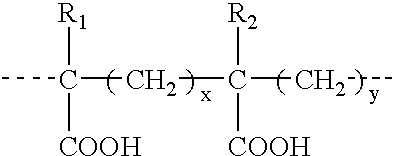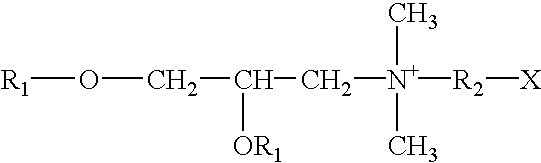Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1036 results about "Immunity response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Immune response is the body's response caused by its immune system being activated by antigens. The immune response can include immunity to pathogenic microorganisms and its products, allergies, graft rejections, as well as autoimmunity to self-antigens.
Humanization of antibodies
InactiveUS20050042664A1Limited diversityFast and less labor intensive productionHybrid immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
The present invention provides methods of re-engineering or re-shaping an antibody from a first species, wherein the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody does not elicit undesired immune response in a second species, and the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody retains substantially the same antigen binding-ability of the antibody from the first species. In accordance with the present invention, a combinatorial library comprising the CDRs of the antibody from the first species fused in frame with framework regions derived from a second species can be constructed and screened for the desired modified antibody. In particular, the present invention provides methods utilizing low homology acceptor antibody frameworks for efficiently humanizing an antibody or a fragment thereof. The present invention also provides antibodies produced by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c]-quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof
Thiazolo-, oxazolo- and selenazolo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof are described including methods of manufacture and the use of novel intermediates. The compounds are immunomodulators and induce cytokine biosynthesis, including interferon and / or tumor biosynthesis, necrosis factor, and inhibit the T-helper-type 2 immune response. The compounds are further useful in the treatment of viral and neoplastic diseases.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
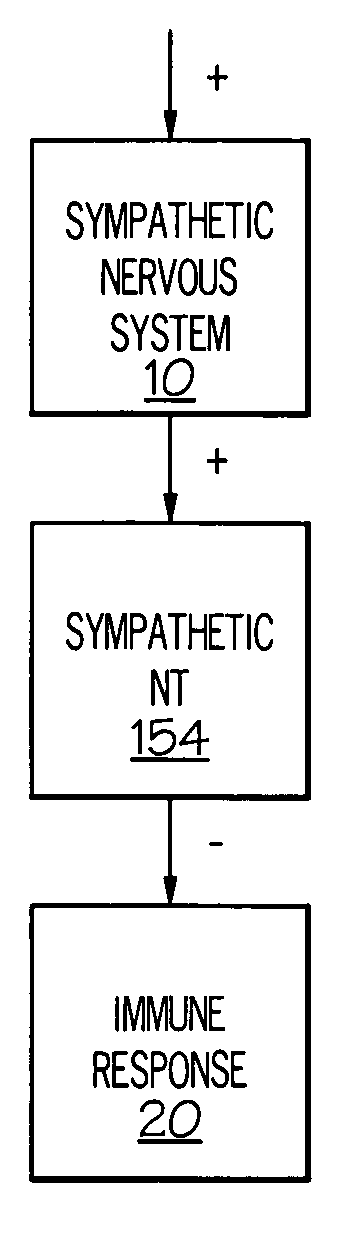
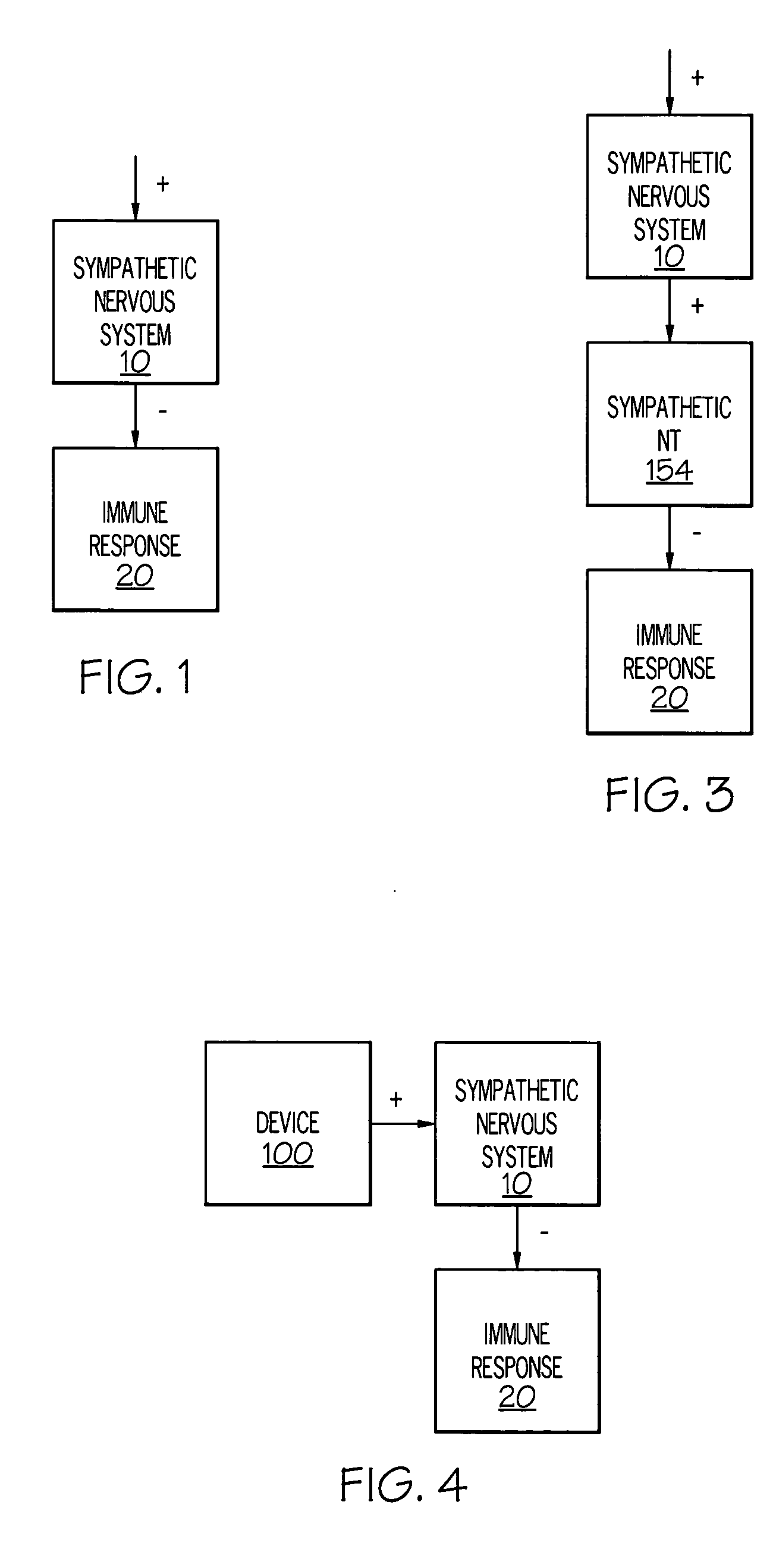
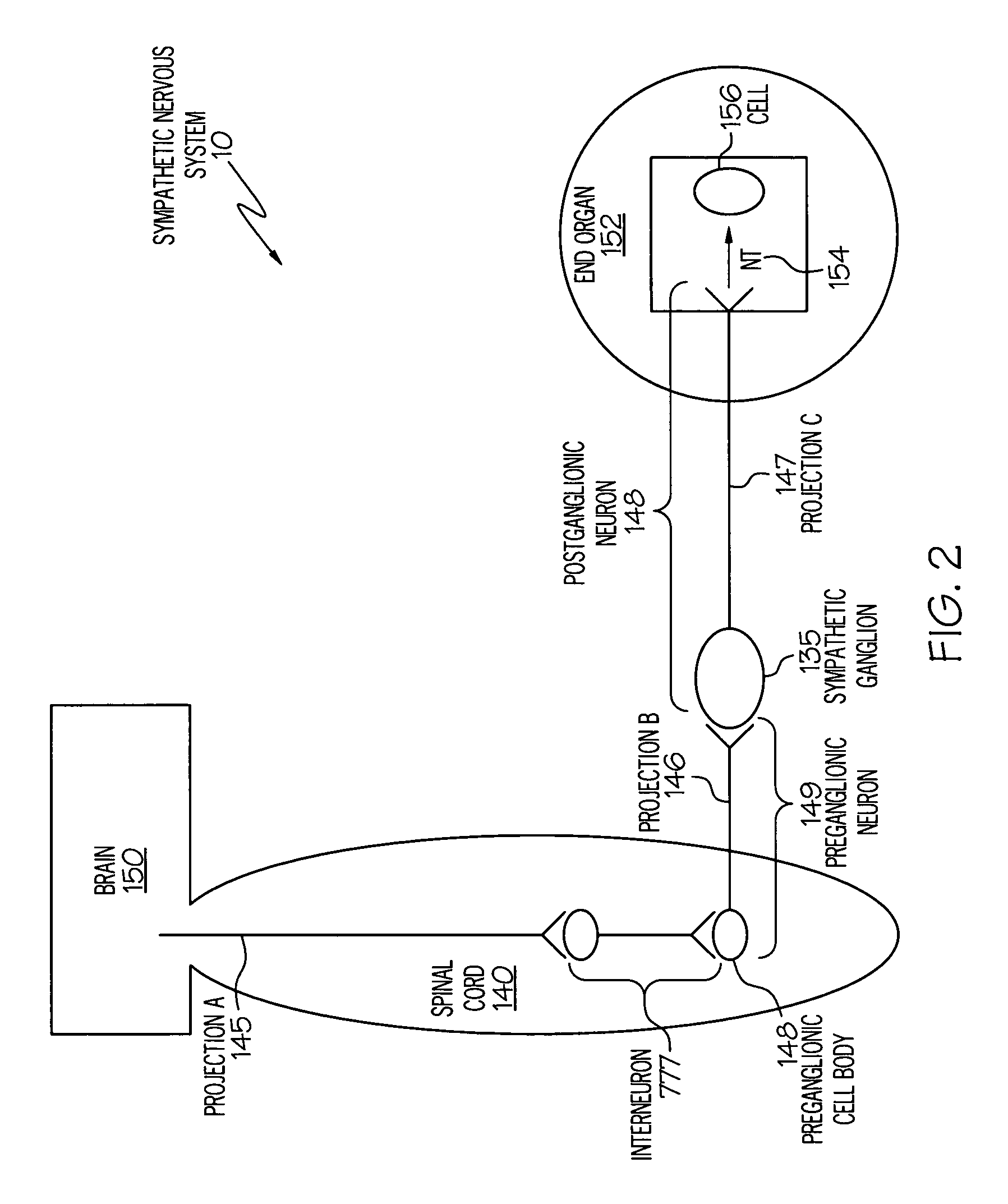
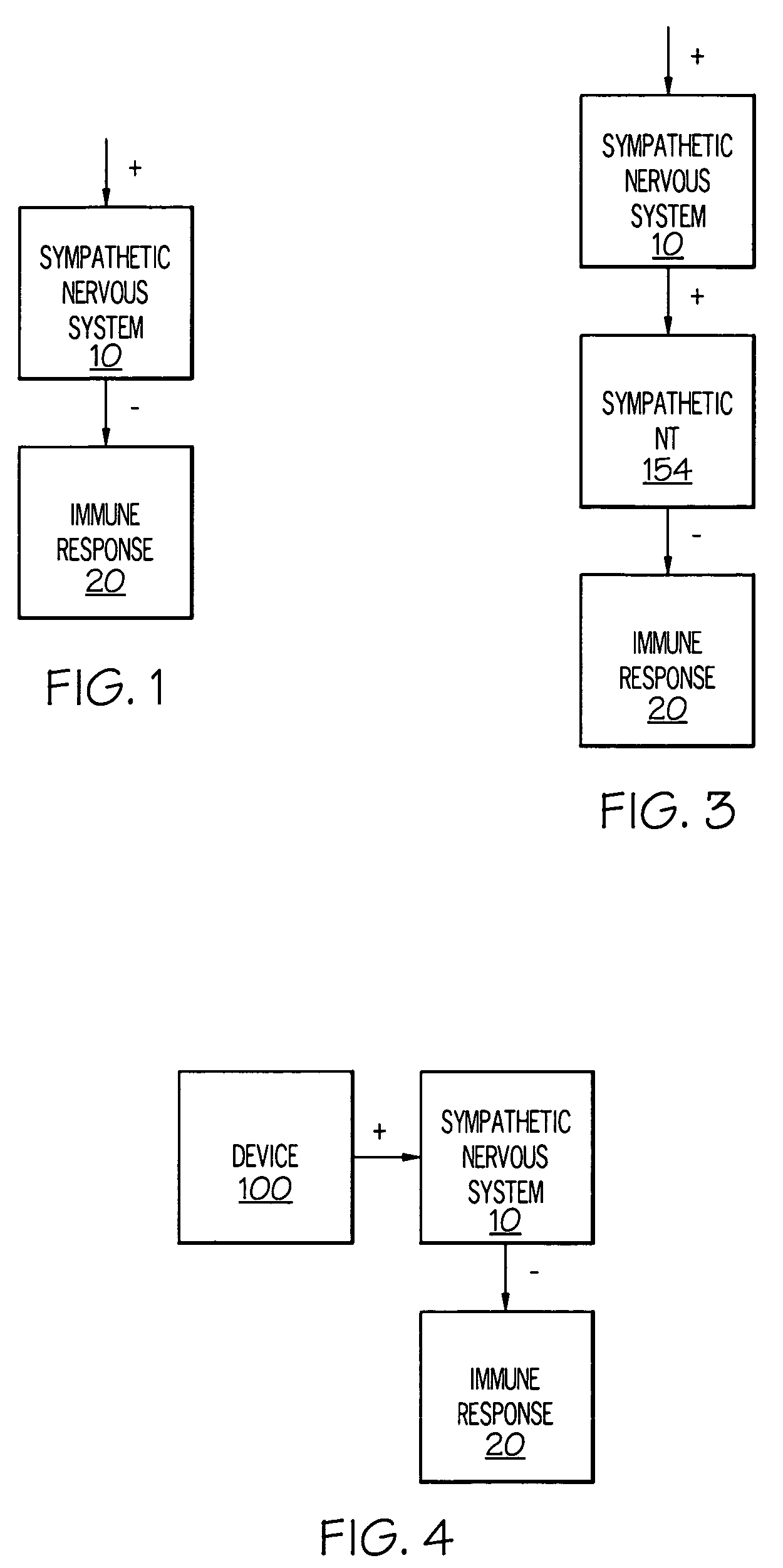
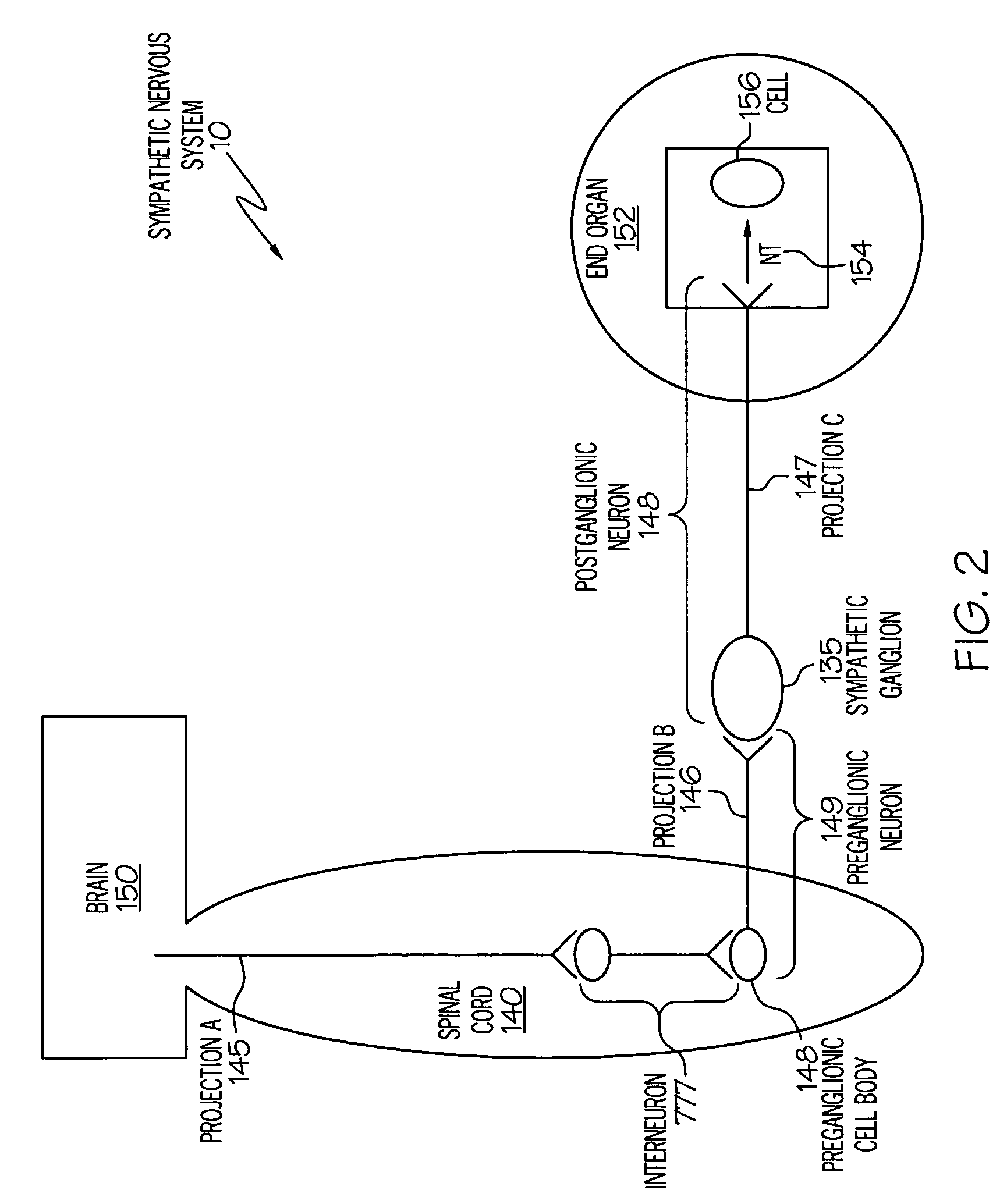
Device and method for inhibiting release of pro-inflammatory mediator
InactiveUS20050075702A1Great flexibilityGreat specificitySpinal electrodesArtificial respirationNervous systemDrug
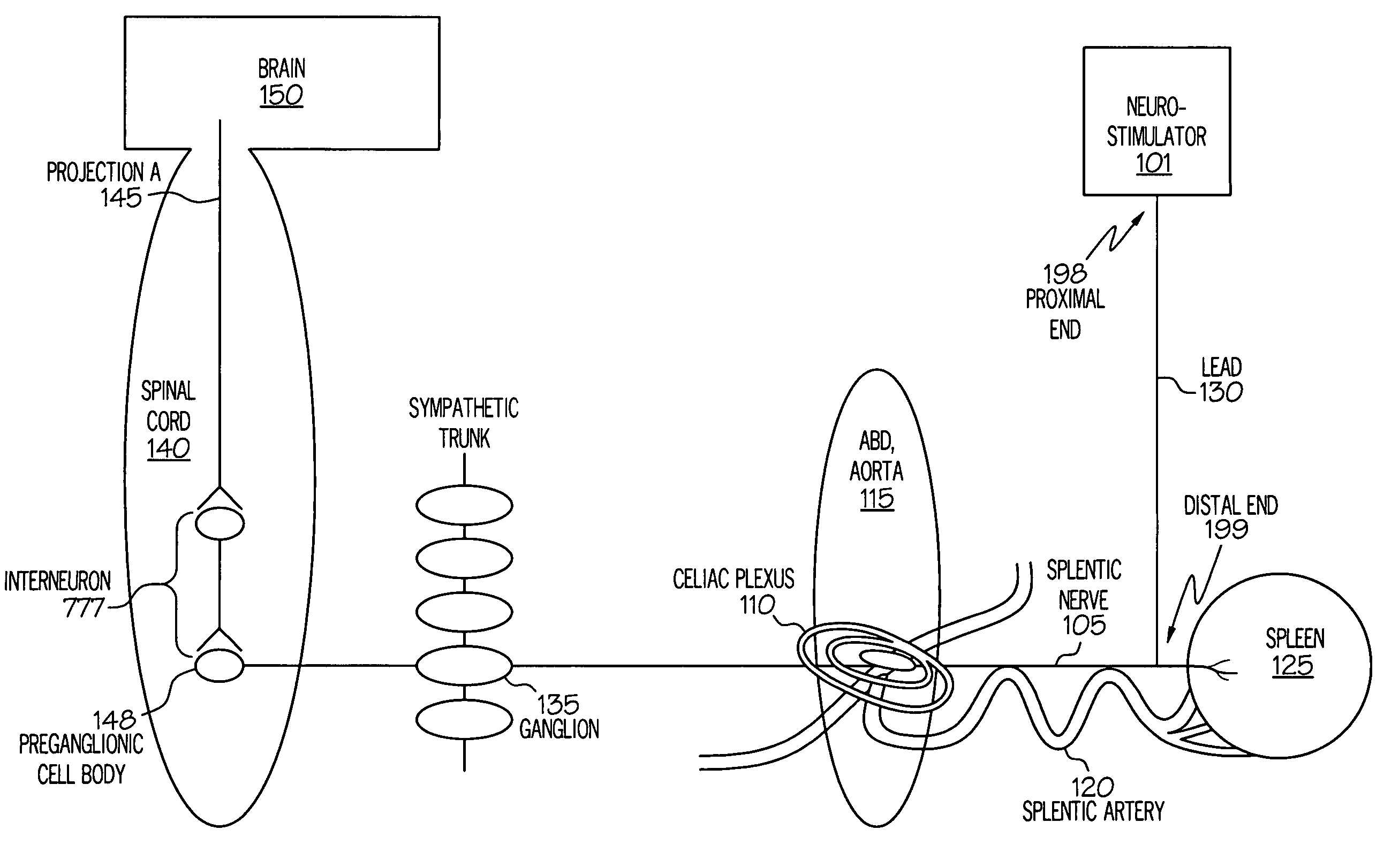
