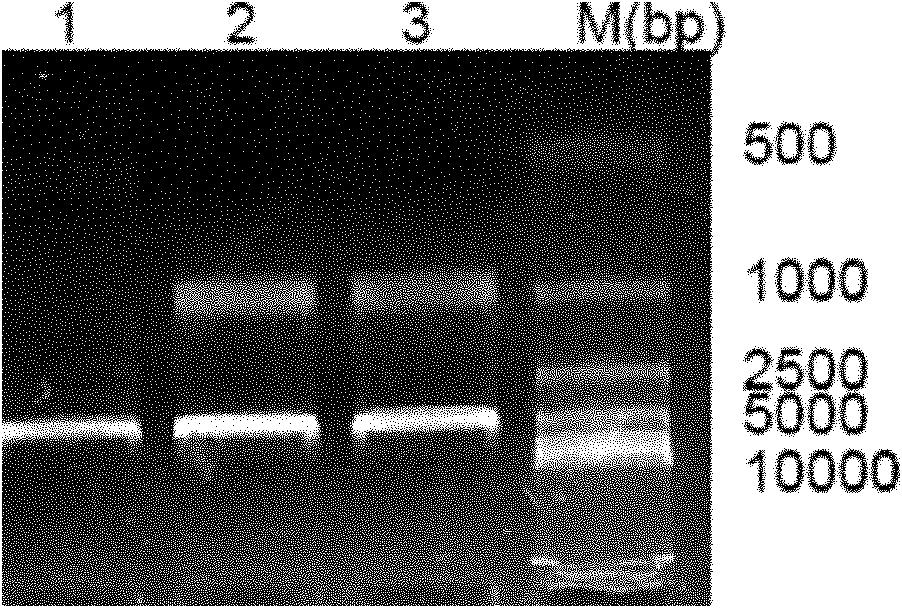
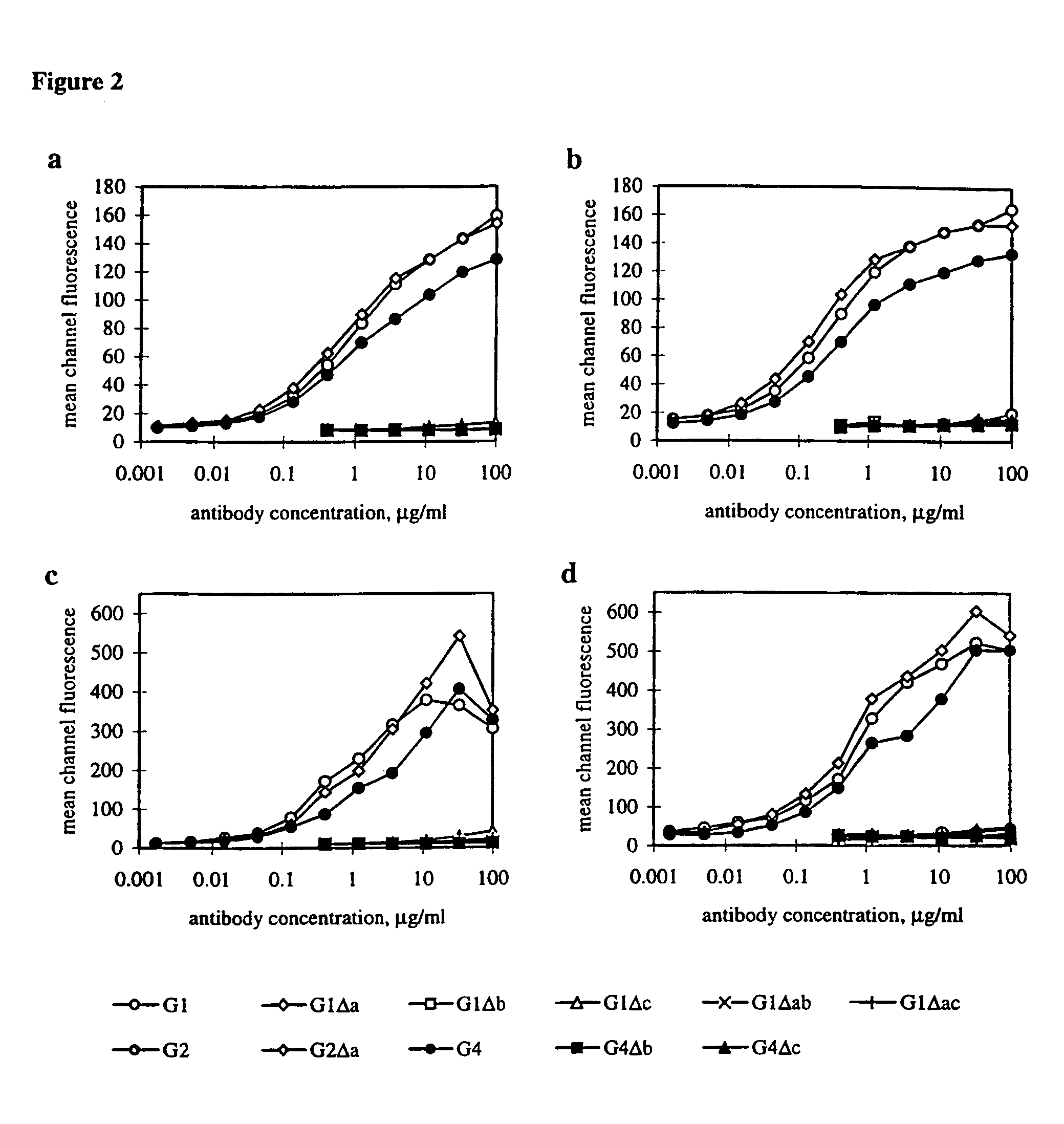
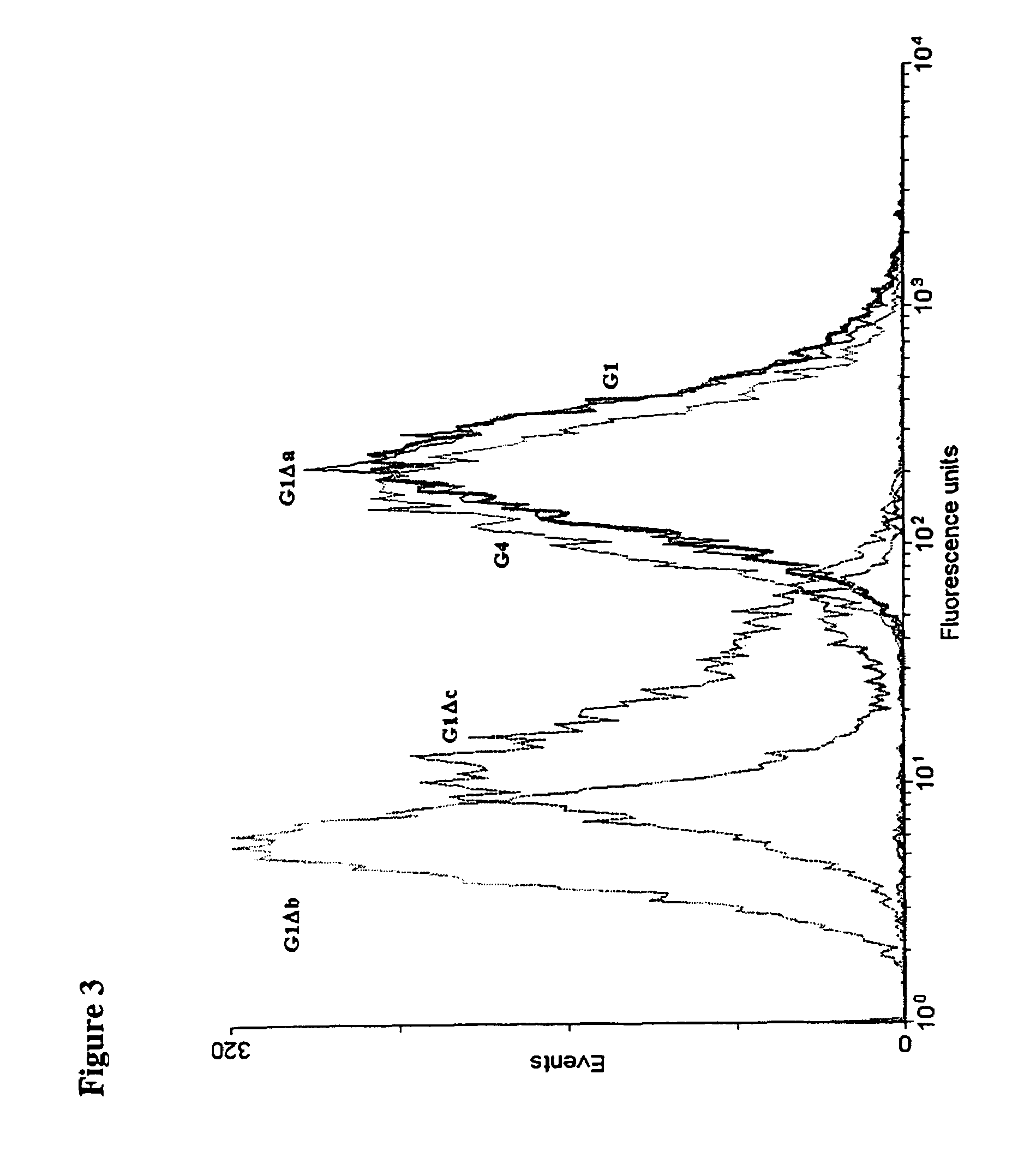
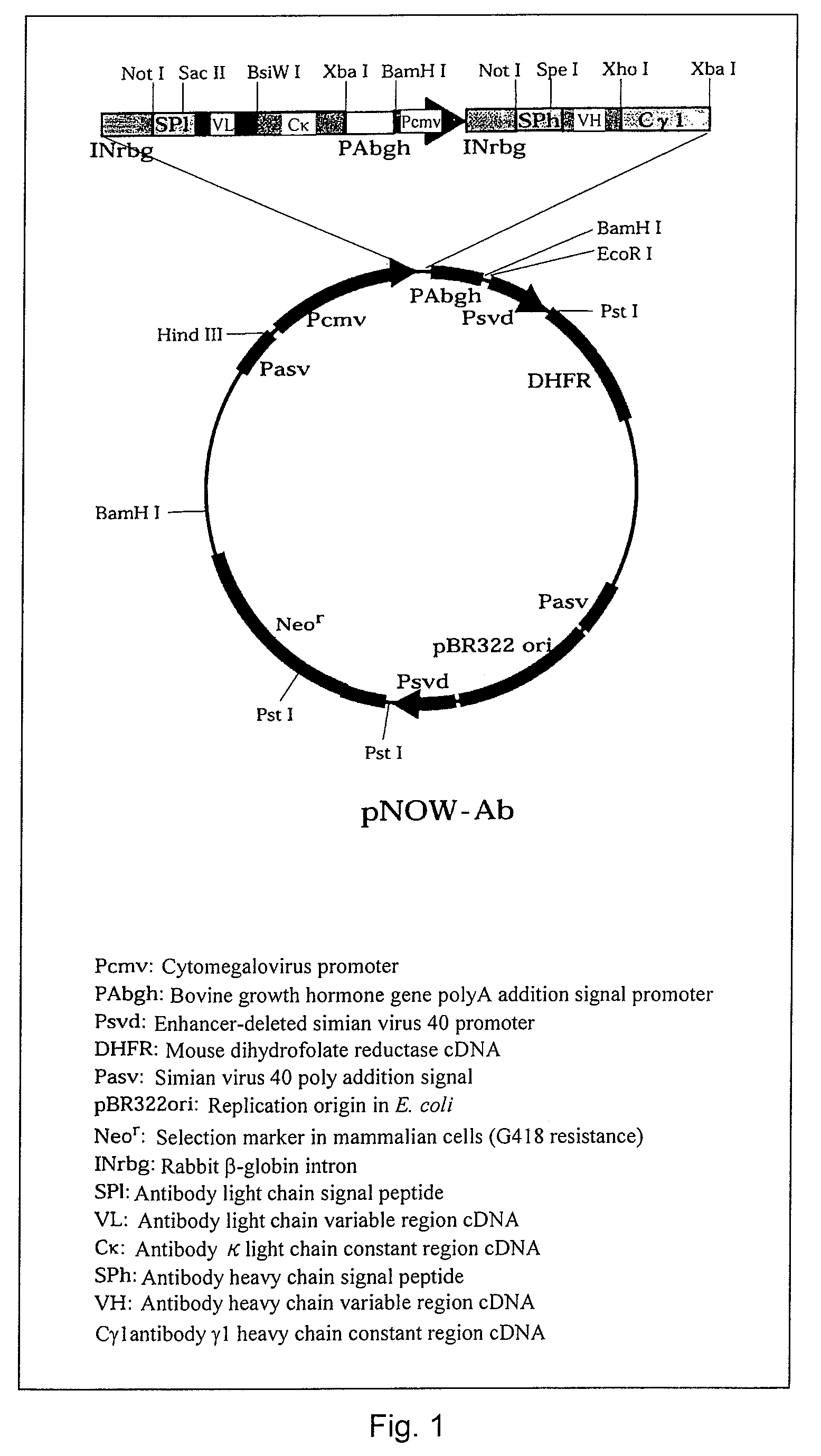
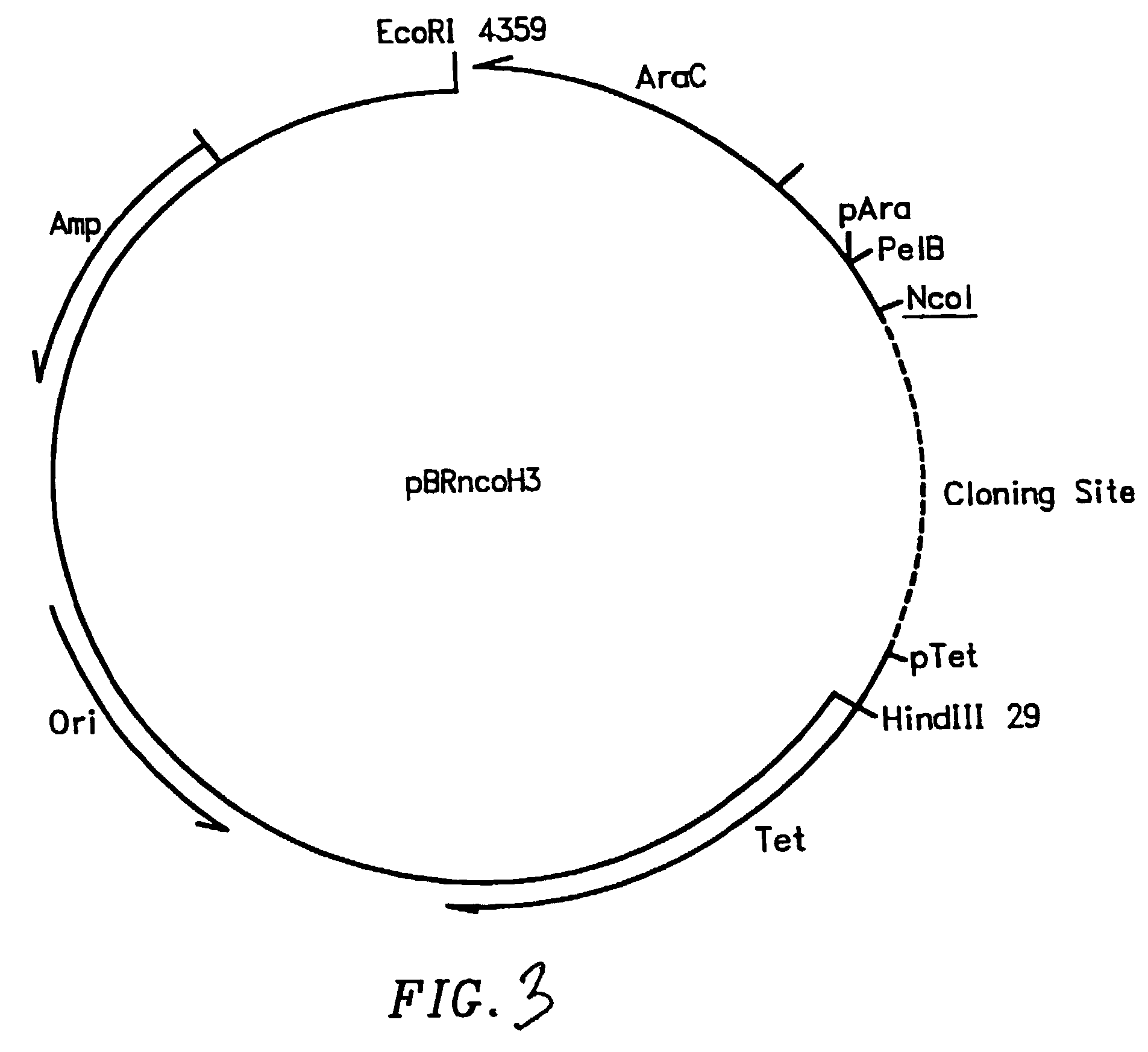
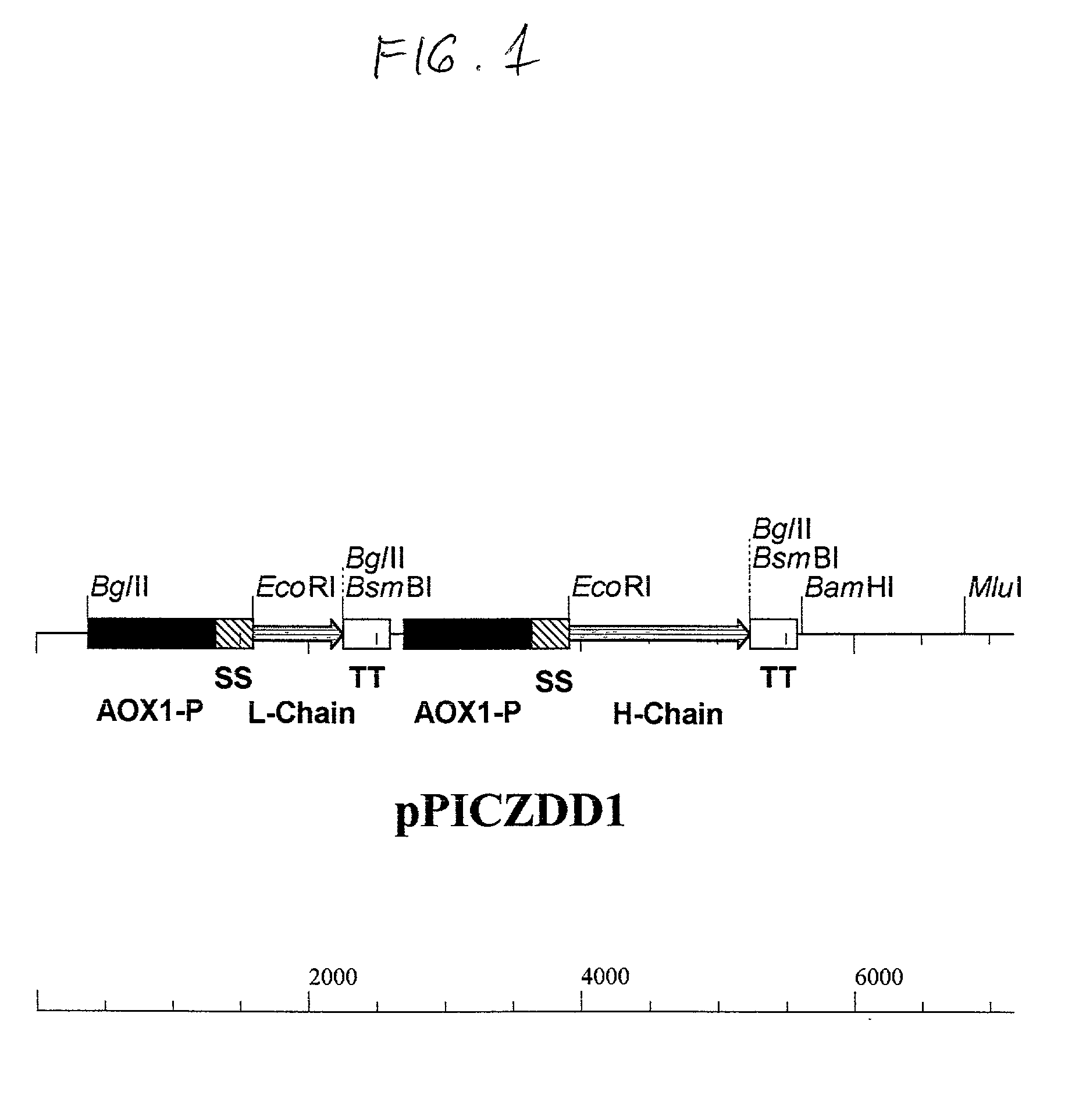
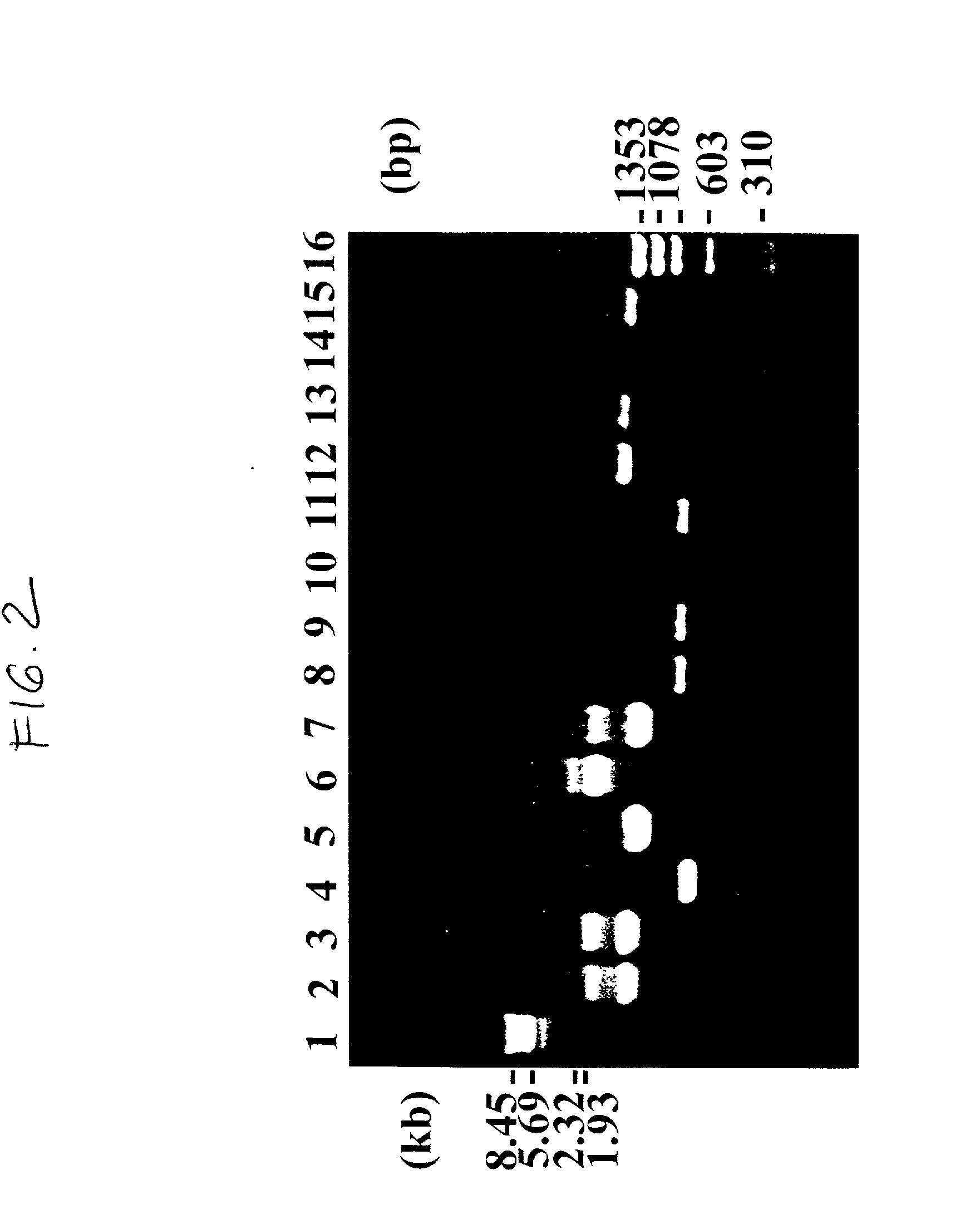
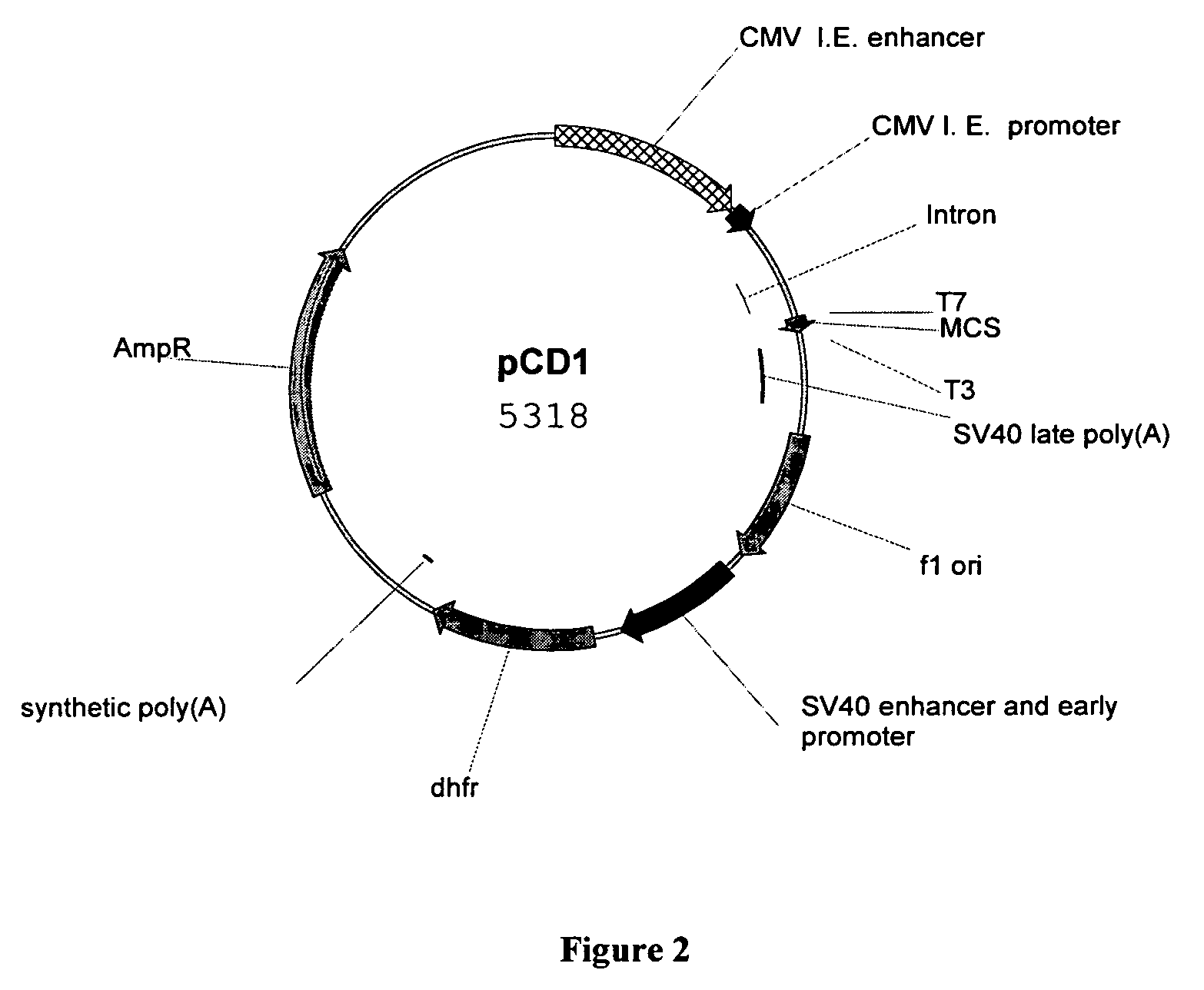
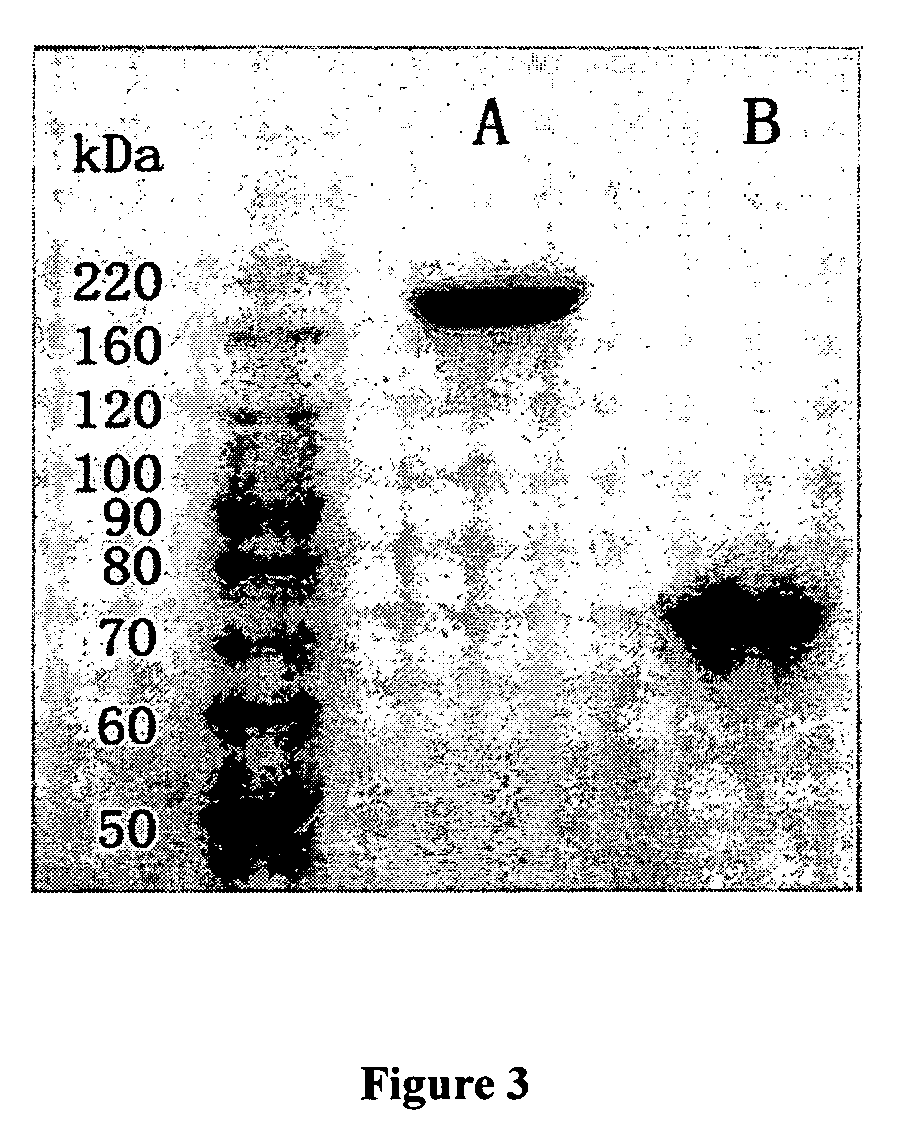
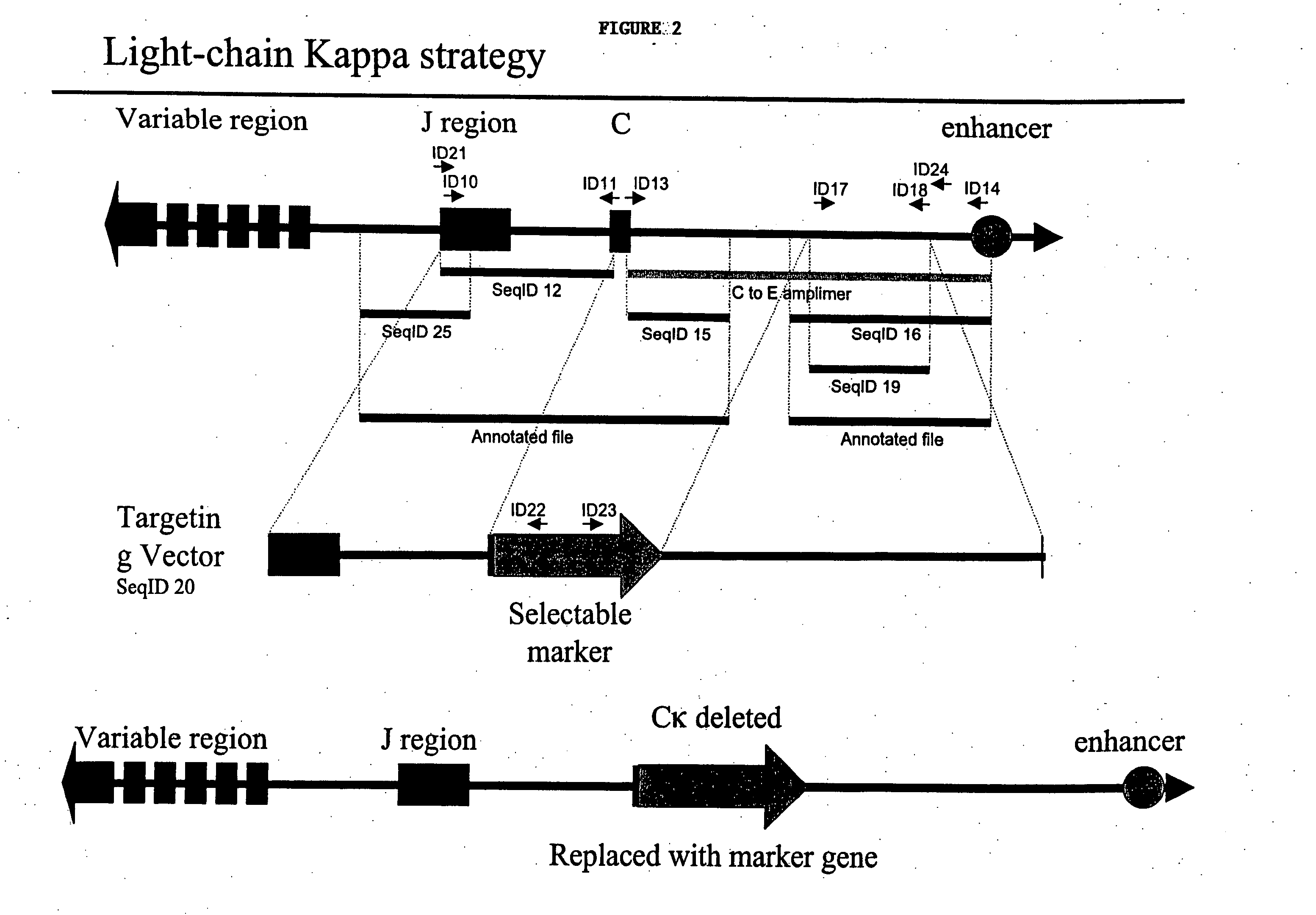
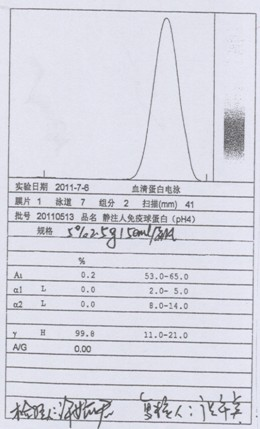
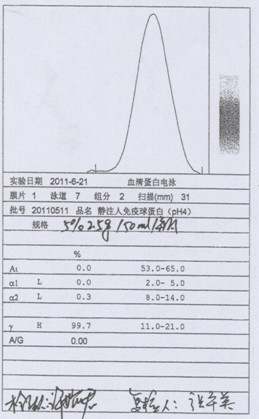
