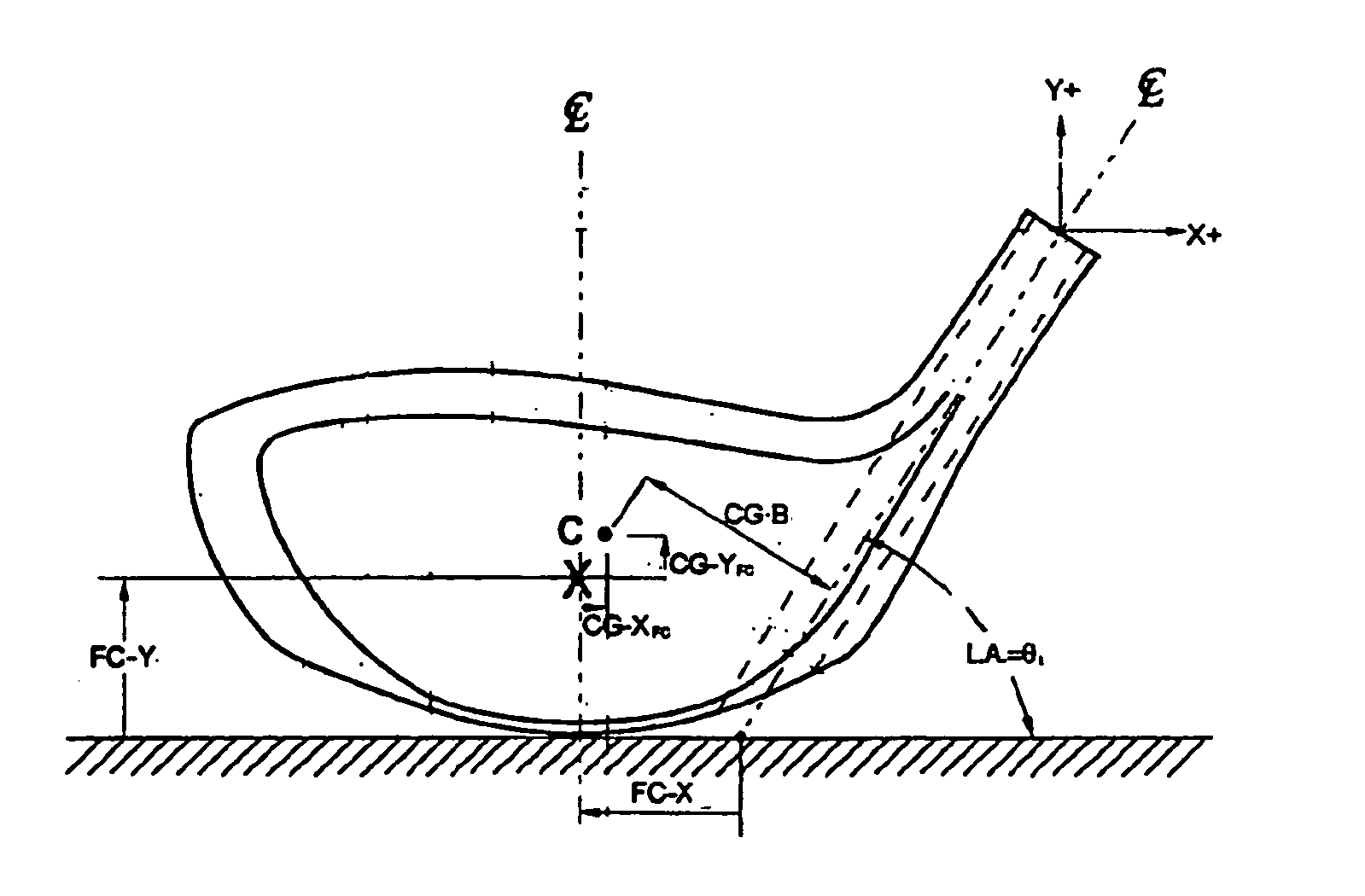
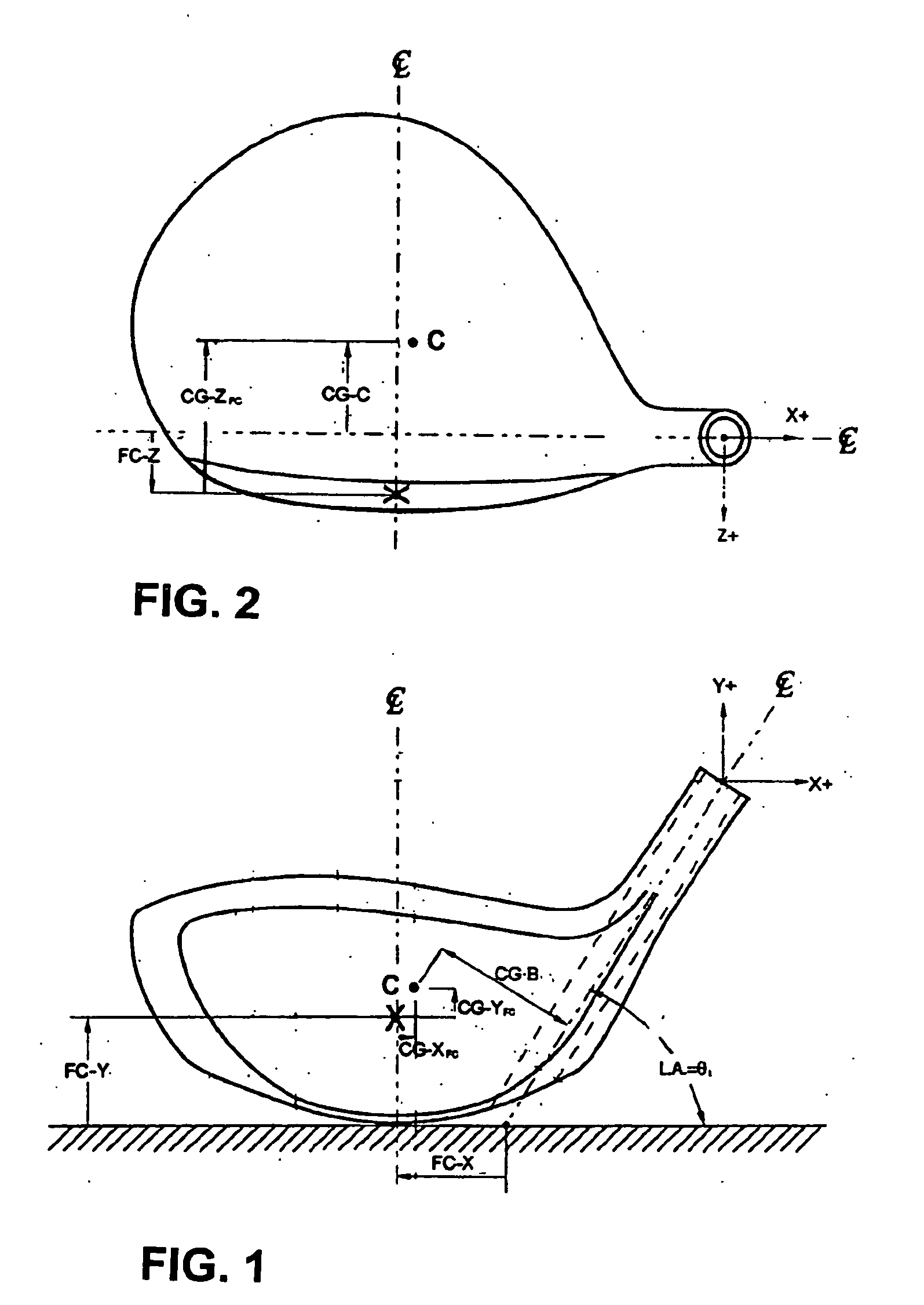
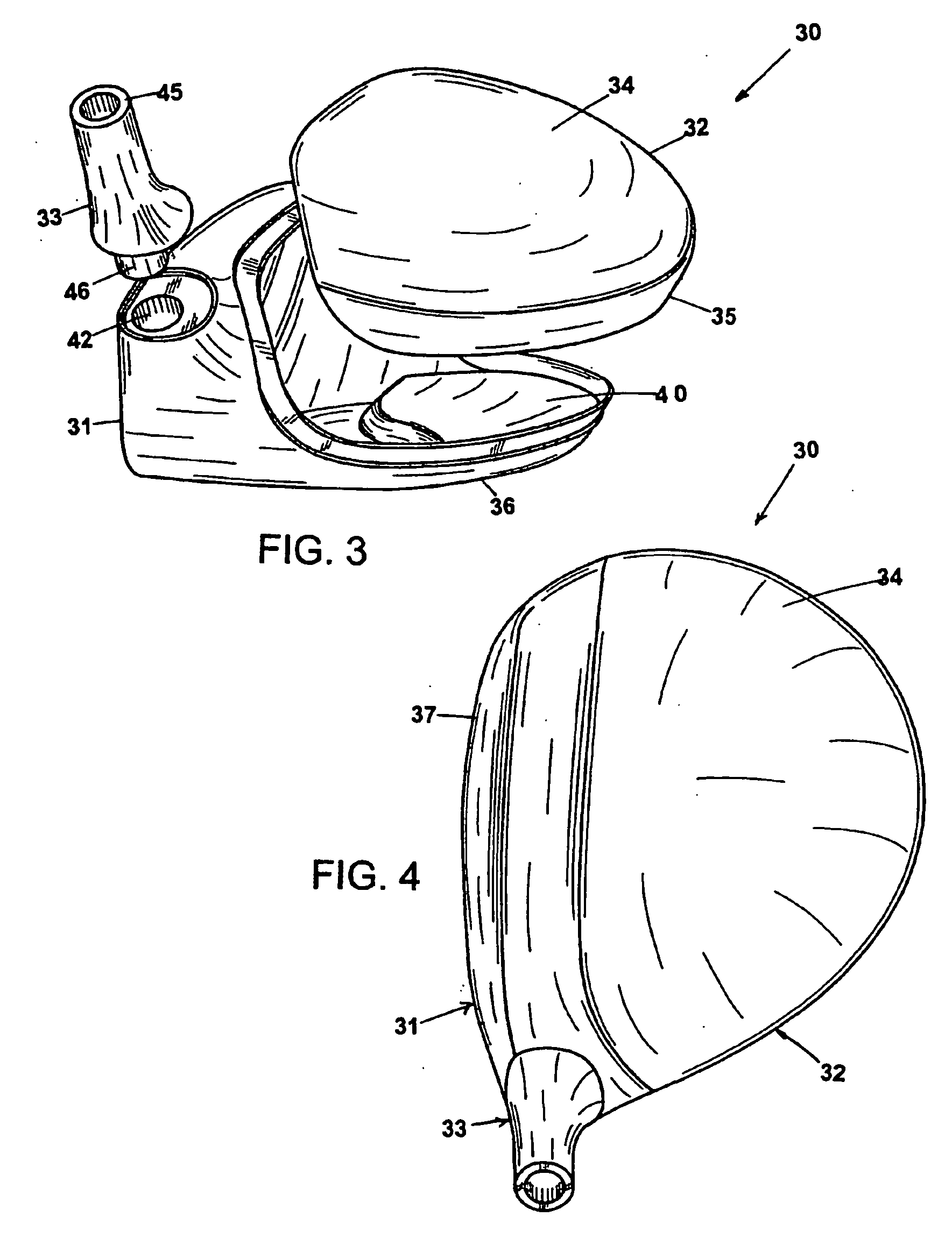
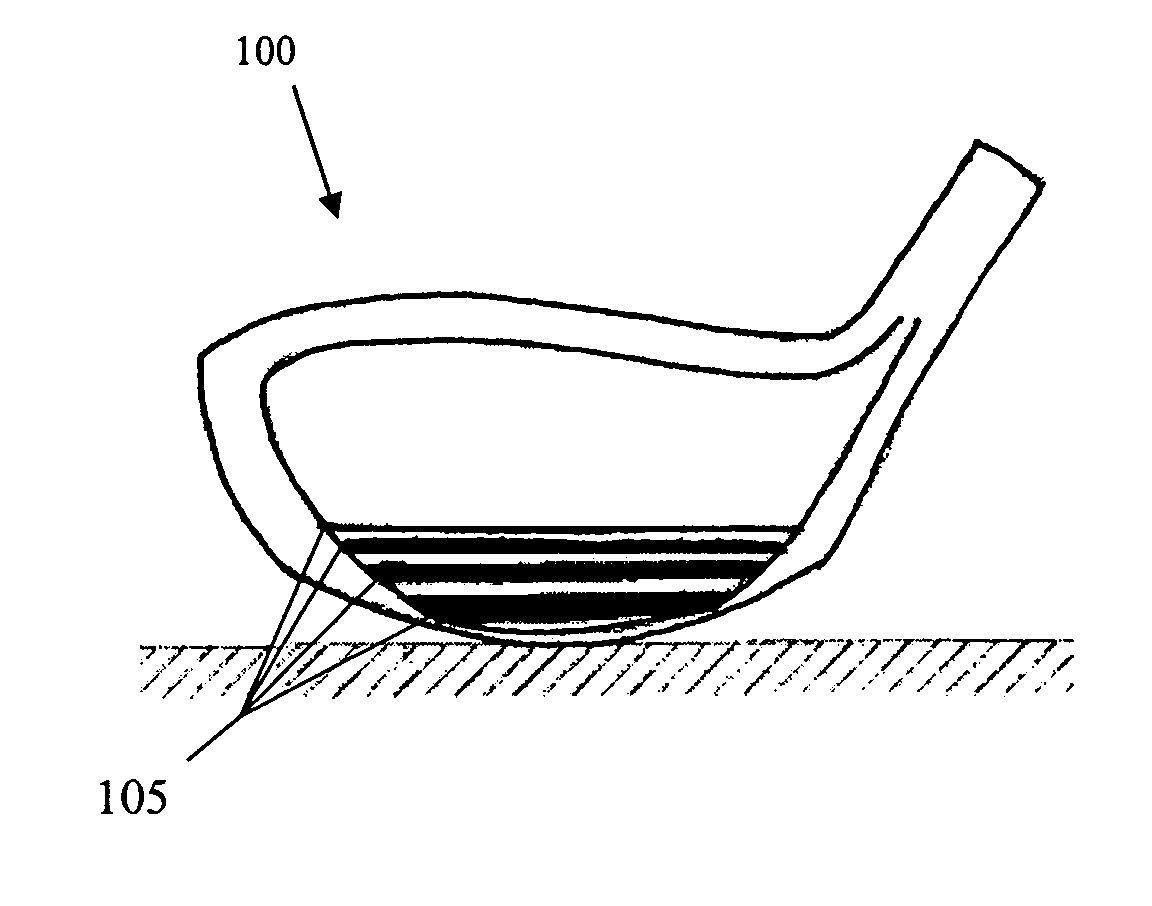
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
204 results about "Launch angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
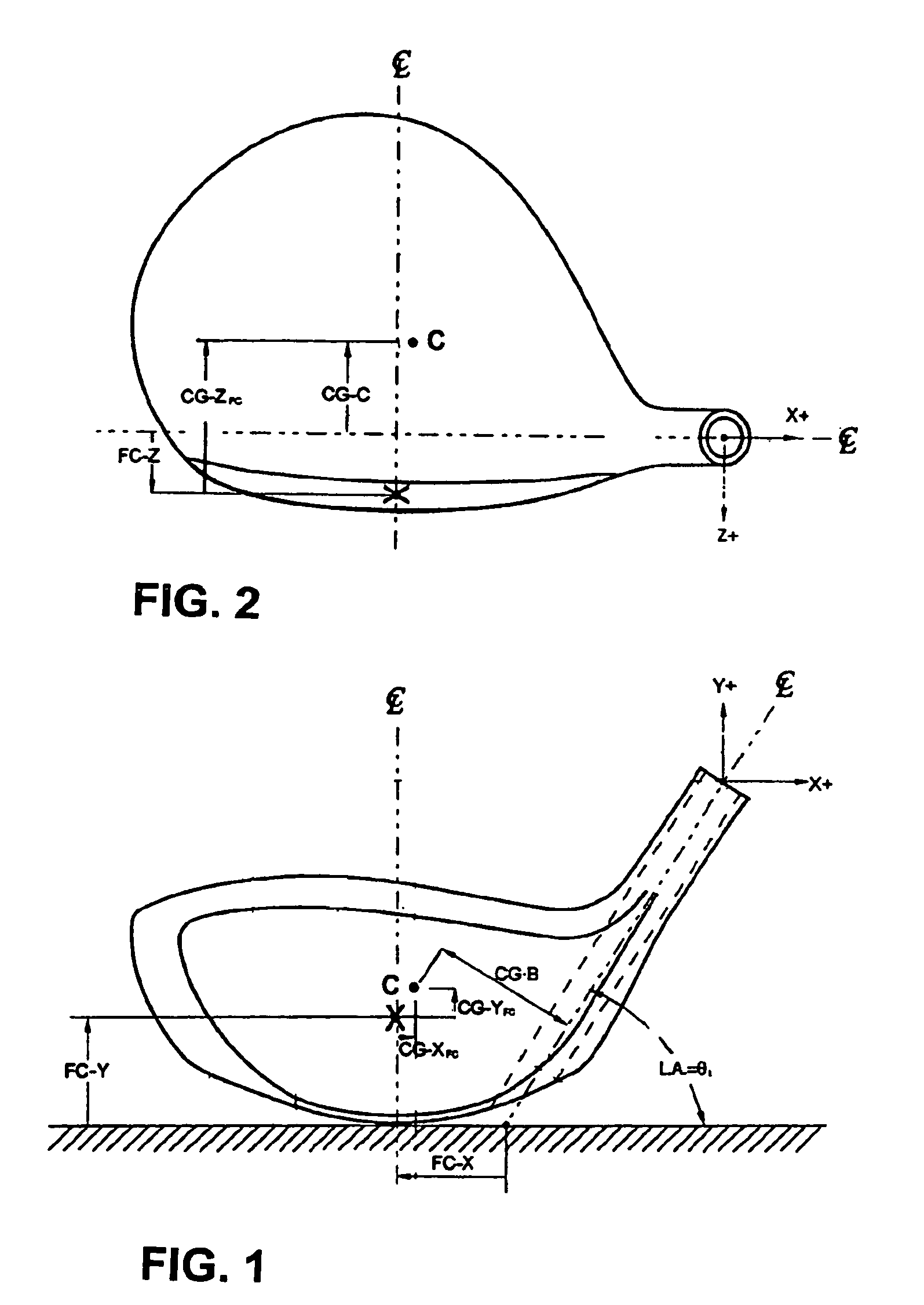
In fiber optic telecommunications, the launch angle has the following meanings: The angle, with respect to the normal, at which a light ray emerges from a surface. The beam divergence at an emitting surface, such as that of a light-emitting diode, laser, lens, prism, or optical fiber end face. At an end face of an optical fiber, the angle between an input ray and the fiber axis. If the end face of the fiber is perpendicular to the fiber axis, the launch angle is equal to the angle of incidence.
