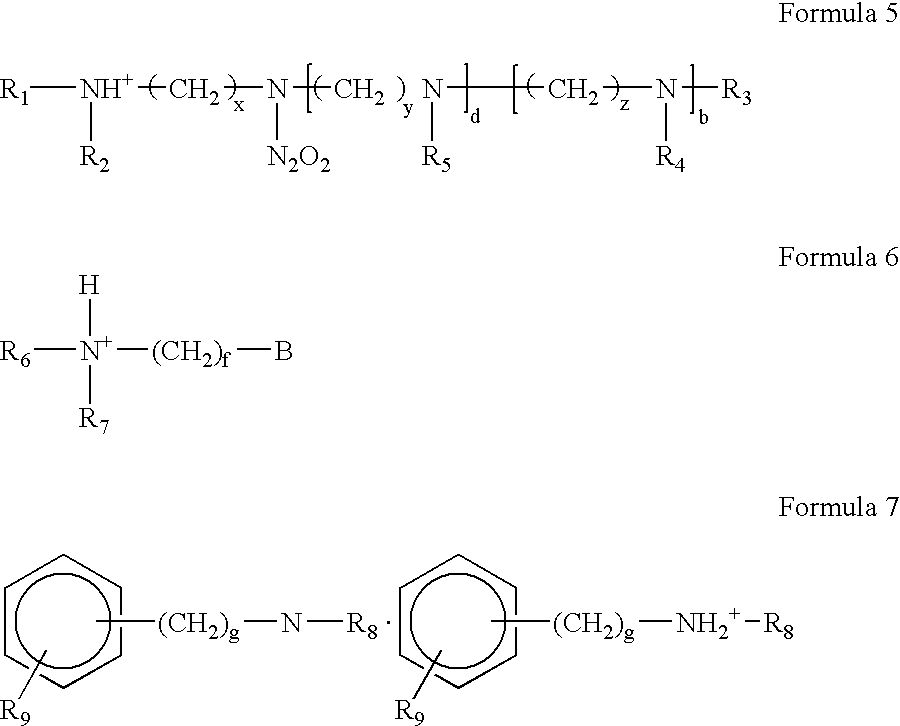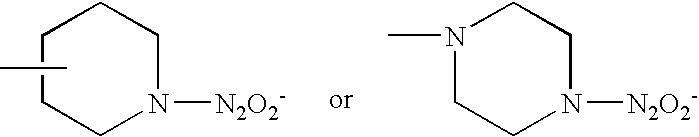Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
354results about How to "Prevent restenosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
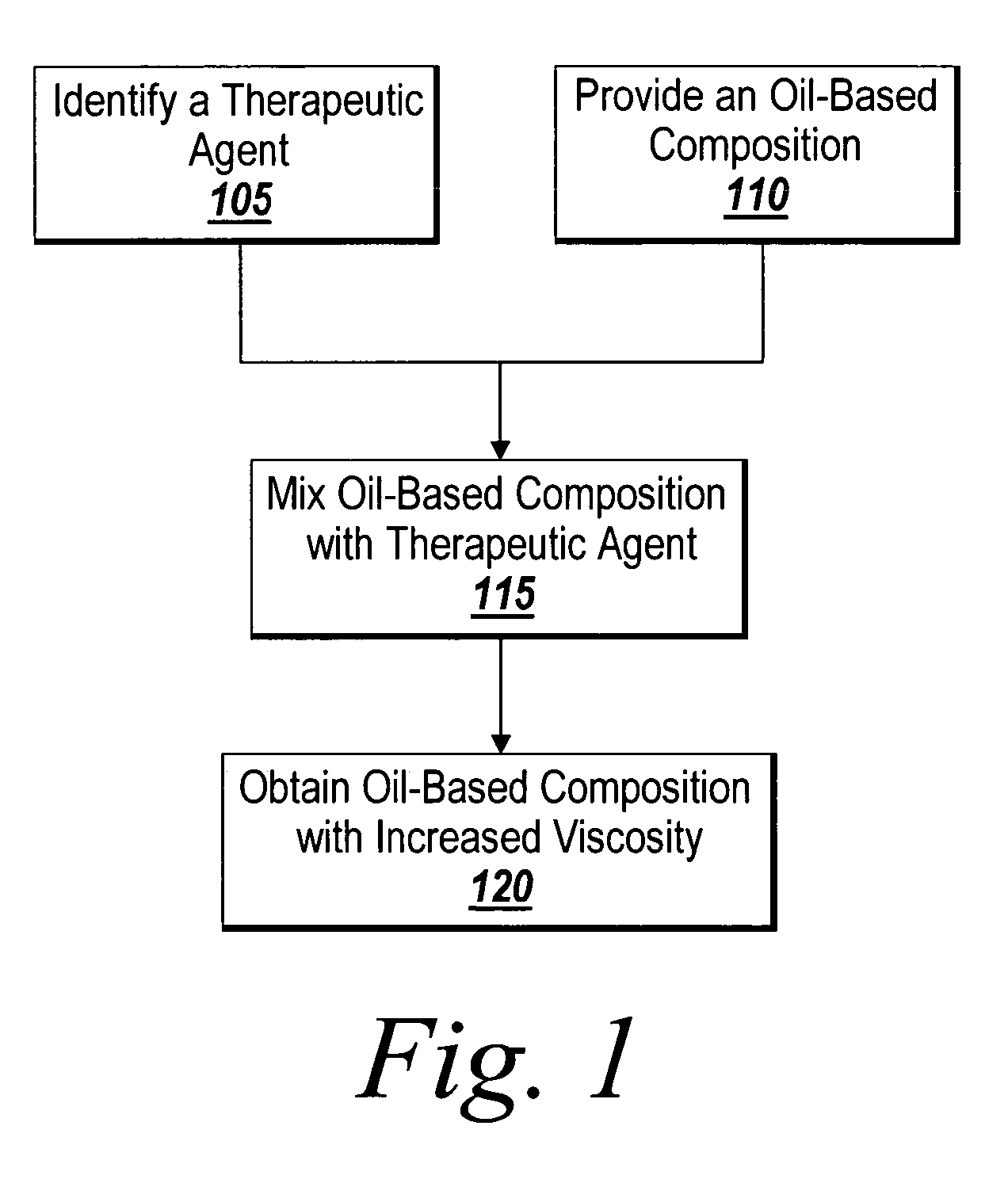
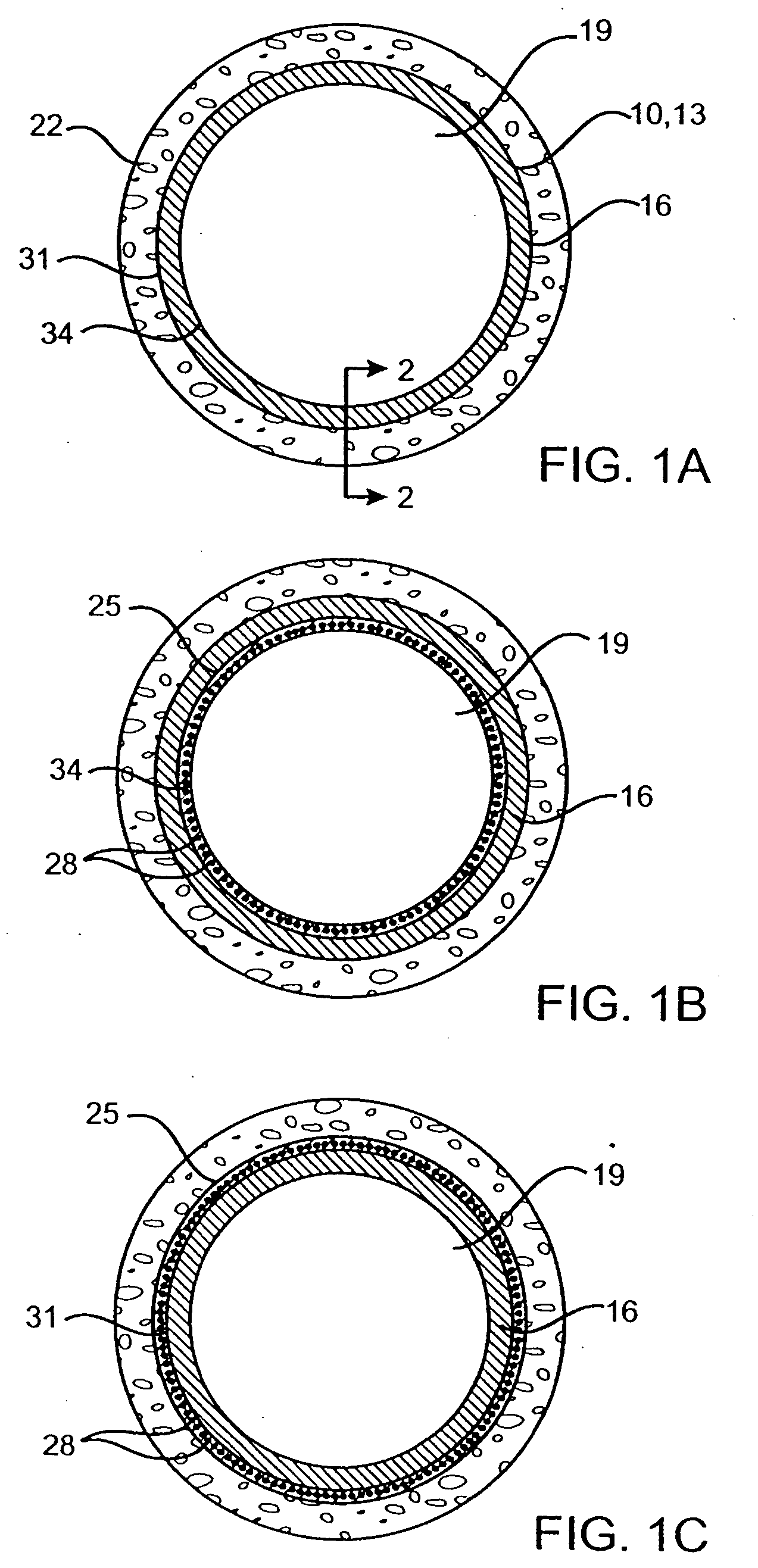
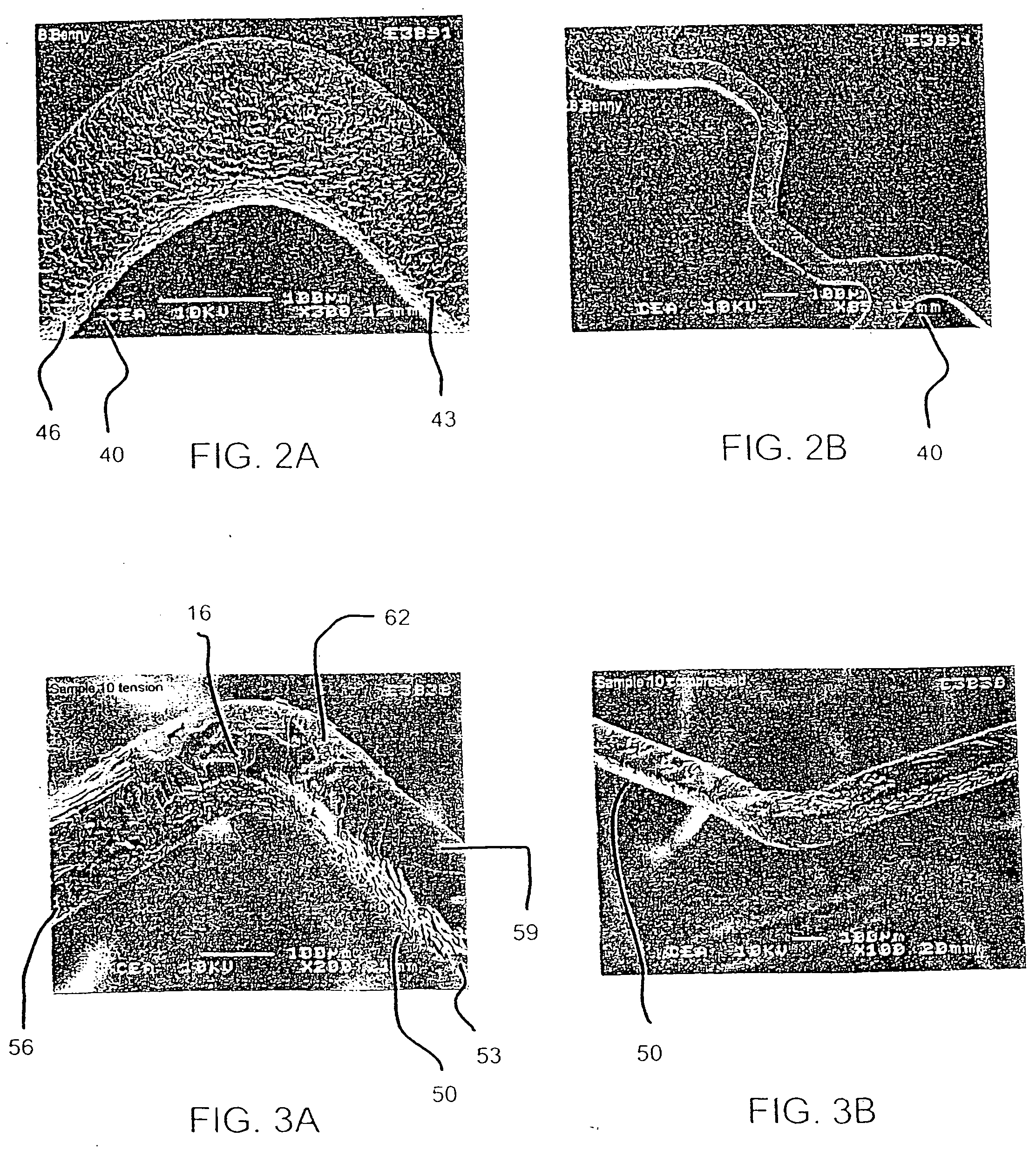
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
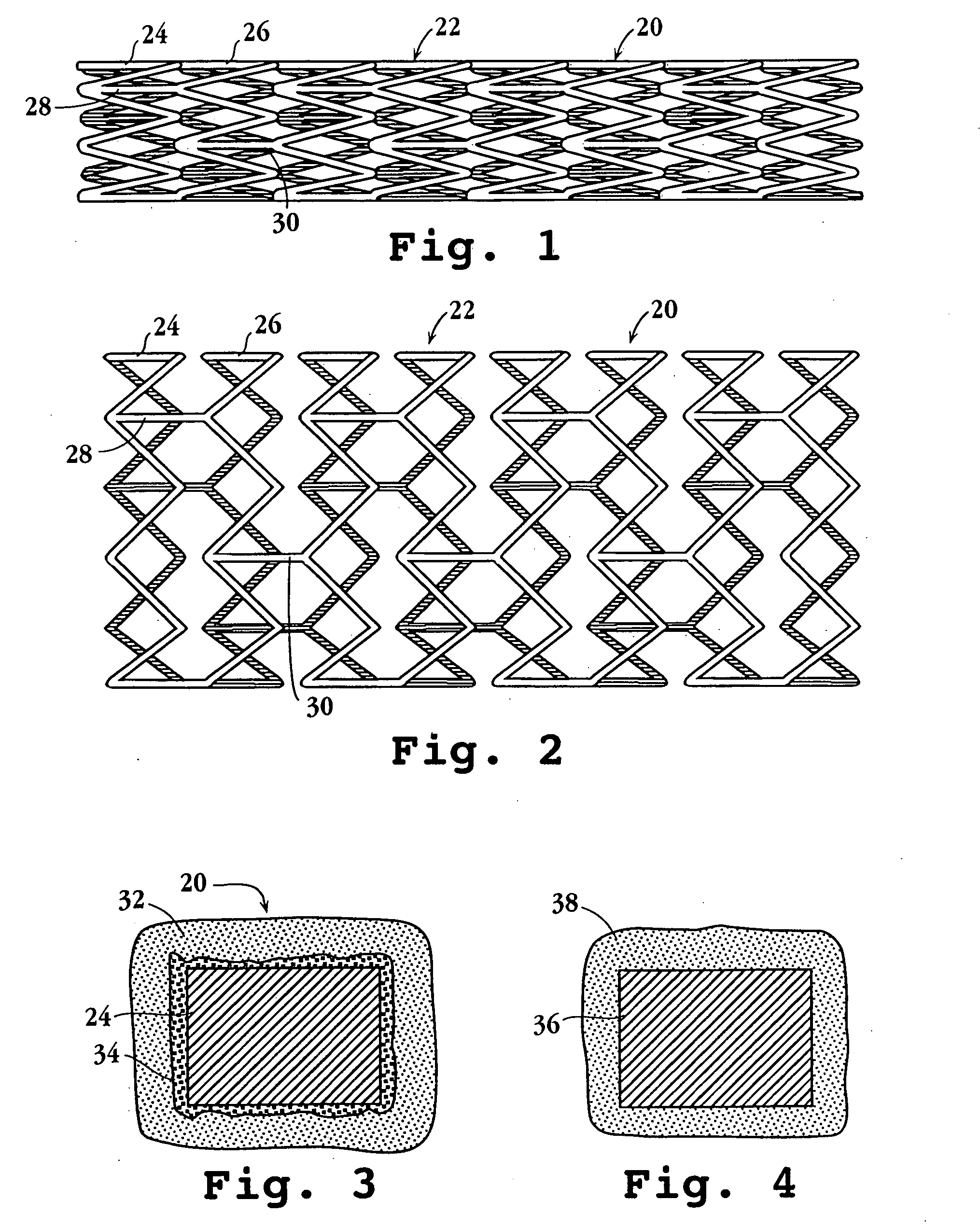
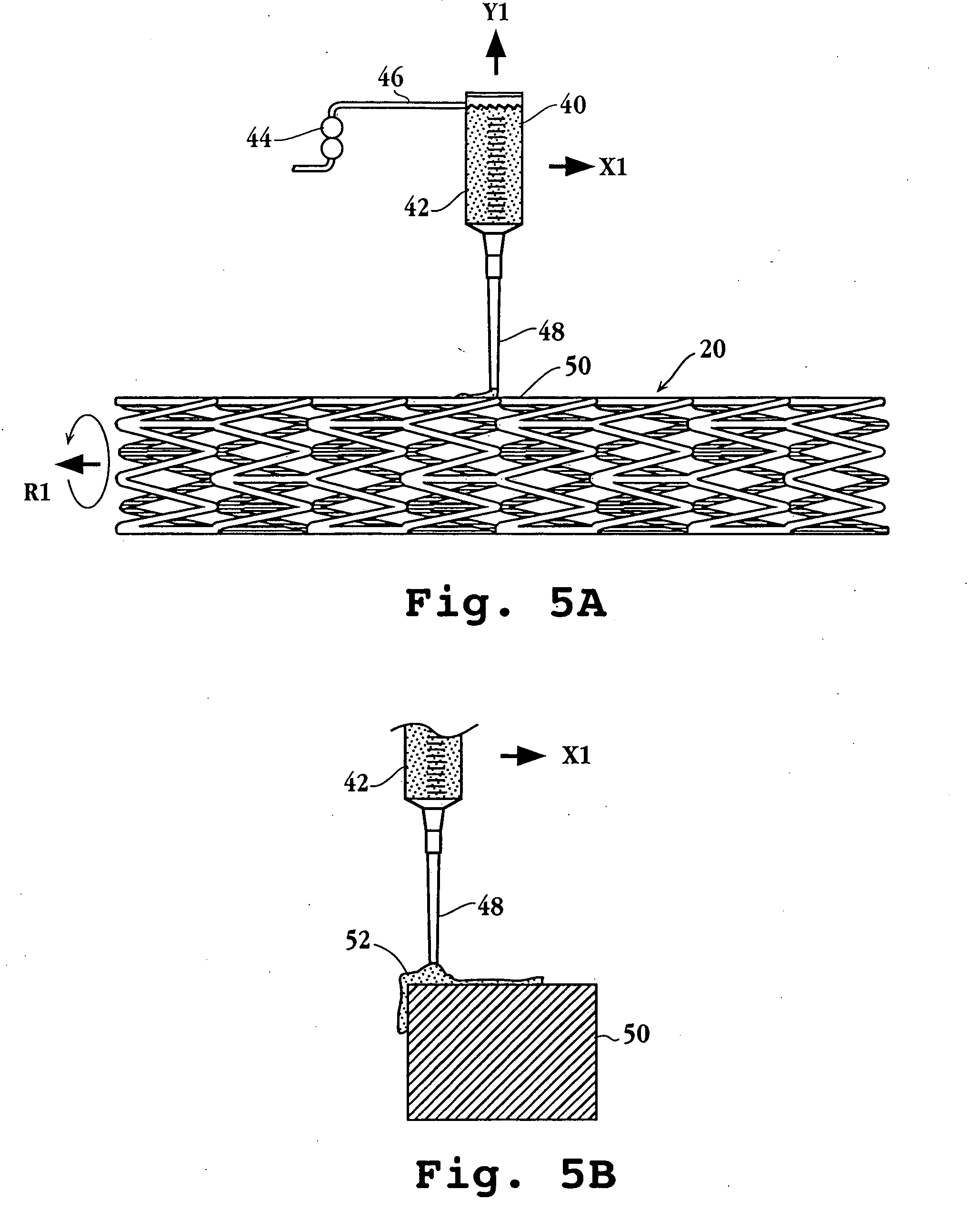
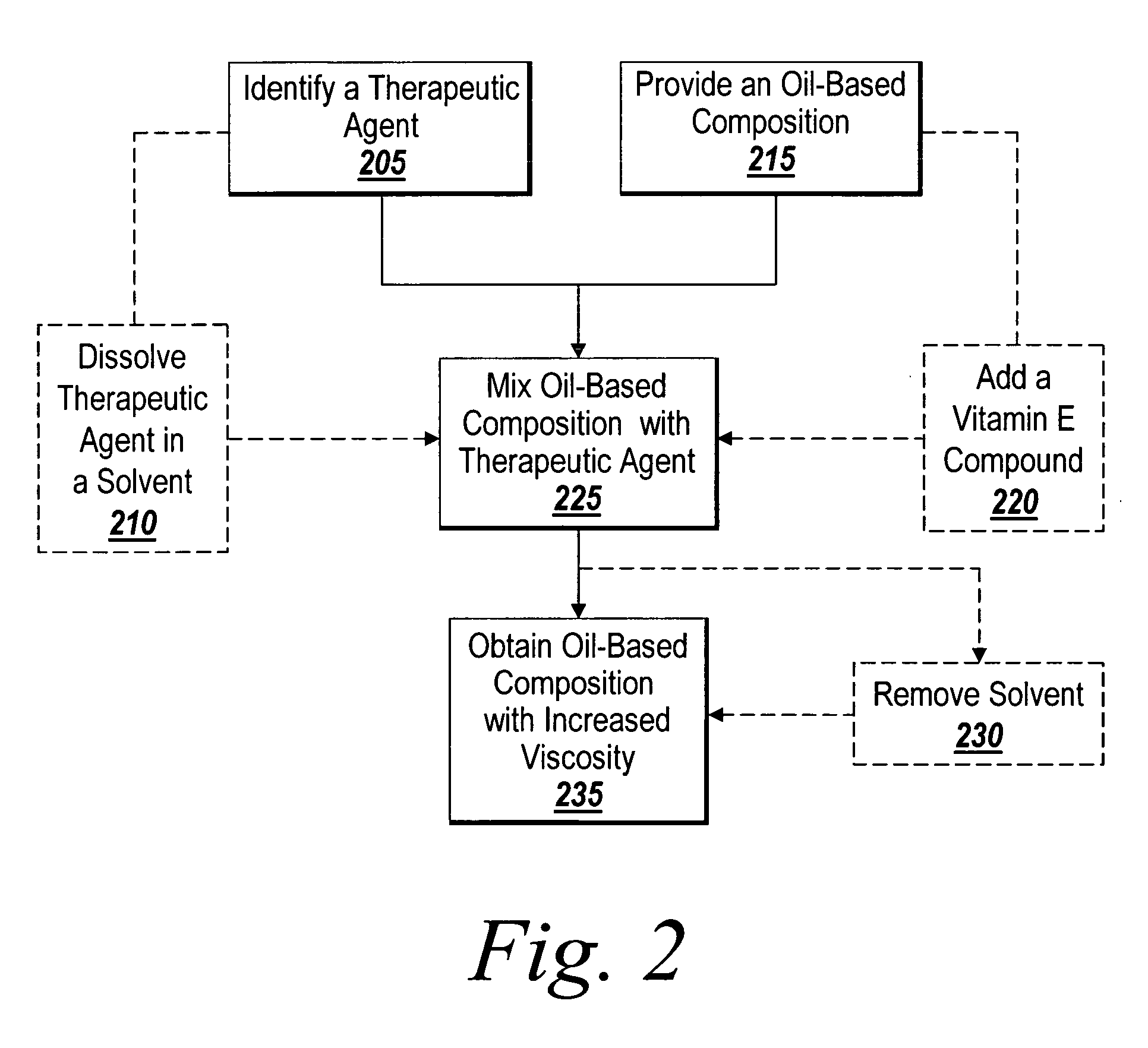
Drug-delivery endovascular stent and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20050038505A1Prevent restenosisEfficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPolymer substrateInsertion stent
An intravascular stent and method for inhibiting restenosis, following vascular injury, is disclosed. The stent has an expandable, linked-filament body and a drug-release coating formed on the stent-body filaments, for contacting the vessel injury site when the stent is placed in-situ in an expanded condition. The coating releases, for a period of at least 4 weeks, a restenosis-inhibiting amount of a monocyclic triene immunosuppressive compound having an alkyl group substituent at carbon position 40 in the compound. The stent, when used to treat a vascular injury, gives good protection against clinical restenosis, even when the extent of vascular injury involves vessel overstretching by more than 30% diameter. Also disclosed is a stent having a drug-release coating composed of (i) 10 and 60 weight percent poly-d / -lactide polymer substrate and (ii) 40-90 weight percent of an anti-restenosis compound, and a polymer undercoat having a thickness of between 1-5 microns.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
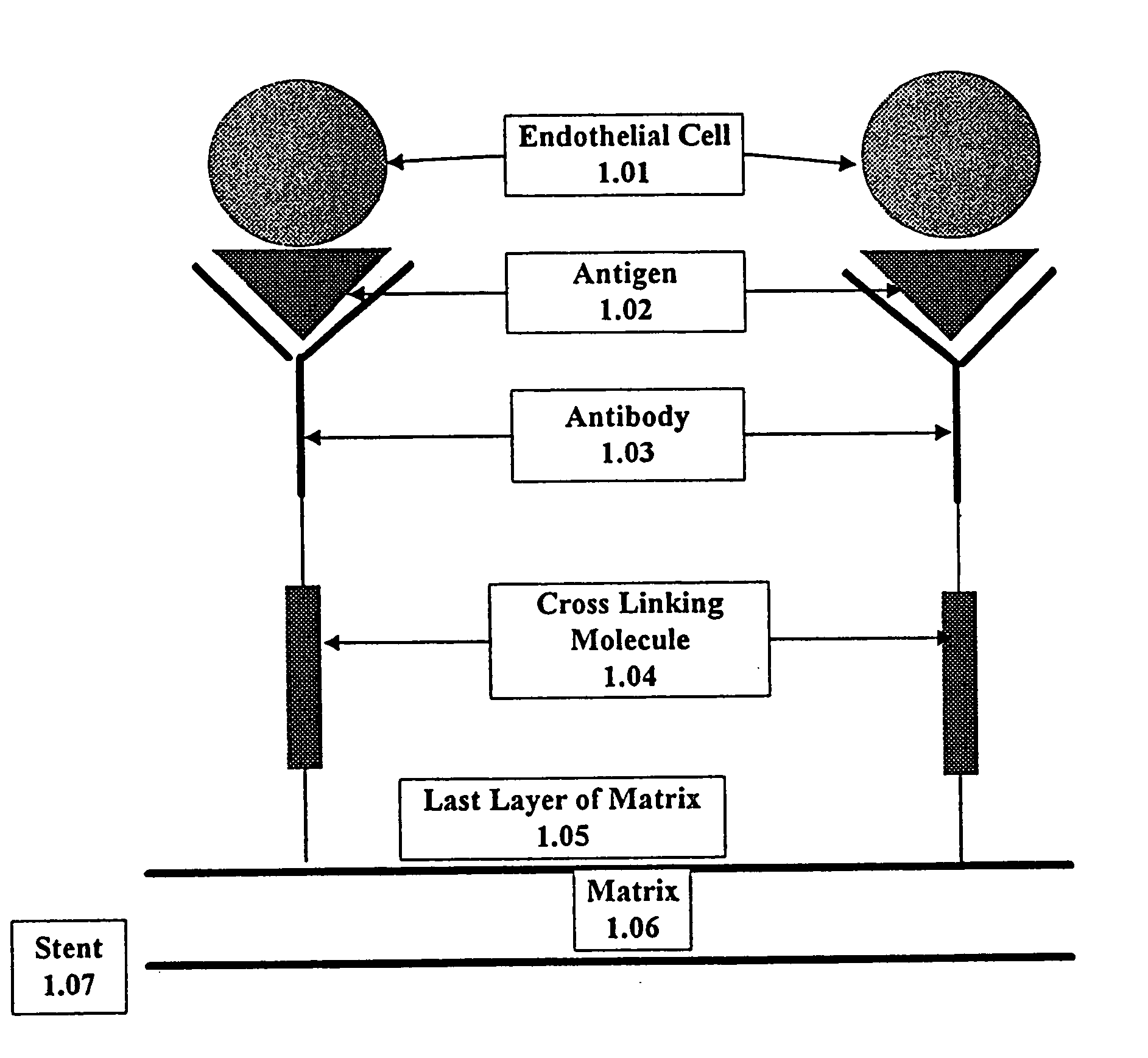
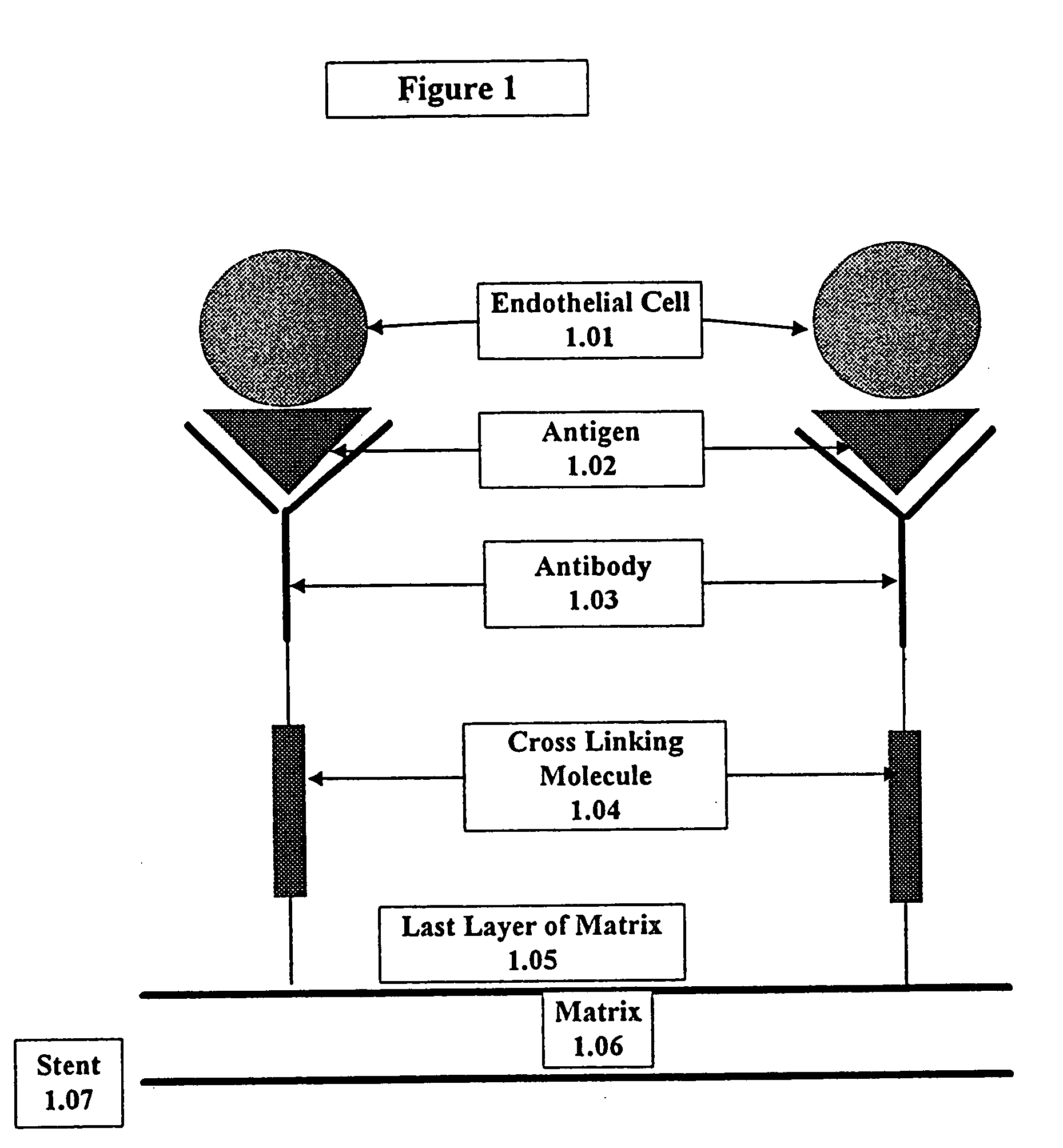
Medical device with coating that promotes cell adherence and differentiation
InactiveUS20030229393A1Improve prognosisPrevent restenosisOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesAntigenPercent Diameter Stenosis
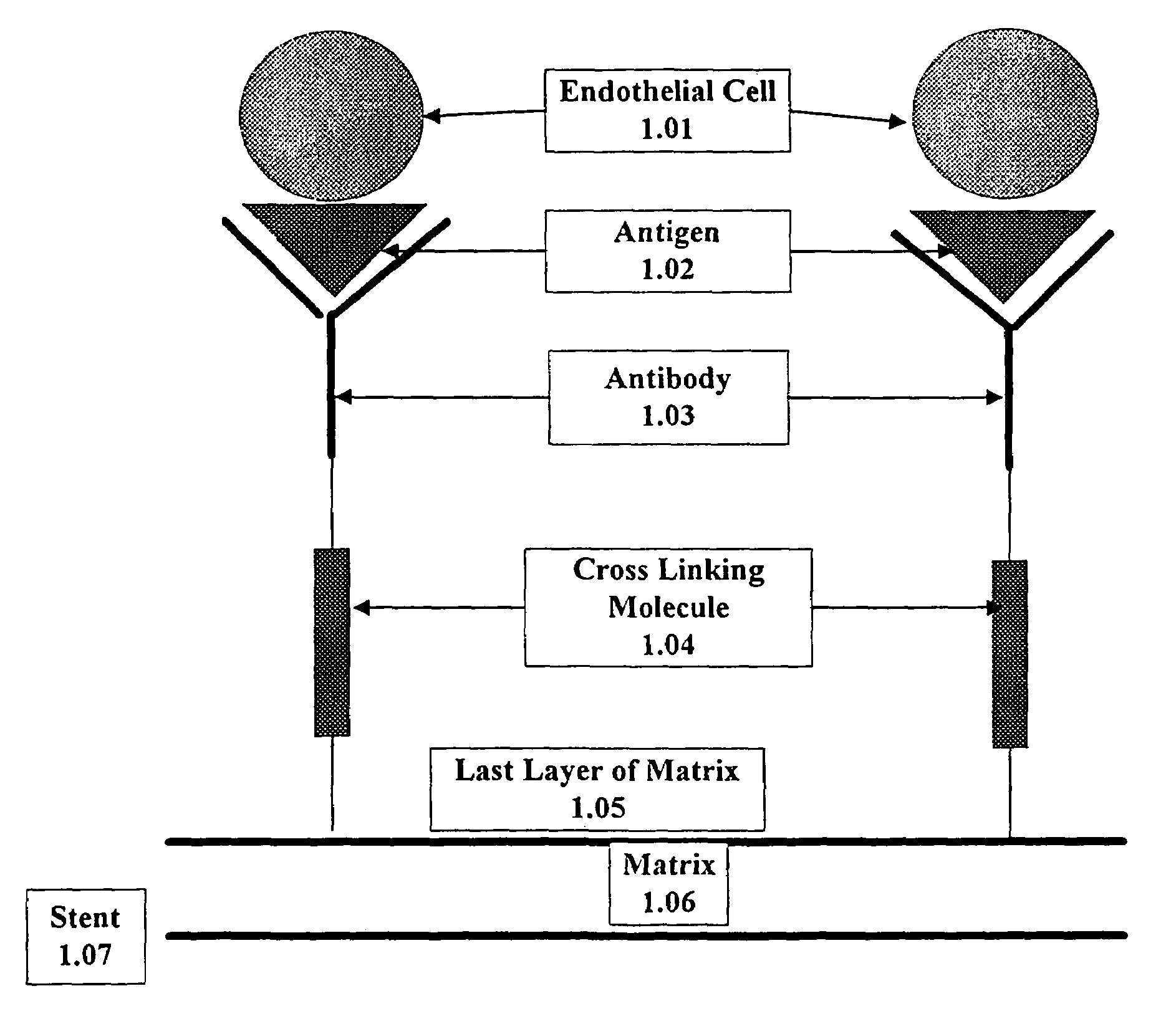
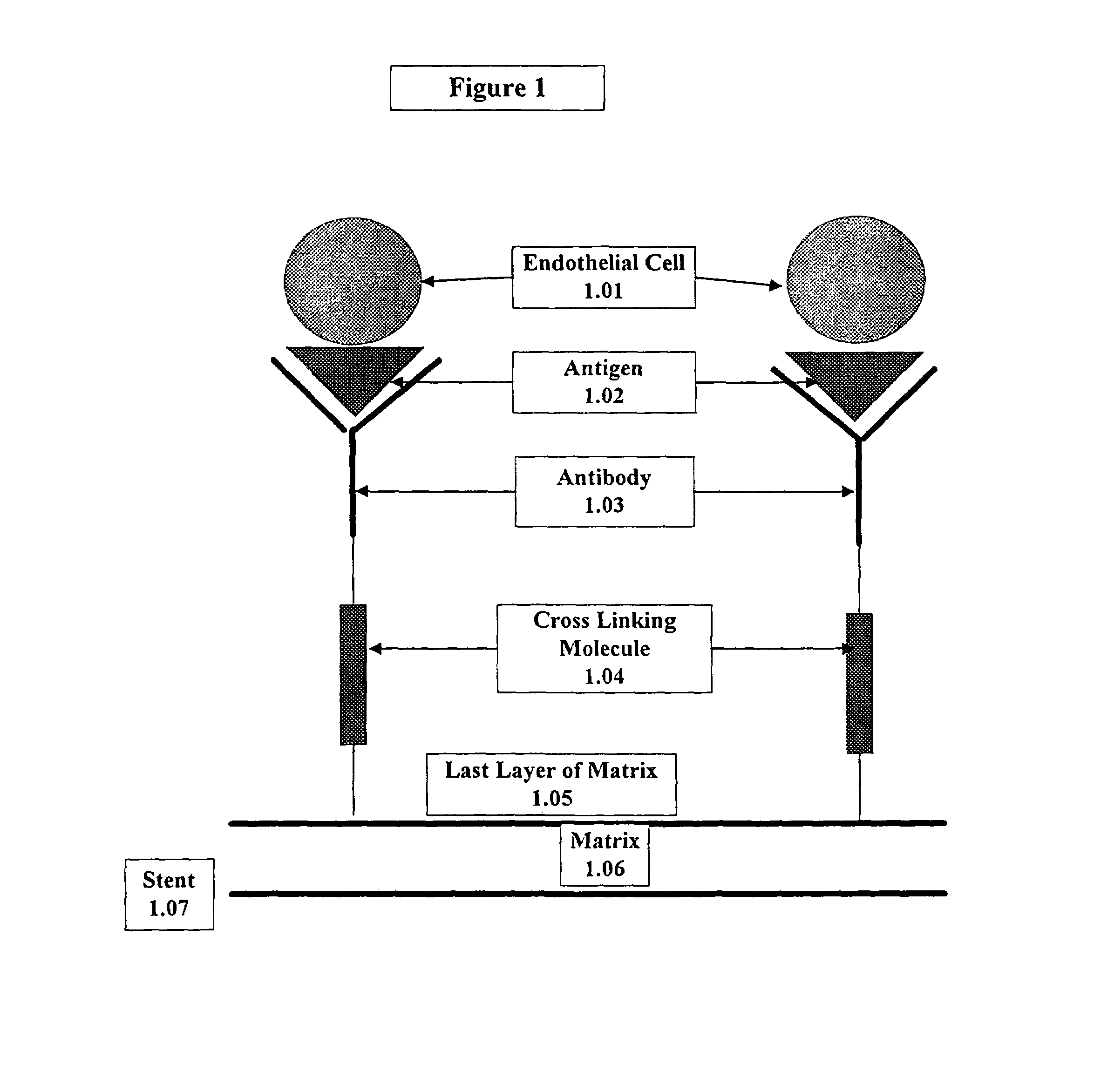
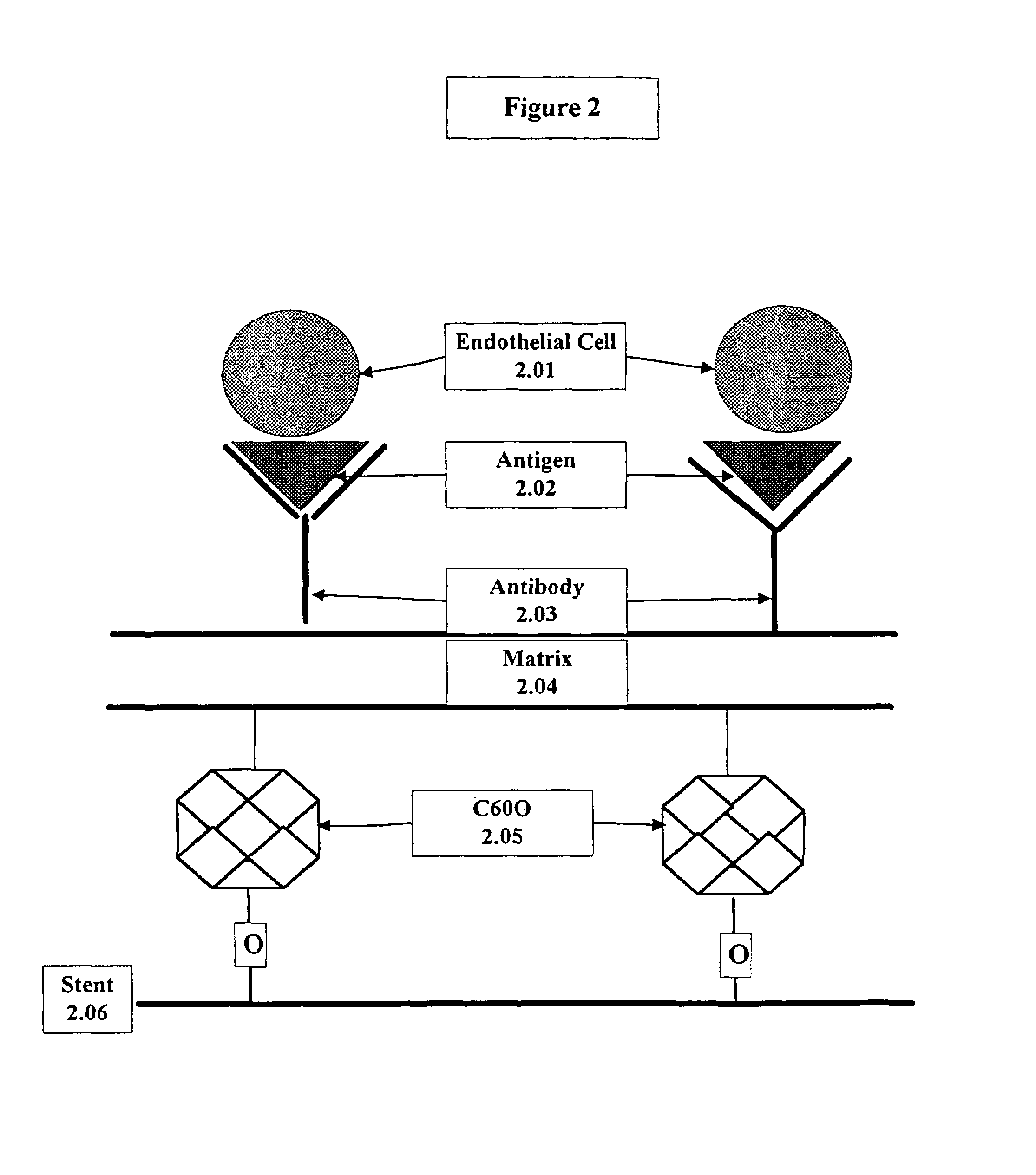
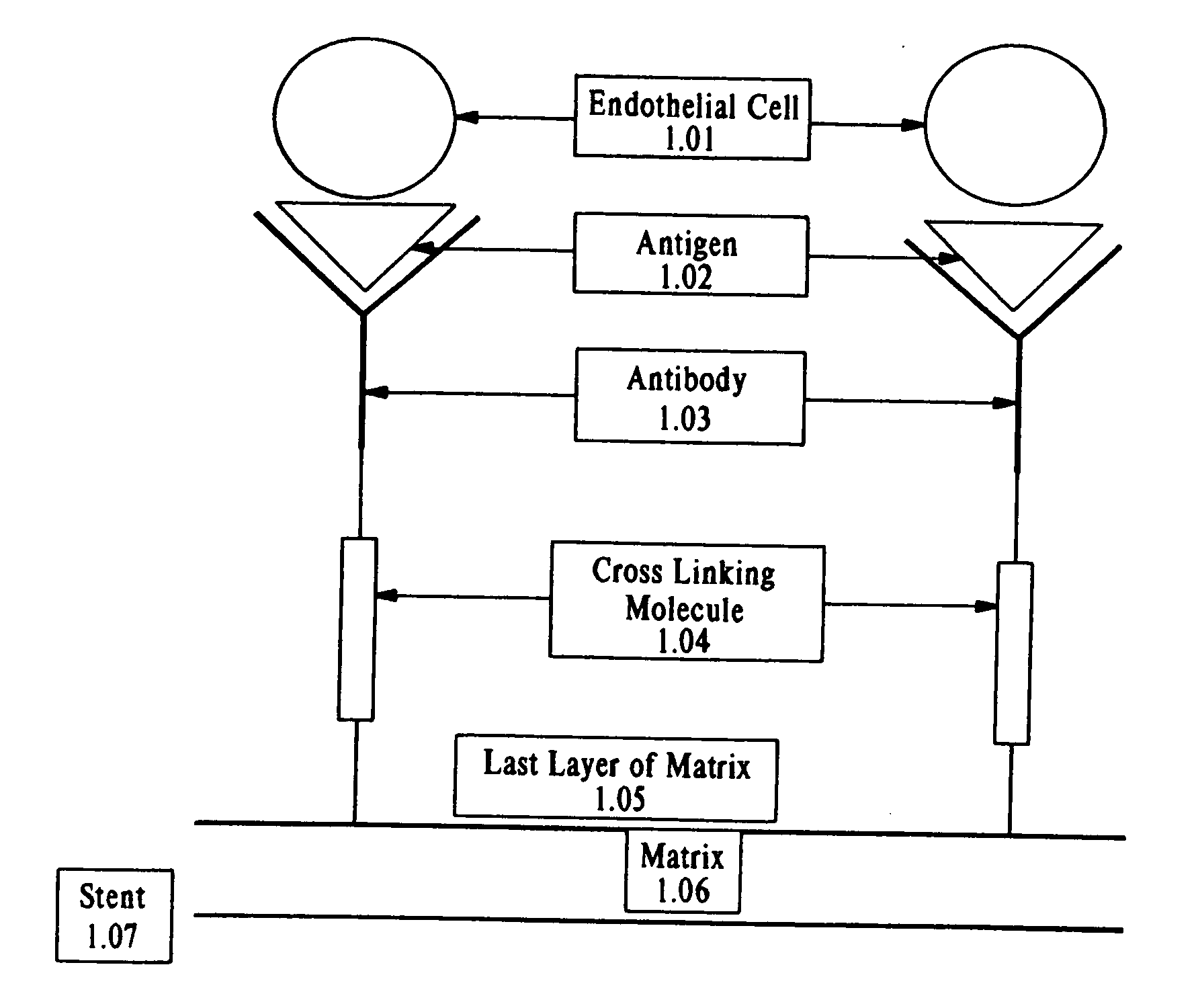
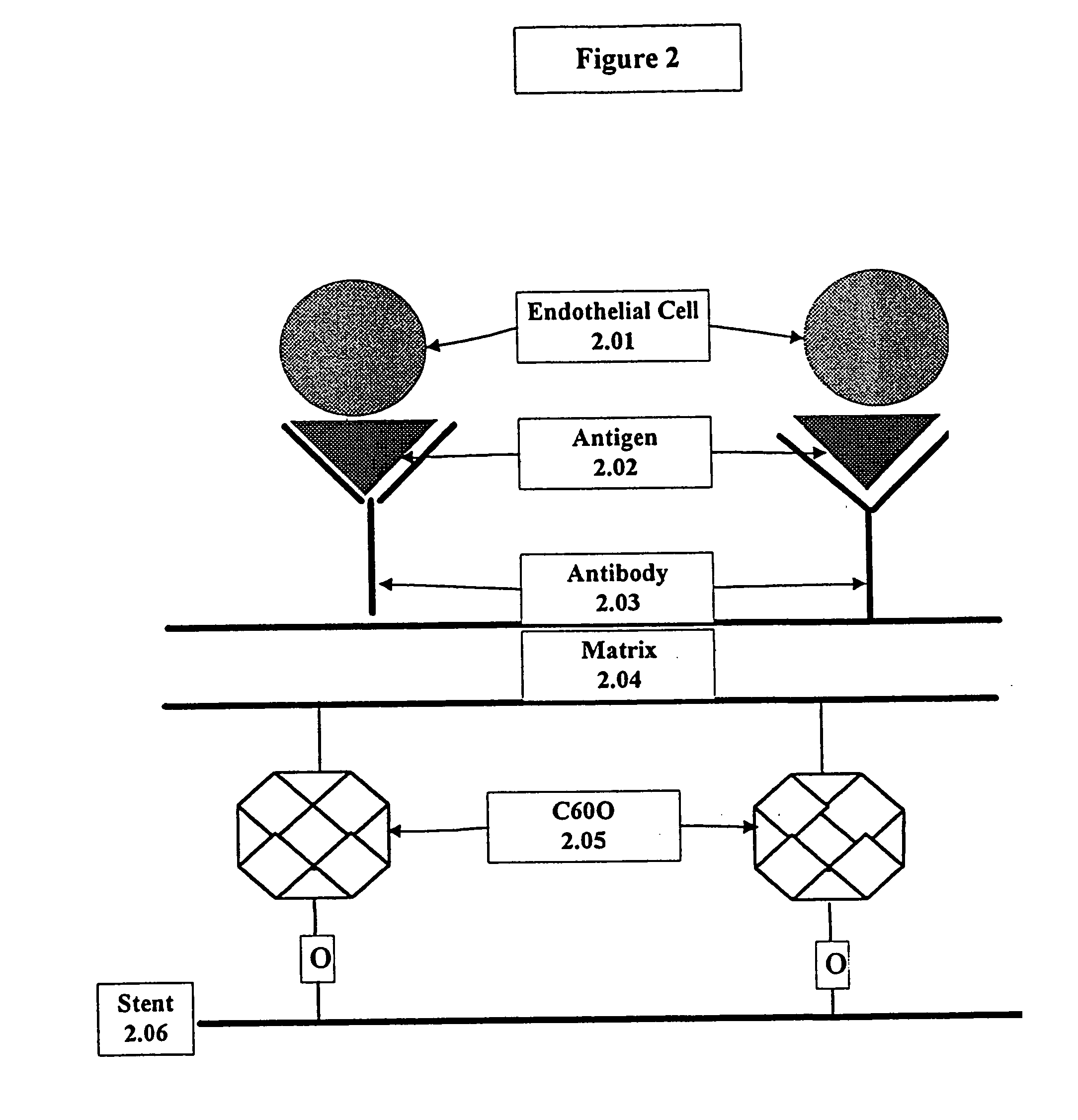
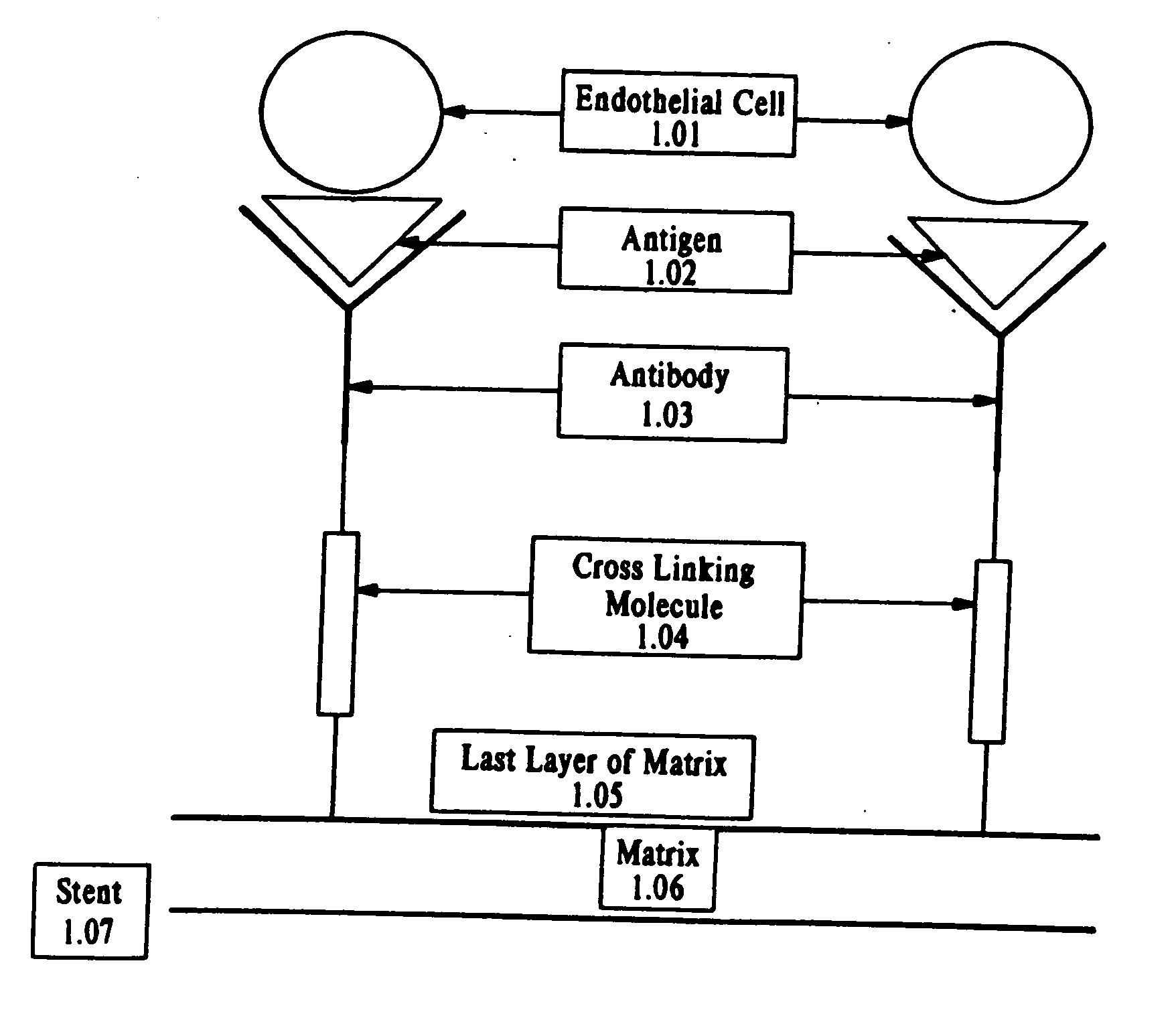
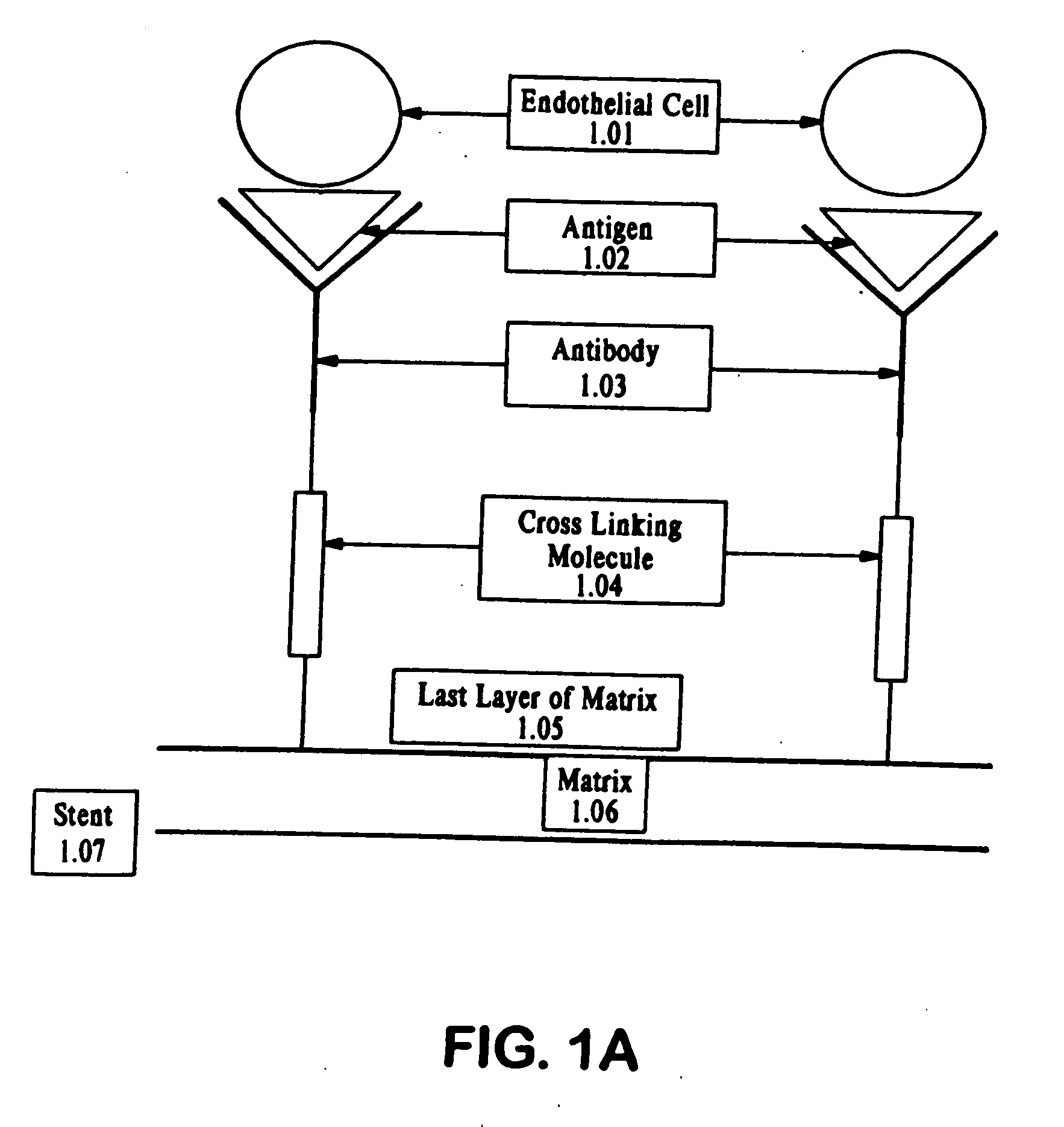
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Delivery of therapeutic capable agents
The present invention provides improved stents and other prostheses for delivering substances to vascular and other luminal and intracorporeal environments. In particular, the present invention provides for therapeutic capable agent eluting stents with minimized undesirable loss of the therapeutic capable agent during expansion of the stent.
Owner:ALTAI MEDICAL TECH
Progenitor endothelial cell capturing with a drug eluting implantable medical device
InactiveUS20050271701A1Increased formationSmooth migrationStentsHeart valvesProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is coated with a pharmaceutical composition consisting of a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises a ligand such as an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Liquid and low melting coatings for stents
