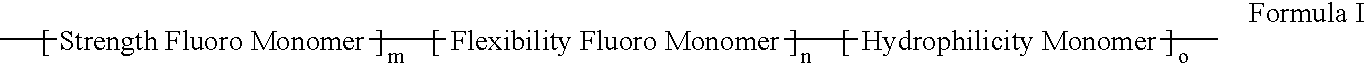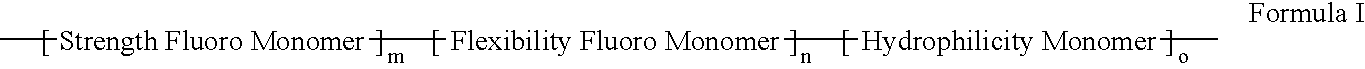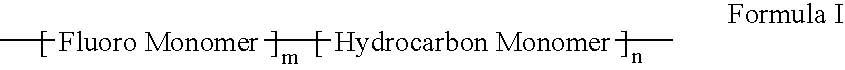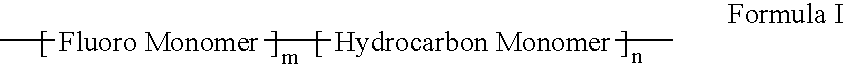Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
212 results about "Total occlusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
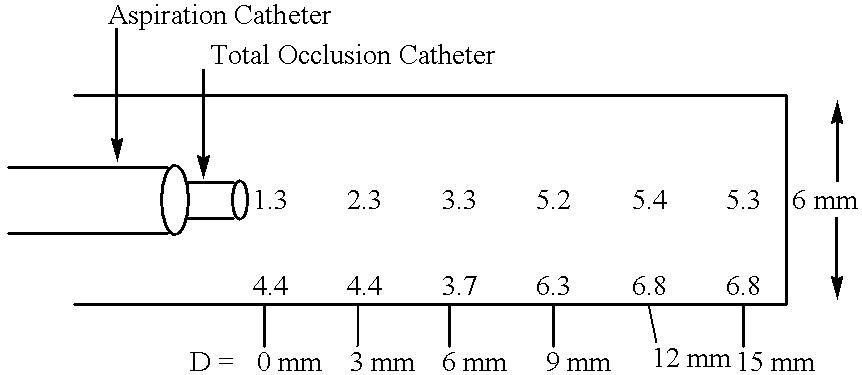
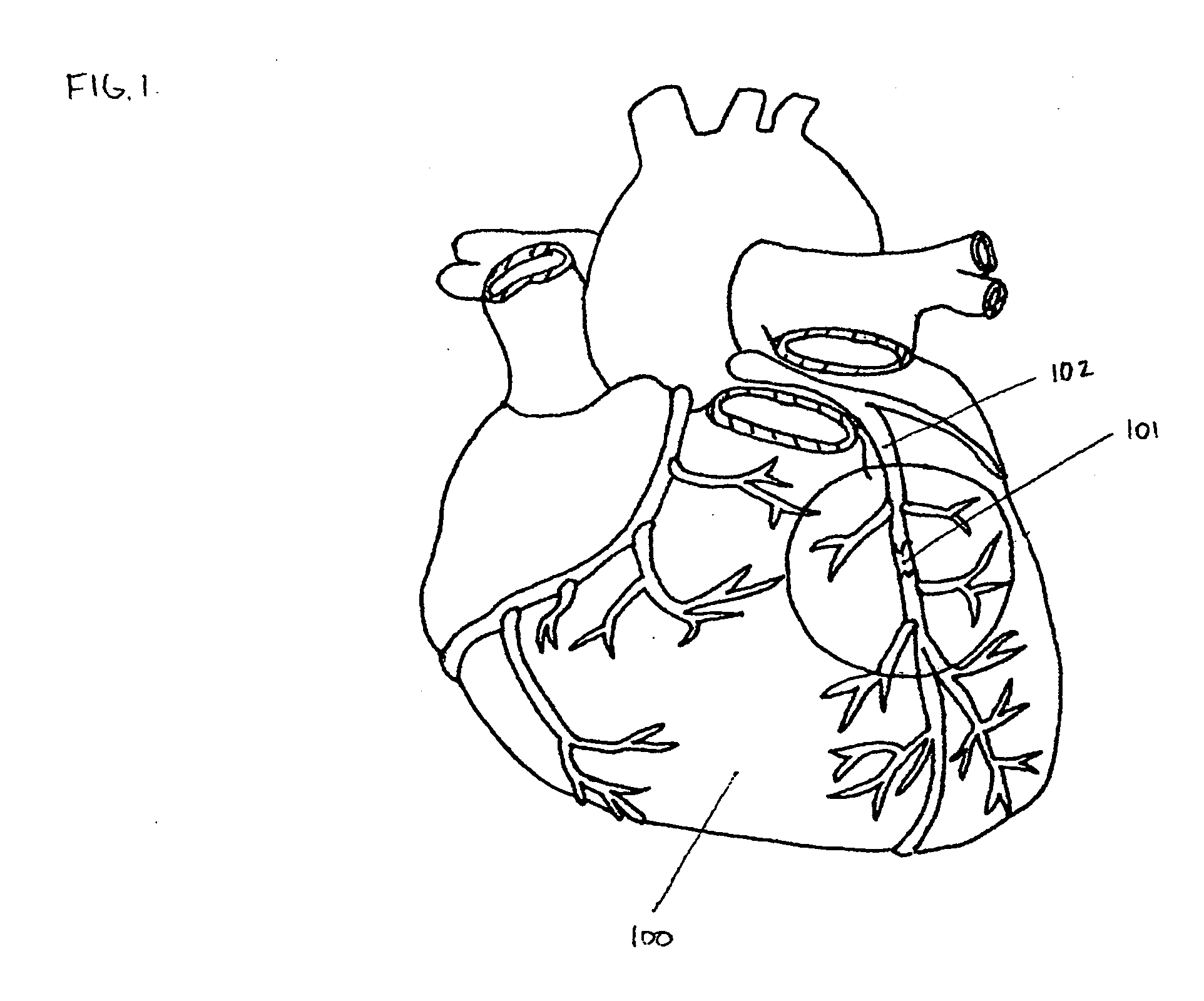
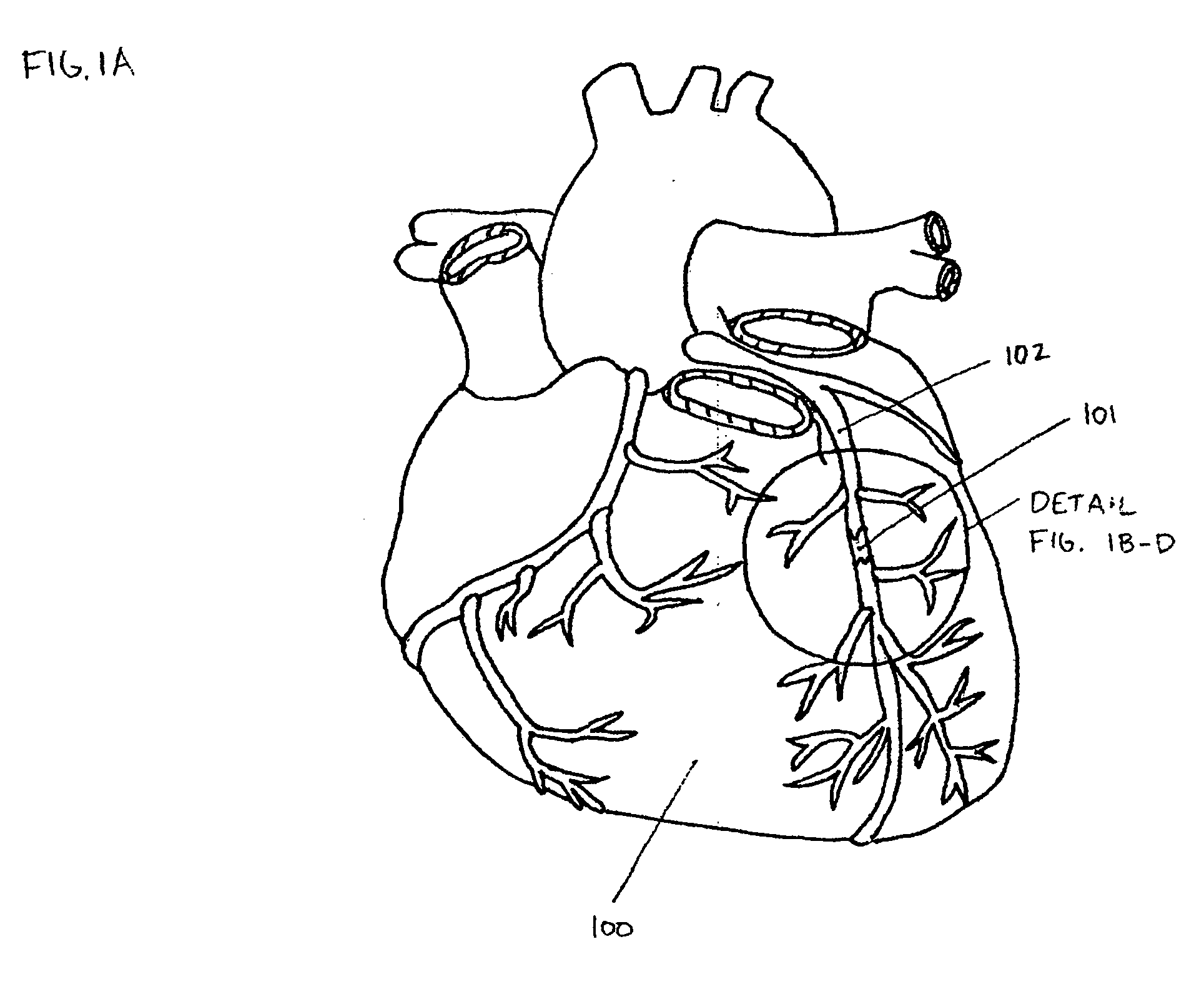
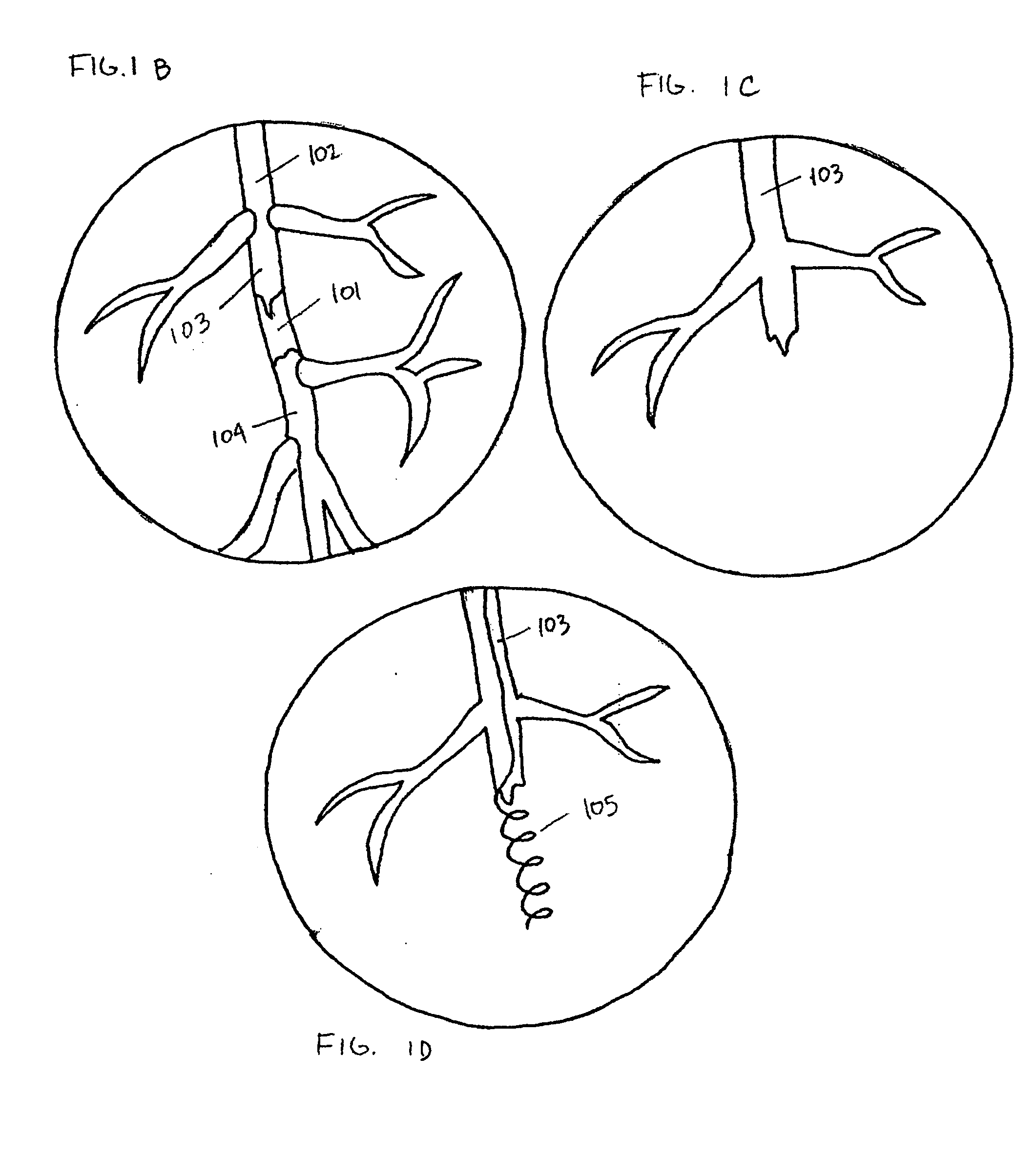
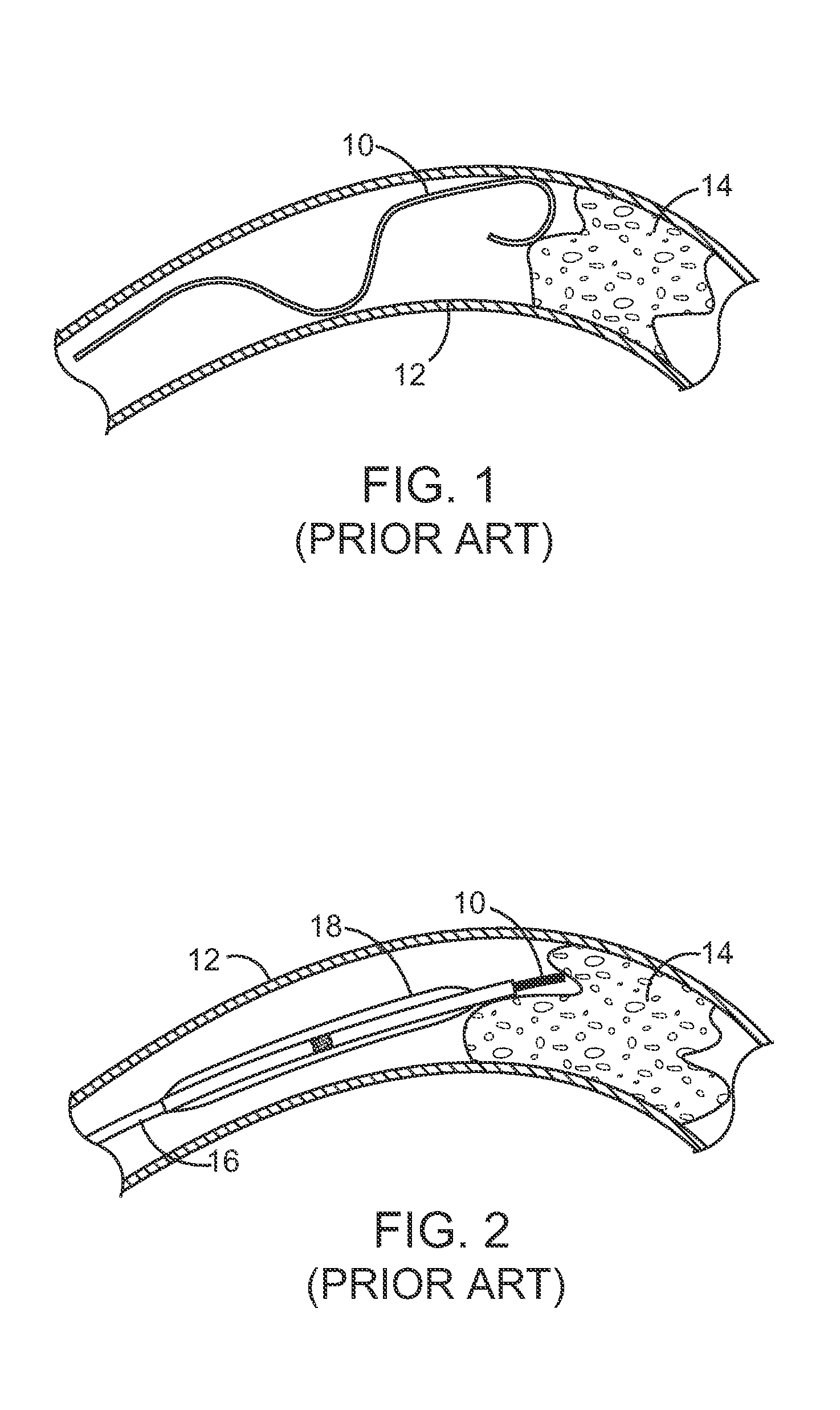
A chronic total occlusion (CTO) is defined as the complete obstruction of a coronary artery, exhibiting TIMI 0 or TIMI 1 flow, with an occlusion duration of >3 months.
