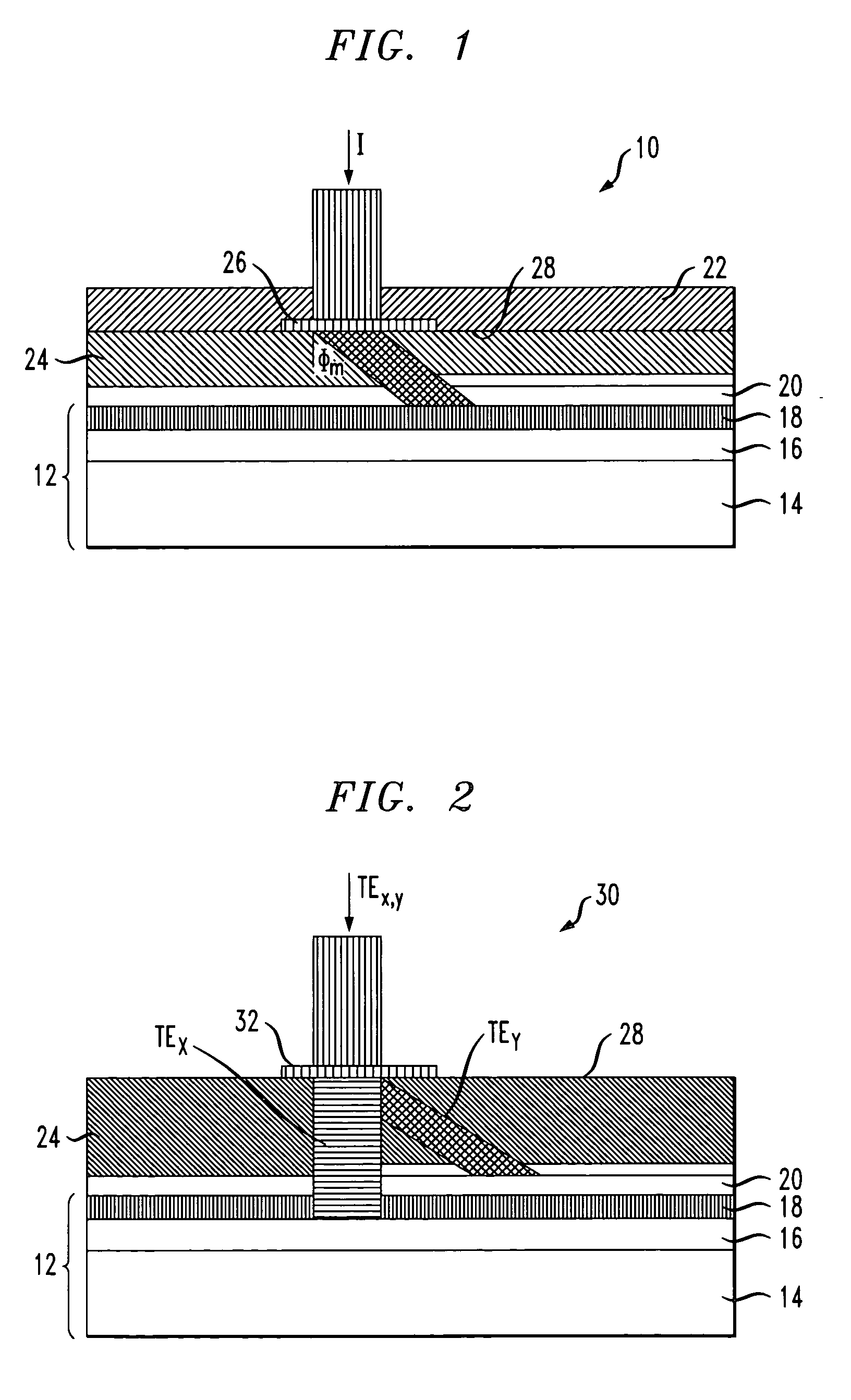
Head structure for thermally-assisted recording (TAR) disk drive
ActiveUS20120113770A1Combination recordingRecord information storageVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A thermally-assisted recording (TAR) head structure has a semiconductor substrate as the head carrier with a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) on its front surface, a TAR head formed directly on the VCSEL, and a highly reflecting third mirror on its back surface. The semiconductor substrate serves as an extended cavity for the VCSEL. The TAR head is fabricated on the outer surface of the VCSEL in the same manner as proposed for fabrication of a TAR head on a conventional slider. The TAR head includes a conventional read head and write head, and an optical waveguide with a grating coupler and a near-field transducer (NFT). The laser radiation is output through a partially reflecting output mirror of the VCSEL through the front surface to the grating coupler, which turns the incoming laser radiation 90 degrees and directs it into the waveguide from where it is directed to the NFT.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
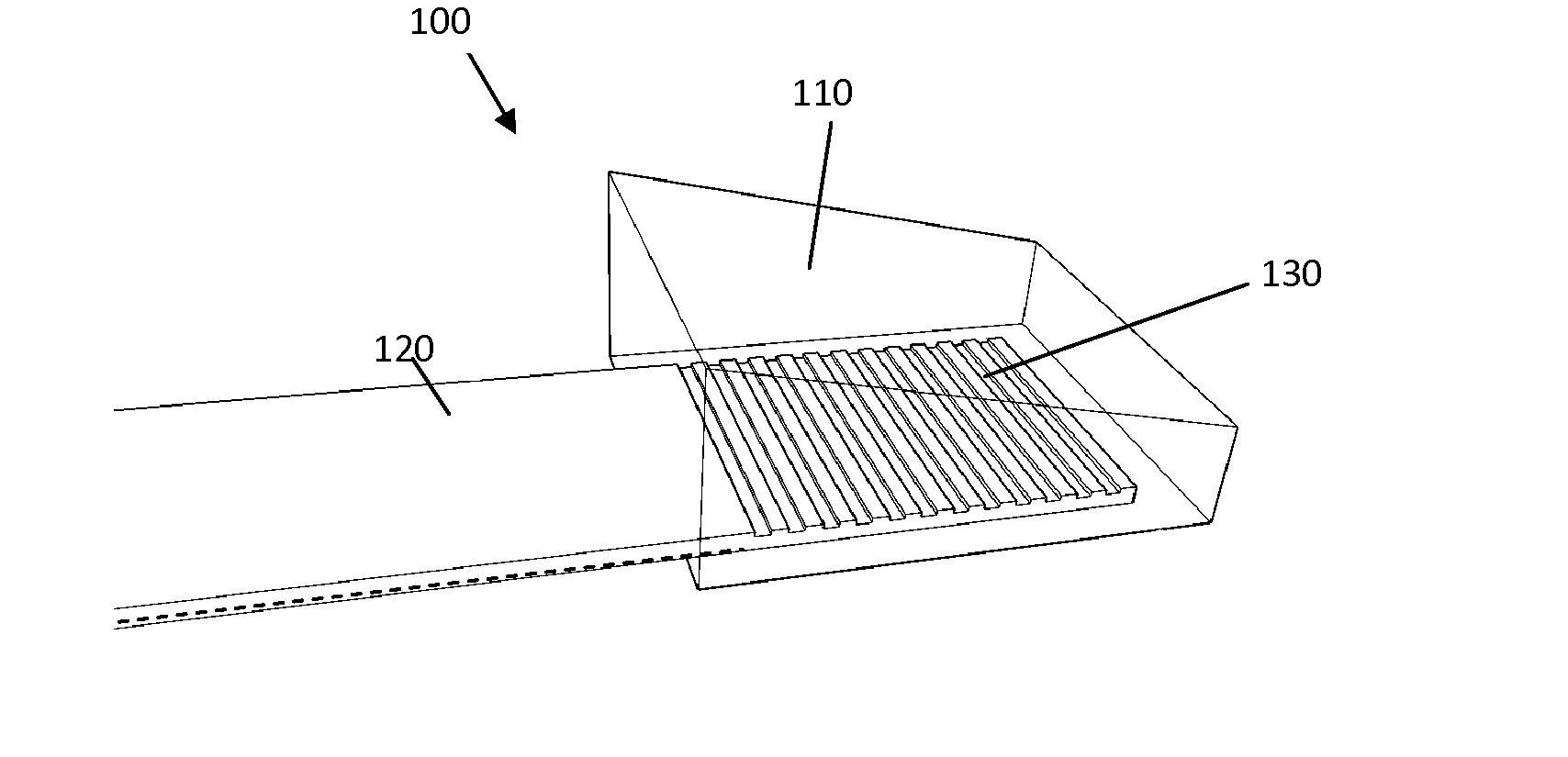
Integrated Photonics Device
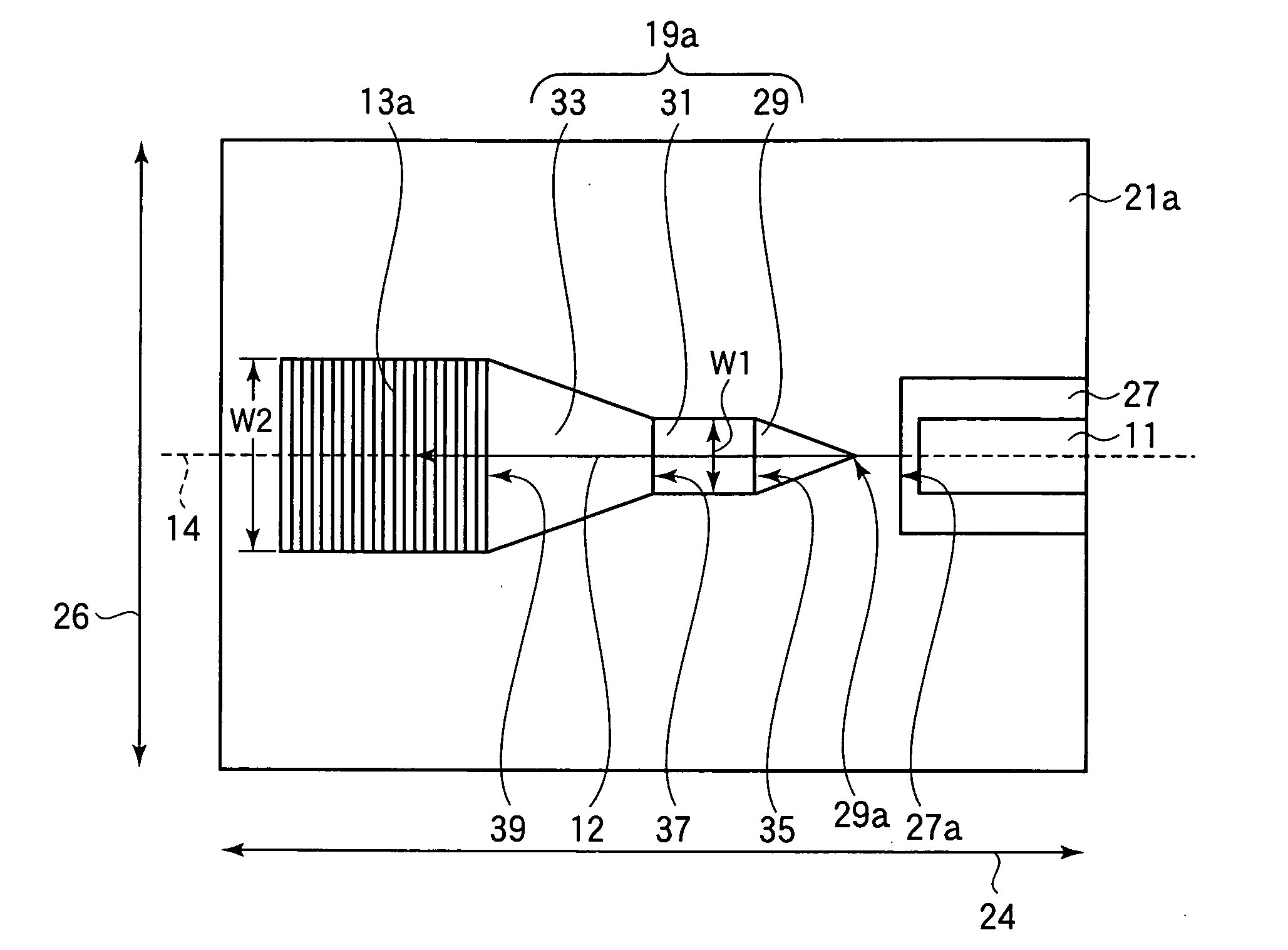
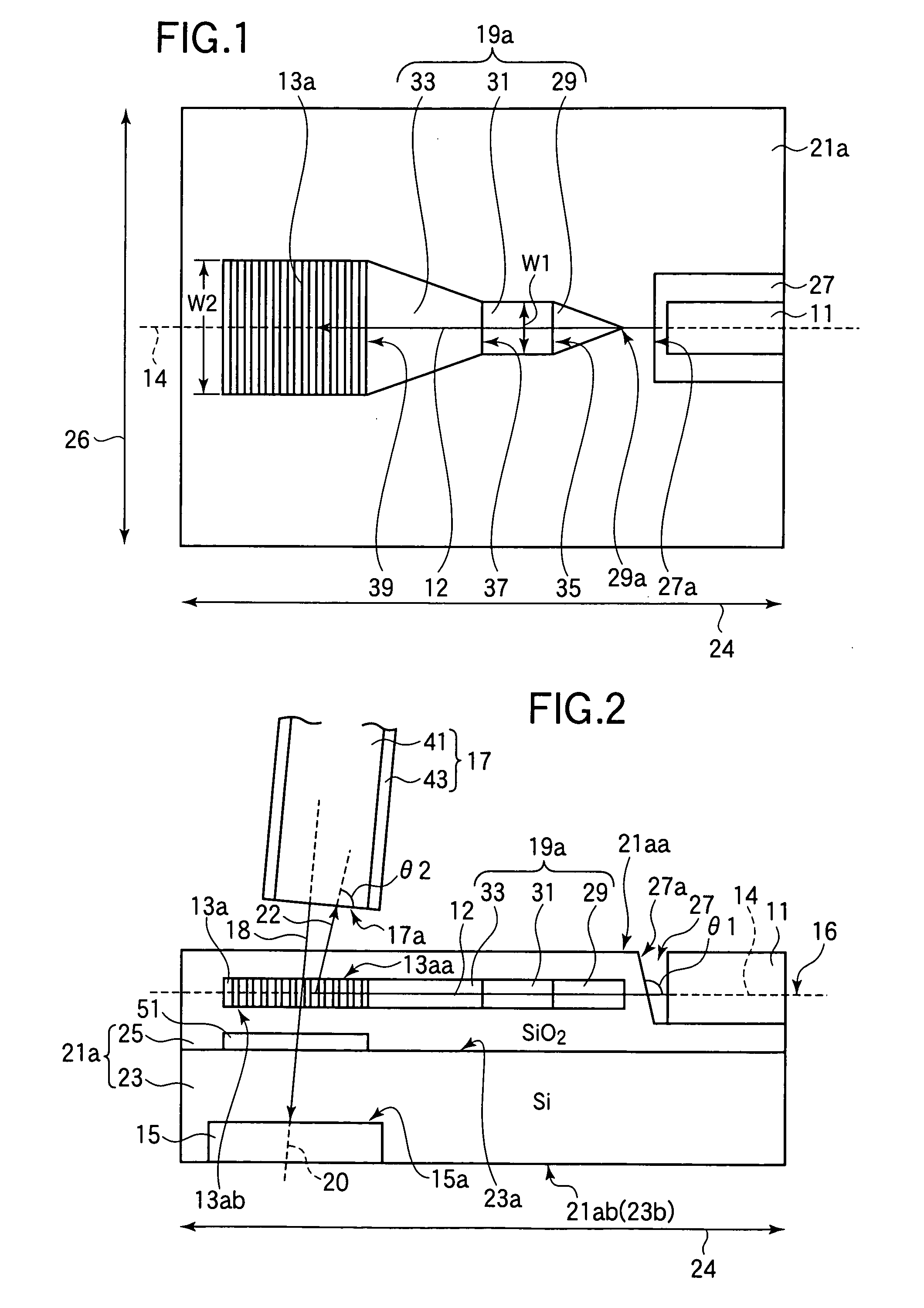
