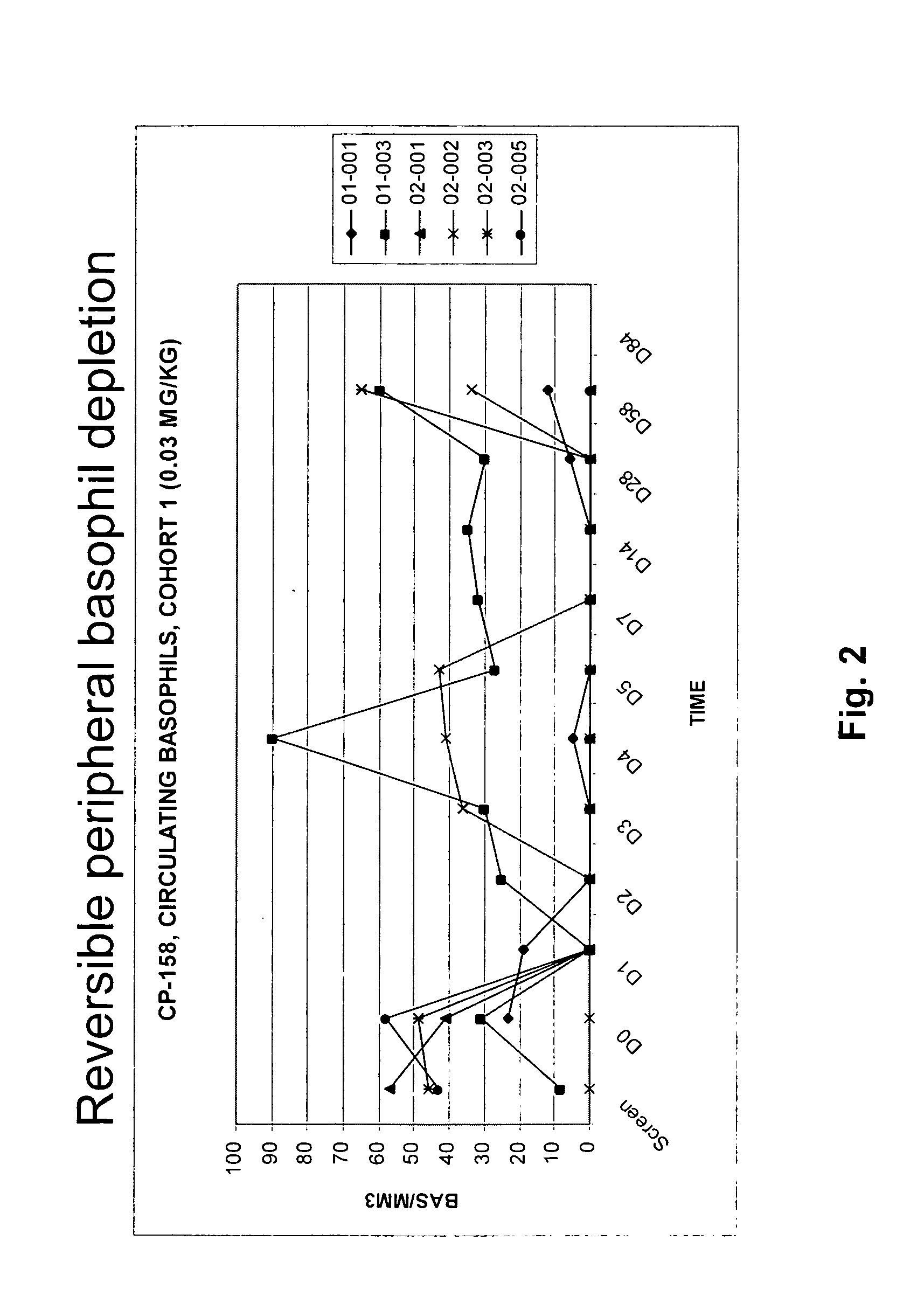
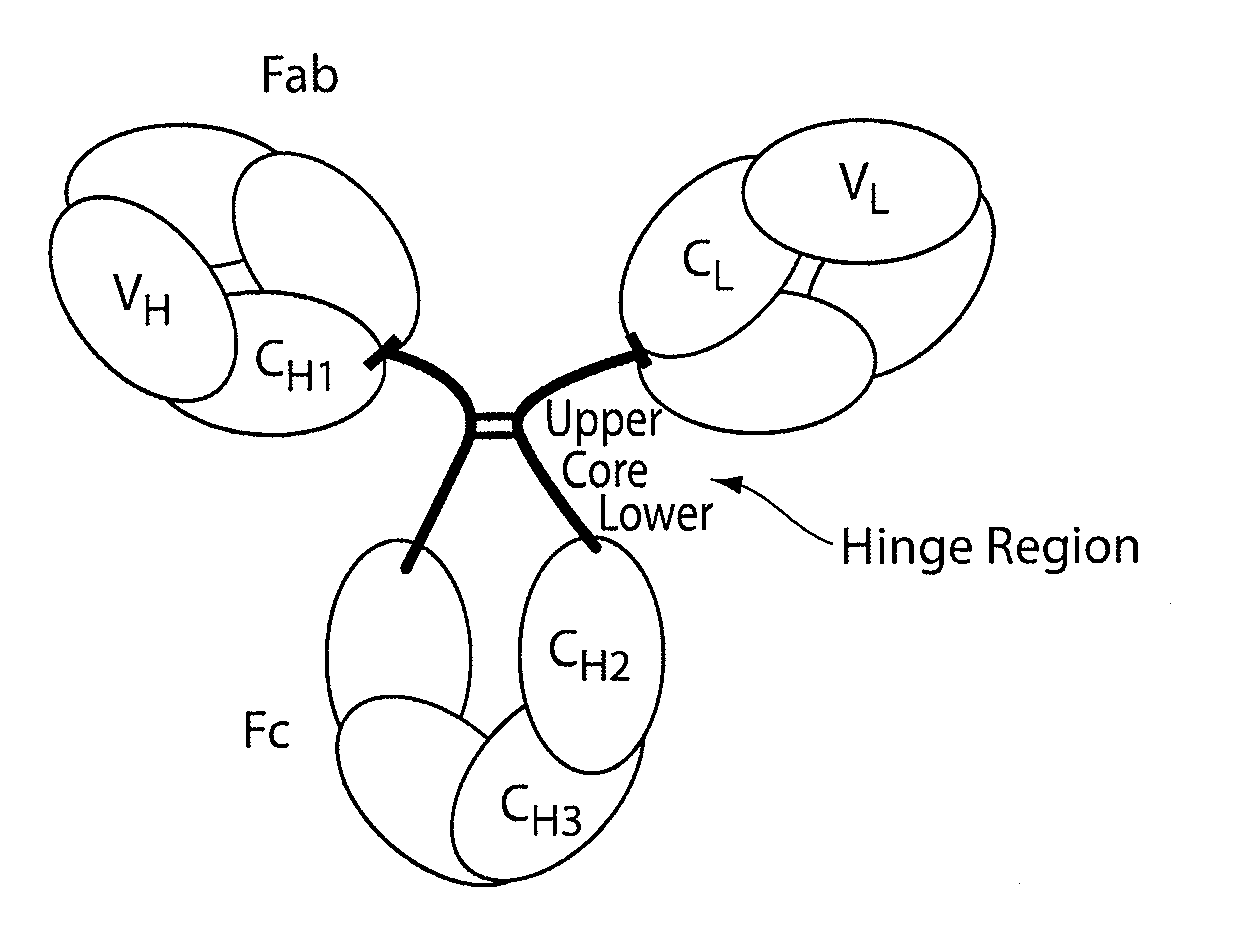
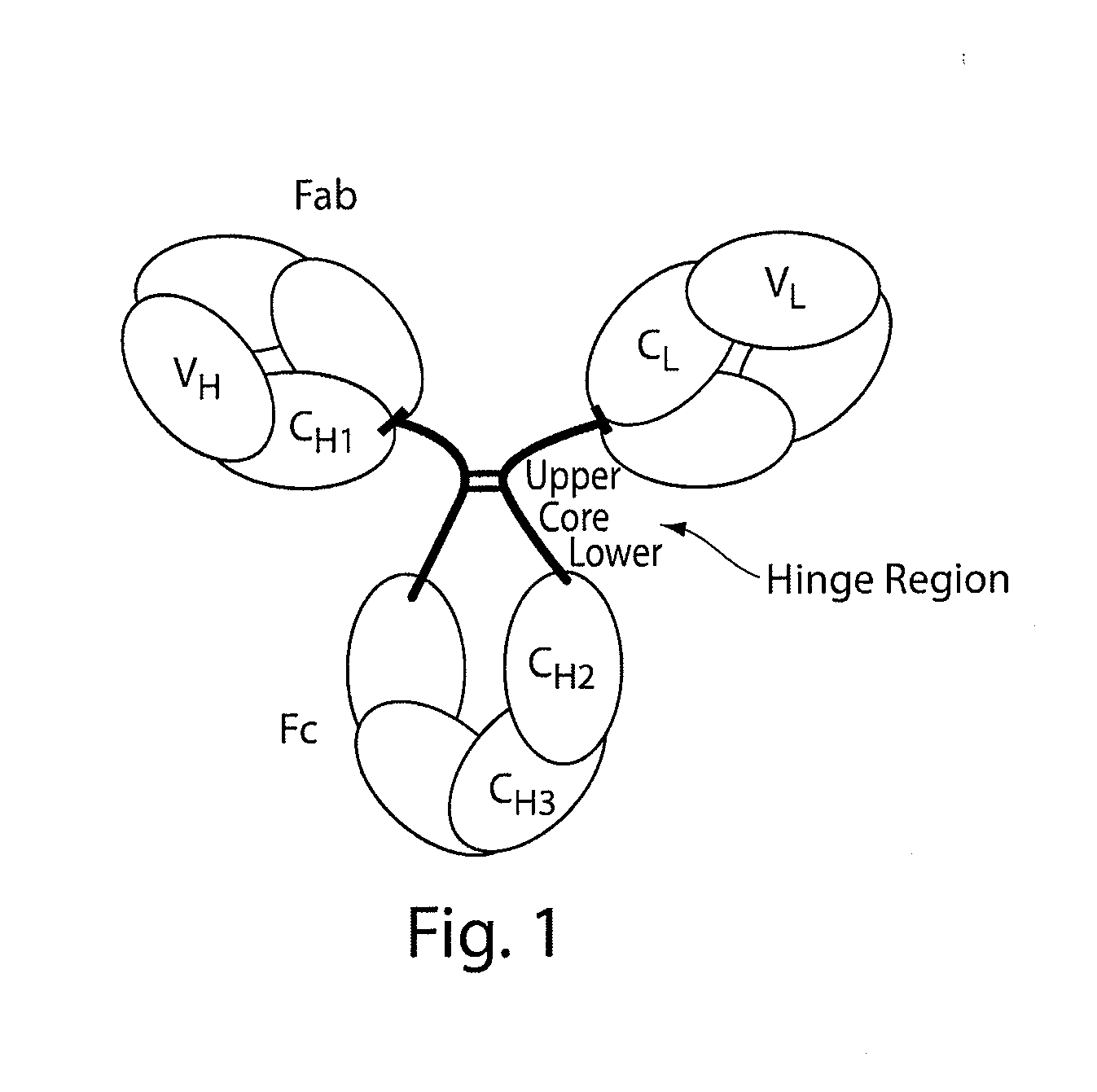
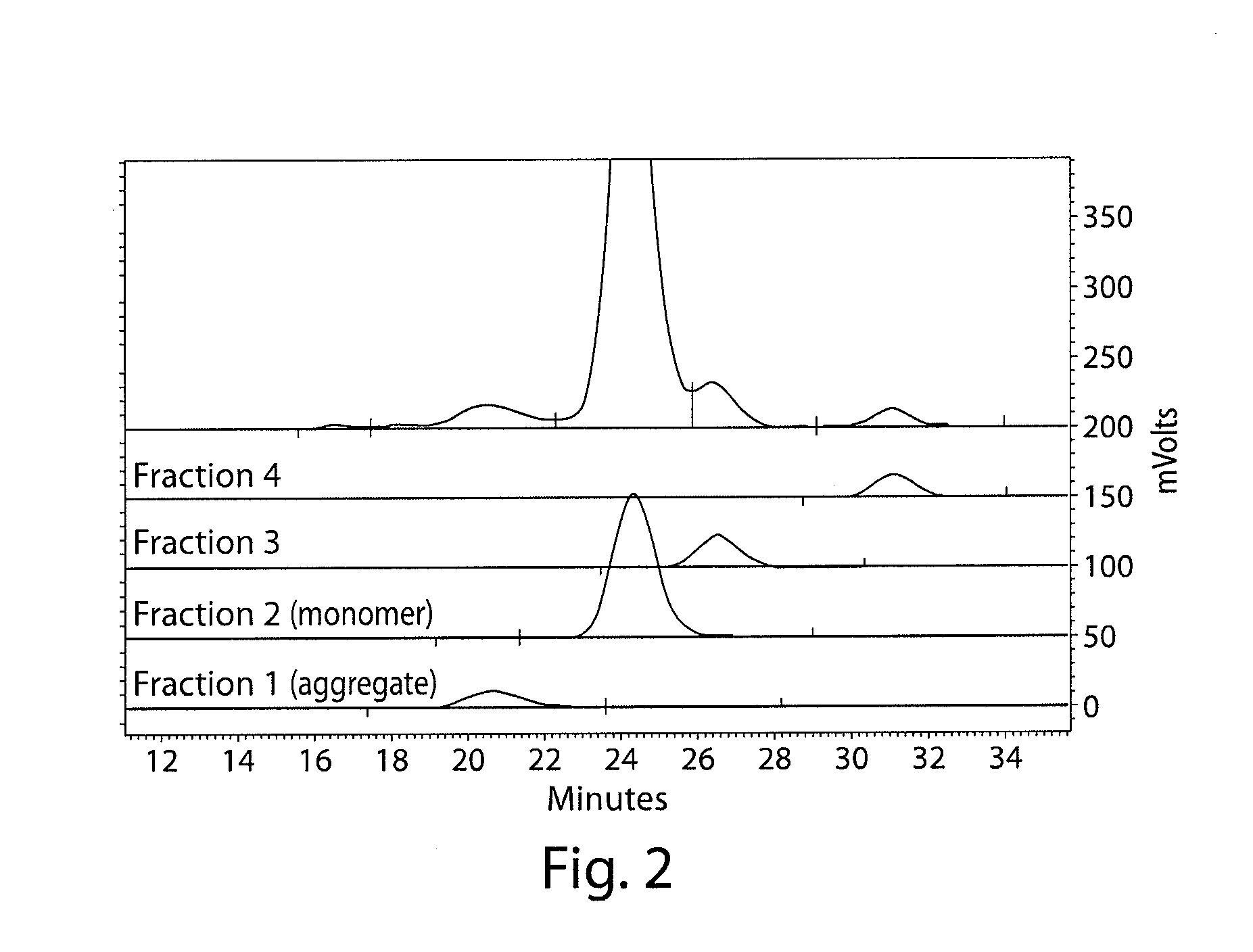
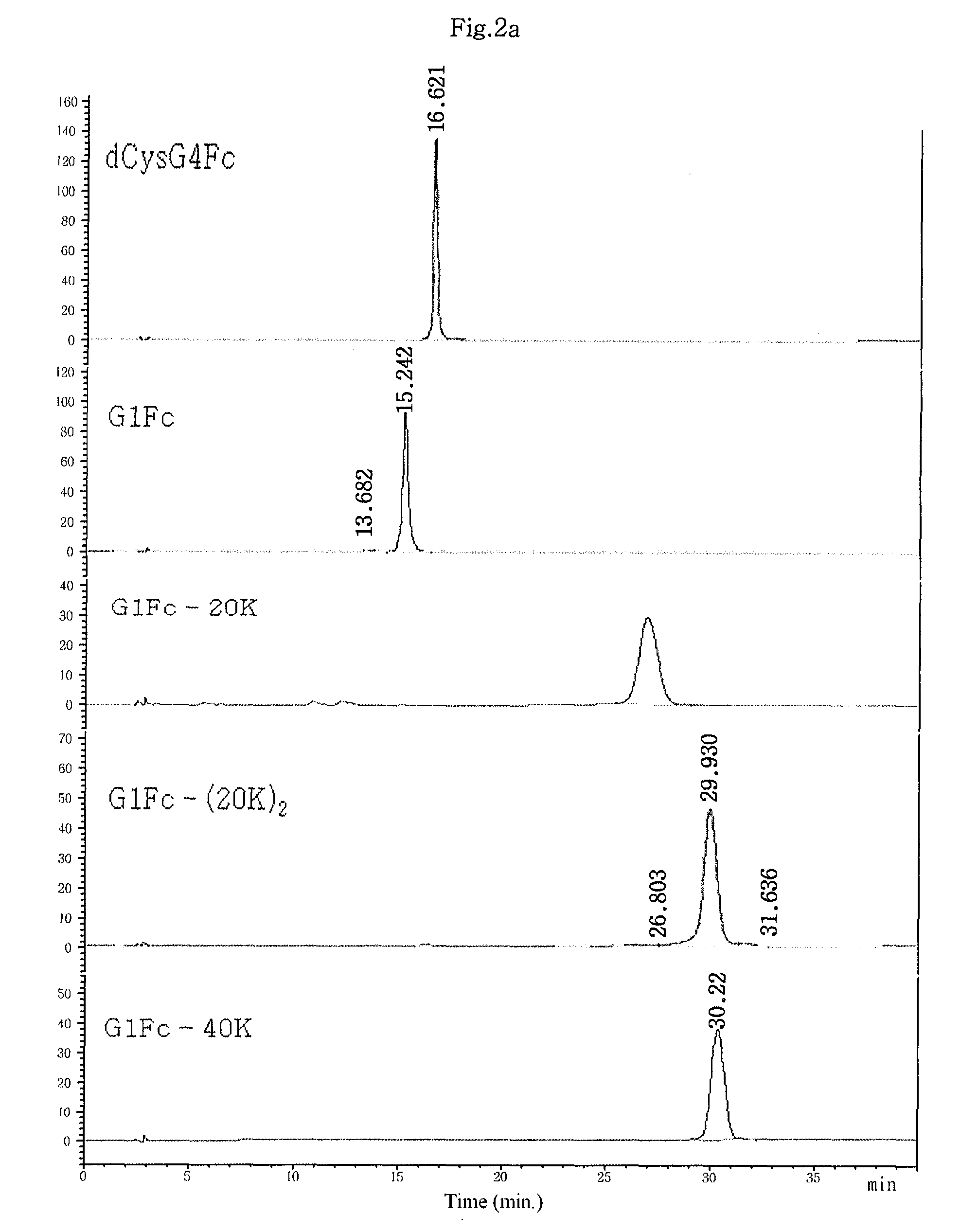
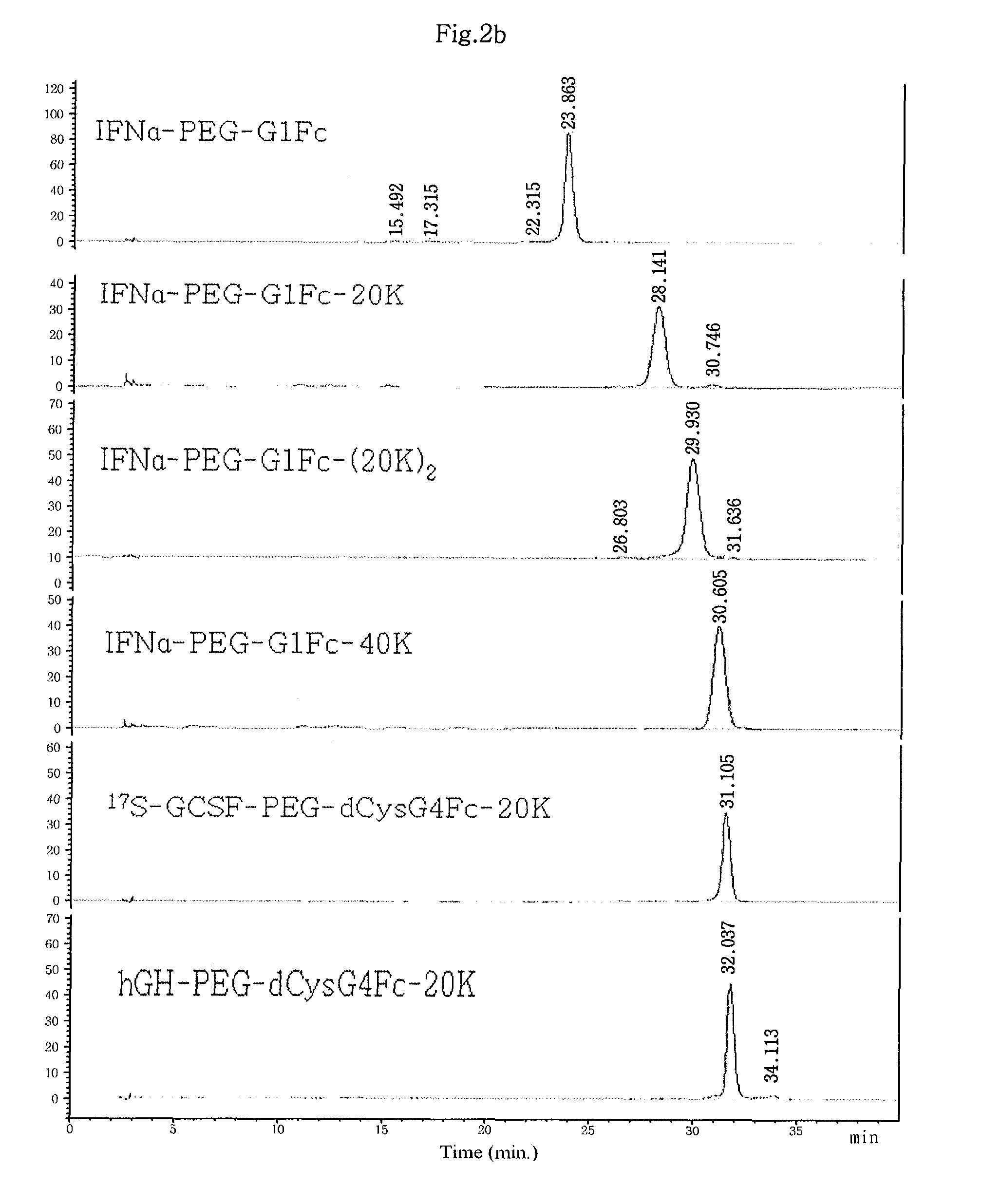
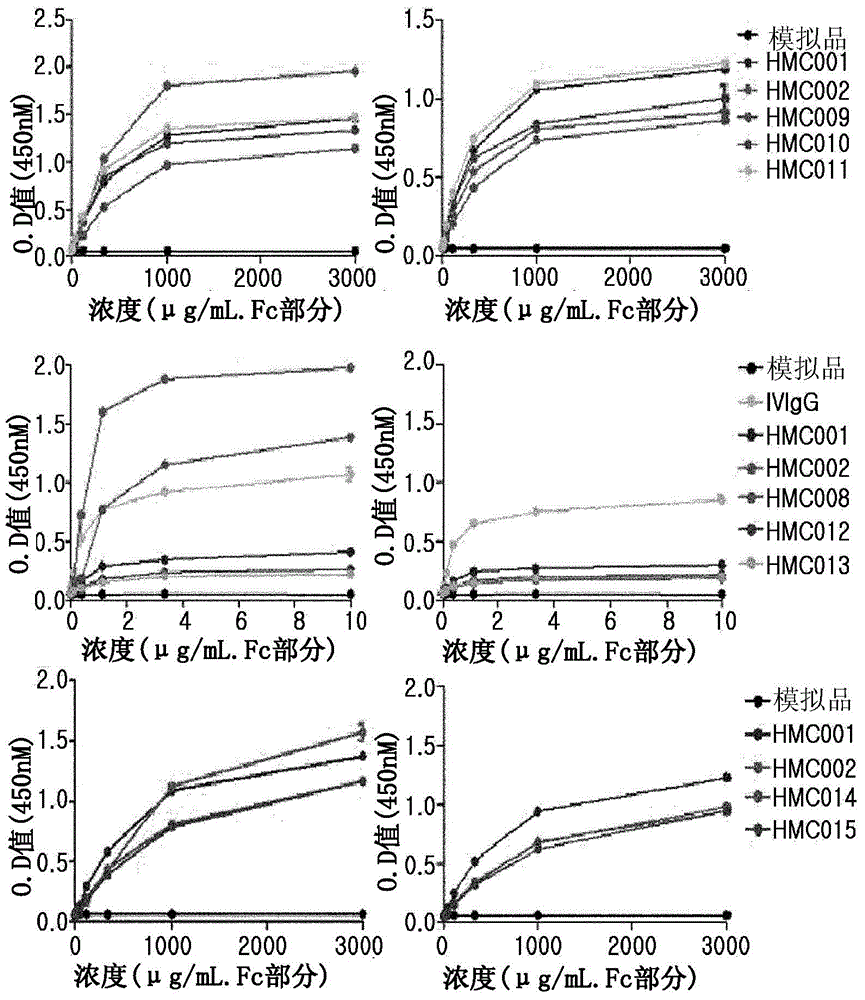
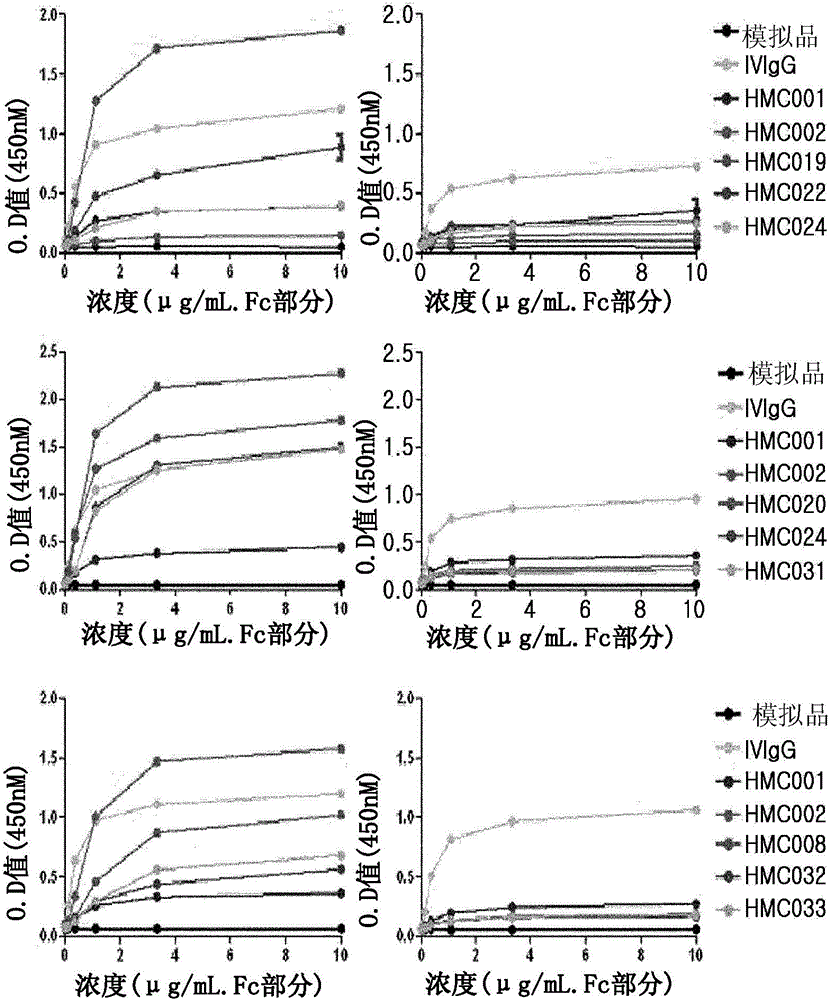
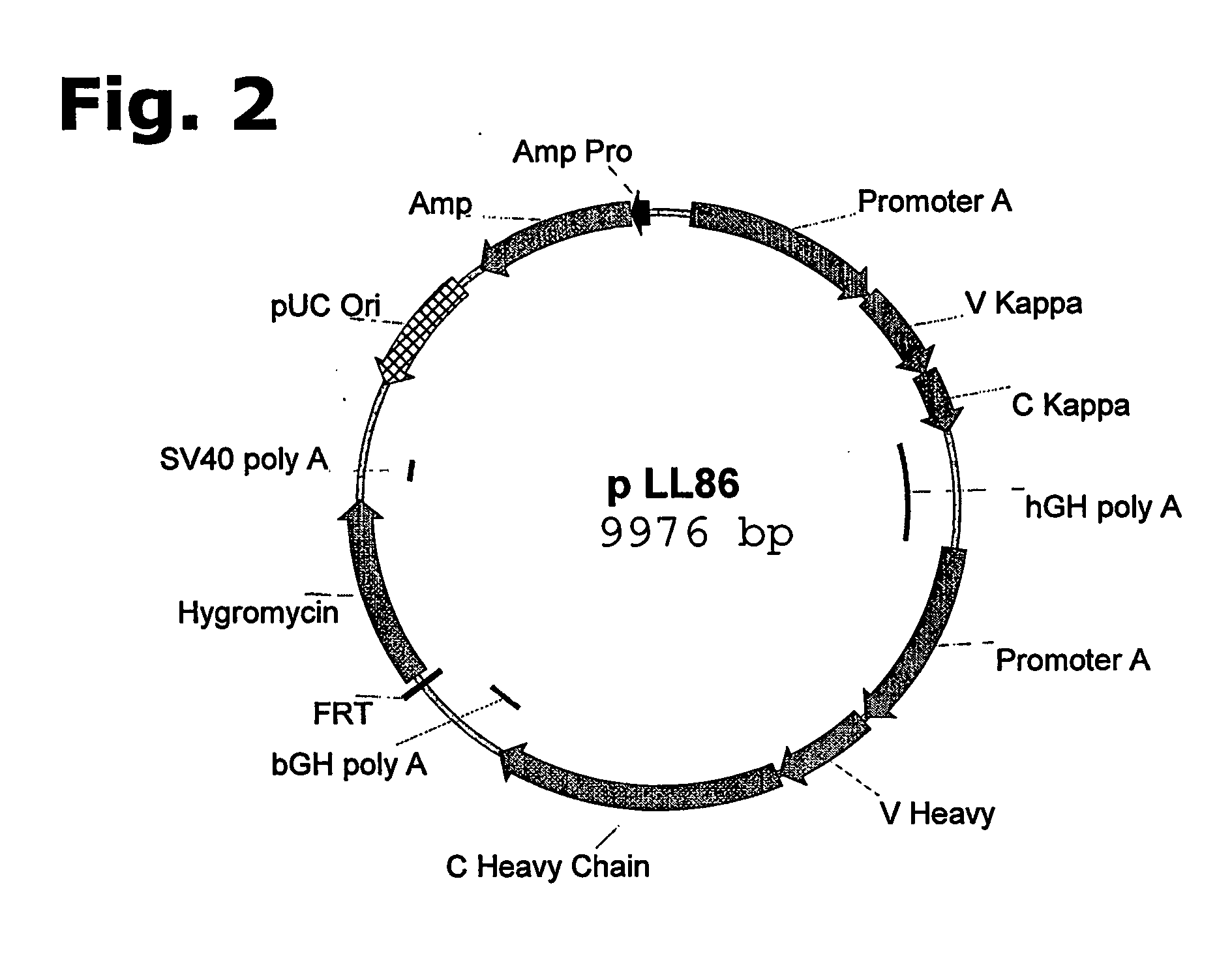
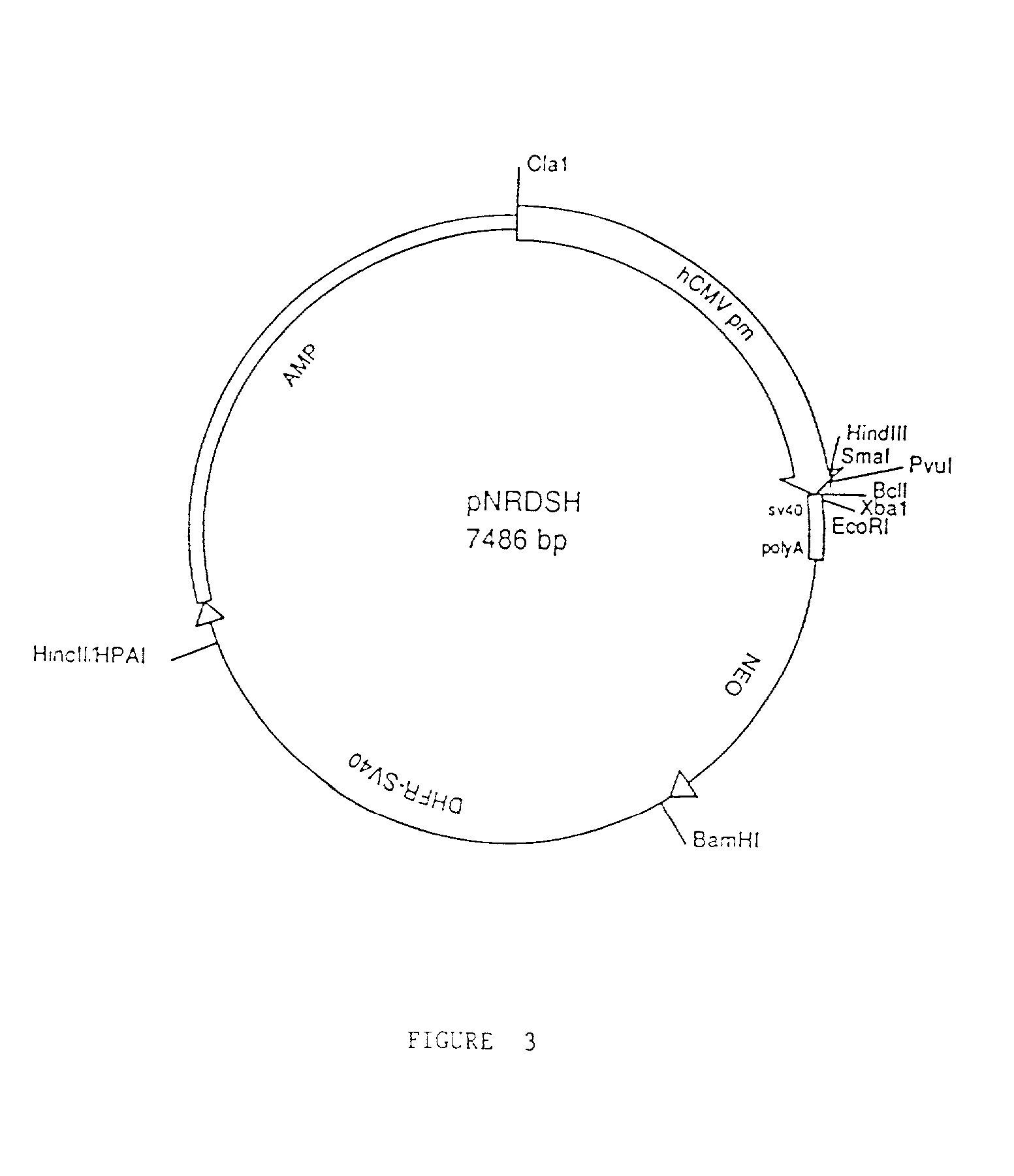
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
