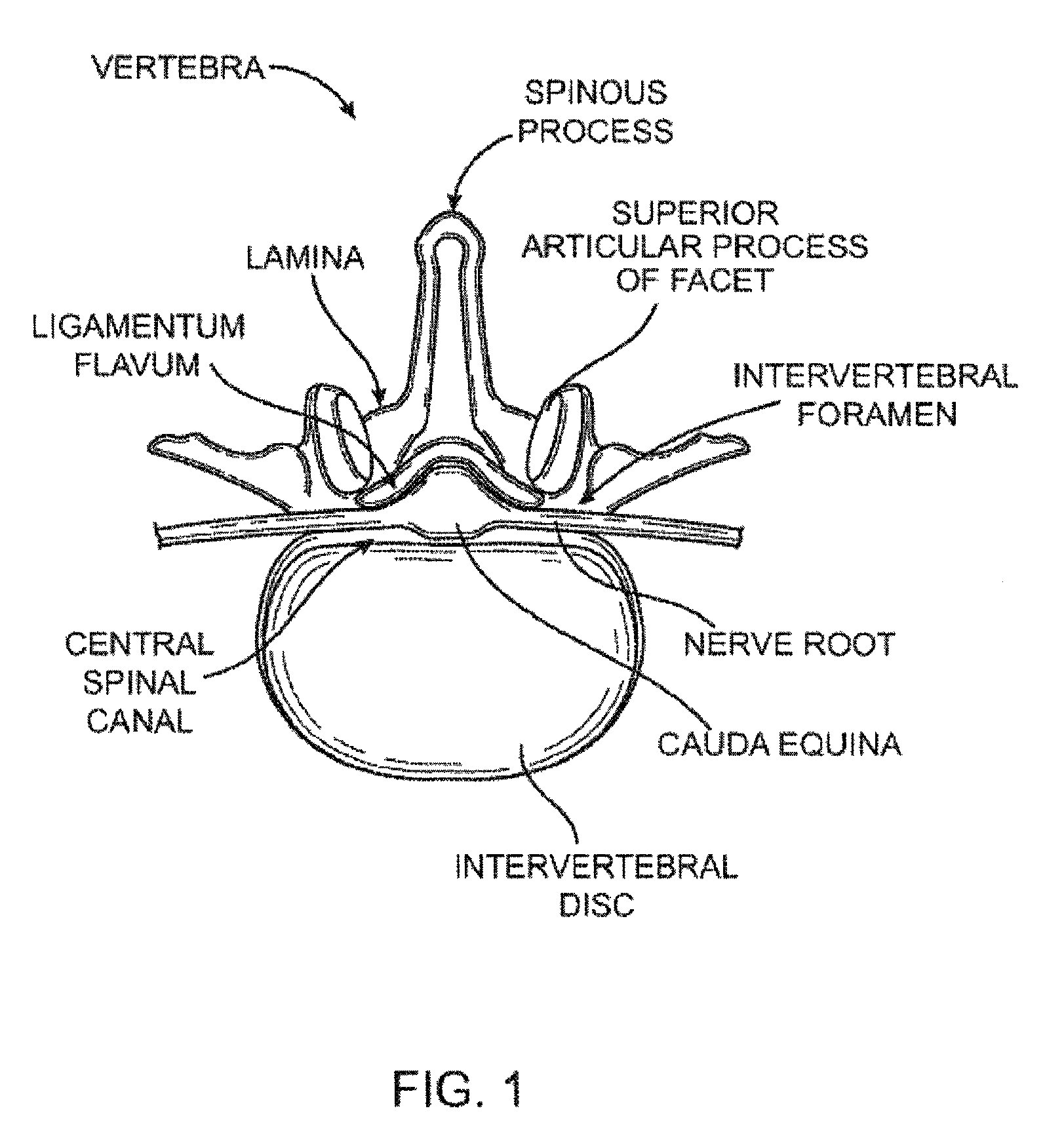
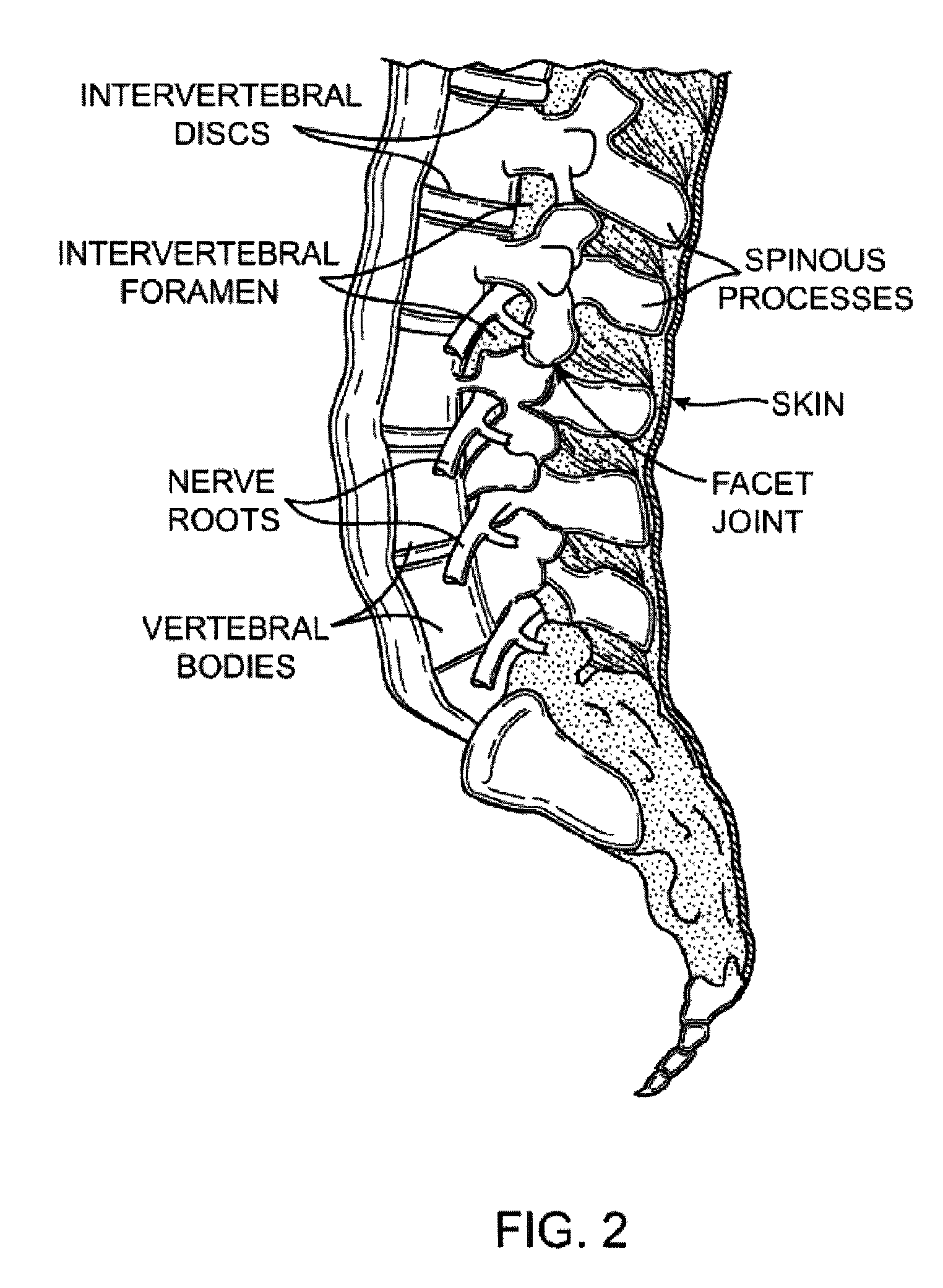
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2826results about "Spinal electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
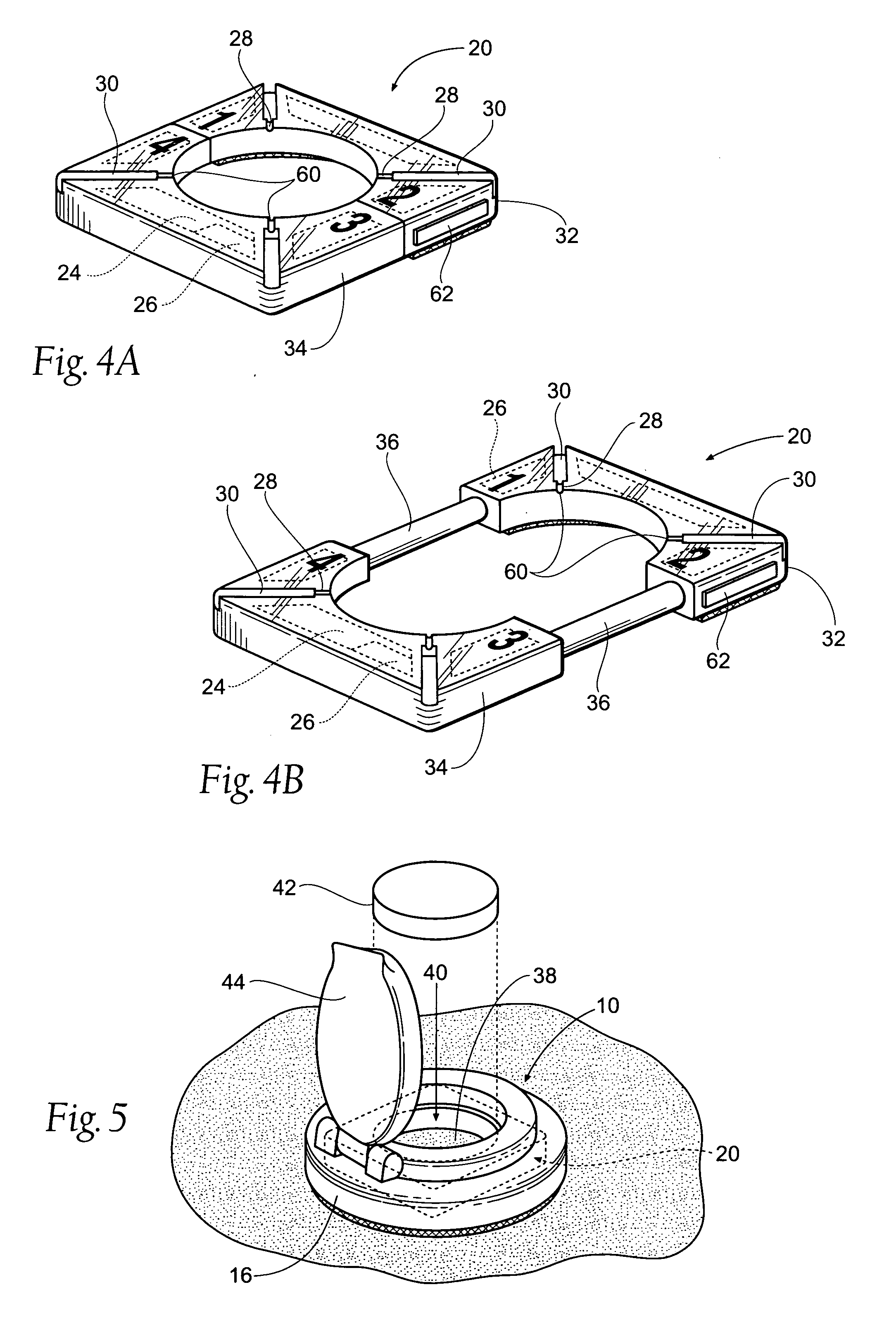
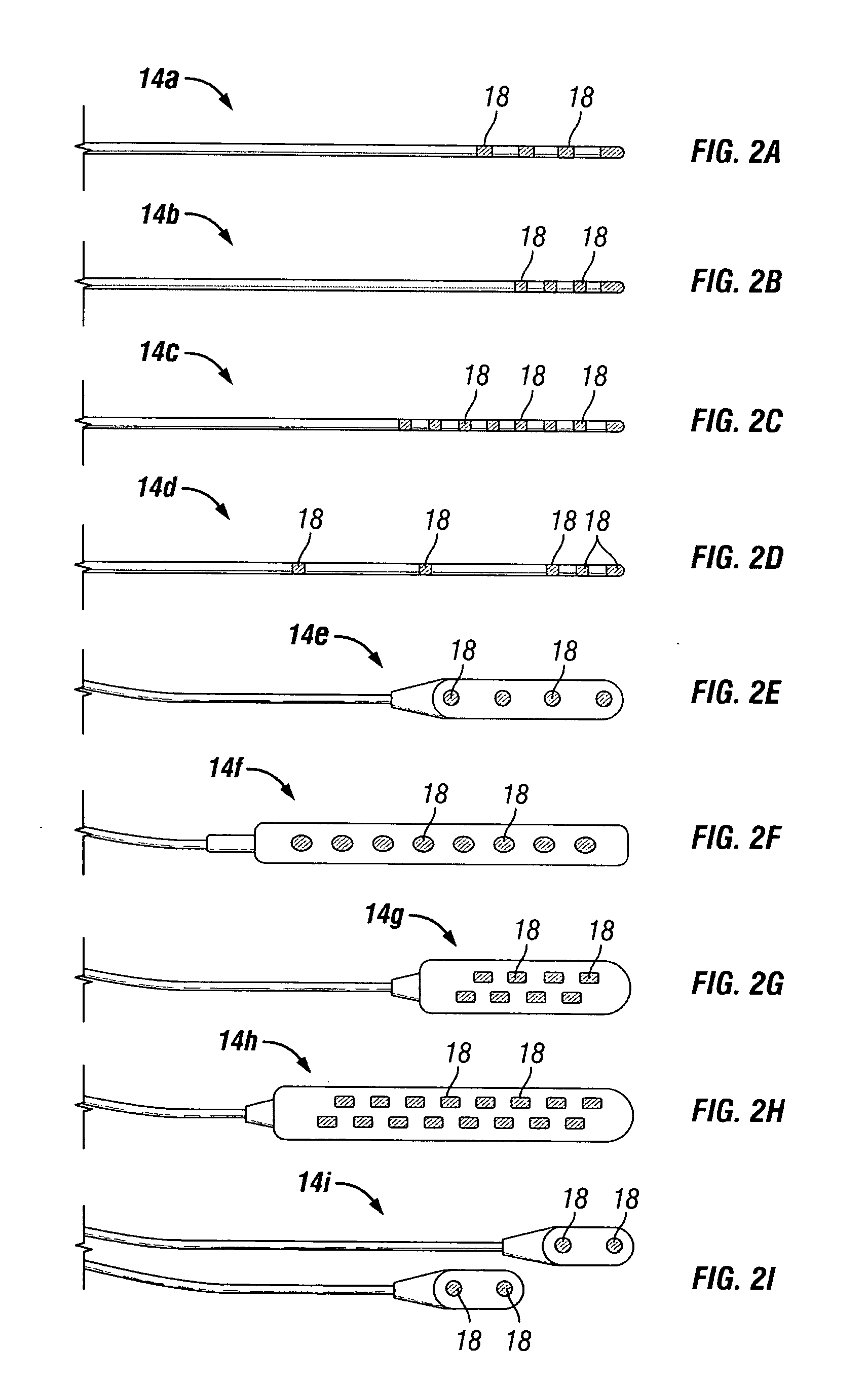
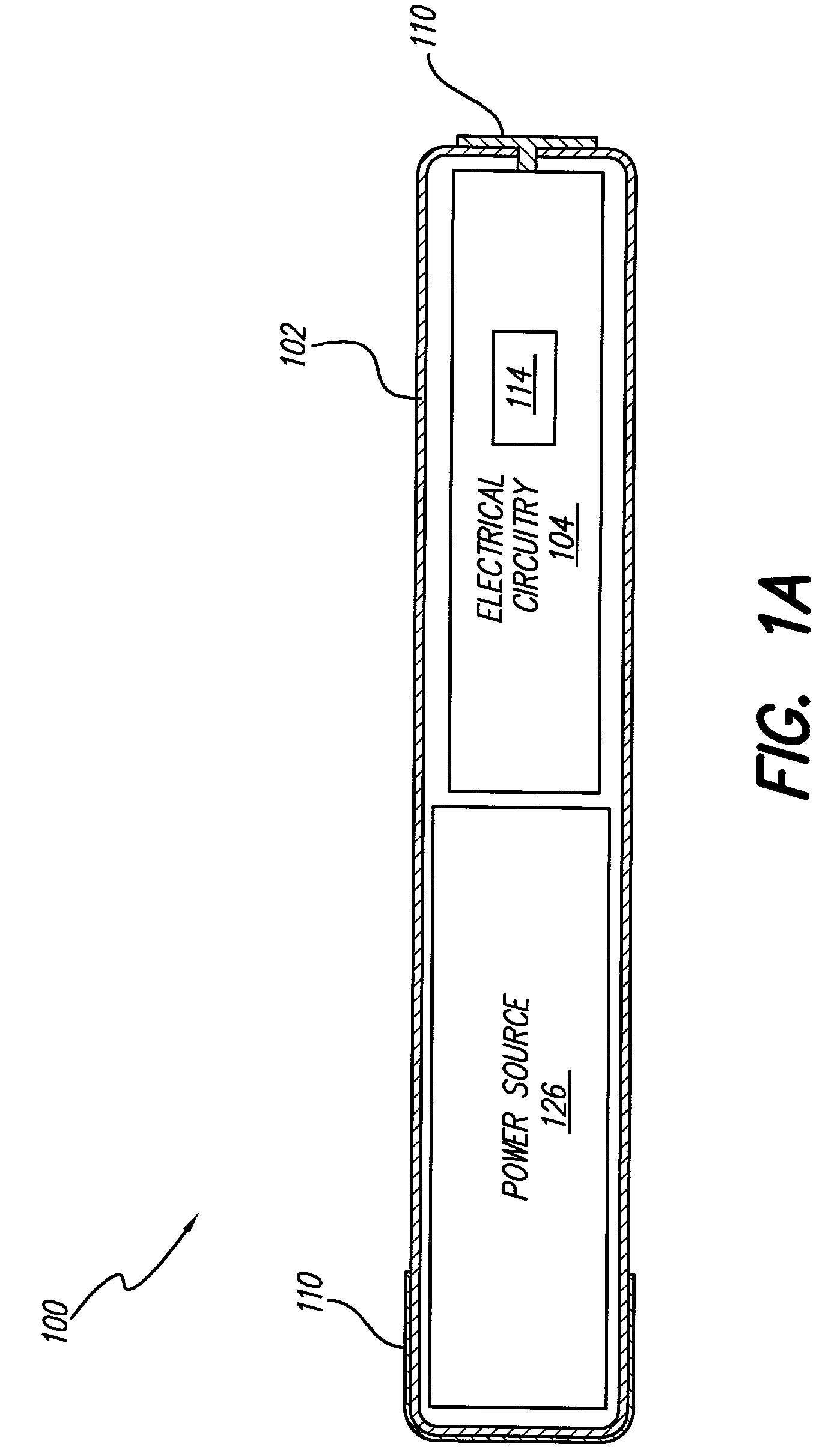
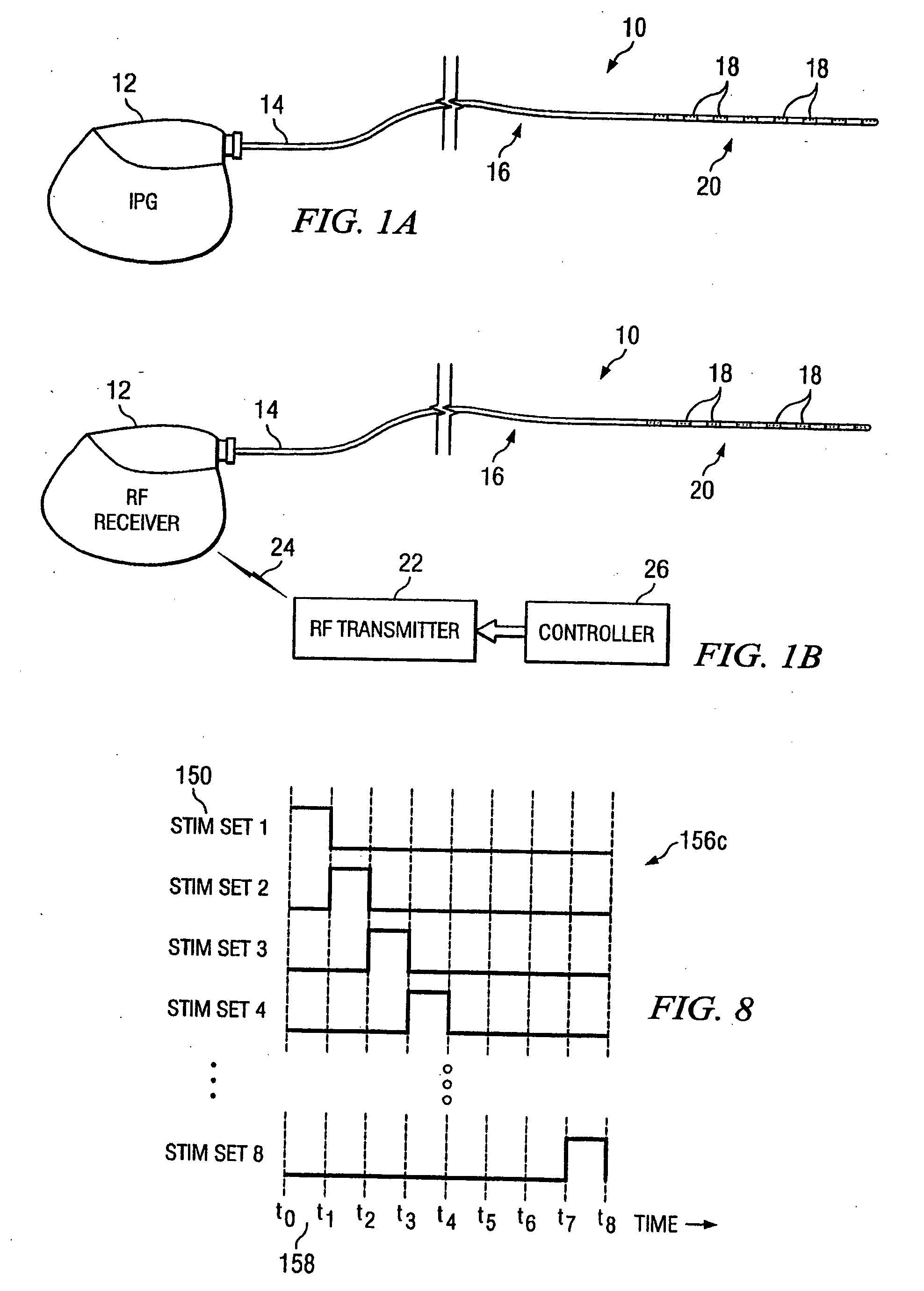
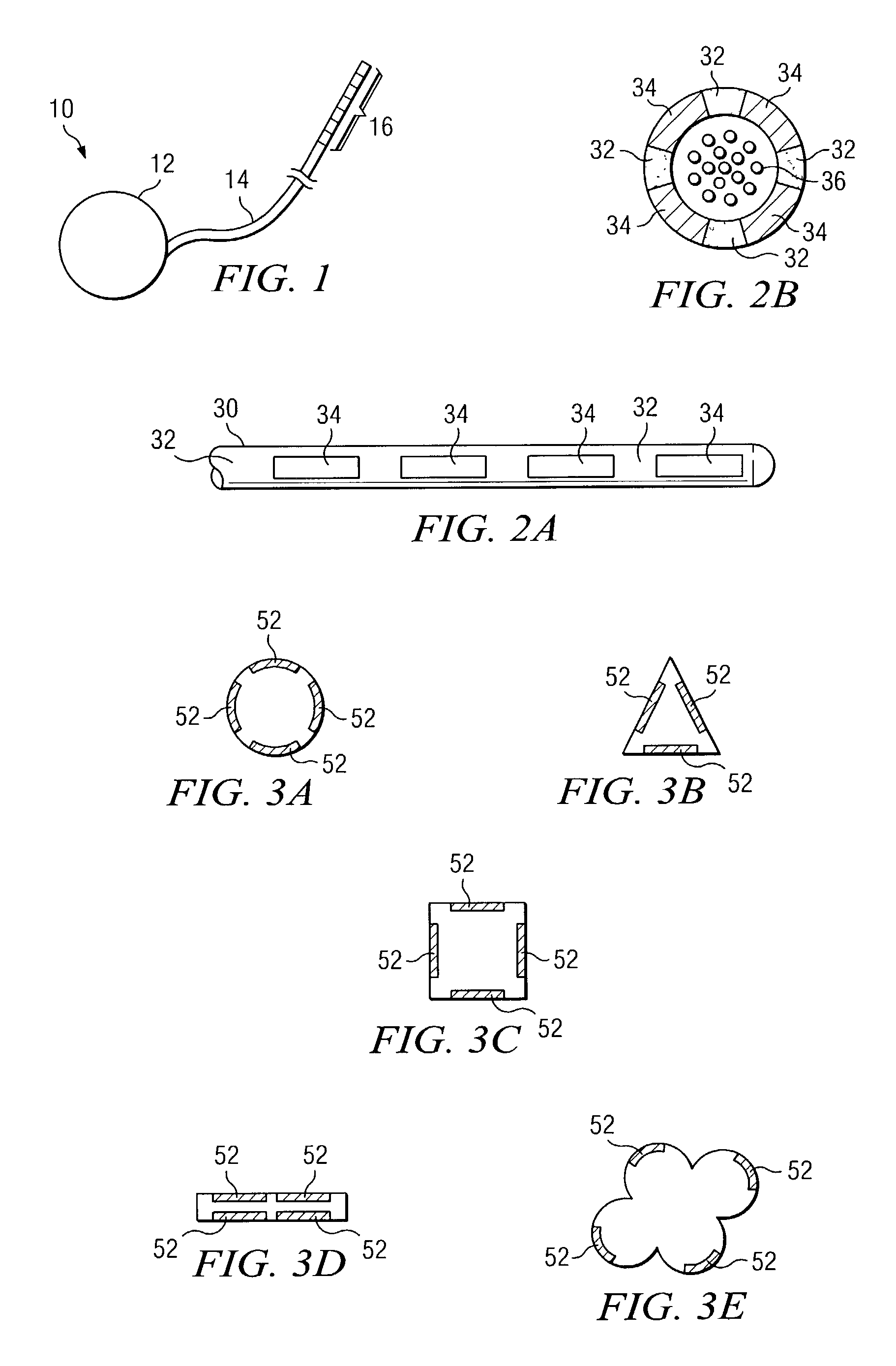
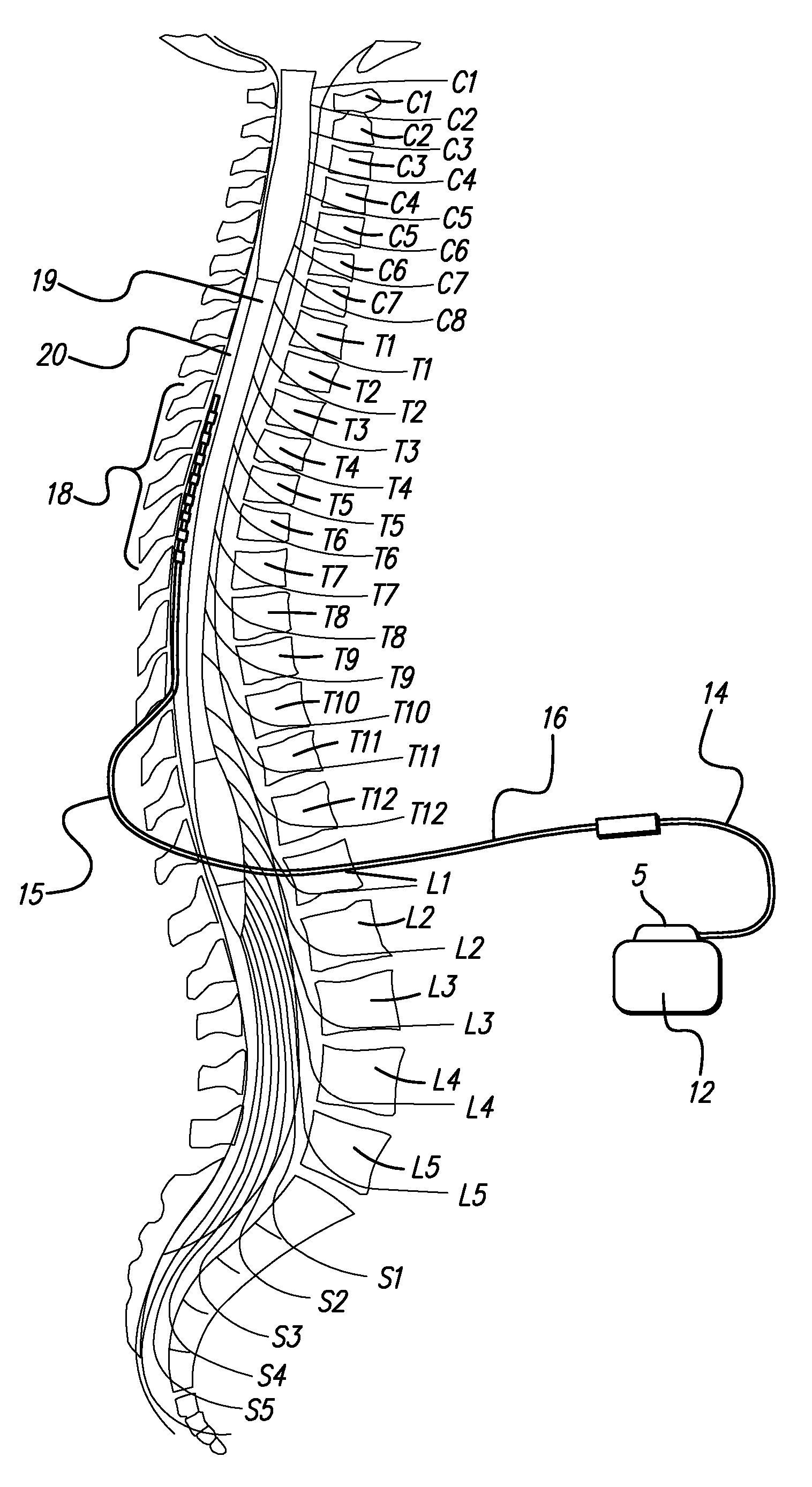
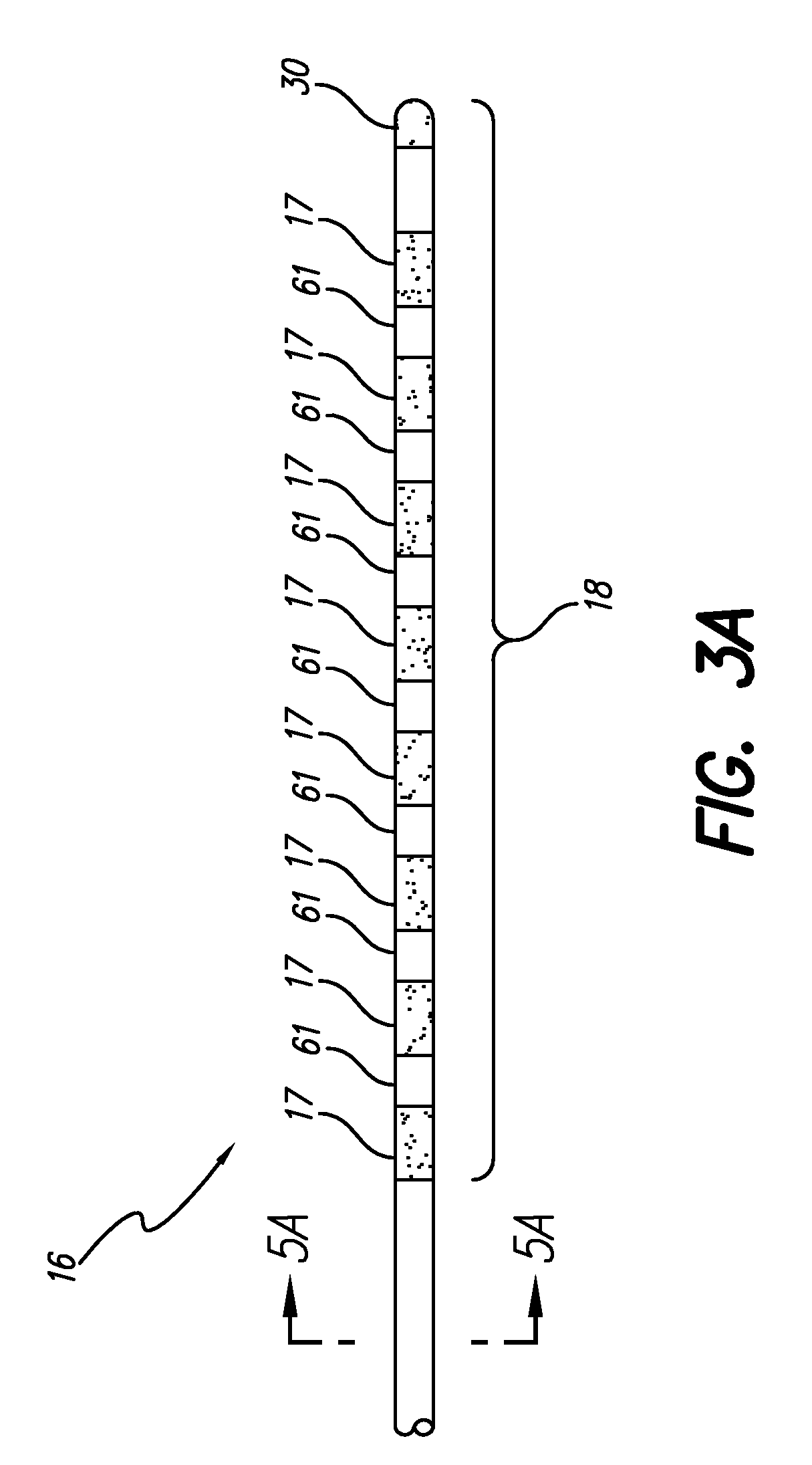
Rechargeable spinal cord stimulator system
InactiveUS6895280B2Provide comfortAvoid displacementSpinal electrodesCircuit arrangements on support structuresReal-time clockElectrical battery
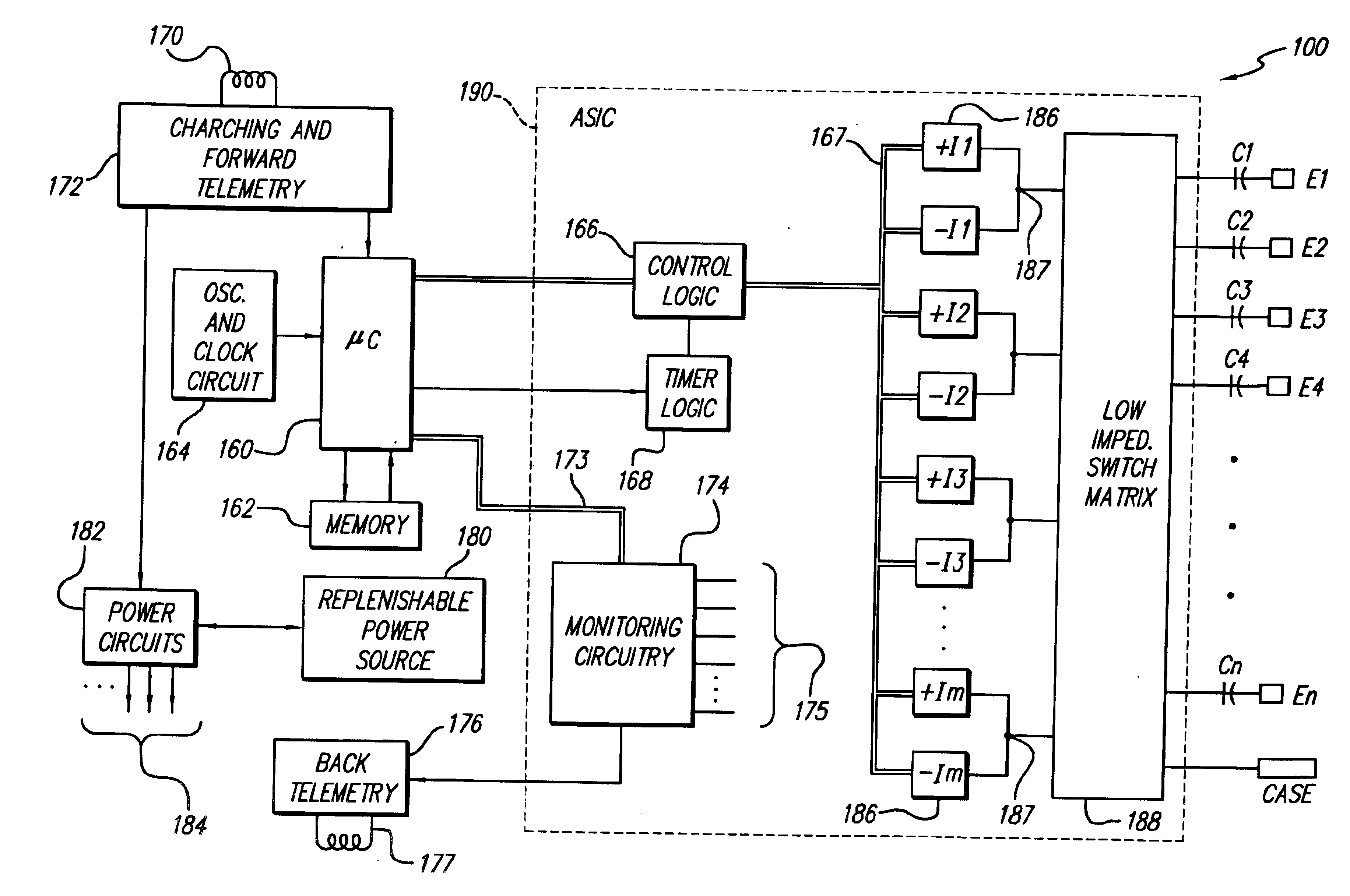
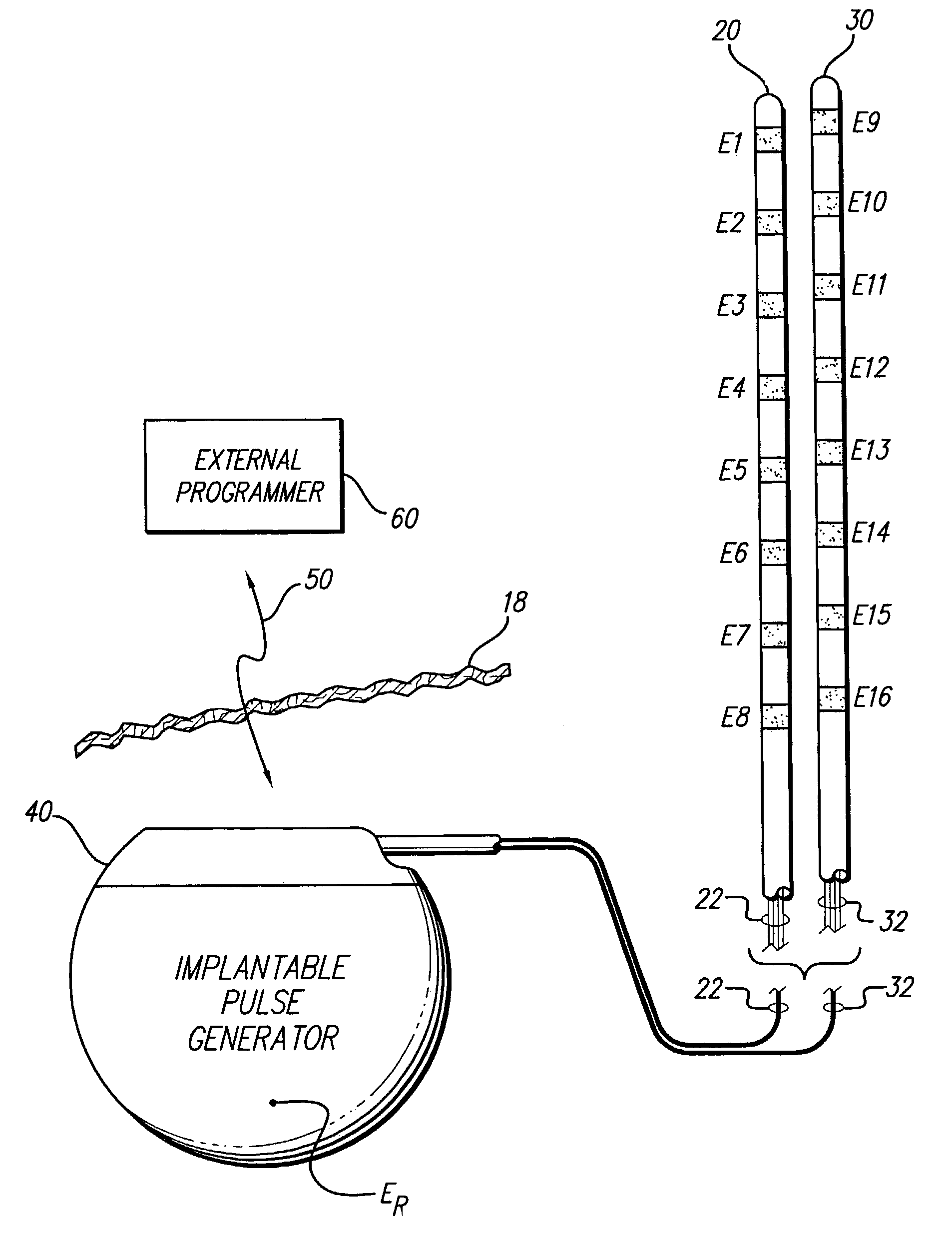
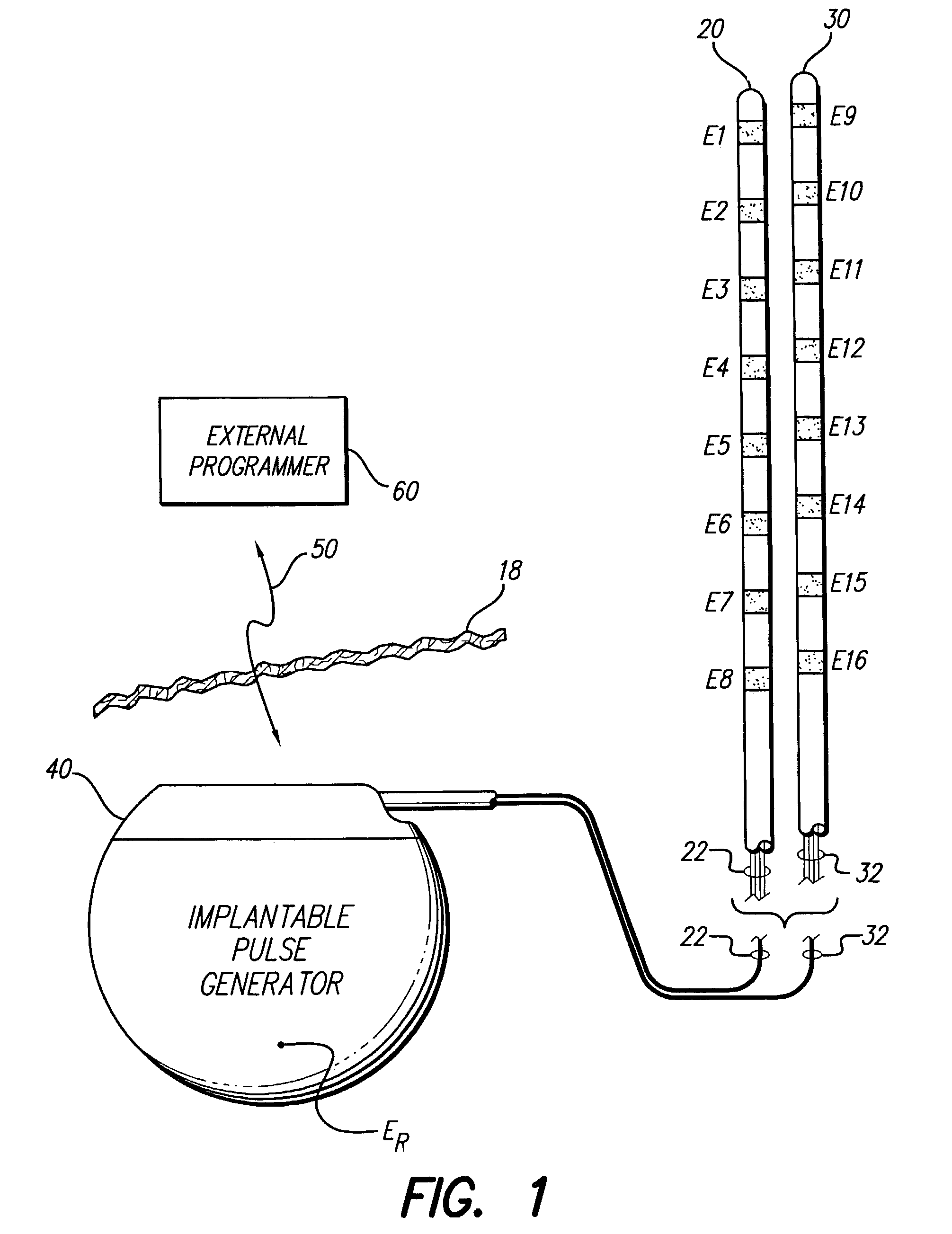
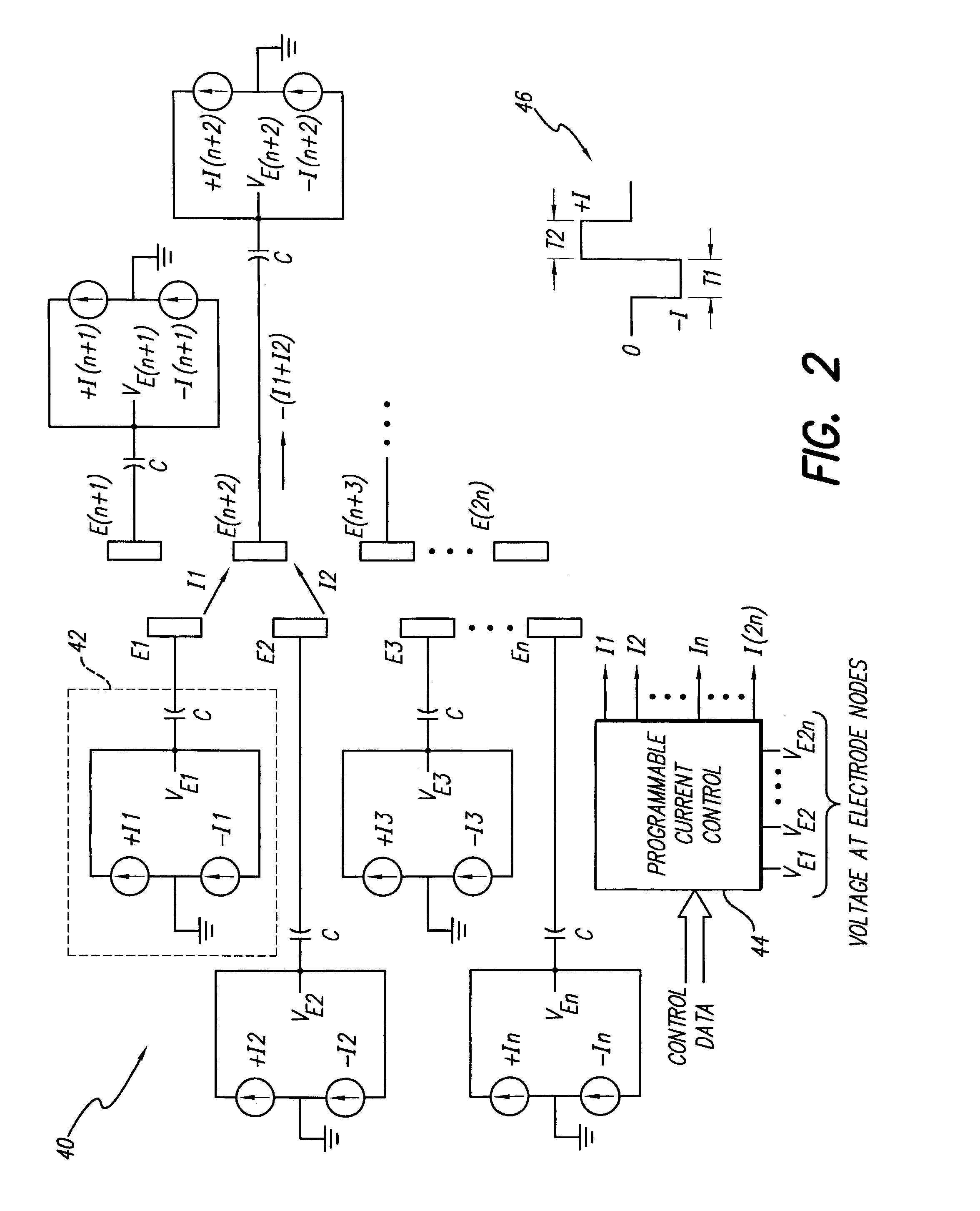
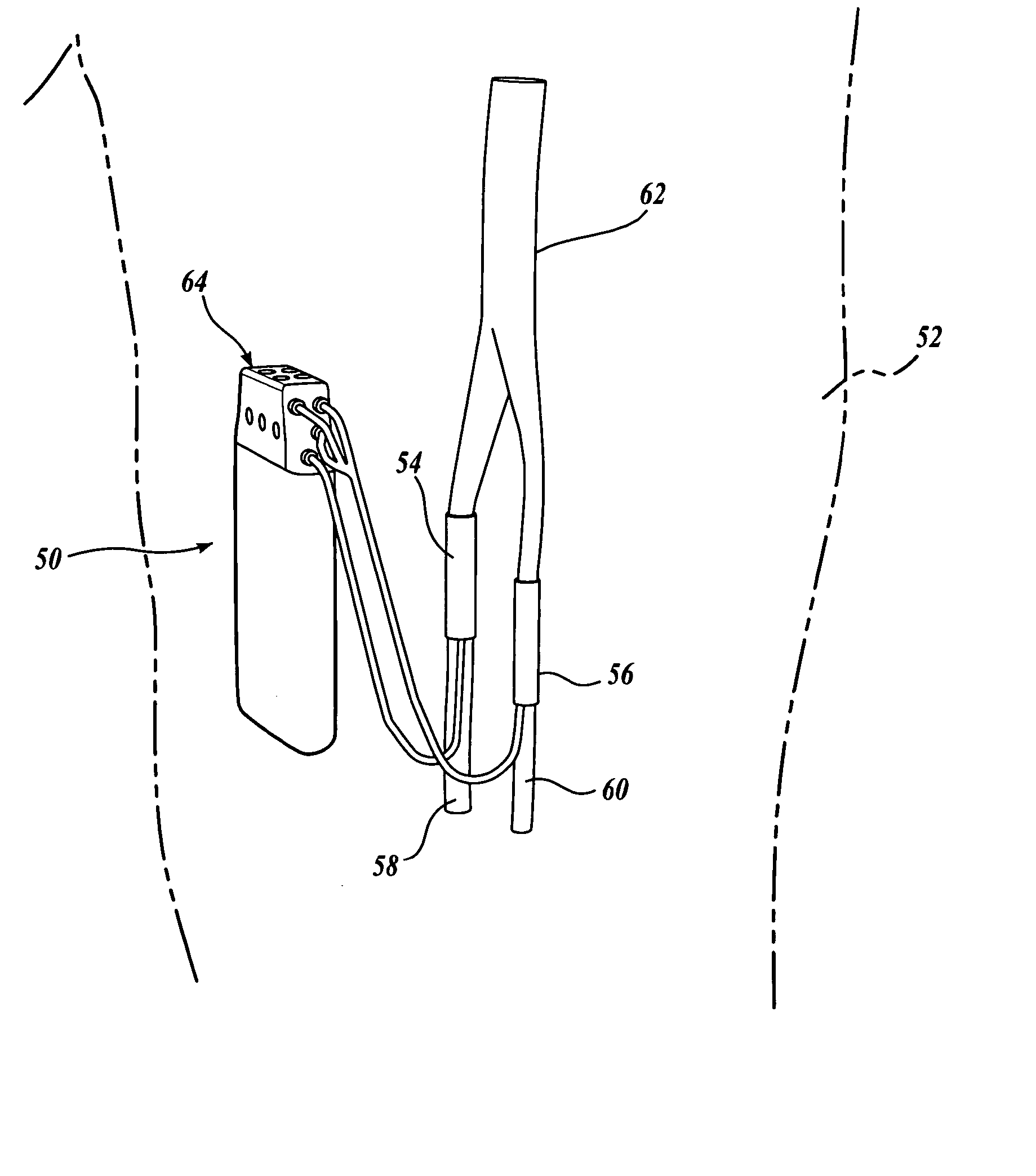
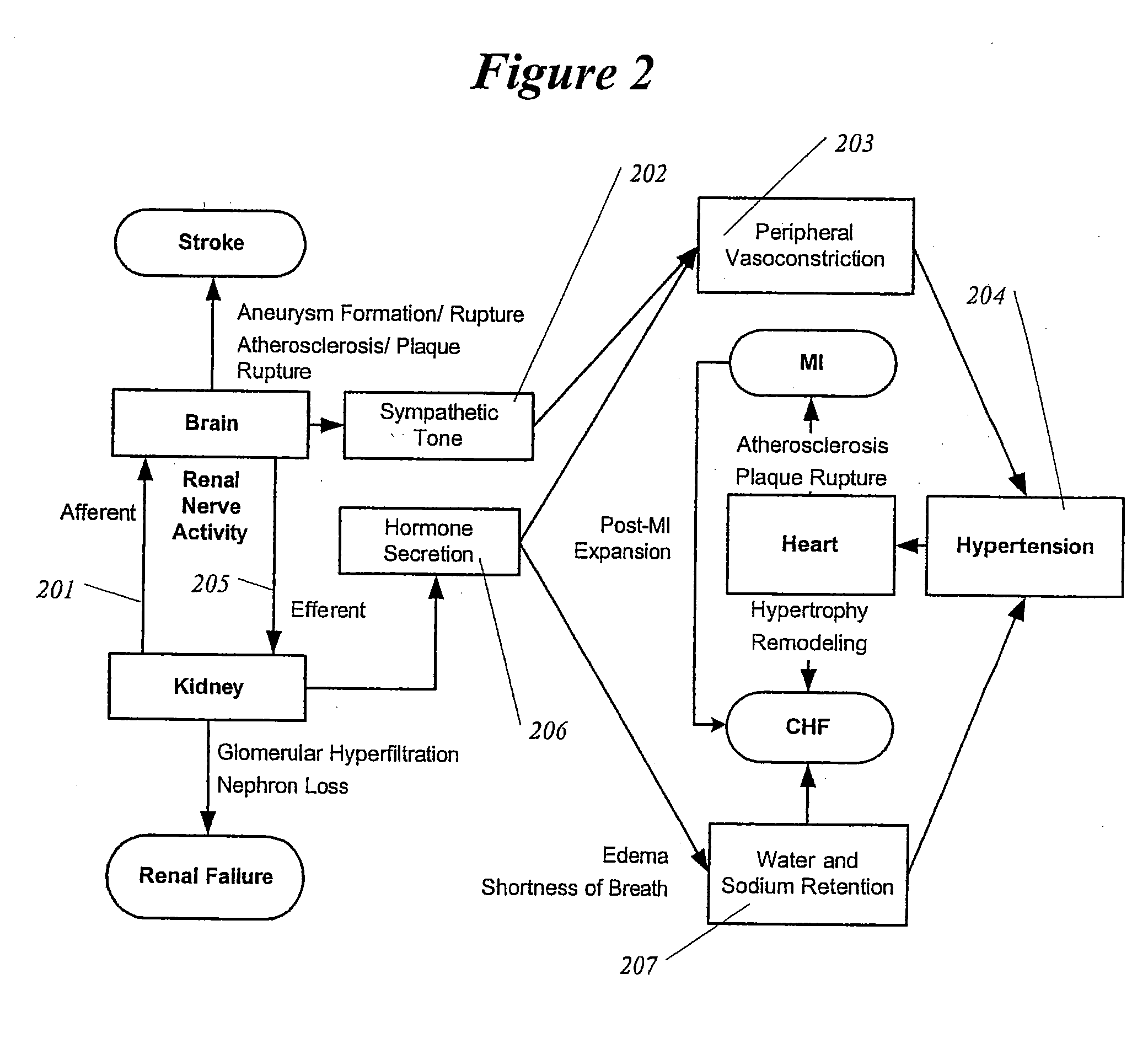
A spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system includes multiple electrodes, multiple, independently programmable, stimulation channels within an implantable pulse generator (IPG) which channels can provide concurrent, but unique stimulation fields, permitting virtual