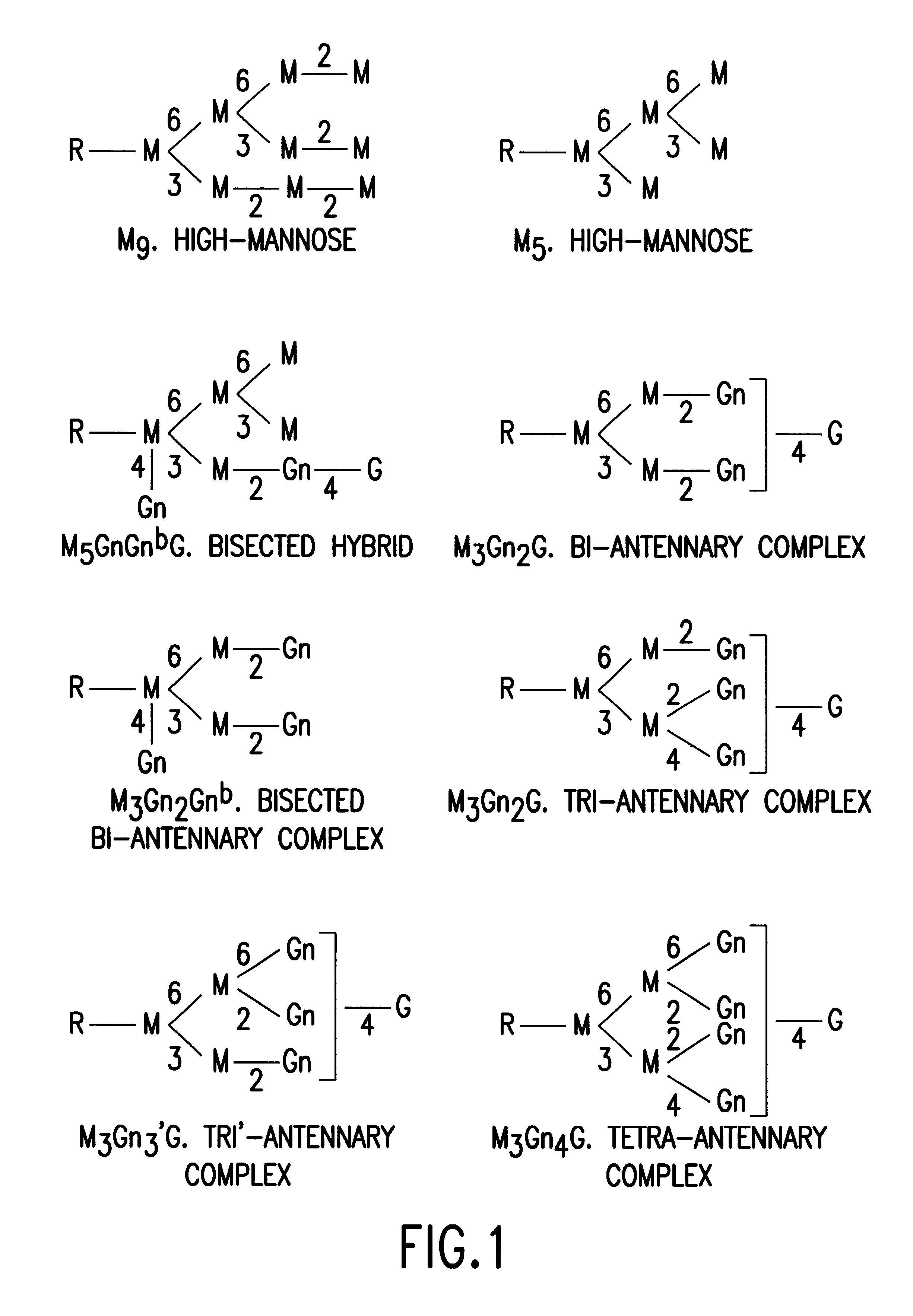
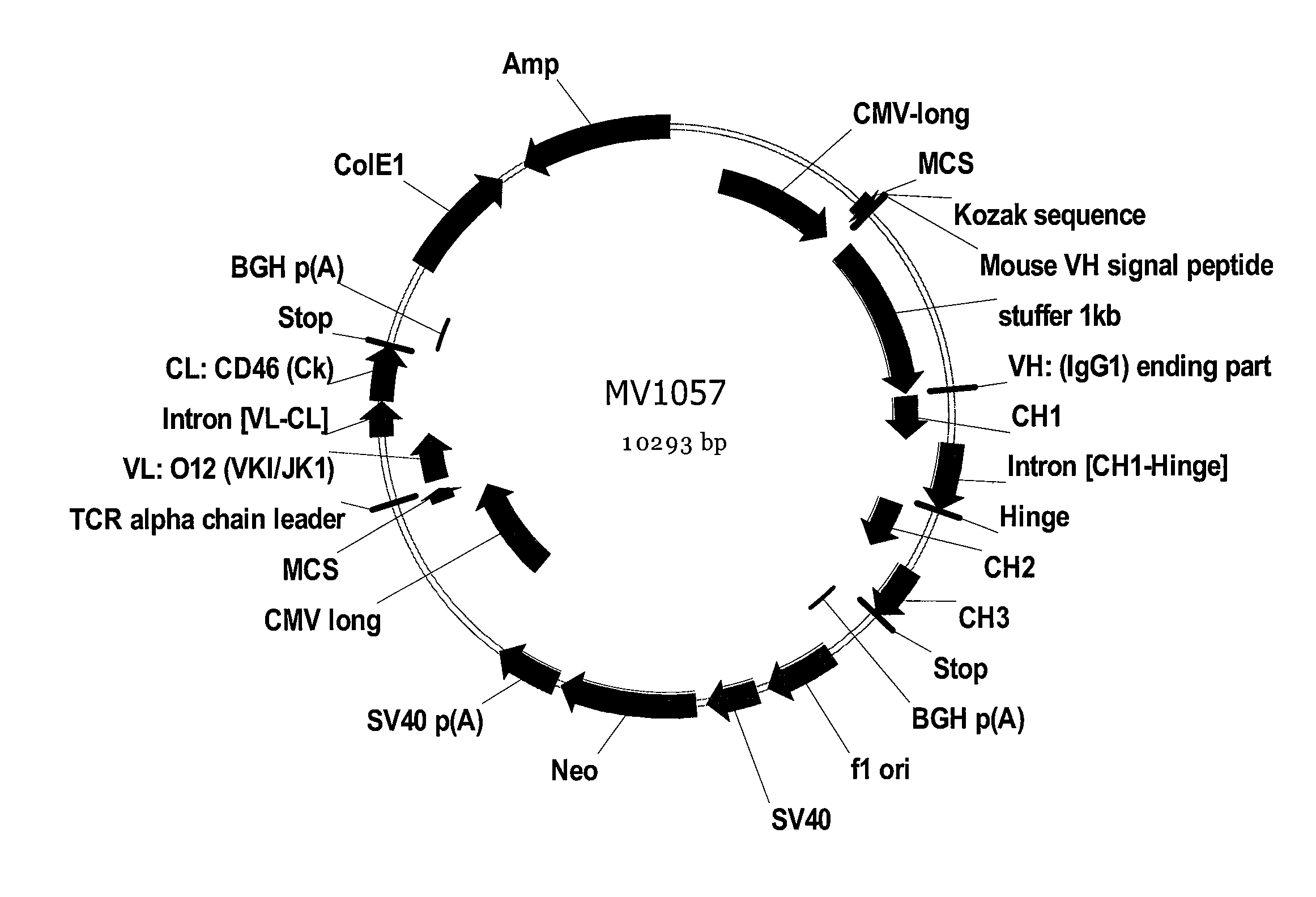
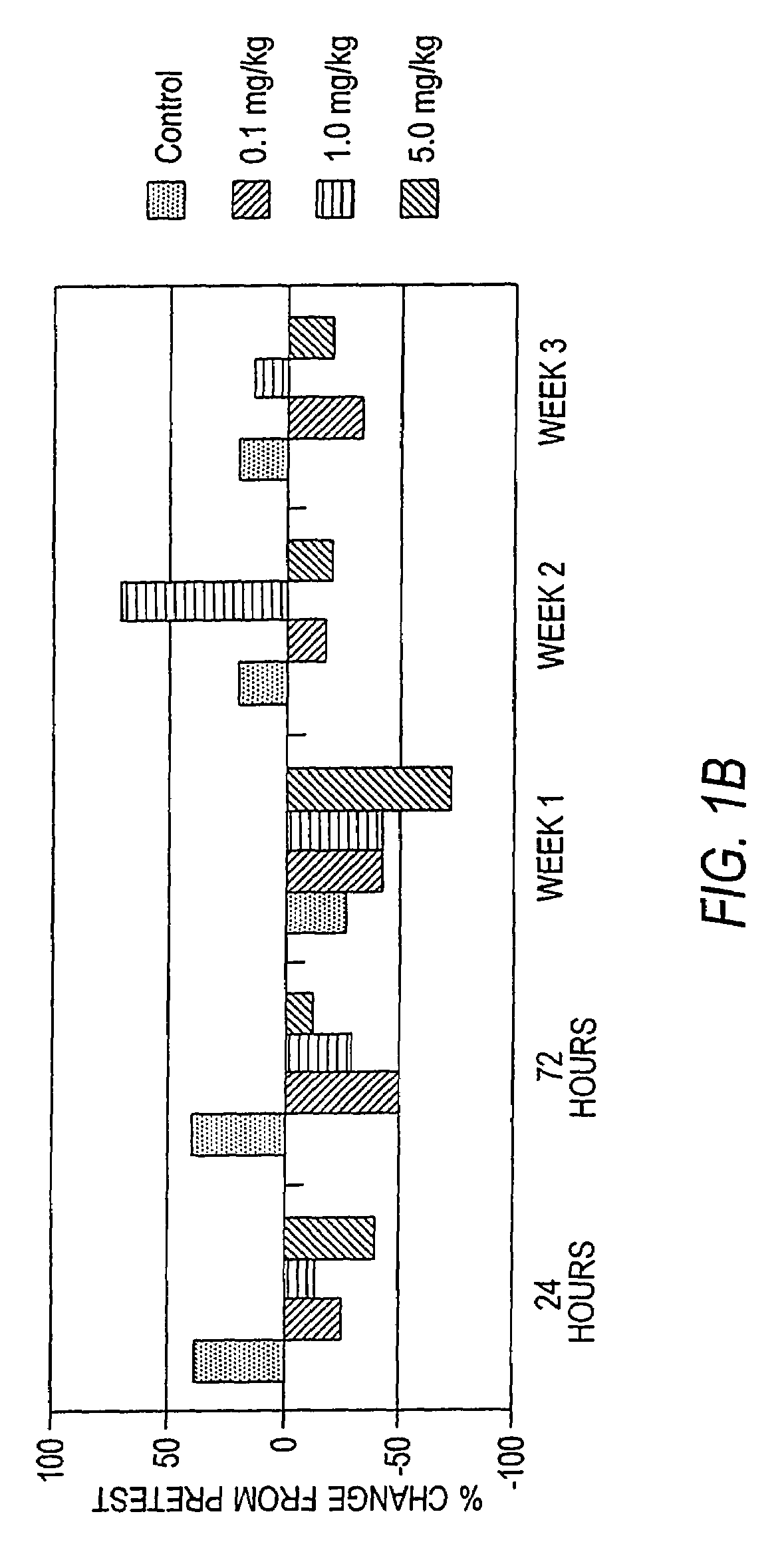
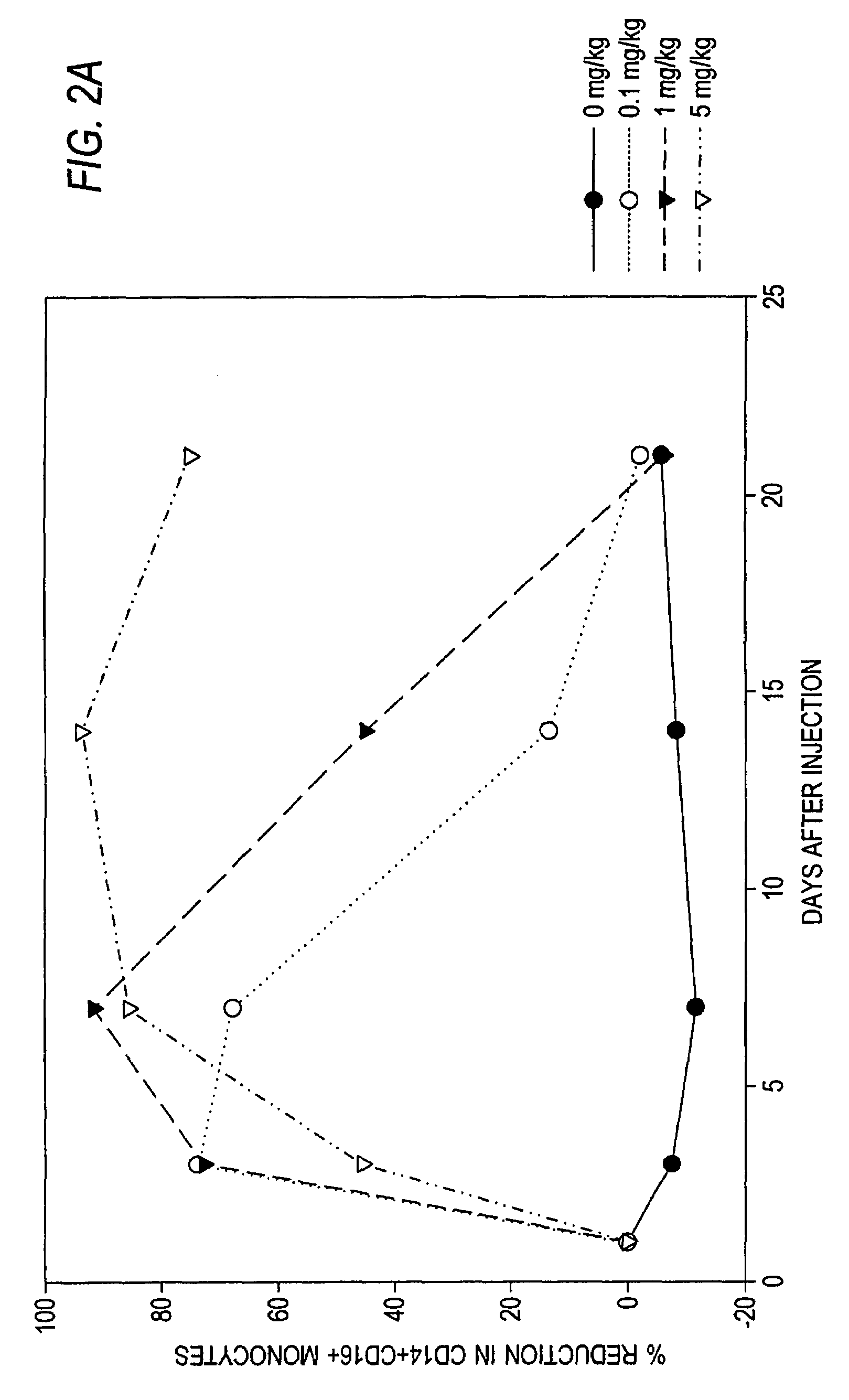
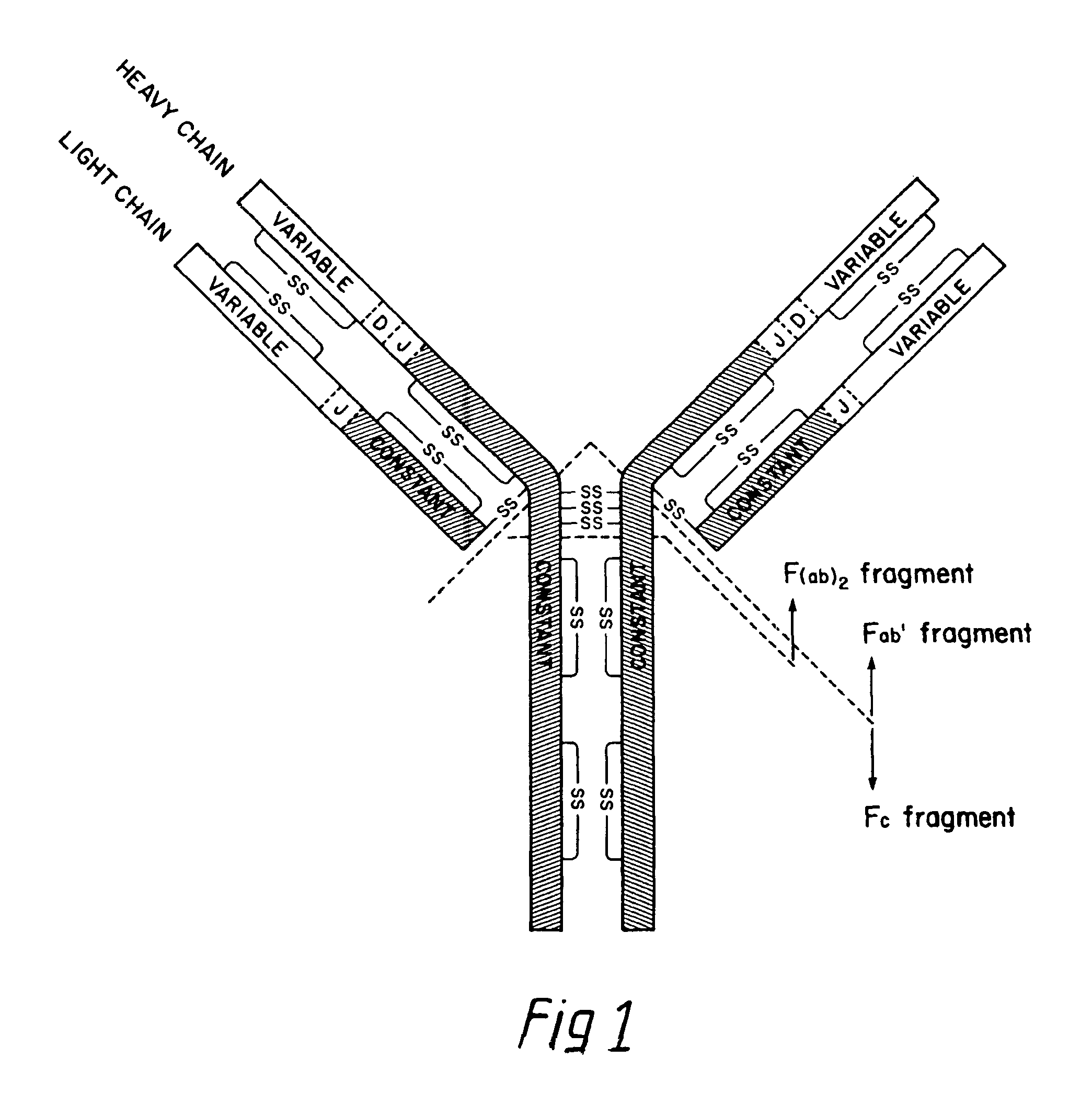
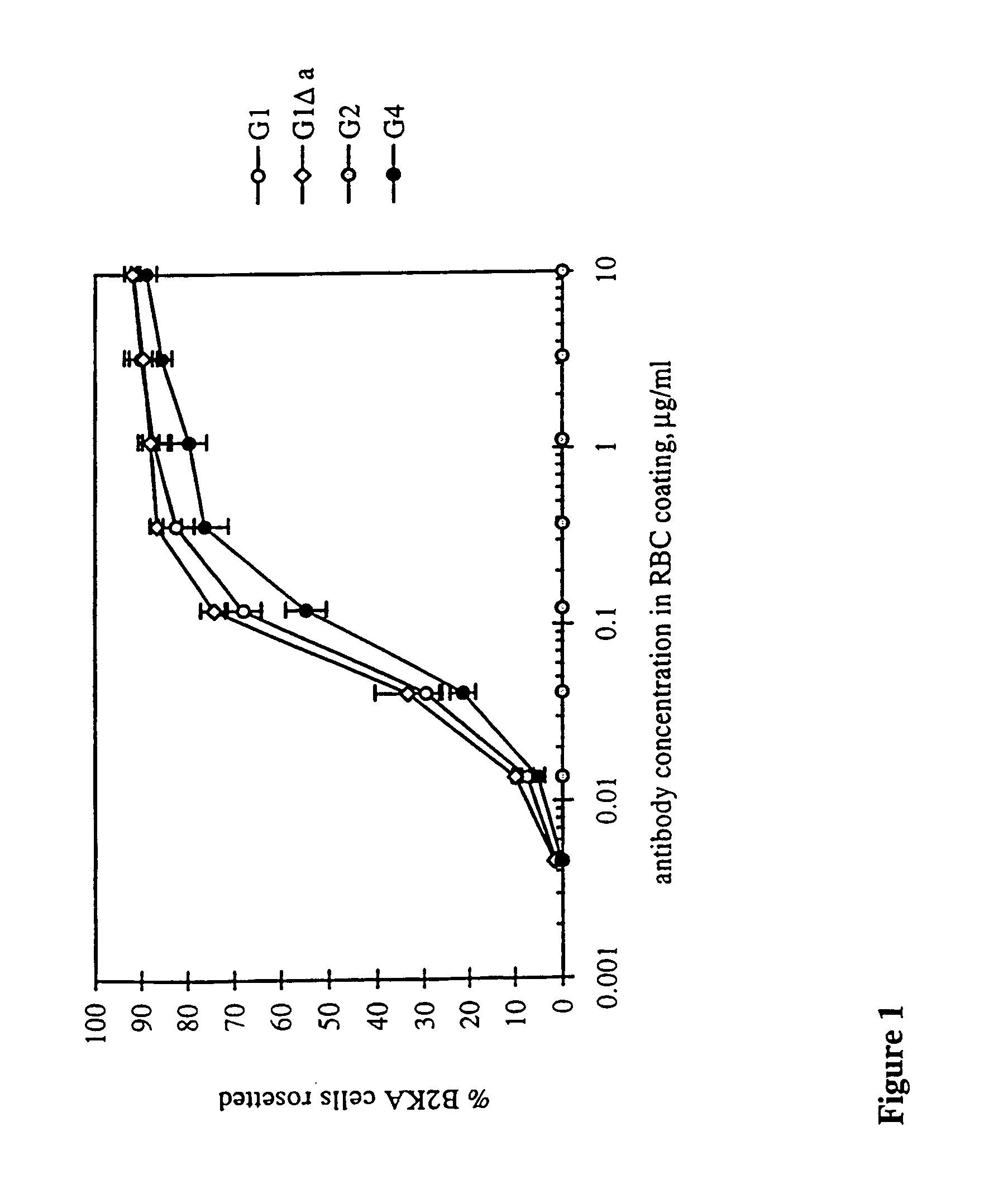
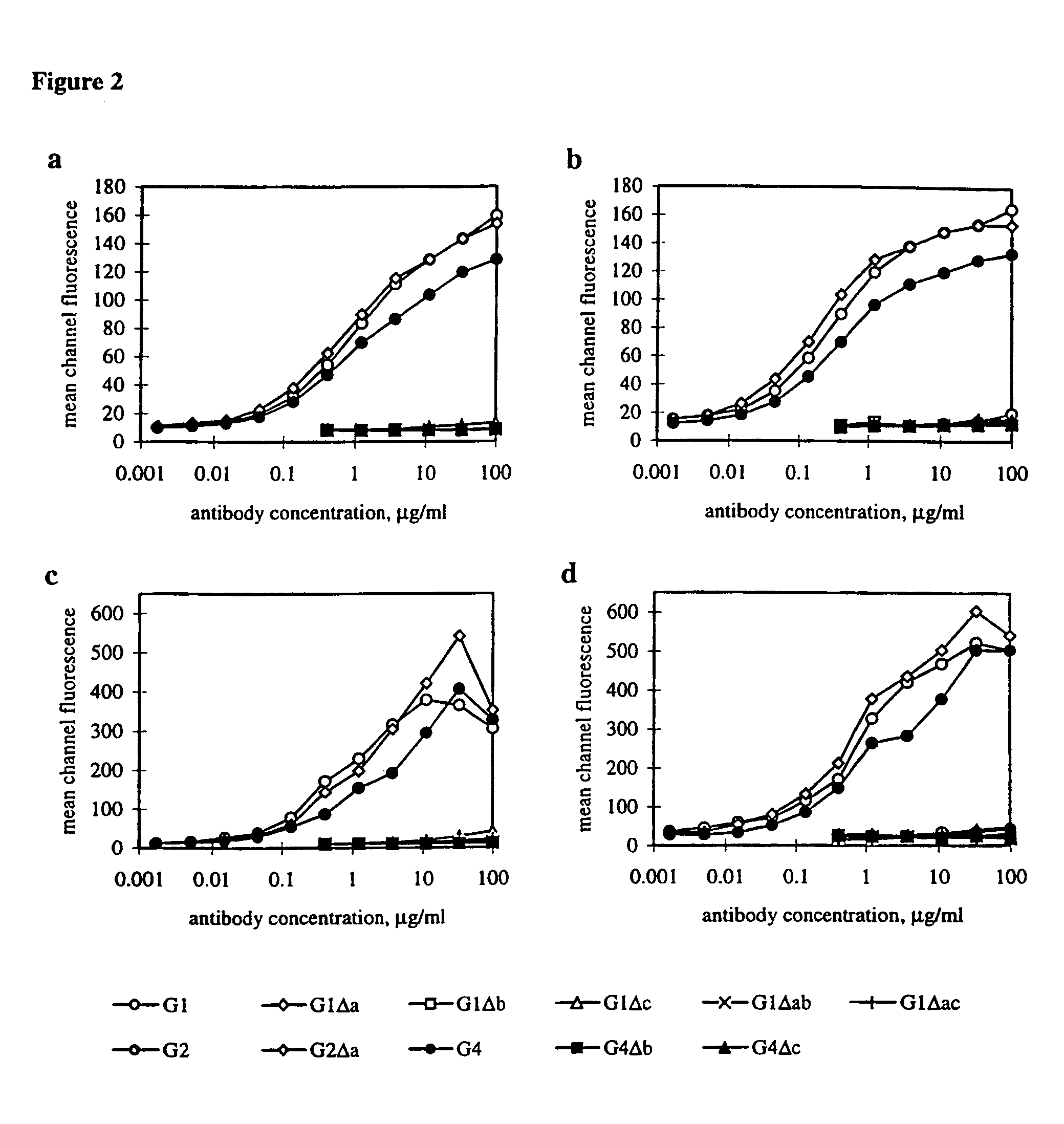
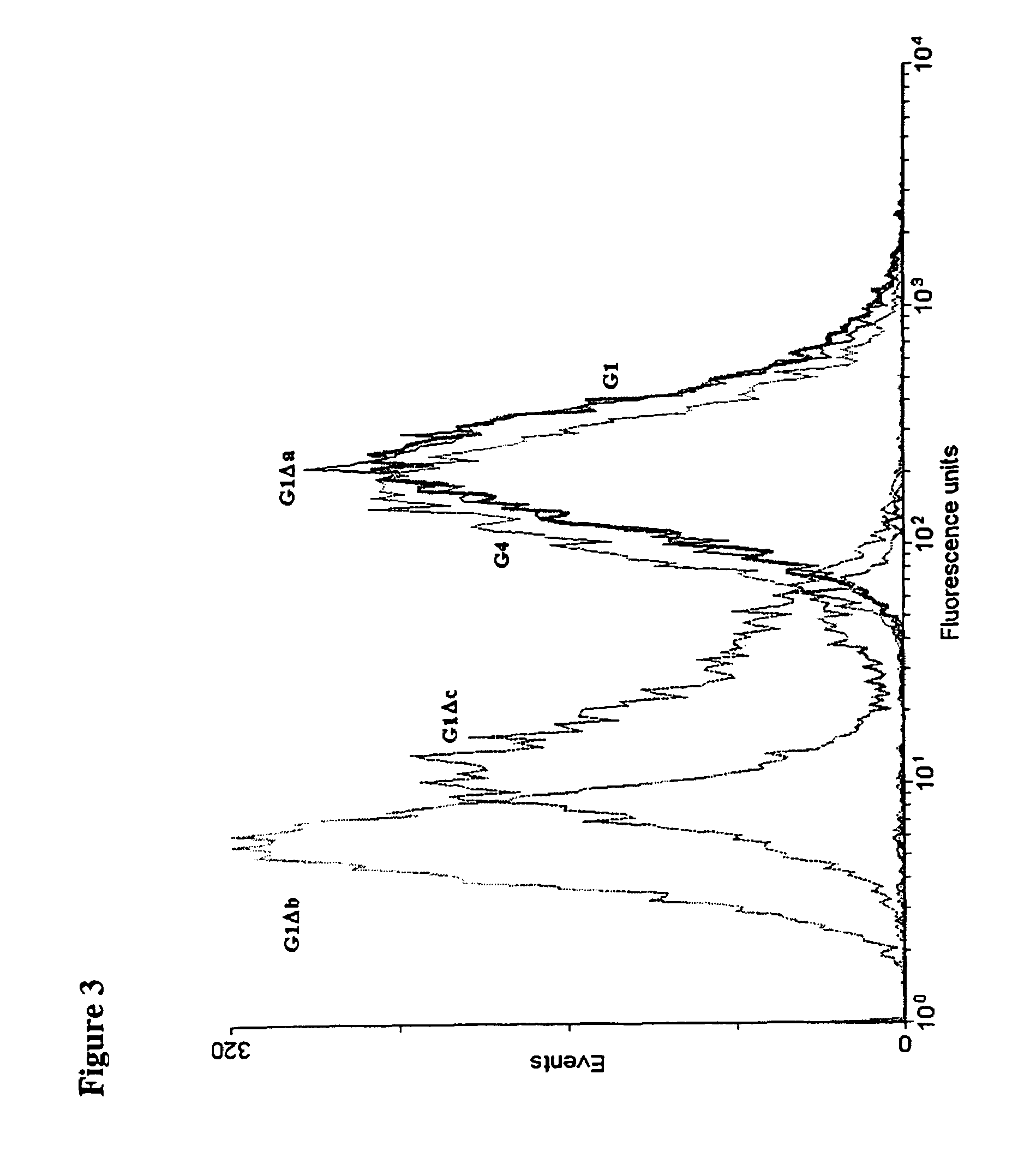
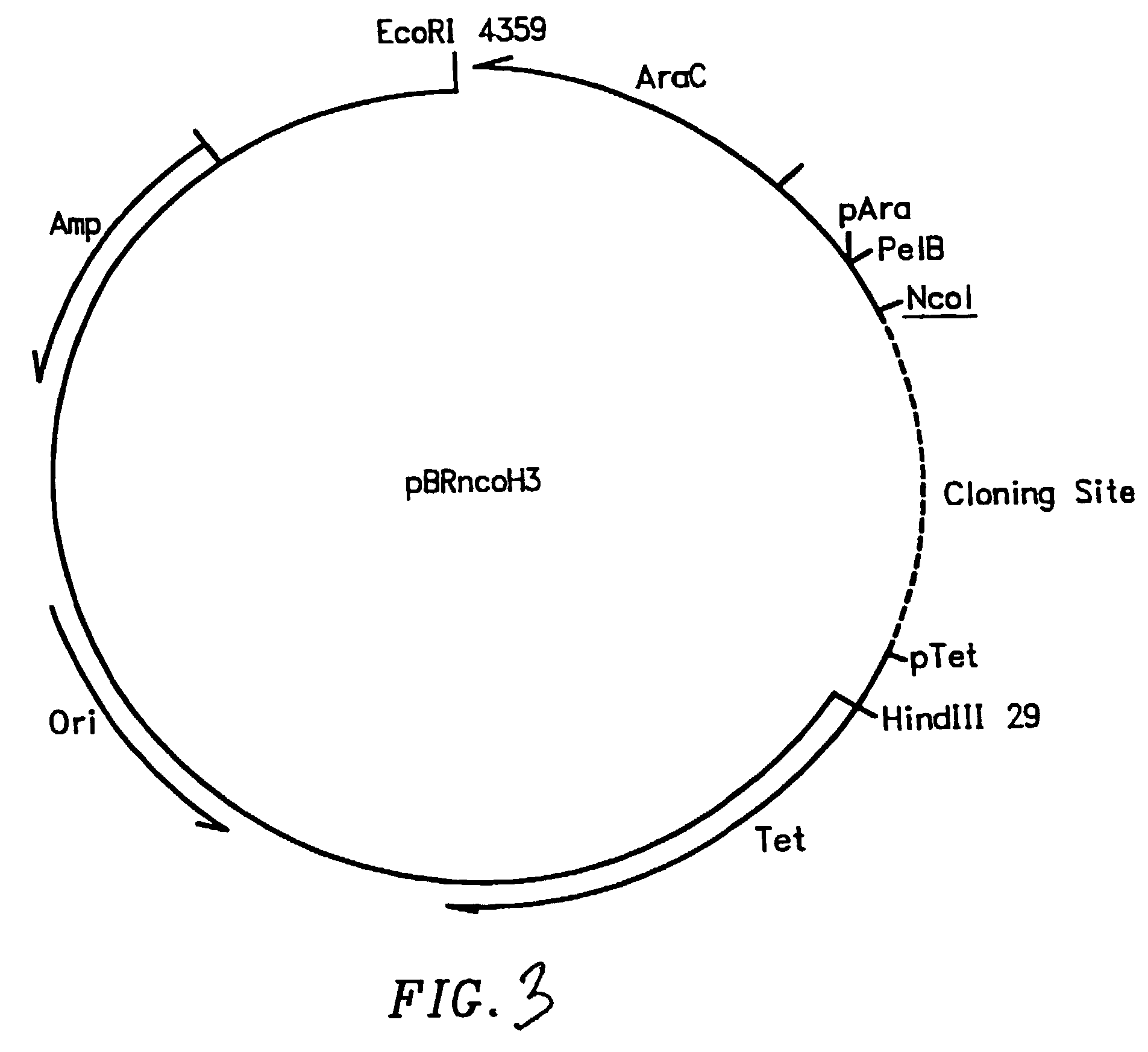
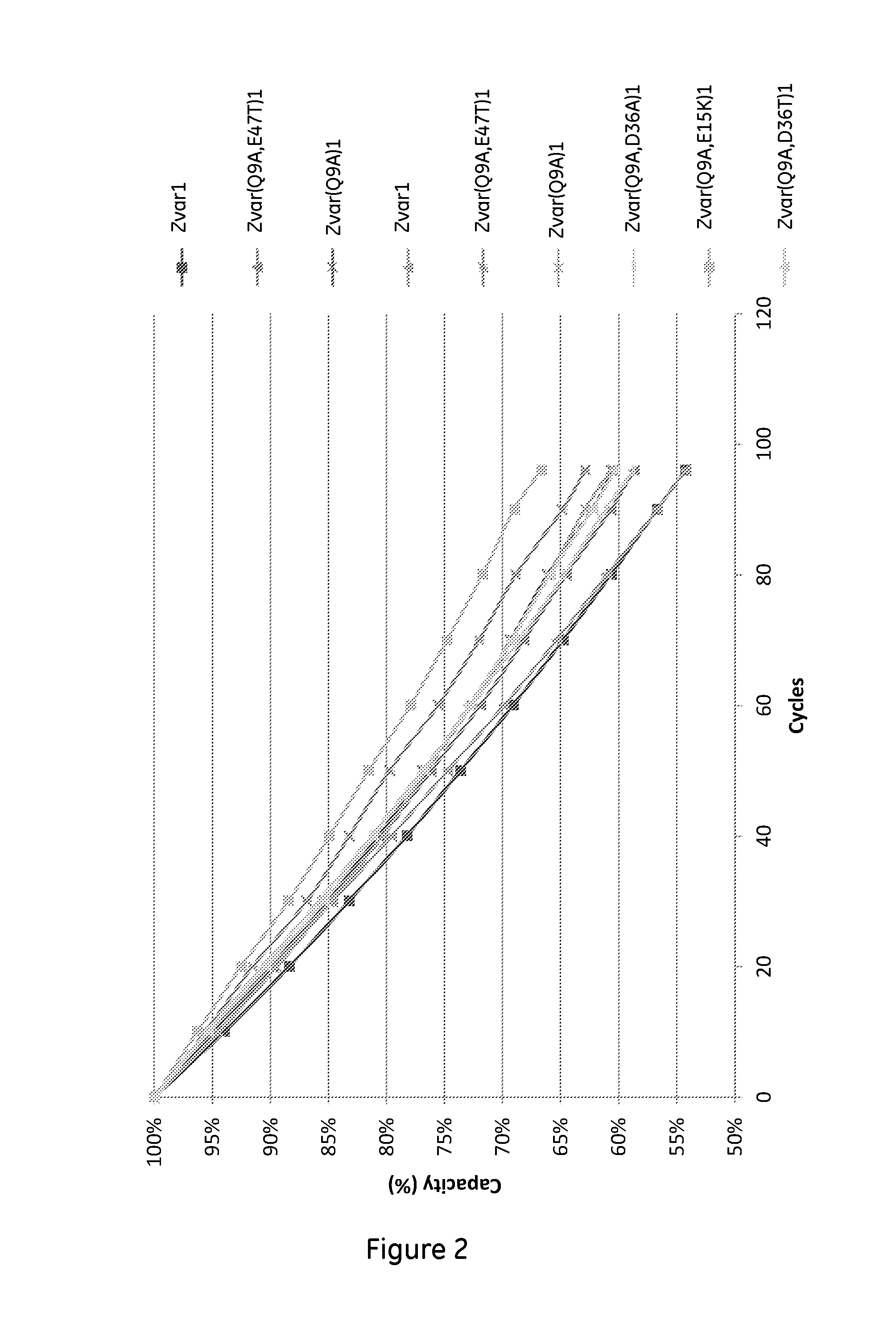
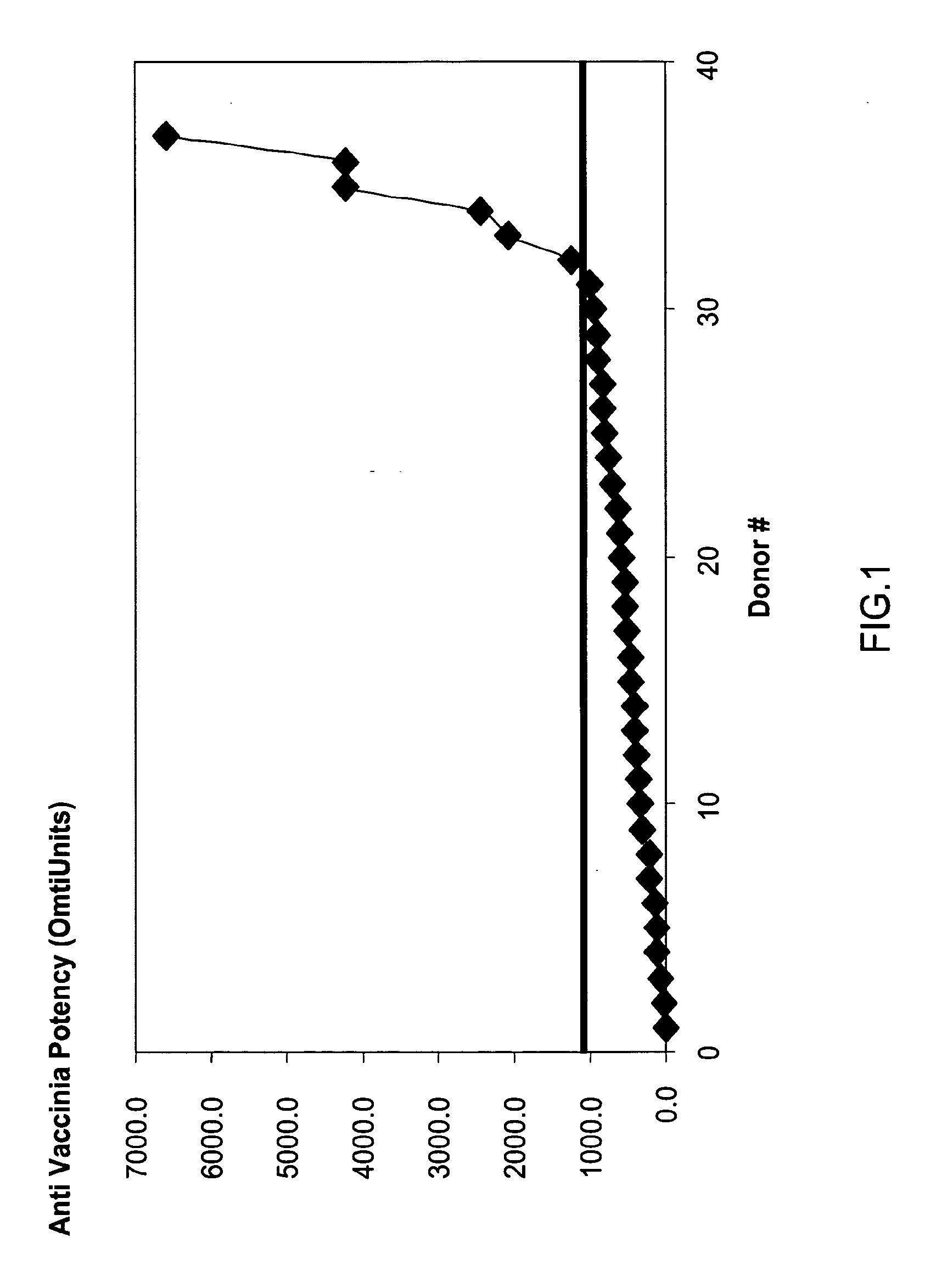
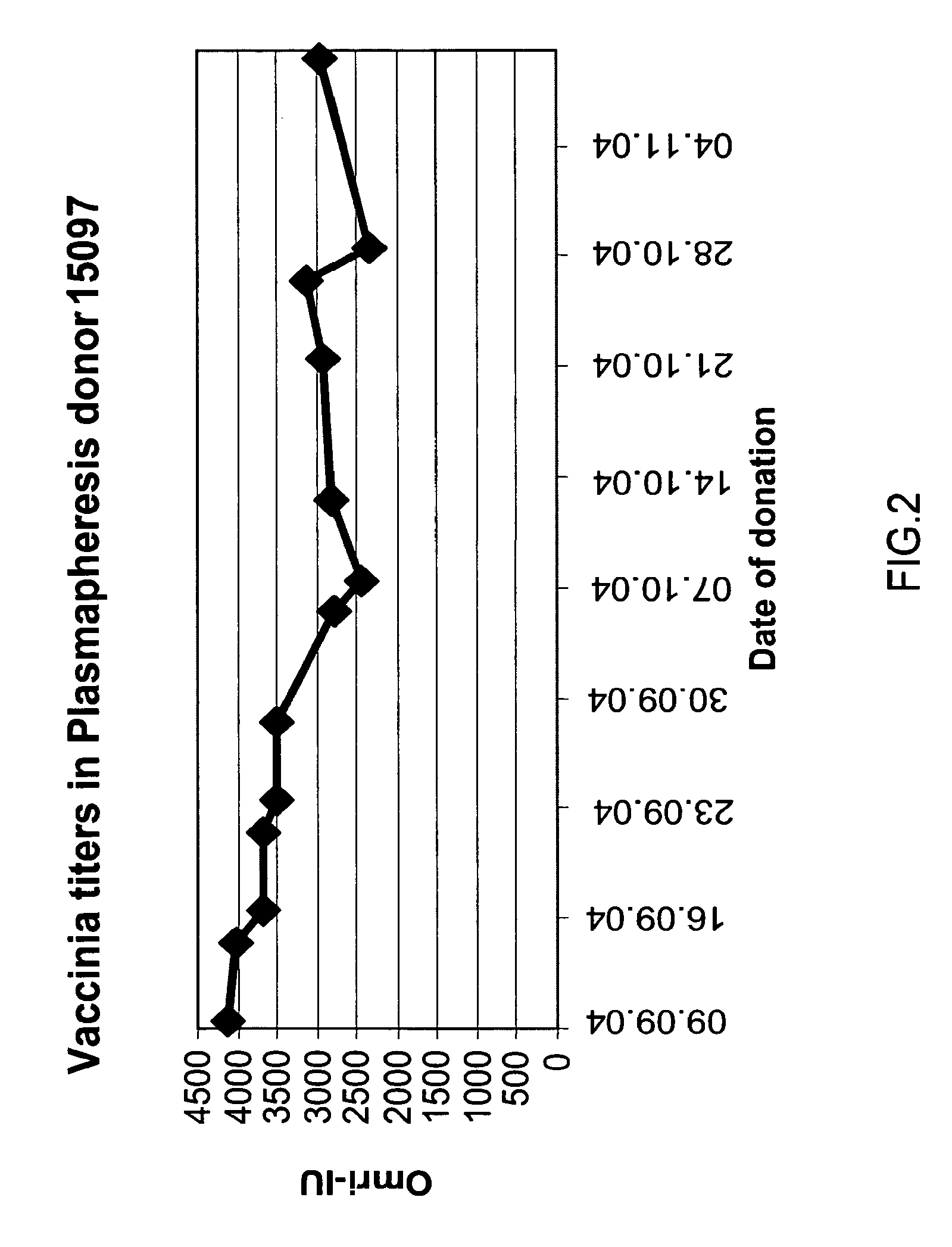
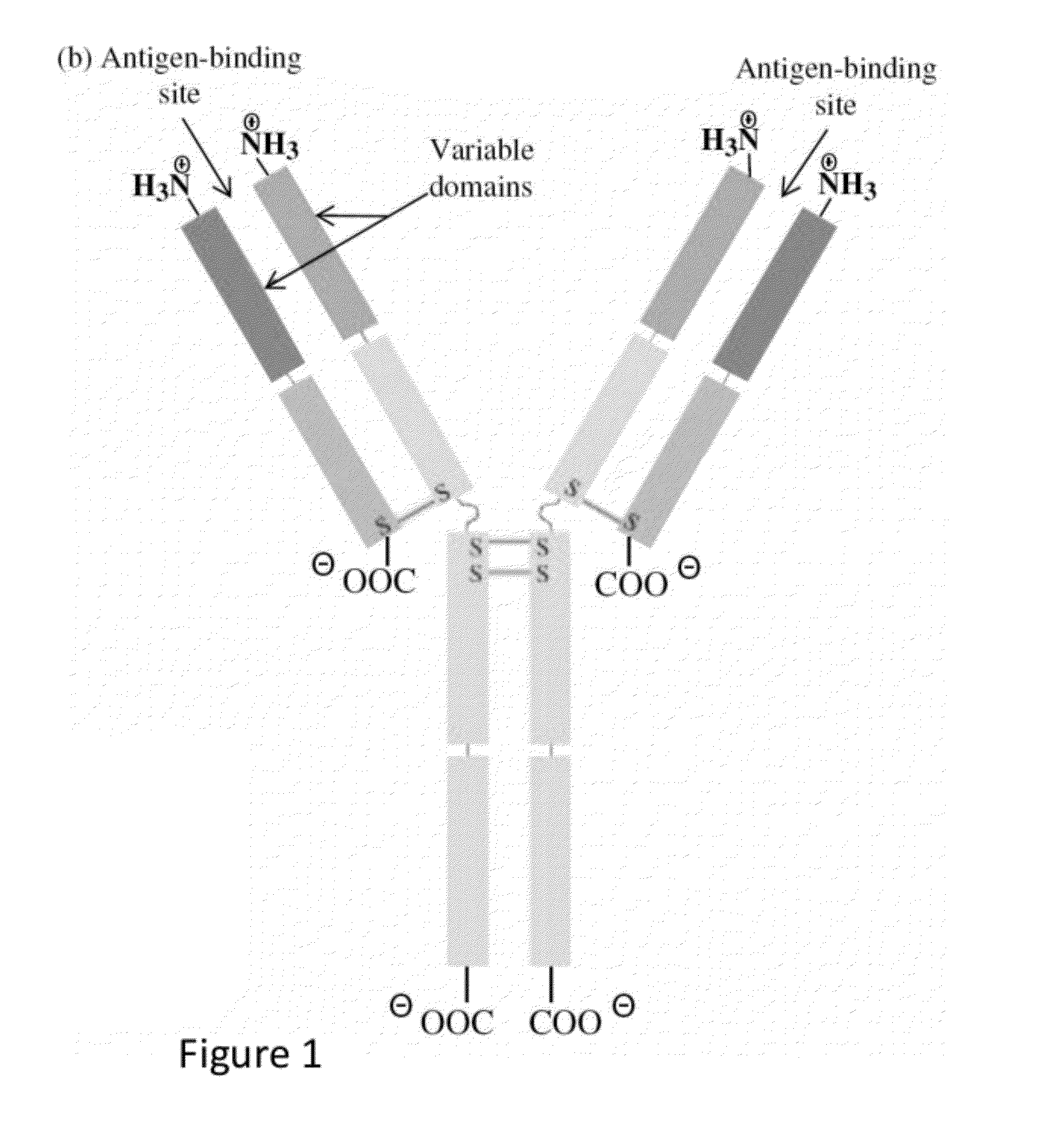
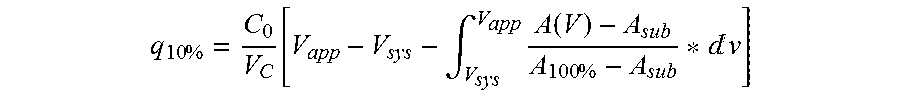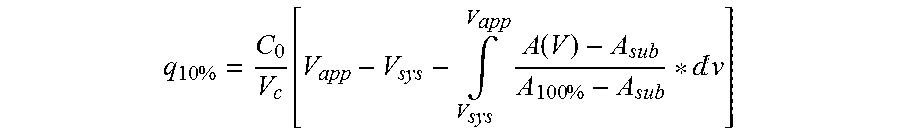Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "Immunoglobulin IgE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An immunoglobulin E (IgE) test measures the level of IgE, a type of antibody. Antibodies are made by the immune system to protect the body from bacteria, viruses, and allergens. IgE antibodies are normally found in small amounts in the blood, but higher amounts can be a sign that the body overreacts to allergens.
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS6602684B1Increase healing valueEnhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicityNanotechFungiAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Antibody producing non-human mammals
ActiveUS20100146647A1Low variabilityLow immunogenicityAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman animalDNA rearrangement
Owner:MERUS NV
Antibody producing non-human mammals
InactiveUS20100069614A1Easy to openEasy maintenanceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalDNA rearrangement
Described are transgenic, non-human animals comprising a nucleic acid encoding an immunoglobulin light chain, whereby the immunoglobulin light chain is human, human-like, or humanized. The nucleic acid is provided with a means that renders it resistant to DNA rearrangements and / or somatic hypermutations. In one embodiment, the nucleic acid comprises an expression cassette for the expression of a desired molecule in cells during a certain stage of development in cells developing into mature B cells. Further provided is methods for producing an immunoglobulin from the transgenic, non-human animal.