320 results about "Immunoglobulin Fc" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
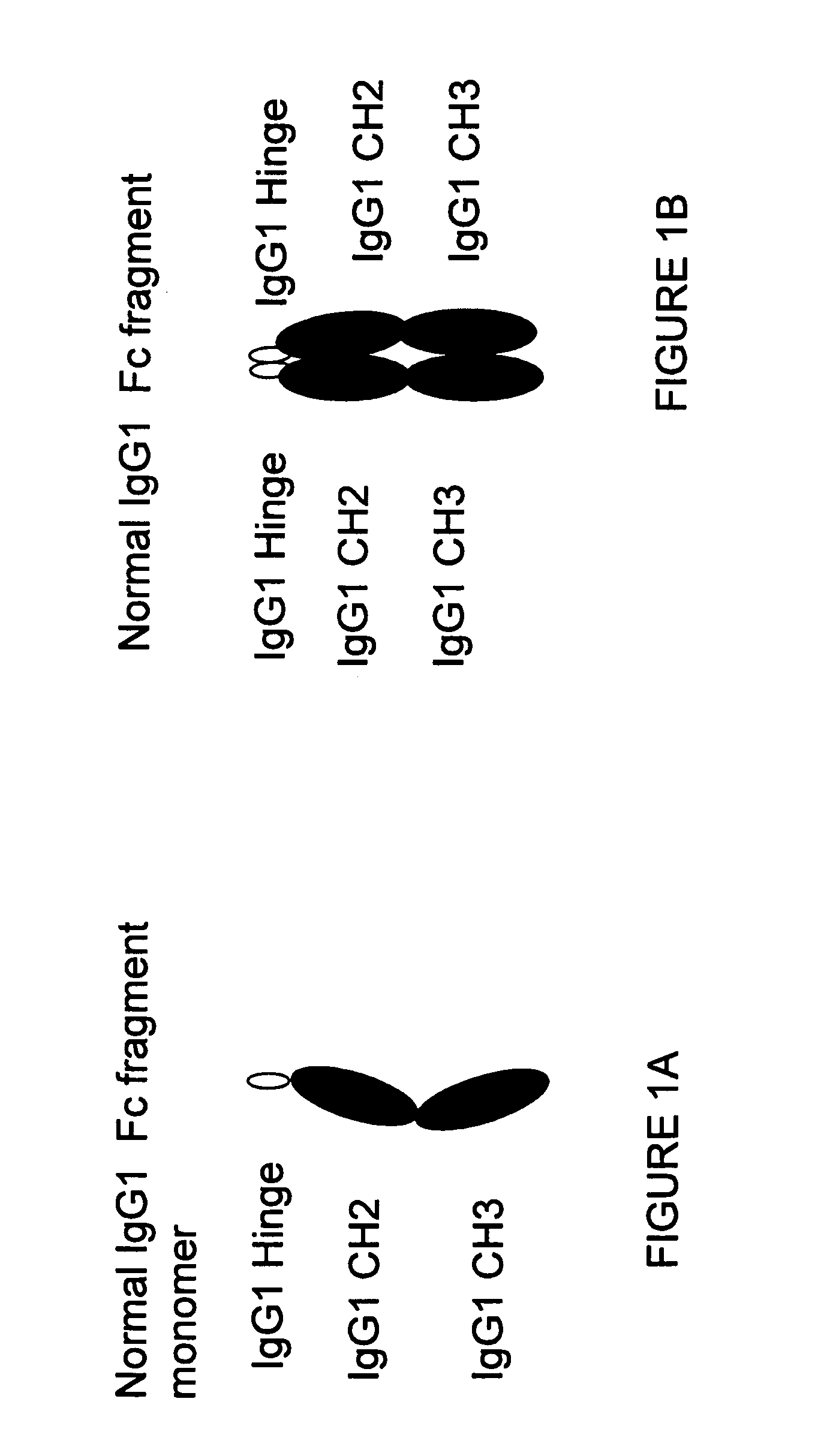
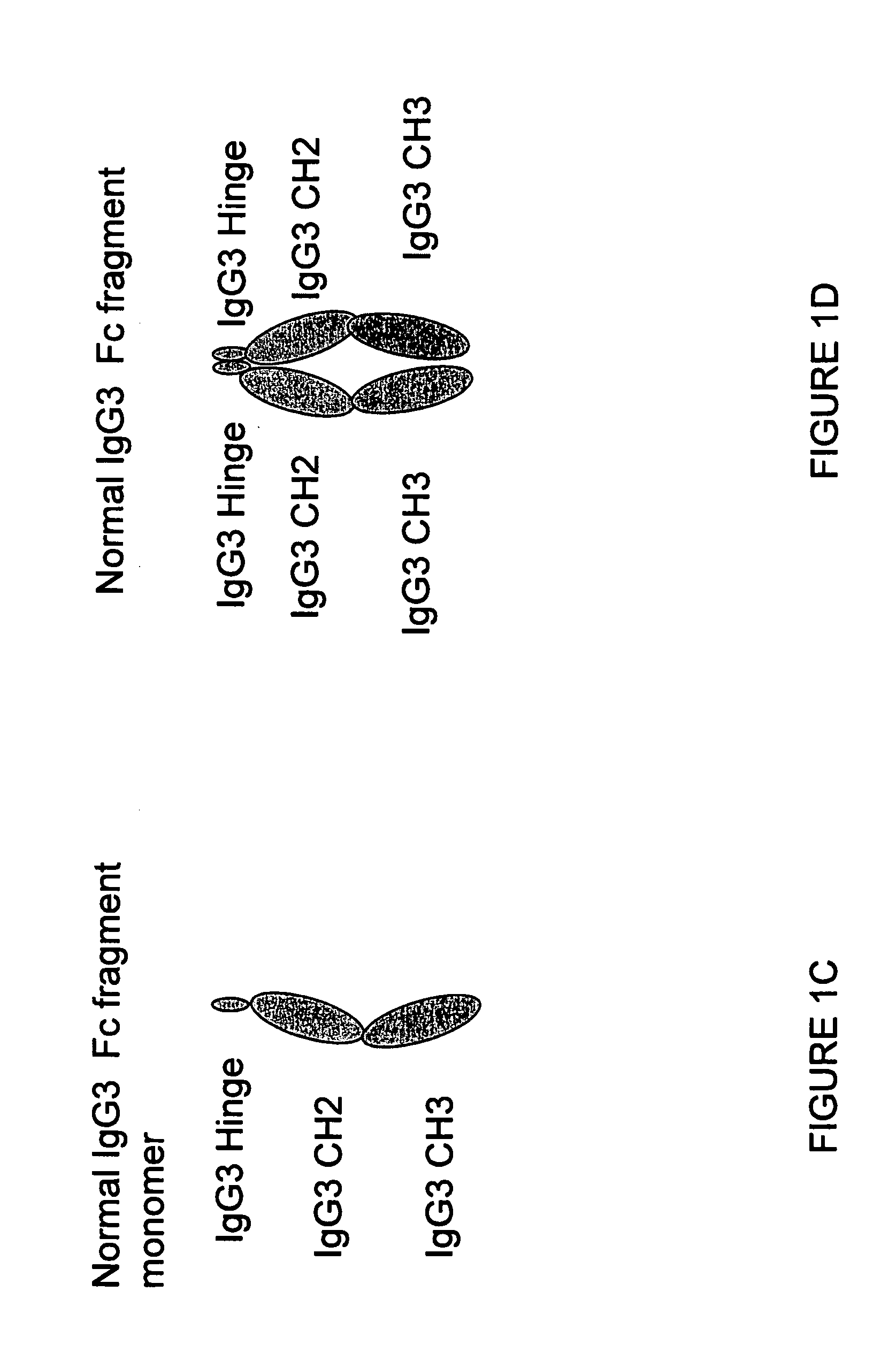
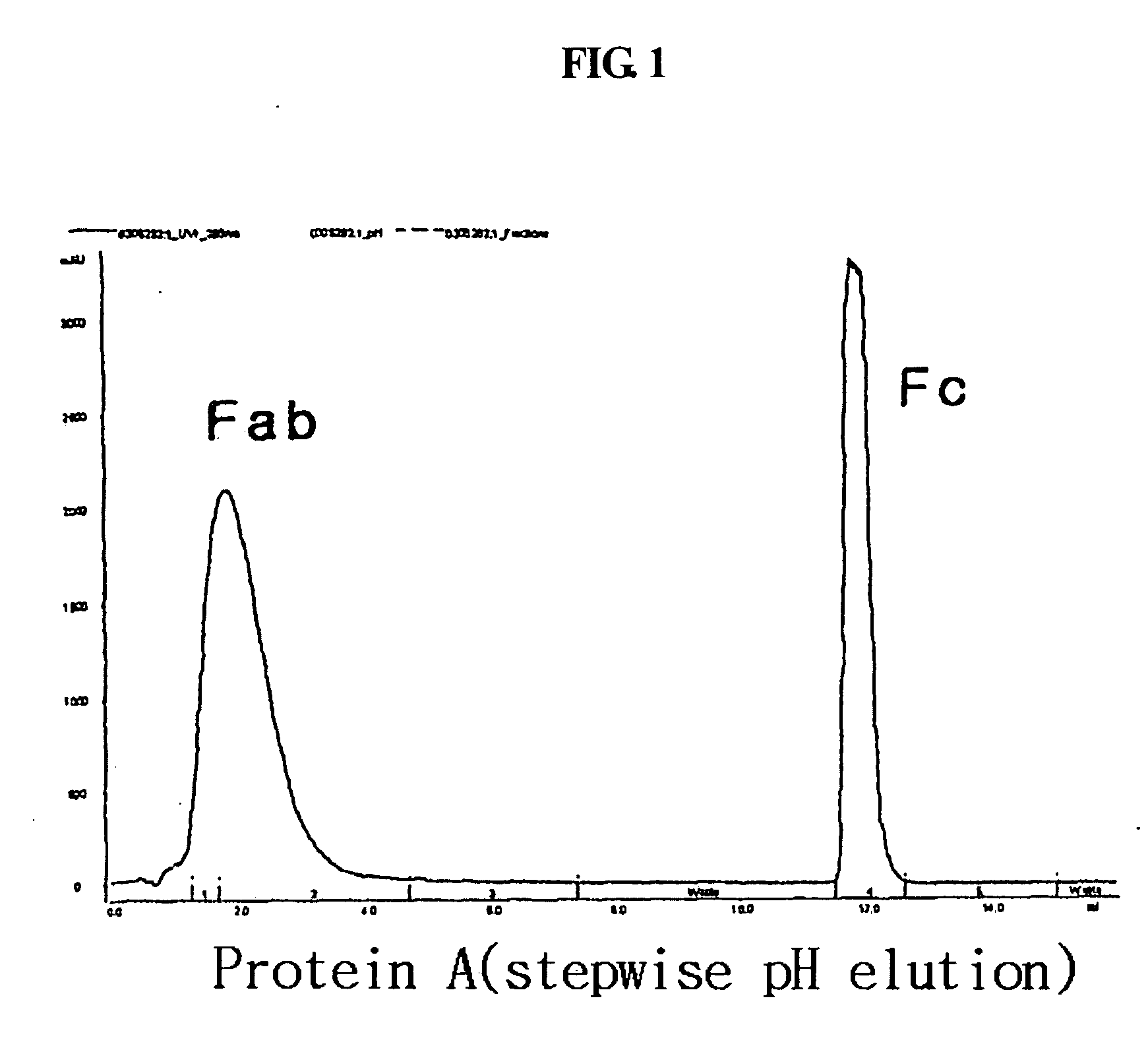
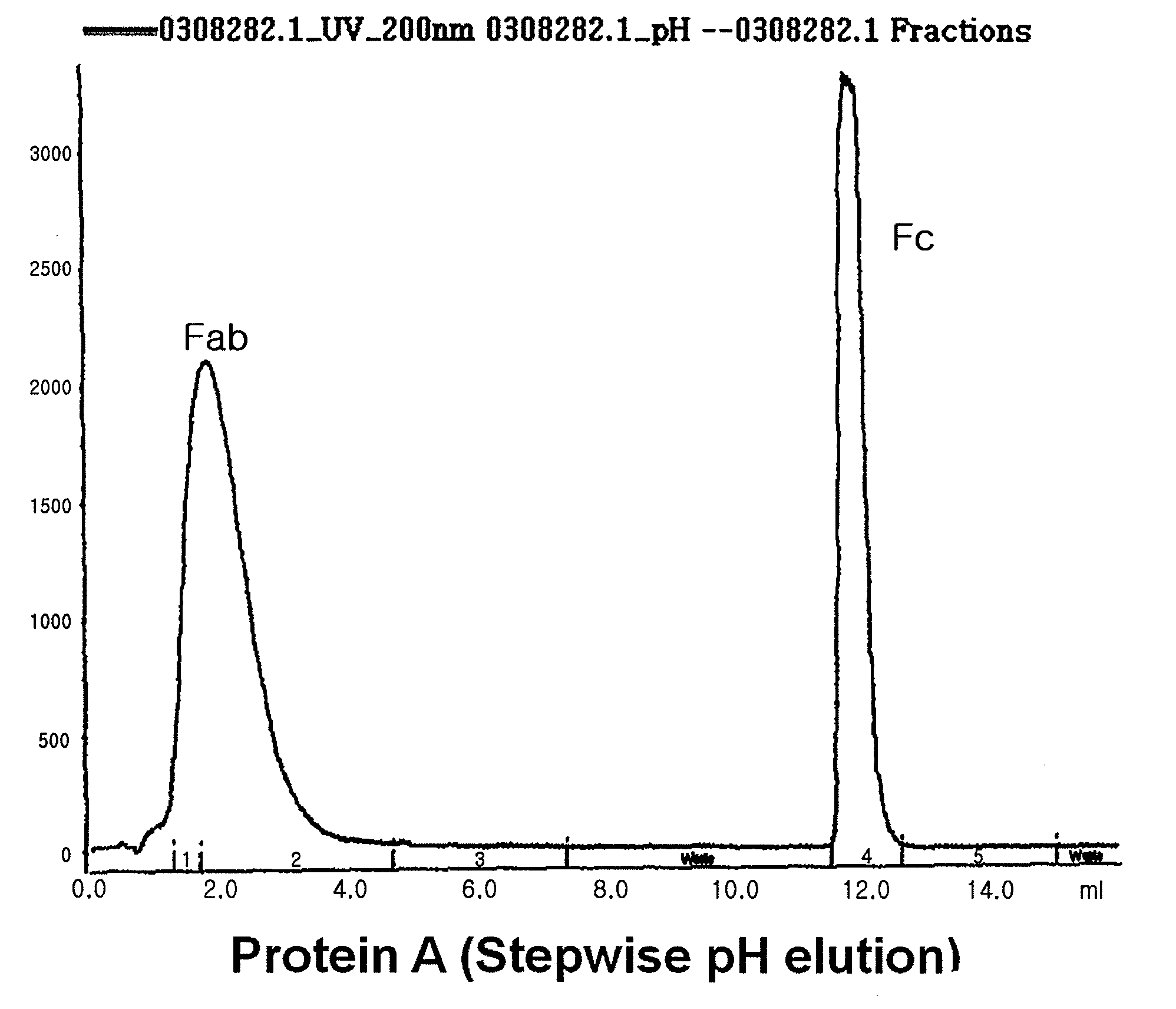
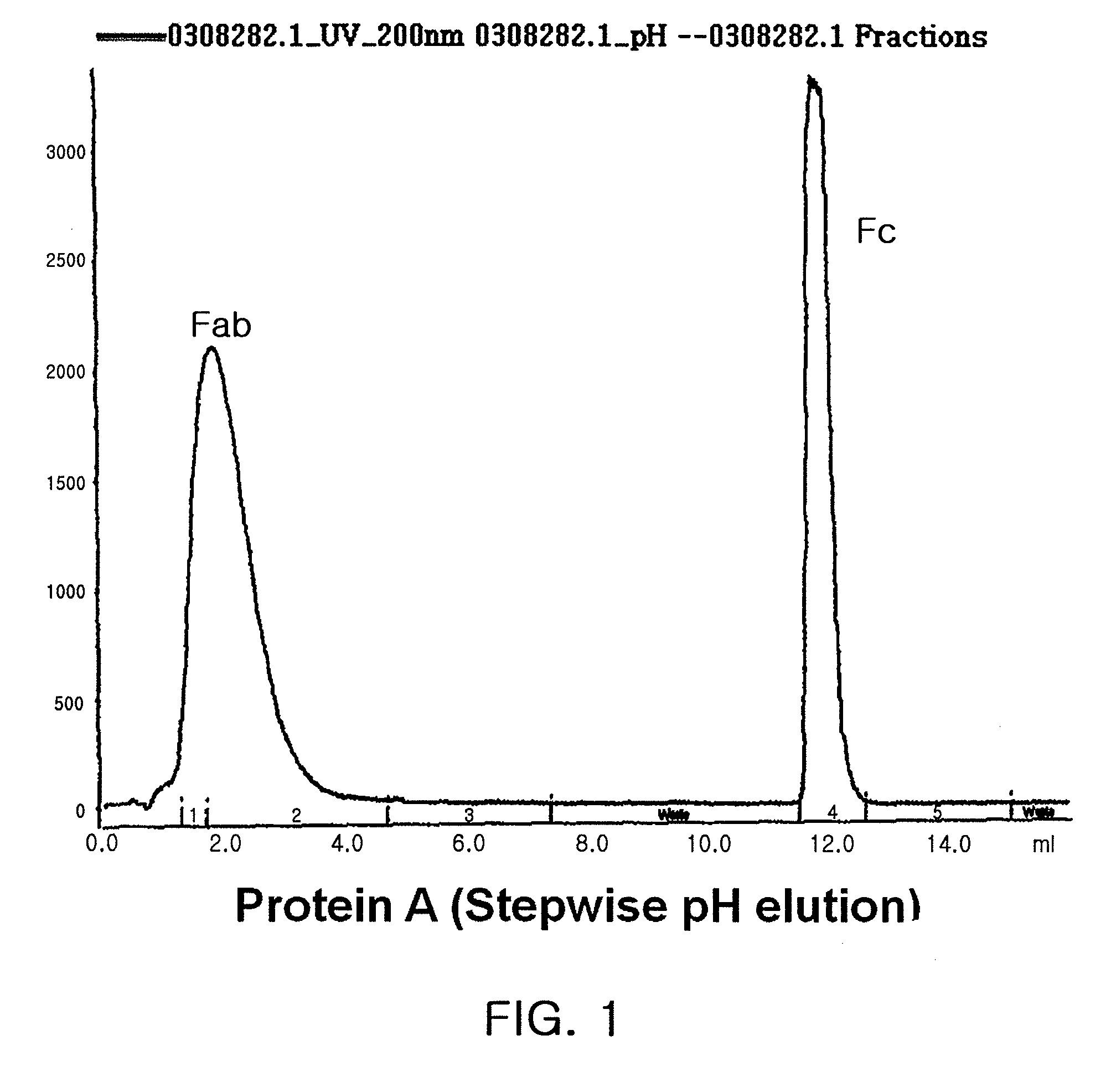
A protein product that results from the digestion of antibodies with papain and is comprised of the second and third constant regions of the antibody heavy chain.