electrodes to be realized. The SCS system includes a replenishable power source (e.g., rechargeable battery), that may be recharged using transcutaneous power transmissions between antenna coil pairs. An external charger unit, having its own rechargeable battery can be used to charge the IPG replenishable power source. A real-time clock can provide an auto-run schedule for daily stimulation. An included bi-directional telemetry link in the system informs the patient or clinician the status of the system, including the state of charge of the IPG battery. Other processing circuitry in the IPG allows electrode impedance measurements to be made. Further circuitry in the external battery charger can provide alignment detection for the coil pairs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Guidewire exchange systems to treat spinal stenosis
Guidewire exchange systems, devices and methods, for positioning and actuating surgical devices in a desired position between two tissues in a patient's body are described. A guidewire may be coupled to a surgical device for positioning and actuating (e.g., urging against a target tissue). The guidewire may be exchanged between different surgical devices during the same procedure, and the guidewire and surgical devices may be releaseably or permanently coupled. The surgical device generally includes one or more guidewire coupling members. A system may include a guidewire and a surgical device having a guidewire coupling member. Methods, devices and systems may be used in open, less-invasive or percutaneous surgical procedures.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC +1
Portable assemblies, systems and methods for providing functional or therapeutic neuromuscular stimulation
InactiveUS20080154335A1Easy to carryNo discomfortSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectricityMedicine
Neuromuscular stimulation assemblies, systems, and methods make possible the providing of short-term therapy or diagnostic testing by providing electrical connections between muscles or nerves inside the body and stimulus generators or recording instruments mounted on the surface of the skin outside the body. Neuromuscular stimulation assemblies, systems, and methods may include a steerable introducer that defines an interior lumen sized and configured to shield a percutaneous electrode from contact with tissue during advancement to a desired position within tissue.
