Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4020 results about "Spins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The spins (as in having "the spins") is an adverse reaction of intoxication that causes a state of vertigo and nausea, causing one to feel as if "spinning out of control", especially when lying down. It is most commonly associated with drunkenness or mixing alcohol with other psychoactive drugs such as cannabis. This state is likely to cause vomiting, but having "the spins" is not life-threatening unless pulmonary aspiration occurs.
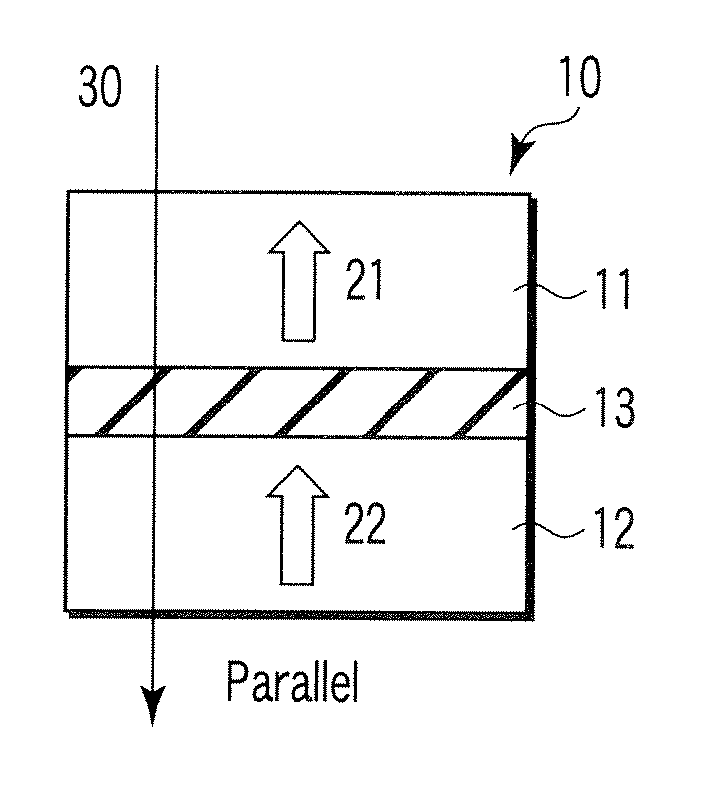
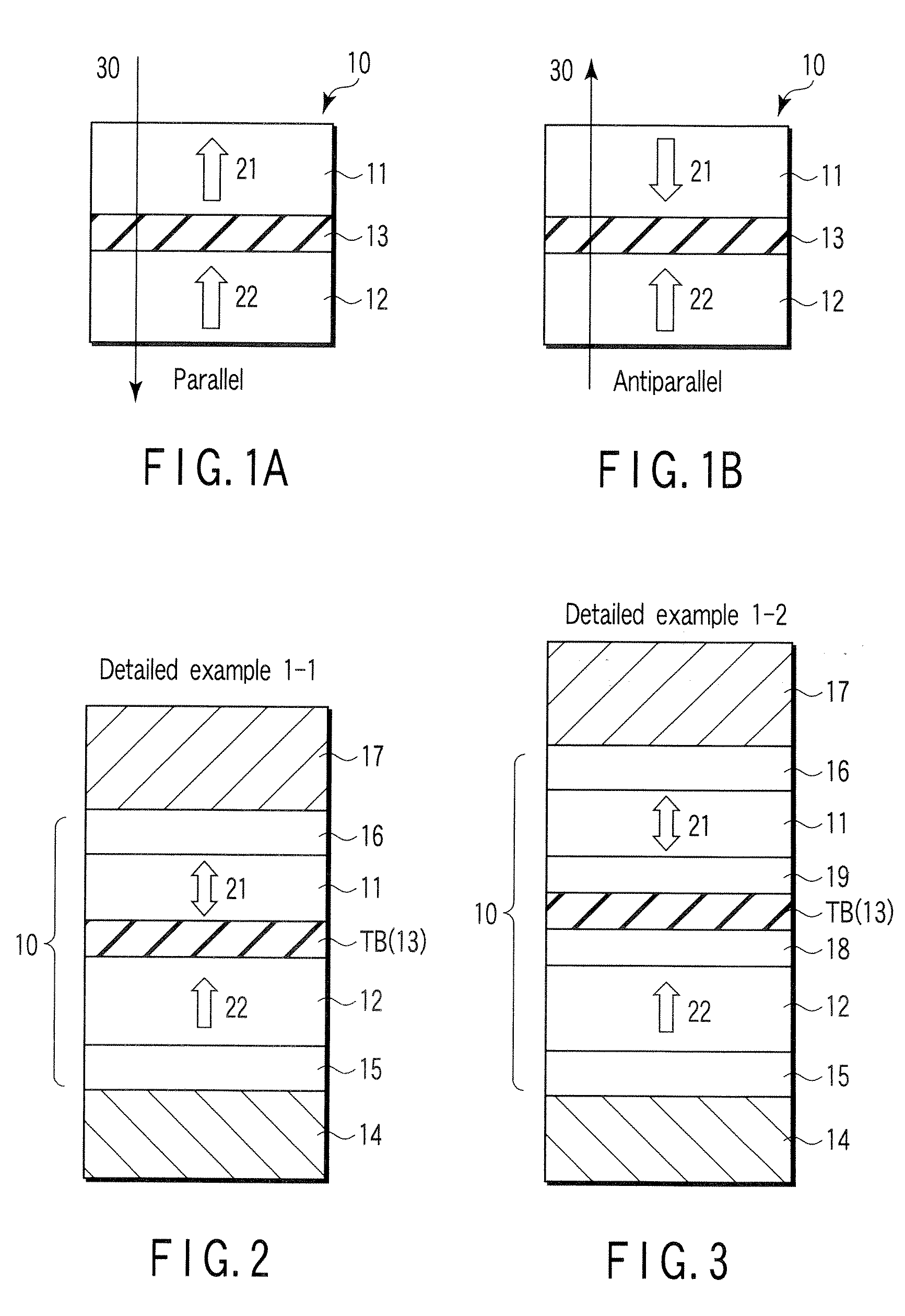
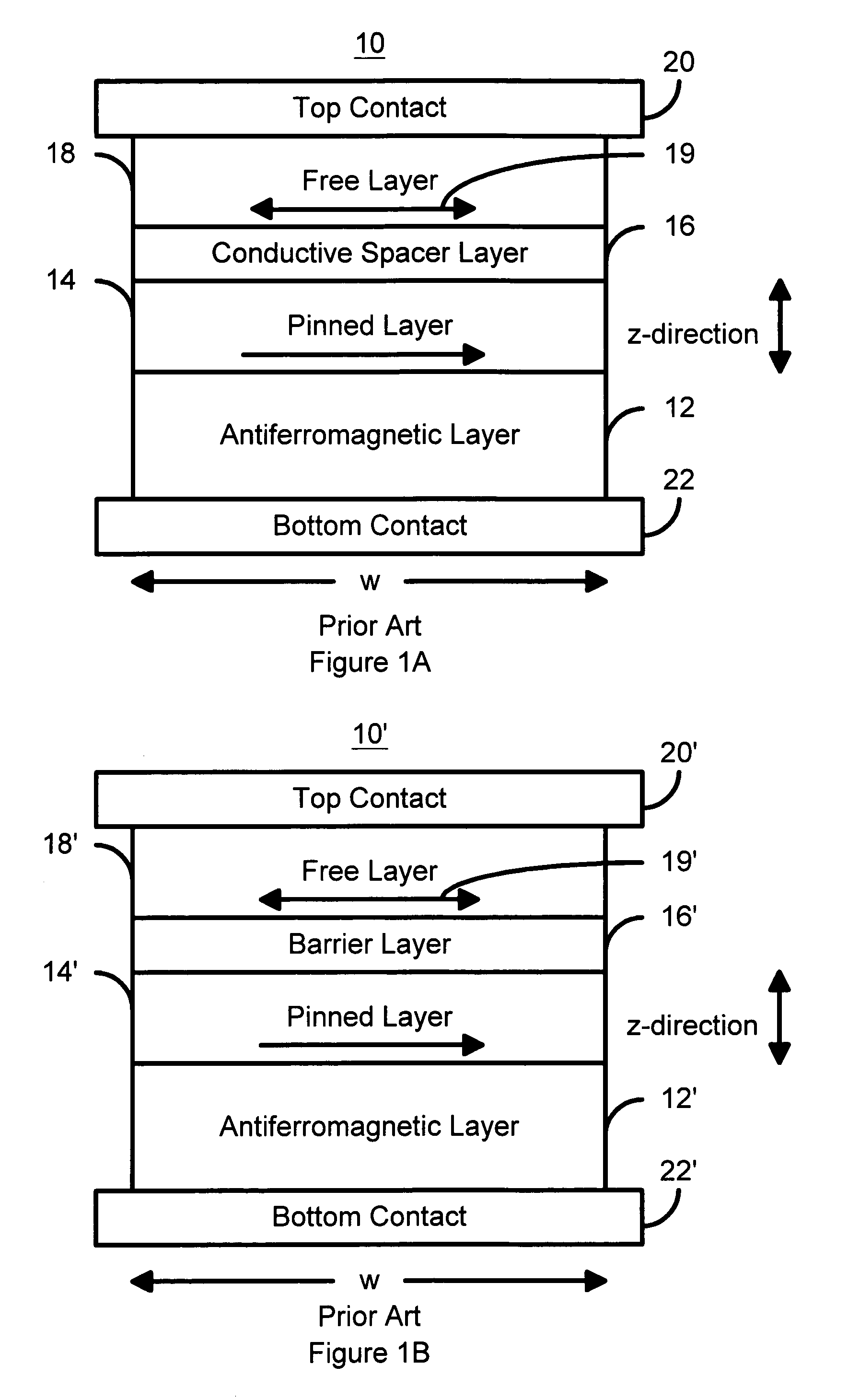
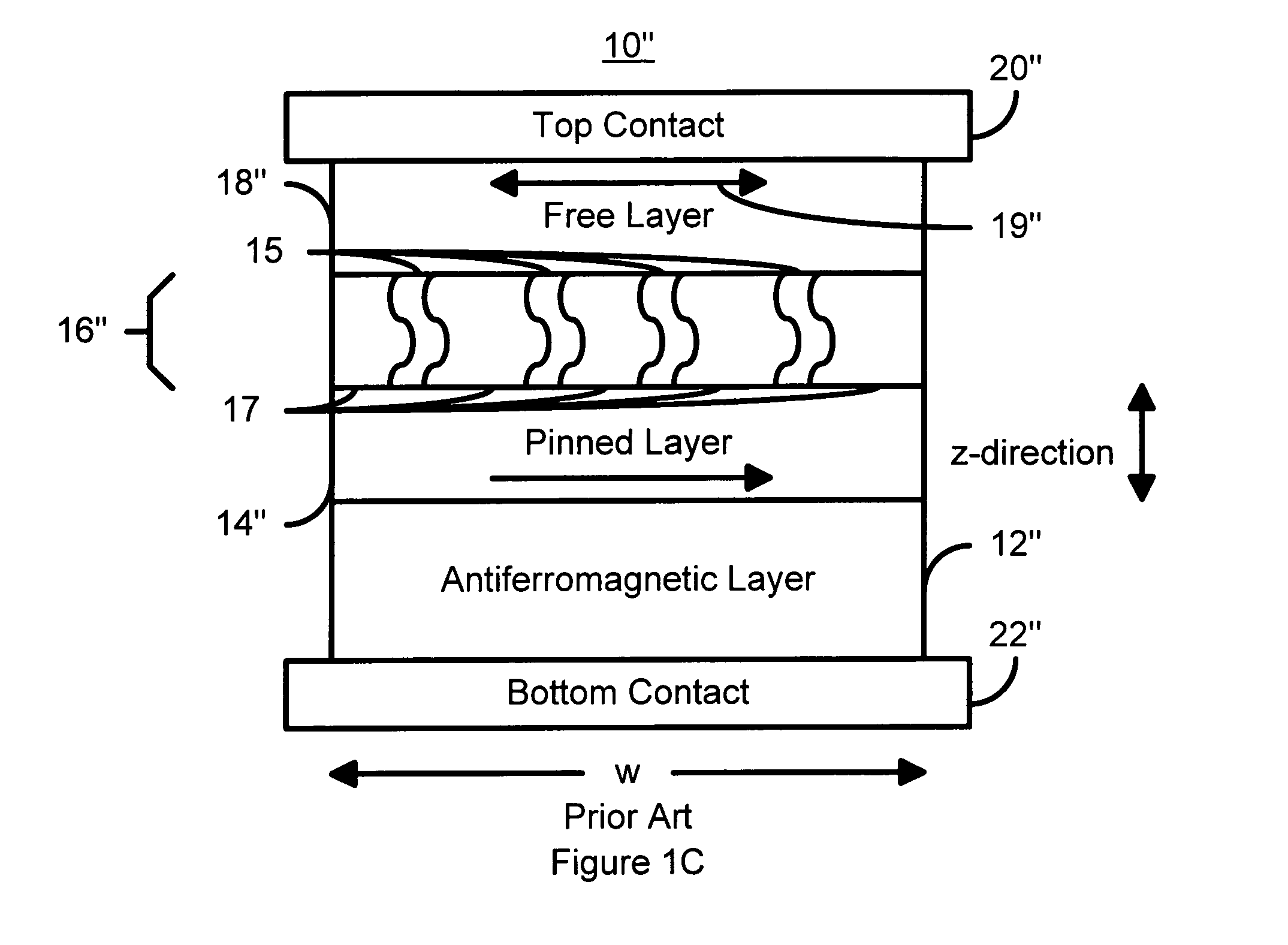
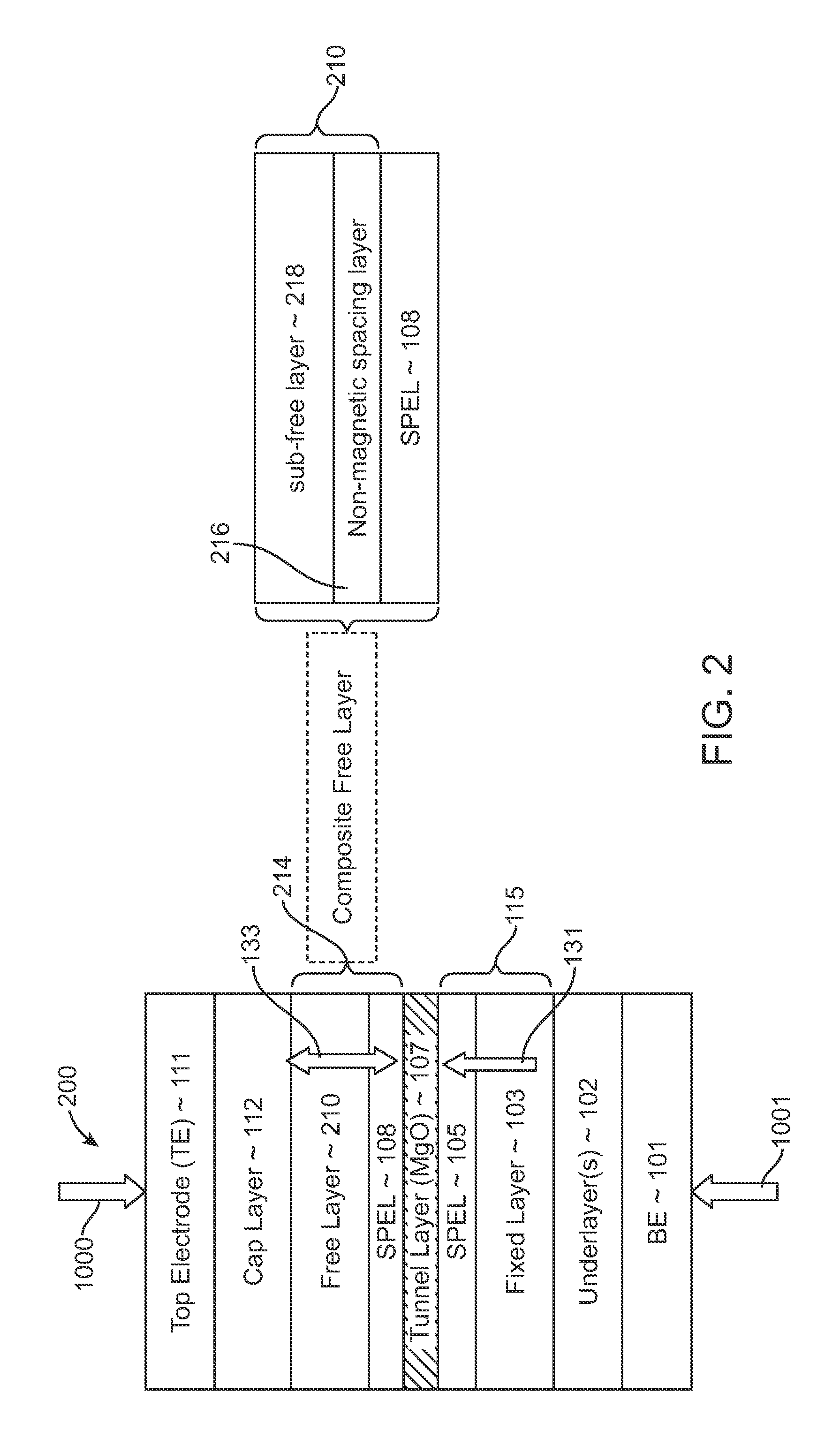
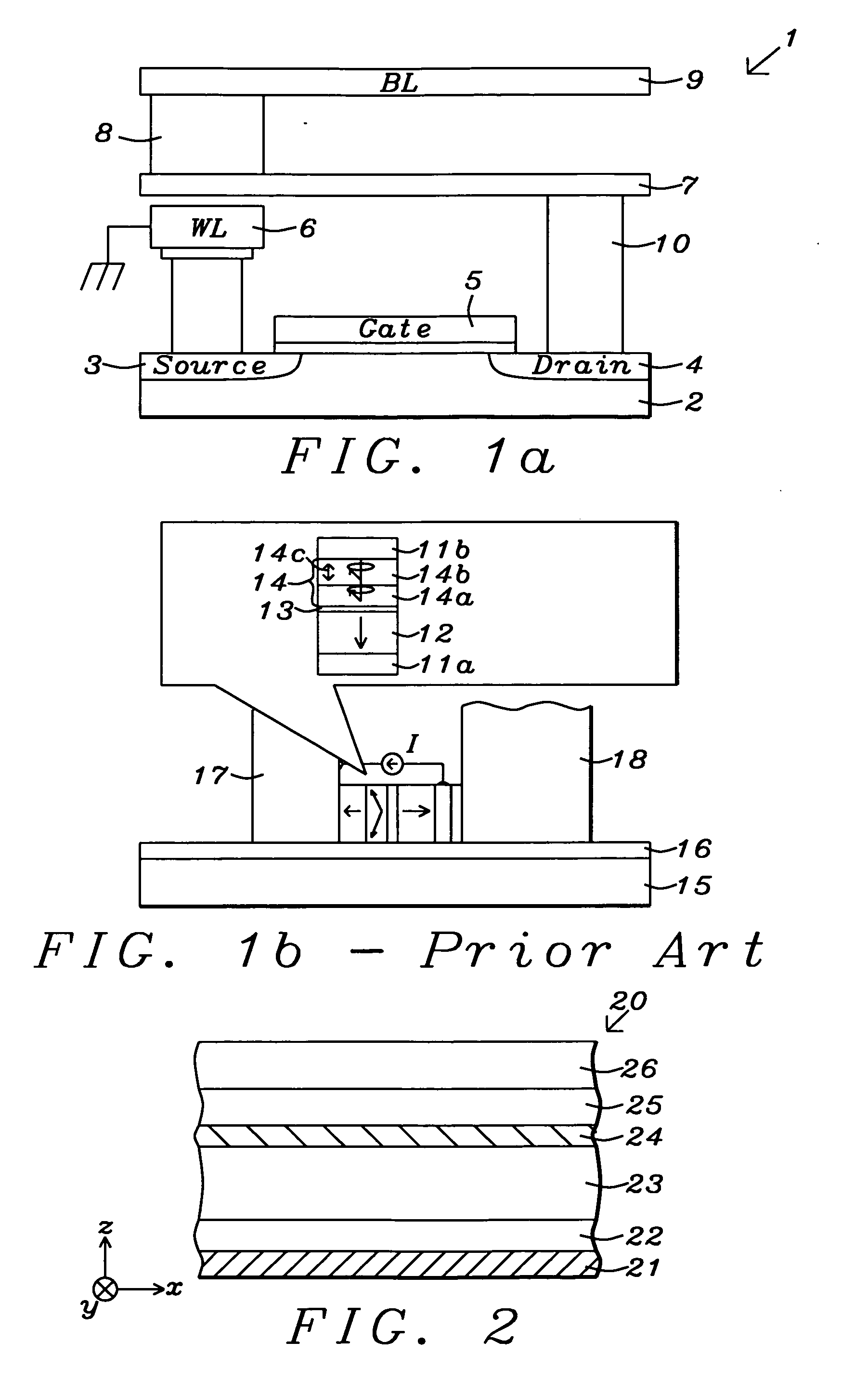
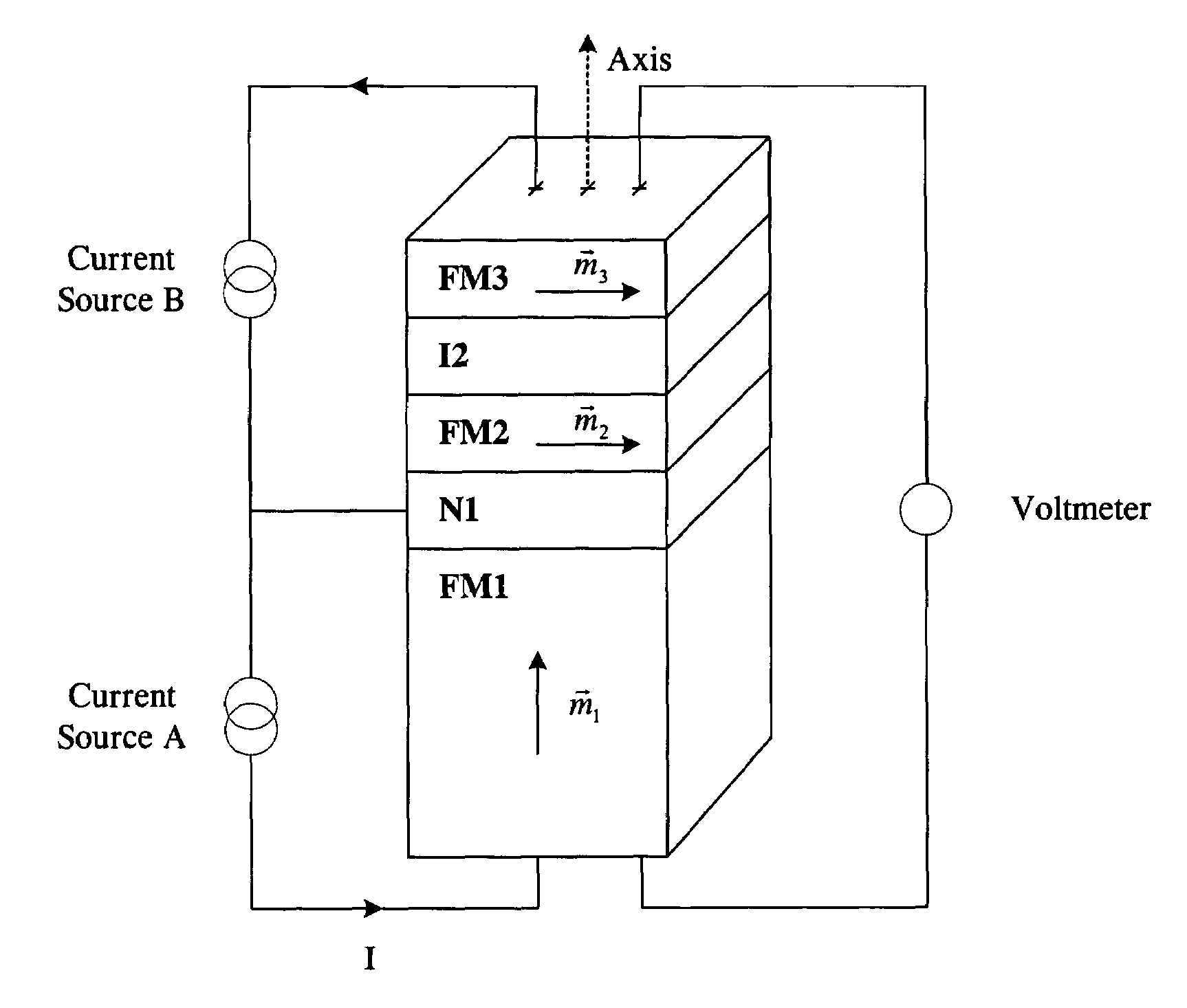
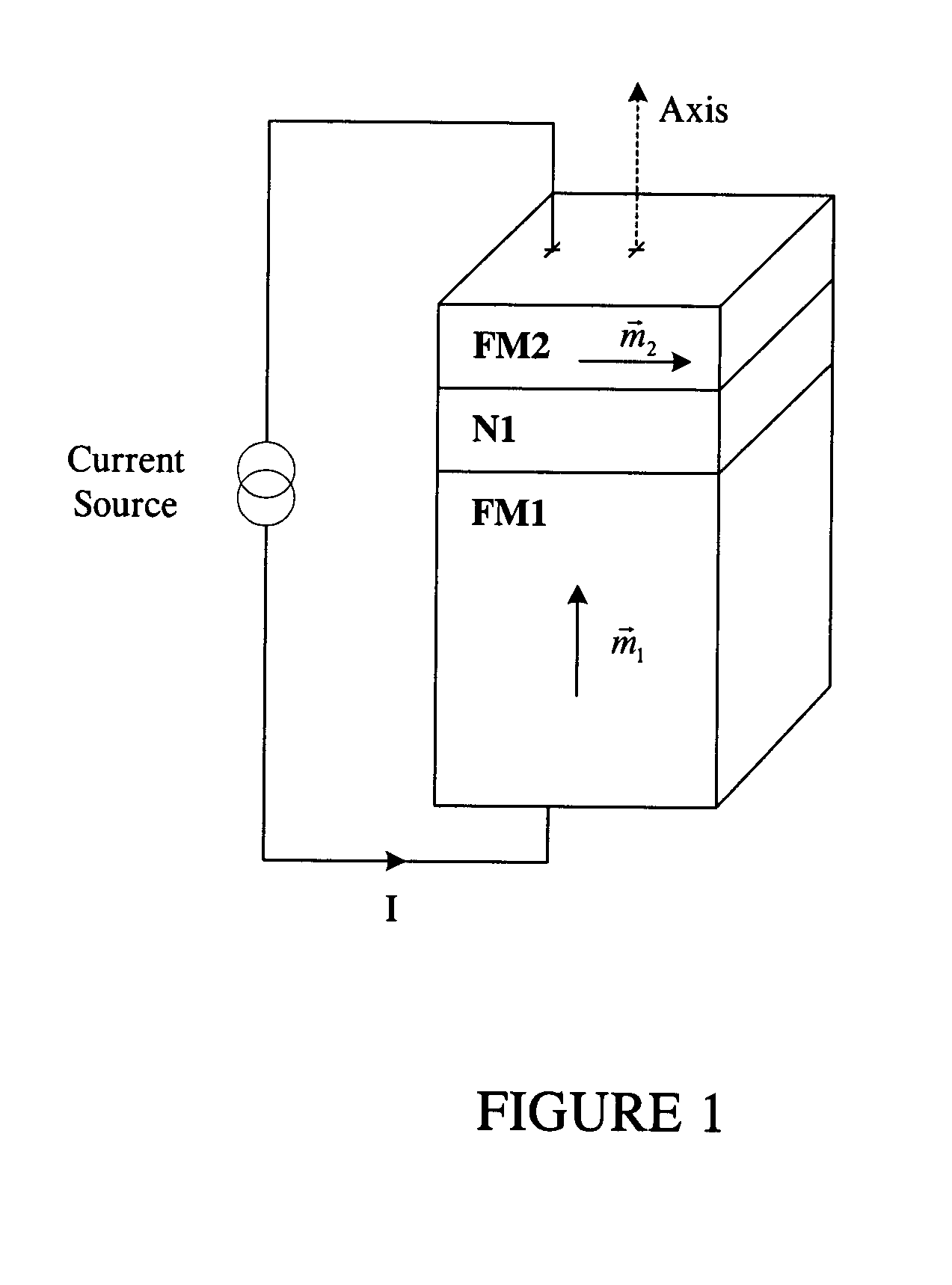
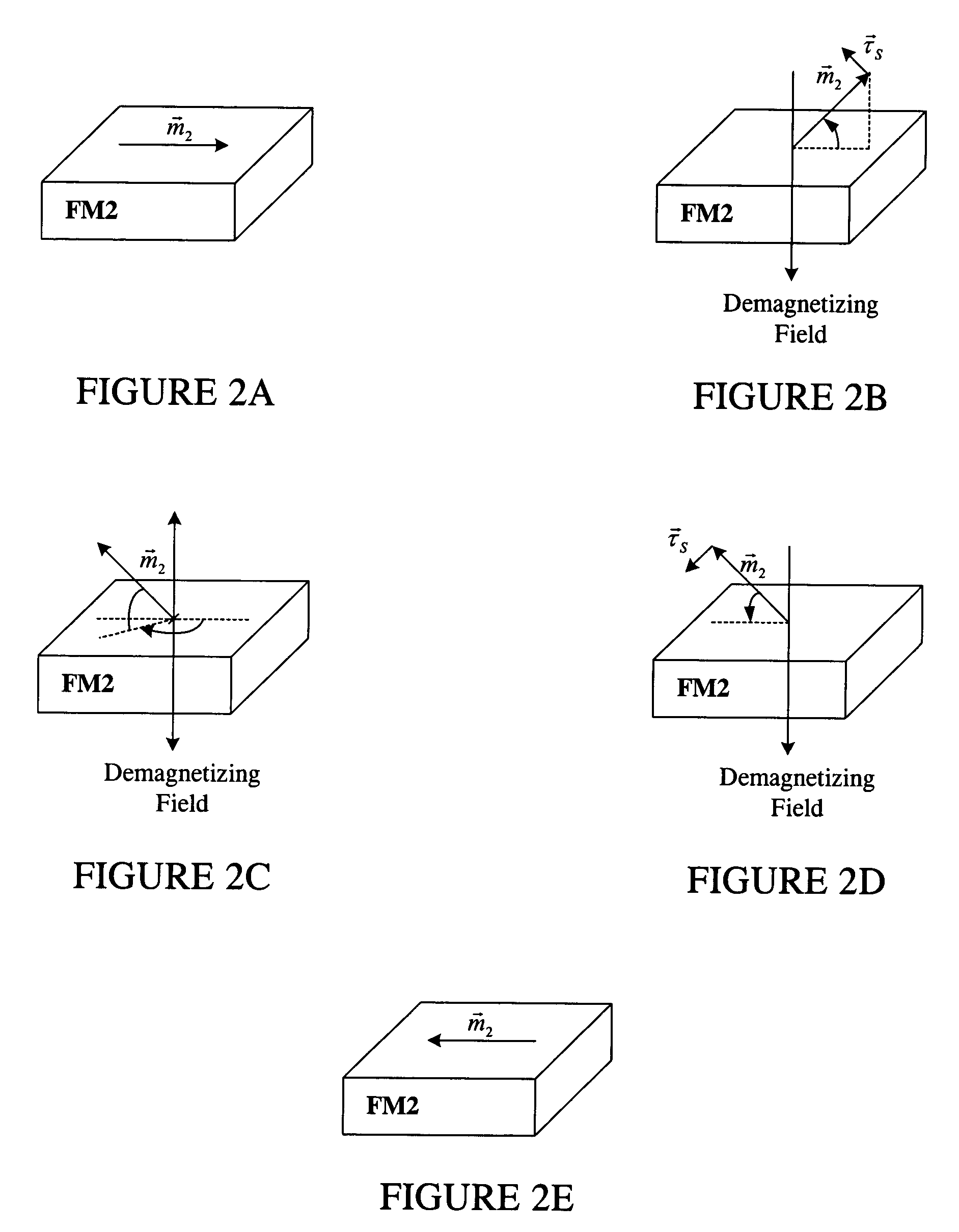
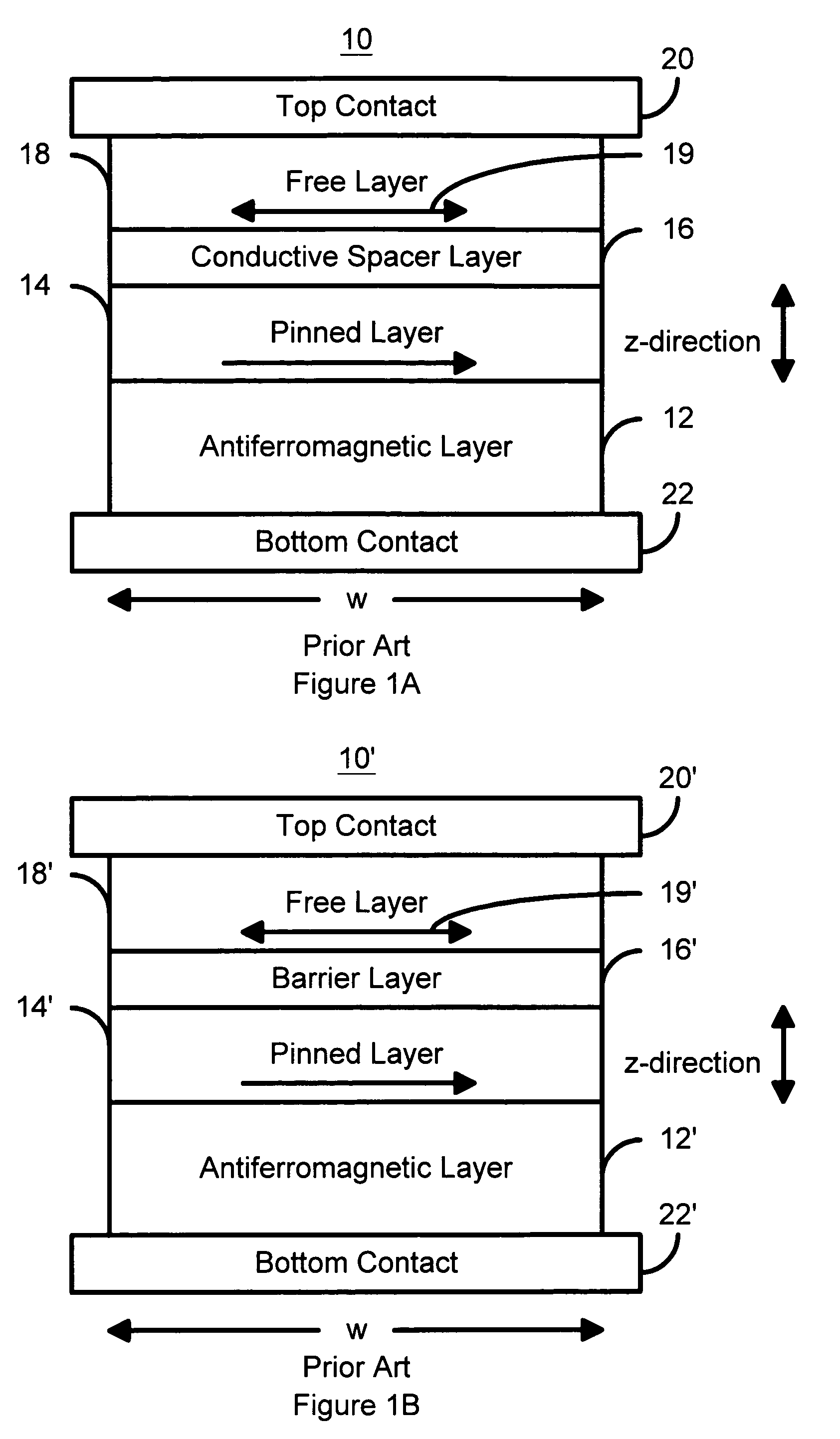
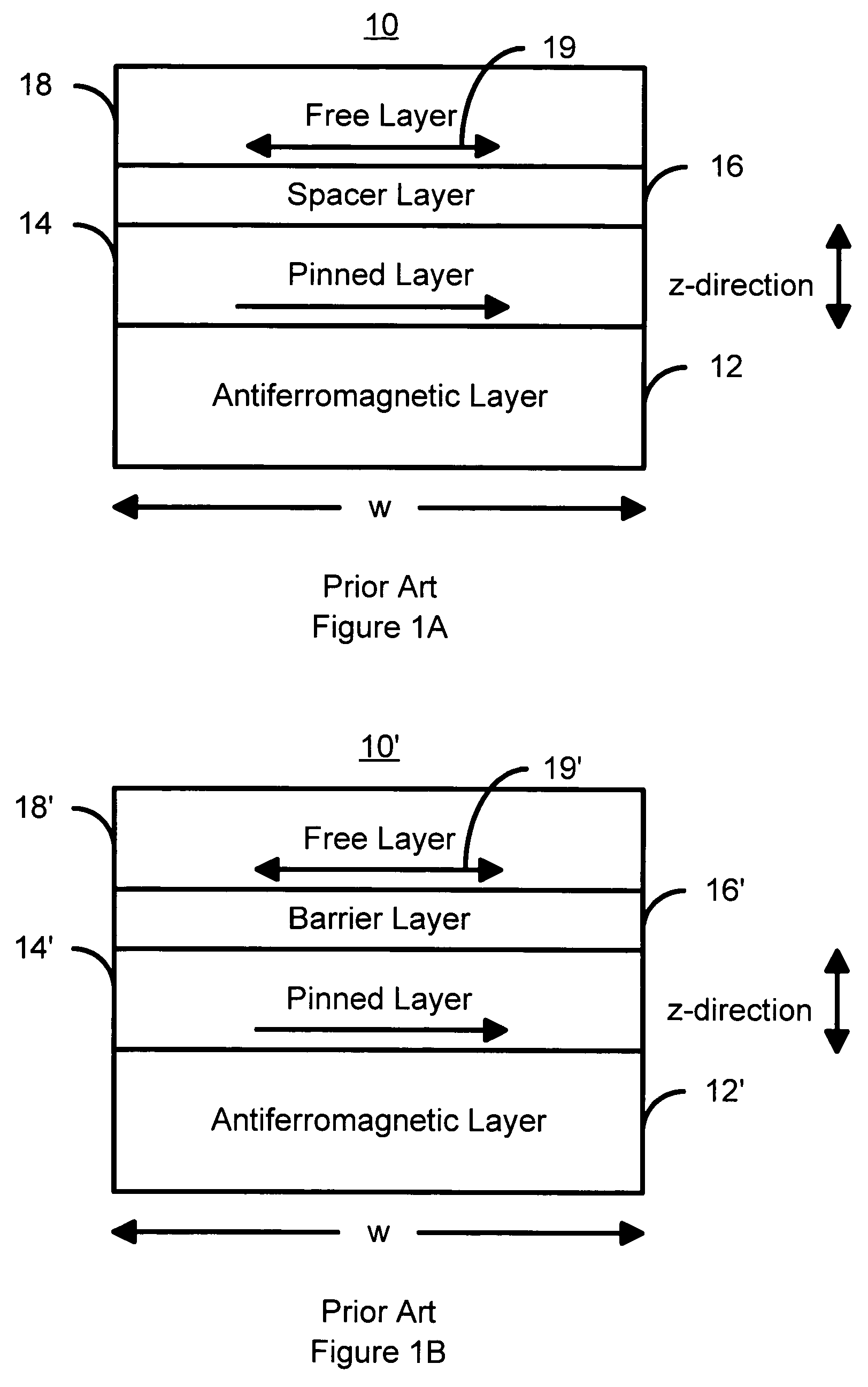
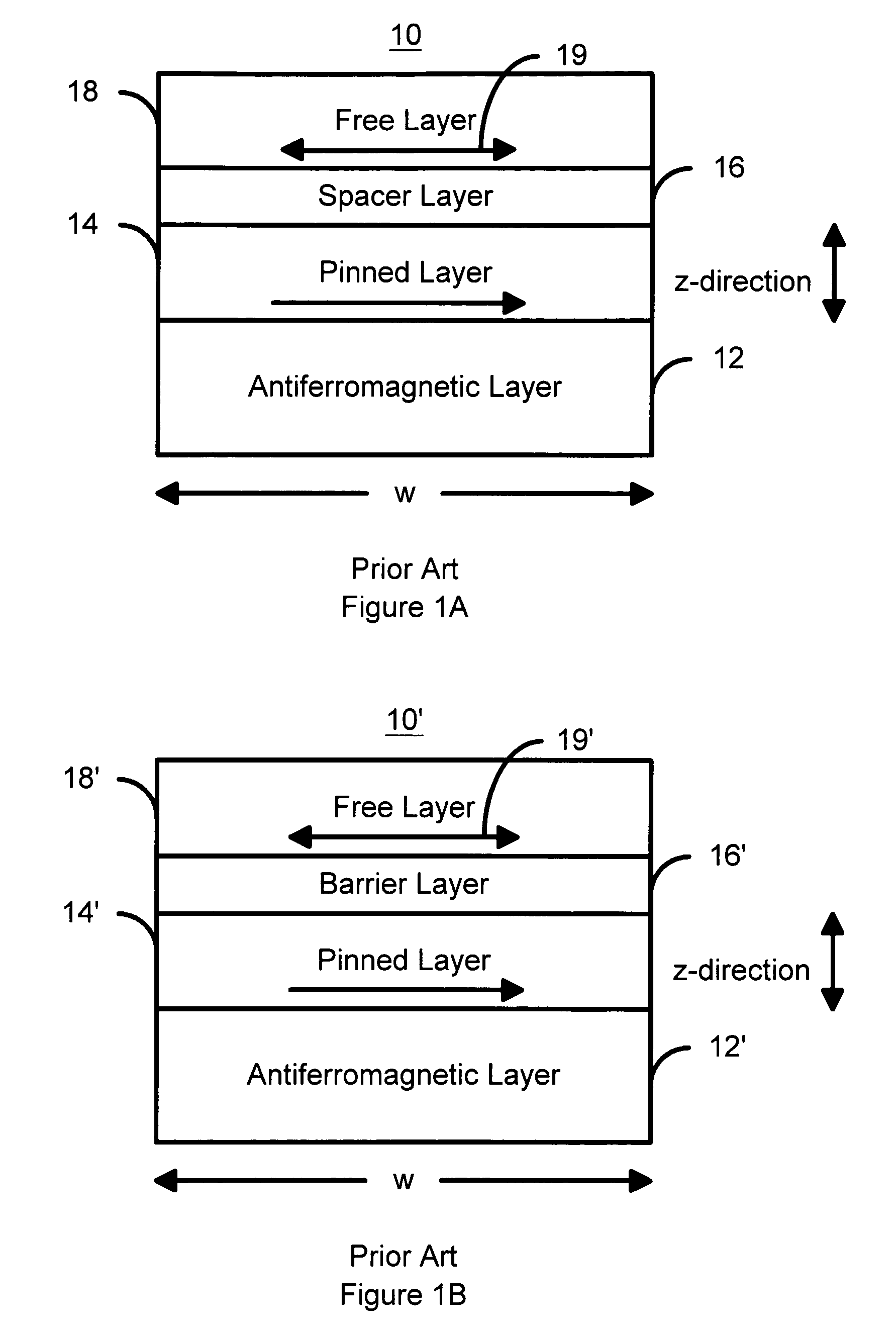
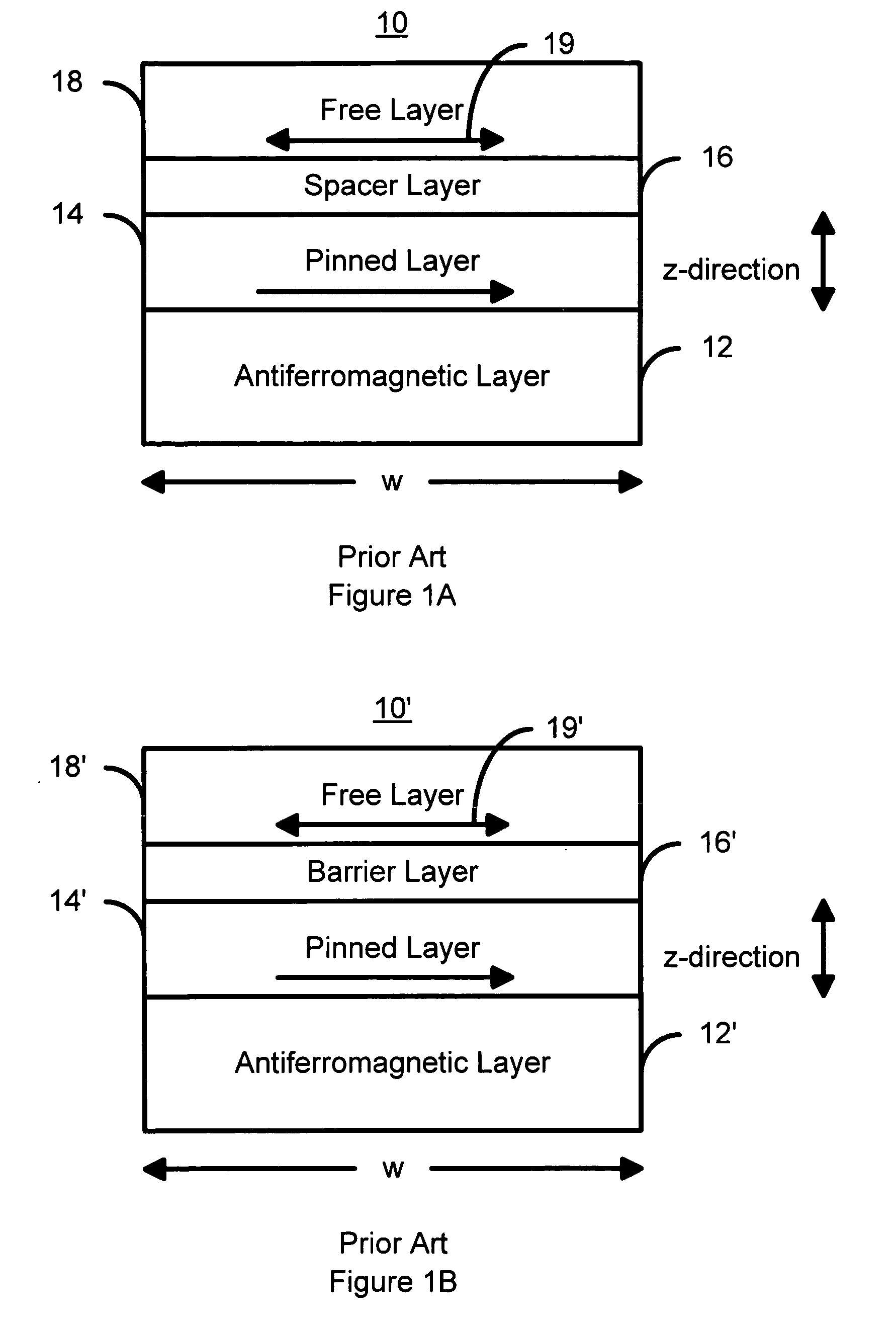
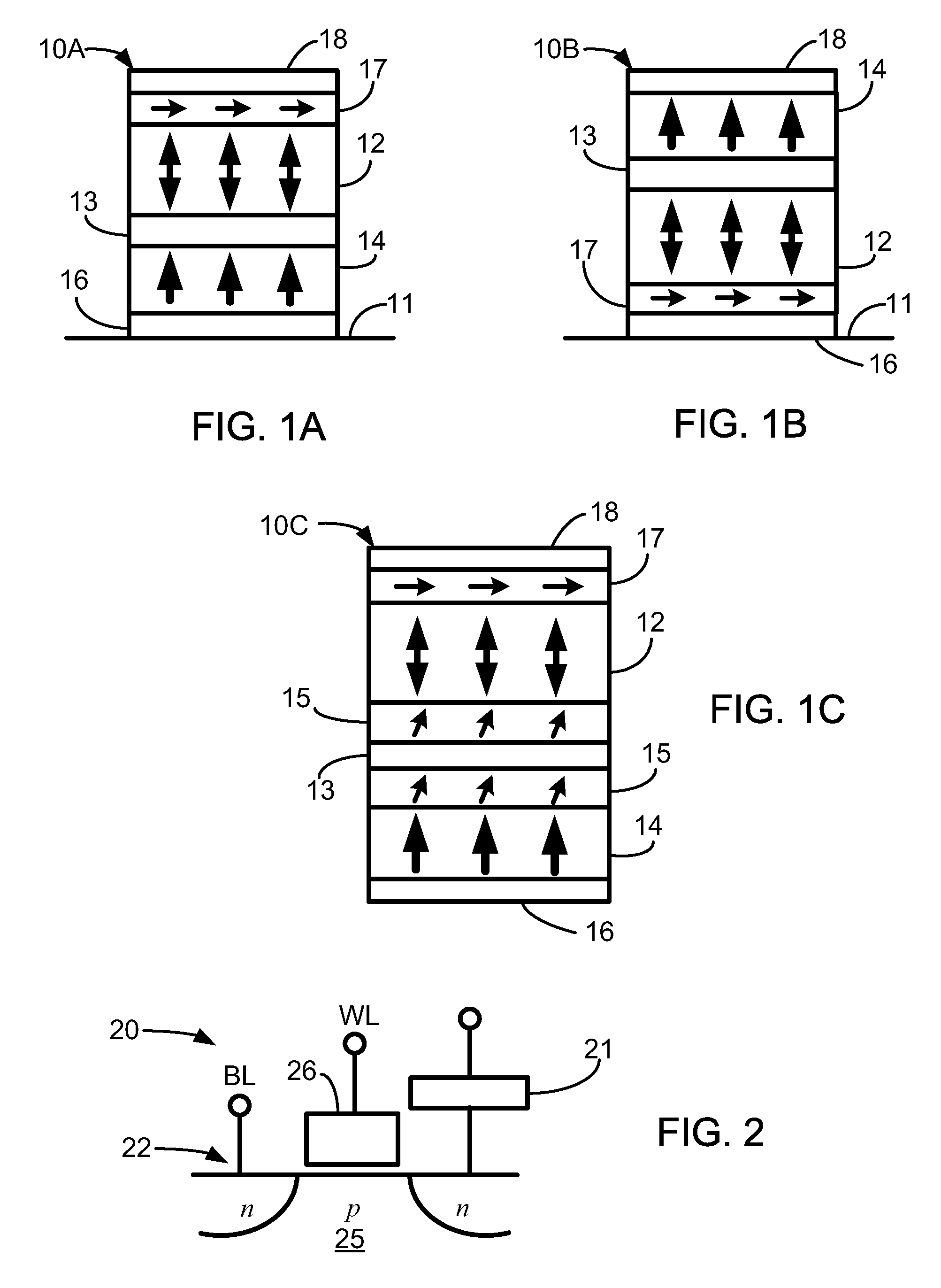
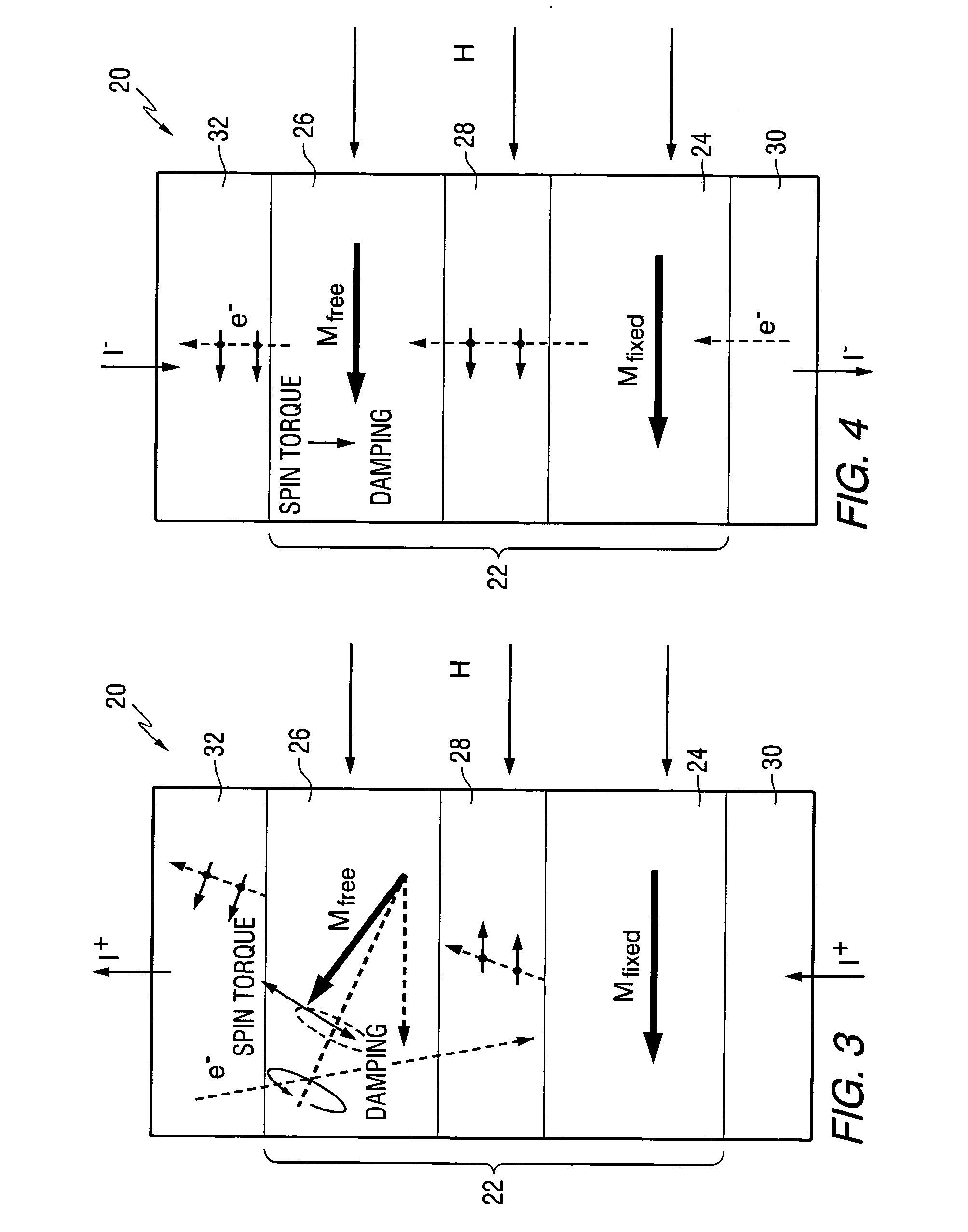
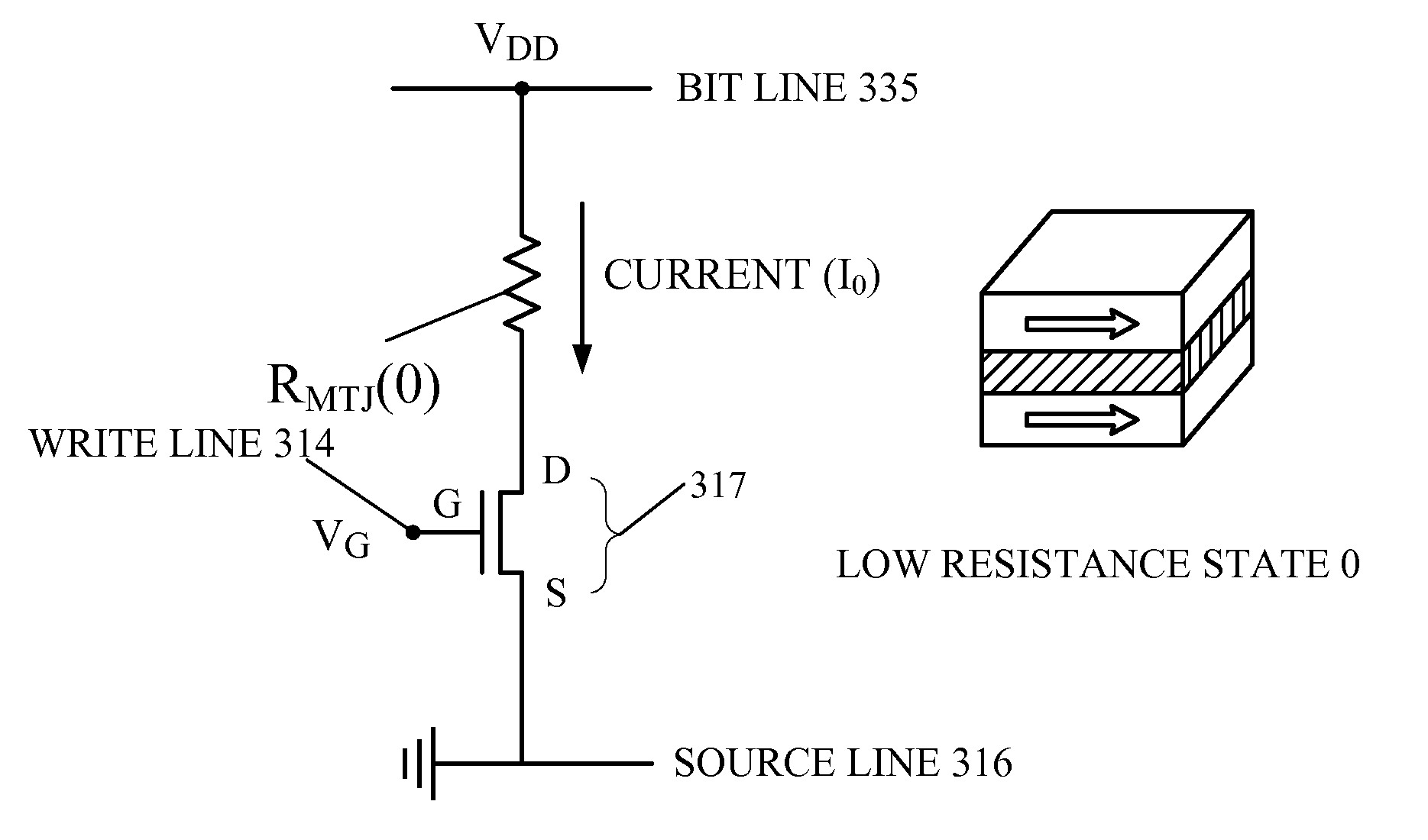
Magnetostatically coupled magnetic elements utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
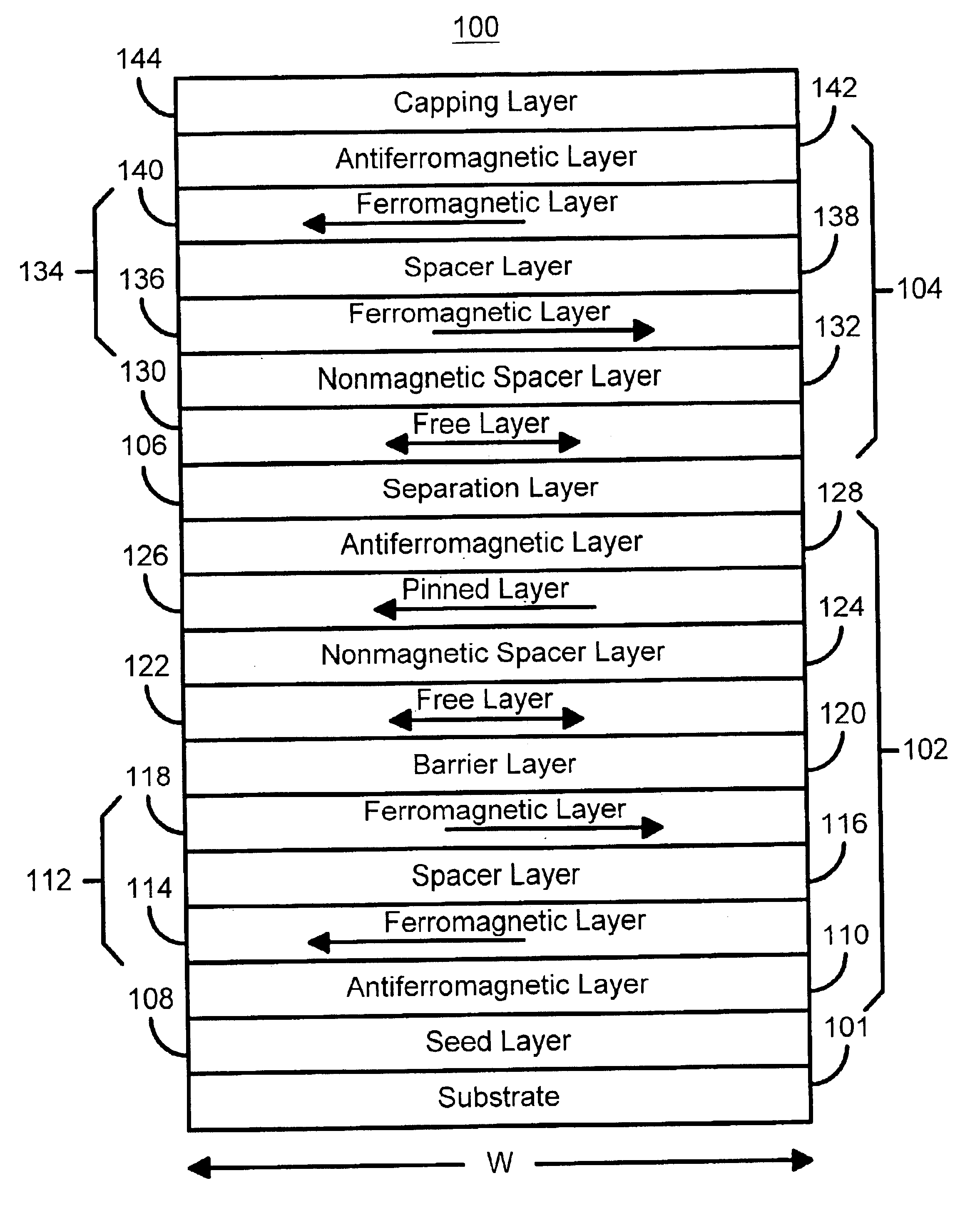
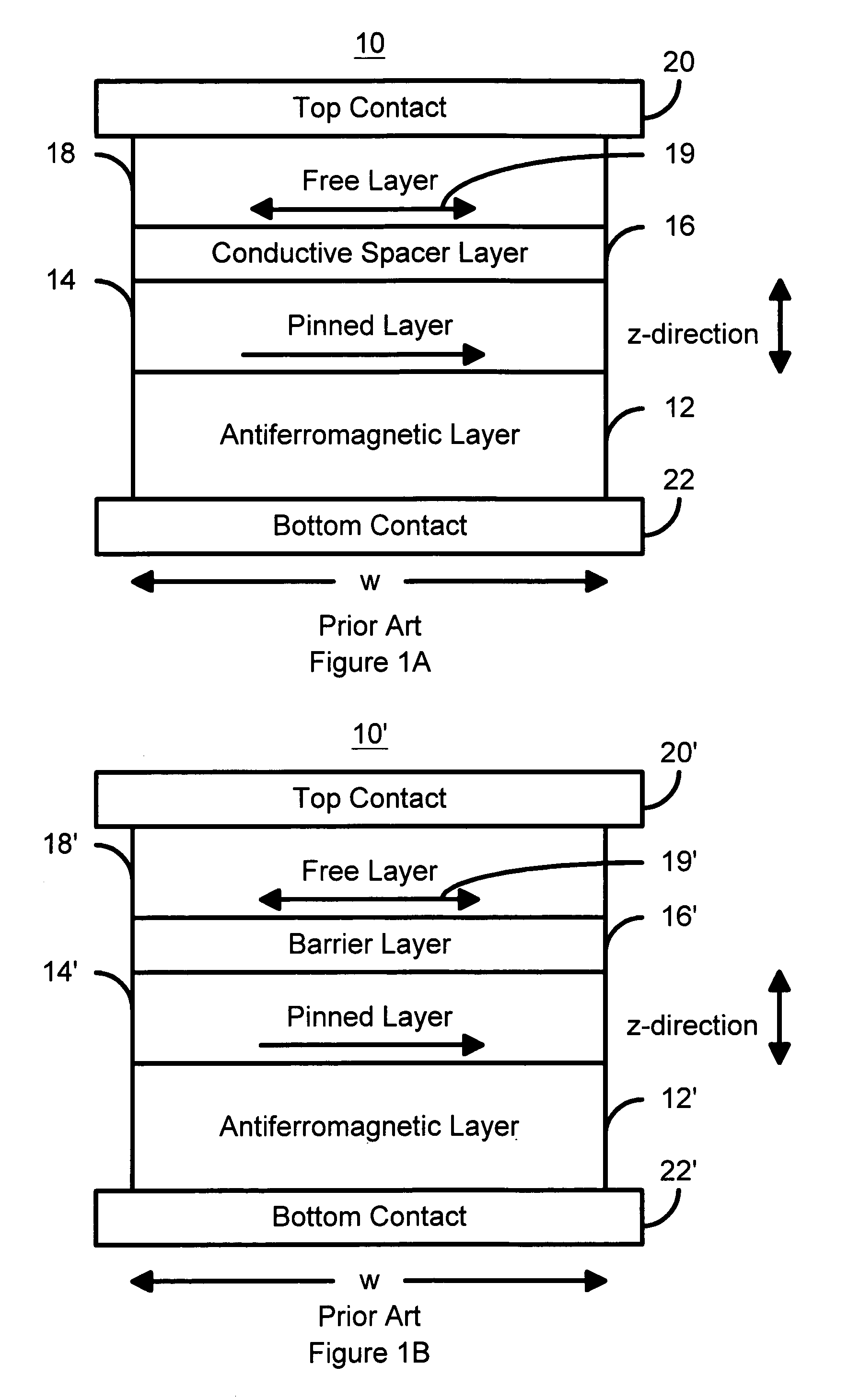