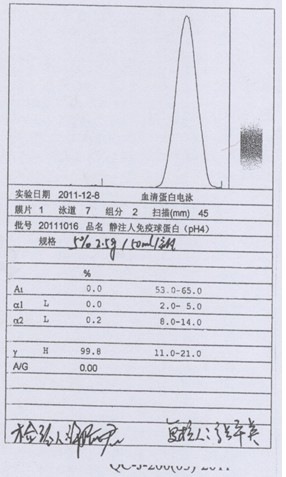
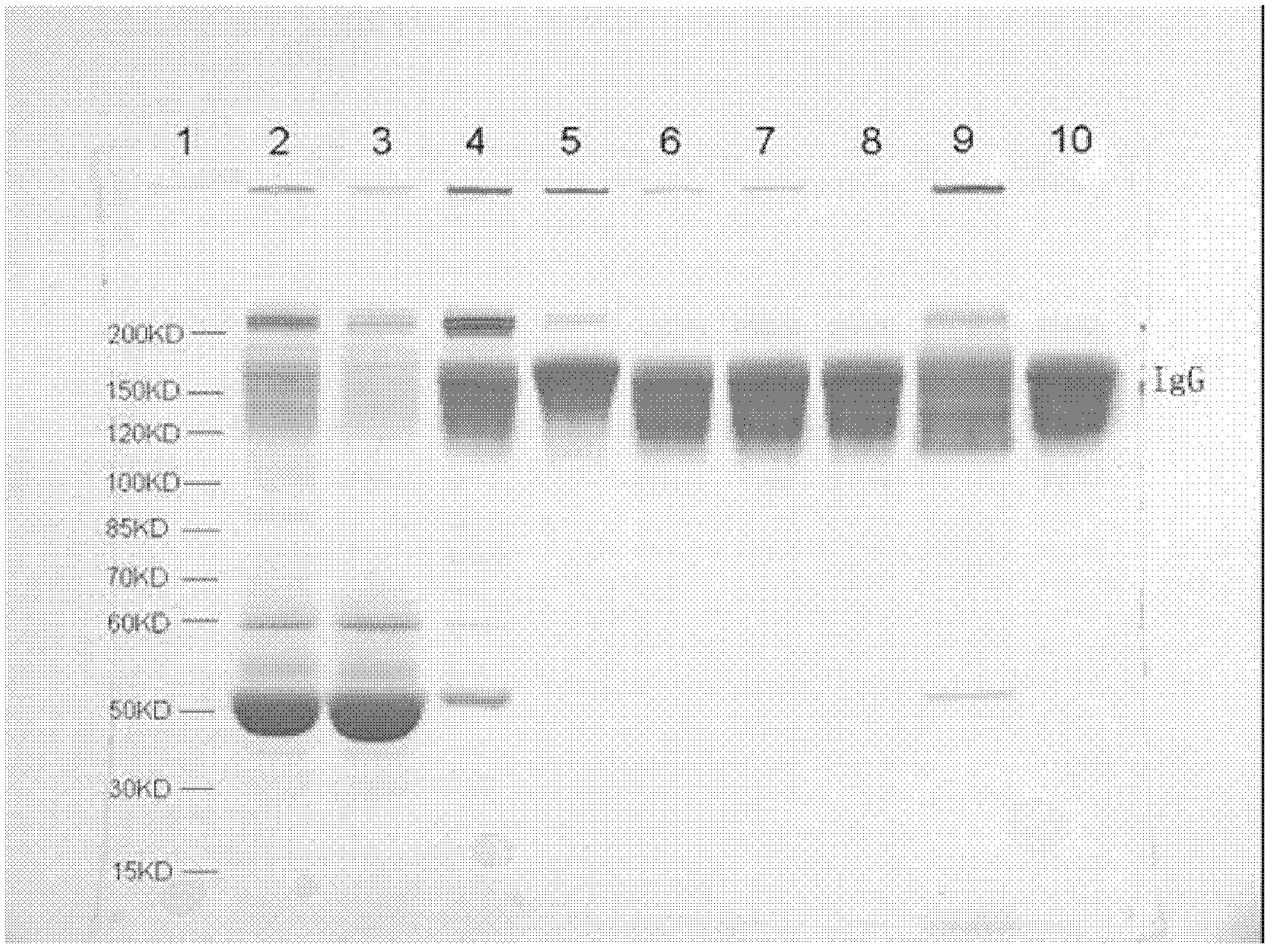Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
266 results about "Human immunoglobulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human immunoglobulin is made from human blood plasma. It contains antibodies against a large number of viruses. Human immunoglobulin therapy first occurred in the 1930s and a formulation for injection into a vein was approved for medical use in the United States in 1981.