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
ActiveUS20130148925A1Short focal lengthClear processLaser detailsCoupling light guidesLaser processingLight beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Three-piece solid golf ball
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
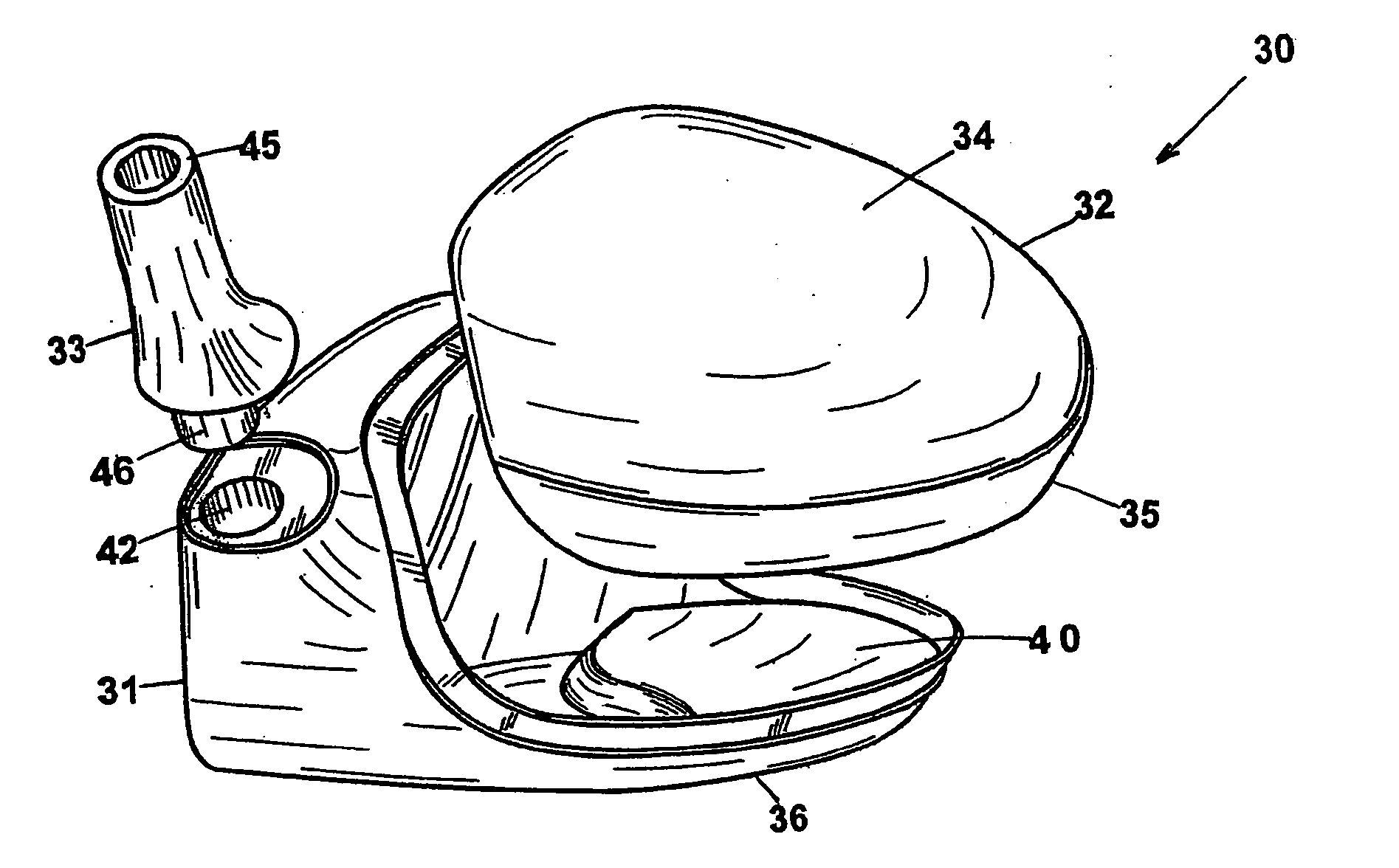
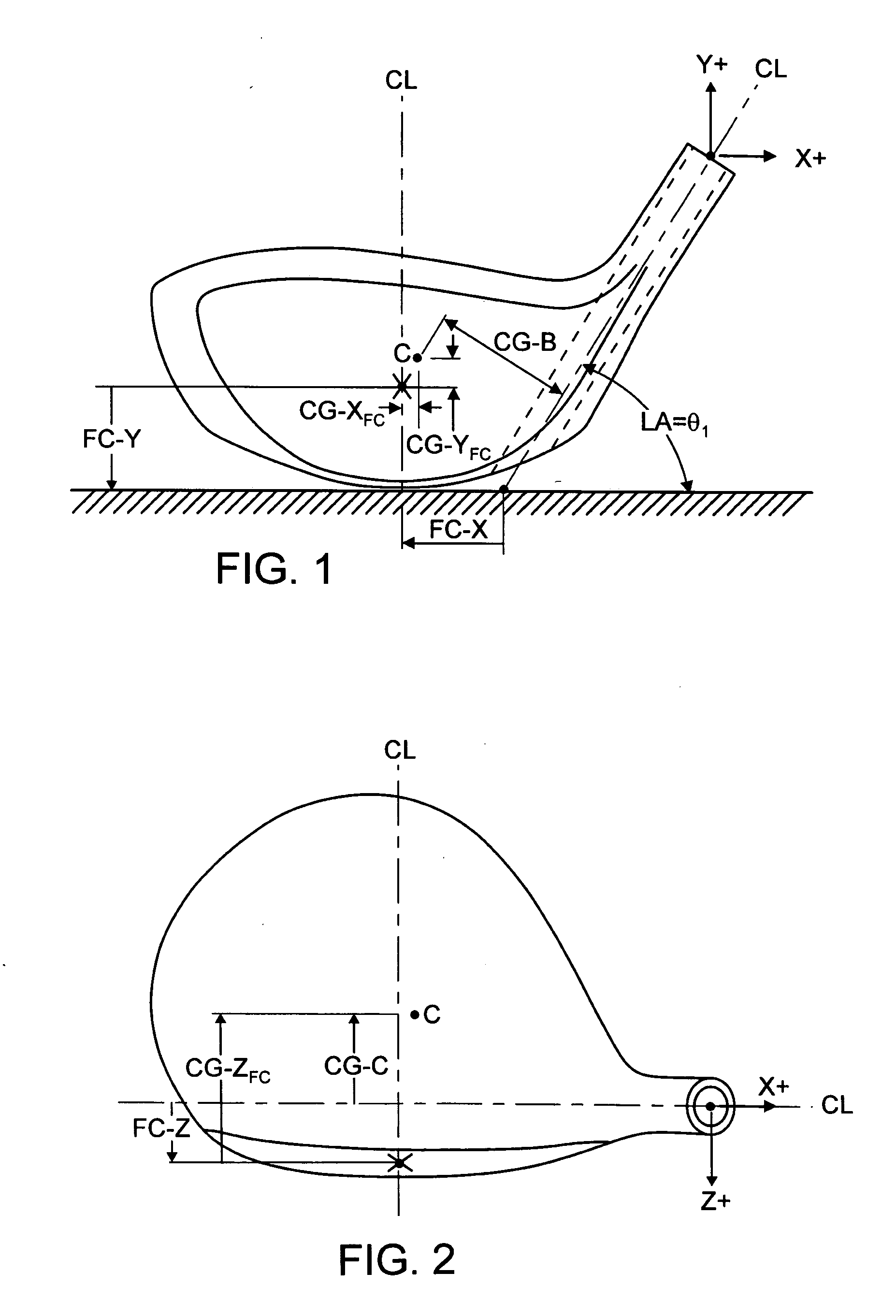
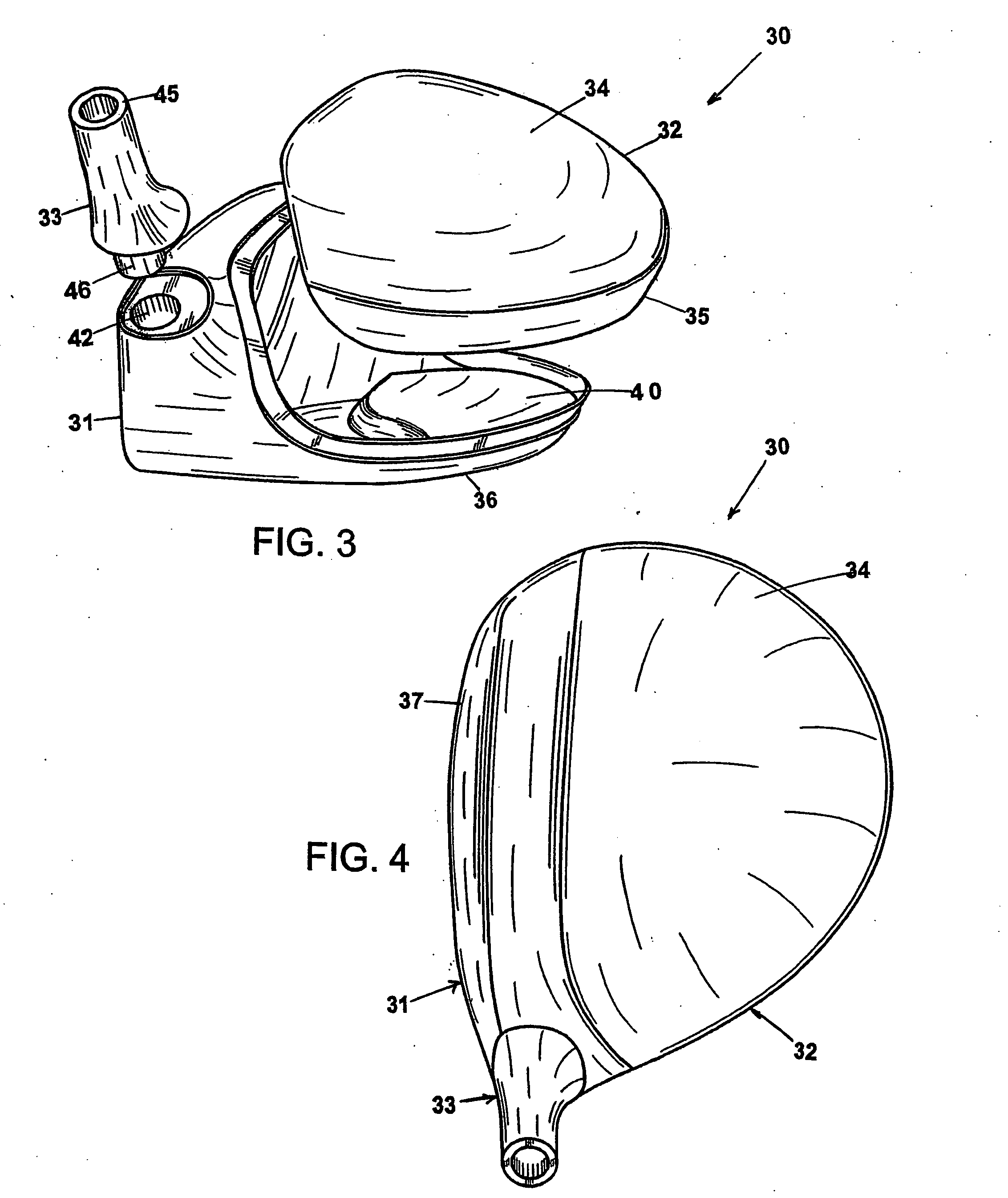
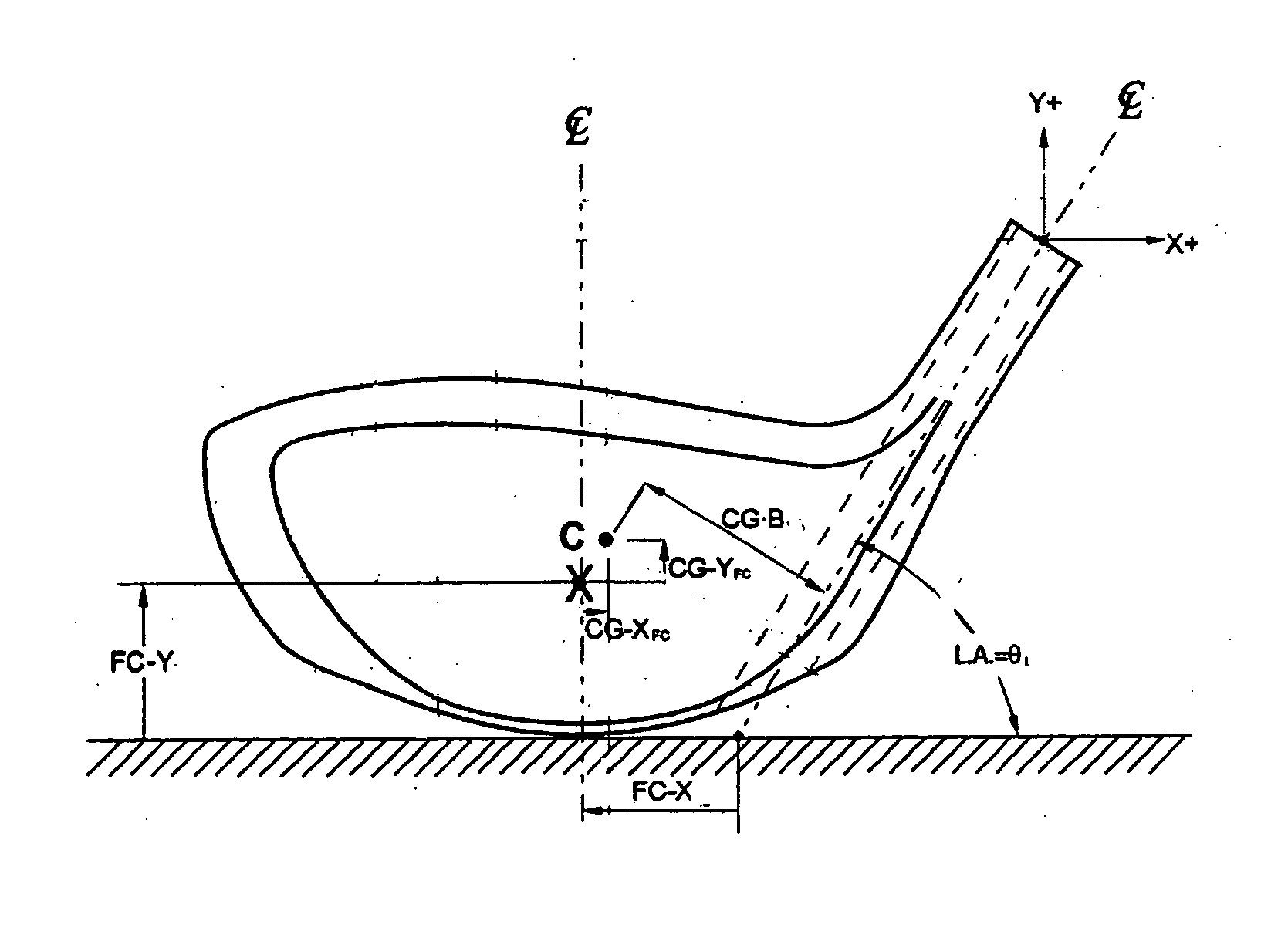
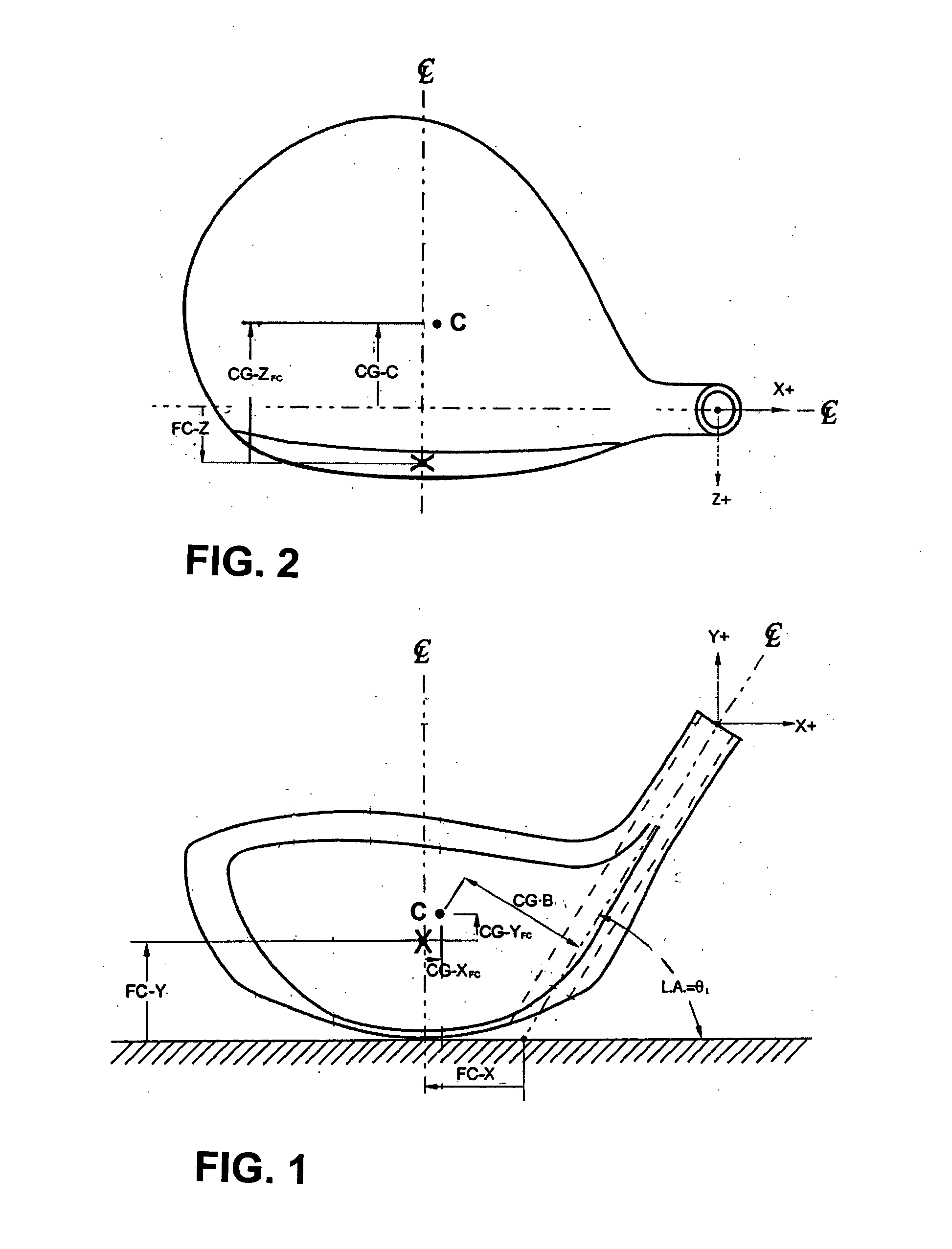
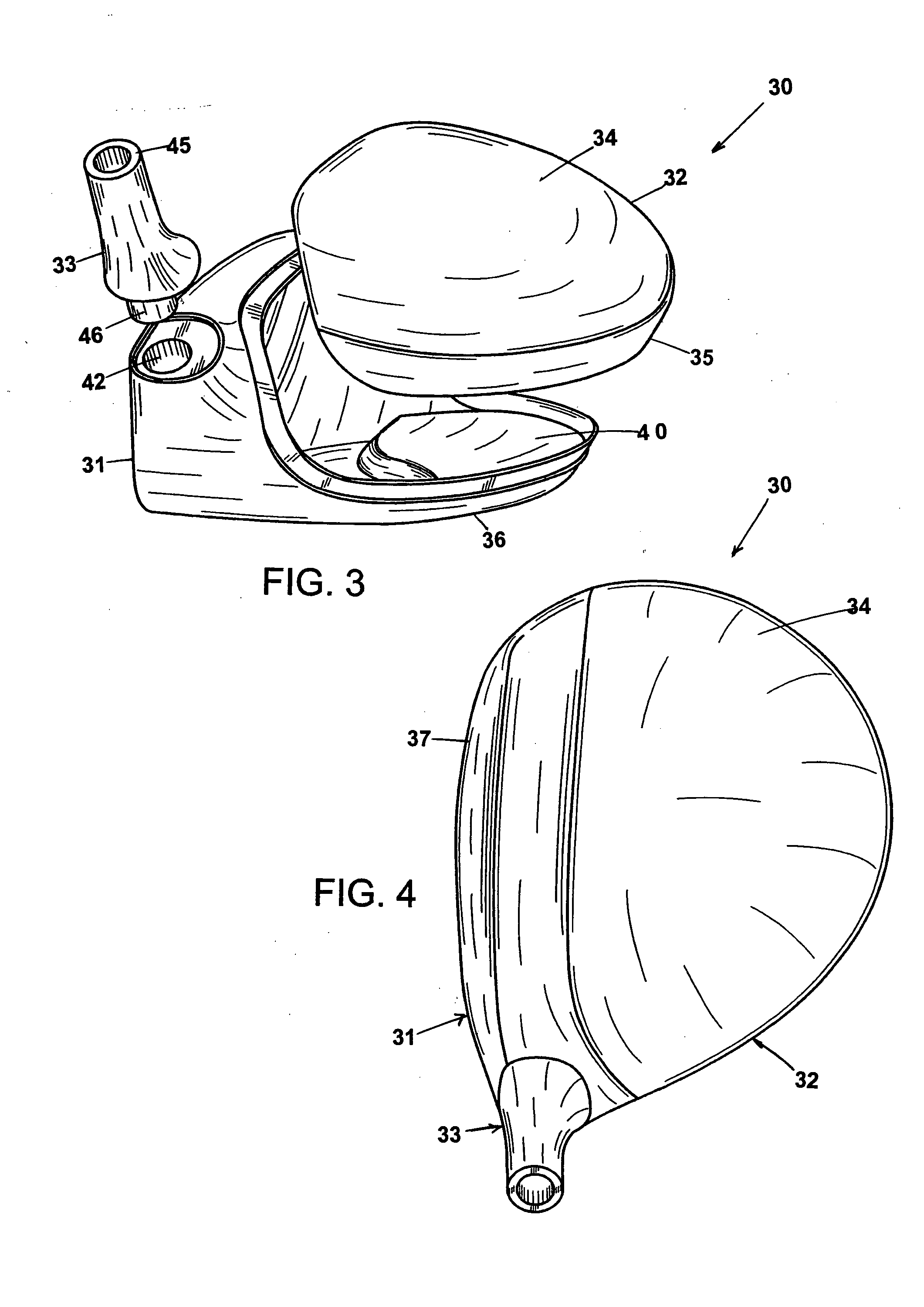
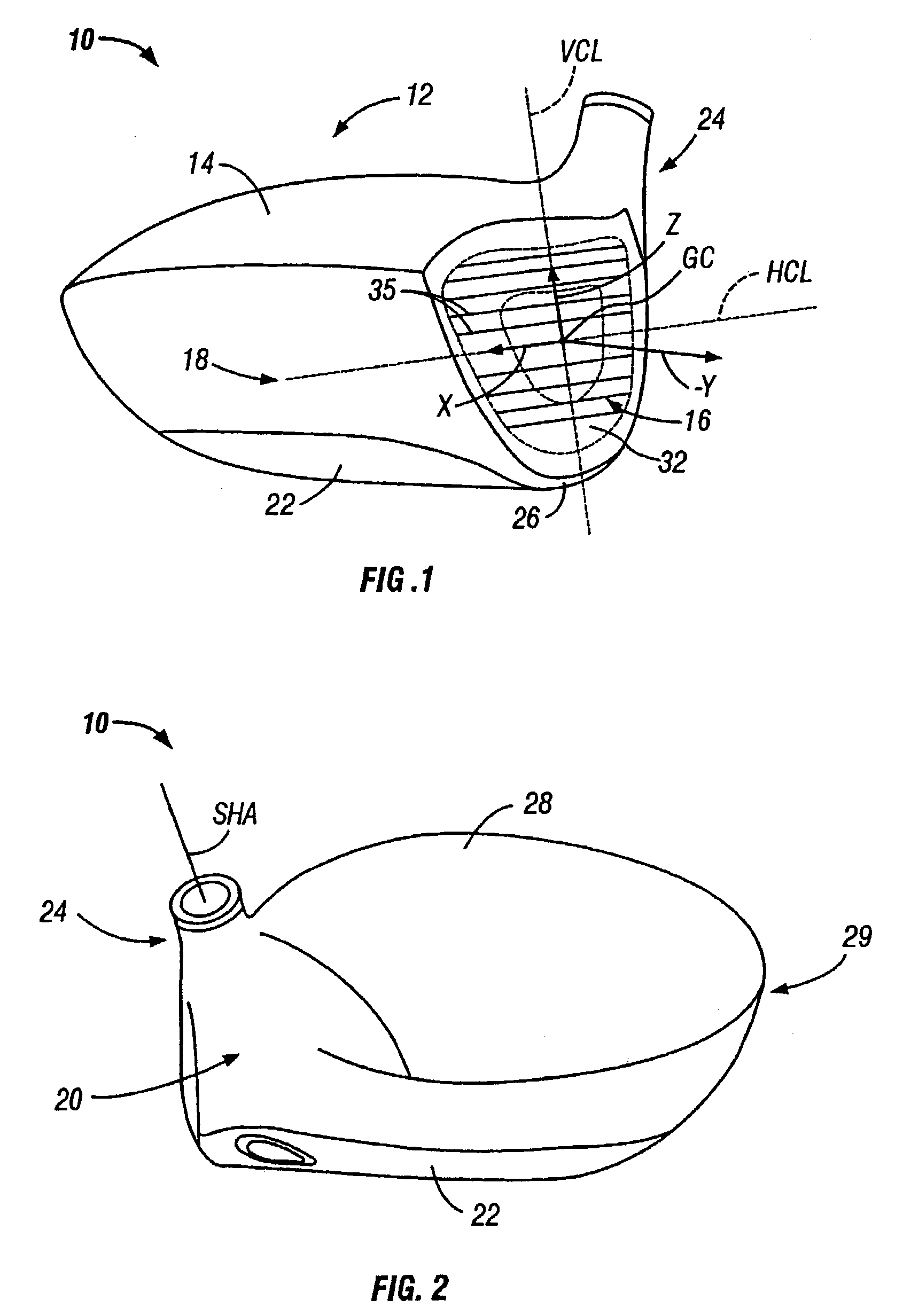
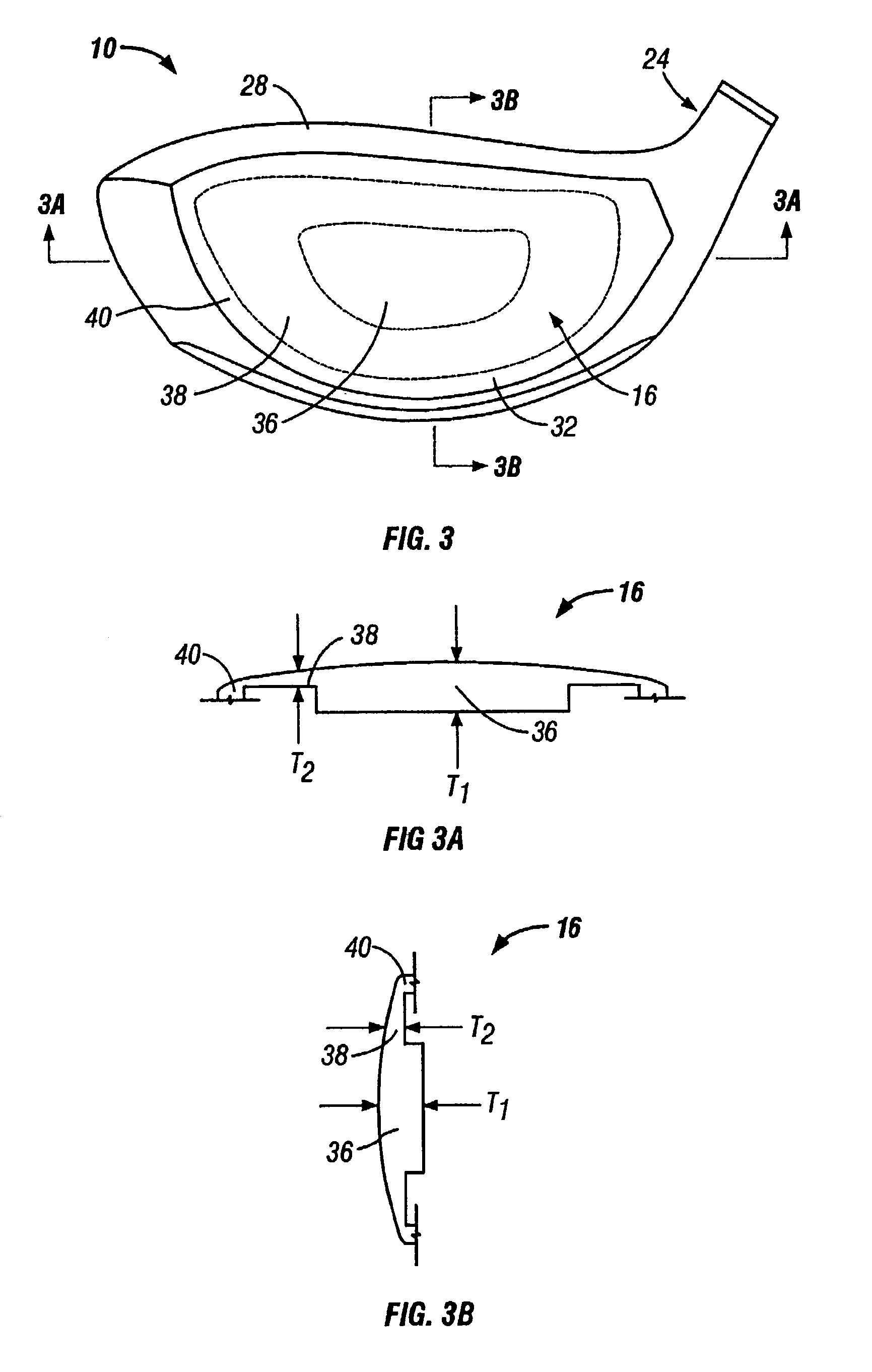
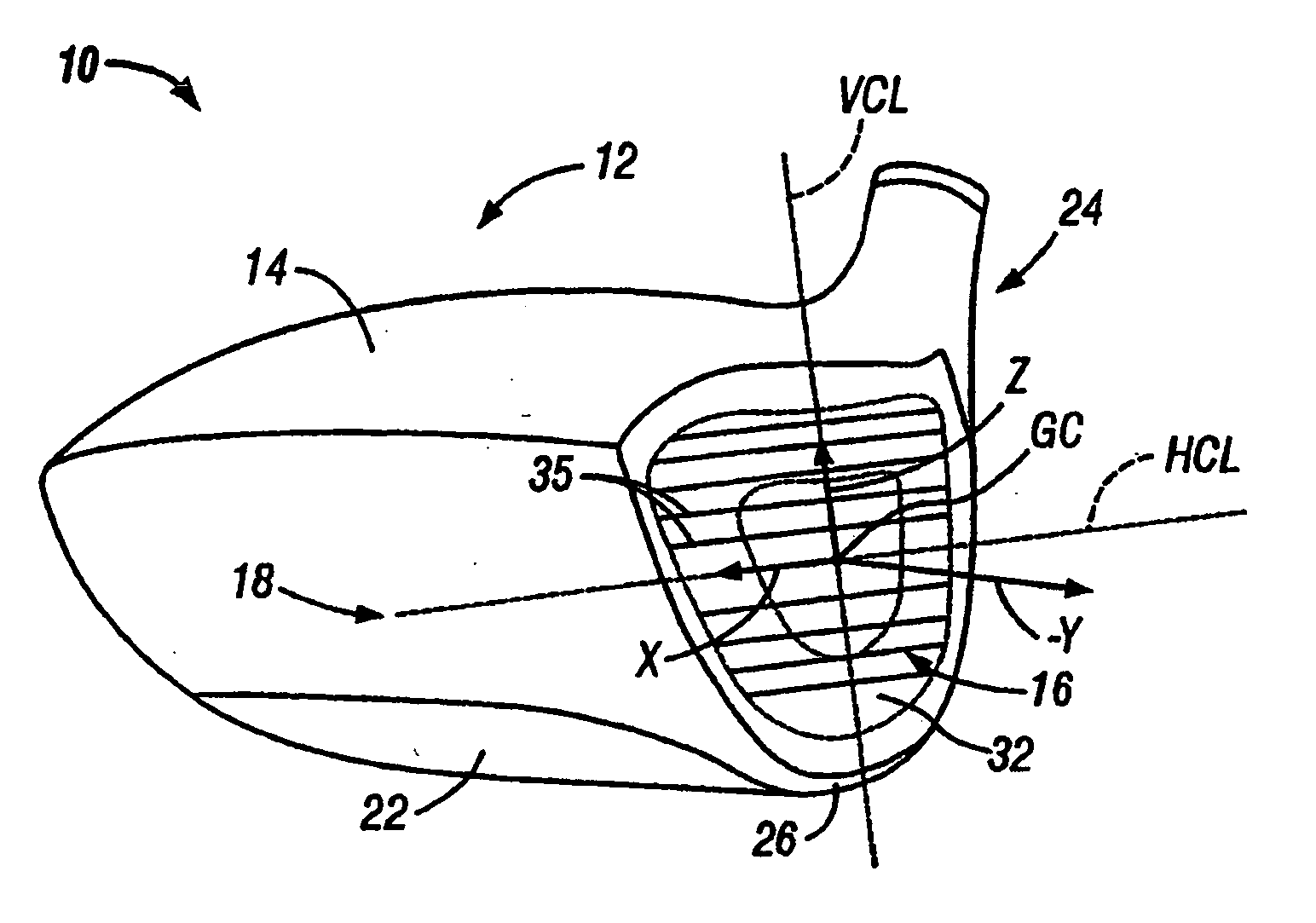
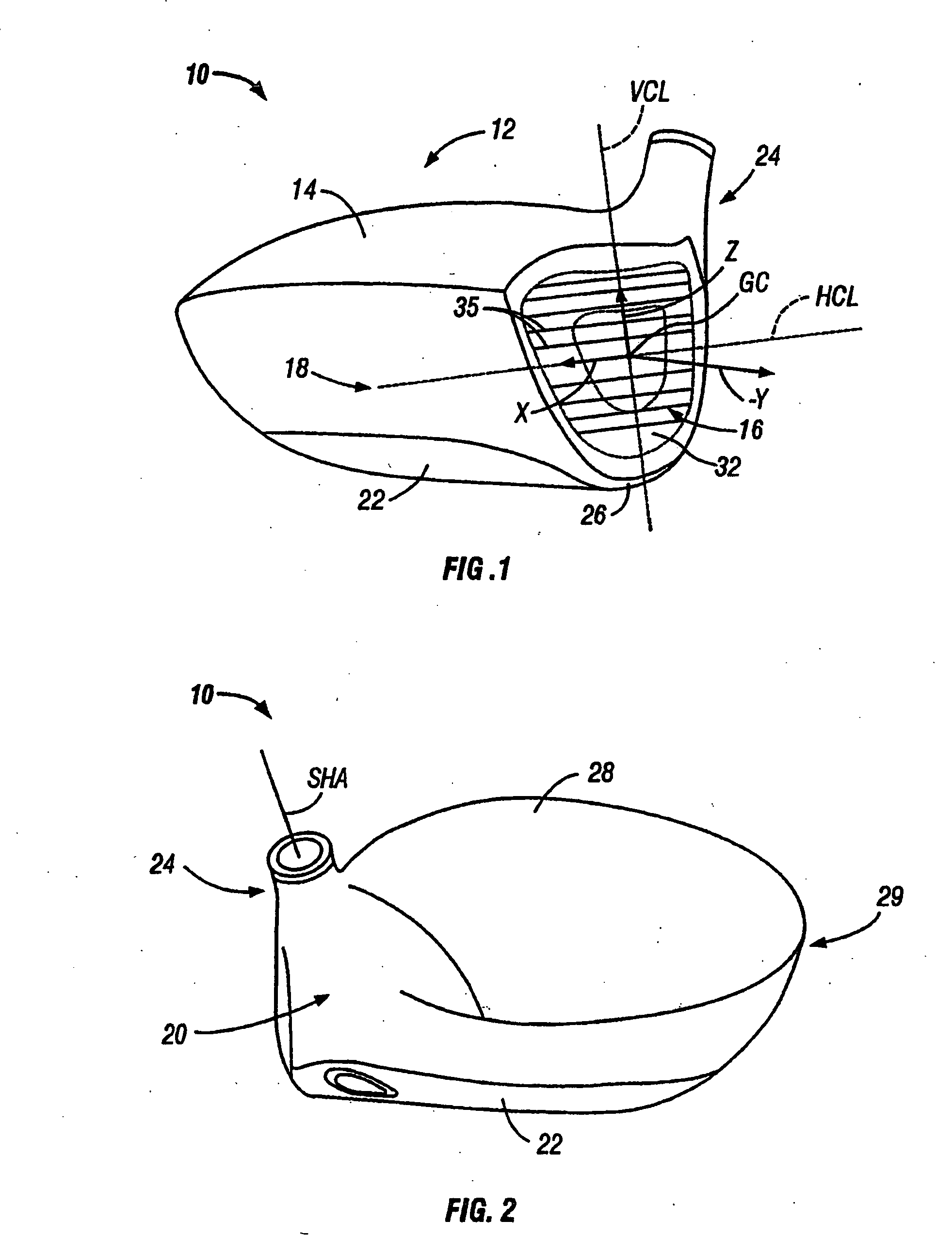
Golf club head
InactiveUS20060116218A1Increase deflectionSlow down the spin rateGolf clubsRacket sportsElastomerCoefficient of restitution
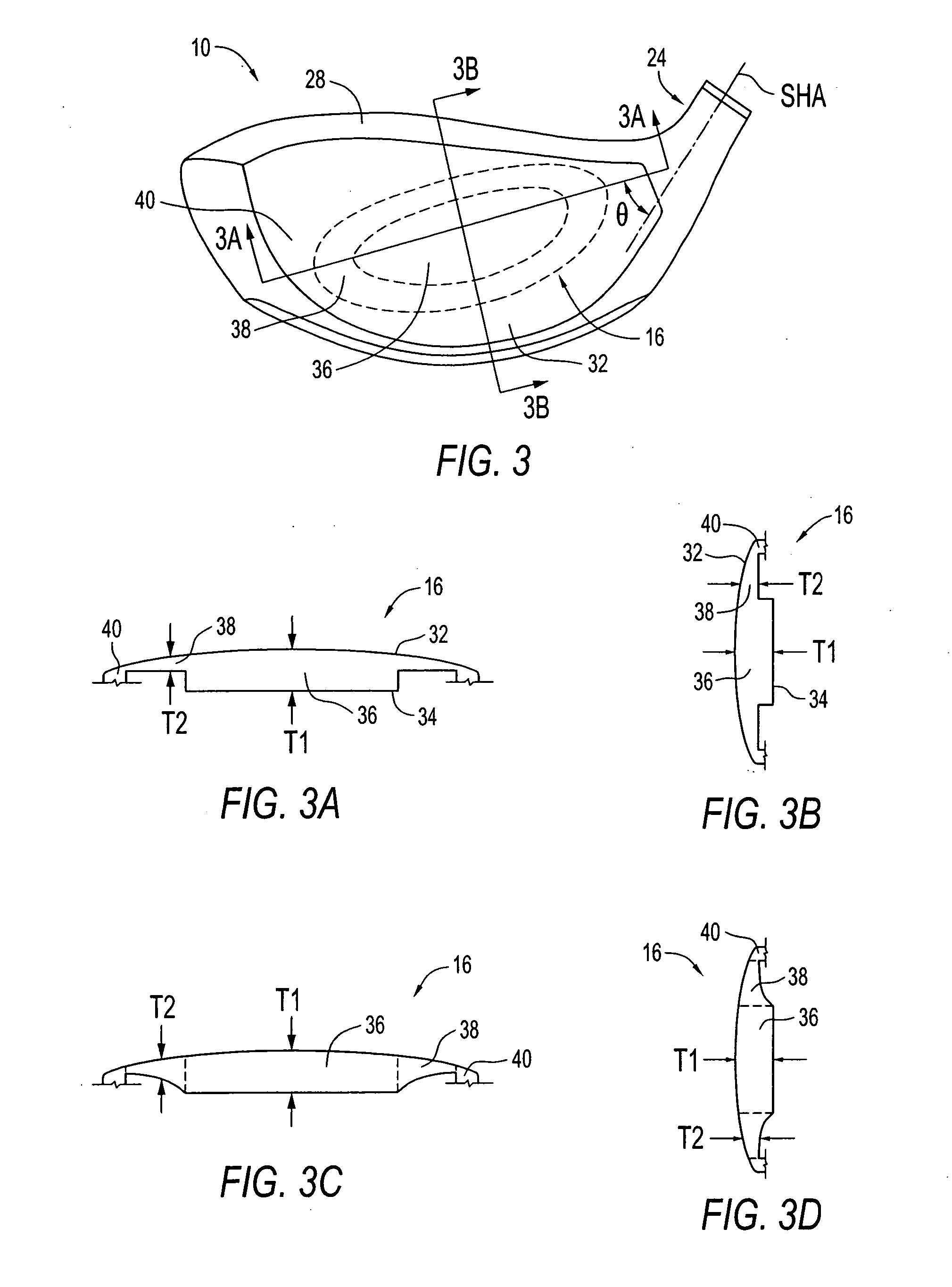
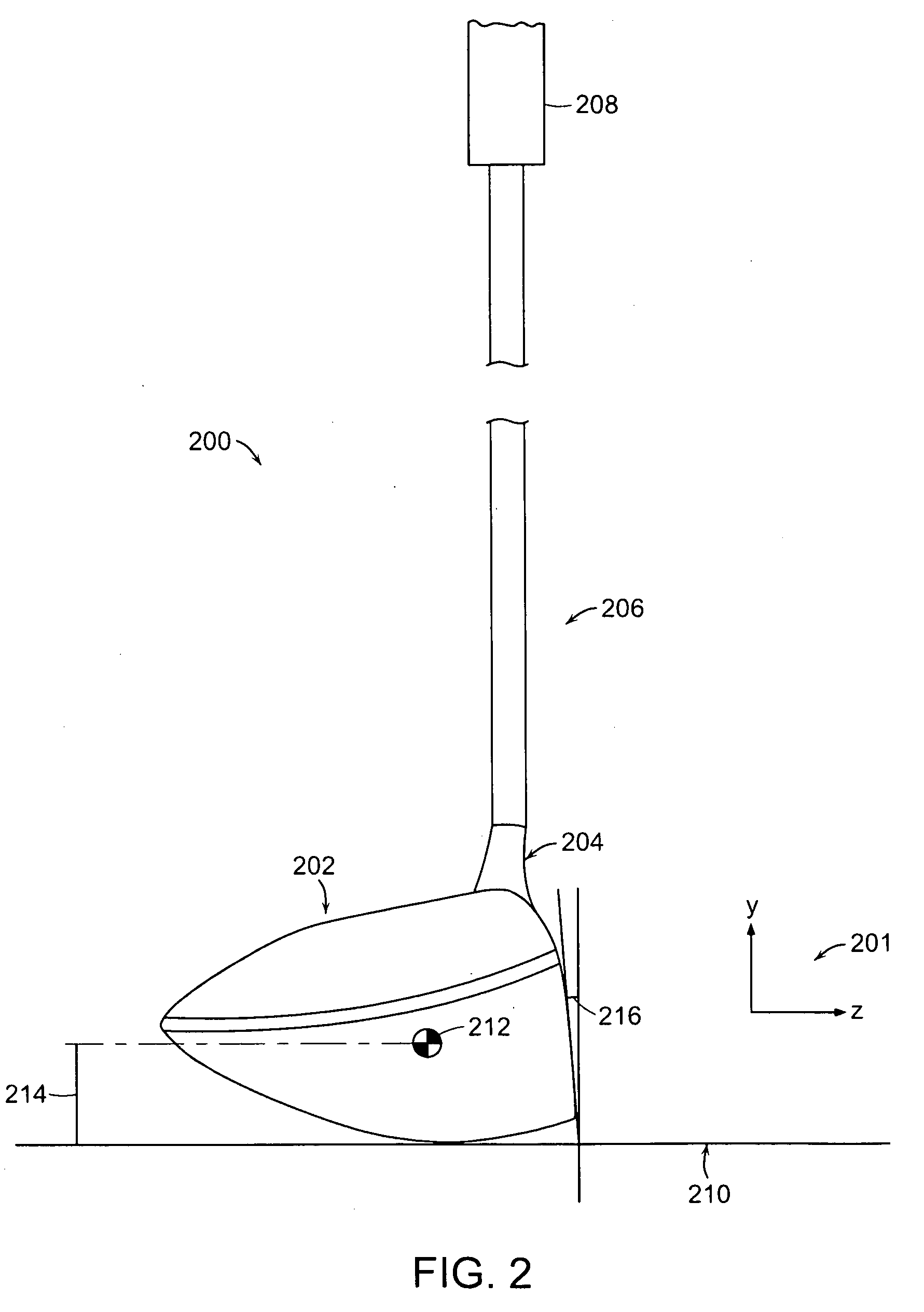
A metal wood golf club head is provided having a front face with an impact zone including a compliant area. Preferably, the compliant area is disposed in an upper portion of the front face. Preferably, a through-slit is provided in the front face to form the compliant area. The through-slit may be an elongated slot substantially parallel to a top of the front face and may include an elastomeric reinforcement. The compliant area creates an ultra-low center of gravity relative to the geometric face center, resulting in higher launch angles and spin rate ratios. The compliant area upwardly shifts the coefficient of restitution to the geometric center of the face and thereby increases the carry distance of a golf ball hit off the club head.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Multi-component golf club head
InactiveUS20050059508A1Lower center of gravityGolf clubsRacket sportsHigh densityCoefficient of restitution
A metal wood golf club head adapted for attachment to a shaft, with a body comprising of a first body portion and a second body portion, each portion constructed of a different density material. Combining a high density material in the first body portion with a low density material in the second body portion, creates an ultra-low center of gravity relative to the geometric face center, resulting in higher launch angles and spin rate ratios. Thickening the lower area of the front face lowers the center of gravity and upwardly shifts the coefficient of restitution to the geometric center of the face
