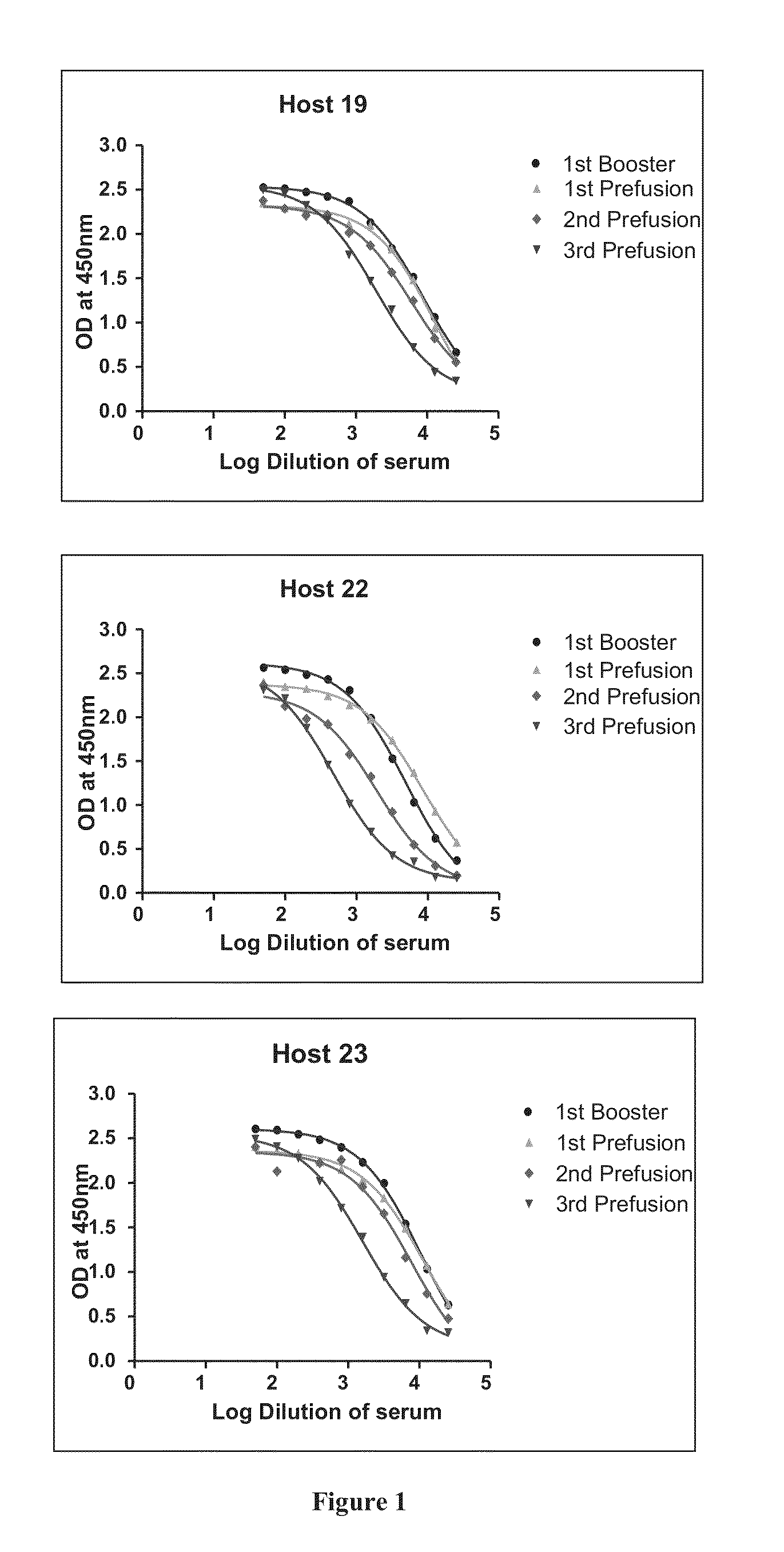
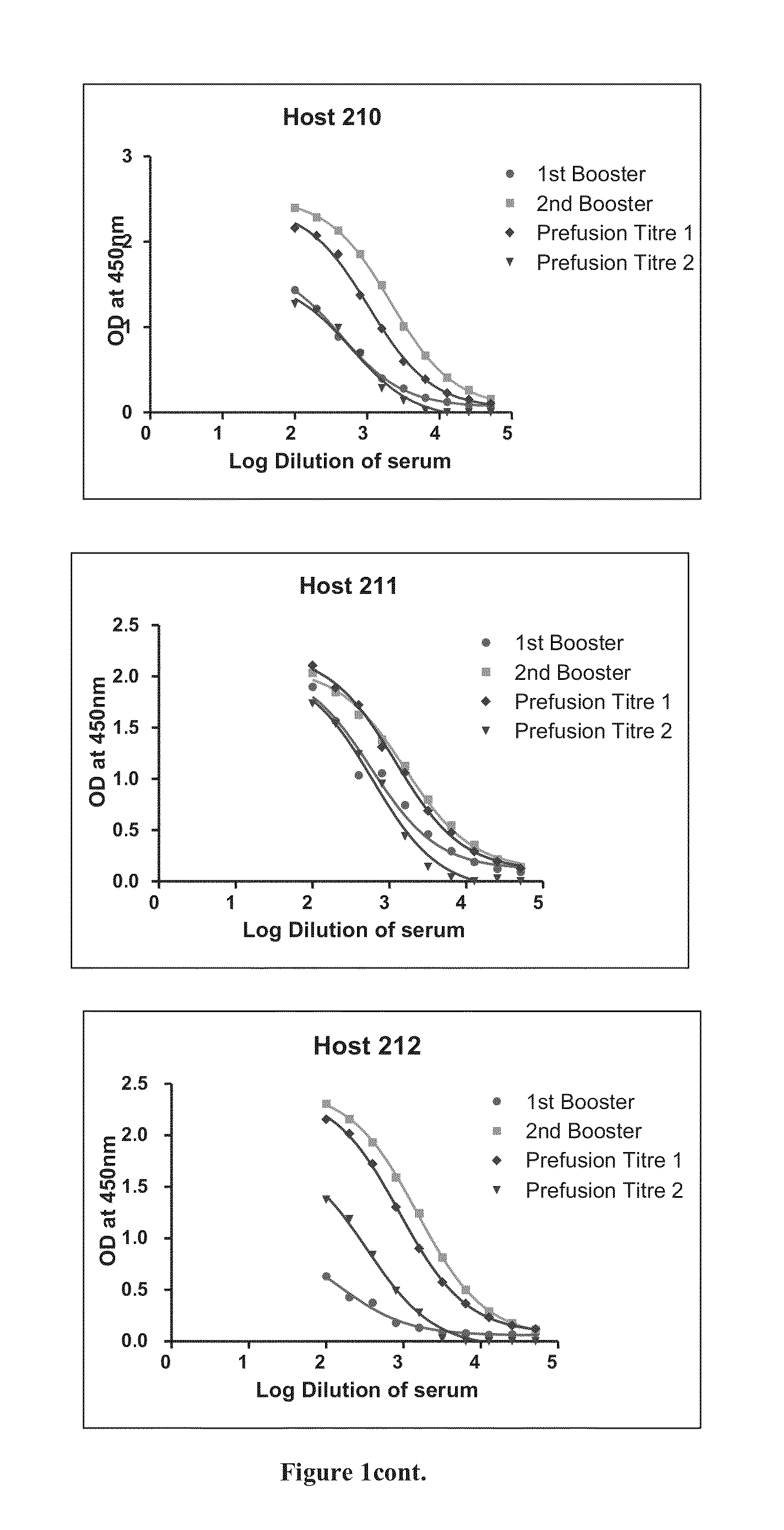
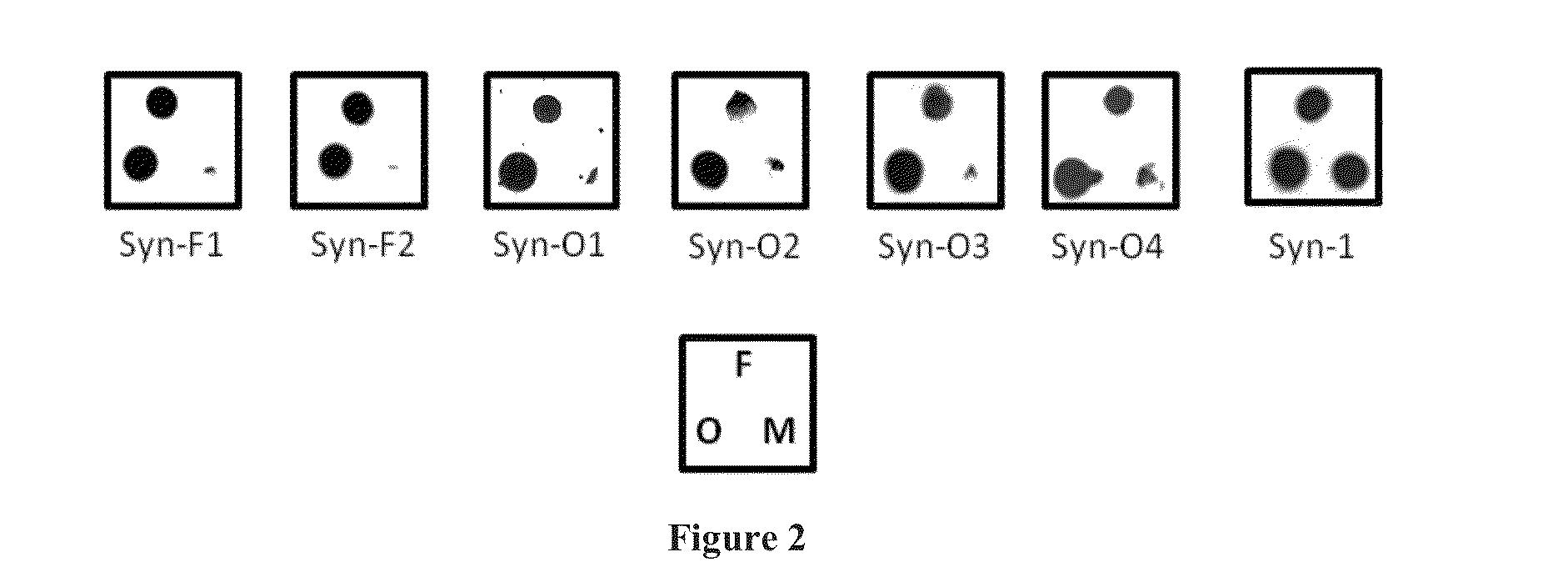
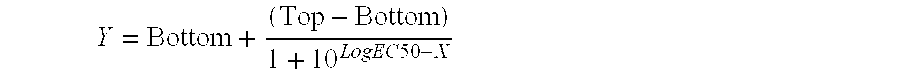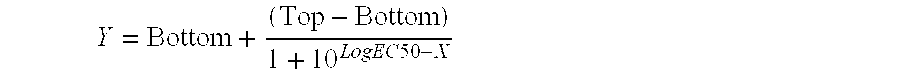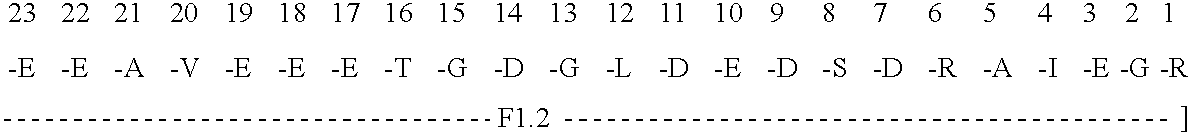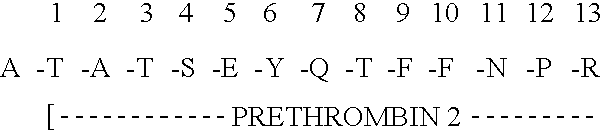Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160 results about "Low affinity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A low affinity connection is used to handle a low affinity request. Each connection handles one request at a time. A low affinity request will operate just as efficiently on any server.
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: photoselection of nucleic acid ligands and solution selex
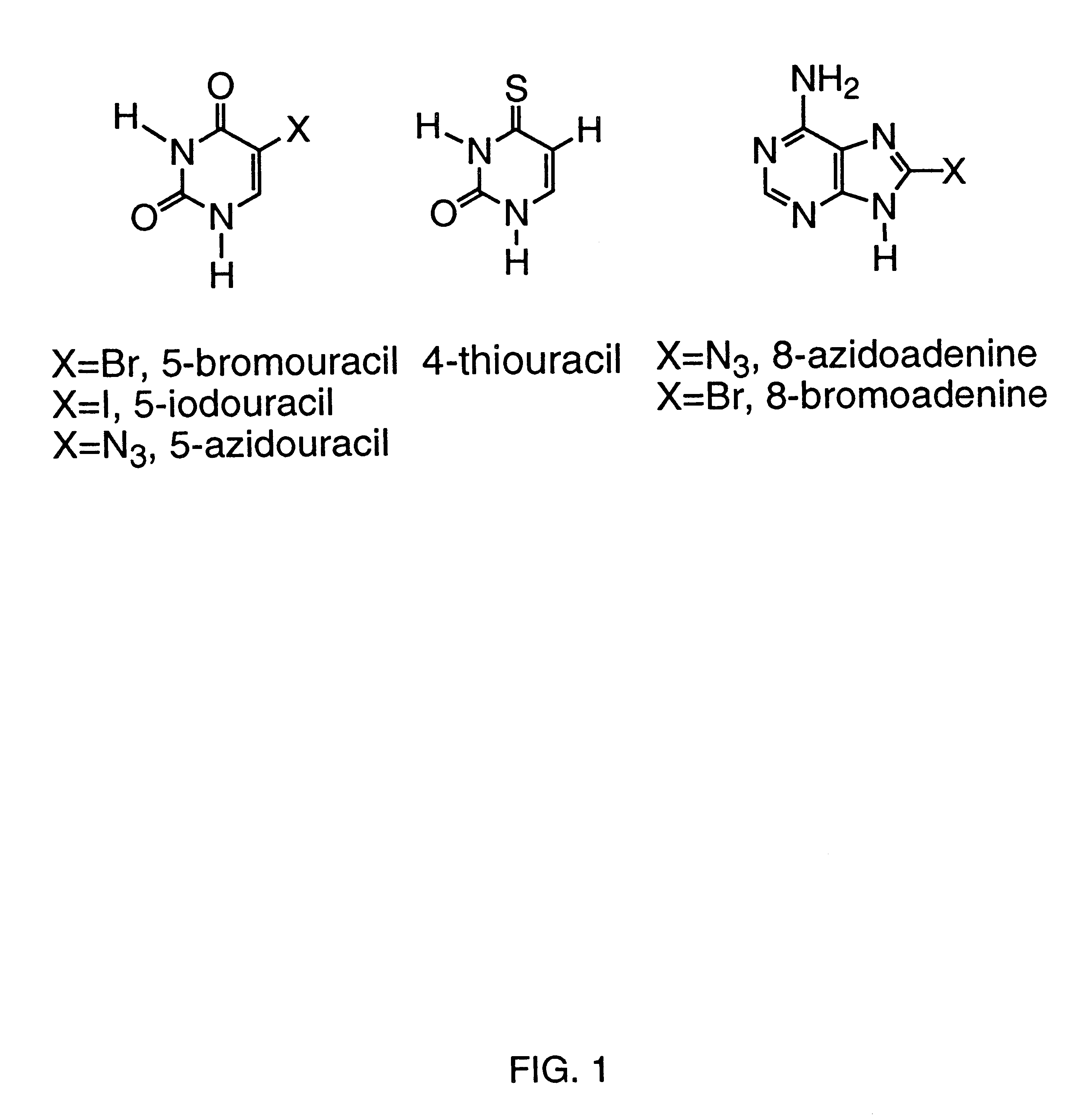
A method for identifying nucleic acid ligands to target molecules using the SELEX procedure wherein the candidate nucleic acids contain photoreactive groups and nucleic acid ligands identified thereby are claimed. The complexes of increased affinity nucleic acids and target molecules formed in the procedure are crosslinked by irradiation to facilitate separation from unbound nucleic acids. In other methods partitioning of high and low affinity nucleic acids is facilitated by primer extension steps as shown in the figure in which chain termination nucleotides, digestion resistant nucleotides or nucleotides that allow retention of the cDNA product on an affinity matrix are differentially incorporated into the cDNA products of either the high or low affinity nucleic acids and the cDNA products are treated accordingly to amplification, enzymatic or chemical digestion or by contact with an affinity matrix.
Owner:SOMALOGIC INC
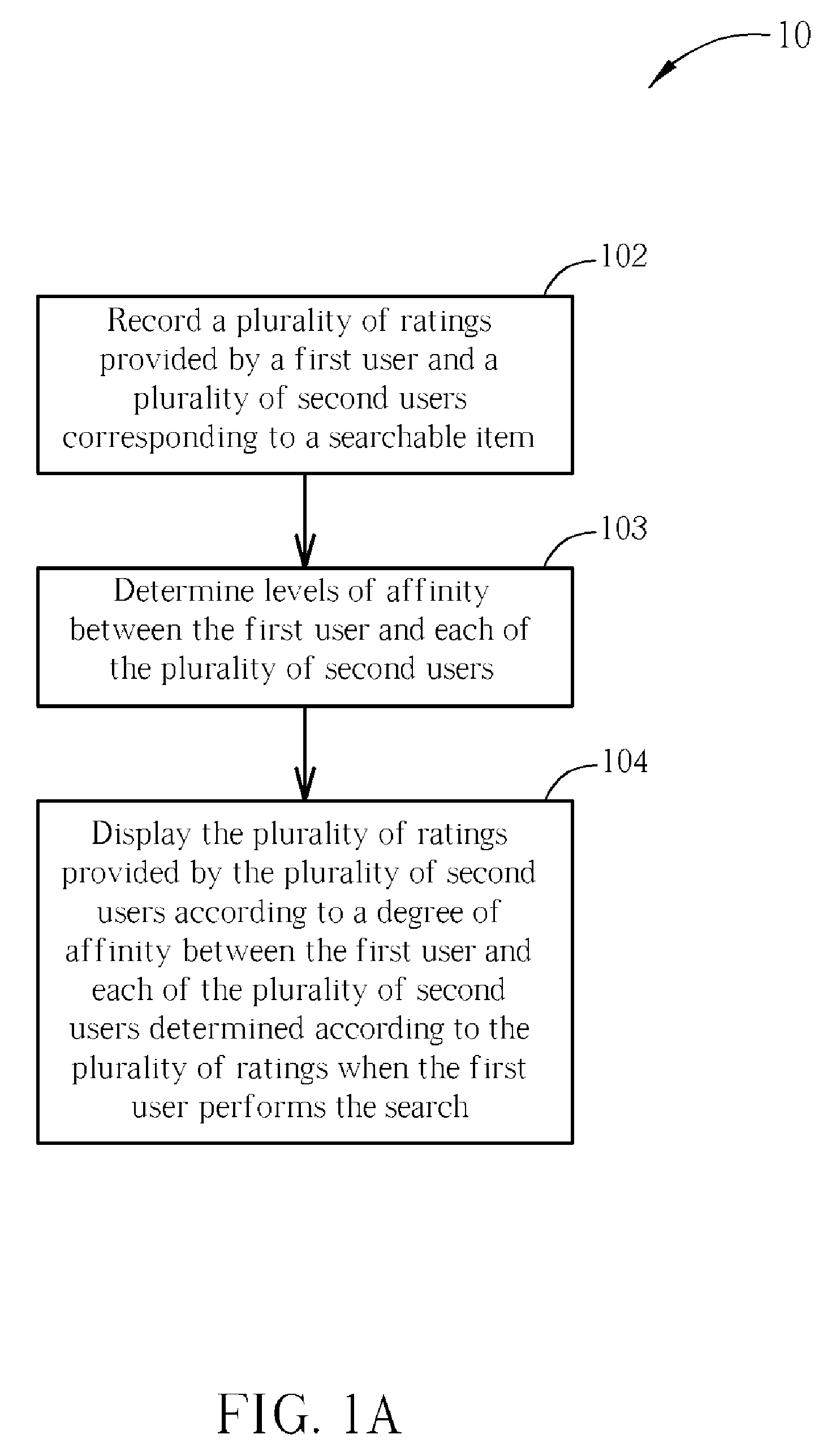
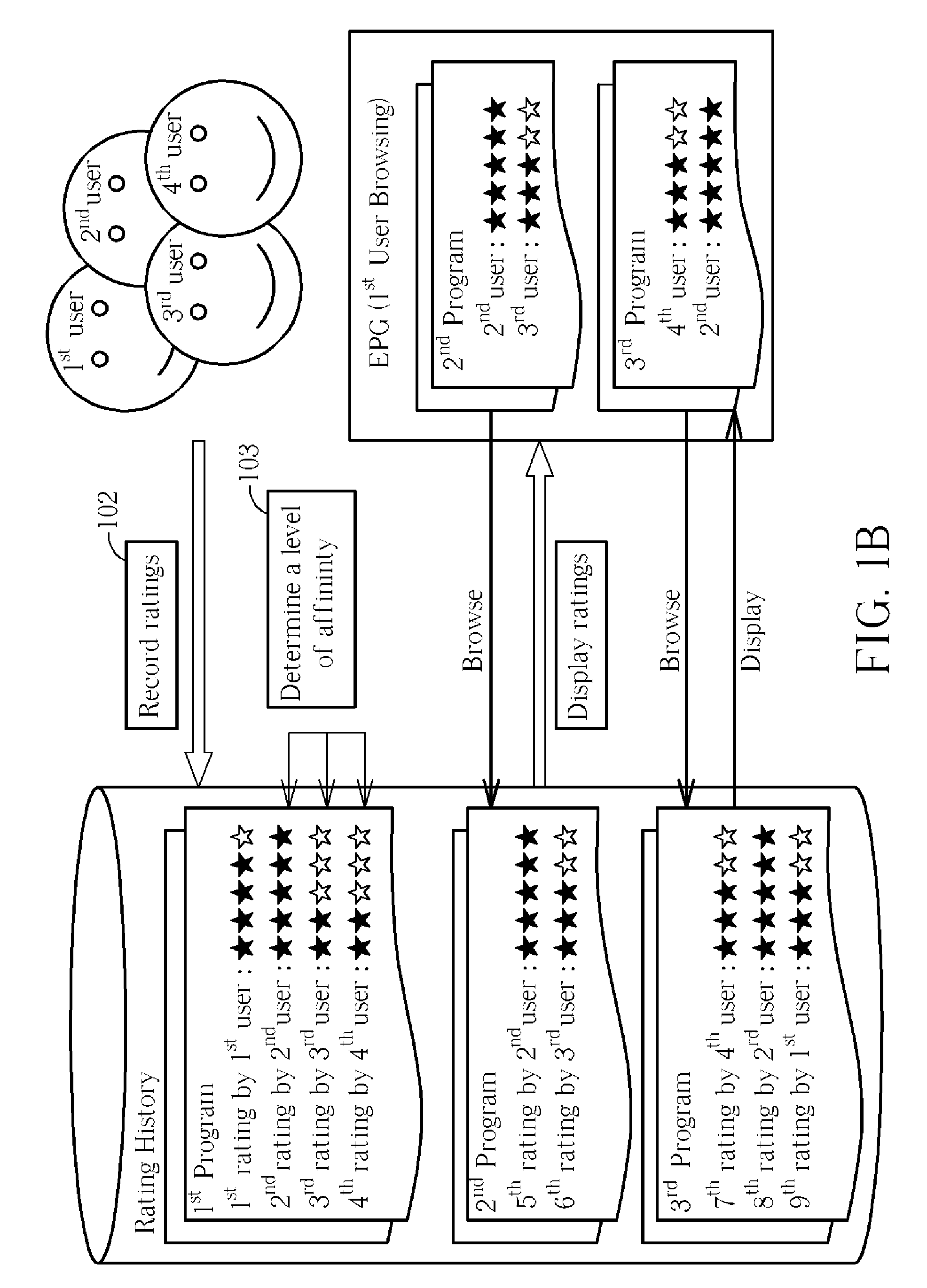
Method for displaying search results in a browser interface
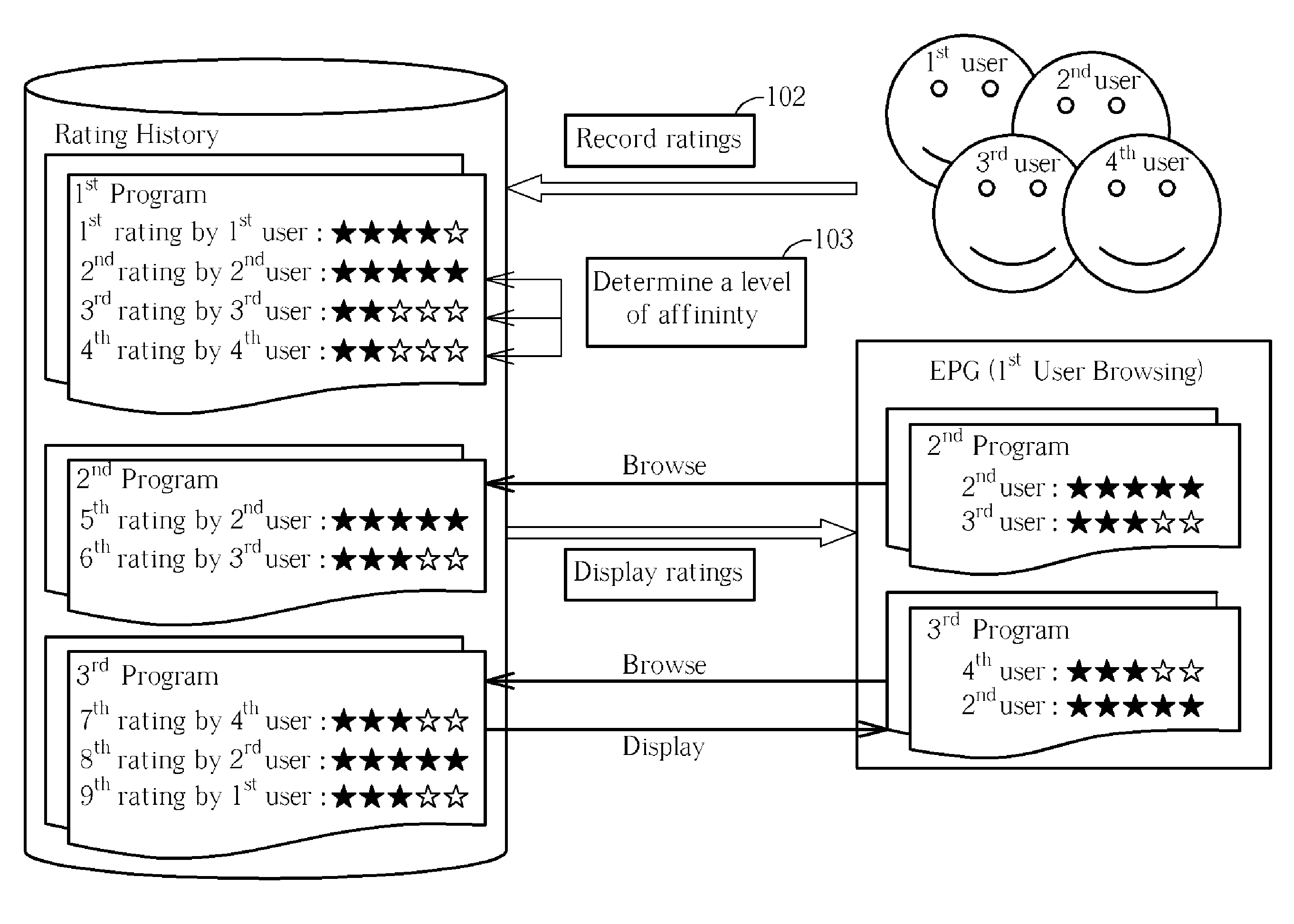
ActiveUS20090234828A1High affinityTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalLow affinityLower affinity
A level of affinity between a first user and many other users is considered when prioritizing content display when browsing, and ratings display when searching for programs in an electronic program guide or in a browser interface of a playback software application. Ratings from users who have high affinity with the first user are shown with priority over ratings from users who have low affinity with the first user. And, when browsing, programs rated highly by users having high affinity with the first user are shown with priority over programs rated poorly by the users having high affinity with the first user, and programs rated highly by users having low affinity with the first user.
