Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Cerebral blood volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
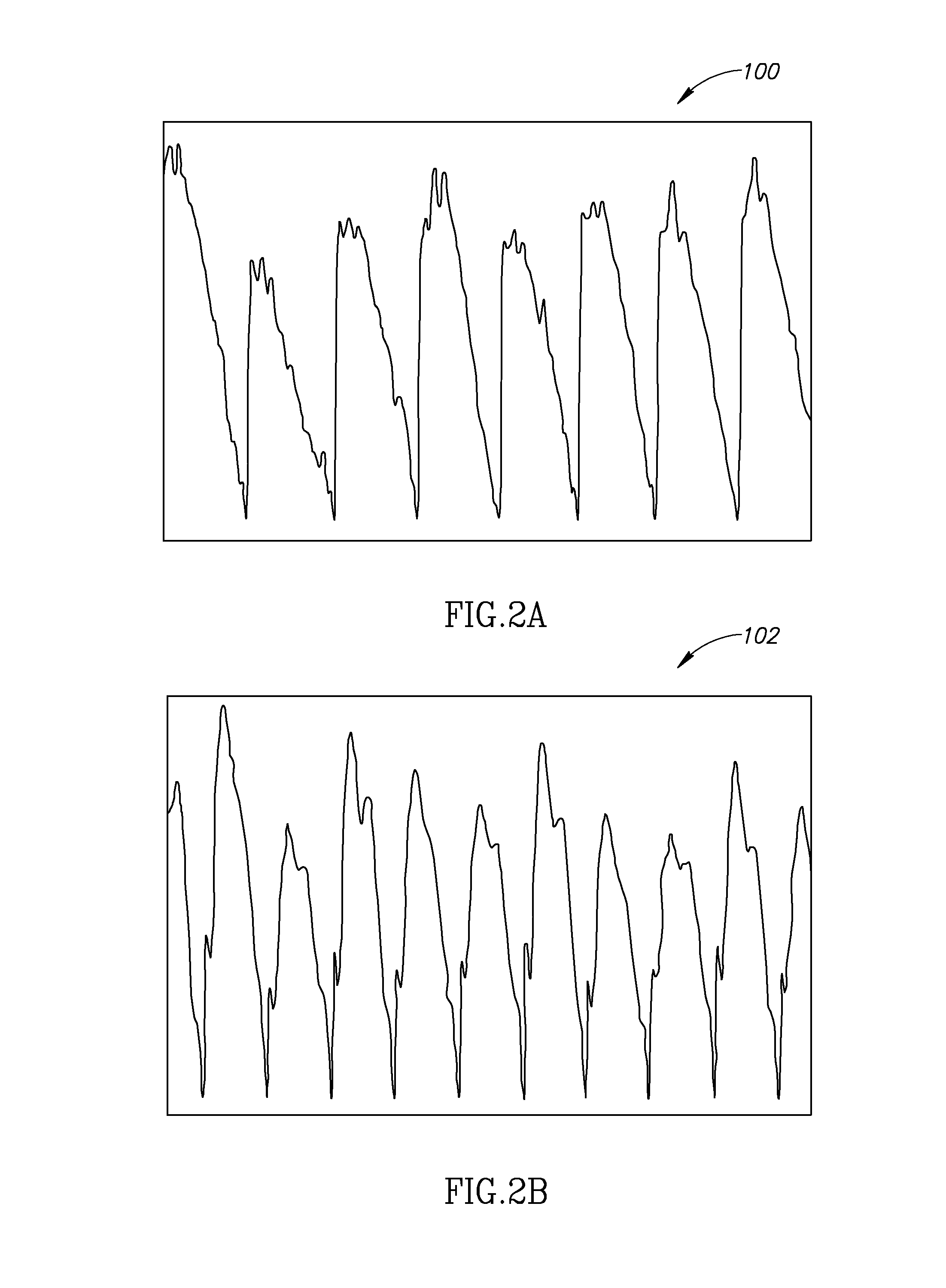
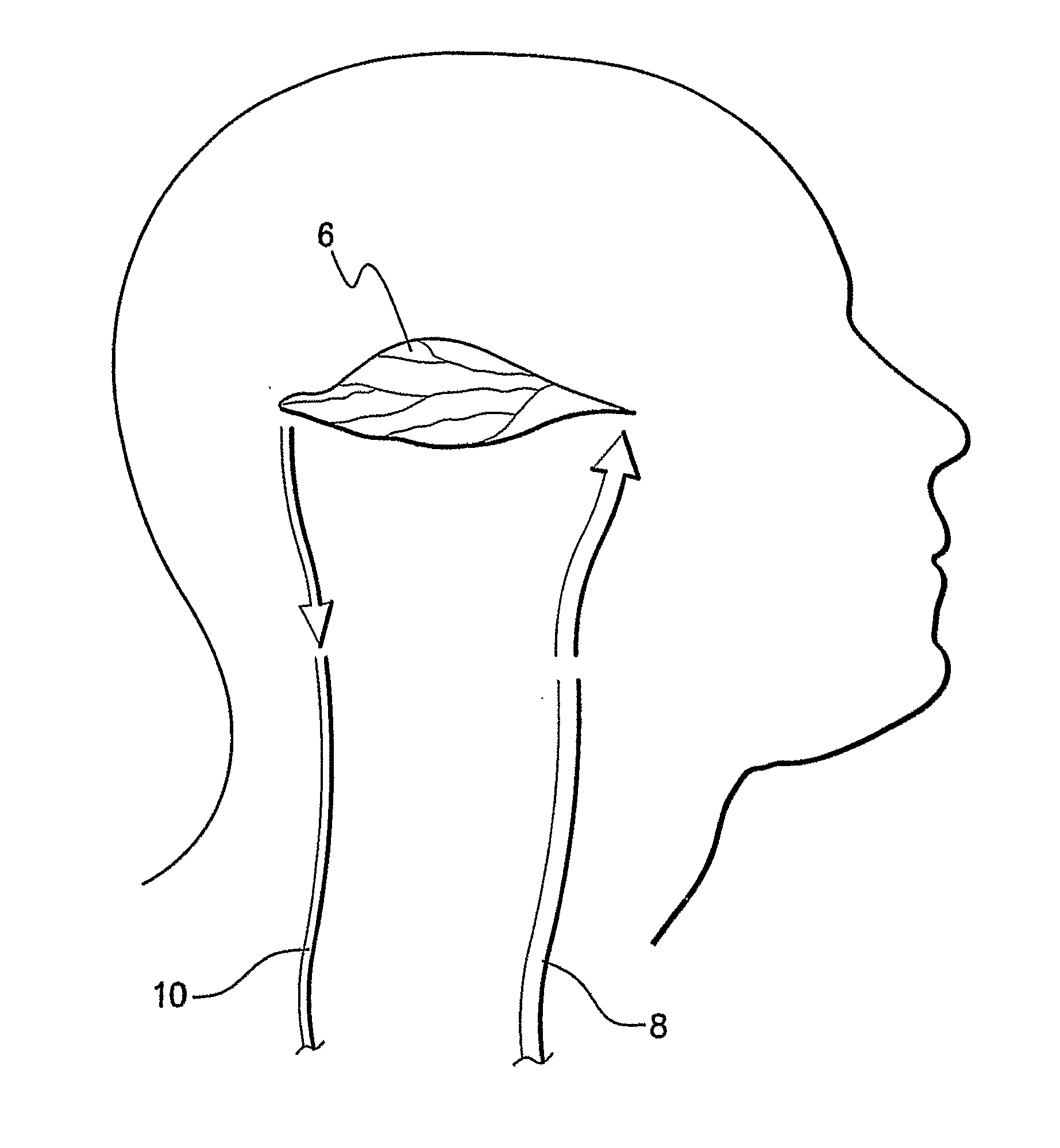
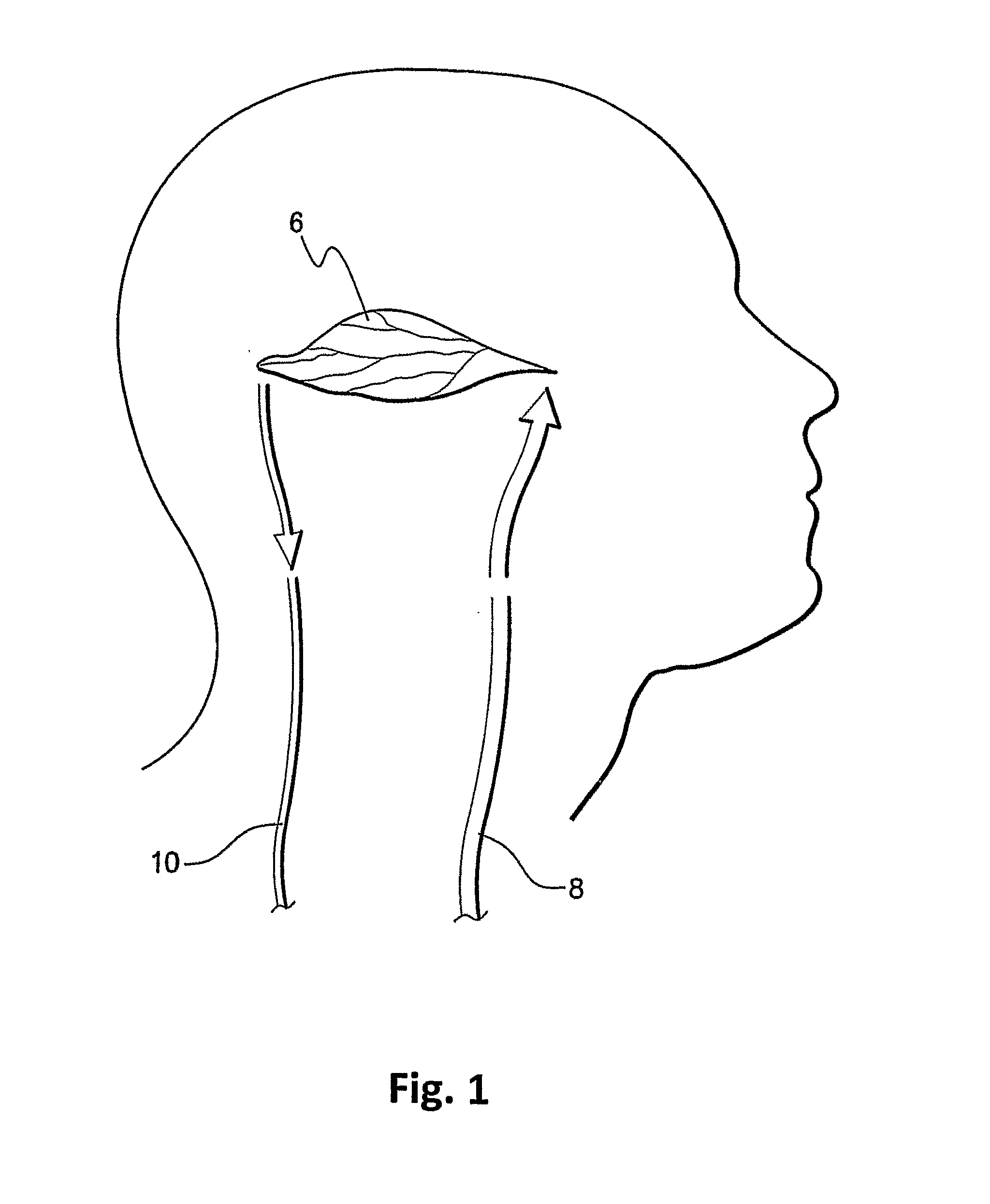
Cerebral Blood Volume (CBV): Describes the blood volume of the cerebral capillaries and venules per cerebral tissue volume. Mean Transit Time (MTT): Measures the length of time a certain volume of blood spends in the cerebral capillary circulation.
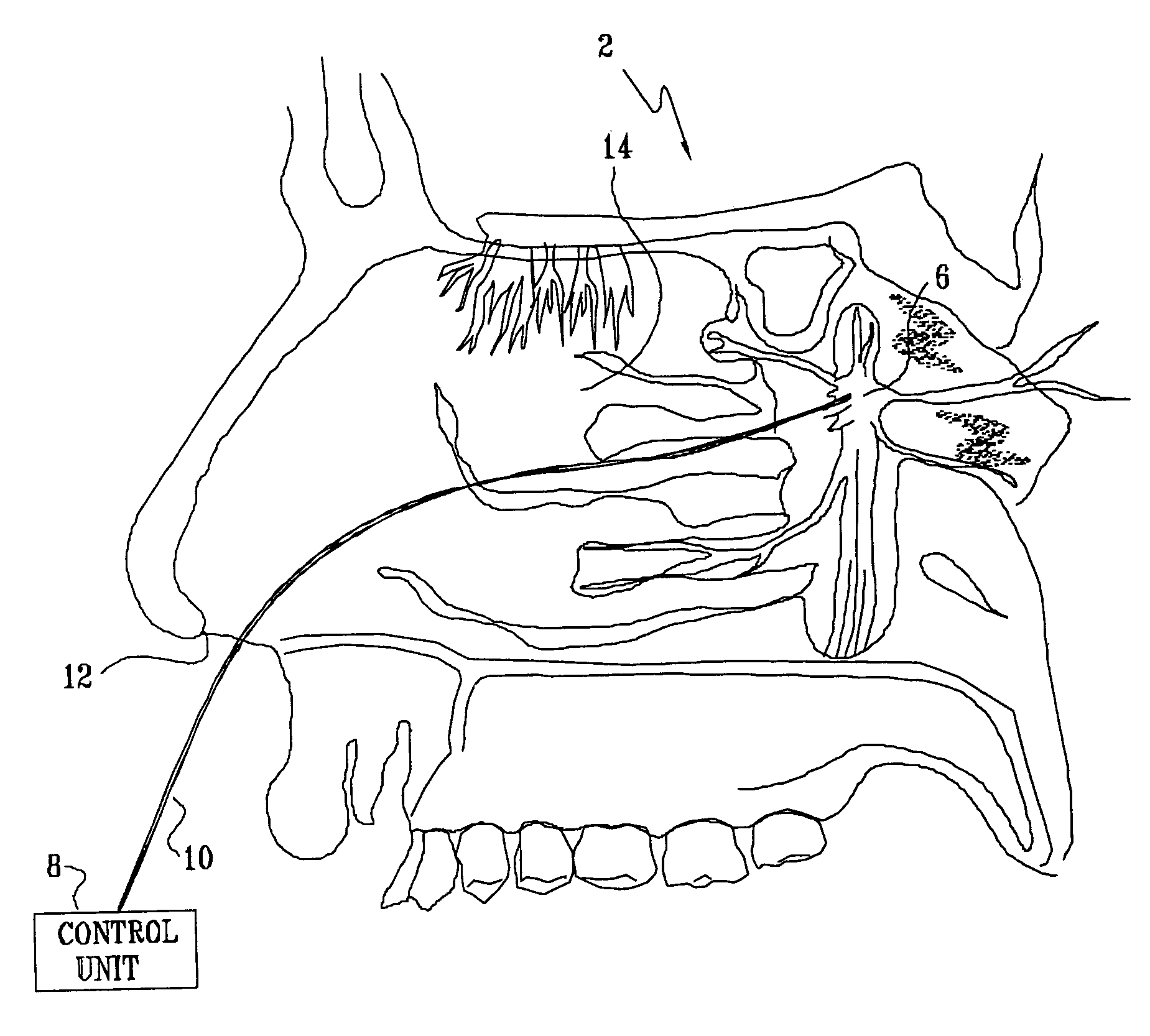
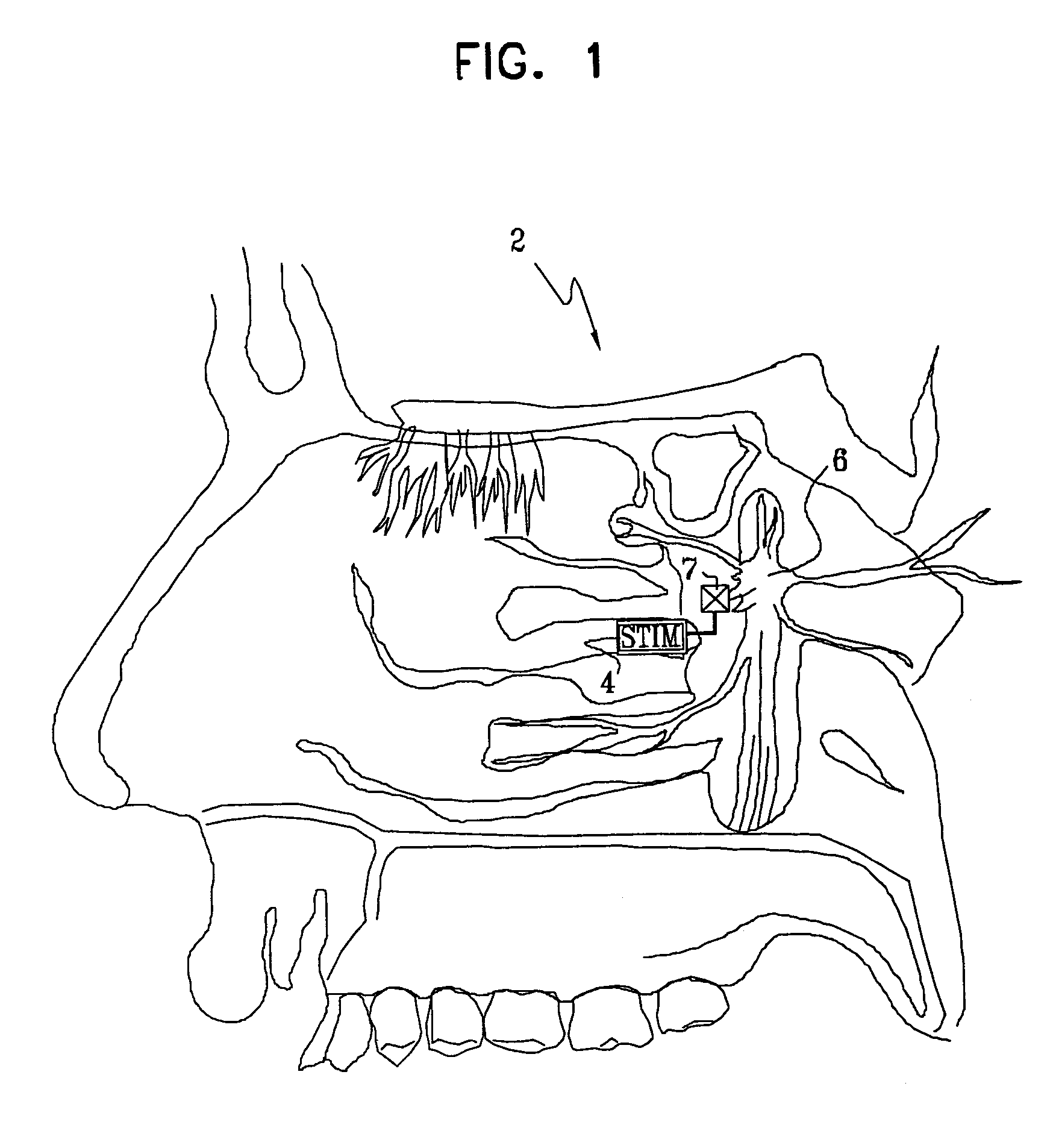
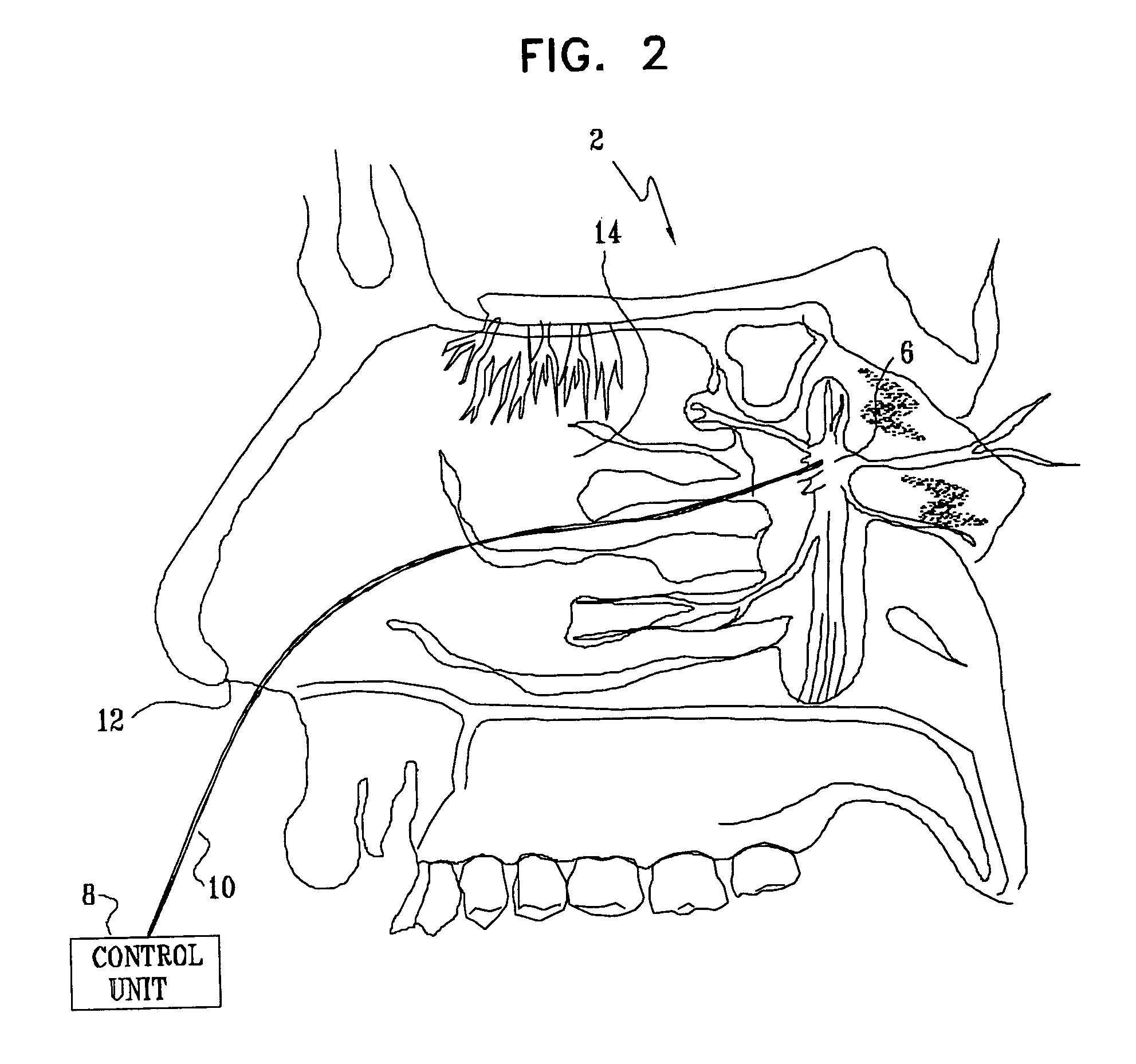
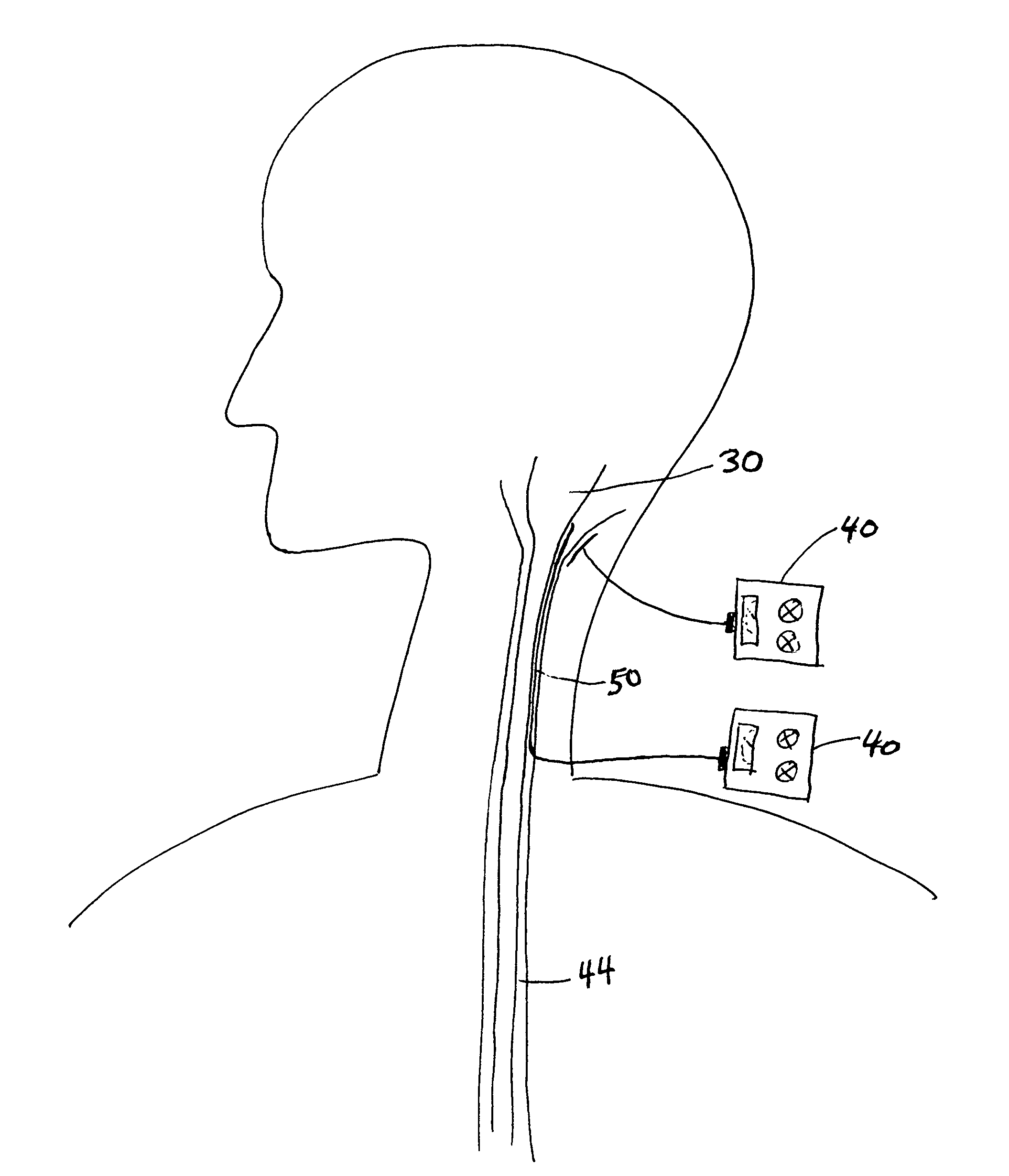
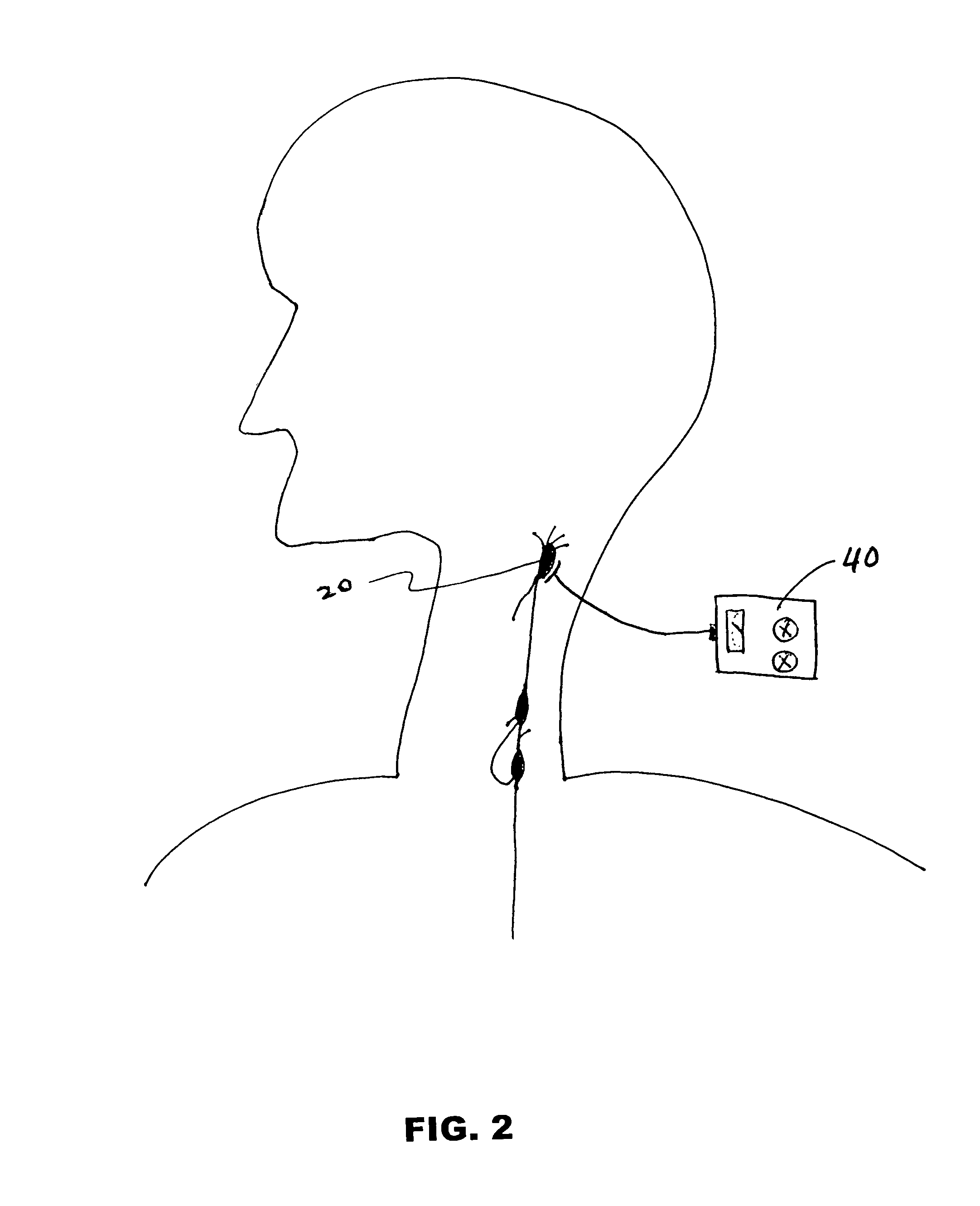
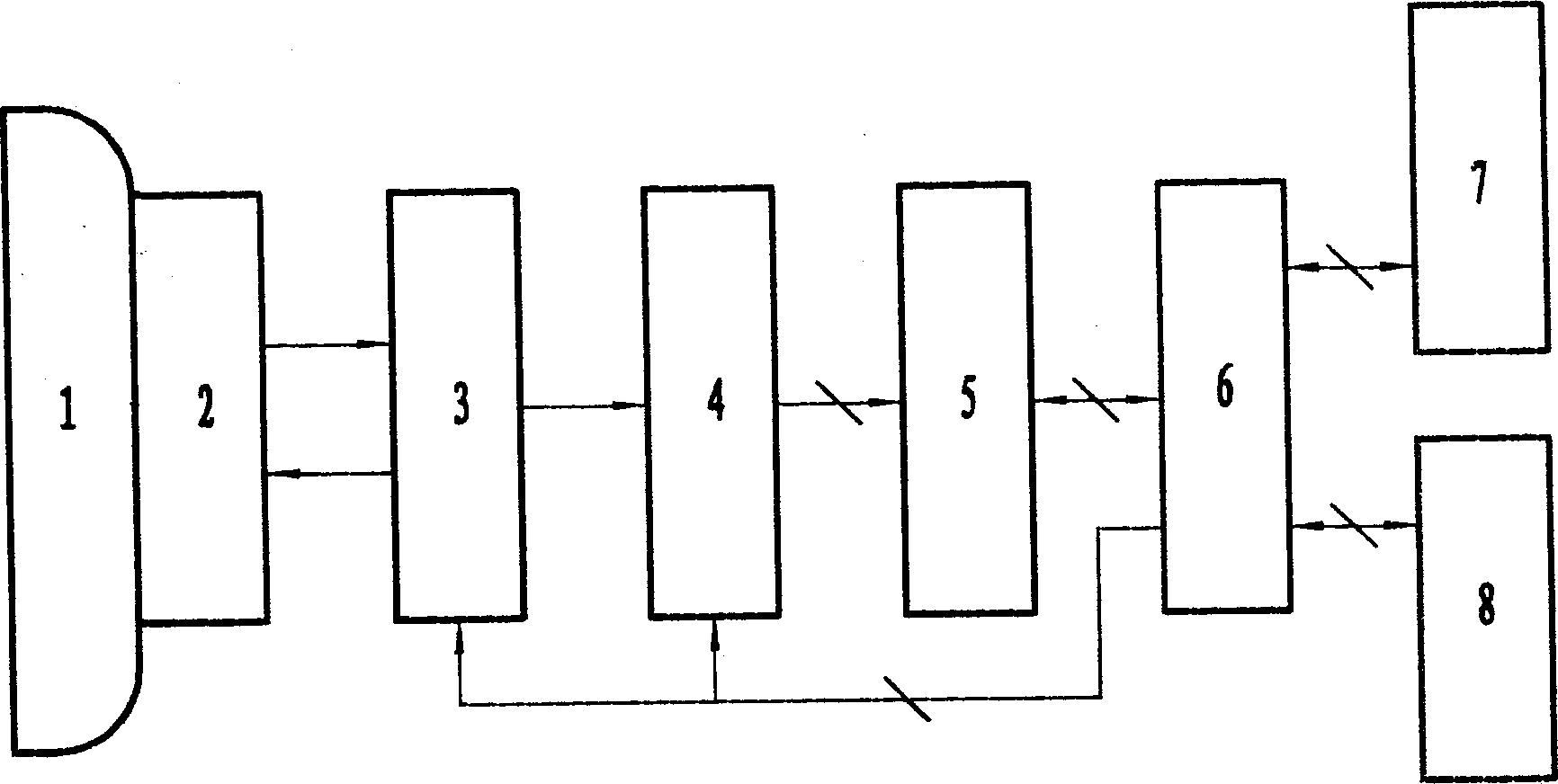
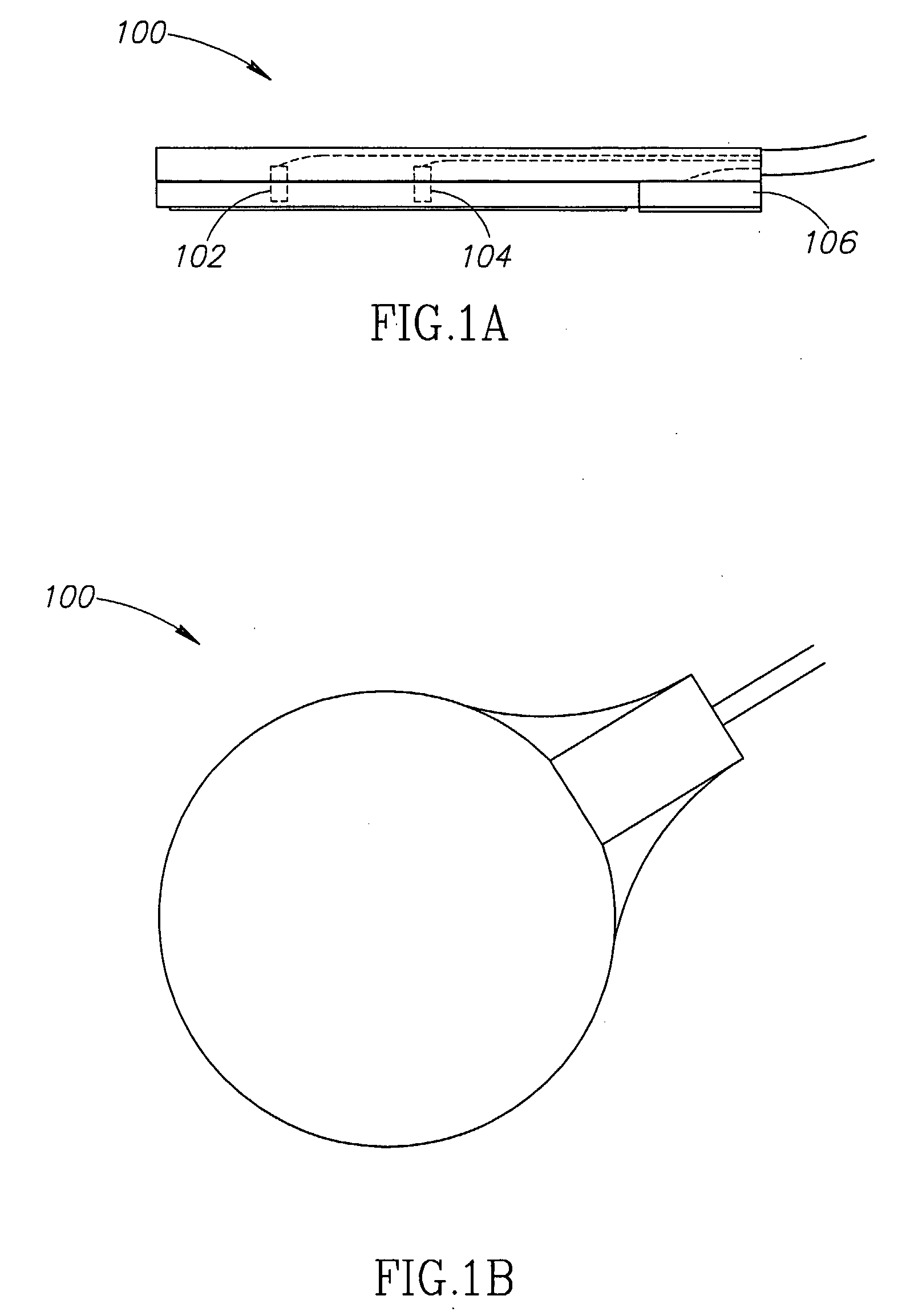
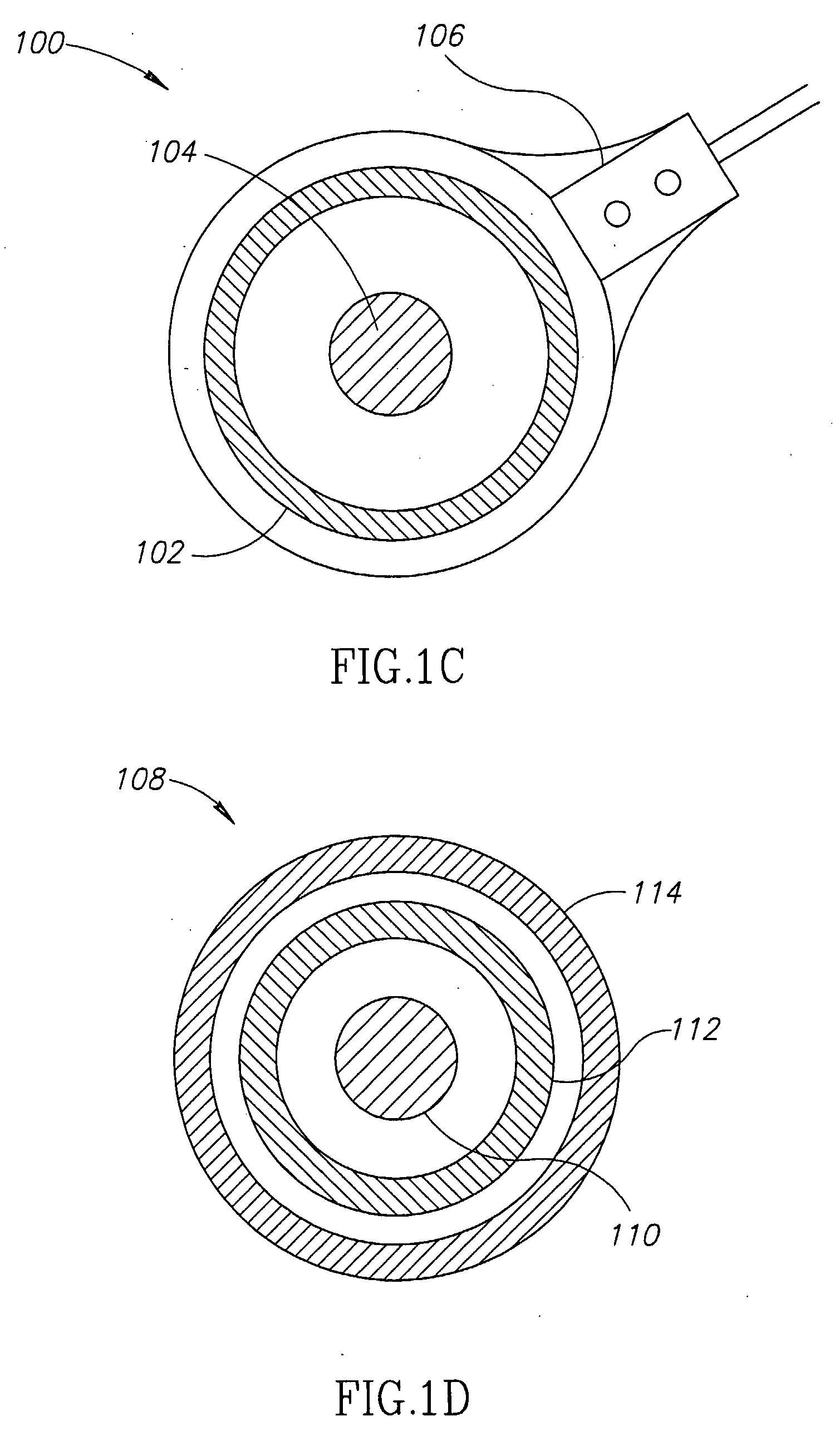
Method and apparatus for stimulating the sphenopalatine ganglion to modify properties of the BBB and cerebral blood flow
InactiveUS7120489B2Promote absorptionPermeability of BBB is increasedHead electrodesBlood flow measurement devicesCerebral blood volumeRetinal blood flow
Apparatus for modifying a property of a brain of a patient is provided, including one or more electrodes (7), adapted to be applied to a site selected from a group of sites consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (6) of the patient and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG. A control unit (8) is adapted to drive the one or more electrodes to apply a current to the site capable of inducing (a) an increase in permeability of a blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the patient, (b) a change in cerebral blood flow of the patient, and / or (c) an inhibition of parasympathetic activity of the SPG.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
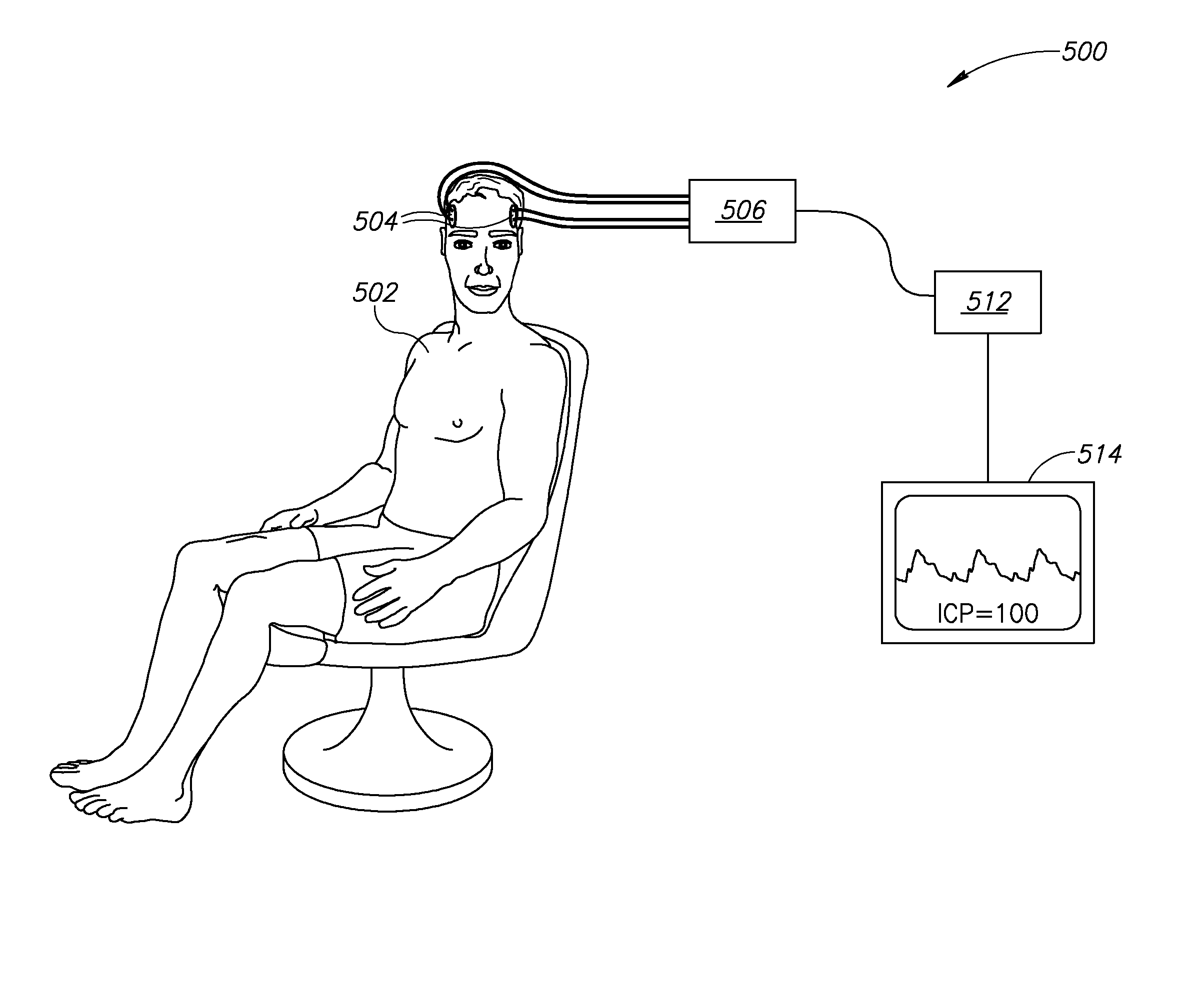
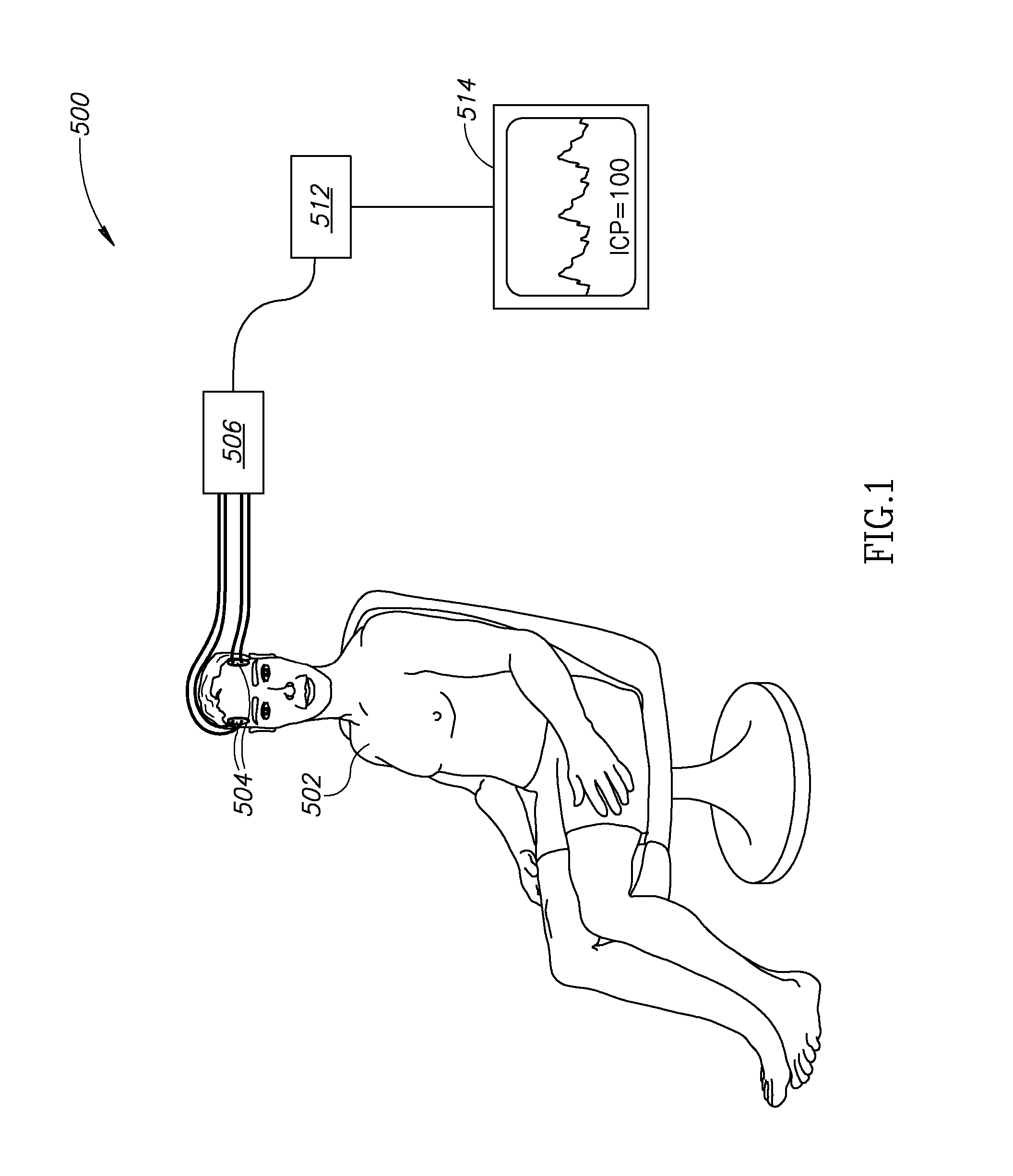
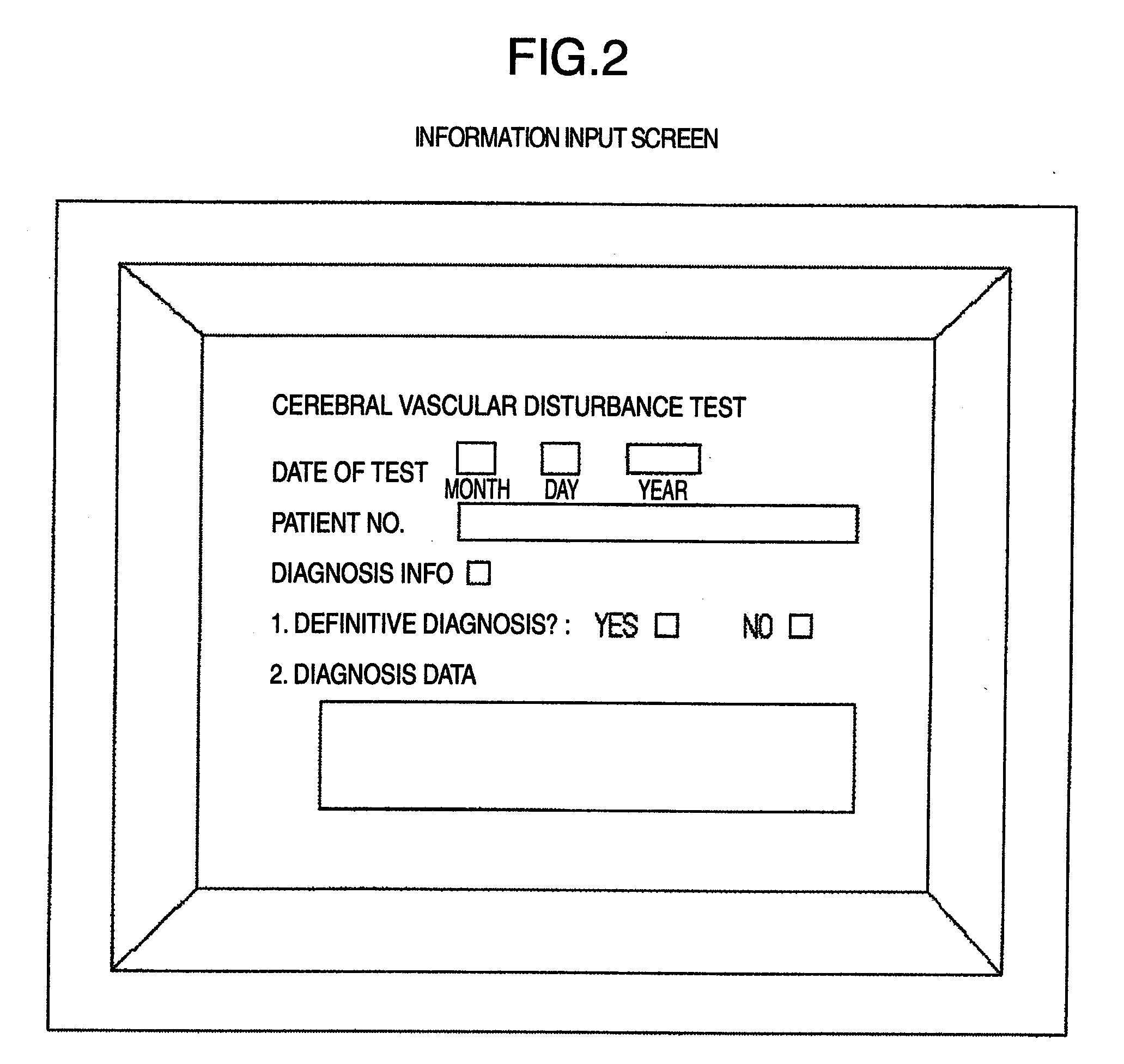
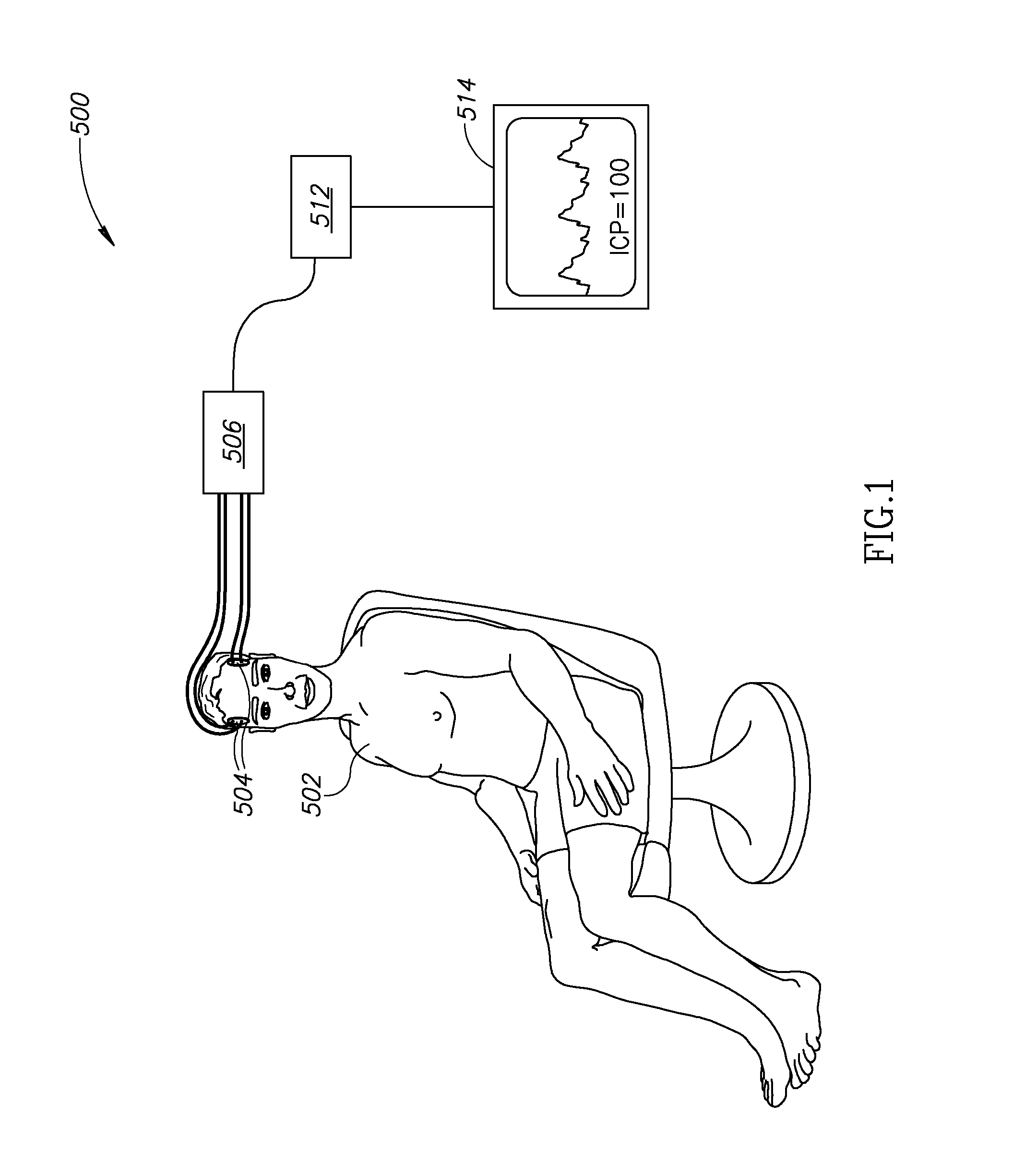
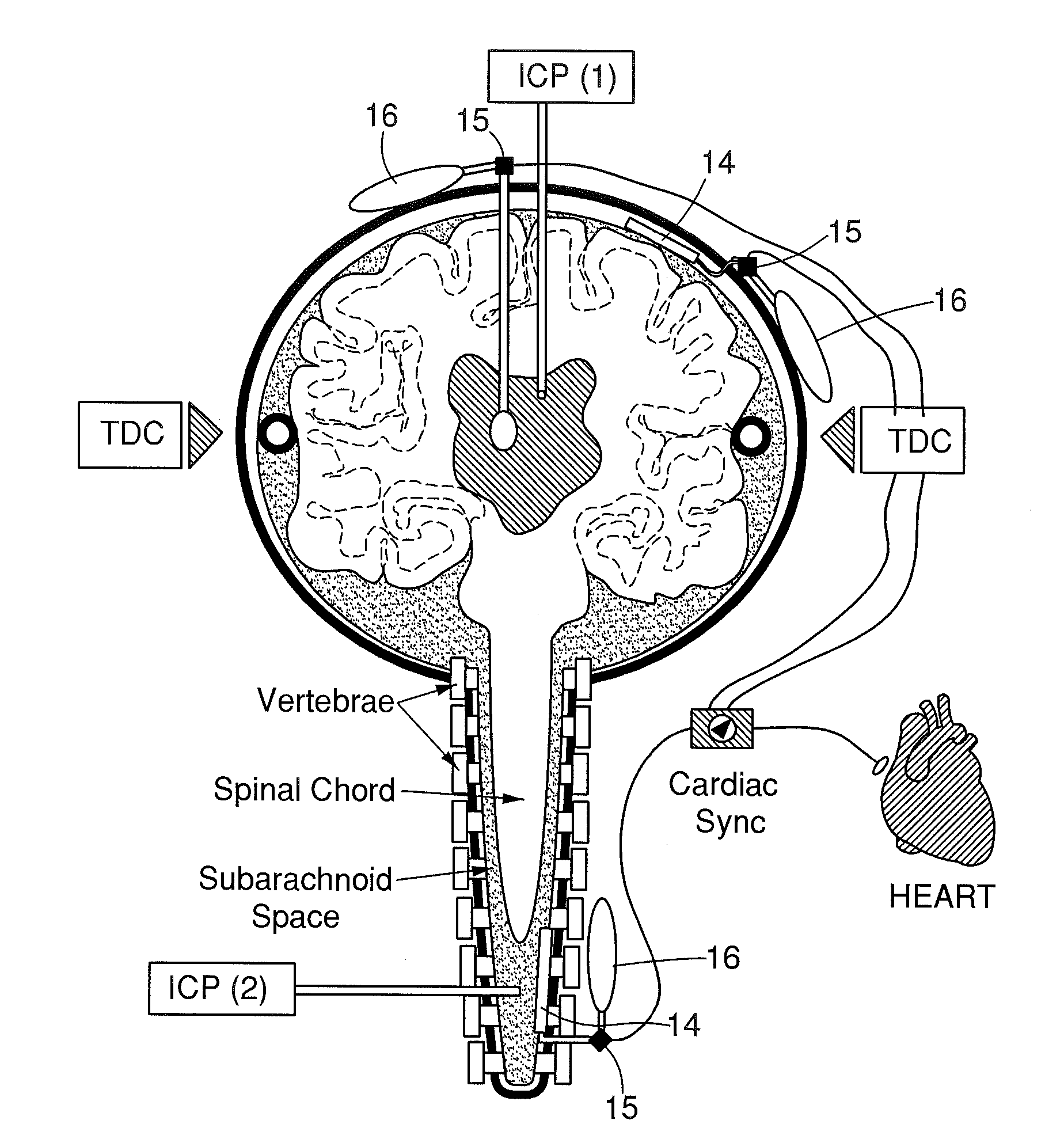
Non-Invasive Intracranial Monitor
InactiveUS20070287899A1Less compliantSpread quicklyEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceHemodynamics
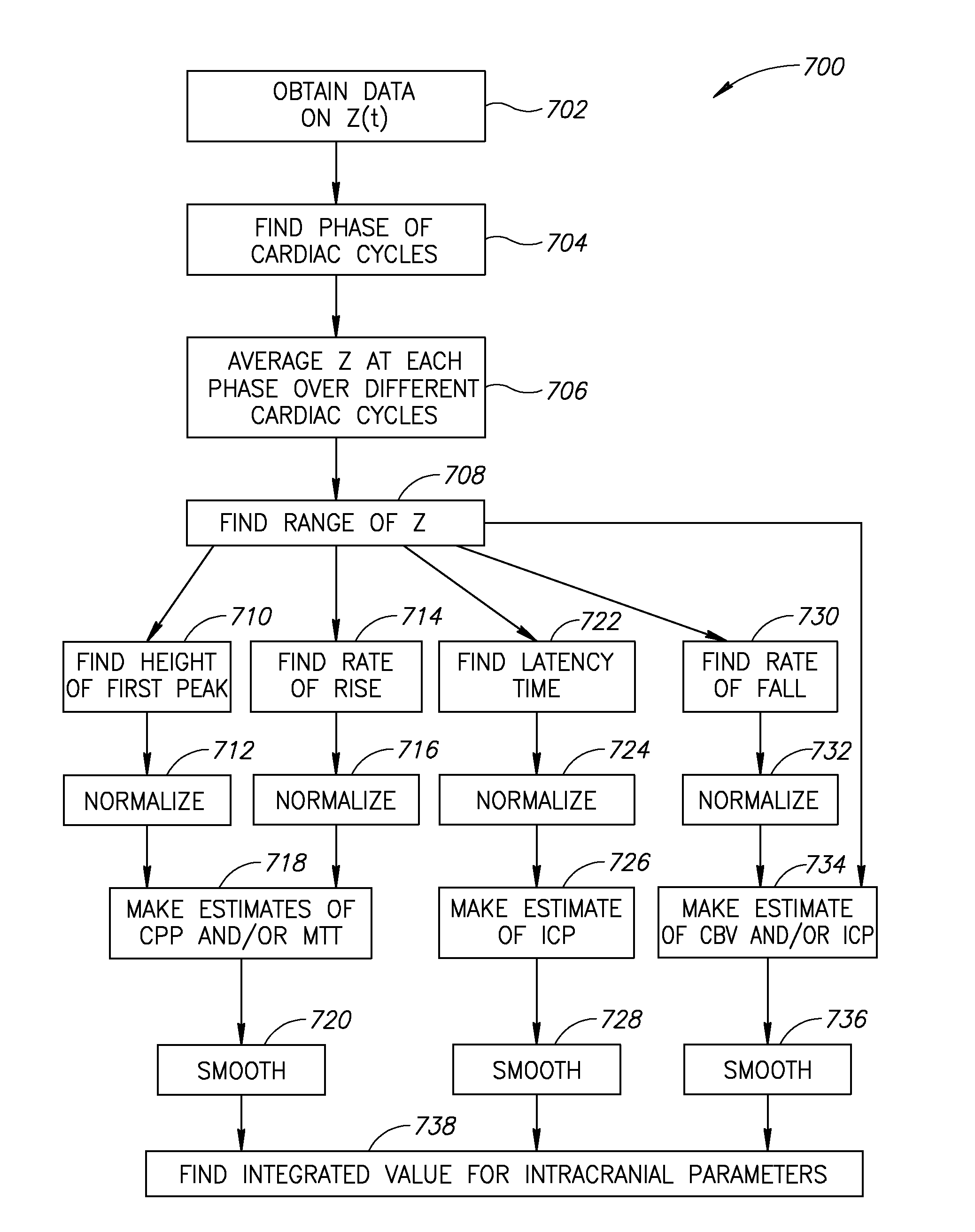
A method of estimating at least one intracranial hemodynamic parameter in a subject, the method comprising: a) obtaining data of changes in electrical impedance across the subject's head as a function of time; b) analyzing the data; and c) estimating one or more of intracranial pressure, cerebral blood volume, and a factor related to at least one of cerebral perfusion pressure and a mean transit time through cerebral capillaries.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
Enhancement of cerebral blood flow by electrical nerve stimulation
InactiveUS7340298B1Increase cerebral blood flowElectrotherapySubarachnoid spaceCerebral blood volume
A method for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient. A electrical stimulating device is provided. The electrical stimulating device is applied to the patient at a region adjacent the cervical sympathetic chain, the brain stem, the head, or the sympathetic nervous system. The electrical stimulating device is applied by any route selected from transcutaneous, subcutaneous, and subarachnoid. The electrical stimulating device is activated to stimulate or inhibit nerve impulses of the cervical sympathetic chain, thereby producing vasodilation in the cerebral vasculature, thereby increasing cerebral blood flow. Devices for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient are also described.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Shunt for redistributing atrial blood volume