Stimulation of one or more neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, including the splenic nerve, to attenuate an immune response, including an inflammatory immune response, is discussed. Devices and systems to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system to attenuate an immune response are also discussed. Devices discussed include pulse generators and drug pumps. Systems are described as optionally having one or more sensors and operator instructions. In specific examples, stimulation of the splenic nerve of pigs with a pulse generator is shown to be safe and effective in attenuating a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
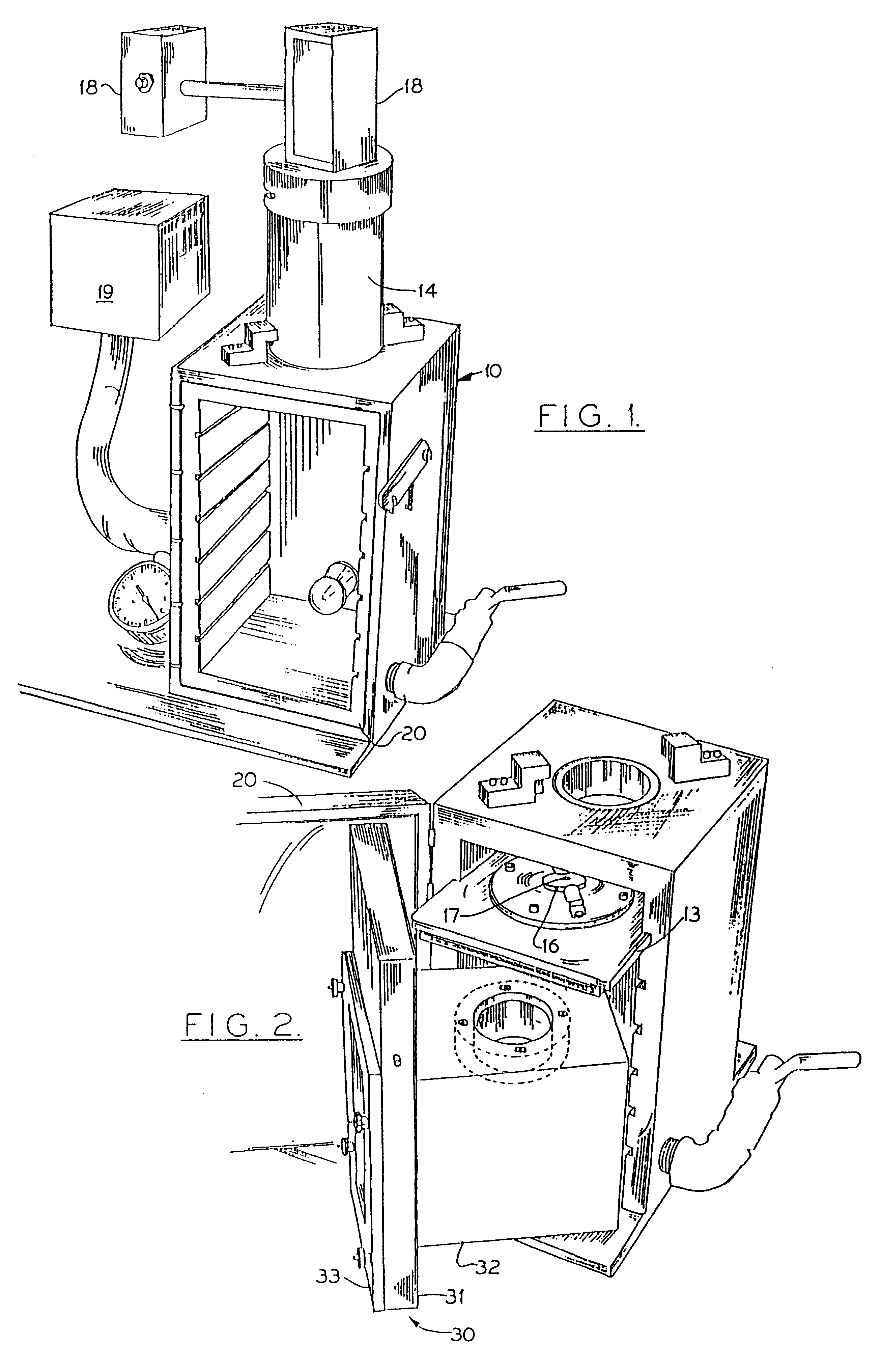
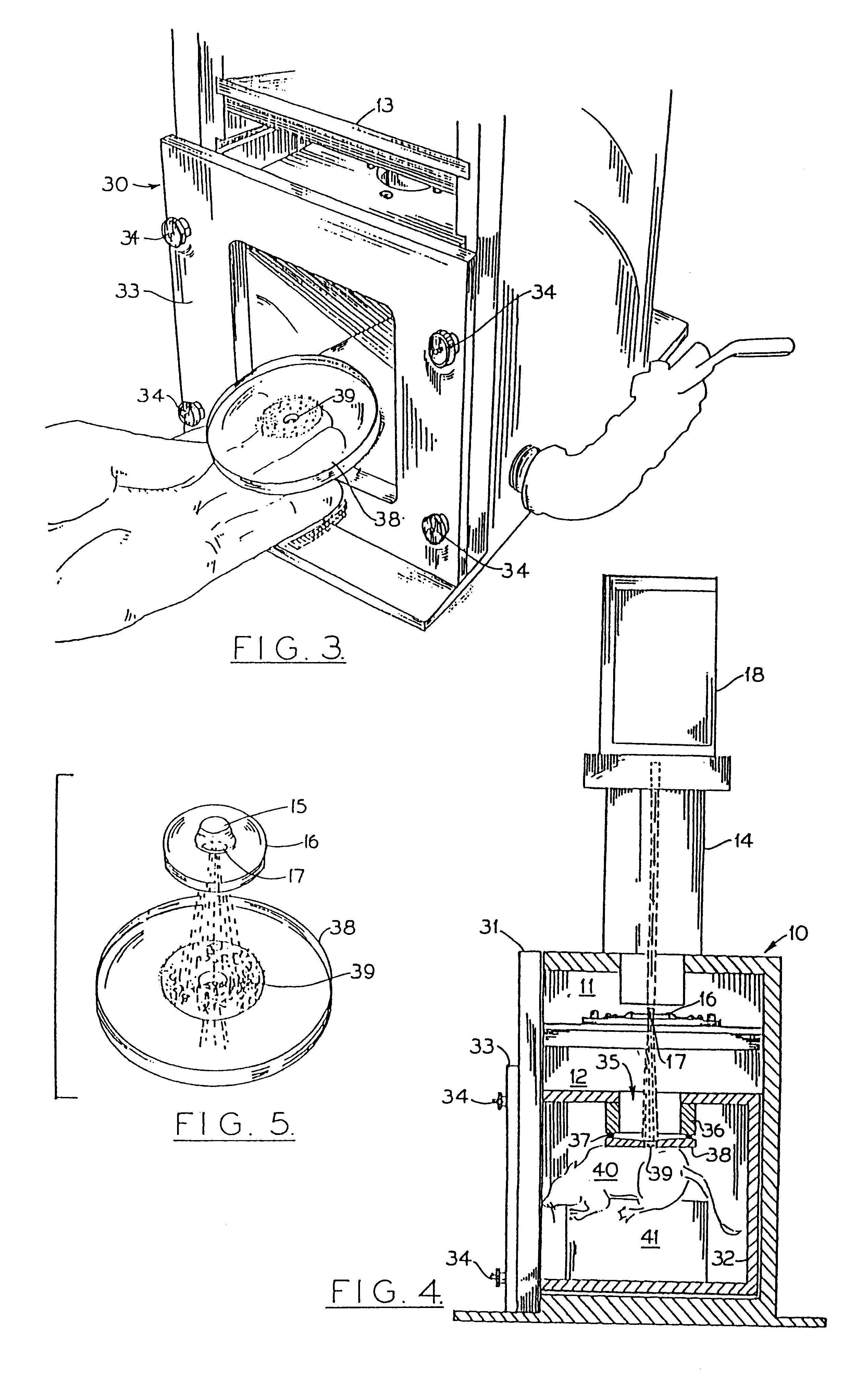
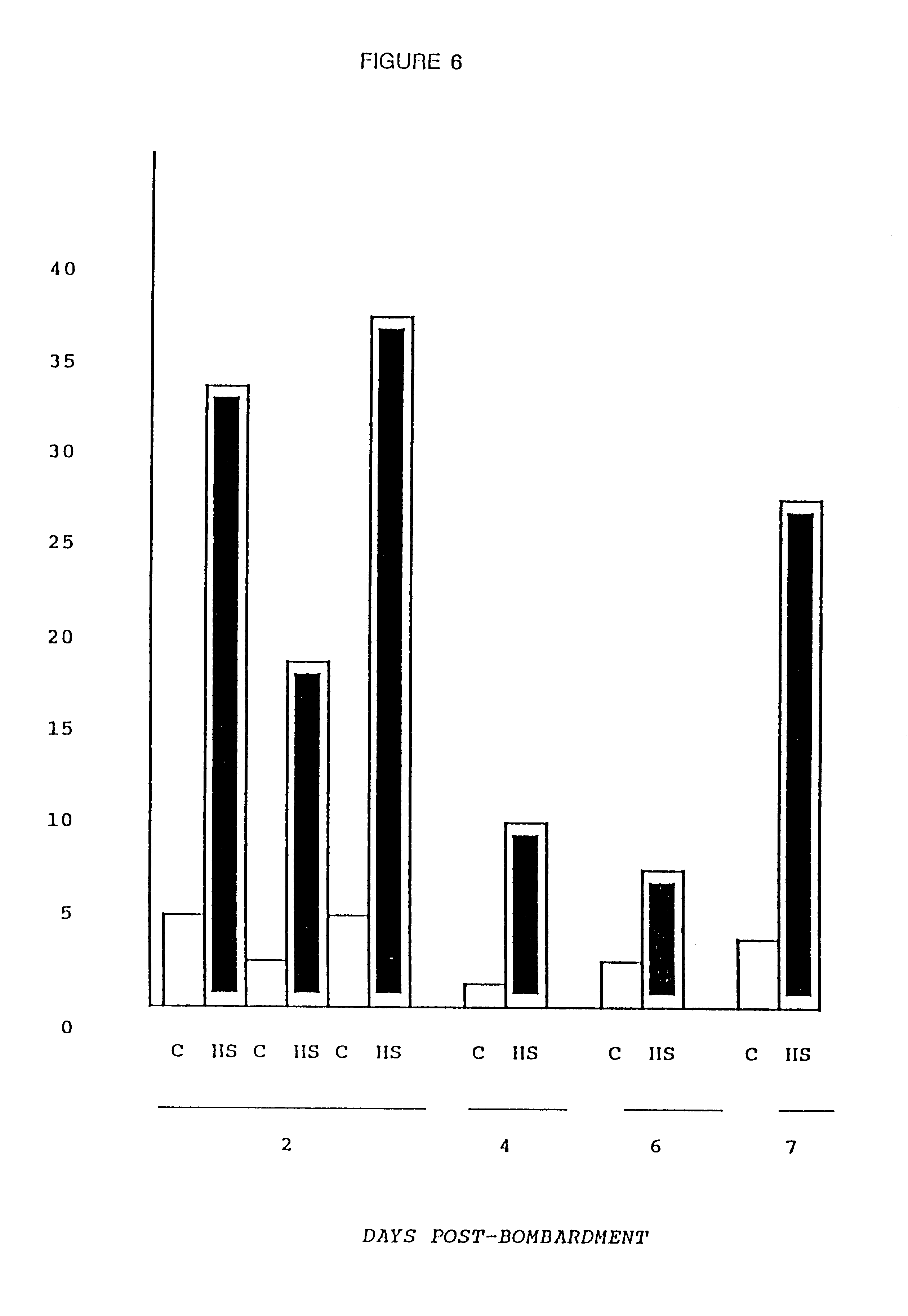
Particle-mediated bombardment of DNA sequences into tissue to induce an immune response
InactiveUS6194389B1Genetic material ingredientsMicroinjection basedNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
A method of transferring a gene to vertebrate cells is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing microprojectiles, the microprojectiles carrying polynucleic acid sequences, the sequences comprising, in the 5' to 3' direction, a regulatory sequence operable in the tissue cells and a gene positioned downstream of the regulatory sequence and under the transcriptional control thereof; and (b) accelerating the microprojectiles at the cells, with the microprojectiles contacting the cells at a speed sufficient to penetrate the cells and deposit the polynucleic acid sequences therein. Preferably, the target cells reside in situ in the animal subject when they are transformed. Preferred target cells are dermis or hypodermis cells, and preferred genes for insertion into the target cells are genes which code for proteins or peptides which produce a physiological response in the animal subject.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
Vaccine composition containing synthetic adjuvant
ActiveUS20080131466A1Elicit immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsNatural productAdditive ingredient
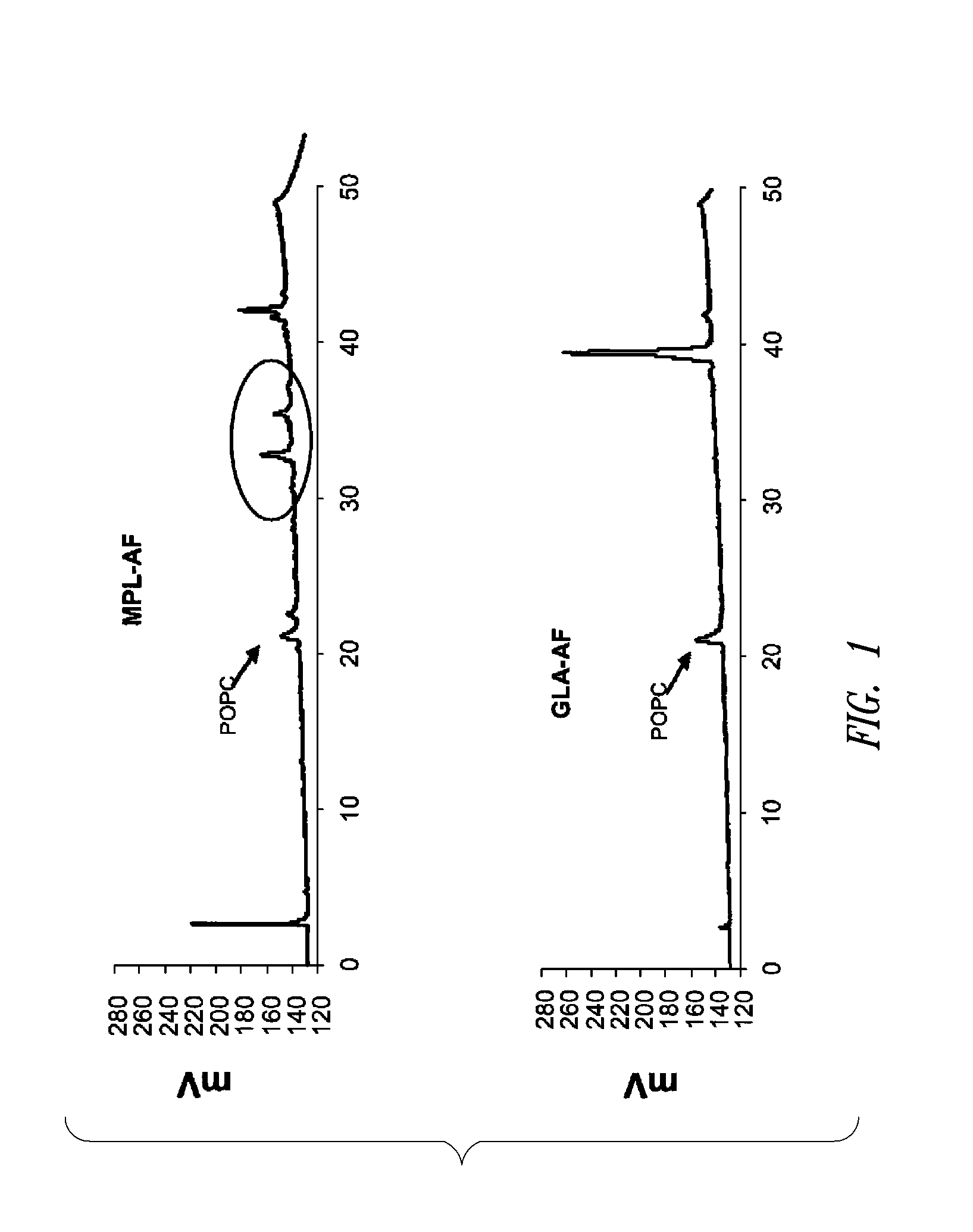
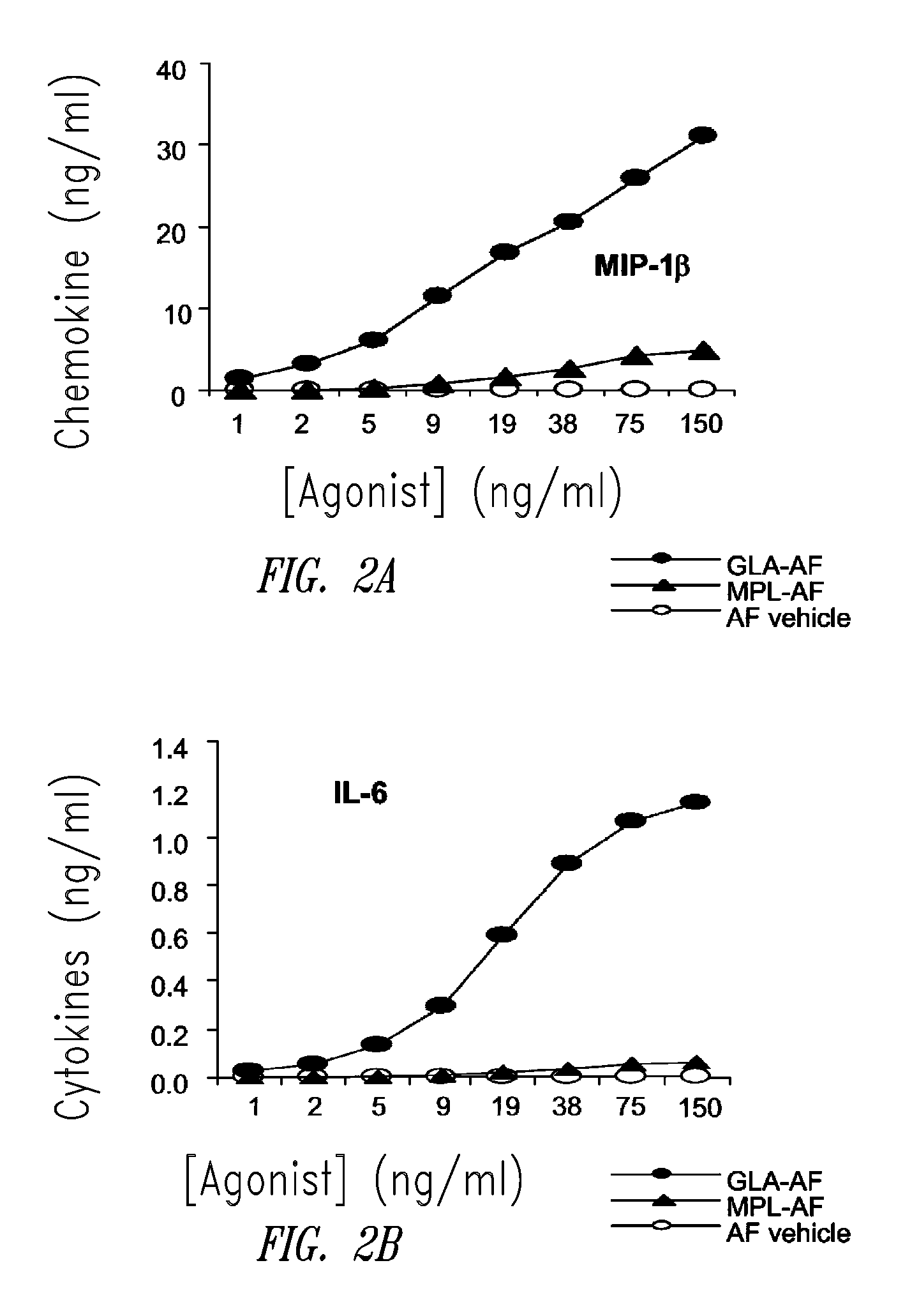
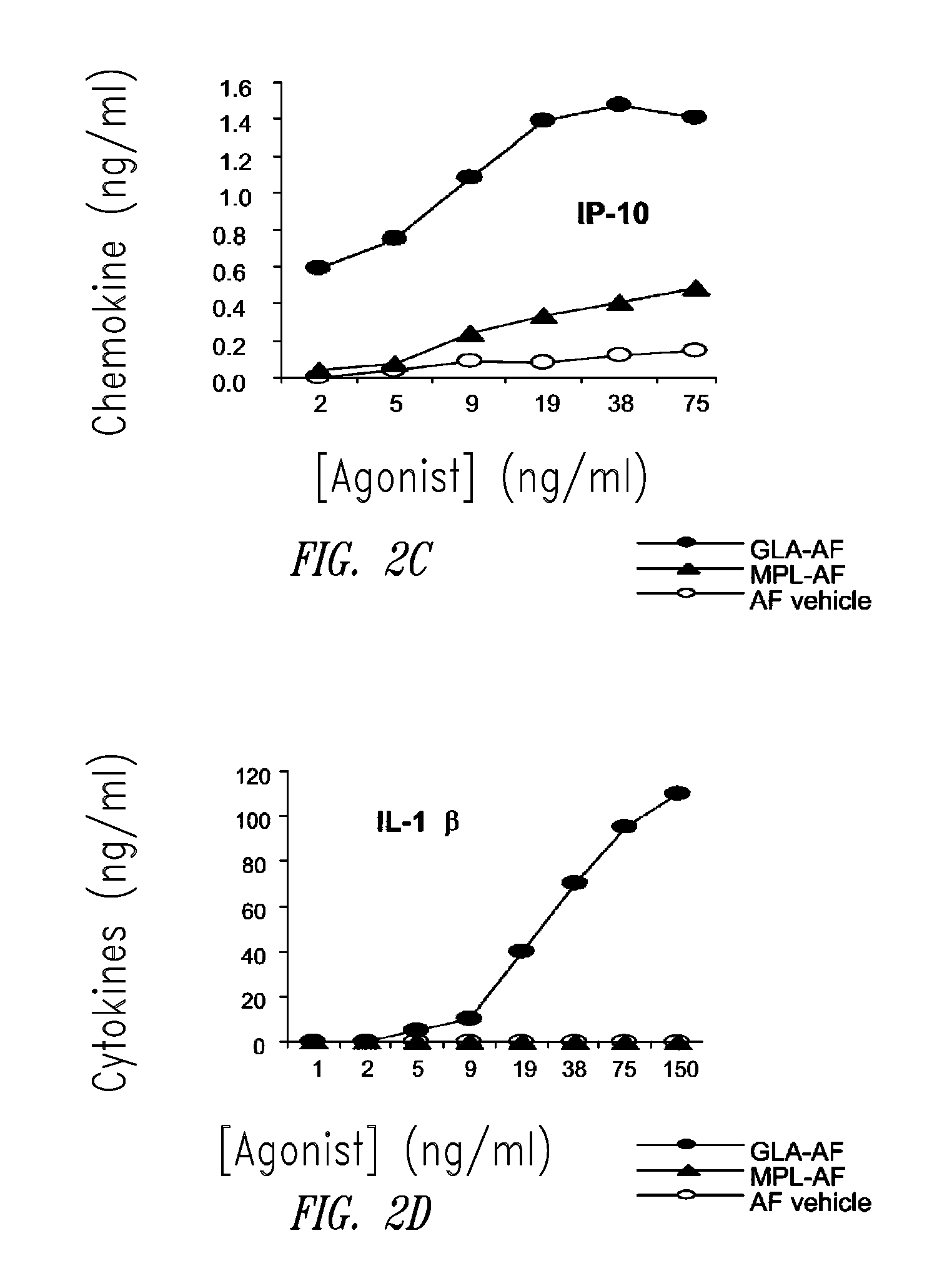