Owner:CYBERLINK
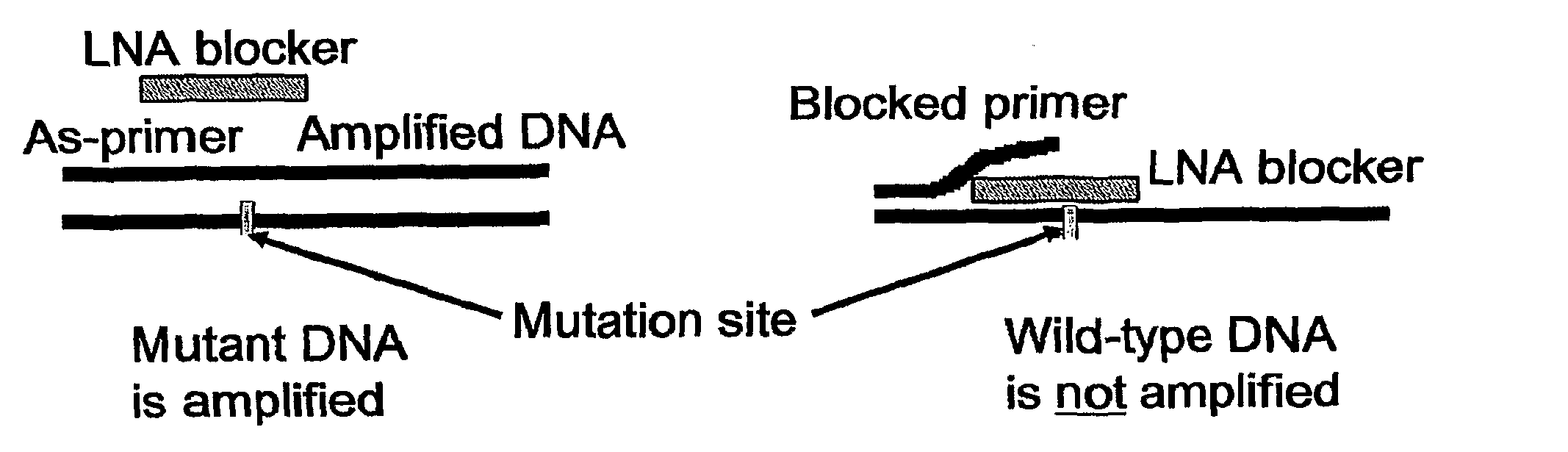
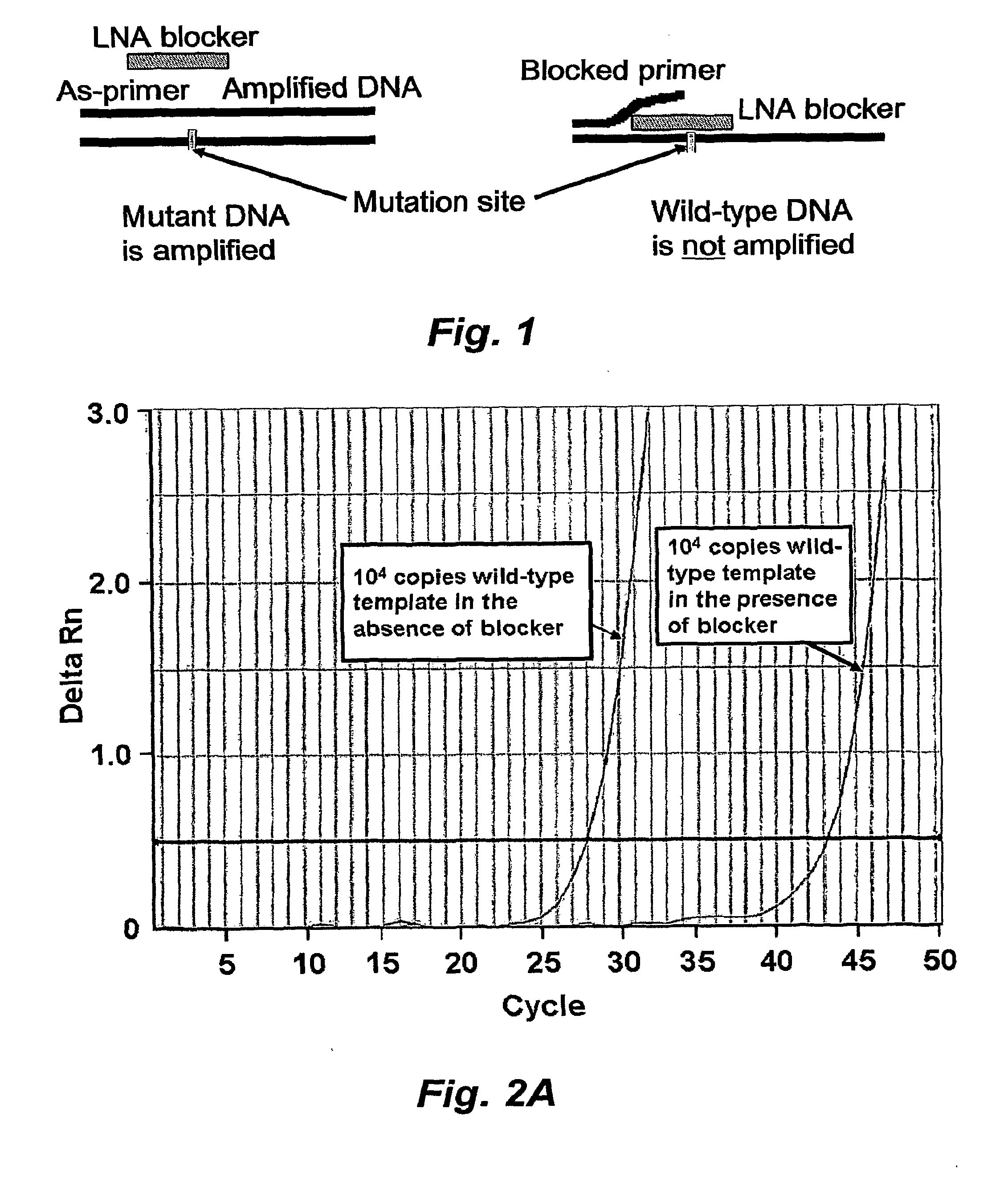
Selective amplification of minority mutations using primer blocking high-affinity oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20100009355A1Avoid detectionPreferential amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationLow affinityNucleic Acid Probes
In certain embodiments this invention pertains to methods of detecting and / or quantifying rare mutant nucleic acids in populations of nucleic acids in which the wild-type nucleic acids are in substantially greater abundance than the rare mutants. In various embodiments the methods utilize short high affinity oligonucleotides targeted to the wild type rather than the minority or mutant sequence. Rather than directly detecting mutant DNA, these probes block detection of wild type DNA. These “blocker” probes can be used in combination with longer “detection” probes or PCR primers to amplify and / or identify the minority mutation in, e.g., clinical specimens. The combination of short high affinity blocker probes and longer, lower affinity detection probes eliminates the single base specificity / complexity tradeoff in the design of nucleic acid probes.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
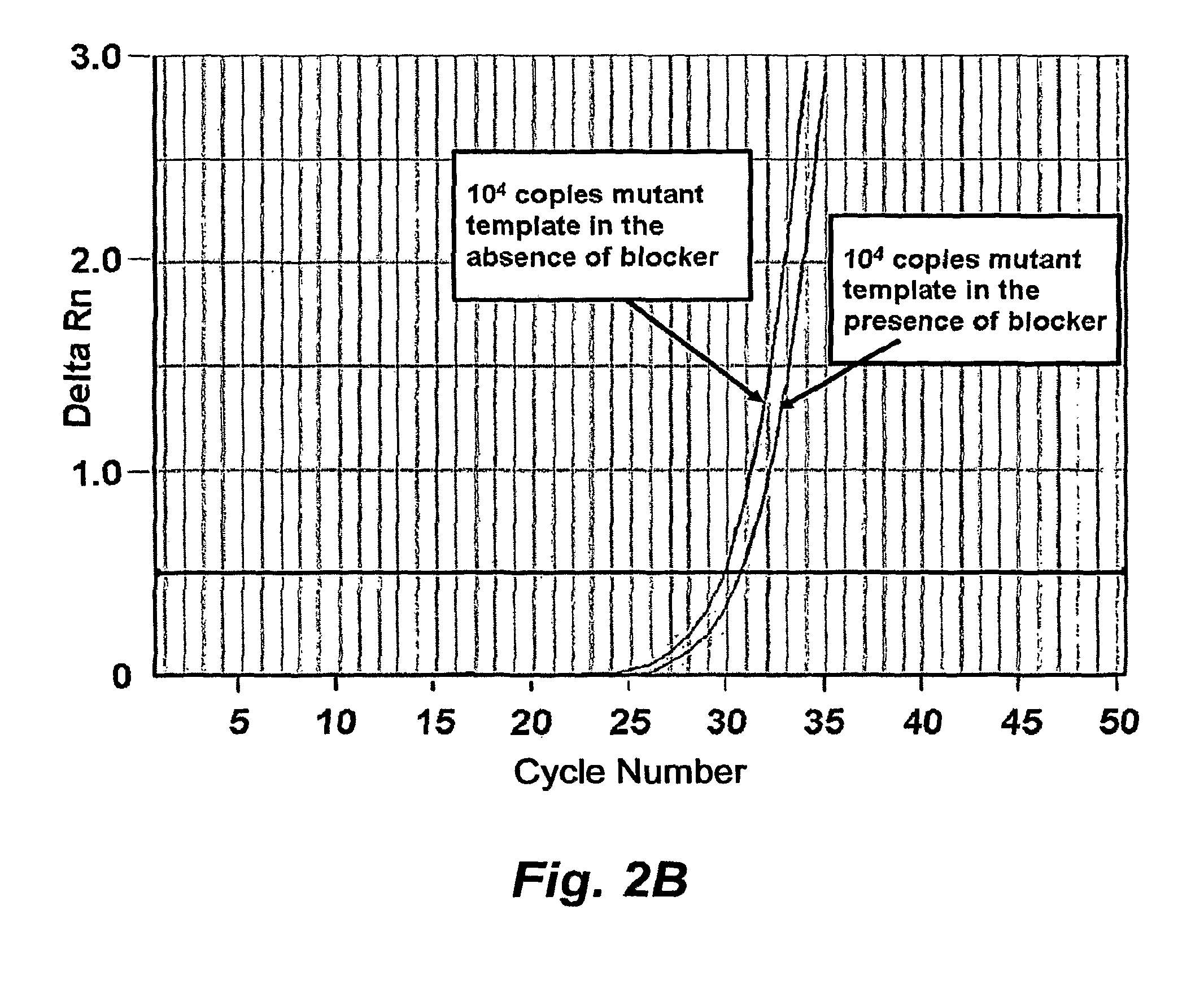
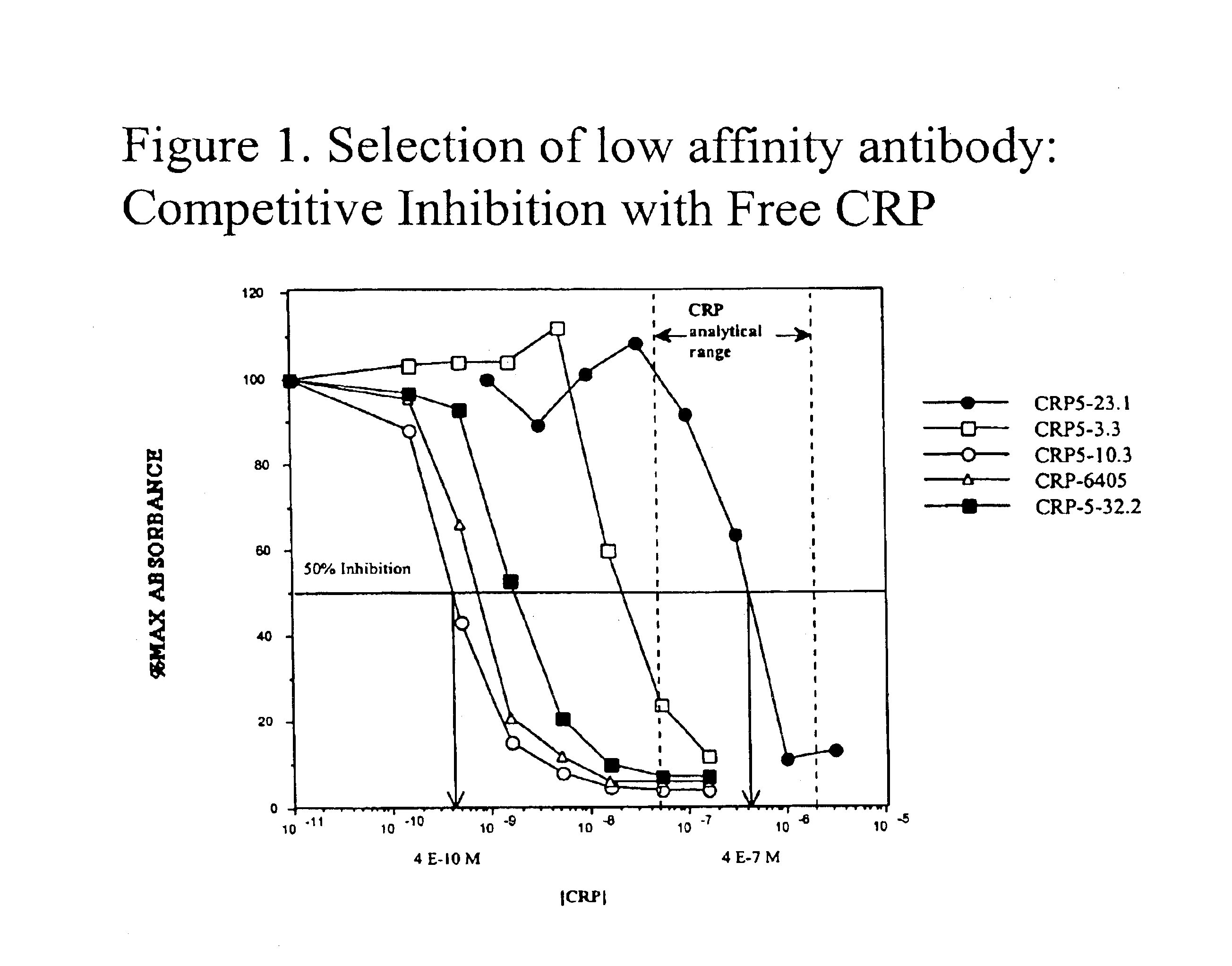
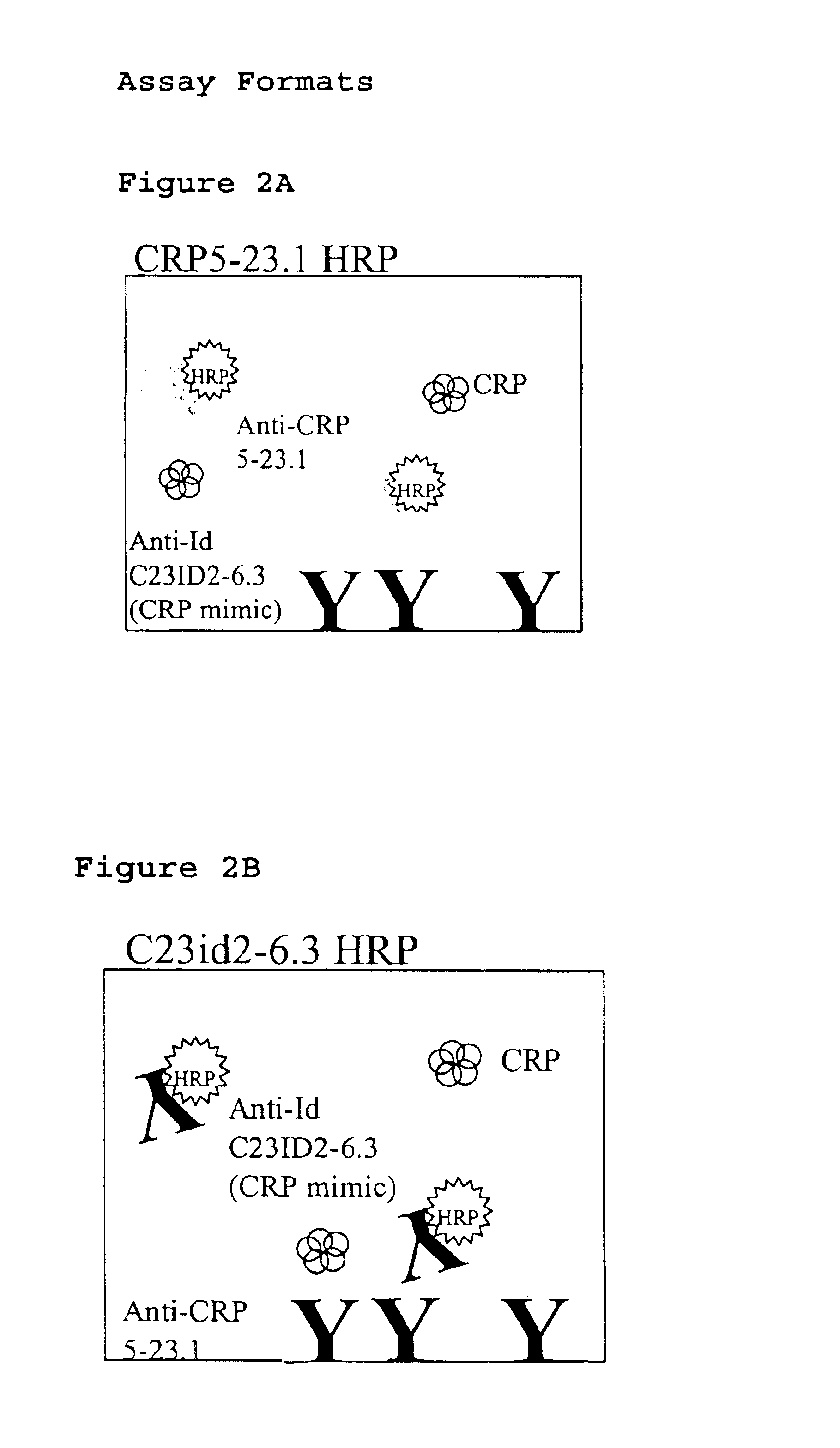
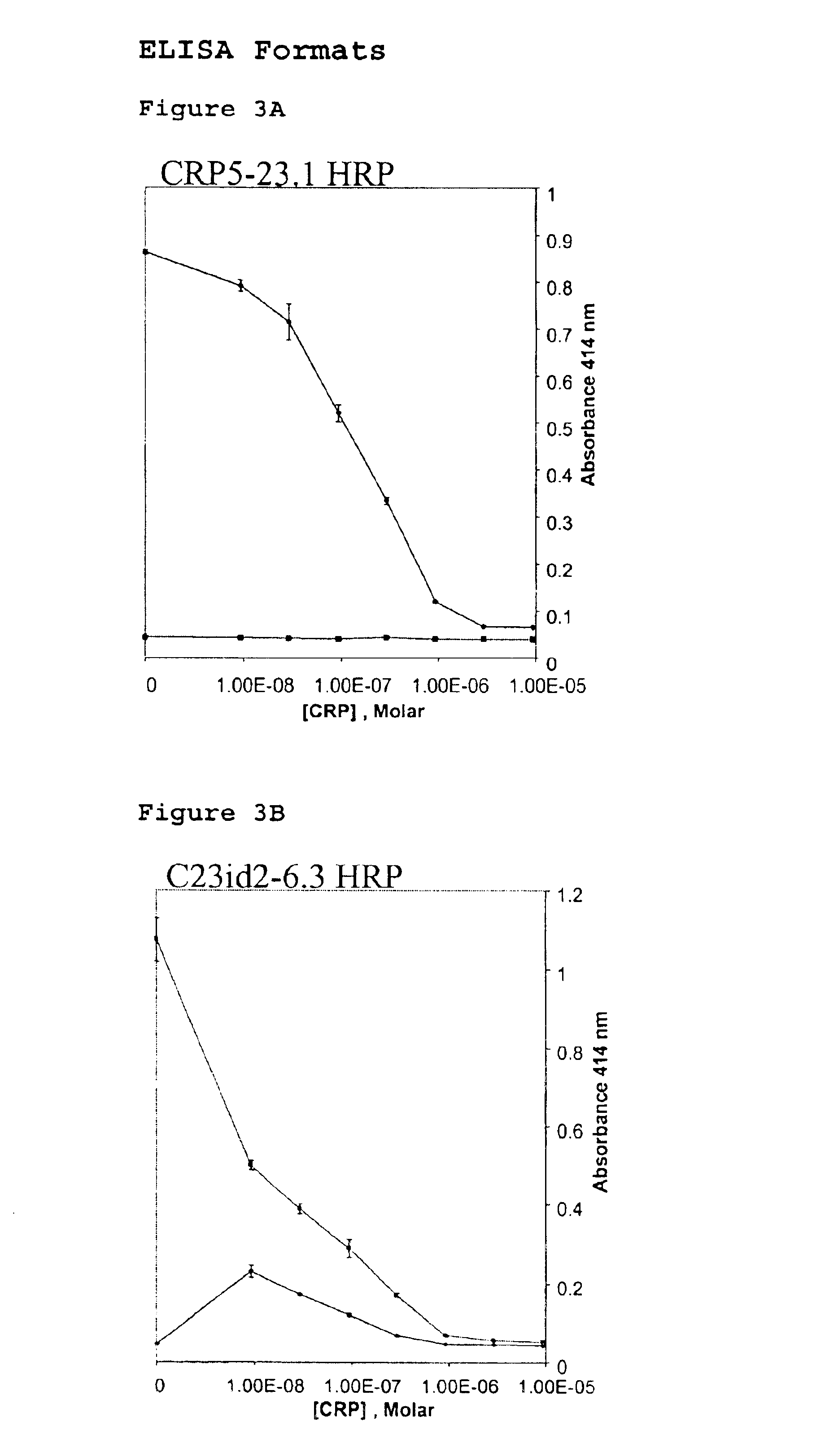
Immunoassay for C-reactive protein
InactiveUS6838250B2High affinityWeak affinityAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansLow affinityAntigen
The present invention relates to new CRP immunoassay compositions. The compositions include a low affinity anti-human CRP monoclonal antibody, and an antiidiotypic antibody raised against it. The invention further provides a method for obtaining antiidiotypic monoclonal antibody populations directed to an antibody that is specific for a high concentration, high molecular weight target antigen.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Semiconductor light source with electrically tunable emission wavelength
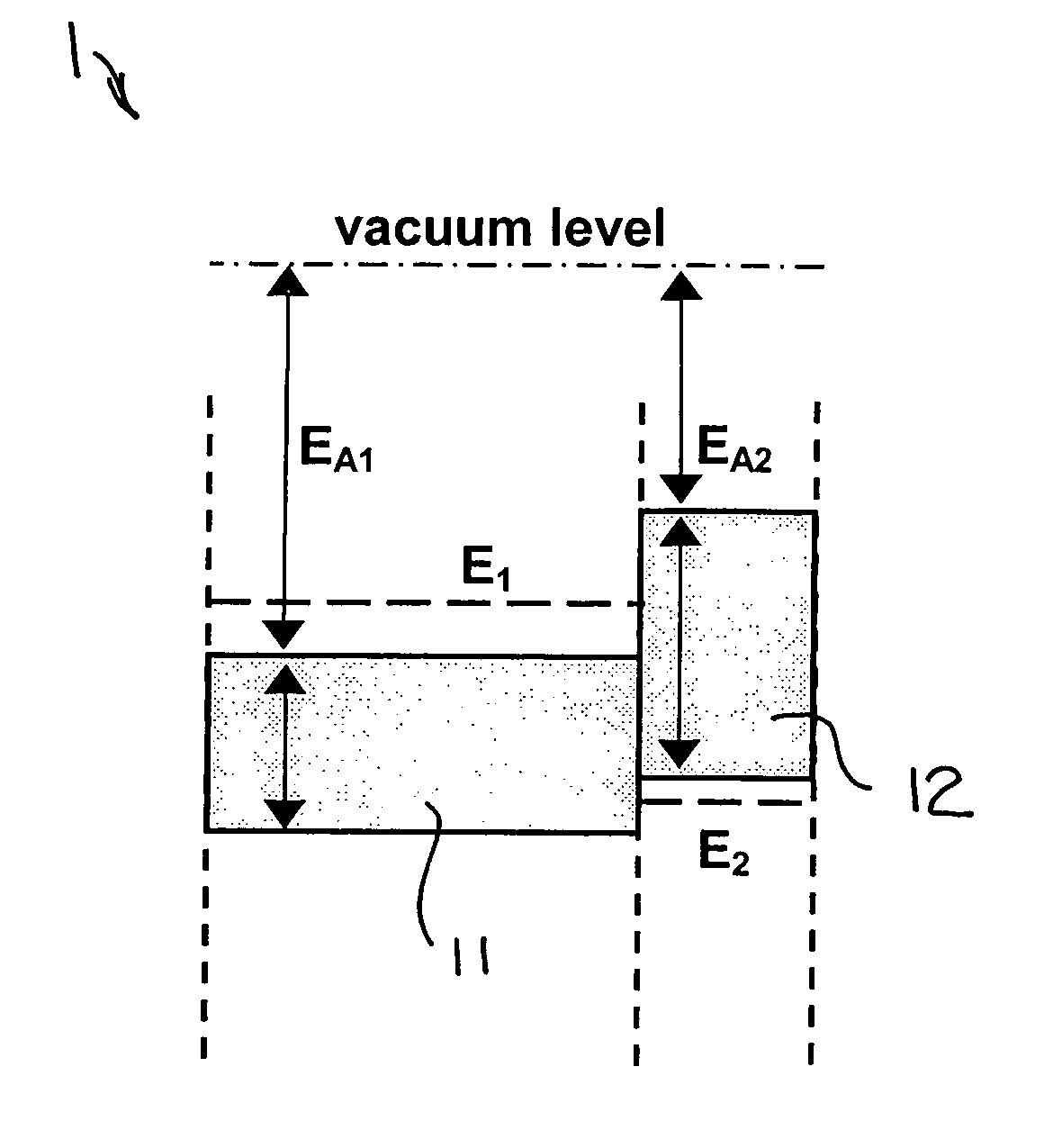
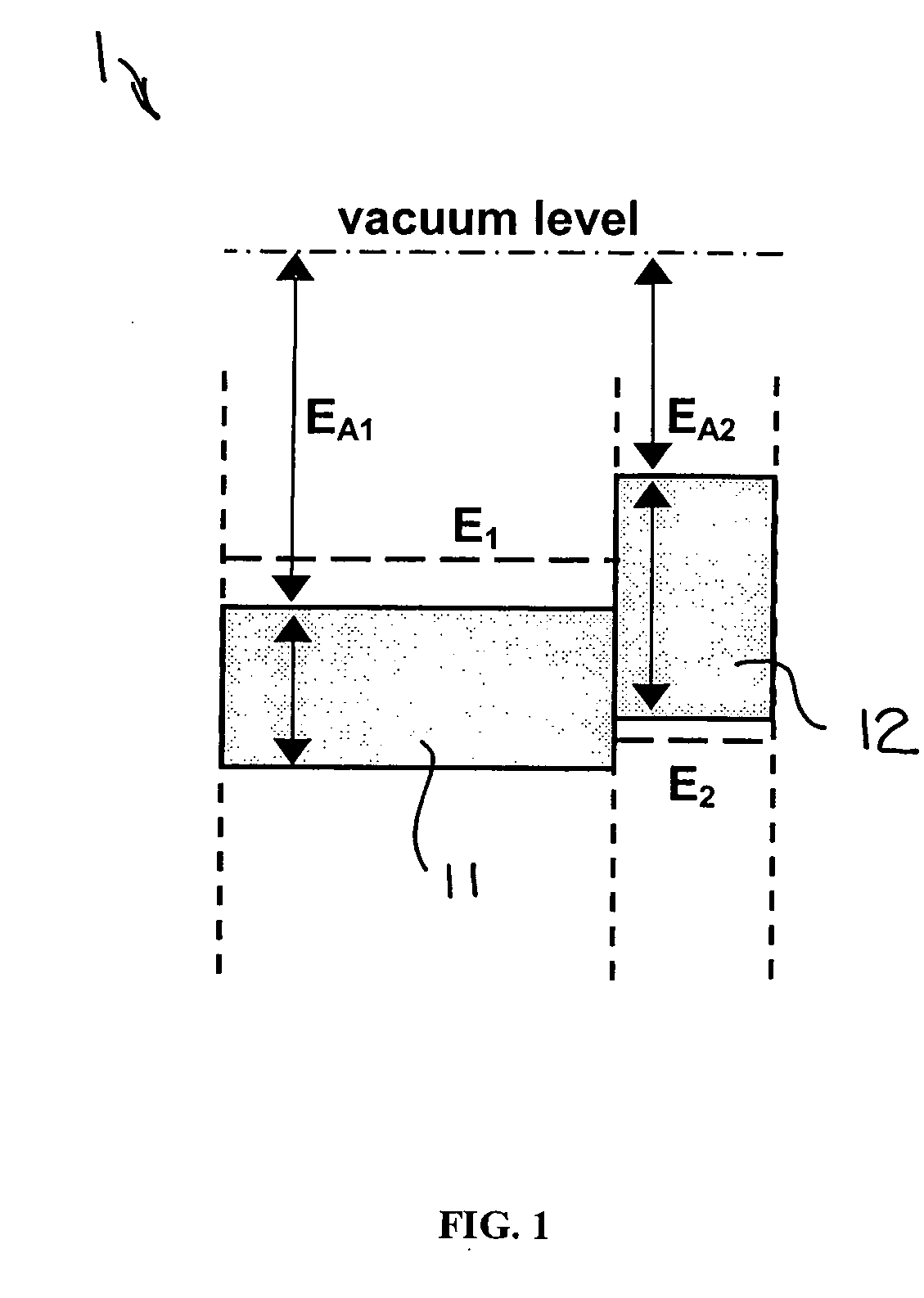
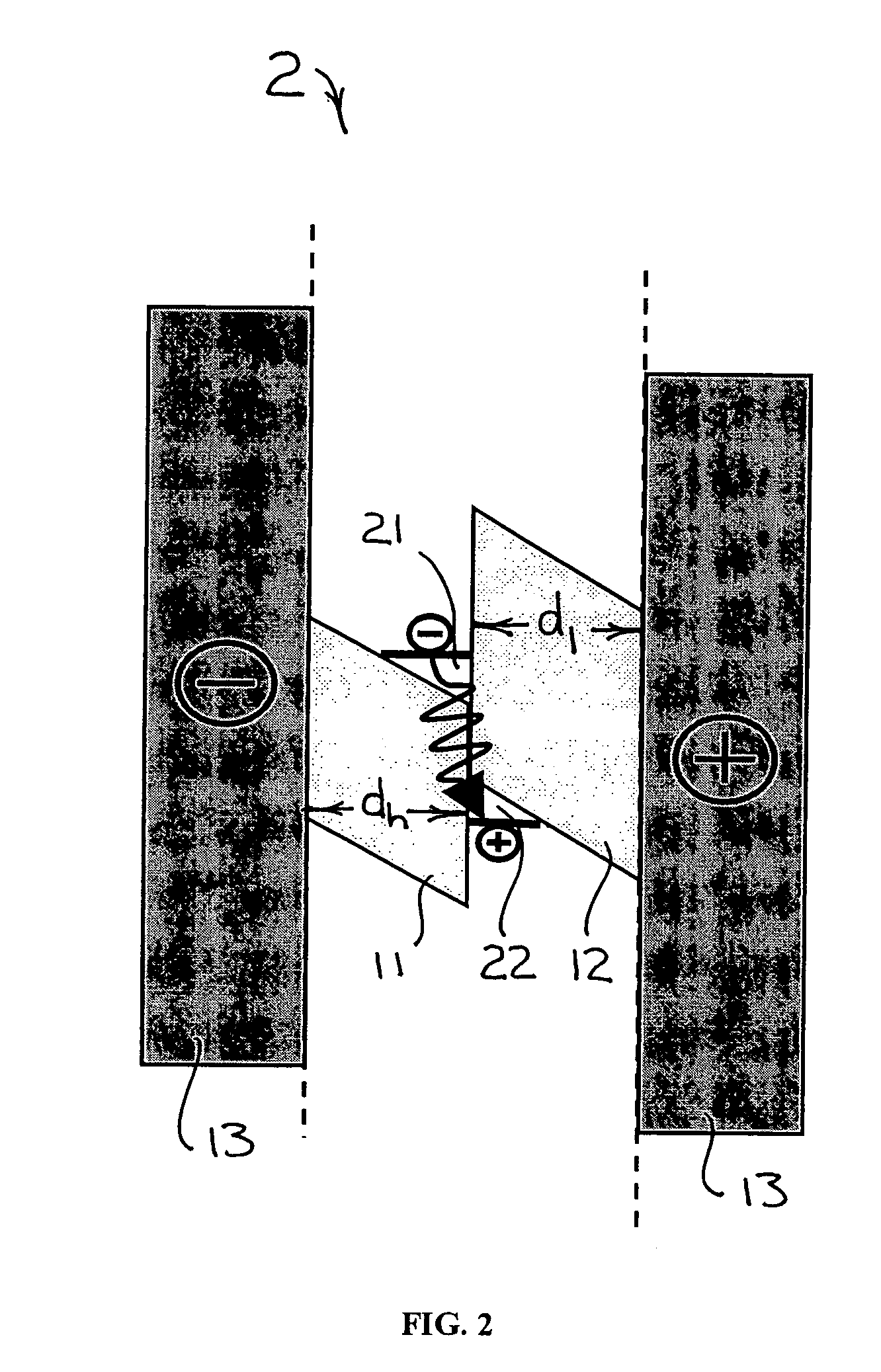
A semiconductor light source is disclosed comprising a substrate, lower and upper claddings, a waveguide region with imbedded active area, and electrical contacts to provide voltage necessary for the wavelength tuning. The active region includes single or several heterojunction periods sandwiched between charge accumulation layers. Each of the active region periods comprises higher and lower affinity semiconductor layers with type-II band alignment. The charge carrier accumulation in the charge accumulation layers results in electric field build-up and leads to the formation of generally triangular electron and hole potential wells in the higher and lower affinity layers. Nonequillibrium carriers can be created in the active region by means of electrical injection or optical pumping. Radiative recombination occurs between the electrons and holes, accumulated in the ground states of the triangular potential wells formed in the high- and low-affinity layers of each active region periods. The ground state energy in the triangular wells and the radiation wavelength can be tuned by changing the voltage drop across the active region.
