Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
335 results about "Sympathetic nervous system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
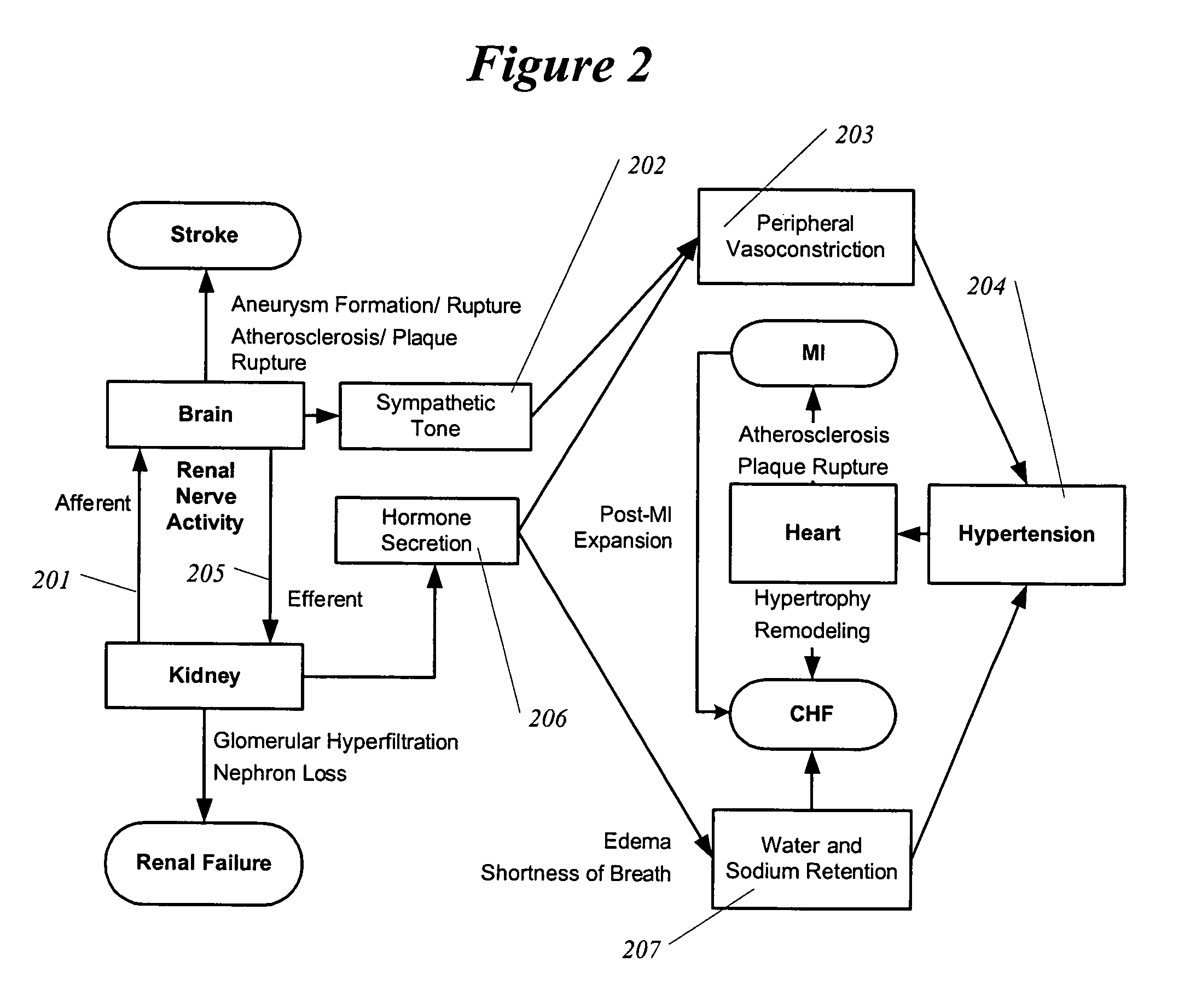
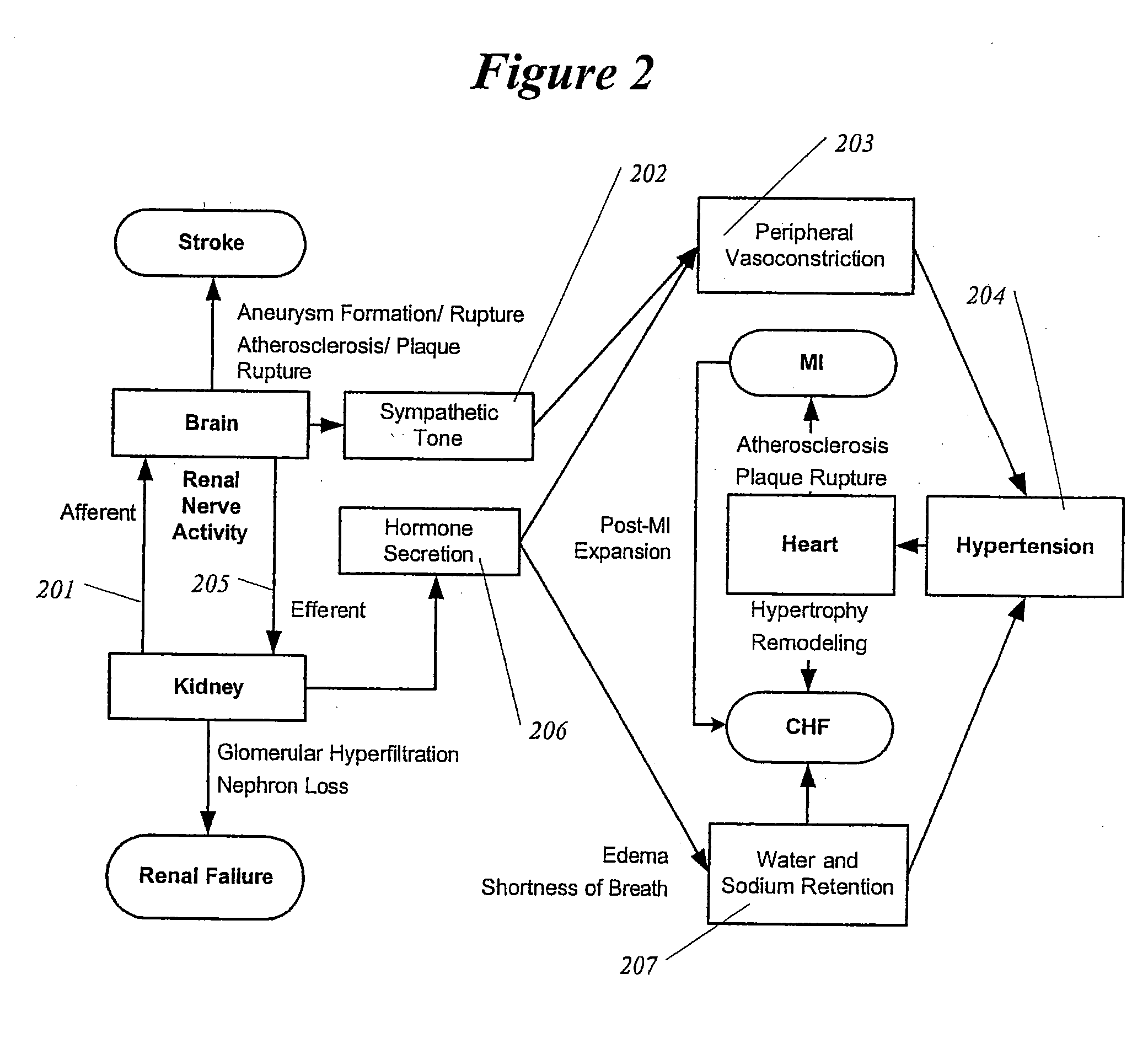
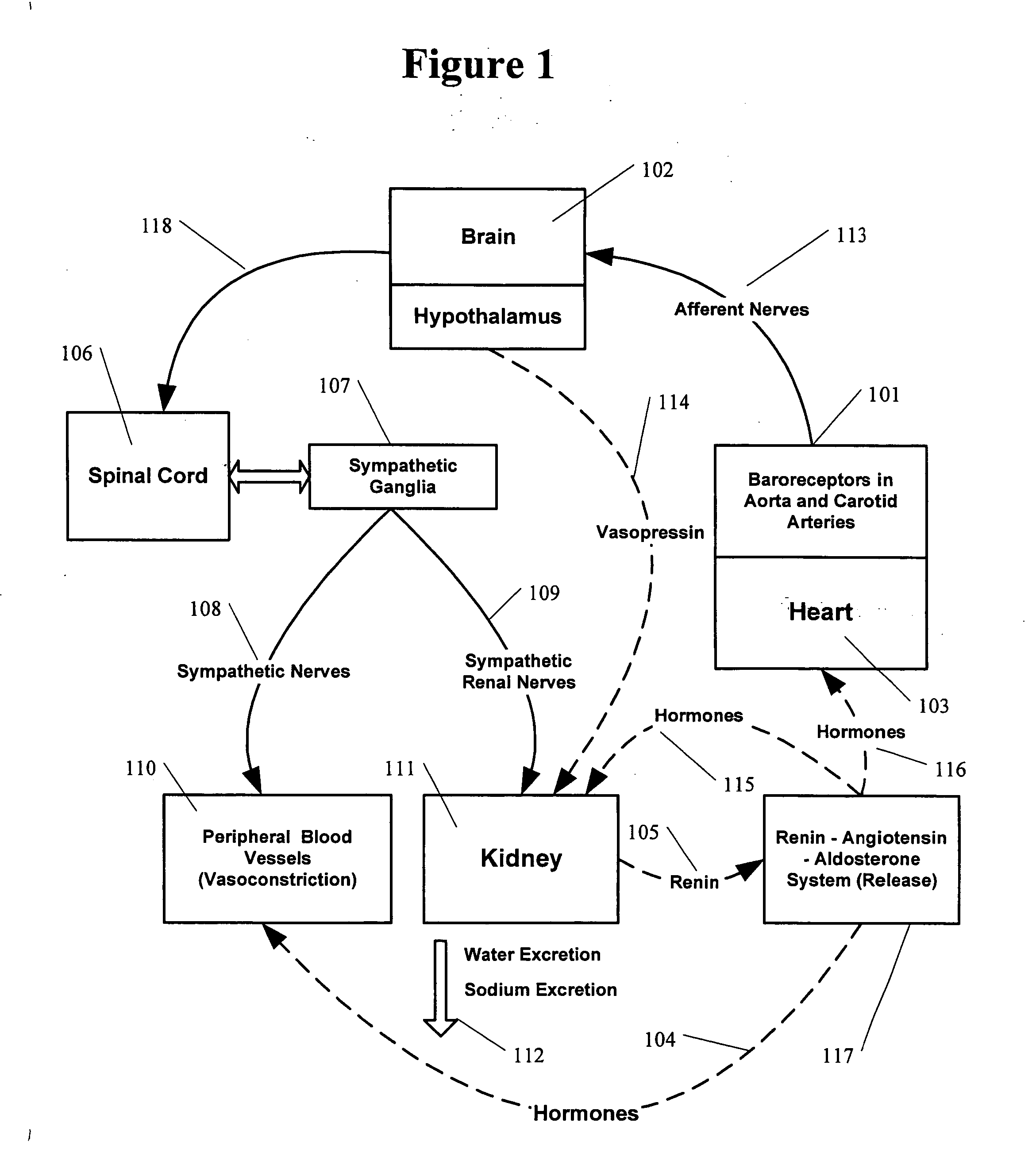
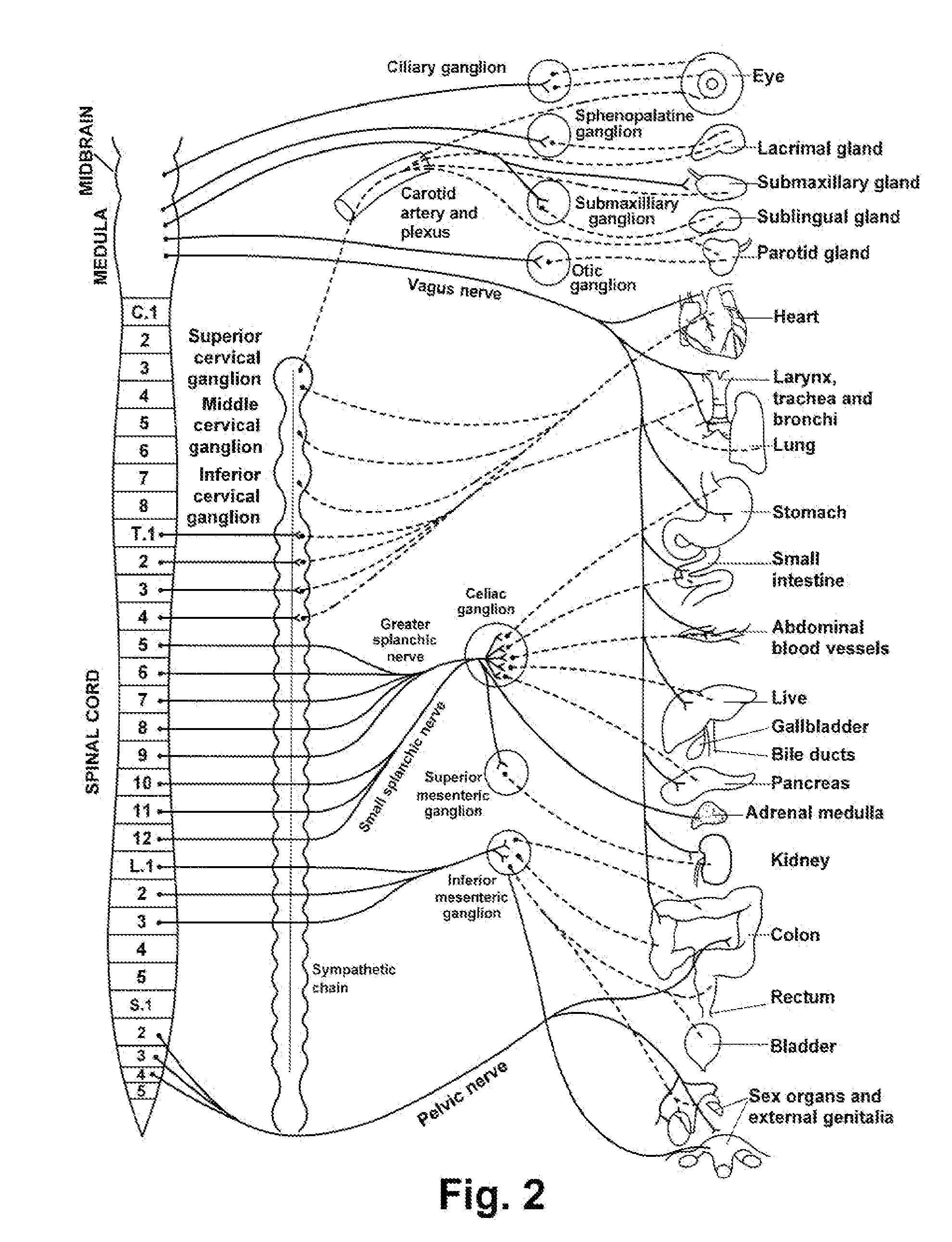
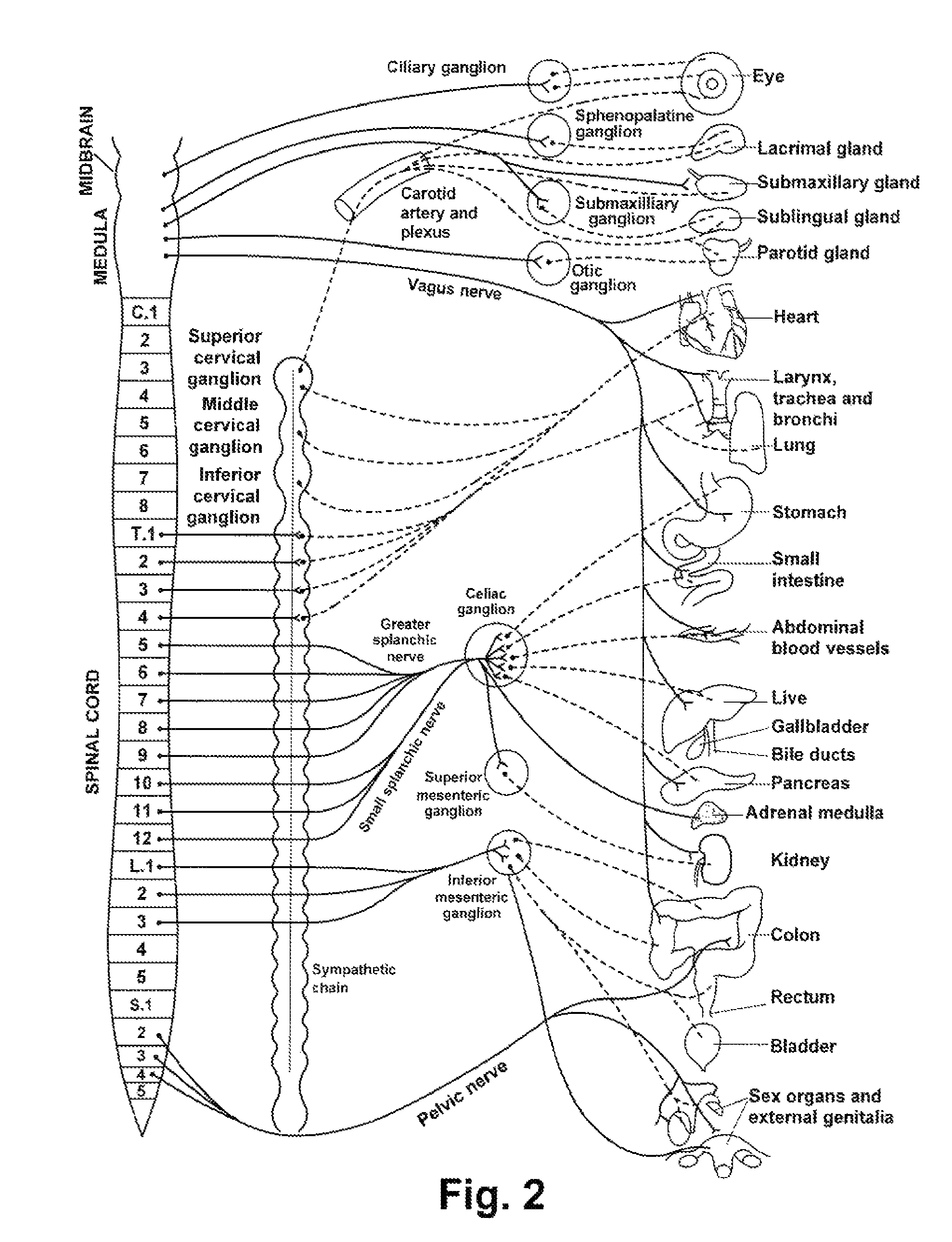
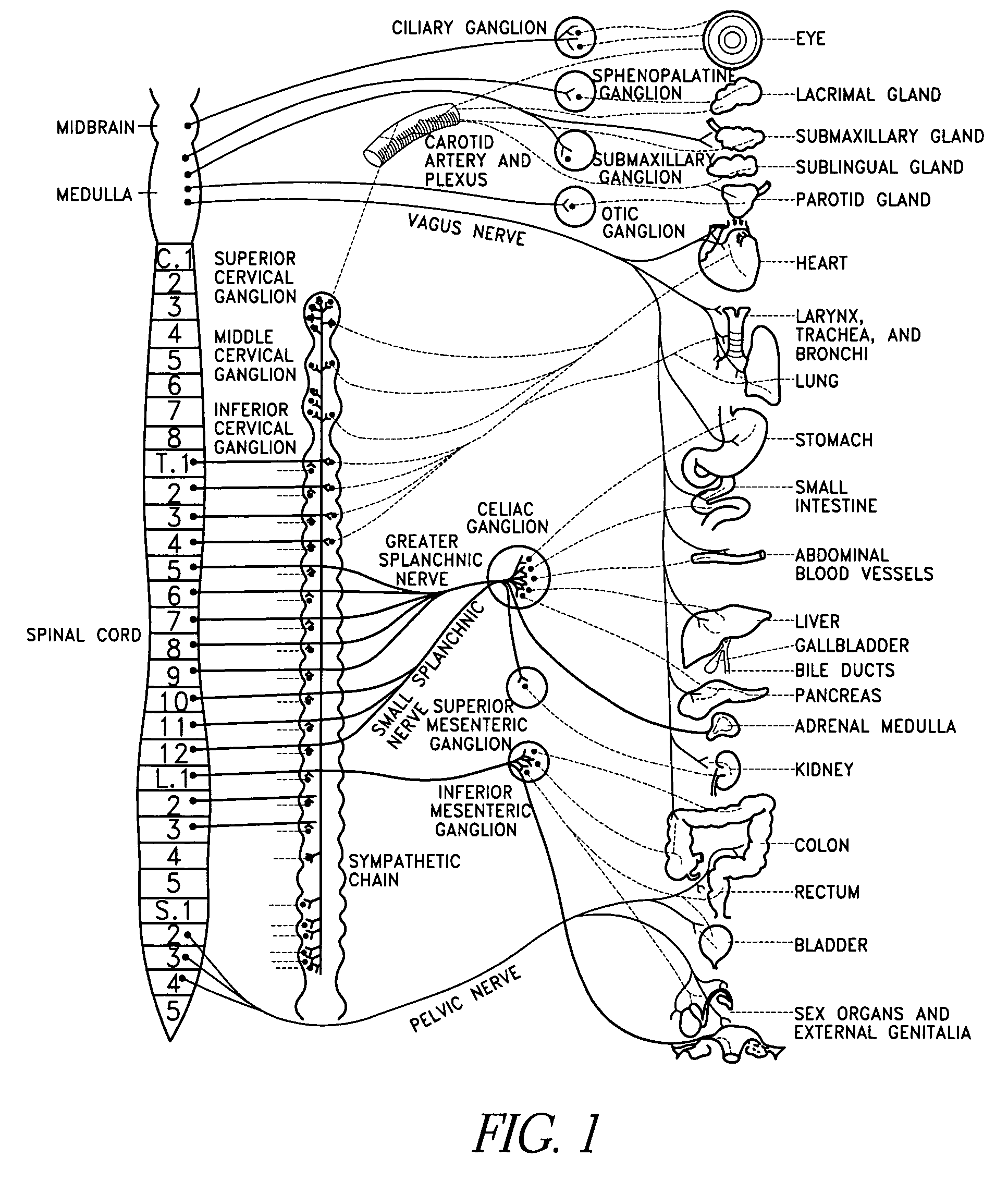
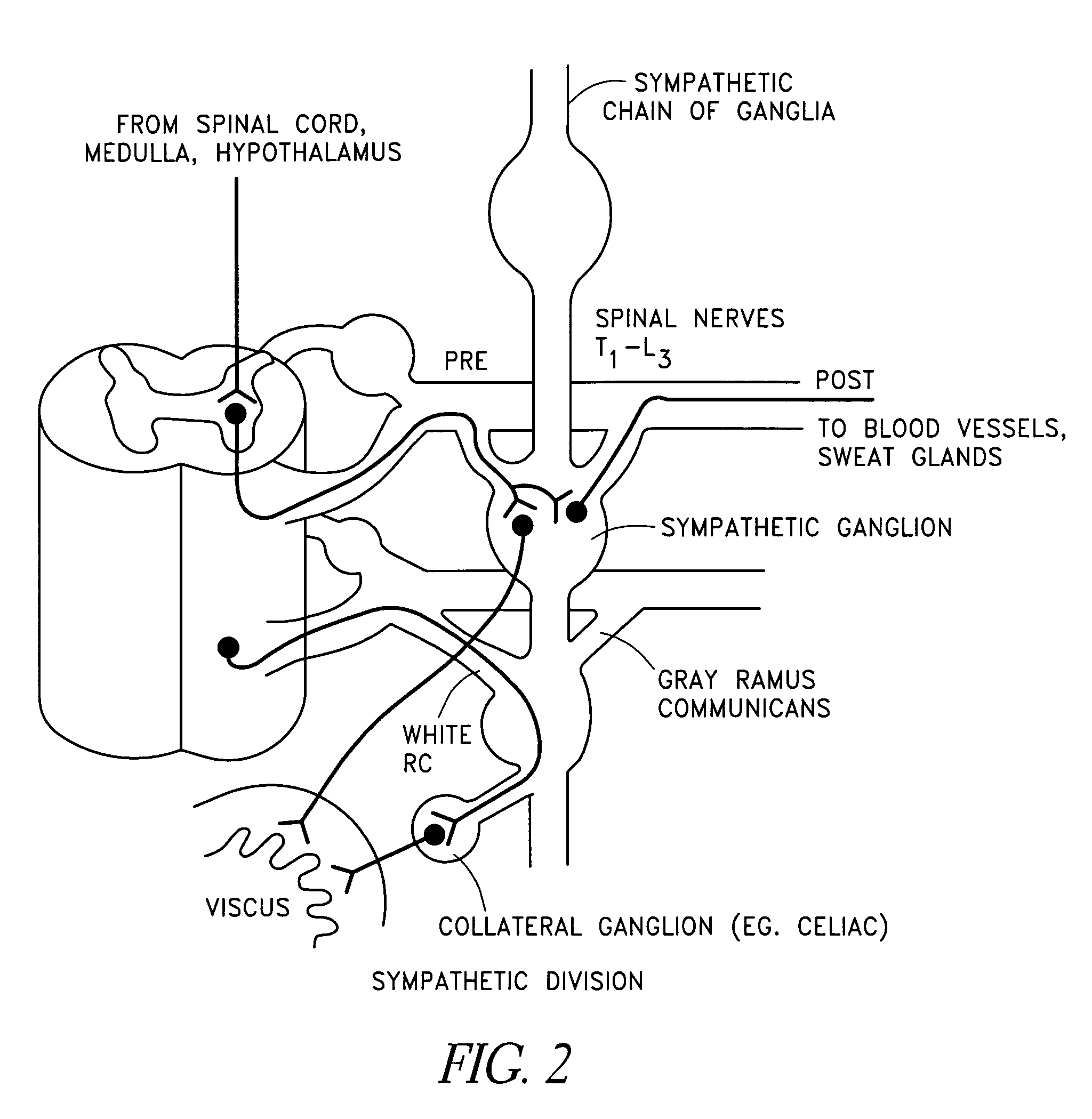
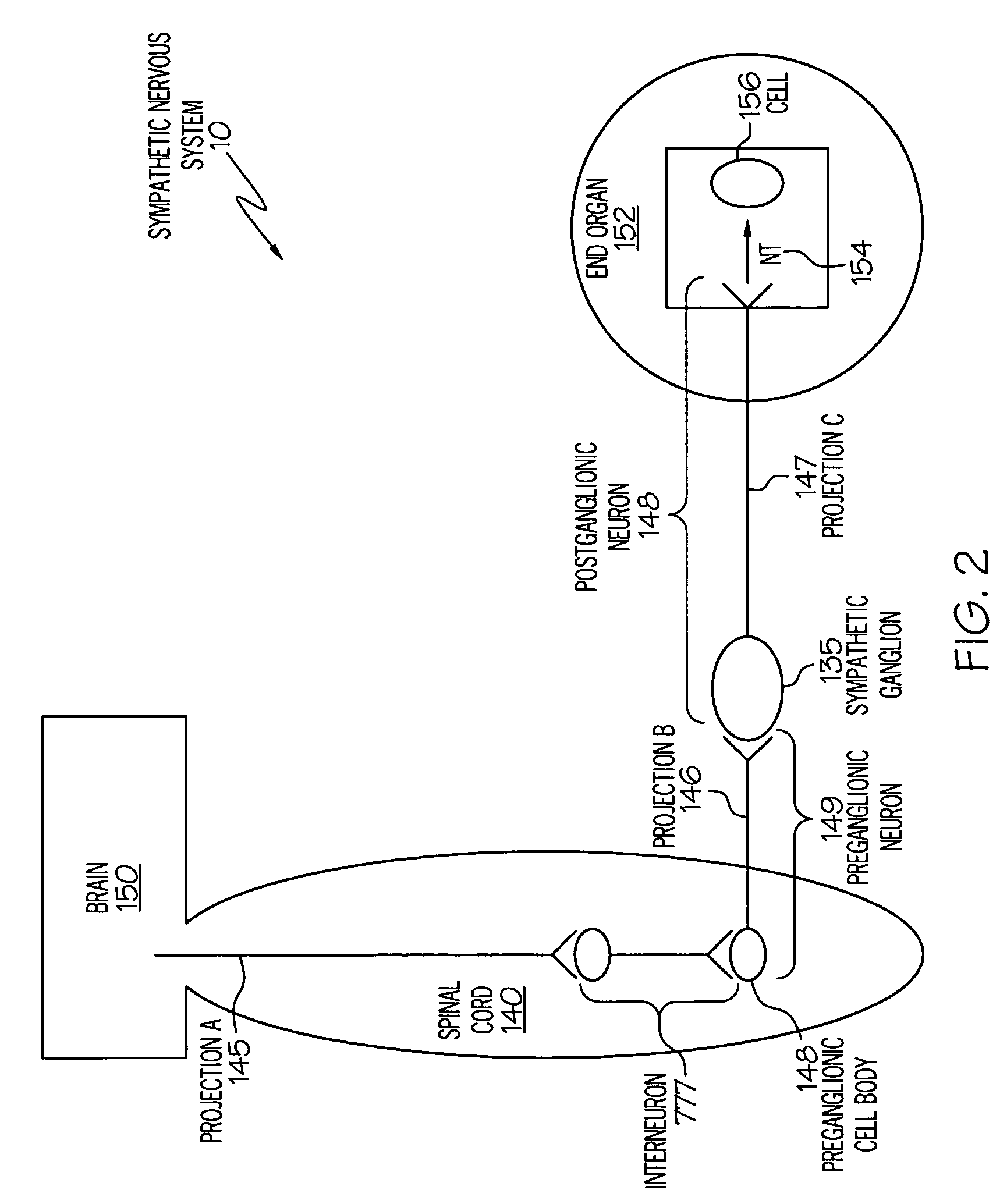
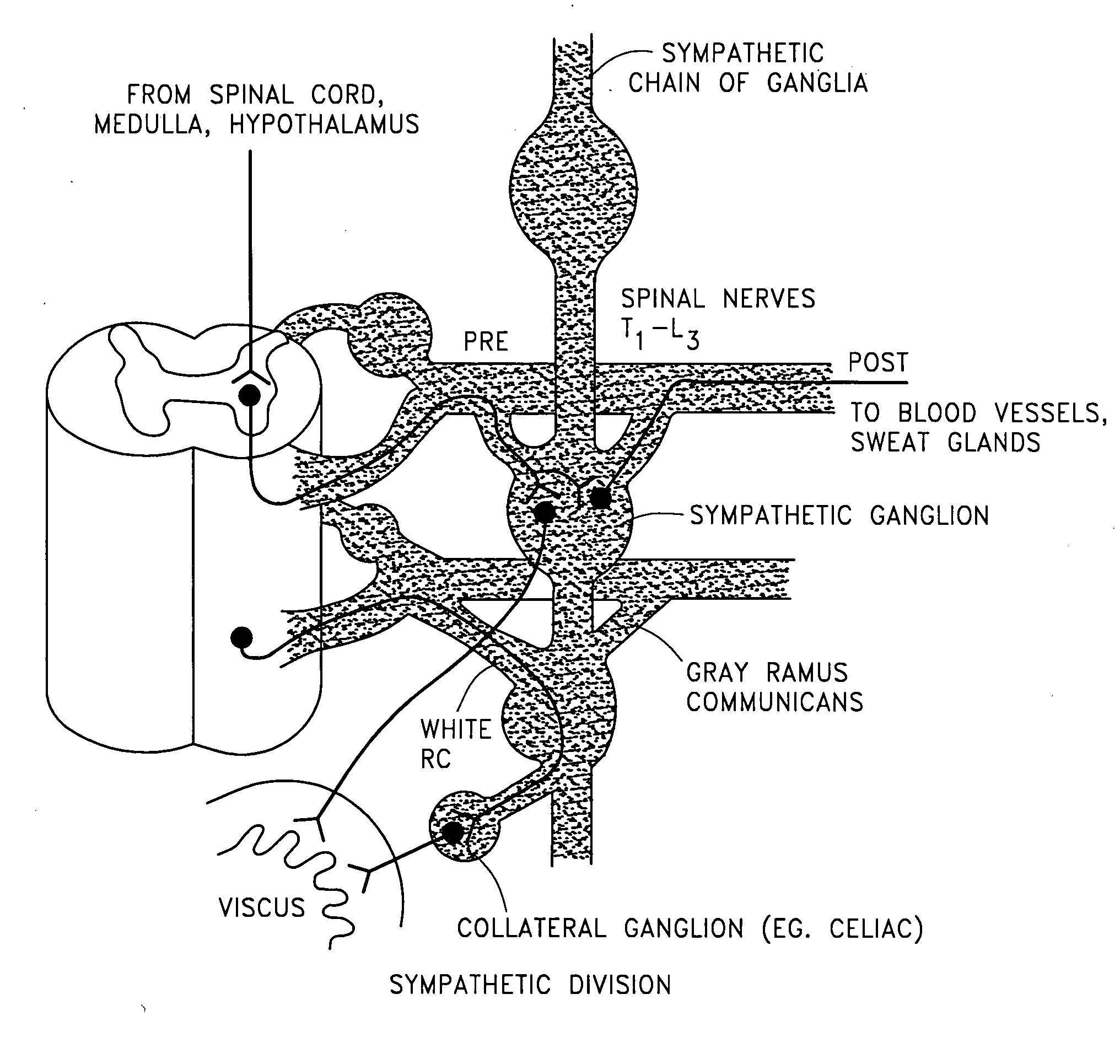
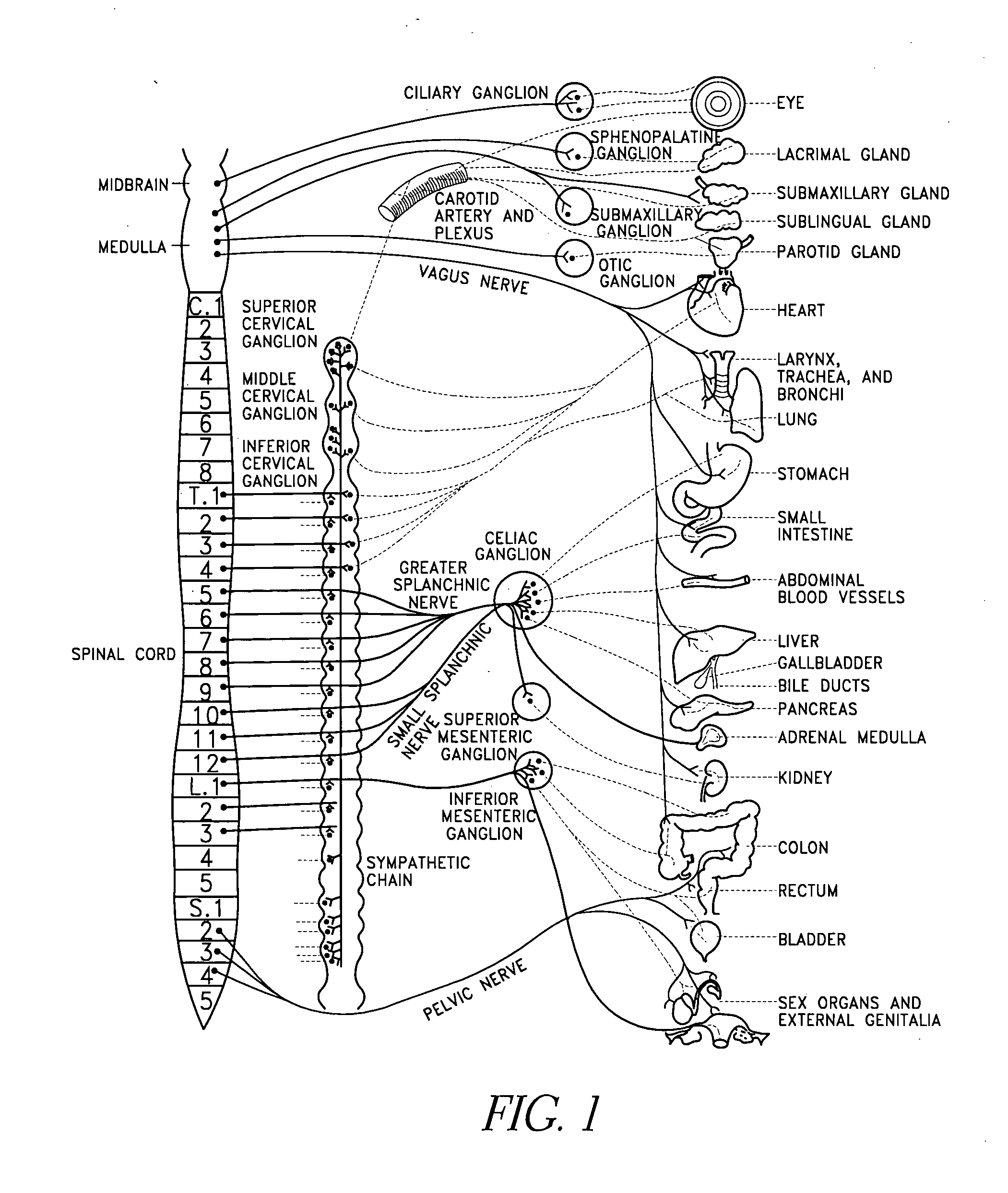
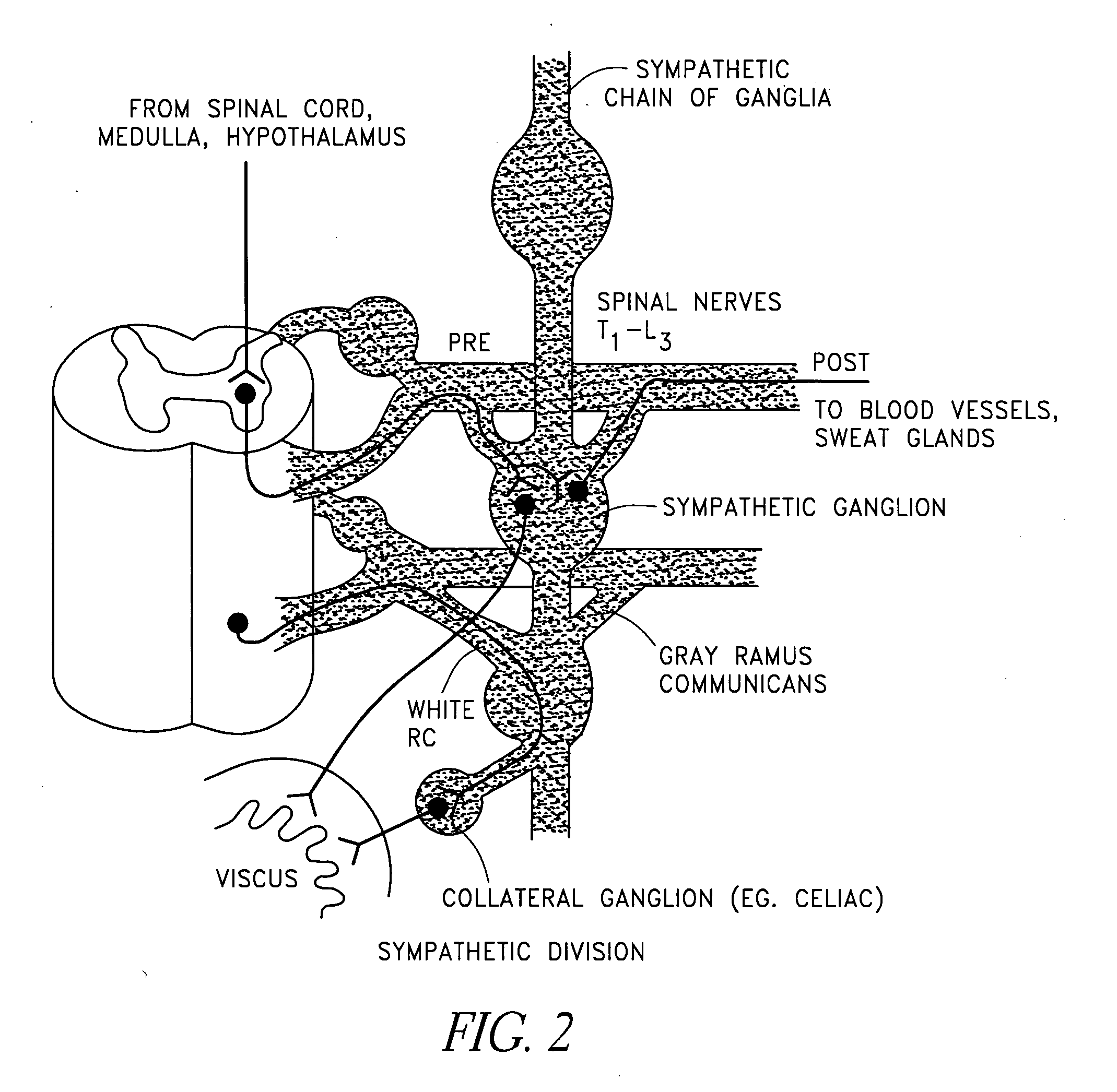
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the other being the parasympathetic nervous system. (The enteric nervous system (ENS) is now usually referred to as separate from the autonomic nervous system since it has its own independent reflex activity.)