The present invention relates to an integrated photonic device (100) operatively coupleable with an optical element (300) in a first coupling direction. The integrated photonic device (100) comprises an integrated photonic waveguide (120) and a grating coupler (130) that is adapted for diffracting light from the waveguide (120) into a second coupling direction different from the first coupling direction. The integrated photonics device also comprises a refractive element (110) disposed adjacent the grating coupler (130) and adapted to refract the light emerging from the grating coupler (130) in the second coupling direction into the first coupling direction.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
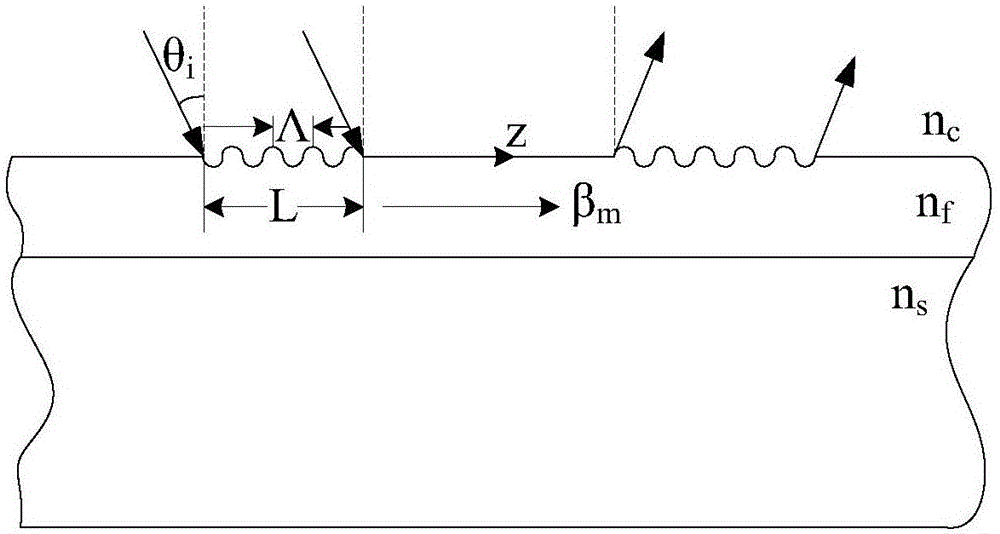
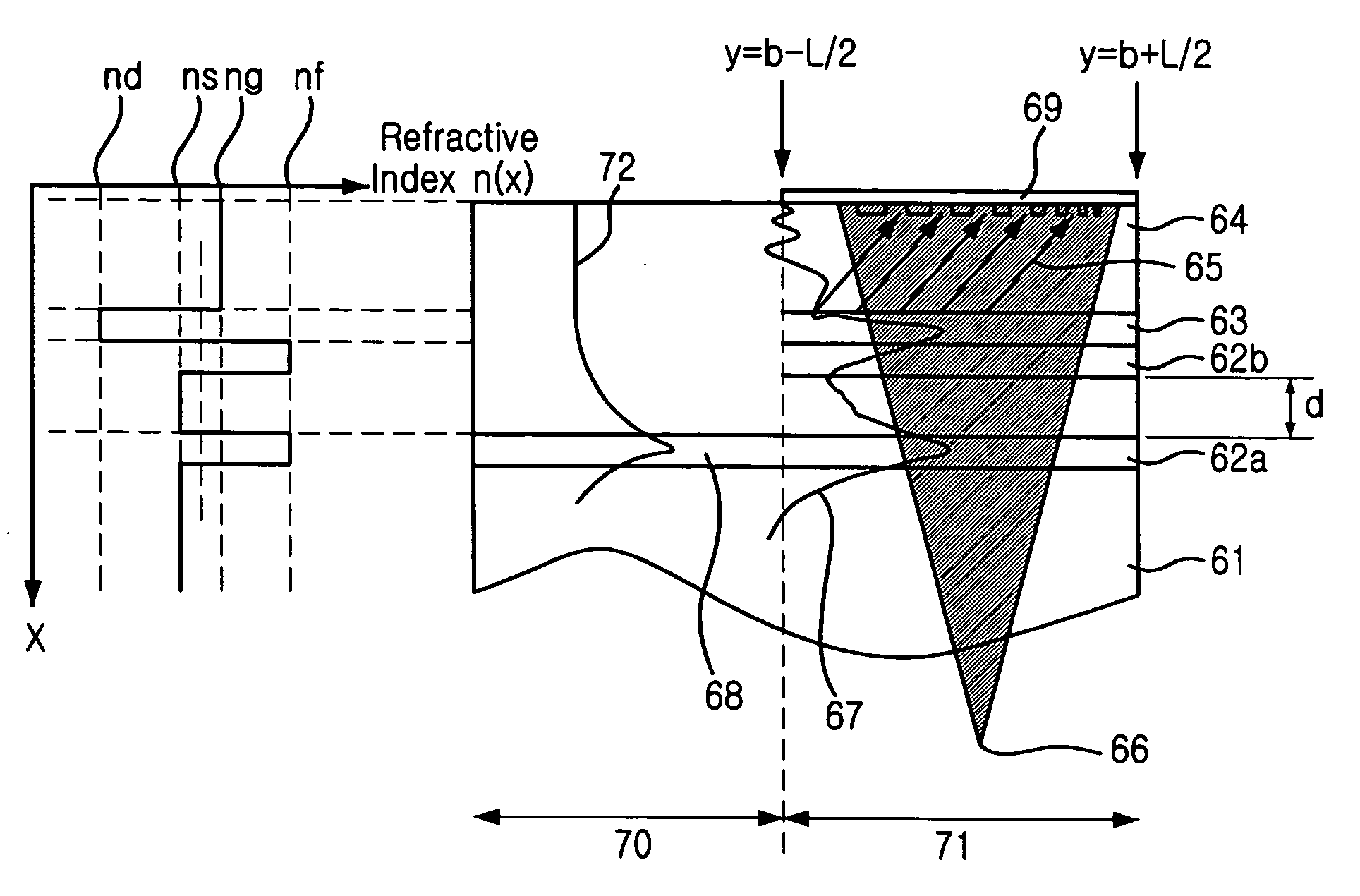
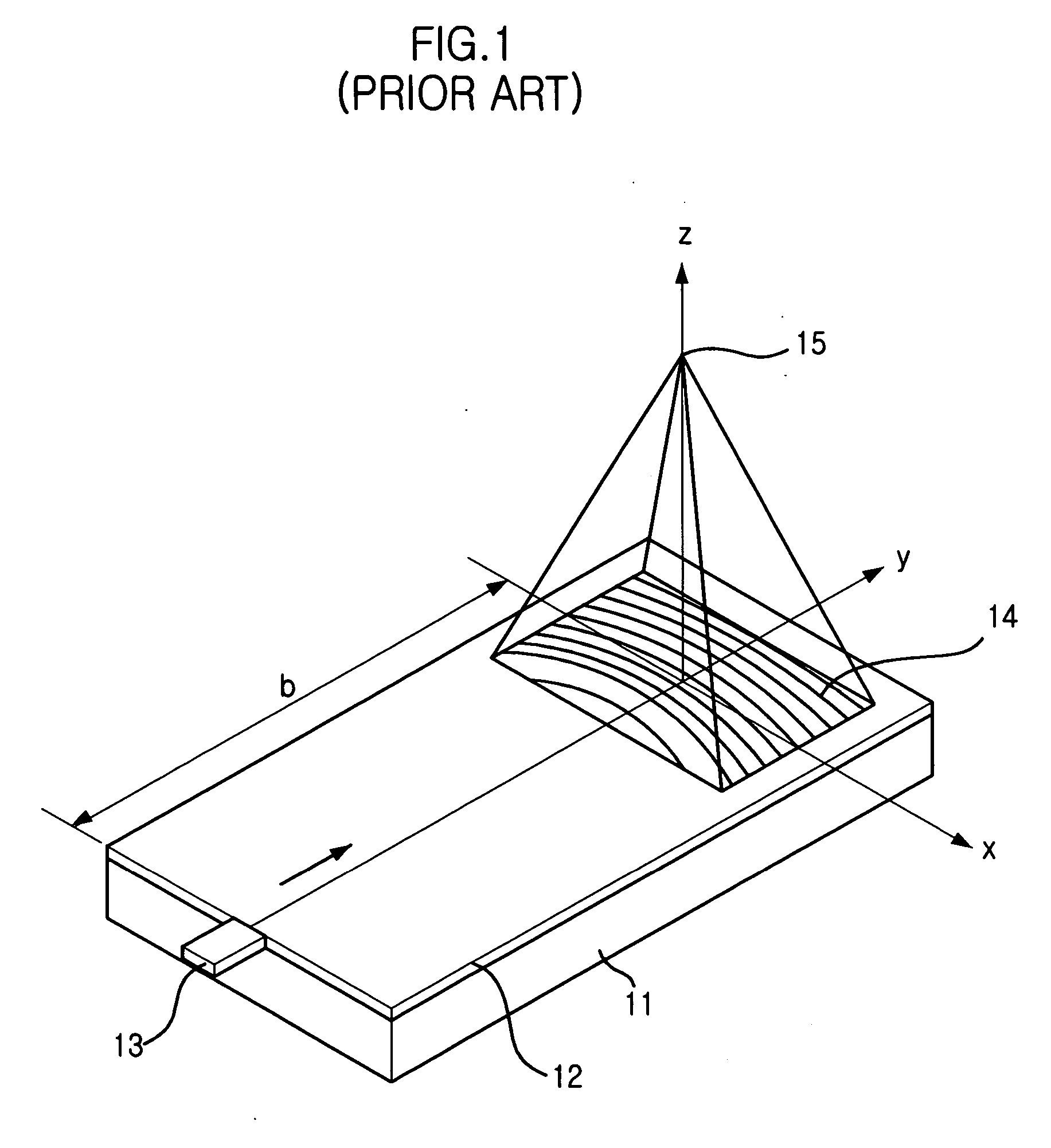
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
InactiveUS20050008294A1Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
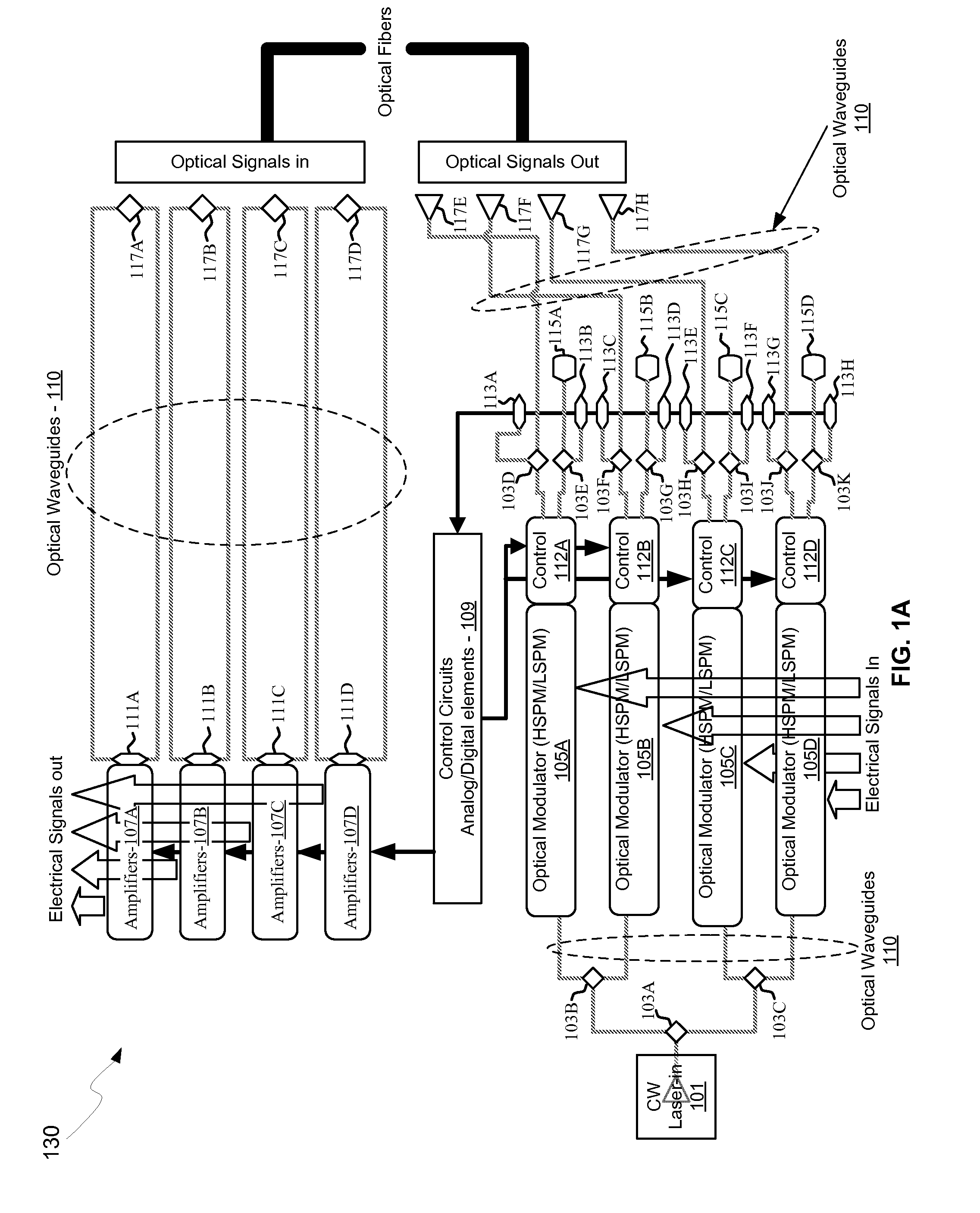
Method and system for multi-mode integrated receivers
A method and system for multi-mode integrated receivers are disclosed and may include receiving an optical signal from an optical fiber coupled to a chip comprising a photonic circuit. The photonic circuit may comprise an optical coupler, one or more multi-mode