Owner:MAXION TECH +1
Melanocortin 1 receptor selective compounds
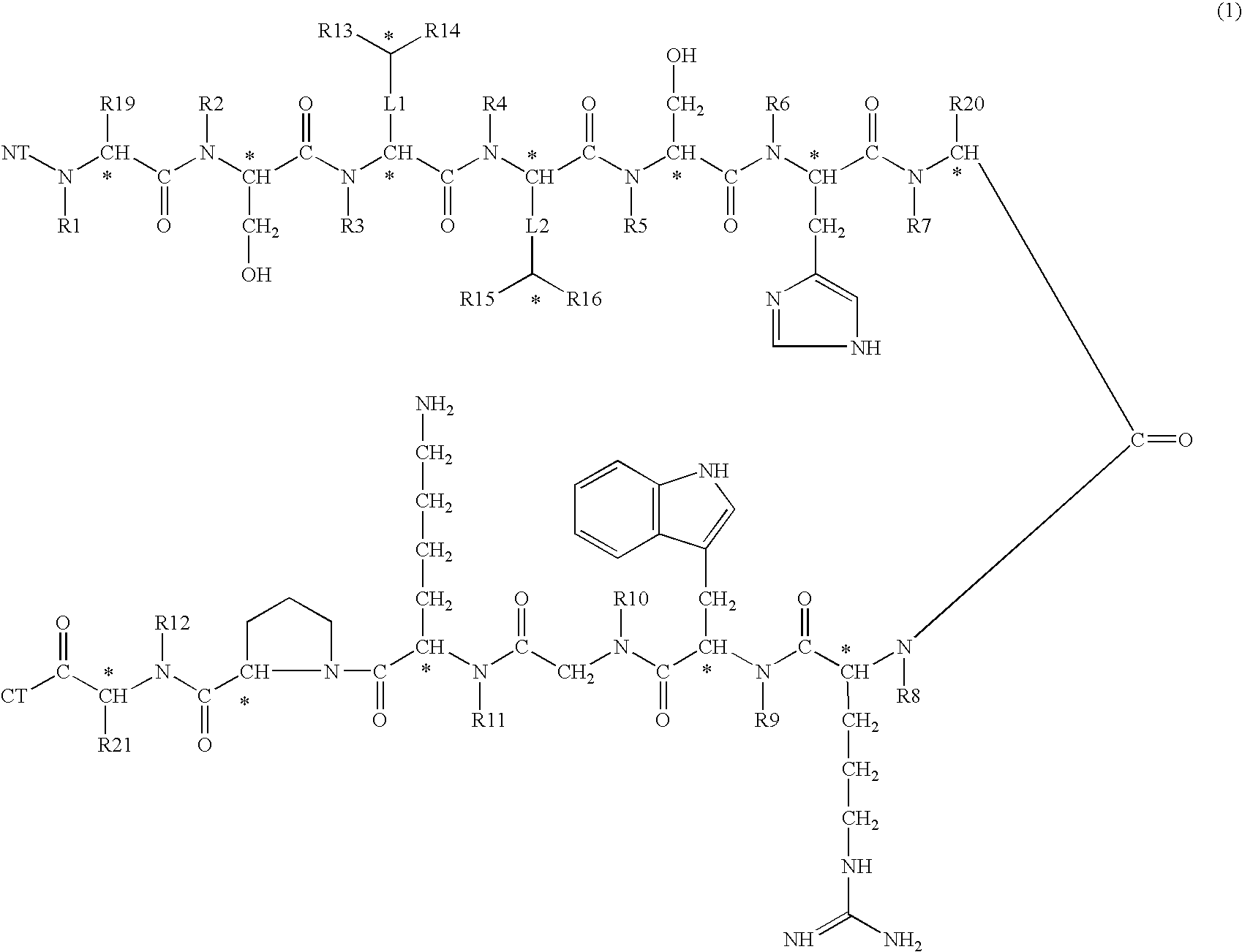
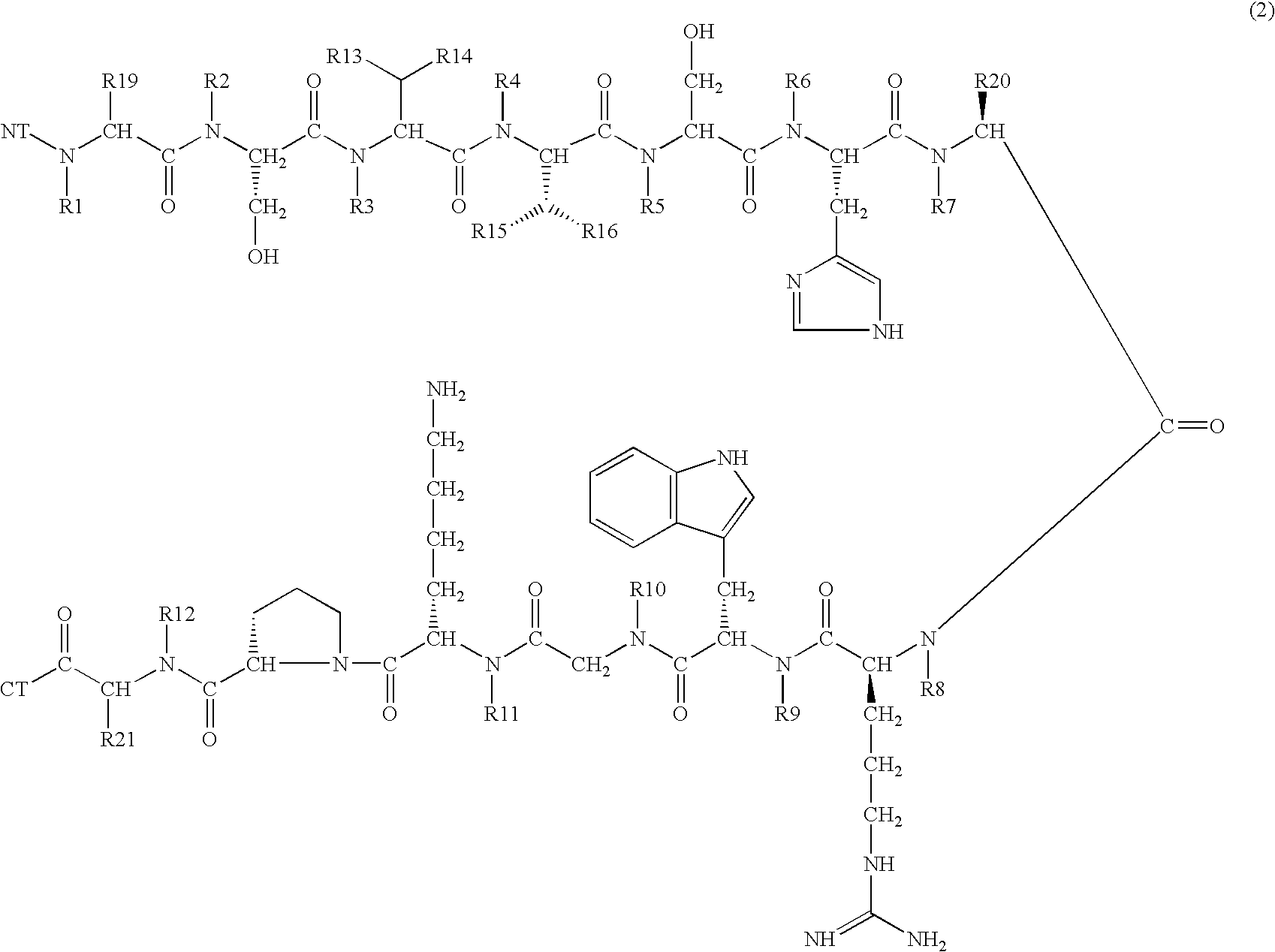
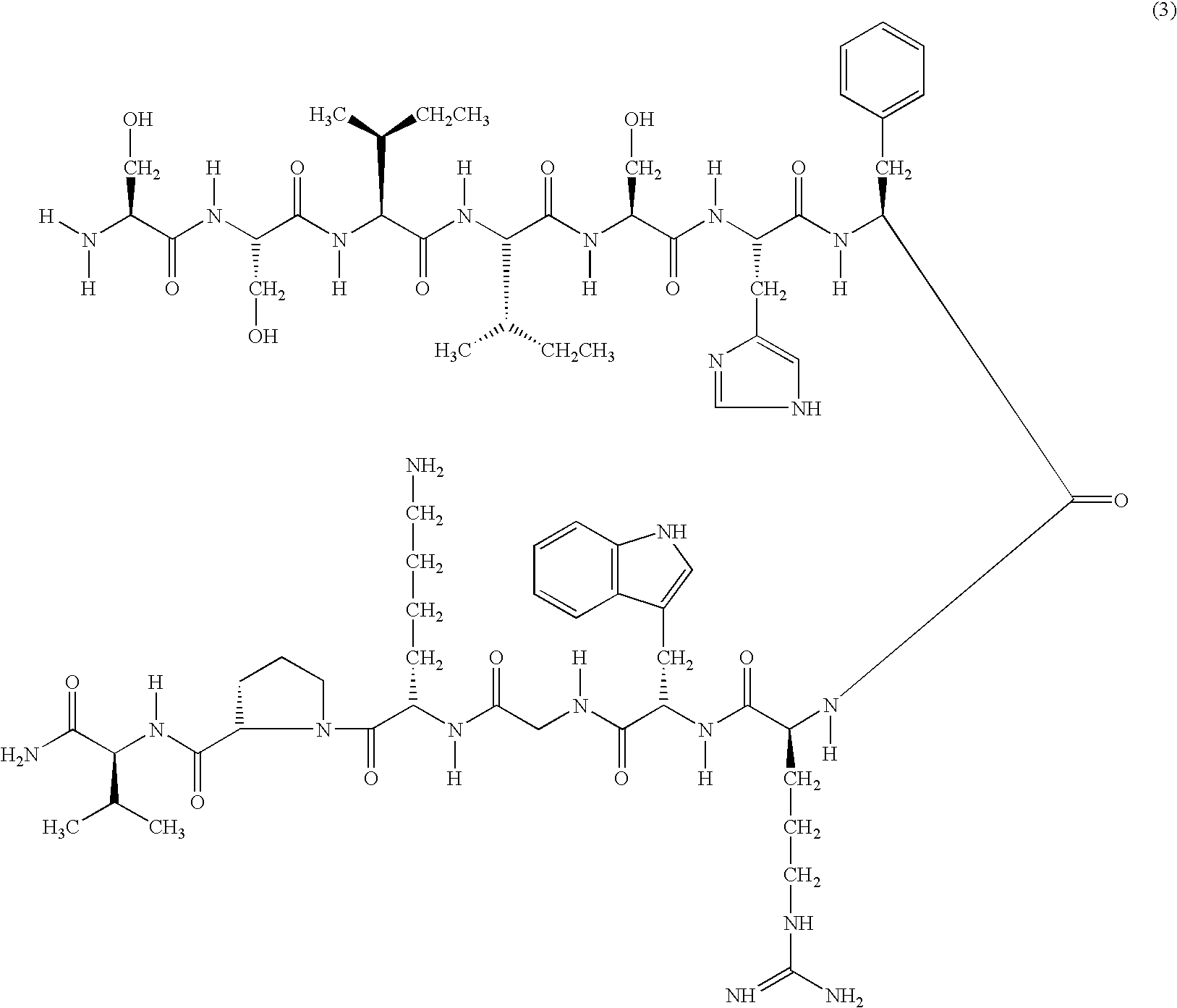
A compound of general formula (1) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11 and R12 are H or methyl, R13, R14, R15 and R16 are H or alkyl, wherein L1 and L2 are linkers selected from single bond, methyl, ethyl, wherein R19, R20 and R21 are H or —CH2X, NT is selected from H, hydroxyl, alkyl, aminoacid, aminoacid analogue, polypeptide and functional group, CT is selected from hydrogen, hydroxyl, alkyl, aminoacid, aminoacid analogue, polypeptide and functional group shows high selectivity and high affinity for MC1-receptors in combination with effective stimulation or inhibiton of cAMP formation in MC1-receptor expressing cells but low affinity for other subtypes of MC-receptors and may be used to treat a wide range of inflammatory conditions. Also disclosed is a DNA molecule and a corresponding vector encoding the compound, a fusion protein comprising a copy of it, a vector comprising DNA encoding the fusion protein, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound.
Owner:ACTION PHARM AS
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS20090246206A1Decreasing activity of tyrosine kinaseModulating biological activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsLow affinitySurface marker
Methods for improving the specific binding ability of bispecific binding compositions are described. The bispecific binding compositions are able to target cells by a high affinity targeting domain to a target cell surface marker and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, wherein the binding of each domain to its respective cell surface marker increases or decreases, as desired, the biological activity of the respective cell surface markers. The invention further provides bispecific binding agents for use in the methods, as well as uses for the agents.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS20120208234A1Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityADAMTS Proteins
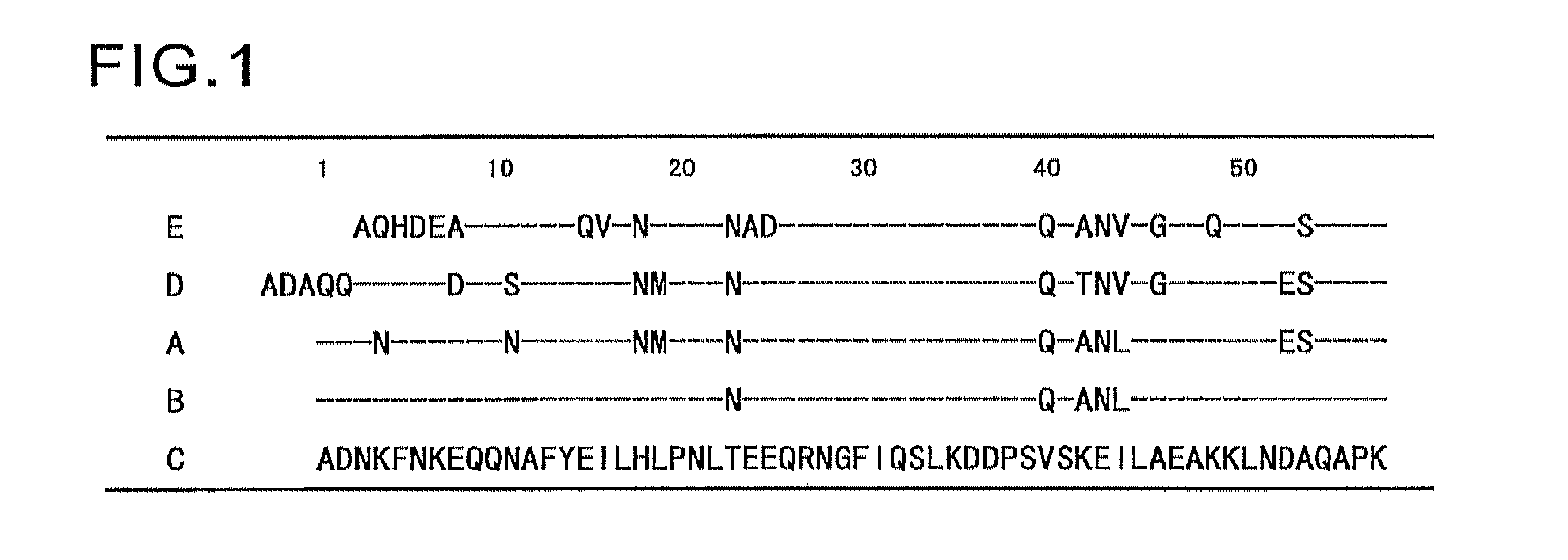
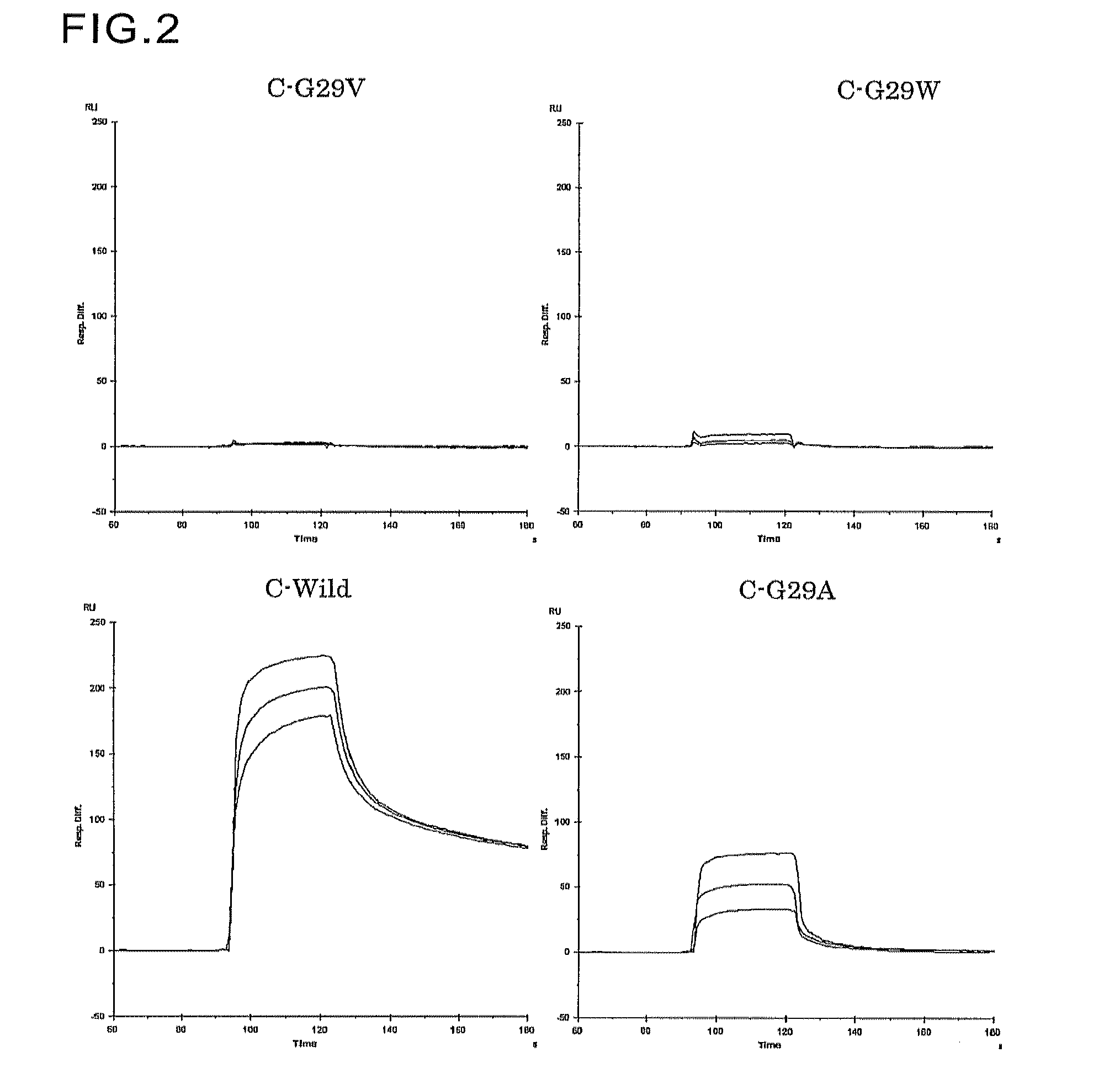
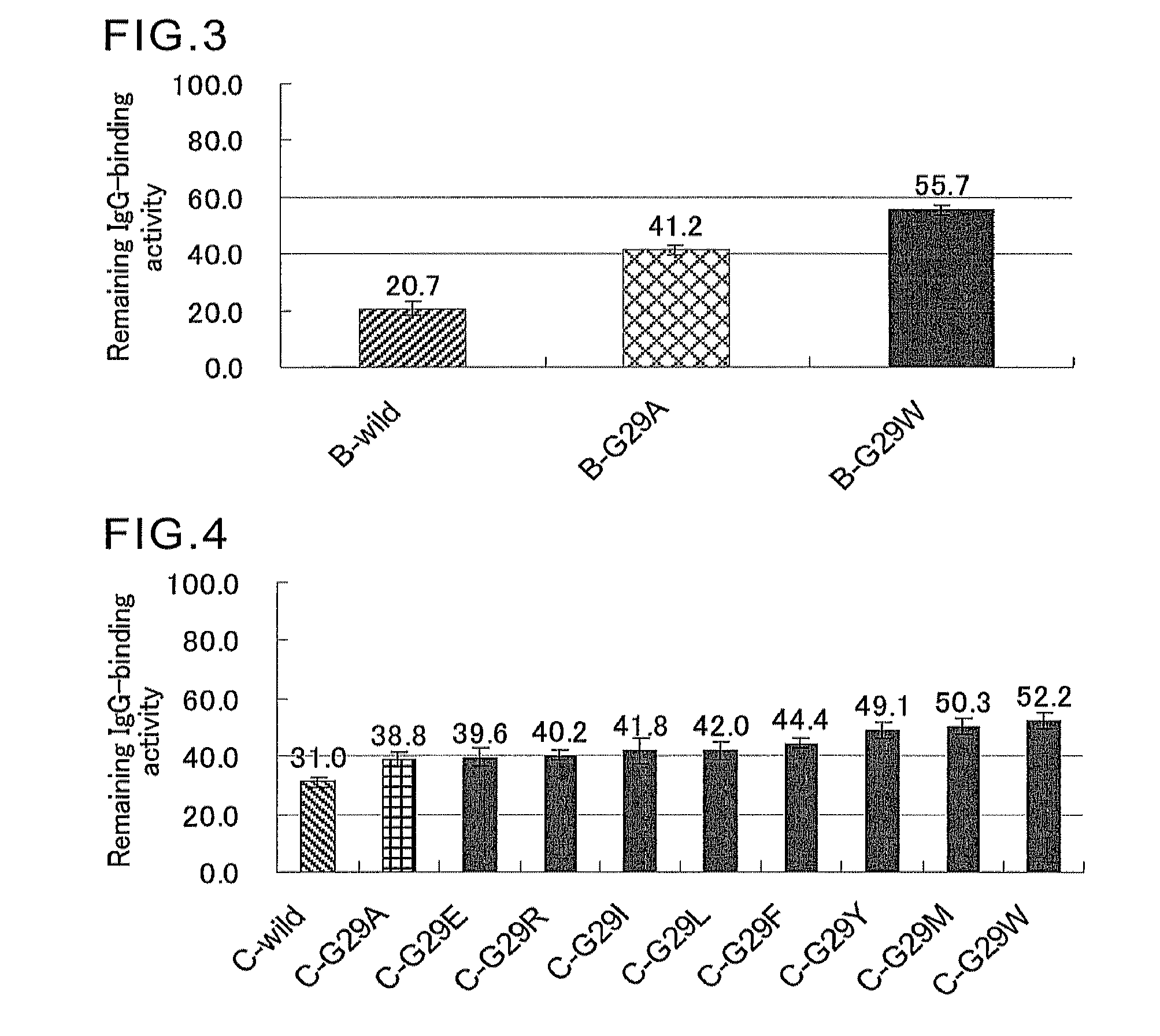
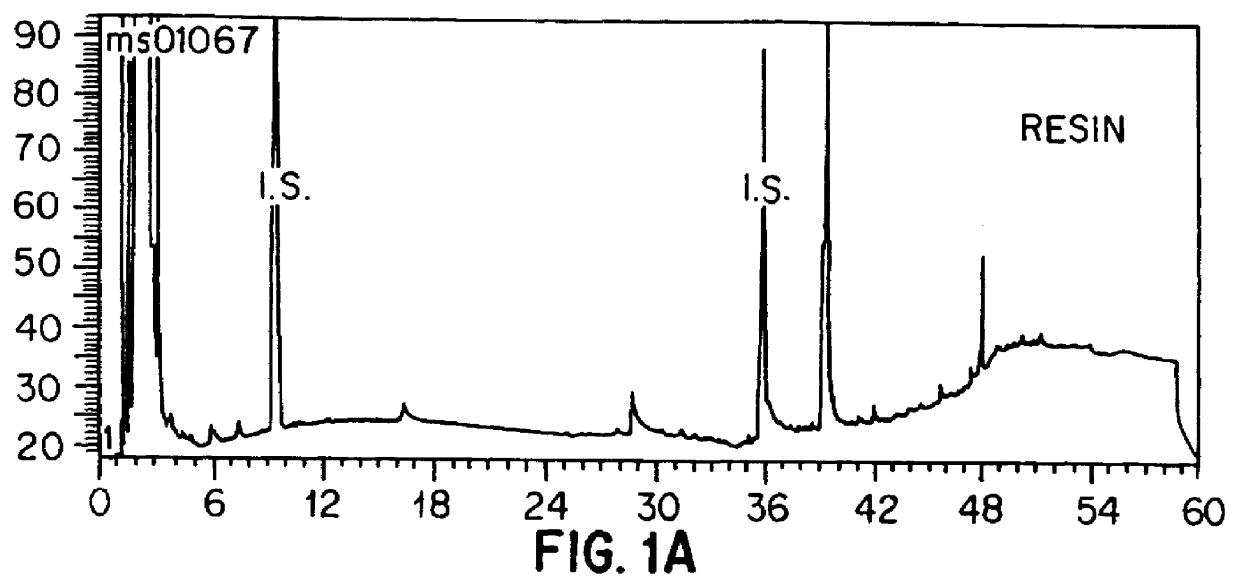
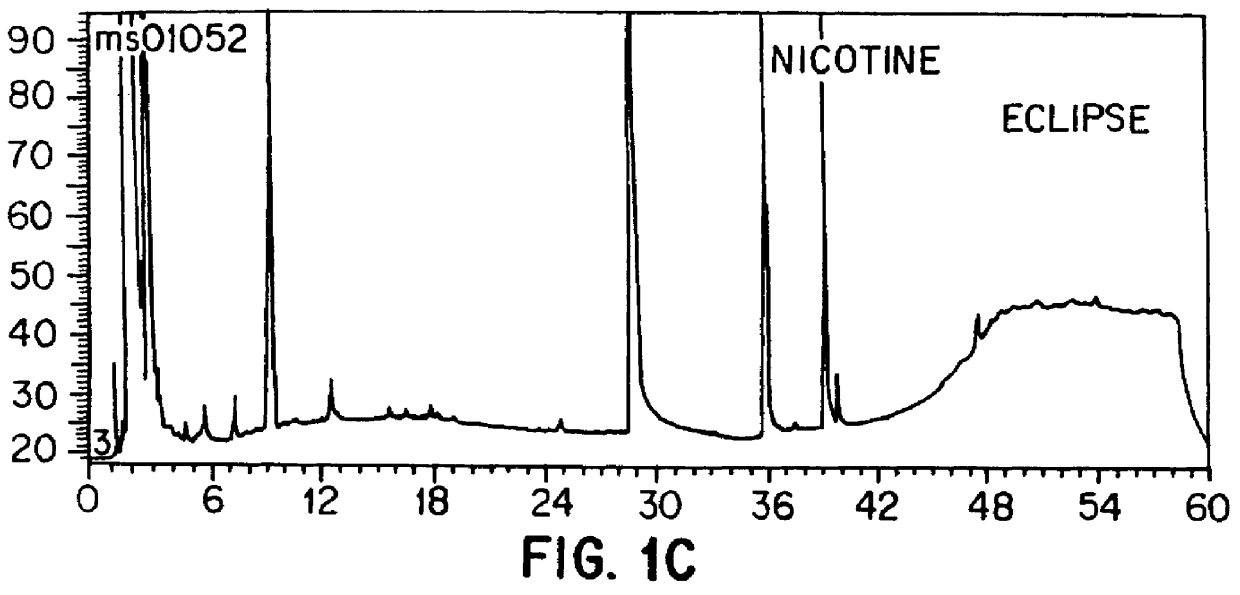
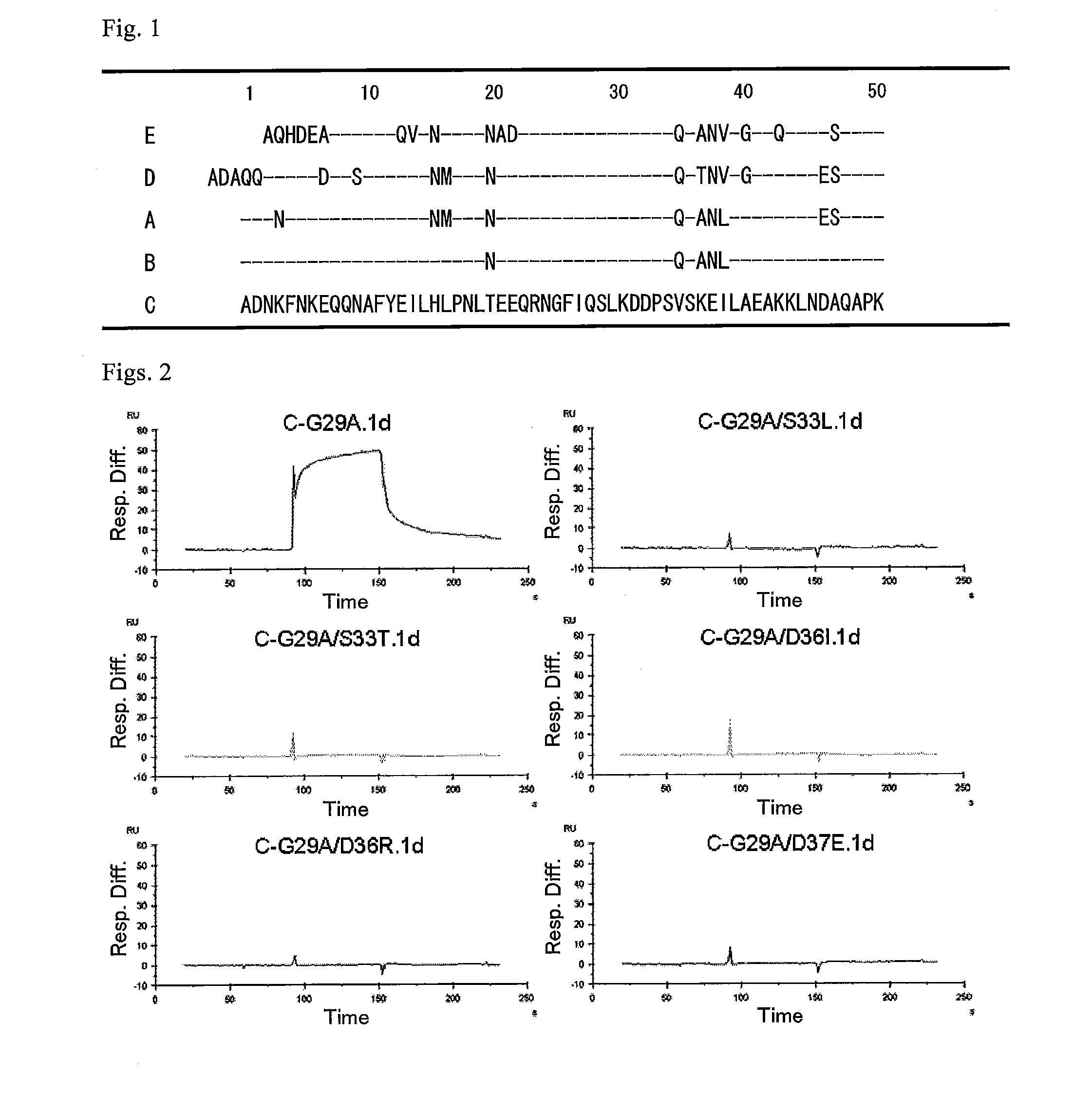
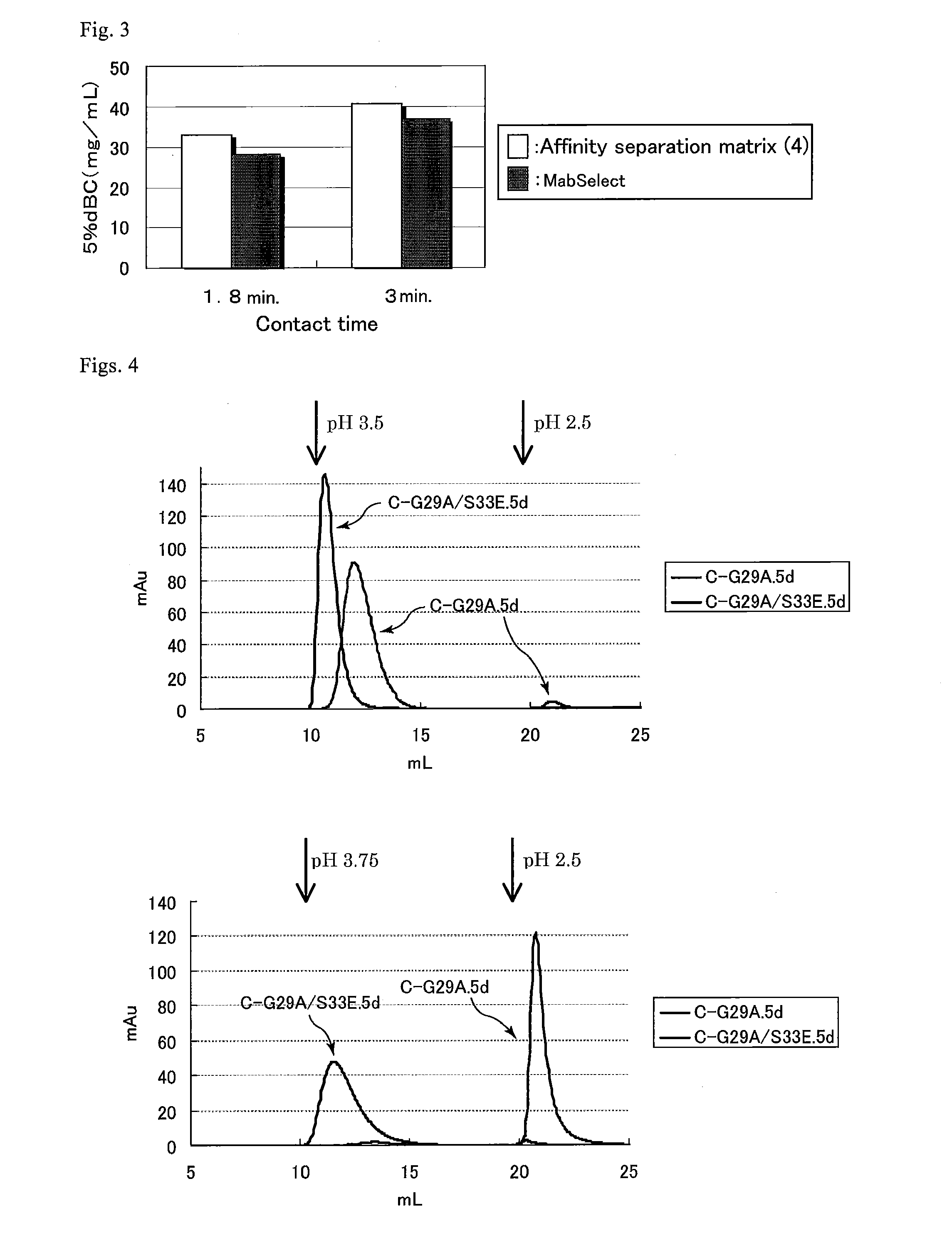
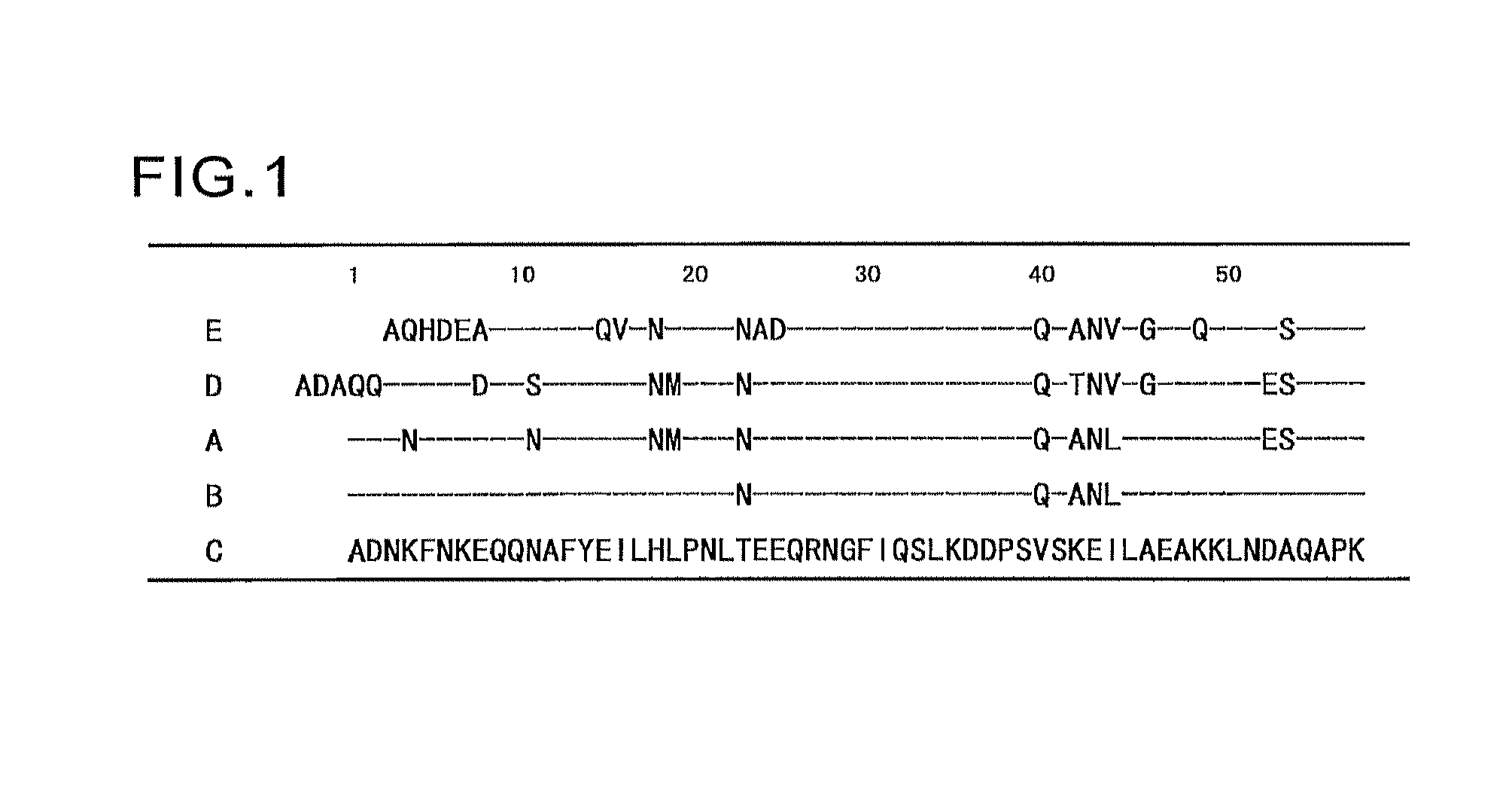
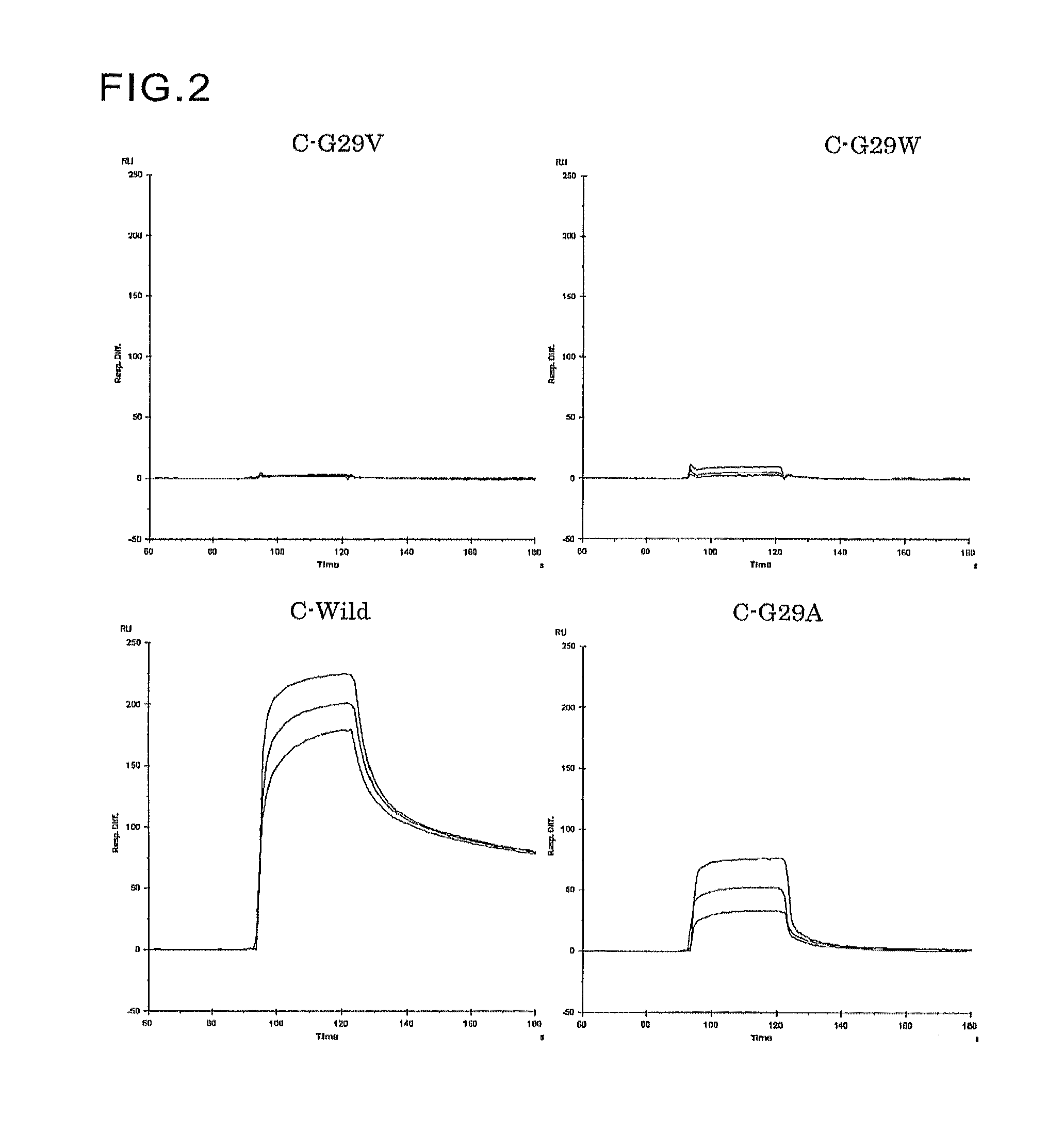
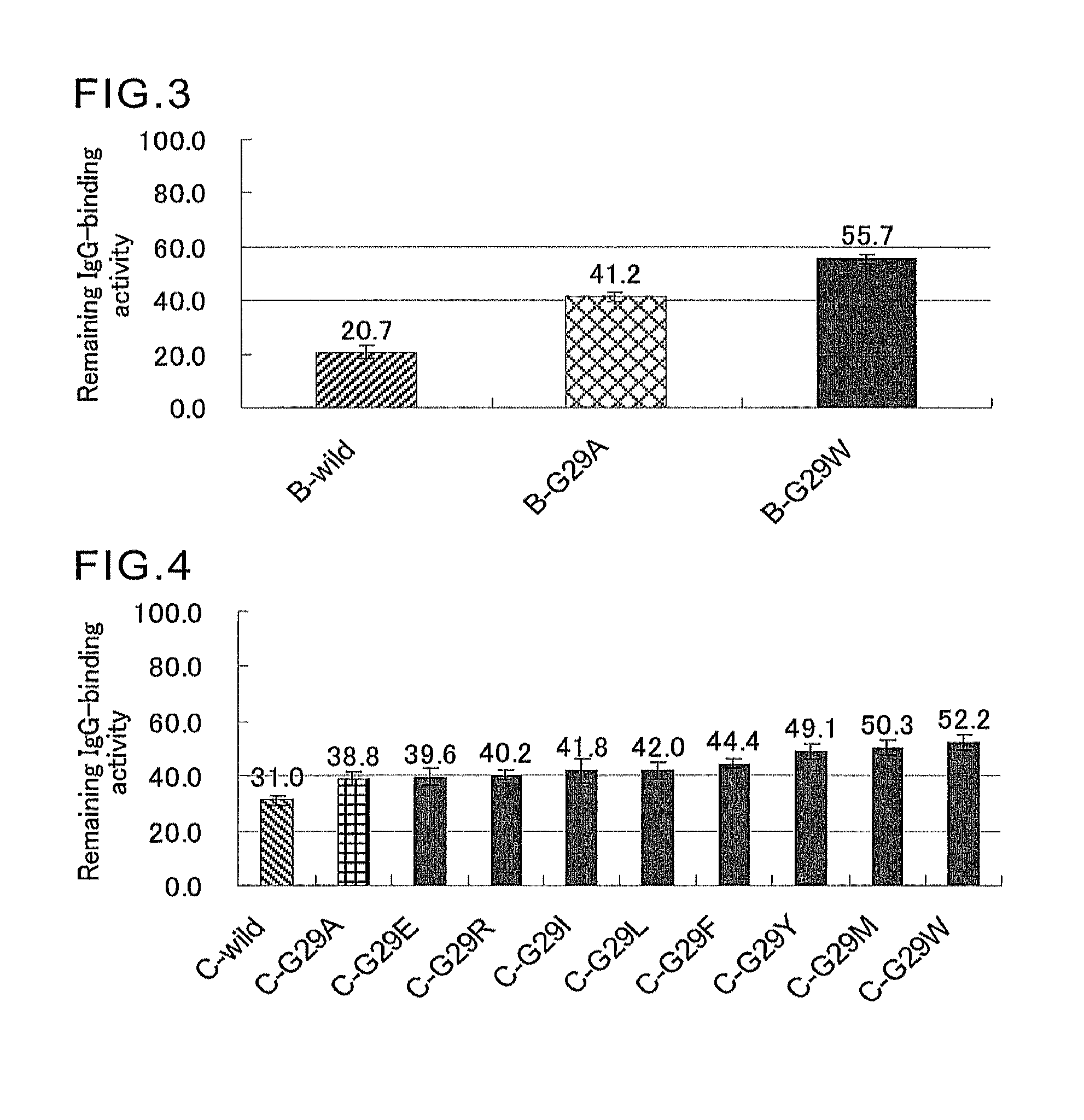