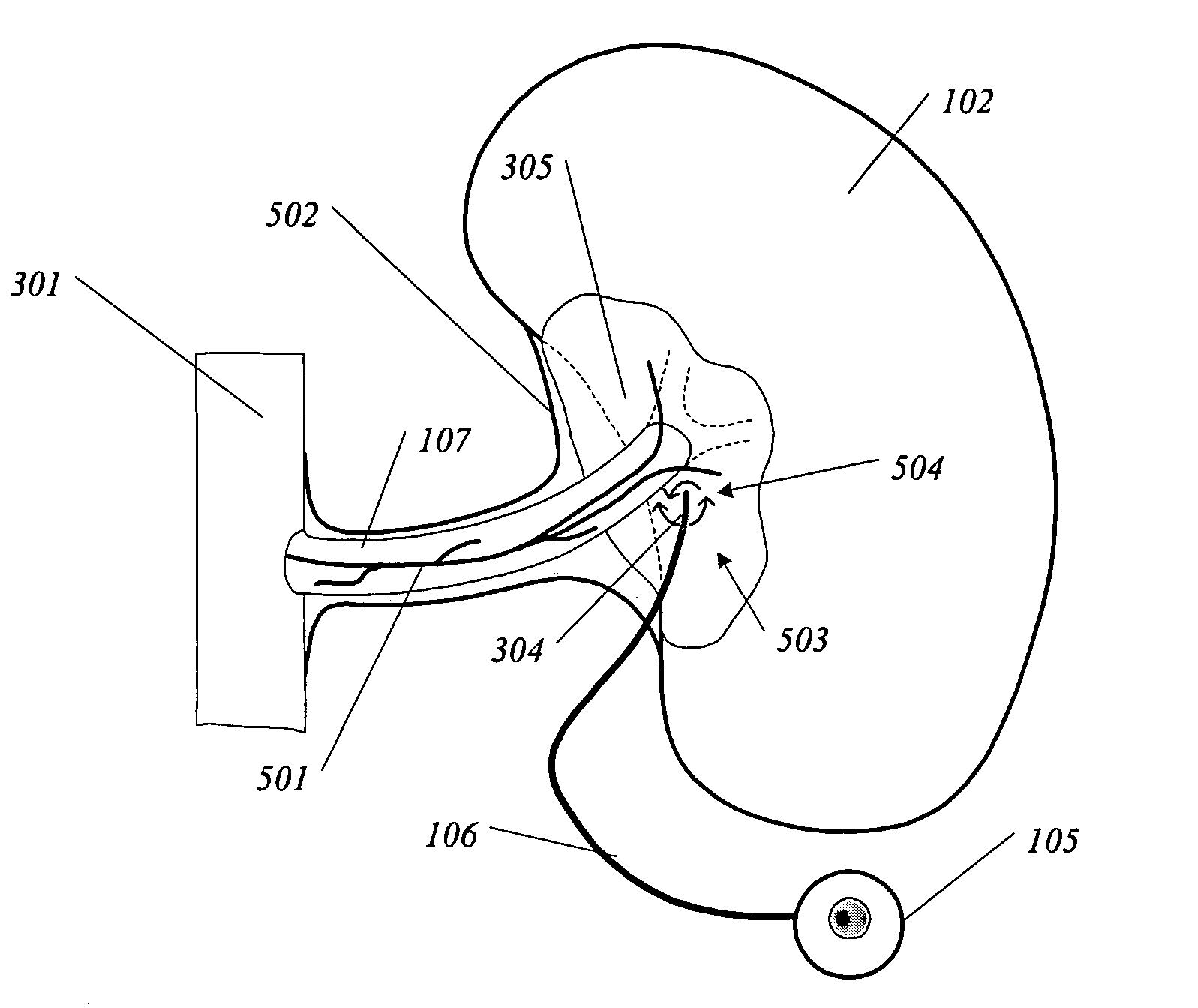
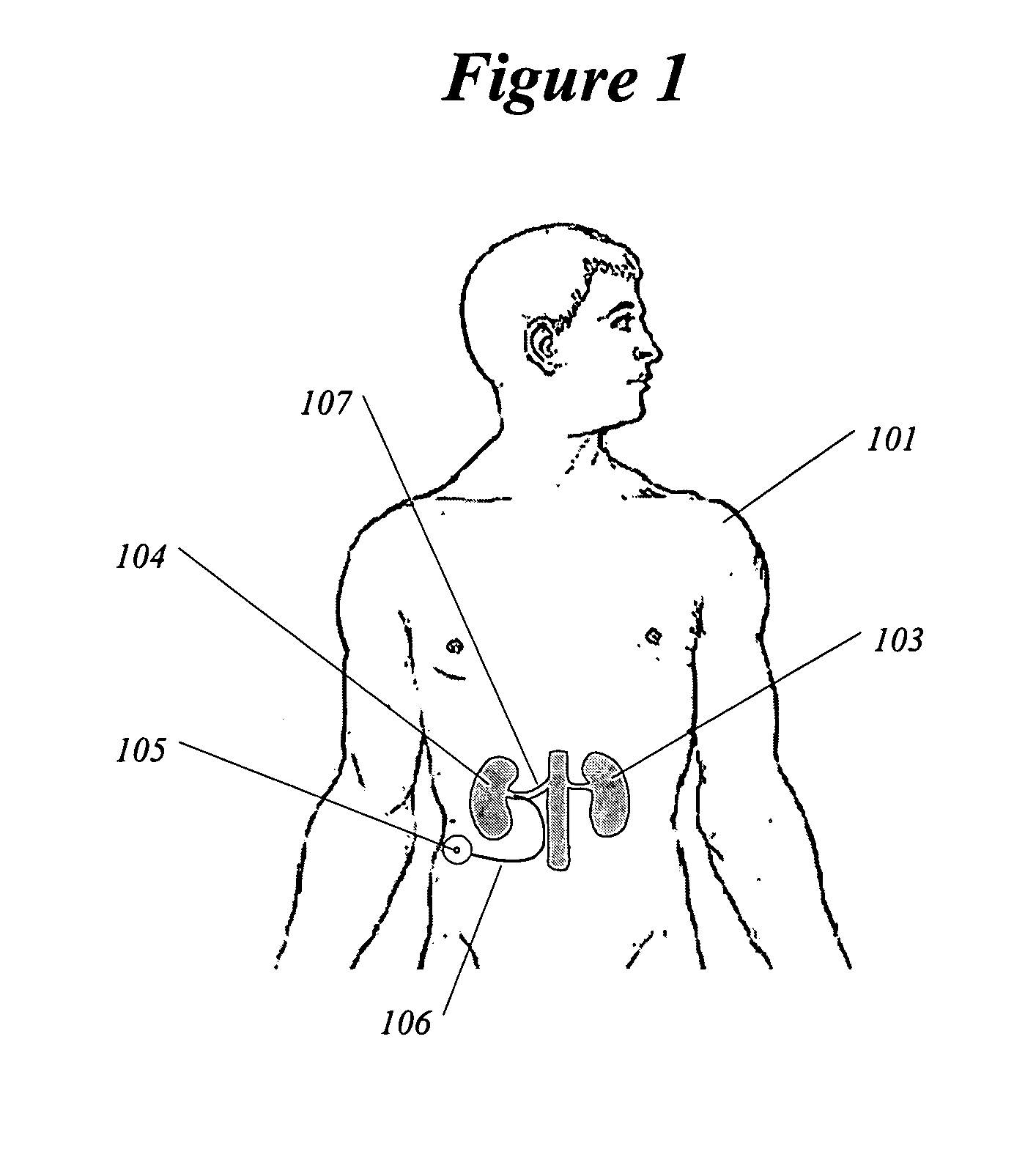
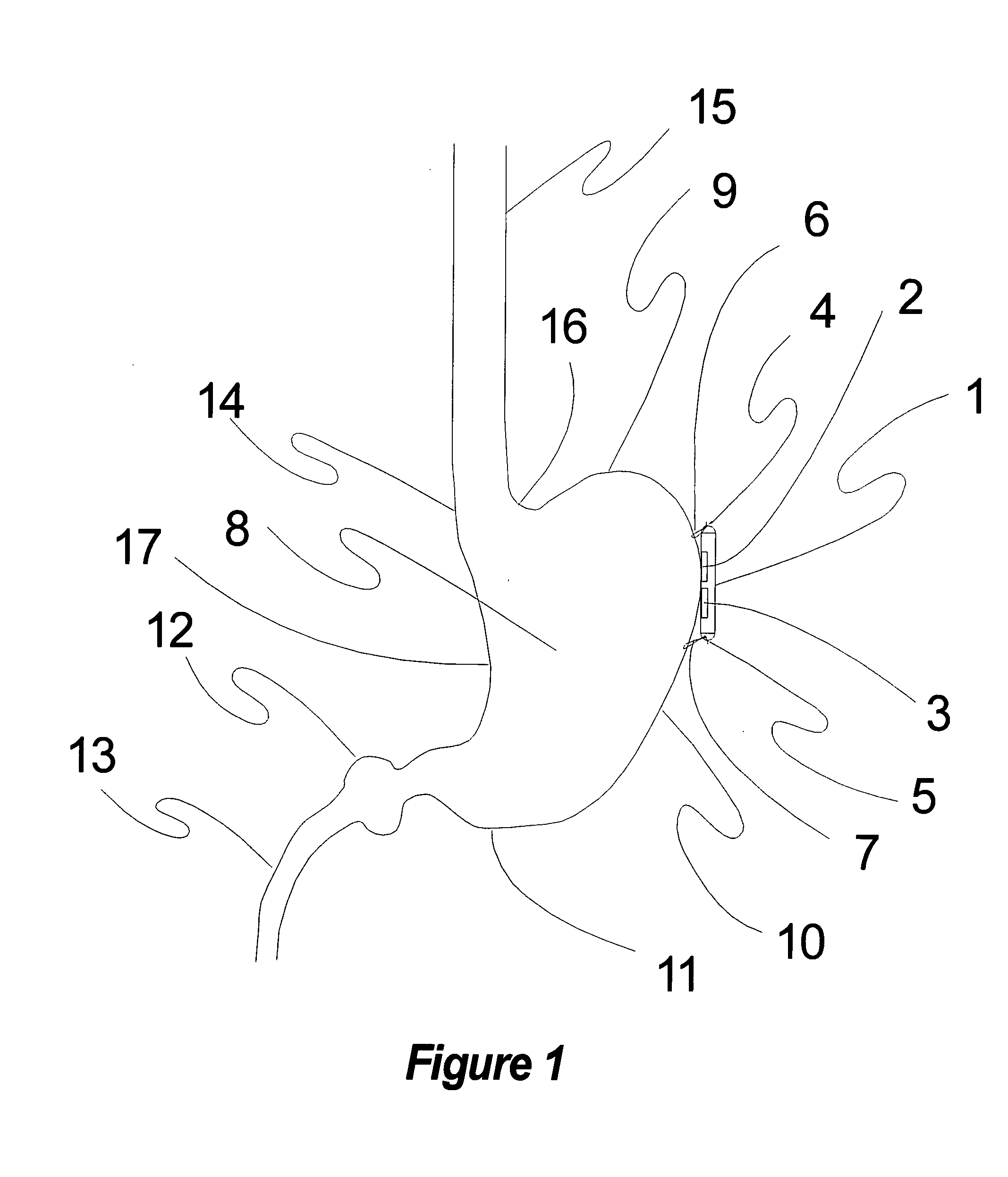
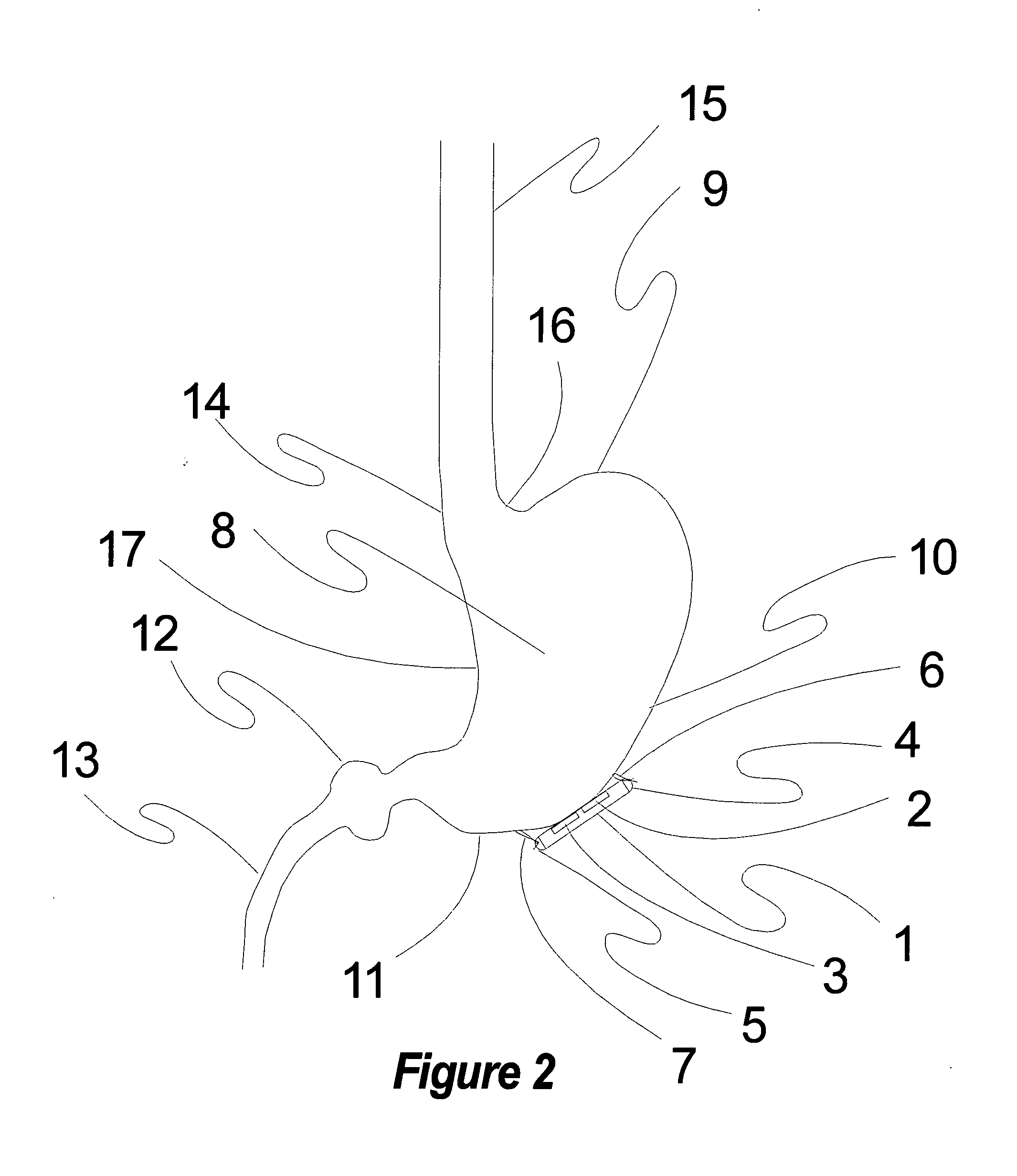
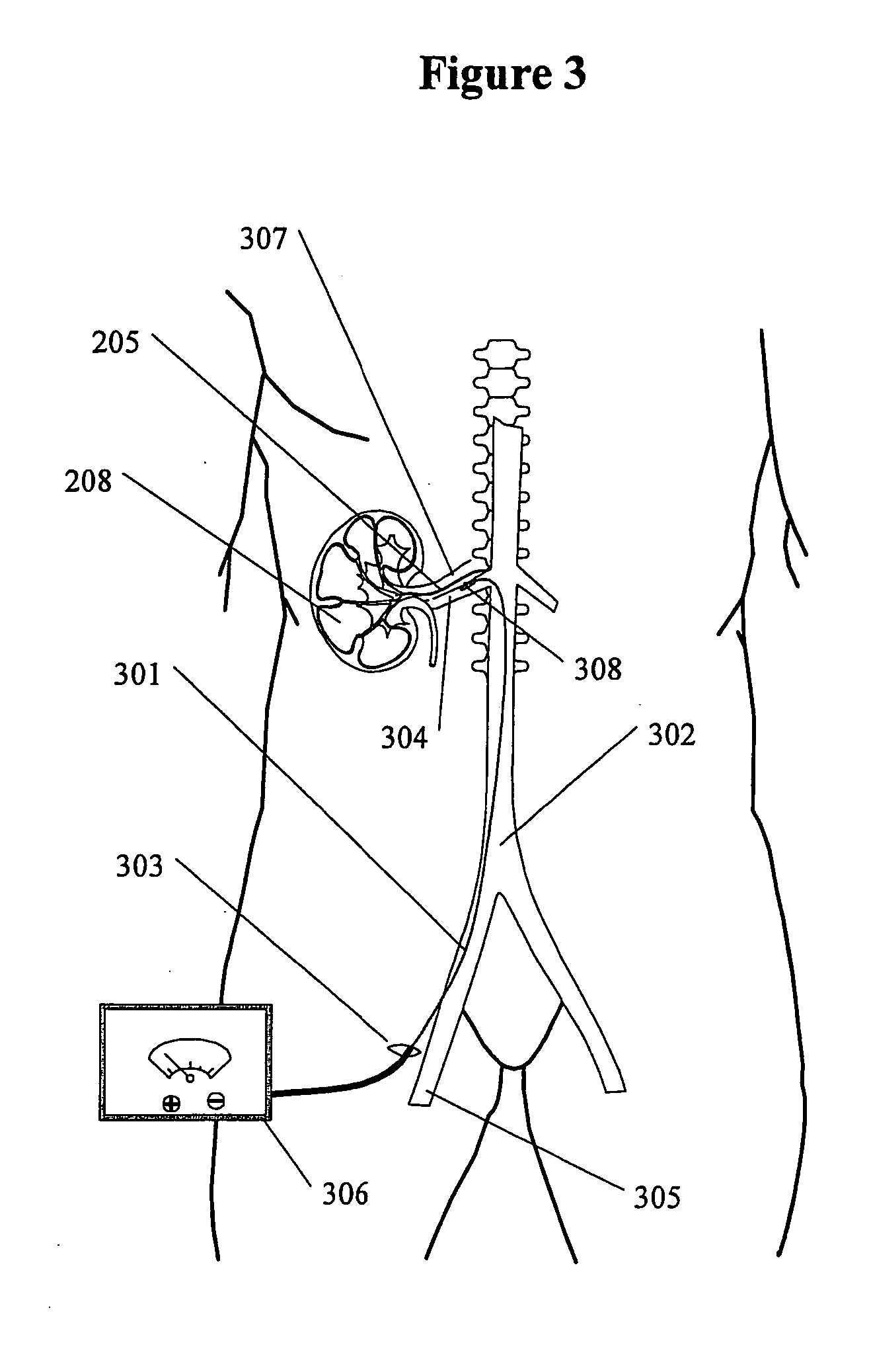
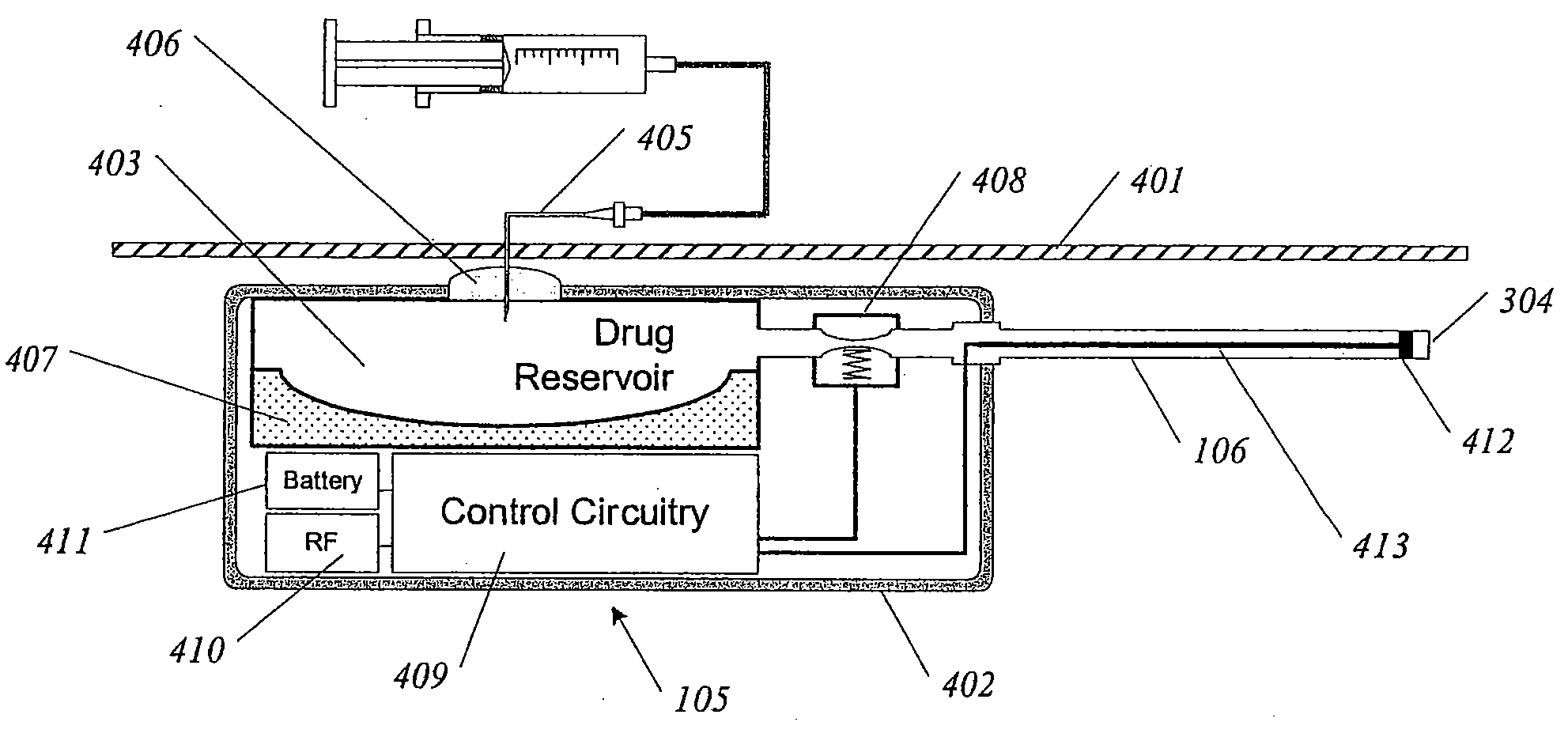
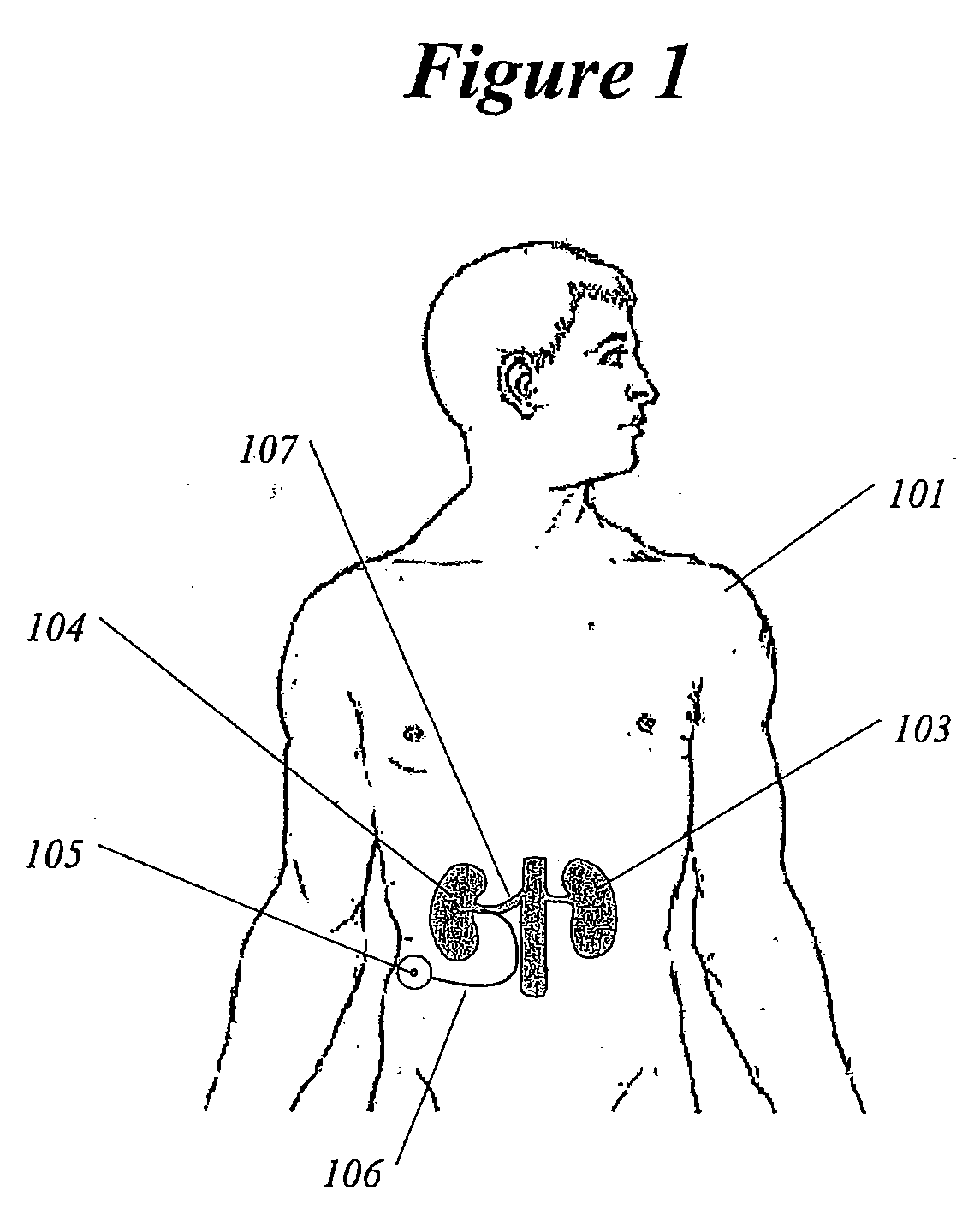
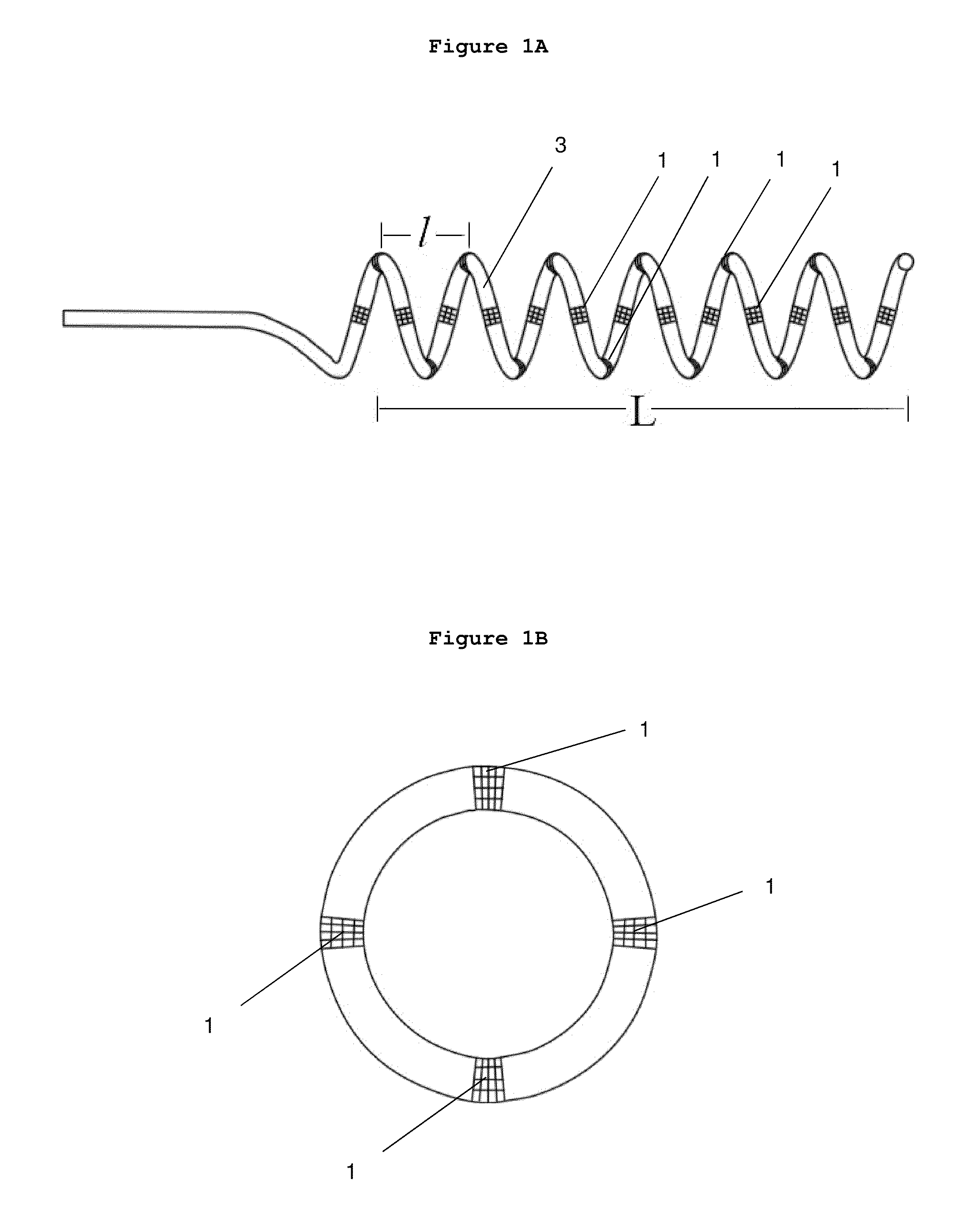
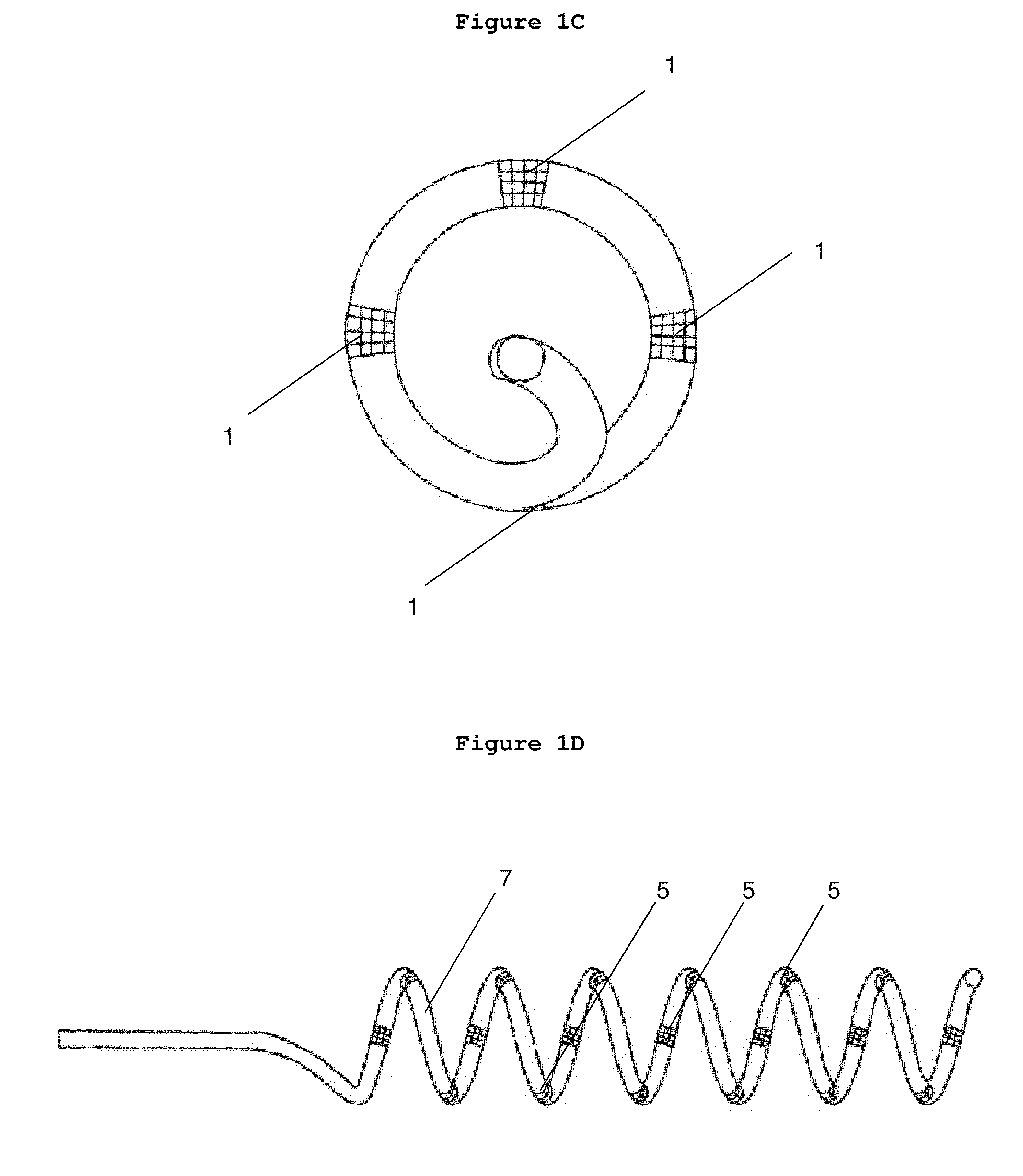
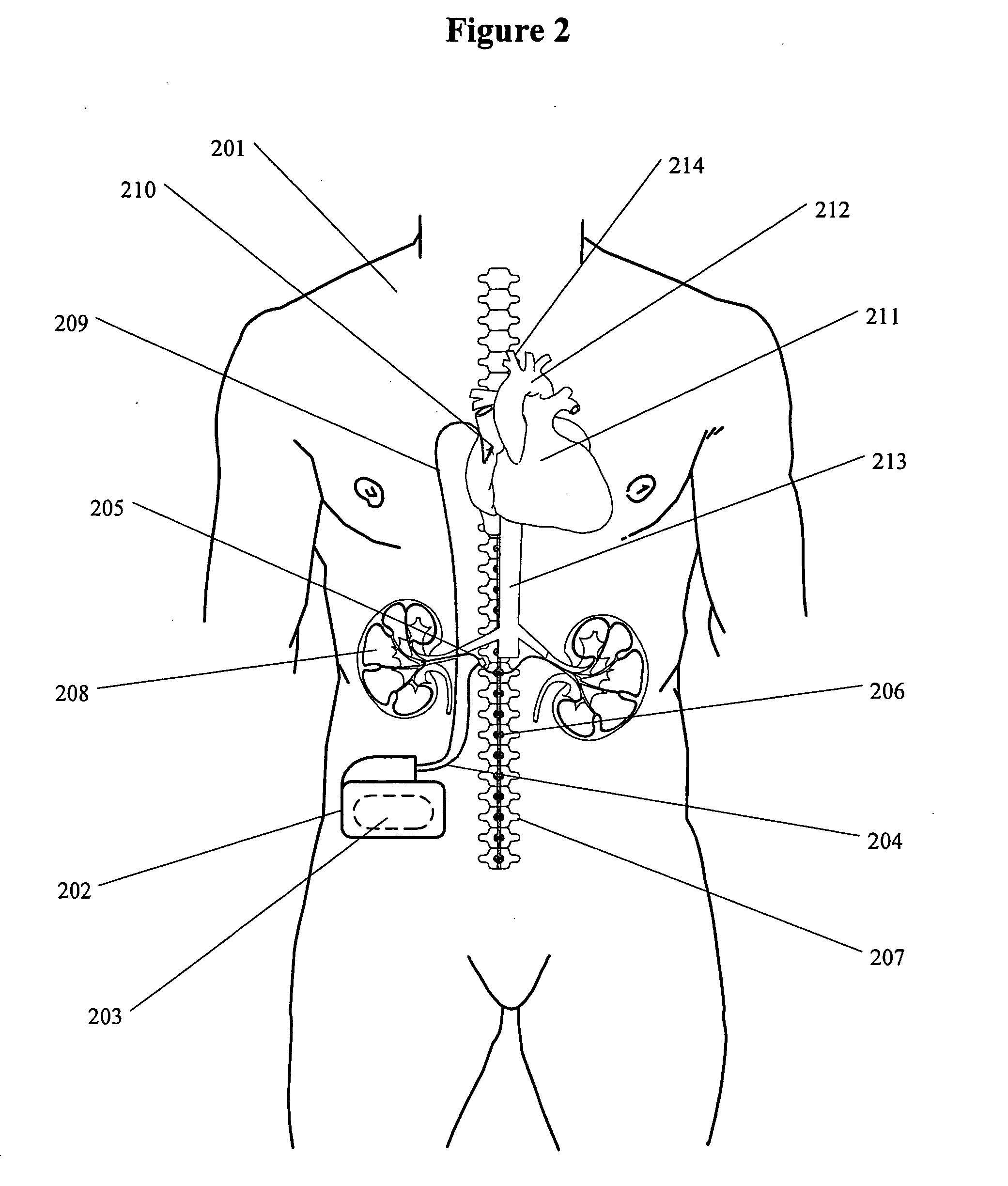
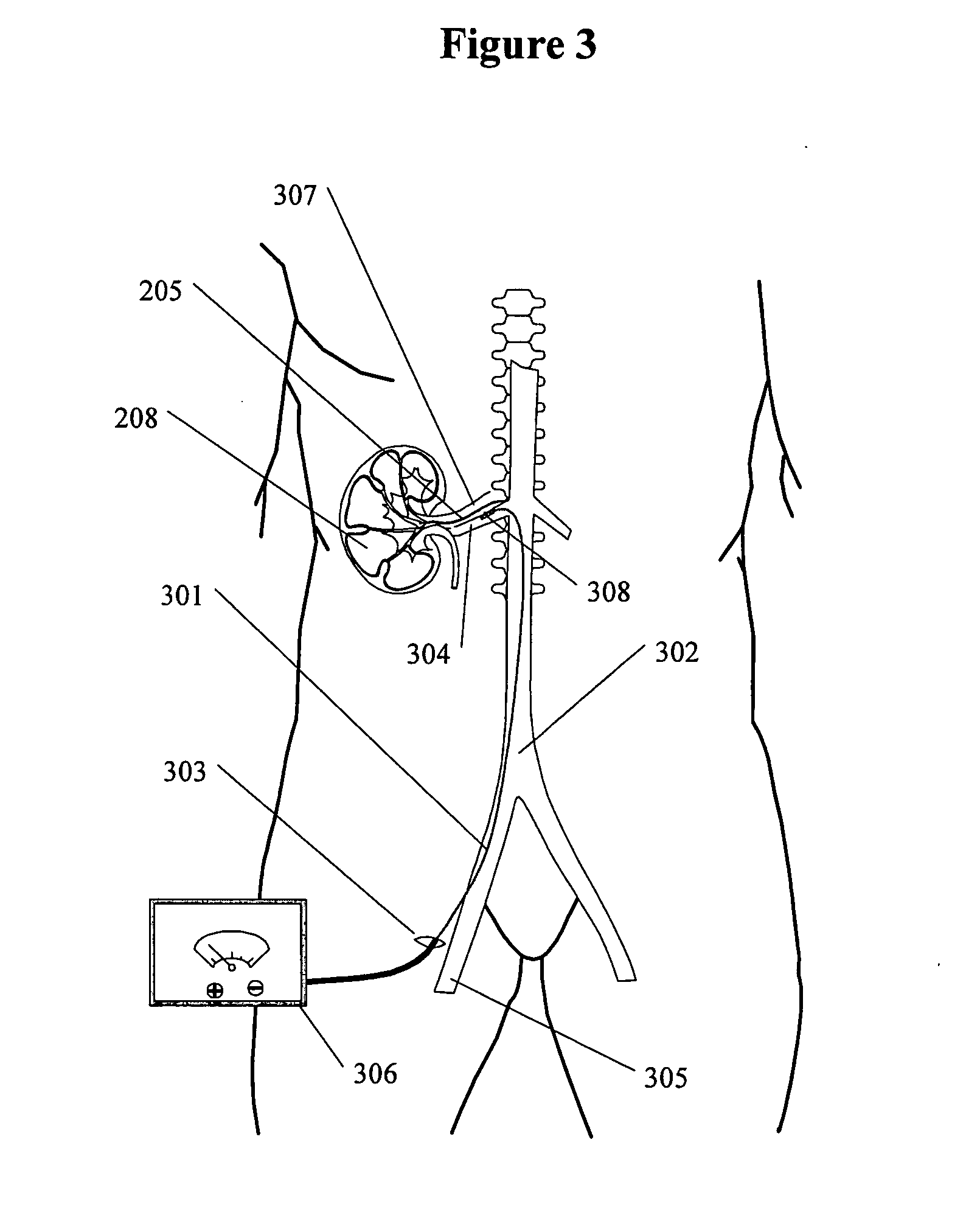
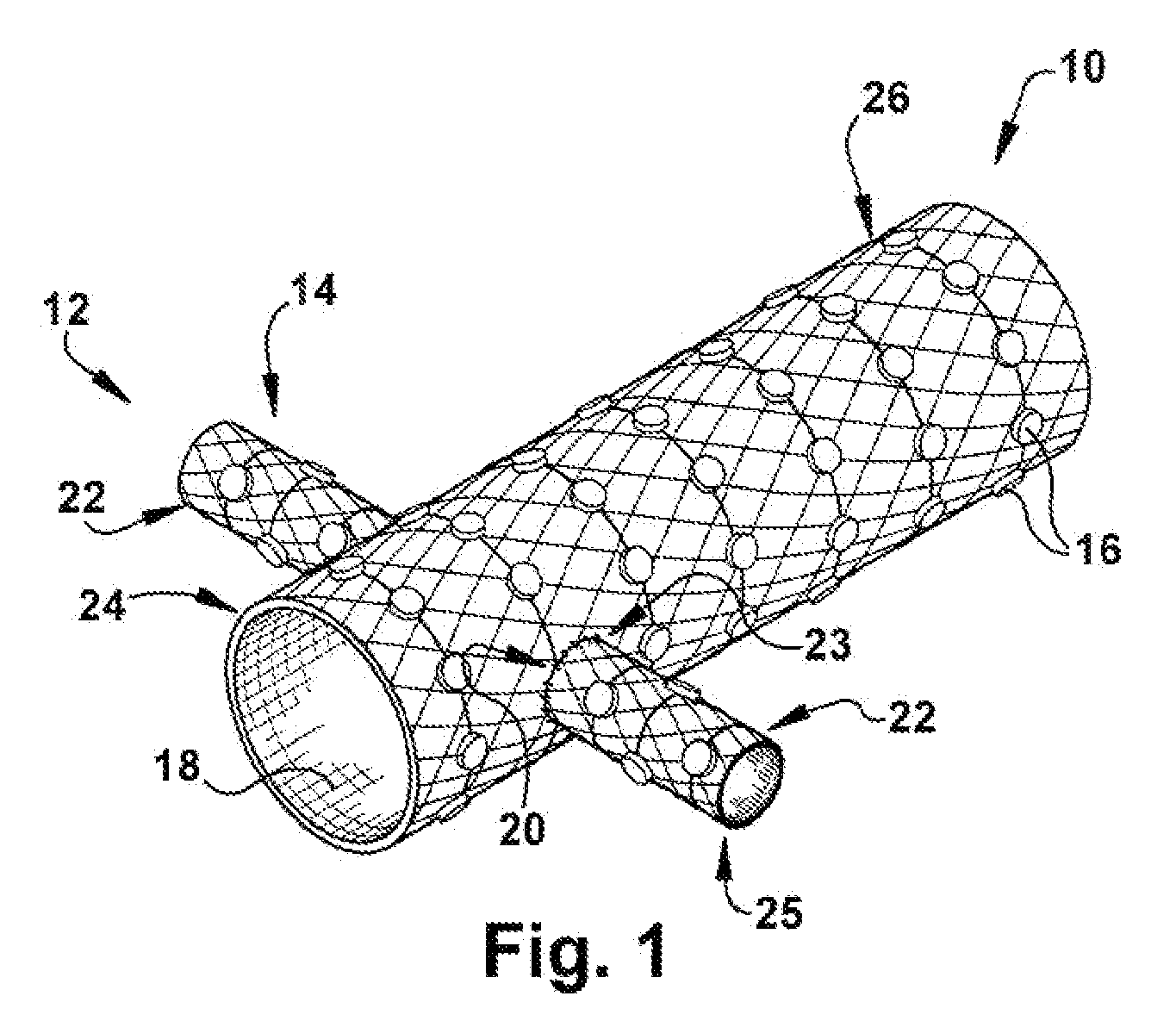
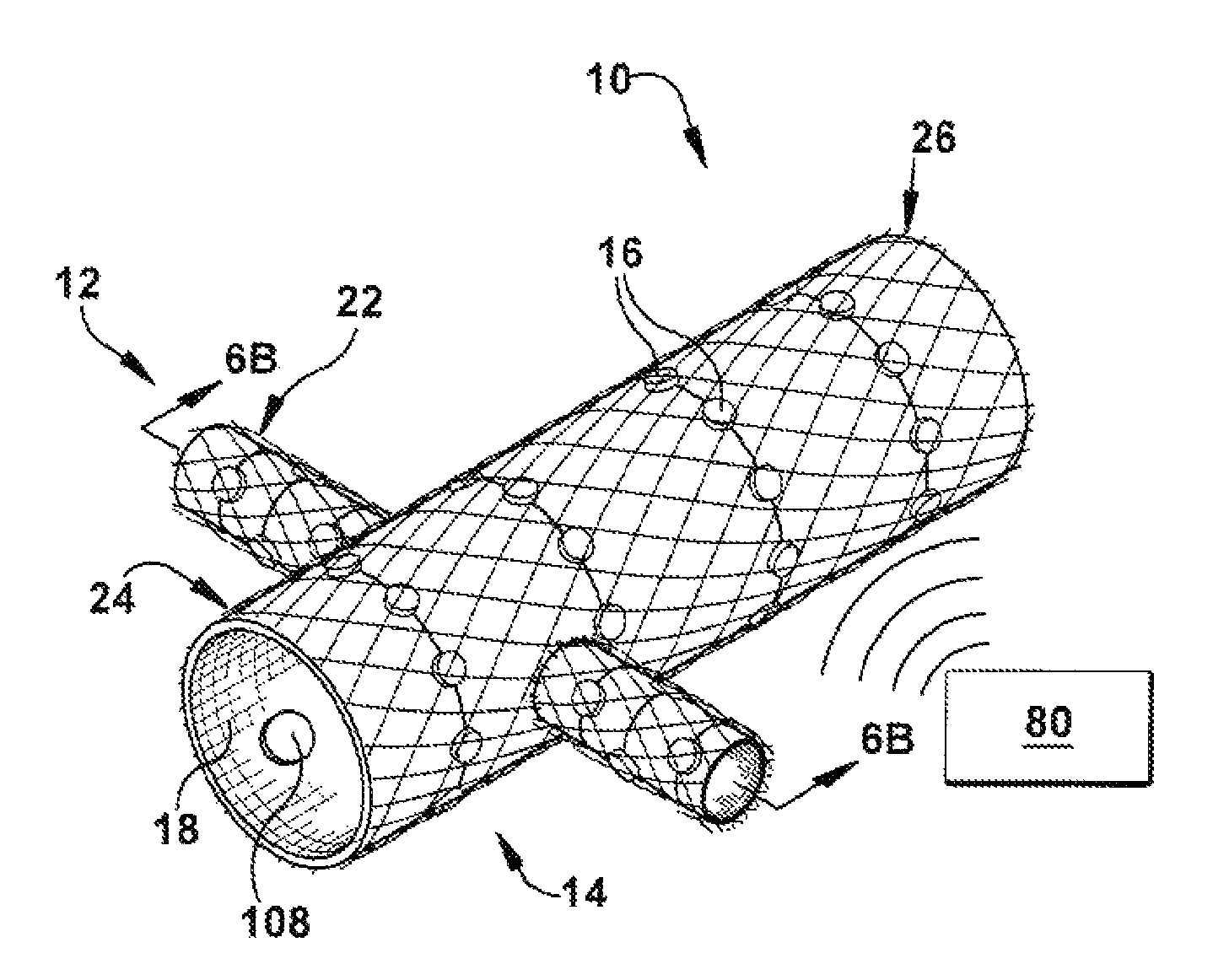
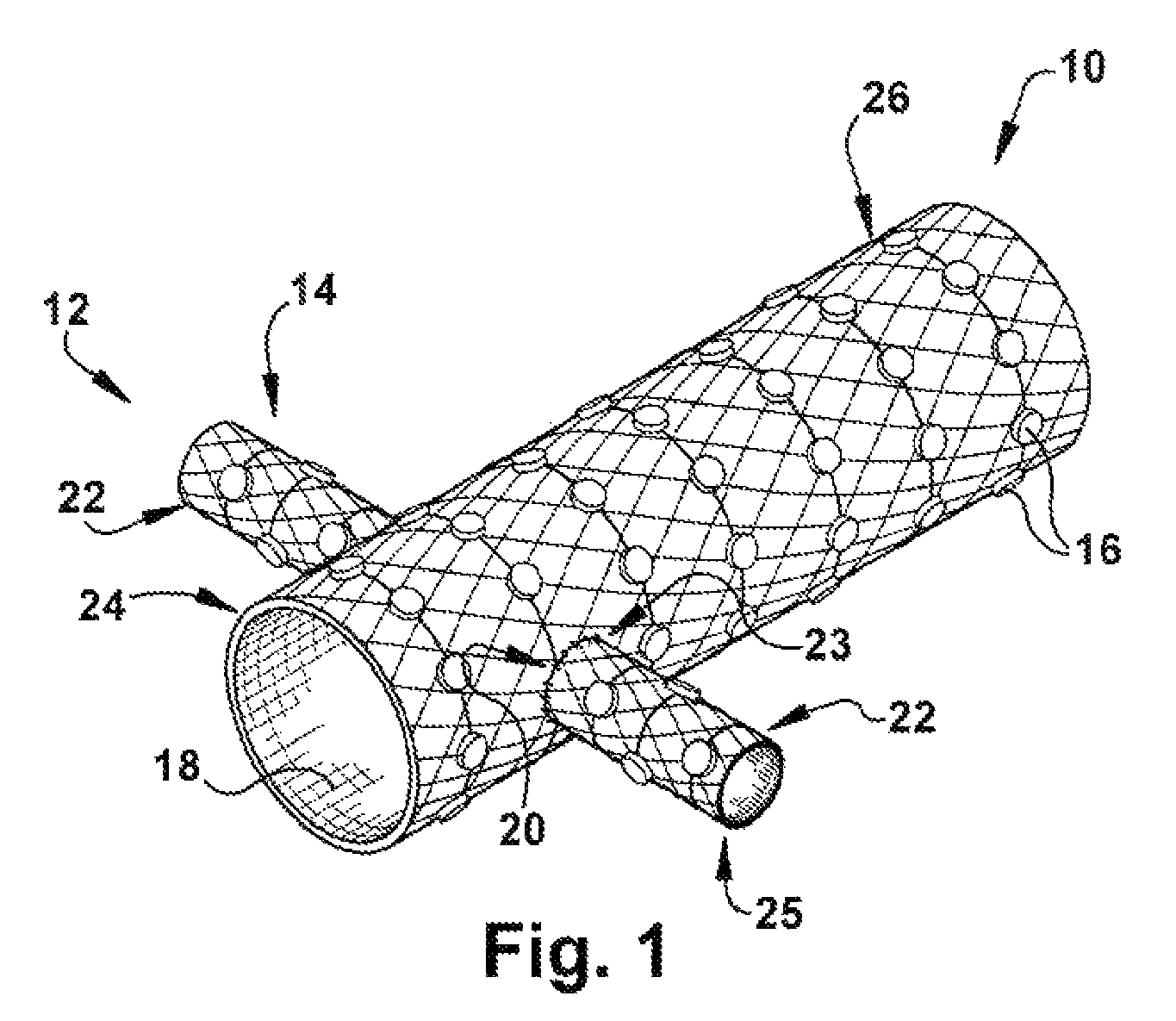
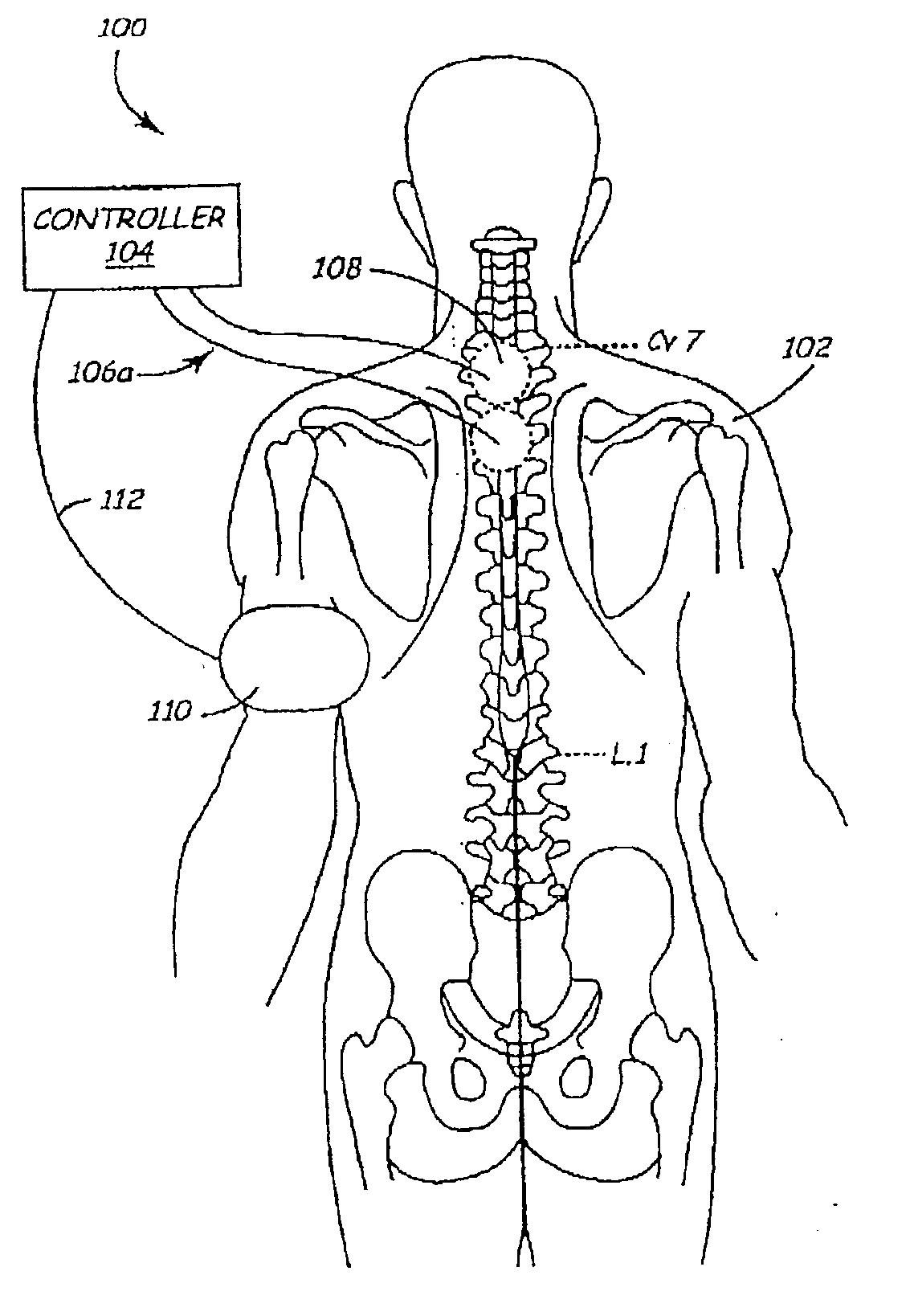