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a corresponding memory are disclosed. In one aspect, the method and system include providing a dual spin tunnel / valve structure and at least one spin valve. The dual spin tunnel / valve structure includes a nonmagnetic spacer layer between a pinned layer and a free layer, another pinned layer and a barrier layer between the free layer and the other pinned layer. The free layers of the dual spin tunnel / valve structure and the spin valve are magnetostatically coupled. In one embodiment a separation layer resides between the dual spin tunnel / valve structure and the spin valve. In another aspect, the method and system include providing two dual spin valves, a spin tunneling junction there between and, in one embodiment, the separation layer. In both aspects, the magnetic element is configured to write to the free layers using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Spin-on carbon compositions for lithographic processing
The invention described herein is directed towards spin-on carbon materials comprising polyamic acid compositions and a crosslinker in a solvent system. The materials are useful in trilayer photolithography processes. Films made with the inventive compositions are not soluble in solvents commonly used in lithographic materials, such as, but not limited to PGME, PGMEA, and cyclohexanone. However, the films can be dissolved in developers commonly used in photolithography. In one embodiment, the films can be heated at high temperatures to improve the thermal stability for high temperature processing. Regardless of the embodiment, the material can be applied to a flat / planar or patterned surface. Advantageously, the material exhibits a wiggling resistance during pattern transfer to silicon substrate using fluorocarbon etch.