An object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having better antibody dissociation properties in the presence of an acid than conventional engineered Protein A ligands and a further object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having higher alkali resistance. The present invention is to provide a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, including an amino acid sequence derived from any of E, D, A, B and C domains of Protein A, wherein at least one Gly residue in the amino acid sequence is replaced with an amino acid other than Ala, and the protein has a lower affinity for an Fab region of an immunoglobulin than a protein including an amino acid sequence in which the Gly residue is replaced with Ala. Also, the present invention is to provide the protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, which has improved chemical stability in an alkaline condition compared to the corresponding domain.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
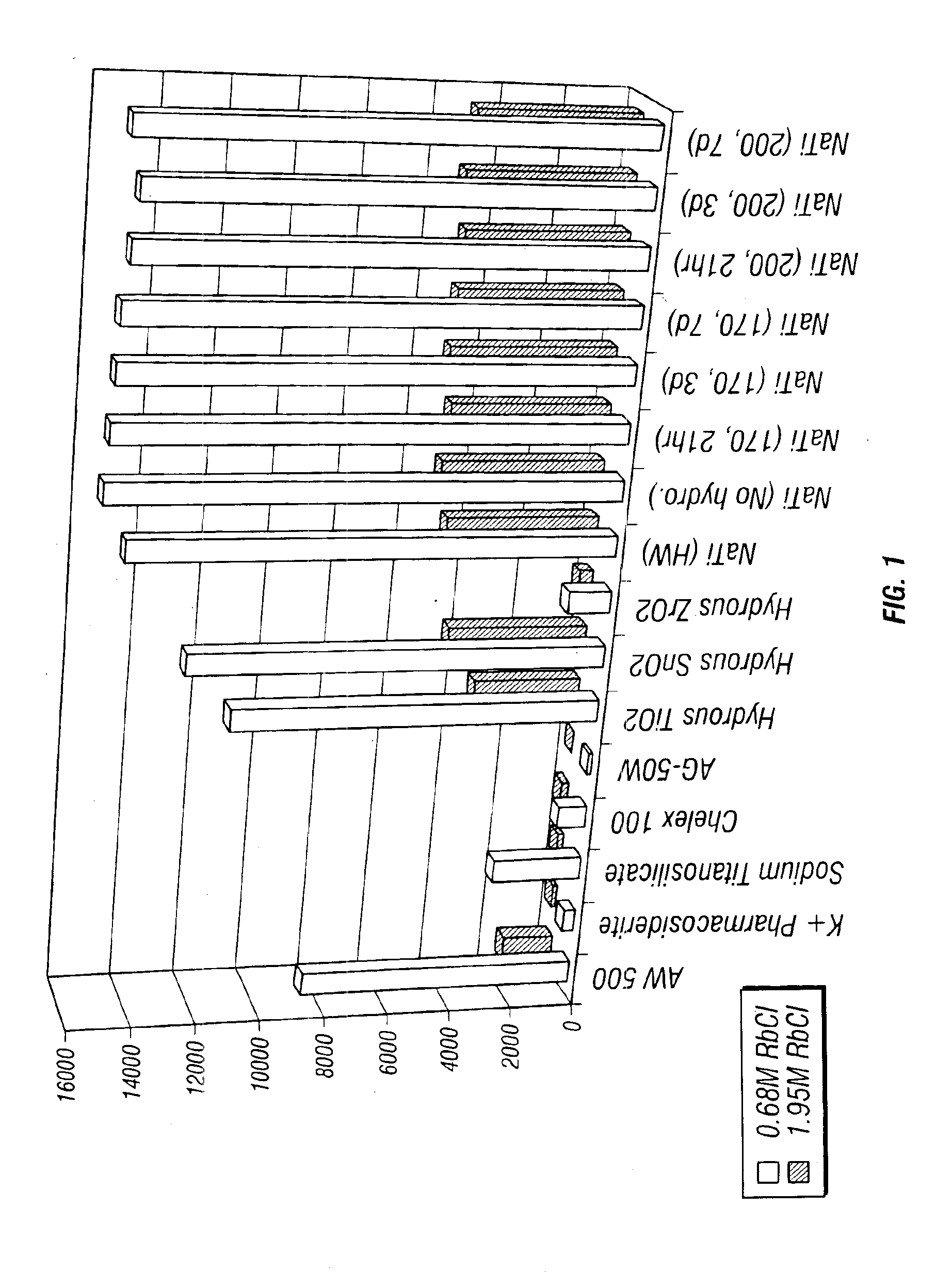
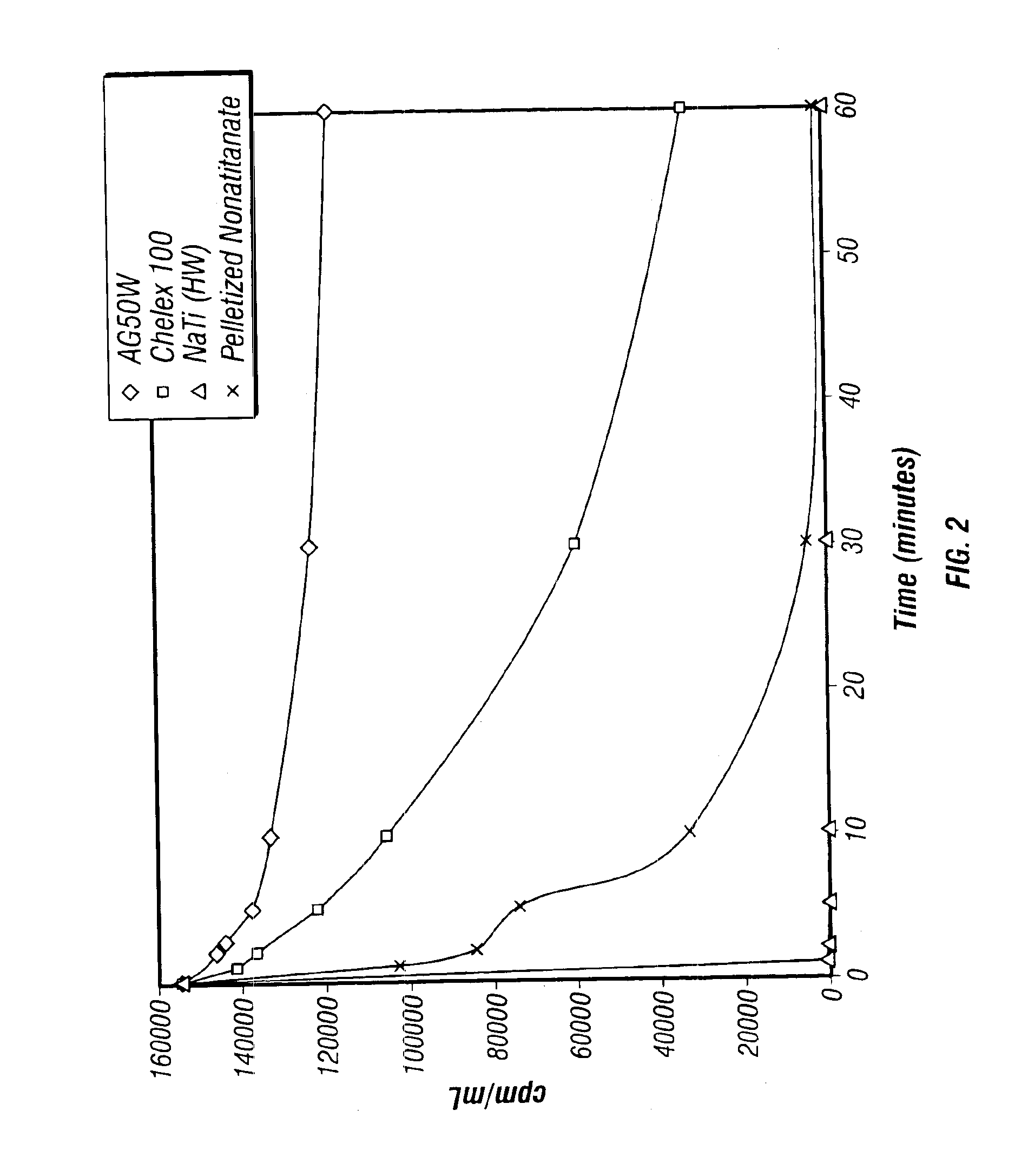
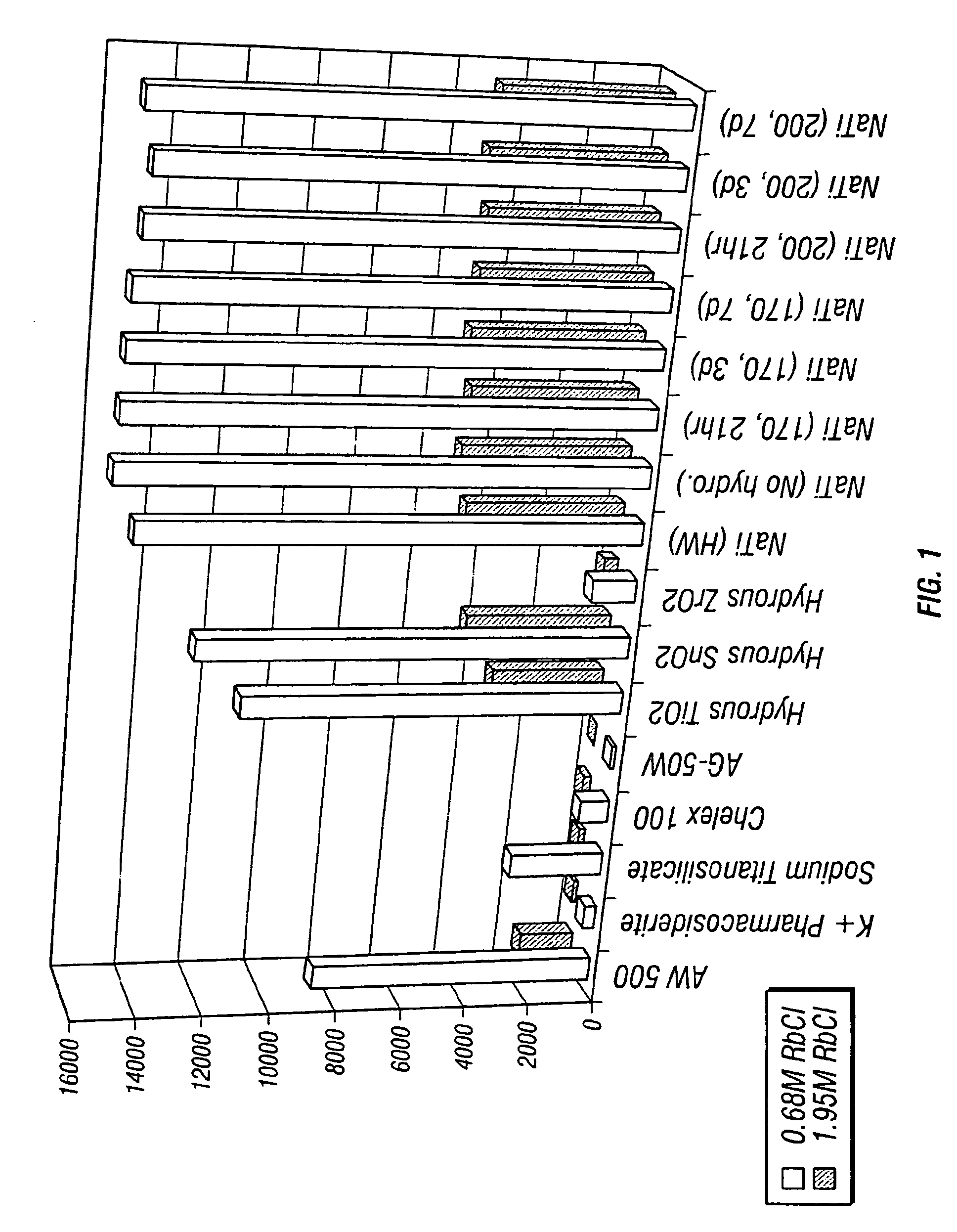
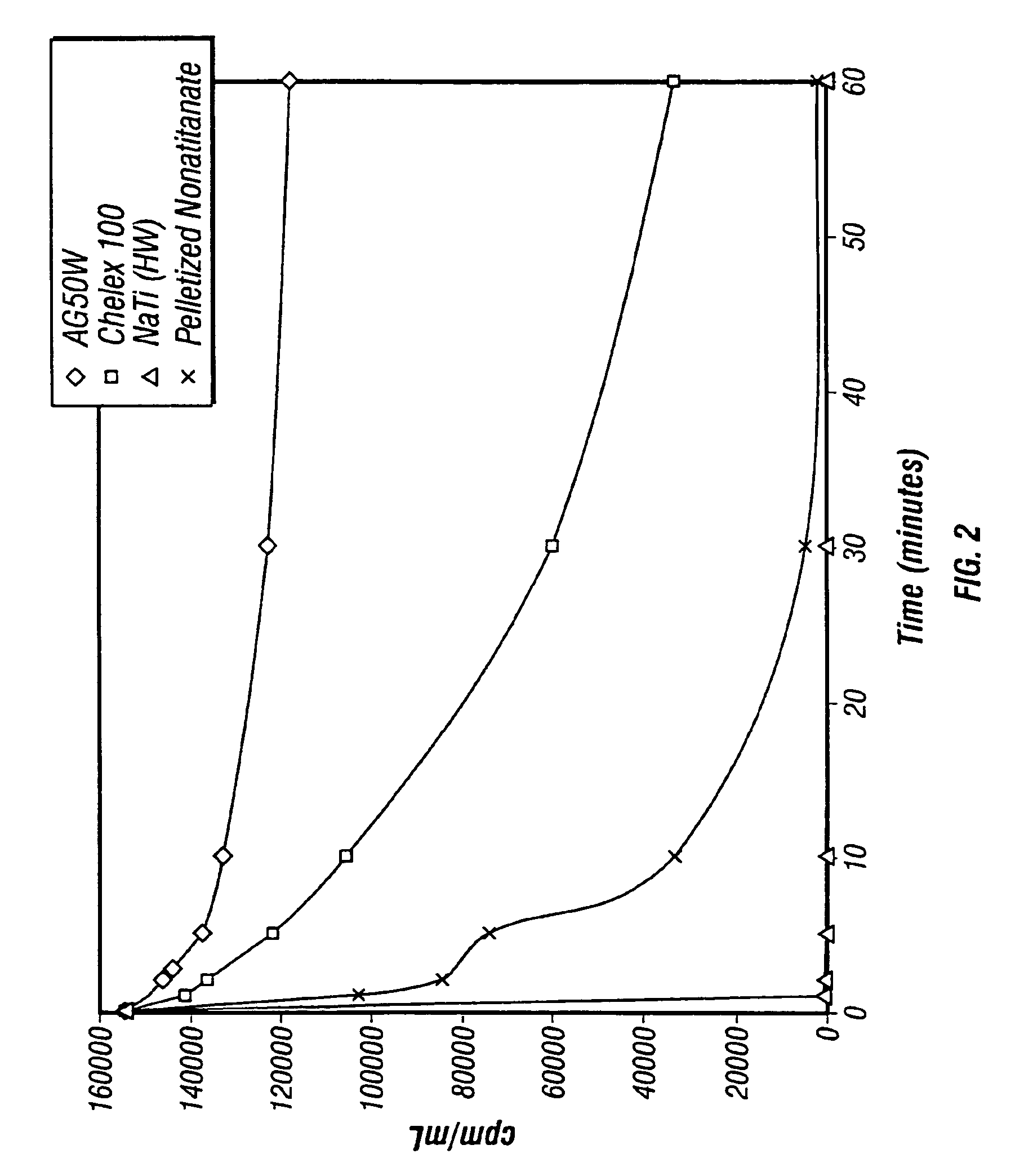
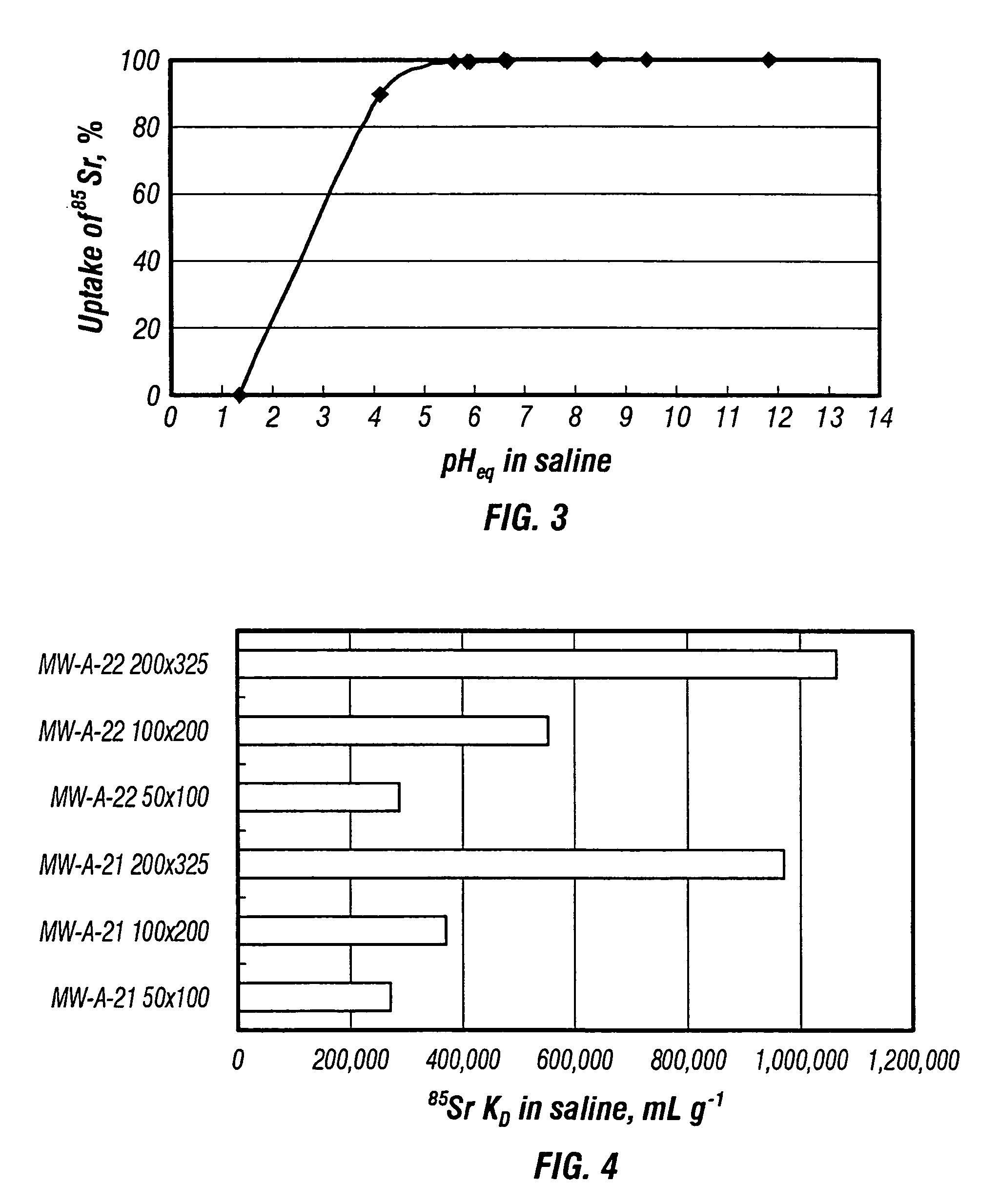
Rubidlum-82 generator based on sodium nonatitanate support, and improved separation methods for the recovery of strontium-82 from irradiated targets
InactiveUS6908598B2Effective recoveryOther chemical processesTransuranic element compoundsLow affinityRubidium
Sodium nonatitanate compositions, a method using the composition for recovery of 82Sr from irradiated targets, and a method using the composition for generating 82Rb. The sodium nonatitanate materials of the invention are highly selective at separating strontium from solutions derived from the dissolution of irradiated target materials, thus reducing target processing times. The compositions also have a very low affinity for rubidium, making it an ideal material for use as a 82Rb generator. Sodium nonatitanate materials of this type both improve the recovery of 82Sr and provide a safer, more effective 82Rb generator system.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS20090181022A1Reduced activityModulating biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Rubidium-82 generator based on sodium nonatitanate support, and improved separation methods for the recovery of strontium-82 from irradiated targets
InactiveUS7476377B2Effective recoveryTransuranic element compoundsOther chemical processesLow affinityRubidium
Sodium nonatitanate compositions, a method using the composition for recovery of 82Sr from irradiated targets, and a method using the composition for generating 82Rb. The sodium nonatitanate materials of the invention are highly selective at separating strontium from solutions derived from the dissolution of irradiated target materials, thus reducing target processing times. The compositions also have a very low affinity for rubidium, making it an ideal material for use as a 82Rb generator. Sodium nonatitanate materials of this type both improve the recovery of 82Sr and provide a safer, more effective 82Rb generator system.