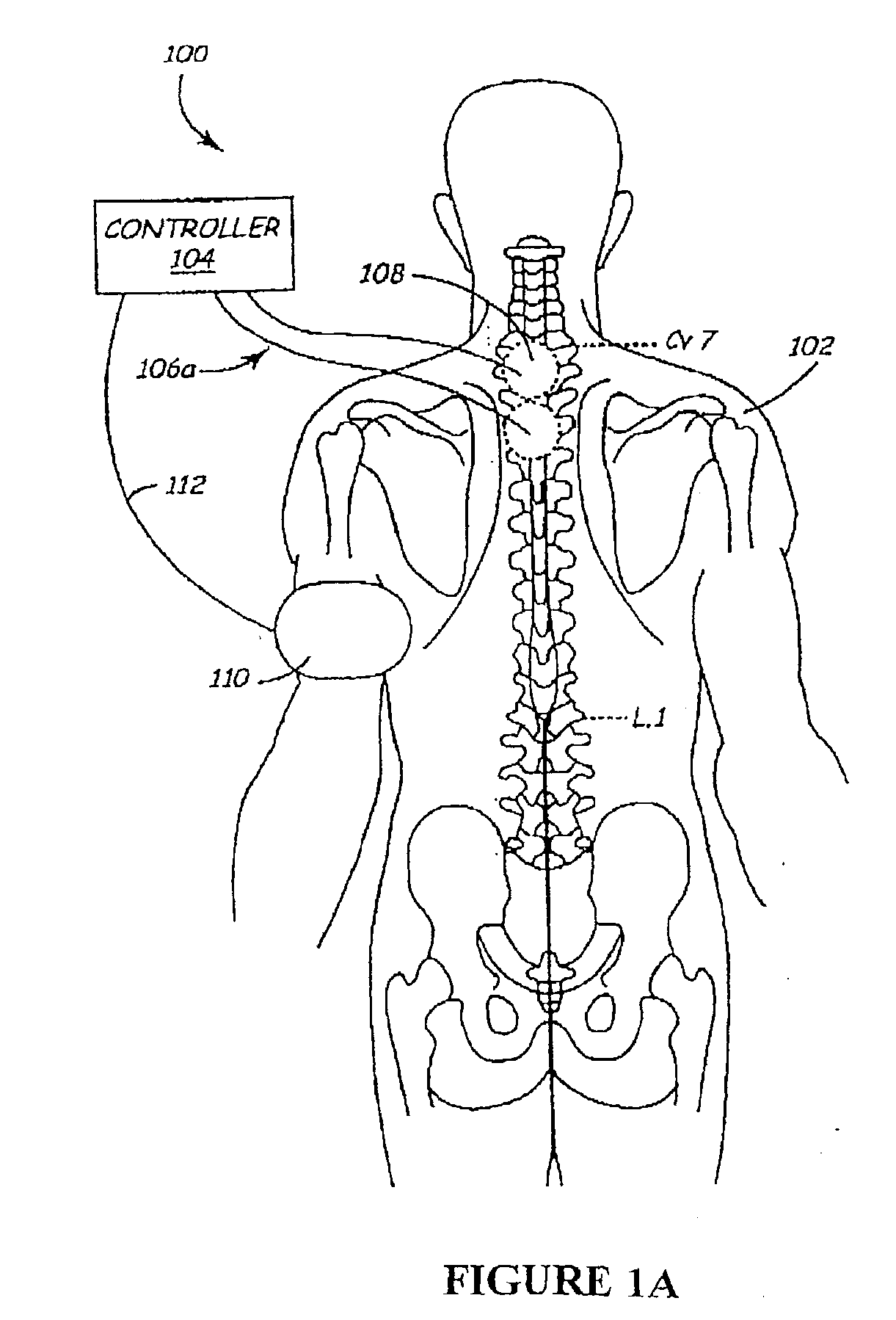
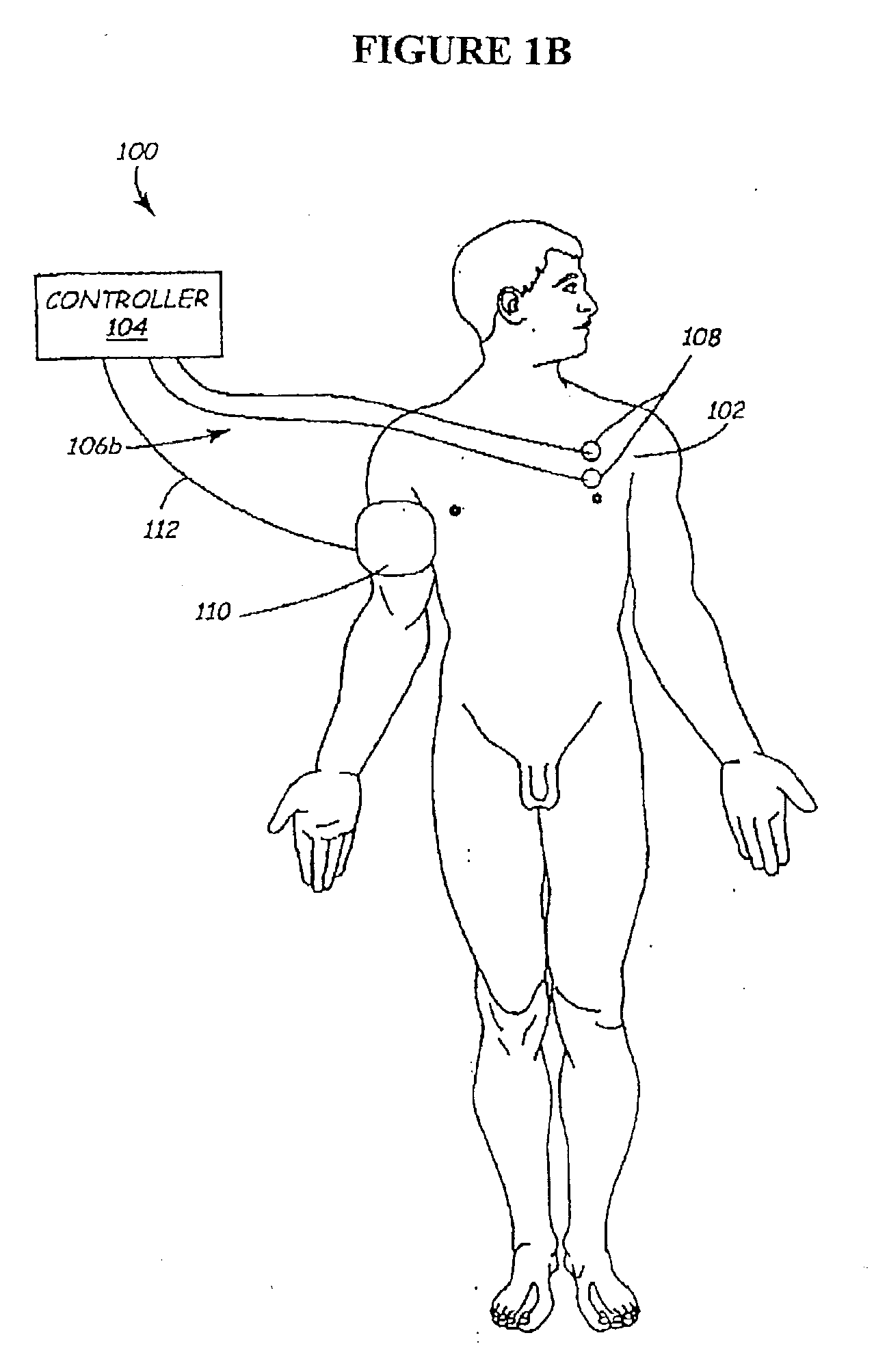
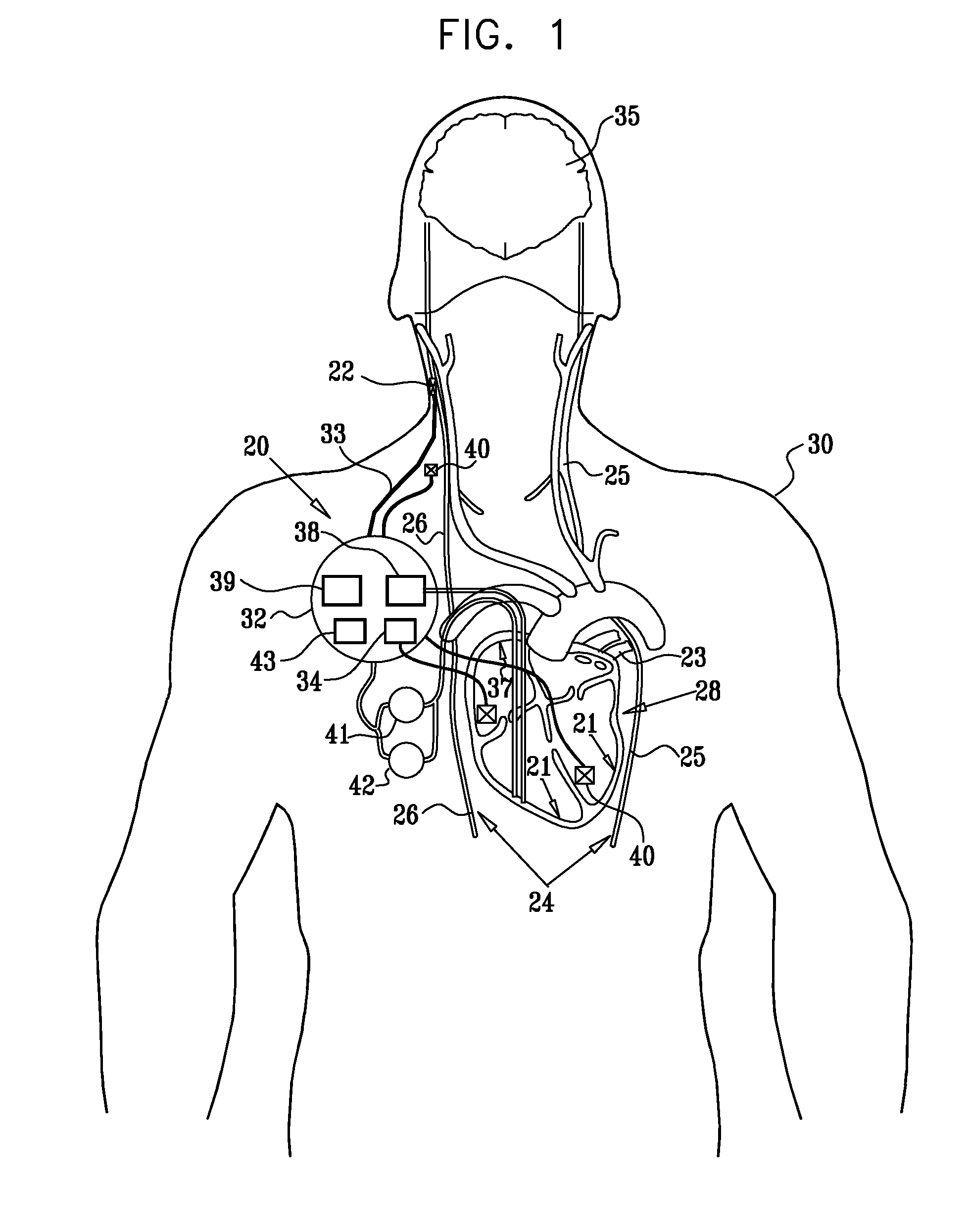
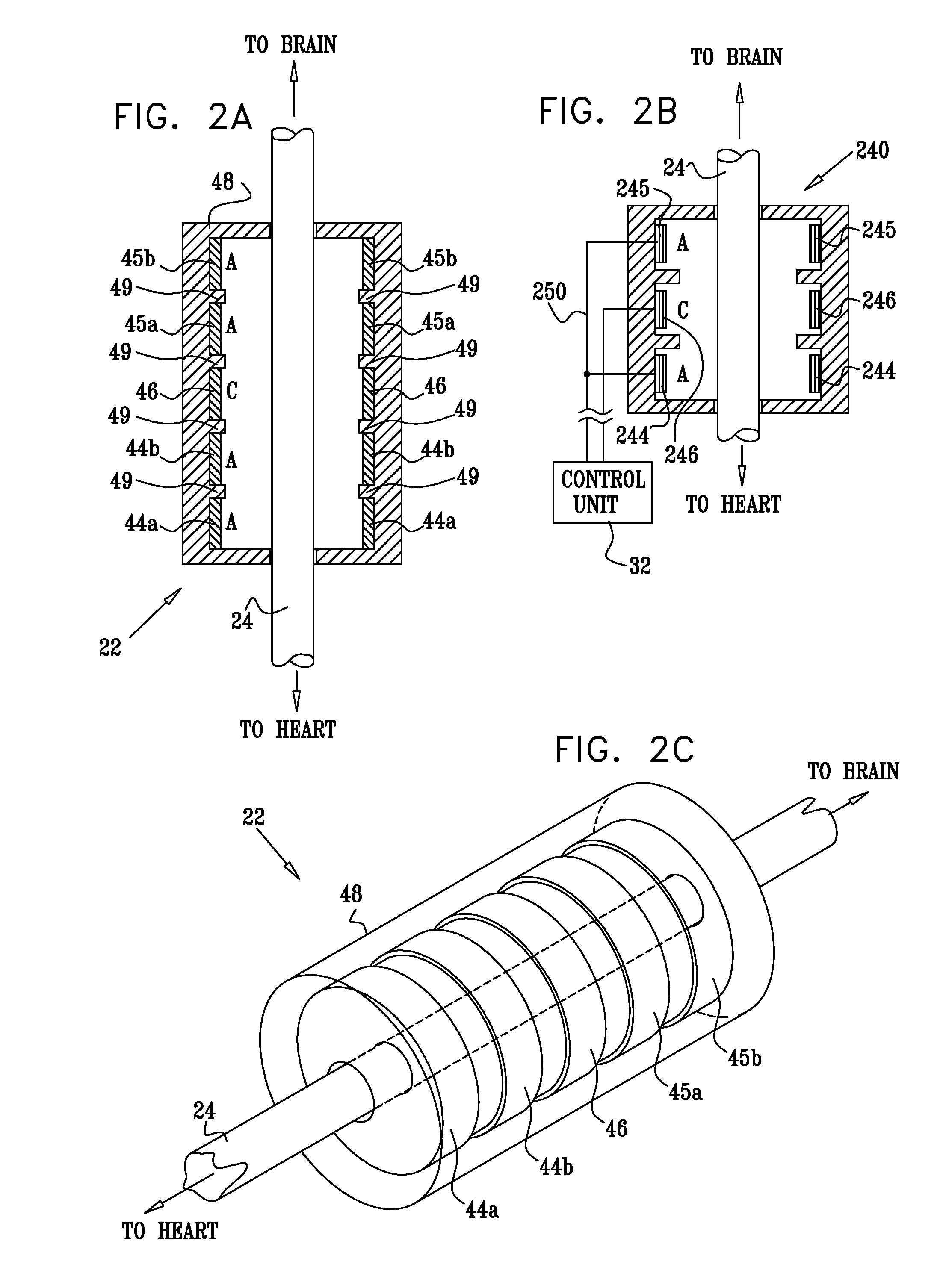
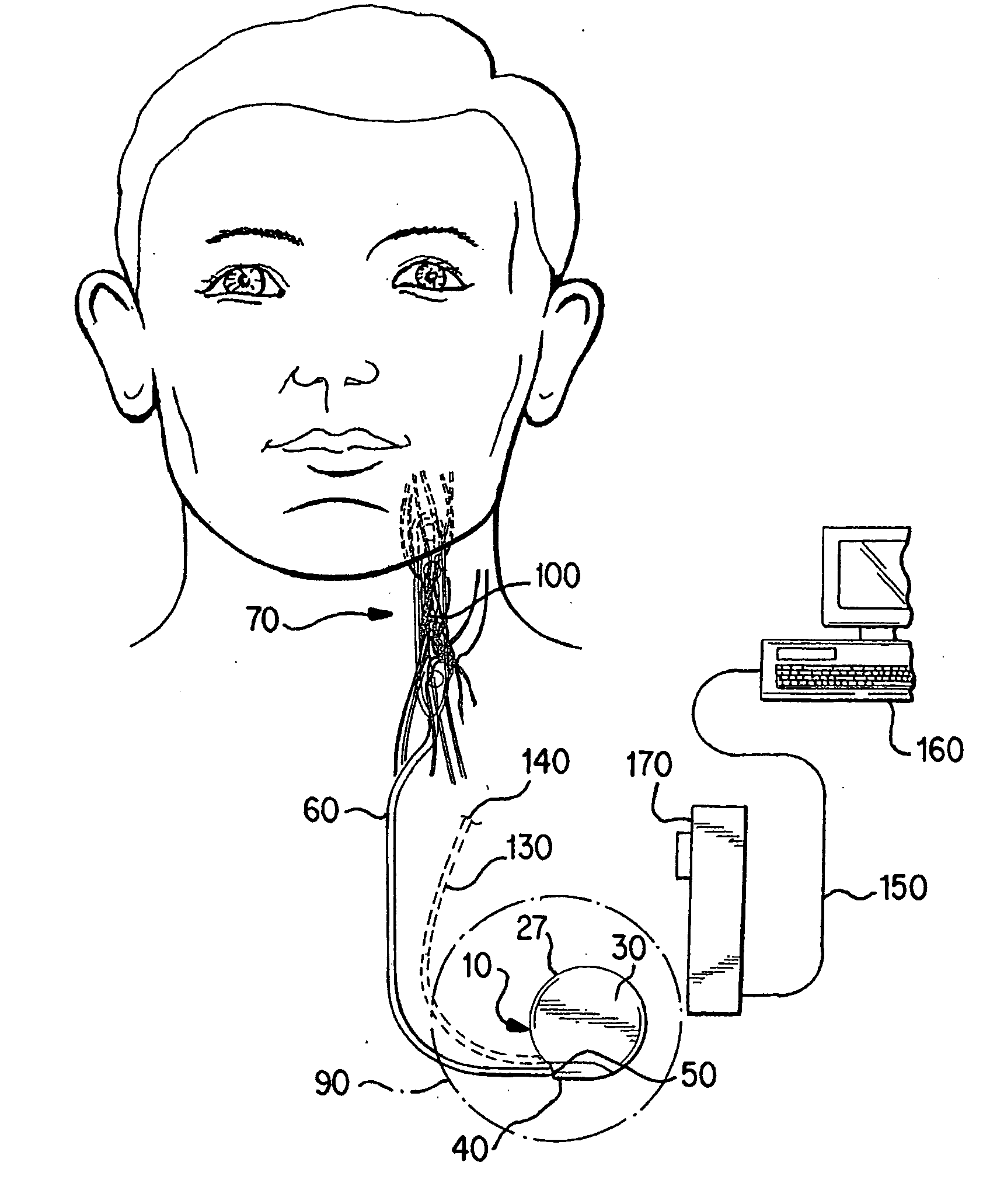
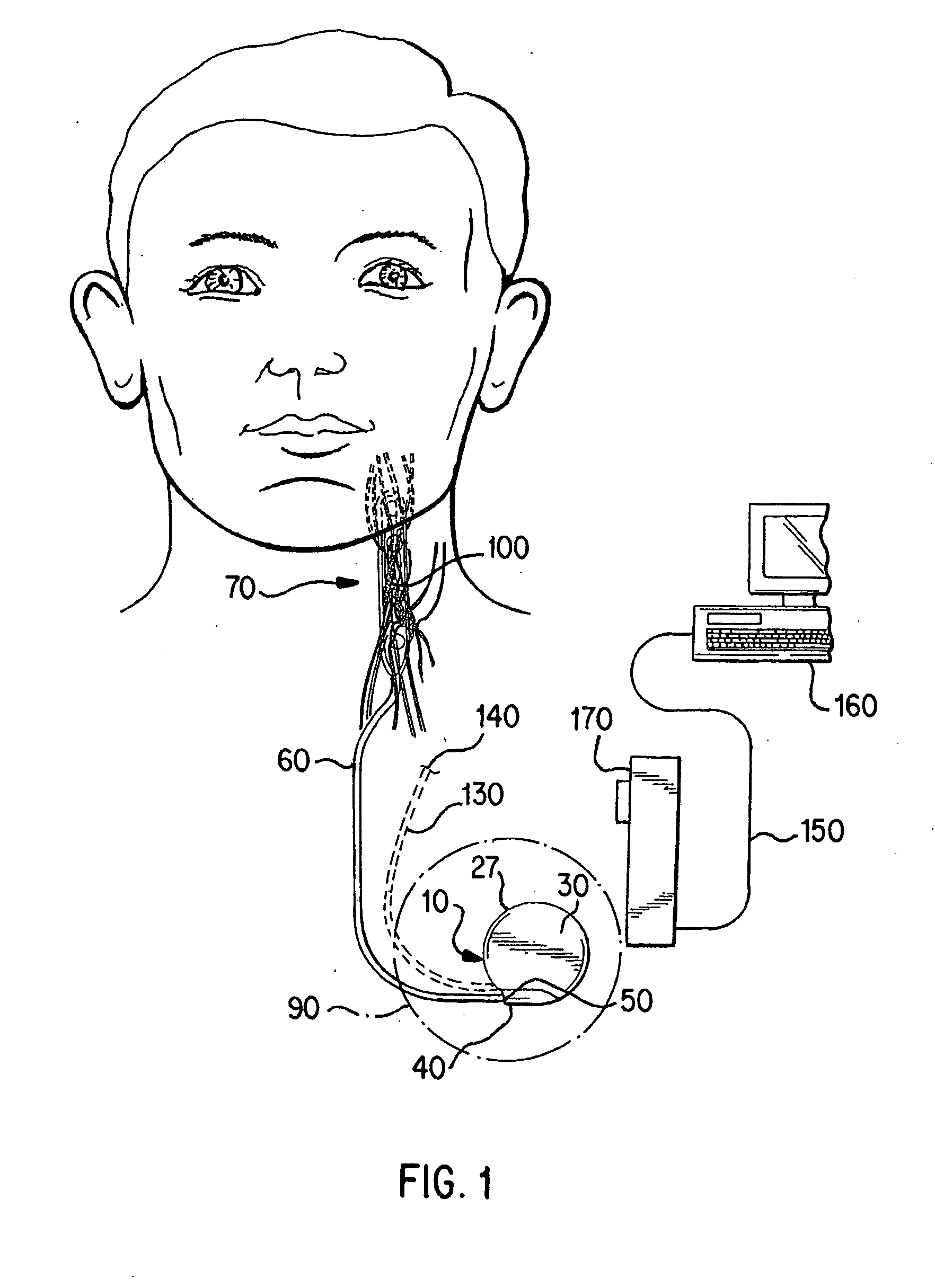
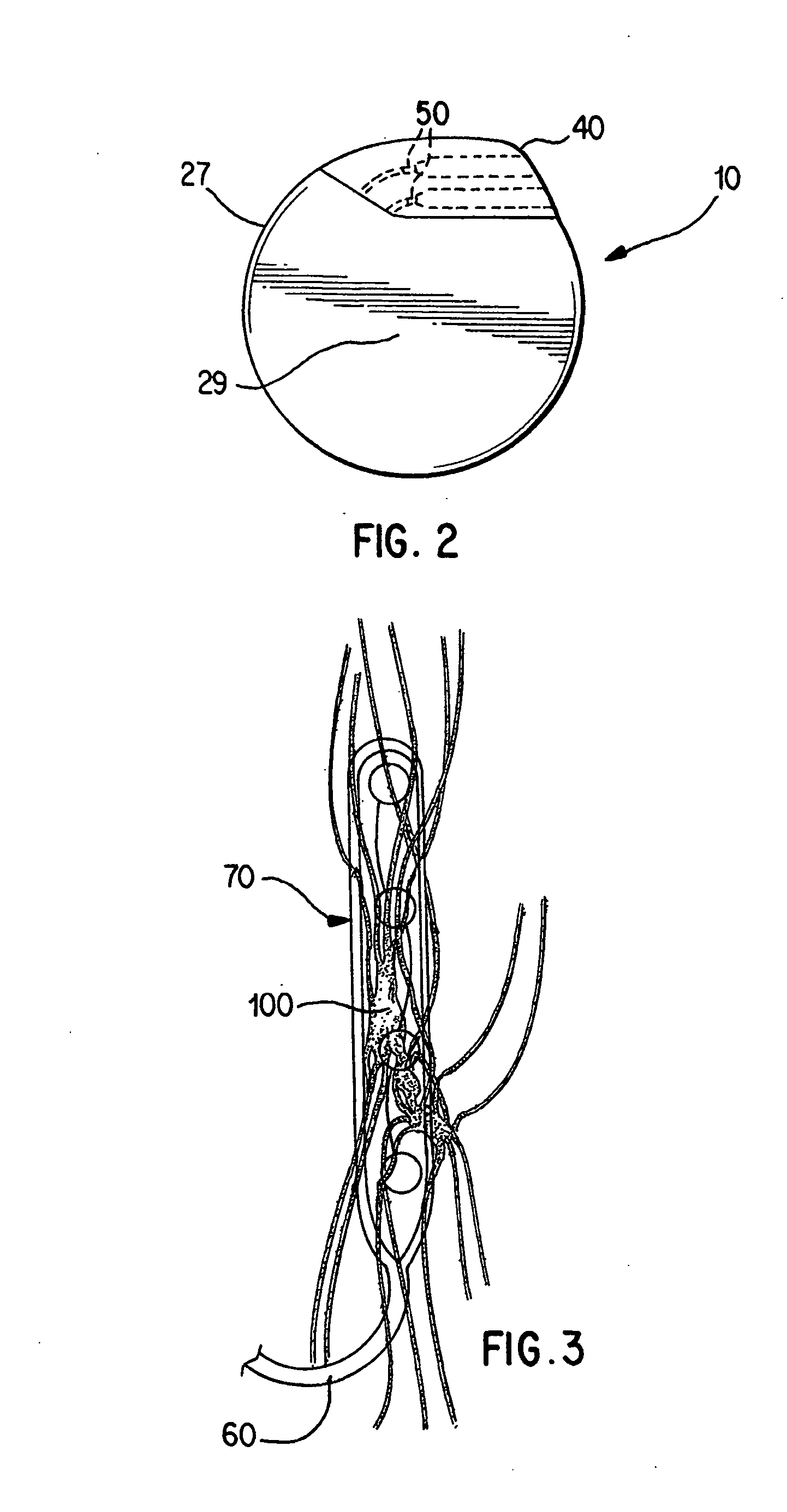
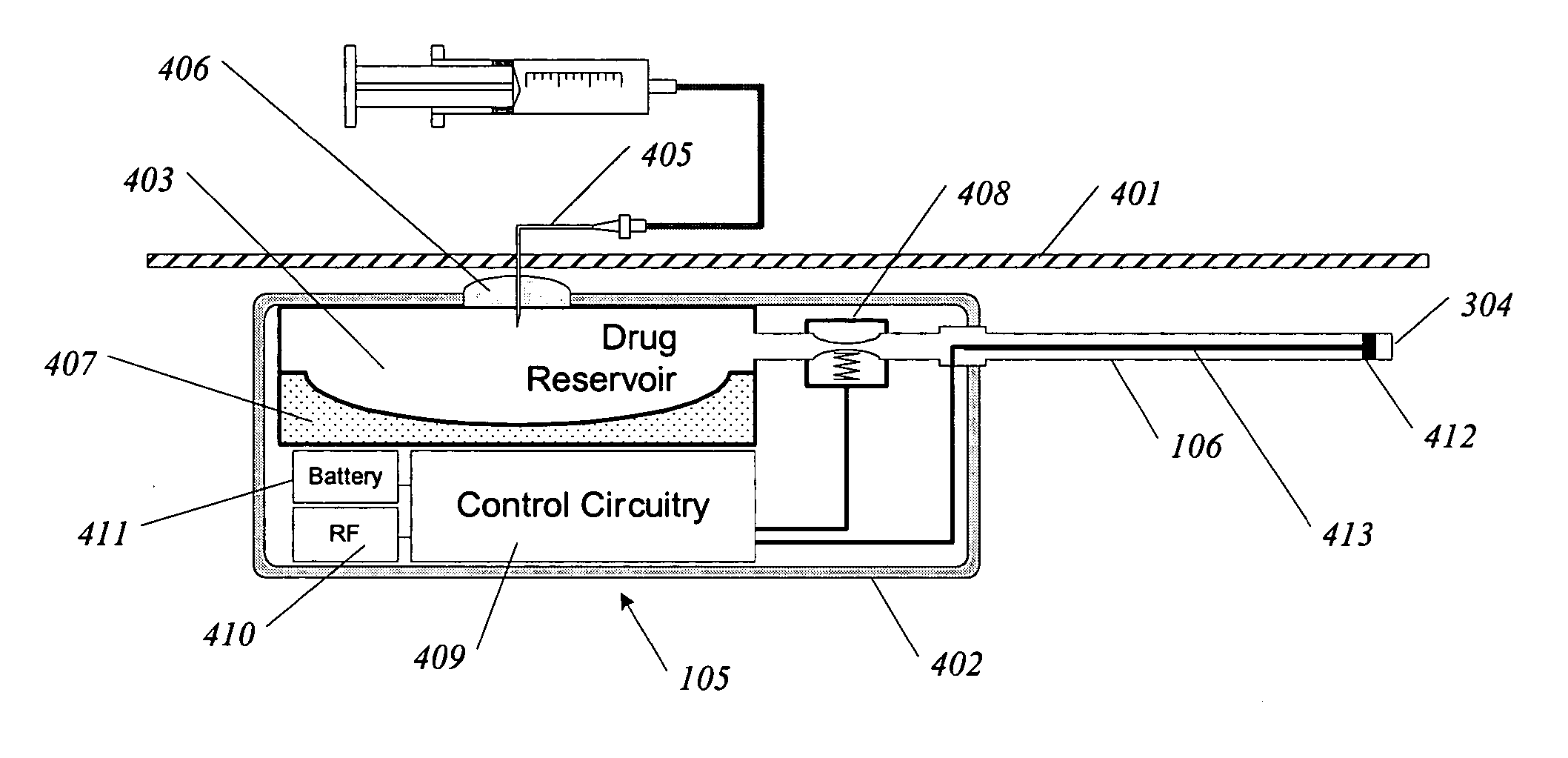
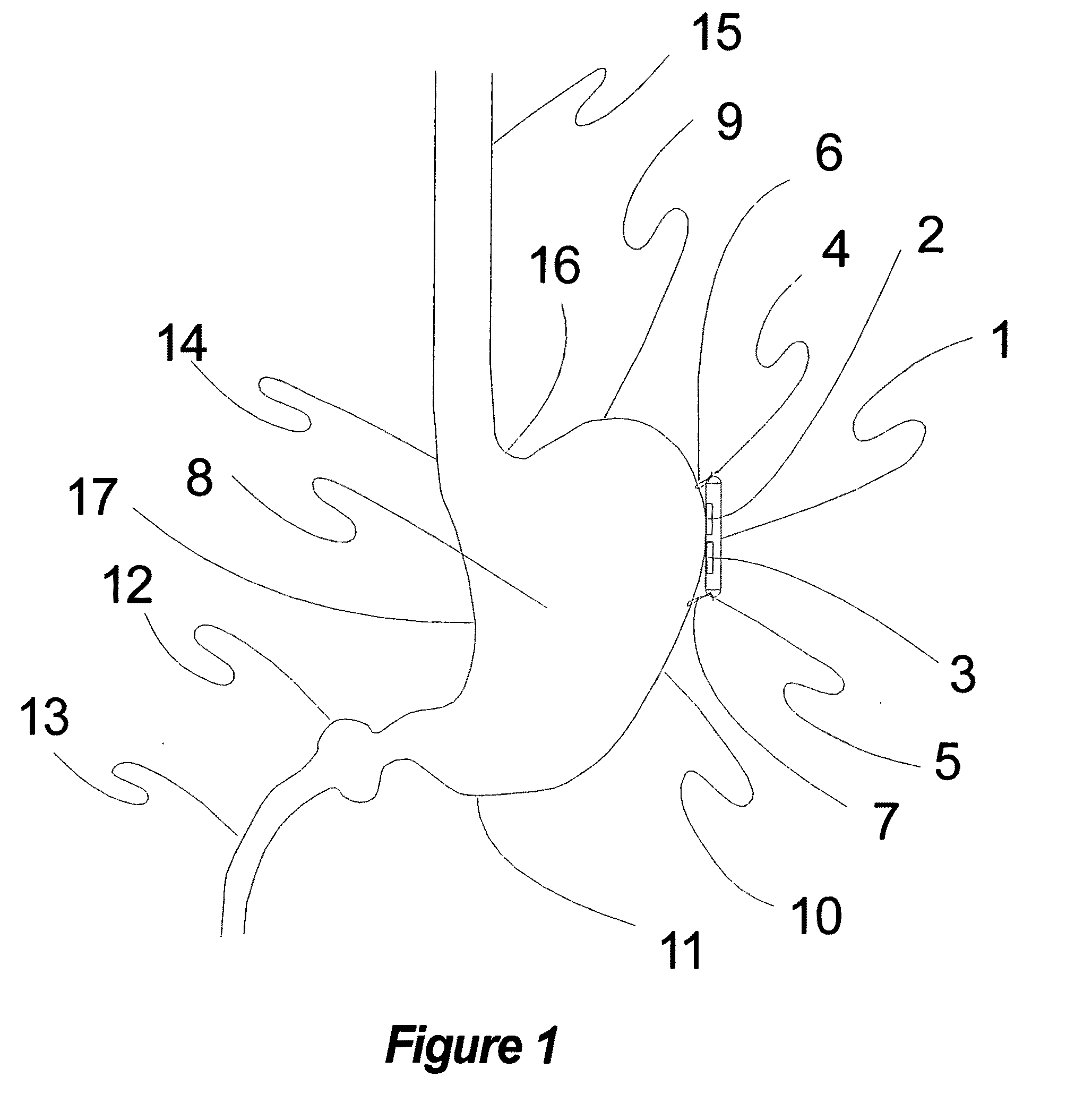
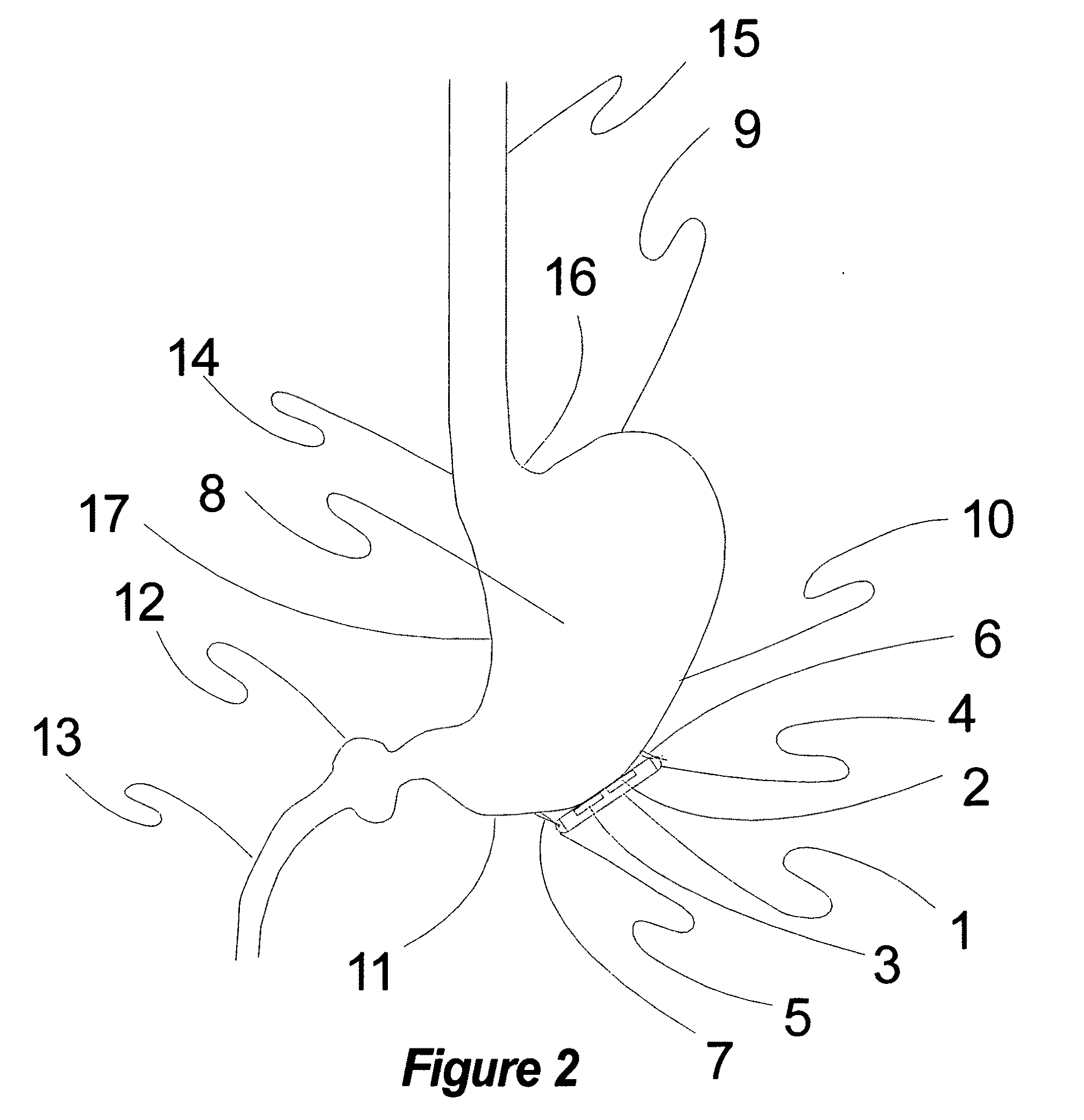
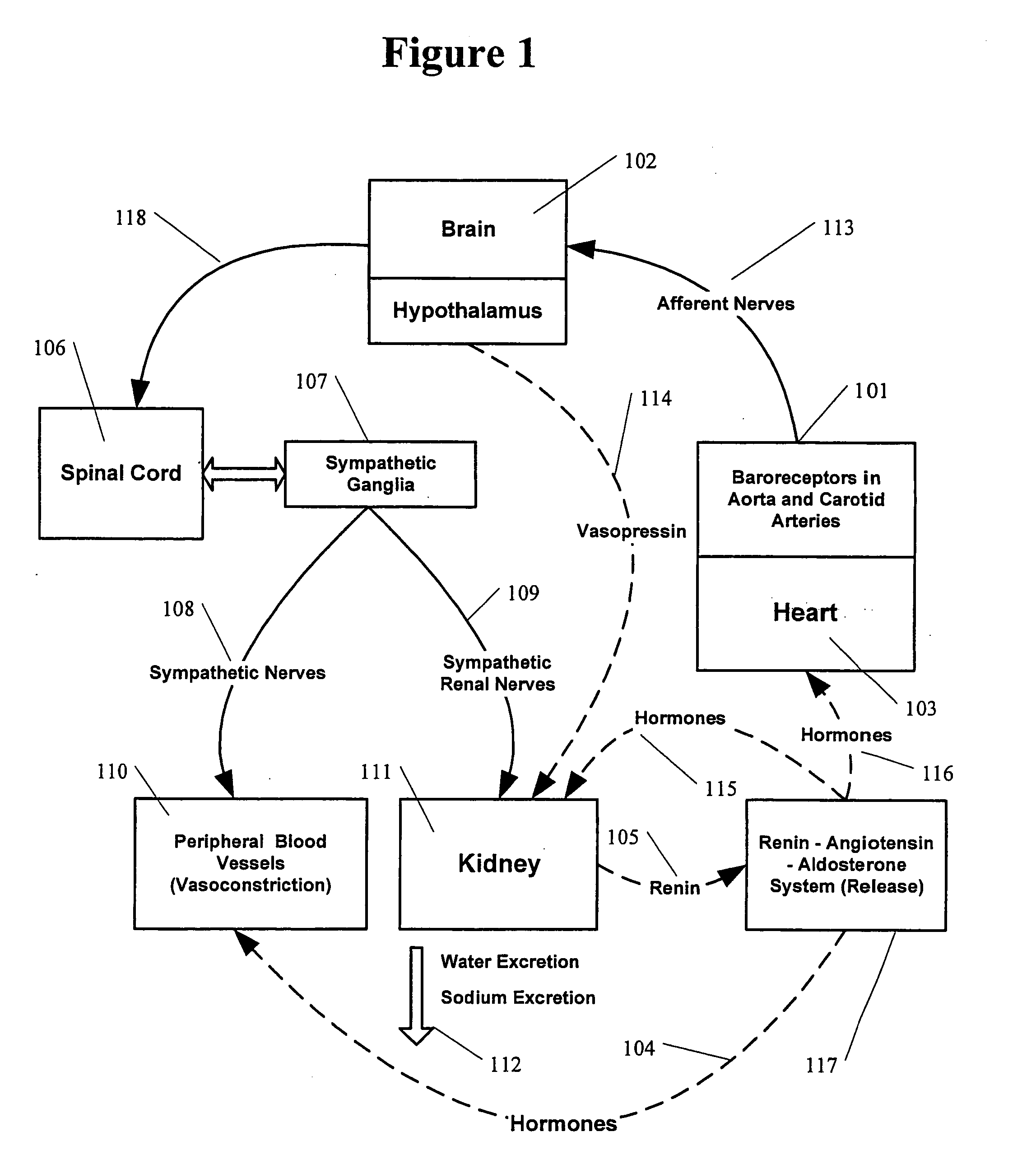
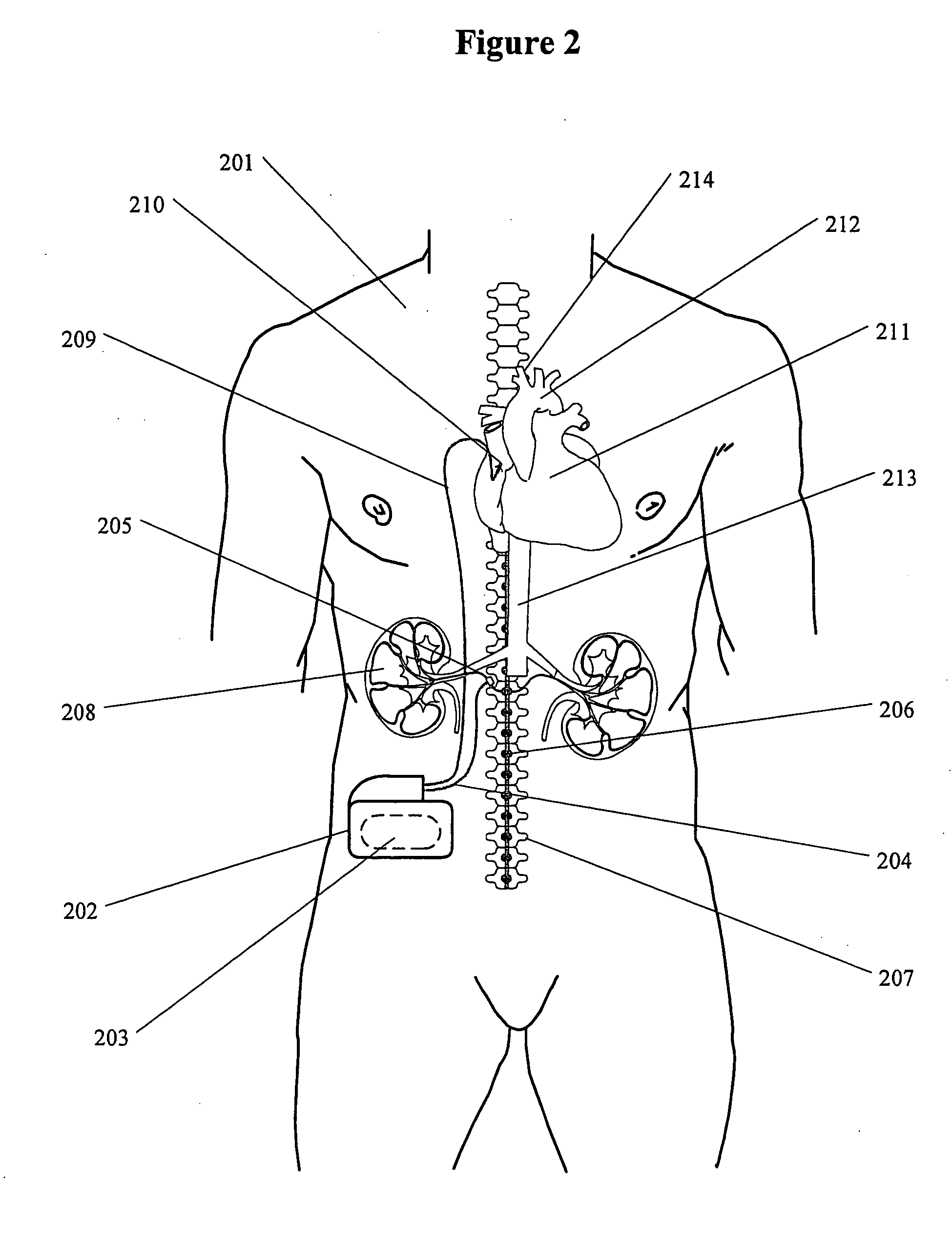