Compositions and methods, including vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for inducing or enhancing an immune response are disclosed based on the discovery of useful immunological adjuvant properties in a synthetic, glucopyranosyl lipid adjuvant (GLA) that is provided in substantially homogeneous form. Chemically defined, synthetic GLA offers a consistent vaccine component from lot to lot without the fluctuations in contaminants or activity that compromise natural-product adjuvants. Also provided are vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions that include GLA and one or more of an antigen, a Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonist, a co-adjuvant and a carrier such as a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:ACCESS TO ADVANCED HEALTH INST
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
ActiveUS7418292B2Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemImmunity response
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
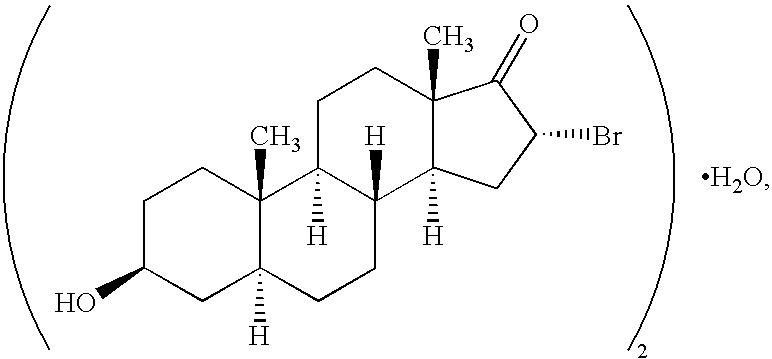
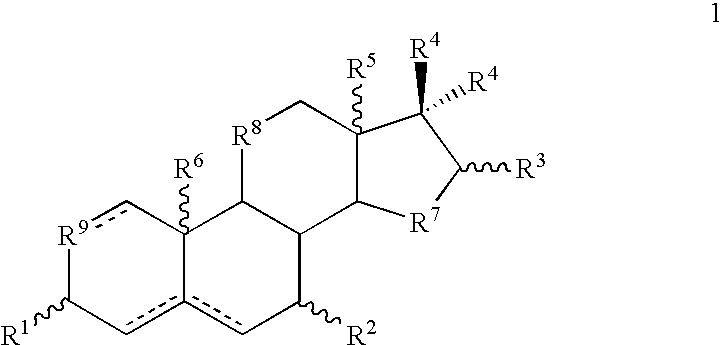
Pharmaceutical compositions and treatment methods
InactiveUS6667299B1Efficient transportReduce yieldAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRegimenKetone
The invention provides compositions comprising, 16alpha-bromo-3beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androstan-17-one hemihydrate and one or more excipients, typically wherein the composition comprises less than about 3% water. The compositions are useful to make improved pharmaceutical formulations. The invention also provides methods of intermittent dosing of steroid compounds such as analogs of 16alpha-bromo-3beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androstan-17-one and compositions useful in such dosing regimens. The invention further provides compositions and methods to inhibit pathogen (viral) replication, ameliorate symptoms associated with immune dysregulation and to modulate immune responses in a subject using certain steroids and steroid analogs. The invention also provides methods to make and use these immunomodulatory compositions and formulations.
Owner:NEURMEDIX +2
Saponin compositions and uses thereof
Owner:ANTIGENICS
Immunisation of large mammals with low doses of RNA
ActiveUS20130149375A1Conveniently preparedImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseMammalImmunity response
RNA encoding an immunogen is delivered to a large mammal at a dose of between 2 μg and 100 μg. Thus the invention provides a method of raising an immune response in a large mammal, comprising administering to the mammal a dose of between 2 μg and 100 μg of immunogen-encoding RNA. Similarly, RNA encoding an immunogen can be delivered to a large mammal at a dose of 3 ng / kg to 150 ng / kg. The delivered RNA can elicit an immune response in the large mammal