Owner:LYNNTECH
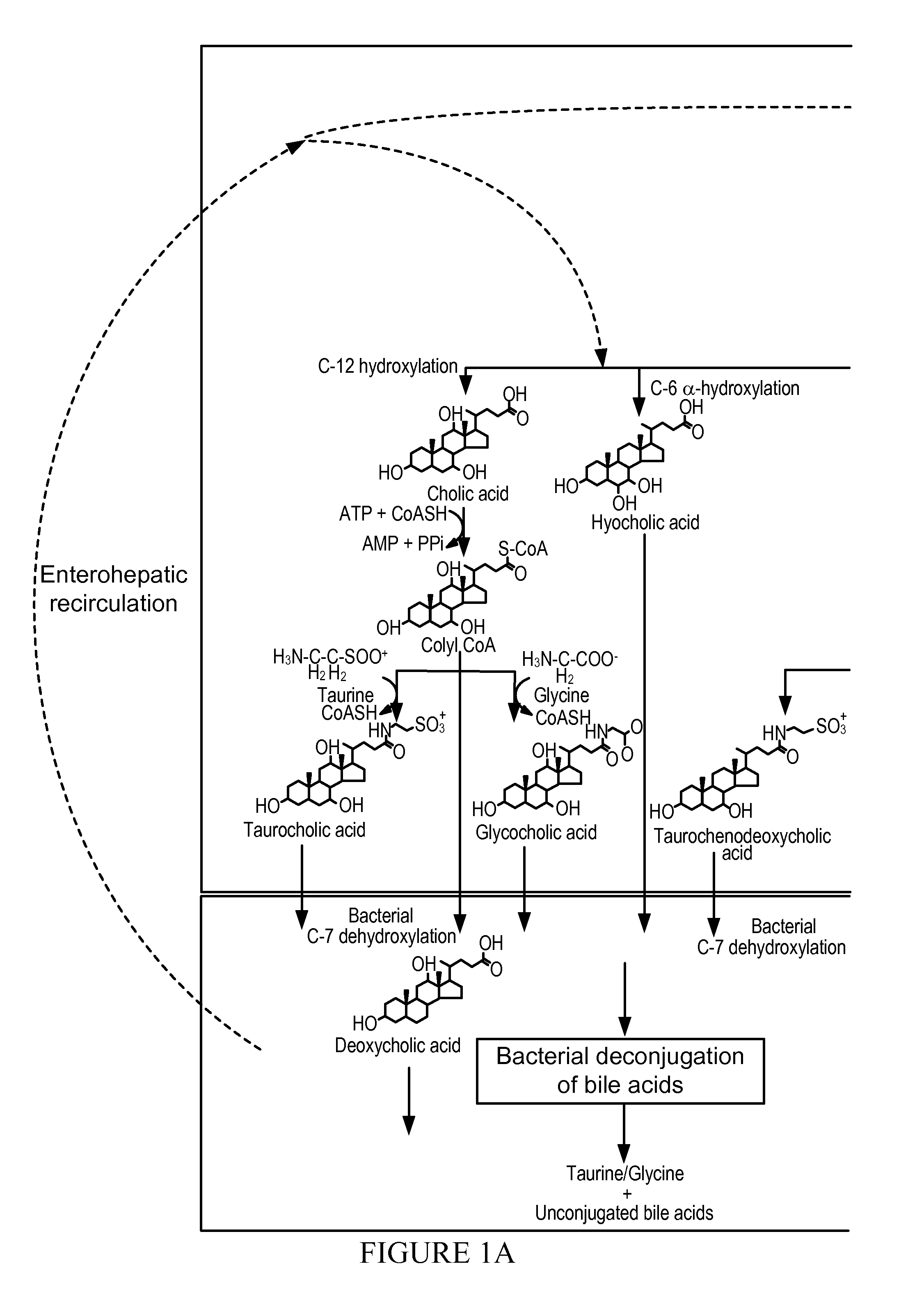
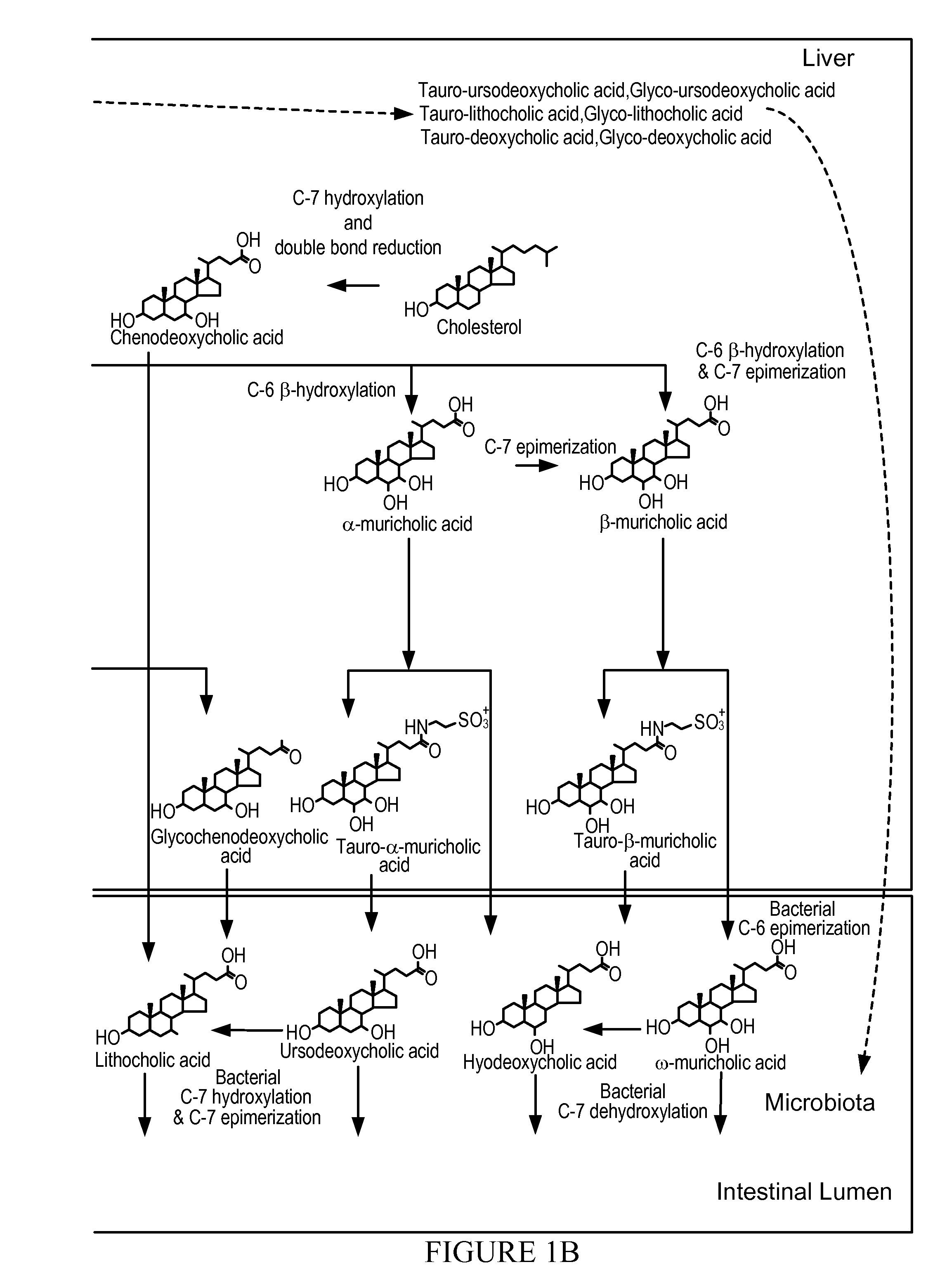
Treatment of Obesity or Diabetes with Bile Acid Sequestrants
InactiveUS20110152204A1Enhances enteroendocrine peptide secretionReduction in blood levelBiocideMetabolism disorderLow affinityDiabetes mellitus
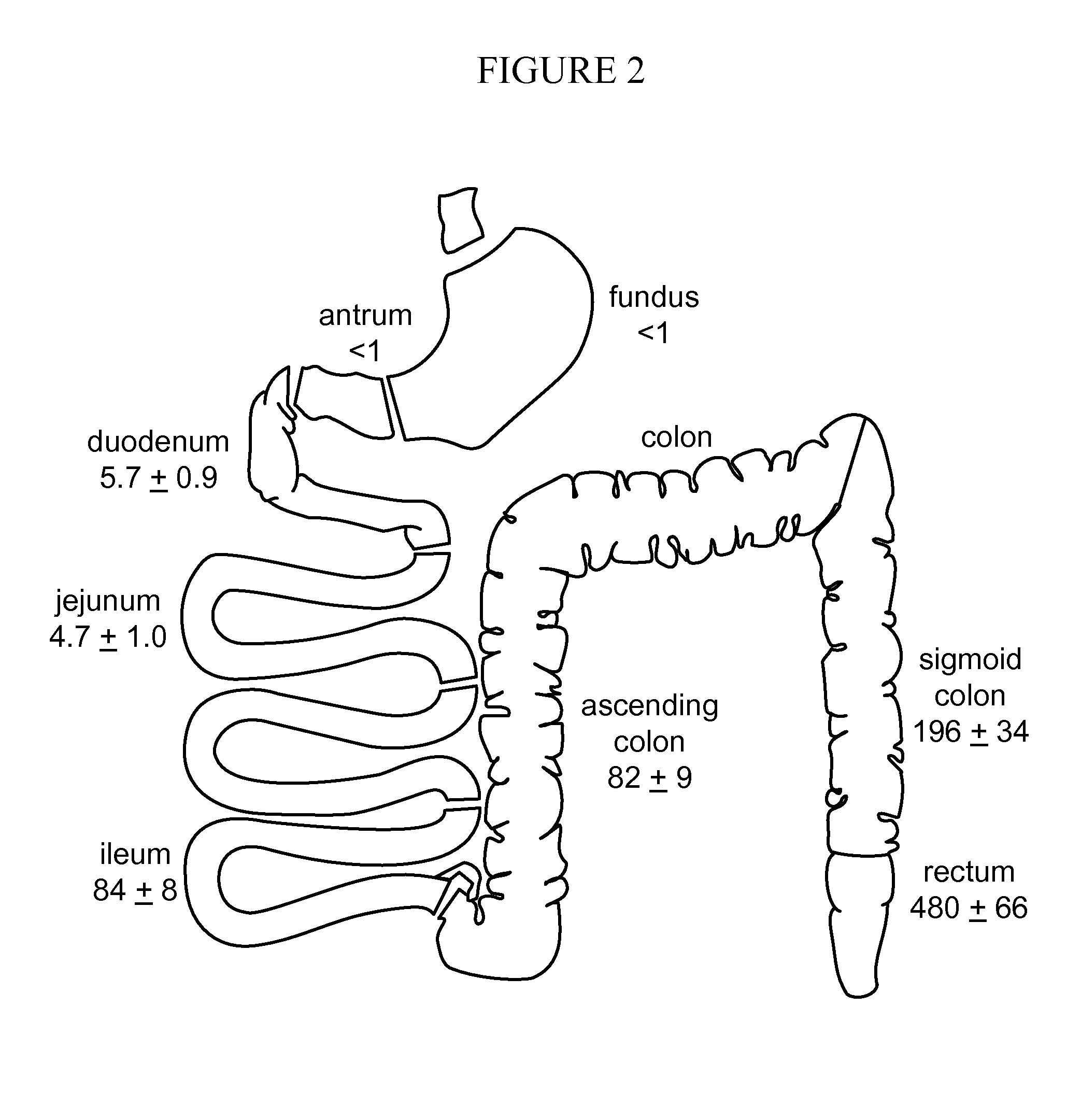
Provided herein are methods of treating obesity and diabetes with labile bile acid sequestrants. An effective amount of a labile bile acid sequestrant may be orally administered to an obese or diabetic individual. A labile bile acid sequestrant provided herein may have a low affinity in the colon or rectum of a human for at least one bile acid or bile acid mimic that stimulates L-cells. A labile bile acid sequestrant may be a non-systemic labile bile acid sequestrant.
Owner:SATIOGEN PHARMA
Bispecific nanobodies
InactiveUS20160251440A1Avoid infectionEasy to neutralizeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntineoplastic agentsLow affinityCancer cell
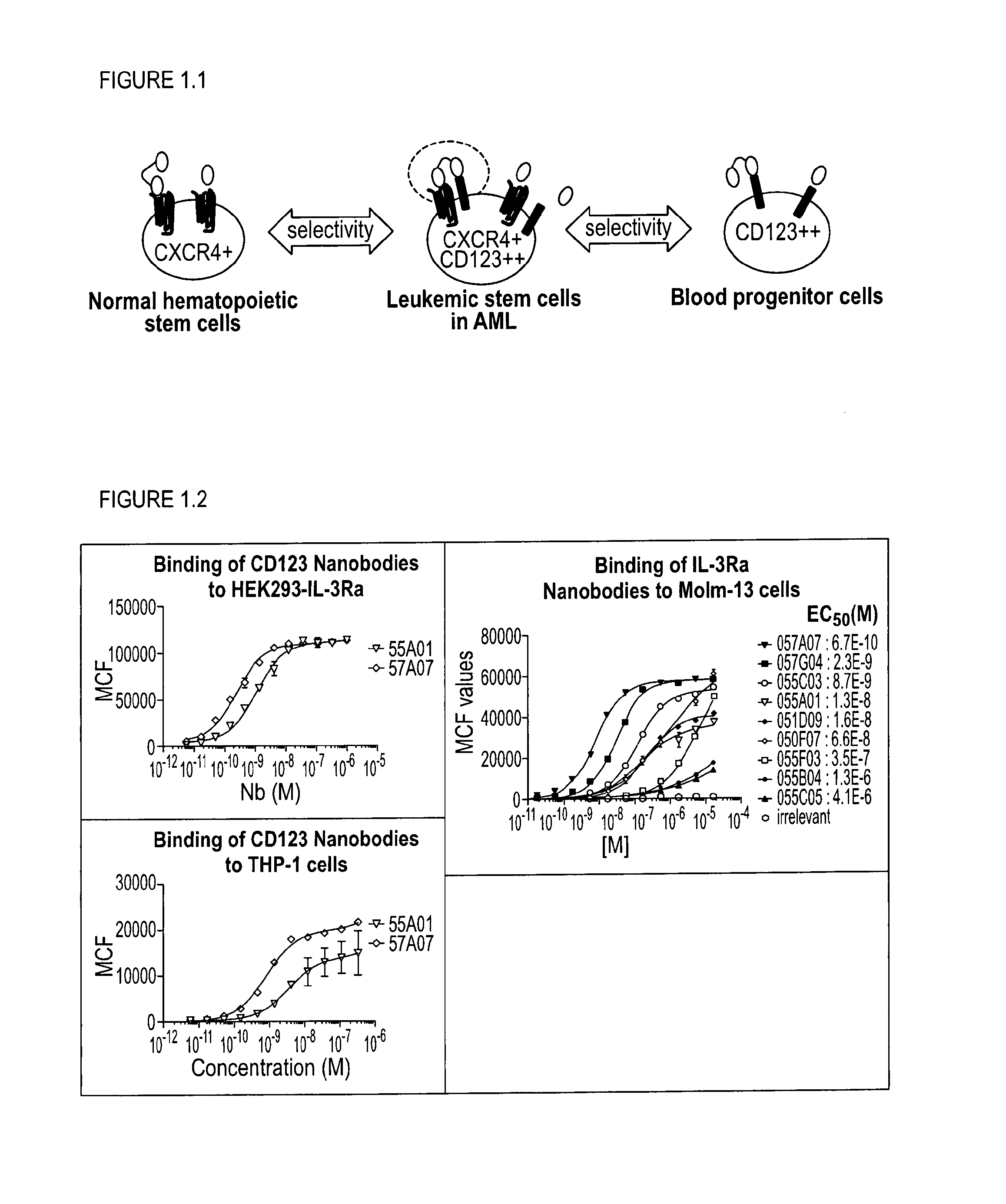
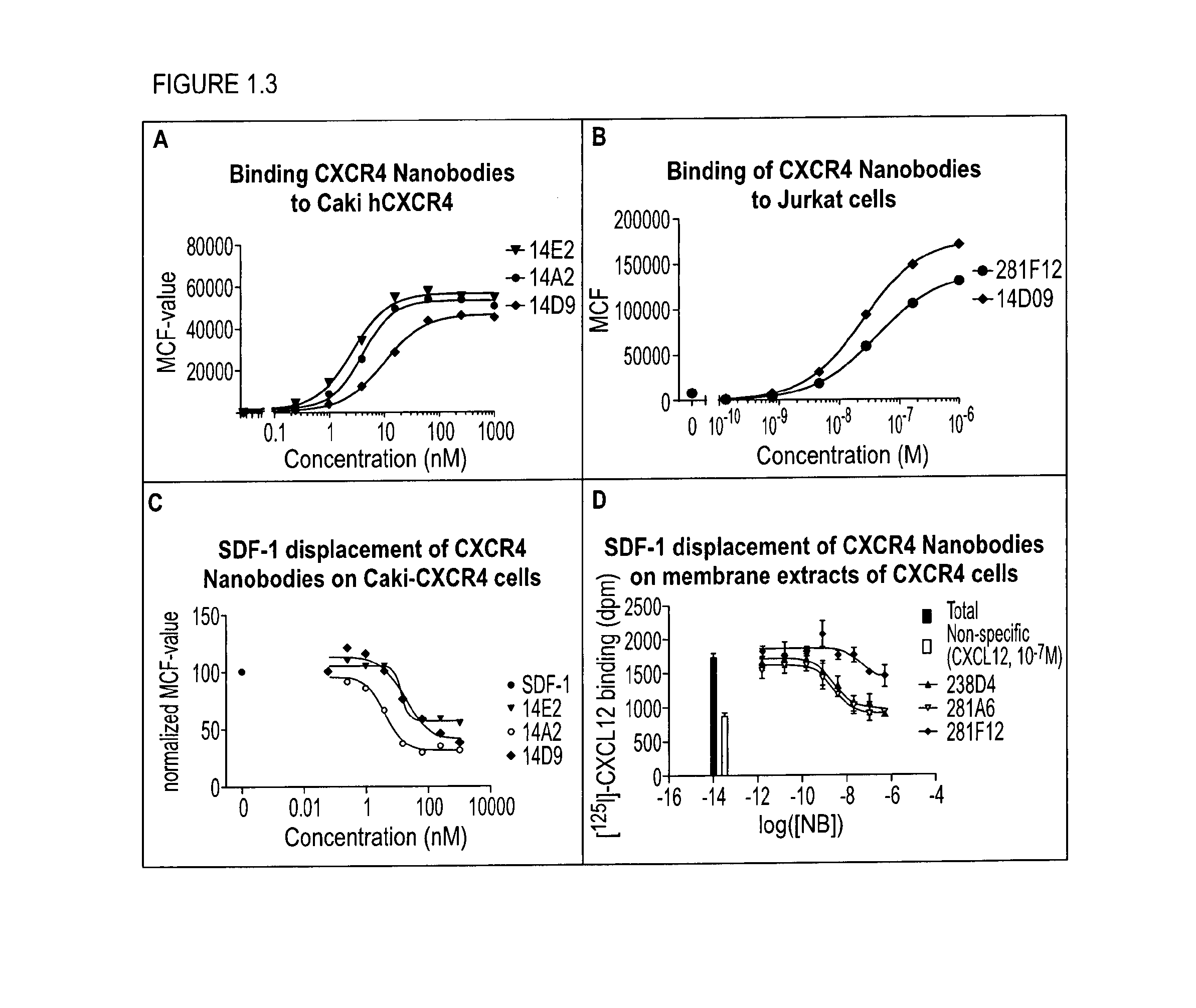
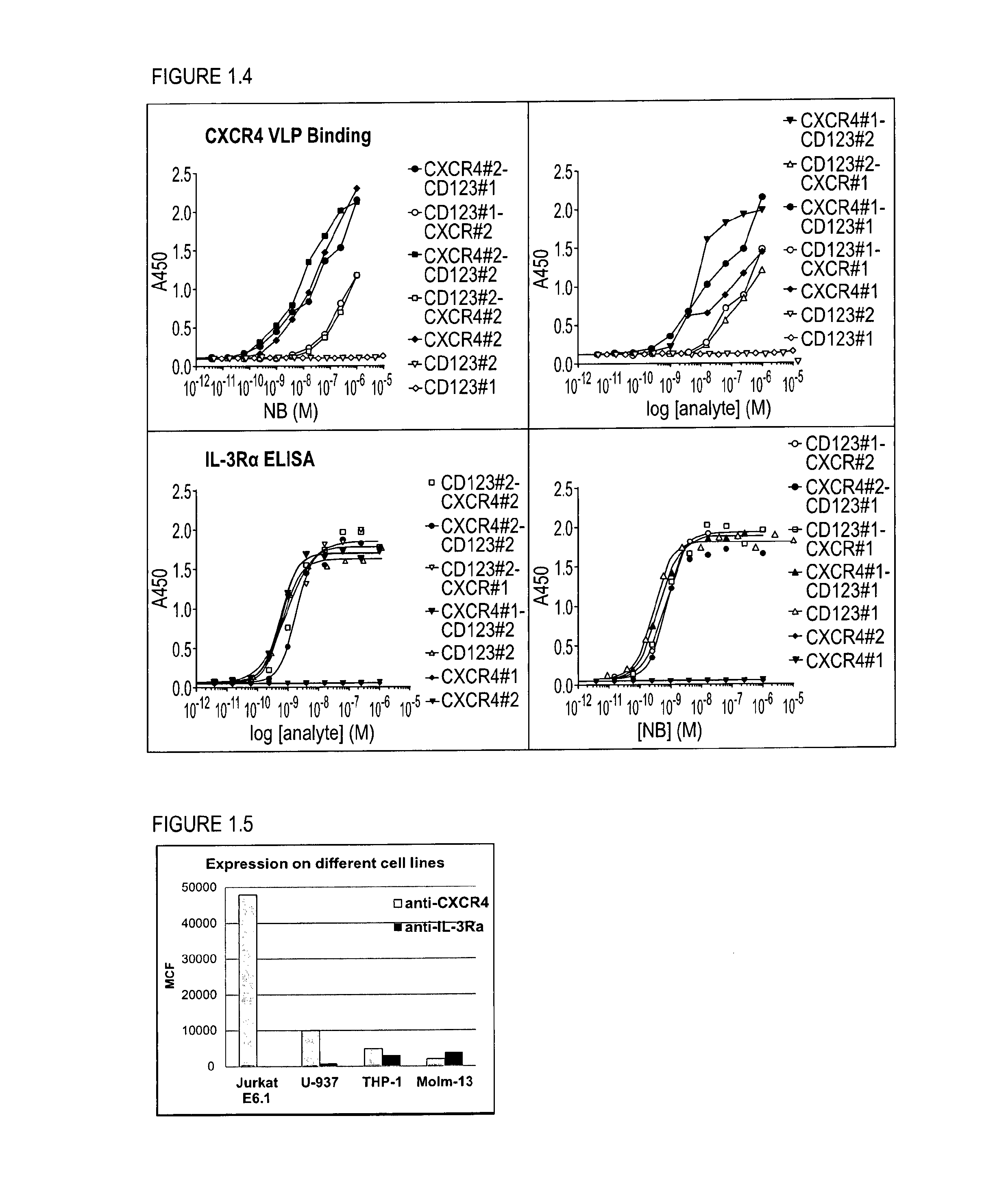
The present disclosure relates to bispecific polypeptides comprising a first and a second immunoglobulin single variable domain (ISV), wherein said first ISV binds to a first target on the surface of a cancer cell with a low affinity and, when bound inhibits a function of said first target, and a said second ISV binds to a second target on the surface of said cell with a high affinity and wherein said first target is different from said second target. The present invention further discloses methods for identifying and making the same.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
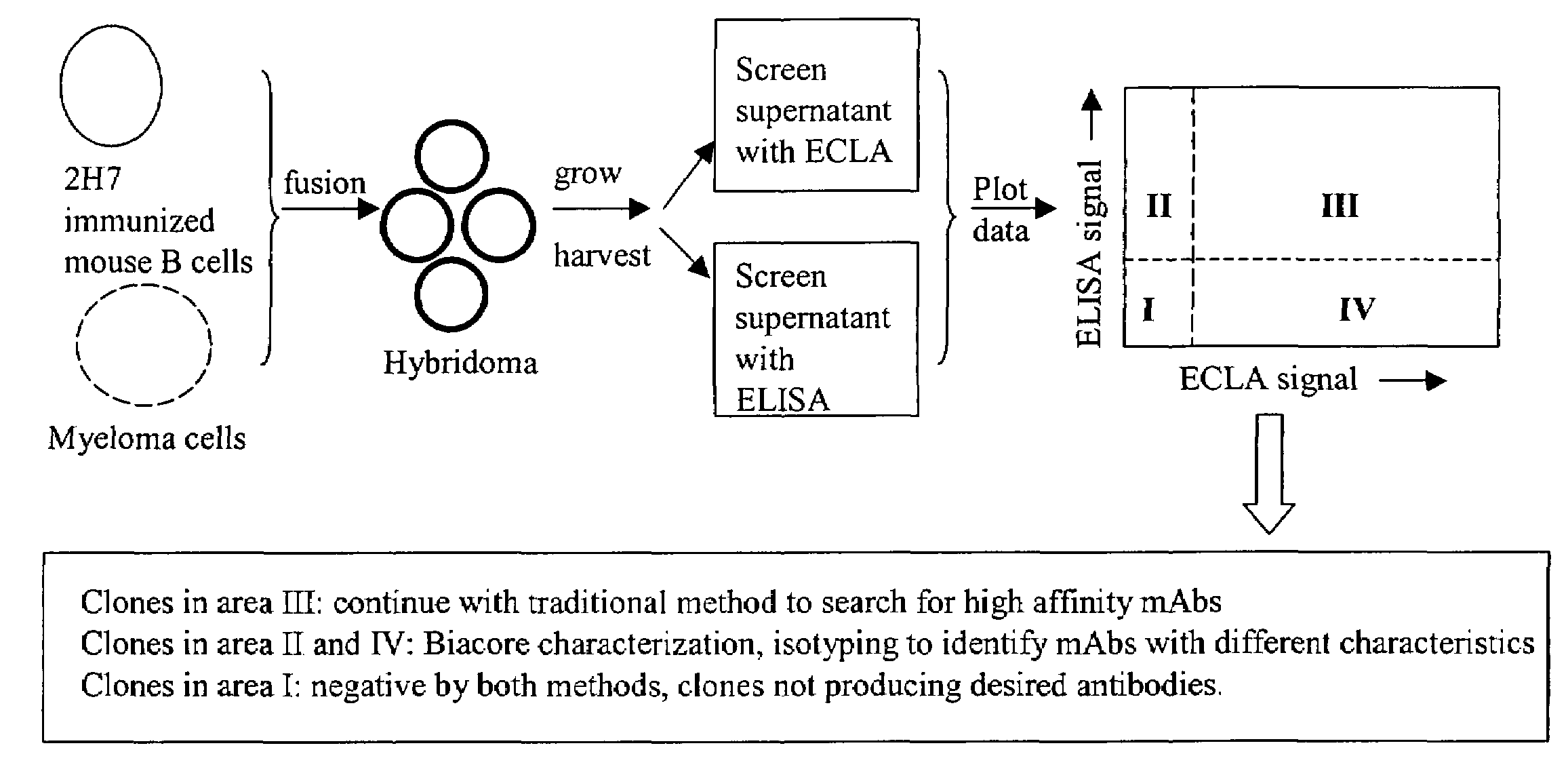
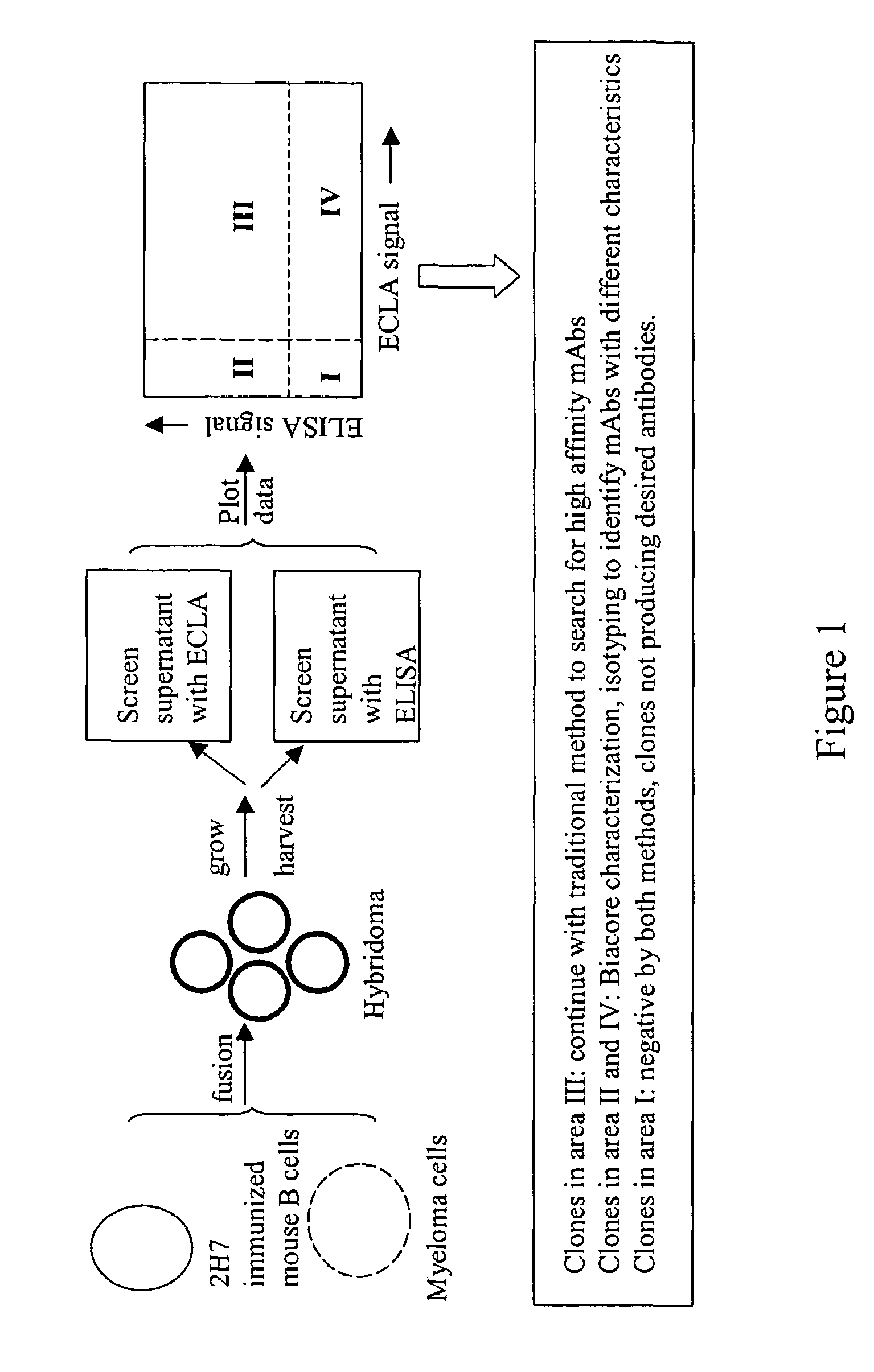
Cross-screening system and methods for detecting a molecule having binding affinity for a target molecule
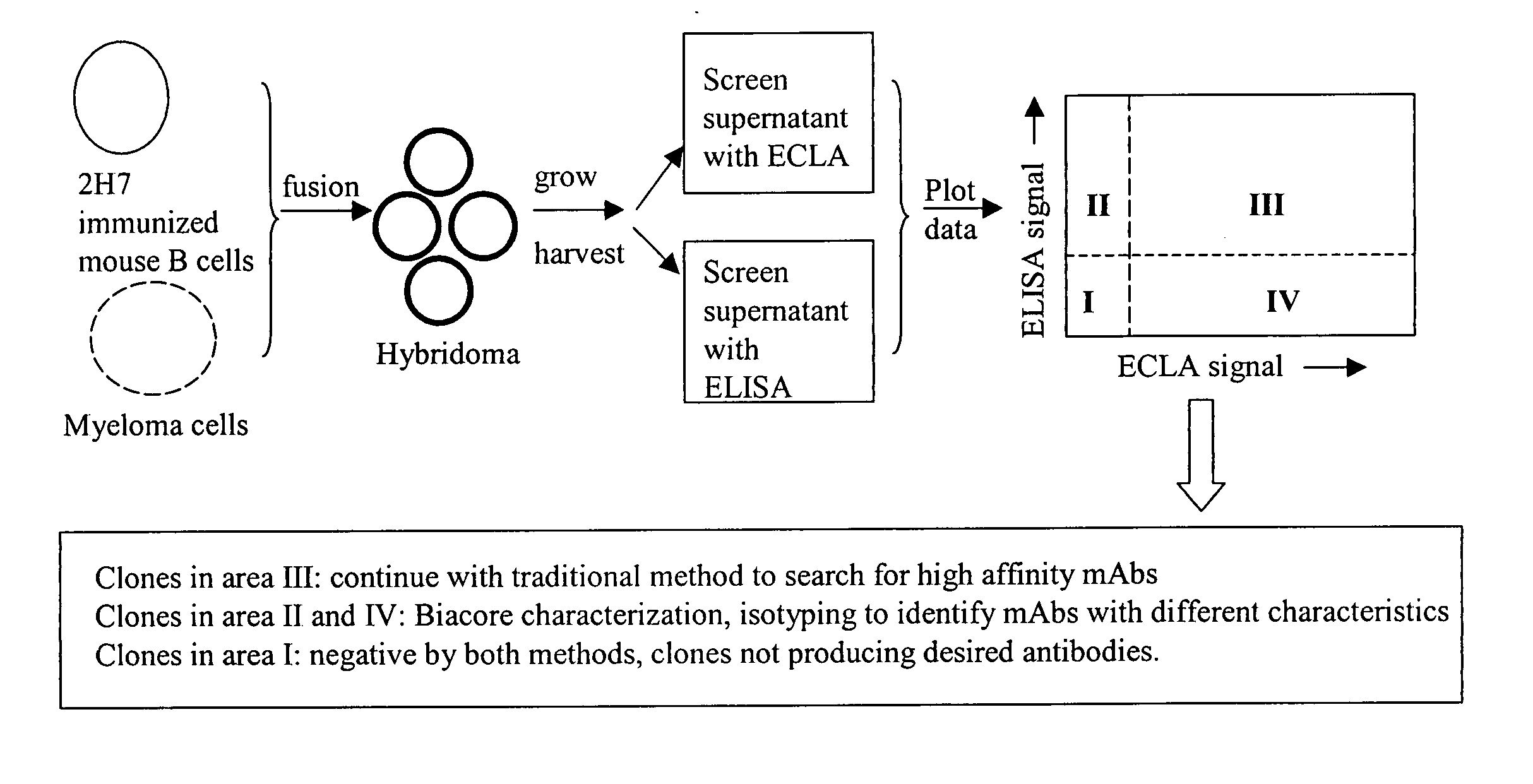
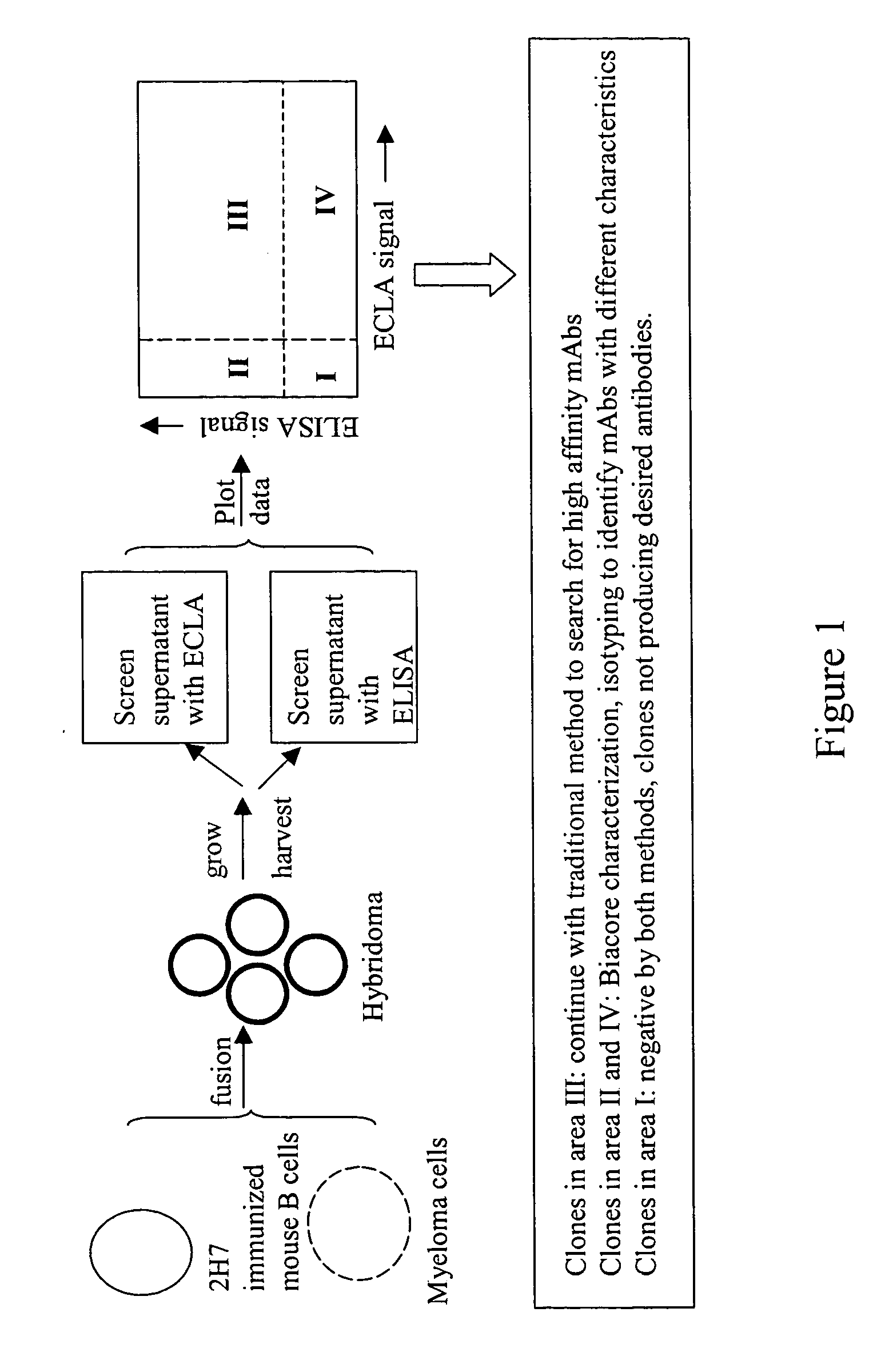