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
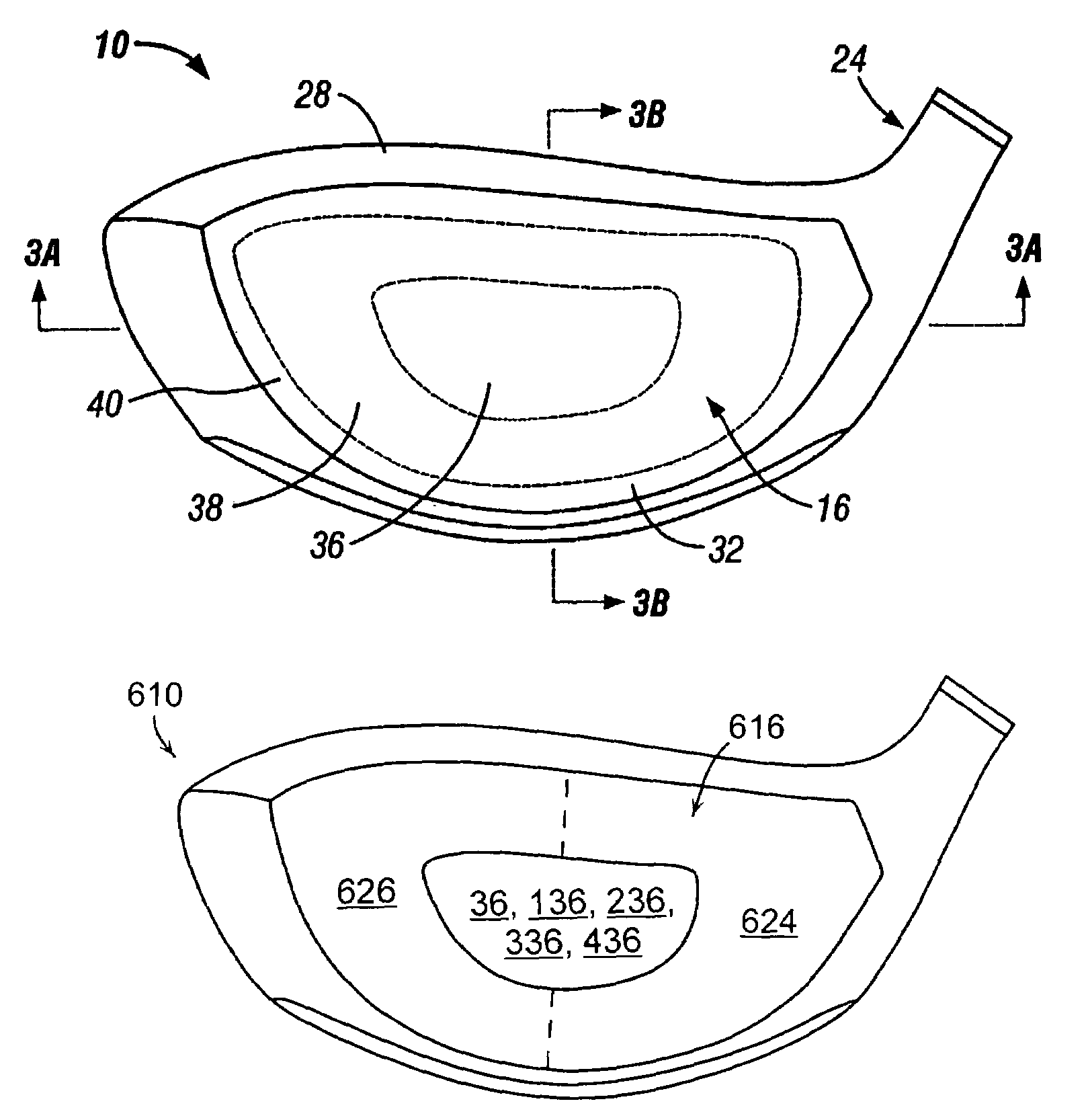
Golf club head with variable flexural stiffness for controlled ball flight and trajectory
InactiveUS7041003B2Increase ball speedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGolf clubsEngineeringControl zone
The present invention relates to a golf club head with a hitting face. The hitting face comprises a directional control portion, which has at least two zones with different flexural stiffness, such that when the hitting face strikes a golf ball the two zones deform differently to selectively control the direction of the flight of the golf ball. The directional control portion may comprise an upper zone and a lower zone, where the upper zone has a lower flexural stiffness. Alternatively, the lower zone has a lower flexural stiffness. On the other hand, the directional control portion may comprise a left zone and a right zone, and either the left or right zone may have a lower flexural stiffness to selectively control the lateral launch angle either to the left of right. The hitting face may further comprise a central zone disposed within the directional control zone, wherein the central zone has a flexural stiffness of at least about three times greater than the flexural stiffness of the directional control zone.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf club head with progressive face stiffness
ActiveUS20060019770A1The material is lowIncrease stiffnessGolf clubsRacket sportsHigh densityCoefficient of restitution
A metal wood golf club head adapted for attachment to a shaft, with a body comprising of a first body portion and a second body portion, each portion constructed of a different density material. Combining a high density material in the first body portion with a low density material in the second body portion, creates an ultra-low center of gravity relative to the geometric face center, resulting in higher launch angles and spin rate ratios. Thickening the lower area of the front face lowers the center of gravity and upwardly shifts the coefficient of restitution to the geometric center of the face.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf club head with progressive face stiffness