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Hapten-carrier conjugates and uses thereof
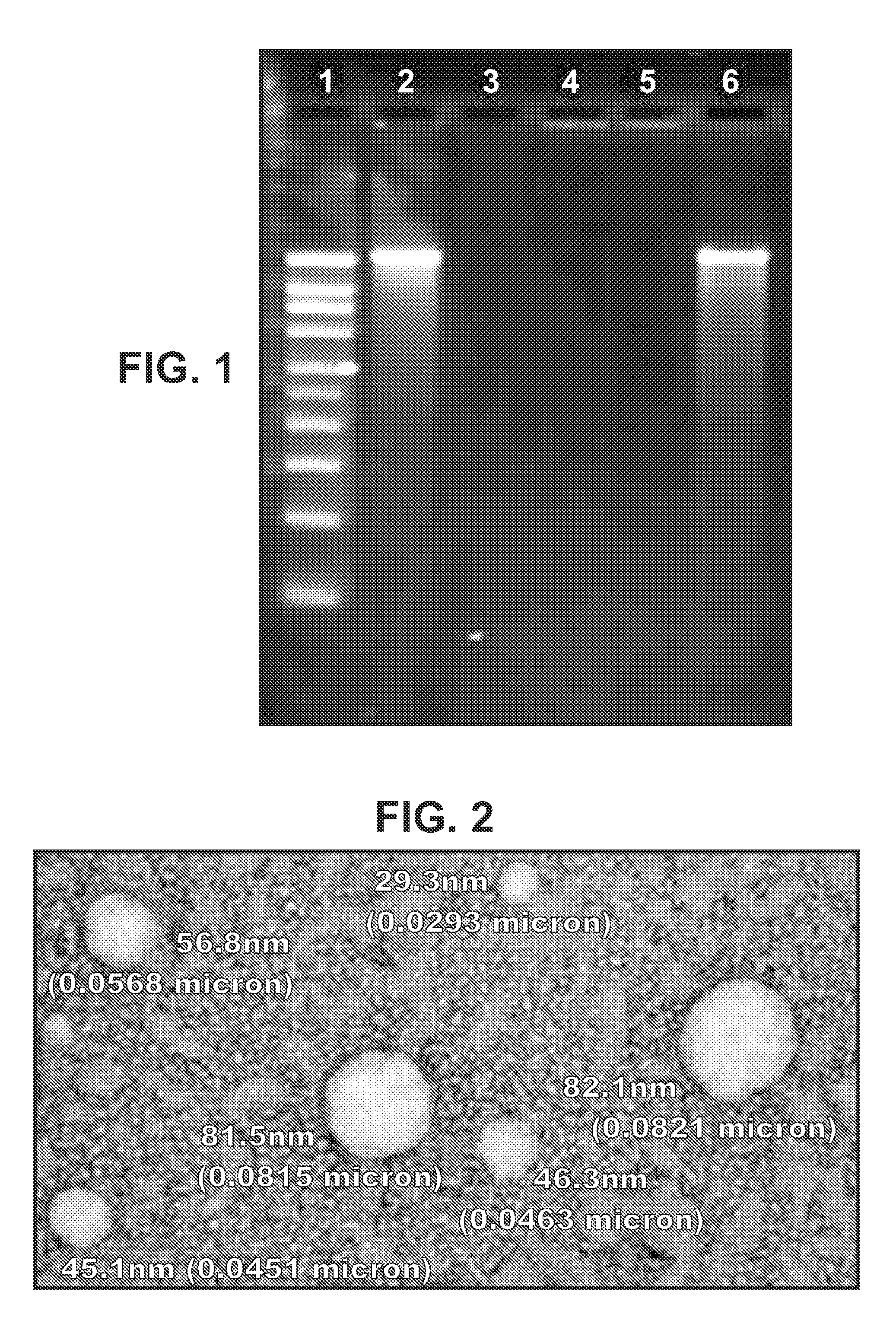
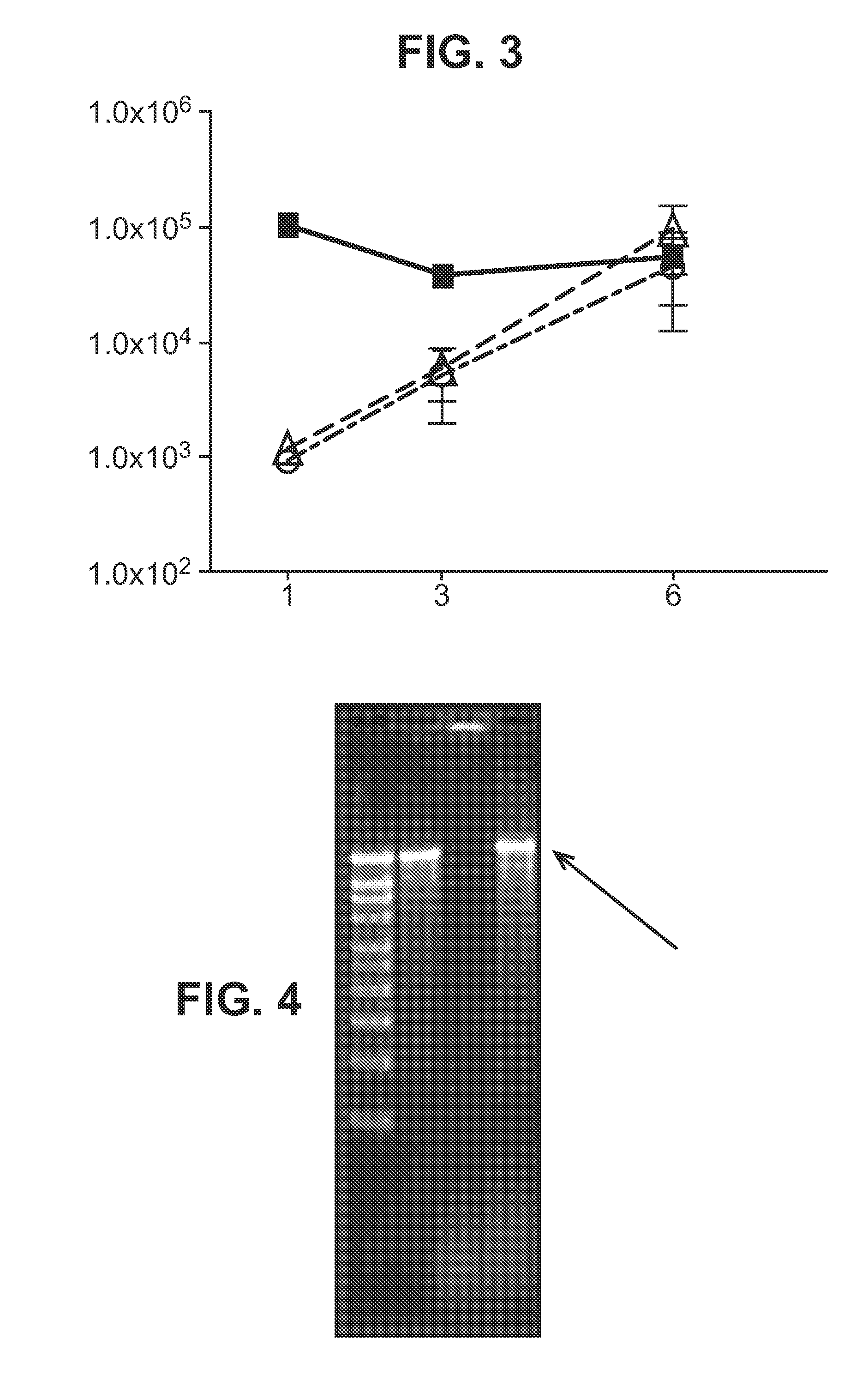
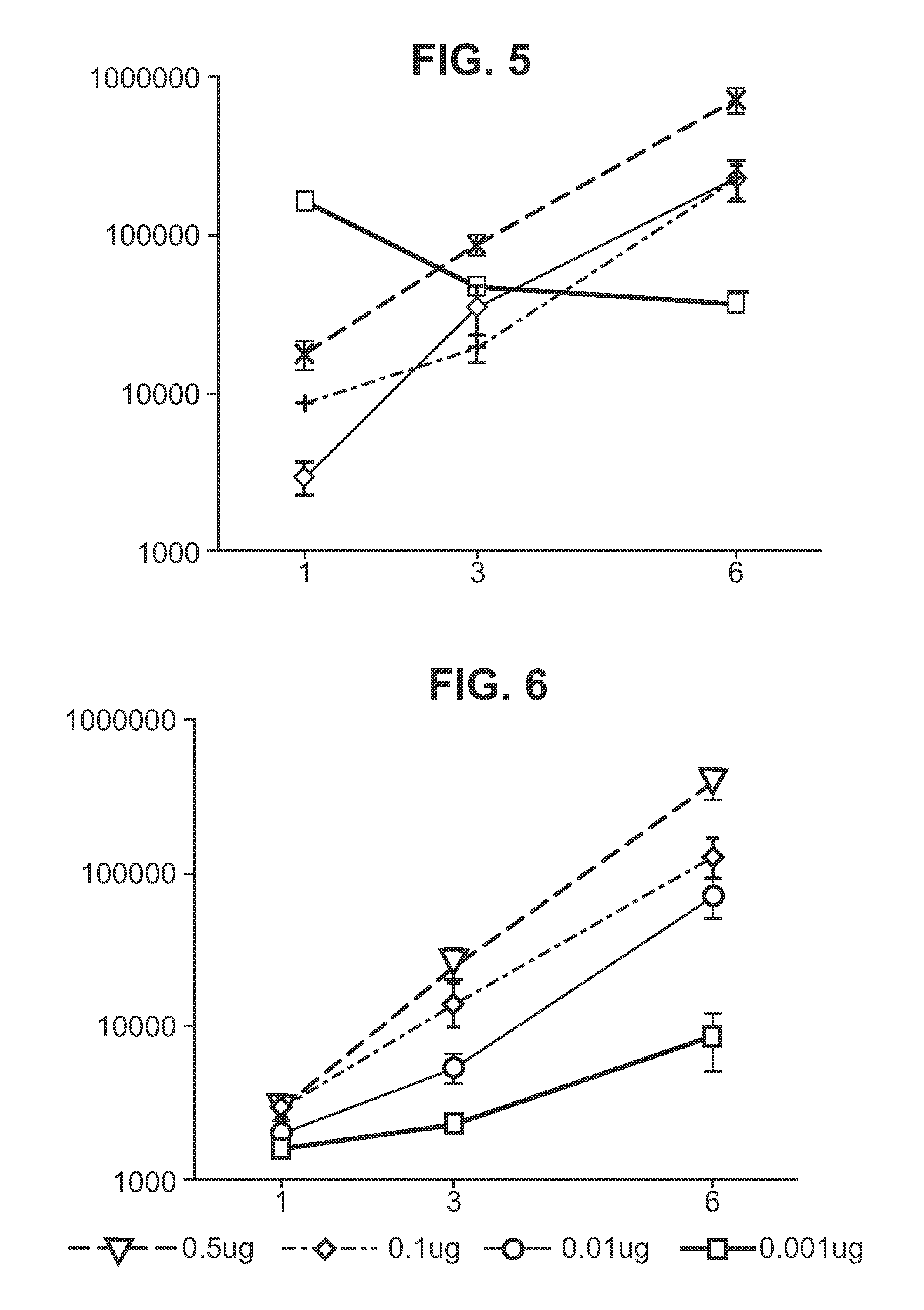
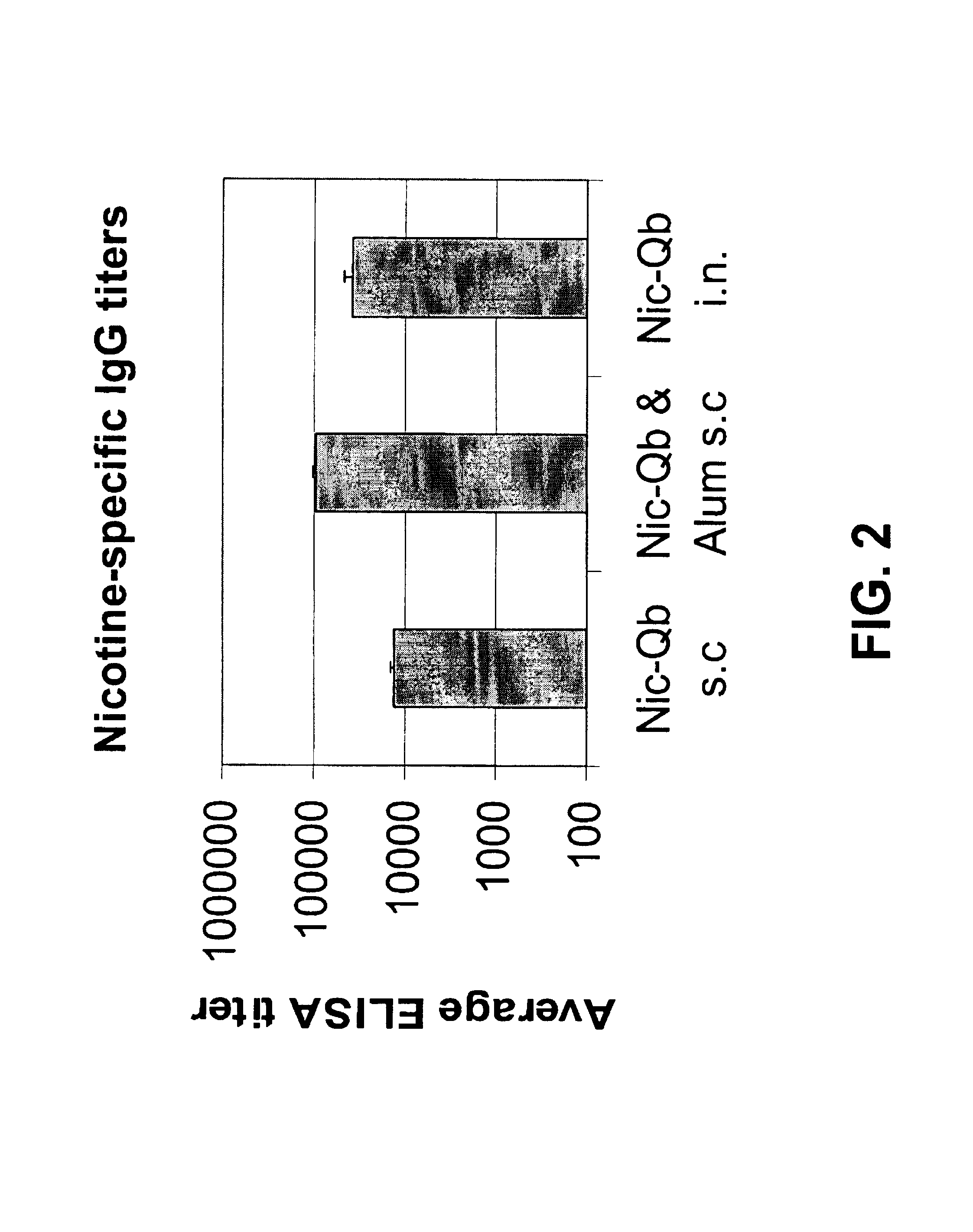
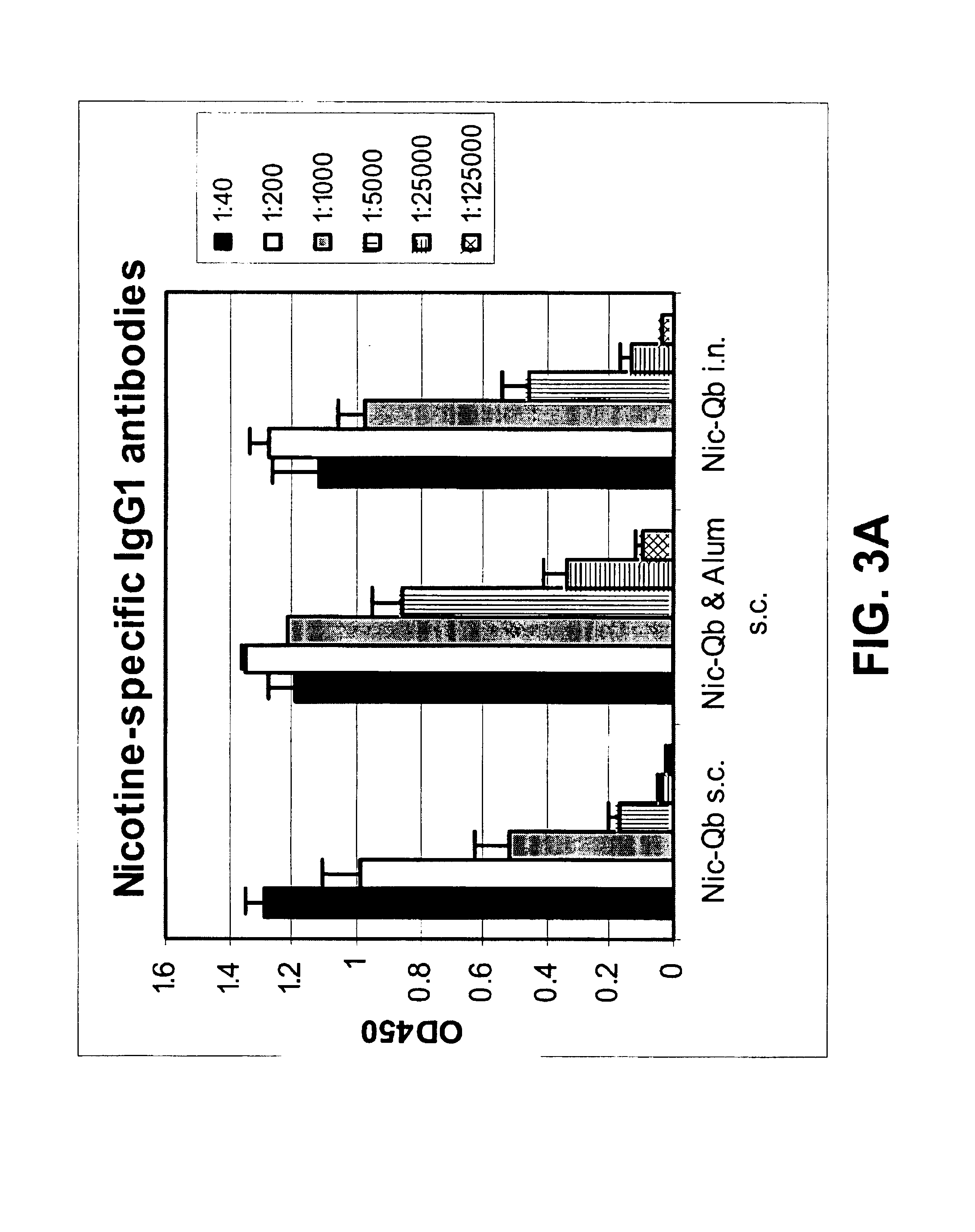
The present invention provides compositions comprising a conjugate of a hapten with a carrier in an ordered and repetitive array, and methods of making such compositions. The conjugates and compositions of the invention may comprise a variety of haptens, including hormones, toxins and drugs, especially drugs of addiction such as nicotine. Compositions and conjugates of the invention are useful for inducing immune responses against haptens, which can use useful in a variety of therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic regimens. In certain embodiments, immune responses generated using the conjugates, compositions and methods of the present invention are useful to prevent or treat addiction to drugs of abuse and the resultant diseases associated with drug addiction.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
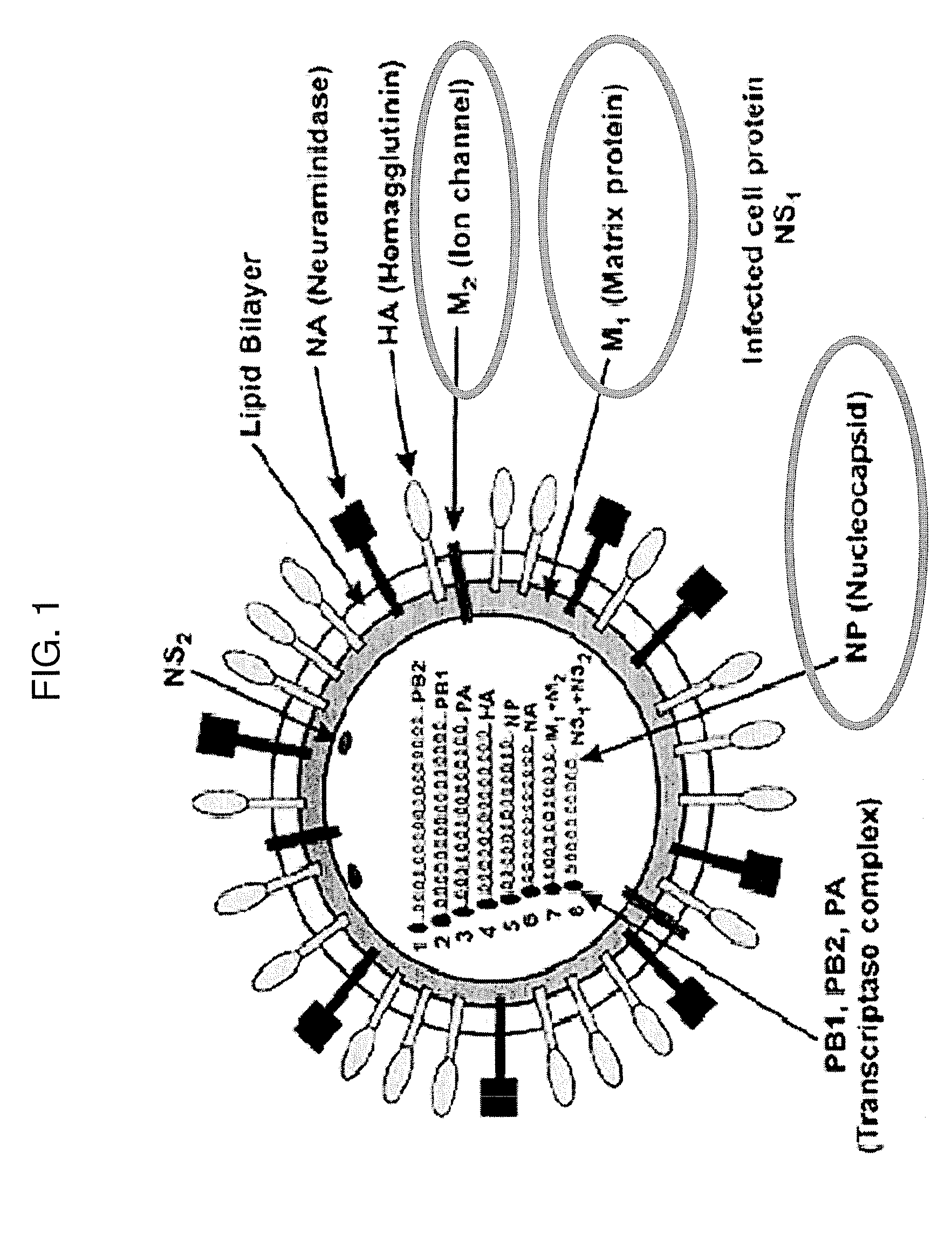
Chimeric viruses presenting non-native surface proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120122185A1Readily immunizeEffective immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEctodomainVirosome
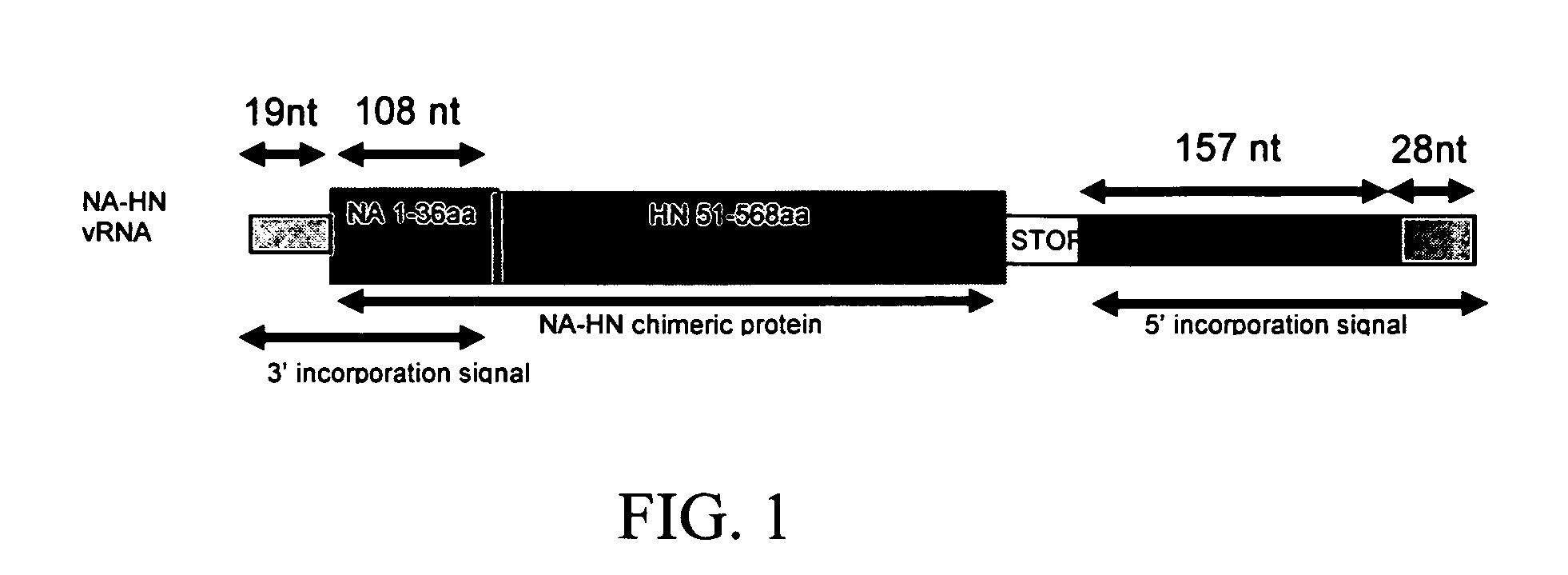
The present invention provides chimeric negative-stand RNA viruses that allow a subject, e.g., an avian, to be immunized against two infectious agents by using a single chimeric virus of the invention. In particular, the present invention provides chimeric influenza viruses engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising an ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an influenza virus protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against influenza virus and the infectious agent. The present invention also provides chimeric Newcastle Disease viruses (NDV) engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising the ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an NDV protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against NDV and the infectious agent.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
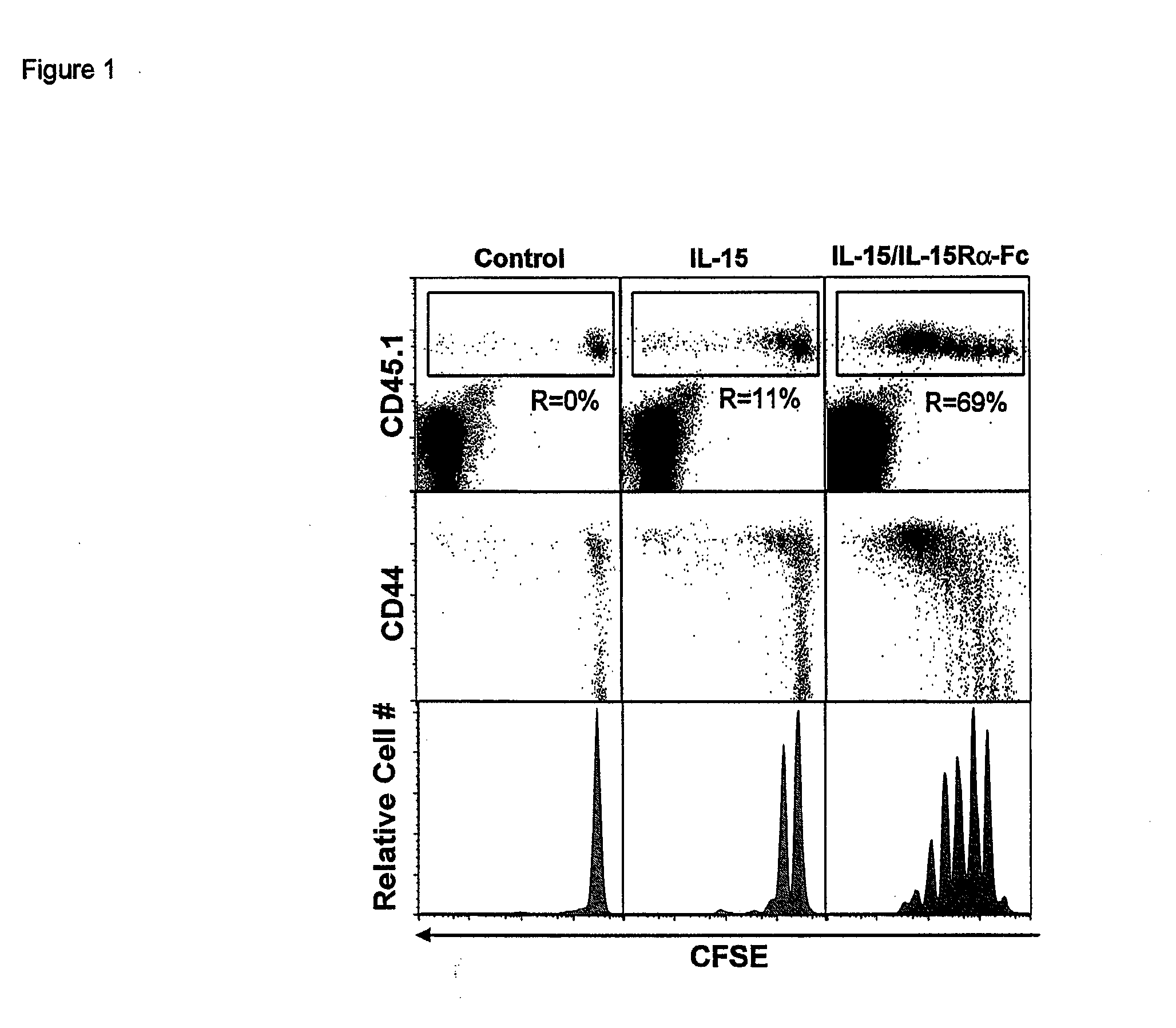
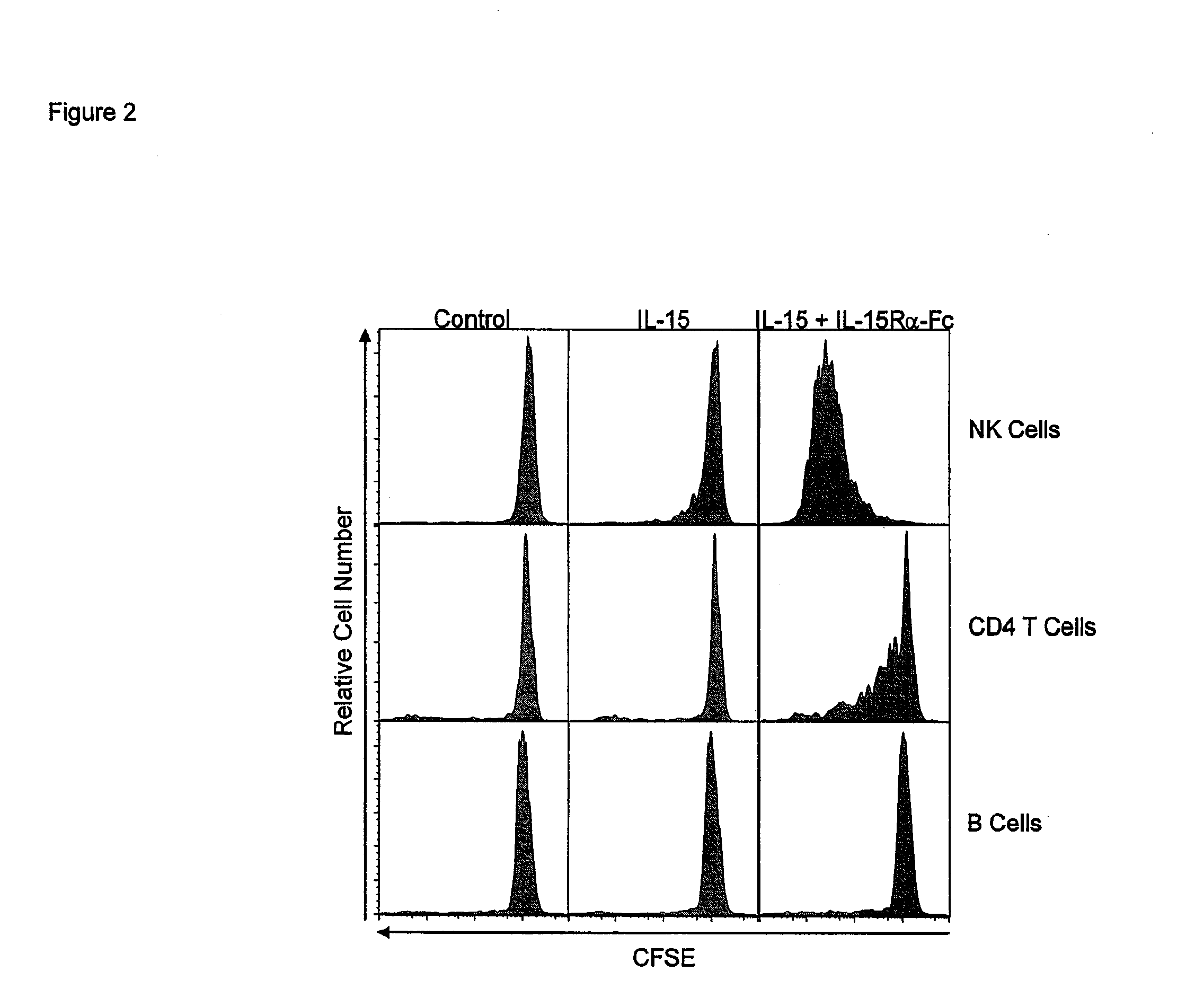
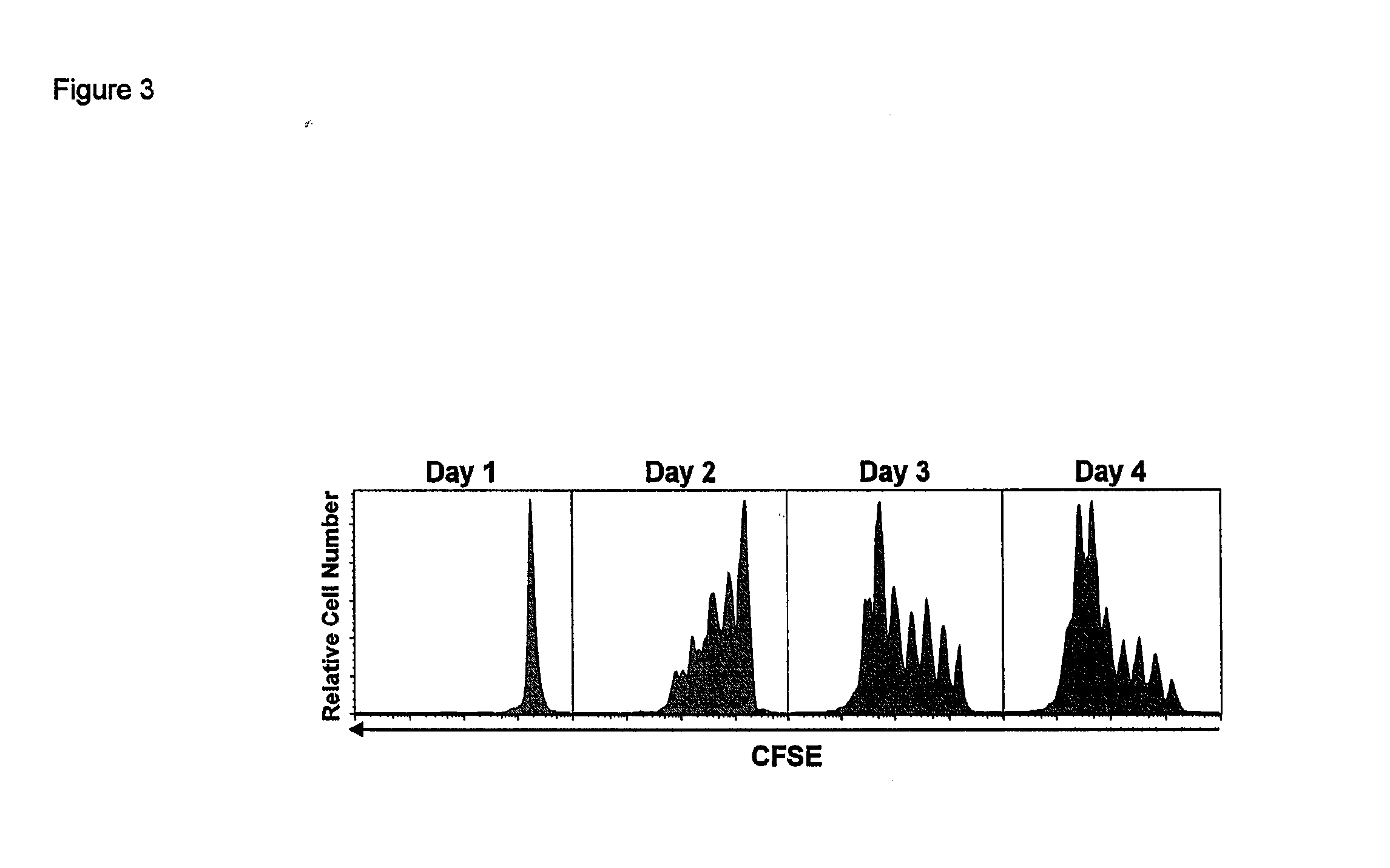
Compositions and Methods for Immunomodulation in an Organism
ActiveUS20120177598A1Long half-lifeGood treatment effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsVaccinationHalf-life
