Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1134results about How to "Easy to implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
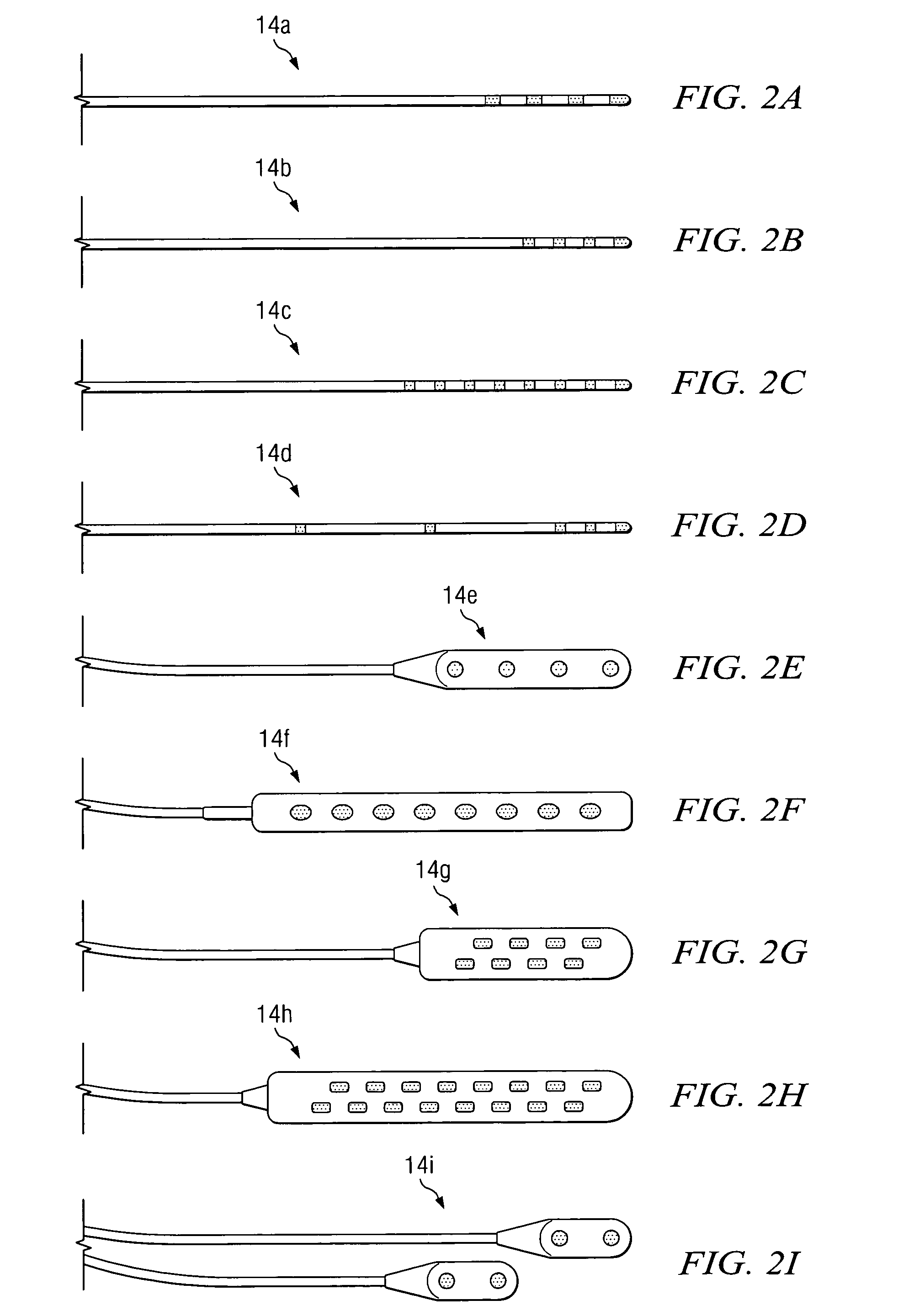
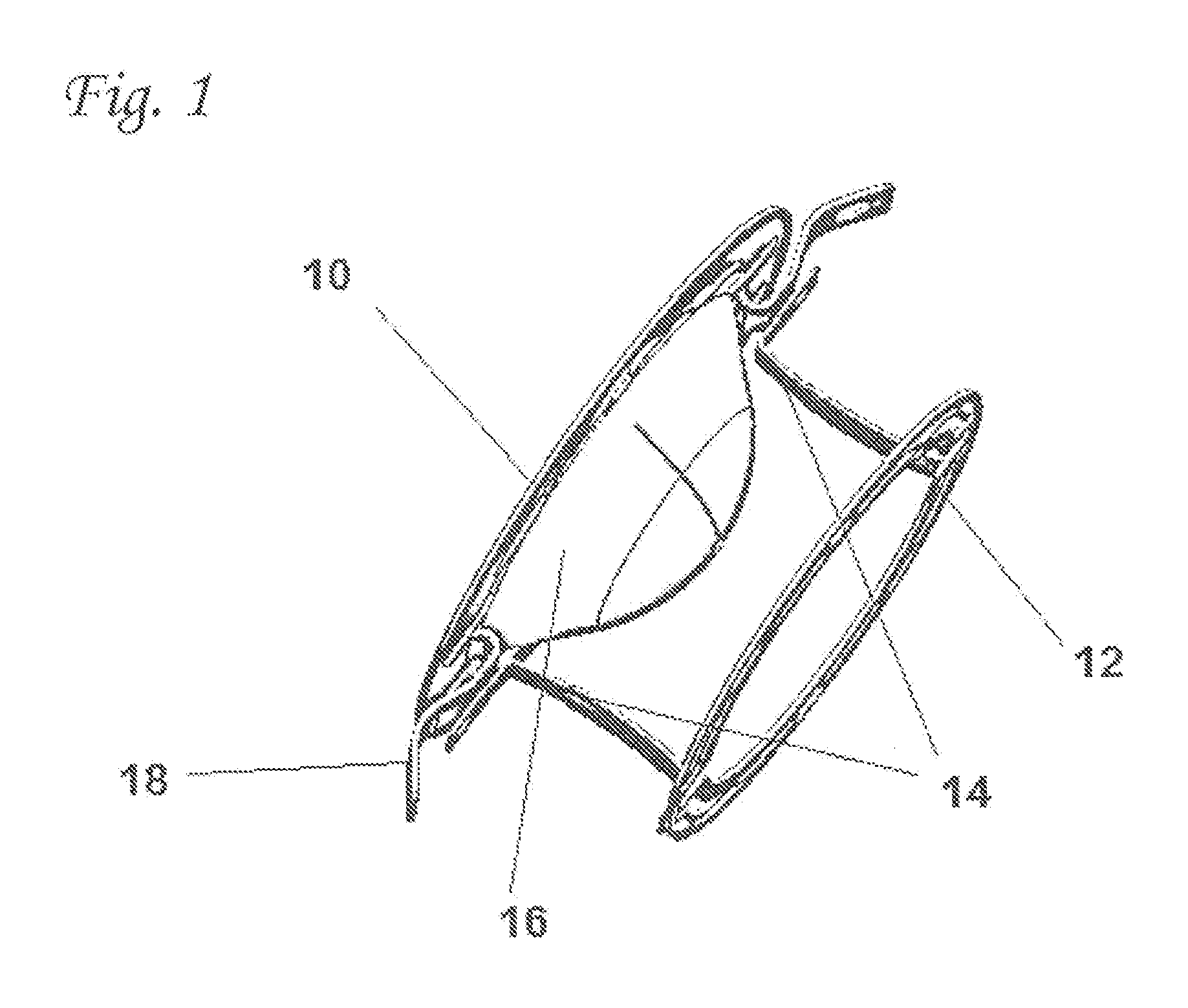
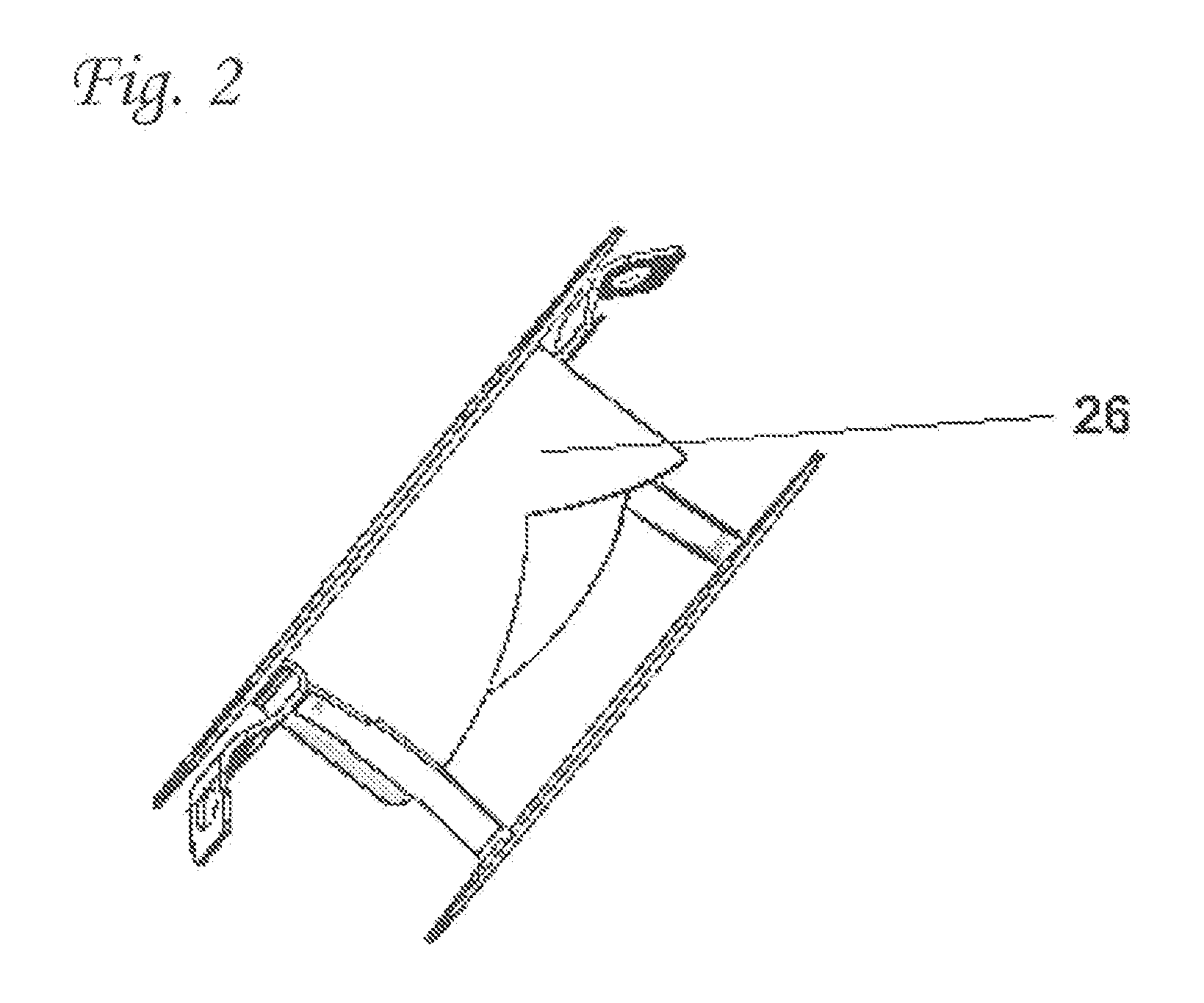
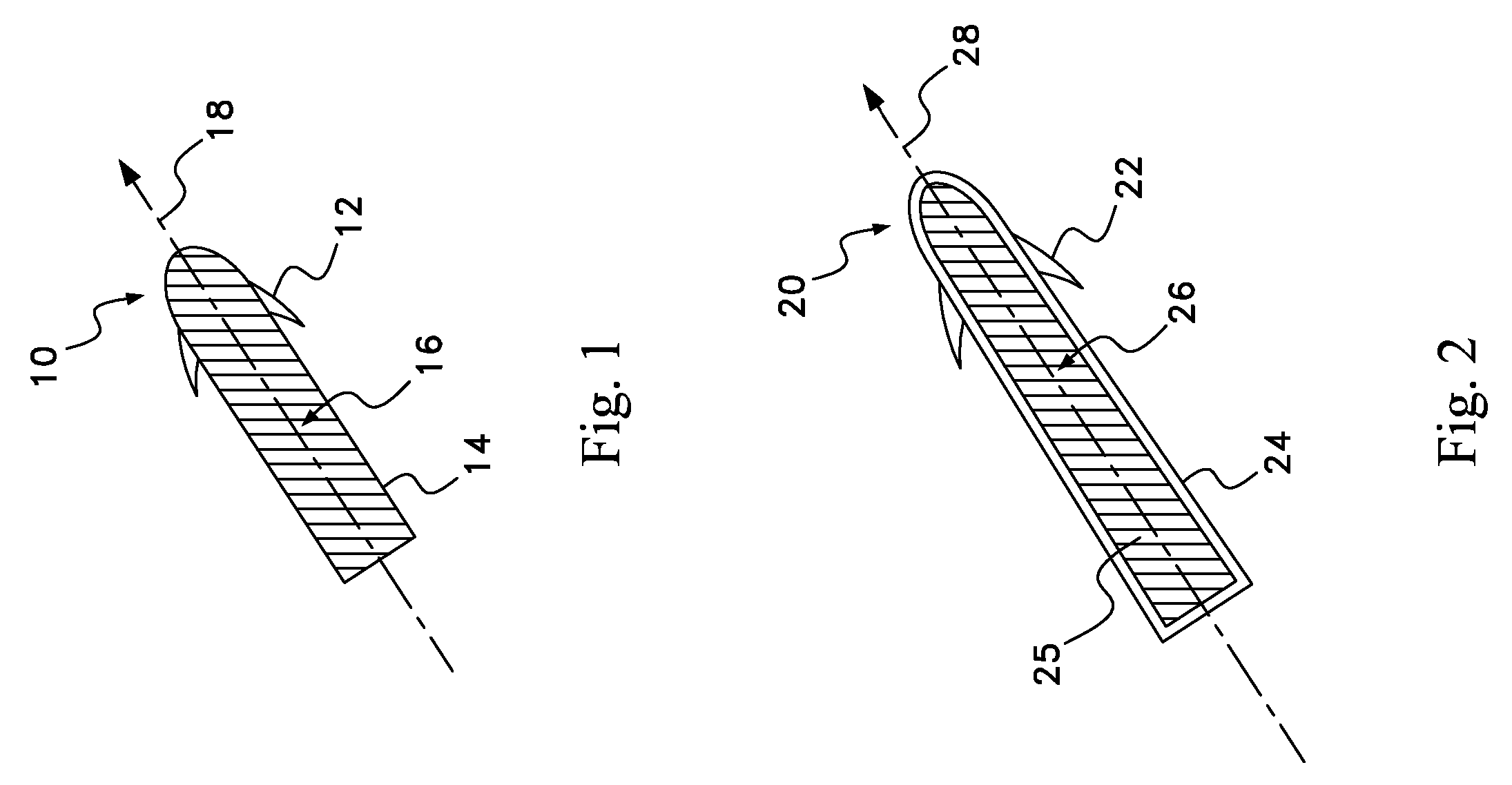
Drug depot implant designs
ActiveUS7727954B2Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injuryChronic pain
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
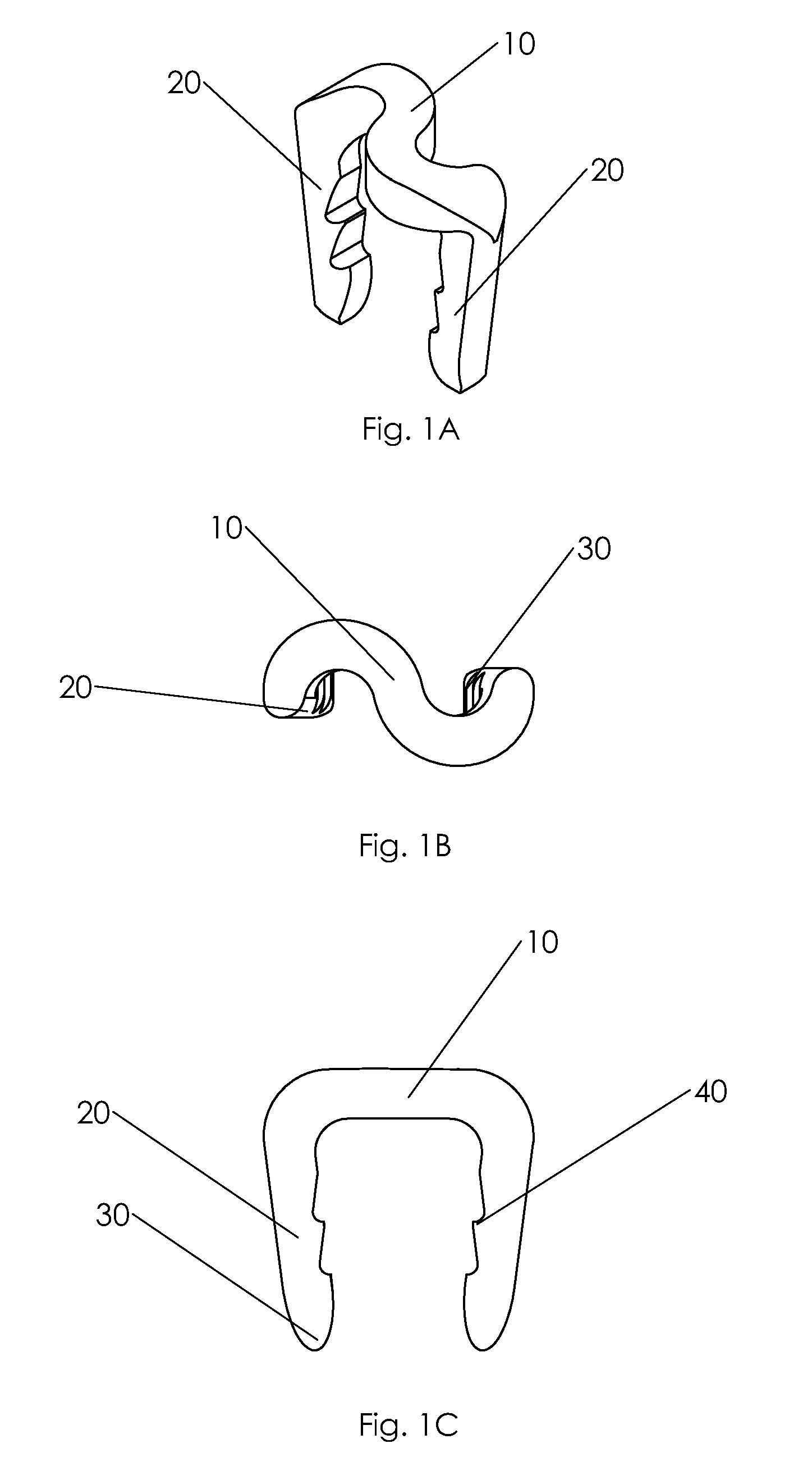
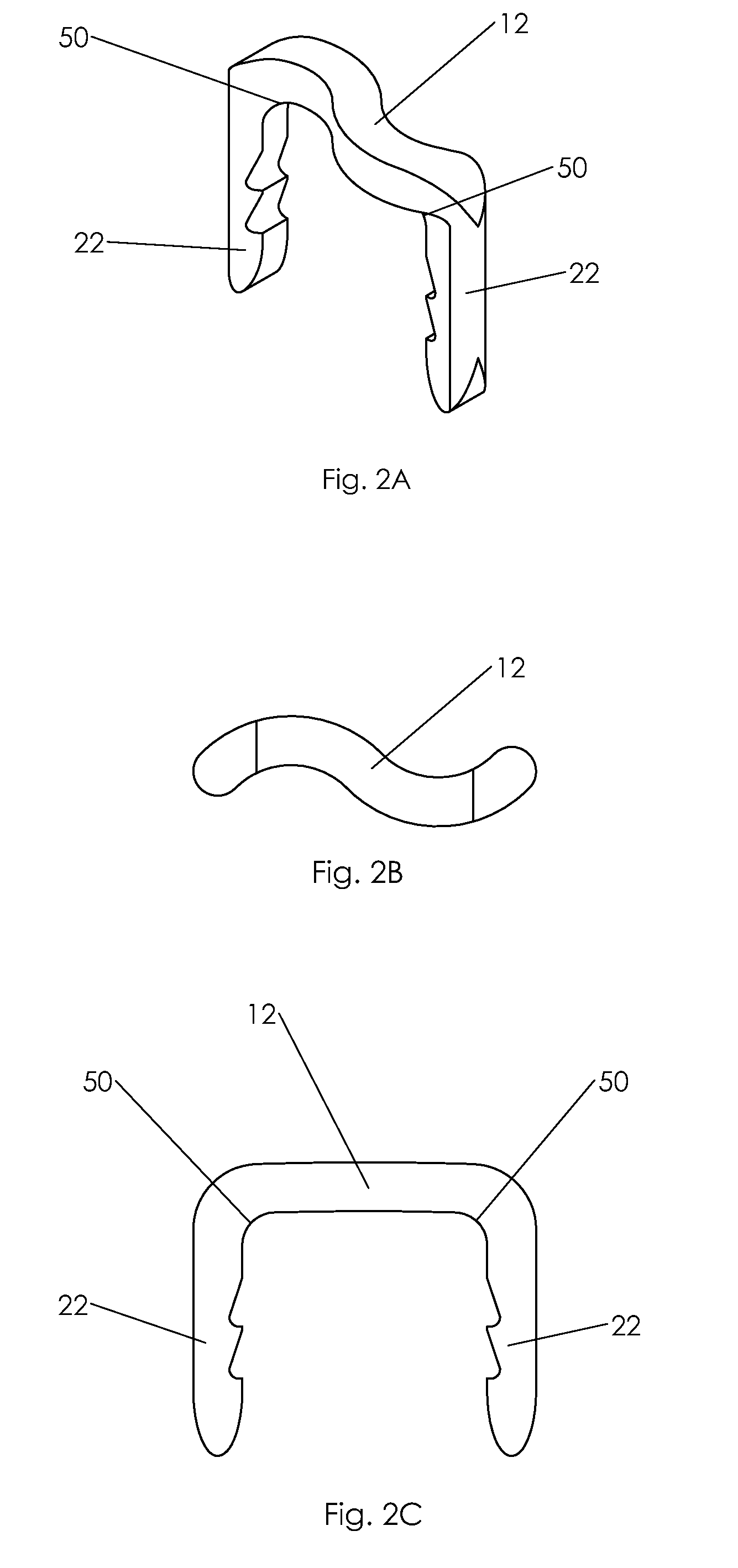
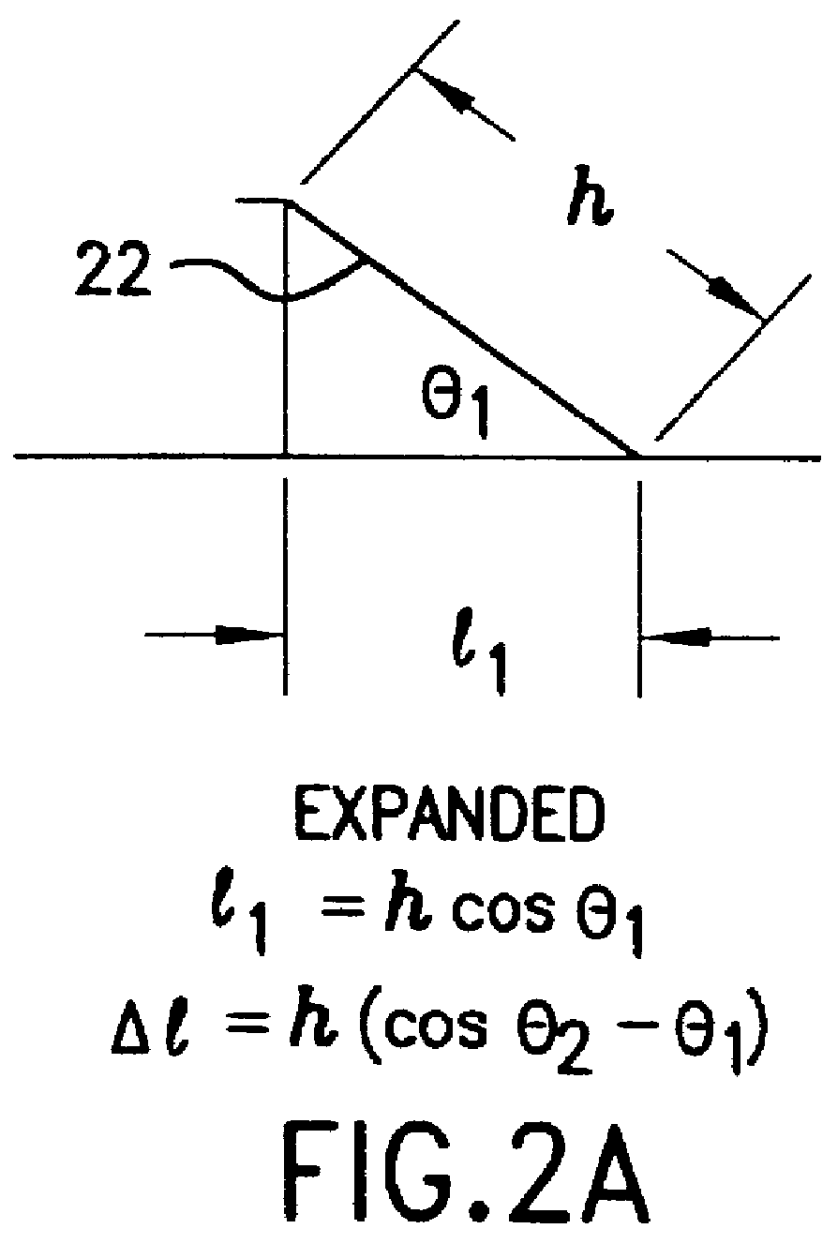
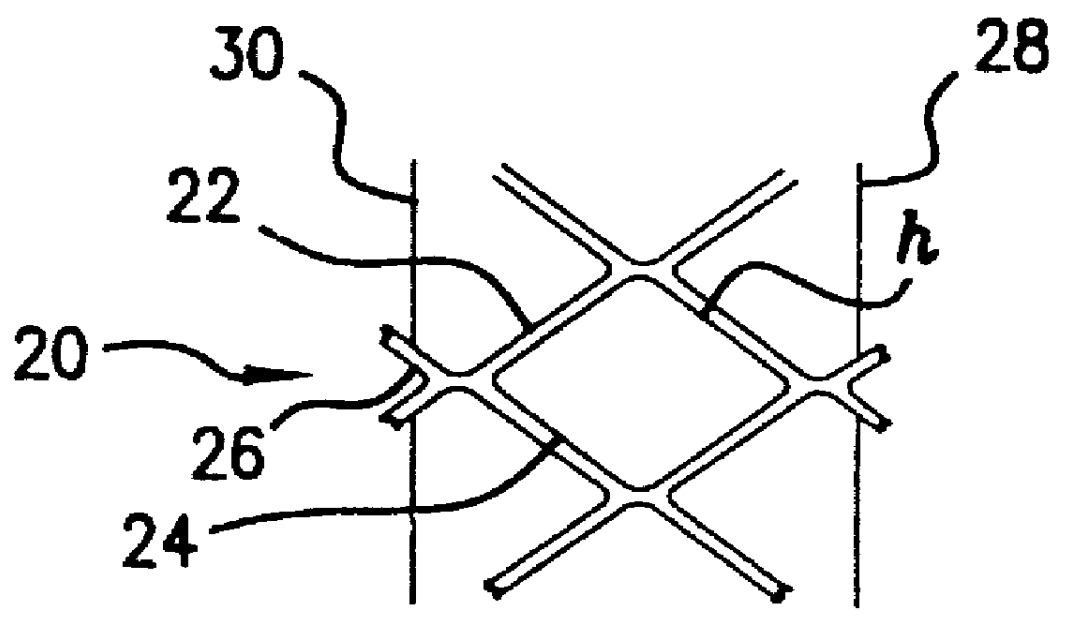
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS9017331B2Stores recoverable mechanical energyEasy to implantPinsInternal osteosythesisShape changeMechanical energy
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
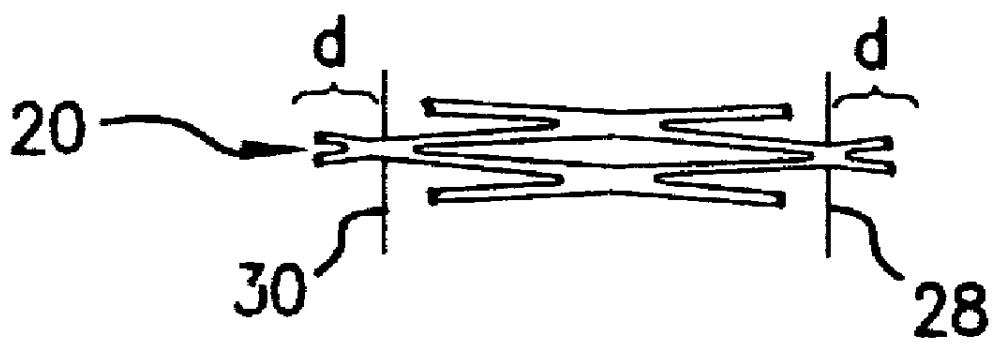
Non-foreshortening intraluminal prosthesis
InactiveUS6106548ADifferent degree of flexibilityVaried flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsProsthesisEngineering
An intraluminal prosthesis is provided with a plurality of annular elements. Each annular element includes a plurality of struts and apices connected to form an annular configuration. Each annular element has a compressed state and an expanded state, and has a longitudinal dimension which is smaller in the expanded state than in the compressed state. A plurality of connecting members connect the apices of adjacent annular elements. The connecting members have a plurality of alternating segments that function to compensate for the smaller longitudinal dimension of each annular element in the expanded state. The stent may be provided with varying flexibility along its length and / or circumference, and may include segments that have different diameters.