Humanized immunoglobulins
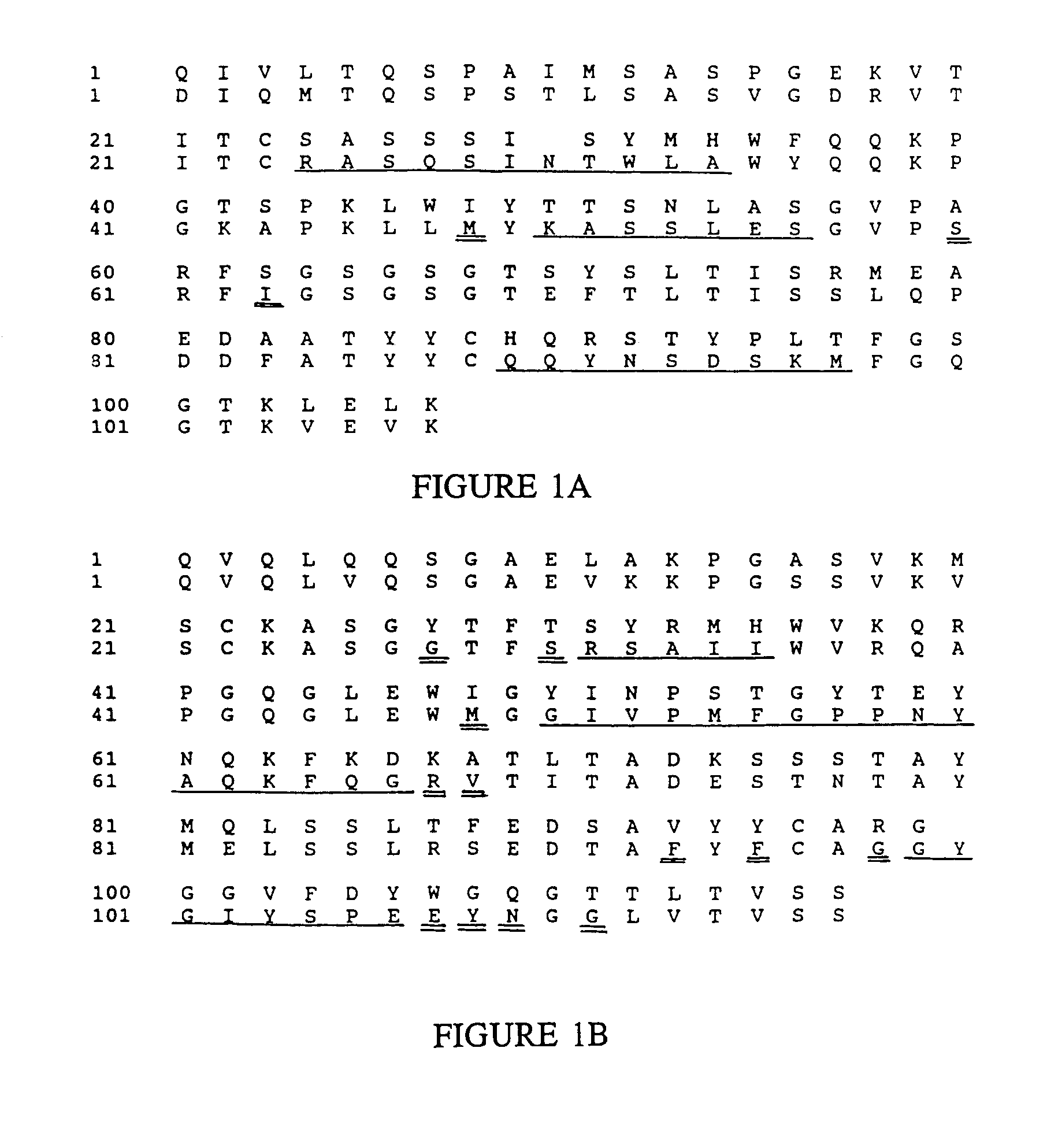
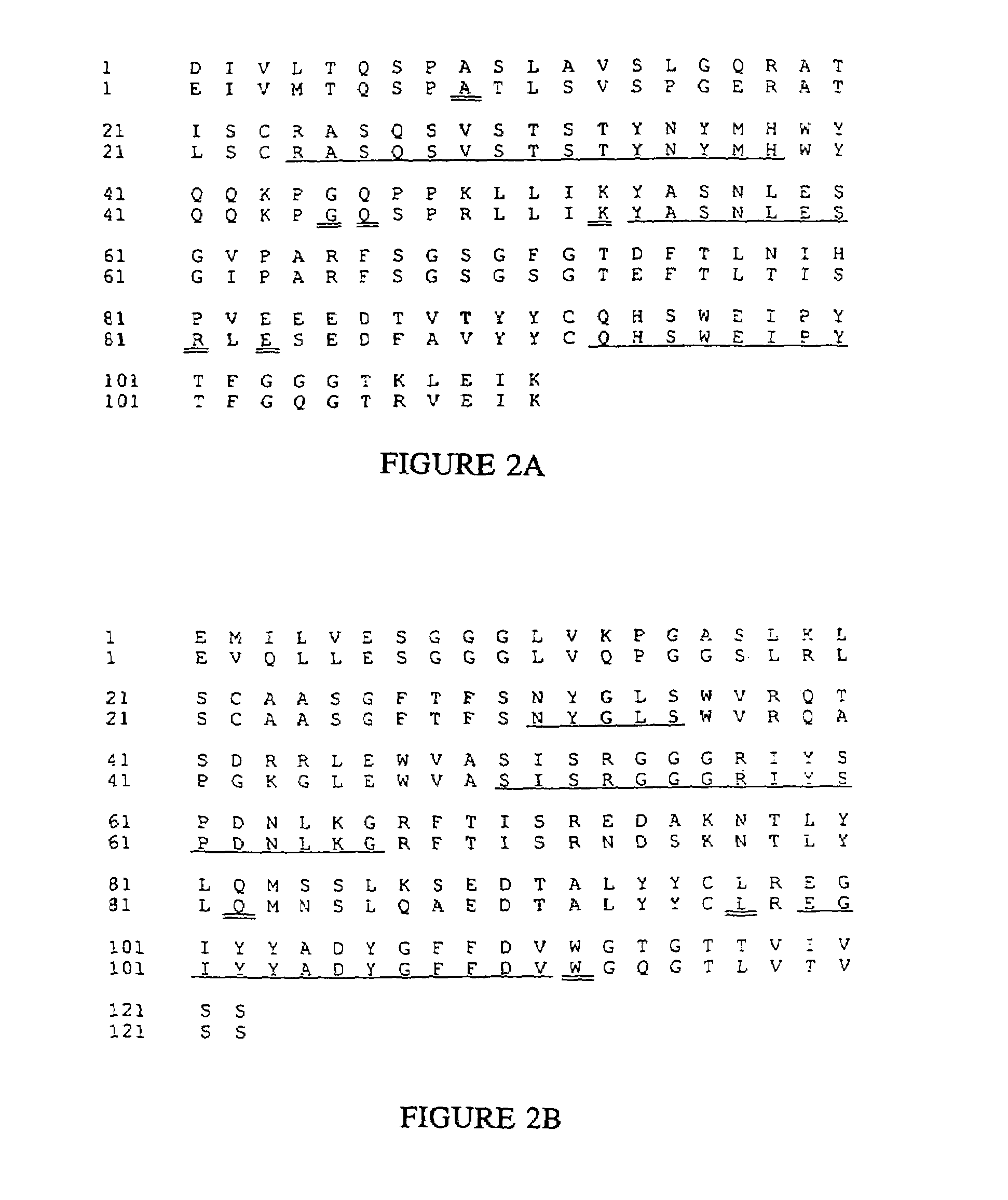
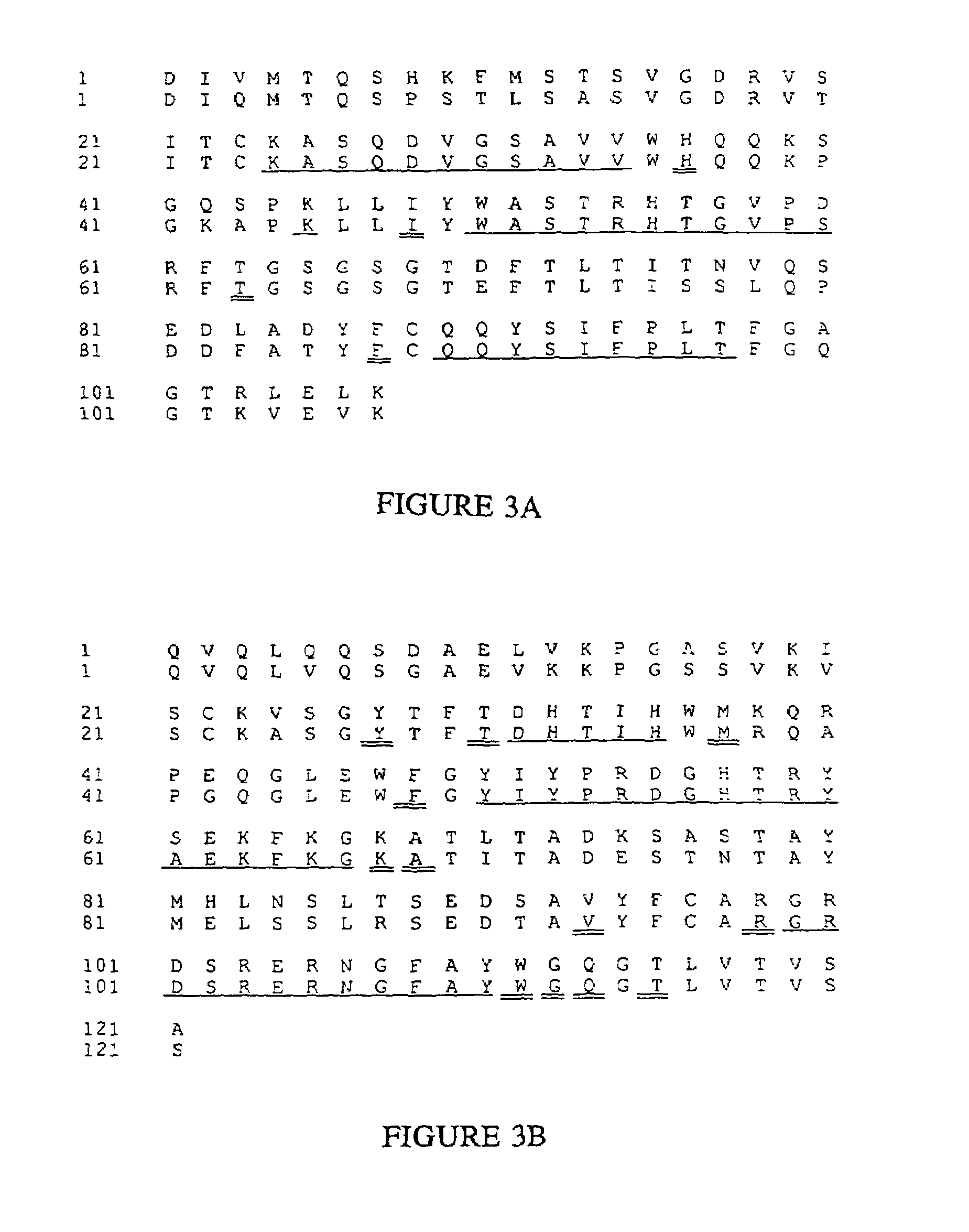
Novel methods for producing, and compositions of, humanized immunoglobulins having one or more complementarity determining regions (CDR's) and possible additional amino acids from a donor immunoglobulin and a framework region from an accepting human immunoglobulin are provided. Each humanized immunoglobulin chain will usually comprise, in addition to the CDR's, amino acids from the donor immunoglobulin framework that are, e.g., capable of interacting with the CDR's to effect binding affinity, such as one or more amino acids which are immediately adjacent to a CDR in the donor immunoglobulin or those within about about 3Å as predicted by molecular modeling. The heavy and light chains may each be designed by using any one or all of various position criteria. When combined into an intact antibody, the humanized immunoglobulins of the present invention will be substantially non-immunogenic in humans and retain substantially the same affinity as the donor immunoglobulin to the antigen, such as a protein or other compound containing an epitope.