InactiveUS20030083740A1Prevent restenosisRestenosis may be prevented or lessenedStentsSurgeryAngioplasty balloonWax
A method for forming liquid coatings for medical devices such as stents and angioplasty balloons is provided. The liquid coatings can be made from biodegradable materials in liquid, low melting solid, or wax forms, which preferably degrade in the body without producing potentially harmful fragments. The liquid coatings may also contain biologically active components, which are released from the coatings through diffusion from the coatings and the degradation of the coatings.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP +1
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
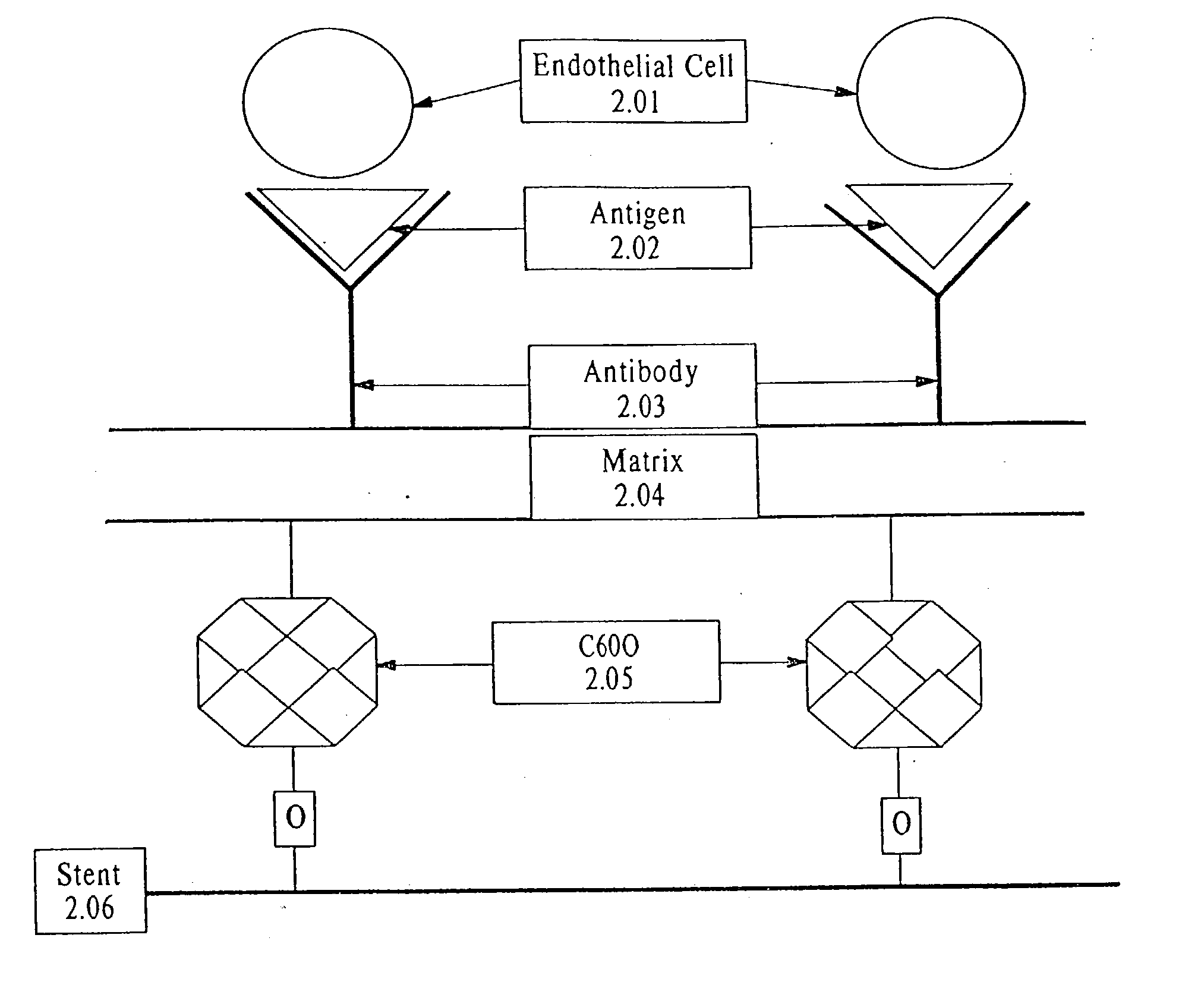
InactiveUS7037332B2Prevent restenosisMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsCell Surface AntigensPercent Diameter Stenosis
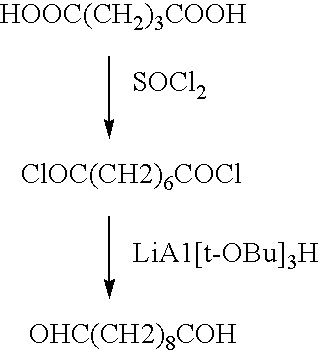
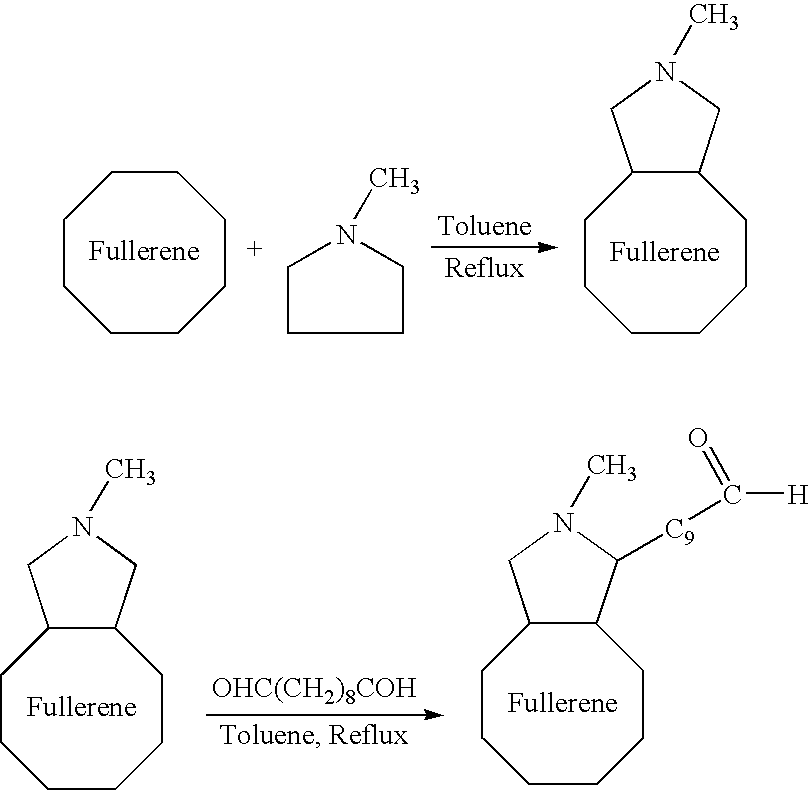
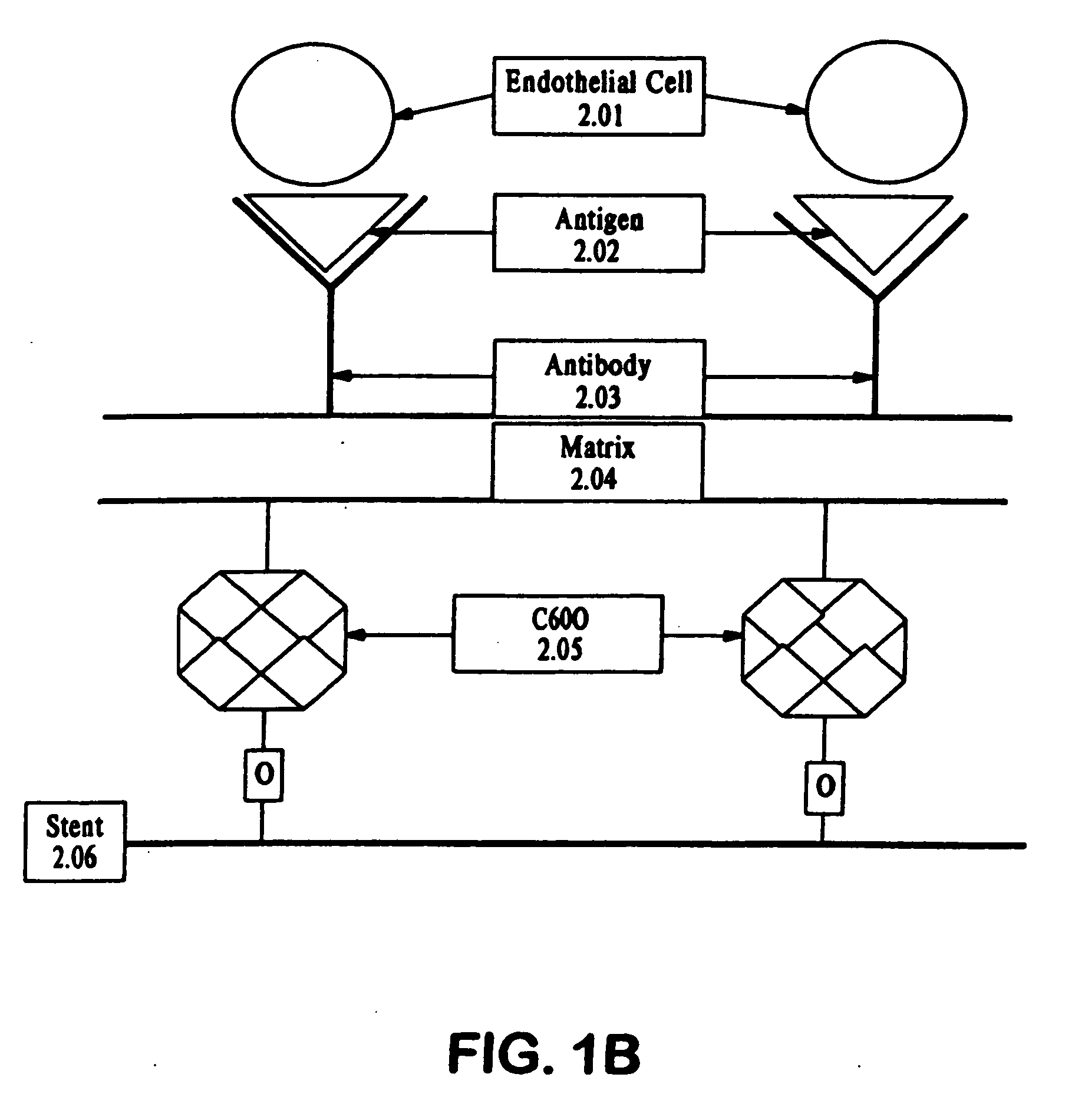
A medical device coated with one or more antibodies and one or more layers of a matrix is disclosed. The antibodies or fragments thereof react with an endothelial cell surface antigen. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for producing the medical device. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of a synthetic material, such as a fullerene, or a naturally occurring material. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote the adherence of cells captured in vivo on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. By facilitating adherence of cells to the surface of the medical device, the disclosed methods and compositions will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Stem cell therapy for cardiac valvular dysfunction
InactiveUS20080050347A1Raise transfer toReduce needBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSexual dysfunctionTricuspid valve function
Disclosed are methods, compounds and compositions useful for treatment of a patient with valvular dysfunction. The invention relates to using stem cells, modified stem cells, derivatives thereof, and agents stimulatory to stem cells in order to substantially ameliorate, and in some cases induce a therapeutic benefit, to a patient suffering from a dysfunction of the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, or pulmonary valve. In some embodiments the invention treats the valve dysfunction itself, whereas in other embodiments treatment of associated cardiac structures is performed. Furthermore, in other embodiments the invention permits physiological compensation for the valve dysfunction, prolonging the time until surgical intervention is needed.
Owner:MEDISTEM LAB
Atherectomy methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20080161840A1Small sizeReduce harmCannulasFluid jet surgical cuttersAtherectomyThree vessels
Apparatus is provided for removing plaque from a blood vessel of a subject, including a catheter shaped to define an opening that is placed in the blood vessel. A pressure source propels a fluid jet through the opening, and a pressure sensor detects a pressure in the blood vessel induced by the jet. A control unit steers the jet in response to the detected pressure. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:VASCURE
