Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
803results about "Fluid jet surgical cutters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
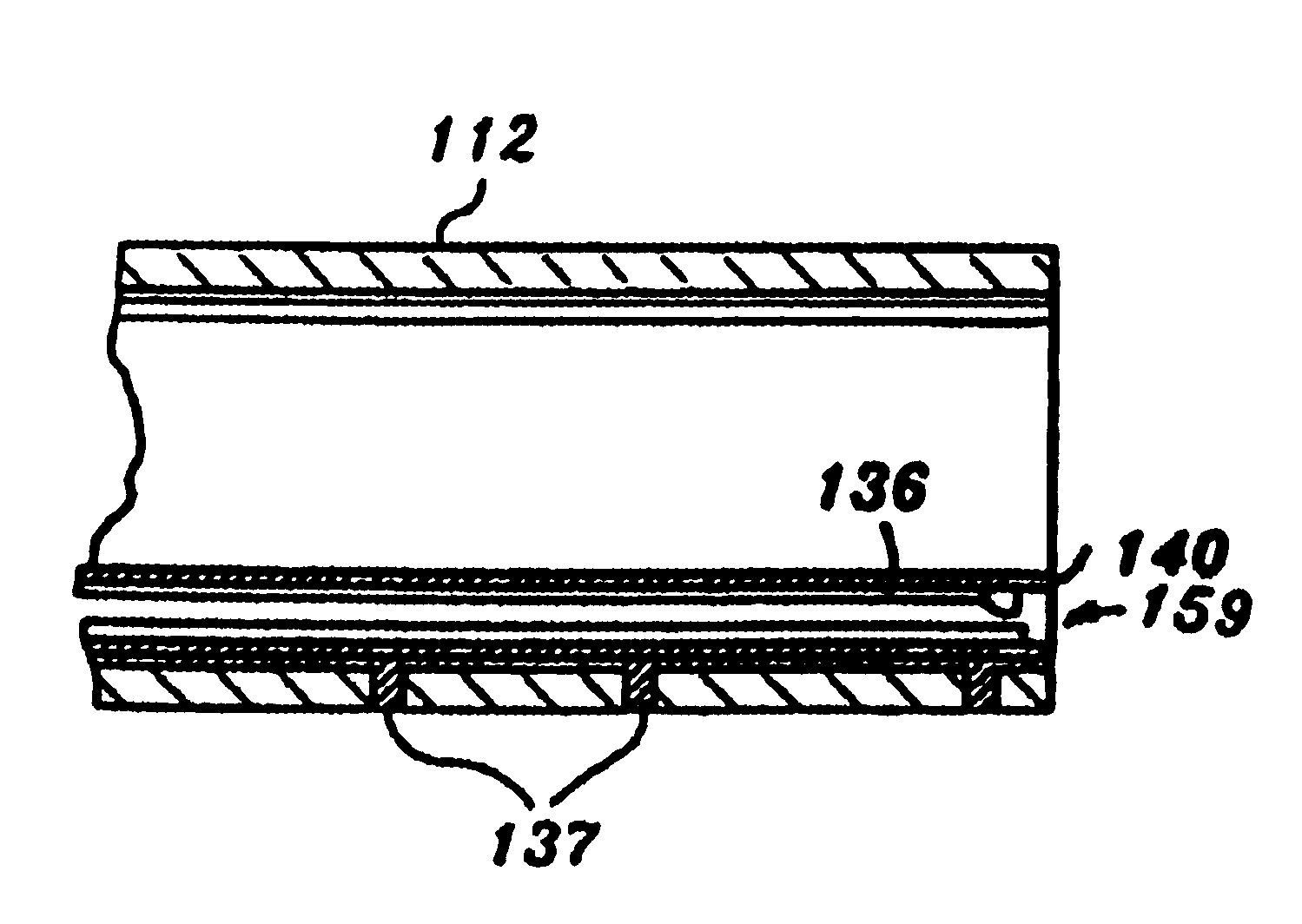
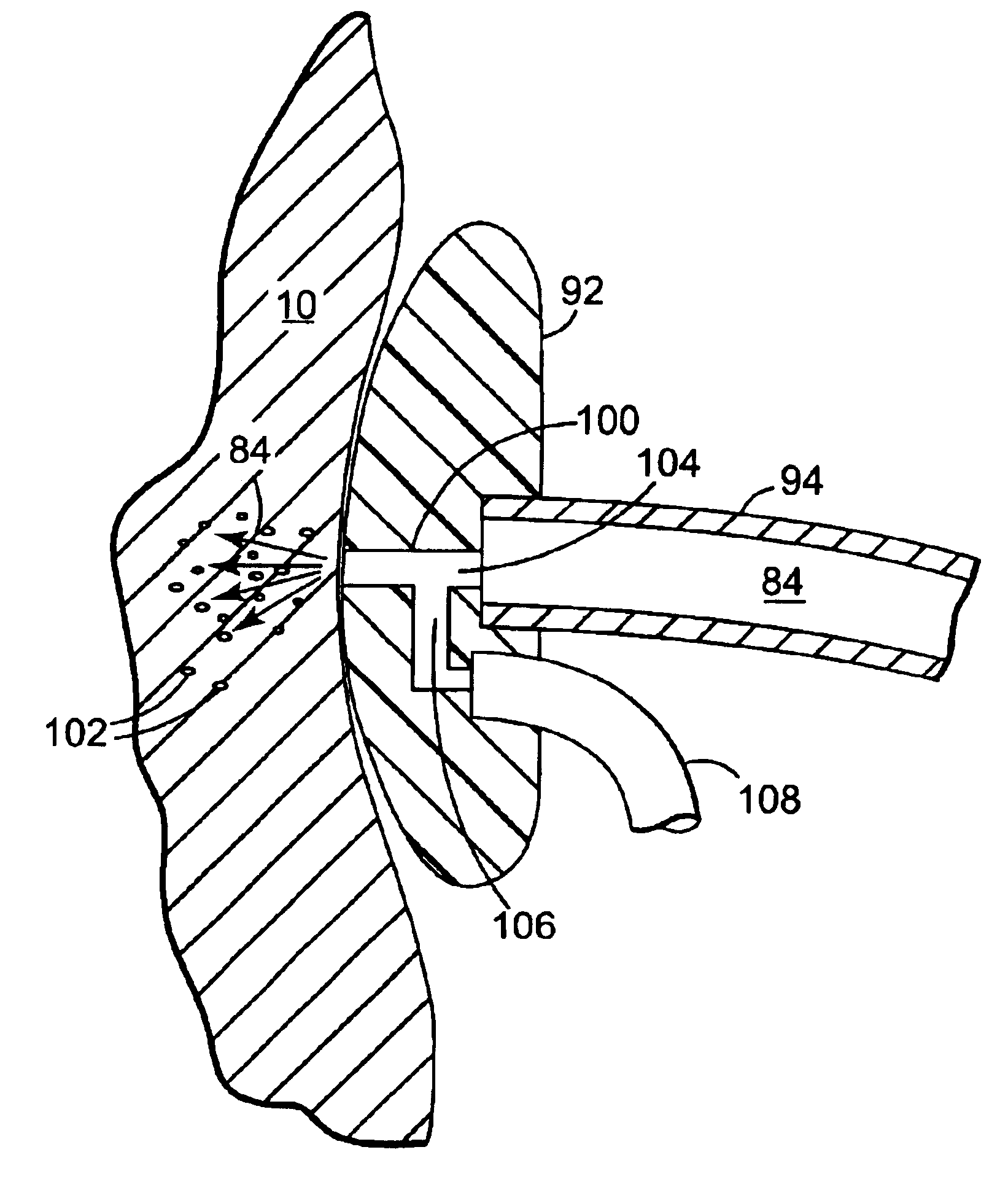
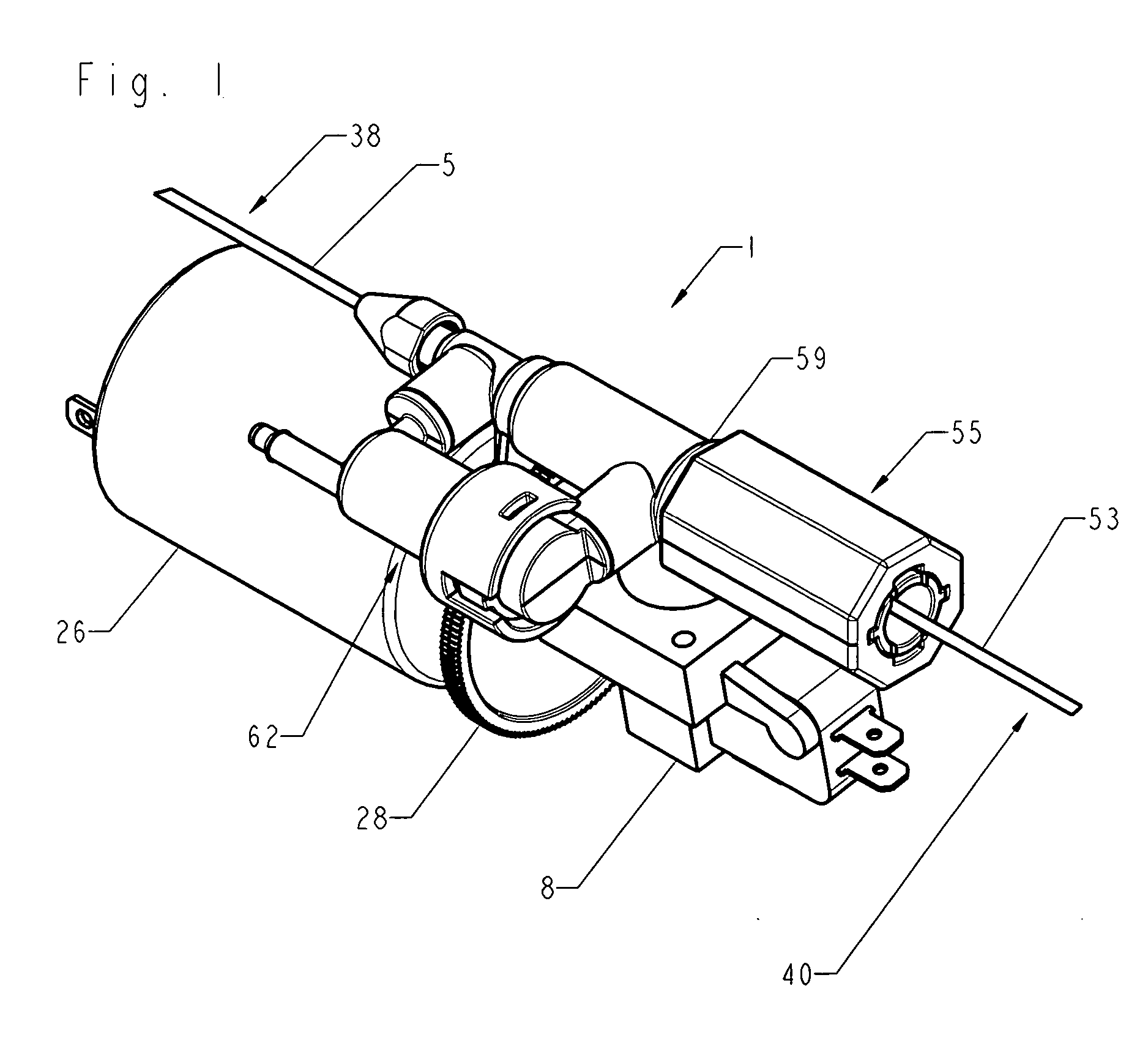
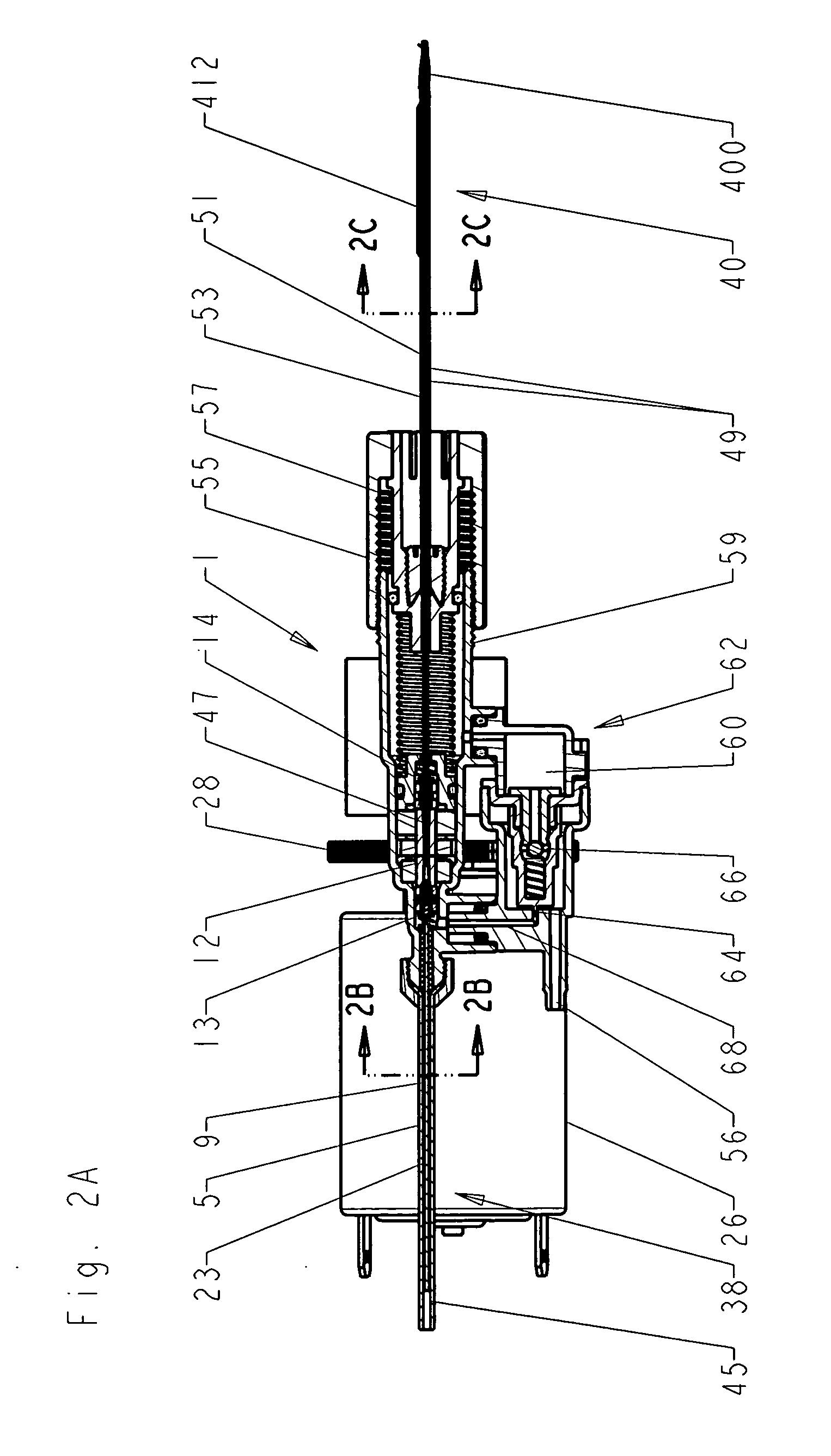
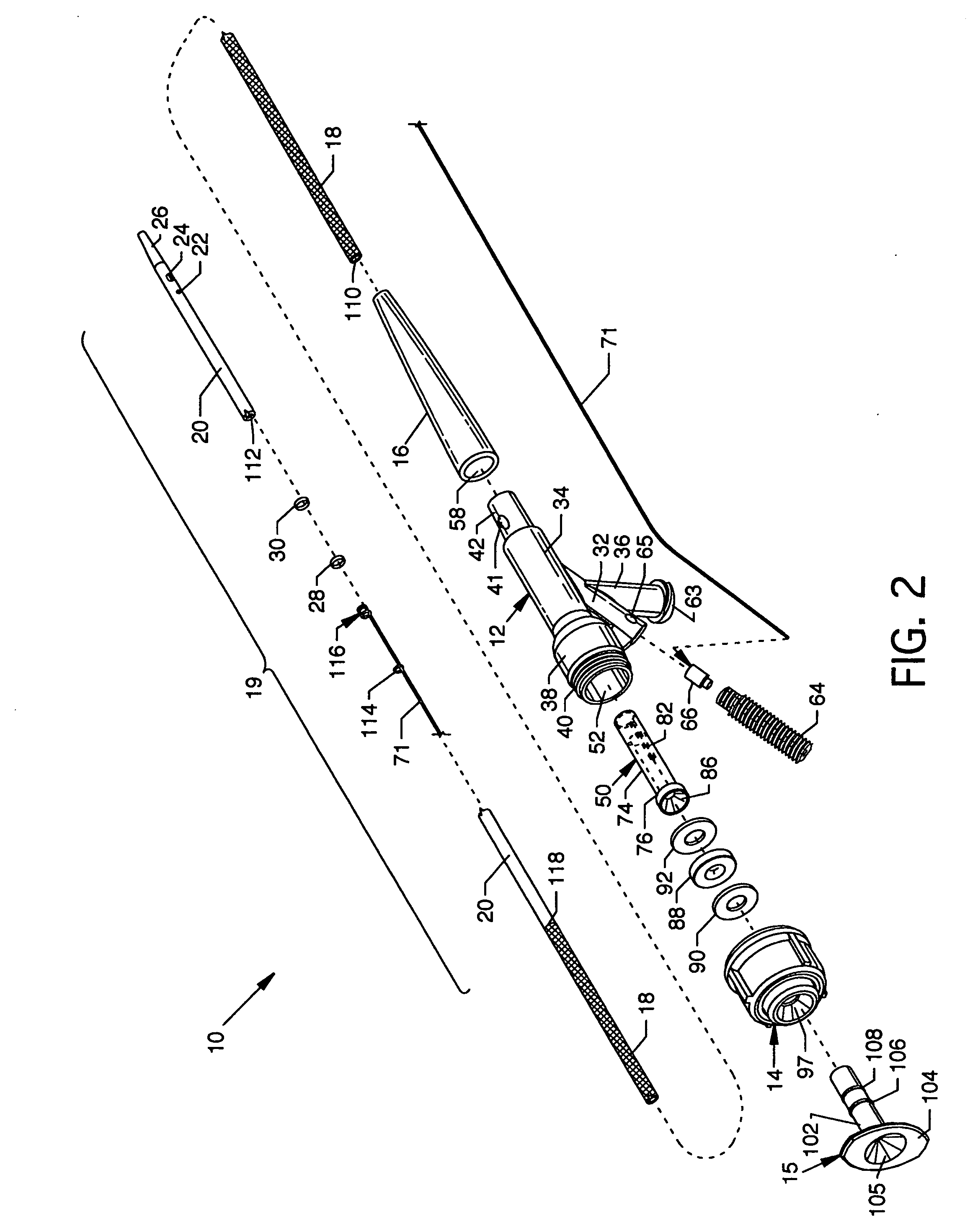
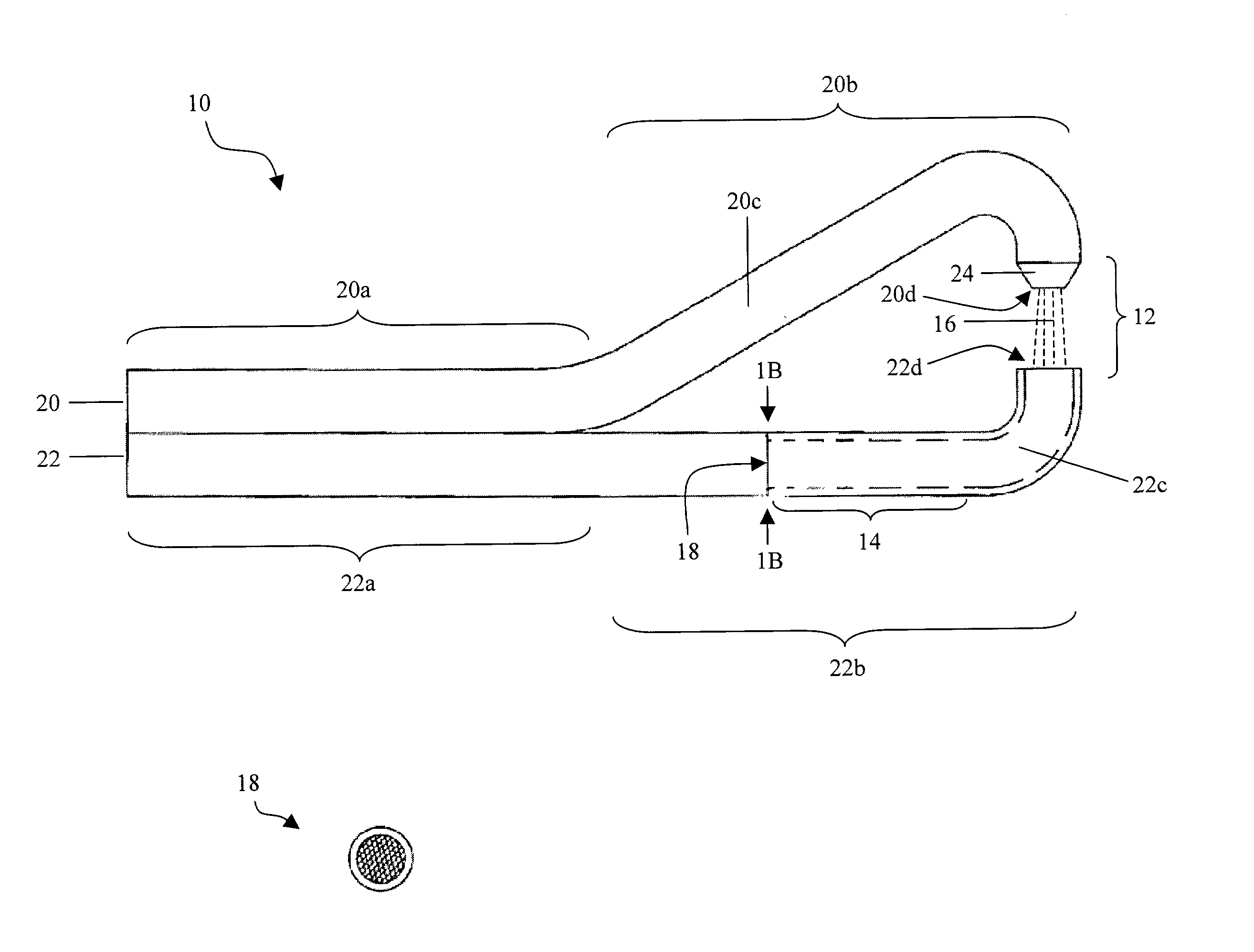
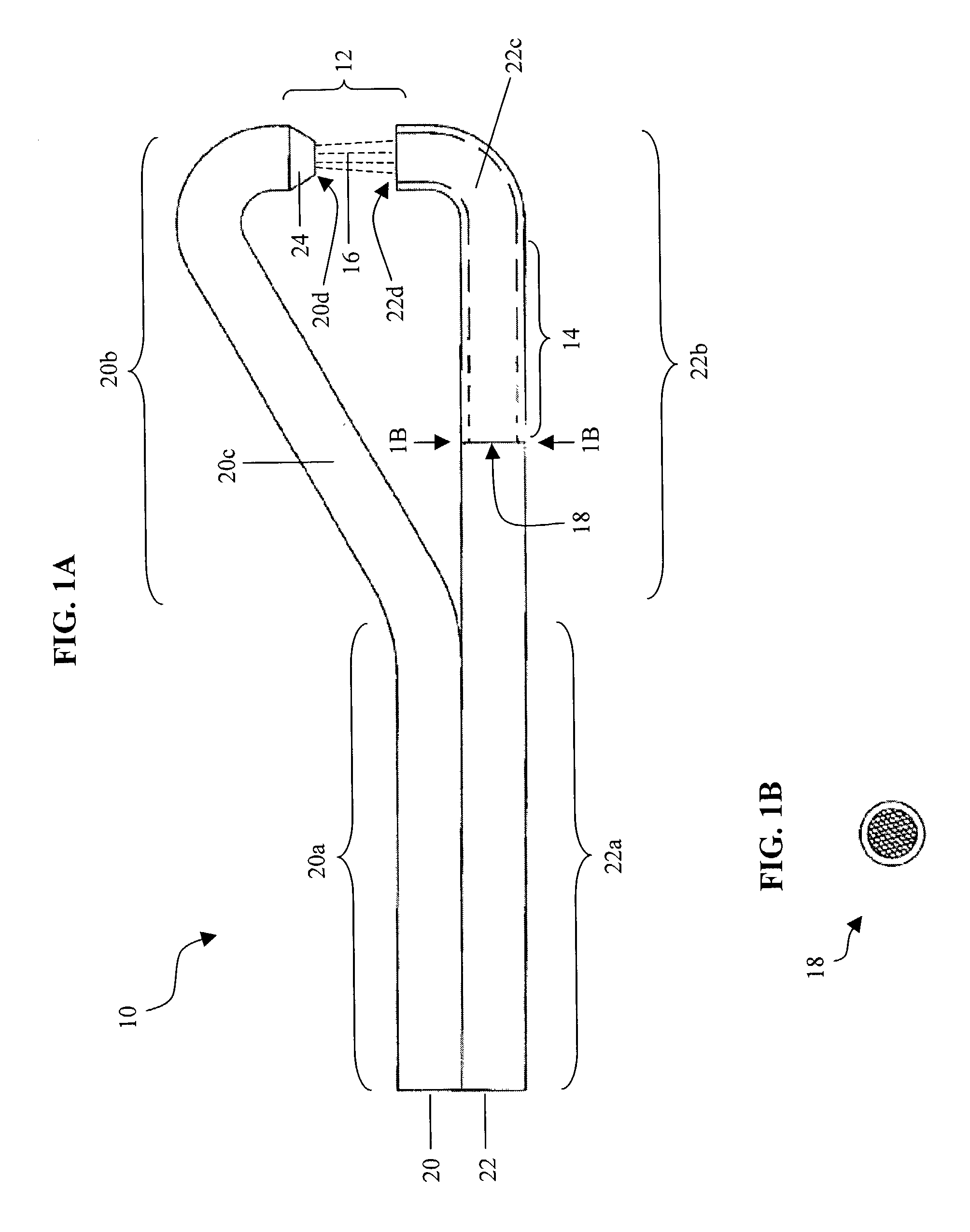
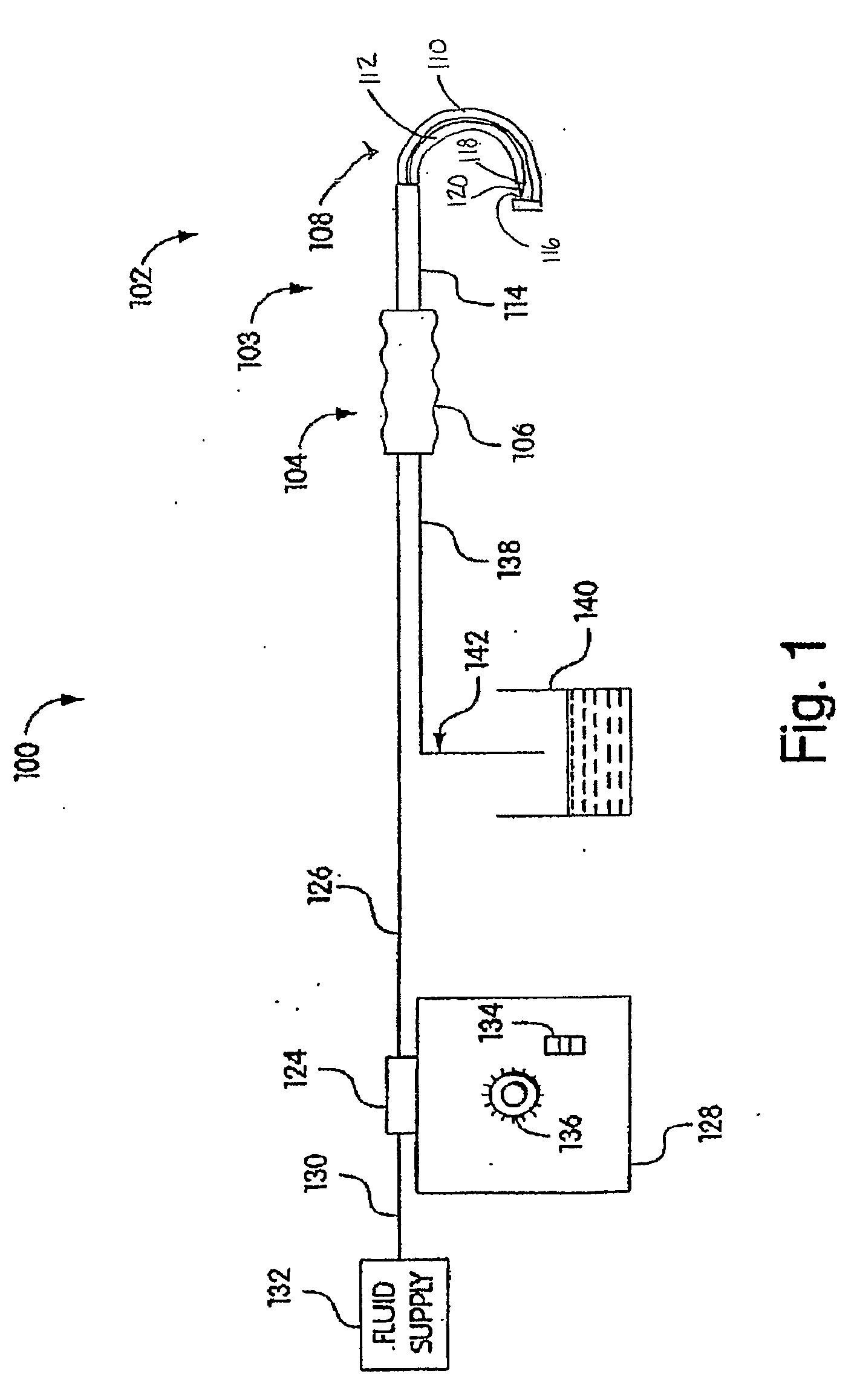
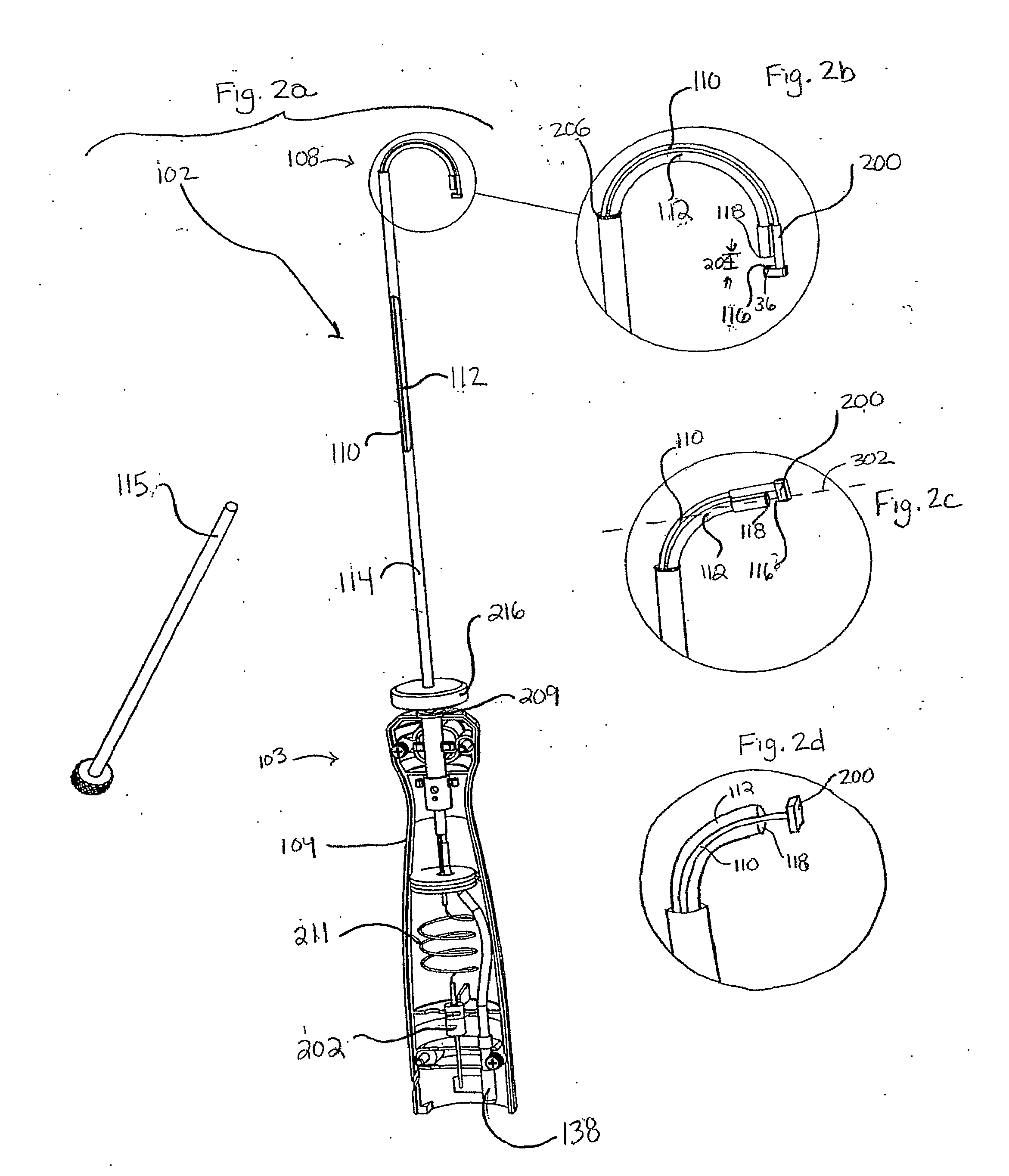
Tissue remover and method
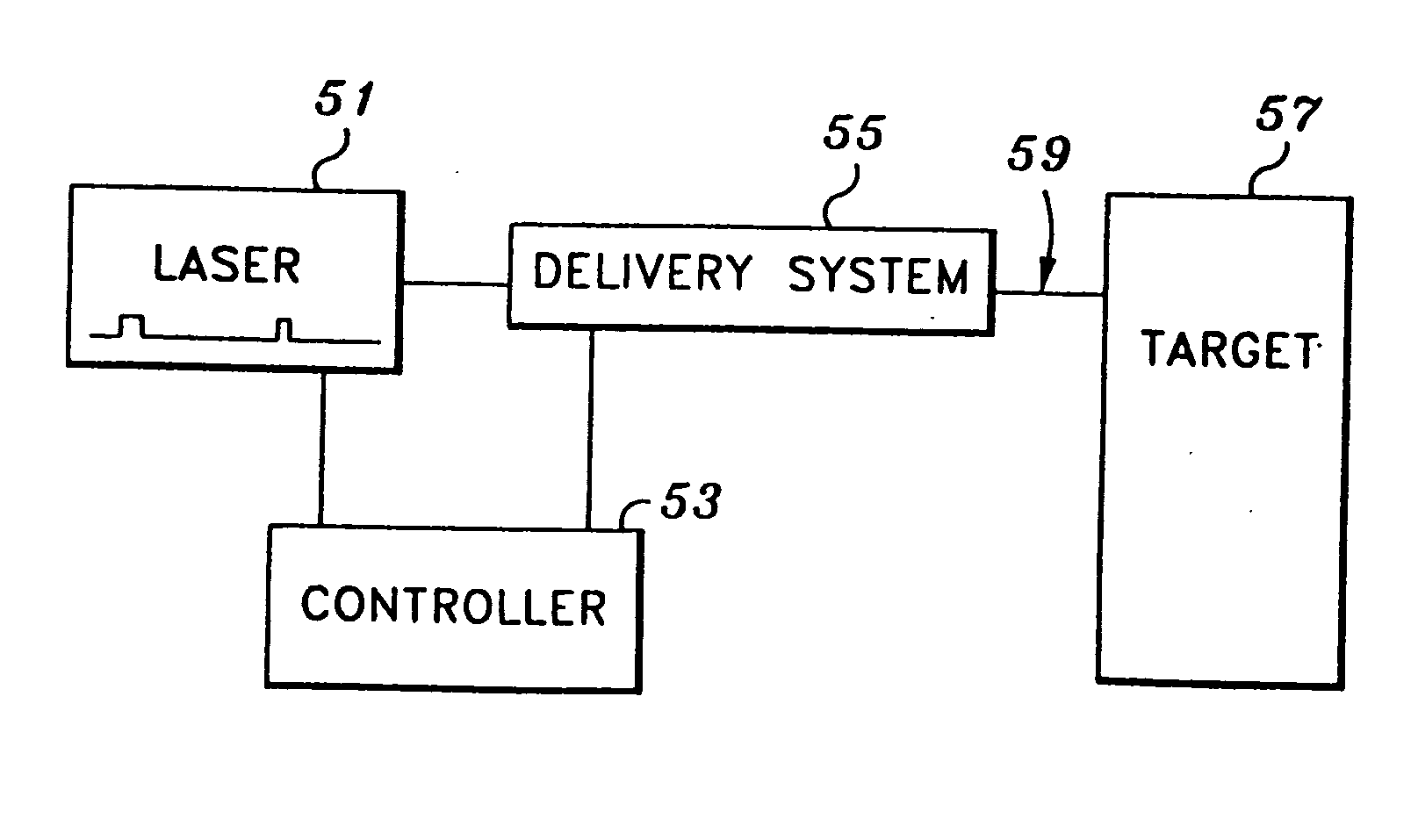
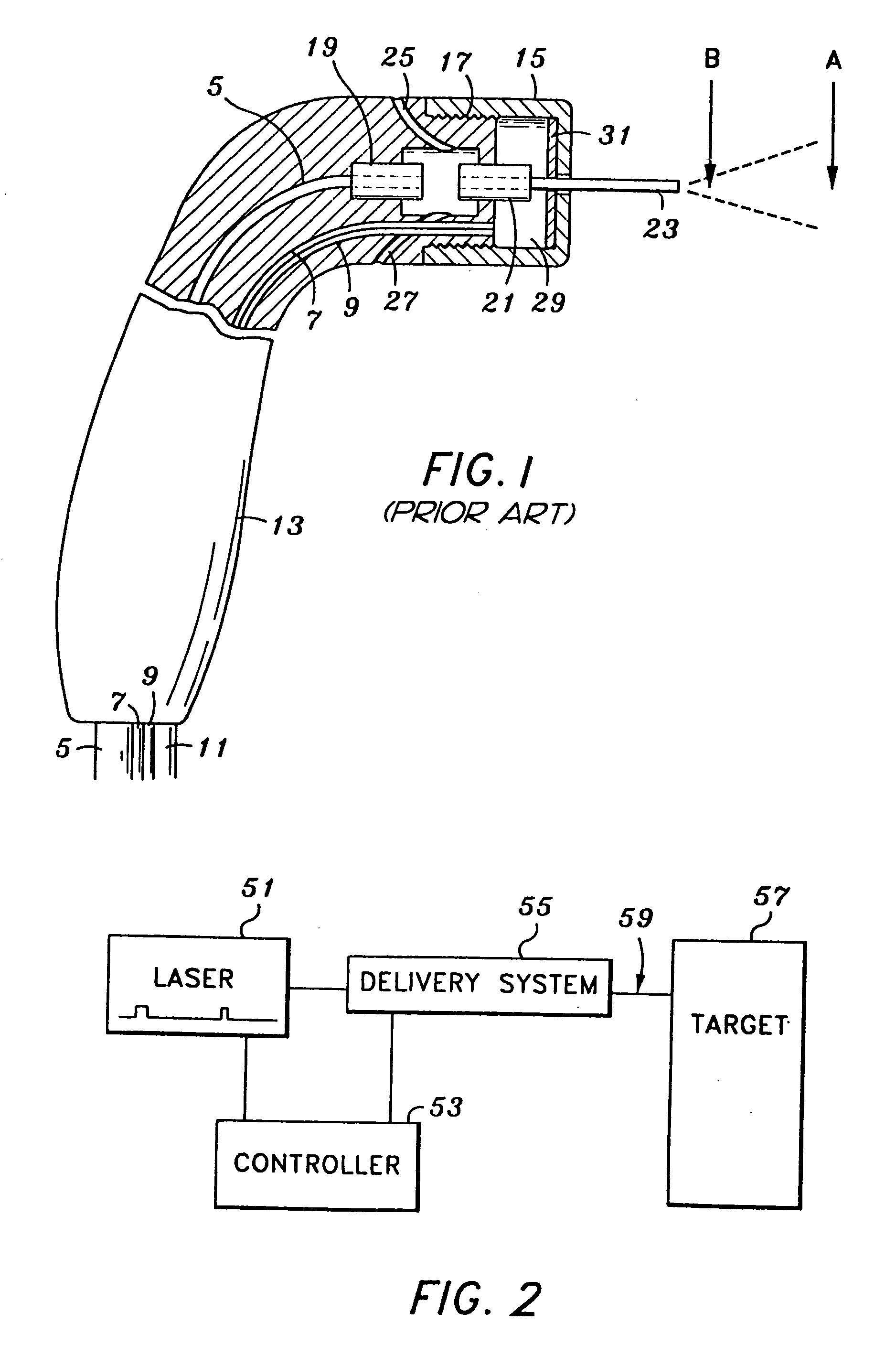
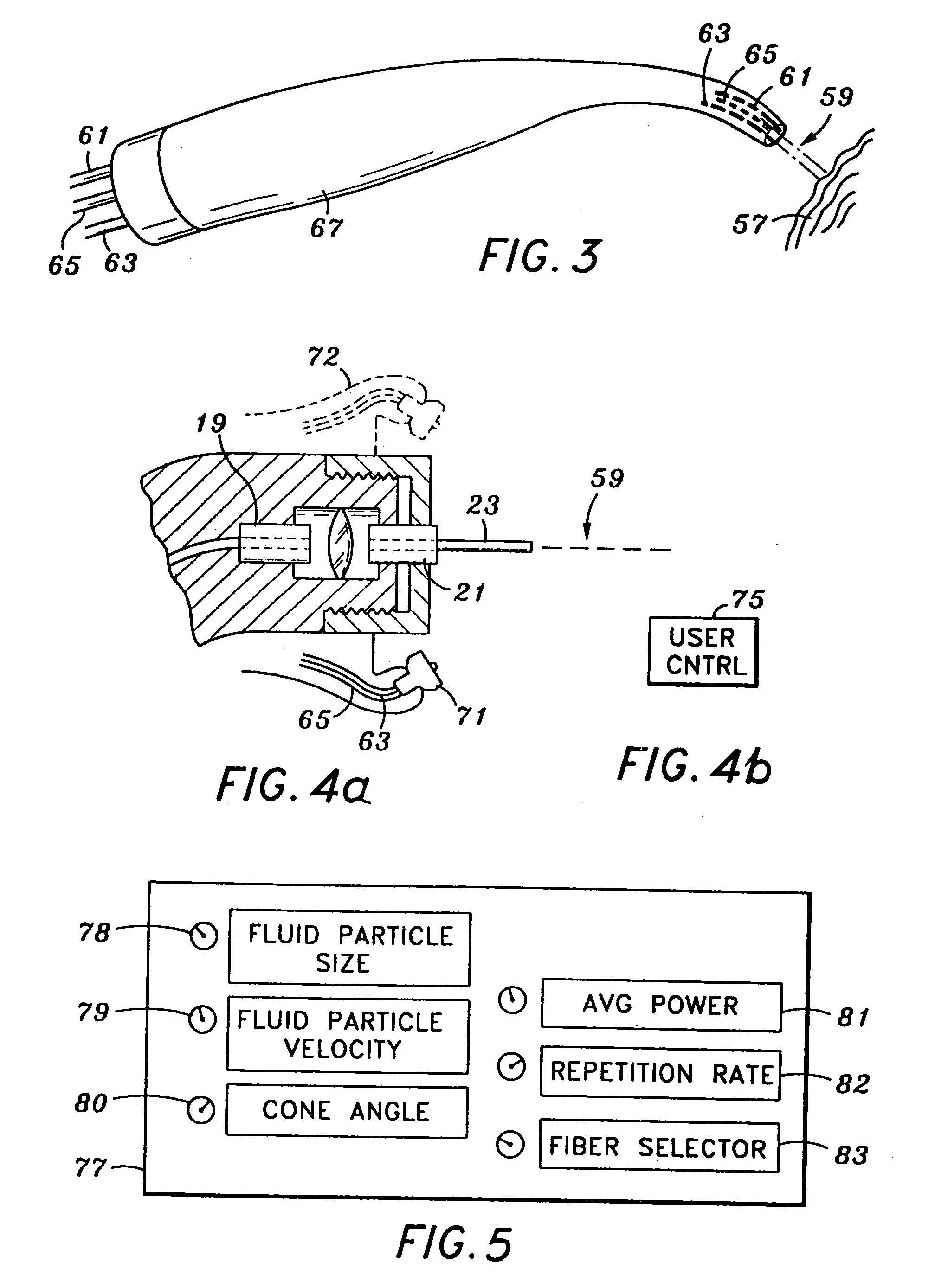
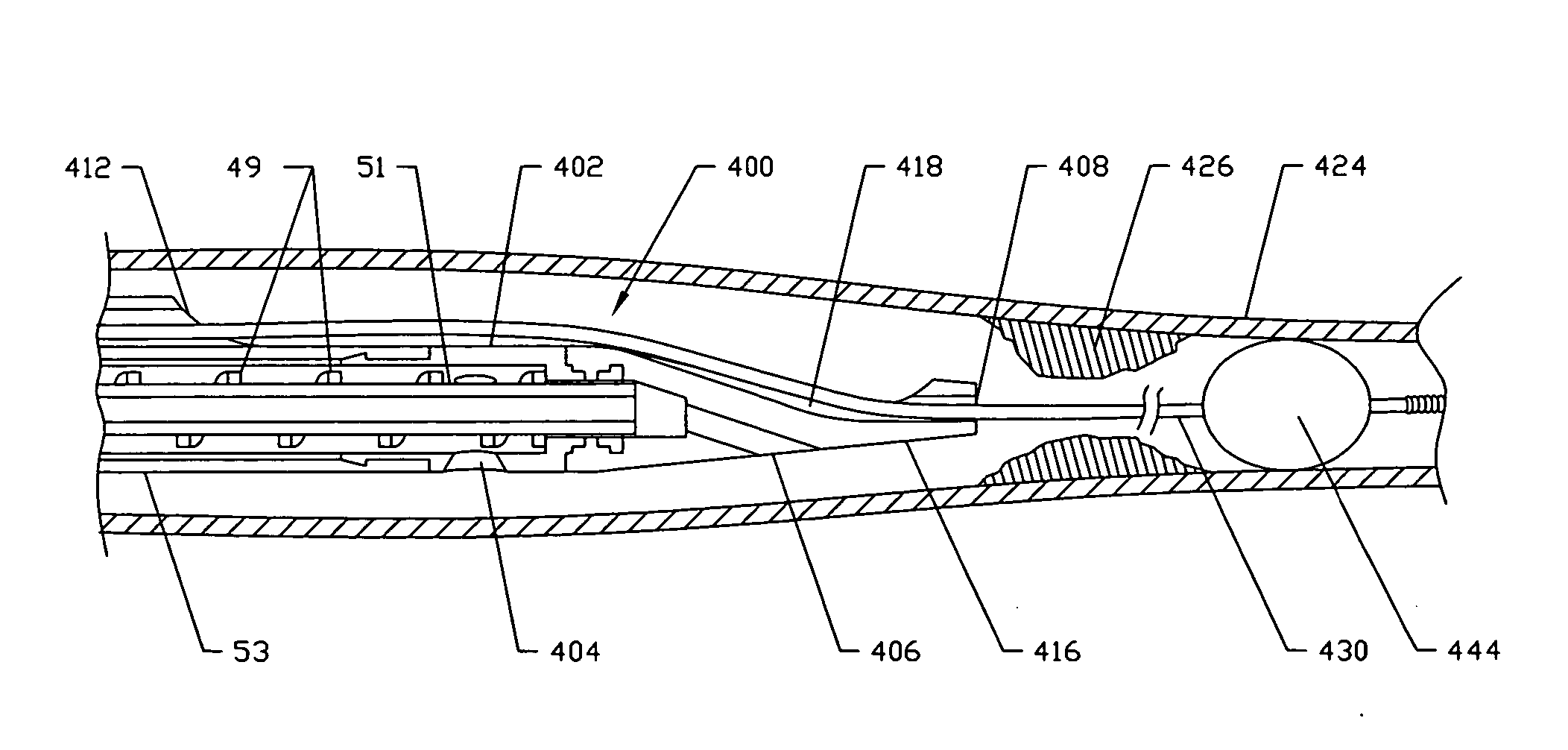
InactiveUS6669685B1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersMedicineCutting force
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Surgical devices incorporating liquid jet assisted tissue manipulation and methods for their use
ActiveUS8162966B2Improving speed and safetyDecreasing fatigue and workloadCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsSpinal columnLiquid jet
Surgical instruments are disclosed that utilize high-pressure liquid jets to perform a variety of useful functions. In certain embodiments, surgical instruments are described incorporating one or more liquid jets utilized to contact tissue excised by a non-liquid jet tissue-cutting component of the surgical instrument. In certain embodiments, a liquid jet of a