Owner:NDI MEDICAL LLC - CHARTER NO 1766209
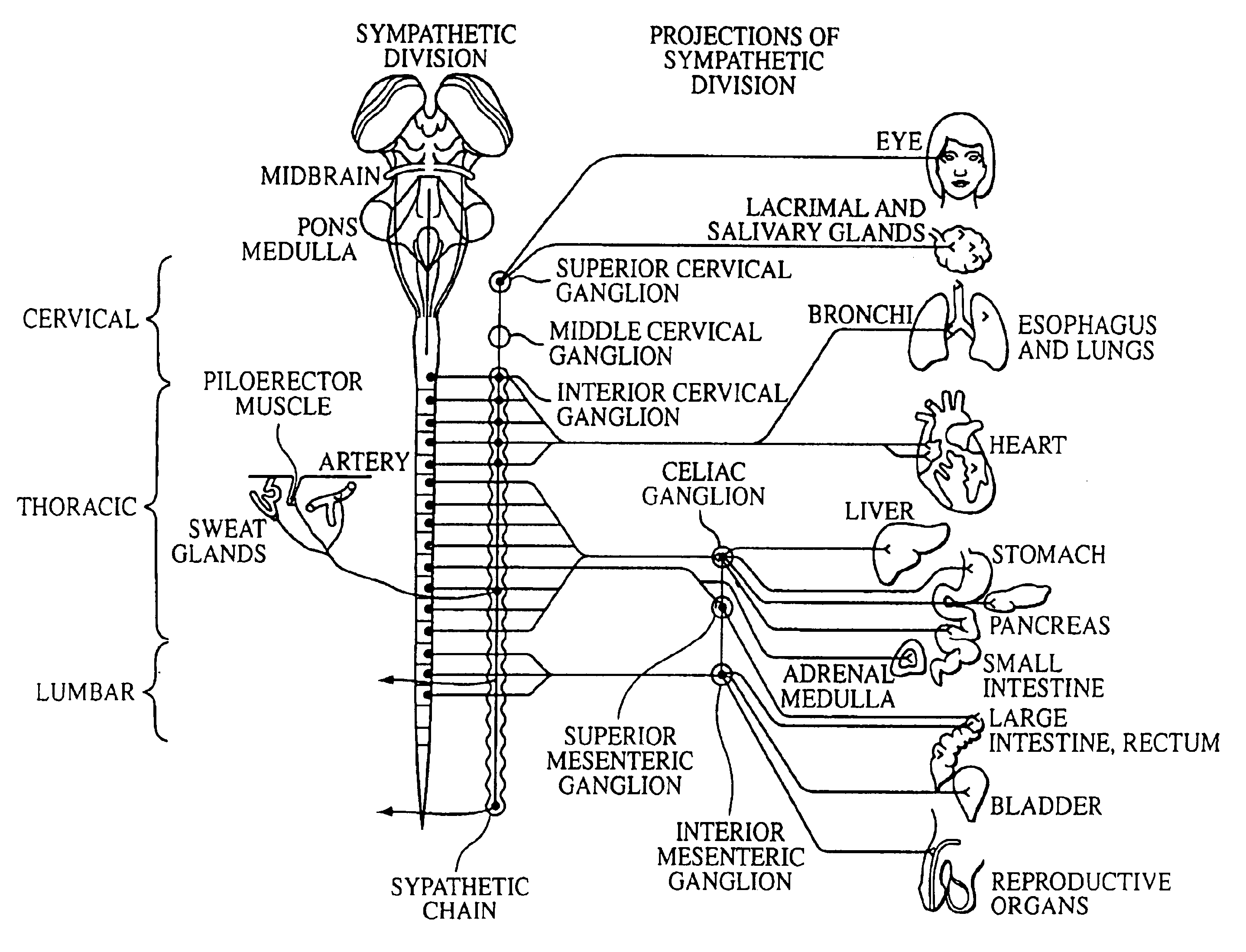
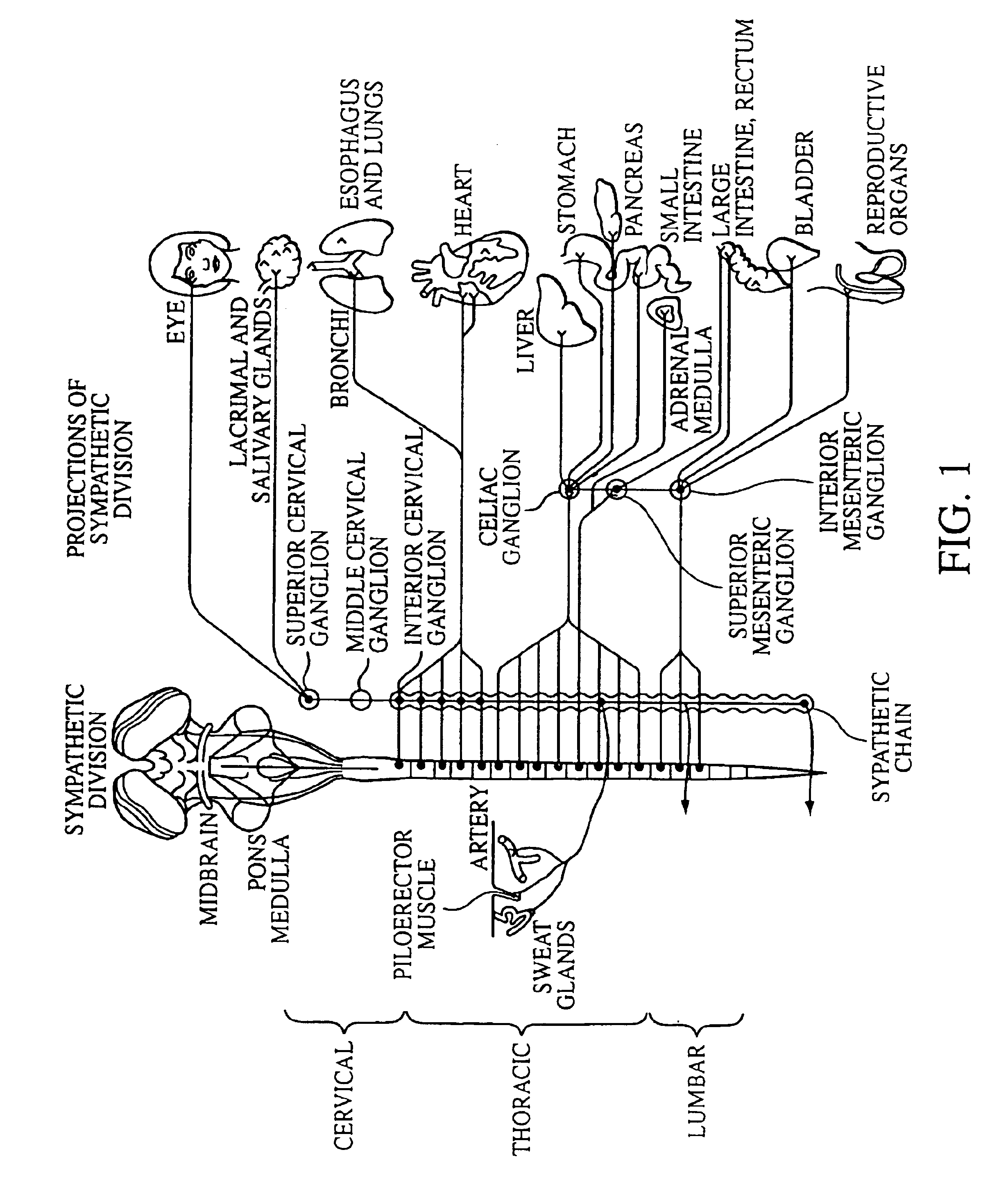
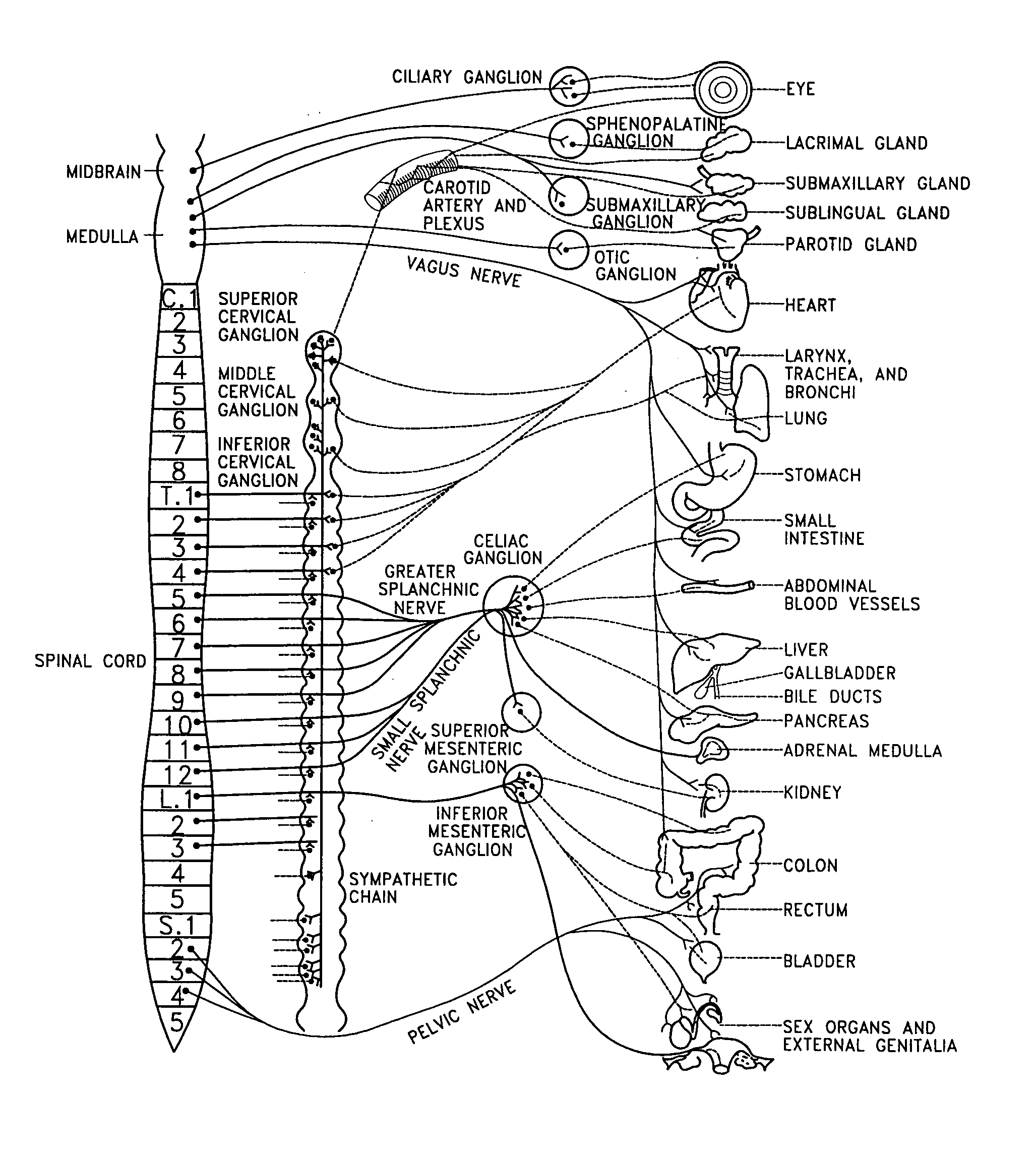
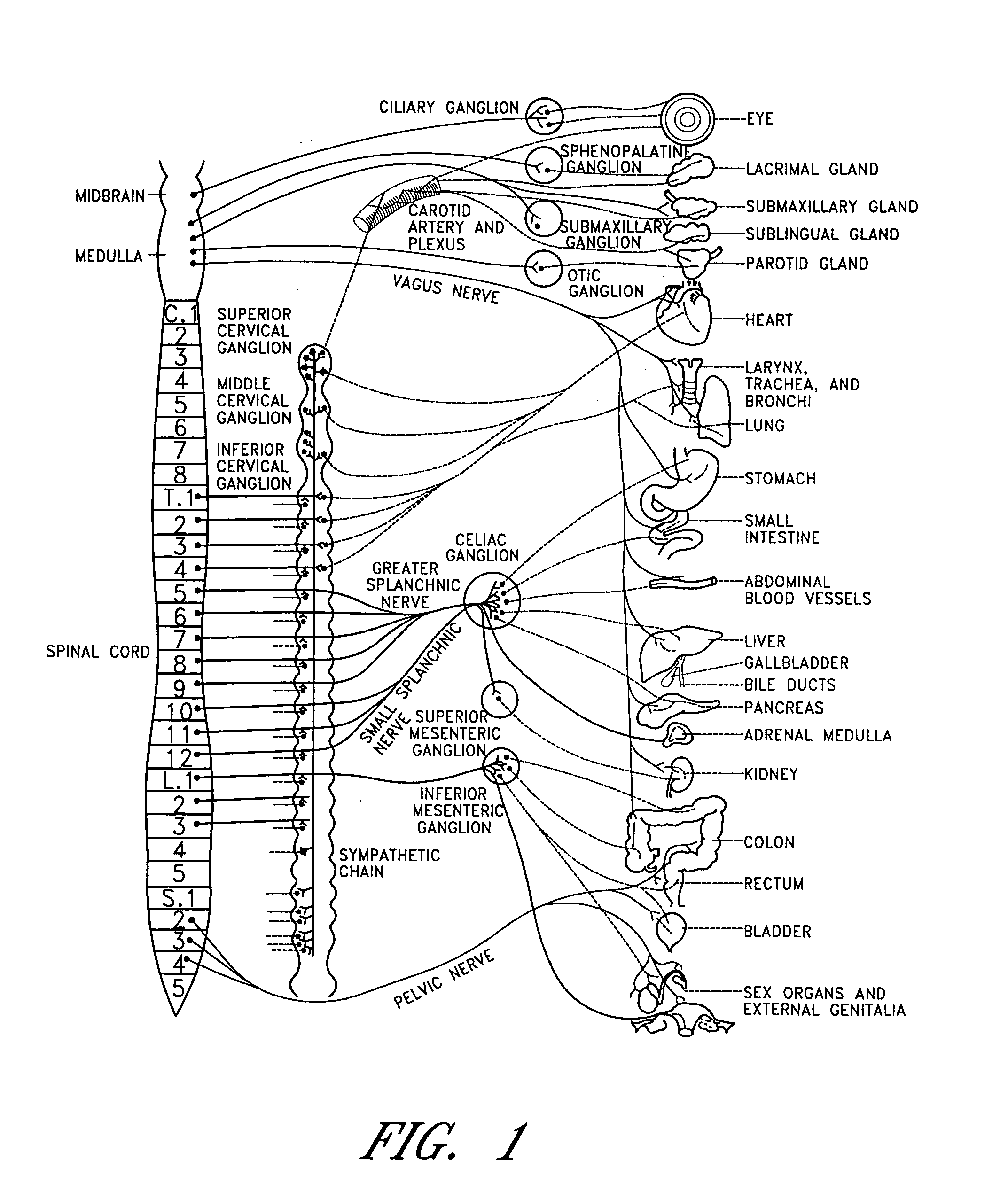
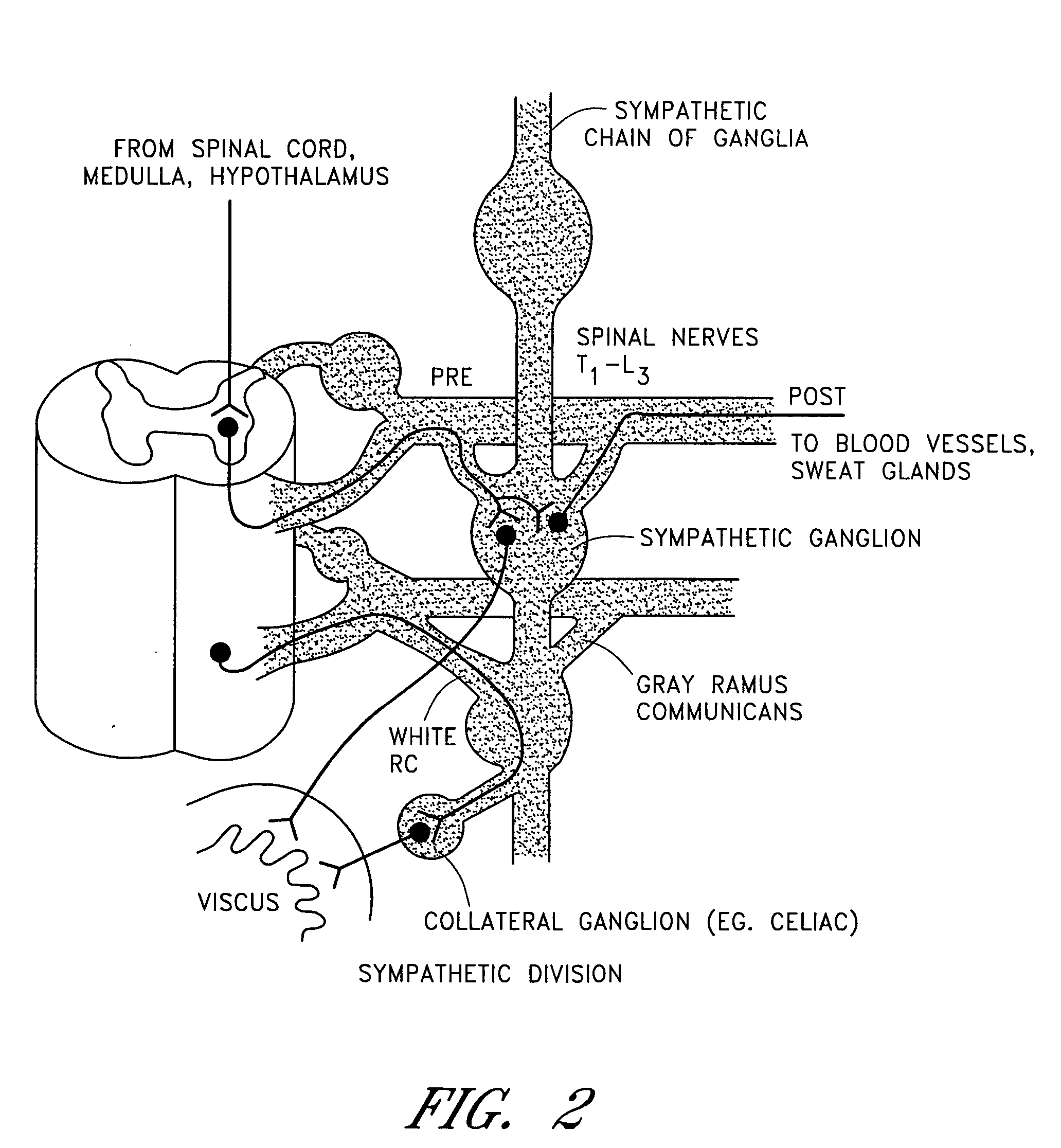
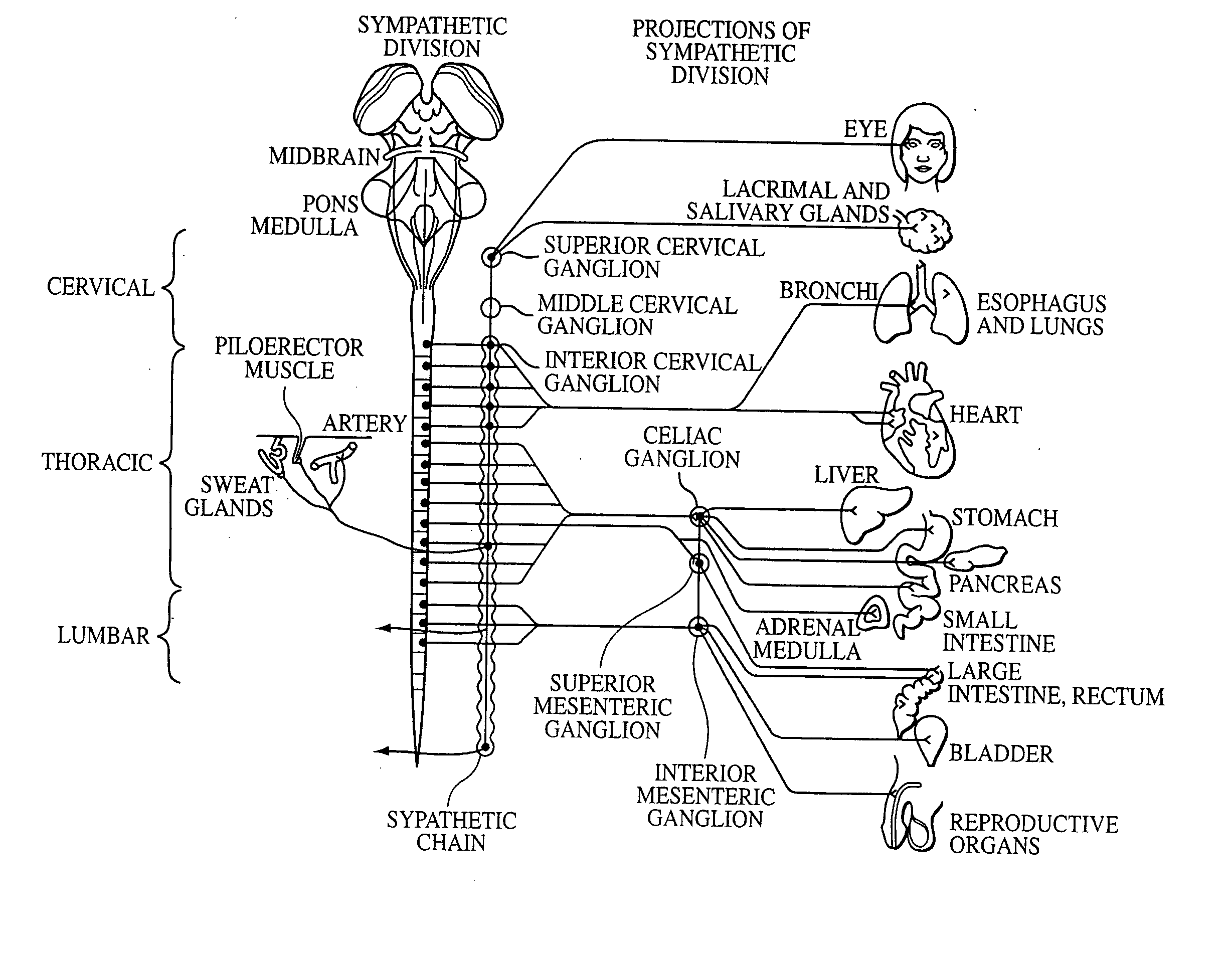
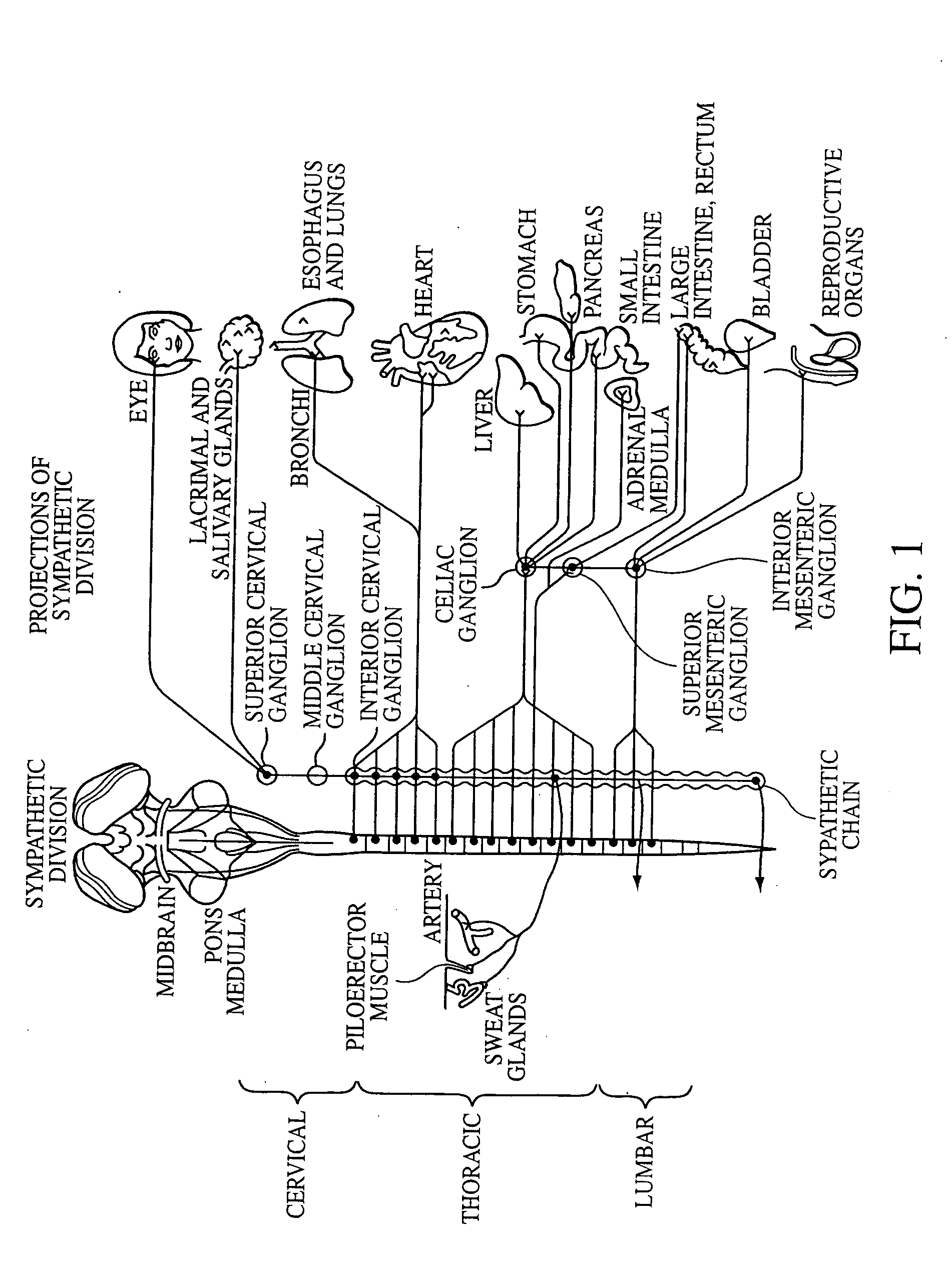
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS6885888B2Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
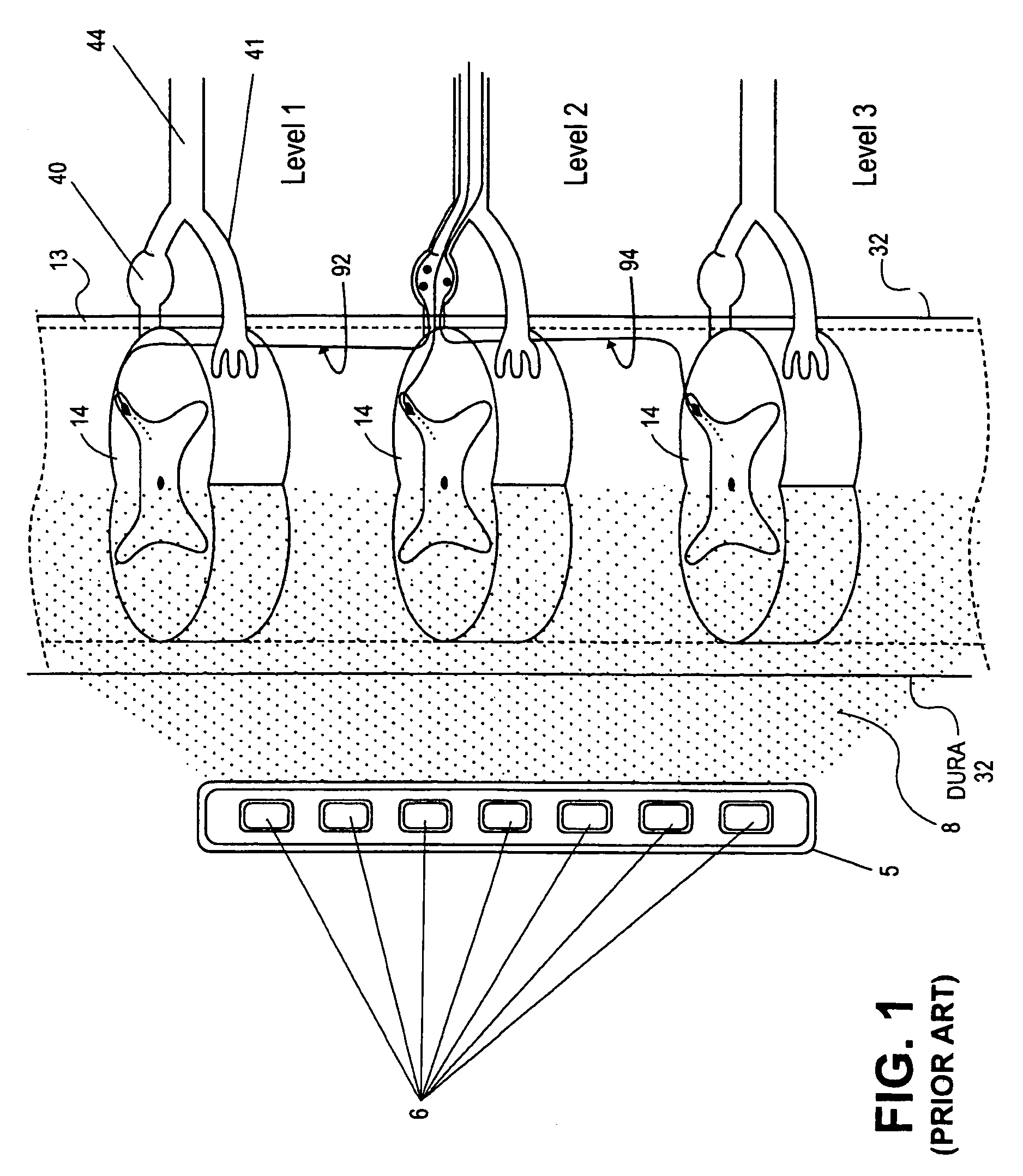
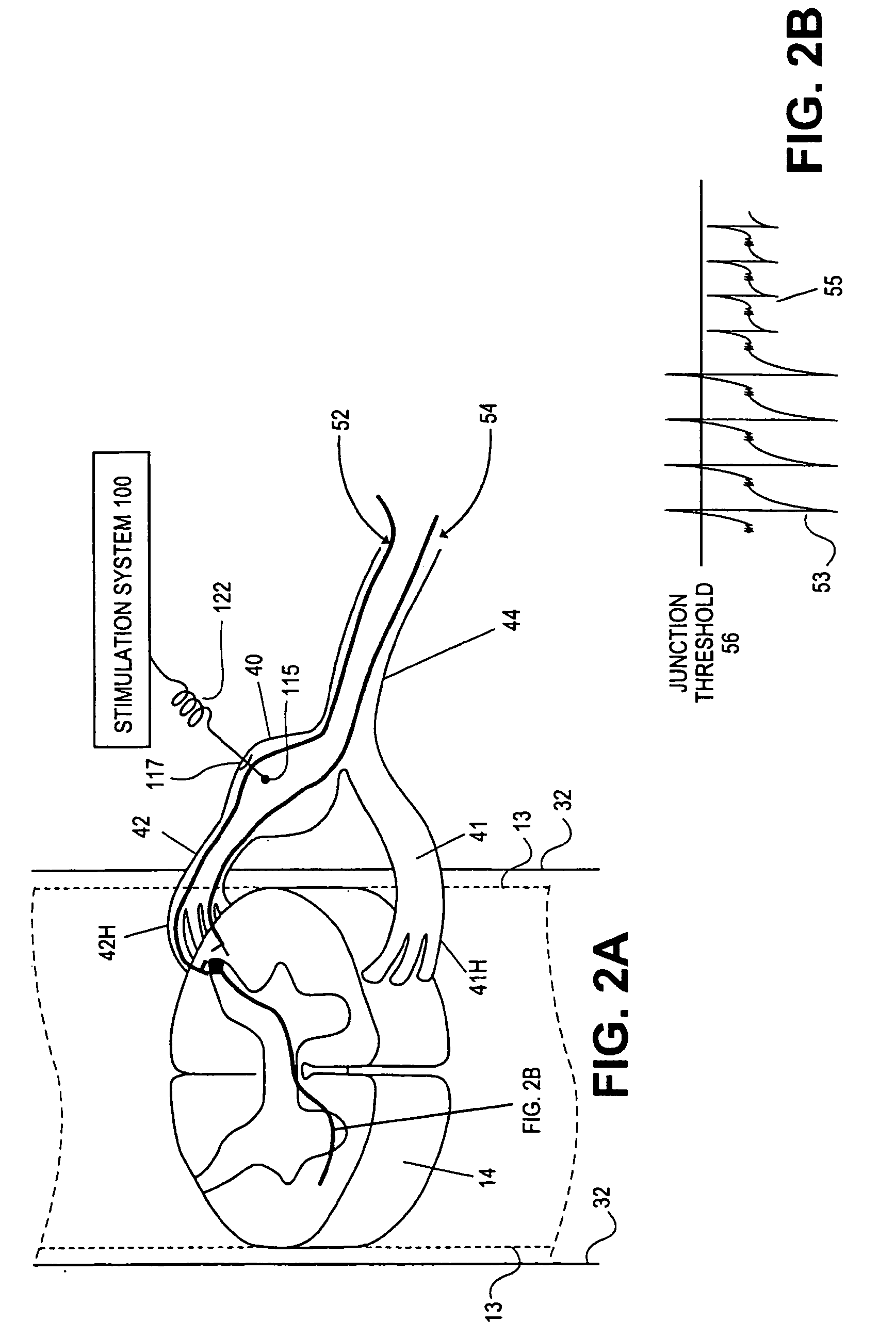
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Fully implantable nerve signal sensing and stimulation device and method for treating foot drop and other neurological disorders
InactiveUS20050010265A1Minimizing battery power consumptionLengthen expected life of batterySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal amplifierPower component
A fully implantable nerve stimulation system includes an event-triggered, closed-loop control unit that detects physiological events from nerve signals and delivers stimulation pulses to a nerve to produce a desired physiological response. The stimulation system includes a low-noise, low-power nerve signal amplifier, accelerometers that detect position and a battery powered processor that selectively powers components in the system to detect physiological events and deliver stimulation pulses with a minimum of battery power.
