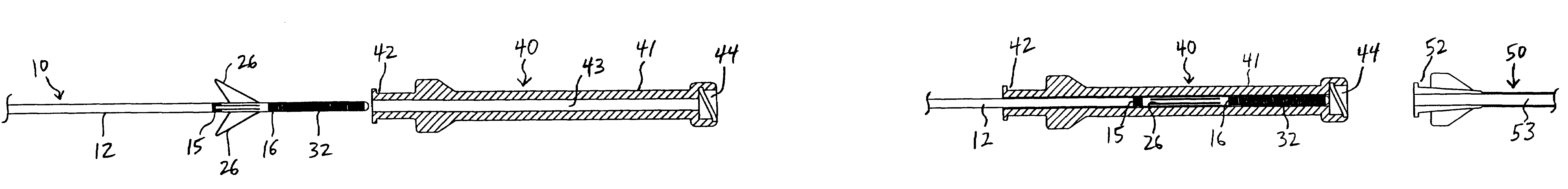Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
753 results about "Cerebral vessel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
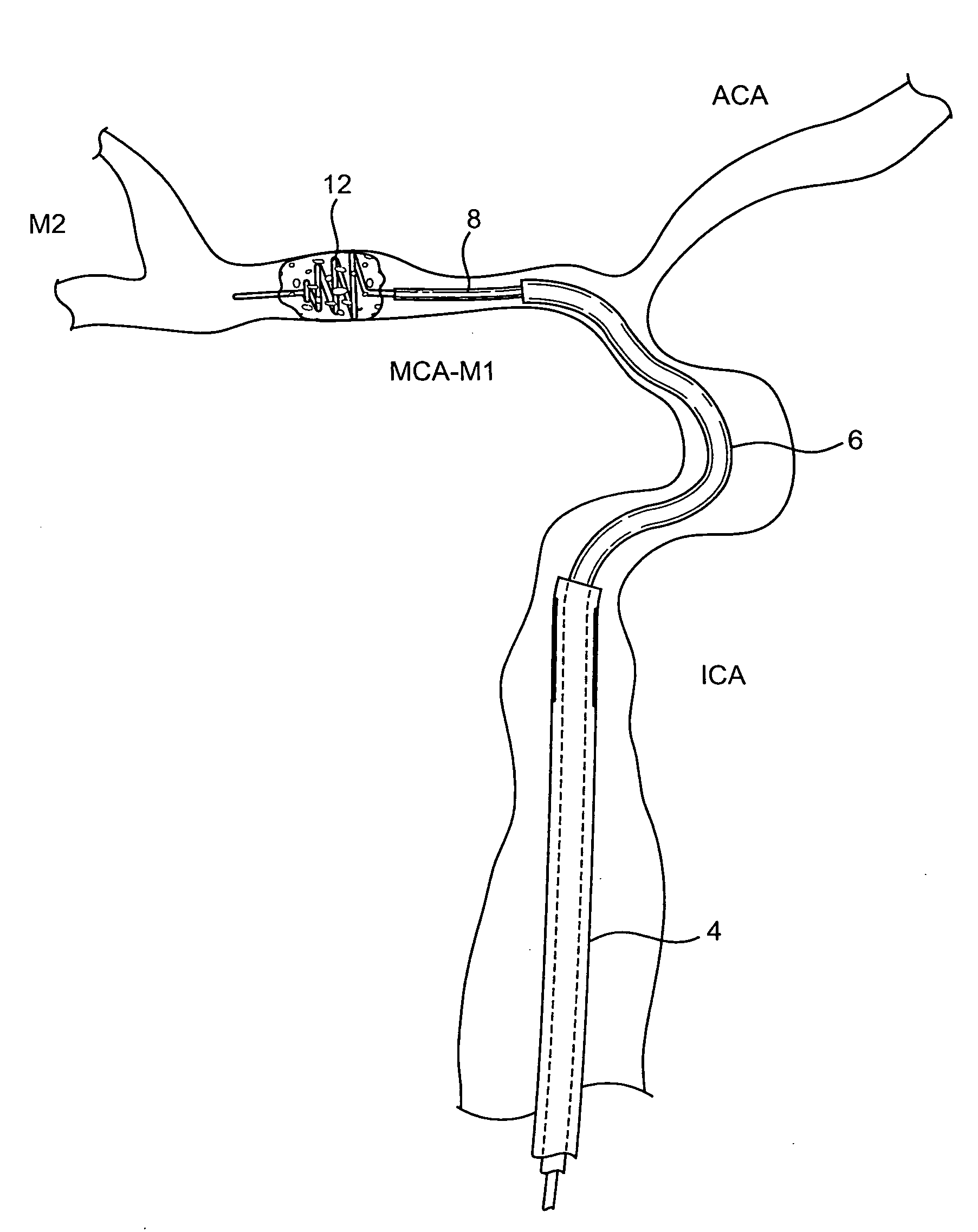
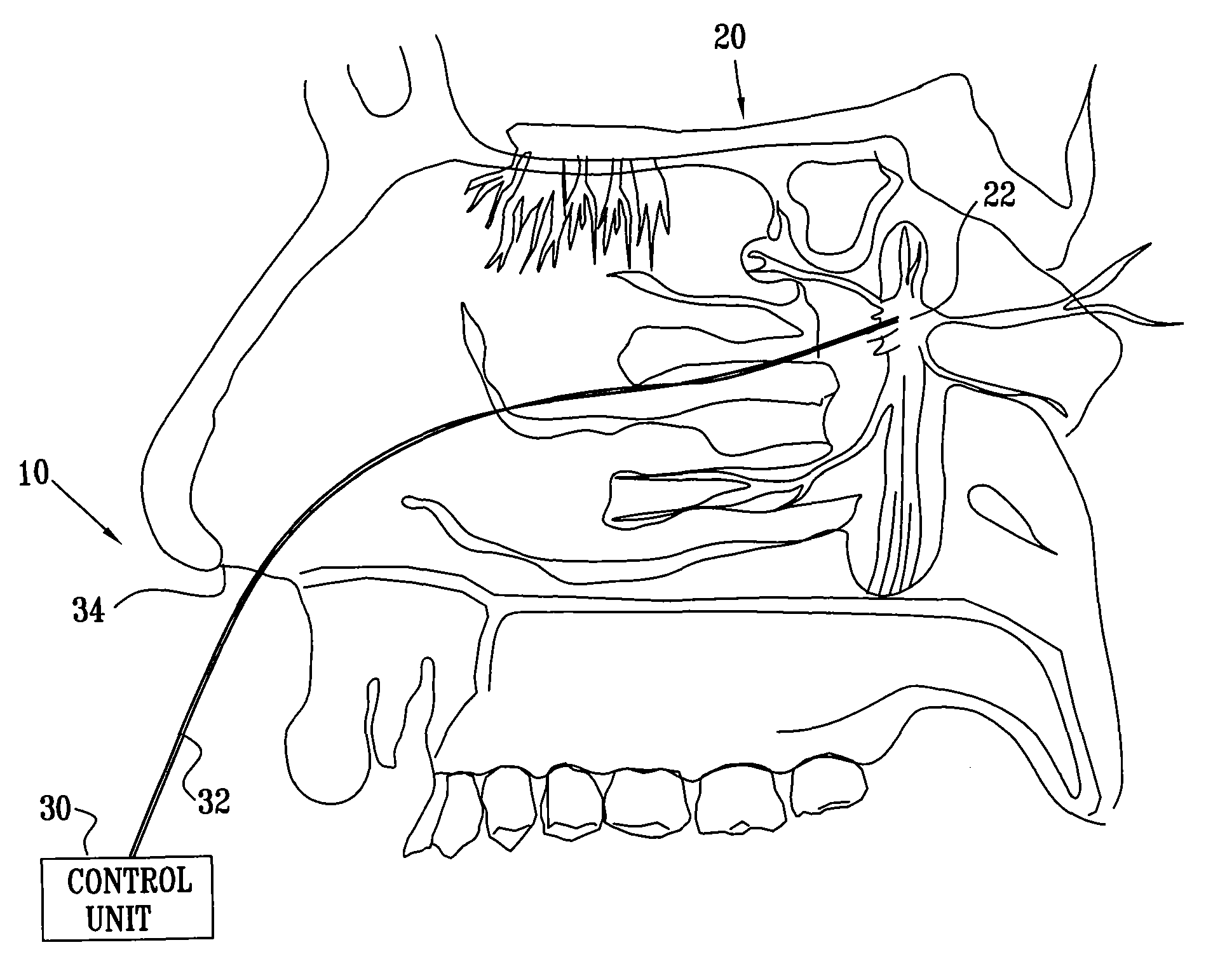
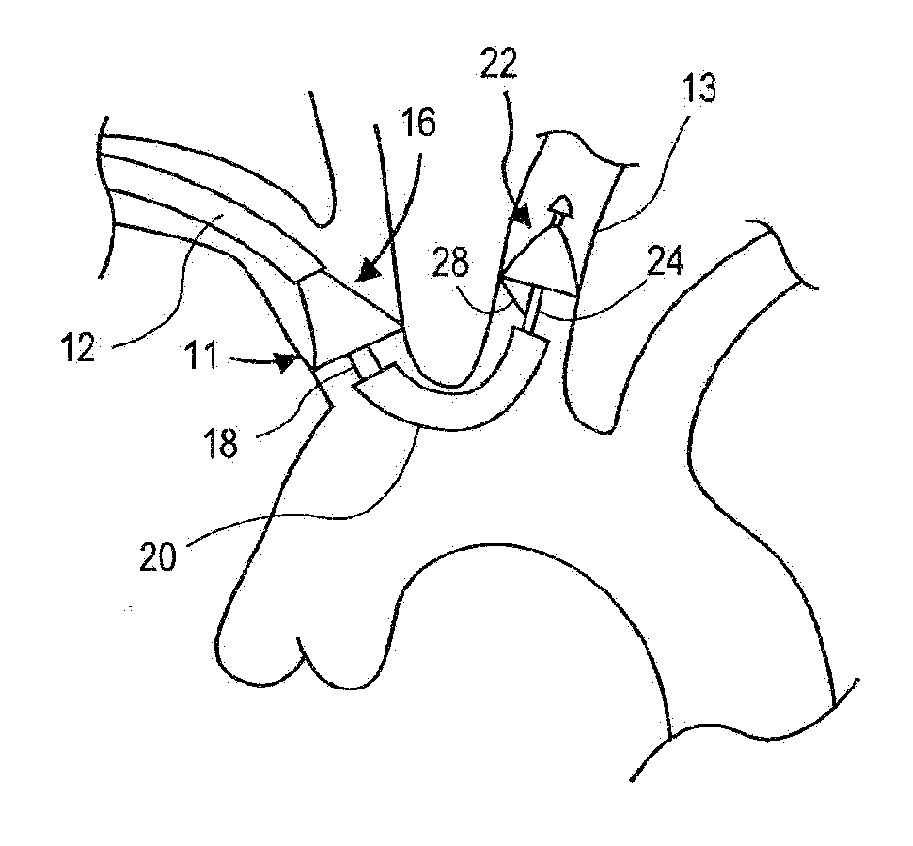
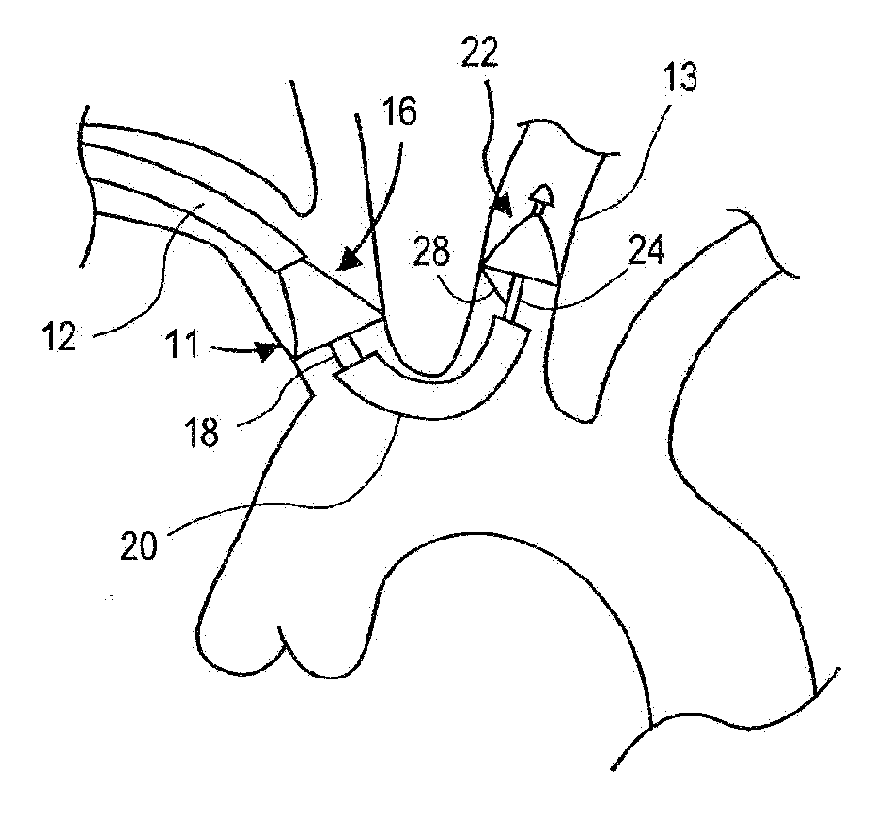
Cerebral Vascular Architecture. The pial vessels are intracranial vessels on the surface of the brain within the pia–arachnoid (also known as the leptomeninges) or glia limitans (the outmost layer of the cortex comprised of astrocytic end-feet) [1].