Owner:PDL BIOPHARMA INCORPORATED
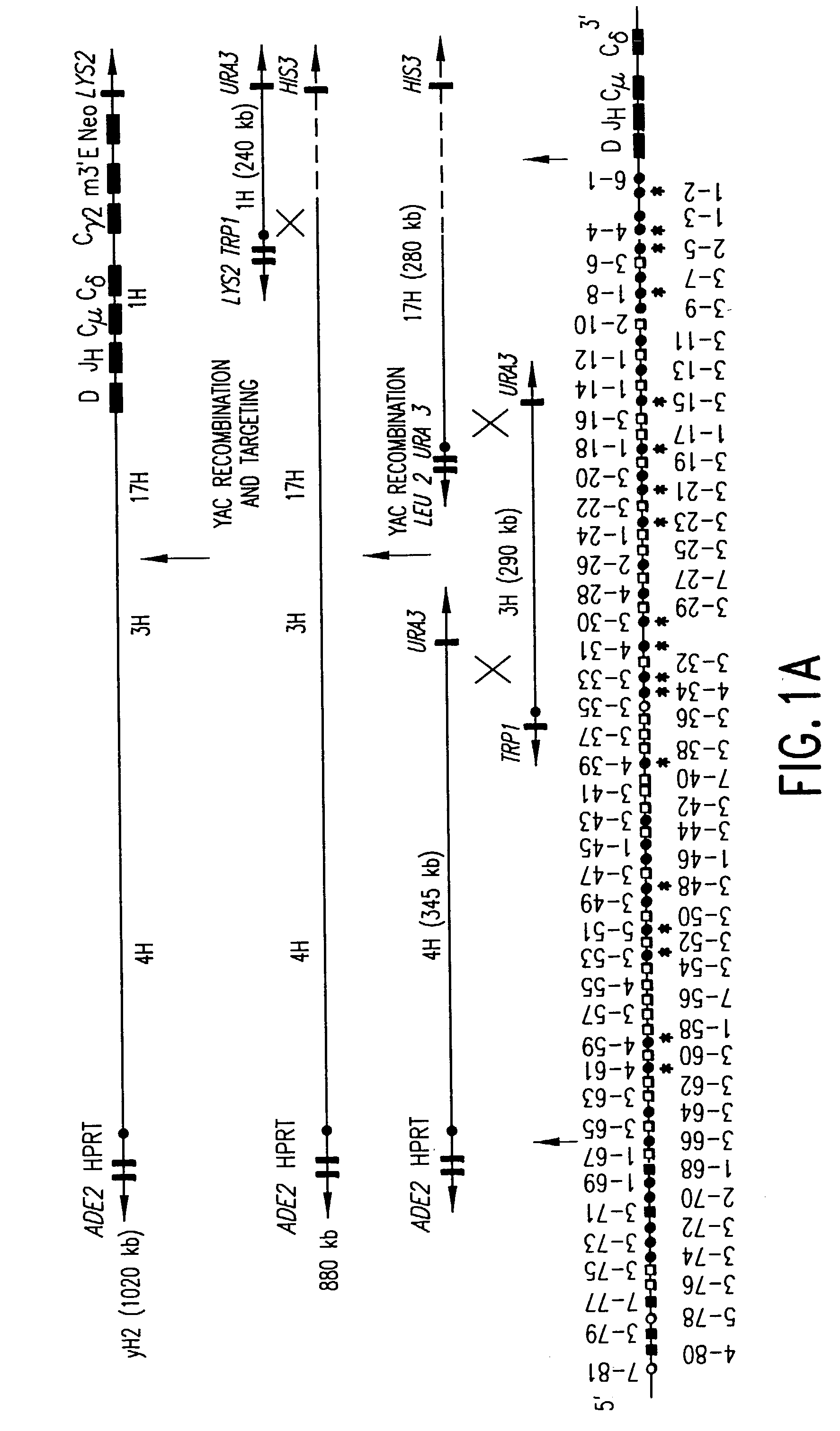
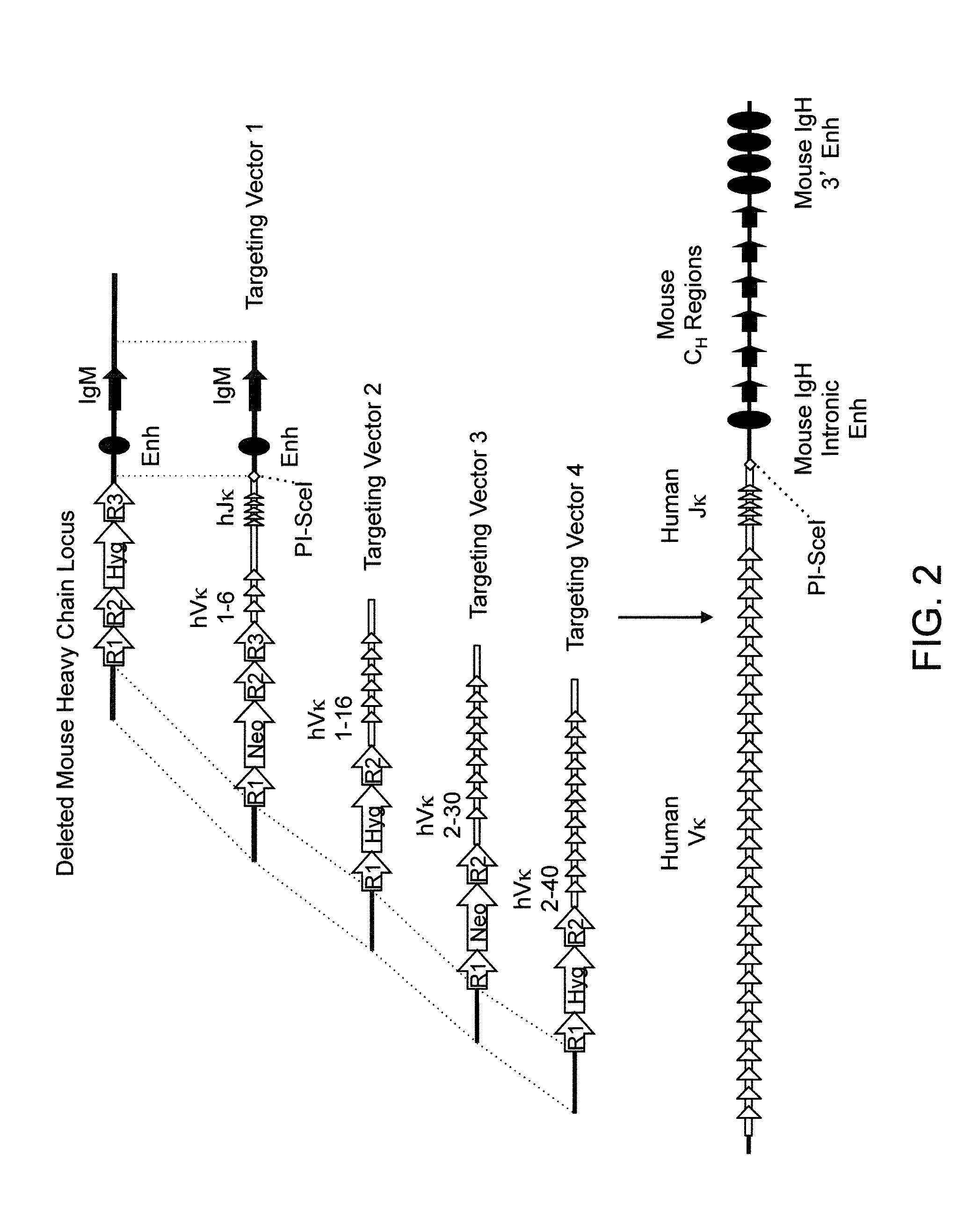
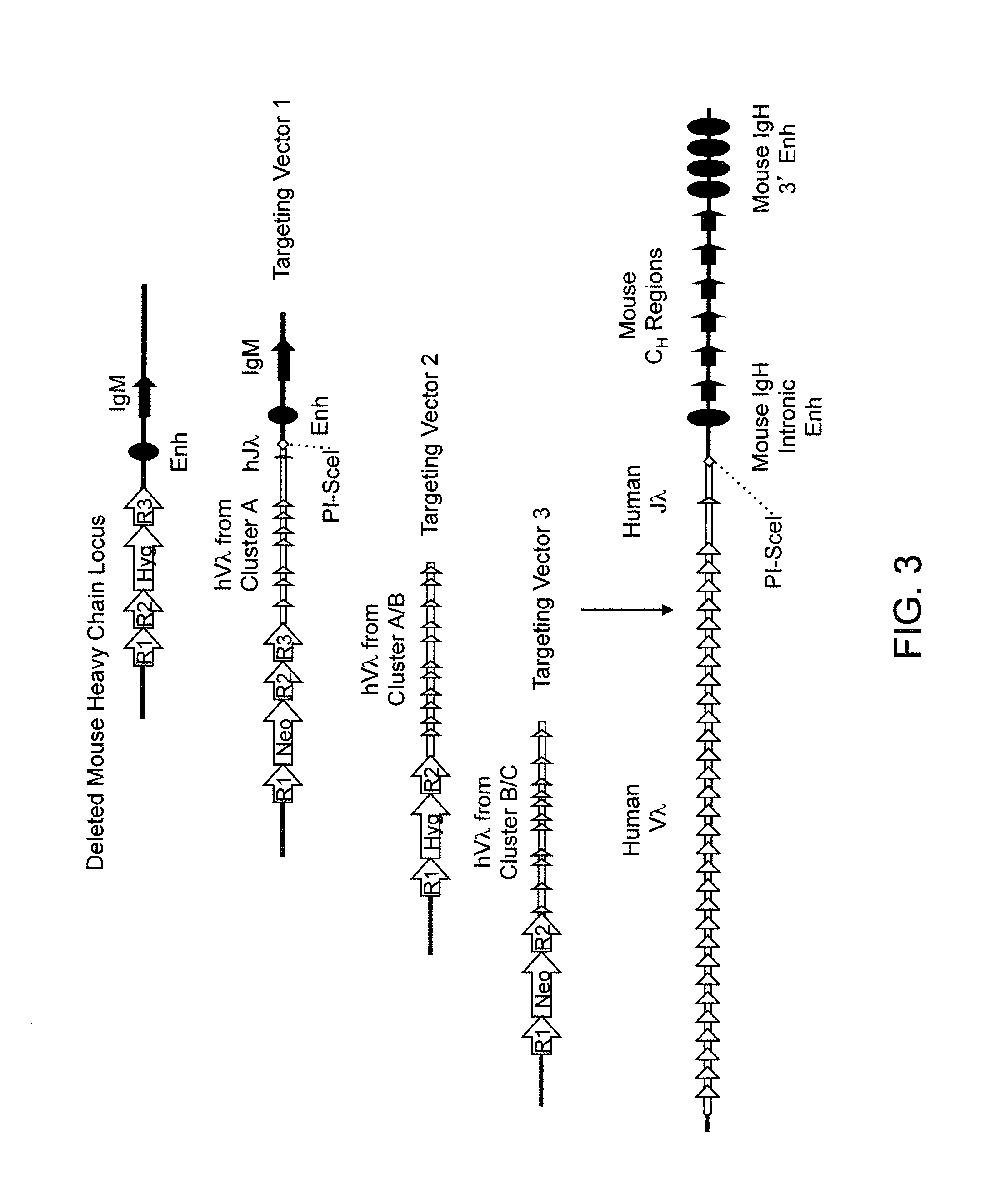
Transgenic mammals having human Ig loci including plural VH and VK regions and antibodies produced therefrom
InactiveUS7064244B2Reduced development and maturation of B-cellsEfficient productionAntipyreticAnalgesicsHuman animalMammal
The present invention relates to transgenic non-human animals that are engineered to contain human immunoglobulin gene loci. In particular, animals in accordance with the invention possess human Ig loci that include plural variable (VH and Vκ) gene regions. Advantageously, the inclusion of plural variable region genes enhances the specificity and diversity of human antibodies produced by the animal. Further, the inclusion of such regions enhances and reconstitutes B-cell development to the animals, such that the animals possess abundant mature B-cells secreting extremely high affinity antibodies.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
Transgenic animals for producing specific isotypes of human antibodies via non-cognate switch regions
InactiveUS7049426B2Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenExon
The present invention provides fully human antibodies in a transgenic animal of a desired isotype in response to immunization with any virtually any desired antigen. The human immunoglobulin heavy chain transgene in the foregoing animals comprises a human constant region gene segment comprising exons encoding the desired heavy chain isotype, operably linked to switch segments from a constant region of a different heavy chain isotype, i.e., a non-cognate switch region. Said additional constant region segment comprises a switch region and human constant region coding segment, wherein the constant region coding segment is operably linked to a switch region that it is not normally associated with, i.e., a non-cognate switch region. In the transgenes of the invention, the non-cognate switch region may be a switch region from a different species than the constant region coding segment. The switch region and membrane exons of the invention may comprise a human gamma-2 constant region and the secreted constant region exons are from a human gamma-1 or a human gamma-4 constant region.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
Method for preparing human immunoglobulin concentrates for therapeutic use
InactiveUS7186410B2Simple processHighly compatibleAntibacterial agentsSerum immunoglobulinsAnion-exchange chromatographyBlood plasma
The invention concerns a method for preparing human immunoglobulin concentrates for therapeutic use, from plasma or a plasma fraction. The method comprises pre-purification and a single anion-exchange chromatography carried out at alkaline pH, thereby enabling the immunoglobulins to be retained on the chromatographic support and fractionated. The method enables to obtain IgG, IgA and IgM concentrates.
Owner:LABE FR DU FRACTIONNEMENT & DES BIOTECH SA
Transgenic mammals having human Ig loci including plural Vh and Vk regions and antibodies produced therefrom
InactiveUS20080098490A1Reduced development and maturation of B-cellsEfficient productionAntipyreticAnalgesicsHuman animalMammal
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
Binding molecules derived from immunoglobulins which do not trigger complement mediated lysis
InactiveUS7597889B1Maximizing numberIncreasing therapeutic potentialOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensHeavy chainImmunoglobulin IgE
Disclosed are binding molecules which are recombinant polypeptides containing: (i) a binding domain capable of binding a target molecule, and (ii) an effector domain having an amino acid sequence substantially homologous to all or part of a constant domain of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain; characterized in that the binding molecule is capable of binding the target molecule without triggering significant complement dependent lysis, or cell mediated destruction of the target, and more preferably wherein the effector domain is capable of specifically binding FcRn and / or FcγRIIb. These are generally based on chimeric domains which are derived from two or more human immunoglobulin heavy chain CH2 domains domains. In preferred embodiments the regions 233-236, and 327-331, are modified, as are further residues to render the molecule null allotypic. Also disclosed are nucleic acids, host cells, production processes and materials, and uses. Pharmaceutical preparations are also disclosed.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody
A murine anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody having cell growth inhibitory activities is disclosed. Cell growth inhibitory activities include apoptosis against human CD20 antigen expressing cells in culture of the CD20 antigen expressing cells without effector cells. The anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody is incorporated into chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in which the amino acid sequences of the variable regions of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and the amino acid sequences of the constant regions of human immunoglobulin are fused. Also a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody is described which includes all of the variable region CDRs of the H chain of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and all of the variable region CDRs of the L chain of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and an amino acid sequence of human immunoglobulin. A nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence of the chimeric or humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody can be expressed in mammalian cells.
Owner:INST OF IMMUNOLOGY
Human antibodies
InactiveUS7135287B1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulin IgEGenetically modified animal
The invention uses the power of display selection methods to screen libraries of human immunoglobulin genes from nonhuman transgenic animals expressing human immunoglobulins. Such screening produces unlimited numbers of high affinity human antibodies to any target of interest.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
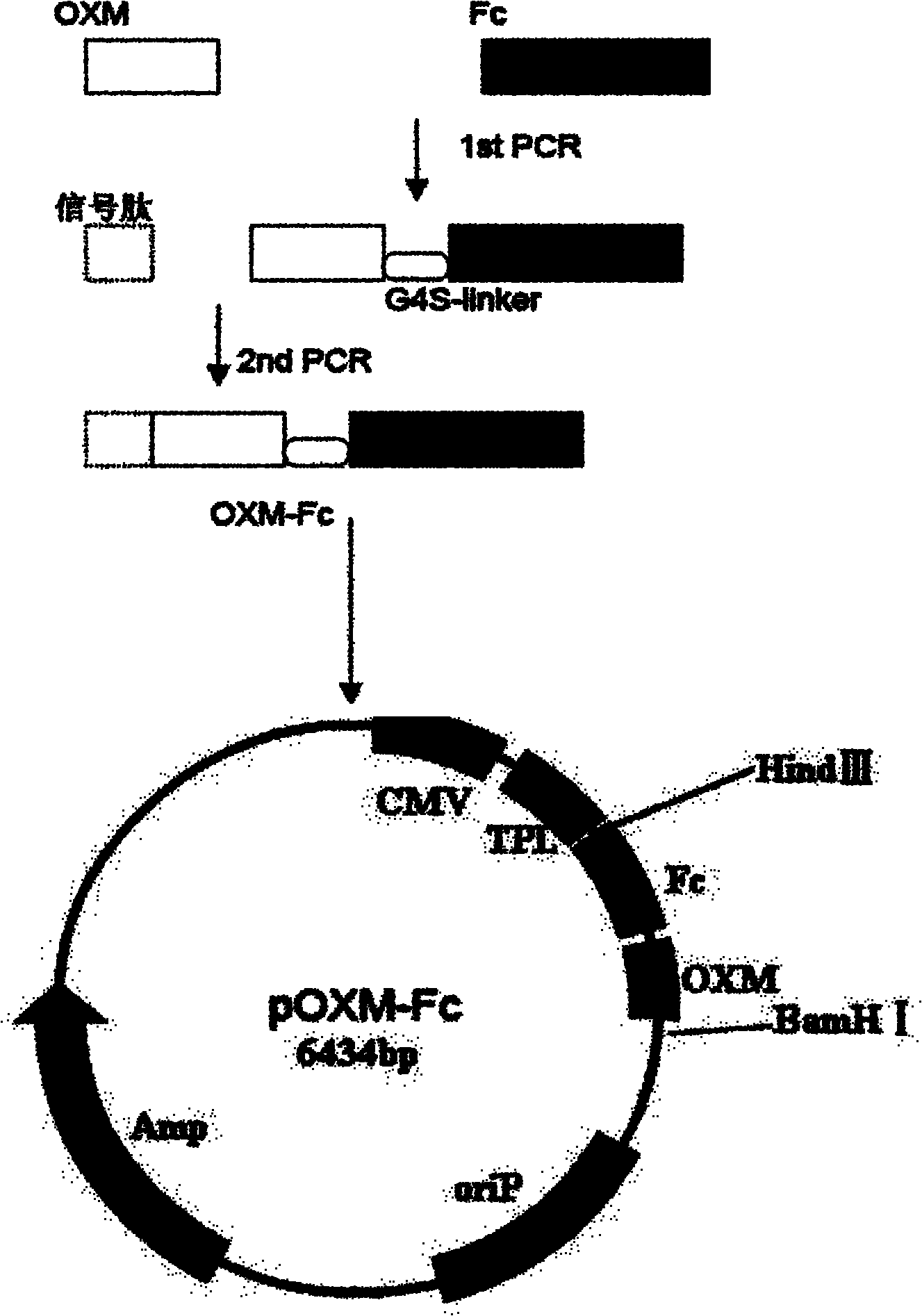
Recombinant oxyntomodulin (OXM) fusion protein, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102010473AExtended half-lifeImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseRecombinant expression
The invention relates to long-acting and stable oxyntomodulin (OXM). An Fc segment of human immunoglobulin G and the human OXM form fusion protein through a connecting peptide. A method for preparing the fusion protein comprises the following steps of: preparing the human OXM and an Fc segment gene of the human immunoglobulin respectively, and connecting the human OXM and the Fc segment gene of the human immunoglobulin to construct connecting segment-containing recombinant expression vectors; and transforming host cells by using the recombinant expression vectors, culturing the host cells and recovering from cell culture and purifying the host cells to obtain the recombinant fusion protein. The fusion protein can be used for preparing medicaments for treating metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
Owner:曹鹏 +1
Humanized Rodents that Express Heavy Chain Containing VL Domains
InactiveUS20130212719A1Reduced fertilityImprove fertilityAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsGenetic MaterialsVariable domain
Non-human animals, tissues, cells, and genetic material are provided that comprise a modification of an endogenous non-human heavy chain immunoglobulin sequence and that comprise an ADAM6 activity functional in a rodent (e.g., a mouse), wherein the non-human animals rearrange human immunoglobulin light chain gene segments in the context of heavy chain constant regions and express immunoglobulin-like molecules comprising human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains fused to heavy chain constant domains that are cognate with human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains fused to light chain constant domains.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
InactiveUS20140013456A1Reduce the binding forceNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsNucleotideGenetically modified crops
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains derived from a limited repertoire of human immunoglobulin light chain variable gene segments that comprise histidine modifications in their germline sequence. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising histidine residues encoded by histidine codons introduced into immunoglobulin light chain nucleotide sequences are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Interfusion protein of human interleukin 15 and Fe
ActiveCN1760209APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsWhite blood cellImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
A human interleukin 15-Fc fusion protein composed of interleukin 15 and the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin, which are linked via joining peptide, the nucleic acid ofr coding it, the expression carrier containing said nucleic acid, its composite medicine for preventing and treating microbial infection and its preparing process are disclosed.
