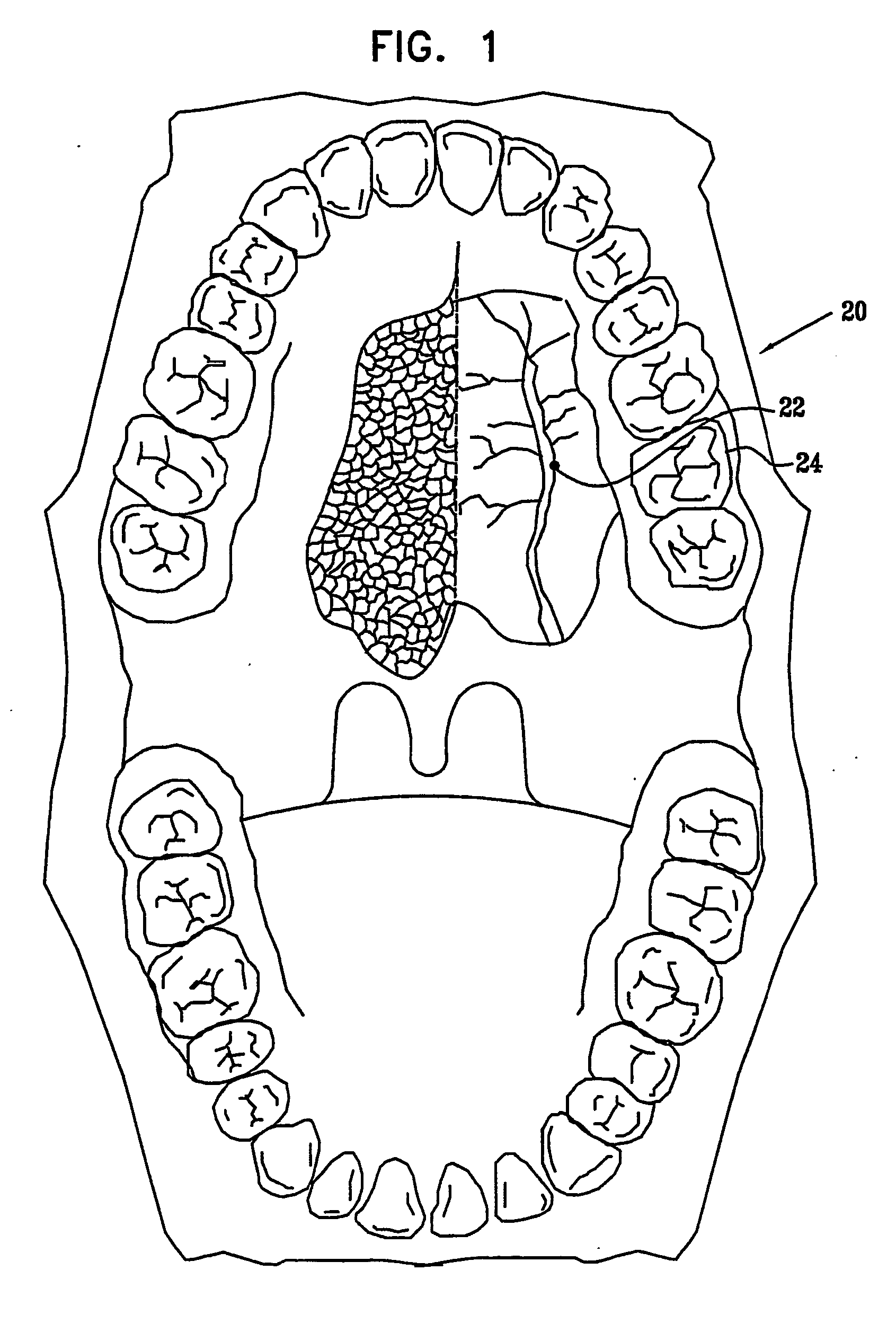
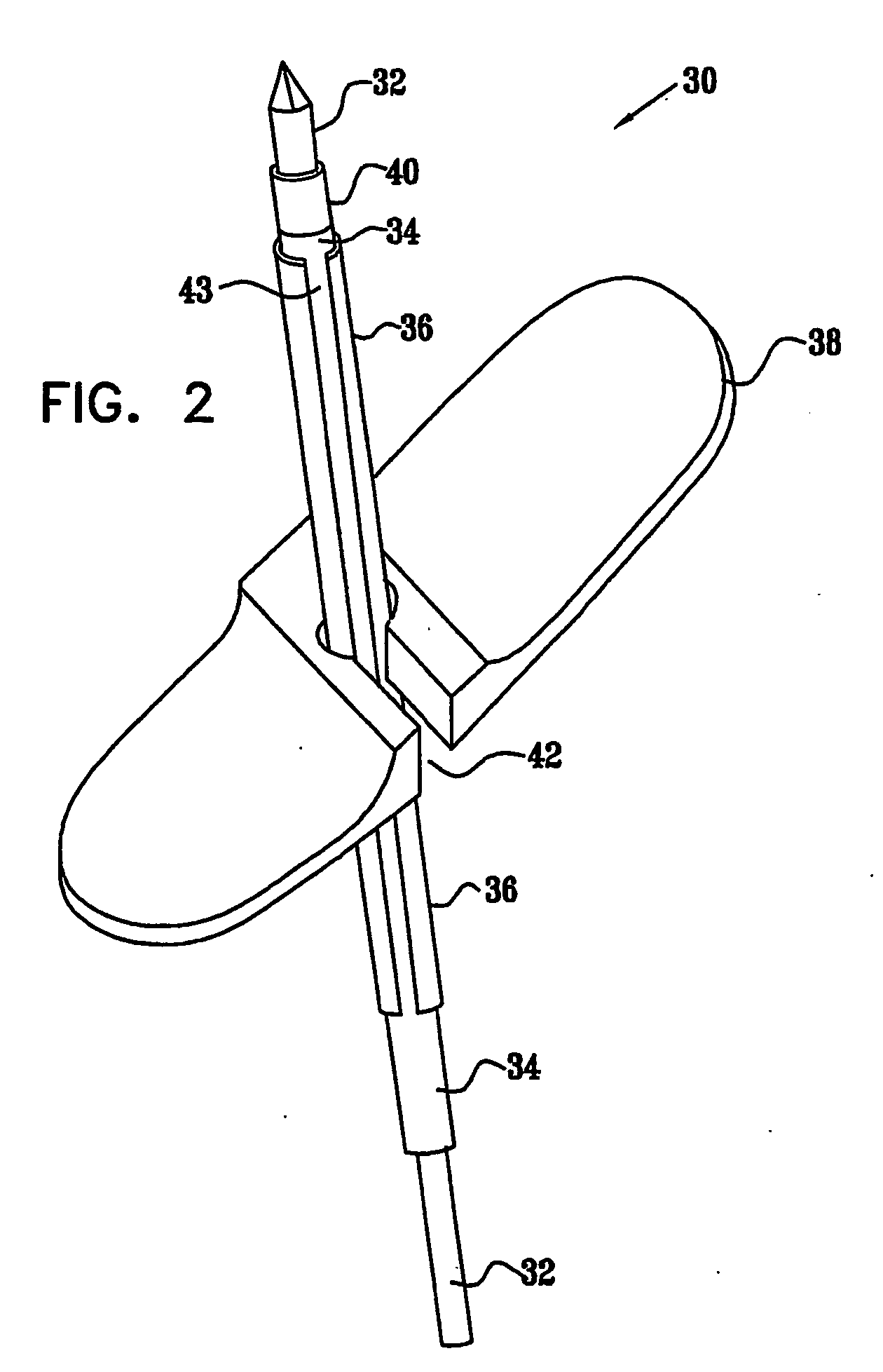
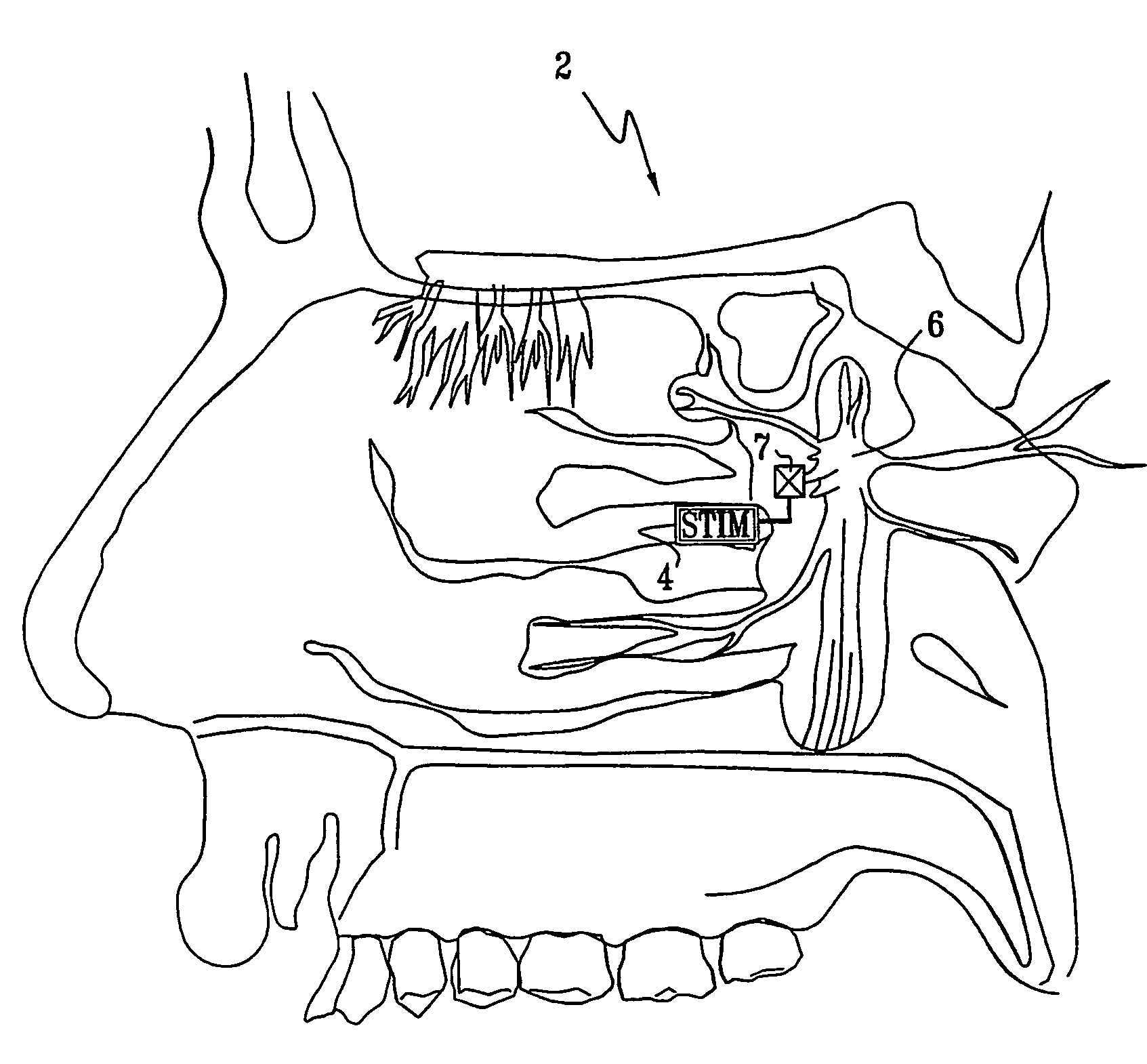
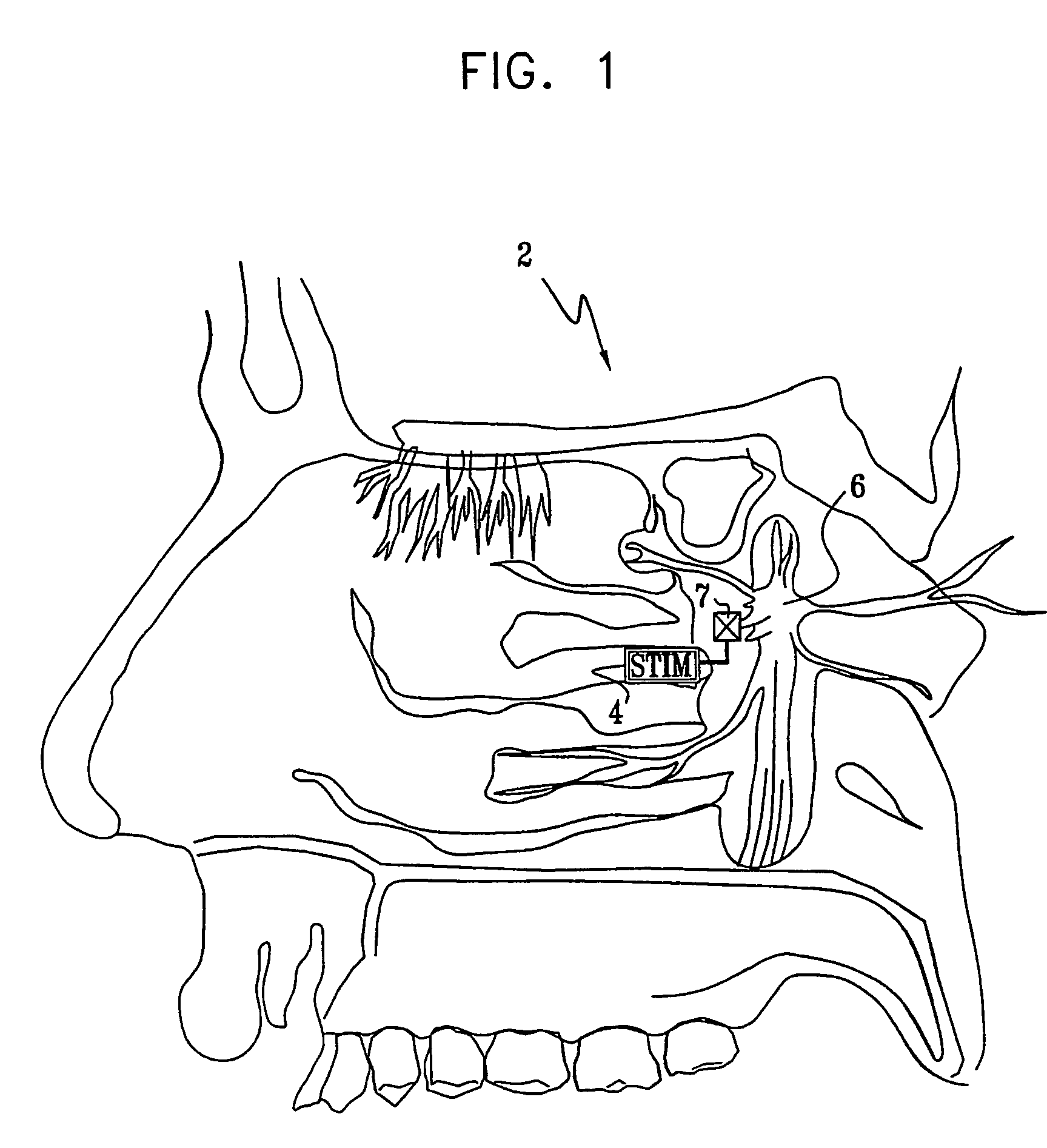
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
391 results about "Ganglion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
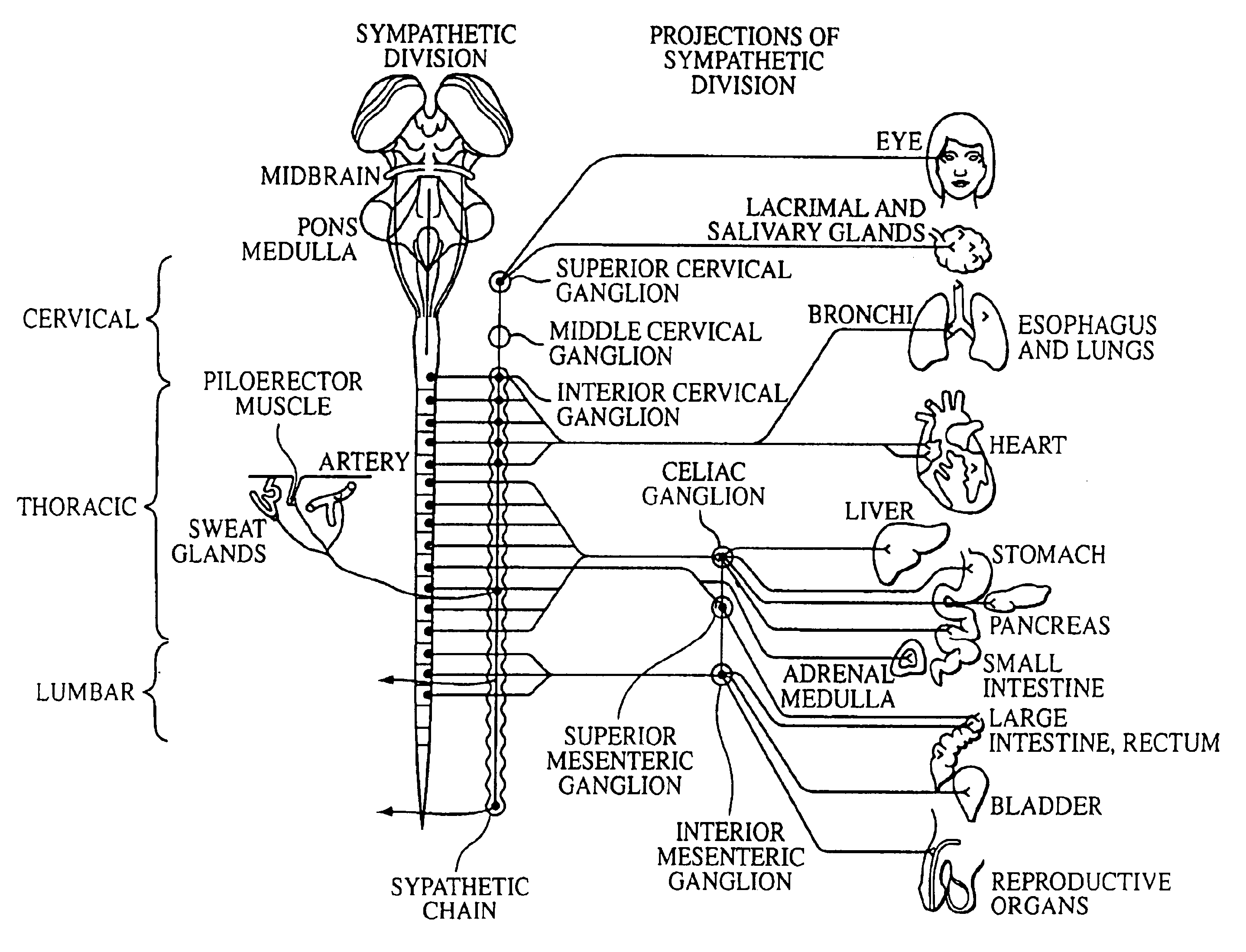
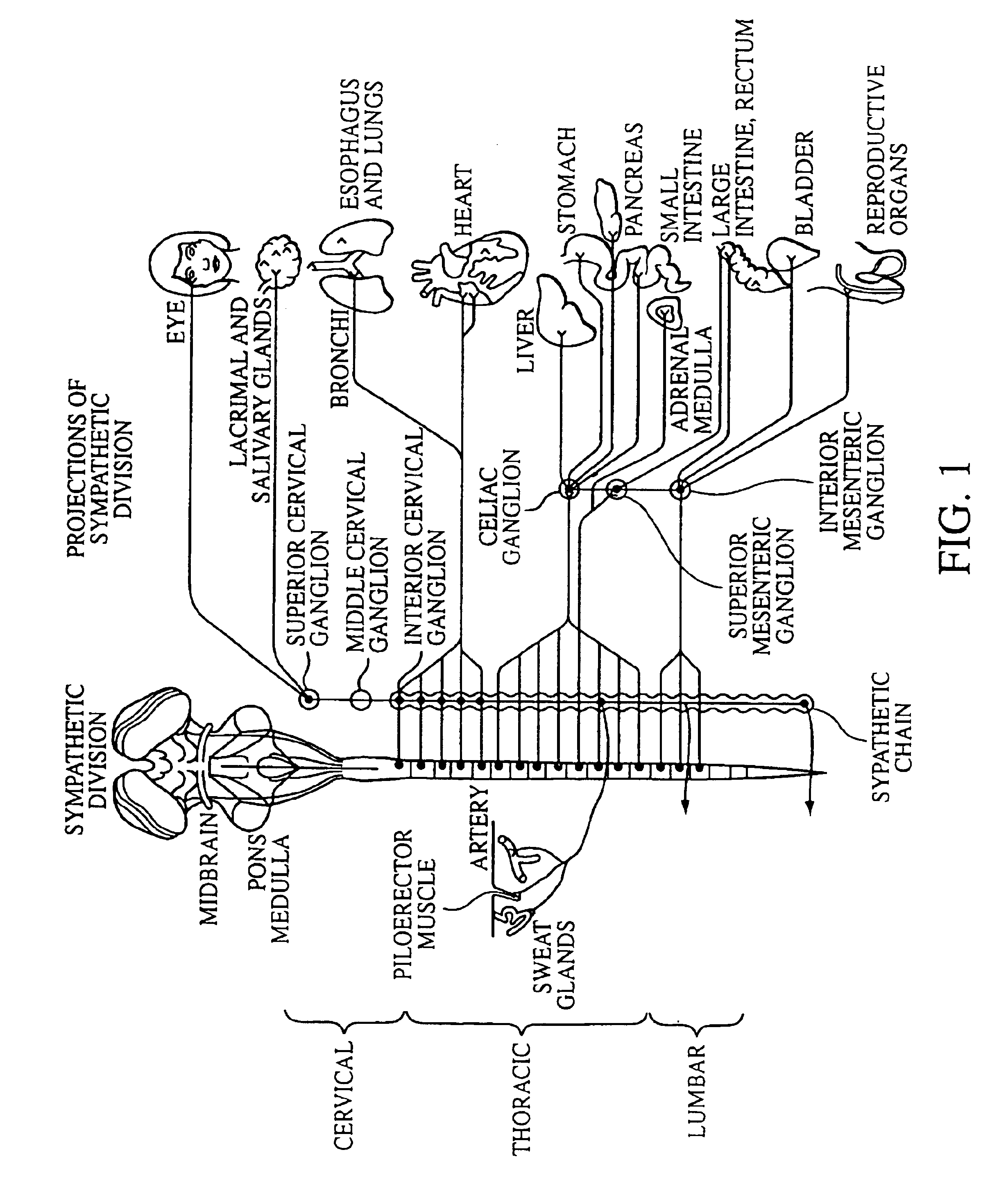
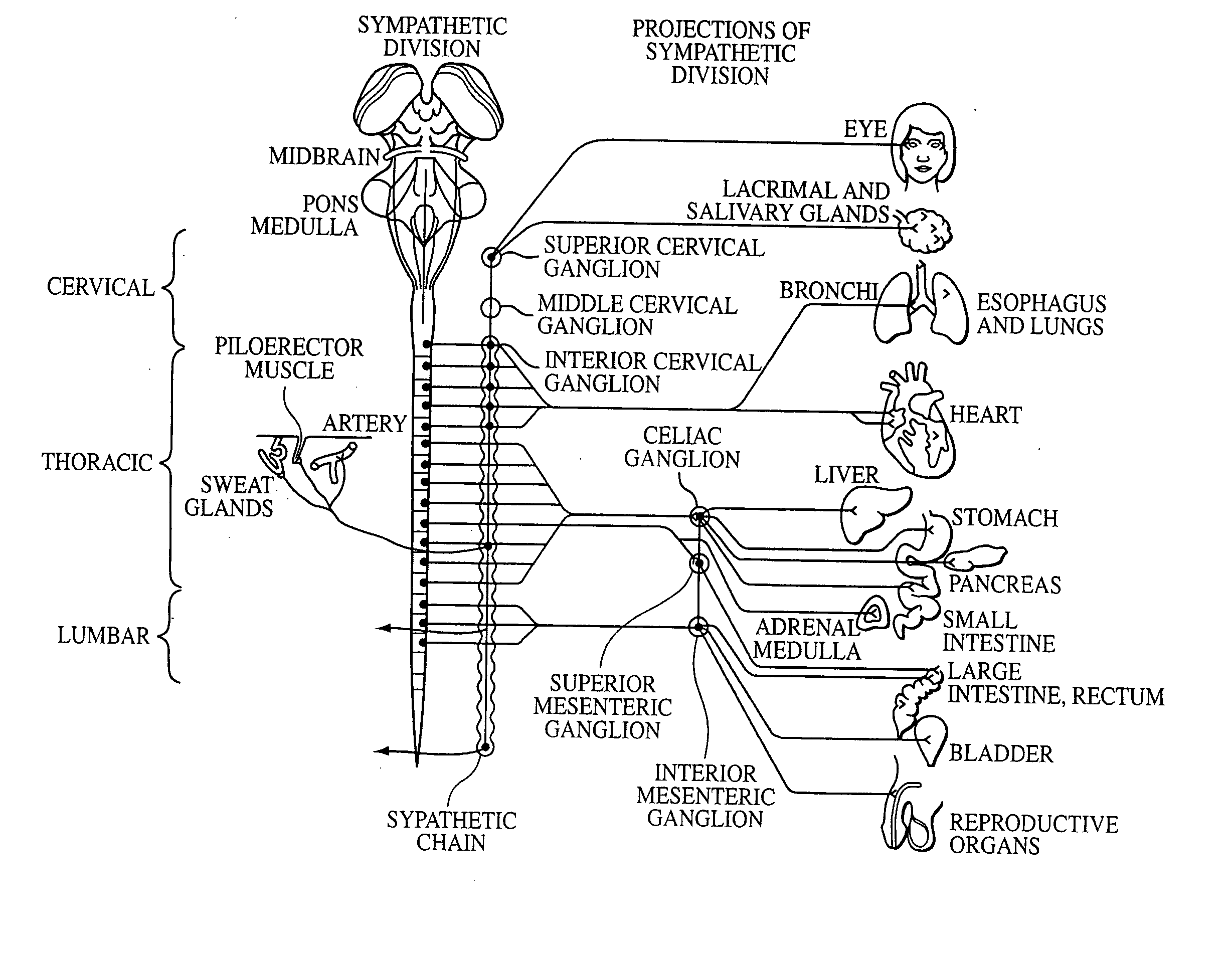
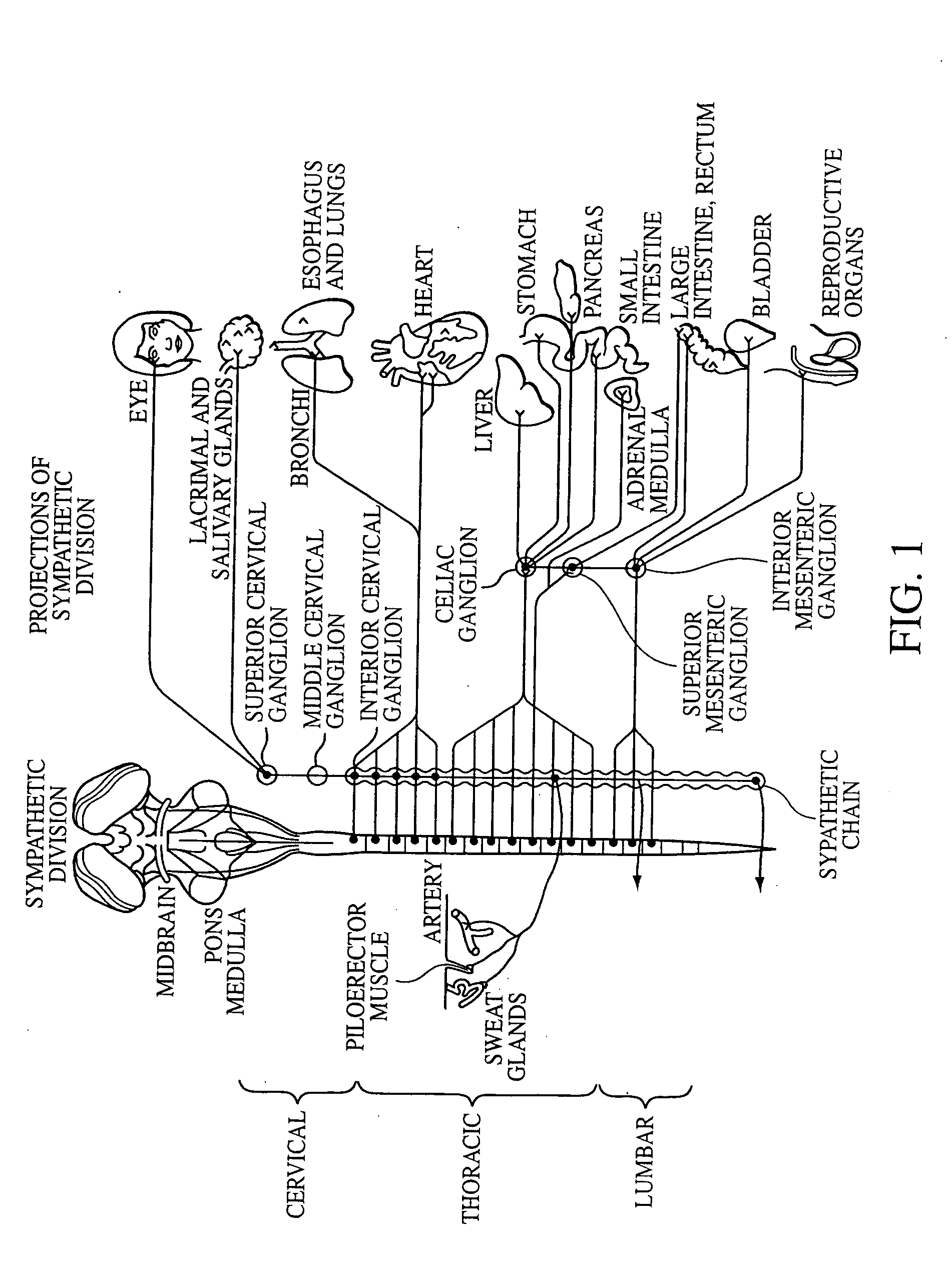
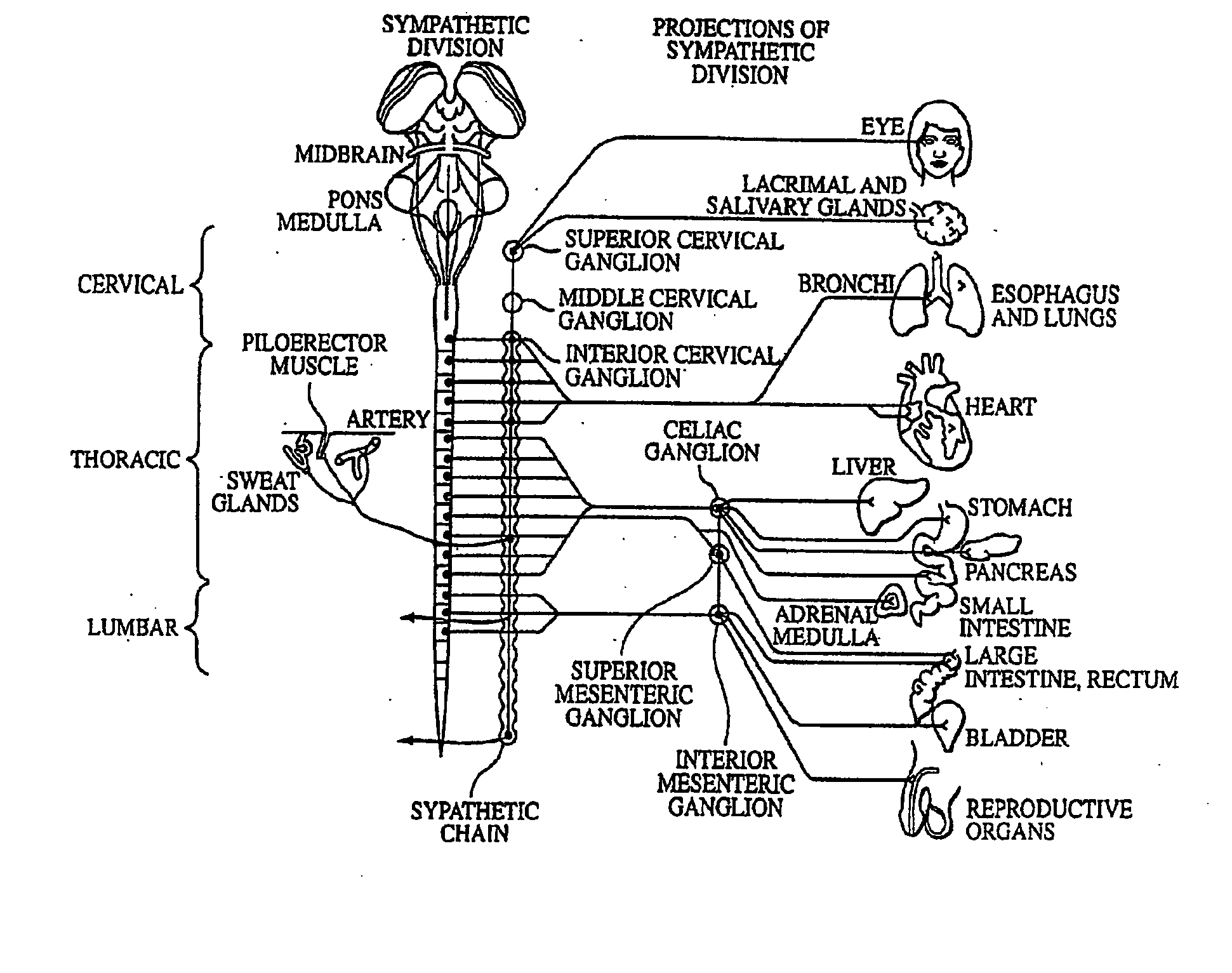
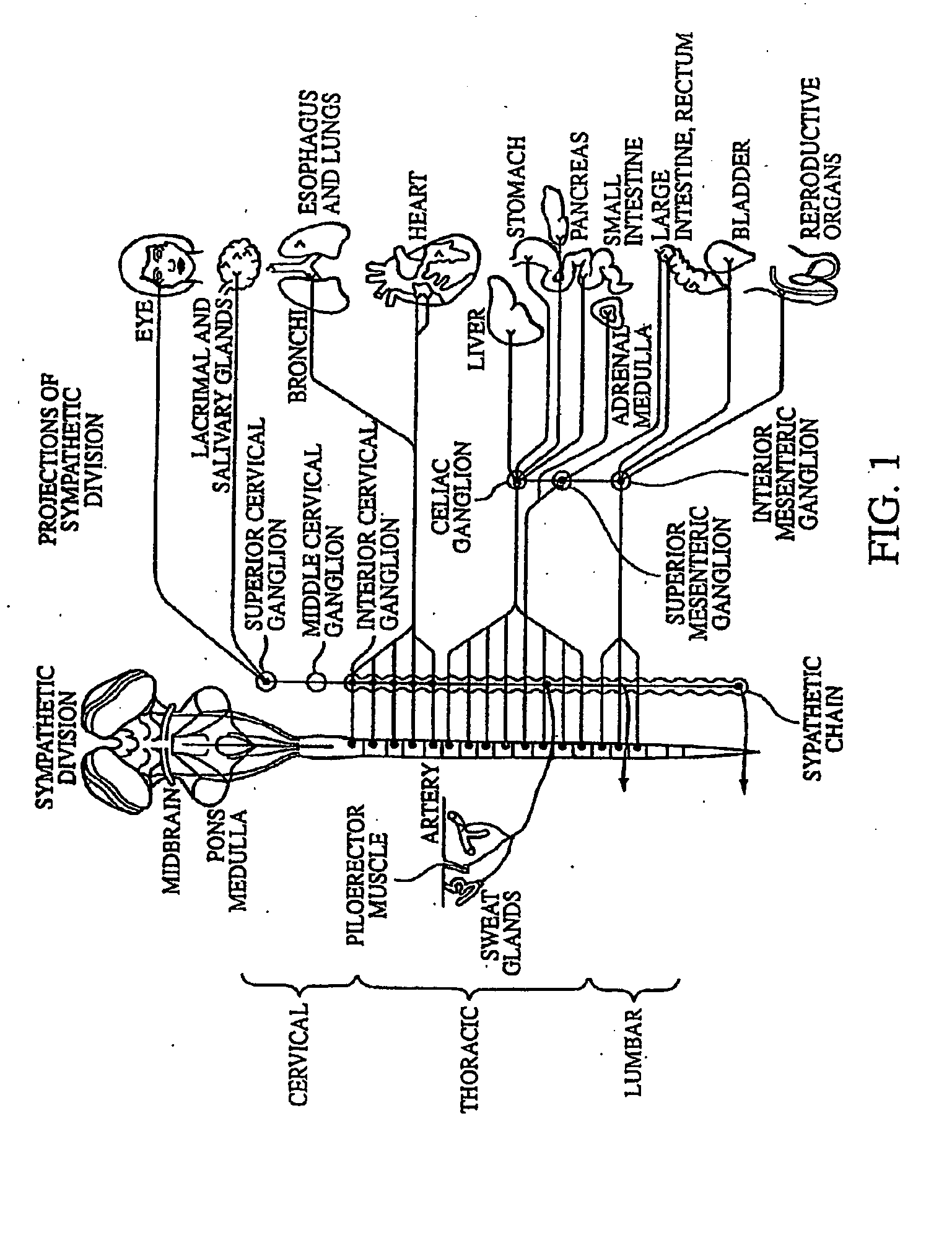
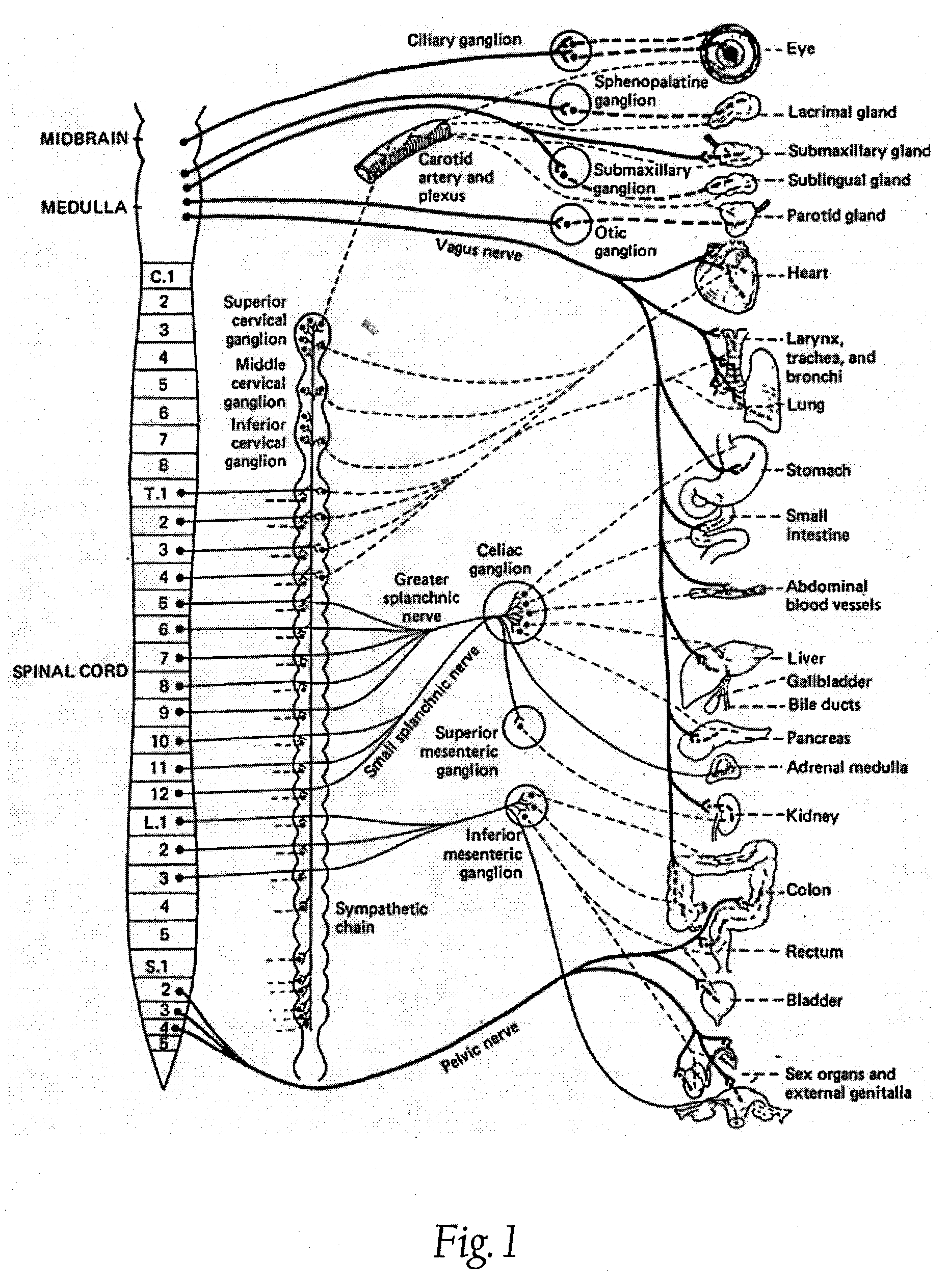
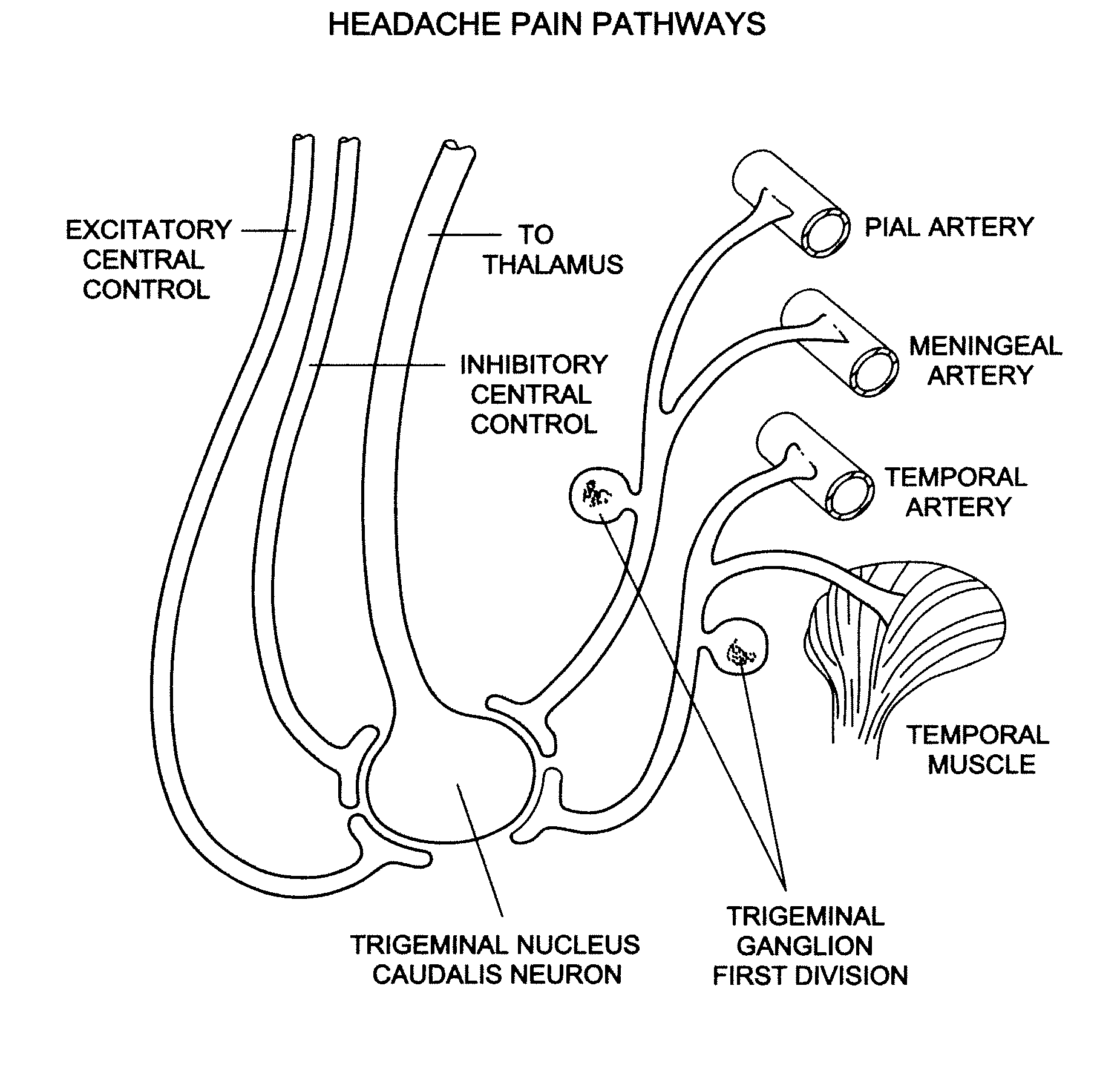
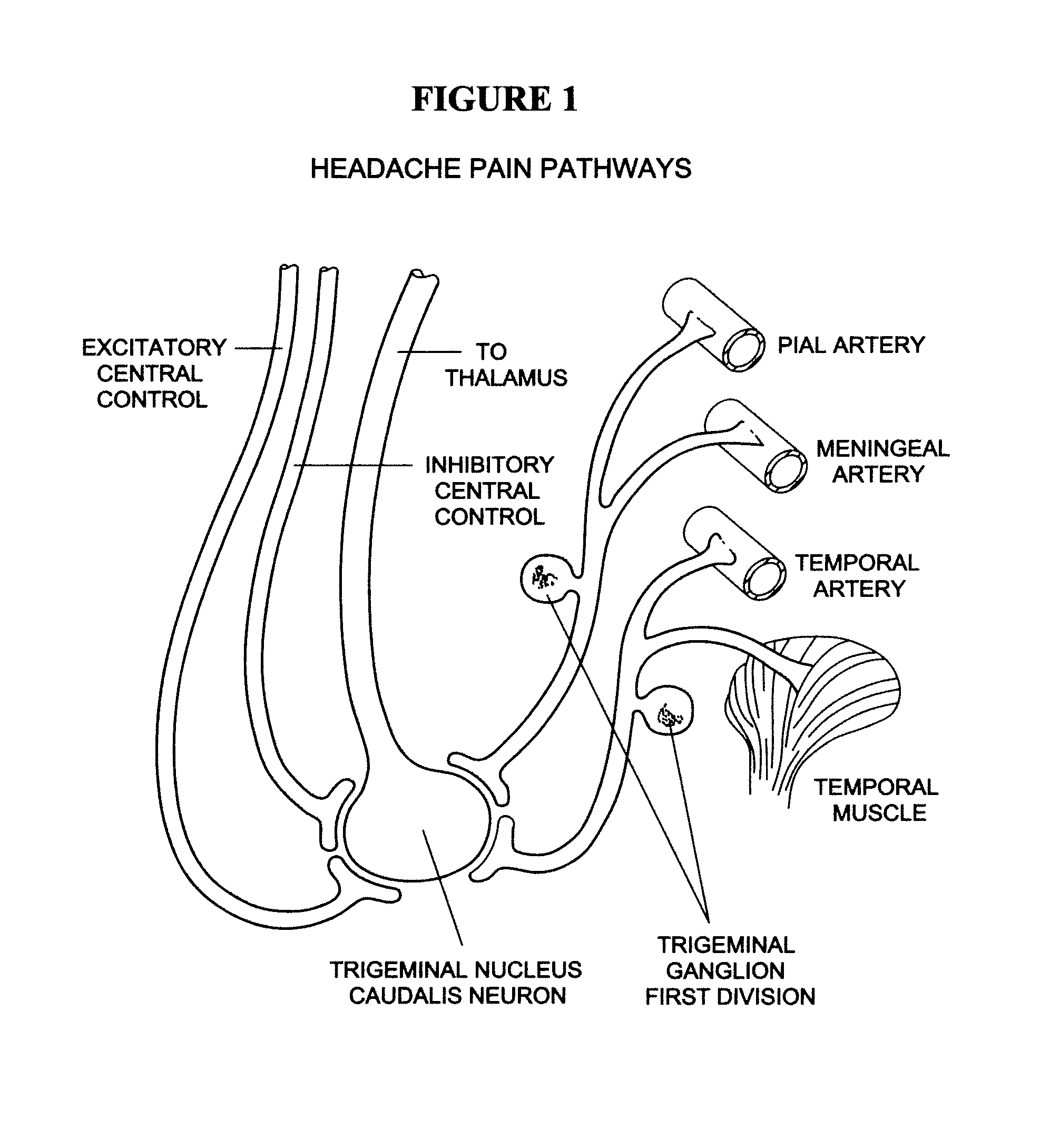
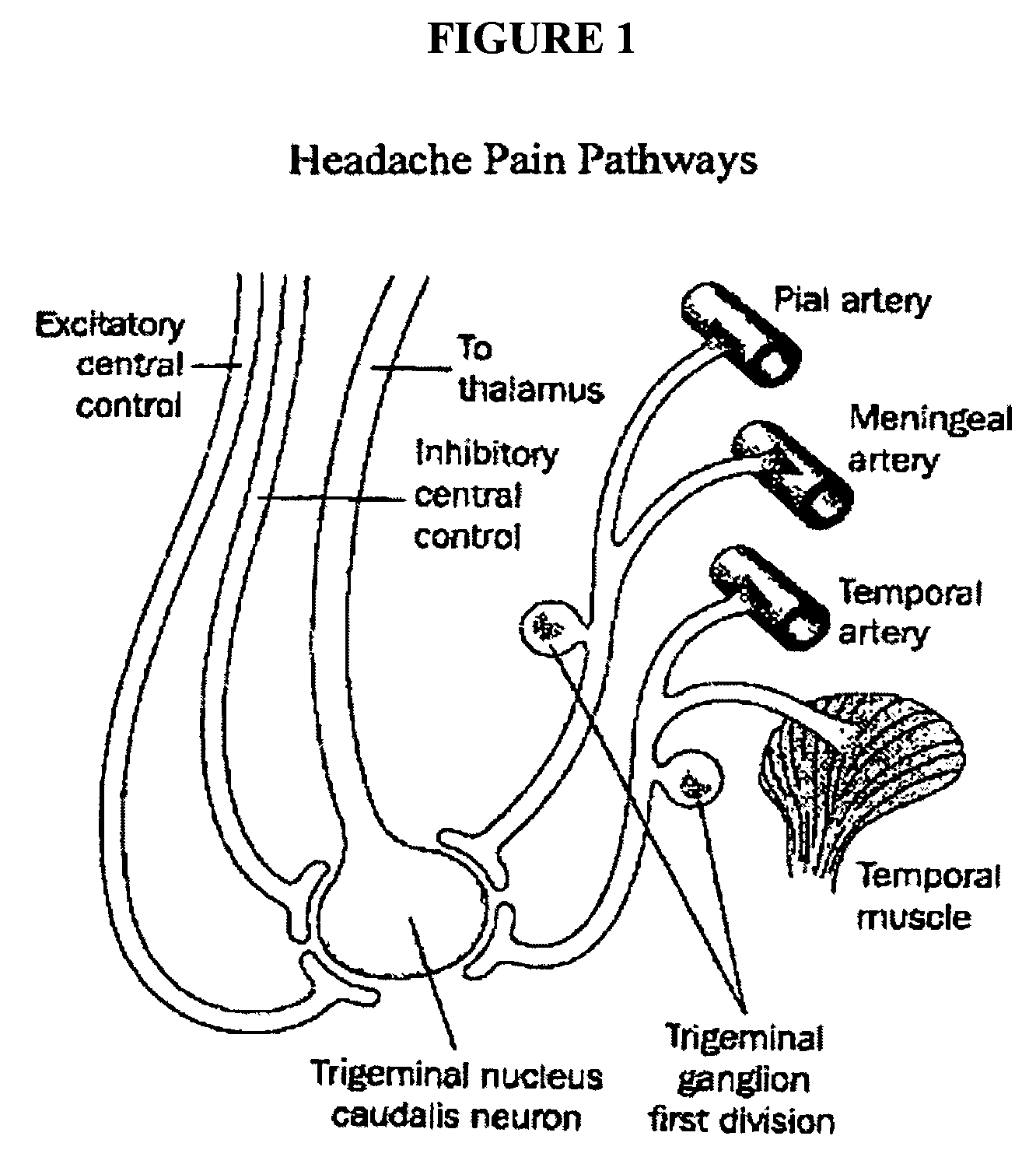
A ganglion is a nerve cell cluster or a group of nerve cell bodies located in the autonomic nervous system and sensory system, mostly outside the central nervous system except certain nuclei. Ganglia house the cell bodies of afferent nerves (input nerve fibers) and efferent nerves (output/motor nerve fibers).
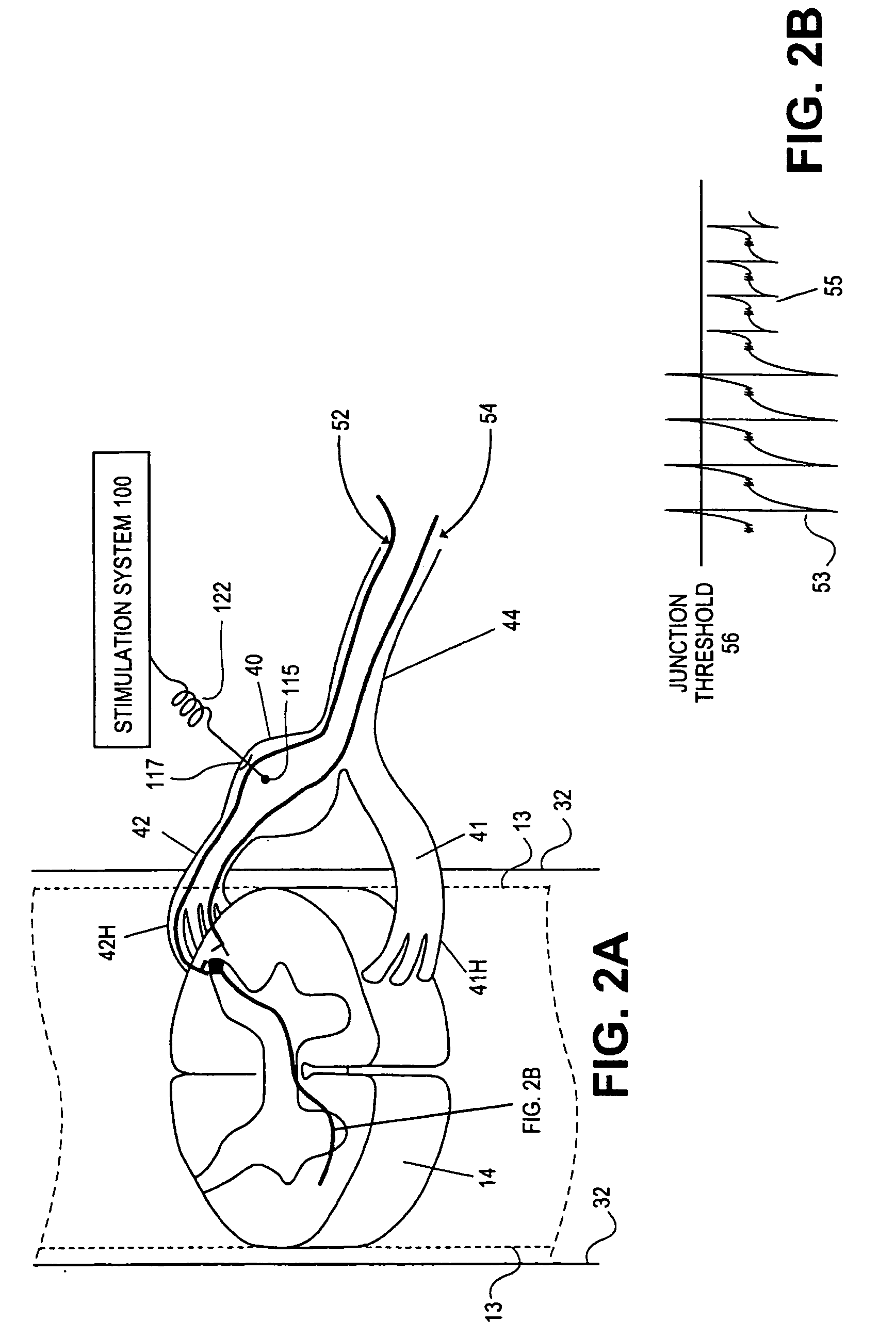
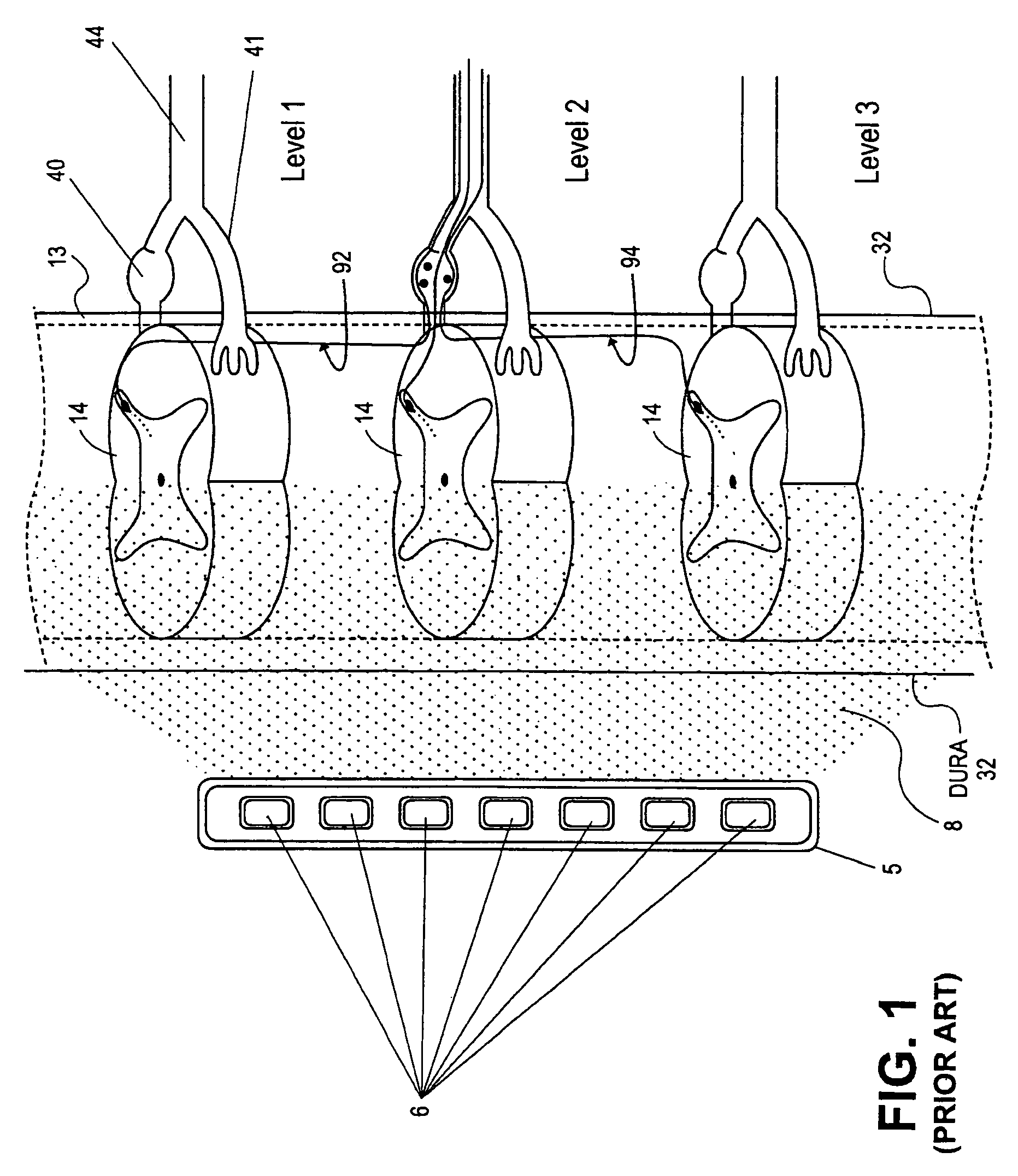
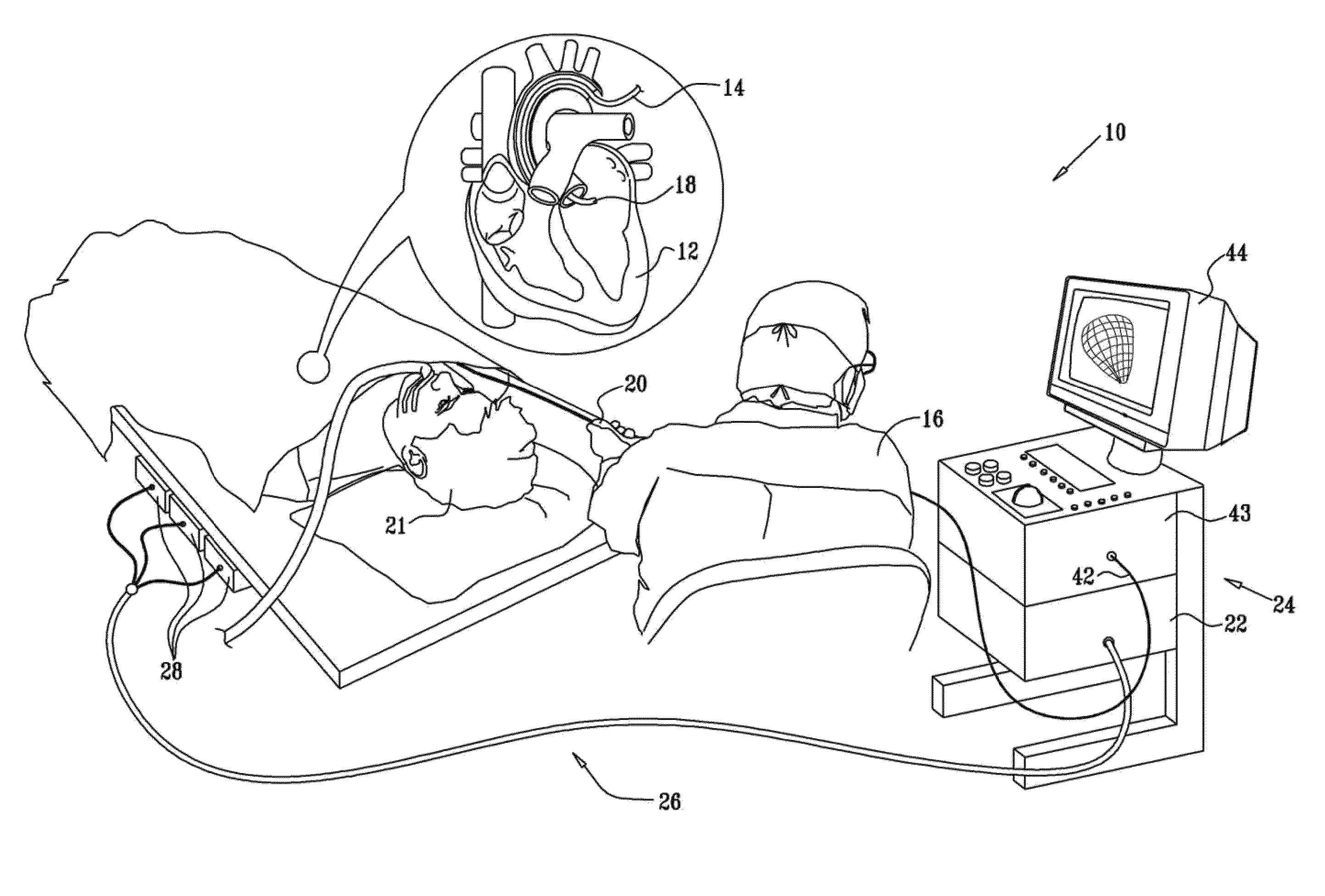
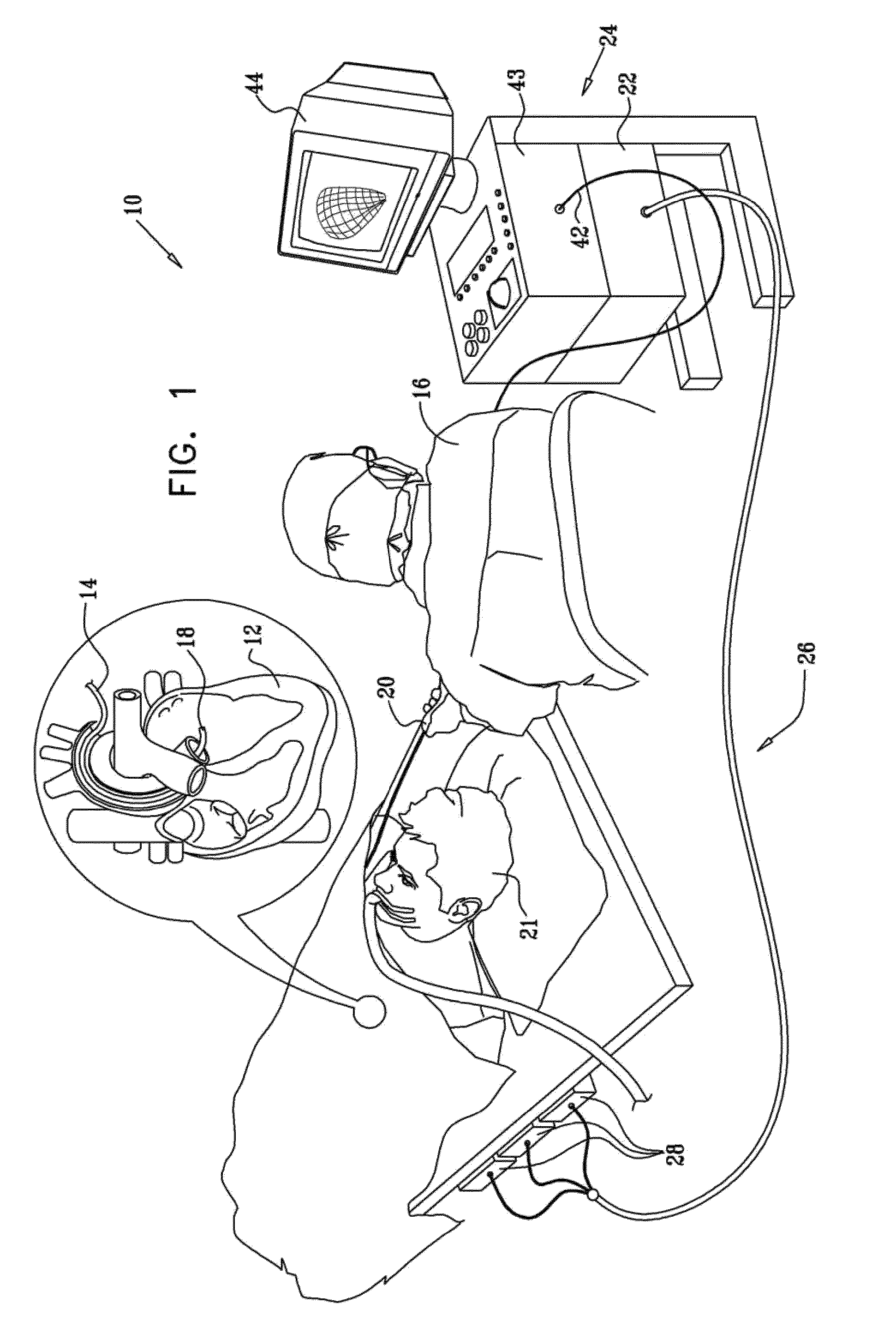
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS6885888B2Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
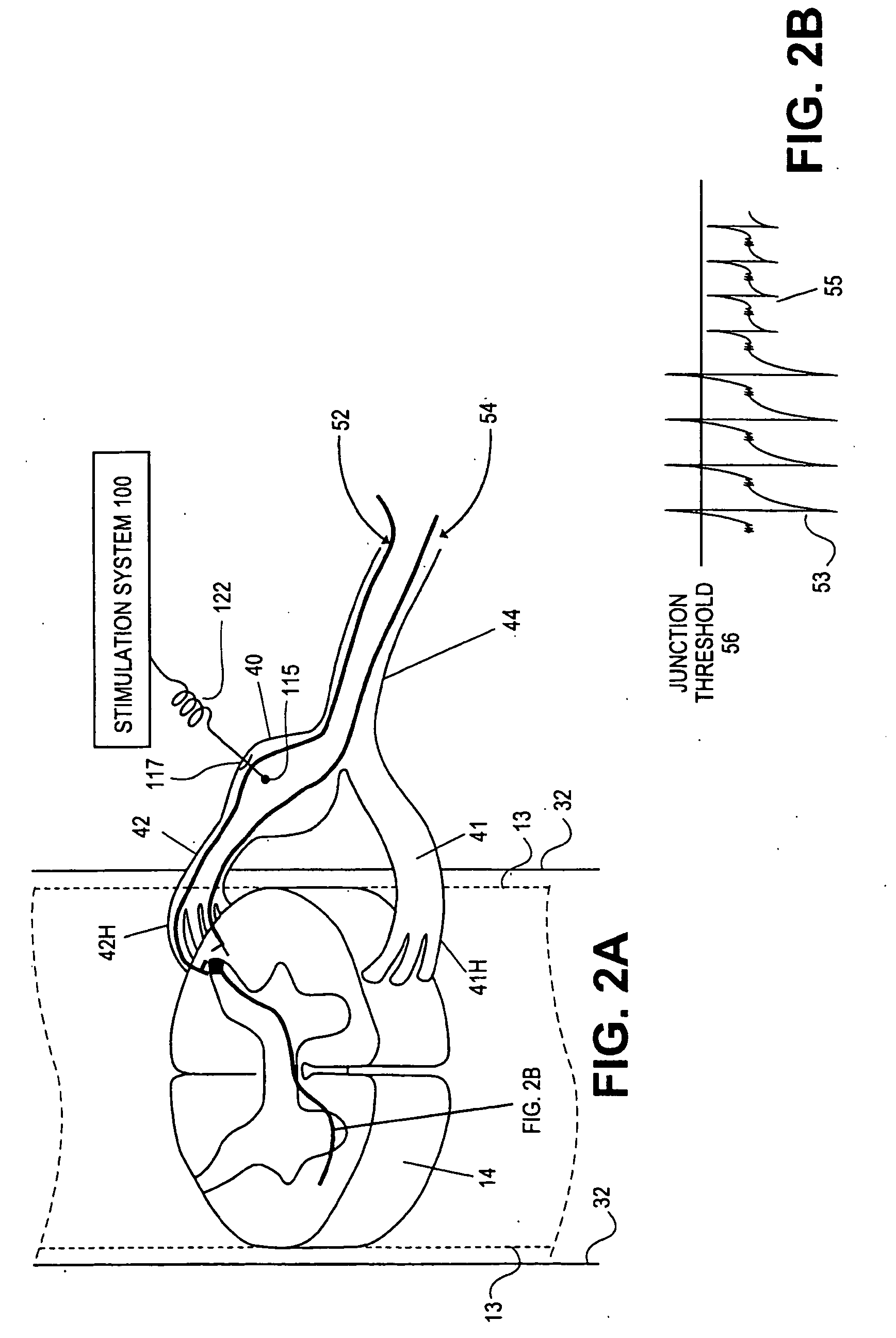
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065573A1Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
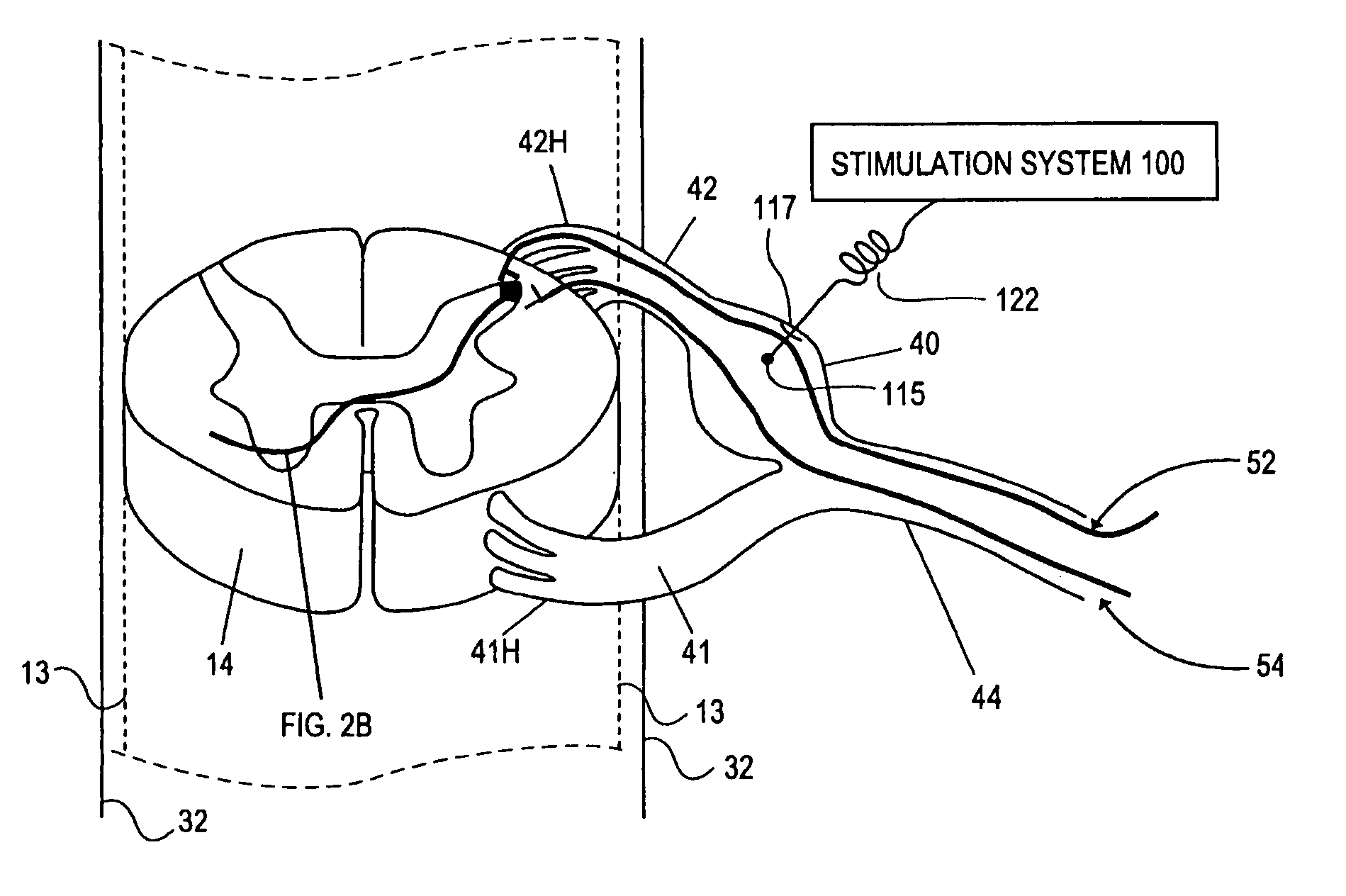
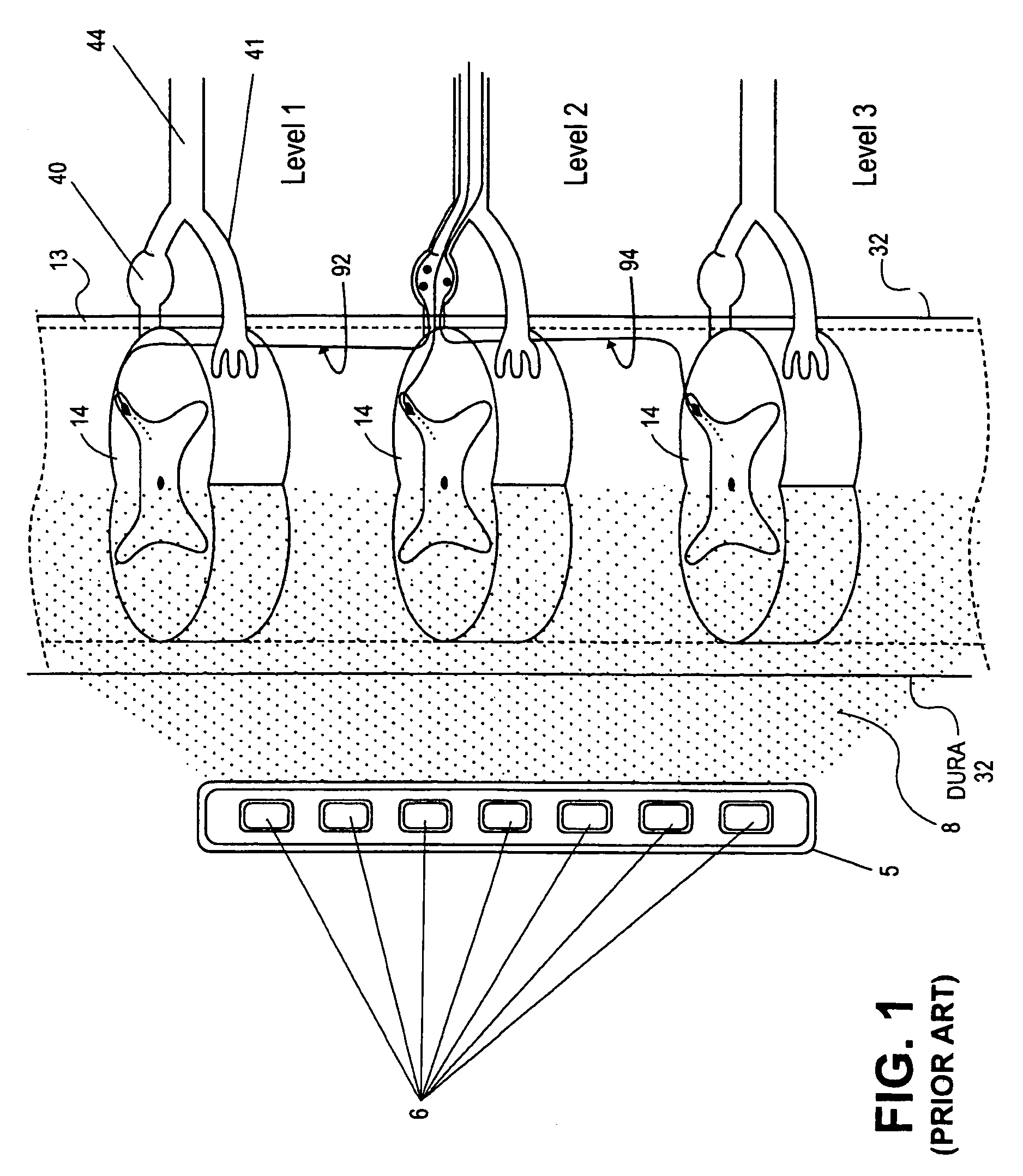
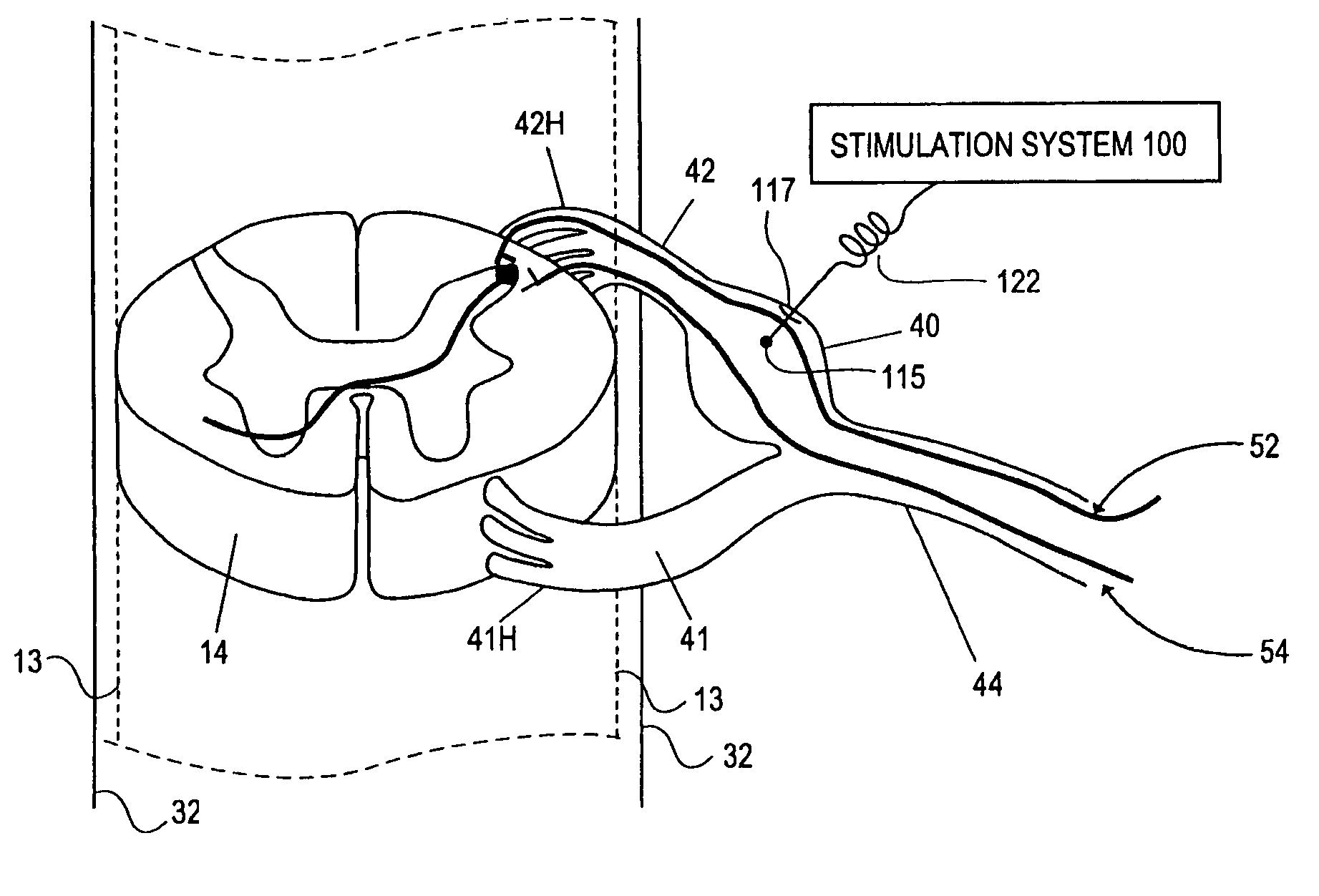
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
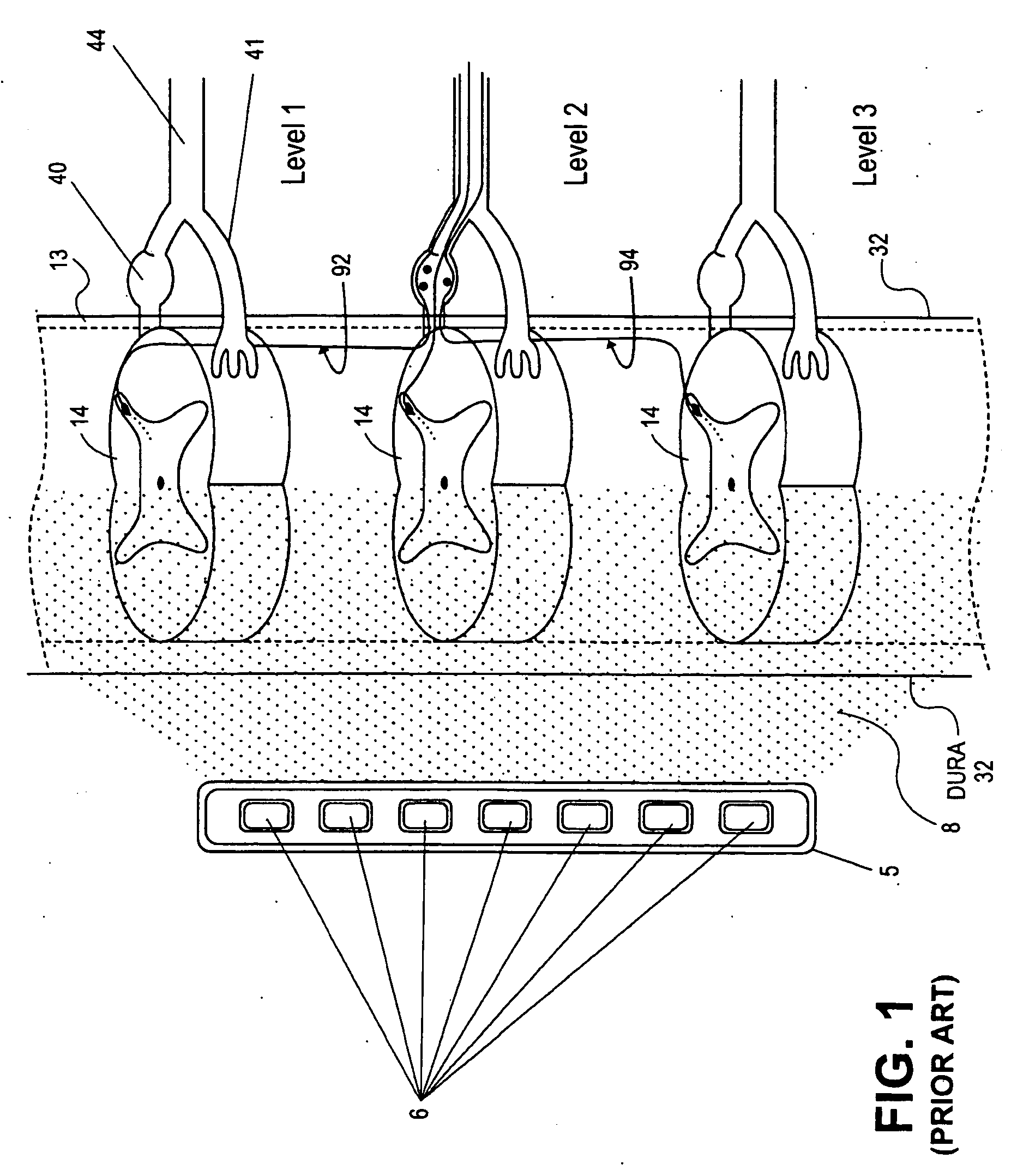
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065562A1Convenient treatmentModulating levelSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
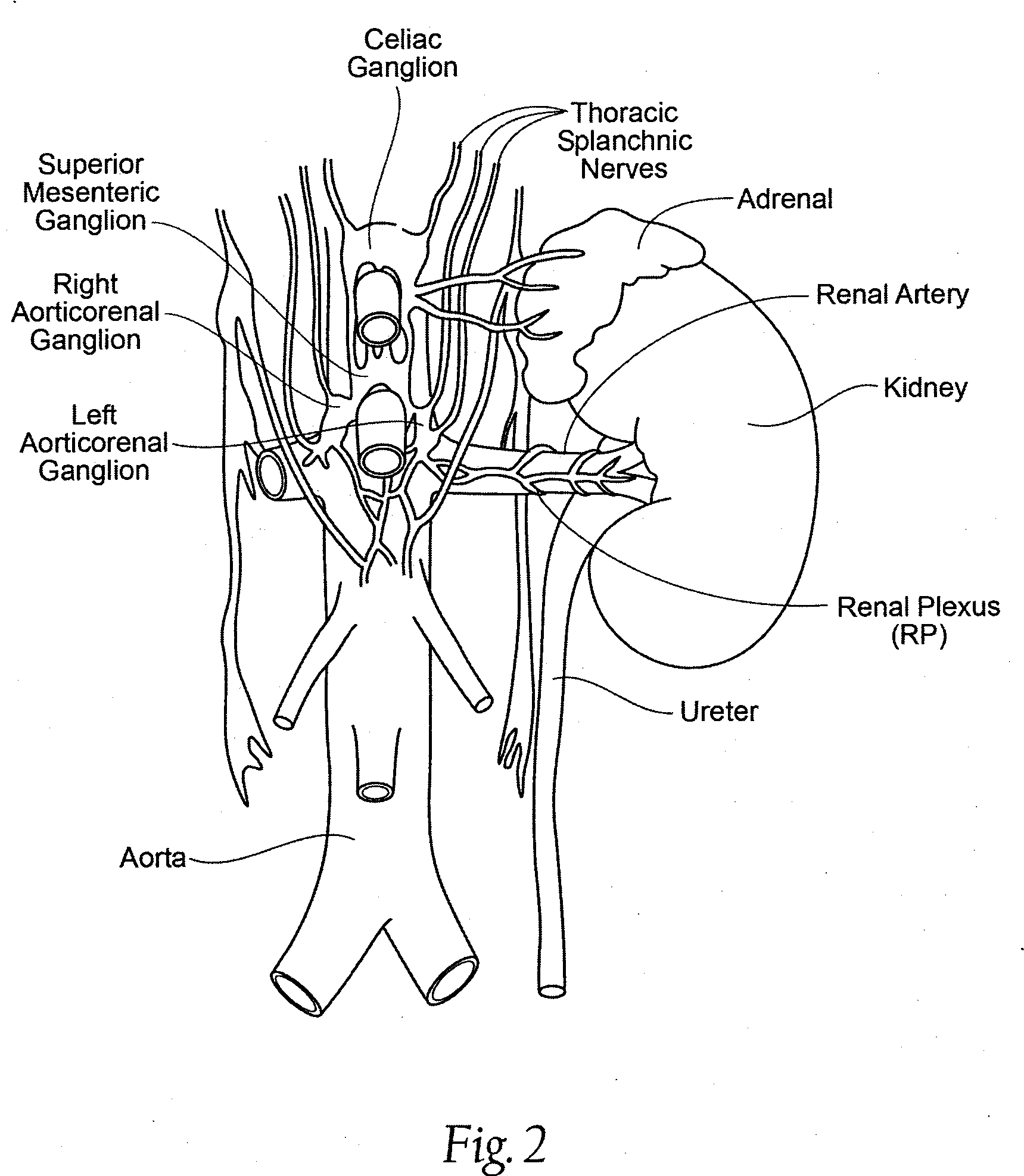
Methods and apparatus for renal neuromodulation via stereotactic radiotherapy
InactiveUS20110200171A1Precise positioningReduce and minimize exposureUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsDiseaseStereotactic radiotherapy