A shunt for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an anchor comprising a neck region, first and second end regions, and a conduit affixed with the anchor that formed of a biocompatible material that is resistant to transmural and translation tissue ingrowth and that reduces a risk of paradoxical embolism.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
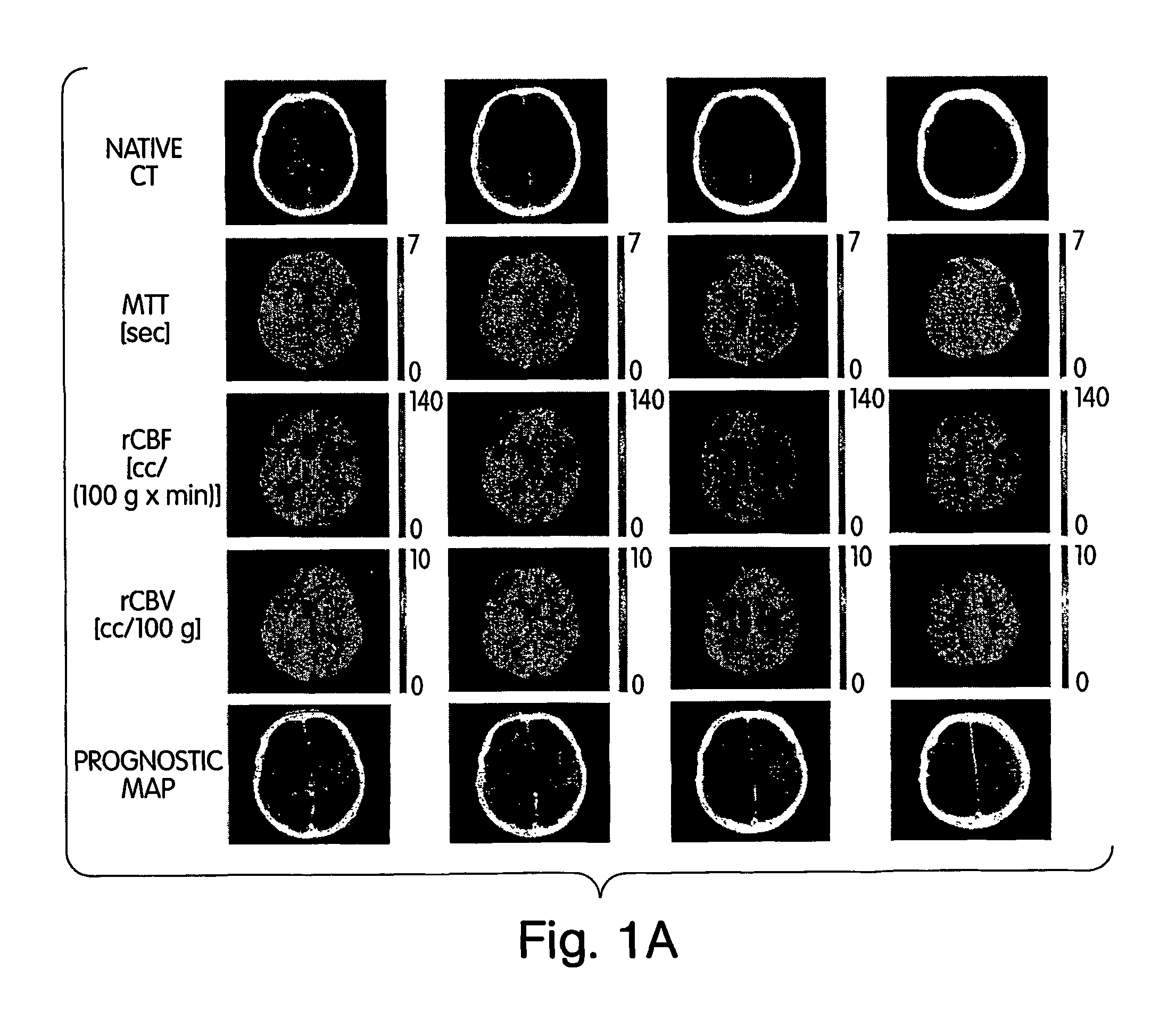
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
InactiveUS20020161292A1Computerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyCerebral blood volume
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second value. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Shunt for redistributing atrial blood volume
ActiveUS20180243071A1Maintains luminal patencyReduce riskHeart valvesWound drainsNormal blood volumeBlood pressure
A shunt for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an anchor comprising a neck region, first and second end regions, and a conduit affixed with the anchor that formed of a biocompatible material that is resistant to transmural and translation tissue ingrowth and that reduces a risk of paradoxical embolism.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Medical oscillating compliance devices and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090177279A1Improve efficiencyStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
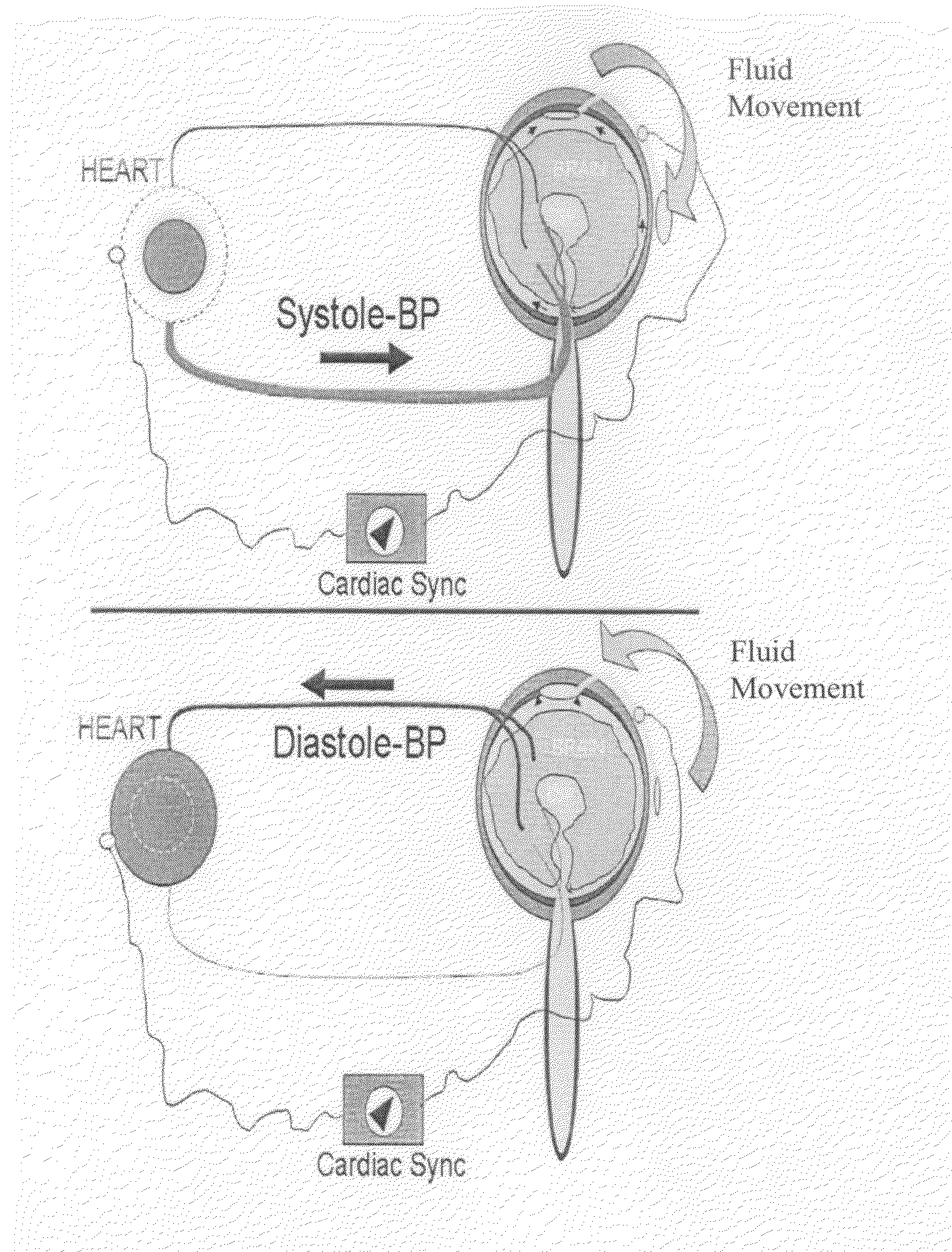
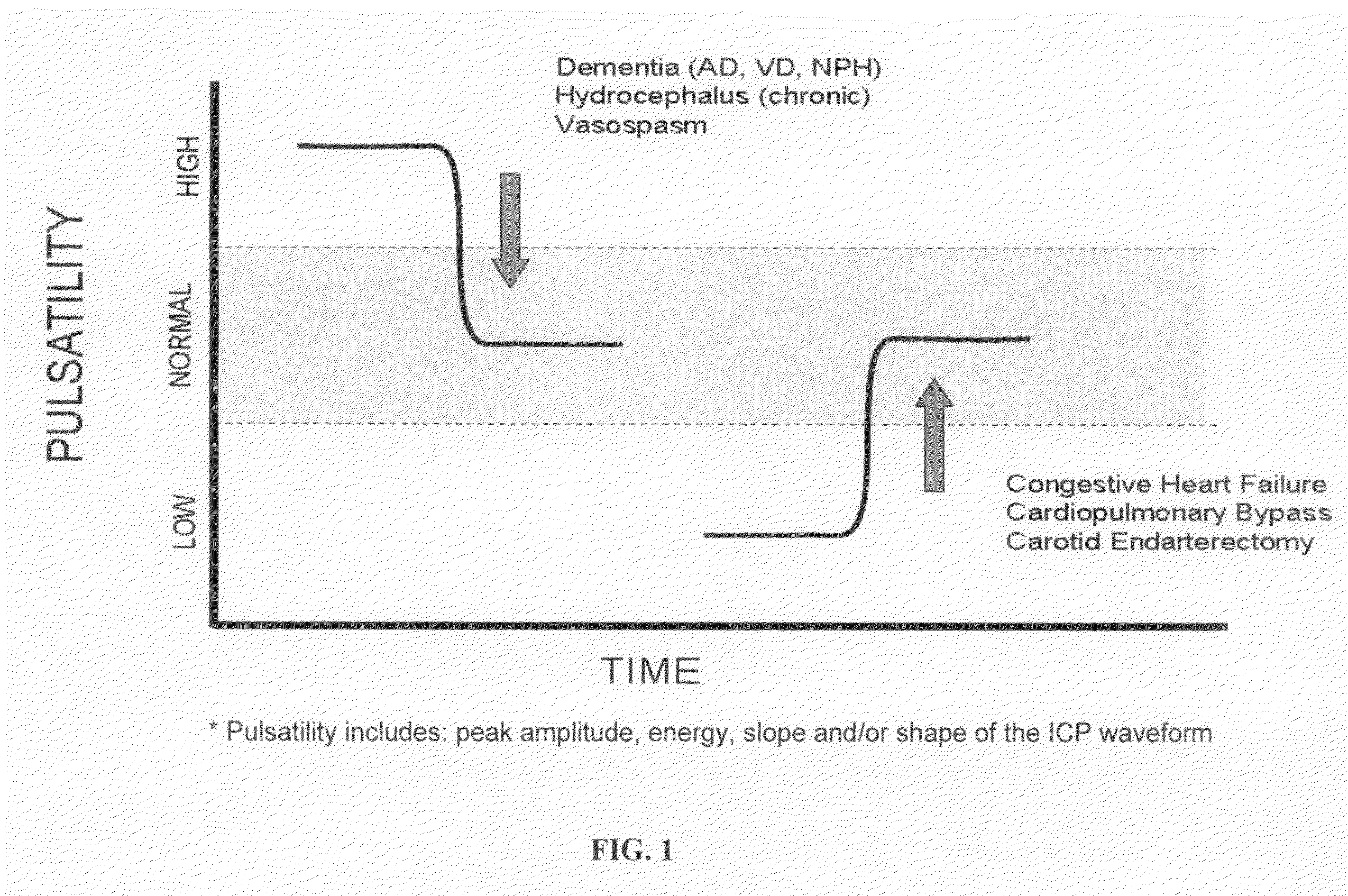
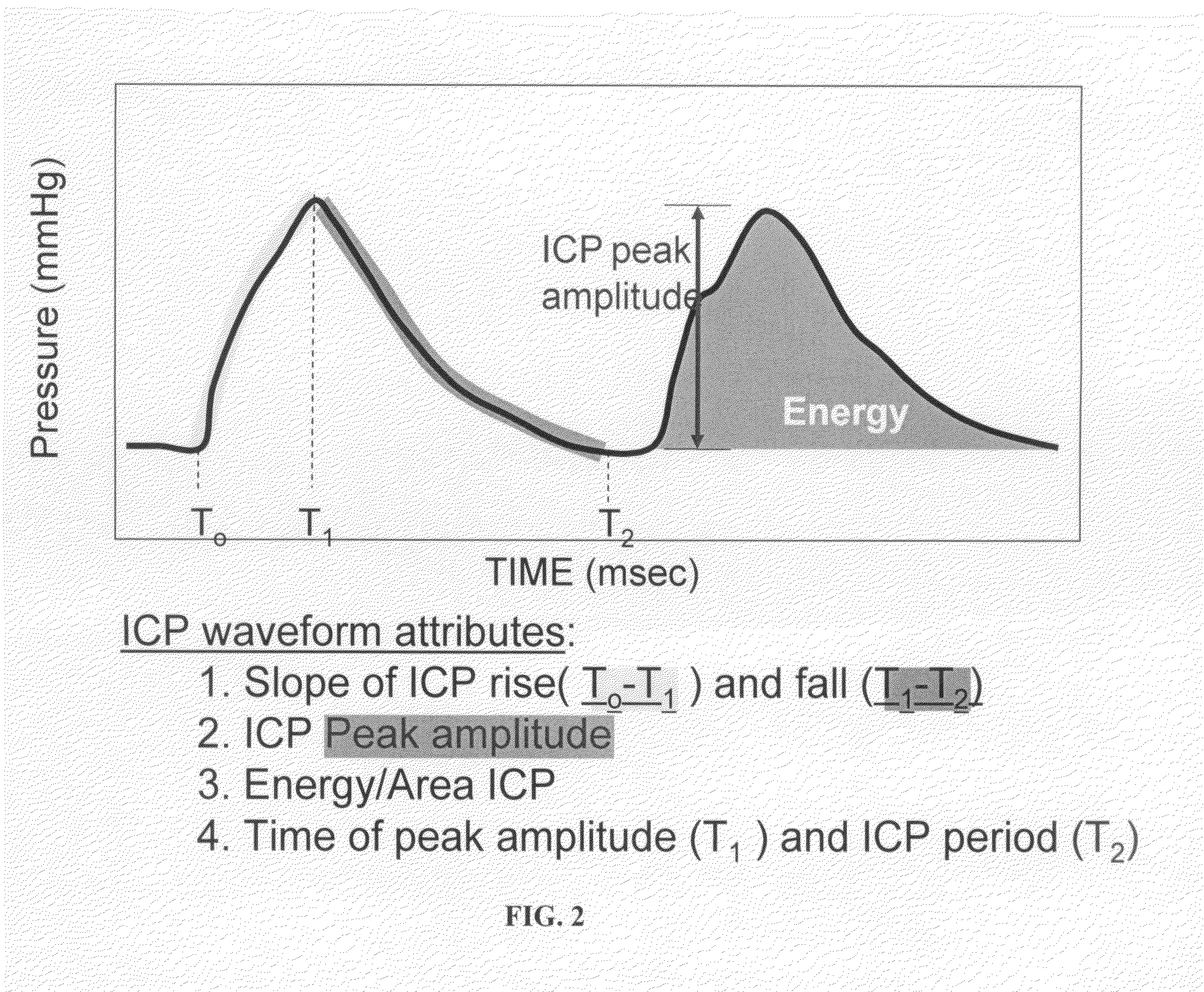
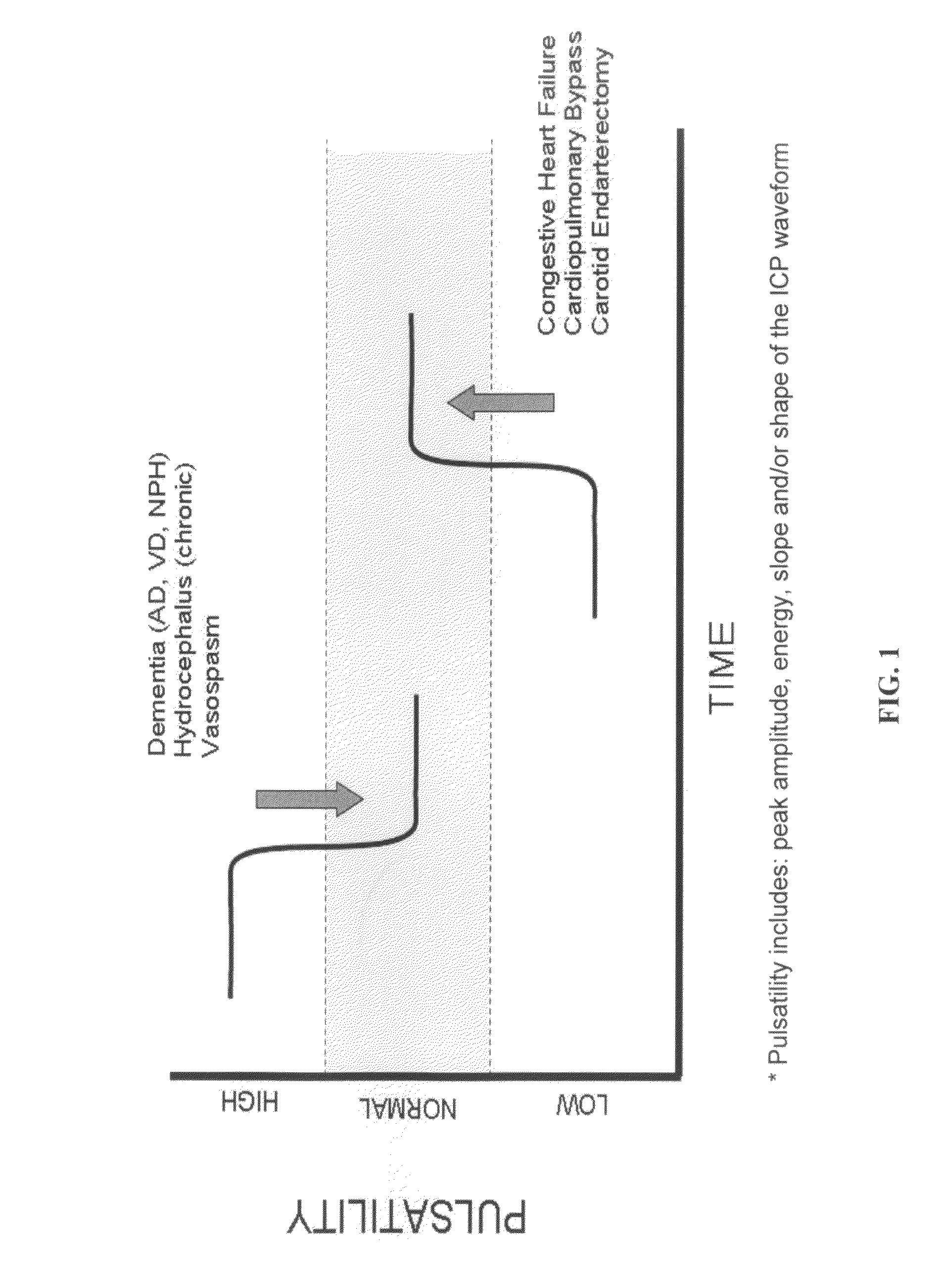
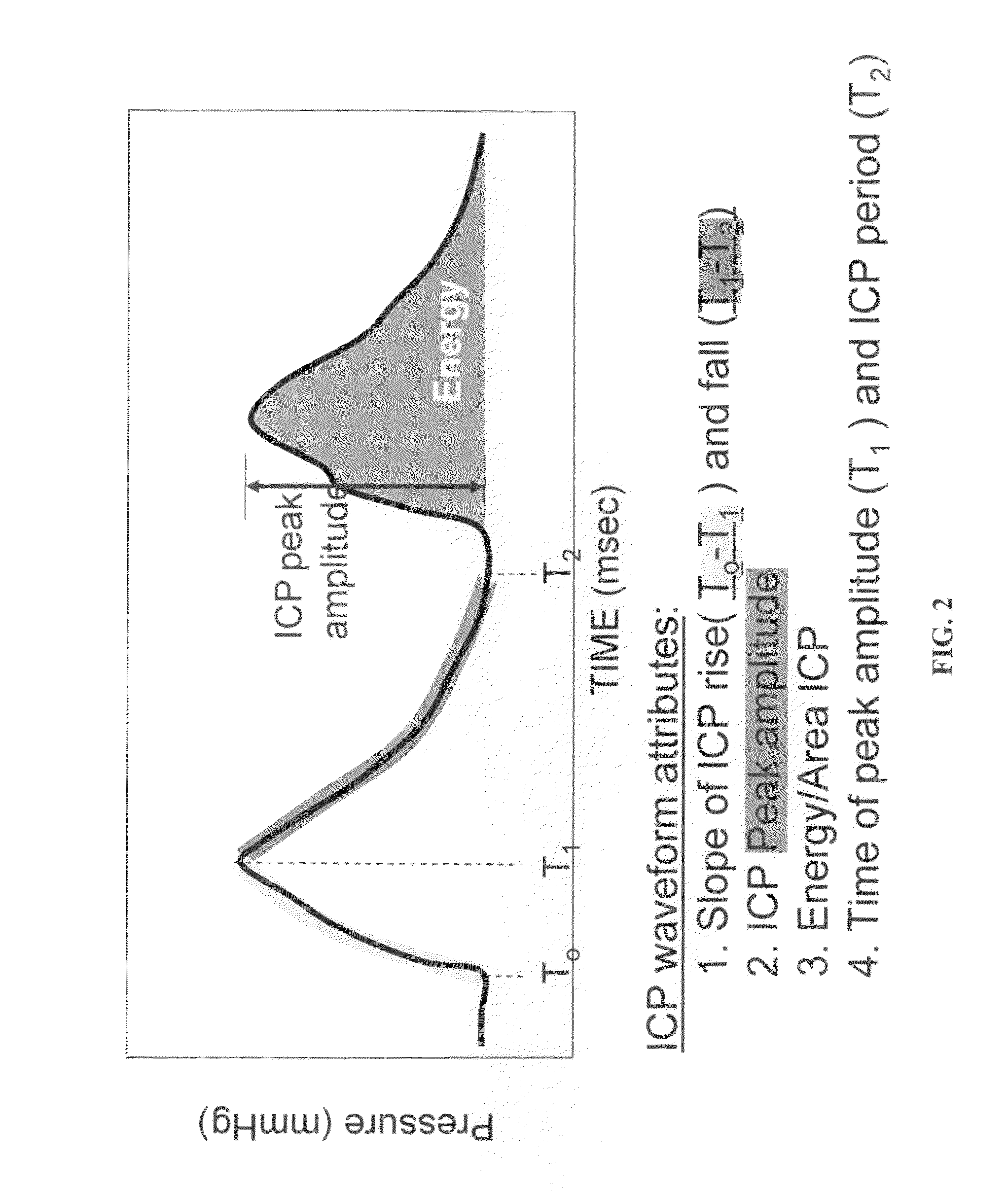
The present invention relates to devices and systems that alter intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform by oscillating the contraction and expansion of a compressible composition within the cranial or spinal cavities such that they increase intracranial capacity. The contraction and expansion of the compressible composition in the oscillating compliance devices can be due to an individual's intracranial pressure, the result of the expansion and compression of a reservoir which is mediated by the contractility of the heart or driven by a pump gaited to a biorhythm. The invention also relates to methods for protecting an individual's brain from abnormal arterial pulsations and for altering an individual's cerebral blood flow using the devices and systems of the invention. The oscillating compliance devices can be used to treat several diseases and / or conditions characterized by altered / abnormal intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform, including hydrocephalus, stroke, dementia and migraine headaches, vasospasms, congestive heart failure, cardiopulmonary bypass or carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Noninvasive 4-d time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS20150327783A1High degree of efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsSystoleCardiac cycle