Owner:MERUS NV
Fab library for the preparation of anti VEGF and anti rabies virus fabs
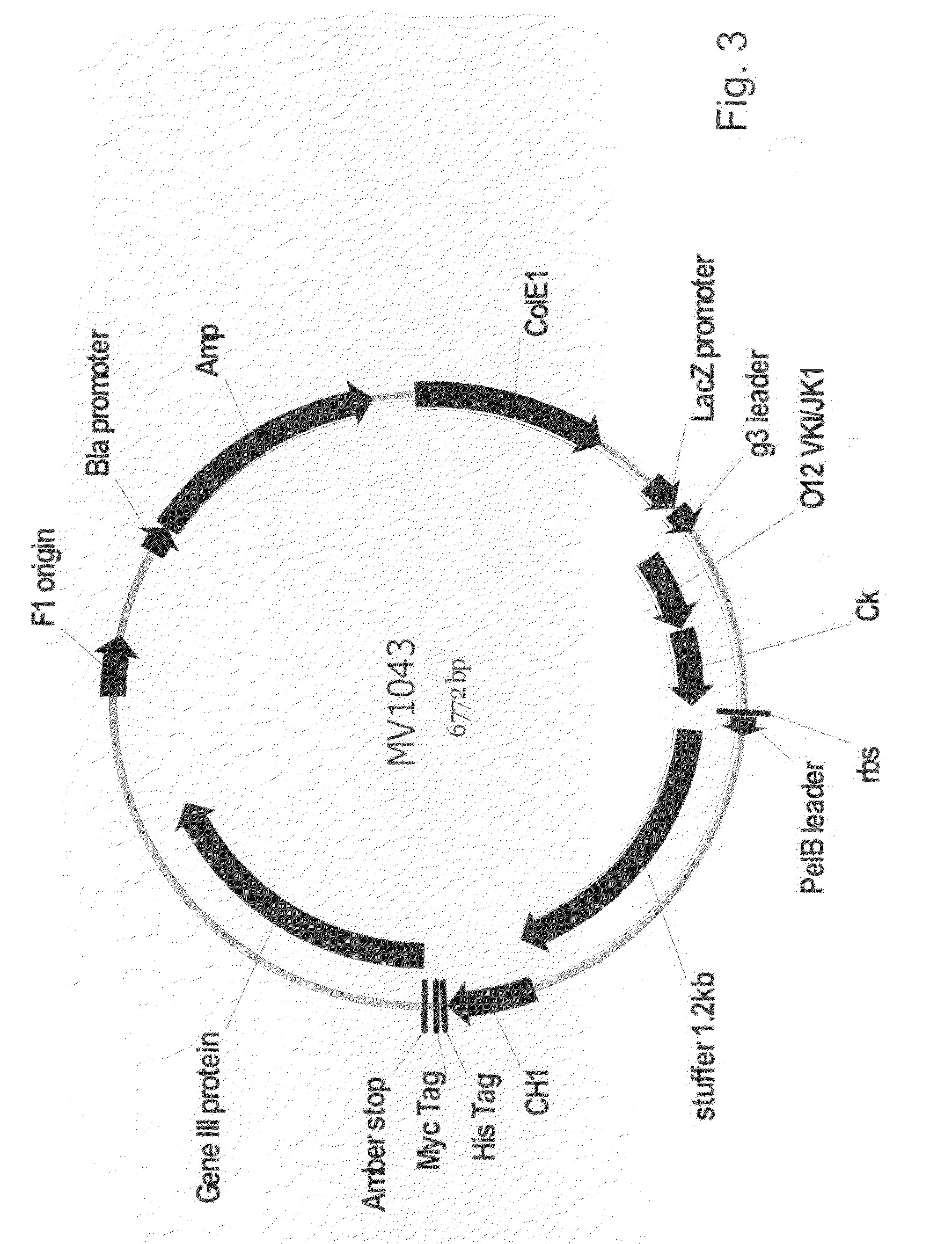
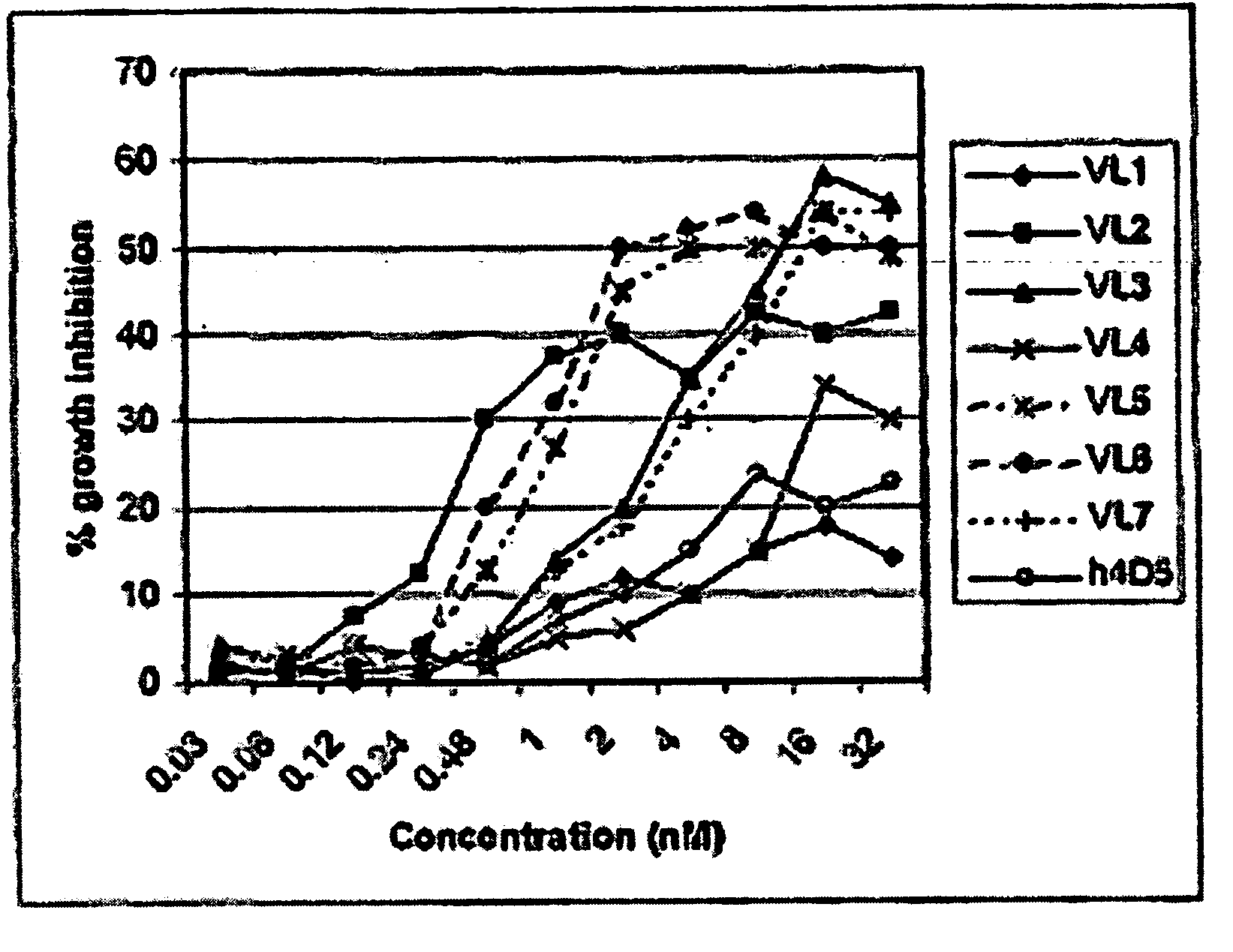
InactiveUS20060160184A1Maintain good propertiesOptimization mechanismAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein moleculesImmunoglobulin IgE
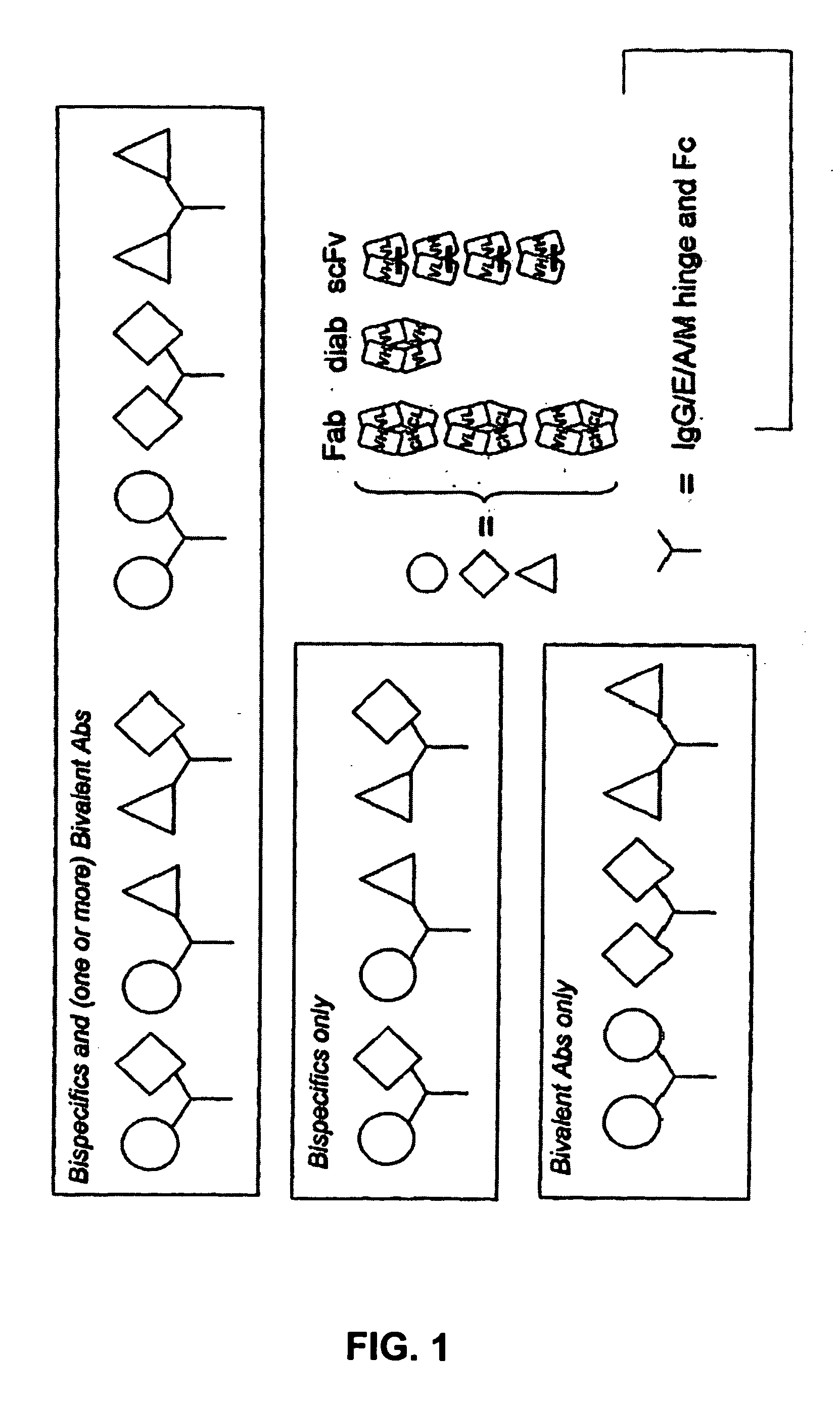
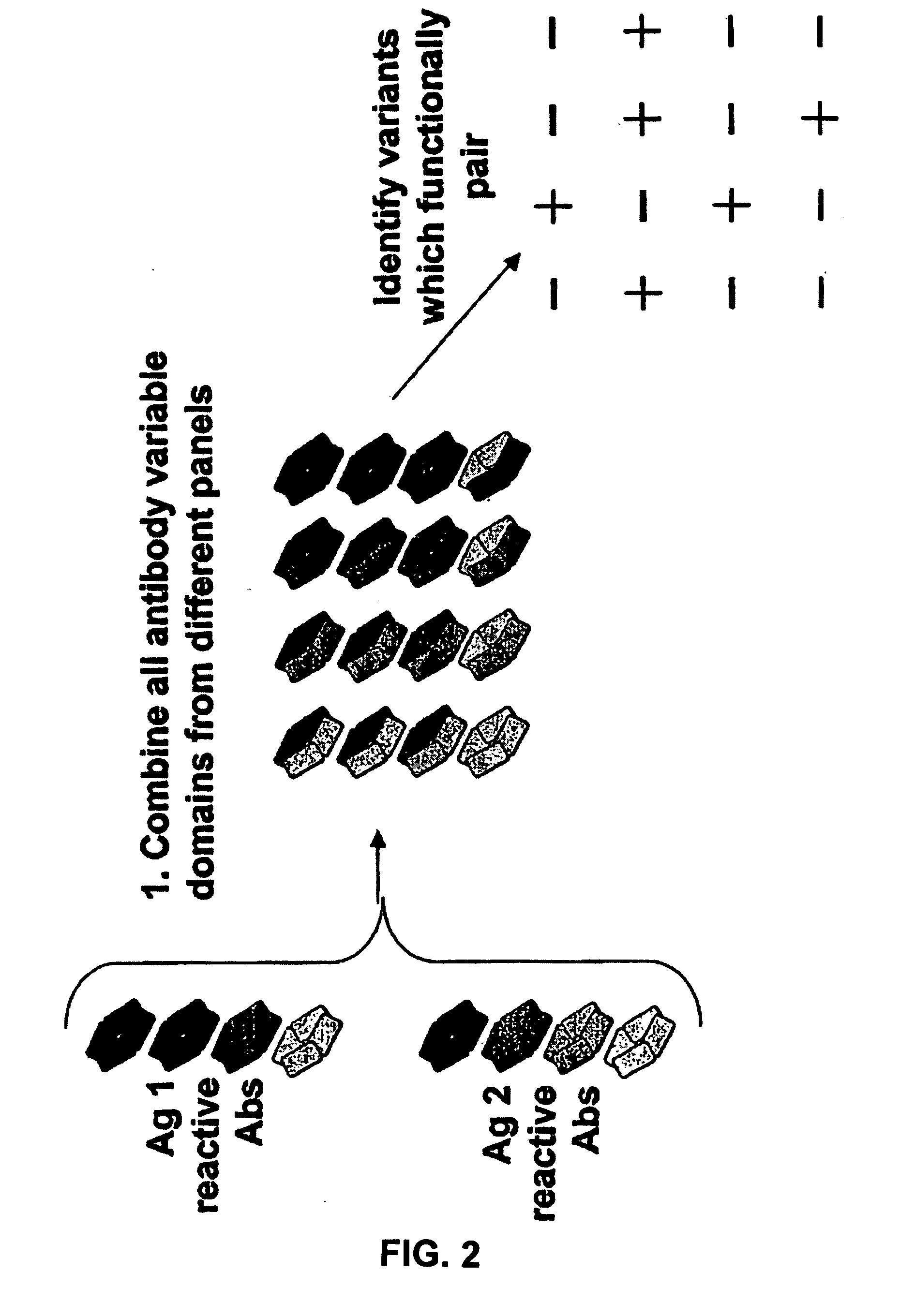
The present invention provides combinations of specific binding proteins, such as immunoglobulins, that are designed to be true combinations, essentially all components of the combination being functional and compatible with each other. The invention further provides a method for producing a composition comprising at least two different proteinaceous molecules comprising paired variable regions, the at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising paired variable regions, at least two proteinaceous molecules having different binding specificities, comprising contacting at least three different variable regions under conditions allowing for pairing of variable regions and harvesting essentially all proteinaceous molecules having binding specificities resulting from the pairing.
Owner:MERUS NV
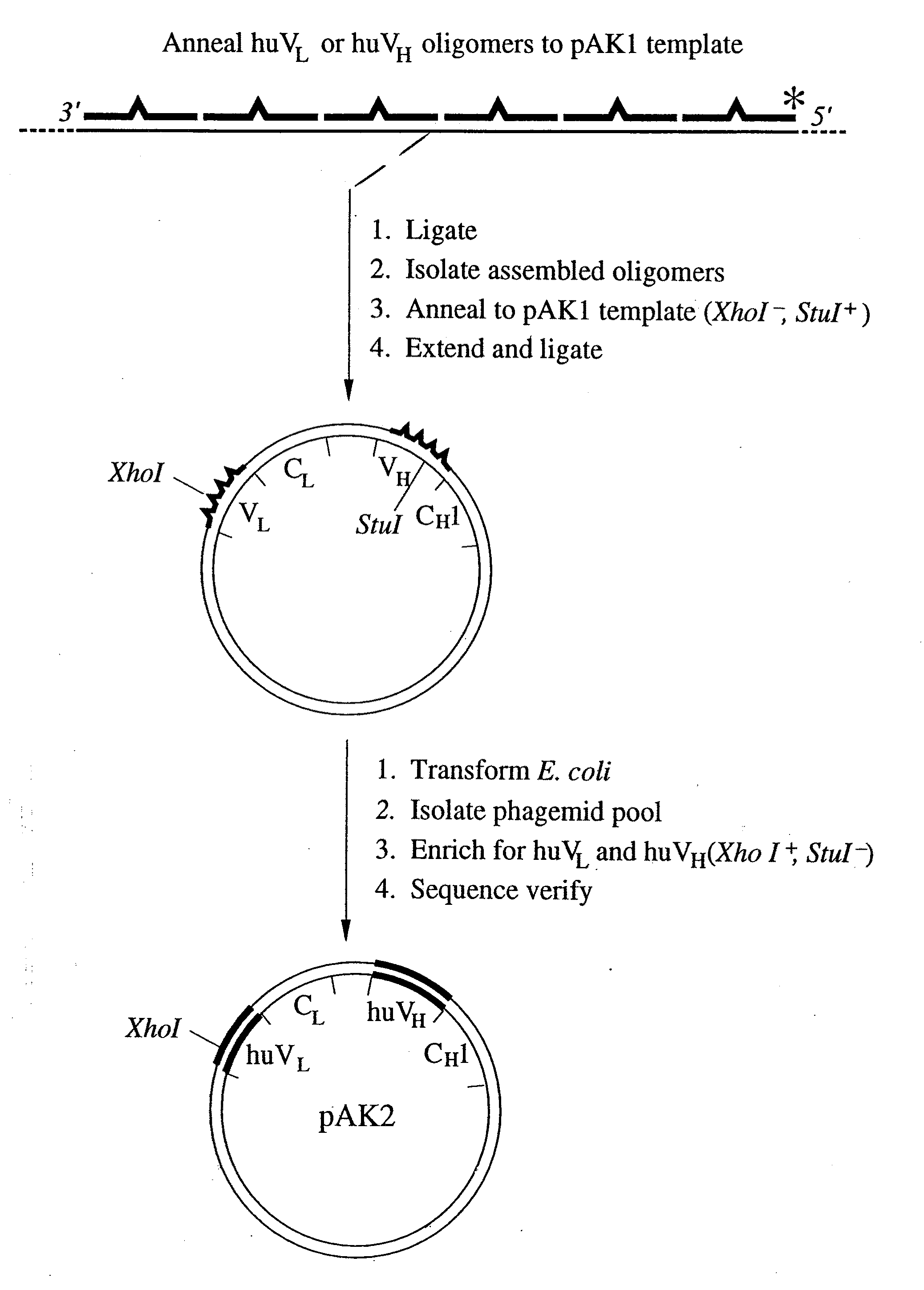
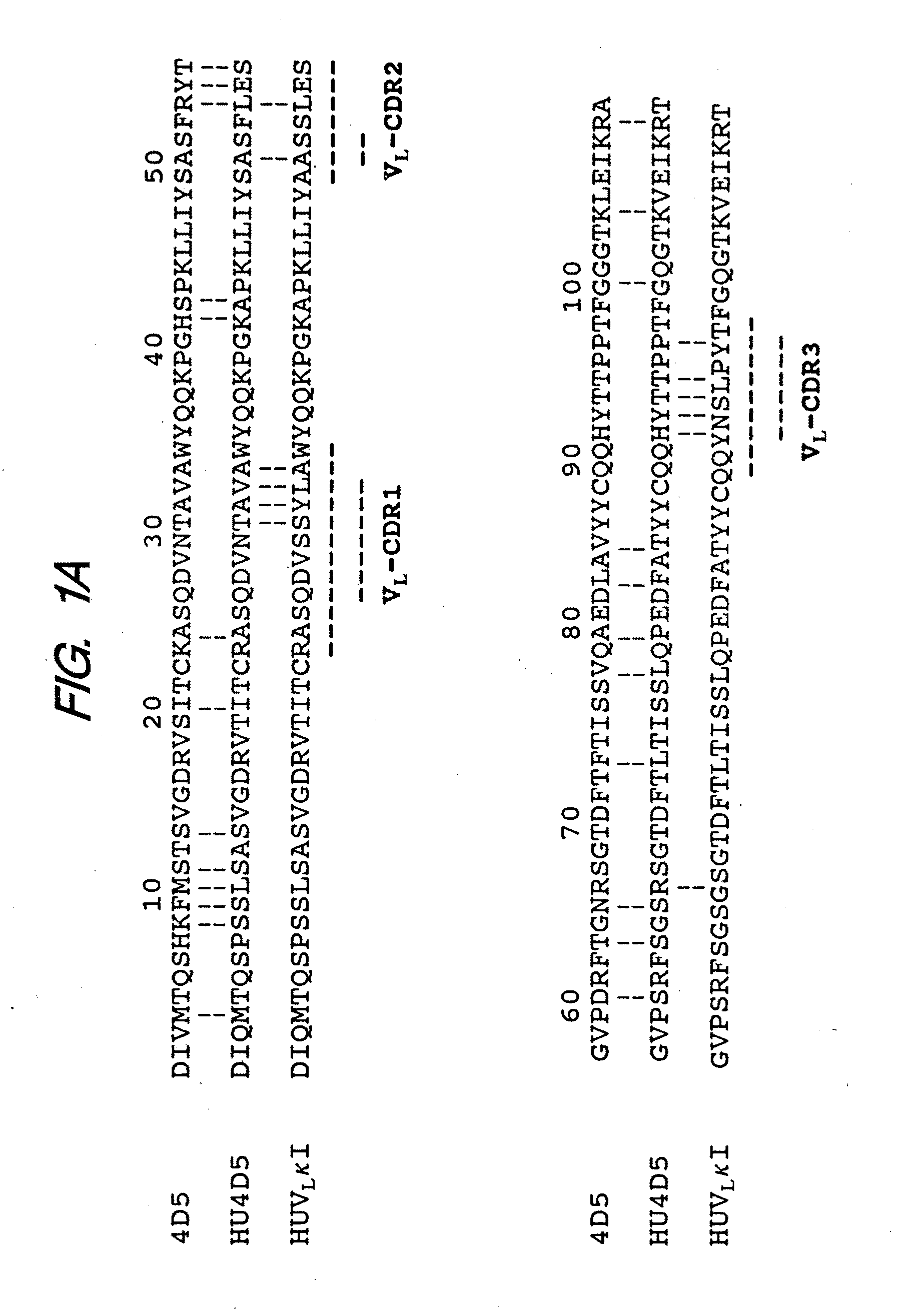
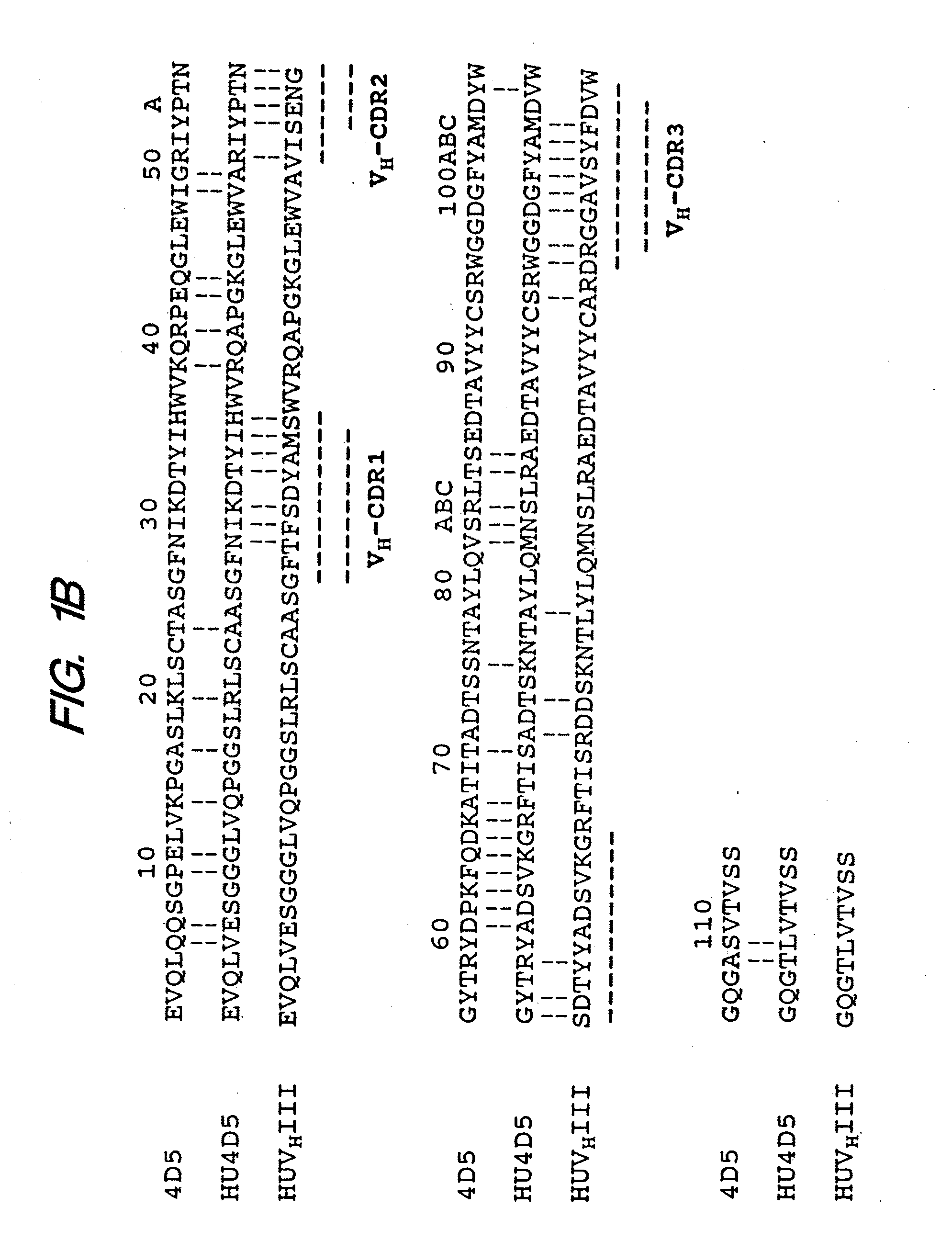
Method for making humanized antibodies
InactiveUS20100016556A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulin IgEHumanized antibody
Variant immunoglobulins, particularly humanized antibody polypeptides are provided, along with methods for their preparation and use. Consensus immunoglobulin sequences and structural models are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Antibodies to M-CSF
The present invention relates to antibodies and antigen-binding portions thereof that specifically bind to a M-CSF, preferably human M-CSF, and that function to inhibit a M-CSF. The invention also relates to human anti-M-CSF antibodies and antigen-binding portions thereof. The invention also relates to antibodies that are chimeric, bispecific, derivatized, single chain antibodies or portions of fusion proteins. The invention also relates to isolated heavy and light chain immunoglobulins derived from human anti-M-CSF antibodies and nucleic acid molecules encoding such immunoglobulins. The present invention also relates to methods of making human anti-M-CSF antibodies, compositions comprising these antibodies and methods of using the antibodies and compositions for diagnosis and treatment. The invention also provides gene therapy methods using nucleic acid molecules encoding the heavy and / or light immunoglobulin molecules that comprise the human anti-M-CSF antibodies. The invention also relates to transgenic animals and transgenic plants comprising nucleic acid molecules of the present invention.