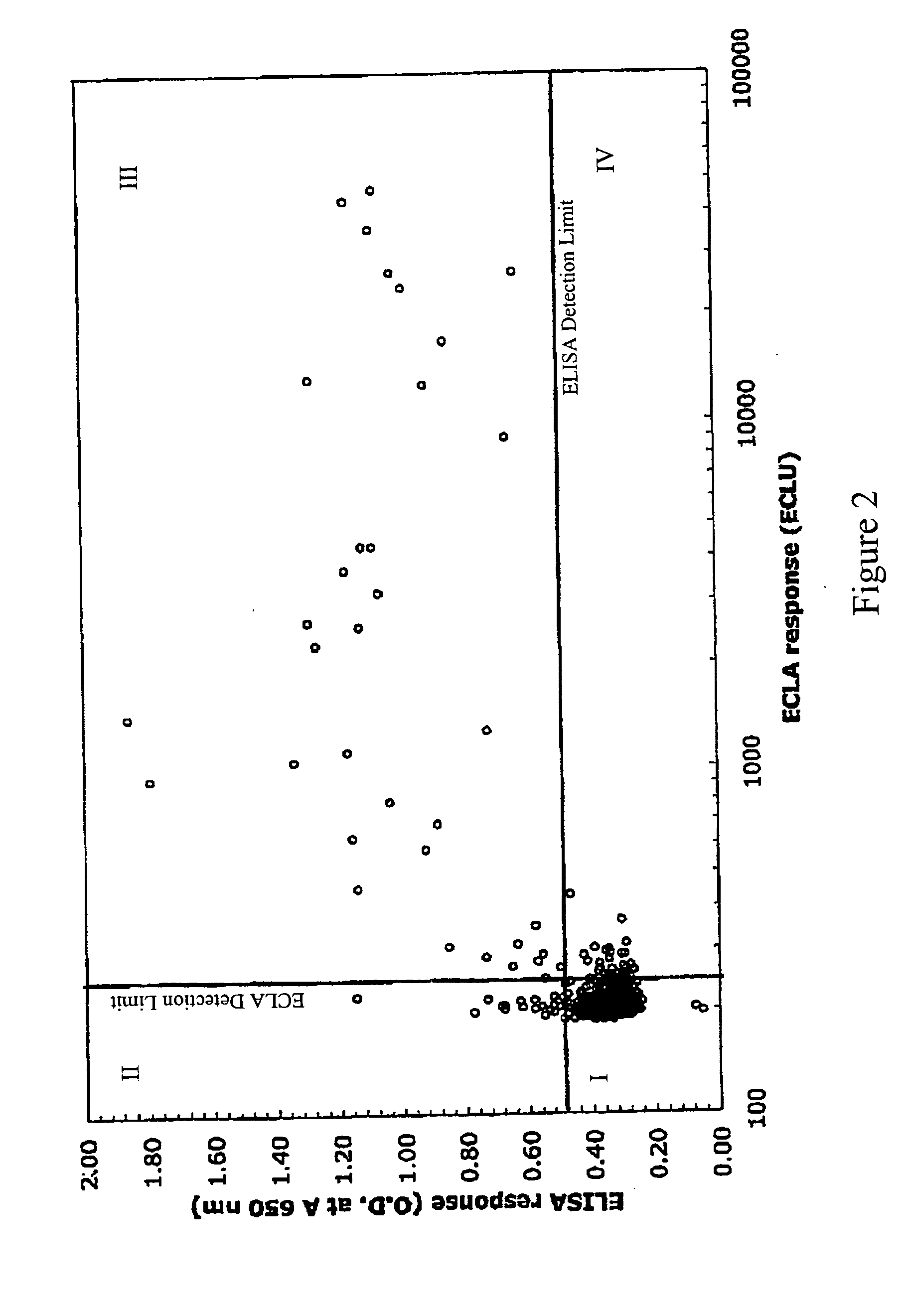
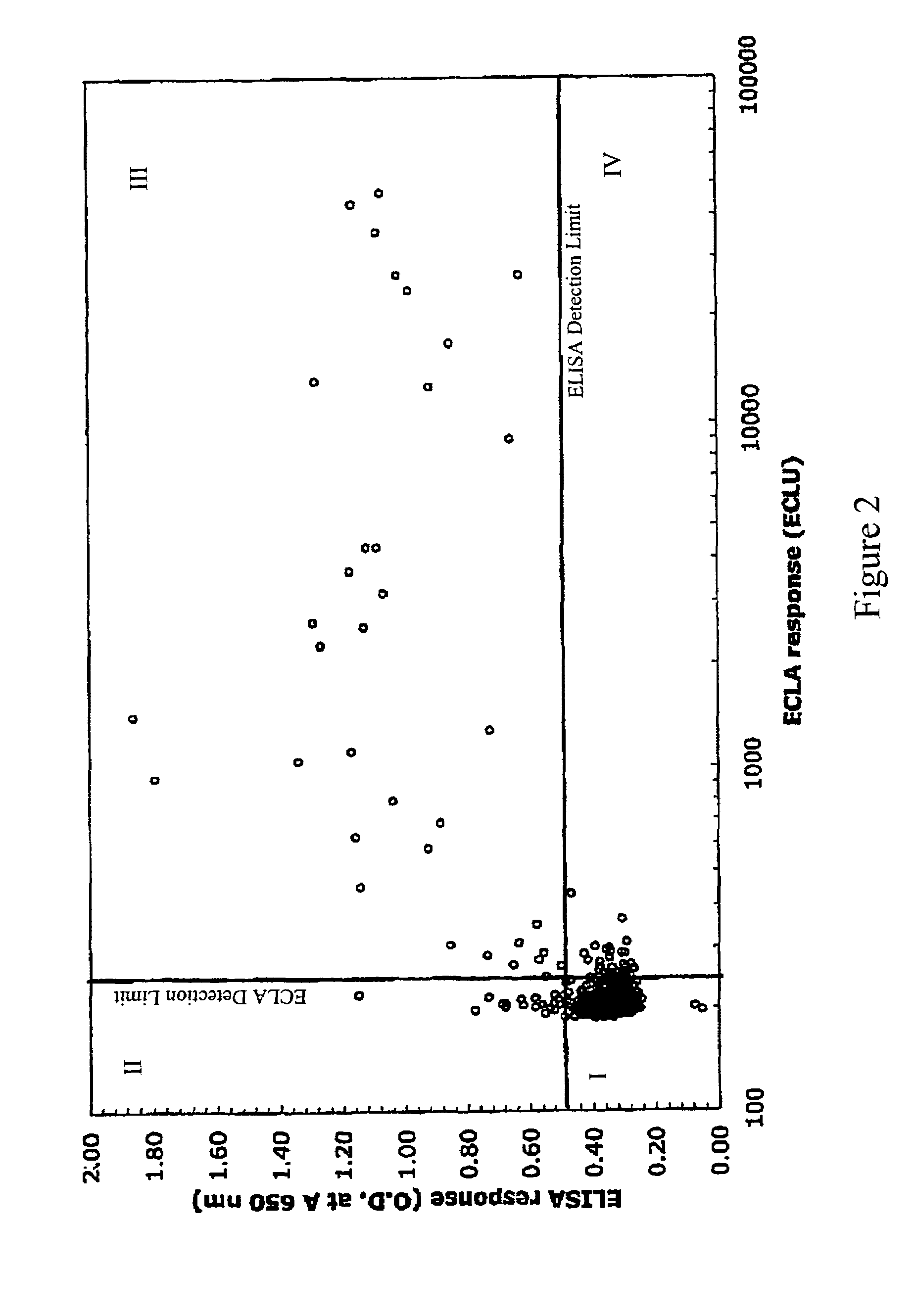
ActiveUS20050255527A1Reduce concentrationSafety and efficacyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLow affinityElectrochemiluminescence
The invention is directed to a cross-screening system and methods of the invention utilizing a combination of an immunoassay (IA) and electrochemiluminescence assay (ECLA) to identify molecules that have binding affinities for a target molecule. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention can detect molecules that have binding affinities for the target molecule below the detection limits of the individual immunoassay or ECLA. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful for generating a pool of candidate analyte molecules enriched in a desired characteristic, such as low binding affinity for a target molecule. Low affinity antibodies identified by the cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful, for example, in assessing the safety and efficacy of biological therapeutics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method and apparatus for the selective removal of specific components from smoke condensates
InactiveUS6119699AHigh capacity bonded phaseEasy to useTobacco treatmentCigar manufactureLow affinitySmoke composition
A smoking article capable of delivering a regulated smoke composition to a smoker, includes: a) a combustible filler wrapped in a combustible sheath; and b) at least one affinity chromatographic filter unit designed to preferentially remove specific targeted components from the smoke disposed within the sheath adjacent the combustible filler. The filter unit includes a mass of silica or resin particles having chemically bonded to their surfaces functional groups which exhibit preferential affinity for the targeted components and which reversibly bind the targeted components to elute components having a lower affinity than a previously bound component.