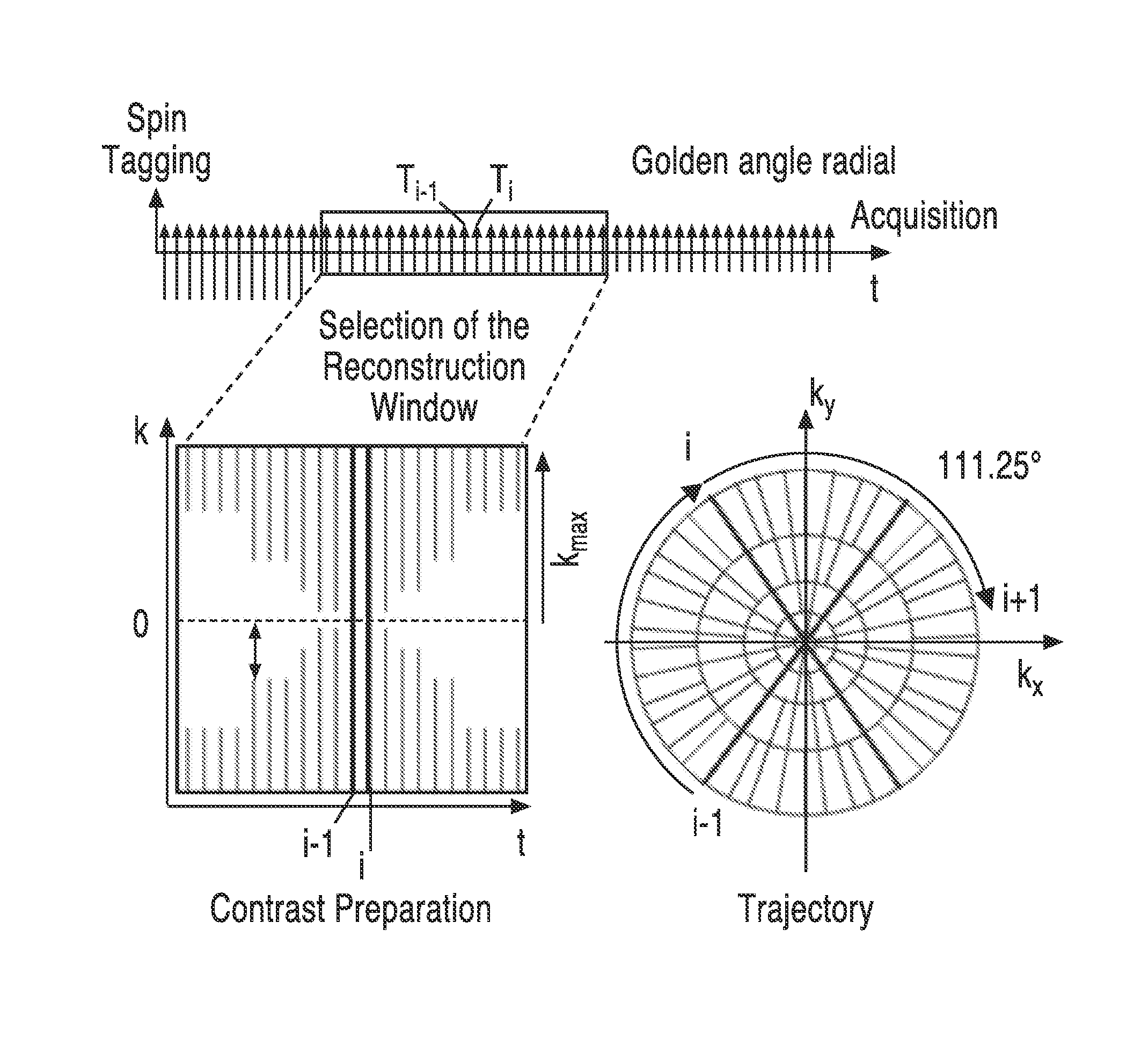
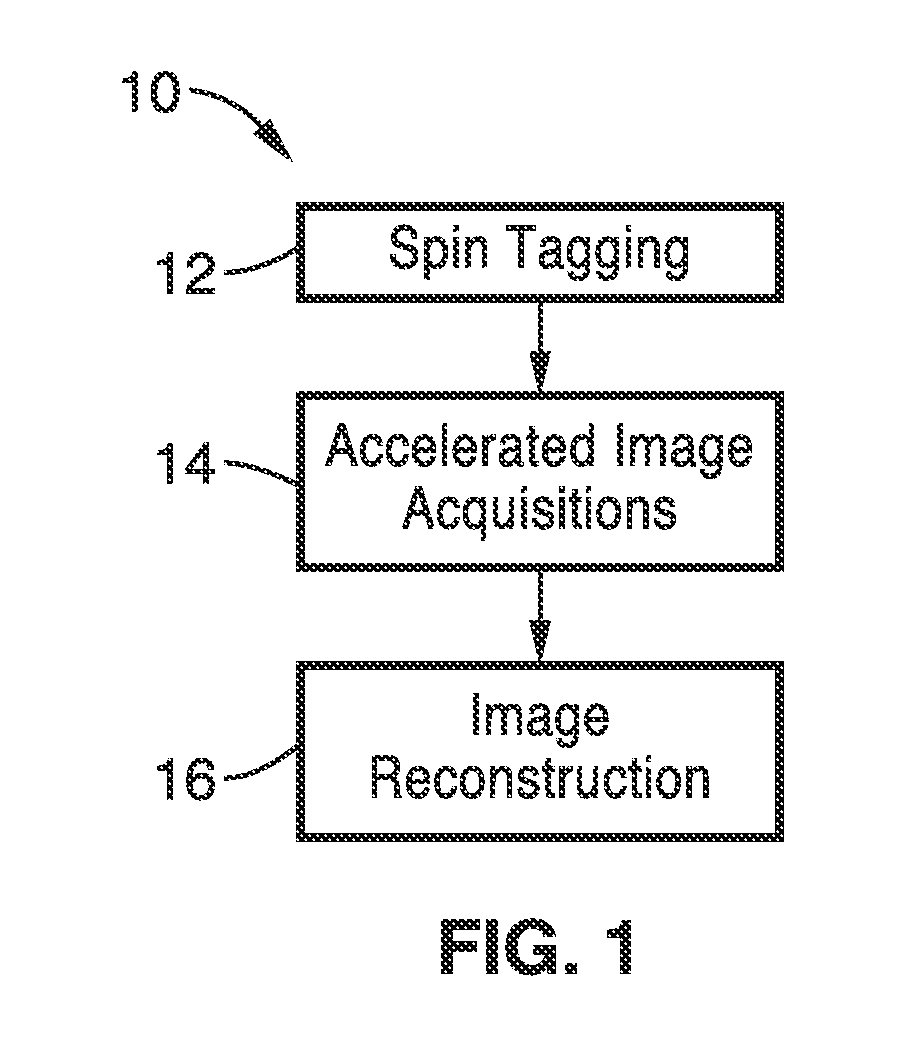
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Perfusion digital subtraction angiography
ActiveUS20190015061A1Improve patient outcomesSustain viabilityImage enhancementImage analysisTime density curveVolumetric Mass Density
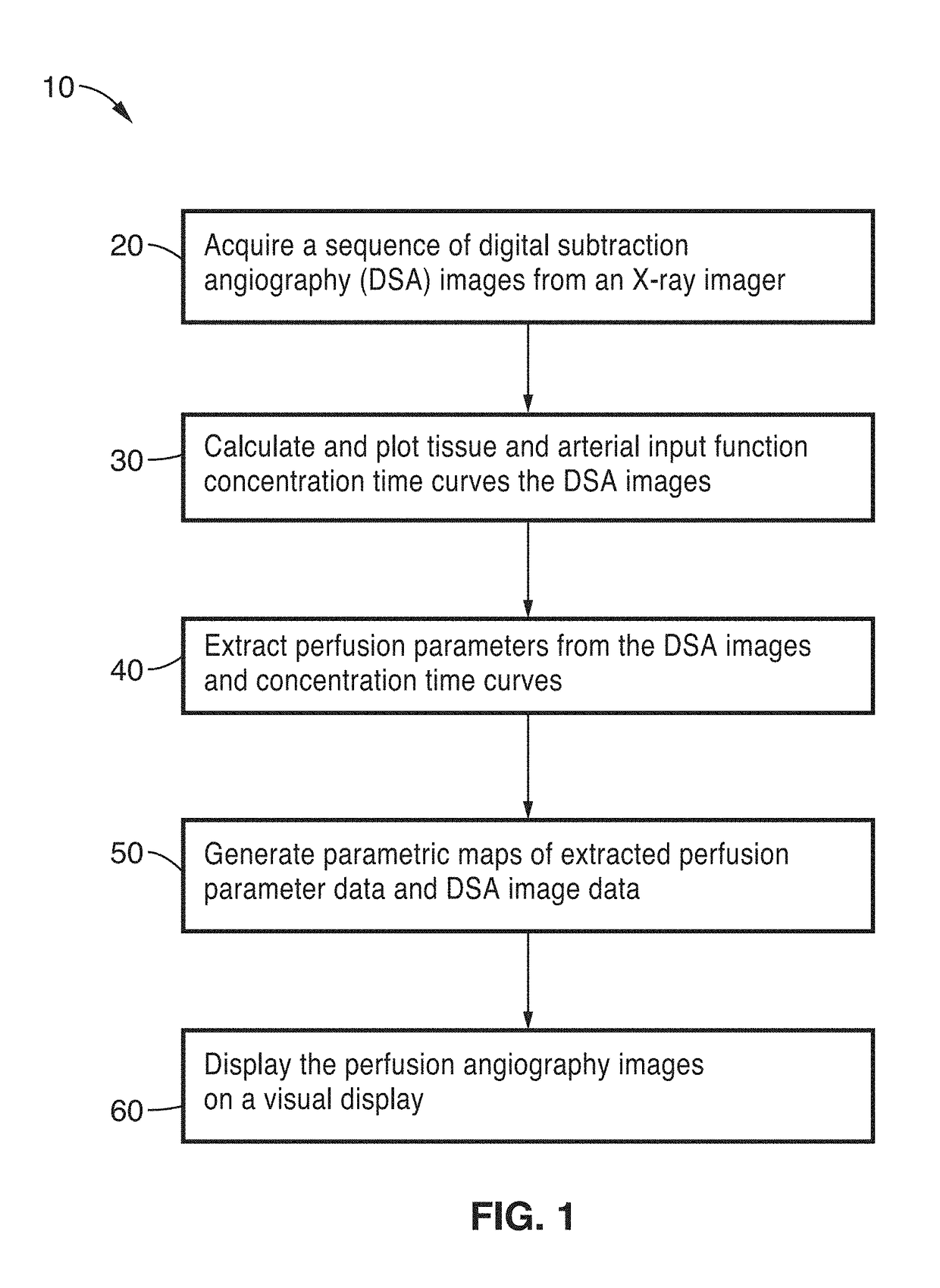
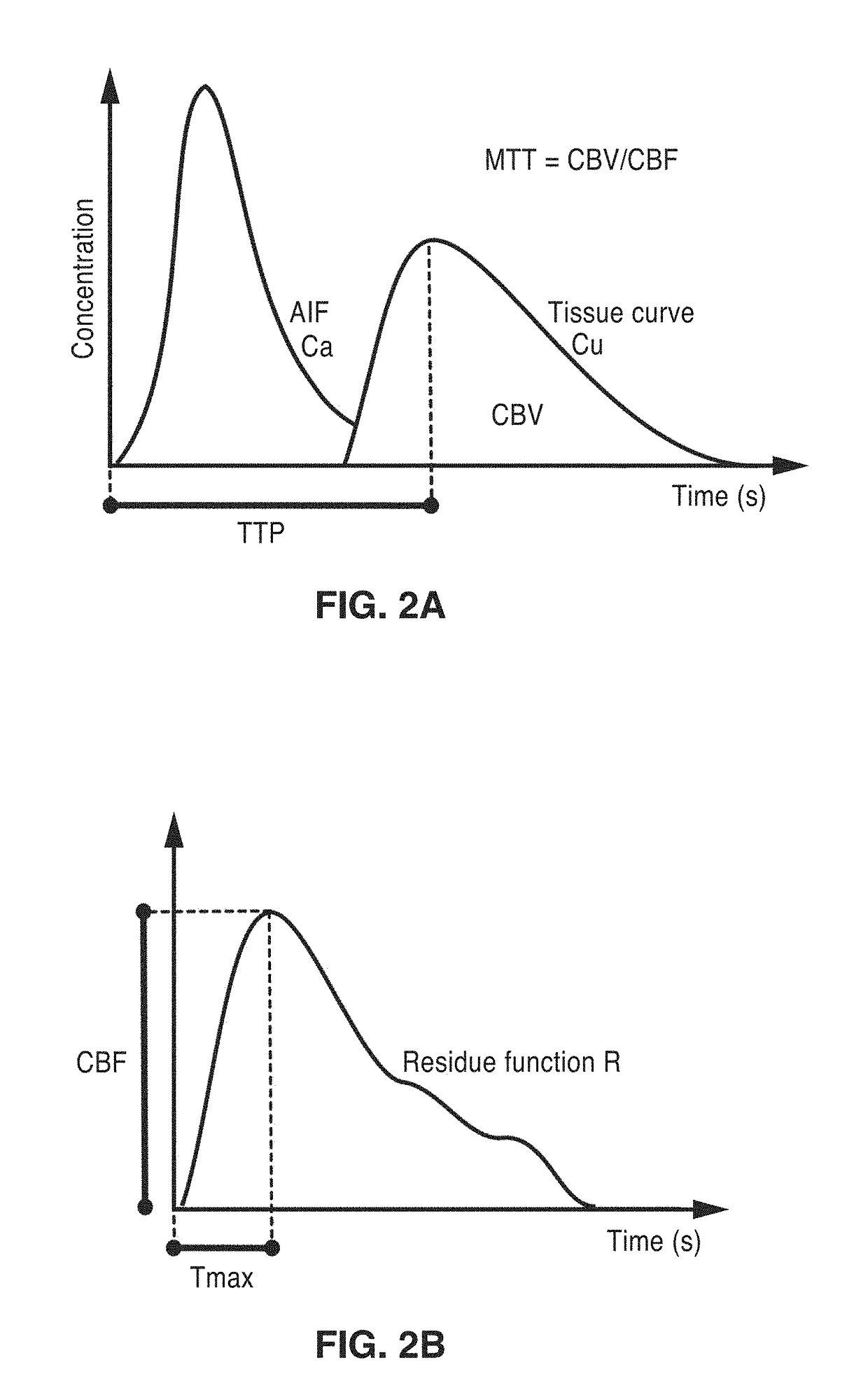
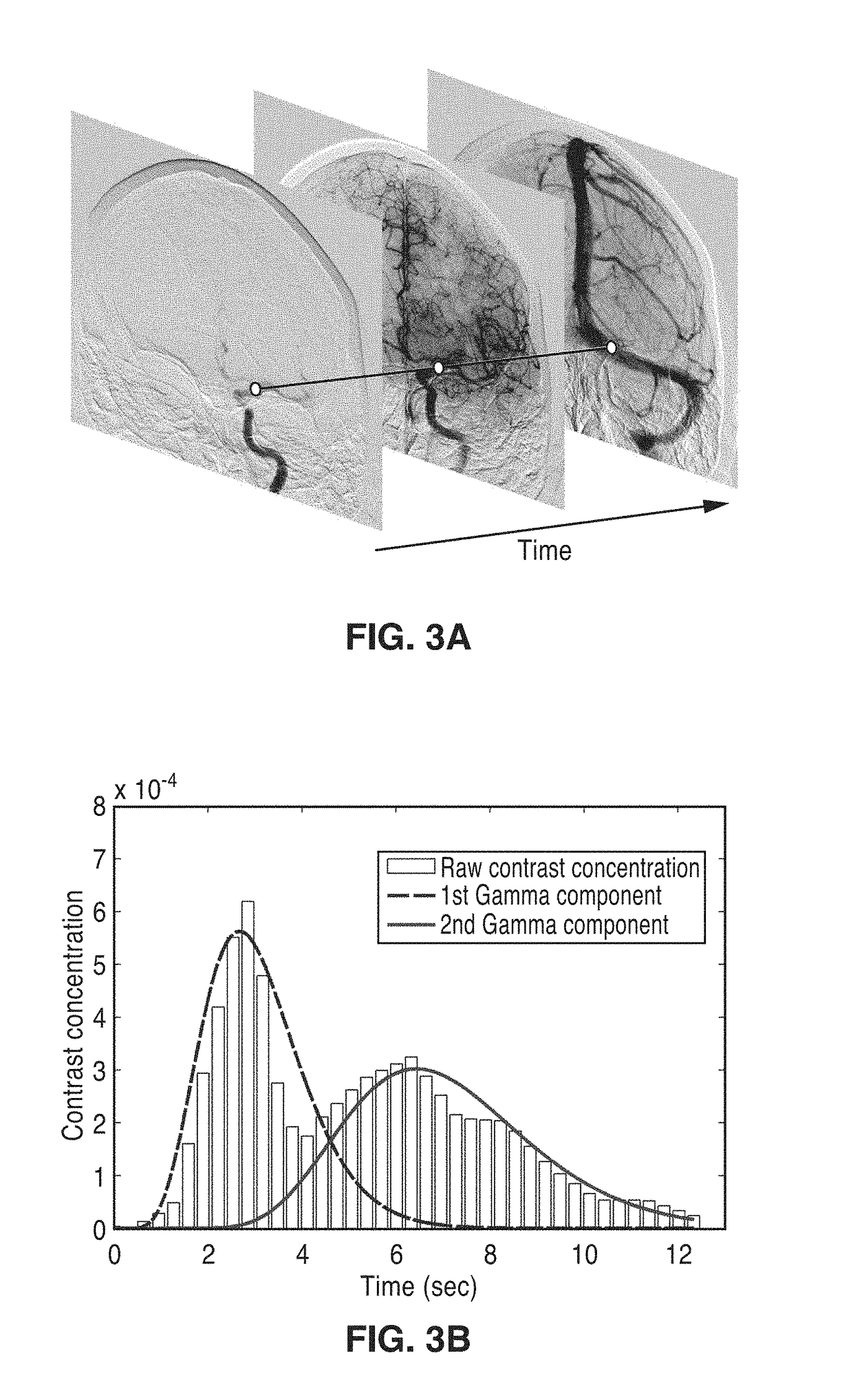
An apparatus and methodological framework are provided, named perfusion angiography, for the quantitative analysis and visualization of blood flow parameters from DSA images. The parameters, including cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV), mean transit time (MTT), time-to-peak (TTP), and Tmax, are computed using a bolus tracking method based on the deconvolution of time-density curves on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Individual contrast concentration curves of overlapping vessels can be delineated with multivariate Gamma fitting. The extracted parameters are each transformed into parametric maps of the target that can be color coded with different colors to represent parameter values within a particular set range. Side by side parametric maps with corresponding DSA images allow expert evaluation and condition diagnosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Embolic deflection device
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Tester for saturation level of cerebral blood oxygen
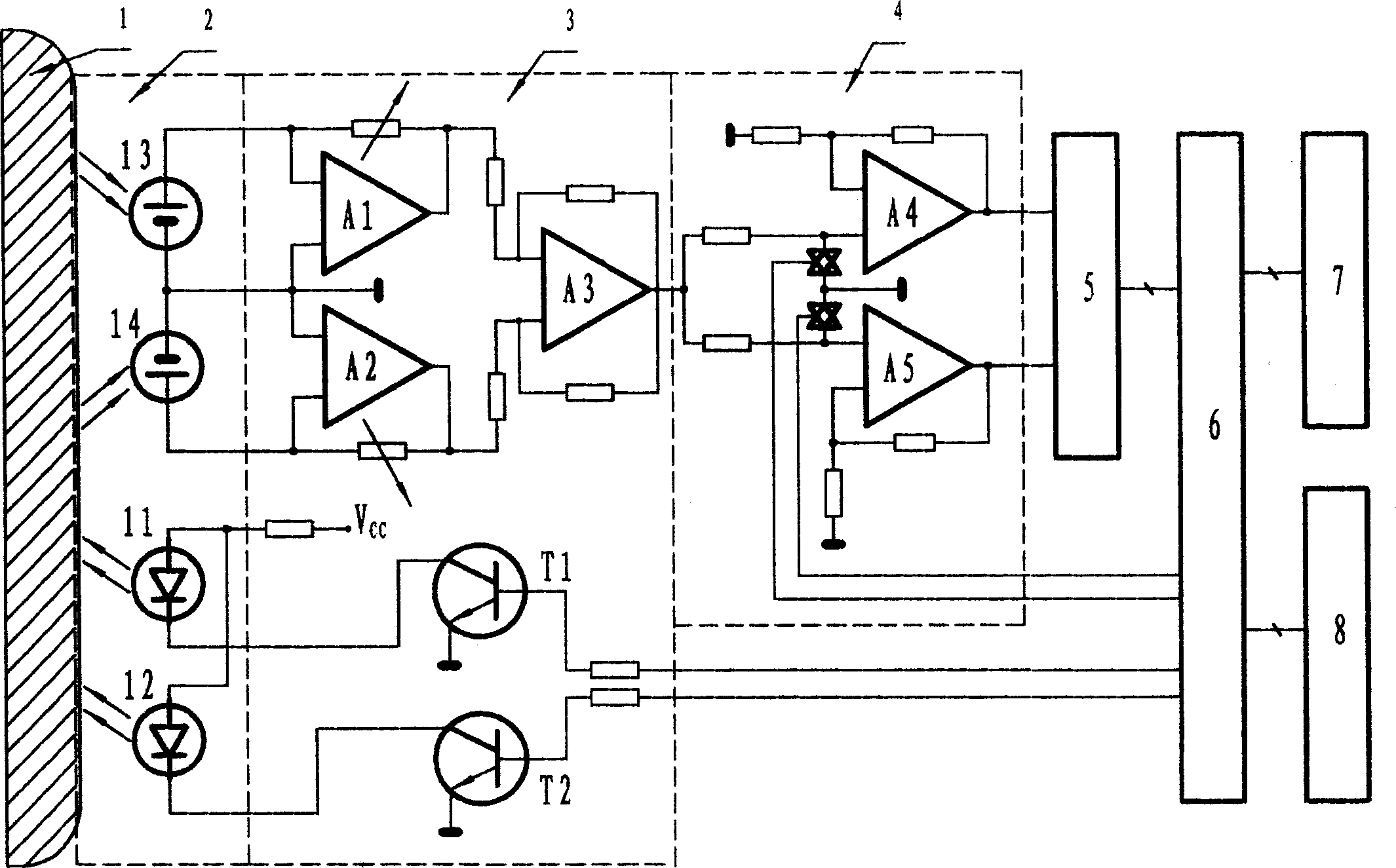
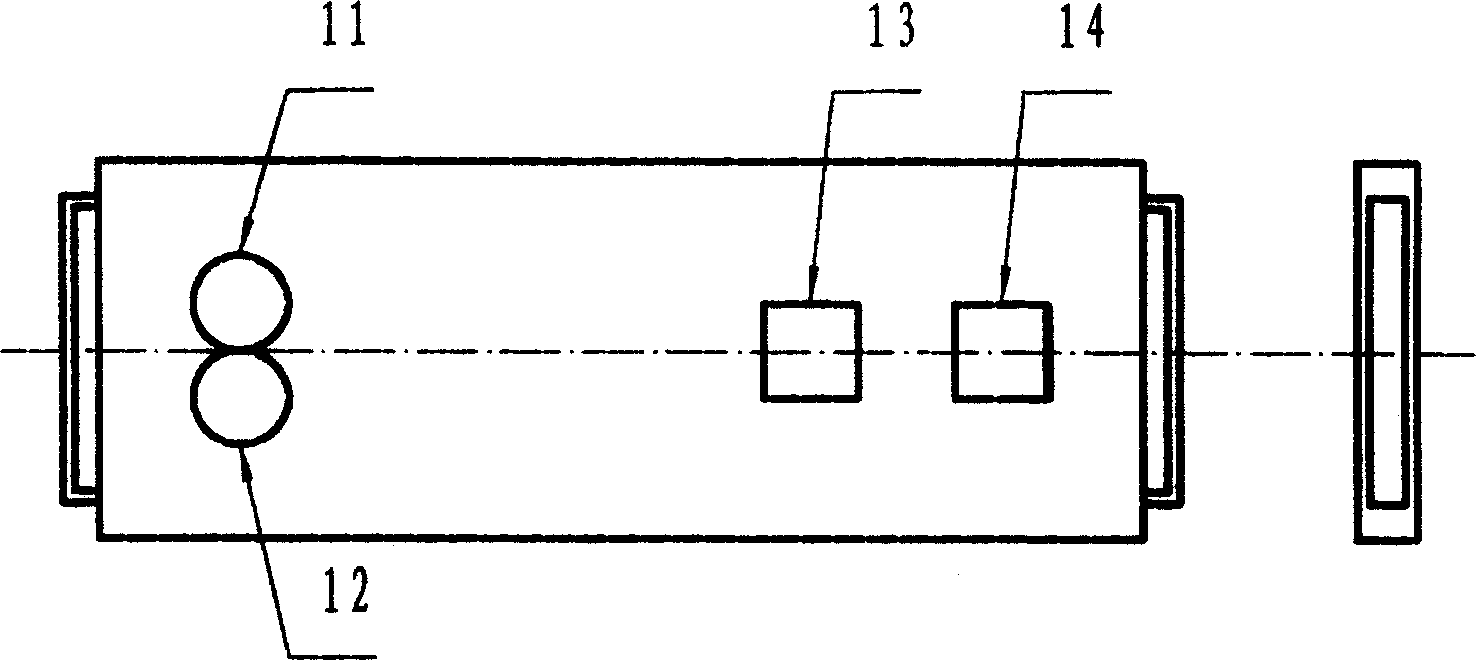
InactiveCN1365649ASimple structureEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSoftware systemDisplay device
A detector for detecting the saturation level of cerebral blood oxygen is composed of probe, synchronous amplifier, A / D converter, single-chip computer system, and display. It features that two LEDs generating different wavelengthes and two light receivers with two photoelectric silicon cells are installed in its probe. The obtained data contains two parts: one is the information about superficial tissue and another is the information about superficial tissue and cerebral blood oxygen. Subtracting one part from another can obtain the information about cerebral blood oxygen. Its advantages include simple structure, high sensitivity and reliability, and low cost.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Cerebral Perfusion Monitor
InactiveUS20080275352A1Grow fastEnhanced signalCatheterSensorsNormal blood volumeCerebral blood volume
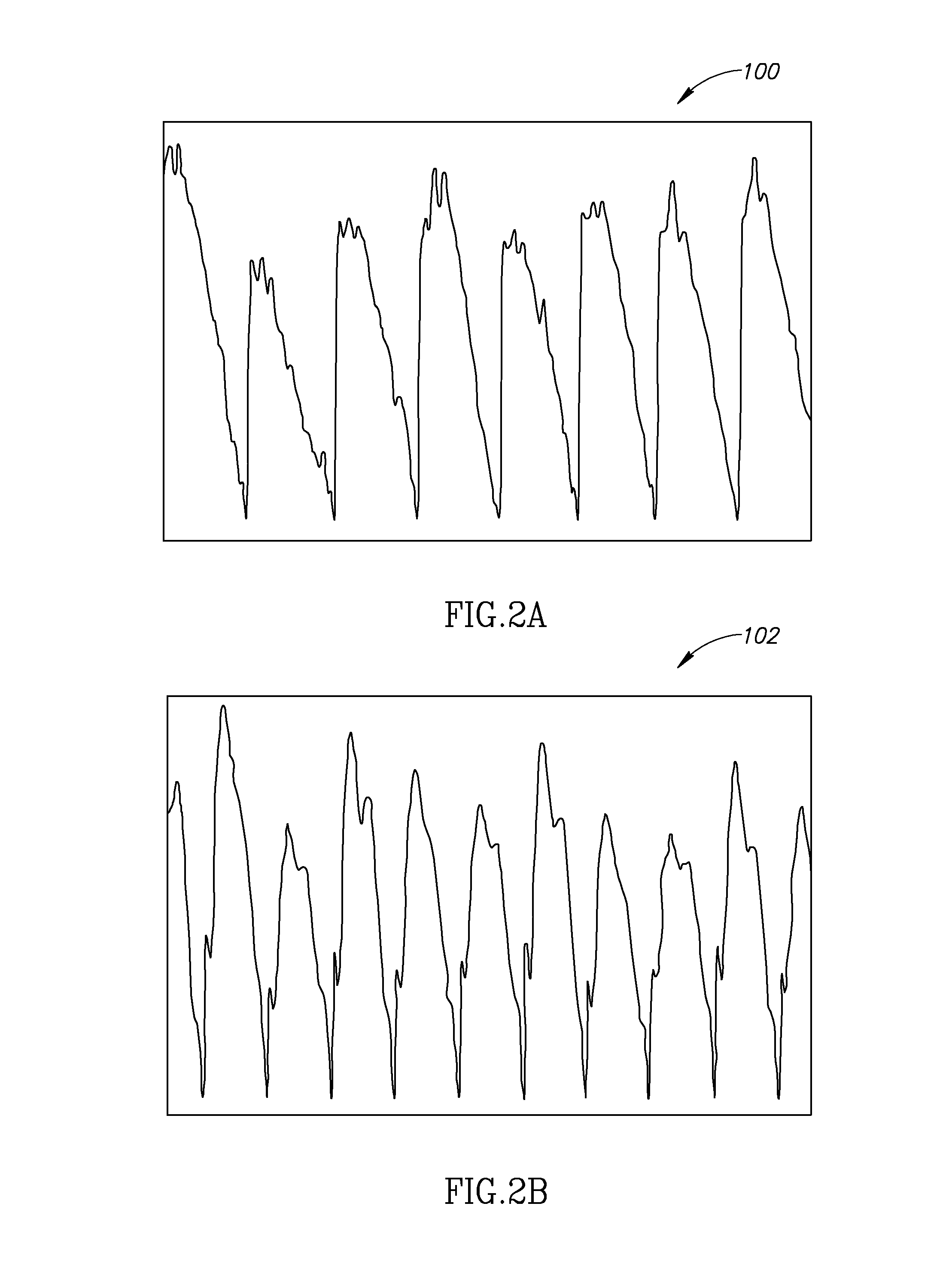
A method of estimating cerebral blood flow includes obtaining a measure of time-varying blood volume in the head, using an impedance plethysmography (102 and 104), obtaining a measure of time-varying blood volume in the scalp, and using the time-varying blood volume in the head and scalp to estimate cerebral blood flow.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
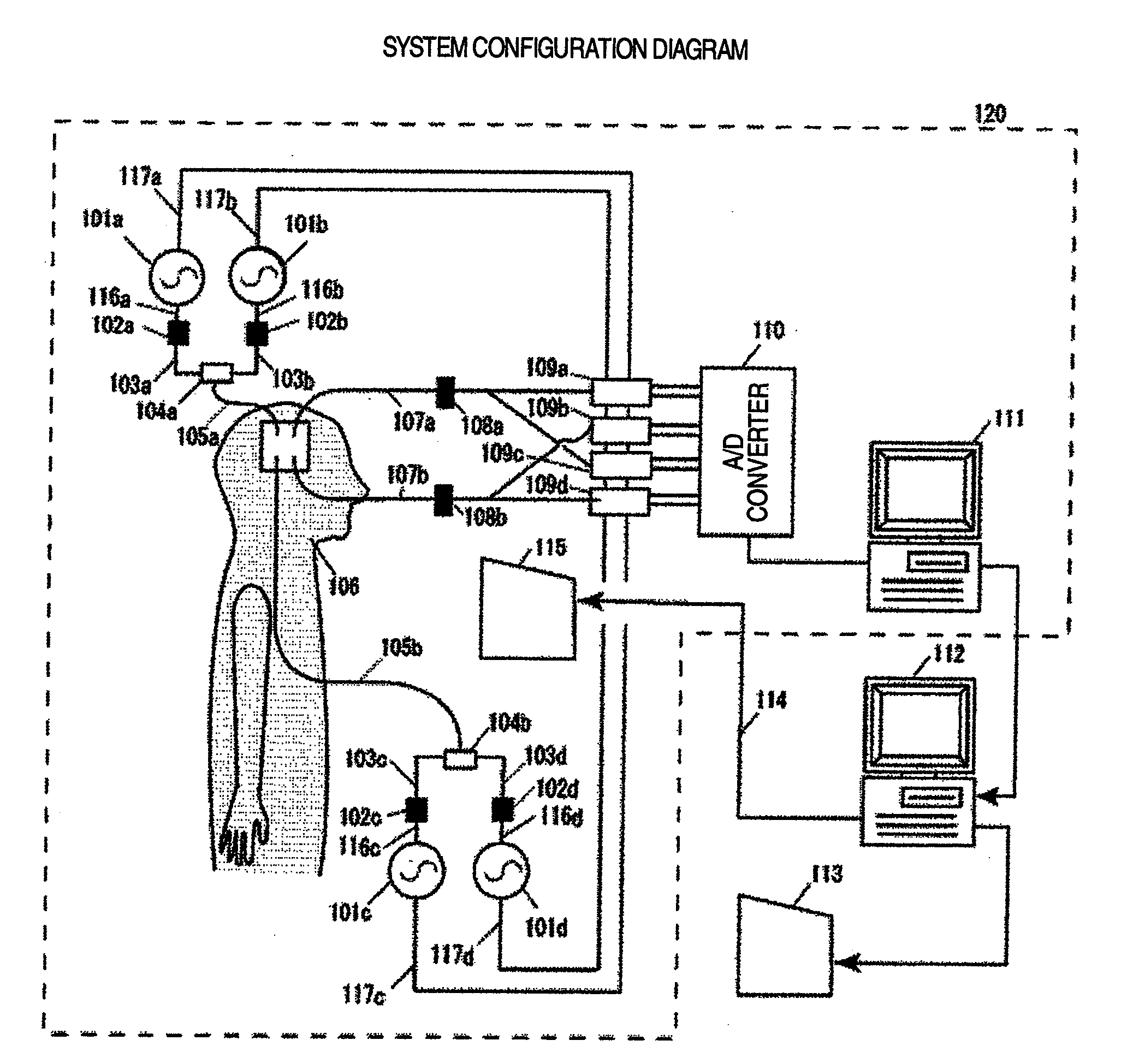
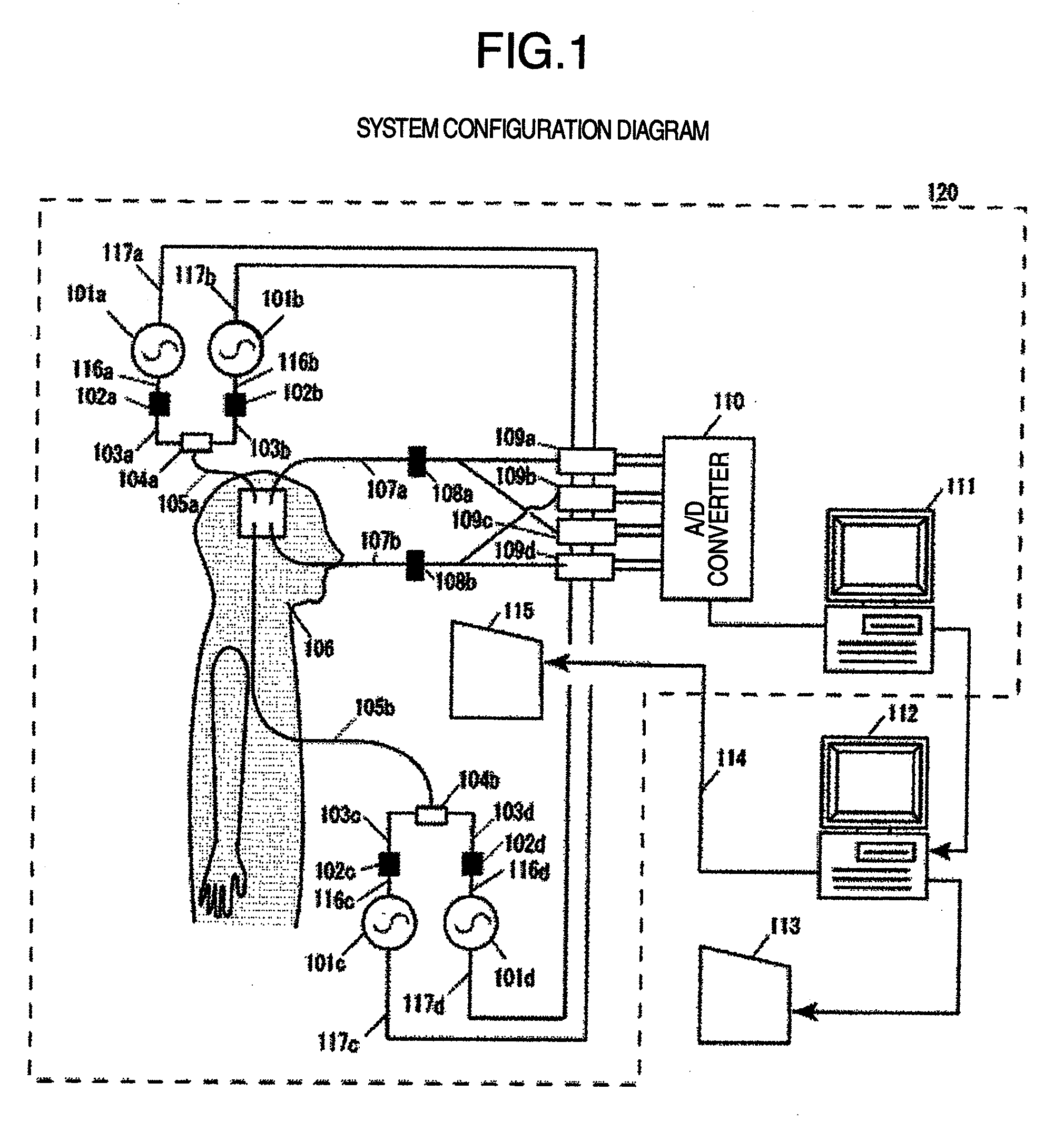
Biological measurement system