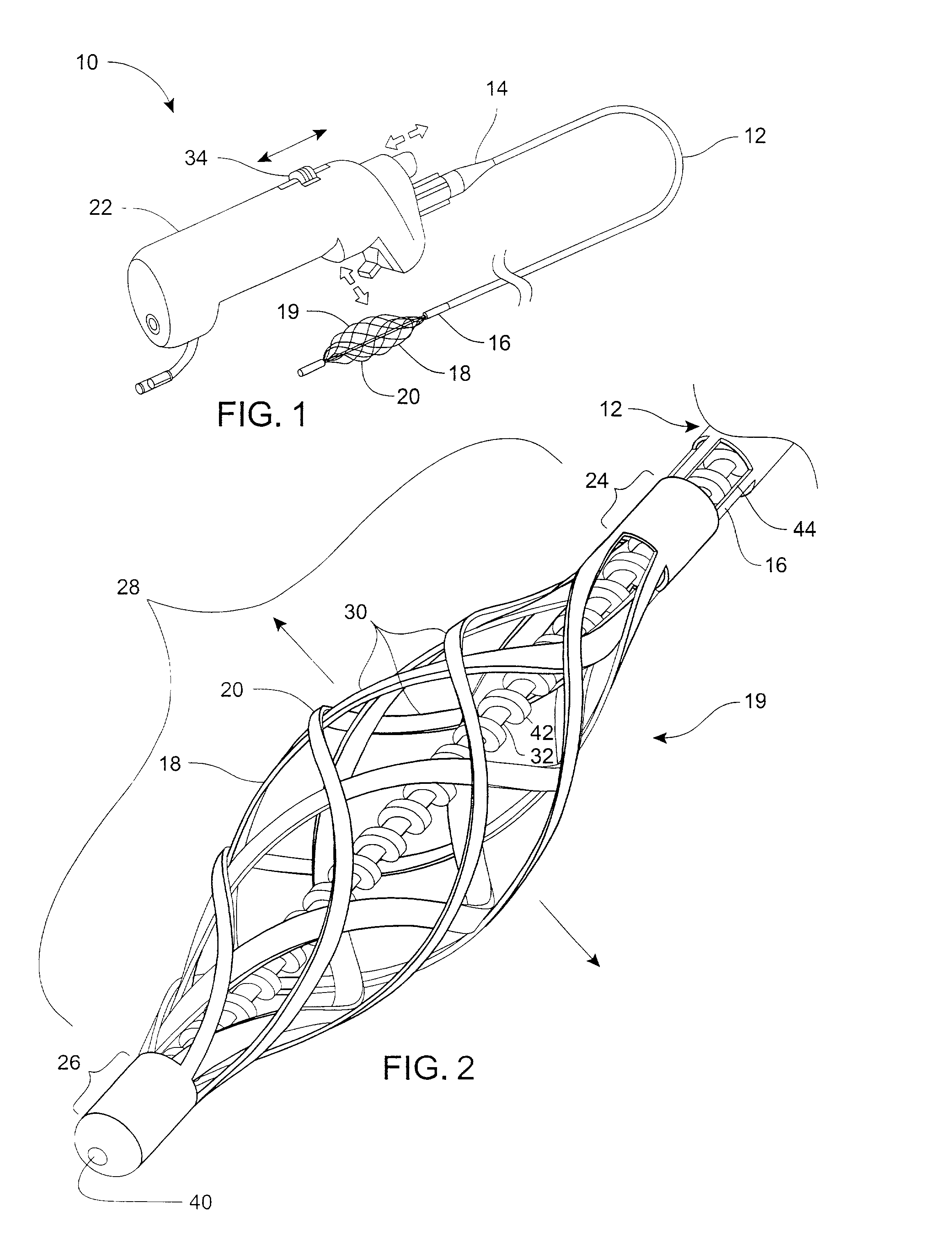
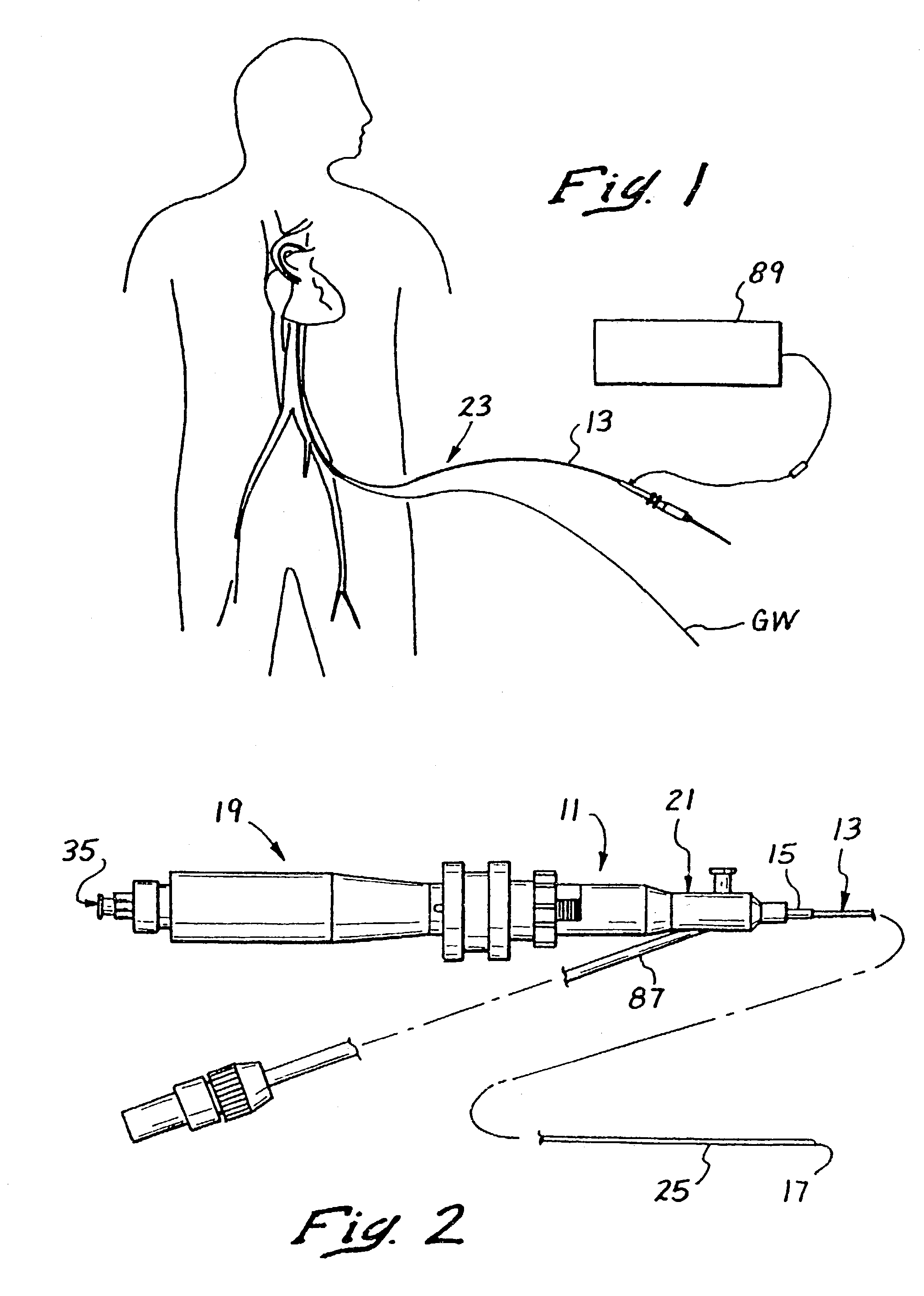
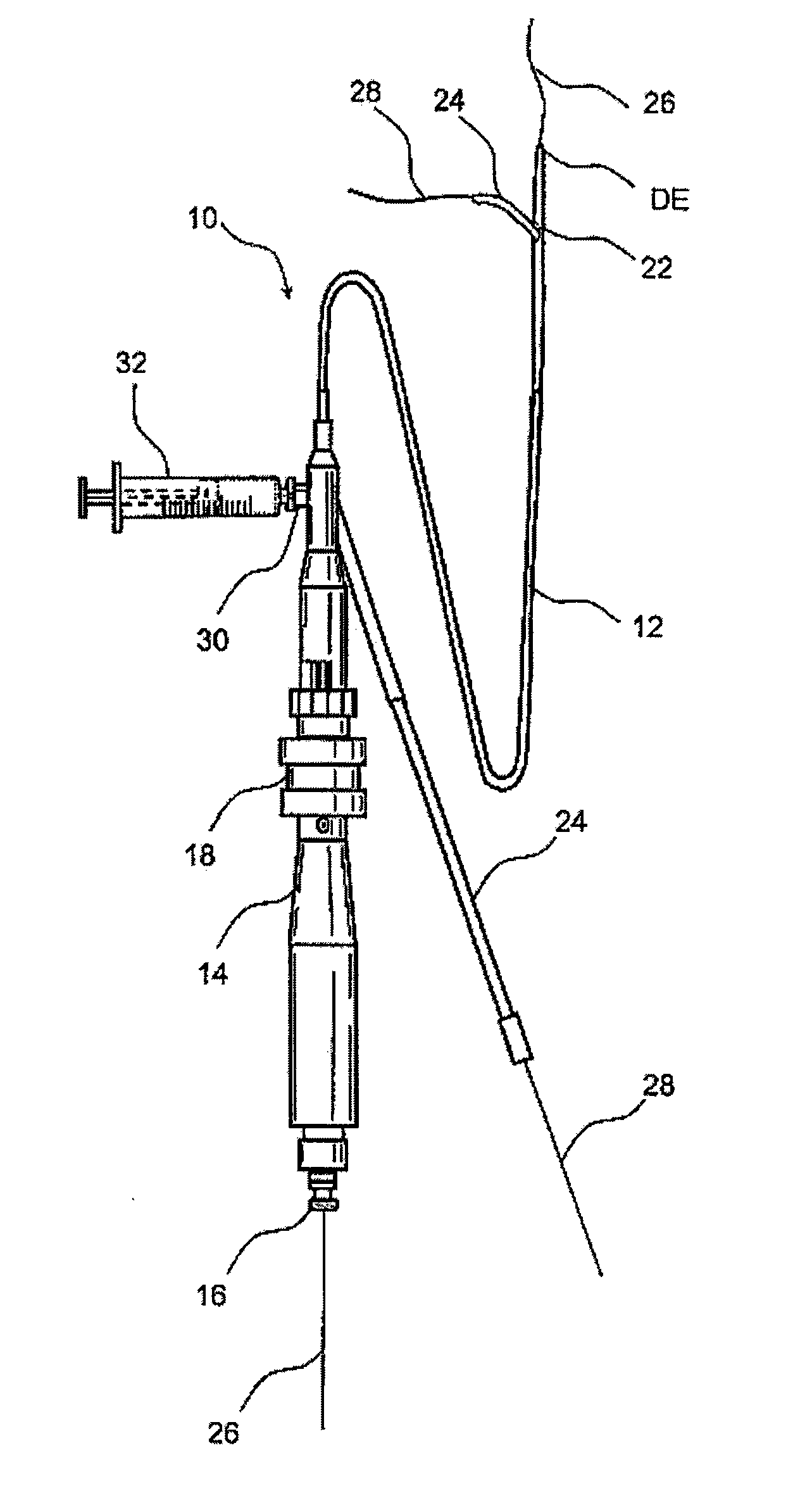
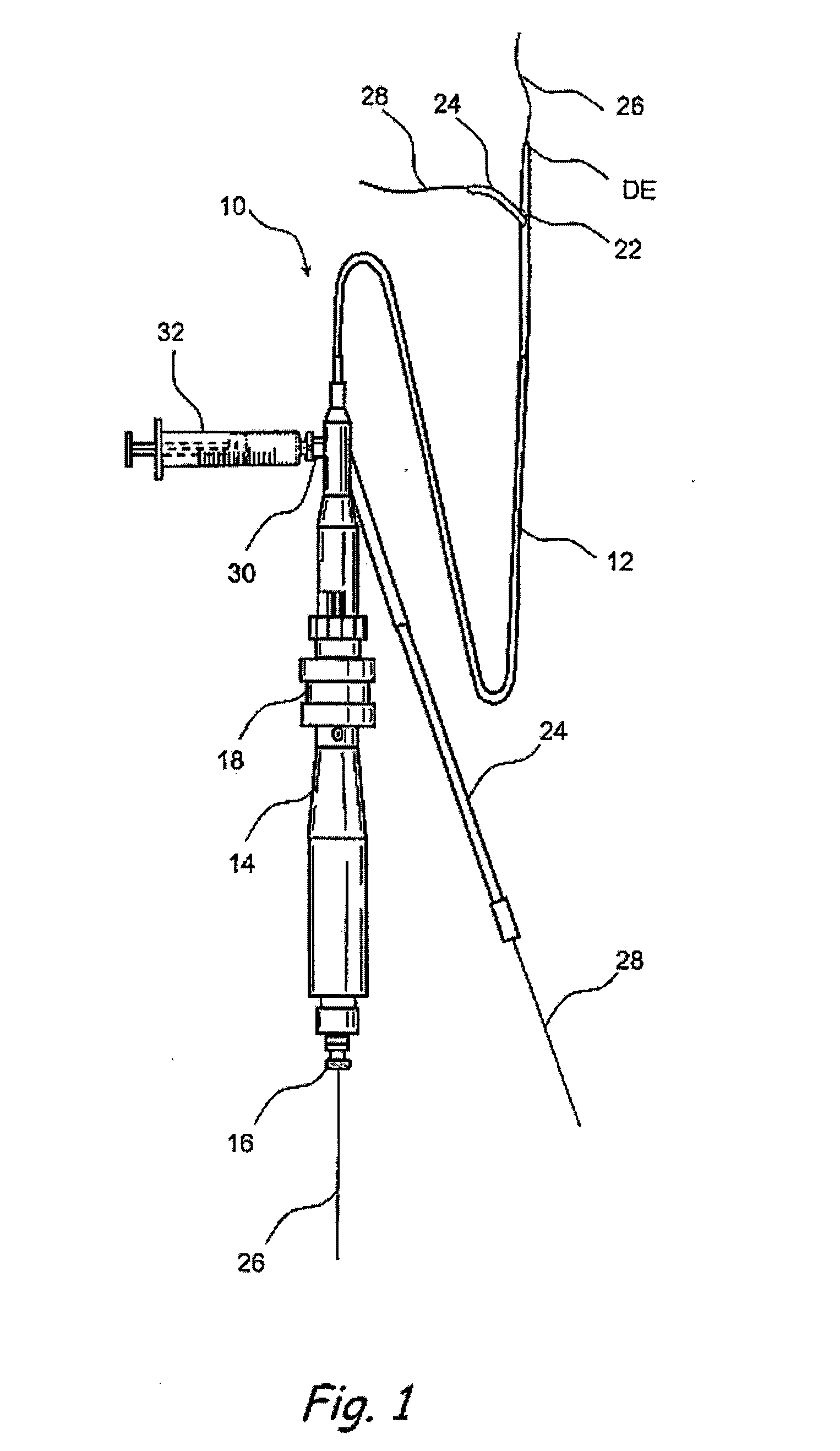
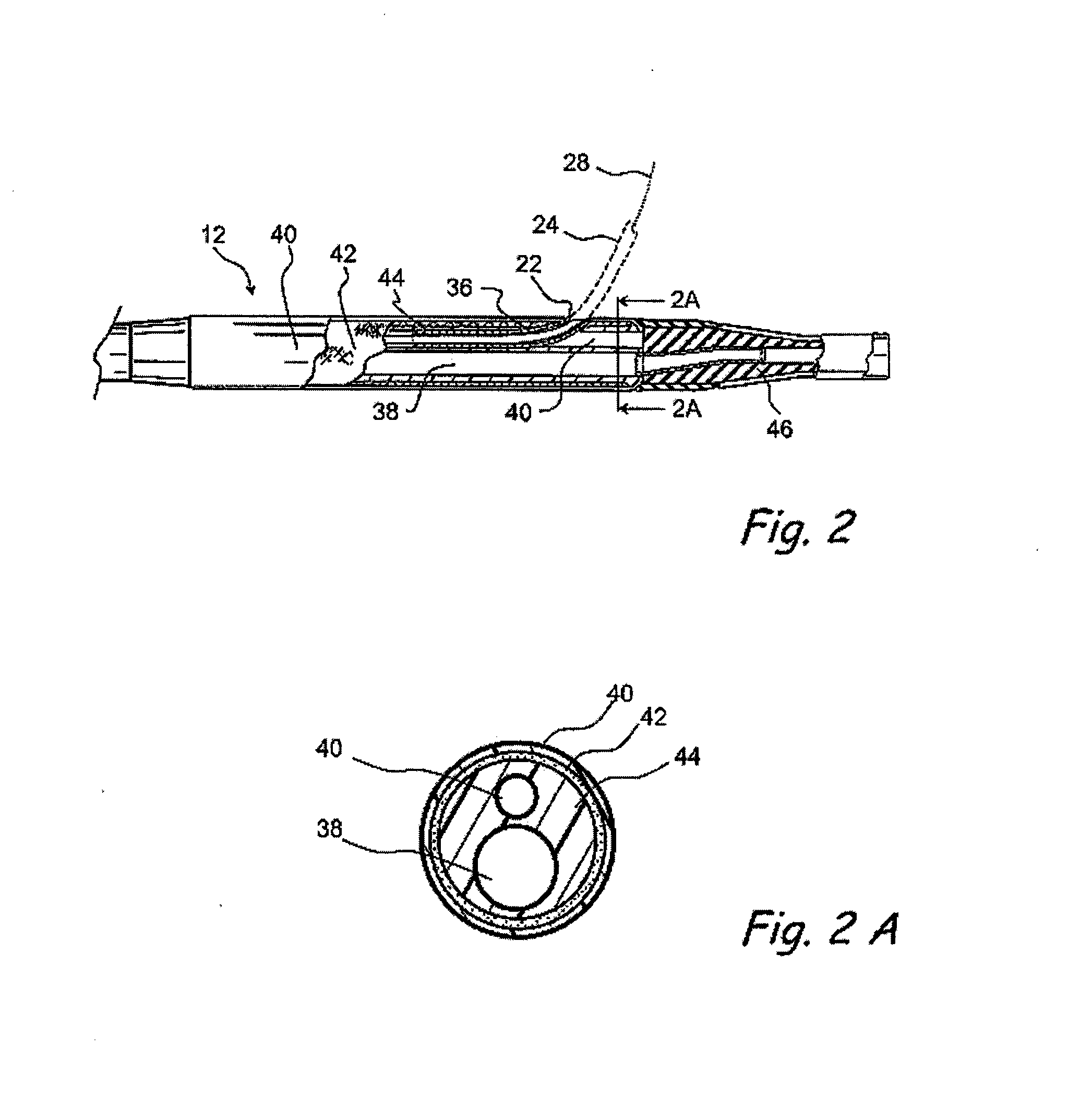
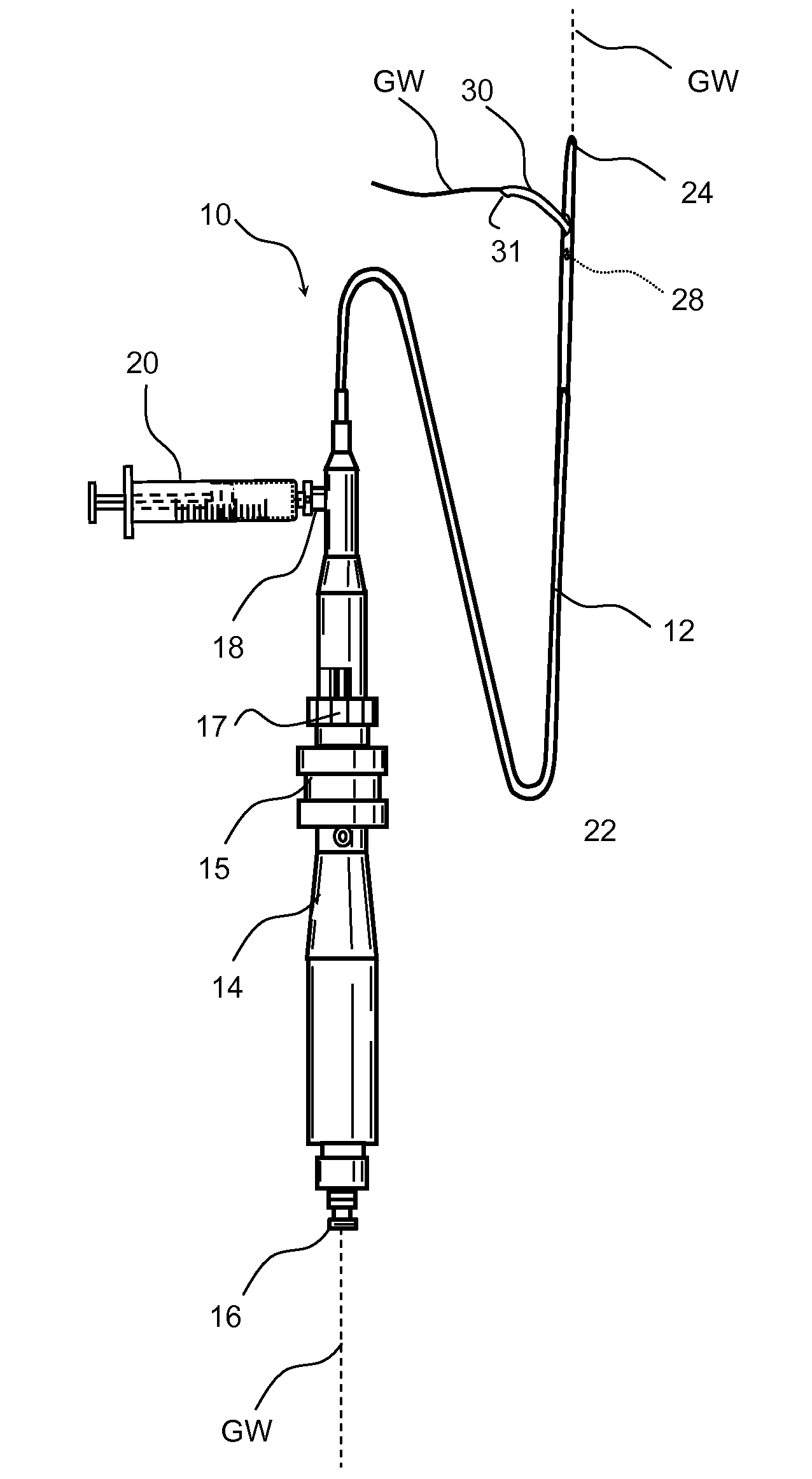
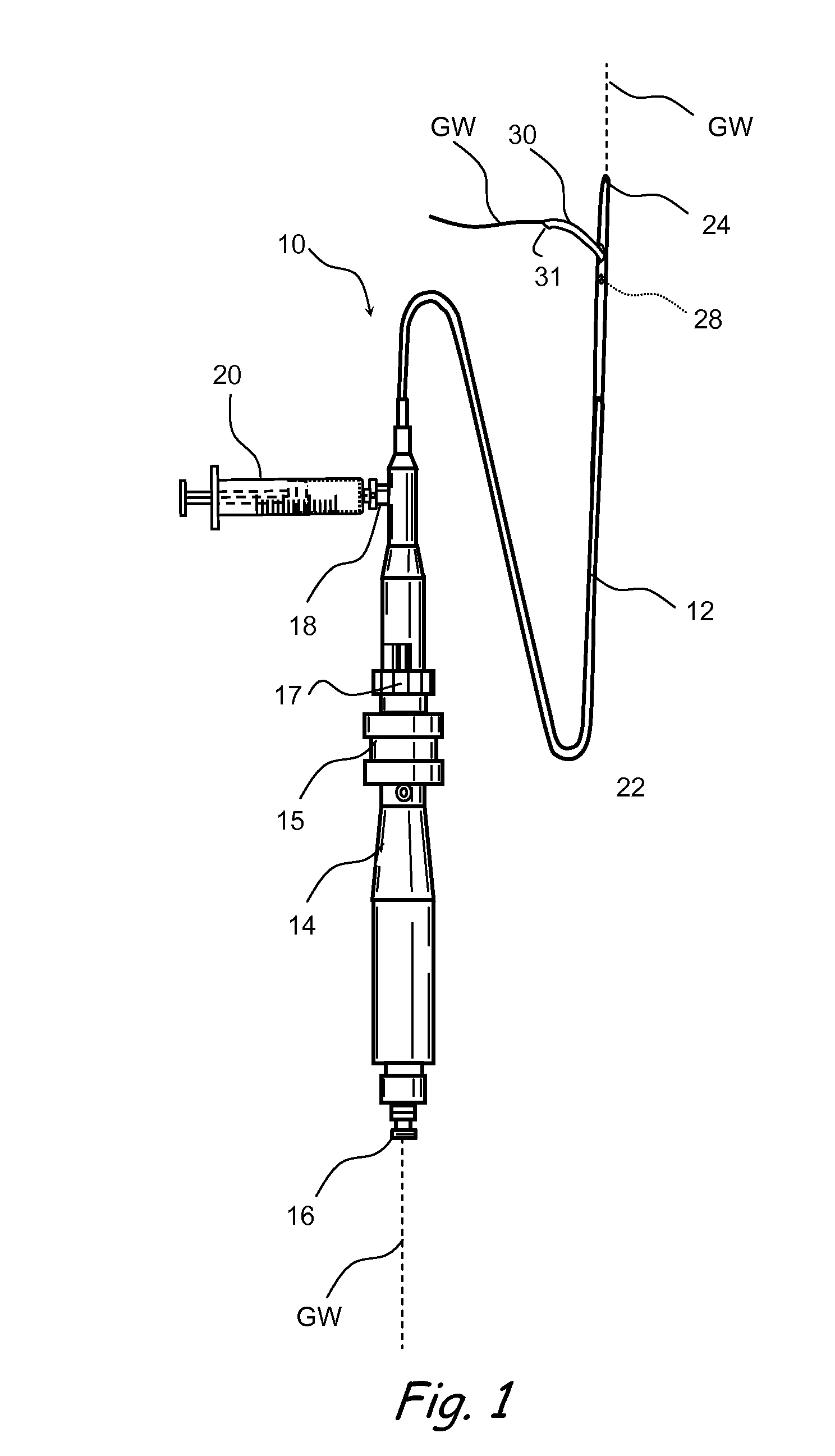
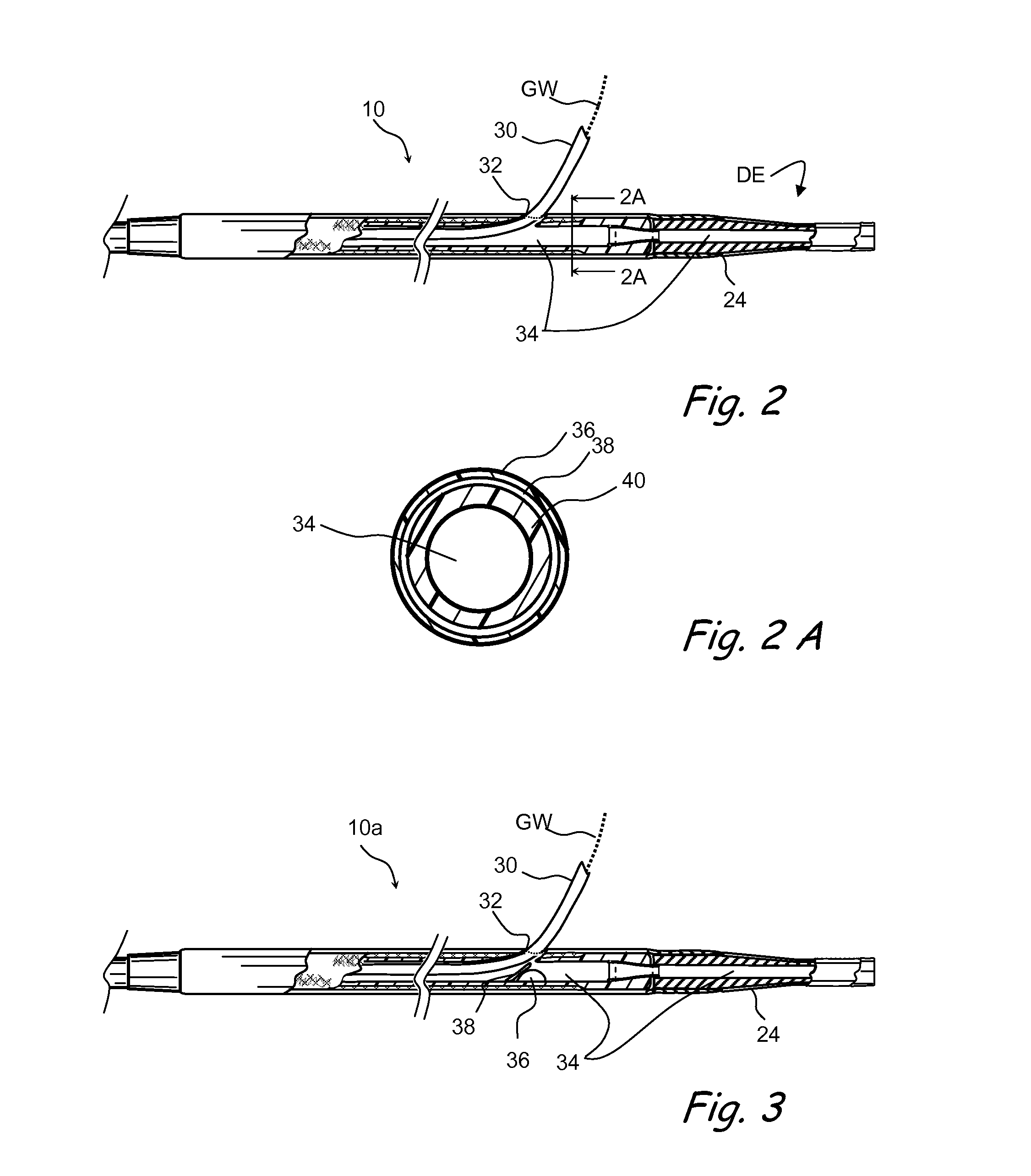
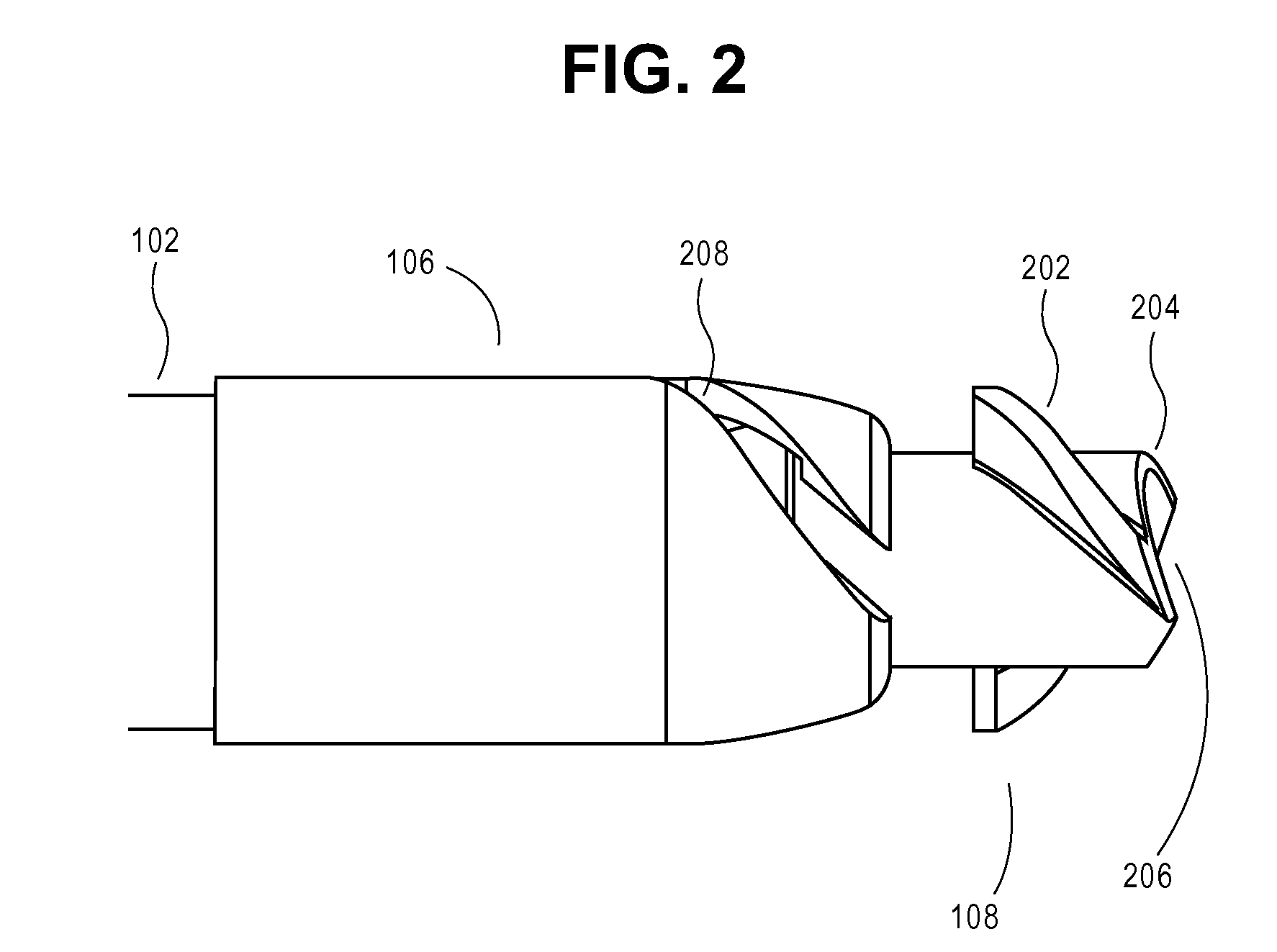
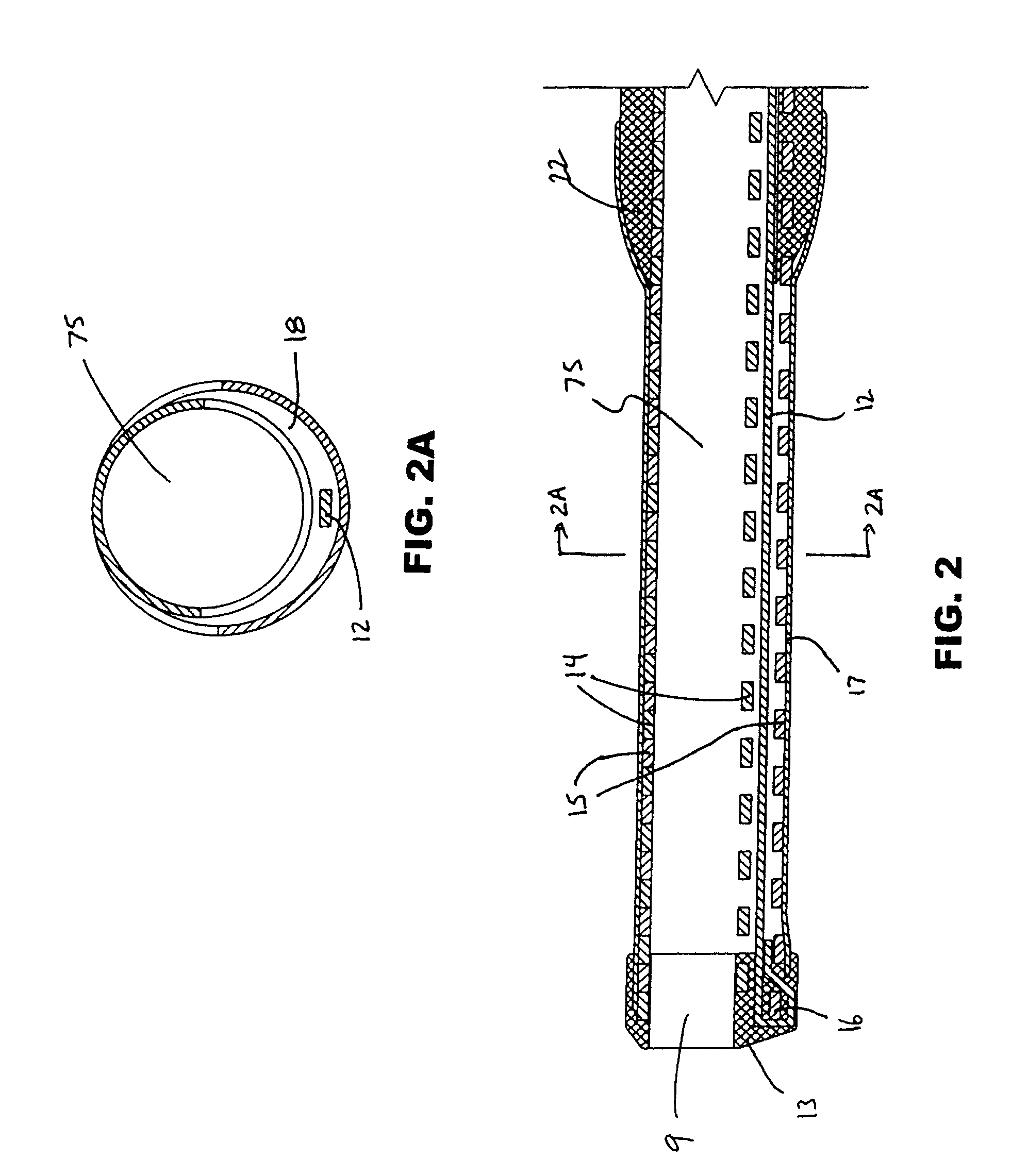
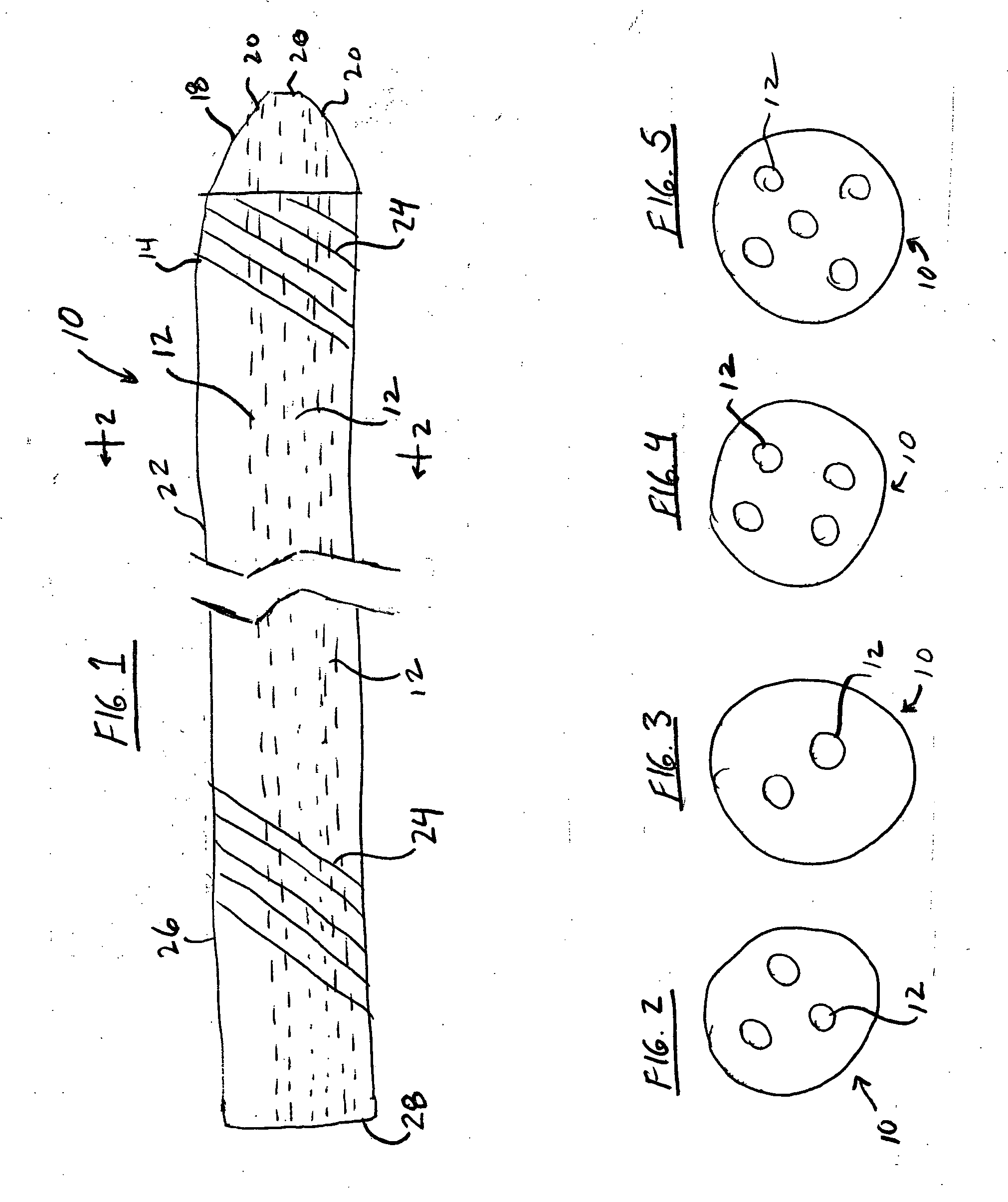
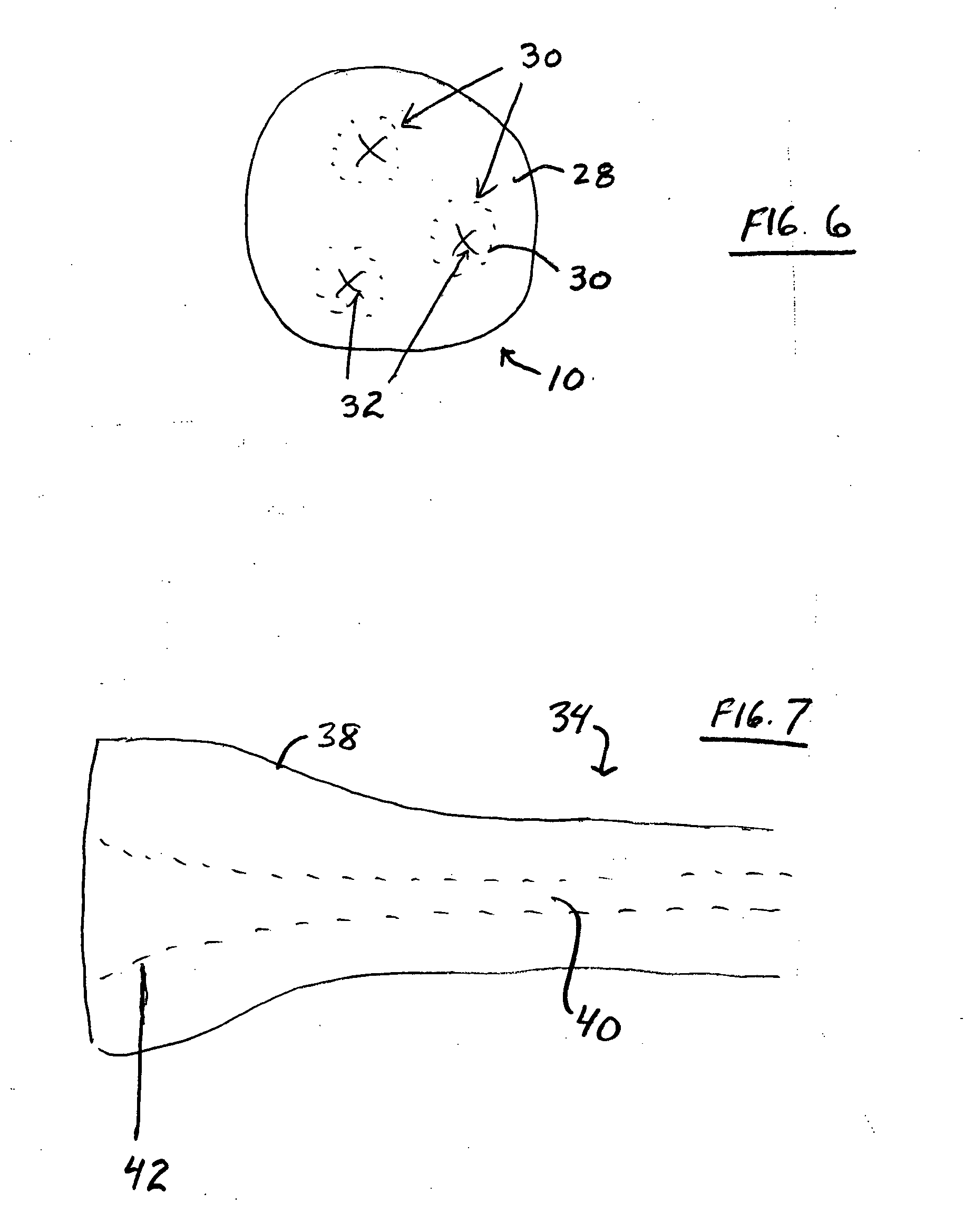
Method and device for locating guidewire and treating chronic total occlusions
InactiveUS20010031981A1Inhibit excessive separationPrevent slidingDiagnosticsDilatorsAtherectomyTotal occlusion
Devices, methods, kits, and methods remove obstructive material from the vasculature and other body lumens. Expansible baskets may be used as cooperating radially expansible shearing members. Helically oriented struts of each basket may wind in a uniform circumferential direction. The struts can be independently flexible, allowing the shearing members to flex axially together. The inner basket may be rotatably driven and may use an axial pump extending proximally from the shearing members and / or a distal penetrator for advancing into an occlusion which inhibits guidewire access. The struts may slide substantially continuously across each other, and may be sufficiently aggressive for highly effective thrombectomy. A rotationally static and axially flexible outer basket may provide a safe, limited atherectomy treatment.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Methods for bypassing total or near-total obstructions in arteries or other anatomical conduits
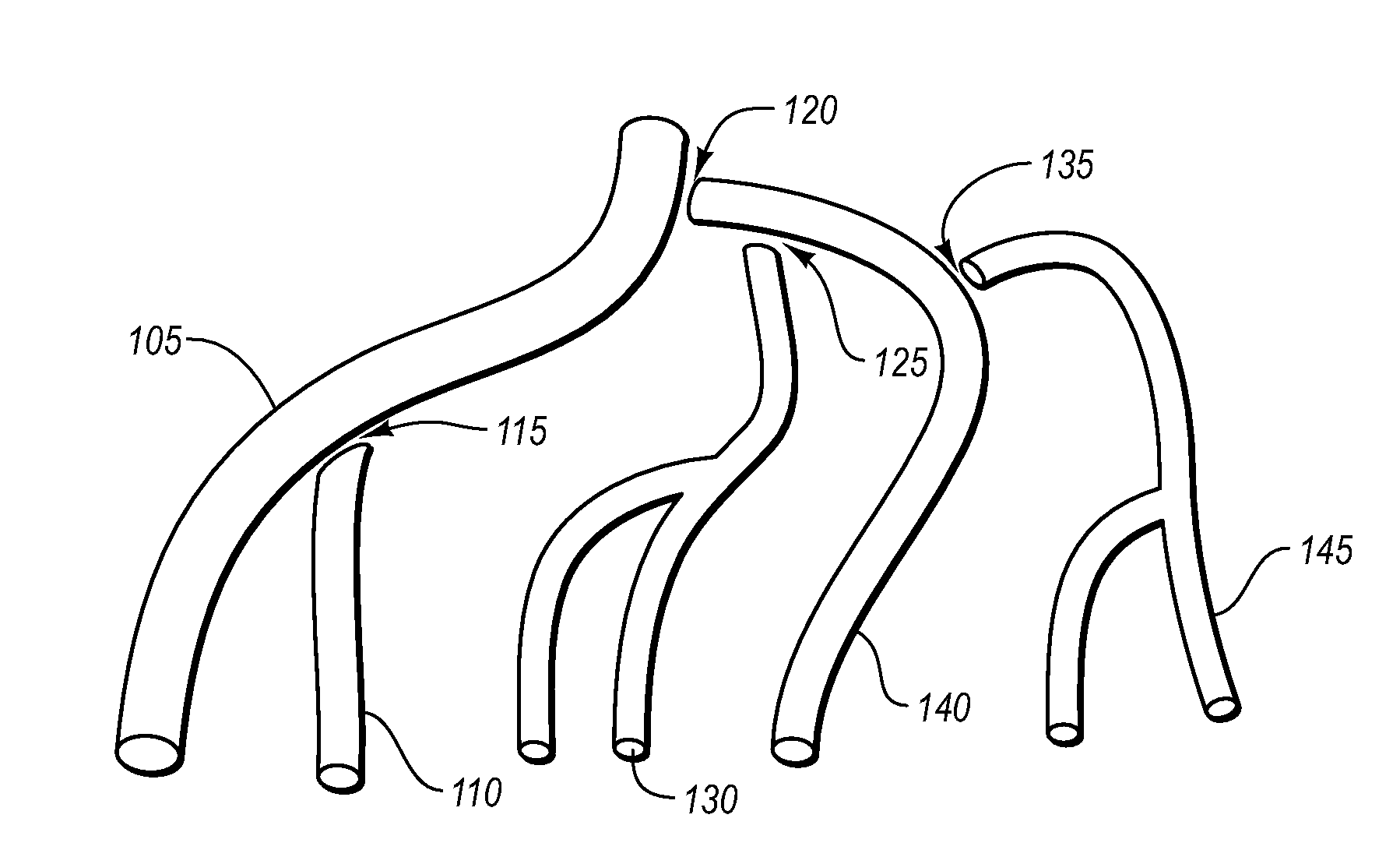
Methods for bypassing total or near-total obstructions in arteries or other anatomical conduits. A guidewire is advanced through the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit upstream of the obstruction and past the obstruction. In navigating past the obstruction, this guidewire may advance through tissue that is located within the wall of the artery or anatomical conduit and / or through tissue that is located outside of the wall of the artery or anatomical conduit. After this guidewire has been advanced past the obstruction, a penetrating catheter that is equipped with an orientation element is advanced over that guidewire. The