Method of thickening a coating using a drug
InactiveUS20060083768A1Prevent restenosisInhibit neointimal growthBiocideStentsNuclear medicineMedical device
A method for the provision of a coating on an implantable medical device results in a medical device having a bio-absorbable coating. The coating includes a bio-absorbable carrier component. In addition to the bio-absorbable carrier component, a dissolved therapeutic agent component can also be provided. The coated medical device is implantable in a patient to effect controlled delivery of the coating, including the dissolved therapeutic agent, to the patient.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
InactiveUS20050043787A1Prevent restenosisPreventing other thromboembolic complicationMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPolyethylene glycol
This invention provides compositions and methods for producing a medical device coated with a matrix and an antibody which reacts with an endothelial cell antigen. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of synthetic material, such as polyurethane, poly-L-lactic acid, cellulose ester or polyethylene glycol. In another embodiment, the matrix is composed of naturally occurring materials, such as collagen, fibrin, elastin, amorphous carbon. In a third embodiment, the matrix may be composed of fullerenes. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote adherence of endothelial cells on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the endothelial cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. Methods of preparing such composition and methods of treating a mammal with atherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstruction are disclosed. By facilitating adherence of endothelial cells to the surface of the medical device, the methods and compositions of this invention will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Use of hyaluronic acid and forms to prevent arterial restenosis
InactiveUS6022866APrevent restenosis of the arterial wallsPrevent restenosisBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPercent Diameter StenosisHyaluronic acid
PCT No. PCT / CA93 / 00388 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 24, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 24, 1995 PCT Filed Sep. 22, 1993 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 07505 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 14, 1994A method is provided of inhibiting the narrowing of the vascular tubular walls of an animal by the proliferation of endothelial cells in the area of trauma after the vascular tubular walls have been traumatized, the method comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective non-toxic amount of a form of hyaluronic acid selected from the group consisting of hyaluronic acid and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof to the animal to inhibit the narrowing of the vascular tubular walls by the proliferation of endothelial cells into the area of trauma.