Owner:BREWER SCI
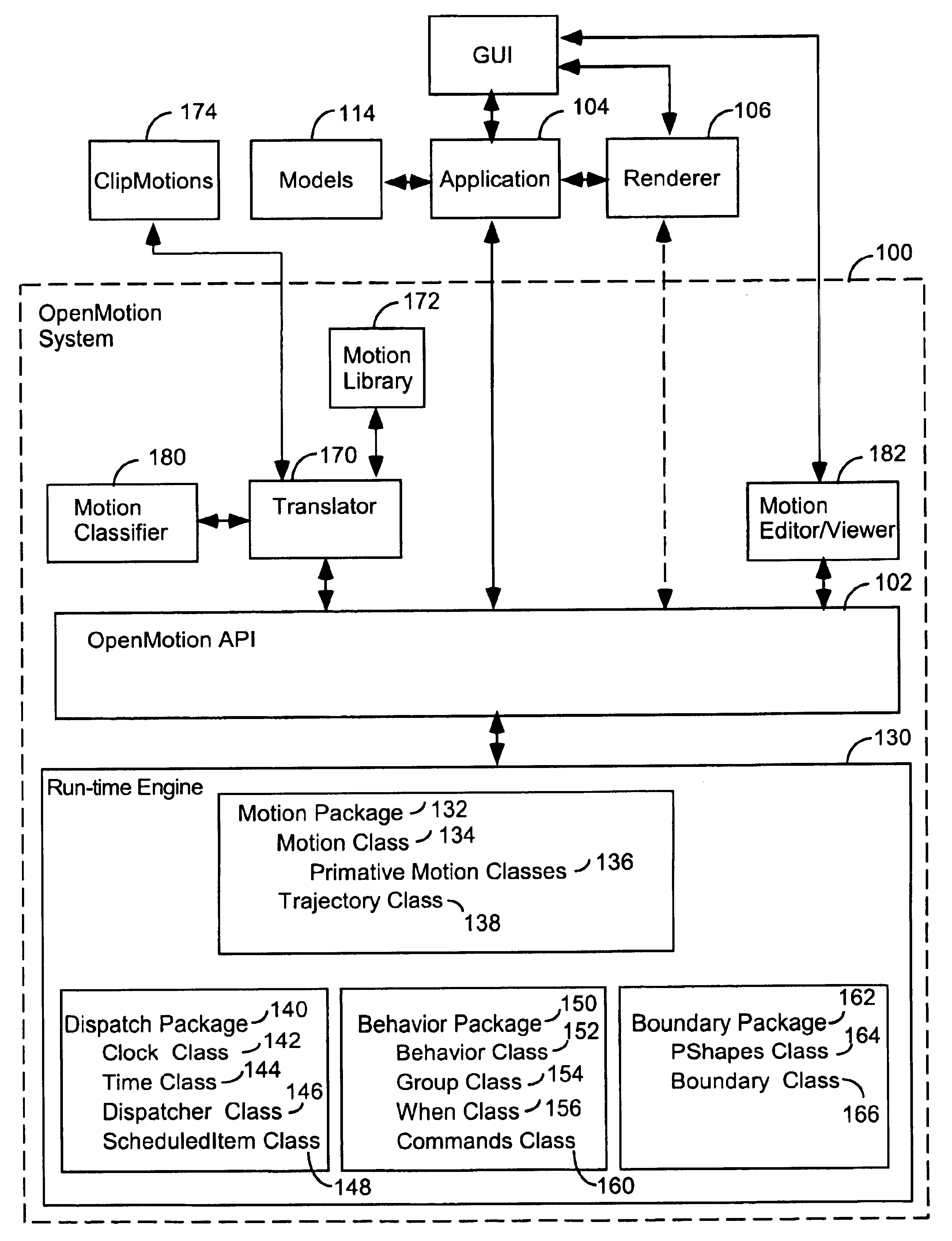
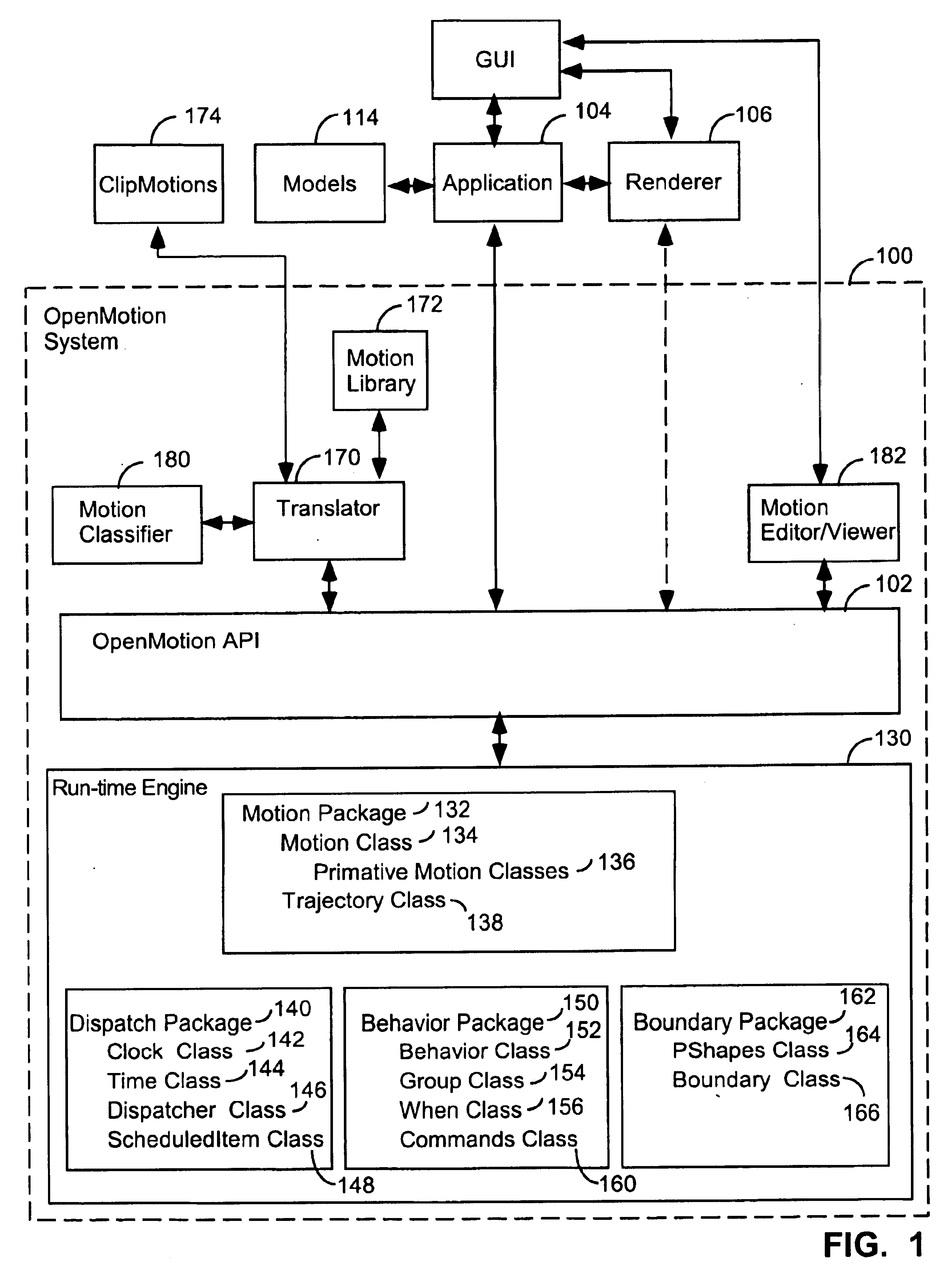
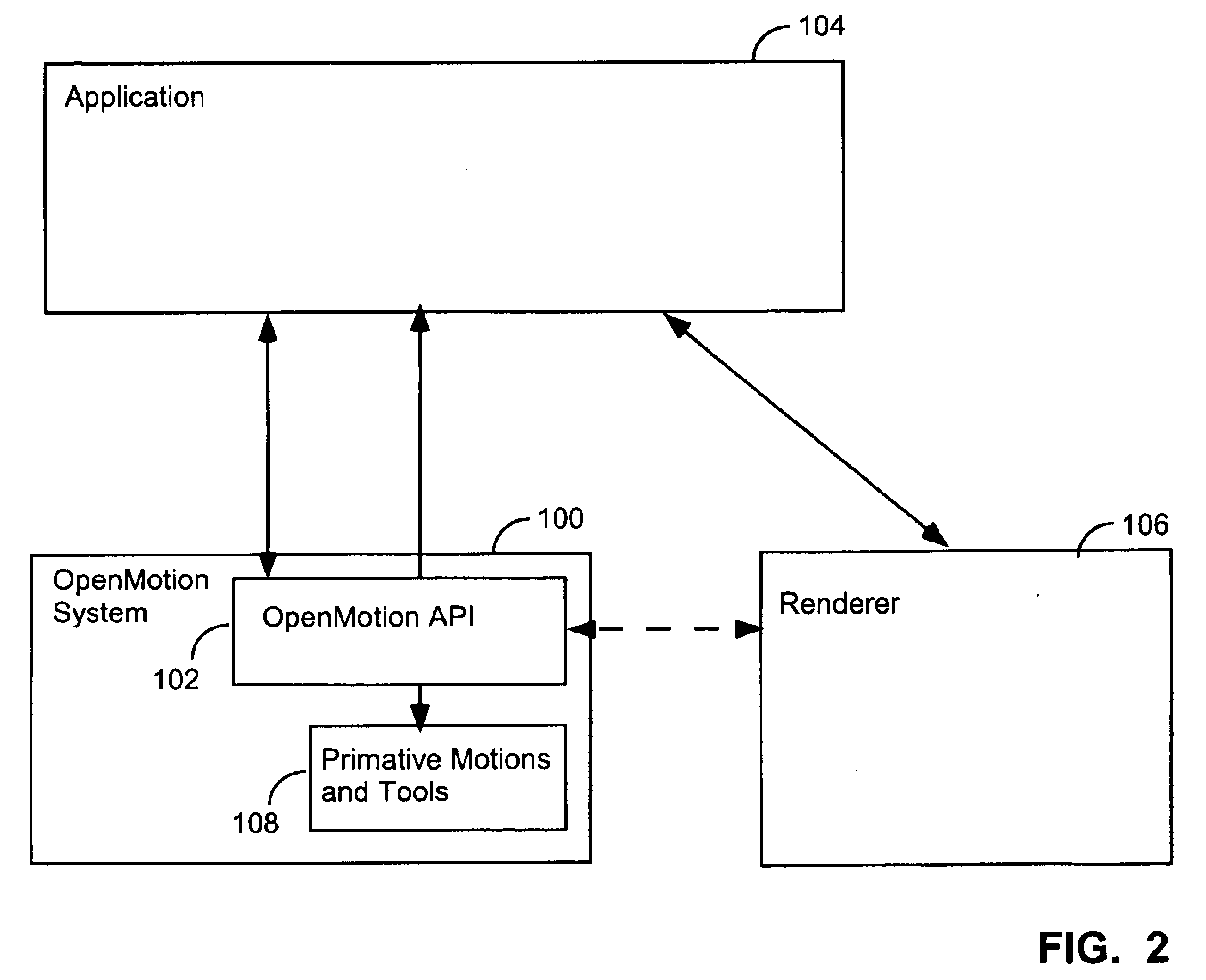
Apparatuses, methods, computer programming, and propagated signals for modeling motion in computer applications
InactiveUS6714201B1Easy to buildThe process is simple and fastComputer controlSimulator controlGraphicsTime function
A hierarchical 3D graphics model can be viewed as a hierarchical graph of its nodes and their associated motions, with the mathematical type of motions graphically indicated. A user can click on a displayed motion to edit it. A motion API provides one or more of the following features: (1) spatial predicate functions; (2) functions for scaling motion intensity; (3) classes for shake, spin, and swing motions; (4) motion classes with a GUI interfaced for defining their duty cycle; (5) functions for defining and computing 0through 2<nd >order derivatives of 3D position and orientation as function of time; (6) behaviors that constrain motions by boundaries in which the constraint is a reflection, clamp, andor onto constraint, or in which the boundary is a composite boundary. Motions can be defined by successive calls to an API and then be saved in a file.
Owner:3D OPEN MOTION
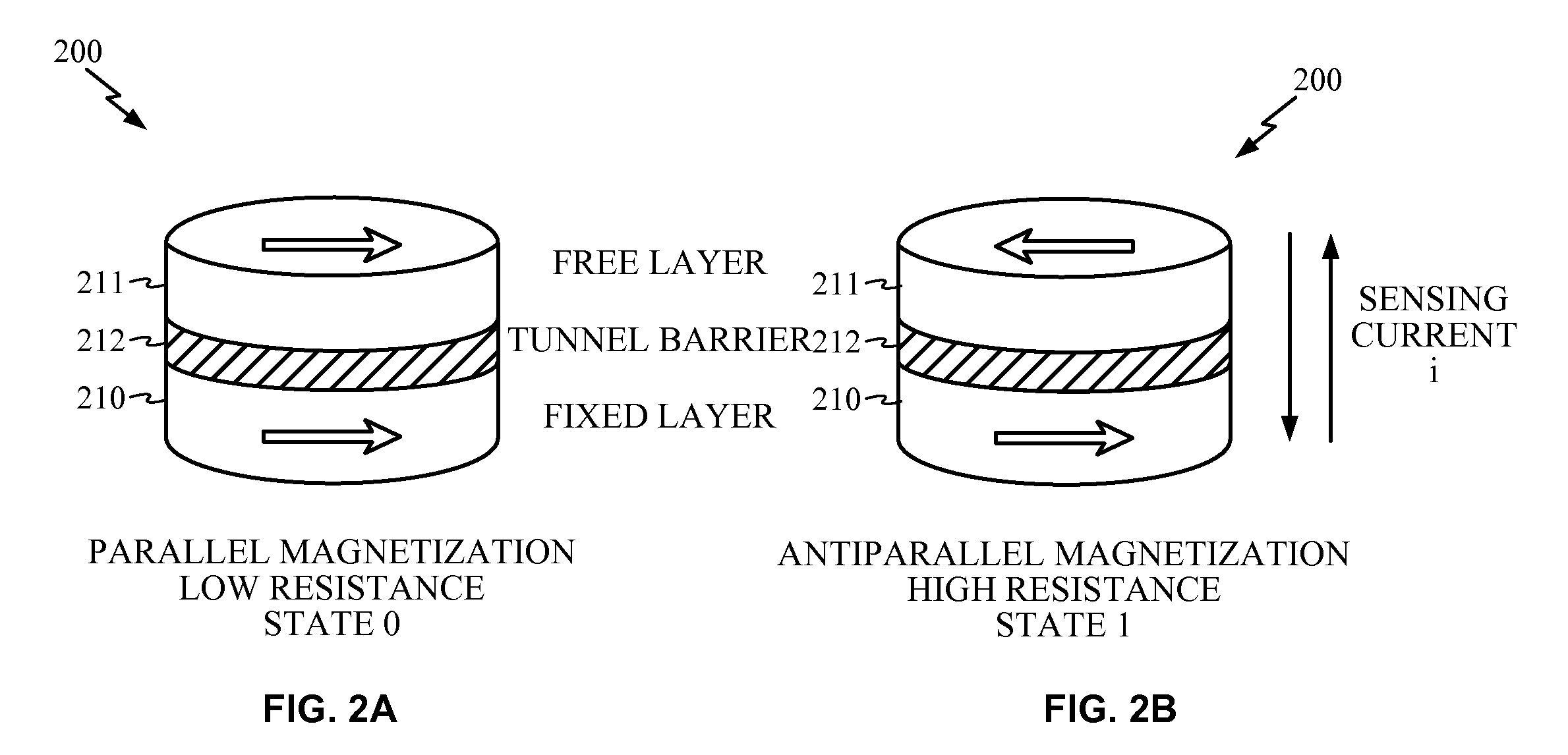
Magnetoresistive element
A magnetoresistive element which records information by supplying spin-polarized electrons to a magnetic material, includes a first pinned layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a first magnetization directed in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, a free layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a second magnetization directed in the direction perpendicular to the film surface, the direction of the second magnetization reversing by the spin-polarized electrons, and a first nonmagnetic layer which is provided between the first pinned layer and the free layer. A saturation magnetization Ms of the free layer satisfies a relationship 0≧Ms<√{square root over ( )}{Jw / (6nAt)}. Jw is a write current density, t is a thickness of the free layer, A is a constant.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Spin barrier enhanced magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7088609B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
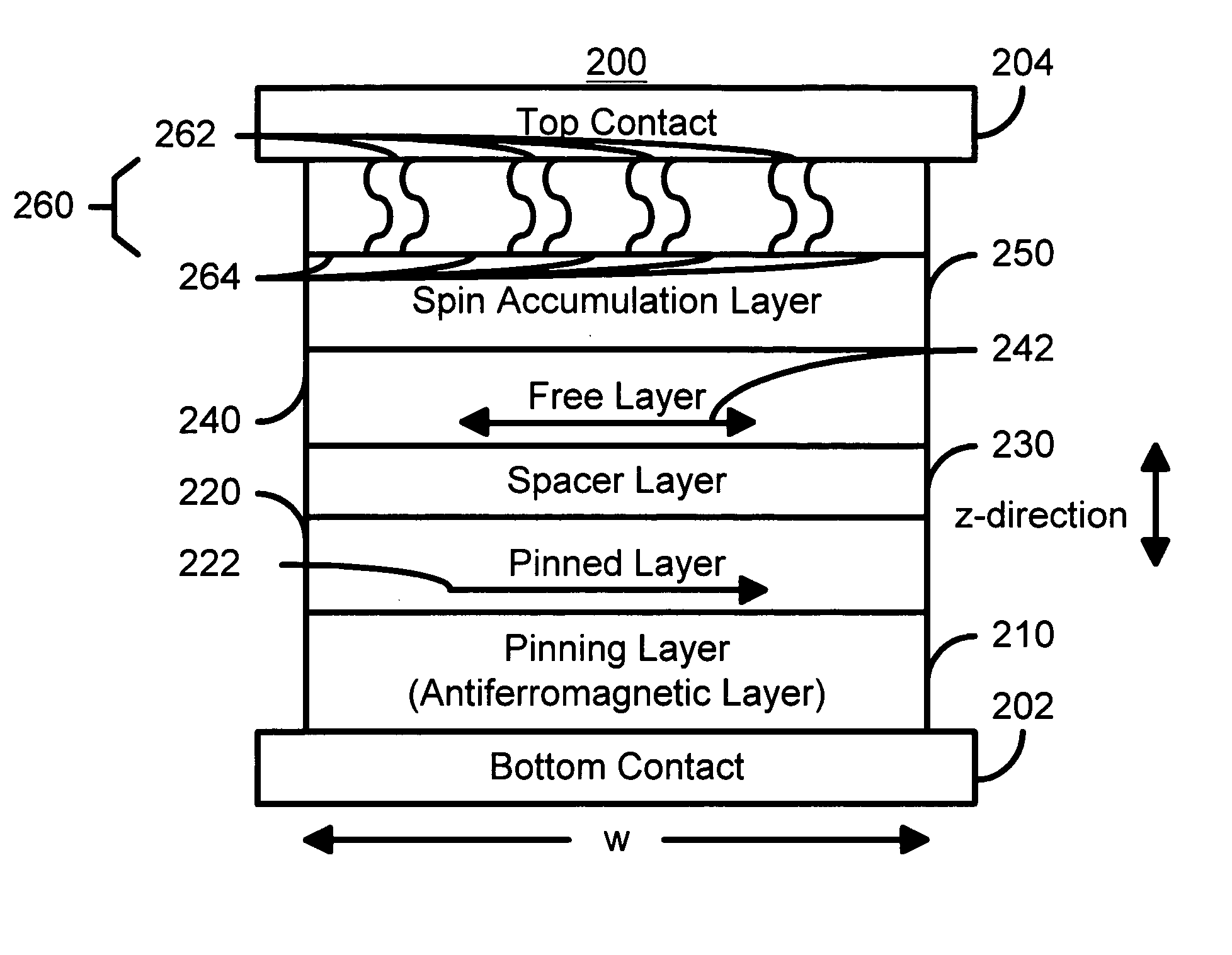
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, spacer, free, and spin barrier layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer layer and the spin barrier layer. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to a damping constant of the free layer. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity, preferably being metallic, and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Thin seeded Co/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular anisotropy for spintronic device applications
ActiveUS20090257151A1Raise the ratioNot to damageMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingPerpendicular anisotropySpins
A spin valve structure for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having a fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying (Co / Ni)x multilayer. The (Co / Ni)x multilayer is deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging Co / Ni interfaces and thereby preserving PMA. As a result, only a thin seed layer is required. PMA is maintained even after annealing at 220° C. for 10 hours. Examples of GMR and TMR spin valves are described and may be incorporated in spin transfer oscillators and spin transfer MRAMs. The free layer is preferably made of a FeCo alloy including at least one of Al, Ge, Si, Ga, B, C, Se, Sn, or a Heusler alloy, or a half Heusler alloy to provide high spin polarization and a low magnetic damping coefficient.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