orientation element is then used to aim a penetrator back into the lumen of the obstructed artery or conduit, downstream of the obstruction. The penetrator is then advanced into the lumen of the obstructed artery or conduit, downstream of the obstruction, and a final guidewire is advanced through the penetrator and into the lumen of the artery or conduit downstream of the obstruction. The catheter (and the guidewire that was initially used to pass the obstruction) may then be removed, leaving the final guidewire in place. A balloon or other tract enlarging device may be used to dilate or otherwise enlarge the bypass tract through which the final guidewire extends. Also, a covered or uncovered stent may be placed within the tract to facilitate flow from the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit upstream of the obstruction, through the newly created bypass tract and back into the lumen of the artery or anatomical conduit downstream of the obstruction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
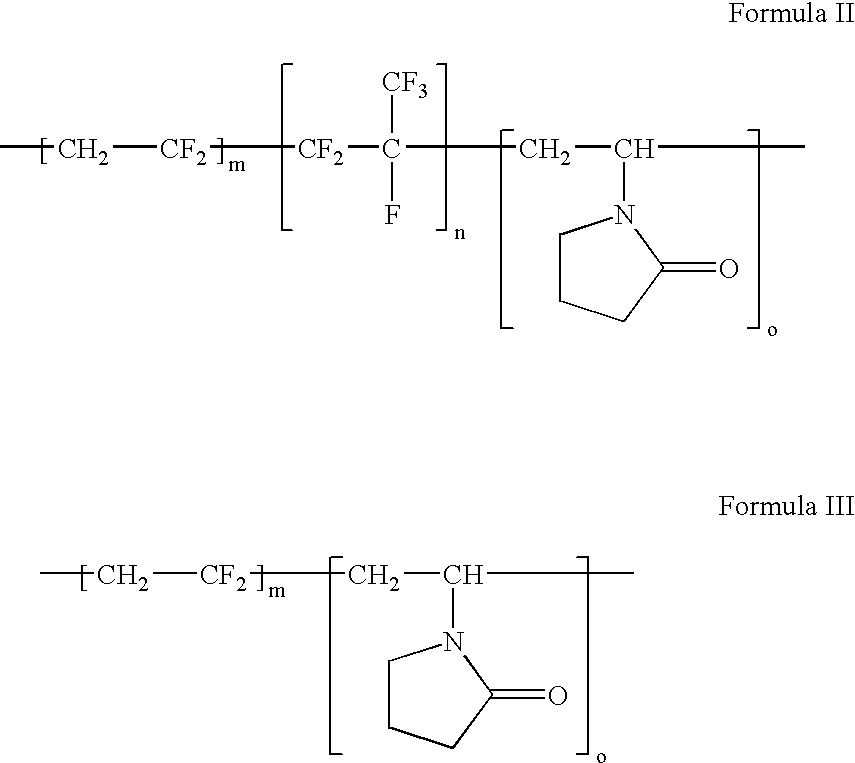
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers
ActiveUS20060047095A1Improve propertiesProvide flexibilityFibre treatmentSurgeryDiseasePolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer of fluorinated monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer of fluorinated monomers or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
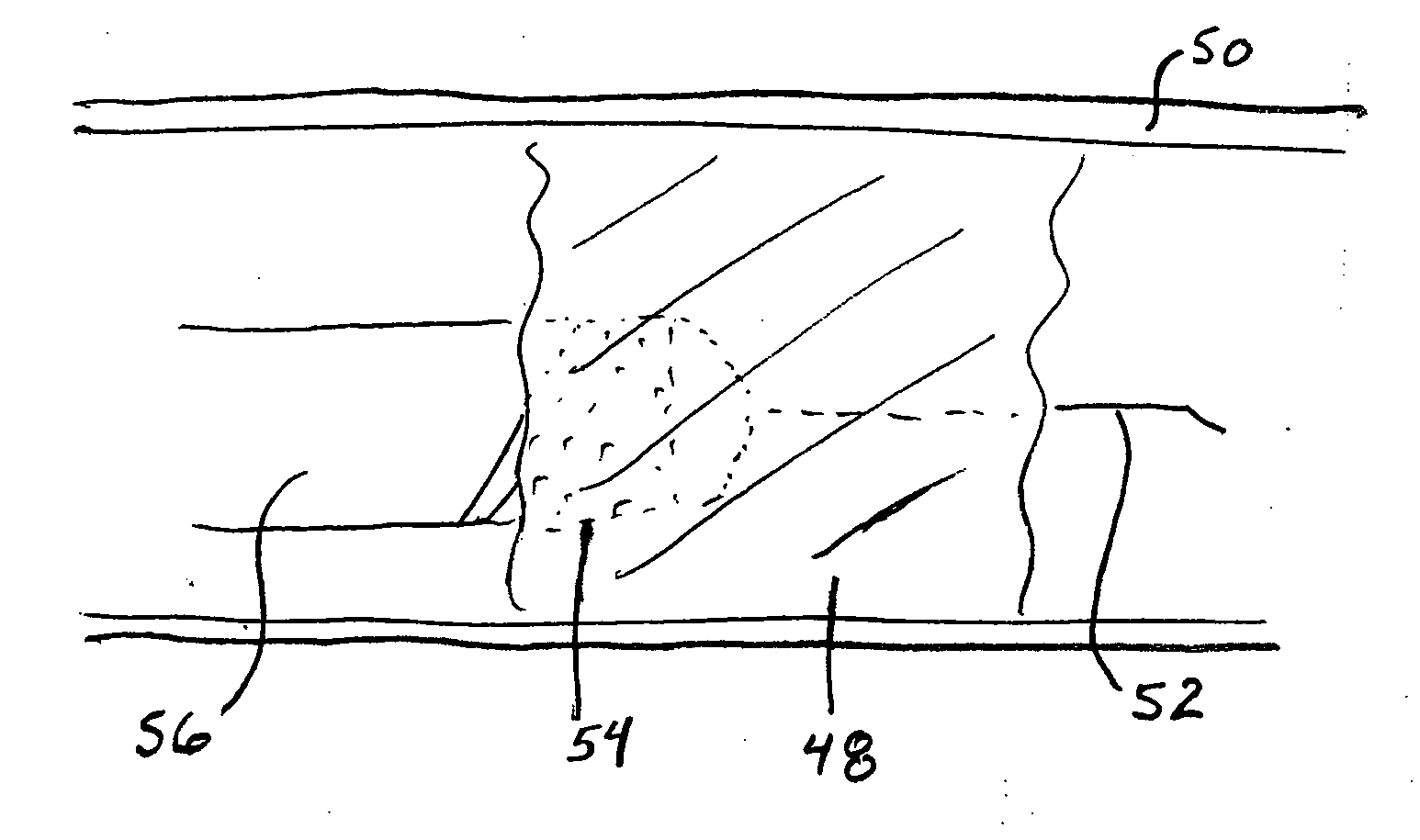
Apparatus and Method for Guided Chronic Total Occlusion Penetration
InactiveUS20080294037A1For accurate placementAvoids and reduces complicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryTotal occlusionIntravascular catheter
An apparatus and method for guided penetration of a chronic total occlusion in a blood vessel are disclosed. The invention is directed to an apparatus that facilitates accurate placement of a drilling tip within a body lumen using ultrasound-based detection to determine the position of the intravascular catheter relative to the vessel occlusion and vessel walls.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
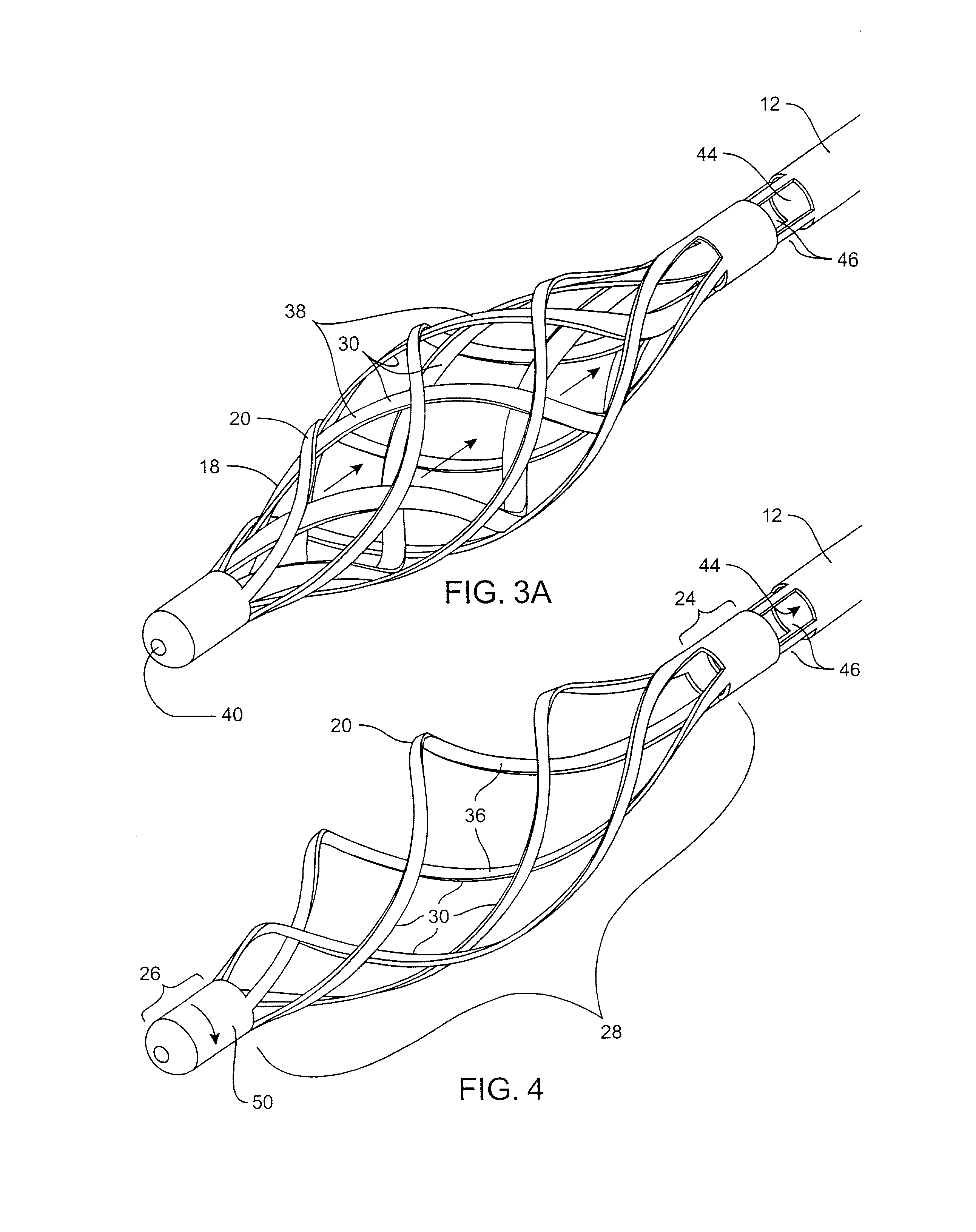
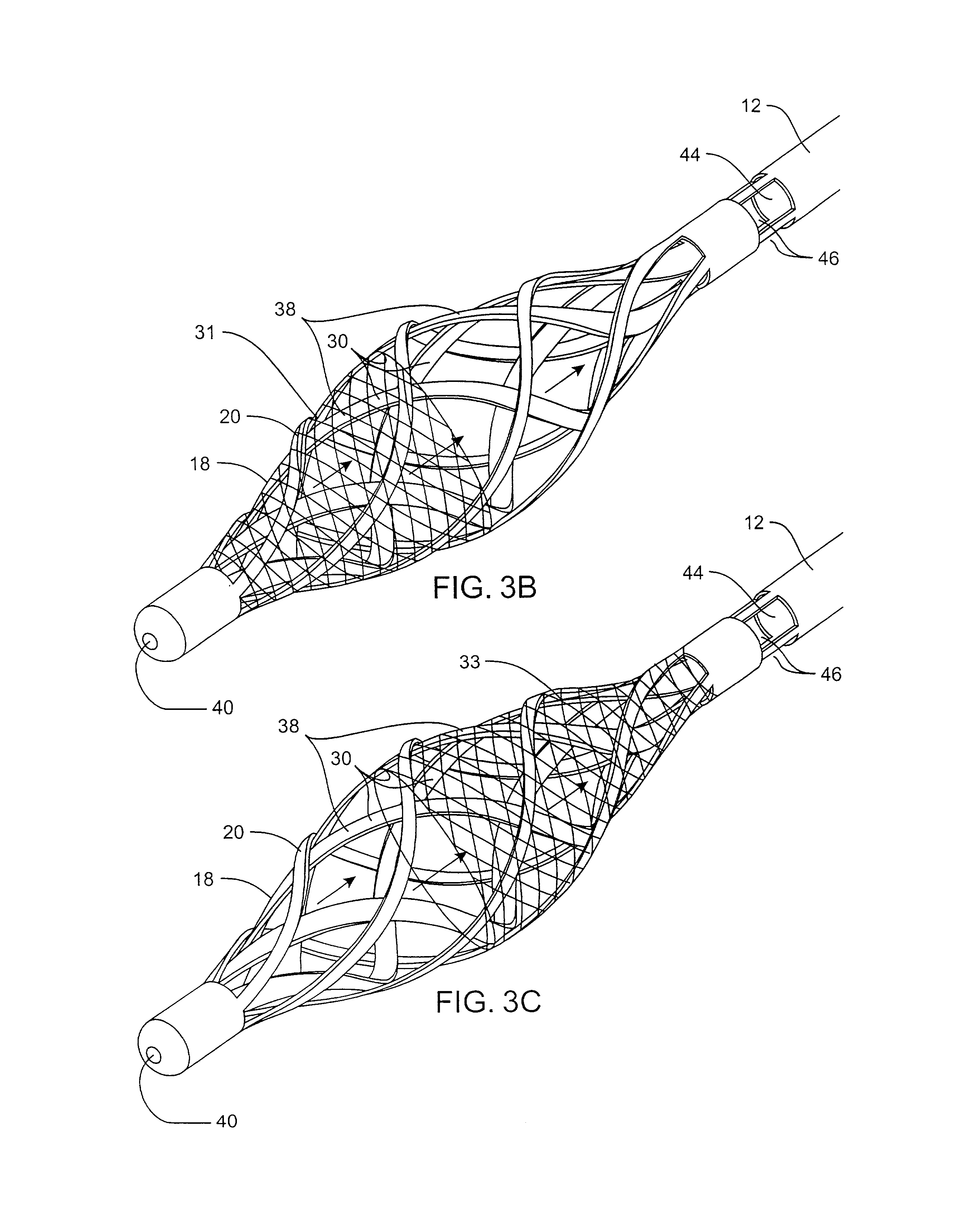
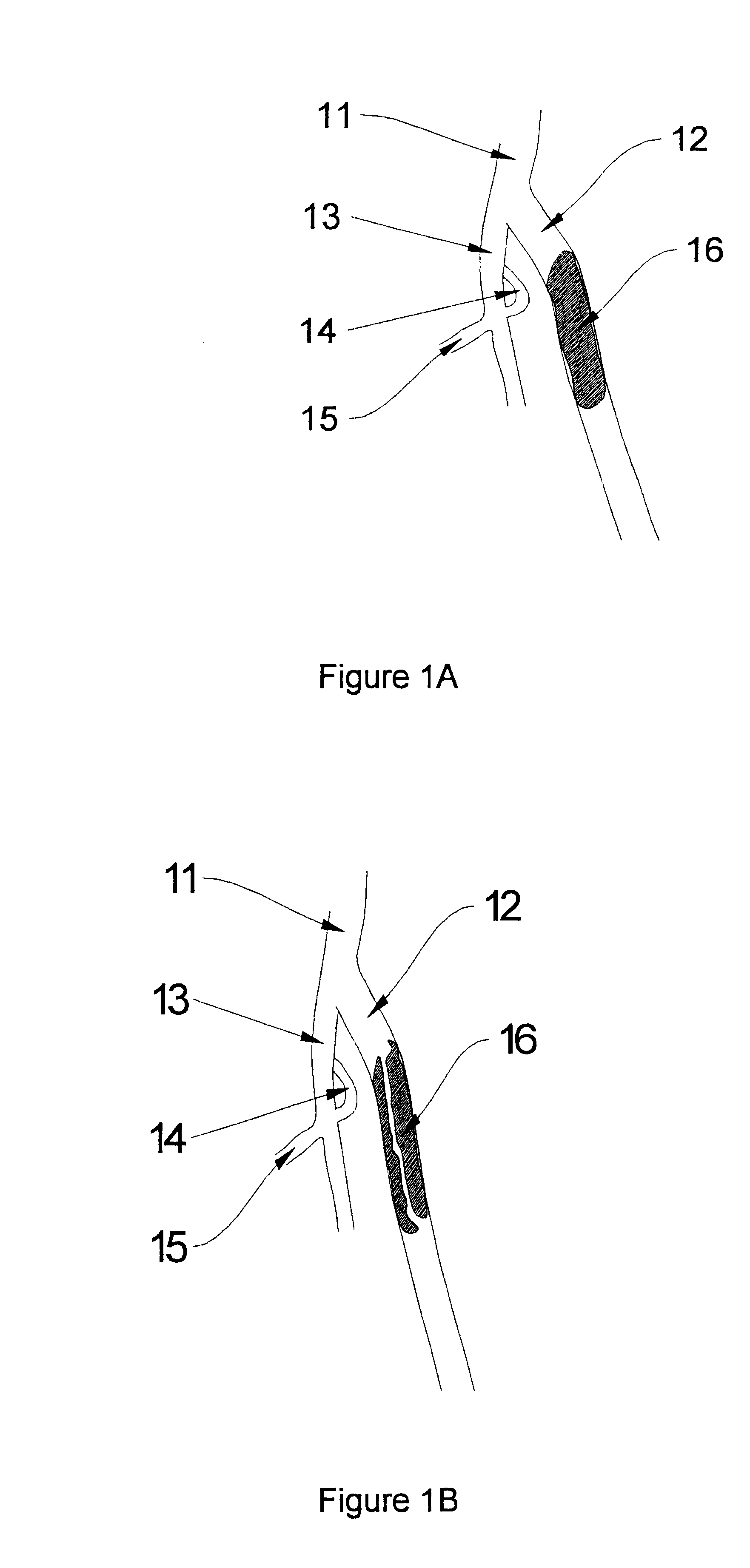
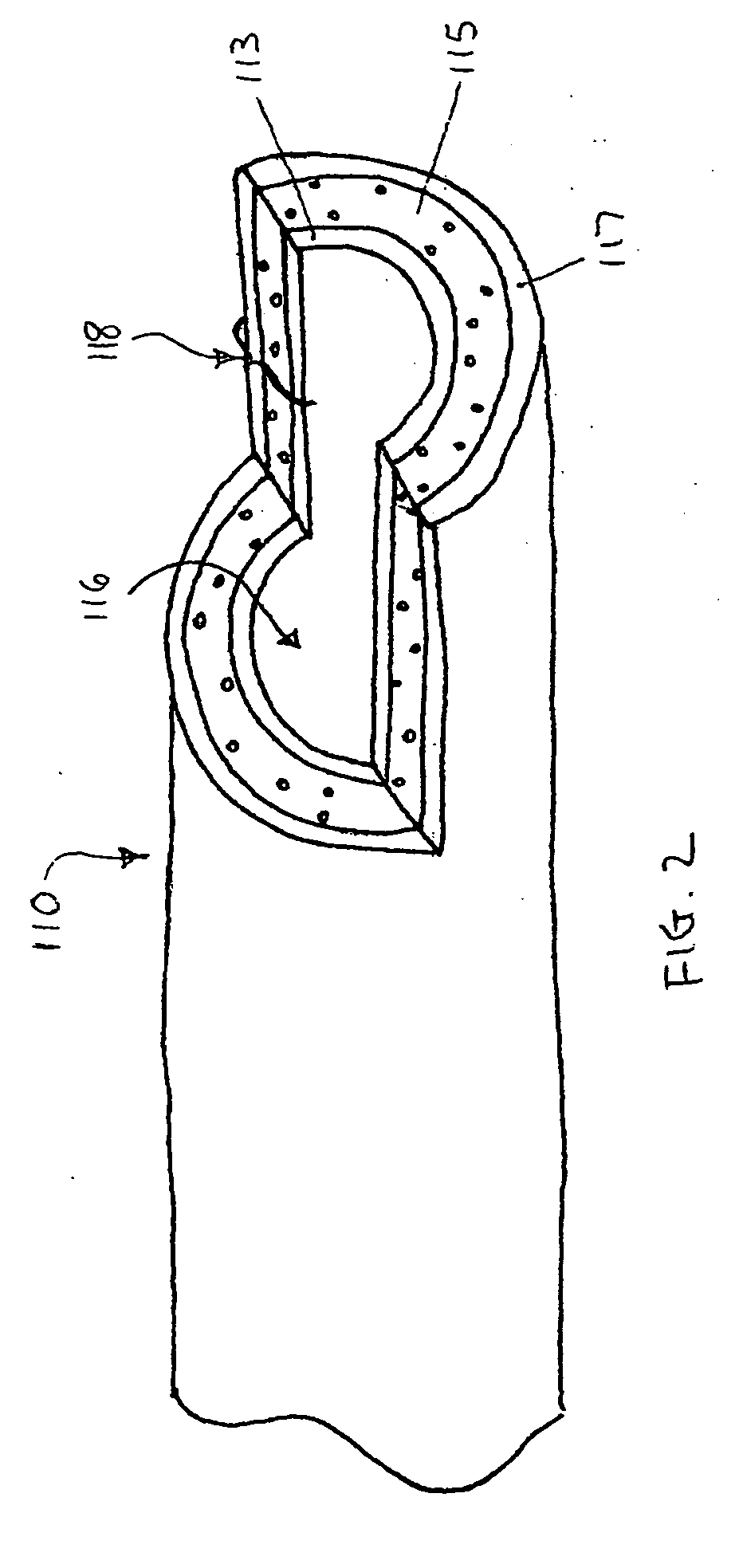
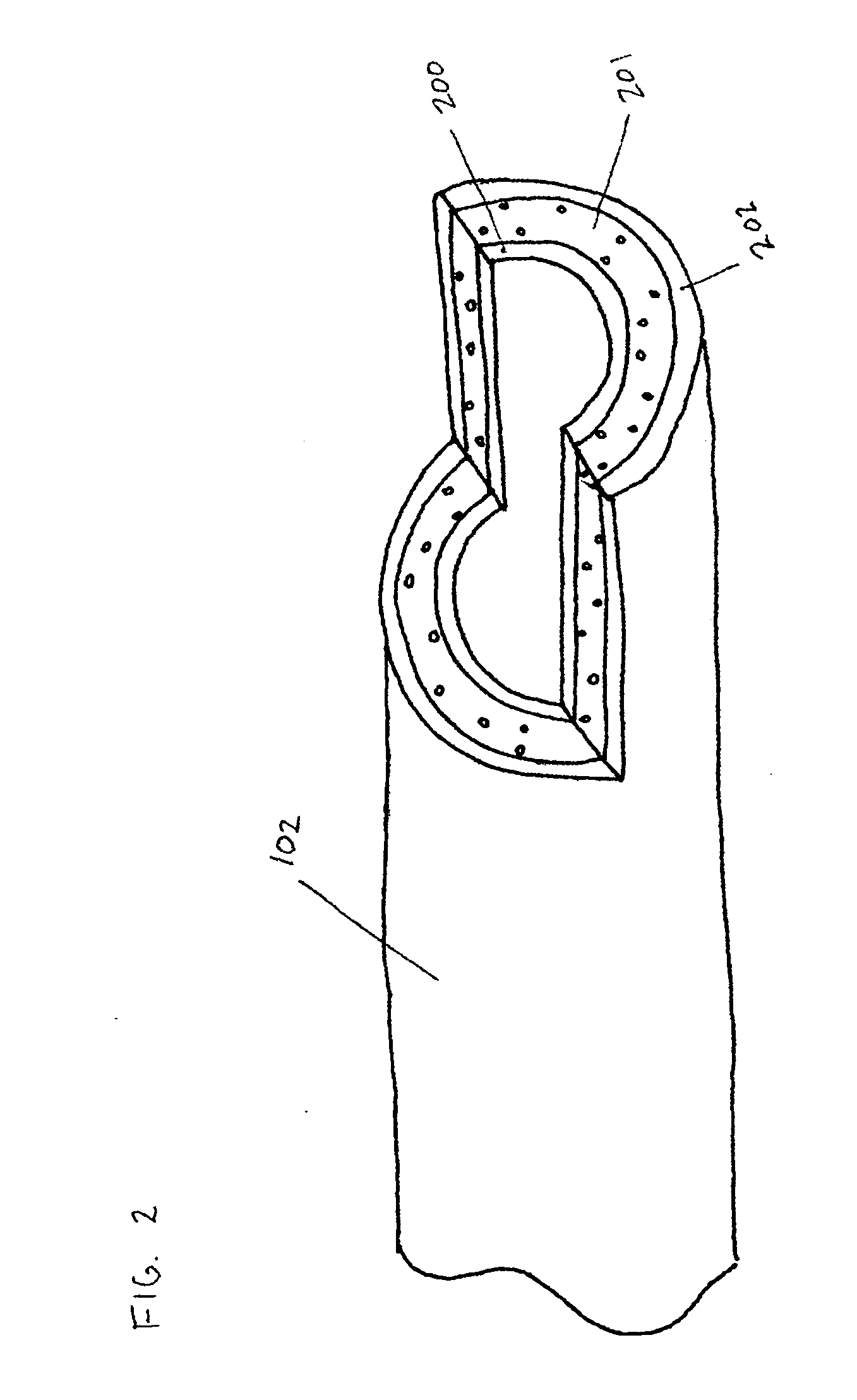
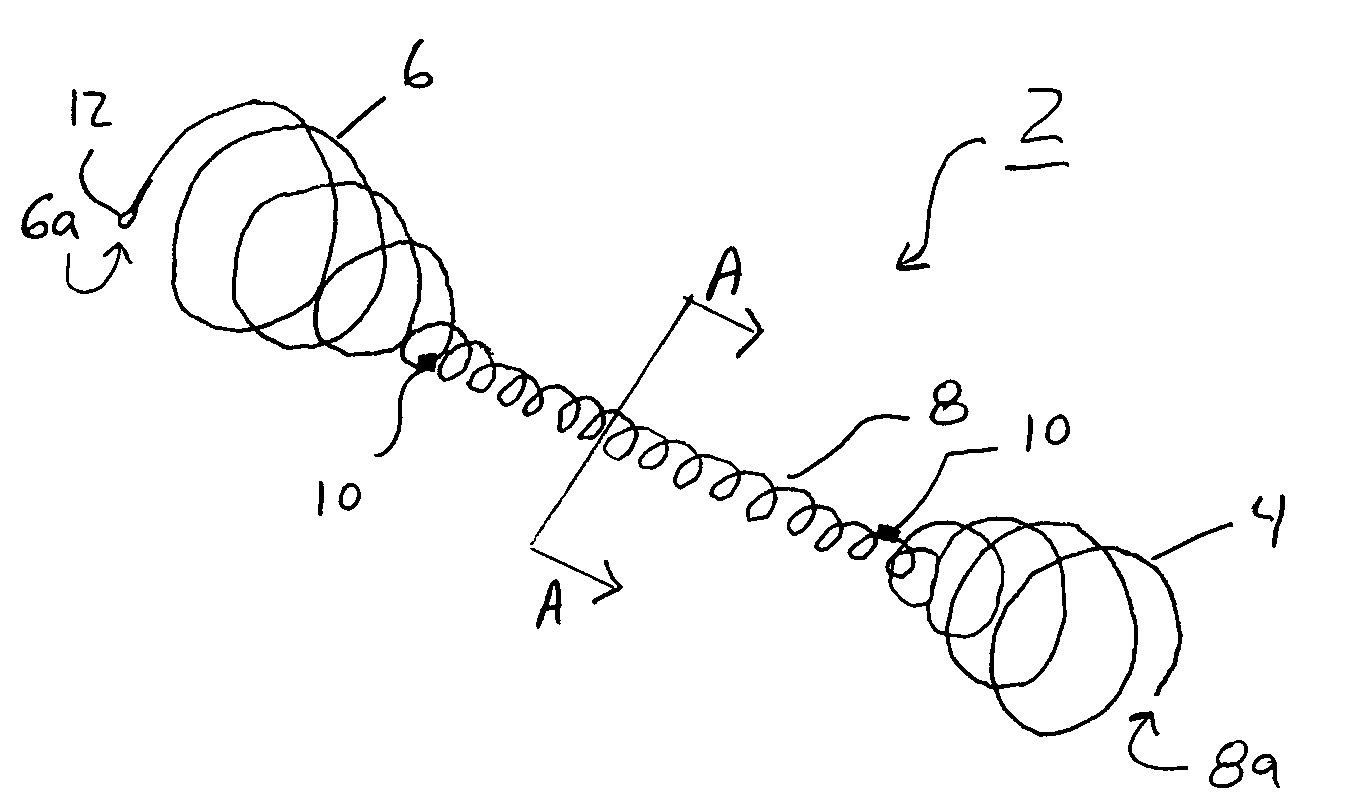