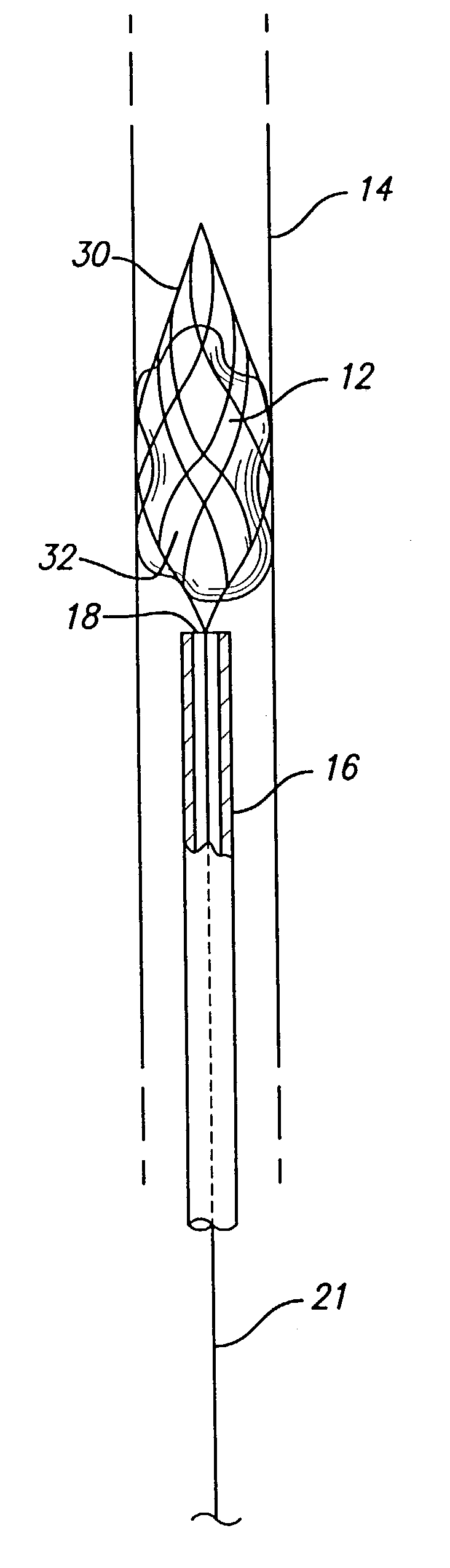
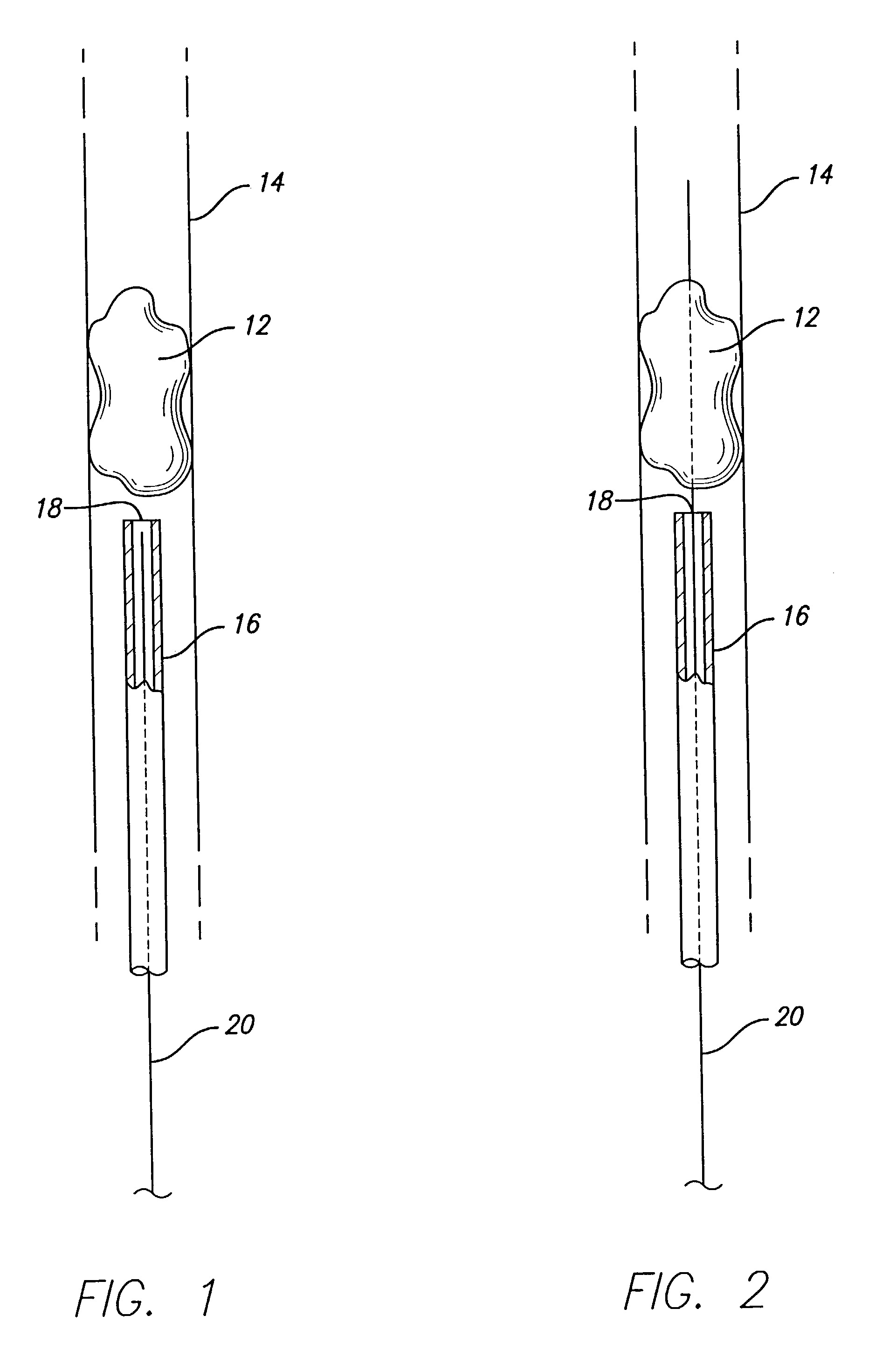
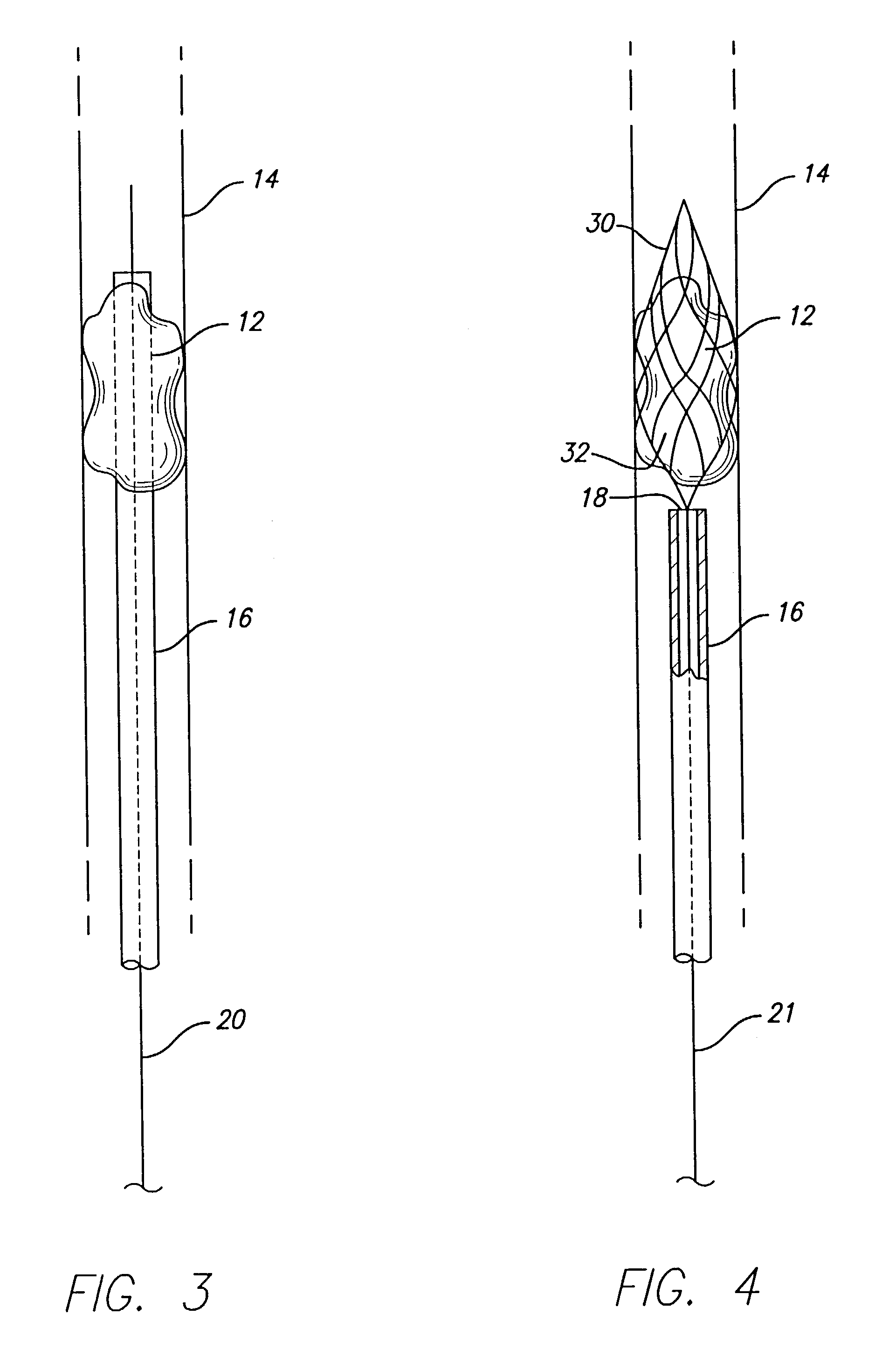
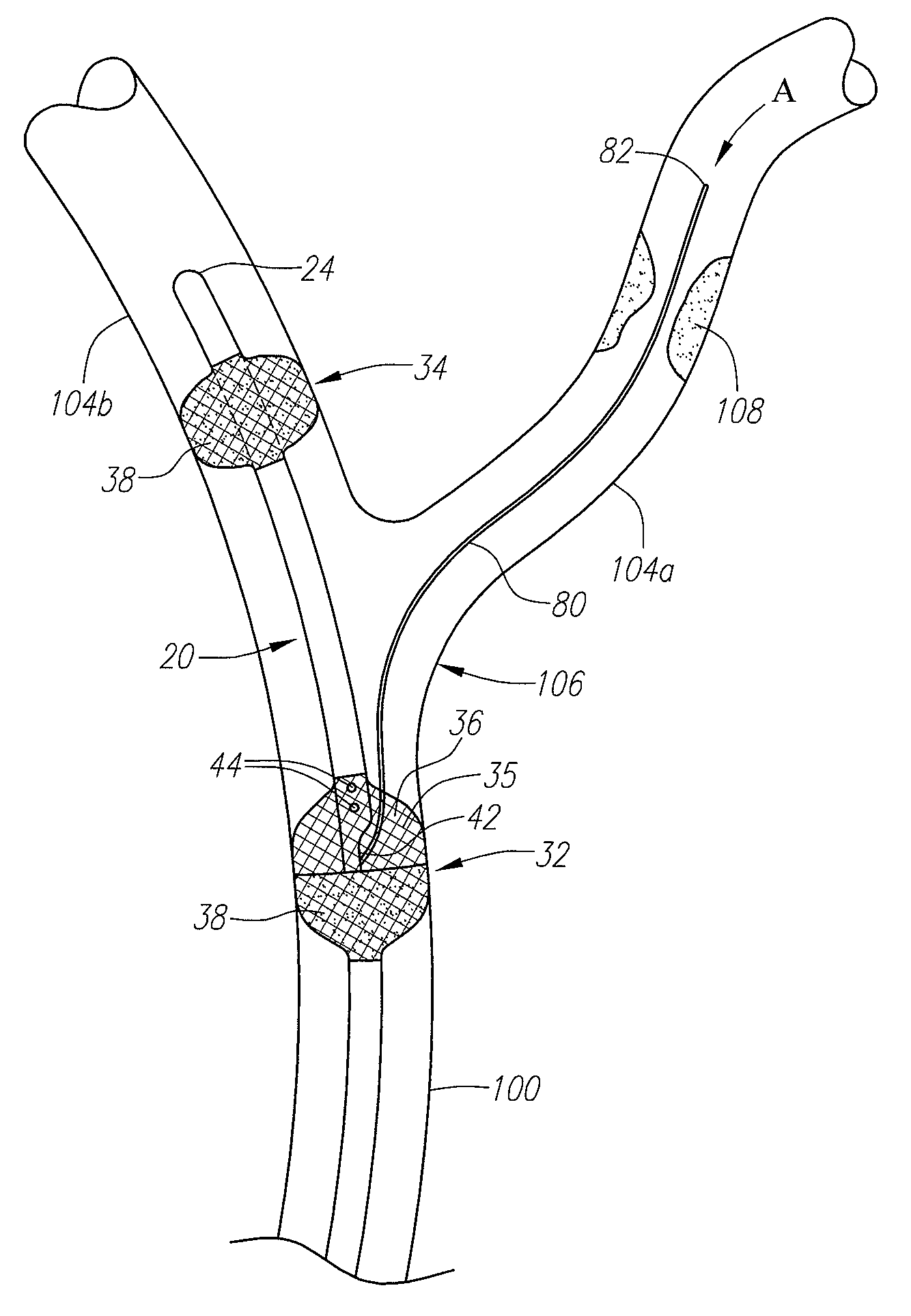
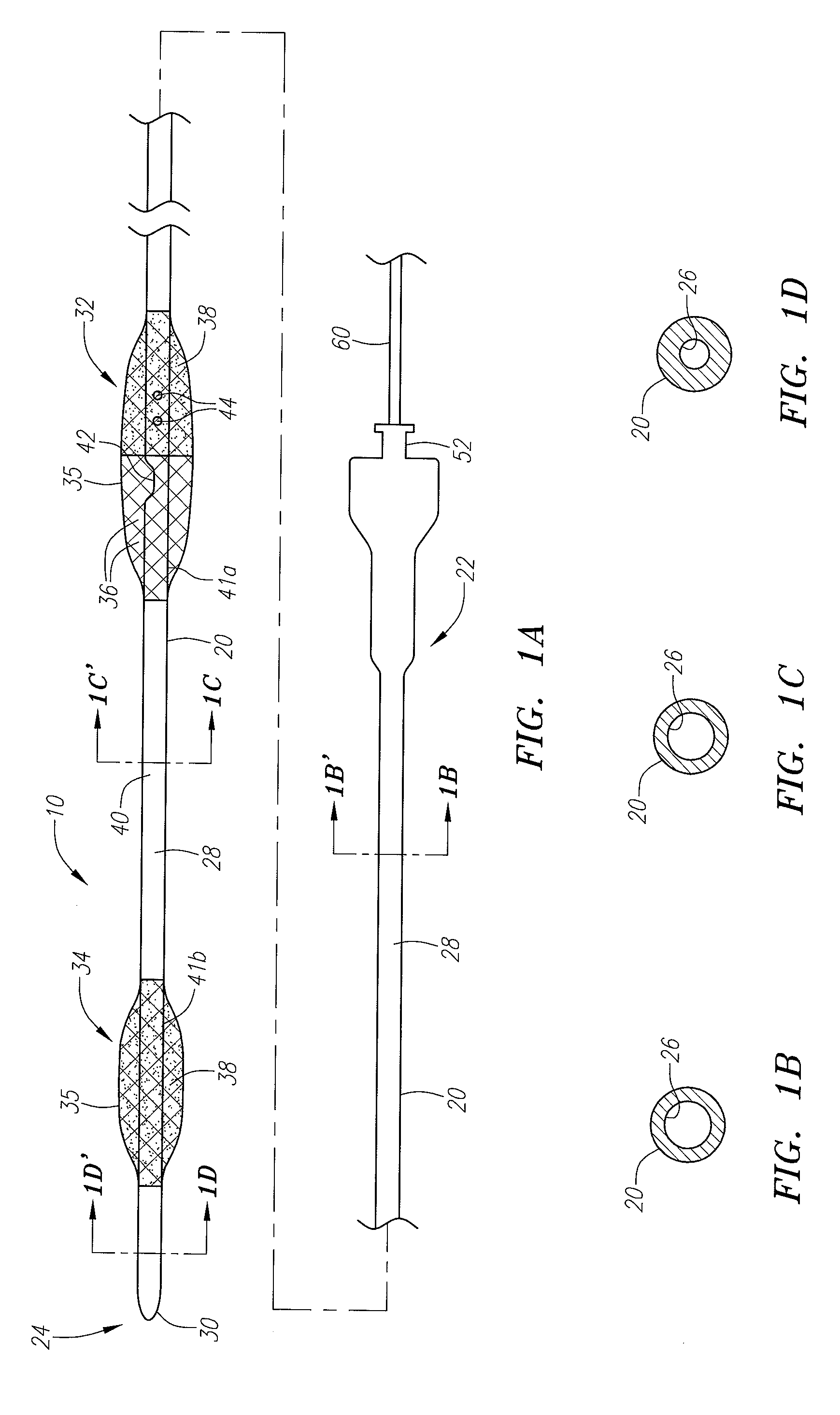
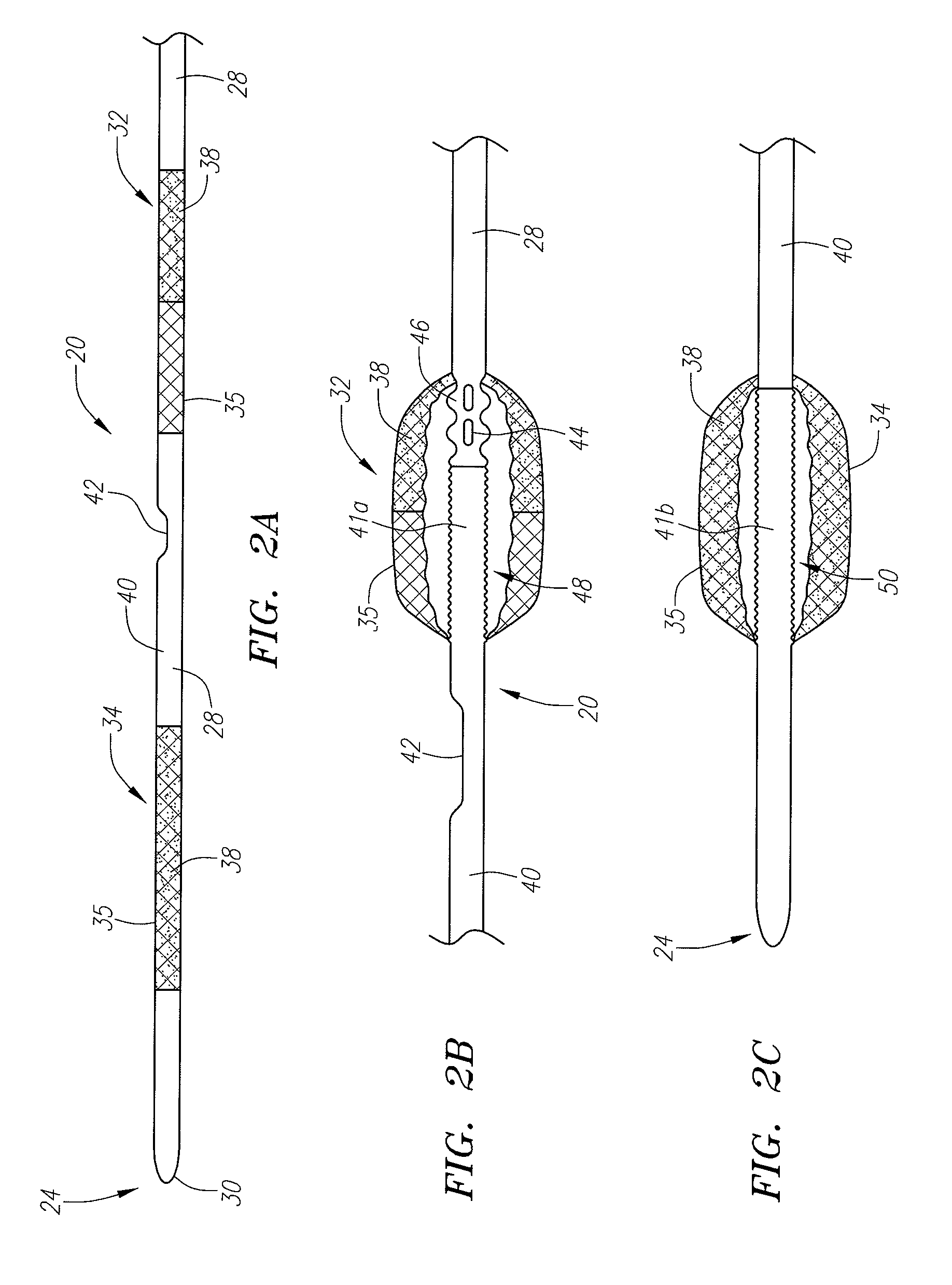
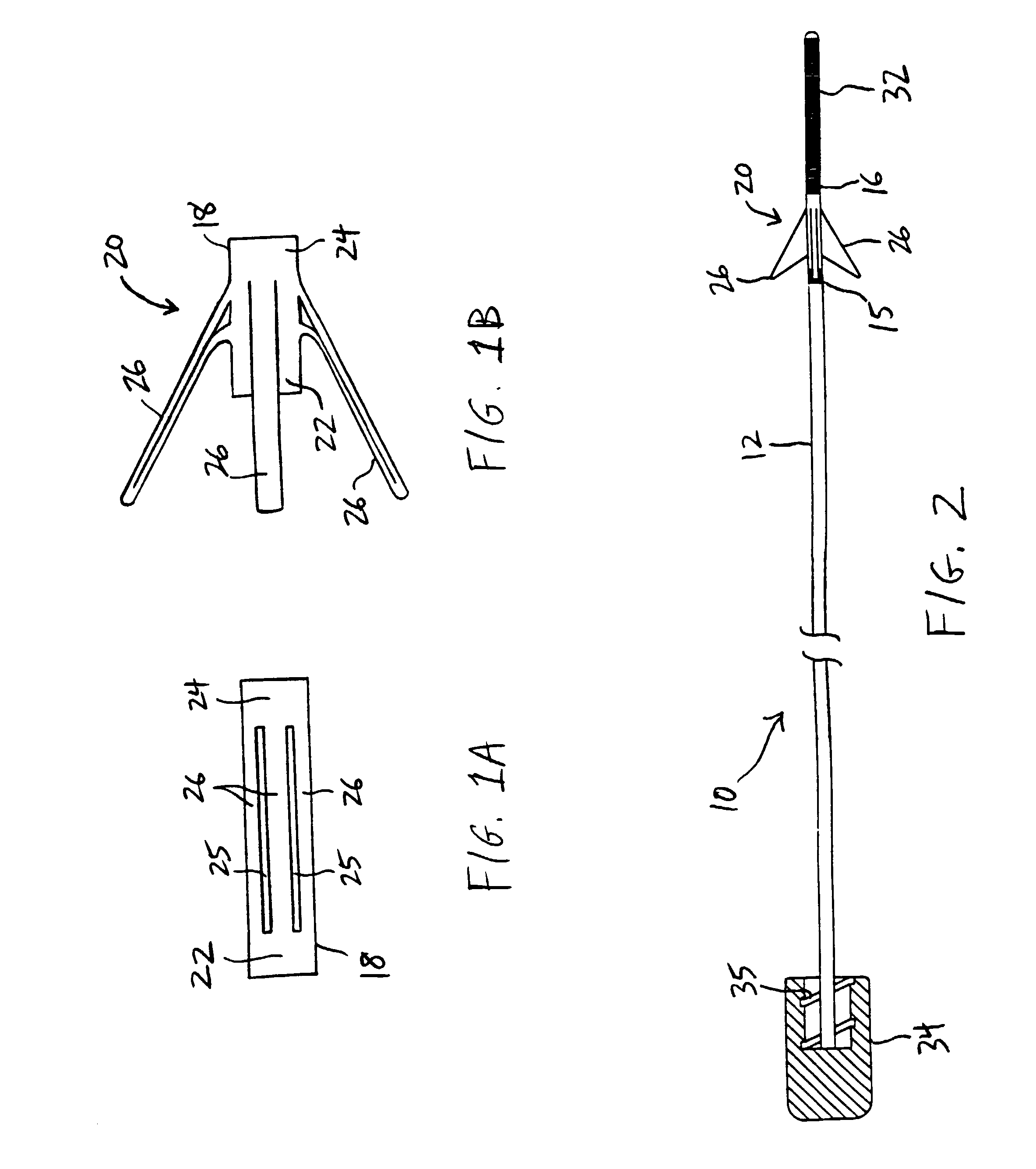
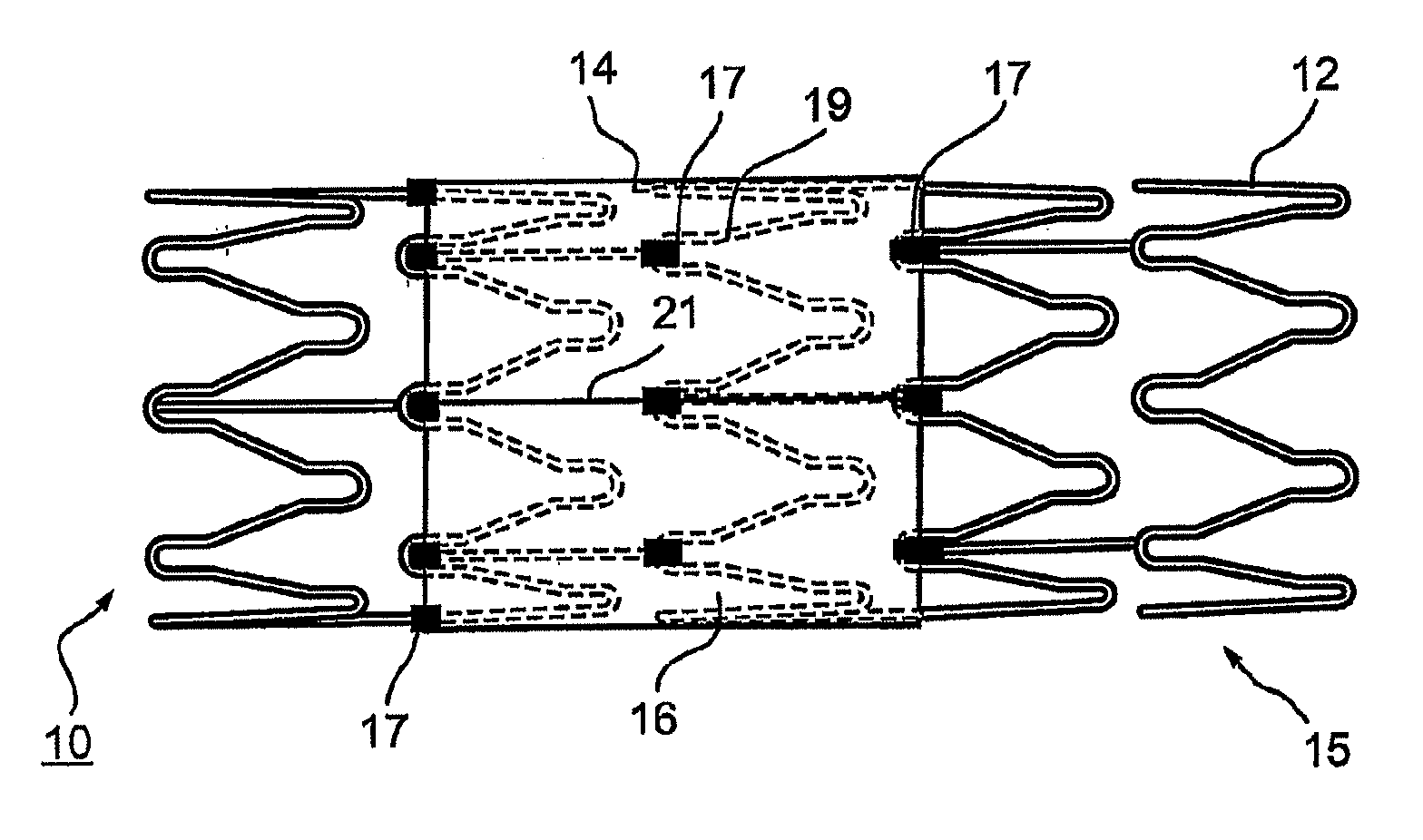
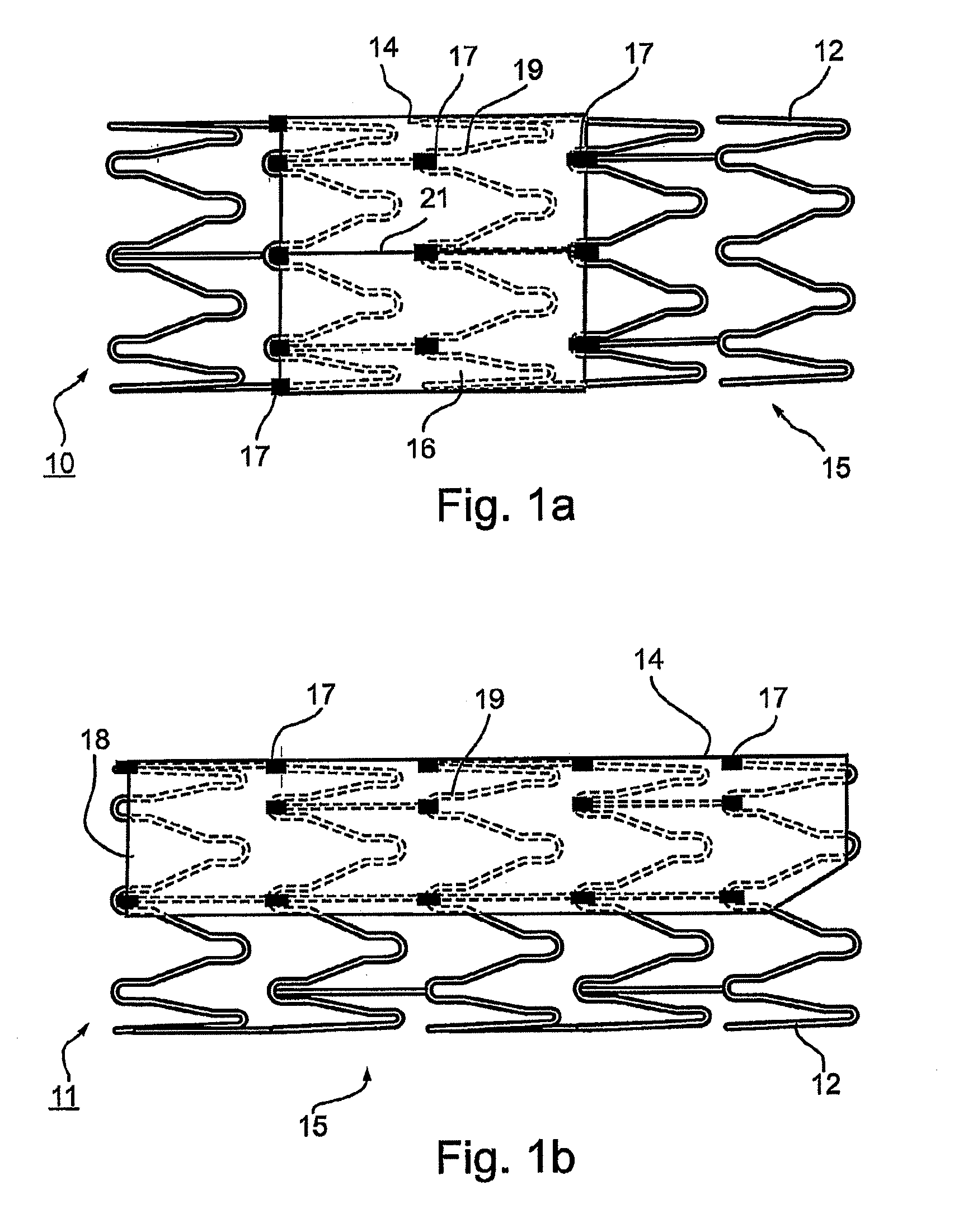
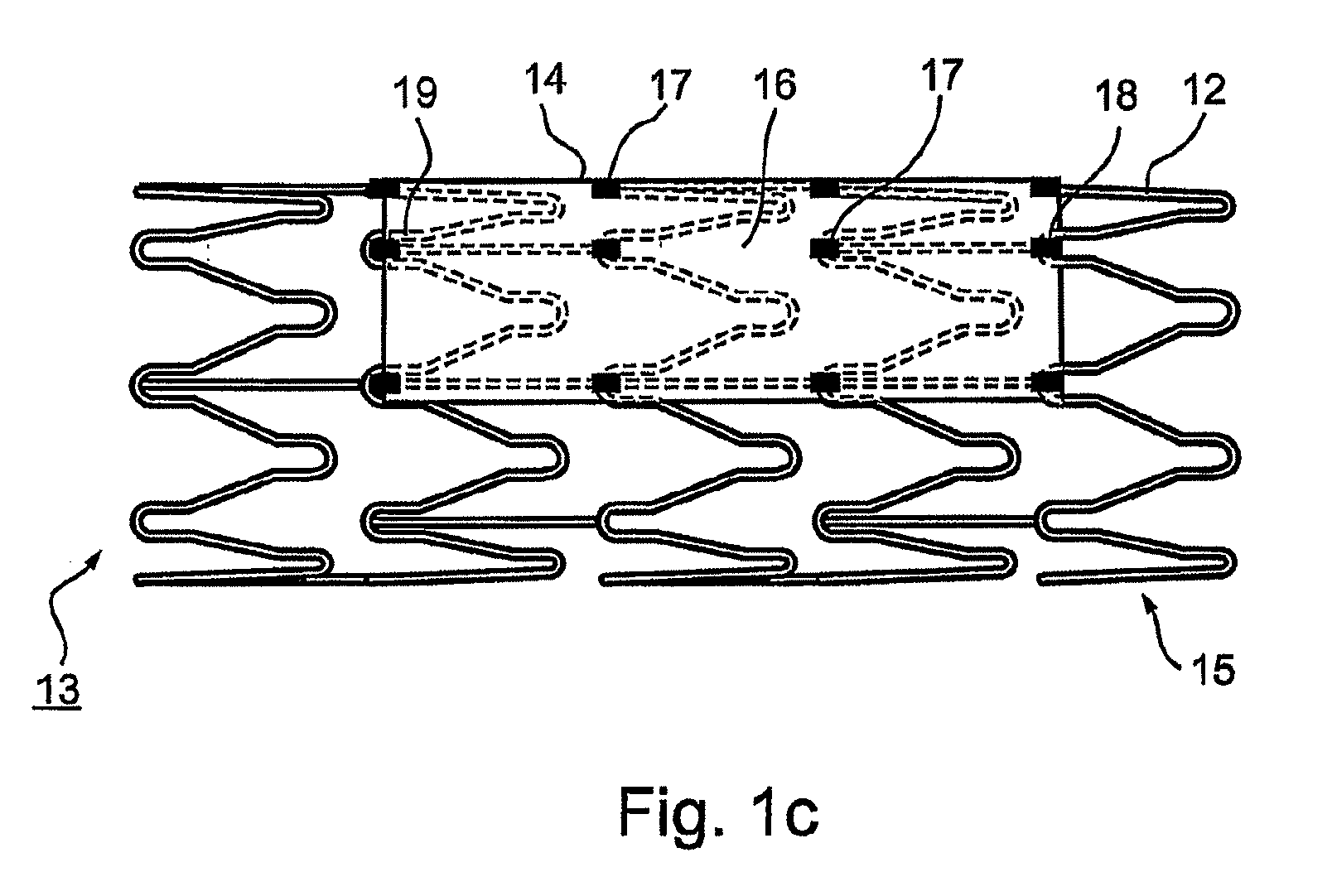
Device for removal of thrombus through physiological adhesion
InactiveUS7004954B1Raise the level of performanceRestoring native blood flowBalloon catheterSurgeryMedicineThrombus
A device that is useful for removing obstructions from vessels. Various embodiments and methods of use are contemplated for the effective removal of obstructions. The disclosed devices utilize a thrombogenic material to promote the formation of fibrin bonds, thus enhancing adhesion. It is further contemplated that the disclosed devices may be used in all vasculature including the cerebral vasculature and the neurovasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
Occlusion device and method of use
ActiveUS20080200946A1Small outer diameterReduce intervention timeStentsSurgeryDistal portionBlood vessel