Owner:ENDOSYST
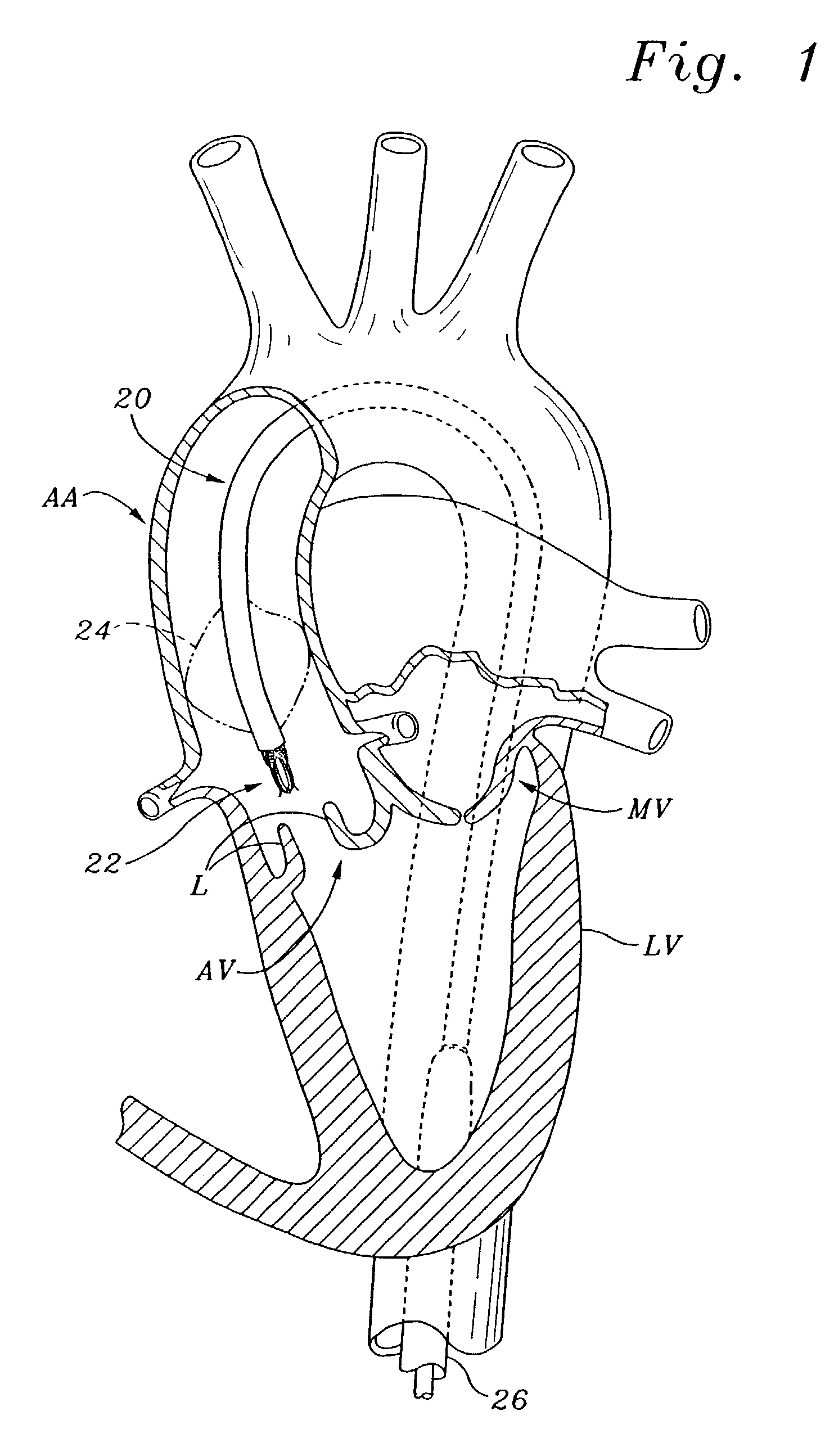
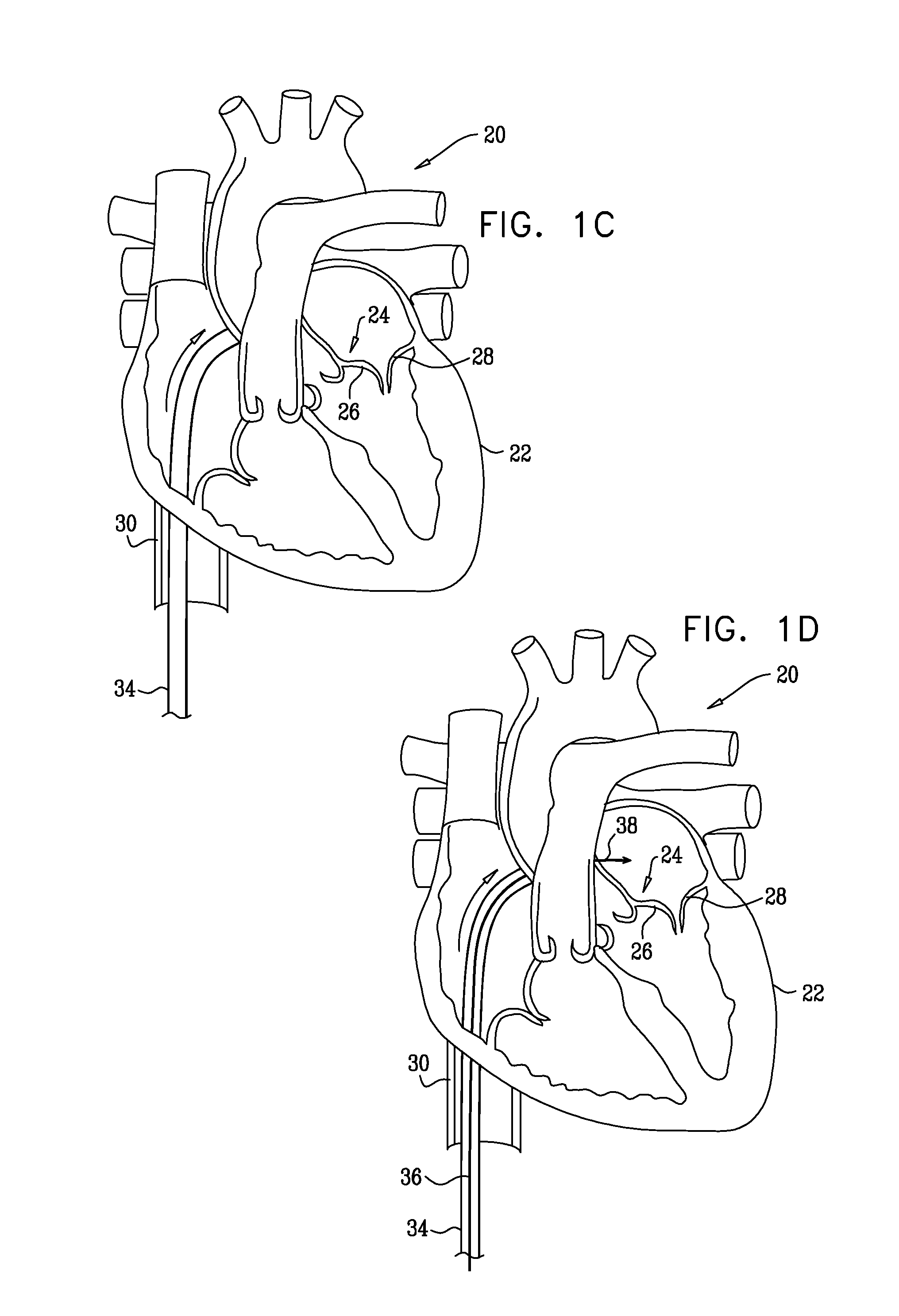
Methods and systems for cardiac valve delivery
The present invention provides systems and methods for the repair, removal, and / or replacement of heart valves. The methods comprise introducing a delivery system into the heart, wherein a prosthesis is disposed on the delivery member attached to the delivery system, advancing the prosthesis to the target site, and disengaging the prosthesis from the delivery member at the target site for implantation. The present invention also provides implant systems for delivering a prosthesis to a target site in or near the heart. In one embodiment of the present invention, the implant system comprises a delivery system, an access system, and a prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Implantable device for vital signs monitoring
InactiveUS20070016089A1Few suture requirementKeep the distanceElectrocardiographyCatheterSubcutaneous implantationDigital storage
An implantable medical device is provided for subcutaneous implantation within a human being. The implantable medical device includes a pair of electrodes for sensing electrical signals from the human being's heart. Electronic circuitry having digital memory is provided with the electronic circuitry designed to record the electrical signals from the heart. The electronics of the electronic circuitry are housed in a case having a tapered shape to facilitate implantation and removal of the implantable medical device.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST +1
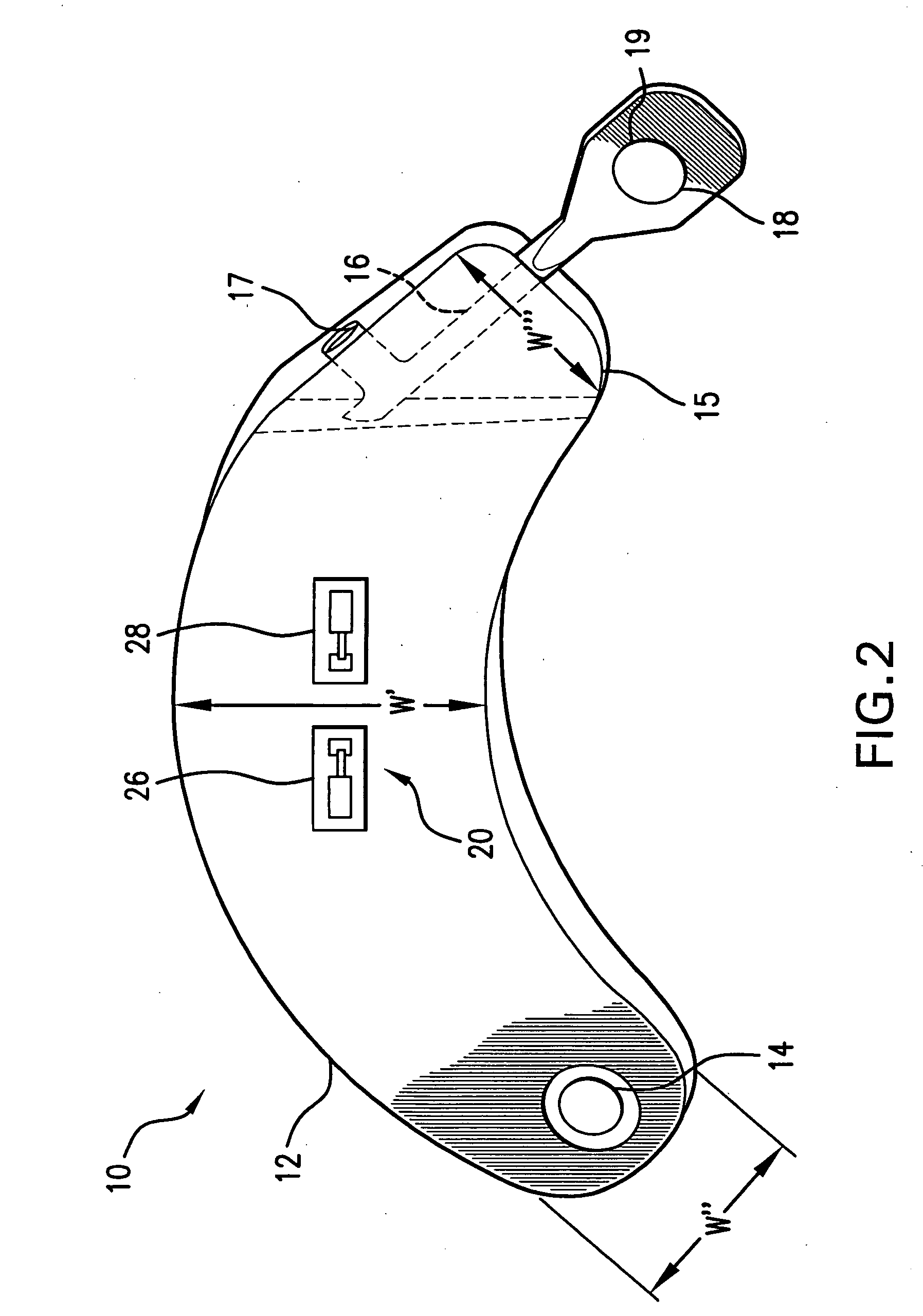
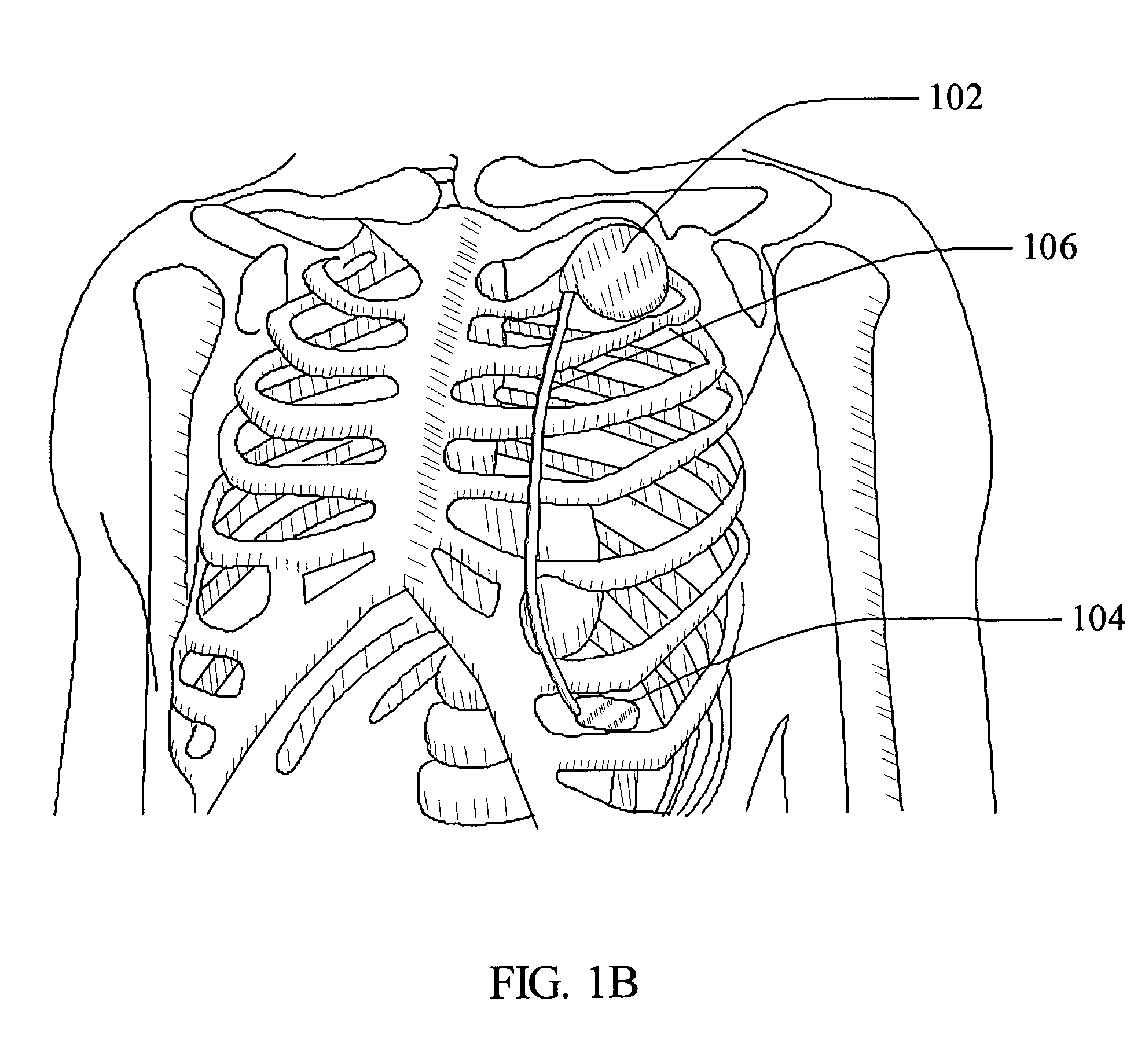
Dynamic stabilization system for the spine
ActiveUS20060293663A1Easy to implantIncrease spacingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacroiliac jointBiomedical engineering
A system for dynamic stabilization of the spine includes a bone engaging fastener configured to be anchored in a vertebra and a deflectable element mounted on the fastener. The deflectable element or bumper is configured and arranged to contact a portion of an adjacent vertebra, such as the facet, during extension of the spine, while offering no resistance during flexion. In certain embodiments, a cable may be fastened to the bone engaging fastener and arranged to contact a portion of the adjacent vertebra, such as the spinous process, during flexion of the spine. In one surgical technique of the invention, a contralateral approach is used to introduce the bone engaging fastener through the deflectable element and into the vertebra.