Owner:4491343 CANADA
Implantable microdevice with extended lead and remote electrode
InactiveUS7949395B2Good anchoring characteristicPreventing tetheringSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesBiomedical engineeringElectronic circuit
An implantable microdevice includes at least one electrode detachably connected to electronic circuitry housed in an hermetically-sealed micro housing. The micro housing has a length no more than about 10 mm. In one embodiment, the electrode is located at a distal end of an electrode lead, and a proximal end of the electrode lead is removably inserted into a connector that forms part of the micro housing.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
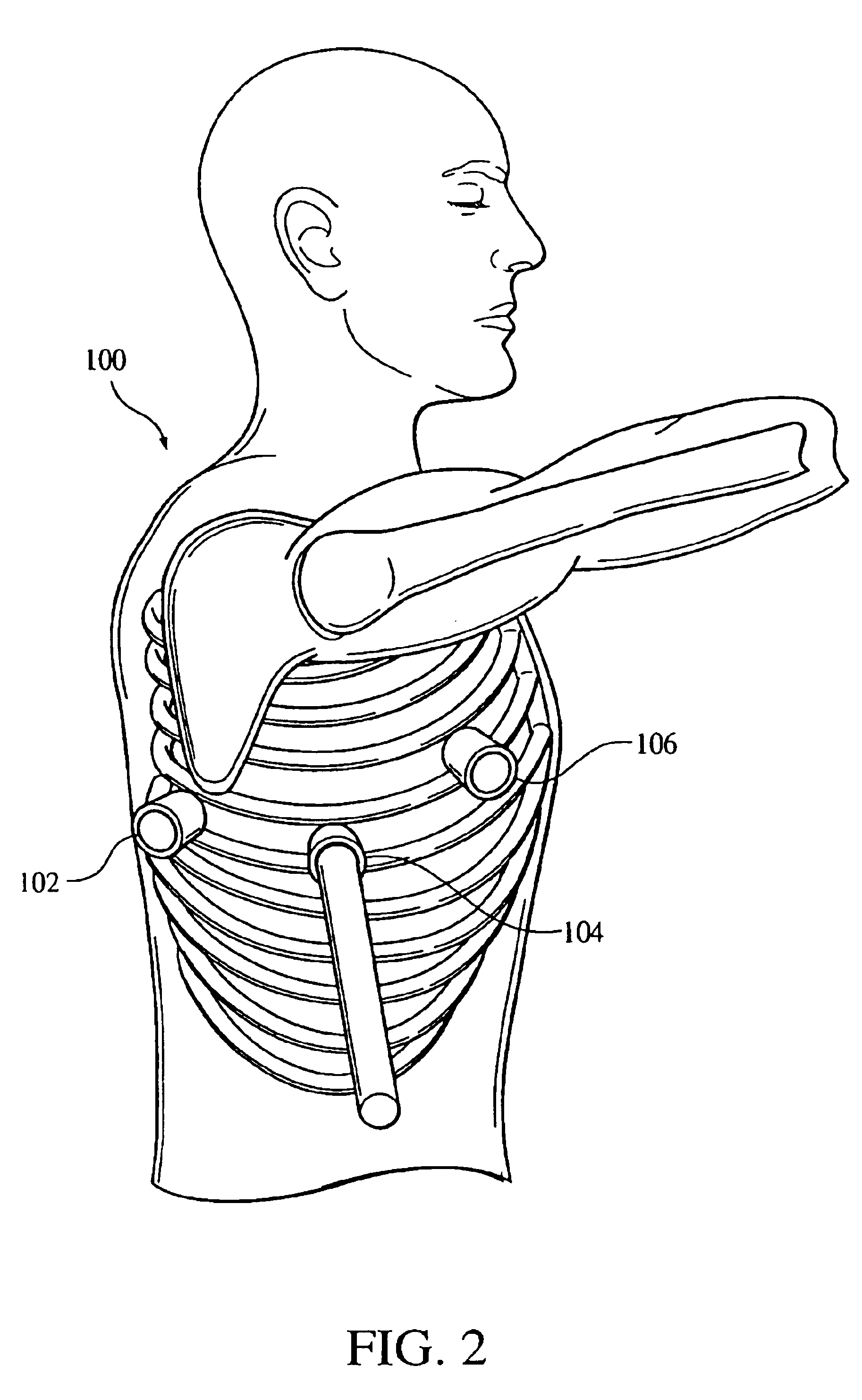
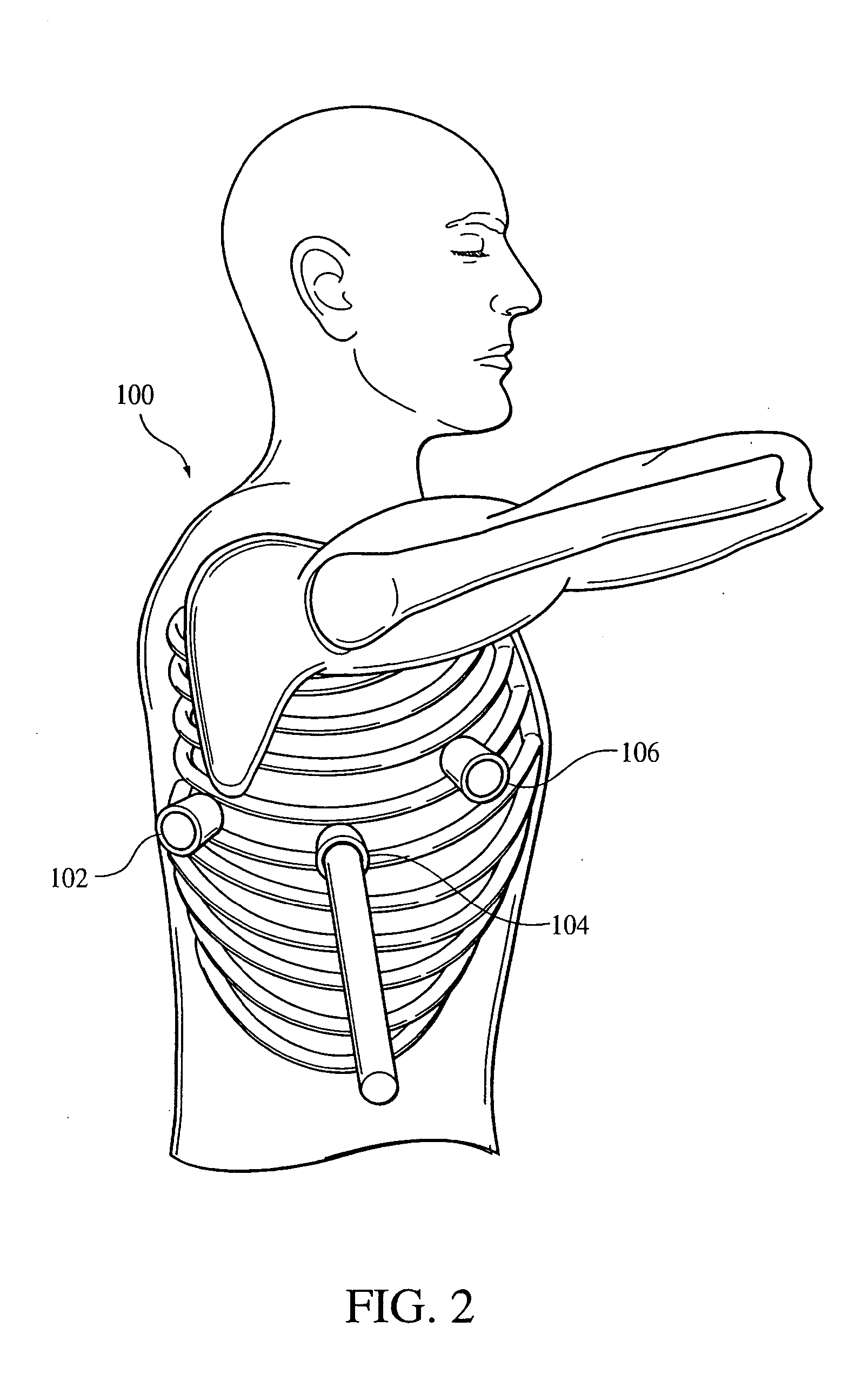
Electrode contact configurations for cuff leads
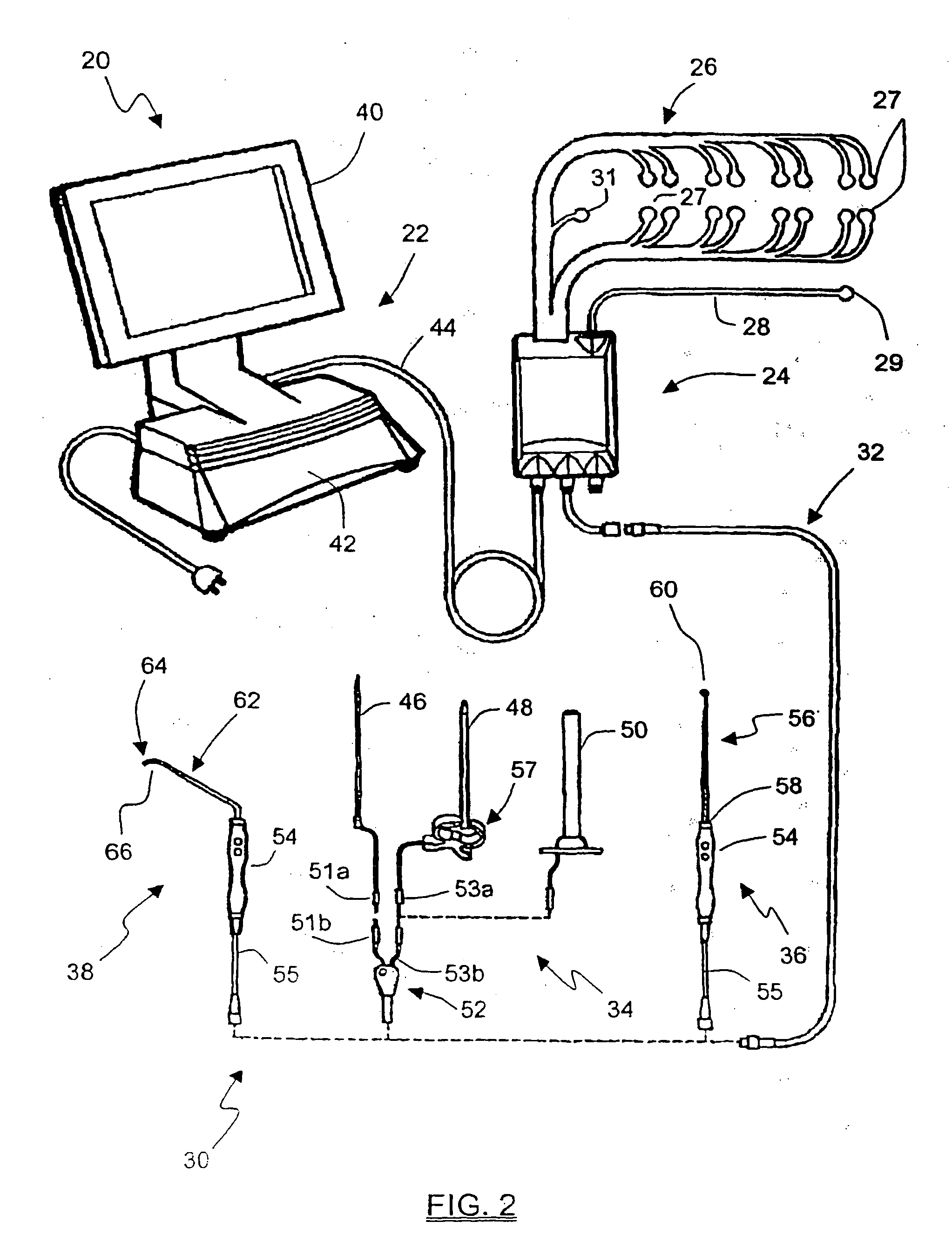
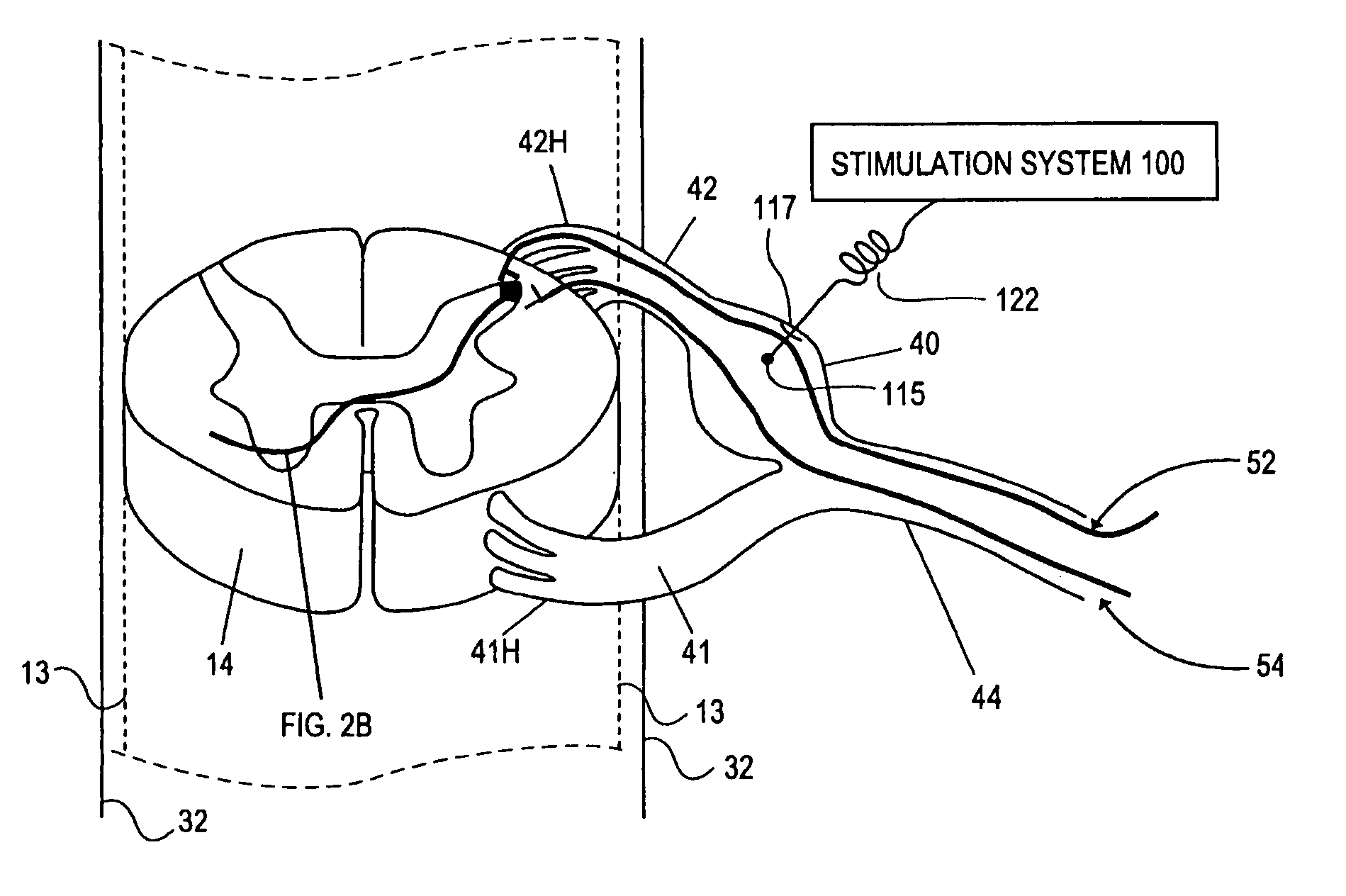
A stimulation system is disclosed that may include a stimulator unit coupled to electrode contacts on a cuff. In one embodiment, the cuff may be placed at least partially around a nerve. The stimulation system may include at least two electrode contacts disposed on the cuff such that a distance between the at least two electrode contacts various along a length of the electrode contacts. In another embodiment, a plurality of electrode contacts are disposed on the cuff such that distances between at least one electrode contact within the plurality of electrode contacts and each electrode contact immediately adjacent to the at least one electrode contact are different. The stimulator unit may also be implantable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Surgical access system and related methods
ActiveUS7207949B2Increase the number ofStructural damageSpinal electrodesElectromyographyDistractionRadiology
A surgical access system including a tissue distraction assembly and a tissue retraction assembly, both of which may be equipped with one or more electrodes for use in detecting the existence of (and optionally the distance and / or direction to) neural structures before, during, and after the establishment of an operative corridor to a surgical target site.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Minimally invasive apparatus for implanting a sacral stimulation lead
Methods and apparatus for implanting a stimulation lead in a patient's sacrum to deliver neurostimulation therapy that can reduce patient surgical complications, reduce patient recovery time, and reduce healthcare costs. A surgical instrumentation kit for minimally invasive implantation of a sacral stimulation lead through a foramen of the sacrum in a patient to electrically stimulate a sacral nerve comprises a needle and a dilator and optionally includes a guide wire. The needle is adapted to be inserted posterior to the sacrum through an entry point and guided into a foramen along an insertion path to a desired location. In one variation, a guide wire is inserted through a needle lumen, and the needle is withdrawn. The insertion path is dilated with a dilator inserted over the needle or over the guide wire to a diameter sufficient for inserting a stimulation lead, and the needle or guide wire is removed from the insertion path. The dilator optionally includes a dilator body and a dilator sheath fitted over the dilator body. The stimulation lead is inserted to the desired location through the dilator body lumen or the dilator sheath lumen after removal of the dilator body, and the dilator sheath or body is removed from the insertion path. If the clinician desires to separately anchor the stimulation lead, an incision is created through the entry point from an epidermis to a fascia layer, and the stimulation lead is anchored to the fascia layer. The stimulation lead can be connected to the neurostimulator to delivery therapies to treat pelvic floor disorders such as urinary control disorders, fecal control disorders, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic pain.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
New stimulation design for neuromodulation
The present application relates to a new stimulation design which can be utilized to treat neurological conditions. The stimulation system produces a burst mode stimulation which alters the neuronal activity of the predetermined site, thereby treating the neurological condition or disorder.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Method, apparatus, and surgical technique for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20060167498A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesSplanchnic nervesDisease
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
Electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS6907295B2Minimize cathode effectWeakening rangeSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowAnatomy
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve. A cathode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a cathodic longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply, a cathodic current to the nerve. A primary inhibiting anode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a primary anodal longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply a primary anodal current to the nerve. A secondary inhibiting anode is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a secondary anodal longitudinal site of the nerve and to apply a secondary anodal current to the nerve, the secondary anodal longitudinal site being closer to the primary anodal longitudinal site than to the cathodic longitudinal site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Renal nerve stimulation method and apparatus for treatment of patients
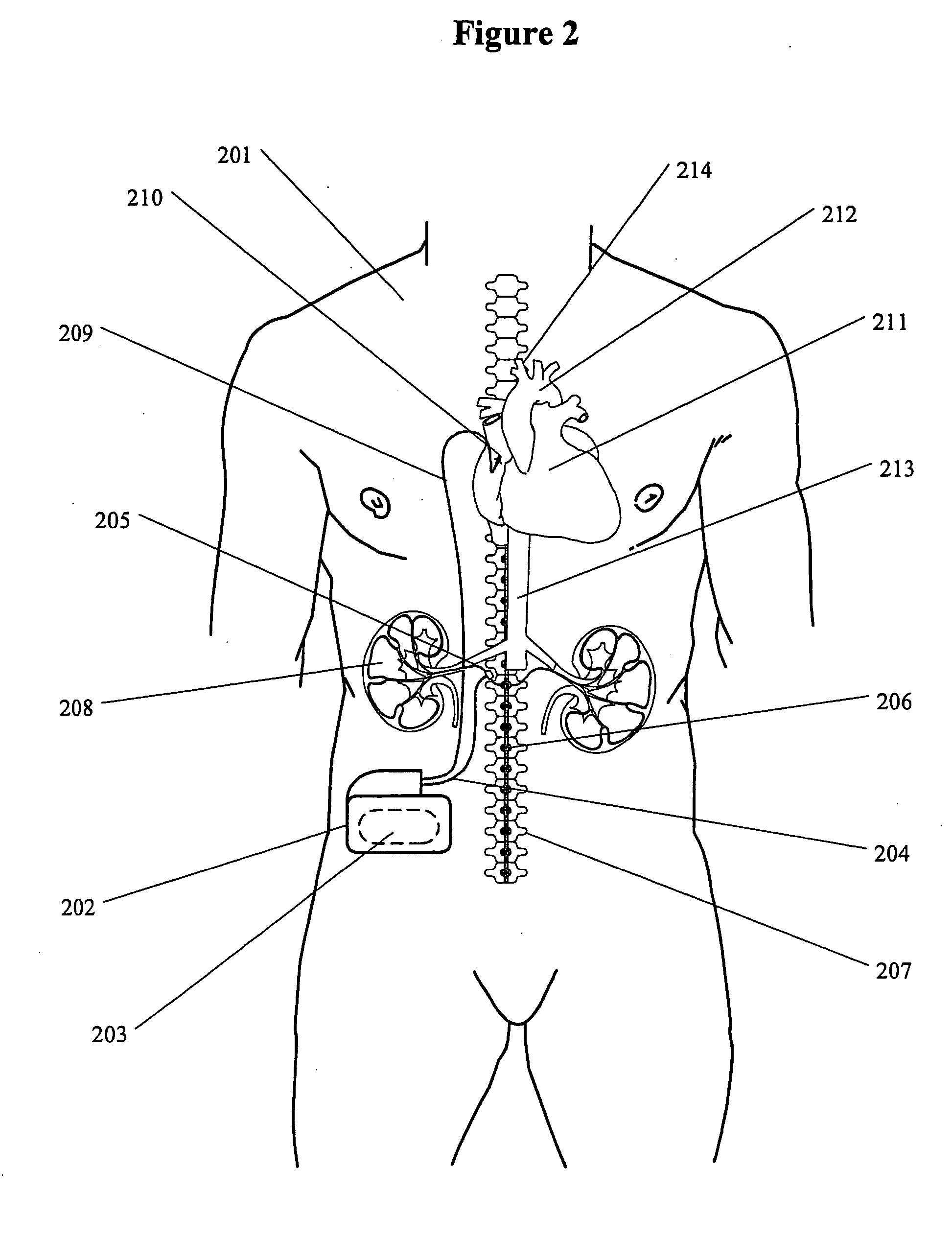
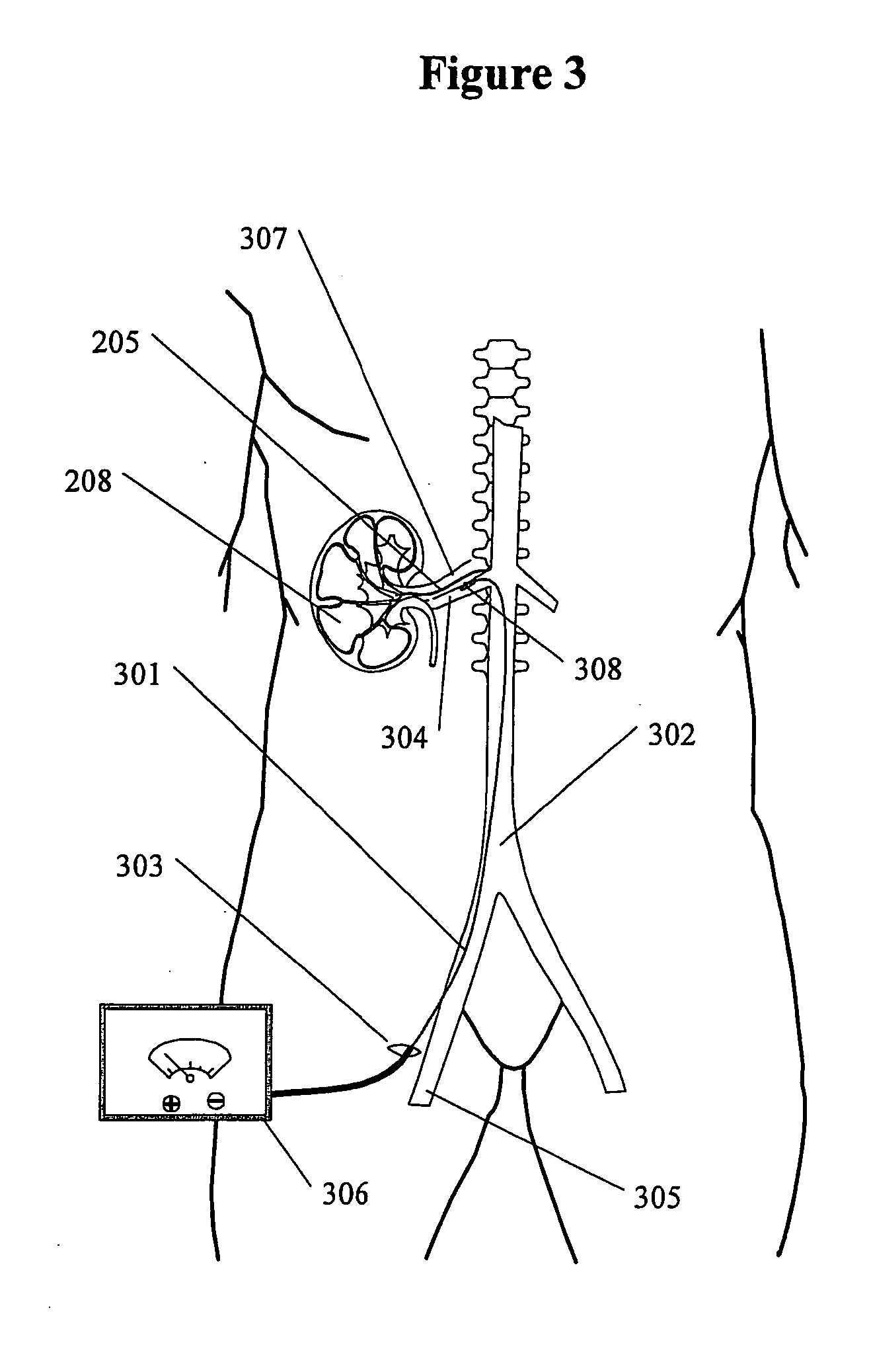
InactiveUS20050228460A1Arrest and slow down progression of diseaseEase of conditionsSpinal electrodesMedical devicesRenal nerveFAILURE KIDNEY
A method and apparatus for treatment of heart failure, hypertension and renal failure by stimulating the renal nerve. The goal of therapy is to reduce sympathetic activity of the renal nerve. Therapy is accomplished by at least partially blocking the nerve with drug infusion or electrostimulation. Apparatus can be permanently implanted or catheter based.