surgical instrument can be utilized for the purpose of excising tissue of a patient immobilized and / or manipulated by the surgical instrument. Also described are surgical devices of the type characterized by curettes, rongeurs, bone punches, bone cutting forceps, morcellators, surgical micrograspers, with functionality and performance supplemented by the integration of a liquid jet. Also disclosed are methods of using certain liquid jet-containing surgical instruments for performing surgical procedures, for example surgical procedures on the spinal column of a patient.
Owner:HYDROCISION
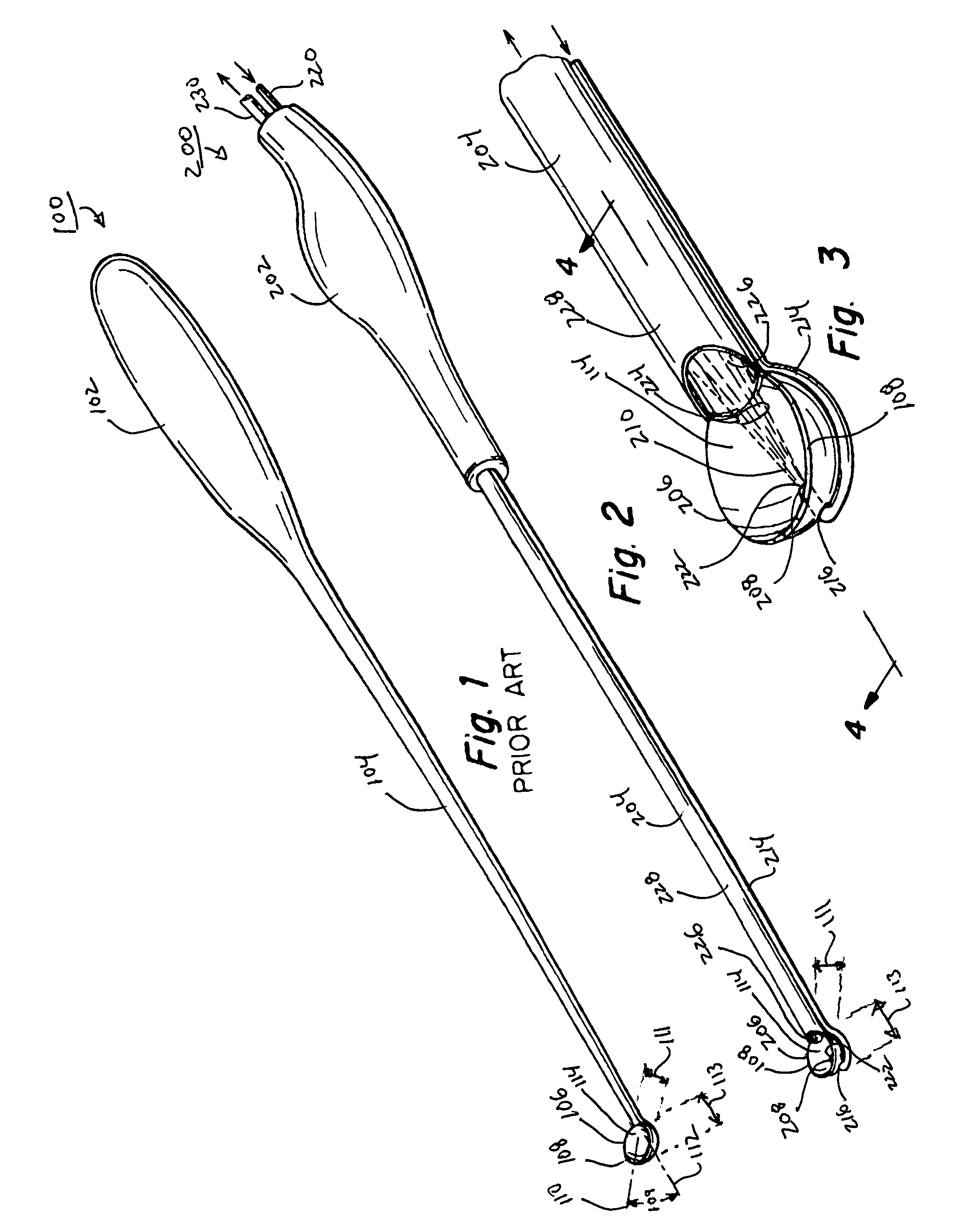
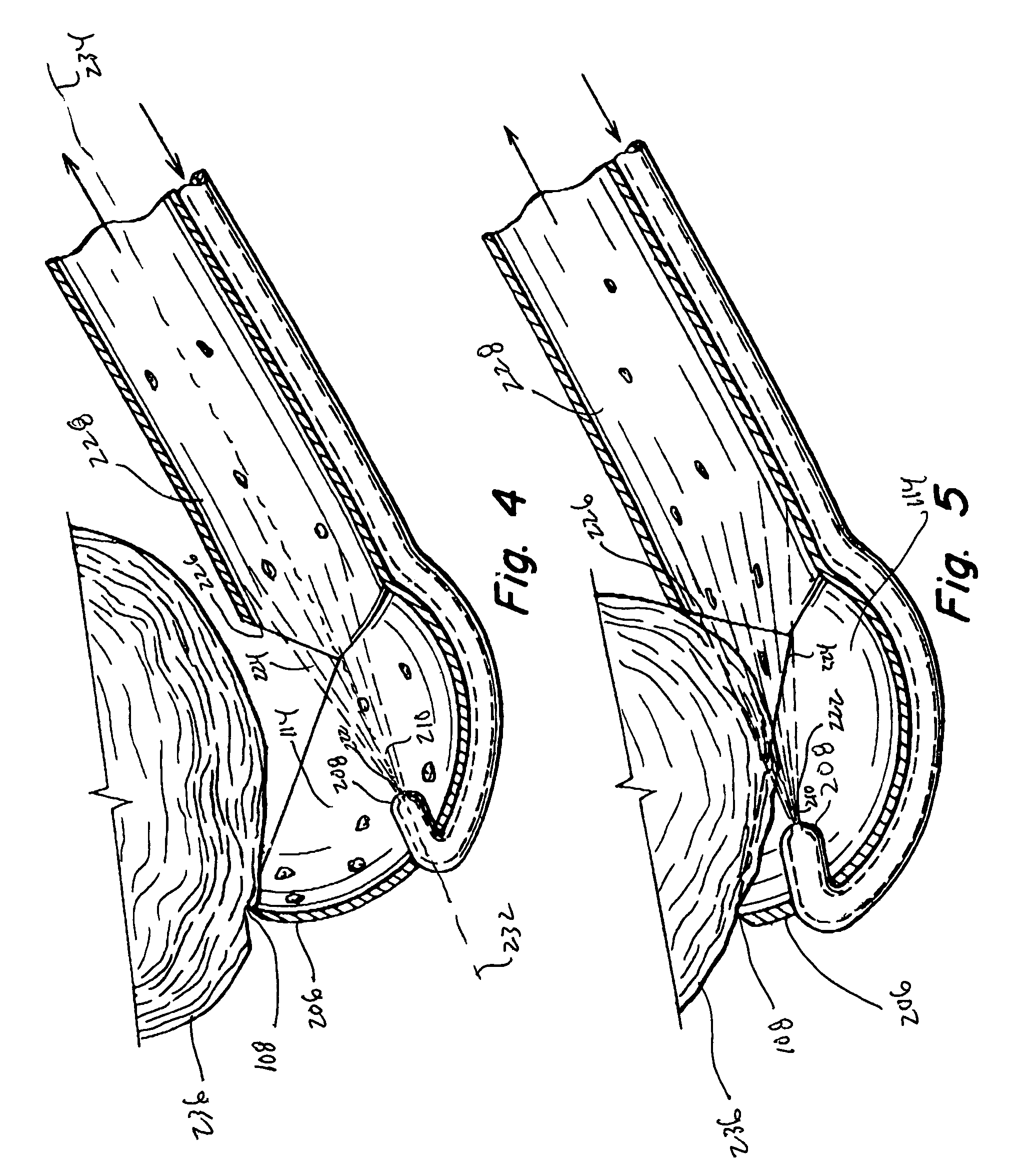
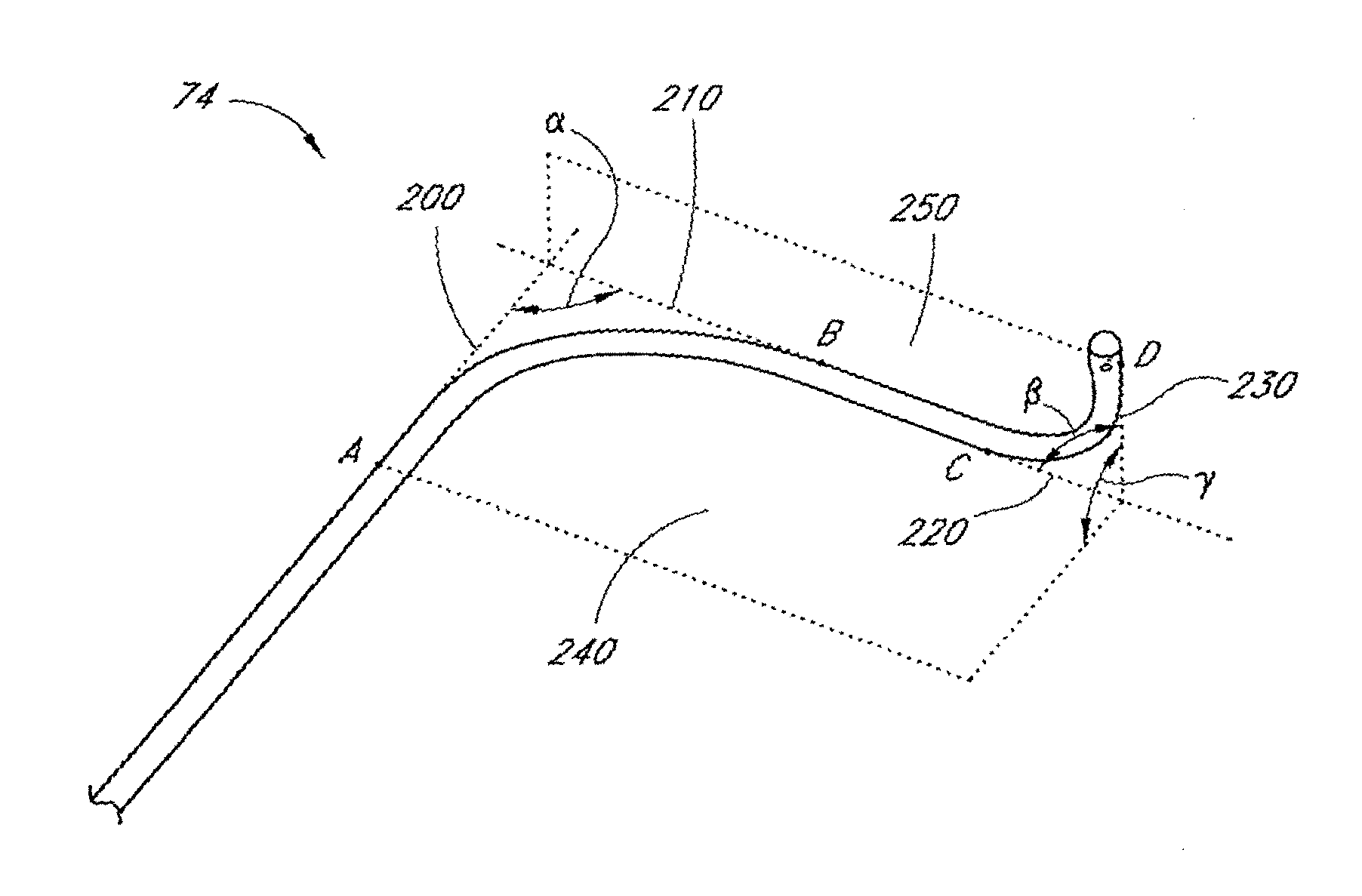
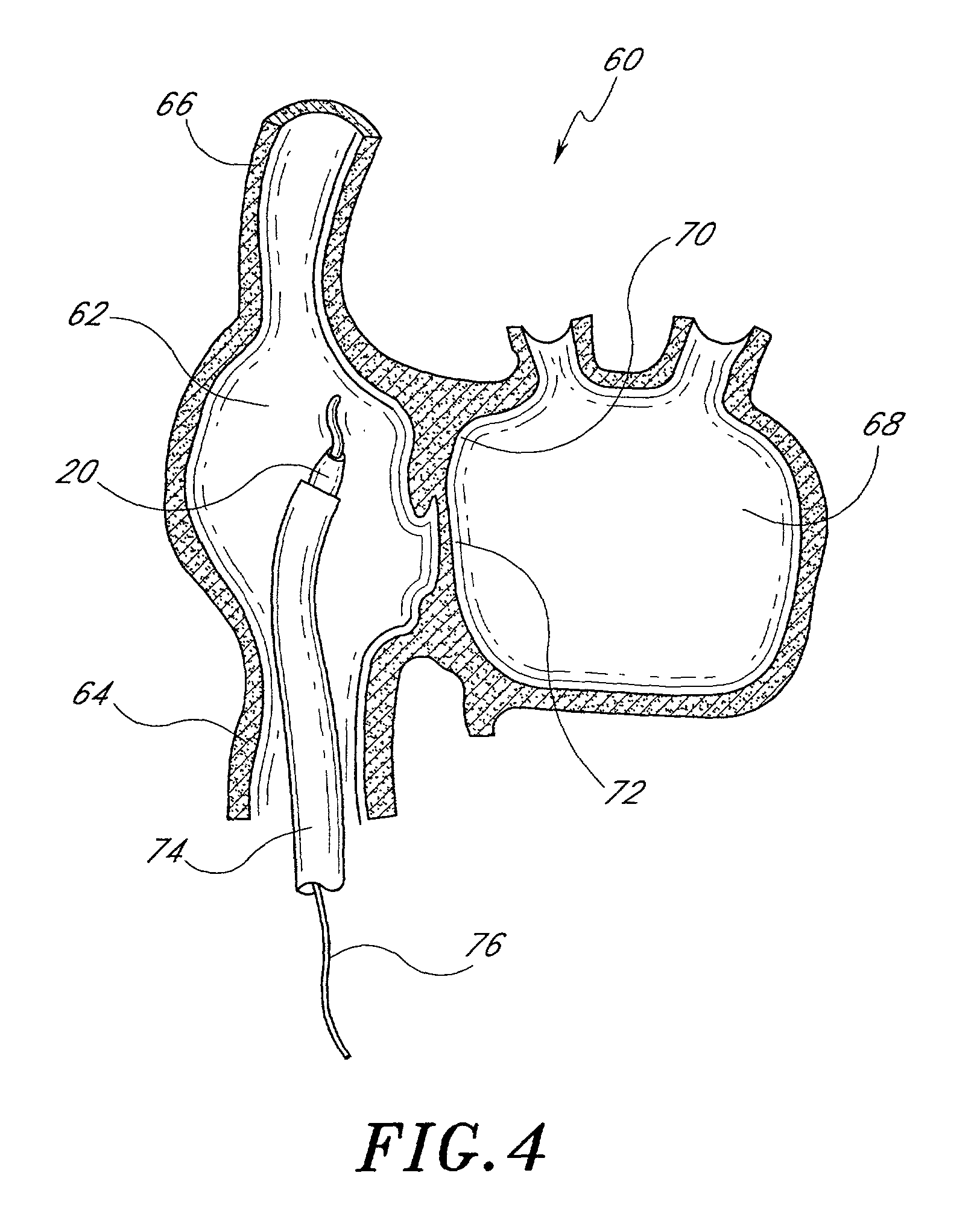
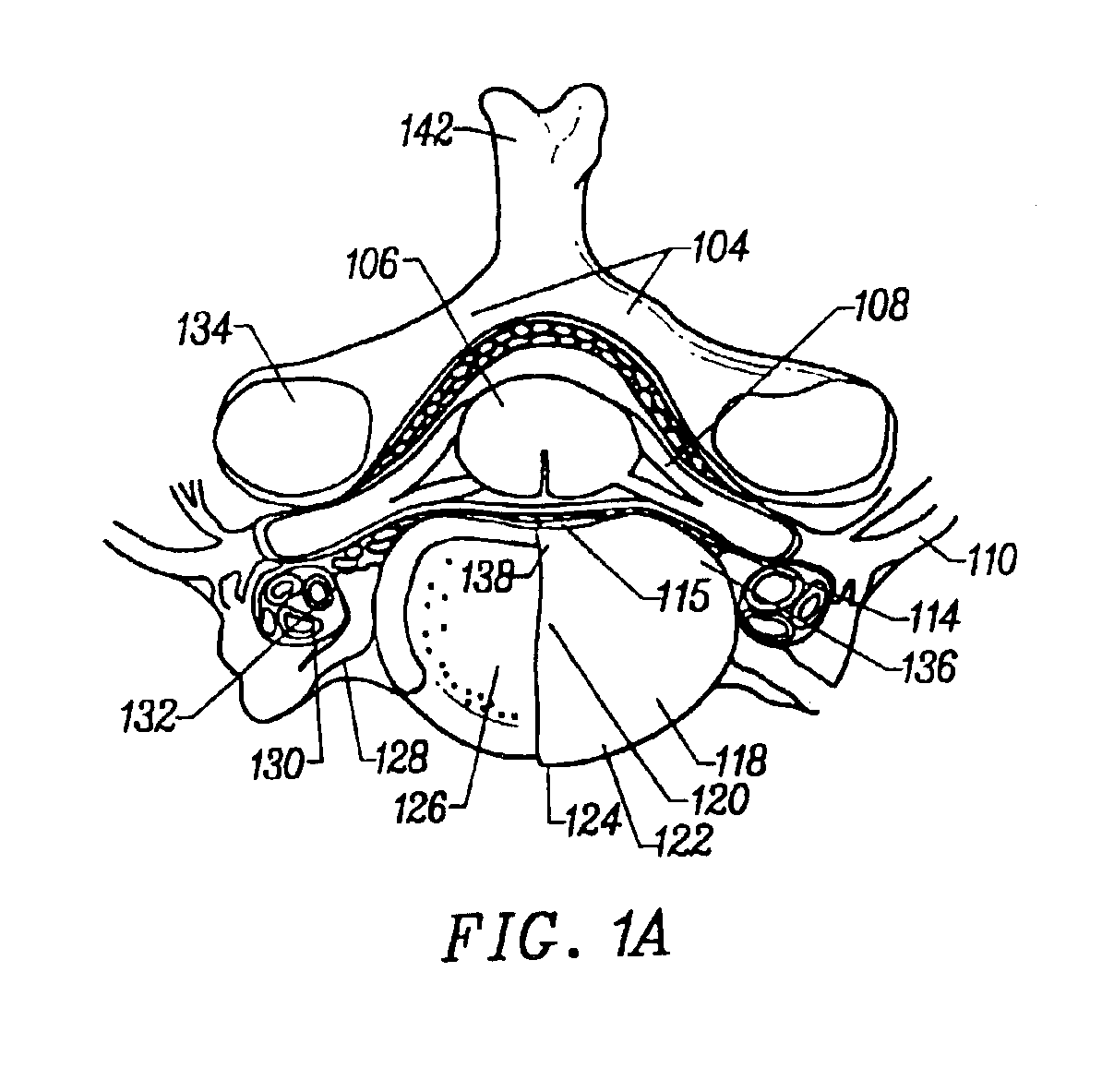
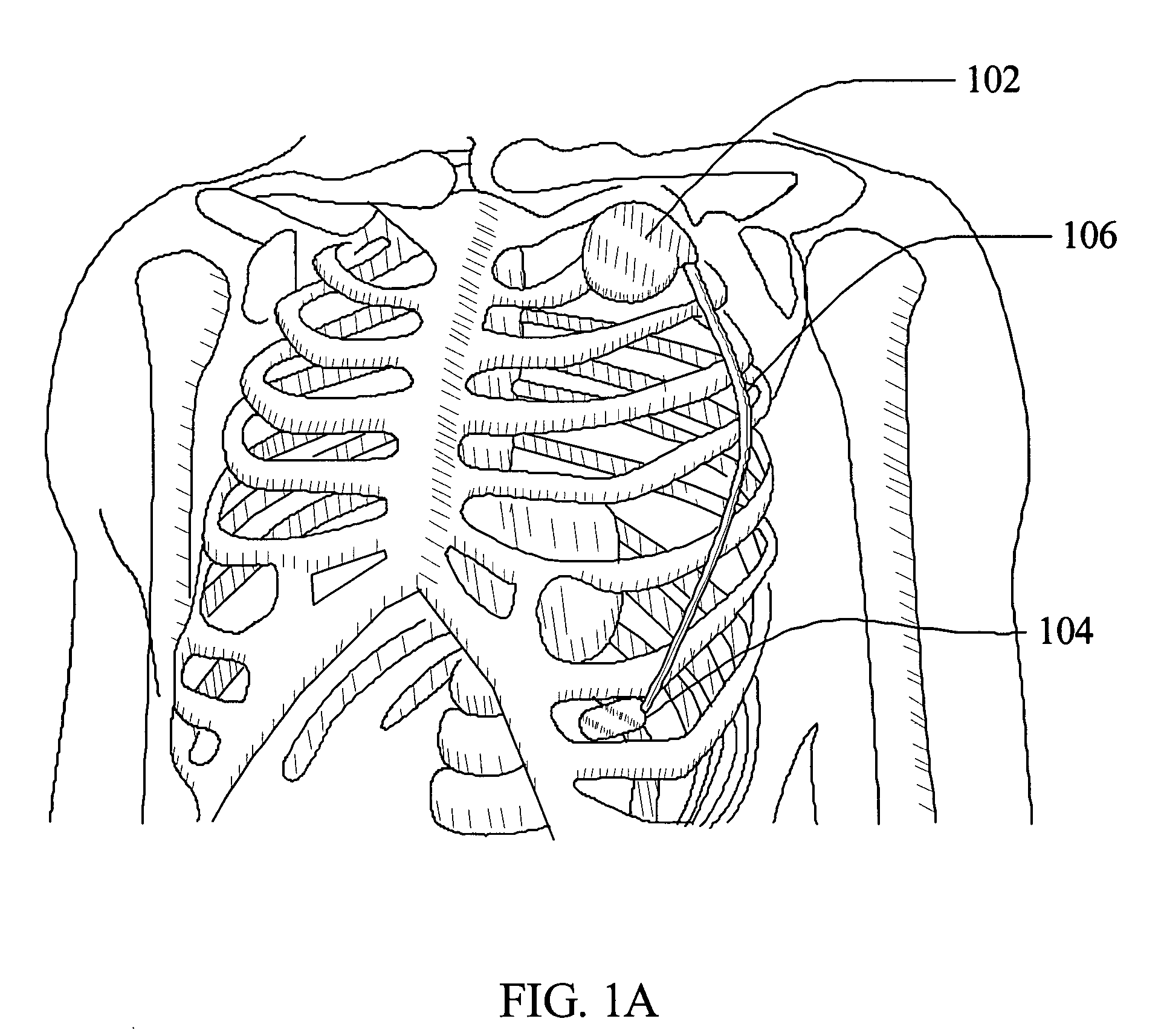
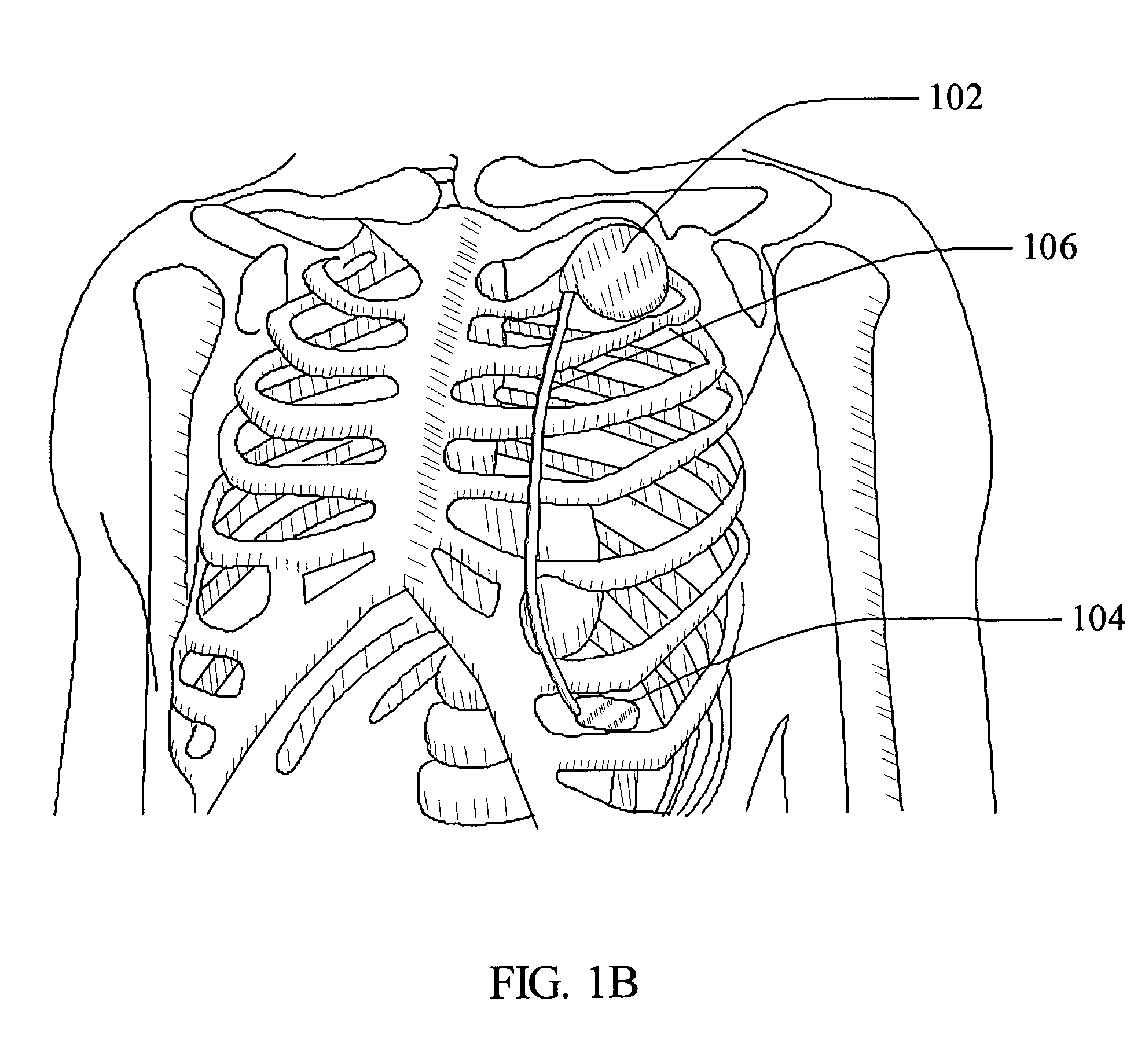
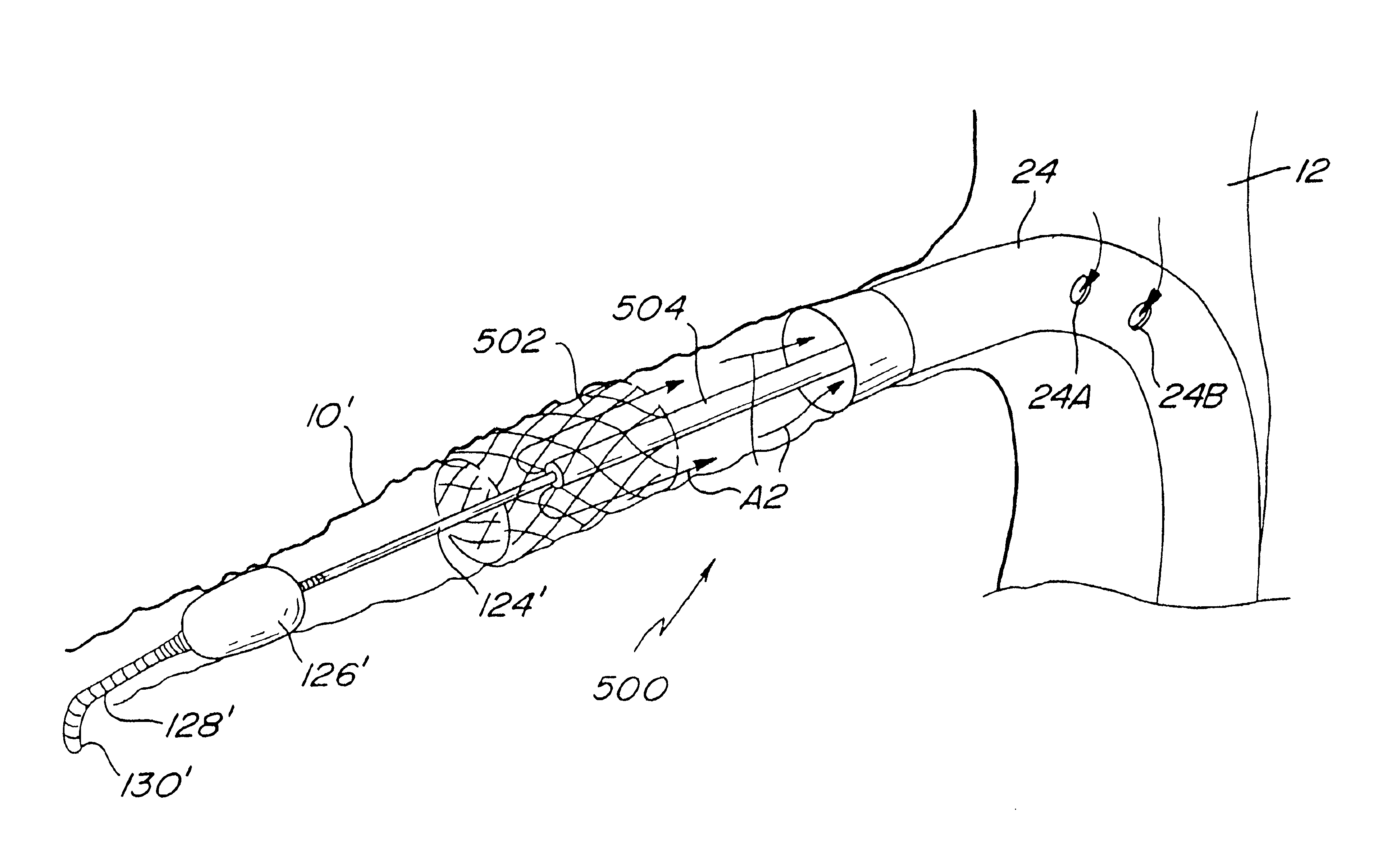
Method and apparatus for accessing the left atrial appendage
Disclosed is an apparatus for facilitating access to the left atrium, and specifically the left atrial appendage. The apparatus may comprise a sheath with first and second curved sections that facilitate location of the fossa ovalis and left atrial appendage. The apparatus may further comprise tissue piercing and dilating structures. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Active drug delivery in the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS20050058701A1Easy accessPromote absorptionInternal electrodesBody temperature measurementMedicineDrug administration