Owner:上海海欣生物技术有限公司
Method of generating single vl domain antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20110123527A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsFermentationSingle-Chain AntibodiesVariable domain
The present invention describes methods of generating single VL domain antibodies, including chimeric single chain antibodies that comprise of a variable region of a human immunoglobulin κ or λ light chain and a non-human constant region. The non-human constant region is devoid of a first constant domain CH1, and the variable region is devoid of a heavy chain variable domain.
Owner:ABLEXIS LLC
Exendin-4 and analog fusion protein thereof
ActiveCN101891823APromote regenerationPromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseMotility
The invention discloses exendin-4, an analog fusion protein thereof, the corresponding polynucleotide sequence, carrier, host cell and pharmaceutical composite and a preparation method and applications of the fusion protein. The fusion protein is prepared by fusing exendin-4 and analog thereof with human immunoglobulin IgG2-Fc through special connecting peptide and has better stability and loner half-life in vivo. The fusion protein can be administered by performing local delivery, using aerosol and using injection. The fusion protein can promote the regeneration and repair of islet beta cells, increase islet beta cells, promote the secretion of insulin and improve the sensitivity of organism to insulin. The fusion protein is used to cure diabetes, adiposity and other diseases which can be benefited by reducing plasma glucose and inhibiting gastrointestinal motility and gastric emptying.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
Functionally assembled antigen-specific intact recombinant antibody and a method for production thereof
Functionally assembled antigen-specific intact recombinant monoclonal antibody produced by transformation of the methylotropic yeast, P. pastoris with mouse / human immunoglobulin genes encoding heavy and light chains. A method for production of the intact monoclonal antibodies, a recombinant yeast expression vector and the antibody-specific MRNA synthesis. A process for a large-scale production of the functionally assembled intact recombinant antibody.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
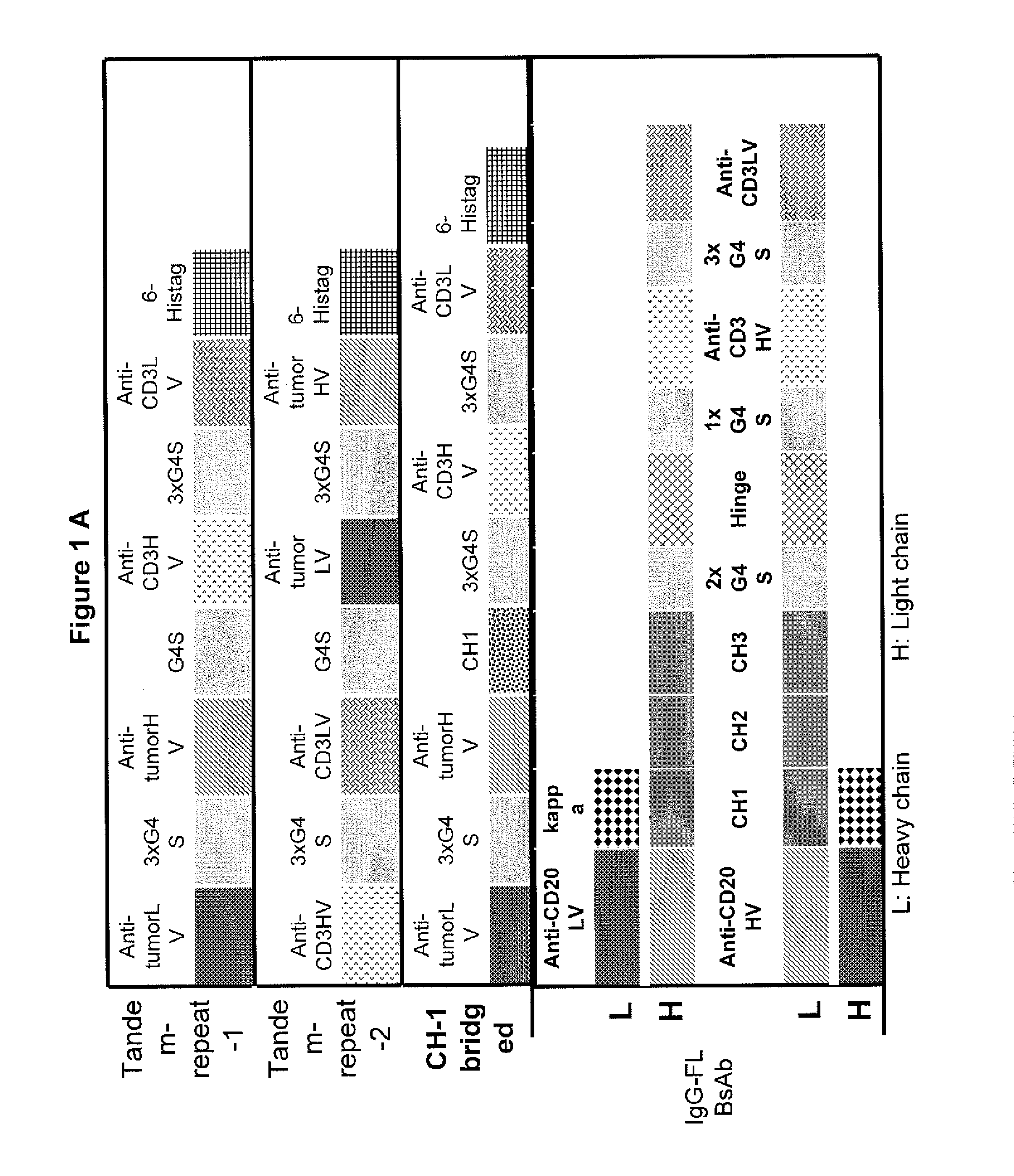
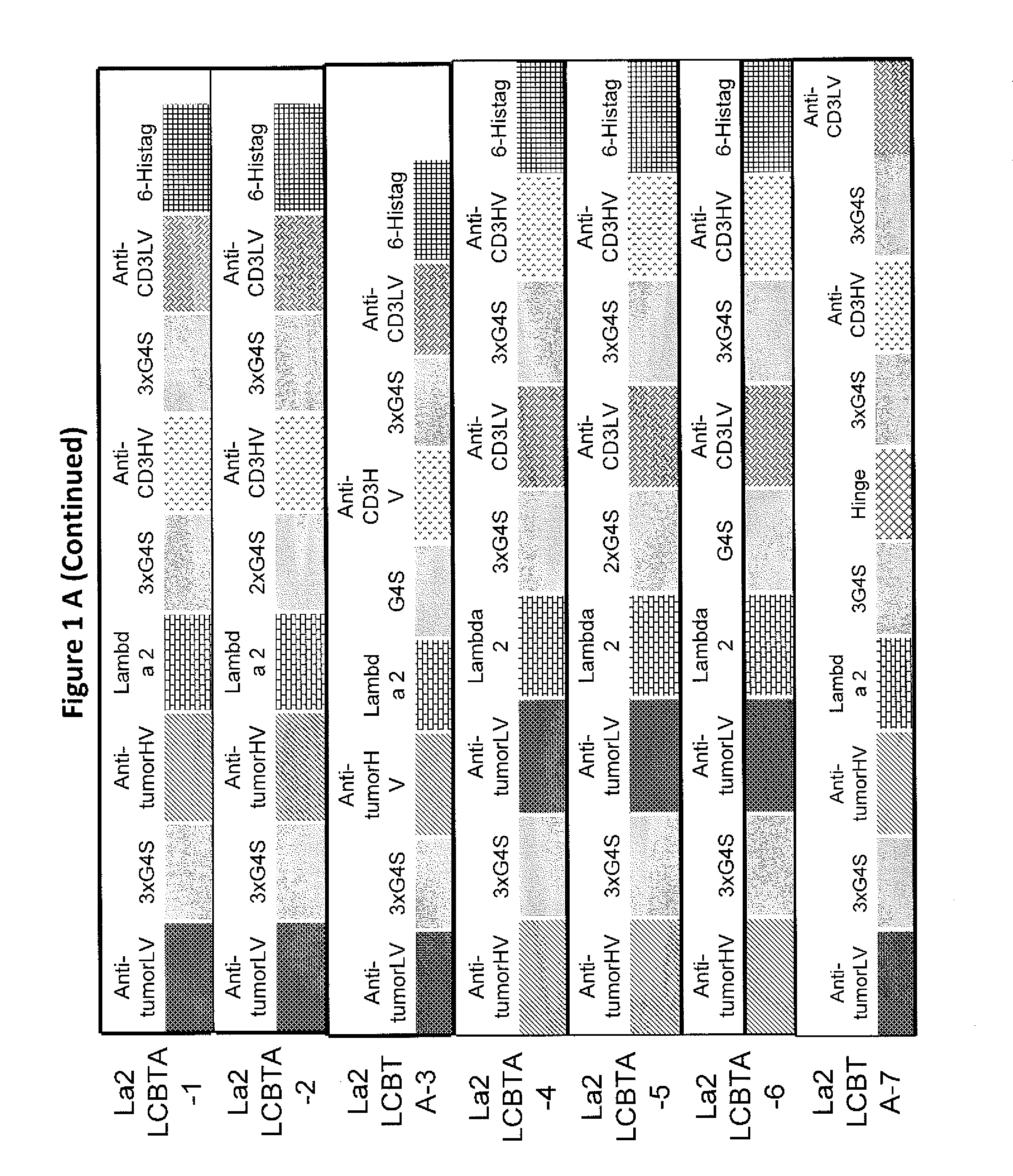
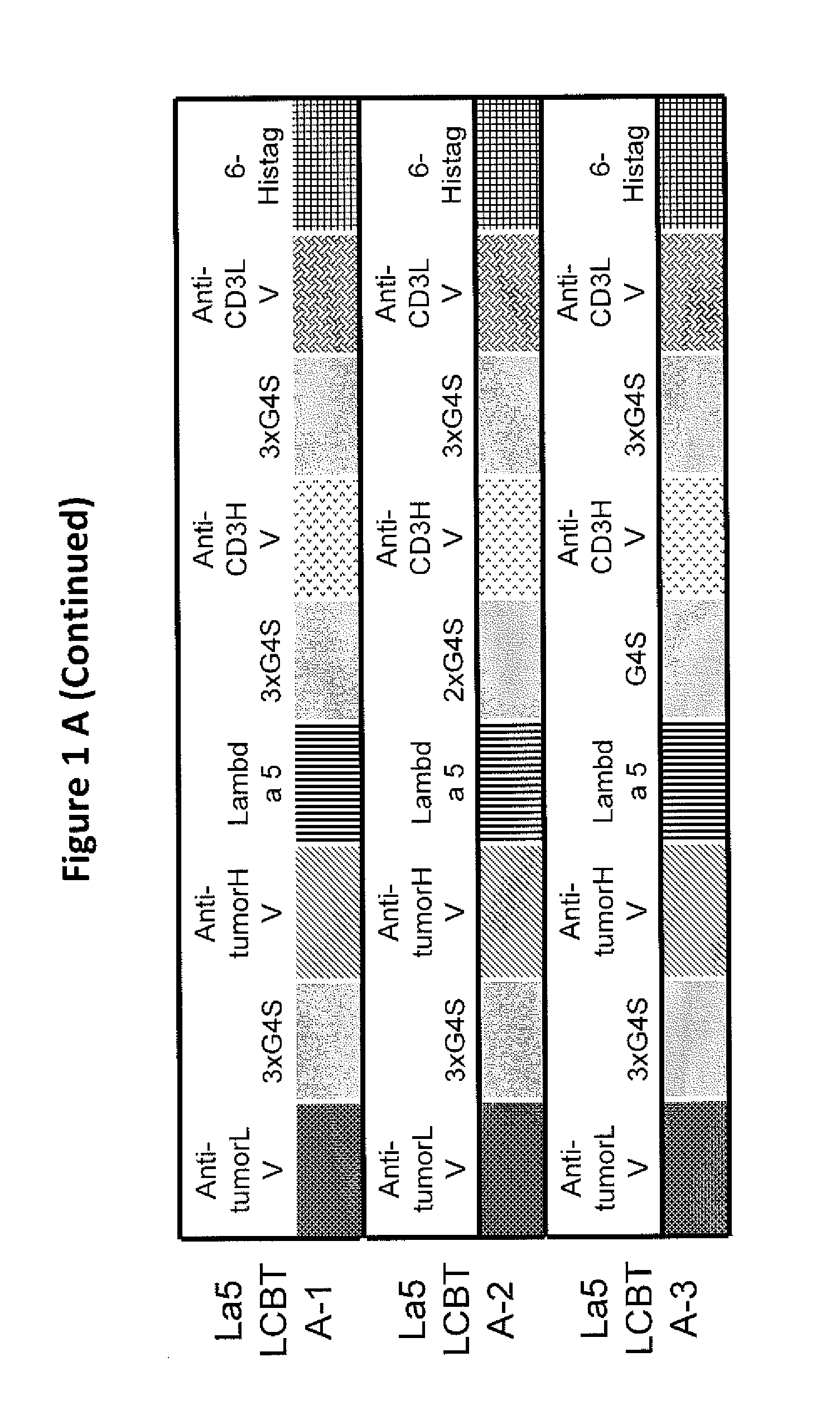
Light chain-bridged bispecific antibody
InactiveUS20130165638A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyClinical therapy
This invention describes a novel format of monomeric bispecific fusion protein with immune activating property for clinical therapies. A bispecific fusion protein includes a first targeting domain with a specificity for a first target of interest; a bridging domain derived from a constant region of a light chain or heavy chain of an immunoglobulin, which may be a human immunoglobulin; and a second targeting domain with a specificity for a second target of interest. The bispecific fusion protein may further include a linker fused to the N-terminus or the C-terminus of the bridging domain. The first targeting domain is fused to the bridging domain and the second targeting domain is fused to the bridging domain or the linker. The linker may include a GGGGS sequence. The first target of interest may be CD20, Her2 / neu, or EpCAM, and the second targeting domain is a T-lymphocyte activating domain.
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY +1
Recombinant human EPO-Fc fusion proteins with prolonged half-life and enhanced erythropoietic activity in vivo
ActiveUS7625564B2Enhanced erythropoietic bioactivityExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeRed blood cell
A recombinant fusion protein comprising a human erythropoietin peptide portion linked to an immunoglobulin peptide portion is described. The fusion protein has a prolonged half-life in vivo in comparison to naturally occurring or recombinant native human erythropoietin. In one embodiment of the invention, the protein has a half-life in vivo at least three fold higher than native human erythropoietin. The fusion protein also exhibits enhanced erythropoietic bioactivity in comparison to native human erythropoietin. In one embodiment, the fusion protein comprises the complete peptide sequence of a human erythropoietin (EPO) molecule and the peptide sequence of an Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin IgG1. The Fc fragment in the fusion protein includes the hinge region, CH2 and CH3 domains of human immunoglobulin IgG1. The EPO molecule may be linked directly to the Fc fragment to avoid extraneous peptide linkers and lessen the risk of an immunogenic response when administered in vivo. In one embodiment the hinge region is a human Fc fragment variant having a non-cysteine residue at amino acid 6. The invention also relates to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding the fusion protein and transfected cell lines and methods for producing the fusion protein. The invention further includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising the fusion protein and methods of using the fusion protein and / or the pharmaceutical compositions, for example to stimulate erythropoiesis in subjects in need of therapy.
Owner:NOVAGEN HLDG CORP
Ungulates with genetically modified immune systems
InactiveUS20060130157A1Eliminate expressionNucleic acid vectorGenetic engineeringGenomic DNAUngulate
The present invention provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional endogenous immunoglobulin loci. The present invention also provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which express xenogenous, such as human, immunoglobulin loci. The present invention further provides ungulate, such as porcine genomic DNA sequence of porcine heavy and light chain immunogobulins. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and medical therapy. In addition, methods are provided to prepare such animals, organs, tissues, and cells.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Transgenic animals and methods of use
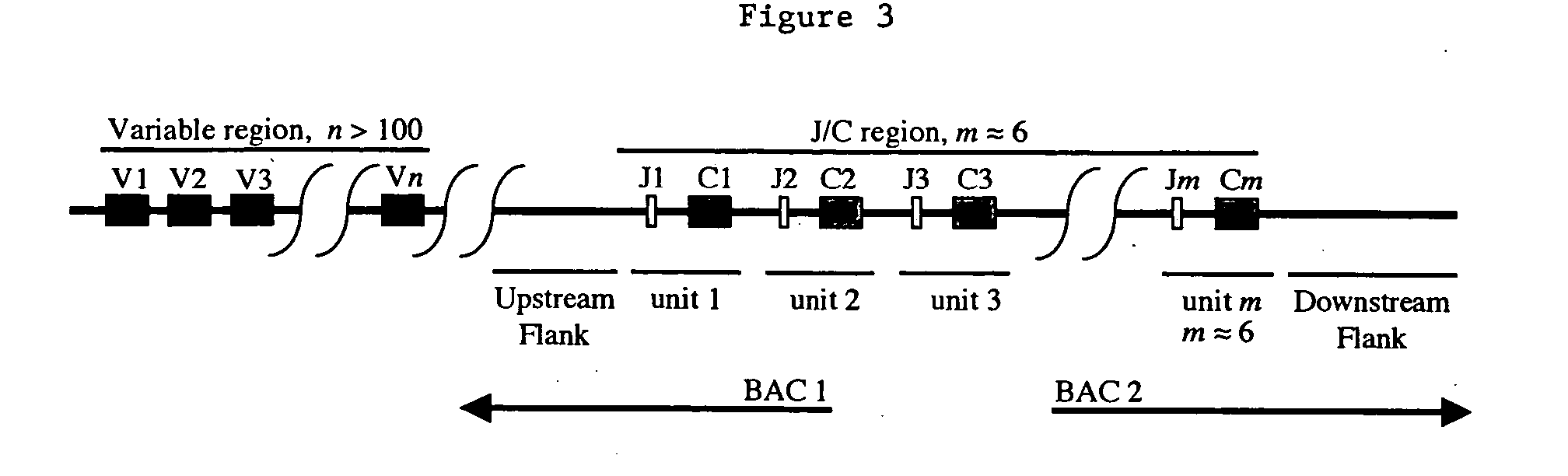
The present invention comprises non-human vertebrate cells and non-human mammals having a genome comprising an introduced partially human immunoglobulin region, said introduced region comprising human VH coding sequences and non-coding VH sequences based on the endogenous genome of the non-human mammal.