The present disclosure describes methods and apparatus for renal neuromodulation via stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of hypertension, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, insulin resistance, metabolic disorder or other ailments. Renal neuromodulation may be achieved by locating renal nerves and then utilizing stereotactic radiotherapy to expose the renal nerves to a radiation dose sufficient to reduce neural activity. A neural location element may be provided for locating target renal nerves, and a stereotactic radiotherapy system may be provided for exposing the located renal nerves to a radiation dose sufficient to reduce the neural activity, with reduced or minimized radiation exposure in adjacent tissue. Renal nerves may be located and targeted at the level of the ganglion and / or at postganglionic positions, as well as at pre-ganglionic positions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Methods and systems for modulating neural tissue
Some embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for modulating neural tissue including systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of targeted neural tissue. Targeted neural tissue may include one or more ganglia including those of the spinal nerves in the dorsal root and the sympathetic chain. Methods also include implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a dorsal root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
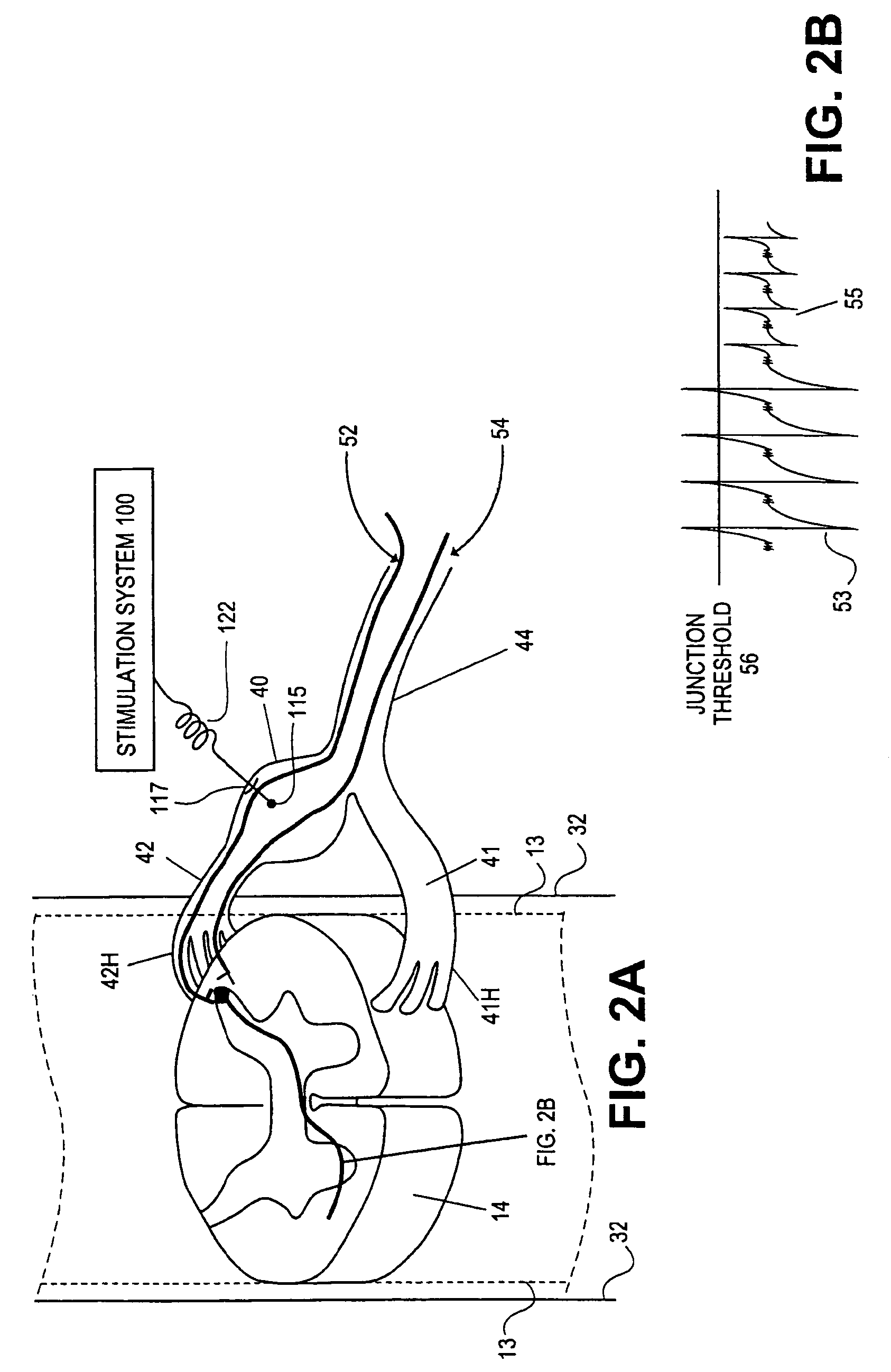
Stimulation for treating and diagnosing conditions
InactiveUS20050159790A1Increasing and reducing cortical blood flowMinimize damageHead electrodesMedical devicesPower flowWhole body
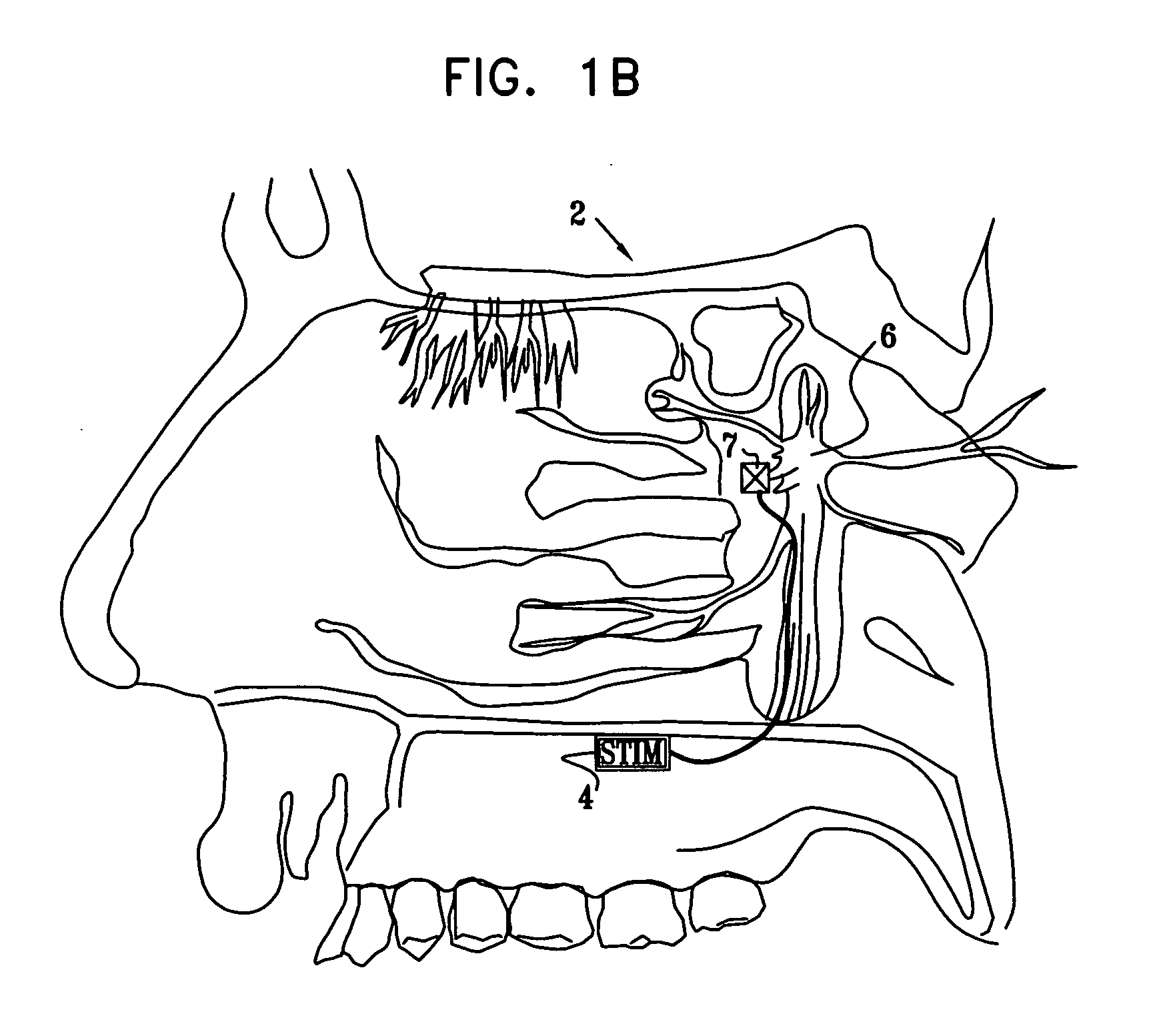
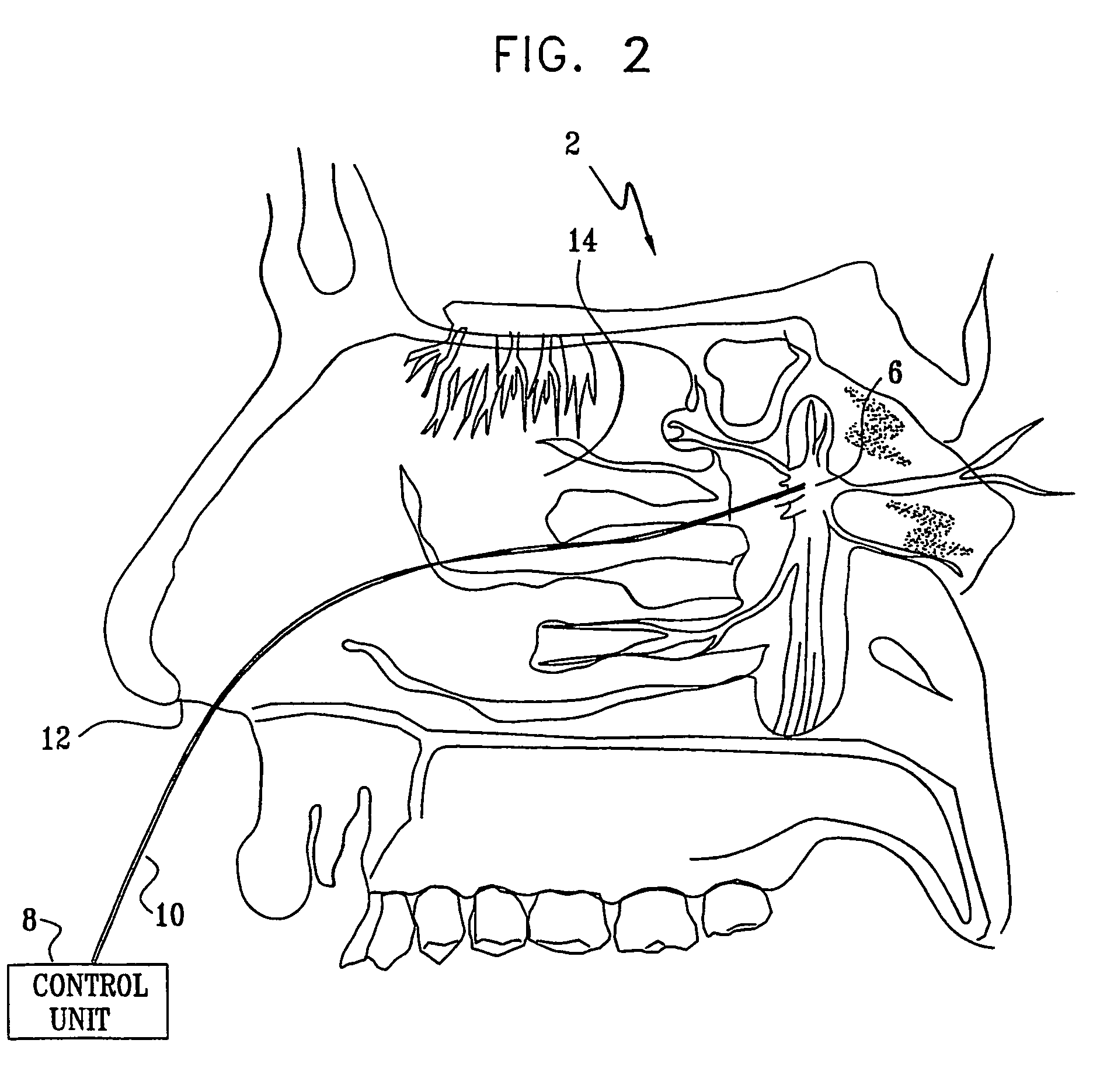
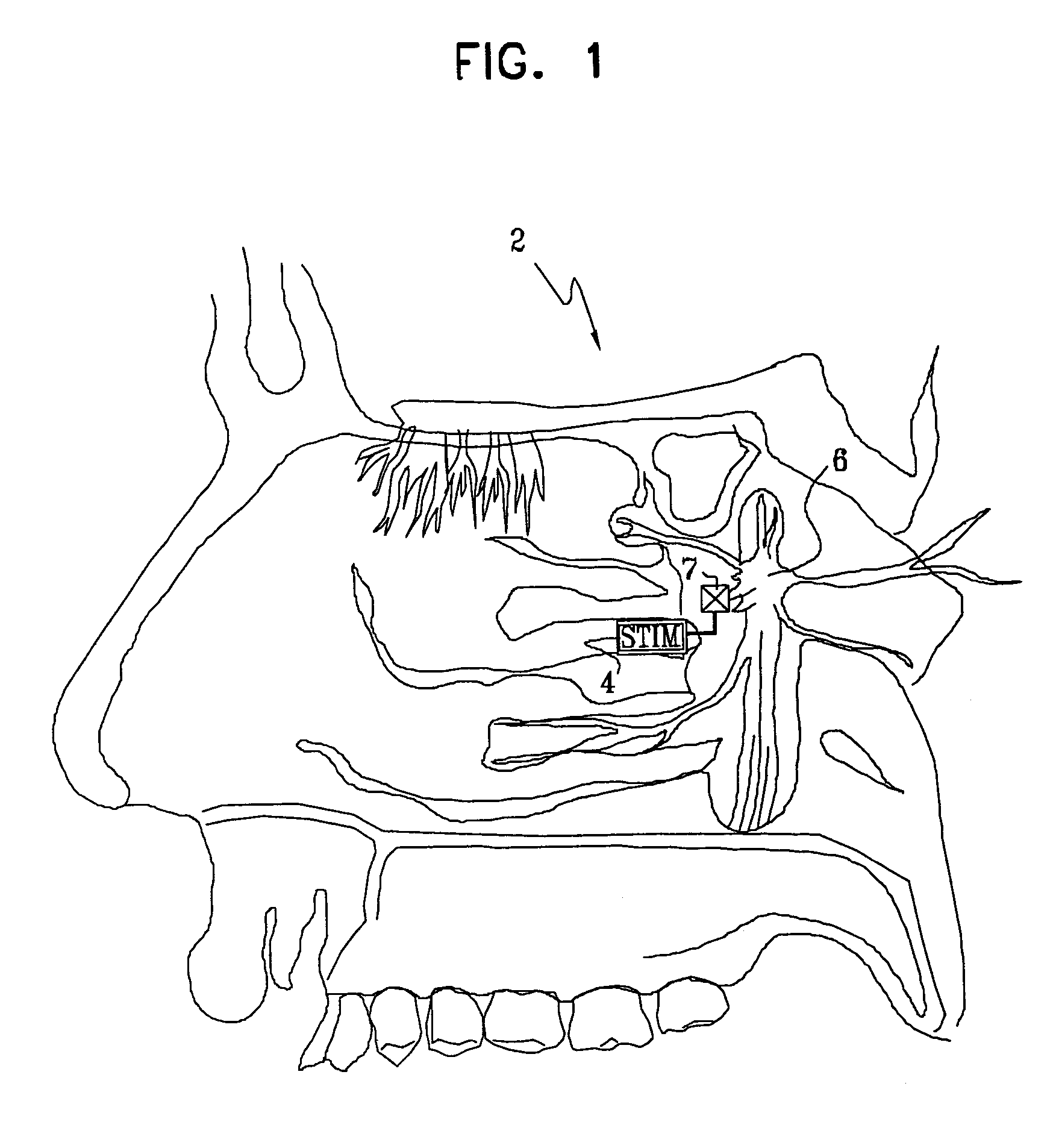
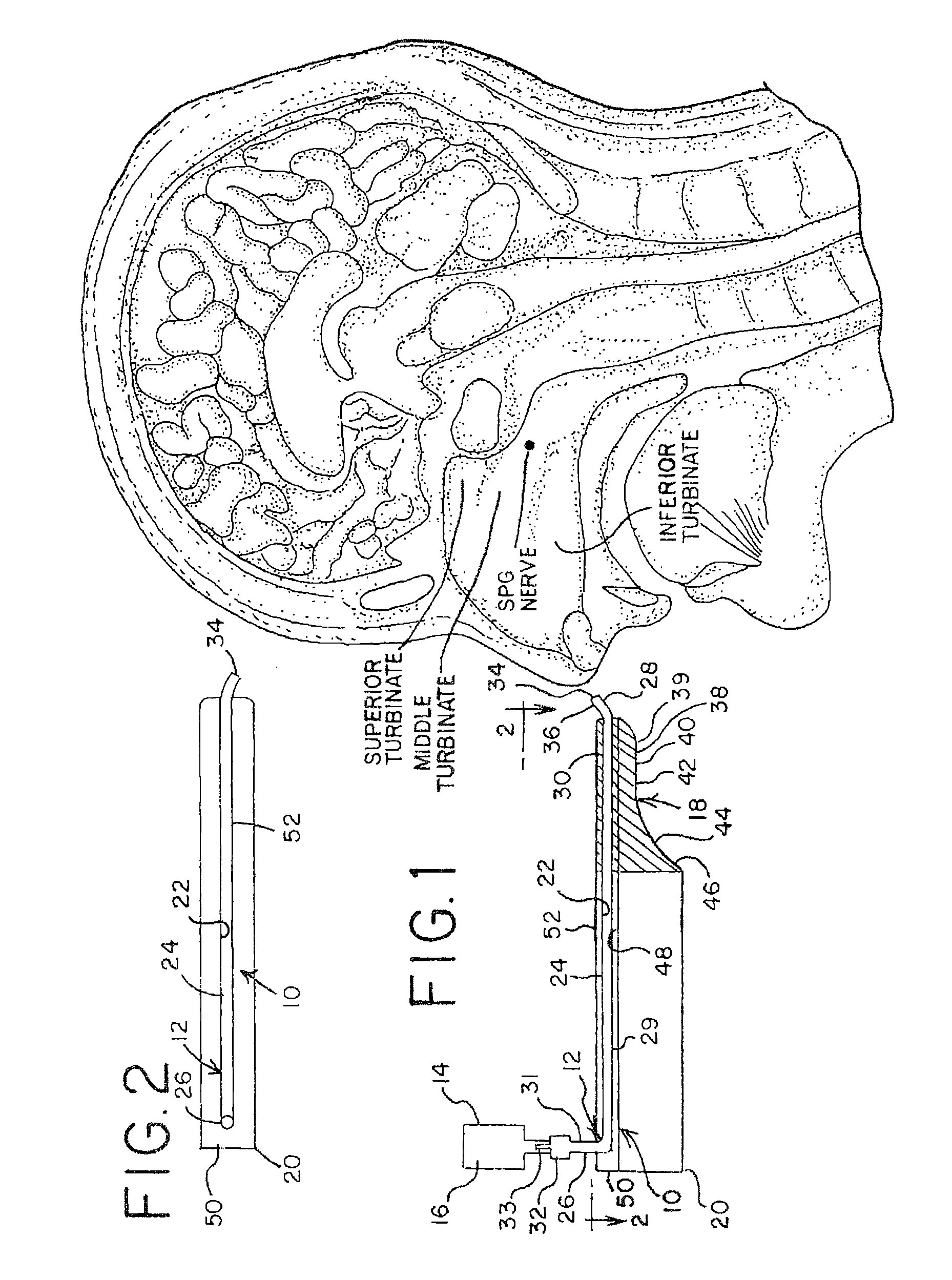
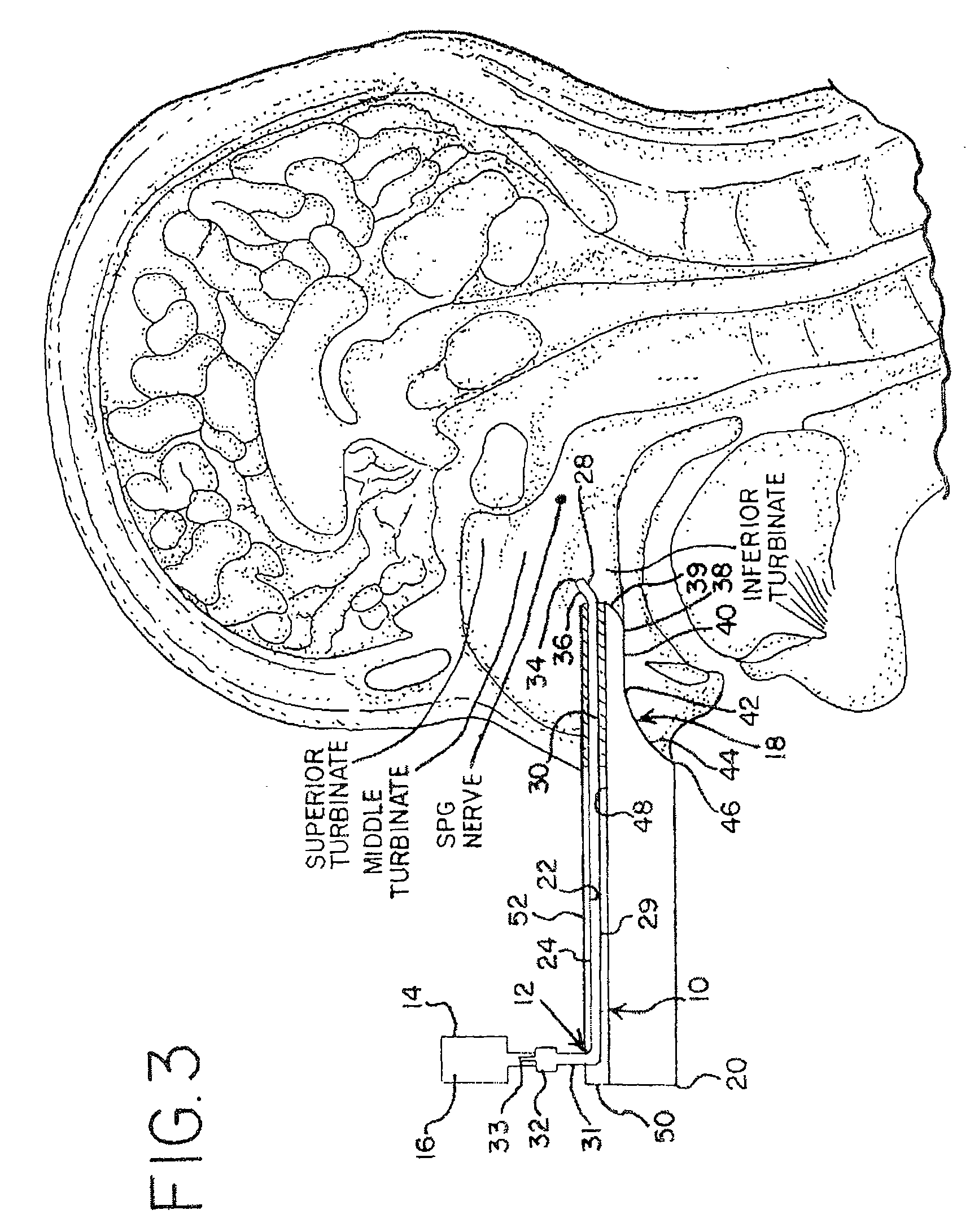
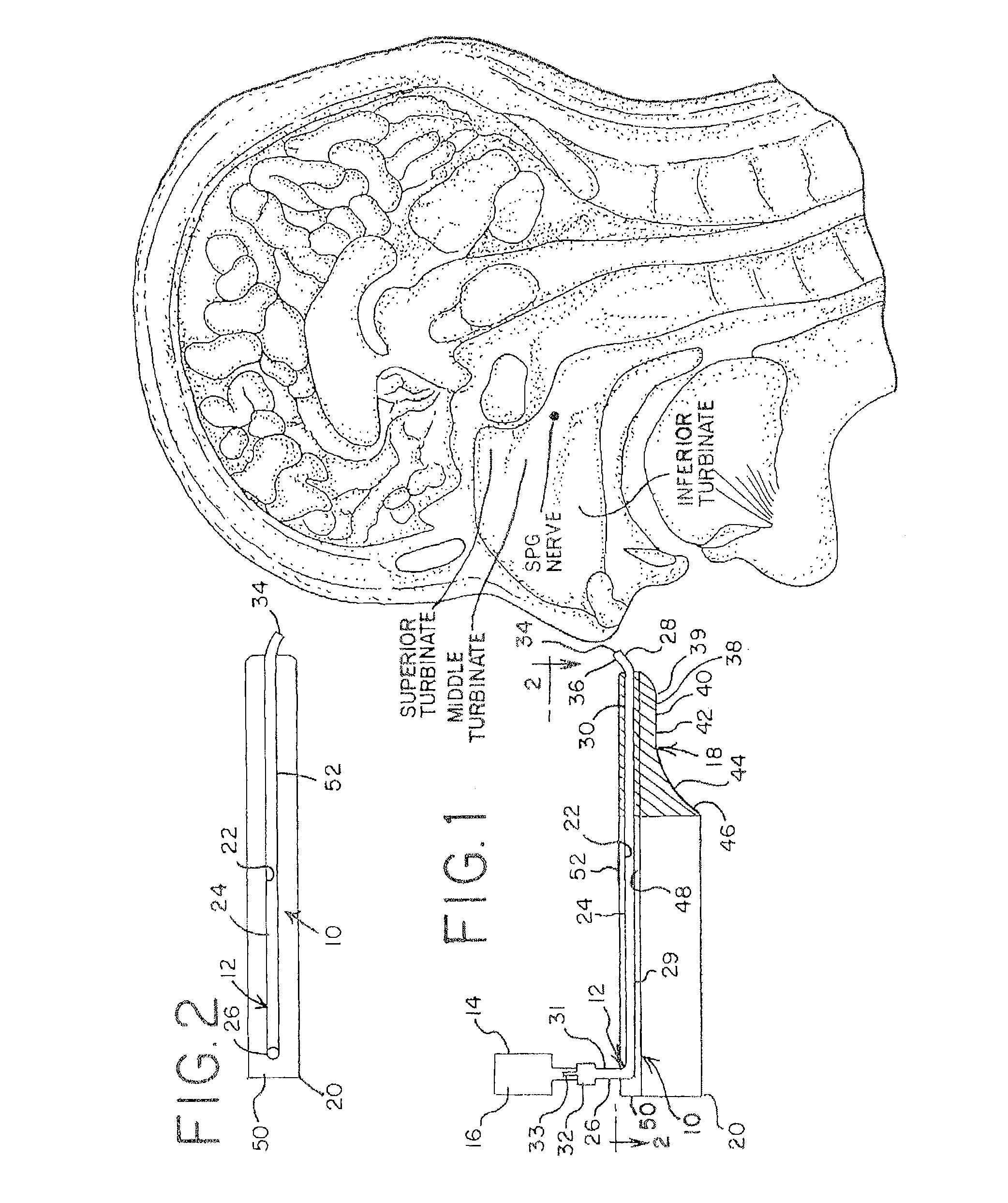
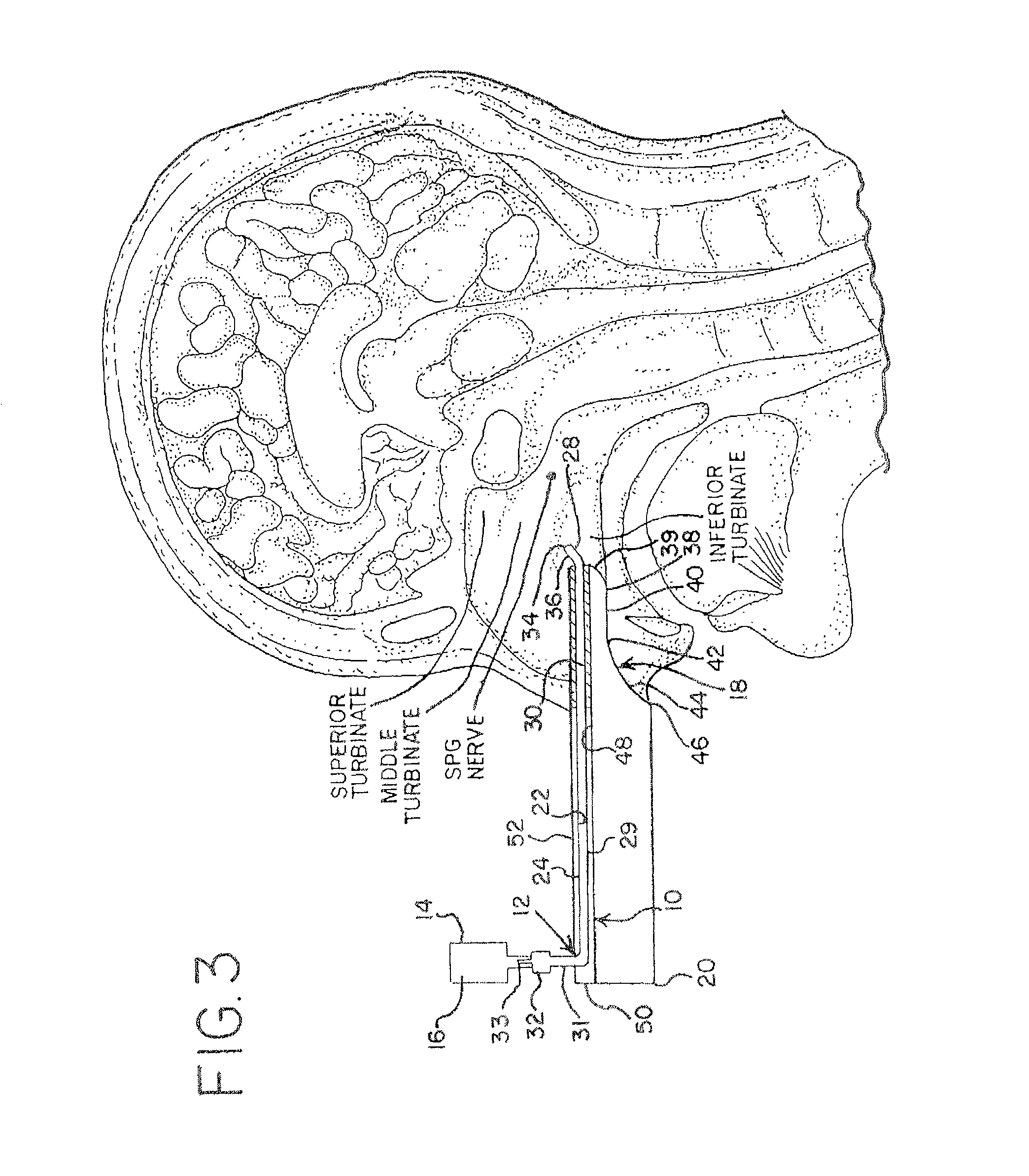