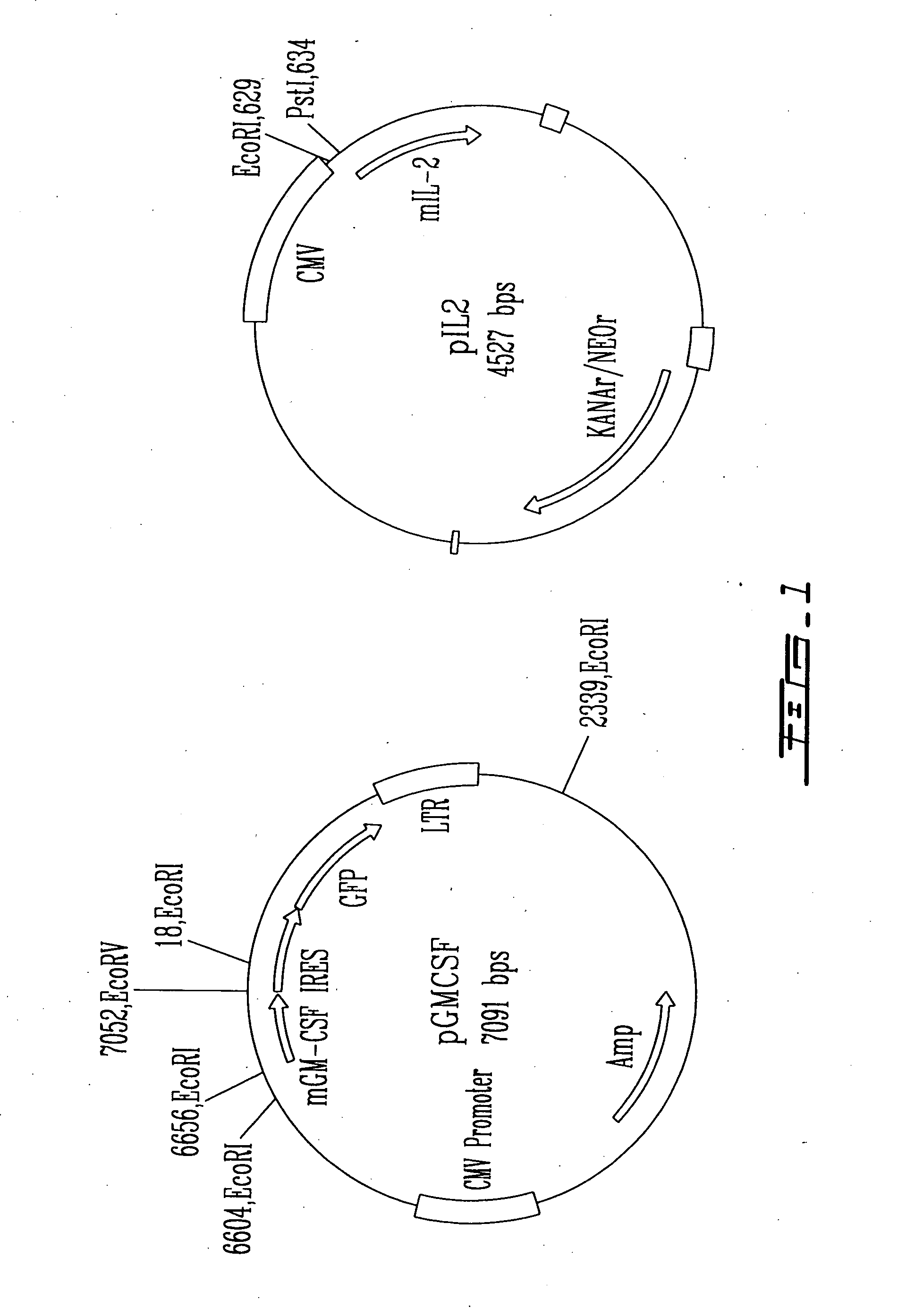
The present invention relates to a therapeutic polypeptide and methods for its creation and use for modulating an immune response in a host organism in need thereof. In particular, the invention relates to the administration to an organism in need thereof, of an effective amount of a pre-coupled polypeptide complex comprising a lymphokine polypeptide portion, for example IL-15 (SEQ ID NO: 5, 6), IL-2 (SEQ ID NO: 10, 12) or combinations of both, and an interleukin receptor polypeptide portion, for example IL-15Ra (SEQ ID NO: 7, 8), IL-2Ra (SEQ ID NO: 9, 11) or combinations of both, for augmenting the immune system in, for example, cancer, SCID, AIDS, or vaccination; or inhibiting the immune system in, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, or Lupus. The therapeutic complex of the invention surprisingly demonstrates increased half-life, and efficacy in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Immunogenic compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140242152A1Enhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryEpitopeImmunogenicity
This invention generally relates to immunogenic compositions that comprise an RNA component and a polypeptide component. Immunogenic compositions that deliver antigenic epitopes in two different forms—a first epitope from a pathogen, in RNA-coded form; and a second epitope from the same pathogen, in polypeptide form—are effective in inducing immune response to the pathogen. The invention also relates to a kit comprising an RNA-based priming composition and a polypeptide-based boosting composition. The kit may be used for sequential administration of the priming and the boosting compositions.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Vaccine composition containing synthetic adjuvant
InactiveUS20090181078A1Promote maturitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVertebrate antigen ingredientsNatural productPharmaceutical drug
Compositions and methods, including vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for inducing or enhancing an immune response are disclosed based on the discovery of useful immunological adjuvant properties in a synthetic, glucopyranosyl lipid adjuvant (GLA) that is provided in substantially homogeneous form. Chemically defined, synthetic GLA offers a consistent vaccine component from lot to lot without the fluctuations in contaminants or activity that compromise natural-product adjuvants. Also provided are vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions that include GLA and one or more of an antigen, a Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonist, a co-adjuvant and a carrier such as a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:INFECTIOUS DISEASE RES INST