Single-chain multiple antigen-binding molecule, its preparation and use
InactiveUS20050004352A1Reduce dissociationLess complexOrganic active ingredientsFungiAntigen bindingVariable domain
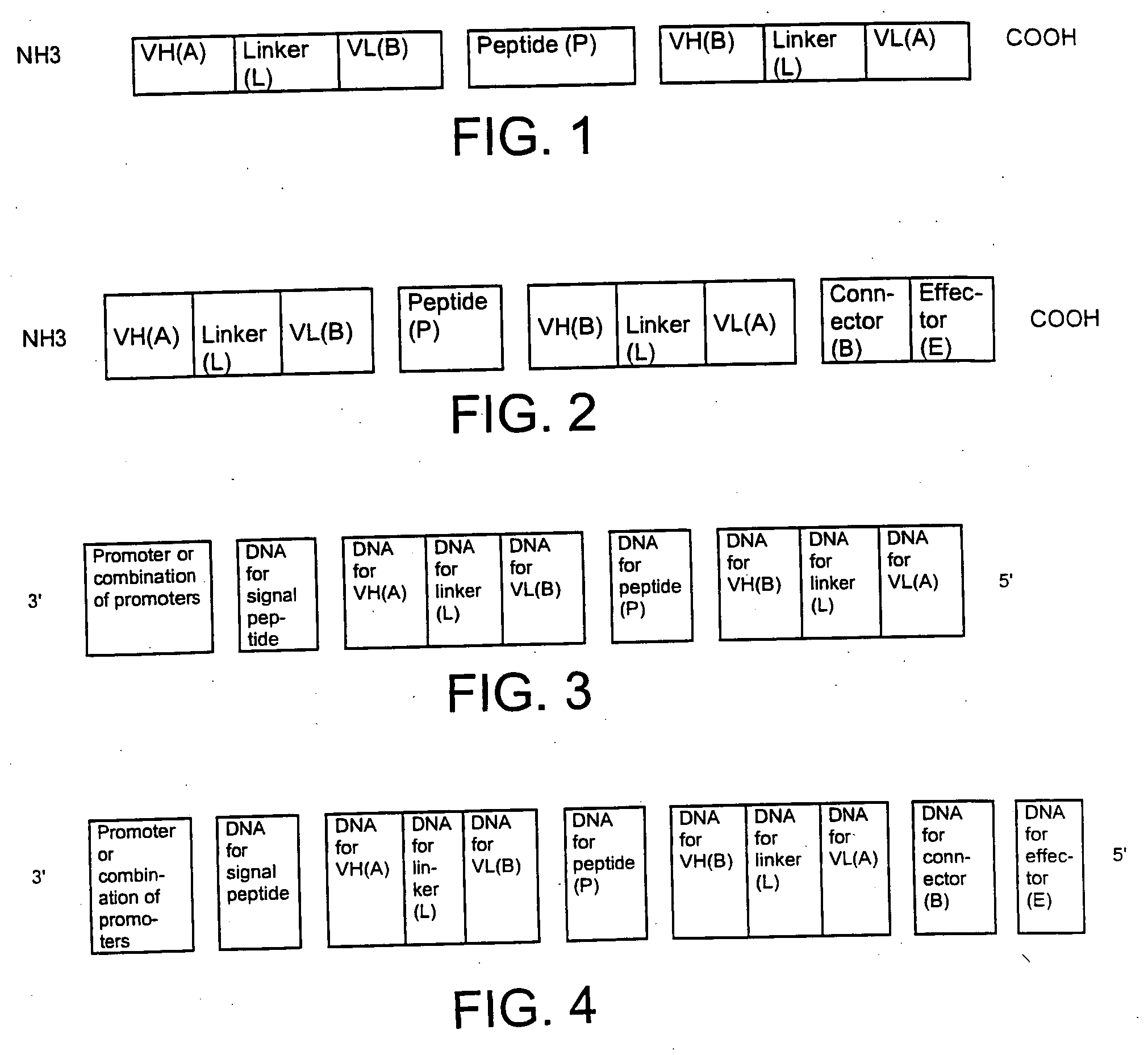
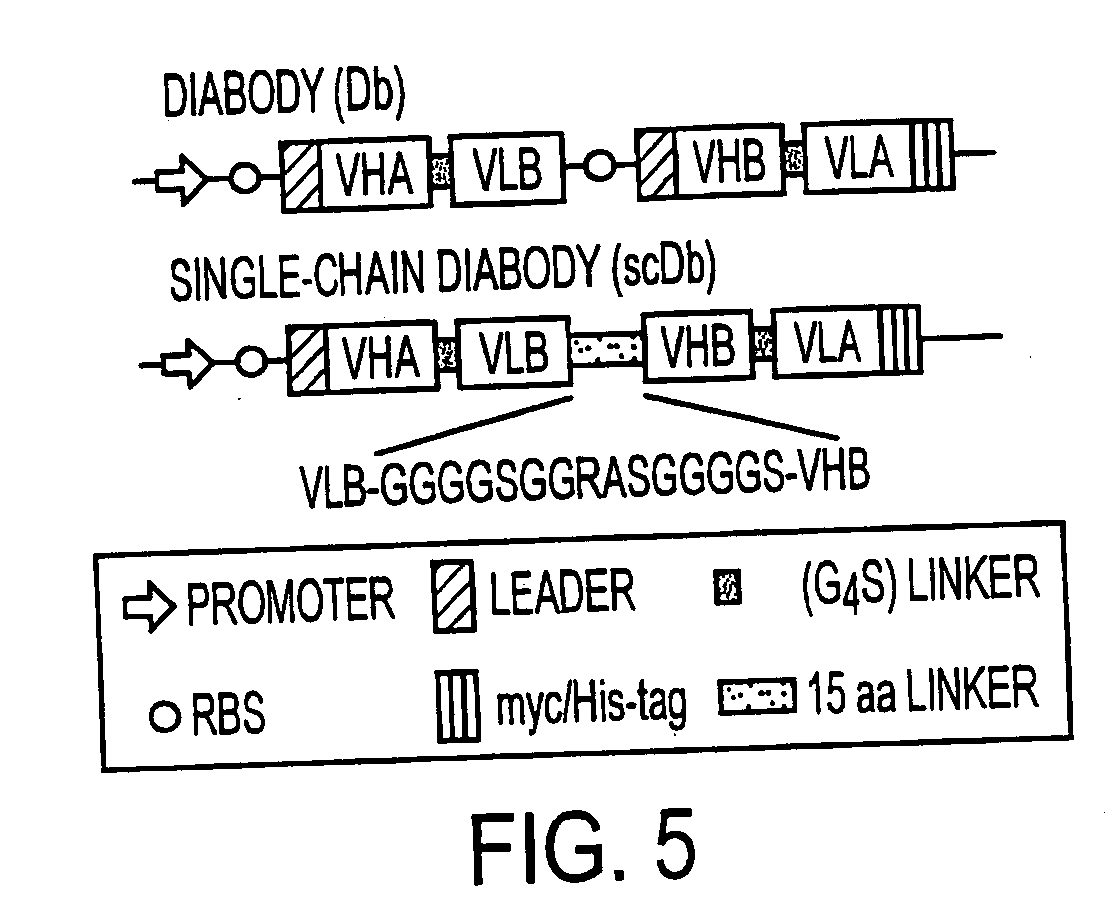
The present invention relates to a single-chain, multiple antigen-binding molecule with diverse variable domains of a heavy and of a light chain of an immunoglobulin, which are connected in the form of a VH-VL construct, which are in turn connected together via a peptide, and to the preparation and use thereof as pharmaceutical or diagnostic aid.
Owner:AFFITECH RESEARCH AS
Immunoglobulin constant region fc receptor binding agents
ActiveUS20100239633A1Wide applicationPathological conditionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseFc(alpha) receptor
IVIG replacement compounds are derived from recombinant and / or biochemical creation of immunologically active biomimetic(s). These replacement compounds are then screened in vitro to assess each replacements compound's efficiency at modulating immune function. Particular replacement compounds are selected for further in vivo validation and dosage / administration optimization. Finally, the replacement compounds are used to treat a wide range of diseases, including inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:GLIKNIK +1
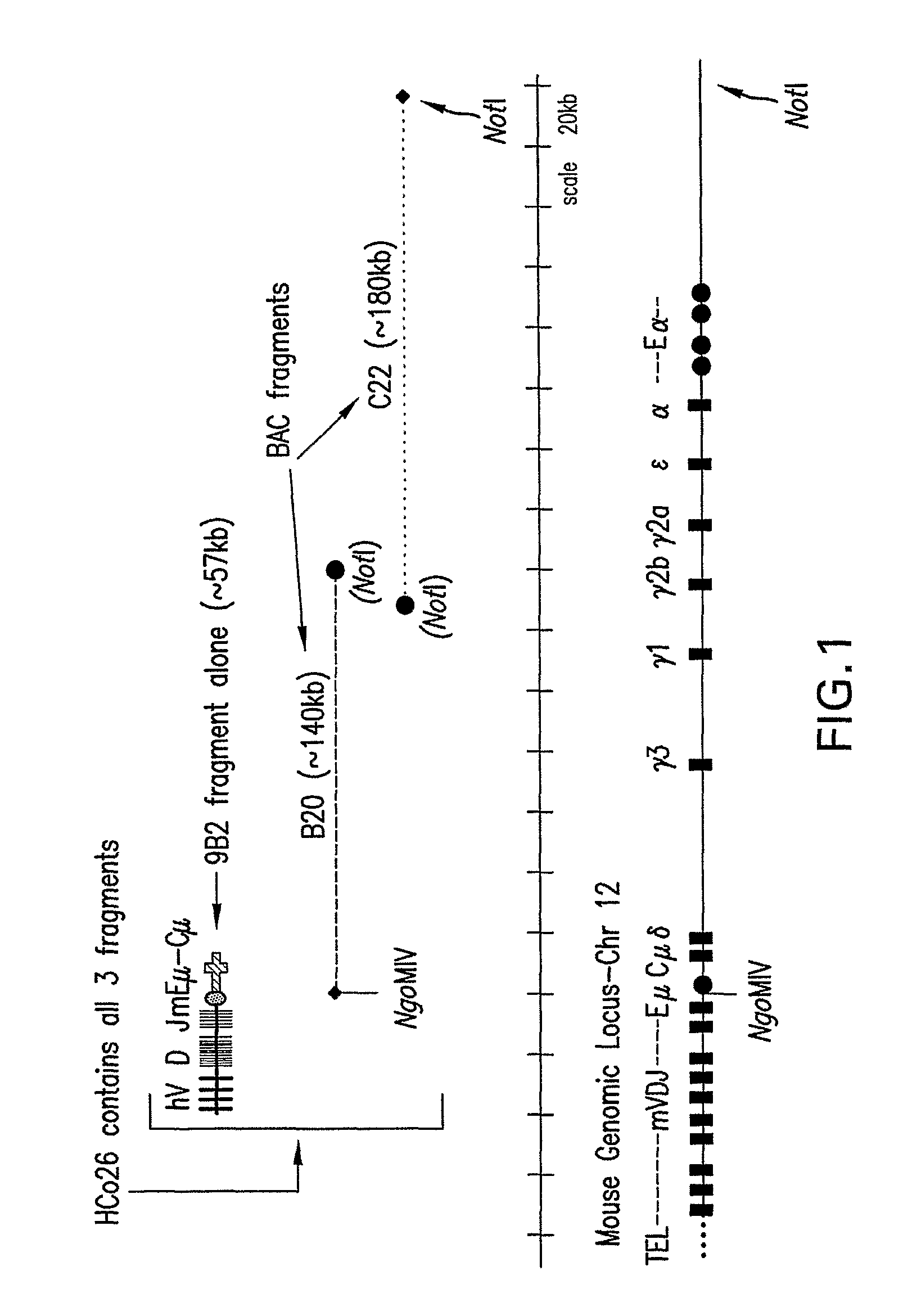
Transgenic animals expressing chimeric antibodies for use in preparing human antibodies
ActiveUS7910798B2Improved trafficking developmentStrengthen associationSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsTransgenesisIn vivo
The invention provides transgene constructs for expressing chimeric antibodies, and transgenic non-human host animals carrying such constructs, wherein the chimeric antibodies comprise human variable regions and constant regions of the non-human transgenic host animal. The presence of immunoglobulin constant regions of the host animal allows for generation of improved antibodies in such transgenic host animals. Subsequently, the chimeric antibodies can be readily converted to fully human antibodies using recombinant DNA techniques. Thus, the invention provides compositions and methods for generating human antibodies in which chimeric antibodies raised in vivo in transgenic mice are used as intermediates and then converted to fully human antibodies in vitro.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Monomeric immunoglobulin Fc domains
InactiveUS20060074225A1Increase contentReduce disulfide bondImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMonomerImmunoglobulin Fc
Design and production of immunoglobulin Fc domains including variants to stabilize their monomeric forms are provided.
Owner:XENCOR
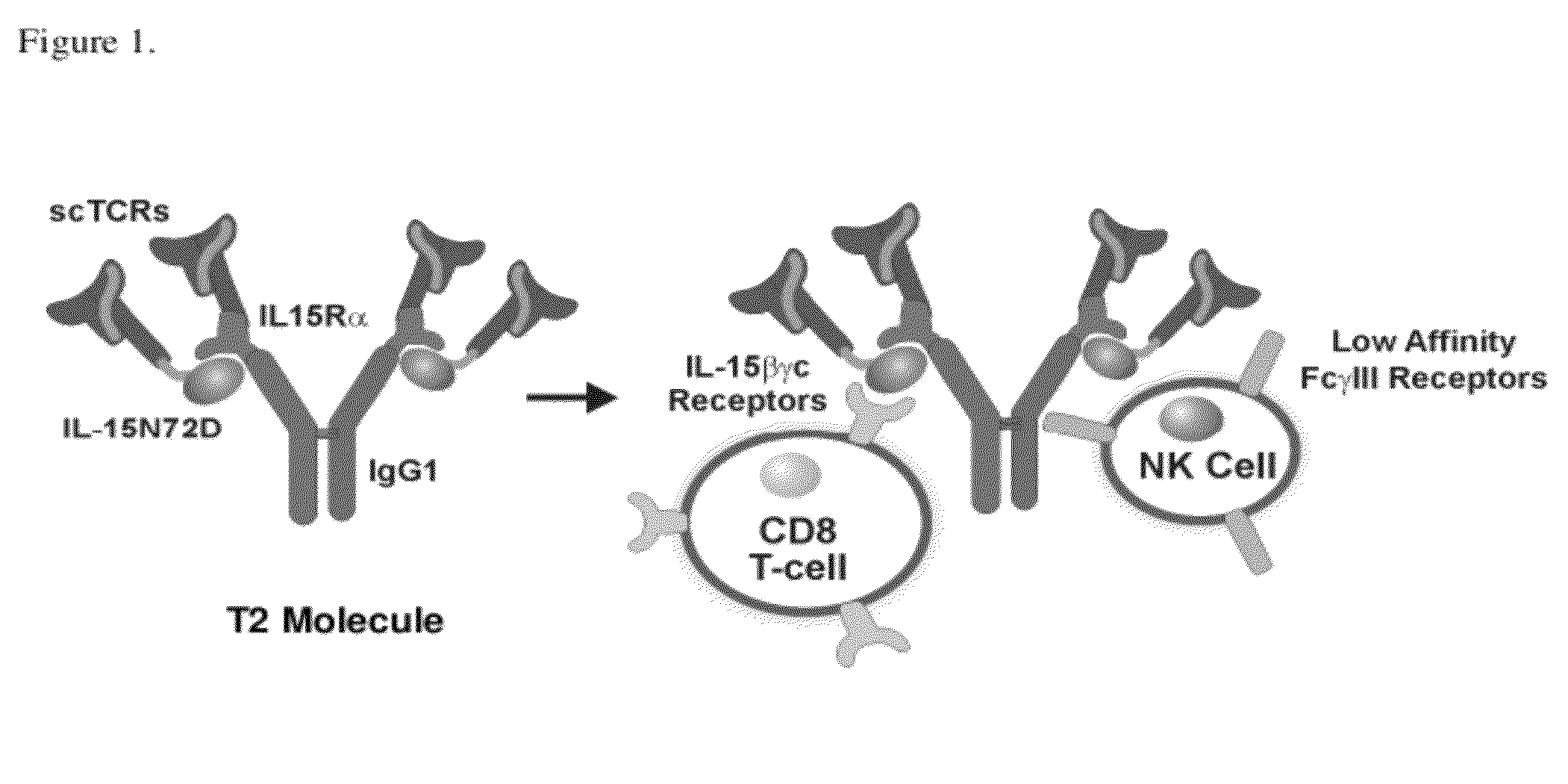
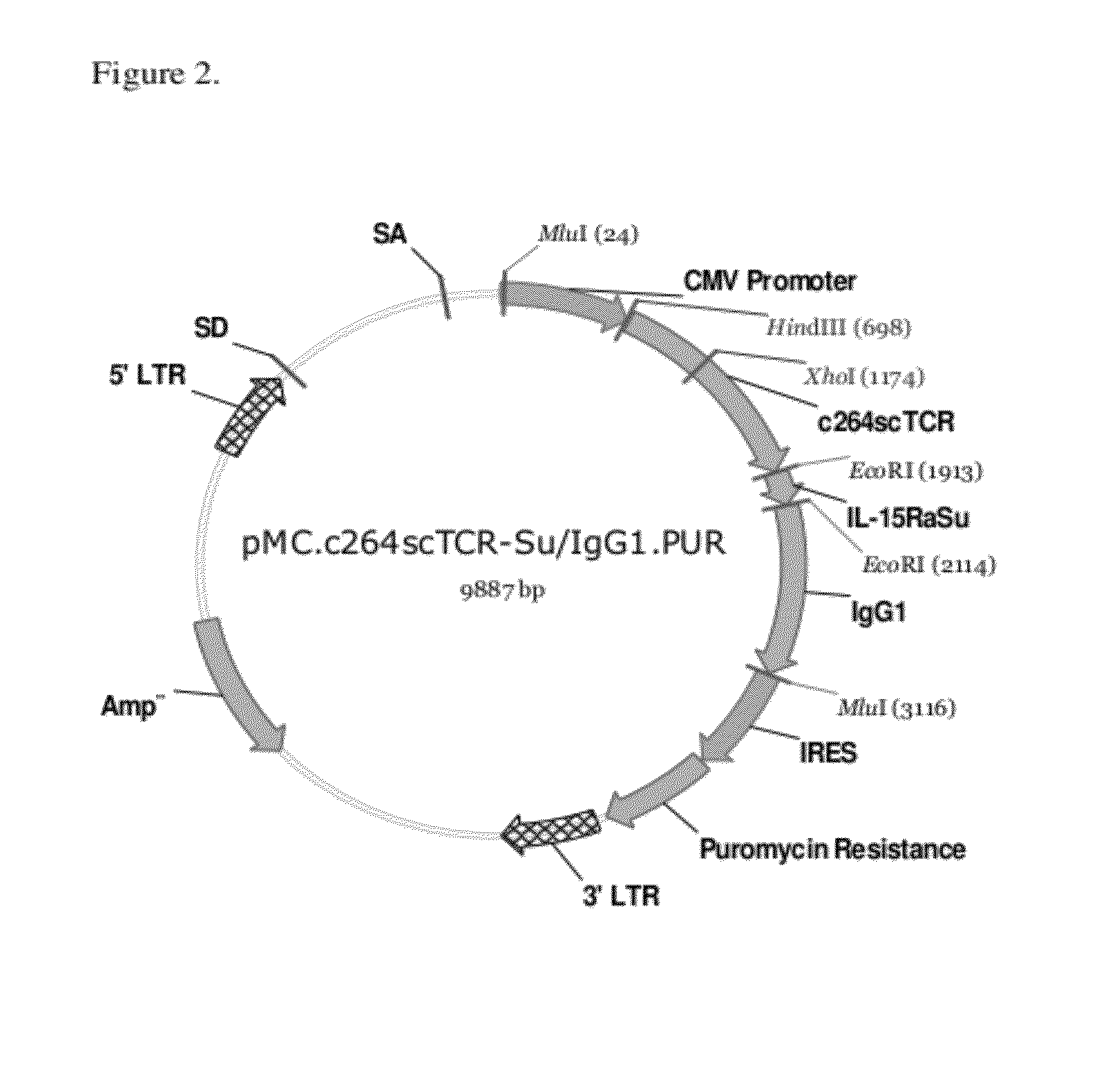
Multimeric IL-15 soluble fusion molecules and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS8507222B2High binding activityAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaInterleukin-15 receptorCoordination complex
The invention provides soluble fusion protein complexes having at least two soluble fusion proteins. The first fusion protein is a biologically active polypeptide covalently linked to an interleukin-15 (IL-15) polypeptide or a functional fragment thereof. The second fusion protein is a second biologically active polypeptide covalently linked to a soluble interleukin-15 receptor alpha (IL-15Rα) polypeptide or a functional fragment thereof. In the complexes of the invention, one or both of the first and second fusion proteins further includes an immunoglobulin Fc domain or a functional fragment thereof; and the first fusion protein binds to the soluble IL-15Rα domain of the second fusion protein to form a soluble fusion protein complex. The invention further provides methods for making and using the complexes of the invention.
Owner:ALTOR BIOSCI LLC
Pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin fc region as a carrier
ActiveUS20060275254A1Prolong the action timePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein targetHalf-life
Disclosed is a novel use of an immunoglobulin Fe fragment, and more particularly, a pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fe fragment as a carrier. The pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fe fragment as a carrier remarkably extends the serum half-life of a drug while maintaining the in vivo activity of the drug at relatively high levels. Also, when the drug is a polypeptide drug, the pharmaceutical composition has less risk of inducing immune responses compared to a fusion protein of the immunoglobulin Fe fragment and a target protein, and is thus useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Binding proteins comprising immunoglobulin hinge and fc regions having altered fc effector functions
Provided herein are binding proteins comprising one or more immunoglobulin Fc region hinge, CH2, and / or CH3 domain wherein one or more hinge and / or constant region CH2 and / or CH3 domain is modified to alter the binding protein's binding affinity and / or specificity for a cognate receptor (e.g., an Fc receptor) and / or to impart one or more new binding specificity(ies) to the hinge and / or constant region that the corresponding unmodified immunoglobulin does not possess (e.g., affinity for distinct class of cognate receptor distinct from the class of cognate receptor to which the unmodified binding protein specifically binds). Binding proteins according to the present invention include, for example, modified antibodies, antibody fragments, recombinant binding proteins, and molecularly engineered binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins, including small modular immunopharmaceutical products (SMIP™ products).
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Methods of reducing eosinophil levels
The present invention relates to a method of reducing the numbers of eosinophils in a human subject comprising administration to a subject an IL-5R binding molecule that comprises (a) a region that specifically binds to the IL-5R and (b) an immunoglobulin Fc region. In a specific embodiment, a method of the invention reduces the number of eosinophils in blood, bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract (e g, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and colon), or lung.