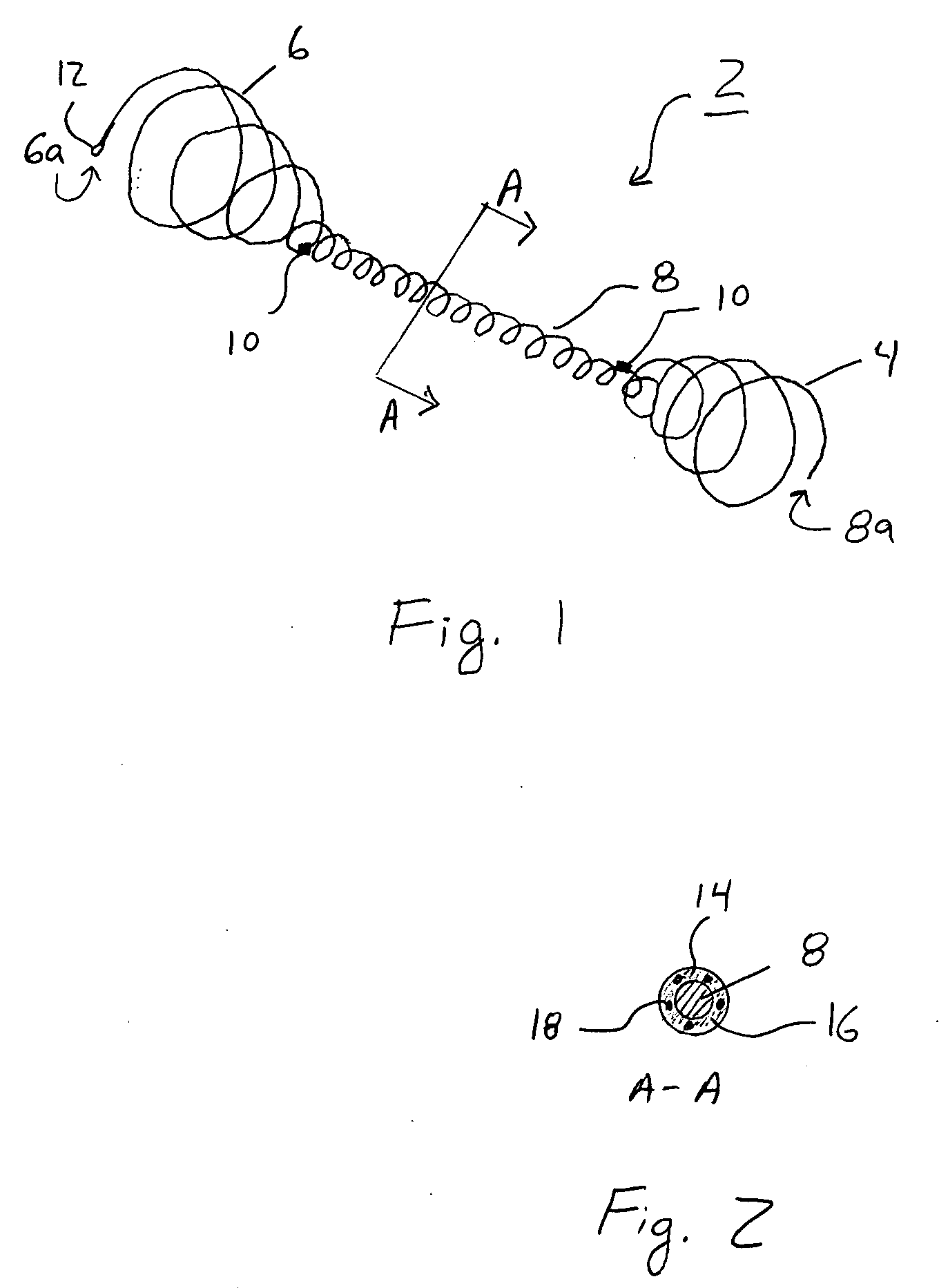
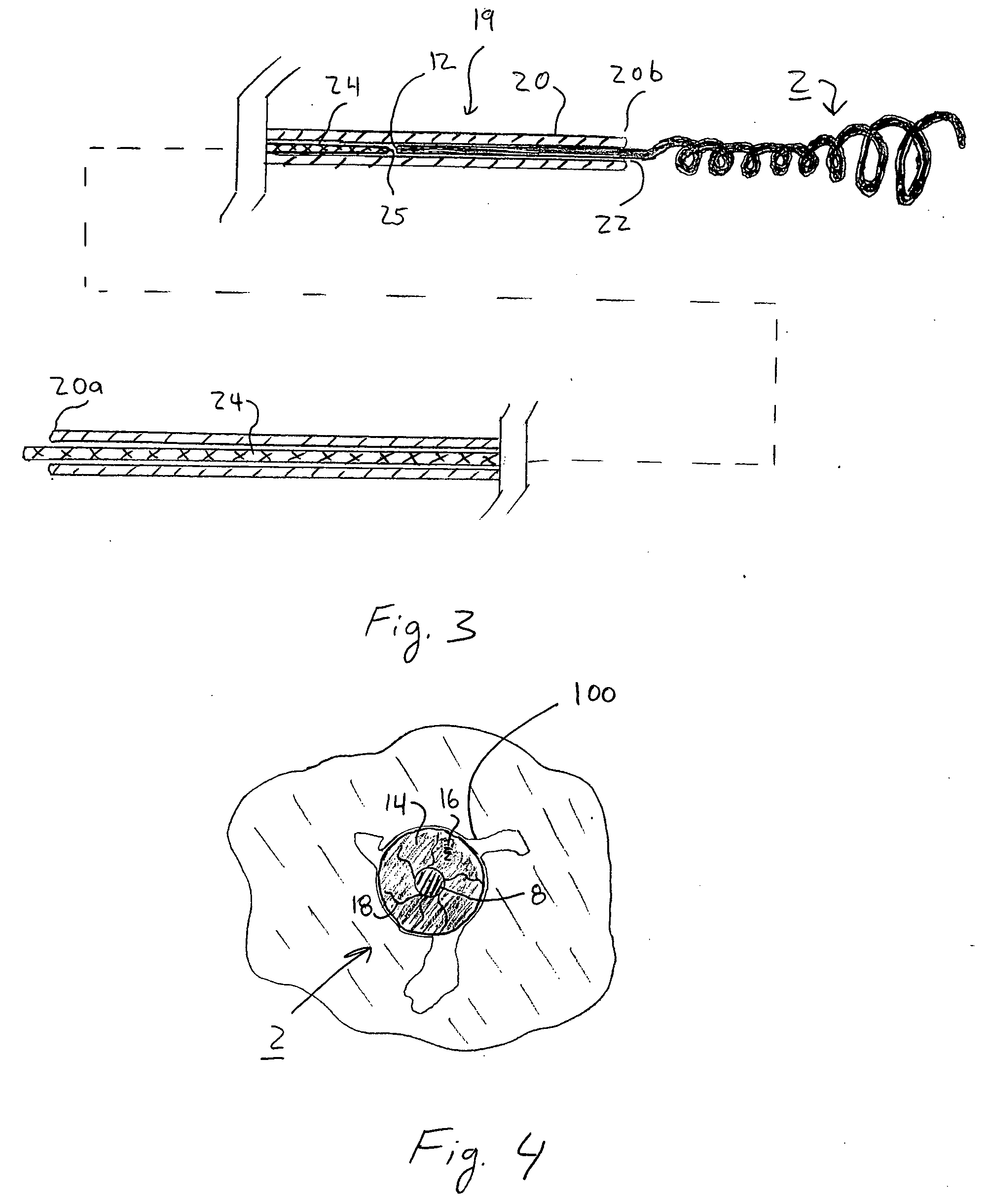
Devices and methods for crossing a chronic total occlusion
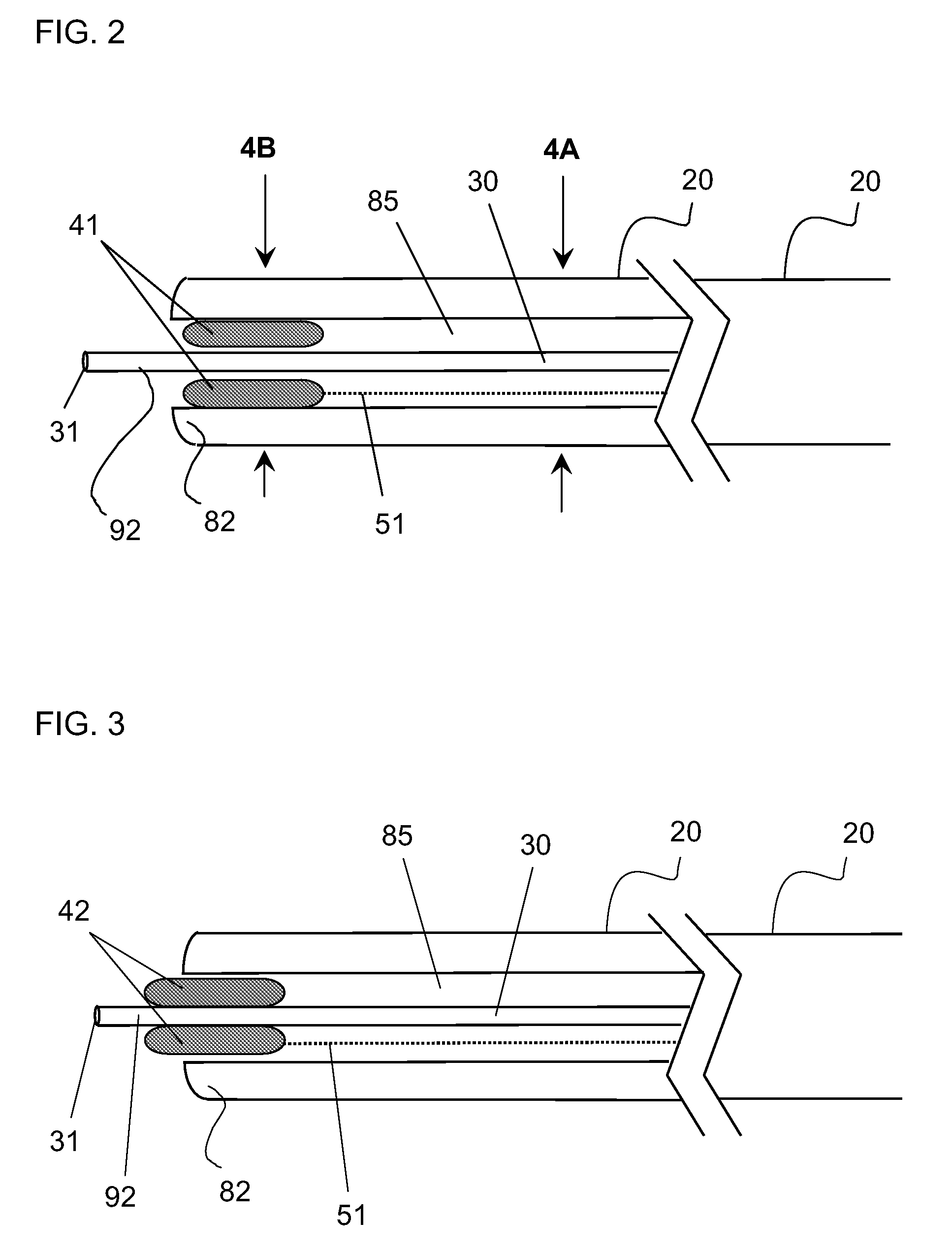
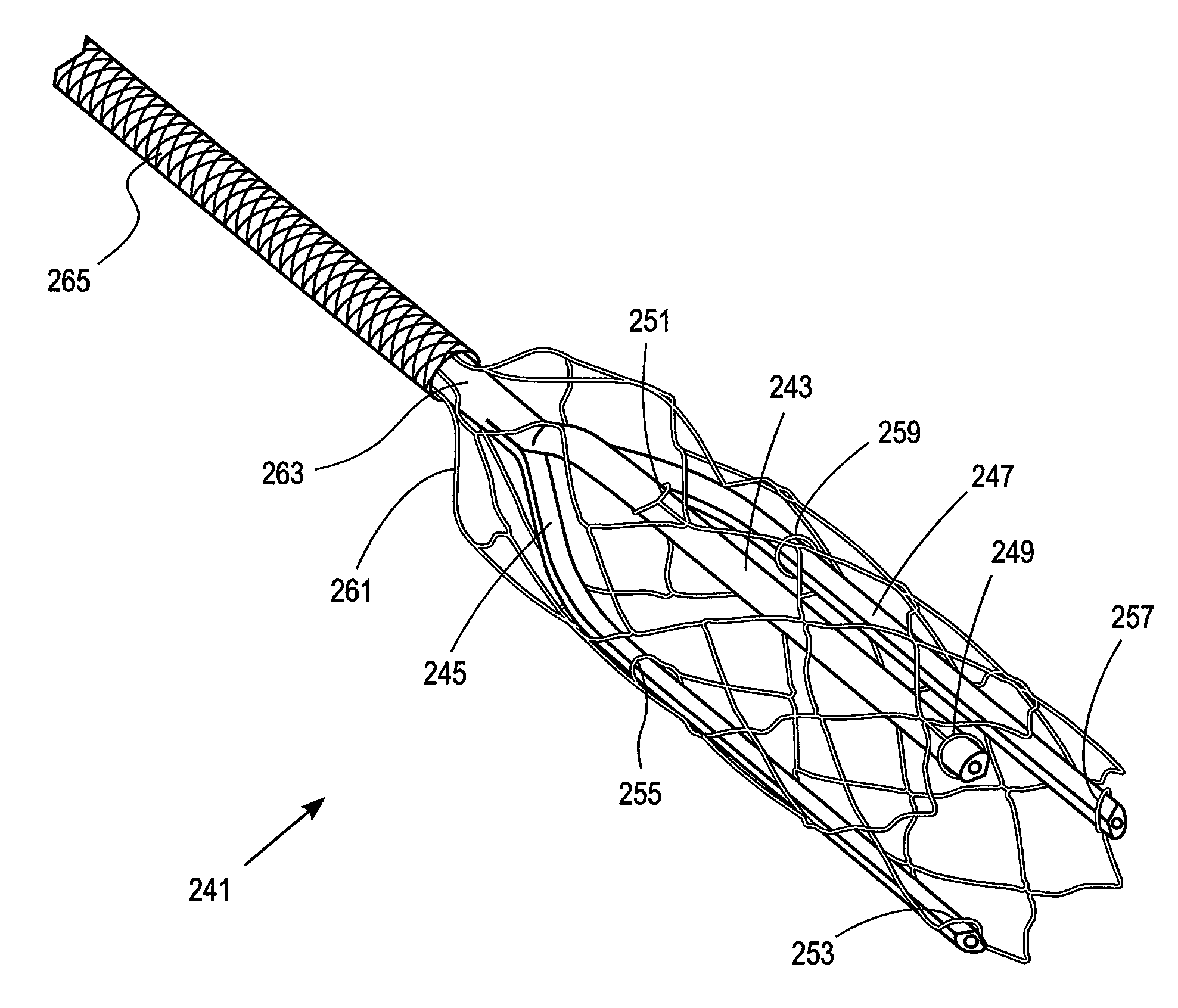
ActiveUS20050049574A1Increase pitchTendency increaseStentsBalloon catheterTotal occlusionHelical coil
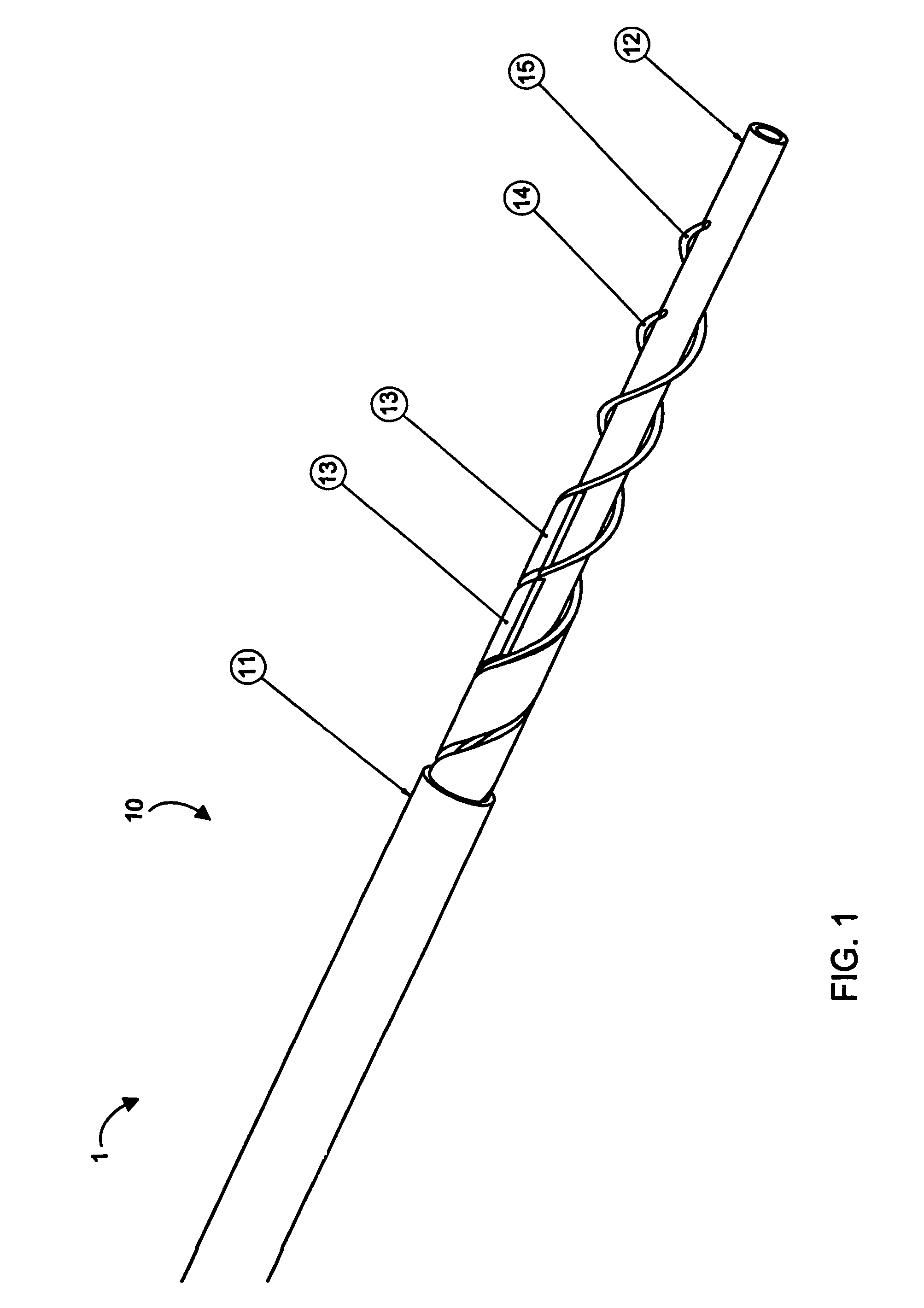
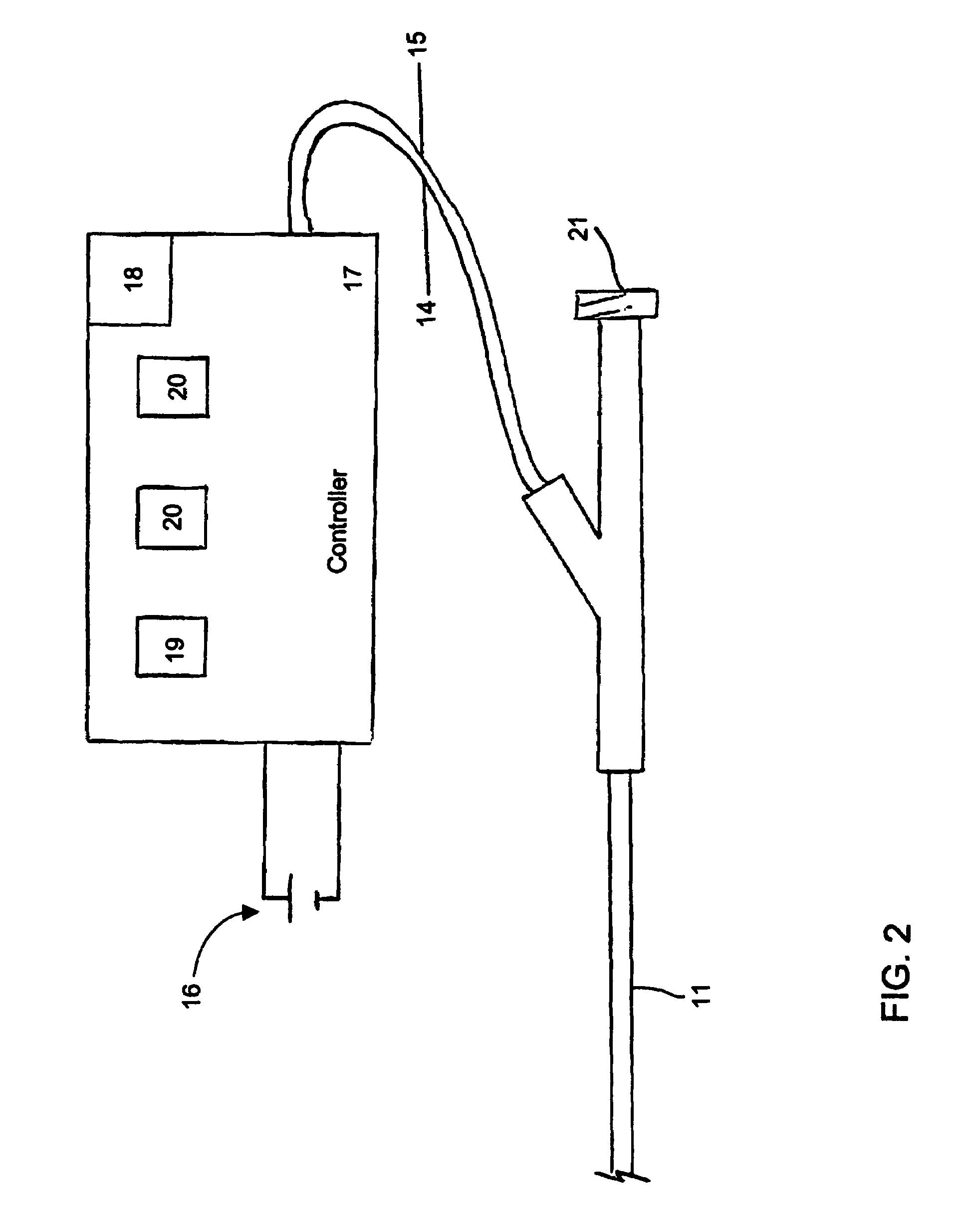
A catheter comprising an elongate tubular member having a proximal end and a distal end, and a deflectable tip at the distal end of the elongate tubular member. The deflectable tip comprises a first helical coil having a first diameter and a second helical coil having a second diameter, the first diameter being larger than the second diameter. The first and second helical coils are arranged in the manner of a double helix. When viewed in cross-section, the first helical coil and the second helical coil are aligned at a first point on a circumference of each coil and misaligned at a second point on the circumference of each coil, where the second point is approximately 180 degrees from the first point. In certain embodiments the catheter further includes a dilatation balloon. Methods of use for crossing a chronic total occlusion are also described.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC +1
Methods for enhancing fluid flow through an obstructed vascular site, and systems and kits for use in practicing the same
Methods of enhancing fluid flow through a vascular site occupied by a vascular occlusion, as well as systems and kits for use in practicing the same, are provided. In practicing the subject methods, the vascular site is flushed simultaneously with a first dissolution fluid (e.g., an organic matter dissolution fluid and / or an inorganic matter dissolution fluid), and a second dissolution fluid attenuating fluid, where flushing is carried out in a manner such that only a surface of the vascular occlusion is contacted with the non-attenuated dissolution fluid. Examples of dissolution fluid / dissolution fluid attenuating fluid pairs include: (1) oxidizing agent fluid and fluid comprising oxidizable neutralizing agent; (2) surfactant fluid and phosphate buffered saline; (3) acidic solution and phosphate buffered saline; etc. Flushing is carried out in this manner for a period of time sufficient for fluid flow through the vascular site to be enhanced, e.g. increased or established. The subject methods, systems and kits for practicing the same find use in the treatment of a variety of different vascular diseases characterized by the presence of vascular occlusions, including both partial and total occlusions.