Owner:WARNER LAMBERT CO LLC +1
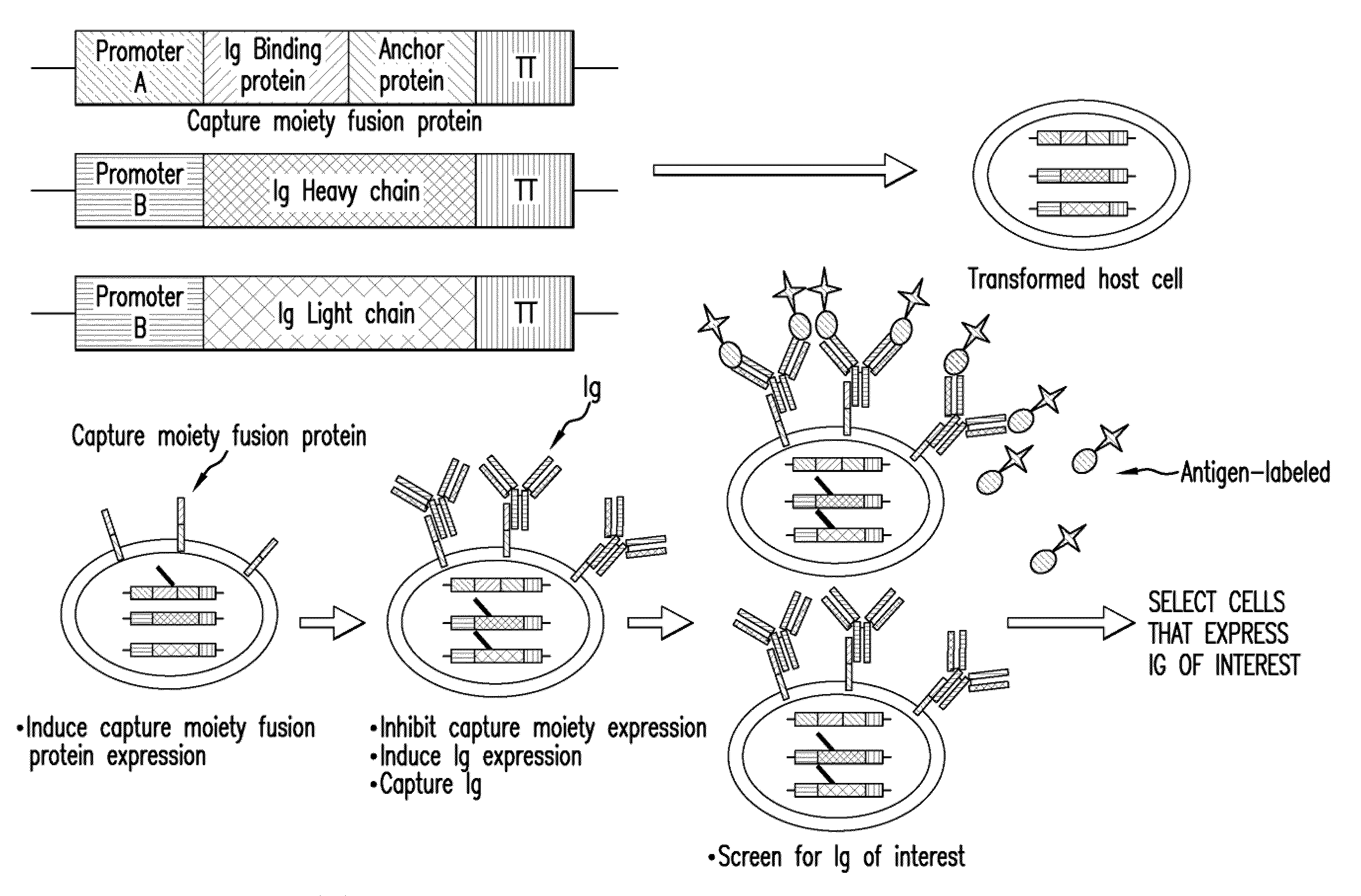
Methods of making antibody heavy and light chains having specificity for a desired antigen
The invention relates to processes for producing an immunoglobulin or an immunologically functional immunoglobulin fragment containing at least the variable domains of the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains. The processes can use one or more vectors which produce both the heavy and light chains or fragments thereof in a single cell. The invention also relates to the vectors used to produce the immunoglobulin or fragment, and to cells transformed with the vectors.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Binding molecules derived from immunoglobulins which do not trigger complement mediated lysis
InactiveUS7597889B1Maximizing numberIncreasing therapeutic potentialOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensHeavy chainImmunoglobulin IgE
Disclosed are binding molecules which are recombinant polypeptides containing: (i) a binding domain capable of binding a target molecule, and (ii) an effector domain having an amino acid sequence substantially homologous to all or part of a constant domain of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain; characterized in that the binding molecule is capable of binding the target molecule without triggering significant complement dependent lysis, or cell mediated destruction of the target, and more preferably wherein the effector domain is capable of specifically binding FcRn and / or FcγRIIb. These are generally based on chimeric domains which are derived from two or more human immunoglobulin heavy chain CH2 domains domains. In preferred embodiments the regions 233-236, and 327-331, are modified, as are further residues to render the molecule null allotypic. Also disclosed are nucleic acids, host cells, production processes and materials, and uses. Pharmaceutical preparations are also disclosed.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Human antibodies
InactiveUS7135287B1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulin IgEGenetically modified animal
The invention uses the power of display selection methods to screen libraries of human immunoglobulin genes from nonhuman transgenic animals expressing human immunoglobulins. Such screening produces unlimited numbers of high affinity human antibodies to any target of interest.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS20120208234A1Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityADAMTS Proteins
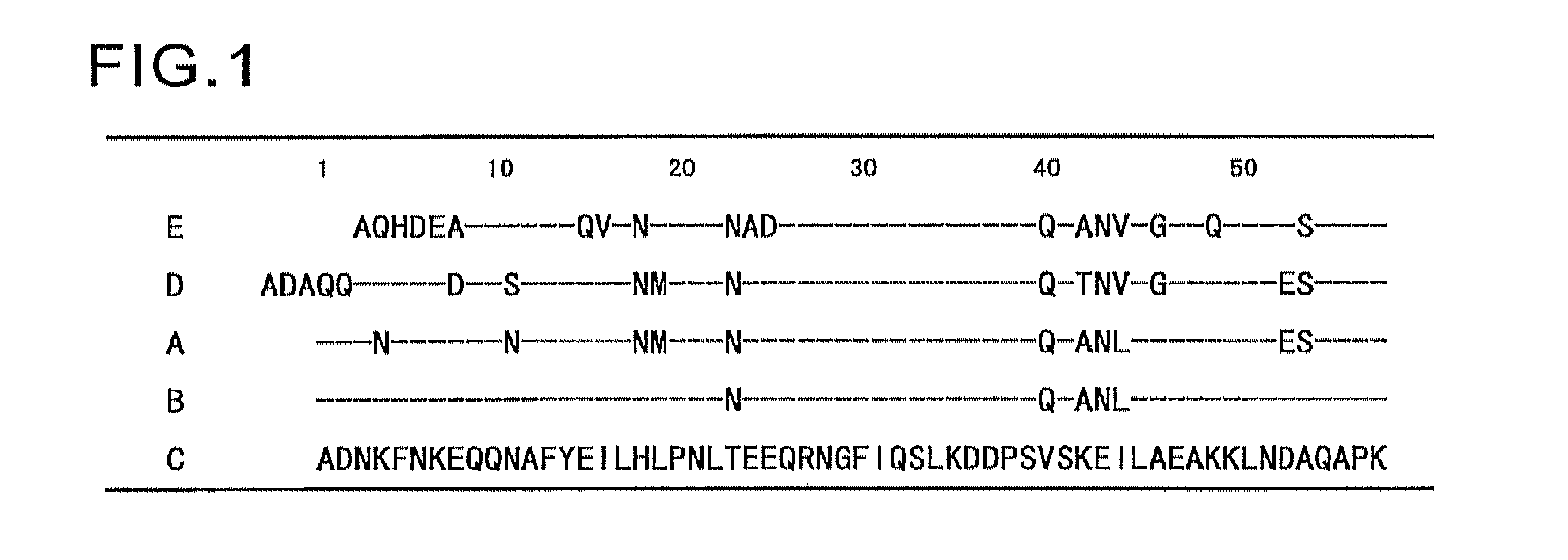
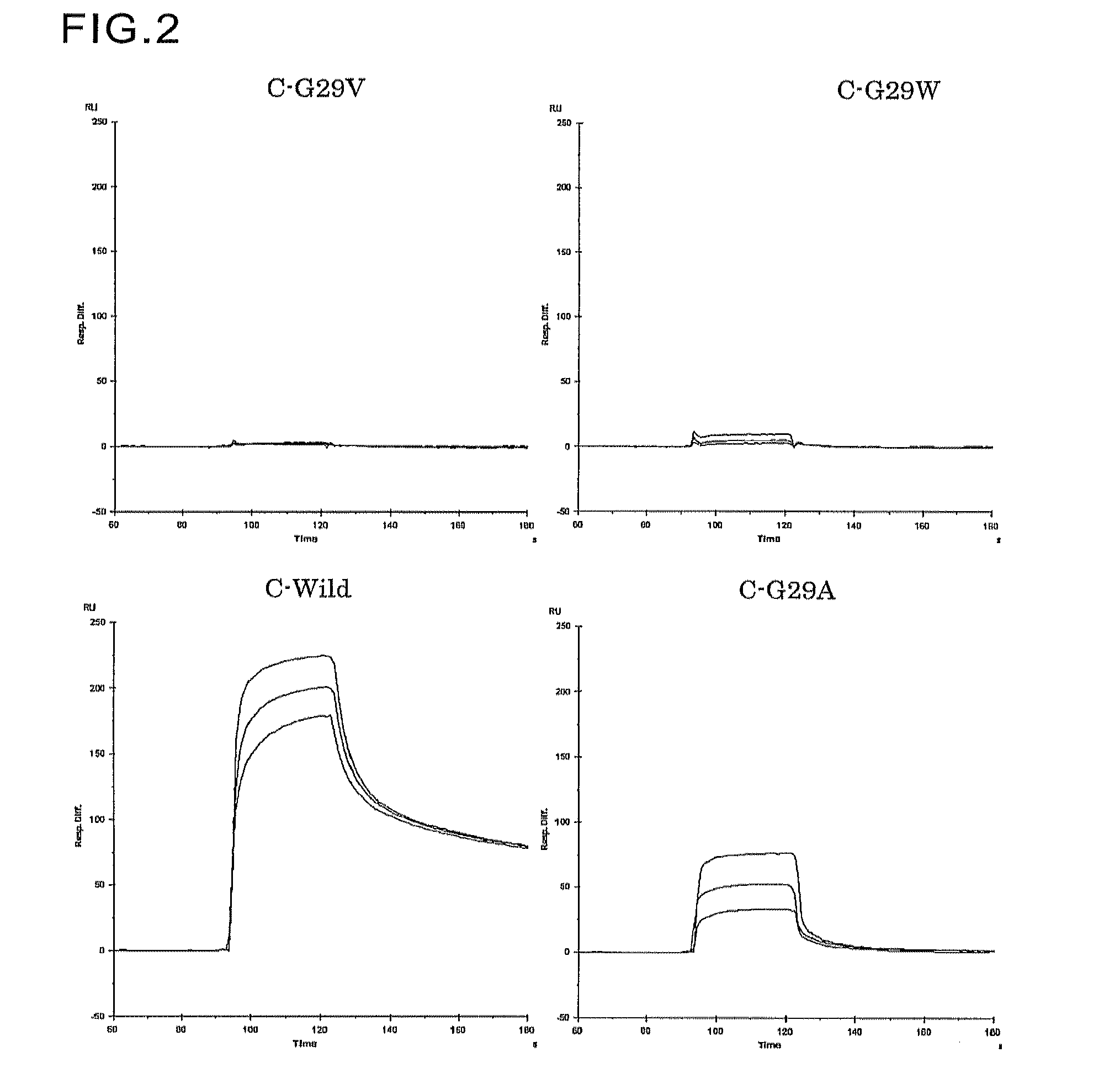
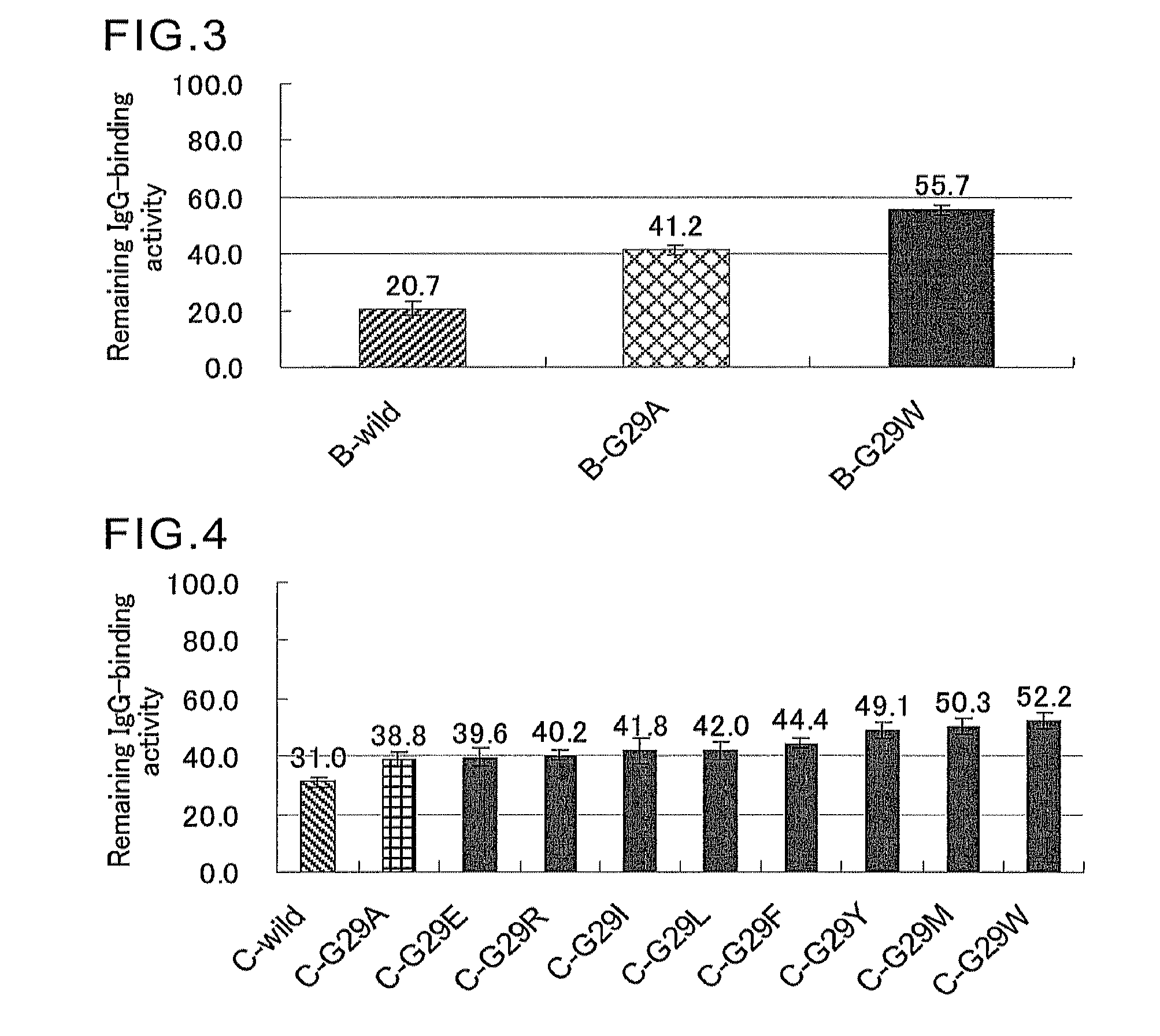
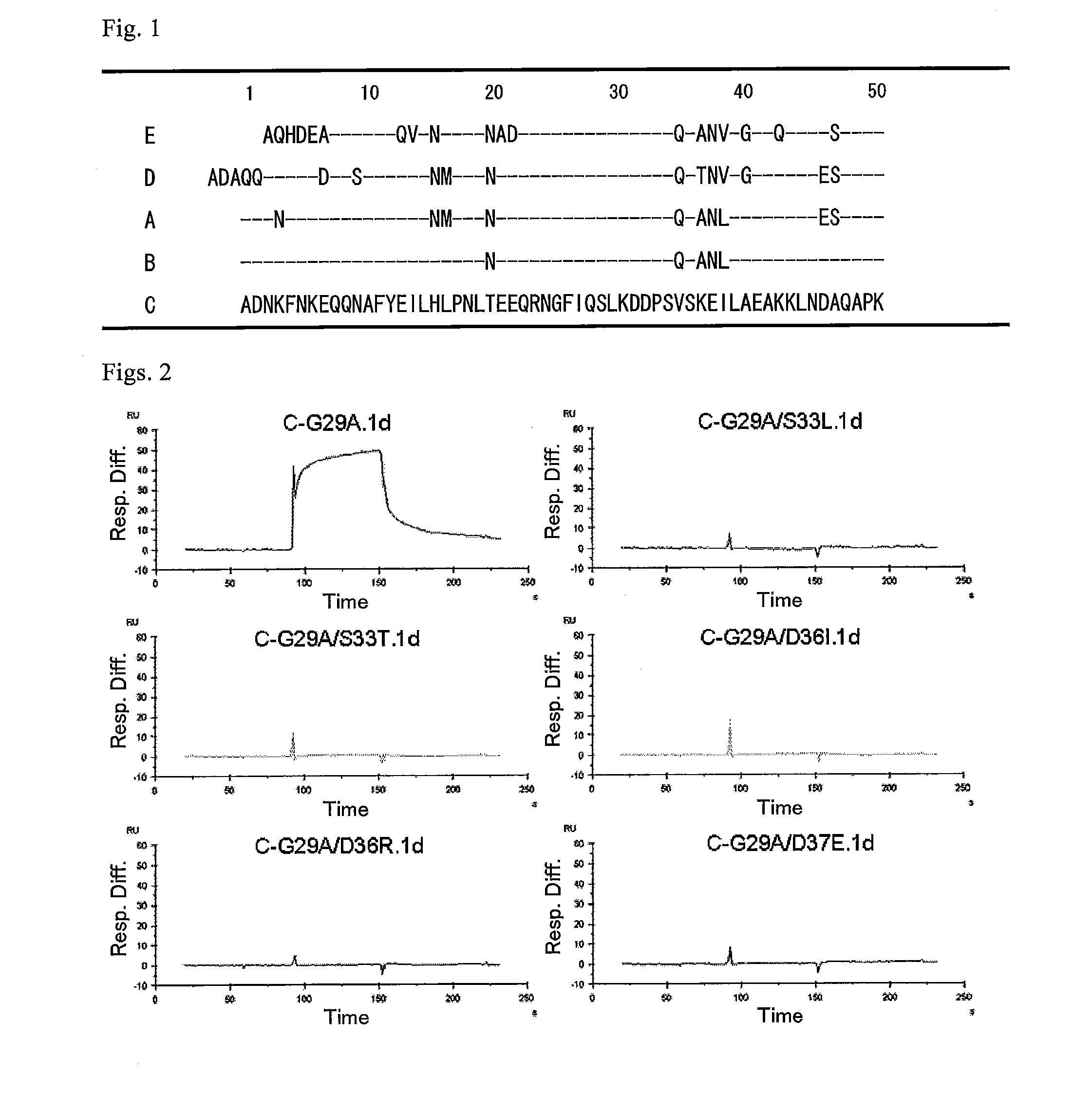
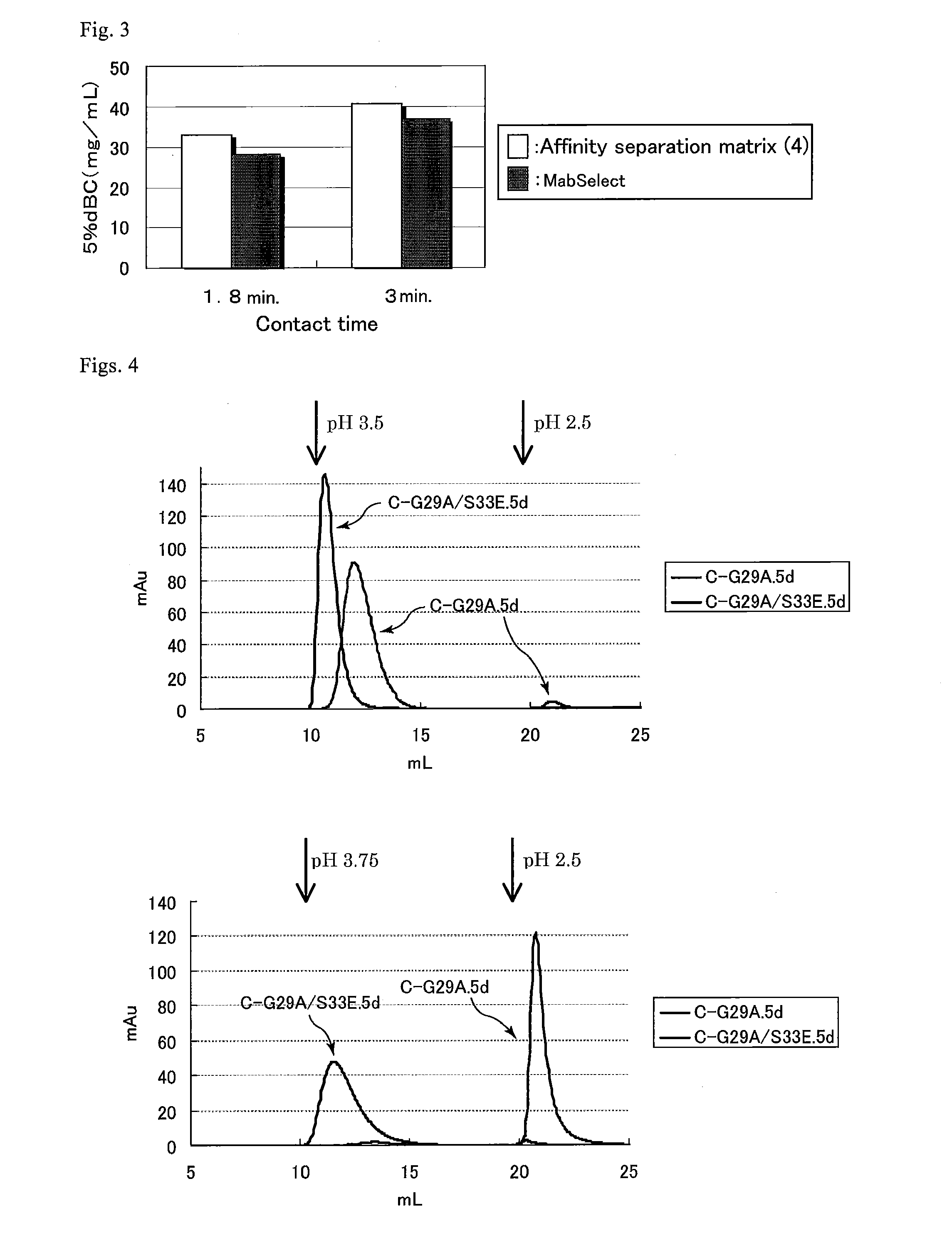
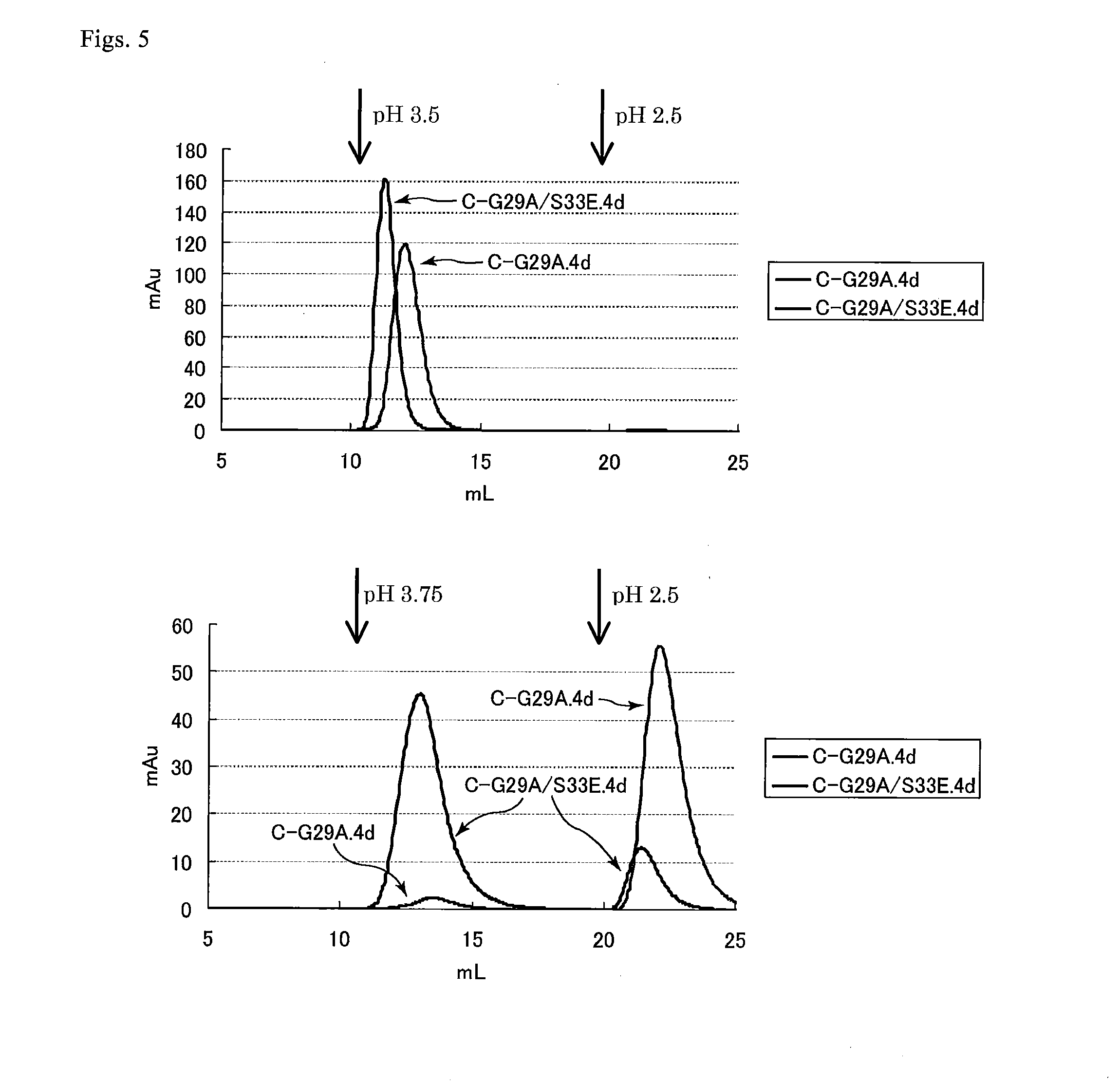
An object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having better antibody dissociation properties in the presence of an acid than conventional engineered Protein A ligands and a further object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having higher alkali resistance. The present invention is to provide a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, including an amino acid sequence derived from any of E, D, A, B and C domains of Protein A, wherein at least one Gly residue in the amino acid sequence is replaced with an amino acid other than Ala, and the protein has a lower affinity for an Fab region of an immunoglobulin than a protein including an amino acid sequence in which the Gly residue is replaced with Ala. Also, the present invention is to provide the protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, which has improved chemical stability in an alkaline condition compared to the corresponding domain.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Surface Display of Whole Antibodies in Eukaryotes