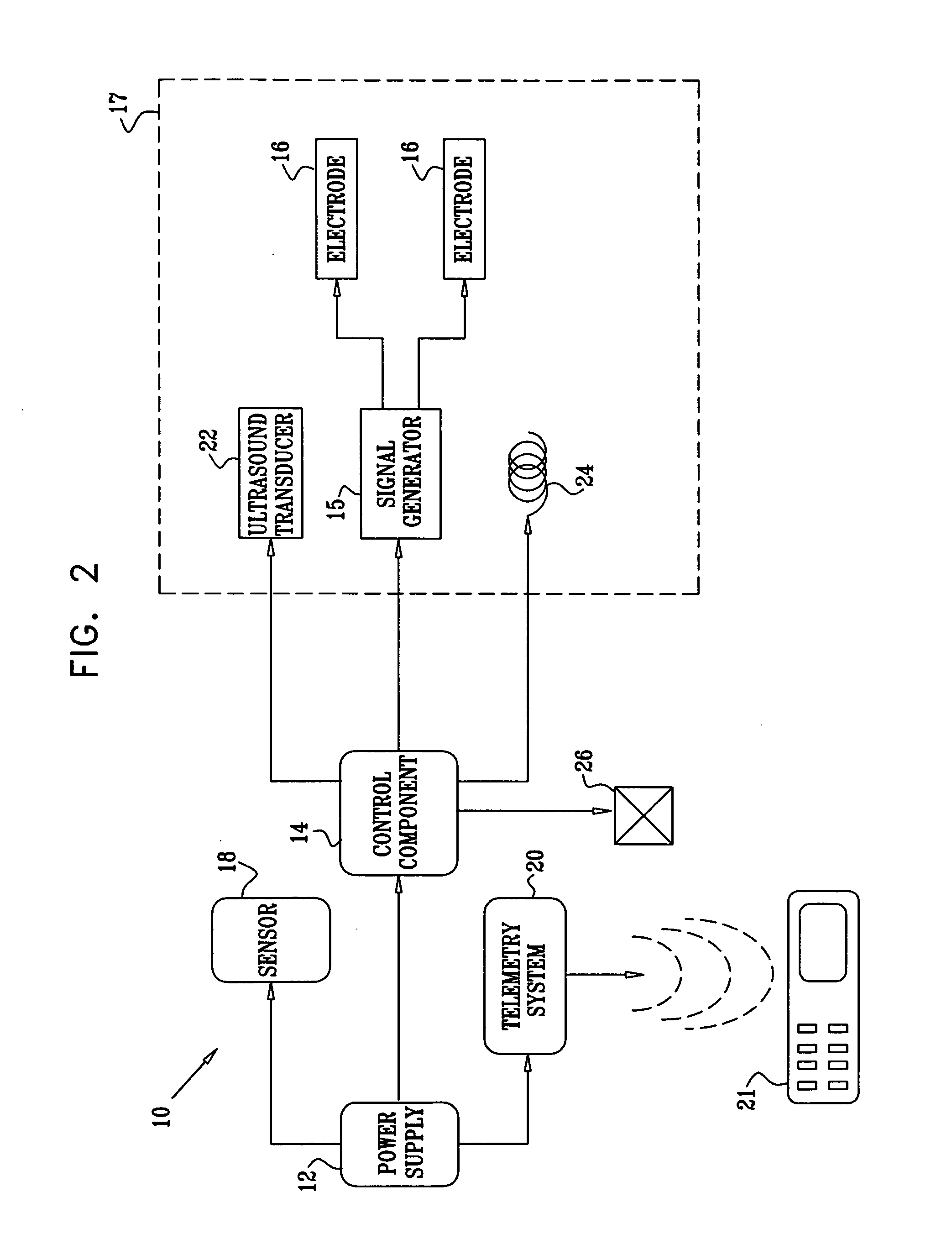
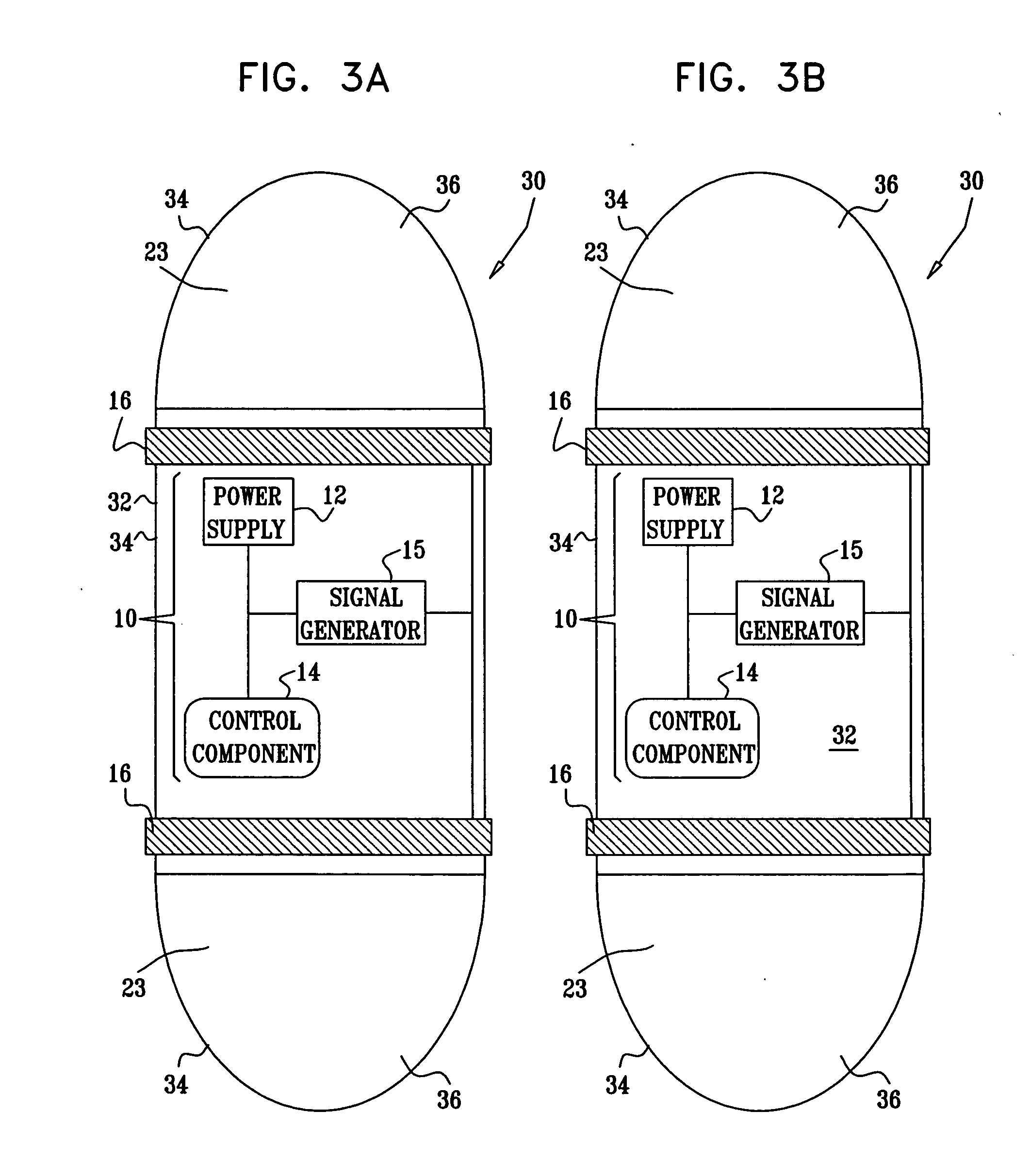
Apparatus for drug administration is provided, including an ingestible capsule, which includes a drug, stored by the capsule, and an environmentally-sensitive mechanism, adapted to change a state thereof responsively to a disposition of the capsule within a gastrointestinal (GI) tract of a subject. The capsule further includes first and second electrodes, and a control component, adapted to facilitate passage of the drug, in response to a change of state of the environmentally-sensitive mechanism, through an epithelial layer of the GI tract by driving the first and second electrodes to apply a series of pulses at a current of less than about 5 mA, at a frequency of between about 12 Hz and about 24 Hz, and with a pulse duration of between about 0.5 milliseconds and about 3 milliseconds.
Owner:E PILL PHARMA
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
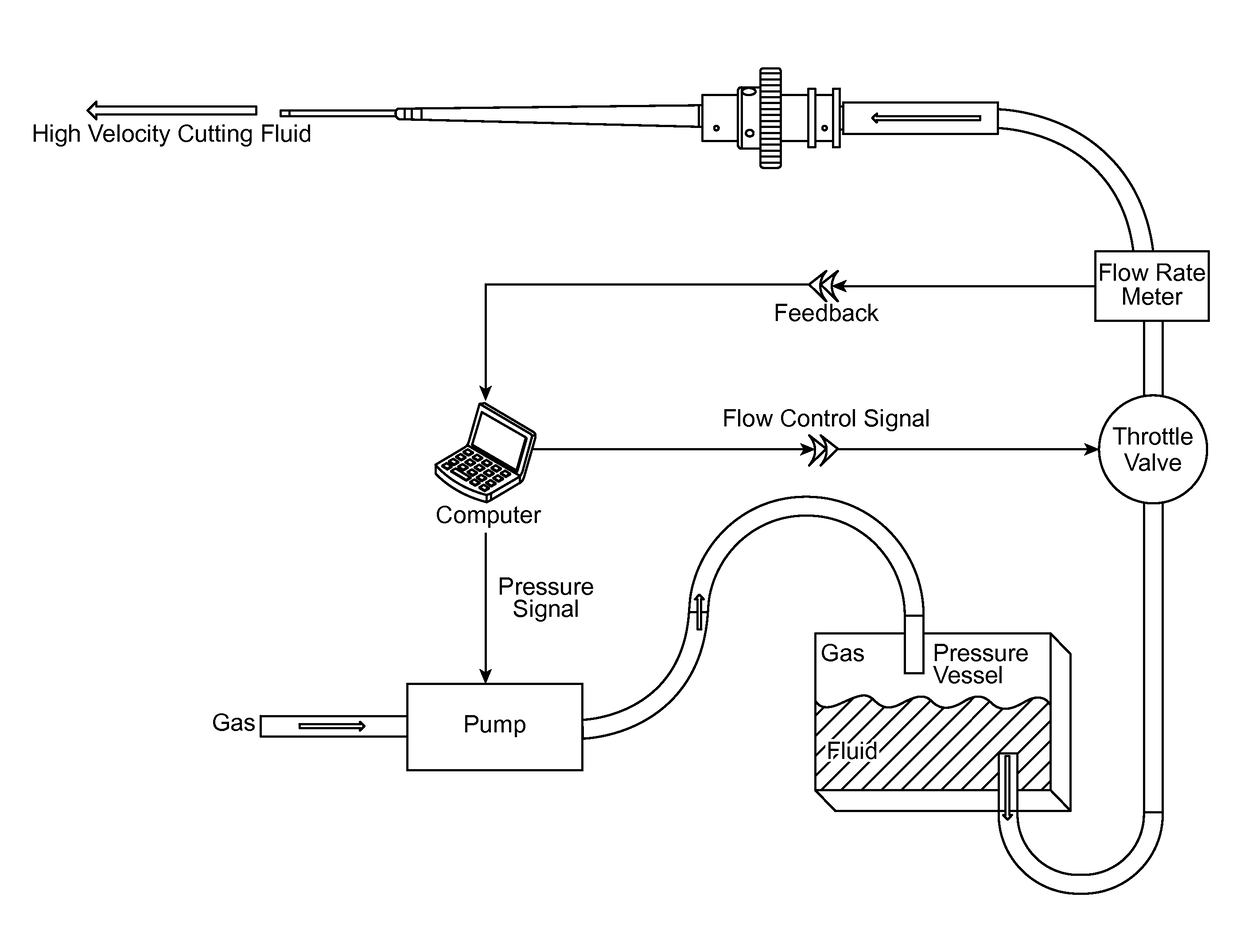
A water jet instrument may be used for manually performing eye surgery such as, cataract, or perform micro-surgery (remove cartilage), or any emulsification technique. The water jet instrument may be manually controlled or controlled by a system with a robotic control. The water jet apparatus defines a jet cutting area that is based at least in part on a flow rate meter and a feedback loop.