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
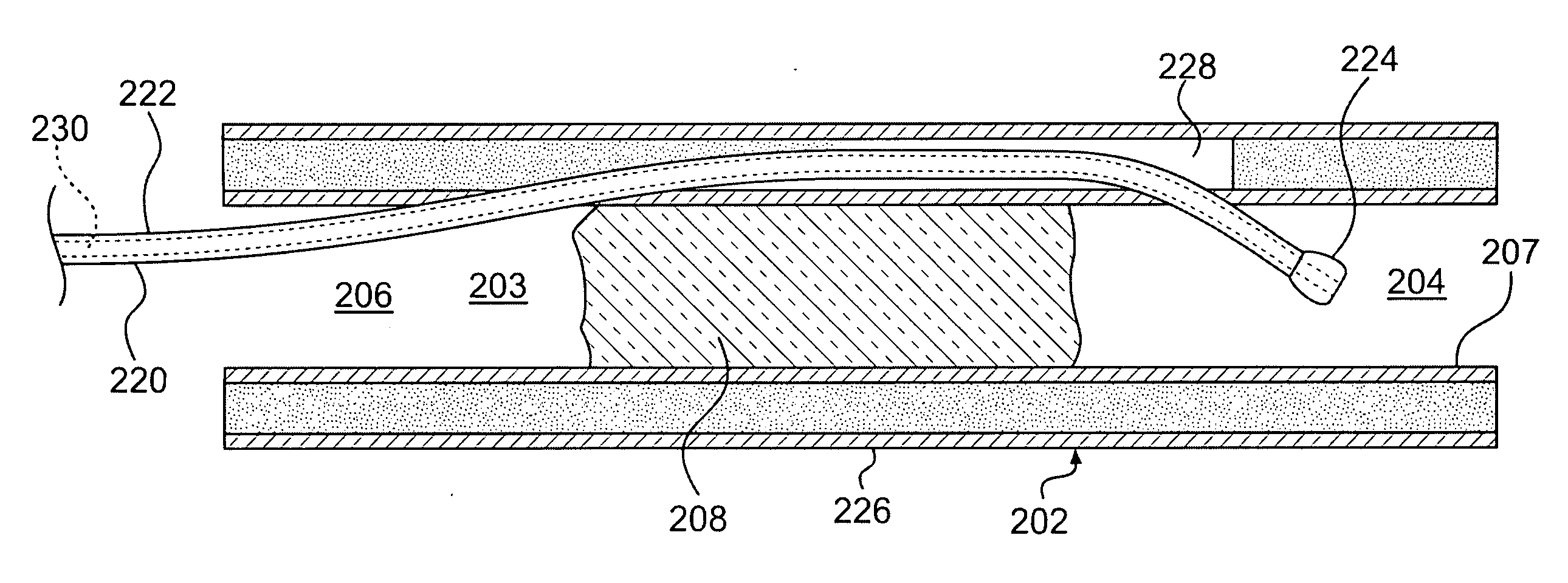
Endovascular devices and methods for exploiting intramural space
ActiveUS20070093780A1Convenient treatmentBypass occlusionStentsMulti-lumen catheterVascular lumenDistal portion
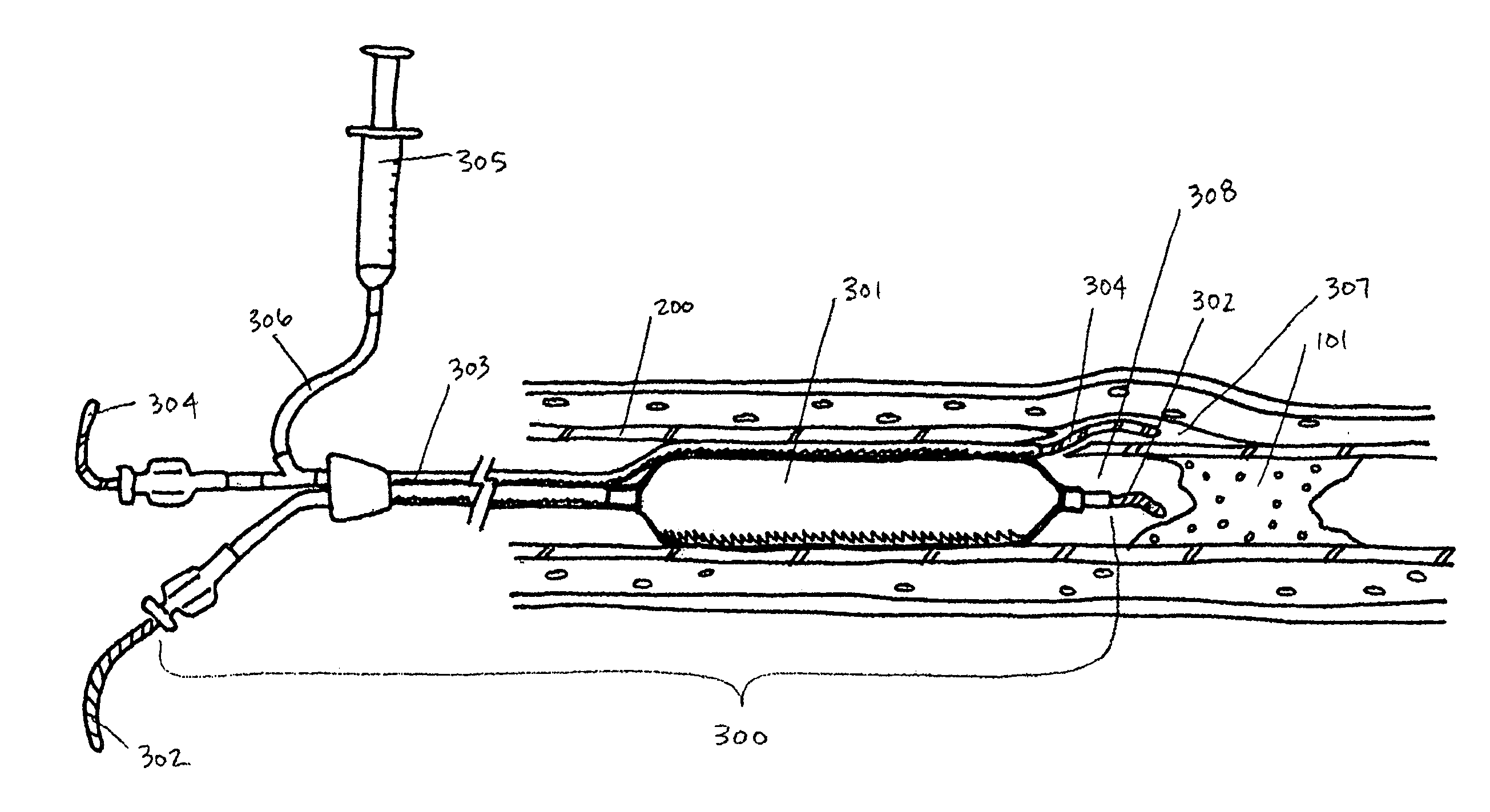
Devices and methods for the treatment of chronic total occlusions are provided. One disclosed embodiment comprises a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method includes providing a first intravascular device having a distal portion with a concave side, inserting the first device into the vascular lumen, positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall, and orienting the concave side of the distal portion toward the vascular lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
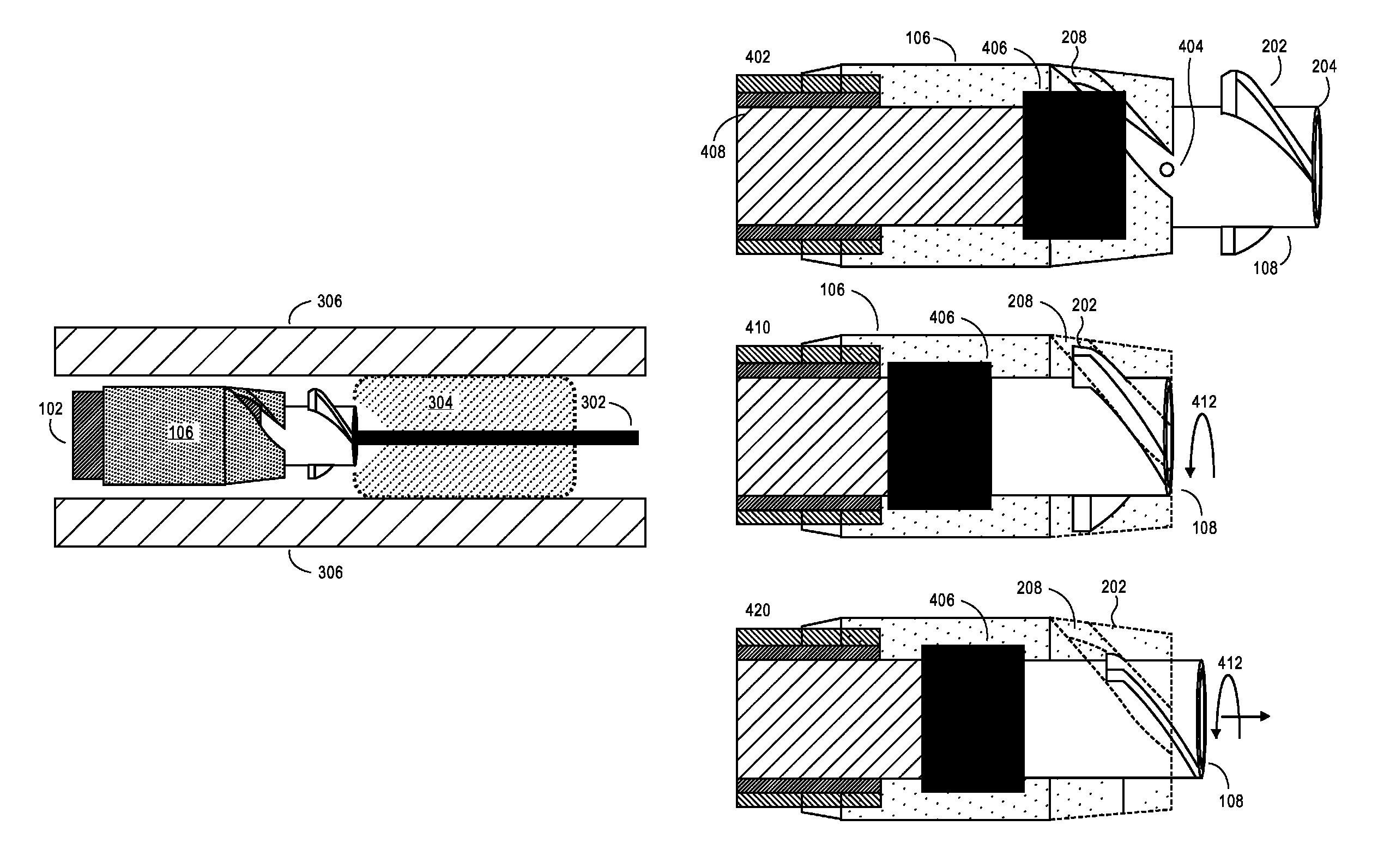
High Torque, Low Profile Catheters and Methods for Transluminal Interventions
ActiveUS20080125748A1Raise the possibilitySmall diameterGuide needlesMulti-lumen catheterBlood vessel occlusionPartial obstruction
Catheter devices having low profile shafts and laterally deployable members (e.g., cannulas, needles, etc.) that may be extended or advanced laterally from the catheter shaft. Also disclosed are methods for bypassing a vascular obstruction (e.g., a chronic total occlusion or other full or partial obstruction) wherein a guidewire is entrapped in a subintimal space adjacent to the obstruction. A catheter of the foregoing character is advanced over the entrapped guidewire and into the subintimal space. The laterally deployable member is then advanced or extended from the subintimal space back into the true lumen of the blood vessel distal to the obstruction. A second guidewire is then advanced through or along the laterally deployable member. The catheter and first guidewire are then removed and one or more working device(s) (balloons, atherectomy devices, setnts, etc.) is / are advanced over the second guidewire and used to establish a subintimal bypass channel through which blood may flow around the obstruction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Low Profile Catheters and Methods for Treatment of Chronic Total Occlusions and Other Disorders