Owner:BIOWA +1
Stable antibody compositions and methods of stabilizing same
InactiveUS20100172862A1Improve propertiesMaintain stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderFractionationAntigen binding
The invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting fractionation of immunoglobulins comprising a lambda light chain based on the observation that iron, in the presence of histidine, results in increased fragmentation of a recombinant fully human IgG molecule containing a lambda light chain due to cleavage in the hinge region. The invention further provides an aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising an antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, that binds the p40 subunit of IL-12 / IL-23 and a buffer system comprising histidine, wherein the formulation has enhanced stability, including enhanced resistance to fragmentation.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
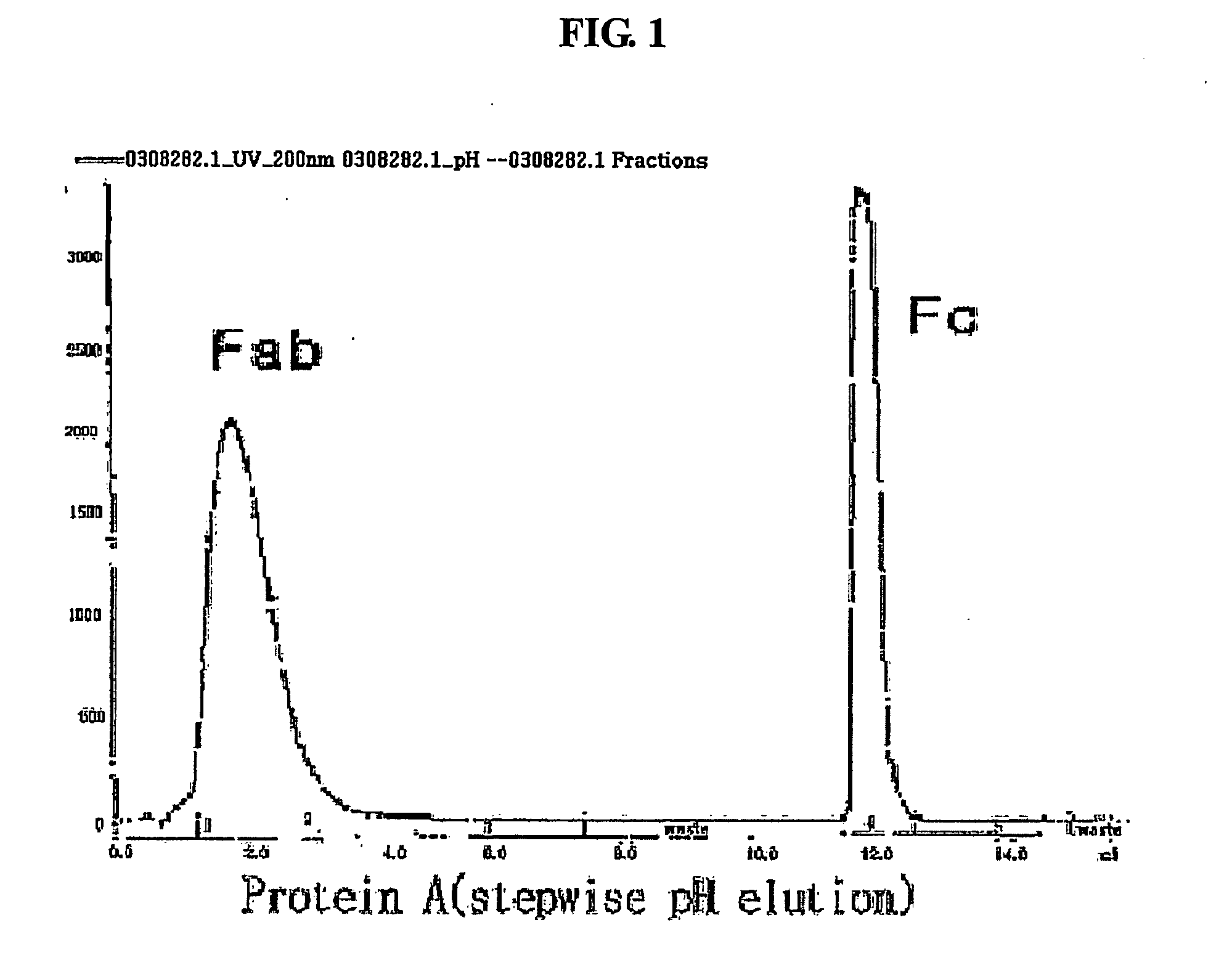
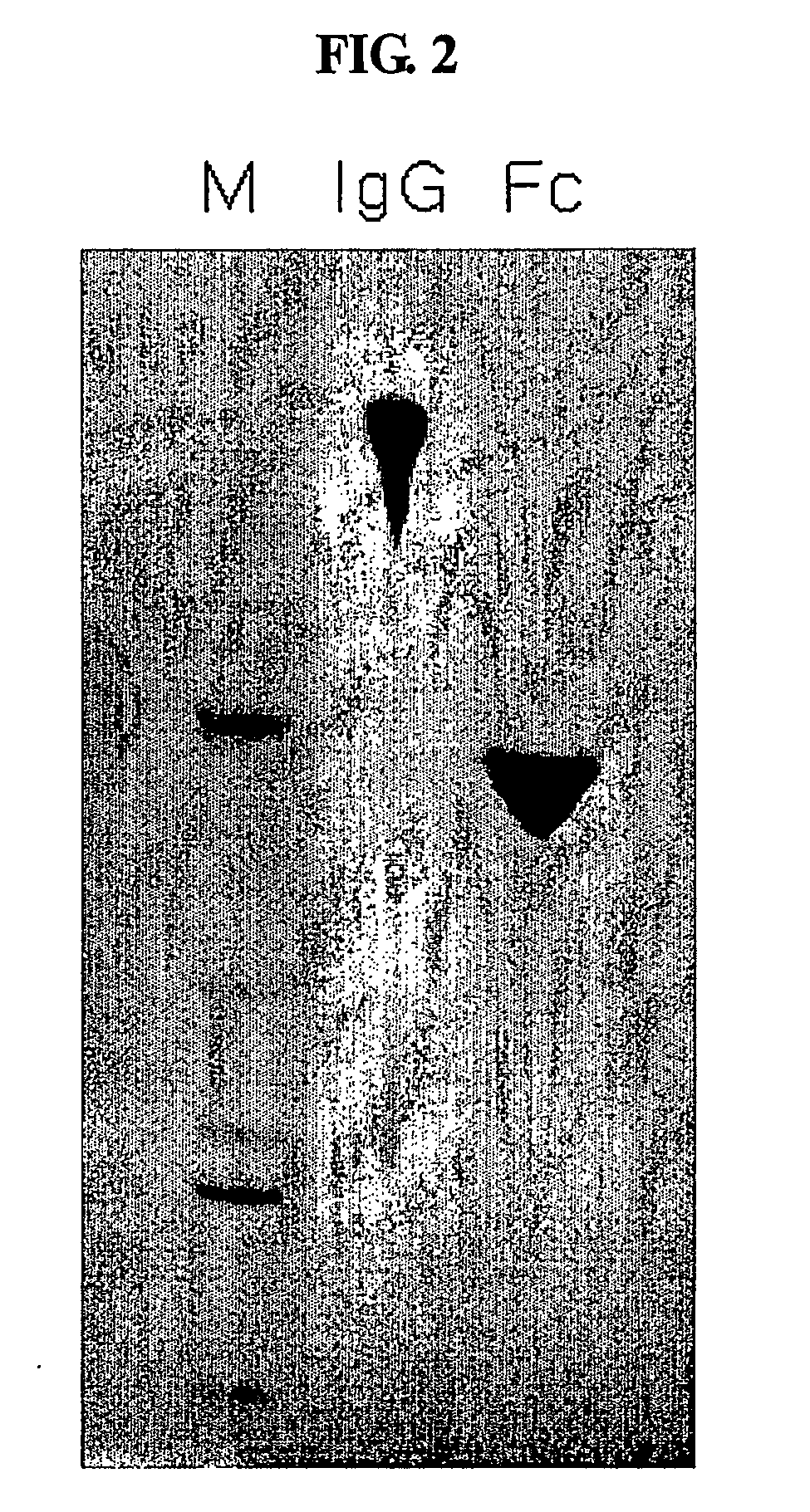
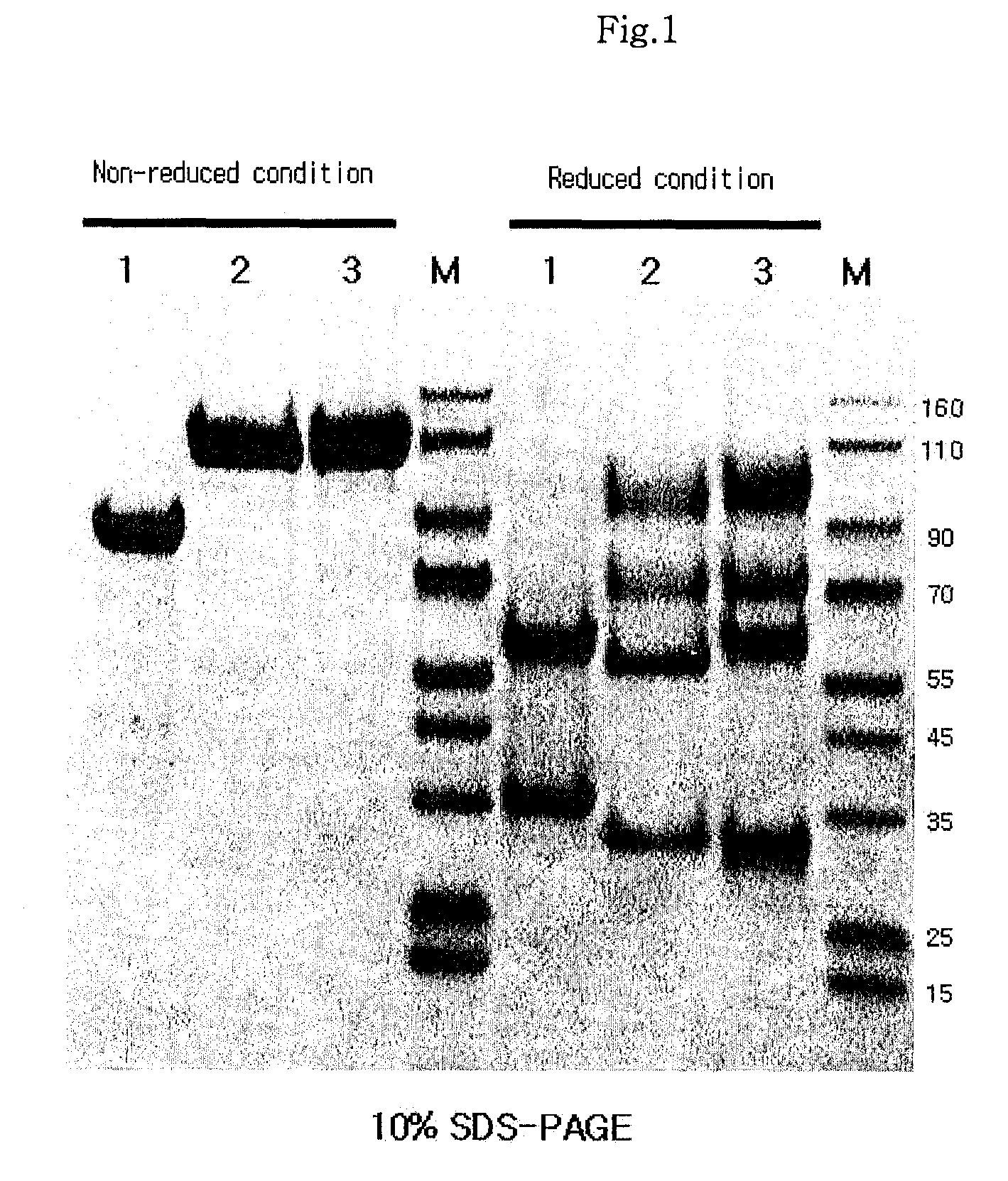
Protein complex using an immunoglobulin fragment and method for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20060269553A1Improve stabilityExtended durationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunological disordersHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
Disclosed are a protein conjugate with improved in vivo duration and stability and the use thereof. The protein conjugate includes a physiologically active polypeptide, a non-peptide polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc fragment. Since the three components are covalently linked, the protein conjugate has extended in vivo duration and enhanced stability for the physiologically active polypeptide. The protein conjugate maintains the in vivo activity at relatively high levels and remarkably increases the serum half-life for the physiologically active polypeptide, with less risk of inducing undesirable immune responses. Thus, the protein conjugate is useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
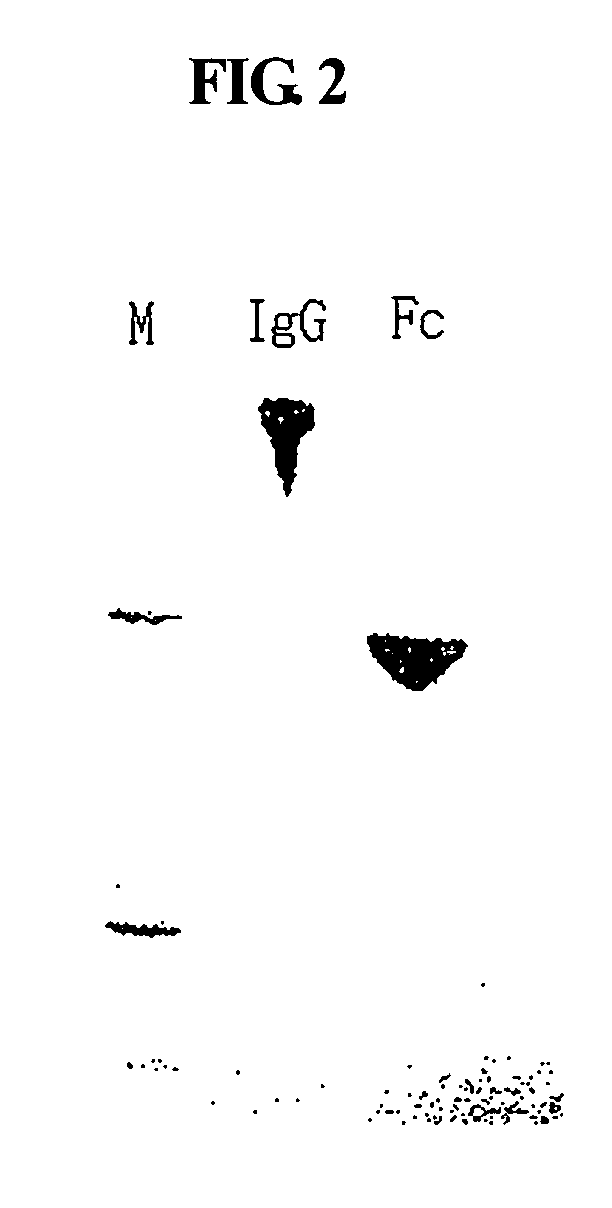
Immunoglobulin Fc fragment modified by non-peptide polymer and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
ActiveUS8124094B2Enhances in vivo duration and stabilityReduced activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiviralsHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
Disclosed are an Fc fragment modified by a non-peptide polymer, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the Fc fragment modified by the non-peptide polymer as a carrier, a complex of the Fc fragment and a drug via a linker and a pharmaceutical composition comprising such a complex. The Fc fragment modified by a non-peptide peptide according to the present invention lacks immunogenicity and effector functions. Due to these properties, the Fc fragment maintains the in vivo activity of a drug conjugated thereto in high levels, remarkably increases the serum half-life of the drug, and remarkably reduces the risk of inducing immune responses.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Immunoglobulin fc variants
ActiveCN104039831AProlong half-life in vivoReduce application frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin Fc variants having an increased binding affinity for FcRn, which is characterized by including one or more amino acid modifications selected from the group consisting of 307S, 308F, 380S, 380A, 428L, 429K, 430S, 433K and 434S (this numbering is according to the EU index) in the constant region of a native immunoglobulin Fc fragment. Owing to the high binding affinity for FcRn, the immunoglobulin Fc variants according to the present invention show more prolonged in vivo half-life, and thus can be used for the preparation of a long-acting formulation of protein drugs.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
An insulinotropic complex using an immunoglobulin fragment
ActiveUS20100105877A1Improve efficacyProlong lifePeptide/protein ingredientsVasoactive intestinal peptidePeptide drugHalf-life
The present invention relates to an insulinotropic peptide conjugate having improved in-vivo duration of efficacy and stability, comprising an insulinotropic peptide, a non-peptide polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc region, which are covalently linked to each other, and a use of the same. The insulinotropic peptide conjugate of the present invention has the in-vivo activity which is maintained relatively high, and has remarkably increased blood half-life, and thus it can be desirably employed in the development of long acting formulations of various peptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
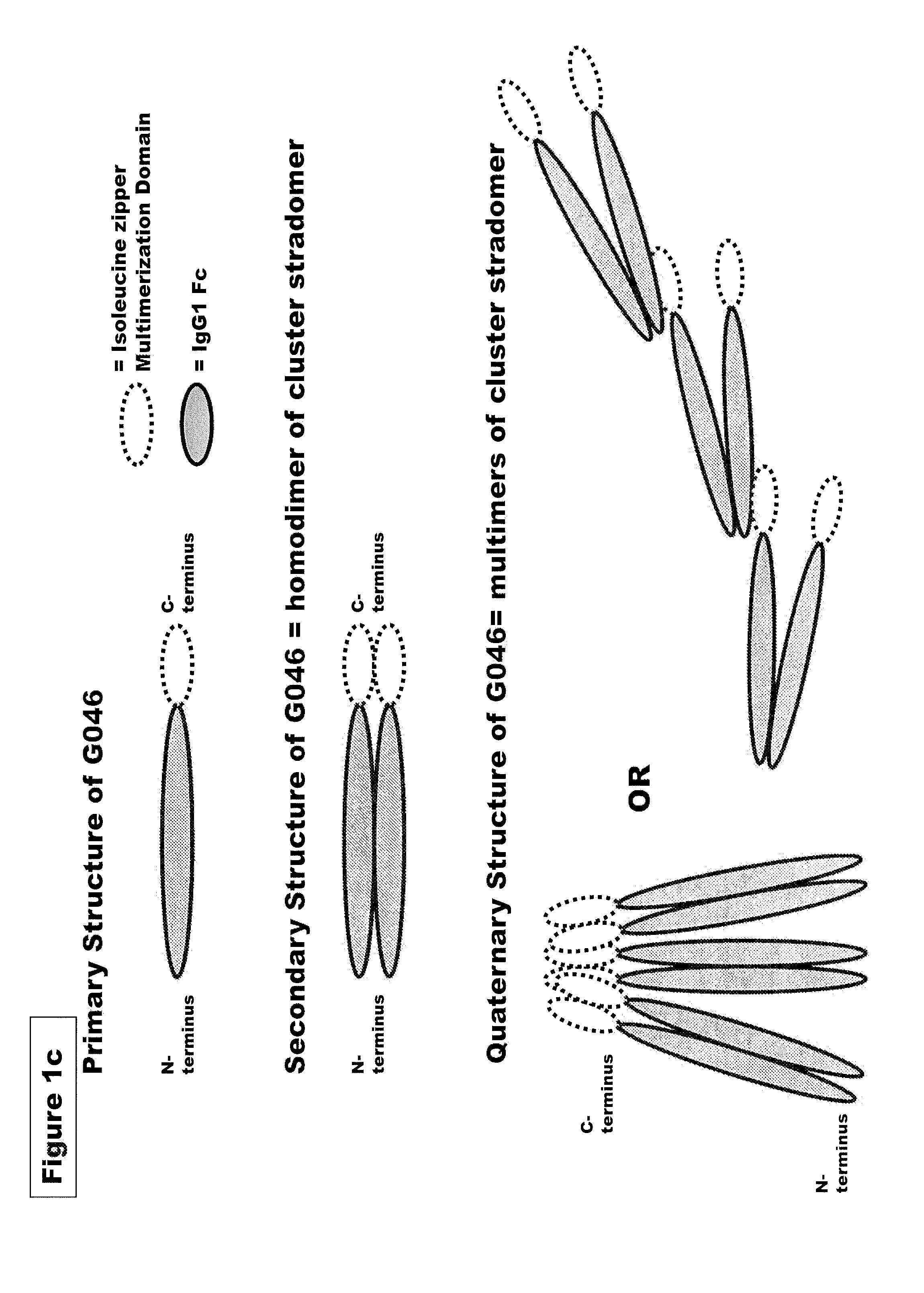
FUSION PROTEINS OF NATURAL HUMAN PROTEIN FRAGMENTS TO CREATE ORDERLY MULTIMERIZED IMMUNOGLOBULIN Fc COMPOSITIONS
InactiveUS20130156765A1High protein loadGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseHuman proteins
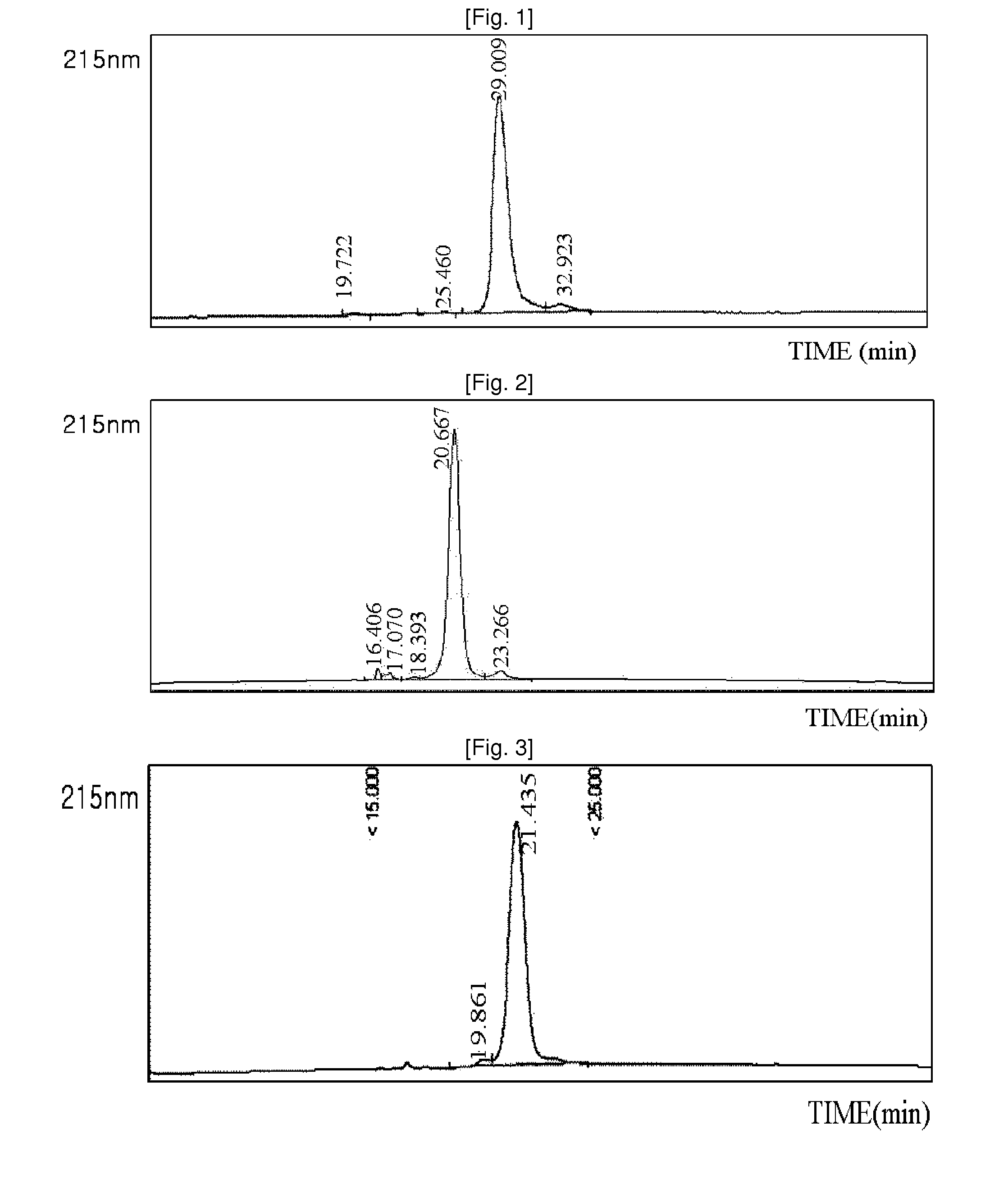
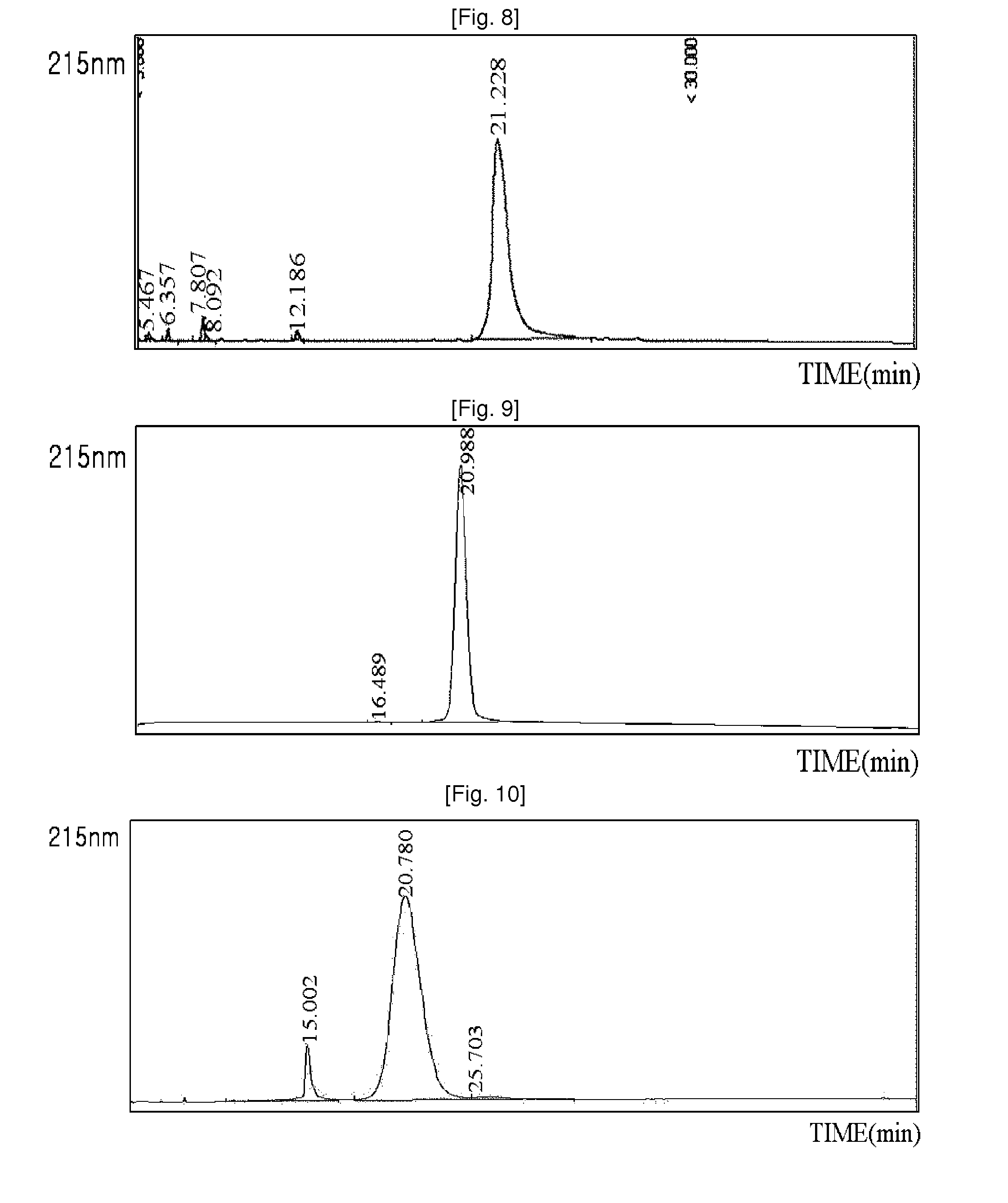
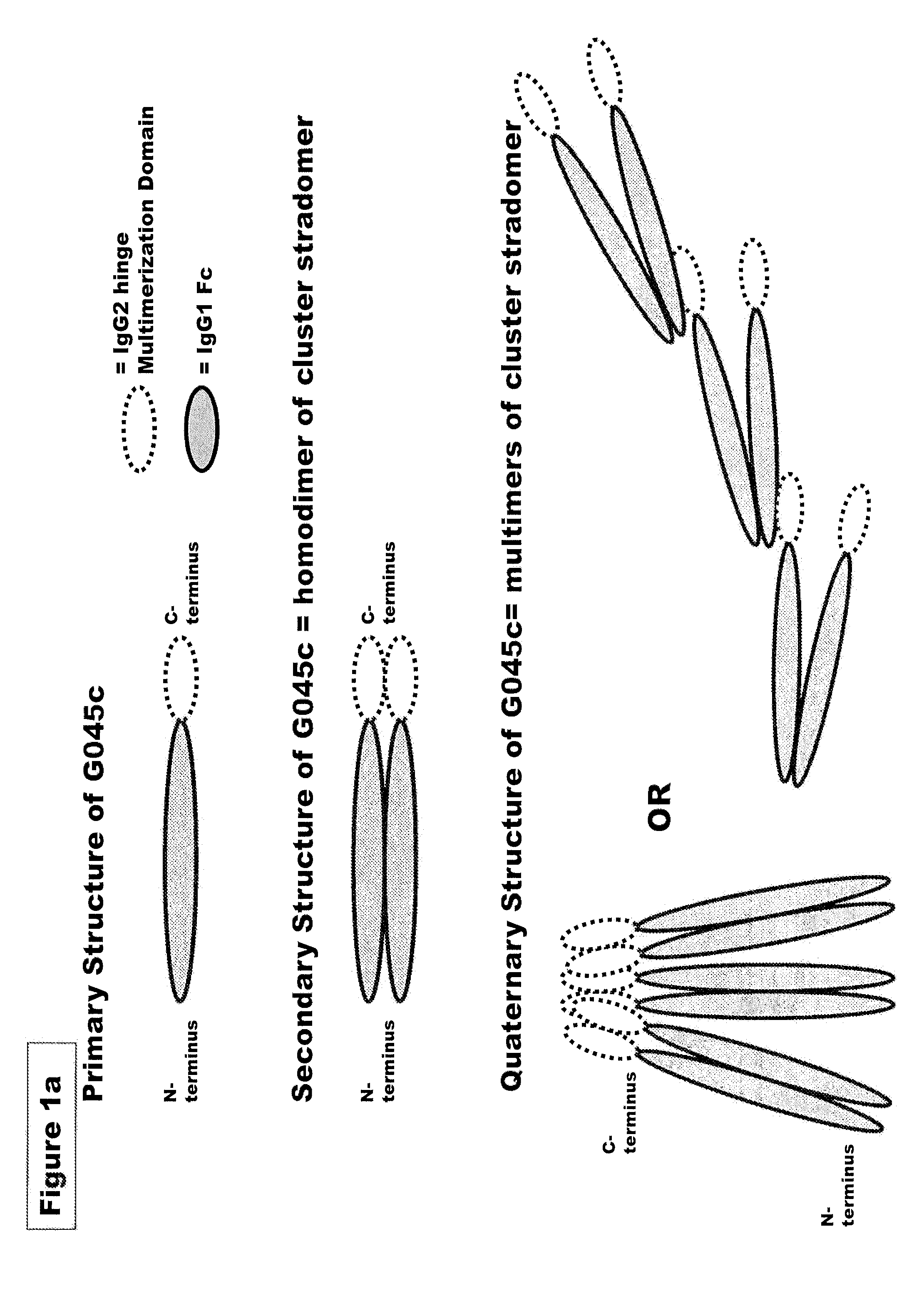
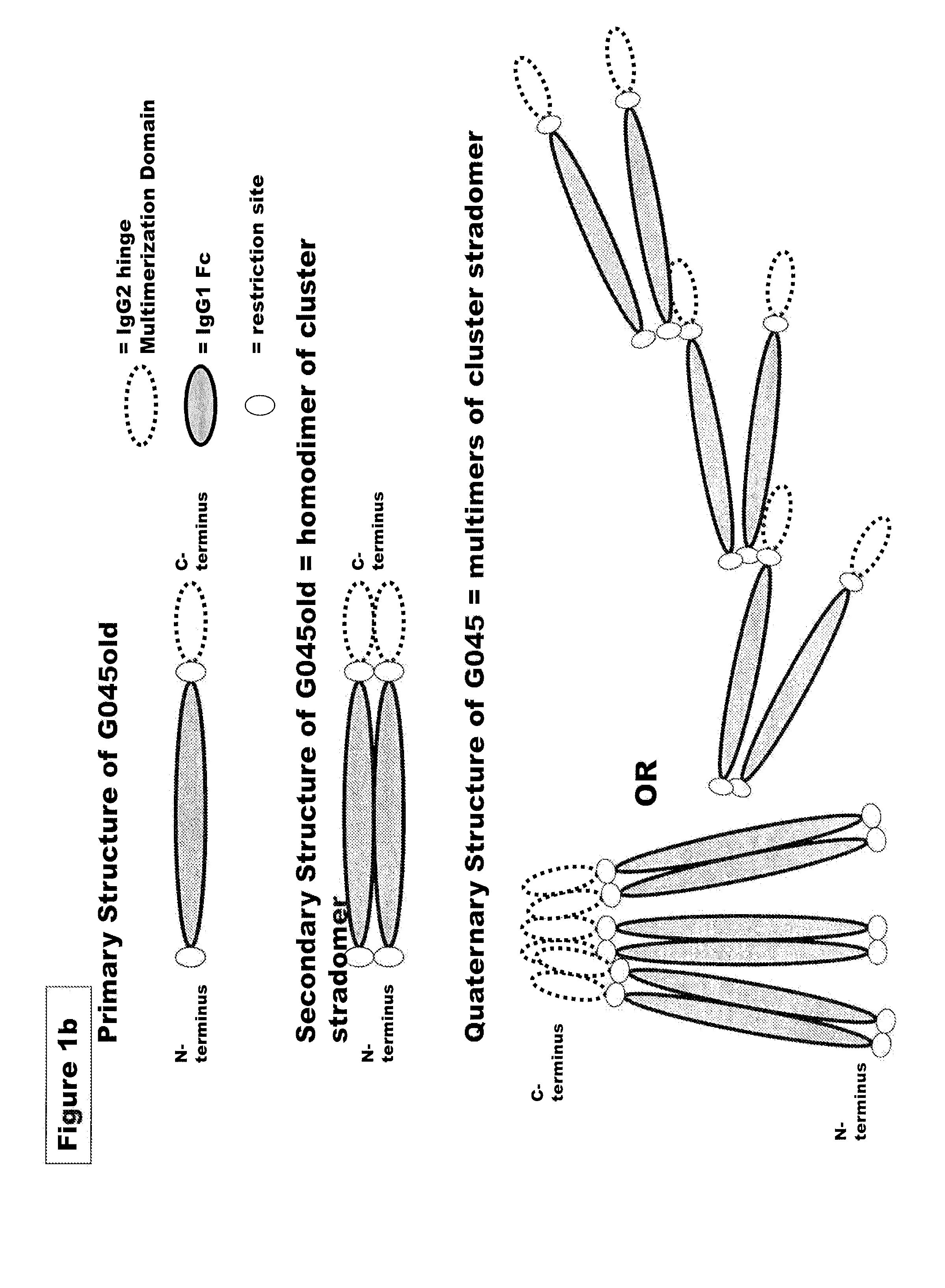
The current invention involves a series of fully recombinant multimerized forms of immunoglobulin Fc which thereby present polyvalent immunoglobulin Fc to immune cell receptors. The fusion proteins exist as both homodimeric and highly ordered multimeric fractions, termed stradomers. In comparison to the homodimeric fraction, purified multimeric stradomers have higher affinity and avidity for Fc Rs with slower dissociation and are useful in the treatment and prevention of disease. The current invention demonstrates that directly linking IgG1 Fc regions to multimerization domains leads to enhanced multimerization and biological activity.