ActiveUS20100009866A1Stabilize cytoplasmic mRNAImprove translation efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningYeastAntigen
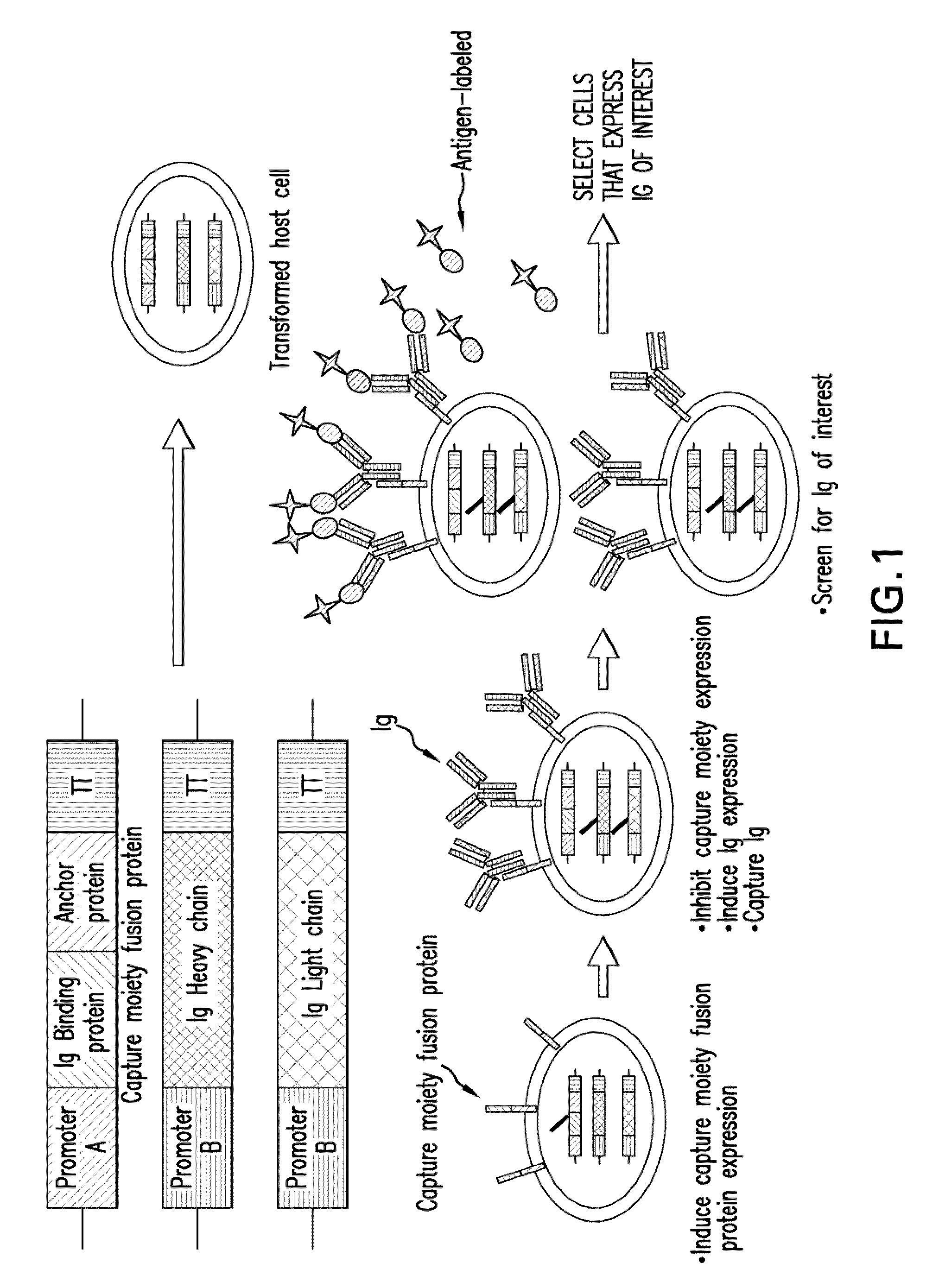
Methods for display of recombinant whole immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin libraries on the surface of eukaryote host cells, including yeast and filamentous fungi, are described. The methods are useful for screening libraries of recombinant immunoglobulins in eukaryote host cells to identify immunoglobulins that are specific for an antigen of interest.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
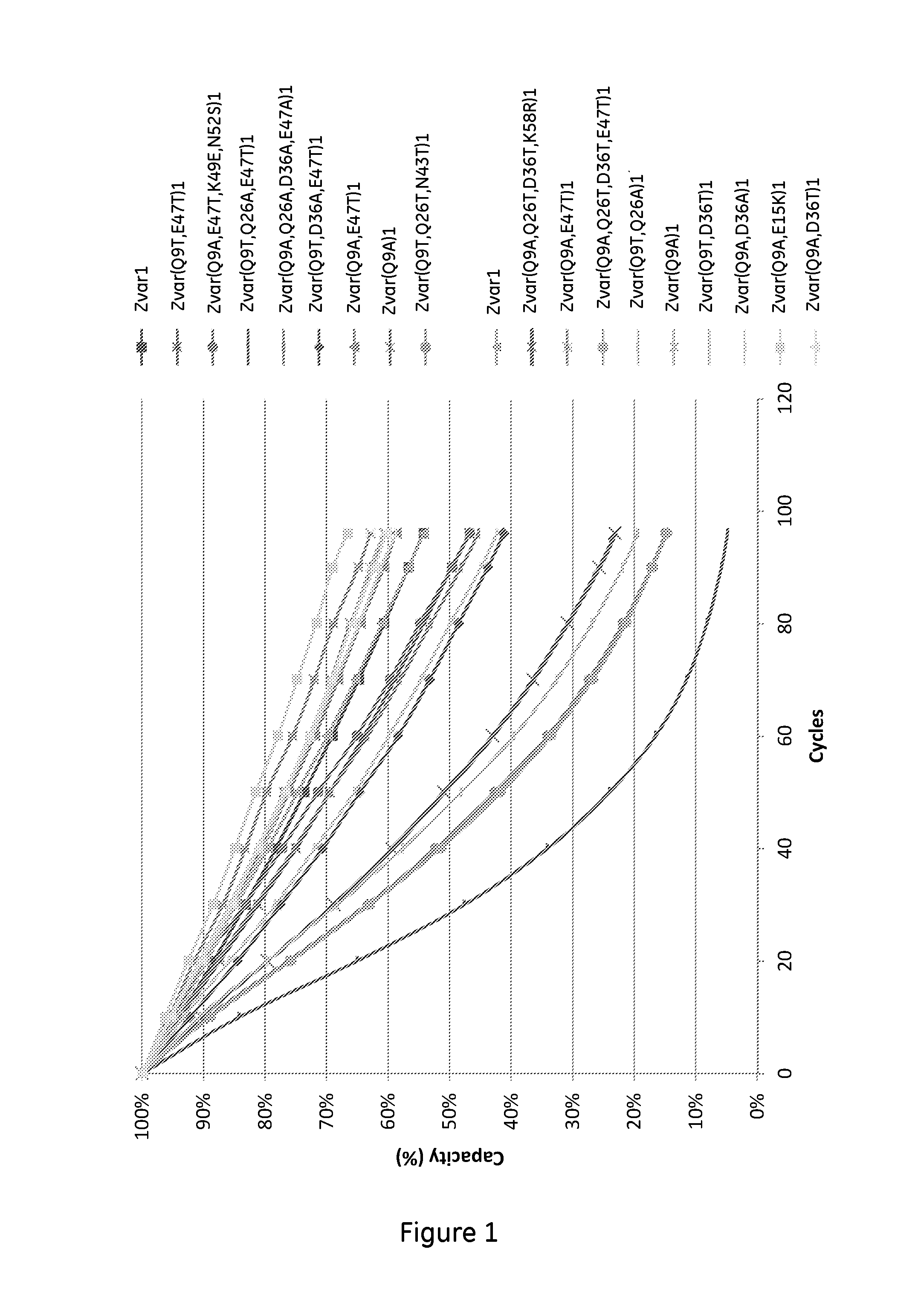
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Polypeptides
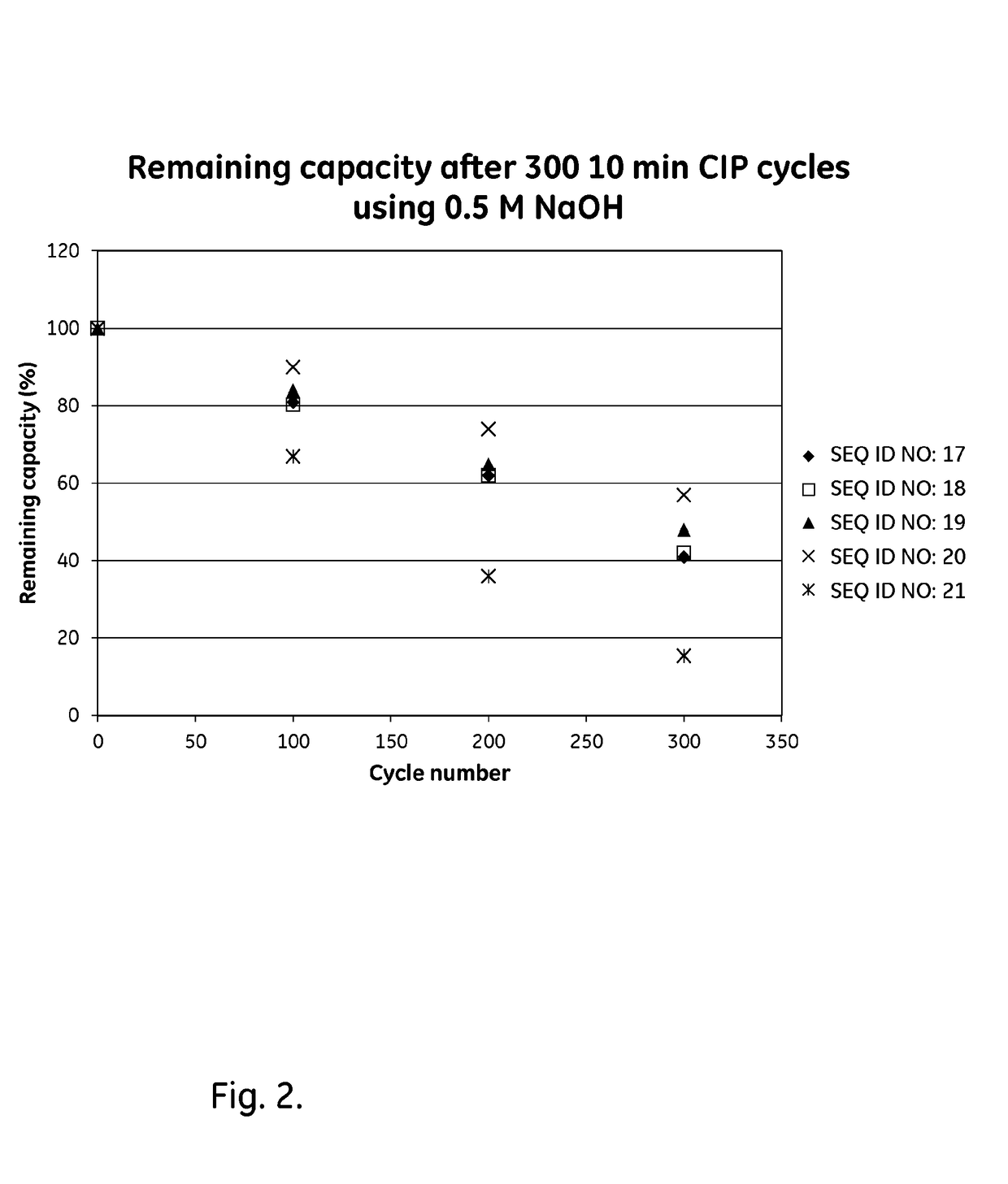
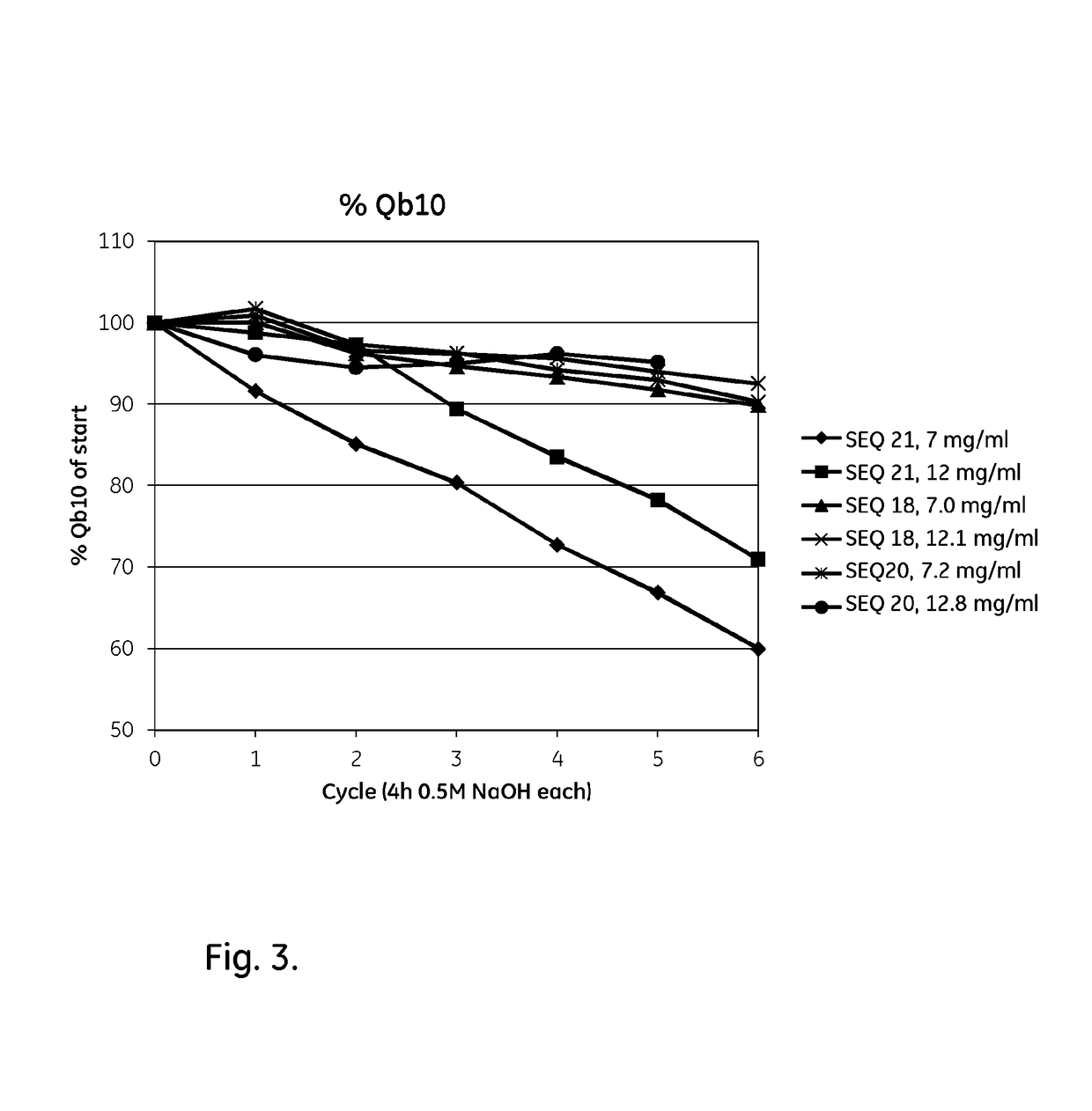
ActiveUS20170334954A1Improved alkaline stabilityImprove stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationArginineFc binding
An Fc-binding polypeptide of improved alkali stability, comprising a mutant of an Fc-binding domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as defined by SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5, SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7, SEQ ID NO:22, SEQ ID NO 51 or SEQ ID NO 52 wherein at least the asparagine or serine residue at the position corresponding to position 11 in SEQ ID NO:4-7 has been mutated to an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glutamic acid, lysine, tyrosine, threonine, phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, alanine, histidine and arginine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Protein capable of binding specifically to immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS20130096276A1Excellent antibody dissociation propertyEasy to separateBacteriaSugar derivativesLow affinityAmino acid substitution
An object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having better antibody dissociation properties in the acidic condition compared with known engineered Protein A ligands. The present invention provides a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, including an amino acid sequence obtained by introducing, into an amino acid sequence derived from any of E, D, A, B and C domains of Protein A, at least one amino acid substitution at any one or more of amino acid residues corresponding to positions 31 to 37 of the A, B and C domains (positions 29 to 35 of the E domain, positions 34 to 40 of the D domain), which are conserved in all the domains, the protein having a lower affinity for an Fab region of an immunoglobulin than a protein having the amino acid sequence before introduction of the substitution.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Antigenic fusionprotein carrying Galalpha1,3Gal epitopes
InactiveUS6943239B2Effective absorptionEasy and cheap to produceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeImmunoglobulin IgE
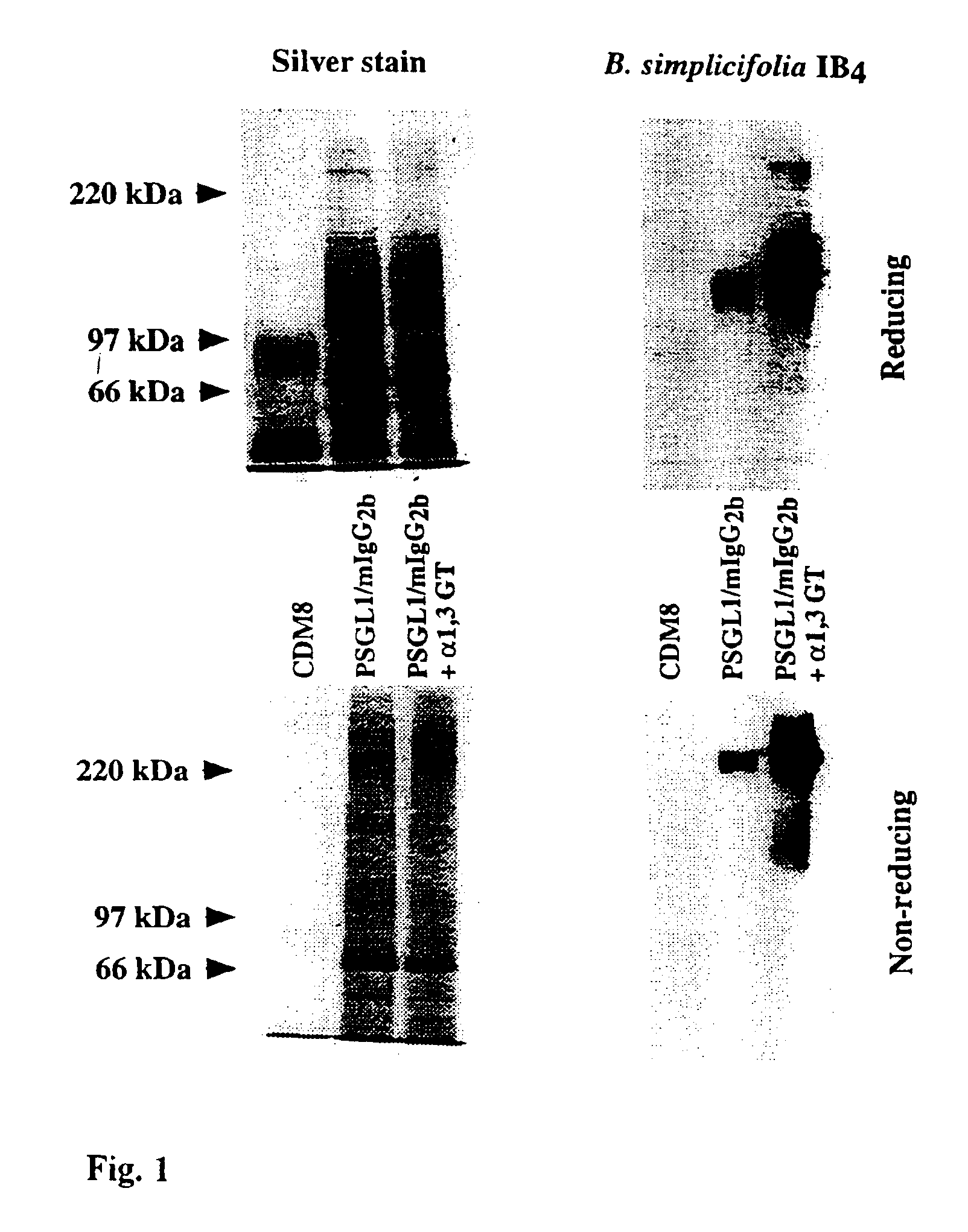
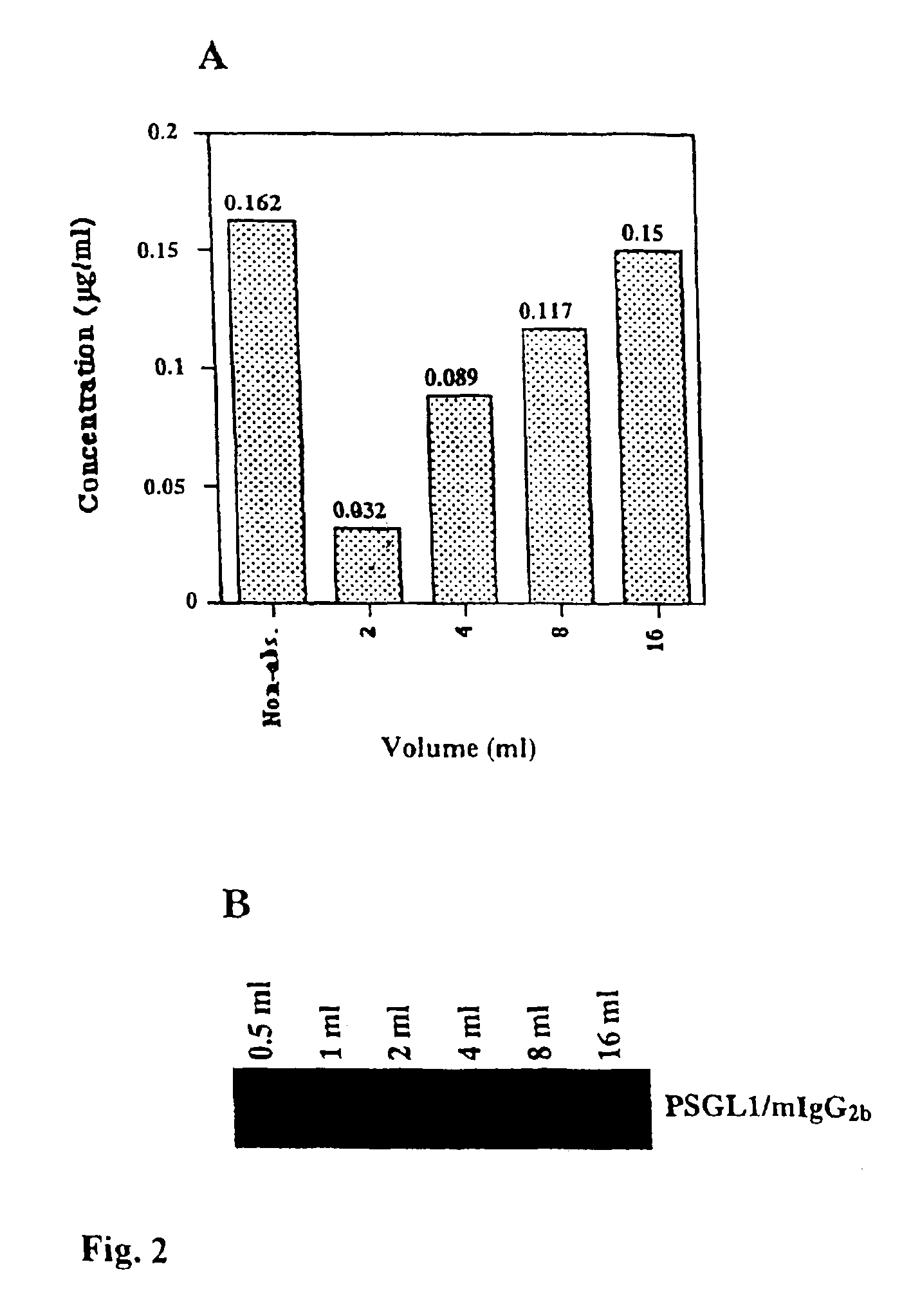
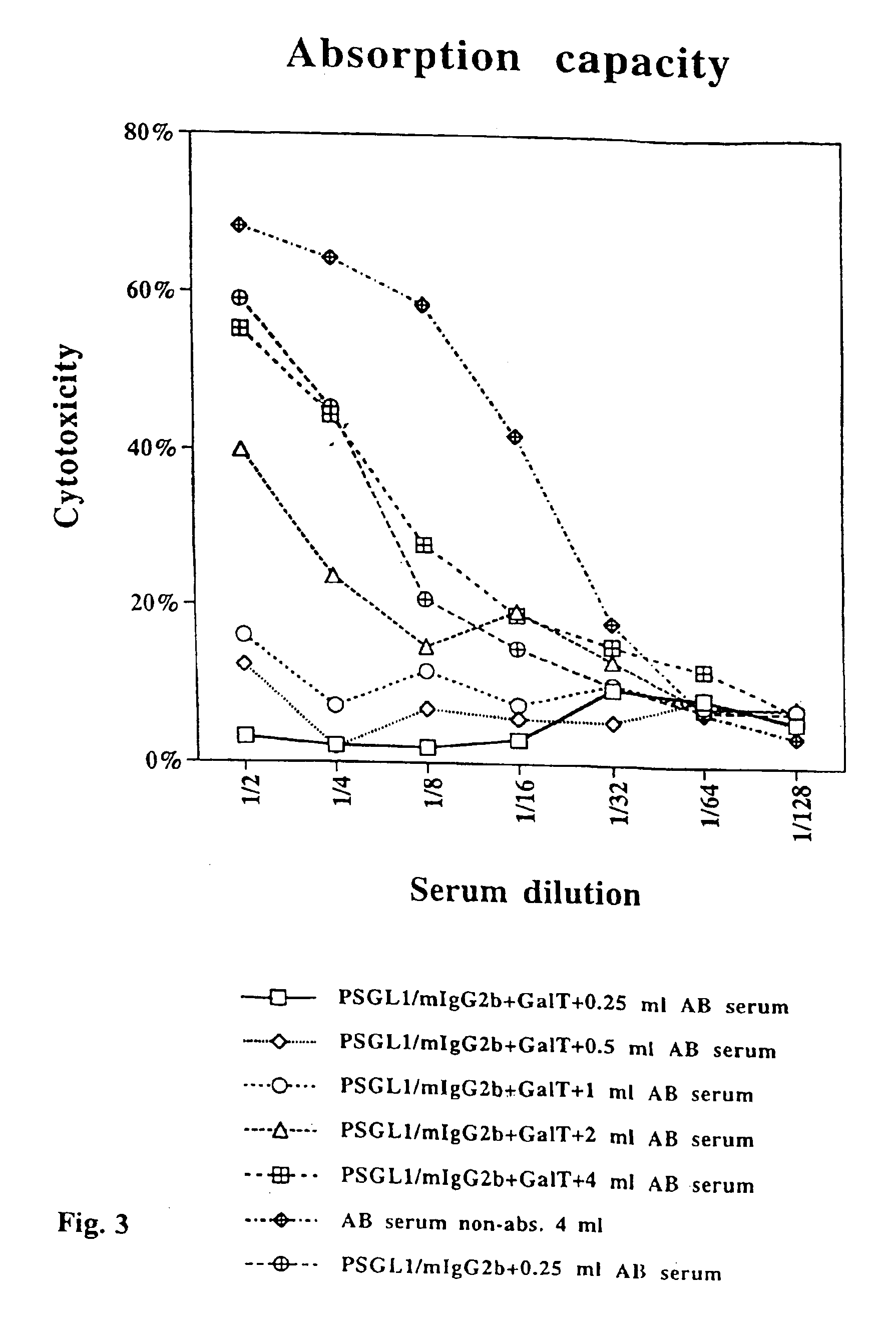
The present invention relates to an antigenic fusionprotein, which carries multiple Galα1,3Gal epitopes. The fusion protein according to the invention may also be comprised of a heavily glycosylated mucin part, which mediates binding to selectins, such as PSGL-1, and a part, which exhibits immunoglobulin properties, such as the Fc part of IgG. The fusionprotein according to the invention is preferably used as an absorber to prevent a hyperacute rejection of a xenotransplant, such as a pig tissue or organ transplanted into a human patient. In addition, the invention relates to a method for the prevention of hyperacute rejection reaction in a patient who is to receive a xenotransplant.