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
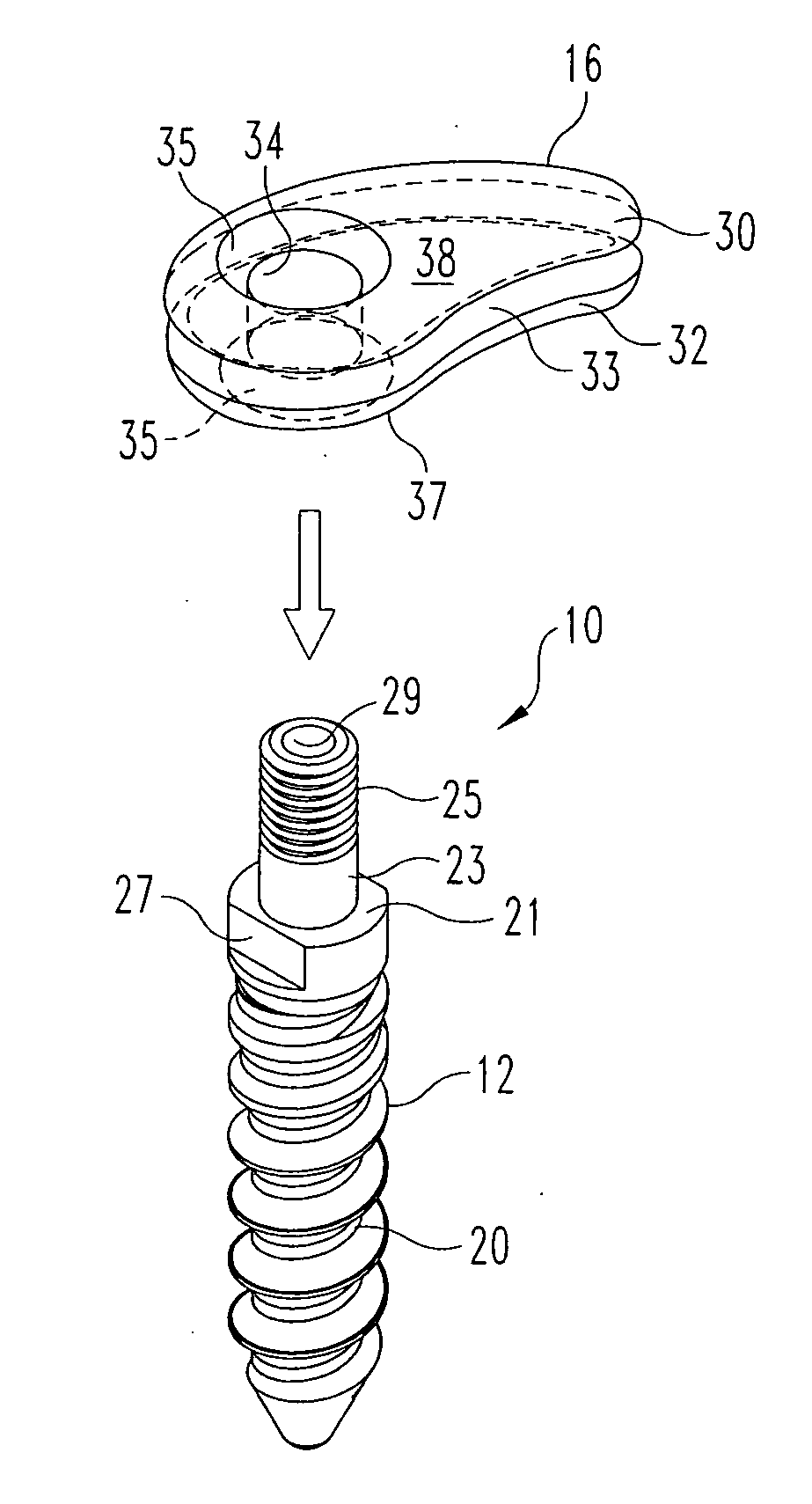
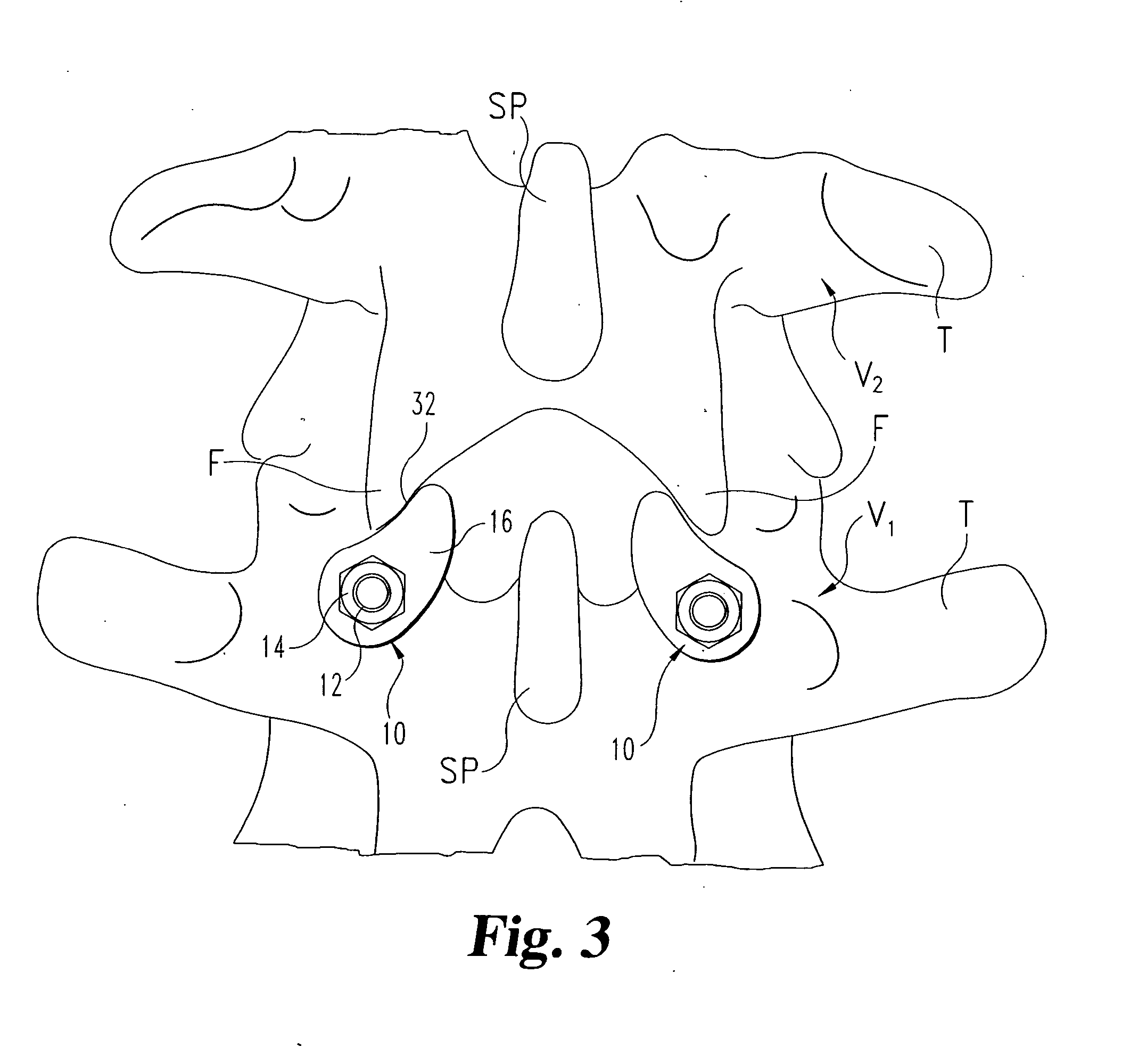
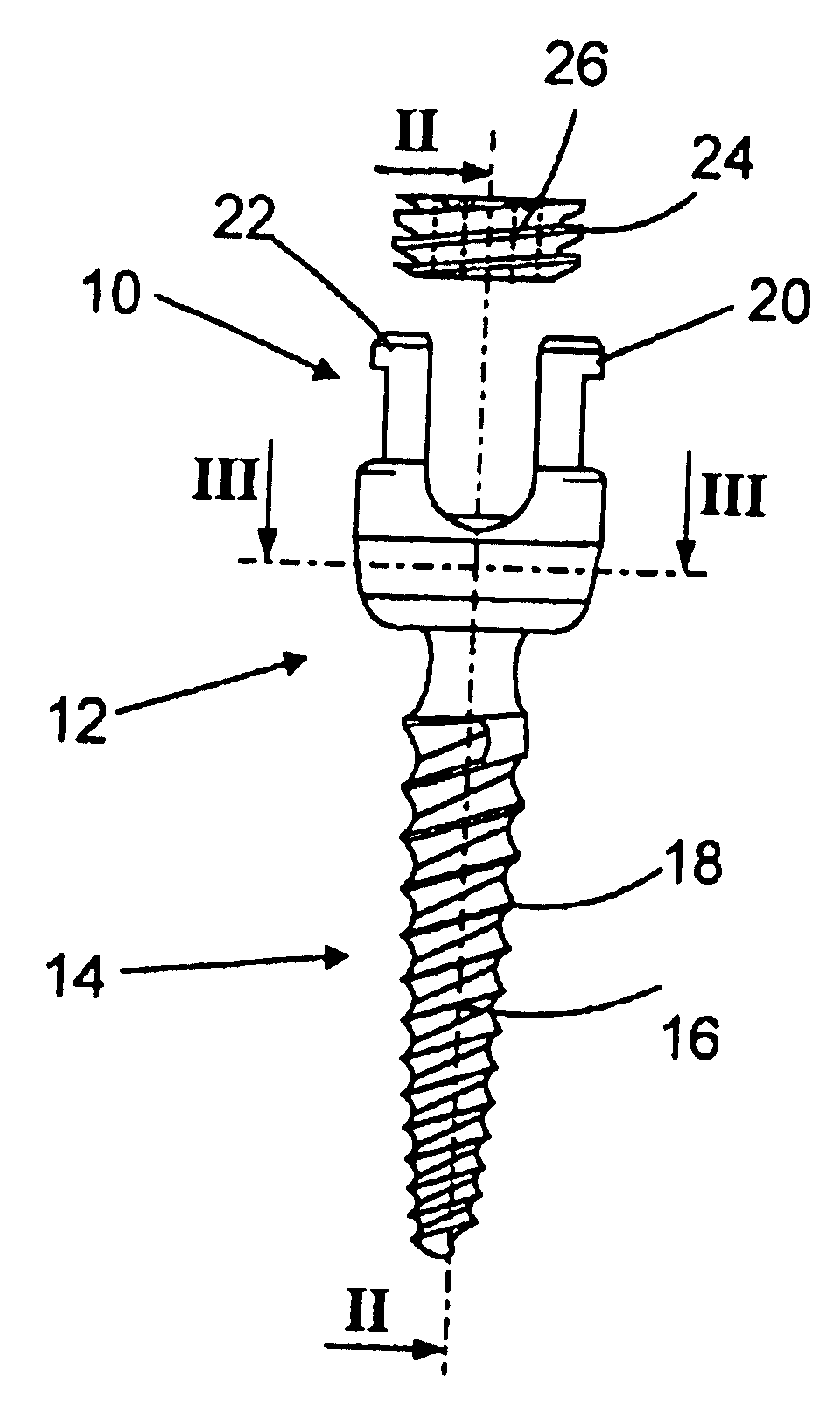
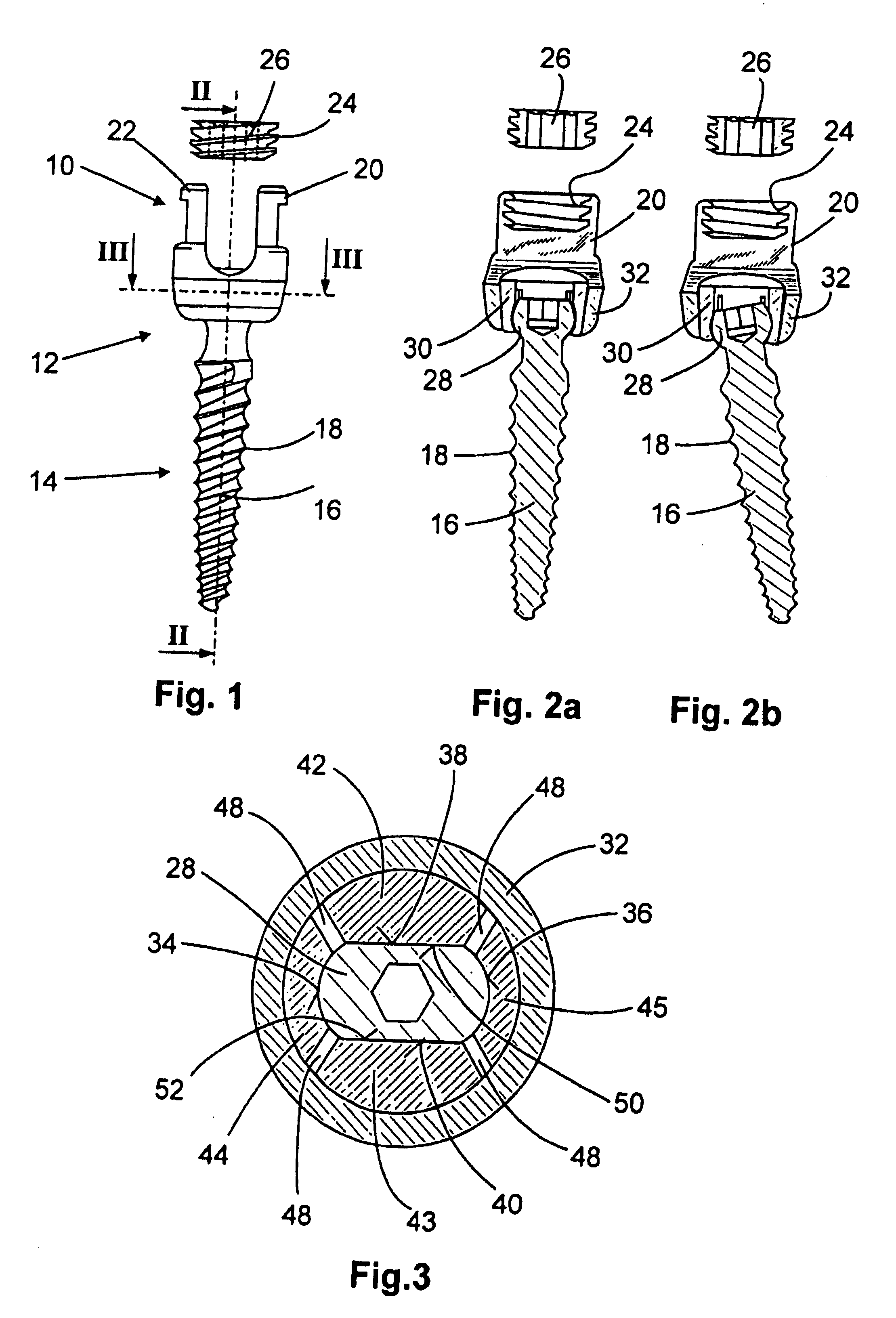
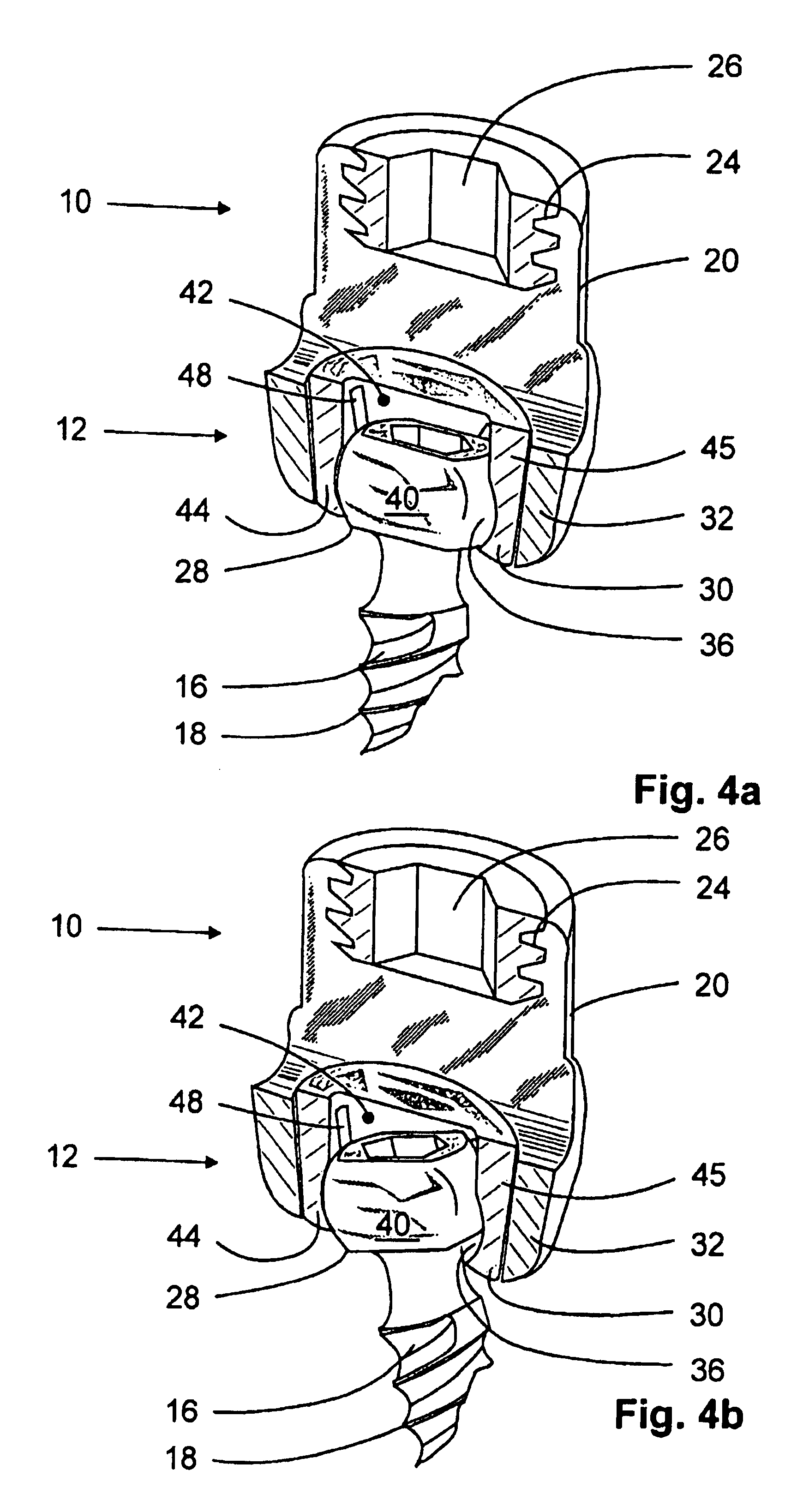
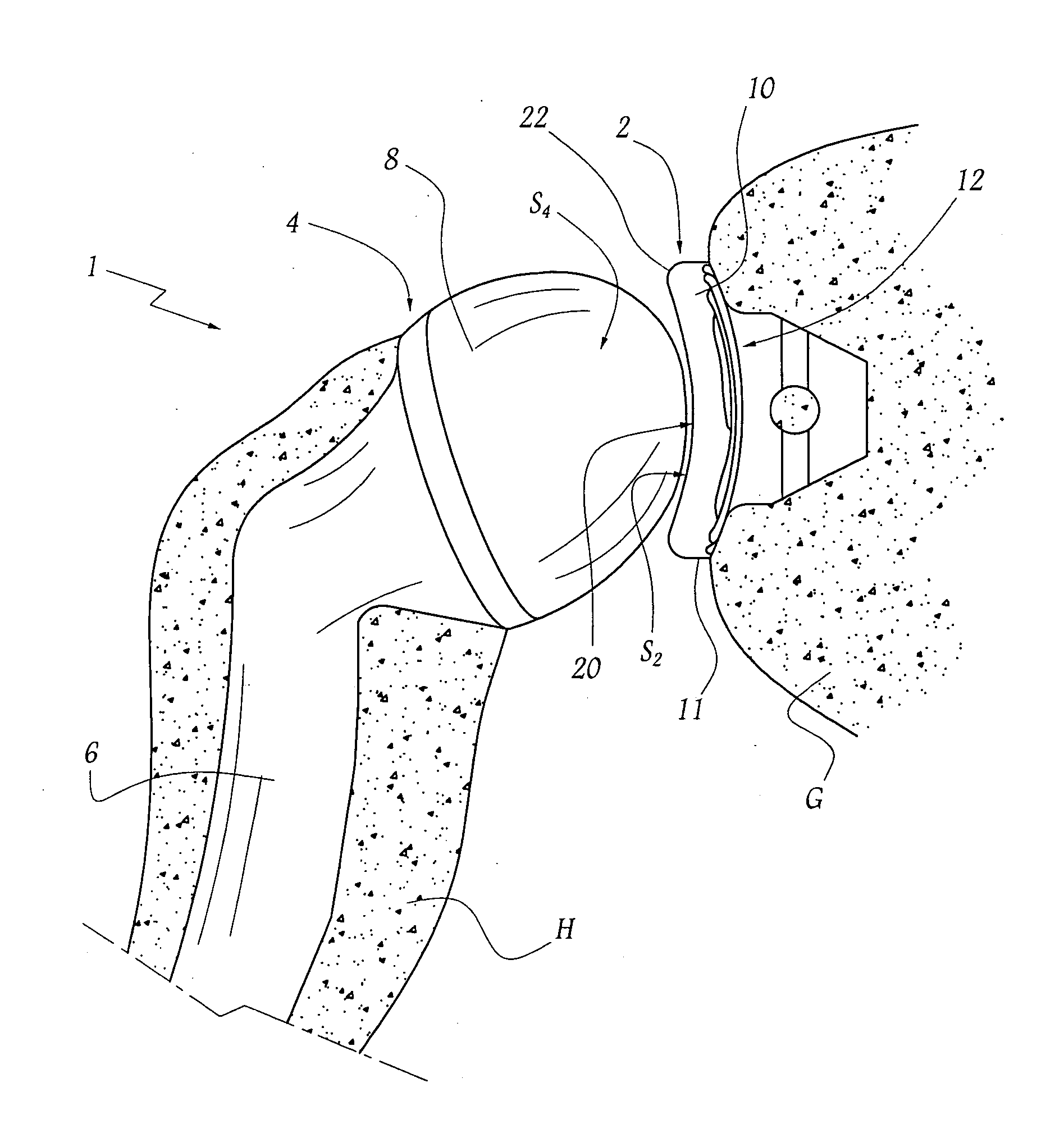
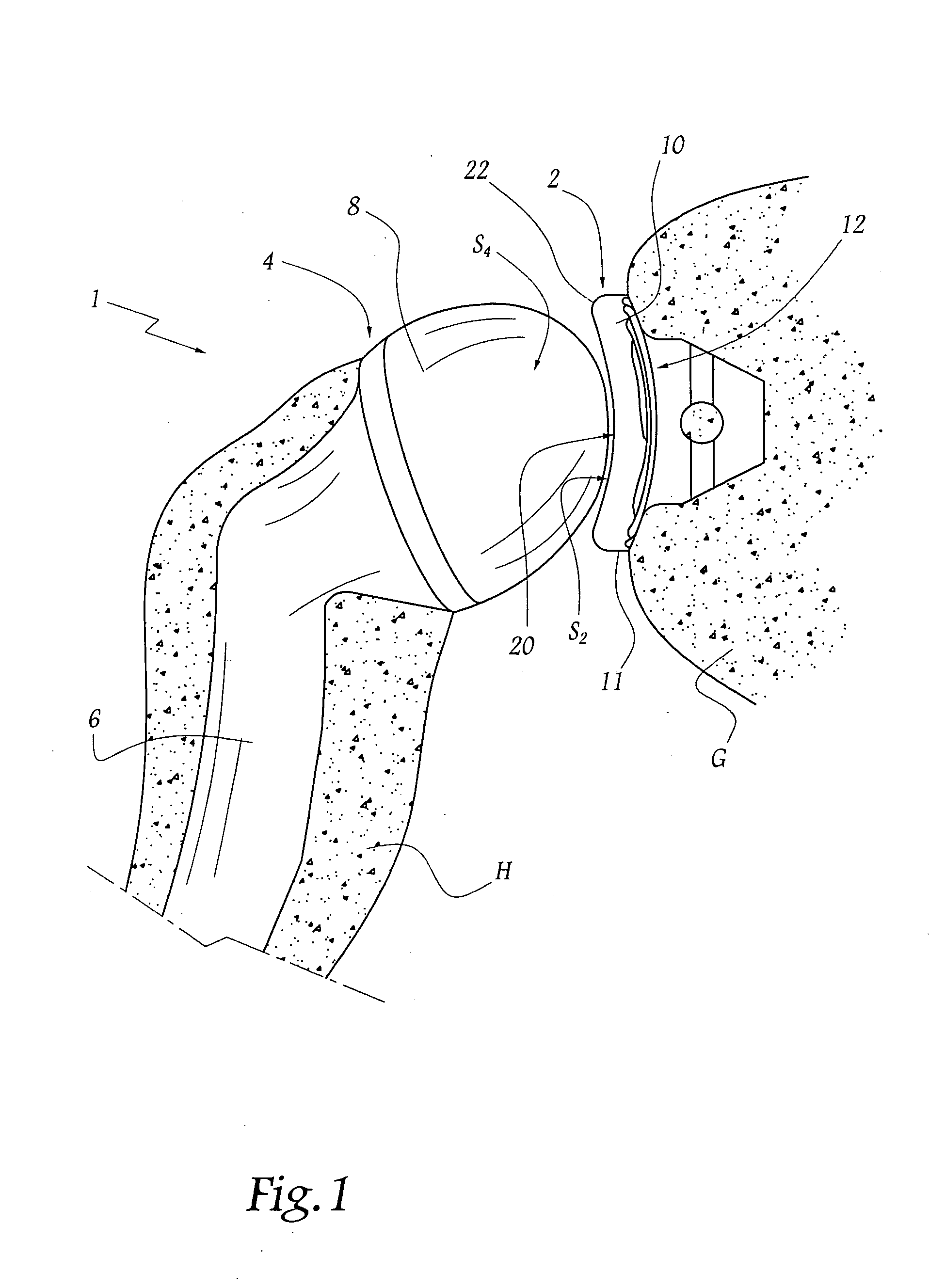
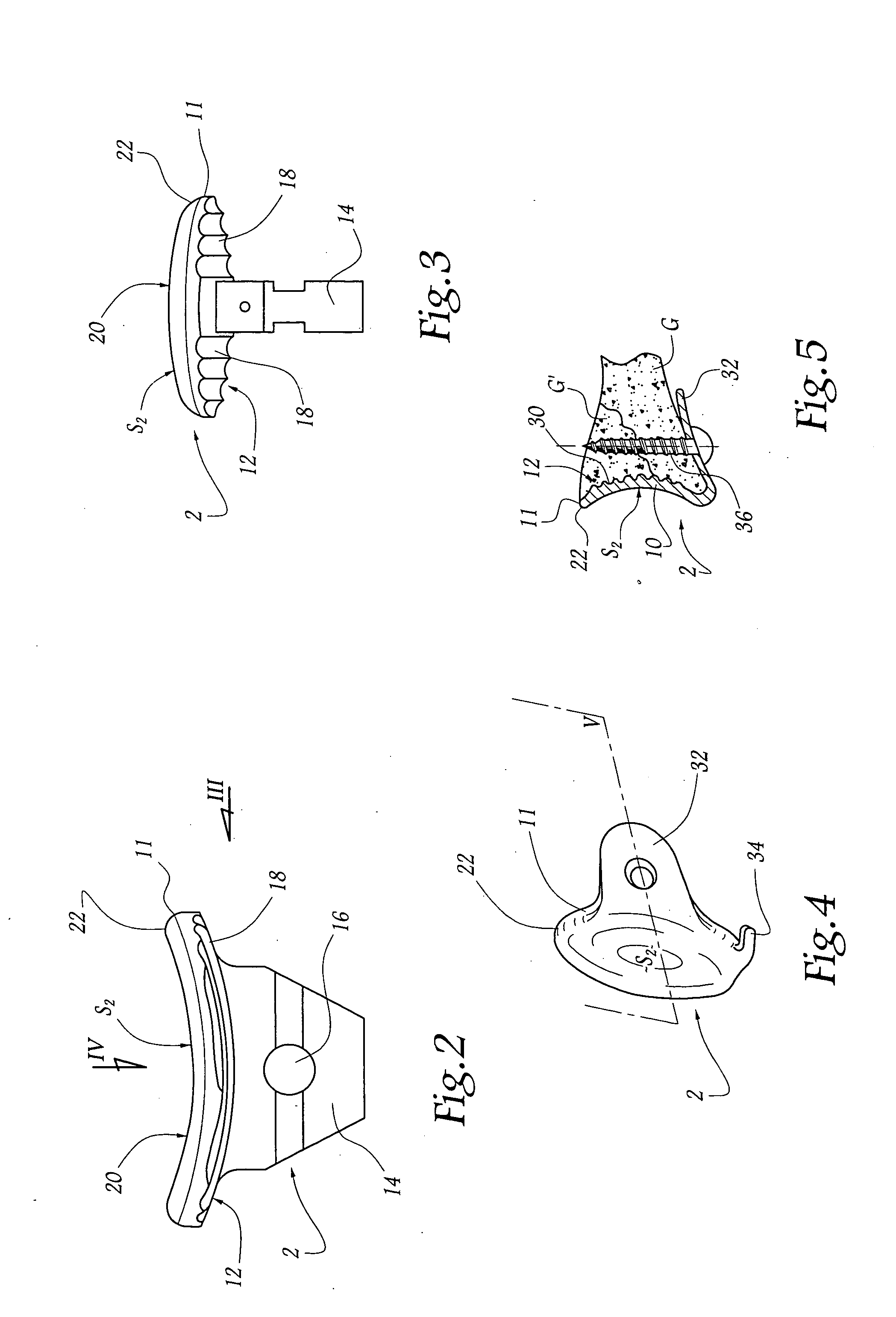
Anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertrebal column on a vertreba
InactiveUS20060155277A1Lower clamping surfaceLower requirementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringLumbar vertebral column
The invention relates to an anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertebral column on a vertebra, comprising a retaining means (10) for receiving the rod, a safety element (26) placed on the retaining means and working against the rod, a securing element (14) which can be placed on the body of the vertebra, and a clamping device (12) which is arranged between the retaining means (10) and the securing element (14), comprising a ring-shaped mount (32), a partially conical-segment shaped bearing (28) and an intermediate element (30) which is embedded in the mount (32) and which engages the bearing, whereby the mounting (32) is moveable in a removed state in relation to the bearing (28), whereas the mount (32) is maintained in a clamped state on the bearing (28) by means of the intermediate element (30). The mount (32) is rigidly connected to the retaining means (10) and the bearing (28) is rigidly connected to the securing element (14). In order to enable said type of anchoring element, despite the fact that it is displaceably retained, to transmit relatively large amounts of force from the rod to the body of the vertebra without causing slipping, the bearing (28) comprises flat guiding surfaces (38, 40) which are formed laterally on two opposite sides (34, 36), and the intermediate element (30) is provided with corresponding counter surfaces (50, 52).