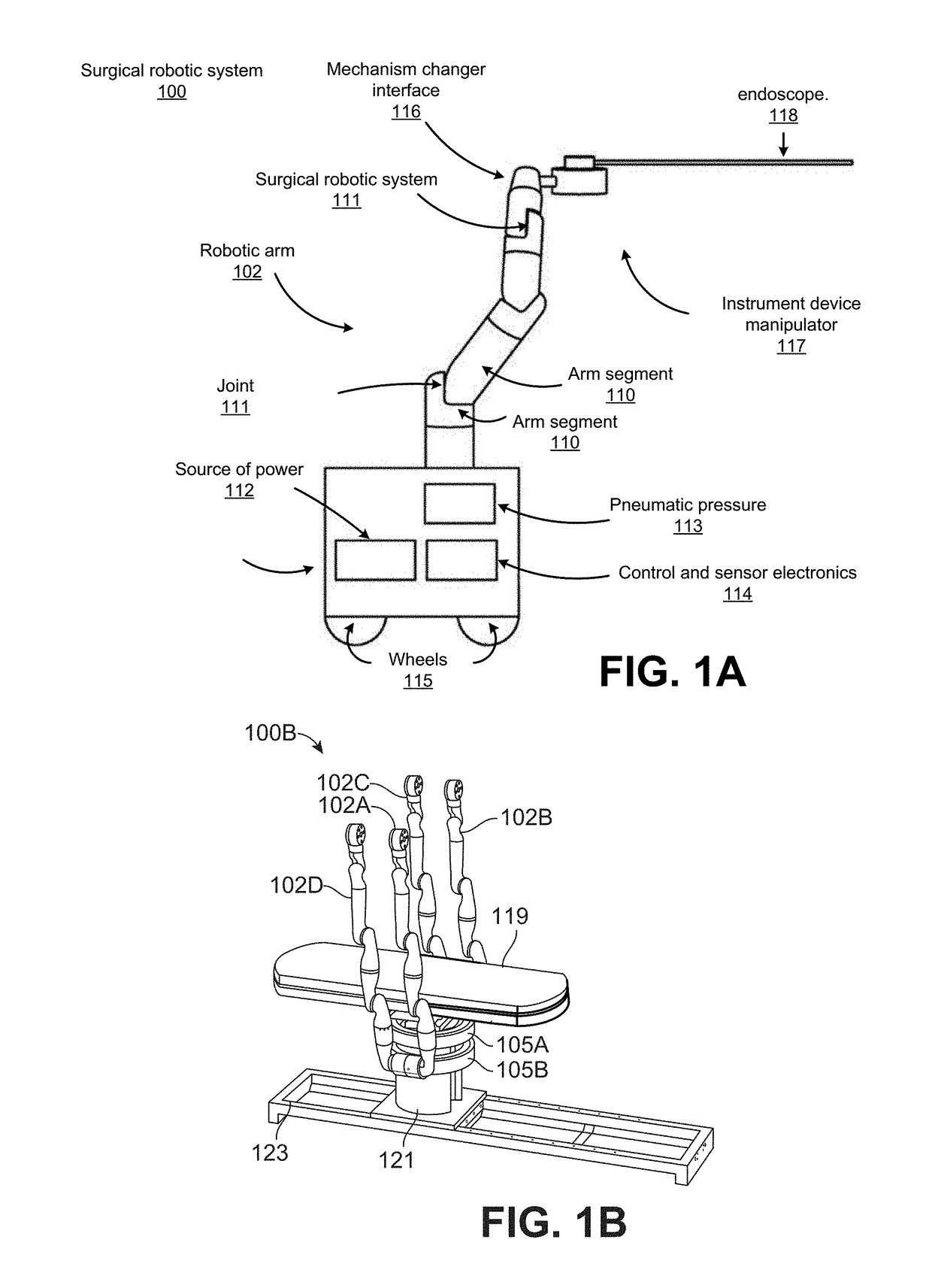
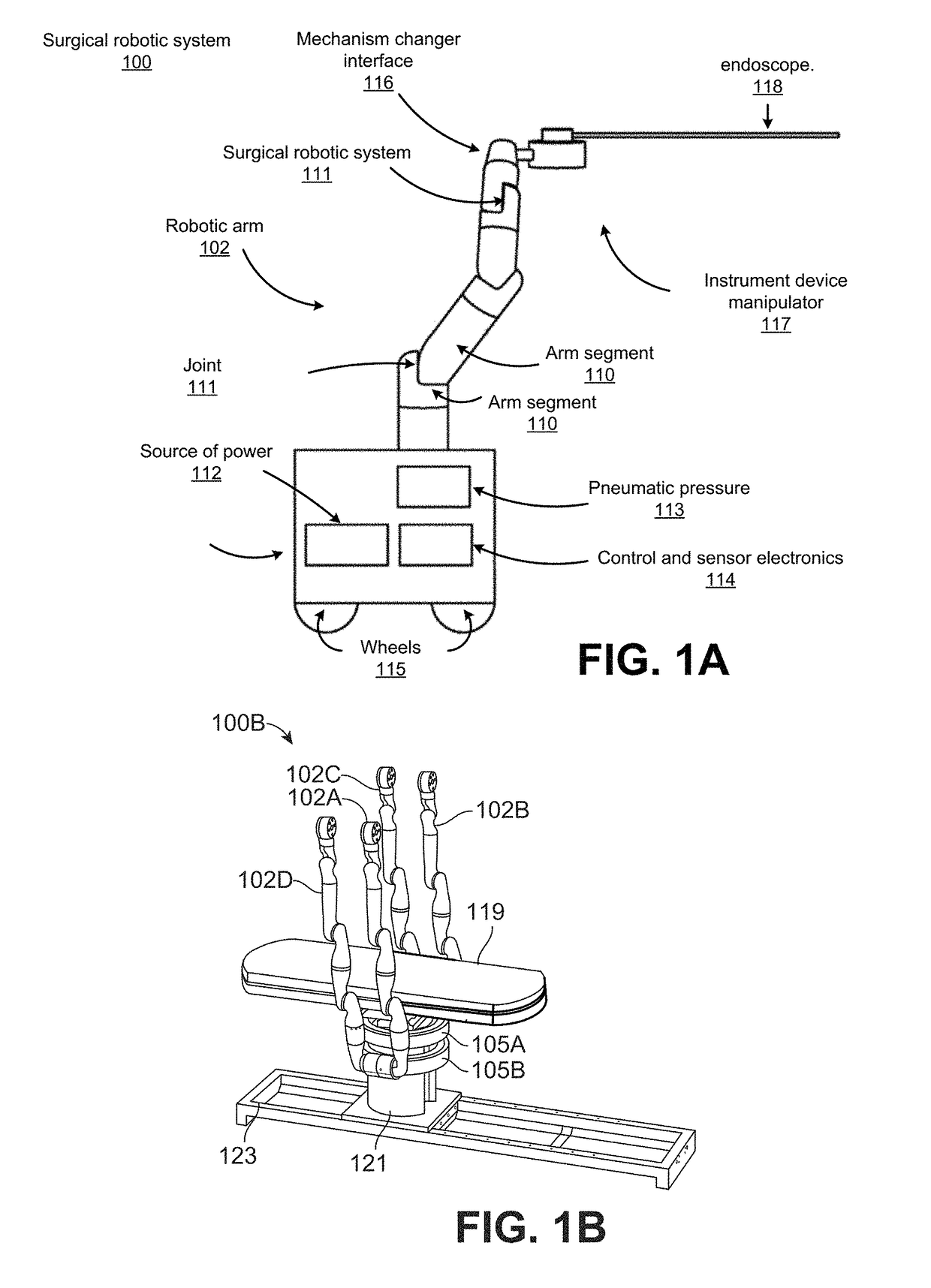
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Method and apparatus for treating annular fissures in intervertebral discs
InactiveUS6997941B2Sufficient energyReduce pressureElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisSufficient timeMedicine
A device is described that may be positioned at a location in an intervertebral disc for diagnosis or treatment of the disc. Treatment may include, for example, applying energy or removing material, and may decrease intradiscal pressure. Radiofrequency energy may be applied. A percutaneous method of repairing a fissure in the annulus pulposus comprises placing an energy source adjacent to the fissure and providing sufficient energy to the fissure to raise the temperature to at least about 45-70° C. and for a sufficient time to cause the collagen to weld. An intervertebral fissure also can be treated by placing a catheter with a lumen adjacent to the fissure and injecting sealant into the fissure via the catheter, thereby sealing the fissure. An intervertebral fissure additionally can be treated by providing a catheter having a distal end, a proximal end, a longitudinal axis, and an intradiscal section at the catheter's distal end on which there is at least one functional element. The next step is applying a force longitudinally to the proximal of the catheter which is sufficient to advance the intradiscal section through the nucleus pulposus and around an inner wall of an annulus fibrosus, but which force is insufficient to puncture the annulus fibrosus. Next the functional element is positioned at a selected location of the disc by advancing or retracting the catheter and optionally twisting the proximal end of the catheter. Then the functional unit treats the annular fissure. Optionally, there is an additional step of adding a substance to seal the fissure. An externally guidable intervertebral disc apparatus also is disclosed.
Owner:NEUROTHERM
Method and apparatus for accessing the left atrial appendage
Disclosed is an apparatus for facilitating access to the left atrium, and specifically the left atrial appendage. The apparatus may comprise a sheath with first and second curved sections that facilitate location of the fossa ovalis and left atrial appendage. The apparatus may further comprise tissue piercing and dilating structures. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:ATRITECH INC
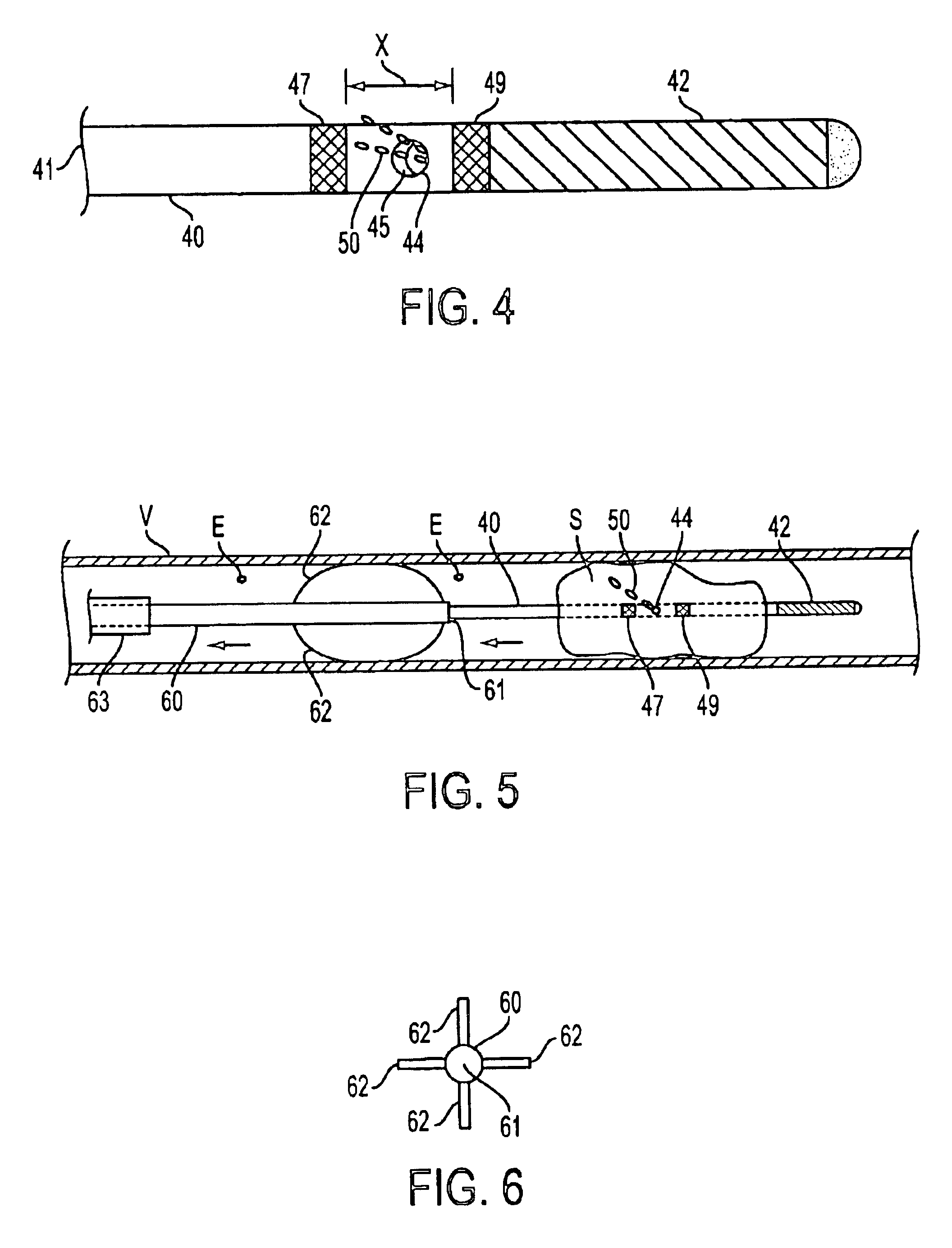
Tissue remover and method
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A non-thermal tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced mechanical cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with an aspiration inlet port adjacent the cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the aspiration inlet port and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
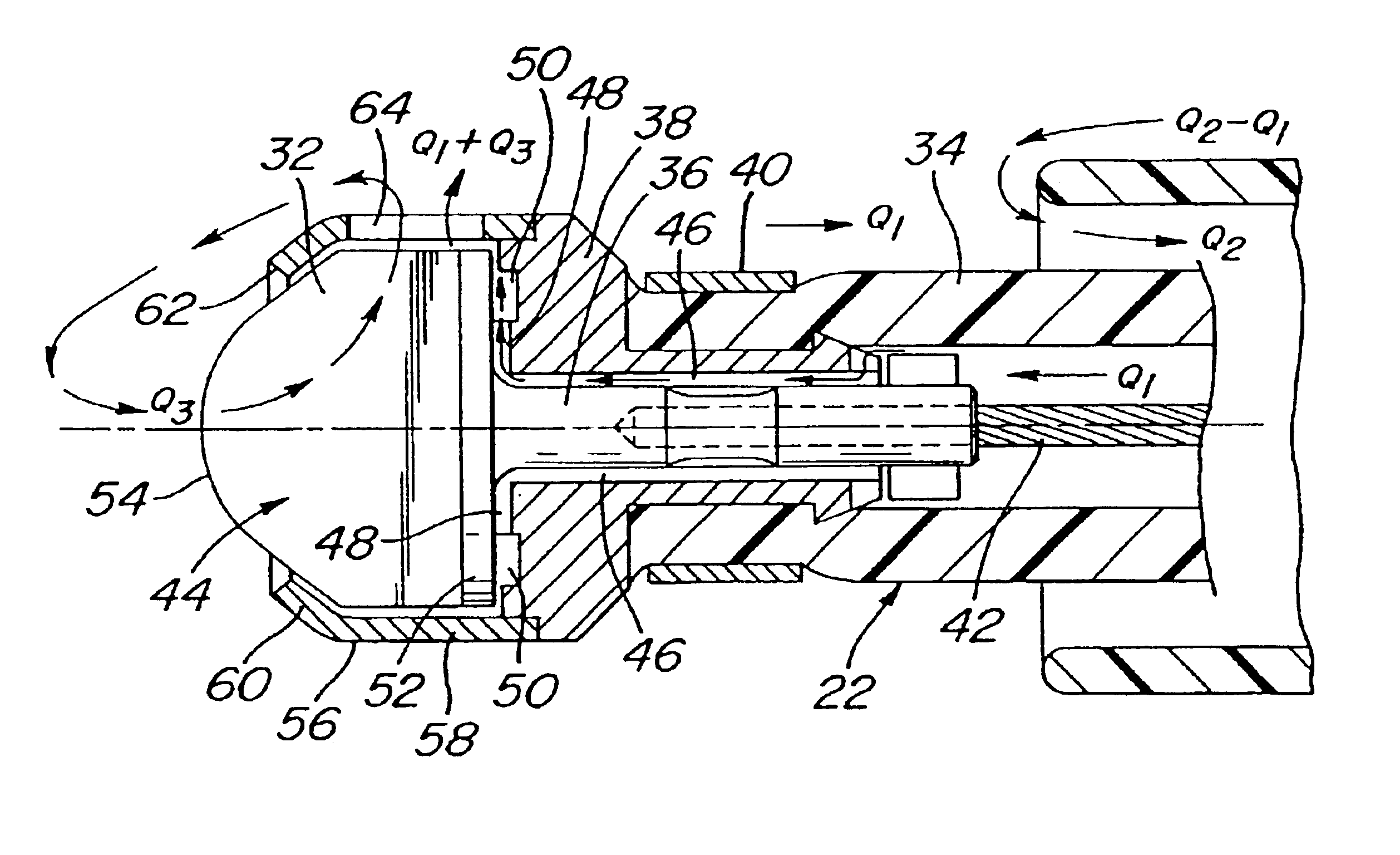
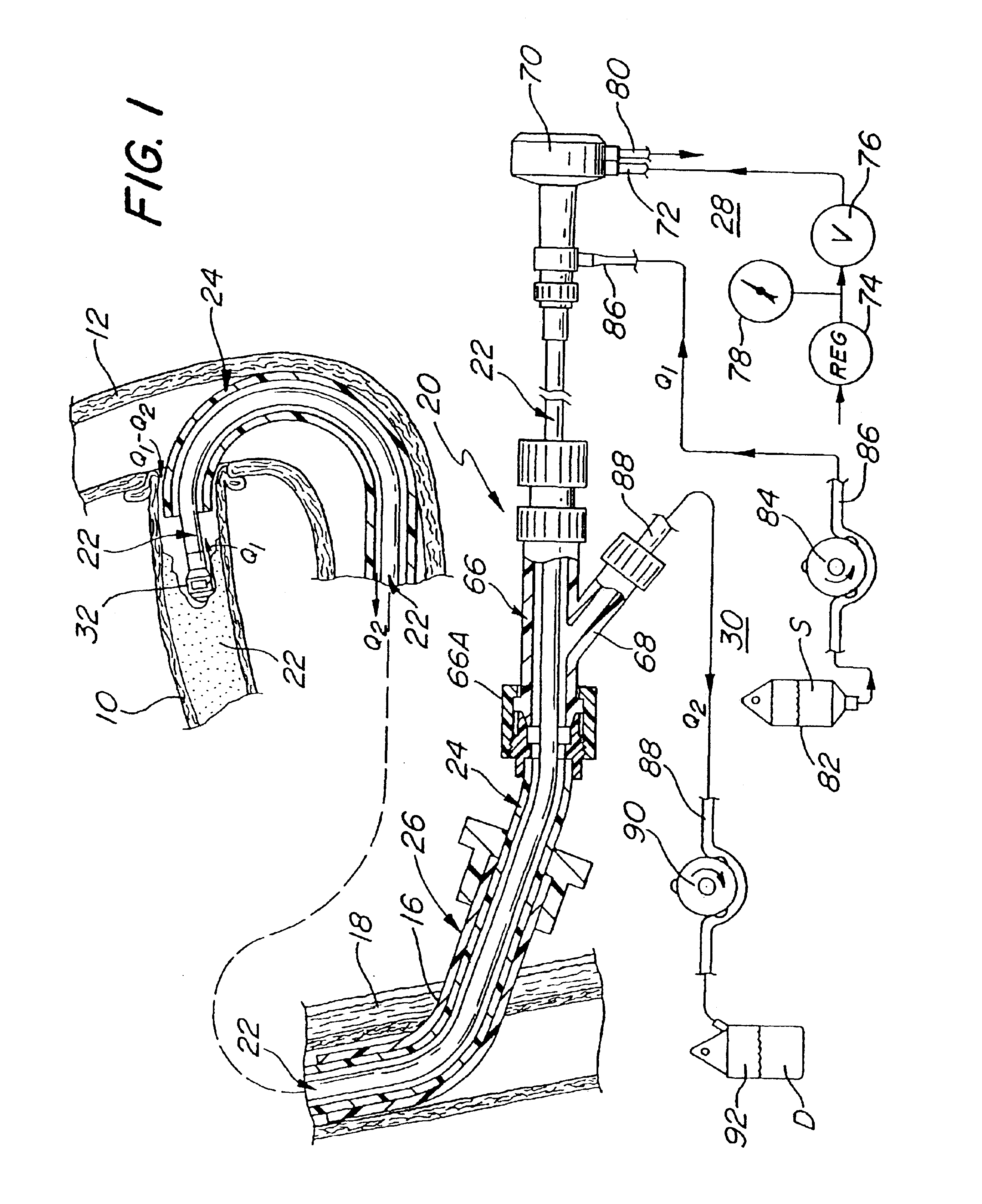
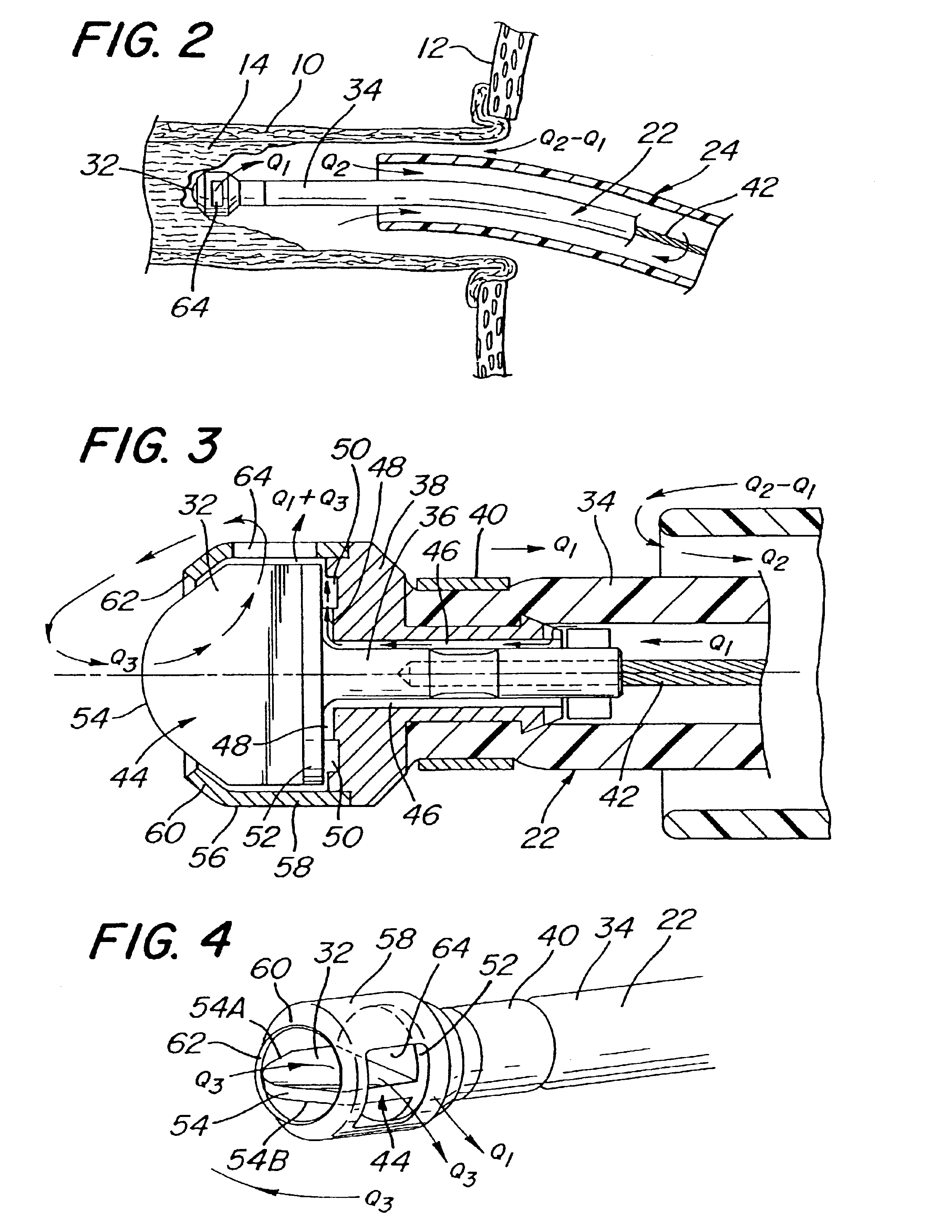
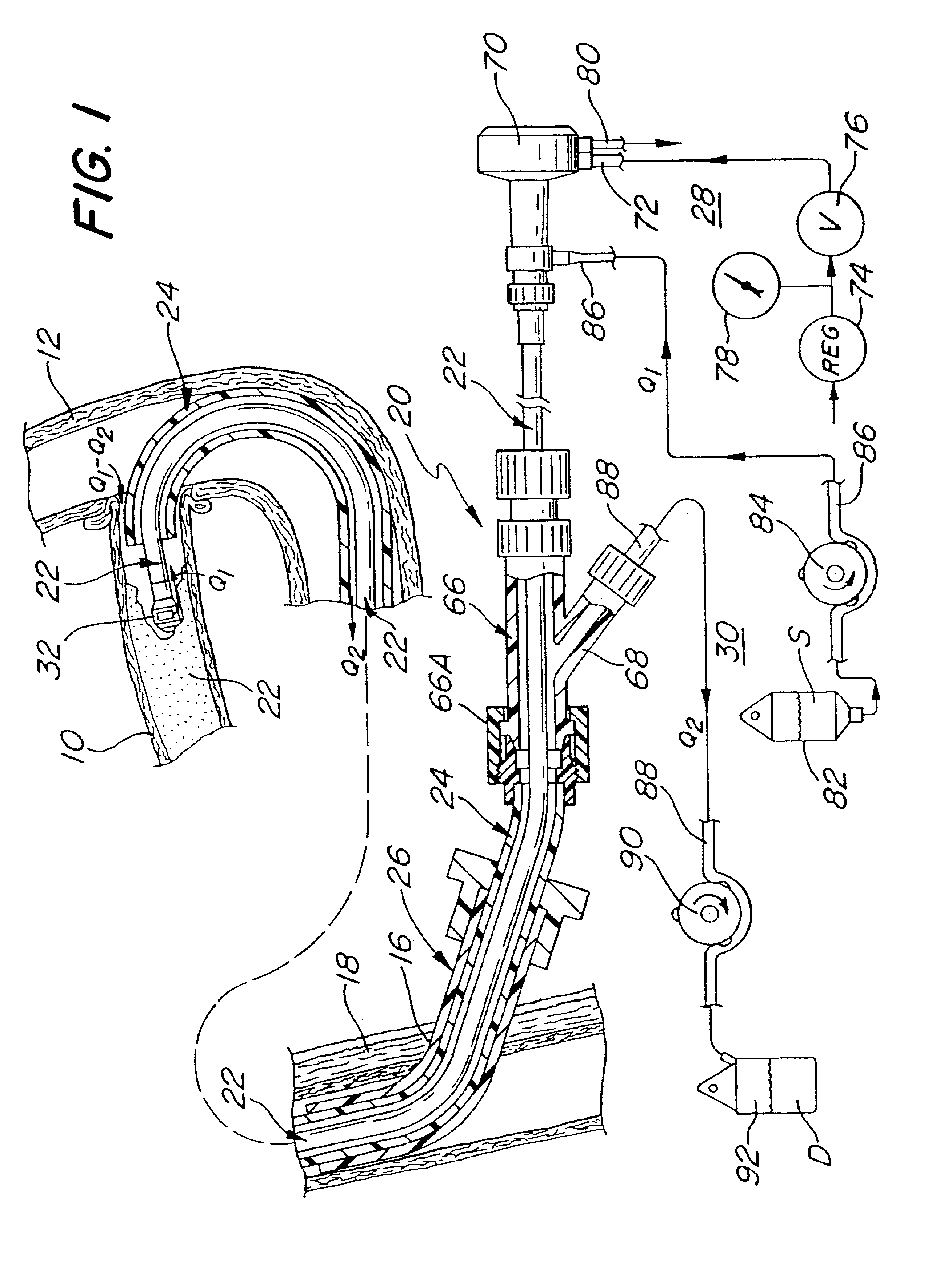
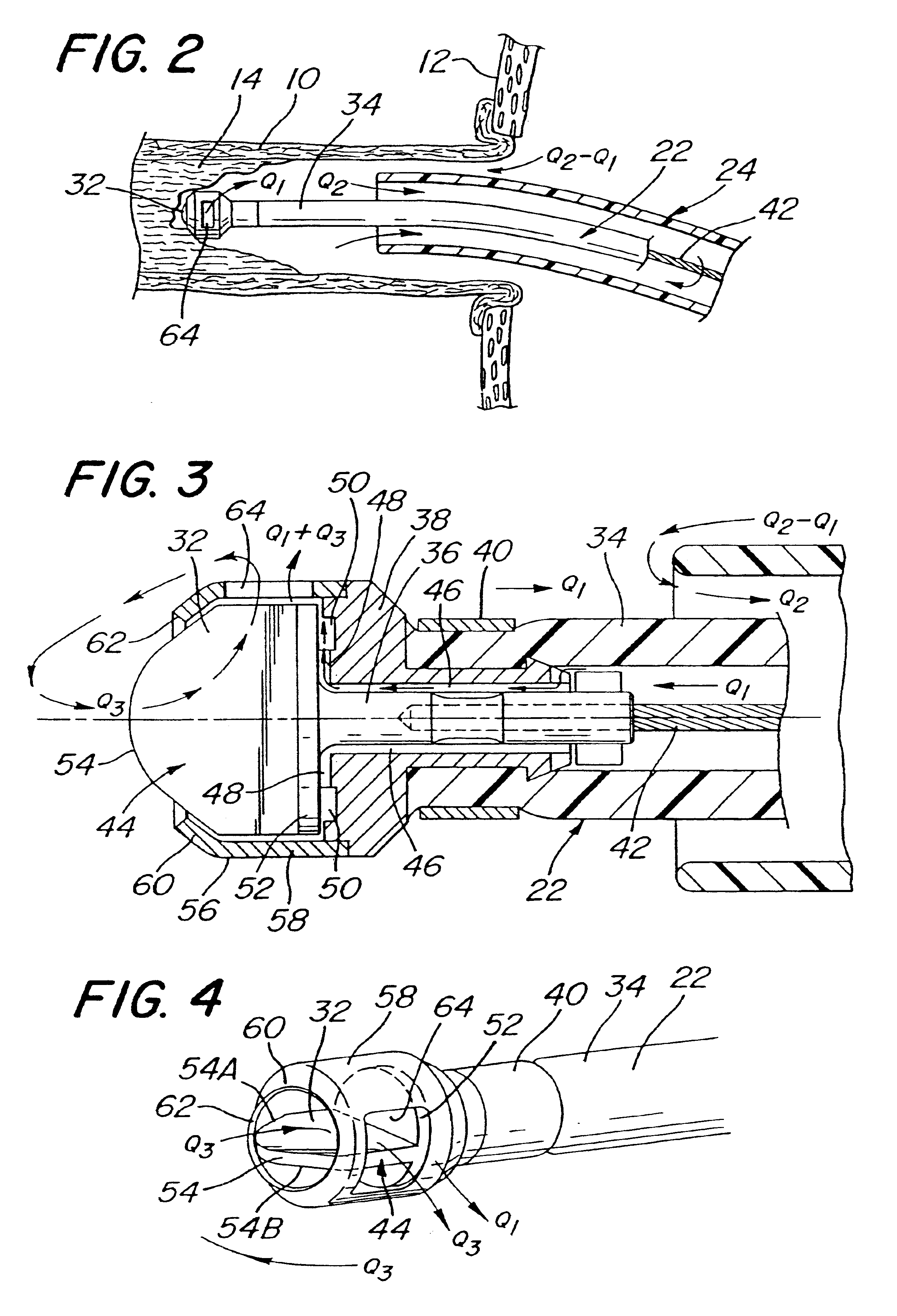
System and method of use for revascularizing stenotic bypass grafts and other occluded blood vessels
InactiveUS6843797B2Effectively revascularizingSafely revascularizingBalloon catheterCannulasAtherectomyThree vessels
A system and method for opening a lumen in an occluded blood vessel, e.g., a coronary bypass graft, of a living being. The system comprises an atherectomy catheter having a working head, e.g., a rotary impacting impeller, and a debris extraction sub-system. The atherectomy catheter is located within a guide catheter. The working head is arranged to operate on, e.g., impact, the occlusive material in the occluded vessel to open a lumen therein, whereupon some debris may be produced. The debris extraction sub-system introduces an infusate liquid at a first flow rate adjacent the working head and withdraws that liquid and some blood at a second and higher flow rate, through the guide catheter to create a differential flow adjacent the working head, whereupon the debris is