Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3904results about "Blood flow measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
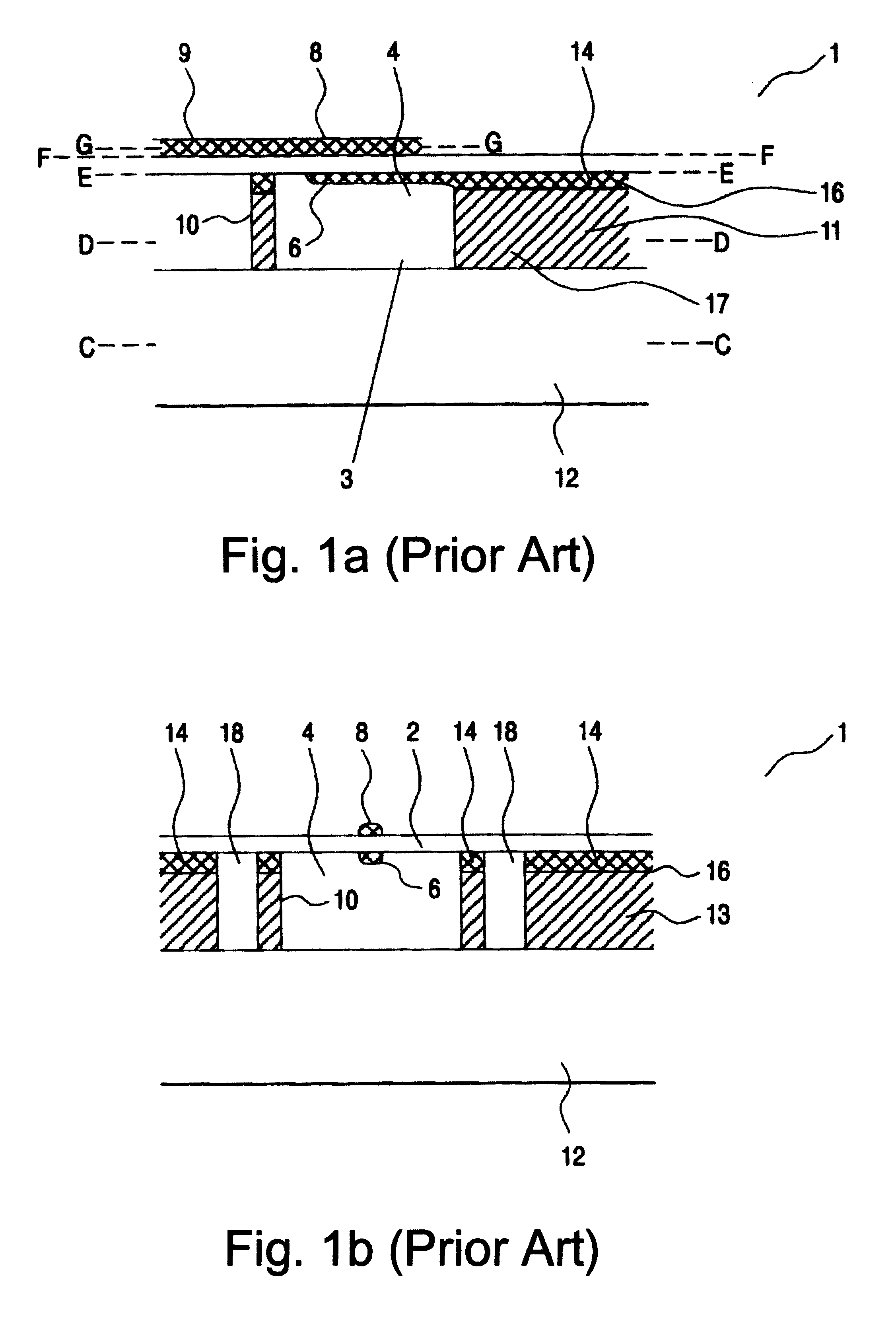
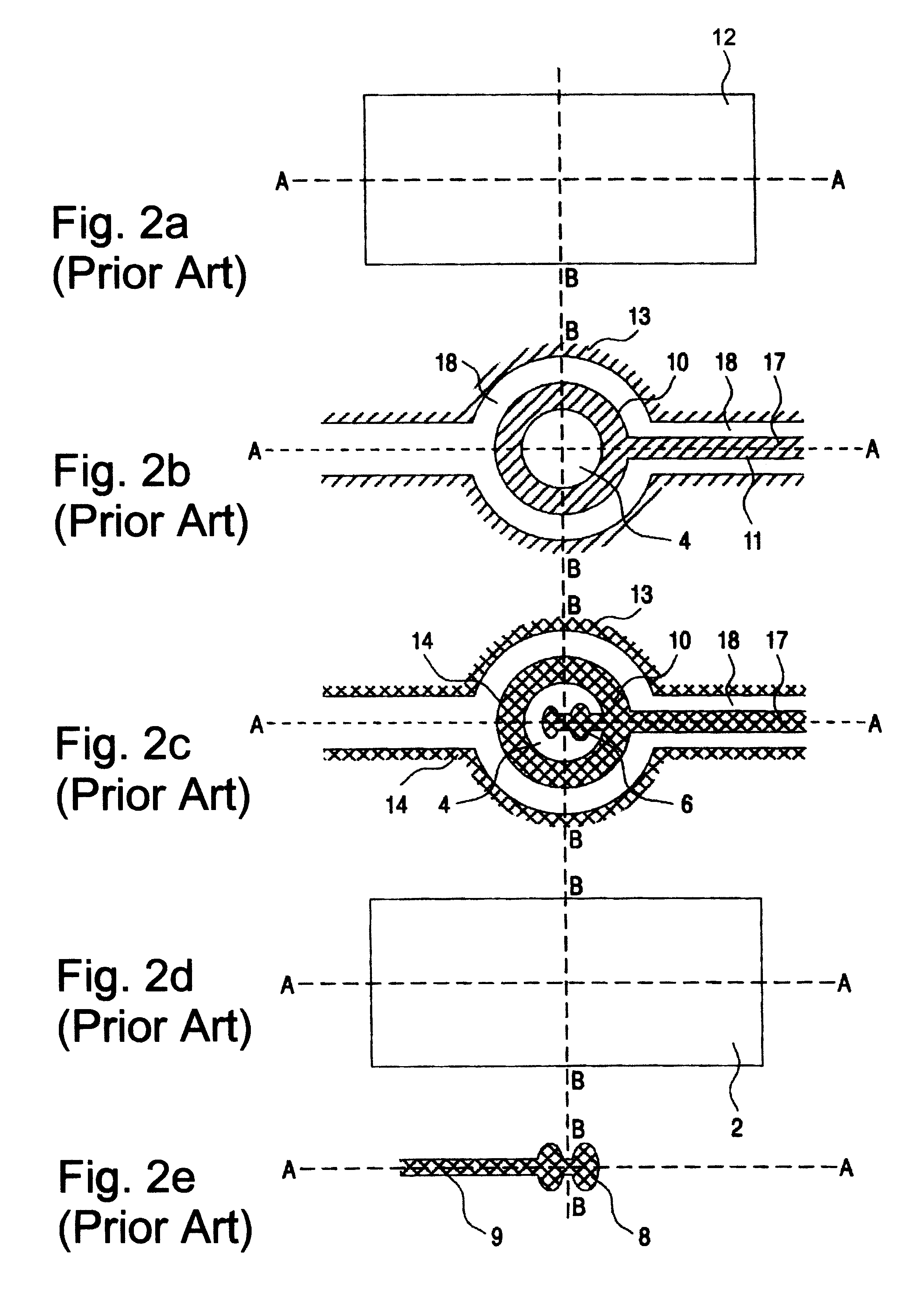
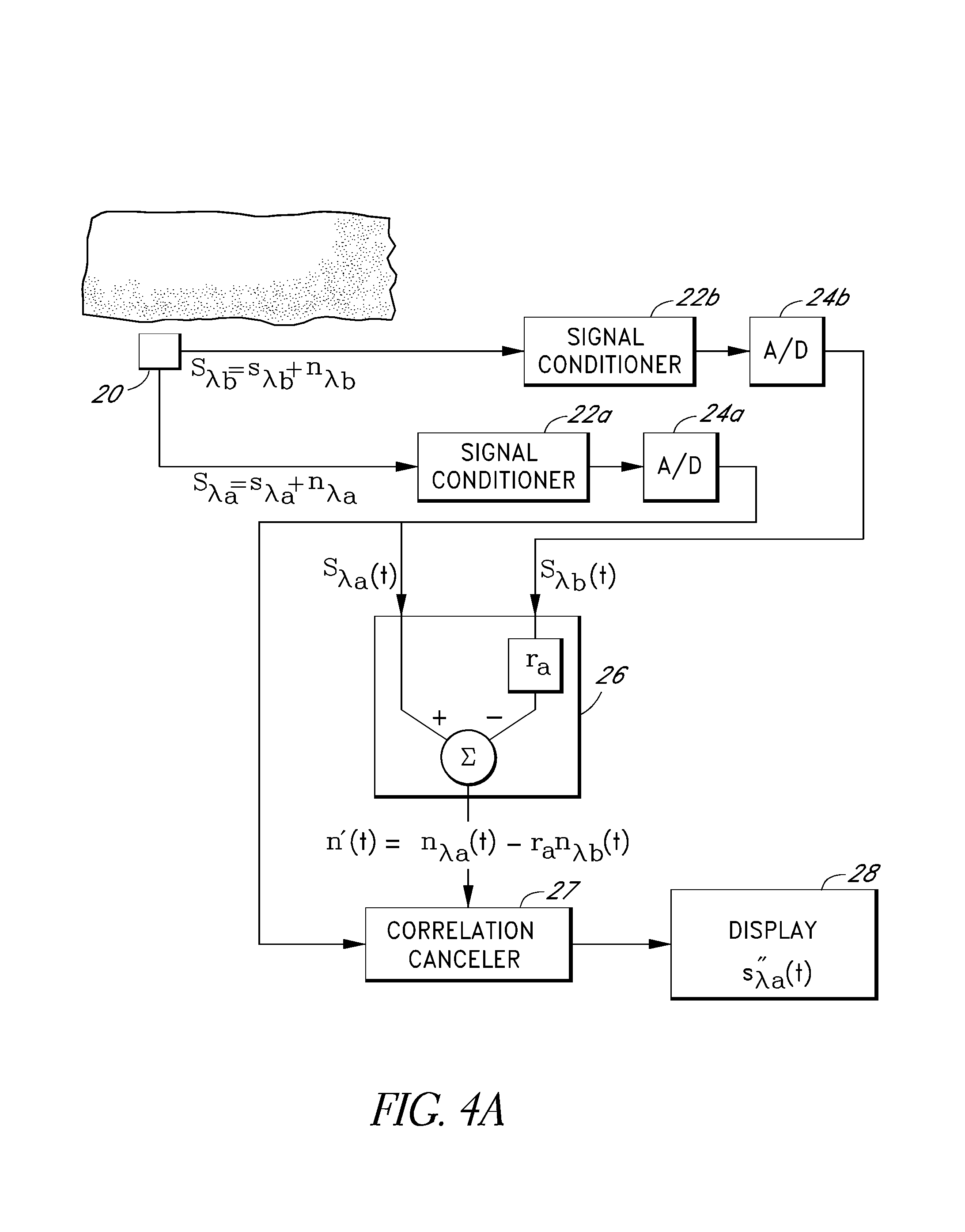
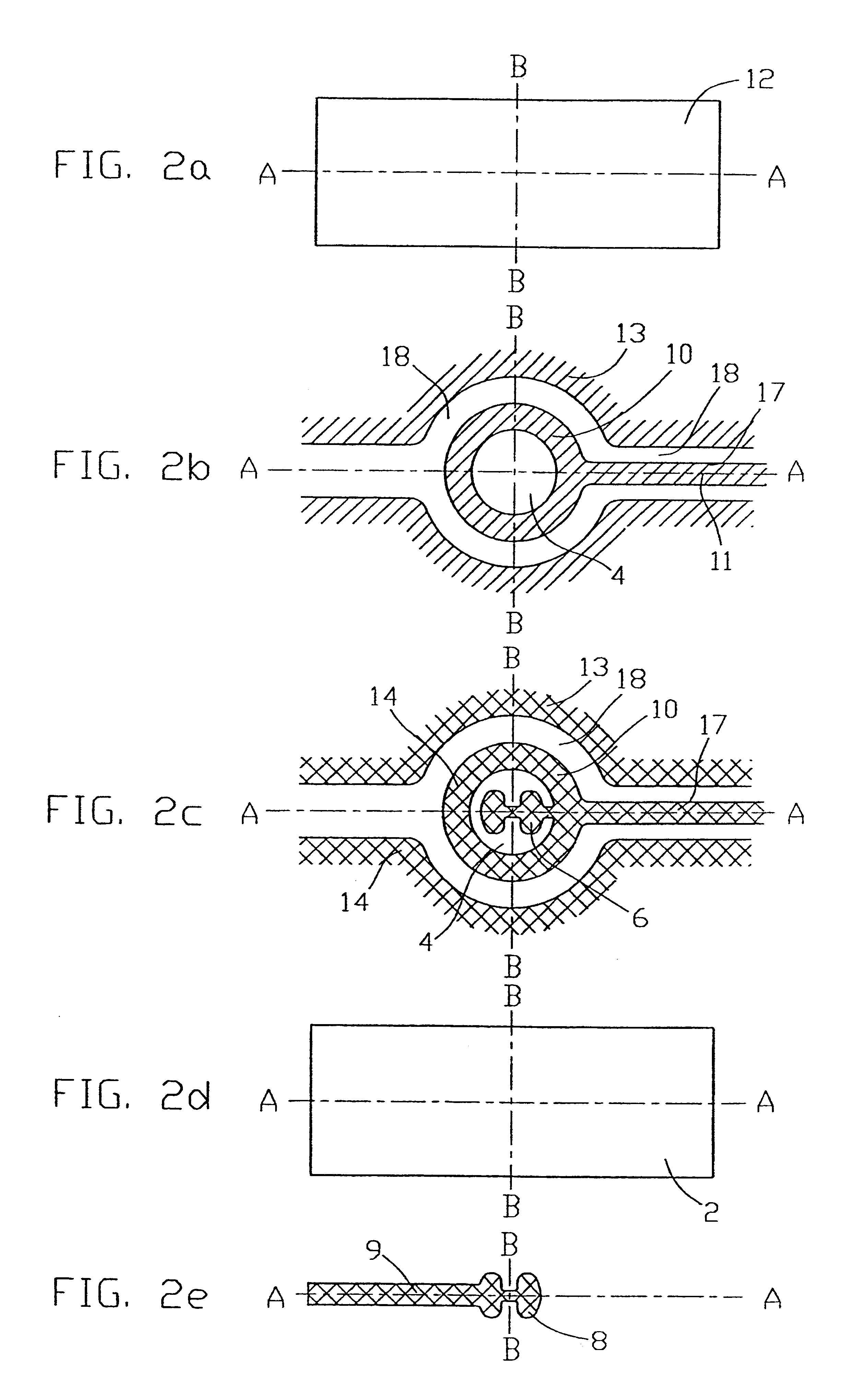
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUSRE38476E1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
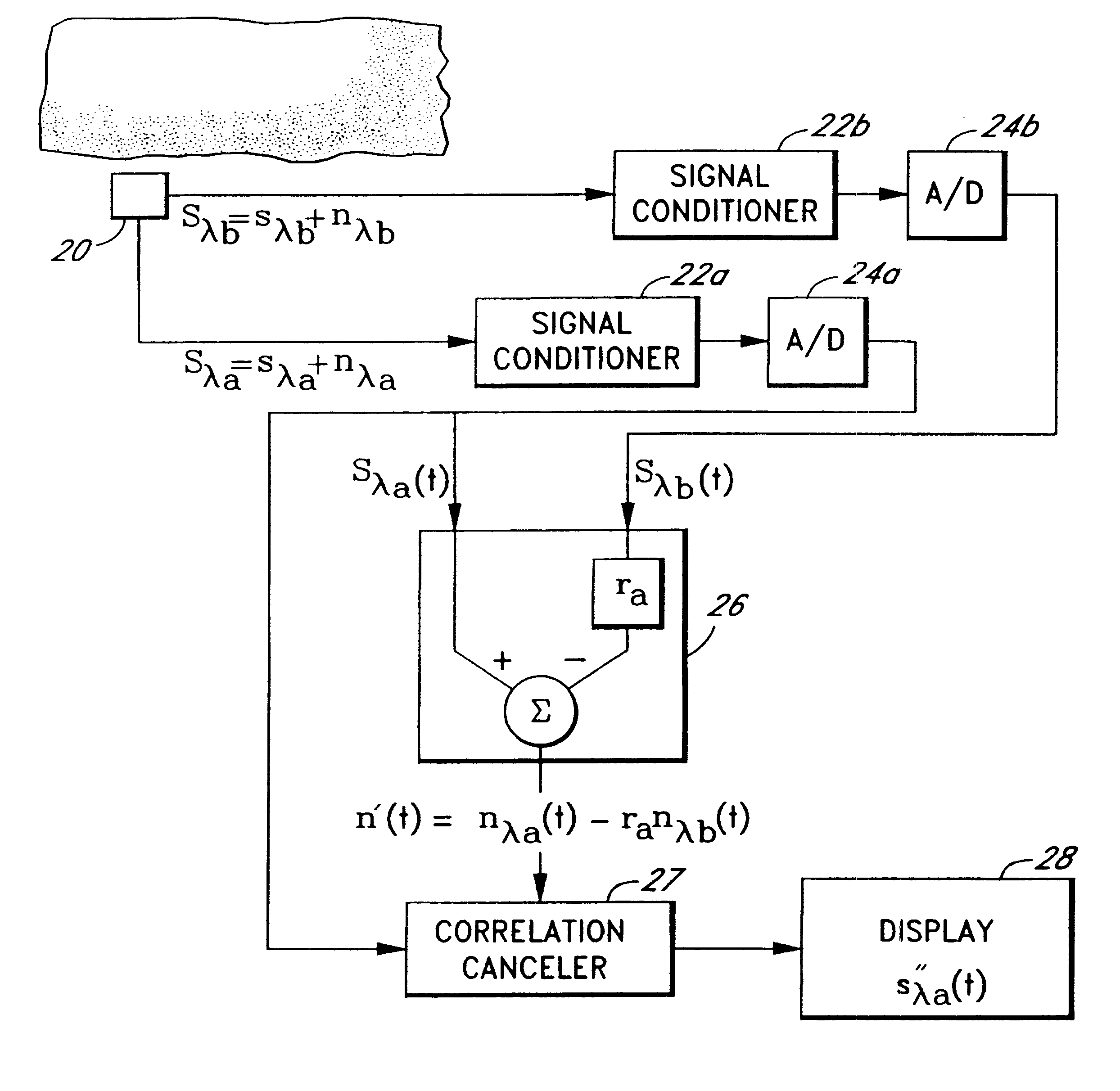
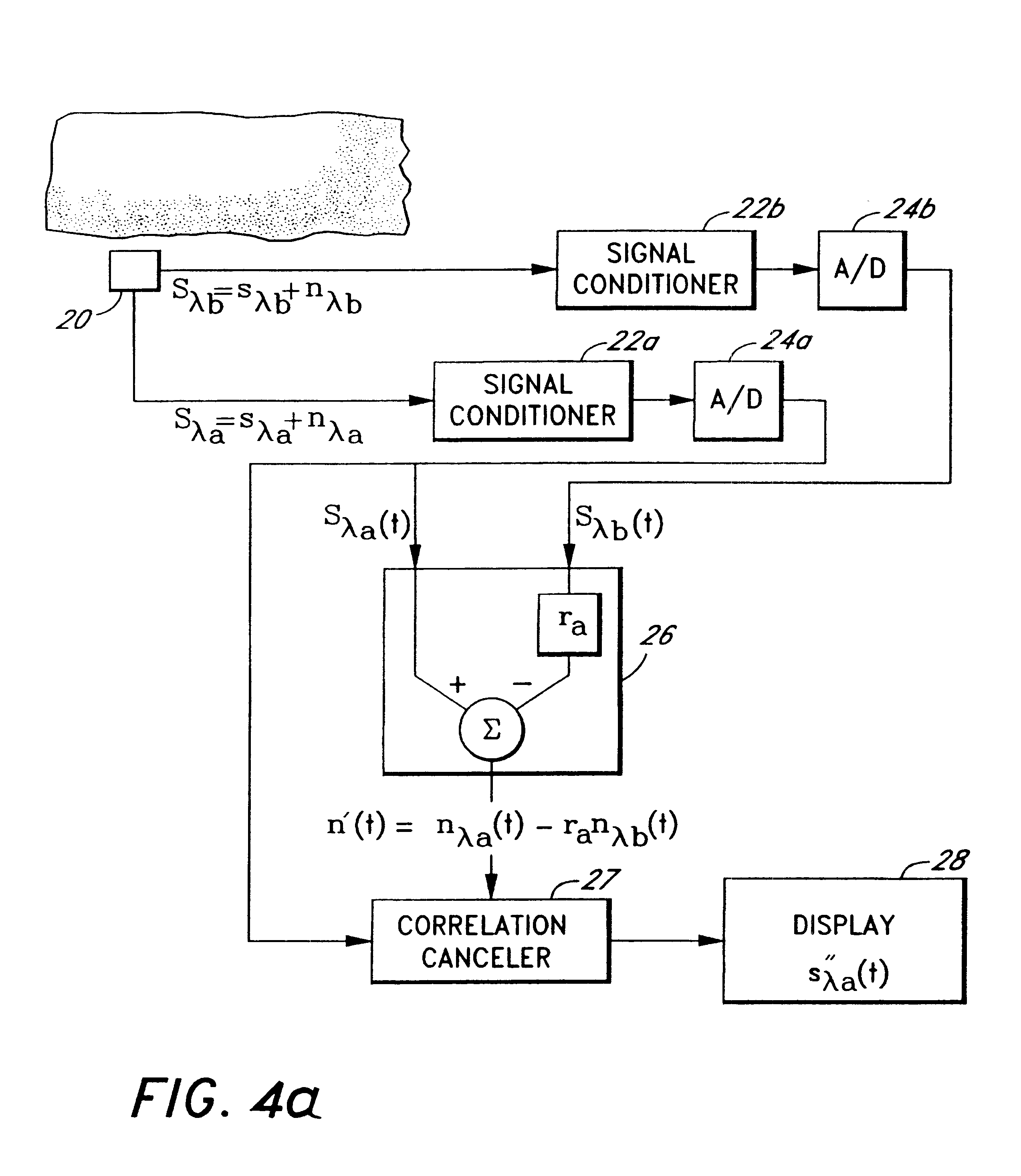
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Surgical instruments with sensors for detecting tissue properties, and system using such instruments
ActiveUS9204830B2Avoiding and detecting failurePredict successDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setPatient state
A system is provided that furnishes expert procedural guidance based upon patient-specific data gained from surgical instruments incorporating sensors on the instrument's working surface, one or more reference sensors placed about the patient, sensors implanted before, during or after the procedure, the patient's personal medical history, and patient status monitoring equipment. Embodiments include a system having a surgical instrument with a sensor for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue of the patient, which signal is converted into a current dataset and stored. A processor compares the current dataset with other previously stored datasets, and uses the comparison to assess a physical condition of the subject tissue and / or to guide a procedure being performed on the tissue.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
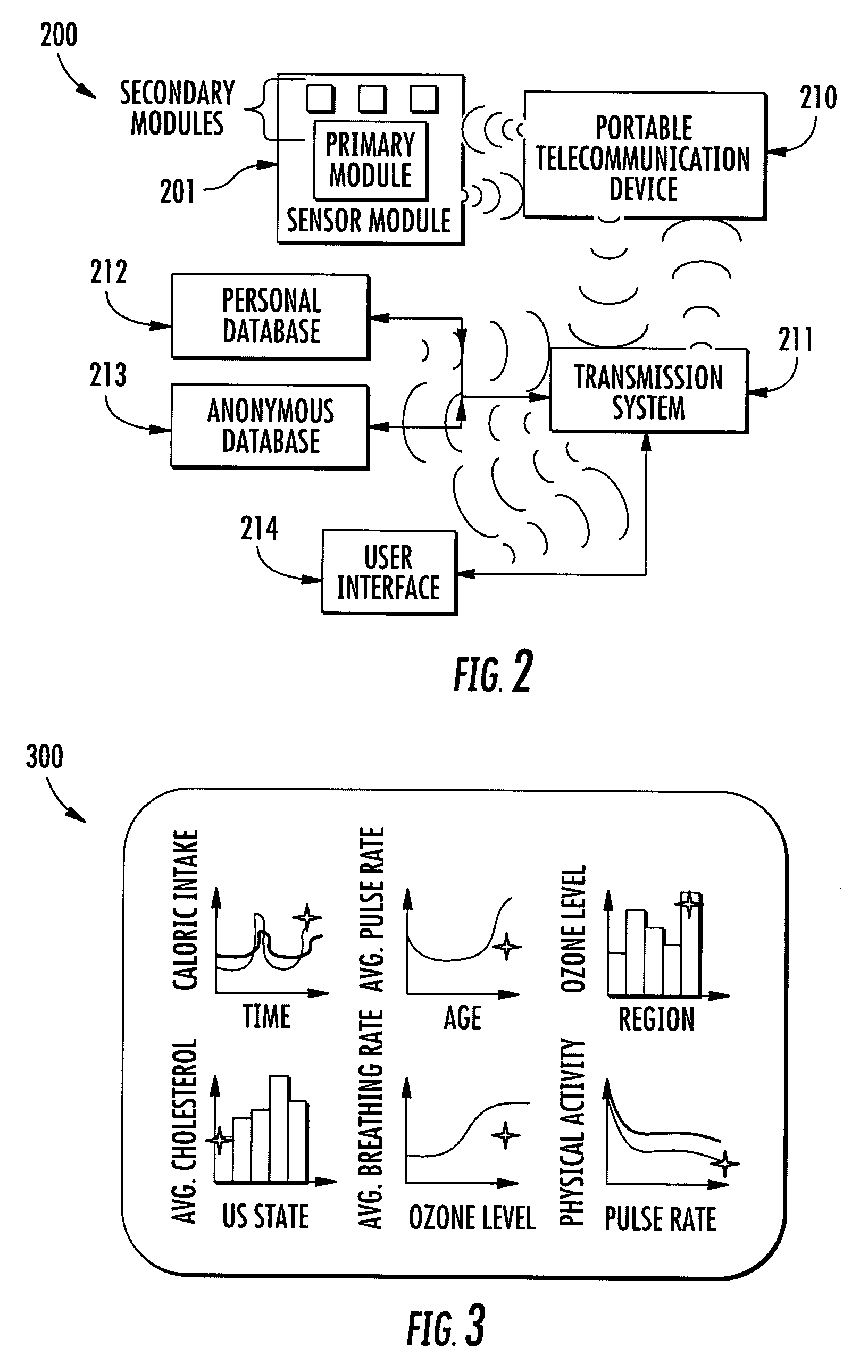
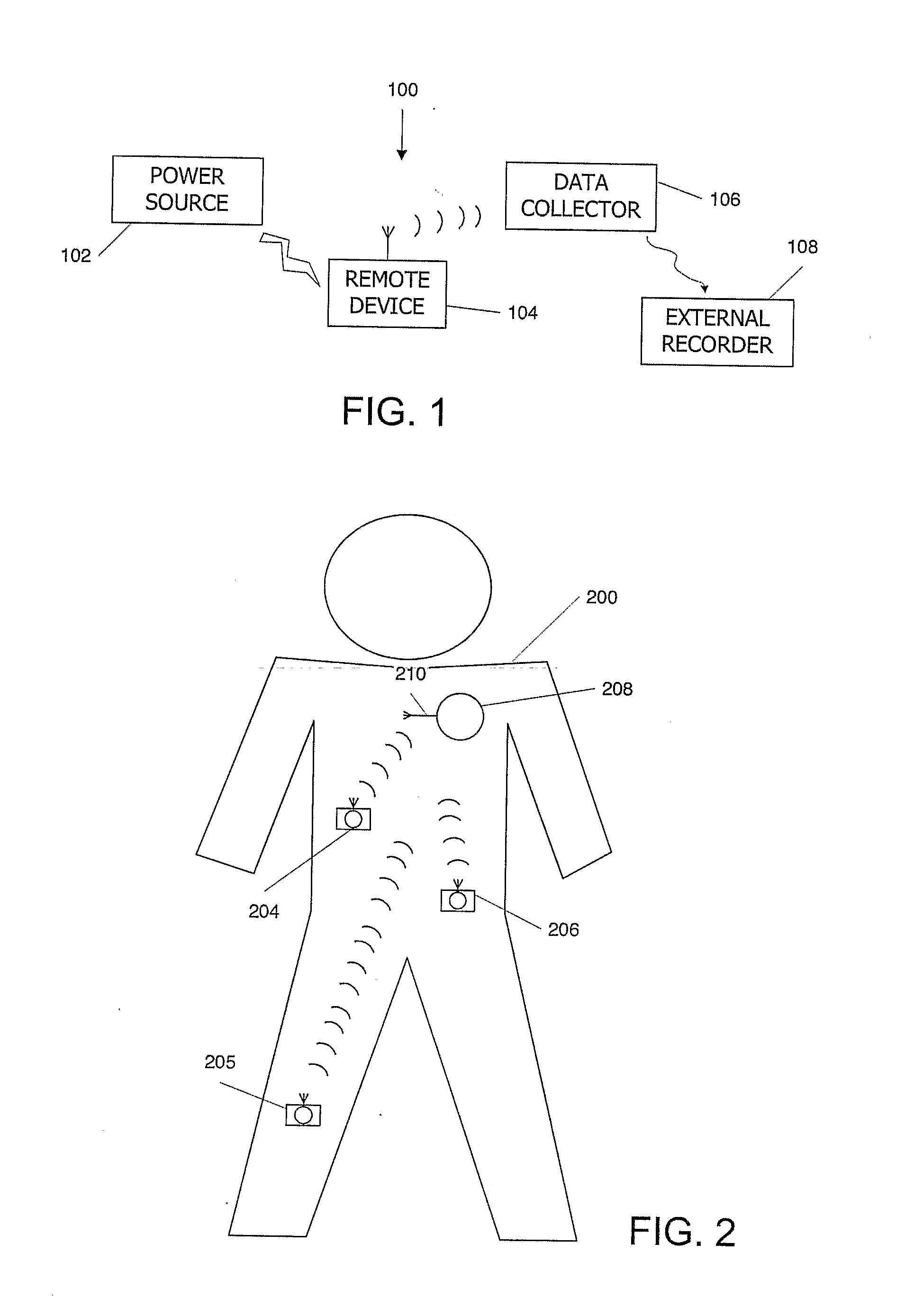
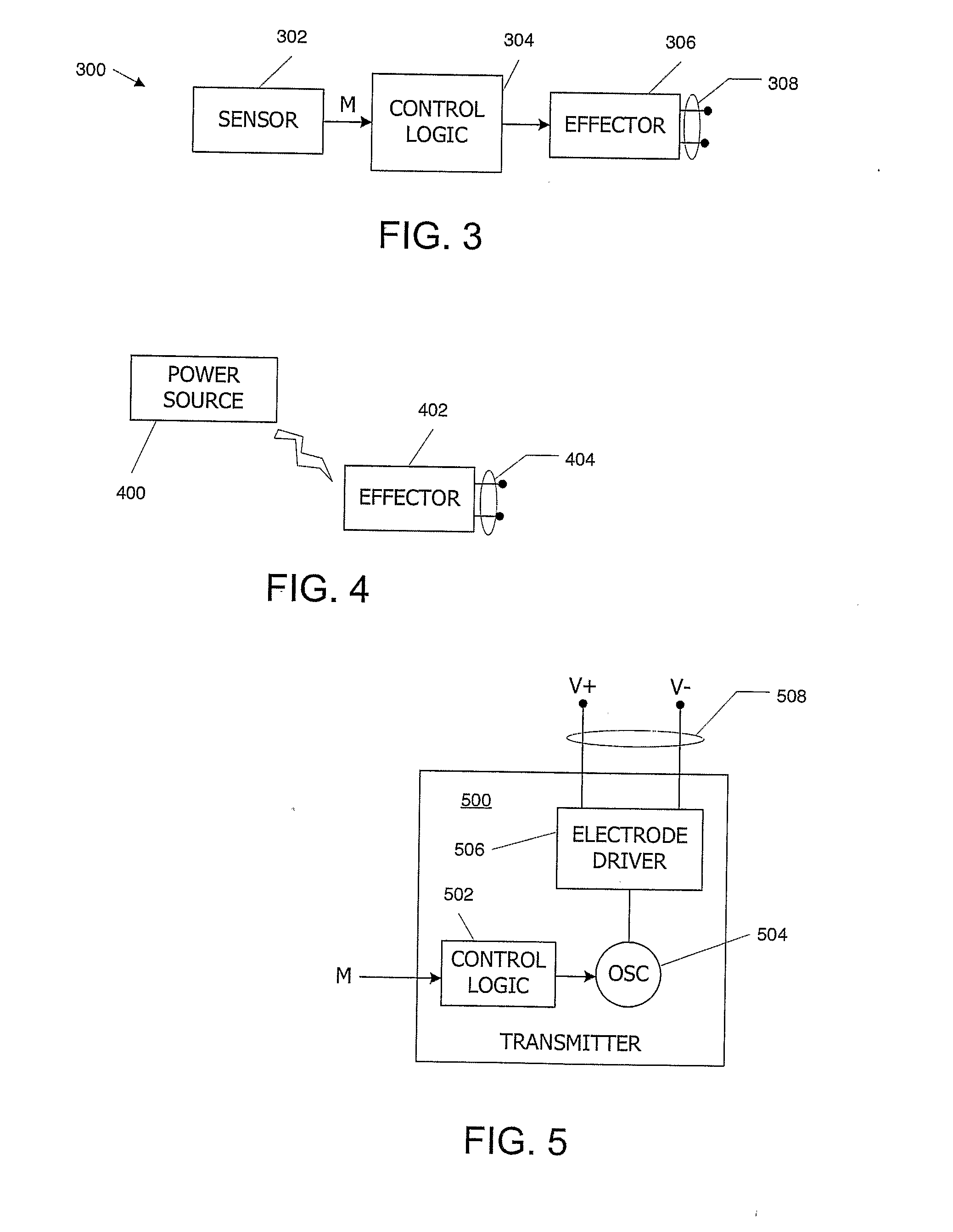
Telemetric apparatus for health and environmental monitoring
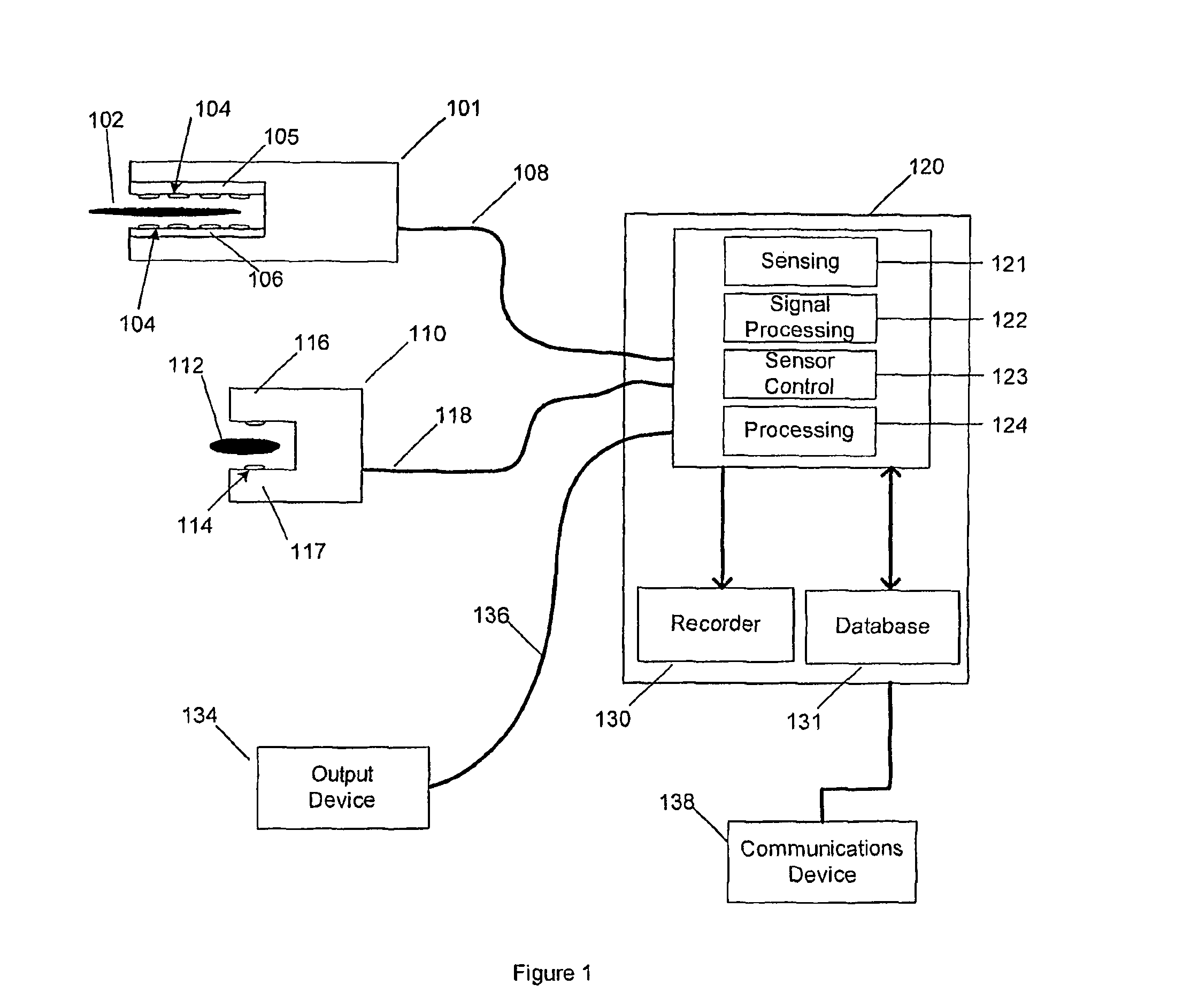
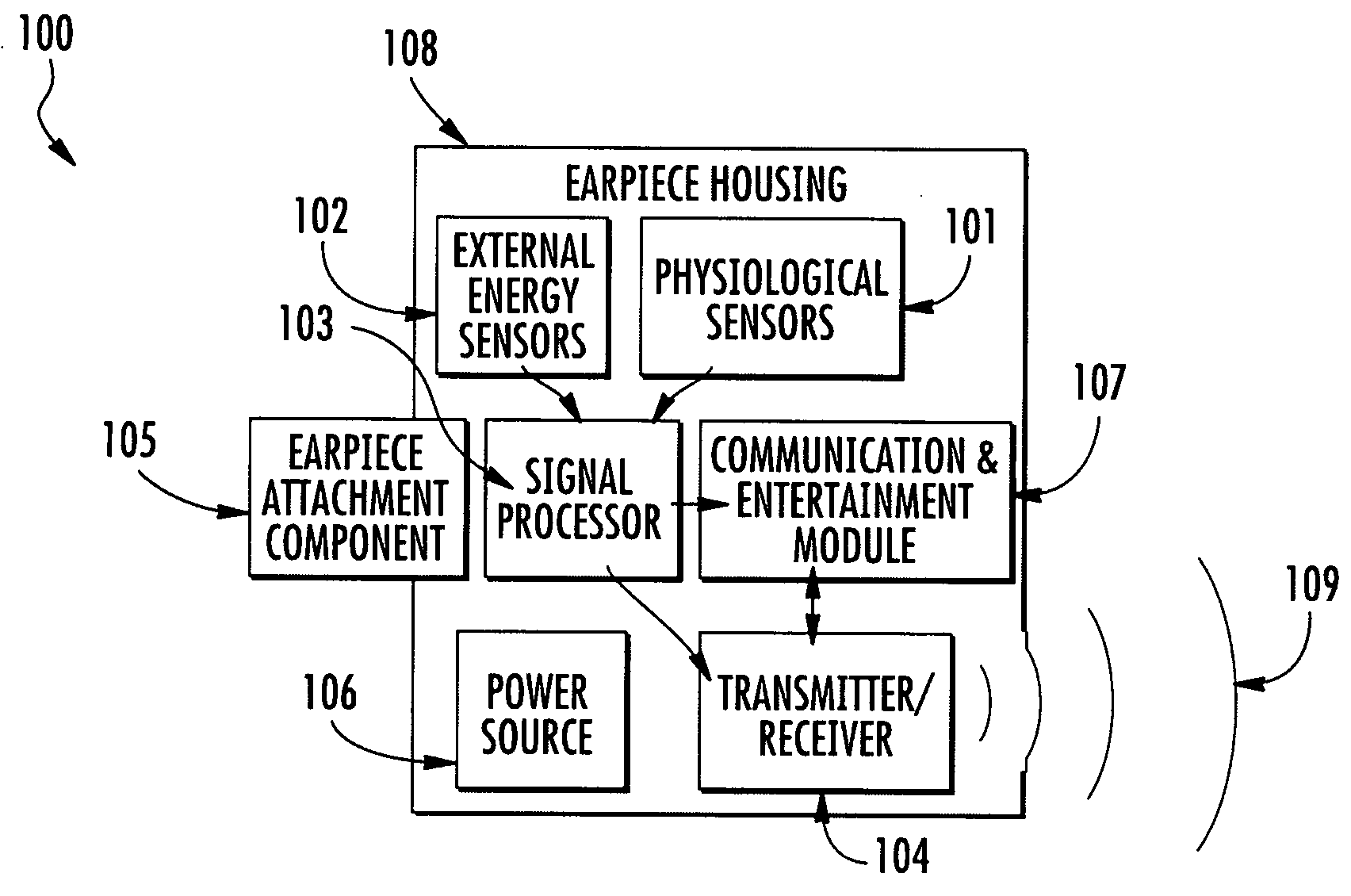
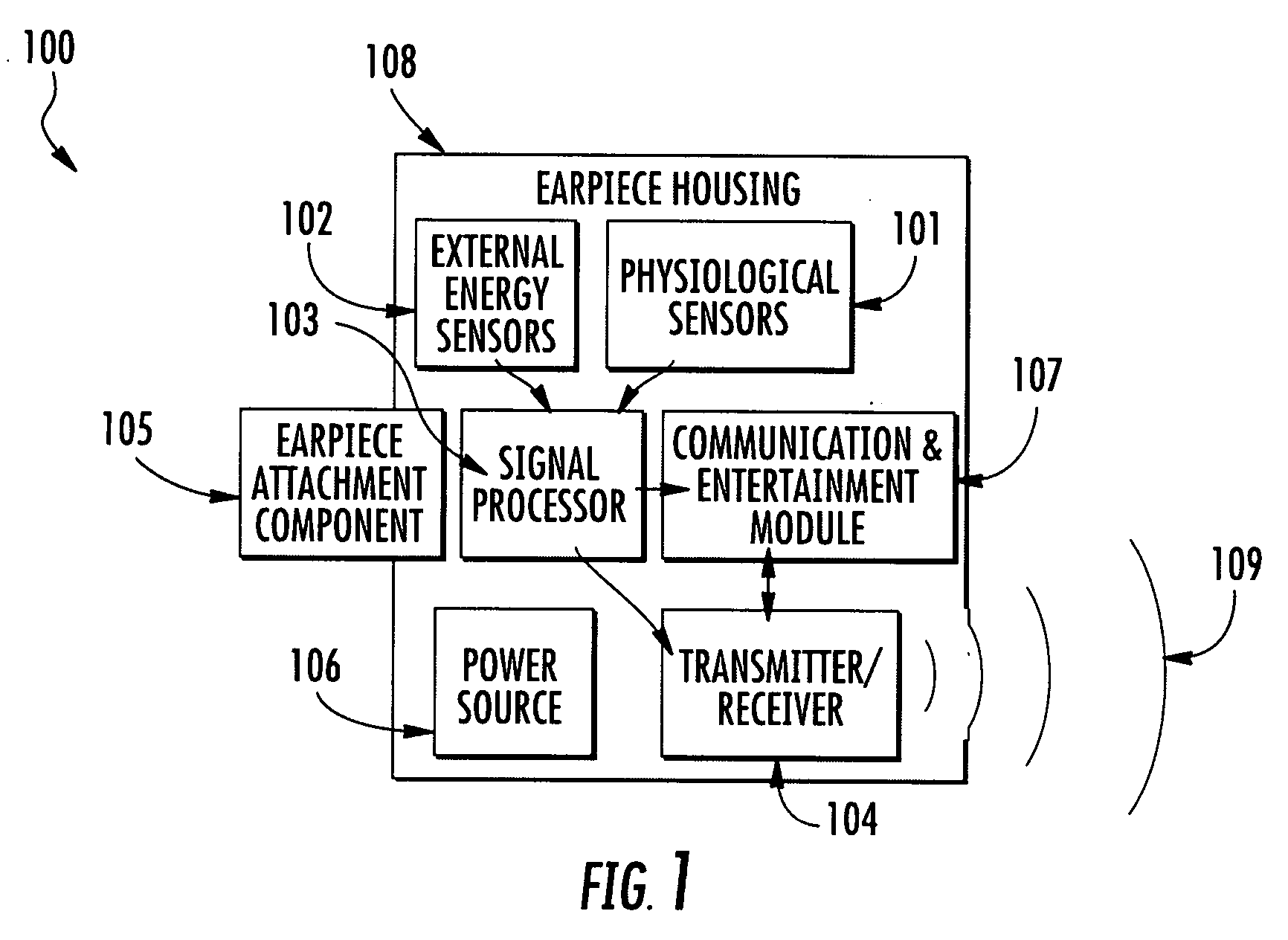
Wearable apparatus for monitoring various physiological and environmental factors are provided. Real-time, noninvasive health and environmental monitors include a plurality of compact sensors integrated within small, low-profile devices, such as earpiece modules. Physiological and environmental data is collected and wirelessly transmitted into a wireless network, where the data is stored and / or processed.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
Surgical instrument with detection sensors
Aspects of the present disclosure are presented for a surgical instrument having one or more sensors at or a near an end effector and configured to aide in the detection of tissues and other materials and structures at a surgical site. The detections may then be used to aide in the placement of the end effector and to confirm which objects to operate on, or alternatively, to avoid. Examples of sensors include laser sensors used to employ Doppler shift principles to detect movement of objects at the surgical site, such as blood cells; resistance sensors to detect the presence of metal; monochromatic light sources that allow for different levels of absorption from different types of substances present at the surgical site, and near infrared spectrometers with small form factors.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