Owner:GLIKNIK
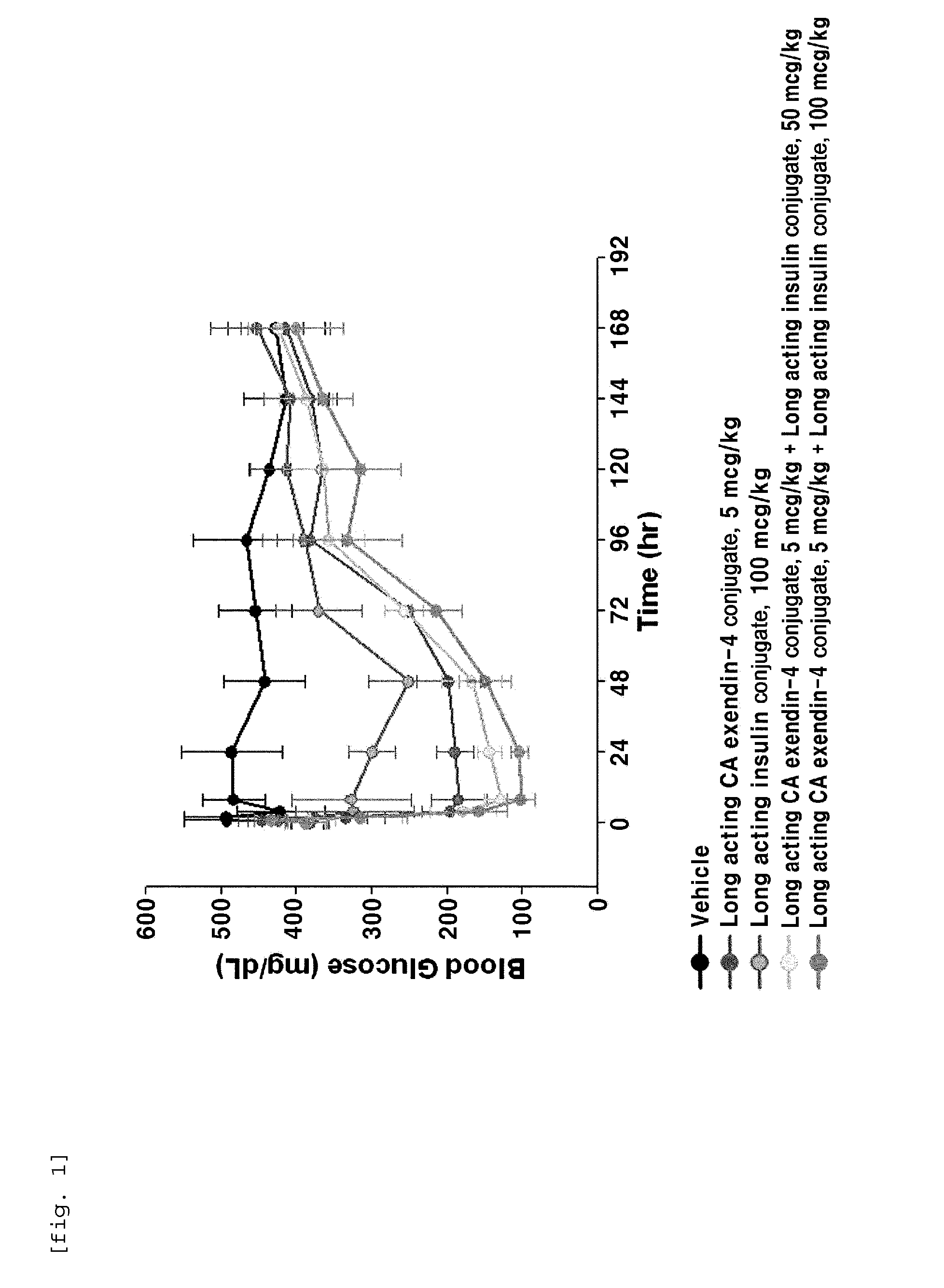
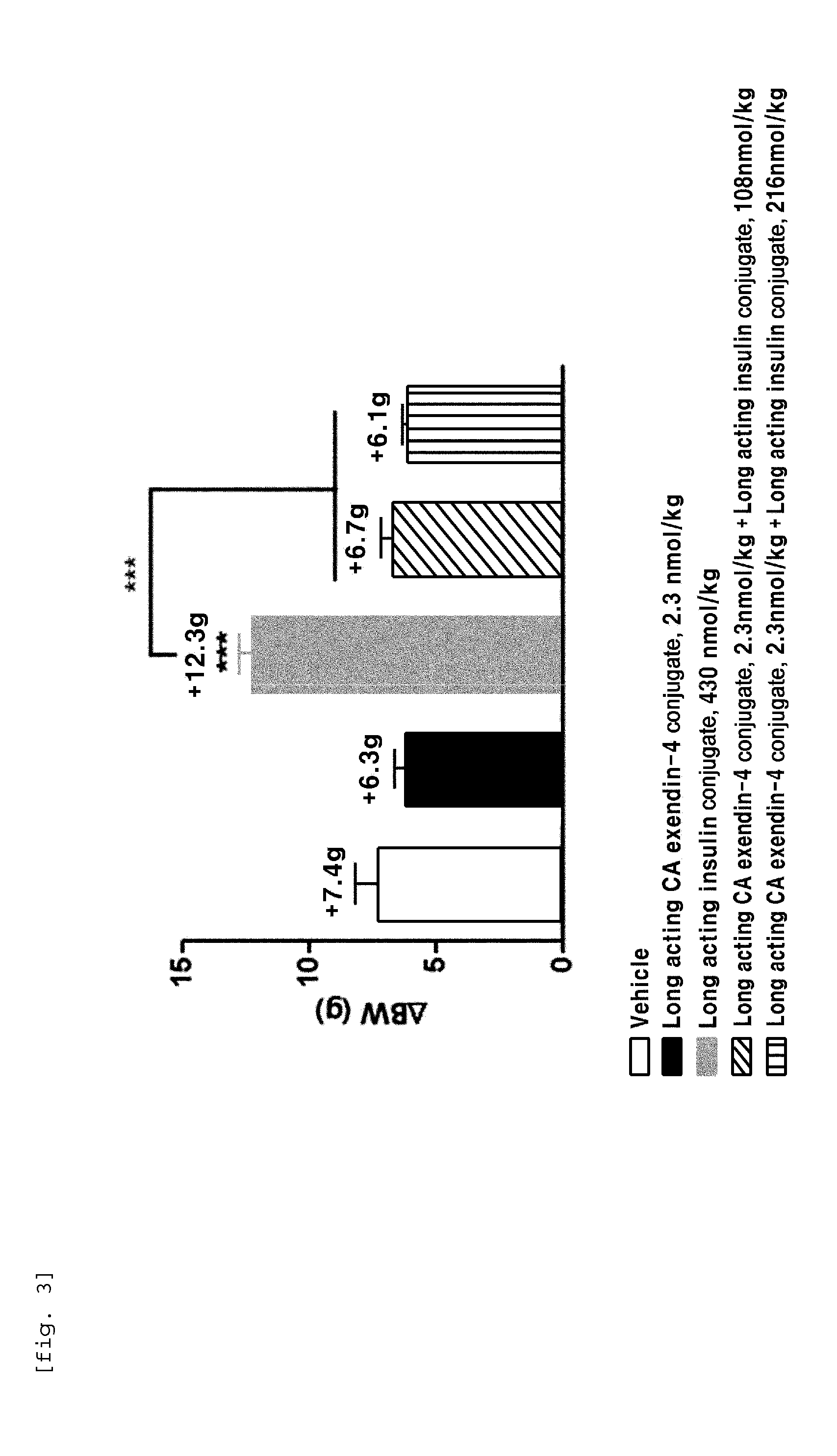
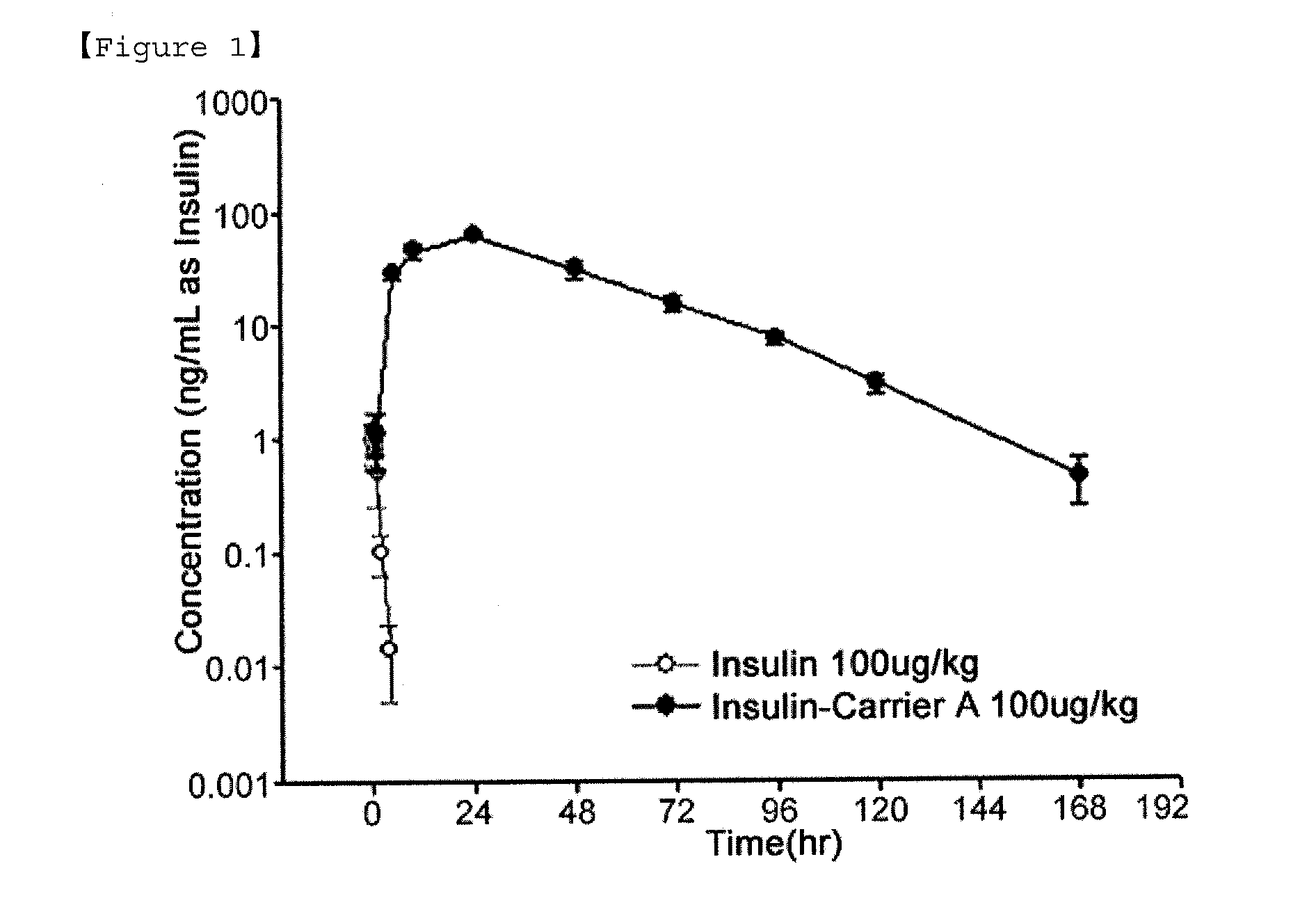
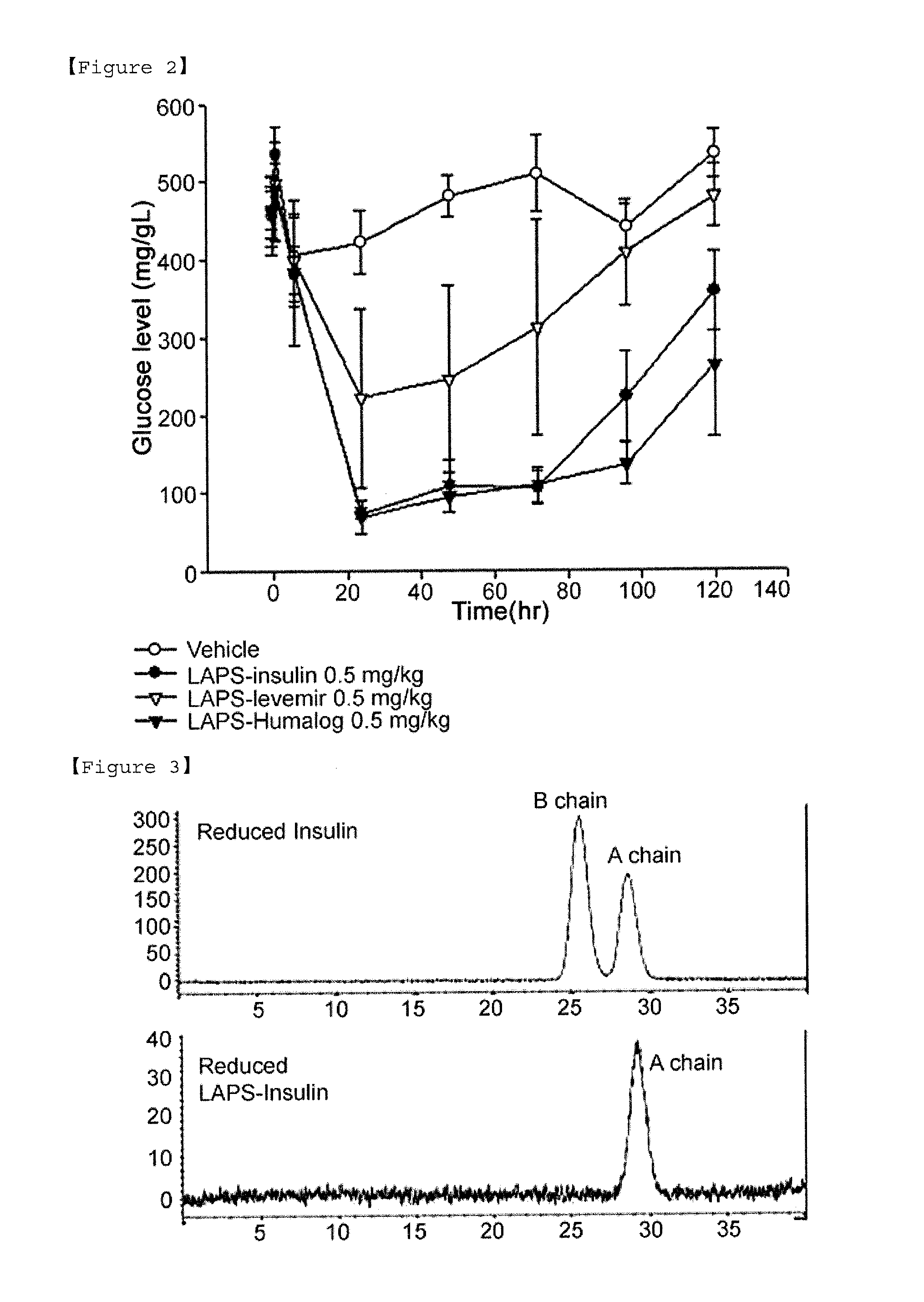
Composition for treating diabetes comprising long-acting insulin conjugate and long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate
ActiveUS20140120120A1Good treatment effectImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderIn vivoWeight gain
The present invention relates to a composition for the prevention or treatment of diabetes comprising a long-acting insulin conjugate and a long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate, and a therapeutic method for the treatment of diabetes, and more particularly, concurrent administration of the long-acting insulin conjugate and the long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate inhibits weight gain caused by insulin treatment, and vomiting and nausea caused by insulinotropic peptide treatment, and reduces the required dose of insulin, thereby remarkably improving drug compliance. Moreover, each of the long-acting insulin conjugate and the long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate of the present invention is prepared by linking insulin or insulinotropic peptide with an immunoglobulin Fc region via a non-peptidyl linker, thereby showing improved in-vivo duration of efficacy and stability.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
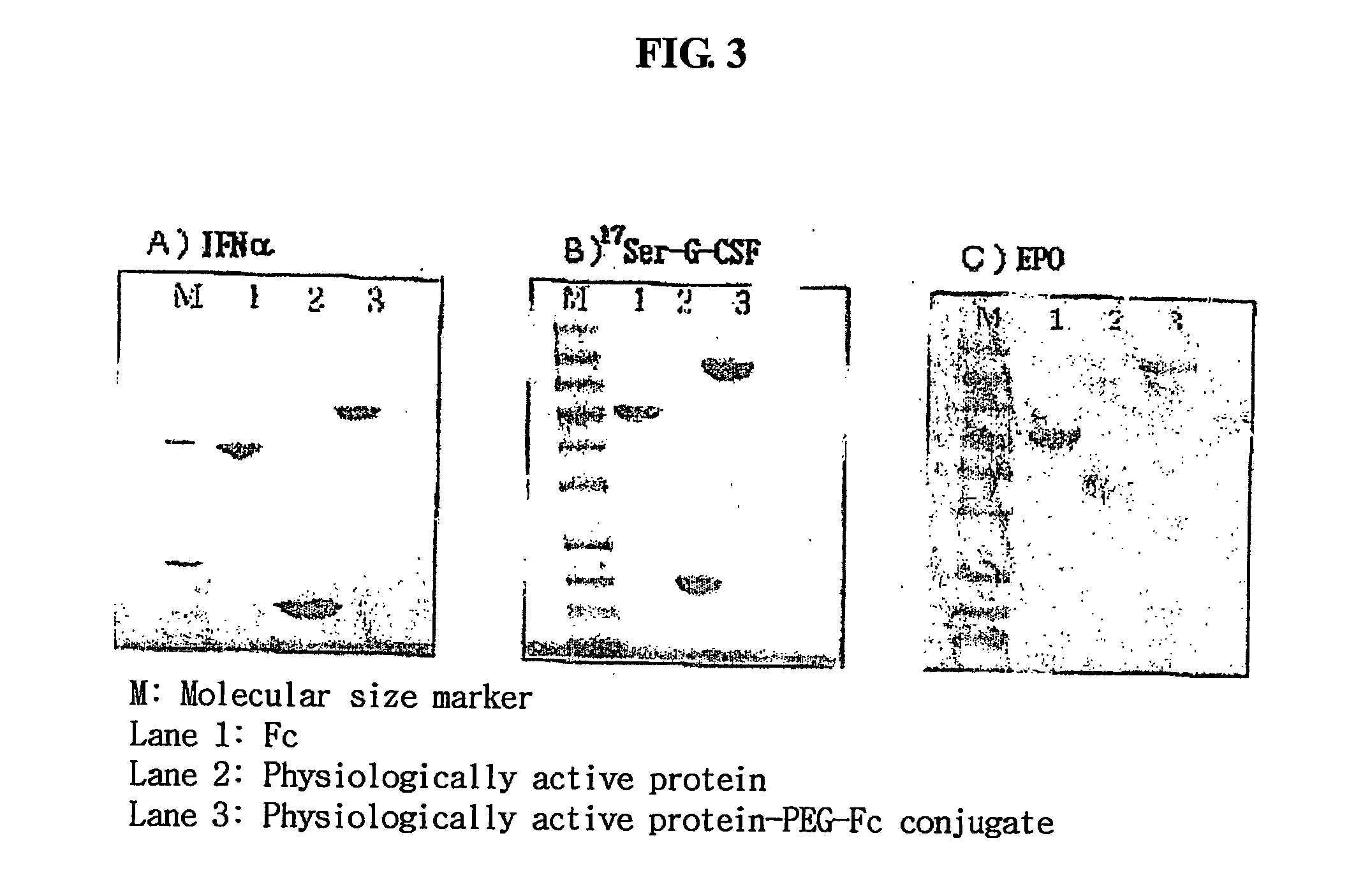
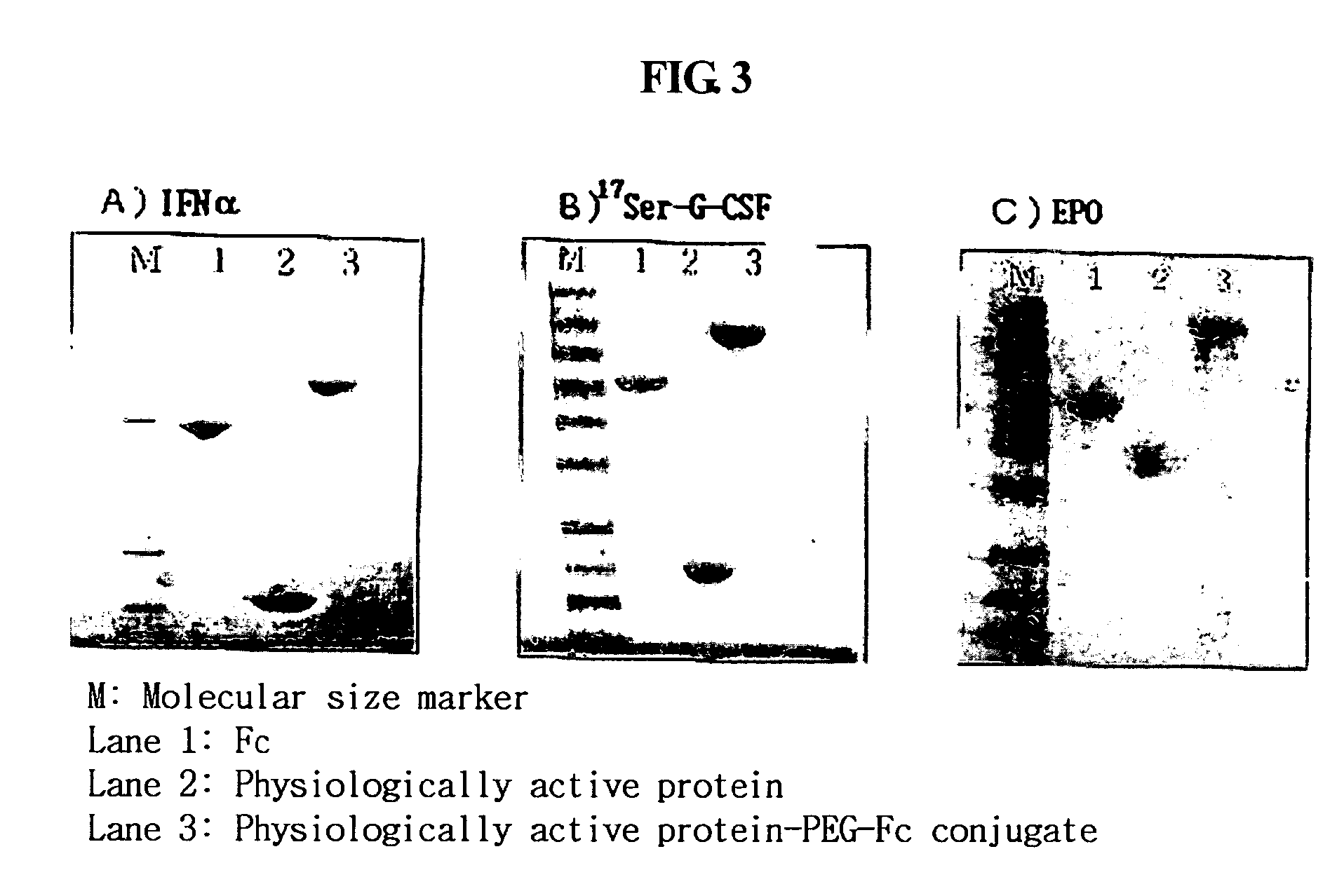
Expression and export of interferon-alpha proteins as Fc fusion proteins
InactiveUS20050042729A1Promote productionEfficient productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRNA SequenceHepatitis
Disclosed are nucleic acid sequences, for example, DNA or RNA sequences, which encode an immunoglobulin Fc-Interferon-alpha fusion protein. The nucleic acid sequences can be inserted into a suitable expression vector and expressed in mammalian cells. Also disclosed is a family of immunoglobulin Fc-Interferon-alpha fusion proteins that can be produced by expression of such nucleic acid sequences. Also disclosed are methods of using such nucleic acid sequences and / or fusion proteins for treating conditions, for example, hepatitis, which are alleviated by the administration of interferon-alpha.