ActiveUS7651412B2The material is lowIncrease stiffnessGolf clubsRacket sportsHigh densityCoefficient of restitution
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Method and apparatus for measuring ball launch conditions
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf club head with variable flexural stiffness for controlled ball flight and trajectory
InactiveUS20060094531A1Increase ball speedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGolf clubsEngineeringControl zone
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
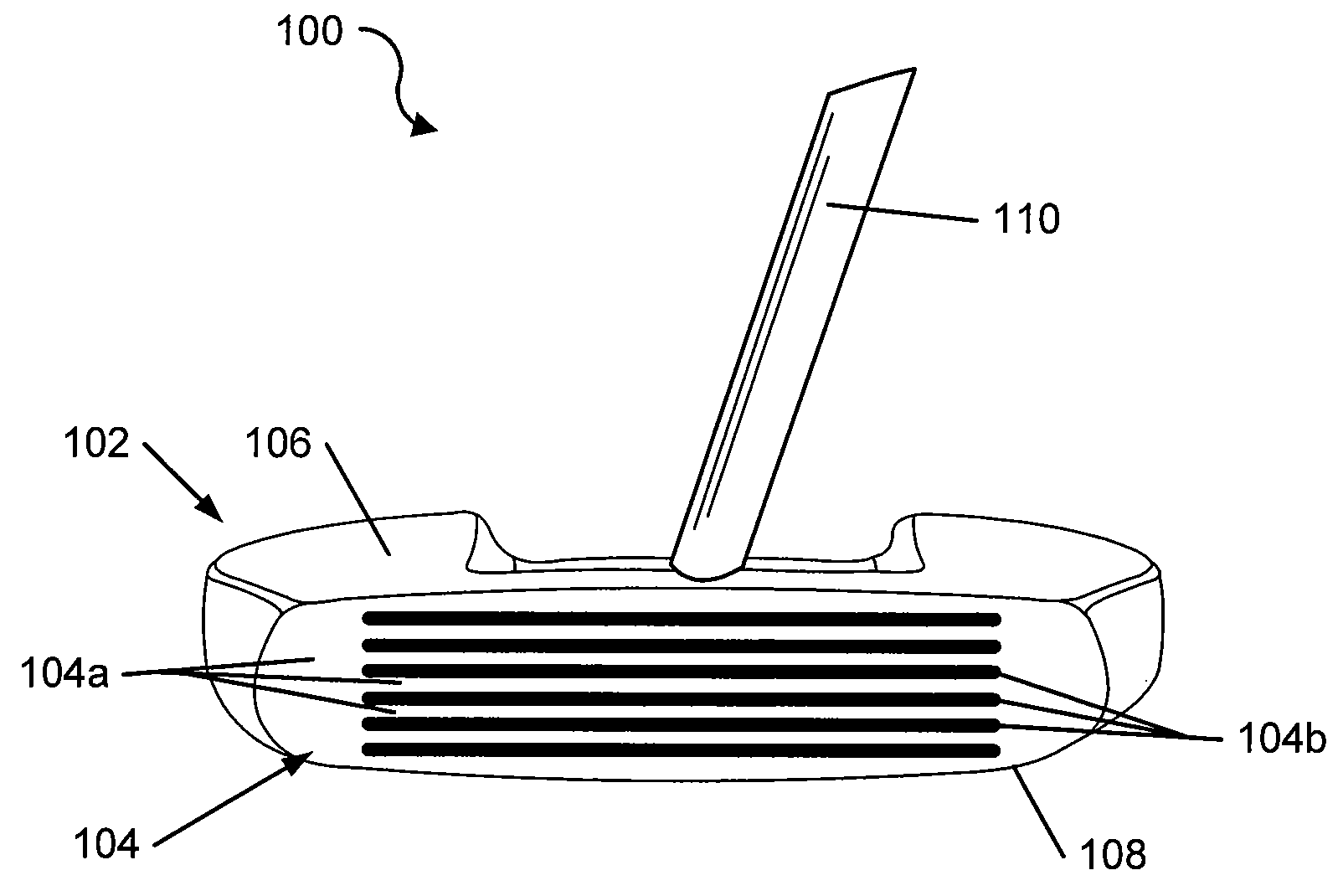
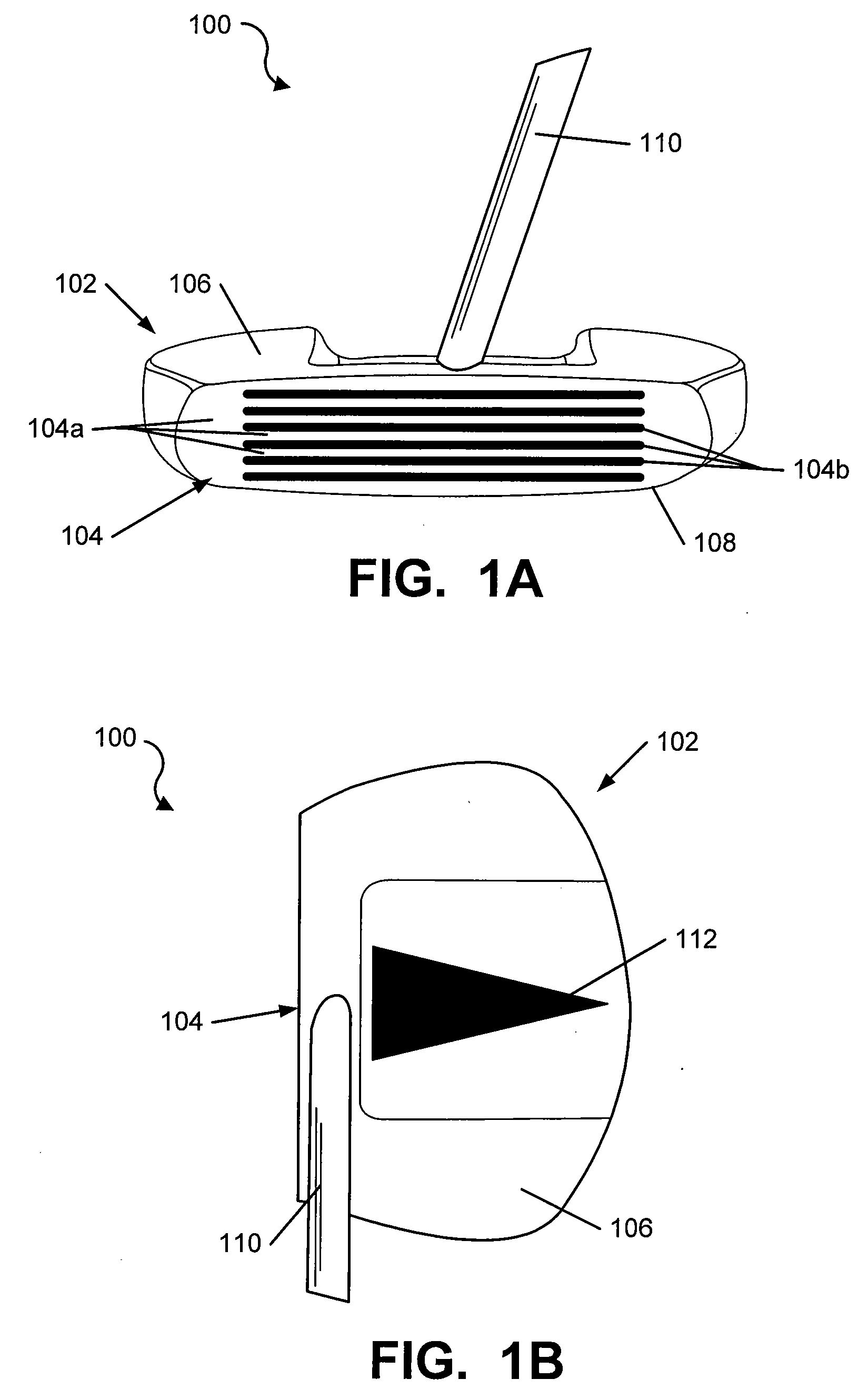
Putter Heads and Putters Including Polymeric Material as Part of the Ball Striking Face
ActiveUS20090286620A1Lighten the structureImprove featuresGolf clubsRacket sportsHardnessEngineering
Putters include a putter body having a ball striking face member made of a material having a first hardness characteristic. A cavity is defined in the putter body behind the ball striking face member, and plural openings are defined in the ball striking face member extending rearward with respect to the ball striking face member and into the cavity. A polymeric material at least partially fills the openings and the cavity, wherein the polymeric material has a second hardness characteristic that is softer than the first hardness characteristic. The ball striking face member and the polymeric material exposed in at least some of the openings provide a ball striking surface of the putter. The ball striking surface may include grooves or scorelines to affect the launch angle, spin, and / or roll of the ball during a putt. Methods for making such putter devices also are described.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
Projector
InactiveUS6877862B2Adjustment of set up easierRealize automatic adjustmentTelevision system detailsProjectorsOptoelectronicsLaunch angle
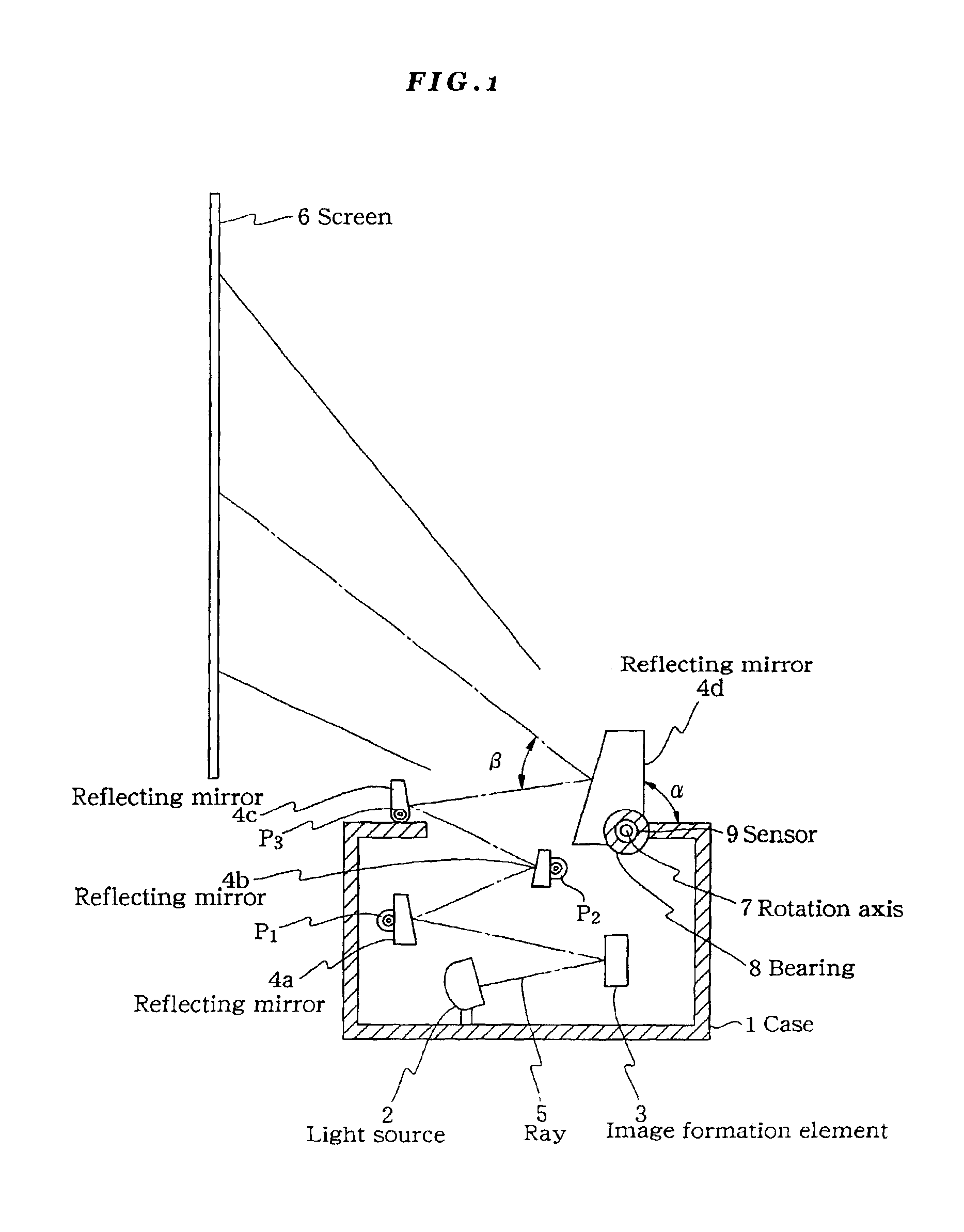
A reflecting mirror 4d has a rotation axis 7 which is inserted into a bearing 8 of a case 1. Accordingly, the reflecting mirror 4d is capable of rotating with respect to the case 1 and only the reflecting mirror 4d is capable of adjusting the set up angle α made with the case 1. When the set up angle is changed, the reflecting angle of the projected ray on the reflecting mirror 4d is also changed. Therefore, the launching angle of the projected ray 5 with respect to the case 1 can be adjusted.