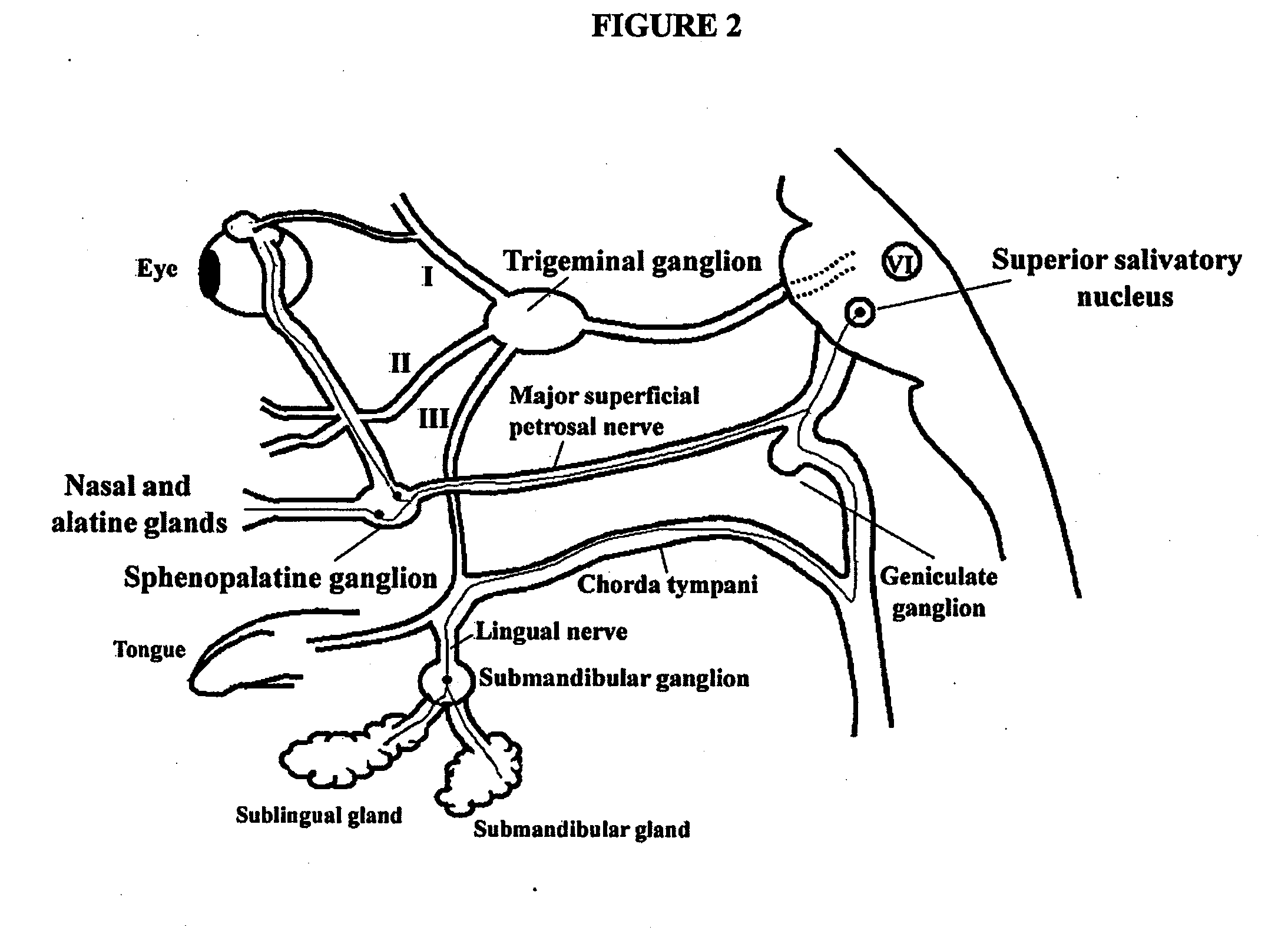
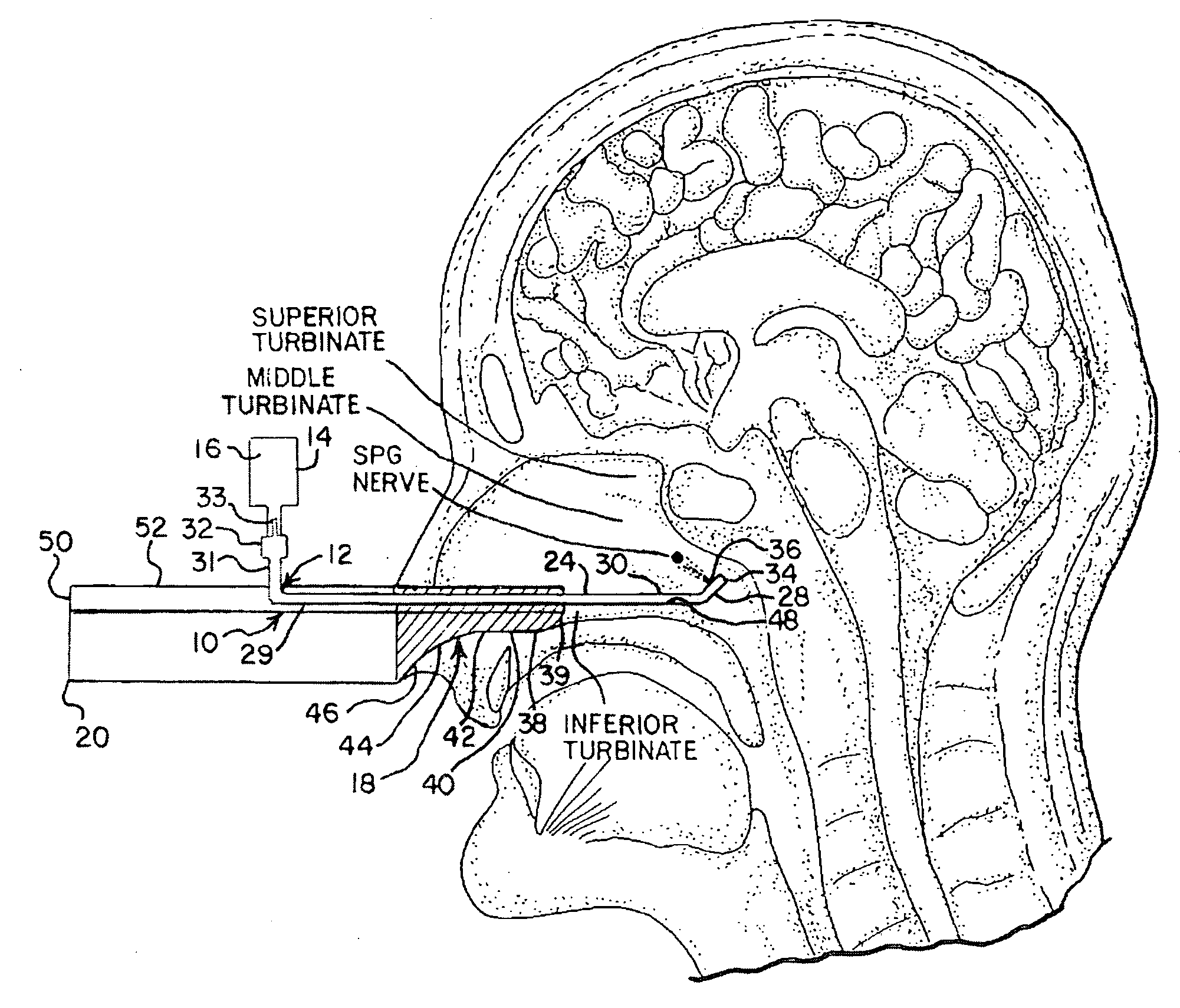
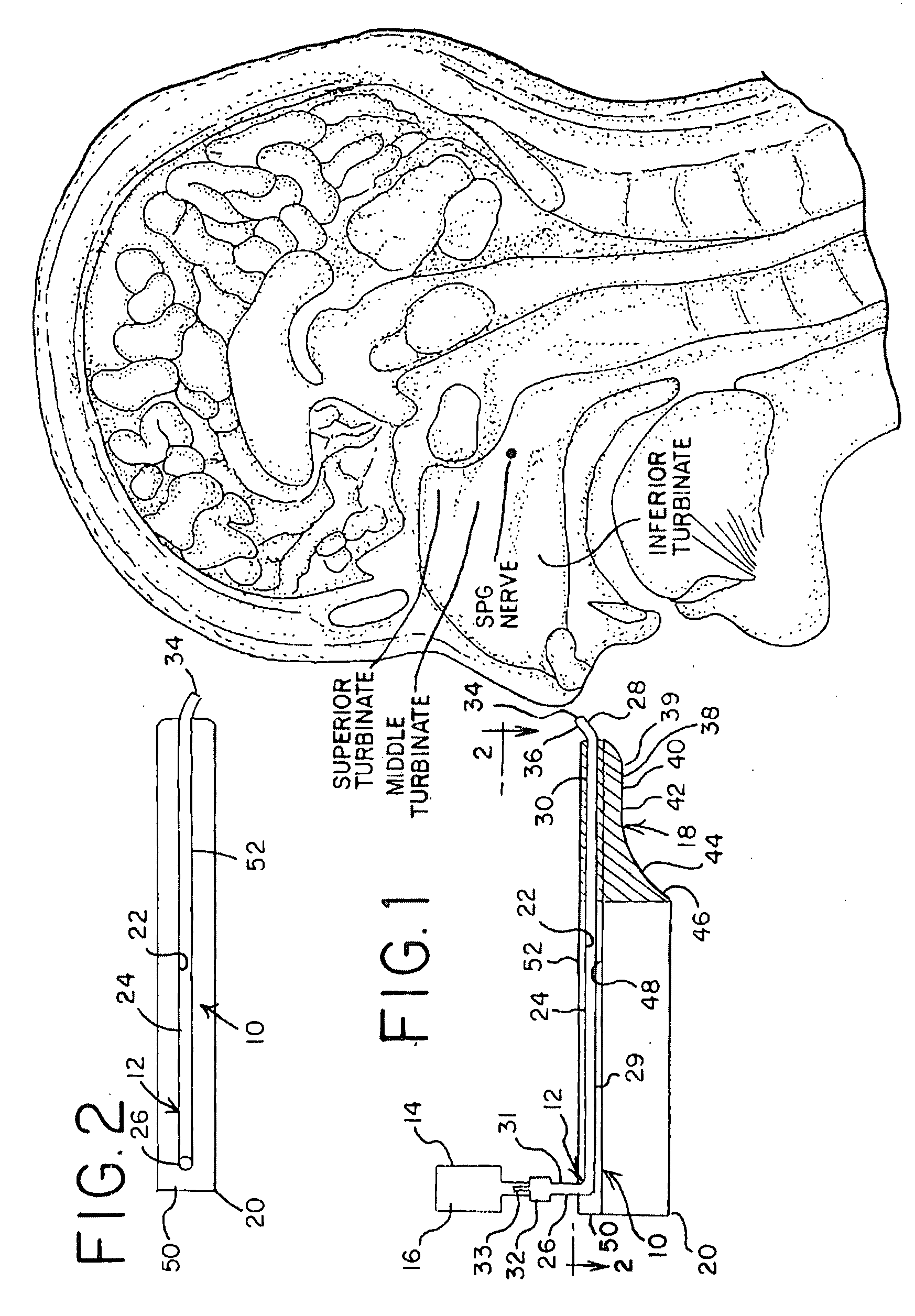
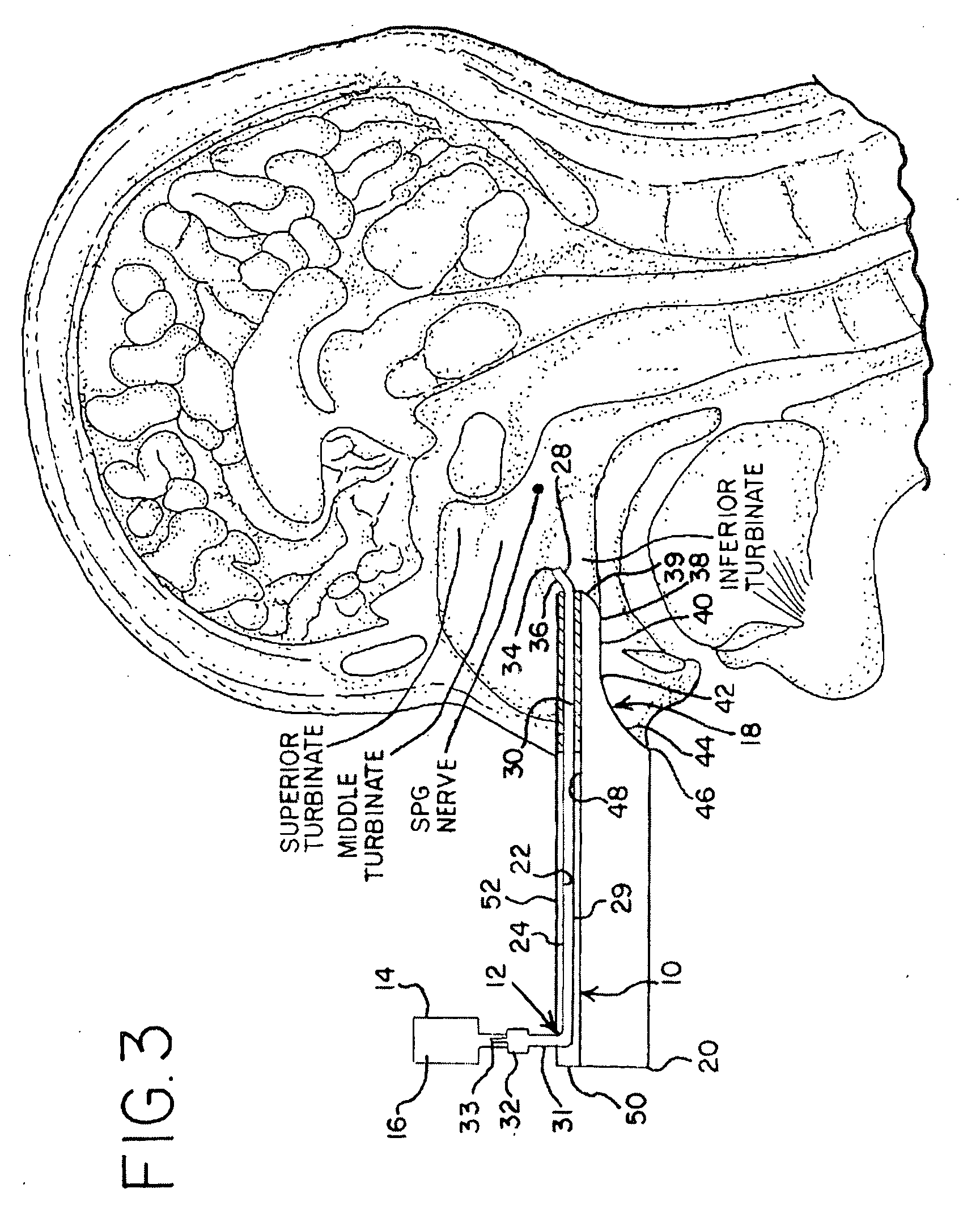
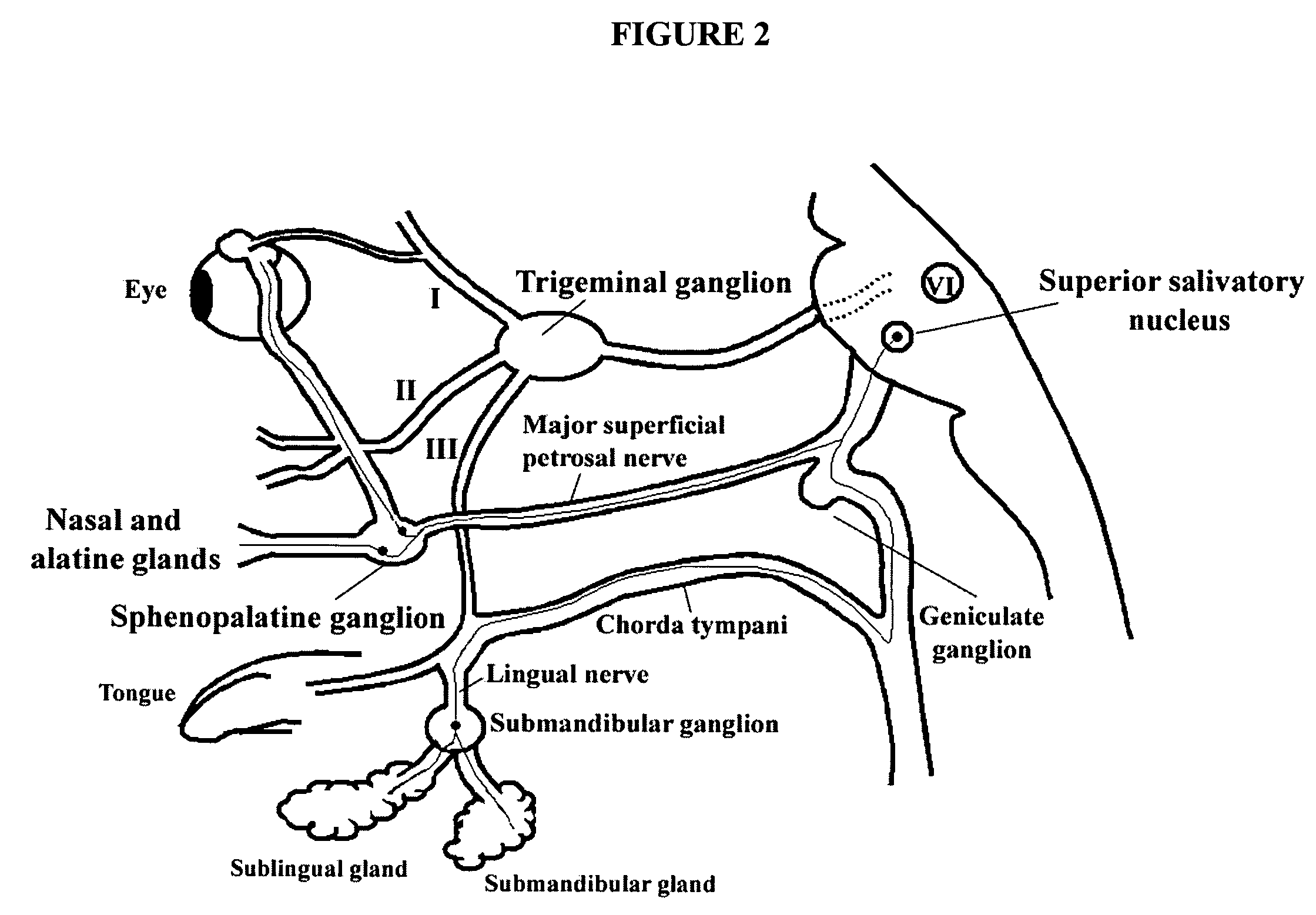
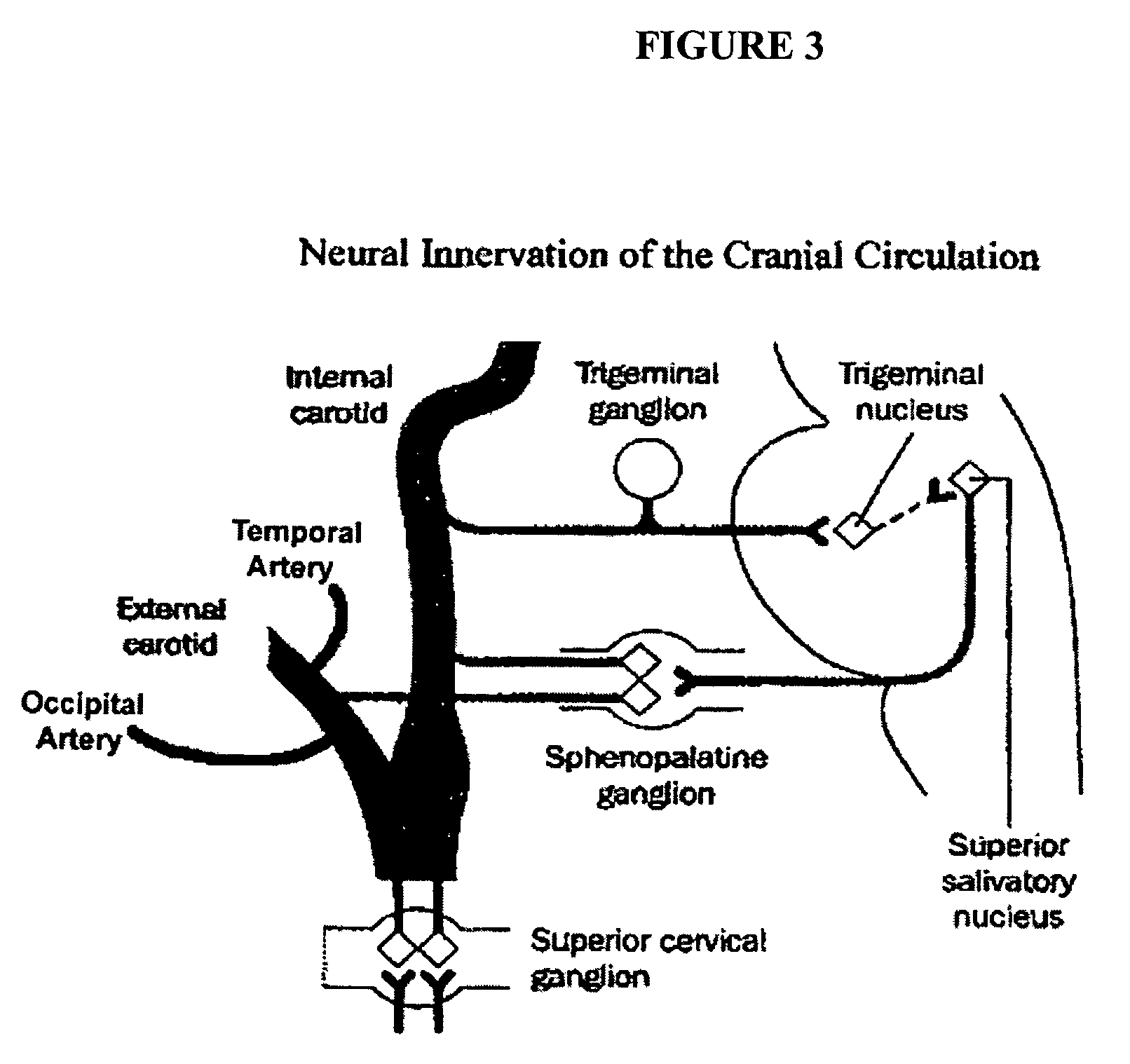
A method is provided for facilitating a diagnosis of a condition of a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) of the subject, and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG, and configuring the current to increase conductance of molecules from brain tissue of the subject through a blood brain barrier (BBB) of the subject into a systemic blood circulation of the subject. The method also includes sensing a quantity of the molecules from a site outside of the brain of the subject, following initiation of application of the current.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
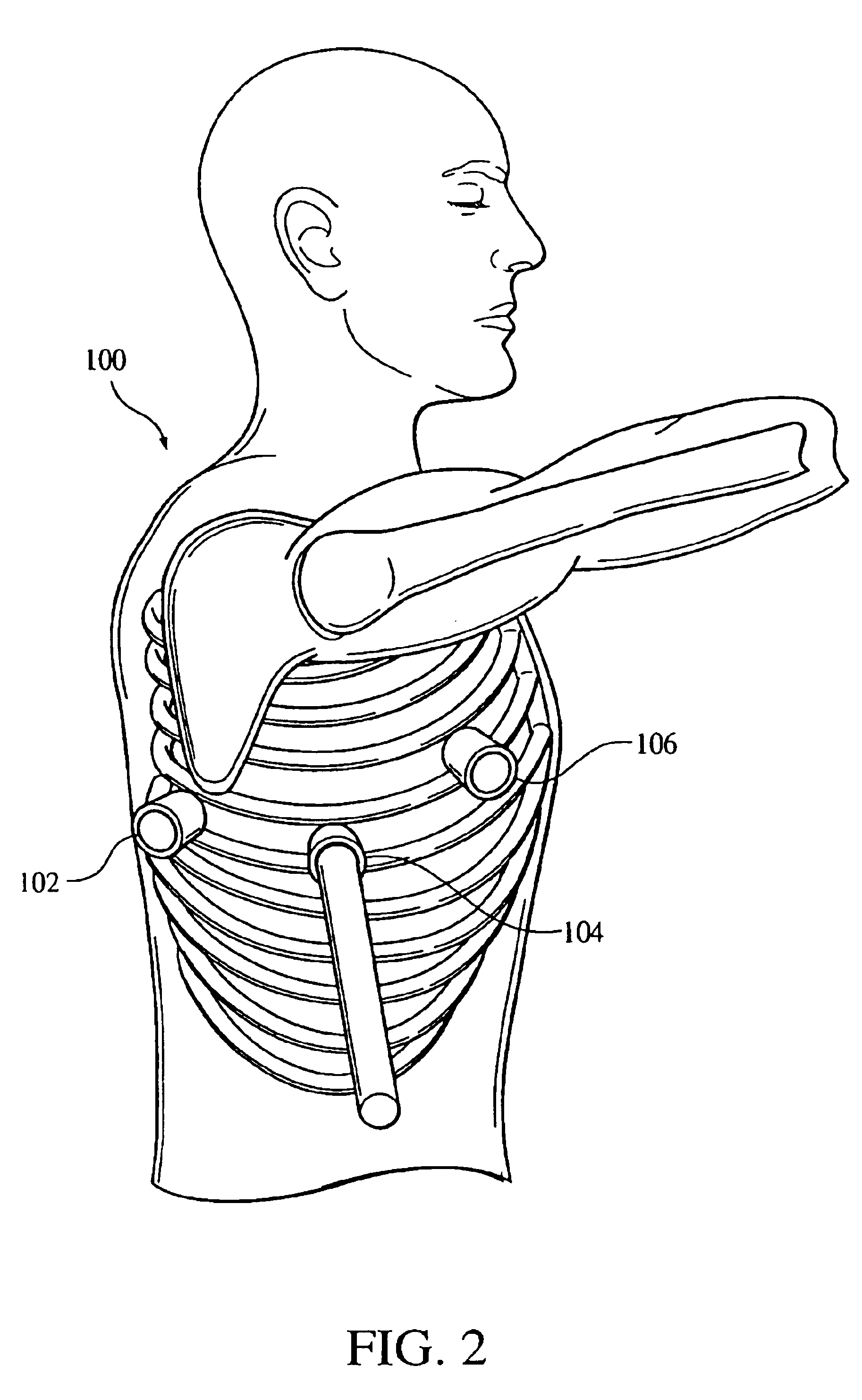
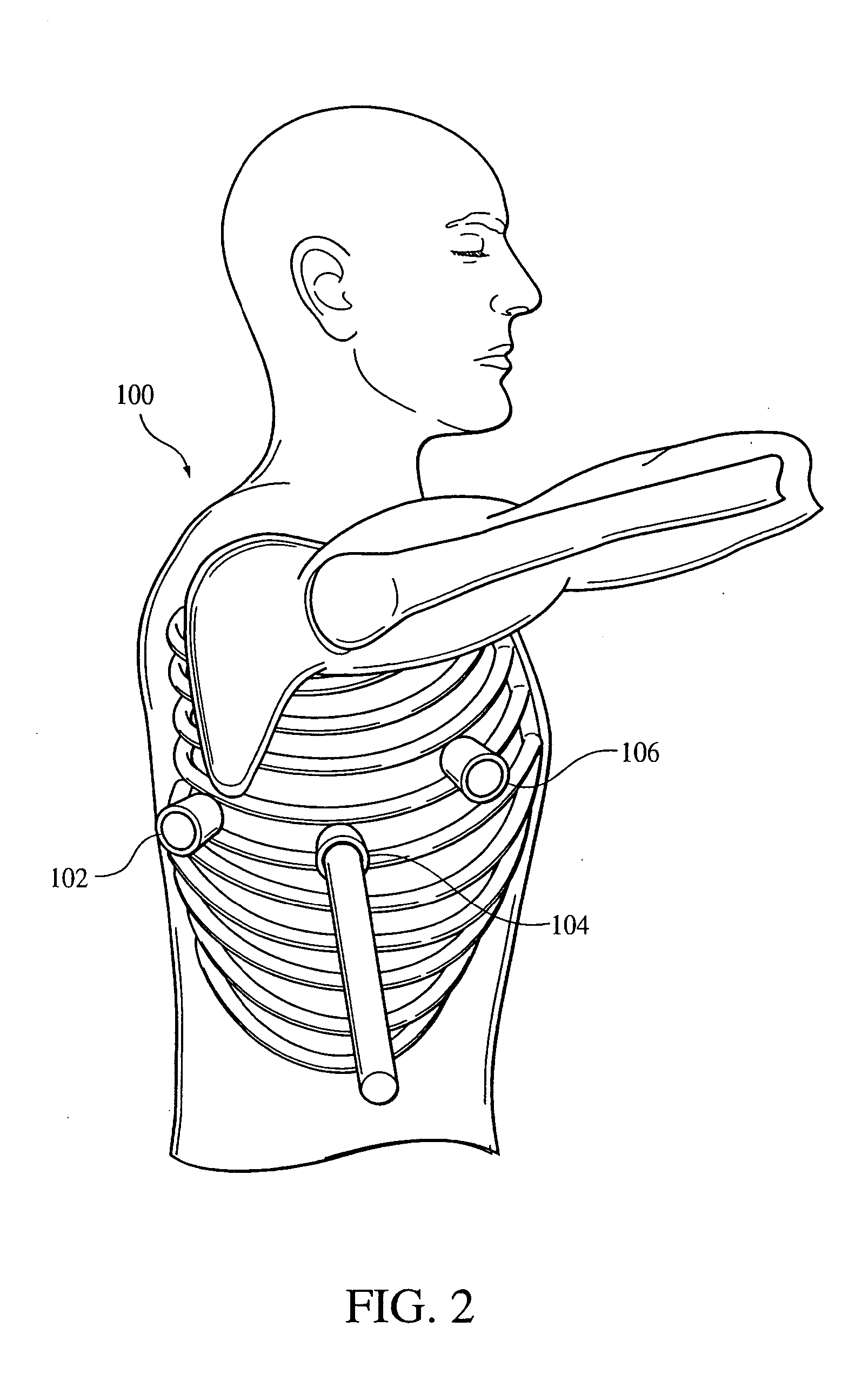
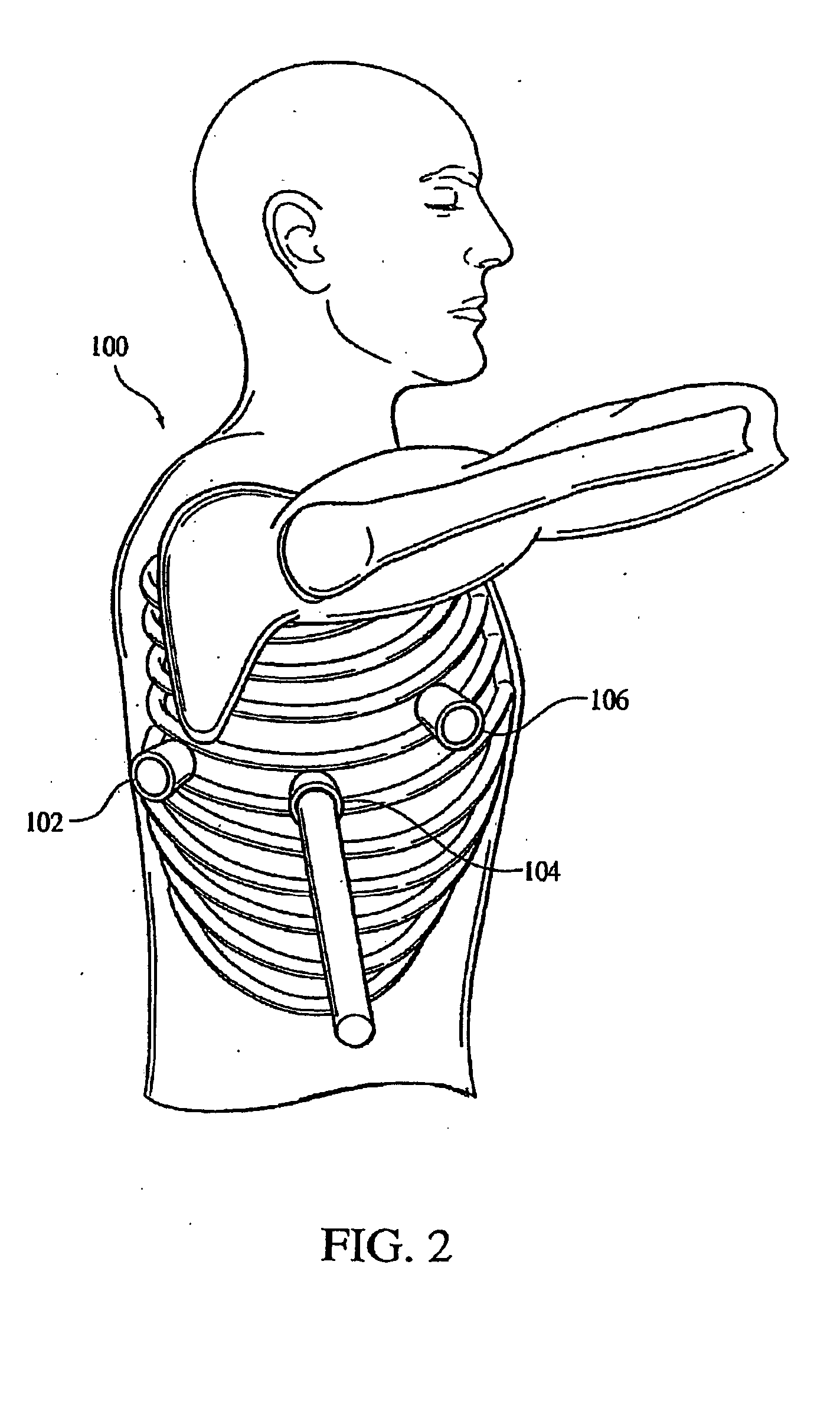
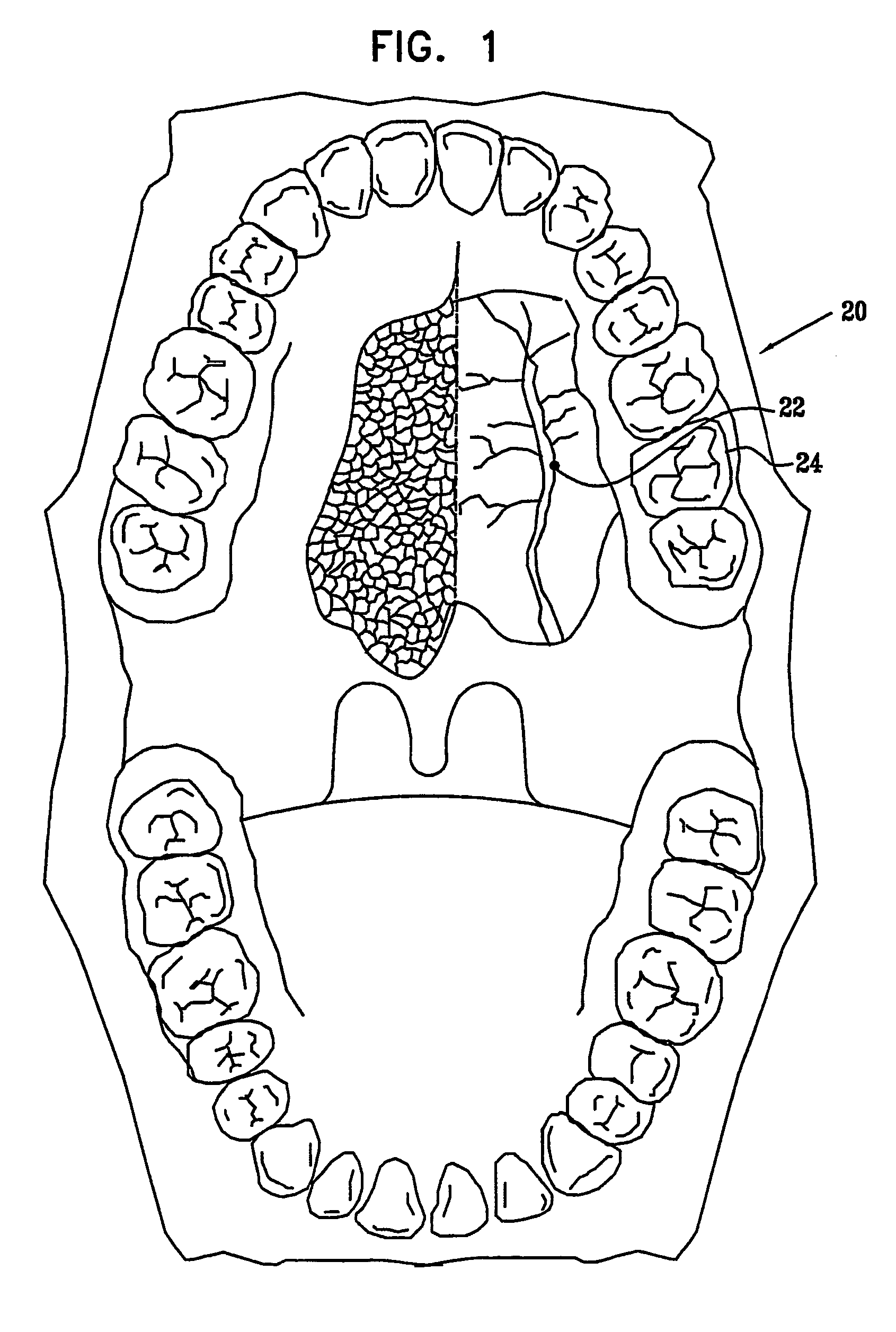
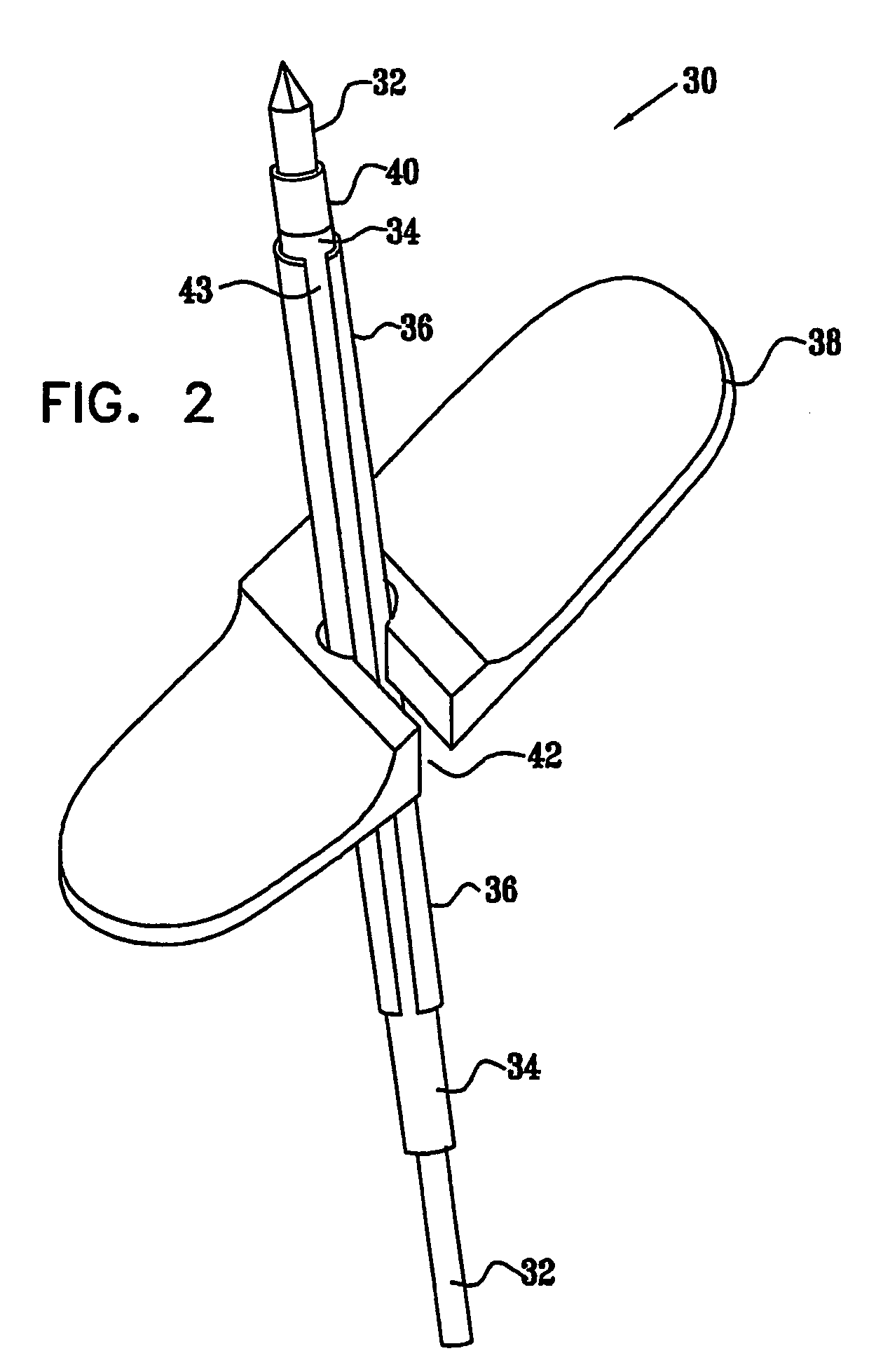
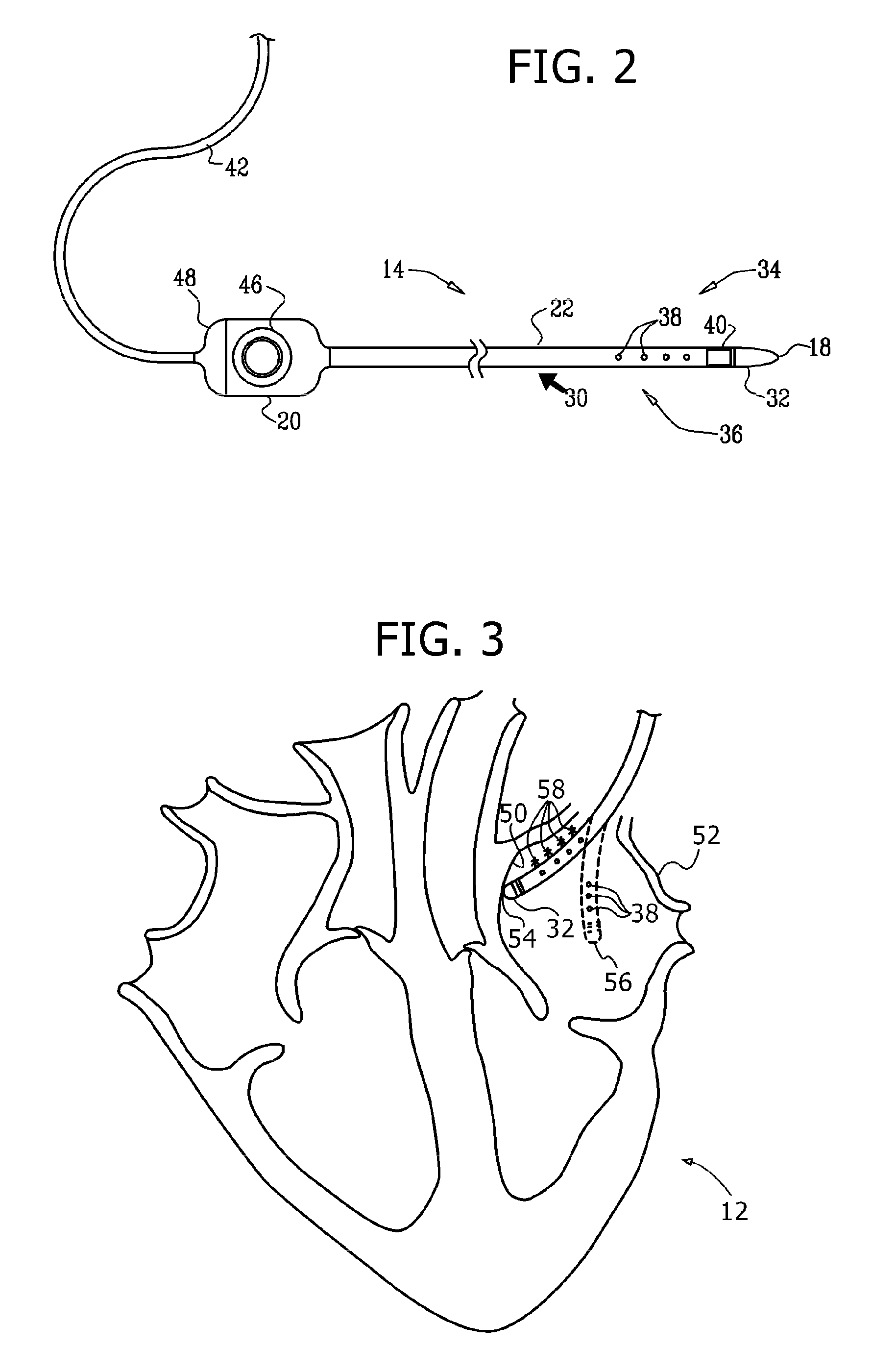
Delivery device for stimulating the sympathetic nerve chain
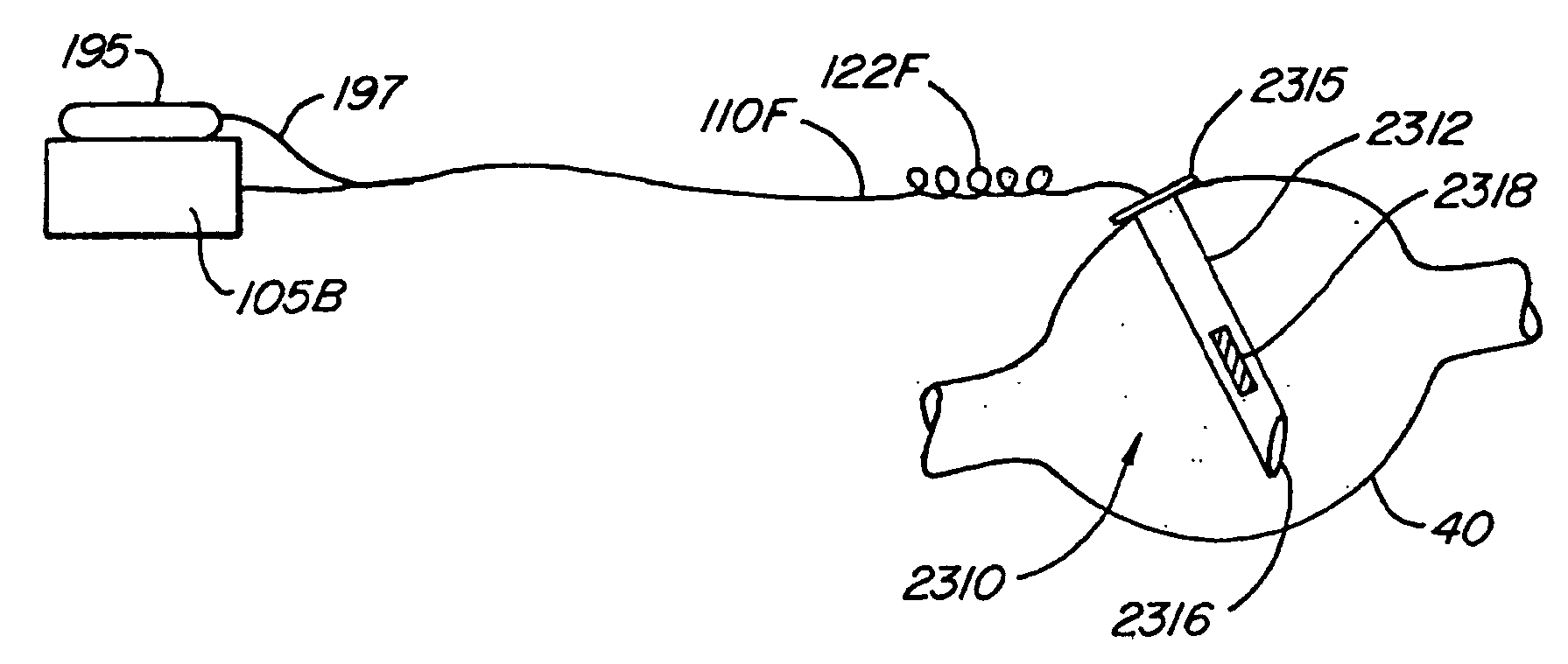
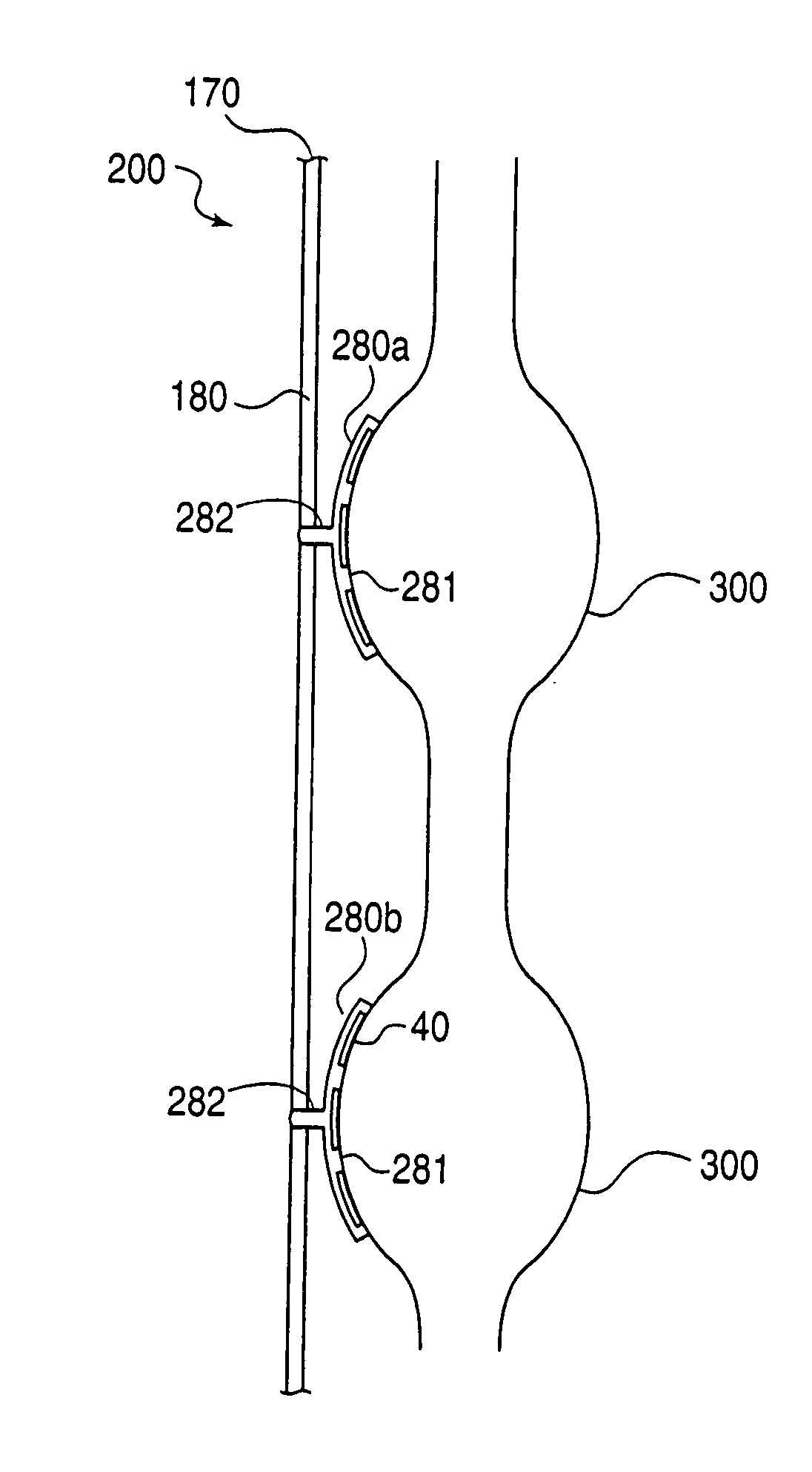
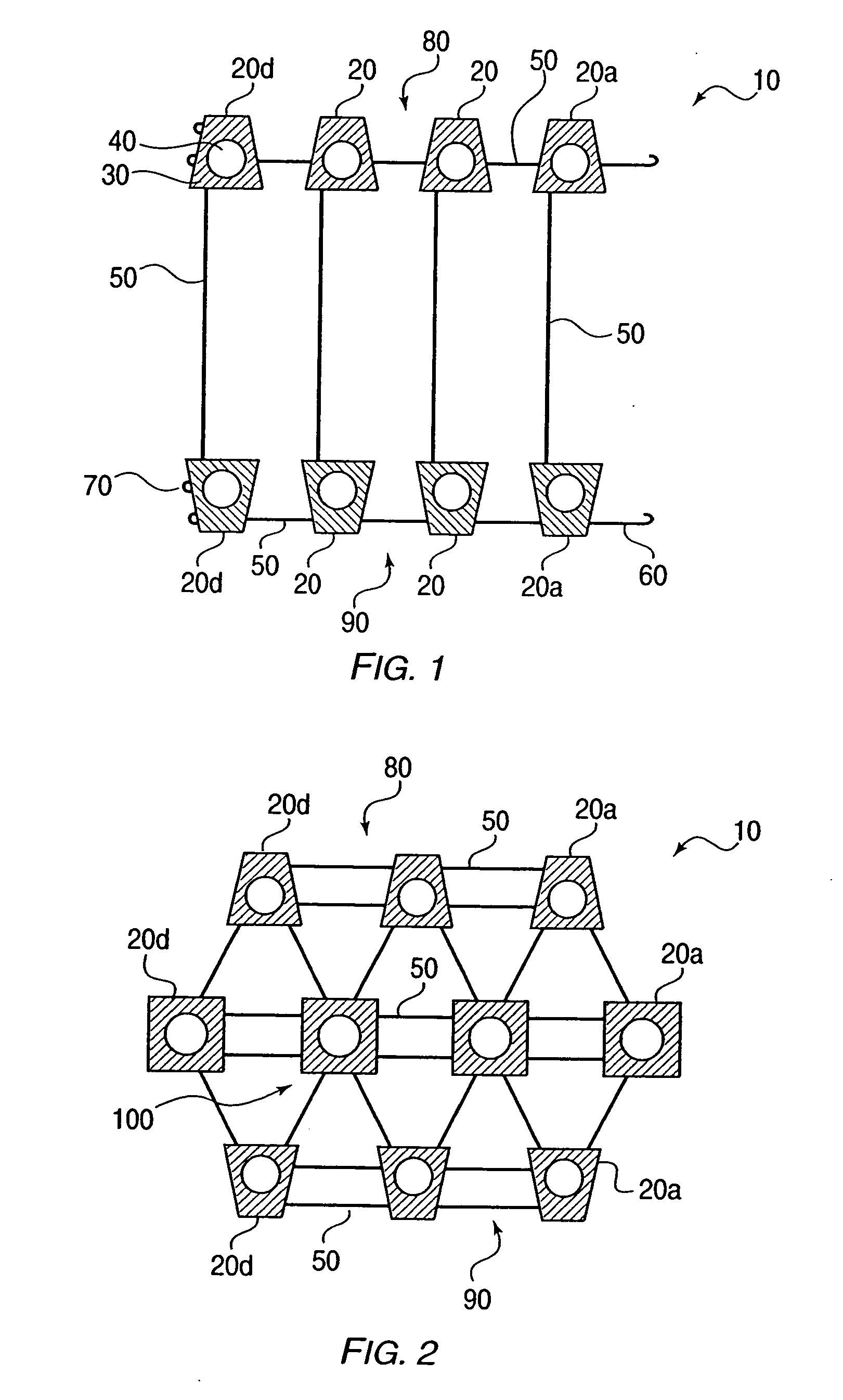
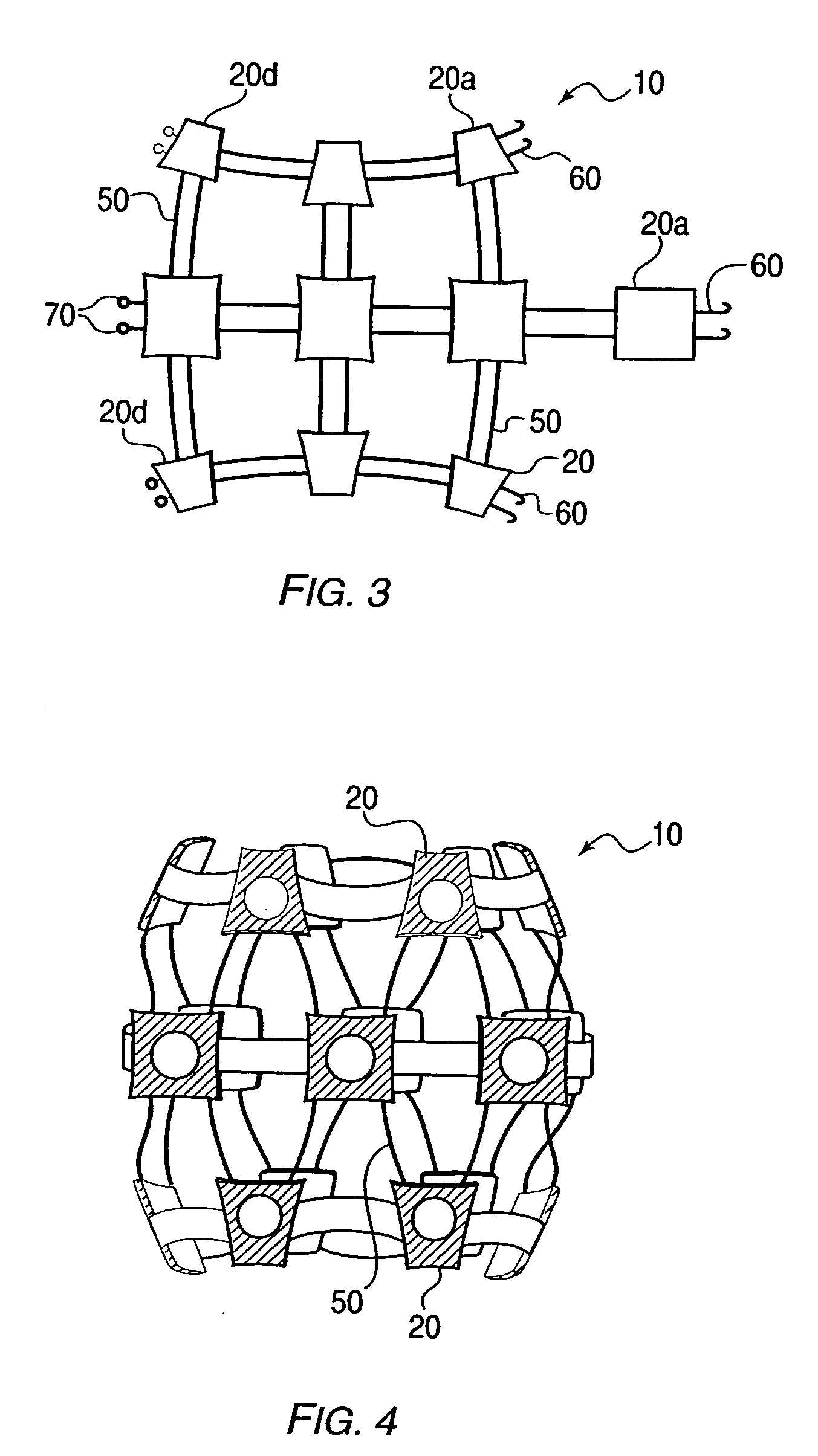
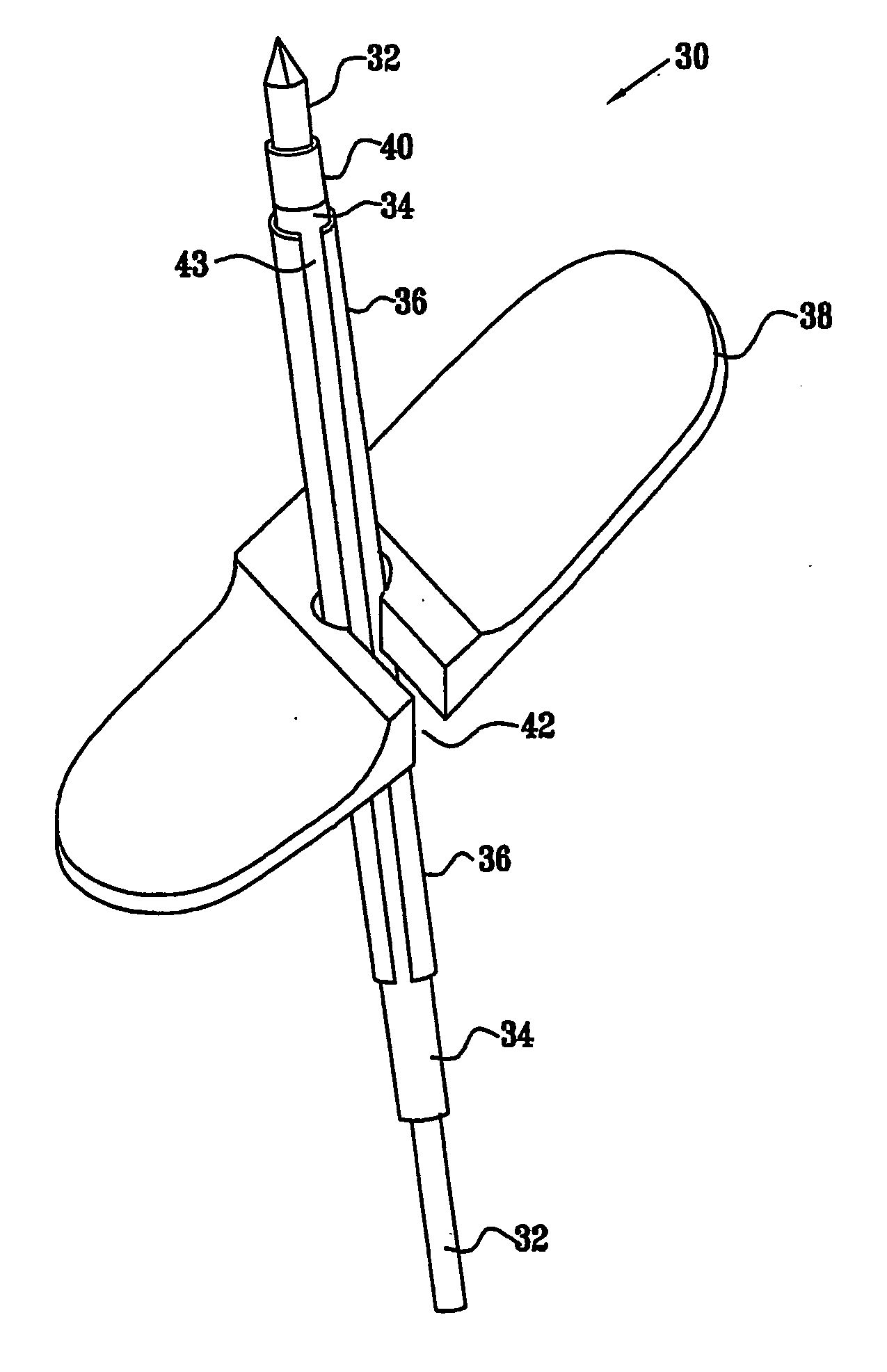
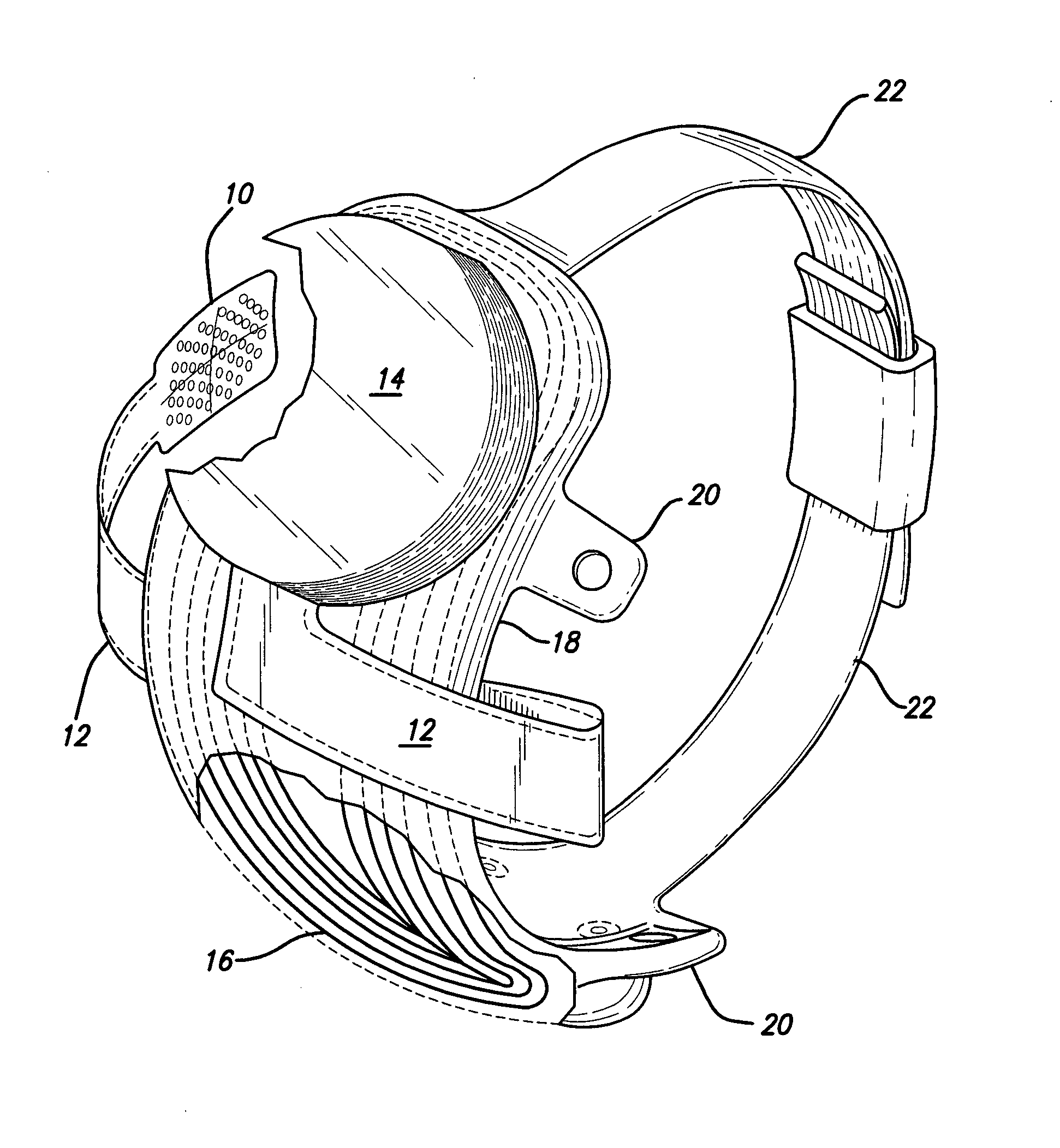
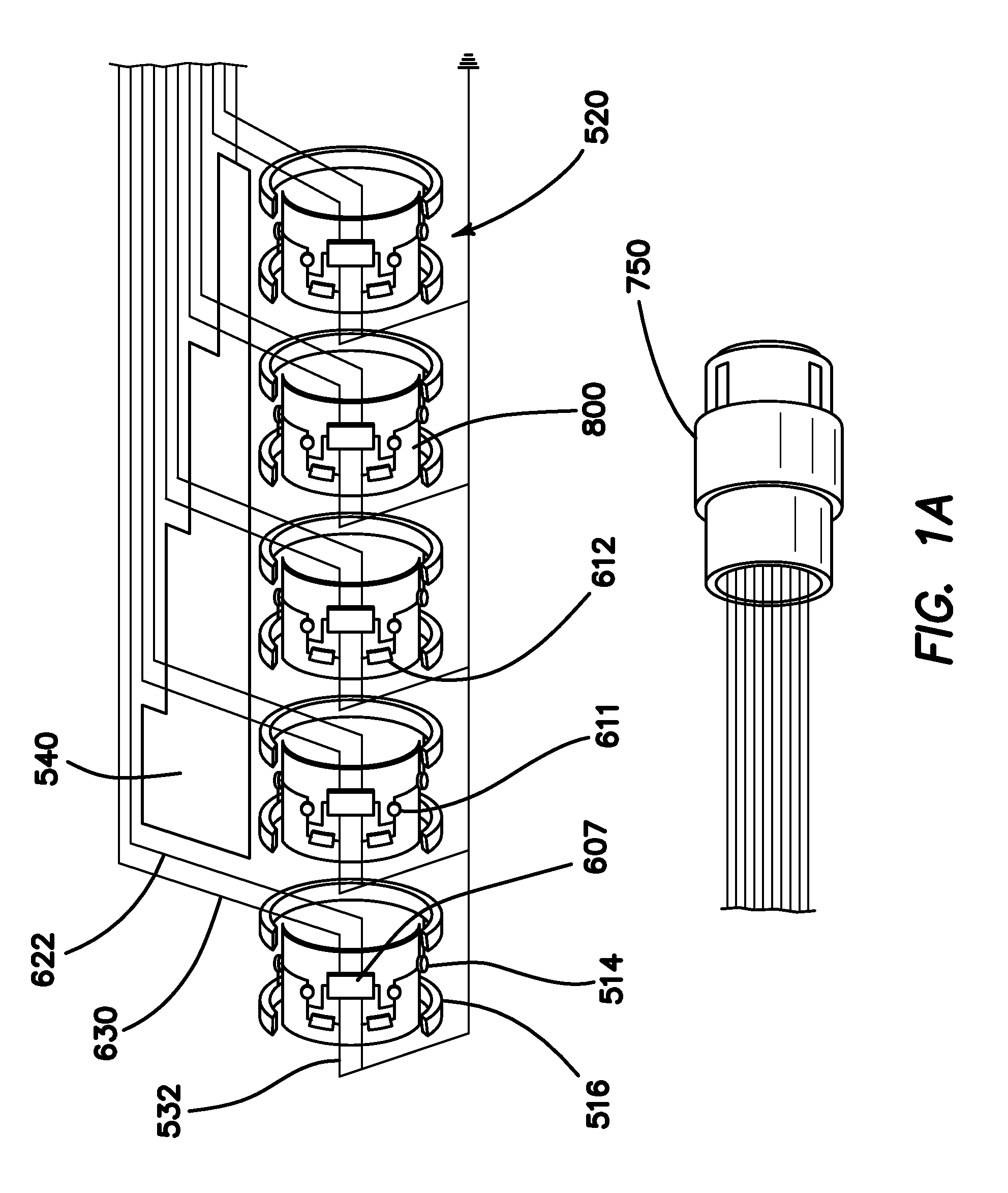
The present invention provides a device and assembly for electrically and / or chemically stimulating individual ganglion and a plurality of ganglia of the nervous system, and particularly to ganglia of the sympathetic nerve chain. A device is provided that generally wraps around an individual ganglion and conforms to the shape of the ganglion without exerting excessive pressure on the ganglion to damage the ganglion. An assembly is also provided that includes an axially elongated shaft that can be positioned adjacent to the sympathetic nerve chain and that can receive a plurality of ganglion