Owner:PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS +1
Extracorporeal pressure shock wave device
ActiveUS8556813B2Reduce edemaReduce inflammationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAcousticsFocal volume
Owner:SANUWAVE INC
Implantable stent with endothelialization factor
InactiveUS20060085062A1Promote endothelializationStrong adhesionStentsSurgeryEndoluminal stentInsertion stent
A stent is provided in combination with a growth factor, specifically pleiotrophin or an analog or derivative thereof, which promotes endothelialization of the stent and re-endothelialization of the stented region of an injured site in a body lumen. In particular applications, the stent is an endolumenal stent and the growth factor promotes healing via endothelialization and substantially prevents restenosis. The growth factor is delivered from the stent formulated as a protein or peptide, or as a gene transfer vector. Methods for the treatment of vascular injury using pleiotrophin are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Method and apparatus for treating aneurysms
A balloon catheter for isolating and treating an aneurysm in a vessel. The catheter including one or more inflatable balloons for defining an isolated volume within the vessel and for preventing any blood flow from coming into contact with the interior walls of the vessel outside the isolated volume. The catheter further including a lumen for injecting into the isolated volume a crosslinking agent, such as glutaraldehyde, for toughening the aneurysmal vessel wall.
Owner:LESCHINSKY BORIS
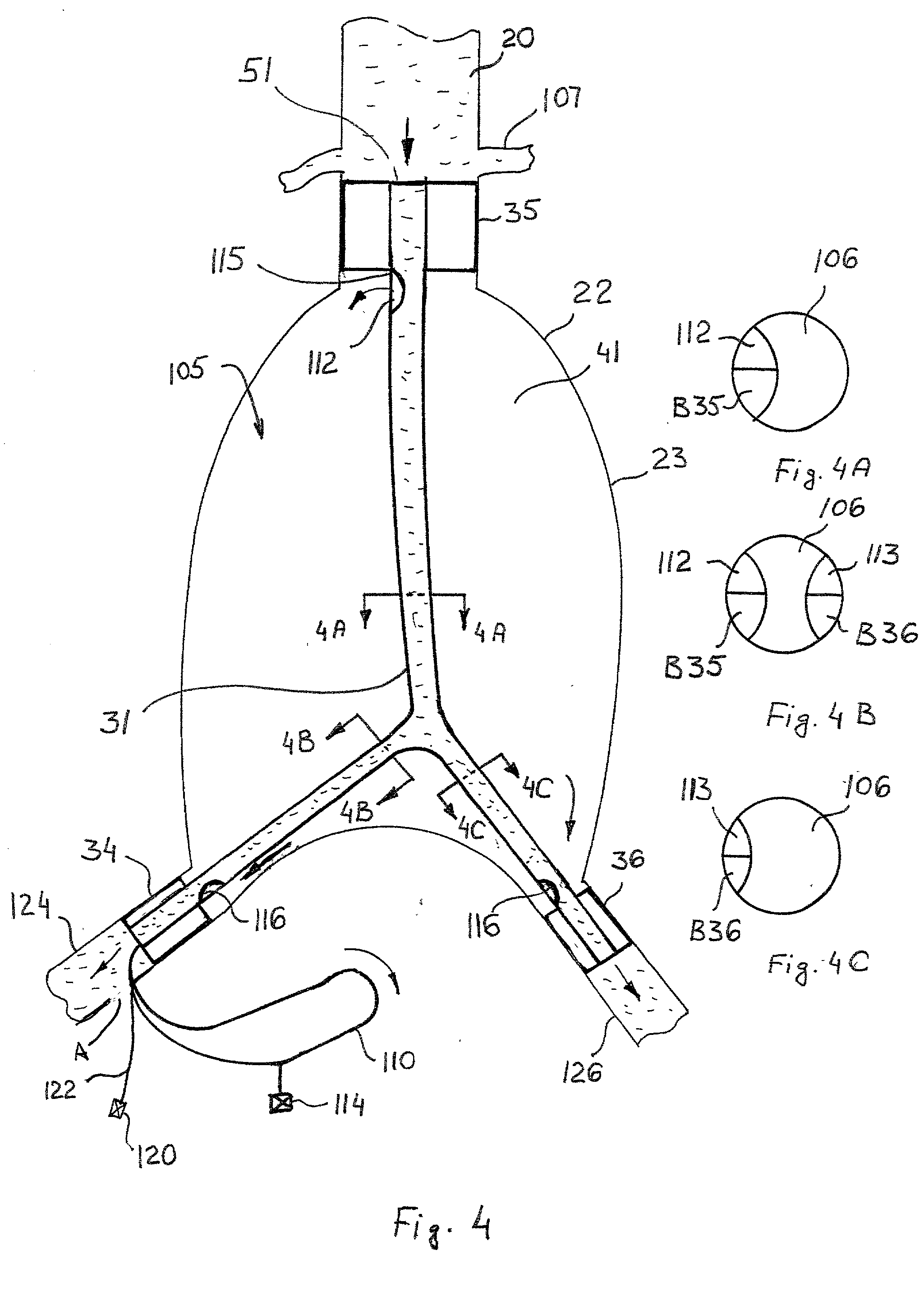
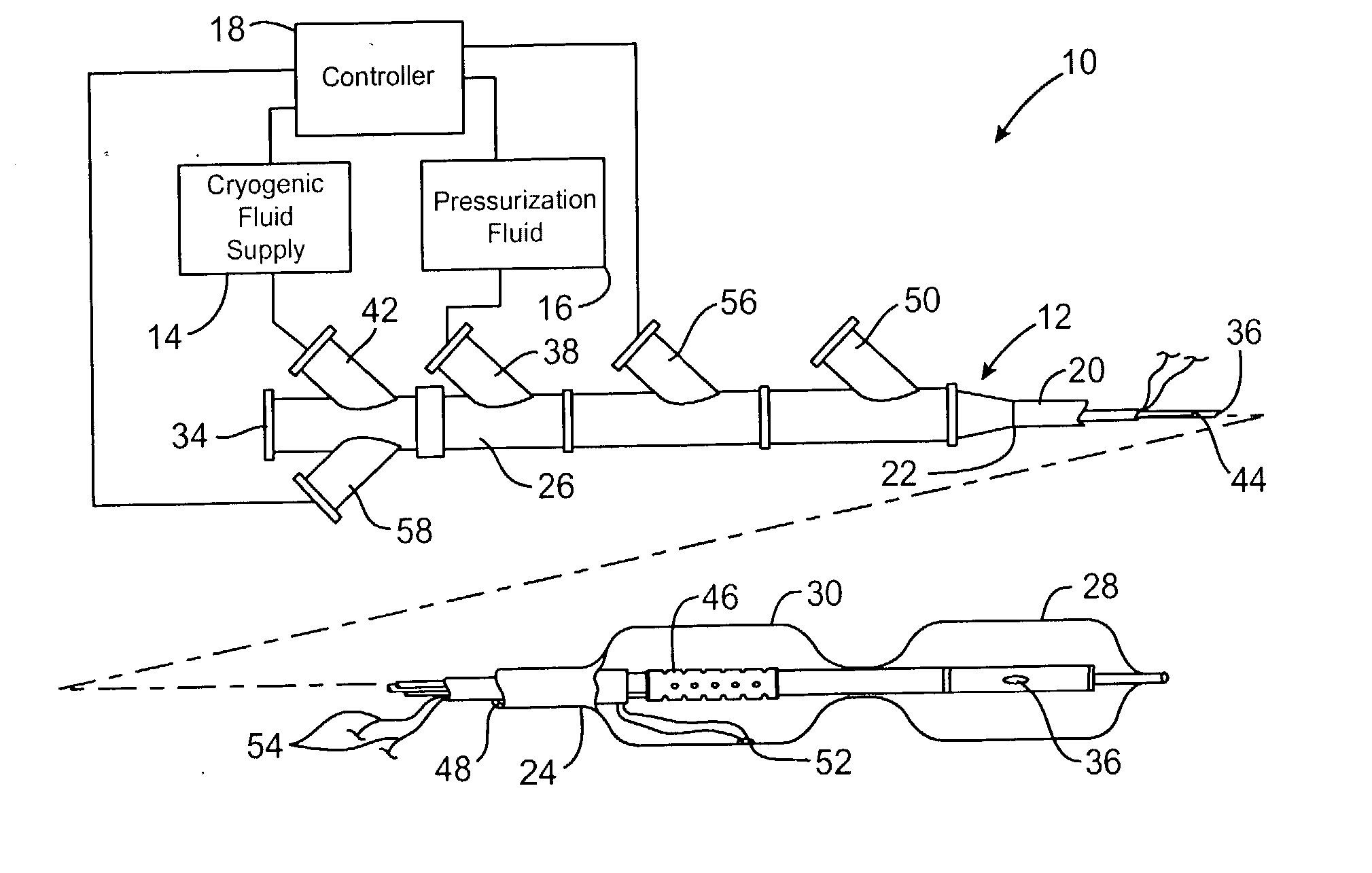
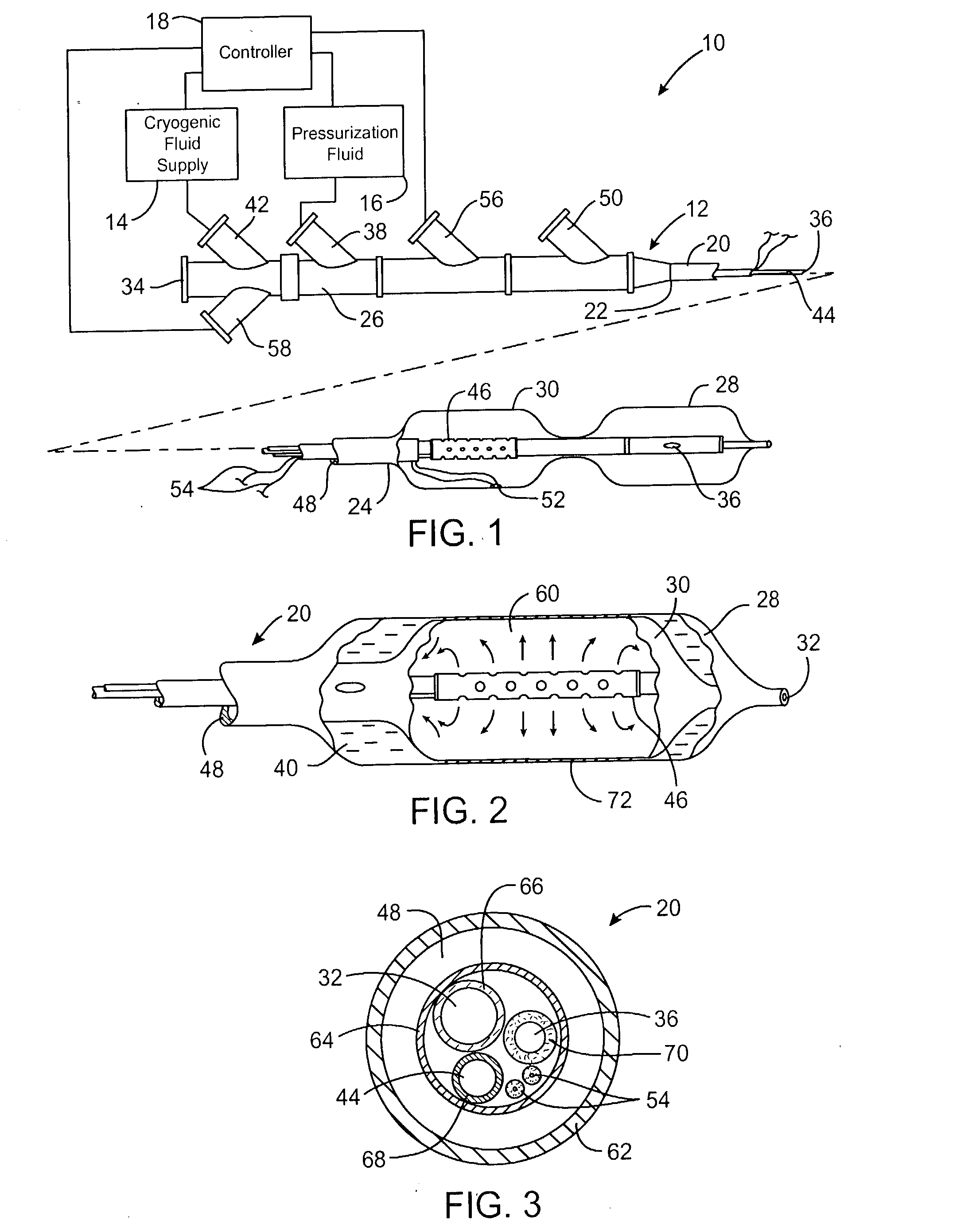
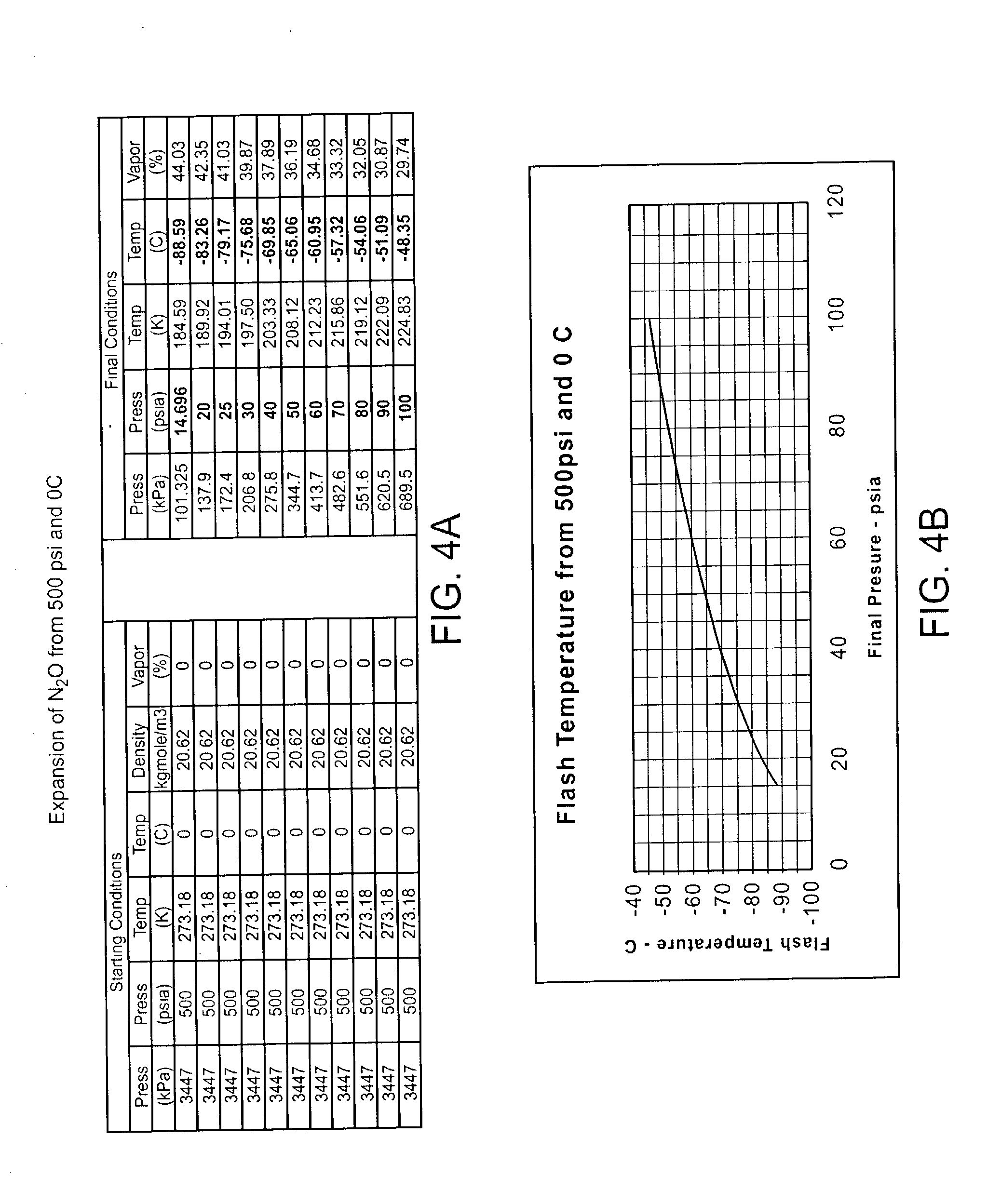
Cryogenically enhanced intravascular interventions
InactiveUS20030109912A1Reduce stenosisPrevent restenosisCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
Techniques and devices for treating atherosclerotic disease use controlled cryogenic cooling, often in combination with angioplasty and / or stenting. A combination cryogenic / angioplasty catheter may cool the diseased blood vessel before, during, and / or after dilation. Controlled cooling of the vessel wall reduces actual / observed hyperplasia as compared to conventional uncooled angioplasty. Similar reductions in restenosis may be provided for other primary treatments of the blood vessel, including directional arthrectomy, rotational arthrectomy, laser angioplasty, stenting, and the like. Cooling of vessel wall tissues will often be performed through plaque, and the cooling process will preferably take the thermodynamic effects of the plaque into account.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
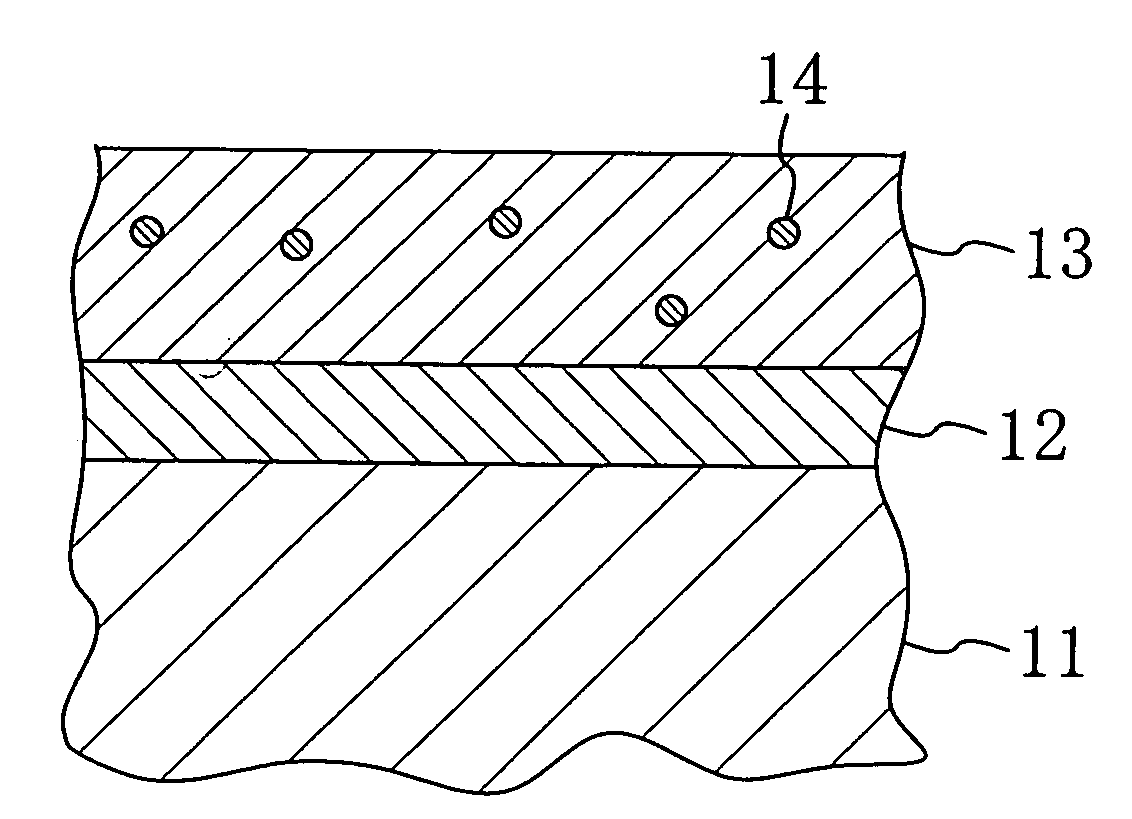
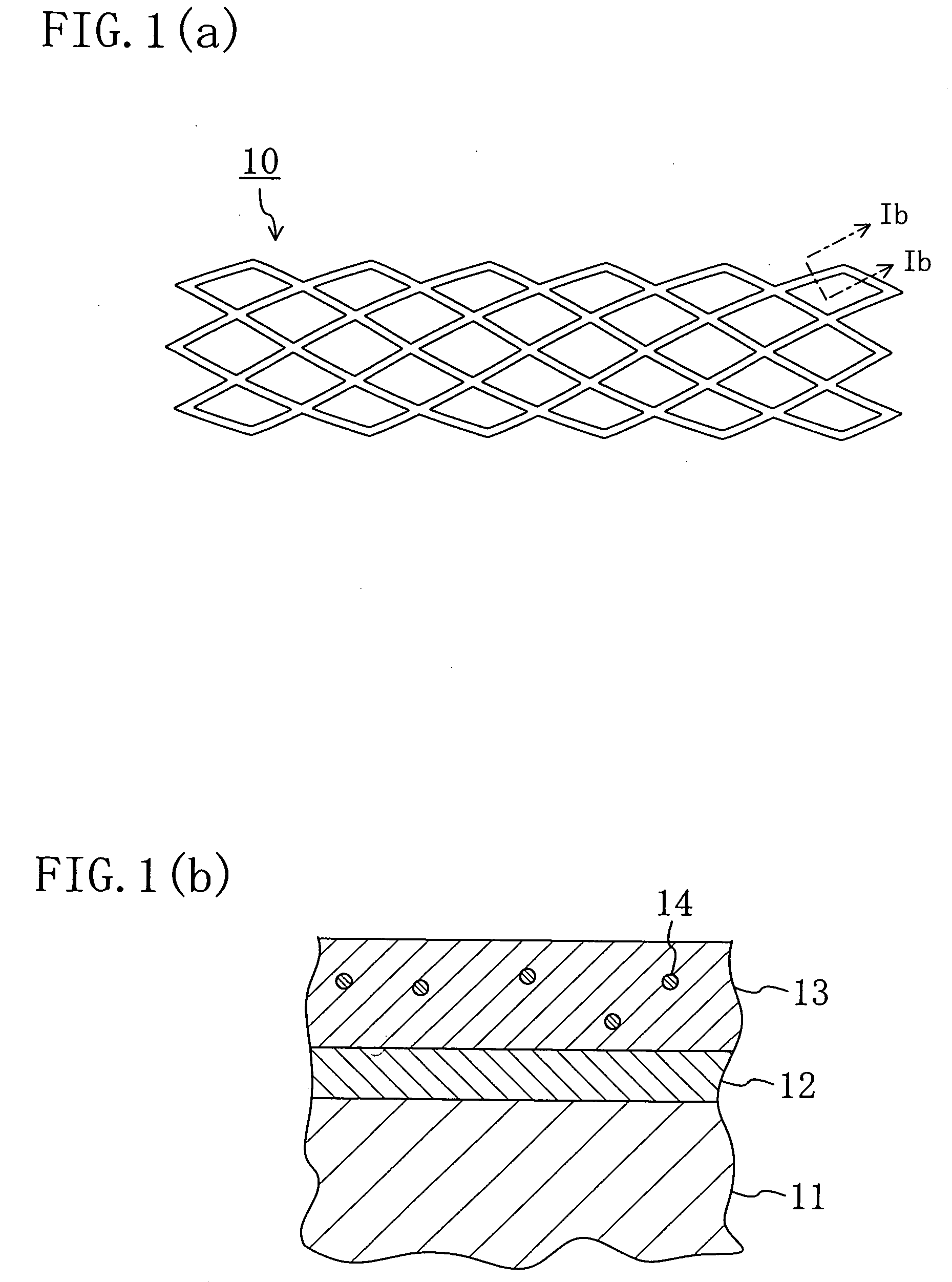
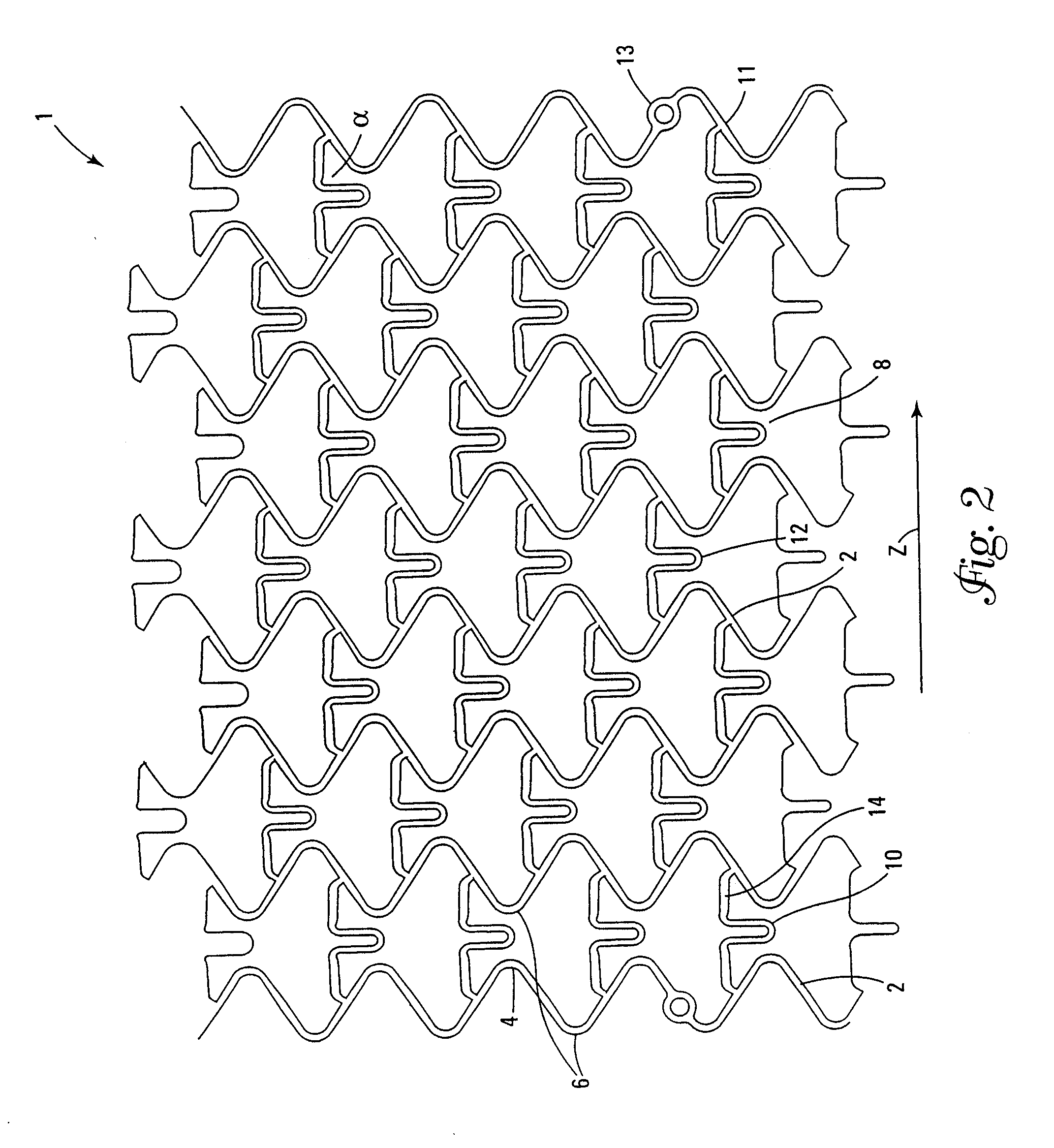
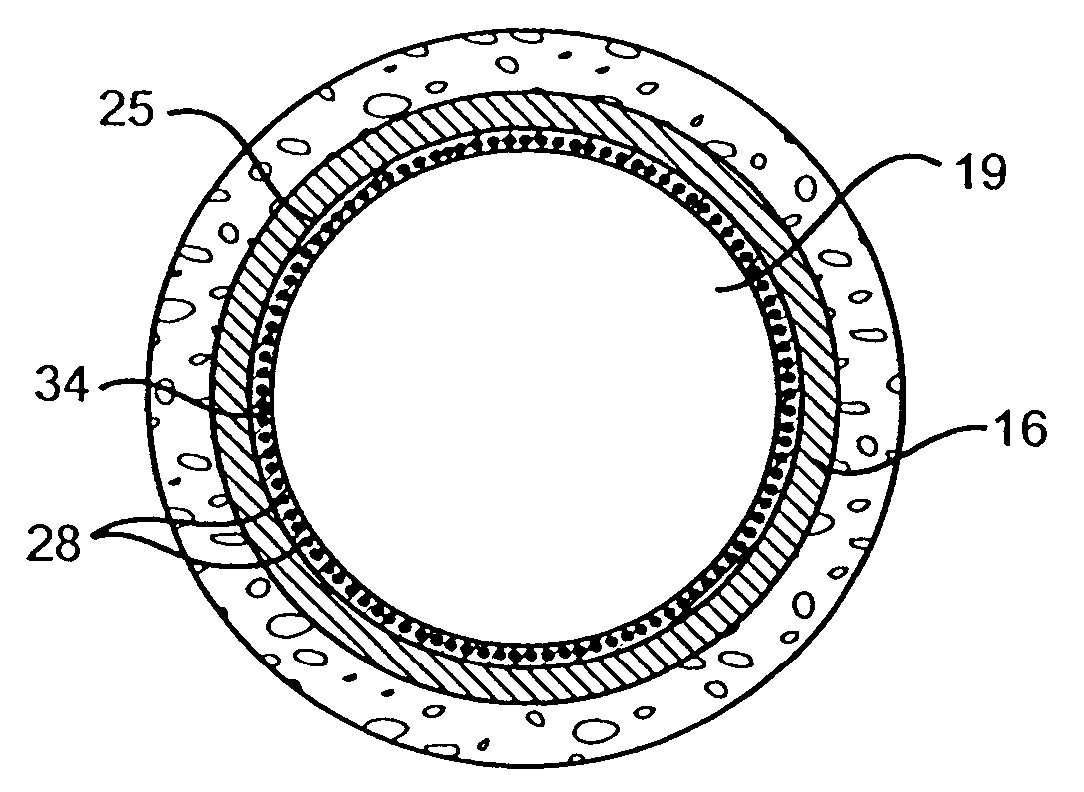
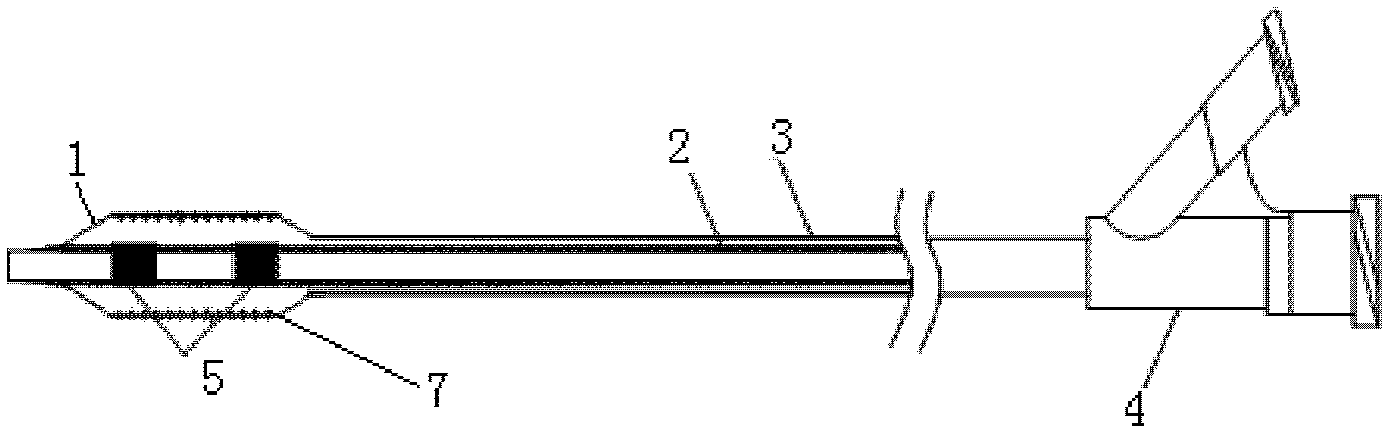