Owner:EMD LEXIGEN RES CENT CORP
Enhancing the circulating half-life of antibody-based fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060194952A1Extended half-lifeReduced binding affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
Disclosed are methods for the genetic construction and expression of antibody-based fusion proteins with enhanced circulating half-lives. The fusion proteins of the present invention lack the ability to bind to immunoglobulin Fc receptors, either as a consequence of the antibody isotype used for fusion protein construction, or through directed mutagenesis of antibody isotypes that normally bind Fc receptors. The fusion proteins of the present invention may also contain a functional domain capable of binding an immunoglobulin protection receptor.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
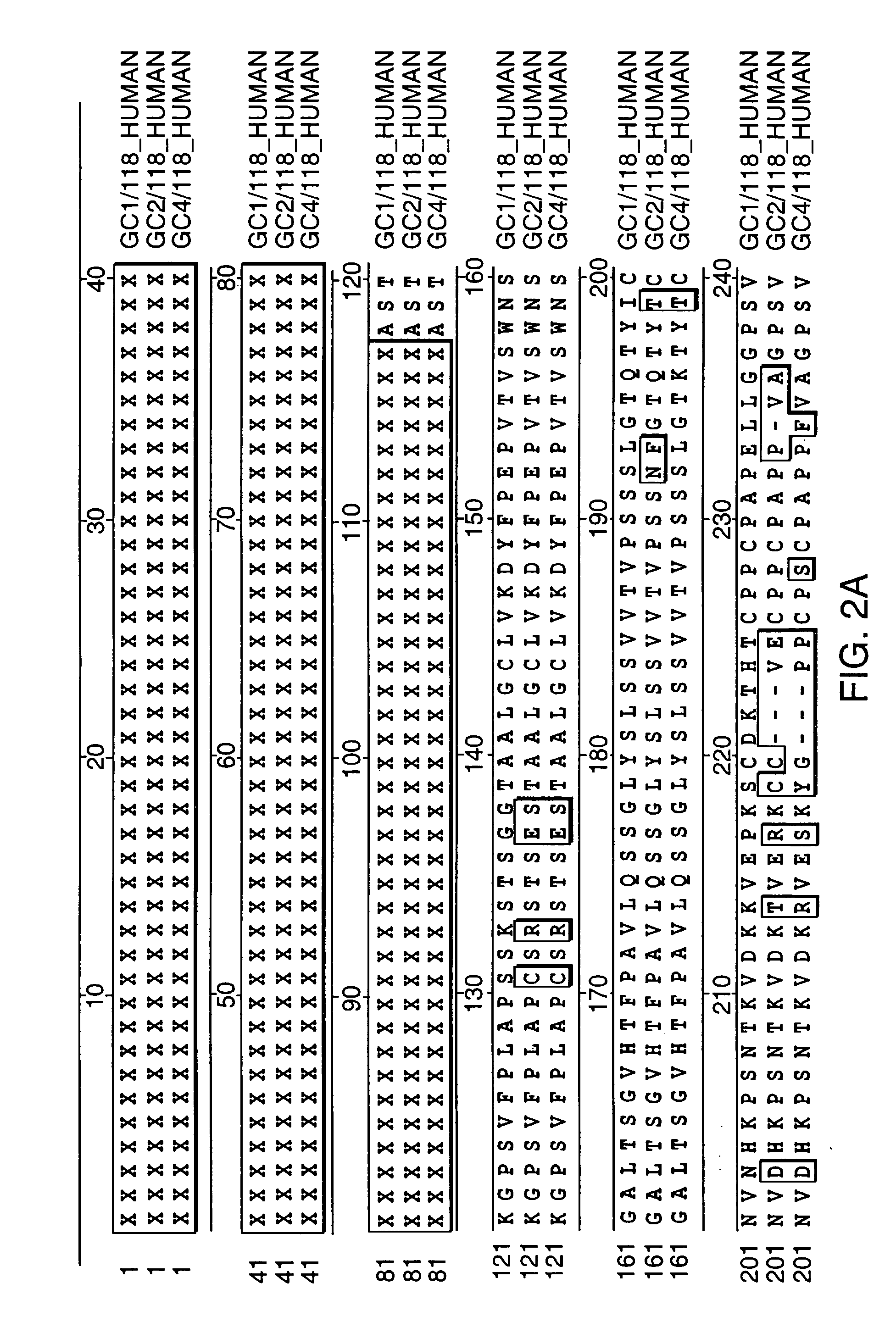
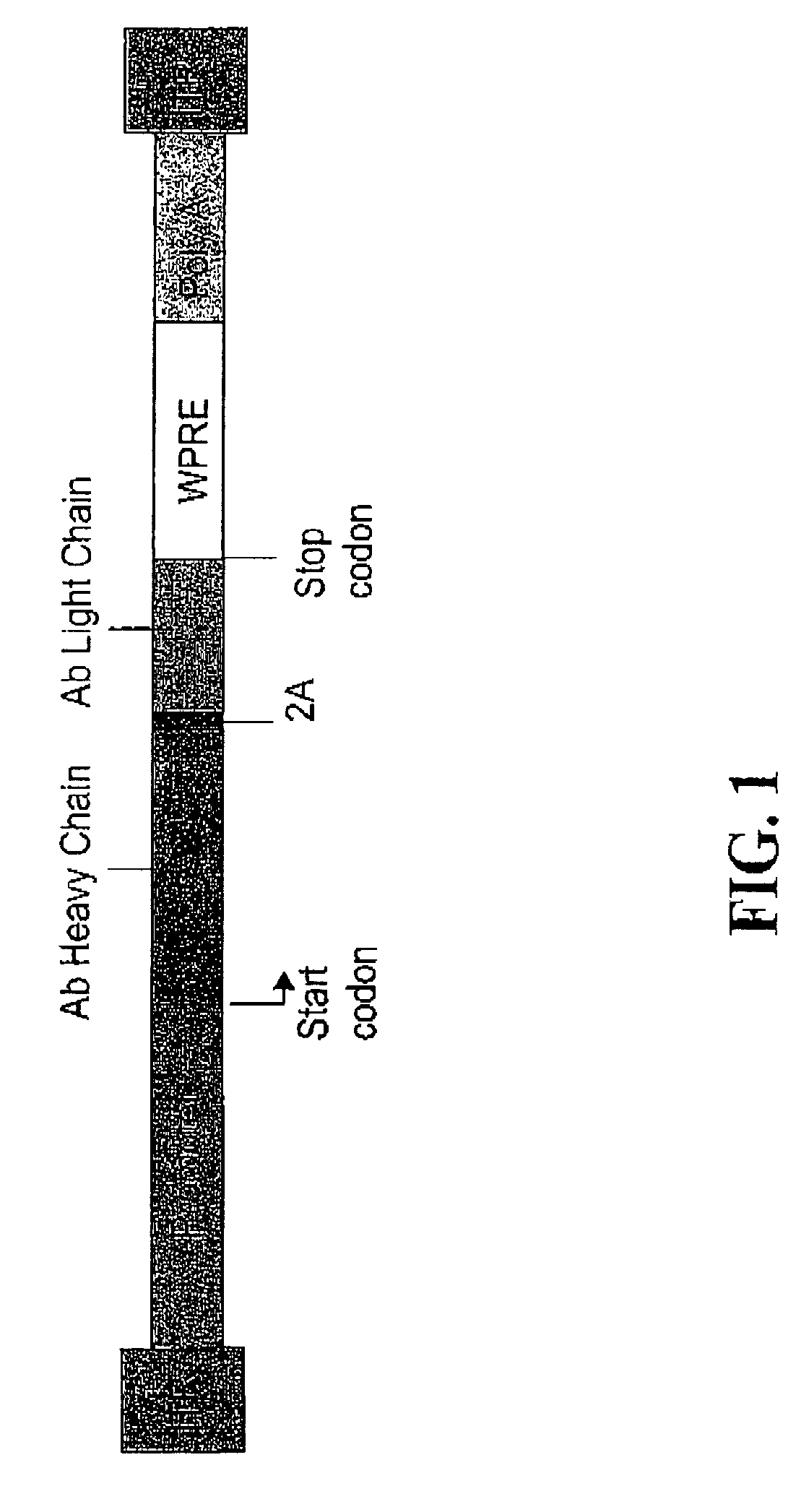
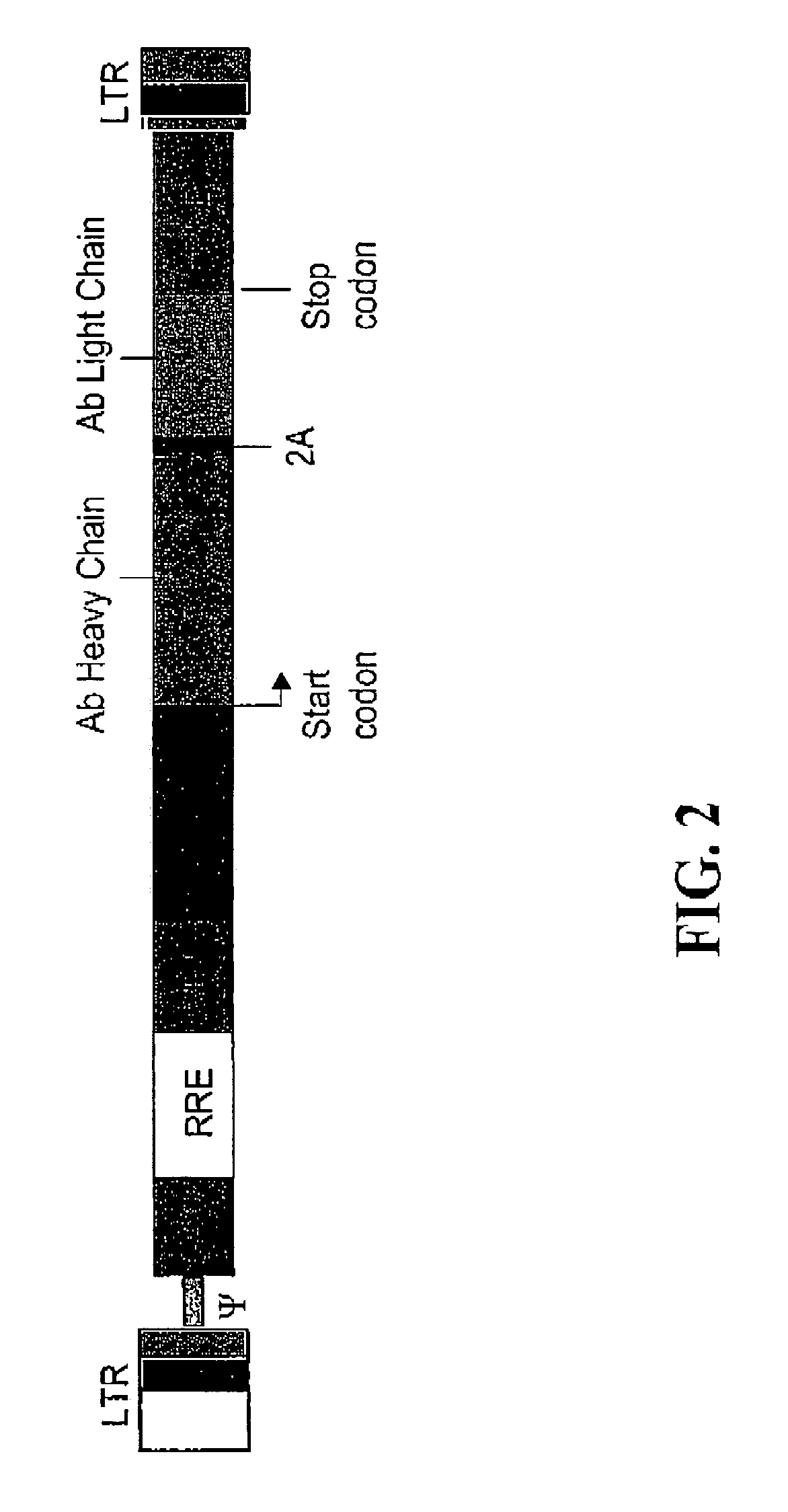
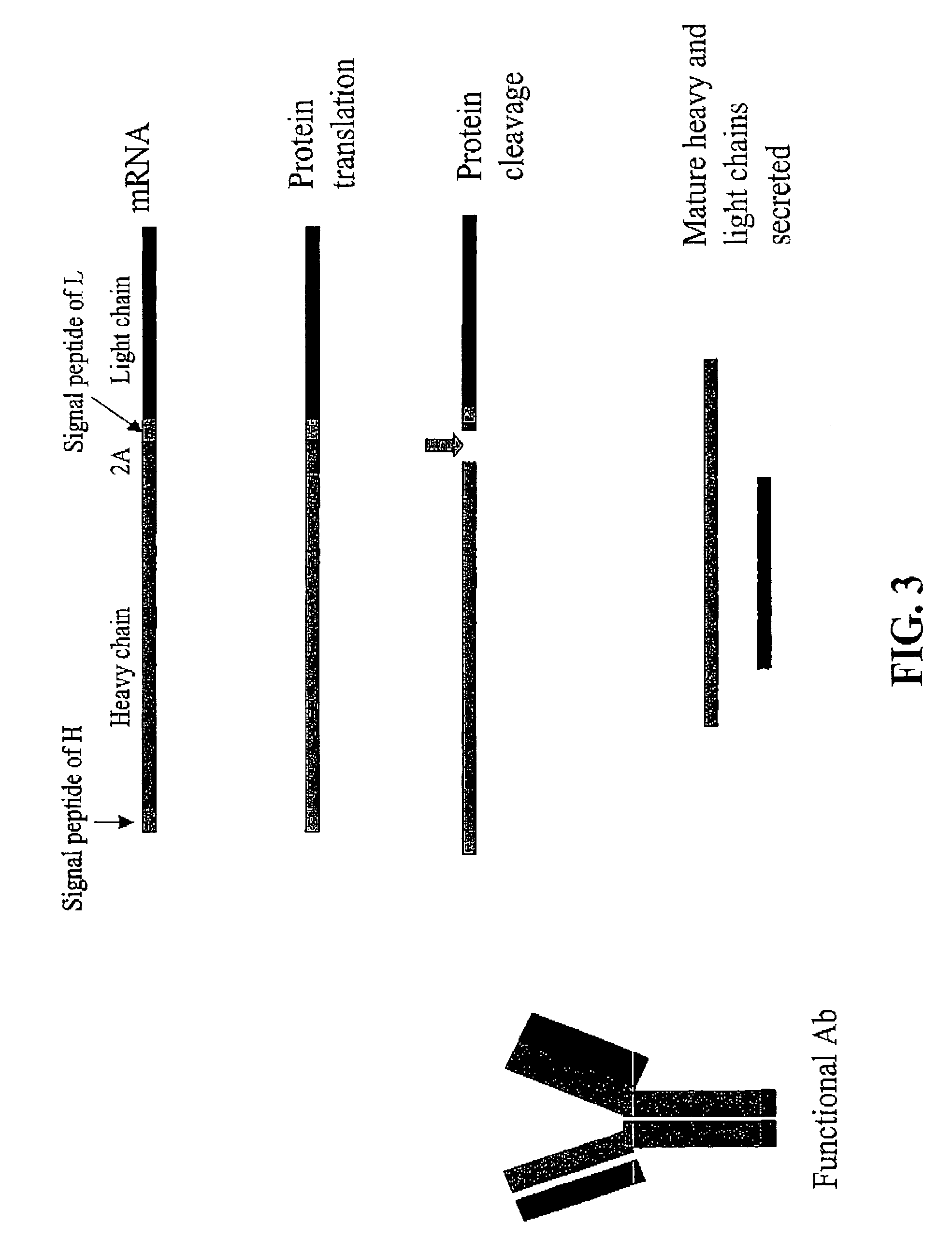
Compositions and methods for enhanced expression of immunoglobulins from a single vector using a peptide cleavage site
Single vector constructs for expression of an immunoglobulin molecule or fragment thereof and methods of making and using the same are described. The vectors comprise a self-processing cleavage sequence between a first and second immunoglobulin coding sequence allowing for expression of a functional antibody molecule using a single promoter. The vector constructs include the coding sequence for a self-processing cleavage site and may further include an additional proteolytic cleavage sequence which provides a means to remove the self processing peptide sequence from an expressed immunoglobulin molecule or fragment thereof. The vector constructs find utility in methods for enhanced production of biologically active immunoglobulins or fragments thereof in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:BIOSANTE PHARMA
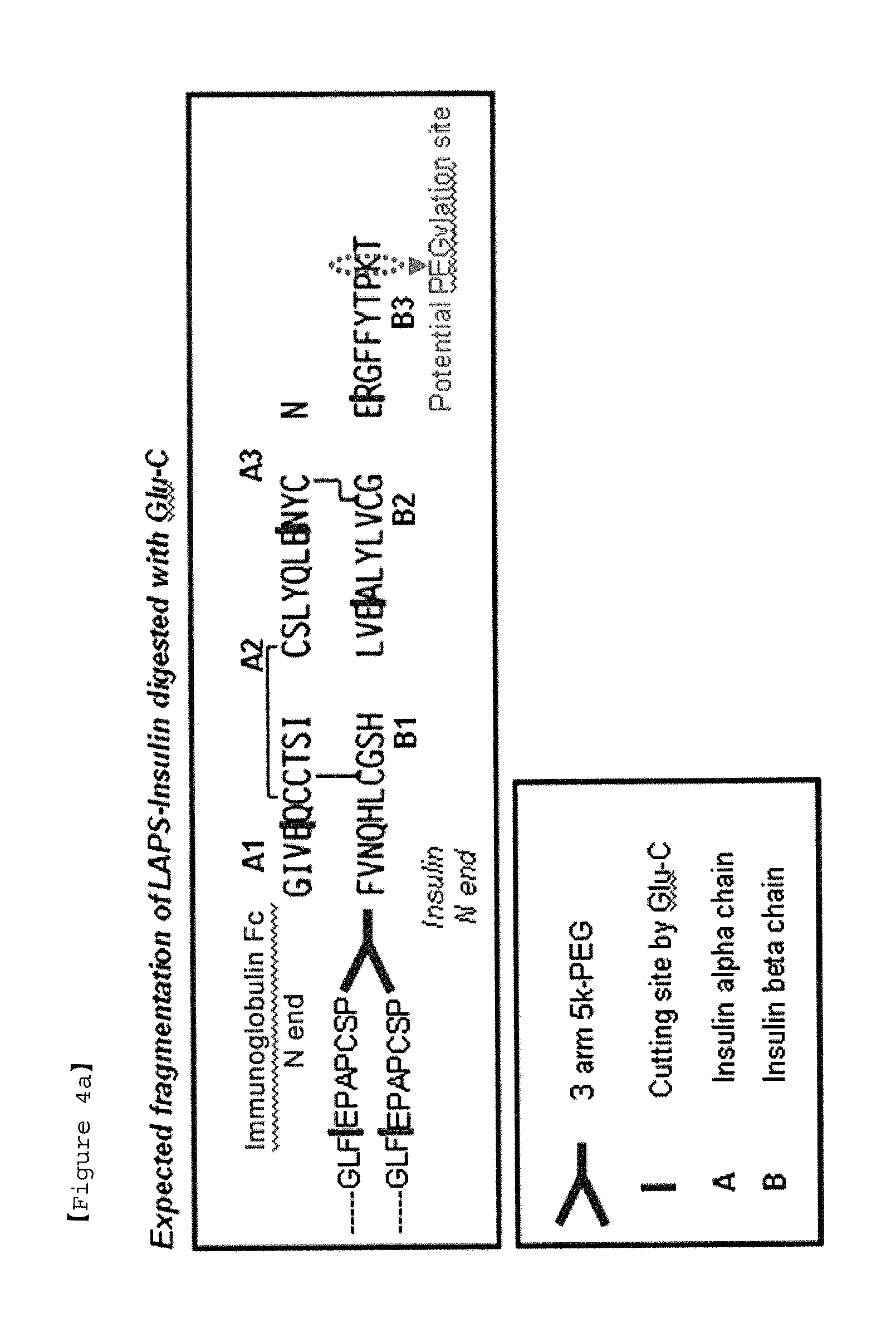
Insulin conjugate using an immunoglobulin fragment
ActiveUS20130028918A1Improve the level ofExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to an insulin conjugate having improved in vivo duration and stability, which is prepared by covalently linking insulin with an immunoglobulin Fc region via a non-peptidyl polymer, a long-acting formulation comprising the same, and a preparation method thereof. The insulin conjugate of the present invention maintains in vivo activity of the peptide at a relatively high level and remarkably increases the serum half-life thereof, thereby greatly improving drug compliance upon insulin treatment.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Human monoclonal antibodies to activin receptor-like kinase-1
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Method for producing antibody fragments
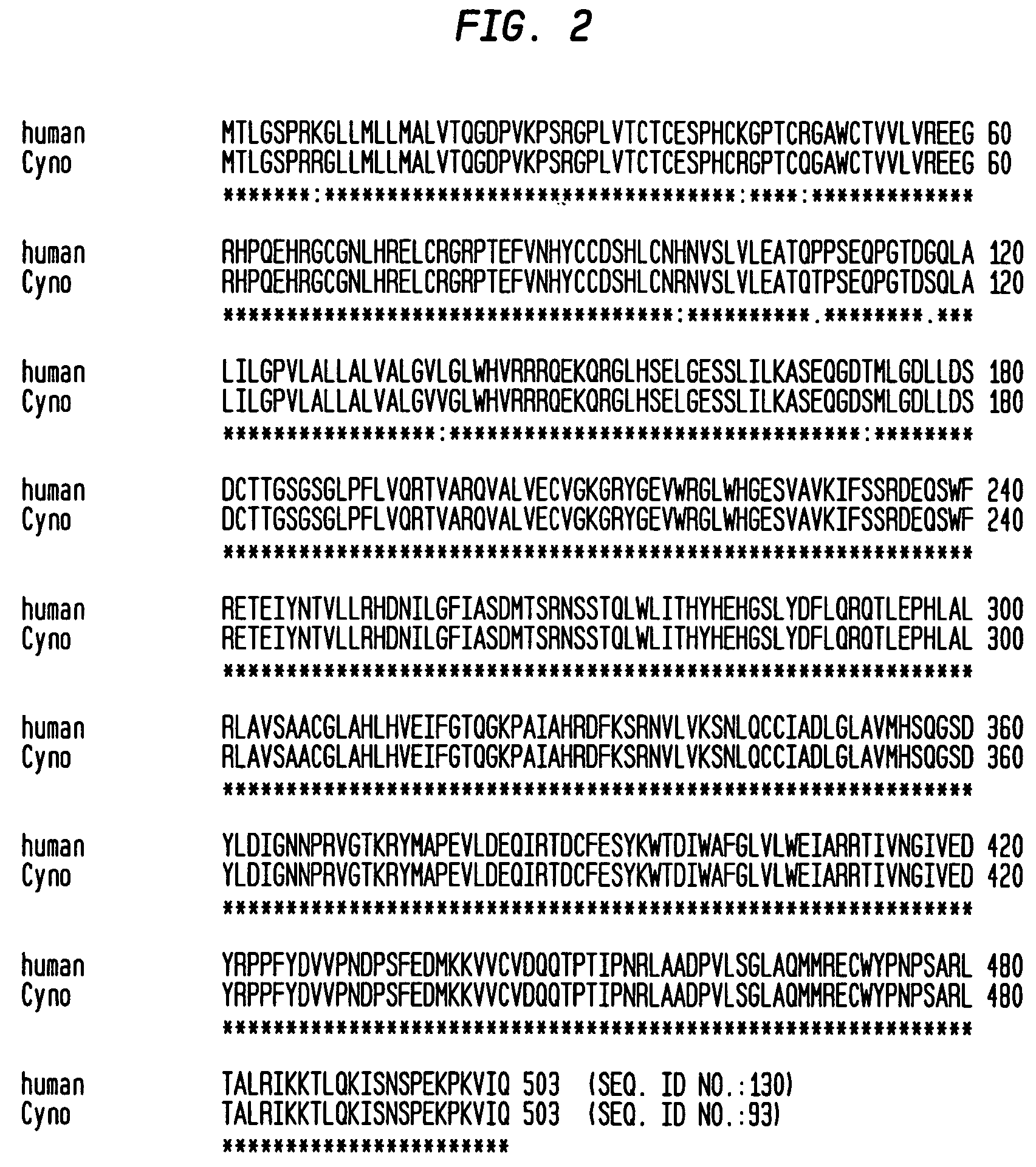
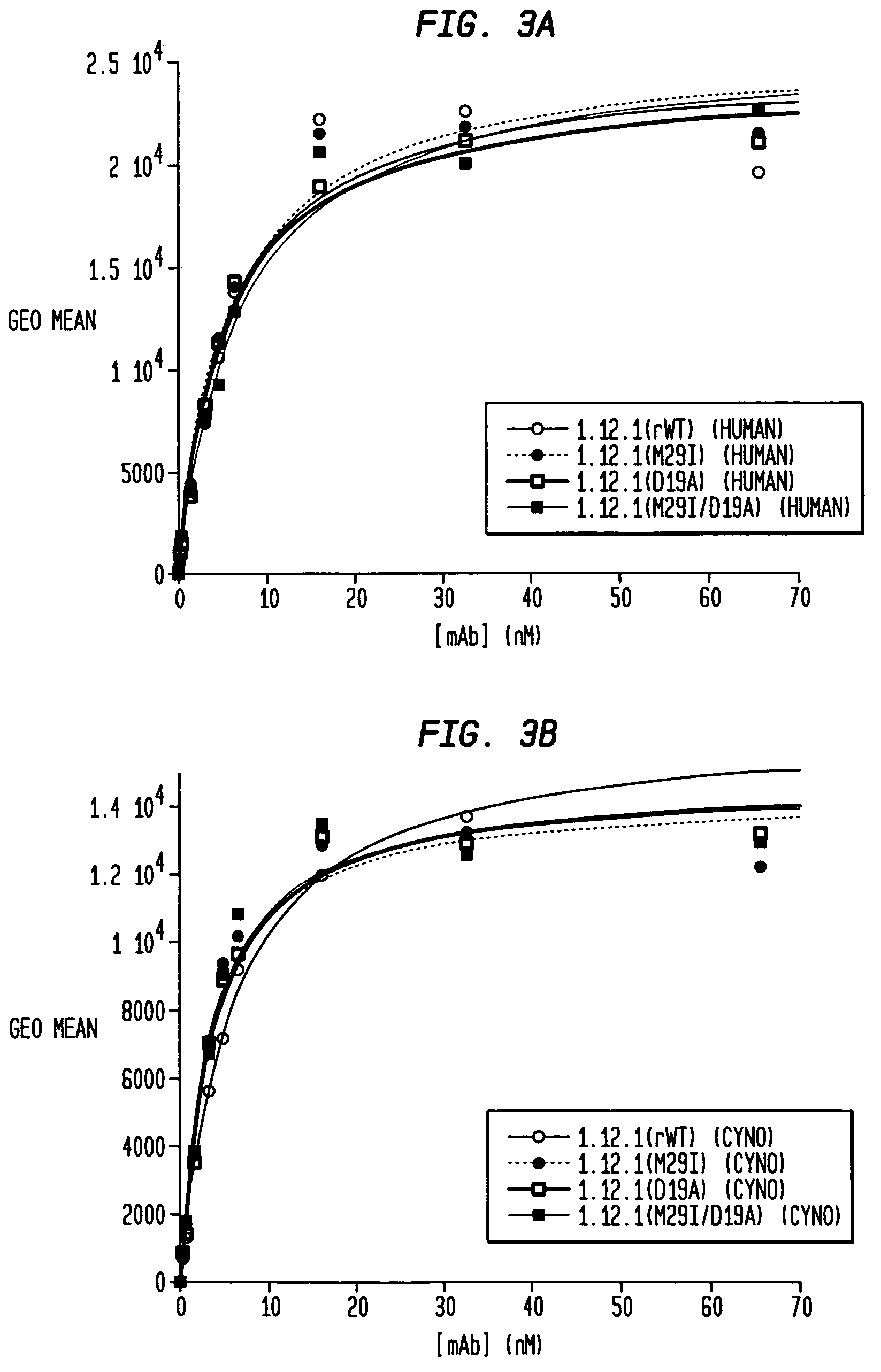
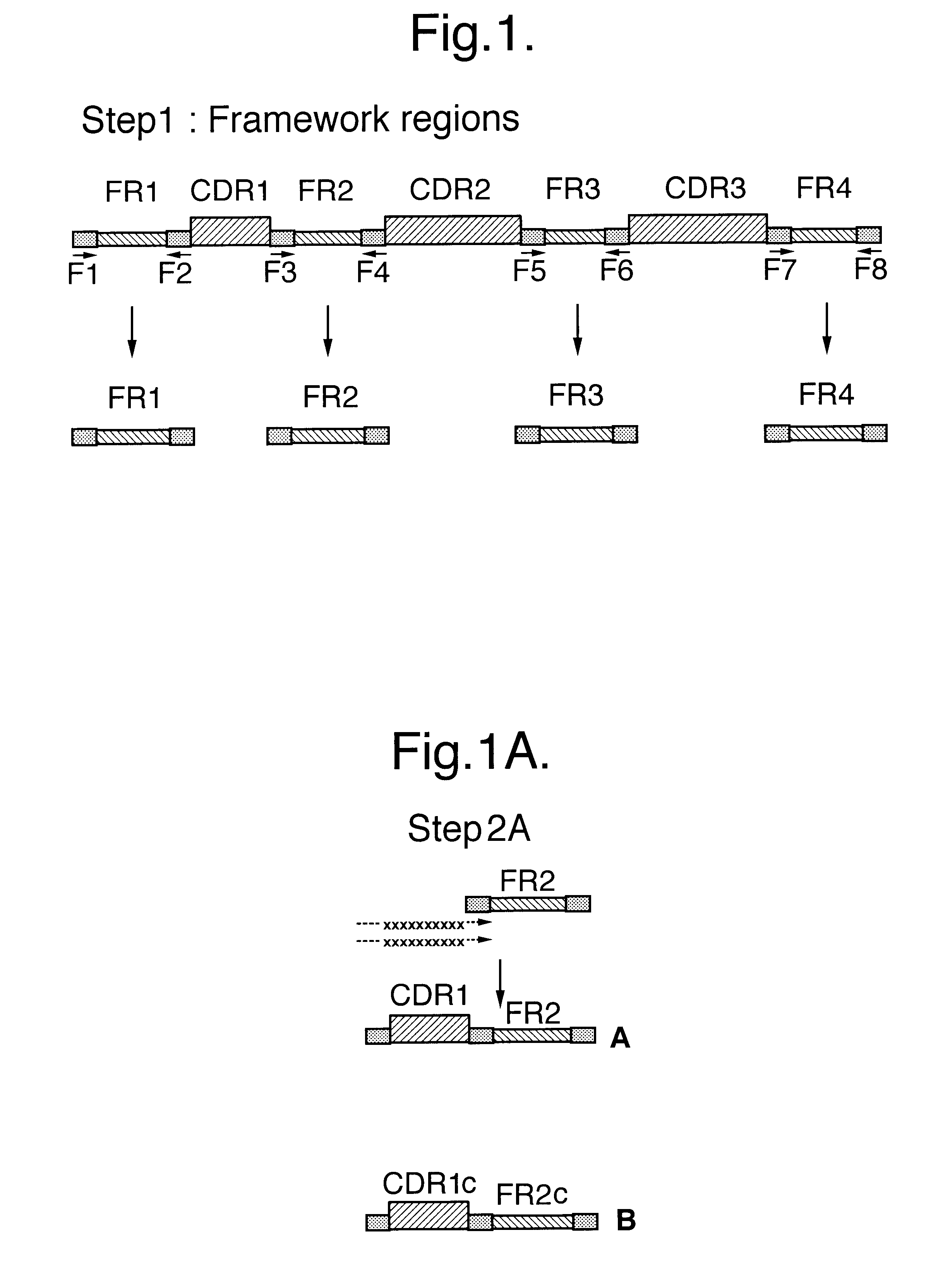
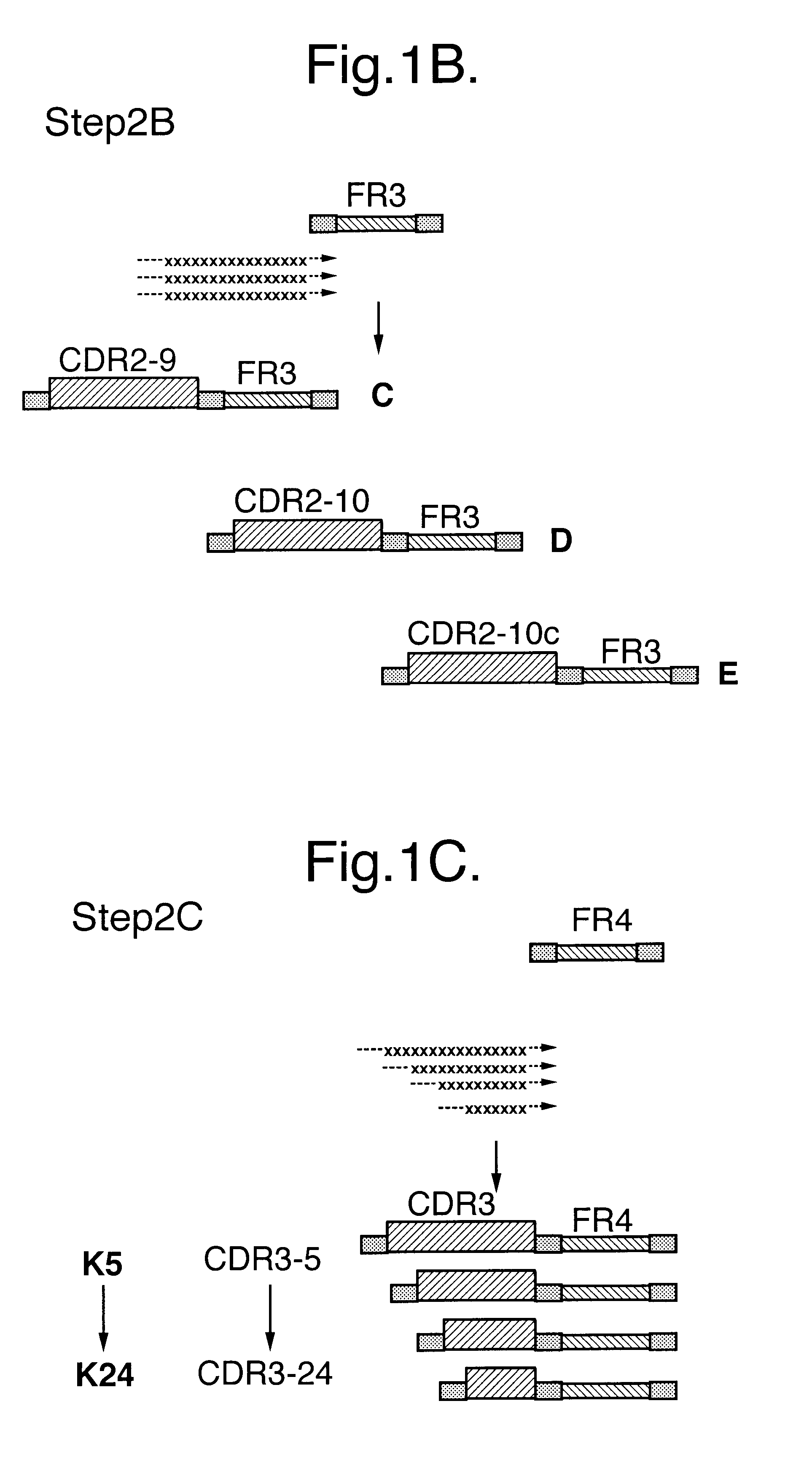
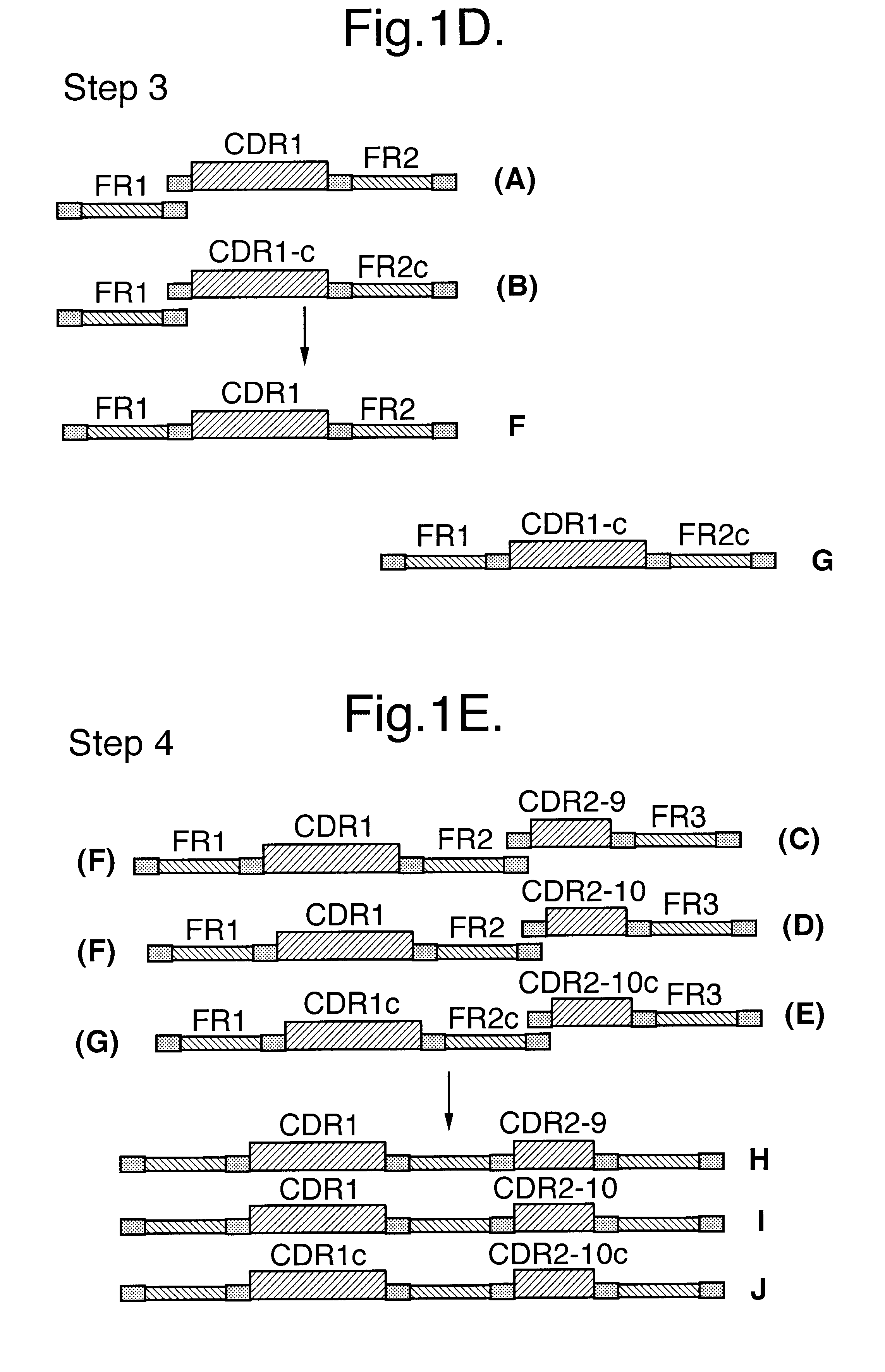
InactiveUS6399763B1Sugar derivativesMicroorganism librariesExpression LibraryComplementarity determining region
An expression library comprising a repertoire of nucleic acid sequences cloned from a non-immunized source, each nucleic acid sequence encoding at least part of a variable domain of a heavy chain derived from an immunoglobulin naturally devoid of light chains (VHH) wherein the extent of sequence variability in the library is enhanced compared to the corresponding naive expression library by introducing mutations in one or more of the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of the nucleic acid sequences or by generating alternative combinations of CDR and framework sequences not naturally present in the naive library repertoire. Also disclosed is the use of such a library in preparing antibodies, more particularly antibody fragments.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Insulinotropic peptide conjugate using an immunoglobulin fc