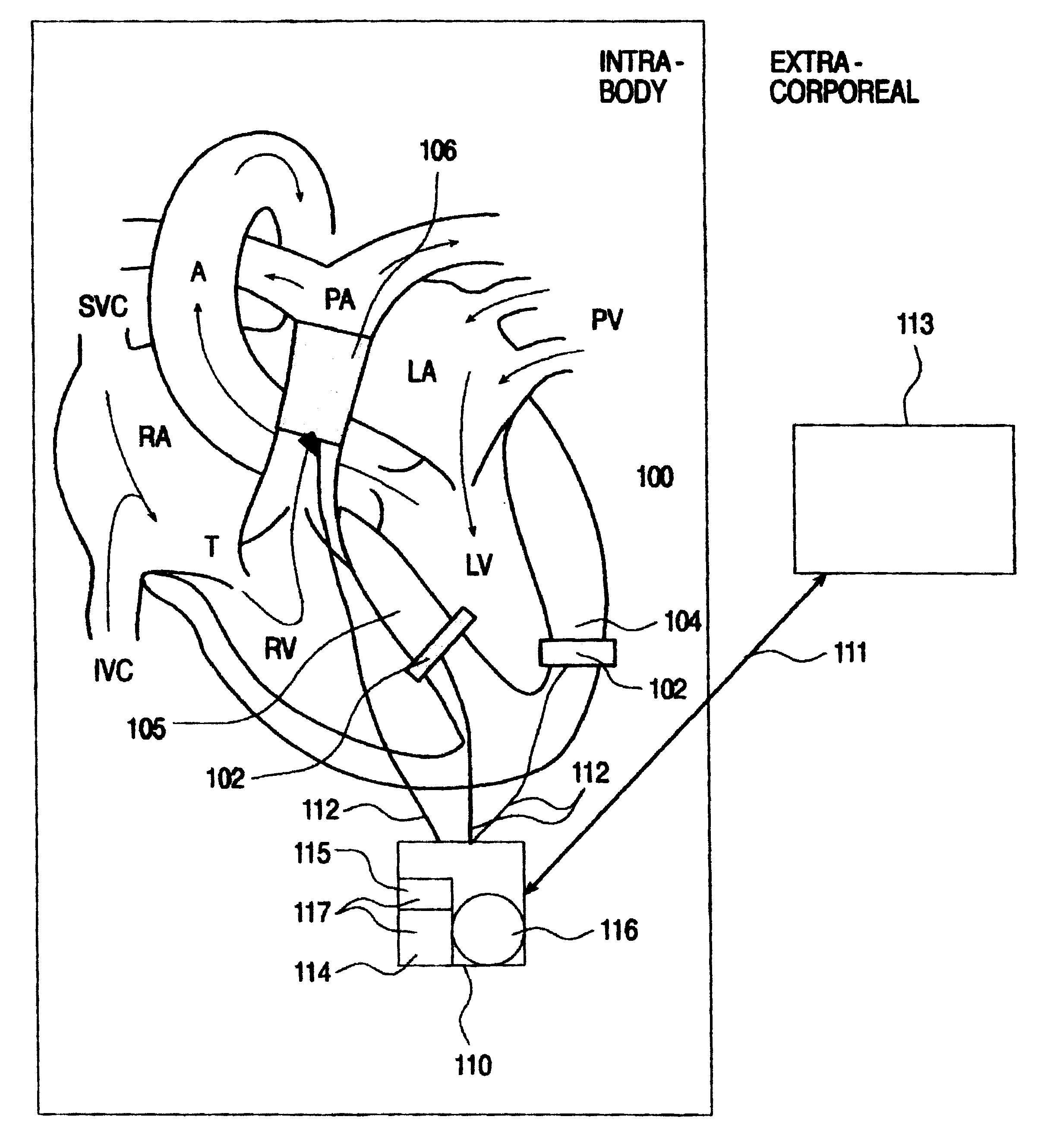
System and method for monitoring a parameter associated with the performance of a heart
An intrabody implantable system for long-term, real time monitoring of at least one parameter associated with heart performance. The system includes (a) a first sensor being implantable within a heart and being for collecting information pertaining to a pressure in a first cavity of the heart; (b) at least one additional sensor being implantable in an blood vessel supporting blood flow into or out of a second cavity of the heart, the at least one additional sensor being for collecting information pertaining to a pressure and a flow within the blood vessel; and (c) at least one device implantable in the body and being in data communication with the first sensor and the at least one additional sensor, the at least one device being for receiving the information pertaining to the pressure in the first cavity of the heart and the information pertaining to the pressure and the flow within the blood vessel and for relaying the information pertaining to the pressure in the first cavity of the heart and the information pertaining to the pressure and the flow within the blood vessel outside the body.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS8560034B1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
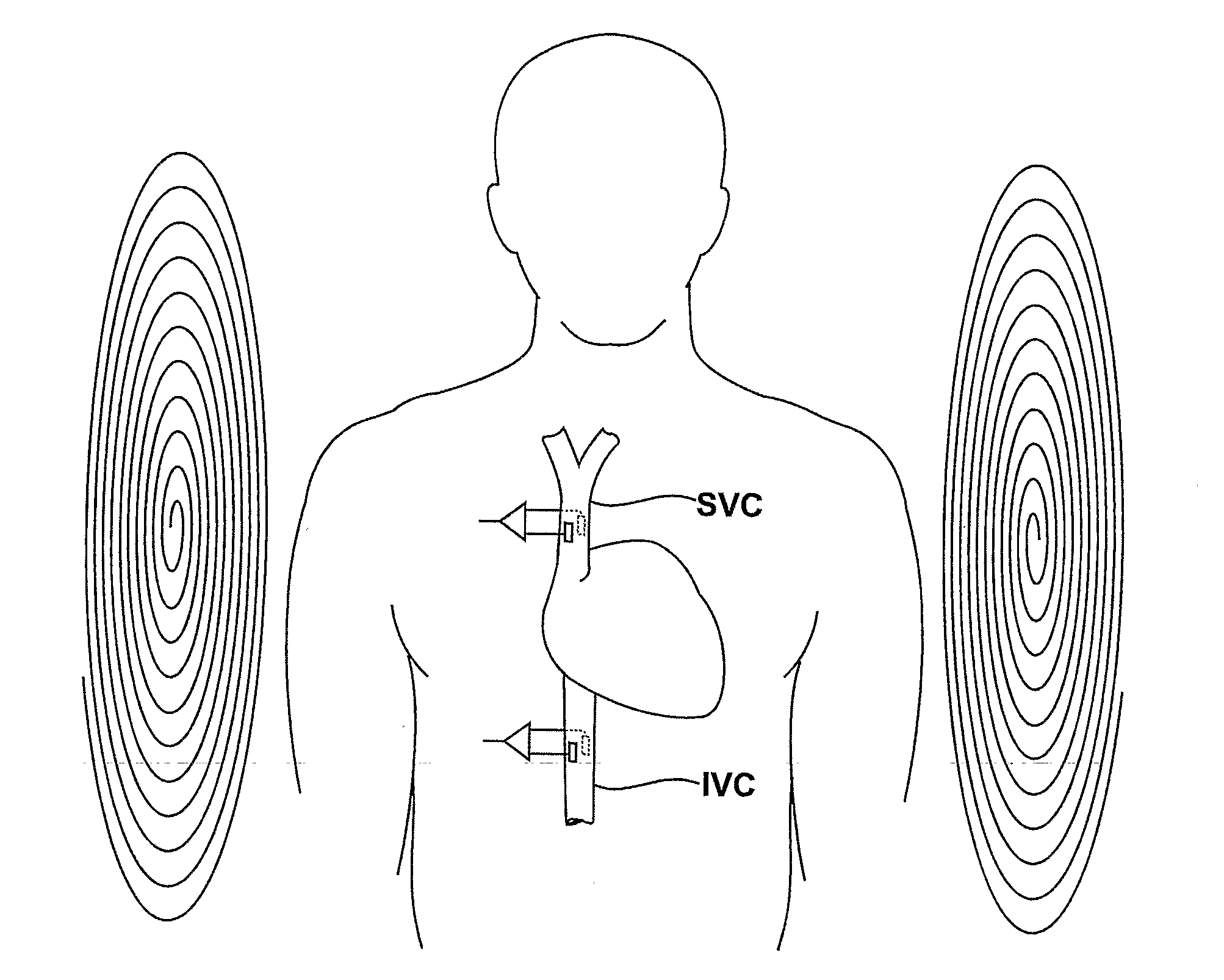
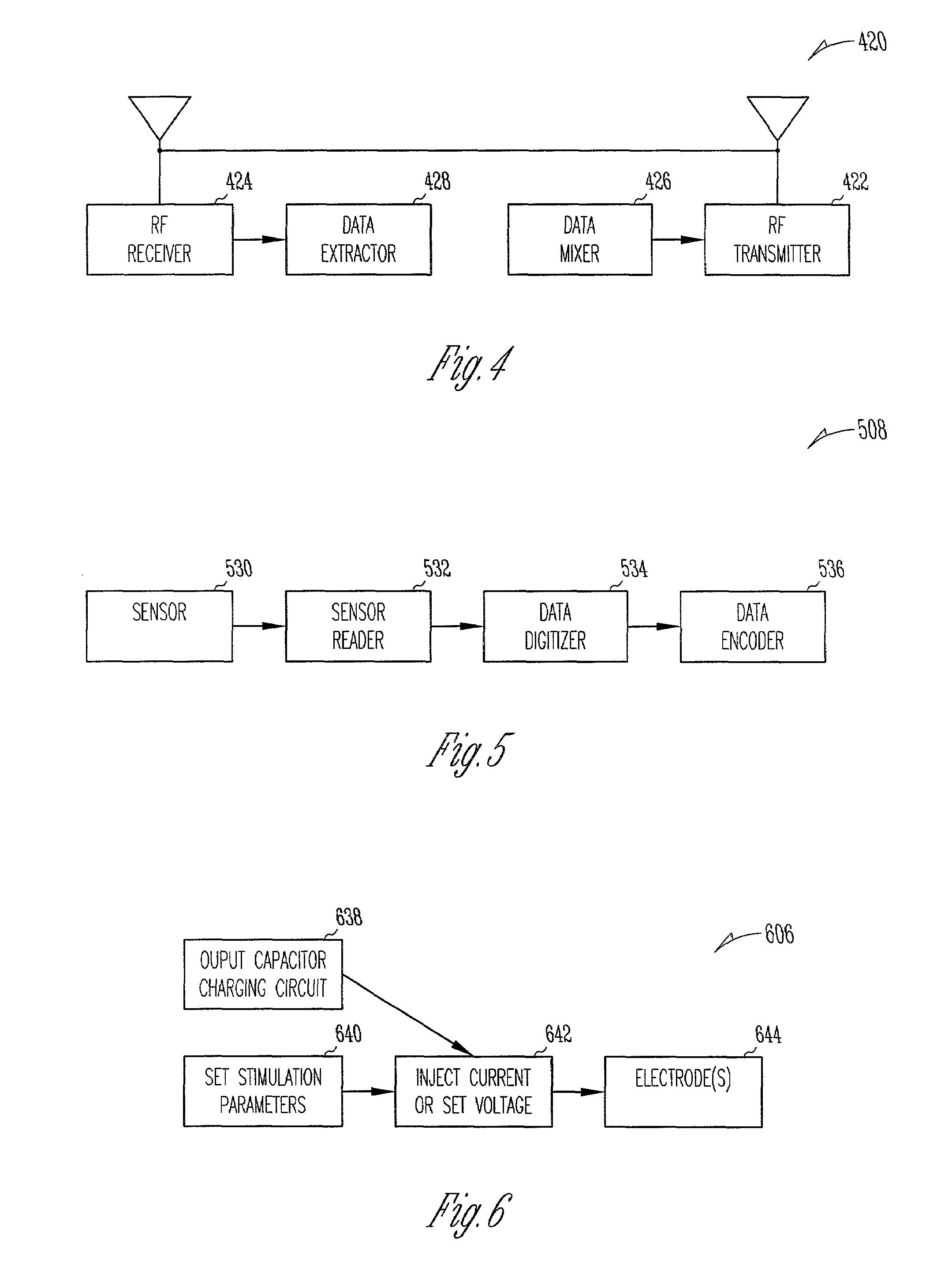
Medical Diagnostic and Treatment Platform Using Near-Field Wireless Communication of Information Within a Patient's Body
ActiveUS20080306359A1Efficient communicationSmall sizeElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit arrangementsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides implantable systems that communicate wirelessly with each other using a unique format that enables devices configurations and applications heretofore not possible. Embodiments of the present invention provide communication apparatuses and methods for exchanging information with implantable medical devices. In some embodiments, two implantable devices communicate with each other using quasi-electrostatic signal transmission in a long wavelength / low frequency electromagnetic band, with the patient's body acting as a conductive medium.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
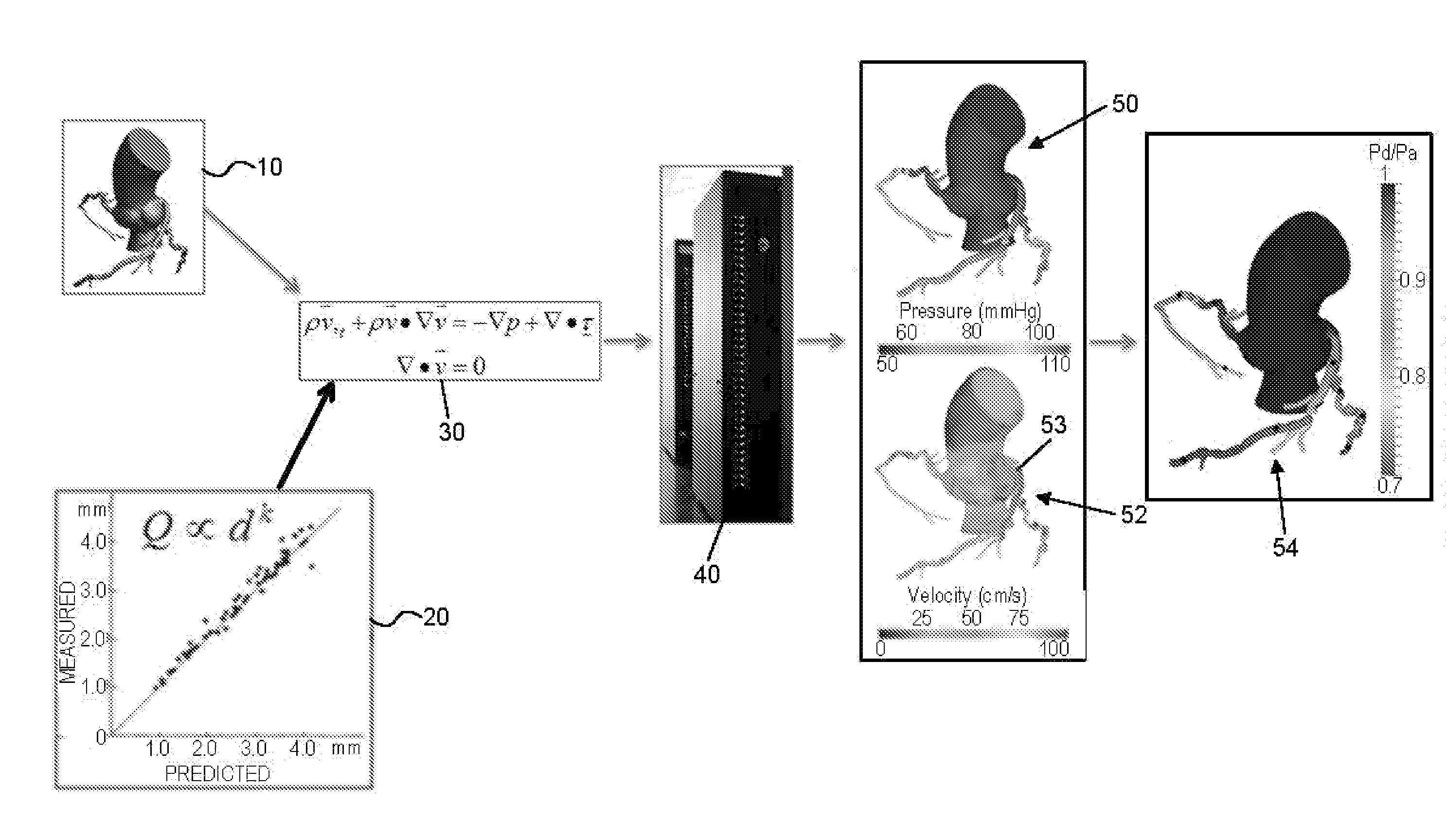
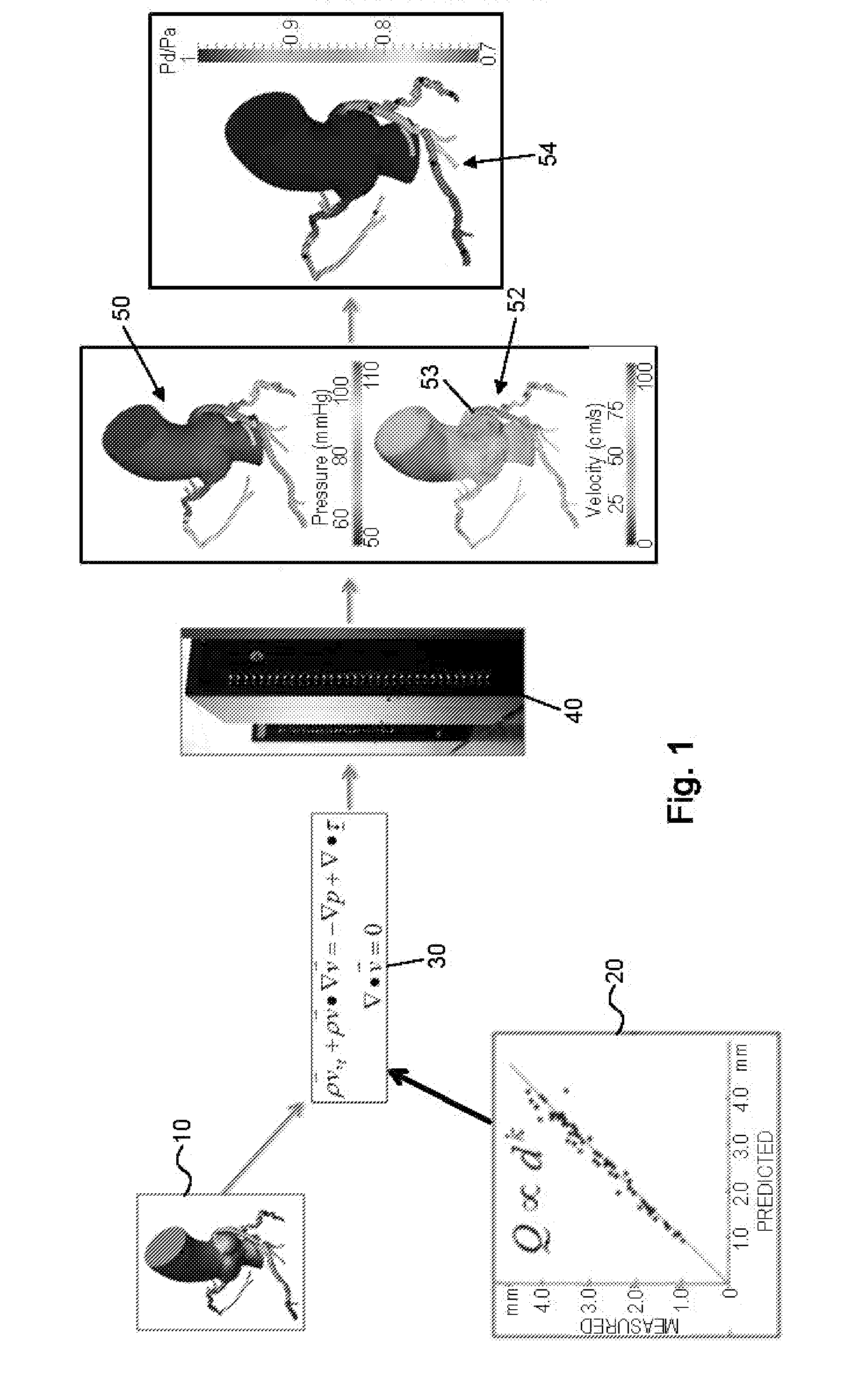
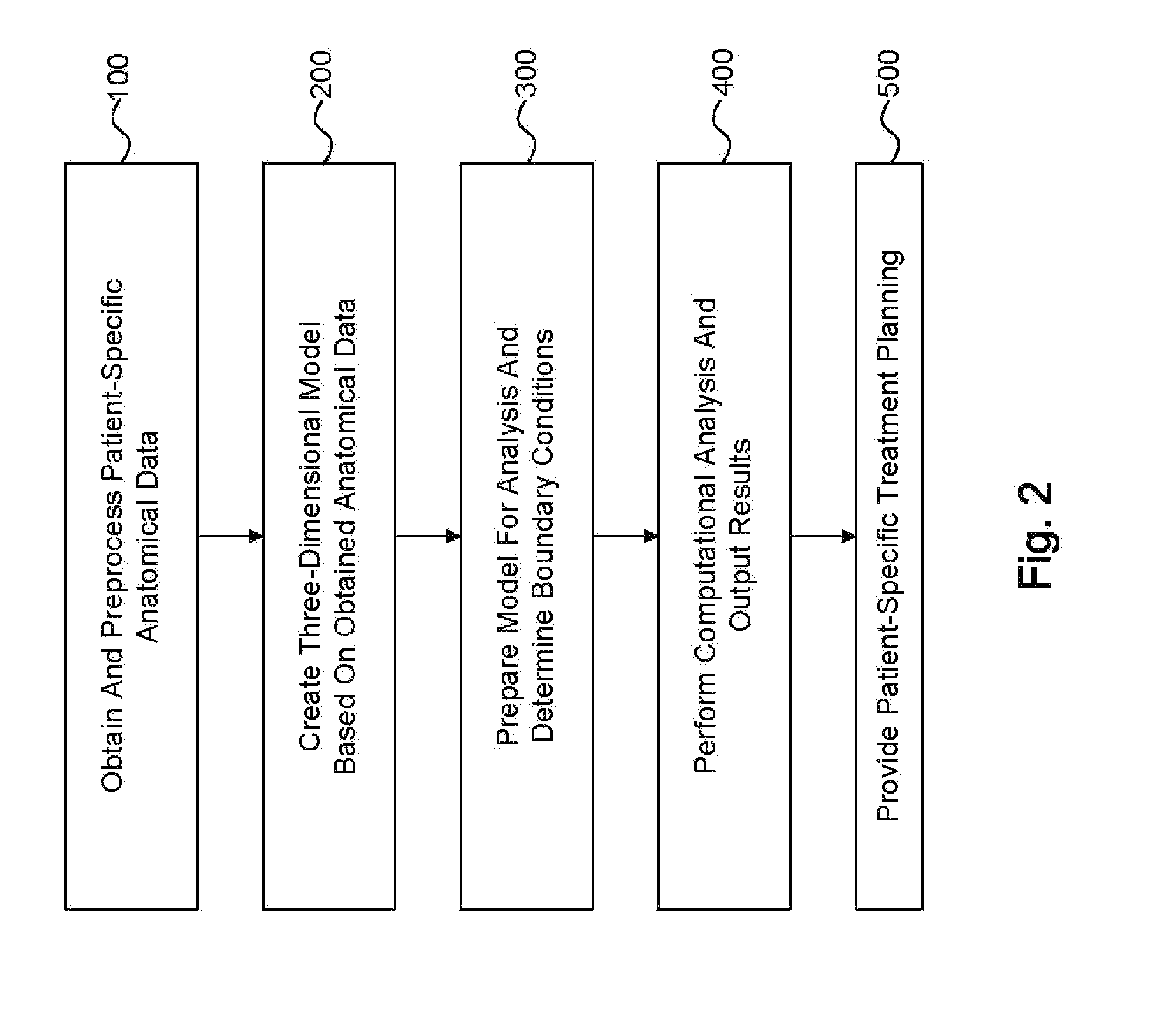
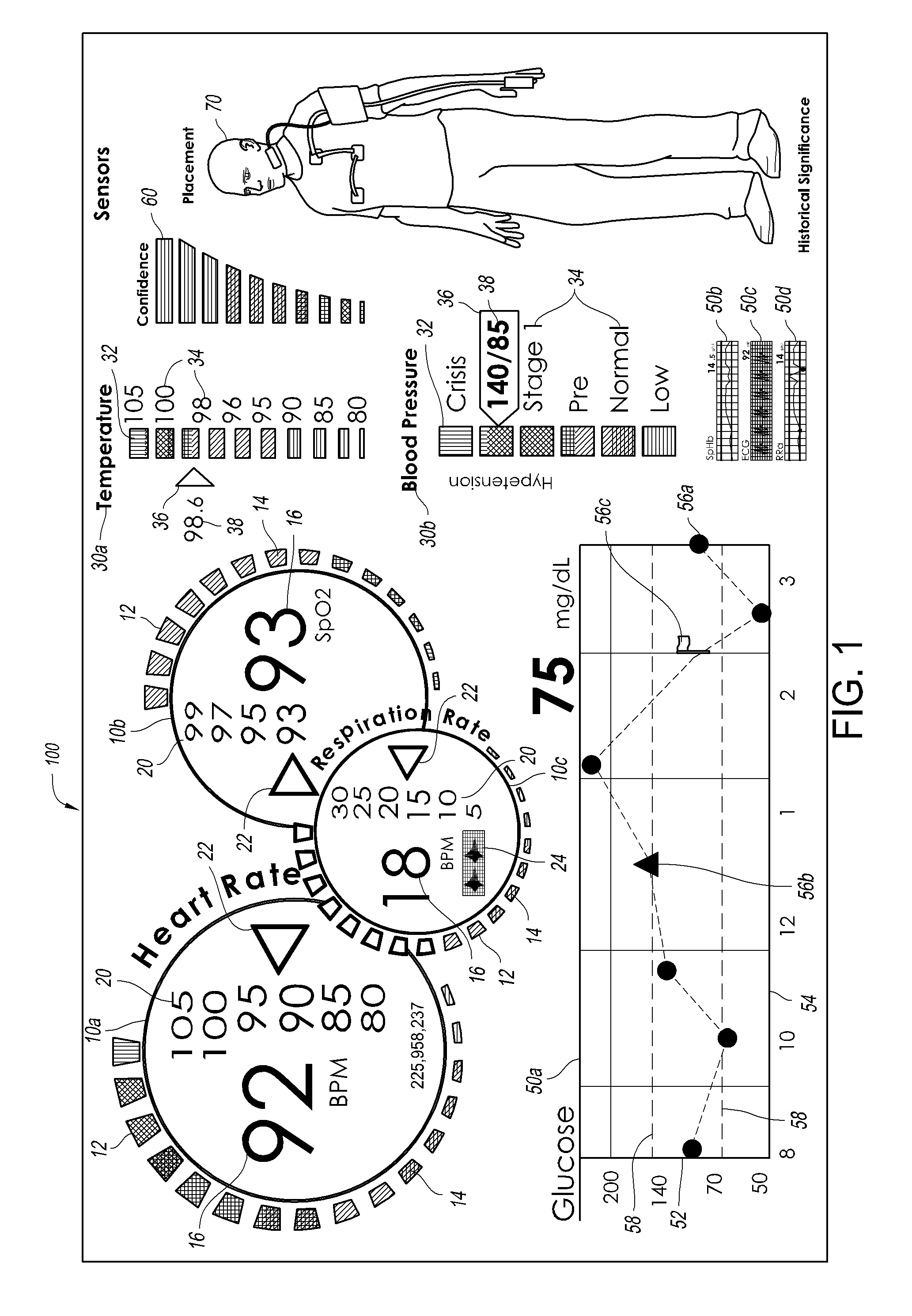