This invention measures cerebral blood volume changes to evaluate, from properties of low-frequency components of such changes and heart rate changes calculated by analysis, a distribution of cerebral blood vessel hardness and its with-time change to thereby estimate and display diseased and dangerous portions based on the evaluation. Briefly, the above-noted object is attainable by a biological measurement system having a cerebral blood volume measurement unit which measures a regional cerebral blood volume of a body under test, an analyzer unit that analyzes a signal measured by the cerebral blood volume measurement unit, an extraction unit for extracting, based on an output of the analysis unit, information concerning a regional cerebral blood vessel state of the test body, and a display unit which displays a measurement result of the cerebral blood volume measurement unit, an analysis result of the analyzer unit or an extraction result of the extraction unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Non-invasive intracranial monitor
InactiveUS8211031B2Less compliantSpread quicklyEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceHemodynamics
A method of estimating at least one intracranial hemodynamic parameter in a subject, the method comprising:a) obtaining data of changes in electrical impedance across the subject's head as a function of time;b) analyzing the data; andc) estimating one or more of intracranial pressure, cerebral blood volume, and a factor related to at least one of cerebral perfusion pressure and a mean transit time through cerebral capillaries.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
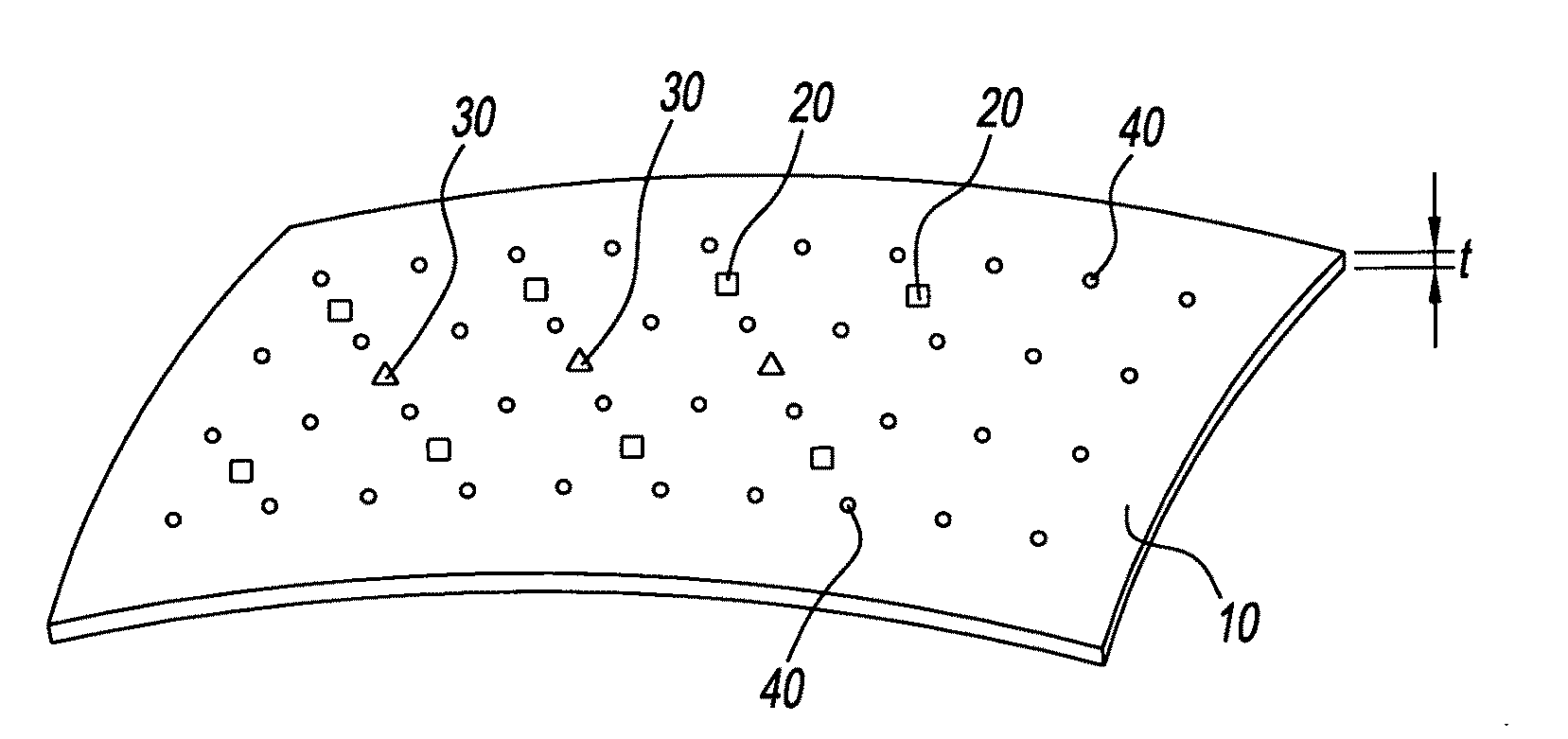
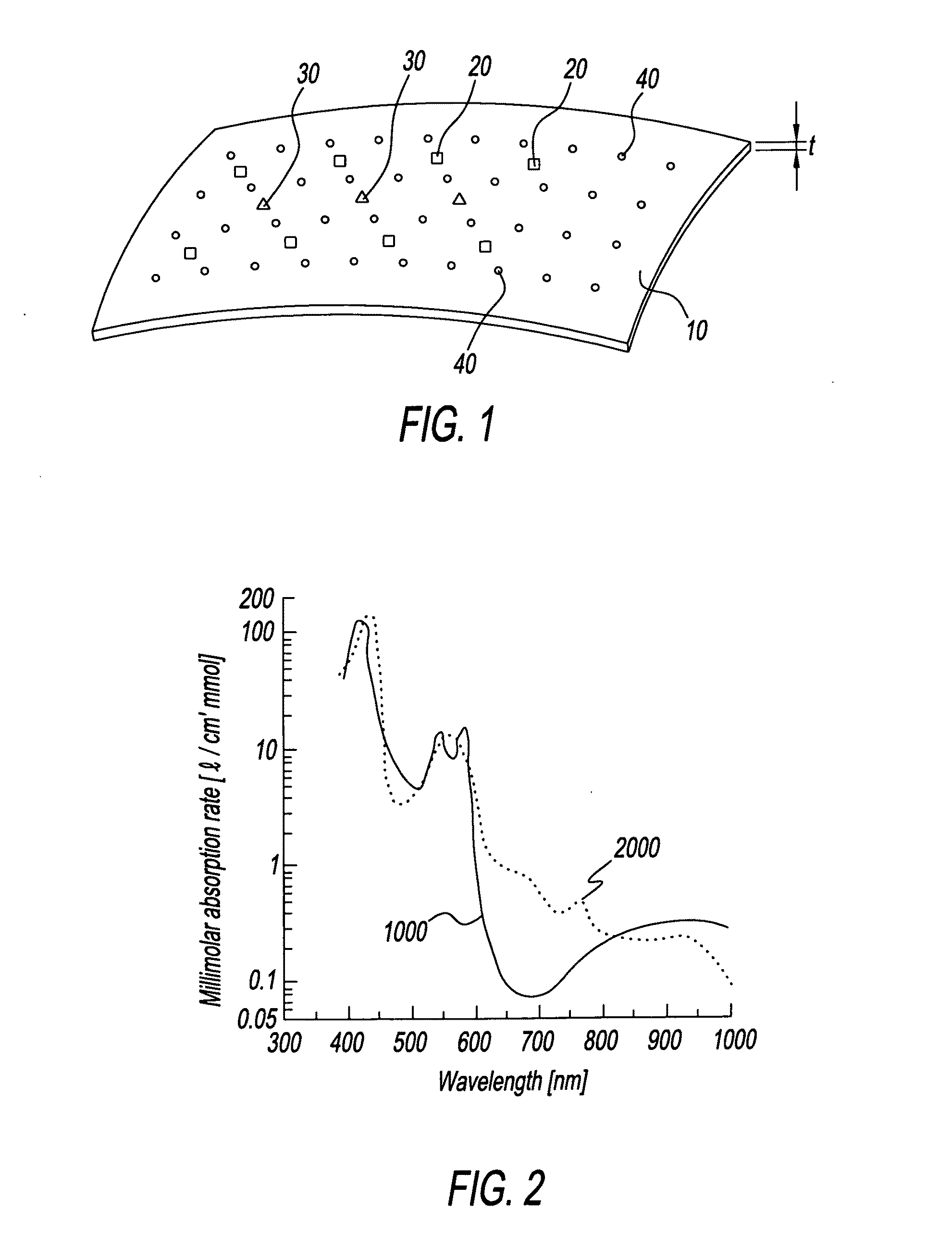
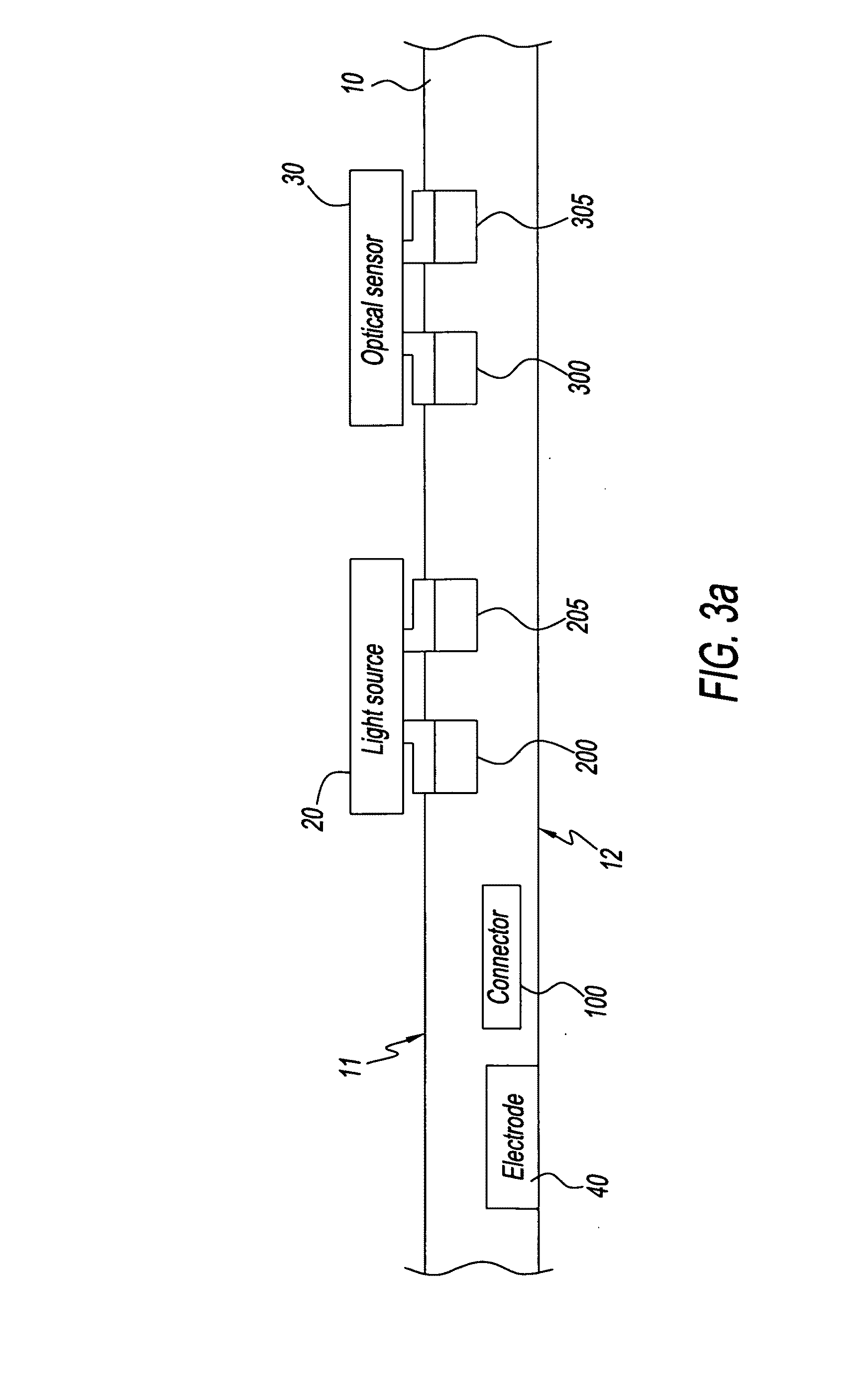
Apparatus for detecting brain conditions
InactiveUS20100241006A1Minimize damageSmall sizeScattering properties measurementsCatheterDiseaseBrain condition
Disclosed embodiments relate to an apparatus for detecting brain conditions. The apparatus for detecting brain conditions may include: a layer which is located adjacent to the brain of a living body; a light source which is formed on the layer and irradiates light to the brain; and an optical sensor which is formed on the layer adjacent to the light source and detects the light scattered from the brain. Since detection is possible at a location relatively adjacent to the brain, the apparatus for detecting brain conditions may improve accuracy and reliability of detection. The apparatus for detecting brain conditions may be used to detect brain conditions such as cerebral oxygenation, cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow, etc. or to monitor brain activities, or to diagnose and / or localize the disease foci in case of neurovascular disease such as stroke including hemorrhage or bleeding, into or around the brain or brain tumors or epilepsy, etc. Since the apparatus for detecting brain conditions has a relatively flexible structure, damage to the brain tissue may be minimized.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Medical oscillating compliance devices and uses thereof
ActiveUS8956379B2Improve efficiencyServomotor componentsSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