The present invention relates to an insulinotropic peptide conjugate having improved in-vivo duration of efficacy and stability, comprising an insulinotropic peptide, a non-peptide polymer and a carrier substance, which are covalently linked to each other, and a use of the same. The insulinotropic peptide conjugate of the present invention has the in-vivo activity which is maintained relatively high, and has remarkably increased blood half-life, and thus it can be desirably employed in the development of long acting formulations of various peptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising An Immunoglobulin FC Region as a Carrier
Disclosed is a novel use of an immunoglobulin Fc fragment, and more particularly, a pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fc fragment as a carrier. The pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fc fragment as a carrier remarkably extends the serum half-life of a drug while maintaining the in vivo activity of the drug at relatively high levels. Also, when the drug is a polypeptide drug, the pharmaceutical composition has less risk of inducing immune responses compared to a fusion protein of the immunoglobulin Fc fragment and a target protein, and is thus useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Angiogenesis inhibiting fusion protein and its use
ActiveCN1706867AImprove stabilityReduced stabilityHybrid peptidesAngiogenesis growth factorADAMTS Proteins
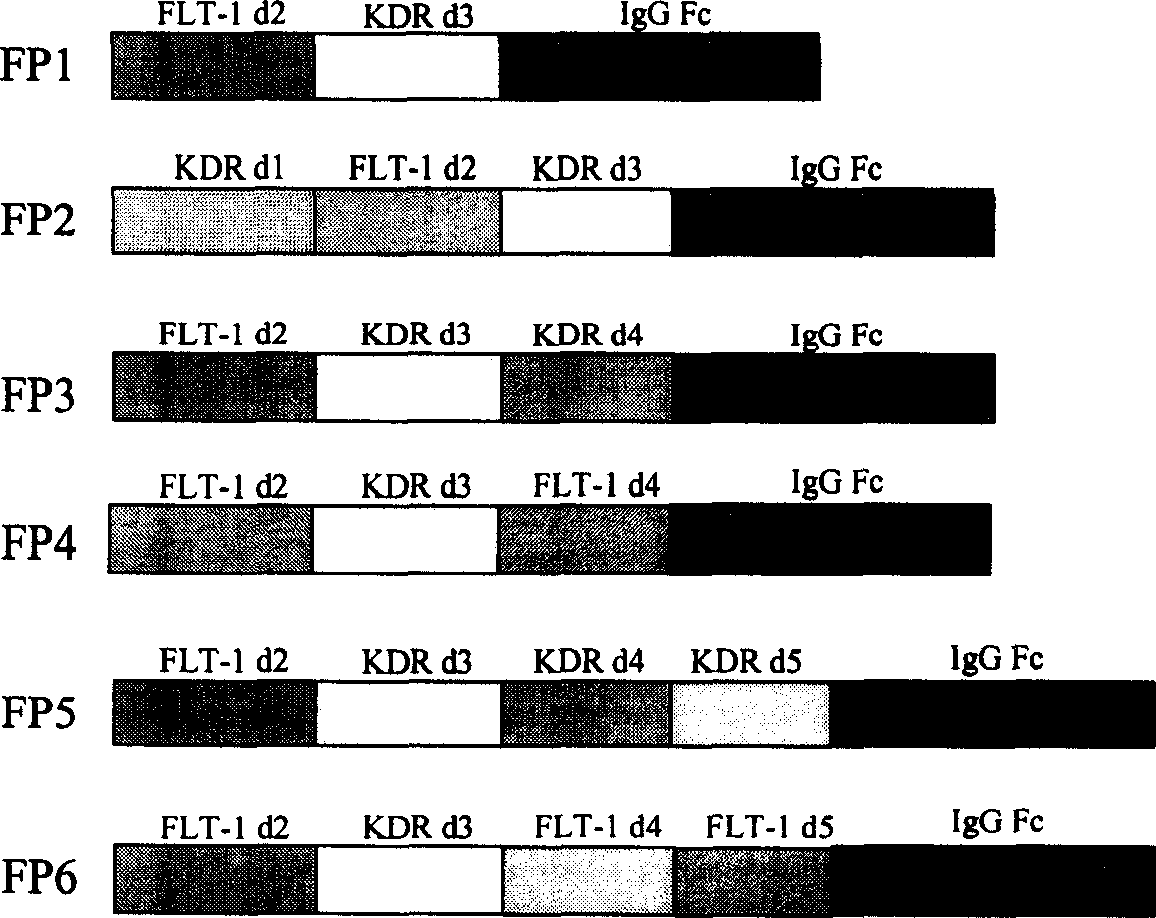
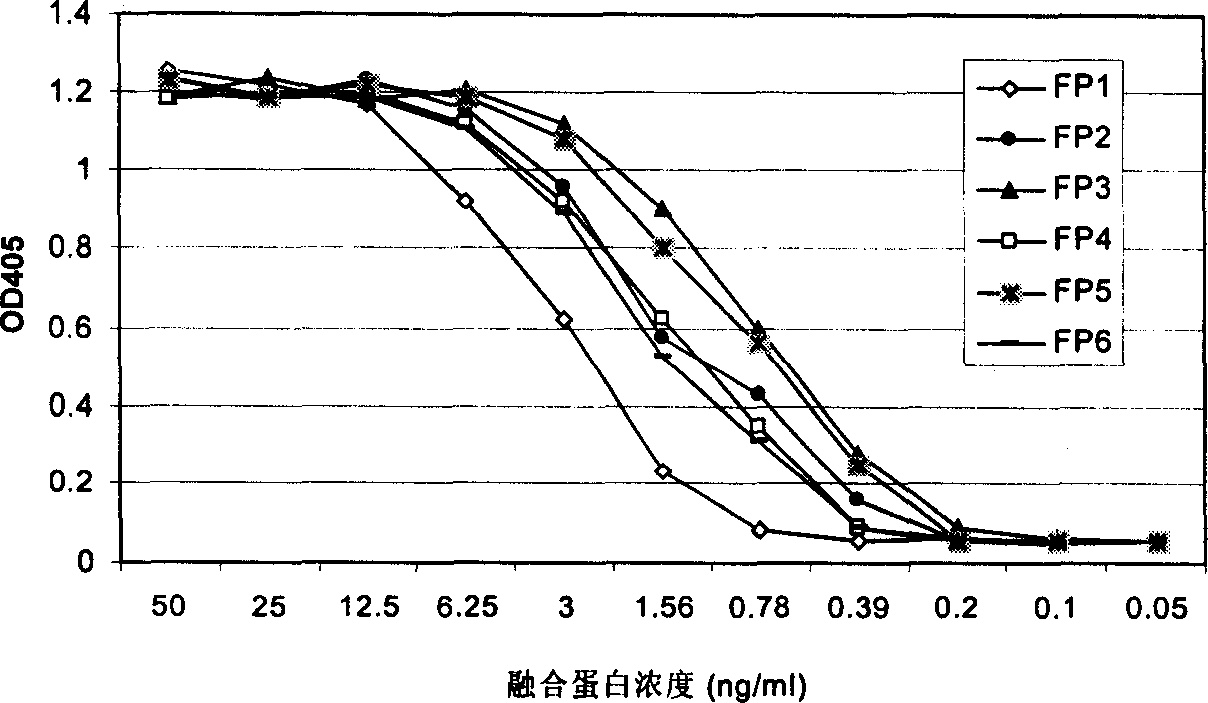
The present invention relates to one kind of angiogenesis inhibiting fusion protein and its use. The fusion proteins of the present invention are produced through fusing FLT-1 segment, KDR segment and immunoglobulin Fc segment, and are named as FP1, FP2, FP3, FP4, FP5 and FP6. The amino acid sequences FLT-1 D2, FLT-1 D4, KDR, D1, KDR D3, KDR D4 and FP3 in the immunoglobulin-like area of FLT-1 and KDR are shown in the sequence lists 1-6, and FP3 coded DNA sequence is shown in the sequence list 7.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
Antibodies and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20090285813A1Low immunogenicityNervous disorderAntipyreticSynthetic antibodyFramework region
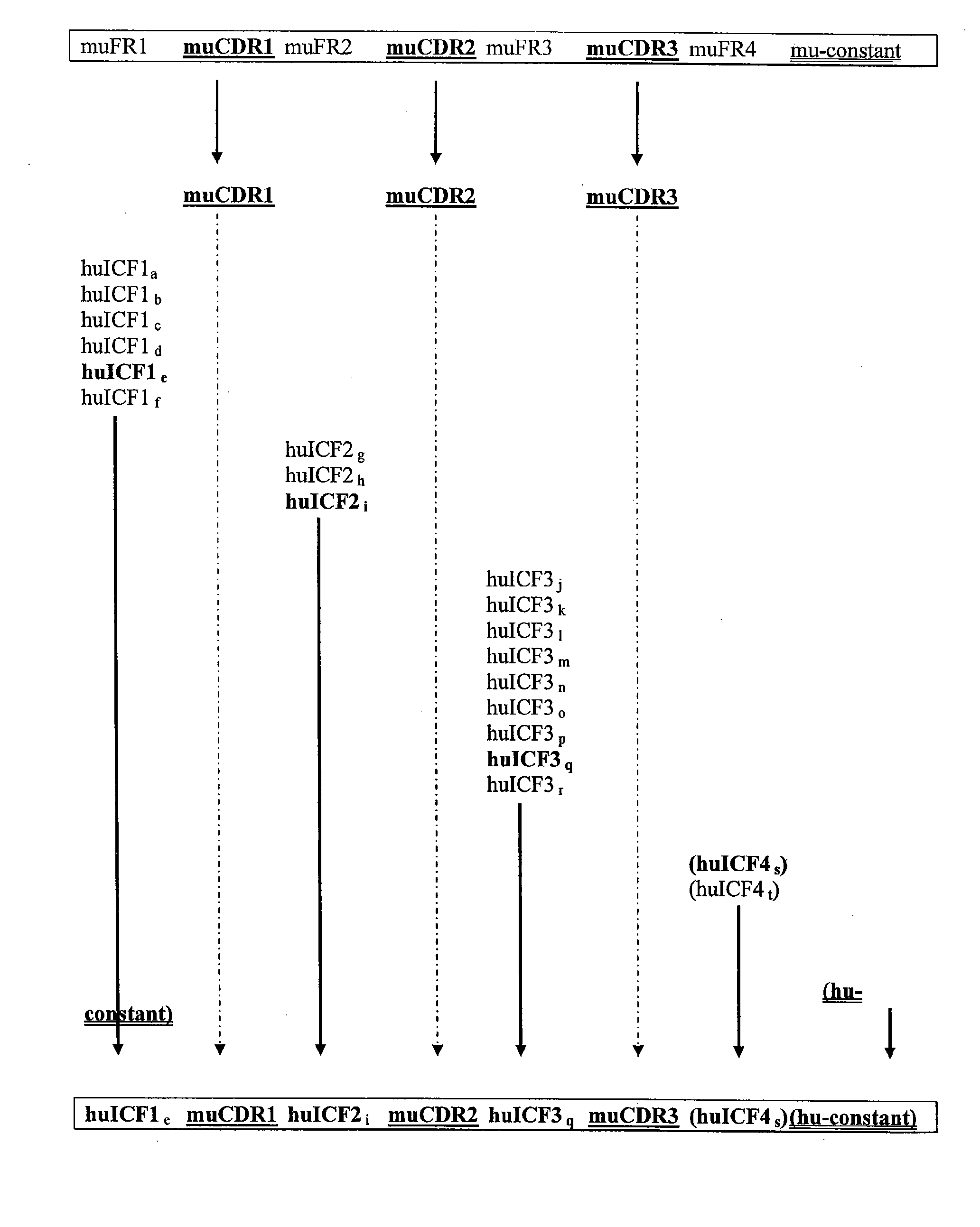
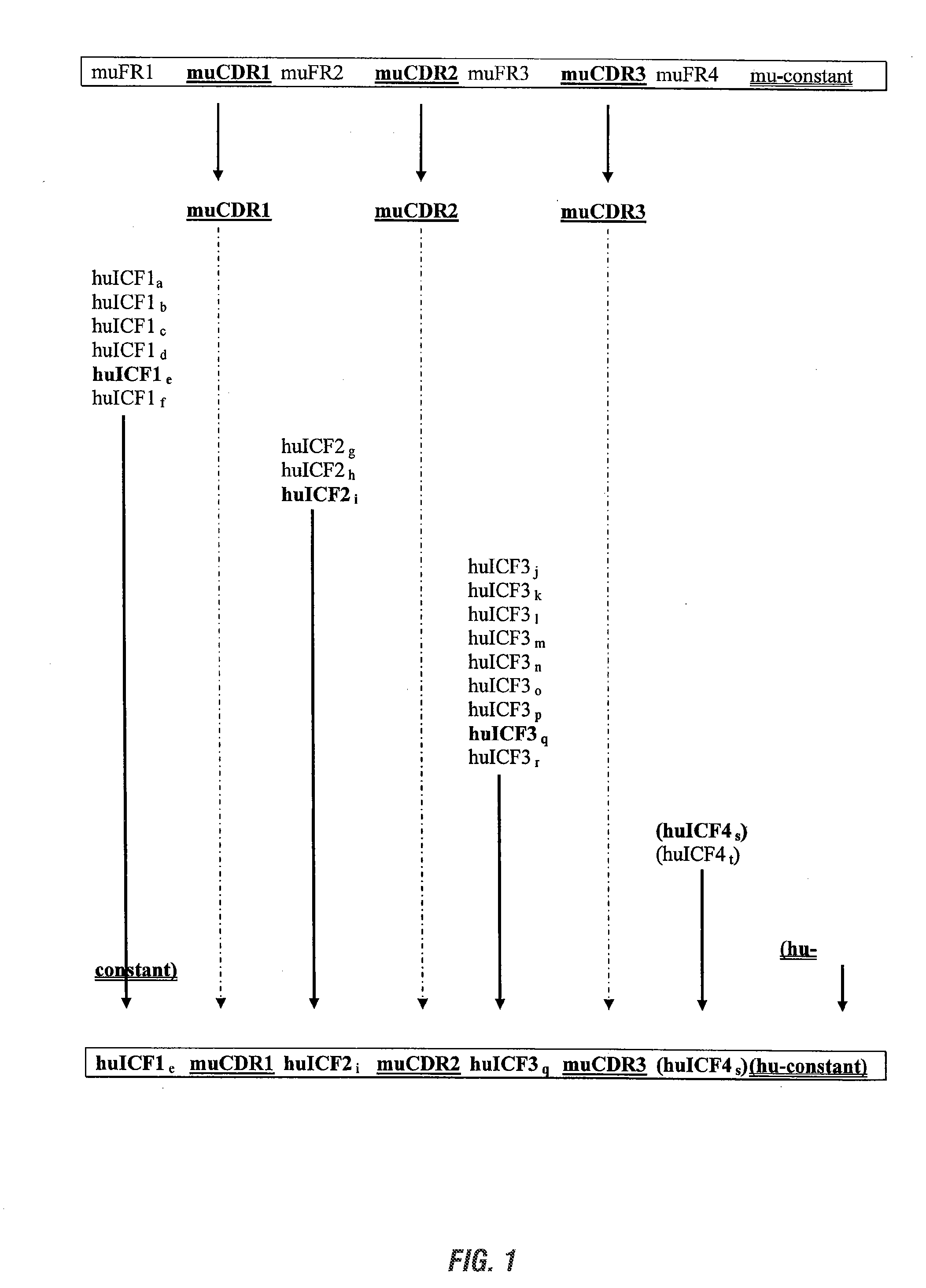
The invention provides antibodies, including chimeric human antibodies, recombinant antibodies, synthetic anti-bodies, and the nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for making and using these immunoglobulins. The invention provides recombinant and synthetic polypeptide and nucleic acid embodiments of these polypeptides and / or antibodies. The invention also provides polypeptides comprising, or consisting of, consensus human framework regions, or “Independently Consensused Frameworks (ICFs)”, nucleic acids encoding them, and libraries and kits comprising these ICFs and / or antibodies of the invention, individually and in combinatorial libraries and combinations.
Owner:MMRGLOBAL
Method for manufacturing recombinant polyclonal proteins
InactiveUS20060275766A1Minimizing unwanted batch-to-batch variationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide librariesPresent methodPlasma derived
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
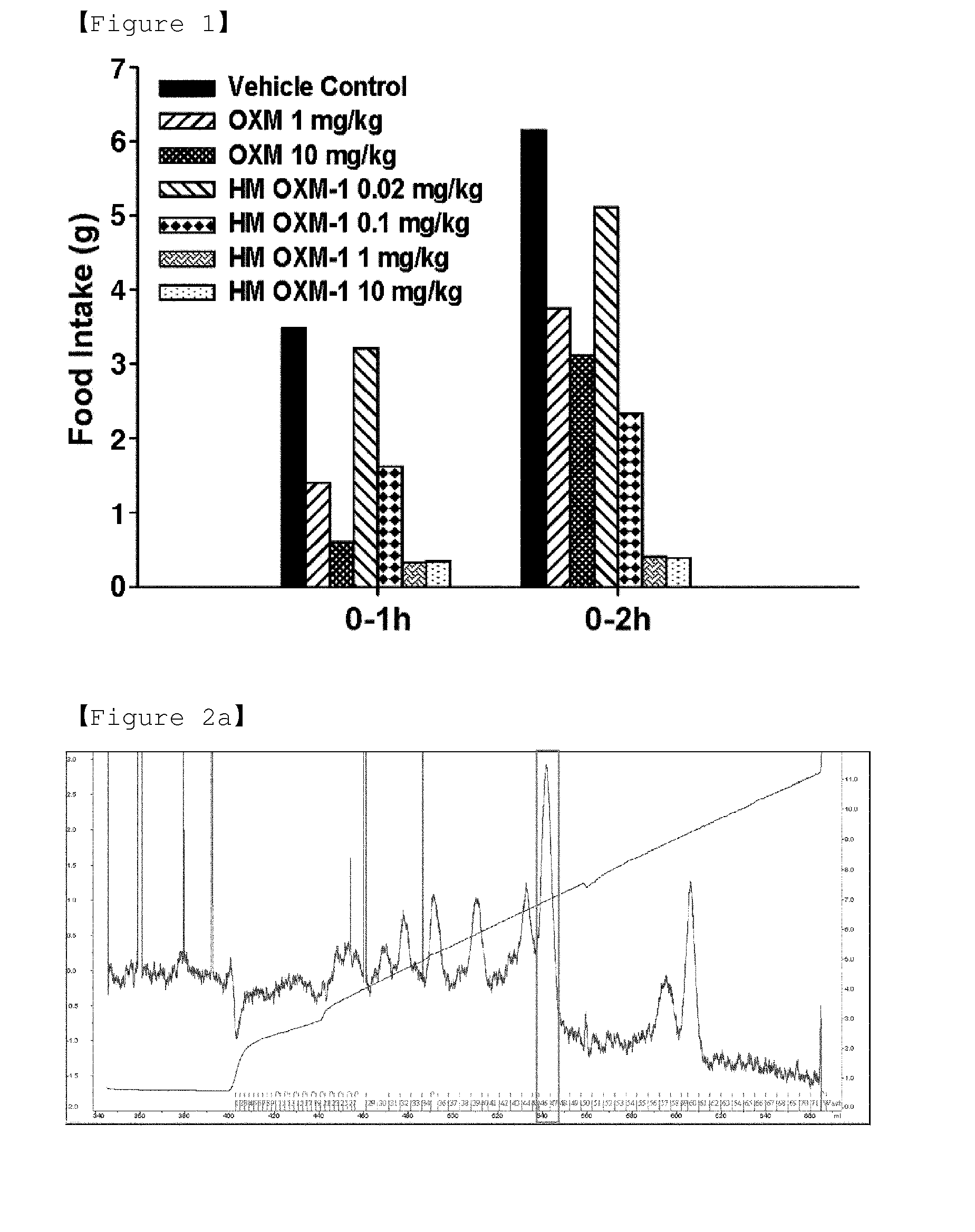
Conjugate comprising oxyntomodulin and an immunoglobulin fragment, and use thereof
ActiveUS20140212440A1Reduces food intakeSuppresses gastric emptyingPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectReceptor activation