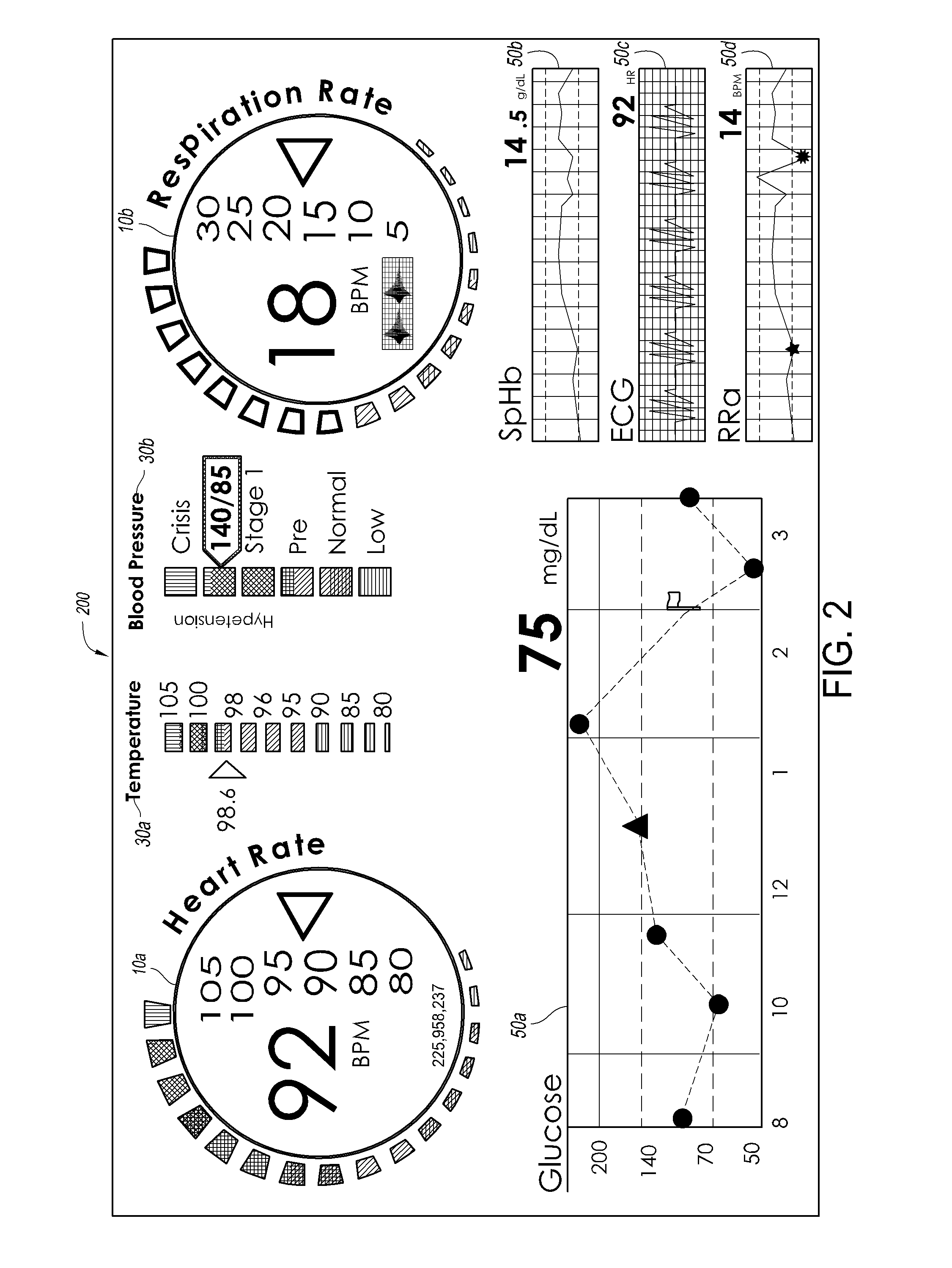
Method and system for patient-specific modeling of blood flow
Embodiments include a system for determining cardiovascular information for a patient. The system may include at least one computer system configured to receive patient-specific data regarding a geometry of the patient's heart, and create a three-dimensional model representing at least a portion of the patient's heart based on the patient-specific data. The at least one computer system may be further configured to create a physics-based model relating to a blood flow characteristic of the patient's heart and determine a fractional flow reserve within the patient's heart based on the three-dimensional model and the physics-based model.
Owner:HEARTFLOW
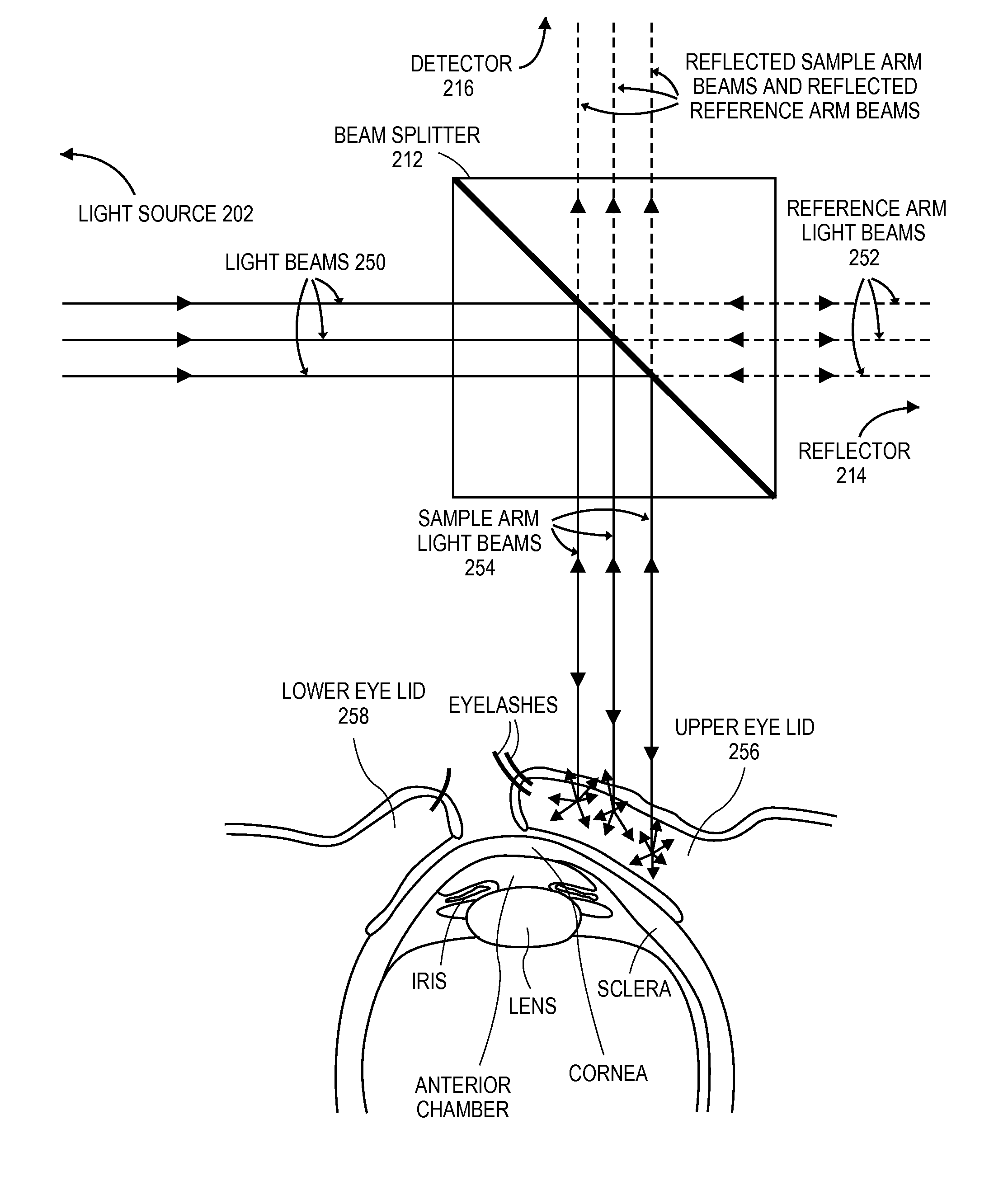
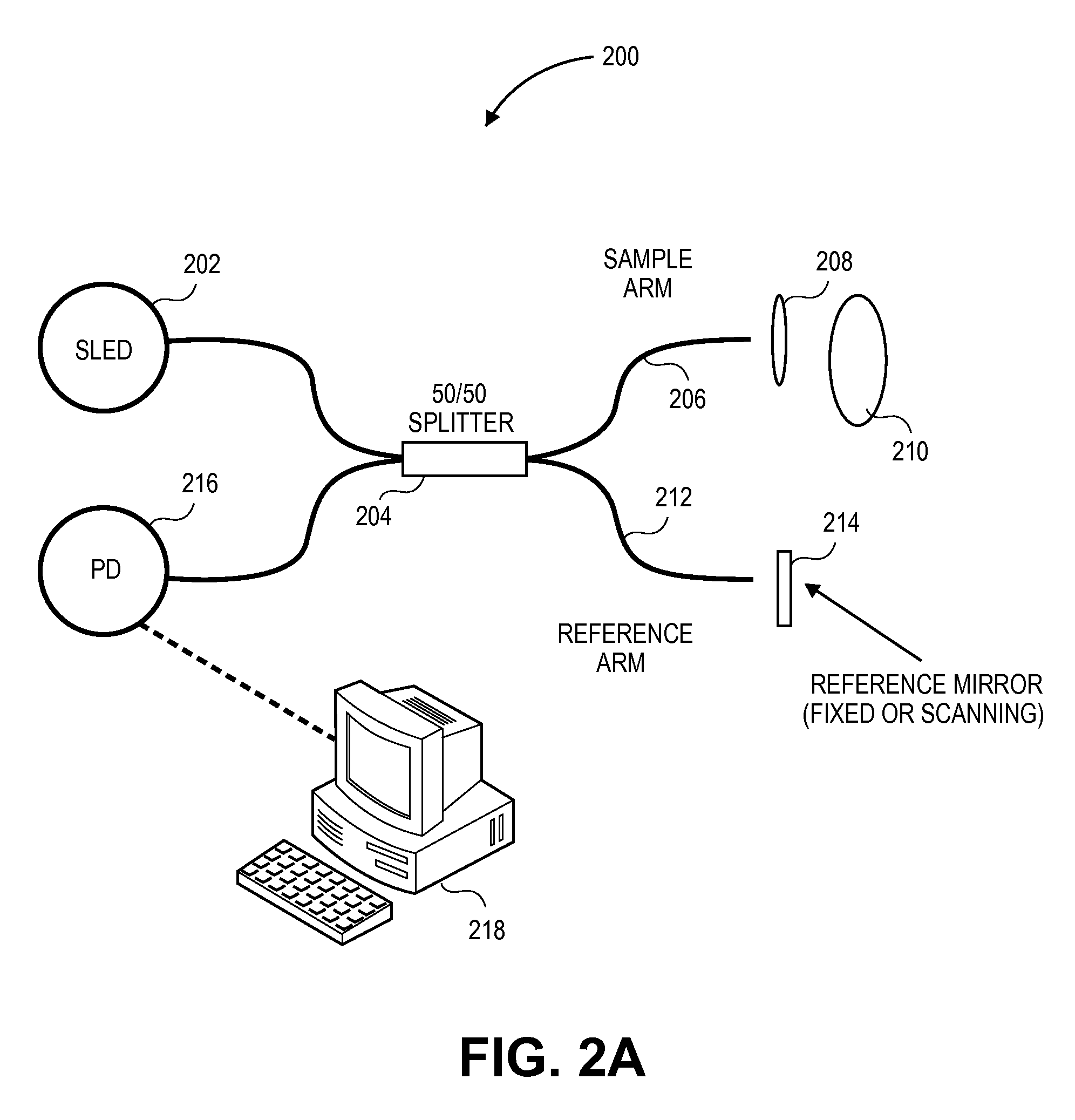
Patient monitor for monitoring microcirculation
A patient monitor capable of measuring microcirculation at a tissue site includes a light source, a beam splitter, a photodetector and a patient monitor. Light emitted from the light source is split into a reference arm and a sample arm. The light in the sample arm is directed at a tissue site, such as an eyelid. The reflected light from the tissue site is interfered with the light from the reference arm. The photodetector measures the interference of the light from both the sample arm and the reference arm. The patient monitor uses the measurements from the photodetector to calculate the oxygen saturation at the tissue site and monitor the microcirculation at the tissue site.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
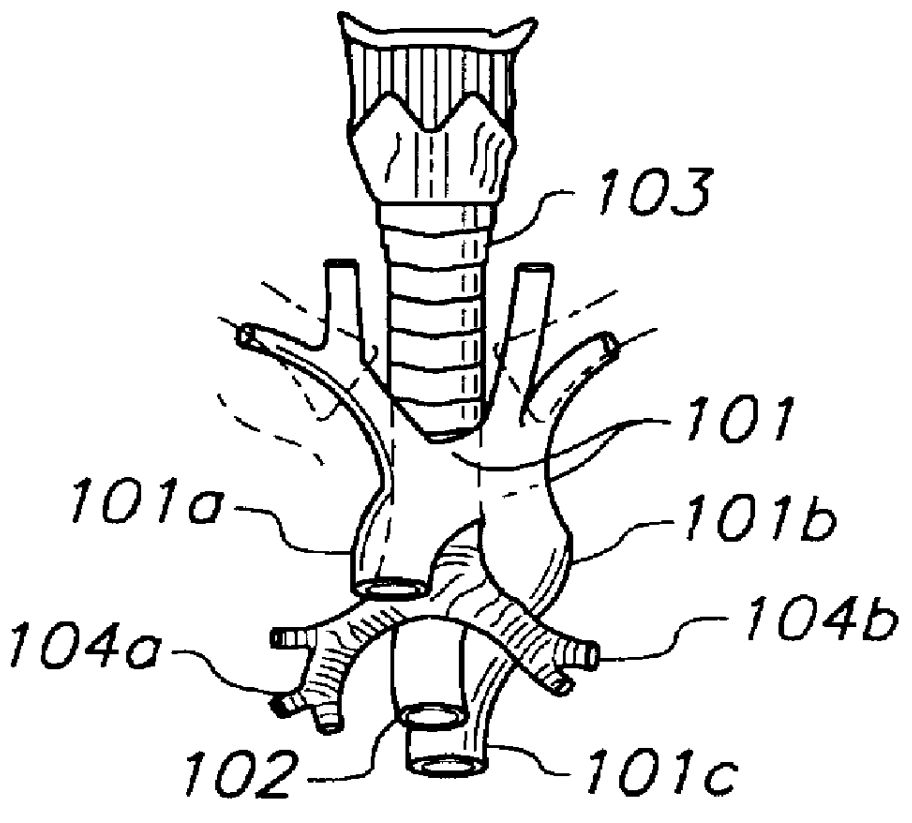
Apparatus and methods of bioelectrical impedance analysis of blood flow
InactiveUS6095987AAccurately and non-invasively and continuously measuring cardiac outputCatheterSensorsBioelectrical impedance analysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus and methods are provided for monitoring cardiac output using bioelectrical impedance techniques in which first and second electrodes are placed in the trachea and / or bronchus in the vicinity of the ascending aorta, while an excitation current is injected into the thorax via first and second current electrodes, so that bioelectrical impedance measurements based on the voltage drop sensed by the first and second electrodes reflect voltage changes induced primarily by blood flow dynamics, rather than respiratory or non-cardiac related physiological effects. Additional sense electrodes may be provided, either internally, or externally, for which bioelectrical impedance values may be obtained. Methods are provided for computing cardiac output from bioelectrical impedance values. Apparatus and methods are also provided so that the measured cardiac output may be used to control administration of intravenous fluids to an organism or to optimize a heart rate controlled by a pacemaker.