withdrawn in the infusate liquid and blood for collection outside the being's body. The introduction of the infusate liquid may also be used to establish an unbalanced flow adjacent the working head to enable the atherectomy catheter to be steered hydrodynamically. A guide wire having an inflatable balloon on its distal end may be used with the atherectomy catheter to block the flow of debris distally, while enabling distal tissues to be perfused with an oxygenating liquid. At least one flow control port may be provided in the guide catheter to prevent collapse of the vessel being revascularized. A cradle is provided to fix the guide catheter and guide wire in position within the body of the being while enabling the atherectomy catheter to be advanced along the guide wire and through the guide catheter.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
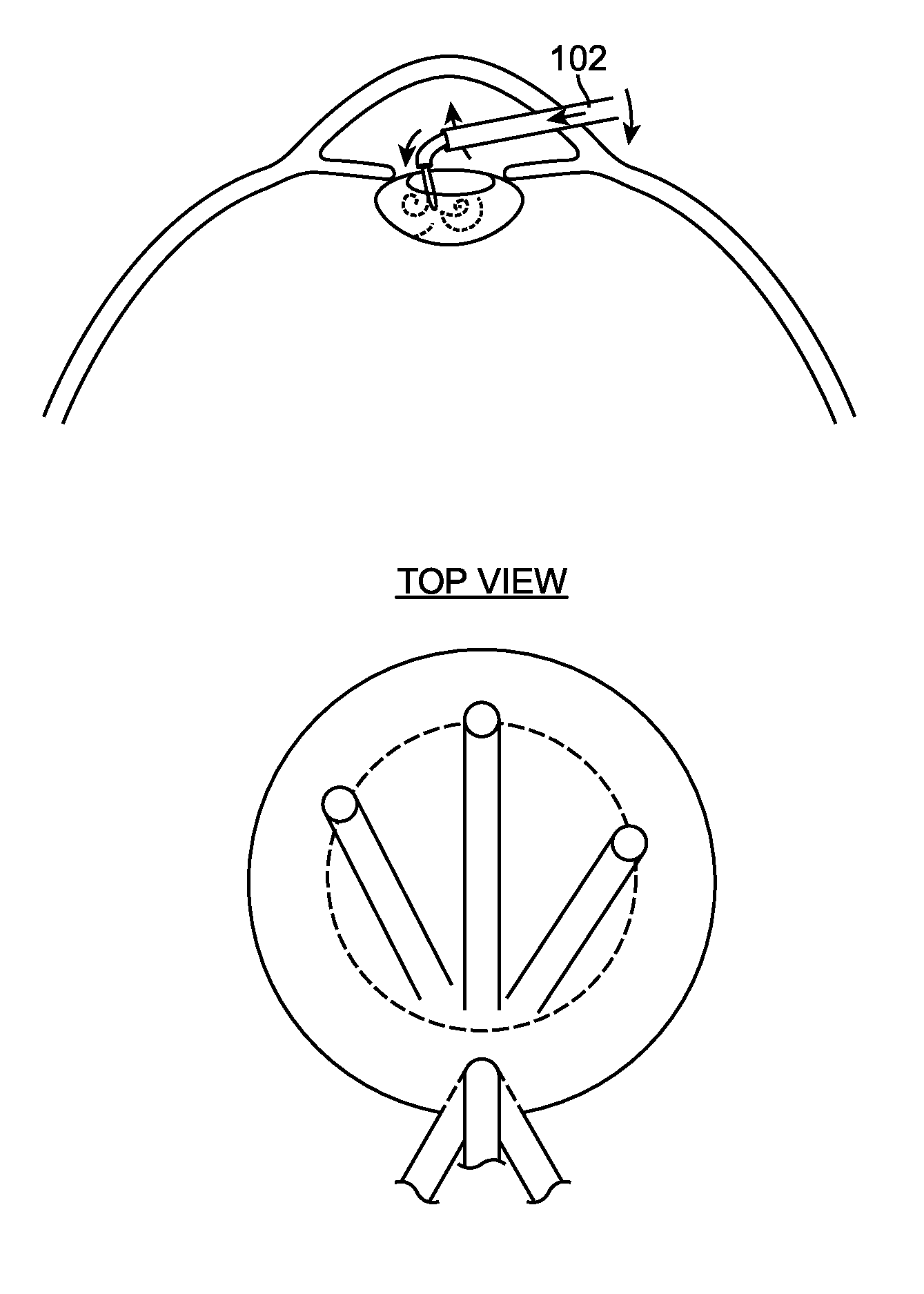
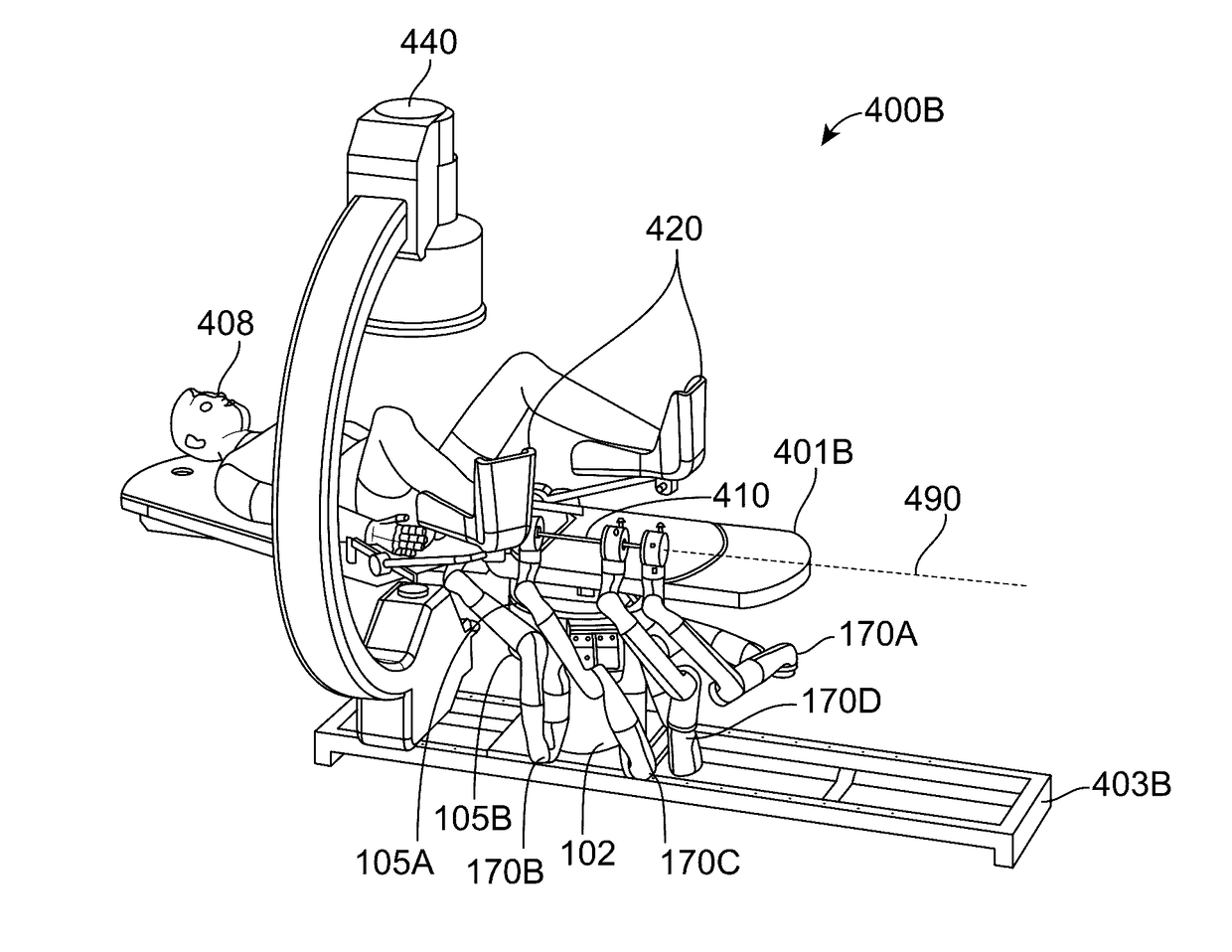
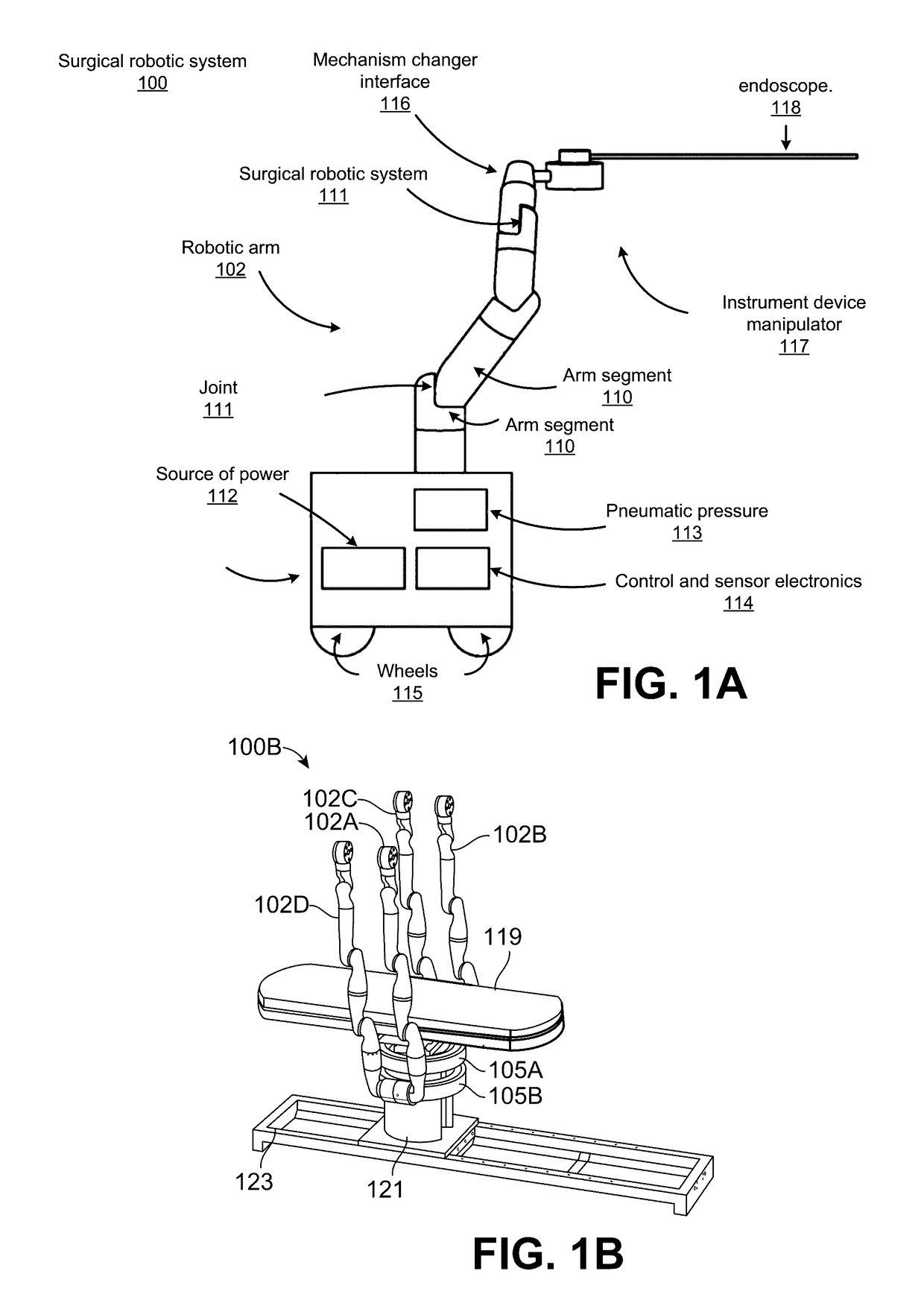
Object capture with a basket
ActiveUS9949749B2Easy to carryEasy to catchEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsURETEROSCOPERobotic arm
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Basket apparatus
ActiveUS9955986B2Easy to carryEasy to catchEndoscopesSurgical systems user interfaceMechanical engineeringEndoscope
A basket apparatus is described that assists in removing objects from within a patient. The apparatus includes a number of pull wires, each pull wire physically coupled to a different capstan that individually actuates one of the pull wires. The apparatus also includes an outer support shaft itself including a number of channels through which the pull wires traverse. The portions of the pull wires extending out of the outer support shaft form a basket of adjustable size, shape, and position. The pull wires are attached together at a tip located at a distal end of the basket apparatus. By controlling the actuation of the various pull wires, the basket's shape, position size can be manipulated to reposition the basket around an object located within a patient, independent of or in conjunction with motion of the remainder of the apparatus or an associated endoscope.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
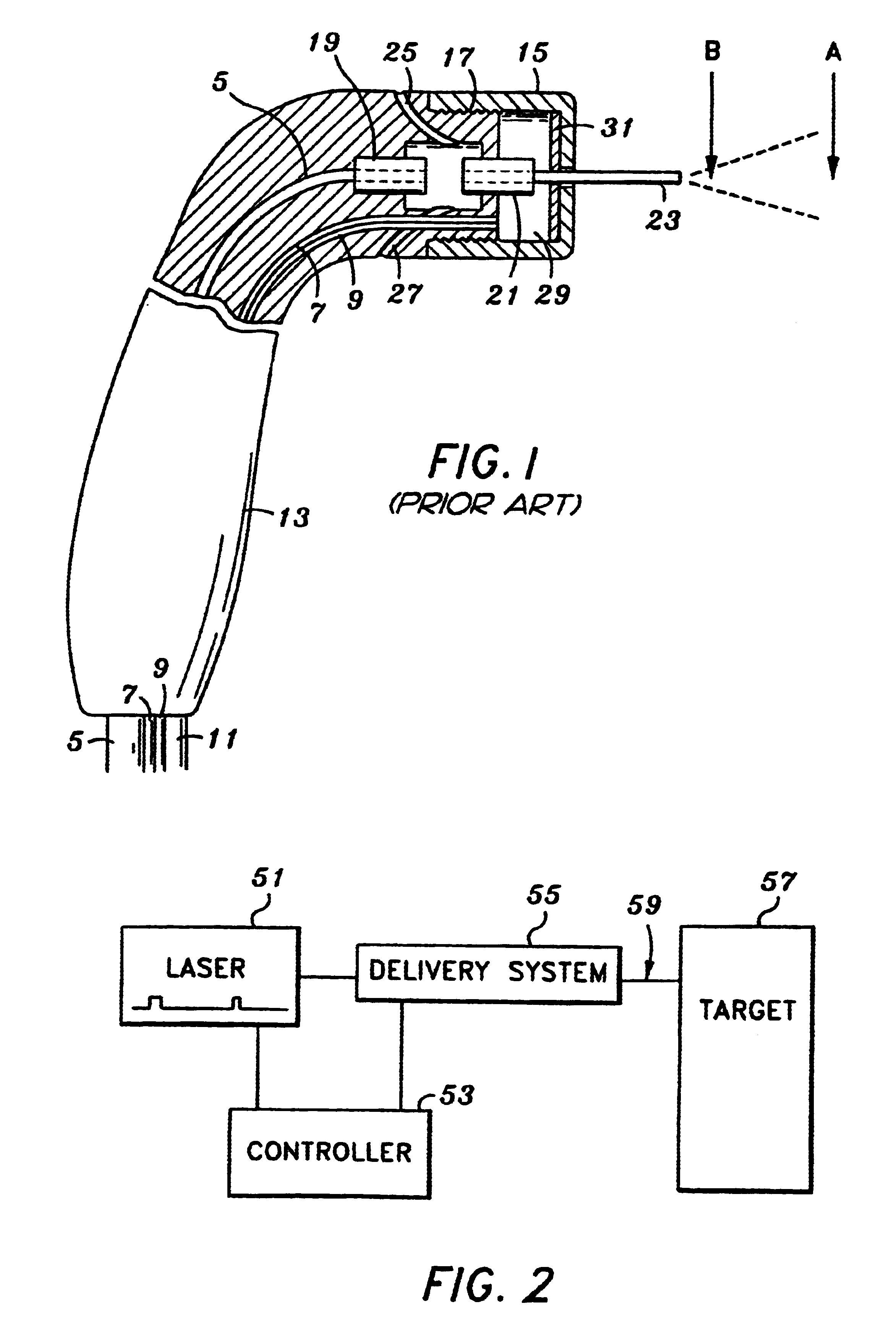
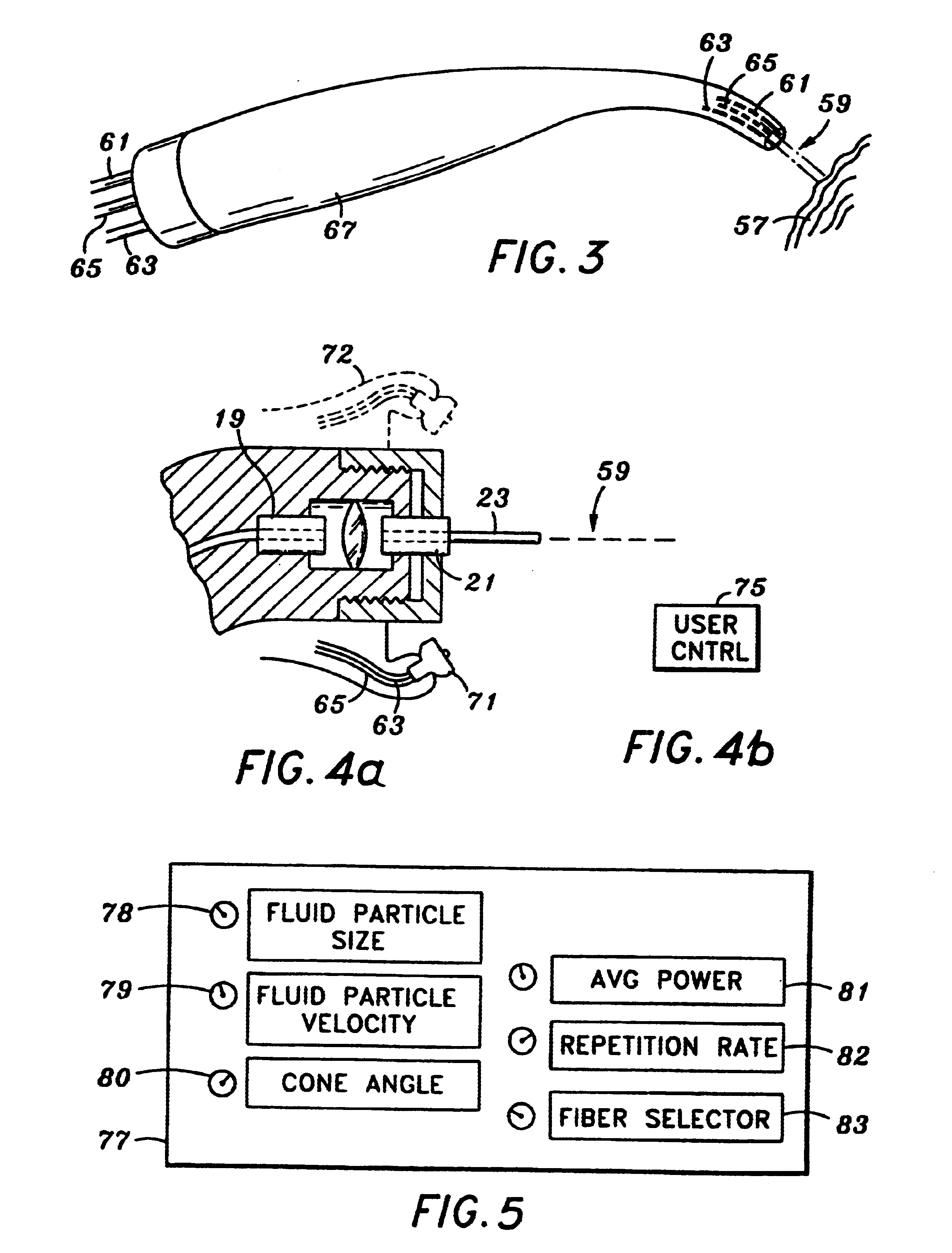
Medical instrument and method of use
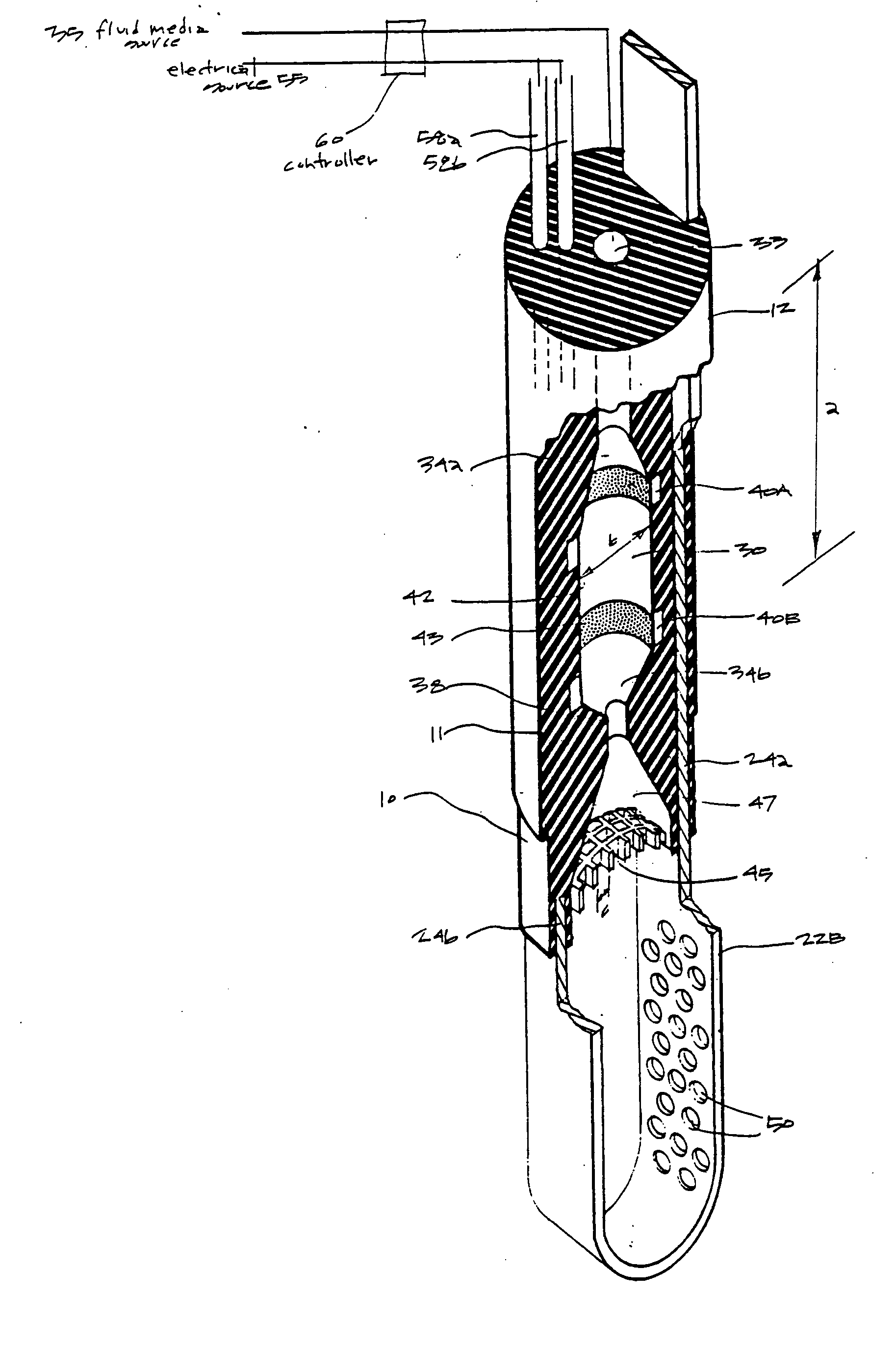
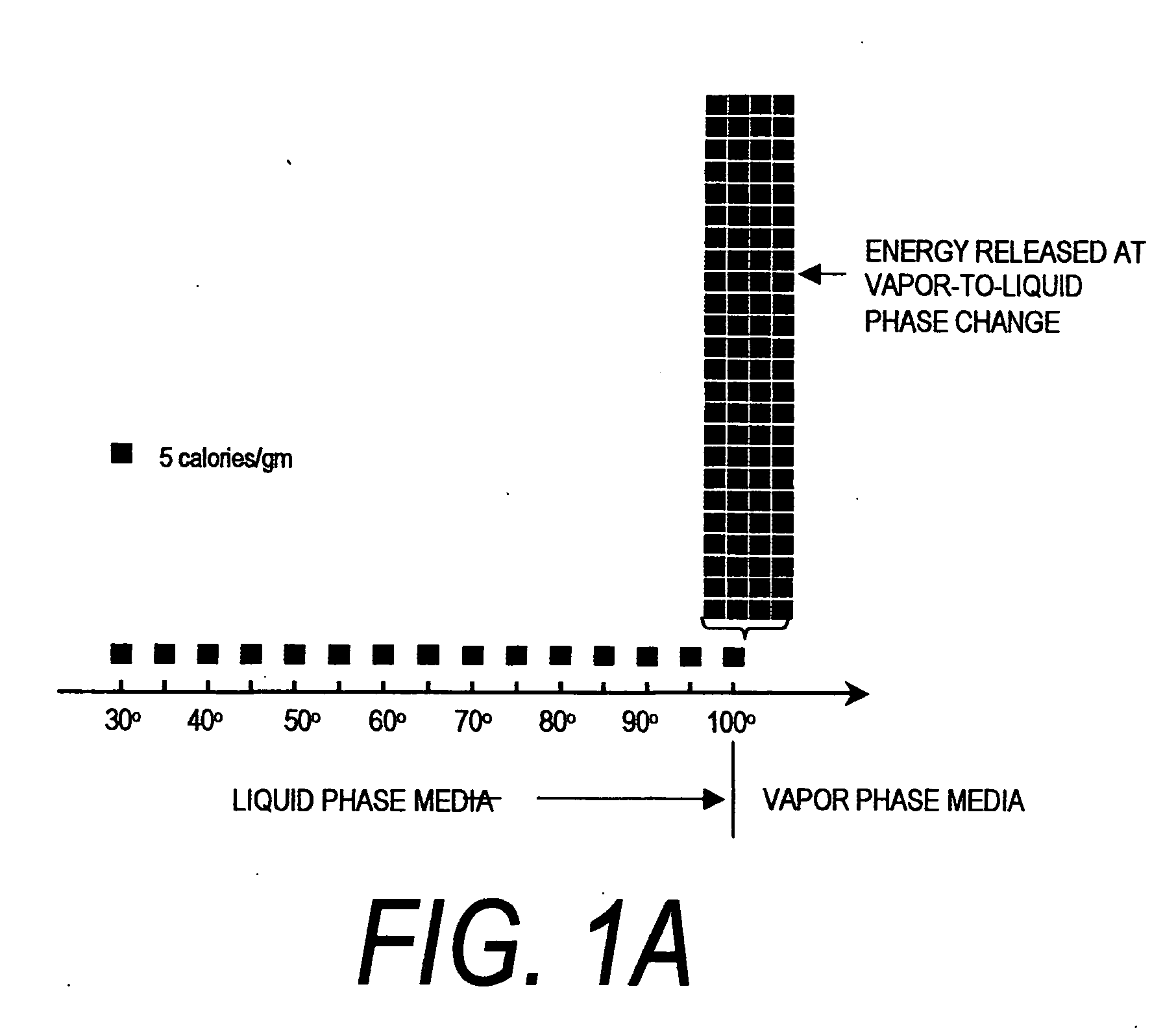
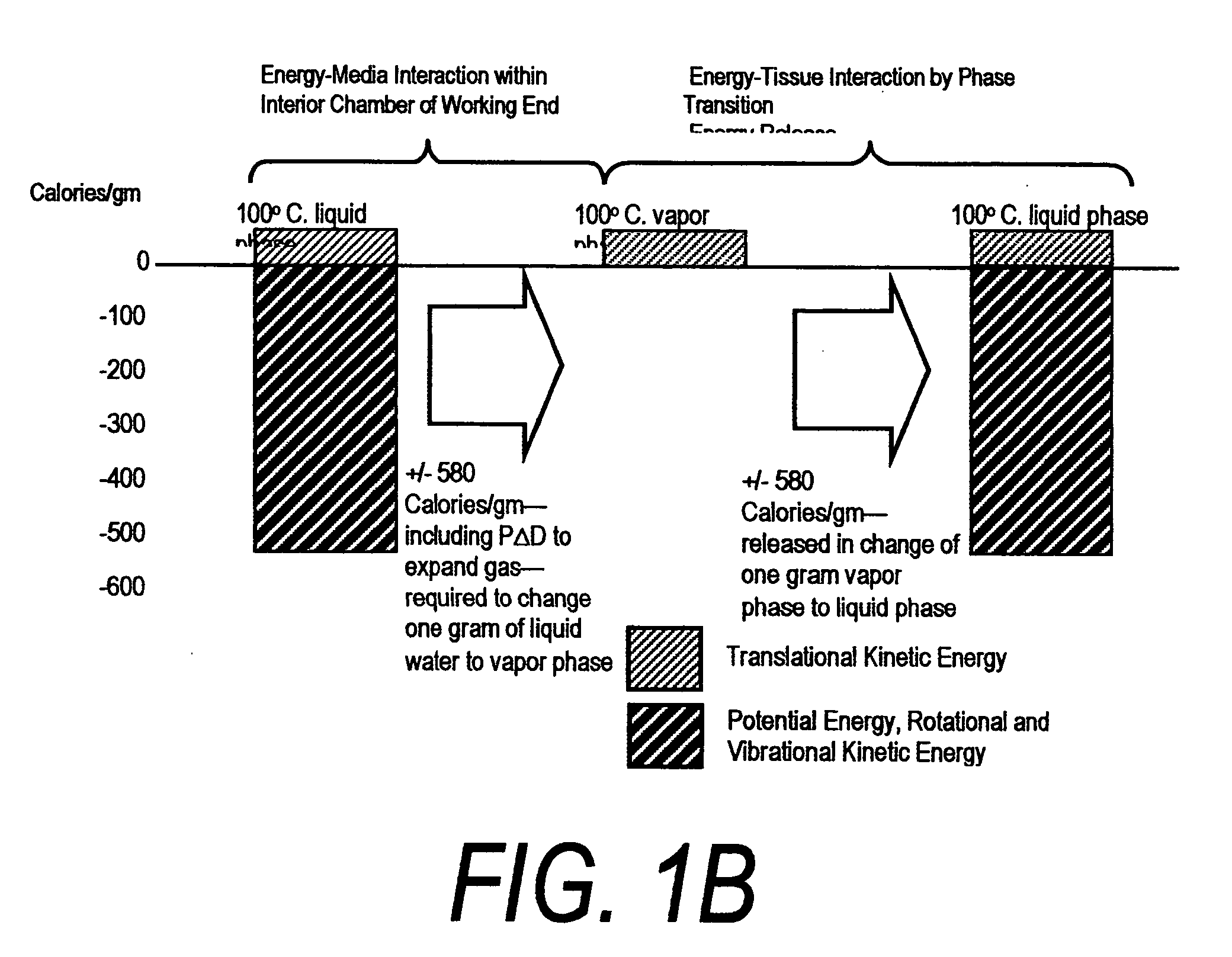
ActiveUS20060135955A1Simple methodFluid jet surgical cuttersSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instrumentVapor phase
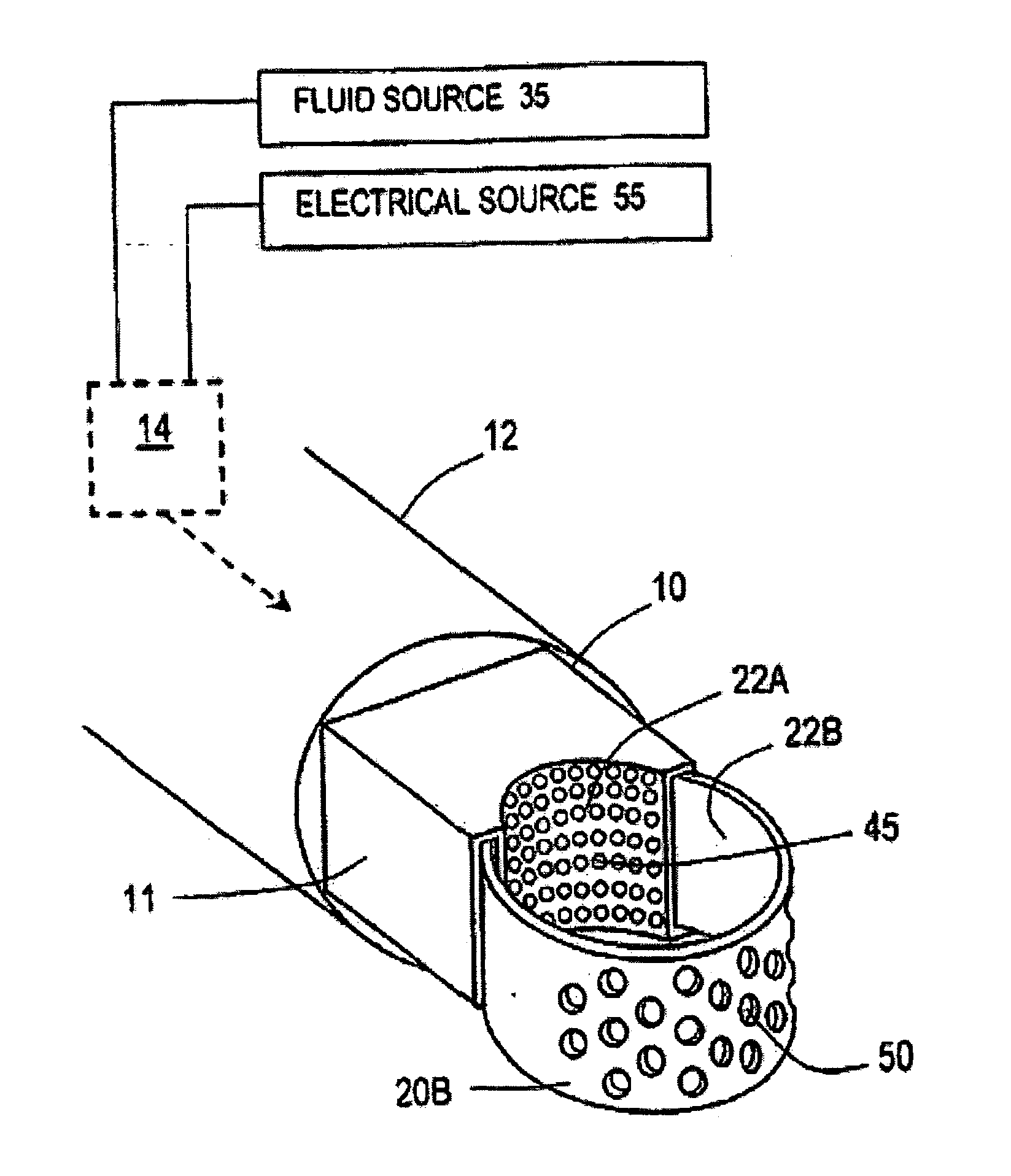
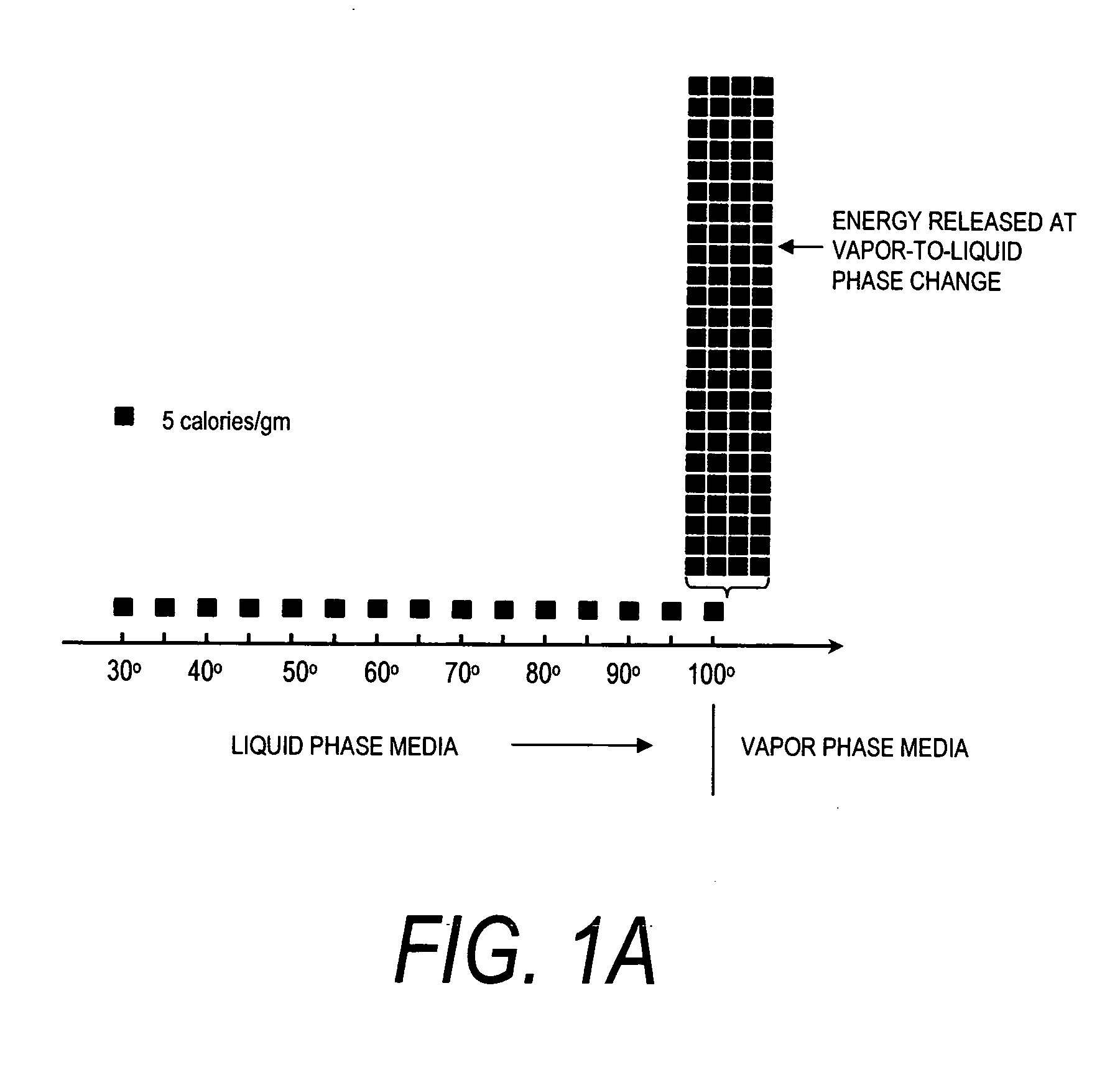
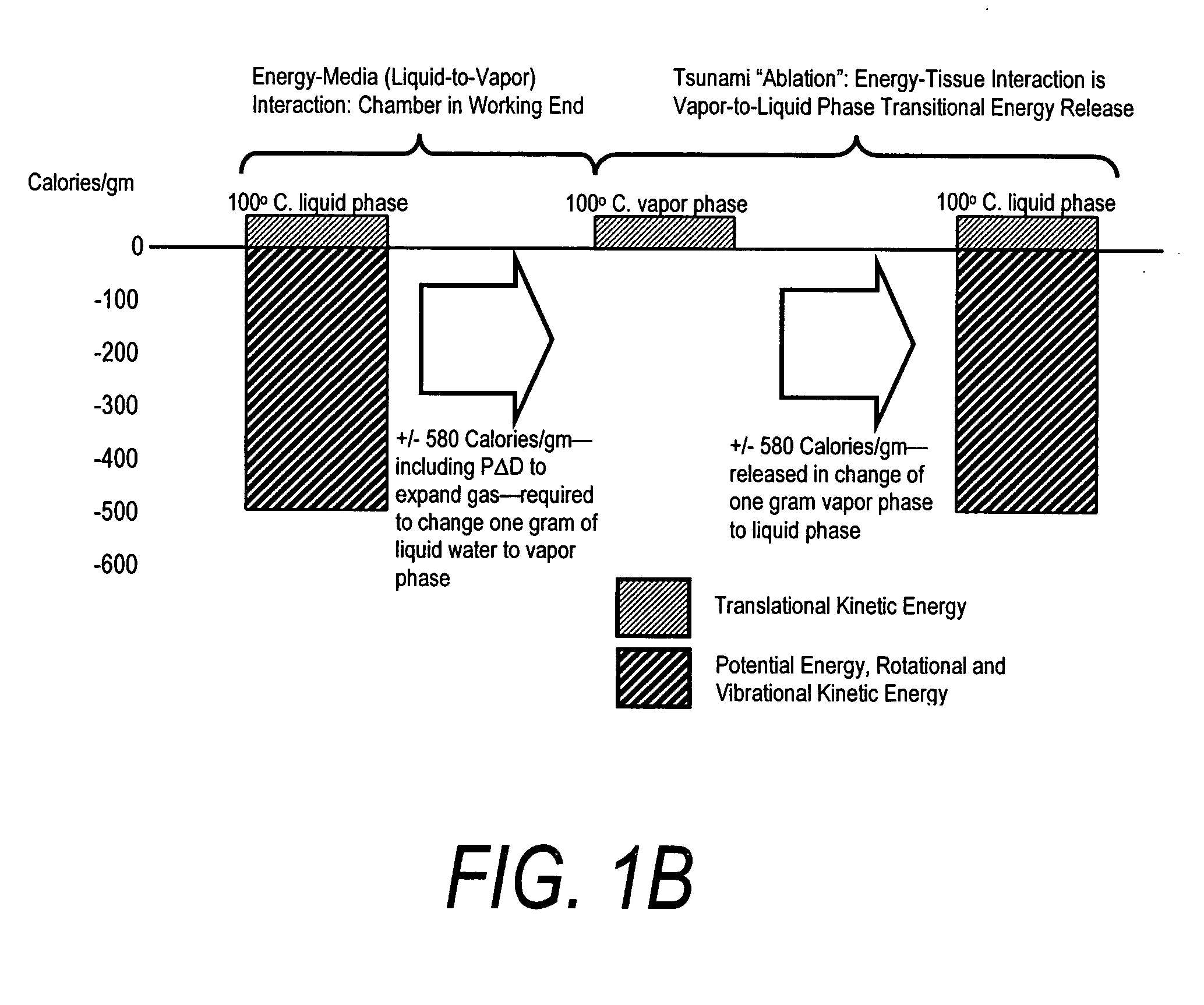
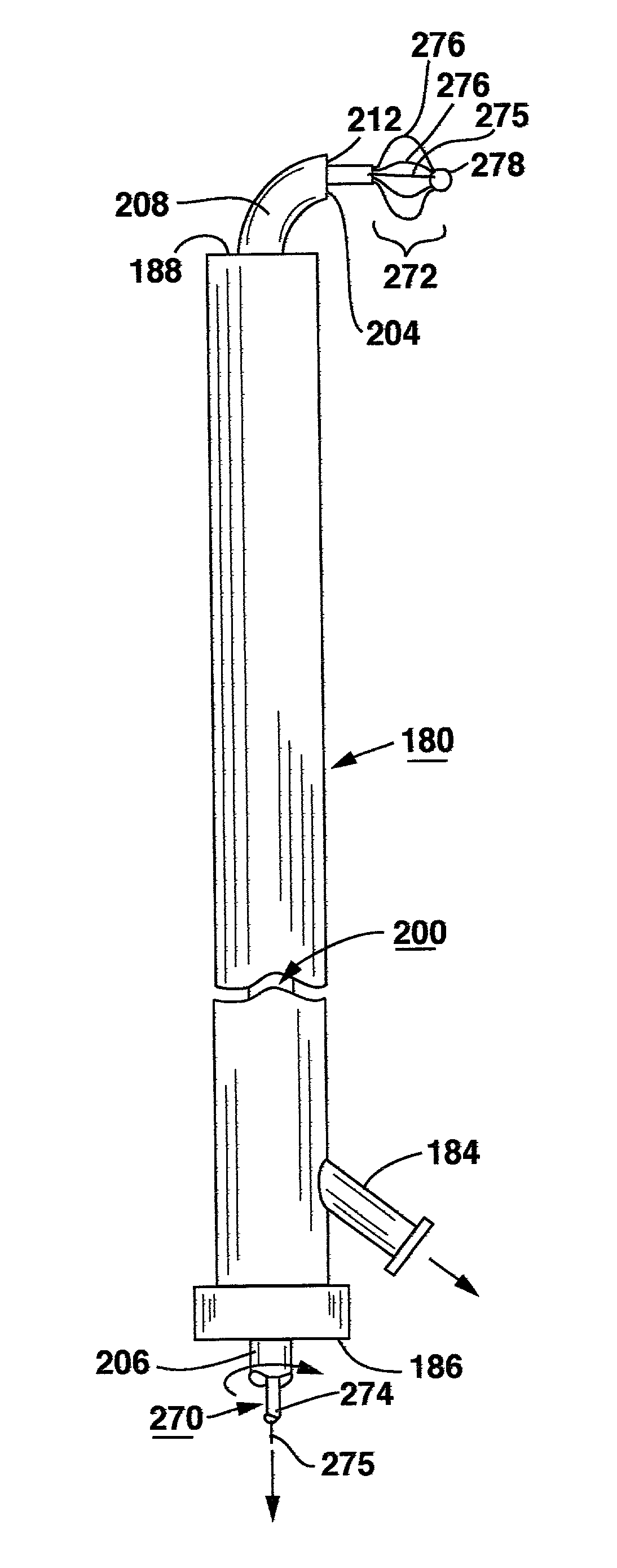
This invention relates to surgical instruments for applying energy to tissue. In one embodiment, an elongated introducer has a handle portion that includes an interior chamber that is supplied with a biocompatible liquid under pressure. An energy source causes a liquid-to-vapor phase change within the interior chamber and ejects a flow of vapor media from the working end of the introducer. The flow of vapor is controlled by a computer controller to cause a selected pressure, a selected volume of vapor, and an optional aspiration of vapor condensate. Contemporaneous with tissue contact, the vapor undergoes a vapor-to-liquid phase transition which delivers large amount of energy to the targeted tissue. In one embodiment, the system is configured for volumetric removal of tissue by means of high velocity ejection of a vapor media from a first vapor port proximate to soft tissue wherein the vapor-to-liquid phase change of the media applies energy to the tissue. The system provides a second port coupled to a suction source that cooperates with the first vapor port to suction tissue debris from the targeted site.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Medical instruments and techniques for treating pulmonary disorders
ActiveUS20080132826A1Enhance tissue remodelingReducing lung volumeMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersThermal energyDisease