stimulators that can slidably engage with the outer surface of the shaft. As additional ganglia are desired to be stimulated, each of the plurality of ganglion stimulators can be added to the shaft to engage the outer surface of the shaft and can be positioned adjacent to the ganglia desired to be stimulated.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
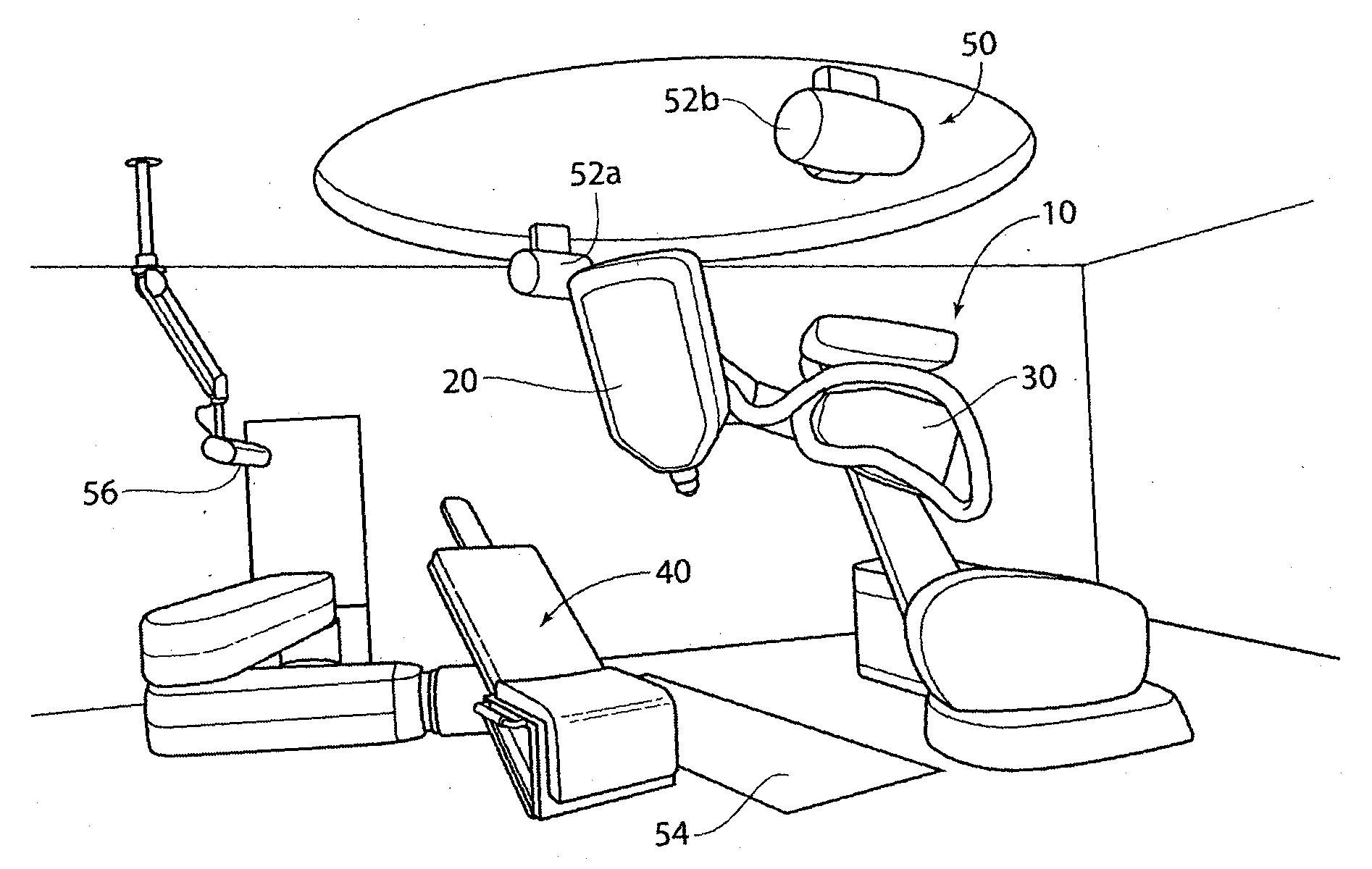
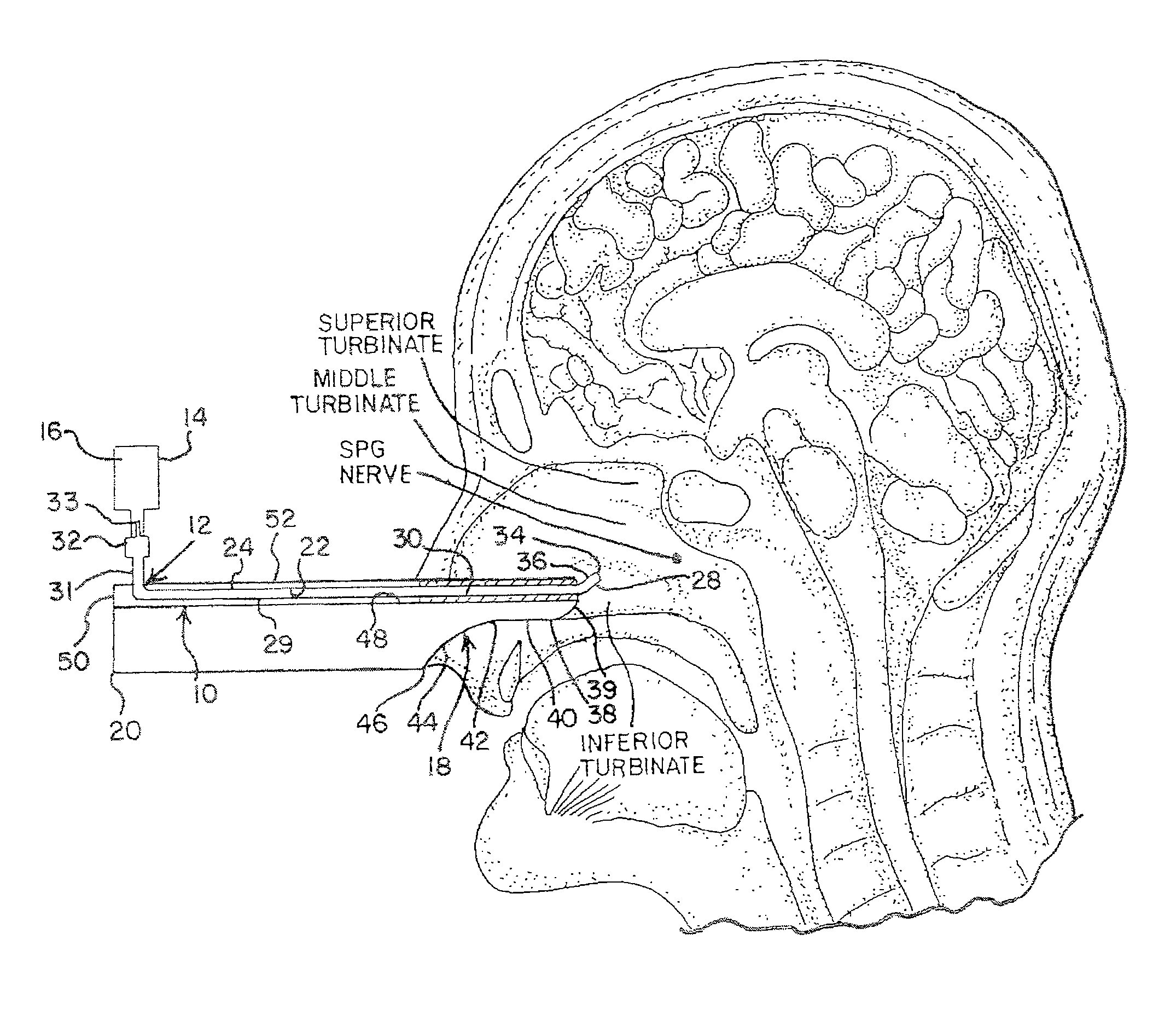
Surgical tools and techniques for stimulation
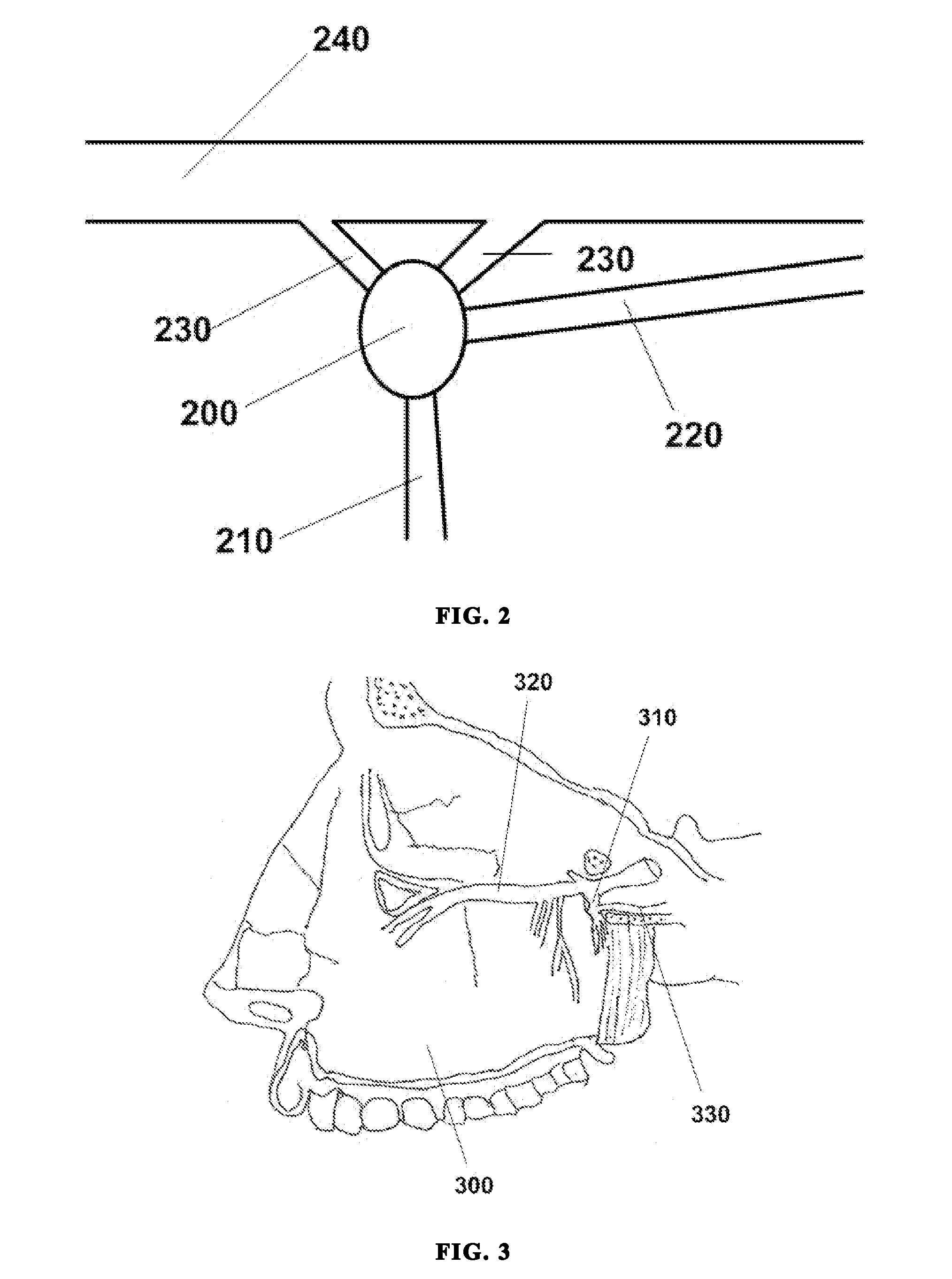
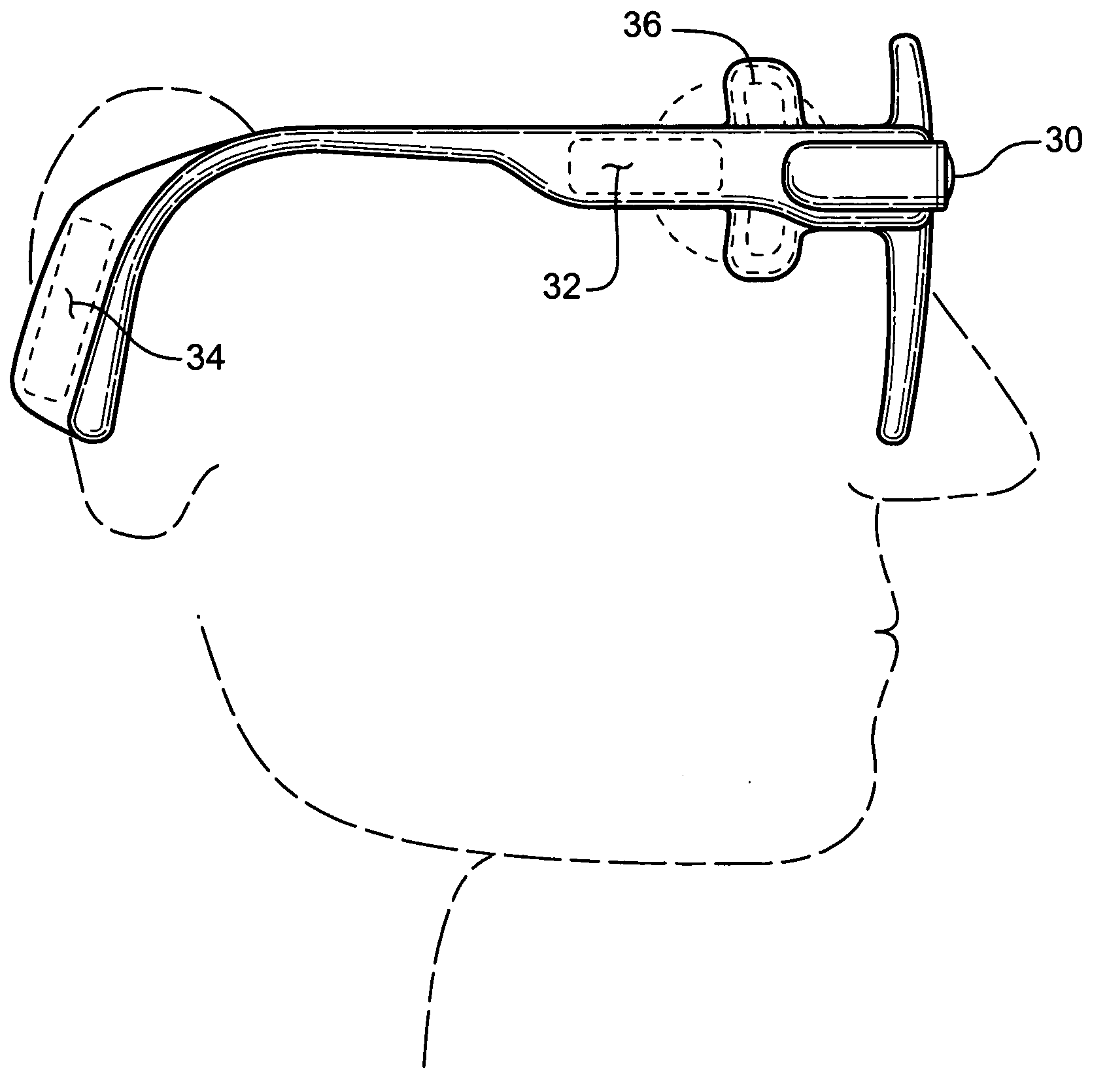
ActiveUS20060195169A1Reduce patient discomfortModulate permeability of the blood-brain-barrierHead electrodesSurgeryGreater palatine canalSurgery
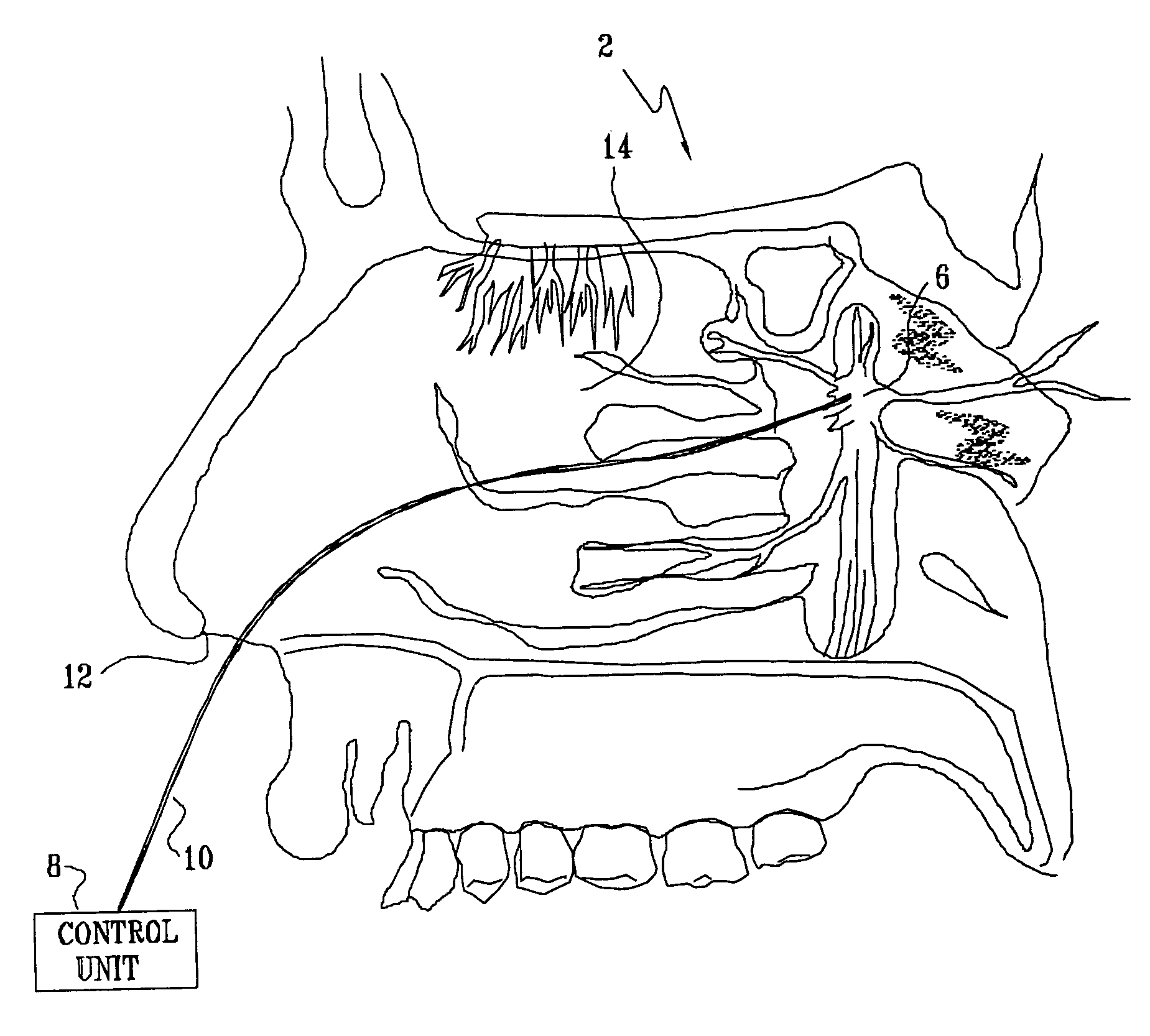
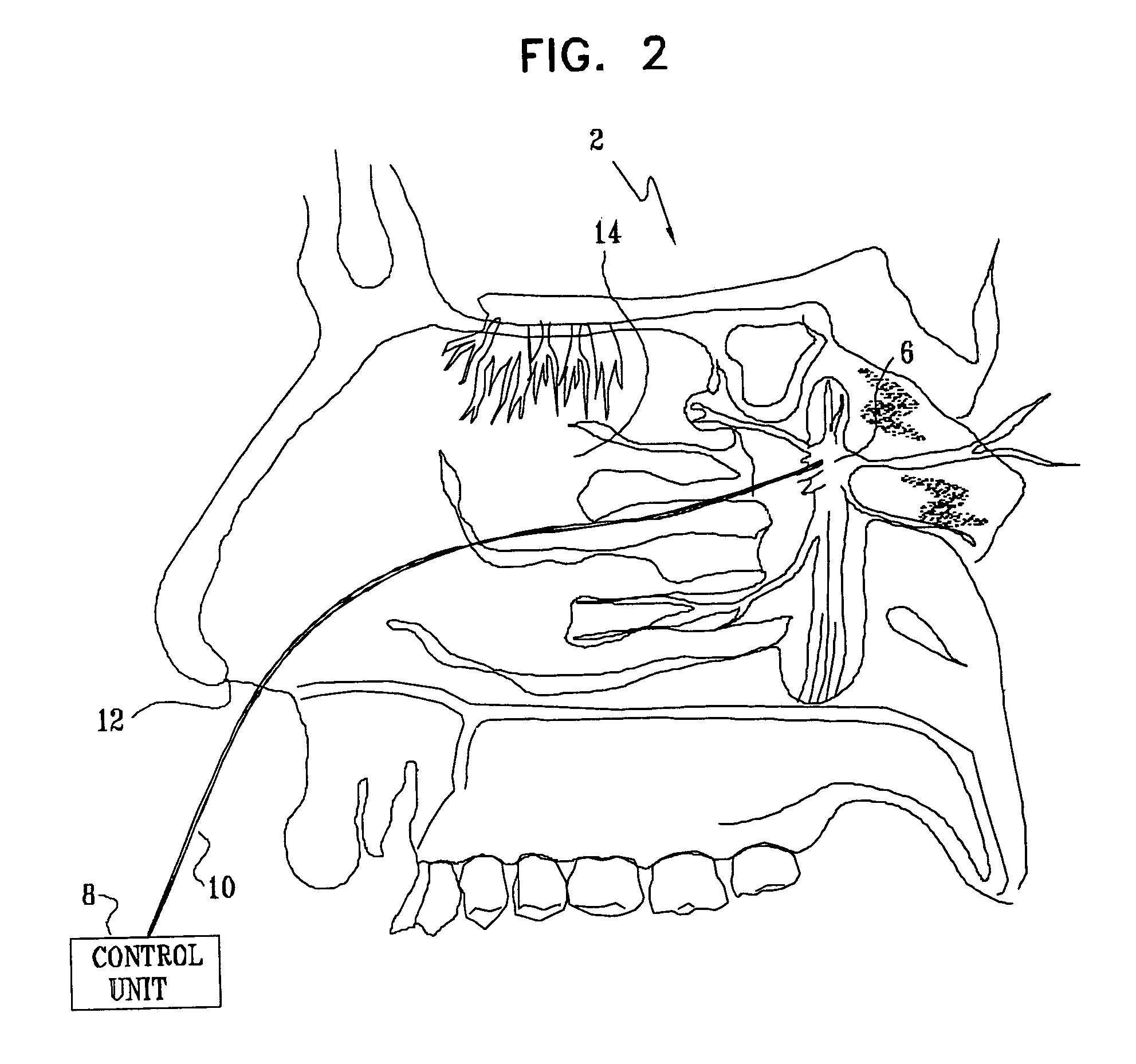
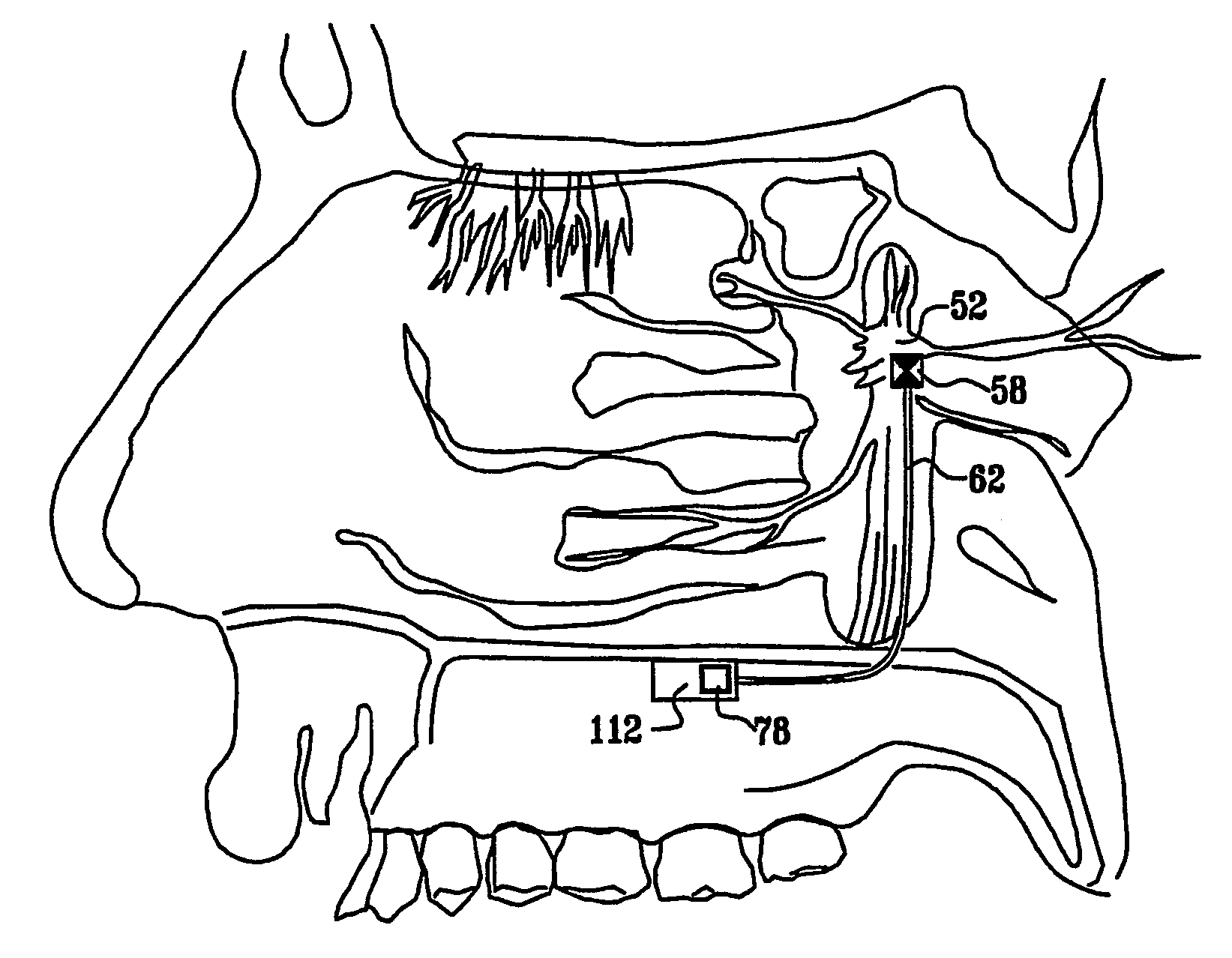
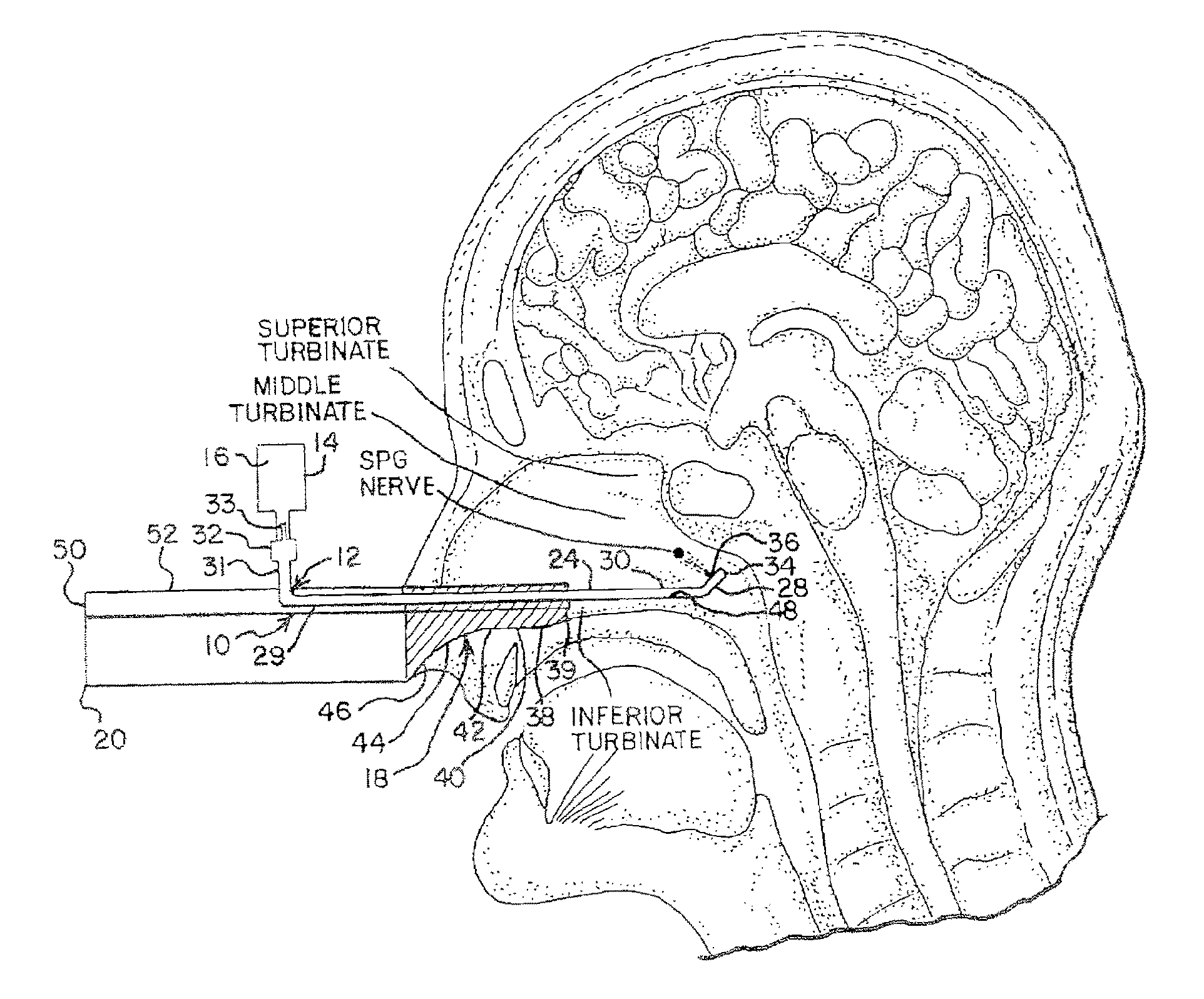
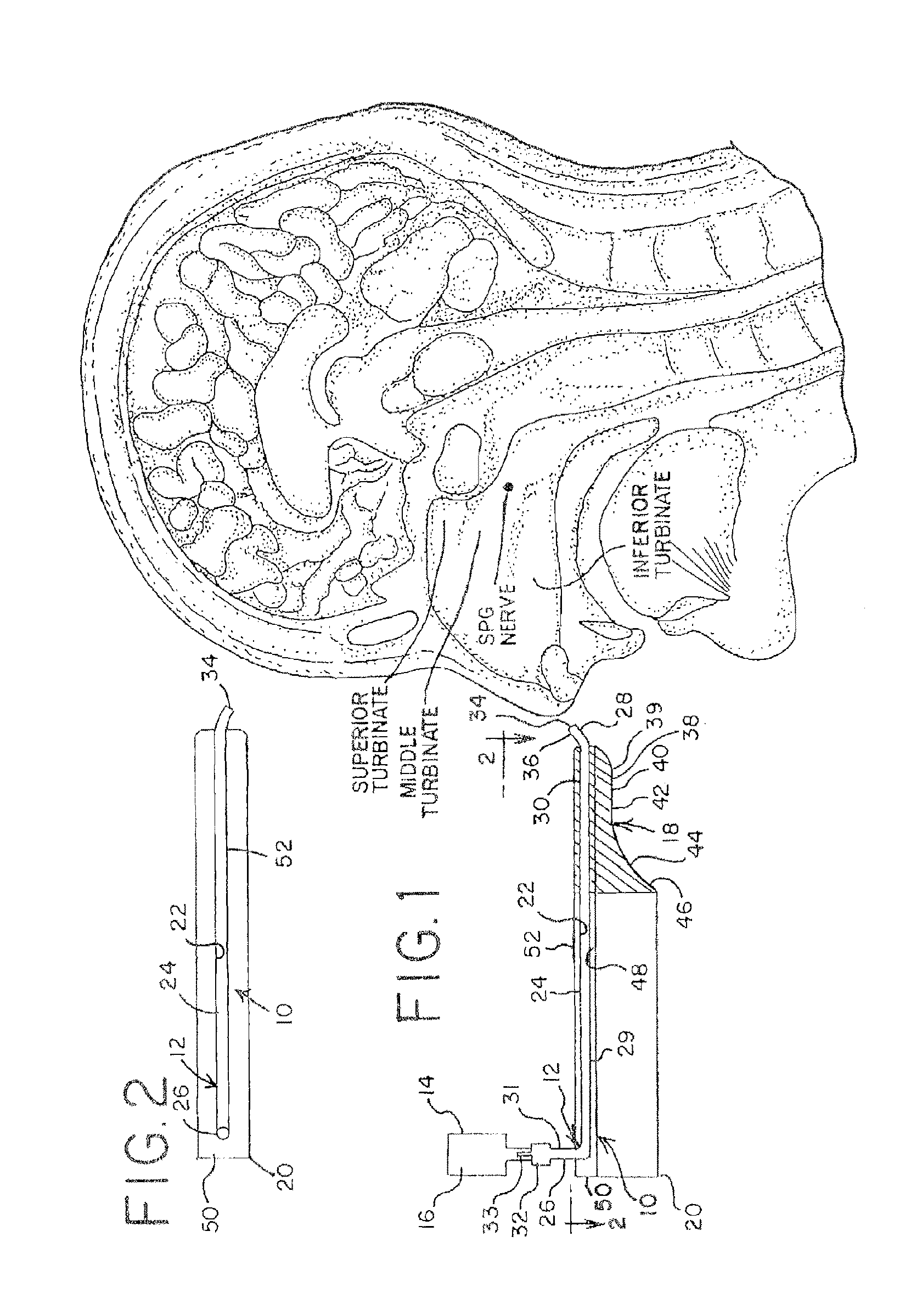
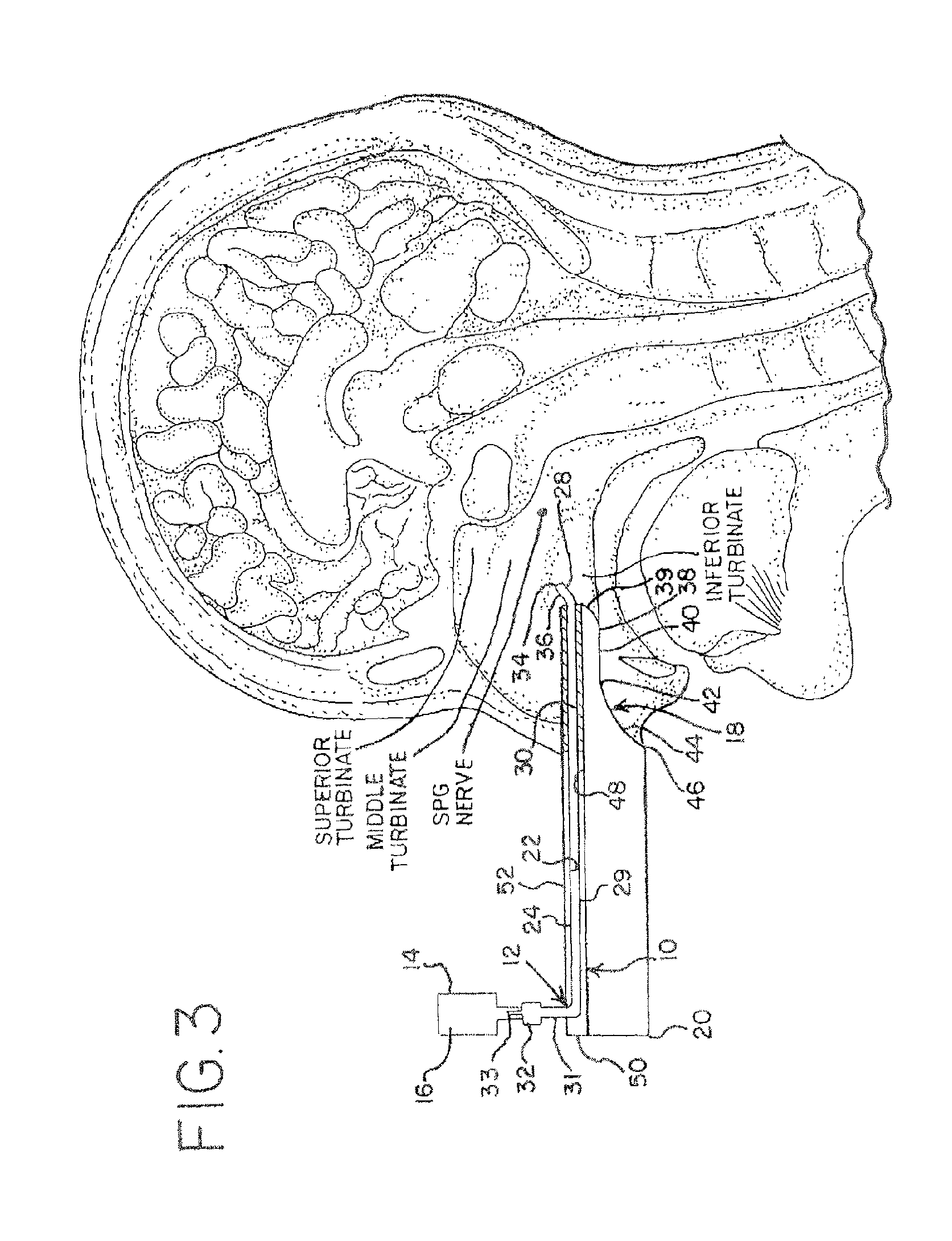
Apparatus for treating a subject is provided, the apparatus comprising (a) a stimulation device (352), adapted to be implanted in a vicinity of a site selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (52) of the subject and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG; and (b) a connecting element (356), coupled to the stimulation device (352), and adapted to be passed through at least a portion of a greater palatine canal (282) of the subject. Also provided is a method for implanting a treatment stimulation device (352) in a vicinity of a site of a subject, the method comprising passing the device (352) through a greater palatine foramen (22) of the subject, and bringing the device (352) into contact with the vicinity of the site, the site selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (52) of the subject and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Methods and systems for management of alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS7640062B2Increasing molecular passageHeart defibrillatorsImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseMedicine