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS6978174B2Shorten the progressResolution of overloadPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseNephropathy
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump eluting implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Method, apparatus, and surgical technique for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20060167498A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesSplanchnic nervesDisease
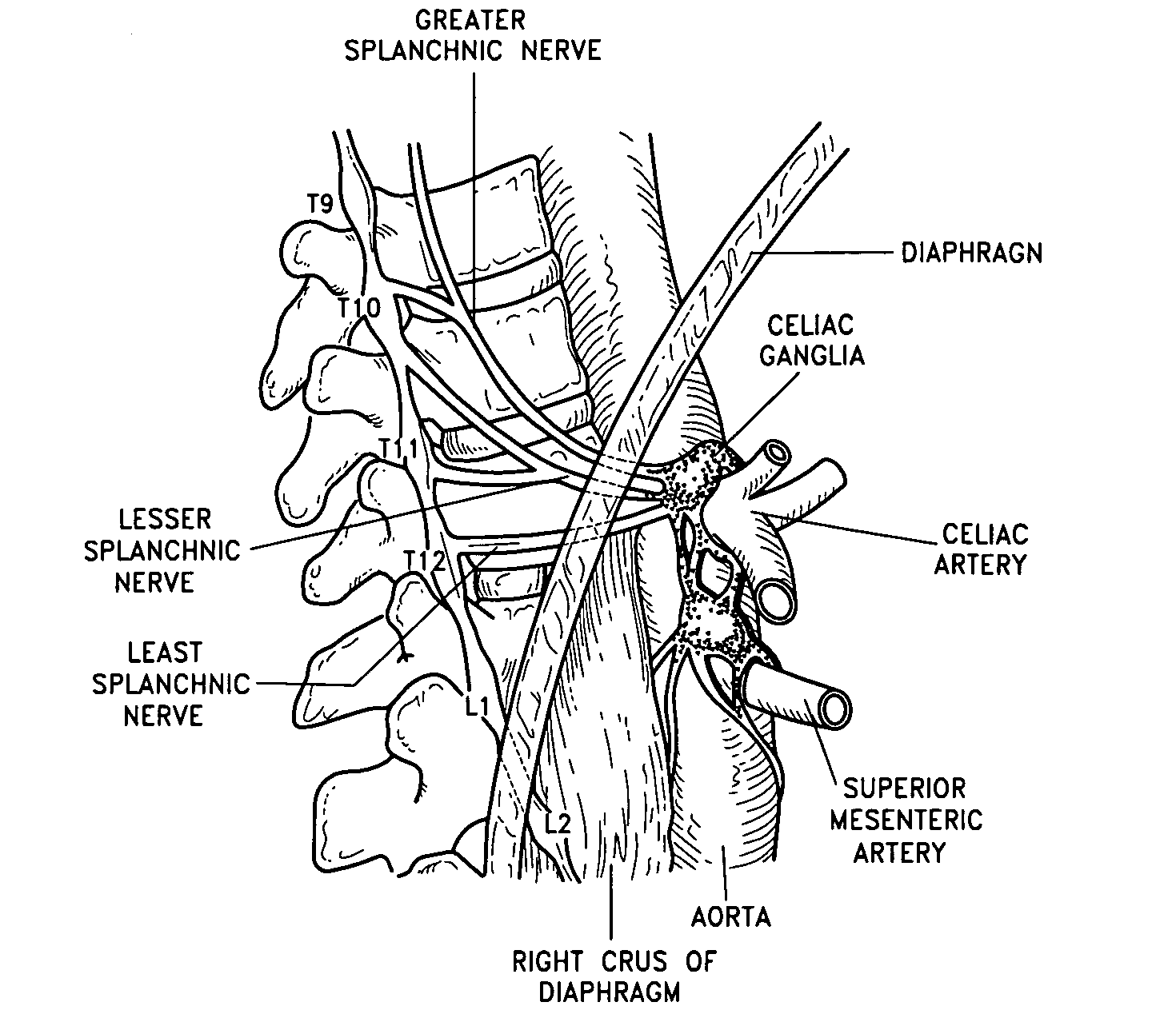
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
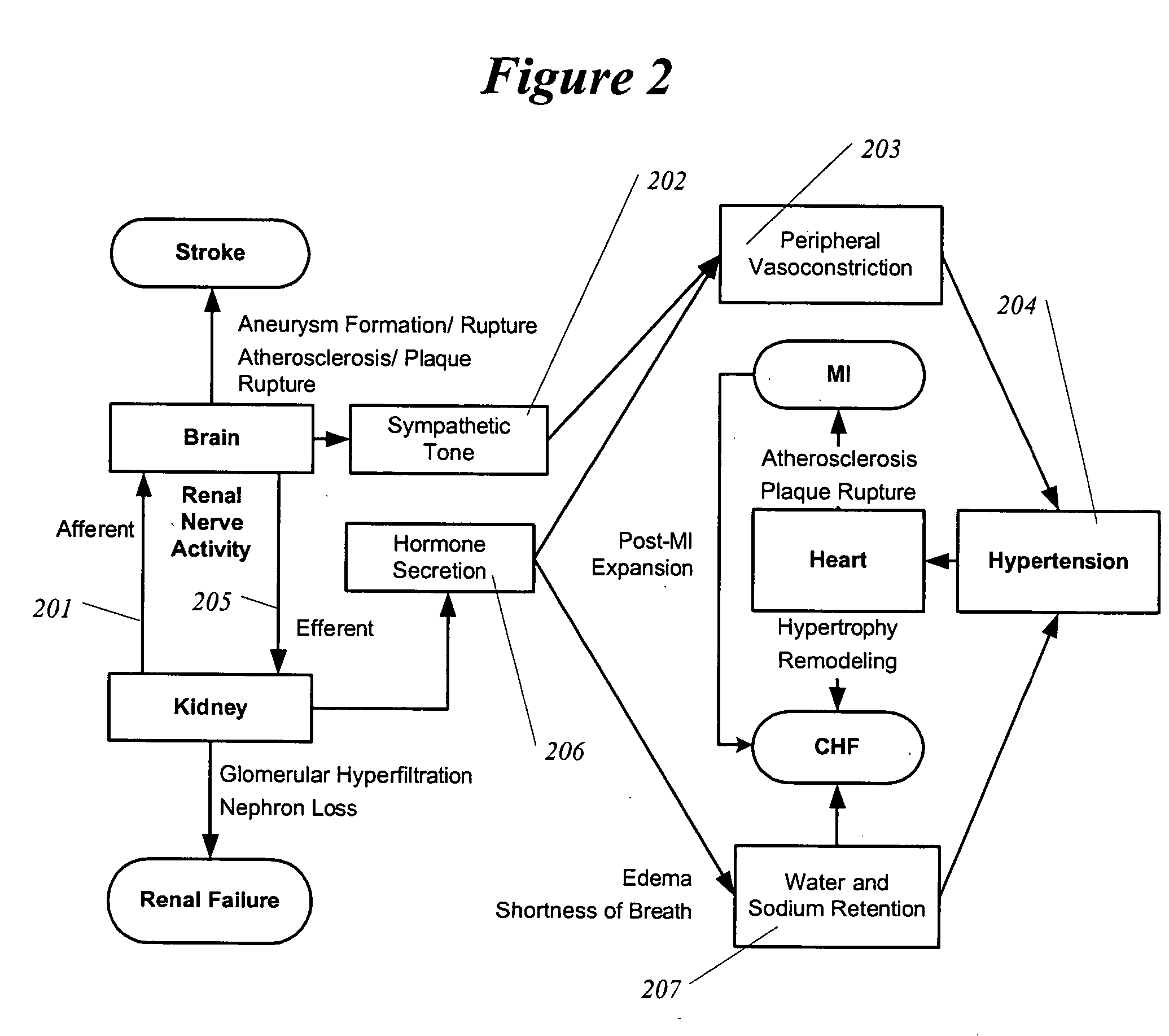
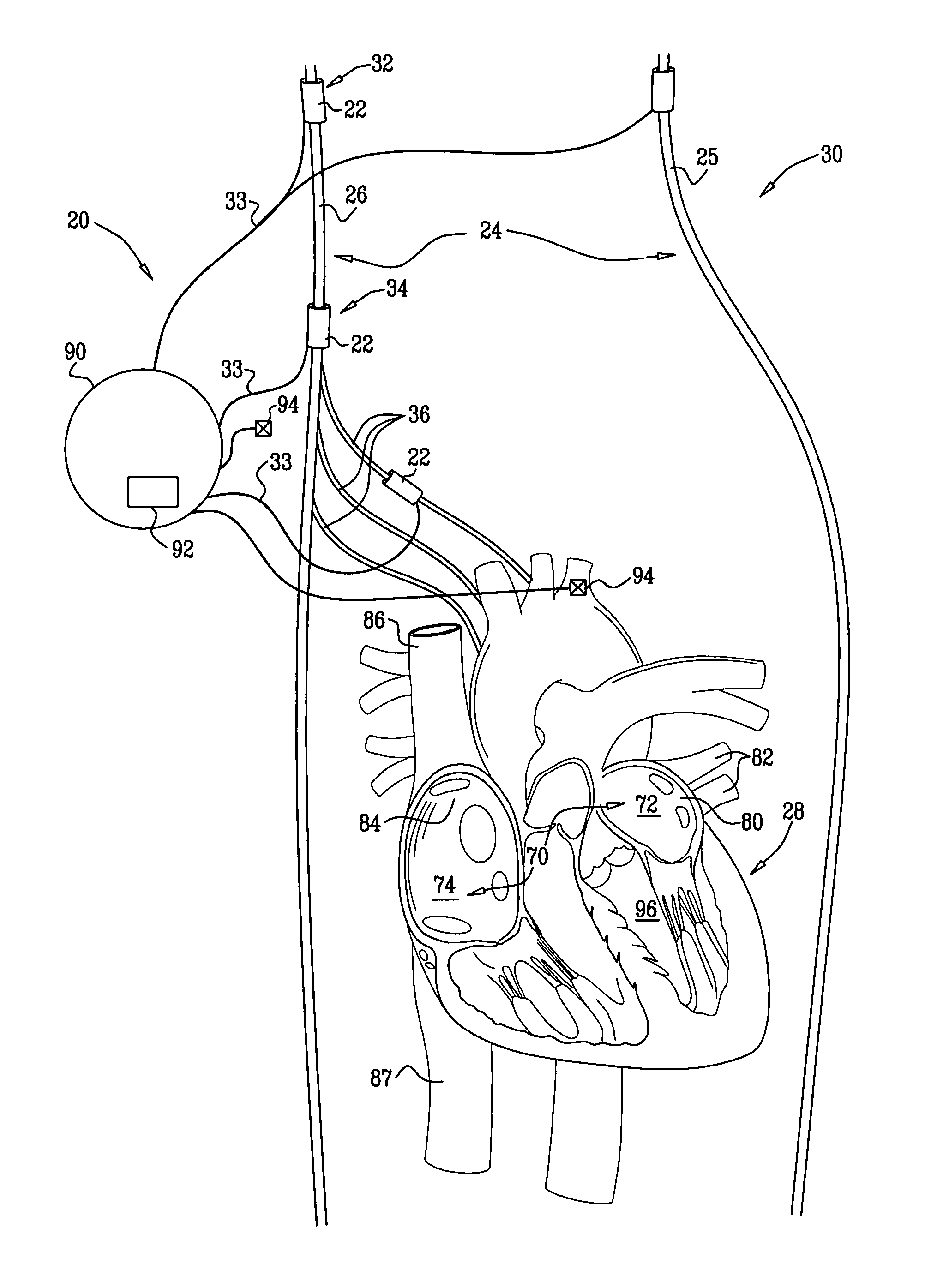