Owner:TRIANNI INC
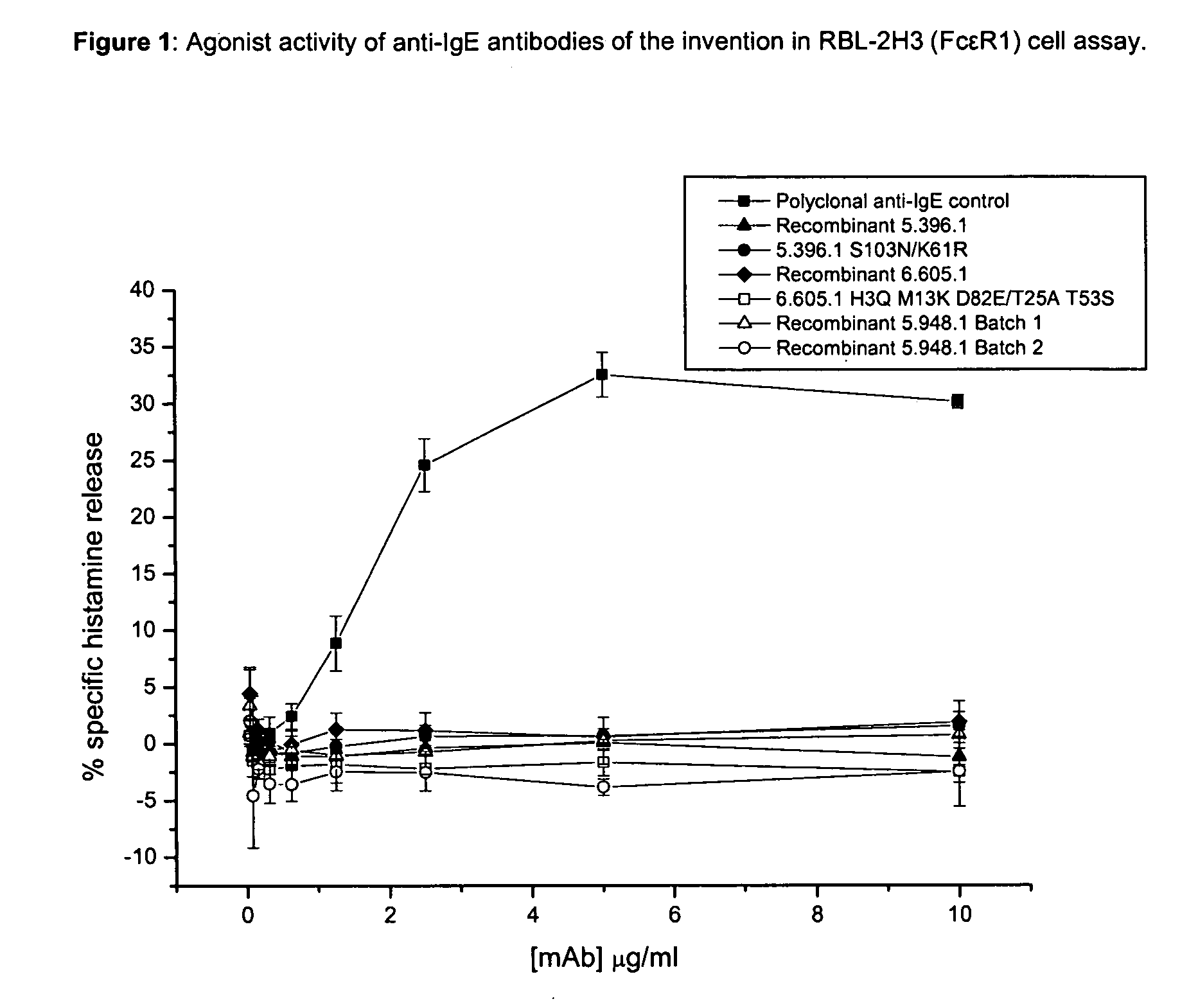
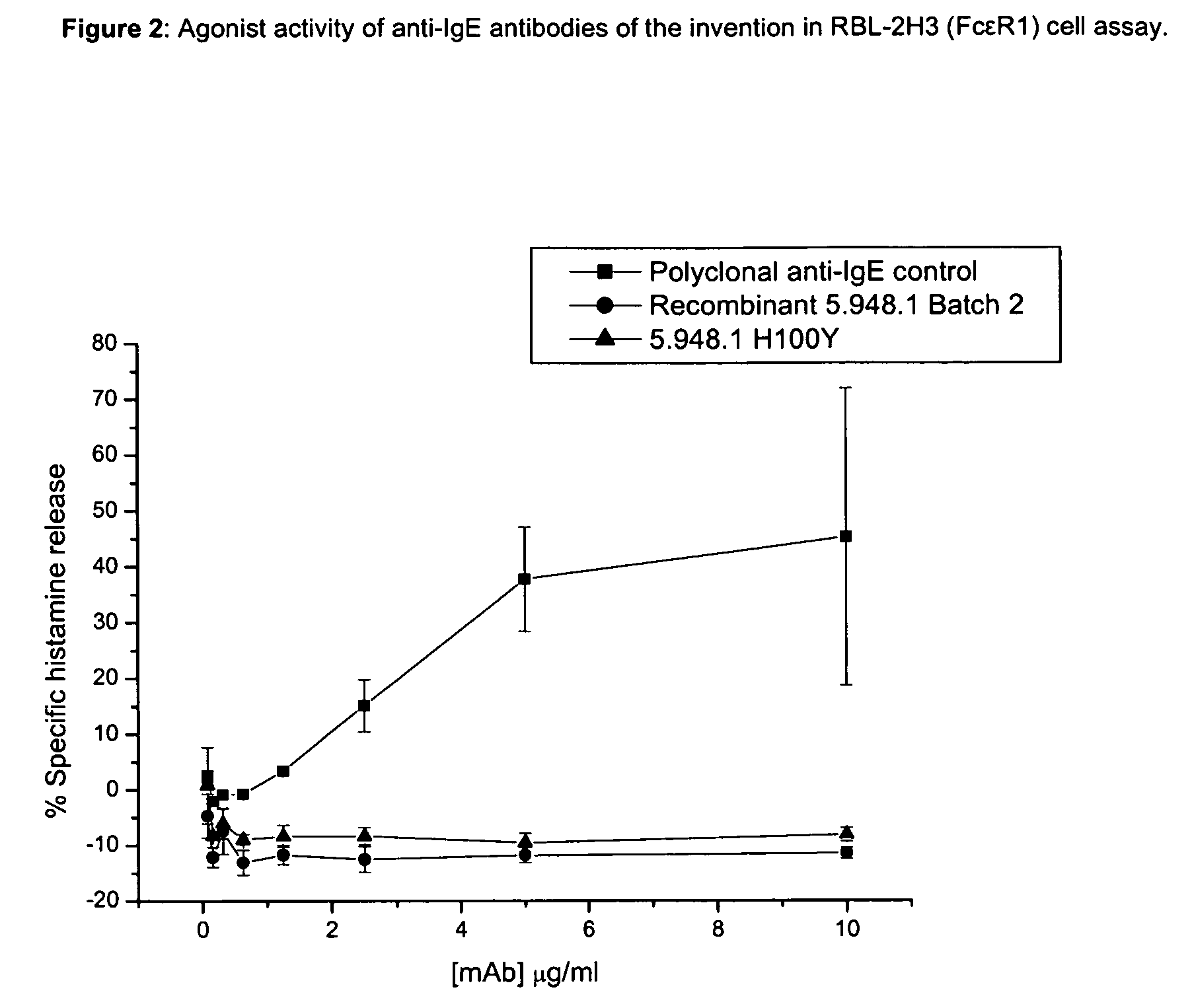
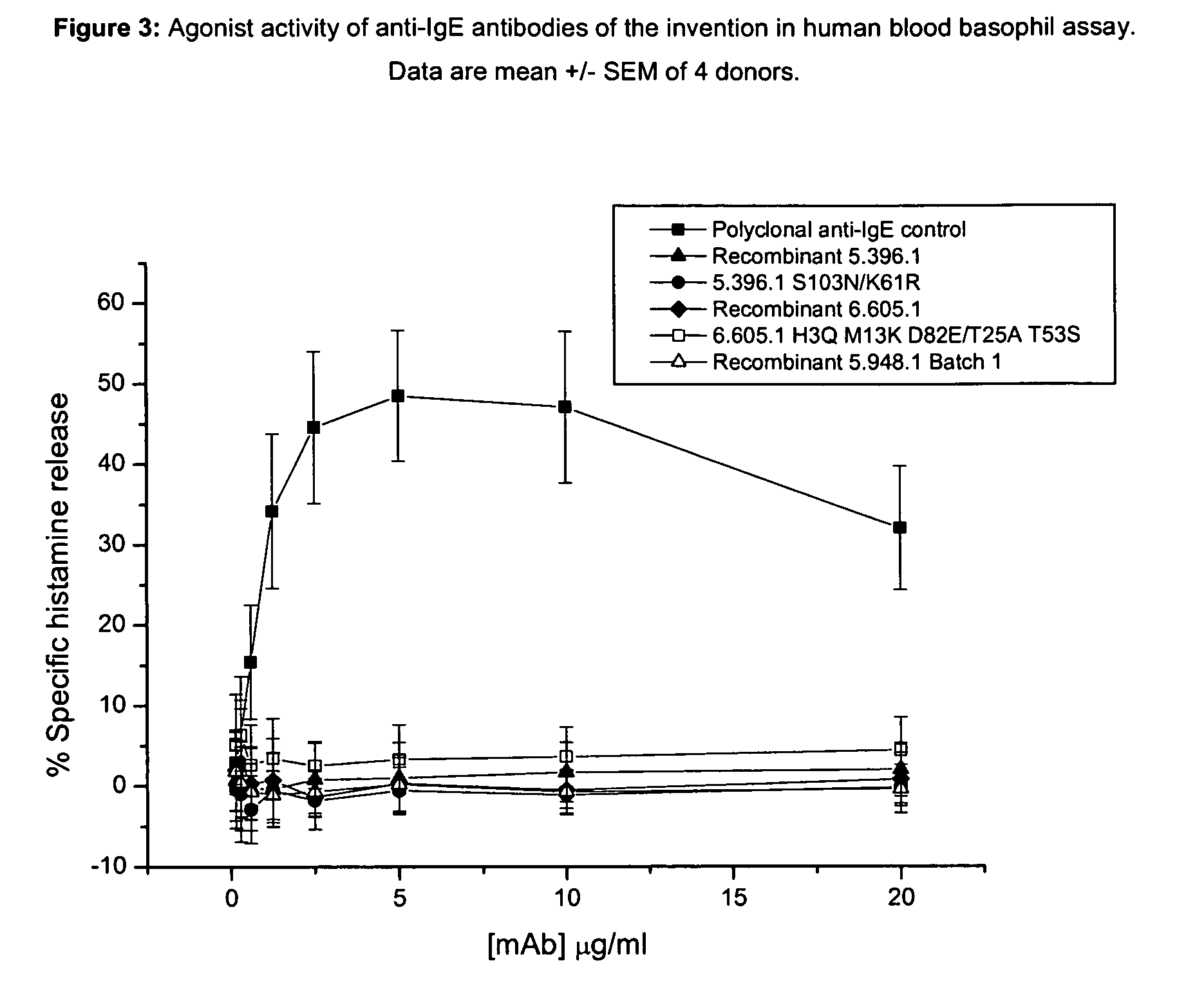
Anti-IgE antibodies
The present invention relates to novel human antibodies specifically directed against human immunoglobulin E (anti-IgE). The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating asthma, in particular allergic asthma, as well as other IgE-mediated disorders including allergic rhinitis and food allergies.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
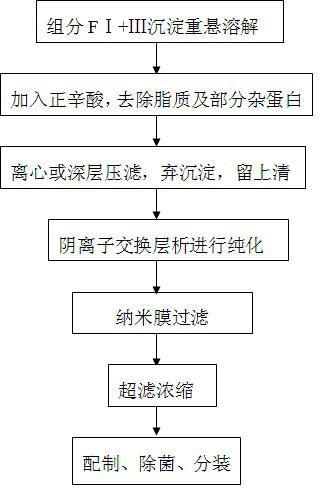
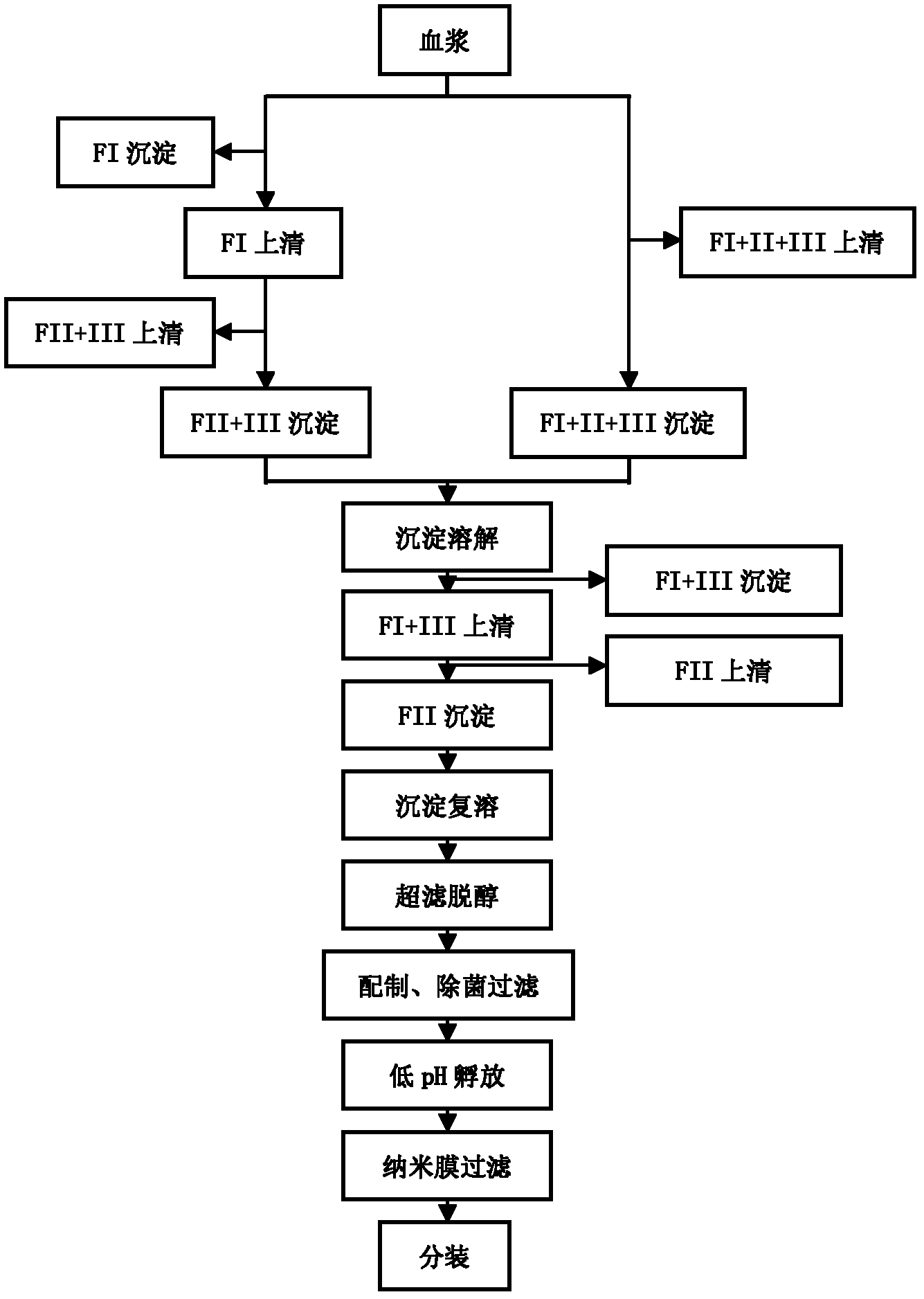
Method for purifying human immunoglobulin from separated component I+III of blood plasma
ActiveCN102250240ARealize comprehensive utilizationAvoid pollutionPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsBiotechnologyUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for separating and purifying human immunoglobulin from a component I+III of blood plasma, and aims to provide a high-efficiency method for recovering high-purity human immunoglobulin. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: a, fully dissolving component I+III precipitate; b, precipitating with octylic acid and removing lipid and a part of impurity protein to prepare IgG (Immunoglobulin G); c, purifying through anion exchange column chromatography; and d, collecting flow-through liquid, performing membrane nanofiltration, ultrafiltration and concentration, preparing the human immunoglobulin, sterilizing and packaging. The method has the beneficial effects of capability of being operated at the room temperature, simple and short steps, high yield, low energy consumption and high output and is suitable for mass production; comprehensive utilization of the blood plasma is fully realized; the time of the entire production process is shortened; the cost is reduced; extremely considerable economic benefit can be produced; the safety of a product is guaranteed by using two virus inactivation / elimination methods of different mechanisms; the environmental pollution is avoided; and the method has high economic and social values.
