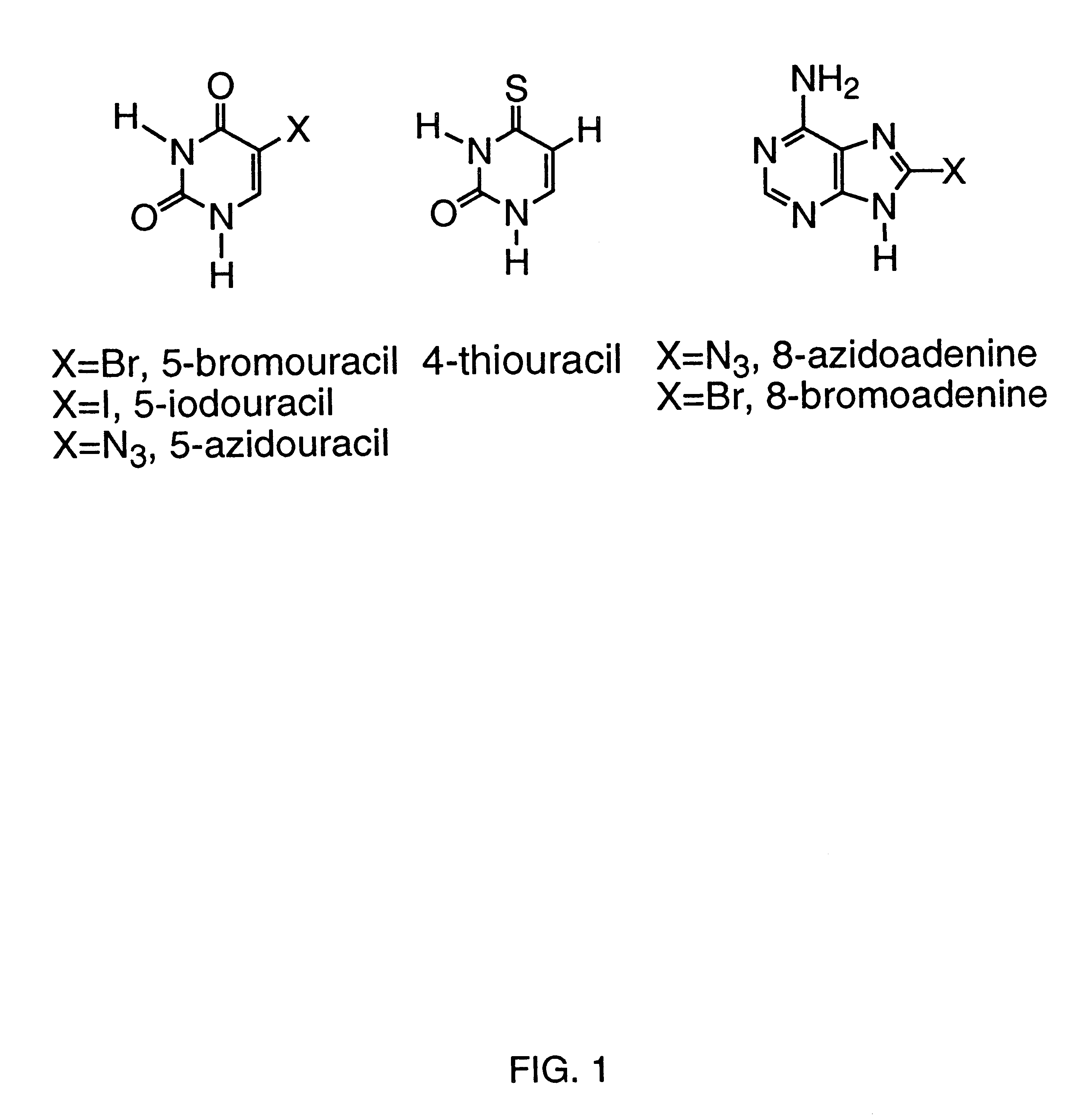
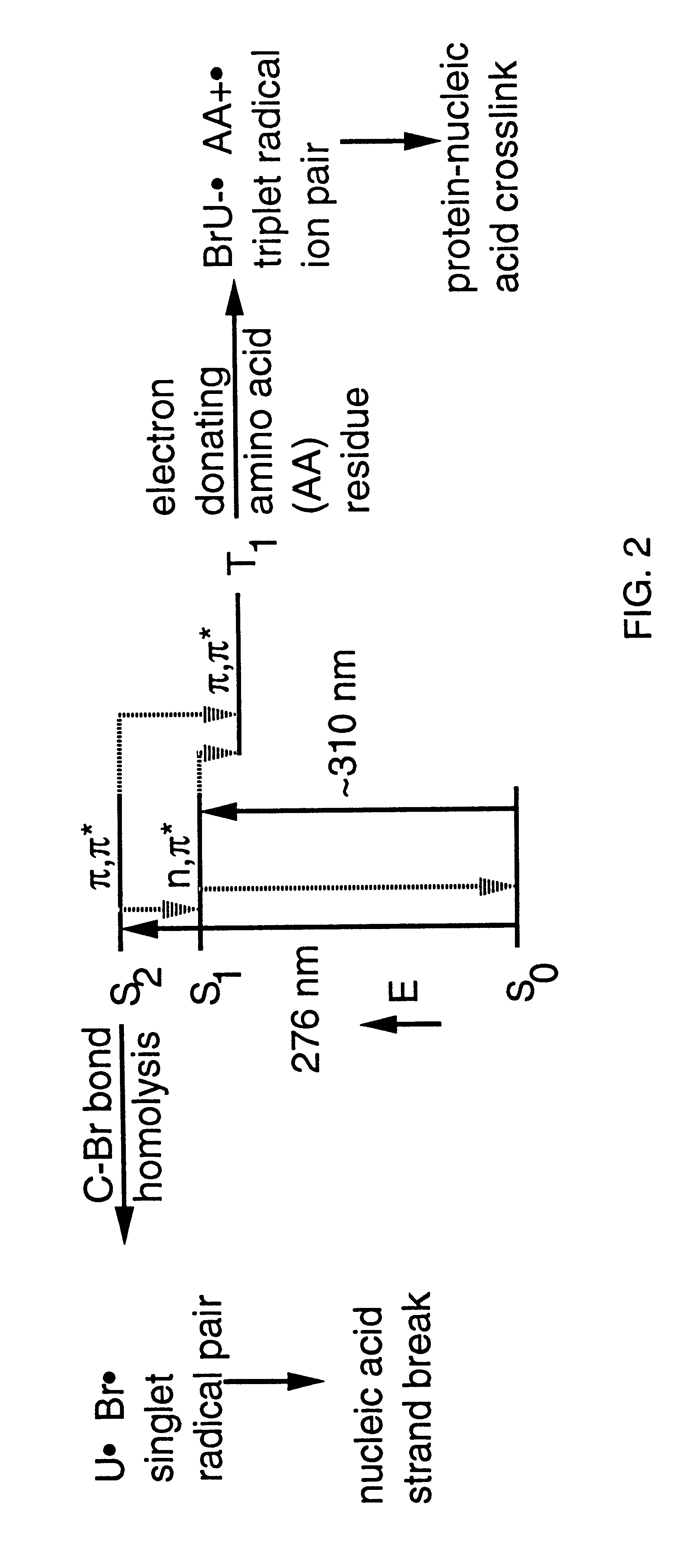
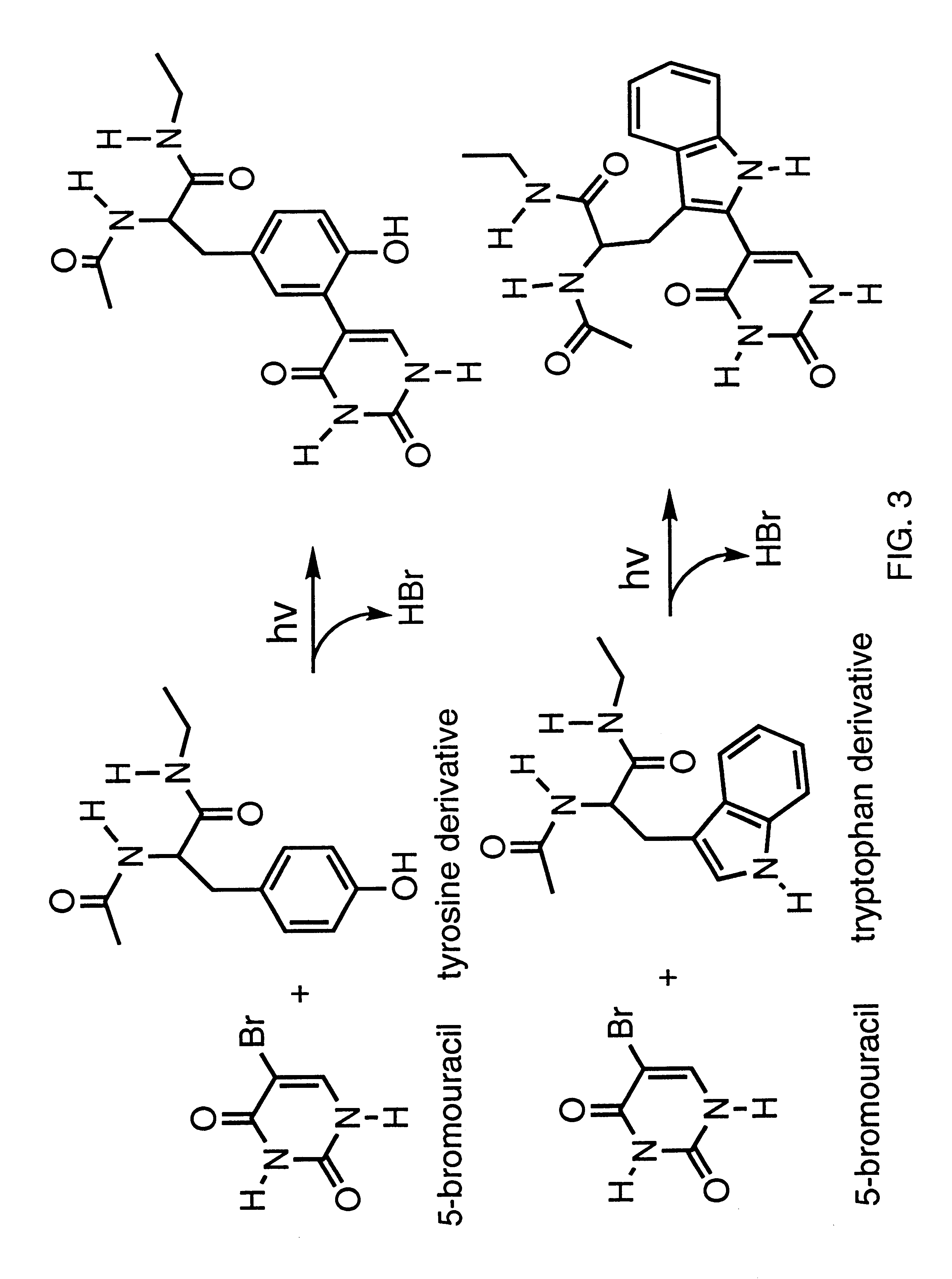
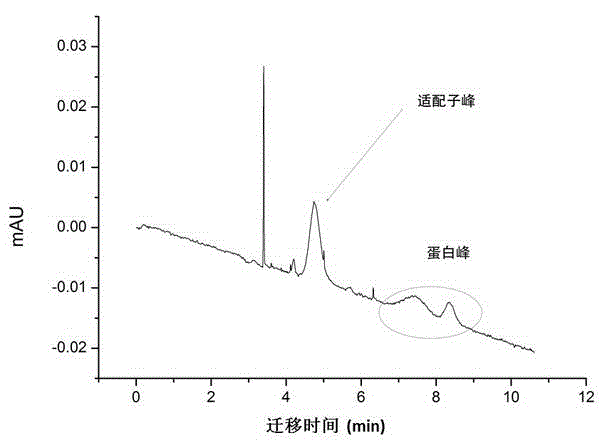
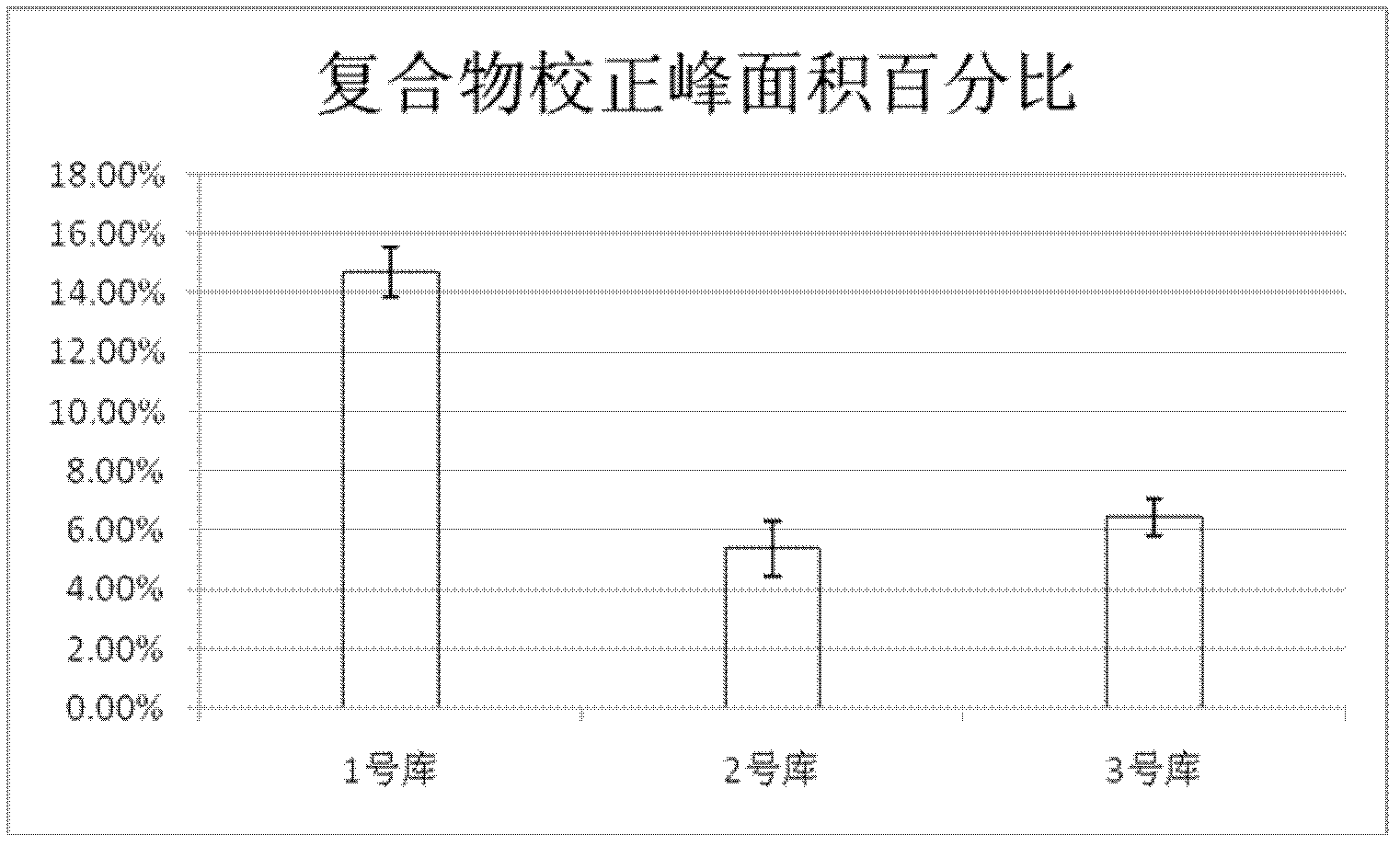
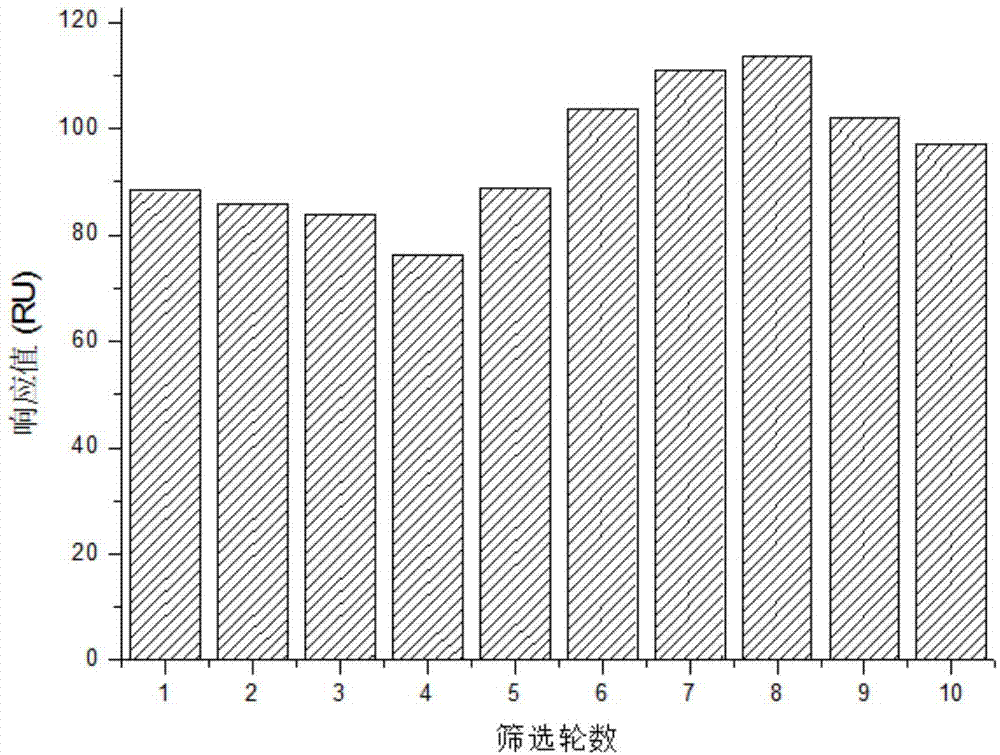