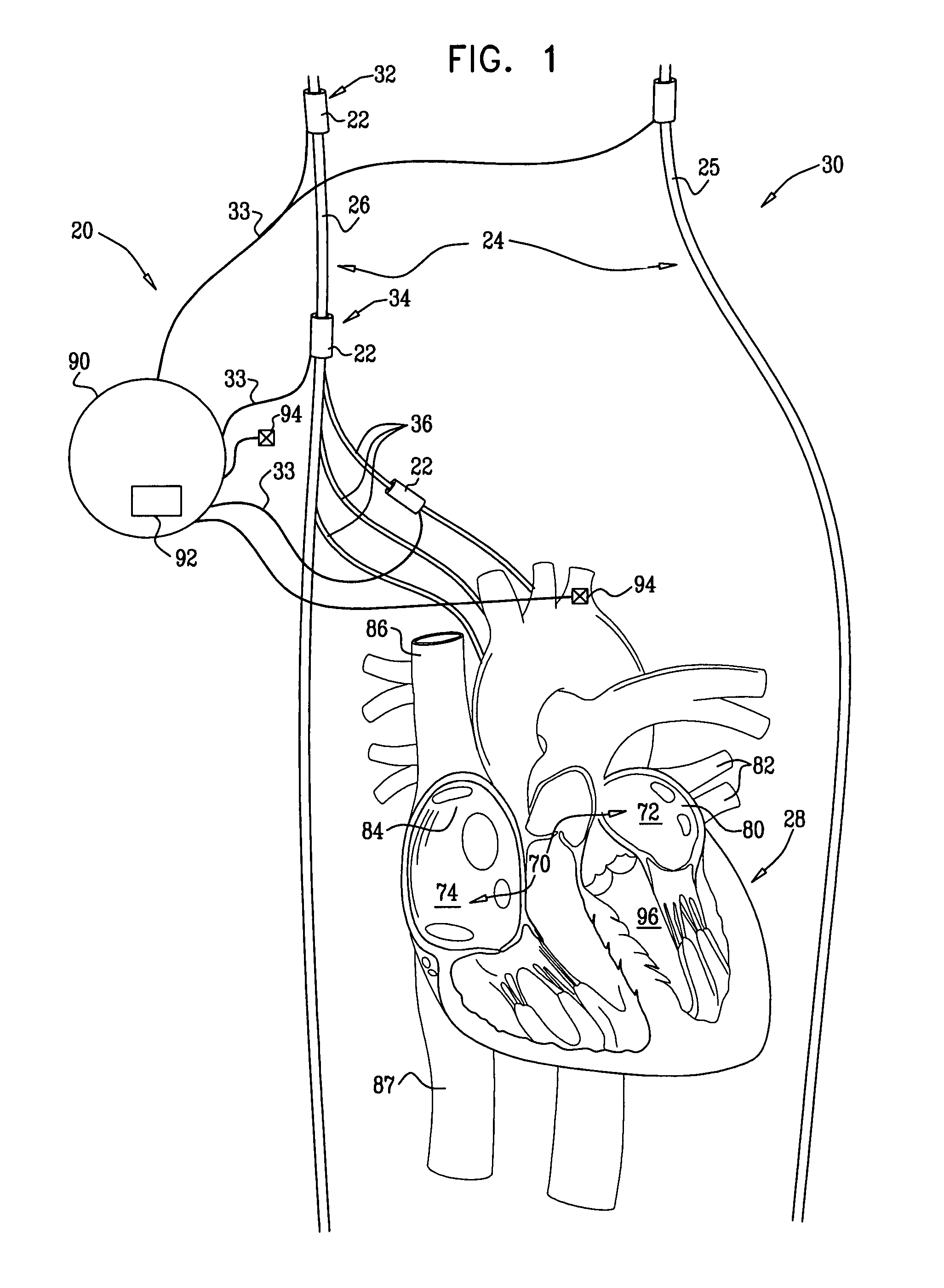
Renal nerve stimulation method and apparatus for treatment of patients
InactiveUS20050228460A1Arrest and slow down progression of diseaseEase of conditionsSpinal electrodesMedical devicesRenal nerveFAILURE KIDNEY
A method and apparatus for treatment of heart failure, hypertension and renal failure by stimulating the renal nerve. The goal of therapy is to reduce sympathetic activity of the renal nerve. Therapy is accomplished by at least partially blocking the nerve with drug infusion or electrostimulation. Apparatus can be permanently implanted or catheter based.