optical waveguides, and a detector. The received optical signal may be coupled to a plurality of optical modes in the one or more multi-mode optical waveguides, which are communicated to a detector to generate an electrical signal from the communicated modes. The optical coupler may comprise a grating coupler. The chip may comprise a CMOS chip, and the optical fiber may comprise a single-mode or a multi-mode fiber. The detector may comprise a germanium or silicon-germanium photodiode, and / or a waveguide detector. The optical fiber may be coupled to a top surface of the chip and the multi-mode optical waveguides may comprise rib waveguides.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High time-resolution ultrasensitive optical detector, using grating coupling
InactiveUS20090020701A1Improve time resolutionImprove detection efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesGratingImage resolution
This detector is intended to detect at least one photon and comprises a dielectric substrate (30), of index nO; a detecting element (32) forming a serpentine, placed on the substrate and generating a signal using the energy of the photon(s); a dielectric grating, formed of lines of index nH, alternating with lines of index nB, avec nH>nO and nH>nB, the grating being placed above the detecting element, the set grating-element presenting a resonant absorption in a given incidence and for a given polarisation; and a superstratum (40) having a refractive index ni, this superstratum being placed above the one-dimensional dielectric grating, nH being furthermore greater than ni.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electro-optic array interface
InactiveUS20050248829A1Improve interconnect densityStatic indicating devicesScattering properties measurementsAngle of incidencePolymer dielectrics
A grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator is disclose. A electro-optic polymer dielectric is deposited on the metallic surface of a diffraction grating to provide a metal / dielectric interface. A surface plasmon will propagate at the metal / dielectric interface in a resonant condition, e.g., when the metal surface is illuminated by transverse magnetic (TM) polarized light of the appropriate wavelength, angle of incidence and phase velocity. In the present invention, phase velocity is controlled by the diffraction grating. A transparent electrode deposited on the electro-optic layer allows an electrical potential to be applied across the electro-optic polymer. The applied electrical potential (voltage) changes the index of refraction of the electro-optic polymer, thereby disrupting the resonant condition to