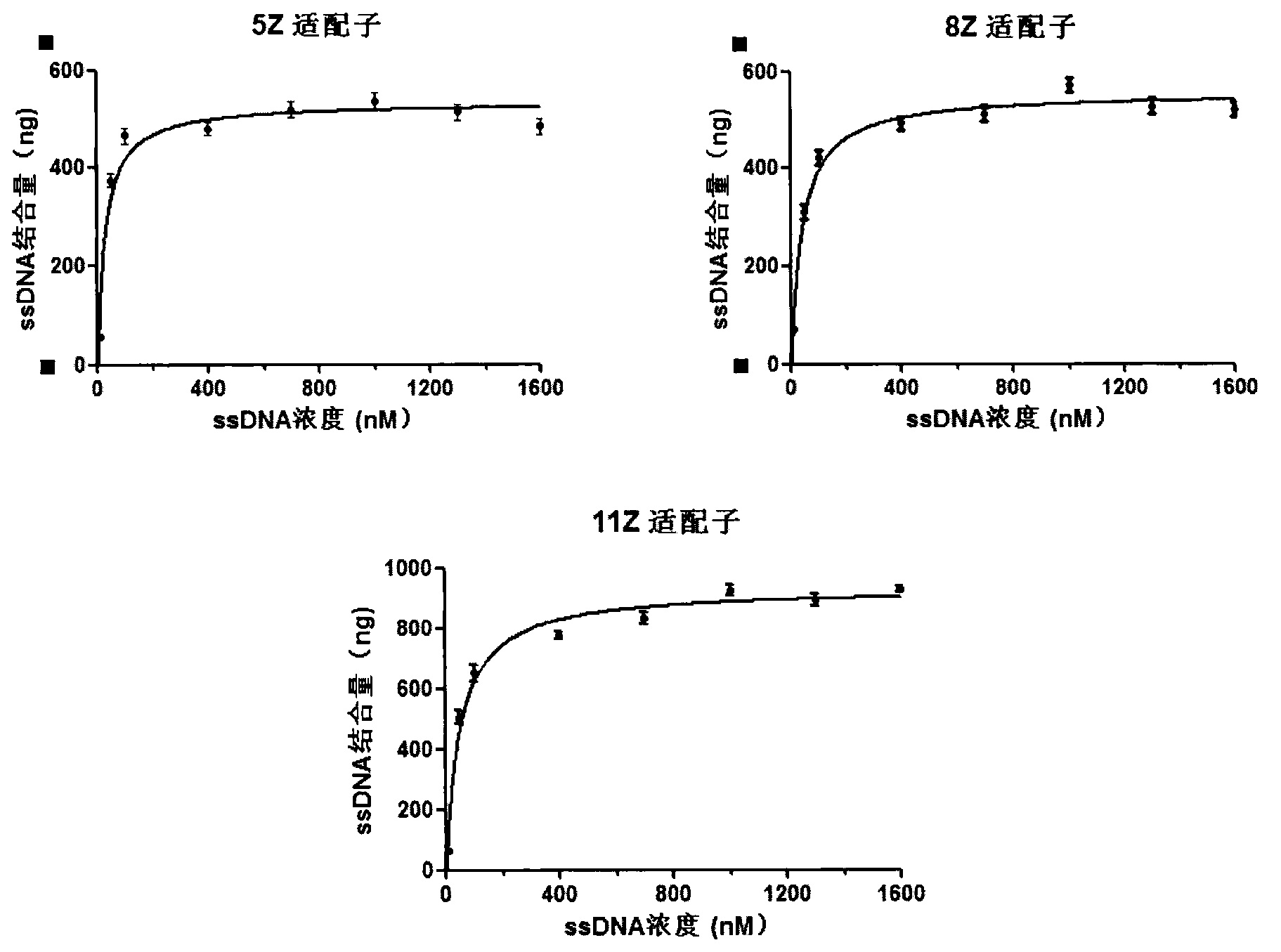
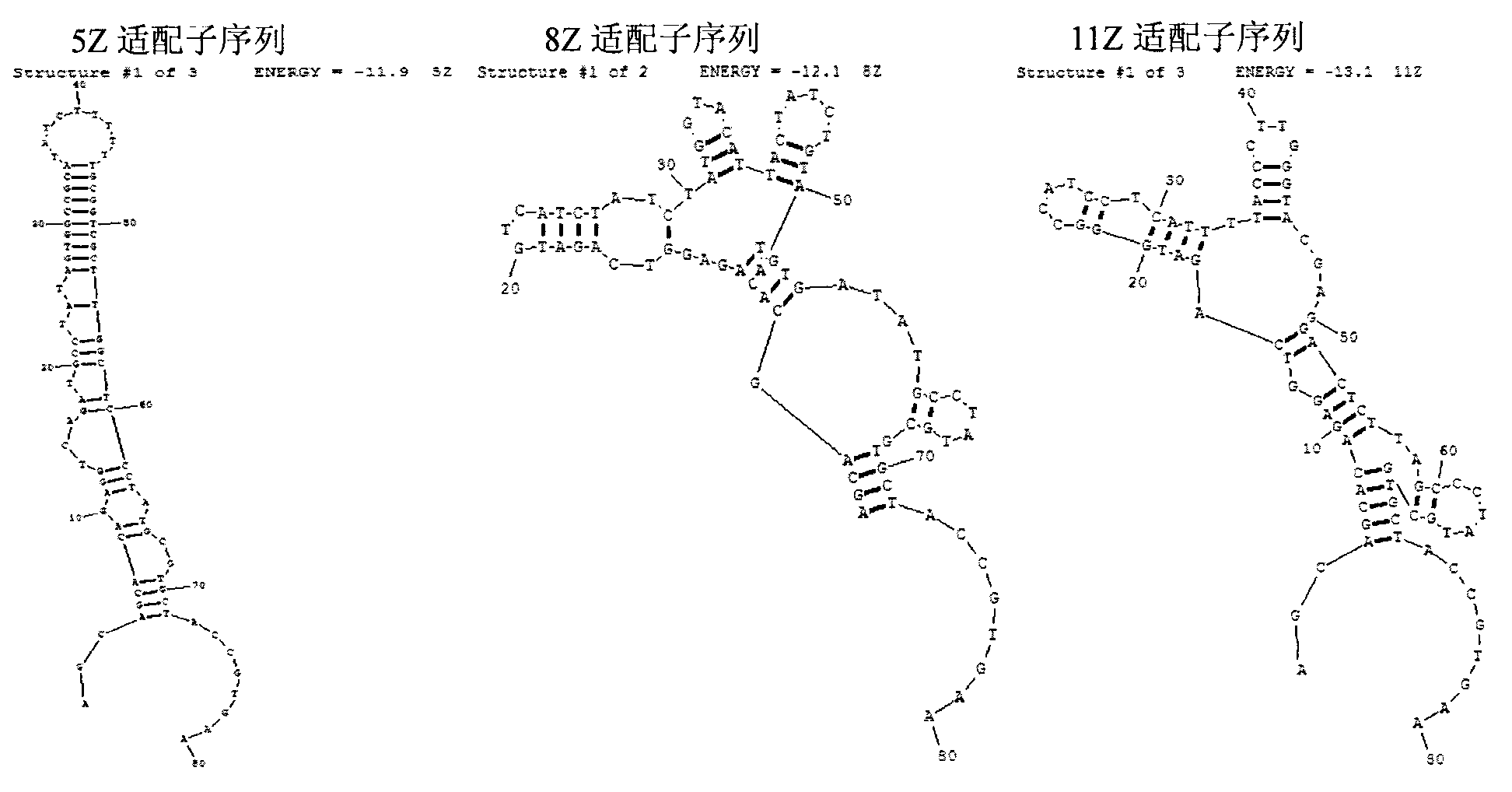
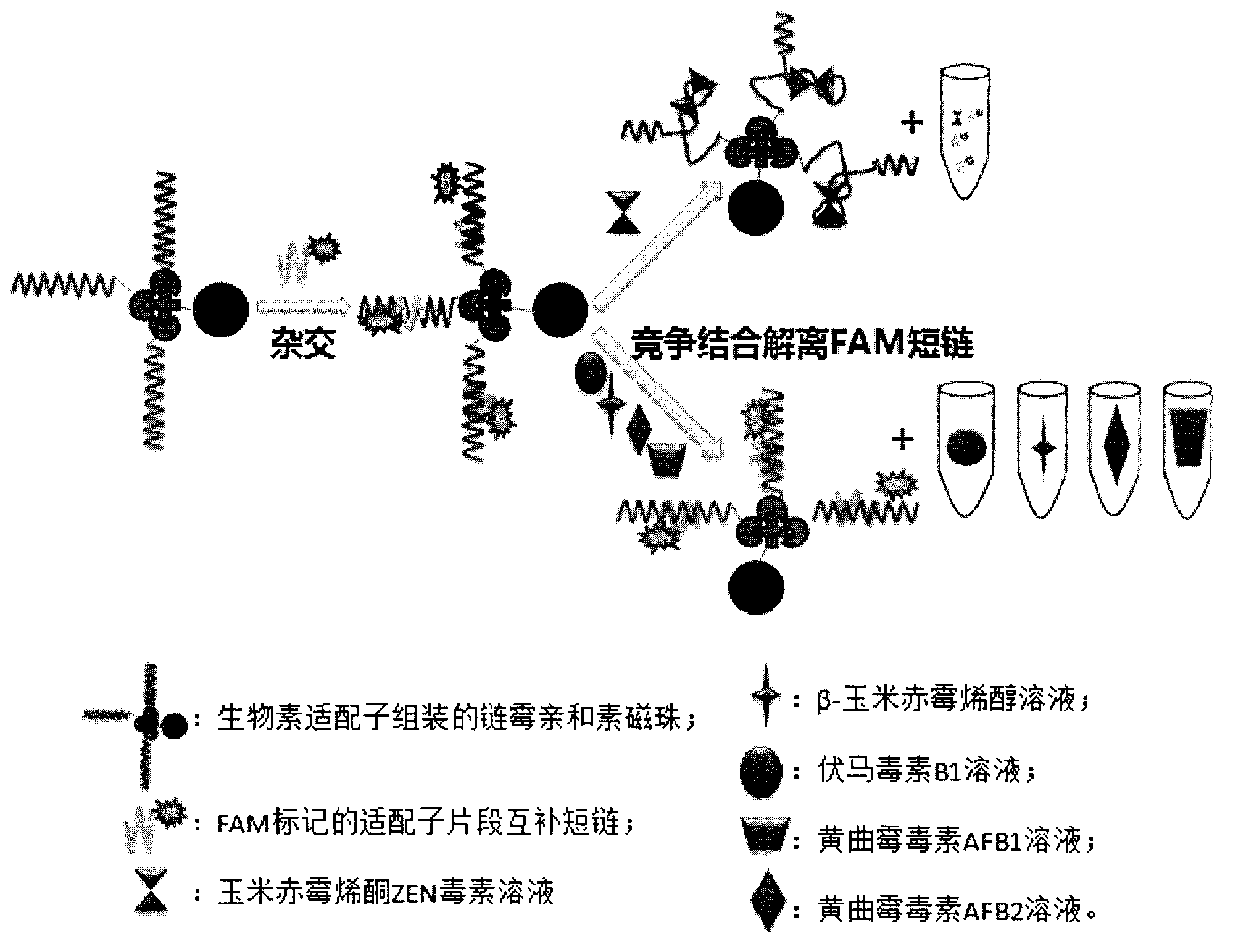
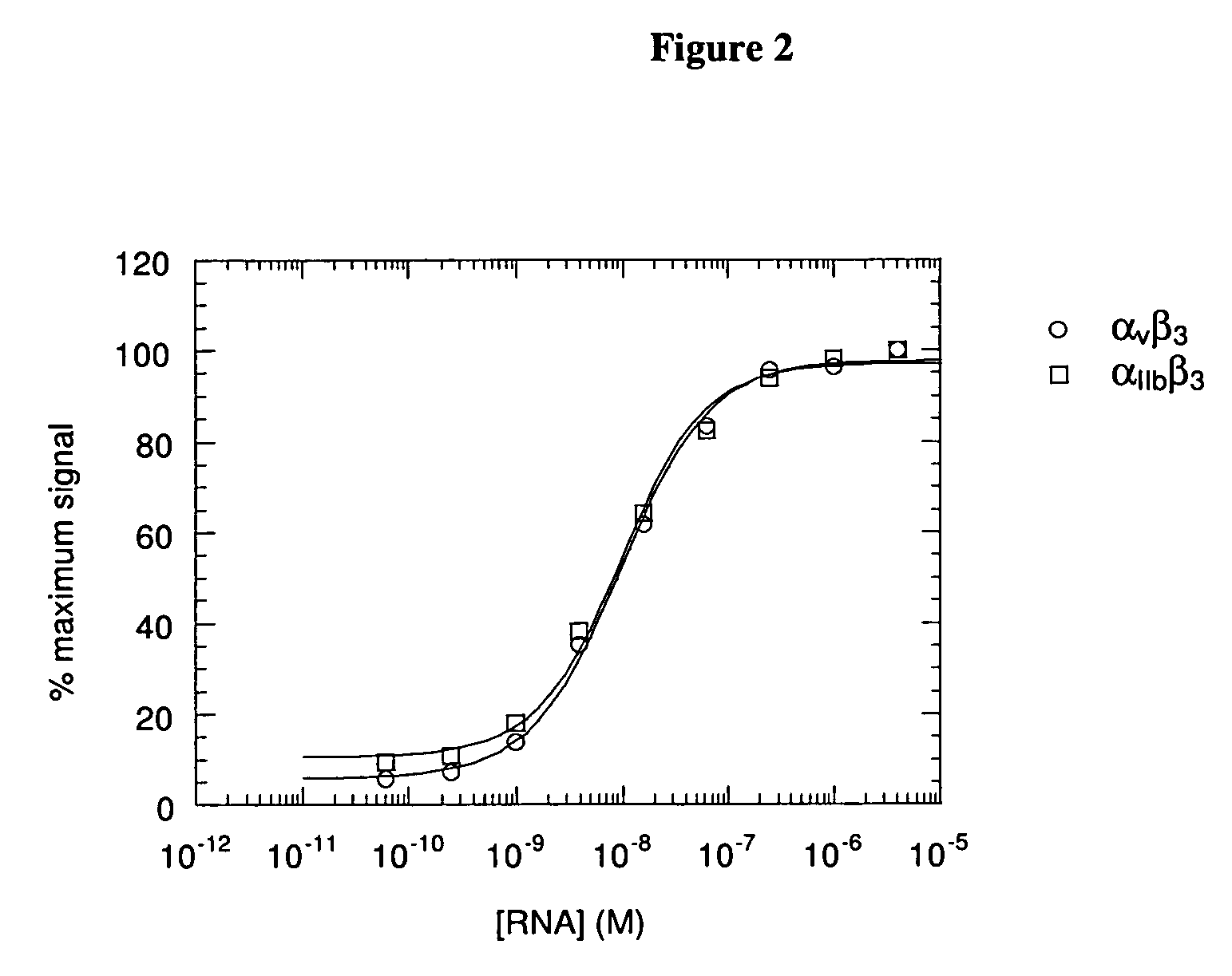
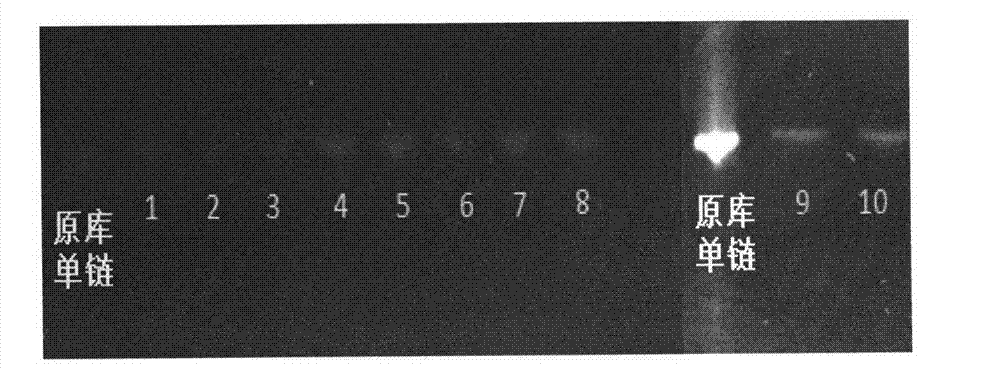
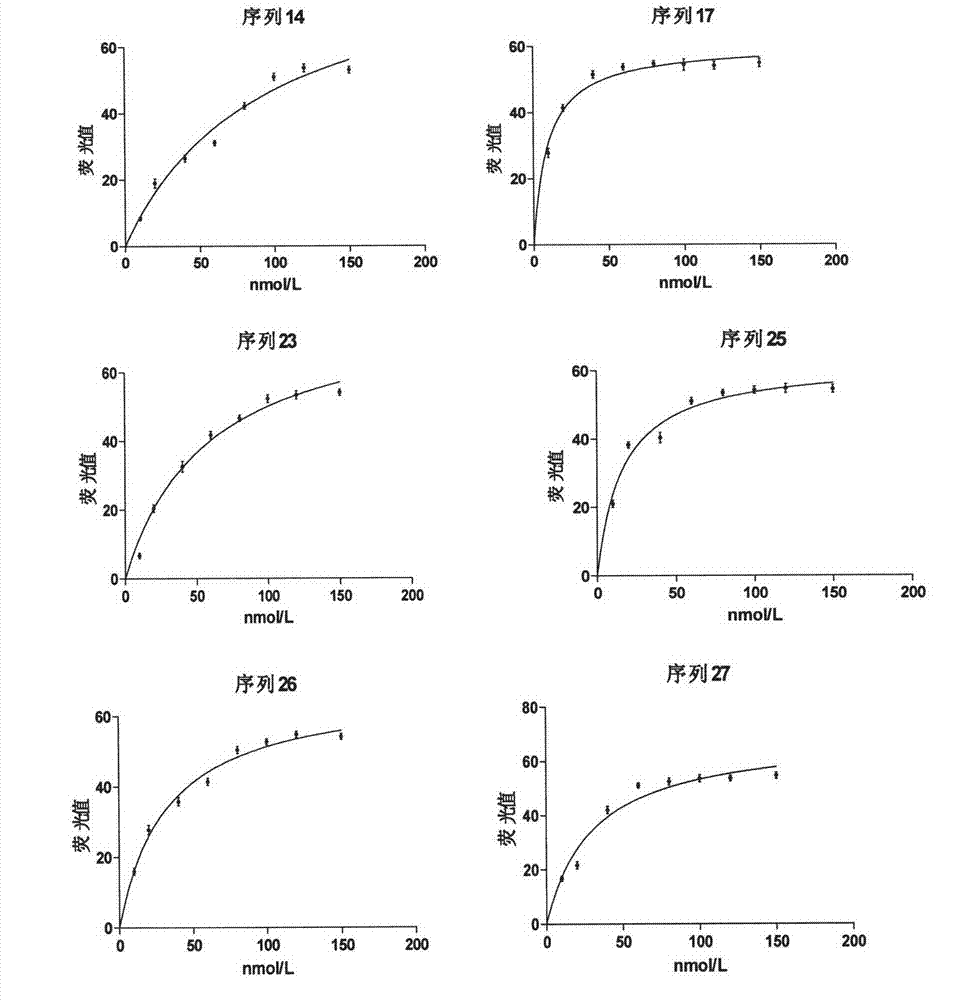