Owner:LEVIN HOWARD R +1
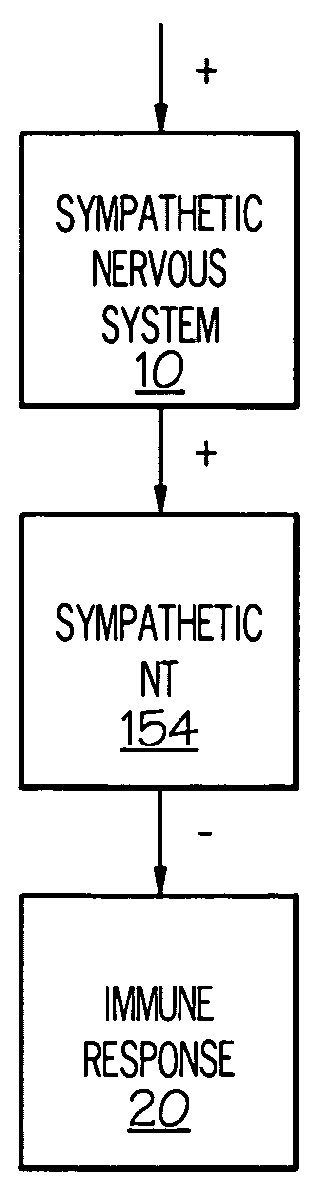
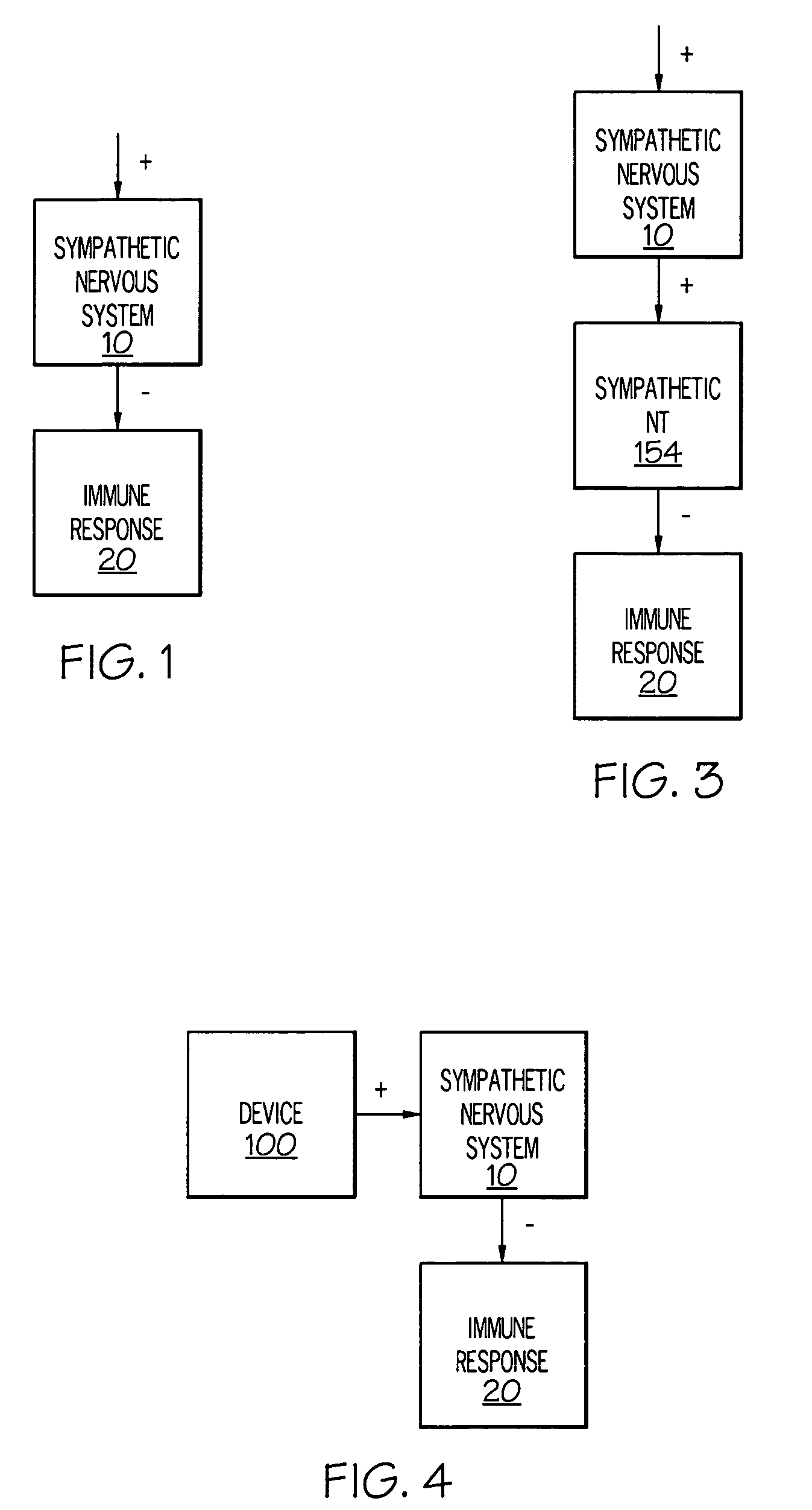
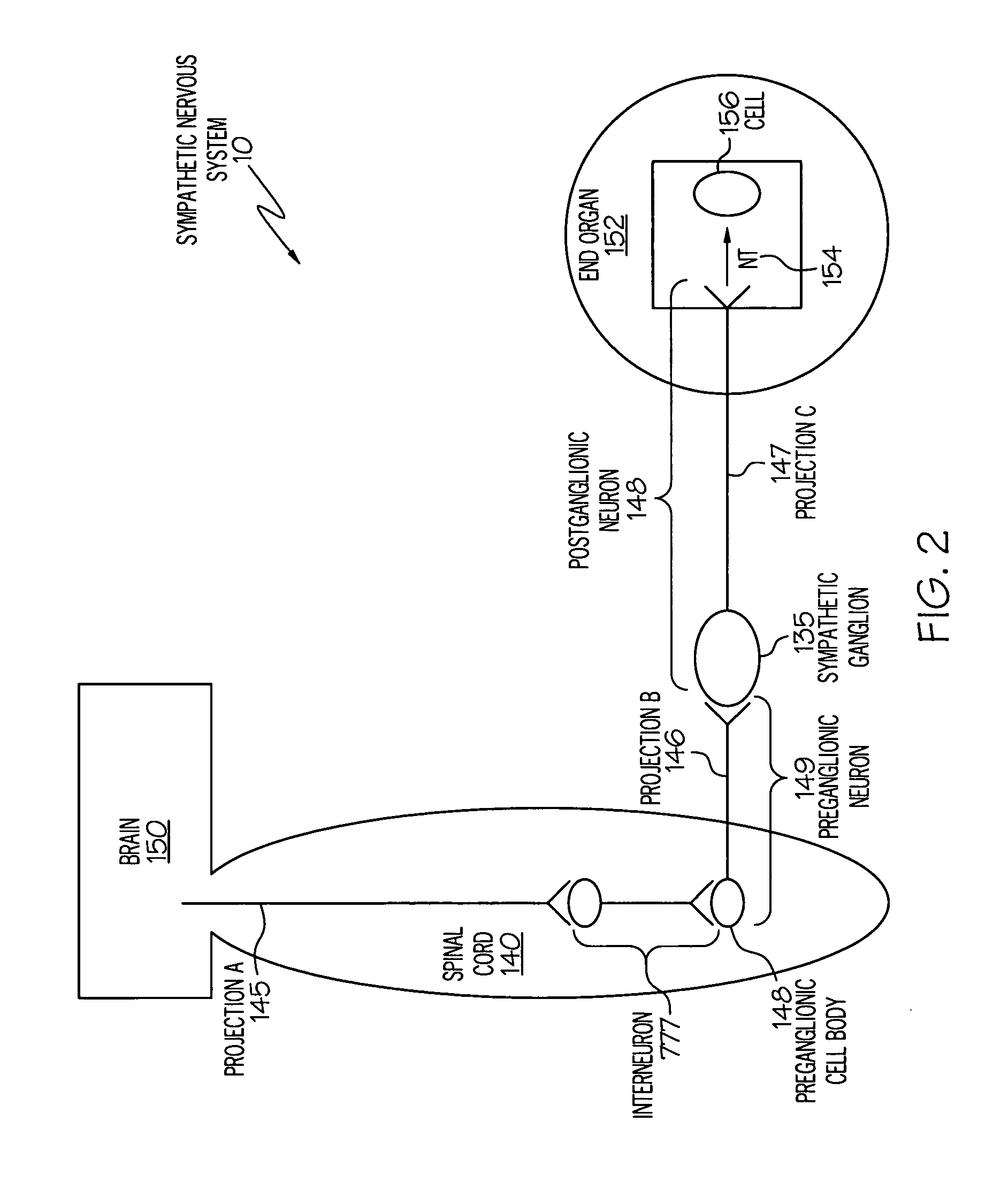
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
ActiveUS20050075701A1Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemNeuron
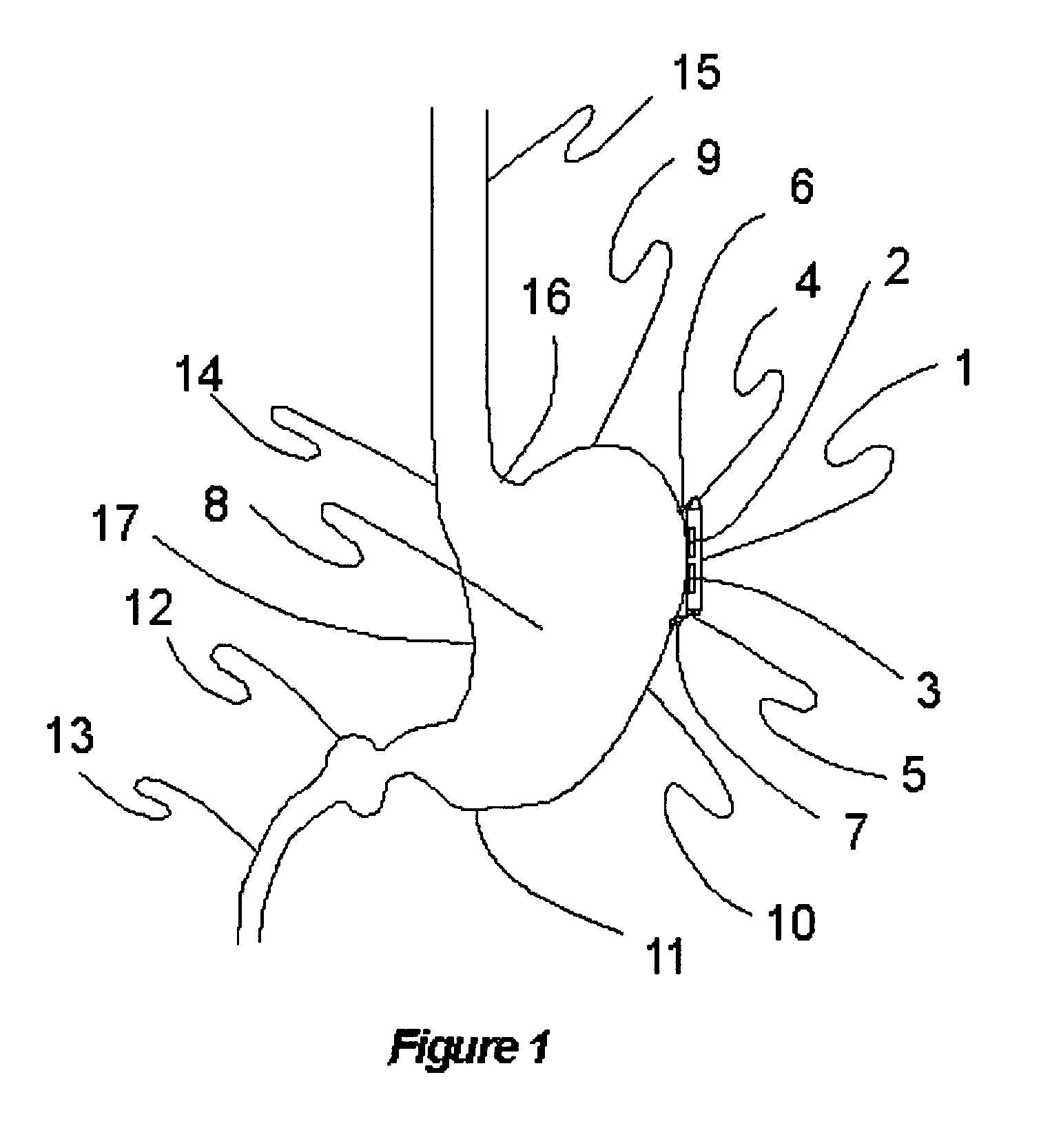
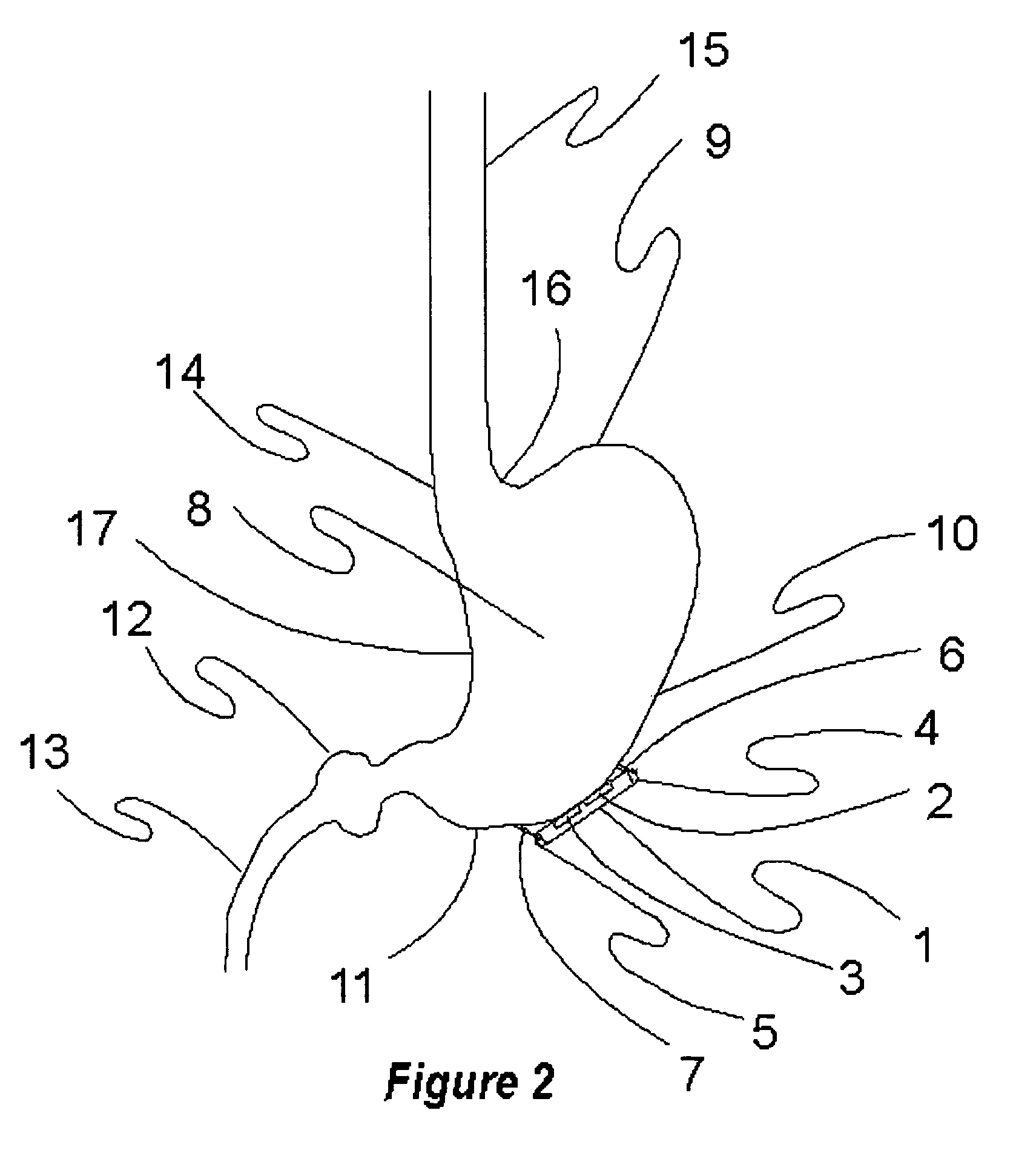
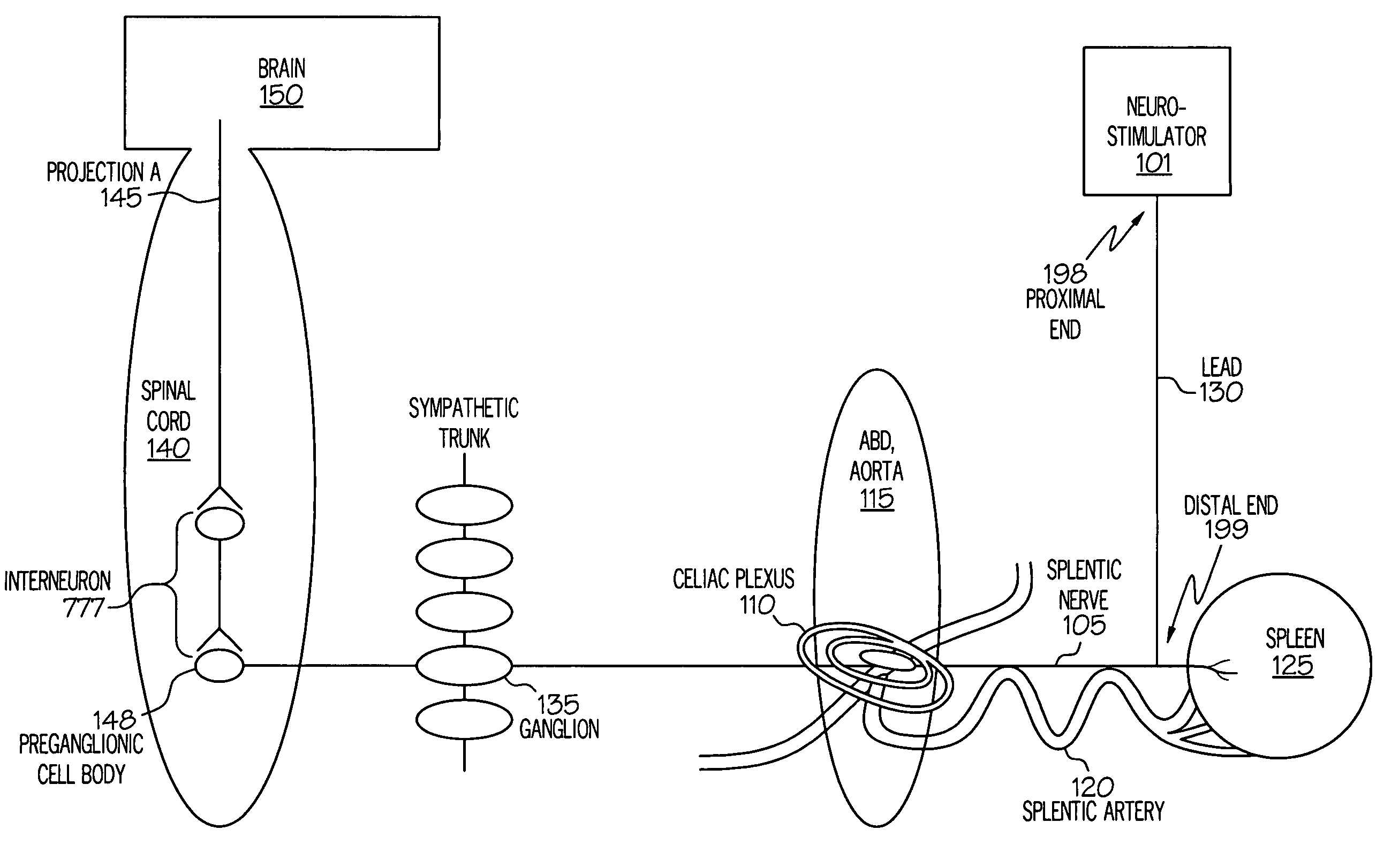
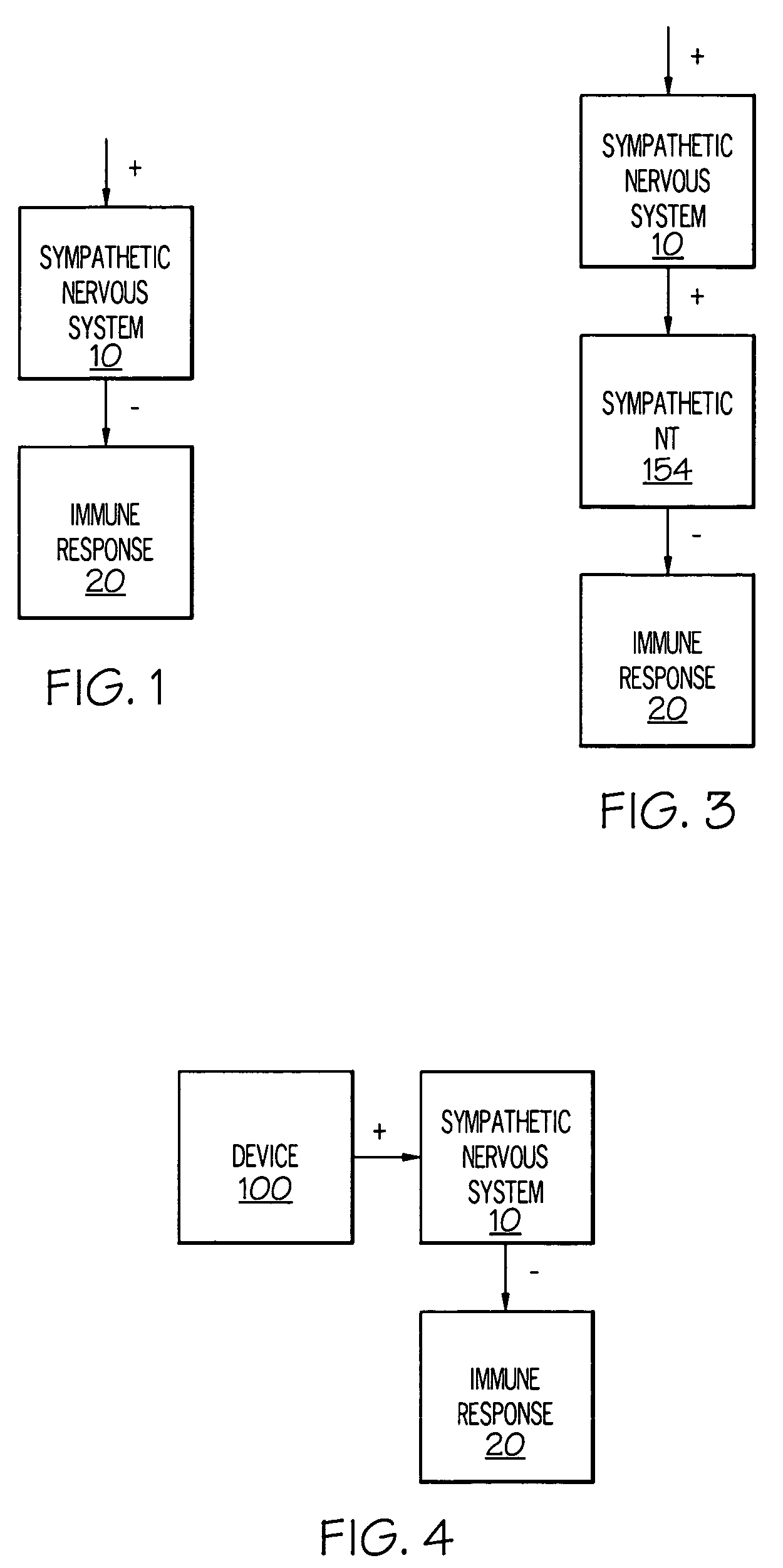
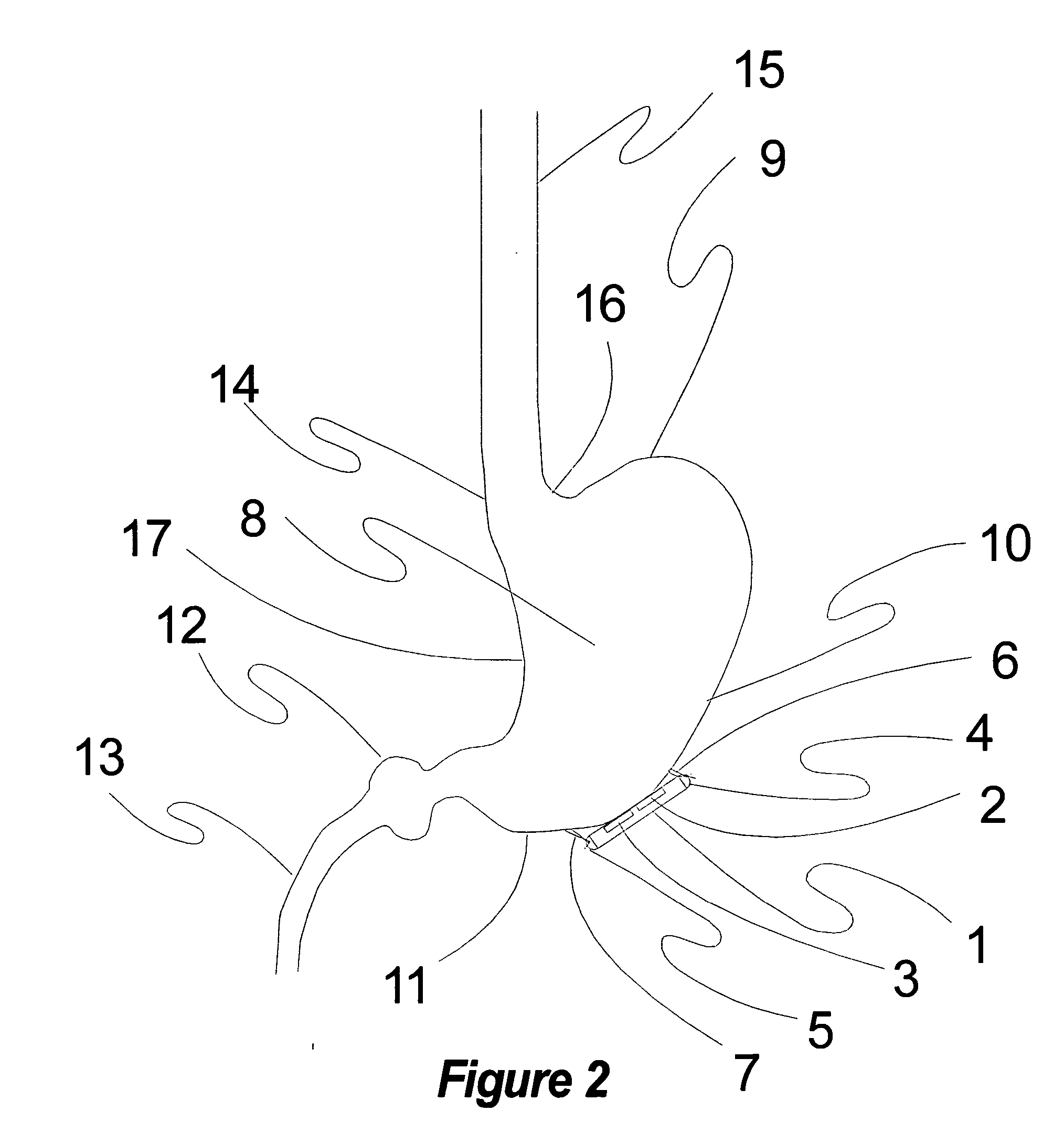
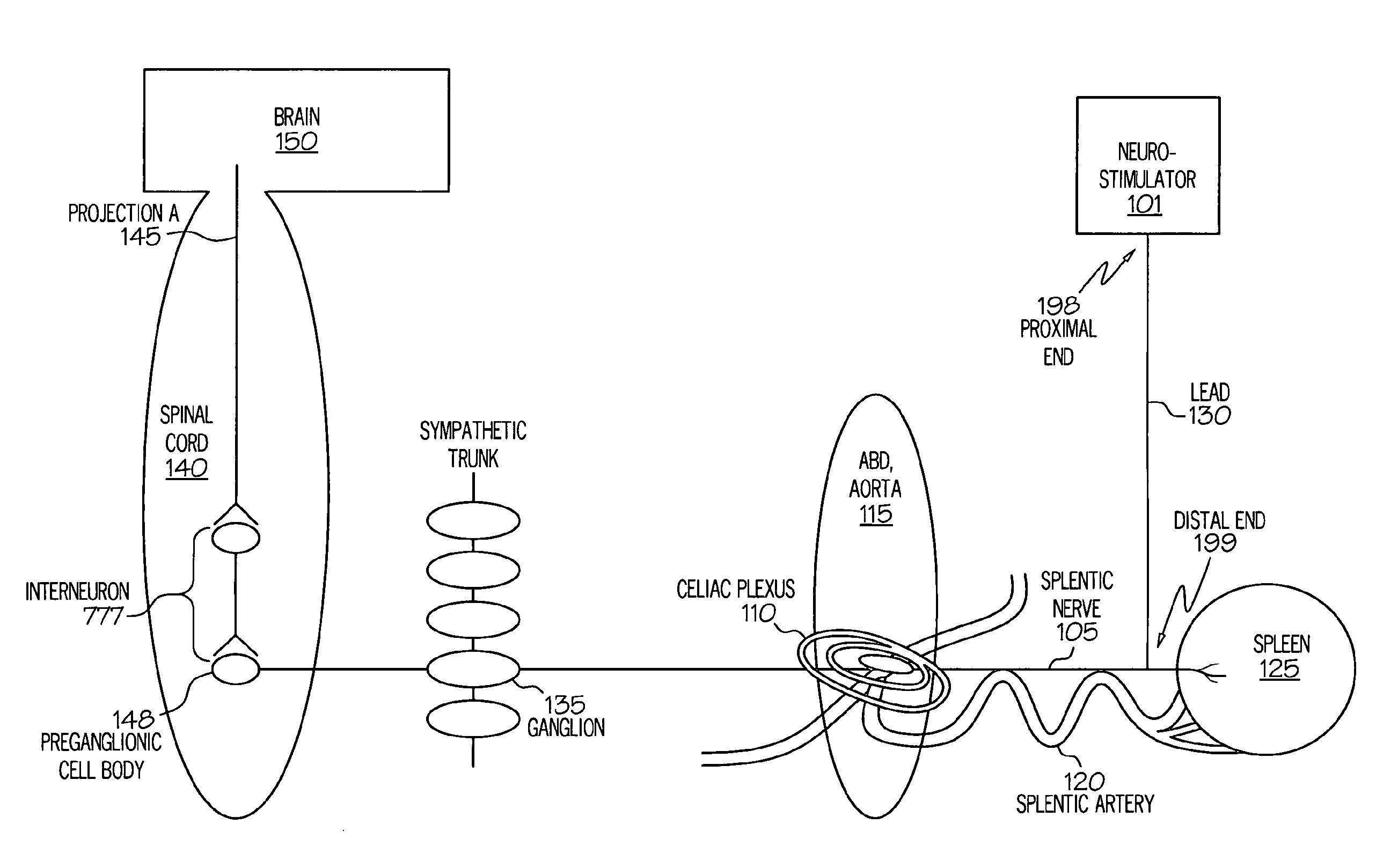
Stimulation of one or more neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, including the splenic nerve, to attenuate an immune response, including an inflammatory immune response, is discussed. Devices and systems to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system to attenuate an immune response are also discussed. Devices discussed include pulse generators and drug pumps. Systems are described as optionally having one or more sensors and operator instructions. In specific examples, stimulation of the splenic nerve of pigs with a pulse generator is shown to be safe and effective in attenuating a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS20080213331A1Shorten the progressResolution of overloadSpinal electrodesMedical devicesDiseaseRenal nerve
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump or a drug eluding implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:ARDIAN
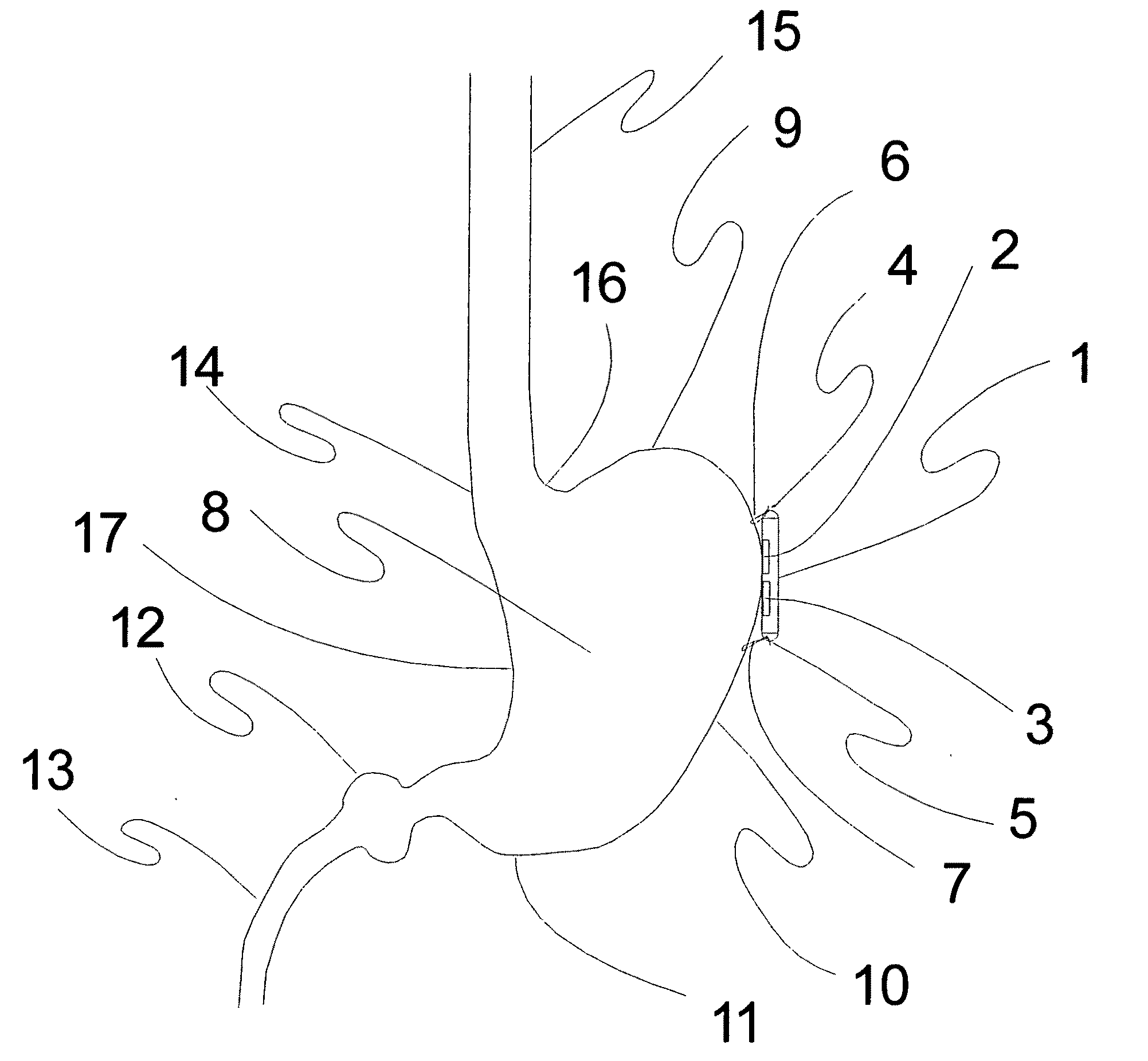
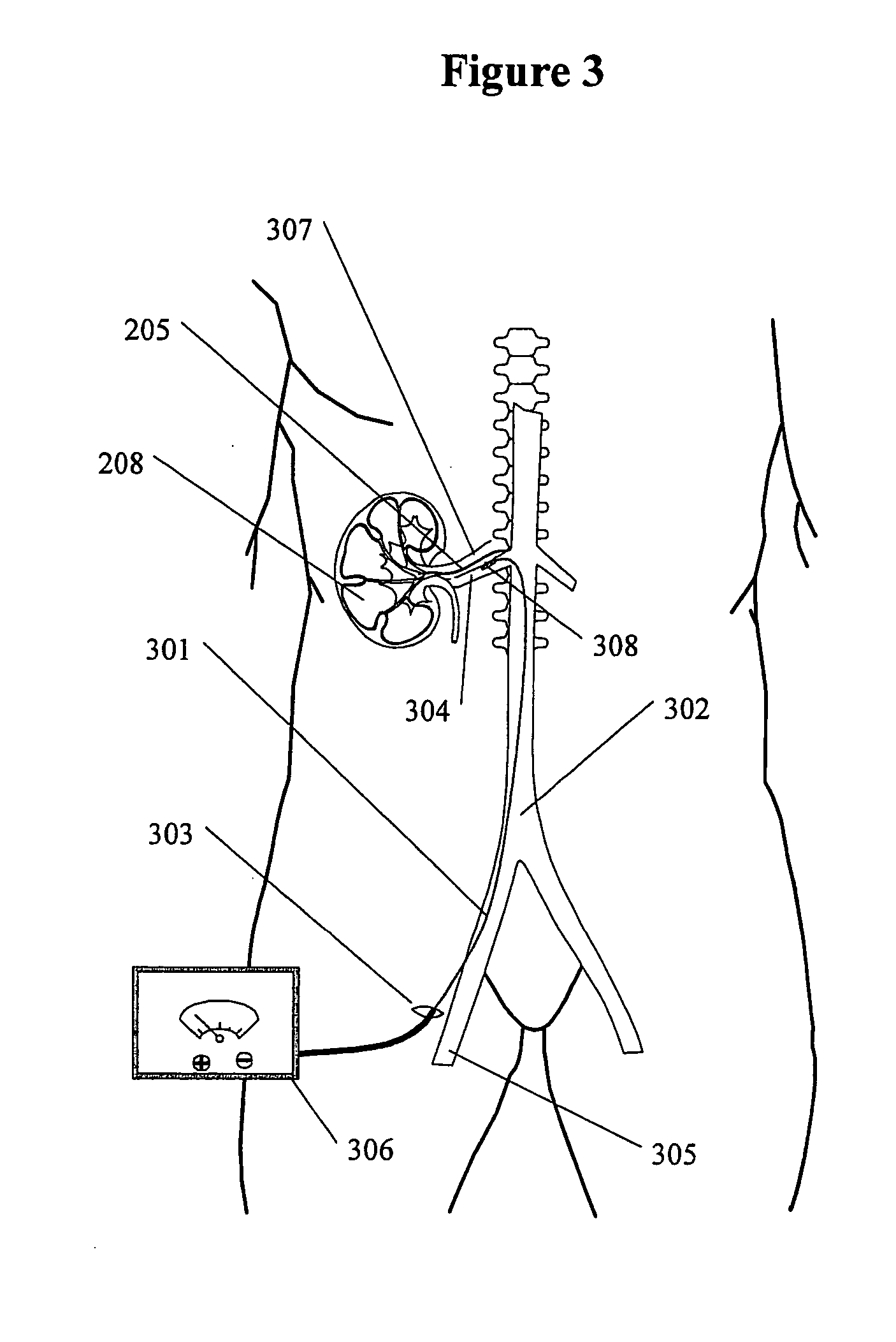
Mapping sympathetic nerve distribution for renal ablation and catheters for same
This invention provides methods for mapping and ablating renal nerves to treat disease caused by systemic renal nerve hyperactivity, e.g. hypertension, heart failure, renal failure and diabetes. Also provided are catheters for performing the mapping and ablating functions.