Owner:ECOM MED
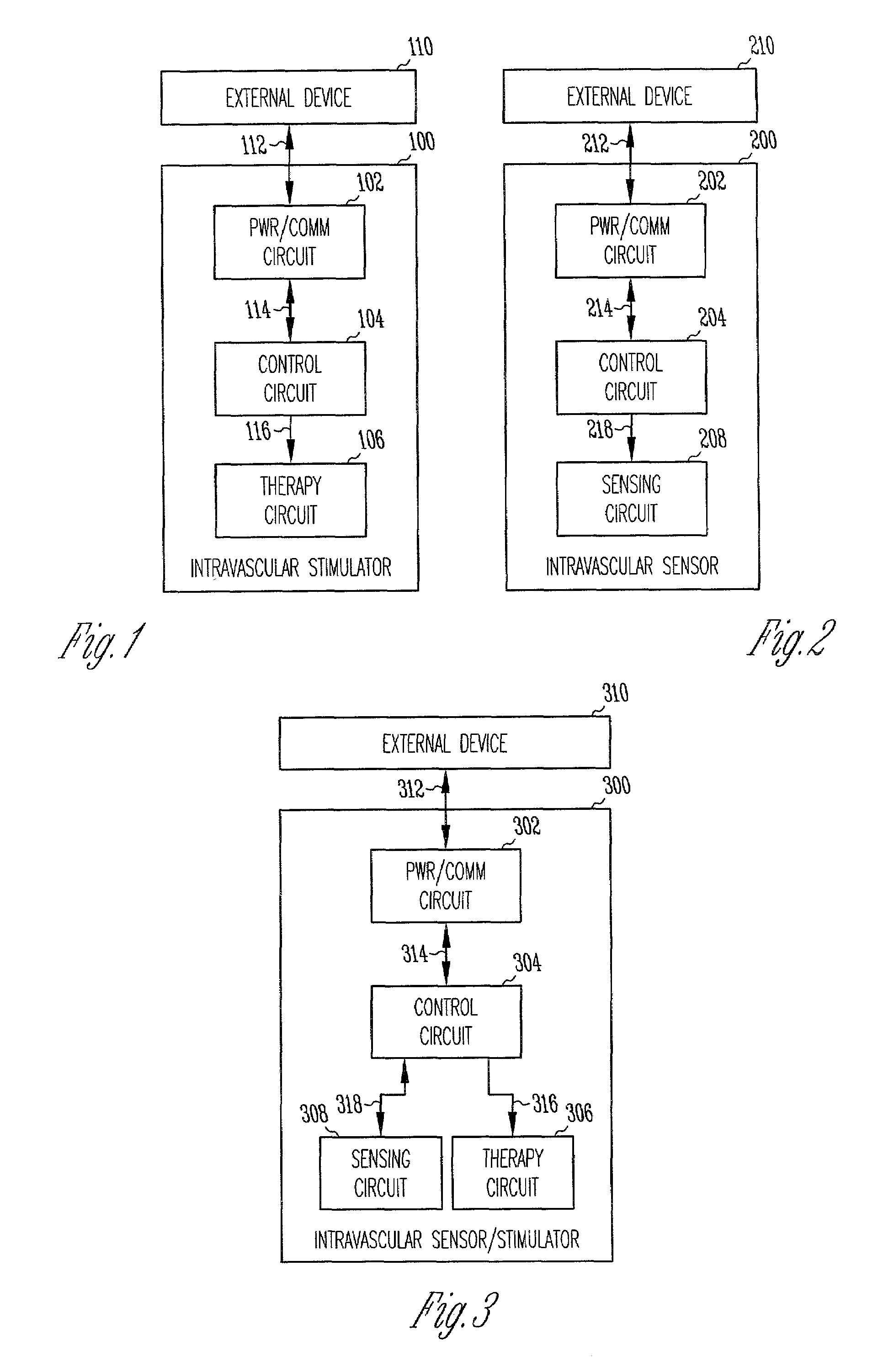
Chronically-implanted device for sensing and therapy
InactiveUS7236821B2Easy to solvePrevent restenosisStentsEndoradiosondesElectricityTherapeutic Devices
Systems, devices and methods are provided for providing sensing and therapy functions using a chronically-implanted device. According to one embodiment, the device includes a structure adapted to be chronically placed within a biosystem, and further includes sensing circuitry and therapy-providing circuitry attached to the structure. The sensing circuitry is adapted to sense mechanical parameters in the biosystem. The therapy-providing circuitry is adapted to provide therapy to the biosystem. According to various embodiments of the device, the sensing circuitry is further adapted to sense electrical and / or chemical parameters in the biosystem, and / or is adapted to provide electrical therapy and / or to provide drug-eluting therapy. One embodiment of the device includes a stent-like structure adapted to be chronically placed intravascularly in the biosystem.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
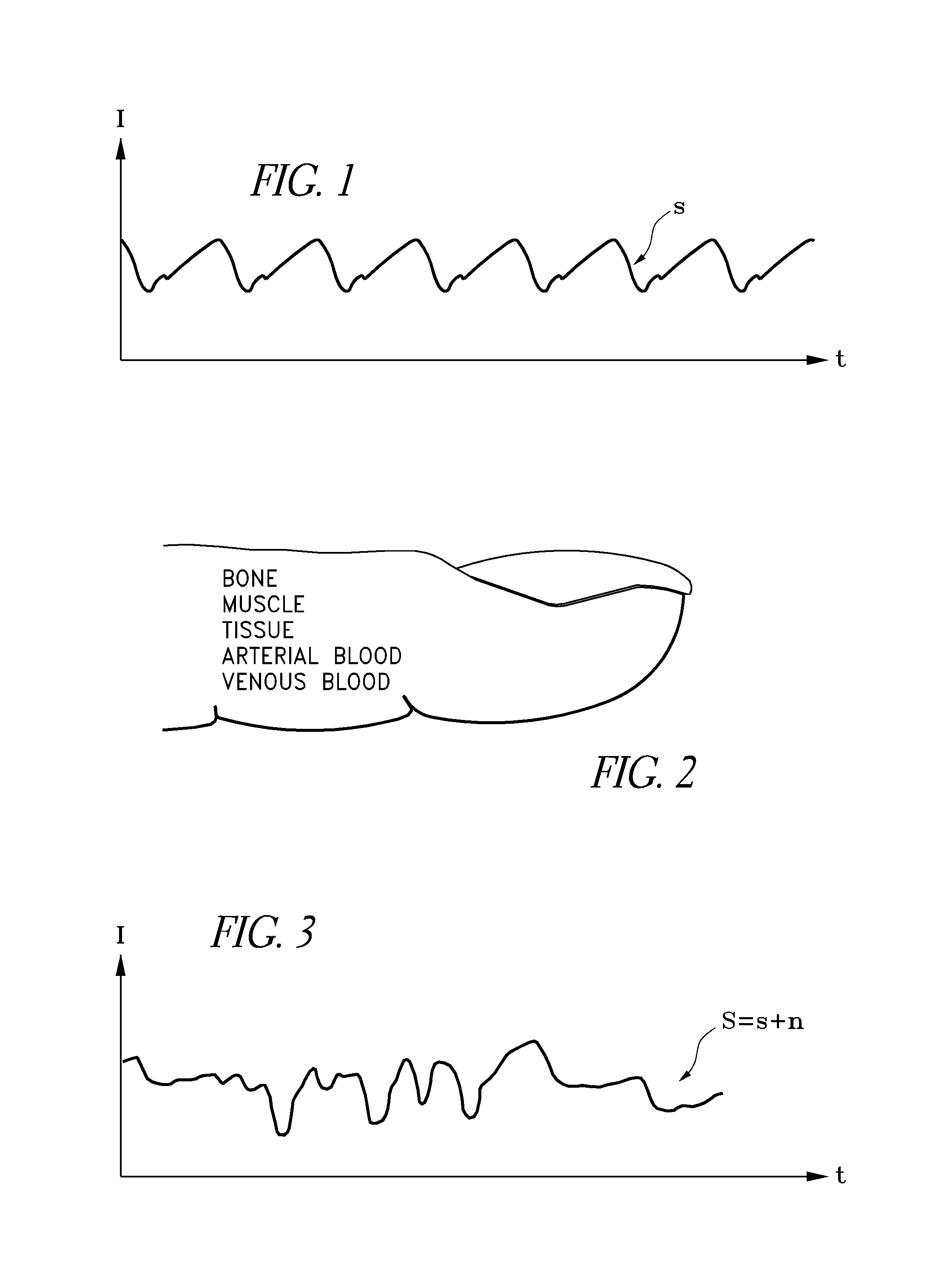
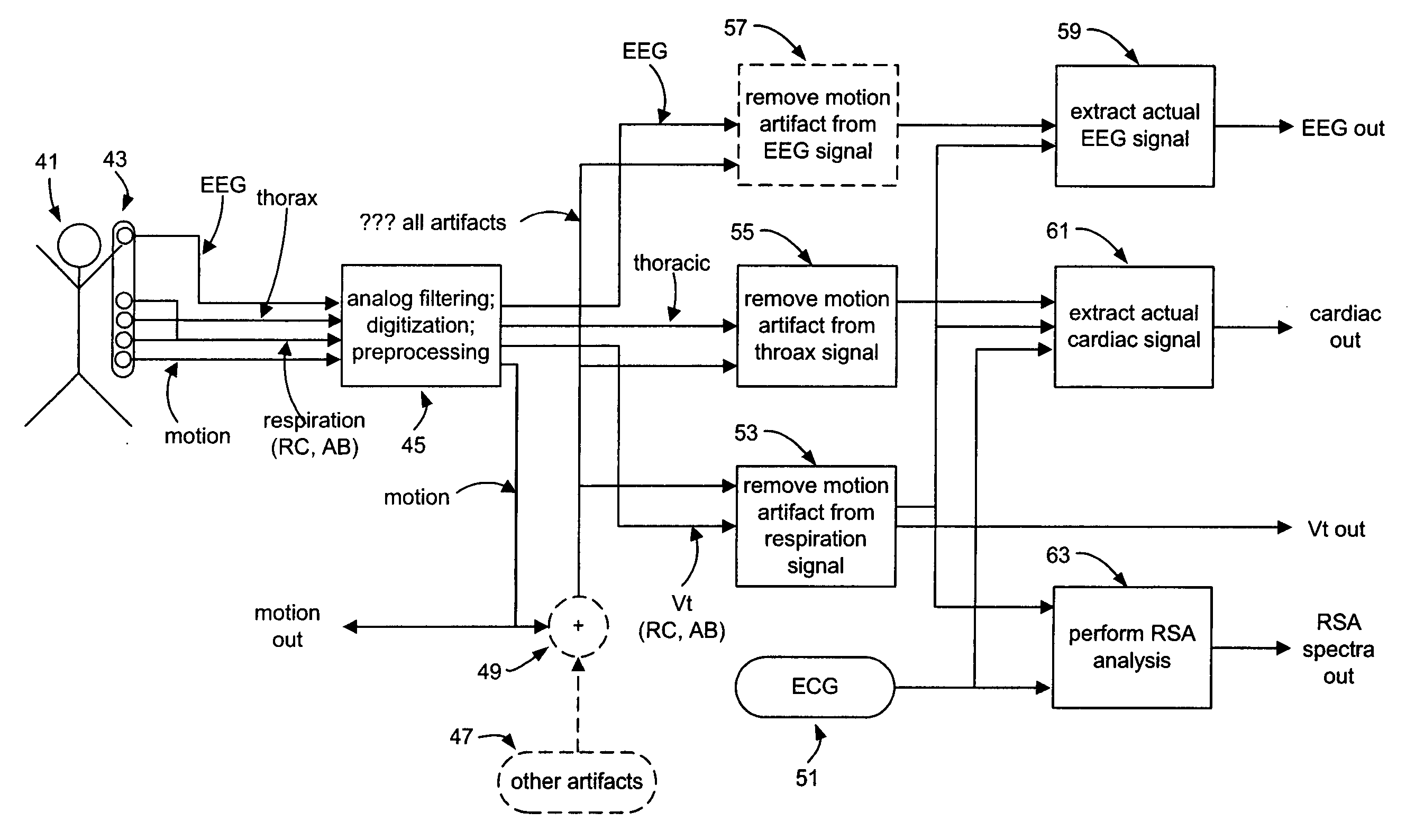
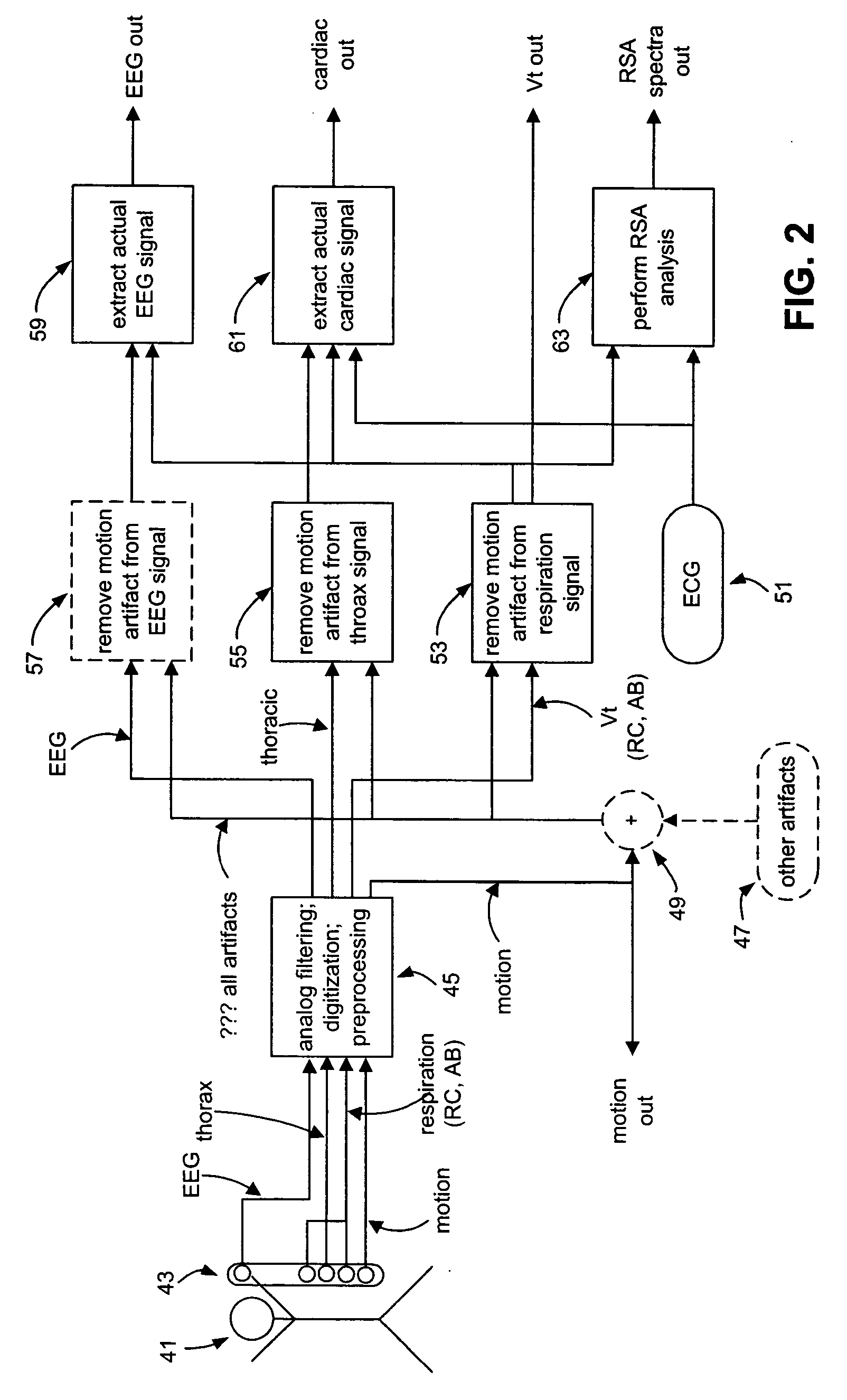
Method and system for processing data from ambulatory physiological monitoring
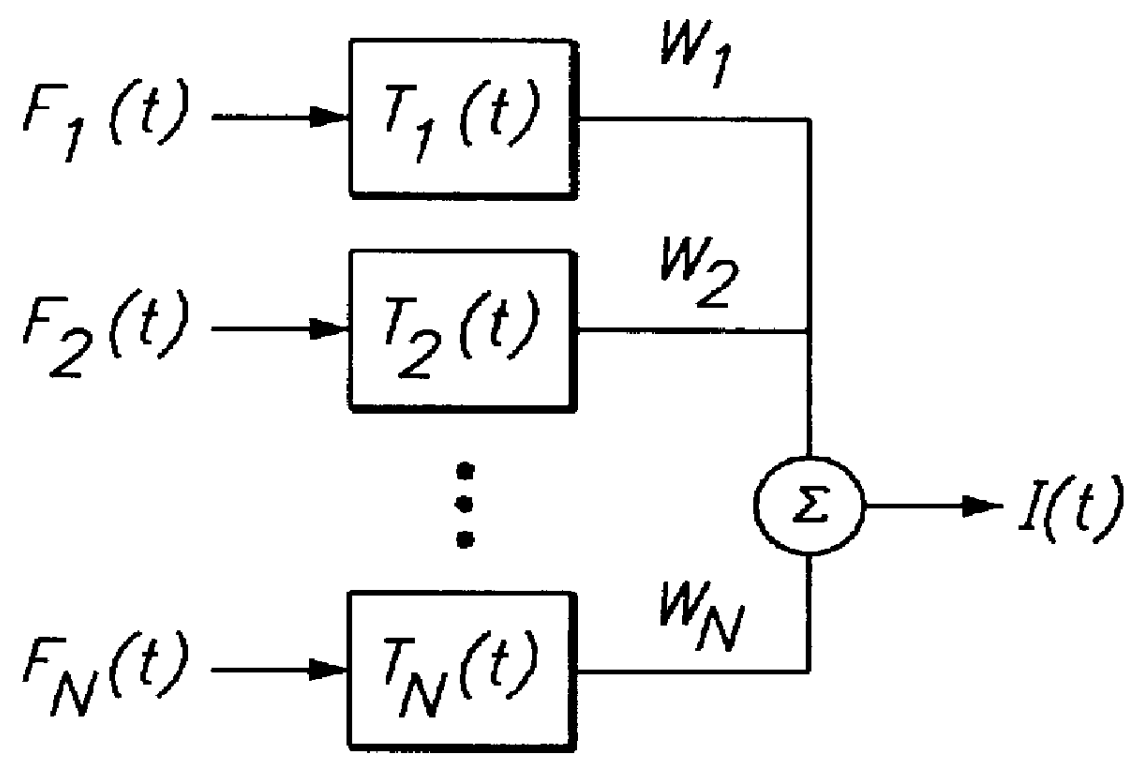
ActiveUS20050240087A1Improved robust and reliable extractionAvoid injuryElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPhysiological monitoringEngineering
This invention provides methods and systems for the analysis of data returned from monitoring multiple physiological parameters of a subject, especially from ambulatory multiple parameter monitoring. The methods and systems remove motion artifacts from signals and separate multiple components of single signals due to two or more physiological systems or processes. Each output signal is are preferably free from motion artifacts and reflects primarily functioning of only a single physiological system or process.
Owner:ADIDAS
Deployment device, system and method for medical implantation
A deployment device for deploying a self-expansible medical implant at a target location in a body cavity, is provided. While generally, the expansion of self-expansible structures tends to be abrupt, and the impact of expansion may cause injury, a two-stage expansion process of the present invention minimizes the impact of exapnsion. Additionally, an ability to manuever the medical imlant into position, after the first stage of expansion, provides for accurate positioning. Thus the present invention is of a deployment device for precise and well-controlled manner of deployment, so as to minimize damage to the cavity wall and to position the implant accurately at the target location. The deployment device includes: an inner tube; an outer tube; and an implant received on the inner tube and enclosed by the outer tube. The implant has a self-expansible anchoring element which is in a contracted condition when enclosed by the outer tube, expands to a partially-expanded condition when the outer tube is retracted, and expands to a fully-expanded condition when the inner tube is removed.. The implant is deployed by introducing the deployment device to the target location in the body cavity; retracting the outer tube with respect to the implant such that the anchoring element self-expands from its contracted condition to its partially-expanded condition; and withdrawing the inner tube from the implant such that the anchoring element self-expands from its partially-expanded condition to its fully-expanded condition to firmly fix the implant at the target location within the body cavity.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
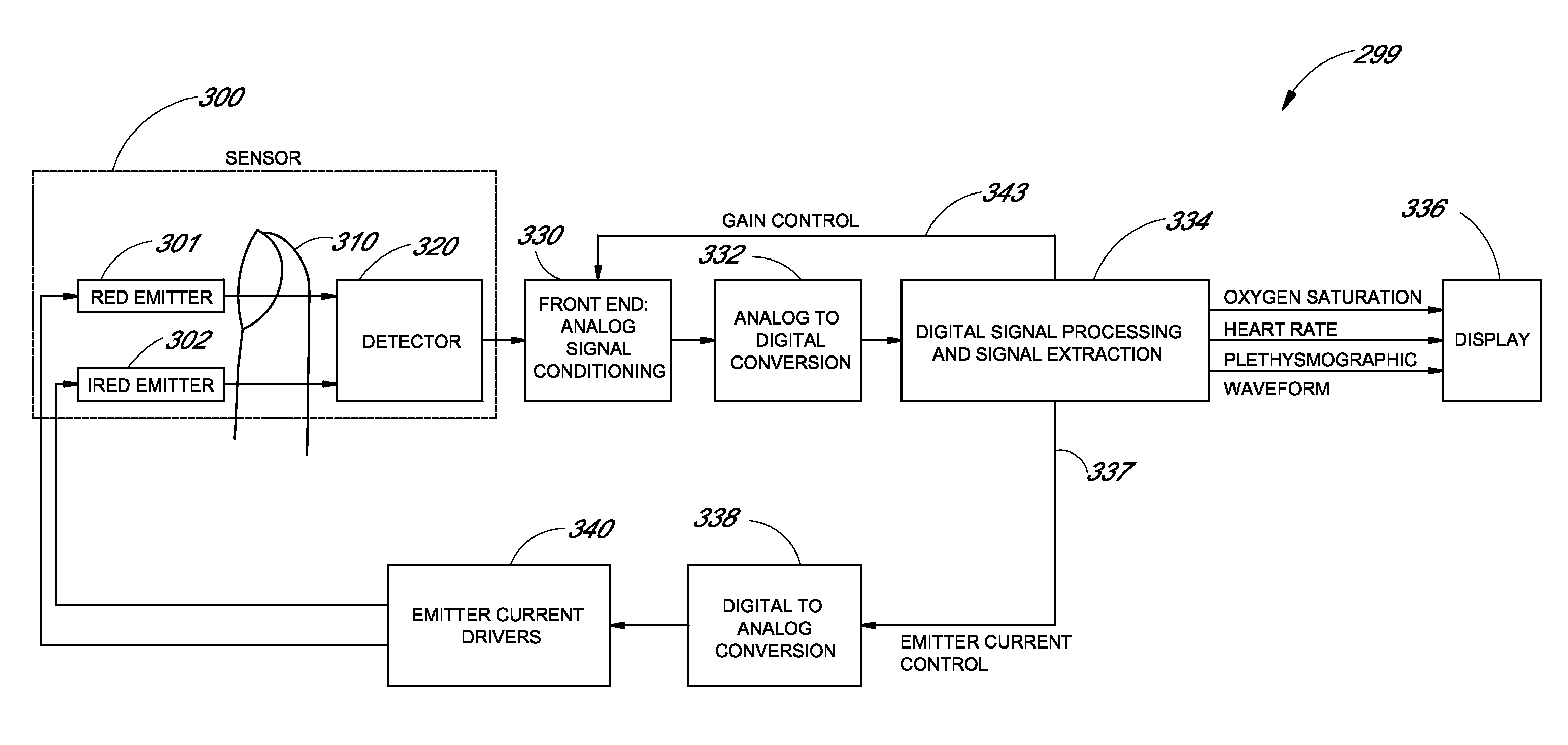
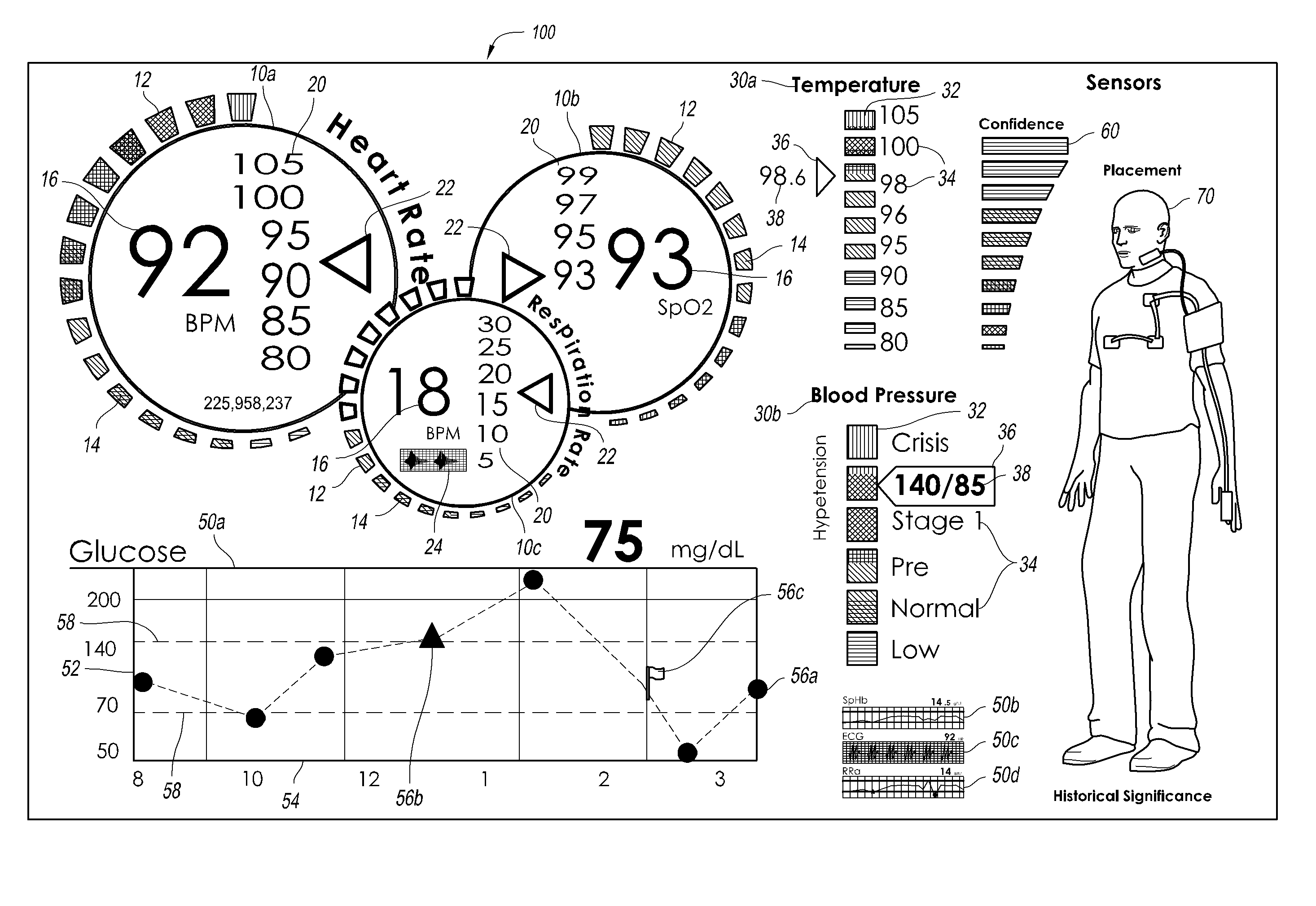
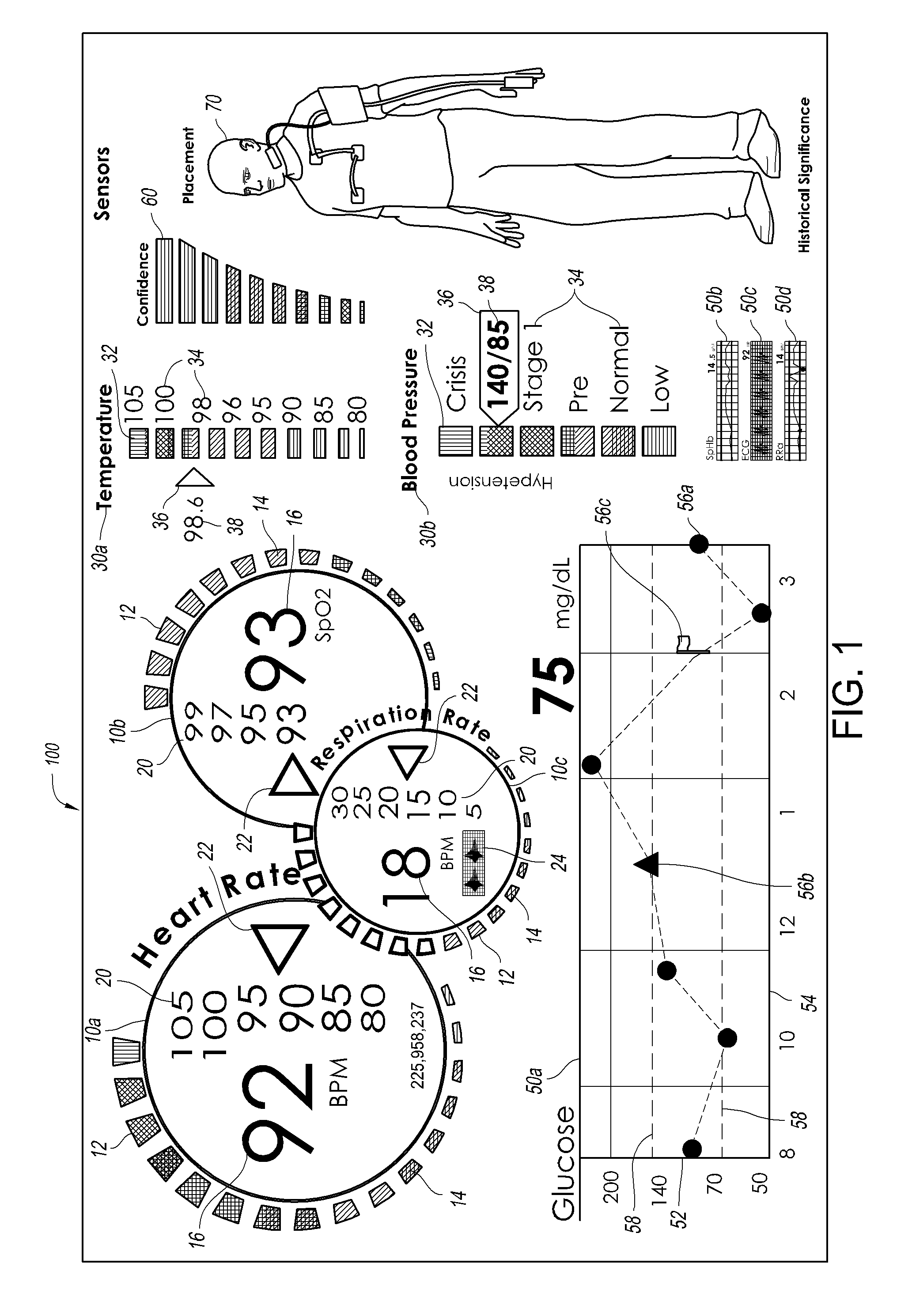
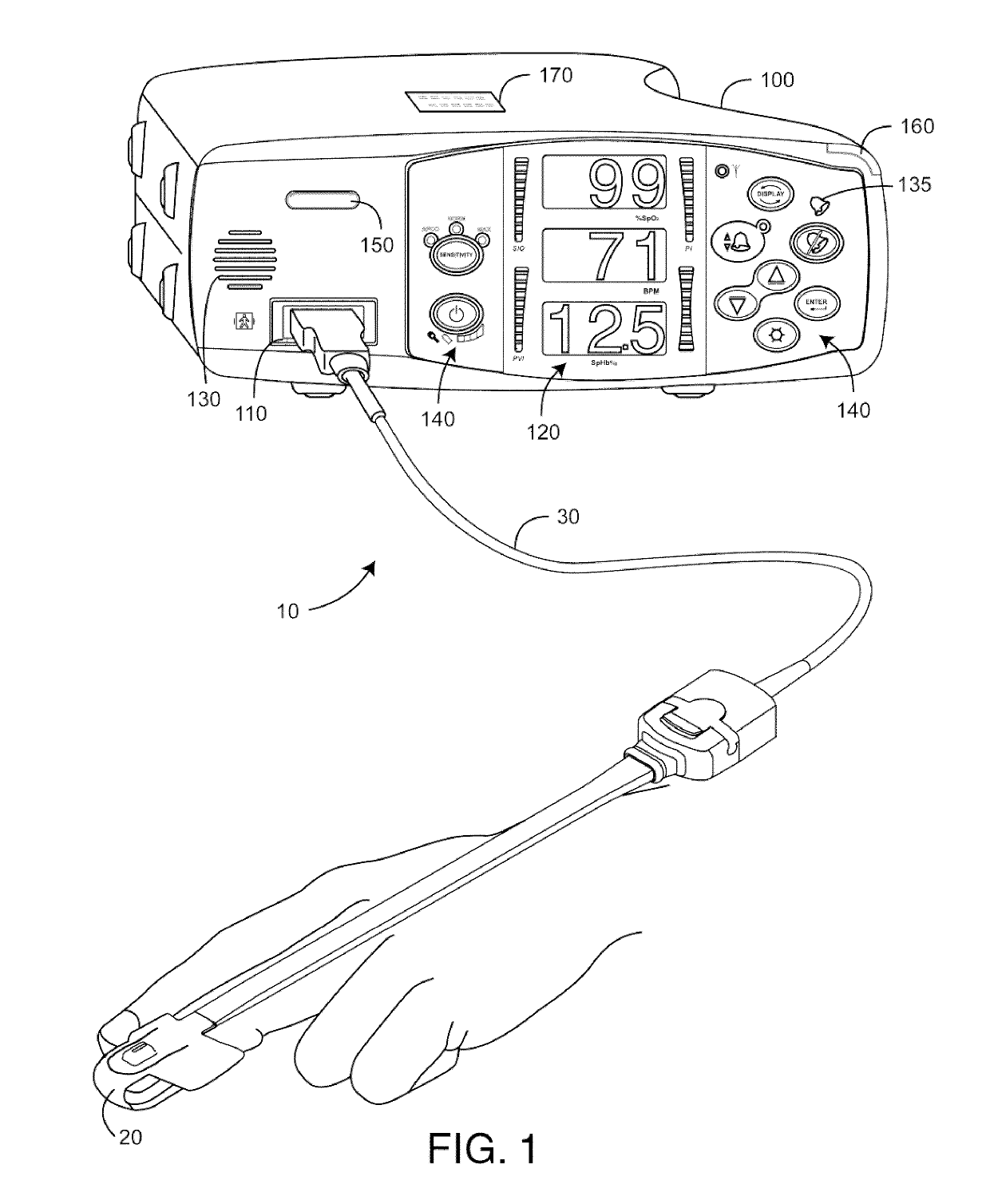
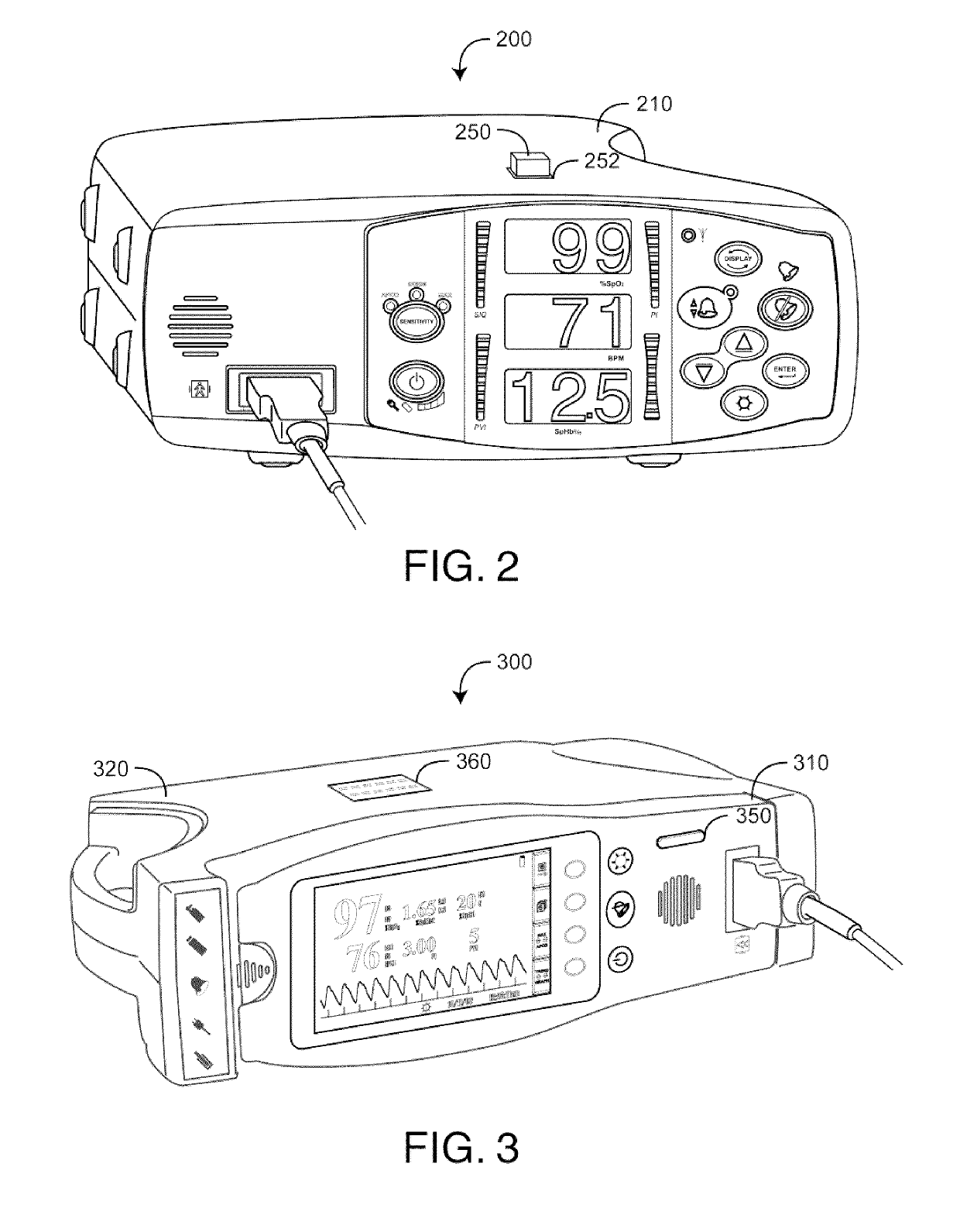
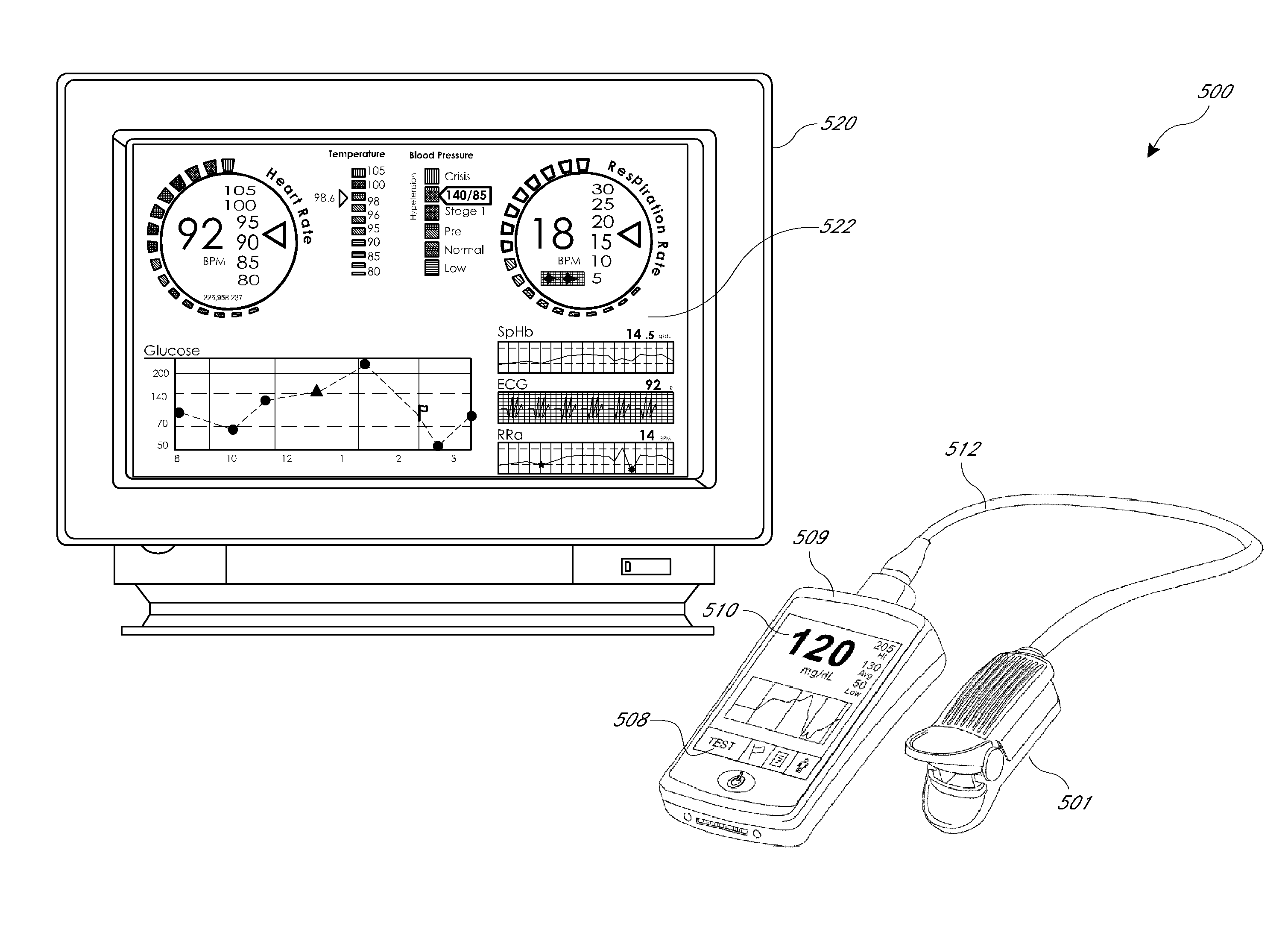
Configurable patient monitoring system