Owner:SHANDONG TAIBANG BIOLOGICAL PROD CO LTD
Ganglioside-associated recombinant antibodies and the use thereof in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors
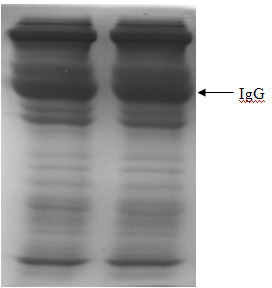
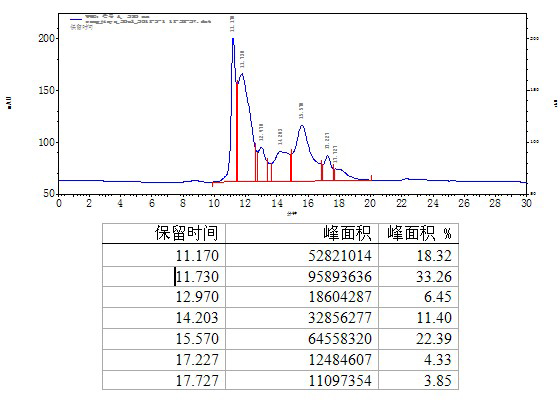
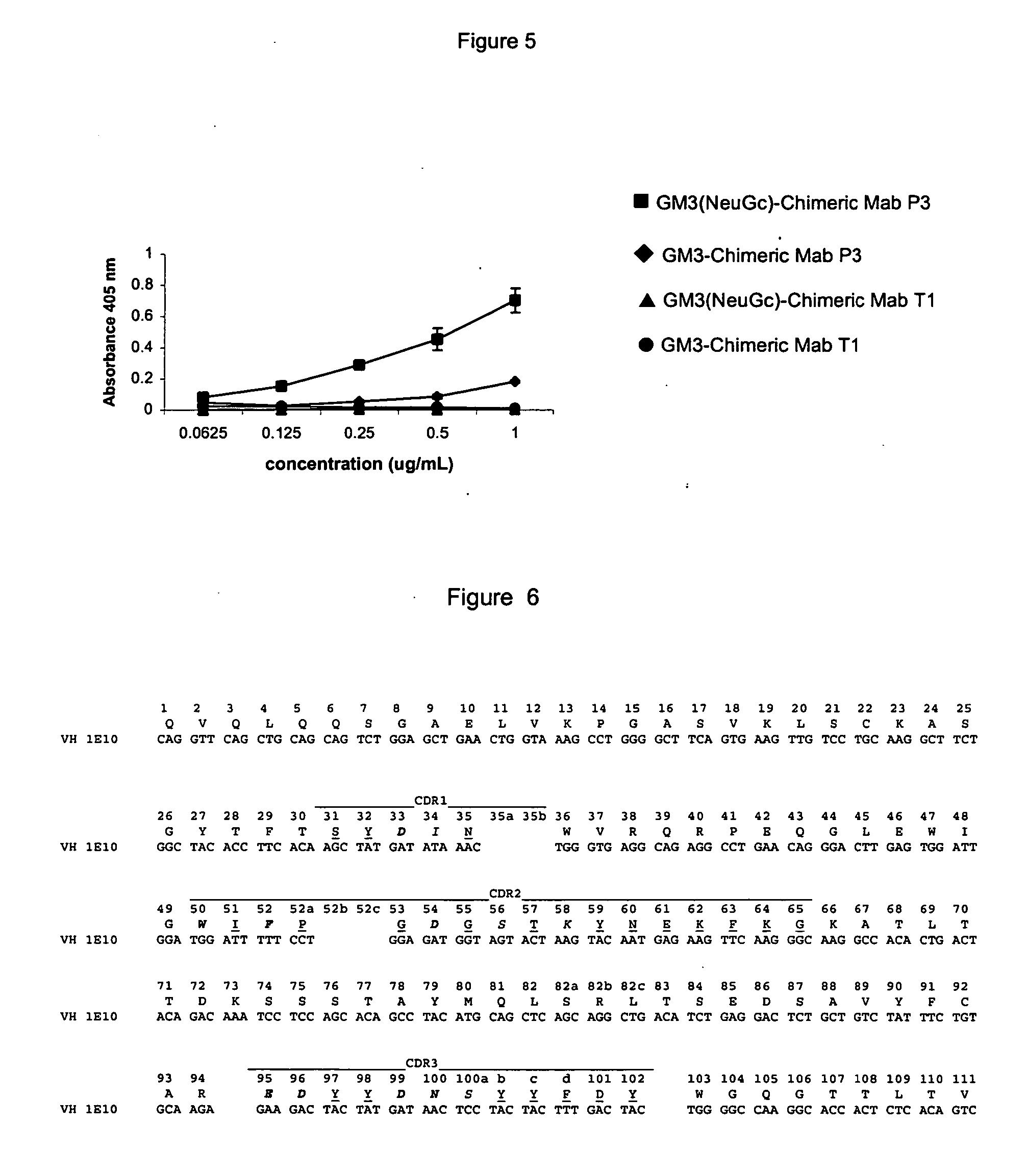
The present invention is related with the obtaining of modified antibodies by means of the DNA recombinant technology from the murine monoclonal antibody P3 (MAb P3) produced by the hybridoma cell line deposited under Budapest Treaty with accession number ECACC 94113026 and from its anti-idiotype murine monoclonal antibody 1E10(MAbai 1E10) produced by the hybridoma cell line with deposit number ECACC 97112901, with the objective of achieving monoclonal antibodies which preserve the biological function of specific binding to the antigen of the original antibodies, but being at the same time less immunogenic. The chimeric antibodies of the invention contain the variable domains of the murine immunoglobulin and the constant regions of the human immunoglobulin; and those humanized, besides containing the constant regions of the human immunoglobulins, they are modified in the region of the murine frameworks (FRs) and in particular in those zones that could be in an antigenic site for the T cells, so several positions of the FRS are human as well. These antibodies can be used in the diagnosis and therapy of different types of tumors. The present invention is also related with use of the antibodies for therapeutical and diagnostic purposes.
Owner:CENT DE INMUNOLOGIA MOLECULAR CENT DE INMUNOLO
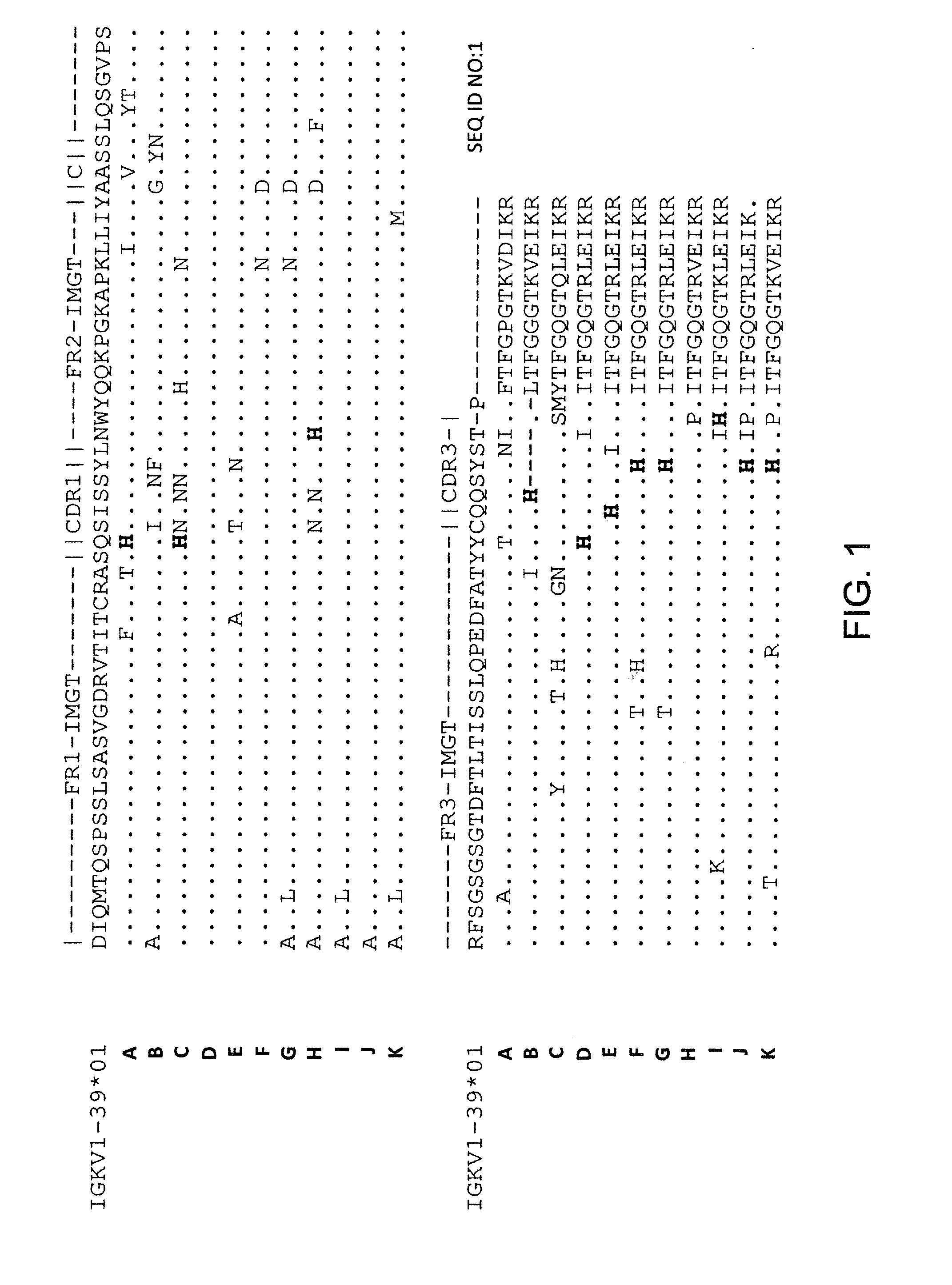
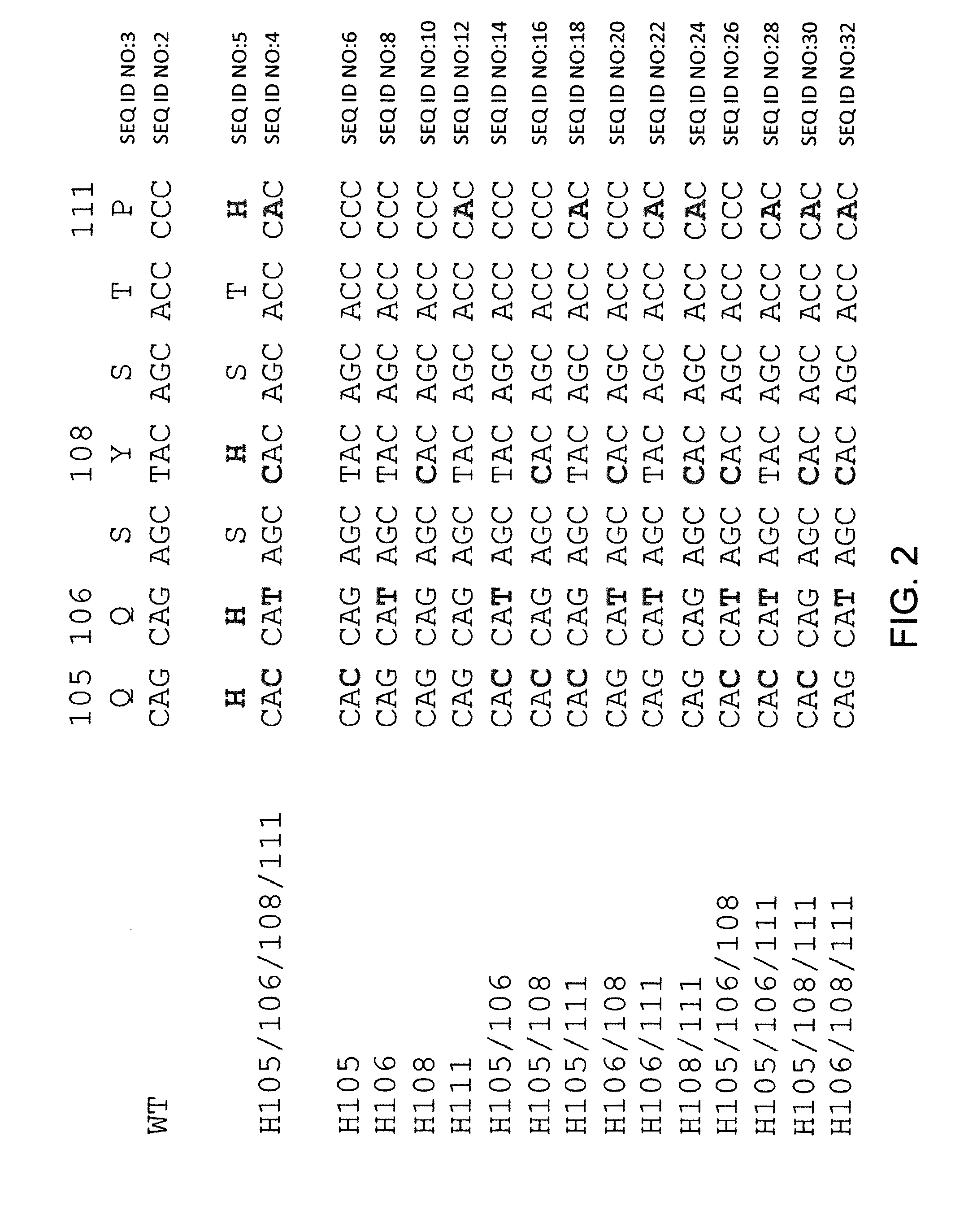
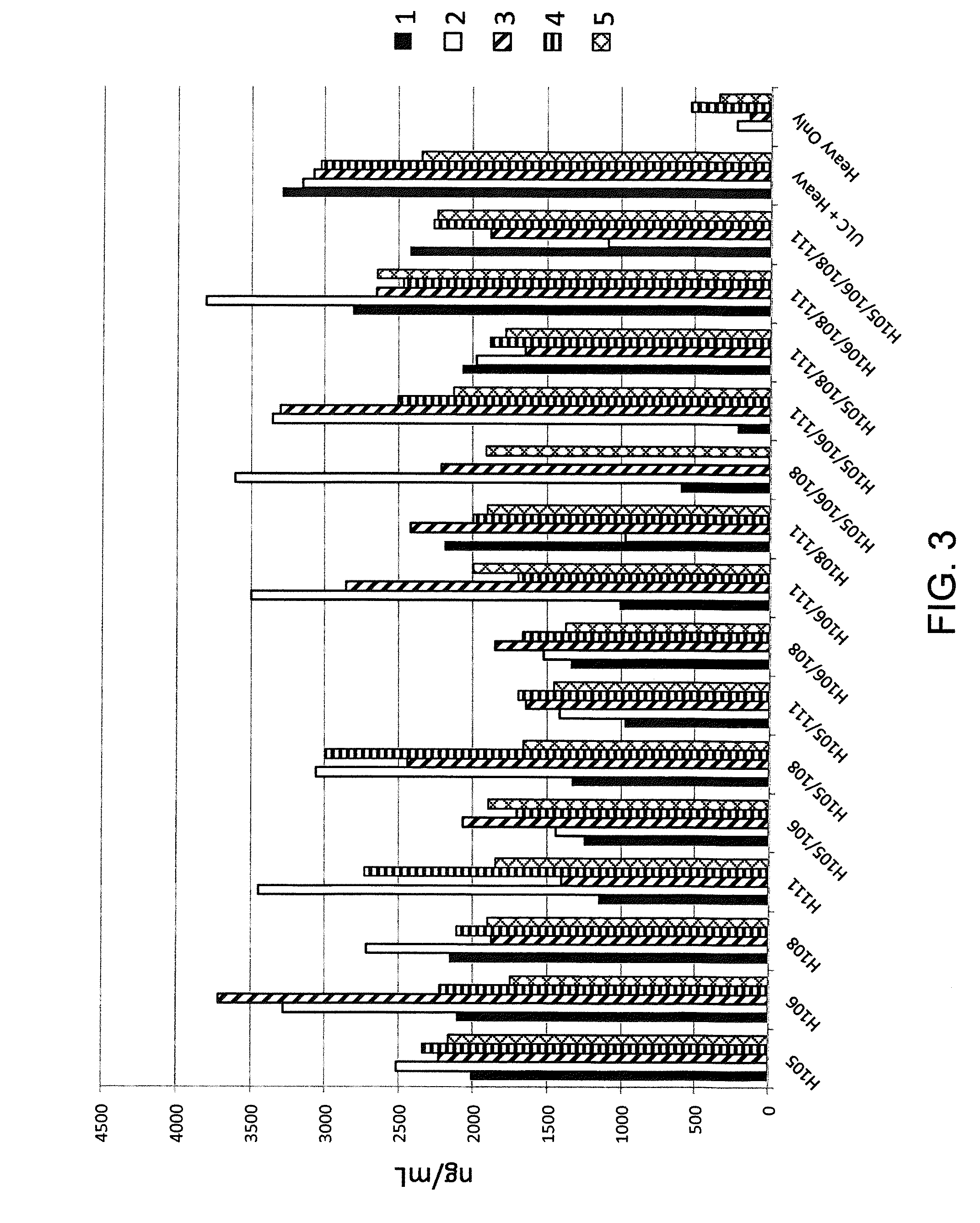
Nucleic acids encoding superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies
The present invention relates to one or more nucleic acid(s) encoding a binding molecule specifically binding to a human CD28 molecule, comprising(a) a nucleic acid sequence encoding a VH region and a nucleic acid sequence encoding a VL region comprising CDRs in a human immunoglobulin framework, wherein(i) the CDRs of the VH region (CDR-H) comprise the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 2 or 18 (CDR-H3), 4 or 20 (CDR-H2) and 6 or 22 (CDR-H1) or are encoded by the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1 or 17 (CDR-H3), 3 or 19 (CDR-H2) and 5 or 21 (CDR-H1); and(ii) the CDRs of the VL region (CDR-L) comprise the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 8 or 24 (CDR-L3), 10 or 26 (CDR-L2) and 12 or 28 (CDR-L1) or are encoded by the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 7 or 23 (CDR-L3), 9 or 25 (CDR-L2) and 11 or 27 (CDR-L1); and(b) a nucleic acid sequence encoding the constant region of a human IgG1 or IgG4 antibody.