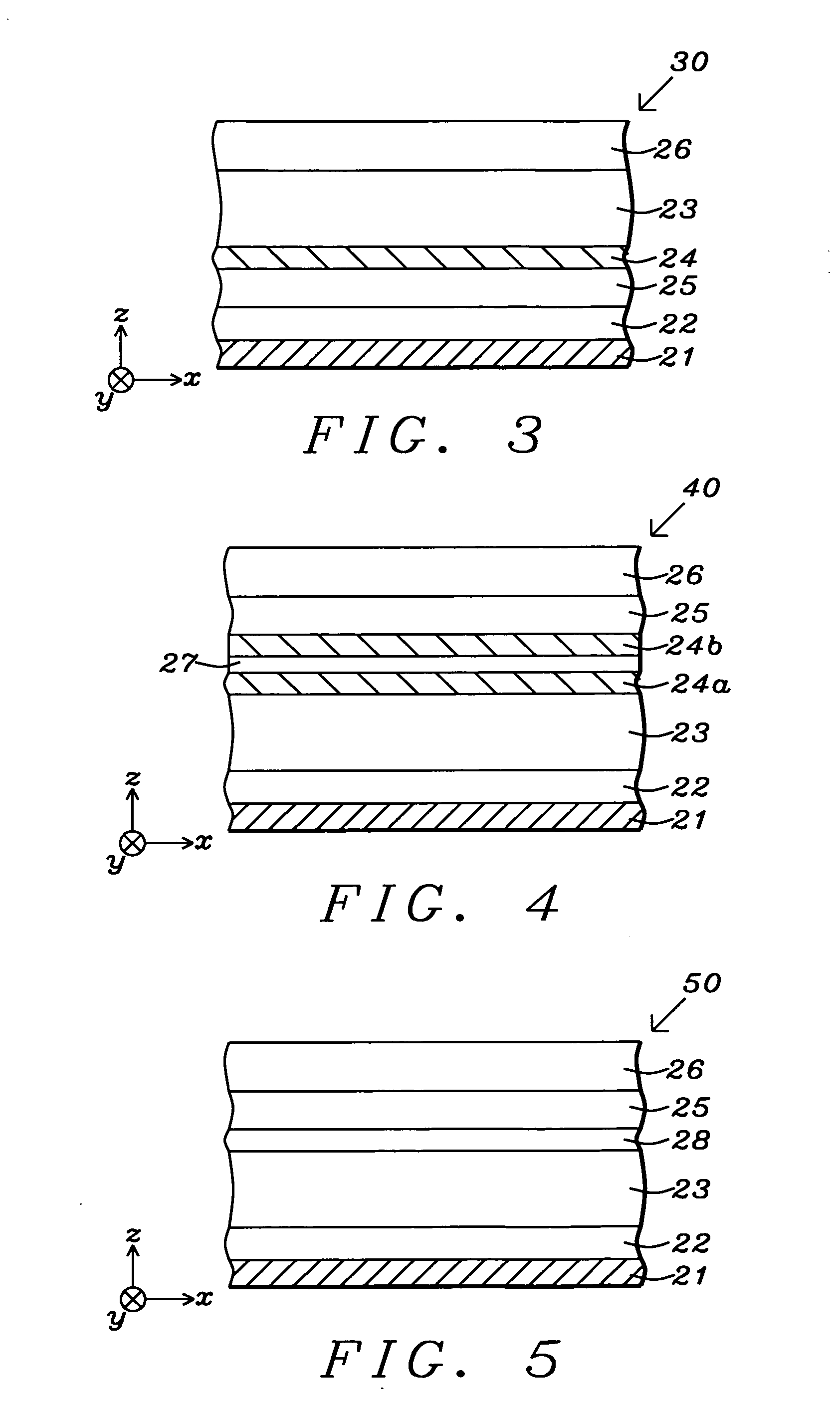
Spin barrier enhanced dual magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7057921B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes first pinned, spacer, free, spin barrier, and second pinned layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer and spin barrier layers. The spin barrier layer is between the free and second pinned layers. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to the free layer damping constant. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
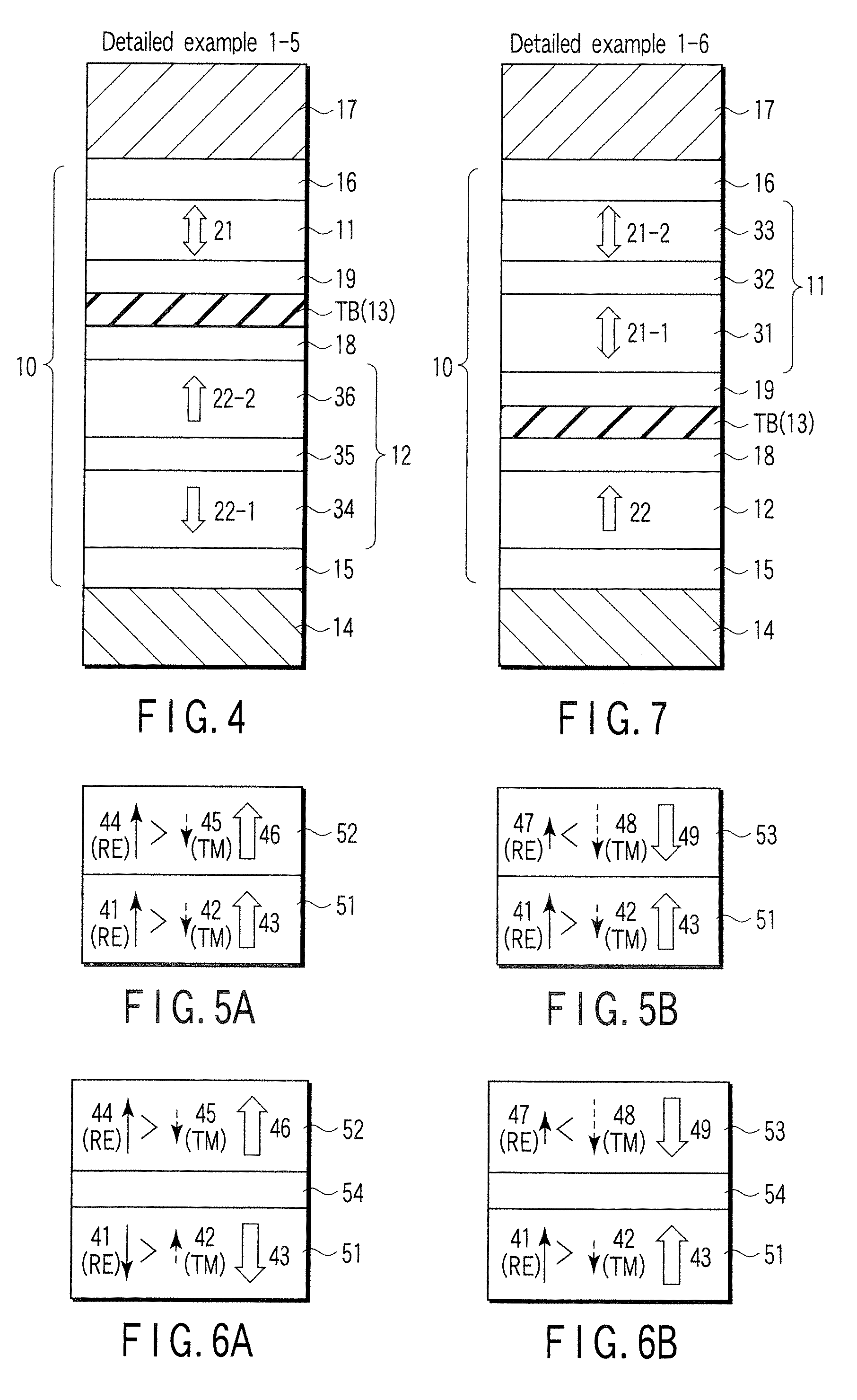
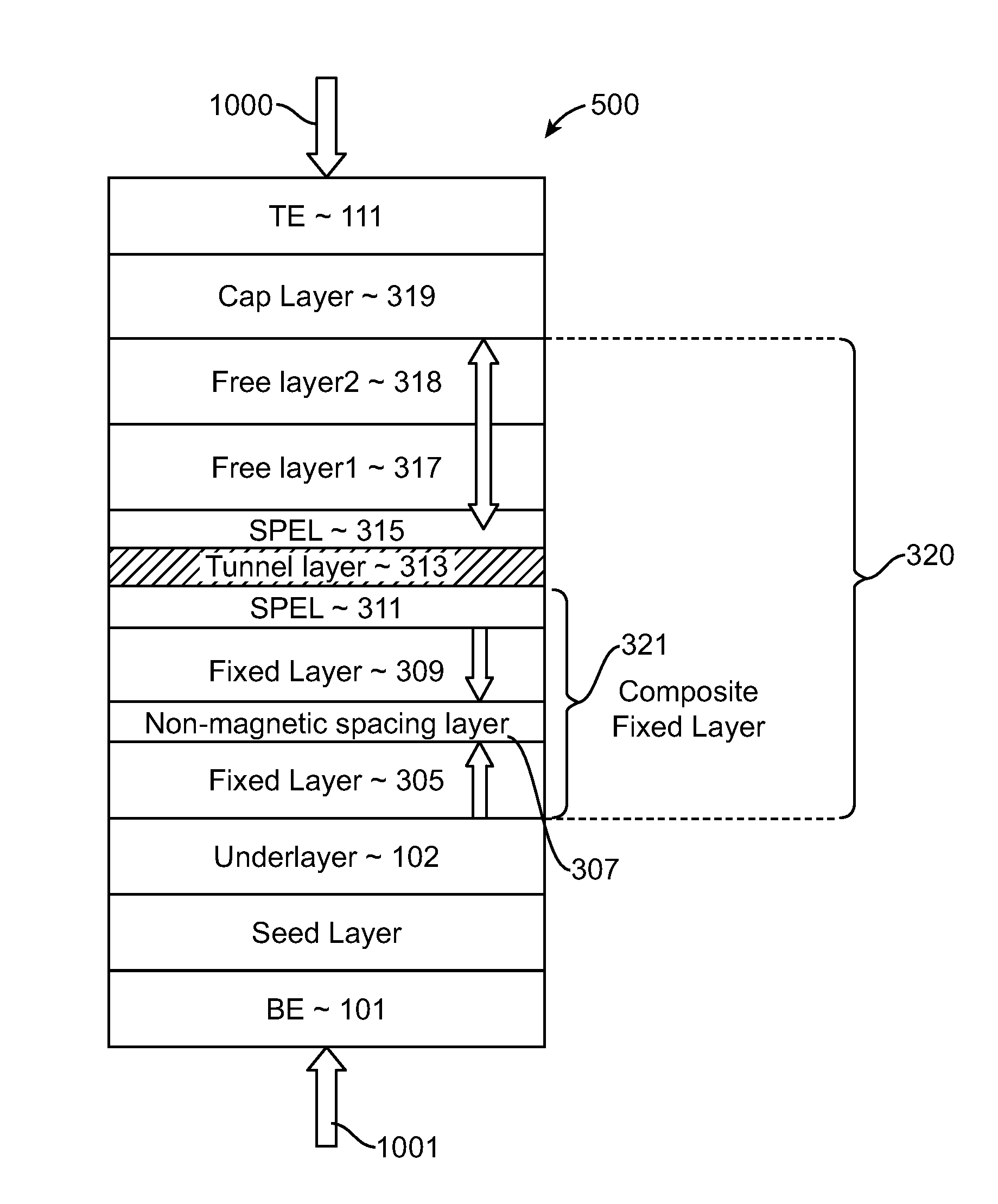
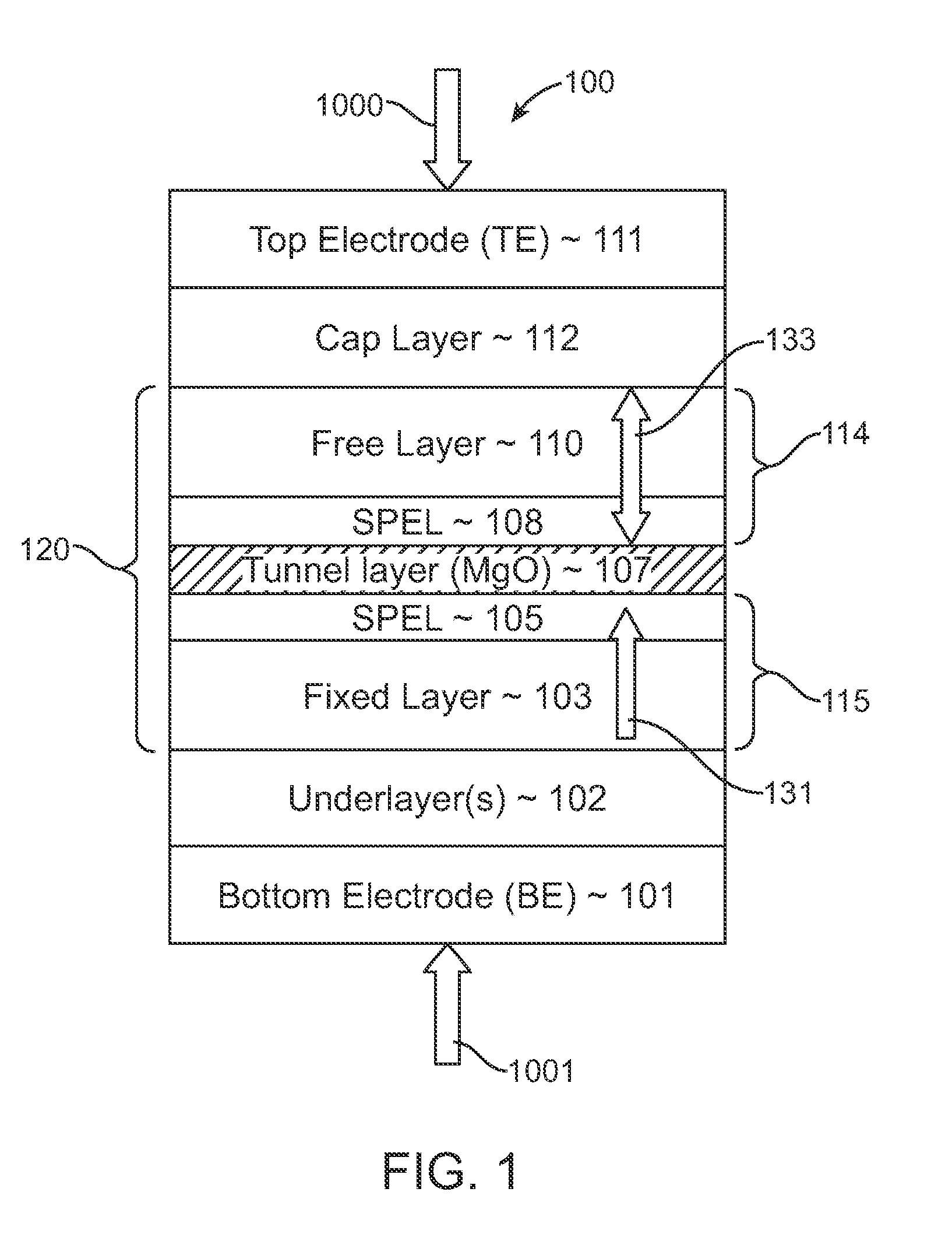
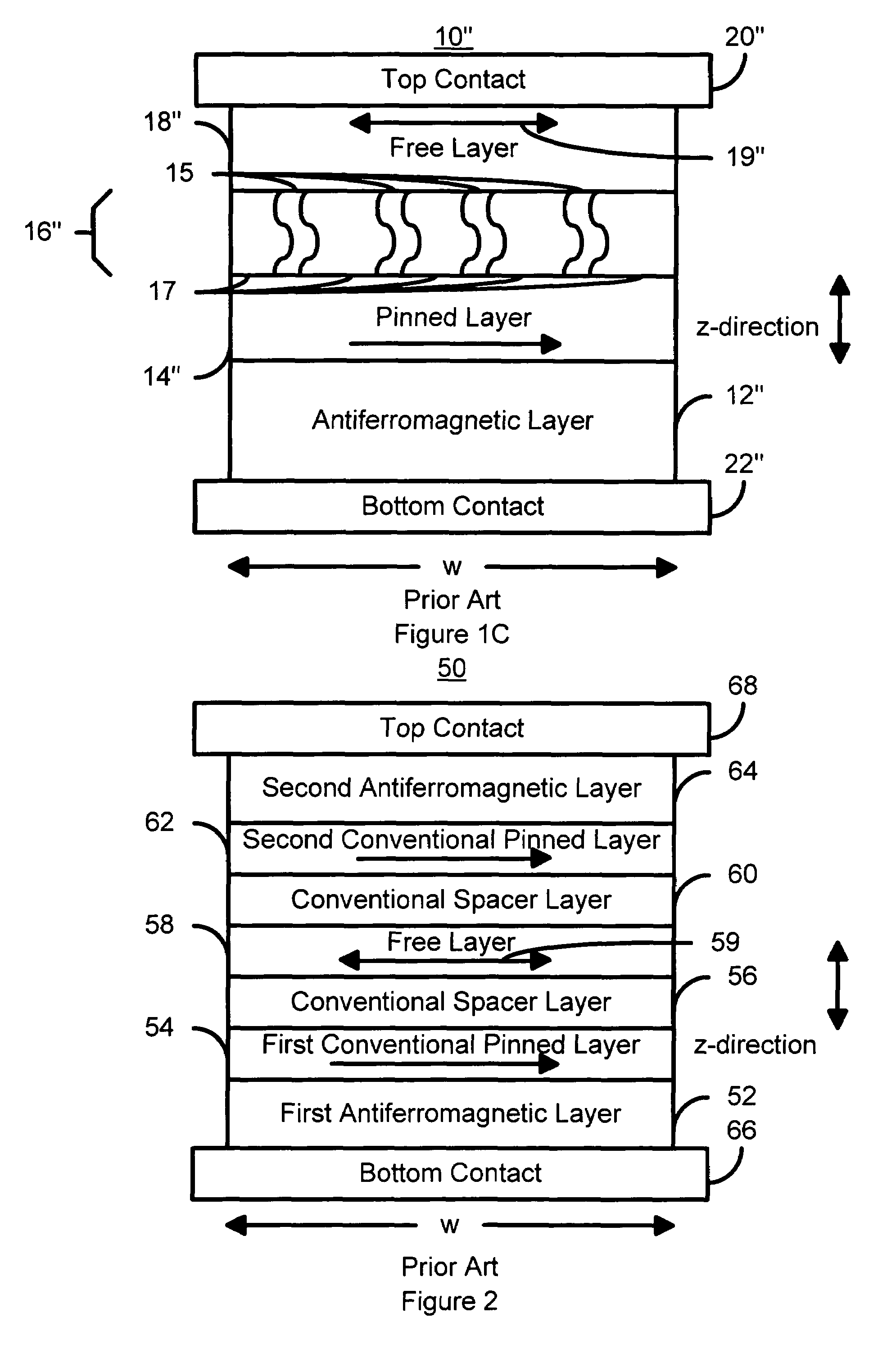
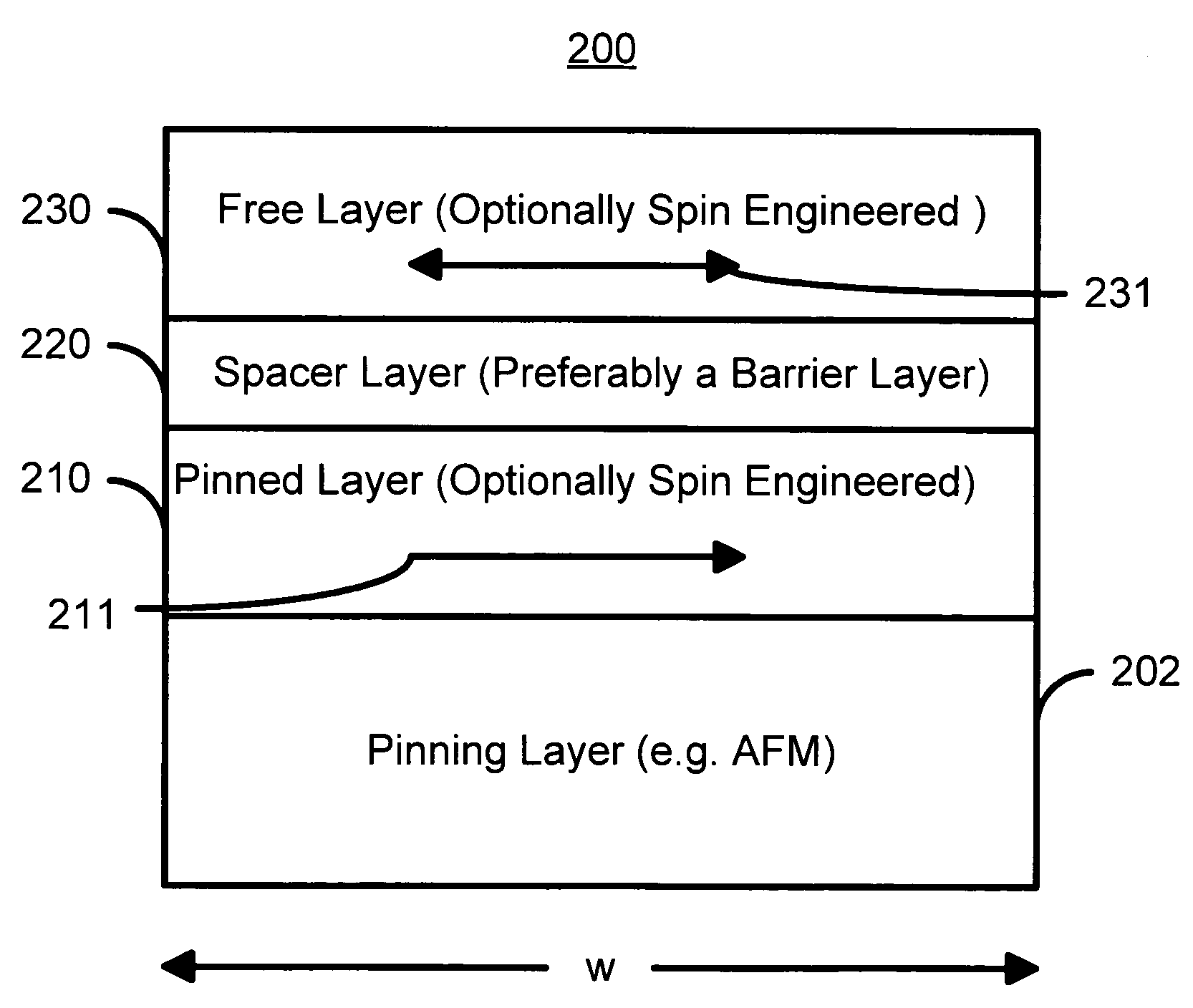
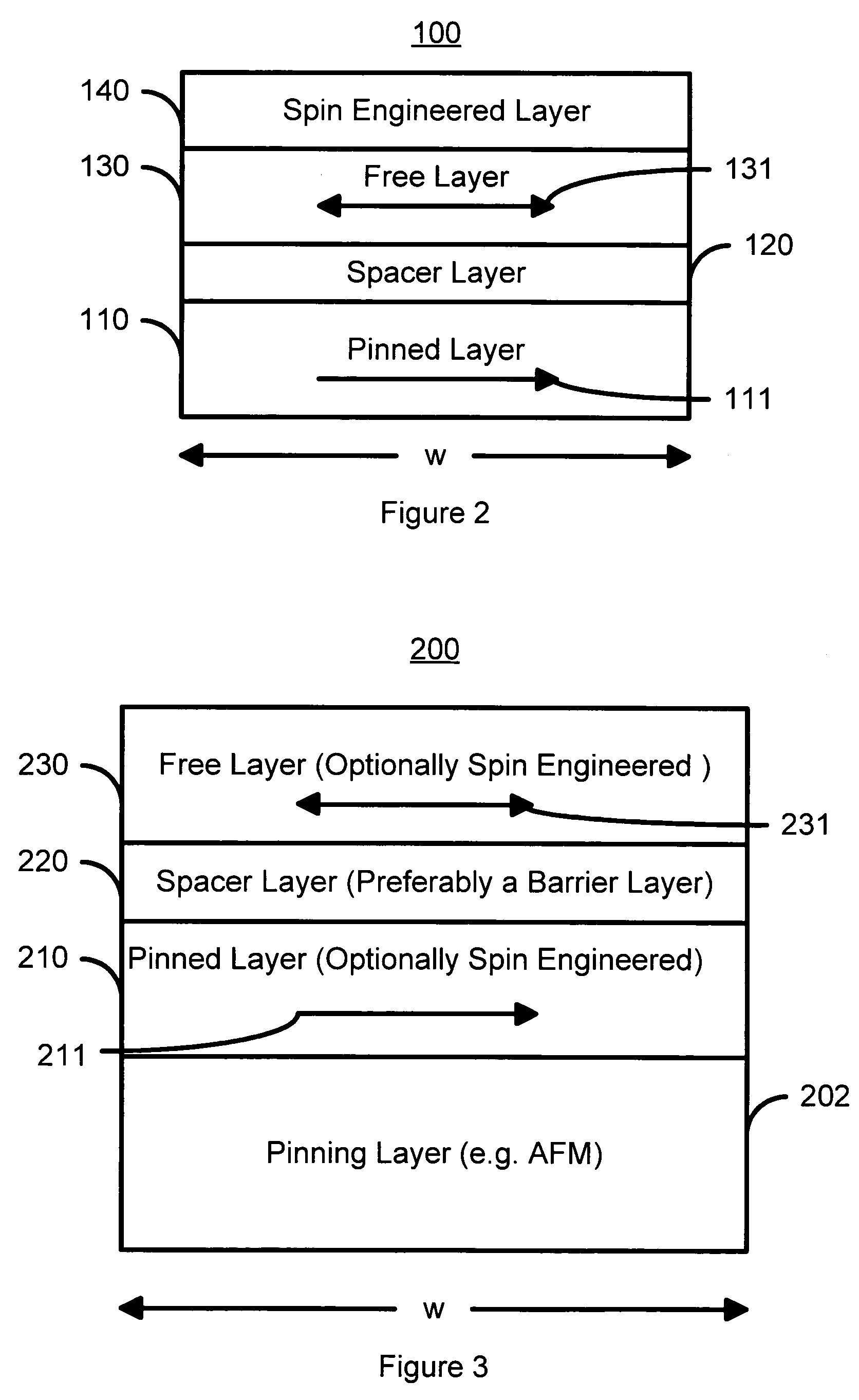
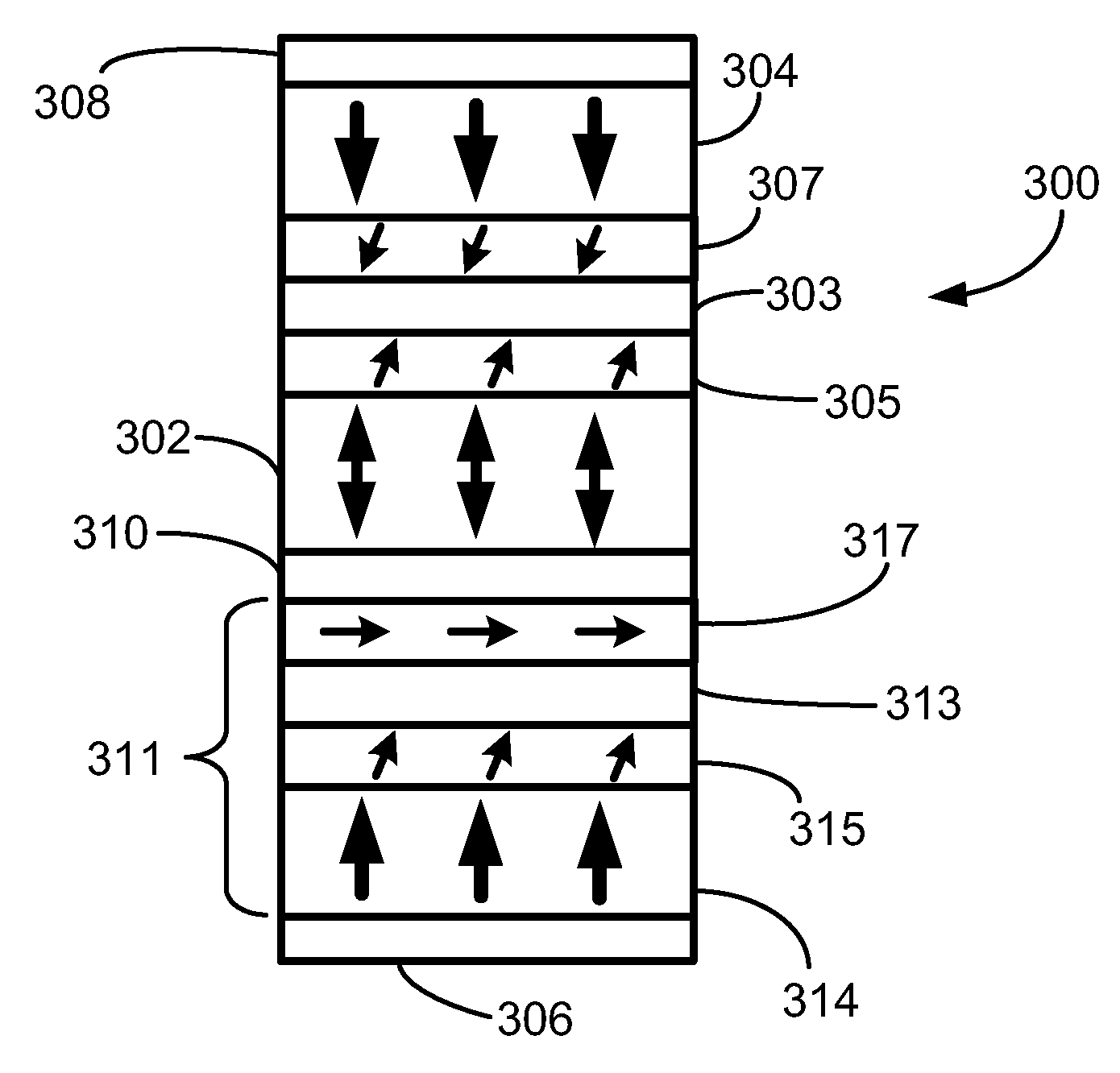
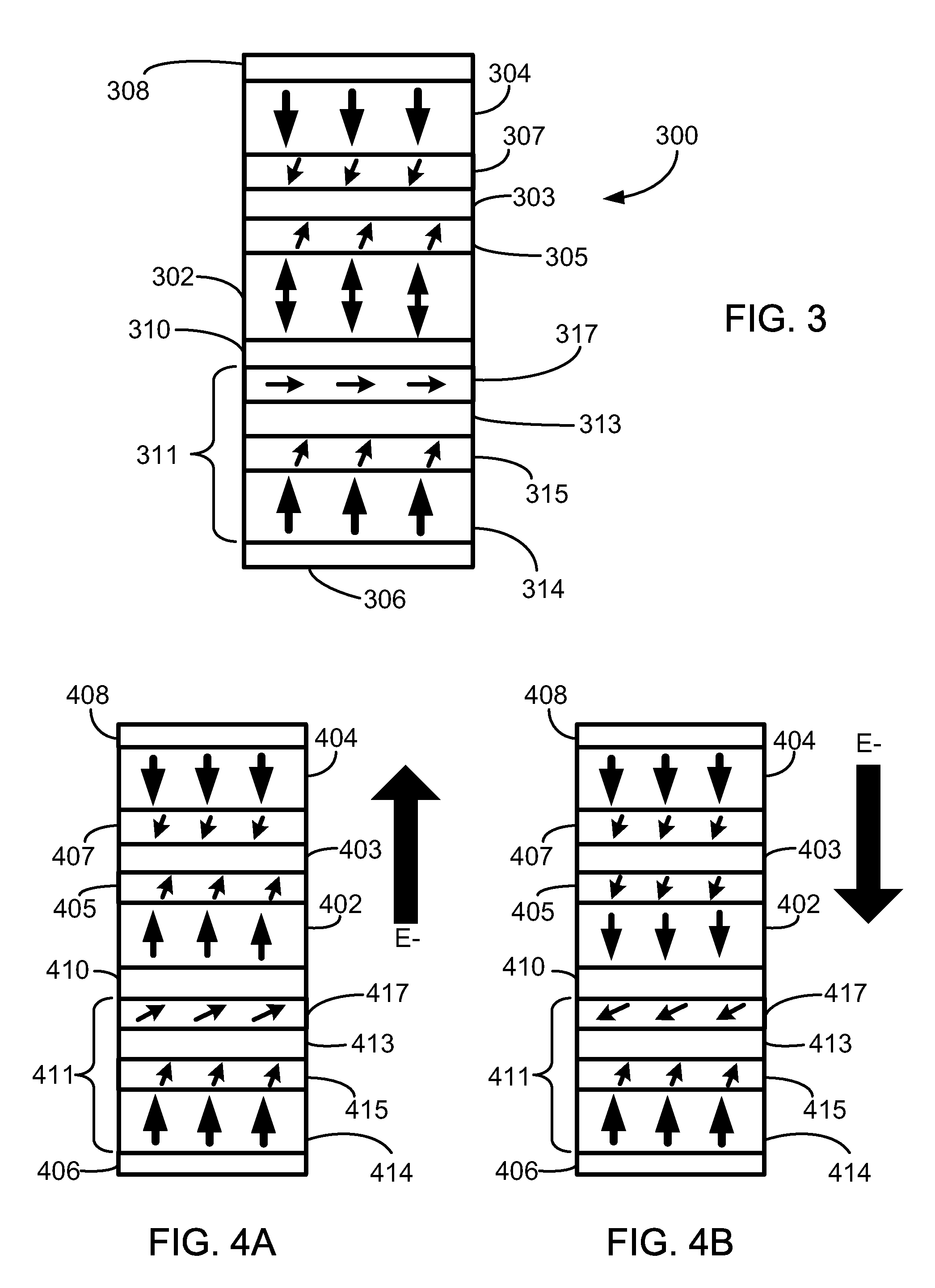
Magnetic elements with spin engineered insertion layers and MRAM devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7369427B2Lower average currentReduce consumptionNanomagnetismGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpinsSpin transfer
A method and system include providing a pinned layer, a free layer, and a spacer layer between the pinned and free layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. In one aspect, the method and system include providing a spin engineered layer adjacent to the free layer. The spin engineered layer is configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. In another aspect, at least one of the pinned, free, and spacer layers is a spin engineered layer having an internal spin engineered layer configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. In this aspect, the magnetic element may include another pinned layer and a barrier layer between the free and pinned layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
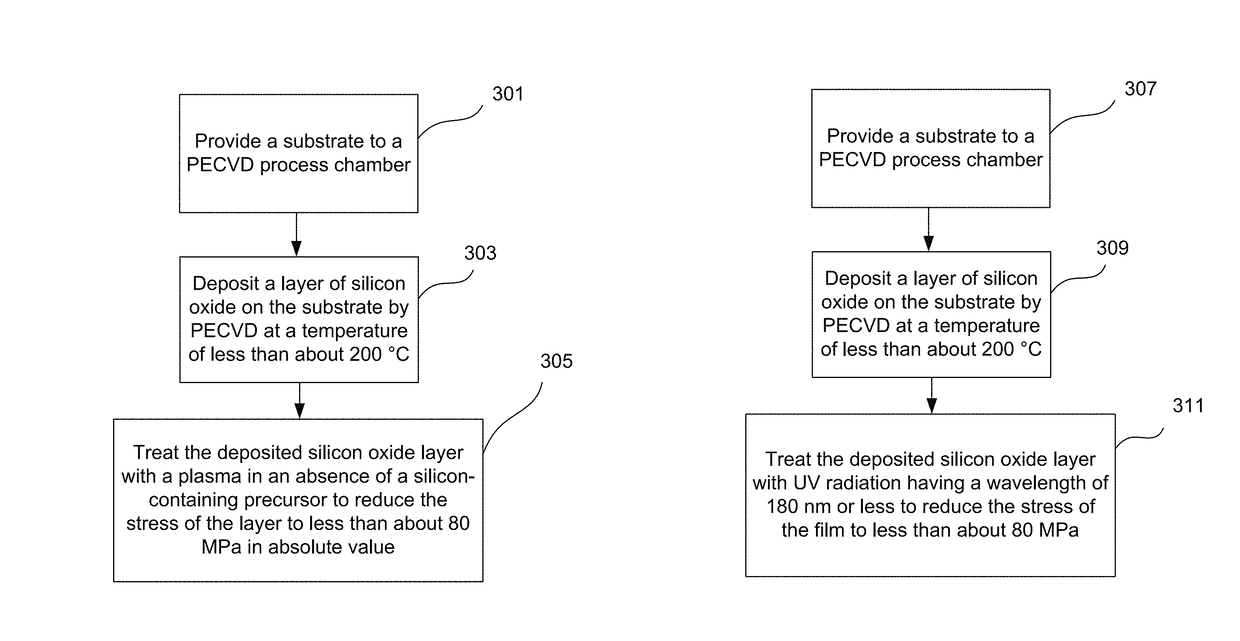
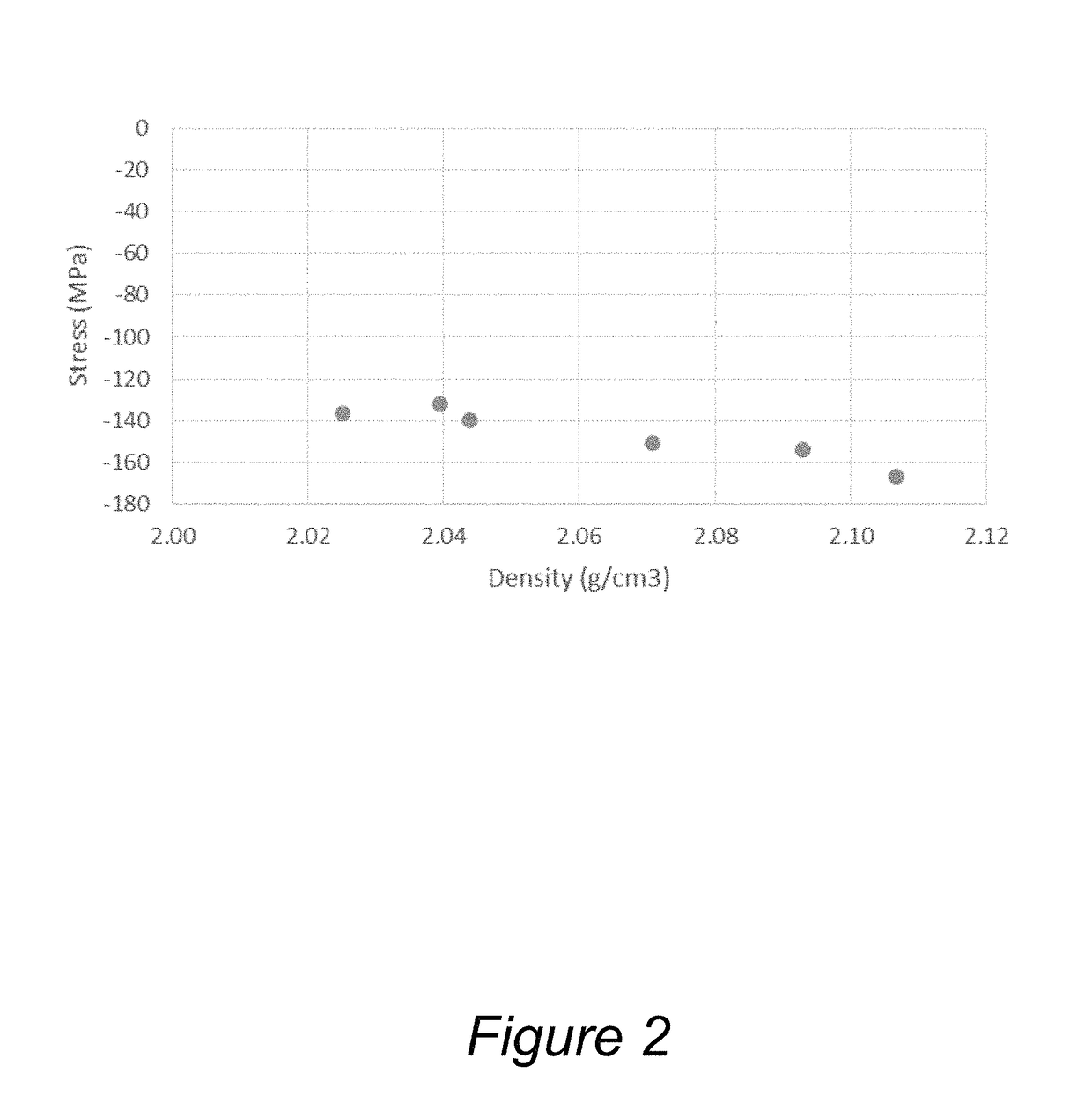
Low temperature formation of high quality silicon oxide films in semiconductor device manufacturing
ActiveUS9847221B1Relieve pressureReduce film stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricDevice material
Silicon oxide layer is deposited on a semiconductor substrate by PECVD at a temperature of less than about 200° C. and is treated with helium plasma to reduce stress of the deposited layer to an absolute value of less than about 80 MPa. Plasma treatment reduces hydrogen content in the silicon oxide layer, and leads to low stress films that can also have high density and low roughness. In some embodiments, the film is deposited on a semiconductor substrate that contains one or more temperature-sensitive layers, such as layers of organic material or spin-on dielectric that cannot withstand temperatures of greater than 250° C. In some embodiments the silicon oxide film is deposited to a thickness of between about 100-200 Å, and is used as a hardmask layer during etching of other layers on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Novel magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) to reduce spin transfer magnetization switching current
ActiveUS20080179699A1Reduce magnetic “ dead layer ”Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesLayer interfaceSpins
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
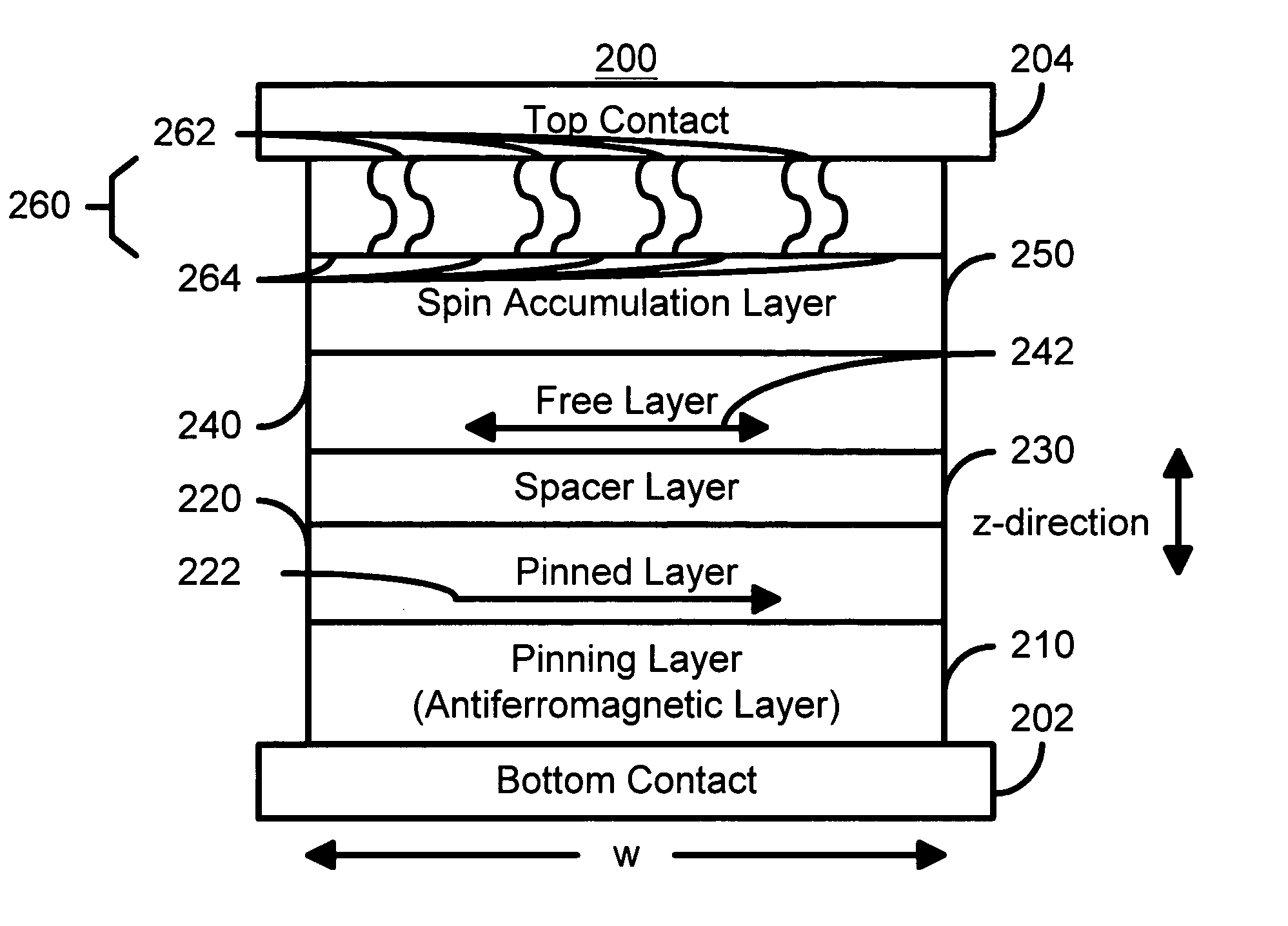
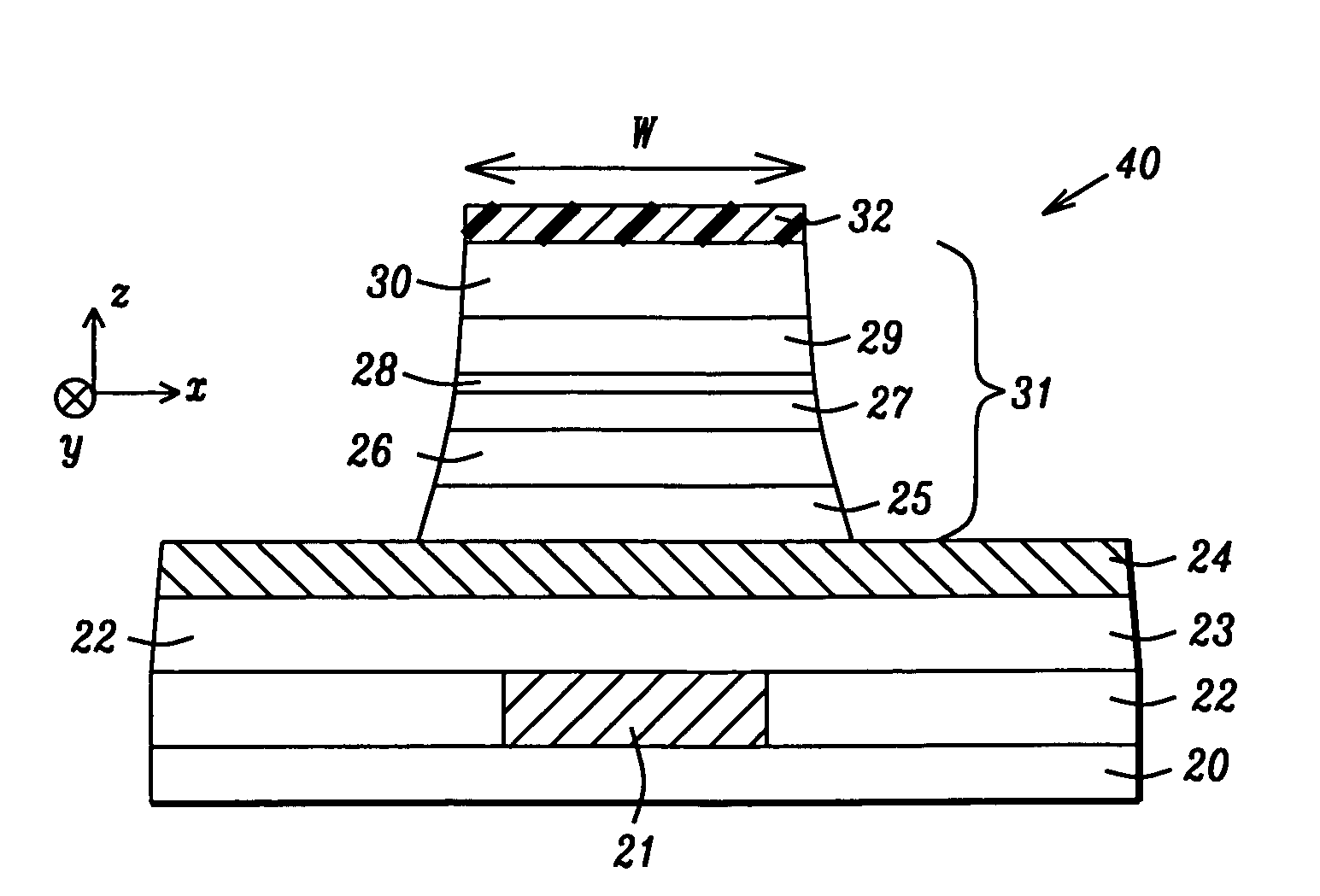
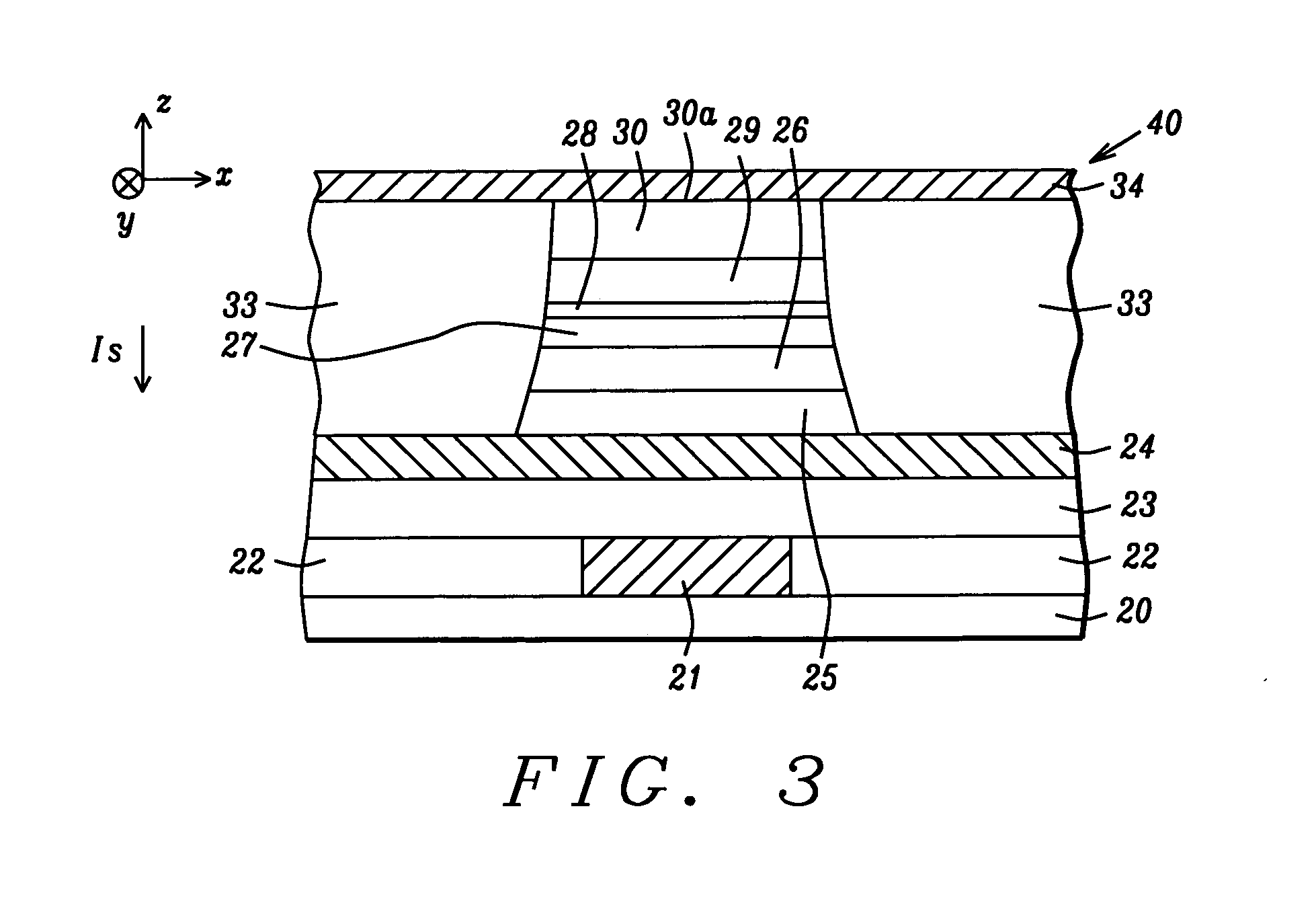
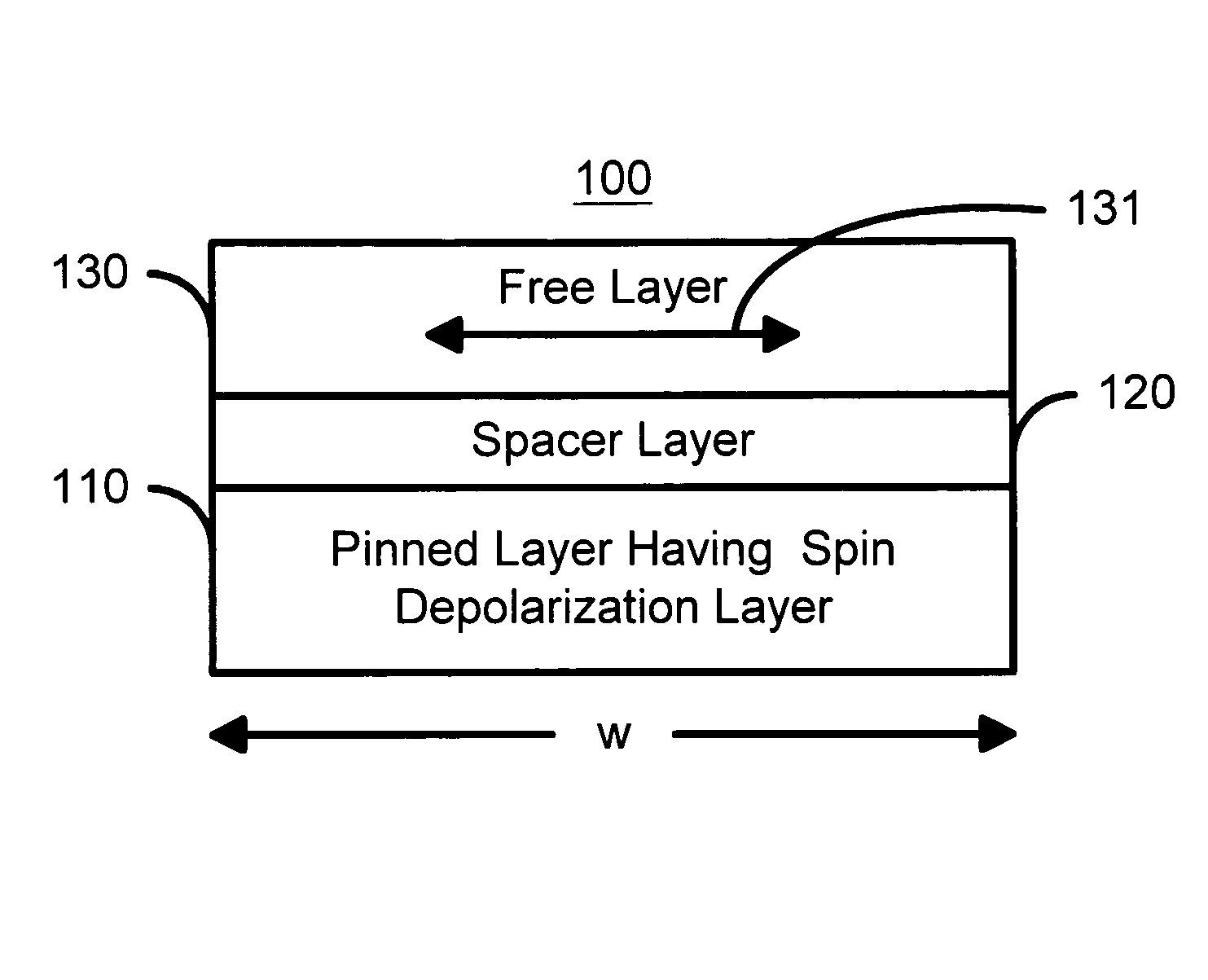