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
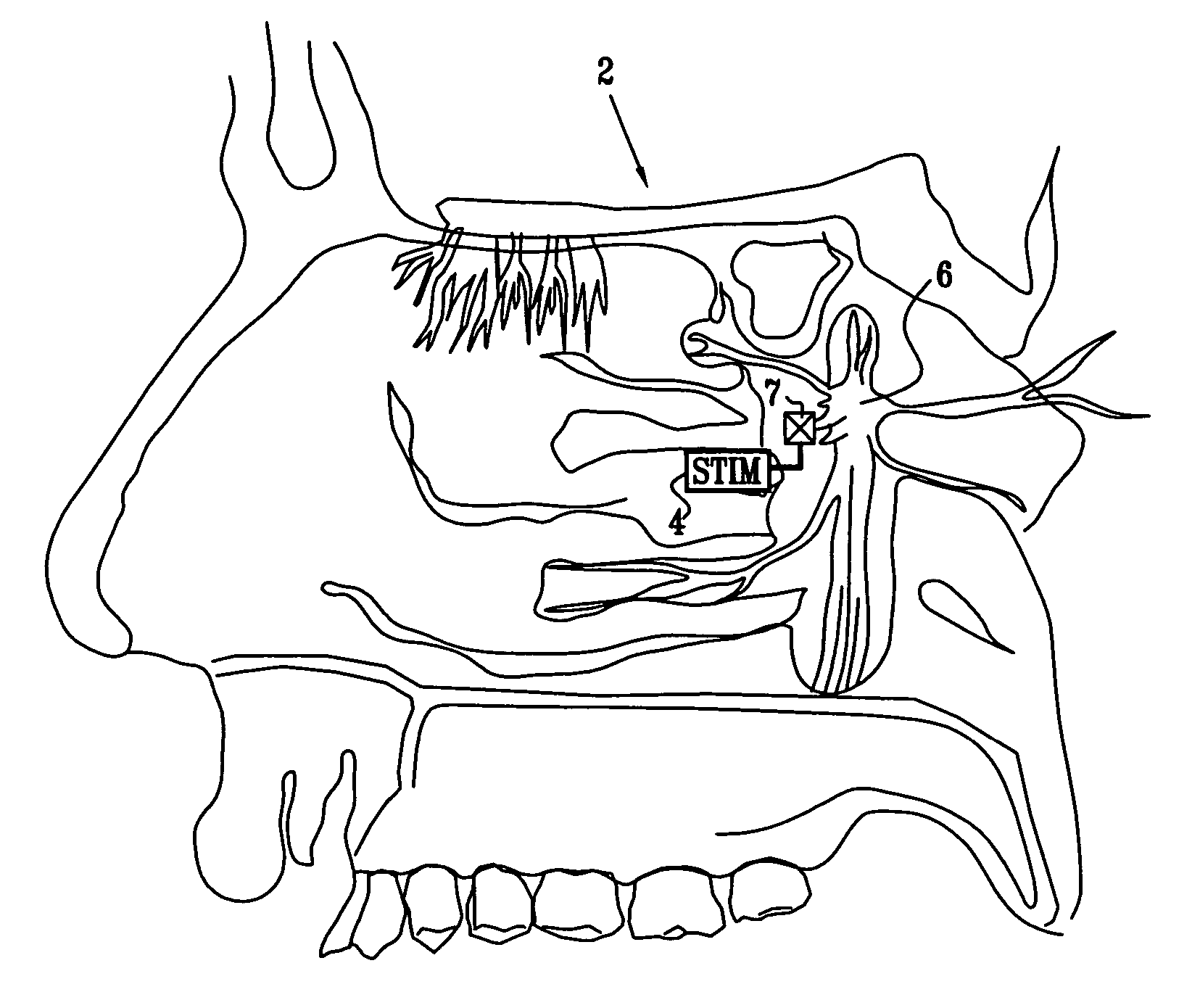
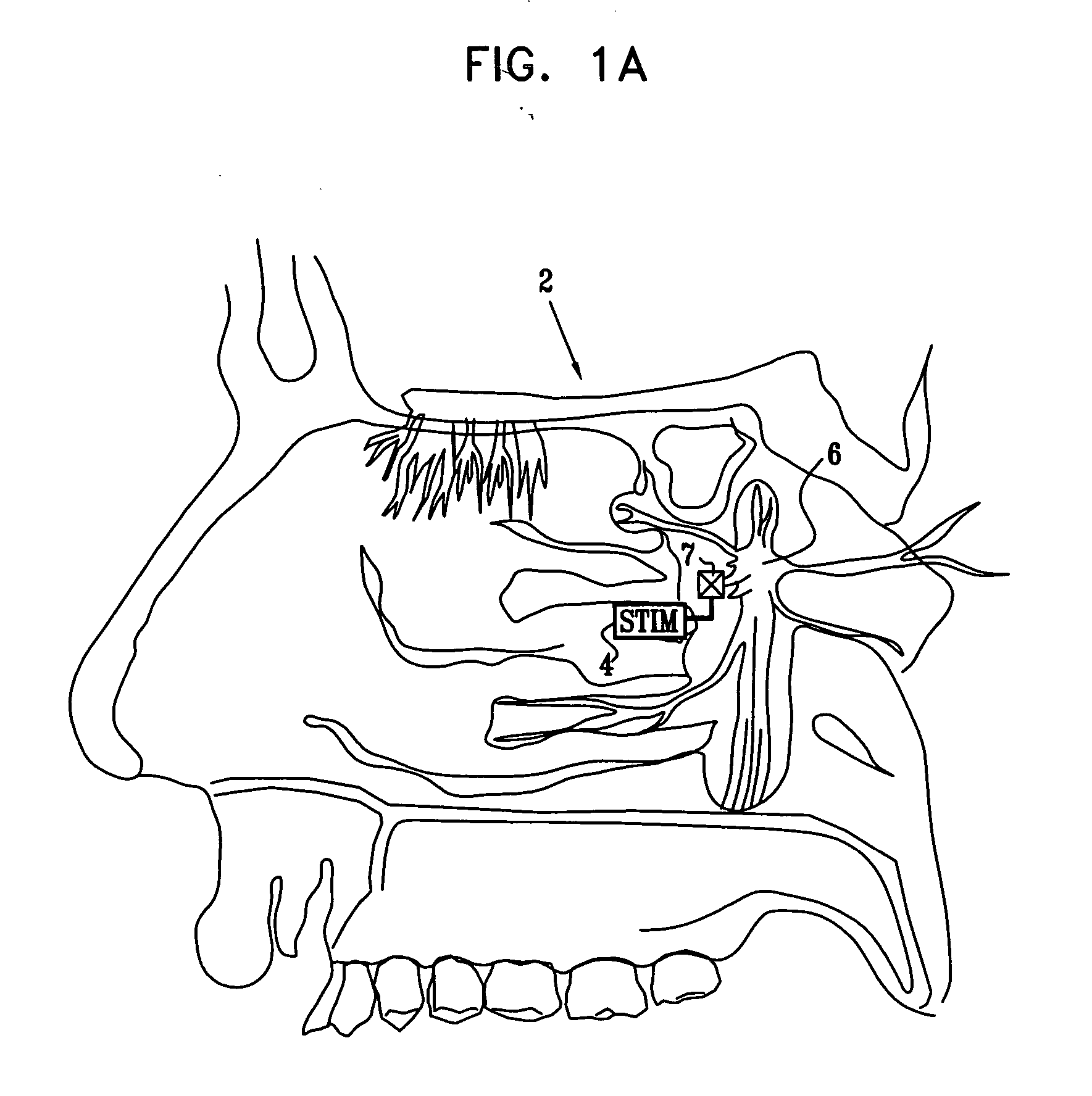
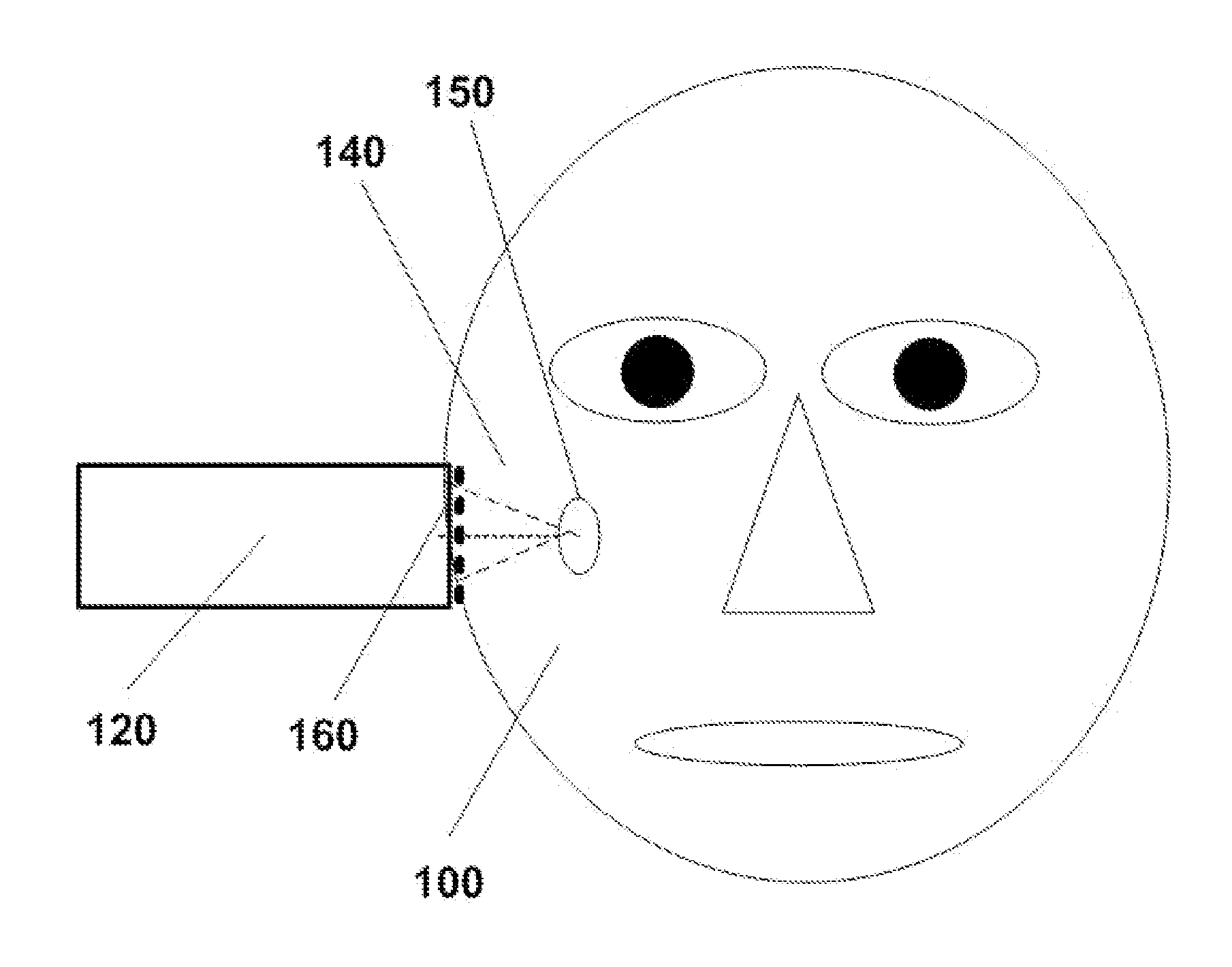
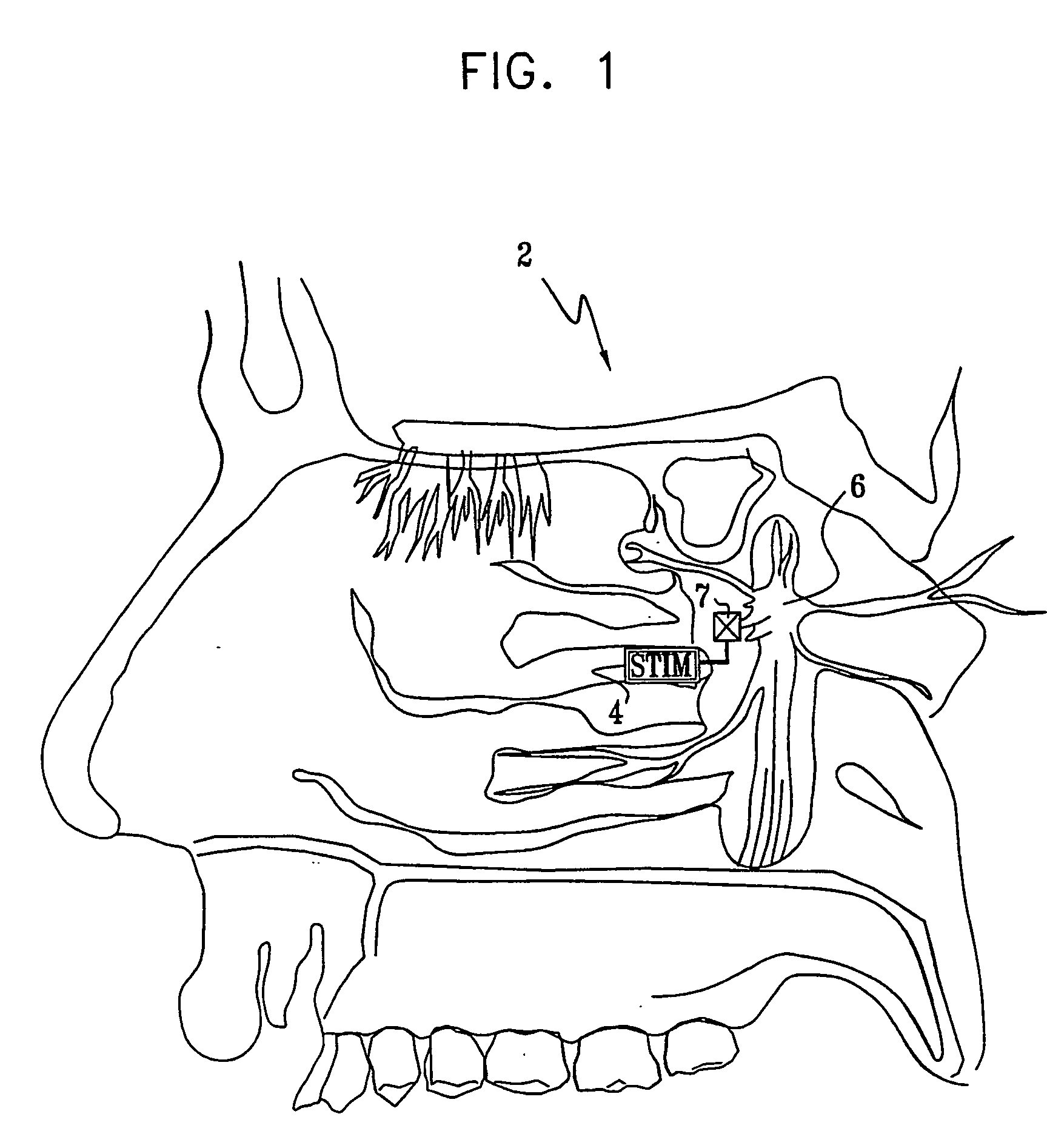
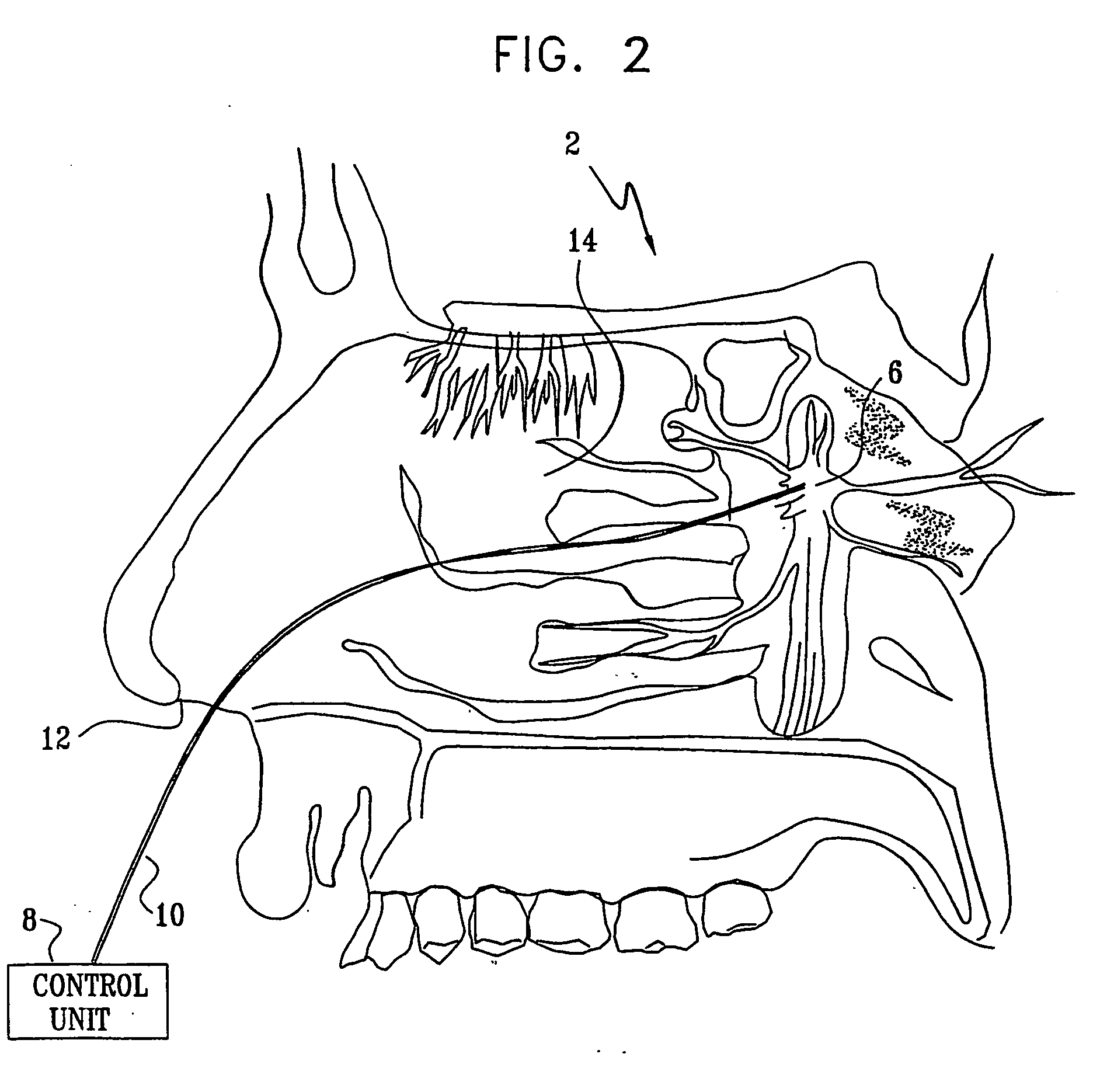
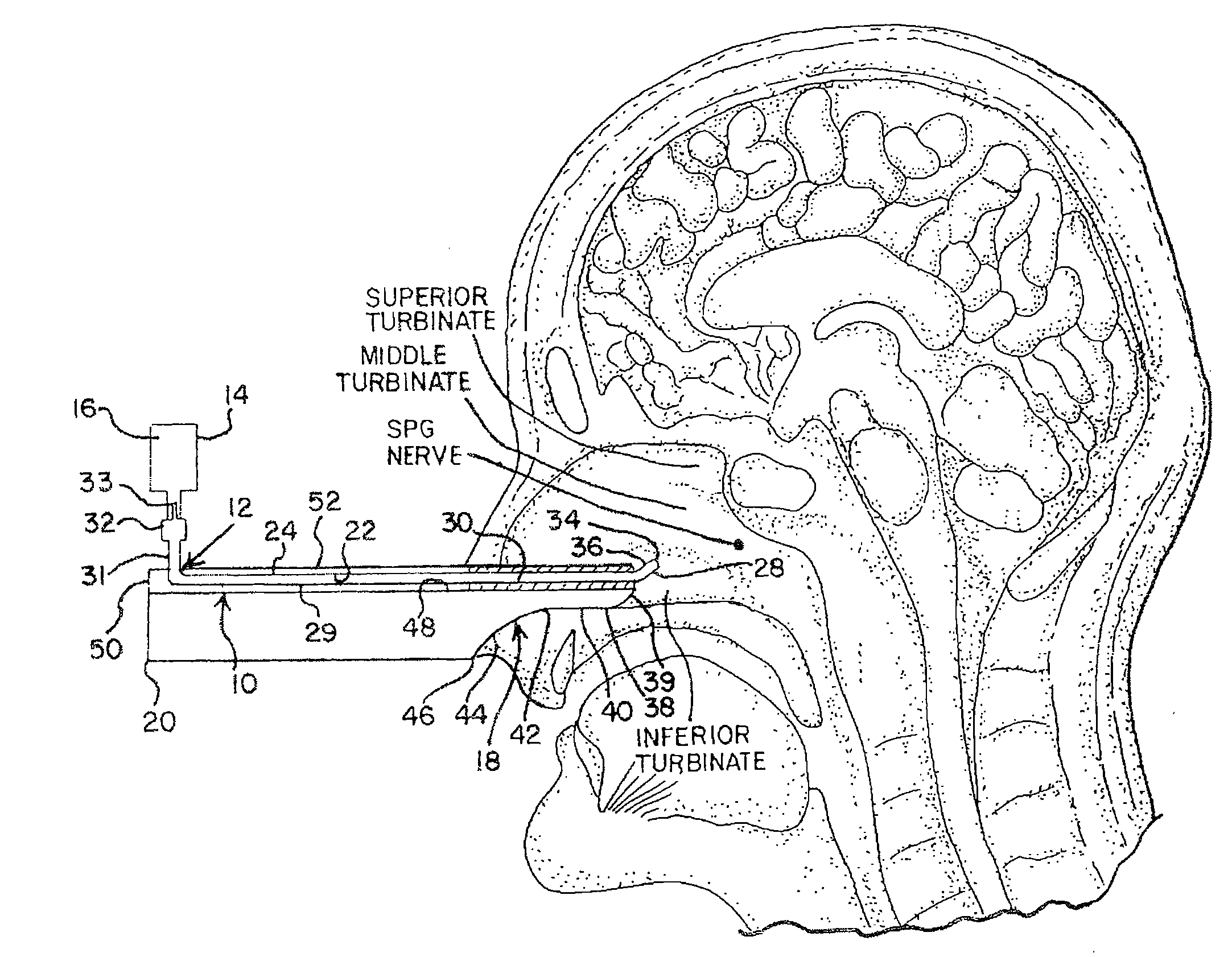
Method and apparatus for stimulating the sphenopalatine ganglion to modify properties of the BBB and cerebral blood flow
InactiveUS7120489B2Promote absorptionPermeability of BBB is increasedHead electrodesBlood flow measurement devicesCerebral blood volumeRetinal blood flow
Apparatus for modifying a property of a brain of a patient is provided, including one or more electrodes (7), adapted to be applied to a site selected from a group of sites consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (6) of the patient and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG. A control unit (8) is adapted to drive the one or more electrodes to apply a current to the site capable of inducing (a) an increase in permeability of a blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the patient, (b) a change in cerebral blood flow of the patient, and / or (c) an inhibition of parasympathetic activity of the SPG.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
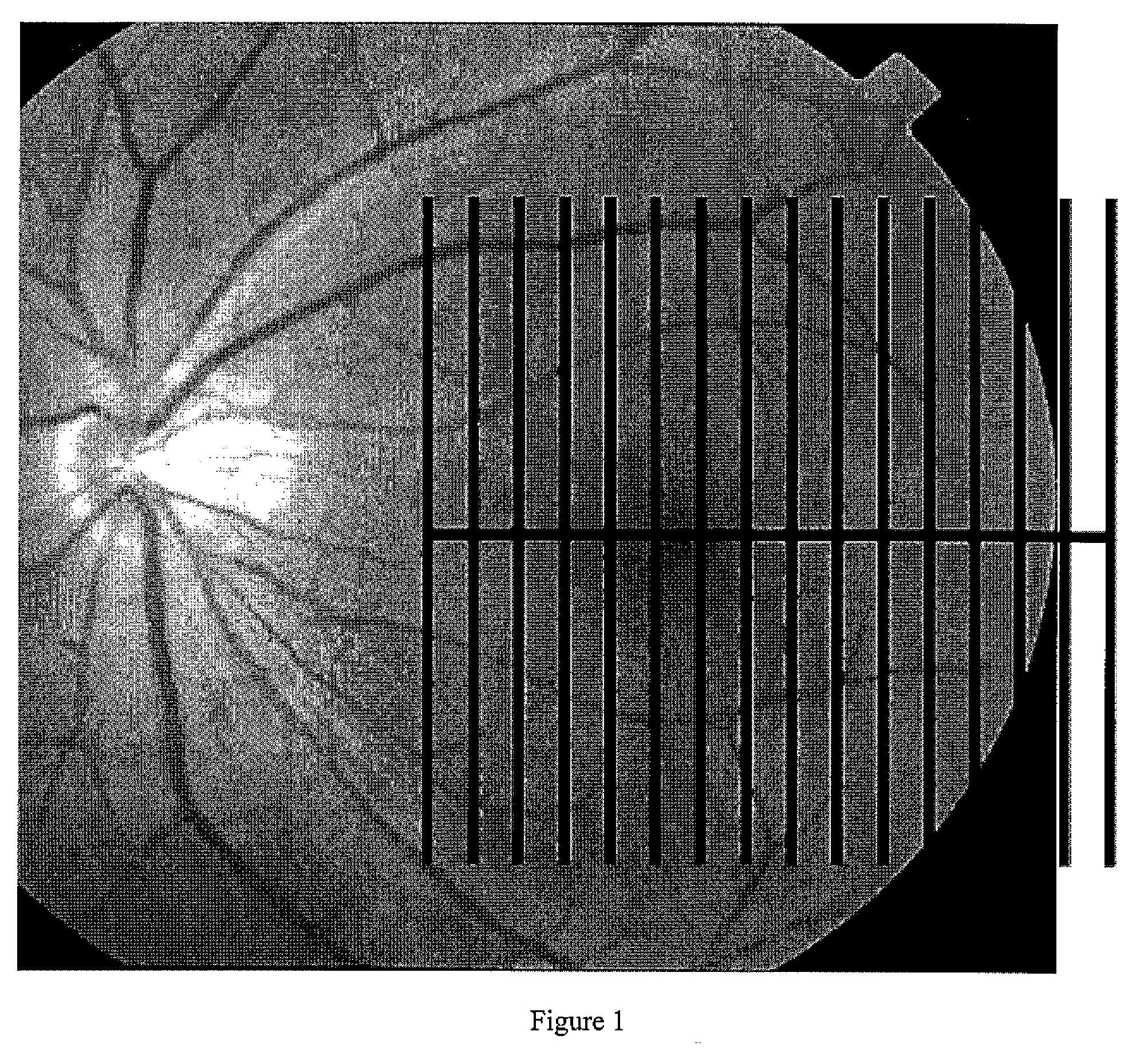
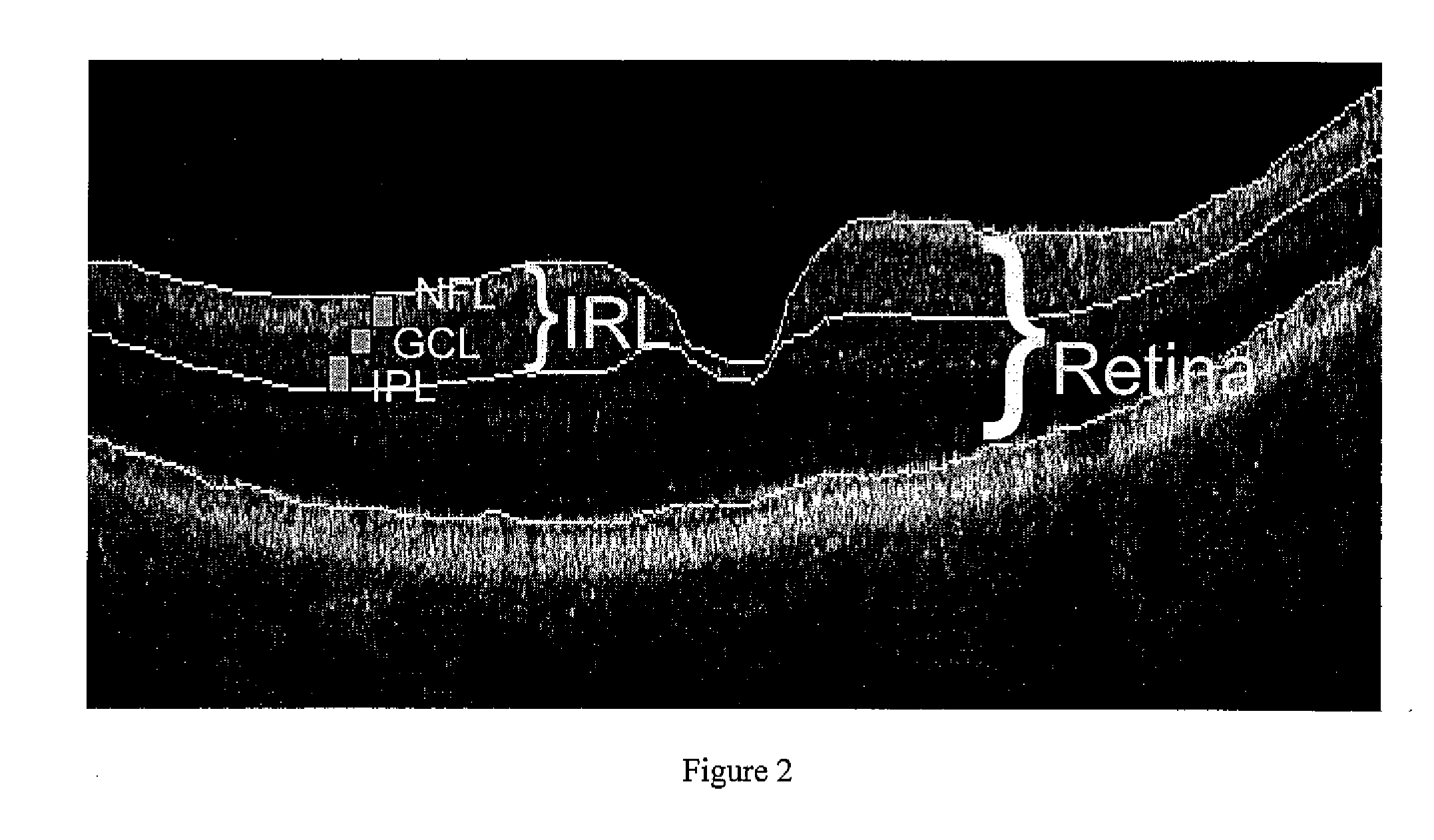
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Ultrasound neuromodulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion
InactiveUS20110190668A1Effective treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Disclosed are methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation of the Sphenopalatine Ganglion and associated neural structures vidian nerve and / or sphenopalatine nerve using an ultrasound transducer to treat migraine and cluster headaches as well as other indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. Treatment may be unilateral or bilateral.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Mimicking neural coding in retinal ganglion cells with short pulse electrical stimulation