Owner:SYMAP MEDICAL (SUZHOU) LIMITED
Renal nerve stimulation method and apparatus for treatment of patients
InactiveUS20050234523A1Arrest and slow down progression of diseaseEase of conditionsSpinal electrodesMedical devicesRenal nerveFAILURE KIDNEY
A method and apparatus for treatment of heart failure, hypertension and renal failure by stimulating the renal nerve. The goal of therapy is to reduce sympathetic activity of the renal nerve. Therapy is accomplished by at least partially blocking the nerve with drug infusion or electrostimulation. Apparatus can be permanently implanted or catheter based.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
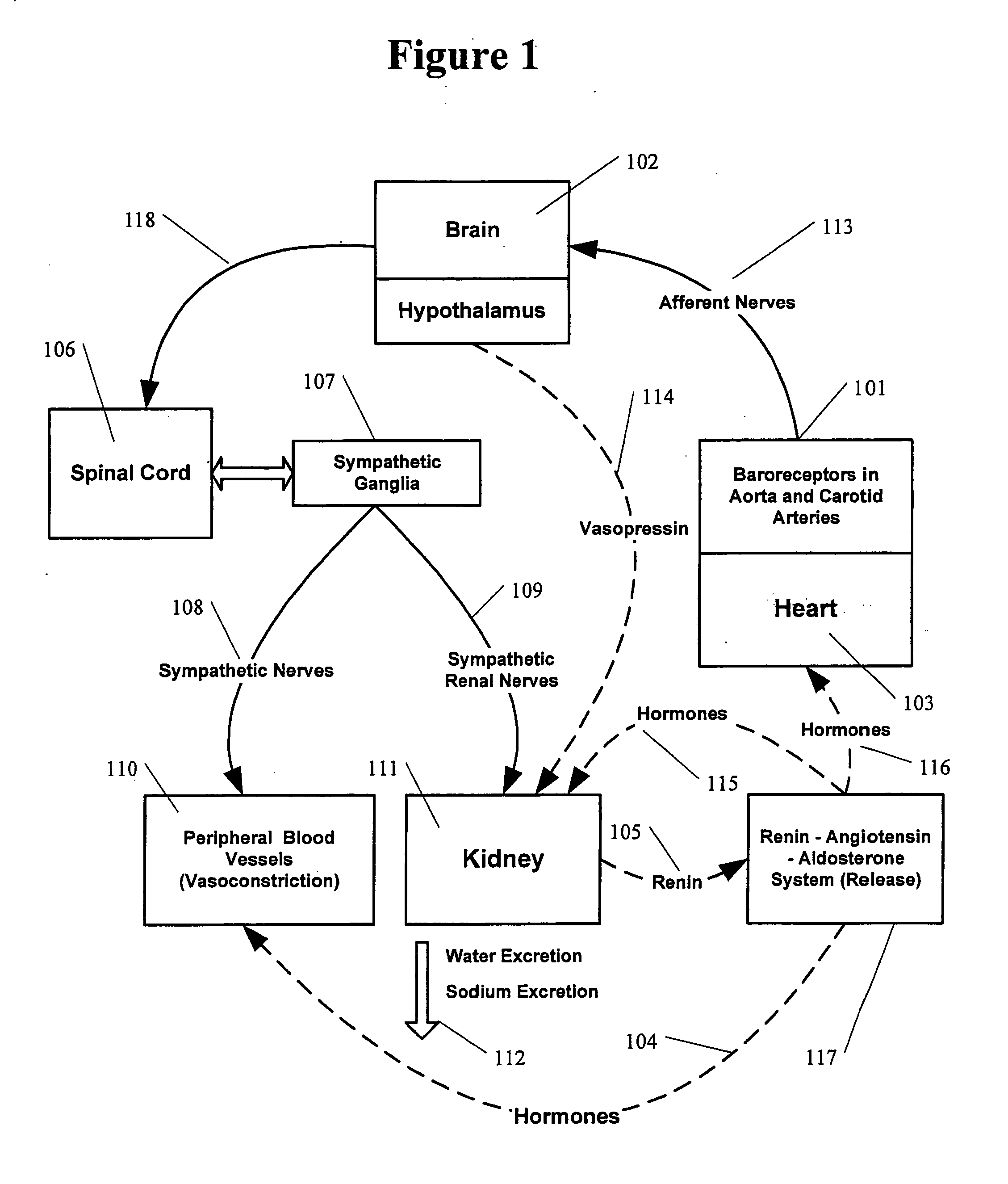
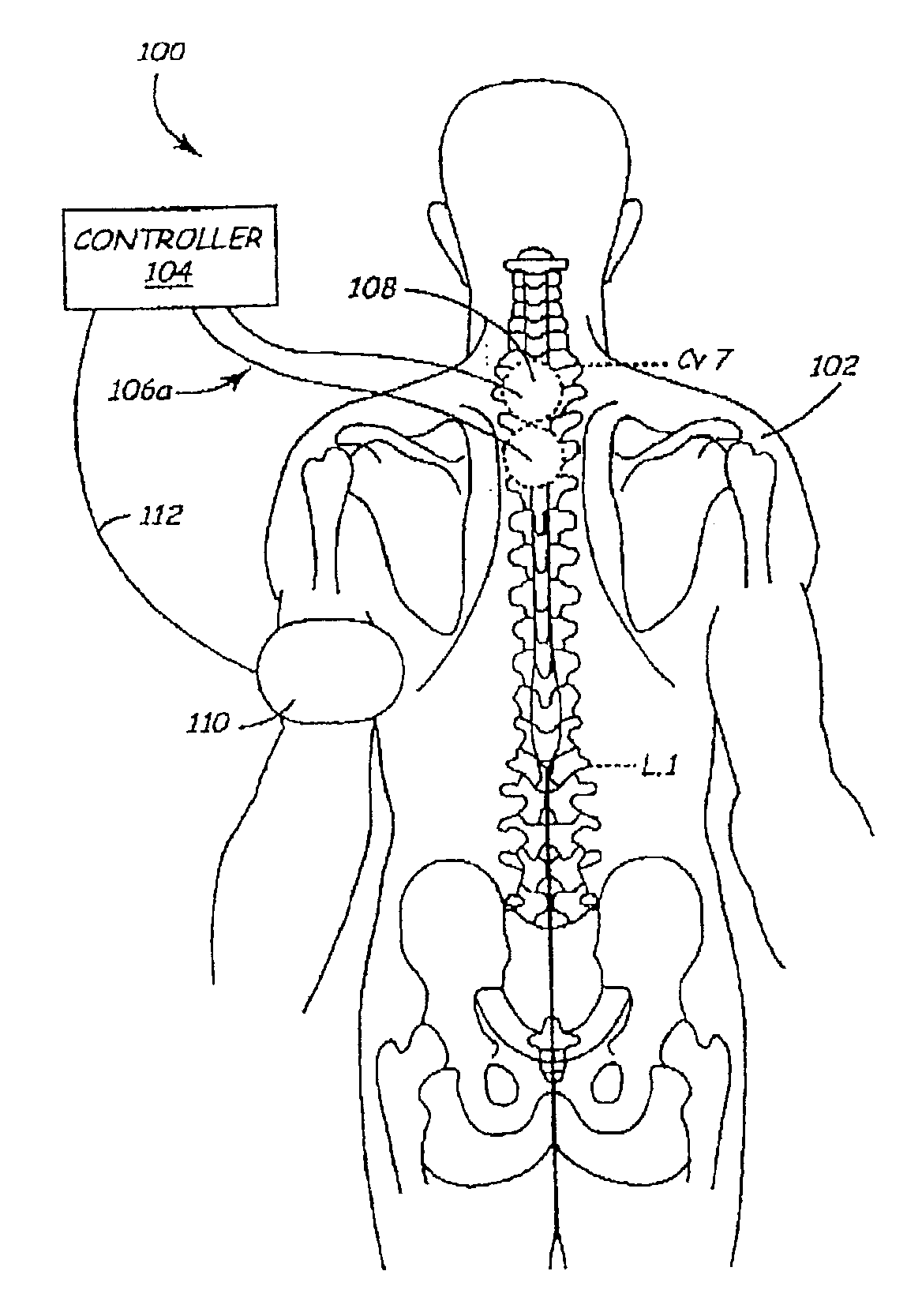
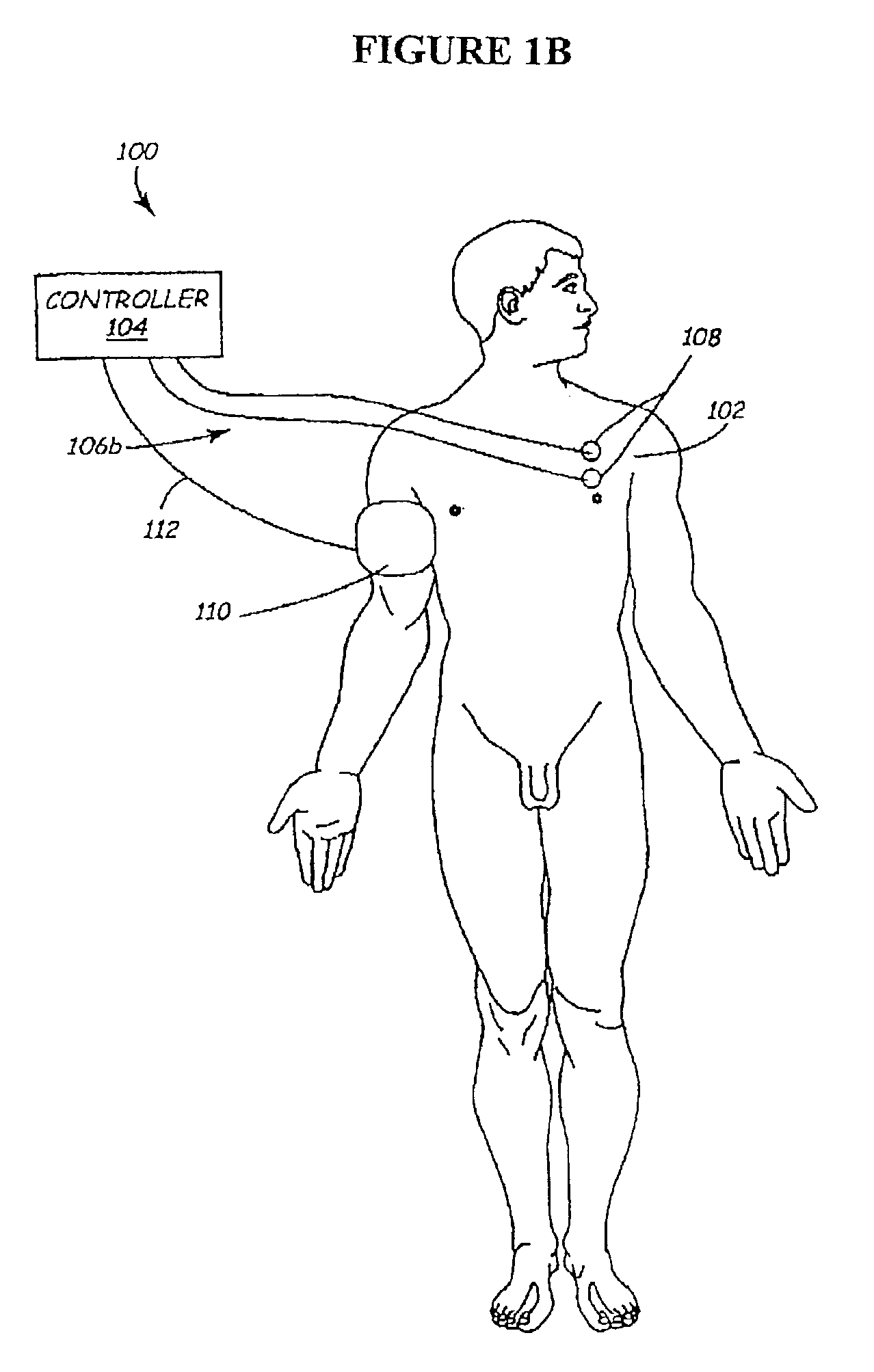
Methods and apparatus for the regulation of hormone release
ActiveUS7221979B2Modulate hormone levelPrevent hormone imbalancesInternal electrodesExternal electrodesCatecholamineElectrical stimulations
A method and apparatus for delivering corrective therapy through hormone regulation is provided. Inhibition of sympathetic fibers by spinal cord stimulation is used to regulate the levels of hormones such as catecholamines, renin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. The invention utilizes a closed or open loop feedback system in which physiological parameters such as the concentrations of hormones and sympathetic indicators such as heart rate and urine production are monitored and used to determine the appropriate level of neurostimulation. The site of electrical stimulation includes, but is not limited to, the spinal cord at levels T7–L2 and the associated neural fibers within a region of the T7–L2 dermatomes
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
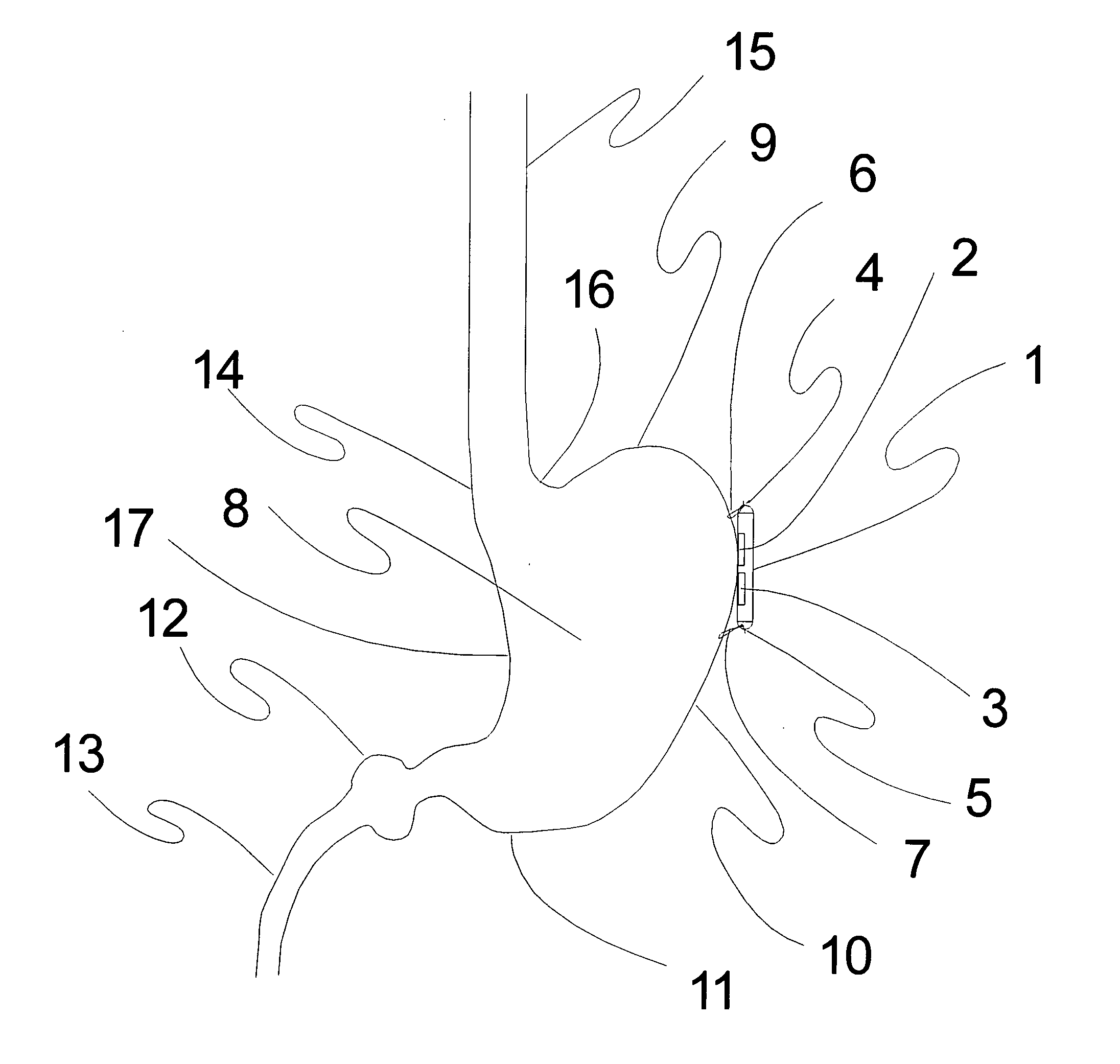
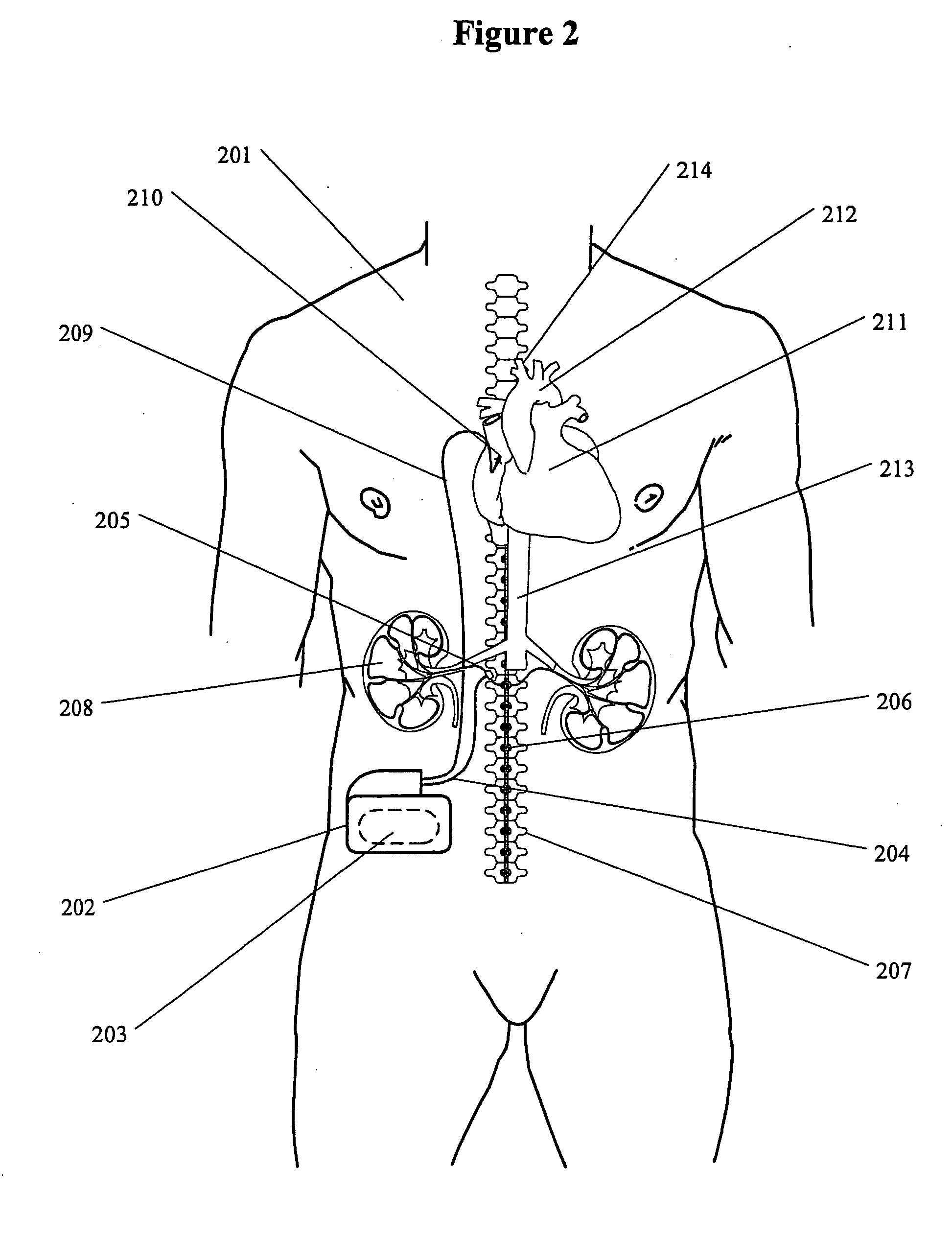
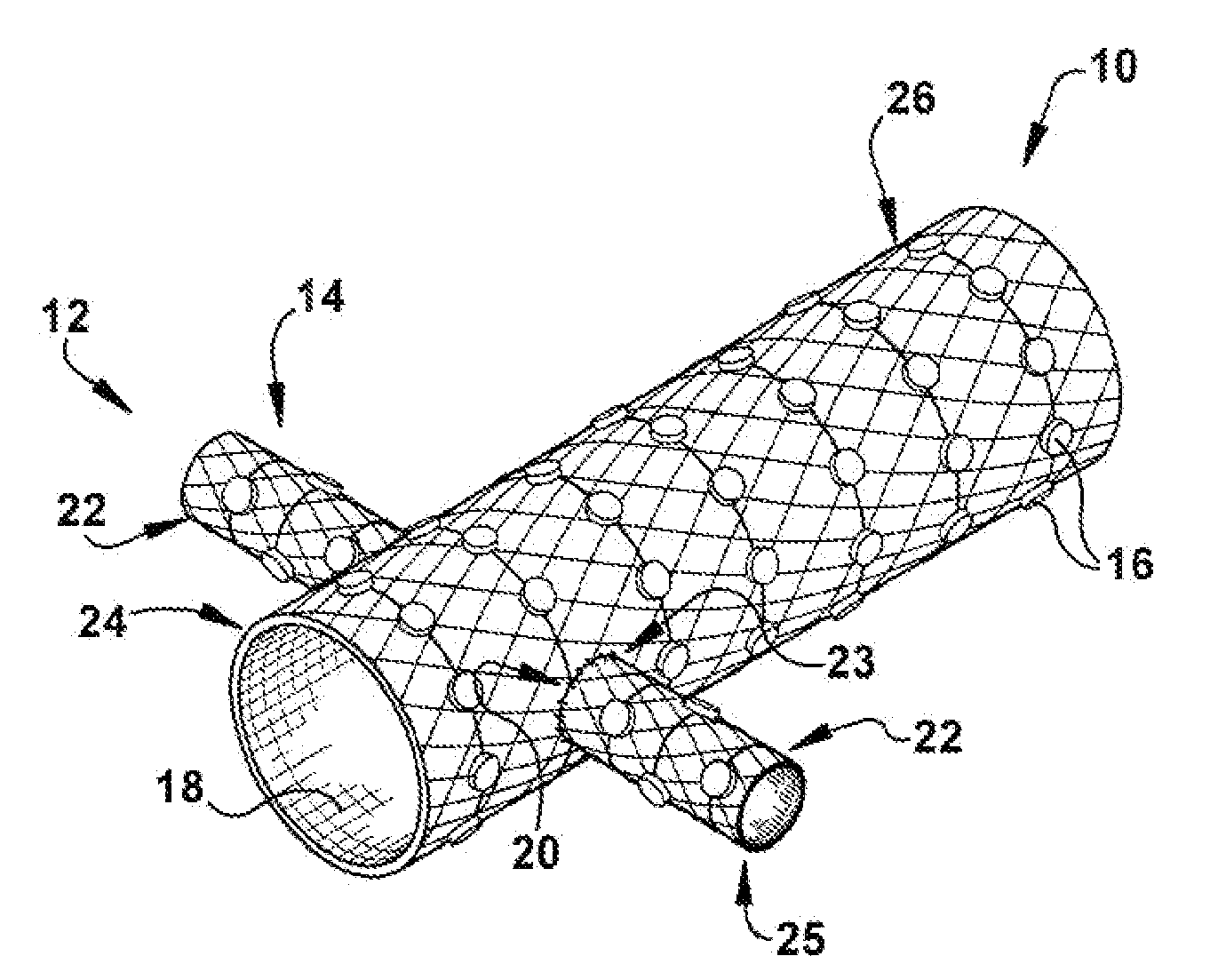
Method and apparatus for renal neuromodulation
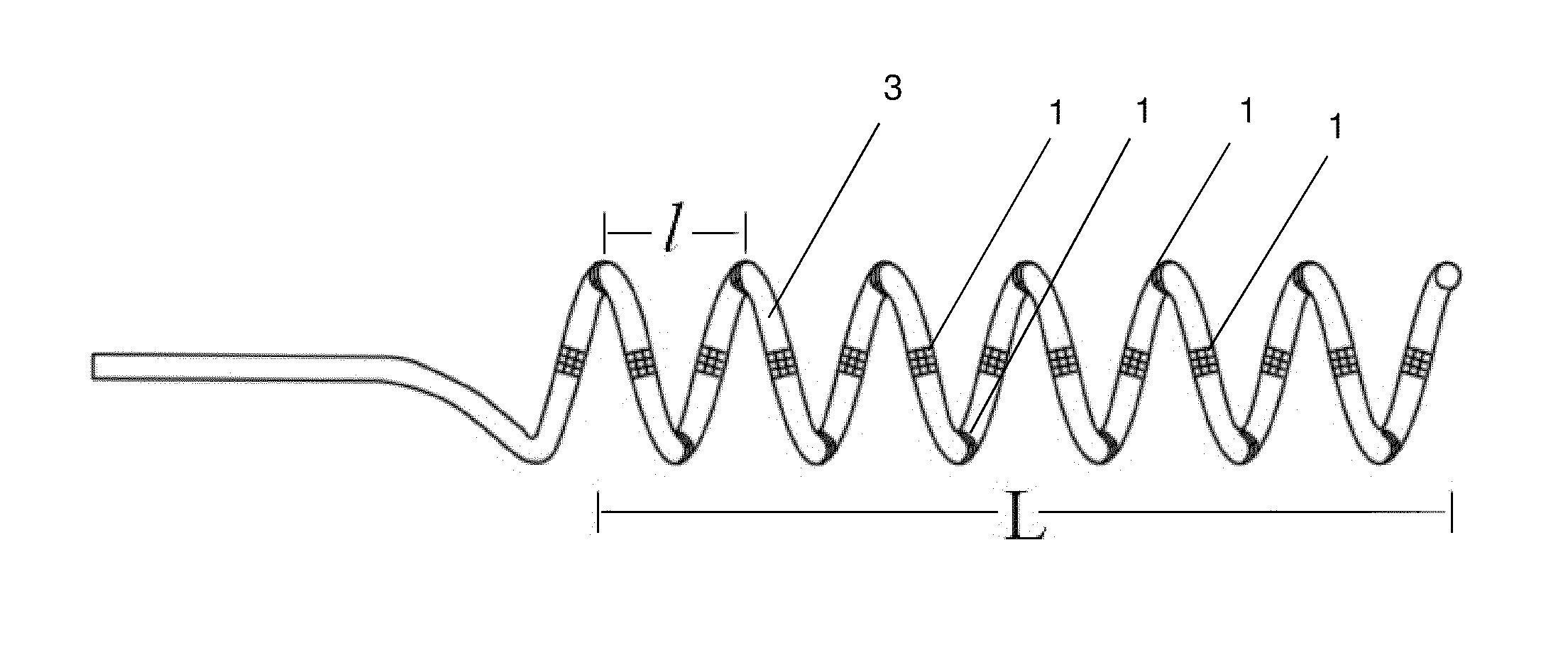
An apparatus for renal neuromodulation includes an expandable support member having a main body portion for engaging a wall of a blood vessel proximate a renal vasculature and at least one electrode connected with the main body portion. The at least one electrode is arranged to selectively deliver electric current to a desired location where modulation of the sympathetic nervous system is effective to alter renal function. The apparatus further includes an insulative material attached to at least a portion of the main body portion for isolating blood flow through the vessel from the electric current delivered by the at least one electrode.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and apparatus for renal neuromodulation
An apparatus for renal neuromodulation includes an expandable support member having a main body portion for engaging a wall of a blood vessel proximate a renal vasculature and at least one electrode connected with the main body portion. The at least one electrode is arranged to selectively deliver electric current to a desired location where modulation of the sympathetic nervous system is effective to alter renal function. The apparatus further includes an insulative material attached to at least a portion of the main body portion for isolating blood flow through the vessel from the electric current delivered by the at least one electrode.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Electrical and magnetic stimulators used to treat migraine/sinus headache and comorbid disorders
Non-invasive electrical nerve stimulation devices and magnetic stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of treating medical disorders using energy that is delivered noninvasively by such devices. The disorders comprise migraine and other primary headaches such as cluster headaches, including sinus symptoms that resemble an immune-mediated response (“sinus” headaches), irrespective of whether those symptoms arise from an allergy that is co-morbid with the headache. The disclosed methods may also be used to treat other disorders that may be co-morbid with migraine headaches, such as anxiety disorders. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, one or both of the patient's vagus nerves are stimulated non-invasively. In other embodiments, parts of the sympathetic nervous system and / or the adrenal glands are stimulated.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Methods and apparatus for the regulation of hormone release
A method and apparatus for delivering corrective therapy through hormone regulation is provided. Inhibition of sympathetic fibers by spinal cord stimulation is used to regulate the levels of hormones such as catecholamines, renin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. The invention utilizes a closed or open loop feedback system in which physiological parameters such as the concentrations of hormones and sympathetic indicators such as heart rate and urine production are monitored and used to determine the appropriate level of neurostimulation. The site of electrical stimulation includes, but is not limited to, the spinal cord at levels T7-L2 and the associated neural fibers within a region of the T7-L2 dermatomes
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Parasympathetic nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20120303080A1Optimal ventricular rateSlow heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowMedicine
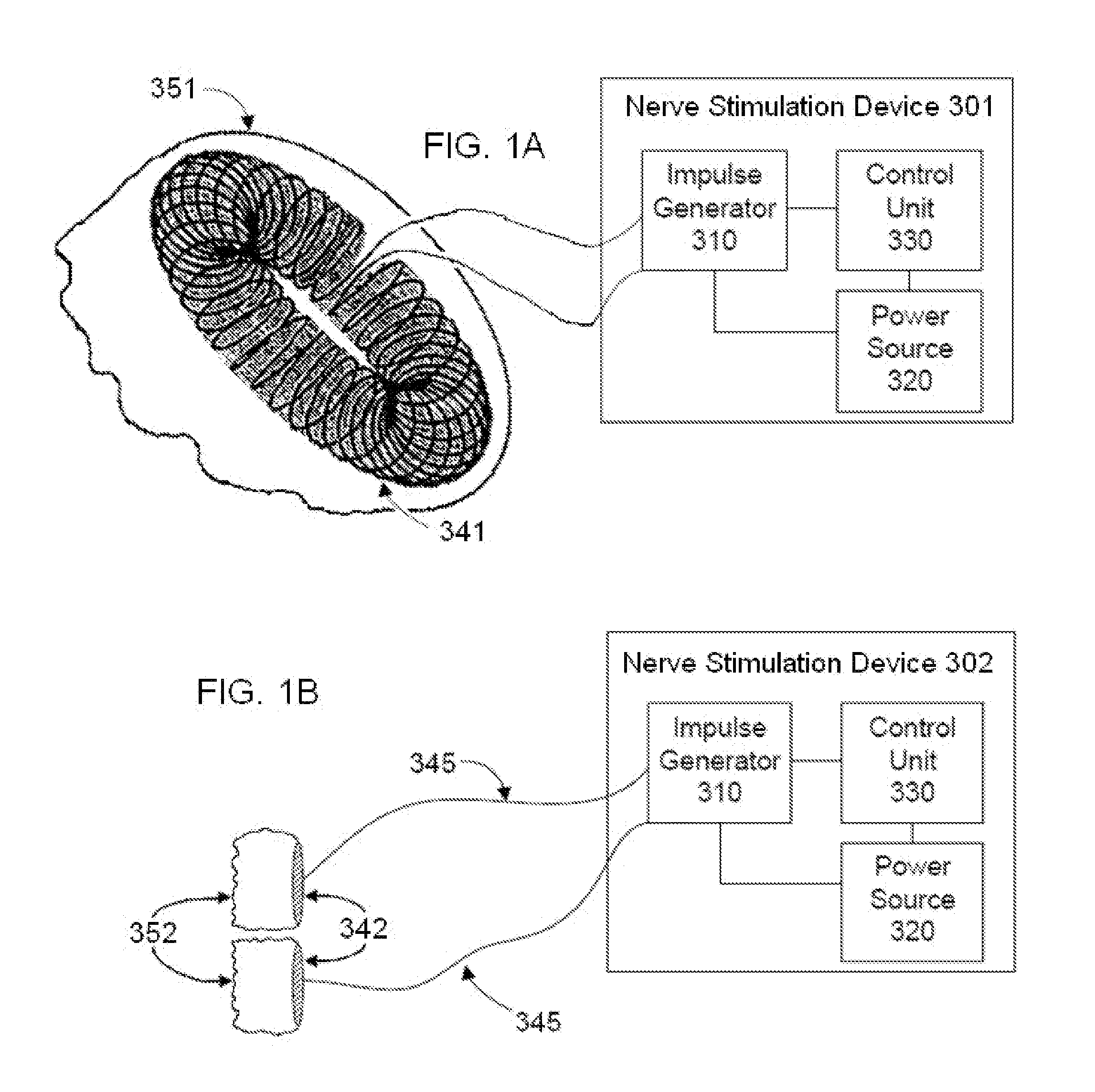
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by coupling an electrode device to a site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue; driving, by a control unit, the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the site not responsively to any physiological parameters sensed by any device directly or indirectly coupled to the control unit; and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wireless electric modulation of sympathetic nervous system
InactiveUS7236822B2Increased energy expenditureReducing food intakeInternal electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseNervous system
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders, by wireless electrical activation or inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by wirelessly stimulating the greater splanchnic nerve or other portion of the sympathetic nervous system using a wireless electrode inductively coupled with a radiofrequency field. The source of radiofrequency energy may be internal or external to the patient. This nerve activation can result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Treatment of renal hypertension or carotid sinus syndrome with adventitial pharmaceutical sympathetic denervation or neuromodulation
ActiveUS20110104061A1Improve concentrationOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsRenal HypertensionsCvd risk
Sympathetic nerves run through the adventitia surrounding renal arteries and are critical in the modulation of systemic hypertension. Hyperactivity of these nerves can cause renal hypertension, a disease prevalent in 30-40% of the adult population. Hypertension can be treated with neuromodulating agents (such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II inhibitors, or aldosterone receptor blockers), but requires adherence to strict medication regimens and often does not reach target blood pressure threshold to reduce risk of major cardiovascular events. A minimally invasive solution is presented here to reduce the activity of the sympathetic nerves surrounding the renal artery by locally delivering neurotoxic or nerve-blocking agents into the adventitia. Extended elution of these agents may also be accomplished in order to tailor the therapy to the patient.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
Nerve stimulation for treatment of syncope
InactiveUS20070027497A1Augmentation of vasomotor toneDeterring and preventing faintingElectrotherapySympathetic nervous systemPhysical therapy
A method and apparatus for treating a syncope disorder is disclosed. The method comprises coupling a first electrode to a sympathetic nerve of the patient, and then applying a first therapeutic electrical signal to the electrode to stimulate the sympathetic nerve, wherein the stimulation causes an increase in the blood pressure of the patient to a level that is above a predetermined threshold level, whereby dizziness or fainting by the patient is deterred or prevented.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Method and apparatus for neuromodulation and physiologic modulation for the treatment of metabolic and neuropsychiatric disease
InactiveUS7529582B1Delay is slowIncrease pressureUltrasound therapySpinal electrodesSplanchnic nervesAfferent Neurons