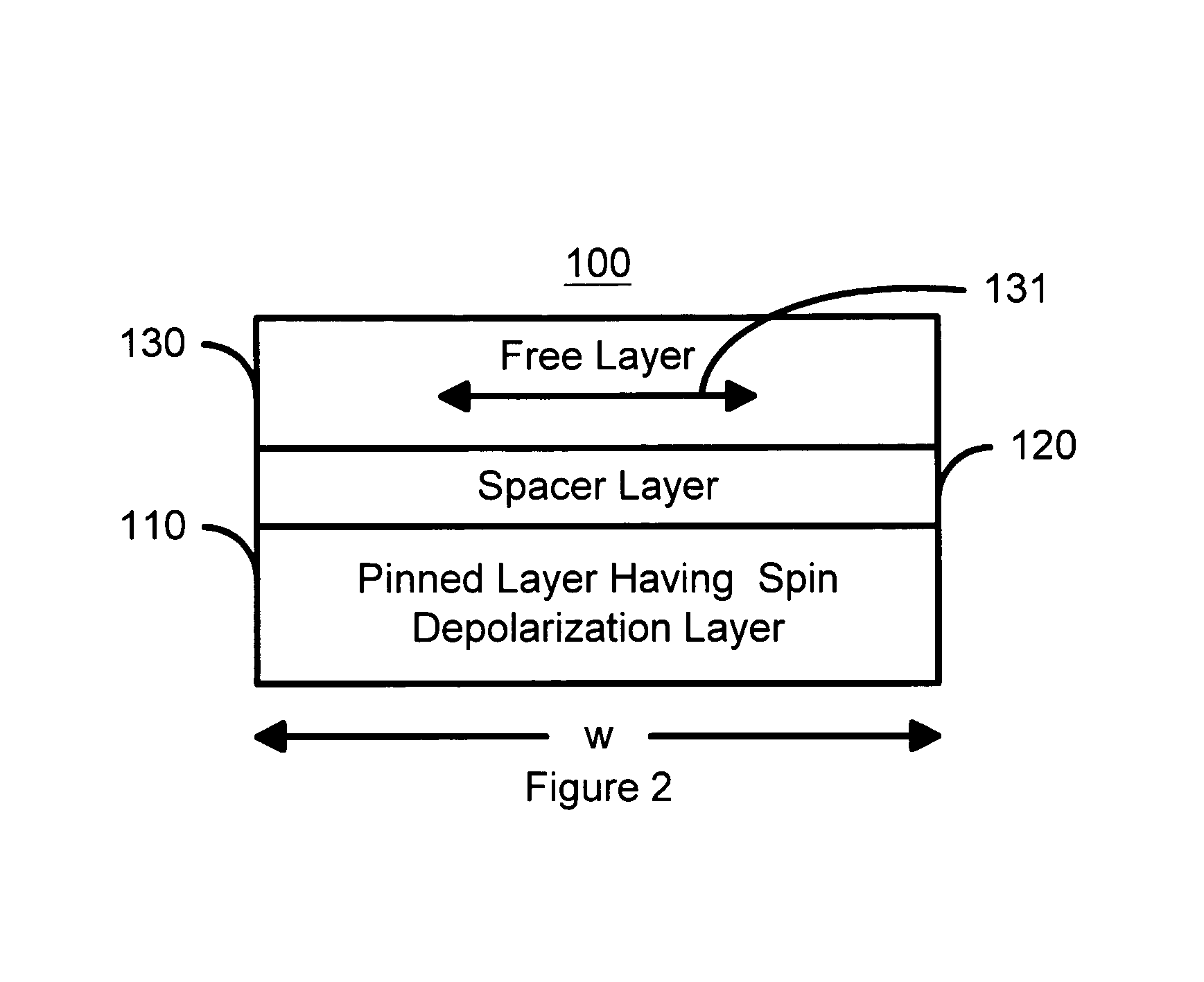
Spin transfer magnetic elements with spin depolarization layers
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method and system include providing a free layer, a spacer layer, and a pinned layer. The free layer is ferromagnetic and has a free layer magnetization. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The pinned layer includes first and second ferromagnetic layers having first and second magnetizations, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a spin depolarization layer. Residing between the first and second ferromagnetic layers, the nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and promotes antiparallel orientations between the first and second magnetizations. The spin depolarization layer is configured to depolarize at least a portion of a plurality of electrons passing through it. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer magnetization to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
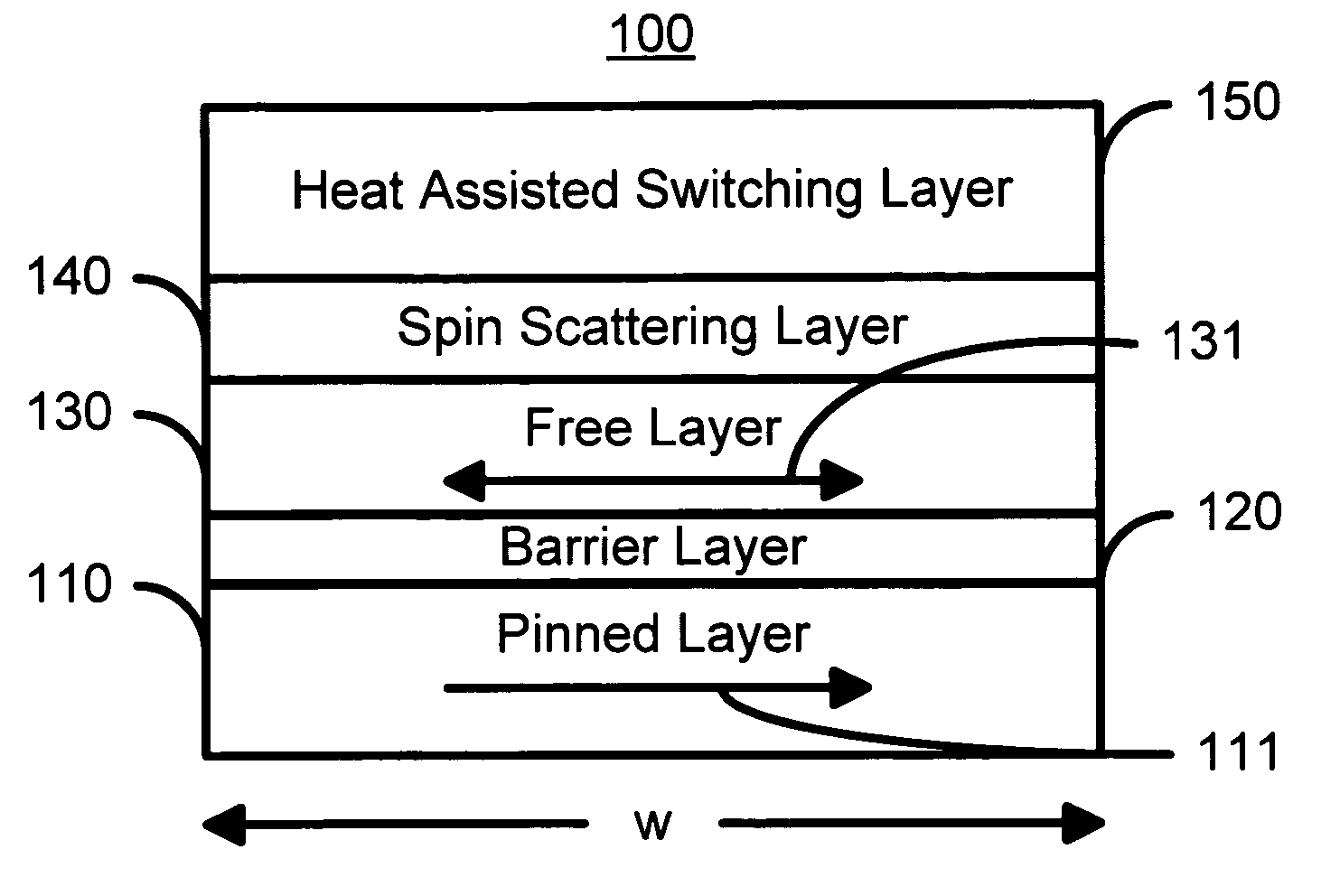
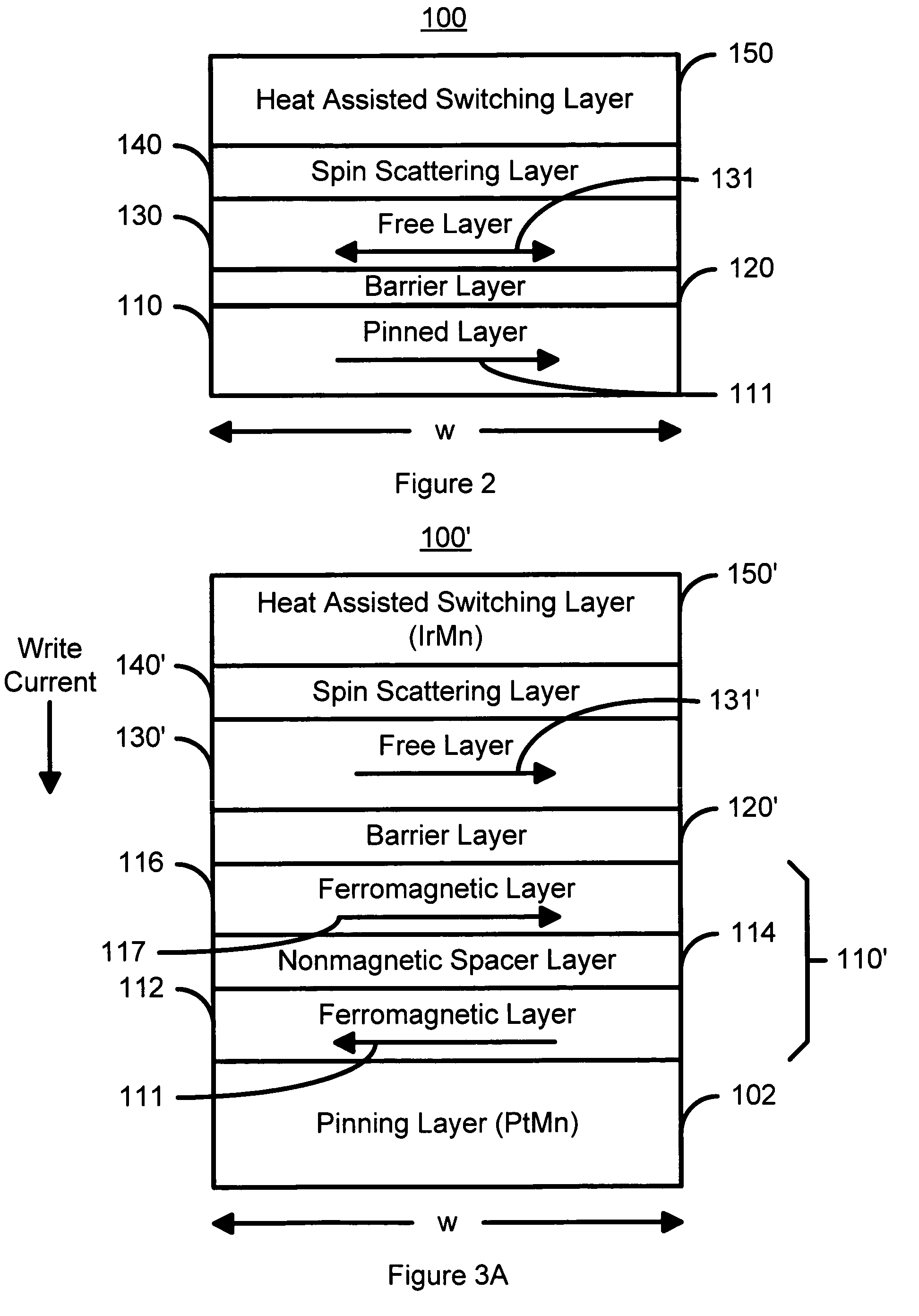
Spin scattering and heat assisted switching of a magnetic element
ActiveUS7126202B2Improve thermal stabilityStrong scatteringNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpinsThermal stability
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The magnetic element include providing a pinned layer, a spacer layer, and a free layer. The method and system also include providing a heat assisted switching layer and a spin scattering layer between the free layer and the heat assisted switching layer. The spin scattering layer is configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. The heat assisted switching layer is for improving a thermal stability of the free layer when the free layer is not being switched. Moreover, the magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Magnetic stack having assist layer
A magnetic memory cell having a ferromagnetic free layer and a ferromagnetic pinned reference layer, each having an out-of-plane magnetic anisotropy and an out-of-plane magnetization orientation and switchable by spin torque. The cell includes a ferromagnetic assist layer proximate the free layer, the assist layer having a low magnetic anisotropy less than about 500 Oe. The assist layer may have in-plane or out-of-plane anisotropy.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
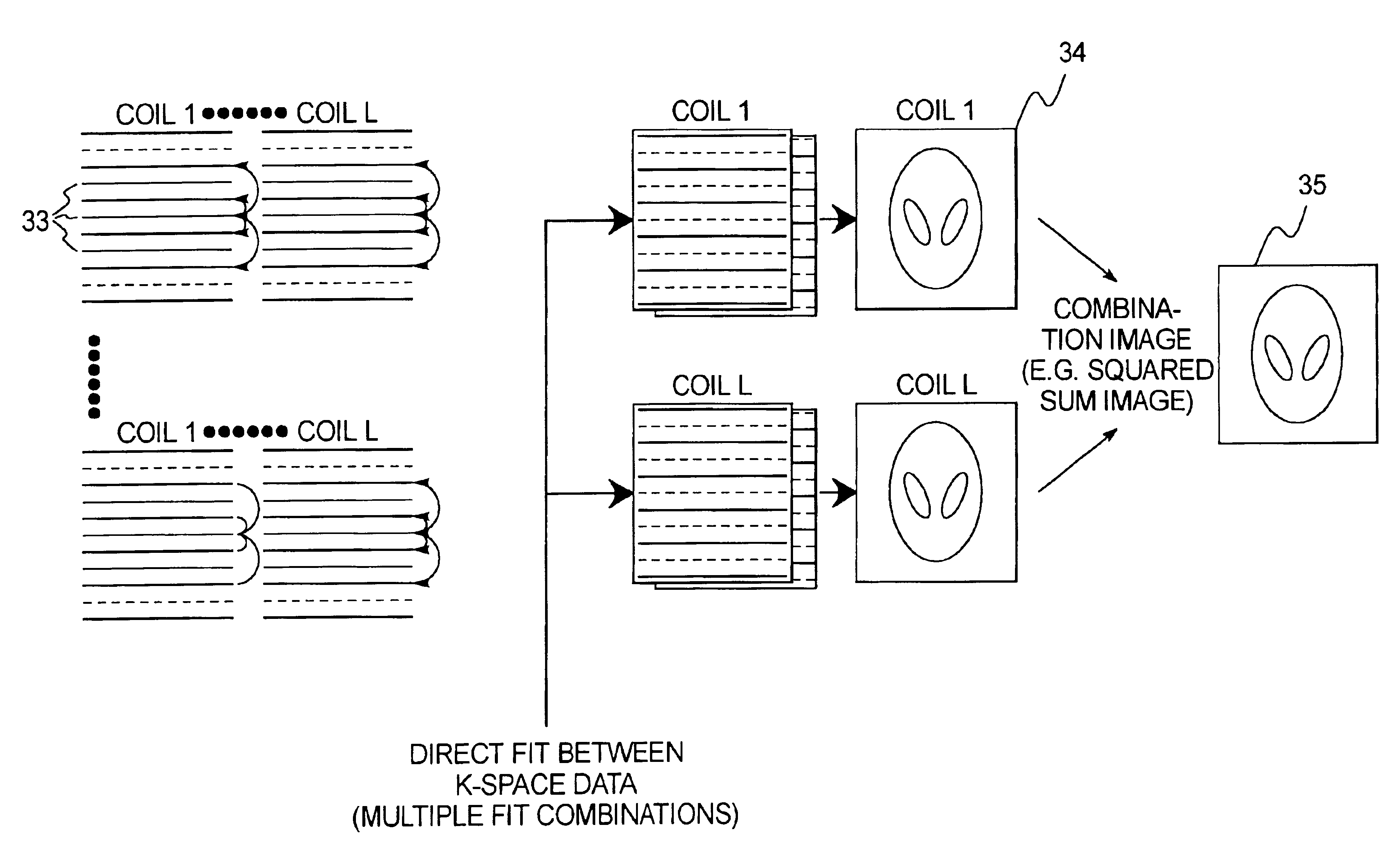
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus employing partial parallel acquisition, wherein each coil produces a complete k-space datasheet
InactiveUS6841998B1Quality improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDatasheetData set
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an interconnected region of a human body on the basis of a partially parallel acquisition (PPA) by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of the radio-frequency signals produced by the excited nuclear spins, a number of spin excitations and measurements of an RF response signal are implemented simultaneously in every component coil of a number of RF reception coils. As a result a number of response signals are acquired that form a reduced dataset of received RF signals for each component coil. Additional calibration data points are acquired for each reduced dataset. A complete image dataset is formed for each component coil on the basis of the reduced dataset for that component coil and at least one further, reduced dataset of a different component coil. A spatial transformation of the image dataset of each component coil is implemented in order to form a complete image of each component coil.