Owner:NEC DISPLAY SOLUTIONS LTD
Method and system for selecting a golf club
A method for selecting a golf club suitable for a golfer includes the steps of (a) obtaining at least one of head speed and hit-ball data (initial velocity, launch angle, backspin, side spin, and travel distance) when a golfer hits a golf ball with a golf club; (b) obtaining ideal hit-ball data of the golfer on the basis of the at least one of head speed and hit-ball data obtained in step (a); and (c) selecting a golf club suitable for the golfer on the basis of the ideal hit-ball data obtained in step (b).
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Composite metal wood club
InactiveUS20060293118A1Increased bending stiffnessIncrease elasticityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGolf clubsSurface layerHigh density
A metal wood golf club head adapted for attachment to a shaft, comprising of a body portion and a crown portion, each portion constructed of a different density material. Combining a high-density material in the body portion, with a low-density material in the crown portion, creates an ultra-low center of gravity relative to the geometric face center, resulting in higher launch angles and spin rate ratios. The material for the crown portion is preferably a composite. The crown portion comprises an inner surface layer of a vibration dampening material. The transverse surfaces of the crown and body portions creating a gap that is filled with a shock absorption material such as putty or a rubber based structural adhesive.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Multi-piece solid golf ball
ActiveUS20120100933A1Improve controllabilityFeel goodGolf ballsSolid ballsRubber materialEngineering
A multi-piece solid golf ball has a core, an envelope layer encasing the core, an intermediate layer encasing the envelope layer, and a cover which encases the intermediate layer and has formed on a surface thereof a plurality of dimples. The envelope layer is formed of an inner envelope layer, an intermediate envelope layer and an outer envelope layer. The inner, intermediate and outer envelope layers, the intermediate layer and the cover are each formed primarily of a resin material which may be of the same or different types, and the core is formed primarily of a rubber material. The cover has a material hardness which is the same as or lower than the core center hardness. One of the inner layers has a material hardness which is higher than either or both of the cover material hardness and the average core hardness (defined as the arithmetic mean of the core surface hardness and the core center hardness). The golf ball, even when used by those golfers among professionals and skilled amateurs who, on striking a ball with a driver, tend to generate shots having a rather low spin rate and a low launch angle, has an excellent flight performance and also excellent controllability in the short game that are acceptable to such users. In addition, it has a good feel on impact and an excellent scuff resistance.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
High launch and low spin golf ball and golf club combination
The present invention is directed to a golf club and golf ball combination that maximizes the distance of travel when the golf club strikes the golf ball. More specifically, a golf club and golf ball combination capable of generating a higher launch angle combined with the lower spin rate to maximize the distance. The golf club in accordance with the present invention may generally have a lower center of gravity, a higher loft angle, or may even have a coating on the club face that optimizes the coefficient of friction between the golf club and the golf ball. The golf ball in accordance with the present invention may generally have a ratio of the coefficient of lift (CL) near the beginning of flight to the coefficient of lift near the end of the flight within a range that maximizes flight distance, with similar ratios in appropriate ranges for the coefficient of drag (CD) and the lift-to-drag ratio (CL / CD).
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
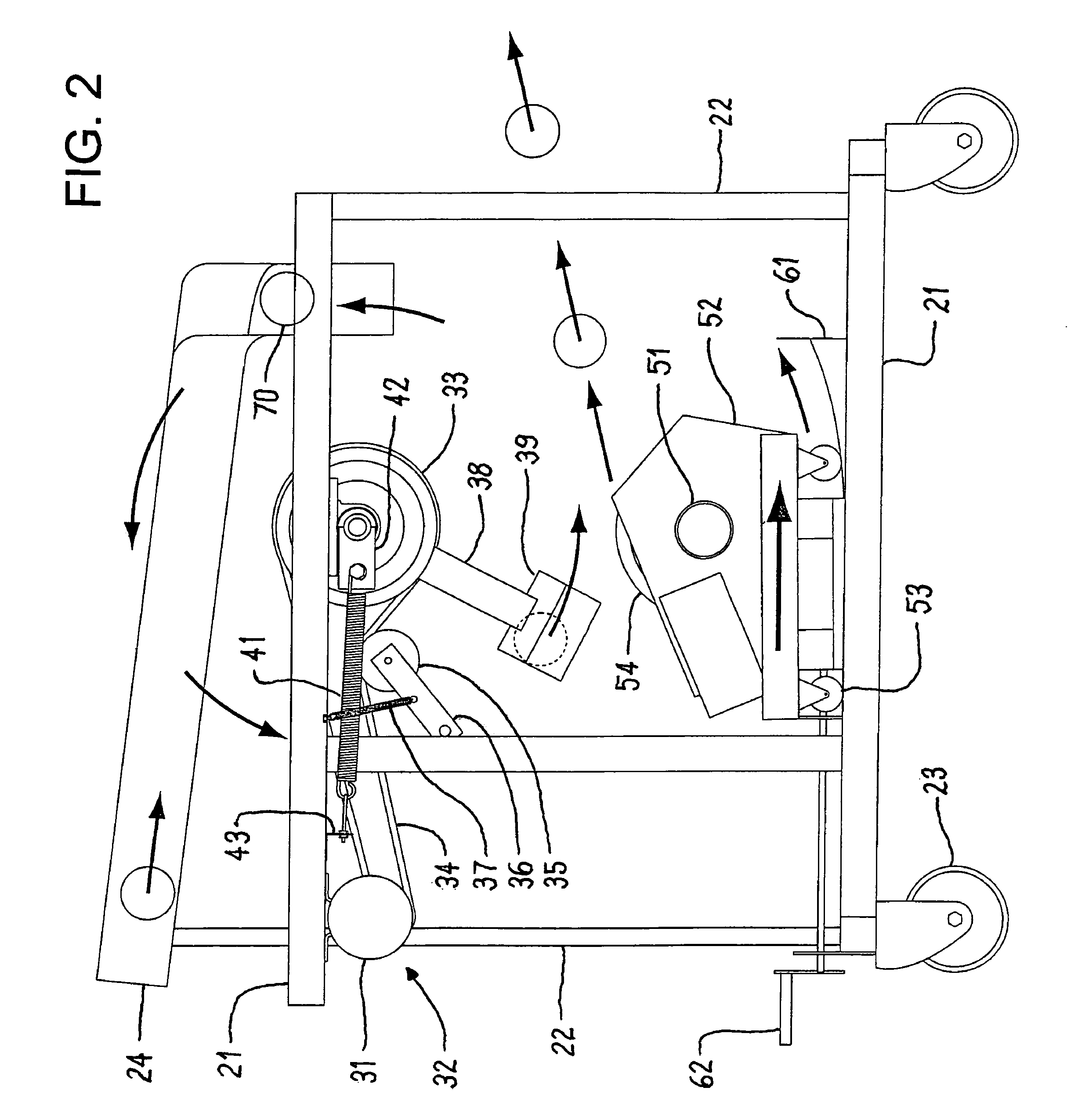
Pitching machine
InactiveUS7806788B1Light weightReduce manufacturing costLiquid ejecting gunsCompressed gas gunsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A pitching machine contains a pitching arm that vertically rotates at a speed of about 5 to 15 rpm, picks up a ball from the ball cradle at a pick-up point in its rotation, and then releases the ball at a release point in its rotation to provide a first velocity component to the ball. The pitching machine also contains a wheel that vertically rotates at a speed of about 300 to 3000 rpm. The wheel is positioned at the release point of the pitching arm to provide a second velocity component to the ball and to pitch the ball at an initial launch angle.
Owner:NEUMAN DANIEL R
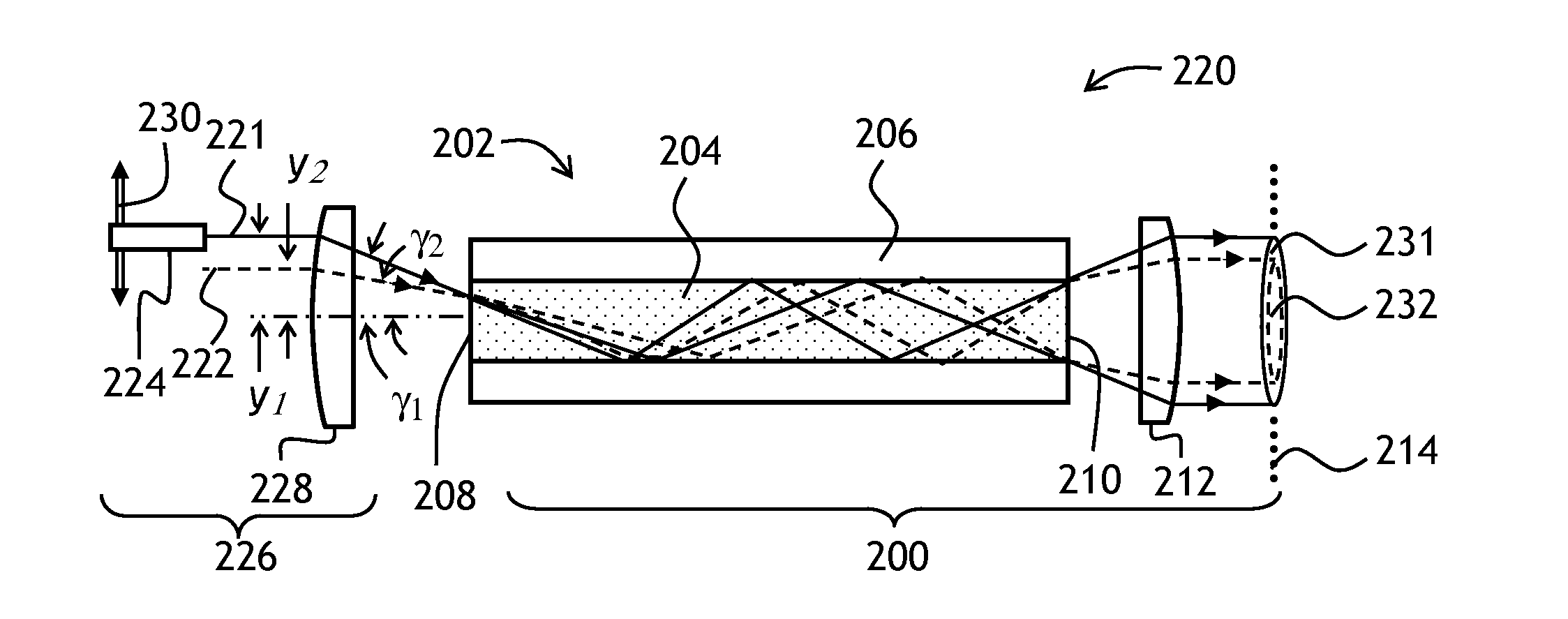
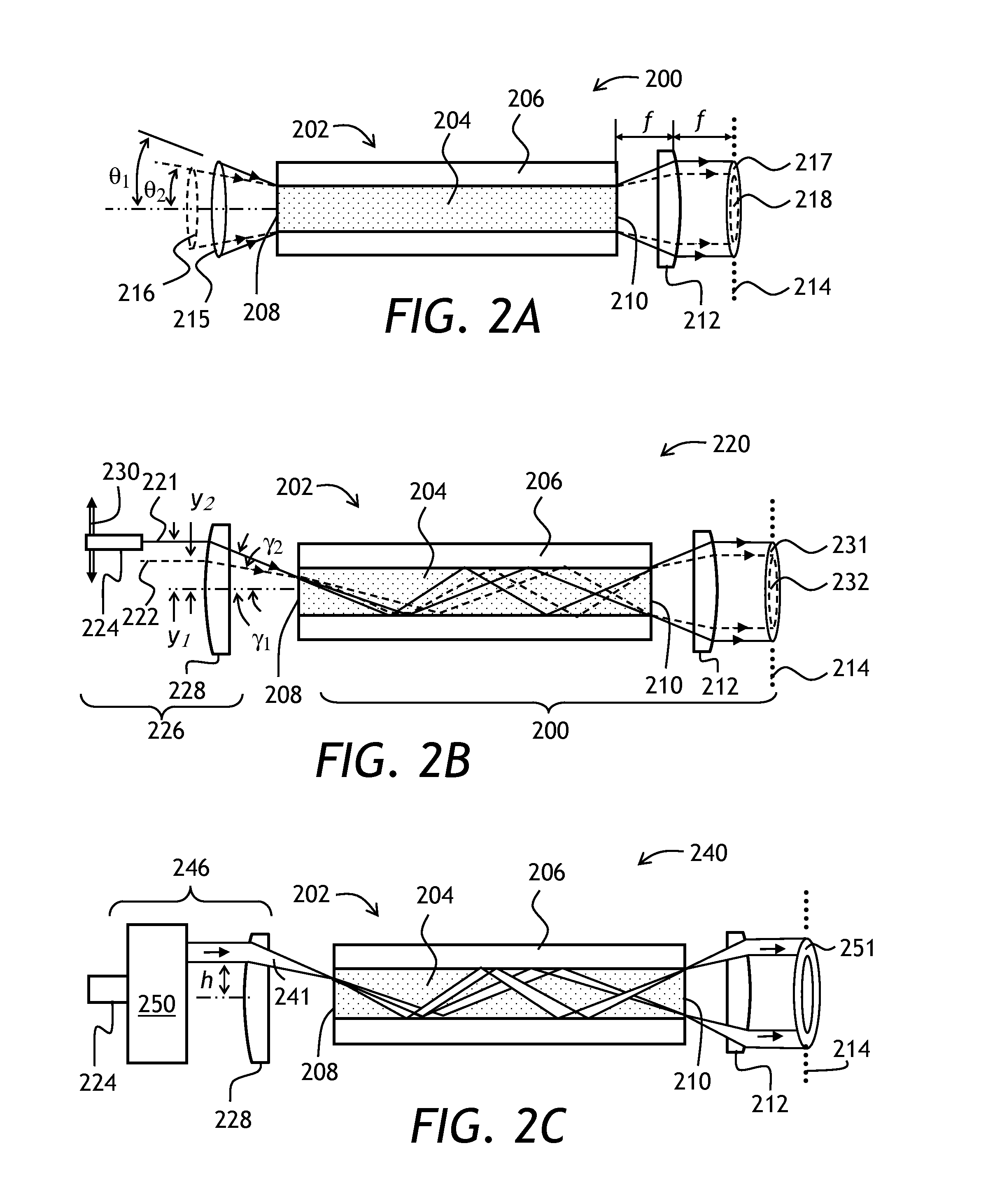
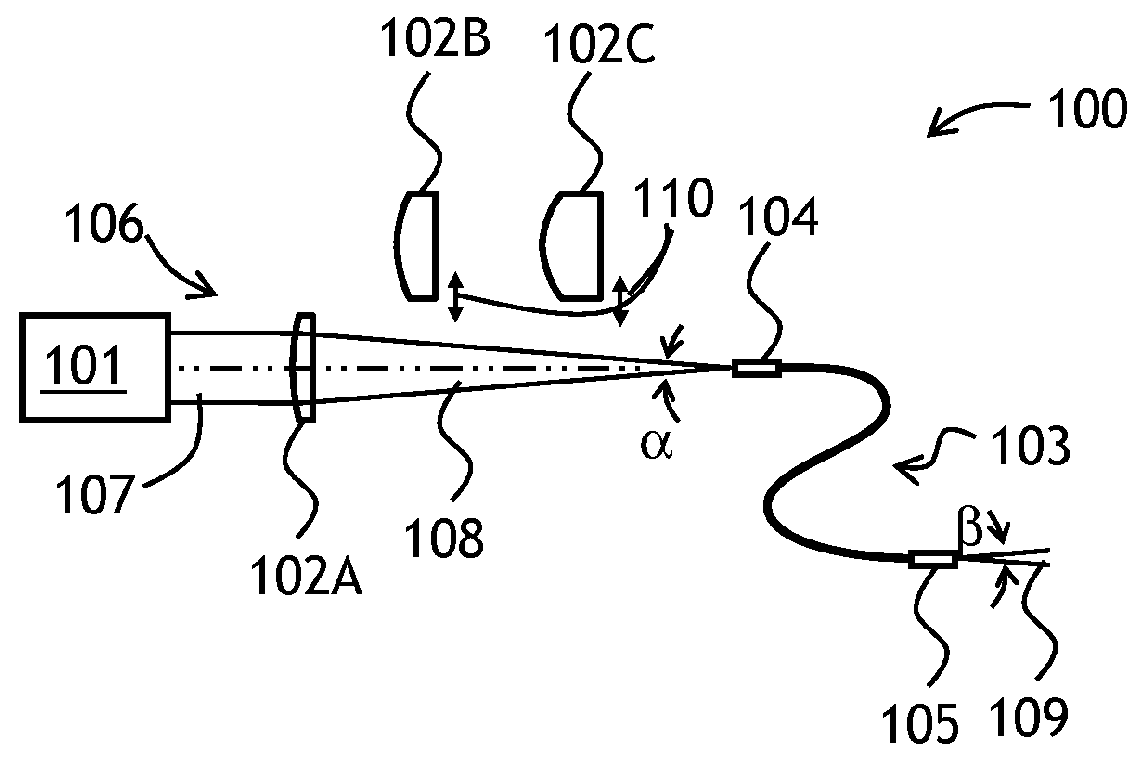
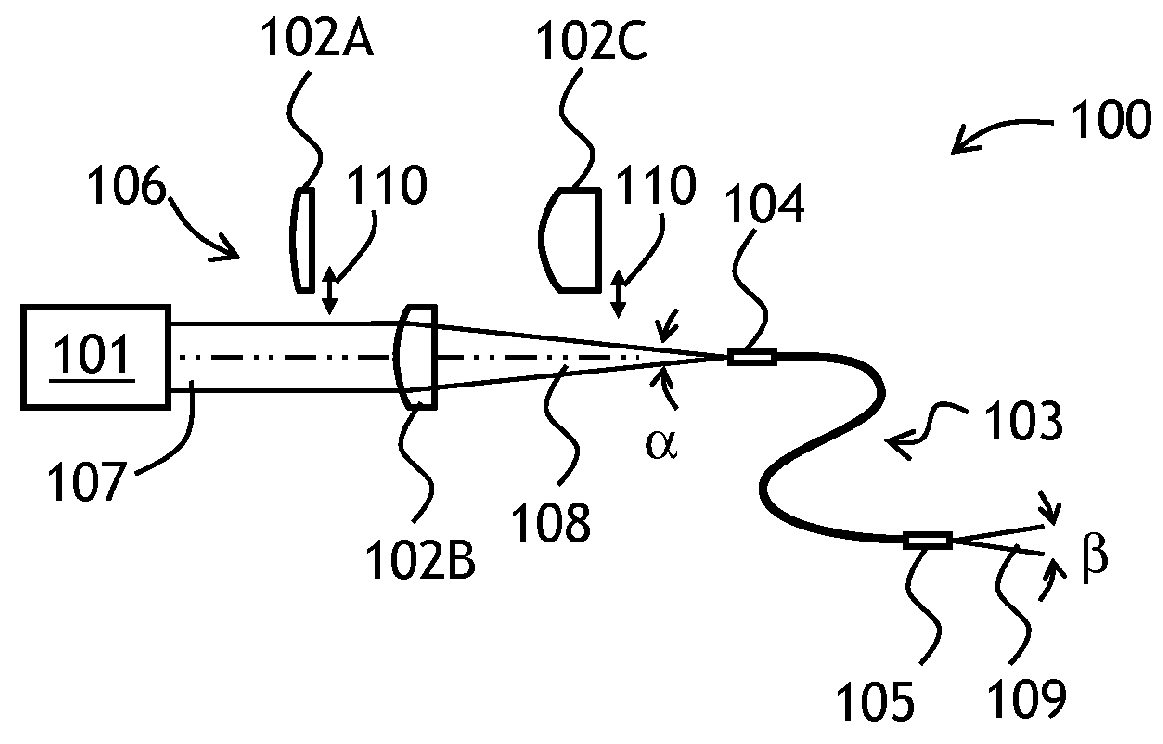
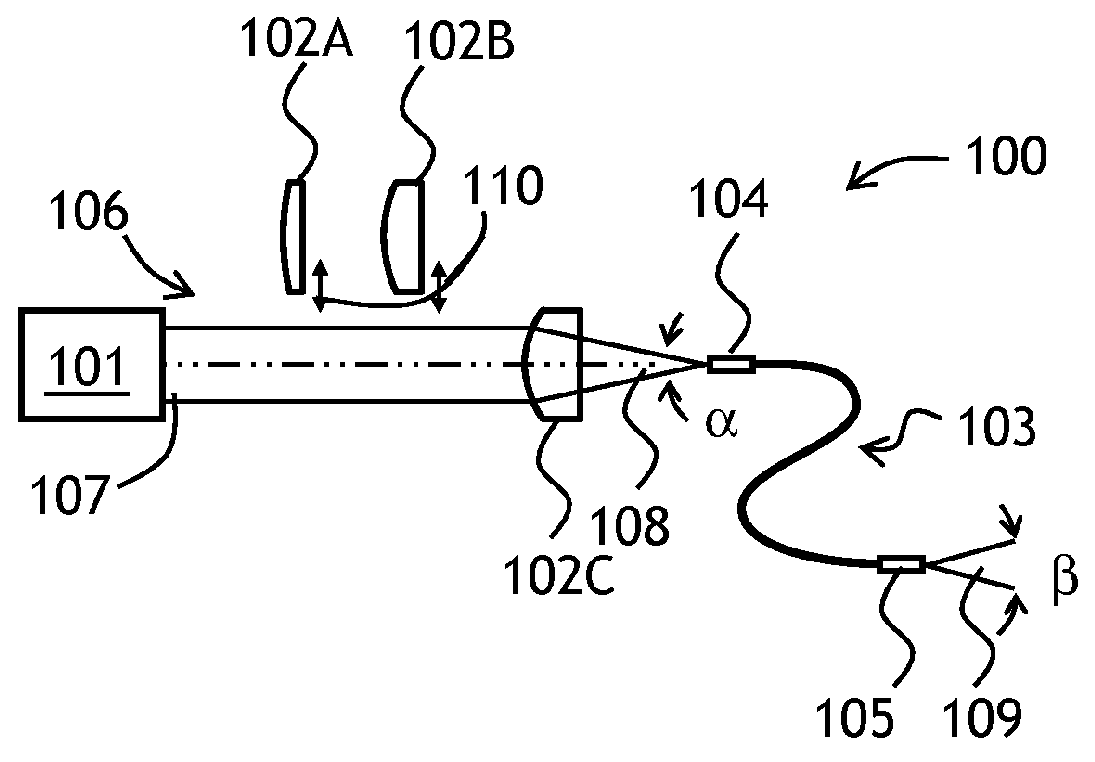
Self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system capable of bilaterally receiving and transmitting laser beams
ActiveCN103311790ARealize two-way sending and receivingAchieving Synchronous Adaptive CorrectionLaser output parameters controlActive medium shape and constructionOptical fiber couplerHigh pressure
The invention discloses a self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system capable of bilaterally receiving and transmitting laser beams. The self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system comprises a coupling or collimating lens, a connecting sleeve, an optical fiber end face positioner, a first optical fiber, a three-port optical fiber circulator, a second optical fiber, a third optical fiber, a laser, a photoelectric detector, a control platform and a high-voltage amplifier, wherein the optical fiber end face positioner comprises a flexible crossed beam, a bimorph driver, a damping material, a boss and a fixed seat. Due to the adoption of the self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system, the light beam arriving angle errors caused by factors such as atmosphere turbulence, mechanical vibration, thermal distortion and the like can be corrected adaptively; and meanwhile, according to the reversibility principle of a light path, the transmitting angle correction of emitted collimating light beams is also realized. The self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system has an important application prospect in the field of optical fiber-based laser space application, such as free space laser communication, laser precise positioning and laser radar.