The present invention relates to devices and systems that alter intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform by oscillating the contraction and expansion of a compressible composition within the cranial or spinal cavities such that they increase intracranial capacity. The contraction and expansion of the compressible composition in the oscillating compliance devices can be due to an individual's intracranial pressure, the result of the expansion and compression of a reservoir which is mediated by the contractility of the heart or driven by a pump gaited to a biorhythm. The invention also relates to methods for protecting an individual's brain from abnormal arterial pulsations and for altering an individual's cerebral blood flow using the devices and systems of the invention. The oscillating compliance devices can be used to treat several diseases and / or conditions characterized by altered / abnormal intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform, including hydrocephalus, stroke, dementia and migraine headaches, vasospasms, congestive heart failure, cardiopulmonary bypass or carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Imaging Correlates of Neurogenesis With MRI
InactiveUS20090246145A1Decreased neurogenesisBlood volume expansionBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
This invention provides a method for treating a mammalian subject afflicted with a disorder associated with reduced neurogenesis in the subject's hippocampal dentate gyrus which comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound which increases cerebral blood volume in the subject's hippocampal dentate gyrus by a percentage greater than that by which it increases the cerebral blood volume in the subject's hippocampal CA1 region, thereby treating the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method and system for mapping tissue status of acute stroke
ActiveUS20110229003A1Minimize impactMotion compensationImage enhancementImage analysisCerebral blood volumeIschemic lesion
The current invention provides a method of identifying a ischemic lesion. The method includes loading perfusion imaging data into an electronic memory element and deriving perfusion maps from the perfusion imaging data, where the perfusion maps include a cerebral blood volume (CBV) map and an arterial delay time (DT) map, which utilize arterial delay and dispersion effects. Ischemic pixels are determined from the perfusion imaging data, where the DT is greater than a predetermined first threshold value and the CBV is below a second threshold value and the infarct portion of the ischemic lesion is determined, where DT is greater than a predetermined third threshold value and / or the CBV is below a forth threshold value. A cluster analysis is applied to all of the determined ischemic lesion and infarct pixels and the penumbra is then determined, where mismatch regions between the ischemic lesion and the infarct core define the penumbra.
Owner:APOLLO MEDICAL IMAGING TECH
Method for calculating brain blood volume on basis of stable status method
InactiveCN102119856AReduce the impactReduce dependenceComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringBrain ctClinical trial