Owner:LEVIN HOWARD R +1
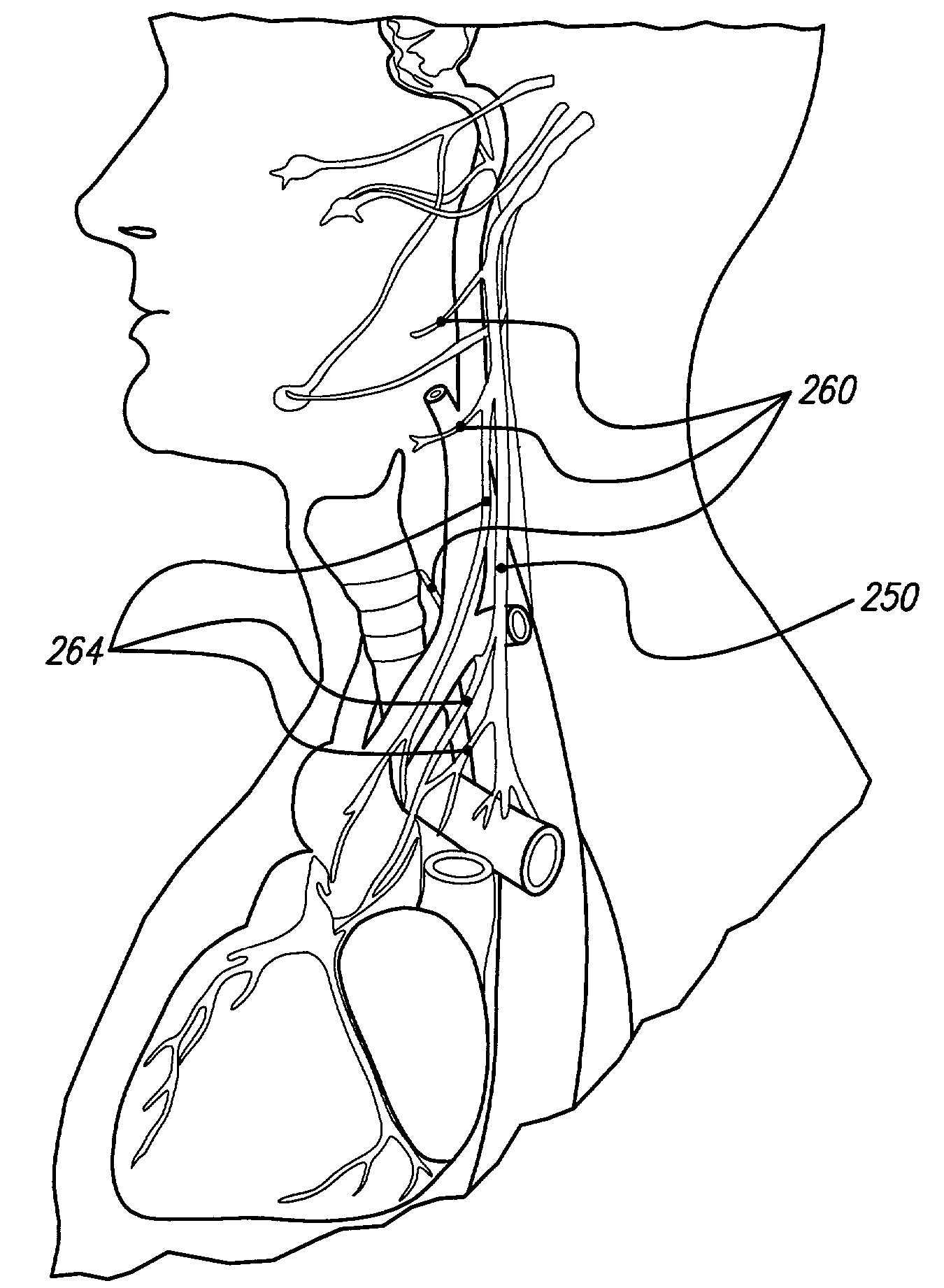
Vagus nerve stimulation via unidirectional propagation of action potentials
ActiveUS7292890B2Less power consumptionExcessive stimulationSpinal electrodesSurgerySide effectMedicine
Methods of stimulating a vagus nerve include providing at least one implantable stimulator with at least two electrodes, configuring the electrodes to apply stimulation that unidirectionally propagates action potentials along a vagus nerve, and applying the stimulation to the vagus nerve to effectively select afferent fibers, thereby treating at least one of epilepsy and depression while limiting side effects of bidirectional stimulation. At least one of the electrodes comprises a leadsless electrode.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method of routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors
The invention provides an implant, system and method for electrically stimulating a target tissue to either activate or block neural impulses. The implant provides a conductive pathway for a portion of electrical current flowing between surface electrodes positioned on the skin and transmits that current to the target tissue. The implant has a passive electrical conductor of sufficient length to extend from subcutaneous tissue located below a surface cathodic electrode to the target tissue. The conductor has a pick-up end which forms an electrical termination having a sufficient surface area to allow a sufficient portion of the electrical current to flow through the conductor, in preference to flowing through body tissue between the surface electrodes, such that the target tissue is stimulated to either activate or block neural impulses. The conductor also has a stimulating end which forms an electrical termination for delivering the current to the target body tissue.
Owner:2249020 ALBERTA LTD
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
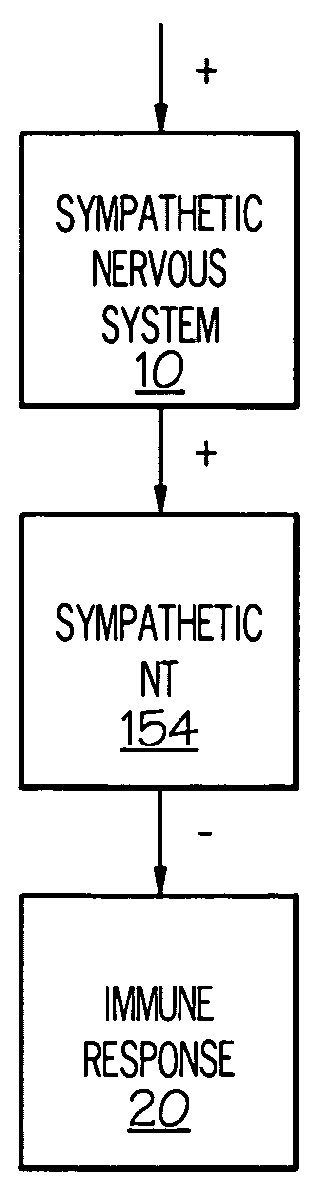
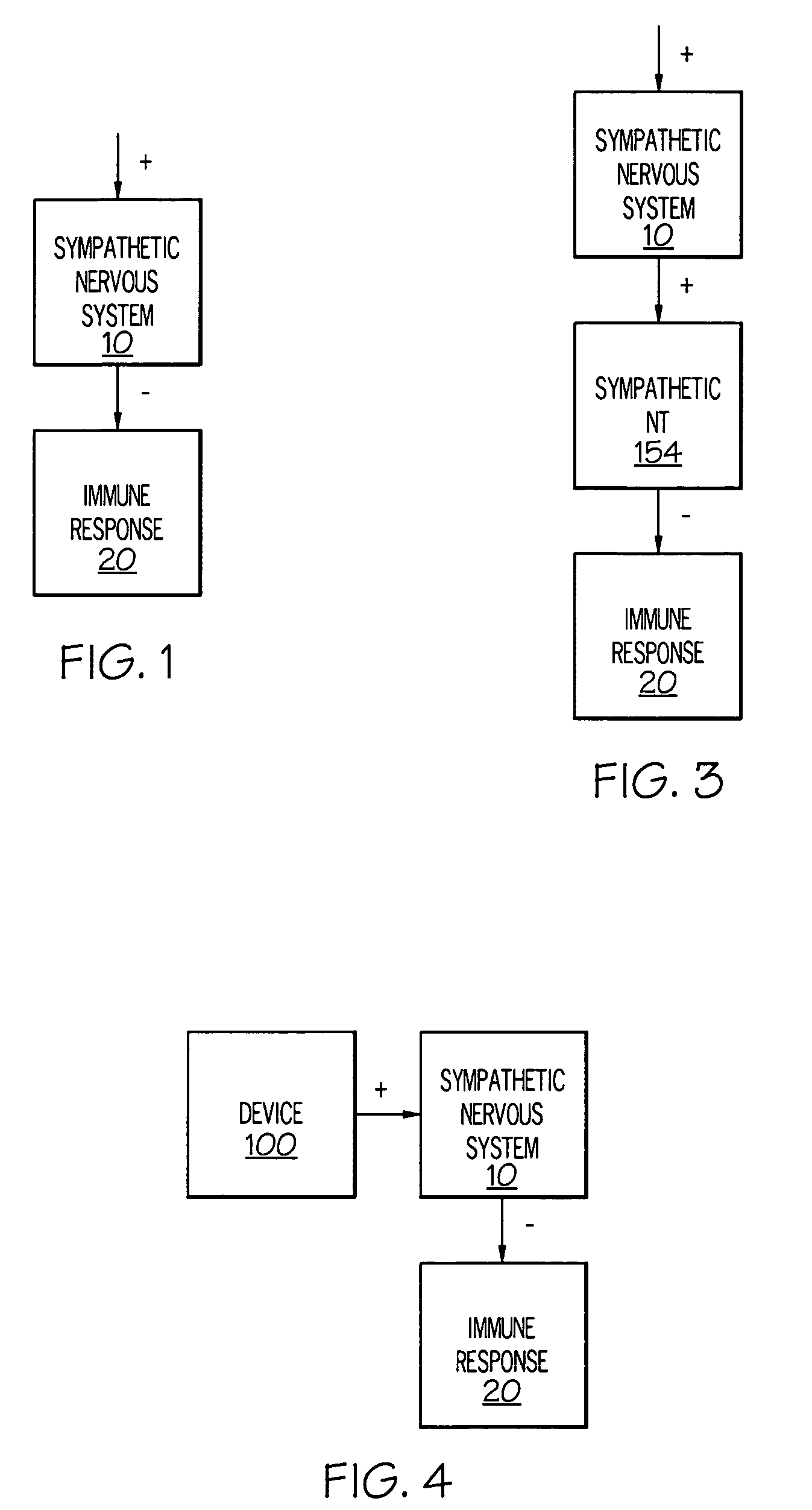
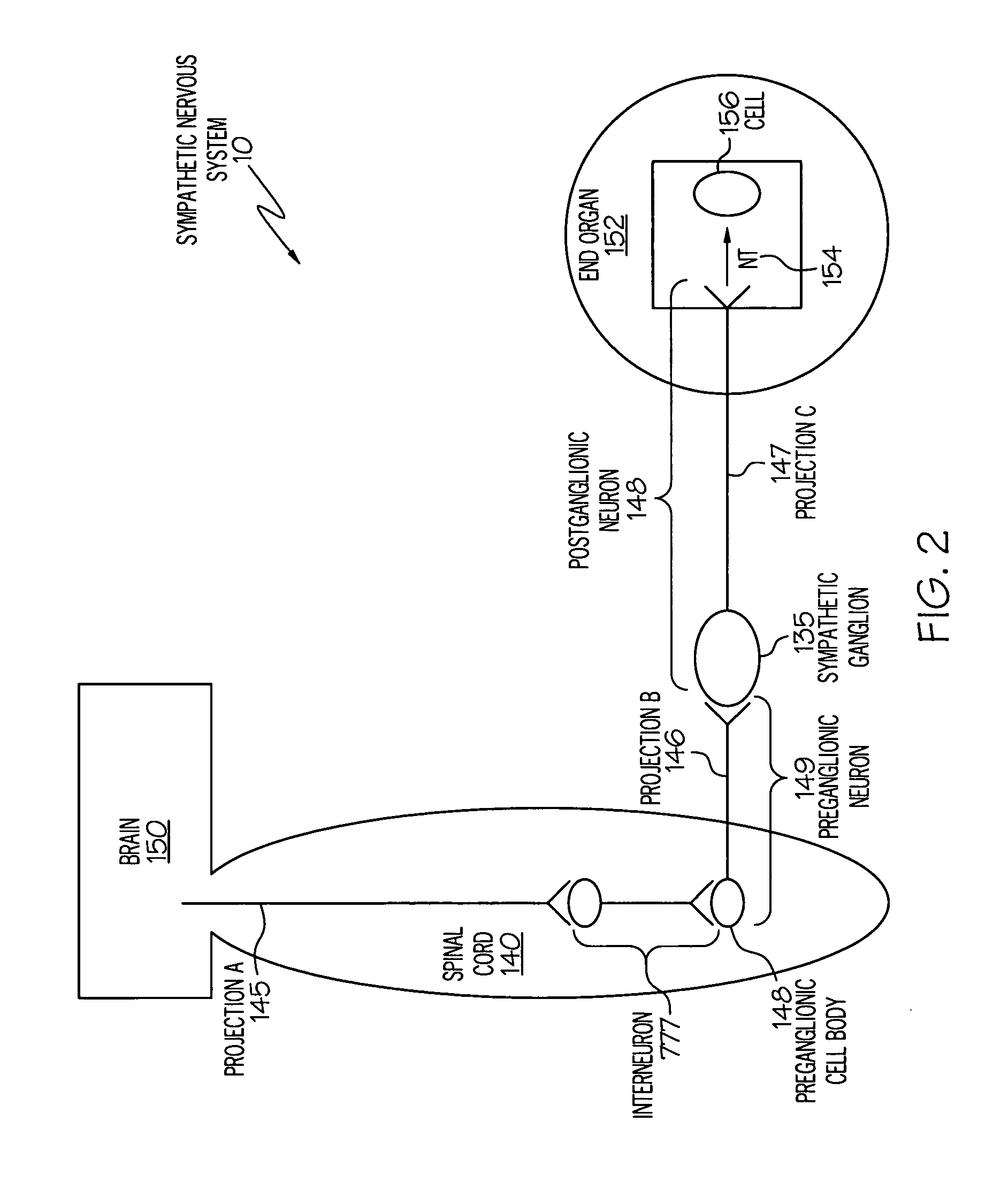
ActiveUS20050075701A1Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemNeuron
Stimulation of one or more neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, including the splenic nerve, to attenuate an immune response, including an inflammatory immune response, is discussed. Devices and systems to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system to attenuate an immune response are also discussed. Devices discussed include pulse generators and drug pumps. Systems are described as optionally having one or more sensors and operator instructions. In specific examples, stimulation of the splenic nerve of pigs with a pulse generator is shown to be safe and effective in attenuating a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Access and tissue modification systems and methods
Described herein are methods and systems for precisely placing and / or manipulating devices within the body by first positioning a guidewire or pullwire through the body from a first location, around a curved pathway, and out of the body through a second location, so that the distal and proximal ends of the guidewire extend from the body, then pulling a device into position using the guidewire. The device to be positioned within the body is coupled to the proximal end of the guidewire, and the device is pulled into the body by pulling on the distal end of the guidewire that extends from the body. The device may be bimanually manipulated by pulling the guidewire distally, and an attachment to the device that extends proximally, allowing control of both the proximal and the distal ends. In this manner devices (and particularly implants such as innerspinous distracters, stimulating leads, and disc slings) may be positioned and / or manipulated within the body. Devices to modify tissue may also be positioned or manipulated so that a target tissue within the body is modified.