Antigen delivery platforms
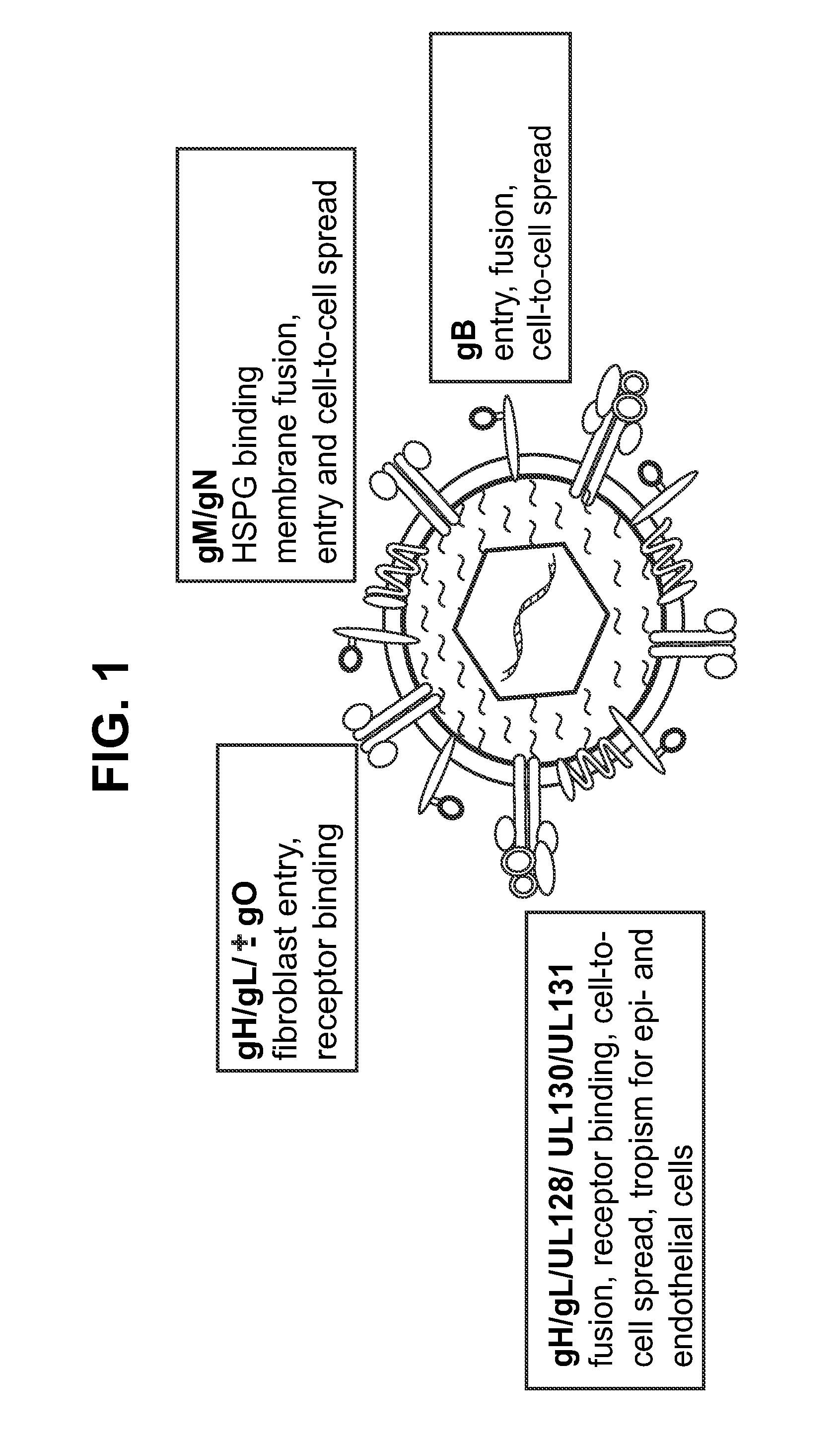
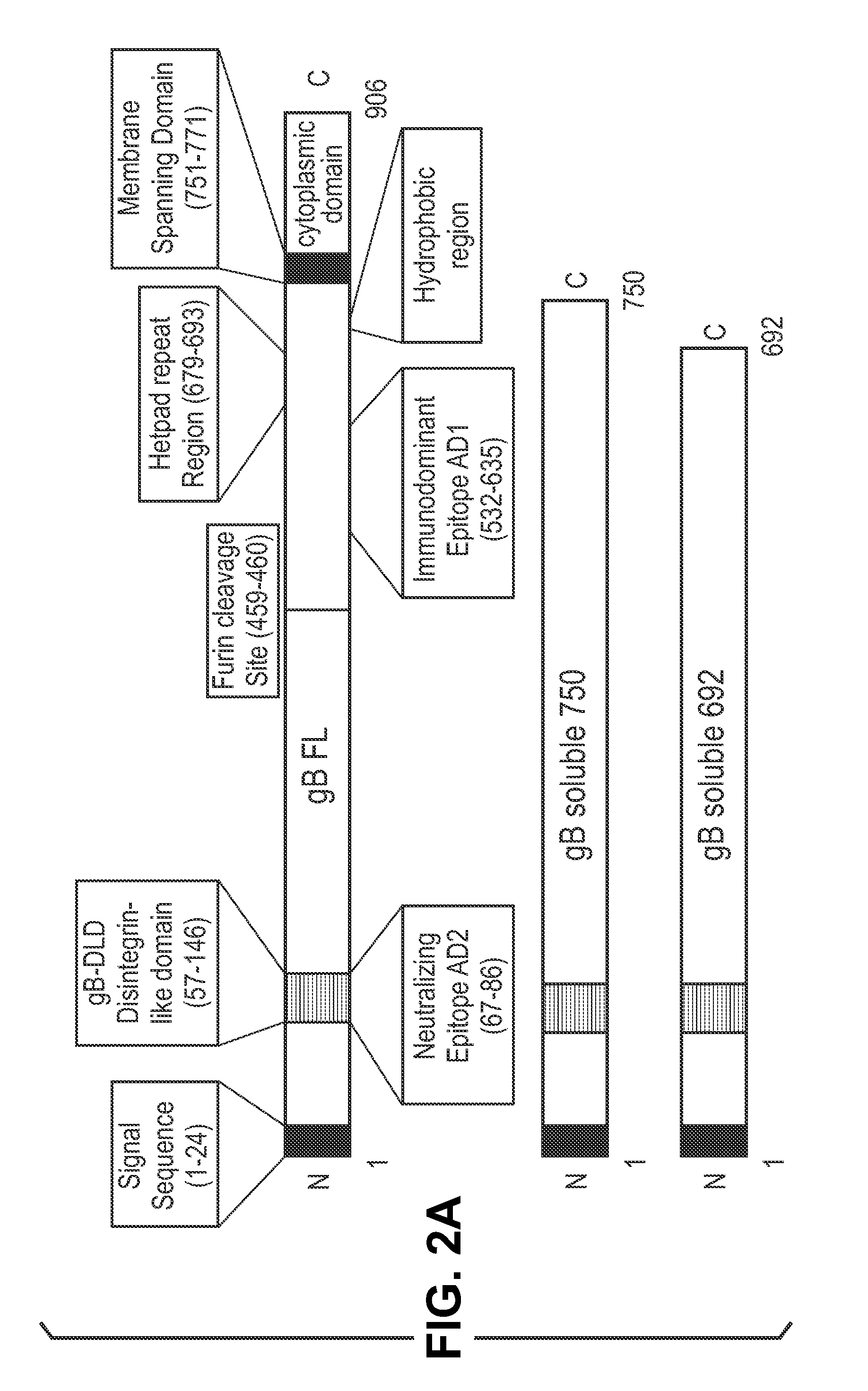
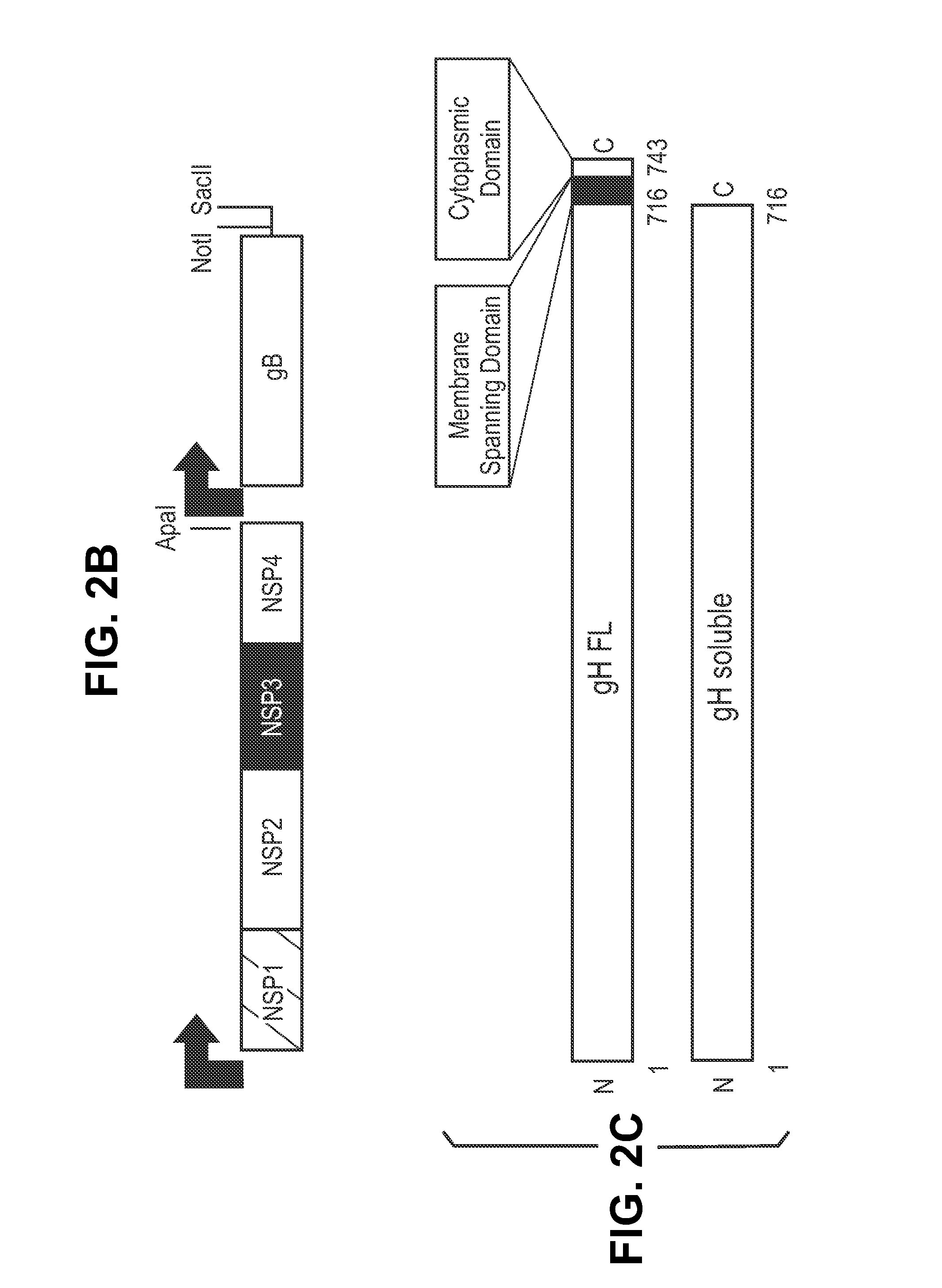
InactiveUS20140030292A1Improve stabilityAvoid reduce stimulationSsRNA viruses positive-senseFusion with post-translational modification motifAntigen deliveryHerpes simplex virus DNA
This disclosure provides platforms for delivery of herpes virus proteins to cells, particularly proteins that form complexes in vivo. In some embodiments these proteins and the complexes they form elicit potent neutralizing antibodies. Thus, presentation of herpes virus proteins using the disclosed platforms permits the generation of broad and potent immune responses useful for vaccine development.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Programmed immune responses using a vaccination node
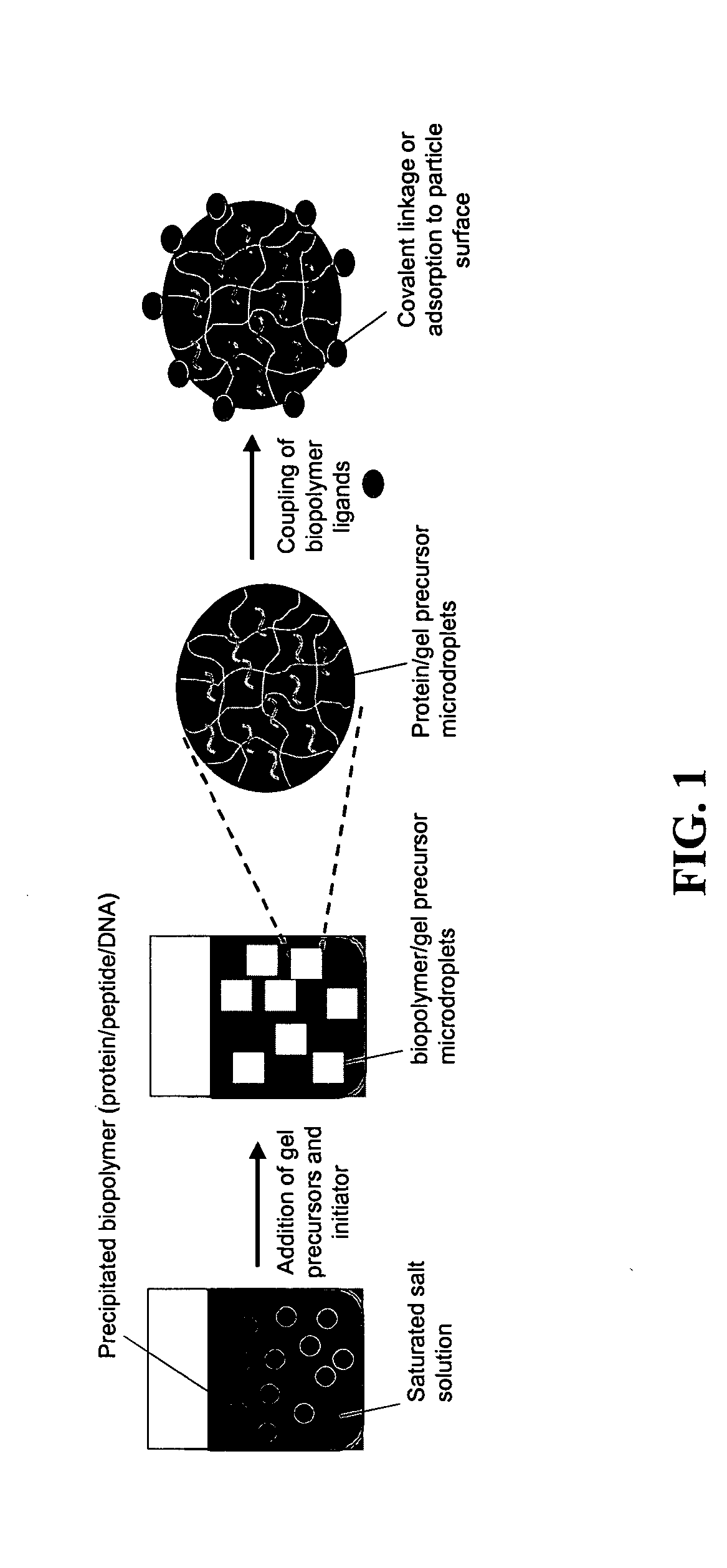
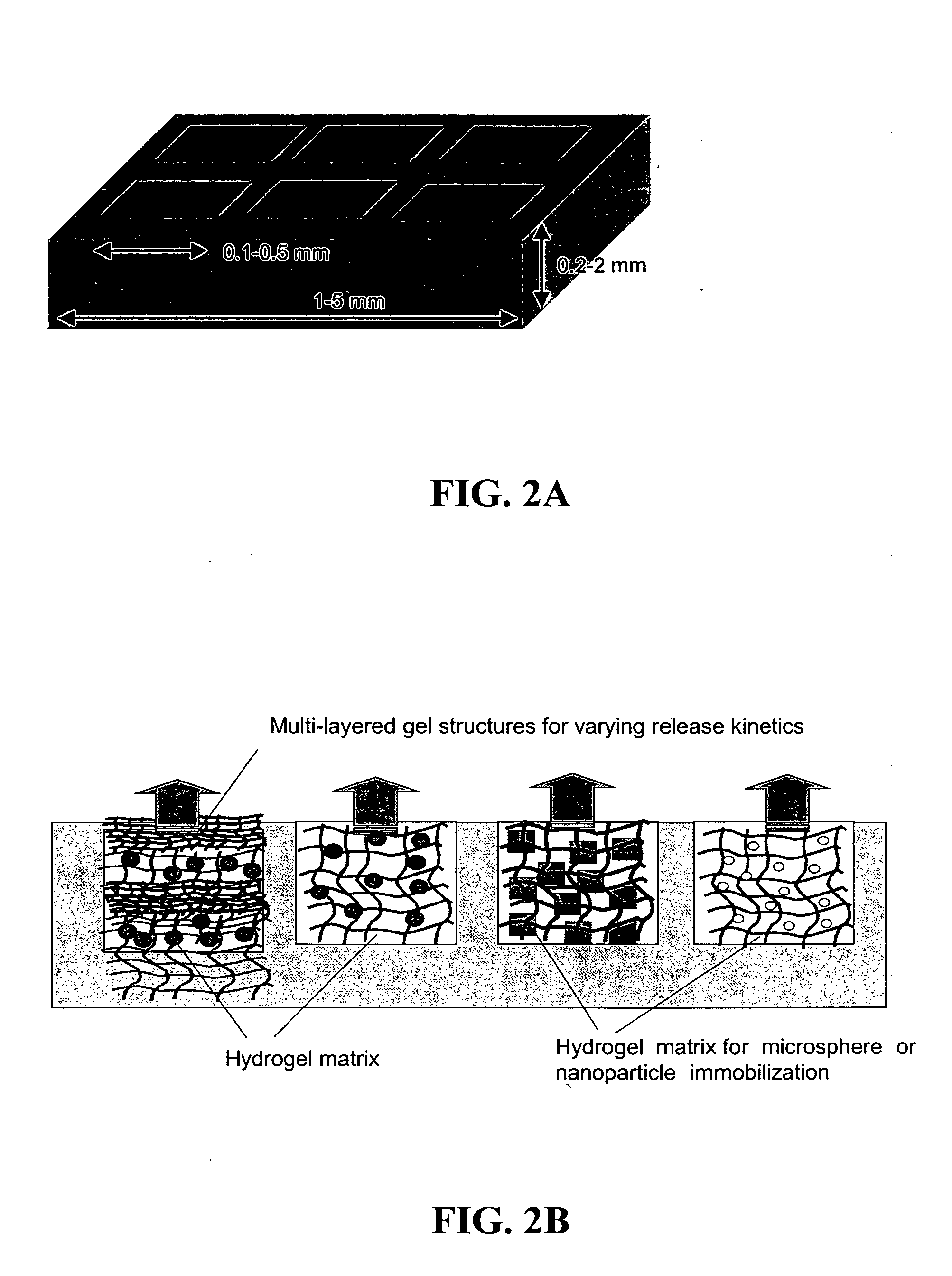
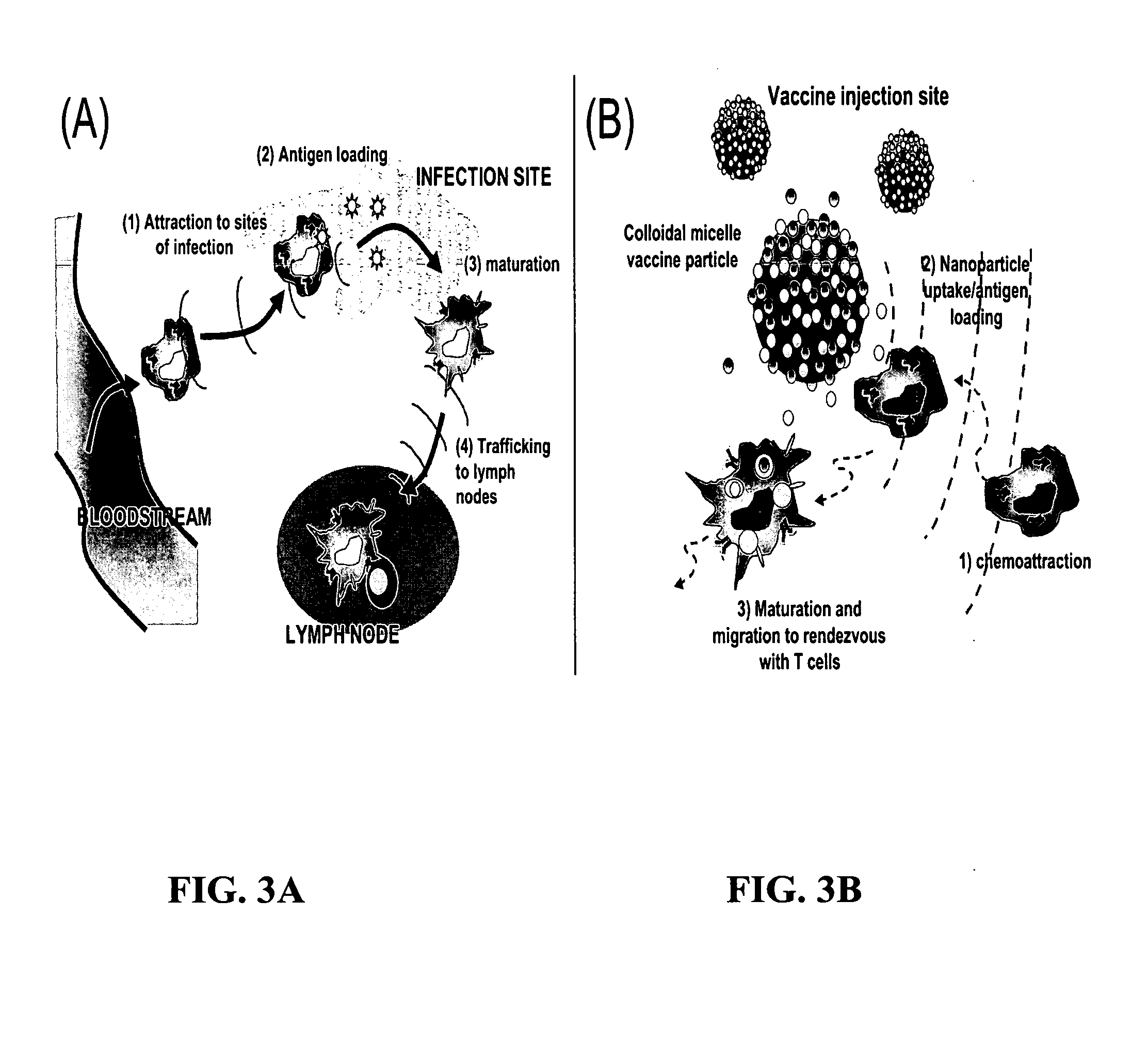
The present invention provides compositions and methods for modulating immune responses to antigens. One aspect of the present invention relates to a particle-based antigen delivery system (vaccination node) that comprises a hydrogel particle capable of both antigen presentation and DC activation. The VN may further comprise a chemoattractant-loaded microsphere capable of attracting DCs to the site of administration. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the VN to modulate antigen presenting cells activation for the prevention and / treatment of various diseases, such as infectious diseases, cancers and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:VAXDESIGN
Anti-HLA-DR antibody
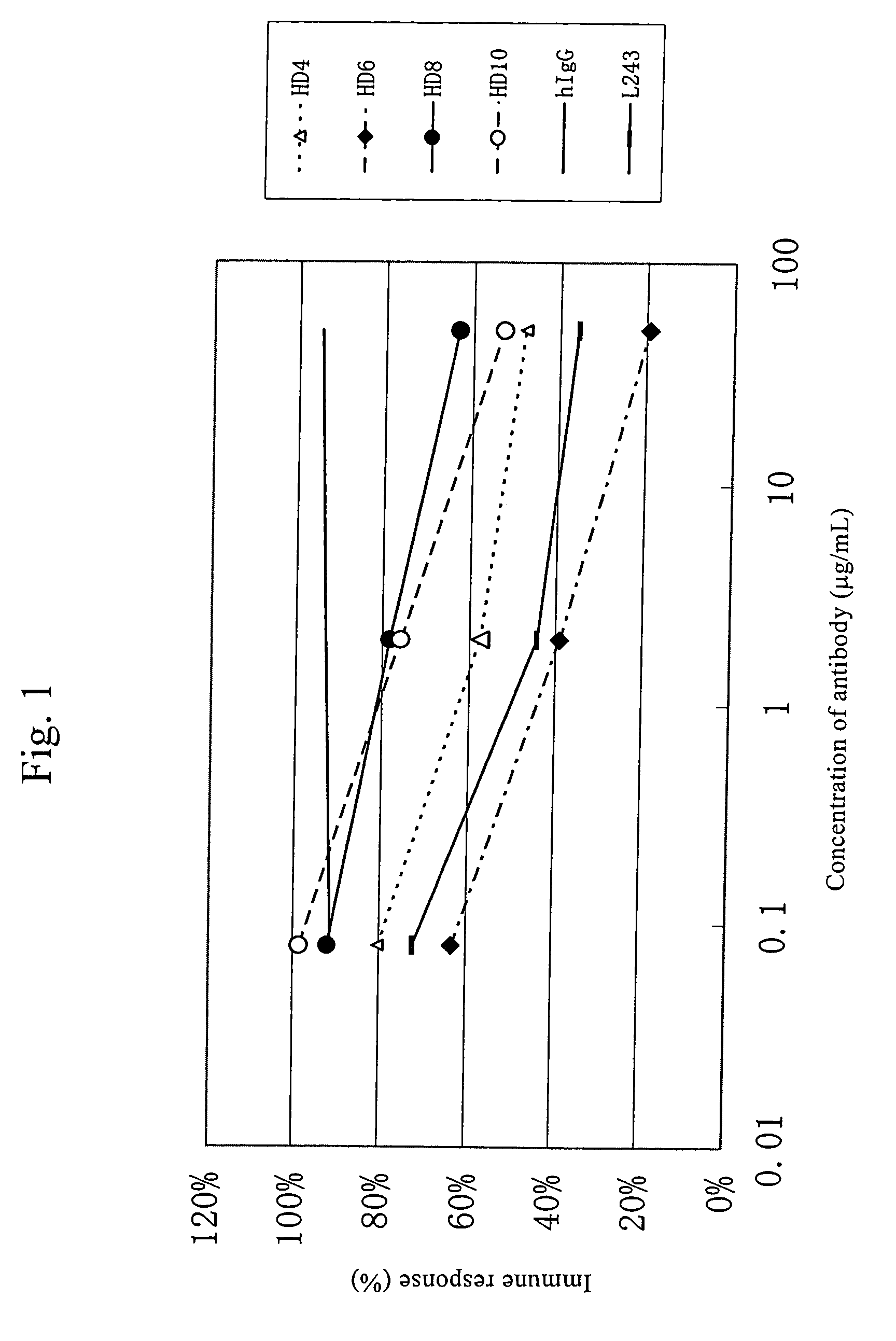
InactiveUS7262278B2Suppress lowering survival ratioSurvival ratioFungiBacteriaCancer cellMonoclonal antibody
This invention provides an anti-HLA-DR monoclonal antibody. This invention relates to an antibody binding to HLA-DR or a functional fragment thereof having (a) life-extending effects in nonhuman animals bearing HLA-DR-expressing cancer cells and (b) activity of suppressing immune responses lower than that of L243, or an antibody binding to HLA-DR or a functional fragment thereof exhibiting immunosuppressive activity equivalent to or higher than that of the mouse anti-HLA-DR monoclonal antibody L243 (ATCC HB-55).