A patient monitoring system can display one or more configurable health monitors on a configurable user interface. The health indicators are configured to display a physiological signal from a patient. The patient monitoring system can calculate ranges of values for the health indicator that correspond to a status of the patient. The health indicators can display different outputs based on the value of the physiological signal.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
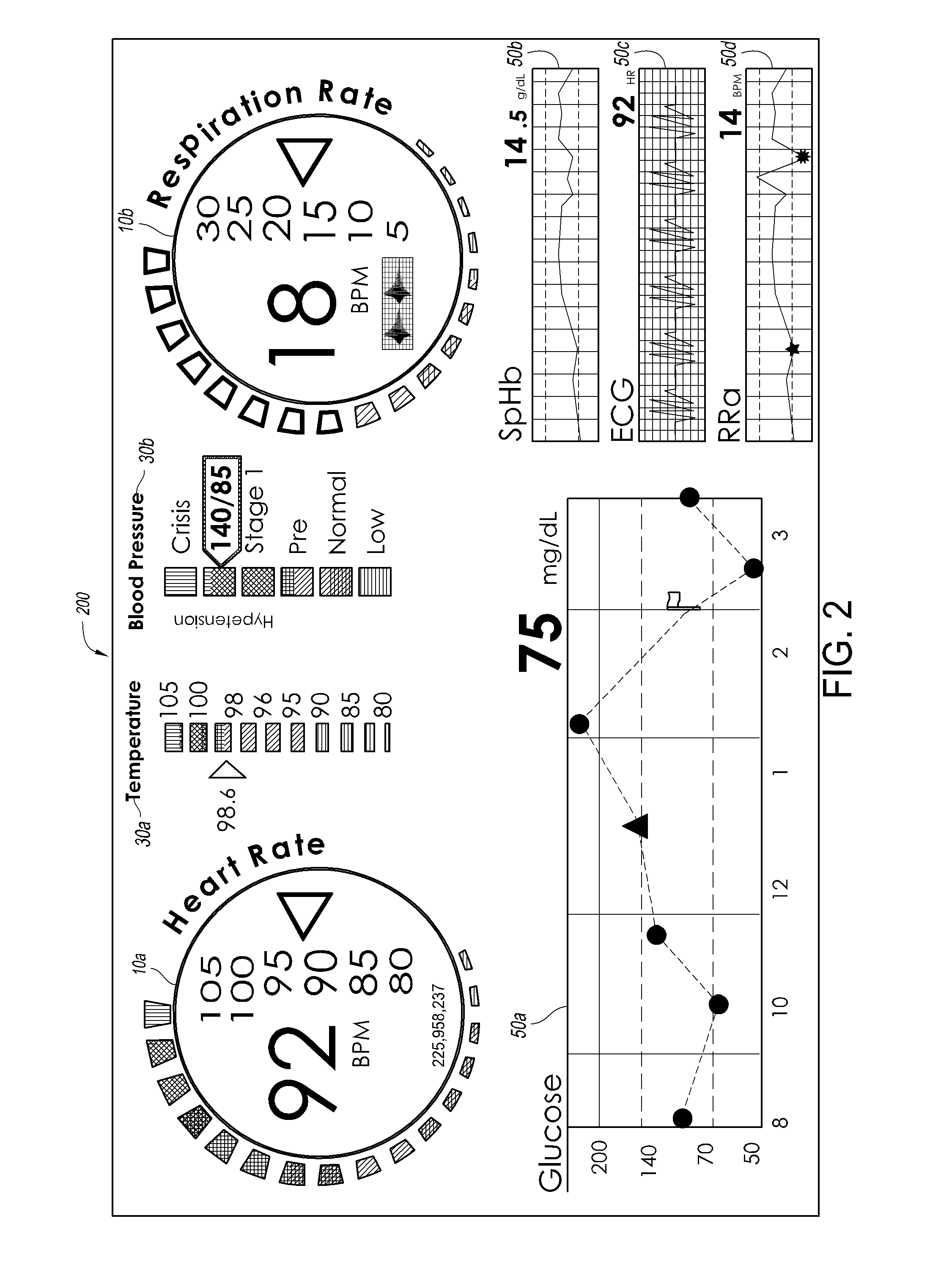
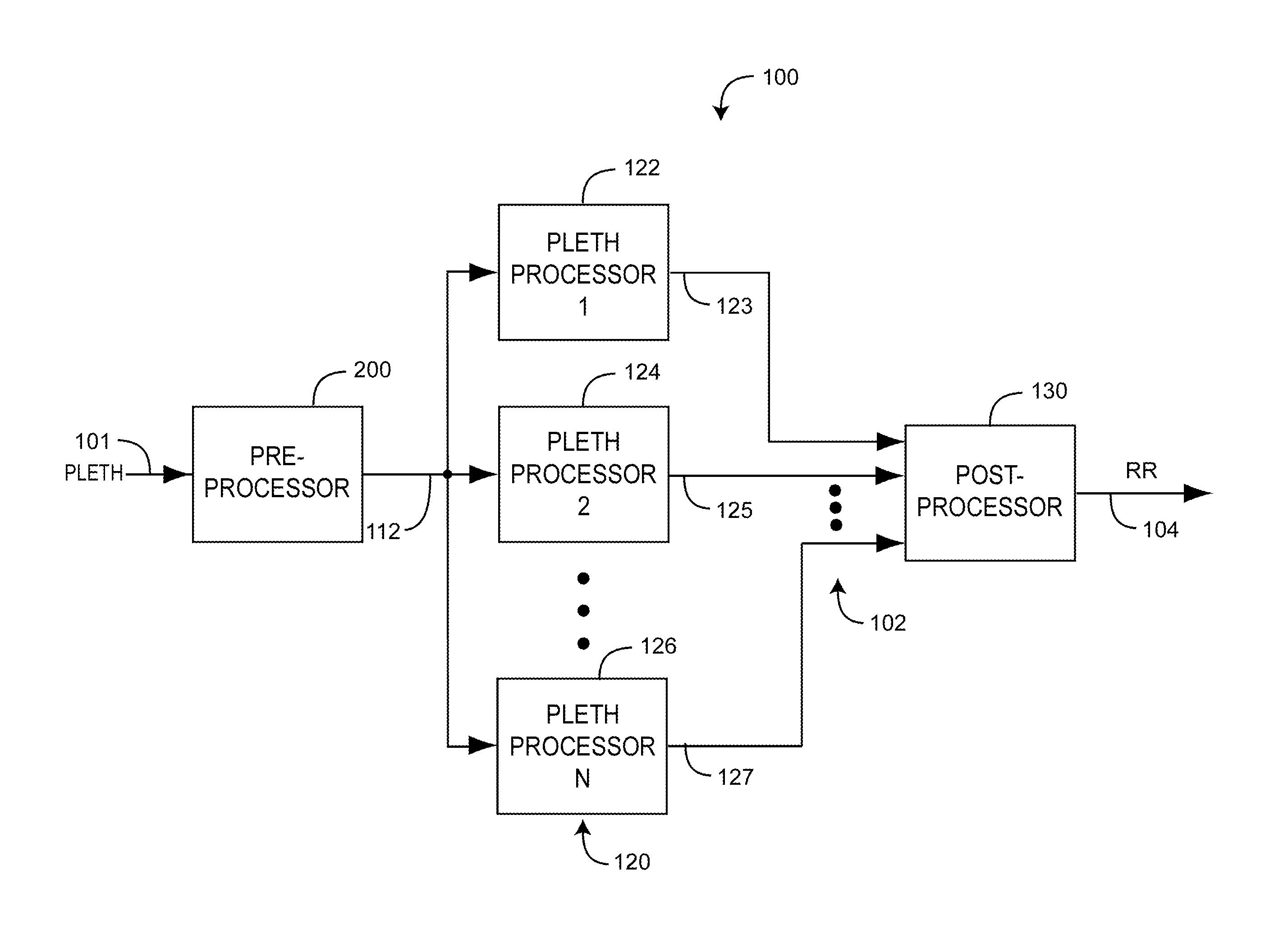
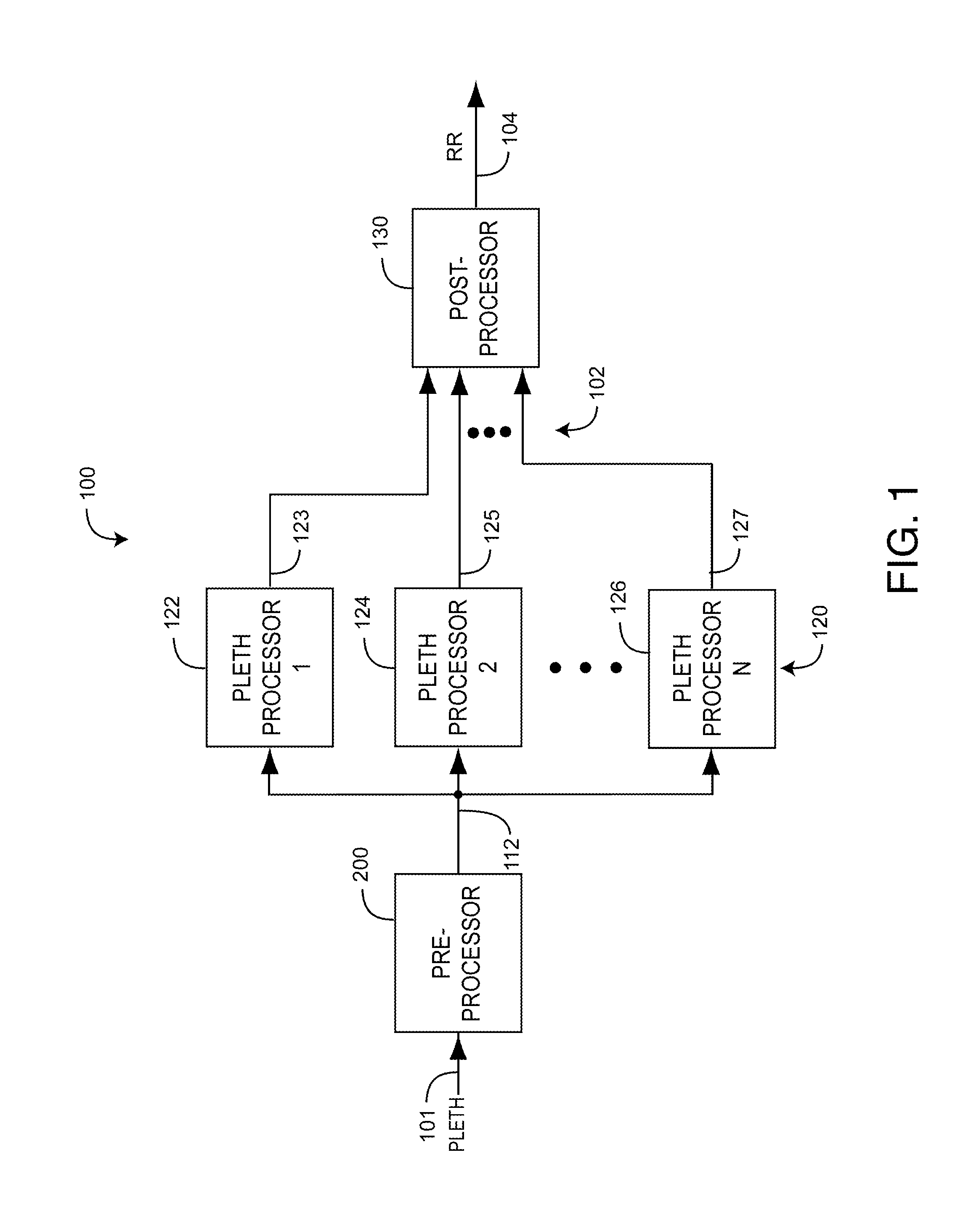
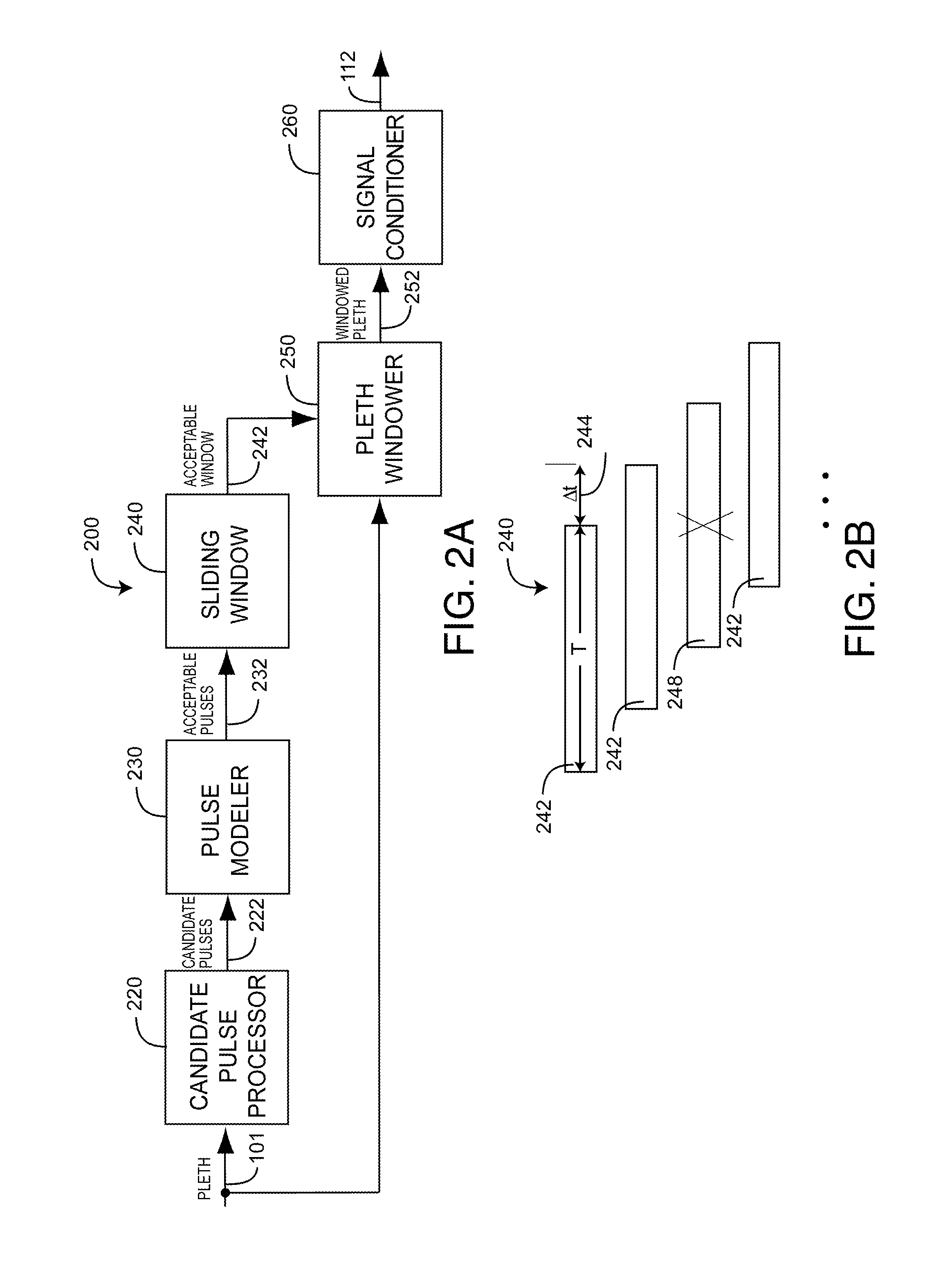
Plethysmographic respiration processor
ActiveUS9307928B1Improve accuracyImprove robustnessHealth-index calculationRespiratory organ evaluationRadiologyNormal blood volume
A plethysmographic respiration processor is responsive to respiratory effects appearing on a blood volume waveform and the corresponding detected intensity waveform measured with an optical sensor at a blood perfused peripheral tissue site so as to provide a measurement of respiration rate. A preprocessor identifies a windowed pleth corresponding to a physiologically acceptable series of plethysmograph waveform pulses. Multiple processors derive different parameters responsive to particular respiratory effects on the windowed pleth. Decision logic determines a respiration rate based upon at least a portion of these parameters.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
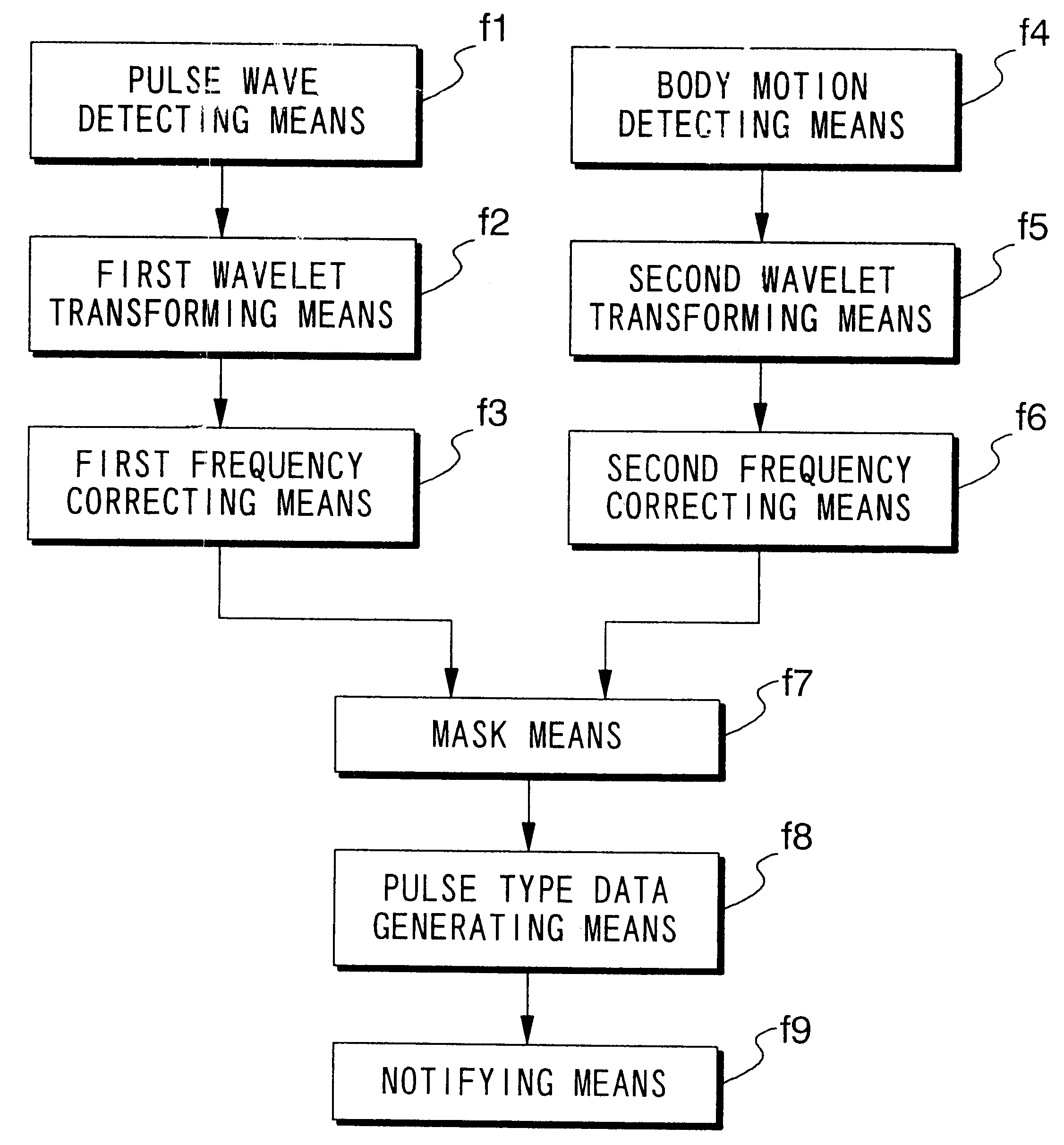
Pulse wave diagnosing device
When pulse waveform MH is detected by pulse wave detection sensor unit 130, wavelet transformer 10 performs wavelet transformation on pulse waveform MH and generates analyzed pulse wave data MKD. This analyzed pulse wave data MKD consists of a time region in which one heartbeat is divided into eighths, and the frequency region of 0-4 Hz which has been divided into eighths. Frequency corrector 11 generates corrected pulse wave data MKD' by performing frequency correction on analyzed pulse wave data MKD. Pulse type data generator 12 compares corrected pulse wave data MKD' over each frequency-time region, and generates pulse type data ZD indicating the type of pulse. Display 13 displays the pulse type for pulse waveform MH based on pulse type data ZD.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
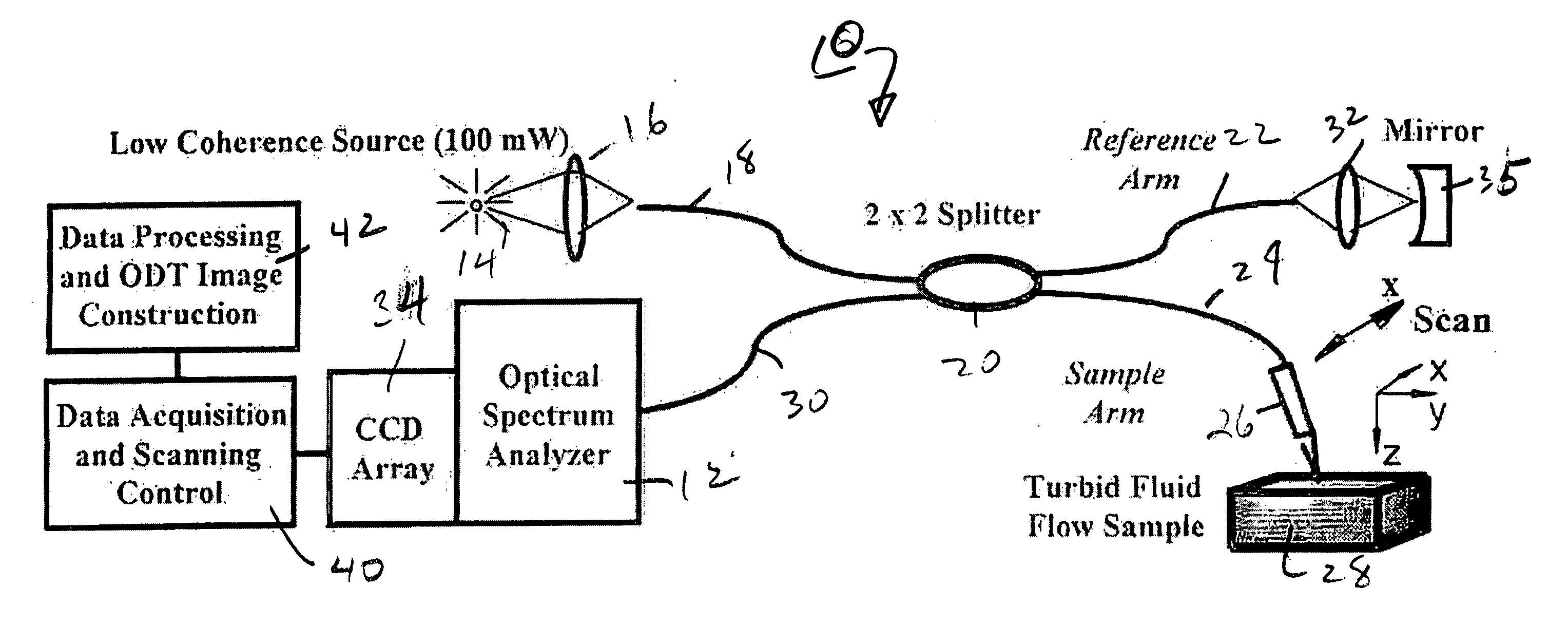
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
ActiveUS20050171438A1Accurate settingImprove system sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood flowIn vivo
A method for tomographic imaging comprises the steps of providing a source of at least partially coherent radiation and a frequency-swept laser source through an interferometer; phase modulating the radiation in the interferometer at a modulation frequency for elimination of DC and autocorrelation noises as well as the mirror image; detecting interference fringes of the radiation backscattered from the sample into the interferometer to obtain a spectral signal; transforming the spectral signal of the detected backscattered interference fringes to obtain a time and location dependent signal, including the Doppler shift and variance, at each pixel location in a data window; and generating a tomographic image of the fluid flow in the data window and of the structure of the scanned fluid flow sample in the data window from the time and location dependent signal. The apparatus comprises a system for tomographic imaging operating according to the above method.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Surgical instruments including sensors
ActiveUS10624616B2Evaluation of blood vesselsDead animal preservationRegional perfusionSurgical device
A surgical instrument includes a handle portion, first and second jaw members operably coupled to the handle portion, and first and second sensors associated with the first or second jaw members. The first sensor is configured to measure local perfusion in tissue grasped between the first and second jaw members, and the second sensor is configured to measure a pressure applied to the tissue by the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