Owner:SUNG MICHAEL T
Protein capable of binding specifically to immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS20130096276A1Excellent antibody dissociation propertyEasy to separateBacteriaSugar derivativesLow affinityAmino acid substitution
An object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having better antibody dissociation properties in the acidic condition compared with known engineered Protein A ligands. The present invention provides a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, including an amino acid sequence obtained by introducing, into an amino acid sequence derived from any of E, D, A, B and C domains of Protein A, at least one amino acid substitution at any one or more of amino acid residues corresponding to positions 31 to 37 of the A, B and C domains (positions 29 to 35 of the E domain, positions 34 to 40 of the D domain), which are conserved in all the domains, the protein having a lower affinity for an Fab region of an immunoglobulin than a protein having the amino acid sequence before introduction of the substitution.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
POLYMERIC IMMUNOGLOBULIN FUSION PROTEINS THAT TARGET LOW AFFINITY FCyRECEPTORS
InactiveUS20090117133A1Small size range and conformationPromote generationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityNACHT domain
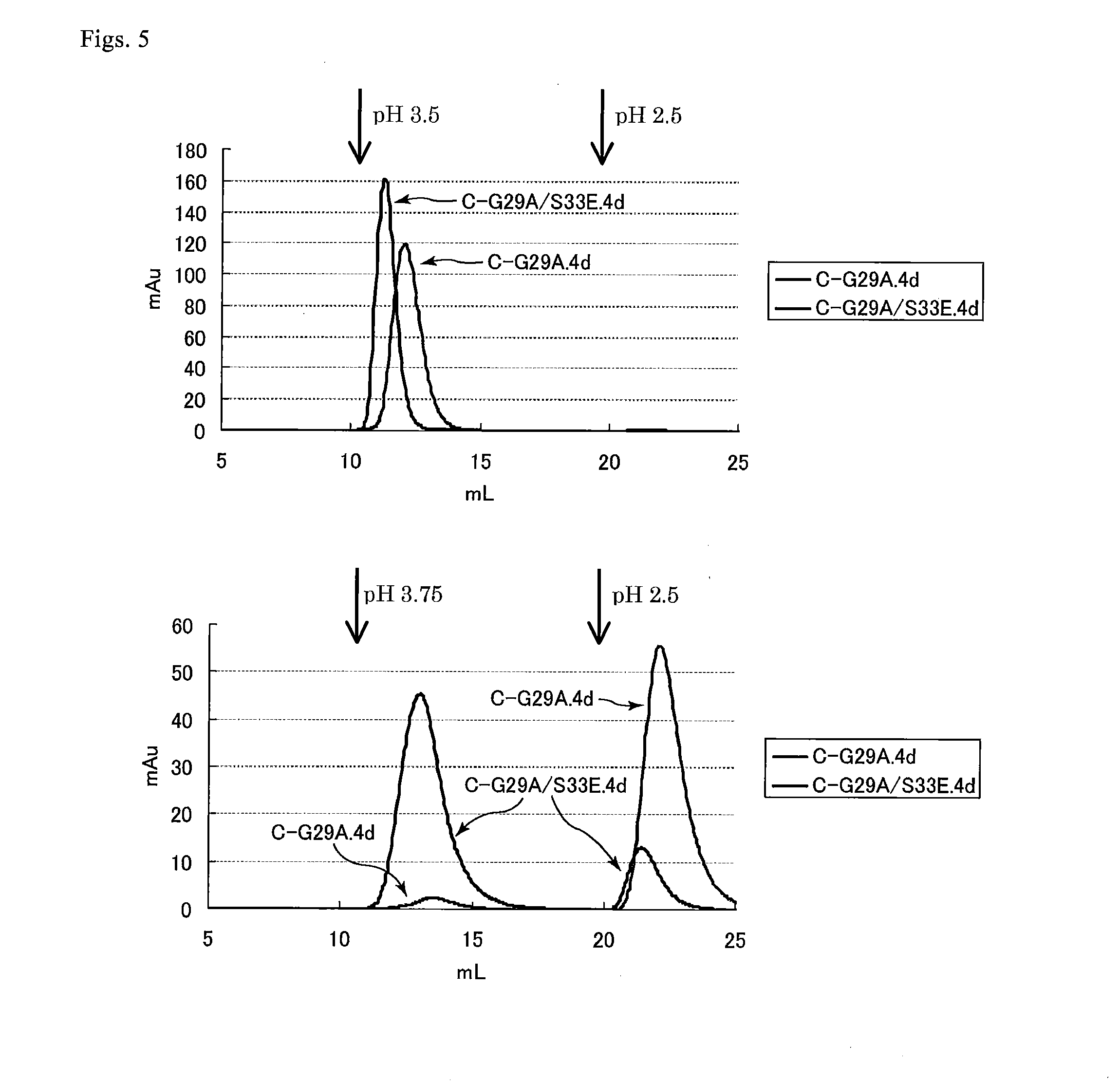
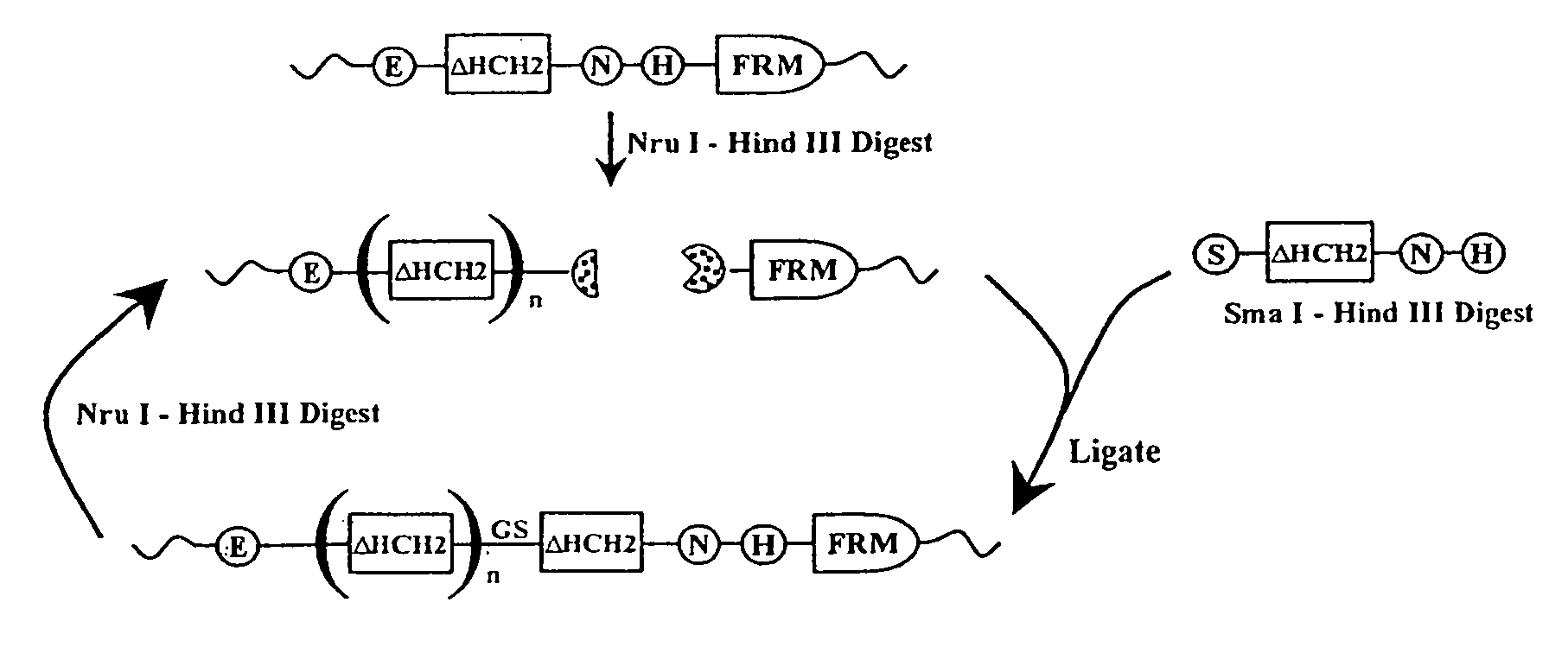
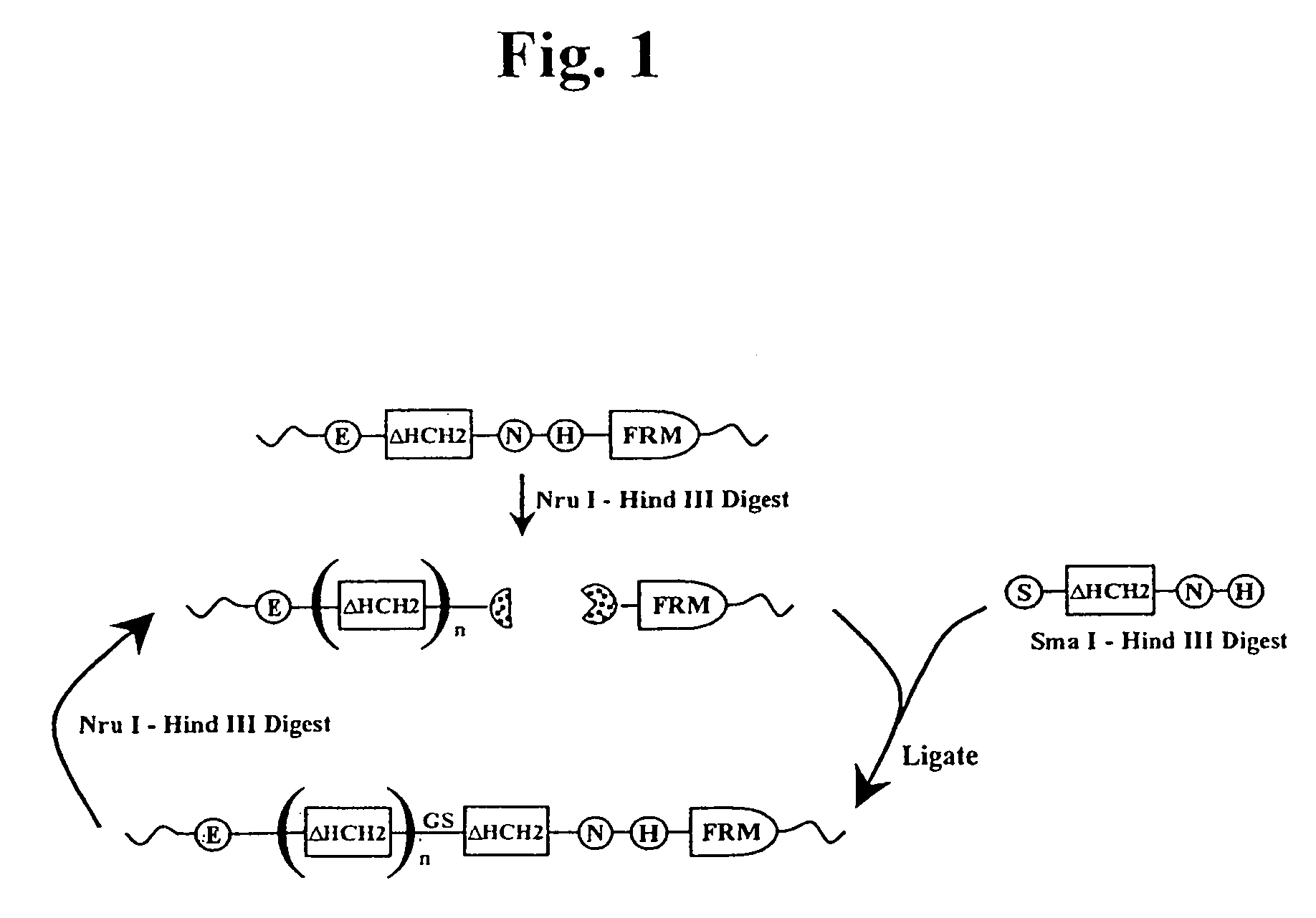
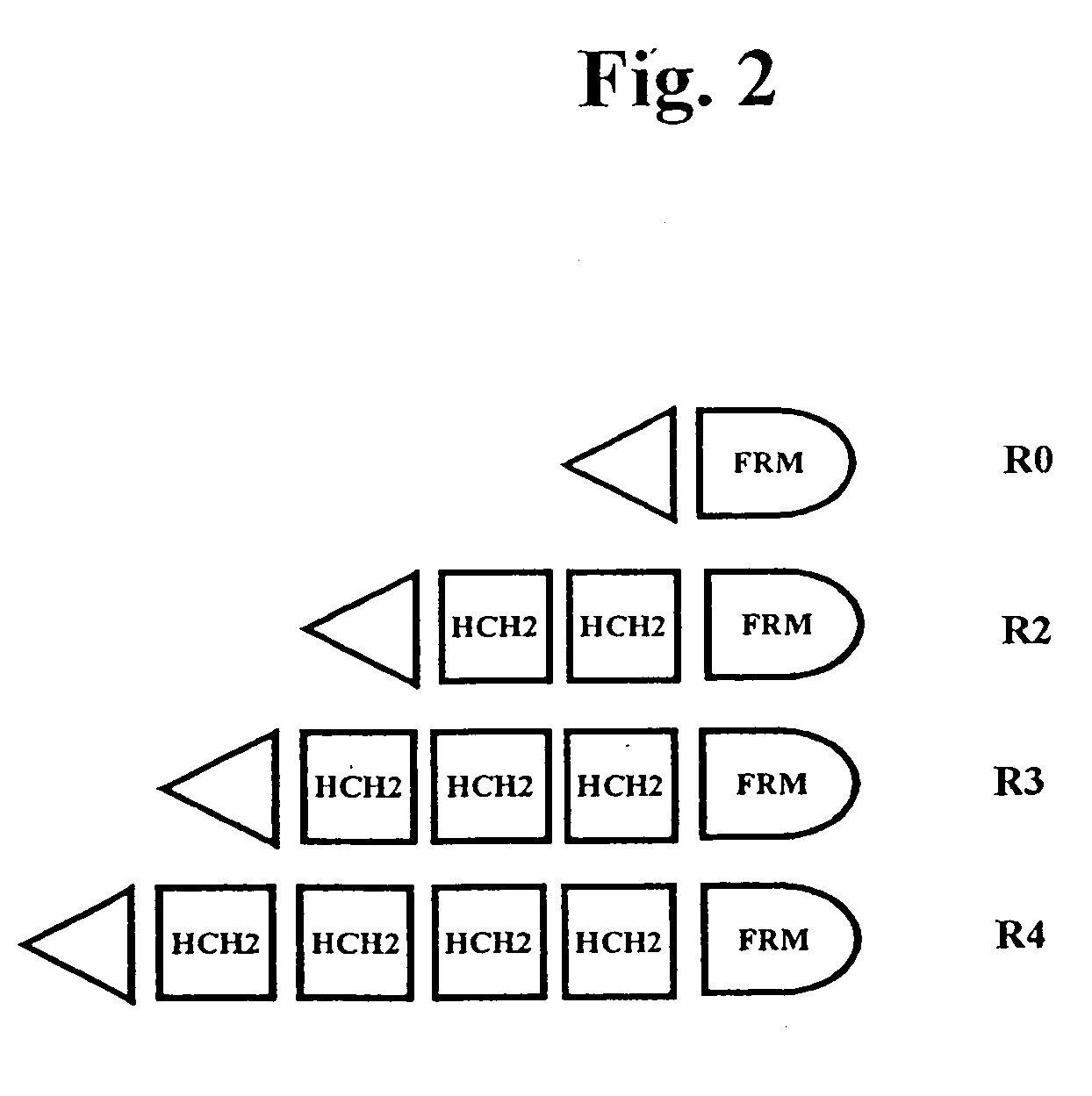
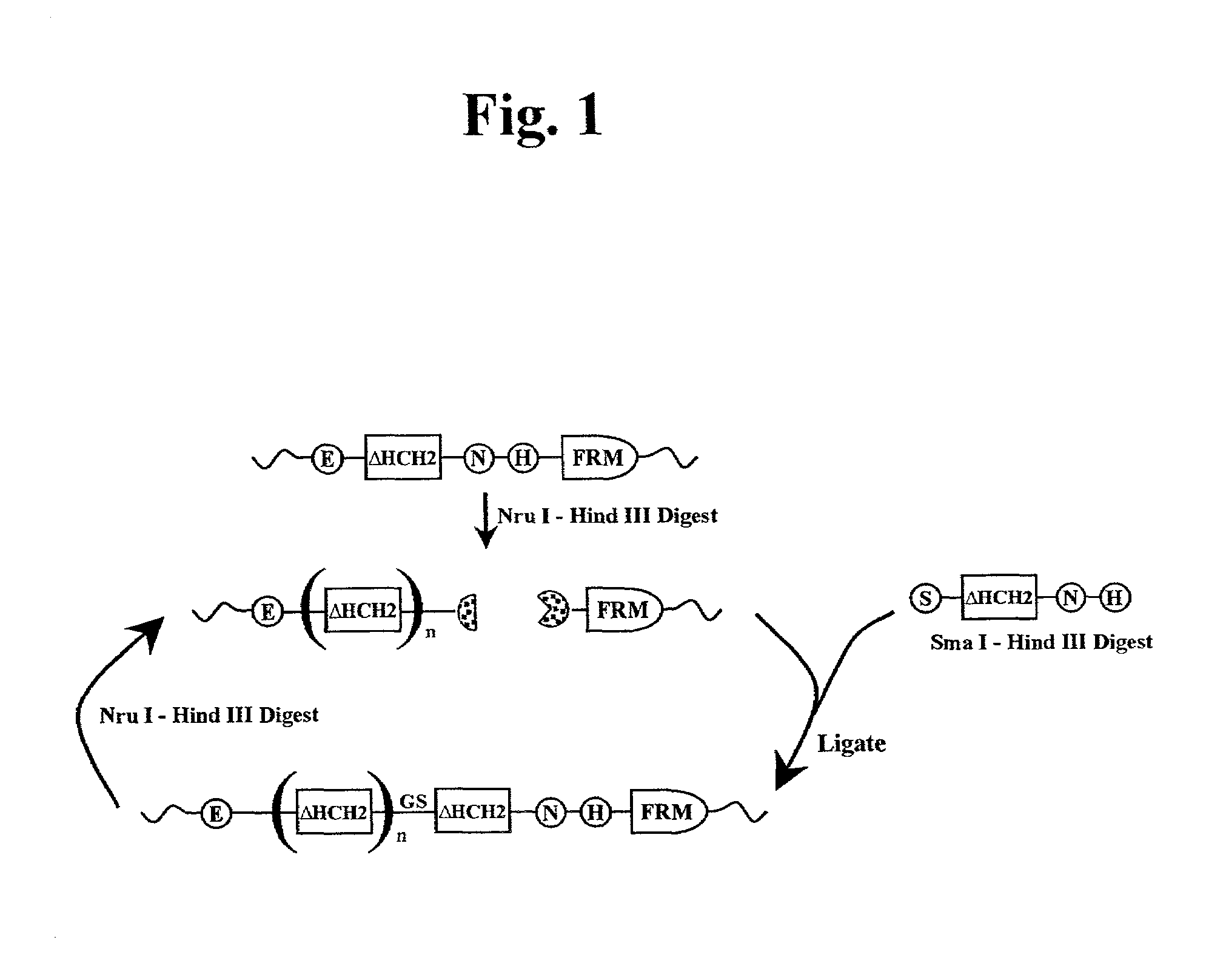
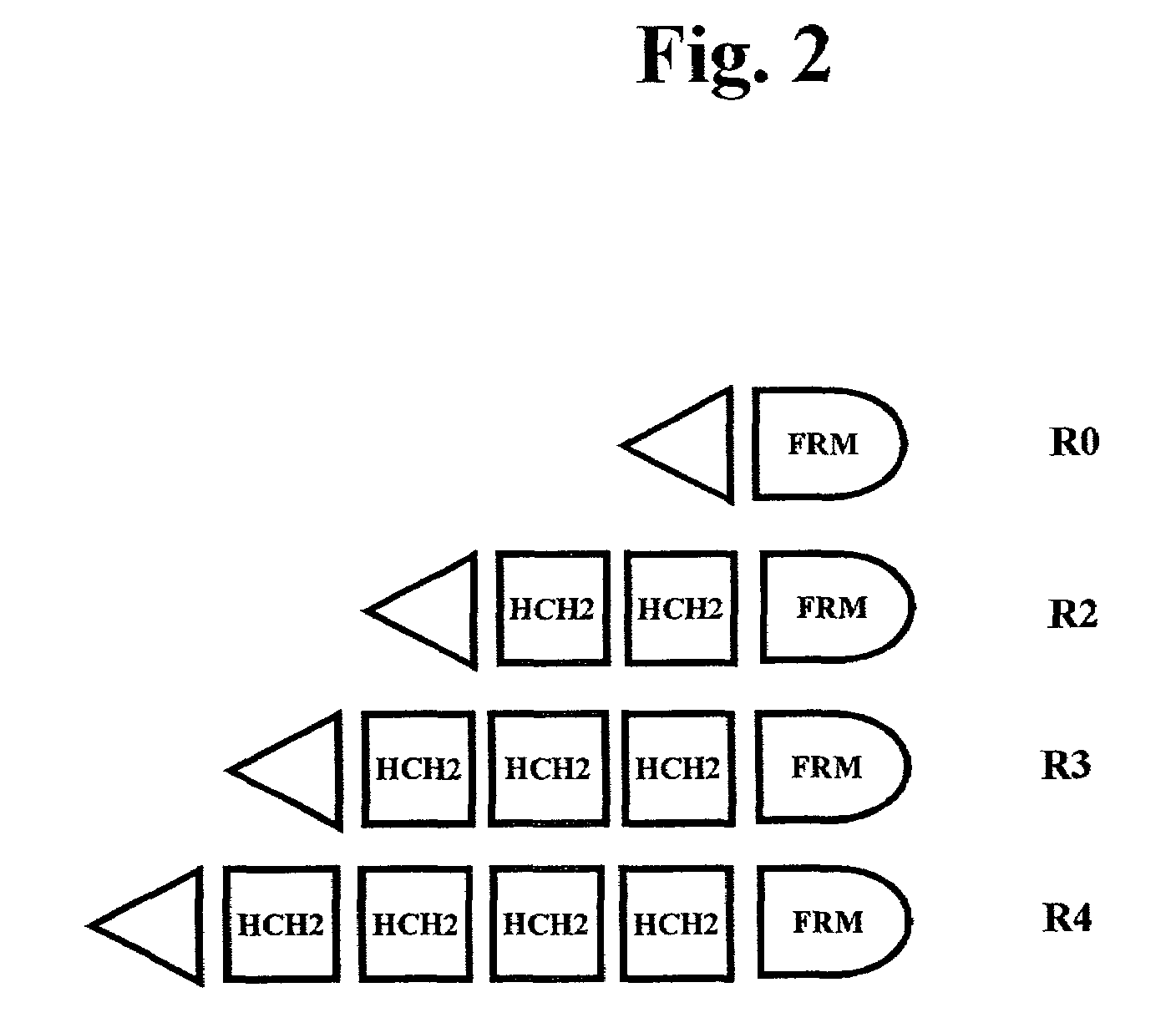
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fission proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS8124085B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Polymeric immunoglobulin fusion proteins that target low-affinity Fcγreceptors
ActiveUS7511121B2Improve effectivenessModerating disease severitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFusion Protein ExpressionLow affinity
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fusion proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
Alpha-synuclein antibodies and uses thereof
The invention describes antibodies having a high affinity for aggregated forms of α-synuclein and a low affinity for monomeric forms of α-synuclein. The antibodies are useful in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Bispecific recombinant protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108864290AImprove securityAvoid killingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLow affinityTumor target
The invention discloses bispecific recombinant protein. The bispecific recombinant protein comprises a high-affinity tumor-targeted arm and a low-affinity fusion protein for blocking interaction of CD47 and SIRPalpha, wherein an antibody corresponding to the high-affinity tumor-targeted arm is not combined with the CD47, and the bonding affinity to target antigens on tumor cells is at least 6 times of the bonding affinity of the monomeric fusion protein and dimer corresponding to the low-affinity fusion protein for blocking the interaction of the CD47 and the SIRPalpha to the CD47 on the tumorcells; the low-affinity fusion protein for blocking mutual action of the CD47 and SIRPalpha contains SIRPalpha extracellular truncation. The invention also discloses a nucleic-acid molecule for encoding the recombinant protein and application of the recombinant protein and the nucleic-acid molecule in preparation of medicines for treating tumors. The bispecific recombinant protein disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the bonding abundance of tumor targeting saturation of the recombinant protein with the function of adjusting macrophage is obviously improved by the bispecific recombinant protein, the side effect of the non-tumor targeting is reduced and the application value is large clinically.
Owner:SHANGHAI JMT BIO INC
Oligomers with improved off-target profile
ActiveCN104955950AOff-target binding is not easySugar derivativesActivity regulationLow affinityOligomer
Owner:GUANGDONG MAIJINJIA BIOTECH CO LTD
Making method of organic-inorganic hybrid separating membrane
InactiveCN104415668AInhibition of agglomerationImproved separation propertiesSemi-permeable membranesLow affinityHollow fibre
The invention relates to a making method of an organic-inorganic hybrid separating membrane. Present making methods of organic-inorganic hybrid membranes are characterized in that inorganic particles are directly added into an organic polymer membrane casting liquid, and have the problems of easy agglomeration caking, uneven dispersion and poor membrane making repeatability due to high surface energy of inorganic particles and low affinity with the polymer membrane material. The method comprises the following steps: modifying the surface of the inorganic nanoparticles in order to reduce the surface energy and enhance the compatibility with the polymer membrane material; and mixing the surface modified inorganic nanoparticles with the polymer membrane material, an additive and a solvent to obtain the membrane casting liquid, and making the flat or hollow fiber organic-inorganic hybrid separating membrane through a traditional phase transformation technology. Compared with the prior art, the method significantly inhibits the agglomeration phenomenon of the inorganic nanoparticles, improves the dispersion of the inorganic nanoparticles in the membrane casting liquid, and has better membrane making repeatability. The organic-inorganic hybrid separating membrane made in the invention has good separation characteristic, mechanical strength and anti-pollution performance.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
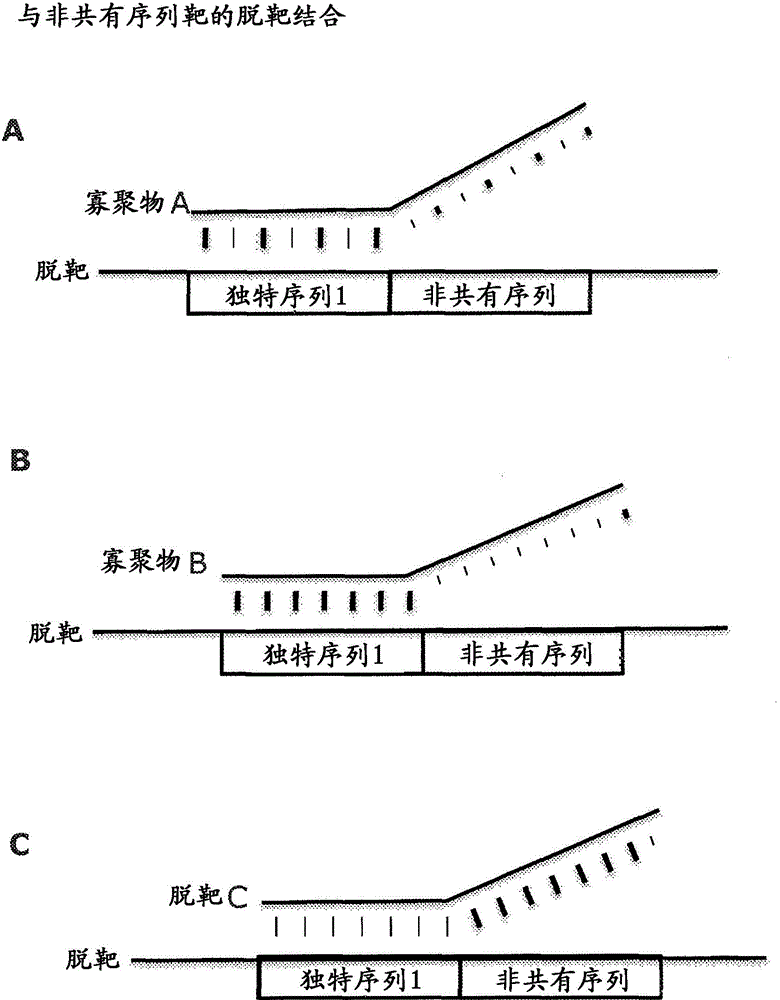