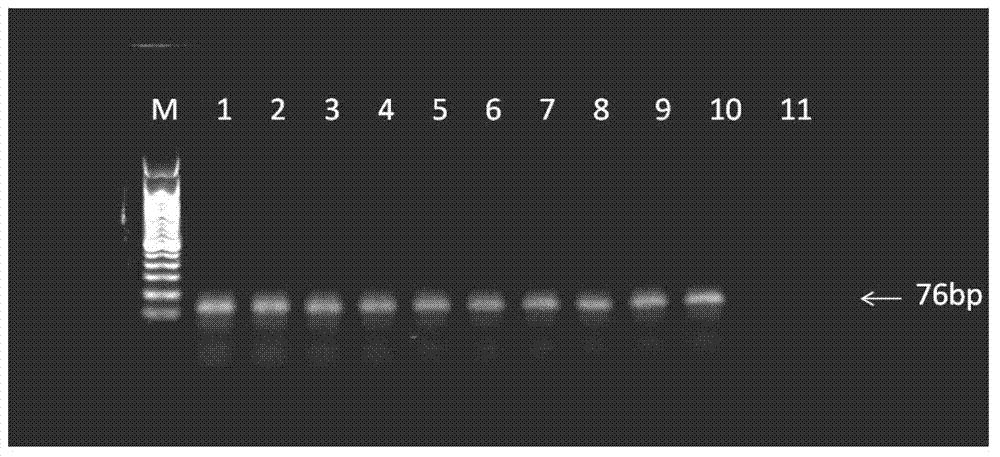Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
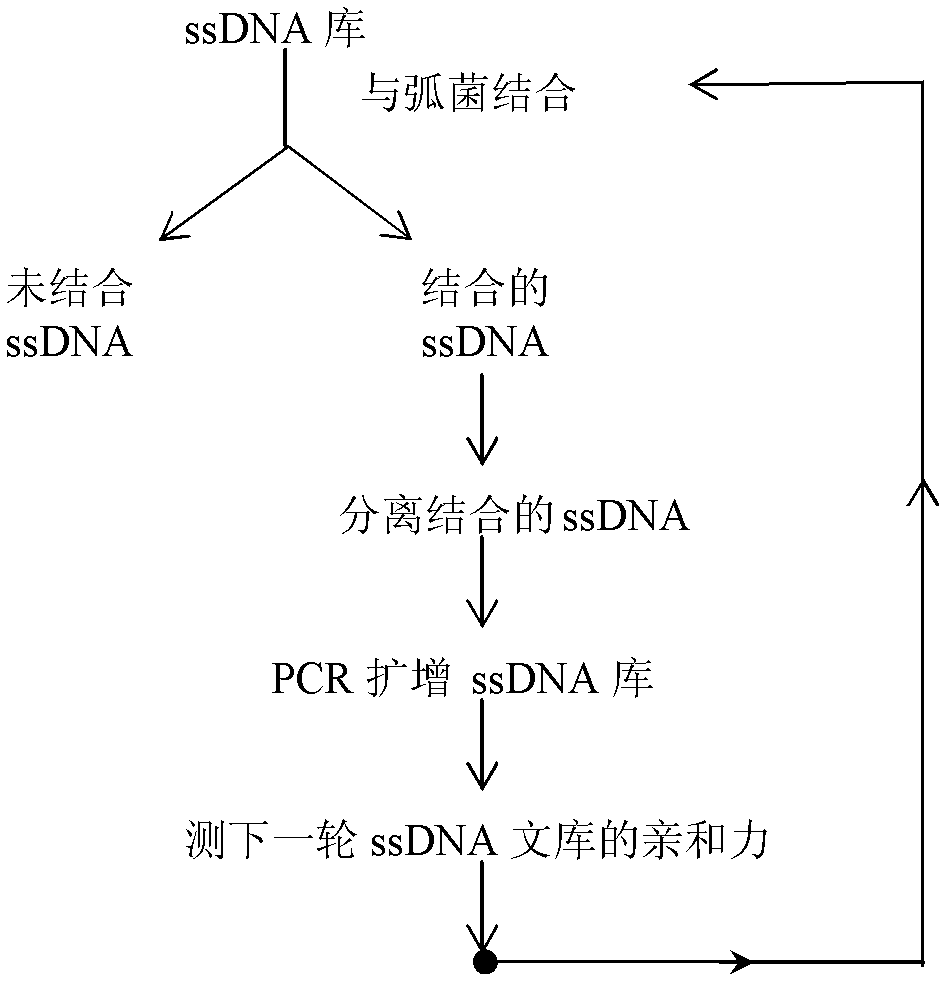
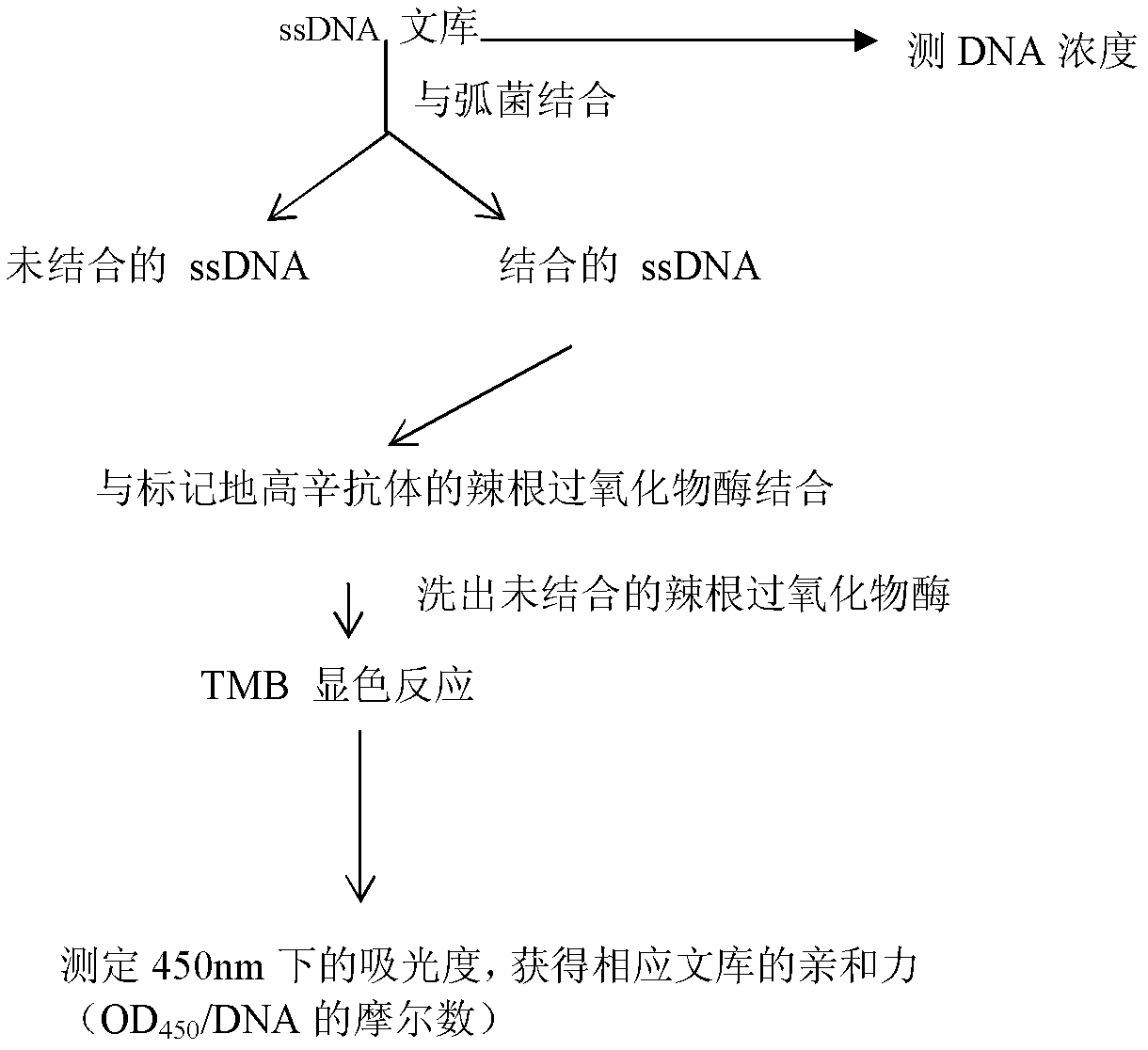
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), also referred to as in vitro selection or in vitro evolution, is a combinatorial chemistry technique in molecular biology for producing oligonucleotides of either single-stranded DNA or RNA that specifically bind to a target ligand or ligands. These single-stranded DNA or RNA are commonly referred to as aptamers. Although SELEX has emerged as the most commonly used name for the procedure, some researchers have referred to it as SAAB (selected and amplified binding site) and CASTing (cyclic amplification and selection of targets) SELEX was first introduced in 1990. In 2015 a special issue was published in the Journal of Molecular Evolution in the honor of quarter century of the SELEX discovery.