Owner:RECOPHARMA AB
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Polypeptides
ActiveUS20160159857A1Highly selective bindingImproved alkaline stabilitySolid sorbent liquid separationDepsipeptidesTryptophanMutant
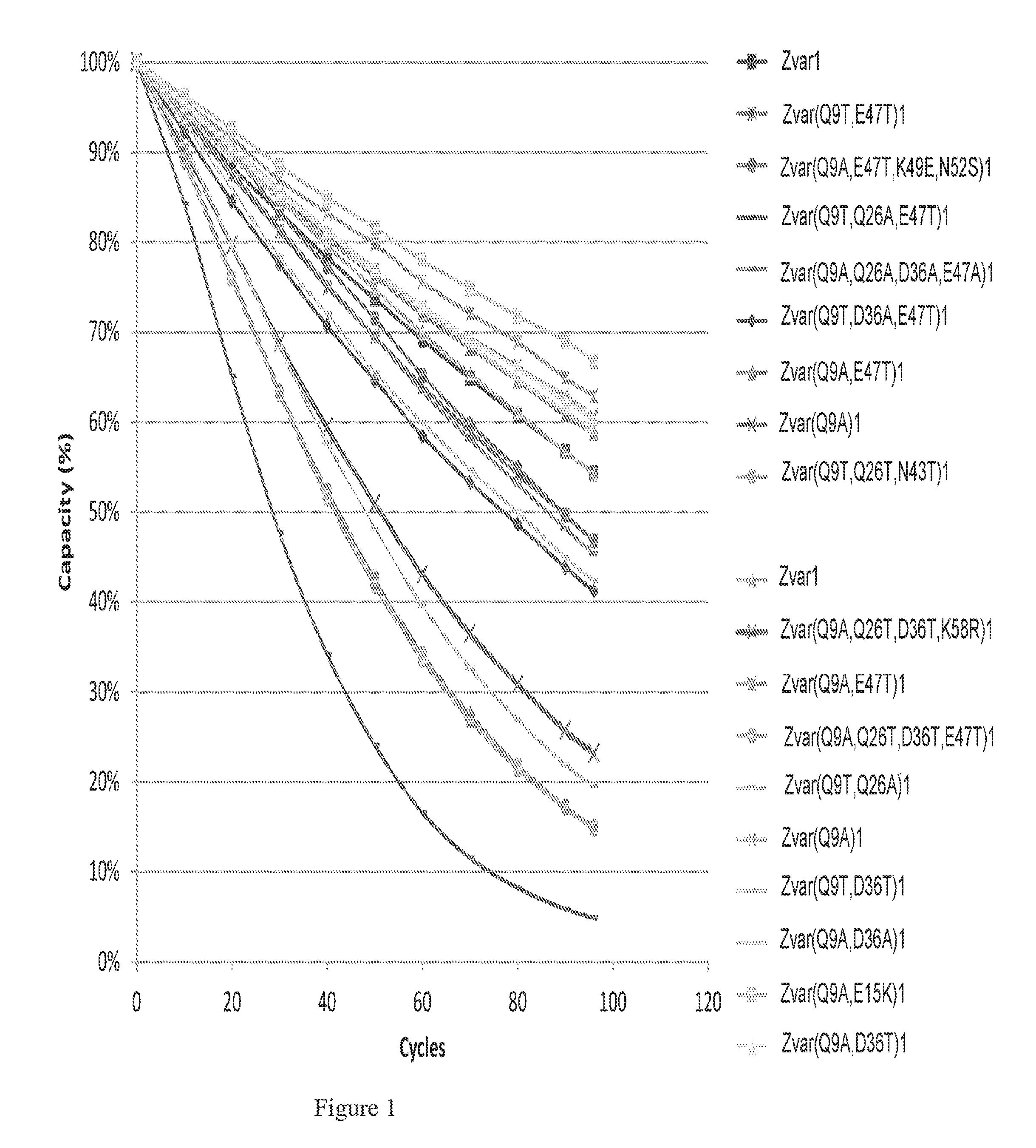
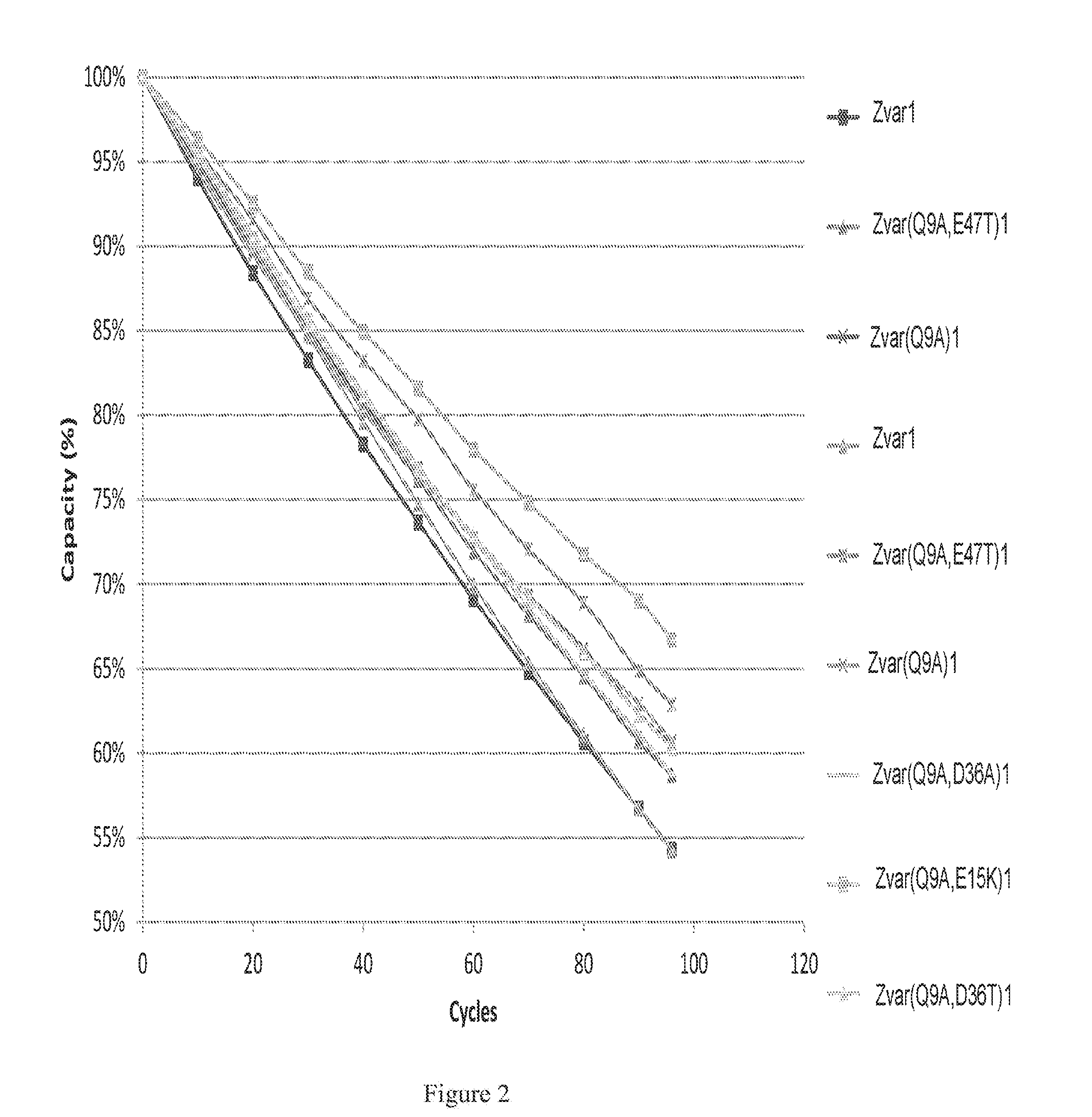
The invention discloses a polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, comprising at least the mutation wherein the glutamine residue at position 9 has been mutated to a tryptophan, leucine, glutamic acid, valine or lysine. The invention also discloses multimers of the polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
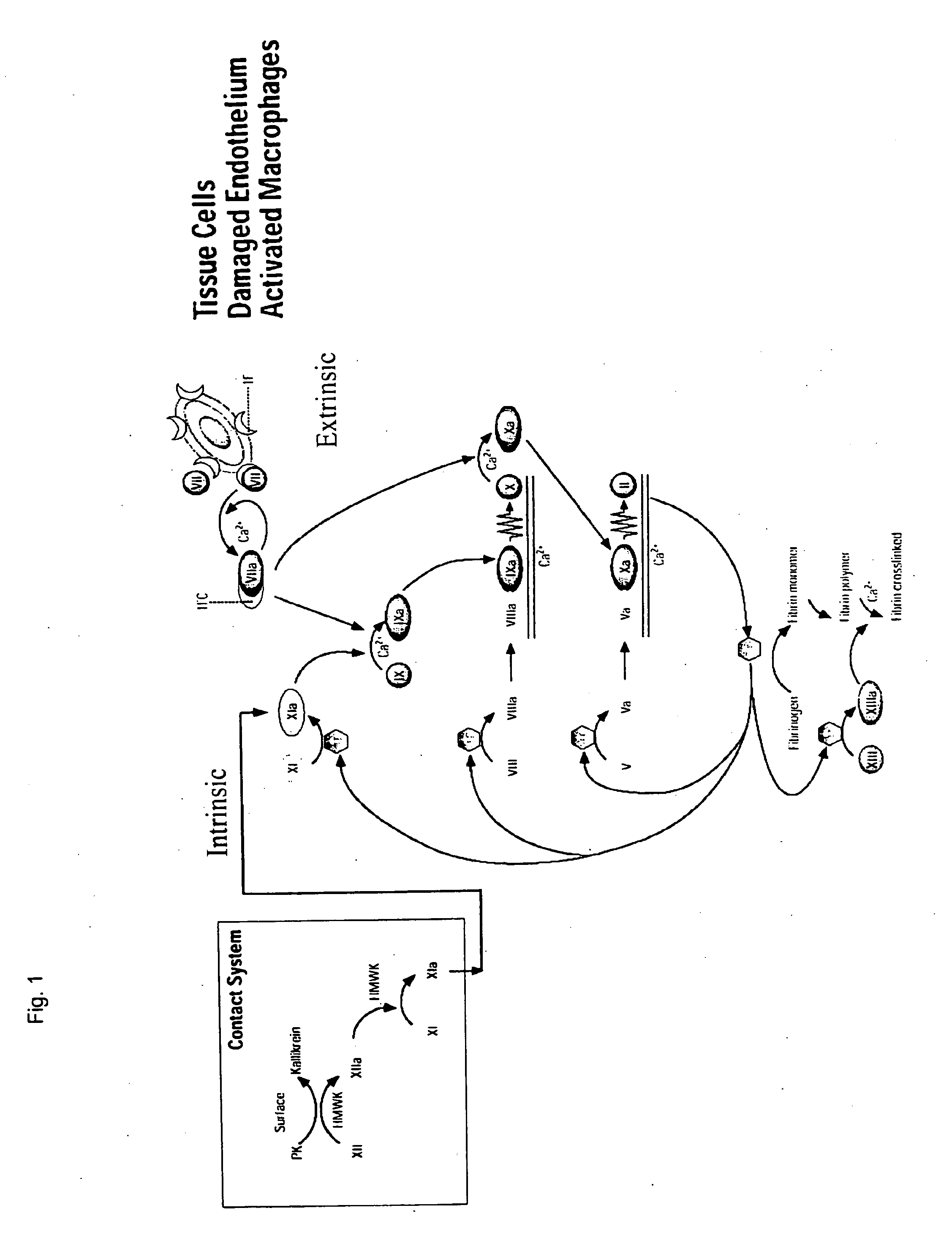
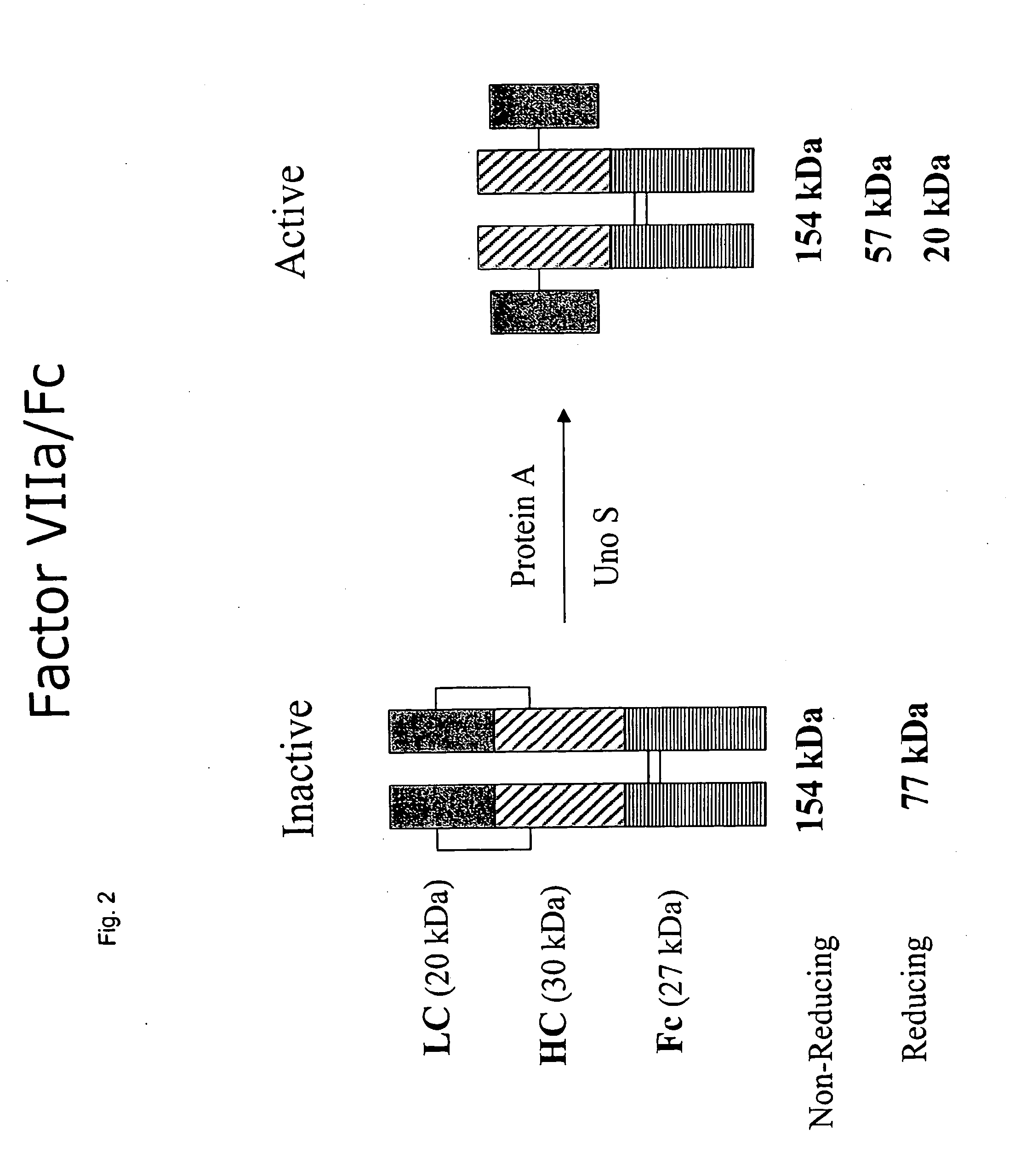
CLOTTING FACTOR-Fc CHIMERIC PROTEINS TO TREAT HEMOPHILIA
ActiveUS20110182896A1Reduce riskEffective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesHemostatic DisordersImmunoglobulin IgE
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
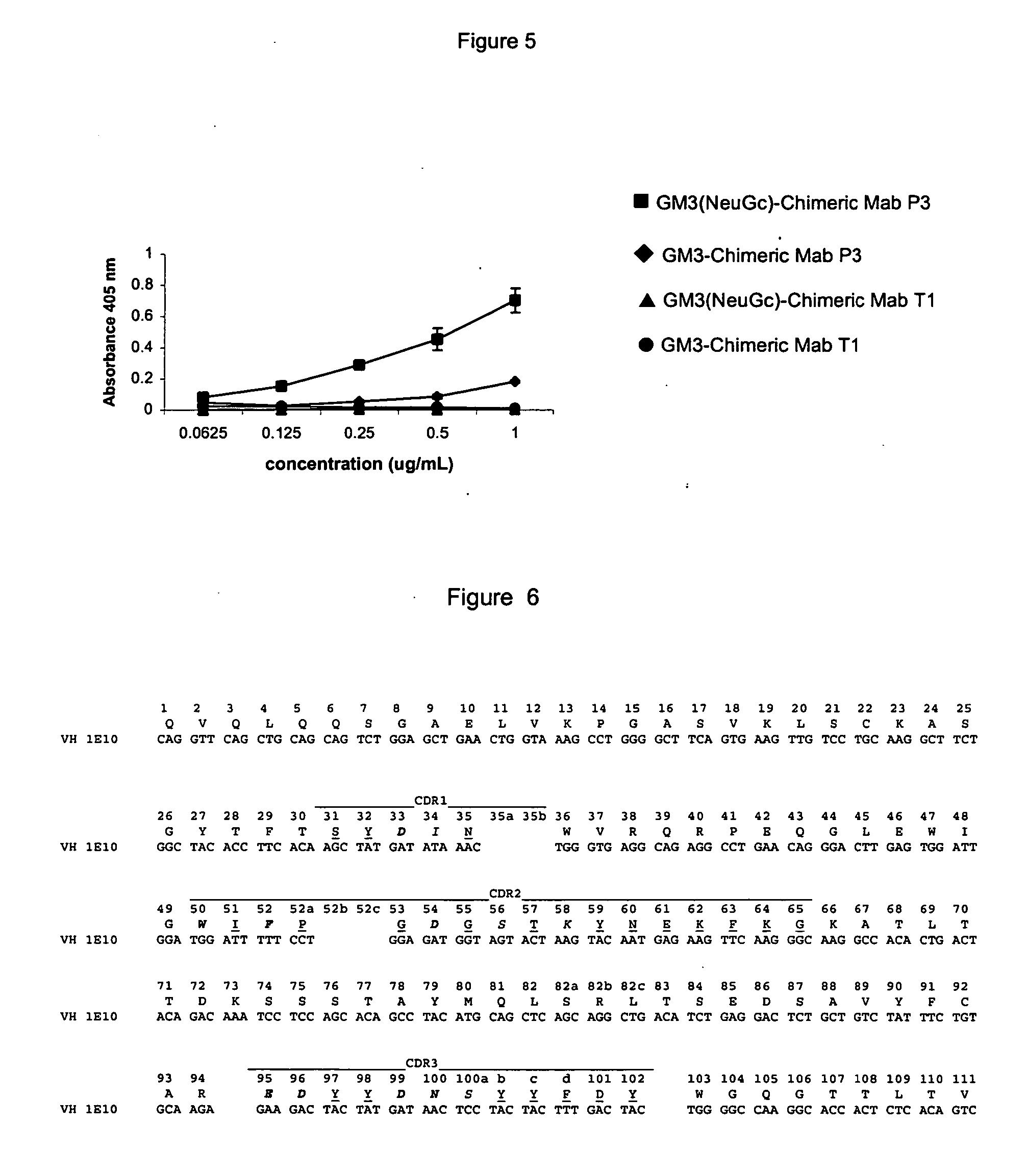
Ganglioside-associated recombinant antibodies and the use thereof in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors
The present invention is related with the obtaining of modified antibodies by means of the DNA recombinant technology from the murine monoclonal antibody P3 (MAb P3) produced by the hybridoma cell line deposited under Budapest Treaty with accession number ECACC 94113026 and from its anti-idiotype murine monoclonal antibody 1E10(MAbai 1E10) produced by the hybridoma cell line with deposit number ECACC 97112901, with the objective of achieving monoclonal antibodies which preserve the biological function of specific binding to the antigen of the original antibodies, but being at the same time less immunogenic. The chimeric antibodies of the invention contain the variable domains of the murine immunoglobulin and the constant regions of the human immunoglobulin; and those humanized, besides containing the constant regions of the human immunoglobulins, they are modified in the region of the murine frameworks (FRs) and in particular in those zones that could be in an antigenic site for the T cells, so several positions of the FRS are human as well. These antibodies can be used in the diagnosis and therapy of different types of tumors. The present invention is also related with use of the antibodies for therapeutical and diagnostic purposes.
Owner:CENT DE INMUNOLOGIA MOLECULAR CENT DE INMUNOLO
Anti-human cardiac troponin I specific monoclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101942416AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesSocial benefitsMortality rate
The invention relates to an anti-human cardiac troponin I hybridoma cell line, with the preservation number of CGMCCNO. 3951, and a monoclonal antibody secreted from the anti-human cardiac troponin I hybridoma cell line CGMCC3951. The class and subclass of immunoglobulin of the monoclonal antibody are respectively IgG and IgG3 and the monoclonal body is specifically combined with human cardiac troponin I; the potency is 1:16000 and the affinity constant is 1.08x10 to 9mol / L. By applying the monoclonal antibody of the invention to clinical diagnosis, the study on complete localization of diagnosis kit for cardiac troponin I is tremendously promoted, correctness of clinical diagnosis and prognosis for cardiovascular diseases is enhanced while suffering of patients and death rate are both reduced, thus prominent economical and social benefits are obtained.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Interleukin-2 fusion proteins and uses thereof
The present invention generally relates to fusion proteins of immunoglobulins and interleukin-2 (IL-2). More particularly, the invention concerns fusion proteins of immunoglobulins and mutant IL-2 that exhibit improved properties for use as therapeutic agents, e.g. in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. In addition, the present invention relates to polynucleotides encoding such fusion proteins, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods for producing the fusion proteins of the invention, and to methods of using them in the treatment of disease.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG +1
Human body important parasite antigen chip and method for making same
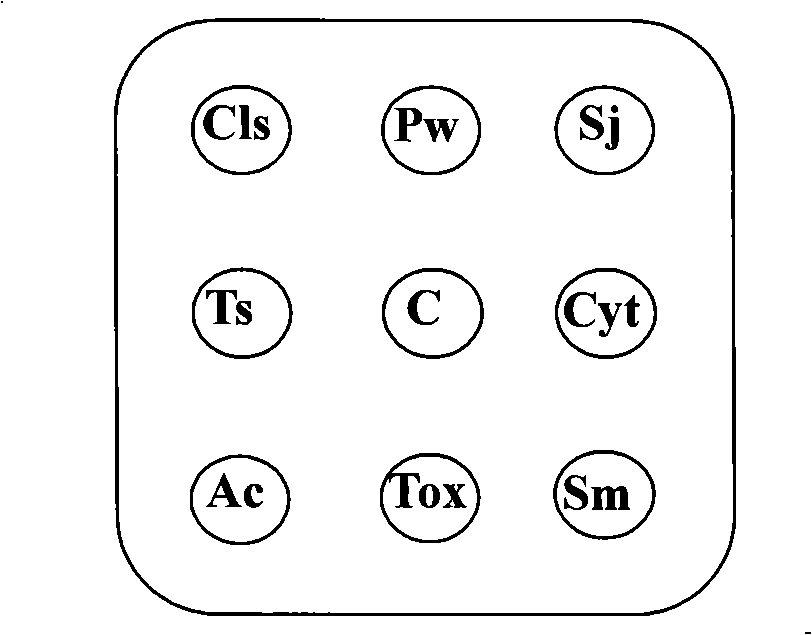