A method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO DANIEL J
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
ActiveUS7418292B2Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemImmunity response
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Nerve stimulation techniques
InactiveUS20140046407A1Avoid damageInhibit migrationSpinal electrodesCatheterControl cellPhysical therapy
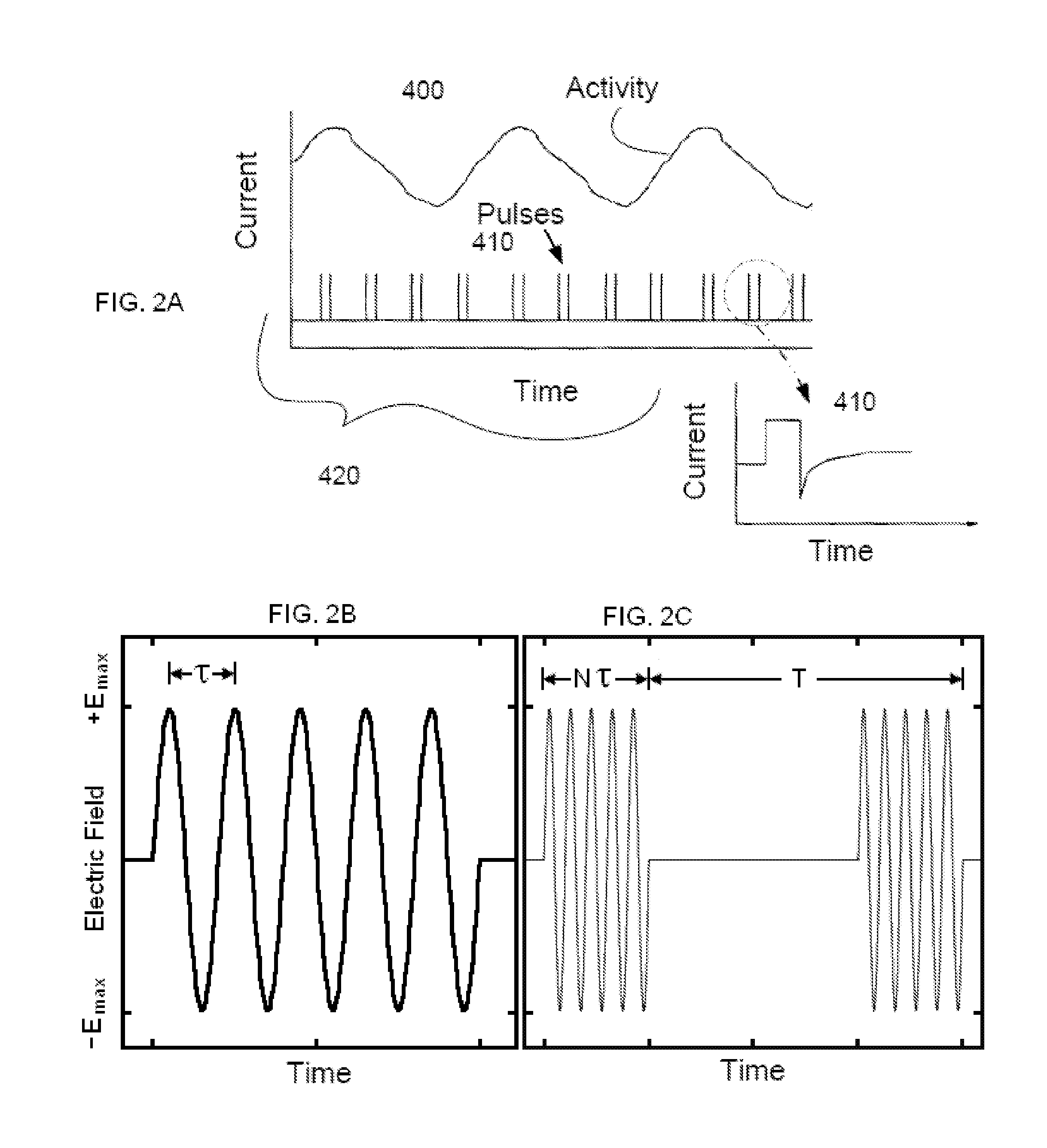
An electrode device is configured to be coupled to a parasympathetic site of a subject. A control unit is configured to drive the electrode device to apply a current in bursts of one or more pulses, during “on” periods that alternate with low stimulation periods, wherein at least one of the low stimulation periods immediately following the at least one of the “on” periods has a low stimulation duration equal to at least 50% of the “on” duration; set the current applied on average during the low stimulation periods to be less than 20% of the current applied on average during the “on” periods; and ramp a number of pulses per burst during a commencement of the at least one of the “on” periods and / or a conclusion of the at least one of the “on” periods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method, apparatus, surgical technique, and stimulation parameters for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20070162085A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesHead electrodesSplanchnic nervesAfferent Neurons
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
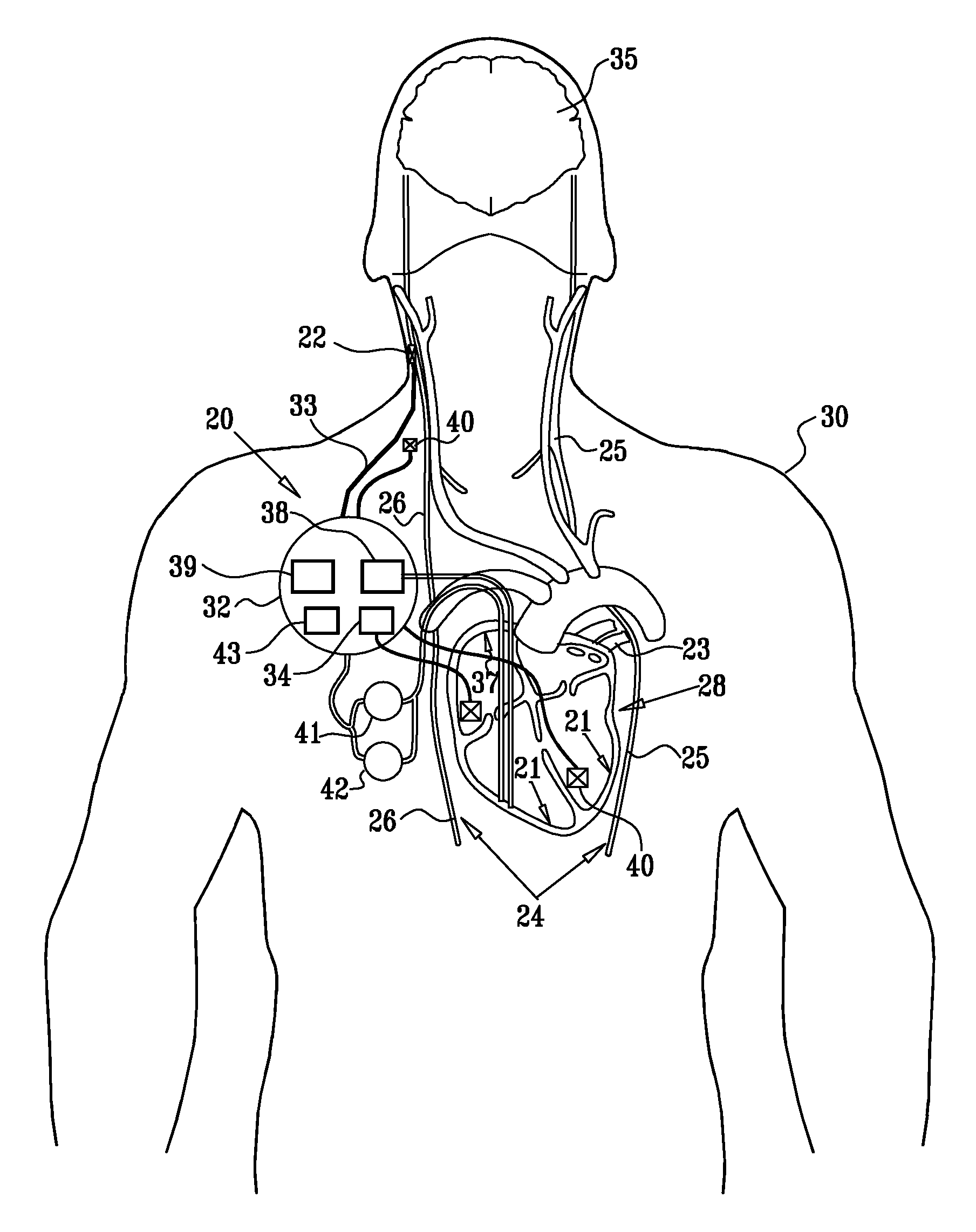
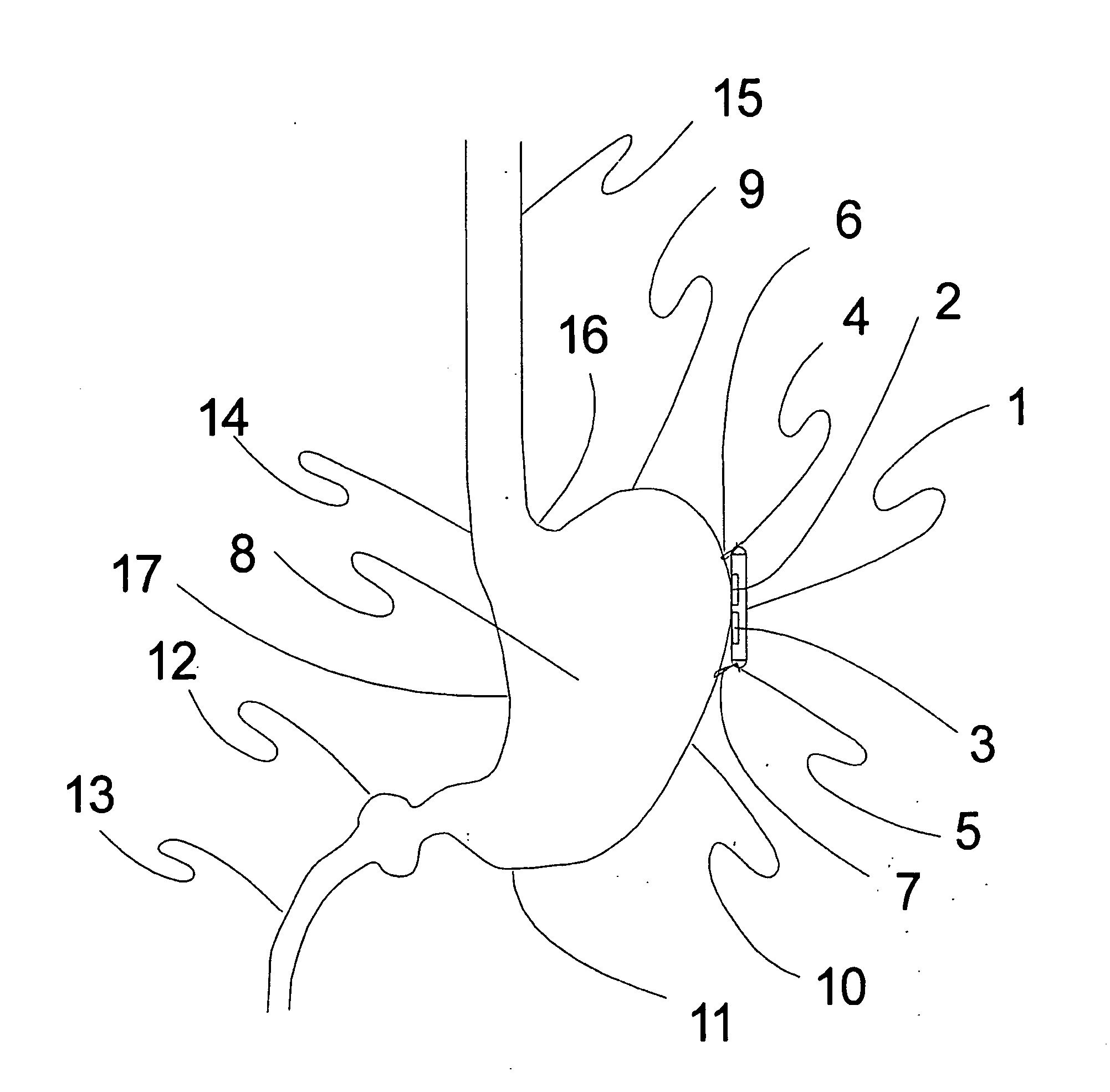
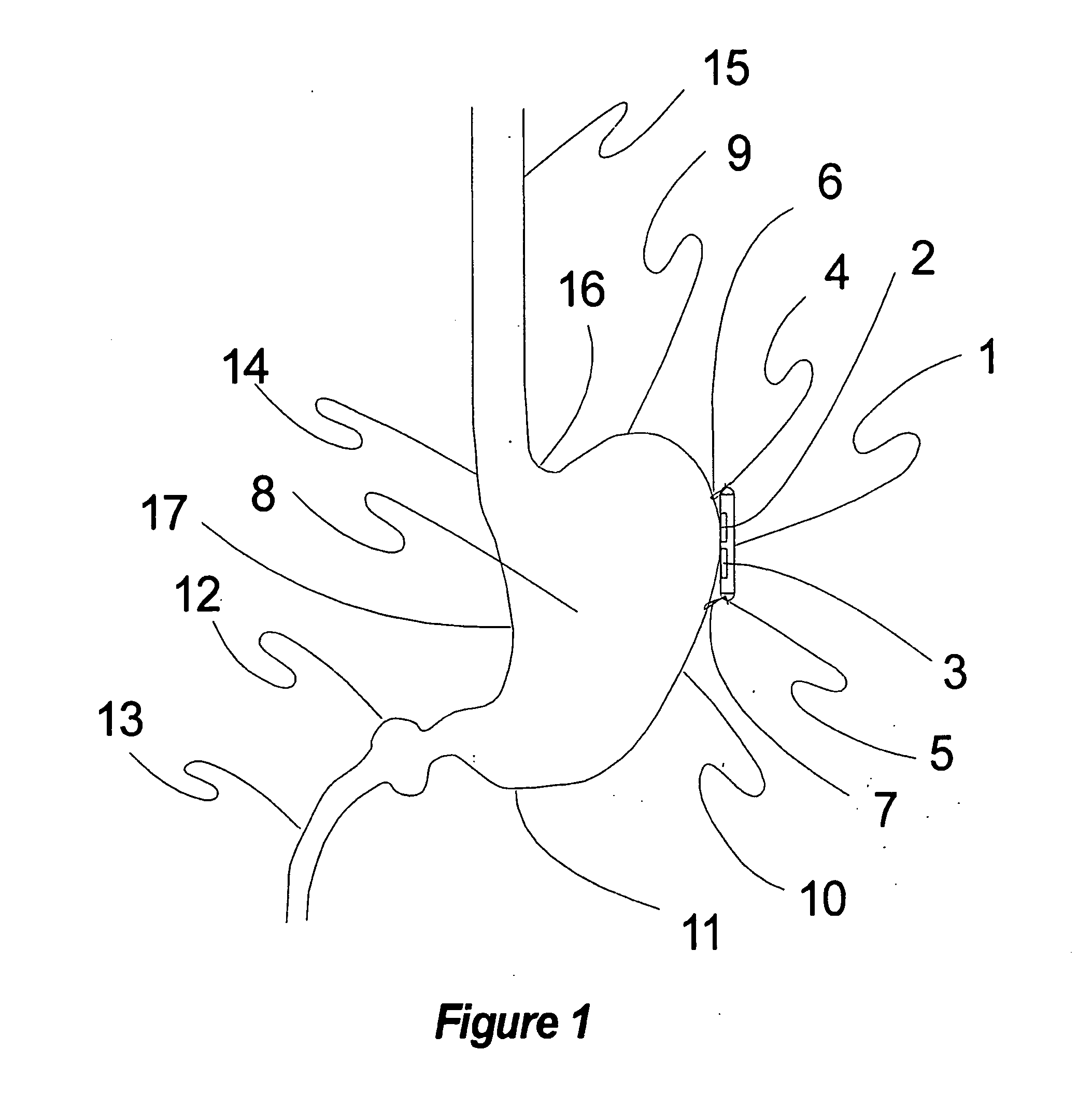
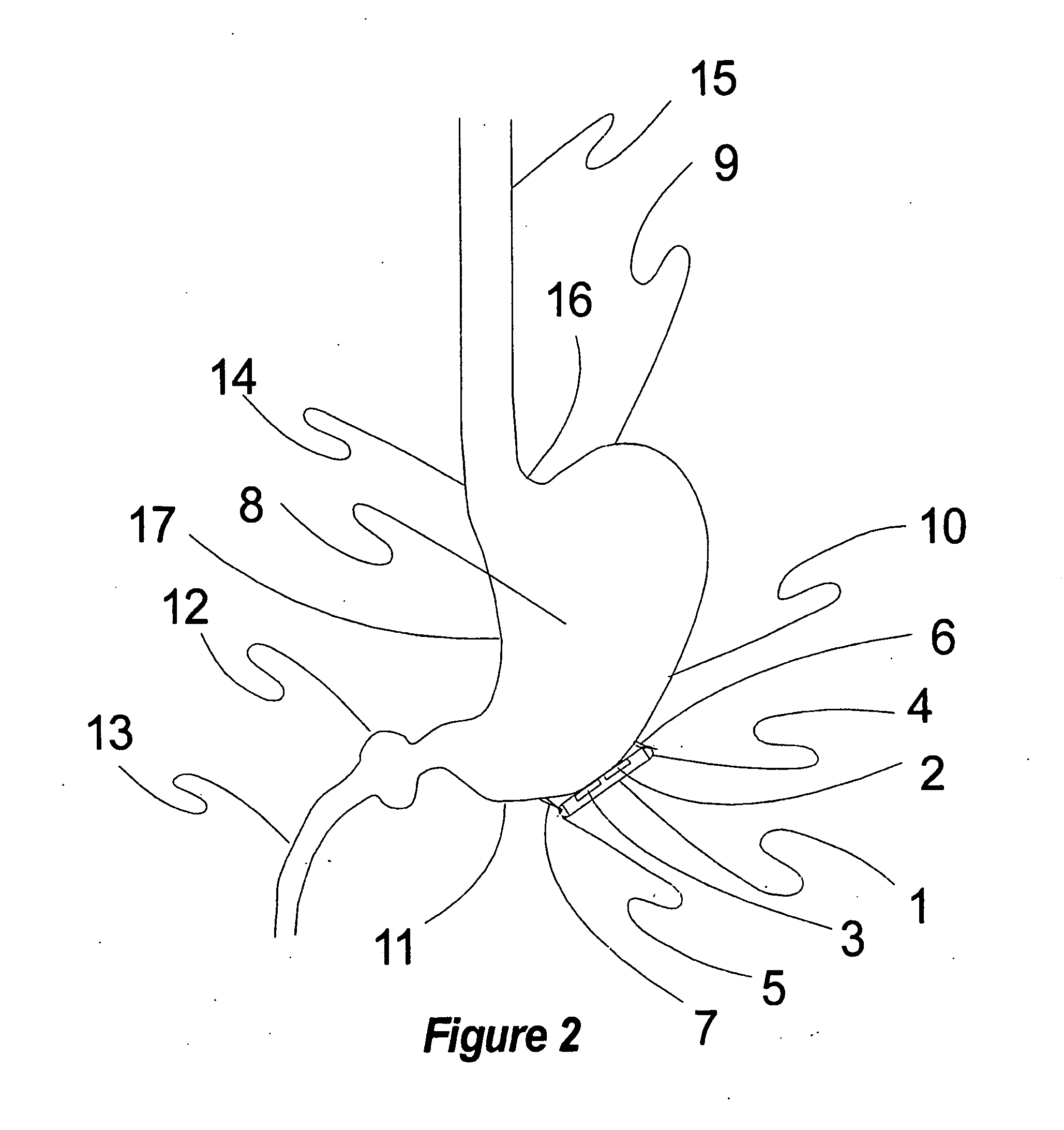
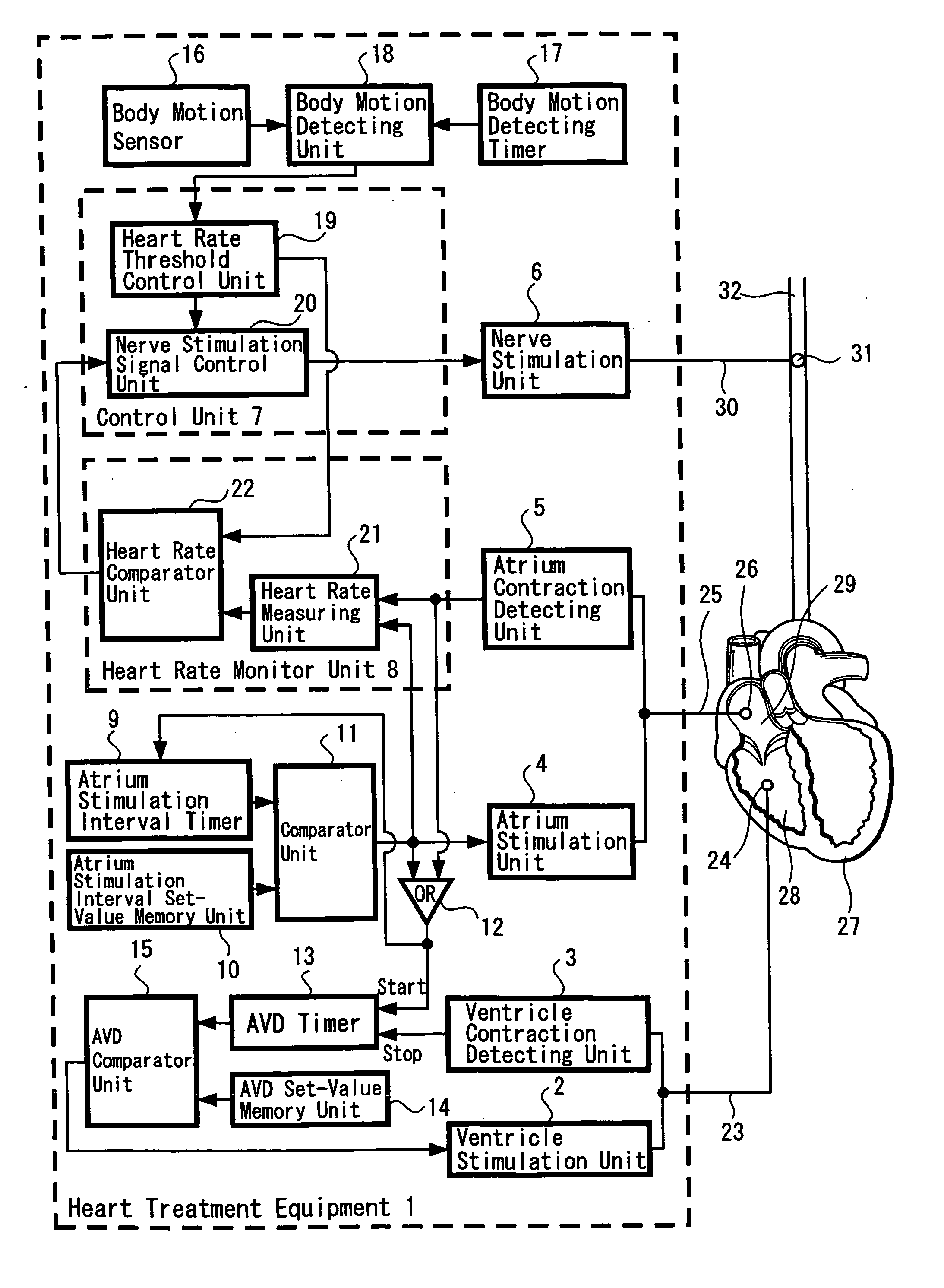
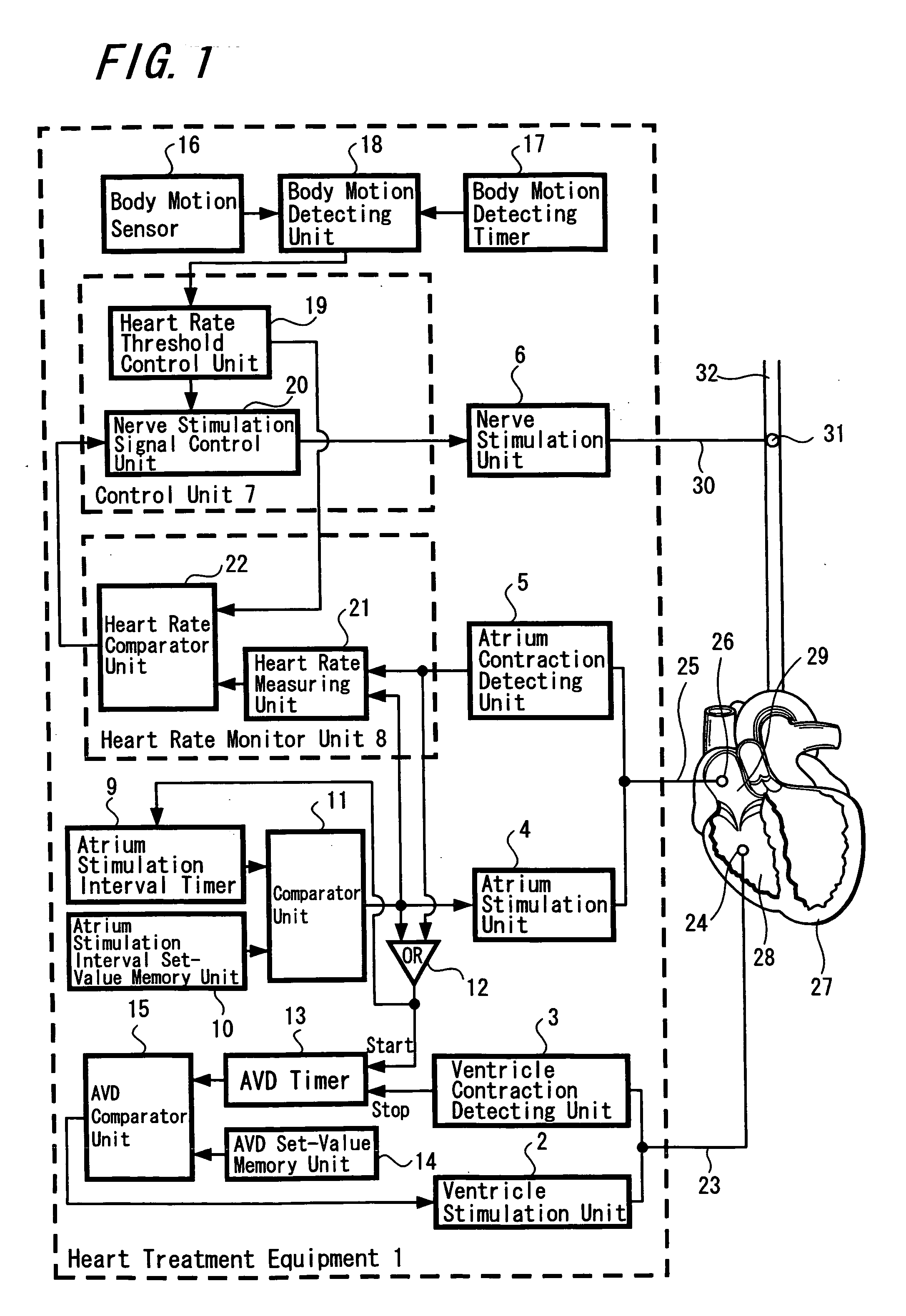
Heart treatment equipment and heart treatment method
InactiveUS20060052831A1Prevent fatal arrhythmia occurrenceIncrease physical exercise tolerable abilityHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringBiological bodySympathetic tone
Heart treatment equipment and a heart treatment method directed to prevention of a fatal arrhythmia by detecting a physical exercise or a mental stress by using a sensor and thereafter controlling the vagus nerve stimulation, wherein sensor means for detecting various living body information for generating a signal which designates degree of a sympathetic tone is provided and heart rate threshold for carrying out the vagus nerve stimulation is adjusted according to the living body information detected by the sensor means. Further, a nerve stimulation parameter for adjusting the strength of the vagus nerve stimulation is adjusted in response to the degree of the patient sympathetic tone.
Owner:KAISHA TERUMO KABUSHIKI
Method, apparatus, and surgical technique for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20060116736A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomUltrasound therapySpinal electrodesDiseaseSplanchnic nerves
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
Device and method for inhibiting release of pro-inflammatory mediator
ActiveUS20060287678A1Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationNervous systemNeuron
Stimulation of one or more neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, including the splenic nerve, to attenuate an immune response, including an inflammatory immune response, is discussed. Devices and systems to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system to attenuate an immune response are also discussed. Devices discussed include pulse generators and drug pumps. Systems are described as optionally having one or more sensors and operator instructions. In specific examples, stimulation of the splenic nerve of pigs with a pulse generator is shown to be safe and effective in attenuating a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of biochemical treatment of persistent pain
InactiveUS20050152905A1Reduce releaseAvoid exposureBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterleukin 6Interleukin-1beta
This invention relates to a method for the biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders by inhibiting the biochemical mediators of inflammation in a subject comprising administering to said subject any one of several combinations of components that are inhibitors of biochemical mediators of inflammation. Said process for biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders is based on Sota Omoigui's Law, which states: ‘The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response’. Sota Omoigui's Law of Pain unifies all pain syndromes as sharing a common origin of inflammation and the inflammatory response. The various biochemical mediators of inflammation are present in differing amounts in all pain syndromes and are responsible for the pain experience. Classification and treatment of pain syndromes should depend on the complex inflammatory profile. A variety of mediators are generated by tissue injury and inflammation. These include substances produced by damaged tissue, substances of vascular origin as well as substances released by nerve fibers themselves, sympathetic fibers and various immune cells. Biochemical mediators of inflammation that are targeted for inhibition include but are not limited to: prostaglandin, nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-alpha, interleukin 1-beta, interleukin-4, Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, histamine and serotonin, substance P, Matrix Metallo-Proteinase, calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide as well as the potent inflammatory mediator peptide proteins neurokinin A, bradykinin, kallidin and T-kinin.
Owner:OMOIGUI OSEMWOTA SOTA
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS20050192638A1Shorten the progressResolution of overloadPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsRenal nerveImplanted device
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump or a drug eluding implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Method and apparatus for conformal electrodes for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of obesity and other conditions
InactiveUS20090118780A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesHead electrodesAfferent NeuronsAutonomic Denervation
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for user control and operation of physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, metabolic disease, and other conditions. This includes programming of neuromodulatory signal for the modulation of autonomic neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate tissues, including the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety and efferent neurons to modulate metabolism. The apparatus and methods include a conformal neuromodulator array which facilitates minimally invasive placement of neuromodulators in communication with target tissues.
Owner:DILORENZO DANIEL JOHN
Parasympathetic stimulation for termination of non-sinus atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS8060197B2Avoid stimulationHigh strengthElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Splanchnic nerve stimulation for treatment of obesity
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating the greater splanchnic nerve or other portion of the sympathetic nervous system using an electrode. This nerve activation can result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Renal nerve stimulation method and apparatus for treatment of patients
InactiveUS20050228459A1Reduce sympathetic nerve stimulationReduce functionSpinal electrodesMedical devicesRenal nerveFAILURE KIDNEY
A method and apparatus for treatment of heart failure, hypertension and renal failure by stimulating the renal nerve. The goal of therapy is to reduce sympathetic activity of the renal nerve. Therapy is accomplished by at least partially blocking the nerve with drug infusion or electrostimulation. Apparatus can be permanently implanted or catheter based.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Methods and Devices for Treating Hypertension
Devices, systems and methods are described which control blood pressure and nervous system activity by stimulating baroreceptors. By selectively and controllably activating baroreceptors and / or nerves, the present invention reduces blood pressure and alters the sympathetic nervous system; thereby minimizing deleterious effects on the heart, vasculature and other organs and tissues. A baroreceptor activation device or other sensory activation device is positioned near a dermal bone to provide the treatment.
Owner:SYMPARA MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com