Owner:成都芯智锐光科技有限公司
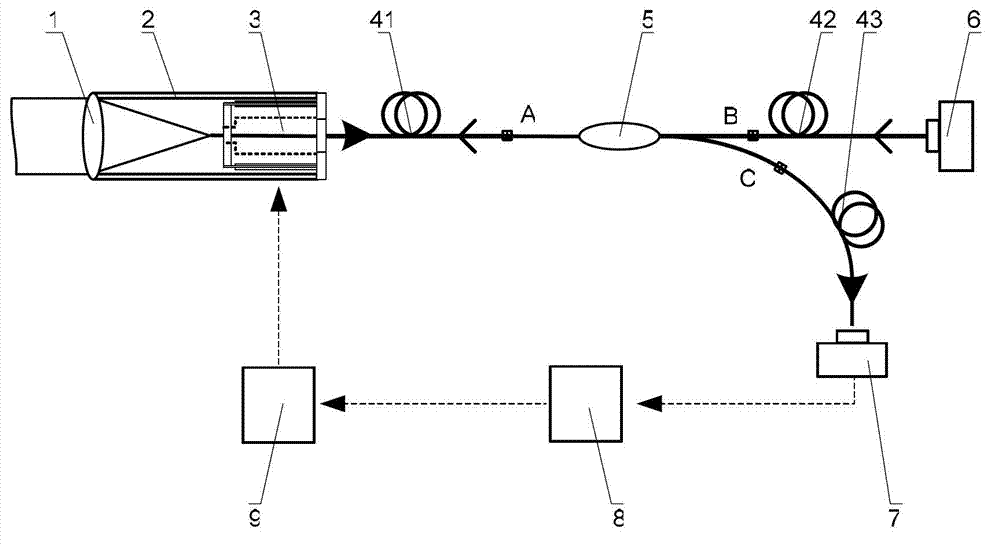
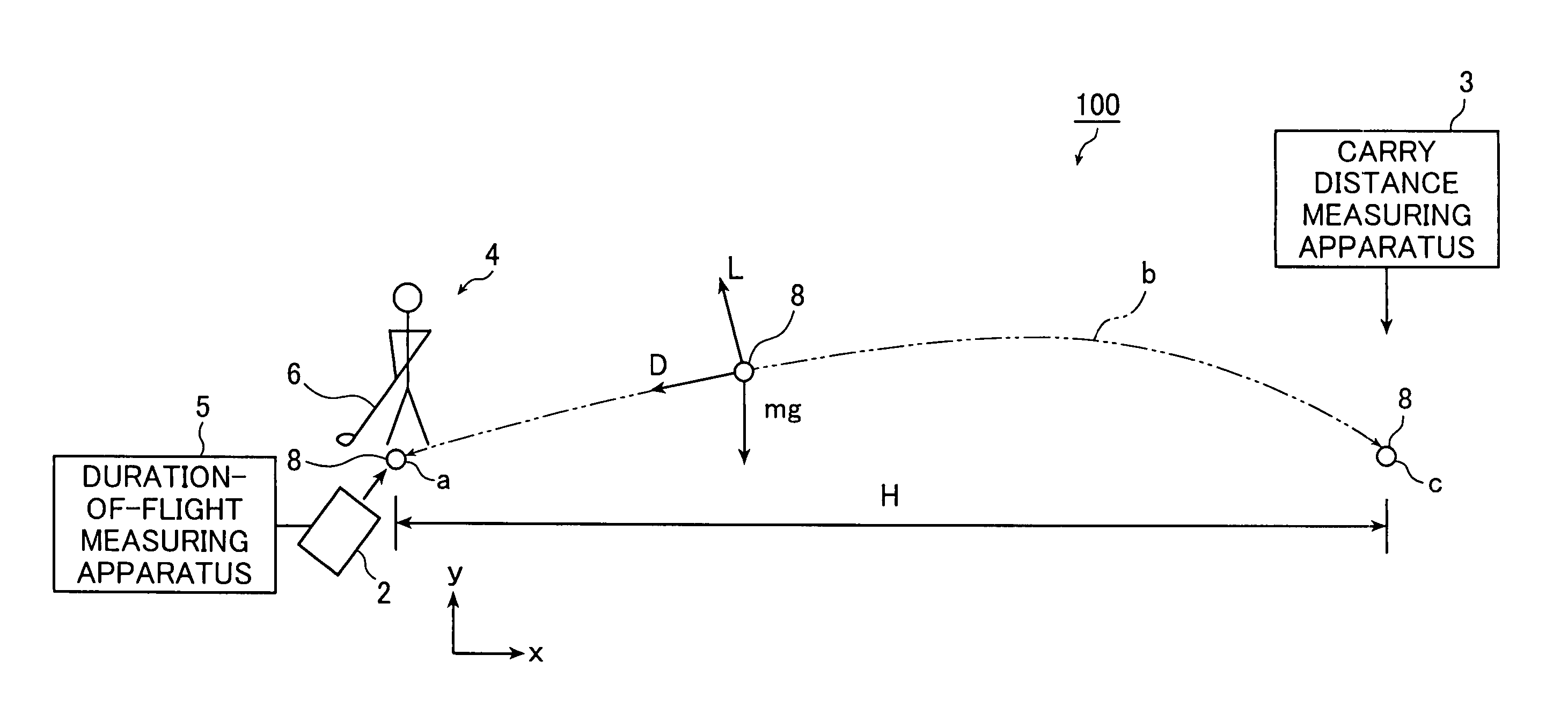
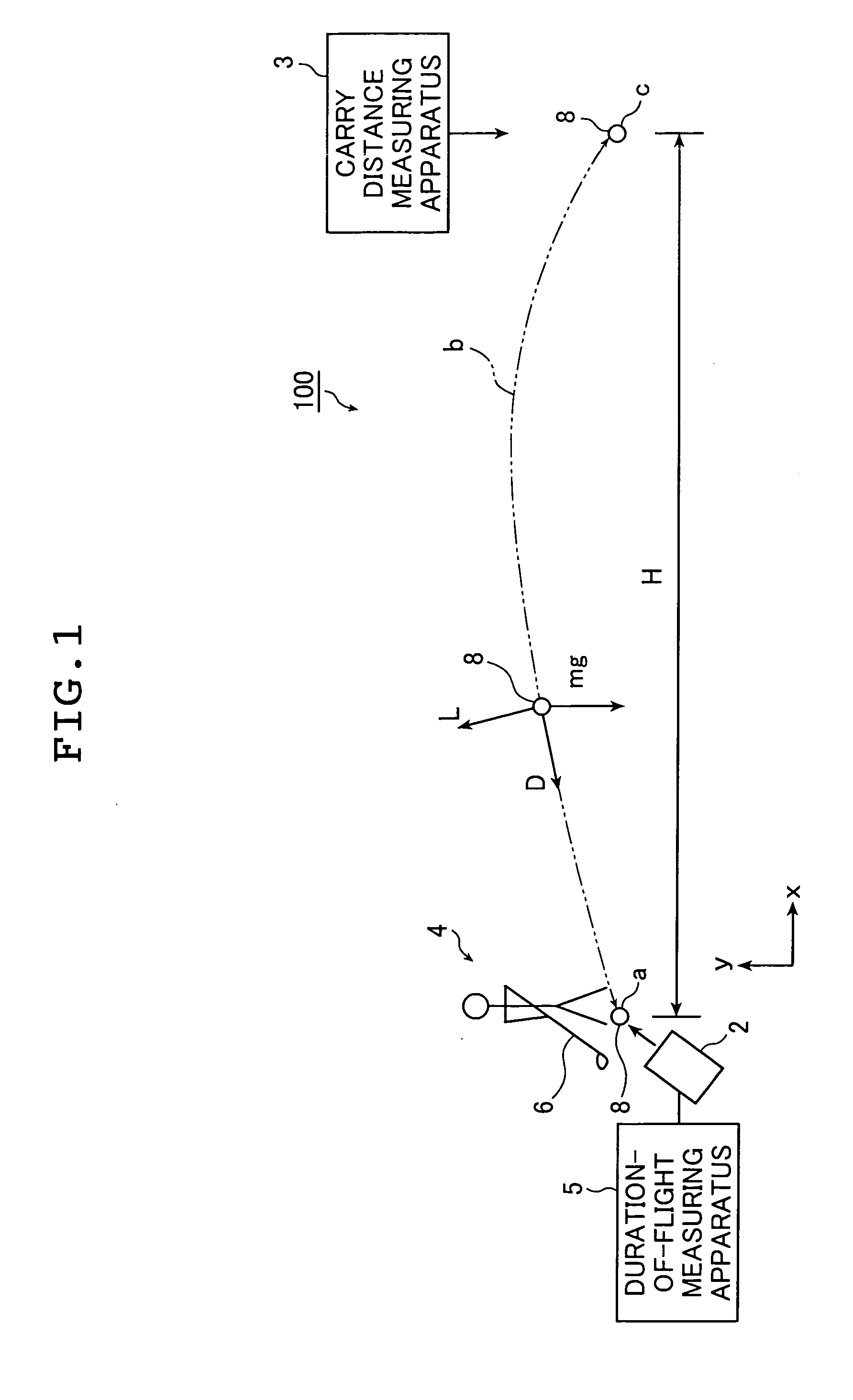
Golf ball trajectory computing system and method of computing trajectory of golf ball
A trajectory of a struck golf ball from when the golf ball is struck until the golf ball lands is computed by a golf ball trajectory computing system. The system comprises: an initial trajectory measuring portions that measures an initial velocity, a launch angle, and a backspin rate of the golf ball immediately after impact thereof; a carry distance measuring portion that measures a carry distance of the golf ball from an impact point to a landing point where the golf ball lands; a duration-of-flight measuring portion that measures a duration of flight of the golf ball from impact thereof until the golf ball lands; and a computing portions that computes a trajectory of the golf ball based on the measured initial velocity, the measured launch angle, and the measured backspin of the golf ball immediately after impact, and the carry distance and the duration of flight of the golf ball.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
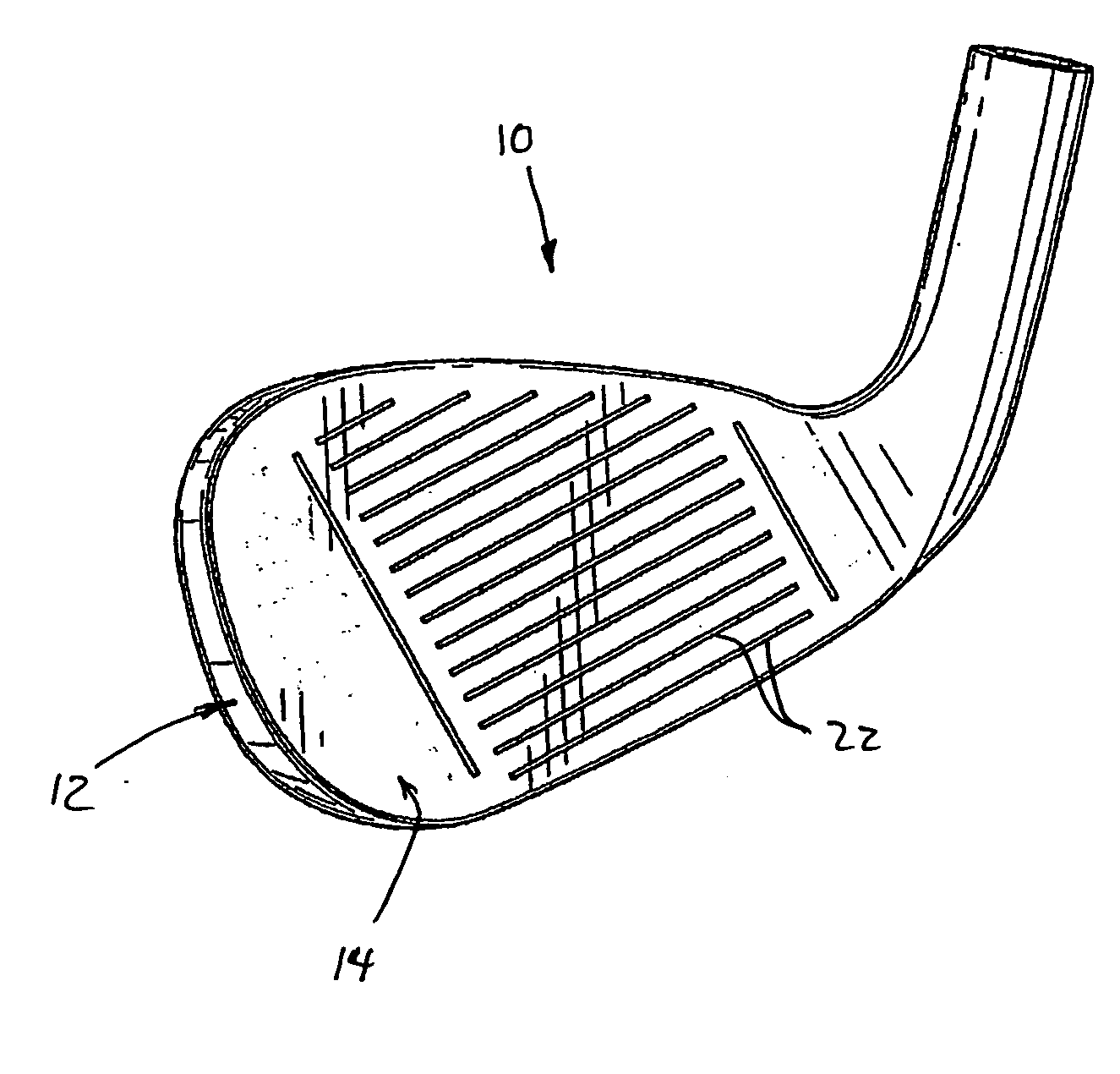
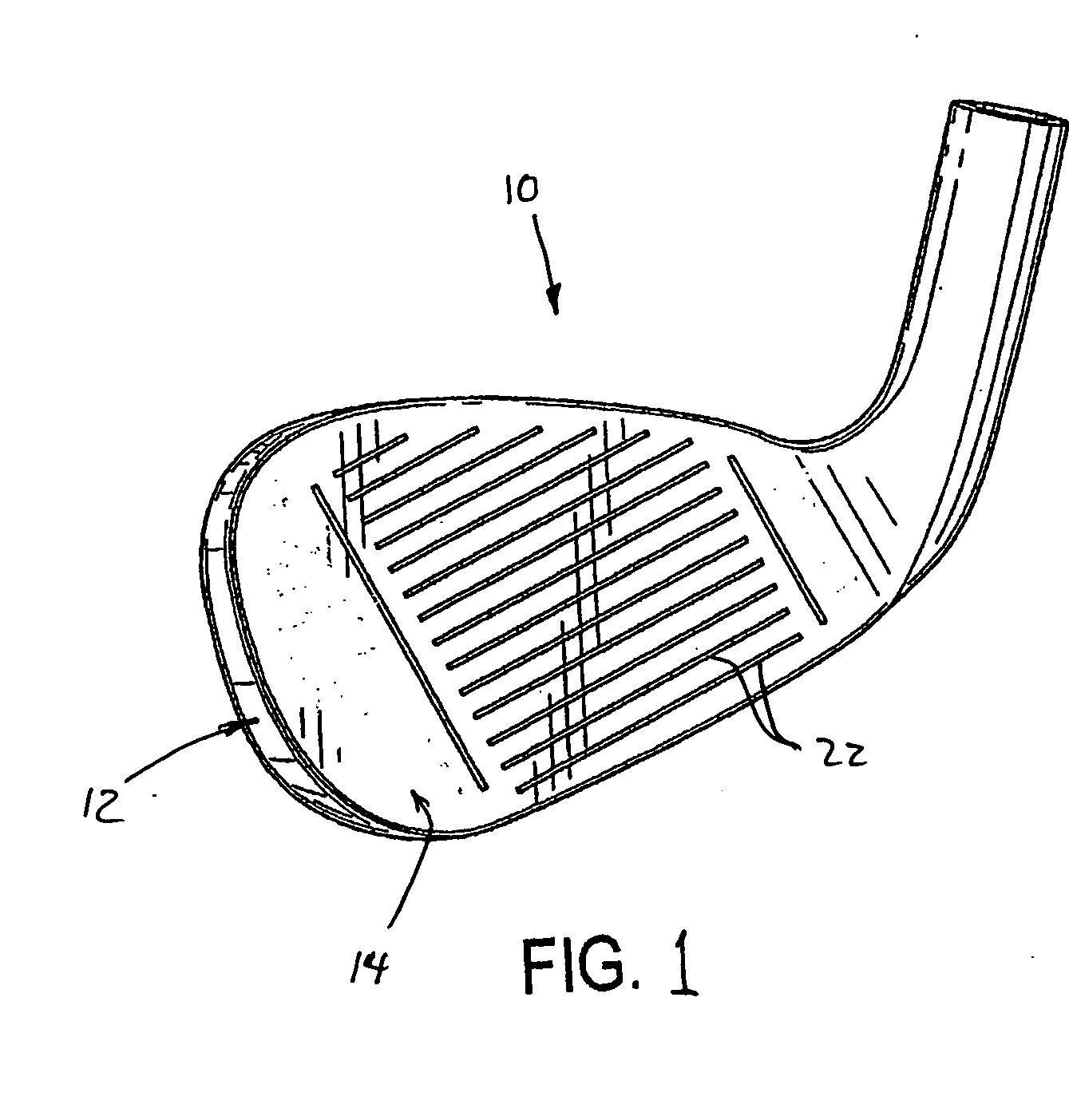
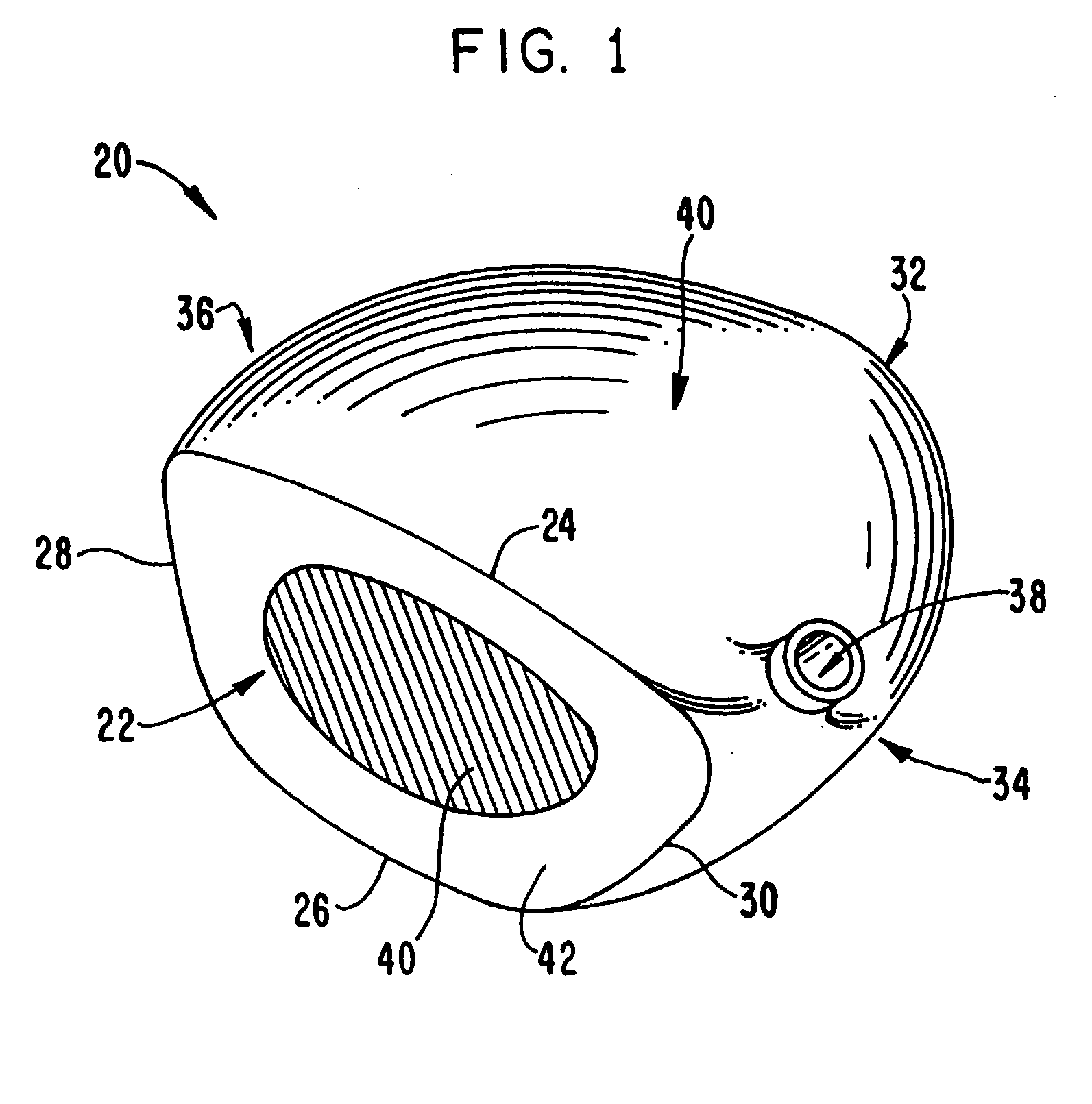
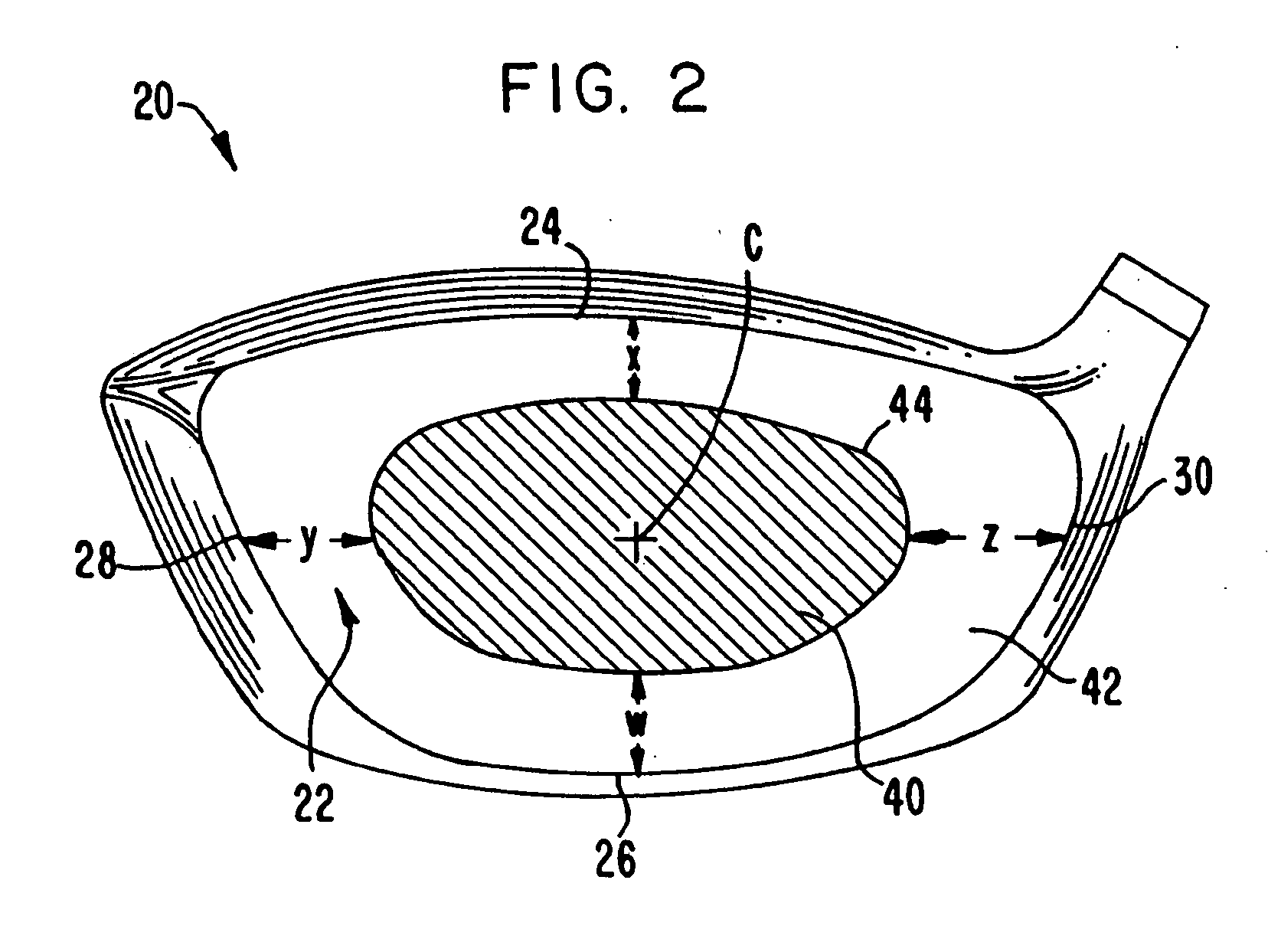
Golf club striking face and method of manufacture
A golf club head in accordance with the invention includes a front wall defining a forward striking face having an engineered texture thereon. The engineered texture includes a prescribed, regular pattern of discrete, geometric shapes spaced at least 0.1 mm apart from each other, each shape having a volume that is less than 0.0007 mm3. Preferred methods of manufacturing the engineered texture of the forward striking face include treating the face by chemical etching, precision micro-saw-cutting, and laser cutting. The engineered texture enhances the performance of the golf club head upon striking a golf ball, providing one or more of an increased high backspin, a lower launch angle, and a higher ball speed, as compared to a golf club head not incorporating such an engineered texture.
Owner:MDW TECH
Liquid crystal grating coupling
A tunable optical coupling arrangement for use with a relatively thin (generally sub-micron thickness) silicon waveguiding layer of a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. The arrangement comprises a multi-layer structure including a substrate for supporting one or more diffractive optical elements and a layer of tunable liquid crystal material. The multi-layer structure is disposed over a conventional SOI substrate including the thin silicon waveguiding layer, where the refractive index of the liquid crystal material can be modified to adjust the deflection of an input optical beam through the various diffractive optical elements and present an optimized launch angle into the silicon waveguiding layer, thus reducing insertion loss at the waveguiding layer.
Owner:SIOPTICAL INC +1
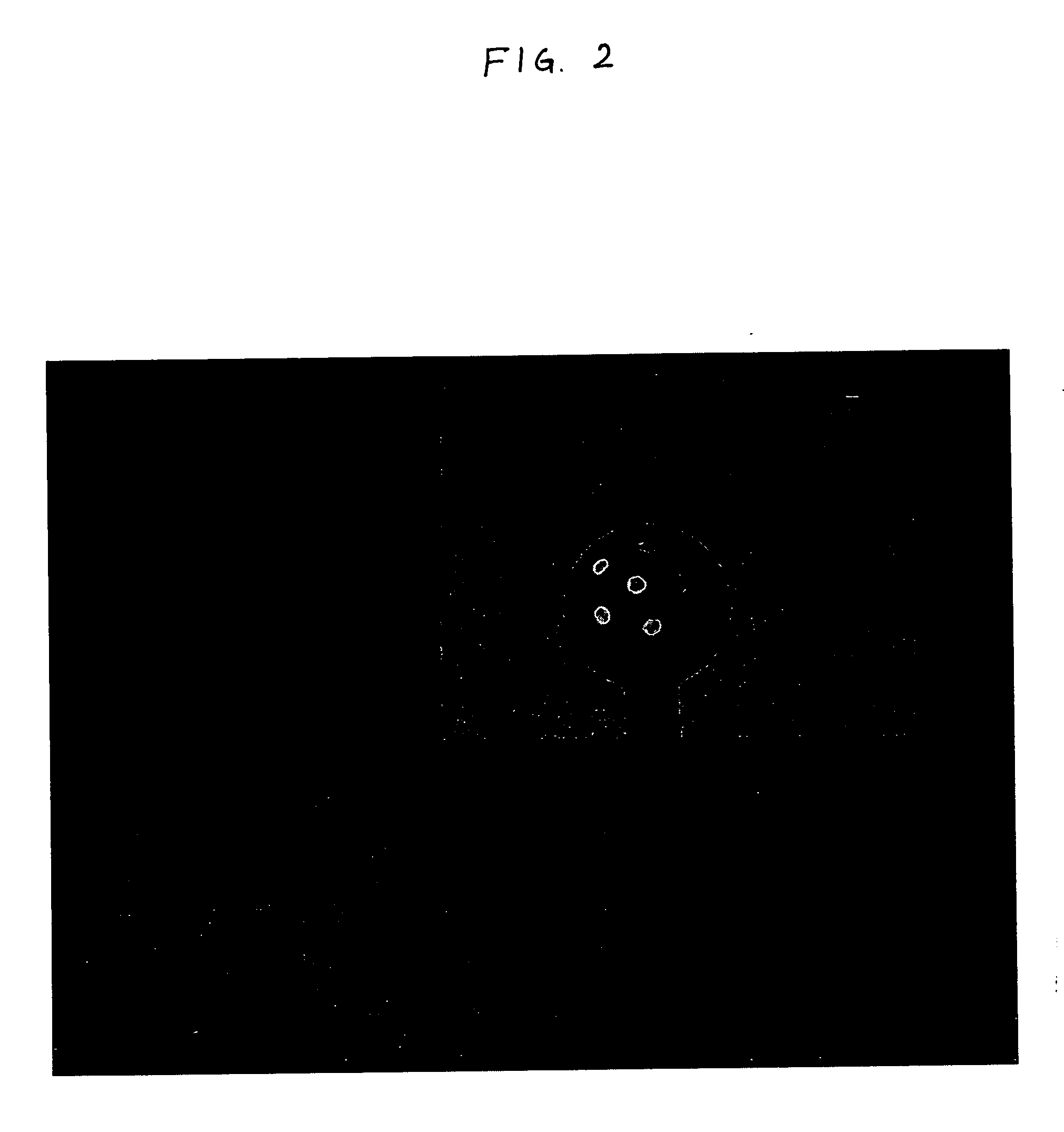
Method and apparatus for measuring ball launch conditions
A method and apparatus for measuring ball launch conditions is disclosed. Specifically, the accuracy of the calculations used to determine the kinematic characteristics may be increased. A background image of a field of view, without a golf ball present, may be acquired. Two or more images of a golf ball in motion are then be acquired based on positive or negative imaging. The background image is subtracted from each of the two or more images of the golf ball. After subtracting the background image, the two or more images of the golf ball are analyzed to determine the location of the circular perimeter of the golf ball. Based on the location of the circular perimeter of the golf ball, the location of the center of the golf ball may be calculated. Knowing the location of the center of the golf ball increases the accuracy of measurements of kinematic characteristics such as sidespin, backspin, velocity, and launch angle.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Arrangements for reducing wavelength sensitivity in prism-coupled SOI-based optical systems