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to an antigen chip used for detecting human parasites antigens in serum and a preparation method thereof. The invention spots antigen array of parasites which are seriously harmful to human body, Schistosoma, Lung fluke, Clonorchis sinensis, Cysticercosis, Sparganum mansoni, Trichina, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Toxoplasma gondii, and the like, on a solid phase membrane carrier, and specific gamma immunoglobulin (IgG) of human parasites in serum is detected by a specially made vertical flow chip detect device, and the detecting marker is colloid gold second antibody conjugate or colloid gold protein A conjugate of fresh color. IgG antibodies in serum specially bind with the antigens on the membrane in percolation process layer upon layer, and human IgG which specially binds with the antigens is detected by the colloid gold marker. Detecting of a plurality of parasites antigen indexes in serum sample can be finished within several minutes. The device and the method have the advantages of high throughput, simple operation, convenient use and being suitable for parasitic diseases clinical test and serum-epidemiological investigation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
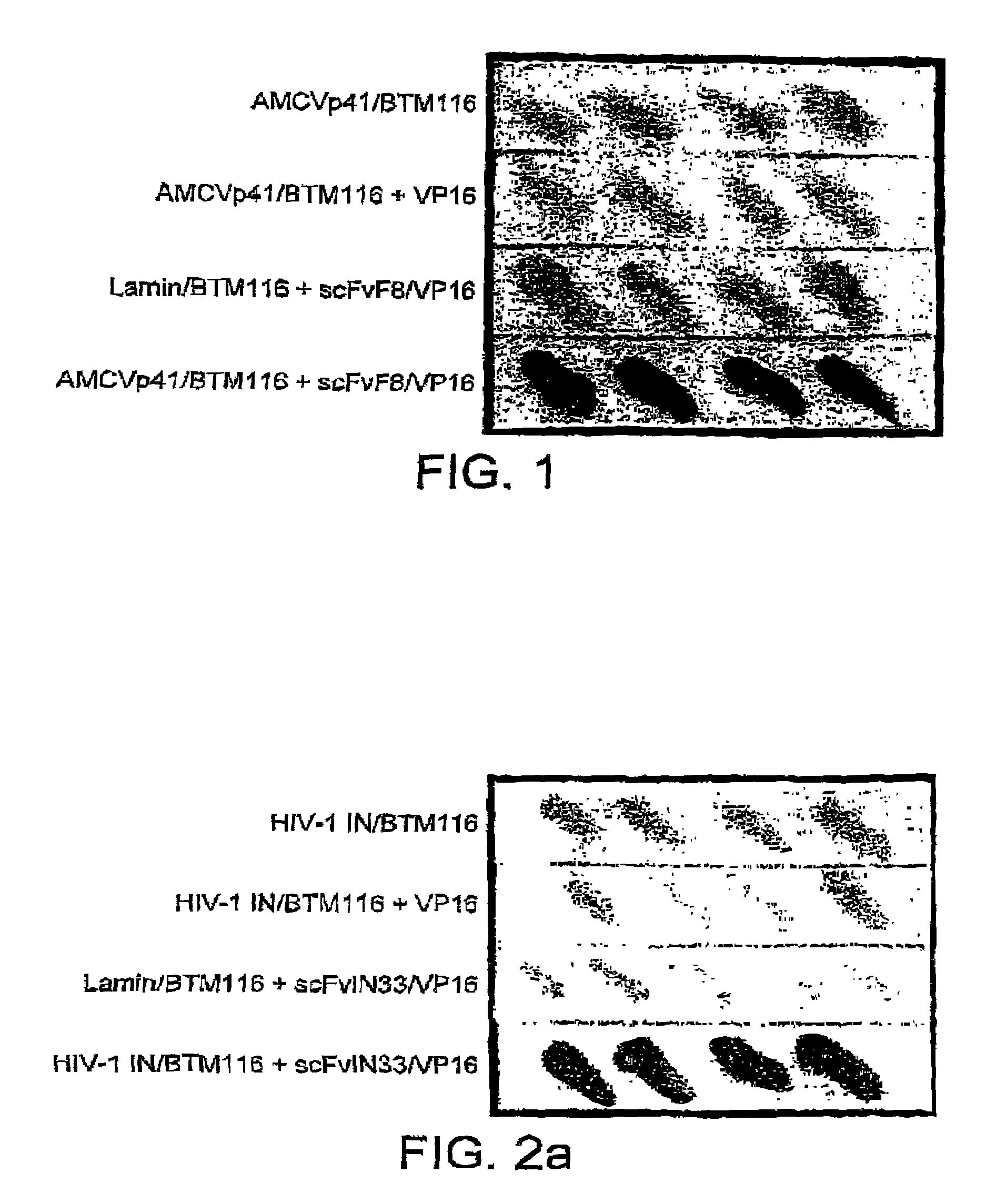
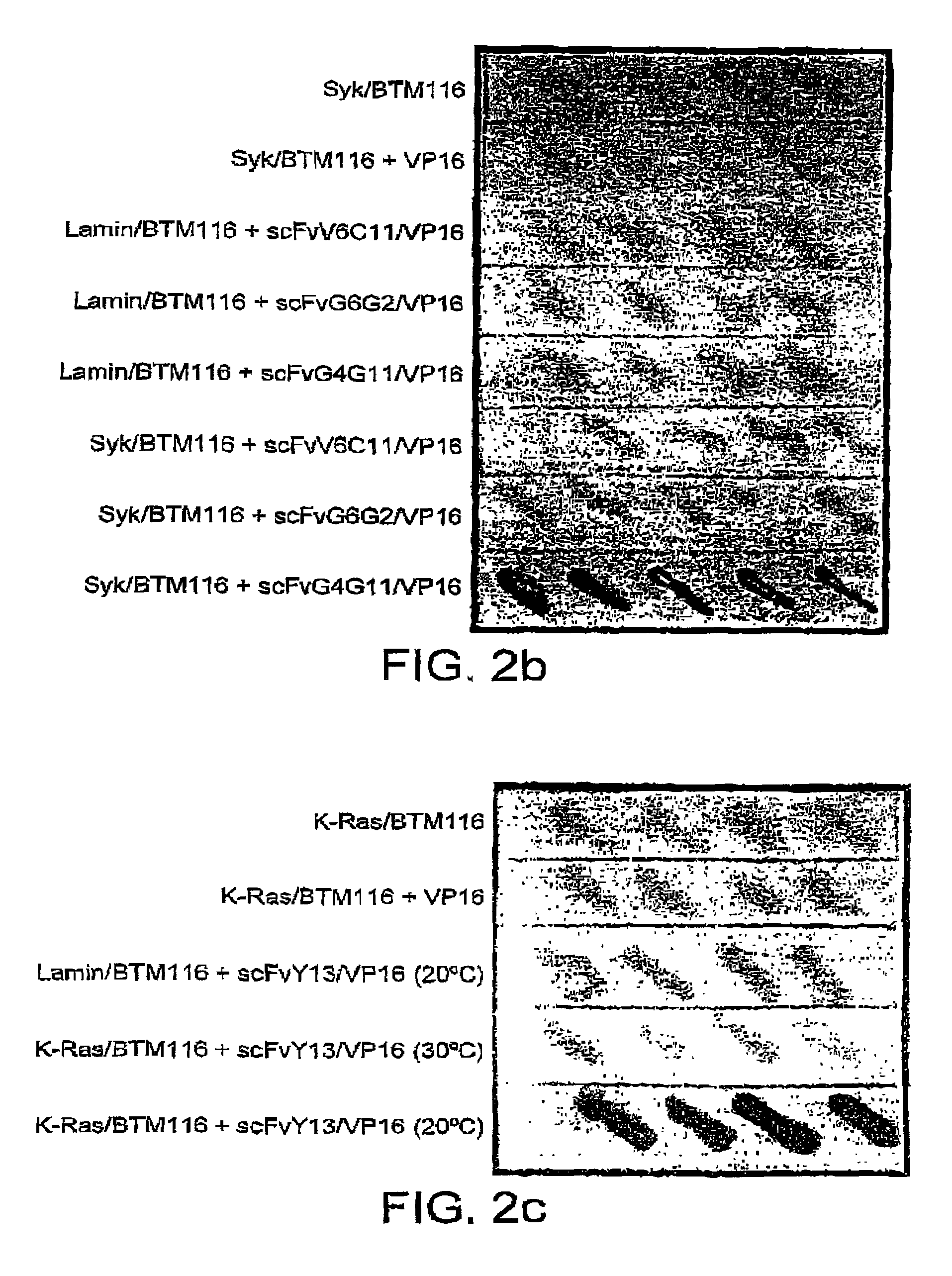
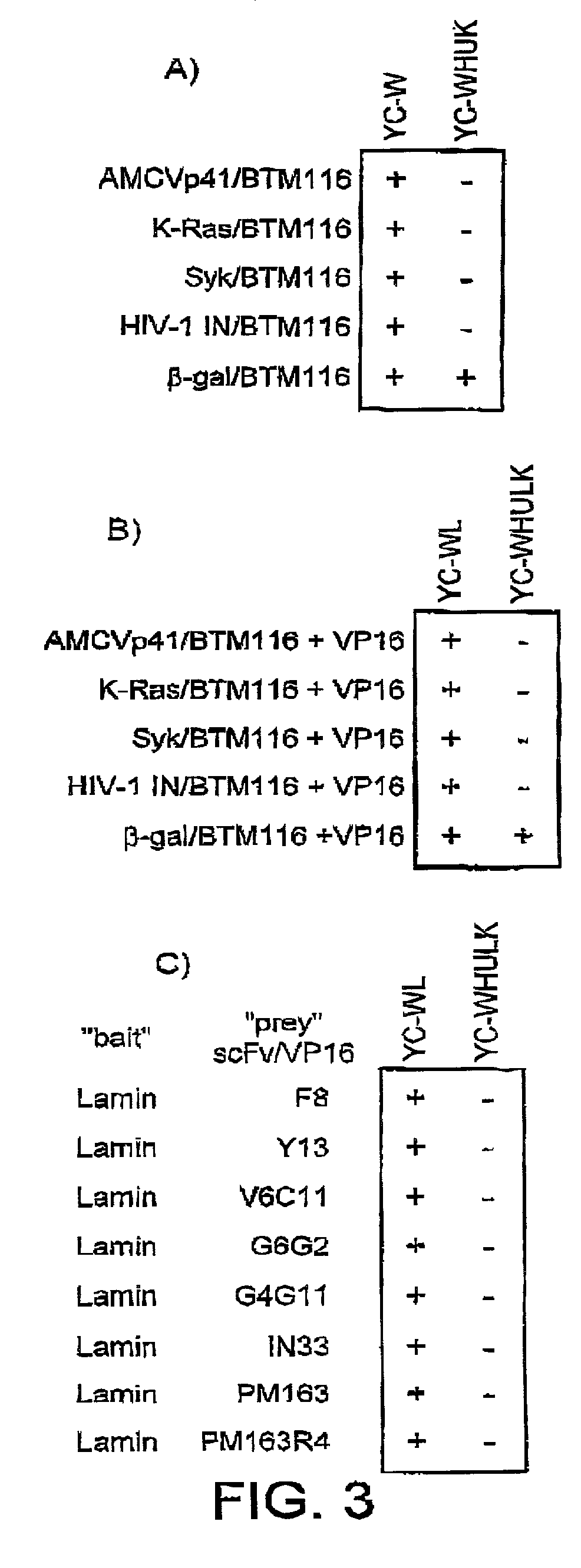
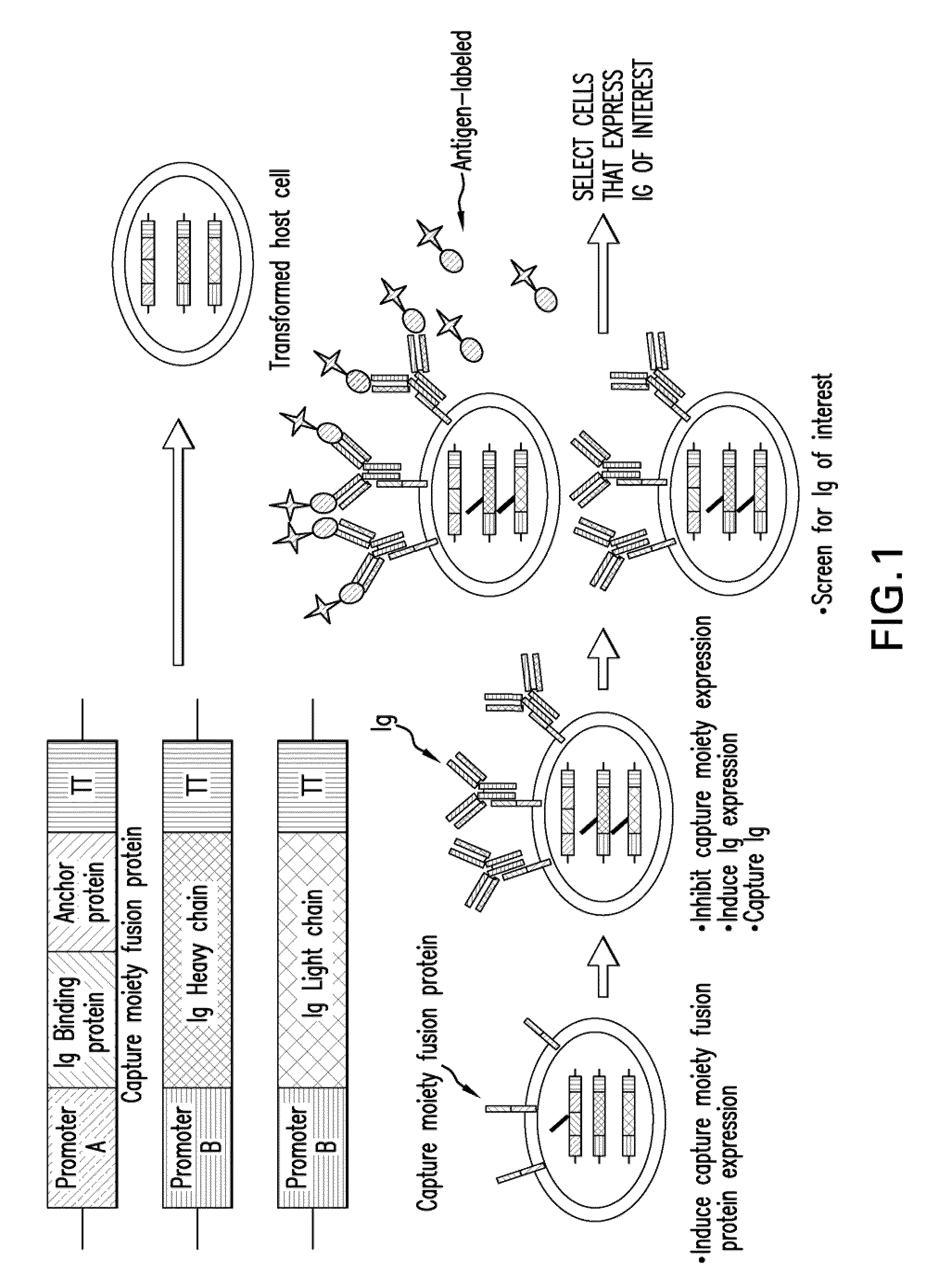
Selection of intracellular immunoglobulins
A general immunoglobulin-target assay system is provided, in which a positive outcome (the generation of a signal) depends only on the intracellular interaction of immunoglobulin with target. This can be accomplished for many immunoglobulins expressed in yeast and / or in mammalian cells and allows the selection of immunoglobulins which are capable of functioning in an intracellular environment.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +2
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding polypeptides
ActiveUS20160159855A1Improved alkaline stabilityHighly selectiveSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulin IgEMutant
A polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A, as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, wherein at least the glutamine residue at position 9 has been mutated to an amino acid other than asparagine. The invention also discloses multimers of said polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
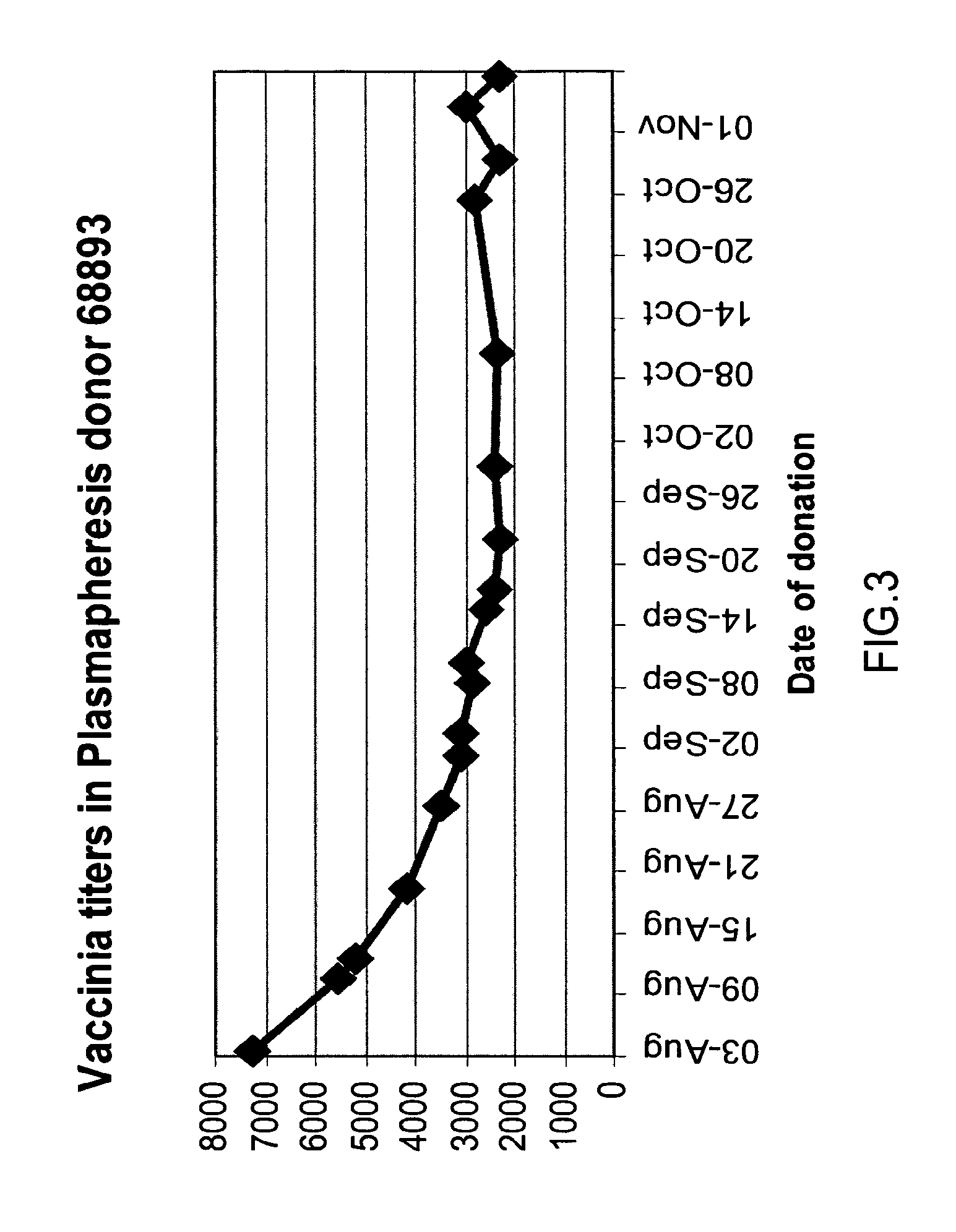
Intravenous immunoglobulin composition
ActiveUS20130011388A1Reduce riskEasy to managePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpecific antibodyHigh titre
A concentrated, immunoglobulin composition for treating subjects vaccinated against or infected with a pathogenic microorganism, is made by (a) selecting a population of individuals previously vaccinated against antigens associated with the pathogenic microorganism; (b) identifying very high titre individuals by determining the level of specific antibodies immunoreactive with the pathogenic microorganism in the blood of the individuals; (c) combining blood from the very high titre individuals; and (d) purifying and / or concentrating the product of step (c). A concentrated immunoglobulin composition can include specific antibodies immunoreactive with a pathogenic microorganism, wherein the titre of specific antibodies is at least 5 times higher than the average titre of specific antibodies of a population of individuals previously vaccinated against antigens associated with the pathogenic microorganism. The composition has a relatively high protein concentration and a low percentage of protein aggregates. The pathogenic microorganism is preferably smallpox virus or vaccinia virus.
Owner:OMRIX BIOPHARM
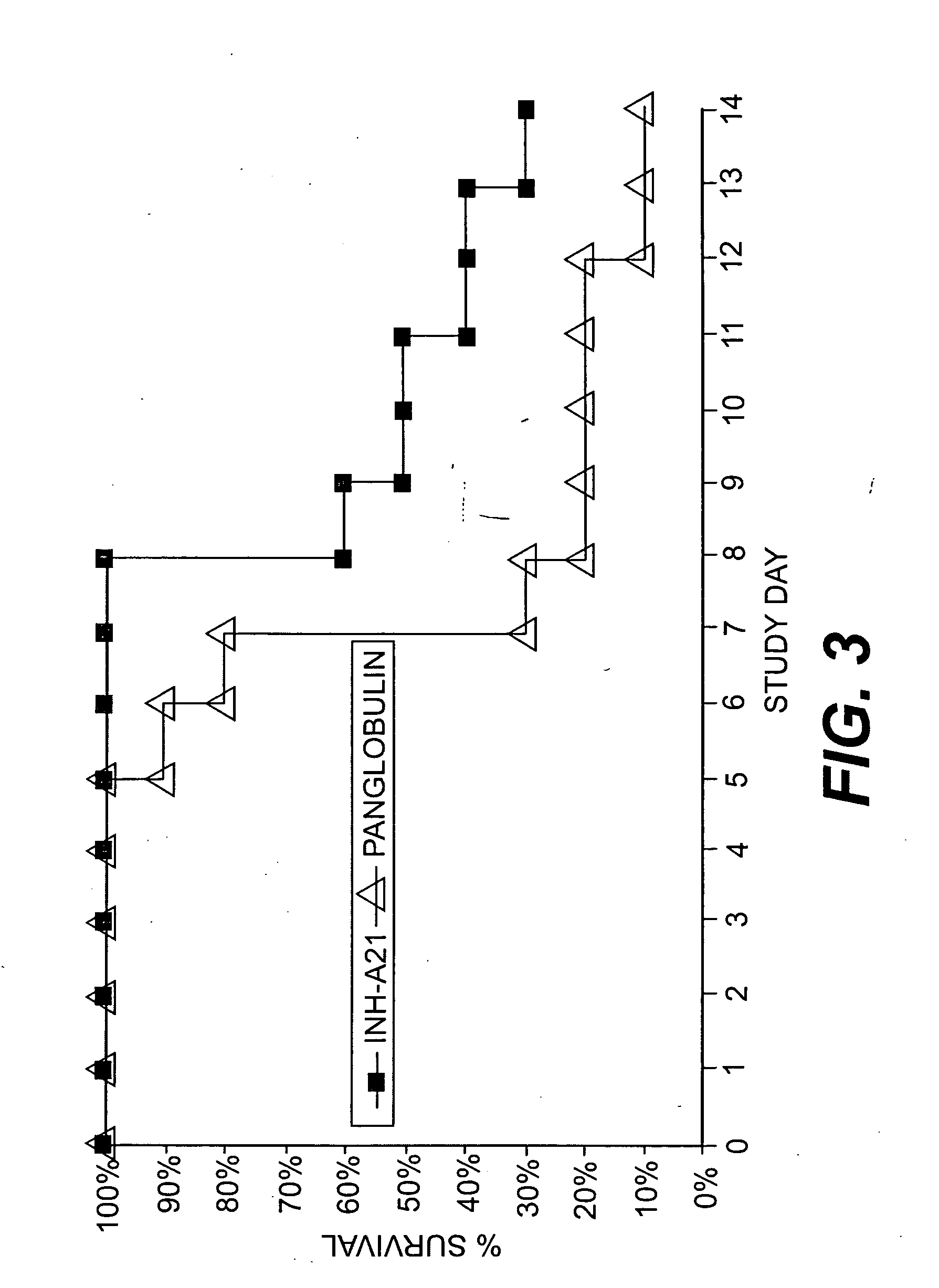
Method of inhibiting Candida-related infections using donor selected or donor stimulated immunoglobulin compositions
InactiveUS20050287146A1Inhibit growthInhibit severityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisYeastStaphylococcus
A method for treating or preventing infections from yeast of the Candida species is provided wherein an immunoglobulin composition containing high titers of antibodies to staphylococcal adhesins ClfA and SdrG is administered in an amount effective to inhibit the growth and progression of Candidial infections. The compositions and methods of the present invention are advantageous in that they can be used to treat both staphylococcal and Candidial infections at the same time, and they are particularly effective in treating or preventing late-onset sepsis in neonates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Methods and reagents for creating monoclonal antibodies
ActiveUS20120308555A1Reduce the likelihood of occurrenceImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHeavy chainMonoclonal antibody
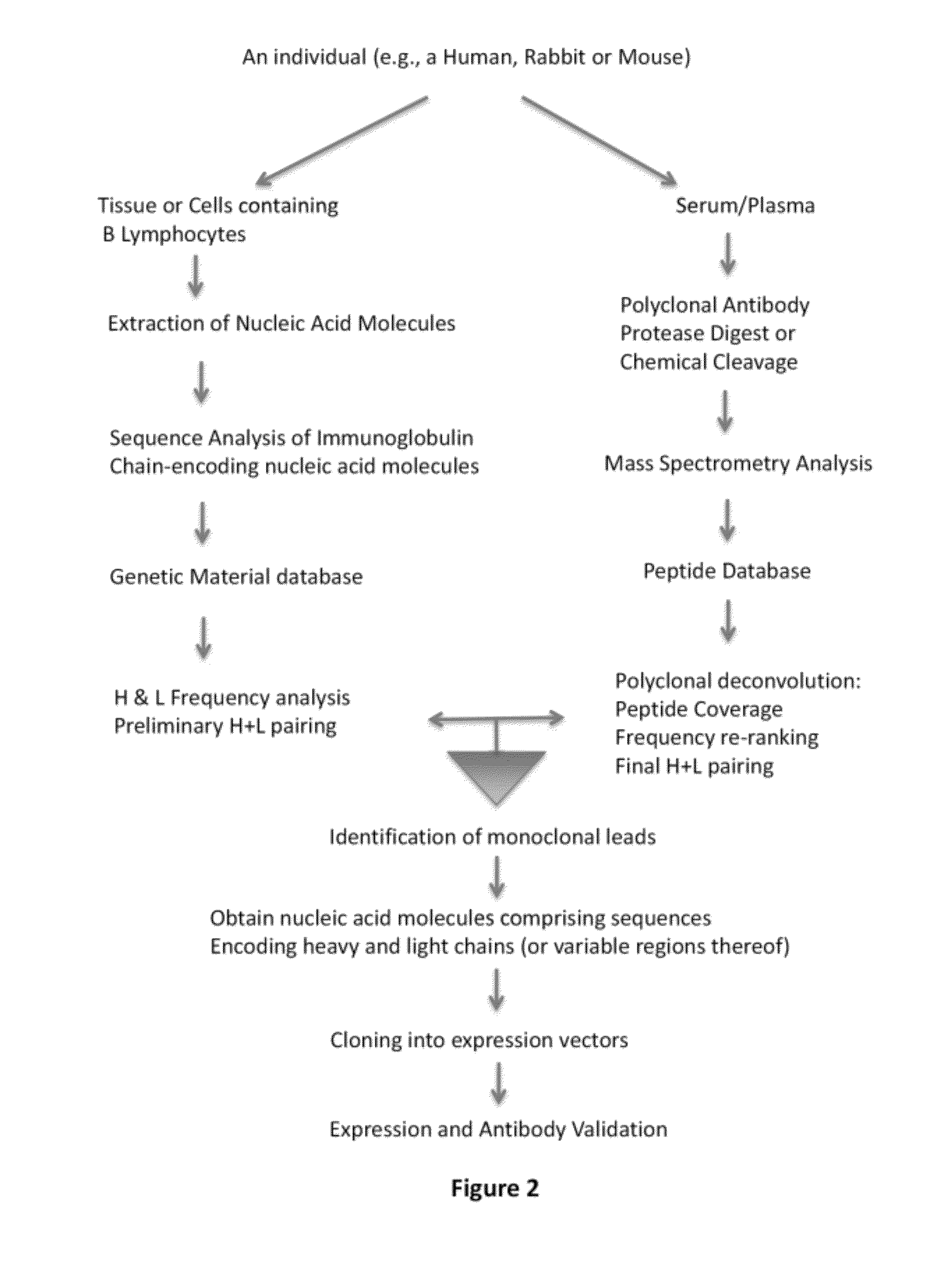