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: photoselection of nucleic acid ligands and solution selex
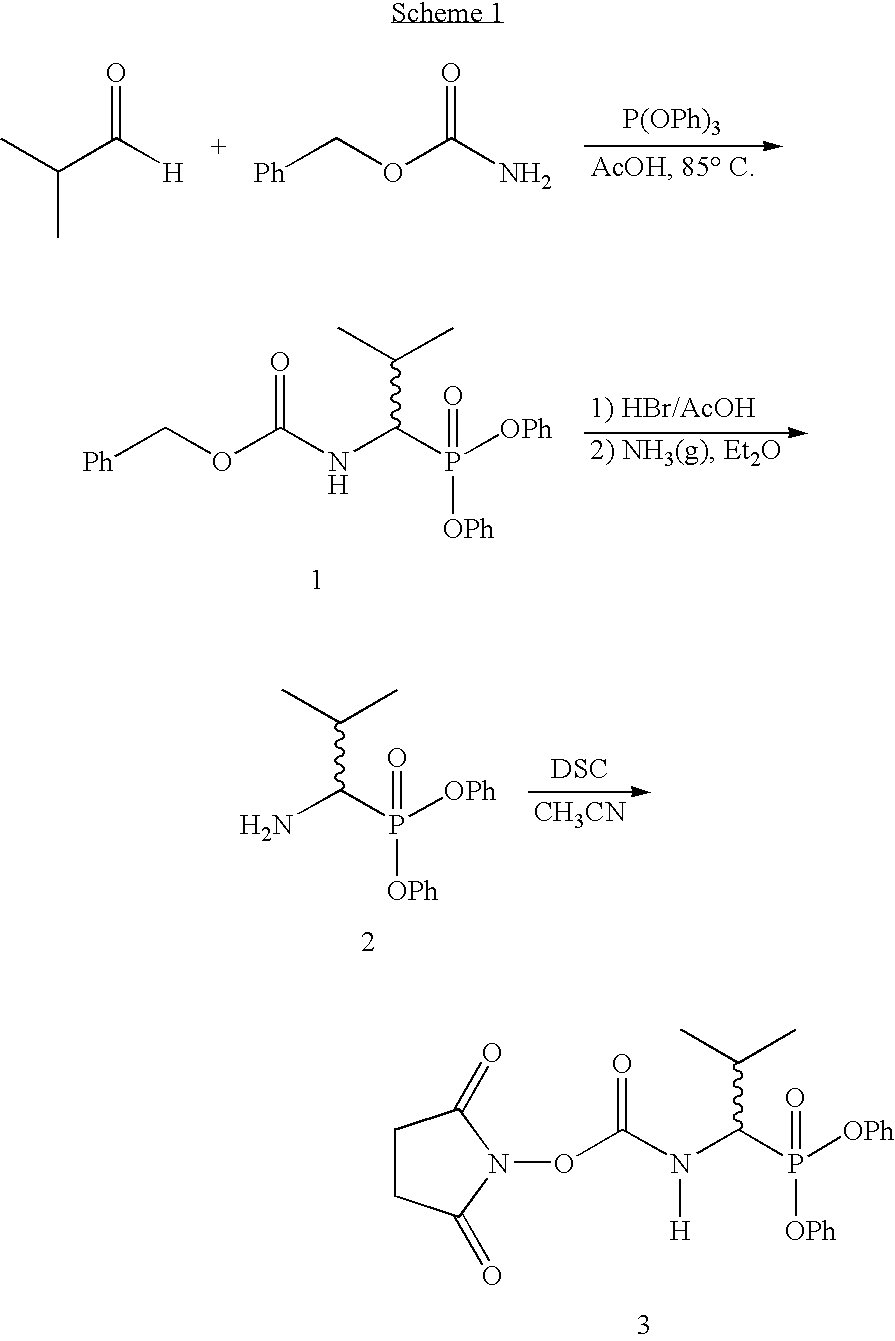
A method for identifying nucleic acid ligands to target molecules using the SELEX procedure wherein the candidate nucleic acids contain photoreactive groups and nucleic acid ligands identified thereby are claimed. The complexes of increased affinity nucleic acids and target molecules formed in the procedure are crosslinked by irradiation to facilitate separation from unbound nucleic acids. In other methods partitioning of high and low affinity nucleic acids is facilitated by primer extension steps as shown in the figure in which chain termination nucleotides, digestion resistant nucleotides or nucleotides that allow retention of the cDNA product on an affinity matrix are differentially incorporated into the cDNA products of either the high or low affinity nucleic acids and the cDNA products are treated accordingly to amplification, enzymatic or chemical digestion or by contact with an affinity matrix.
Owner:SOMALOGIC INC
Aptamer capable of being in specific binding to TS/MDEP protein in gastric cancer cells
InactiveCN104818278ALow costSimple methodBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerProtein target
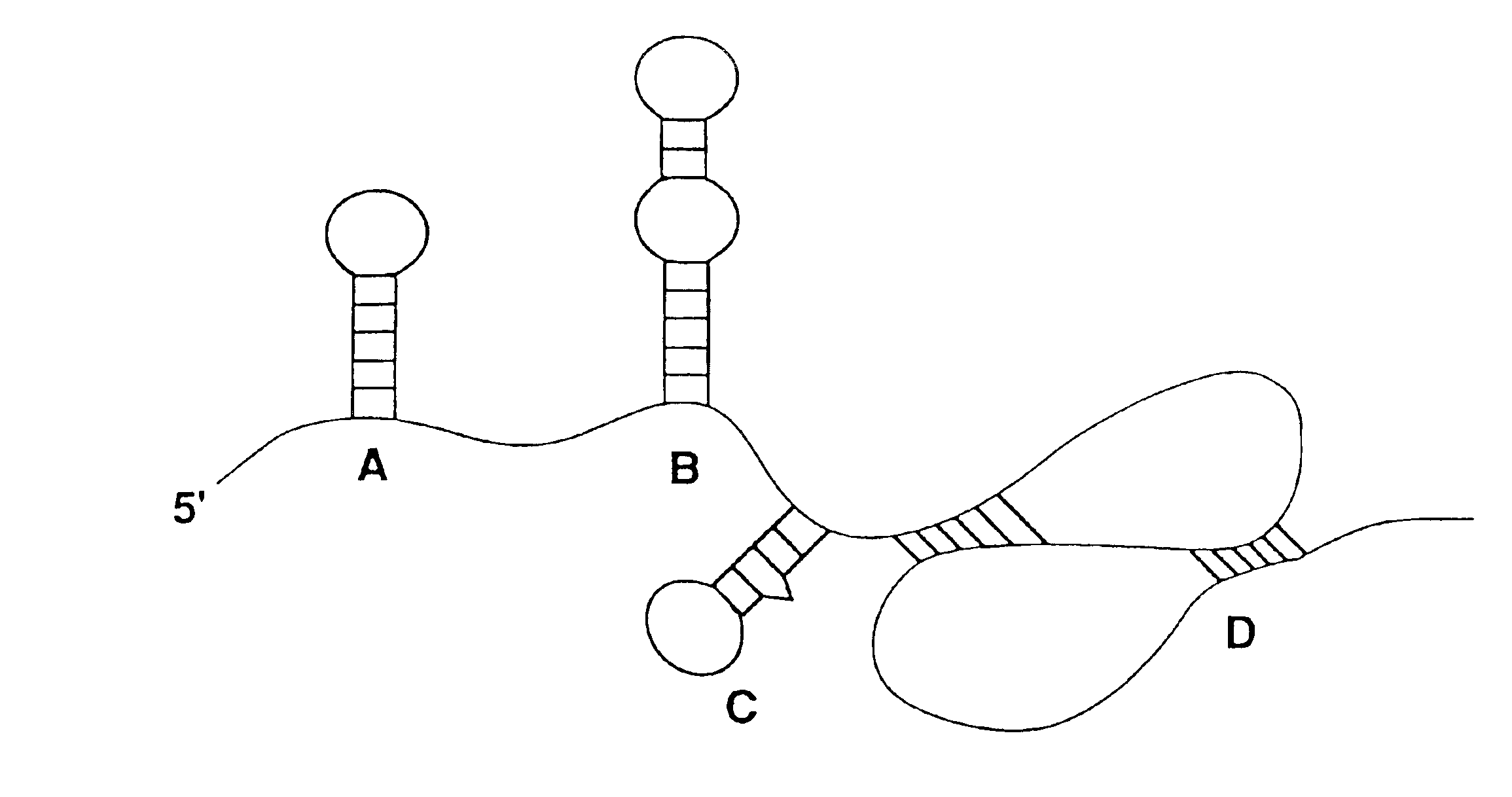
The invention discloses a targeted artificial TS / MDEP protein nucleic acid aptamer and a sequence thereof. A new combinatorial chemistry technology SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) is applied, the TS / MDEP protein serves as a target protein, and a DNA aptamer capable of being in specific binding to the TS / MDEP protein is screened from a single-chain RNA random library. The aptamer can form a special stem-loop structure in a random sequence area and can be in specific and high-affinity binding to the TS / MDEP protein or targeted binding to gastric cancer cells. The RNA aptamer provides a specific and efficient marker molecule for the gastric cancer diagnosis and treatment field, as well as a new choice for developing gastric cancer diagnosis reagents and gastric cancer treatment medicines.