The invention relates to a method for calculating brain blood volume. The method is used for calculating the brain blood volume on the stable status CT (Computed Tomography) brain perfusion imaging principle. The method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out common whole brain CT scanning to obtain a brain tissue structure image before contrast agent injection; injecting the contrast agent to the vessel exciting area to reach the stable status, and obtaining the brain tissue structure image of the same position; (3) deleting an overhigh brain blood volume value with a vessel pixel deleting method, and deleting the interference of the artery in the existing area to the brain blood content measuring value; (4) and calculating the brain blood flow value of the brain tissue by calculating the ratio of the brain tissue to the signal change in the vessel according to a formula. With the method, all brain scanning can be carried out and the radial dosage of the perfusion scanning can be reduced, thus the method for calculating brain blood volume can be widely applied into the clinical trial.
Owner:姜卫剑 +1
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
InactiveUS20040138549A1Character and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsRadiologyCerebral blood volume
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second dvalue. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Method for auxiliary assessment of ischemic disease risk based on magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image
InactiveCN110490871AEffective assessment methodImage enhancementImage analysisHead movementsDisease cause
The invention provides an automatic image processing and displaying method based on a magnetic resonance cerebral perfusion image, which is used for assisting in evaluating cerebral ischemia disease risks and is characterized by comprising spatial deformation, multi-parameterization, brain map coverage and a method for evaluating ischemic cerebral disease risks. The image space deformation methodcomprises the following steps: head movement correction, which is used for adjusting a space difference generated by head movement in a cerebral perfusion imaging process; and standard brain registration: taking the standard brain as a reference to realize standardization of the imported cerebral perfusion image. The multi-parameterization is used for converting the original nuclear magnetic datainto cerebral image perfusion parameters such as cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume and artery arrival time, wherein the coverage brain map is used for enabling the parameterized cerebral perfusion image data to cover standard brain maps of different templates to form different regions of interest, and calculating average parameter values of the different regions of interest.The standard cerebral map comprises a cerebral artery blood supply area and an early CT scoring area of an Albetan stroke project. The ischemic brain disease risk assessment method is used for comparing the averageparameter value of the region of interest with a reference range, displaying the differentiation degree and automatically displaying the region of interest beyond the reference range. According to the invention, multi-parameter automatic partitioning and quantitative processing from nuclear magnetic cerebral perfusion original number to ischemic cerebral disease early-stage risk assessment are realized, and an effective assessment method is provided for early-stage screening, early-stage diagnosis and early-stage treatment of cerebral ischemic diseases.