A method, device and system for stimulating visual tissue, typically in the retina or visual cortex, to achieve an artificial percept of light or image. The method includes providing stimulating electrodes suitable for placement in proximity to the visual tissue and generating a series of short-duration stimulation signals having a duration of less than about 0.5 milliseconds each. The short-duration stimulation signals are applied through the stimulating electrodes with varying frequencies that are substantially matched to a spiking range of frequencies of at least one ganglion cell for perceiving brightness or image.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Surgical tools and techniques for stimulation
ActiveUS7636597B2Reduce patient discomfortModulate permeability of the blood-brain-barrierHead electrodesSurgeryGreater palatine canalNeural tract
Apparatus for treating a subject is provided, the apparatus comprising (a) a stimulation device (352), adapted to be implanted in a vicinity of a site selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (52) of the subject and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG; and (b) a connecting element (356), coupled to the stimulation device (352), and adapted to be passed through at least a portion of a greater palatine canal (282) of the subject. Also provided is a method for implanting a treatment stimulation device (352) in a vicinity of a site of a subject, the method comprising passing the device (352) through a greater palatine foramen (22) of the subject, and bringing the device (352) into contact with the vicinity of the site, the site selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (52) of the subject and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Methods and systems for management of alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20060020299A1Reduce deliveryPain reliefHeart defibrillatorsImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineGanglion-Like Cell