The present invention relates to a conjugate comprising oxyntomodulin, an immunoglobulin Fc region, and non-peptidyl polymer wherein the conjugate being obtainable by covalently linking oxyntomodulin to immunoglobulin Fc region via non-peptidyl polymer, and a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention or treatment of obesity comprising the conjugates. The conjugate comprising oxyntomodulin and the immunoglobulin Fc of the present invention reduces food intake, suppresses gastric emptying, and facilitates lipolysis without side-effects, unlike native oxyntomodulin, and also shows excellent receptor-activating effects and long-term sustainability, compared to native oxyntomodulin. Thus, it can be widely used in the treatment of obesity with safety and efficacy.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
CTLA4-Cgamma4 fusion proteins
InactiveUS20020114814A1Reduce complement activating abilityReduced effector functionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAutoimmune responses
CTLA4-immunoglobulin fusion proteins having modified immunoglobulin constant region-mediated effector functions, and nucleic acids encoding the fusion proteins, are described. The CTLA4-immunoglobulin fusion proteins comprise two components: a first peptide having a CTLA4 activity and a second peptide comprising an immunoglobulin constant region which is modified to reduce at least one constant region-mediated biological effector function relative to a CTLA4-IgG1 fusion protein. The nucleic acids of the invention can be integrated into various expression vectors, which in turn can direct the synthesis of the corresponding proteins in a variety of hosts, particularly eukaryotic cells. The CTLA4-immunoglobulin fusion proteins described herein can be administered to a subject to inhibit an interaction between a CTLA4 ligand (e.g., B7-1 and / or B7-2) on an antigen presenting cell and a receptor for the CTLA4 ligand (e.g. CD28 and / or CTLA4) on the surface of T cells to thereby suppress an immune response in the subject, for example to inhibit transplantation rejection graft versus host disease or autoimmune responses.
Owner:GRAY GARY S +4
Nucleic acids encoding superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies
The present invention relates to one or more nucleic acid(s) encoding a binding molecule specifically binding to a human CD28 molecule, comprising(a) a nucleic acid sequence encoding a VH region and a nucleic acid sequence encoding a VL region comprising CDRs in a human immunoglobulin framework, wherein(i) the CDRs of the VH region (CDR-H) comprise the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 2 or 18 (CDR-H3), 4 or 20 (CDR-H2) and 6 or 22 (CDR-H1) or are encoded by the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1 or 17 (CDR-H3), 3 or 19 (CDR-H2) and 5 or 21 (CDR-H1); and(ii) the CDRs of the VL region (CDR-L) comprise the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 8 or 24 (CDR-L3), 10 or 26 (CDR-L2) and 12 or 28 (CDR-L1) or are encoded by the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 7 or 23 (CDR-L3), 9 or 25 (CDR-L2) and 11 or 27 (CDR-L1); and(b) a nucleic acid sequence encoding the constant region of a human IgG1 or IgG4 antibody.
Owner:THERAMAB
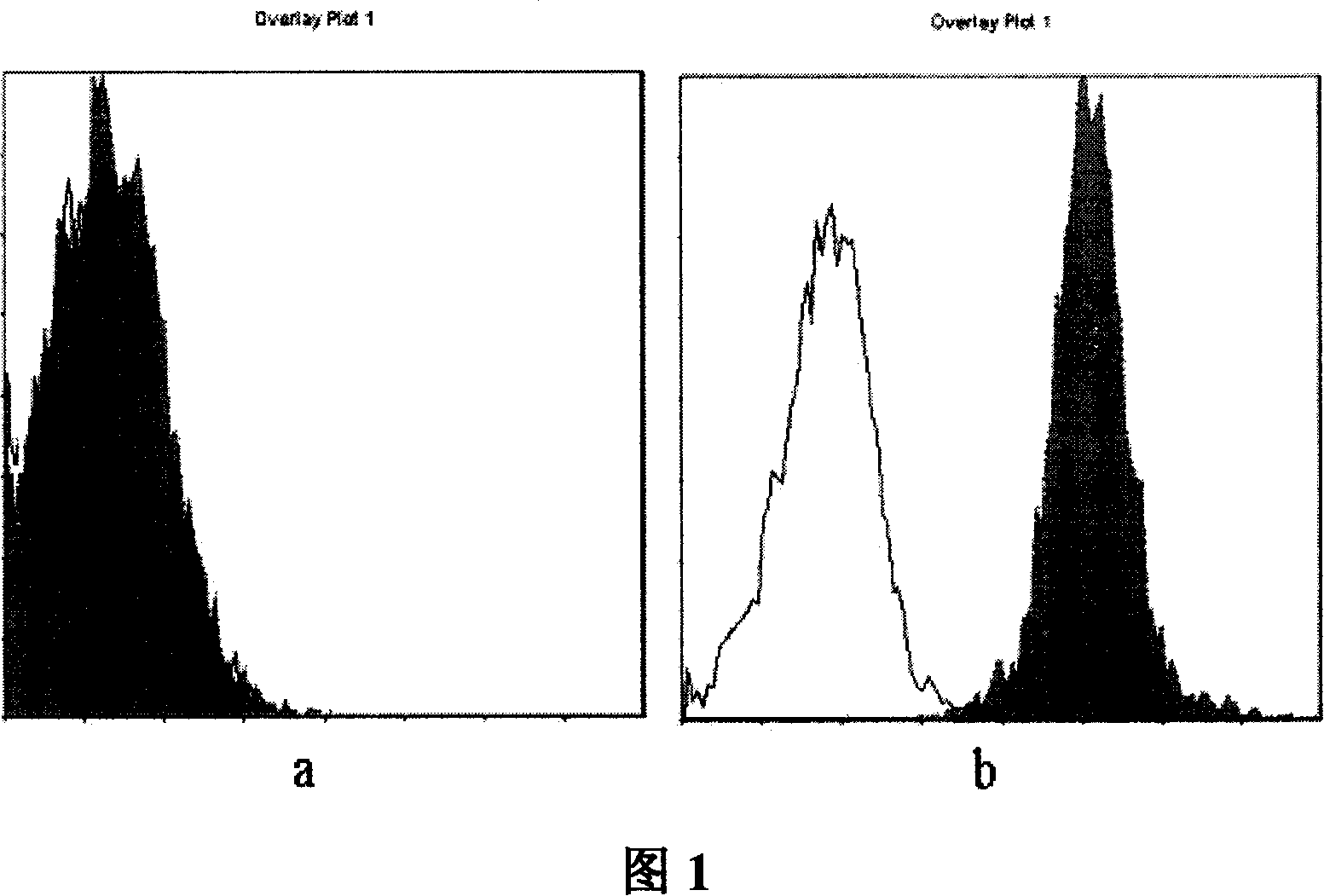
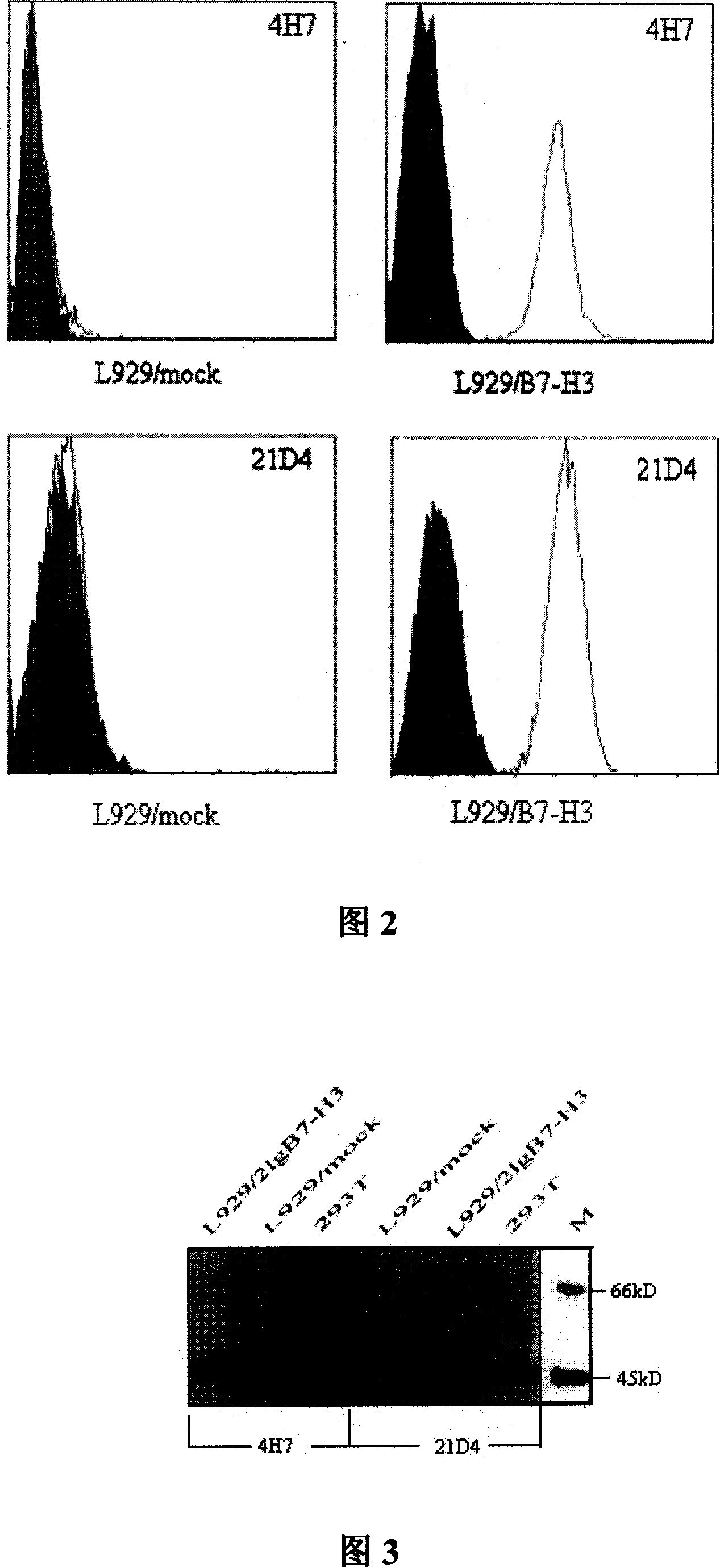
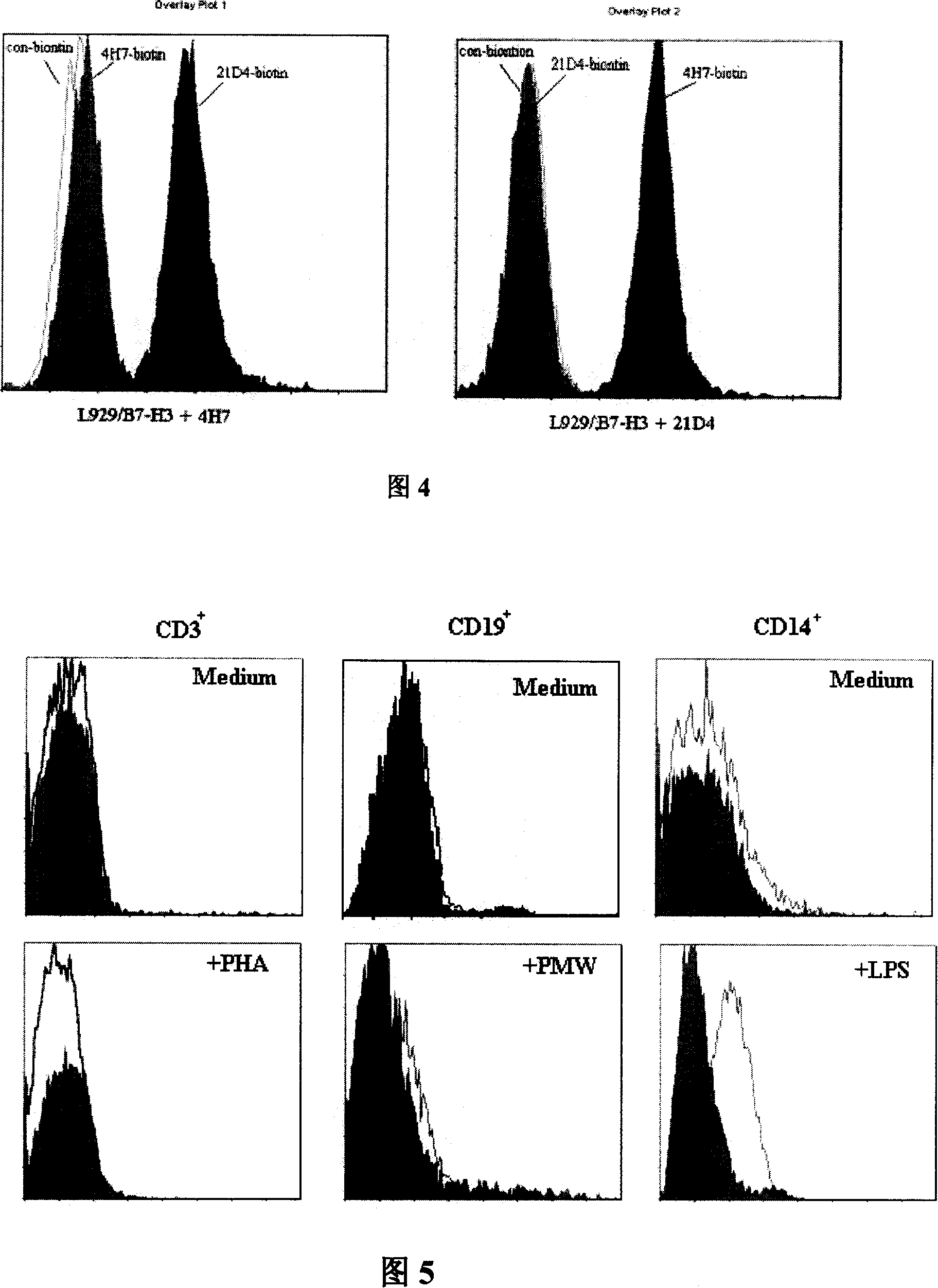
Preparation for anti human B7-H3 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN101104639AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsDendritic cellMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to binding proteins or polypeptides of a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, specifically relates to an anti-human B7-H3 monoclonal antibodies 4H7 and 21D4, a preparation method of the monoclonal antibodies, and the applications of the monoclonal antibodies in tumor (gastric cancer) prognostic evaluation and in being used as a marked molecule for identification of human dendritic cells (DC).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com