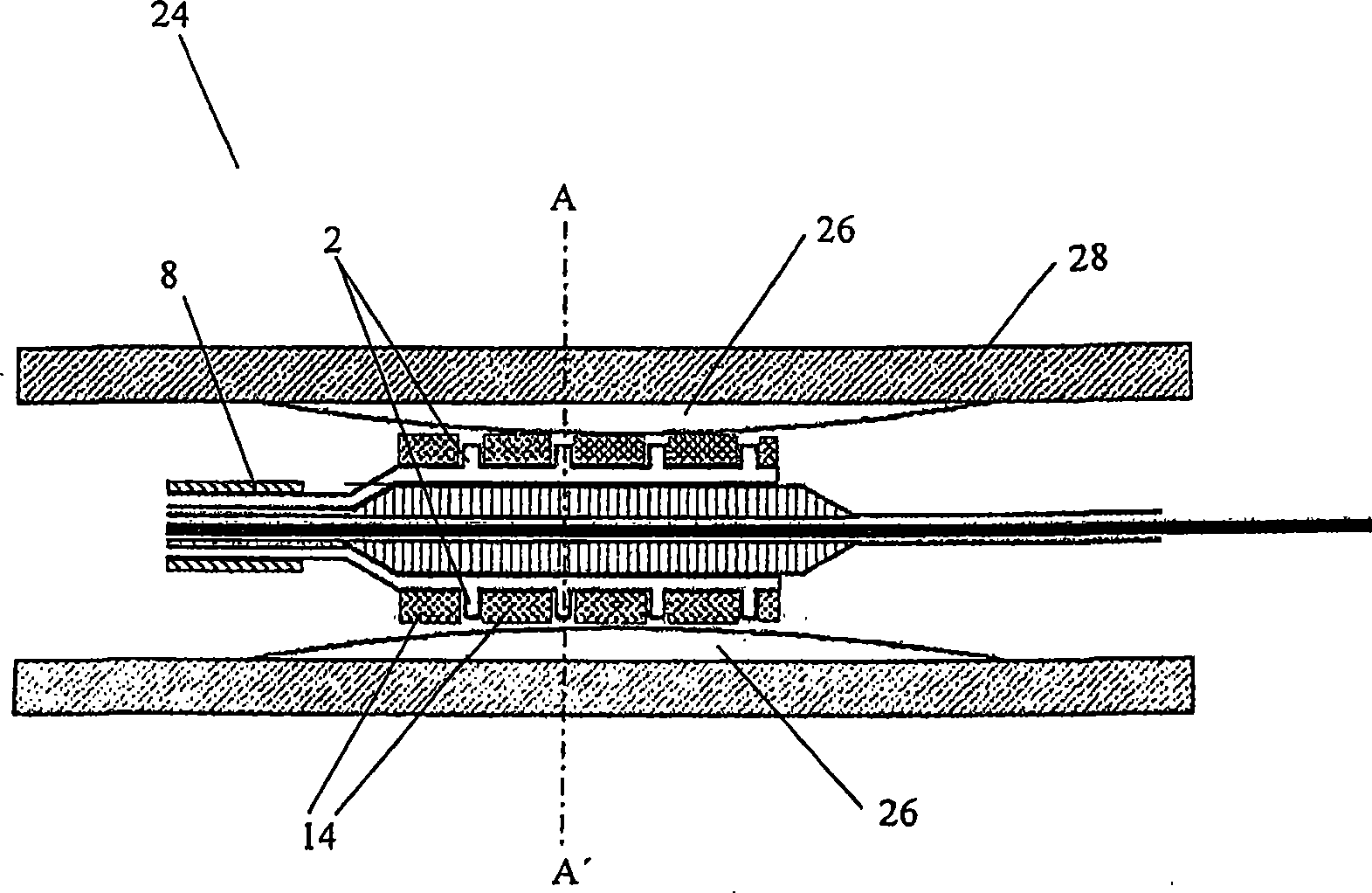
Stent and Method For Fabricating the Same
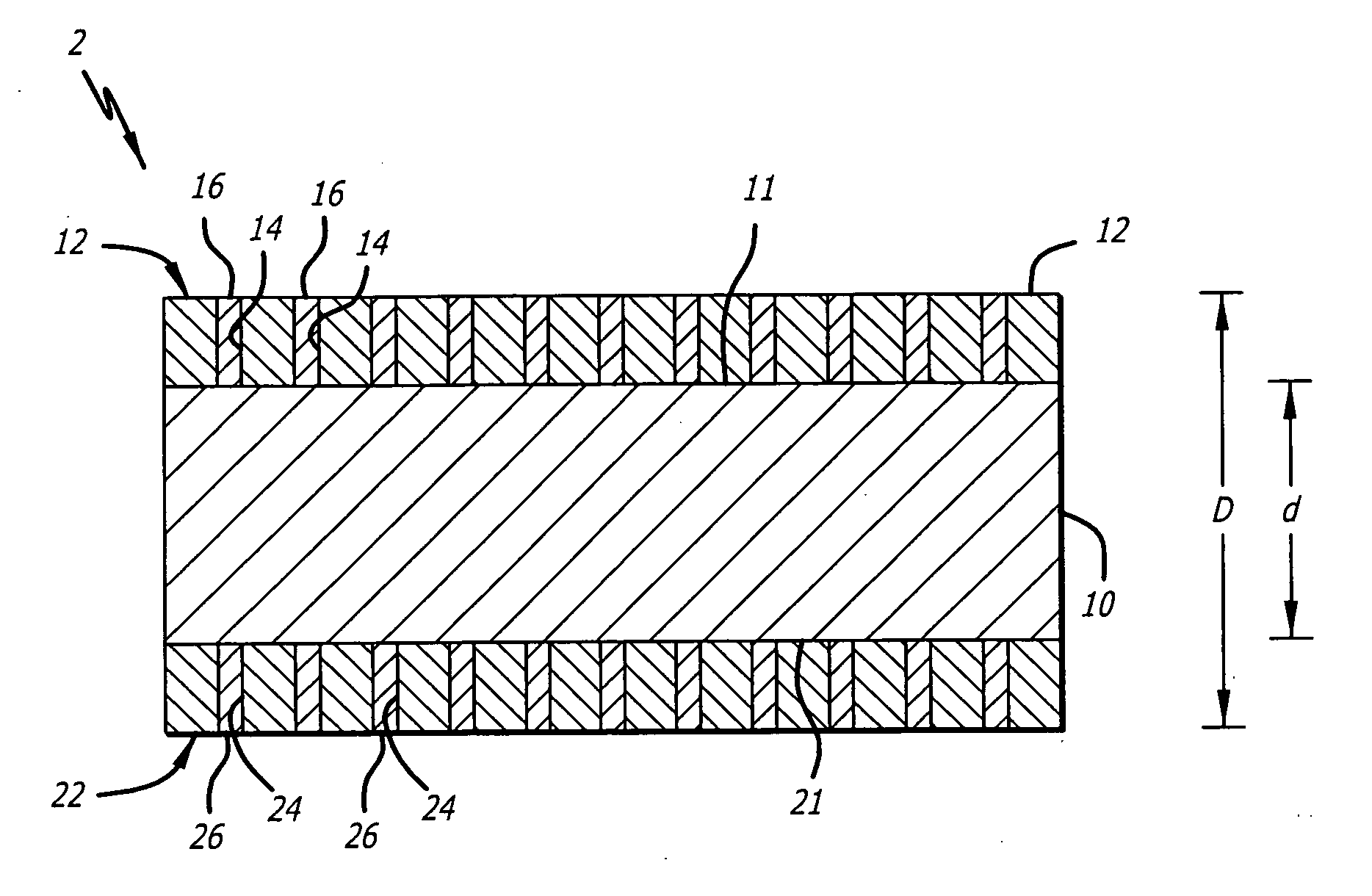
A stent includes a tubular stent body 11, a diamond-like carbon film 12 formed on the surface of the stent body 11 and having an activated surface, and a polymer layer 13 immobilized on the surface of the diamond-like carbon film. The polymer layer 13 contains a drug 14 having an effect to prevent restenosis, and the drug 14 is gradually released from the polymer layer 13.
Owner:TOYO ADVANCED TECH CO LTD +1
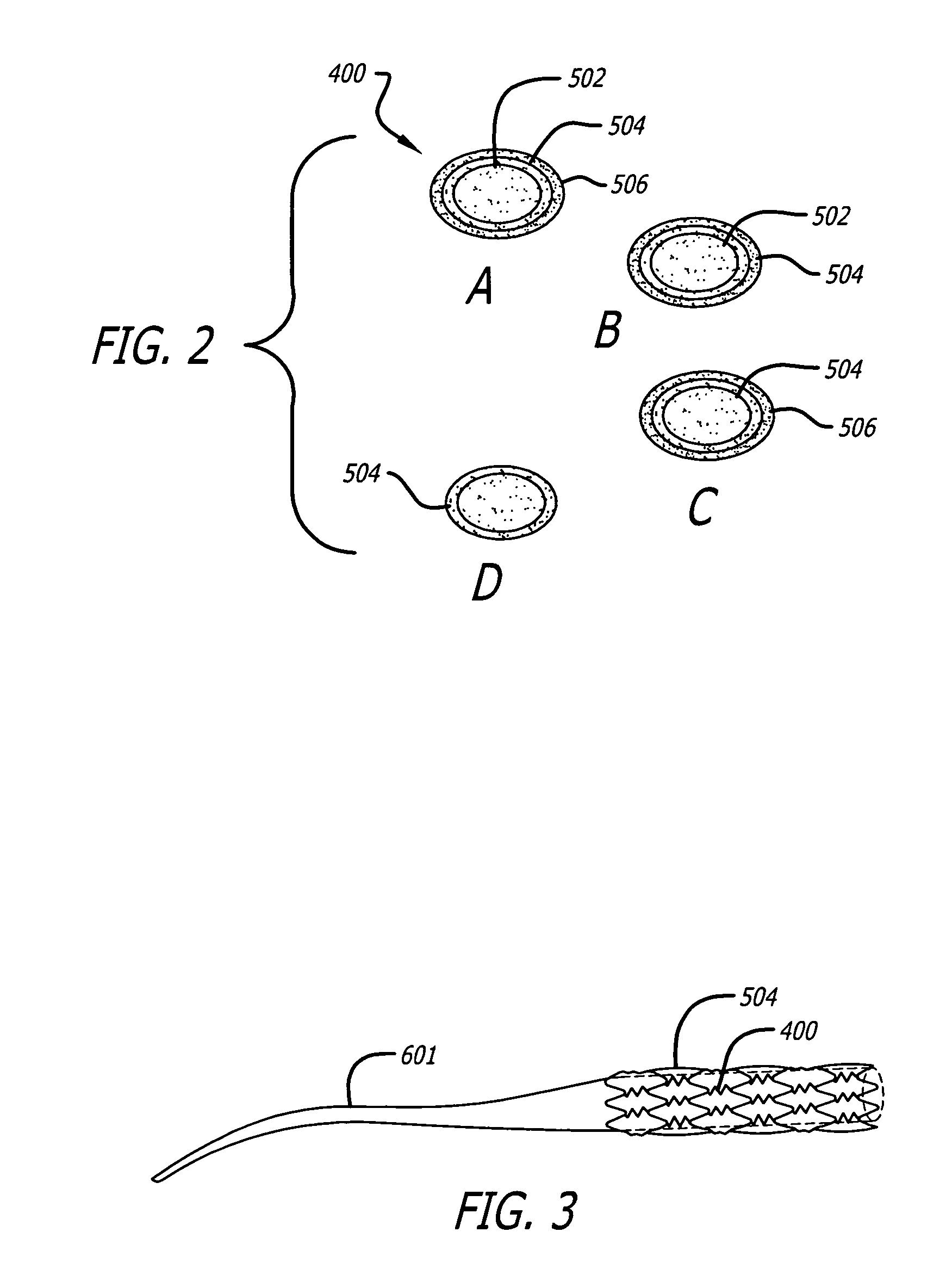
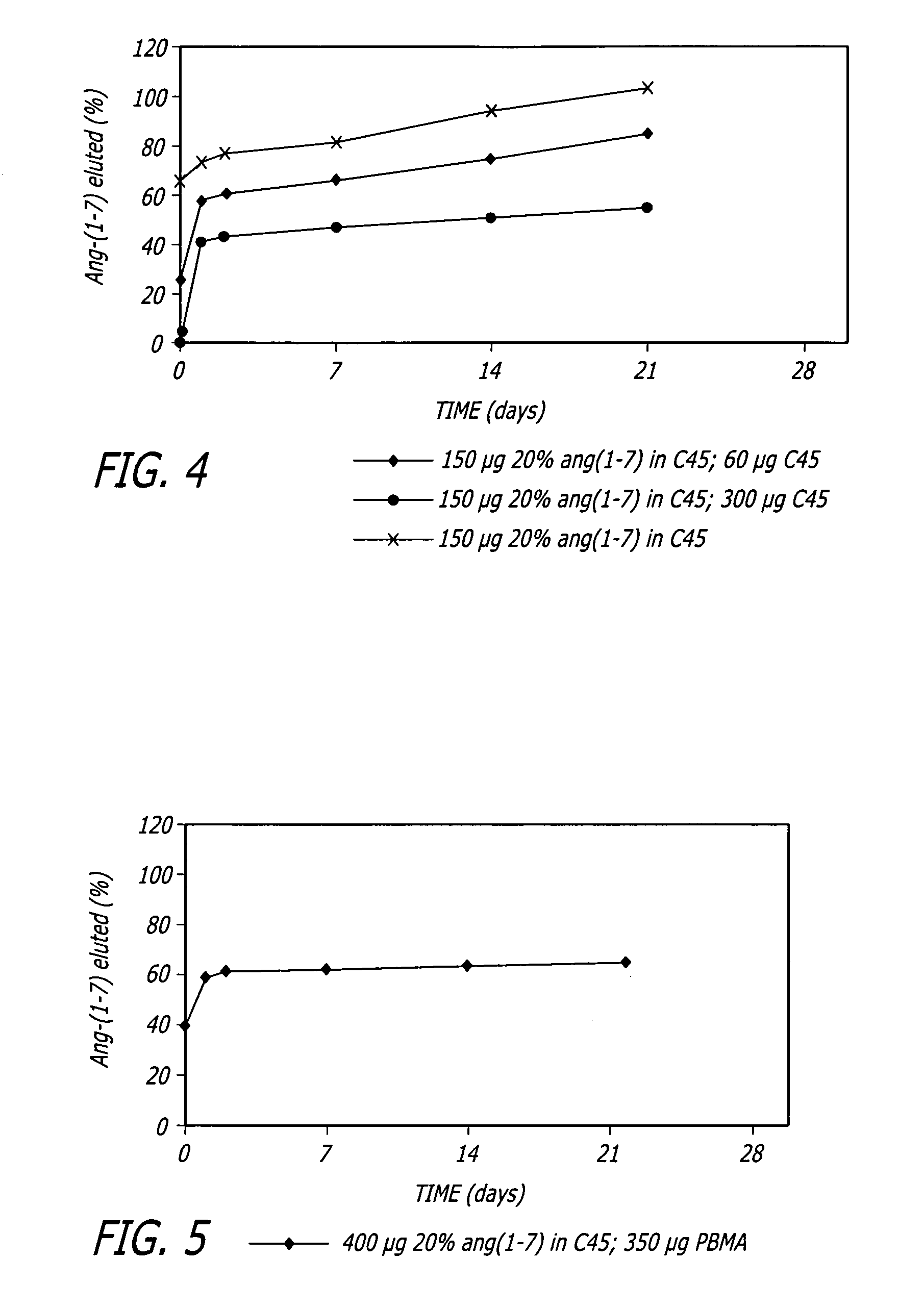
Angiotensin-(1-7) eluting polymer-coated medical device to reduce restenosis and improve endothelial cell function
InactiveUS7176261B2Function increasePrevent restenosisAngiotensinsPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular endotheliumPercent Diameter Stenosis
Medical devices with polymer coatings designed to control the release of angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonists from medical devices are disclosed. The present application also discloses providing vascular stents with angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonist-containing controlled-release coatings. Methods for treating or inhibiting post-stent implantation restenosis as well as improving vascular endothelial function in patients are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
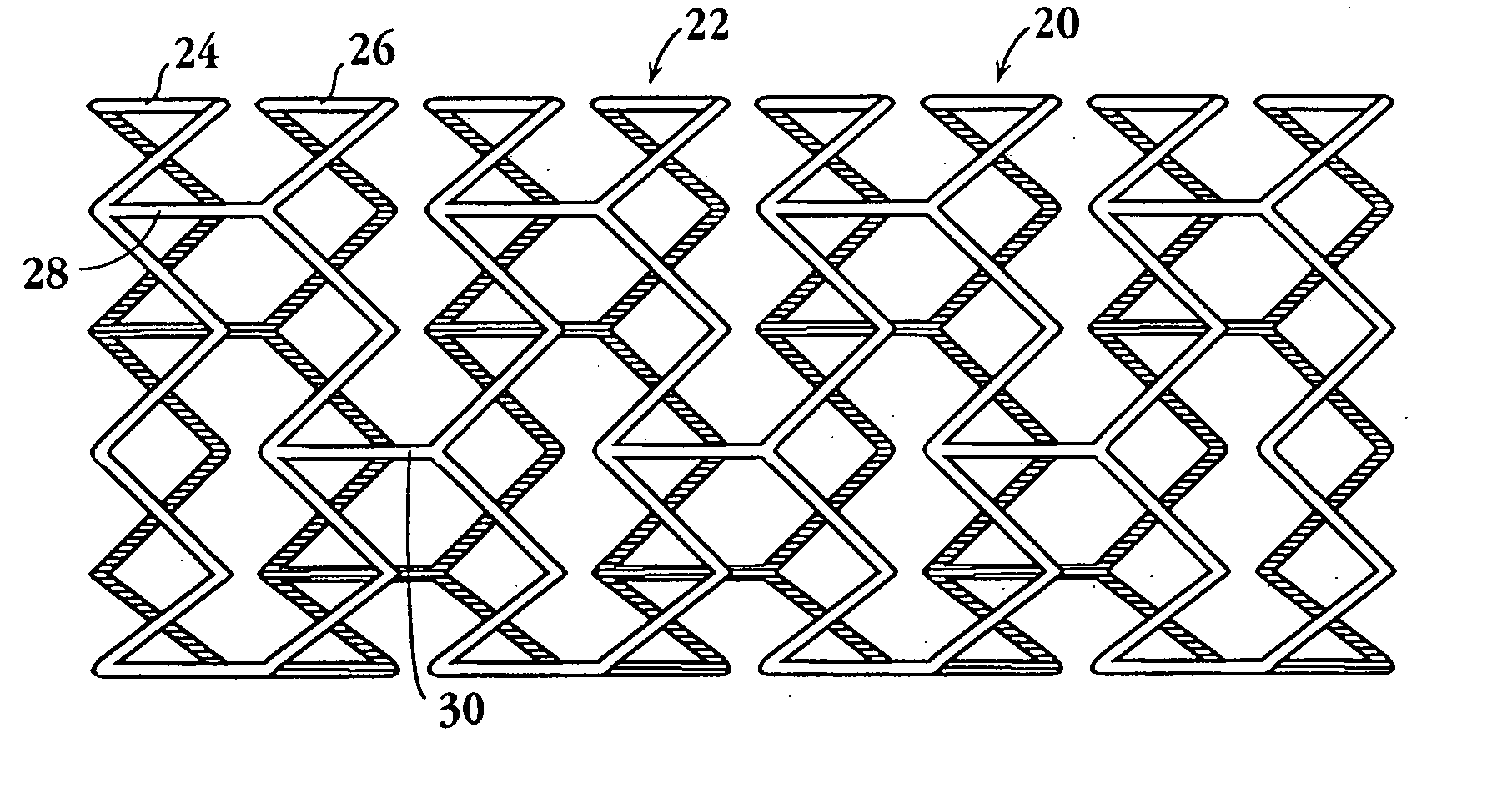
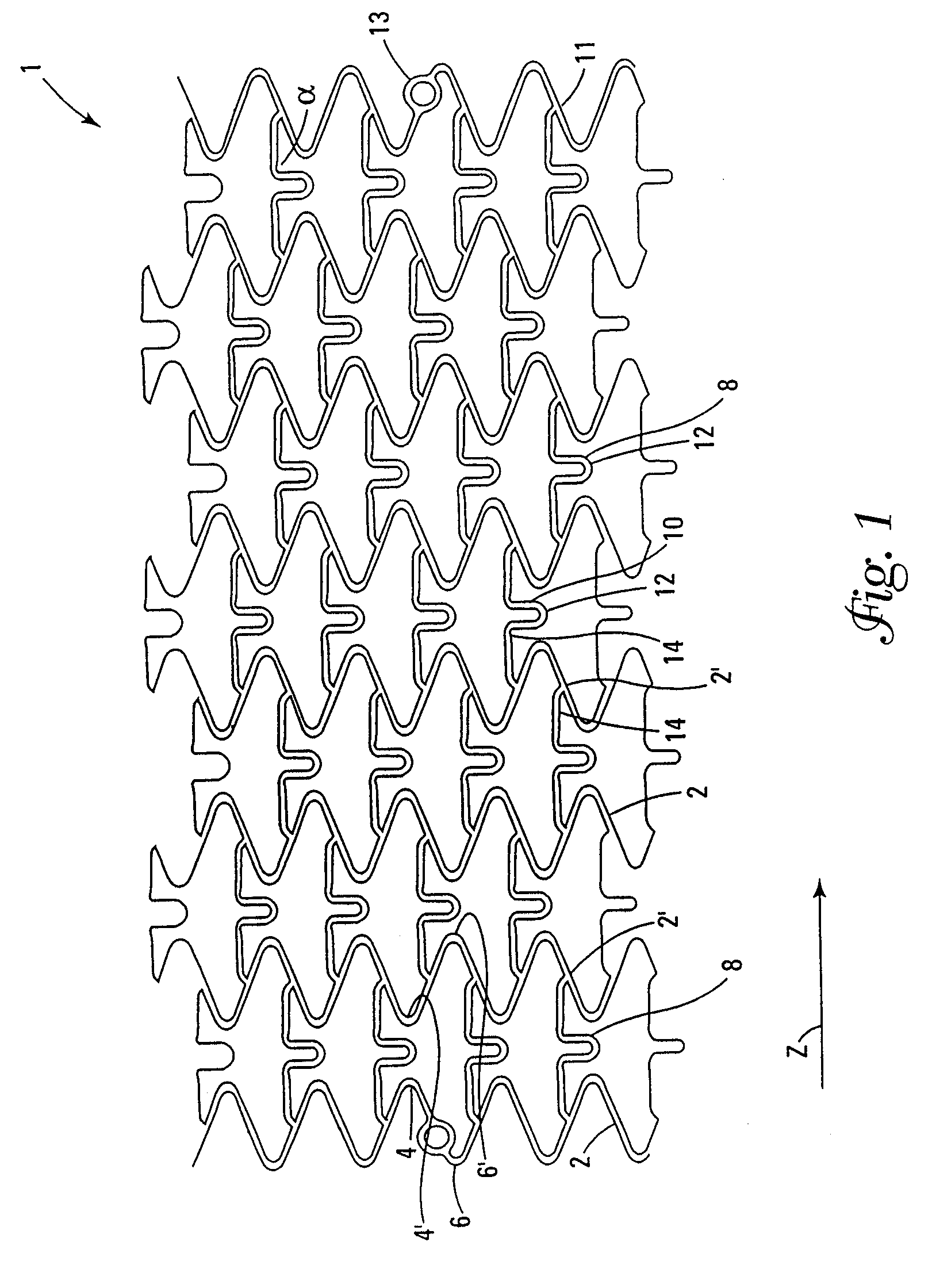
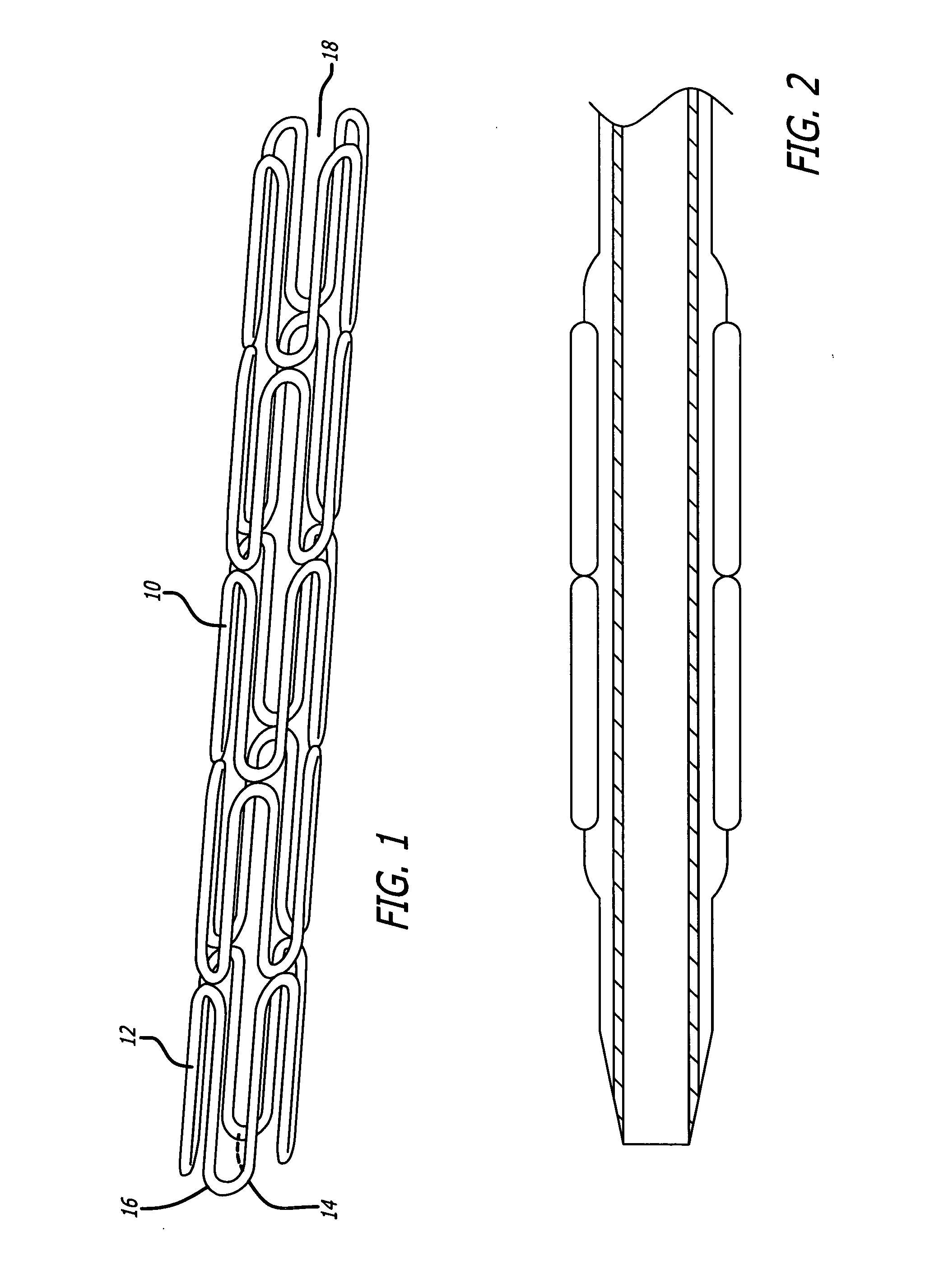
Stents for angioplasty
This invention is a stent having a substantially tubular body defining a longitudinal axis comprising first and second adjacent annular segments, each segment defining a substantially sinusoidal shape having a plurality of peaks and valleys, the peaks of the first segment extending toward the second segment and being aligned longitudinally with the valleys of the second segment. The stent has a plurality of bridge elements having a U-shaped portion between first and second connector arms, the first connector arm of one bridge element being connected between a first peak and a first valley of the first segment and the second connector arm being connected between a first peak and a first valley of the second segment.
Owner:SORIN BIOMEDICA CARDIO SRL
Methods for the inhibition of neointima formation
Restenosis is inhibited through local delivery of anti-restenotic agents including angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; nicotine receptor agonists, agents that increase concentrations of nitric oxide, anti-angiogenic agents, agonists of the TGF-beta receptor; death domain receptor ligands; and thrombin inhibitors. In one embodiment of the invention, the localized delivery is effected through the use of a stent modified for delivery of the agent at the site of injury from balloon angioplasty.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Drug-eluting stents coated with non-nucleotide P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound
InactiveUS20060121086A1Inhibit contractionInhibit cell proliferationBiocideStentsLeiomyocyteThrombosis prevention
The present invention provides a drug-eluting stent, wherein the stent is coated with one or more non-mucleotide P2Y12 receptor antagonist compounds or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or hydrate thereof. When the stent is placed in a narrowed or damaged arterial vessel, a therapeutically effective amount of the P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound is eluted continuously from the stent to the local environment of the stent. The P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound-eluting stents are useful in preventing thrombosis and restenosis, and are effective in inhibiting the contraction of vascular smooth muscle cells, inhibiting cell proliferation, and reducing inflammation.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
Delivery of therapeutic capable agents
InactiveUS20060212109A1Reduce generationReduce releasePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInsertion stentProsthesis
The present invention provides improved stents and other prostheses for delivering substances to vascular and other luminal and intracorporeal environments. In particular, the present invention provides for therapeutic capable agent eluting stents with minimized undesirable loss of the therapeutic capable agent during expansion of the stent.
Owner:ALTAI MEDICAL TECH
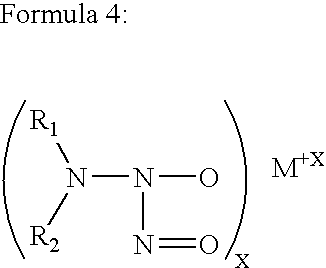
Highly cross-linked, extremely hydrophobic nitric oxide-releasing polymers and methods for their manufacture and use
InactiveUS20050079148A1Prevent restenosisLong duration of NO releaseAntibacterial agentsSuture equipmentsCross-linkDivinylbenzene
Extremely hydrophobic nitric oxide (NO) releasing polymers are disclosed. The extremely hydrophobic NO-releasing polymers provided are extensively cross-linked polyamine-derivatized divinylbenzene diazeniumdiolates. These polymers can be loaded with extremely high NO levels and designed to release NO in manners than mimic natural biological systems. The NO-releasing extremely hydrophobic polymers provided can maintain a sustained NO release for periods exceeding nine months. Also provided are related medical devices made using these NO-releasing extremely hydrophobic polymers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
InactiveUS20070055367A1Improved prognosisInhibit intimal hyperplasiaMaterial nanotechnologyStentsAntigenProgenitor
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUS MEDICAL TECH +1
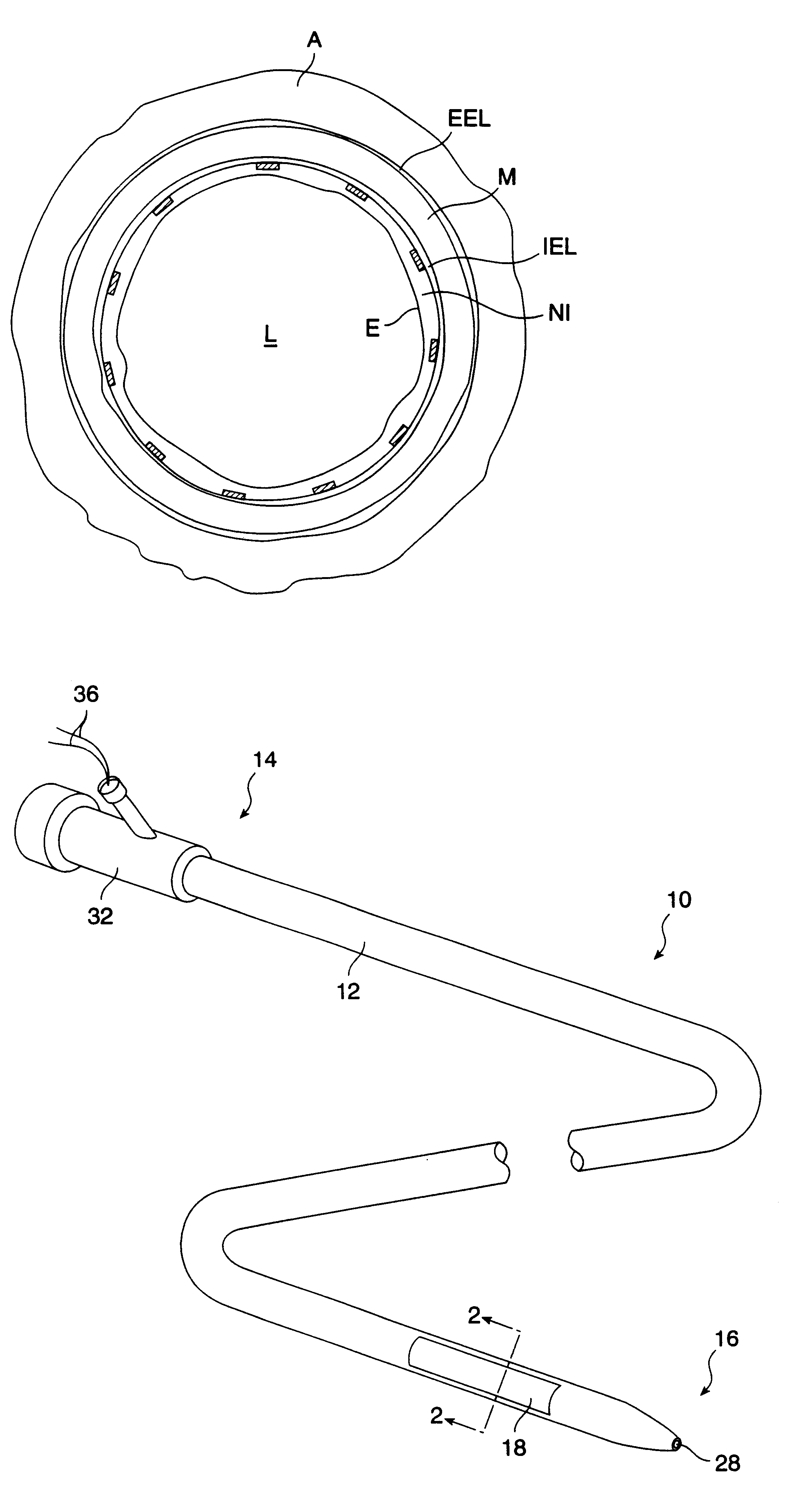
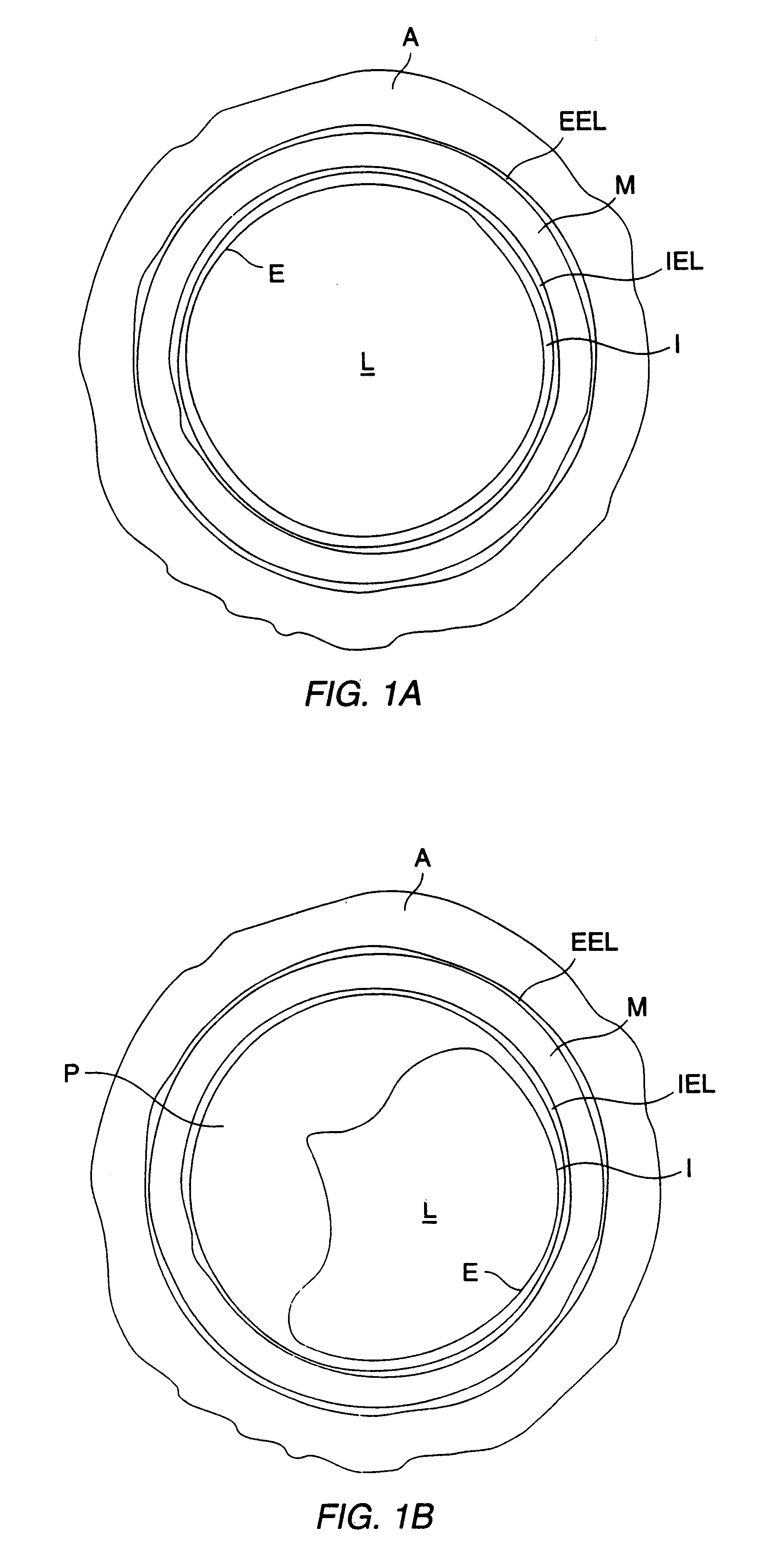
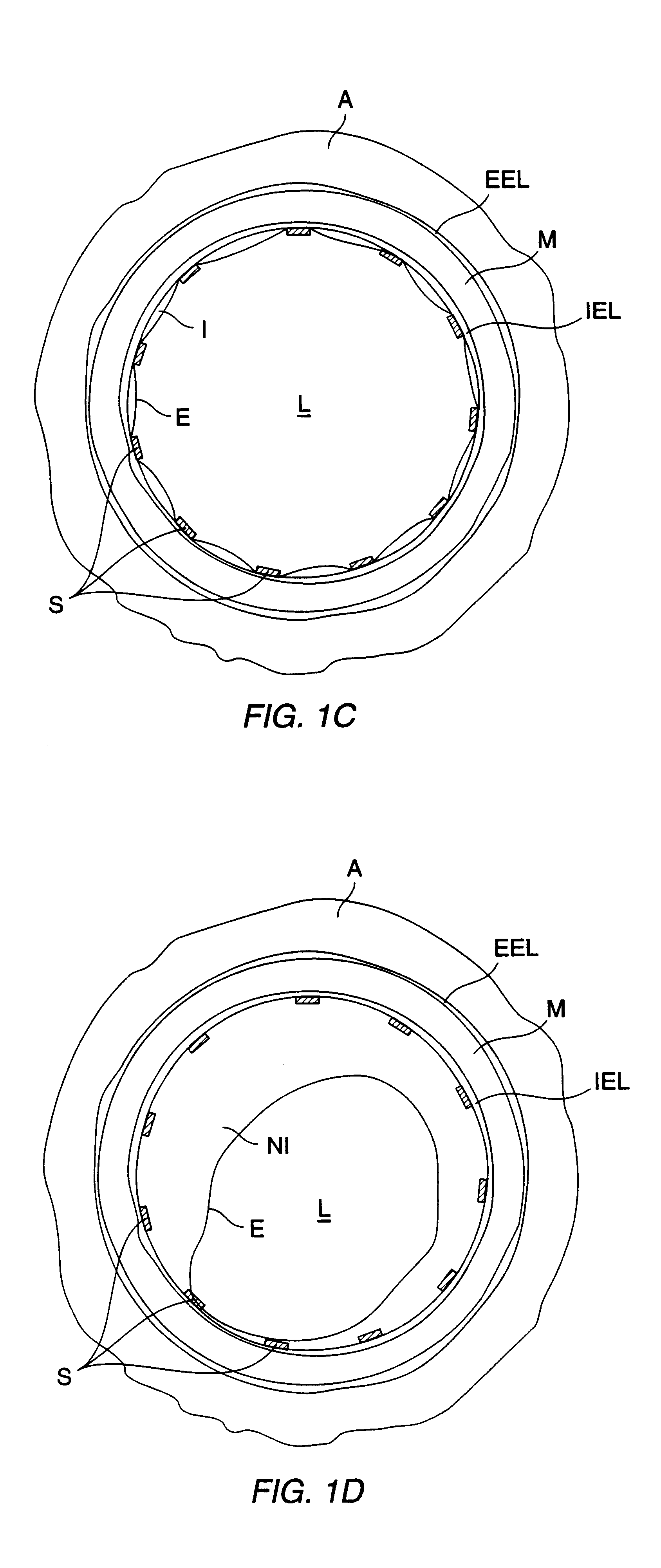
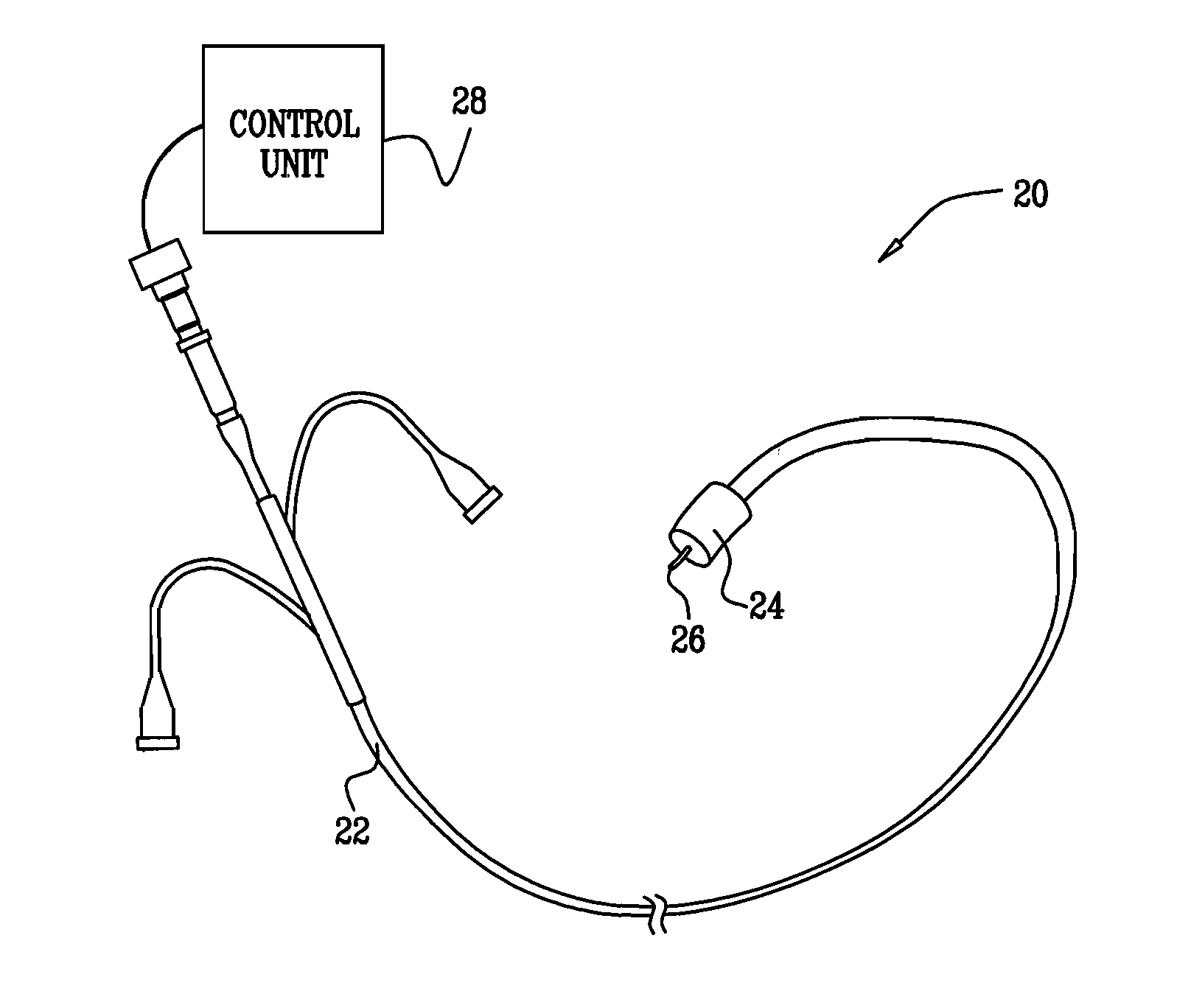
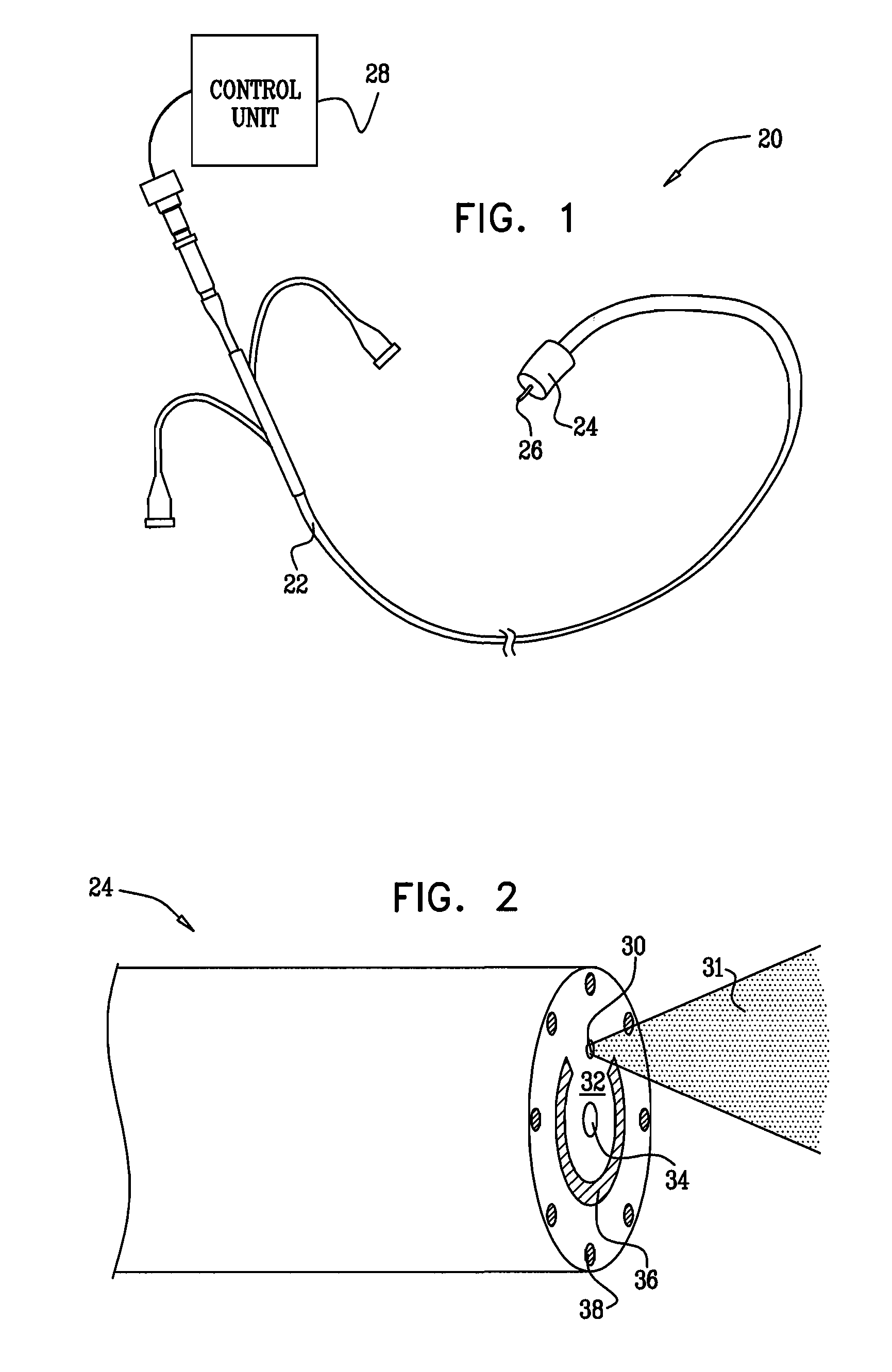
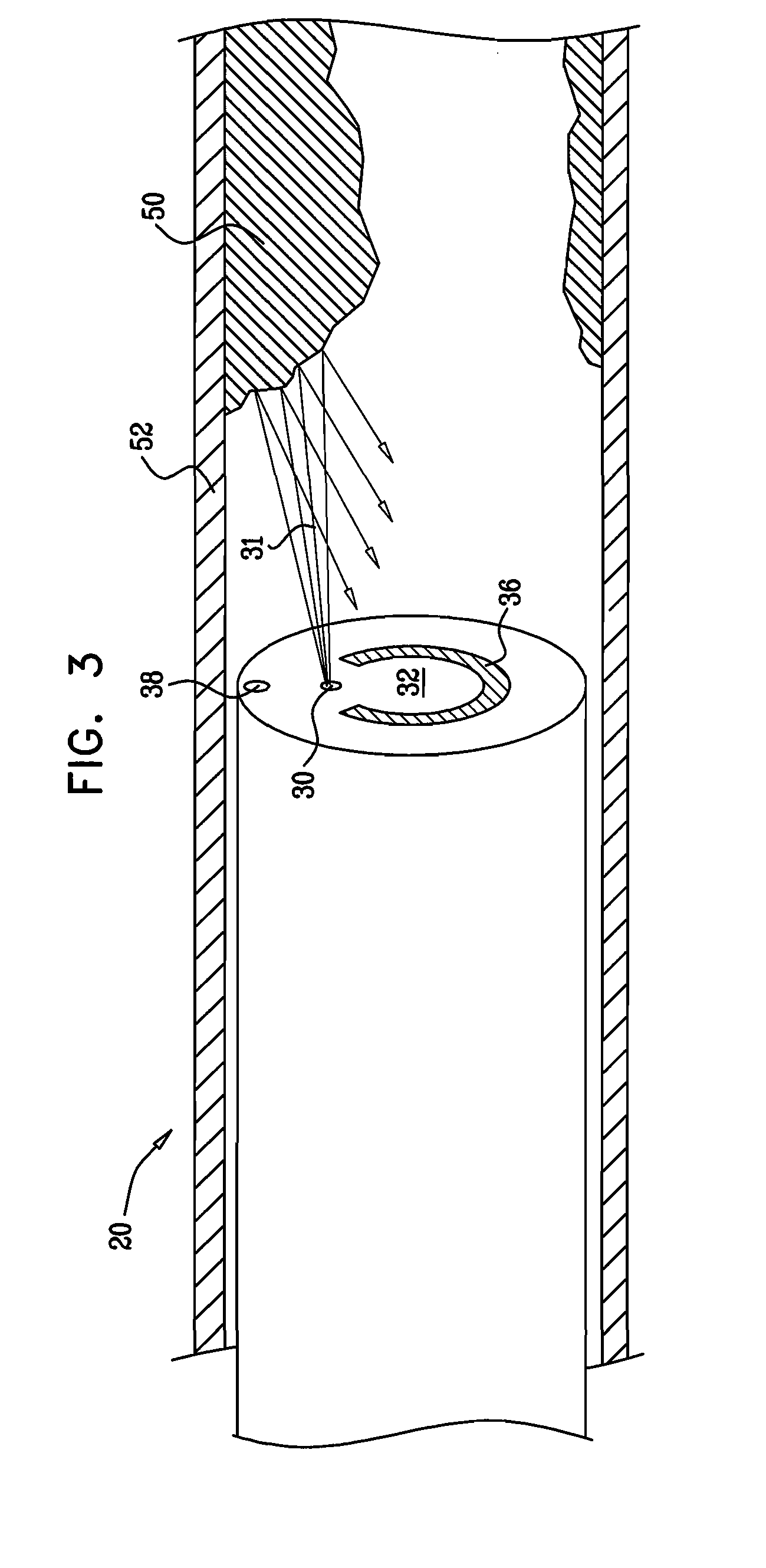
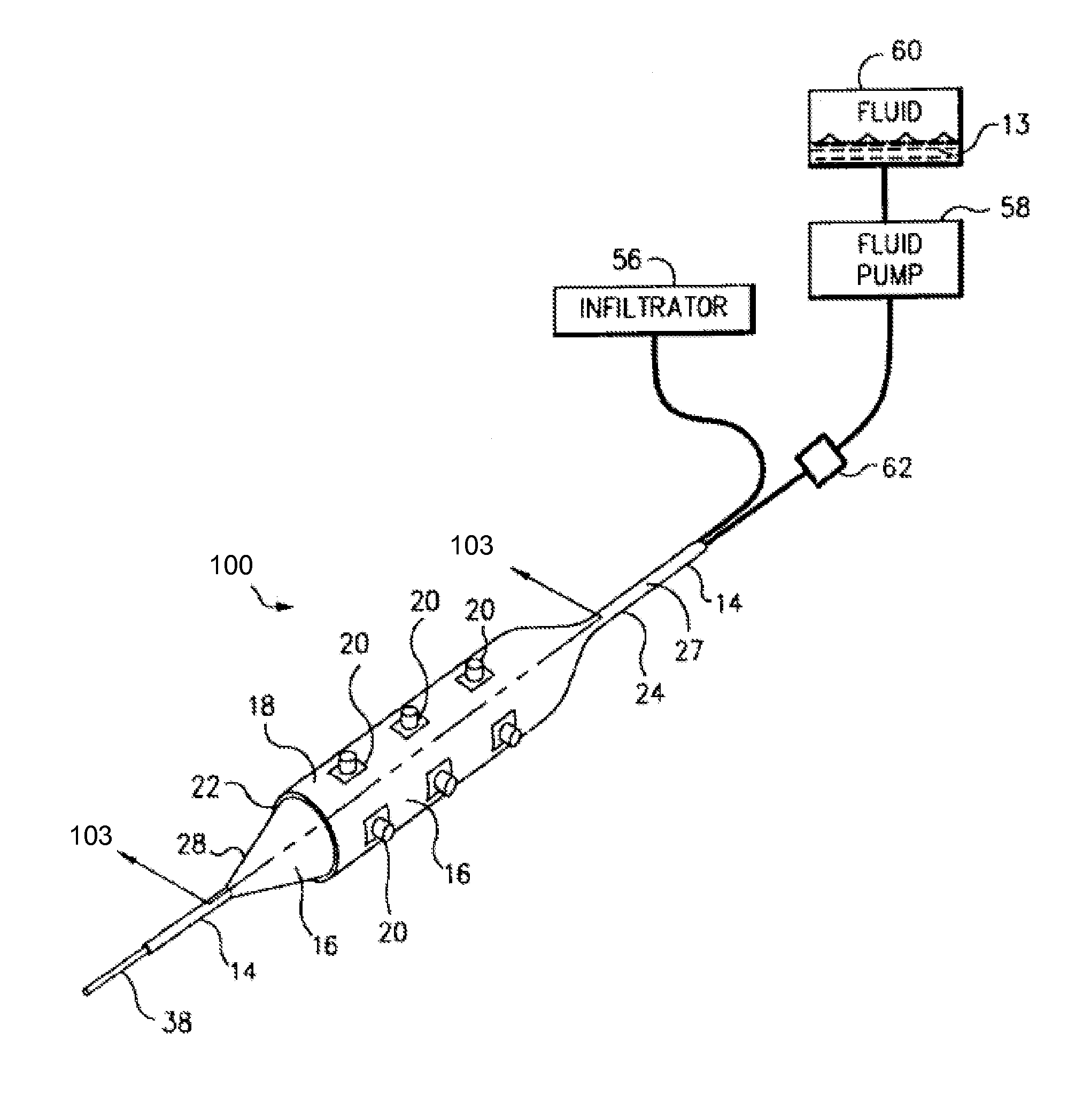