Owner:METZ STAVENHAGEN PETER
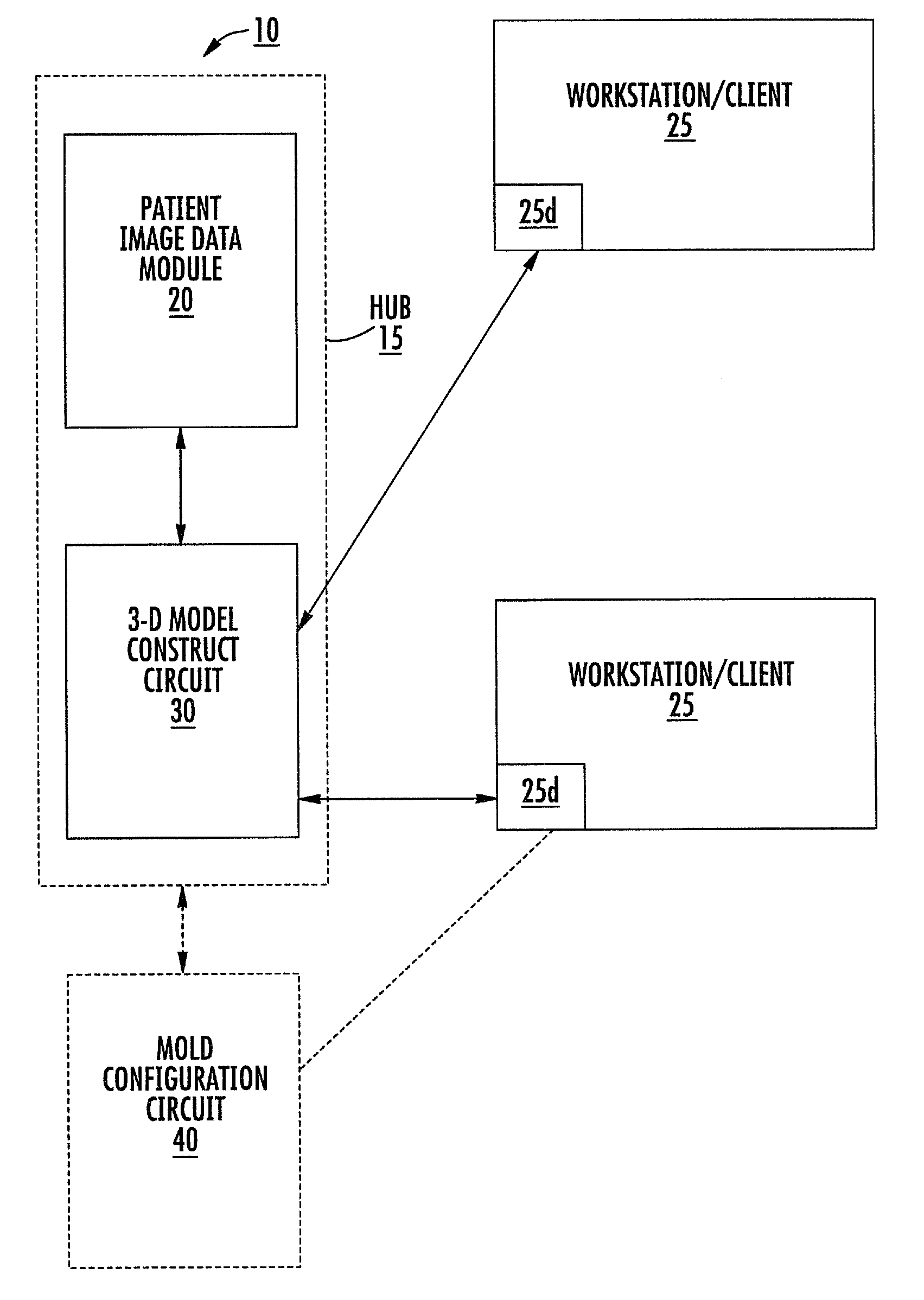
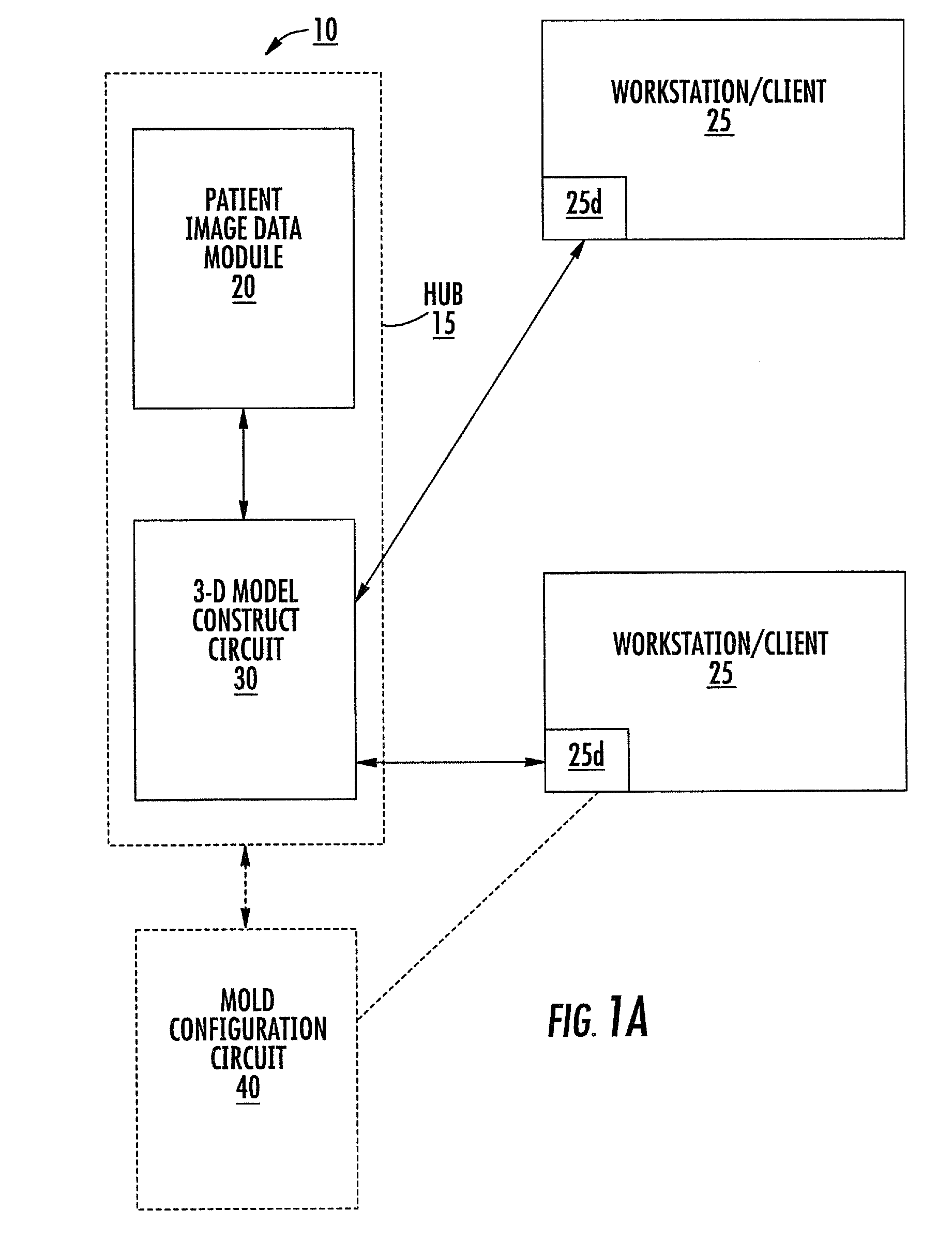
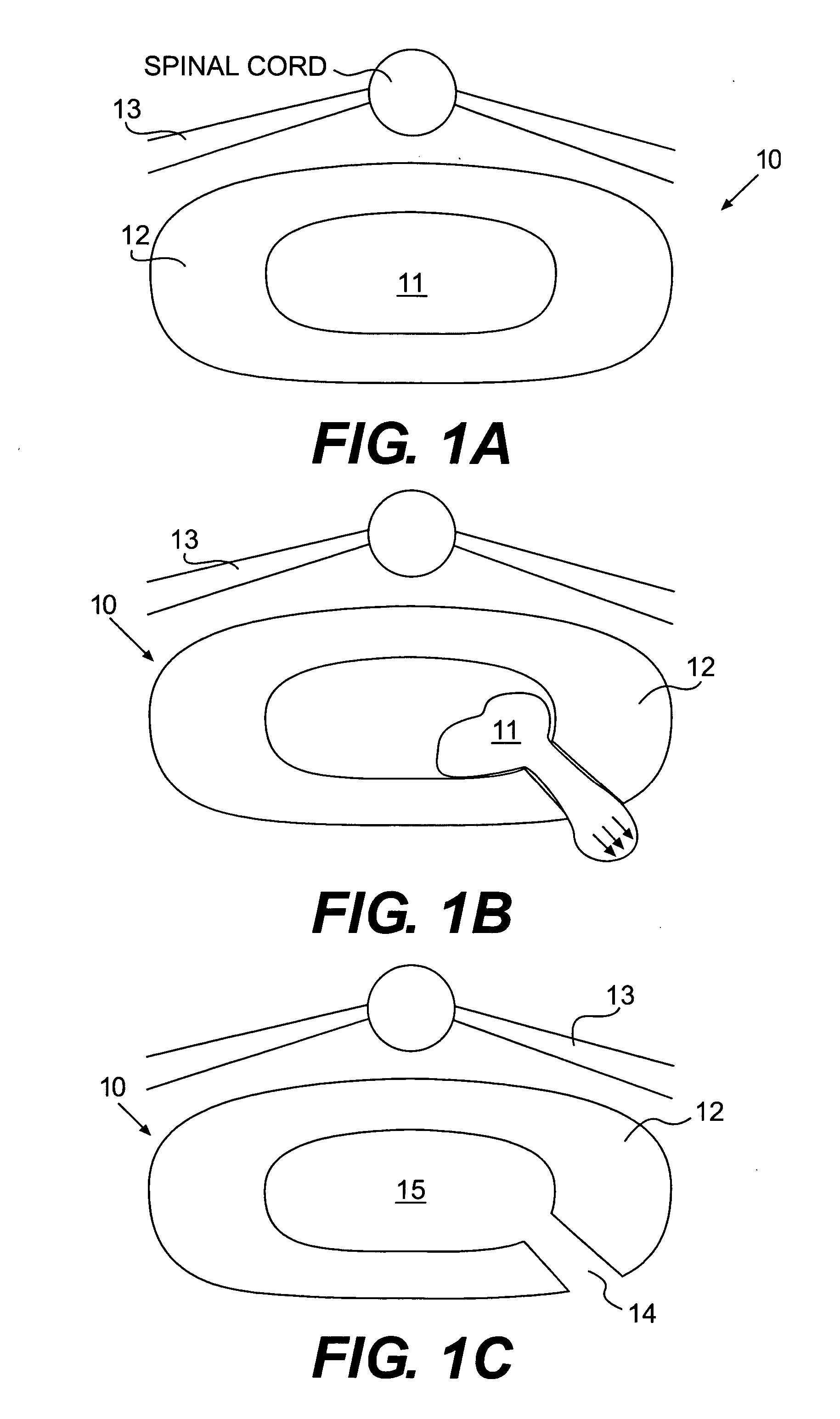
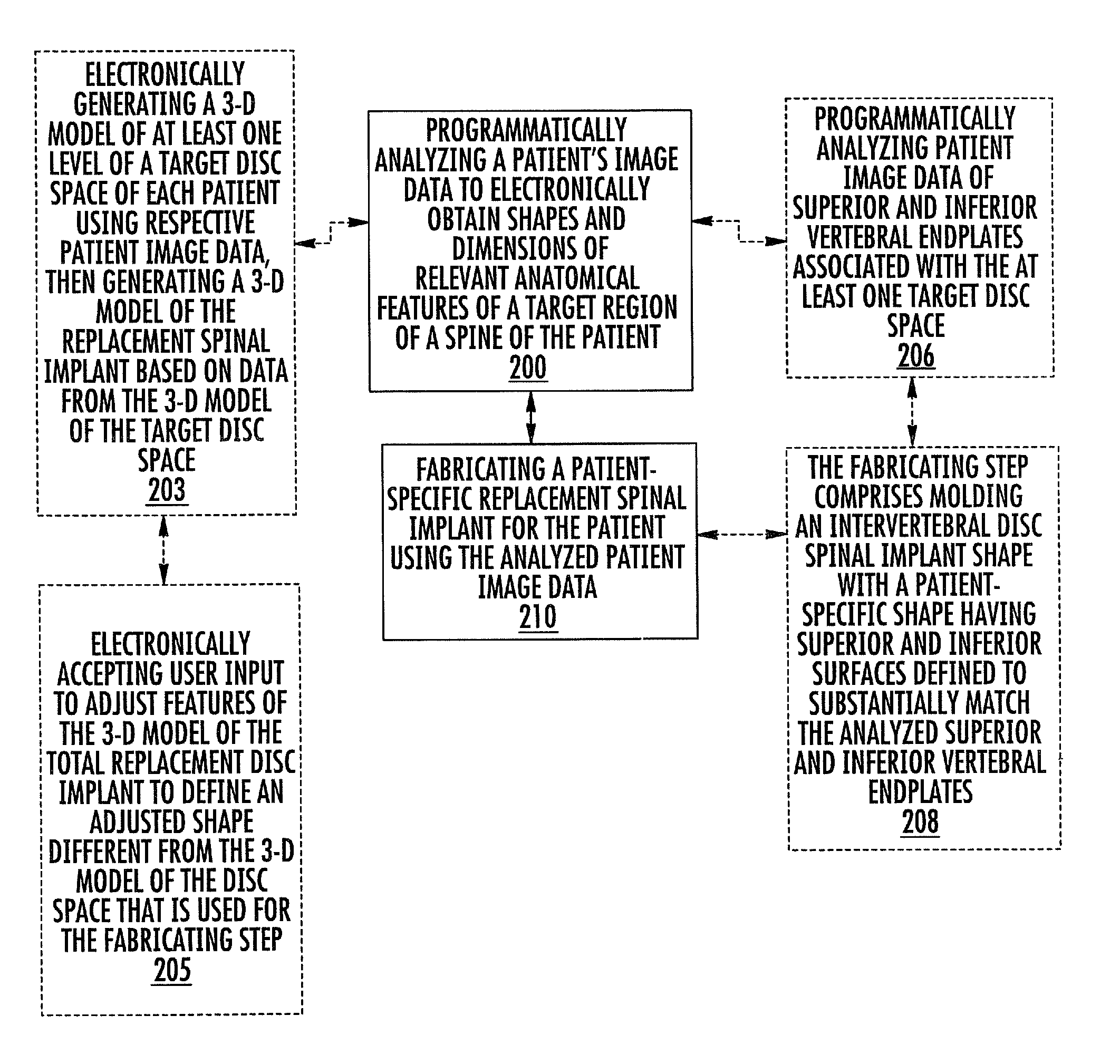
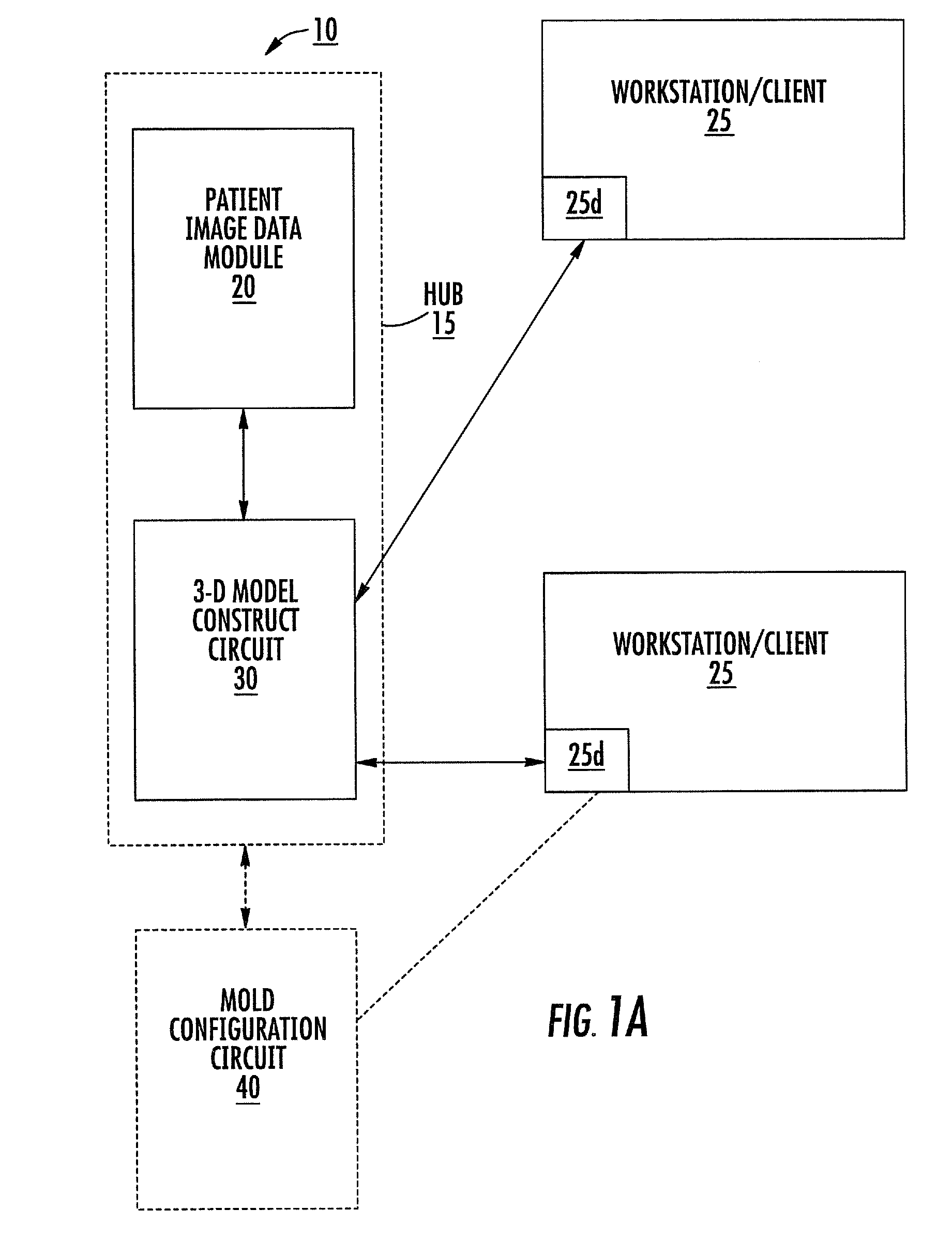
Patient-specific spinal implants and related systems and methods
InactiveUS20070276501A1Ease of implantationEasy to implantAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantPatient specific
Methods and systems for generating custom implants by programmatically analyzing a patient's image data to electronically obtain shapes and dimensions of relevant anatomical features of a target region of the patient; and fabricating a patient-specific replacement implant for the patient using the analyzed patient image data. Related patient-specific spinal implants are also described.