ActiveUS6917730B2Coupling efficiency is maximizedReduce thicknessCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSurface layerPrism
An optical coupling system for use with multiple wavelength optical signals provides improved coupling efficiency between a free-space optical beam and a relatively thin, surface layer of an SOI structure (“SOI layer”), allowing for sufficient coupling efficiency (greater than 50%) over a predetermined wavelength range. An evanescent coupling layer, disposed between a coupling prism and an SOI layer, is particularly configured to improve the coupling efficiency. In one embodiment, the thickness of the evanescent layer is reduced below an optimum value for a single wavelength, the reduced thickness improving coupling efficiency over a predetermined wavelength range around a defined center wavelength. Alternatively, a tapered thickness evanescent coupling layer may be used to improve coupling efficiency (or a combination of reduced thickness and tapered configuration). Optical beam steering can be combined with a modified evanescent coupling layer to control the input beam launch angle and further improve coupling efficiency.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Microlen array based laser beam divegence angle testing method
InactiveCN101013030AAvoid the difficult problem of not easy to measure accuratelyConveniently Realize Real-Time MeasurementsLaser detailsUsing optical meansObservational errorLight spot
The invention is a laser beam divergence angle testing method based on the micro-lens array, and the invention belongs to the optical field, specifically relating to the laser beam divergence angle testing method. It overcomes the existing deficiencies of the existing beam scattered angle method with larger measurement error and less measurement real-time feature. It includes the following steps: the measured beam is incidence to the telescope system, matching the output beam diameter and the micro-lens array shape, and the micro-lens array contains mXn matrix sub-lens; using micro-lens array to divide the measured beam into the sub-beams, and through CCD to detect the launch angle of each sub-beam, and through statistical method to calculate the measured beam divergence angle, the measurement accuracy reaching 0.1mu rad. Because this method does not require the measurement light spot diameter, it avoids the problem that the light spot diameter is difficult to be accurately measured. This method in the invention is only measuring in the one position of the optical path; therefore the method can facilitate to realize the real-time measurement of the beam divergence angle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wedge type golf club head
ActiveUS8579729B2Mitigate the ballspeed increaseOverall wedge shot distance constantGolf clubsRacket sportsGravity centerEngineering
A wedge type golf club head is disclosed herein where the wedge type golf club head has enhanced performance characteristics such as improved backspin, ball speed, and launch angle. More specifically, the present invention relates to a wedge type golf club head having an adjustable center of gravity, where the center of gravity may be adjusted based on different backing profiles that comprises at least one hollow chamber. The wedge type golf club head disclosed above may also have a thickened topline, wherein the thickness of the topline progressively changes as a function of the loft angle of the wedge type golf club head.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Multi-piece solid golf ball
InactiveUS7121959B1Soft and good shot feelImprove flight performanceGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringHardness
The invention provides a multi-piece solid golf ball having soft, good shot feel, excellent flight performance, high rebound characteristics and high launch angle, when hit by golfers who swing a golf club at high or low head speed using all golf clubs, namely, a driver to an iron club, a putter. The multi-piece solid golf ball has a core having an inner core and an outer core covering the inner core, and at least one layer covering the core; the inner core has a diameter of 30 to 40.4 mm and surface hardness of 60 to 85 JIS-C, and center JIS-C hardness of the inner core lower than the surface hardness by 5 to 30; the outer core has a thickness of 0.2 to 1.3 mm, and a surface JIS-C hardness of the outer core lower than the surface hardness of the inner core by 2 to 30.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