produce an optically detectable change in reflectance of incident light from the metal layer. The disclosed grating coupled surface plasmon resonance optical modulator may be configured as an electronically or optically addressable array.
Owner:CIENCIA
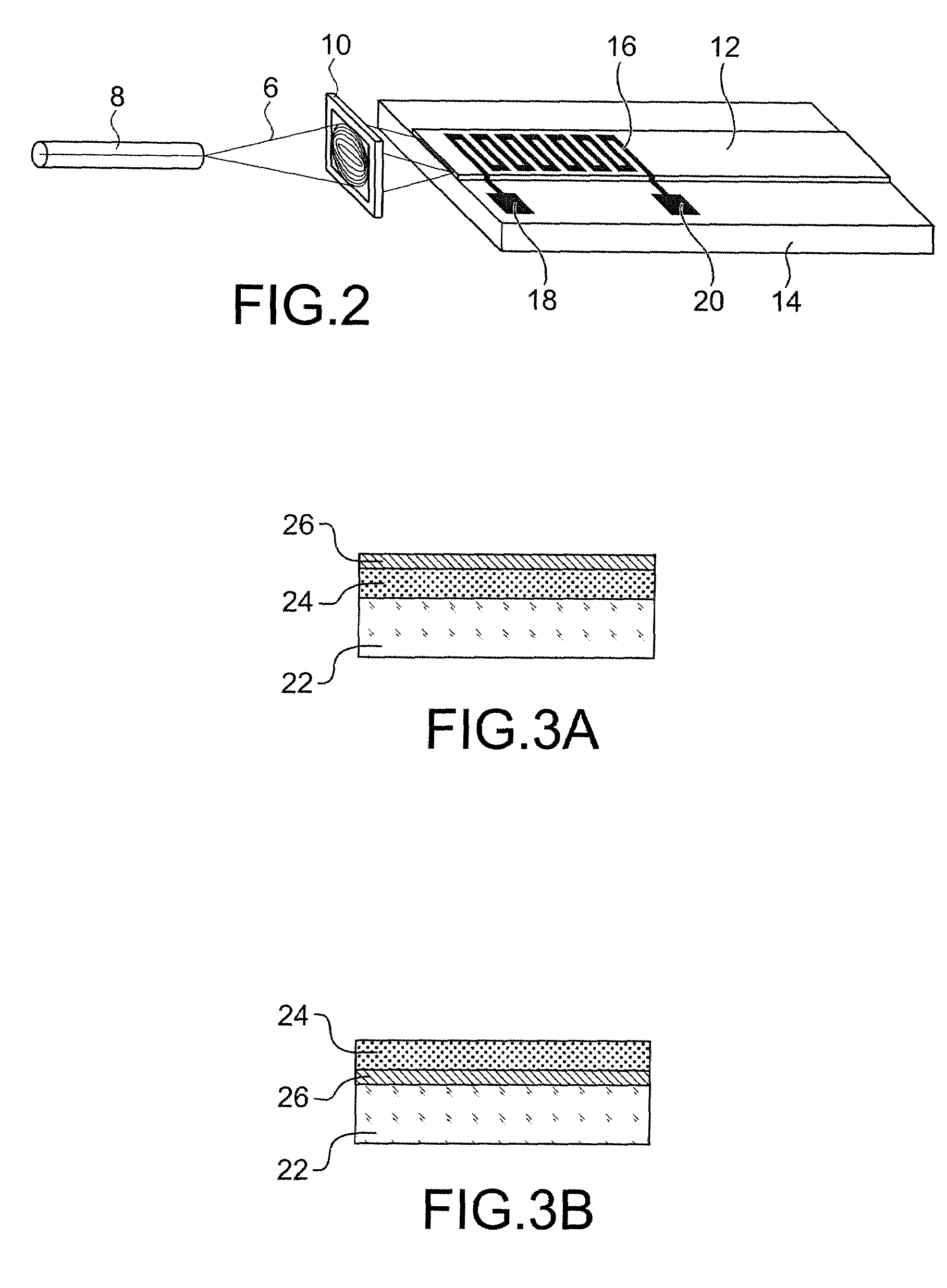
Integrated optical assembly apparatus and integrated fabrication method for coupling optical energy
A novel optical assembly apparatus for coupling optical energy and a related method for creating the novel optical assembly apparatus are disclosed. In one embodiment, the novel optical assembly apparatus includes a high-index contrast waveguide constructed on a semiconductor die or another base substrate with an aligned optical coupling section, a grating coupler etched onto a surface, a micro mirror with an acute angle relative to the surface, and a waveguide taper that narrows an optical beam width. A light ray entered into the optical coupling section is redirected by the micro mirror to form a perpendicular ray entry angle with the grating coupler. The grating coupler then efficiently couples the light ray with the waveguide taper, which in turn narrows the optical beam width. The light ray may originate from a semiconductor die or from an optical fiber, which is purposefully aligned with the high-index contrast waveguide.