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
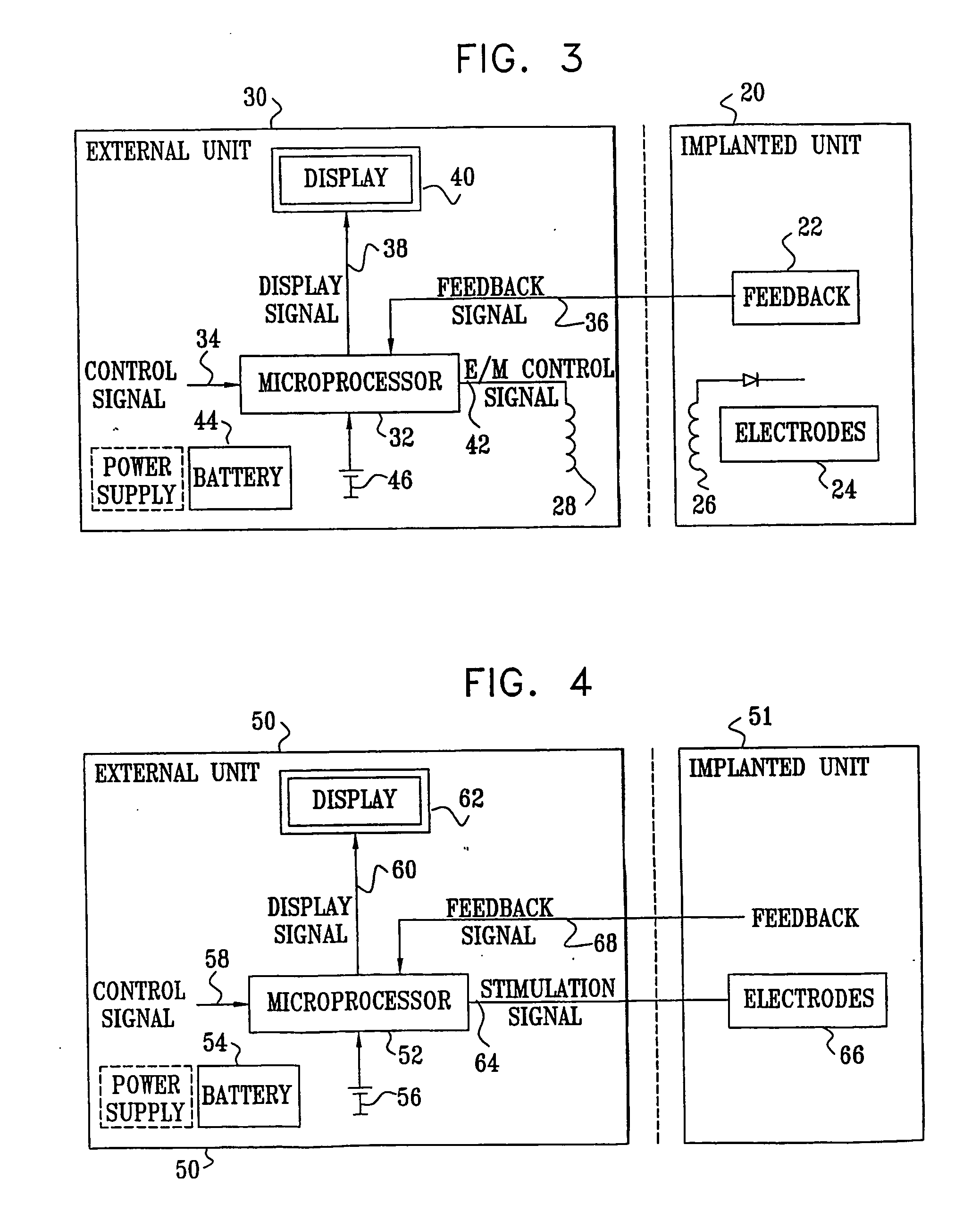
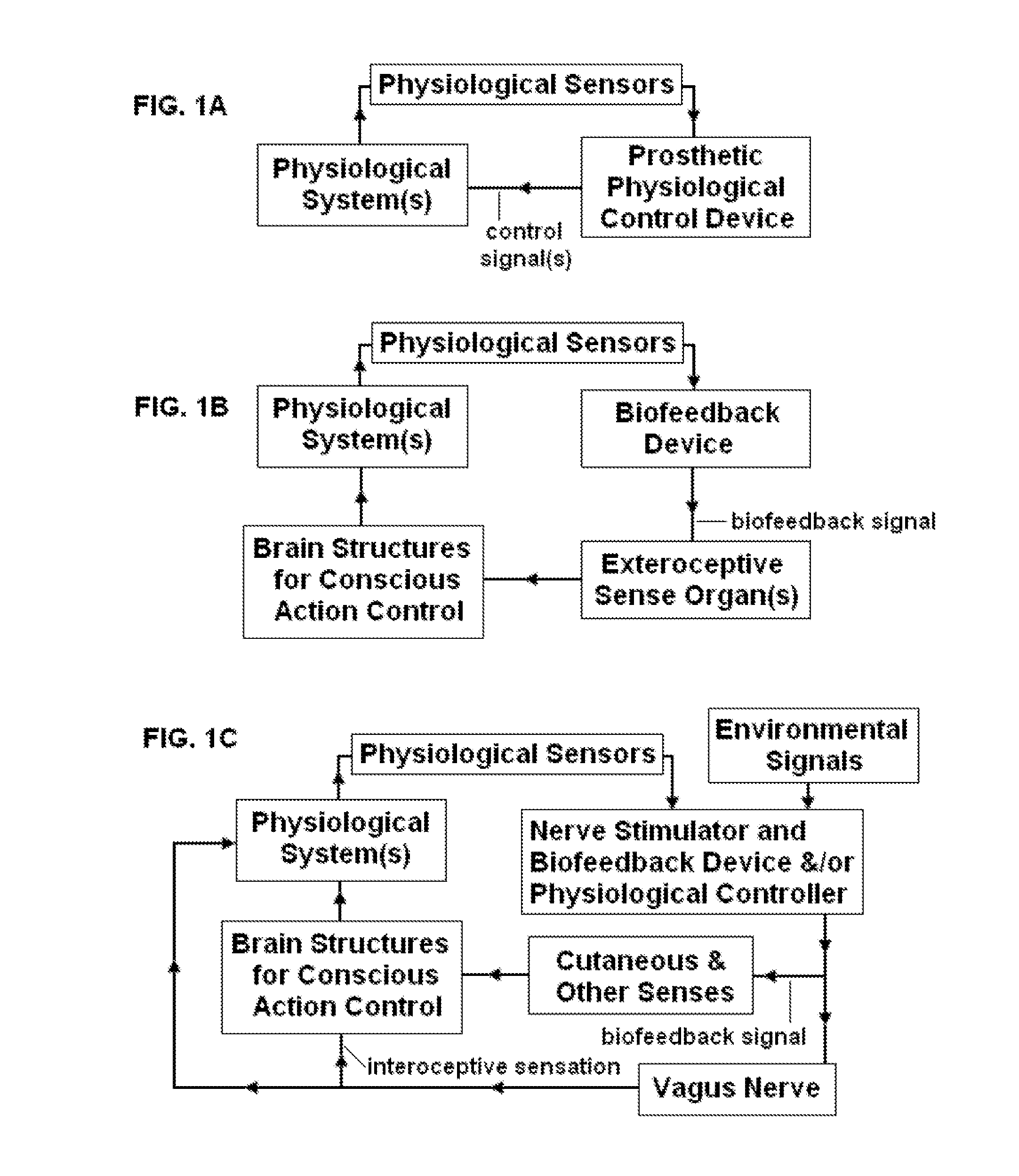
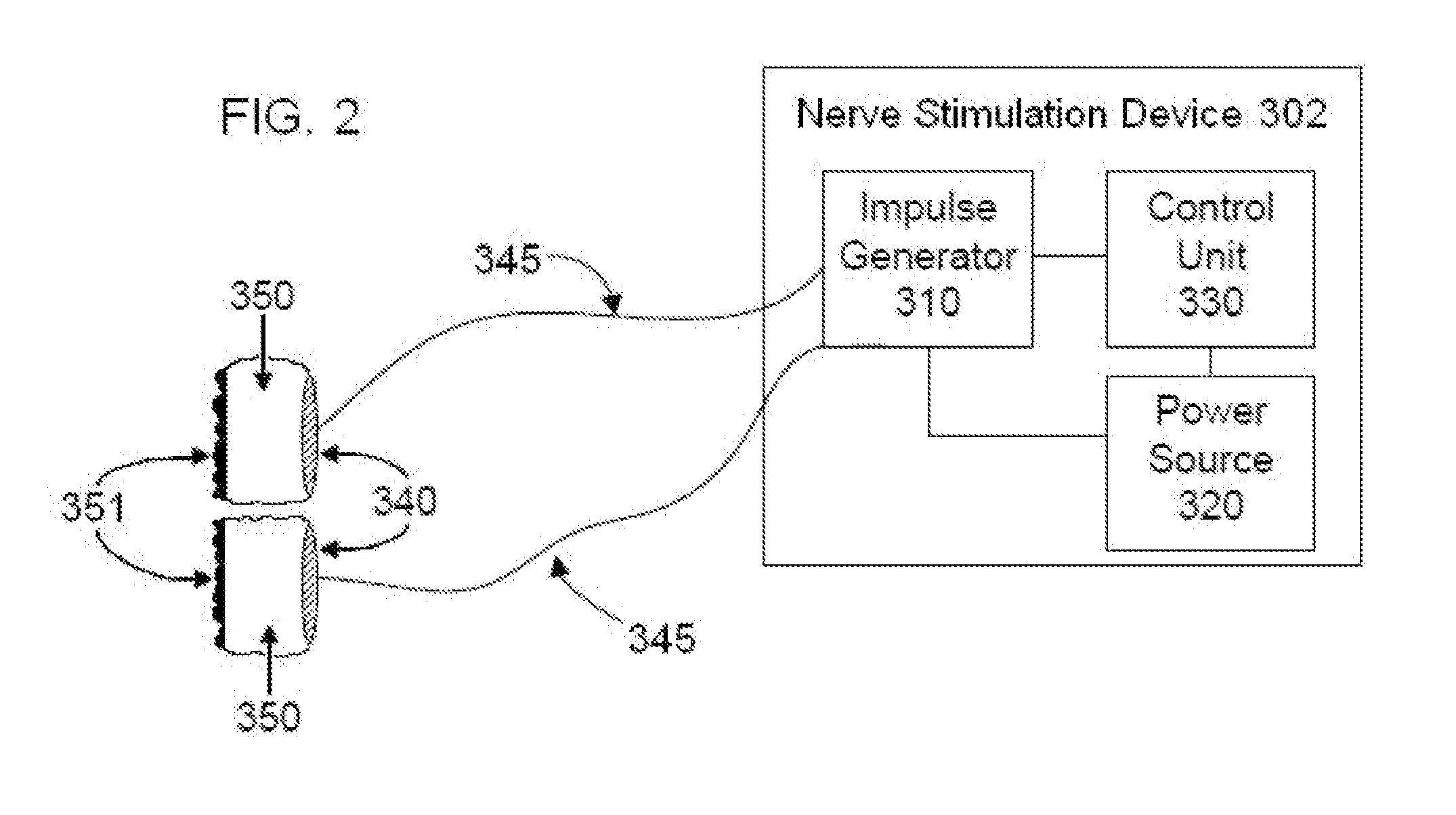
Systems and methods of biofeedback using nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20150142082A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationRR intervalMedicine
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed that are used to treat a medical condition, by electrical stimulation of a nerve or nerve ganglion, used in conjunction with biofeedback. The system comprises a stimulator that applies electrical impulses sufficient to modulate a nerve at a target site within the patient. A sensor measures a physiological output from the patient, such as heart rate variability, and a property of the stimulation signal is varied based on the physiological output.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Methods for Ameliorating Pain and Devices for Delivering a Medicament
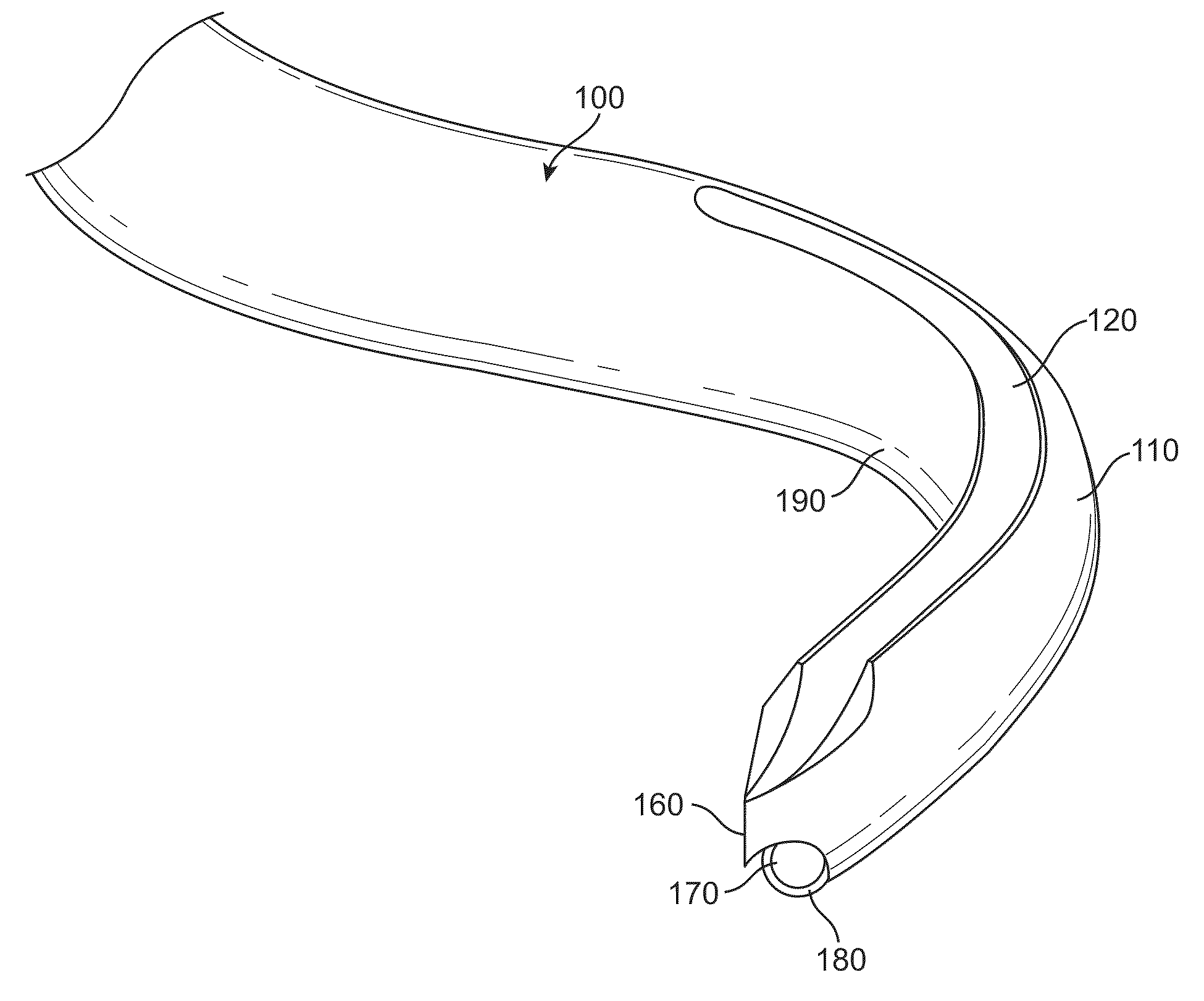
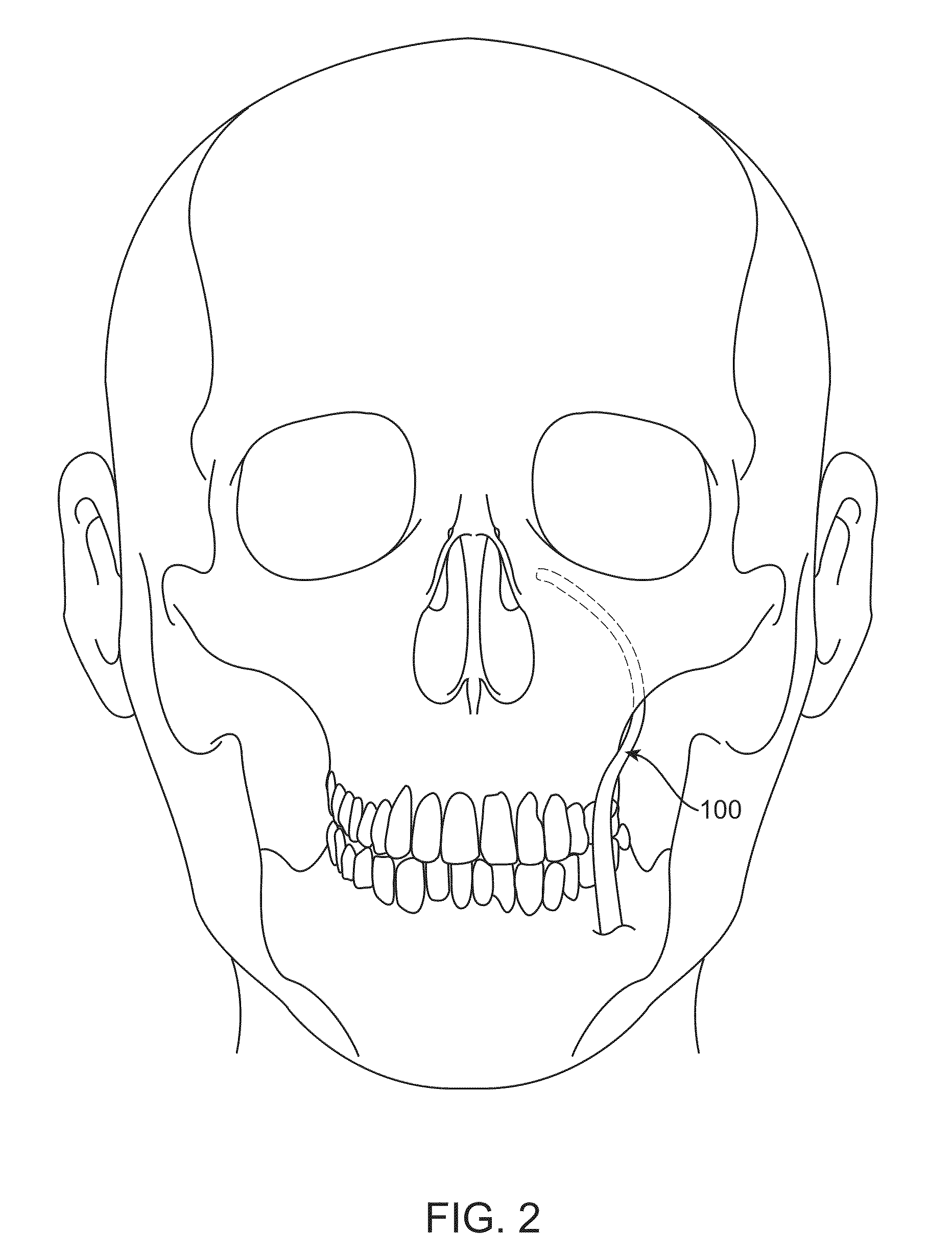
A method for delivering medicament such as for ameliorating pain in a patient includes introducing an injector through a nasal passage of the patient into a region substantially medial and / or posterior and / or inferior to a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) of the patient; and delivering a medicament from the injector superiorly and / or laterally and / or anteriorly towards the SPG. A device for delivering a medicament to a patient in need thereof includes (a) an injector containing a first end configured to remain outside a nasal passage of the patient and a second end configured for entry into the nasal passage of the patient; and (b) an introducer configured for engagement with a nostril of the patient and containing a passageway configured for slidably receiving the injector. The injector is moveable between a storage position preceding the engagement and an engaging position pursuant to the engagement.