Owner:安影科技(北京)有限公司
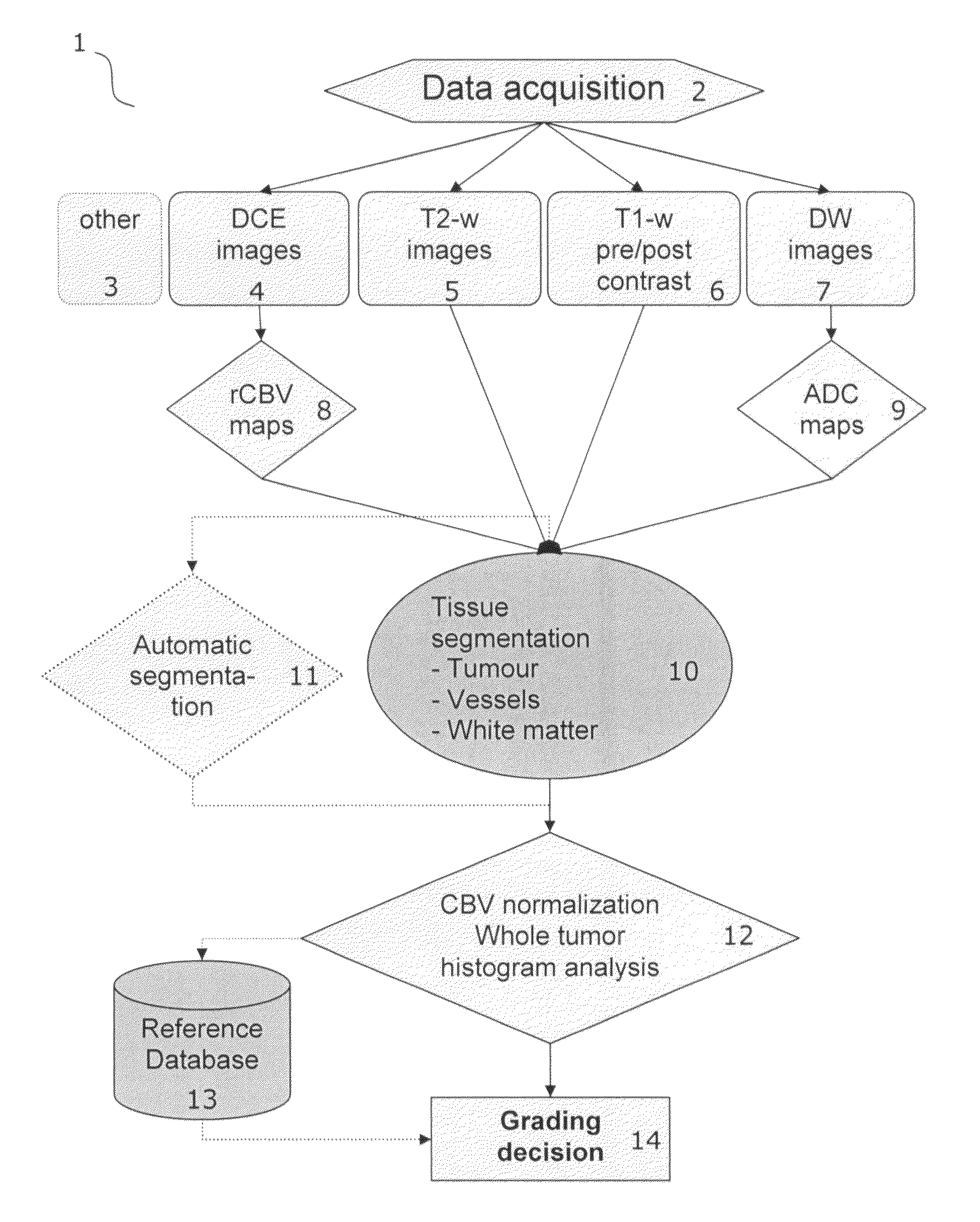
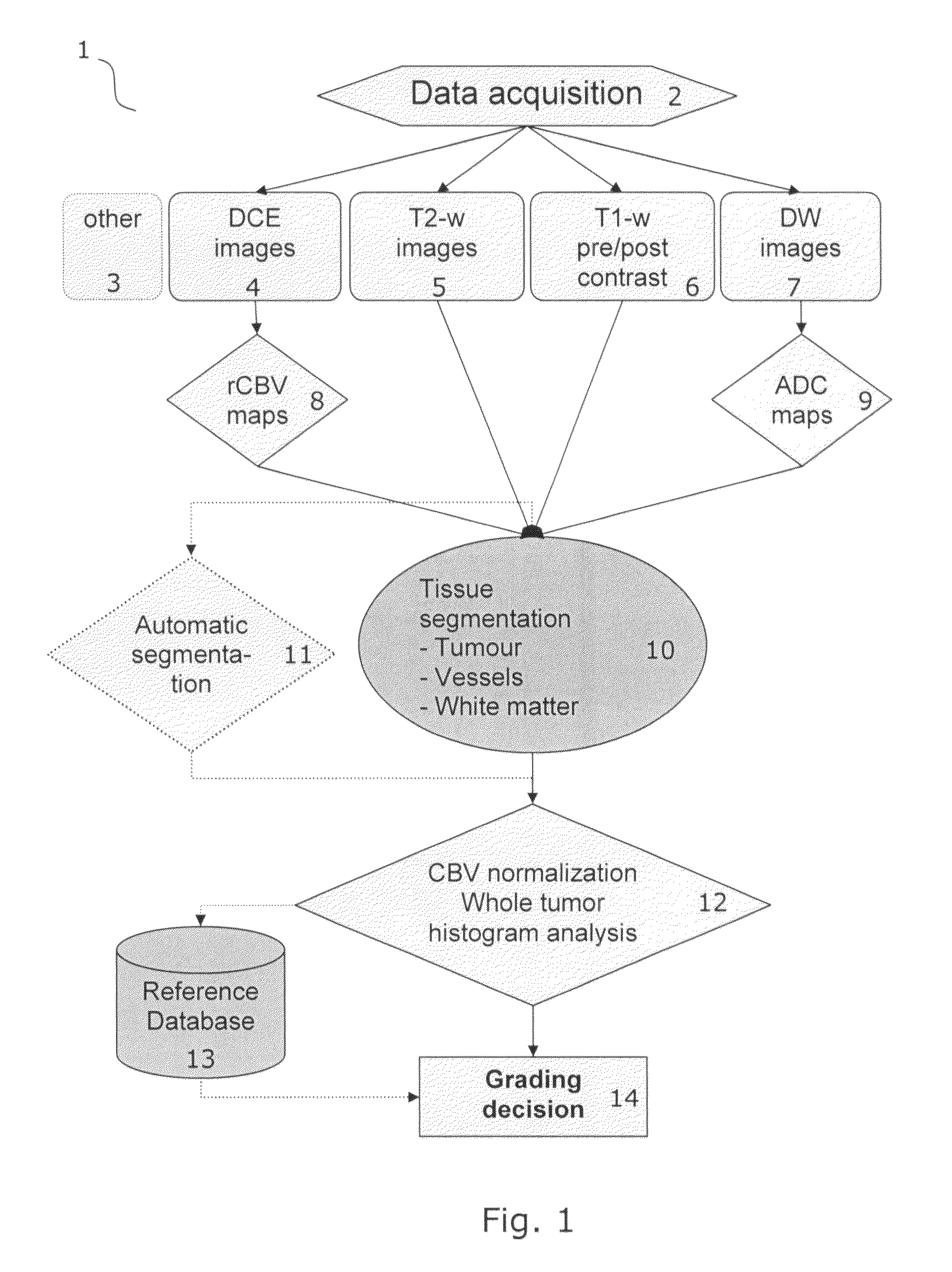
Tumor grading from blood volume maps
An embodiment of the invention is to make possible a non-invasive grading of a tumor based on parameters determined from a frequency distribution (histogram) of values in a map representing cerebral blood volume (CBV) or cellular metabolism in the tumor. The method is especially applicable to brain tumors such as gliomas where histological grading is difficult. The invention provides a precise and consistent grading since it relies on values selected from the whole tumor (not just from hot spots); since it takes the diversity or heterogeneity of the vascularization into account by analyzing the frequency distribution (not just a mean value); and since it involves and allows for a more automated procedure wherein any subjective contributions from human operators is not critical to the resulting grading. CBV maps may be obtained by perfusion imaging using MRI or CT scanning. Cellular metabolism maps may be obtained from a glucose metabolism map obtained by positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
Cerebral blood flow measuring device, system and helmet
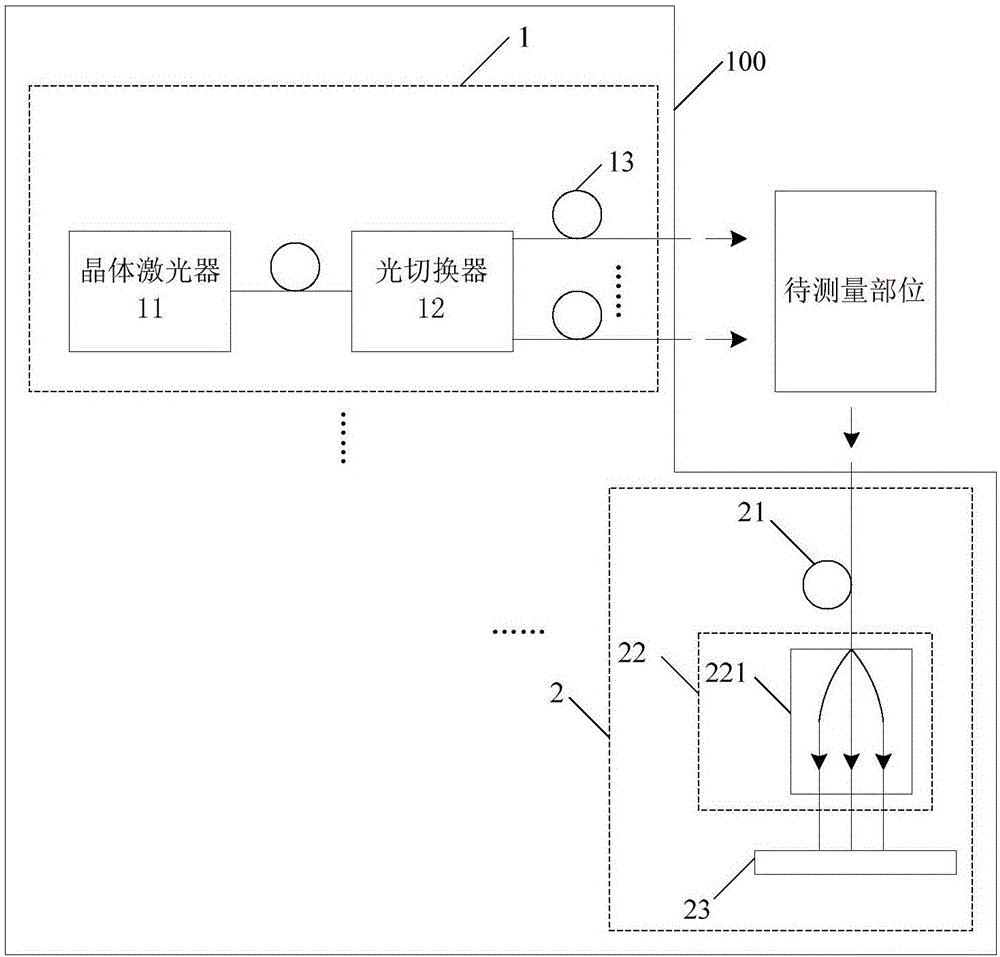
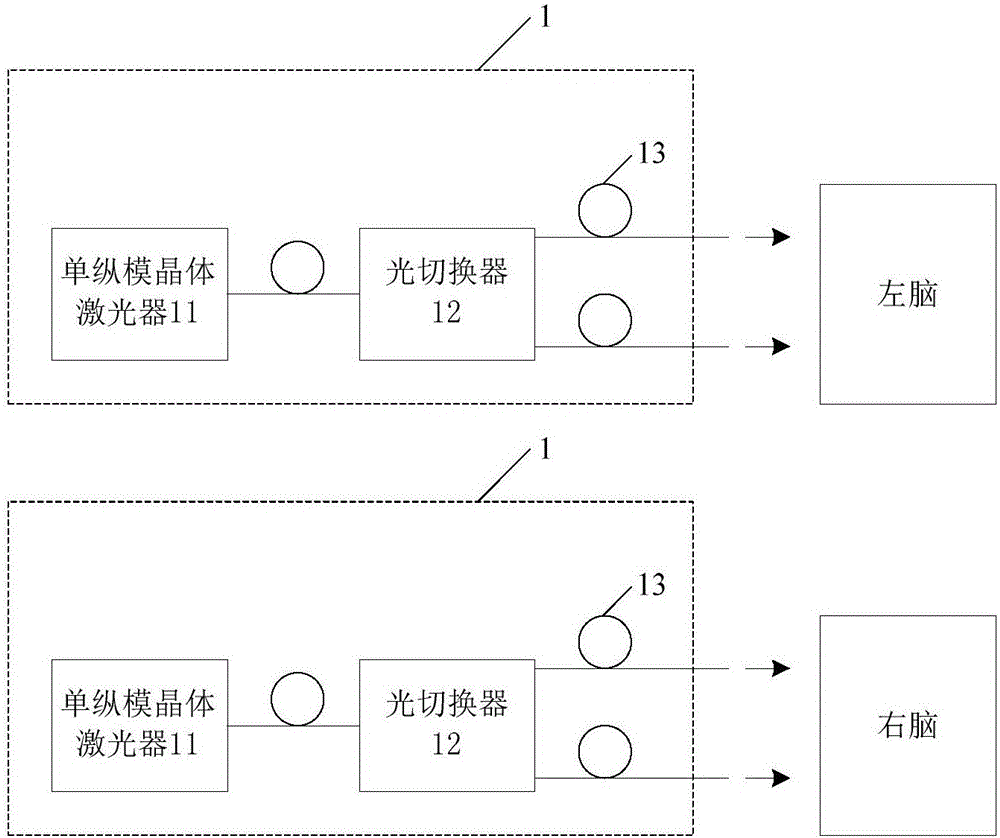
PendingCN106236068AReduce volumeImprove anti-interference abilitySensorsBlood flow measurementSilicon photomultiplierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a cerebral blood flow measuring device, a cerebral blood flow measuring system and a helmet, wherein the cerebral blood flow measuring device comprises at least one group of light source device and at least two groups of detection devices; the light source device comprises a single longitudinal mode crystal laser, an optical switch and radiation optical fibers; an output end of the single longitudinal mode crystal laser is connected to an input end of an optical switch; an output end of the optical switch is connected to the at least two radiation optical fibers so as to switch a beam of inputted laser light into at least two beams of laser light and output the at least two beams of laser light; by virtue of the radiation optical fibers, the laser light is transmitted to a to-be-measured part; each detection device comprises a single mode fiber, a collimation device and a silicon photomultiplier; by virtue of the collimation device, received laser light, which is outputted by the single mode fiber, is uniformly transmitted to a receiving window of the silicon photomultiplier; and the silicon photomultiplier is used for converting a received optical signal into an electric signal and for outputting the electric signal. The cerebral blood flow measuring device disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in time sampling rate, high in signal to noise ratio, small in volume, good in portability and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Device and method for measuring blood flow in an organ
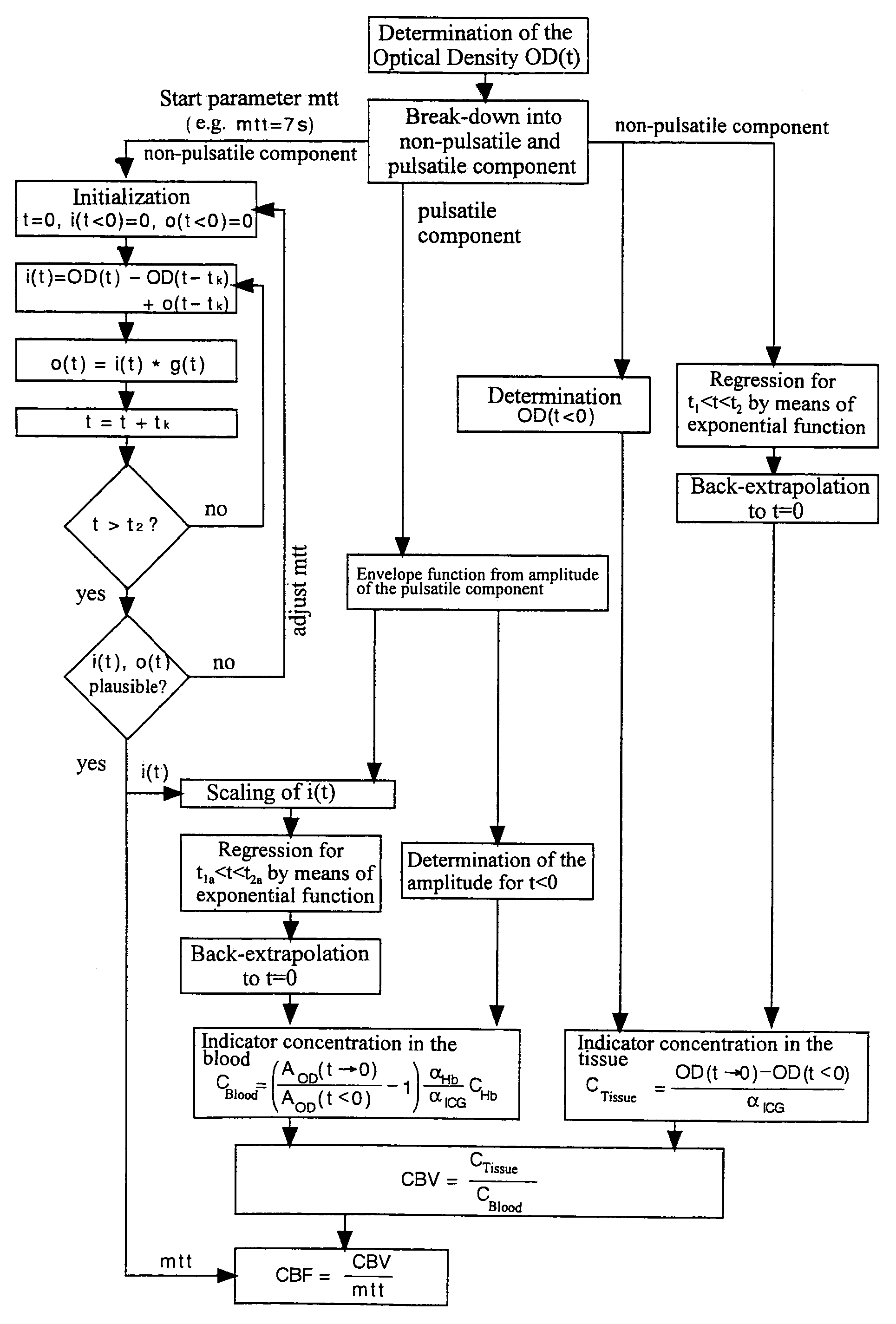
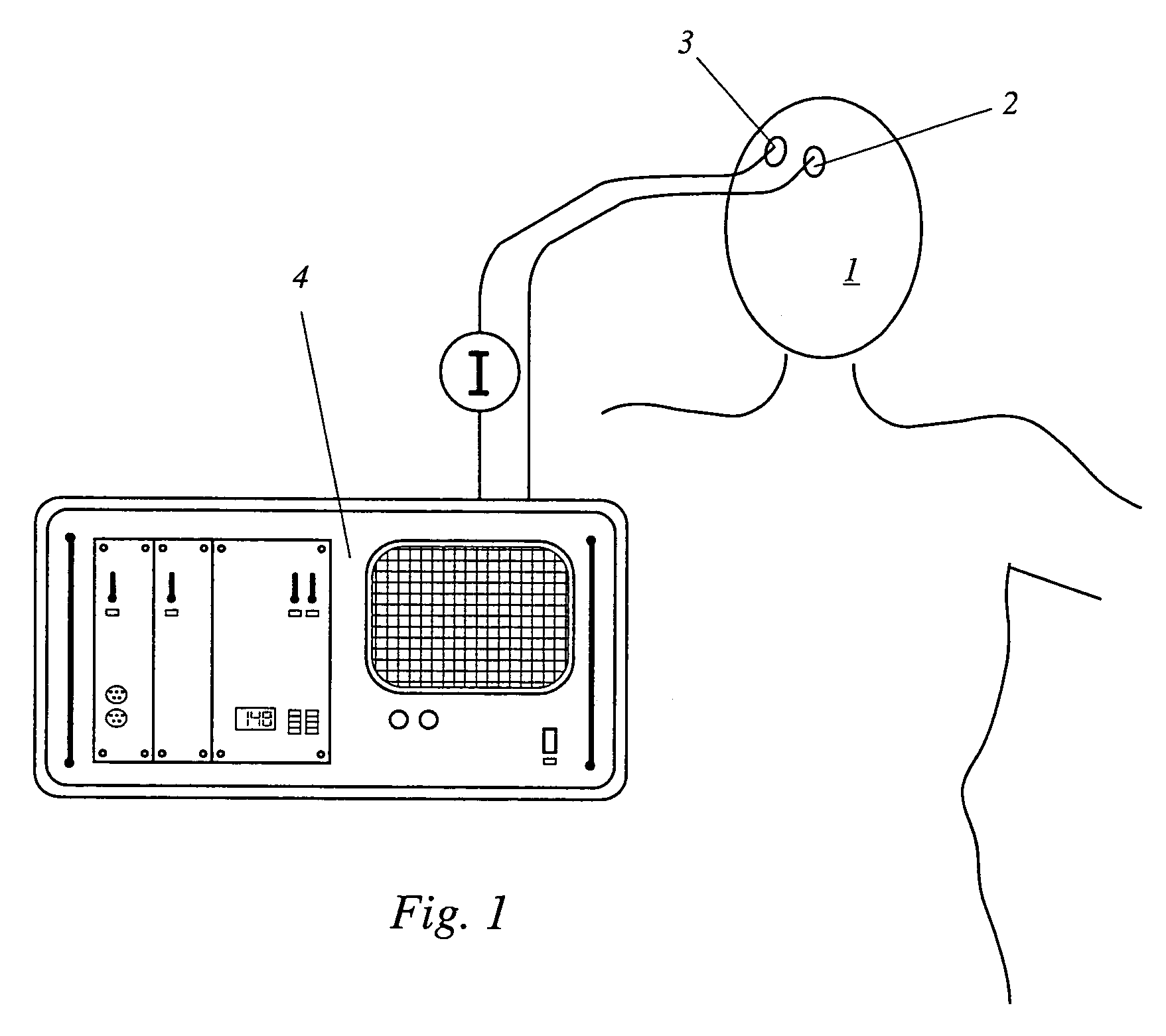
ActiveUS7529576B2Great accuracy in determination of blood flowAccuracy of evaluation be lessRadiation pyrometryCatheterBlood flowNear infrared radiation
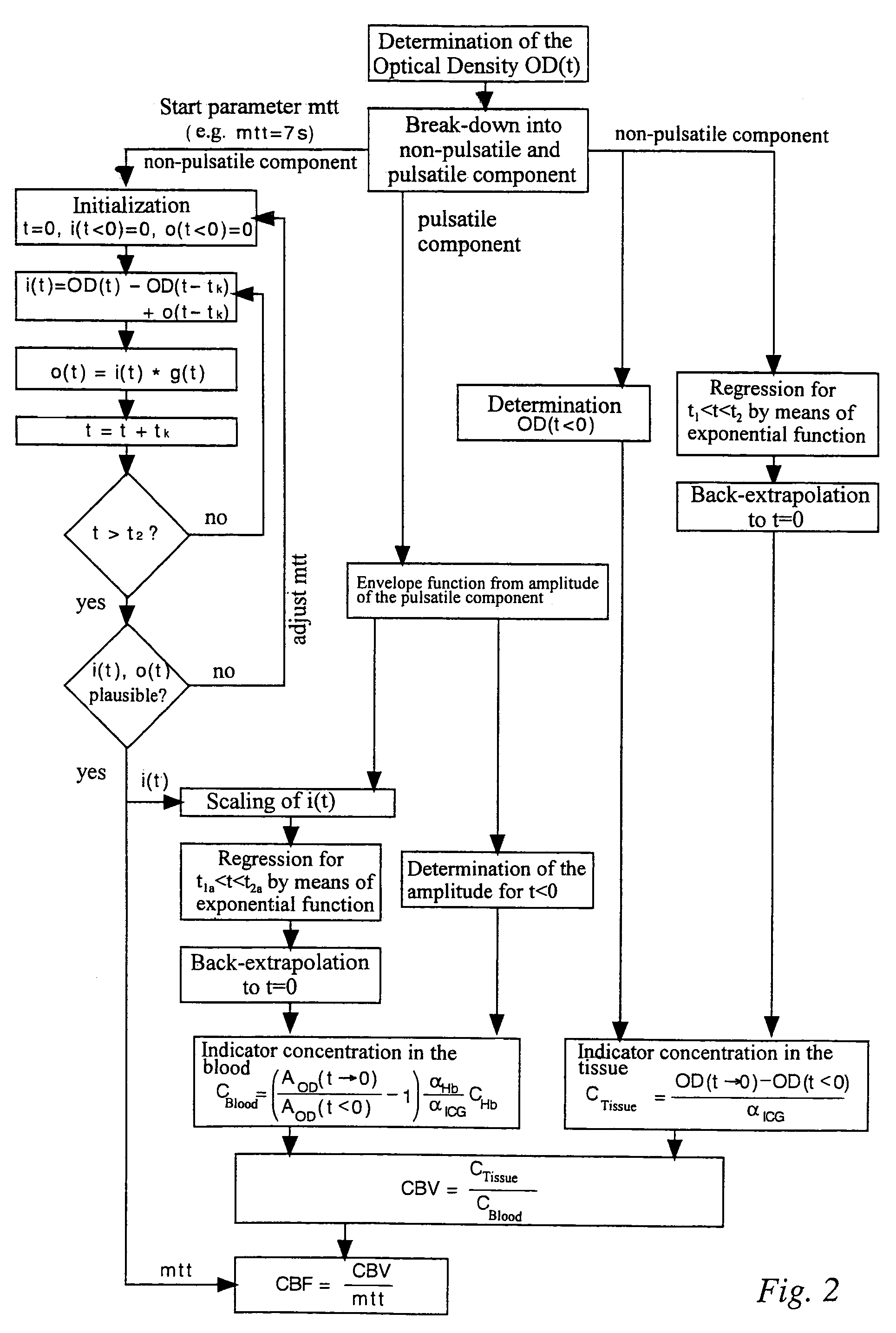
A device has a source for emitting near infrared radiation into cerebral tissue, a sensor for detecting radiation exiting from the tissue, and an evaluation unit which detects the exiting radiation as an input signal having pulsatile and non-pulsatile components and is programmed to determine the concentration of an injected indicator in the tissue from the non-pulsatile signal component, iteratively determine an inflow function characterizing cerebral blood flow by varying a mean transit time until reaching a stop criterion, determine indicator concentration relative to cerebral blood volume from the inflow function and the pulsatile signal component, calculate cerebral blood volume by dividing indicator concentration in the tissue by indicator concentration relative to cerebral blood volume, calculate cerebral blood flow by dividing the cerebral blood volume by the mean transit time when the stop criterion has been reached, and scale the inflow function using values determined from the pulsatile signal component.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
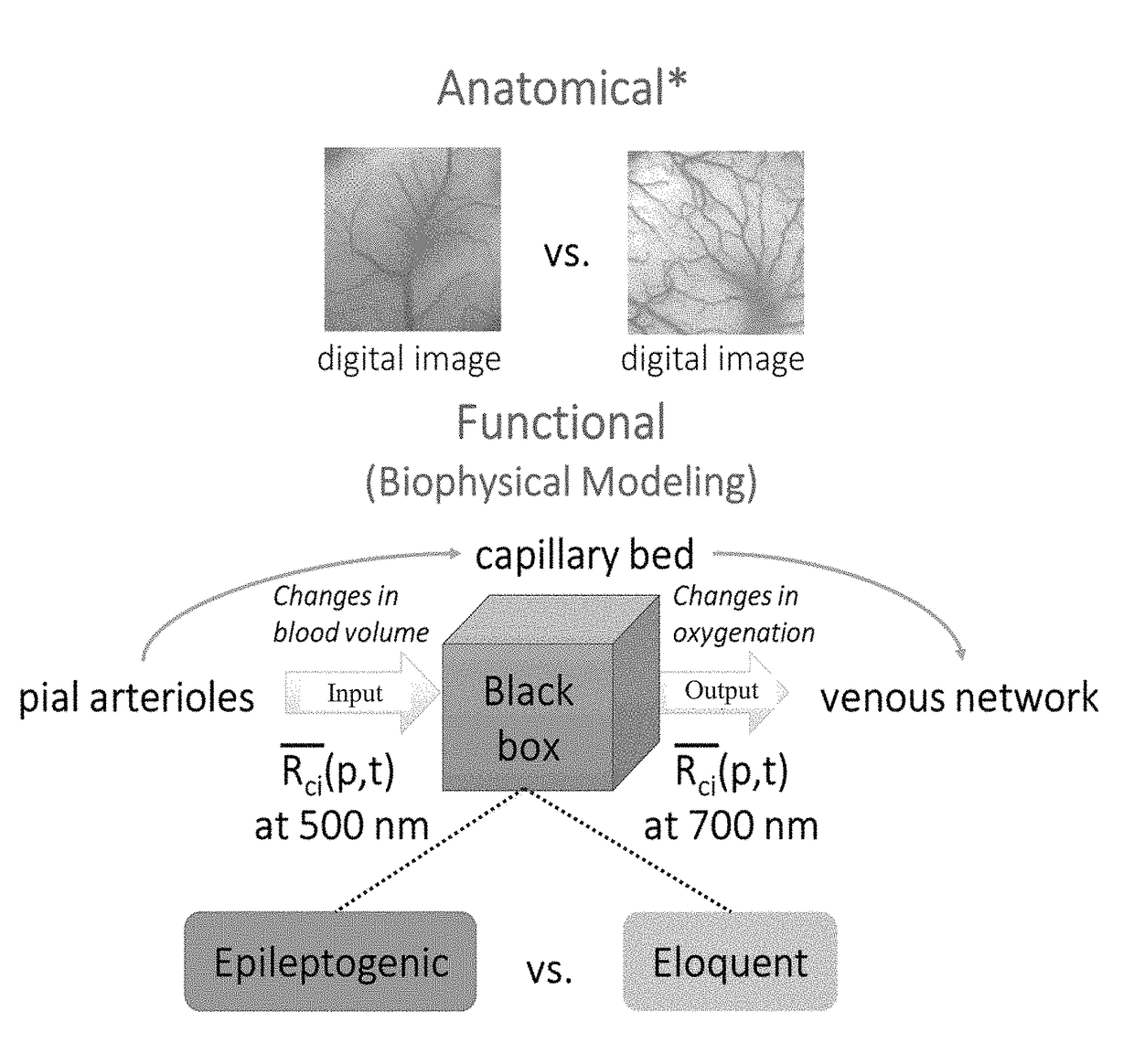
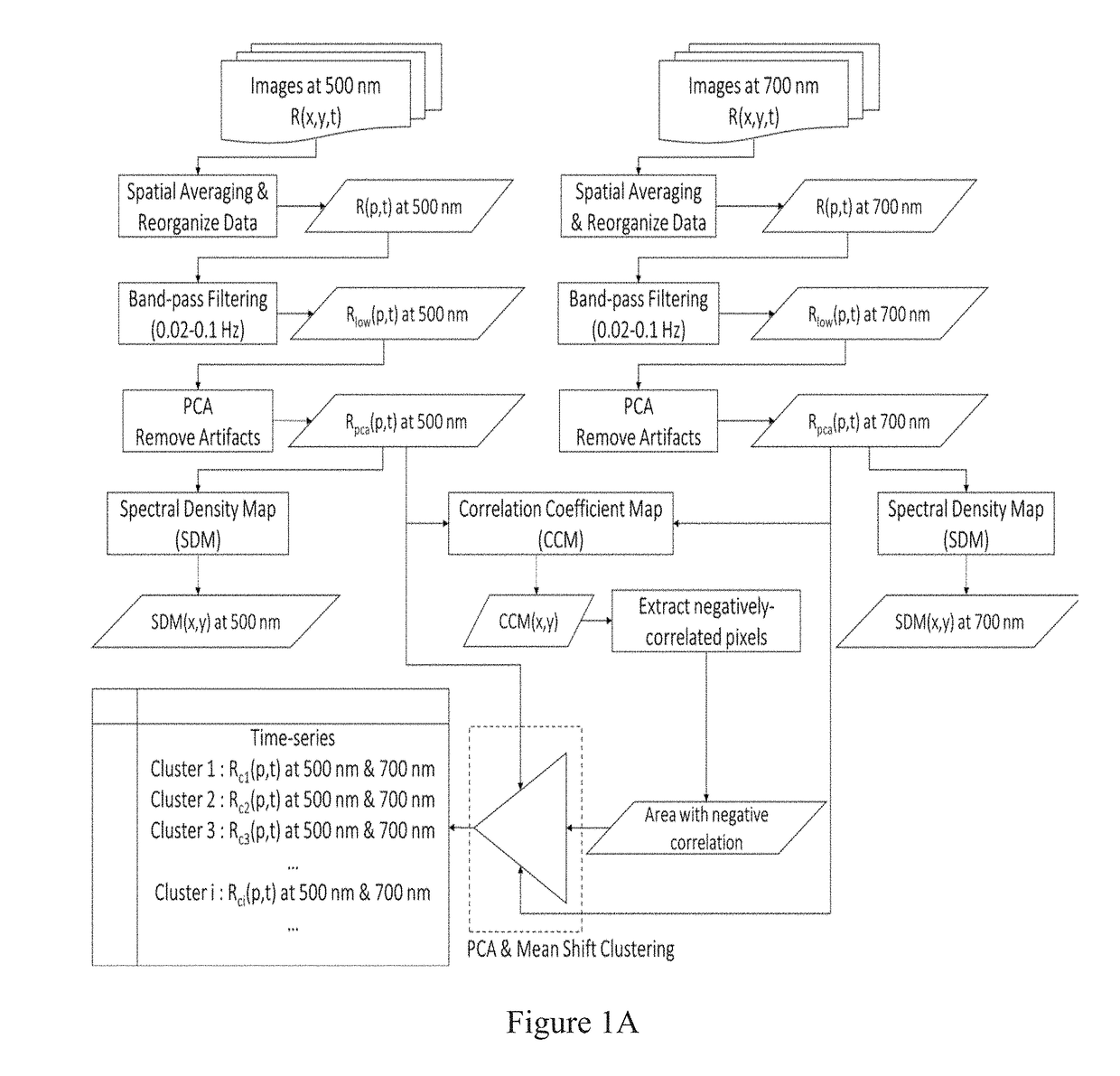
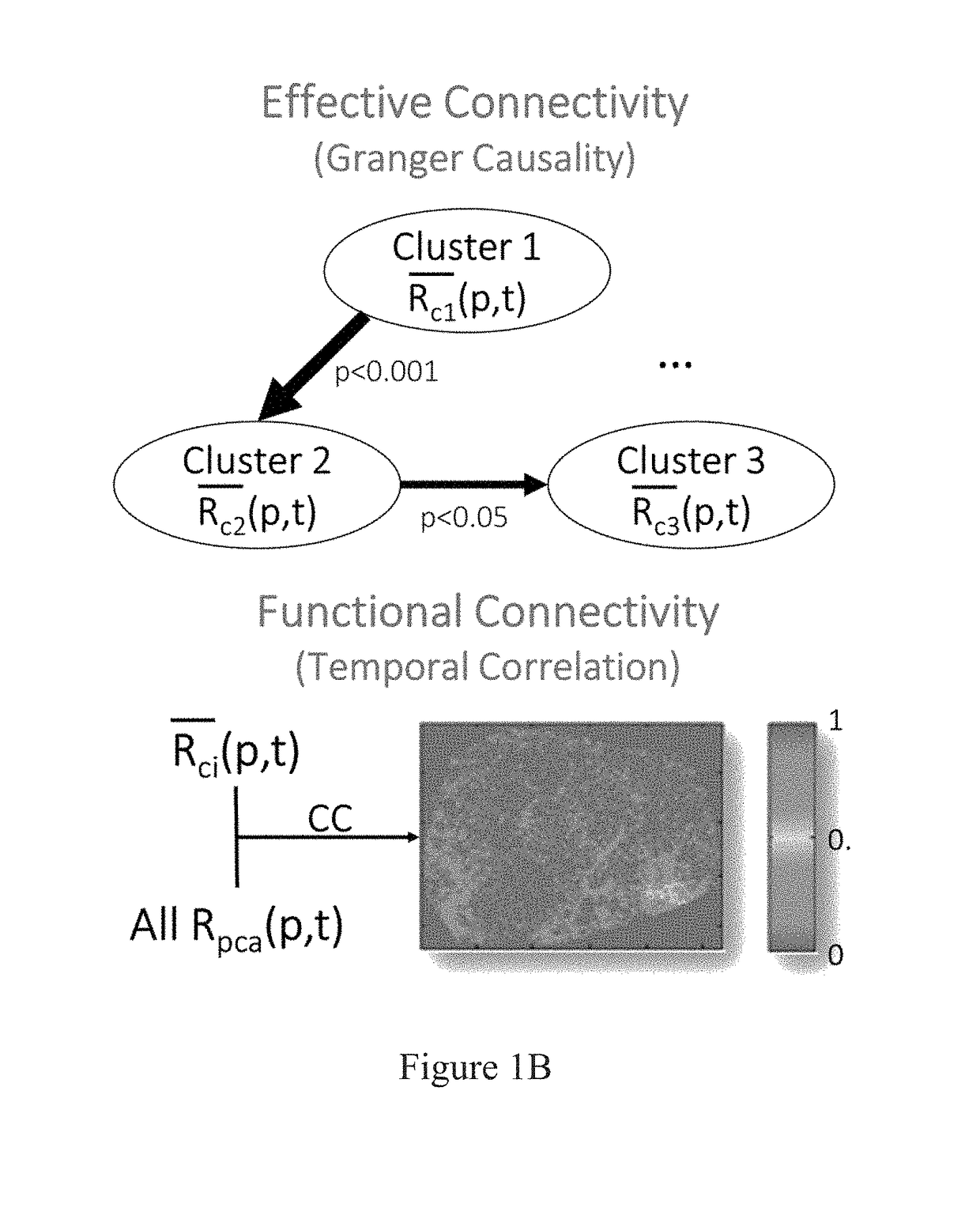
Hybrid spectroscopy imaging system for intraoperative epileptic cortex detection
Methods and systems that detect and differentiate epileptogenic from eloquent and normal cortices are provided. A method for identifying epileptogenic cortices in a brain may include detecting areas in the brain that are undergoing cerebral blood volume low frequency oscillations, detecting areas in the brain that are undergoing blood oxygenation low frequency oscillations; mapping clusters of the brain in which the cerebral blood volume low frequency oscillations are negatively correlated with the blood oxygenation low frequency oscillations, and analyzing the time based relationship between the clusters of the brain that are undergoing negatively correlated low frequency oscillations to determine cause areas, which are areas of the brain that are causing negatively correlated low frequency oscillations to occur elsewhere.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Mouse MRI for drug screening
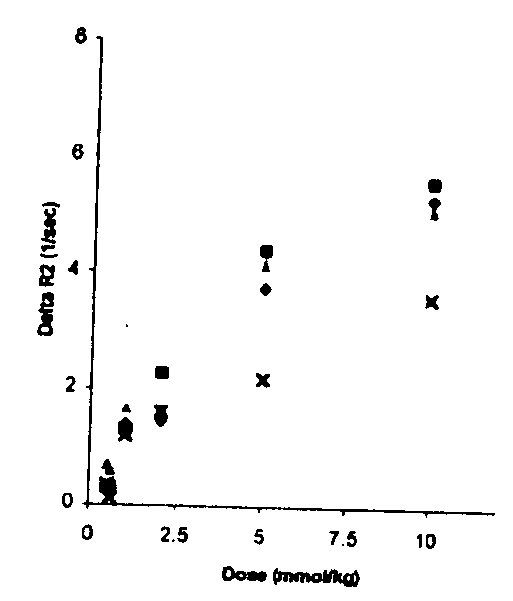
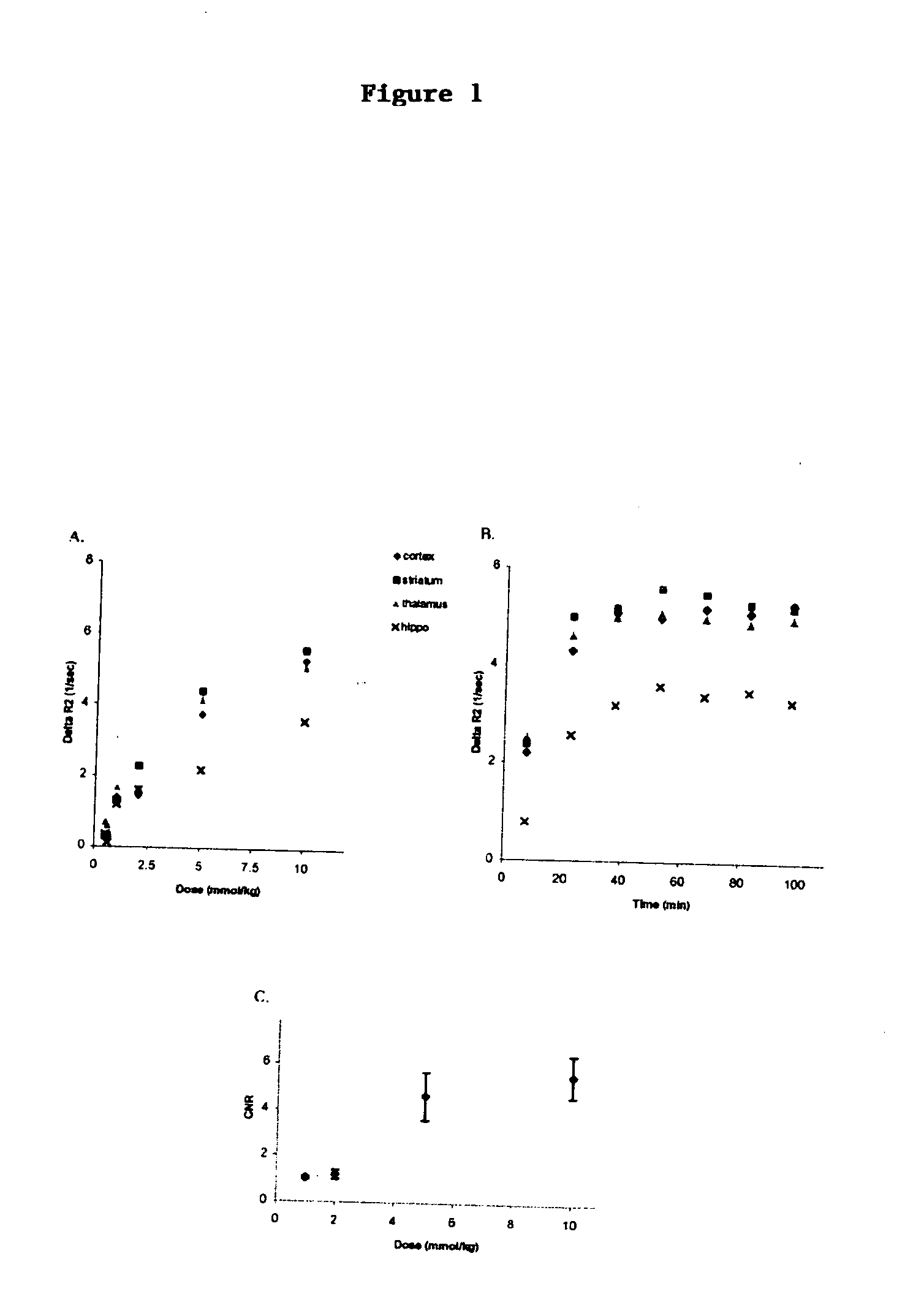
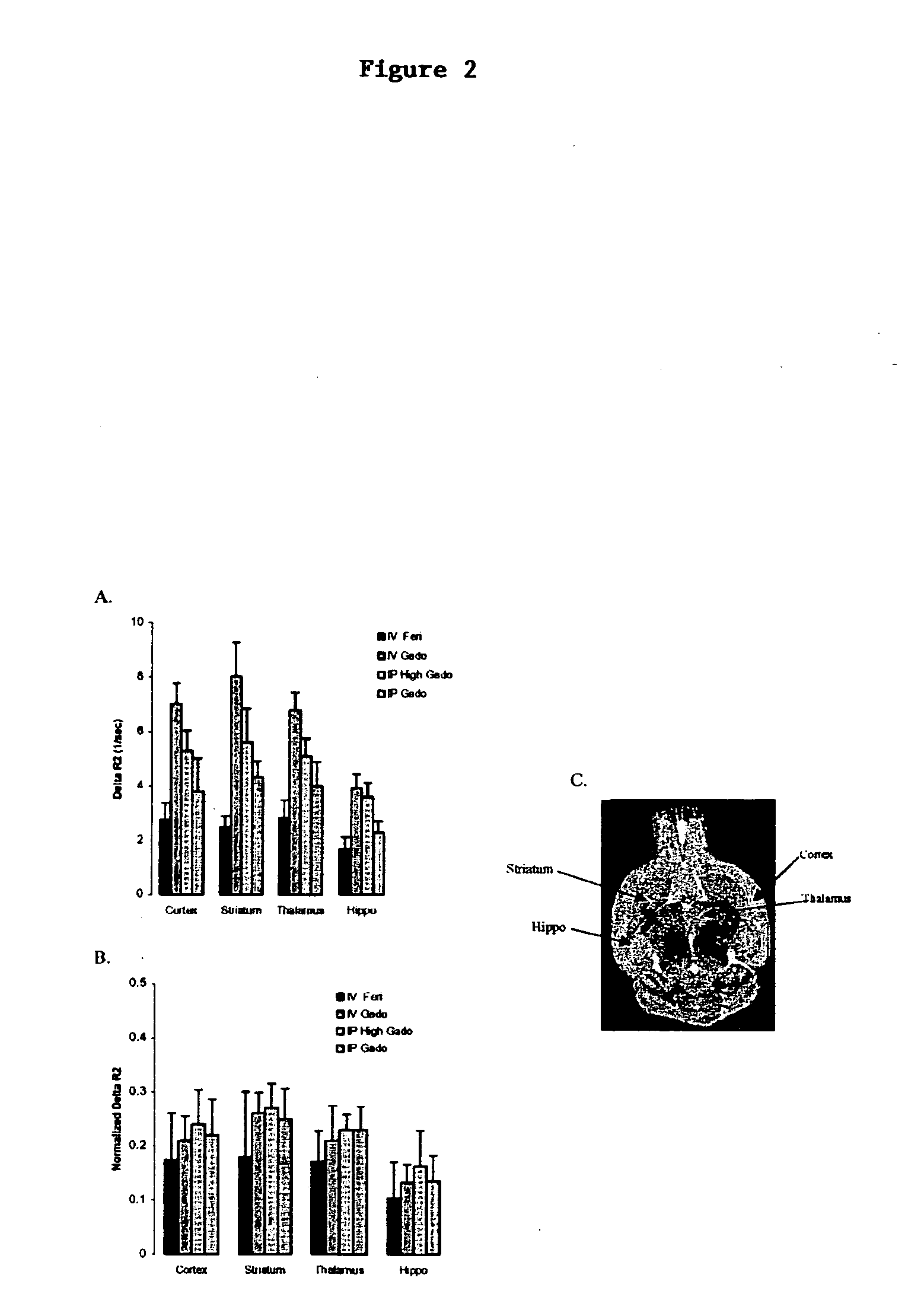