Owner:GRISWOLD MARK
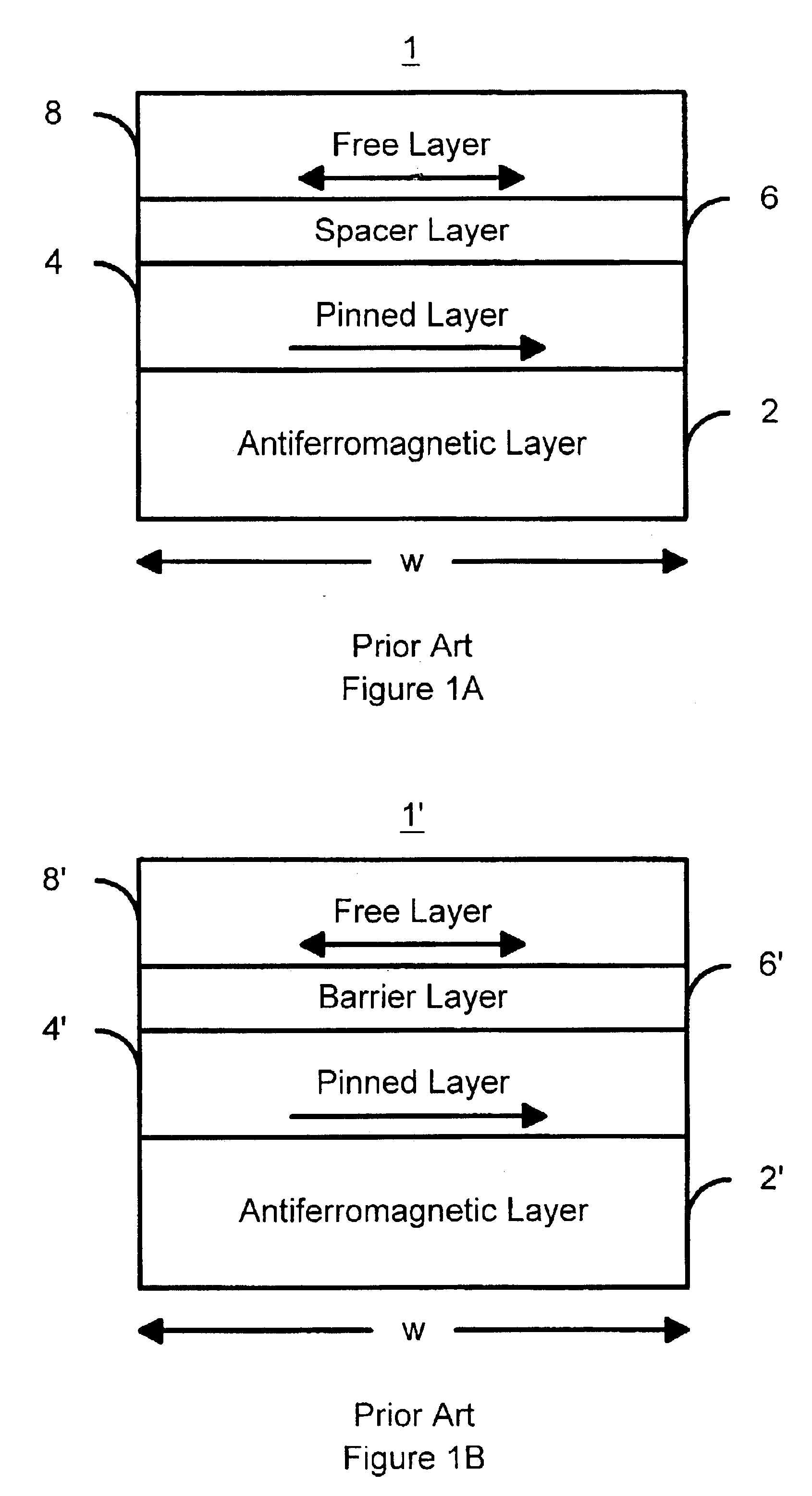
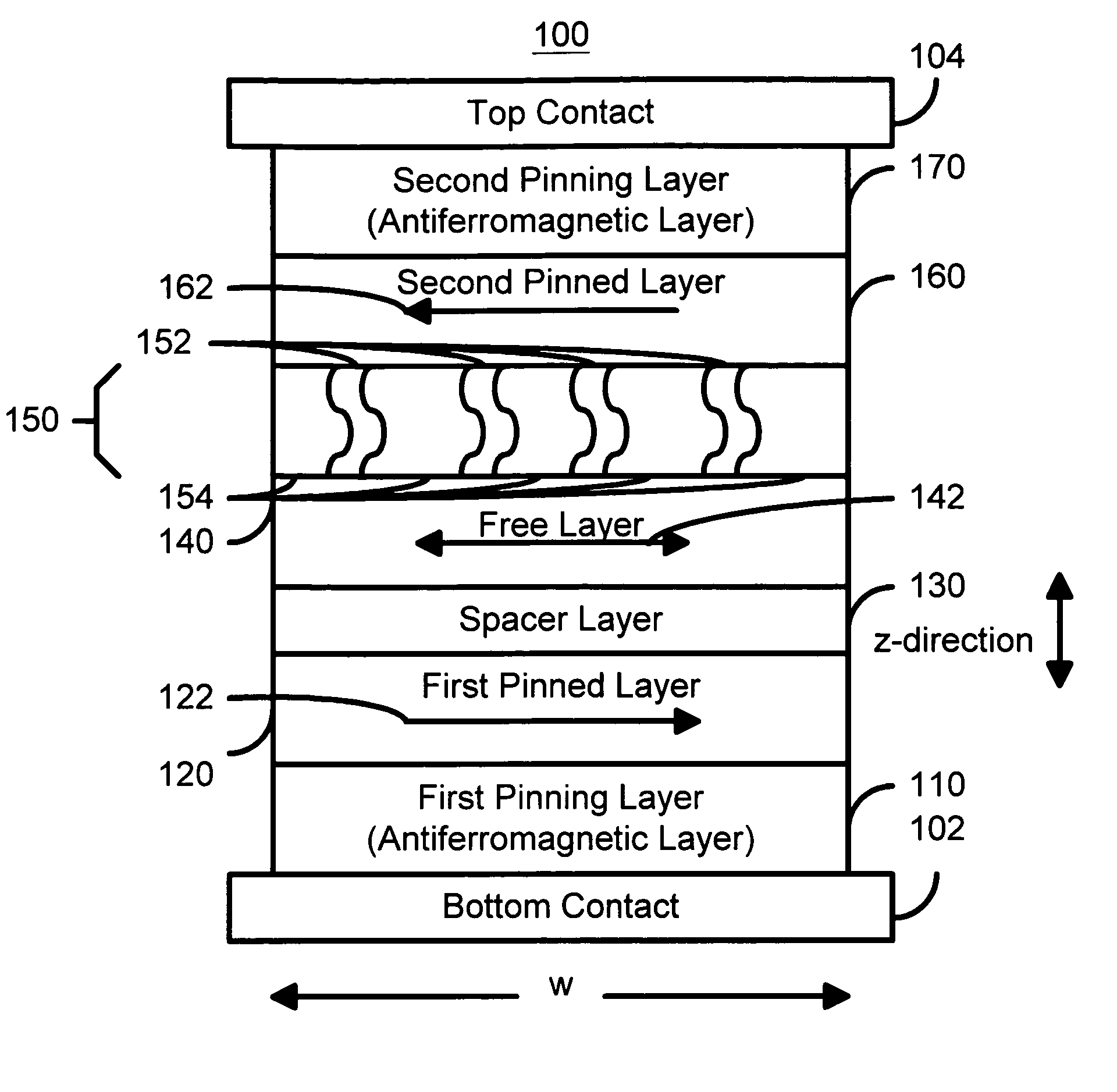
Spin-valve type magnetoresistance sensor and thin-film magnetic head
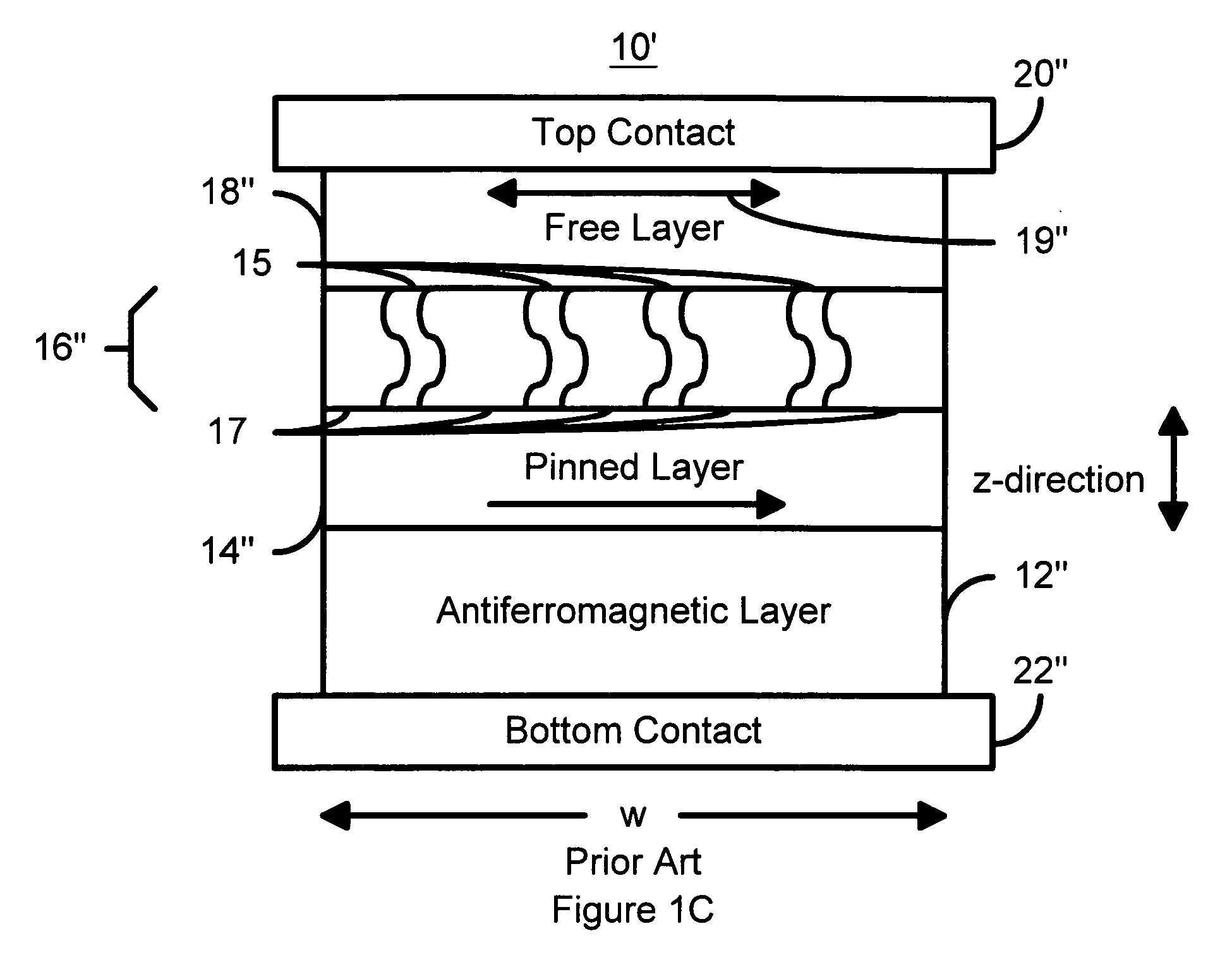
A method and apparatus of a spin-type magnetoresistance sensor having a free and pinned magnetic layer stacked with a non-magnetic interposed layer are disclosed. Specifically, the spin-valve type magnetoresistance sensor of the present invention is equipped with a free ferromagnetic layer, a pinned ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic spacer layer which is sandwiched between the aforementioned ferromagnetic layers, an anti-ferromagnetic layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned pinned ferromagnetic layer and which is used to pin the direction of magnetization of said pinned ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic back layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned free ferromagnetic layer and which is stacked on the opposite side the free ferromagnetic layer from the aforementioned nonmagnetic spacer layer, and an electron-reflective layer which is disposed adjacent to the aforementioned back layer and which is stacked on the opposite side of the back layer from the aforementioned free ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
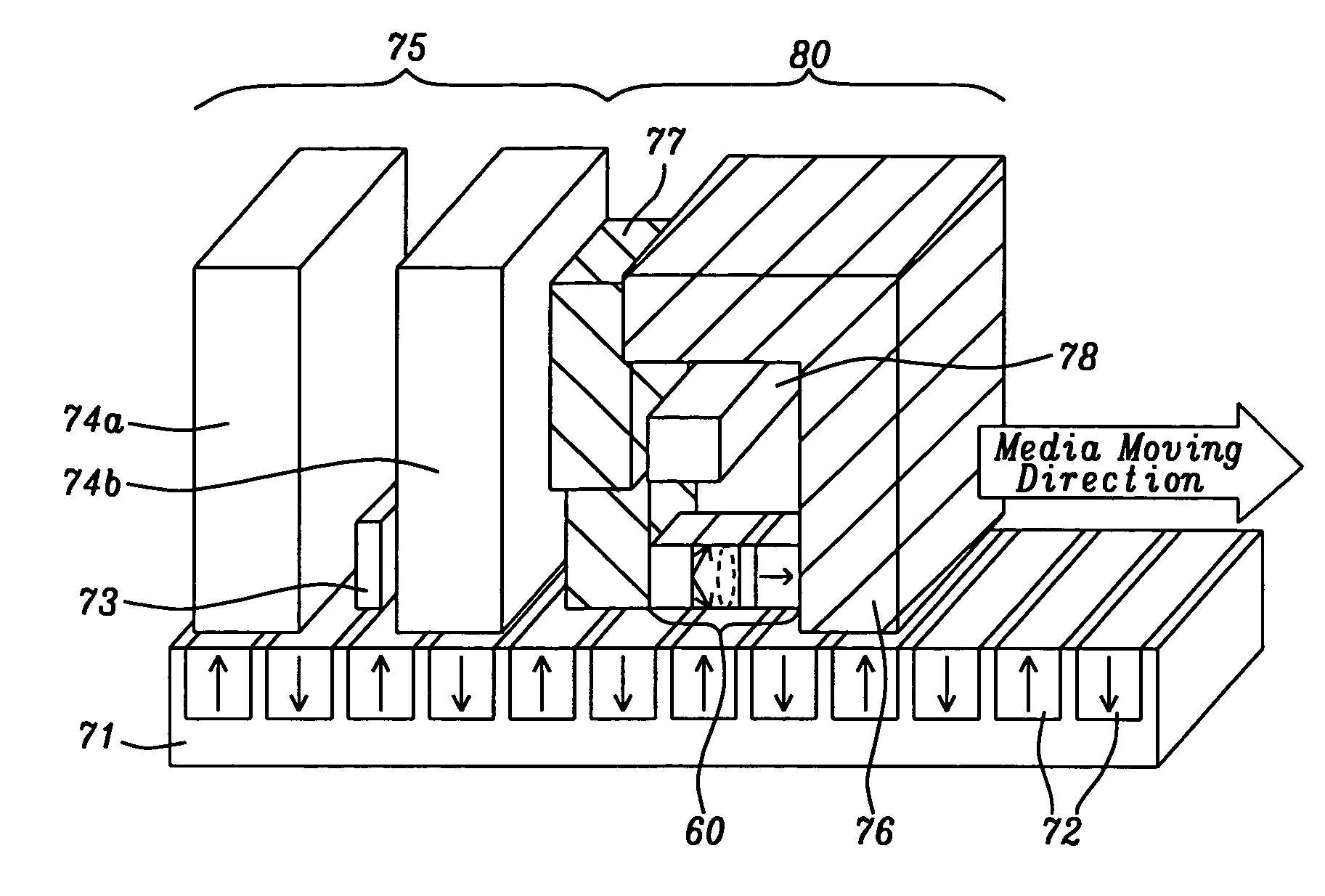
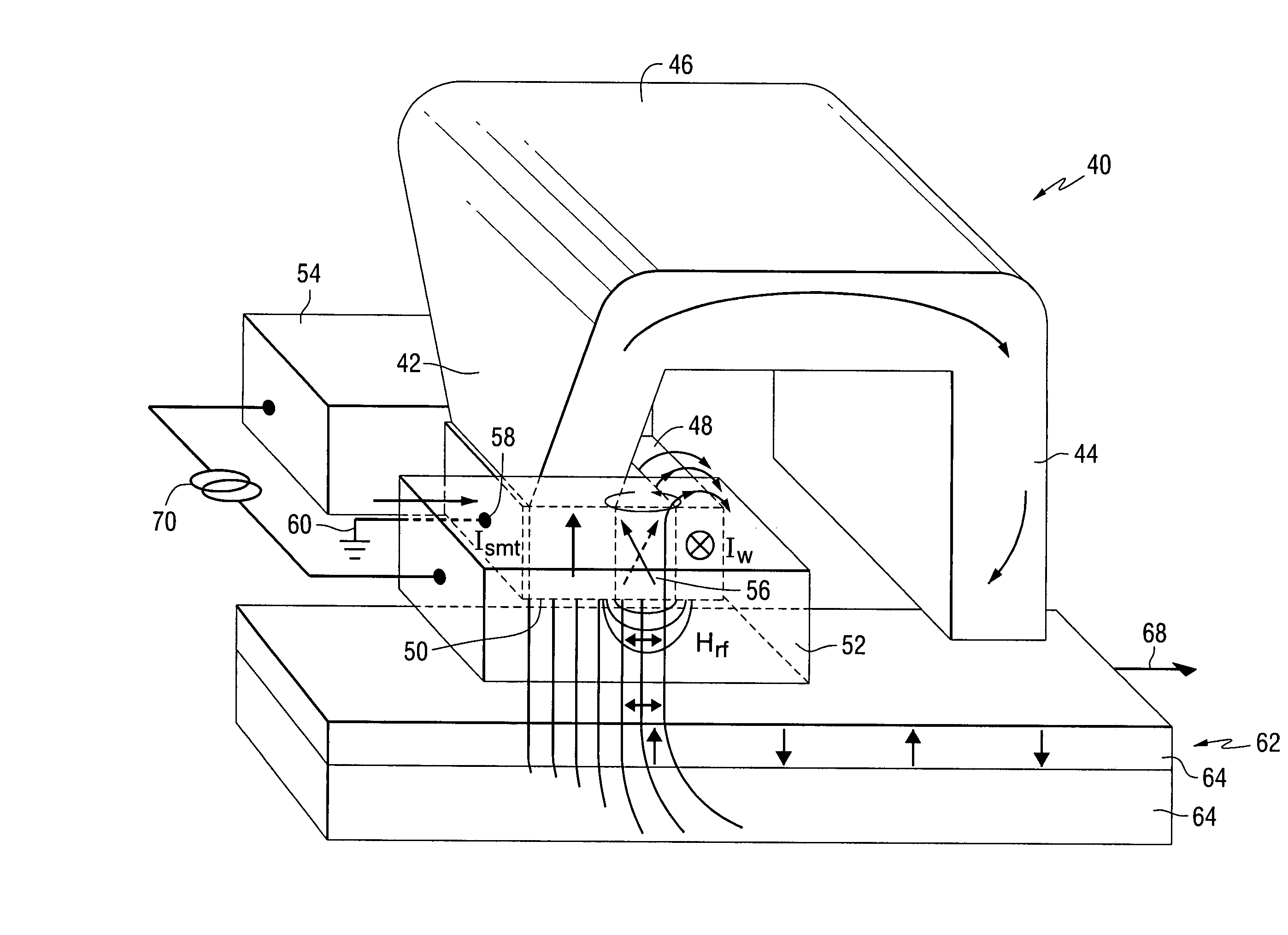
WAMR writer with an integrated spin momentum transfer driven oscillator for generating a microwave assist field
InactiveUS20080112087A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsInter layerSpins
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Spin barrier enhanced magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS20050254287A1Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, spacer, free, and spin barrier layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer layer and the spin barrier layer. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to a damping constant of the free layer. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity, preferably being metallic, and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Method and systems using prediction of outcome for launched objects
InactiveUS20070167247A1Improve forecast accuracyReduce errorsGymnastic exercisingBall sportsElectricityDisplay device
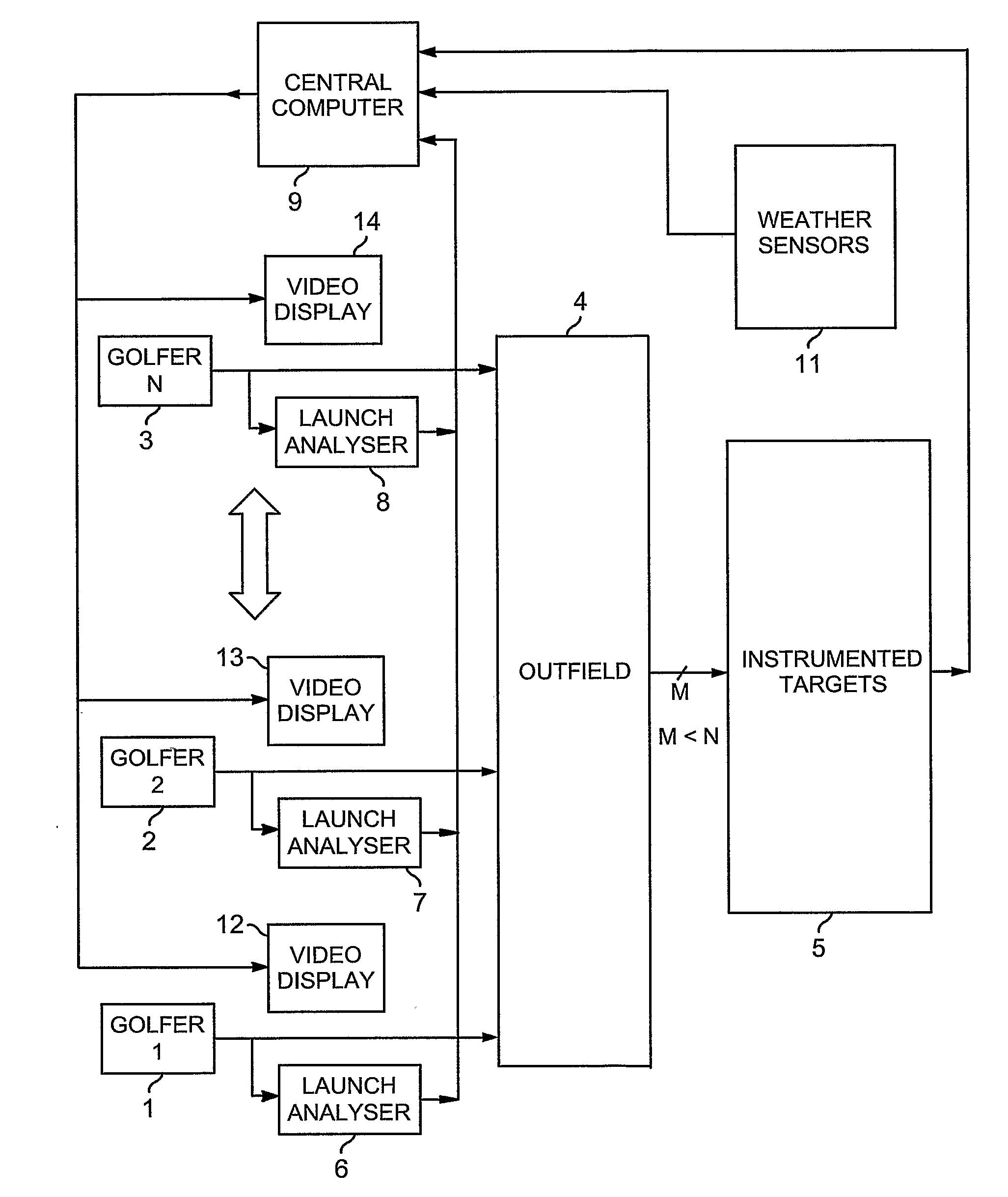
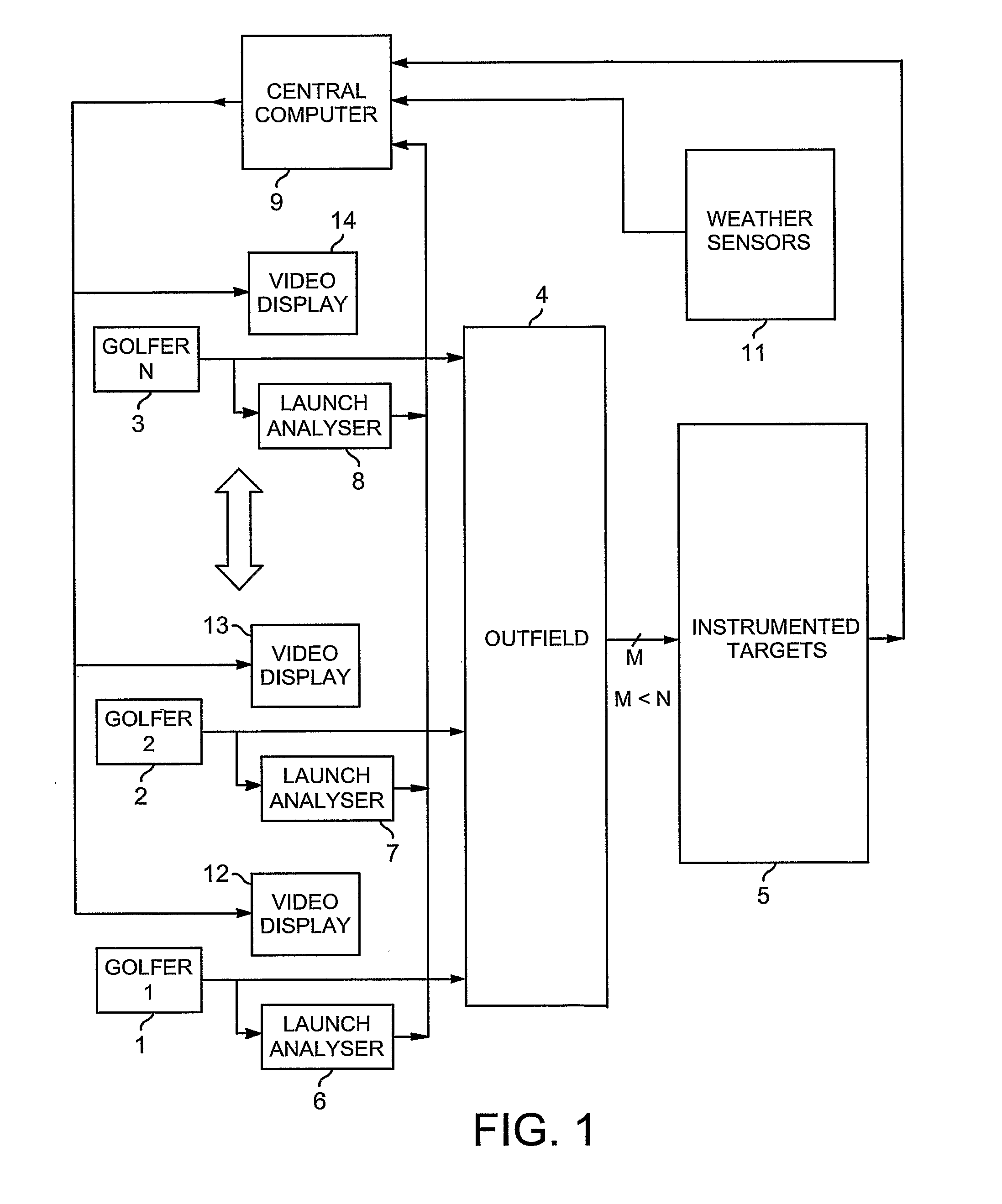
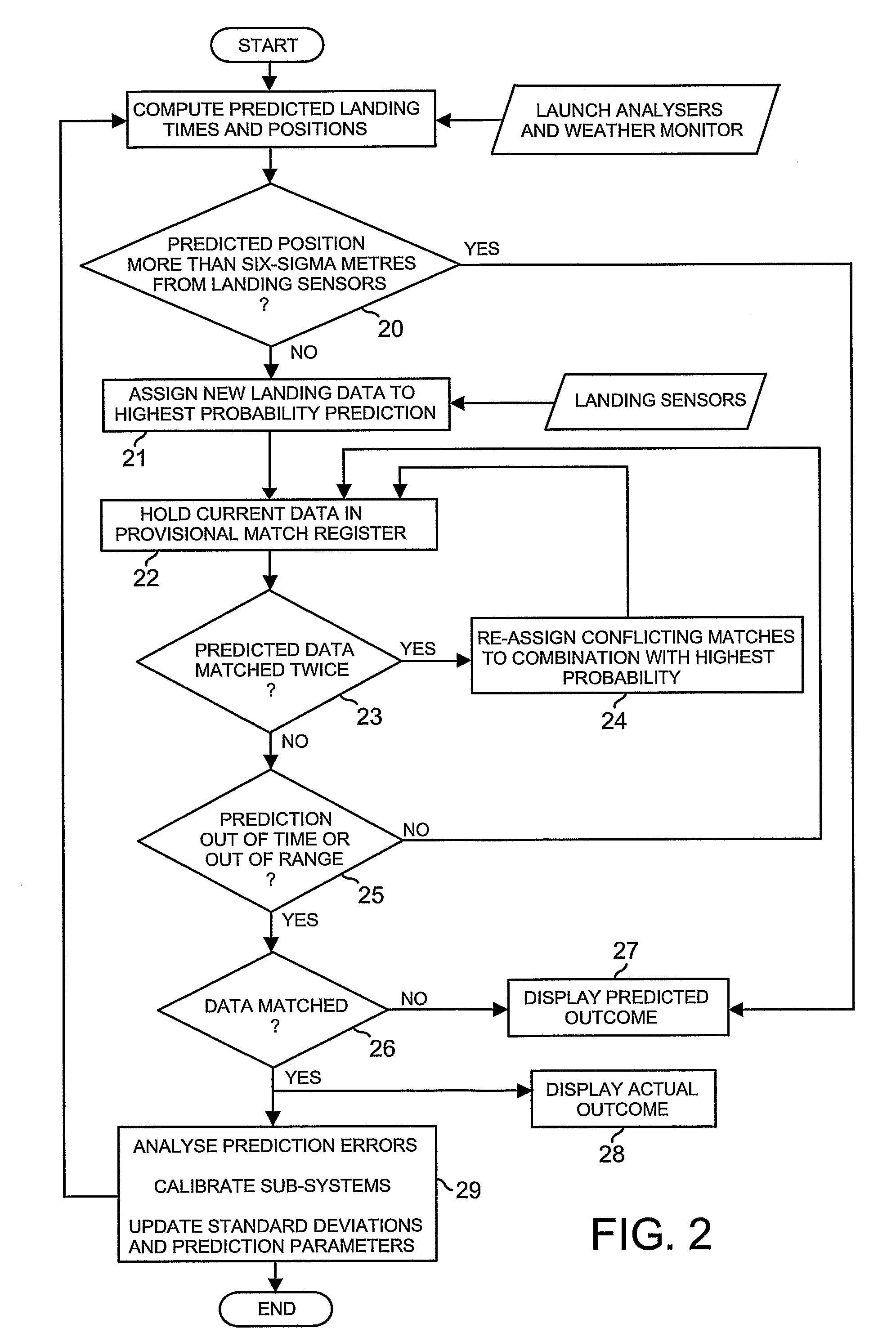
Each golfer (1-3) on a golf range (4) has an individual display (12-14) showing at least a predicted outcome of each of his / her shots, and a launch-analyser (6-8) to measure velocity vectors of the ball and / or club at strike for central-computation (9) of the prediction. Vibration and piezo-cable sensors (54,55;68,69) at instrumented targets (5;41-45,47) distributed throughout the range (4), detect the presence of balls arriving in their respective locations for matching with launched balls using the computed predictions and probability; active or passive radio-frequency identification and location of balls may also be used. Where a match is found, error between predicted and actual outcome is applied to adaptive correction of the prediction-computing process, and the actual outcome is displayed to the golfer instead of the prediction. Ball and / or club velocity vectors, and ball spin, at launch are measured from light changes occurring in detection planes (96,97;105;114-117;134;144-146) defined by slit apertures (94,95;104), and resulting from retro-reflection from ball (91;110;131) and / or club (130).