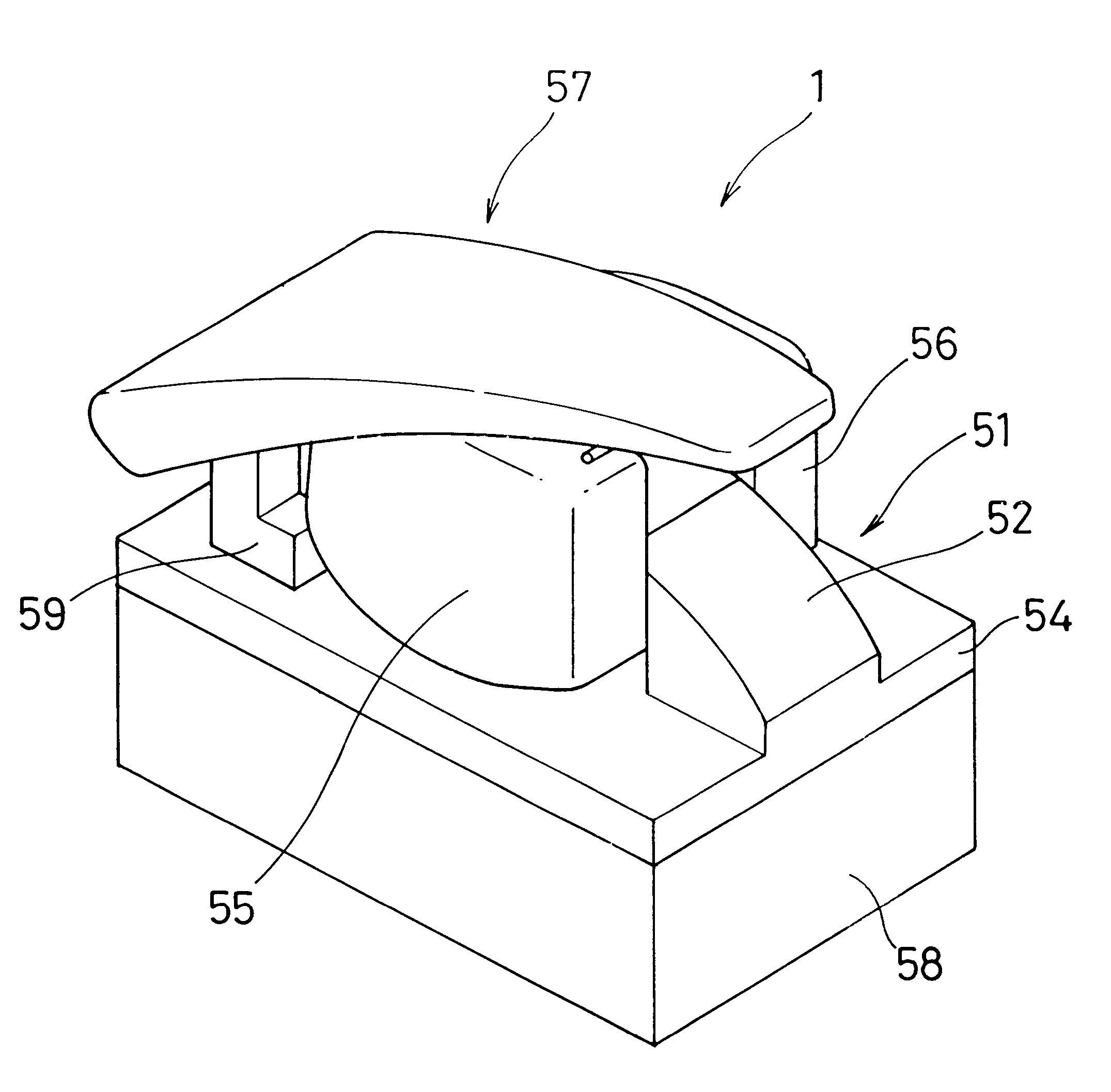
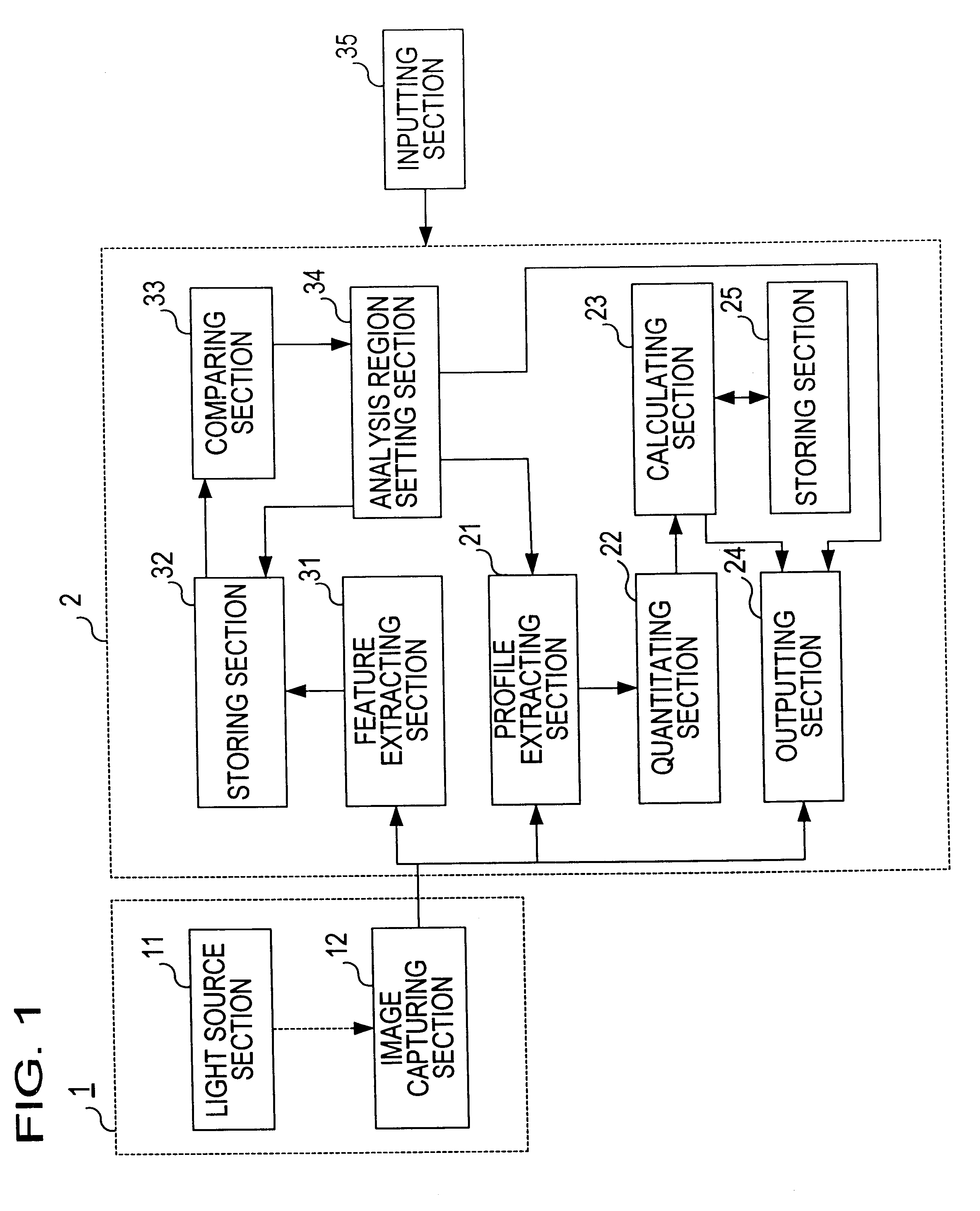
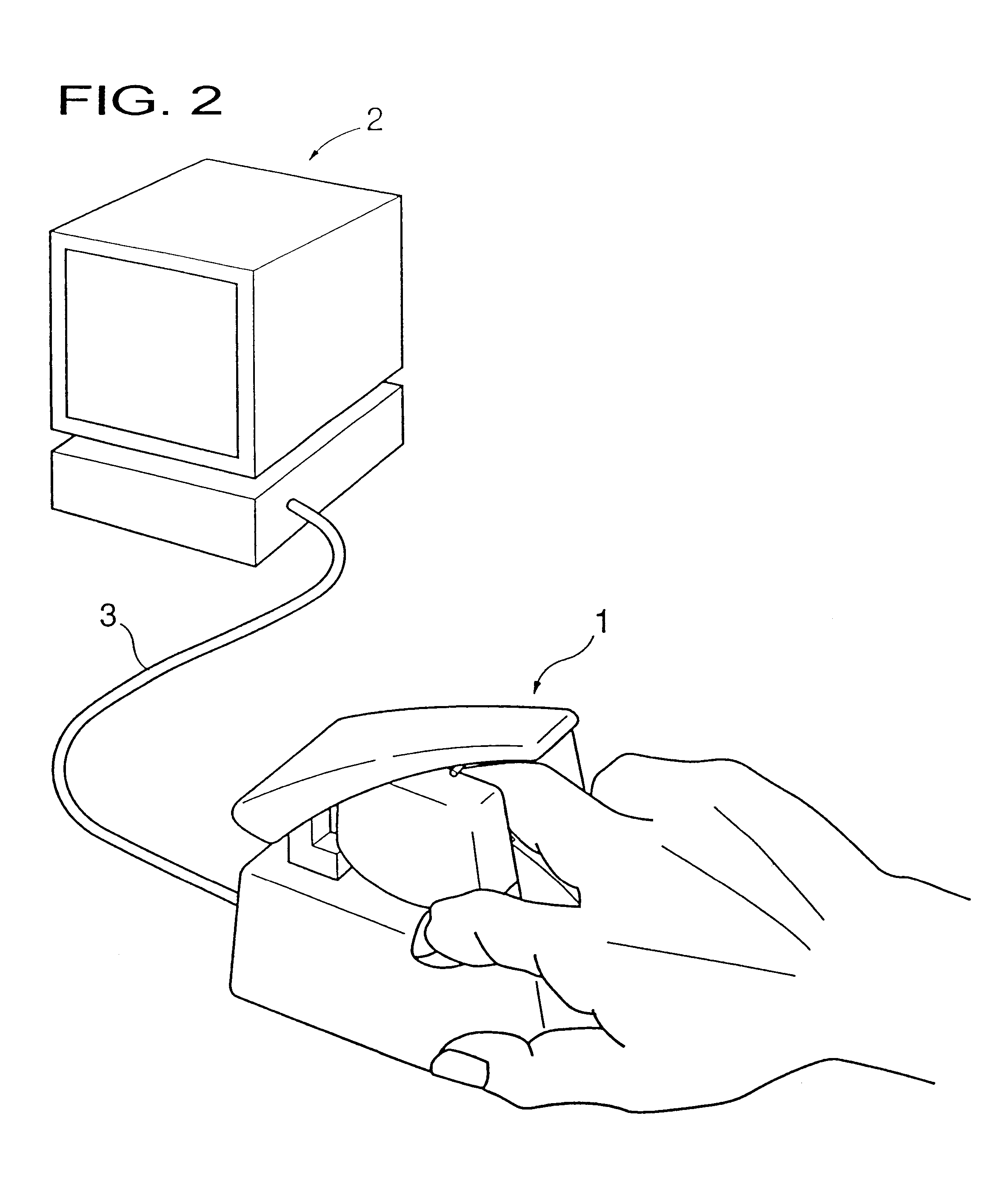
Living body inspecting apparatus and noninvasive blood analyzer using the same
The purpose is to fix a portion of a living body, which is an object of measurement, stably without strain and to acquire accurate inspection results with good reproducibility. An apparatus for capturing an image of a living body includes: a base for mounting a portion of a living body to be inspected; two sidewall members capable of holding the mounted portion of the living body therebetween from both sides; a light source section for supplying a light to the portion of the living body held on the base and between the sidewall members; and a light receiving section for detecting optical information from the portion of the living body supplied with the light, and a non-invasive apparatus for living body inspection including the above apparatus for capturing an image of a living body in which the light receiving section includes an image capturing element, and an analyzing section for calculating information on blood flowing through a blood vessel by analyzing an image of a tissue including the blood vessel obtained by the image capturing element.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
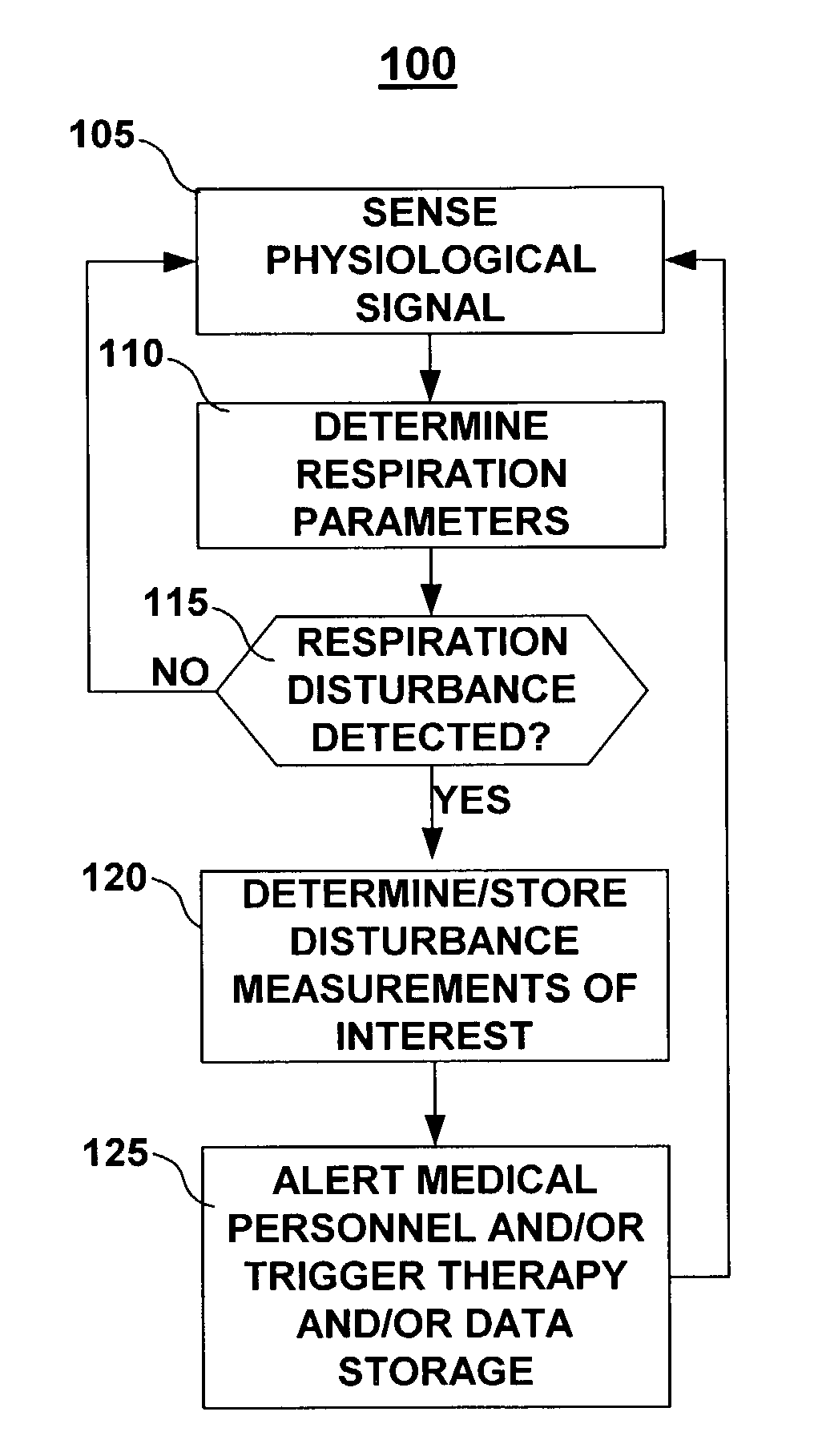
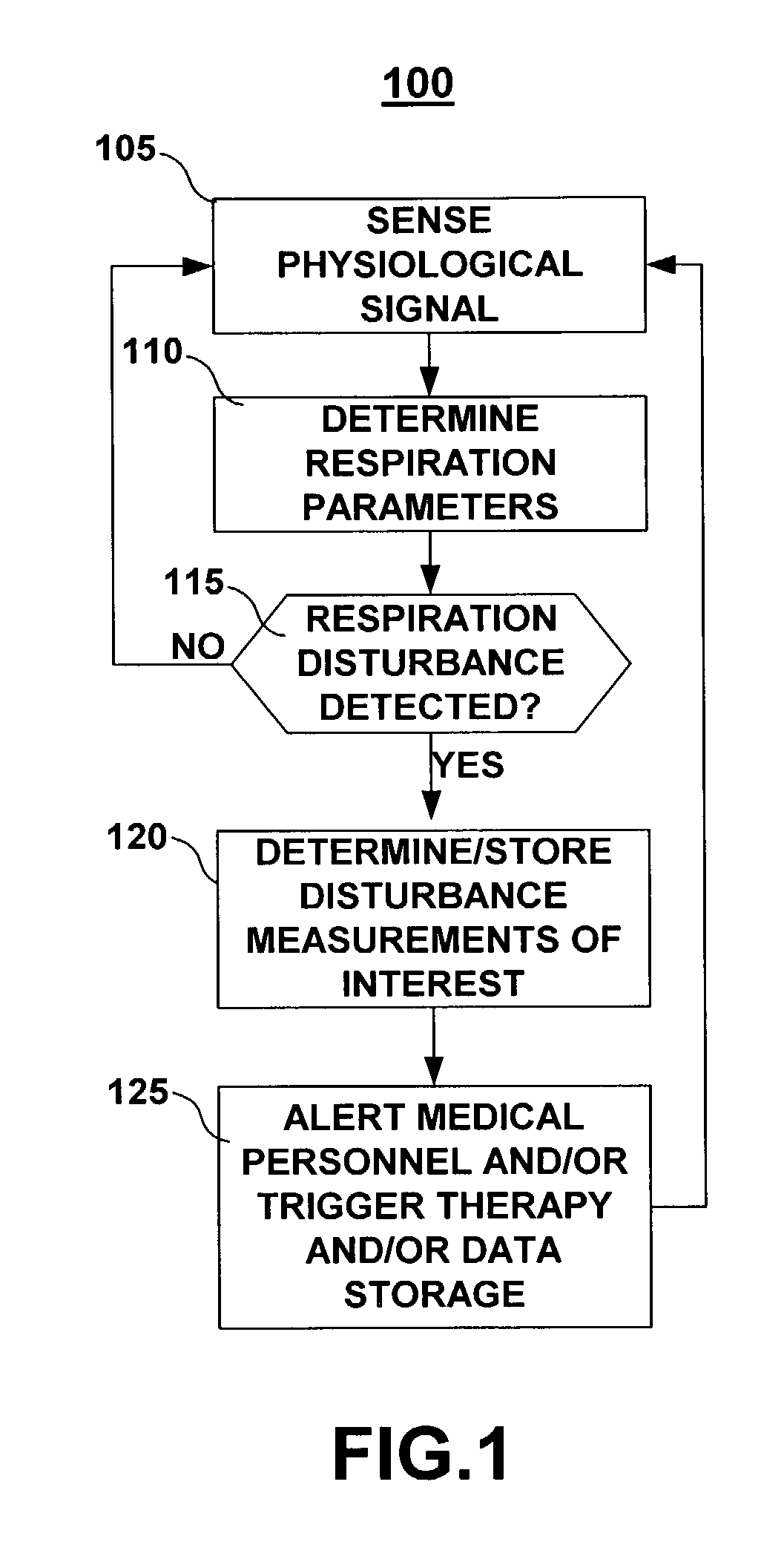
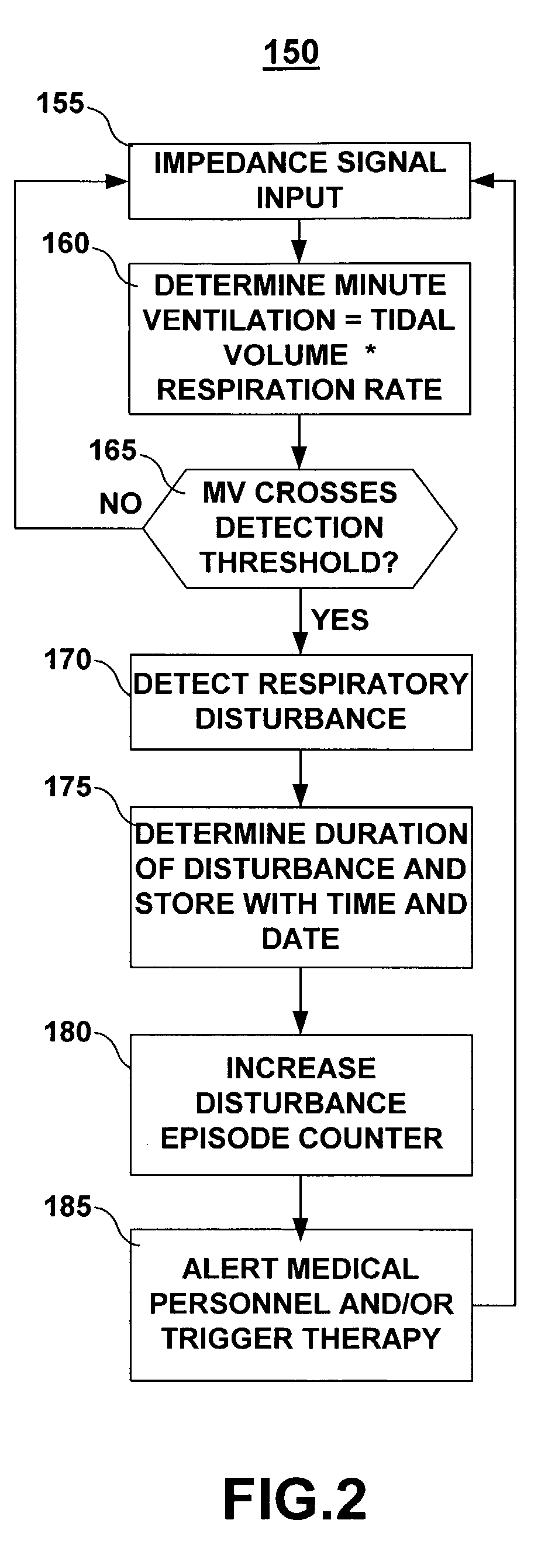
Method and apparatus for detecting respiratory disturbances
ActiveUS7160252B2Easy to identifyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAnesthesiaMedical device
A system and method for monitoring respiration including sensing a signal that varies with respiration, deriving a respiration parameter, applying criteria for detecting a respiration disturbance and determining one or more respiratory disturbance metrics. The system preferably includes an implantable sensor with an associated implantable medical device such that chronic respiration monitoring is possible. The implantable medical device may execute methods for detecting and measuring respiratory disturbances or may store data to be transferred to an external device for detecting and measuring respiratory disturbances. Respiratory disturbance detection may trigger a responsive action such as physiological data storage, a change in therapy delivery, or a clinician warning. Assessment of cardiac function may be made based on metrics of respiratory disturbances or a measure of circulatory delay time following detection of a respiratory disturbance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
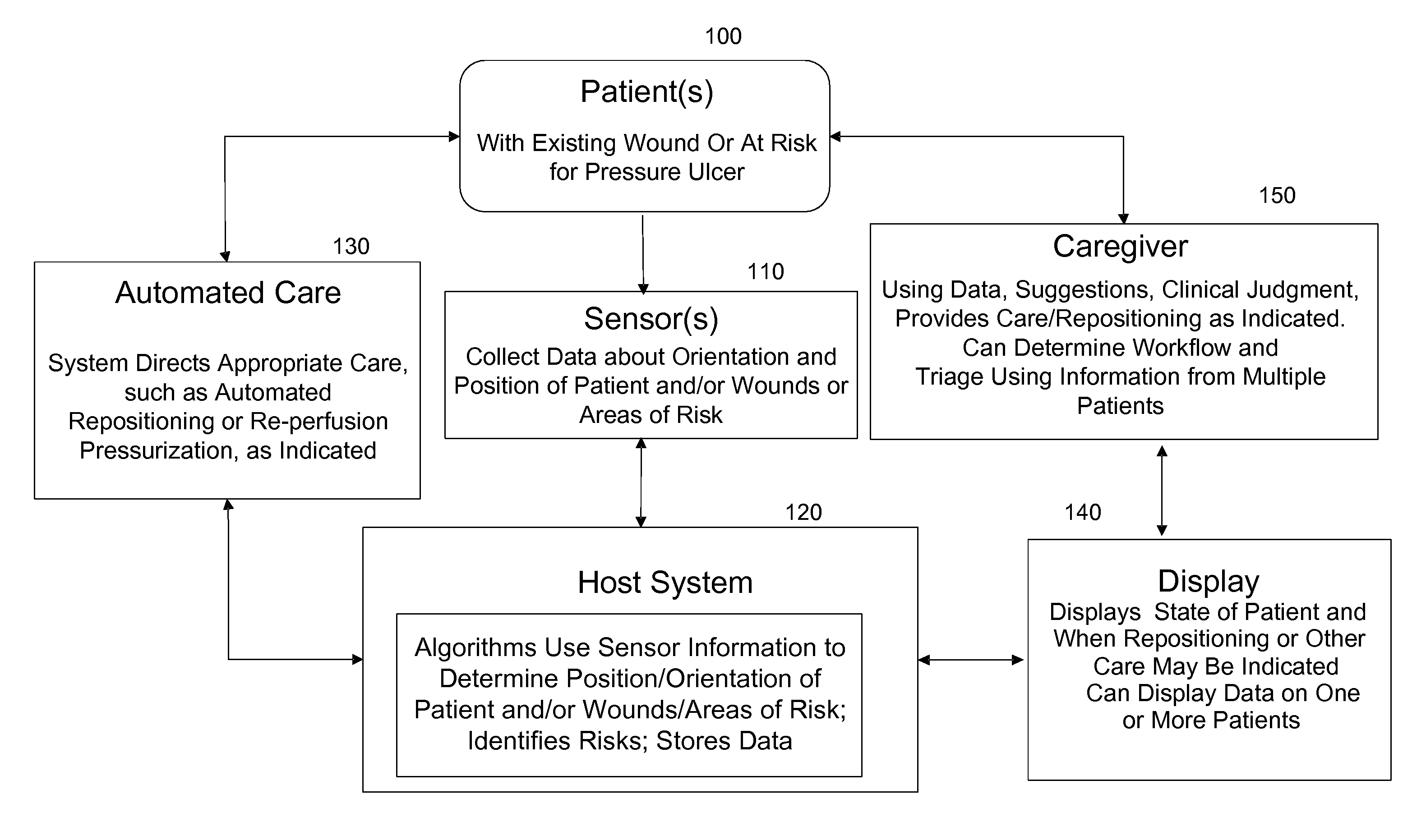
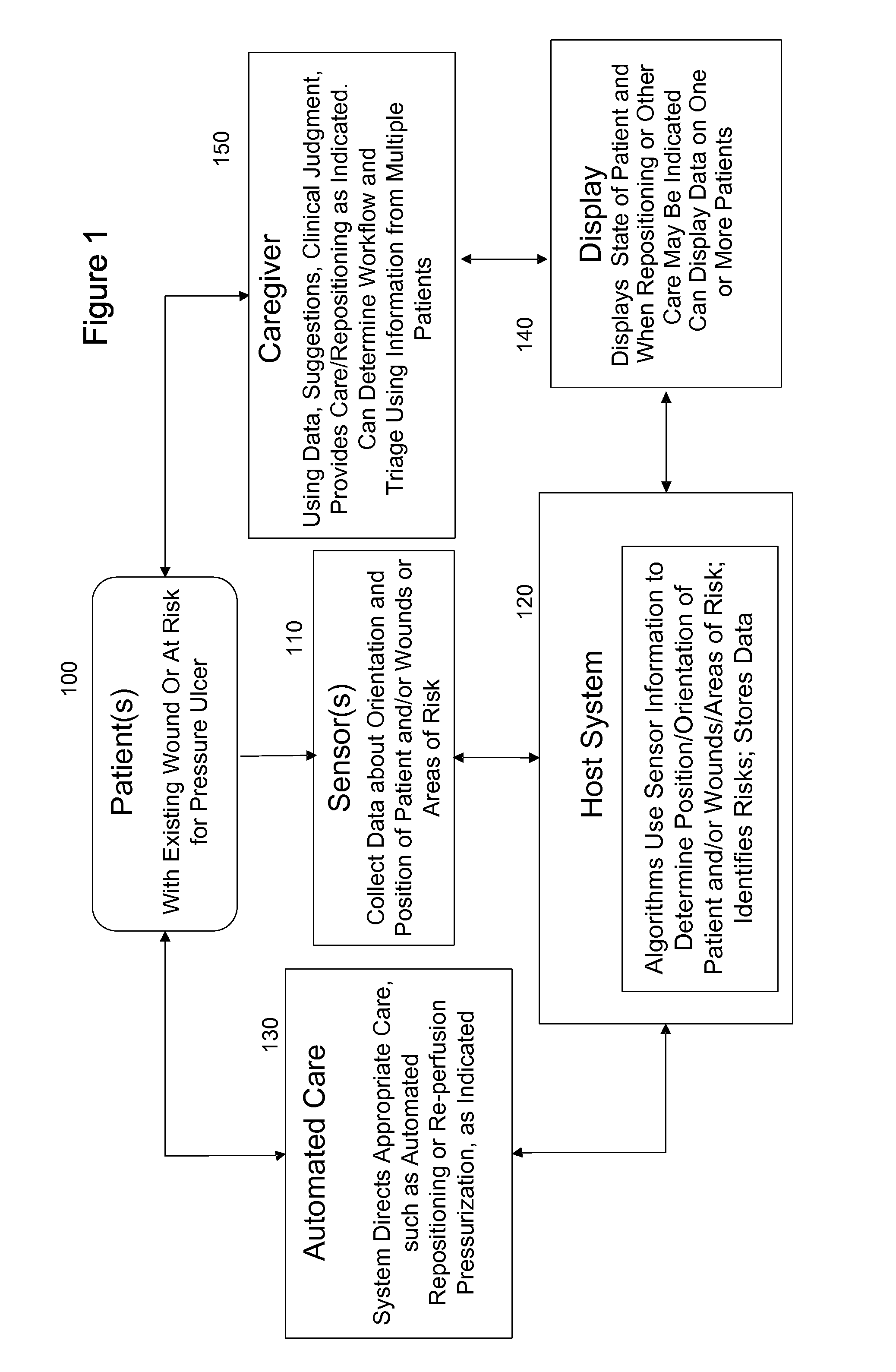
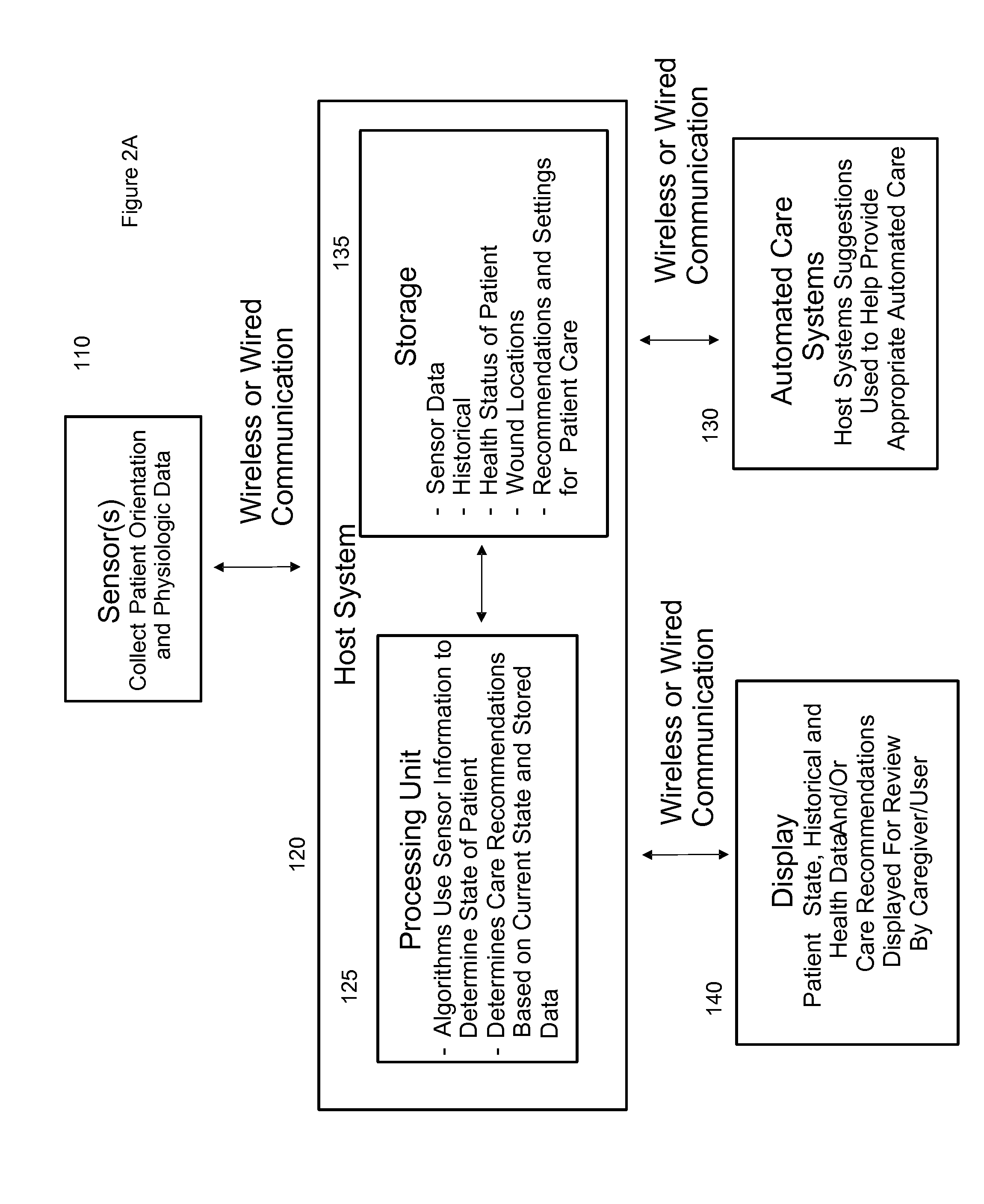
Systems, devices and methods for preventing, detecting and treating pressure-induced ischemia, pressure ulcers, and other conditions
ActiveUS20110263950A1Minimize and eliminate physical contactPromote blood circulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperating chairsAccelerometerPatient characteristics
A system for monitoring medical conditions including pressure ulcers, pressure-induced ischemia and related medical conditions comprises at least one sensor adapted to detect one or more patient characteristic including at least position, orientation, temperature, acceleration, moisture, resistance, stress, heart rate, respiration rate, and blood oxygenation, a host for processing the data received from the sensors together with historical patient data to develop an assessment of patient condition and suggested course of treatment. In some embodiments, the system can further include a support surface having one or more sensors incorporated therein either in addition to sensors affixed to the patient or as an alternative thereof. The support surface is, in some embodiments, capable of responding to commands from the host for assisting in implementing a course of action for patient treatment. The sensor can include bi-axial or tri-axial accelerometers, as well as resistive, inductive, capactive, magnetic and other sensing devices, depending on whether the sensor is located on the patient or the support surface, and for what purpose.