In some embodiments, the invention relates to methods for creating a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to antigen. The method may start from a polyclonal population of antibodies such as a non-specific polyclonal population or a polyclonal population of antibodies that specifically bind to the antigen. The method includes obtaining nucleic acid molecules encoding heavy and light immunoglobulin chains (or variable regions thereof) of multiple immunoglobulins from an animal; obtaining mass spectra information of peptide fragments of a population of polyclonal immunoglobulins that specifically bind to an antigen of choice; comparing and / or correlating the mass spectra information of the peptide fragments of the polyclonal immunoglobulins with predicted mass spectra information of predicted amino acid sequences encoded by the nucleic acid molecules, and then assembling the heavy and light chains to create an antibody (or variable region thereof) that specifically binds to the antigen.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
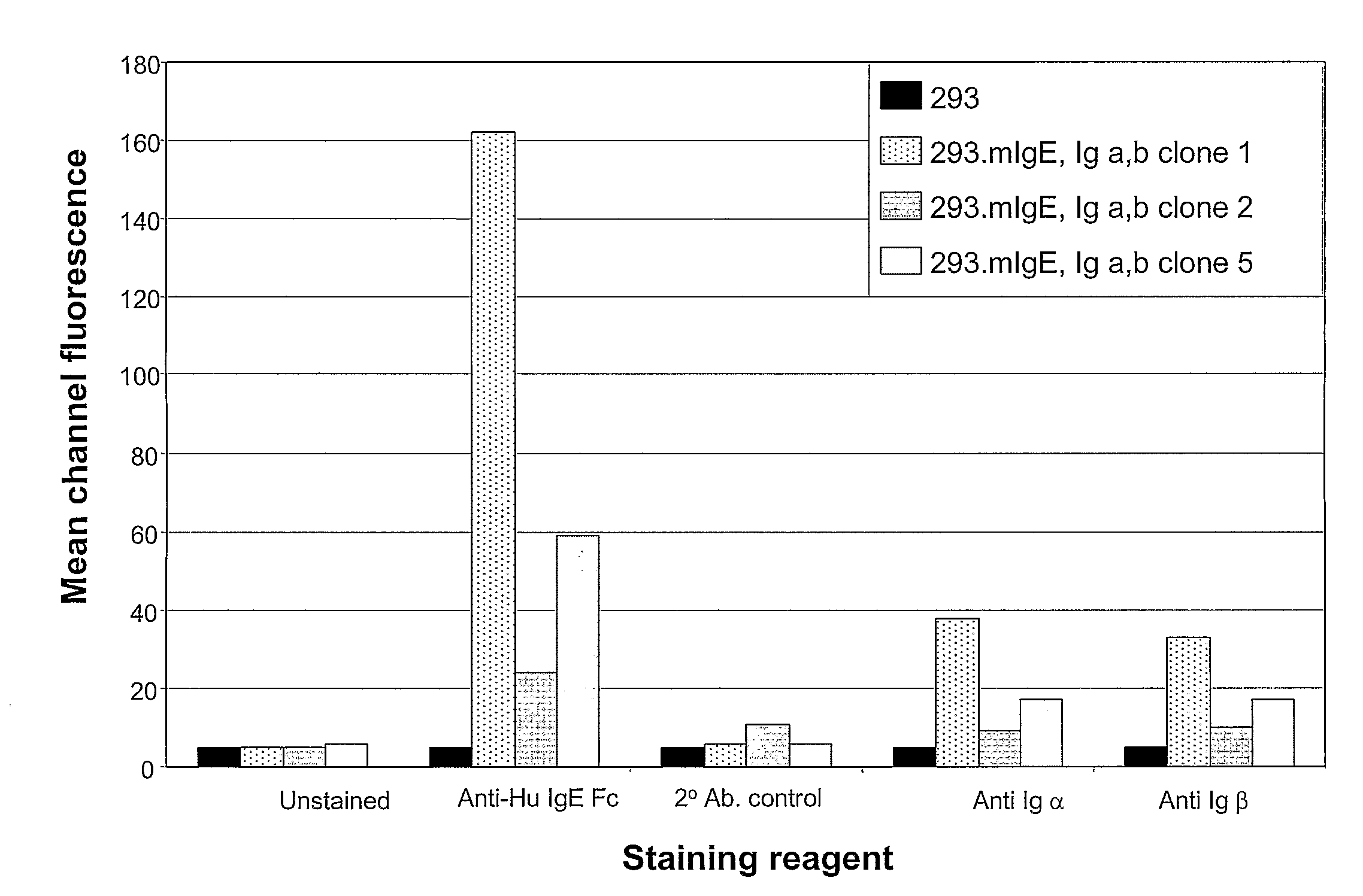
Method of Identifying Membrane Ig Specific Antibodies and Use Thereof for Targeting Immunoglobulin-Producing Precursor Cells
The present invention relates to the discovery of antibodies that bind to novel epitopes present on membrane-anchored immunoglobulins and which bind to these novel epitopes on the surface of B cells and plasma cells. In addition, the antibodies of the present invention can mediate ADCC and can be useful to deplete those B cells and plasma cells expressing the novel epitopes of the invention. The antibodies of the present invention can be useful for the treatment of B cell-mediated diseases and diseases caused by monoclonal expansion of B cells. Accordingly the present invention also provides compositions and methods for the prevention, management, treatment or amelioration of B cell-mediated diseases and diseases caused by monoclonal expansion of B cells.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Truncated recombinant major outer membrane protein antigen (R56) of orientia tsutsugamushi strains Karp, Kato and gilliam and its use in antibody based detection assays and vaccines
A recombinant, refolded non-fusion polypeptide expressed from a truncated r56 gene of the causative agent of scrub typhus, Orientia tsutsugamushi for the Karp, Kato and Gilliam strains has been produced. The invention is useful for detecting prior exposure to scrub typhus, screening for and / or identification of at least one infectious strain-similarity (i.e. a Karp-like, Kato-like or Gilliam-like strain) based on its strength of reaction toward a truncated protein and as a component in vaccine formulations and production of immune globulins for passive prophylaxis and immunity in subjects.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Mycoplasma Hyopneumoniae Vaccine
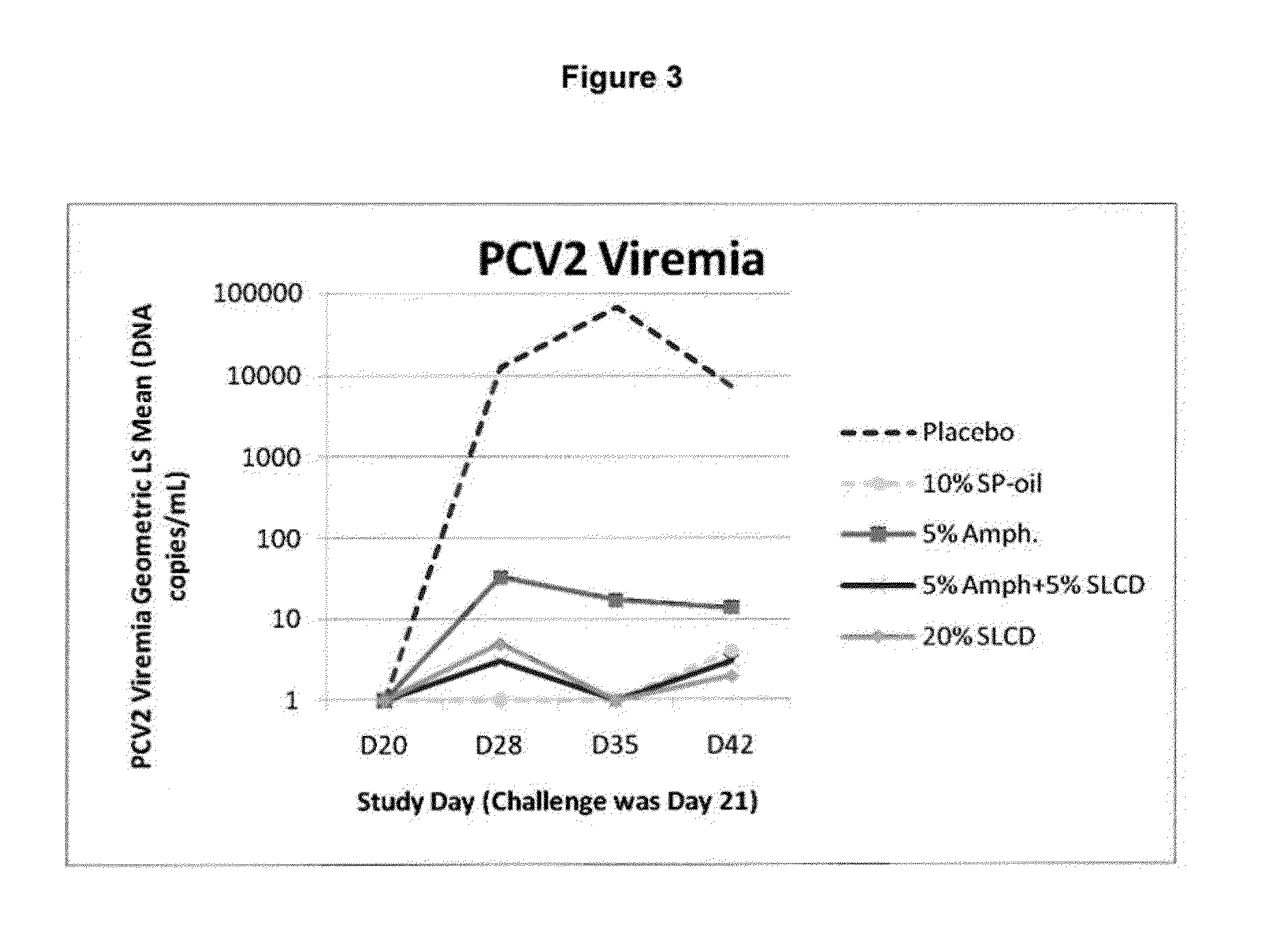
ActiveUS20130266601A1Antibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses positive-senseImmunoglobulin IgEMycoplasma hyopneumoniae
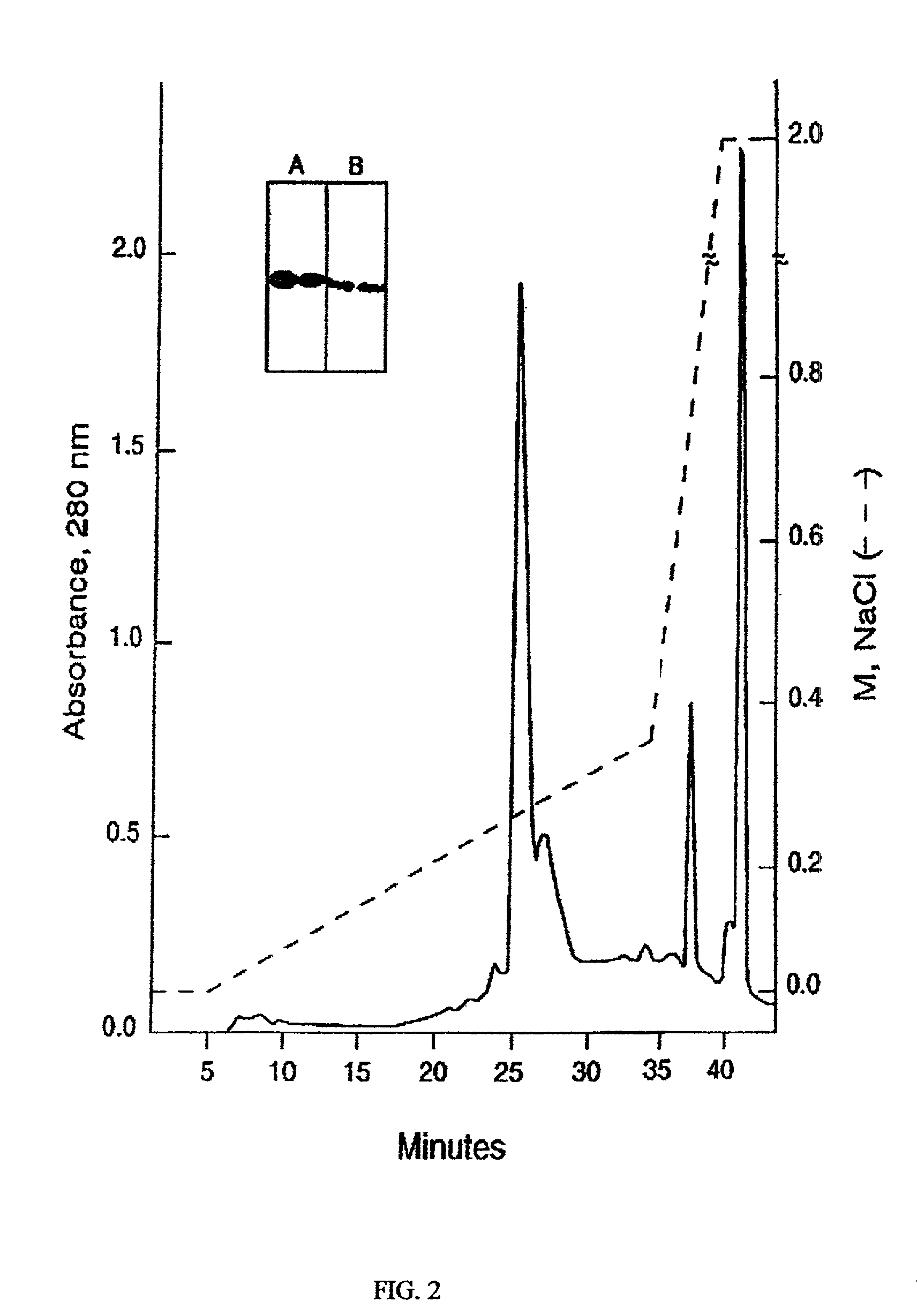
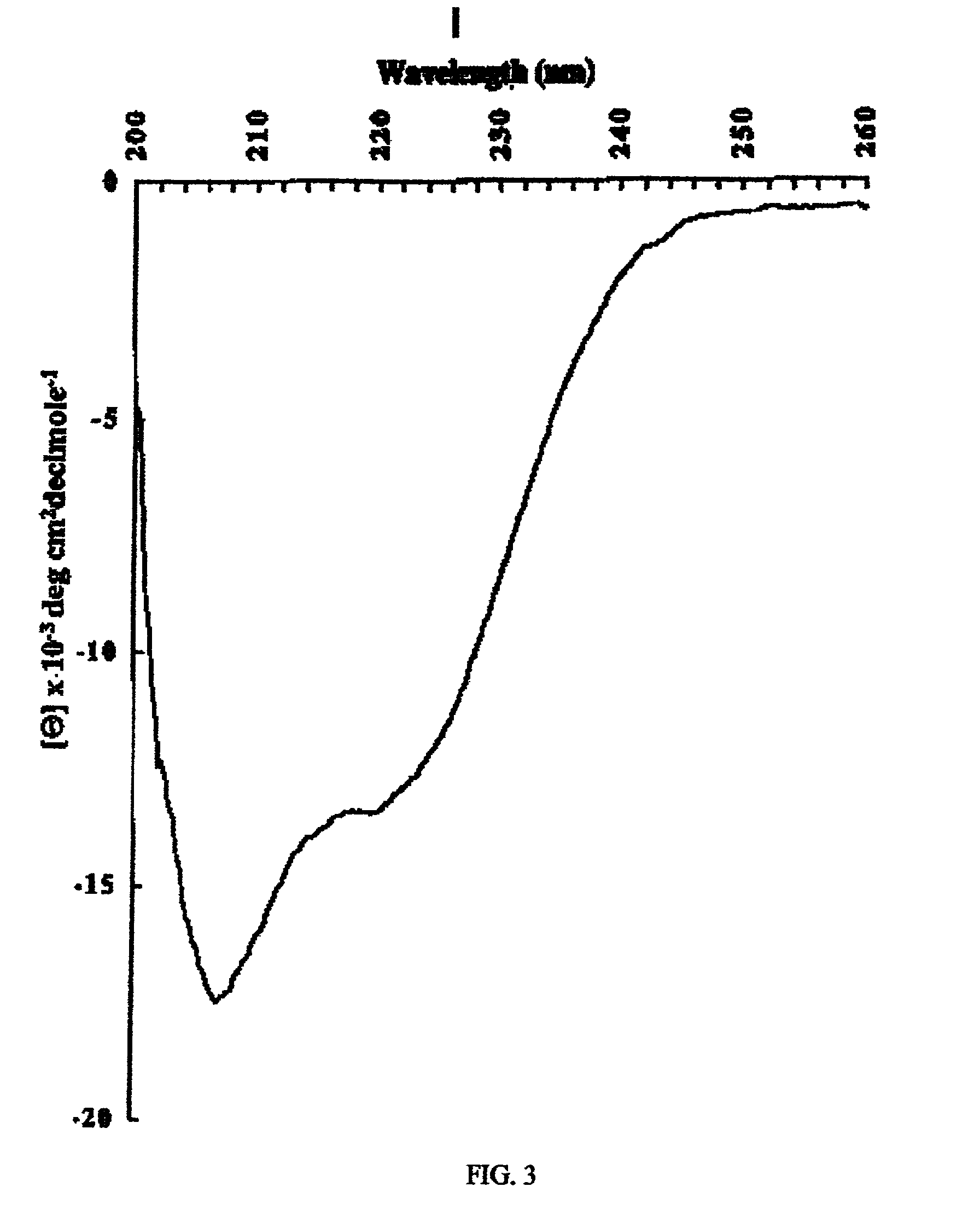
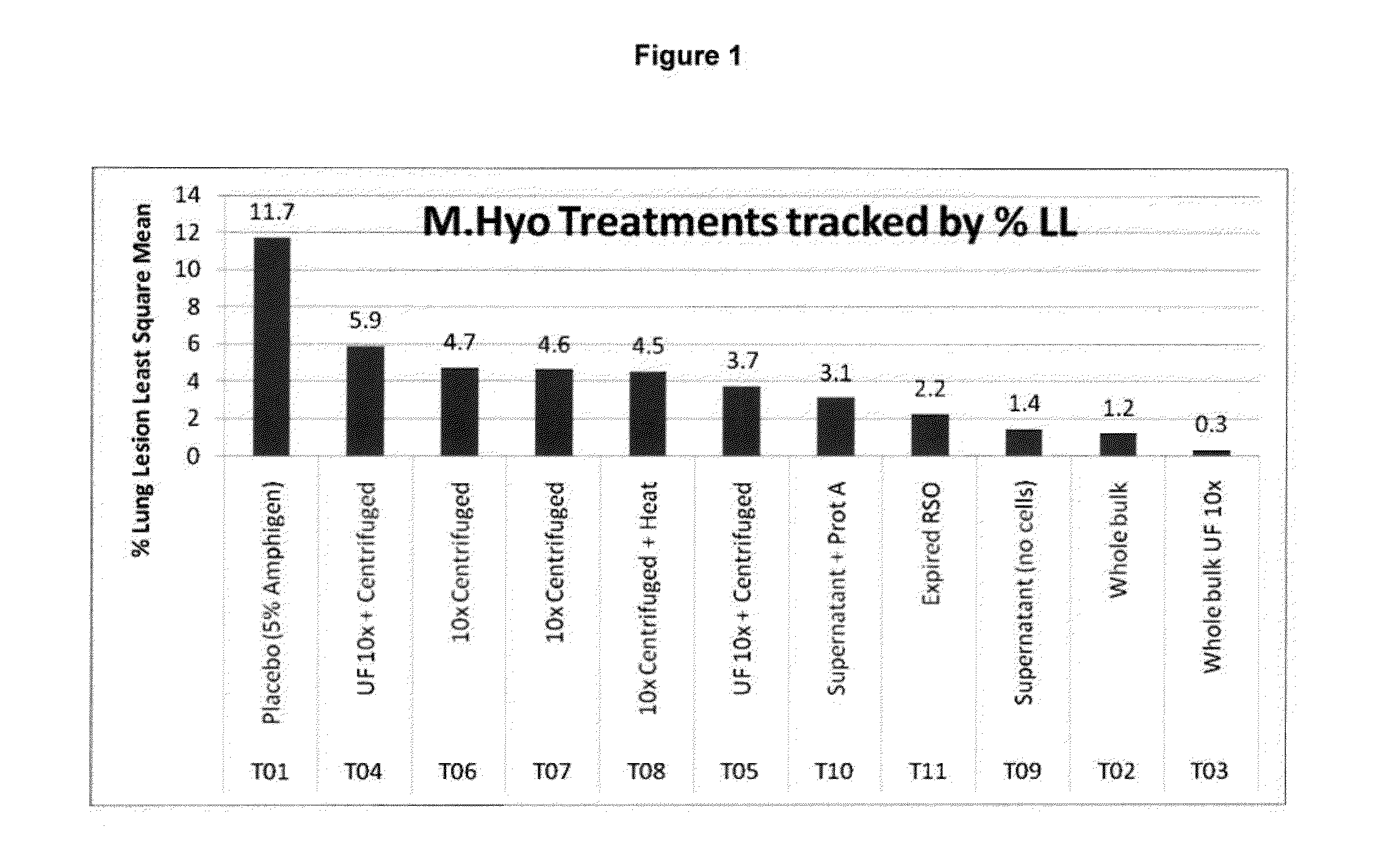
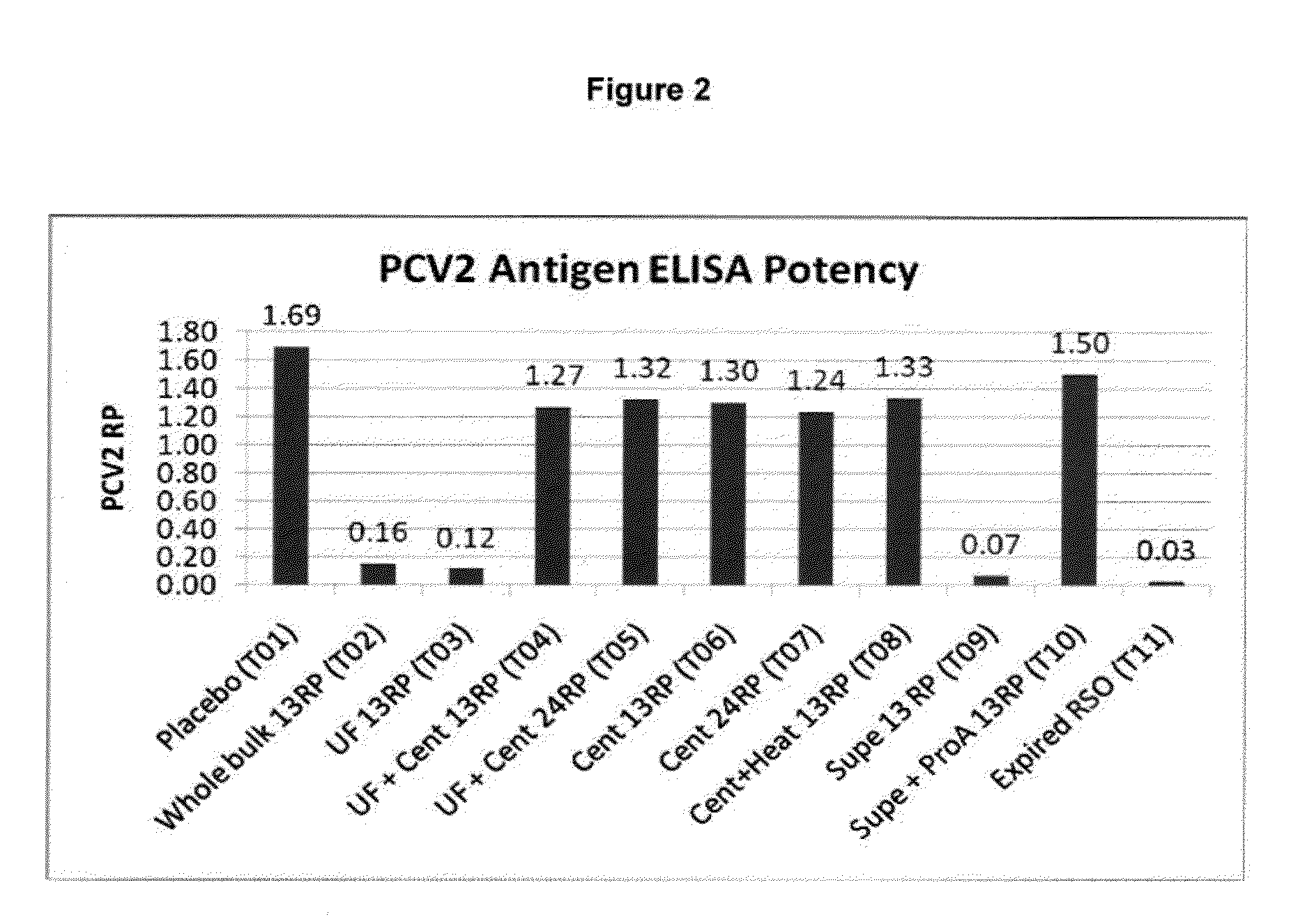
This invention provides an immunogenic composition including a soluble portion of a Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (M.hyo) whole cell preparation, wherein the soluble portion of the M.hyo preparation is substantially free of both (i) IgG and (ii) immunocomplexes comprised of antigen bound to immunoglobulin.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Surface display of whole antibodies in eukaryotes
ActiveUS8067339B2Avoid difficult choicesStabilize cytoplasmic mRNAAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningAntigenYeast
Methods for display of recombinant whole immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin libraries on the surface of eukaryote host cells, including yeast and filamentous fungi, are described. The methods are useful for screening libraries of recombinant immunoglobulins in eukaryote host cells to identify immunoglobulins that are specific for an antigen of interest.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
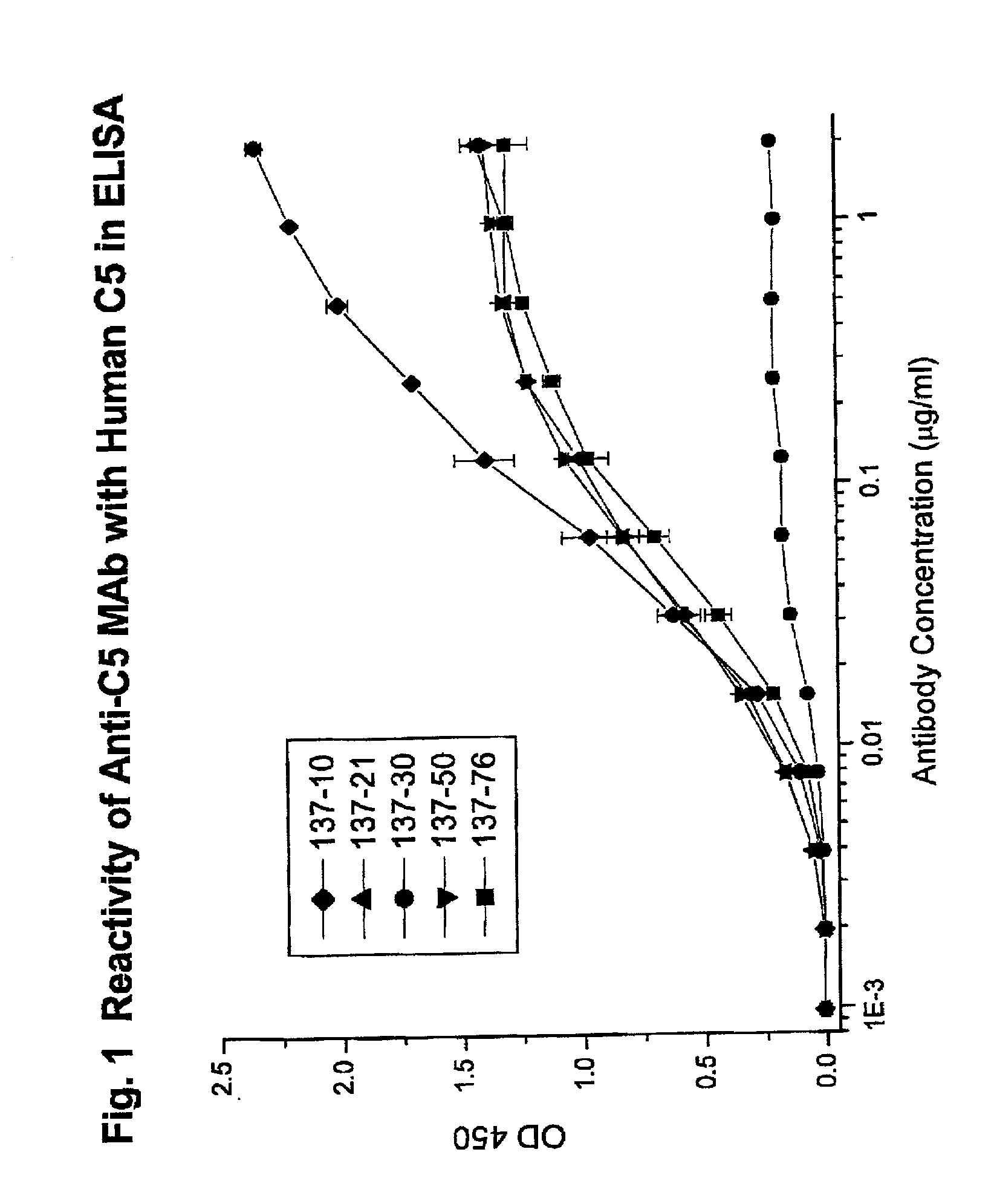
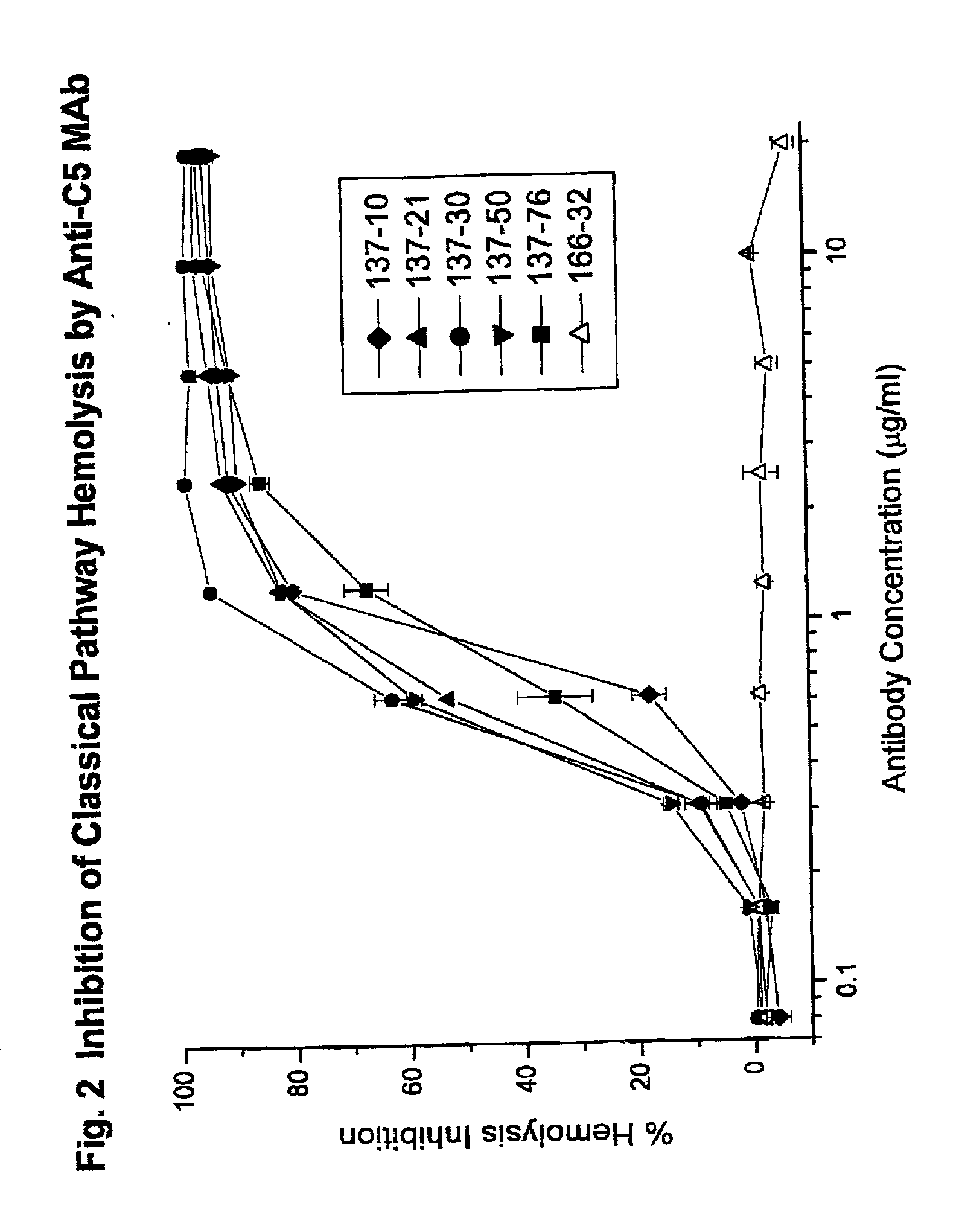
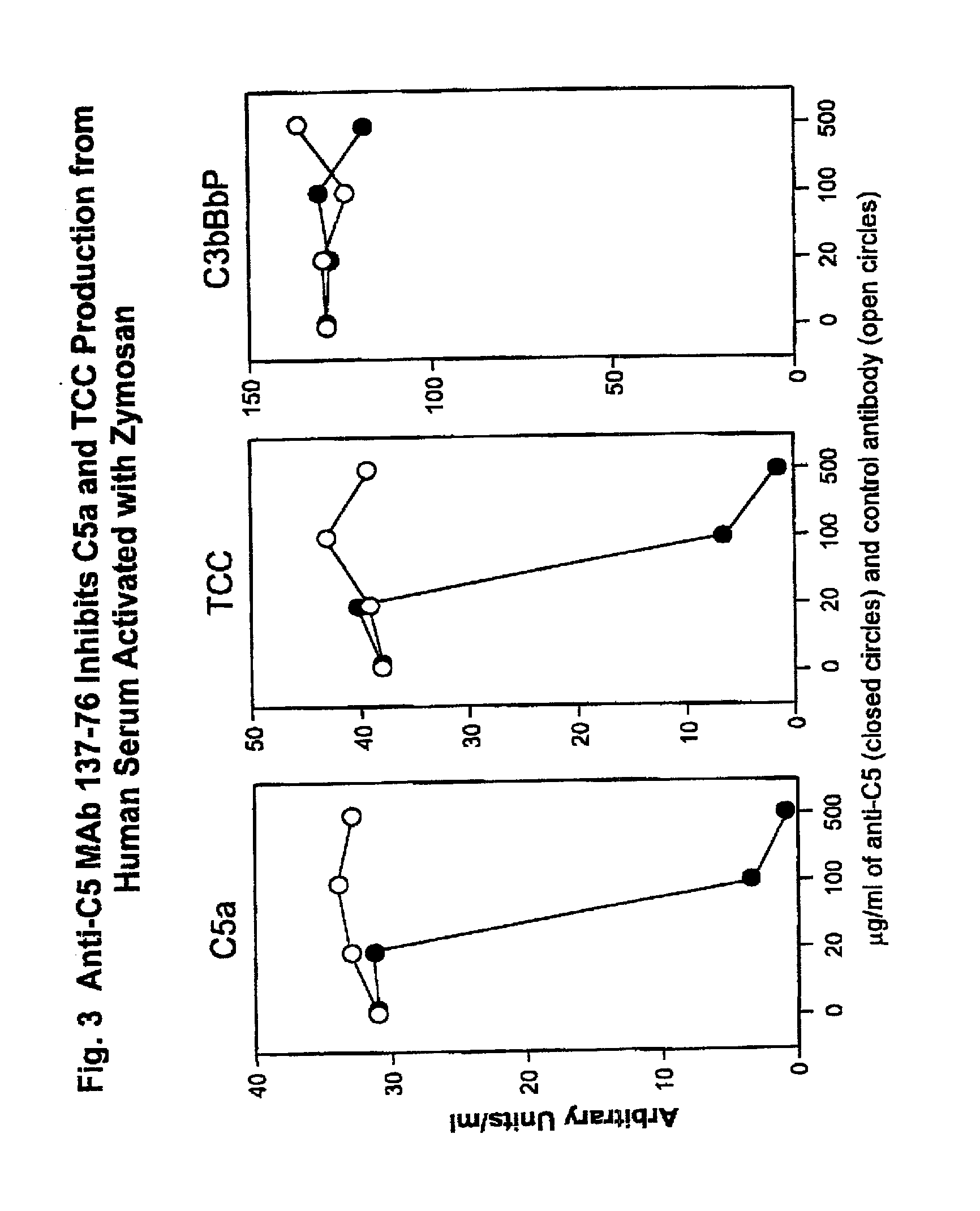
Inhibition of complement C5 activation for treatment and prevention of delayed xenograft/acute vascular rejection
InactiveUS20020041875A1Avoid problemsHigh affinityAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAcute vascular rejectionBiological activation
The invention relates to C5 inhibitors, which inhibit type II endothelial cell activation, wherein the inhibition is manifested by the suppression of E-selectin. These inhibitors are useful in treatment of delayed xenograft rejection or acute vascular rejection. The inhibitors include antibody molecules, as well as homologues, analogues and modified or derived forms thereof, including immunoglobulin fragments like Fab, F(ab')2 and Fv, small molecules, including peptides, oligonucleotides, peptidomimetics and organic compounds. Examples of monoclonal antibodies, which bind to and inhibit C5, were generated and are designated MAb 137-76 and MAb 137-30.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com