Owner:LINDSAY LTD
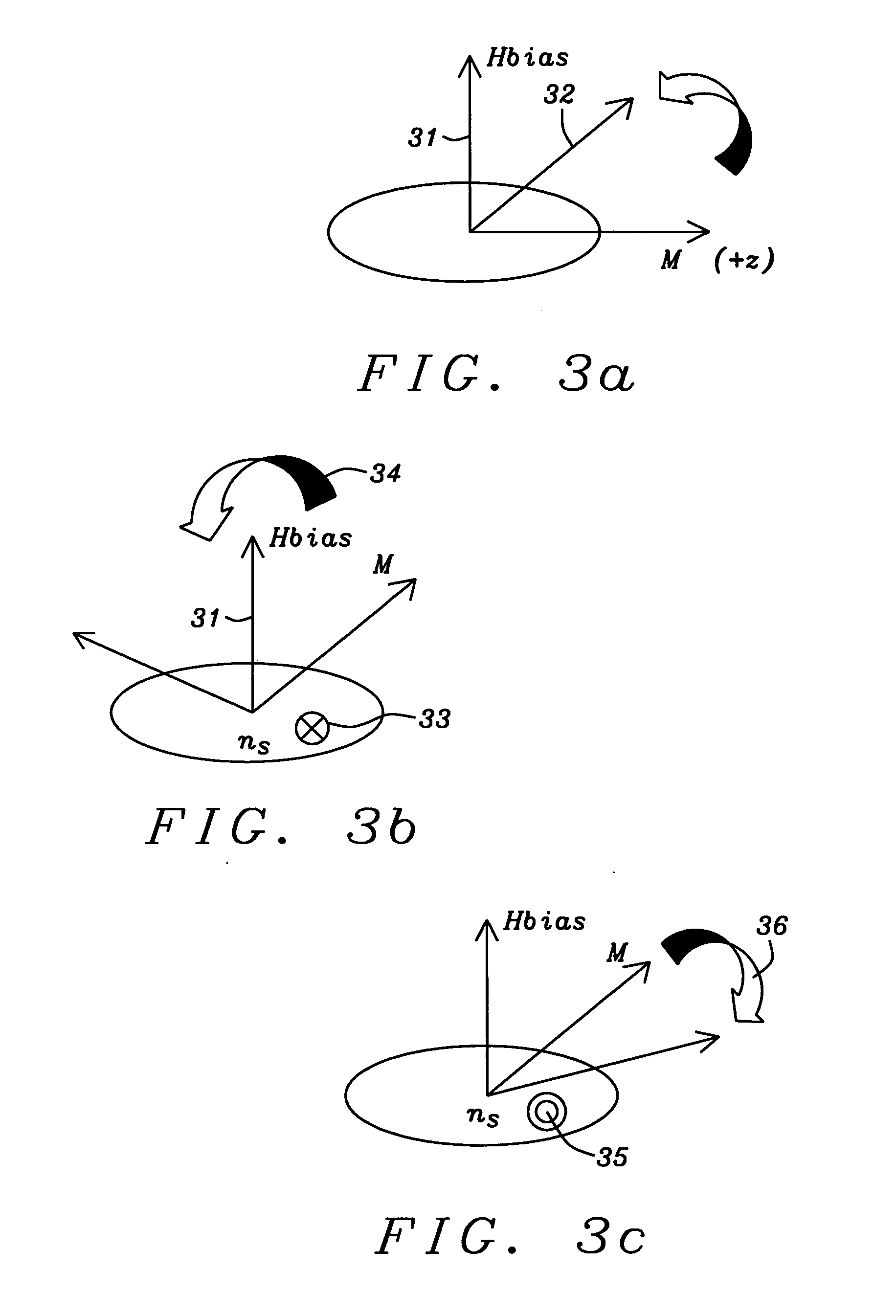
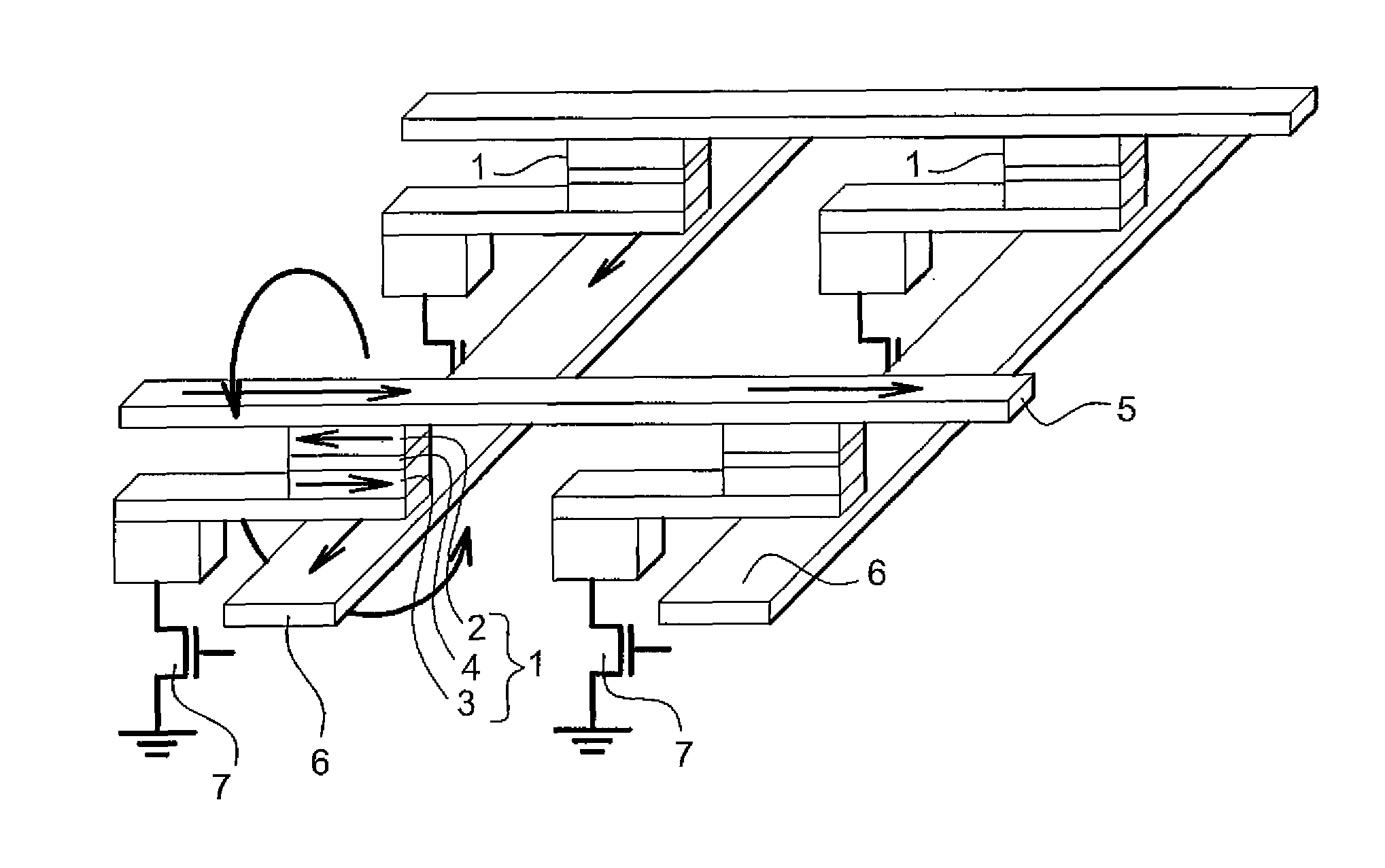
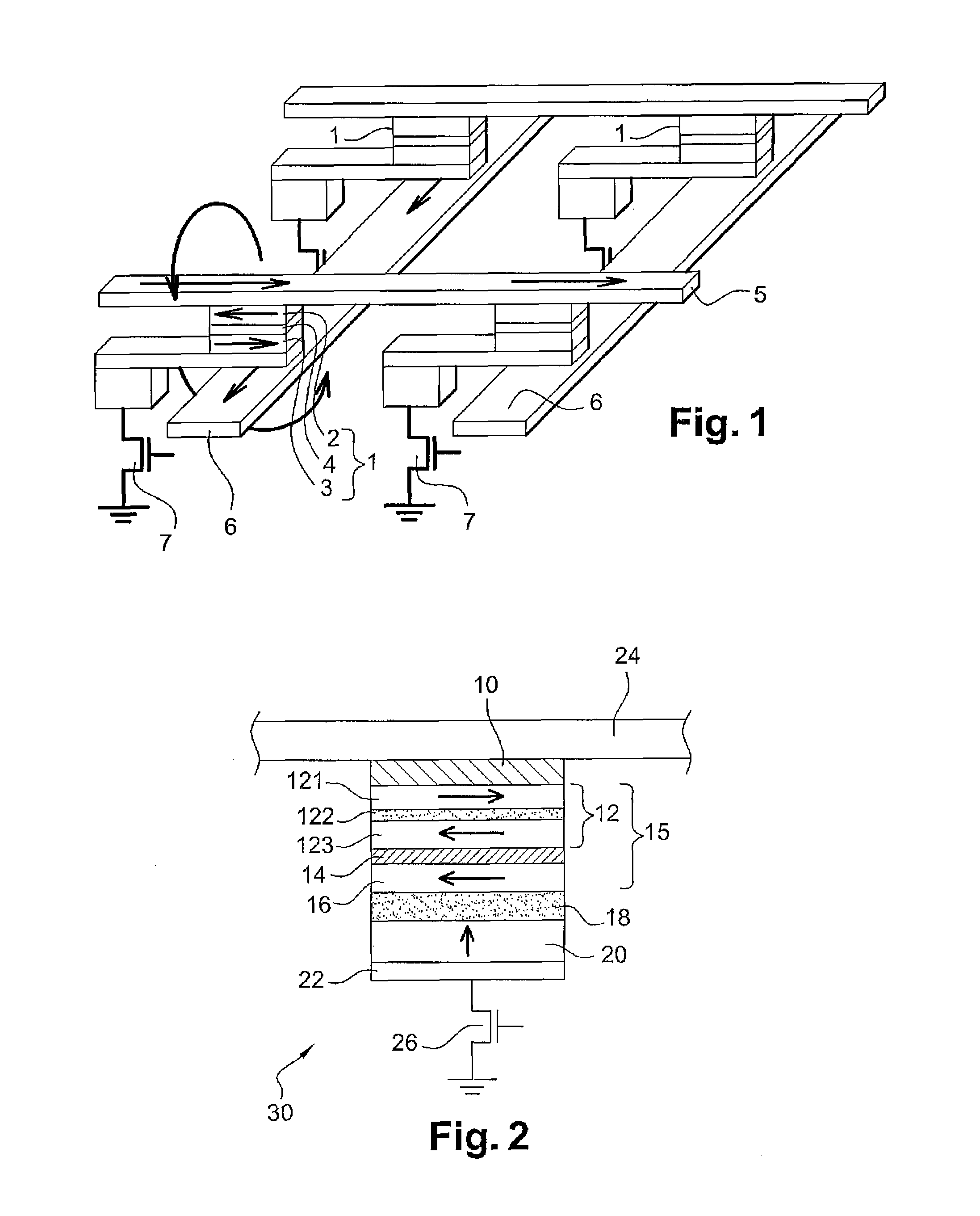
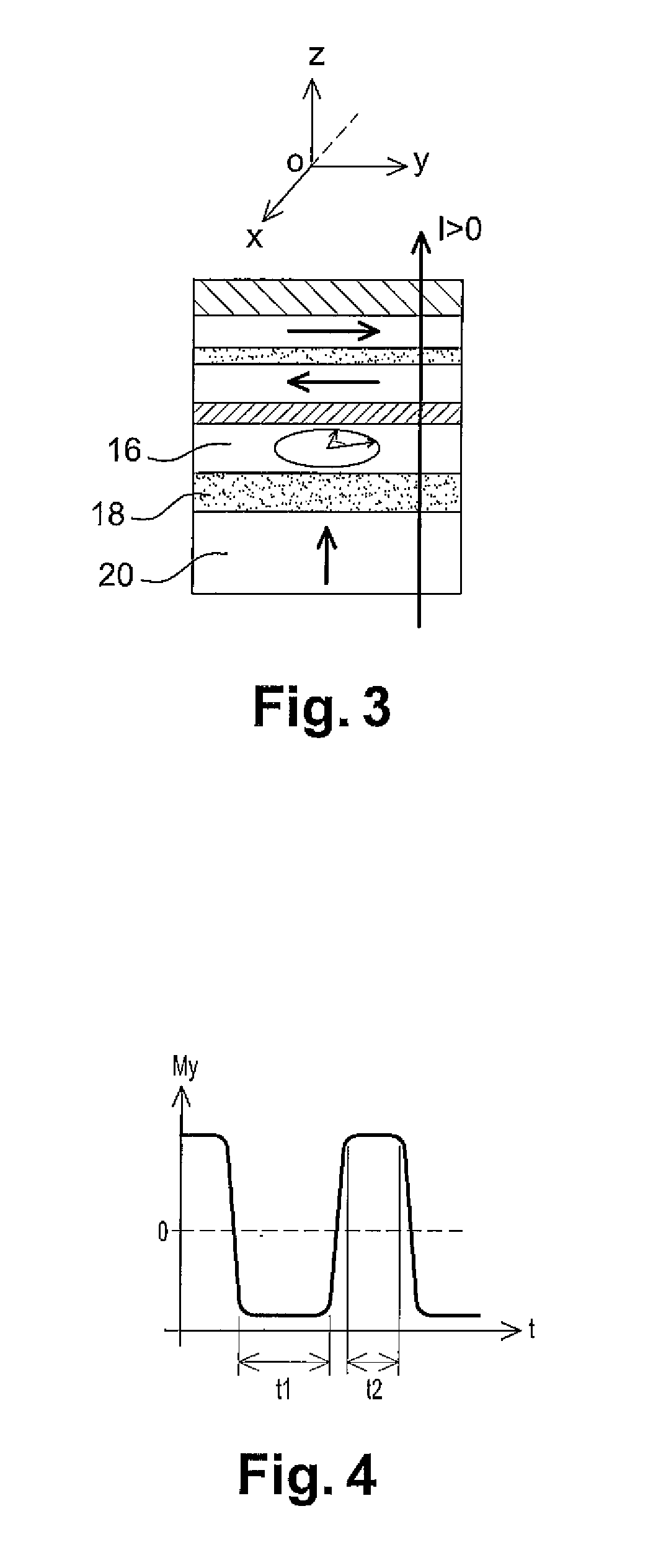
Spin transfer MRAM device with magnetic biasing
ActiveUS20080151614A1Strict controlSignificant power savingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpinsSpin transfer
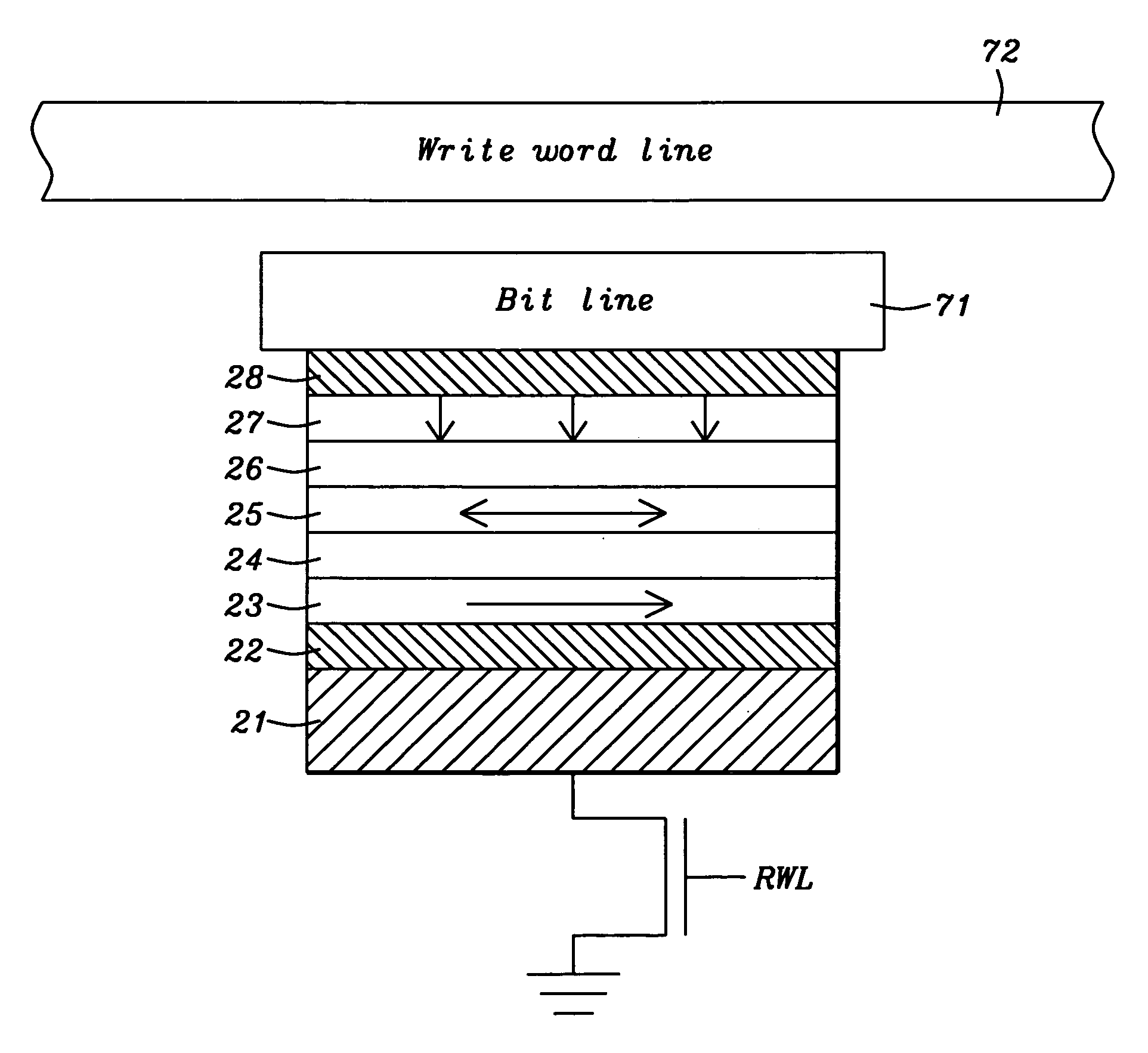
The addition of segmented write word lines to a spin-transfer MRAM structure serves to magnetically bias the free layer so that the precessional motion of the magnetization vector that is set in play by the flow of spin polarized electrons into the free layer allows said magnetic vector to be switched rather than to oscillate between two easy axis directions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Spin polarised magnetic device
ActiveUS8279666B2Reducing the stochastic fluctuations in the magnetisation reversal timeTotal current dropNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic storageSpins
A magnetic device includes a magnetic reference layer with a fixed magnetization direction located either in the plane of the layer or perpendicular to the plane of the layer, a magnetic storage layer with a variable magnetization direction, a non-magnetic spacer separating the reference layer and the storage layer and a magnetic spin polarizing layer with a magnetization perpendicular to that of the reference layer, and located out of the plane of the spin polarizing layer if the magnetization of the reference layer is directed in the plane of the reference layer or in the plane of the spin polarizing layer if the magnetization of the reference layer is directed perpendicular to the plane of the reference layer. The spin transfer coefficient between the reference layer and the storage layer is higher than the spin transfer coefficient between the spin polarizing layer and the storage layer.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT POLYTECHN DE GRENOBLE +2
Gate Level Reconfigurable Magnetic Logic
ActiveUS20100039136A1Write currentIncrease current densitySolid-state devicesDigital storageSignal onRandom access memory
A re-programmable gate logic includes a plurality of non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits in parallel, wherein the circuits are re-configurable to implement or change a selected gate logic, and the plurality of non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits are each adapted to receive a logical input signal. An evaluation switch in series with the plurality of parallel non-volatile re-configurable resistance state-based memory circuits is configured to provide an output signal based on the programmed states of the memory circuits. A sensor is configured to receive the output signal and provide a logical output signal on the basis of the output signal and a reference signal provided to the sensor. The reconfigurable logic may be implemented based on using spin torque transfer (STT) magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) magnetoresistance random access memory (MRAM) as the re-programmable memory elements. The logic configuration is retained without power.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Magnetic shift register with shiftable magnetic domains between two regions, and method of using the same
InactiveUS7031178B2Highly localized and large magnetic fieldsComparable in costLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerProcessor register
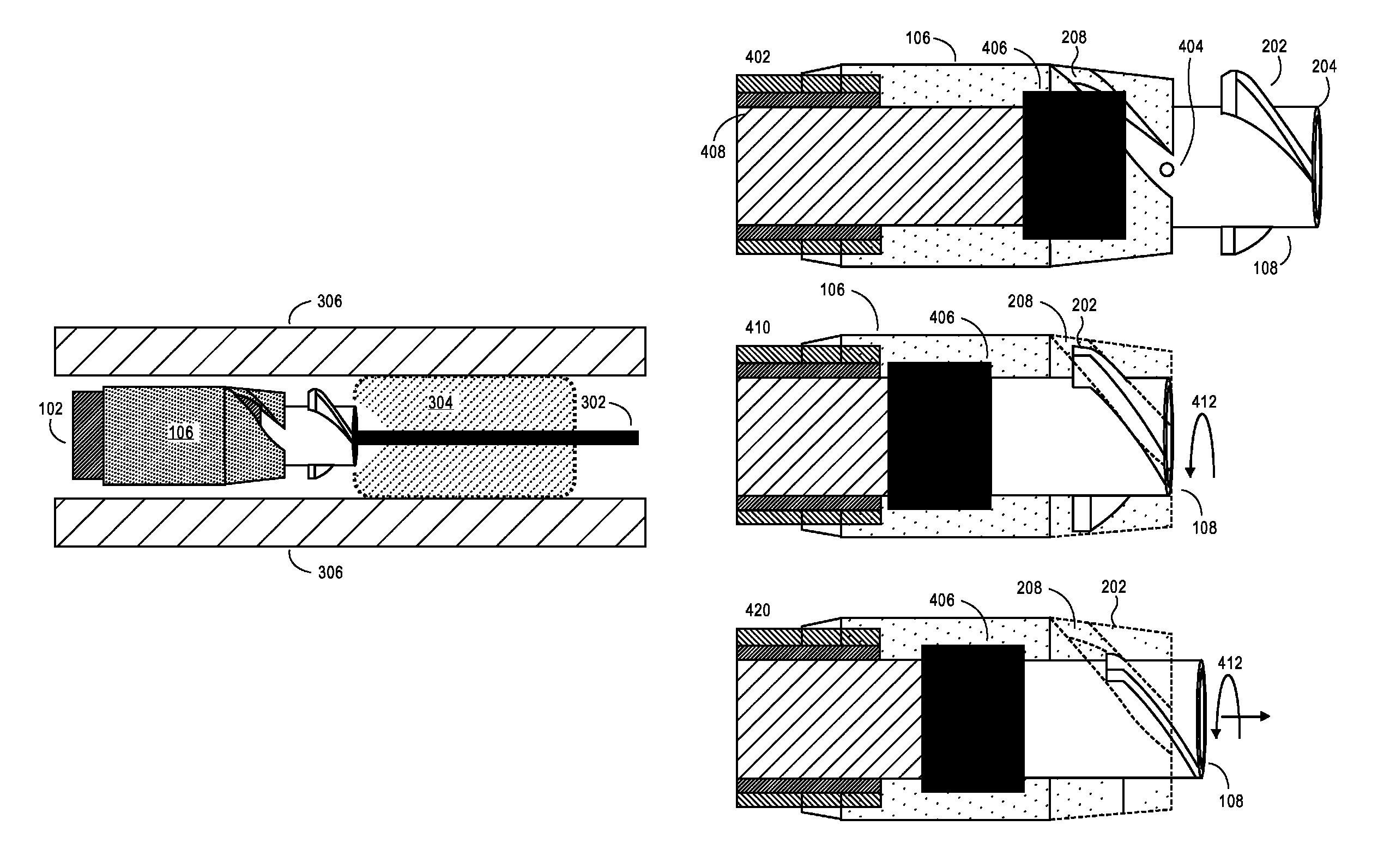
A magnetic shift register uses the inherent, natural properties of domain walls in magnetic materials to store data. The shift register uses spin electronics without changing the physical nature of its constituent materials. The shift register comprises a fine track or strip of magnetic materials. Information is stored as domain walls in the track. An electric current is applied to the track to move the magnetic moments along the track past a reading or writing device. In a magnetic material with domain walls, a current passed across the domain wall moves the domain wall in the direction of the current flow. As the current passes through a domain, it becomes “spin polarized”. When this spin polarized current passes through the next domain and across a domain wall, it develops a circle of spin torque. This spin torque moves the domain wall.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
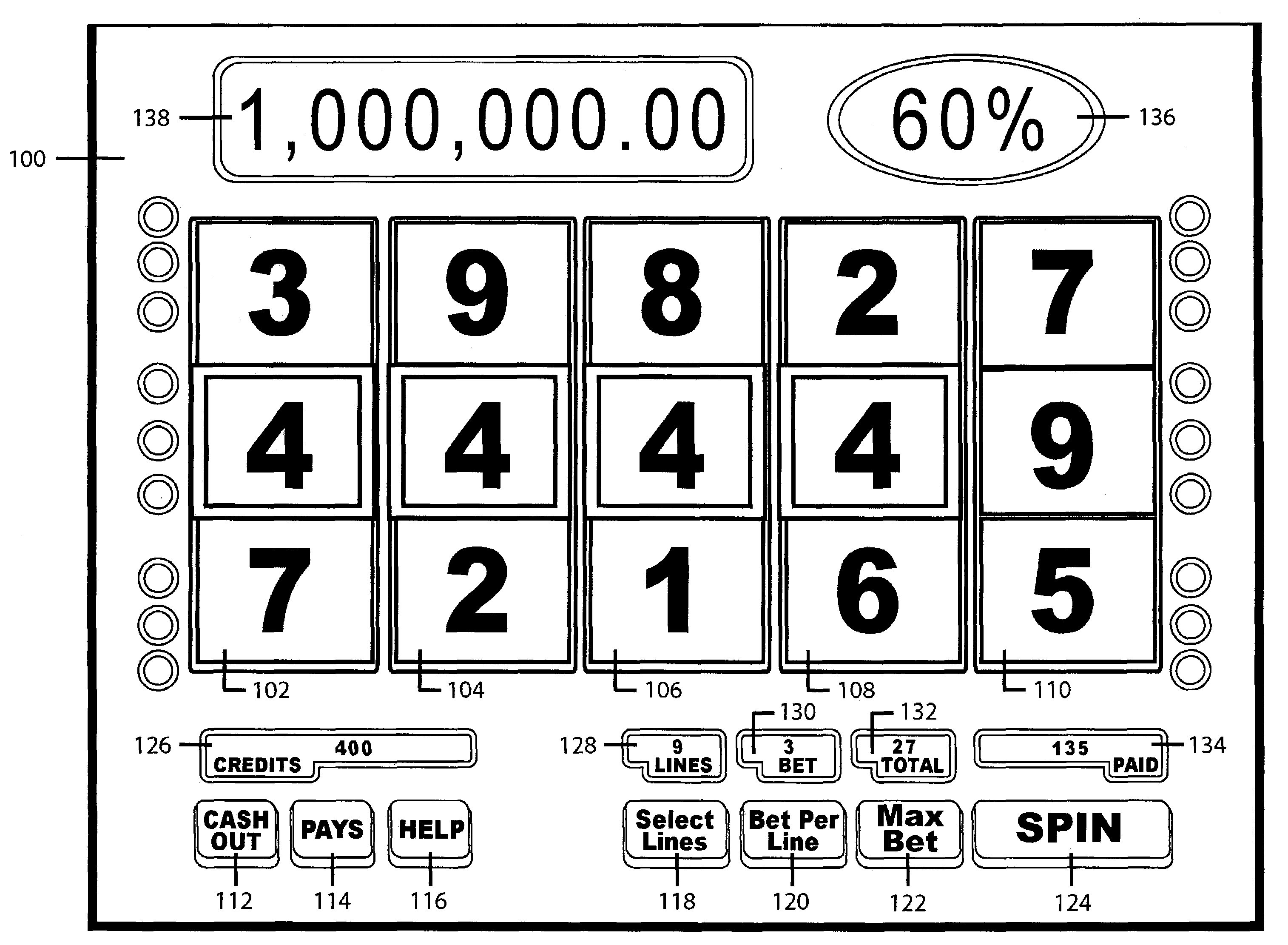
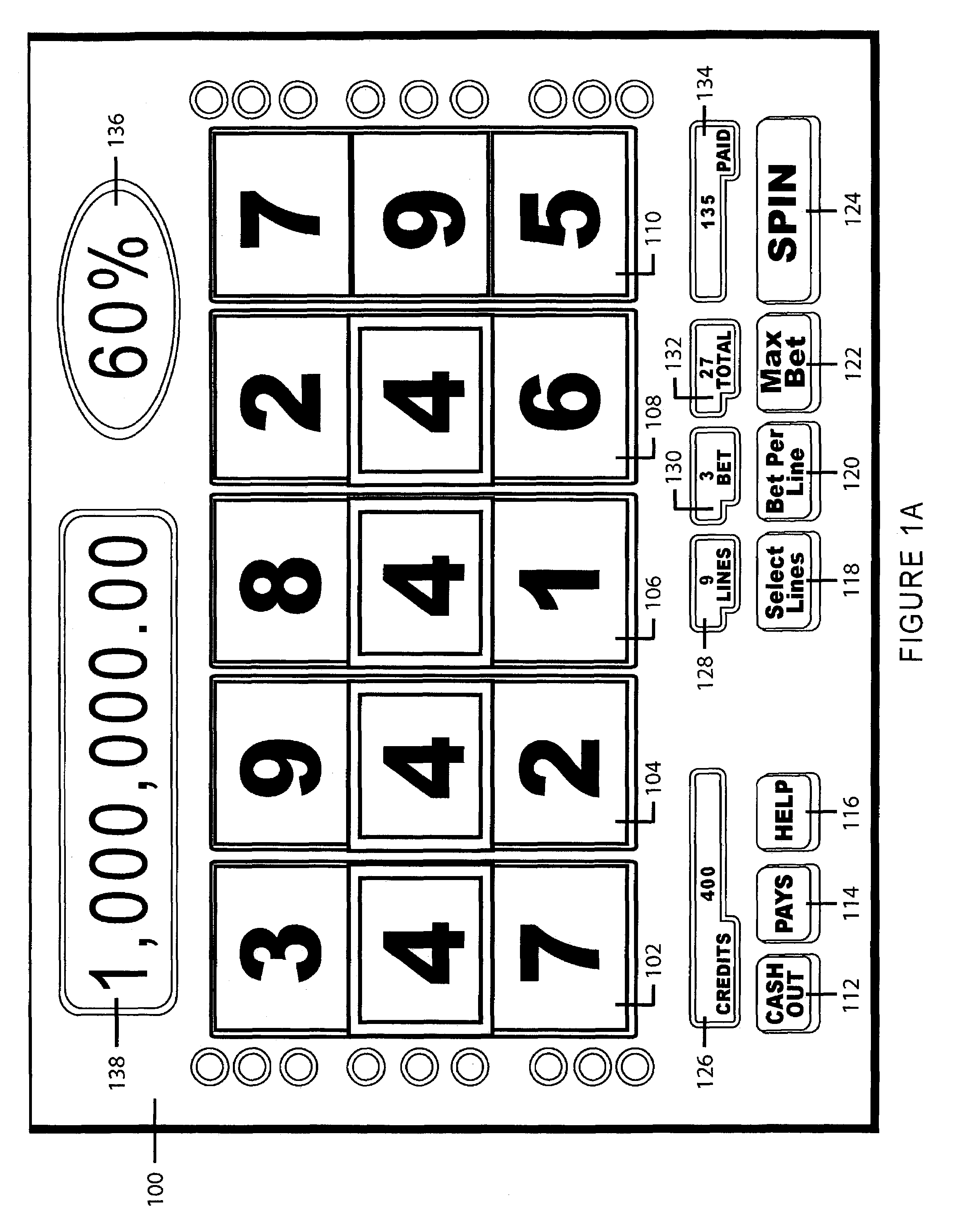
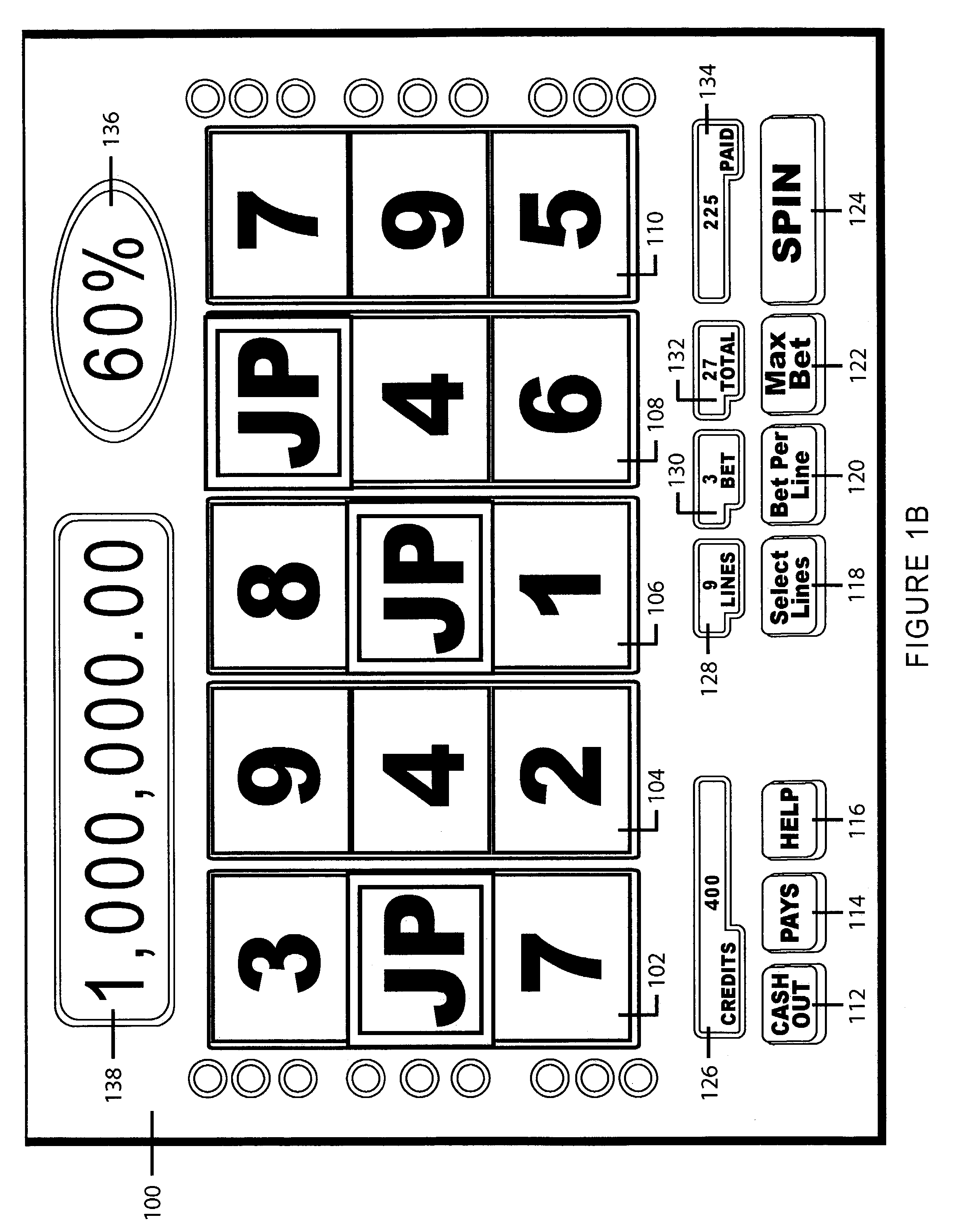
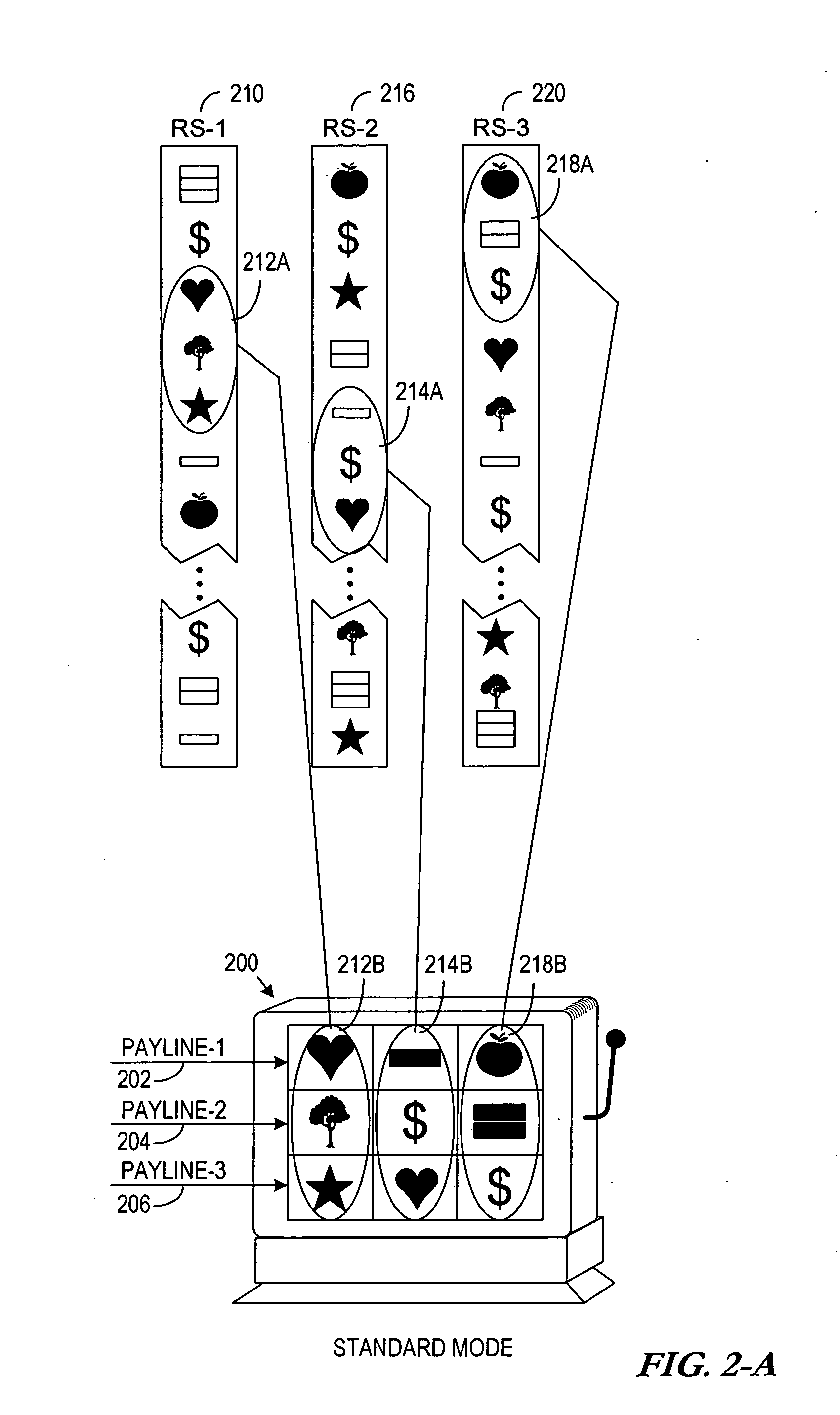
Slot machine game having a plurality of ways to issue a percentage of a progressive award based upon any wager level ("percentage progressive")