Owner:PARTOW TECH LLC
Resonantly enhanced grating coupler
InactiveUS7397987B2Improve system efficiencyImprove efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideGratingCoupling
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods and systems for reducing polarization dependent loss
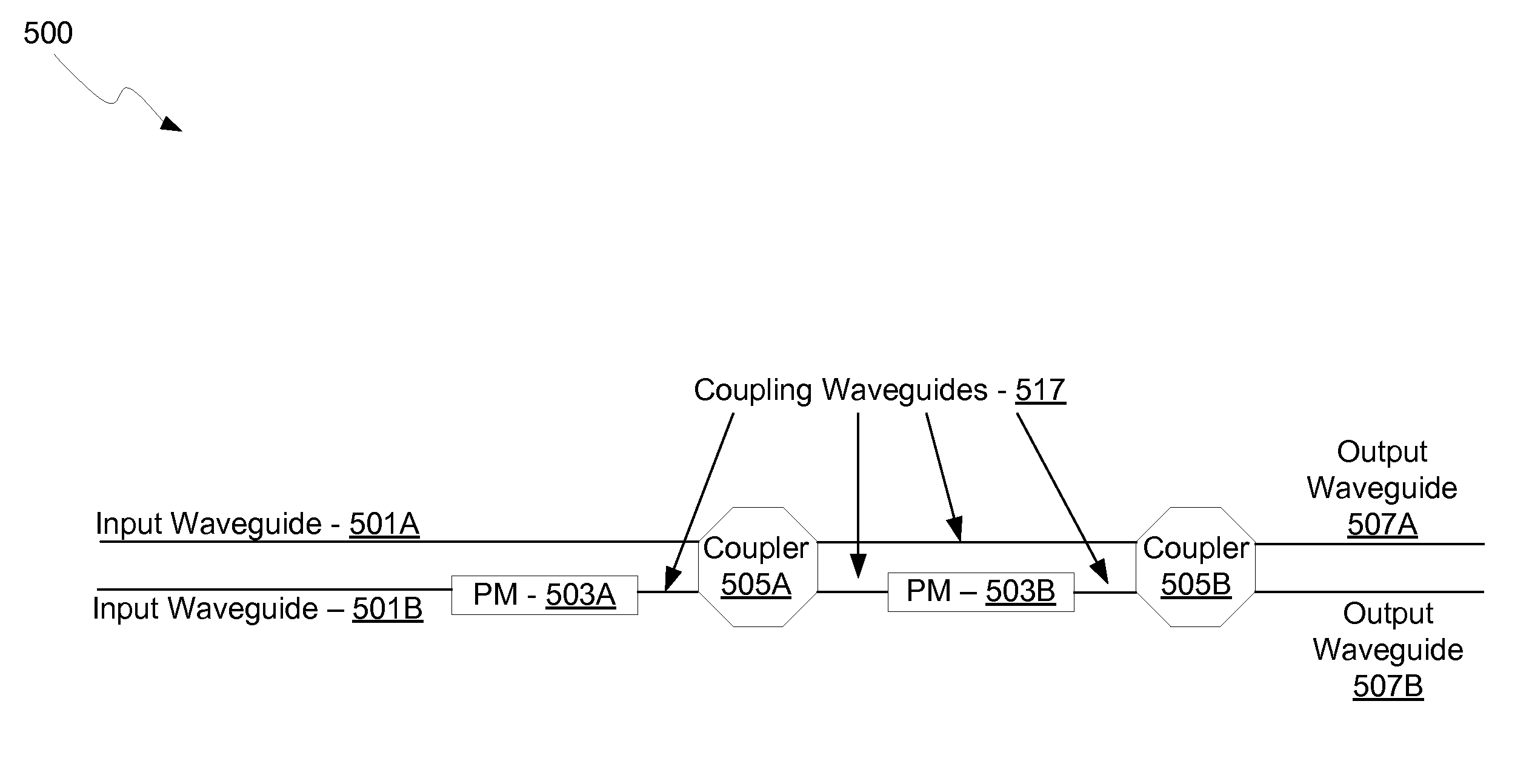
InactiveUS20120207428A1Low and reduced and no polarization dependent lossPolarization lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideGratingPhase shifted
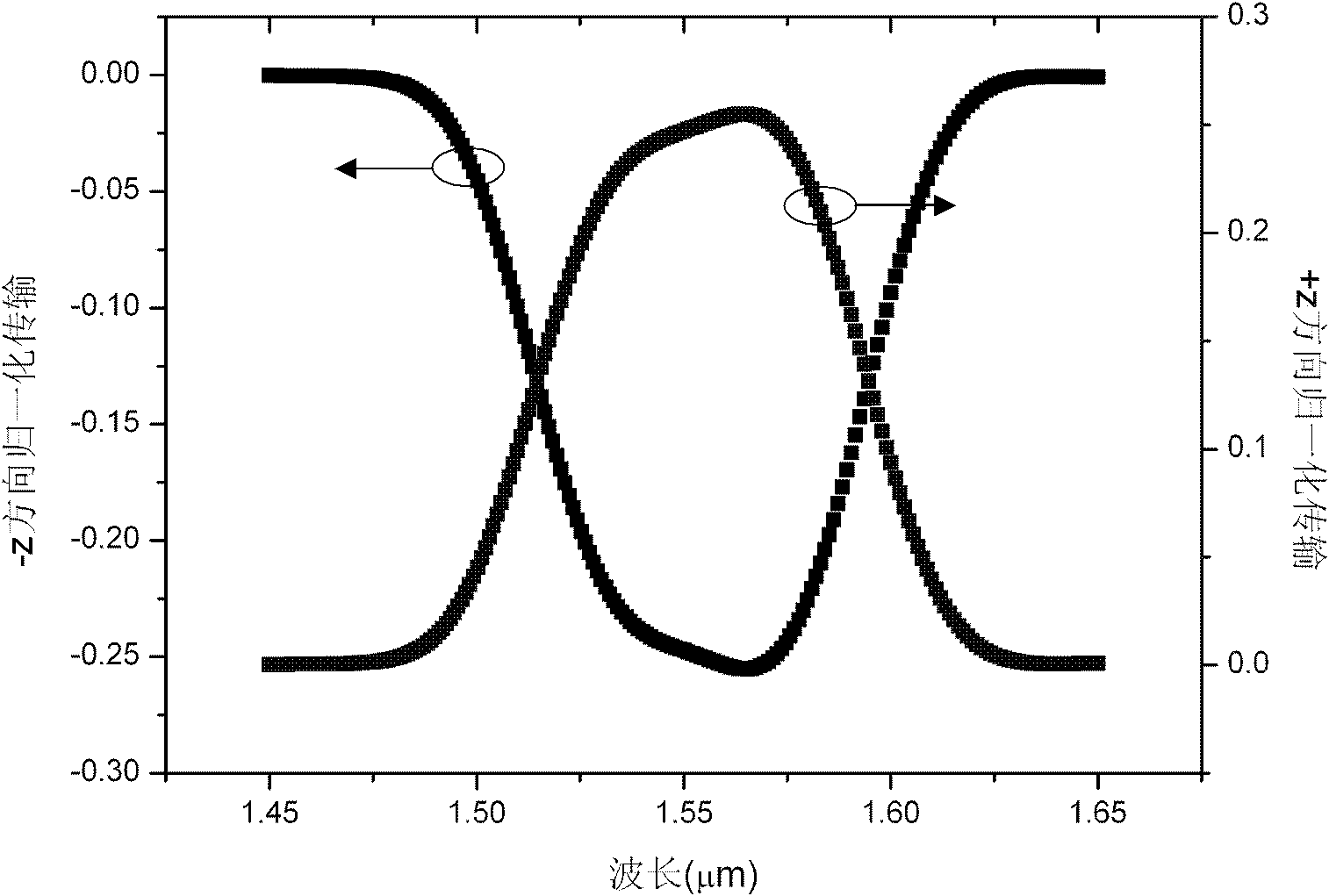
A photonics integrated circuit for processing radiation includes a first-dimensional grating coupler for coupling in radiation, a second two-dimensional grating coupler for coupling out radiation and a waveguide structure having two distinct waveguide arms for splitting radiation received from the first grating coupler and recombining radiation in the second grating coupler. A phase shifting means furthermore is provided for inducing an additional phase shift in at least one of the two distinct waveguide arms thereby inducing a relative phase shift of π between the two distinct waveguide arms so as to provide a TE / TM polarization switch for radiation between the first grating coupler and the second grating coupler.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
Liquid crystal grating coupling
A tunable optical coupling arrangement for use with a relatively thin (generally sub-micron thickness) silicon waveguiding layer of a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. The arrangement comprises a multi-layer structure including a substrate for supporting one or more diffractive optical elements and a layer of tunable liquid crystal material. The multi-layer structure is disposed over a conventional SOI substrate including the thin silicon waveguiding layer, where the refractive index of the liquid crystal material can be modified to adjust the deflection of an input optical beam through the various diffractive optical elements and present an optimized launch angle into the silicon waveguiding layer, thus reducing insertion loss at the waveguiding layer.