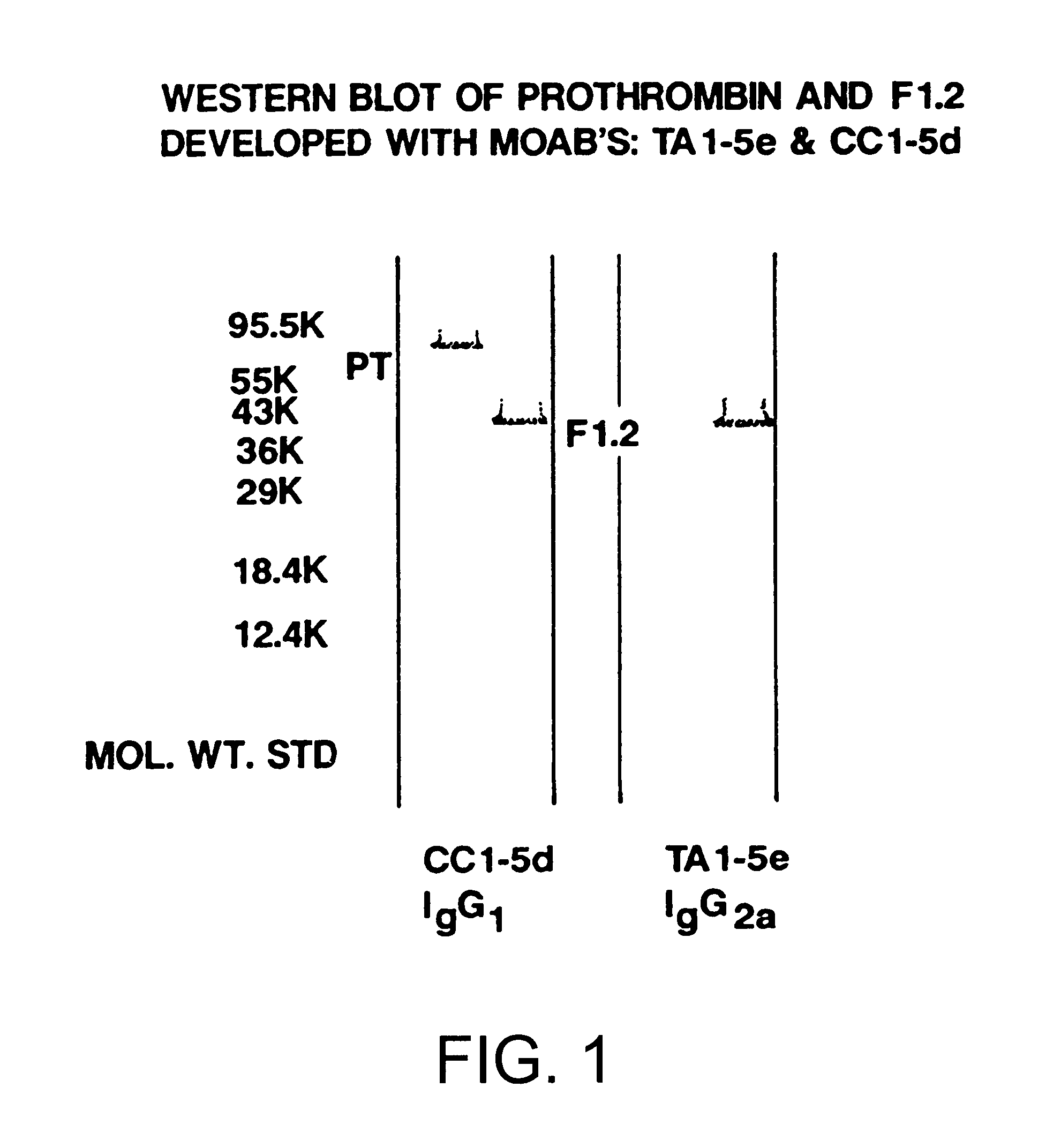
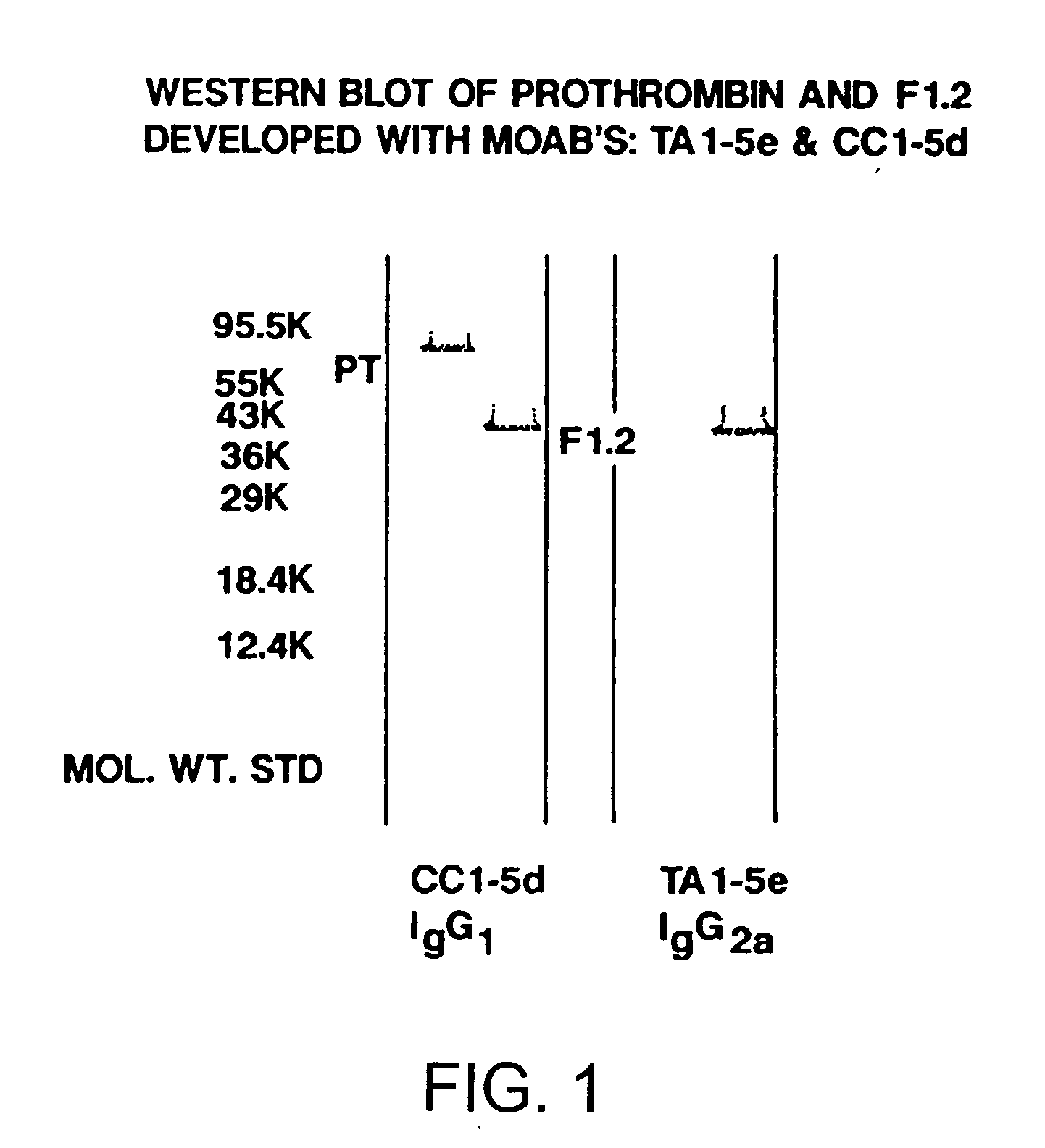
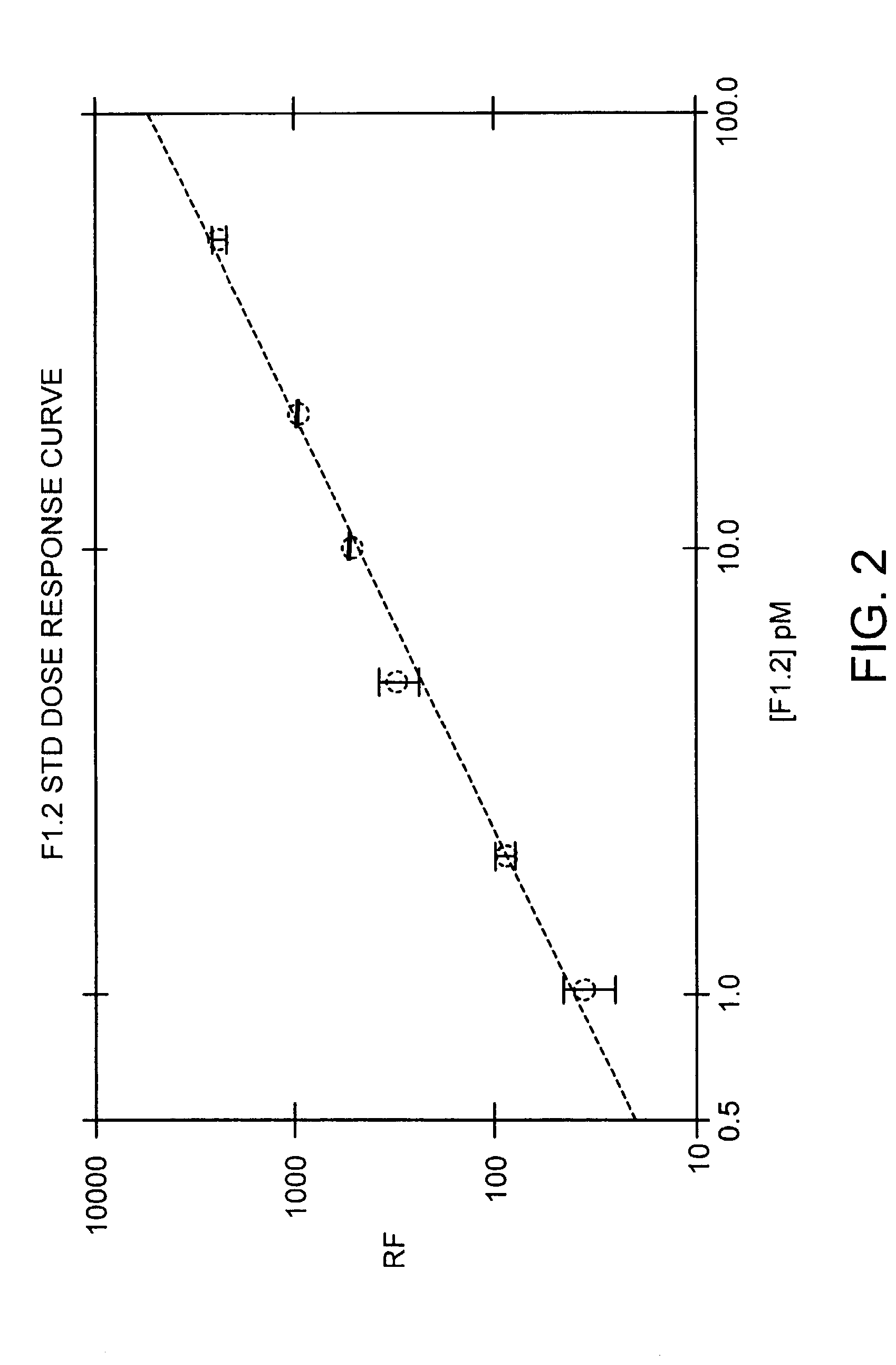
Immunoassay for F1.2 prothrombin fragment
According to the present invention highly specific-low affinity antibodies are generated which allow for the assay of F1.2 in bodily fluids that also contain prothrombin or other plasma proteins. Antibodies having the necessary properties for this assay are made using synthetic polypeptides which mimic the carboxy terminus of F1.2.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS9403883B2Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityLower affinity
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Immunoassay for F1.2 prothrombin fragment
Owner:RUIZ JUAN A +1
Cross-screening system and methods for detecting a molecule having binding affinity for a target molecule
The invention is directed to a cross-screening system and methods of the invention utilizing a combination of an immunoassay (IA) and electrochemiluminescence assay (ECLA) to identify molecules that have binding affinities for a target molecule. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention can detect molecules that have binding affinities for the target molecule below the detection limits of the individual immunoassay or ECLA. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful for generating a pool of candidate analyte molecules enriched in a desired characteristic, such as low binding affinity for a target molecule. Low affinity antibodies identified by the cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful, for example, in assessing the safety and efficacy of biological therapeutics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
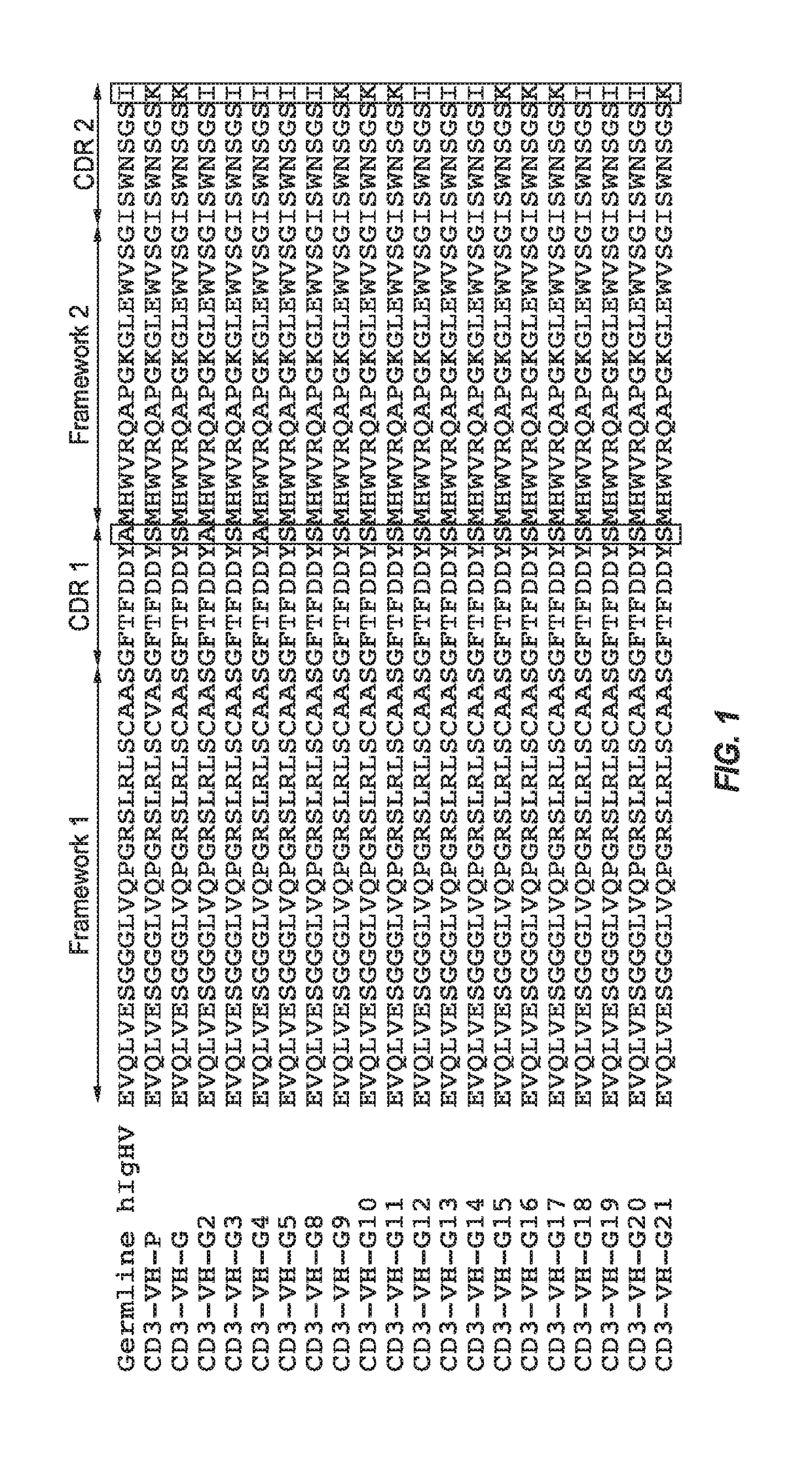
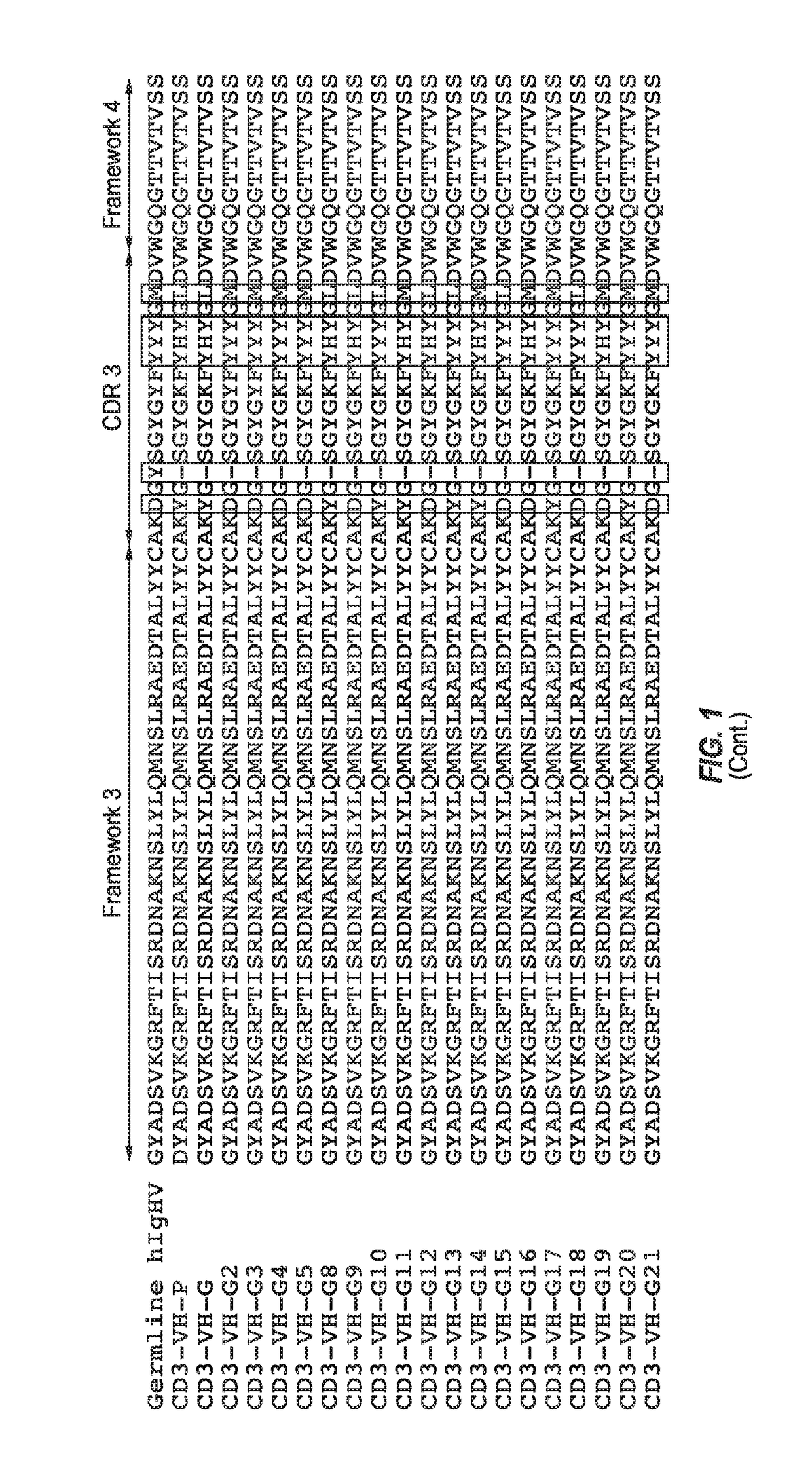
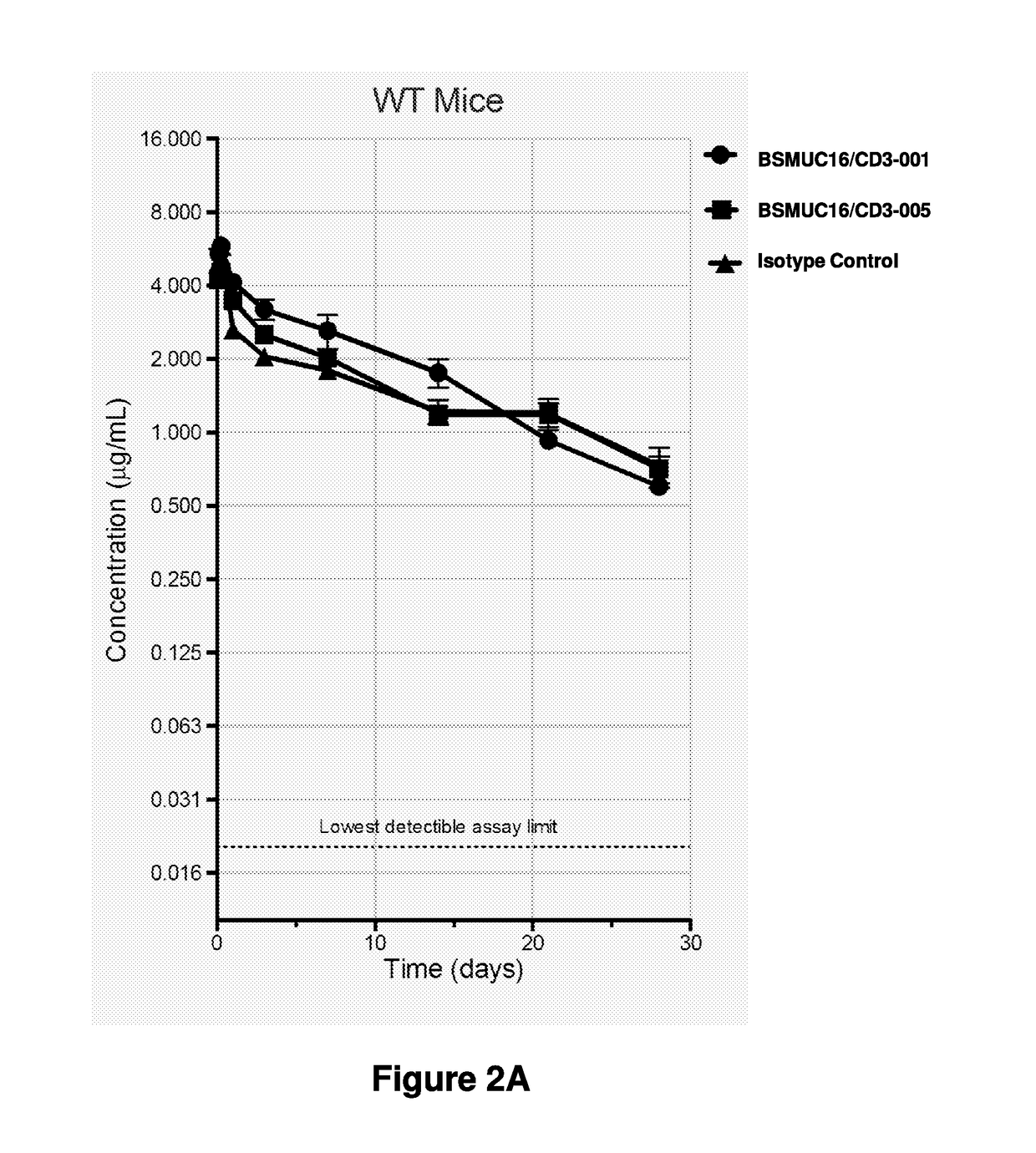
Optimized Anti-CD3 Bispecific Antibodies and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20180355038A1Reduce gapWeak affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLow affinityDisease
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to CD3 with weak or no detectable binding affinity and methods of using the same. According to certain embodiments, the antibodies of the invention bind human CD3 with low affinity and induce human T cell proliferation and hence induce T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells with high efficacy. According to certain embodiments, the present invention provides bispecific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first antigen-binding domain that specifically binds human CD3 with weak or no detectable binding affinity in an in vitro assay, and a second antigen-binding molecule that specifically binds human tumor-associated antigen. In certain embodiments, the bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the present invention are capable of inhibiting the growth of tumors expressing target antigen, such as PSMA. The antibodies and bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the invention are useful for the treatment of diseases and disorders in which an upregulated or induced targeted immune response is desired and / or therapeutically beneficial. For example, the antibodies of the invention are useful for the treatment of various cancers or other diseases where immunotherapy, i.e. effector cell immunomodulation is warranted.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
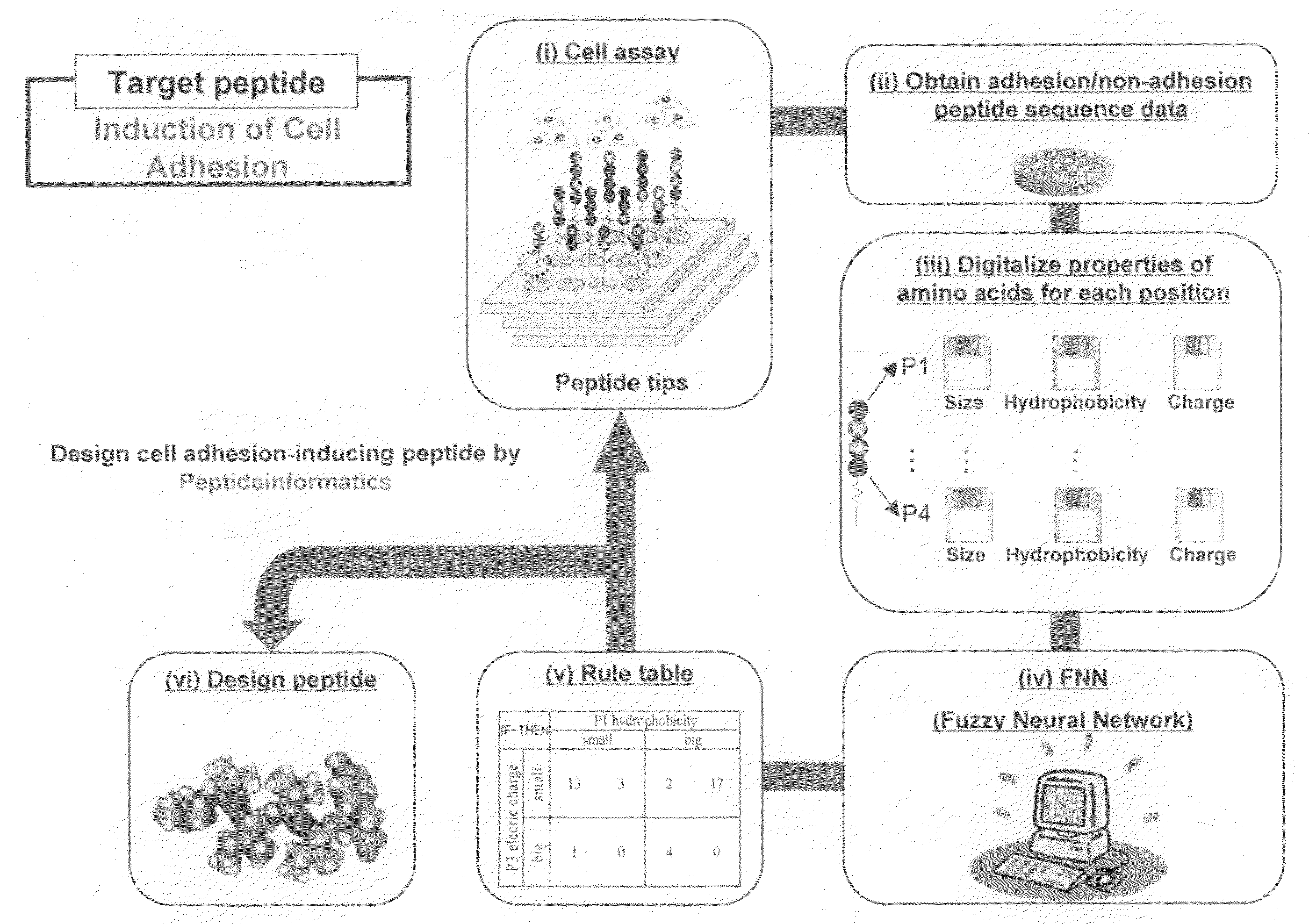
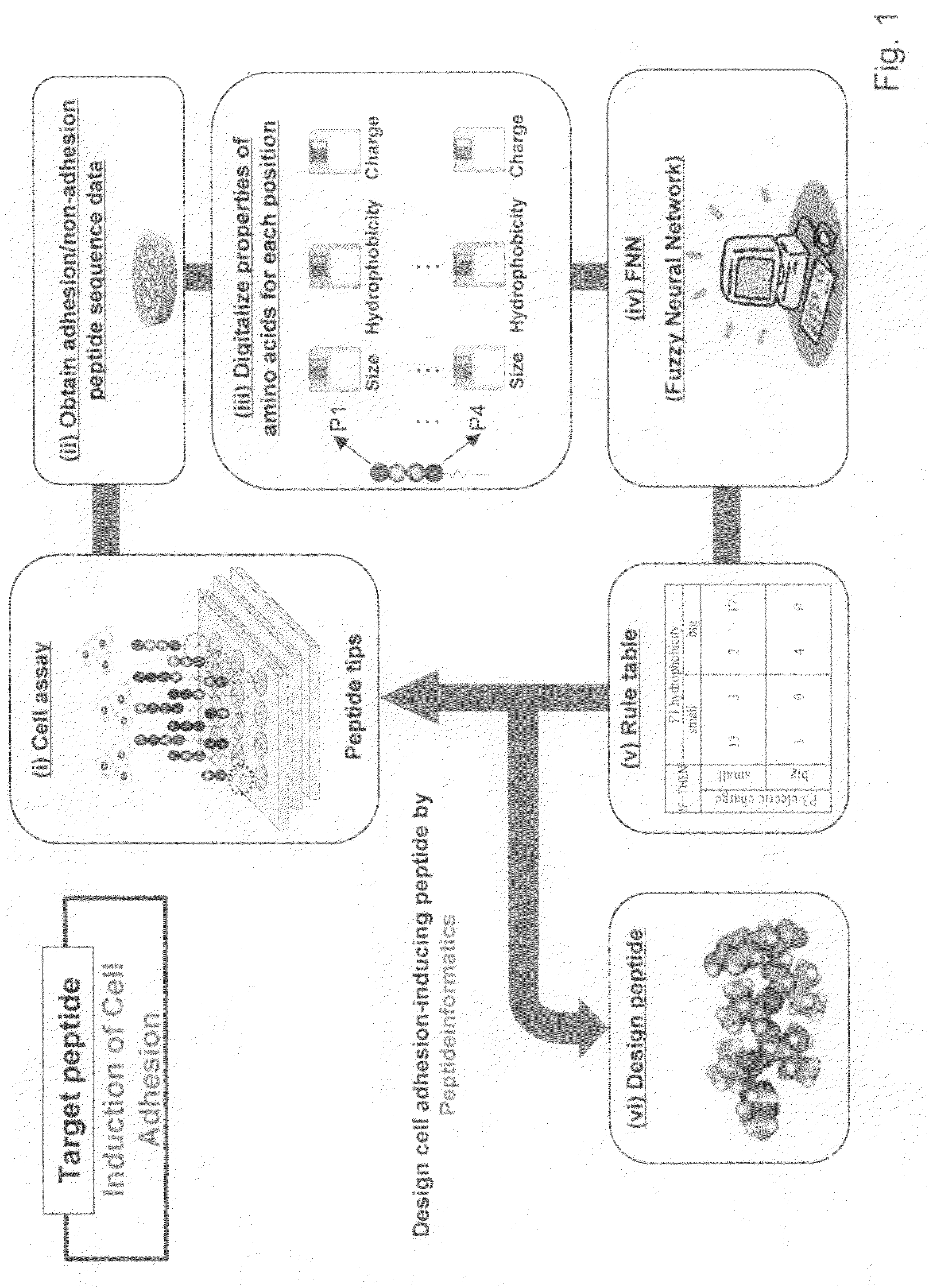
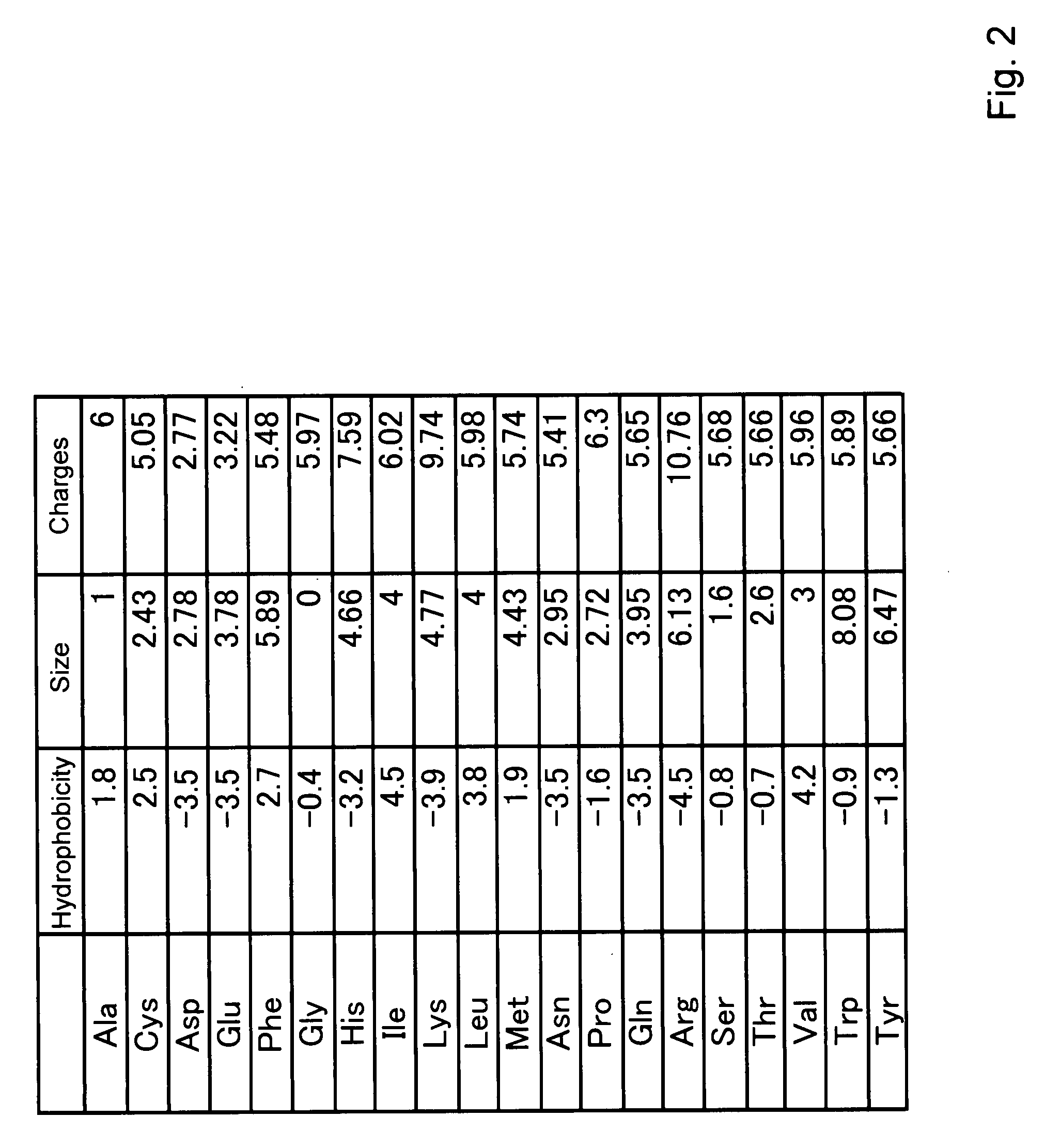
Method of designing high-affinity peptide, method of preparing high-affinity peptides, computer-readable storage medium storing a program for designing high-affinity peptide, apparatus for designing high-affinity peptide, and high-affinity peptide
InactiveUS20080071706A1High affinityEfficiently obtainedPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsLow affinityPeptide sequence
It is an object of the present invention to provide means for efficiently obtaining peptides that exhibit a high affinity toward a given target. Peptides are designed by the steps of (1) performing an affinity assay using a plurality of peptides having different peptide sequences and a target to obtain affinity data for each of the peptide sequences toward the target; (2) selecting high-affinity peptide sequences and low-affinity peptide sequences; (3) digitizing predetermined property(ies) of amino acids for each location from N-terminal or C-terminal to transform each of the selected peptide sequences into numerical data; (4) performing Fuzzy Neural Network analysis by using the obtained numerical data as input variables to construct a prediction model; (5) extracting from the constructed prediction model one or two or more rules wherein the amino acids and the properties are related to each other on one or more locations on the sequences, said rules representing the characteristics of high-affinity peptide sequence; and (6) designing a peptide according to the extracted rules.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Compound Arrays for Sample Profiling
The invention provides arrays of compound for use in profiling samples. The arrays include compounds bind to components of the samples at relatively low affinities. The avidity of compounds binding to components of the samples can be increased by forming arrays such that multivalent components of the samples (e.g., antibodies or cells) can bind to more than one molecule of a compound at the same time. When a sample is applied to an array under such conditions, the compounds of the array bind to component(s) of the sample with significantly different avidities generating a profile characteristic of the sample.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com