A slot machine issues a percentage of one or more progressive awards based upon any wager level (“Percentage Progressive”). In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the Percentage Progressive concept operates as follows:The game displays the total progressive award amount;The player sets the wager;The game displays a Percentage Progressive value based upon the wager level;The player presses the spin button;The reels to spin and stop;The player collects credits for any winning combinations appearing on the reels, including pay table and progressive awards.In the event of a progressive award, the player receives the Percentage Progressive value*total progressive award amount.The preferred embodiment of the present invention, therefore, allows players to participate in progressive awards at any wager level.
Owner:IGT
Gaming using terminating roaming wild positions
ActiveUS20060058095A1Easy to participateApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesGame playerSpins
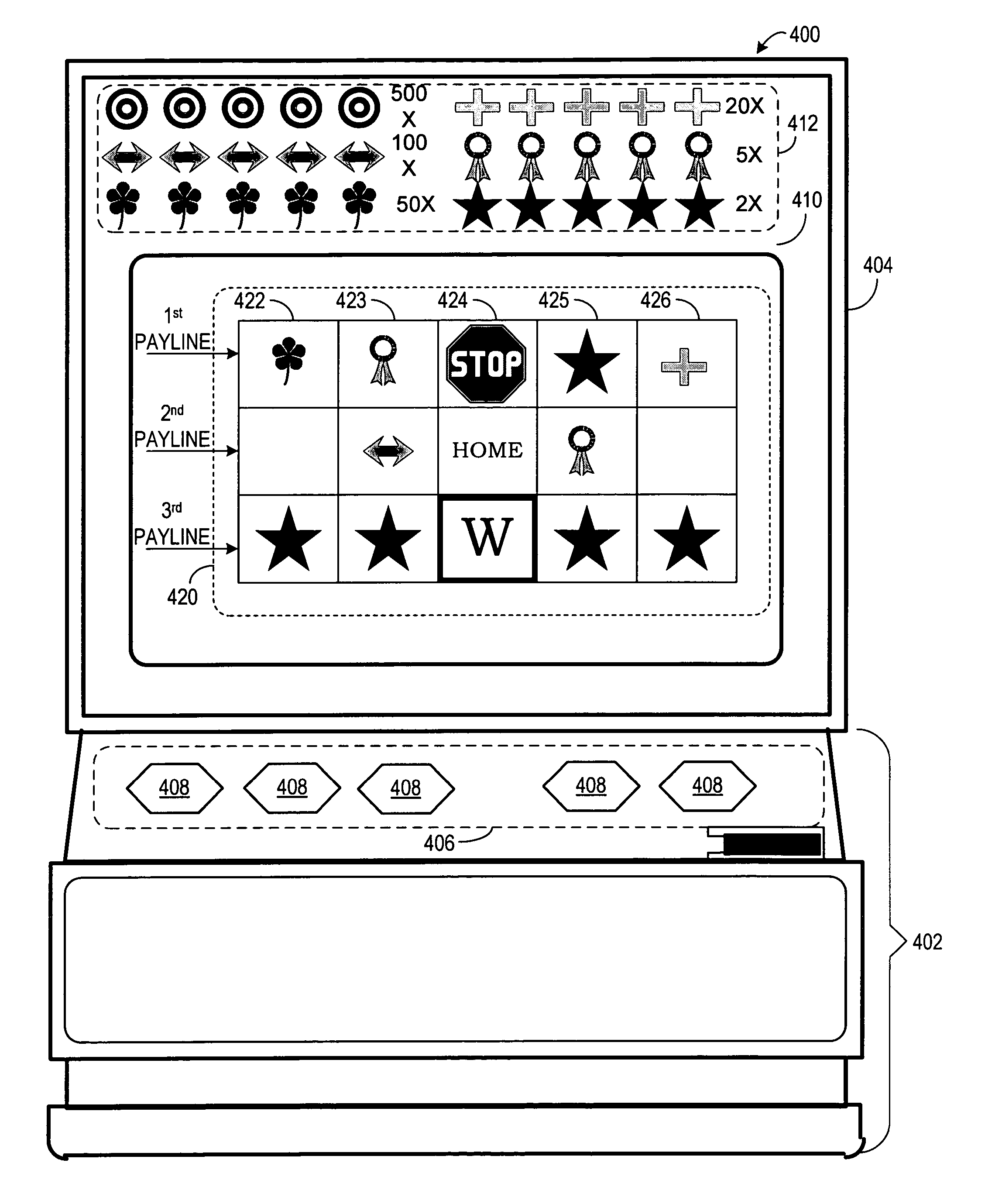
A display grid includes a plurality of grid positions that are presented to a game player. One or more grid positions of the plurality of grid positions are defined as termination positions. One or more wild symbols are moved to grid positions proximate the grid positions associated with the one or more wild symbols using a random process. Winning results are determined using a pay table, based on both the one or more wild symbols and the symbols presented at the grid positions not associated with the one or more wild symbols after a spin. Random movement of the one or more wild symbols to grid positions proximate the grid positions associated with the one or more wild symbols is repeated until the one or more (or all) wild symbols move to the termination positions.
Owner:IGT
Payline system for multiline slot play using an erasing/exposure feature
A method of playing a virtual or virtual / mechanical multireel slot game. A grid of at least 3 rows×3 columns, but preferably 3 rows×5 columns, is presented on a screen, with a second, opaque blanketing layer of color or graphics over the grid, so as to hide symbols on the reels below. After the wager, reels on the bottom layer spin (or are virtually and randomly positioned in any manner), hidden from the player by the blanketing layer. An “erasing” indicium then glides from outside the grid (preferably across the top row of 5 reels, from left to right), over the blanketing layer, erasing the color layer to expose the symbols on the reels below. The indicium preferably (or always) moves in one direction only until it hits the end of a row, the top or bottom of a column, or a revealed symbol that alters movement of the indicium. When the indicium encounters this situation, it may hesitate for a moment, then randomly pick a direction in which to continue. It may continue in the same direction or turn 90° clockwise or 90° counterclockwise. It may even move diagonally. If the indicium turns and continues over the reels, more symbols are revealed until the indicium again reaches a turning point. Payouts are awarded according to a predetermined paytable for single special symbols and / or for sets such as multiple same symbols shown, whether the symbols are contiguous or not.
Owner:PRECEDENT GAMING
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head and magnetic recording and/or reproducing system
InactiveUS6937446B2Efficient use ofControl quantityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsBorideScattering effect
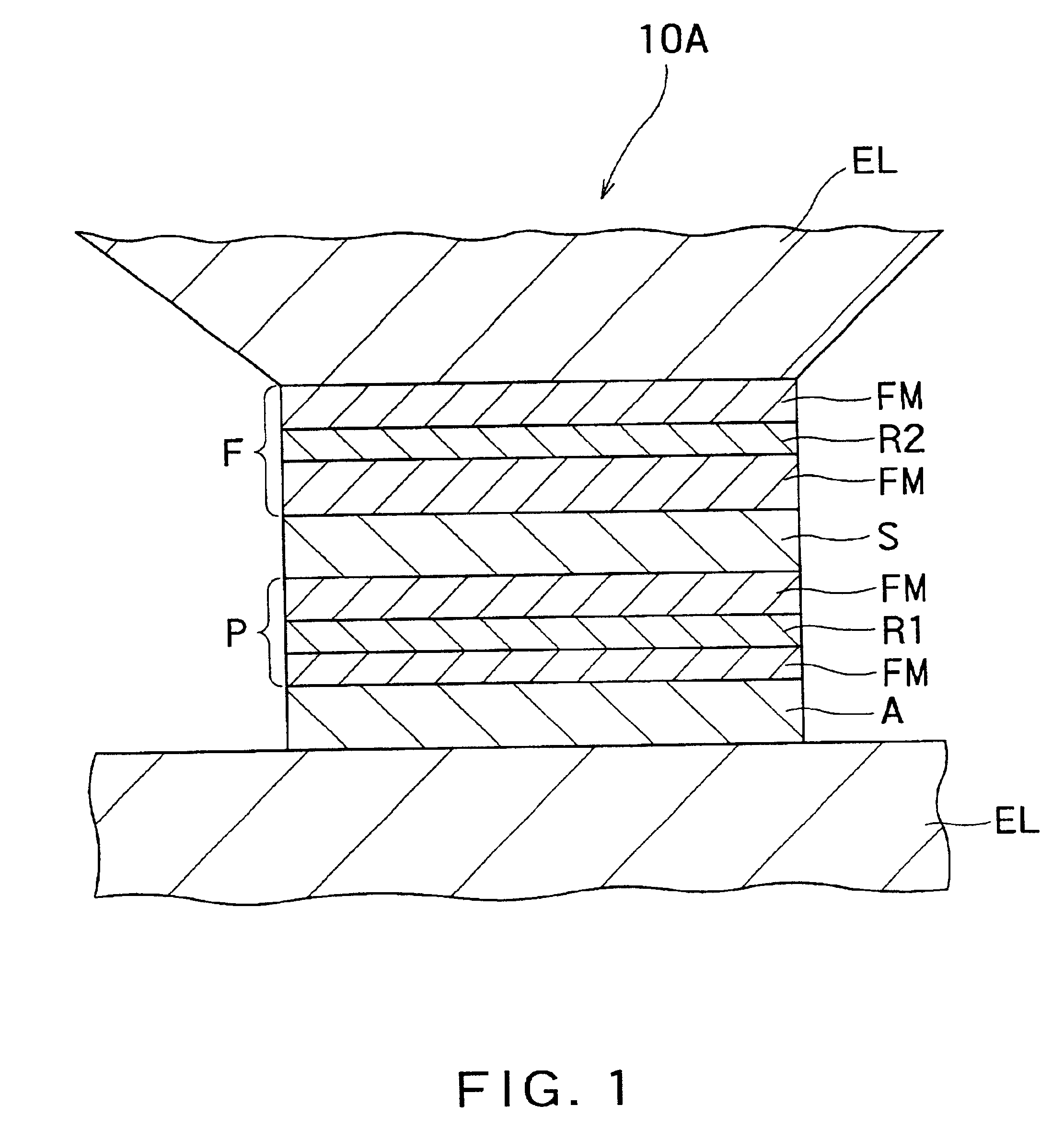
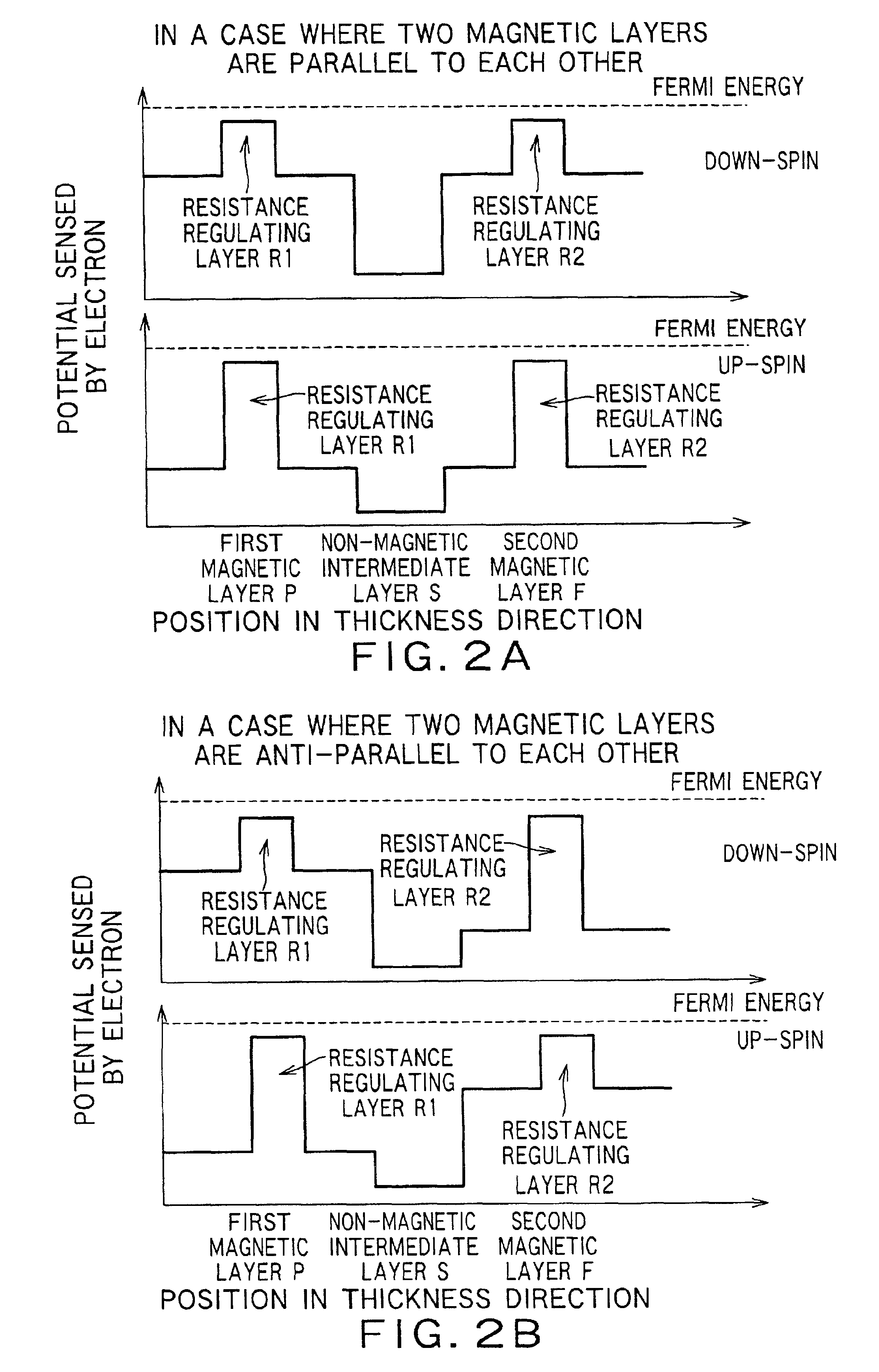
There is provided a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers to be controlled, and a magnetic head and magnetic recording and / or reproducing system using the same. In a magnetoresistance effect element wherein a sense current is caused to flow in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the film, a resistance regulating layer is provided in at least one of a pinned layer, a free layer and an non-magnetic intermediate layer. The resistance regulating layer contains, as a principal component, an oxide, a nitride, a fluoride, a carbide or a boride. The resistance regulating layer may be a continuous film or may have pin holes. Thus, it is possible to provide a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers, while effectively utilizing the scattering effect depending on spin.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Methods and apparatus for isolating platelets from blood
InactiveUS20050186120A1Simple and fast preparationIncrease productionMedical devicesLaboratory glasswaresMedicineRed blood cell
A platelet collection device comprising a centrifugal spin-separator container with a cavity having a longitudinal inner surface. A float in the cavity has a base, a platelet collection surface above the base, an outer surface. The float density is below the density of erythrocytes and above the density of plasma. The platelet collection surface has a position on the float which places it below the level of platelets when the float is suspended in separated blood. During centrifugation, a layer of platelets or buffy coat collects closely adjacent the platelet collection surface. Platelets are then removed from the platelet collection surface. Movement of a float having a density greater than whole blood through the sedimenting erythrocytes releases entrapped platelets, increasing the platelet yield.
Owner:DORIAN RANDEL +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com