A device for protecting cerebral vessels or brain tissue during treatment of a carotid vessel includes a catheter having a distal portion, a proximal portion and a lumen extending therebetween, the catheter including first and second expandable areas for vessel occlusion provided over the length of the catheter. The device further includes an elongate stretching member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the elongate stretching member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state, and wherein the elongate stretching member is retracted proximally relative to the catheter causes the first and second expandable areas to transition from the collapsed state to a radially, or laterally expanded state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Embolectomy catheters and methods for treating stroke and other small vessel thromboembolic disorders
InactiveUS7691121B2Prevent and minimize severityEasy extractionStentsDilatorsThrombosis embolismThromboembolic disorder
Embolectomy catheters, rapid exchange microcatheters, systems and methods for removing clots or other obstructive matter (e.g., thrombus, thromboemboli, embolic fragments of atherosclerotic plaque, foreign objects, etc.) from blood vessels. This invention is particularly useable for percutaneous removal of thromboemboli or other obstructive matter from small blood vessels of the brain, during an evolving stroke or period of cerebral ischemia. In some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters of this invention are advanceable with or over a guidewire which has been pre-inserted through or around the clot. Also, in some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters include clot removal devices which are deployable from the catheter after the catheter has been advanced at least partially through the clot. The clot removal device may included a deployable wire nest that is designed to prevent a blood clot from passing therethrough. The delivery catheter may include telescoping inner and outer tubes, with the clot removal device being radially constrained by the outer tube. Retraction of the outer tube removes the constraint on the clot removal device and permits it to expand to its deployed configuration. An infusion guidewire is particularly useful in conjunction with the embolectomy catheter, and permits infusion of medicaments or visualization fluids distal to the clot.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Aneurysm covering devices and delivery devices
Devices are provided for isolating an aneurysm from the blood vessel, particularly berry aneurysms within the cerebral vasculature. Embodiments of such devices have improved manufacturability, deliverability find isolation of the aneurysm. Delivery systems are also provided for such devices and other devices which may benefit from orientation adjustment during delivery.