Owner:MIMEDX PROCESSING SERVICES LLC
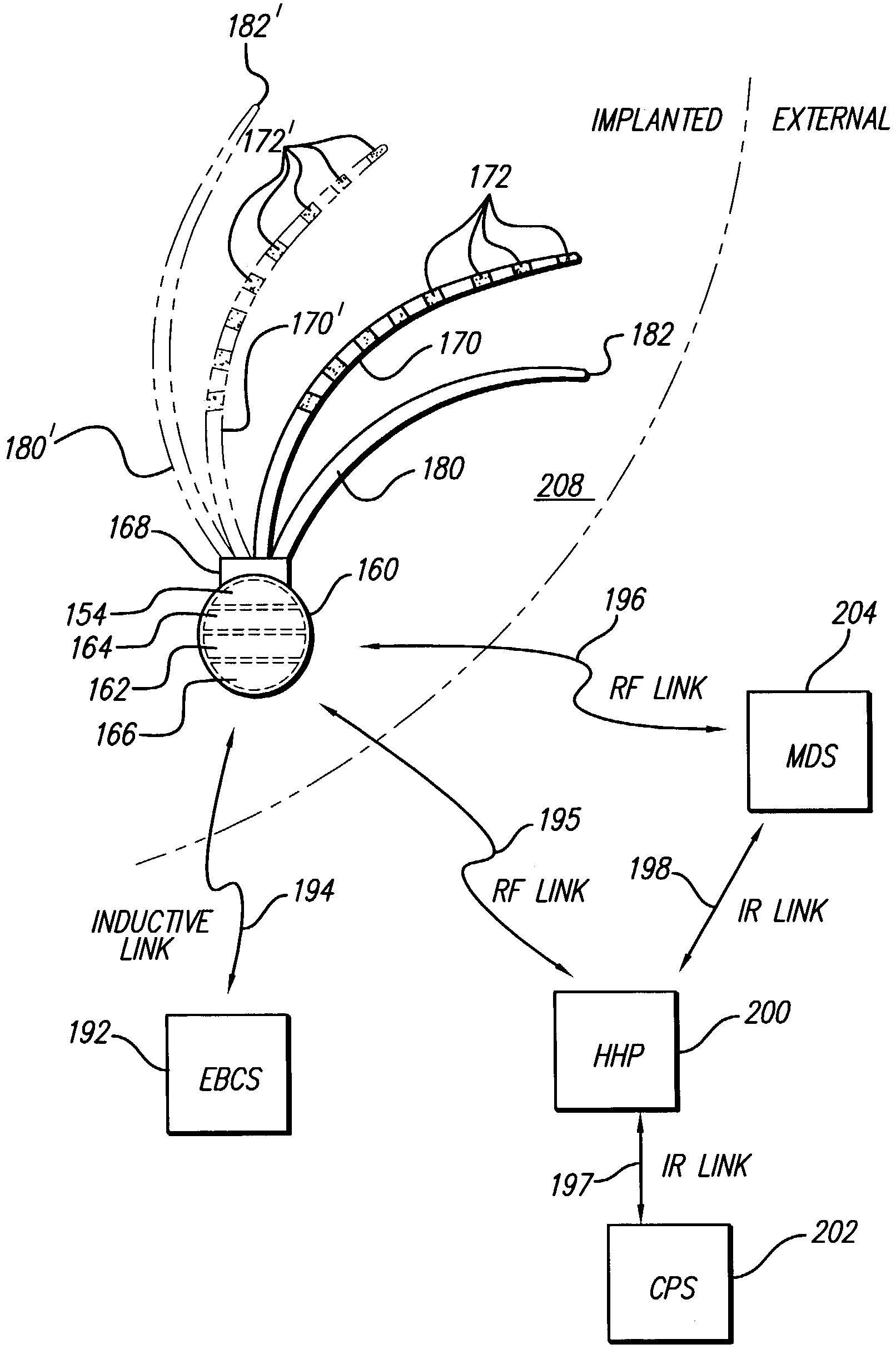
Treatment of epilepsy by brain stimulation
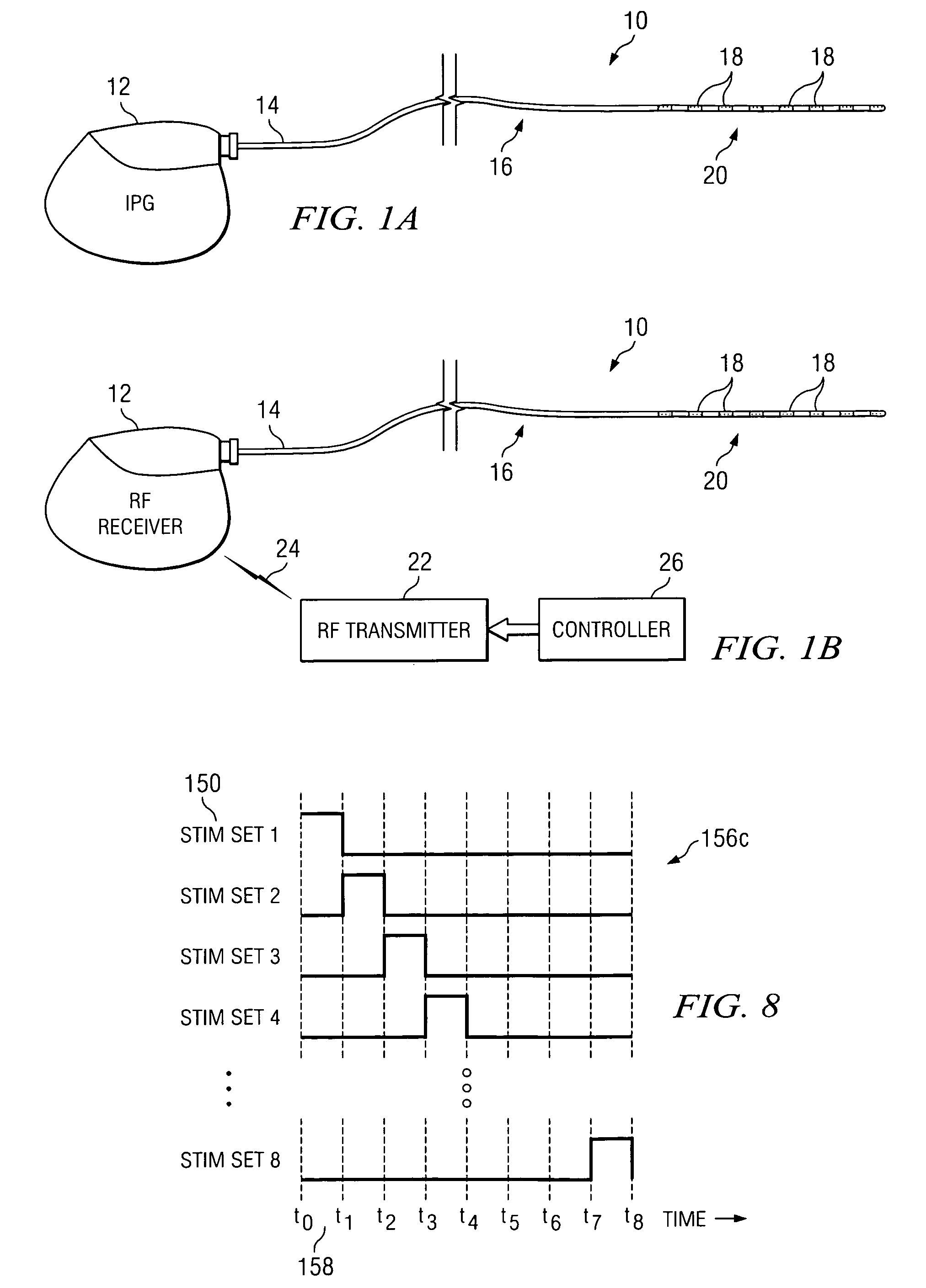
InactiveUS7003352B1Small sizeInhibition amountElectrotherapyPressure infusionMedicineElectrical stimulations
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the brain and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain is used to treat epilepsy. At least one implantable system control unit (SCU) produces electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or drug infusion pulses delivered via a catheter implanted in the brain. The stimulation is delivered to targeted brain structures to adjust the activity of those structures. The small size of the SCUs of the invention allow SCU implantation directly and entirely within the skull and / or brain. Simplicity of the preferred systems and methods and compactness of the preferred system are enabled by the modest control parameter set of these SCU, which do not require or include a sensing feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Intervertebral disc replacement prosthesis
InactiveUS6964686B2Relieve symptomsNot compromising healthJoint implantsSpinal implantsSlice thicknessIntervertebral disk
An intervertebral disc prosthesis that comprises a deformable flexure with an axial cavity, the axial cavity extending along the axis of the flexure, and a slit defined in the perimeter surface of the flexure to provide flexibility to the disc member, the slit having a slit thickness. The slit may be in the form of a coil to impart a spring-like appearance and function. The intervertebral disc prosthesis further comprises a lower disc support housed in the axial cavity and an upper disc support housed in the axial cavity; with the lower and upper disc supports communicating with one another to provide support to the disc. The lower or upper disc support may alternatively be incorporated into the flexure.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
System and method for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerves to treat low back pain
ActiveUS7324852B2Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProximatePeripheral neuron