This invention provides a method for determining the amount of blood in a volume of cerebral tissue (cerebral blood volume) in a mammalian subject comprising (a) acquiring a first magnetic resonance image of the volume of tissue in vivo; (b) administering intraperitoneally to the subject a gadolinium-containing contrast agent in an amount greater than about 1 mg per kg body weight and less than about 20 mg per kg body weight; (c) acquiring a second magnetic resonance image of the volume of tissue in vivo, which second image is acquired at least about 15 minutes after, but not more than about 2 hours after, administering the contrast agent; and (d) determining the amount of cerebral blood volume based on the first and second images.
Owner:SMALL SCOTT +1
Cerebral blood flow auto-regulation index output method, storage medium and ultrasonic equipment
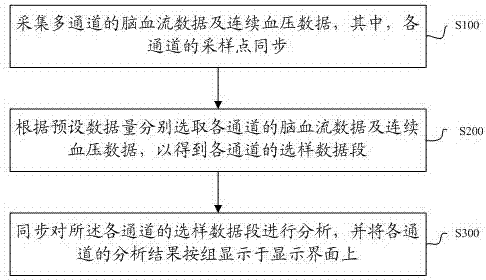
ActiveCN107296627AEasy to useBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsAuto regulationData segment
The invention discloses a cerebral blood flow auto-regulation index output method, a storage medium and ultrasonic equipment. The method includes: acquiring cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data of multiple channels, wherein sampling points of each channel are synchronous; selecting cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data of each channel according to preset data quantity to obtain a sample data segment of each channel; synchronously analyzing the sample data segment of each channel, and displaying analysis results of each channel on a display interface by groups. Since the cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data are acquired synchronously, the synchronously selected data segments are analyzed and the analysis results are displayed on the display interface by groups, real-time synchronous displaying of multiple groups of cerebral blood flow auto-regulation indexes in a transcranial Doppler system is realized, and convenience in use is brought to users.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Method and system for evaluating automatic regulation function of cerebral blood flow through external counterpulsation technique
InactiveCN106264513AEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyCerebral blood volumeCBF - Cerebral blood flow
The invention provides a method for evaluating the automatic regulation function of cerebral blood flow of an individual. The method comprises the following steps that 1, external counterpulsation operation is applied to the individual; 2, continuous blood pressure monitoring and cerebral blood flow speed monitoring are conducted on the individual before the external counterpulsation operation, during the external counterpulsation operation and after the external counterpulsation operation; 3, blood pressure changes and cerebral blood flow speed changes, responding to the external counterpulsation operation, of the individual are recorded, and the automatic regulation function of the cerebral blood flow of the individual is evaluated on the basis of the changes. The invention further provides a system for implementing the method.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Biological measurement system measuring cerebral blood volume changes to find disease or danger
Cerebral blood volume changes are measured to evaluate, from properties of low-frequency components of such changes and heart rate changes calculated by analysis, a distribution of cerebral blood vessel hardness and its change over time to thereby estimate and display diseased and dangerous portions based on the evaluation. This is attainable by a biological measurement system having a cerebral blood volume measurement unit which measures a regional cerebral blood volume of a body under test, an analyzer unit that analyzes a signal measured by the cerebral blood volume measurement unit, an extraction unit for extracting, based on an output of the analysis unit, information concerning a regional cerebral blood vessel state of the test body, and a display unit which displays a measurement result of the cerebral blood volume measurement unit, an analysis result of the analyzer unit or an extraction result of the extraction unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Cerebral blood volume correction method and apparatus, and angiography equipment
ActiveCN104825177AReduce the effect of perfusion symmetryComputerised tomographsTomographyAnatomical structuresBlood flow
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a cerebral blood volume correction method and apparatus. The method comprises steps of: detecting bifurcation points of arteries on each frame of image in an image sequence of cerebral arterial geometries of a patient; for any group of arteries of a same status, selecting areas of interest for the arteries on each frame of image; for each area of interest, extracting a blood flow TIC of the area of interest from the image sequence; according to the TIC of each area of interest, calculating blood flow parameter values of the corresponding artery; for any group of arteries of a same status, calculating blood flow differences between different arteries, and according to the blood flow differences, generating a CBV compensation factor M for each artery; based on the anatomical structure of the 3D CBV image cross section of cerebral arteries of the patient, dividing the cross section into a plurality of artery blood-supply areas, and according to the M of the corresponding artery in each artery blood-supply area, correcting the CBV value of the artery blood-supply area. The cerebral blood volume correction method and apparatus, and angiography equipment provided by the present invention reduce the impact of uneven CM distribution on cerebral perfusion symmetry.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com