A surgical instrument for delivering energy to lung tissue, for example to cause lung volume reduction. In one embodiment, an elongated catheter has a handle portion that includes an interior chamber that is supplied with a biocompatible liquid media under pressure. An energy source delivers energy to the media to cause a liquid-to-vapor phase change within the interior chamber and ejects a flow of vapor media from the working end of the catheter. The delivery of energy and the flow of vapor are controlled by a computer controller to cause a selected pressure and selected volume of vapor to propagate to the extremities of the airways. Contemporaneously, the vapor undergoes a vapor-to-liquid phase transition which delivers a large amount of energy to airway tissue. The thermal energy delivered is equivalent to the heat of vaporization of the fluid media, which shrinks and collapses the treated airways. The treated tissue is the maintained in a collapsed state by means of aspiration for a short interval to enhance tissue remodeling. Thereafter, the patient's wound healing response causes fibrosis and further remodeling to cause permanent lung volume reduction.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
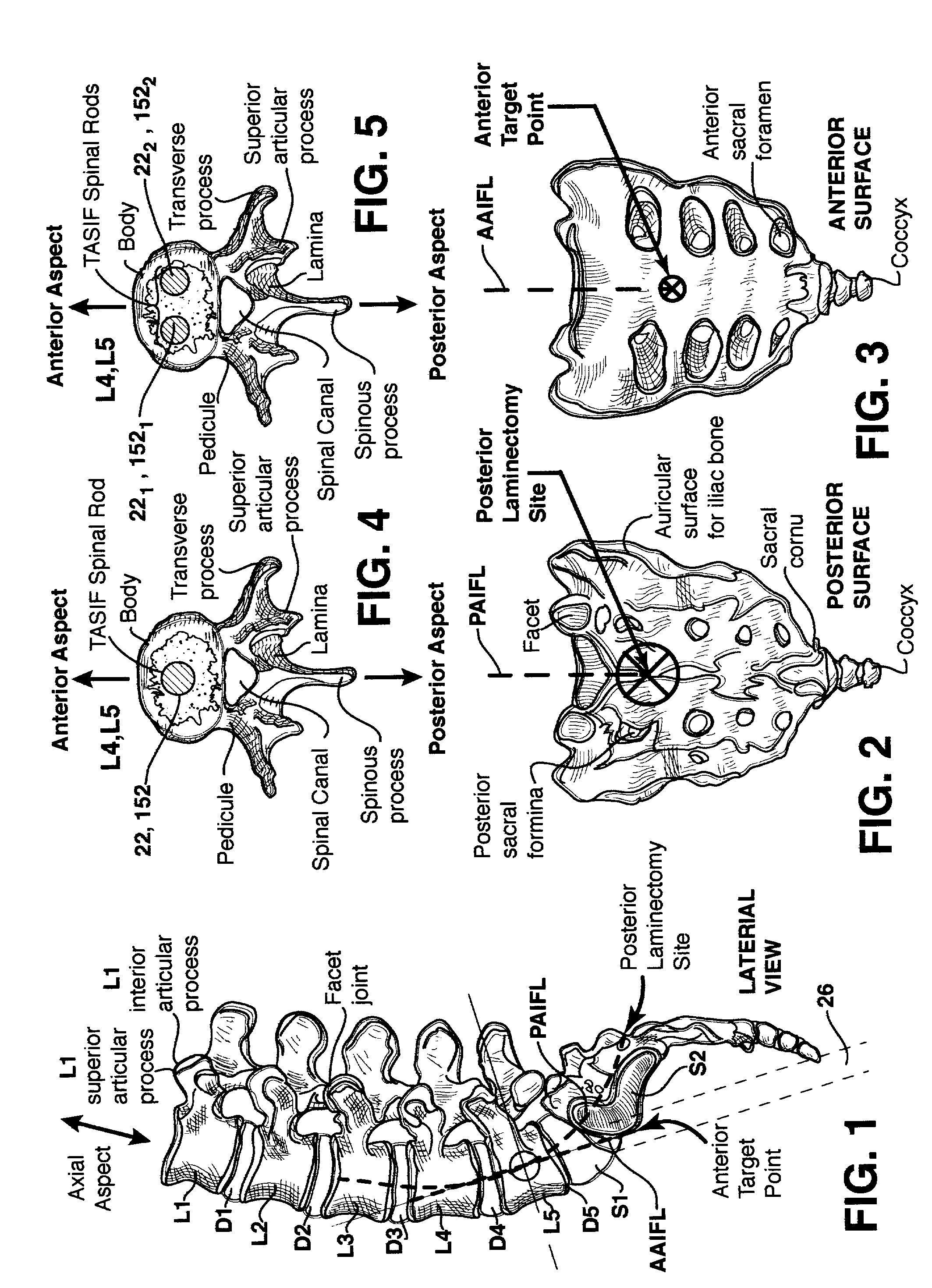
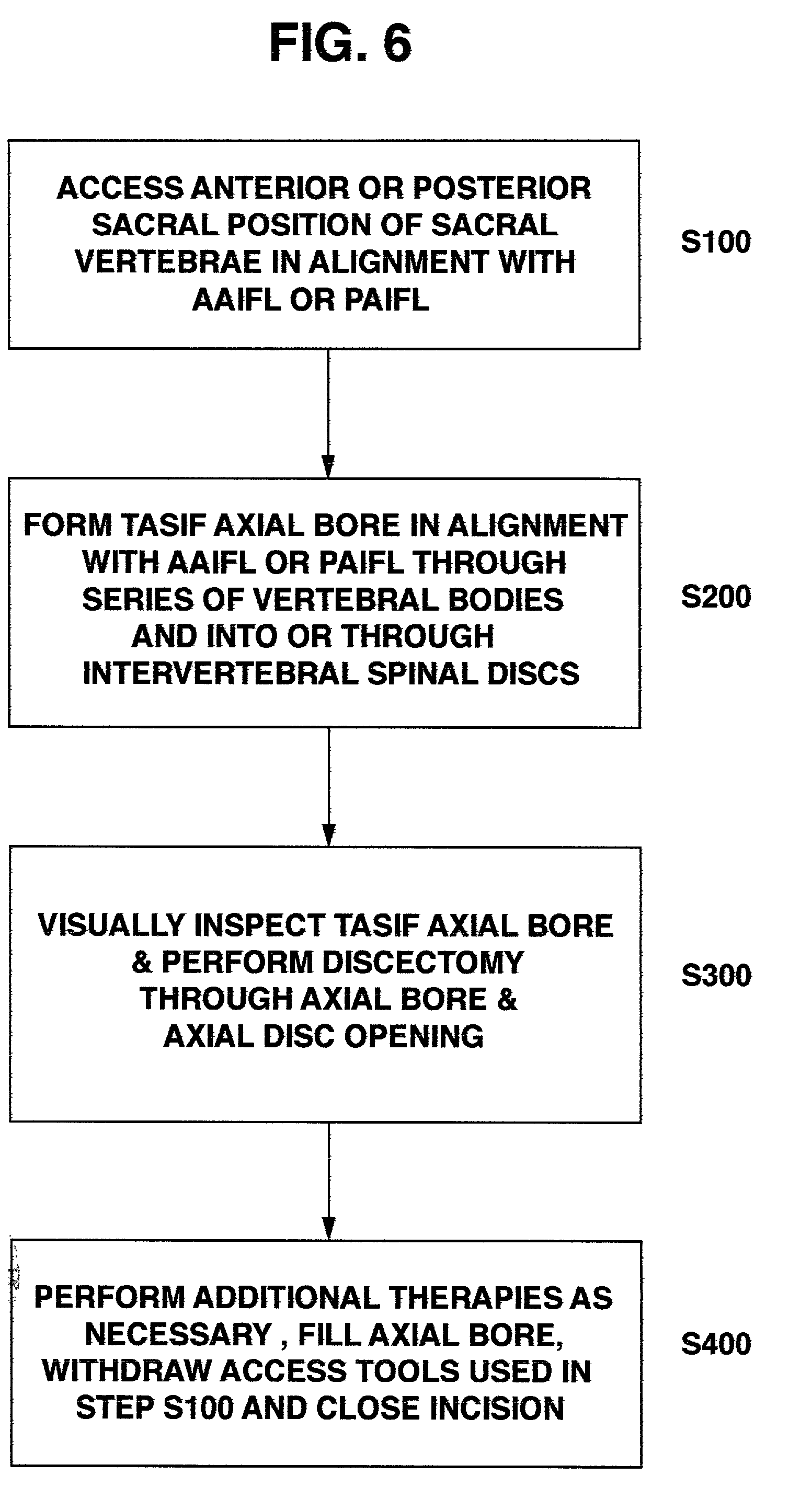
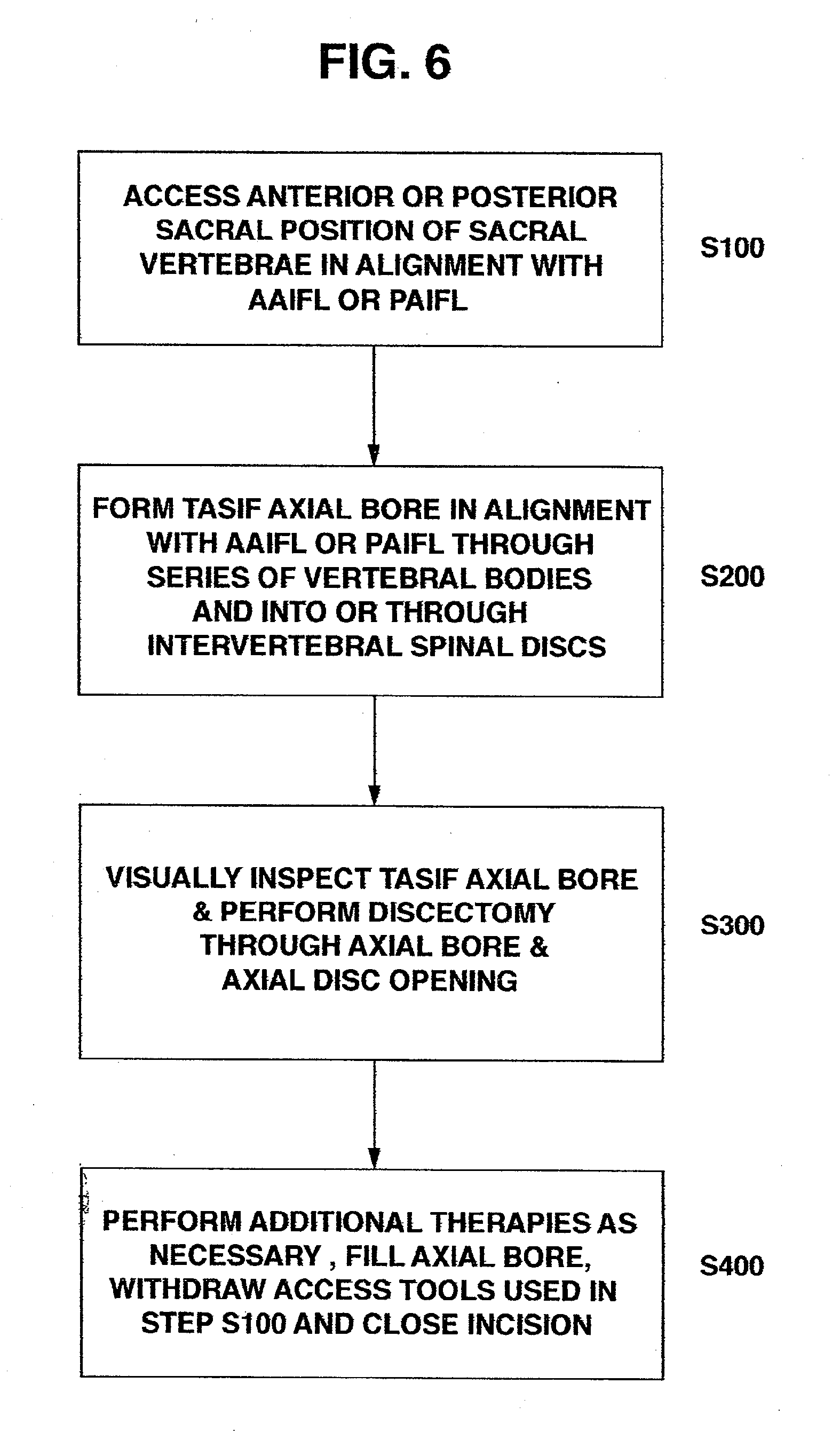
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
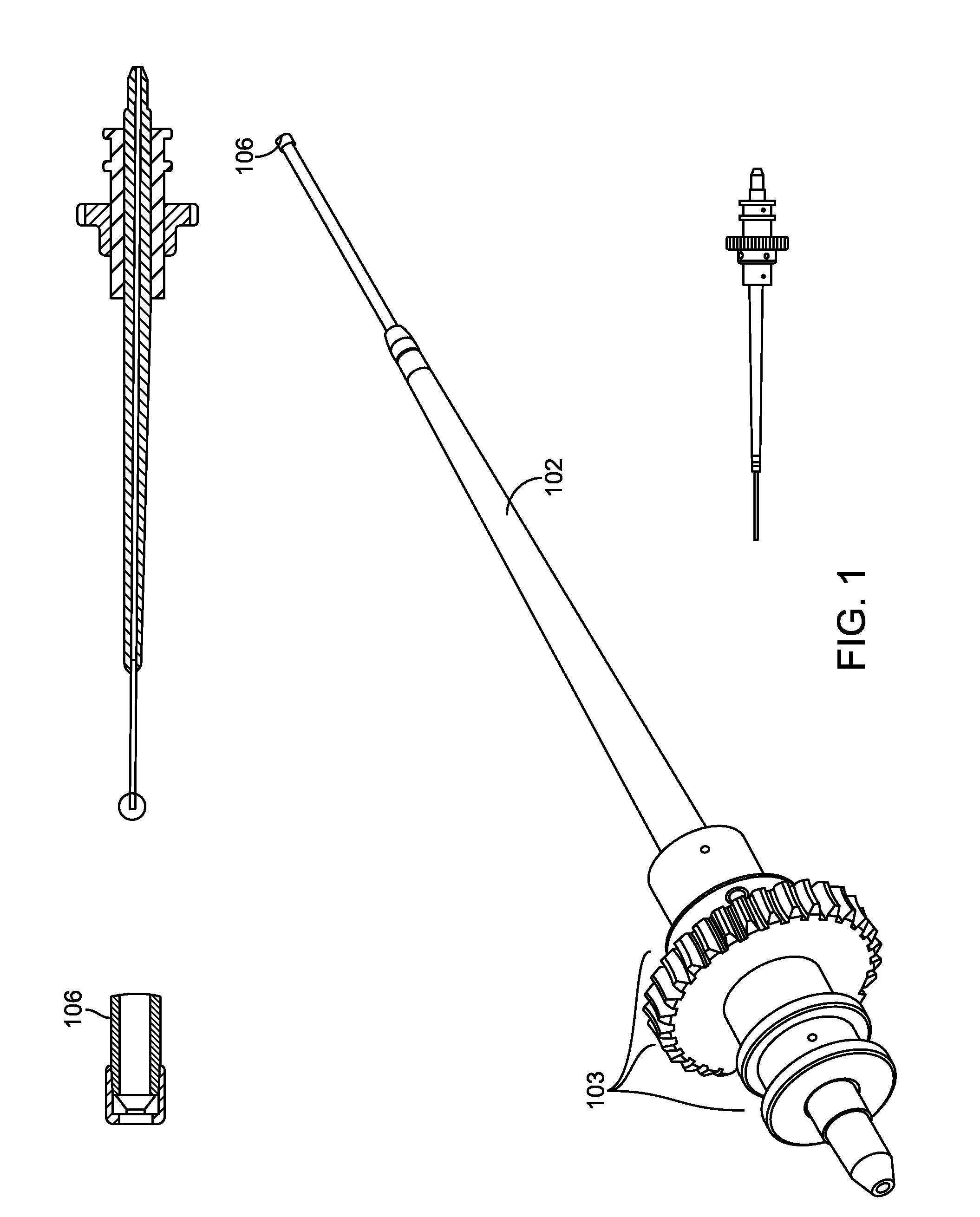
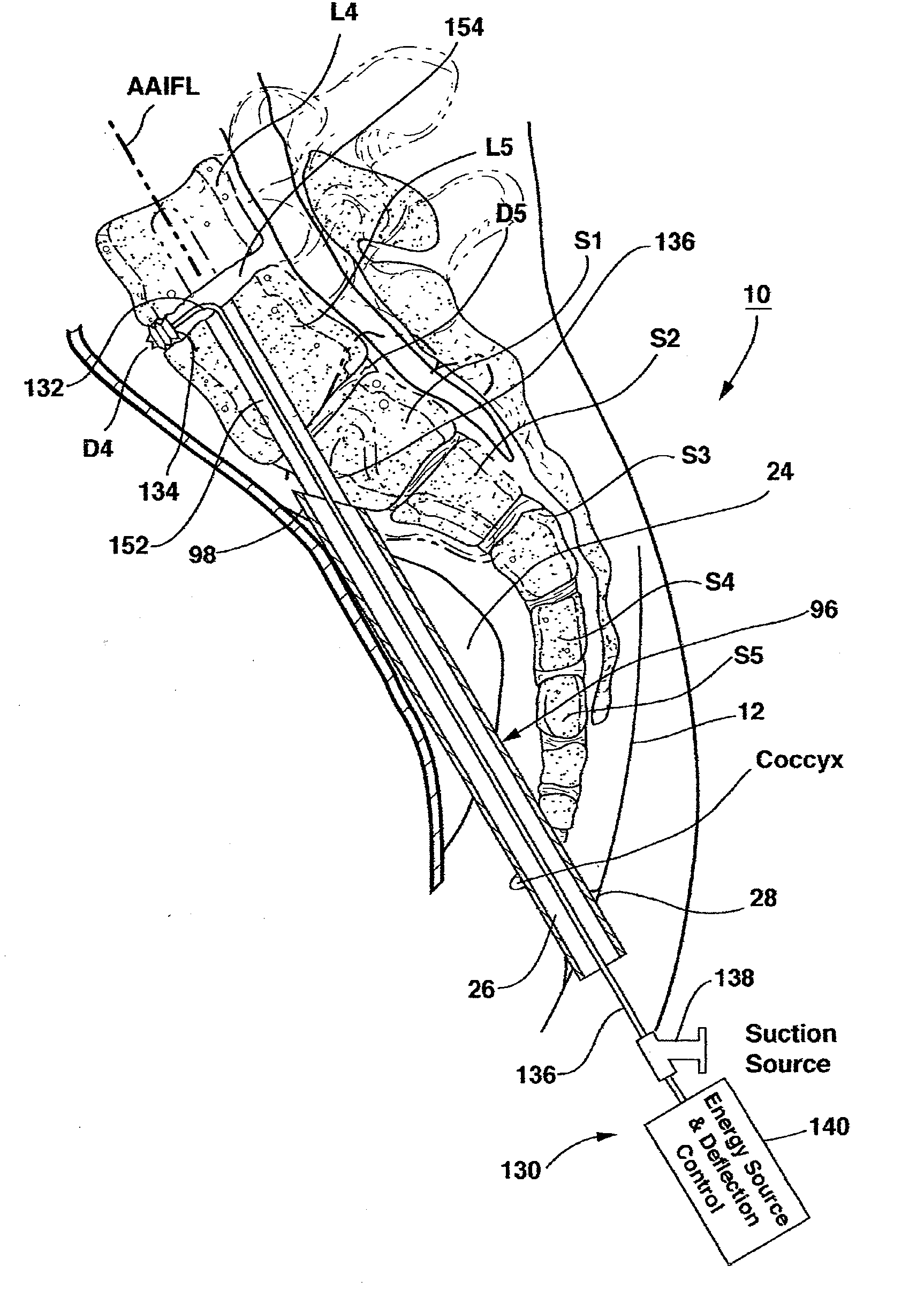
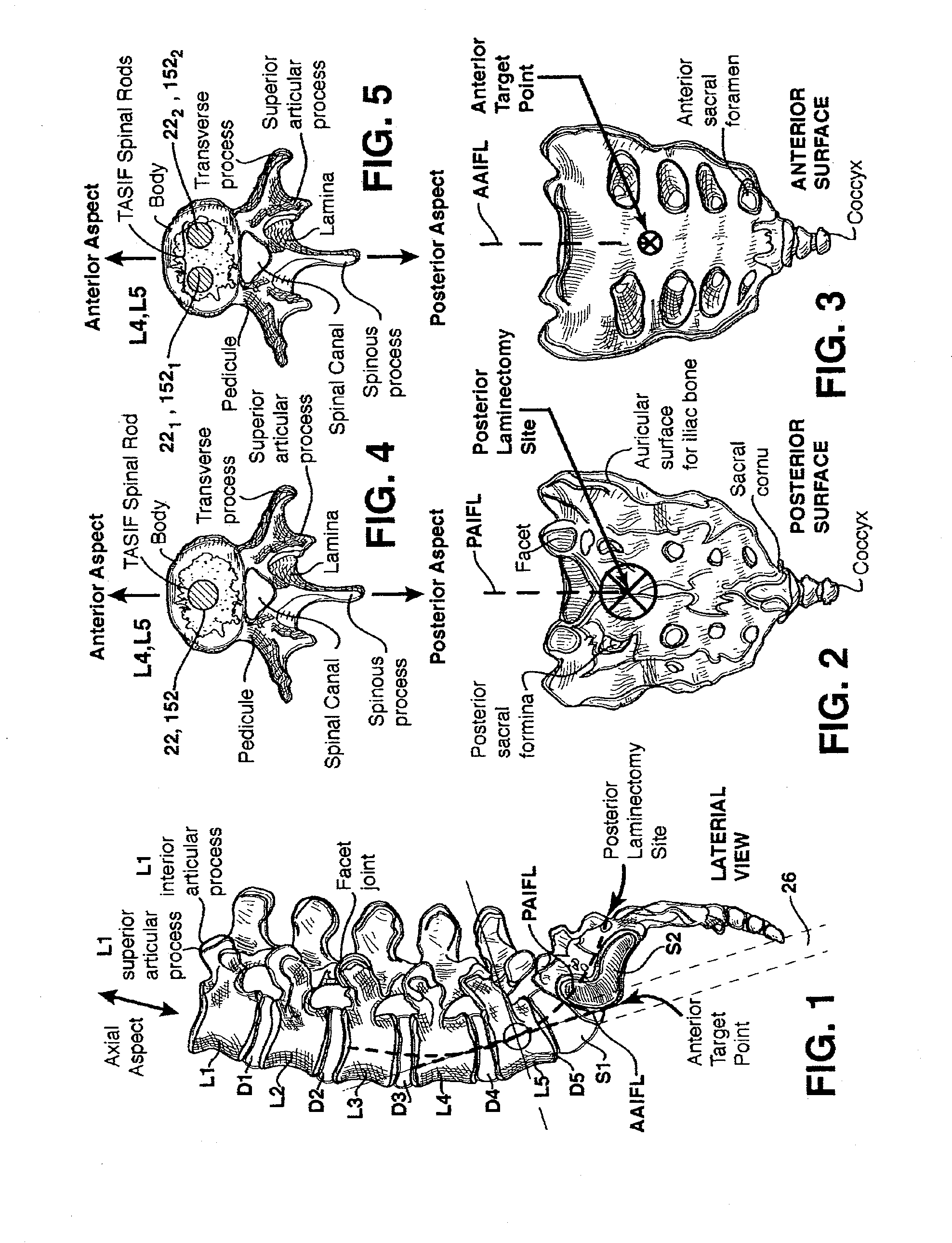
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:TRANSI
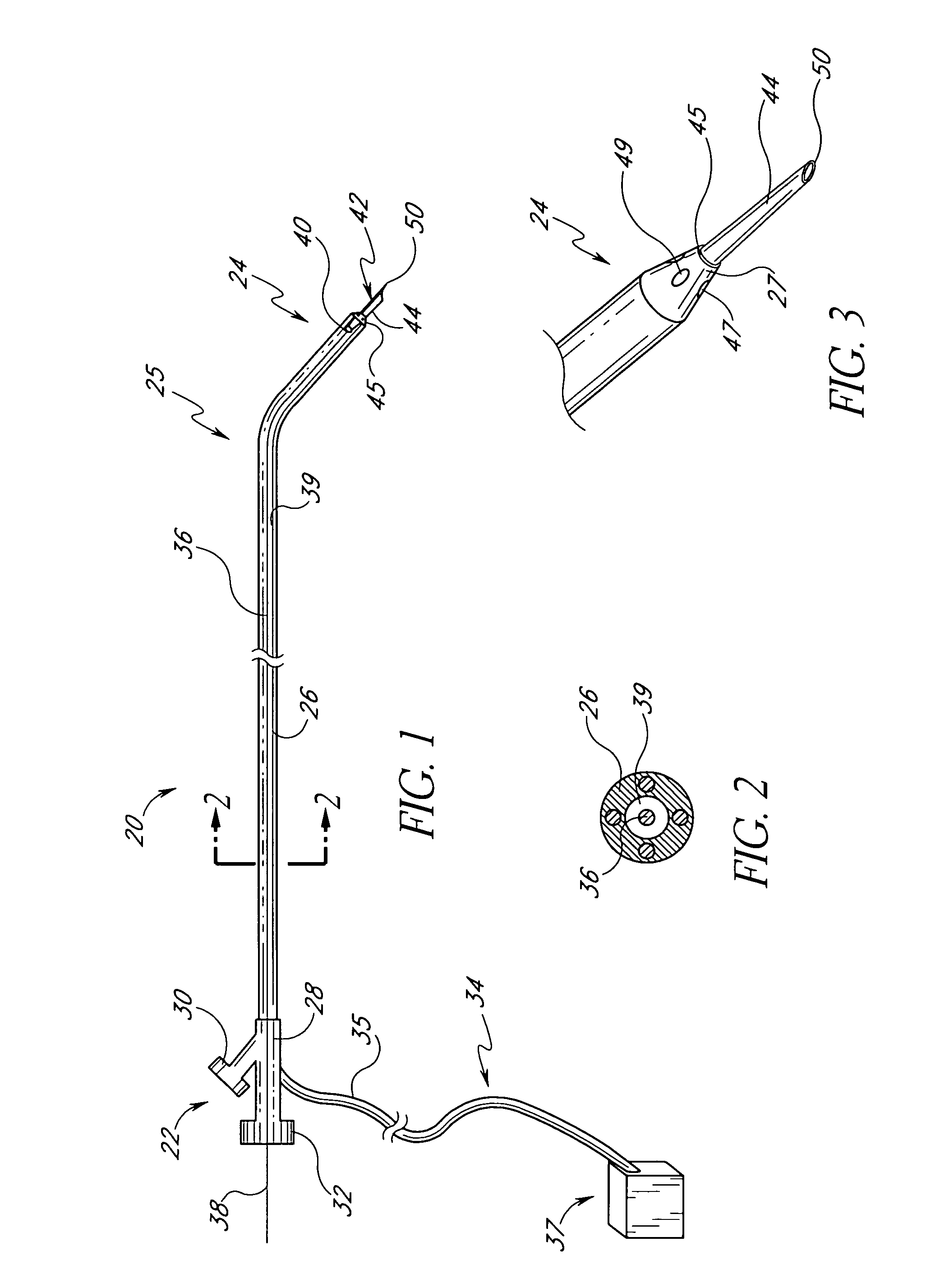
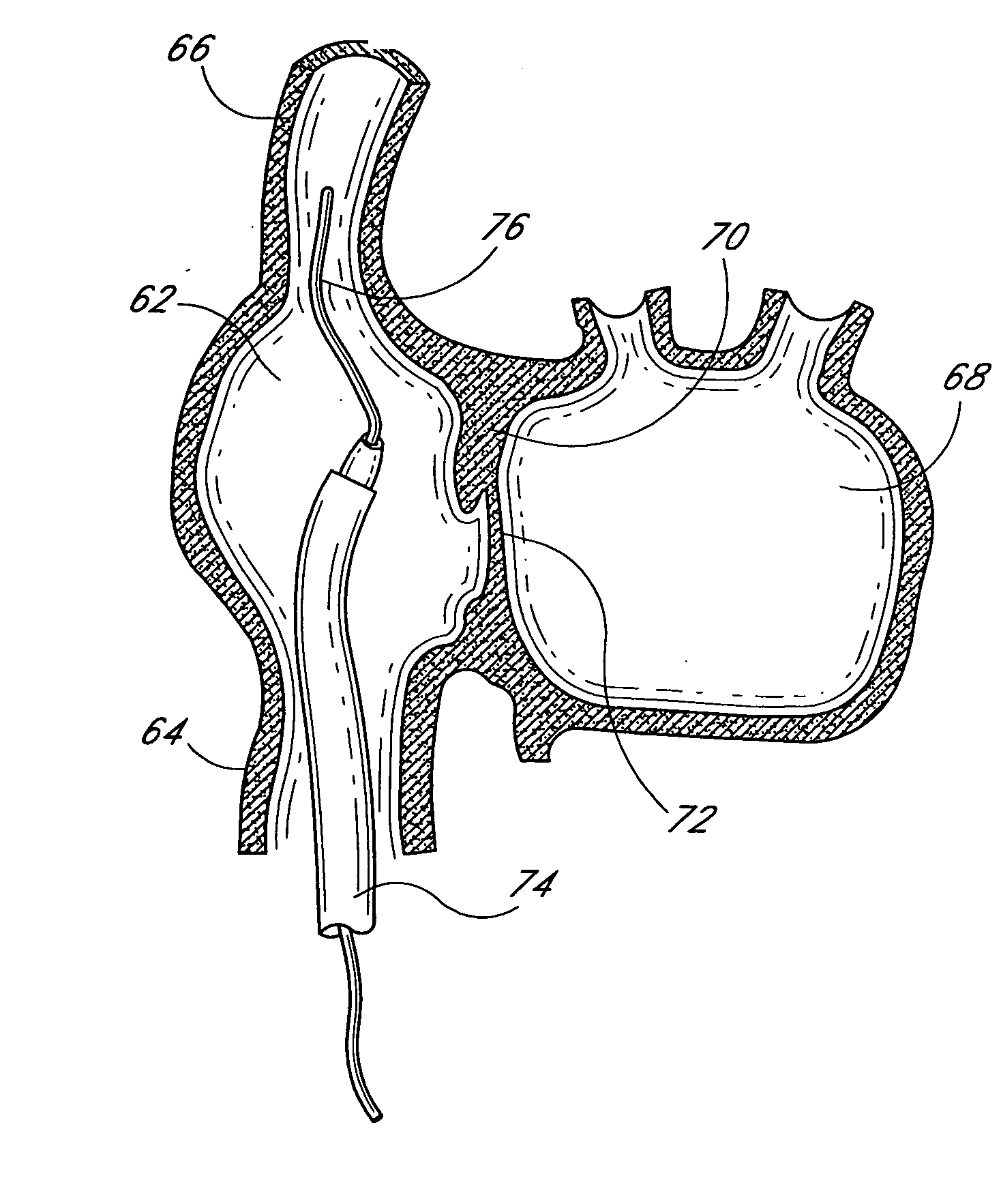
Infusion catheter having an atraumatic tip
The present invention is directed to apparatus and methods for treating a vascular occlusion by providing an infusion catheter having an atraumatic tip and at least one delivery port configured to infuse fluid into the occlusion. The fluid that is infused dilutes the occlusion and reduces adhesion of the occlusion to an intima of the vessel wall, thereby causing the occlusion to dislodge. Emboli generated in the process are directed into an emboli removal catheter for removal.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Ultrasonic subcutaneous dissection tool incorporating fluid delivery
InactiveUS7566318B2Facilitate electrode deliveryEasy to implantDiagnosticsSurgical needlesTransducerEngineering
Ultrasonic dissection instruments and methods provide for fluid delivery during subcutaneous dissection. An ultrasonic dissection tool includes a handle, a transducer and a dissecting member. The dissecting member extends from the distal end of the transducer, and a fluid channel system extends from at least the proximal end to the distal end of the dissecting member. The fluid channel system terminates in a port system. The port system may include one or more apertures, one or more channels, and be adapted to transport fluids such as, for example, irrigation fluids, fluids having analgesics, antibiotics, and combinations of fluids and agents.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method of injecting a drug and echogenic bubbles into prostate tissue
InactiveUS6905475B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsJet injection syringesNeedle Free InjectionEthanol Injection
Method and surgical instrument for treating prostate tissue including a surgical instrument having a main body, a needle deployment port, a needle, first and second handles and a lockout release mechanism to limit needle extension. Additionally, a kit includes the surgical instrument, together with a cystoscope, and optionally a syringe and reservoir of ethanol. The method includes needle-less injection and visualizing the ethanol injection by delivering both an echogenic agent and ethanol either by needle or needle-less injection or by providing an ultrasonically visible marker near the tip of the ethanol delivery cannula. The method also includes extending the needle transversely of the instrument housing using a link assembly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Regimen for treating prostate tissue and surgical kit for use in the regimen