According to one embodiment, a system for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers to treat low back pain is provided. The system includes stimulation electrodes adapted to be implanted in tissue proximate a network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating a painful region of the low back area and to deliver electrical stimulation pulses to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area. The system also includes a stimulation source adapted for implantation into the person's body and operable to generate electrical stimulation pulses for transmission to the electrodes for delivery to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area to relieve pain in the painful region of the low back area.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV +1
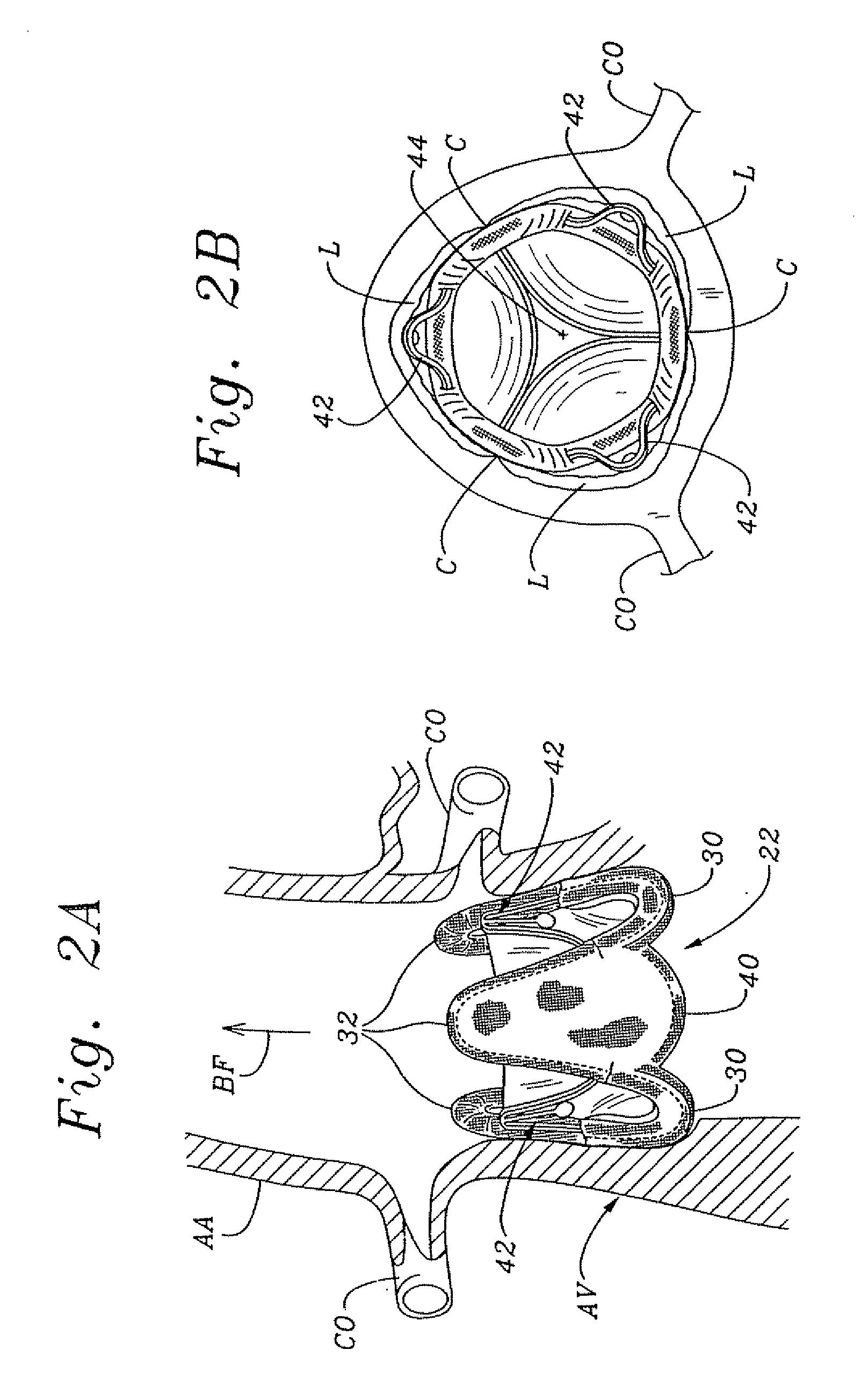
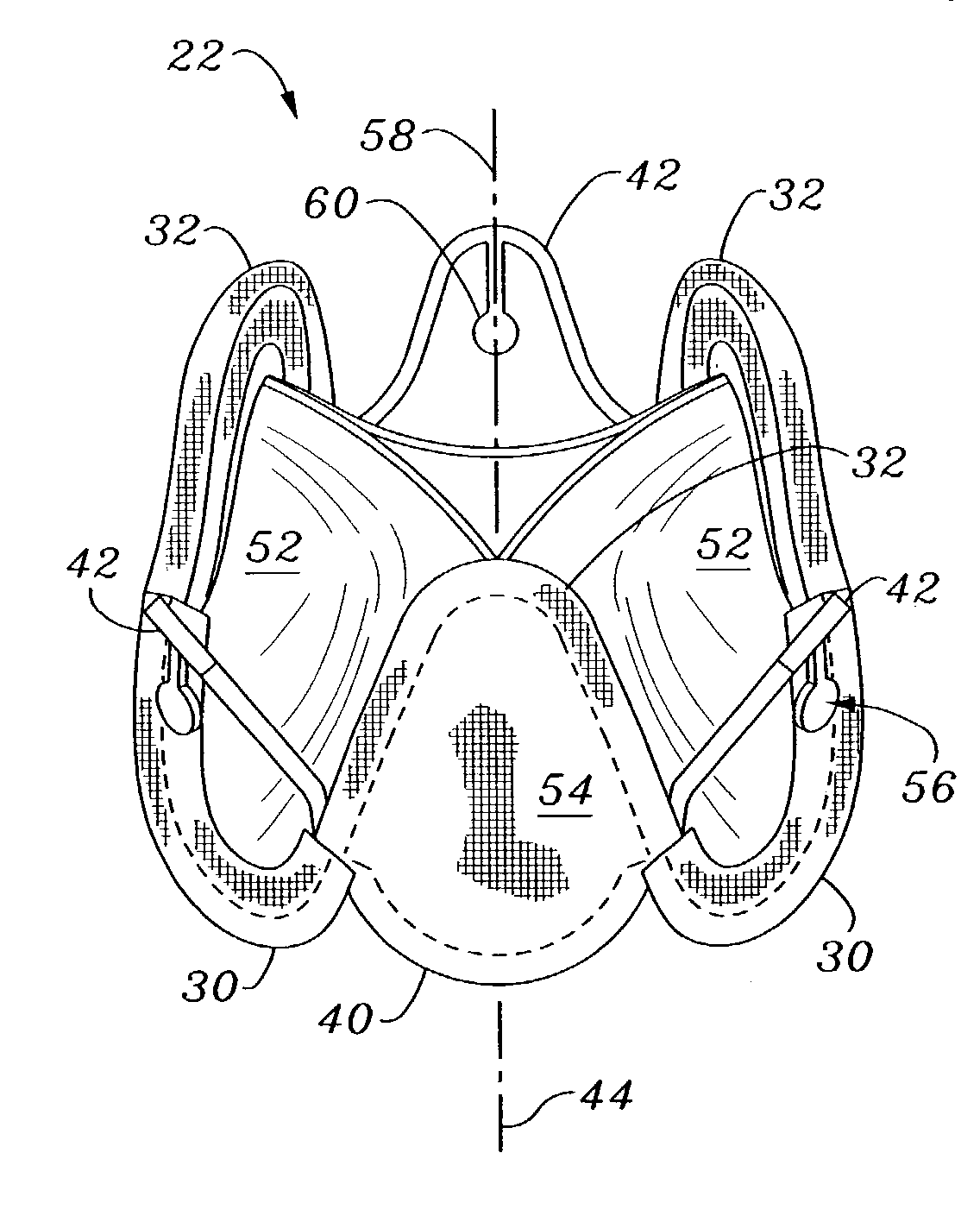
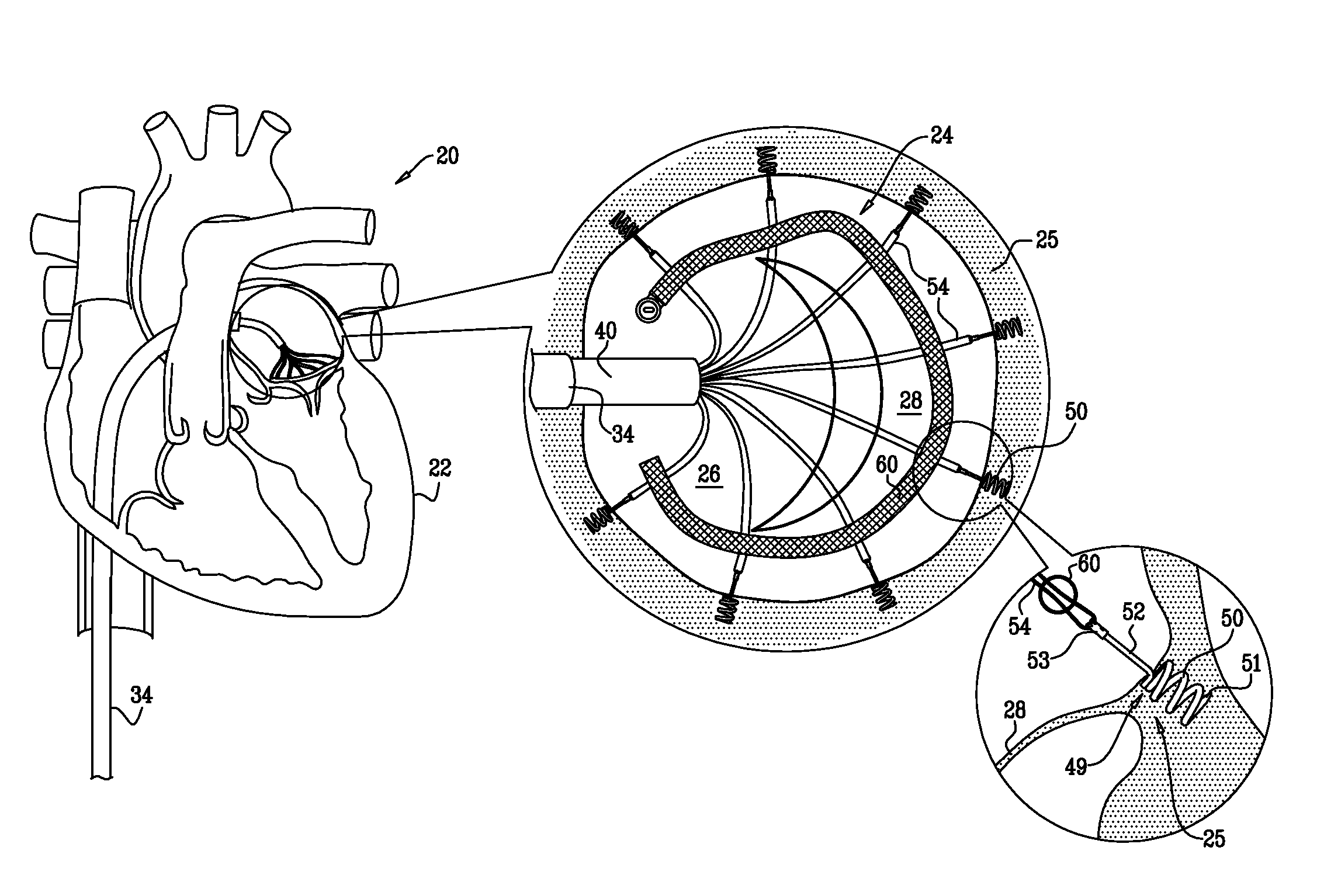
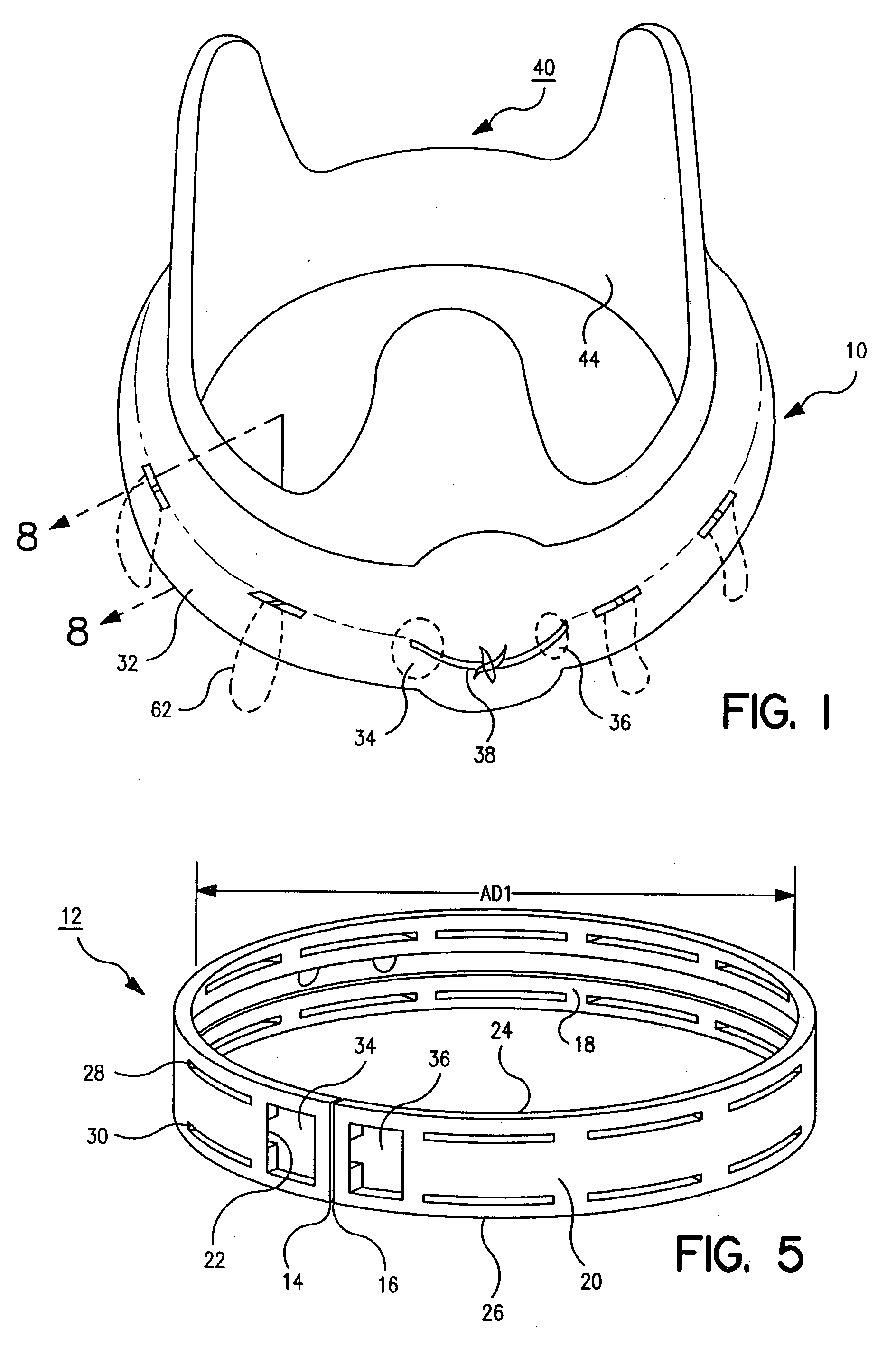
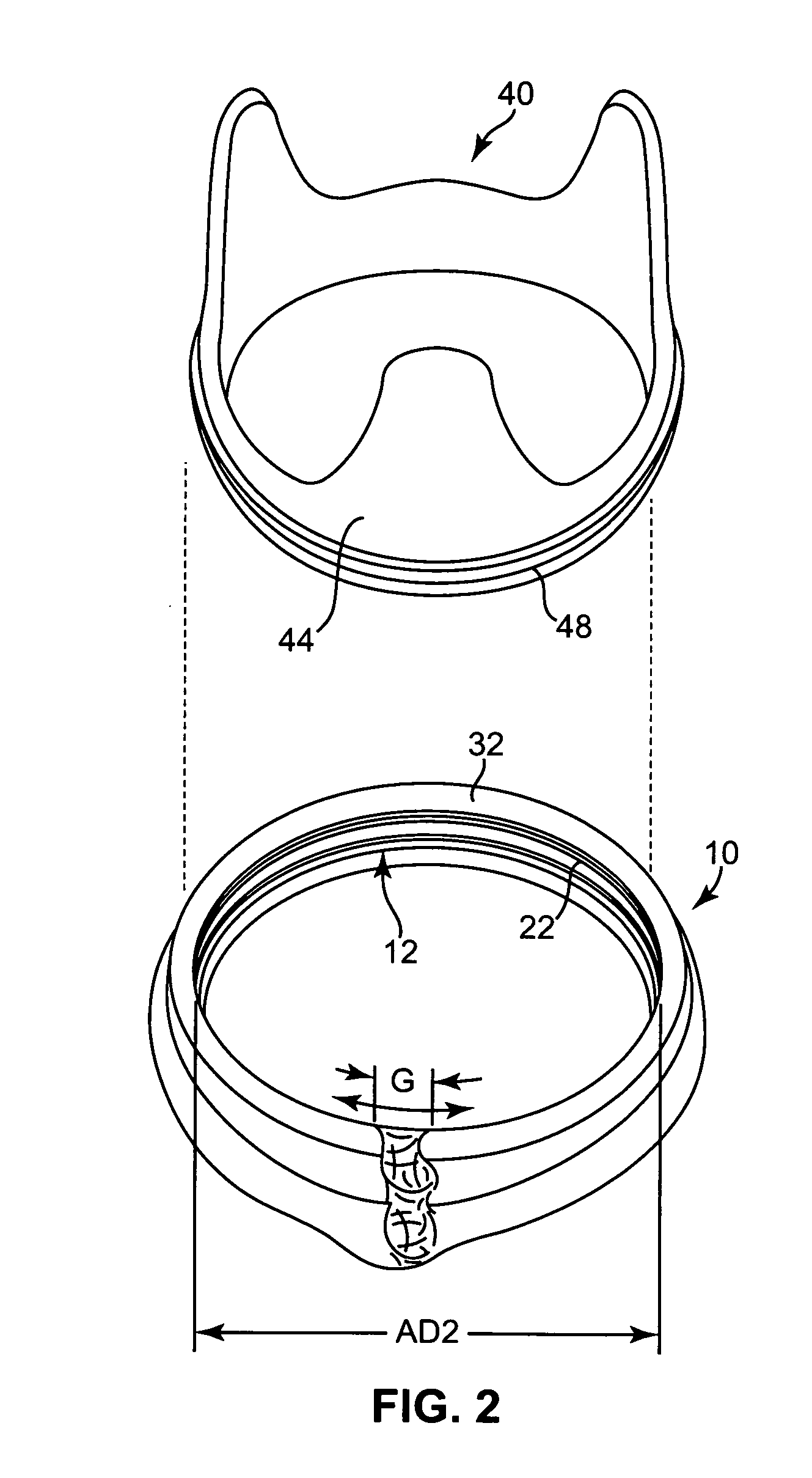
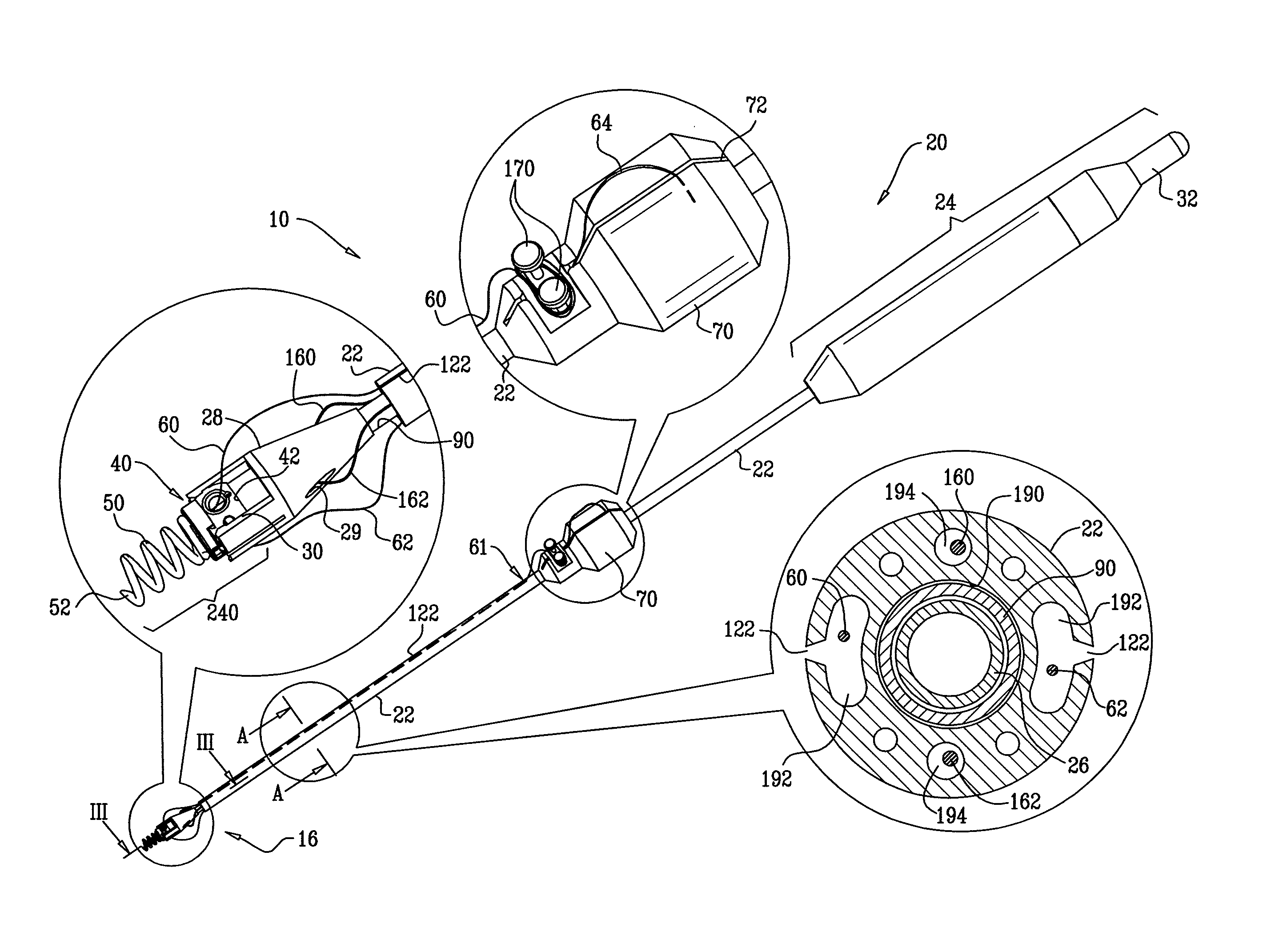
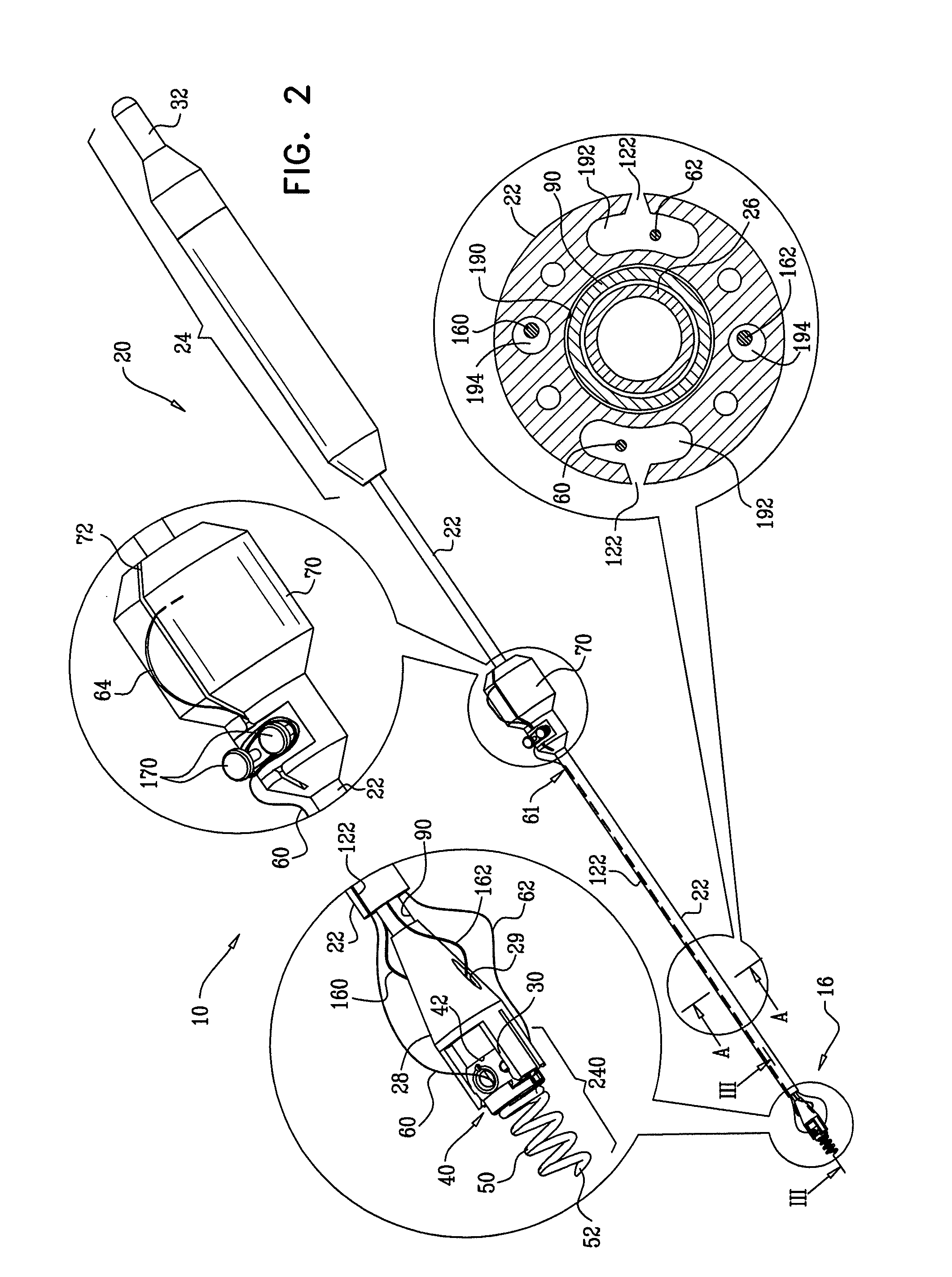
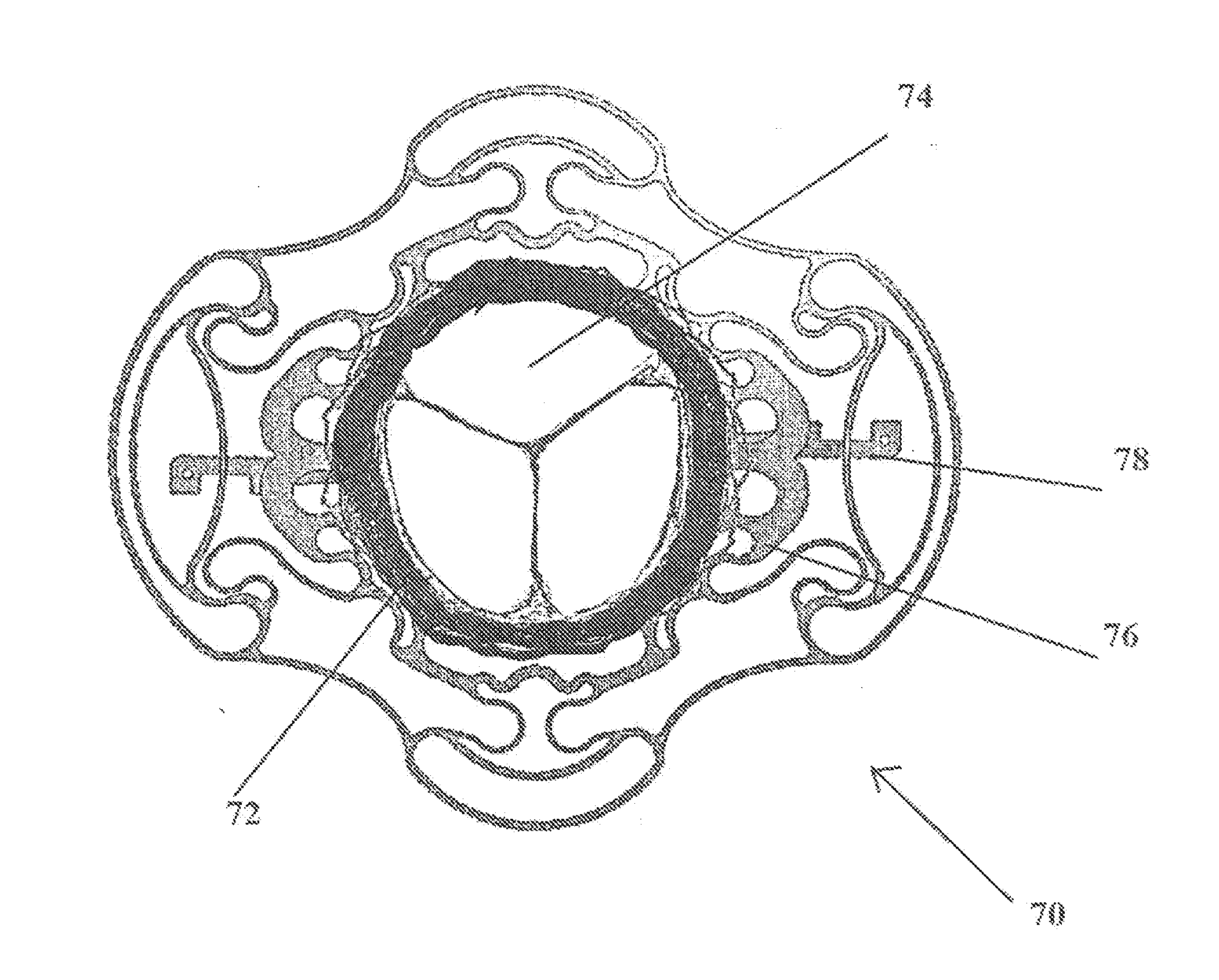
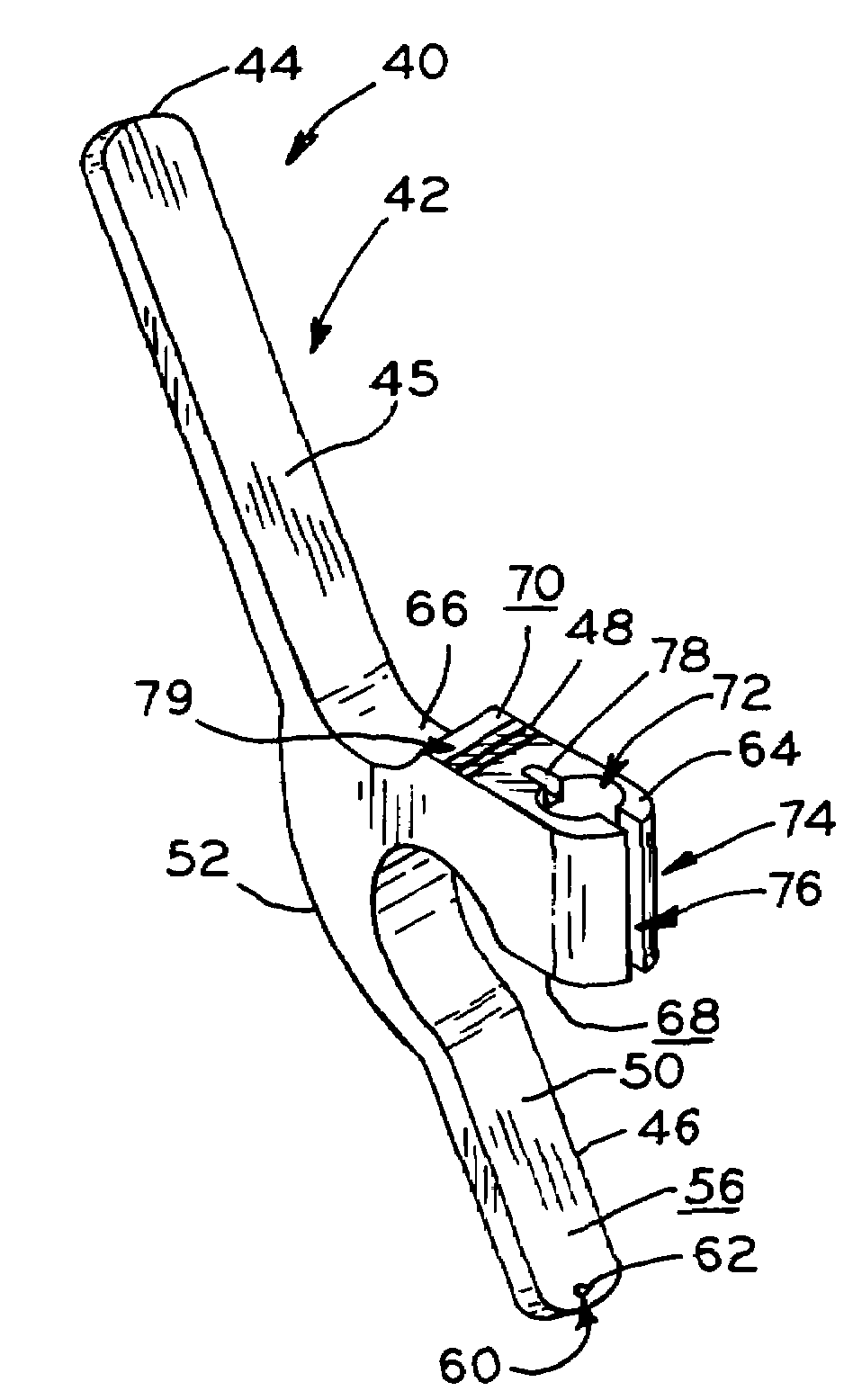
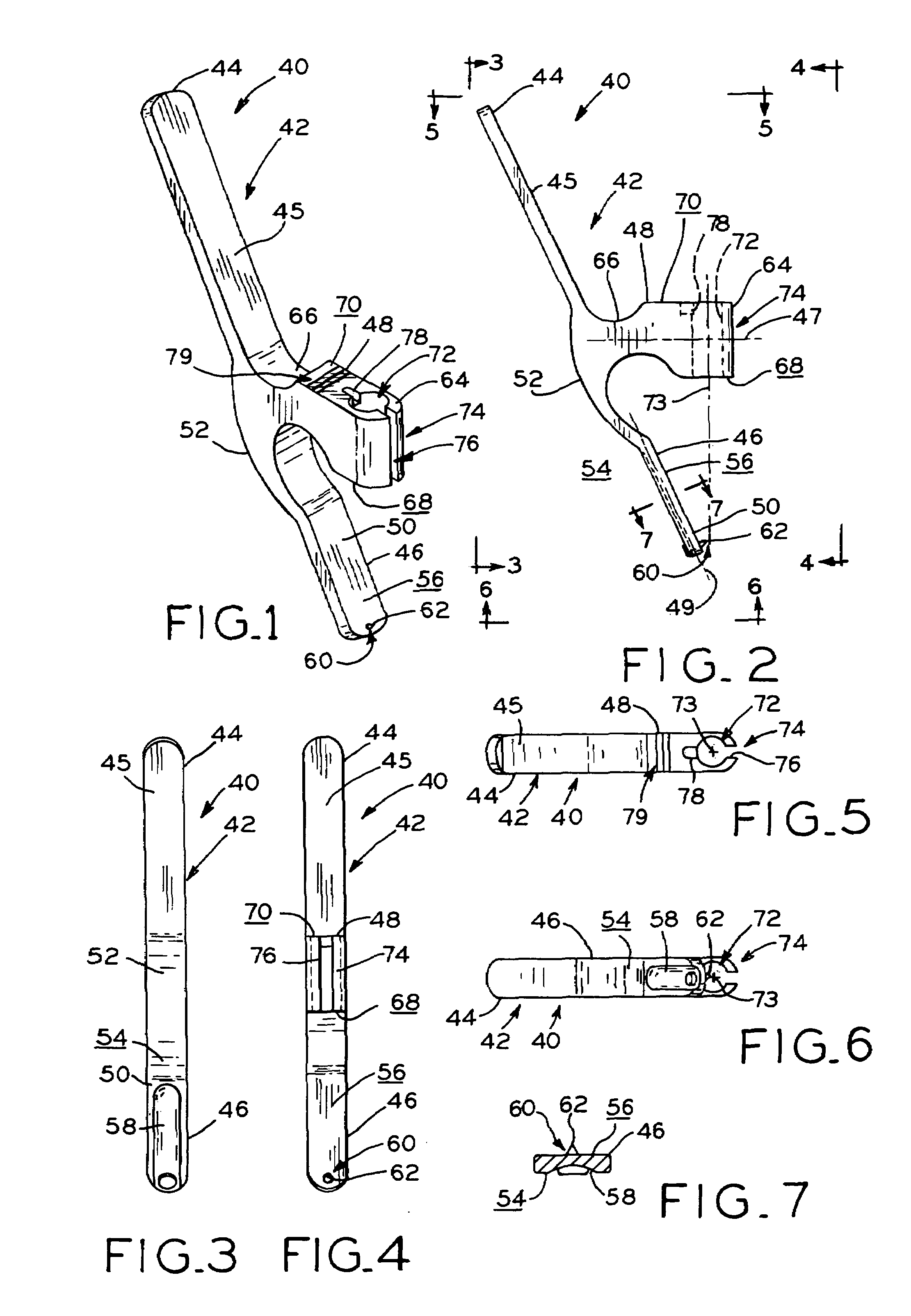
Tissue anchor for annuloplasty device
ActiveUS20110106247A1Facilitate implantationFacilitate couplingSuture equipmentsBone implantBiomedical engineeringFar lateral
Apparatus is provided for use with an implant, the apparatus including a tissue anchor, which comprises a distal tissue coupling element, which is configured to penetrate cardiac tissue, and a proximal implant-penetrating element configured to penetrate the implant. The proximal implant-penetrating element is shaped so as to define a passage therethrough, which passage has at least two openings that are within 1 mm of a proximal end of the implant-penetrating element. The apparatus also comprises a cord configured to be removably passed through the passage. Other applications of the present invention are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
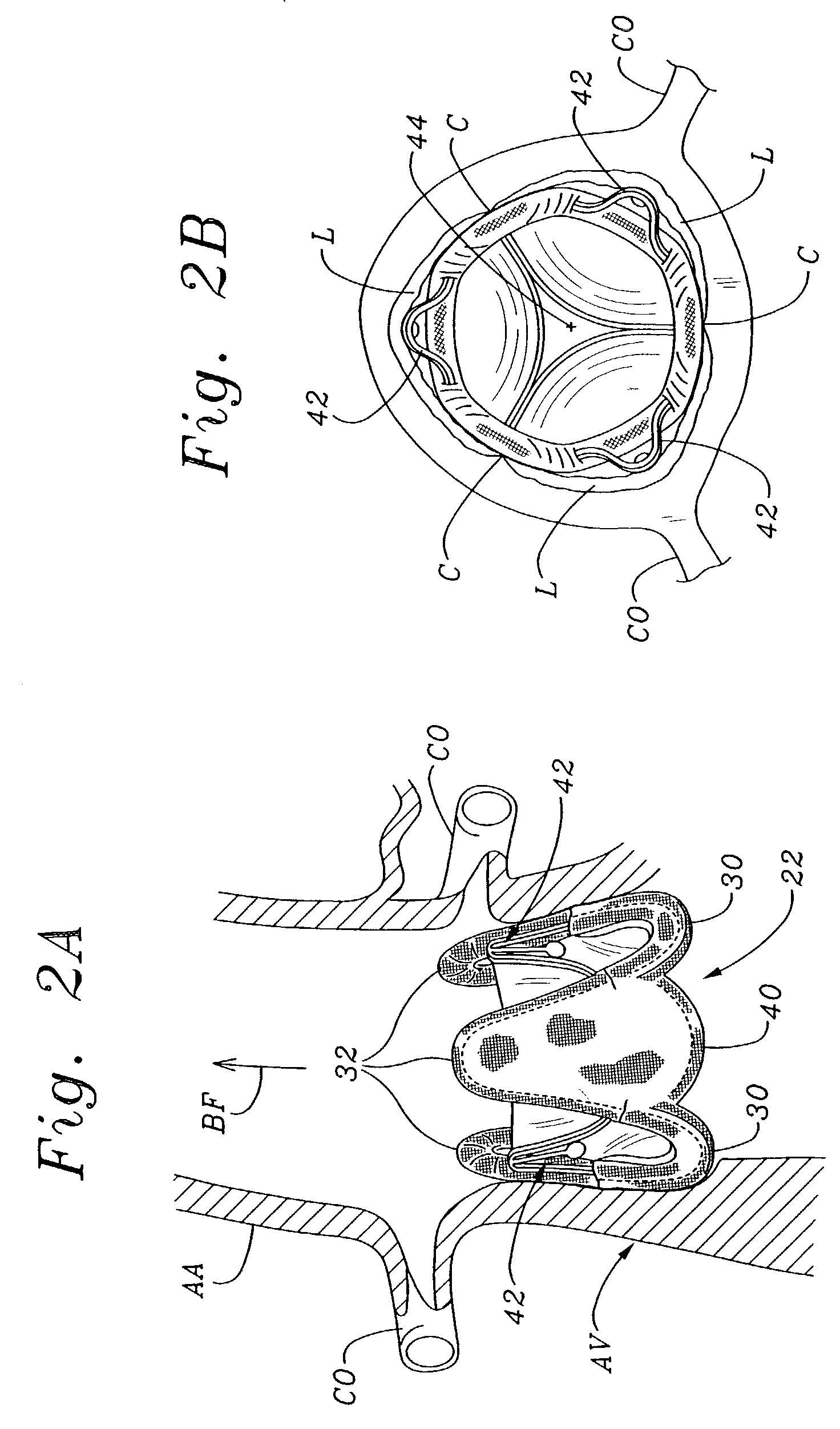
Suturing rings for implantable heart valve prostheses
InactiveUS7172625B2Easy to implantNot diminish the valve annulusDiagnosticsHeart valvesProsthesisCardiac valve prosthesis
Suturing rings and methods of use thereof facilitating initial implantation of new and replacement of dysfunctional tissue or mechanical heart valve mechanisms supported by the suturing ring are disclosed. The suturing ring annulus is adjustable to receive and engage the valve frame of the heart valve mechanism within the annulus. An interlocking mechanism applies restraint to fix the adjusted suturing ring annulus engaged against the valve