Owner:SIOPTICAL INC +1
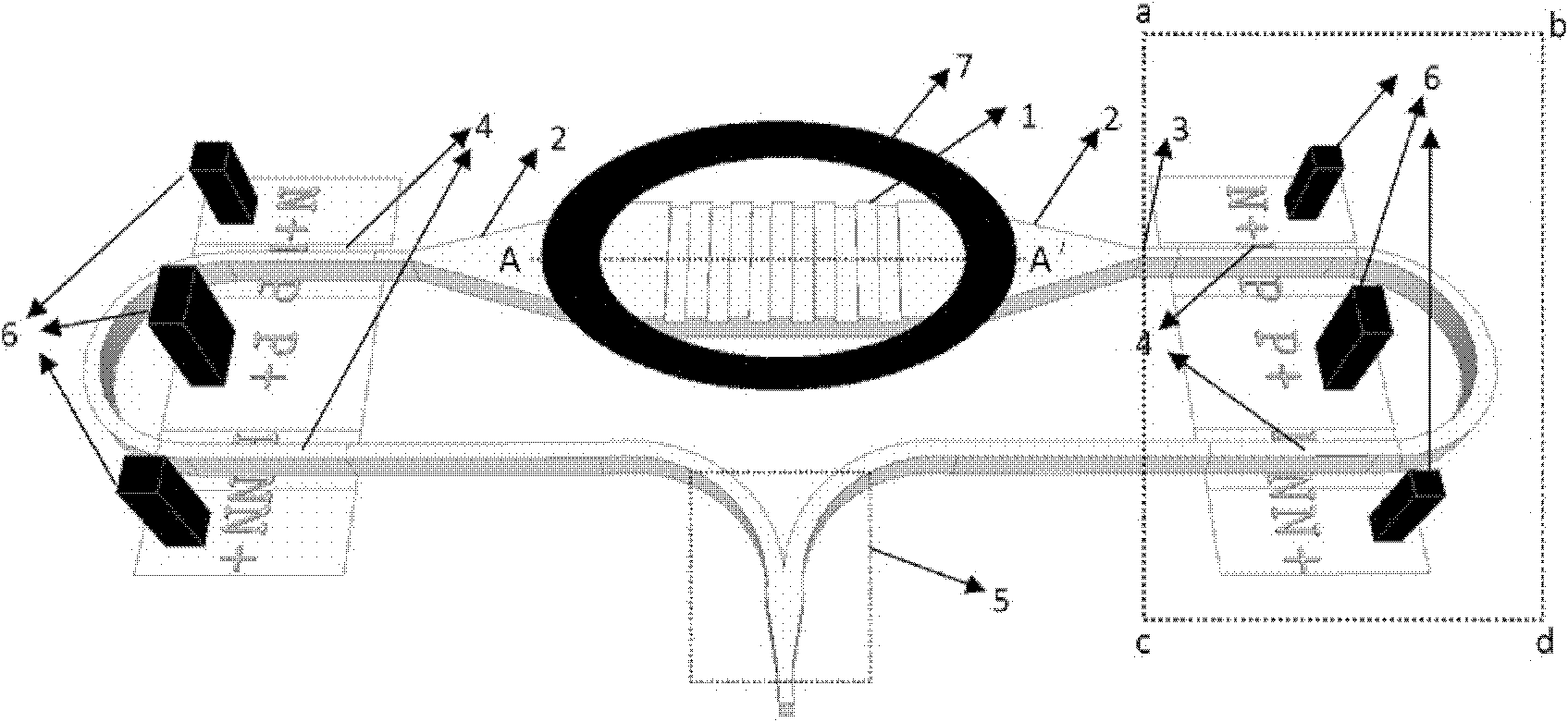
SOI (silicon on insulator) based electrooptical modulator based on symmetrical and vertical grating coupling
ActiveCN102540505AIntegration of coupling and modulation functionsEasy alignmentNon-linear opticsGratingCoplanar waveguide
The invention discloses an SOI (silicon on insulator) based electrooptical modulator based on symmetrical and vertical grating coupling, which comprises a symmetrical and vertical coupling grating, a 3-d B optical beam splitter, two mode converters, two optical phase shift arms, an optical beam combiner, two coplanar waveguide wave traveling electrodes and an annular metal alignment mark, wherein the 3-d B optical beam splitter acts as an interface of the SOI based electrooptical modulator and a single mode fiber or an input end of a coupler and the SOI based electrooptical modulator; the two mode converters act as the connection of a wide wave guide of the symmetrical and vertical coupling grating and a single mode ridge-shaped waveguide; each optical phase shift arm consists of the single mode ridge-shaped waveguide and an electric structure embedded into the single mode ridge-shaped waveguide; the optical beam combiner is used for combining the light in the two optical phase shift arms which are divided by the symmetrical and vertical coupling grating into one beam, thus phase modulation of light is converted into intensity modulation; the coplanar waveguide wave traveling electrodes are respectively positioned on the two optical phase shift arms, form electric contact with the electric structure in the optical phase shift arms, and are used for the loading and transmission of radio frequency / micro wave electrical modulation signals; and the annular metal alignment mark is positioned around the symmetrical and vertical coupling grating, and is used for the alignment of the optical fiber in an optical grating test.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