Owner:MARTIN BRIAN B +1
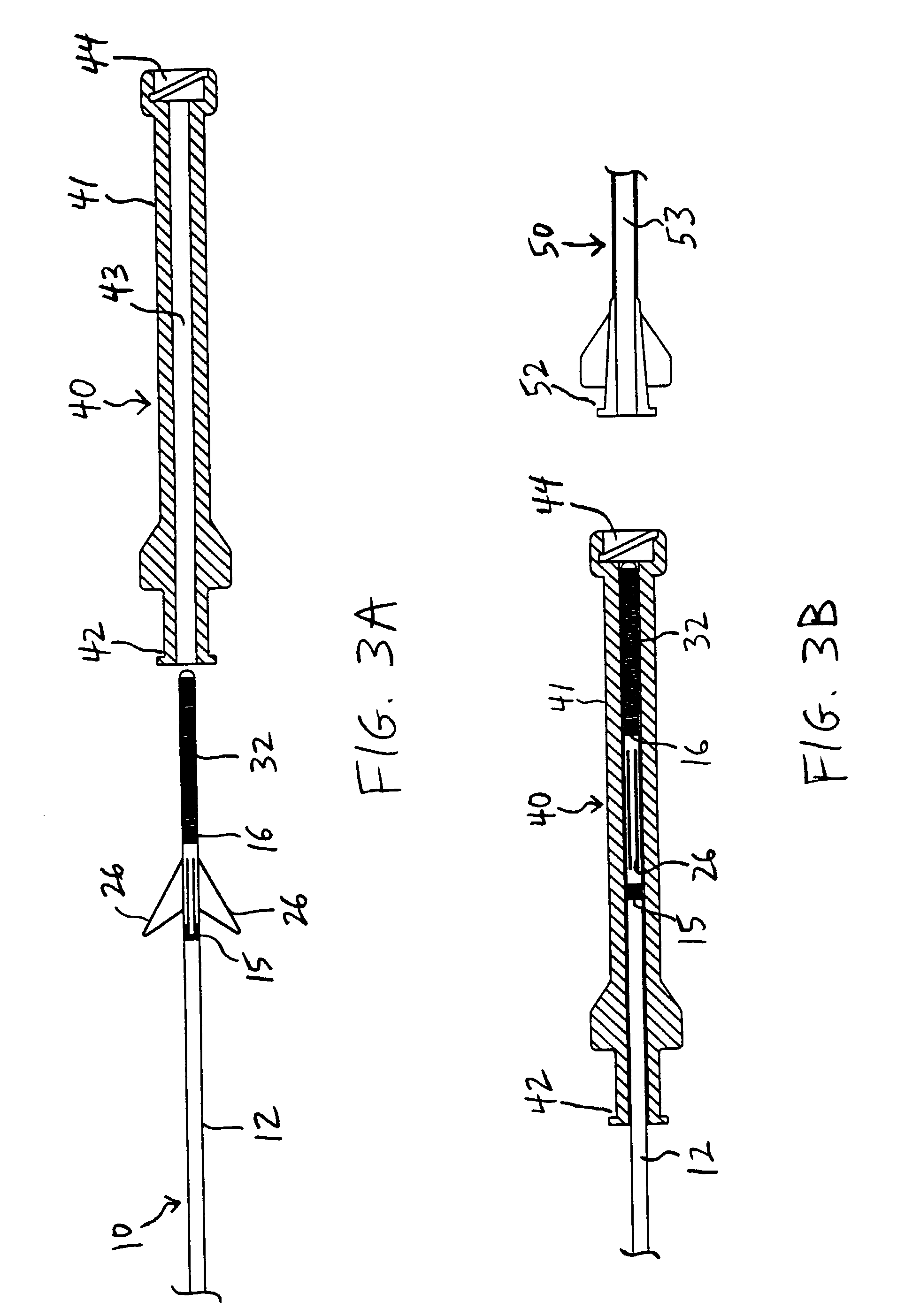
Devices and methods for accessing a cerebral vessel
InactiveUS20100004607A1Guaranteed normal transmissionOptimized and supportStentsSurgeryBlood vesselCatheter device
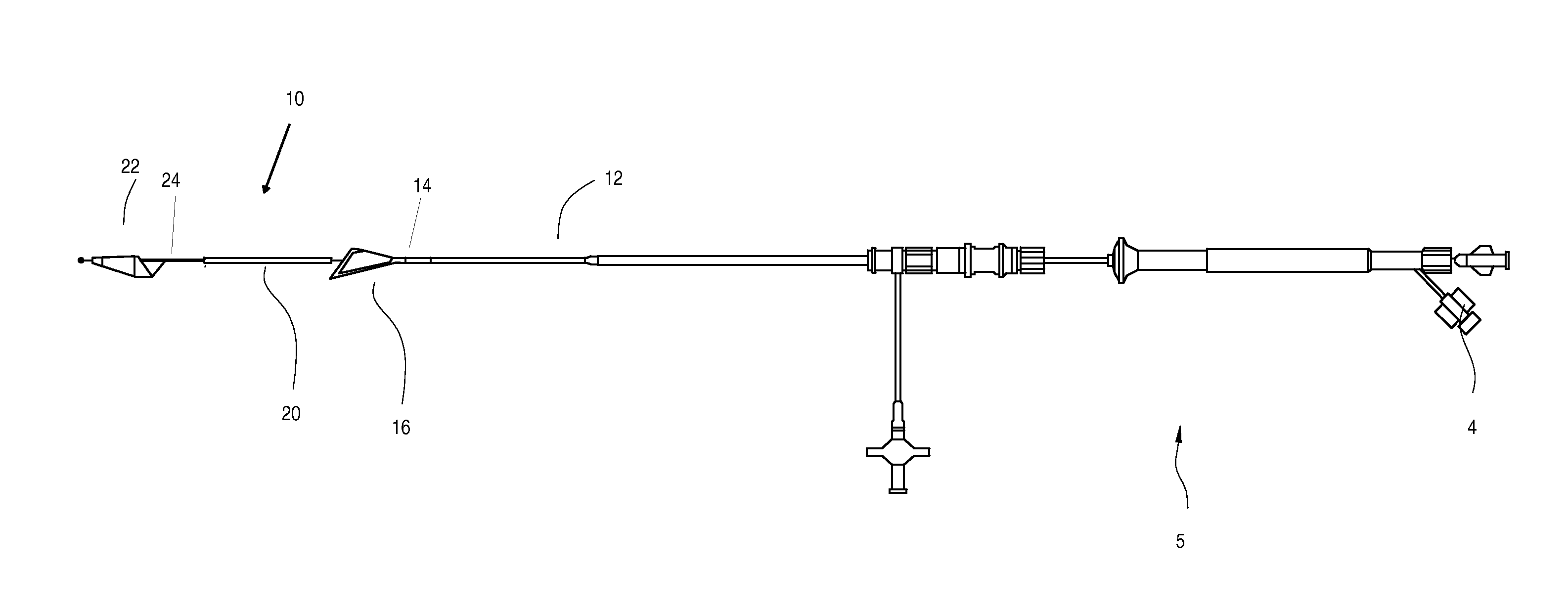
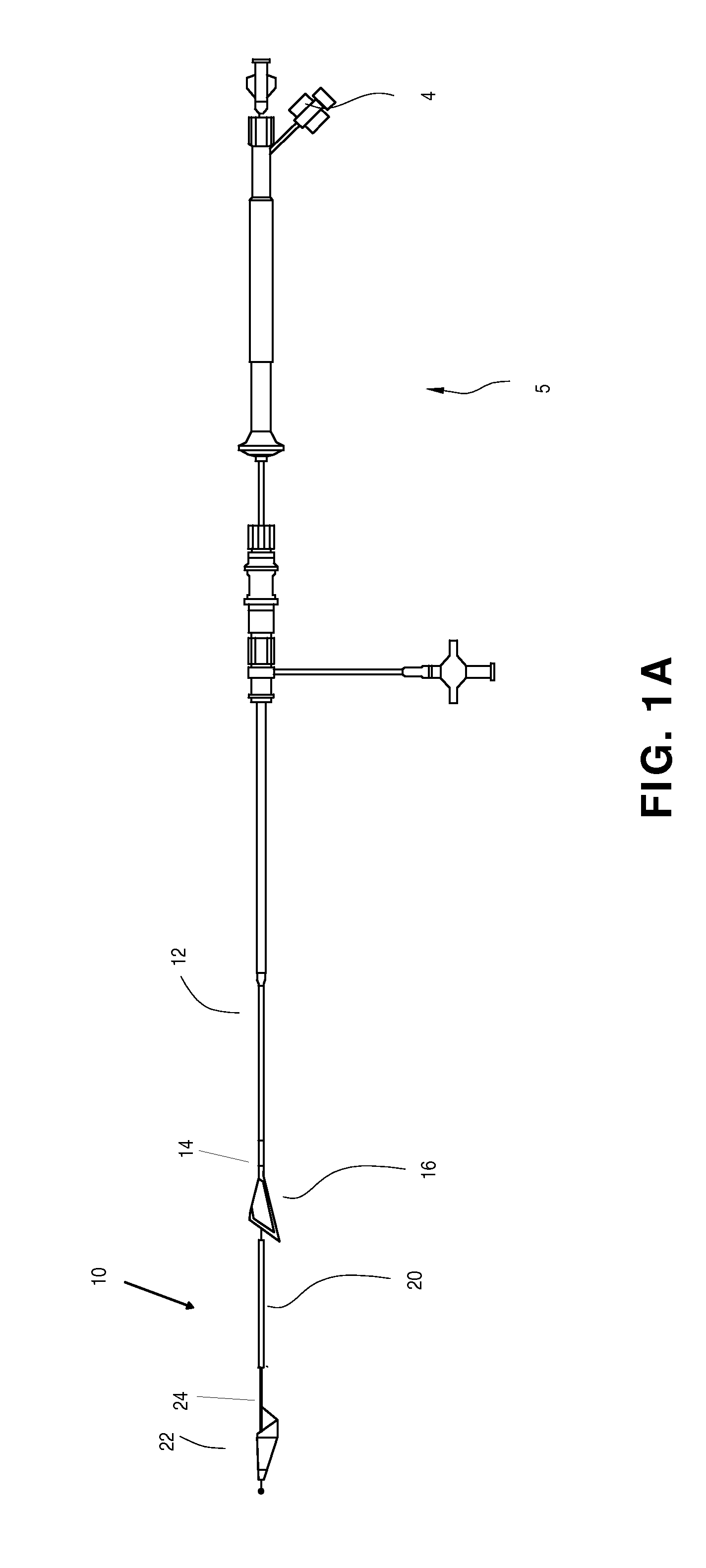
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for accessing a cerebral vessel. The system includes a support catheter, which can be advanced into small and tortuous vessels. By advancing the support catheter nearer to the obstruction then can be achieved with conventional guide catheters, the support catheter reduces the likelihood vessel compression and collapse when manipulating a working catheter.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Devices and methods for removing obstructions from a cerebral vessel
InactiveUS20080082107A1Guaranteed effective force transmissionOptimized advancementStentsSurgeryBlood vesselCatheter device
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for removing an obstruction. The system includes a support catheter which can be advanced into small and tortuos vessels. By advancing the support catheter nearer to the obstruction then can be achieved with conventional guide catheters, the support catheter reduces the likelihood vessel compression and collapse when pulling on the retrieval element.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Embolic protection device for protecting the cerebral vasculature
ActiveUS20120172915A1Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesSurgeryParticulatesEmbolic Protection Devices
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ultrasound Apparatus and Method to Treat an Ischemic Stroke
InactiveUS20080262350A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTransducerIschemic stroke
Owner:CEREVAST THERAPEUTICS
Expandable cerebrovascular sheath and method of use
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, small cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the upper vascular system and has utility in the introduction and removal of therapeutic or diagnostic microcatheters. The access route is through the femoral arteries or the iliac arteries to the cerebrovasculature. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the cerebrovasculature. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device, which is removed prior to the introduction of microcatheters. The sheath can be inserted in a first, small cross-sectional configuration, be expanded diametrically to a second, larger cross-sectional configuration, and then be reduced to a diametrically smaller size for removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Photoacoustic removal of occlusions from blood vessels