frame to support the heart valve mechanism during chronic implantation. Sutures affixing the suturing ring to the valvar rim can be routed and entrapped between the suturing ring annulus and the valve frame when the suturing ring is restraint is applied. The restraint is released to replace a dysfunctional heart valve mechanism and reapplied when a new heart valve mechanism is fitted into the annulus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
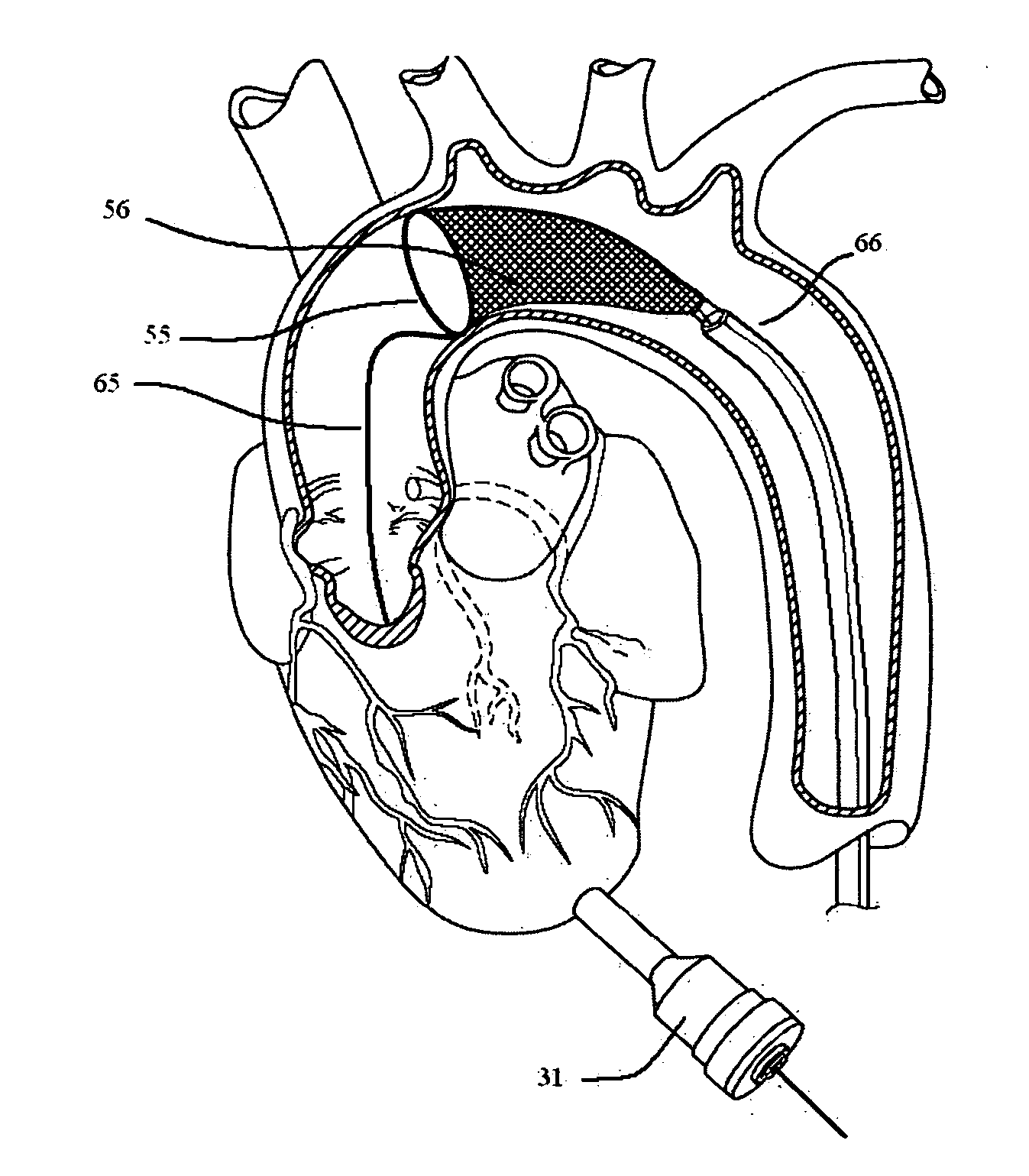
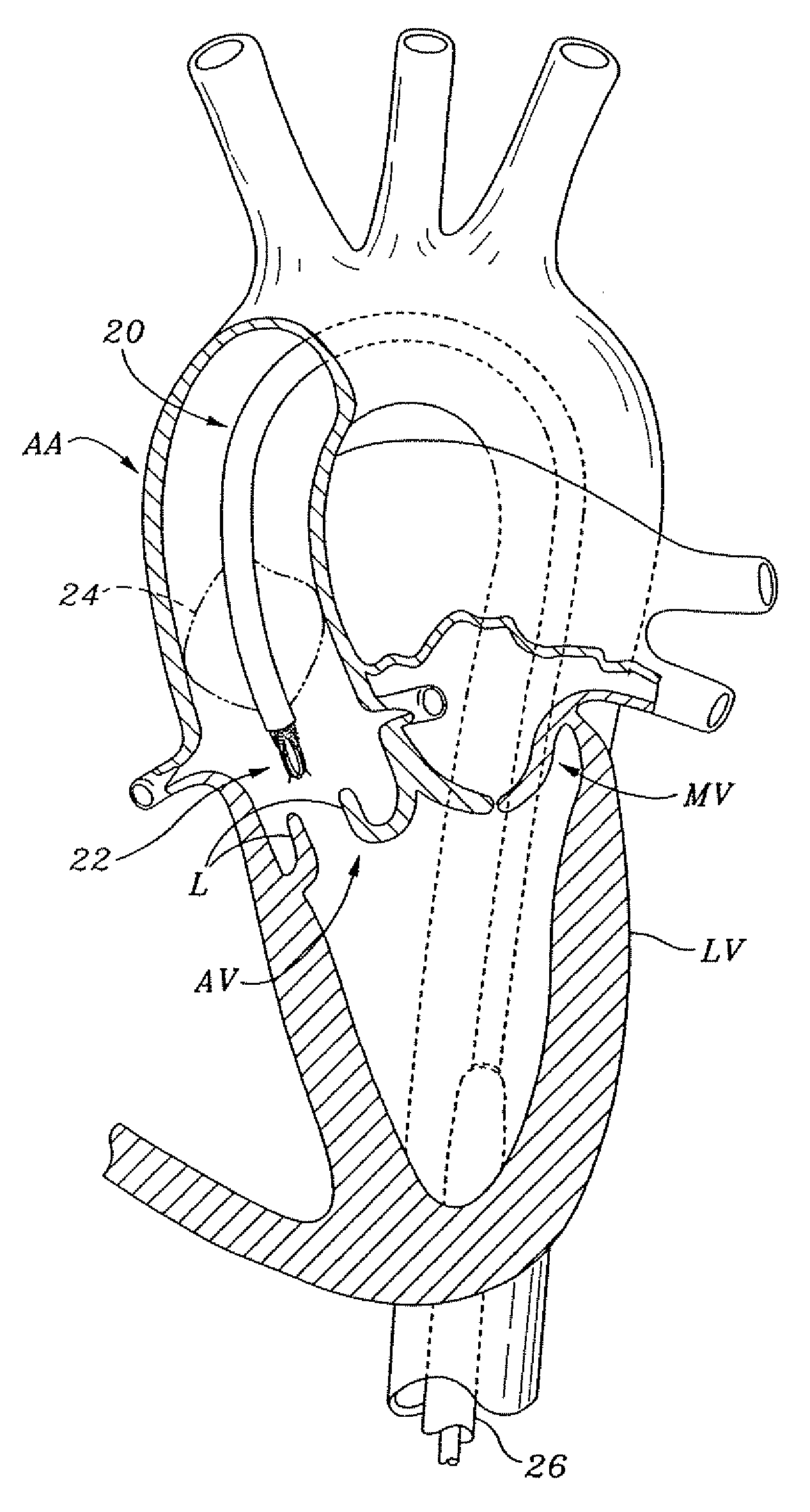
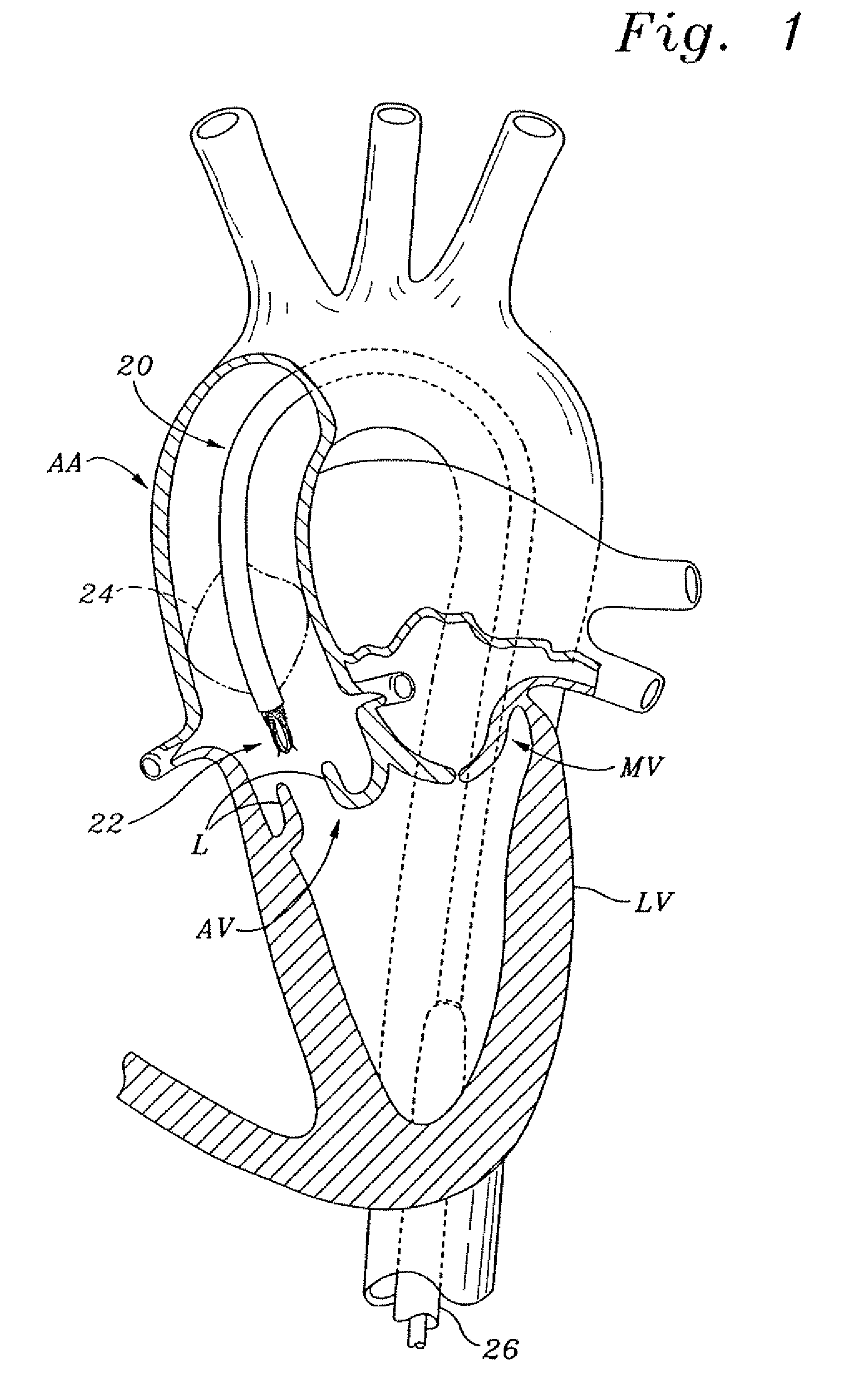
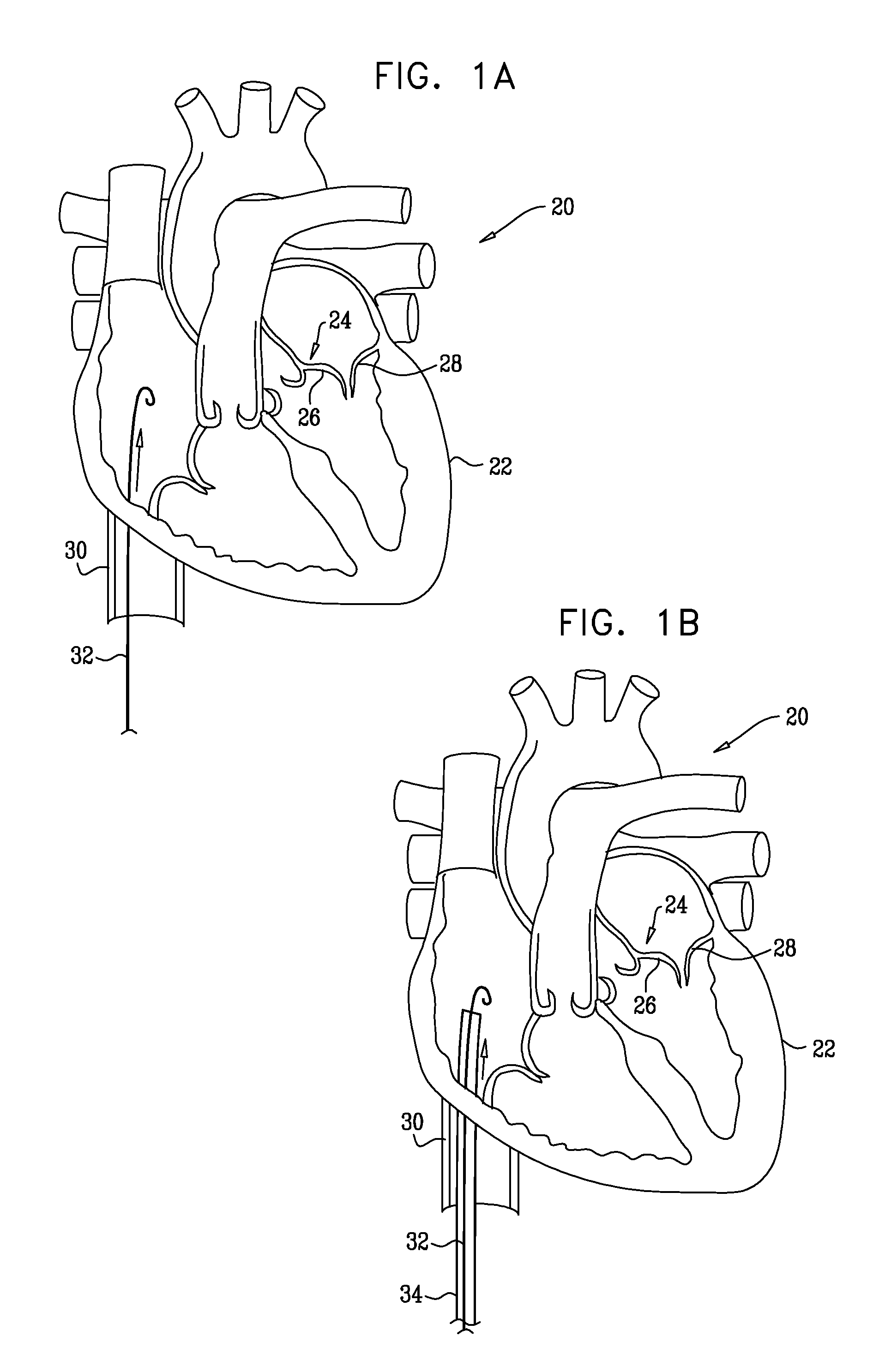
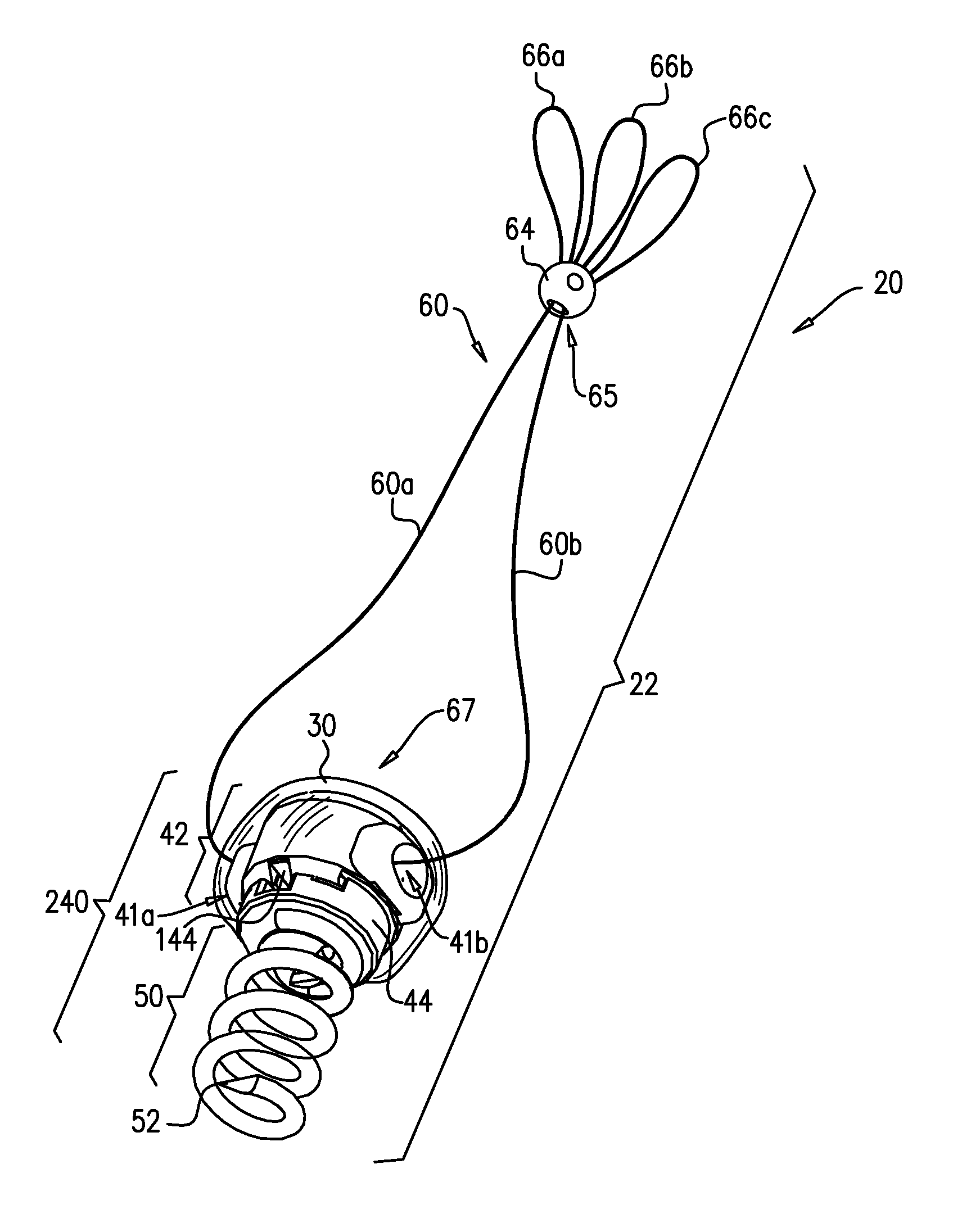
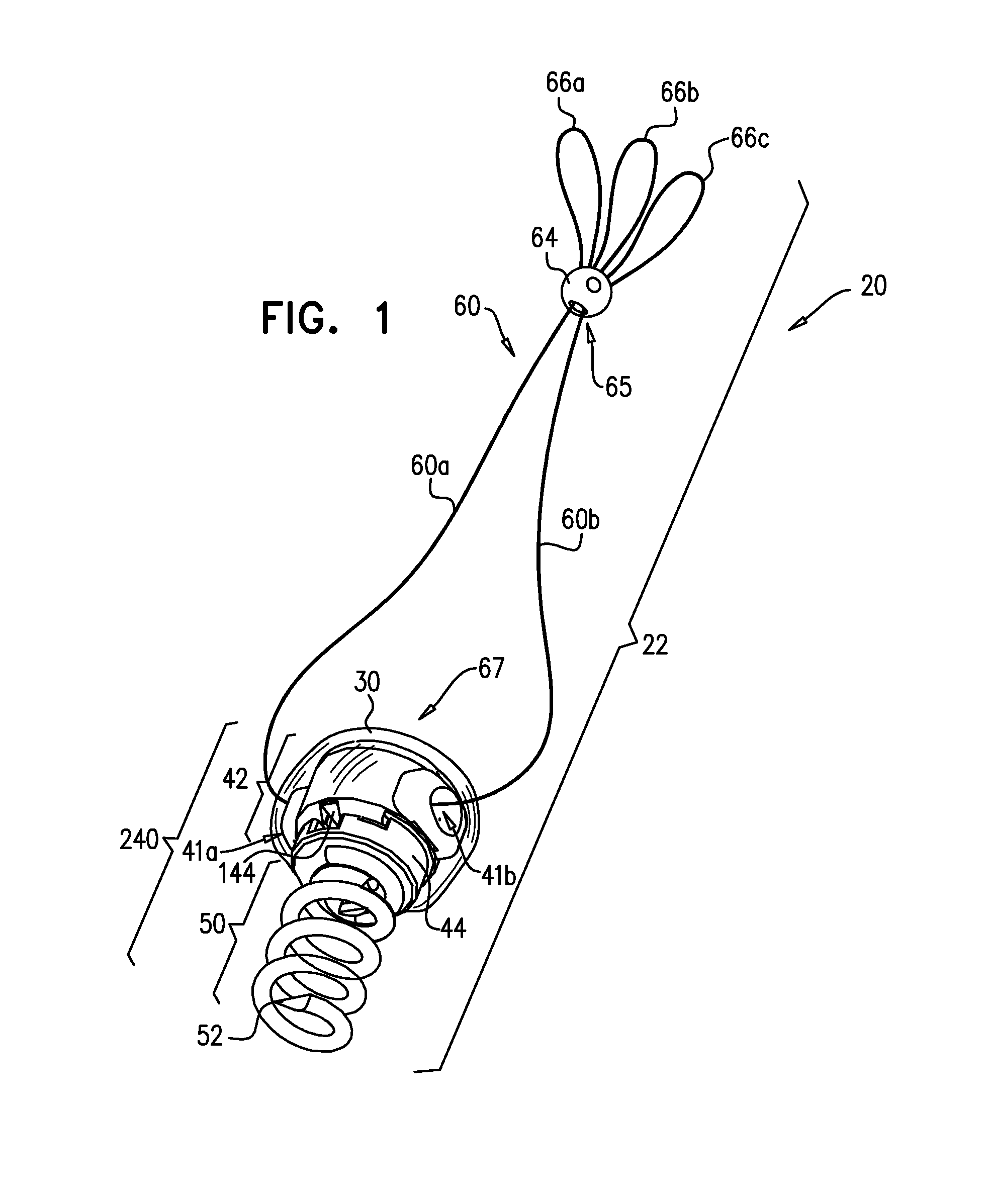
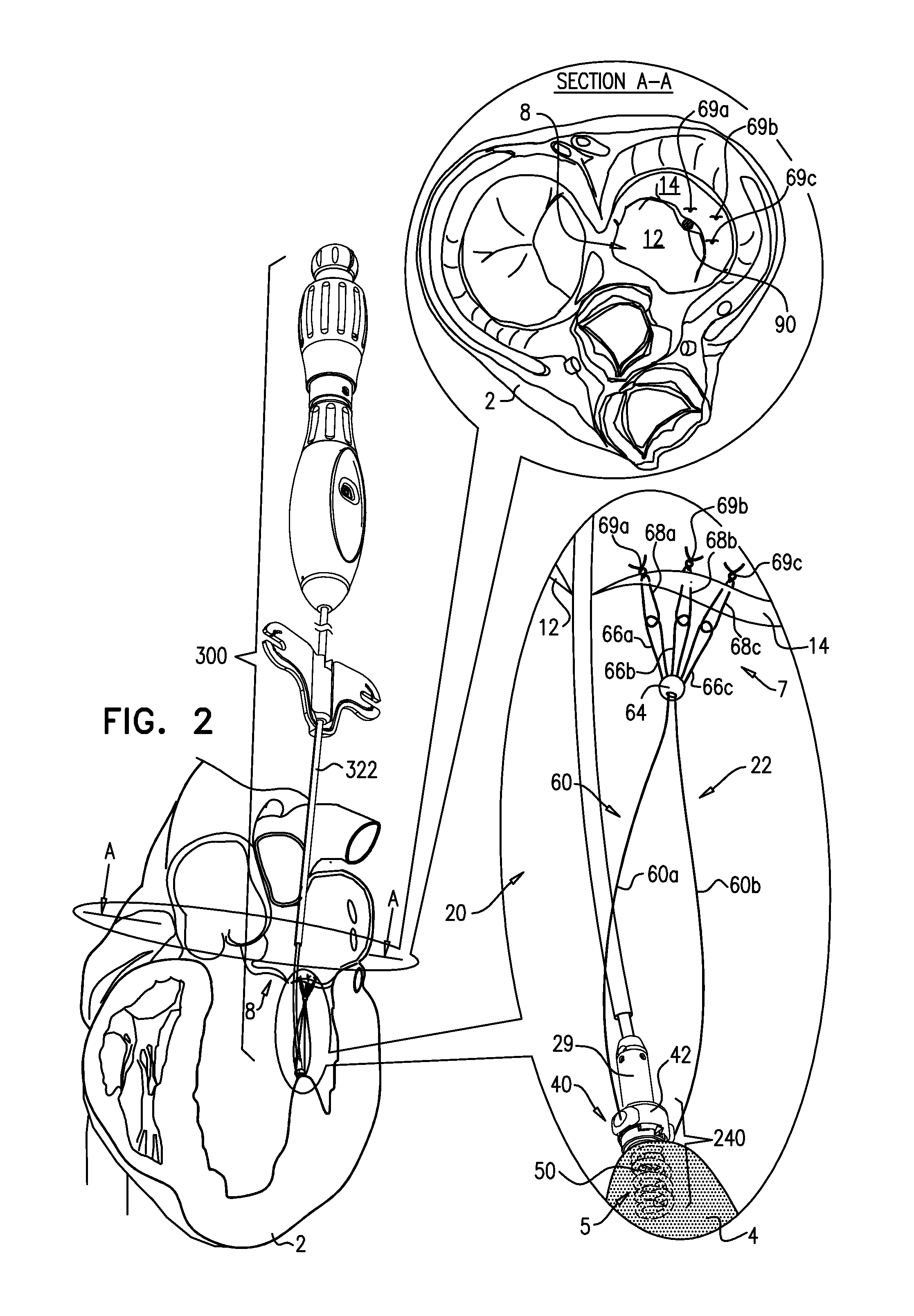
Implantation of repair chords in the heart
A method is provided, including positioning, at an intraventricular site of a ventricle of a patient, a spool coupled to a first end portion of a longitudinal member and coupling a second end portion of the longitudinal member to a portion of tissue facing a lumen of the ventricle. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
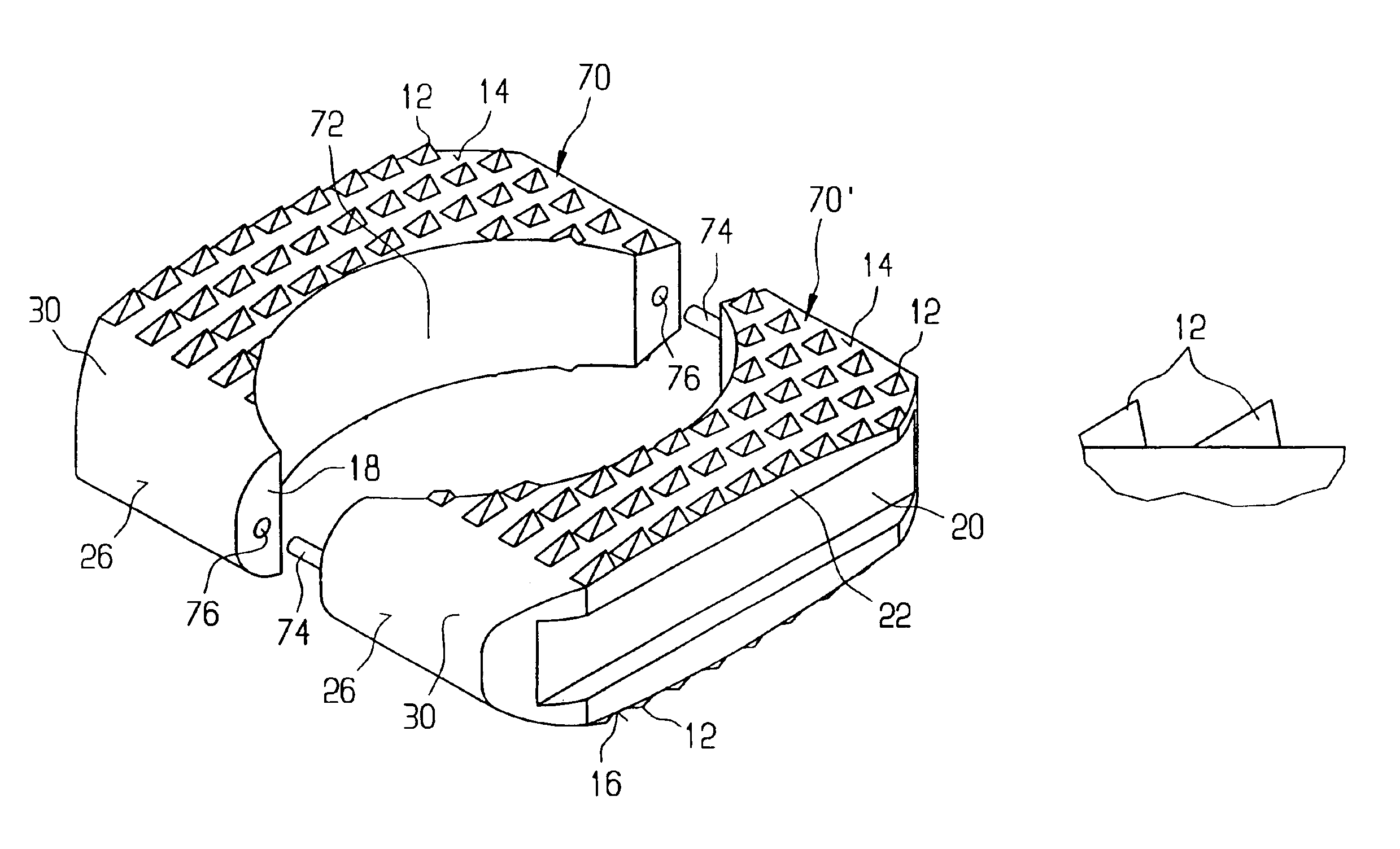
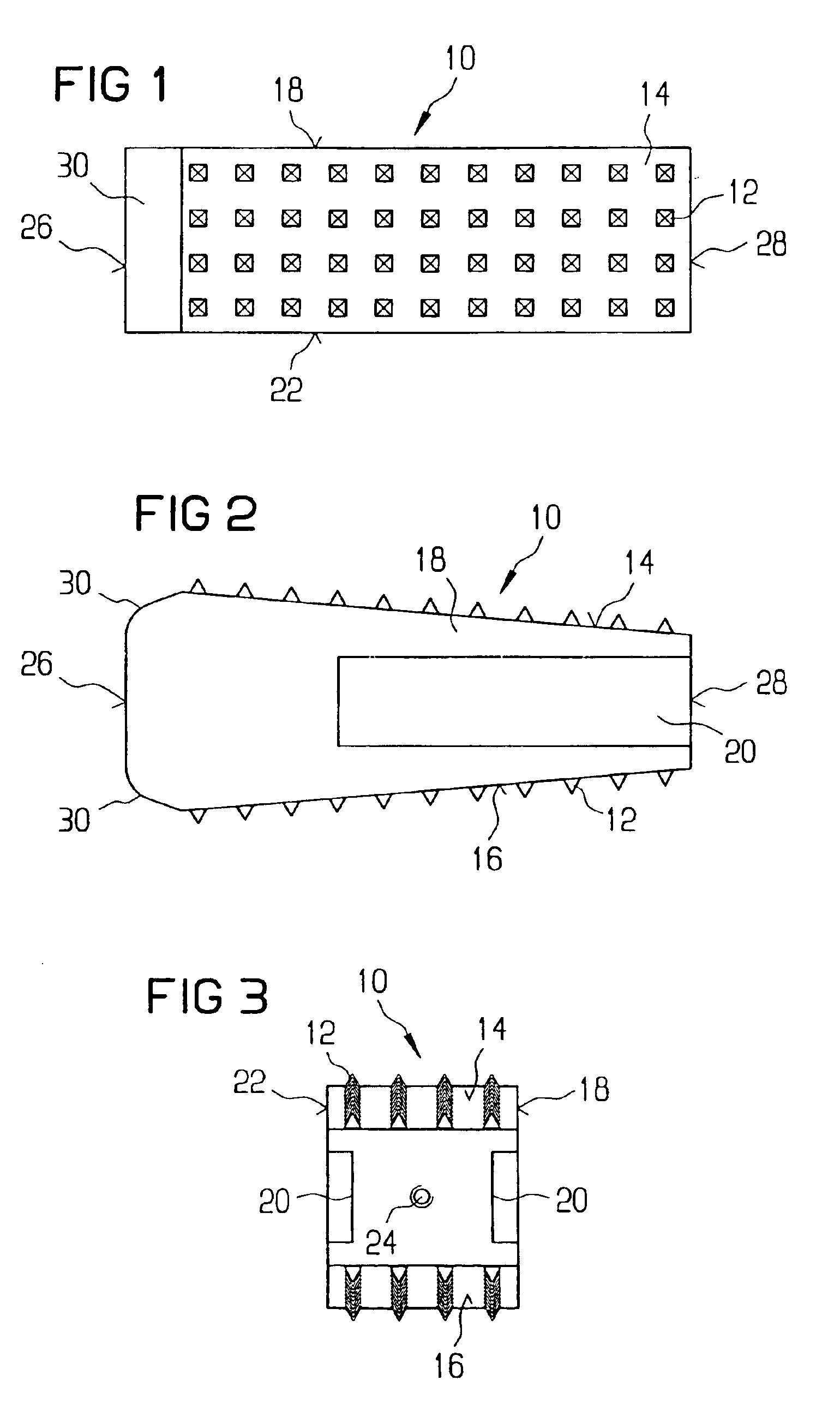
Intervertebral allograft spacer
InactiveUS6986788B2Facilitate implantationEasy to implantBone implantJoint implantsVertebraStress shielding
An allogenic intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant is a piece of allogenic bone conforming in size and shape with a portion of an end plate of a vertebra. The implant has a wedge-shaped profile to restore disc height and the natural curvature of the spine. The top and bottom surfaces of the implant have a plurality of teeth to resist expulsion and provide initial stability. The implant according to the present invention provides initial stability need for fusion without stress shielding.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Surgical articles and methods
InactiveUS7048682B2Improve convenienceProlong surgery timeSuture equipmentsIncision instrumentsMedical disorderSurgical department
Surgical instruments, implantable articles and surgical procedures disclosed for treating medical disorders, particularly incontinence. Improved surgical sling procedures are disclosed. Novel surgical instruments and kits for use in sling procedures are also disclosed. The present invention affords options for surgeons with concomitant advantages to the patient and the healthcare provider.