Owner:XIA TIAN
Integrated Delivery and Visualization Tool for a Neuromodulation System
Methods and apparatus for delivering a neurostimulator to a target tissue are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is a delivery tool comprising a handle portion, an elongate shaft comprising a contoured distal portion, a visualization system embedded in the elongate shaft, and an insertion groove on the elongate shaft configured to deploy the neurostimulator. The contoured distal portion can be shaped and configured to maintain contact with a posterior maxilla and elevate a periosteum off of the posterior maxilla to avoid soft tissue dissection. In some embodiments, the neurostimulator is implanted in close proximity to or touching the sphenopalatine ganglion.
Owner:UNITY HA LLC
Determining locations of ganglia and plexi in the heart using complex fractionated atrial electrogram
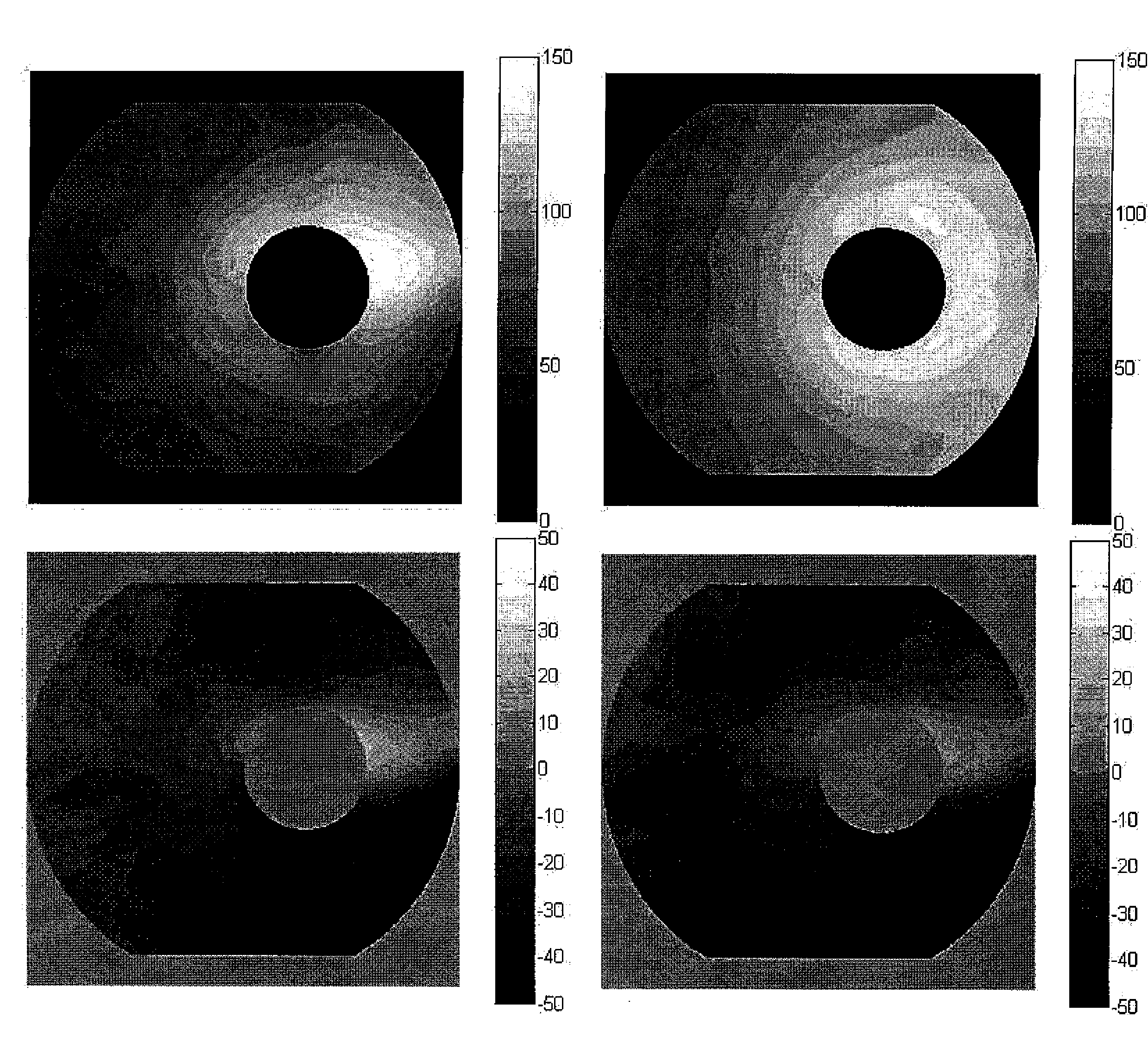
Software and apparatus are provided to automatically detect and map ganglionated plexi that are found within areas of complex fractionated electrograms in cardiac chambers. Electrogram signal are analyzed to count the number of complexes whose amplitude and peak-to-peak intervals meet certain criteria. Functional maps indicating a spatial distribution of the ganglionated plexi and the relative numbers of complex fractionated electrograms are produced for display.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Devices for Delivering a Medicament and Methods for Ameliorating Pain
A device for delivering a medicament to a patient in need thereof includes: (a) an injector including a first end configured to remain outside a nasal passage of the patient and a second end configured for entry into the nasal passage of the patient, wherein the injector is moveable between a storage position and an engaging position; and (b) an introducer configured for engagement with a nostril of the patient, wherein the introducer includes a passageway configured for slidably receiving the injector, and wherein the introducer includes a curvature along a portion thereof adjacent to the passageway. Methods for ameliorating pain in a patient include (a) introducing the injector through the nasal passage of the patient into a region substantially medial and / or posterior and / or inferior to a sphenopalatine ganglion of the patient; and (b) delivering a medicament from the injector superiorly and / or laterally and / or anteriorly towards the sphenopalatine ganglion.
Owner:XIA TIAN
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
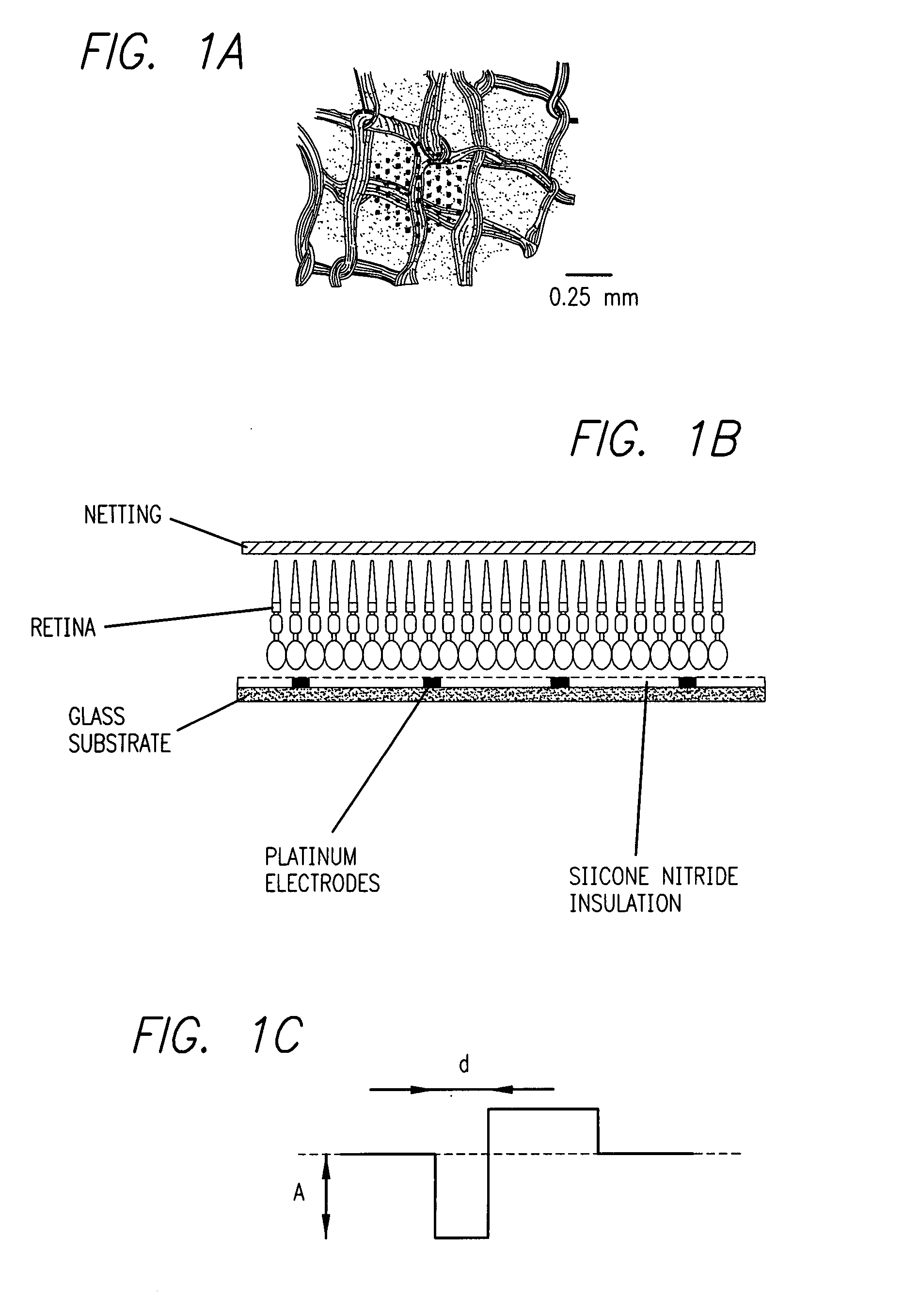
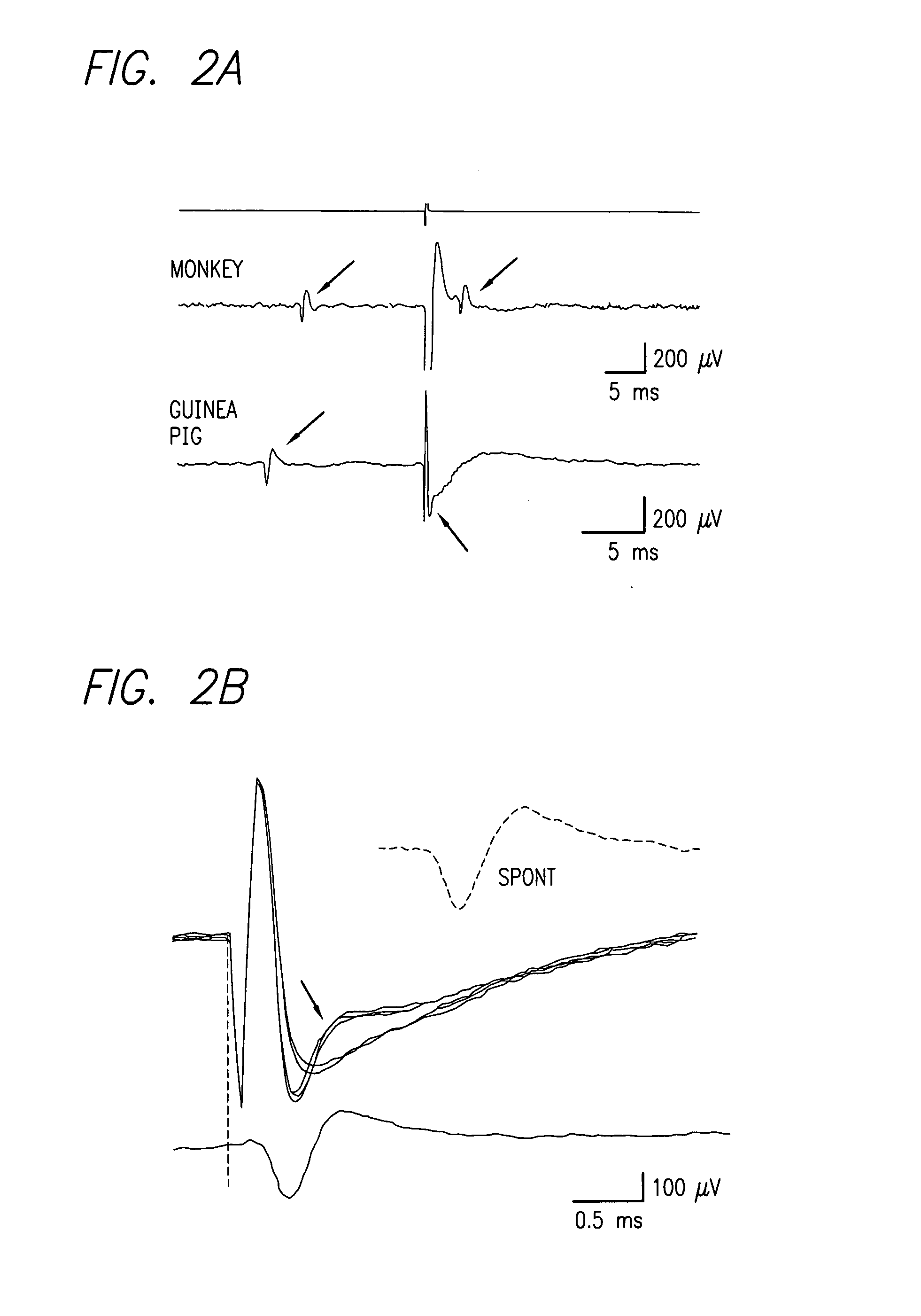
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
Imaging apparatus for imaging a heart
InactiveUS20110230775A1Enhance imageEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac imagingPlexus
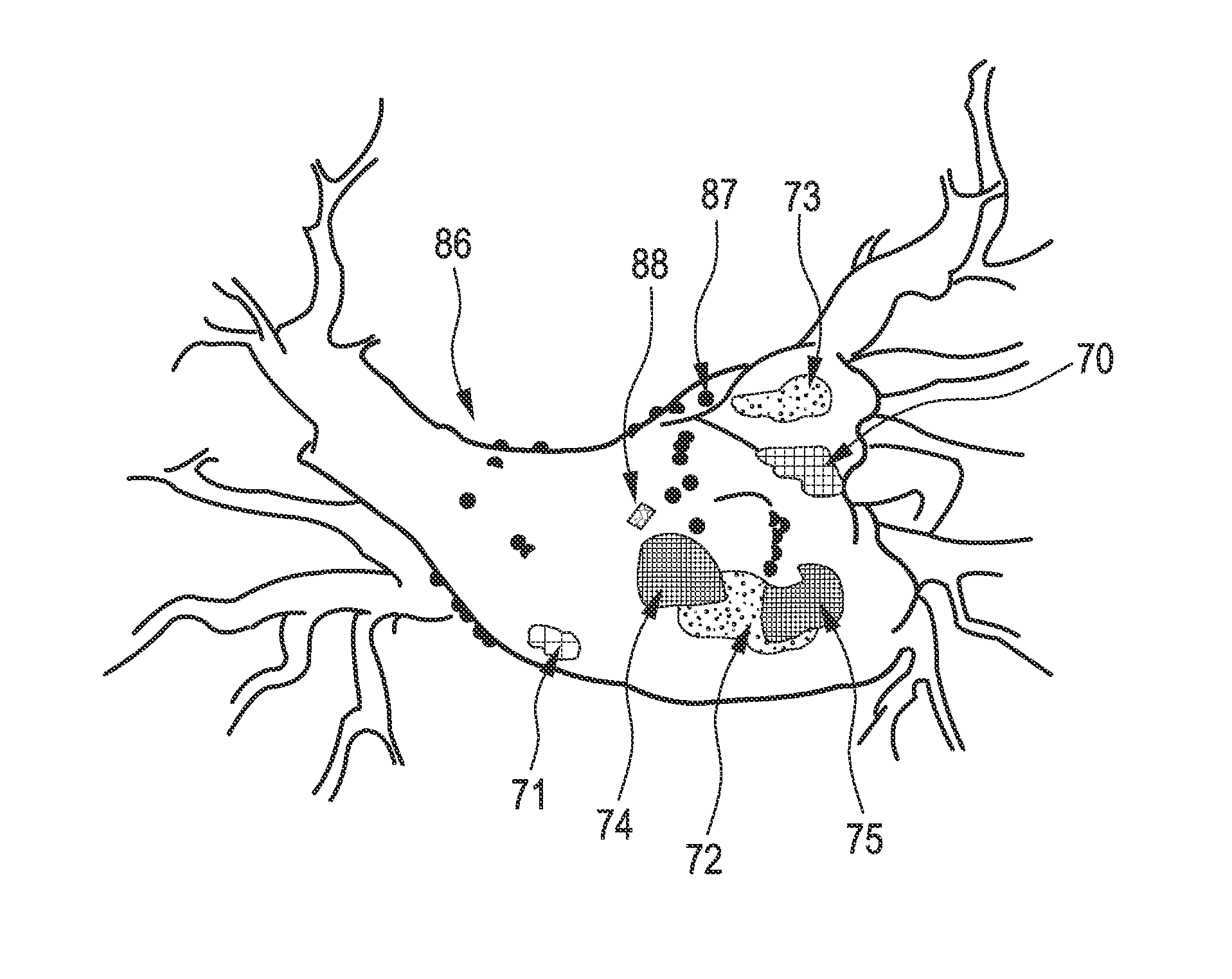
An imaging apparatus for imaging a heart is provided, wherein the imaging of the heart is improved such that conclusions about regions of the heart having an abnormal behaviour can be made more accurate and more optimal. The imaging apparatus comprises a first site determination unit for determining a first site of the heart comprising a first property type like a fractionated electrogram (70,71,74,75) and a second site determination unit for determining a second site comprising a second property type like a ganglionated plexus (72,73). The first site and the second site are causally related and displayed on a display unit. Since the displayed first and second sites are causally related to each other, a further information is given, i.e. the causal relation, which assists a user in finding regions of the heart showing an abnormal behaviour.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
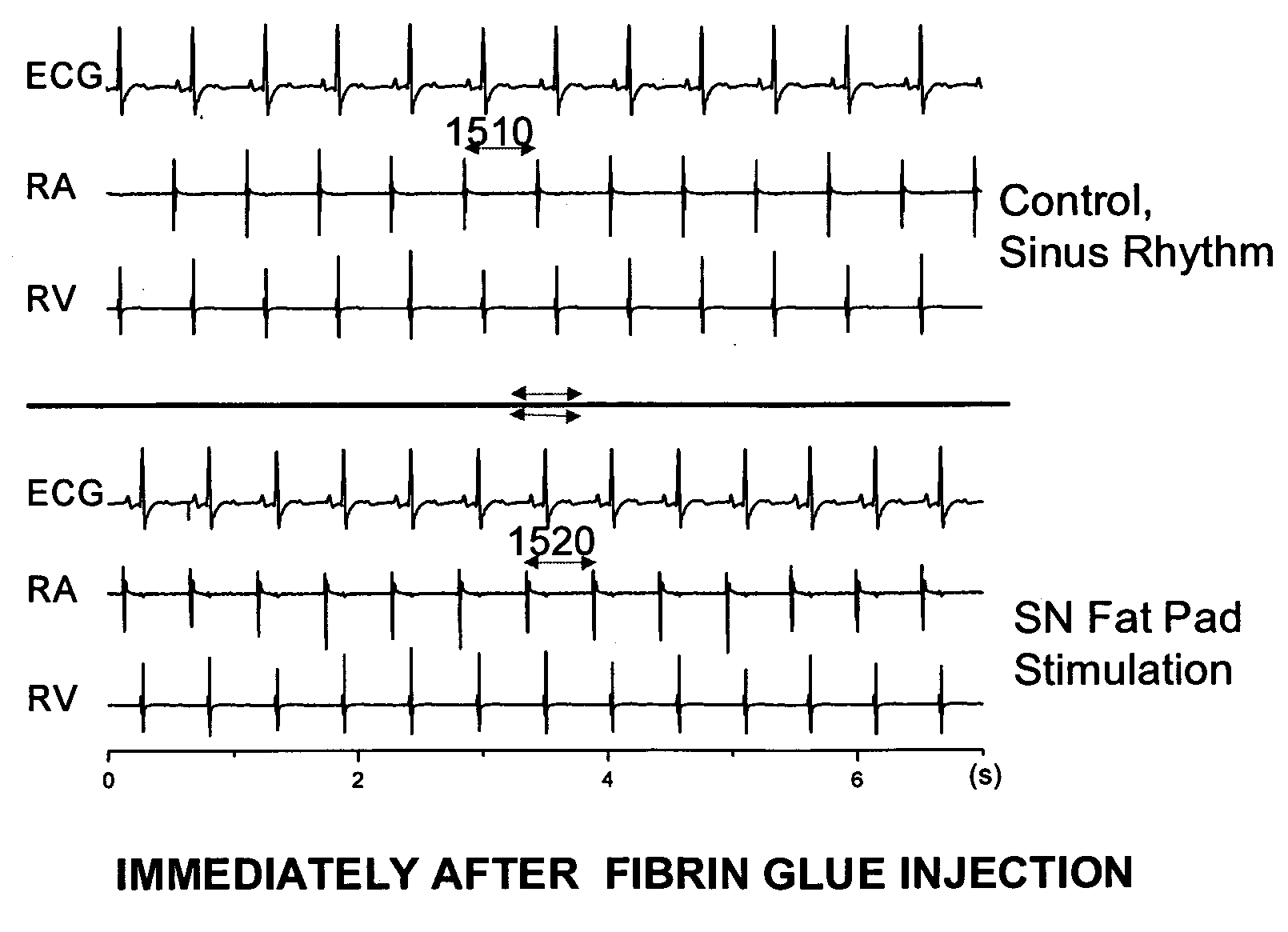
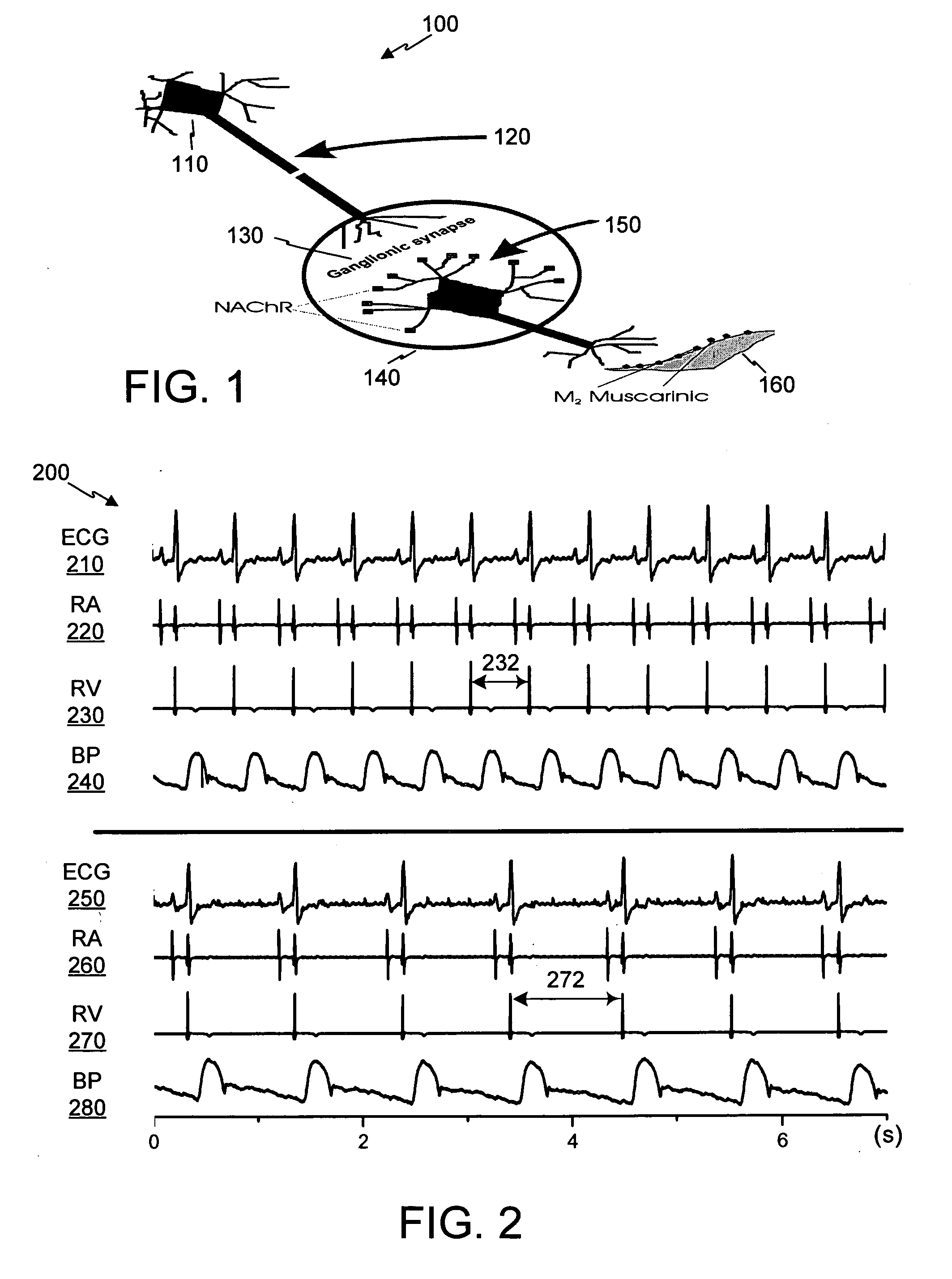
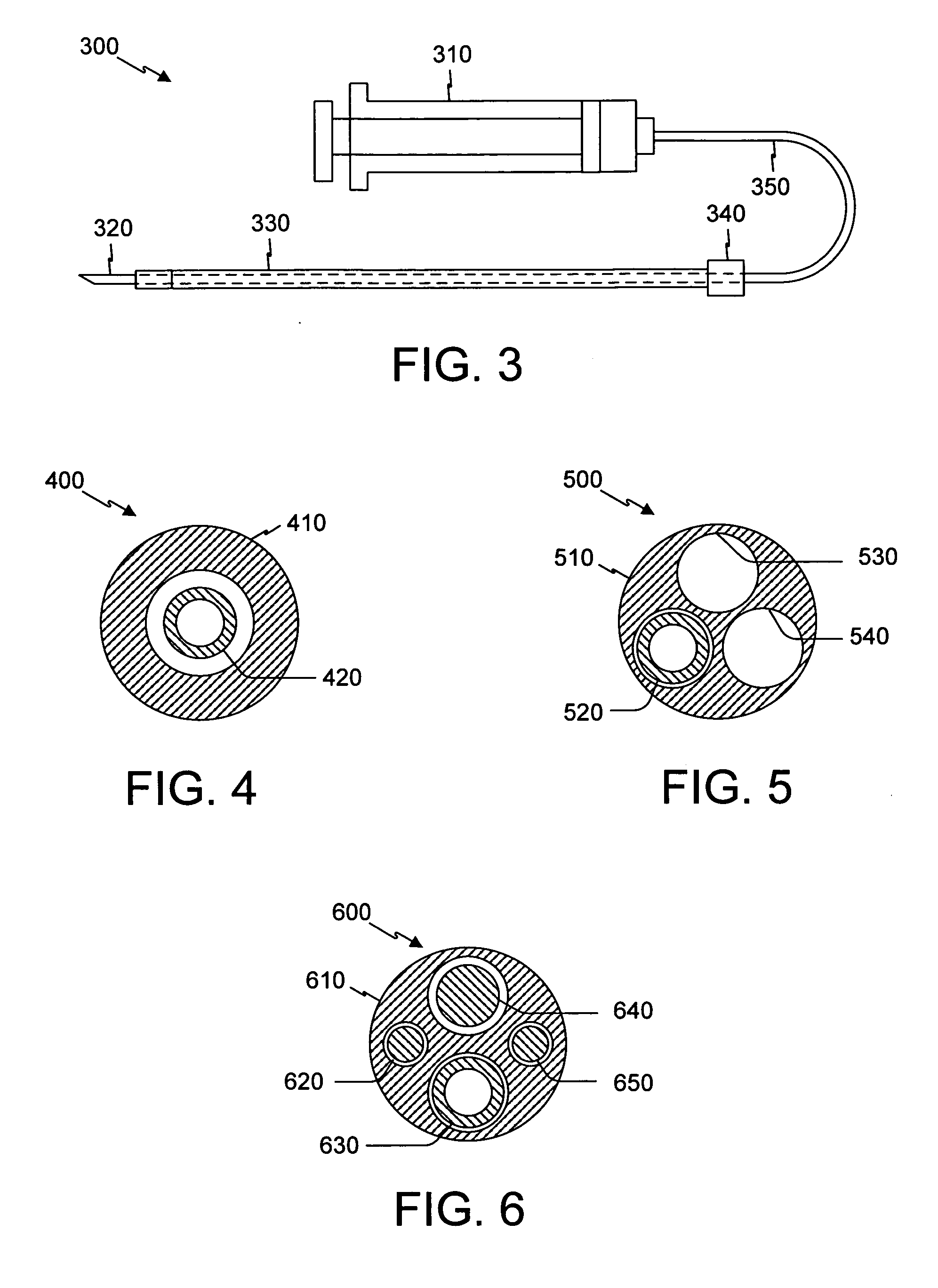
Control of cardiac arrhythmias by modification of neuronal conduction within fat pads of the heart
InactiveUS20050119704A1Efficient modificationPeptide/protein ingredientsInfusion syringesBiopolymerAdventitia
To control cardiac arrhythmias, various conduction-modifying agents include biopolymers, fibroblasts, neurotoxins, and growth factors are introduced either epicardially or endocardially to the fat pads in proximity to the ganglia therein. Any desired technique may be used for injection, including injection from a catheter inserted percutaneously, or direct injection through the epicardial during open heart surgery. Preferably the patient's heart is beating throughout the Injection.
Owner:CARDIOPOLYMERS
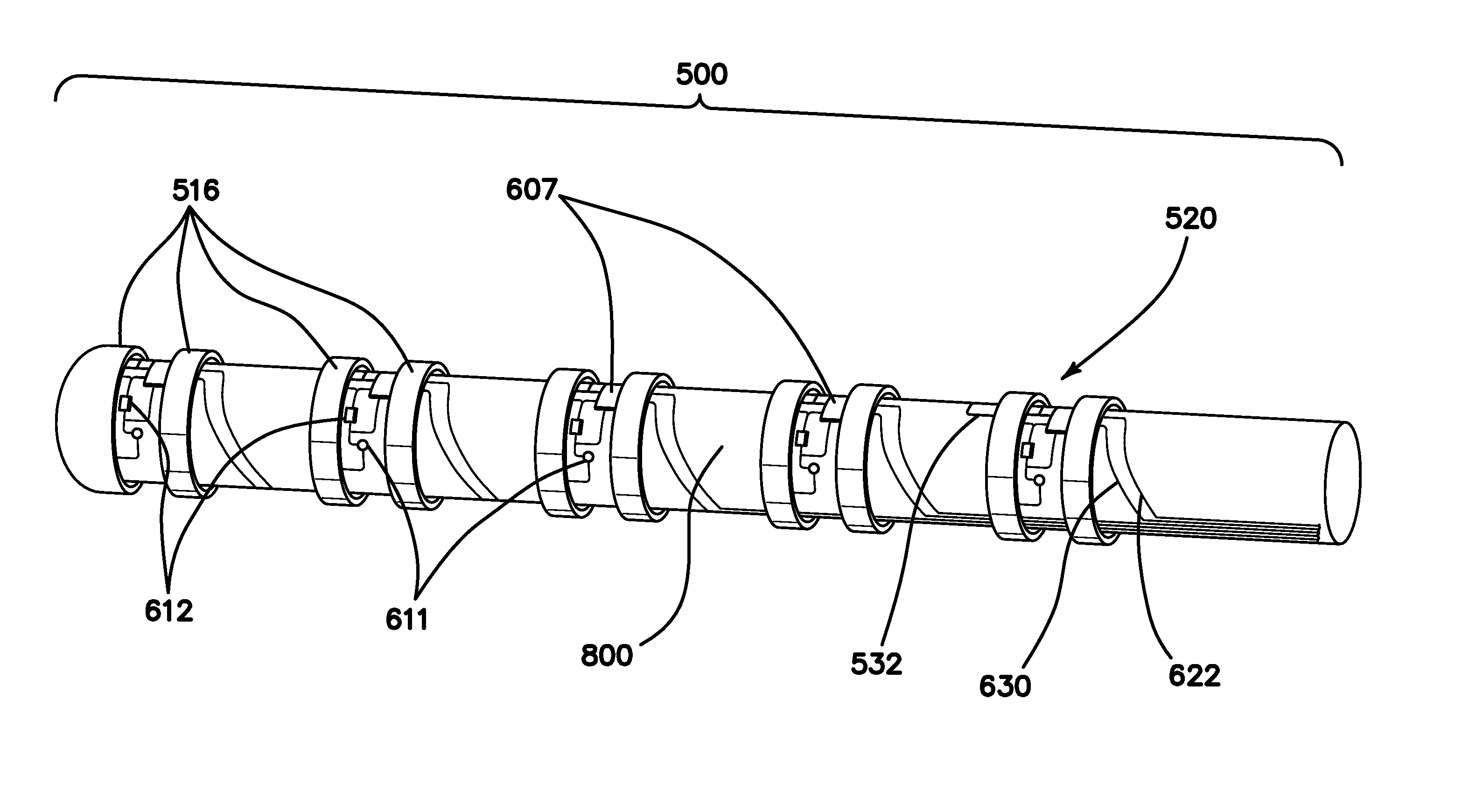
Method and apparatus for measuring biopotential and mapping ephaptic coupling employing a catheter with mosfet sensor array
InactiveUS20140081114A1Simple modelSimple technologyElectroencephalographyCatheterMOSFETSensor array
This invention relates generally to electro-anatomical mapping method and an apparatus using a catheter and more particularly to a mapping catheter having an embedded MOSFET sensor array for detecting local electrophysiological parameters such as biopotential signals within an excitable cellular matrix geometry, for determining physiological as well as electrical characteristics of conduction path and its underlying substrate within the endocardial and epicardial spaces, the arterial structure and in ganglionic plexus. The apparatus with its MOSFET sensor is geometrically configured as a decapolar linear array and optionally with an 8×8 sensor matrix placed on a balloon-like structure.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Targeted delivery of botulinum toxin to the sphenopalatine ganglion
ActiveUS20080279895A1Effective prophylactic treatmentReducing and preventing symptomNervous disorderBacteriaSynapseVascular disease
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Apparatus and Method for Controlling Headaches
InactiveUS20100030187A1Effective and easy to useEffective pain controlMedical devicesMedical atomisersNostrilHeadaches
Owner:XIA TIAN
Targeted delivery of botulinum toxin for the treatment and prevention of trigeminal autonomic cephalgias, migraine and vascular conditions
ActiveUS7655244B2Effective treatmentReducing and preventing symptomBacterial antigen ingredientsNervous disorderSynapseVascular disease
Botulinum toxin, among other presynaptic neurotoxins is used for the treatment and prevention of migraine and other headaches associated with vascular disorders. Presynaptic neurotoxins are delivered focally, targeting the nerve endings of the trigeminal nerve, the occipital nerve and the intranasal terminals of the parasympathetic fibers originating in the Sphenopalatine ganglion. The administration preferably targets the extracranial nerve endings of the trigeminal nerve in the temporal area, the extracranial occipital nerve endings in the occipital area, and the intranasal terminals of the trigeminal nerve and parasympathetic fibers originating in the Sphenopalatine ganglion. The delivery is carried out by way of injection or topically.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Devices for Delivering a Medicament and Connector for Same
A method and device for delivering medicament such as for ameliorating pain in a patient from an injector superiorly and / or laterally and / or anteriorly towards the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG). A device for delivering a medicament to a patient in need thereof includes (a) an injector containing a first end configured to remain outside a nasal passage of the patient and a second end configured for entry into the nasal passage of the patient; and (b) an introducer configured for engagement with a nostril of the patient and containing a passageway configured for slidably receiving the injector. The injector is moveable between a storage position preceding the engagement and an engaging position pursuant to the engagement. The device may further include a locking connection assembly that is useful in other devices.
Owner:XIA TIAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com