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Tolerogenic synthetic nanocarriers to reduce immune responses to therapeutic proteins
ActiveUS20120276109A1Reduce frequencyHigh frequencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryAntigenIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTS
Disclosed are synthetic nanocarrier compositions, and related methods, comprising therapeutic protein APC presentable antigens and immunosuppressants that provide tolerogenic immune responses specific to therapeutic proteins.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
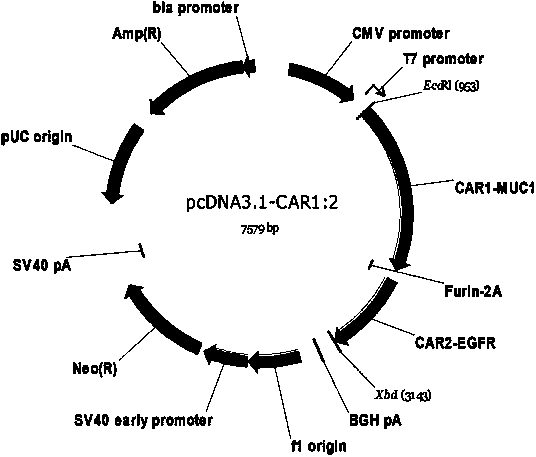
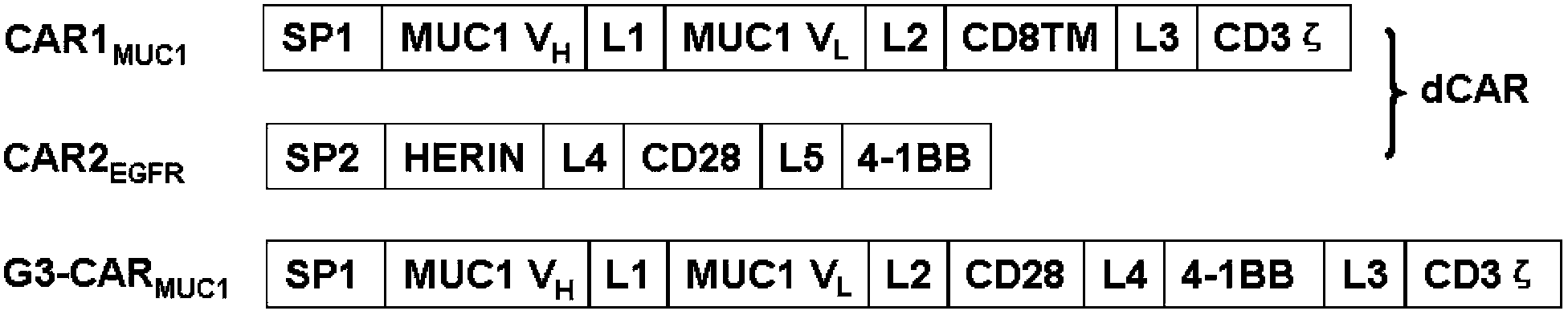
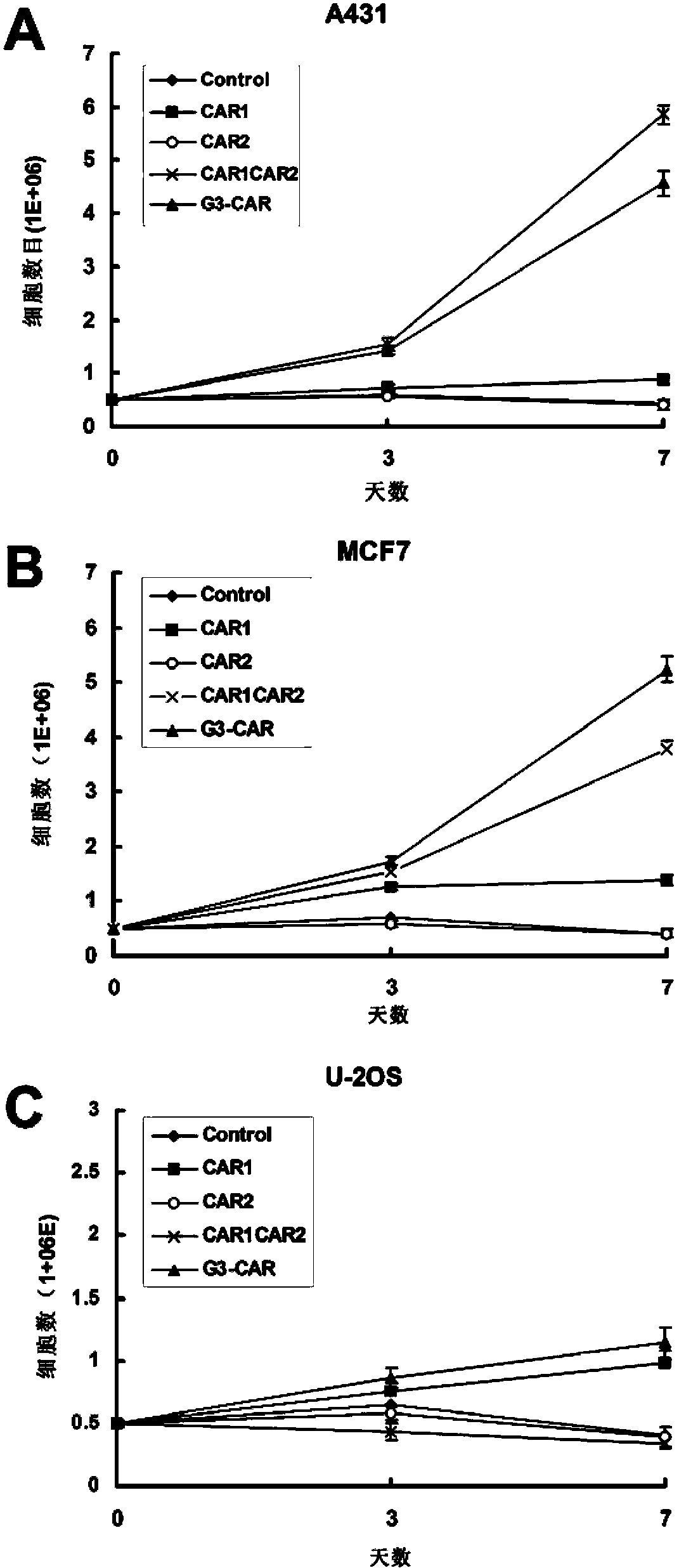
Dual-signal independent chimeric antigen receptors (dsCAR) and uses thereof
ActiveCN103483452APromote proliferationHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorsViral infectious disease
The invention relates to chimeric antigen receptors (CAR), particularly relates to dual-signal independent chimeric antigen receptors (dsCAR), and also relates to immune response cells of the dual-signal independent chimeric antigen receptors (dsCAR) and uses of the immune response cells in preparation of drugs for treatment of malignant tumor and virus infected diseases. In detail, the dual-signal independent chimeric antigen receptors (dsCAR) can respectively identify two different family antigens of tumor cells and can respectively transmit two T-cell-activation related signals. One of the CAR can transmit a first T-cell-activation related signal by combing a ligand of a tumor specific antigen or a tumor-associated antigen to decide T-cell killing specificity, and the other CAR can transmit a second T-cell-activation related signal by combing a ligand of a membrane receptor (such as EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) family protein) widely expressed by the tumor cells to promote T cell activation, proliferation and survival. The dual-signal independent chimeric antigen receptors (dsCAR) can avoid the potential safety problems on the basis of maintaining curative effects of second generation and third generation CAR.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY GRP CO LTD
Novel synthetic chimeric fusion transgene with immuno-therapeutic uses
InactiveUS20050053579A1Reducing tumorigenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInterferon alphaWilms' tumor
The present invention relates to an immuno-therapy conjugate which comprises A-c-B wherein: A and B are different and are compounds selected from the group consisting of cytokines, chemokines, interferons, their respective receptors or a functional fragment thereof; and c is a linker consisting of a bond or an amino acid sequence containing from 1 to 100 residues. The present invention also relates to a vaccine adjuvant comprising the immuno-therapy conjugate of the present invention. The present invention further relates to a method of reducing tumor growth, for inhibiting a viral infection and for improving immune response in a patient.
Owner:GALIPEAU JACQUES +1
Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof
Thiazolo-, oxazolo- and selenazolo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof are described including methods of manufacture and the use of novel intermediates. The compounds are immunomodulators and induce cytokine biosynthesis, including interferon and / or tumor biosynthesis, necrosis factor, and inhibit the T-helper-type 2 immune response. The compounds are further useful in the treatment of viral and neoplastic diseases.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Yeast-based Vaccine for Inducing an Immune Response
InactiveUS20080003239A1Reduces and prevents influenza infectionReduces and prevents infectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideDiseaseYeast form
The invention provided herein relates to vaccines that can be tailored to achieve a desired immune response. Some compositions provided herein are used for preferentially eliciting a humoral immune response while other compositions are useful for preferentially eliciting a cell-mediated response. Combinations of vaccine compositions are also useful for eliciting both types of responses and / or for modulating the type of immune response elicited. The invention also provides methods for eliciting an immune response in an individual by administering the compositions disclosed herein. These immune responses are useful for protecting an individual from various types of diseases, infections, and undesirable conditions.
Owner:GLOBE IMMUNE INC
Novel proteosome-liposaccharide vaccine adjuvant
InactiveUS20030044425A1Increase secretionUniform processSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideImmunotherapeutic agentCytokine
An adjuvant complex composed of bacterial outer membrane protein proteosomes complexed to bacterial liposaccharide is prepared to contain the component parts under a variety of conditions. The complex can be formulated with antigenic material to form immunogenic compositions, vaccines and immunotherapeutics. An induced immune response includes protective antibodies and / or type 1 cytokines is shown for a variety of protocols.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP LAVAL
Targeted multi-epitope dosage forms for induction of an immune response to antigens
InactiveUS20120070493A1Induce and enhance and cytokine productionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAntigenBinding peptide
Provided herein are compositions and methods related to MHC II binding peptides. In some embodiments, the peptides are obtained or derived from a common source. In other embodiment, the peptides are obtained or derived from an infectious agent to which a subject has been repeatedly exposed.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
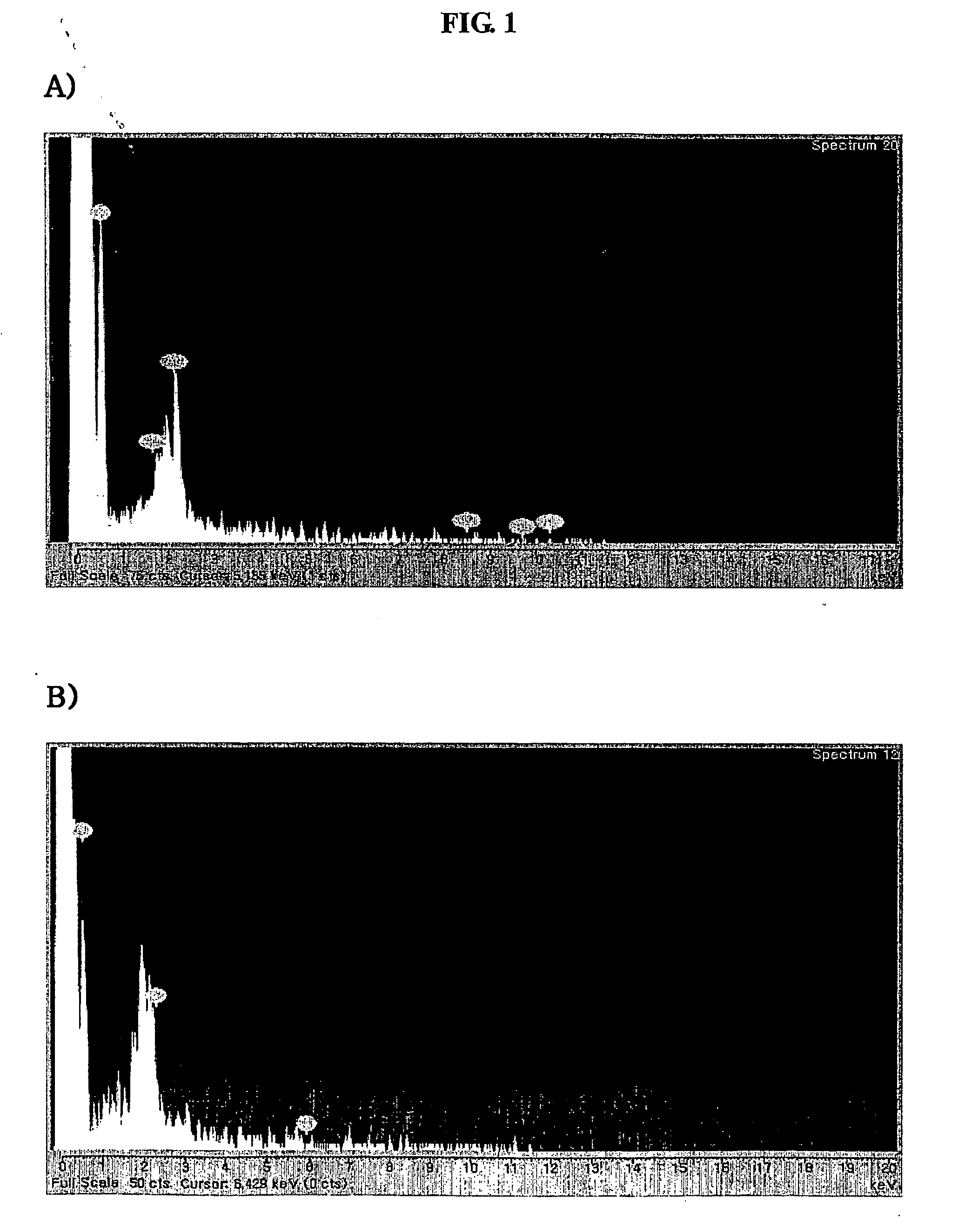
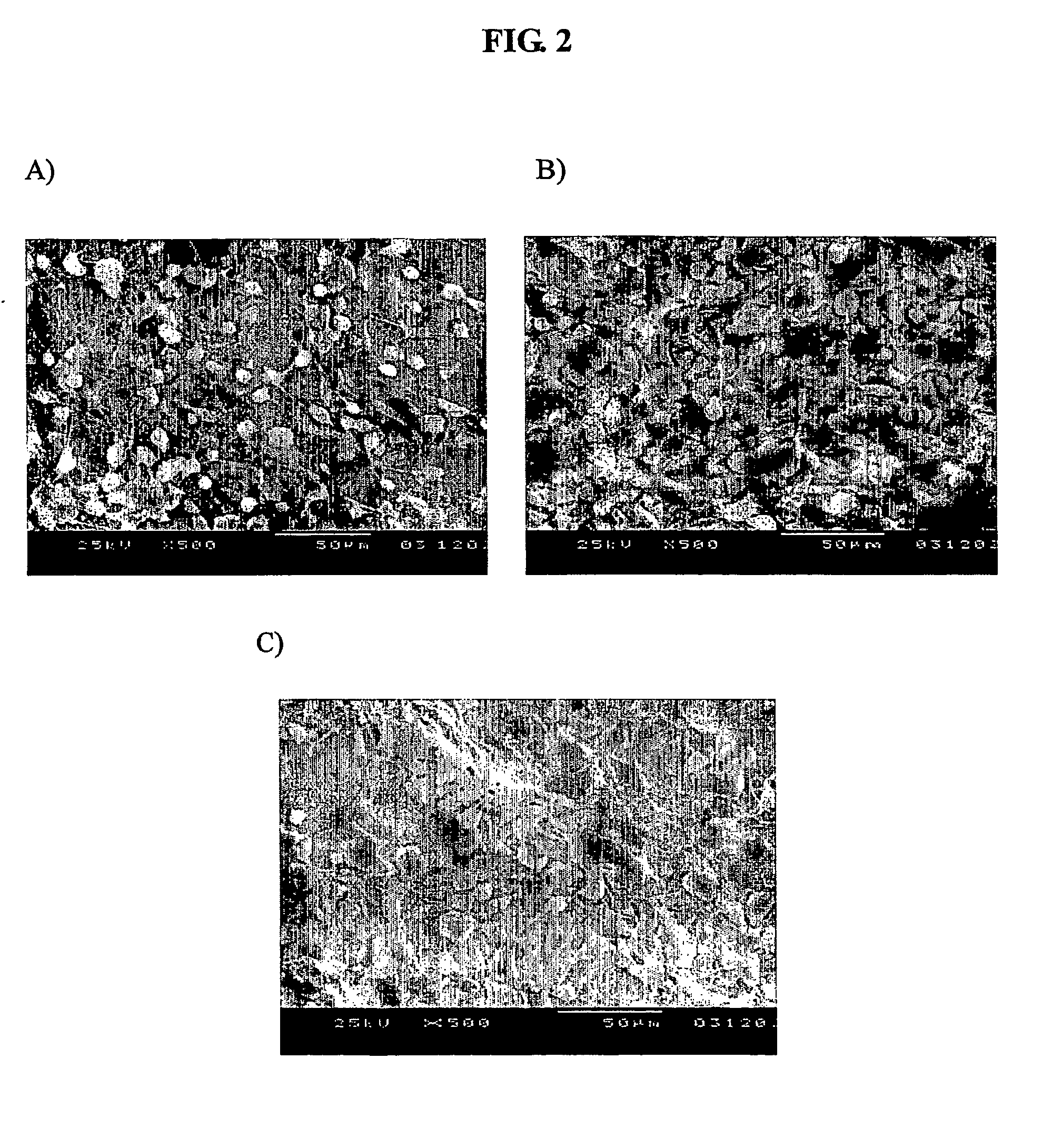
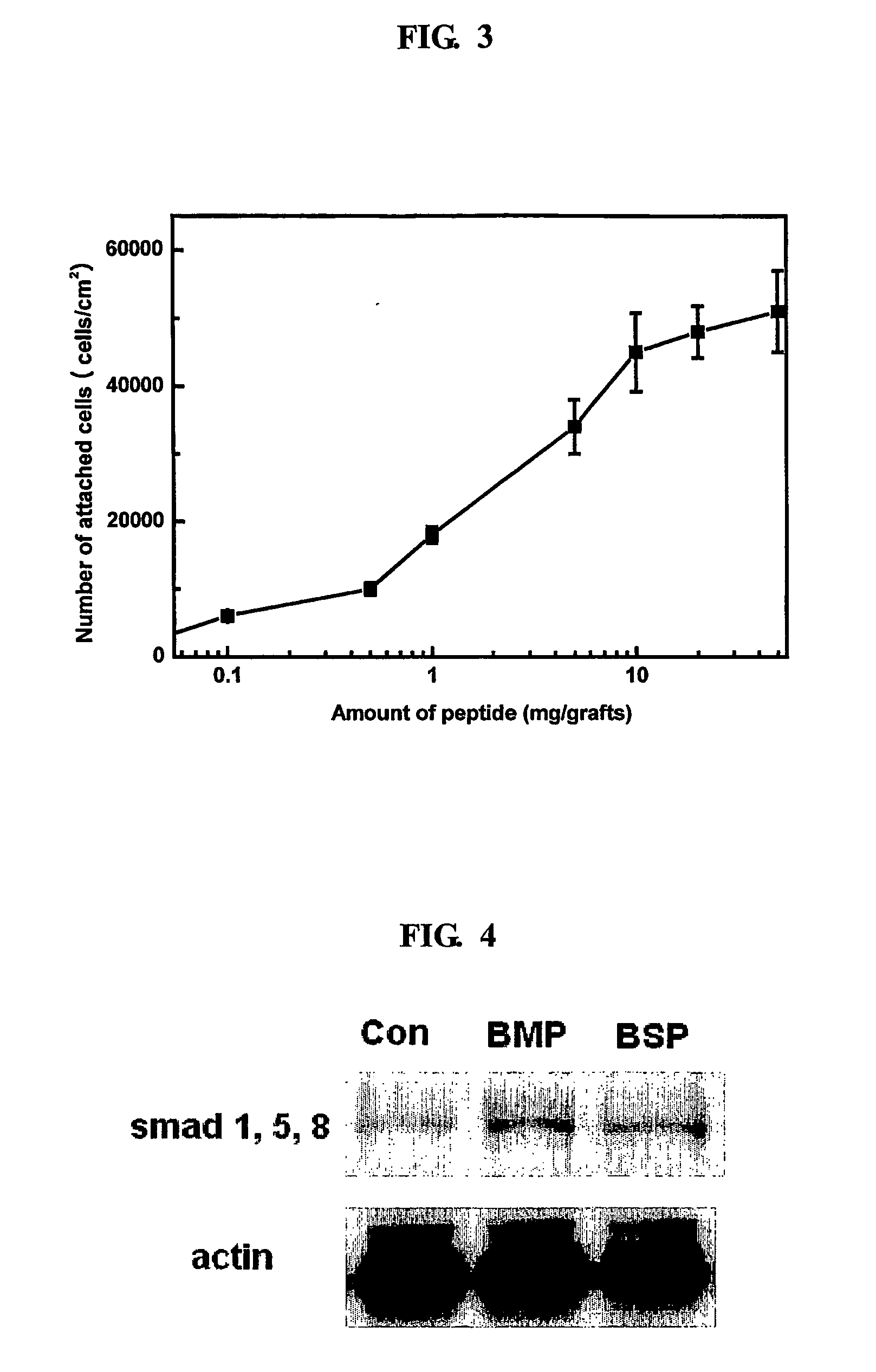