Owner:LEAF HEALTHCARE
Monitor configuration system
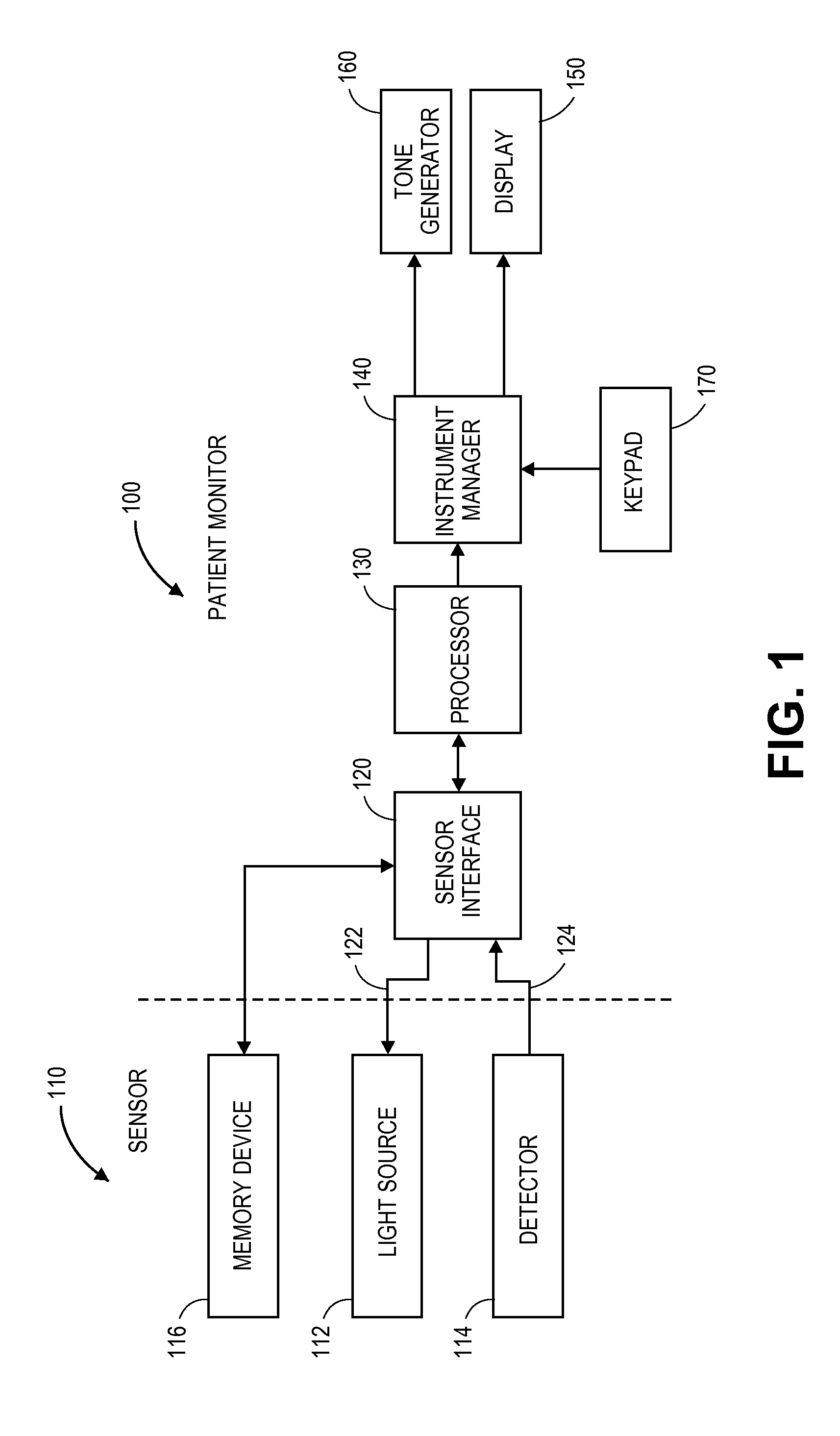
ActiveUS10292664B2Maximum flexibilityOperational flexibilityCatheterSensorsParameter controlLight-emitting diode
A monitor configuration system which communicates with a physiological sensor, the monitor configuration system including one or more processors and an instrument manager module running on the one or more processors. At least one of the one or more processors communicates with the sensor and calculates at least one physiological parameters responsive to the sensor. The instrument manager controls the calculation, display and / or alarms based upon the physiological parameters. A configuration indicator identifies the configuration profile. In one aspect of the invention, the physiological sensor is a optical sensor that includes at least one light emitting diode and at least one detector.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Configurable patient monitoring system
ActiveUS20130211214A1Rapid assessmentEasy to see2D-image generationEvaluation of blood vesselsMonitoring systemEmergency medicine
A patient monitoring system can display one or more configurable health monitors on a configurable user interface. The health indicators are configured to display a physiological signal from a patient. The patient monitoring system can calculate ranges of values for the health indicator that correspond to a status of the patient. The health indicators can display different outputs based on the value of the physiological signal.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
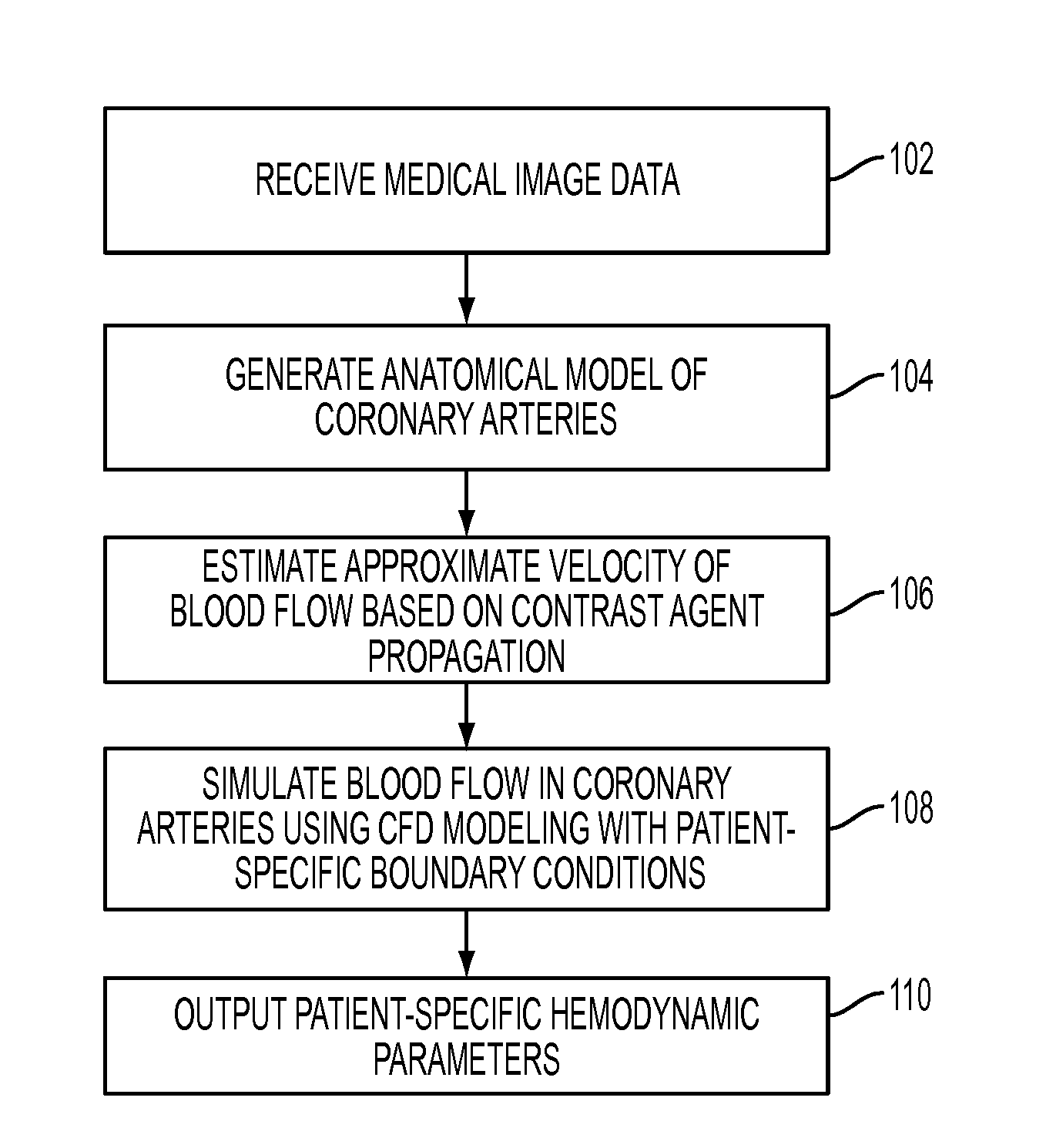
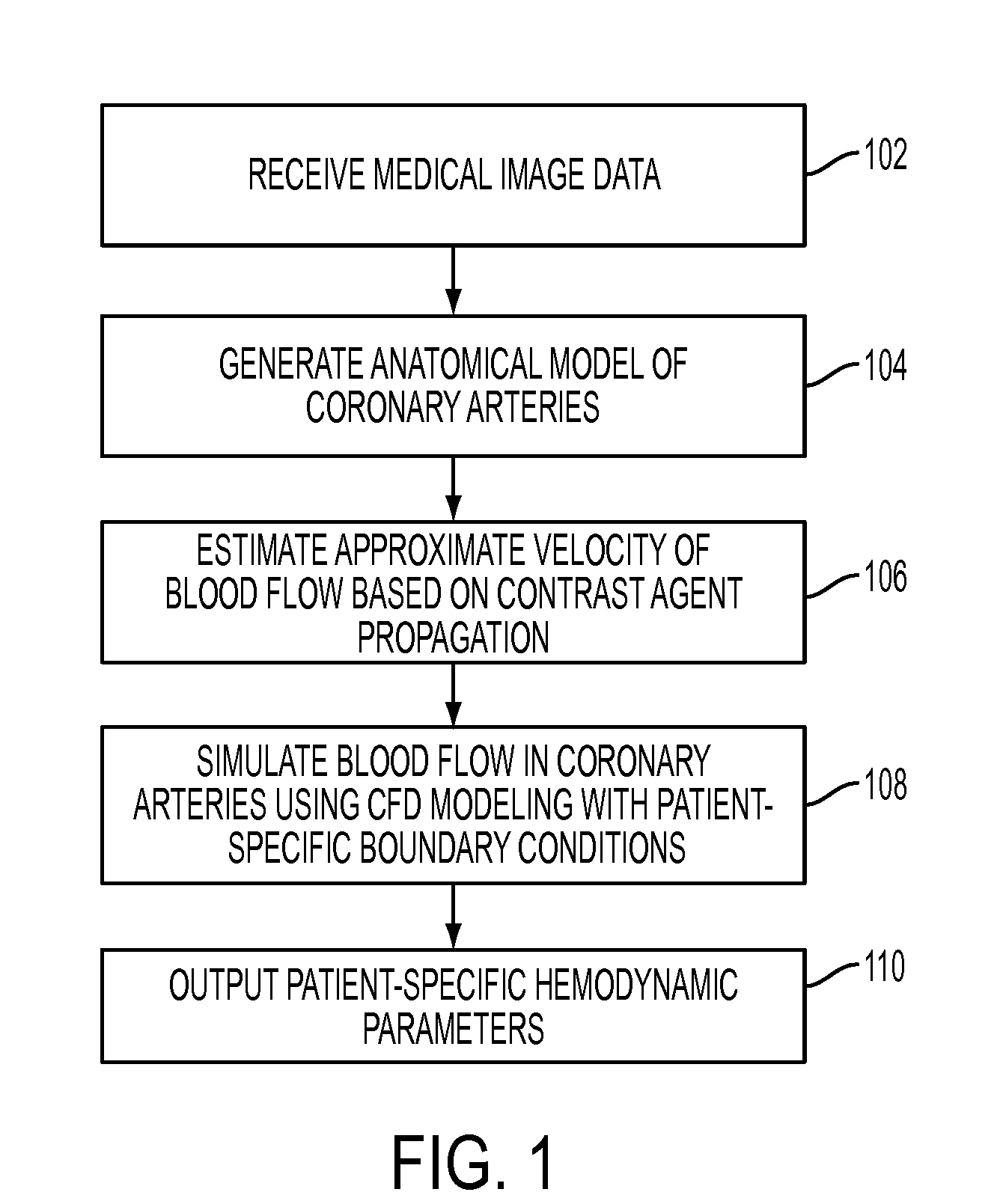
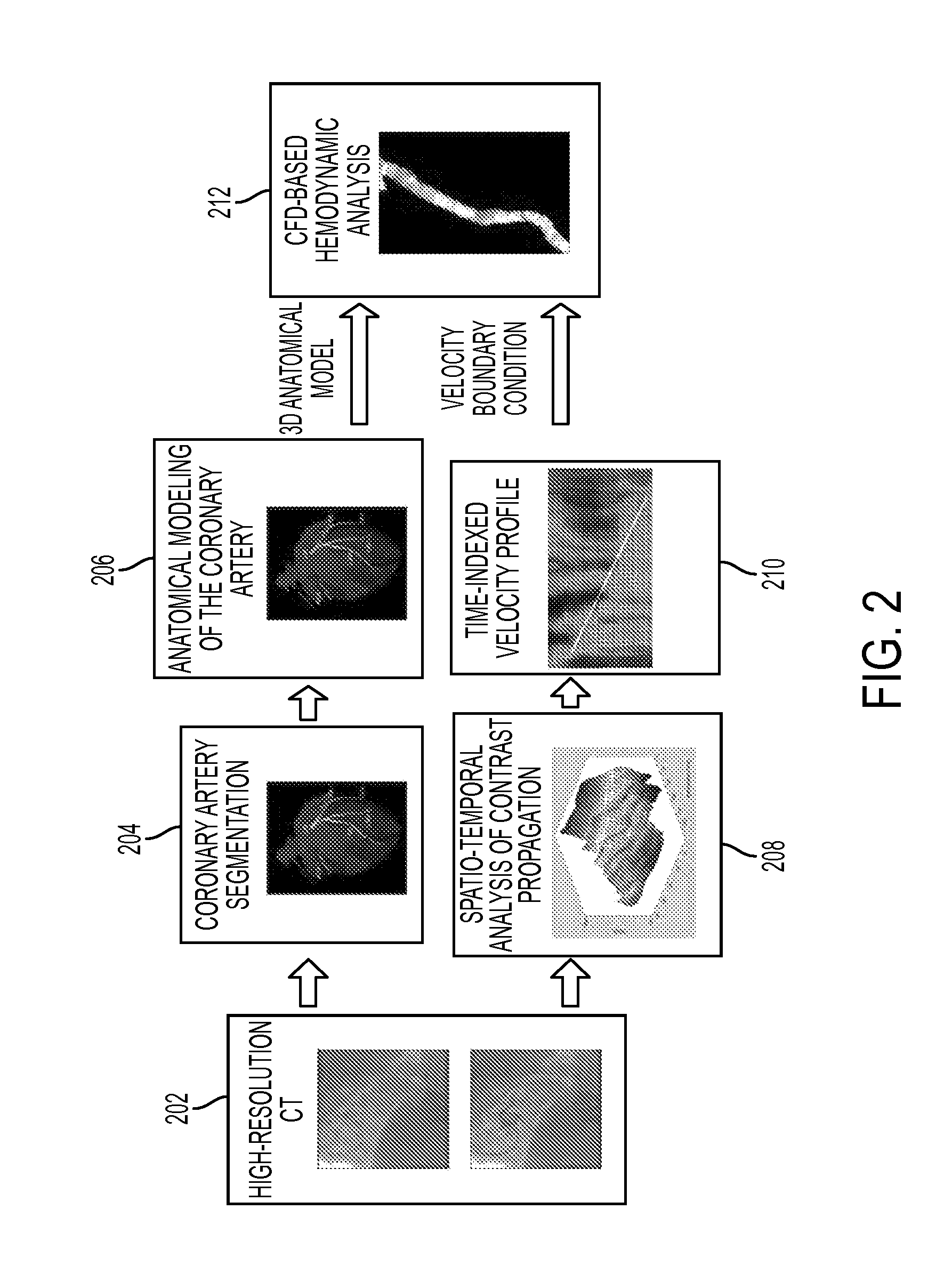
Method and System for Non-Invasive Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease
A method and system for non-invasive patient-specific assessment of coronary artery disease is disclosed. An anatomical model of a coronary artery is generated from medical image data. A velocity of blood in the coronary artery is estimated based on a spatio-temporal representation of contrast agent propagation in the medical image data. Blood flow is simulated in the anatomical model of the coronary artery using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation using the estimated velocity of the blood in the coronary artery as a boundary condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Surgical instruments including sensors
ActiveUS20170172550A1Reduce clamping pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsDead animal preservationMedicinePerfusion
A surgical instrument includes a handle portion, first and second jaw members operably coupled to the handle portion, and first and second sensors associated with the first or second jaw members. The first sensor is configured to measure local perfusion in tissue grasped between the first and second jaw members, and the second sensor is configured to measure a pressure applied to the tissue by the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
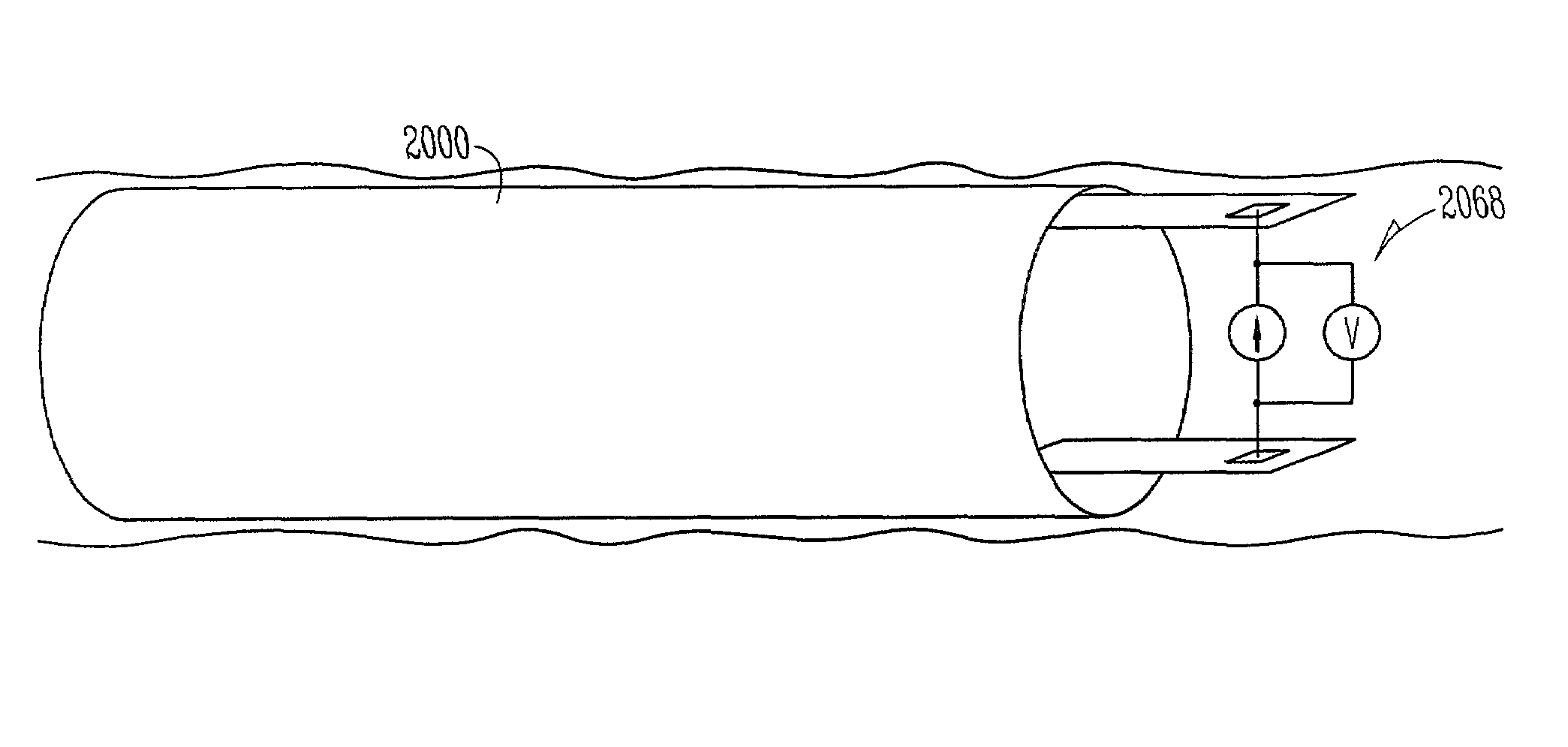
System and method for monitoring pressure, flow and constriction parameters of plumbing and blood vessels
InactiveUS6237398B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringPulsatile flow
The present invention provides a system and method of quantifying flow, detecting a location of an obstruction and quantifying a degree of the obstruction in a pipe characterized in pulsatile flow. The method includes the steps of (a) attaching at least two spaced pressure sensors onto inner walls of the pipe; (b) using the at least two spaced pressure sensors for recording pressure records associated with each of the at least two pressure sensors within the pipe; and (c) using the pressure records for quantifying the pulsatile flow in the pipe, for detecting the location of the obstruction in the pipe and for quantifying the degree of the obstruction in the pipe.