Owner:STASKIN DAVID MD DR
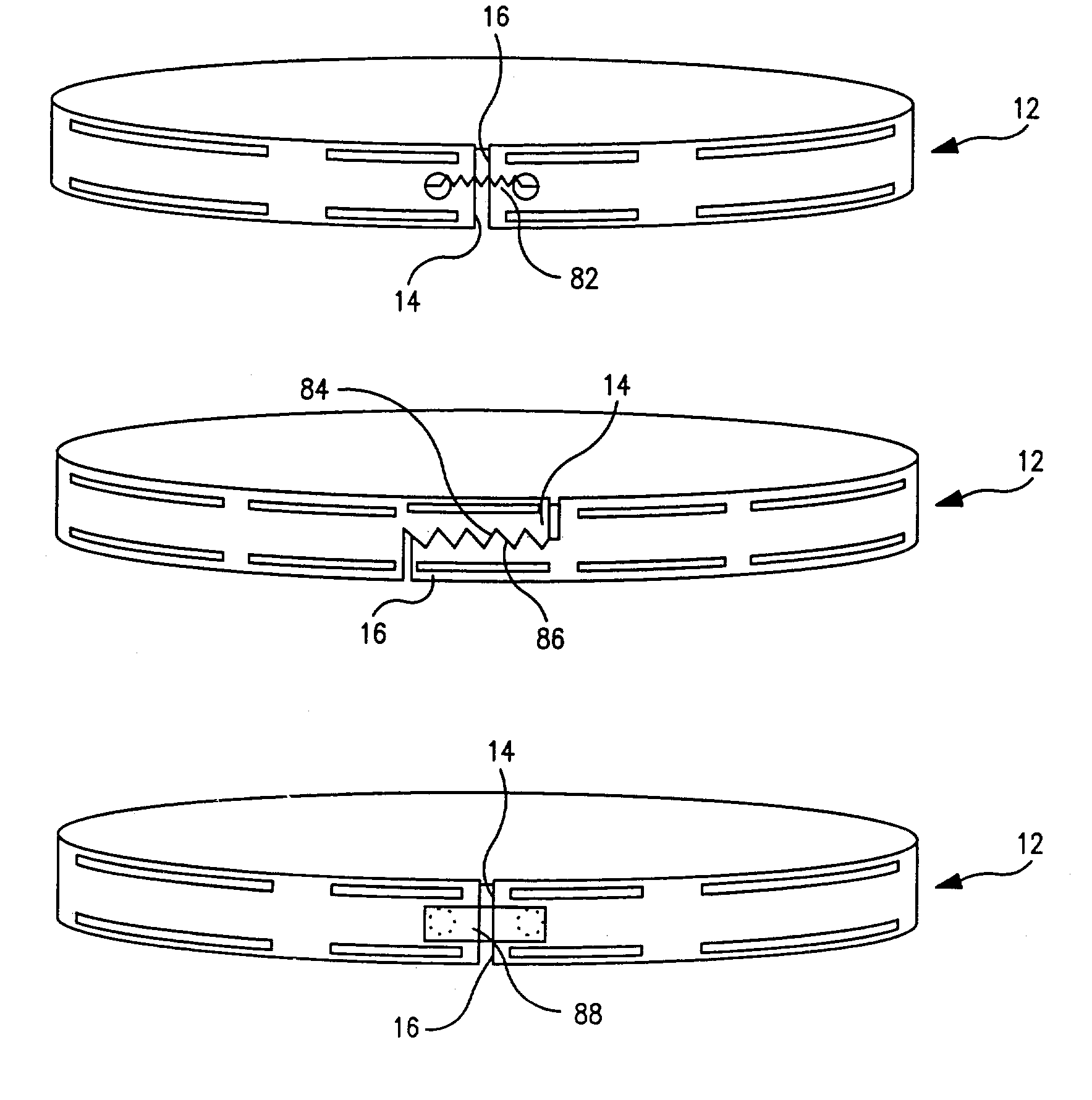
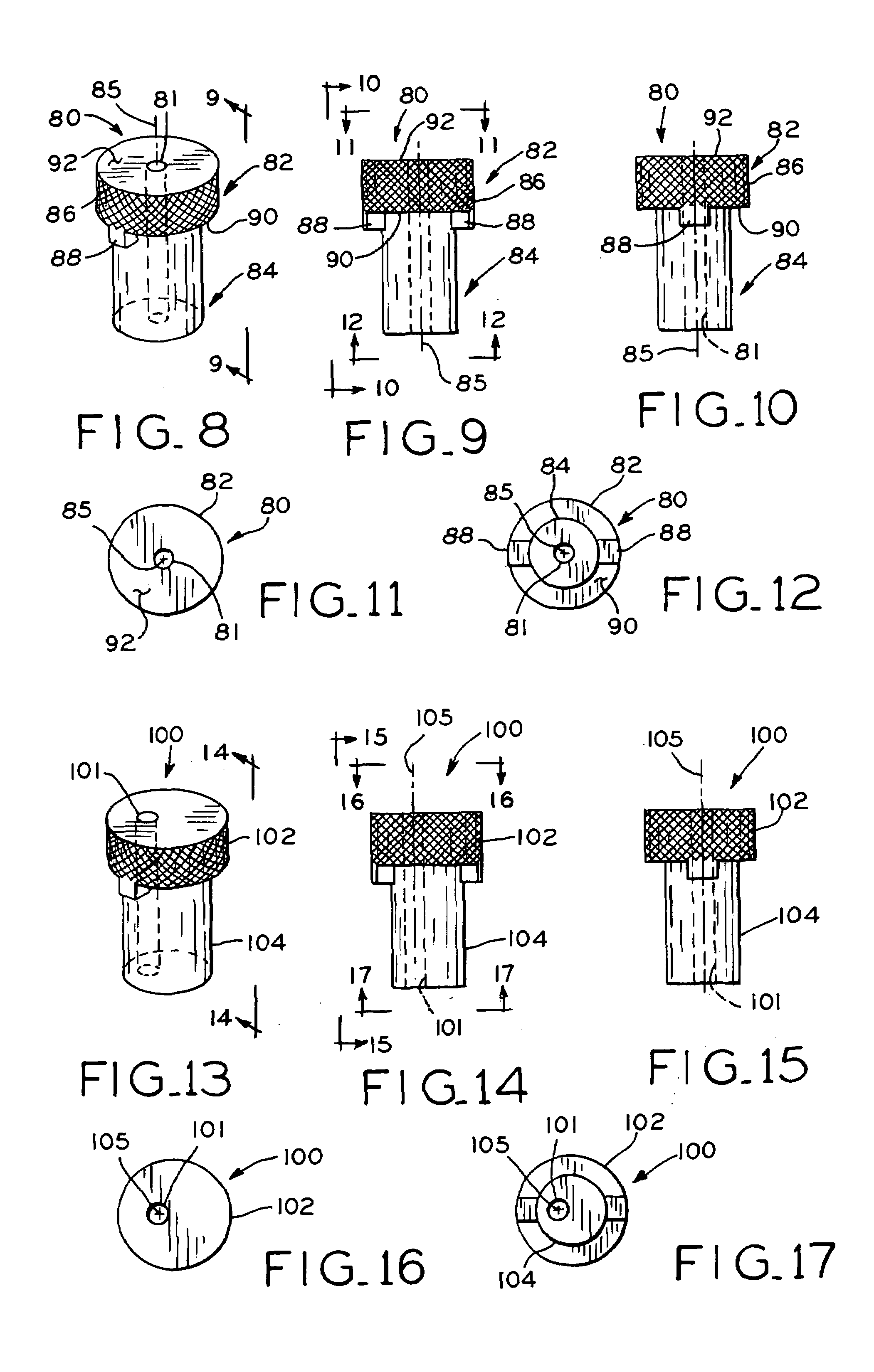
Adjustable artificial chordeae tendineae with suture loops
ActiveUS8790394B2Easy to implantGuaranteed functionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesDistal portionPlantaris tendon
Apparatus is provided, including an artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism and at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea coupled at a distal portion thereof to the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. A degree of tension of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea is adjustable by the artificial-chordeae-tendineae-adjustment mechanism. One or more loops are coupled at a proximal portion of the at least one primary artificial chordea tendinea. The one or more loops are configured to facilitate suturing of the one or more loops to respective portions of a leaflet of an atrioventricular valve of a patient. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Cardiac valve support device fitted with valve leaflets
The present invention provides a cardiac valve support device adapted for endovascular delivery to a cardiac valve, wherein said support device comprises either a single support element with valve leaflets connected thereto or two interconnected support elements having valve leaflets connected to one of said two elements. The invention further encompasses a two-stage method for implanting a replacement cardiac valve, wherein the first stage comprises delivering a valve support device fitted with one or more valve leaflets to a location near a subject's cardiac valve, such that said valve leaflets fulfill the function previously fulfilled by the native valve.
Owner:MVALVE TECH
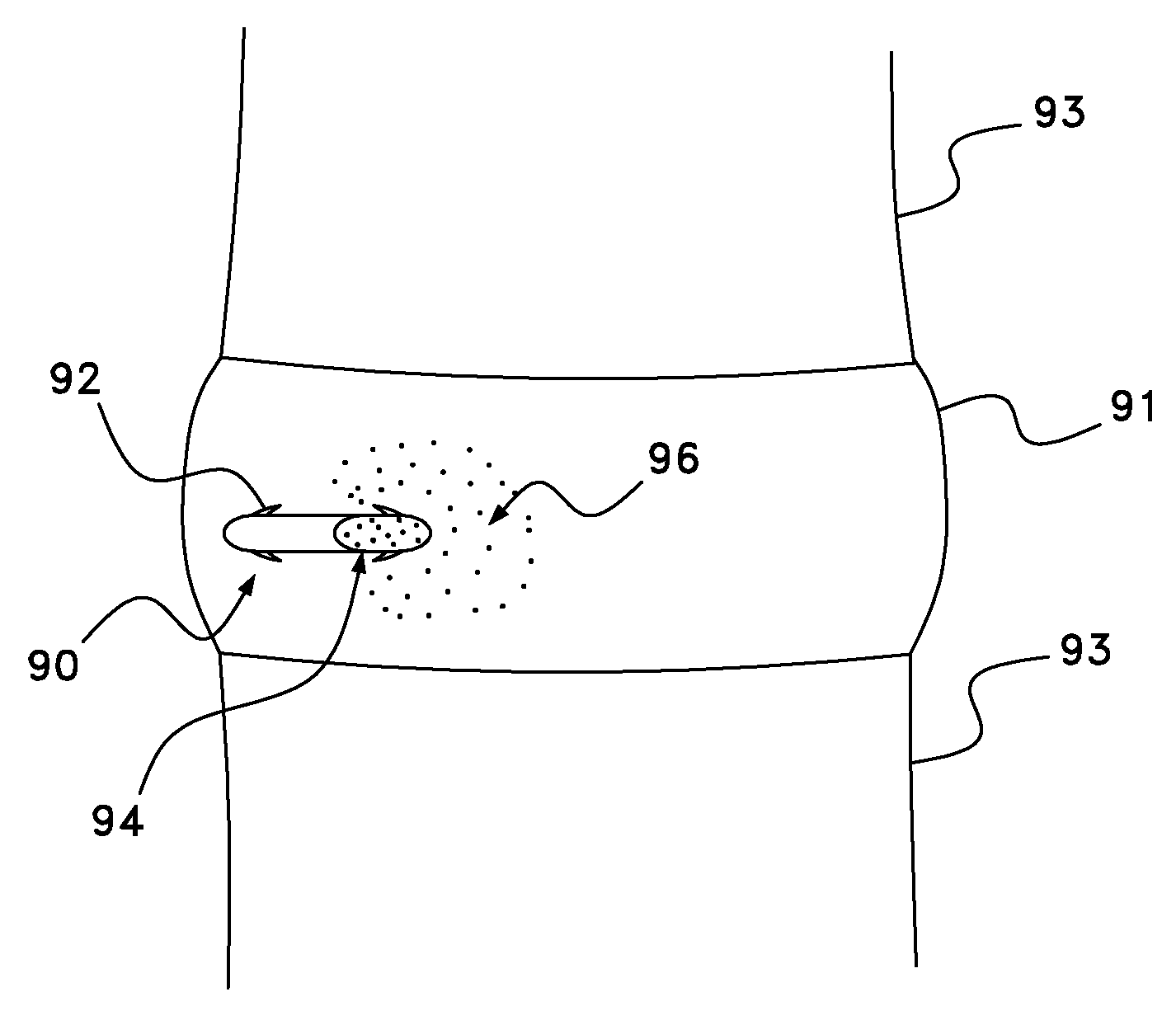
Drug depot implant designs and methods of implantation
ActiveUS20070243225A1Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injurySacroiliac joint
The present invention relates to novel drug depot implant designs for optimal delivery of therapeutic agents to subjects. The invention provides a method for alleviating pain associated with neuromuscular or skeletal injury or inflammation by targeted delivery of one or more therapeutic agents to inhibit the inflammatory response which ultimately causes acute or chronic pain. Controlled and directed delivery can be provided by drug depot implants, comprising therapeutic agents, specifically designed to deliver the therapeutic agent to the desired location by facilitating their implantation, minimizing their migration from the desired tissue location, and without disrupting normal joint and soft tissue movement.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Non-foreshortening intraluminal prosthesis
InactiveUS6475236B1Different degree of flexibilitySame lengthStentsBlood vesselsProsthesisEngineering
An intraluminal prosthesis is provided with a plurality of annular elements. Each annular element includes a plurality of struts and apices connected to form an annular configuration. Each annular element has a compressed state and an expanded state, and has a longitudinal dimension which is smaller in the expanded state than in the compressed state. A plurality of connecting members connect the apices of adjacent annular elements. The connecting members have a plurality of alternating segments that function to compensate for the smaller longitudinal dimension of each annular element in the expanded state. The stent may be provided with varying flexibility along its length and / or circumference, and may include segments that have different diameters.
Owner:ENDOSYST
Implantation of repair chords in the heart
ActiveUS20100161043A1Reduce the overall diameterEasy to implantSuture equipmentsHeart valvesRest stateMechanical elements
Apparatus is provided for adjusting at least one dimension of an implant, including a rotatable structure having first and second openings and a channel extending between the first and second openings. The channel allows passage therethrough of an elongate tool. The second end of the structure has a lower surface having one or more recesses along a circumference thereof. A mechanical element provides a protrusion that is disposed within one of the recesses of the rotatable structure during a resting state of the mechanical element, in a manner that restricts rotation of the rotatable structure. The mechanical clement comprises a depressible portion coupled to the protrusion disposed in communication with the second opening of the lower surface, and configured to dislodge the protrusion from within the recess in response to a force applied thereto by the elongate tool. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Ultrasonic subcutaneous dissection tool incorporating fluid delivery
InactiveUS7566318B2Facilitate electrode deliveryEasy to implantDiagnosticsSurgical needlesTransducerEngineering
Ultrasonic dissection instruments and methods provide for fluid delivery during subcutaneous dissection. An ultrasonic dissection tool includes a handle, a transducer and a dissecting member. The dissecting member extends from the distal end of the transducer, and a fluid channel system extends from at least the proximal end to the distal end of the dissecting member. The fluid channel system terminates in a port system. The port system may include one or more apertures, one or more channels, and be adapted to transport fluids such as, for example, irrigation fluids, fluids having analgesics, antibiotics, and combinations of fluids and agents.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for preparing a glenoid surface
ActiveUS7294133B2Easy to implantEasy to installProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnterior surfaceProsthesis
A method and apparatus for facilitating shoulder arthroplasty by providing a reference to establish version of the glenoid. In one form of the invention, a guide for positioning a guide pin to facilitate implantation of a glenoid prosthesis is provided. To properly position the guide pin, the guide is first oriented with respect to the scapula. A portion of the guide is positioned over the approximate center of the glenoid surface and another portion of the guide is positioned against the anterior surface of the scapula. After the guide is properly positioned, the guide pin is inserted through an aperture in the guide and anchored in the glenoid. Thereafter, the guide pin can serve as an alignment guide for other devices used to modify the glenoid surface. For example, a reamer having a cannulated central shaft can be placed over the guide pin and utilized to resurface the glenoid.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Drug depot implant designs and methods of implantation
ActiveUS20070243228A1Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injurySacroiliac joint
The present invention relates to novel drug depot implant designs for optimal delivery of therapeutic agents to subjects. The invention provides a method for alleviating pain associated with neuromuscular or skeletal injury or inflammation by targeted delivery of one or more therapeutic agents to inhibit the inflammatory response which ultimately causes acute or chronic pain. Controlled and directed delivery can be provided by drug depot implants, comprising therapeutic agents, specifically designed to deliver the therapeutic agent to the desired location by facilitating their implantation, minimizing their migration from the desired tissue location, and without disrupting normal joint and soft tissue movement.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Implant
InactiveUS20060247781A1Small cross sectionPromoting functional performanceBone implantJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringIntervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc nucleus replacement is provided that is configurable into a first configuration to be assumed while the replacement is implanted in the nuclear cavity and a second configuration to be assumed during the procedure of inserting the replacement into the nuclear cavity. The first configuration may have an accordion-like structure formed by a plurality of sections folded in an alternating, zigzag-like manner, and may be sized and shaped to conform to the nuclear cavity. The second configuration may be formed by straightening the plurality of folded sections into an unfolded, elongated, linear member, thereby affording a smaller effective cross-section. The nucleus replacement may be made of an elastic material having shape memory and may be formed so that the first configuration is an unmanipulated or relaxed configuration and the second configuration is a manipulated or unrelaxed configuration.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Patient-specific spinal implants and related systems and methods
InactiveUS8246680B2Easy to implantAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisCustom made implantReplacement implant
Methods and systems for generating custom implants by programmatically analyzing a patient's image data to electronically obtain shapes and dimensions of relevant anatomical features of a target region of the patient; and fabricating a patient-specific replacement implant for the patient using the analyzed patient image data. Related patient-specific spinal implants are also described.
Owner:MIMEDX PROCESSING SERVICES LLC
Tissue anchor for annuloplasty device
ActiveUS8277502B2Easy to implantEnhanced couplingSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsCouplingBiomedical engineering
A method is provided, including coupling, to a first portion of tissue of a patient, a distal tissue coupling element of a tissue anchor. The tissue anchor further includes (a) an implant -coupling element, and (b) a cord, which is removably coupled to the implant-coupling element. The method comprises advancing an implant over the cord until the implant reaches and is coupled to the implant-coupling element. The method further includes restraining the implant from separating from the implant-coupling element, with an implant-restraining element of the implant-coupling element. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Glenoid component of a shoulder prosthesis and complete shoulder prosthesis incorporating such a component
The glenoid component according to the invention comprises a metal body of which the inner face is adapted to be immobilized on the glenoid cavity of a shoulder and of which the outer face bears a concave articulating surface adapted to cooperate with a humeral component. This articulating surface extends on the periphery by a convex surface forming, at least in part, the edge of the body.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com