Bone graft and scaffolding materials immobilized with osteogenesis enhancing peptides on the surface
ActiveUS20070160681A1Improve efficiencyEasy to fixCoffee millsAnimal cellsSurgical operationCell adhesion
The present invention relates to a bone graft material and a scaffold for tissue engineering applications, which have an osteogenesis-promoting peptide immobilized on the surface. More particularly, the invention relates to a bone graft material and a scaffold for tissue engineering applications, which have a cell adhesion-inducing peptide and / or tissue growth factor-derived peptide immobilized on the surface. By the osteogenesis-promoting peptide immobilized on the surface, the inventive bone graft material and scaffold for tissue engineering applications can promote the transition, proliferation and differentiation of cells associated with regeneration, and eventually maximize the regeneration of tissue. Moreover, the peptide immobilized on the surface has low molecular weight, indicating a reduced risk of immune responses upon its application in the body, and can be present in a stable form within the body, thus showing lasting effects. Accordingly, the peptide makes it expedient to perform surgical operations for the regeneration of periodontal tissue, alveolar bone and other bone tissues, and will show high therapeutic effect.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
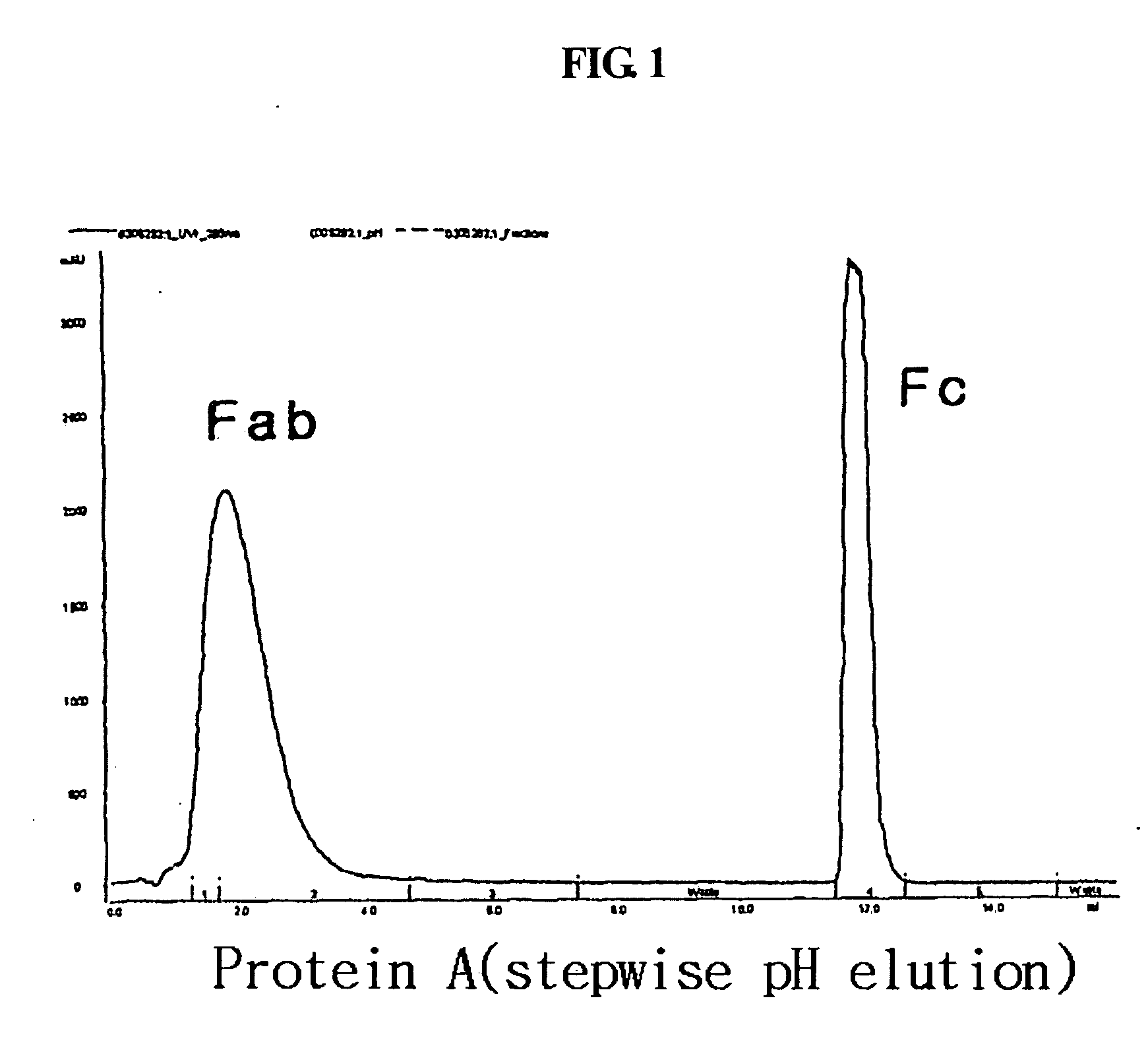
Protein complex using an immunoglobulin fragment and method for the preparation thereof
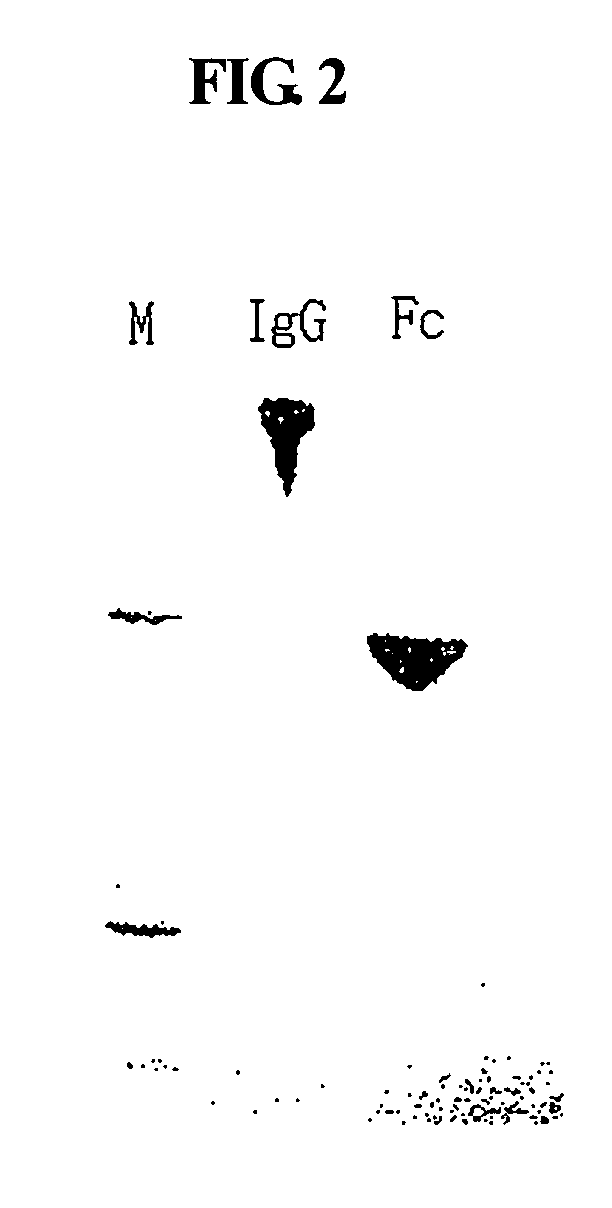
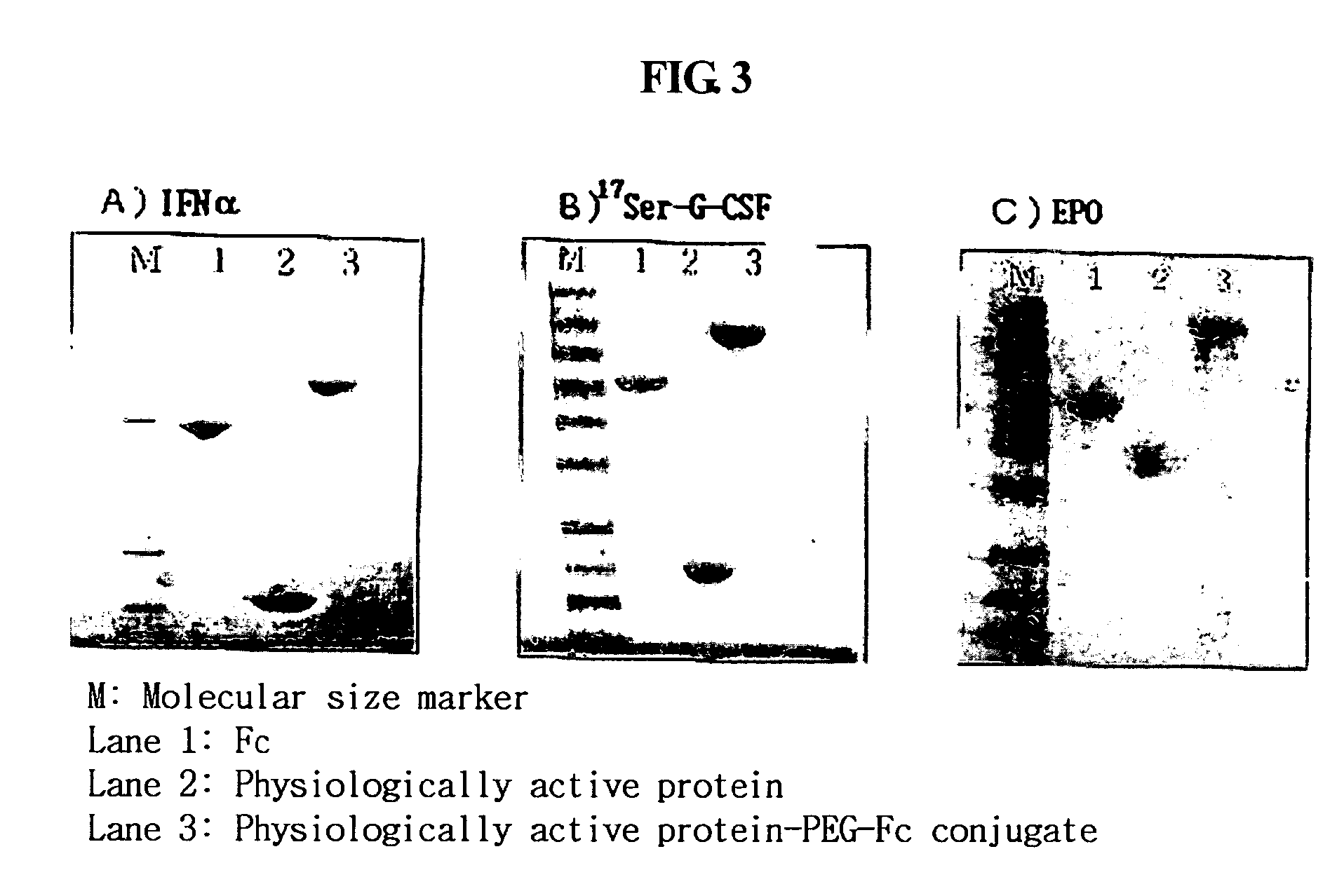
ActiveUS20060269553A1Improve stabilityExtended durationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunological disordersHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
Disclosed are a protein conjugate with improved in vivo duration and stability and the use thereof. The protein conjugate includes a physiologically active polypeptide, a non-peptide polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc fragment. Since the three components are covalently linked, the protein conjugate has extended in vivo duration and enhanced stability for the physiologically active polypeptide. The protein conjugate maintains the in vivo activity at relatively high levels and remarkably increases the serum half-life for the physiologically active polypeptide, with less risk of inducing undesirable immune responses. Thus, the protein conjugate is useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Nanoemulsion therapeutic compositions and methods of using the same
The present invention relates to therapeutic nanoemulsion compositions and to methods of utilizing the same. In particular, nanoemulsion compositions are described herein that find use in the treatment and / or prevention of infection (e.g., respiratory infection (e.g., associated with cystic fibrosis)), in burn wound management, and in immunogenic compositions (e.g., comprising a Burkholderia antigen) that generate an effective immune response (e.g., against a bacterial species of the genus Burkholderia) in a subject administered the immunogenic composition. Compositions and methods of the present invention find use in, among other things, clinical (e.g. therapeutic and preventative medicine), industrial, and research applications.
Owner:NANOBIO CORP
Compositions and methods for eliciting an immune response to escape mutants of targeted therapies
InactiveUS20100034840A1Reduce resistanceSymptoms improvedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMolecular Targeted TherapiesMutant
Provided herein are cells, vectors and viruses in association with a mutant polypeptide that has emerged in response to a therapeutic or prophylactic agent; compositions comprising such cells, vectors and viruses and methods for their use in eliciting an immune response to the mutant polypeptide. In some examples, the immune response is a cellular immune response.
Owner:GLOBE IMMUNE INC
Recombinant vaccine against west nile virus
InactiveUS20030104008A1Inhibition effectEasy to storeSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityNucleotide
Disclosed and claimed are immunogenic compositions to induce an immune response against West Nile (WN) virus, recombinants, for instance recombinant avipox viruses containing and expressing exogenous polynucleotide(s) from WN virus, and methods for making and using the same.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
High cell density process for growth of Listeria
InactiveUS20060121053A1Increase productionIncrease costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenHigh cell
The present invention relates to fed batch culture methods for high cell density growth of Listeria which produce cultures having an OD600 greater than about 2.2 or higher. In particular, the invention provides methods for high cell density growth of Listeria comprising growth in a pH controlled bioreactor and, optionally, the gradual addition of a carbon source, e.g., glucose, with or without one or more additional nutrients, e.g., vitamins, when growth in the initial culture is nearly complete or complete. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention are used to produce Listeria-based compositions, e.g., vaccines comprising Listeria that express a tumor-associated antigen, e.g., an EphA2 antigenic peptide, for eliciting an immune response against hyperproliferative cells.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/74ac572b-d35d-49e9-8ac6-b860065b1a3c/US06323200-20011127-C00001.png)
![Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/74ac572b-d35d-49e9-8ac6-b860065b1a3c/US06323200-20011127-C00002.png)
![Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof Oxazolo, thiazolo and selenazolo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-amines and analogs thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/74ac572b-d35d-49e9-8ac6-b860065b1a3c/US06323200-20011127-C00003.png)