InactiveUS7015253B2Decreasing prostate sizeSmall sizeBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsSteroidal antiandrogenRegimen
The present invention provides treatment regimens for treating diseased prostate tissue, including the steps of chemically ablating prostate tissue and coadministering an antiandrogen. In some embodiments, prostate tissue is chemically ablated by injection of ethanol, or an injectable gel comprising ethanol, into prostate tissue. Steroidal and non-steroidal antiandrogens are suitable antiandrogens. One suitable non-steroidal antiandrogen is bicalutamide. The treatment regimen is suitable for treatment of prostate tissue diseases including benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma. The invention further provides a treatment regimen for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia, including the steps of damaging prostate tissue and coadministering an antiandrogen. Also provided by the present invention is a kit for treating a human male, including a means for necrosing prostate tissue, an antiandrogen drug, and a means for administering the antiandrogen drug. A kit including a first surgical device for delivering a chemoablation fluid to prostate tissue transurethrally, an antiandrogen drug such as bicalutamide, and a second surgical device for administering the antiandrogen drug, is further provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Multifunction device for endoscopic surgery
ActiveUS9308014B2Coagulation facilitatedFacilitate functioningVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFluid jet surgical cuttersForcepsEndoscopic surgery
A multifunction device for endoscopic surgery including a supply means for the supply of at least one fluid and forceps or a clamp which comprise forceps-shaped electrodes with jaw parts for high-frequency surgery. The supply means is formed to dissect tissue by means of a fluid jet at or in a jaw part of the forceps or clamp. The multifunction device is one for both water jet surgery and high-frequency coagulation and / or cutting that occupies no more space than a conventional high-frequency instrument or conventional forceps or clamps.
Owner:ERBE ELEKTROMEDIZIN GMBH
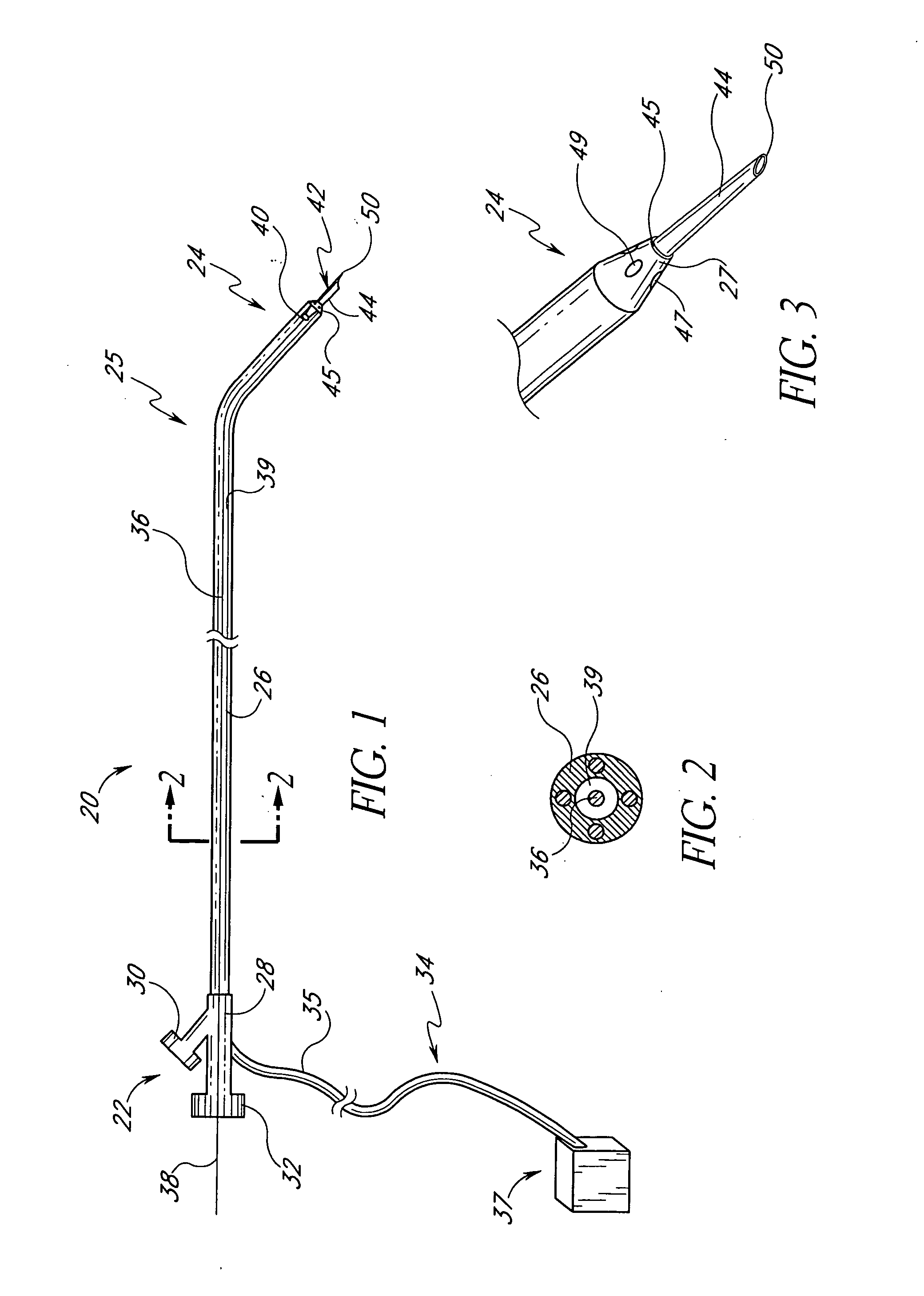
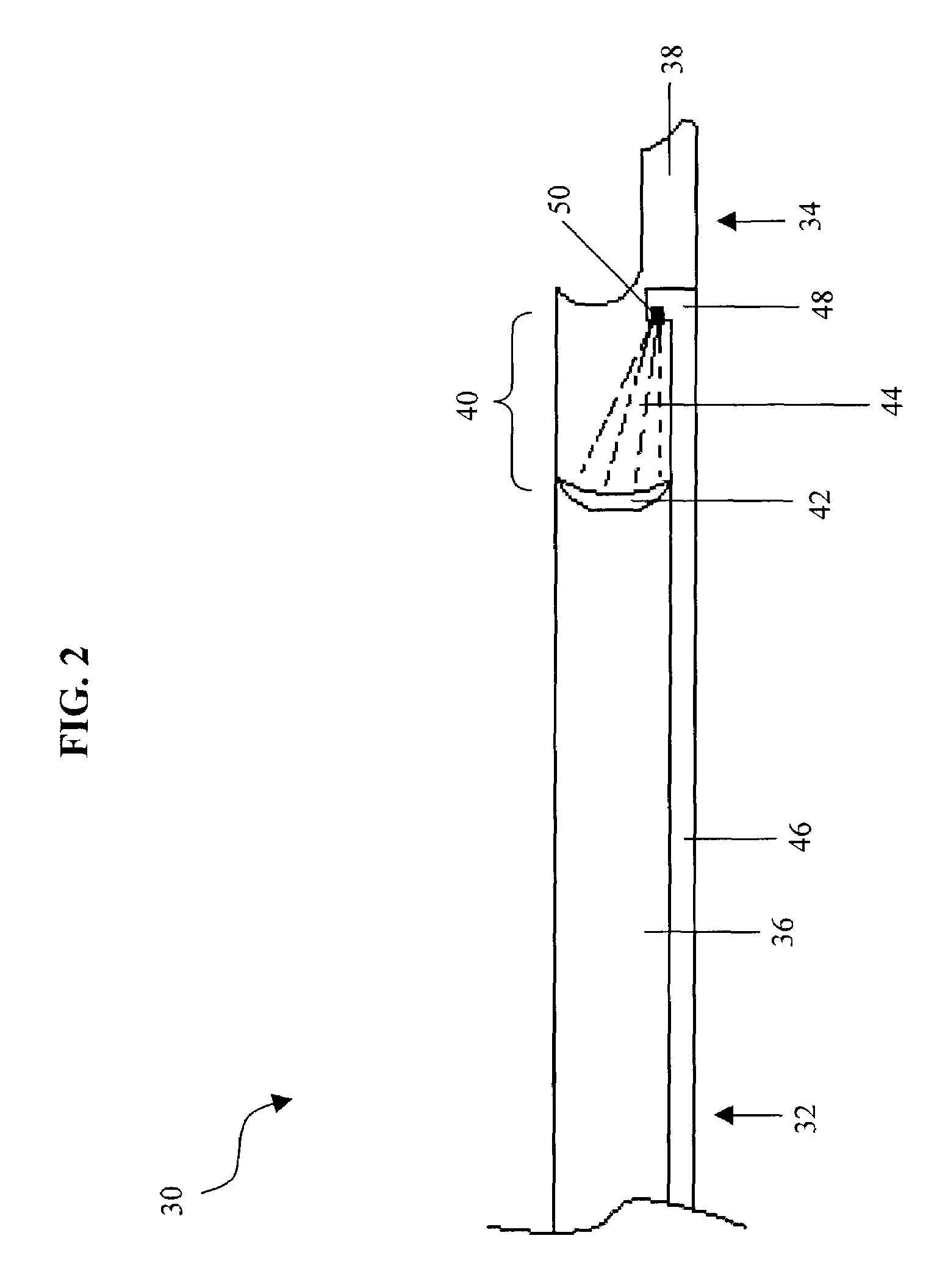
Fluid jet surgical instruments
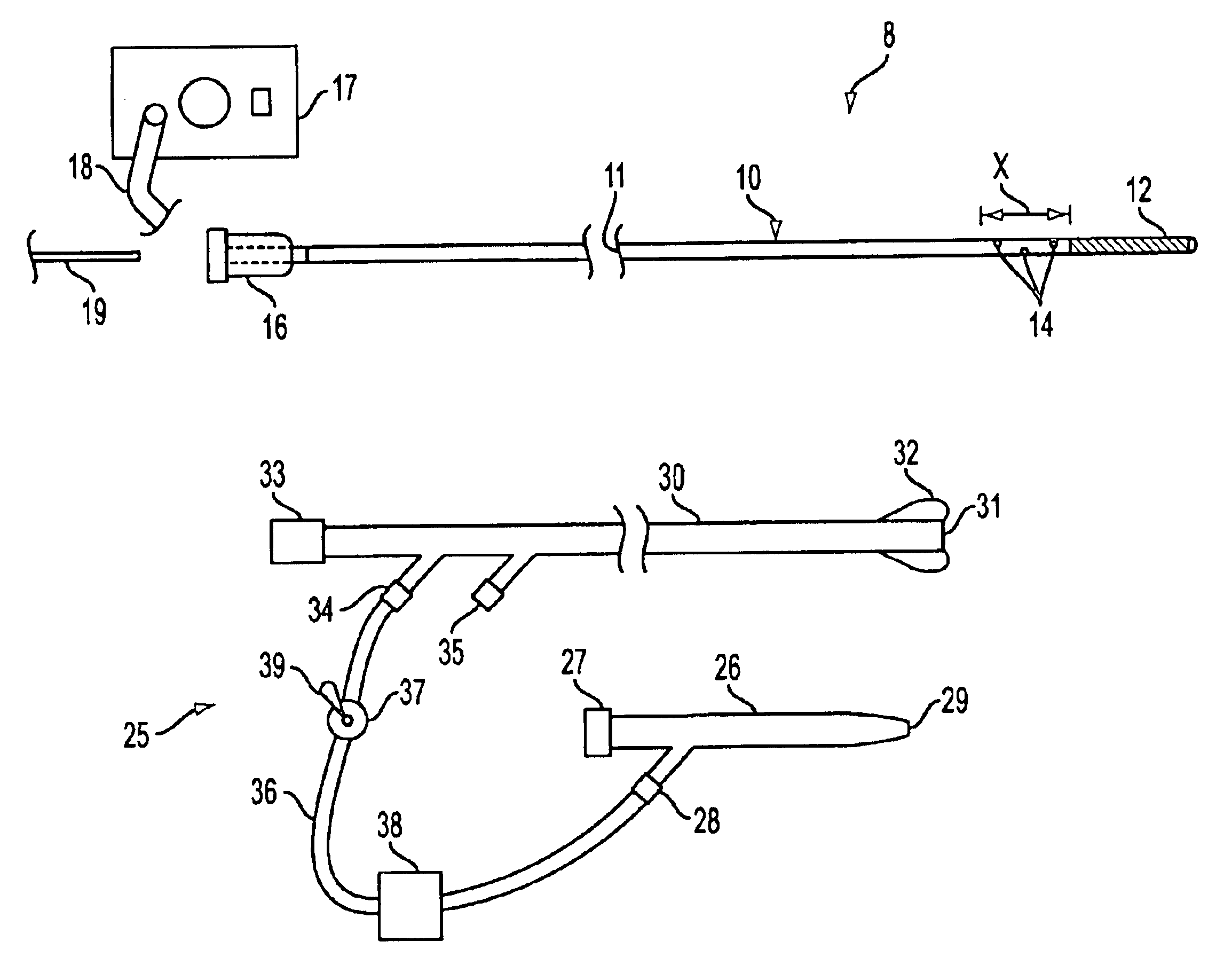
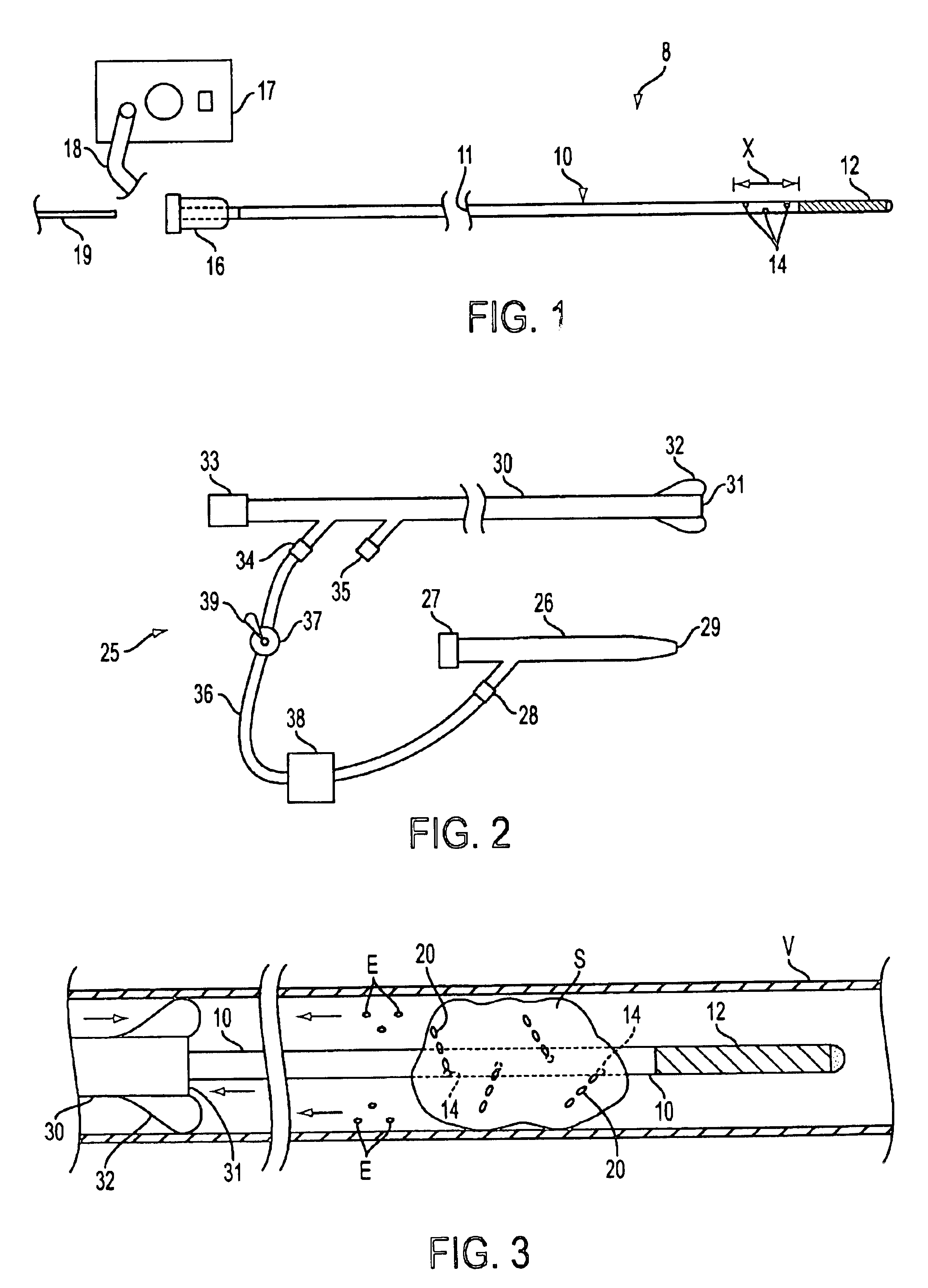
The invention provides a variety of surgical instruments for forming a liquid jet, which are useful for performing a wide variety of surgical procedures. In some embodiments, the invention provides surgical liquid jet instruments having a pressure lumen and an evacuation lumen, where the pressure lumen includes at least one nozzle for forming a liquid jet and where the evacuation lumen includes a jet-receiving opening for receiving the liquid jet when the instrument is in operation. In some embodiments, the pressure lumen and the evacuation lumen of the surgical liquid jet instruments are constructed and positionable relative to each other so that the liquid comprising the liquid jet, and any tissue or material entrained by the liquid jet can be evacuated through the evacuation lumen without the need for an external source of suction. The invention also provides a variety of surgical liquid jet instruments that are constructed and configured specifically for use in a surrounding liquid environment or a surrounding gaseous environment. The invention also provides a variety of surgical liquid jet instruments that are rotatably deployable from an undeployed position, for insertion into the body of a patient, to a deployed position, in which there is a separation distance between the liquid jet nozzle and the jet-receiving opening that defines a liquid jet path length. The invention also provides surgical methods utilizing the inventive surgical liquid jet instruments, and methods for forming components of the surgical liquid jet instruments.