Partial or total occlusions of fluid passages within the human body are removed by positioning an array of optical fibers in the passage and directing treatment radiation pulses along the fibers, one at a time, to generate a shock wave and hydrodynamic flows that strike and emulsify the occlusions. A preferred application is the removal of blood clots (thrombi and emboli) from small cerebral vessels to reverse the effects of an ischemic stroke. The operating parameters and techniques are chosen to minimize the amount of heating of the fragile cerebral vessel walls occurring during this photoacoustic treatment. One such technique is the optical monitoring of the existence of hydrodynamic flow generating vapor bubbles when they are expected to occur and stopping the heat generating pulses propagated along an optical fiber that is not generating such bubbles.
Owner:SELVA MEDICAL +2
Mechanical thrombectomy device for use in cerebral vessels
InactiveUS7029488B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionReduce traumaStentsBalloon catheterThrombusCerebral occlusions
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
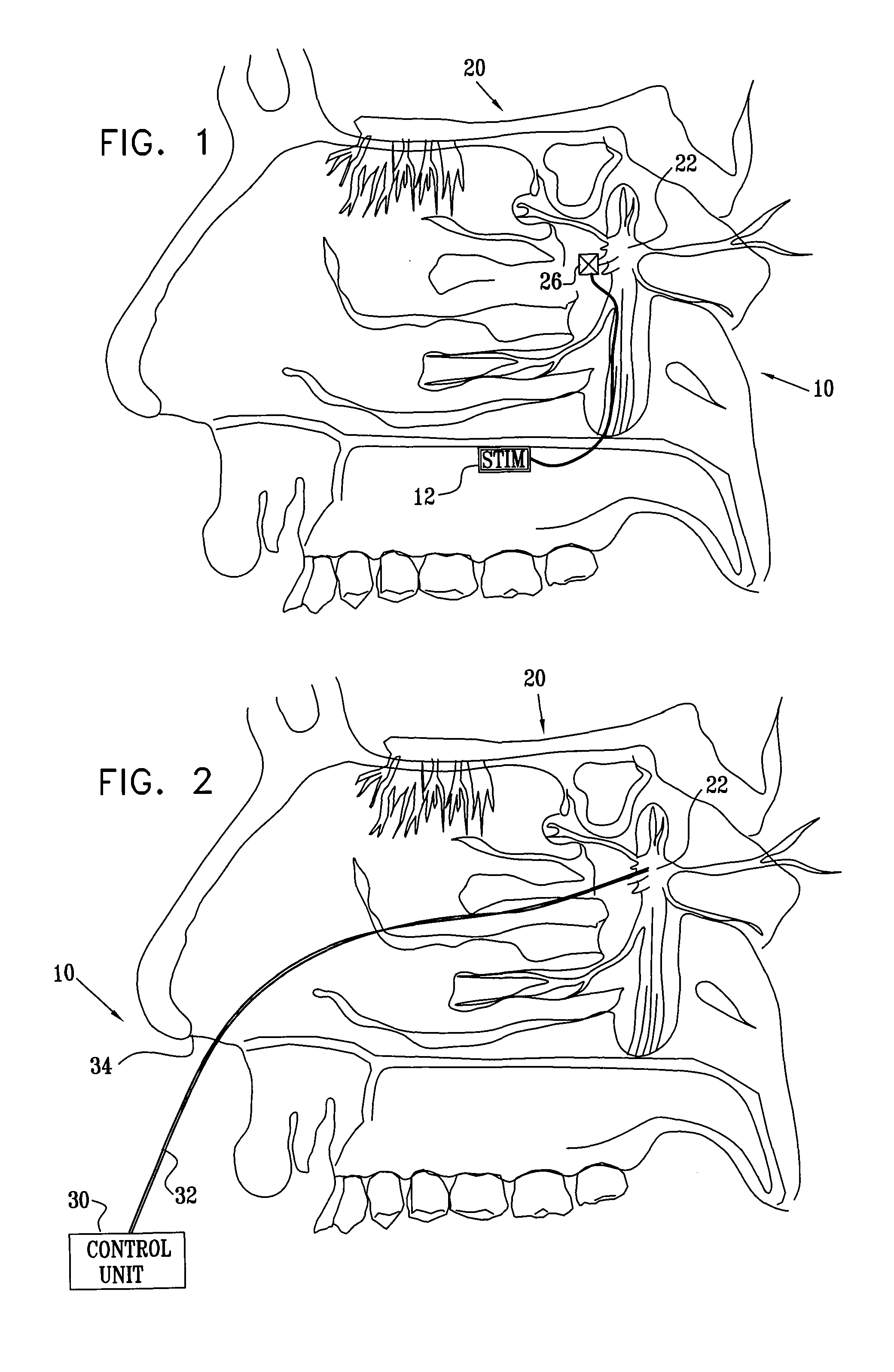
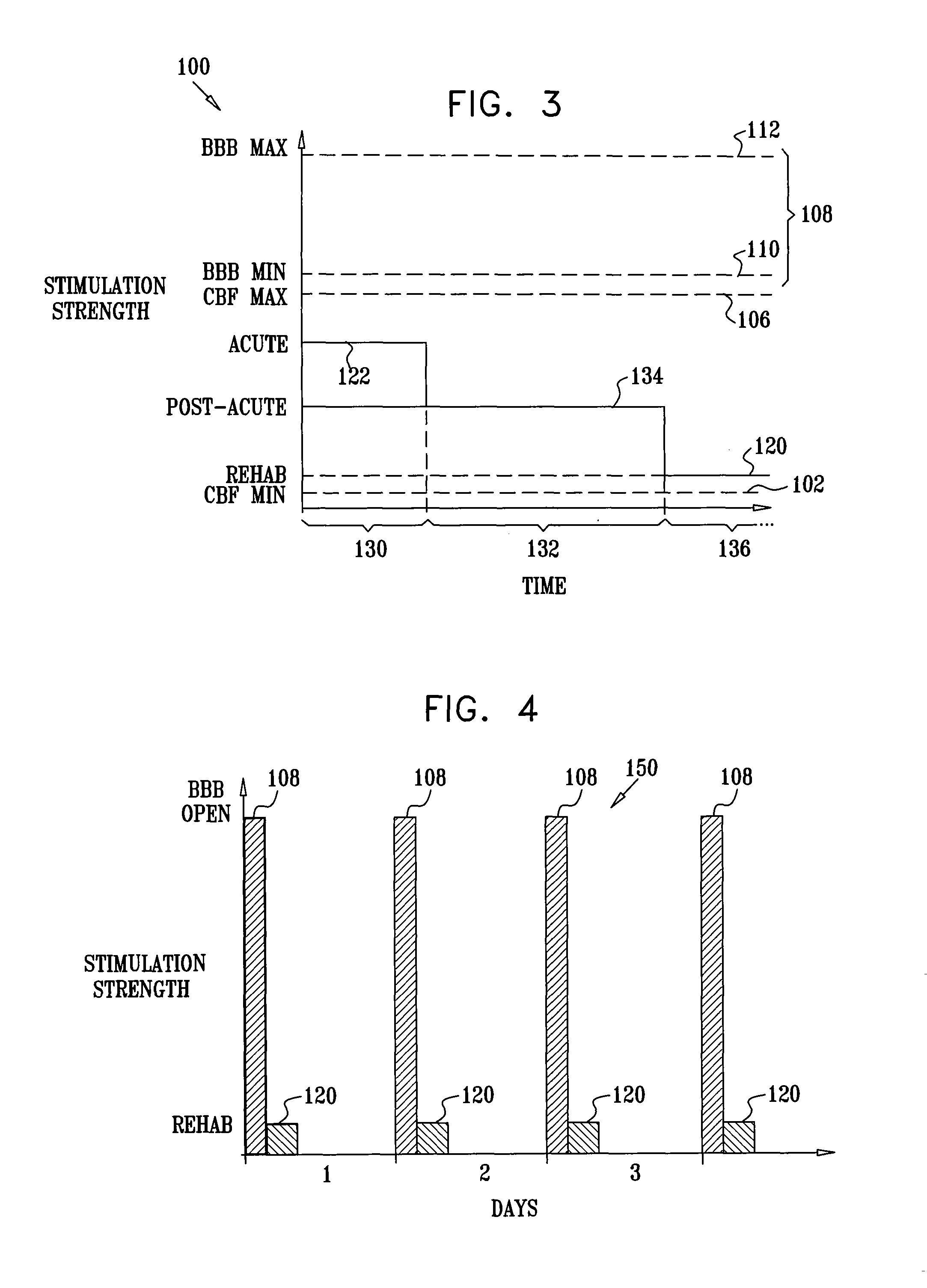
Stimulation for treating brain events and other conditions
ActiveUS20070083245A1Increase cerebral blood flowReduce harmSpinal electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
Apparatus for treatment is provided, including one or more electrodes, configured to be applied to a site of a subject, and adverse cerebrovascular condition treatment functionality. The functionality comprises a control unit configured to drive the one or more electrodes to apply electrical stimulation to the site during a plurality of stimulation periods which includes at least first and last stimulation periods, set an inter-period interval between initiation of the first stimulation period and initiation of the last stimulation period to be at least 24 hours, and configure the stimulation during the first and last stimulation periods to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. The site is selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Aneurysm covering devices and delivery devices
Devices are provided for isolating an aneurysm from the blood vessel, particularly berry aneurysms within the cerebral vasculature. Embodiments of such devices have improved manufacturability, deliverability and isolation of the aneurysm. Delivery systems are also provided for such devices and other devices which may benefit from orientation adjustment during delivery.