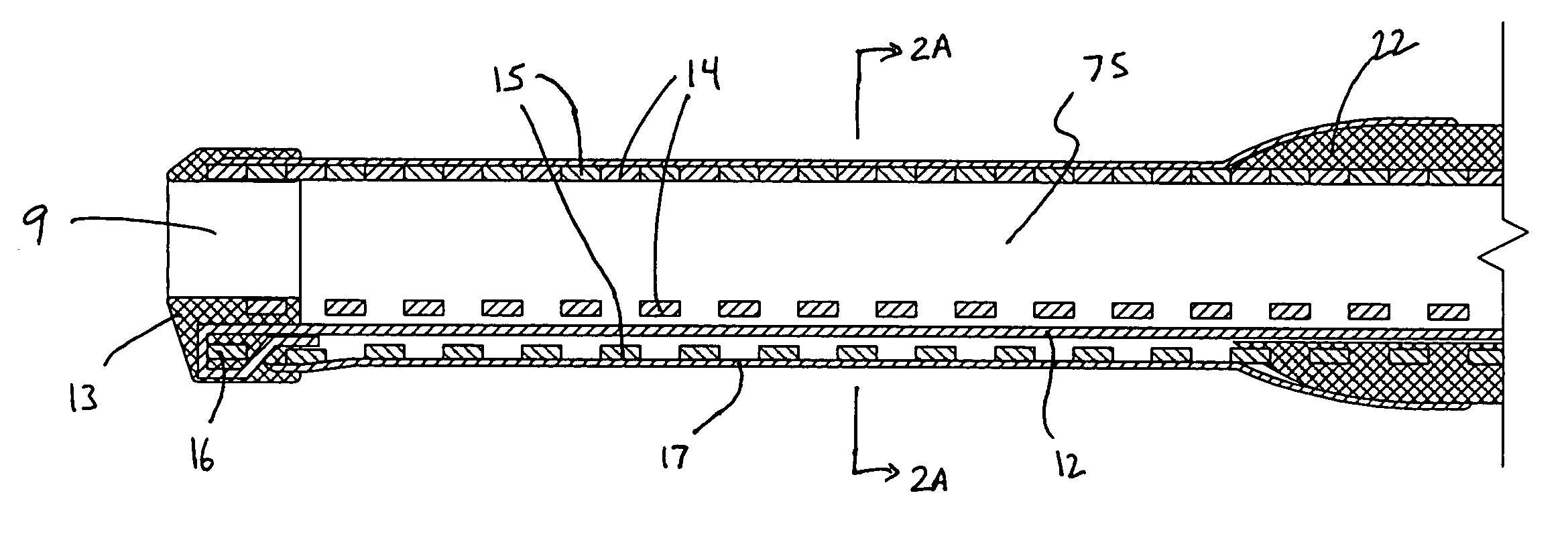
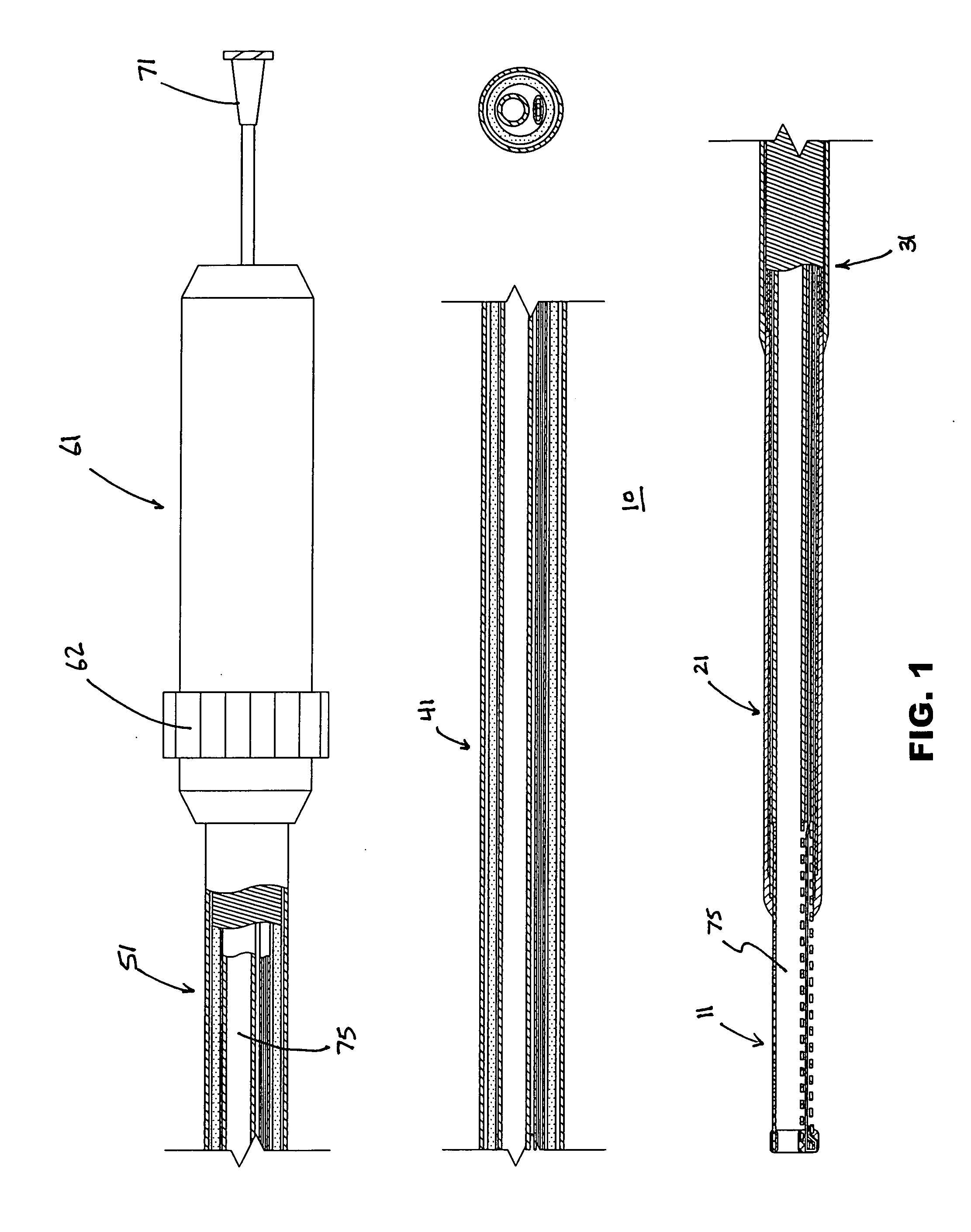
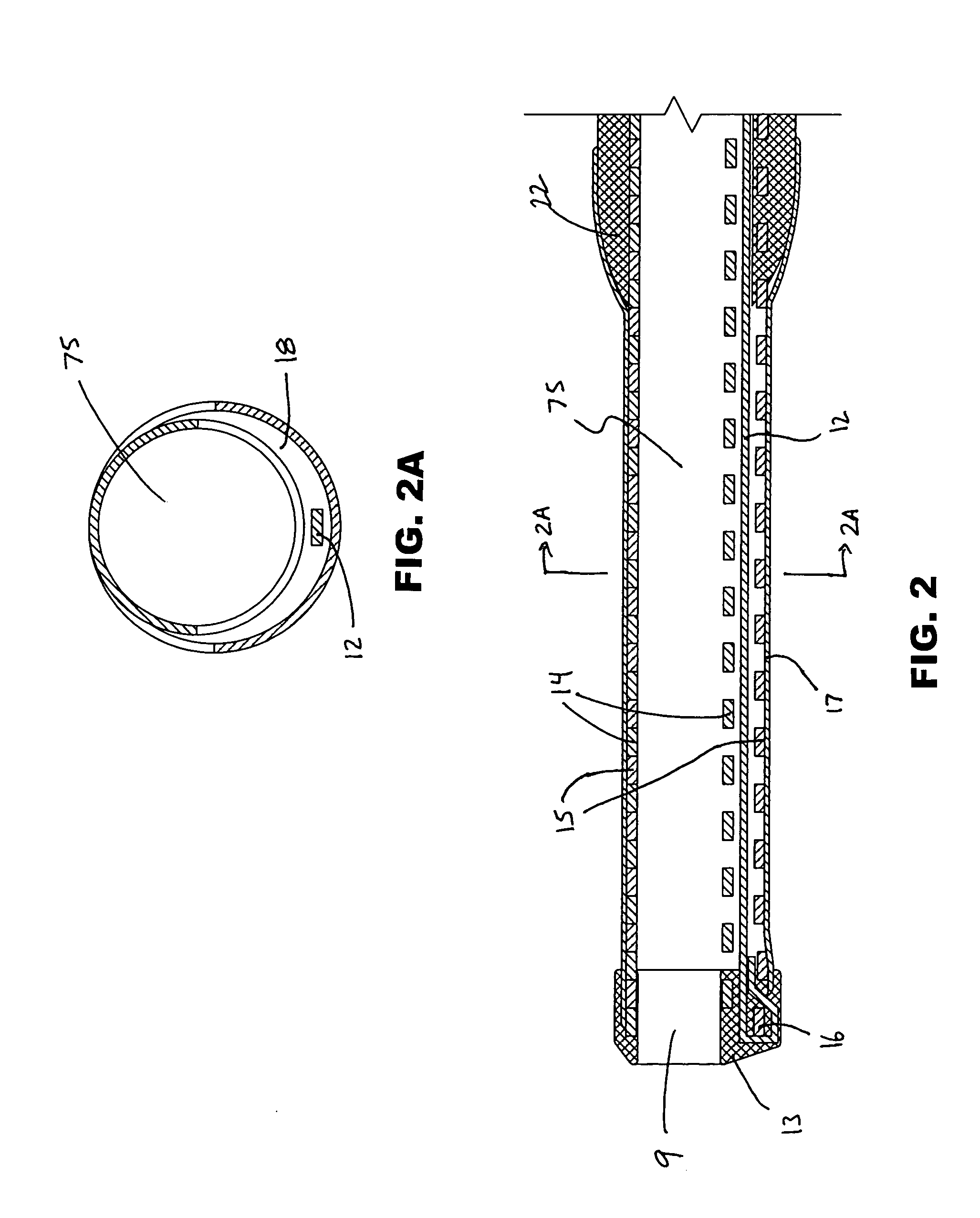
A catheter having a lumen with a distal end opening and a side opening. A tubular member (e.g., needle or other cannula) is moveable between a retracted position where it is within the catheter lumen proximal to the side opening and an extended position where it extends out of the side opening. When the tubular member is in its retracted position its lumen is substantially coaxial with the catheter lumen such that a guidewire may extend through the lumen of the tubular member and out of the distal end opening of the catheter. The guidewire may then be retracted into the lumen of the tubular member and the tubular member may ten be advanced out of the side opening. Thereafter, the same guidewire (or a different guidewire) may be advanced out of the distal end of the tubular member. Also disclosed are methods for using such catheter to redirect a guidewire or other member and for bypassing an obstruction in a blood vessel such as a chronic total occlusion (CTO) of an artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Catheter System and Method for Boring through Blocked Vascular Passages
A rotating cutting head catheter for passage through chronic total occlusions or other refractory atherosclerotic plaque from diseased arteries is disclosed. The catheter's rotating cutting head is designed to reside safely within an outer protective sheath when not in use. The outer protective sheath contains one or more helical groves or slots, and the cutting head contains protruding blades or projections that fit into these helical groves or slots. Application of torque to an inner catheter or wire attached to the cutting head applies spin to the cutting head, and the force of the sheath's helical groves or slots against the cutting head's protruding blades or projections advances the cutting head outward from the protective sheath. Once extended, the cutting head may now rotate freely. The device may use a guidewire to direct the cutting head to the desired position.