Owner:TELESENSE
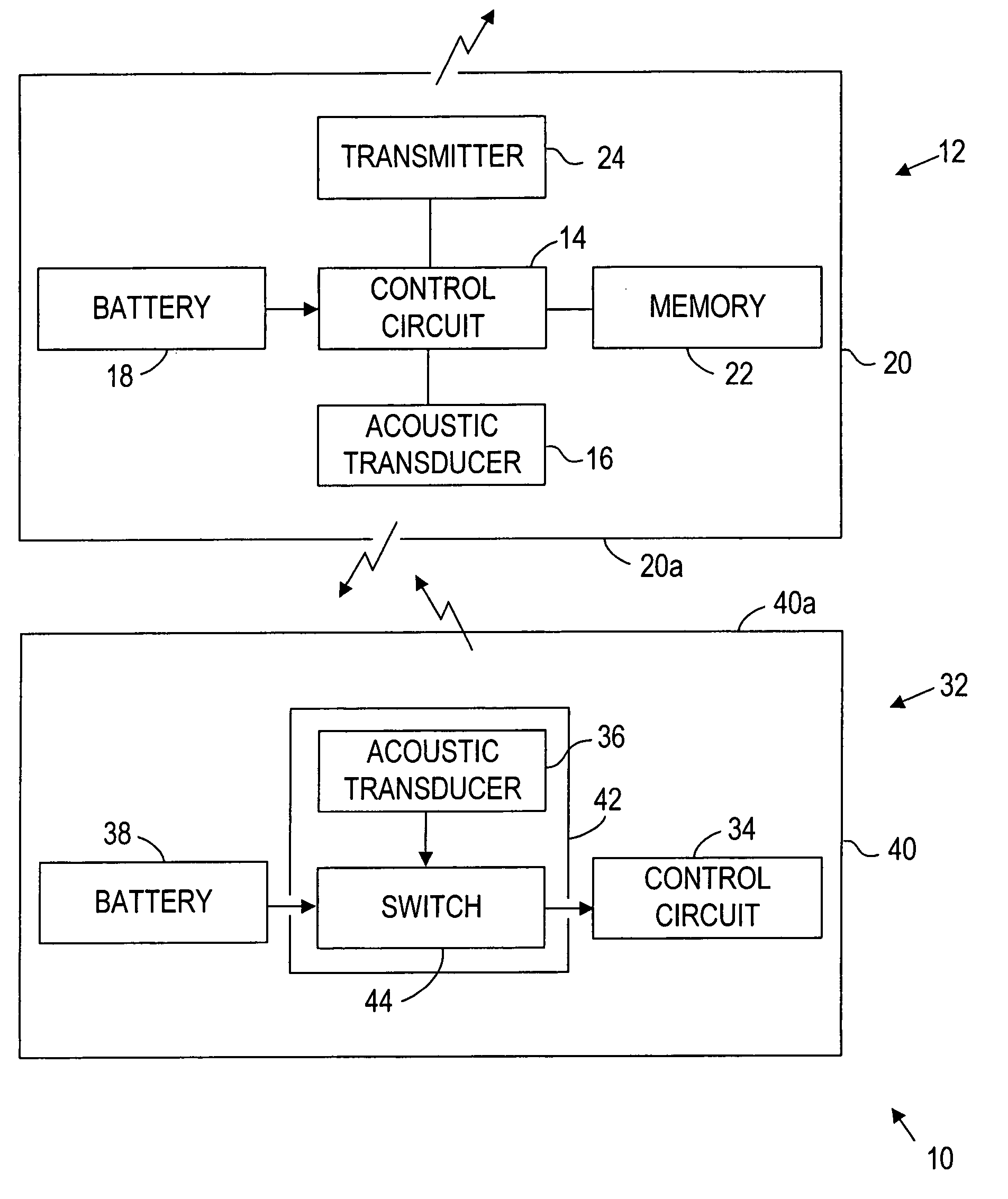
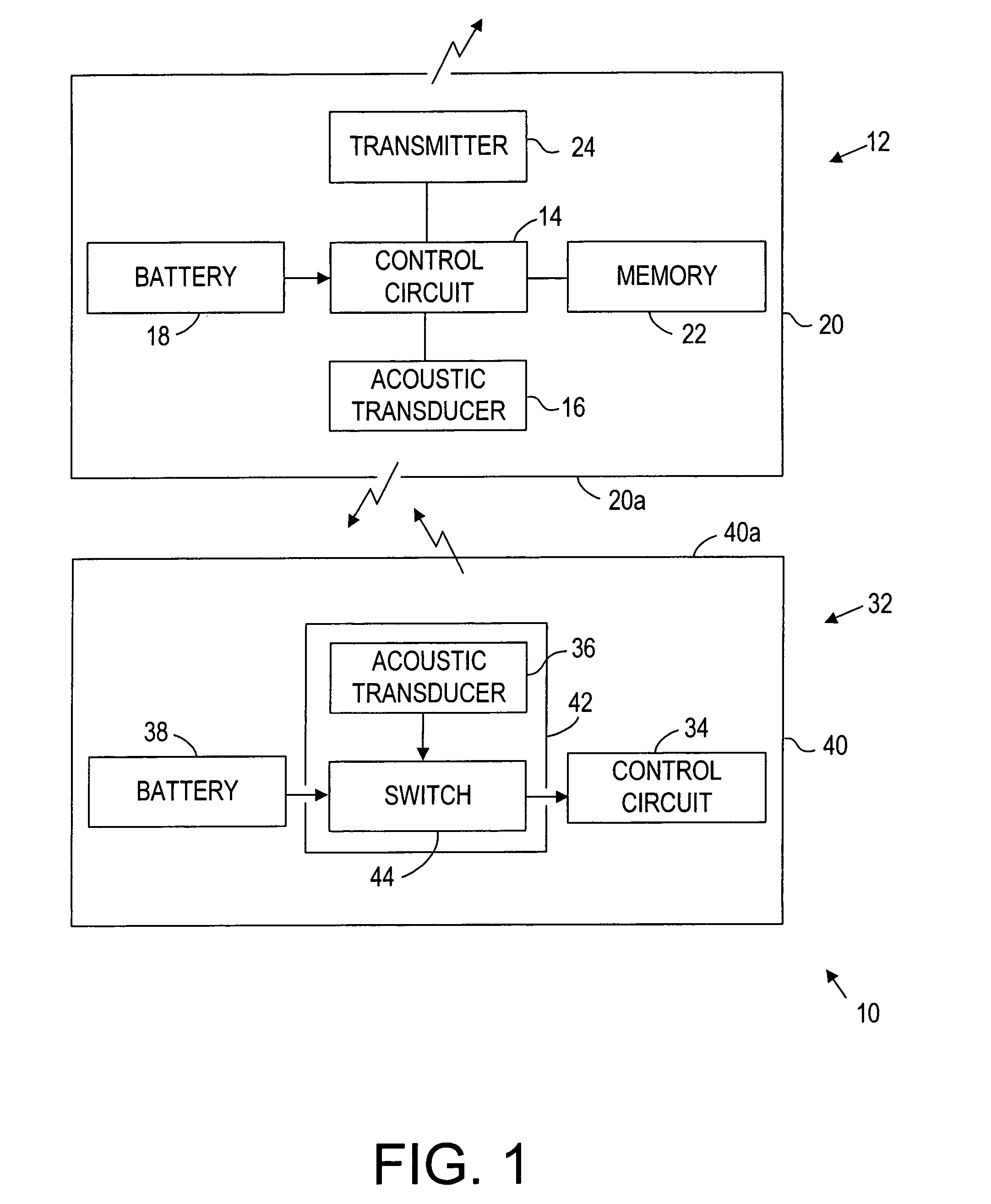
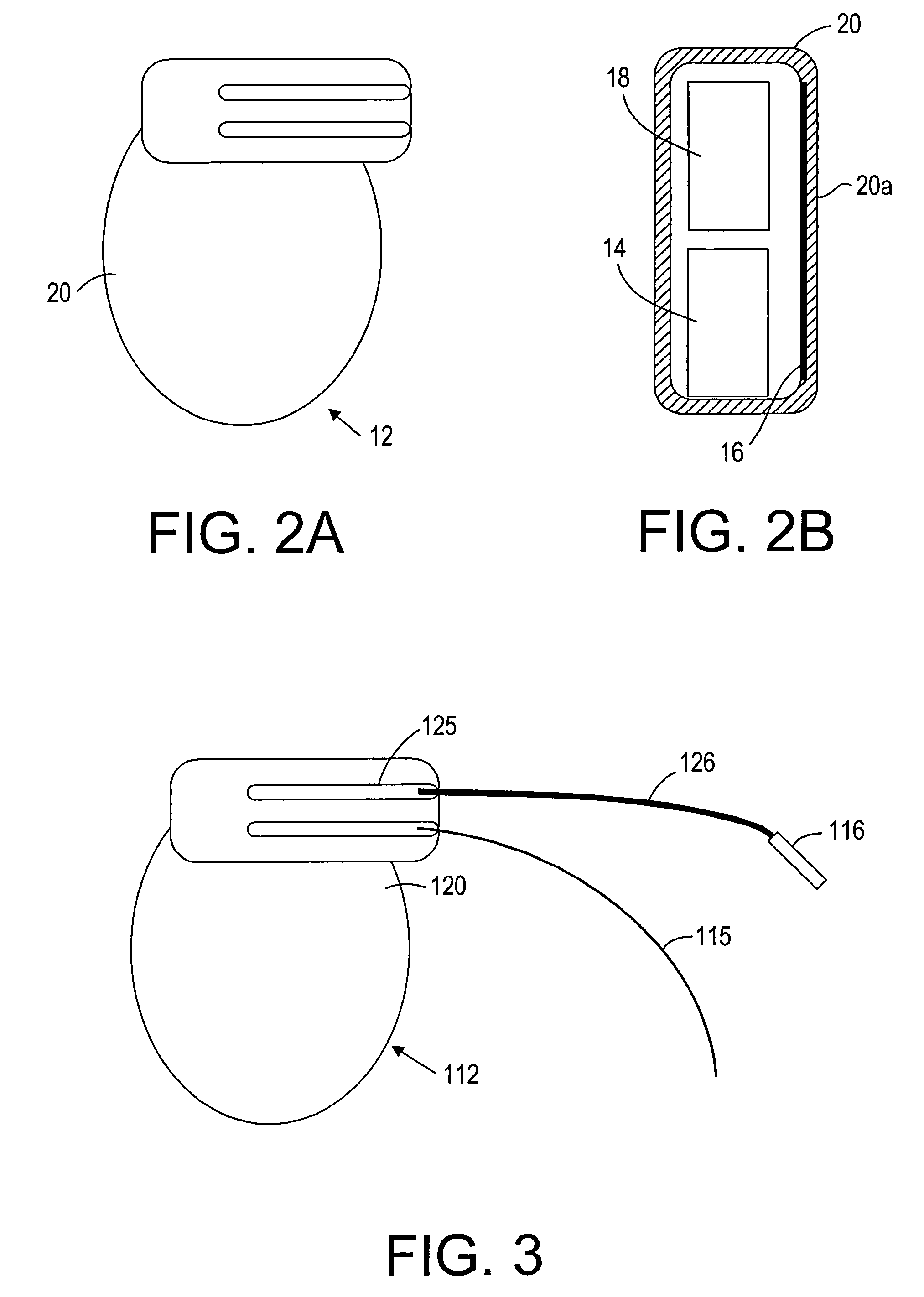
Apparatus and methods using acoustic telemetry for intrabody communications
Systems and methods provide intrabody communication using acoustic telemetry. The system includes a first or control implant including a first acoustic transducer, and a second implant including a switch and a second acoustic transducer coupled to the switch. The second acoustic transducer receives acoustic signals from the first acoustic transducer for closing the switch to activate the second implant. The second implant may include a sensor for measuring a physiological parameter that is transmitted using acoustic signals including the physiological data to the first implant. For example, the second implant may measure pressure in the patient's heart that may be used by the first implant to control a pacemaker. Alternatively, the second implant may blood sugar concentration that may be used by the first implant to control an insulin pump. Alternatively, the first implant may store and transfer the data to an external device for monitoring the patient.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
Endovascular devices and methods of use
ActiveUS20090177090A1StethoscopeHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesBalloon catheterIntravascular device
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Apparatus and methods for monitoring physiological data during environmental interference
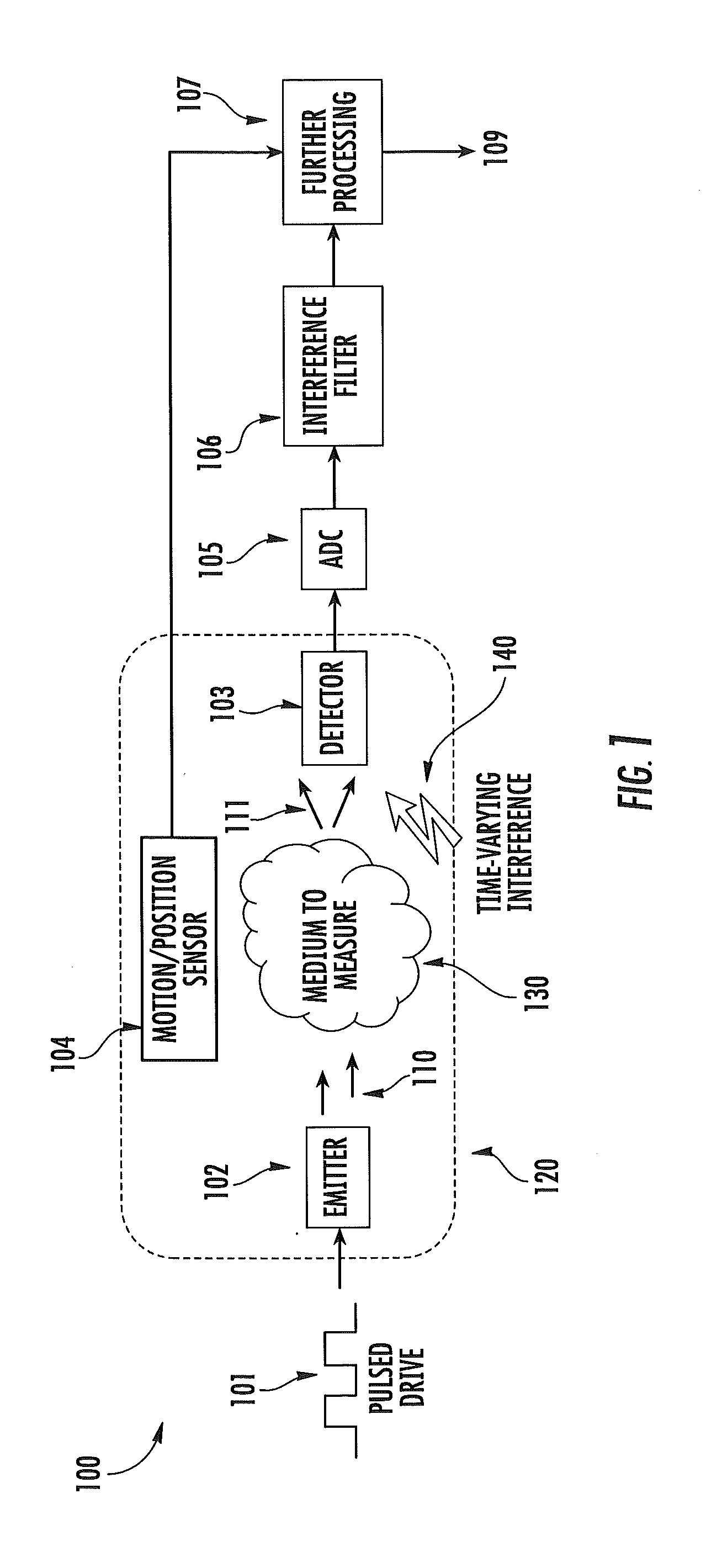
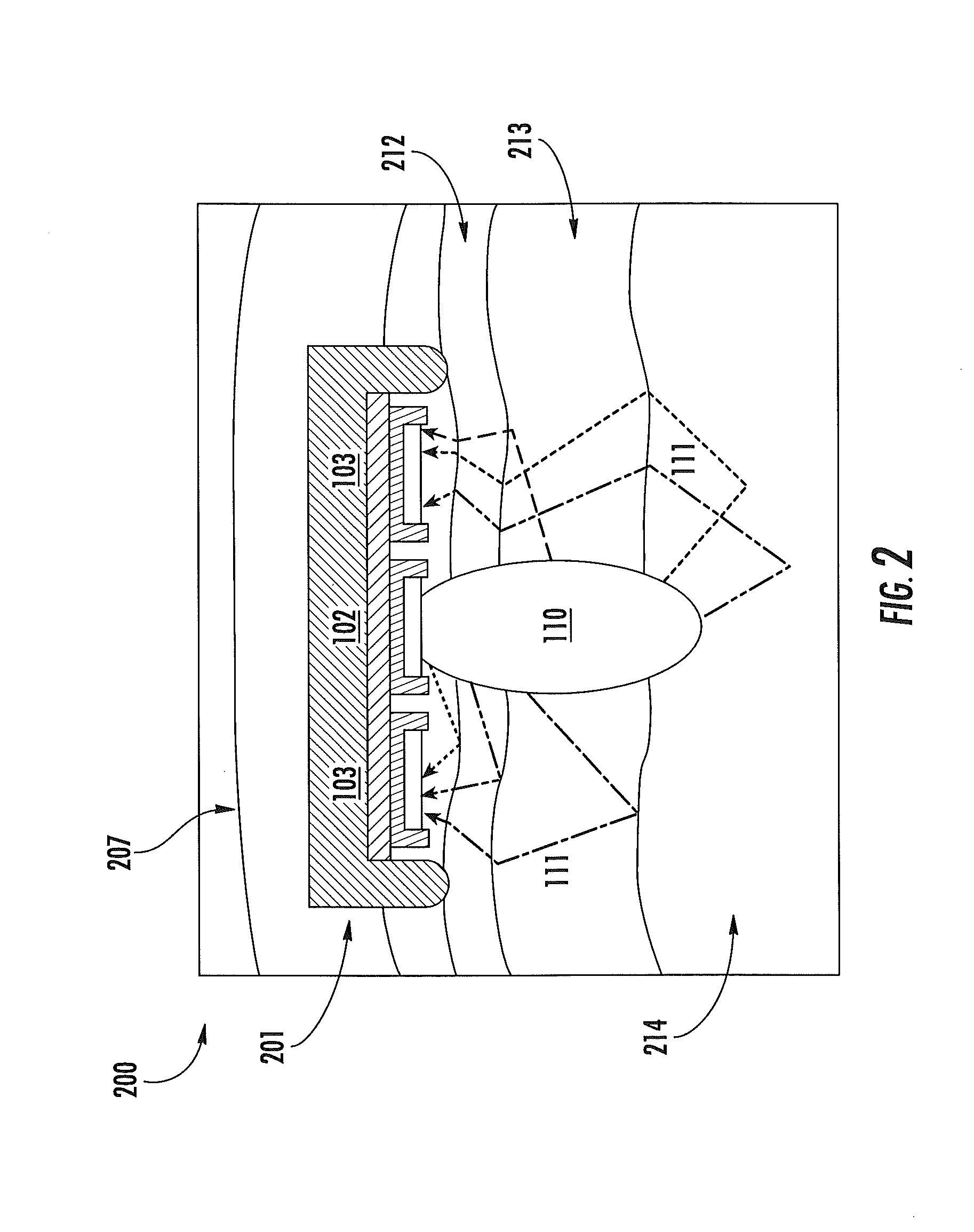
ActiveUS20120197093A1Easy to keepMaximize collectionHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal changeEngineering
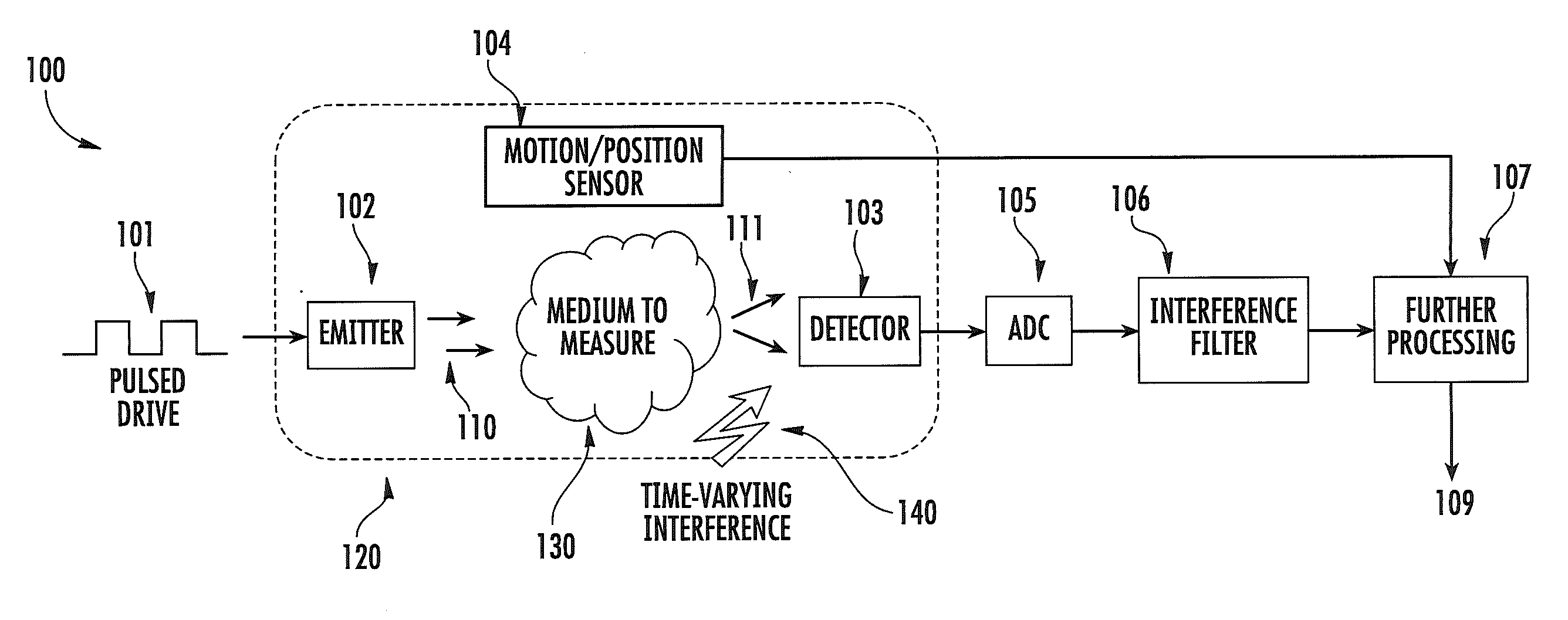
Apparatus and methods for attenuating environmental interference are described. A wearable monitoring apparatus includes a housing configured to be attached to the body of a subject and a sensor module that includes an energy emitter that directs energy at a target region of the subject, a detector that detects an energy response signal—or physiological condition—from the subject, a filter that removes time-varying environmental interference from the energy response signal, and at least one processor that controls operations of the energy emitter, detector, and filter.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com