Owner:BAXANO
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS20080213331A1Shorten the progressResolution of overloadSpinal electrodesMedical devicesDiseaseRenal nerve
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump or a drug eluding implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:ARDIAN
Dynamic nerve stimulation for treatment of disorders
ActiveUS20050065575A1Provide central nervous system satietyIncreased energy expenditureSpinal electrodesDiseasePhysical therapy
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of nerves is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating a nerve using an electrode. Dynamic stimulation through ramped cycling of electrical stimulation, stimulation frequency alteration, and / or duty cycle variance can produce therapeutic benefits.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
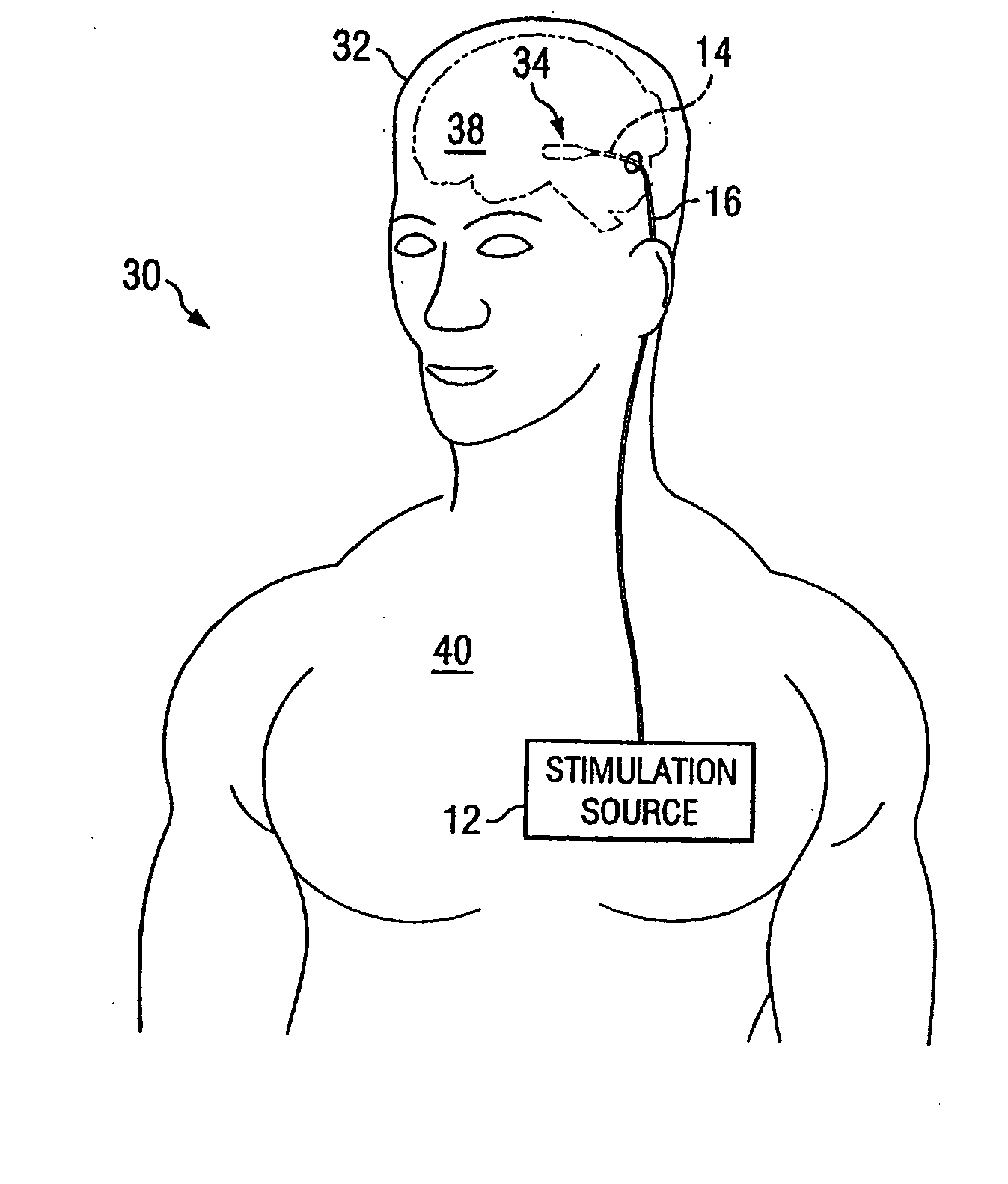
Electrical stimulation system and method for stimulating tissue in the brain to treat a neurological condition
InactiveUS20060004422A1Reduce and eliminate certain problem and disadvantageRemissionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricityMedicine
According to one aspect, a stimulation system is provided for electrically stimulating a predetermined site to treat a neurological condition. The system includes an electrical stimulation lead adapted for implantation in communication with a predetermined site, wherein the site is brain tissue site. The stimulation lead includes one or more stimulation electrodes adapted to be positioned in the predetermined site. The system also includes a stimulation source that generates the stimulation pulses for transmission to the one or more stimulation electrodes of the stimulation lead to deliver the stimulation pulses to the predetermined site to treat a neurological disorder or condition.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
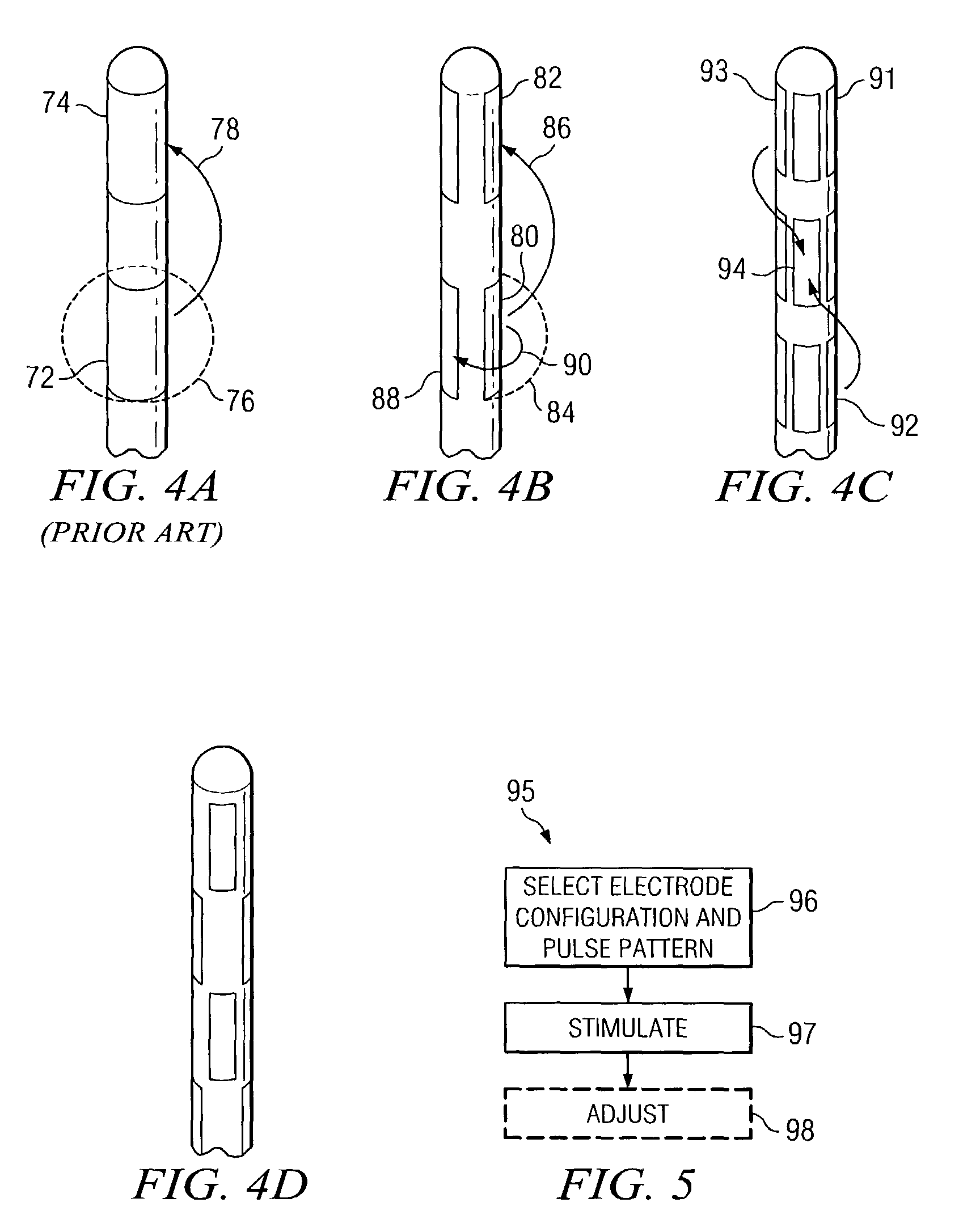
Apparatus for directionally stimulating nerve tissue
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for making such apparatus for providing controlled and directional stimulation patterns for tissue stimulation. The apparatus may be useful in stimulation nervous tissue in the brain, about the spinal cord, on nerve roots, about peripheral nerves, and in muscles, among others. The apparatus includes a implantable pulse generator connected to a lead. The lead has electrodes placed about a perimeter. In addition, the lead may include electrodes placed longitudinally along the axis of the lead. By applying charge differences between circumferentially distributed electrodes, a smaller stimulation field may be established. In addition, by stimulating between electrodes distributed longitudinally on the same side, a directional flow field may be established. Such leads are especially useful in deep brain stimulation as the region in which a stimulation field is strong enough to produce tissue stimulation is directional and minimized.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
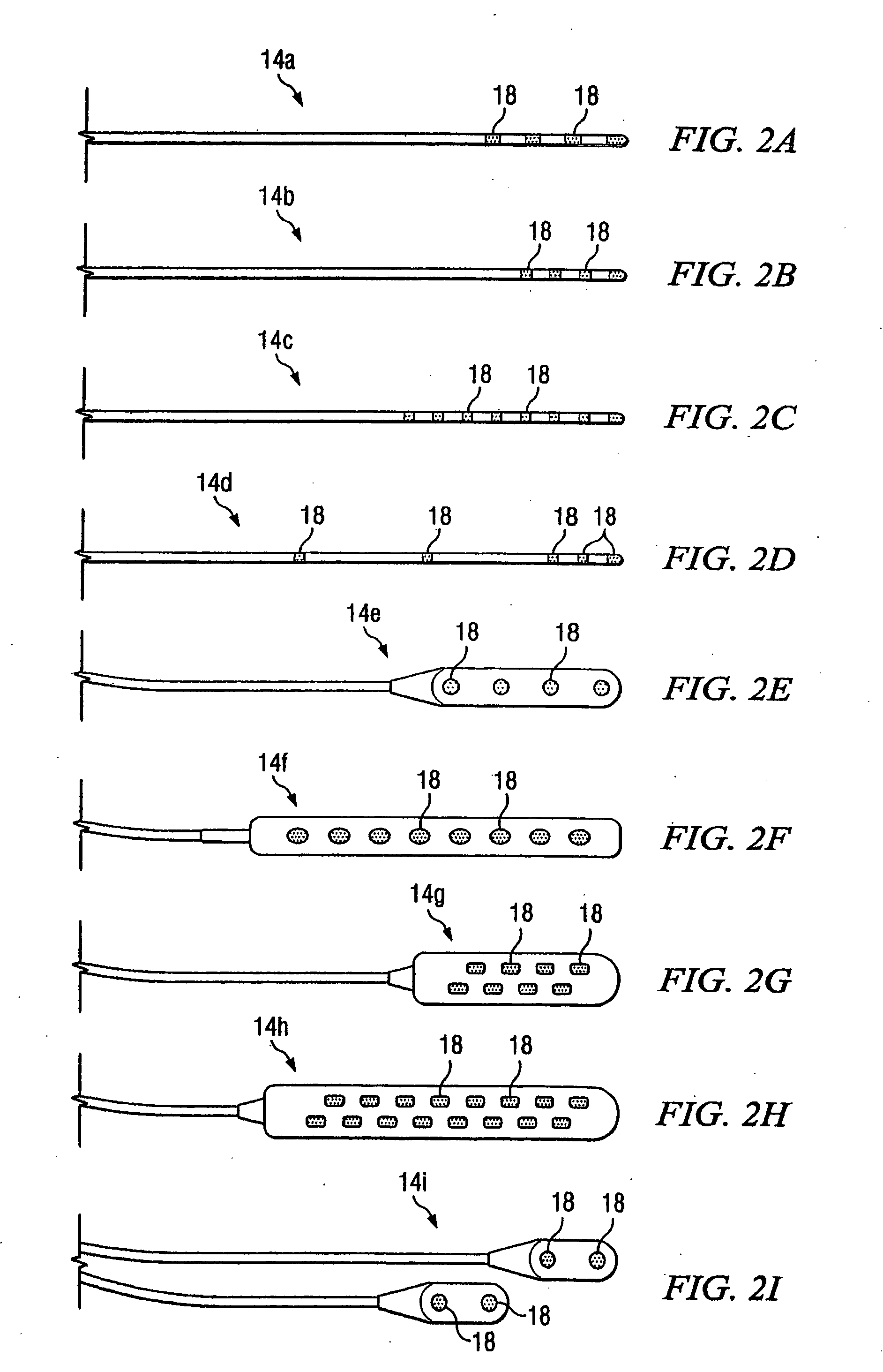
Lead Assembly and Method of Making Same
A lead assembly and a method of making a lead are provided. The lead comprises a terminal, proximal end having a plurality of terminal contacts and material separating the terminal contacts. In one embodiment of the lead, the terminal contacts are separated by a preformed spacer, that may be made from various hard materials such as polyurethane, PEEK and polysulfone. Epoxy may be used to fill spaces at the proximal lead end, including between the spacer and terminal contacts. In one embodiment of the lead, the terminal contacts are separated by epoxy only. The lead may include a plurality of conductor lumens that contain conductors. The lead may also include a stylet lumen for accepting a stylet.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065573A1Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Lead electrode for use in an MRI-safe implantable medical device
A pulse stimulation system configured for implantation into a patient's body comprises a pulse stimulator, a conductive stimulation lead having a proximal end electrically coupled to the pulse simulator and having a distal end, and an electrode assembly coupled to the distal end of the stimulation lead. The electrode assembly comprises an electrode body having a therapy electrode thereon that is electrically coupled to the stimulation lead for delivering therapy to the patient. A floating electrode is configured to contact the patient's body tissue and has a surface area substantially larger than that of the therapy electrode. A filter is coupled between the therapy electrode and the floating electrode for diverting RF energy toward the floating electrode and away from the therapy electrode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Treatment of conditions through modulation of the autonomic nervous system
ActiveUS20050240241A1Decreasing and increasing parasympathetic and activityIncreasing parasympathetic activity/sympathetic activity ratioSpinal electrodesAngle modulation detailsNervous systemAnatomy
Methods are provided for treating a subject for a condition by modulating at least a portion of the subject's autonomic nervous system. In accordance with certain embodiments of the subject methods, at least a portion of a subject's autonomic nervous system is electrically or pharmacologically modulated in a manner that is effective to treat the subject for the condition. The subject methods find use in the treatment of a variety of different conditions, where such conditions include various disease conditions. Also provided are systems and kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:PALO ALTO INVESTORS
Steerable stylet handle assembly
ActiveUS20090187222A1StimulationSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesDistal portionBiomedical engineering
An exemplary steerable stylet handle assembly includes a housing having first and second side walls defining a channel therebetween, a button in communication with the first and second side walls and configured to move distally and proximally within the channel, and a stylet subassembly having an inner stylet wire located at least partially within an outer tubing. The inner stylet wire has a pre-curved portion and is coupled to a proximal portion of the housing. The outer tubing is coupled to the button. Movement of the button within the channel is configured to selectively expose and cover at least a portion of the pre-curved distal portion of the inner stylet wire with the outer tubing.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Leads with spirally arranged segmented electrodes and methods of making and using the leads
One embodiment is a stimulation lead including a lead body comprising a longitudinal surface, a distal end, and a proximal end; and multiple electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead body near the distal end of the lead body. The multiple electrodes include multiple segmented electrodes with each of the segmented electrodes having an exterior surface, an interior surface opposite the exterior surface, a proximal end, and a distal end. At least one of the segmented electrodes includes one or more of a) at least one channel formed in the segmented electrode and extending from the proximal end to the distal end of the segmented electrode, b) an arcuate groove formed in at least one of the distal end surface or the proximal end surface, or c) a notch formed in the segmented electrode and extending from the proximal end to the distal end of the segmented electrode.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and methods for performing surgical procedures and assessments
ActiveUS20050075578A1Easy to useEasy to explainSpinal electrodesCannulasNerve ProximityNeurophysiology
The present invention involves systems and related methods for performing surgical procedures and assessments, including the use of neurophysiology-based monitoring to: (a) determine nerve proximity and nerve direction to surgical instruments employed in accessing a surgical target site; (b) assess the pathology (health or status) of a nerve or nerve root before, during, or after a surgical procedure; and / or (c) assess pedicle integrity before, during or after pedicle screw placement, all in an automated, easy to use, and easy to interpret fashion so as to provide a surgeon-driven system.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods for stimulating a nerve root ganglion
Some embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia. Some other embodiments of the present invention provide methods for selective neurostimulation of one or more dorsal root ganglia as well as techniques for applying neurostimulation to the spinal cord. Still other embodiments of the present invention provide stimulation systems and components for selective stimulation and / or neuromodulation of one or more nerve root ganglia through implantation of an electrode on, in or around a nerve root ganglia in combination with a pharmacological agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com