Owner:TSUNAMI INNOVATIONS
Compositions and methods for improving or preserving brain function
InactiveUS20070179197A1Improve performancePrevent and reduce delayBiocideNervous disorderRegimenExercise performance
The present invention is related to mammalian nutrition and effects thereof in individuals with age associated cognitive decline such as Age Associated Memory Inpairment (AAMI) or a dementing illness such as Alzheimer's disease or related dementia, or Mild Cognitive Impairment, such as improving performance in, or reversal, prevention, reducing and delaying decline in, one or more of cognitive function, memory, behavior, cerebrovascular function, motor function, and / or brain physiology are seen. In particular, the present invention utilizes medium chain triglycerides, in one embodiment, administered as part of a long-term treatment regimen, to preserve or improve learning, attention, motor performance, cerebrovascular function, social behavior, and to increase activity levels, particularly in aging mammals.
Owner:ACCERA INC
Methods, devices, and systems for postconditioning with clot removal
ActiveUS20140155980A1Reduce volumetric flow rateImprove fluid flowStentsBalloon catheterReperfusion injuryThrombus
New devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for preventing, treating, and / or at least minimizing ischemia and / or reperfusion injury by restoring and / or modulating blood flow, particularly in the cerebral vasculature where blood vessels are narrow and tortuous. These devices, systems, and methods make it possible for a clinician to adequately and systematically restore blood flow to ischemic tissue while simultaneously modulating the blood flow to minimize reperfusion injury. New thrombectomy devices and systems, which, for example, expand with greater radial force, further enable improved binding with clots and restoration of blood flow.
Owner:COGNITION MEDICAL
Occlusion device and method of use
InactiveUS20120022572A1Small outer diameterIncrease flexibilityDilatorsOcculdersDistal portionBlood vessel
A device for protecting cerebral vessels or brain tissue during treatment of a carotid vessel includes a catheter having a distal portion, a proximal portion and a lumen extending therebetween, the catheter including first and second expandable areas provided over the length of the catheter. The device includes a first elongate member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the first elongate member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing one of the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state. The device further includes a second elongate member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the second elongate member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing the other of the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Implantable graft assembly and aneurysm treatment
InactiveUS20090069880A1Reduced flexibilityIncrease profile of implantStentsOcculdersVascular implantAneurysm treatment
Disclosed is an implantable graft assembly comprising a graft secured to a expandable tubular frame, the graft only partially covering the frame and the use of the graft assembly in treating an aneurysm, especially a cerebral aneurysm. Disclosed is also a method of treating an aneurysm by deploying an implantable graft assembly. Disclosed is also the use of serous tissue for the preparation of a cerebrovascular implant, especially as a graft, especially as a component of a cerebrovascular implantable graft assembly.
Owner:DESIGN & PERFORMANCE CYPRUS
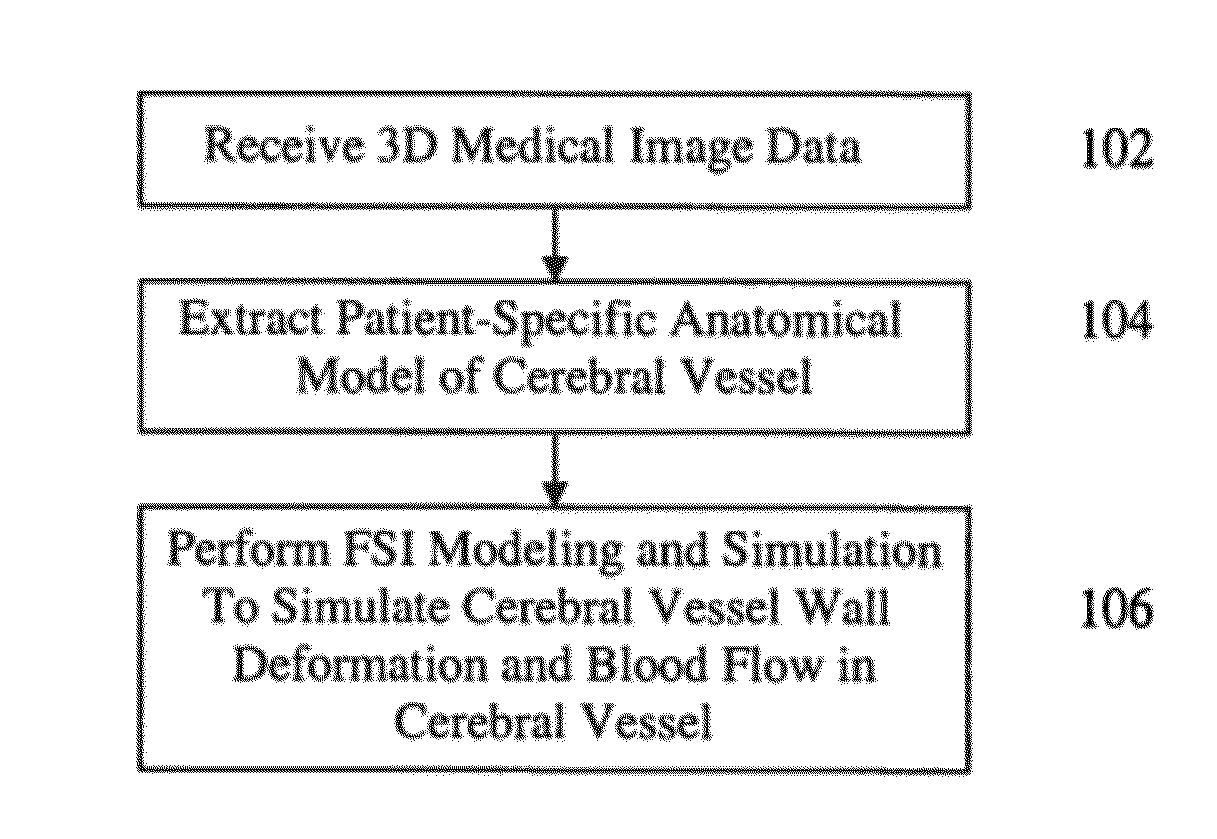
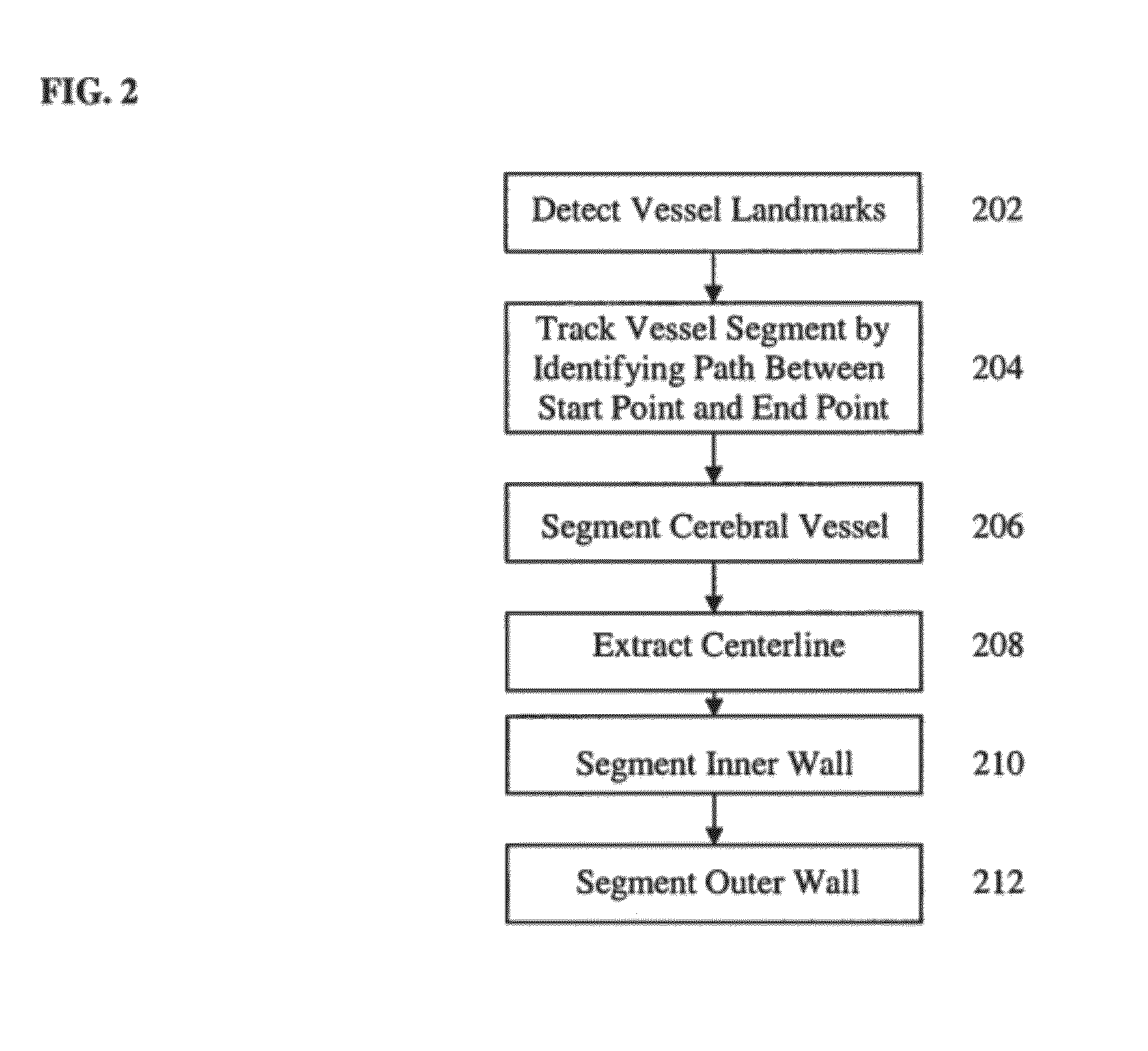
Method and System for Patient-Specific Computational Modeling and Simulation for Coupled Hemodynamic Analysis of Cerebral Vessels
ActiveUS20120203530A1Medical simulationAnalogue computers for distribution networksRadiologySimulation based
A method and system for patient-specific computational modeling and simulation for coupled hemodynamic analysis of cerebral vessels is disclosed. An anatomical model of a cerebral vessel is extracted from 3D medical image data. The anatomical model of the cerebral vessel includes an inner wall and an outer wall of the cerebral vessel. Blood flow in the cerebral vessel and deformation of the cerebral vessel wall are simulated using coupled computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and computational solid mechanics (CSM) simulations based on the anatomical model of the cerebral vessel.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
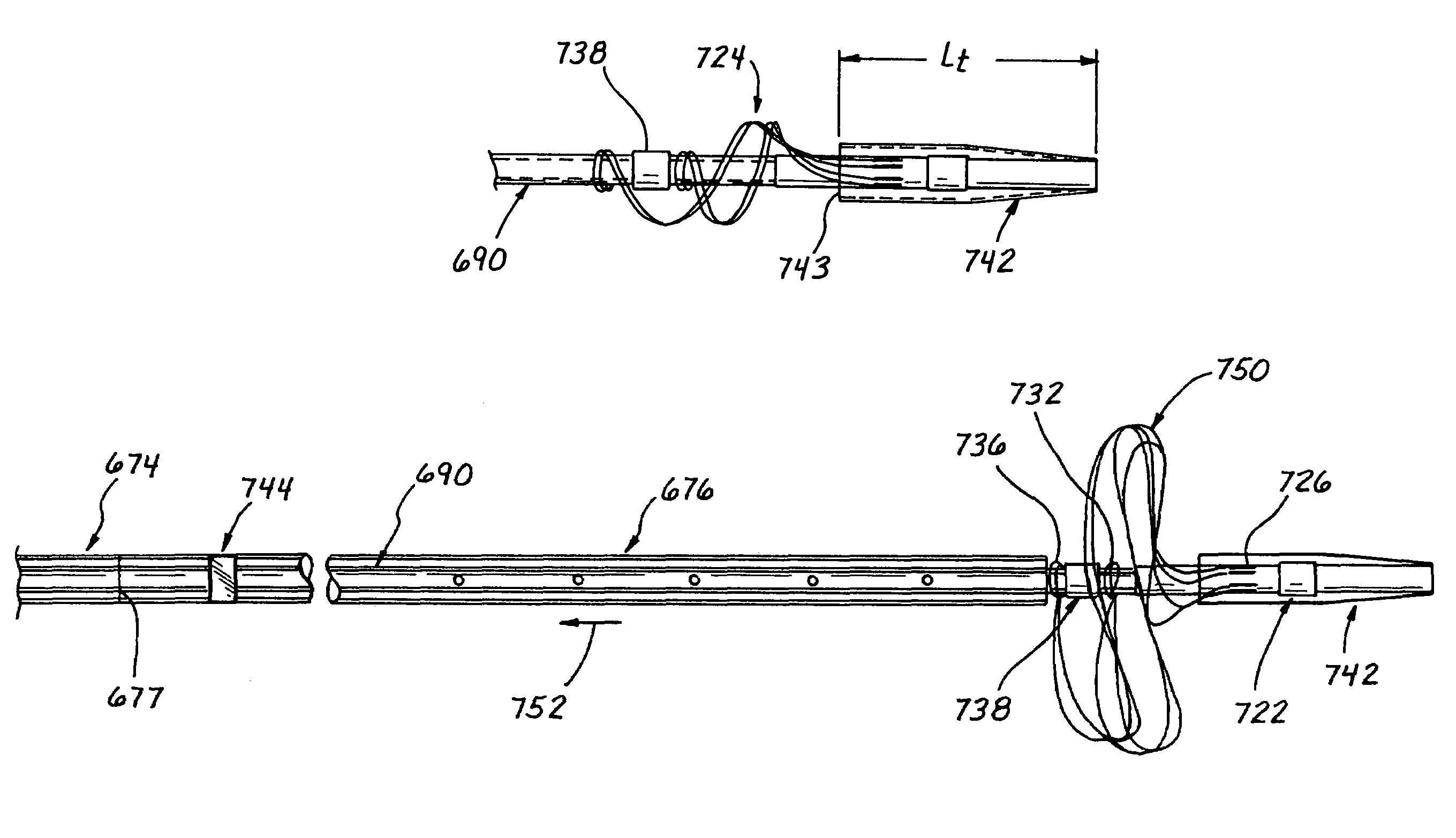
Cerebral vasculature device
Novel cerebral vasculature devices are disclosed, including thrombectomy removal devices that include a continuous braided structure, a proximal portion, a distal portion, and a first expandable portion located between the proximal portion and the distal portion. The braided structure includes a plurality of wires. The proximal portion and the distal portion include polymer imbedded at least partially into the braided structure. The device is useful for removing thrombus from a patient's vasculature.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Electronic cigarette liquid rich in plant flavone
ActiveCN104068467AMeeting smoking needsWill not affect healthTobacco treatmentNicotiana tabacumPropolis
The invention discloses an electronic cigarette liquid rich in plant flavone. The electronic cigarette liquid comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 50-70% of propylene glycol, 5-10% of glycerinum, 5-15% of deionized water, 5-15% of natural flavone extract, 4-8% of tobacco extract, 2-6% of tobacco essence and 2-6% of thickener, wherein the natural flavone extract is the extract obtained by distilling by vapour or extracting a plant mixture by ethyl alcohol, and the total flavonoid content is 20-50% by total flavonoid content; the plant mixture is composed of chuzhou chrysanthemum, iris tectorum roots, propolis, orange peel, grape, peanut coat, lily, radix puerariae, scutellaria baicalensis, roxburgh rose and green tea. The electronic cigarette liquid disclosed by the invention is capable of meeting the smoking needs of smokers; meanwhile, the rich plant flavone has the effects of resisting oxidization, preventing aging, and adjusting immunity, and also has a healthcare effect on heart and cerebral vessels to a certain extent.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ANHUI IND CO LTD