Owner:HYDROCISION
System and method of use for agent delivery and revascularizing of grafts and vessels
InactiveUS6905505B2Effectively revascularizingAvoid flowBalloon catheterCannulasImpellerBiological body
A system and method for opening a lumen in an occluded blood vessel, e.g., a coronary bypass graft, of a living being. The system comprises an atherectomy catheter having a working head, e.g., a rotary impacting impeller, and a debris extraction sub-system. The atherectomy catheter is located within a guide catheter. The working head is arranged to operate on, e.g., impact, the occlusive material in the occluded vessel to open a lumen therein, whereupon some debris may be produced. The debris extraction sub-system introduces an infusate liquid at a first flow rate adjacent the working head and withdraws that liquid and some blood at a second and higher flow rate, through the guide catheter to create a differential flow adjacent the working head, whereupon the debris is withdrawn in the infusate liquid and blood for collection outside the being's body. The introduction of the infusate liquid may also be used to establish an unbalanced flow adjacent the working head to enable the atherectomy catheter to be steered hydrodynamically. A guide wire having an inflatable balloon on its distal end may be used with the atherectomy catheter to block the flow of debris distally, while enabling distal tissues to be perfused with an oxygenating liquid. At least one flow control port may be provided in the guide catheter to prevent collapse of the vessel being revascularized. A cradle is provided to fix the guide catheter and guide wire in position within the body of the being while enabling the atherectomy catheter to be advanced along the guide wire and through the guide catheter.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
A water jet instrument may be used for manually performing eye surgery such as, cataract, or perform micro-surgery (remove cartilage), or any emulsification technique. The water jet instrument may be manually controlled or controlled by a system with a robotic control. The water jet apparatus defines a jet cutting area that is based at least in part on a flow rate meter and a feedback loop.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:BAXANO SURGICAL
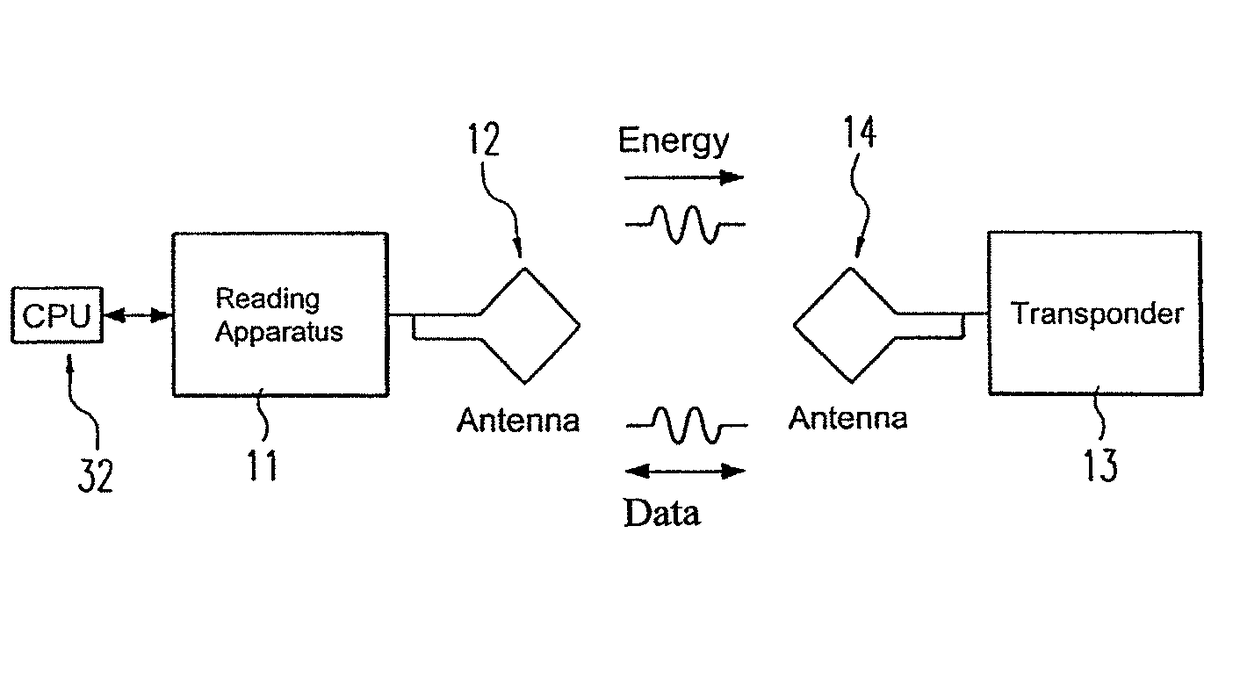
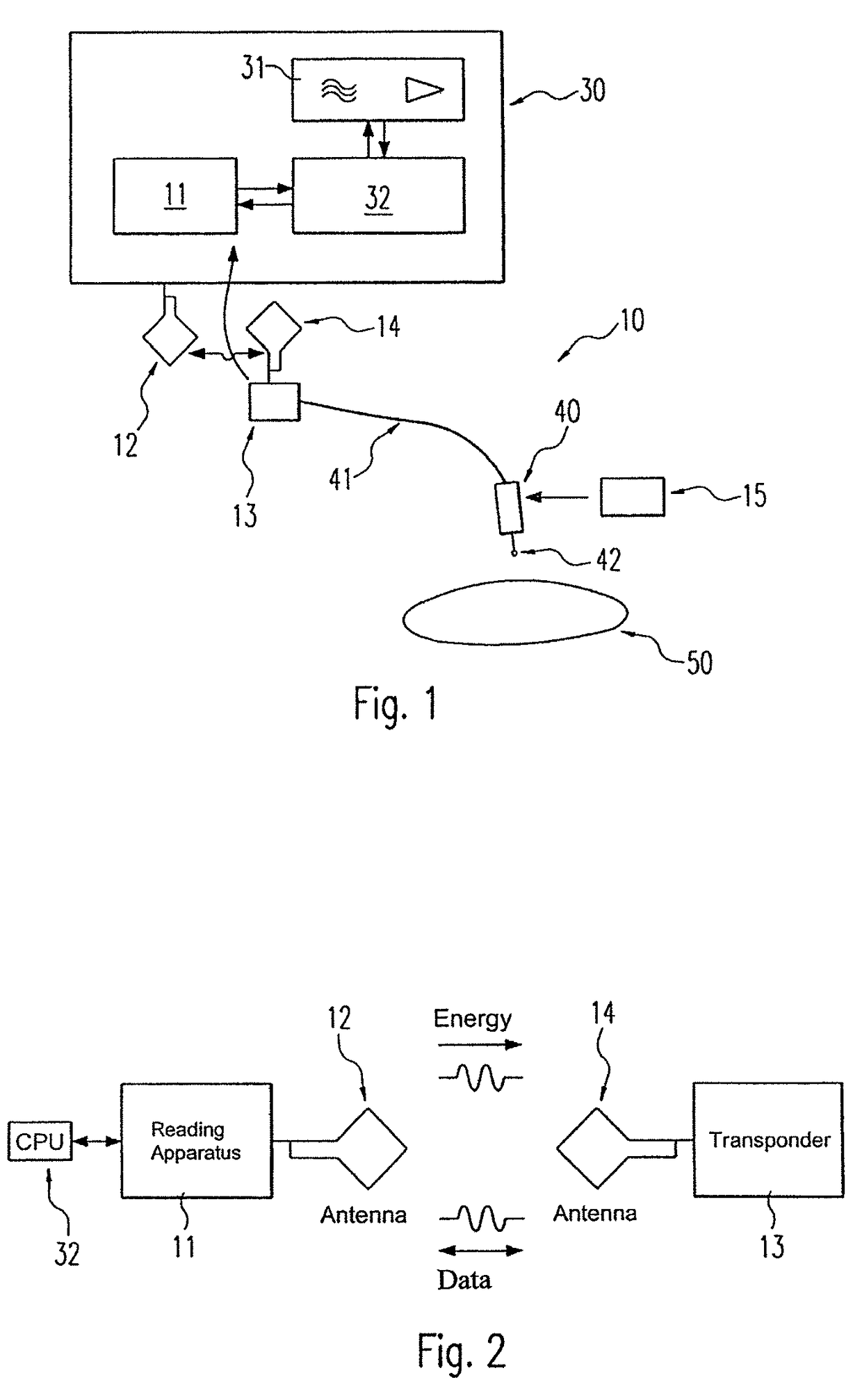
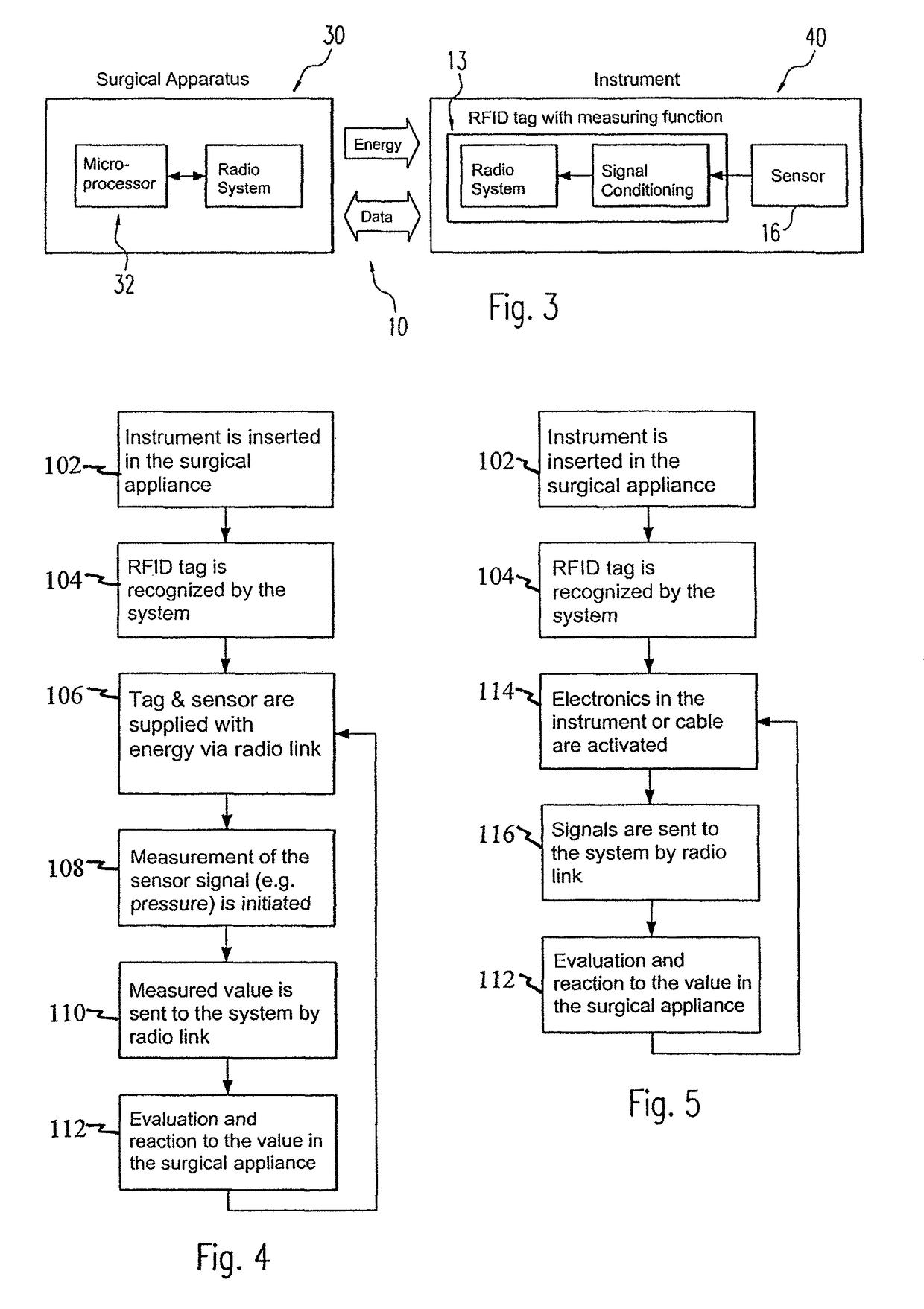
Device for contactless communication and use of a memory device
ActiveUS9622808B2Improve securityDiagnosticsFluid jet surgical cuttersBiomedical engineeringInstrumentation
Owner:ERBE ELEKTROMEDIZIN GMBH
Tissue remover and method
InactiveUS20040068256A1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlFluid jet surgical cuttersSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesCutting forceBiomedical engineering
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
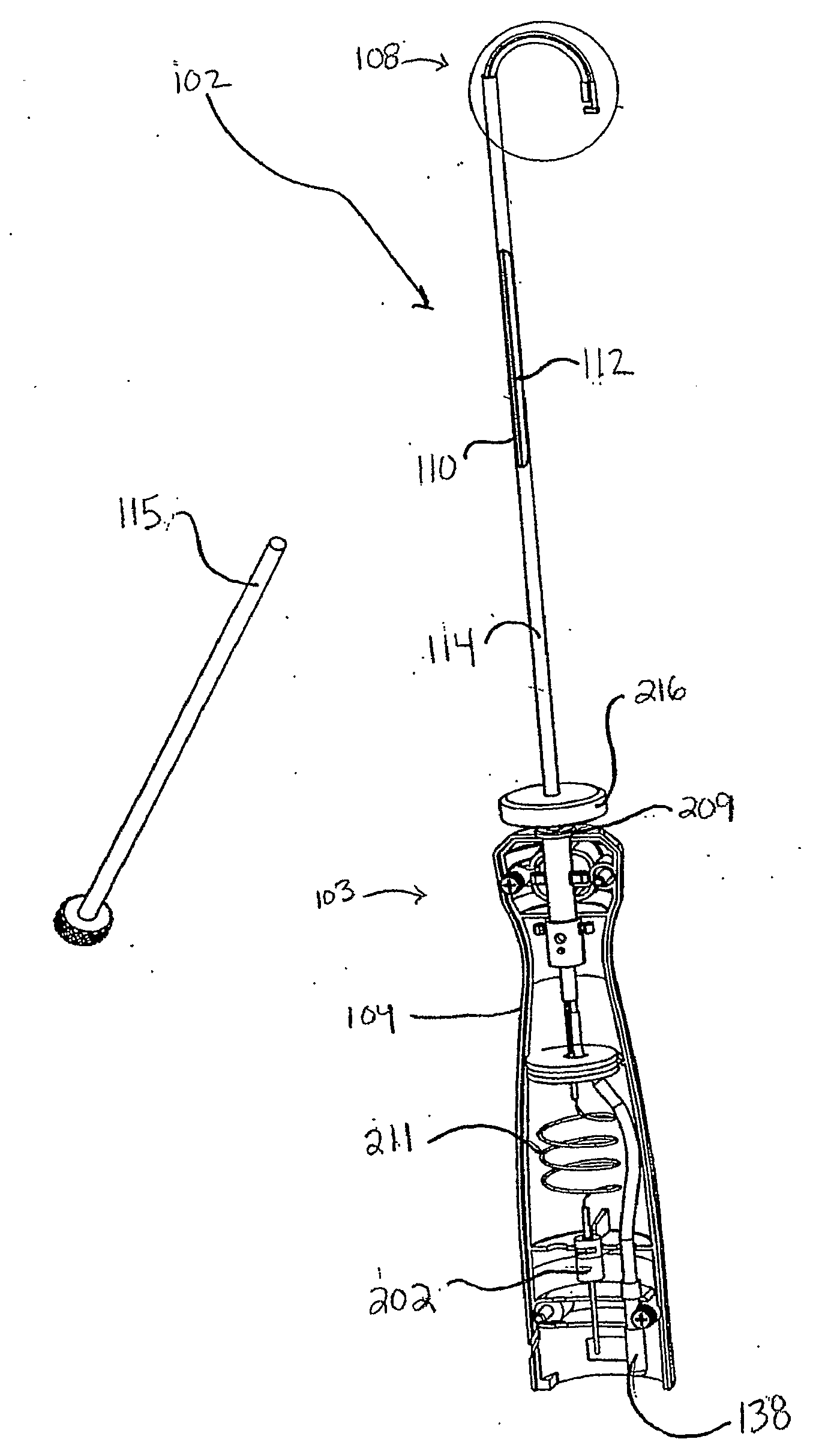
Thrombectomy and soft debris removal device
ActiveUS20050240146A1Efficient removalMinimize associated blood lossStentsBalloon catheterBiological bodyHigh rate
A device suitable for removing material from a living being is provided, featuring an infusate pump, and an aspiration pump, both powered by a motor. The aspiration pump and infusate pump preferably feature a helical pumping mechanism, and operate at a high rate of rotation, thereby ensuring adequate pumping performance and flexibility. Additionally, a narrow crossing profile is maintained, ensuring that the device may reach more tortuous regions of the vasculature.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Enhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomy catheter with backloading manifold
InactiveUS20060129091A1High trafficEnhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomyMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesSuction forceJet flow
An enhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomy catheter with backloading manifold having a distal end with outflow and inflow orifices at one side for producing concentrated cross stream jet flow for selective and concentrated thrombus ablation during thrombectomy procedures. The invention provides for suitable distancing of high powered ablation or suction forces from the near walls of the vasculature. Cross stream flow emanating from the one side of the distal end of the catheter resultantly urges the distal end of the catheter and thus the opposing non-orificed side of the distal end of the catheter toward and against the vascular wall to inhibit contact of the inflow orifice with the vascular wall. Features of the invention include a geometrically configured insert to facilitate the backloading or exchange of guidewires.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
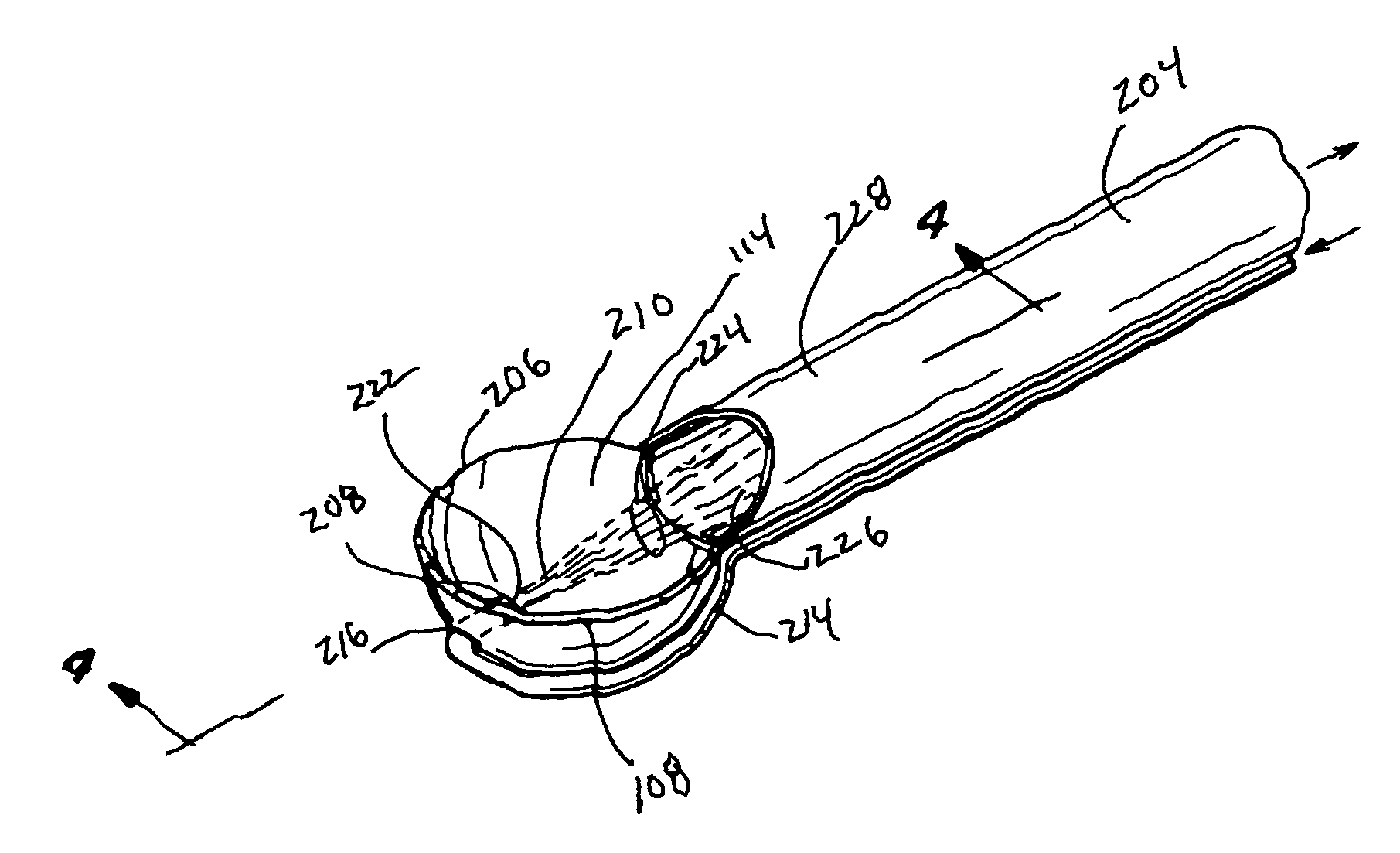
Object removal through a percutaneous suction tube
A method is described for using percutaneous access to a patient to remove an object from a cavity within the patient. The method includes inserting a suction tube into a port created by a percutaneous cut. An endoscope is also advanced into the cavity, however the endoscope passes through a patient lumen rather than through the port. Using a working channel within the endoscope, fluid is irrigated through the cavity. Additionally, a negative pressure is applied to the suction tube, such that the combination of fluid irrigation and negative pressure assist in removing the object from the cavity through the suction tube.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Tissue biopsy and processing device
InactiveUS7115100B2Avoid enteringEfficient receptionWithdrawing sample devicesSurgical needlesTissue biopsyTissue sample
A tissue biopsy and processing device for capturing and processing a tissue sample is provided. In general, the device includes a biopsy member adapted to remove a tissue sample from a patient's body, and a processing apparatus adapted to receive the tissue sample from the biopsy device, and to dissociate and mince the tissue sample in preparation for further use. The processing apparatus can include a tissue reducing chamber in communication with and adapted to receive the tissue sample from the biopsy member, and a tissue processing element associated with the tissue reducing chamber that is effective to dissociate the tissue sample retained within the tissue reducing chamber.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
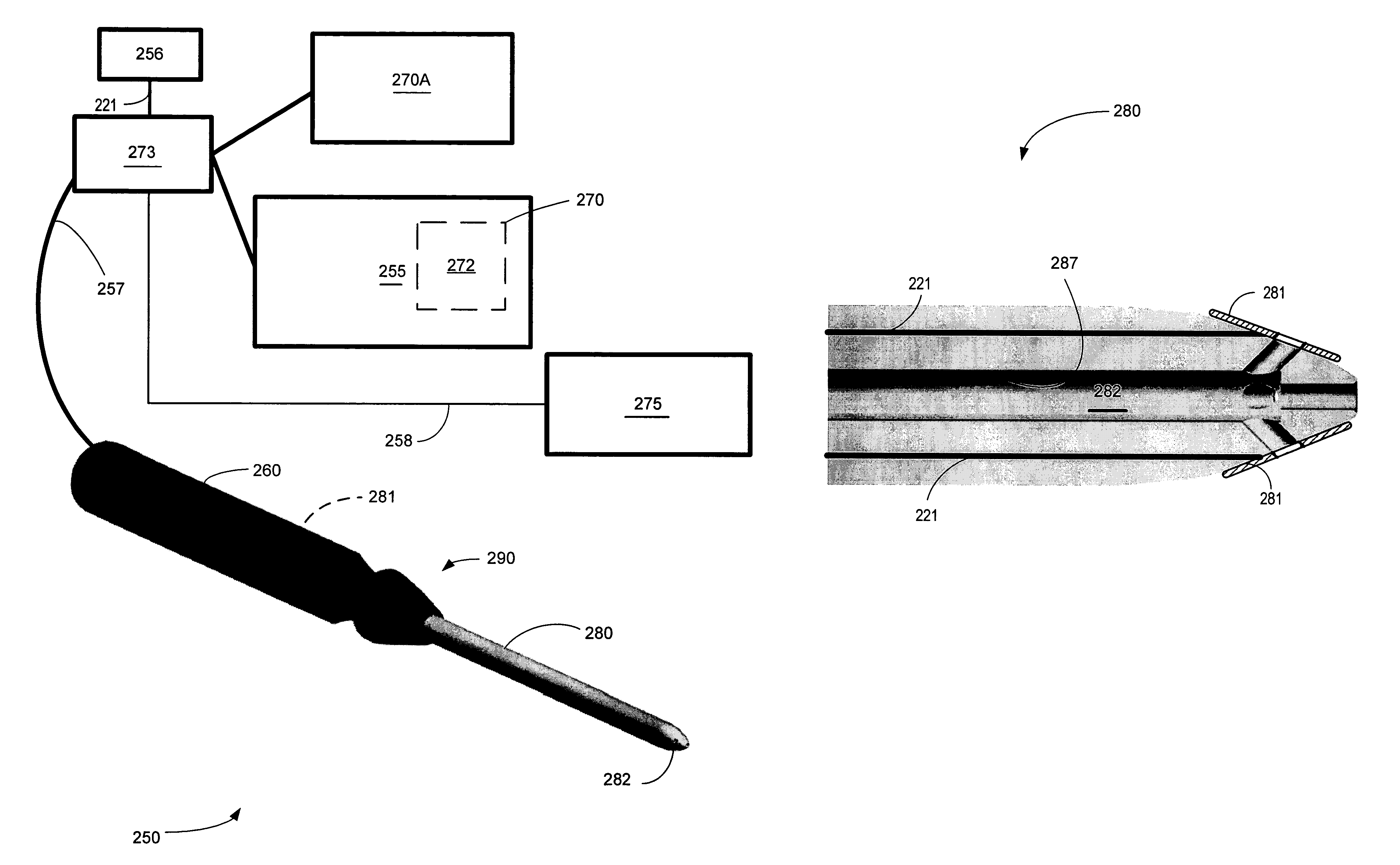
Liquid jet surgical instrument having a distal end with a selectively controllable shape
InactiveUS20100010524A1High burst resistanceFluid jet surgical cuttersMedical atomisersLiquid jetIntervertebral disc
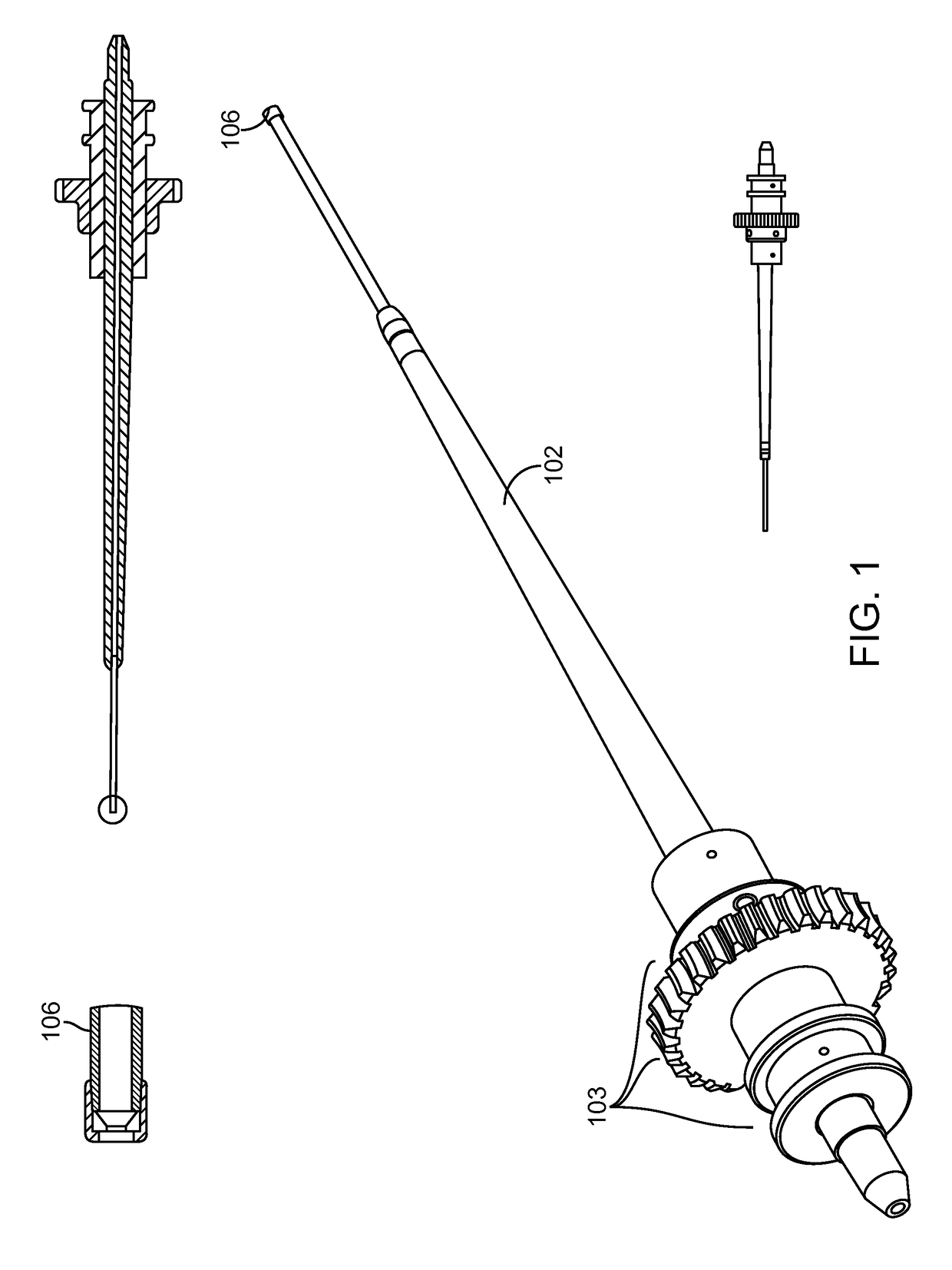
The invention provides a variety of surgical instruments for forming a liquid jet, which are useful for performing a wide variety of surgical procedures. In some embodiments, the invention provides surgical liquid jet instruments having a pressure tube and an evacuation tube, where the pressure tube includes at least one nozzle for forming a liquid jet and where the evacuation tube includes a jet-receiving opening for receiving the liquid jet when the instrument is in operation. In some embodiments, the distal ends of both the pressure and evacuation tubes have a first configuration in a non-relaxed state and a second configuration in a more relaxed state. In some embodiments, a straightener is constructed to selectively control the configuration of the distal ends of both the pressure and evacuation tubes. The invention also provides surgical methods utilizing the inventive surgical liquid jet instruments for cutting or ablating a selected tissue within portions of a patient's spine, such as within the intervertebral disc.
Owner:HYDROCISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com