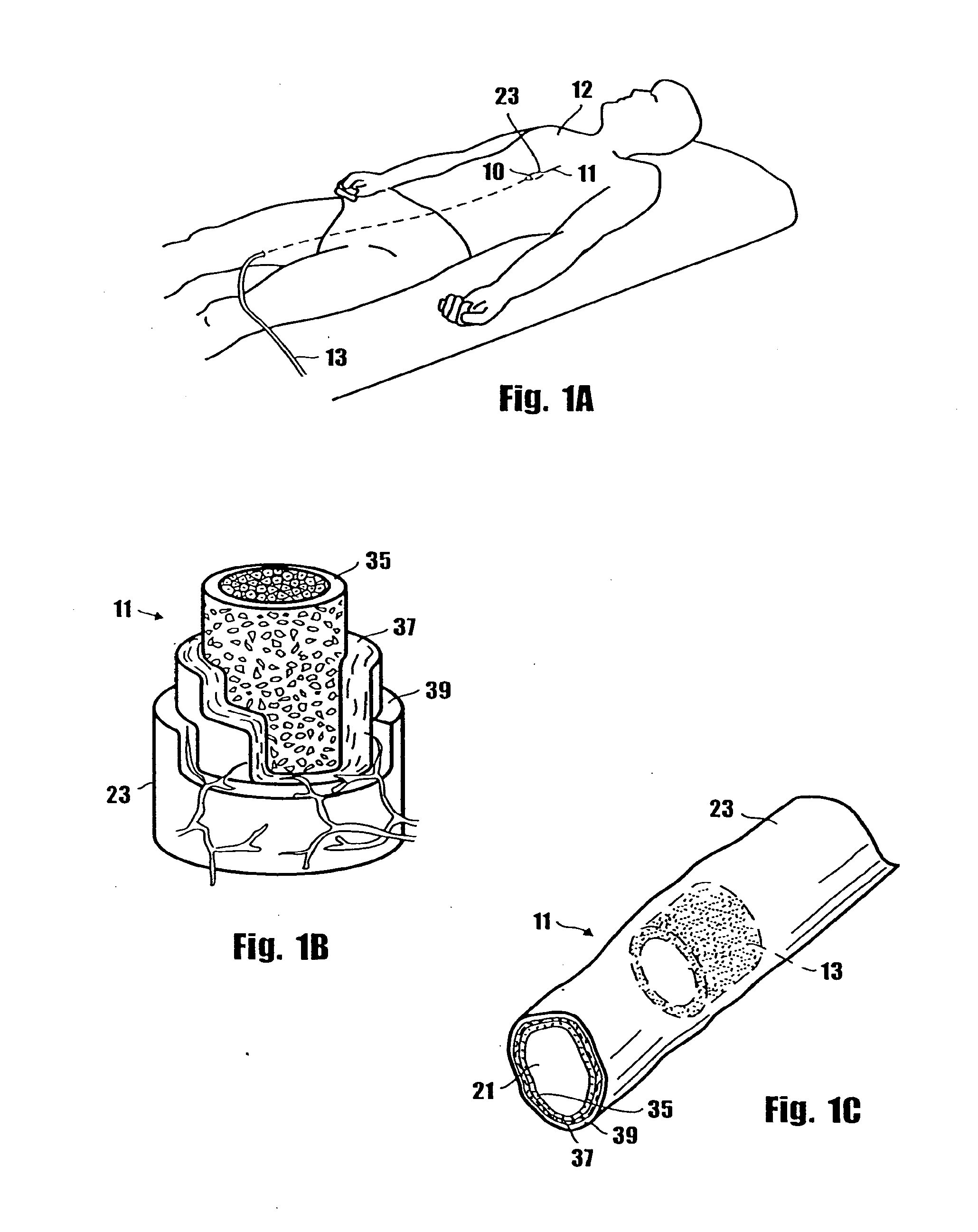
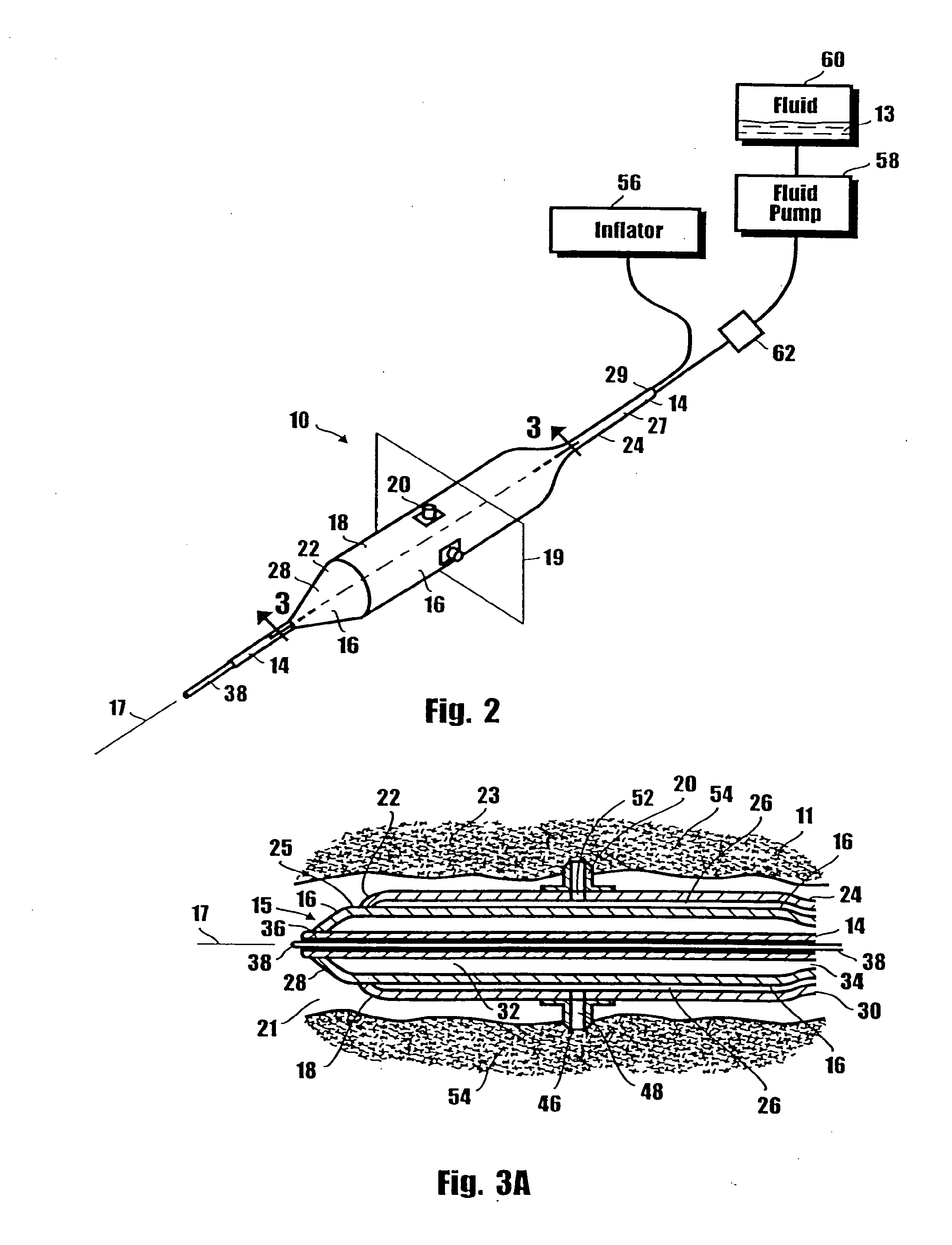
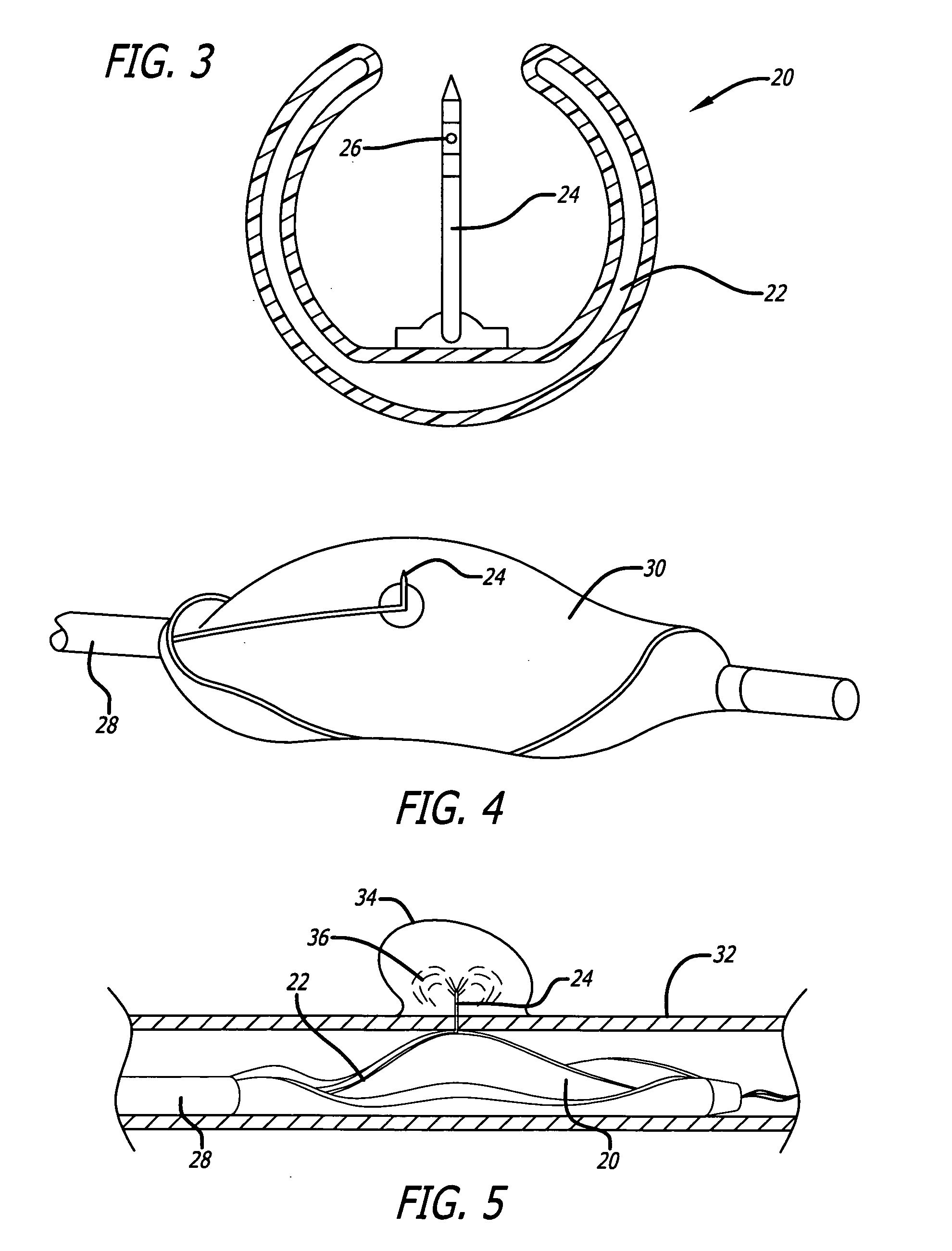
Method for delivering medication into an arterial wall for prevention of restenosis
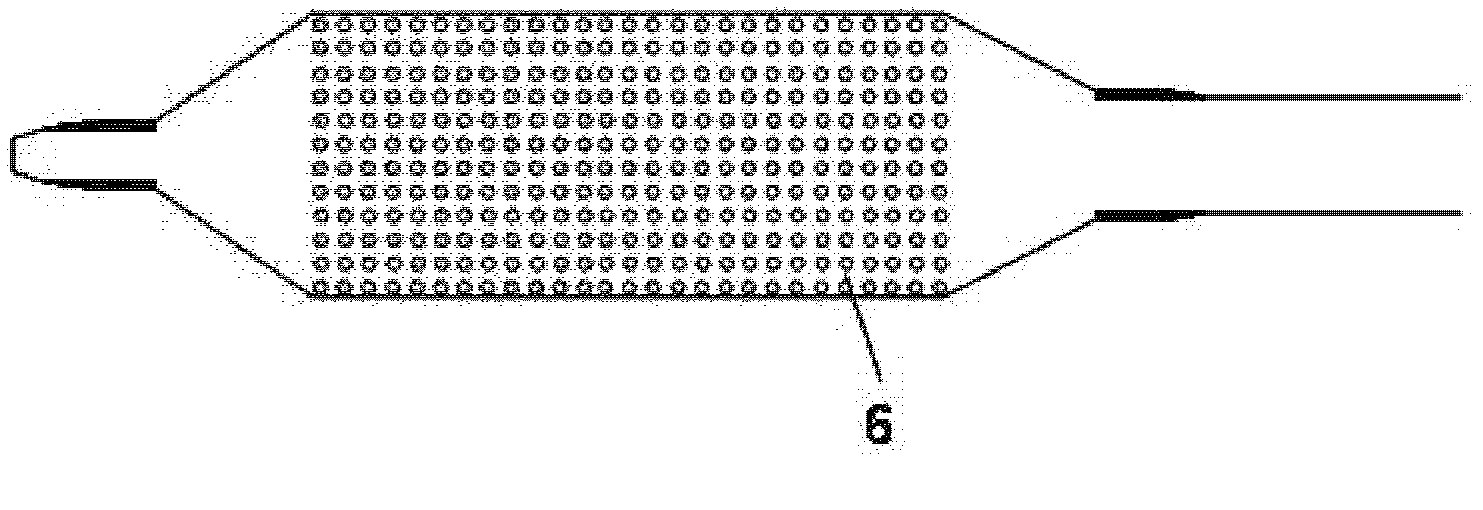
A method for preventing a restenosis within a vessel wall requires a medicament be delivered at predetermined locations into the vessel wall and allowed to subsequently disperse in a predetermined pattern. To deliver the medicament, a catheter with an expanding member is advanced into the vasculature of a patient until the expanding member is located as desired. The expanding member is then expanded to force dispensers into the vessel wall to the proper depth. A medicament is then pumped through the dispensers to create a plurality of equally spaced, localized medicinal deliveries which subsequently disperse to medicate an annulus shaped volume within the vessel wall.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medicine eluting balloon catheter
InactiveCN102512747AReduce lossesFacilitated releaseStentsBalloon catheterBlood Vessel TissuePercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention provides a medicine eluting balloon catheter, which comprises a balloon catheter body and a medicine coating, wherein the balloon catheter body comprises a balloon; the outside surface of the balloon has a plurality of grooves; and the medicine coating is coated on the grooved part and flat part of the outside surface of the balloon. The medicine eluting balloon catheter is characterized in that grooves protrude in a reversed direction when the balloon is fully expanded. The medicine eluting balloon catheter disclosed by the invention can carry more medicines and reduce loss of the medicines in a conveying process; and the medicine eluting balloon catheter directly pour and cast medicines remaining in the grooves into blood through reversed protrusion to accelerate the release of the medicines and to increase the medicine concentration at a target position, so that the medicines can quickly concentrate and act on the target position to well prevent the blood vessel tissue at the target position from regeneration and restenosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
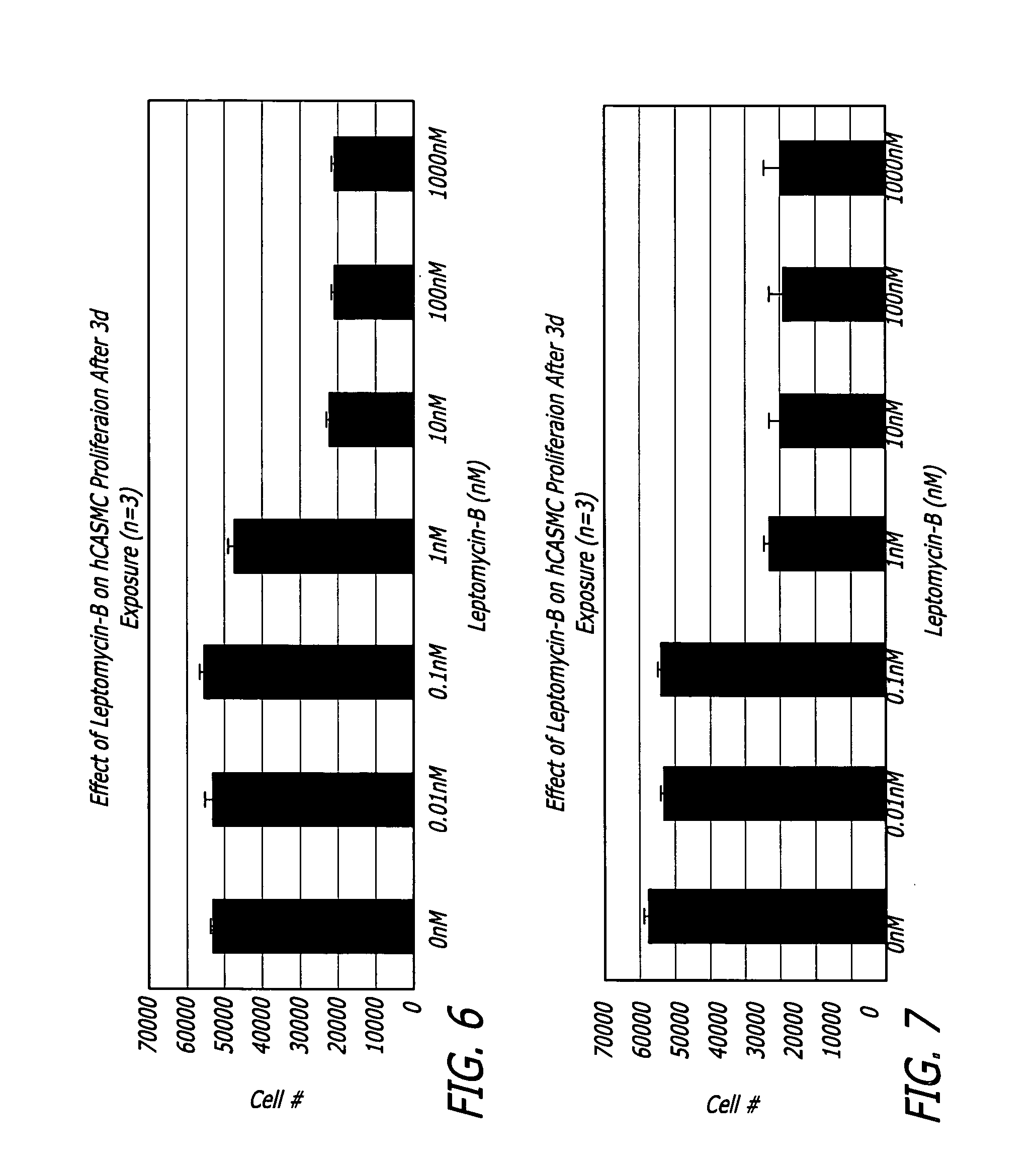
Medical devices and compositions useful for treating or inhibiting restenosis
InactiveUS20060099235A1Reduce needPrevent restenosisBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisMedical device
Medical devices and related methods for making and using same suitable for treating or inhibiting restenosis are proved. Specifically, compositions and methods for I kappa B alpha (IkBα)nuclear factor kβ (NFkβ) complex breakdown inhibition are provided. One embodiment includes a CRM-1 protein binding composition such as leptomycin B. Another embodiment includes a combination of a CRM-1 protein binding composition and a nucleic acid encoding for mammalian IkBα. Medical devices disclosed include catheters and vascular stents.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Compounds useful in coating stents to prevent and treat stenosis and restenosis