Owner:AVINGER
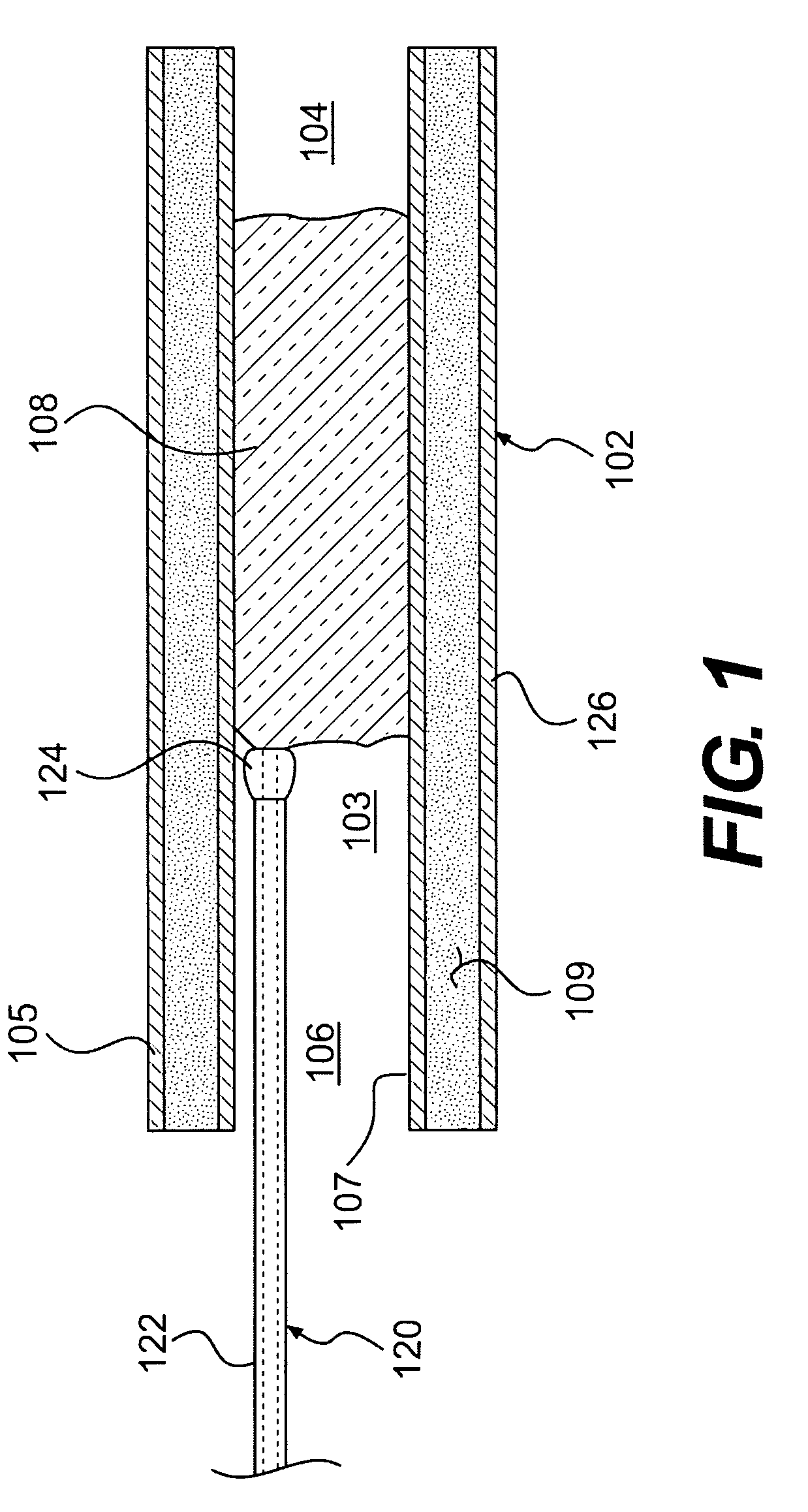
Endovascular devices and methods
Devices and methods for the treatment of chronic total occlusions are provided. One disclosed embodiment comprises a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method includes providing an intravascular device having a distal portion with a side port, inserting the device into the vascular lumen, positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall, directing the distal portion within the vascular wall such that the distal portion moves at least partially laterally, and directing the side port towards the vascular lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
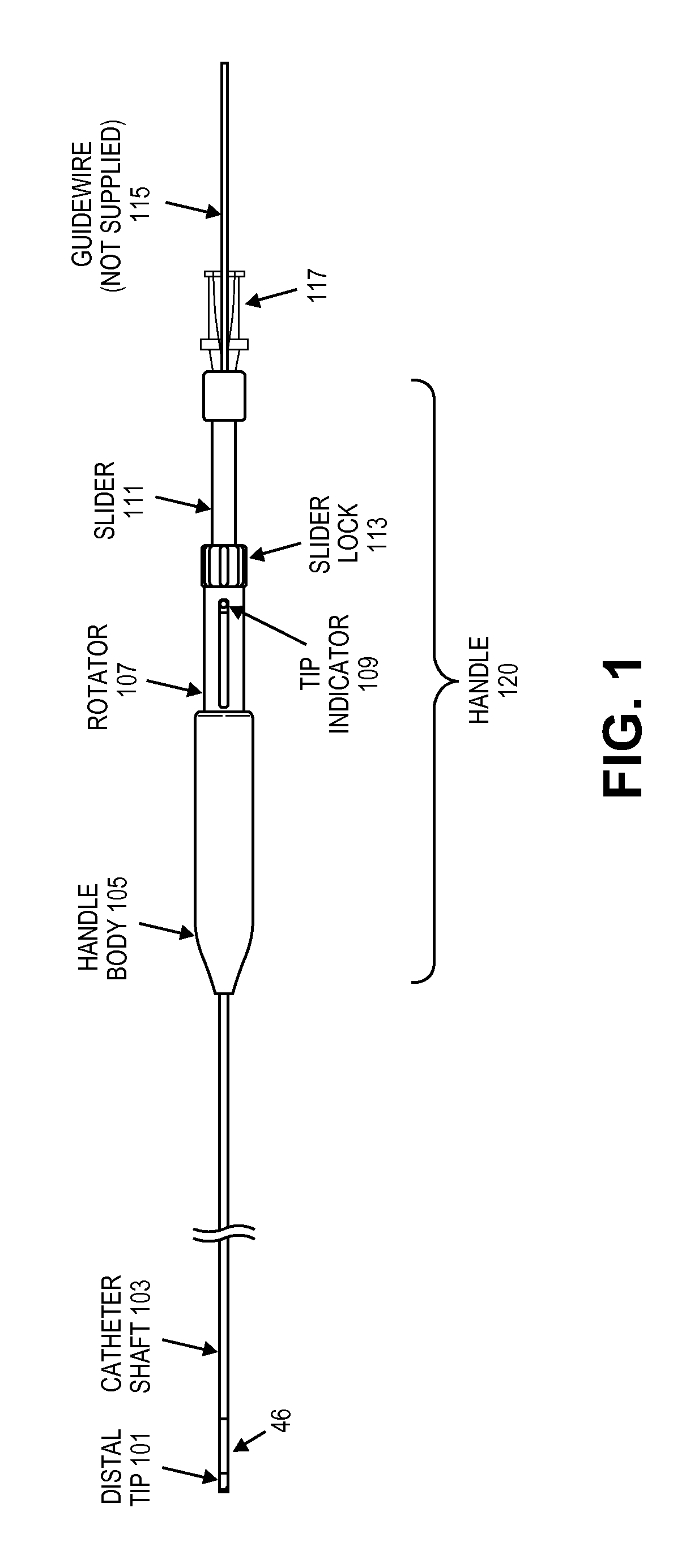
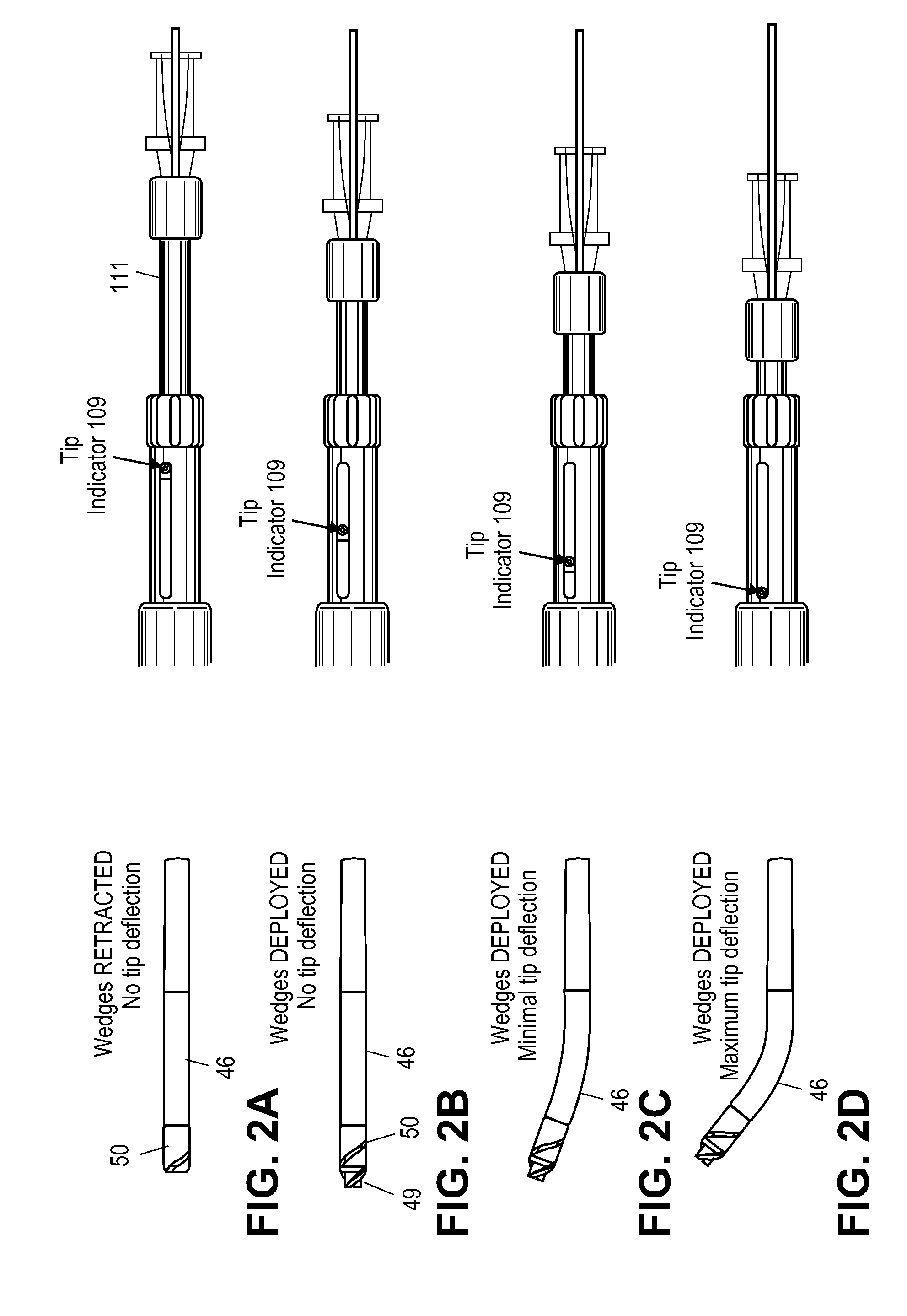
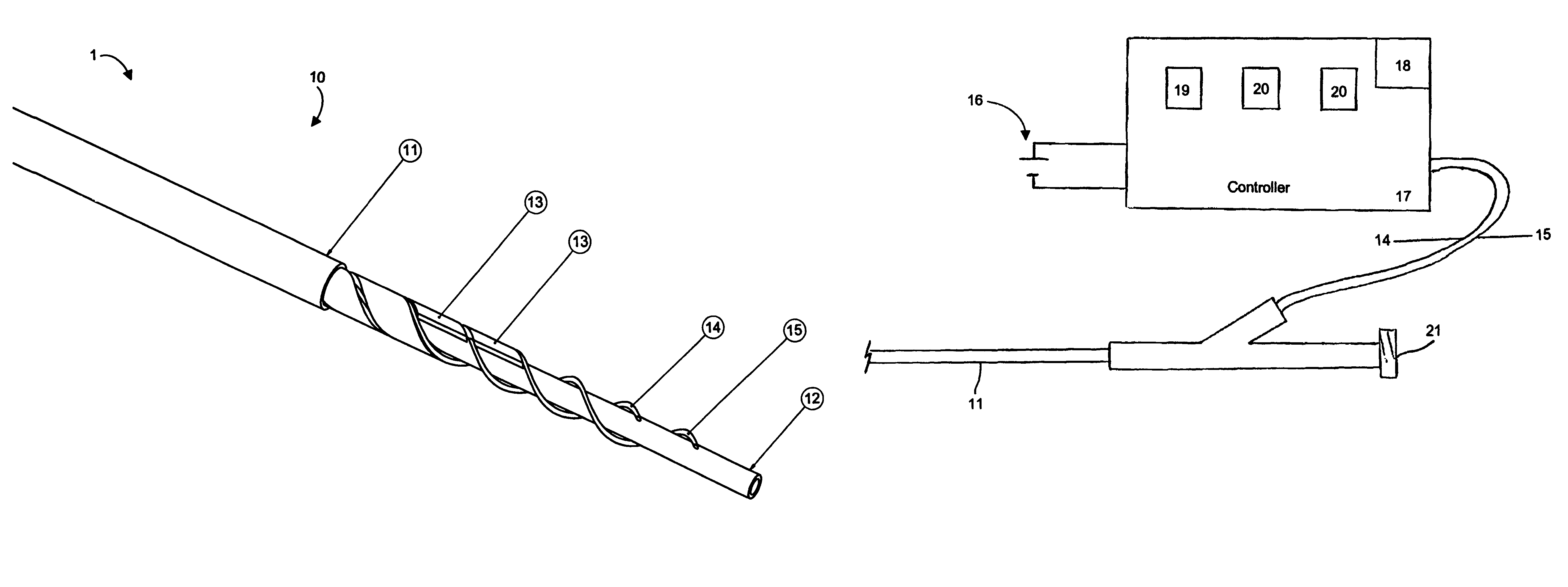
Guidewire support catheter
ActiveUS20100274270A1Better engagementAvoid attenuationEar treatmentCannulasTotal occlusionClockwise
Described herein are guidewire positioning and support devices, method for using them, method of treating a subject using them, and systems including such guidewire positioning and support devices. These devices typically include a rotatable distal tip region that may include one or more wedges. The wedges may be extendable from the rotatable distal tip. The distal end of the device may be steerable, and may be steered while still rotating the distal end of the device. The wedges (which may include sharp forward-cutting blades and blunt lateral portions) can be extended from the distal housing and locked in any position (extended, partially extended or retracted) and rotated clockwise and / or counterclockwise while locked in a retracted, extended or partially extended position. The distal region of the device may also be controllable steered from the proximal end of the device. Systems including these guidewire support catheters are also described, as are method of using them, including methods of treating chronic total occlusions.
Owner:AVINGER
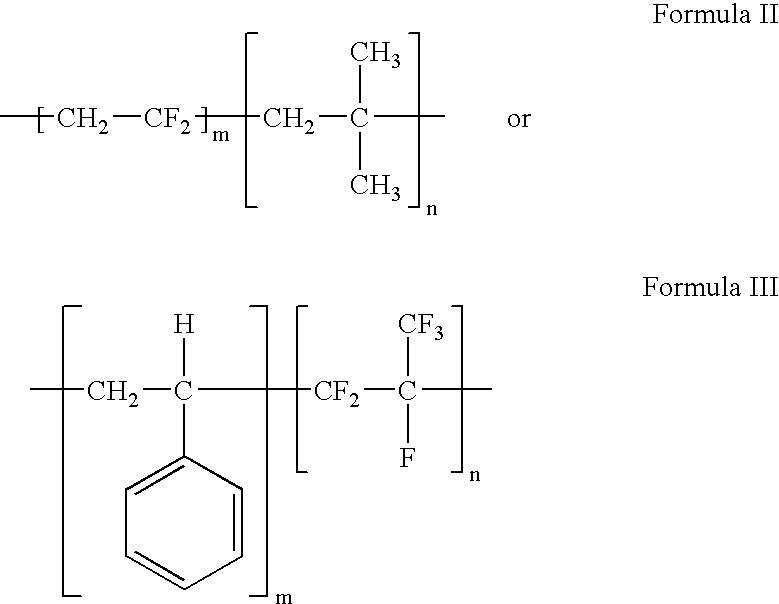
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers
InactiveUS20060134165A1Provide mechanical strengthGive flexibilityStentsSurgeryAbnormal tissue growthPolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer formed of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form an implantable device such as a stent or a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent, which can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Methods for enhancing fluid flow through an obstructed vascular site, and systems and kits for use in practicing the same
Methods of enhancing fluid flow through a vascular site occupied by a vascular occlusion, as well as systems and kits for use in practicing the same, are provided. In practicing the subject methods, the vascular site is flushed simultaneously with a first dissolution fluid (e.g., an organic matter dissolution fluid and / or an inorganic matter dissolution fluid), and a second dissolution fluid attenuating fluid, where flushing is carried out in a manner such that only a surface of the vascular occlusion is contacted with the non-attenuated dissolution fluid. Examples of dissolution fluid / dissolution fluid attenuating fluid pairs include: (1) oxidizing agent fluid and fluid comprising oxidizable neutralizing agent; (2) surfactant fluid and phosphate buffered saline; (3) acidic solution and phosphate buffered saline; etc. Flushing is carried out in this manner for a period of time sufficient for fluid flow through the vascular site to be enhanced, e.g. increased or established. The subject methods, systems and kits for practicing the same find use in the treatment of a variety of different vascular diseases characterized by the presence of vascular occlusions, including both partial and total occlusions.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Endovascular devices and methods for exploiting intramural space
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and methods for crossing a chronic total occlusion
A catheter comprises an elongate tubular member having a proximal end and a distal end, and a deflectable tip at the distal end of the elongate tubular member. The deflectable tip comprises a first helical coil having a first diameter and a second helical coil having a second diameter, the first diameter being larger than the second diameter. The first and second helical coils are arranged in the manner of a double helix. When viewed in cross-section, the first helical coil and the second helical coil are aligned at a first point on a circumference of each coil and misaligned at a second point on the circumference of each coil, where the second point is approximately 180 degrees from the first point. In certain embodiments the catheter further includes a dilatation balloon. Methods of use for crossing a chronic total occlusion are also described.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC +1
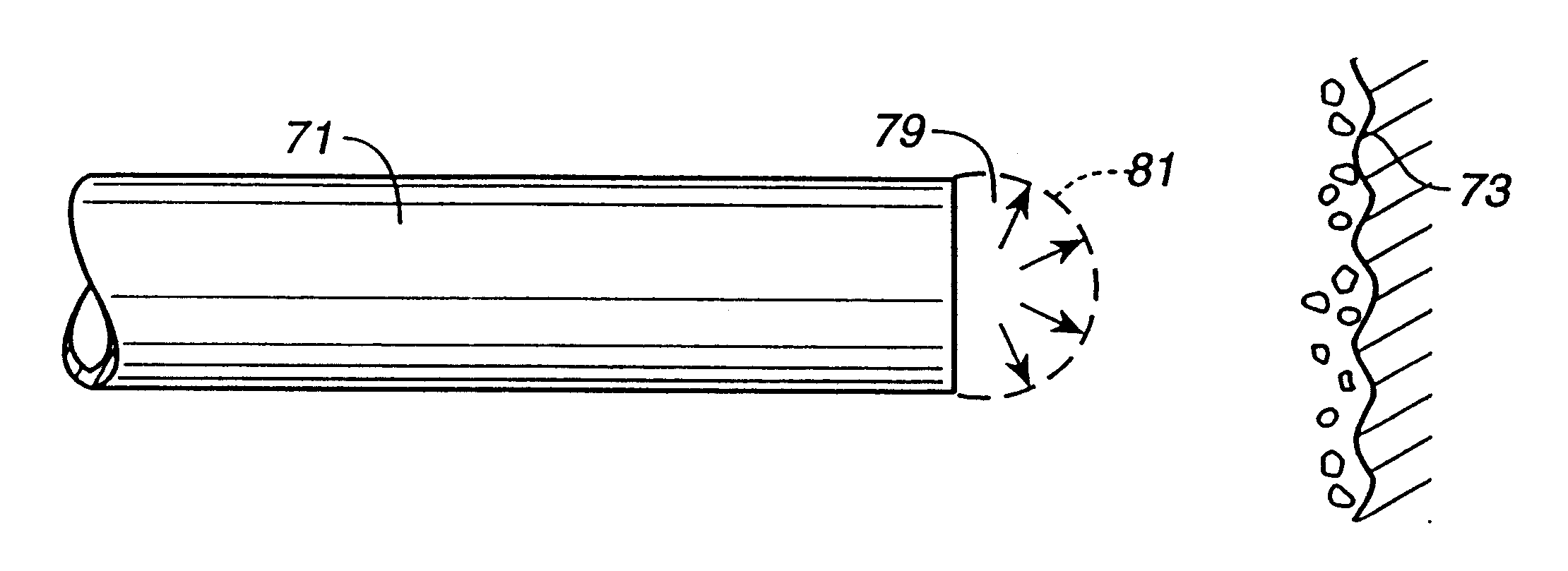
Photoacoustic removal of occlusions from blood vessels
Partial or total occlusions of fluid passages within the human body are removed by positioning an array of optical fibers in the passage and directing treatment radiation pulses along the fibers, one at a time, to generate a shock wave and hydrodynamic flows that strike and emulsify the occlusions. A preferred application is the removal of blood clots (thrombi and emboli) from small cerebral vessels to reverse the effects of an ischemic stroke. The operating parameters and techniques are chosen to minimize the amount of heating of the fragile cerebral vessel walls occurring during this photoacoustic treatment. One such technique is the optical monitoring of the existence of hydrodynamic flow generating vapor bubbles when they are expected to occur and stopping the heat generating pulses propagated along an optical fiber that is not generating such bubbles.