Owner:THERAMAB
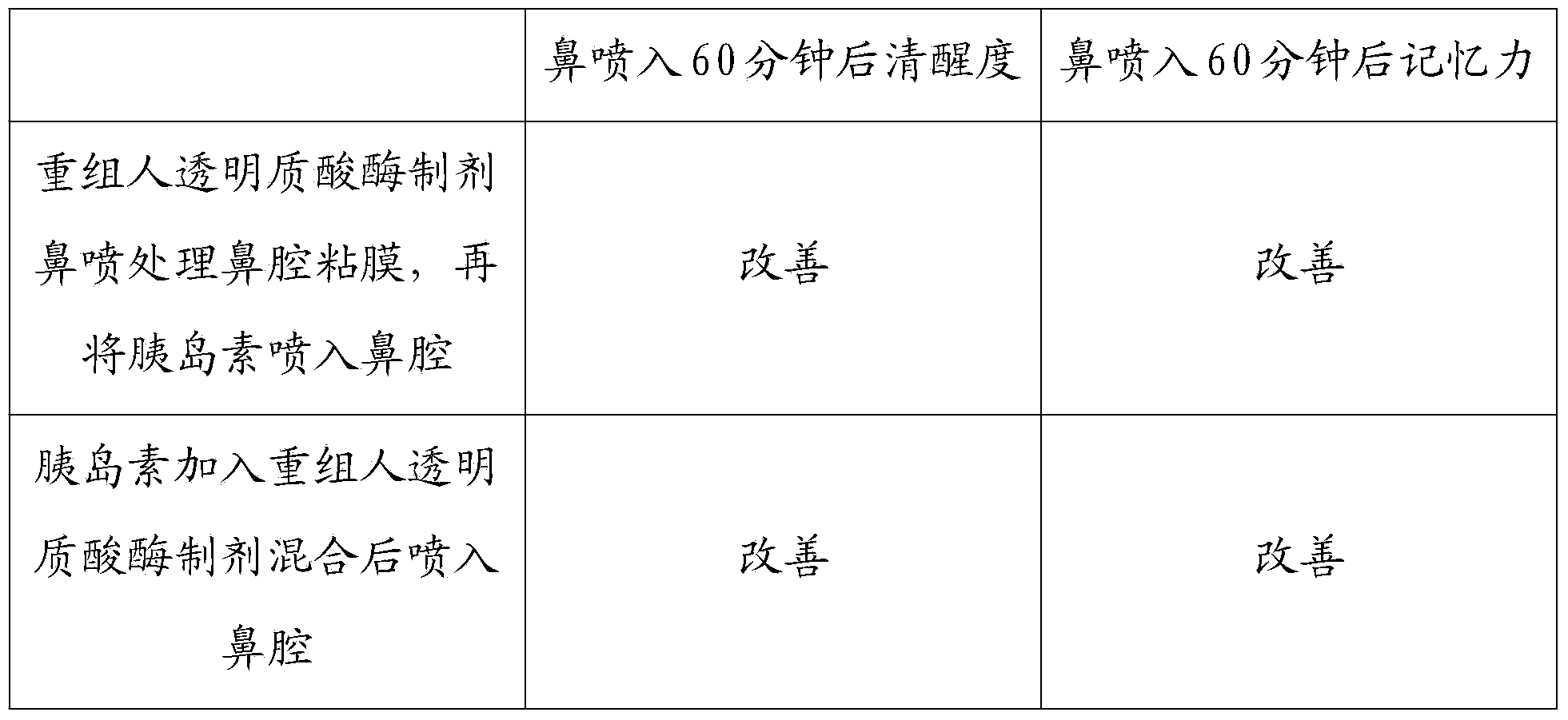
Recombined human hyaluronidase, production and purification method and preparations thereof, use method and application
InactiveCN103468662AImprove permeabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEnzymesNasal cavityDisease
The invention discloses a recombined human hyaluronidase, a production and purification method and preparations of the recombined human hyaluronidase, a use method and application. Recombined human hyaluronidase PH20 or human hyaluronidase human albumin fusion protein PH20-HSA or human hyaluronidase human immunoglobulin IgG2Fc fragment fusion protein PH20-IgFc is adopted by the recombined human hyaluronidase and used in the mucosa or the surface of the skin. The preparations of the recombined human hyaluronidase can be made into different types such as membrane preparations, spray preparations, lotion and freeze-dried powder spray and used for skin infiltration promotion of beauty nutrient substances, skin mucosa infiltration promotion of surface anesthetic, infiltration promotion of skin disease therapeutic medicine, mucosa infiltration promotion of biological tranquillizer, mucosa skin infiltration promotion of growth factors, mucosa infiltration promotion of hypoglycemic drug, mucosa nasal cavity infiltration promotion of nervous centralis nutrient substances and the like.
Owner:惠觅宙
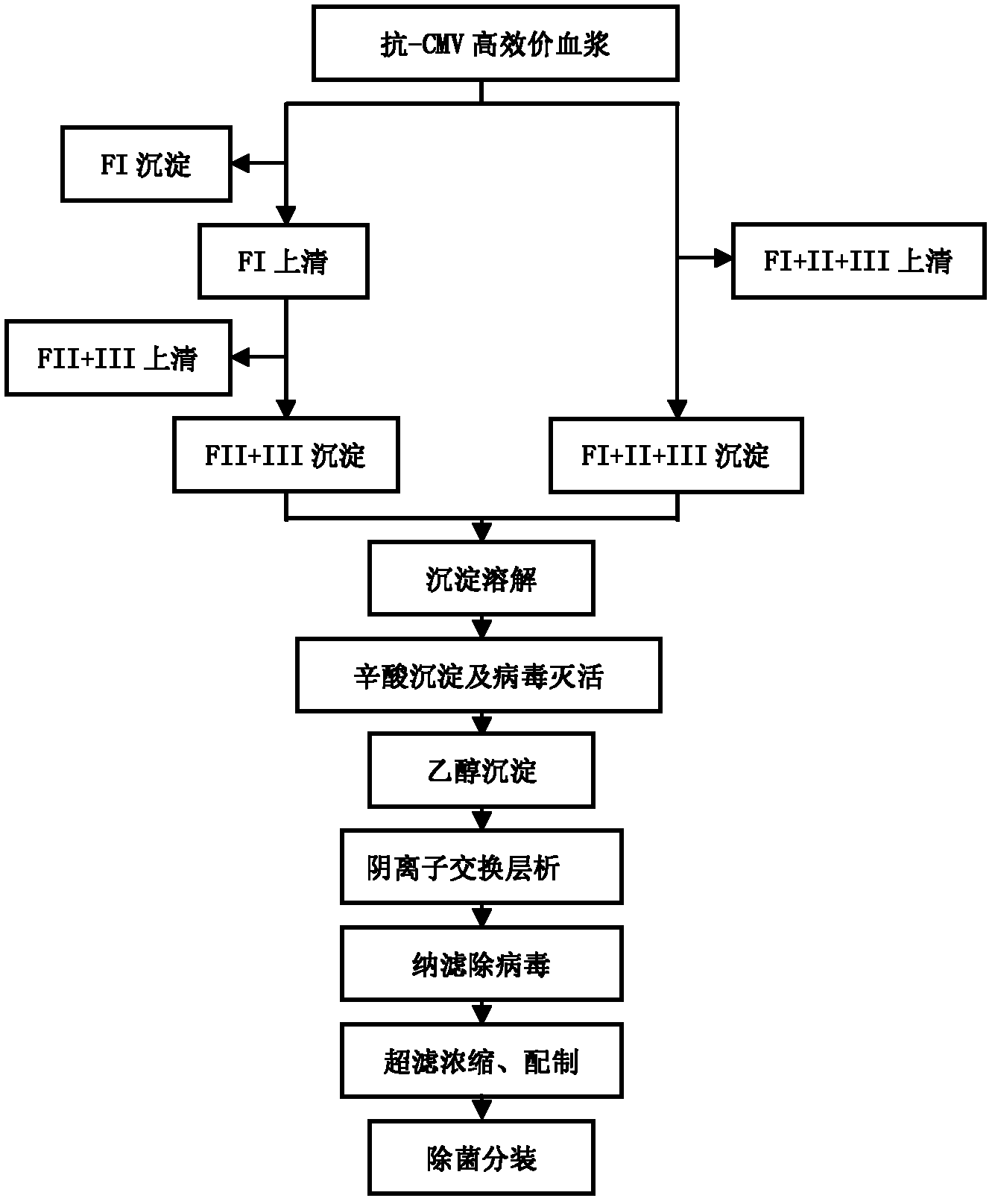
Intravenous injection of cytomegalovirus human immunoglobulin and its preparation method
ActiveCN102286099ASteps to reduce precipitationKeep aliveImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsEthanol precipitationAnion-exchange chromatography
The invention discloses a human cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin for intravenous injection and a preparation method thereof, and aims to improve the purity, yield and safety of the product. In the invention, the specific activity of the human cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin for intravenous injection is not less than 2.5 PEI-U / mg, the anti-CMV titer is not less than 100 PEI-U / ml, the purity is greater than 98.2%, and the protein content is 51-55 mg / ml. Caprylic acid precipitation and anion exchange chromatography are used instead of the partial ethanol precipitation step in the traditional low-temperature ethanol method, thereby keeping IgG in the supernate all the time so as to keep the IgG activity; and processes of caprylic acid virus inactivation and nano film virus removal are used, thereby effectively ensuring the safety of the product. Researches show that the preparation method disclosed by the invention improves the purity, yield and safety of the product, saves the energy and reduces the production cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEIGUANG BIOLOGICAL PROD
Process for preparing human immunoglobulin for intravenous injection
ActiveCN102584934AReduce adverse effectsImprove biological activityPeptide preparation methodsIon exchangeTwo step
The invention relates to a process for preparing human immunoglobulin for intravenous injection, and belongs to the field of biological pharmacy. The precipitate of components II and III in the process for preparing the human immunoglobulin for intravenous injection is treated by a caprylic acid and calcium chloride precipitation method, miscellaneous proteins are removed from the precipitate of the components II and III, and two-step chromatography is performed. Compared with the general caprylic acid precipitation method, the process has the advantages that various blood coagulation factors are effectively removed from a precipitate solution of the components II and III by adding calcium chloride, the stability of the immunoglobulin is improved, and the yield of the product is obviously improved, namely more than 7g of immunoglobulin can be prepared from each liter of blood plasma; upper column chromatographic purification is performed by two ion exchange columns and a chromatographic technology, so that the miscellaneous proteins can be effectively removed, and the purity of the product is over 99.5 percent; and in addition, caprylic acid is added, and viruses are removed and filtered by a DV20 filter element, so that a virus removing effect can be obviously improved, and the safety of clinical medication is improved.
Owner:华润博雅生物制药集团股份有限公司
Interfusion protein of human interleukin 15 and Fe
ActiveCN100334112CPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsWhite blood cellImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
A human interleukin 15-Fc fusion protein composed of interleukin 15 and the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin, which are linked via joining peptide, the nucleic acid ofr coding it, the expression carrier containing said nucleic acid, its composite medicine for preventing and treating microbial infection and its preparing process are disclosed.
Owner:上海海欣生物技术有限公司
Anti-HMFG antibodies and processes for their production
InactiveUS6506881B1Improve featuresPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComplementarity determining regionBinding site
Humanized antibody molecules (HAMs) are described having specificity for human milk fat globule and having an antigen binding site wherein at least one of the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of the variable domains is derived from the mouse monoclonal antibody CTMO1 and the remaining immunoglobulin-derived parts of the HAM are derived from a human immunoglobulin. The HAMs may be chimeric humanized antibodies or CDR-grafted humanized antibodies and are preferably produced by recombinant DNA techniques. The HAMs are useful for in vivo diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:CELLTECH R & D LTD
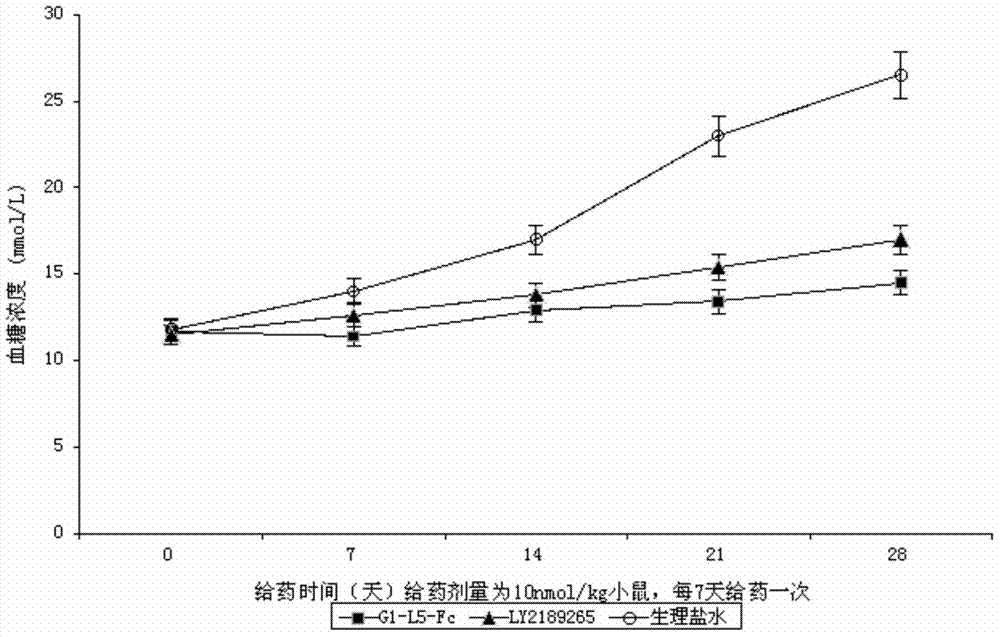
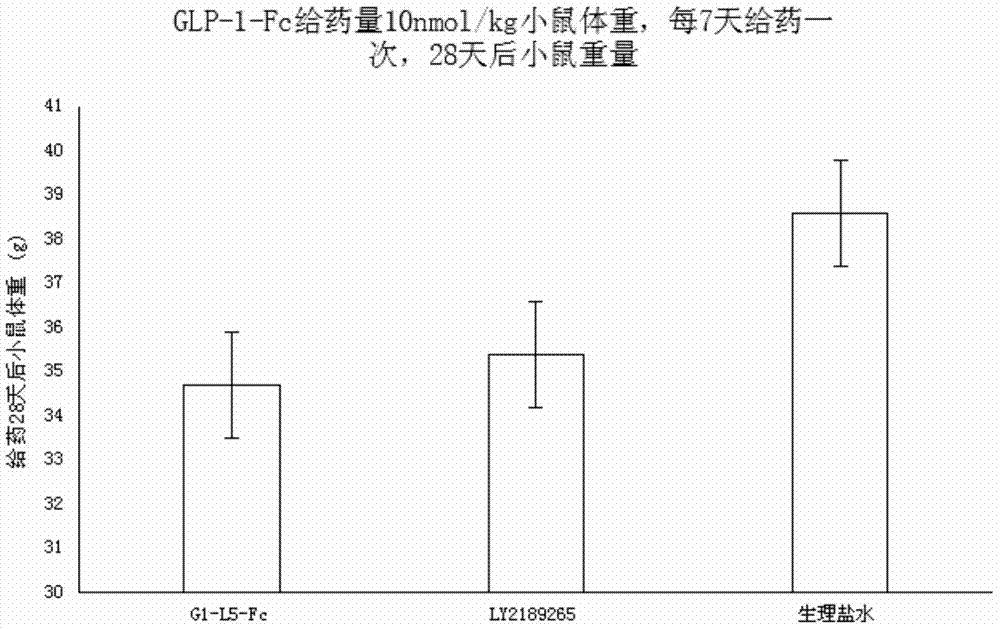
Recombinant human GLP-1-Fc fusion protein
ActiveCN104327187AImprove biological activityWeight controlPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDrug biological activityAmino acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly, relates to a recombinant human GLP-1-Fc fusion protein and a preparation method and an application thereof. The invention provides the recombinant human GLP-1-Fc fusion protein, wherein the recombinant human GLP-1-Fc fusion protein comprises two structural function regions which are respectively a recombinant GLP-1 fragment and a human immunoglobulin Fc fragment, and the recombinant GLP-1 fragment has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQID No.1. The recombinant human GLP-1-Fc fusion protein provided by the invention has the homology with an original GLP-1 molecule reaching 97%, and still maintains excellent biological activity and zoology activity.
Owner:SYNDEGEN SHANGHAI BIOTECH
Recombinant human EPO-Fc fusion proteins with prolonged half-life and enhanced erythropoietic activity in vivo
ActiveUS20070178112A1Enhanced erythropoietic bioactivityExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRed blood cellHalf-life
A recombinant fusion protein comprising a human erythropoietin peptide portion linked to an immunoglobulin peptide portion is described. The fusion protein has a prolonged half-life in vivo in comparison to naturally occurring or recombinant native human erythropoietin. In one embodiment of the invention, the protein has a half-life in vivo at least three fold higher than native human erythropoietin. The fusion protein also exhibits enhanced erythropoietic bioactivity in comparison to native human erythropoietin. In one embodiment, the fusion protein comprises the complete peptide sequence of a human erythropoietin (EPO) molecule and the peptide sequence of an Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin IgG1. The Fc fragment in the fusion protein includes the hinge region, CH2 and CH3 domains of human immunoglobulin IgG1. The EPO molecule may be linked directly to the Fc fragment to avoid extraneous peptide linkers and lessen the risk of an immunogenic response when administered in vivo. In one embodiment the hinge region is a human Fc fragment variant having a non-cysteine residue at amino acid 6. The invention also relates to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding the fusion protein and transfected cell lines and methods for producing the fusion protein. The invention further includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising the fusion protein and methods of using the fusion protein and / or the pharmaceutical compositions, for example to stimulate erythropoiesis in subjects in need of therapy.
Owner:NOVAGEN HLDG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com