System and method for measuring a golfer's ball striking parameters
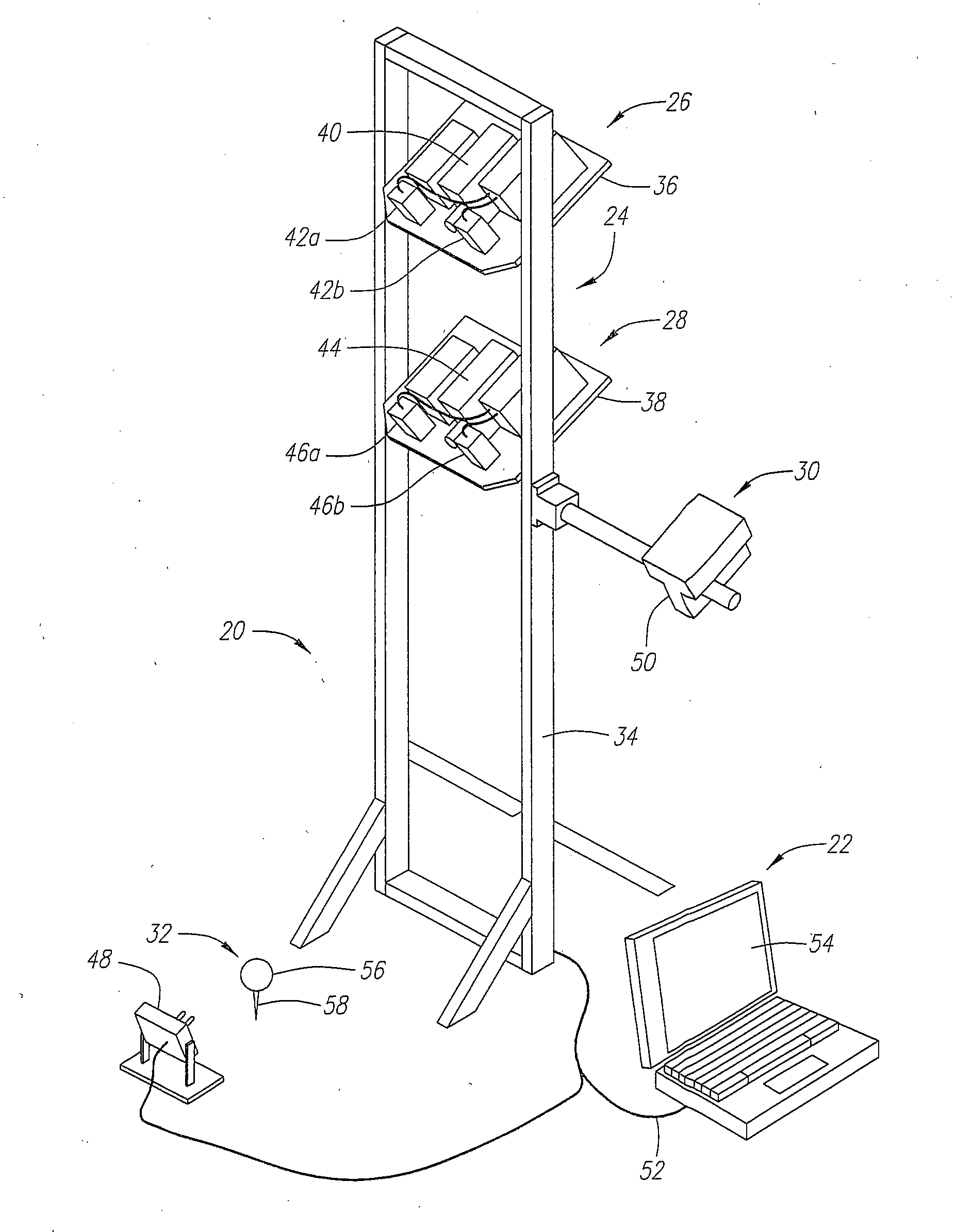
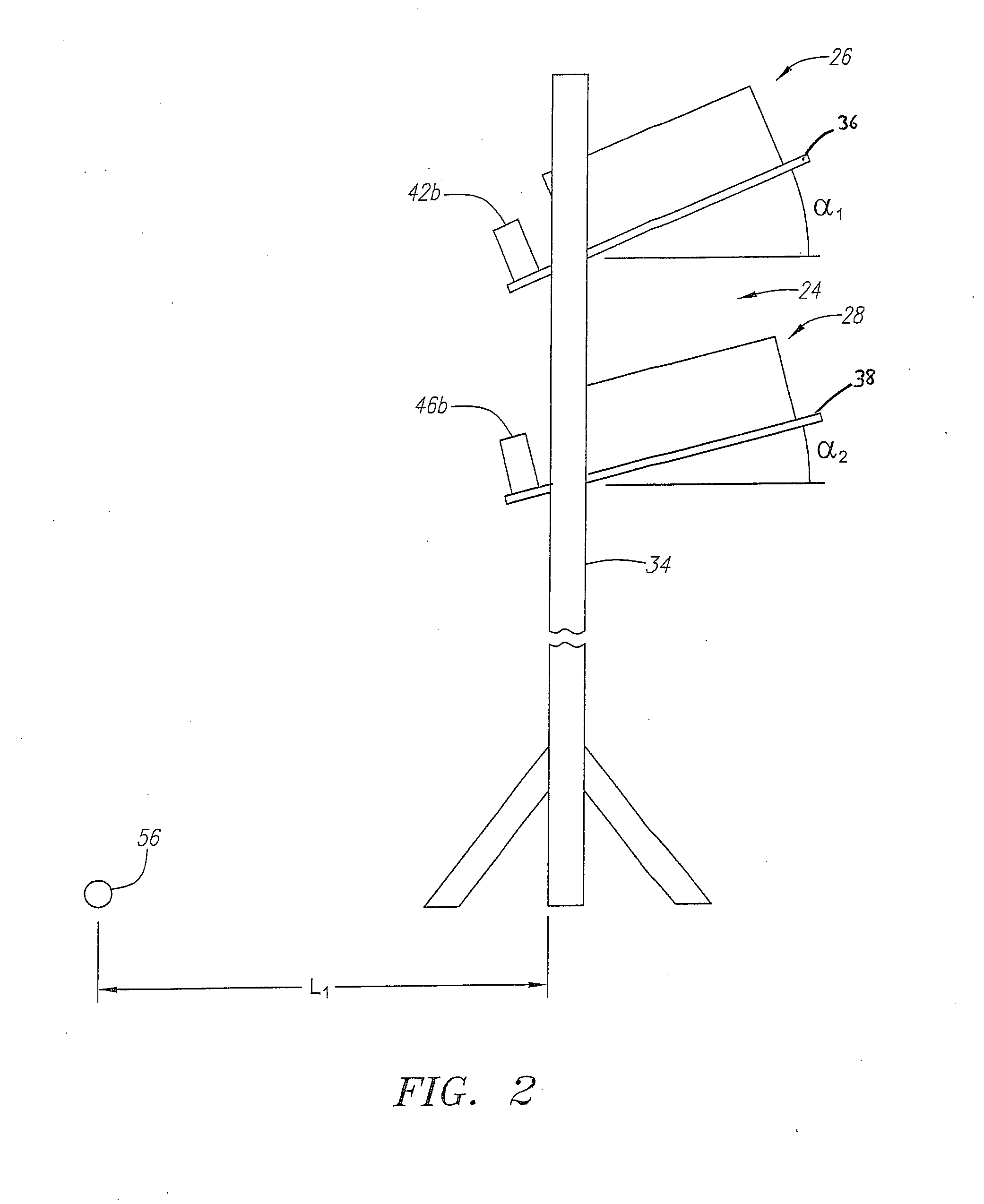
A system (20) for capturing and analyzing golf club information and golf ball information during and after a golfer's swing is disclosed herein. The golf club information includes golf club head orientation, golf club head velocity, and golf club spin. The golf club head orientation includes dynamic lie, loft and face angle of the golf club head. The golf club head velocity includes path of the golf club head, attack of the golf club head and downrange information. The golf ball information includes golf ball velocity, golf ball launch angle, golf ball side angle, golf ball speed manipulation and golf ball orientation. The golf ball orientation includes the true spin of the golf ball, and the tilt axis of the golf ball which entails the back spin and the side spin of the golf ball. The system includes CMOS camera units (26 and 28) and a computer (22).
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
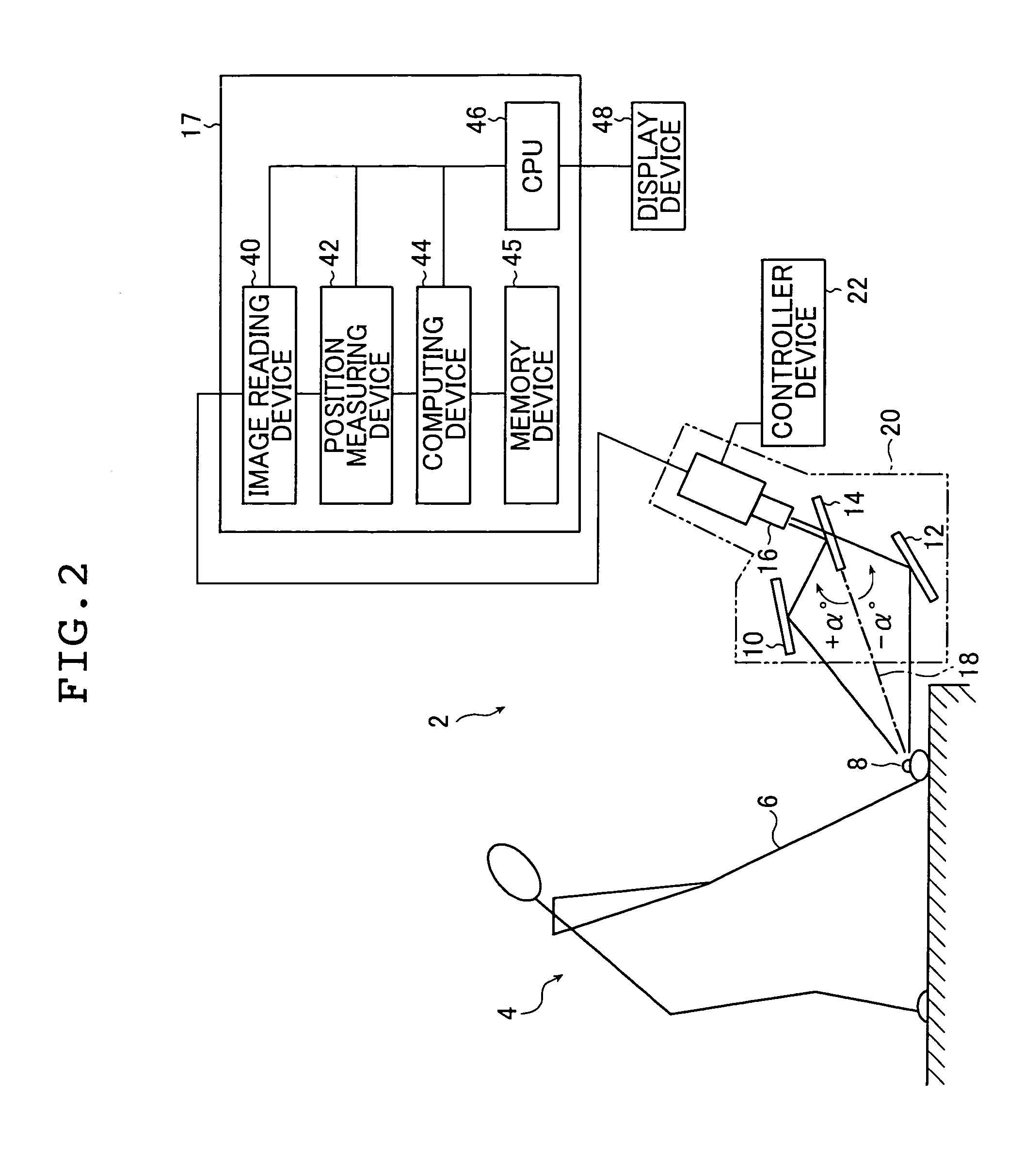
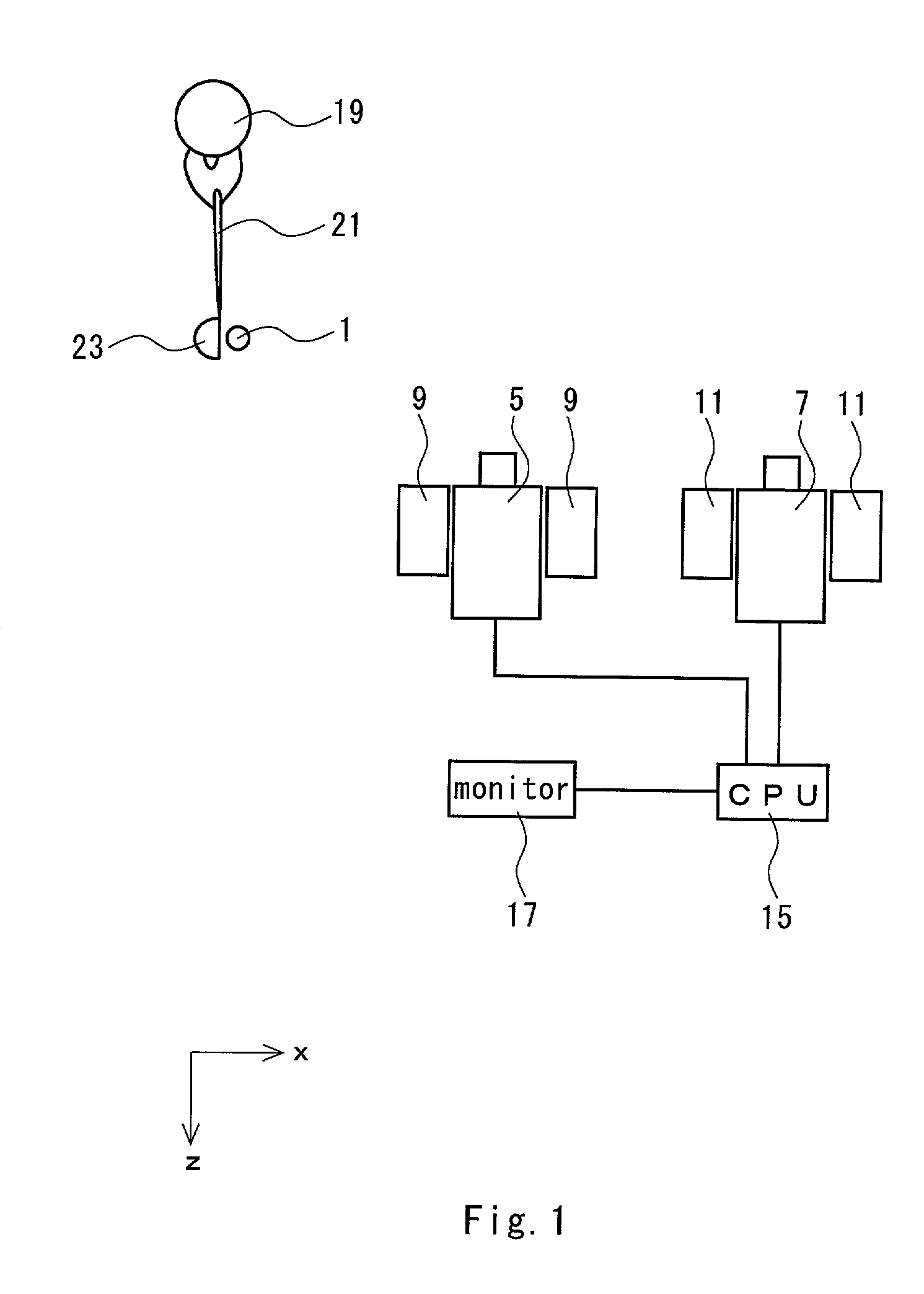
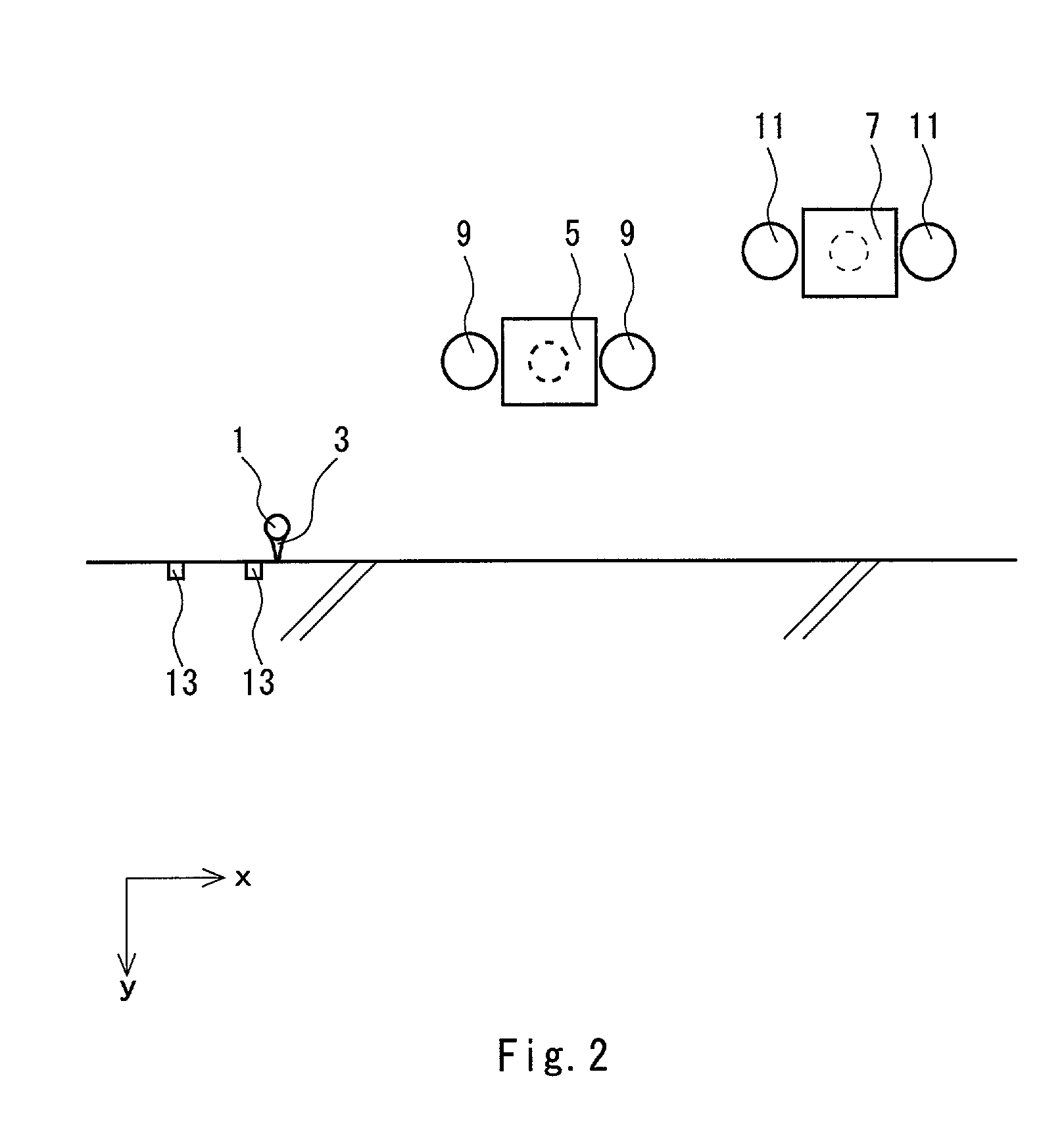
Ball motion measuring apparatus
A ball motion measuring apparatus comprises a tee 3 for mounting a golf ball 1 thereon, a first camera 5, a second camera 7, a pair of first stroboscopes 9, a pair of second stroboscopes 11, a pair of optical sensors 13, a CPU 15 to be a calculating section, and a monitor 17 to be a display section. The first camera 5 and the second camera 7 are CCD cameras having a shutter function. Photographing is carried out by means of the first camera 5 after a predetermined time passes since the golf ball 1 is hit, and the photographing is carried out by means of the second camera 7 after a predetermined time further passes. A magnified image is formed by original image data thus obtained and a read value obtained by pointing the magnified image is subjected to distortion correction or oblique correction so that correction data are obtained. Based on the correction data, a flight speed, a spin rate or a launch angle of the golf ball 1 is calculated.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Golf club head having an alignment marker on its strike face
A golf club head having a hollow metal body with a metal strike face. The metal strike face has a coating applied thereto of a first hue of color that defines an alignment marker for a golfer. The decorative coating covers at least 10% of an entire surface area of the metal strike face, covers the geometric center of the strike face, is bounded by at least a second hue of color that is different than the first hue of color, and does not extend to a periphery of the metal strike face The coating has physical properties that do not affect a launch angle and spin rate of a golf ball hit with the golf club head.
Owner:MACGREGOR GOLF
Projectile and throwing apparatus and game for projectile throwing
An improved projectile throwing apparatus is described comprising a handle, an elongate shaft, and a throwing head for throwing a projectile, such as a golf ball. The throwing head may be interchangeable with golf shafts of varied lengths, with lacrosse shafts, or other shafts to achieve accurate, long distance golf ball throws. The throwing head may be shaped to achieve throws of different distance, launch angle, and trajectory, optionally imparting spin with a retrograde ramp at the distal end of the throwing head. The throwing apparatus is useful for golf-type game play, including for those with physical disabilities, as well as for a training and instructional aid for golf, lacrosse, and other sports.
Owner:EVANS CURTIS ALAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com