Owner:SELVA MEDICAL +2
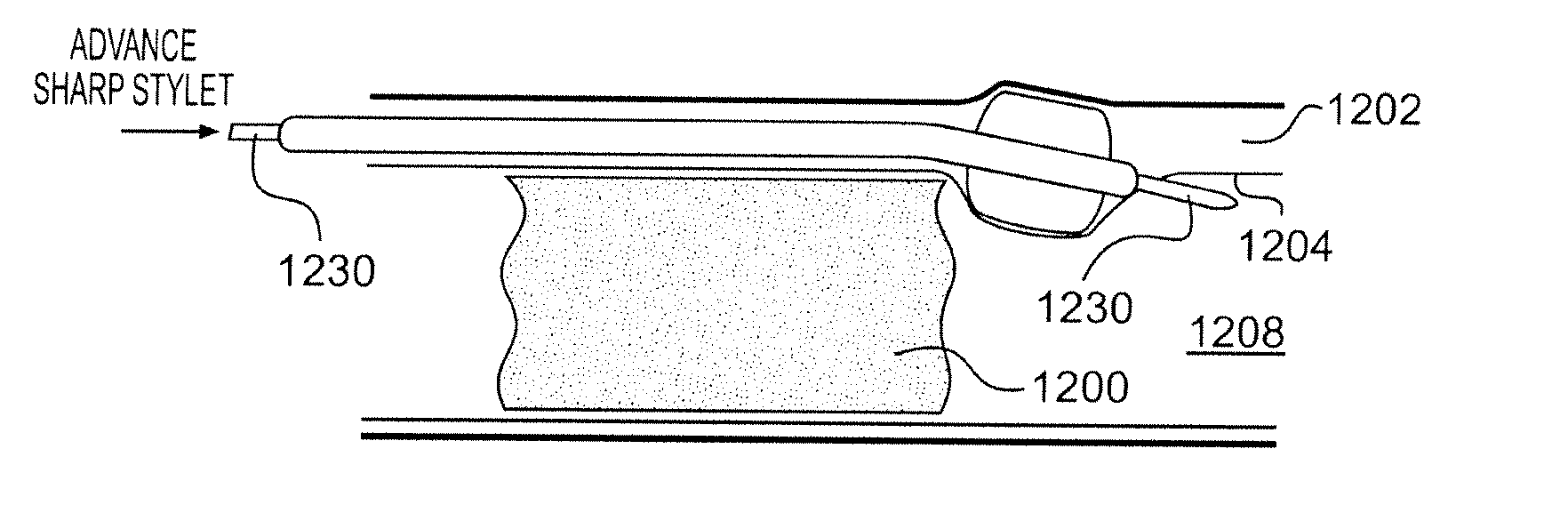
Total occlusion recanalization facilitating device
InactiveUS20050216044A1Easy to insertEnsure safetyMulti-lumen catheterCannulasTotal occlusionComplete occlusion
Owner:HONG MUN K
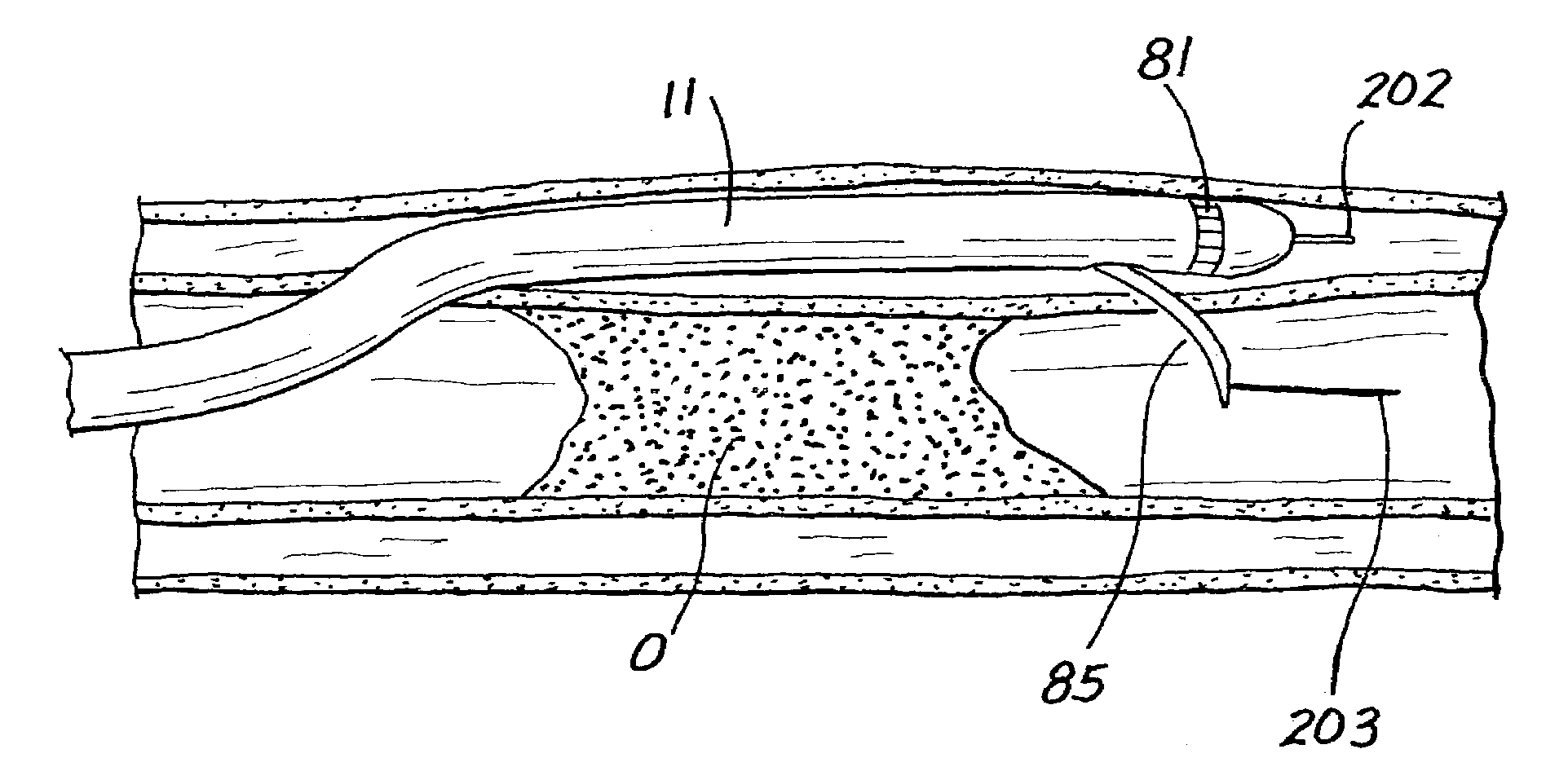
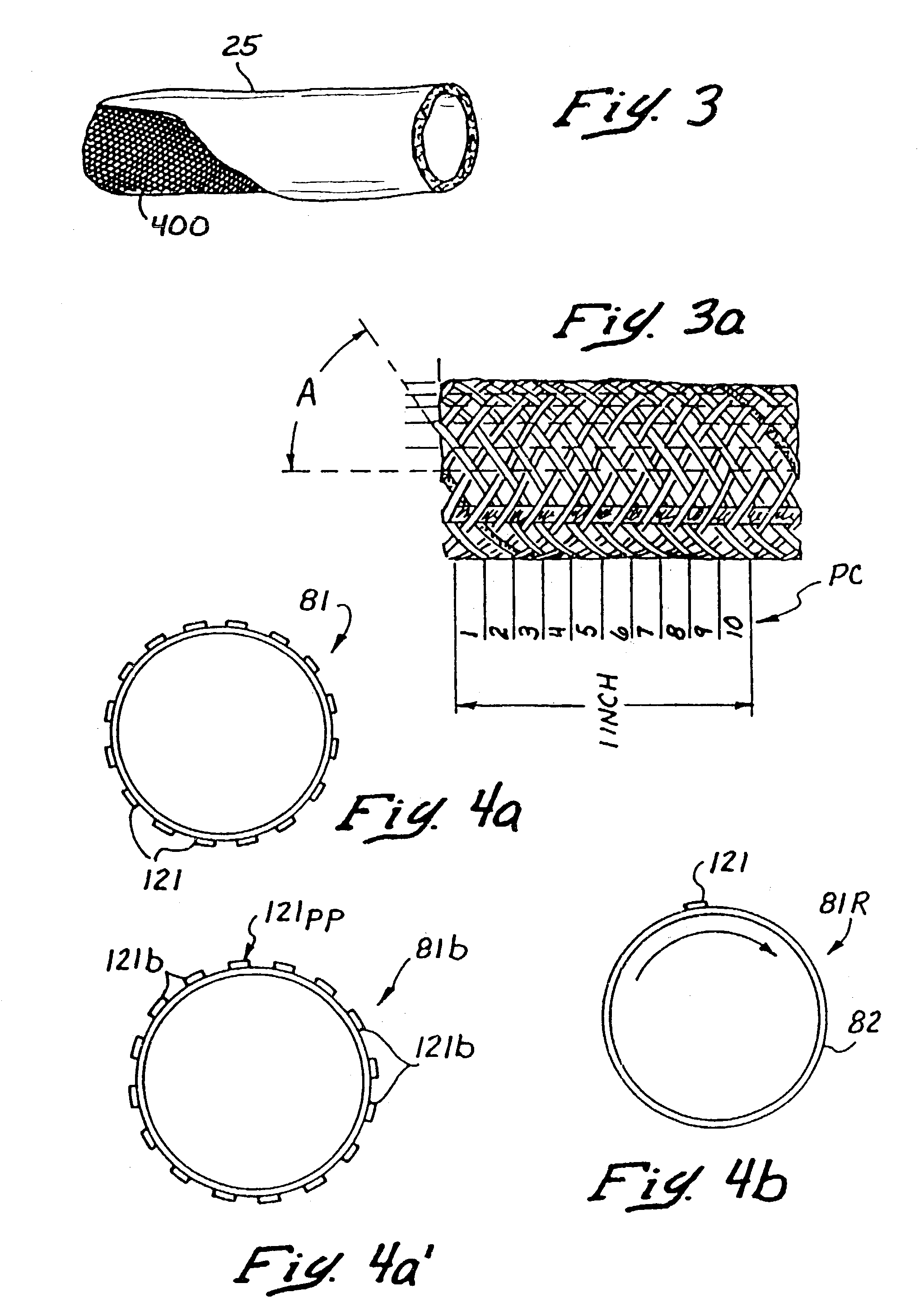
Catheter with controllable stiffness and method for operating a selective stiffening catheter
InactiveUS7559916B2Force applied by the tools on the treatment site can be enhanced and increasedEfficiently advance the guide or crossing wiresMedical devicesCatheterPower controllerTotal occlusion
Owner:SYN VARIFLEX LLC
Endovascular devices and methods
Devices and methods for the treatment of chronic total occlusions are provided. One disclosed embodiment comprises a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method includes providing an intravascular device having a distal portion with a side port, inserting the device into the vascular lumen, positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall, directing the distal portion within the vascular wall such that the distal portion moves at least partially laterally, and directing the side port towards the vascular lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fallopian tube occlusion devices and methods
InactiveUS20070056591A1Safe and effectiveSafe and effective sterilizationFallopian occludersFemale contraceptivesOvulation timesObstetrics
A contraceptive device for placement in a fallopian tube includes expanding distal and proximal anchor members and an expandable elongate member connecting the distal anchor member to the proximal anchor member. An expandable material is disposed on at least a portion of the contraceptive device, whereupon delivery of the contraceptive device, the expandable material expands to completely occlude the fallopian tube. The expandable material may contain a drug, therapeutic agent, or hormone which is released over time to occlude or otherwise prevent the passage of spermazoa through the fallopian tube, or prevent ovulation. The contraceptive device may be delivered non-operatively and provide complete sterilization within a period of days. The device and delivery method obviates the need for follow-up visits to confirm closure of the fallopian tubes.
Owner:MCSWAIN HUGH
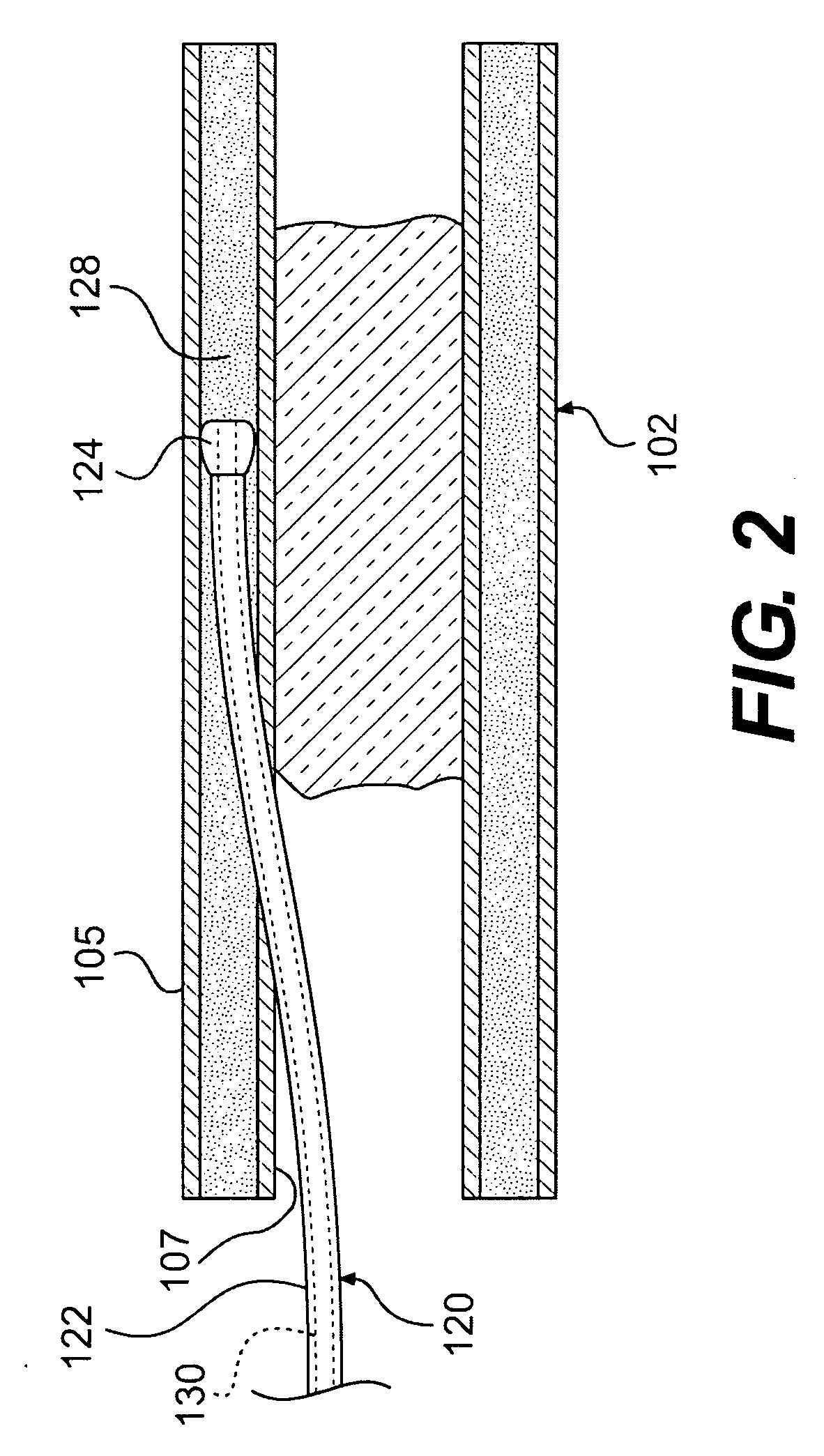
Endovascular devices and methods
ActiveUS20070093783A1Wire advancementAvoid problemsGuide wiresSurgical needlesVascular lumenDistal portion
Devices and methods for the treatment of chronic total occlusions are provided. One disclosed embodiment comprises a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method includes providing an intravascular device having a distal portion with a lumen extending therein; inserting the device into the vascular lumen; positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall; and directing the distal portion within the vascular wall.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Forming vascular diseases within anatomical models
InactiveUS20080076101A1Improve radial strengthArtificial flowers and garlandsSynthetic resin layered productsVascular diseaseAnatomical structures
Anatomical models are provided with simulated plaque, lesion, chronic total occlusion, as well as other vascular diseases that more accurately replicate these abnormalities. In such embodiment, the vascular disease may be formed separate from the structured anatomical model. The formed vascular disease material may then be bonded to or within a PVA material in a separate process from forming this simulated vascular disease, thus providing a replicated specific anatomy structure with an abnormality for demonstrating, testing, and / or developing medical functions and / or devices.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
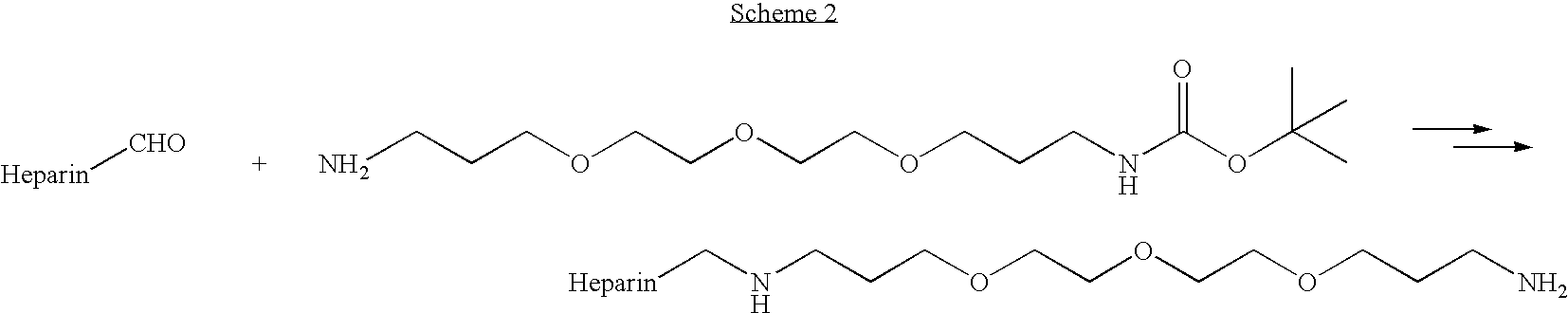
Antifouling heparin coatings
A medical device comprising a coating thereon comprising a biocompatible polymer and heparin is provided herein. Heparin is coupled with the biocompatible polymer via a spacer having a grouping that renders a binding site of the heparin molecule accessible by a binding protein. The medical device can be implanted in a human being for the treatment of a disease such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Methods and devices for crossing chronic total occlusions
The present disclosure is directed to a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method may include providing an intravascular device having a distal portion and a longitudinal axis and inserting the intravascular device into the vascular lumen. The method may further include positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall, rotating the intravascular device about the longitudinal axis, and advancing the intravascular device within the vascular wall.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Catheter apparatus and methods for treating vasculatures
InactiveUS7988646B2Efficiently and effectively passingGuide needlesBalloon catheterTotal occlusionBlood vessel
Owner:ROXWOOD MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device to treat chronic total occlusions
InactiveUS20050119679A1Effective timeSimple, user-friendlyUltrasound therapyCannulasCavitationTotal occlusion
An apparatus and method for using an ultrasonic medical device to treat chronic total occlusions comprises an ultrasonic probe, a transducer, a coupling engaging a proximal end of the ultrasonic probe to a distal end of the transducer and an ultrasonic energy source engaged to the transducer. The ultrasonic probe is inserted into a vasculature and placed in communication with the chronic total occlusion. The ultrasonic energy source produces an ultrasonic energy that is transmitted to the transducer, where the transducer creates a transverse ultrasonic vibration along the ultrasonic probe. The transverse ultrasonic vibration creates a plurality of transverse nodes and a plurality of transverse anti-nodes along the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe, creating cavitation along a portion of the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe to ablate the chronic total occlusion.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Drug-Eluting Device for Treatment of Chronic Total Occlusions
A drug-eluting medical device and method for treating a chronic total occlusion. The drug-eluting medical device is implanted into the chronic total occlusion and elutes a drug that softens or dissolves the plaque of the occlusion over a period of time. After the medical device has resided in the occlusion for an appropriate period of time such that at least a portion of the chronic total occlusion has been softened or dissolved, a guidewire can cross the occlusion and a procedure such as PTCA can be performed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com