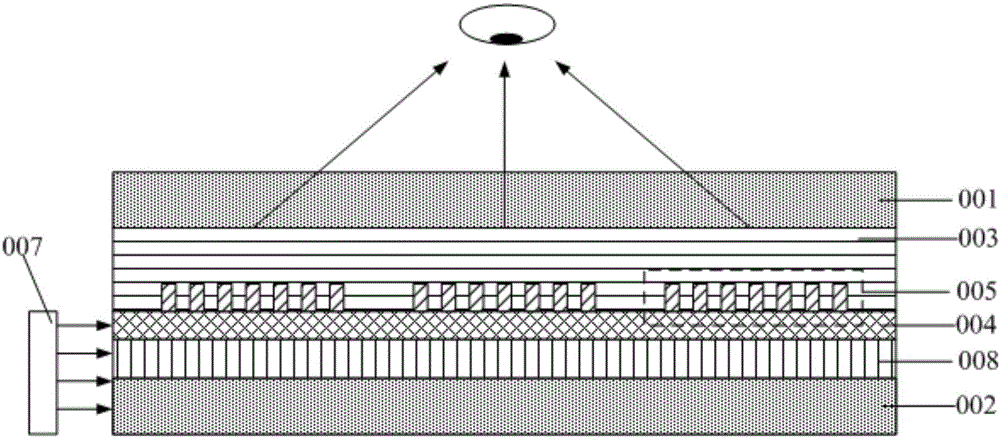
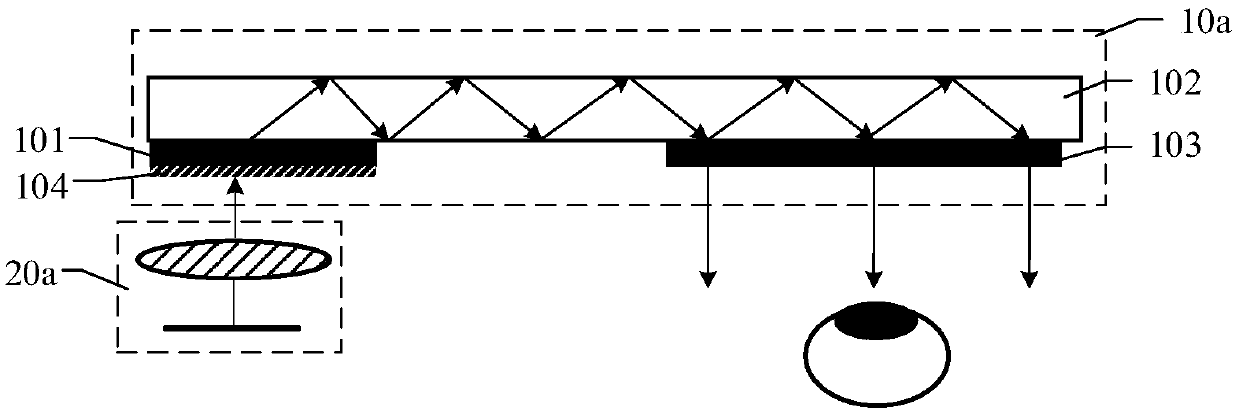
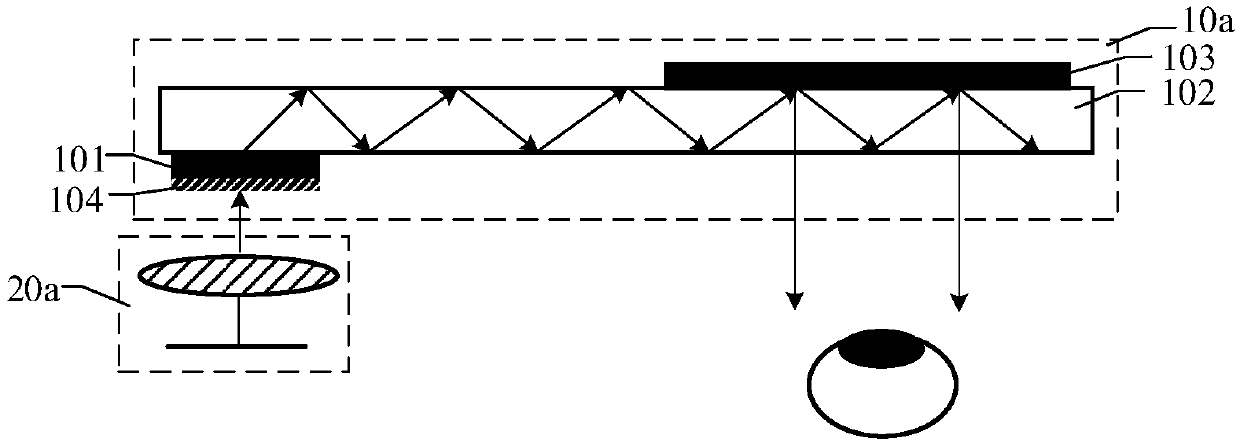
Augmented reality device
An augmented reality device comprises an optical machine and an optical waveguide lens. The optical waveguide lens comprises a dielectric layer, a transmission type coupling-in grating, an optical waveguide and a coupling-out grating. The optical machine is used for generating light, and the dielectric layer is arranged on the surface of one side, close to the optical machine, of the transmission-type coupled grating, and is used for transmitting light to the transmission type coupling-in grating, wherein the refractive index of the dielectric layer is greater than that of the transmission type coupling-in grating; the transmission type coupling-in grating is arranged on the surface of the side, close to the optical machine, of the optical waveguide and used for coupling the light passingthrough the dielectric layer into the optical waveguide, and the optical waveguide is used for transmitting the light coupled in by the transmission type coupling-in grating to the coupling-out grating, and the coupling-out grating is used for coupling out the light in the optical waveguide to human eyes for imaging. Since the dielectric layer with the refractive index greater than that of the transmission type coupled grating is added on the surface of the transmission type coupling-in grating, the optical path of the light passing through the transmission type coupling-in grating can be increased; therefore, more light can be coupled into the optical waveguide, and the coupling efficiency of the transmission type coupling-in grating to the light can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com