InactiveUS20070037739A1Prevent restenosisBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsActive agentPercent Diameter Stenosis
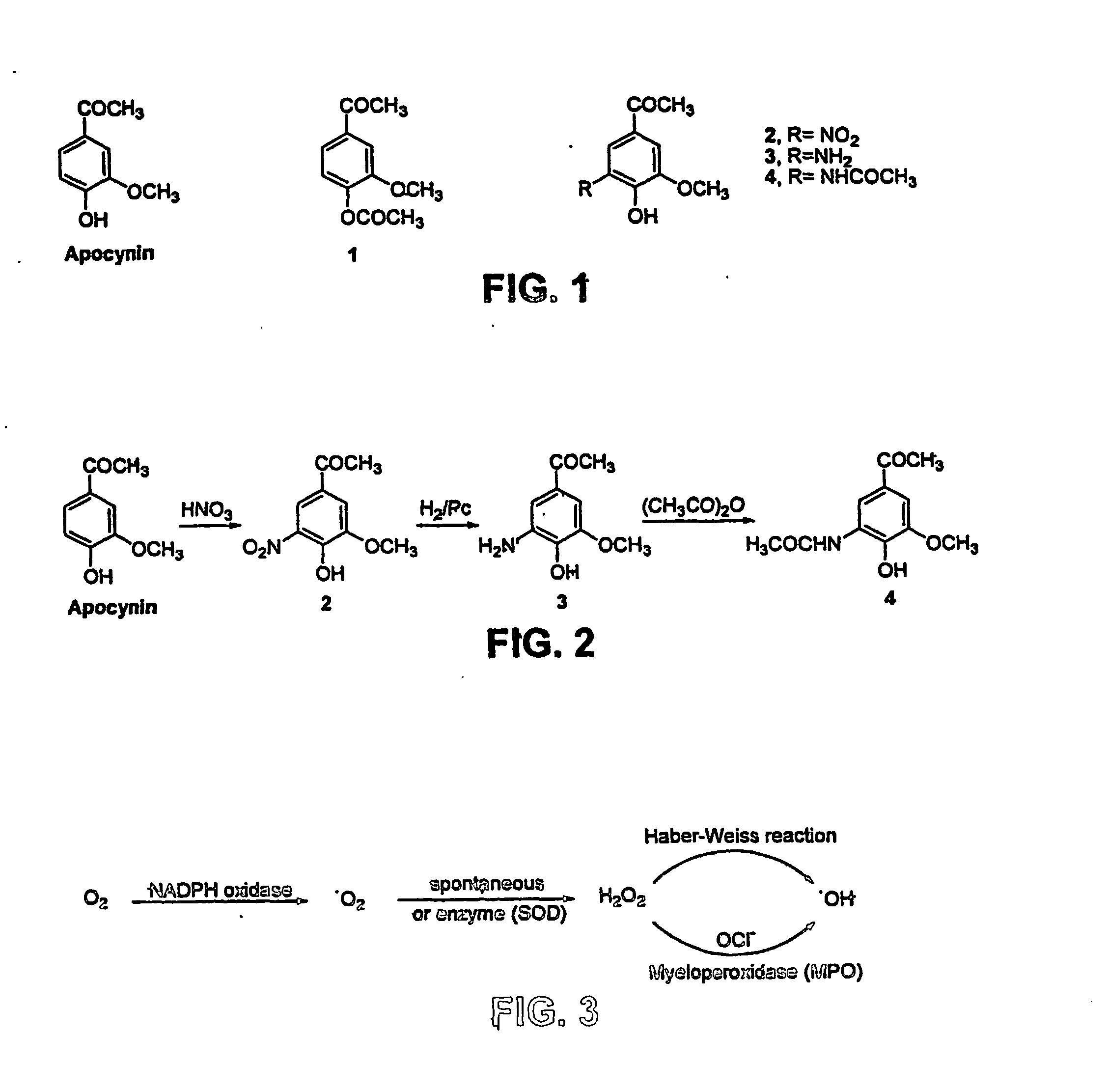
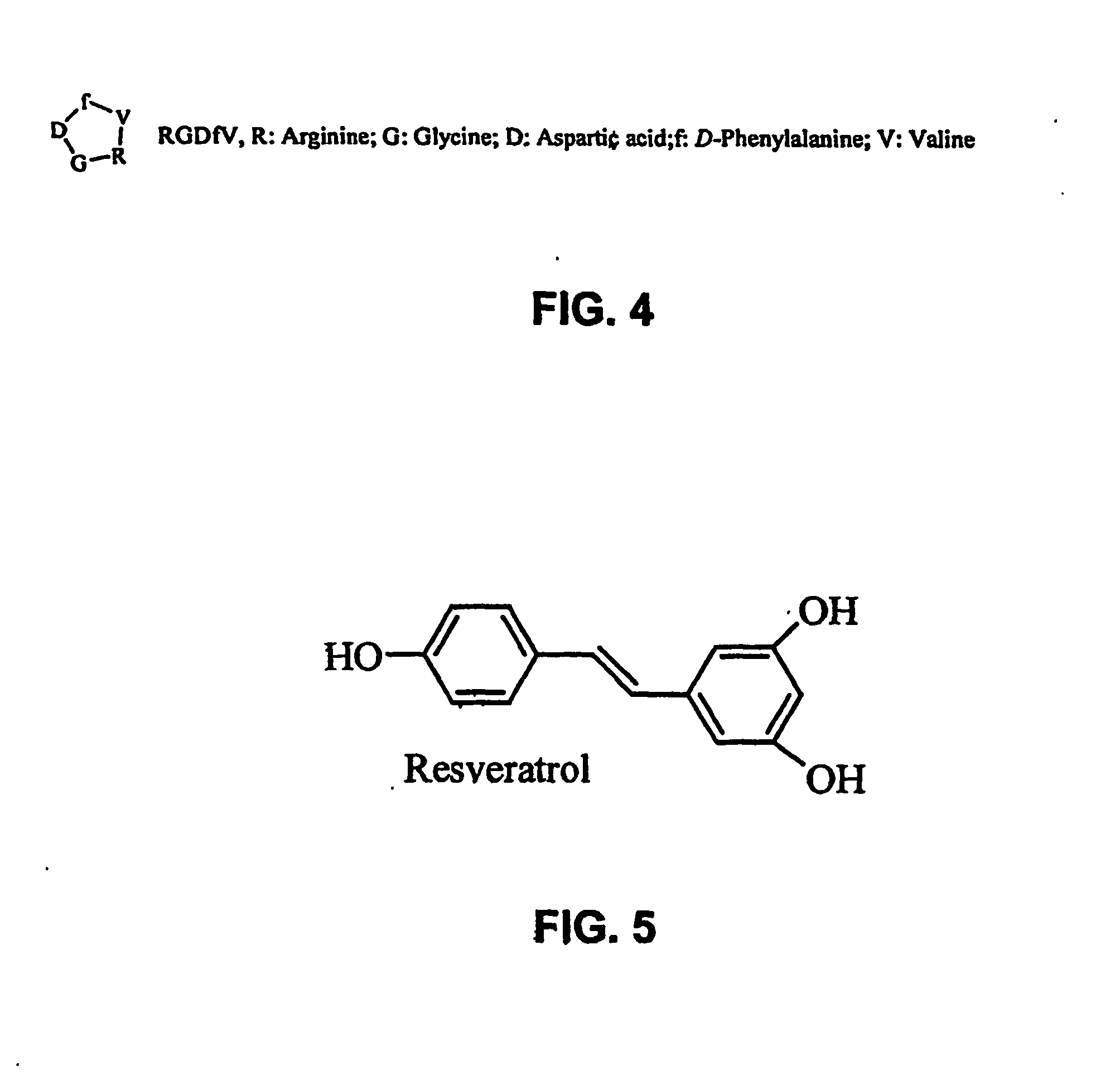
At least one bioactive agent is locally delivered to a location where a stent is implanted within a lumen in a patient's body. The bioactive agent includes a: DNA minor groove binder (such as CC-1065 or Duocarmycin); apocynin; RGD peptide (such as RGDfV); stilbene compound (such as resveratrol); camptothecin; des-aspartate angiotensin I; or ADF; or an analog or derivative thereof; or a combination or blend thereof with at least one other bioactive agent. The bioactive agent is generally locally delivered, such as by elution from the stent. The compounds and methods are of particular benefit for treating or preventing atherosclerosis, stenosis, restenosis, smooth muscle cell proliferation, occlusive disease, or other abnormal lumenal cellular proliferation condition.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
Minimally invasive intravascular treatment device
InactiveCN101420913AReduce retraction resistanceThe delivery method worksStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterAnimal body
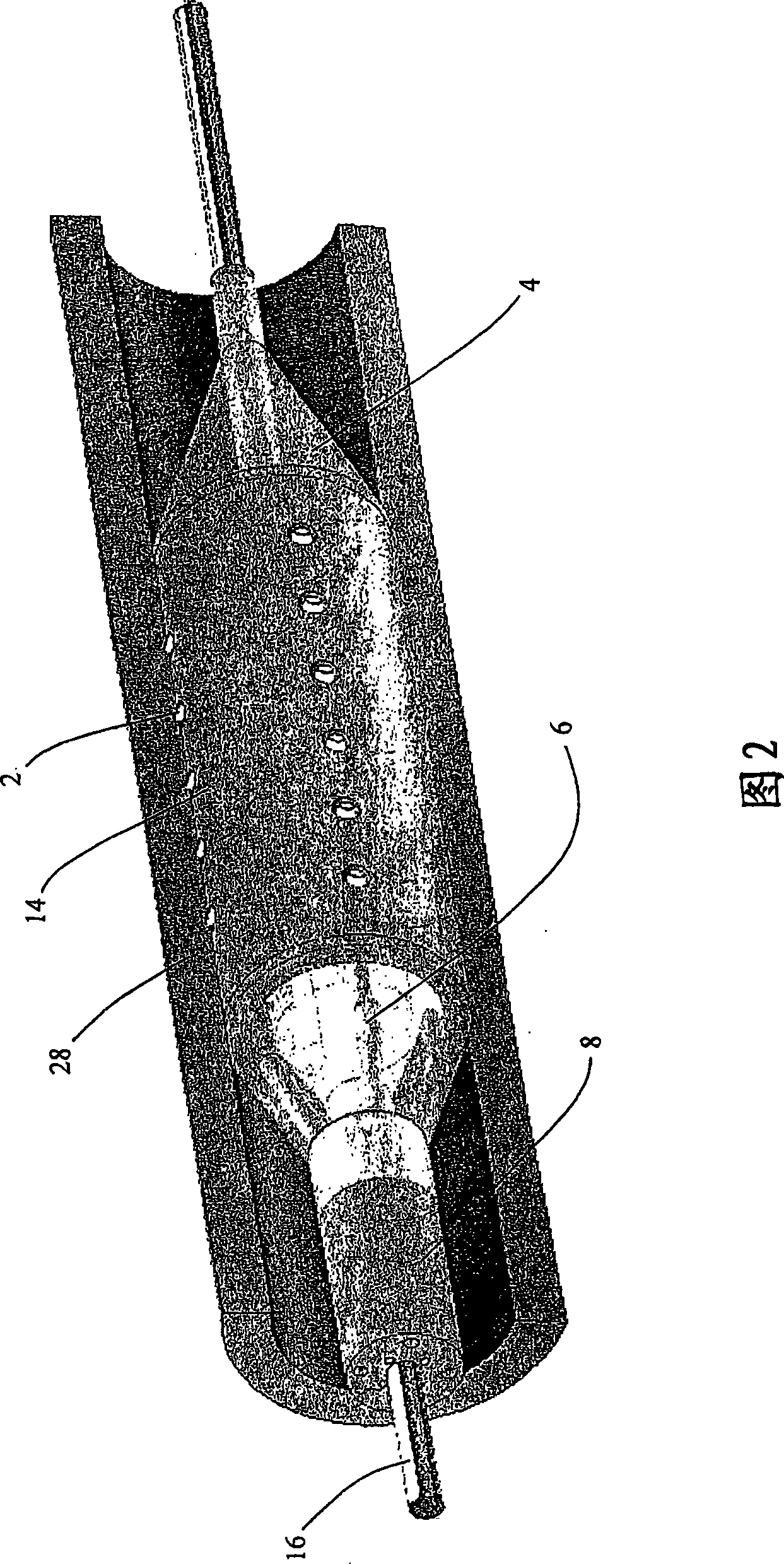
A device for treating a target area of a vessel wall of a vessel within a human or animal body, the device comprising: an expandable portion for radially expanding the device from a contracted configuration allowing travel within the vessel to the target area to an expanded configuration allowing treatment of the target area; a protective sheath stretch-fitted over the expandable portion to exert a compressive force on the expandable portion for radially contracting the device from its expanded configuration to its contracted configuration, and for exerting a compressive force on the expandable portion in its contracted configuration; and at least two spaced apart treatment implements extending radially outwardly from the expandable portion, wherein in the device's contracted configuration the implements are shielded within the protective sheath, and in its expanded configuration the thickness of the sheath decreases to expose the implements for contact with the target area of the vessel wall. A protective sheath for fitting to a device for treating a target area of a vessel wall of a vessel within a human or animal body, a balloon catheter sheath loading device and method for loading a tubular sheath onto a balloon catheter, and a method of treating one or more target areas of a vessel wall within a human or animal body are also disclosed.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com