Devices and methods for accessing a cerebral vessel
InactiveUS20130268050A1Guaranteed normal transmissionOptimized and supportStentsSurgeryBlood vesselCatheter device
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for accessing a cerebral vessel. The system includes a support catheter, which can be advanced into small and tortuous vessels. By advancing the support catheter nearer to the obstruction then can be achieved with conventional guide catheters, the support catheter reduces the likelihood vessel compression and collapse when manipulating a working catheter.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Non-invasive intracranial pressure sensor
A system and method for non-invasively detecting intracranial pressure (ICP) of a living being by detecting impedance mismatches between carotid arteries and cerebral vessels via a reflection of the carotid pressure waveform using a pressure sensor positioned against the palpable carotid artery, as well as analyzing the reflection and comparing the analysis with known cerebral vasculature data, to calculate ICP non-invasively. A remote blood pressure waveform can also be used to compensate for blood system impedance.
Owner:NEURODX DEV
Method and system for determining a cerebrovascular autoregulation state of a patient
A method of diagnosing cerebrovascular autoregulation in a patient includes measuring blood pressure of the patient, measuring, non-invasively, venous oxygen content of the patient's brain substantially simultaneously with the measuring blood pressure, correlating the blood pressure and the venous oxygen content measurements in a time domain, and determining a cerebrovascular autoregulation state of the patient based on the correlating the blood pressure and the venous oxygen content measurements.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Device and Methods for Targeting of Transcranial Ultrasound Neuromodulation by Automated Transcranial Doppler Imaging
InactiveUS20150151142A1Overcome deficienciesReduce amountSurgeryChiropractic devicesSonificationBlood vessel
Methods and systems for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation as well as targeting such neuromodulation in the brain are disclosed. Automated transcranial Doppler imaging (aTCD) of blood flow in the brain is performed and one or more 3-dimensional maps of the neurovasculature are generated. Ultrasound energy is delivered transcranially in conjunction to induce neuromodulation. One or more brain regions for neuromodulation are targeted by using brain blood vessel landmarks identified by aTCD components. The landmarks are used for initial targeting of the neuromodulation to one or more brain regions of interest and / or for maintaining neuromodulation targeting despite user or device movements. Acoustic contrast agents may be employed to generate broadband ultrasound waves locally at the site of target cells. Transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation may be achieved by having confocal ultrasound waves differing in acoustic frequency by a frequency effective for neuromodulation interfere to generate vibrational forces in the brain that induce neuromodulation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
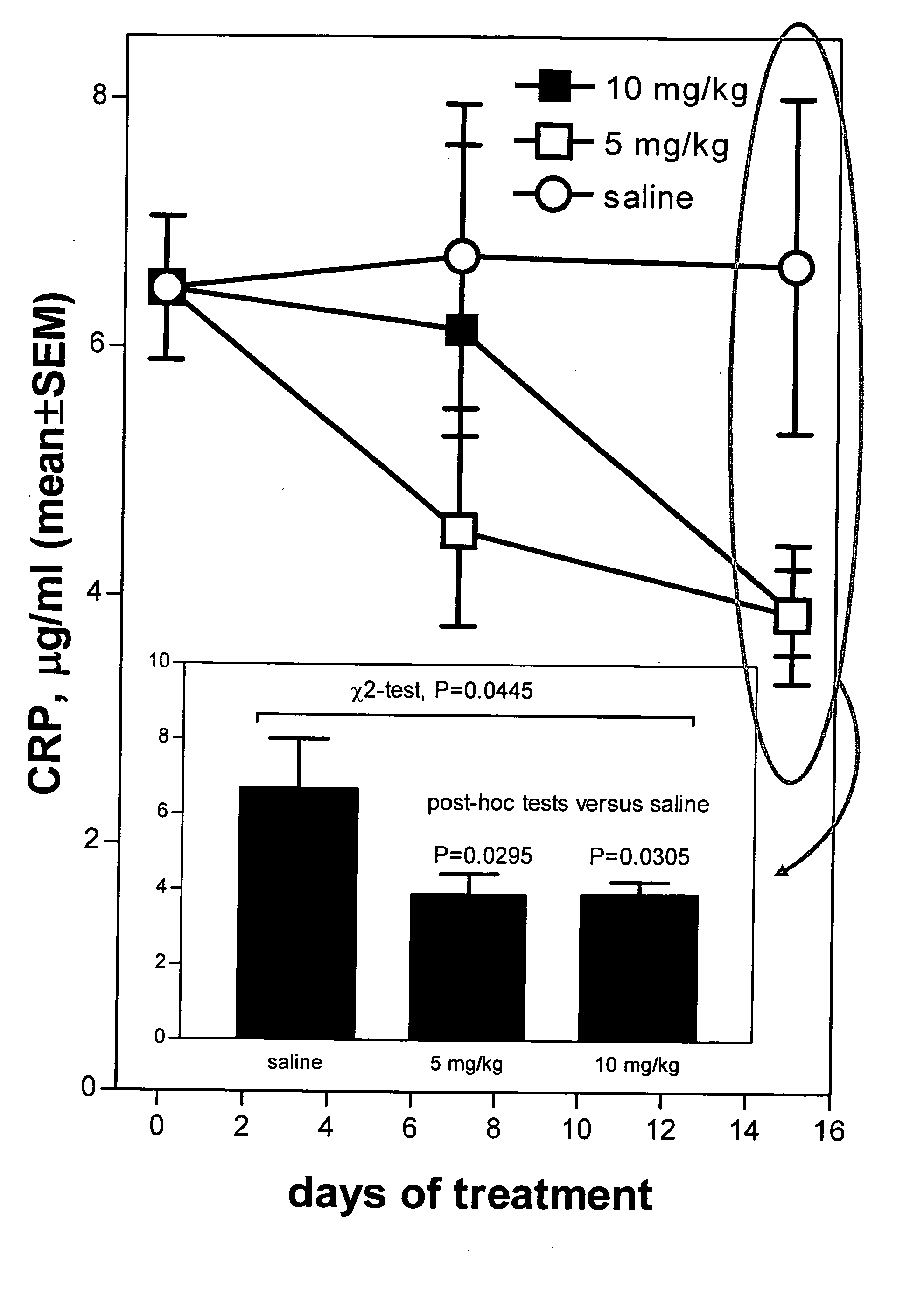
Method of reducing C-reactive protein using growth hormone secretagogues
The present invention relates to a method of reducing C-reactive protein in a subject in need of treatment thereof, wherein the subject is at risk of having or the subject has already had a vascular event or suffering from an inflammatory disease or disorder. In one embodiment, the vascular event is a cardiovascular event (e.g., myocardial infarction). In another embodiment, the vascular event is a cerebrovascular event (e.g., stroke (such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)). In yet another embodiment the vascular event is a peripheral vascular event (e.g., intermittent claudication). The method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of at least one growth hormone secretagogue compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate or solvate thereof. The growth hormone secretagogue can be coadministered with a second growth hormone secretagogue, HMG CoA reductase inhibitor, an ACAT inhibitor, a CETP inhibitor, an anti-inflammatory agent, an ACE inhibitor, a Beta blocker, a cholesterol absorption inhibitor, a nicotonic acid, a fibric acid derivative, a bile acid sequestering agent or a combination thereof.
Owner:HELSINN THERAPEUTICS (US) INC
Method of Isolating the Cerebral Circulation During a Cardiac Procedure
ActiveUS20120172916A1Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesSurgeryParticulatesFilter system
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Deflectable Intravascular Filter
ActiveUS20120172920A1Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesSurgeryParticulatesFilter system
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for detecting blood dynamics of brain blood vessel
InactiveCN1559345AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEvaluation of blood vesselsDiseaseUltrasound doppler
A hemodynamic method and instrument for early diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases features that the Doppler probe and ultrasonography B are used to detect the blood flowing speed, the ultrasonography B is used to detect the physical characteristics of blood vassel, the diameter and wall thickness of blood vessel are measured to obtain the flow of blood in the vessel, and a pressure probe is used to detect blood pressure.
Owner:无锡贝尔森影像技术有限公司
Cerebral vascular reactivity monitoring
InactiveUS20100030054A1Evaluation of blood vesselsCatheterLinear correlationCerebrovascular reactivity
A monitoring device may include logic to receive arterial blood pressure data associated with a patient and receive tissue hemoglobin data associated with the patient. The logic may also calculate a linear correlation between the arterial blood pressure data and the tissue hemoglobin data. The correlation may be used to assess vascular reactivity.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method of accessing the left common carotid artery
ActiveUS8876796B2Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesGuide wiresParticulatesFilter system
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com