Owner:刘红卫
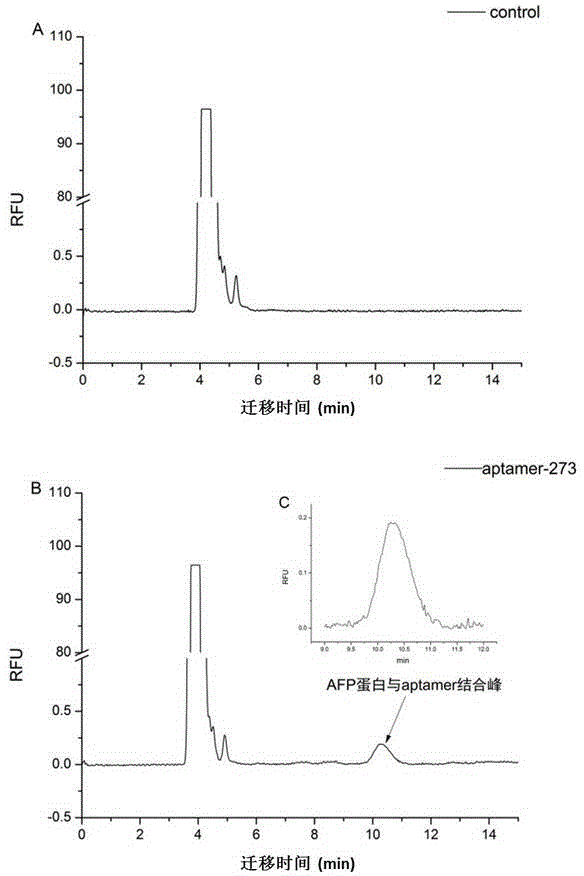
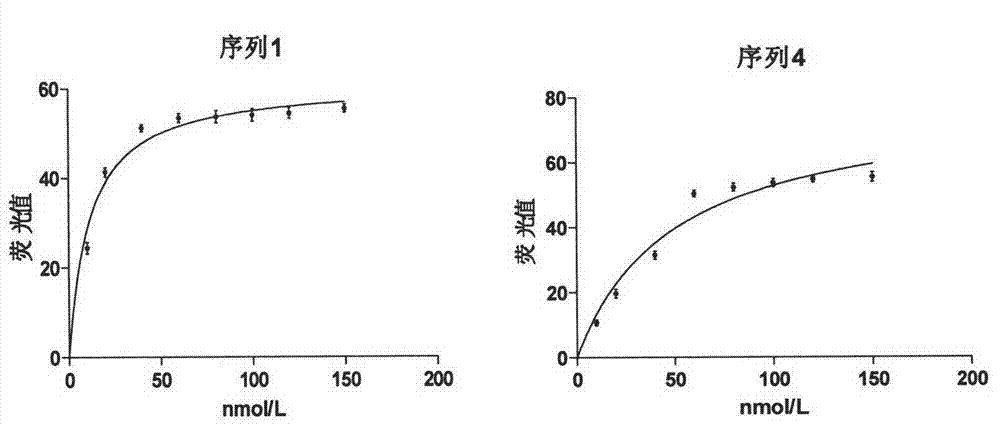
Method for screening aptamer specifically bound with alpha-fetoprotein
InactiveCN104131105AStrong interactionIncrease workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAptamerFetuin b
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
Three oligonucleotide sequences for identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102329862AImprove stabilityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSingle strandOligonucleotide
The invention discloses three oligonucleotide sequences for identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and relates to identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus. The oligonucleotide sequences comprise SEQ ID No. 1-3 (sequence identity number 1-3). The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) oligonucleotide library (5'-TCA GTC GCT TCG CCG TCT CCT TC----N35----GCA CAA GAG GGA GAC CCC AGA GGG-3') for screening; mixing the oligonucleotide library with the vibrio alginolyticus and then performing SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) screening; performing cloning and sequencing on an aptamer-enhanced library after completing the SELEX screening; performing interception in different lengths on high-copy ssDNA emerged in the sequencing result so as to get a series of new sequences, and further constructing complementary sequences of the new sequences; and performing affinity and specificity verification on the obtained new sequences and the complementary sequences thereof so as to get corresponding aptamers.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Group of oligonucleotides aptamers capable of specifically recognizing aflatoxin B1
ActiveCN102952802ALower synthesis costReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerFluorescein
The invention discloses a group of oligonucleotides aptamers capable of specifically recognizing aflatoxin B1. A single-chain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) oligonucleotides aptamer capable of specifically recognizing the aflatoxin B1 is acquired by a systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) technology; the aptamer can be transformed into a report aptamer by a fluorescein mark and the like; the report aptamer is used for detecting the aflatoxin B1; and the aptamer sequence can accurately and rapidly check the aflatoxin B1 in the food; and therefore, the oligonucleotides aptamer has the wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
DNA (Desoxyribonucleic Acid) ligand for specific binding with EPO (erythropoietin), preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102191250AEnhanced interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningA-DNADesoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a DNA (Desoxyribonucleic Acid) ligand for specific binding with EPO (erythropoietin), a preparation method thereof and application thereof, specifically provides a DNA ligand capable of specifically binding with the EPO and a method for screening the ligand by an improved SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) technology, and provides EPO detecting elements with better detecting stability, higher sensitivity, convenience and quickness.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: blended SELEX
InactiveUS7176295B2High affinityDesired effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandIntegrin
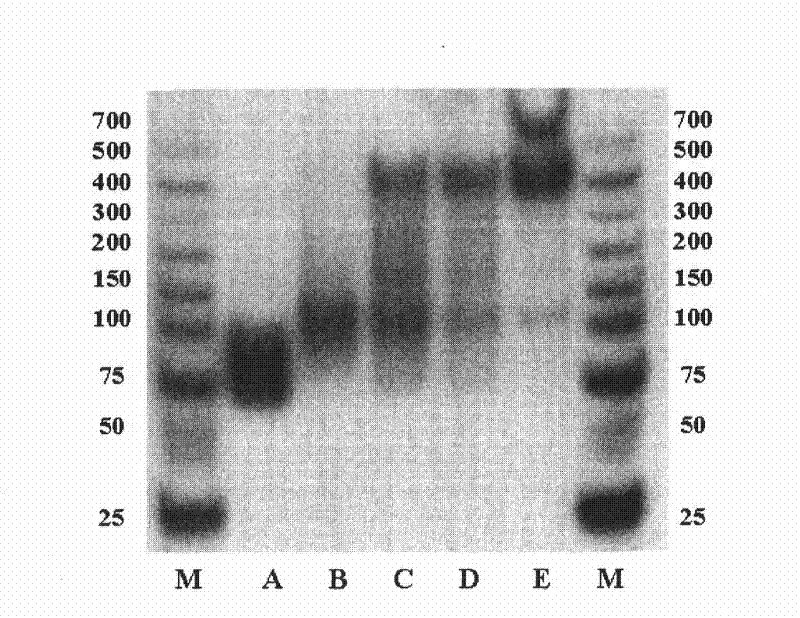
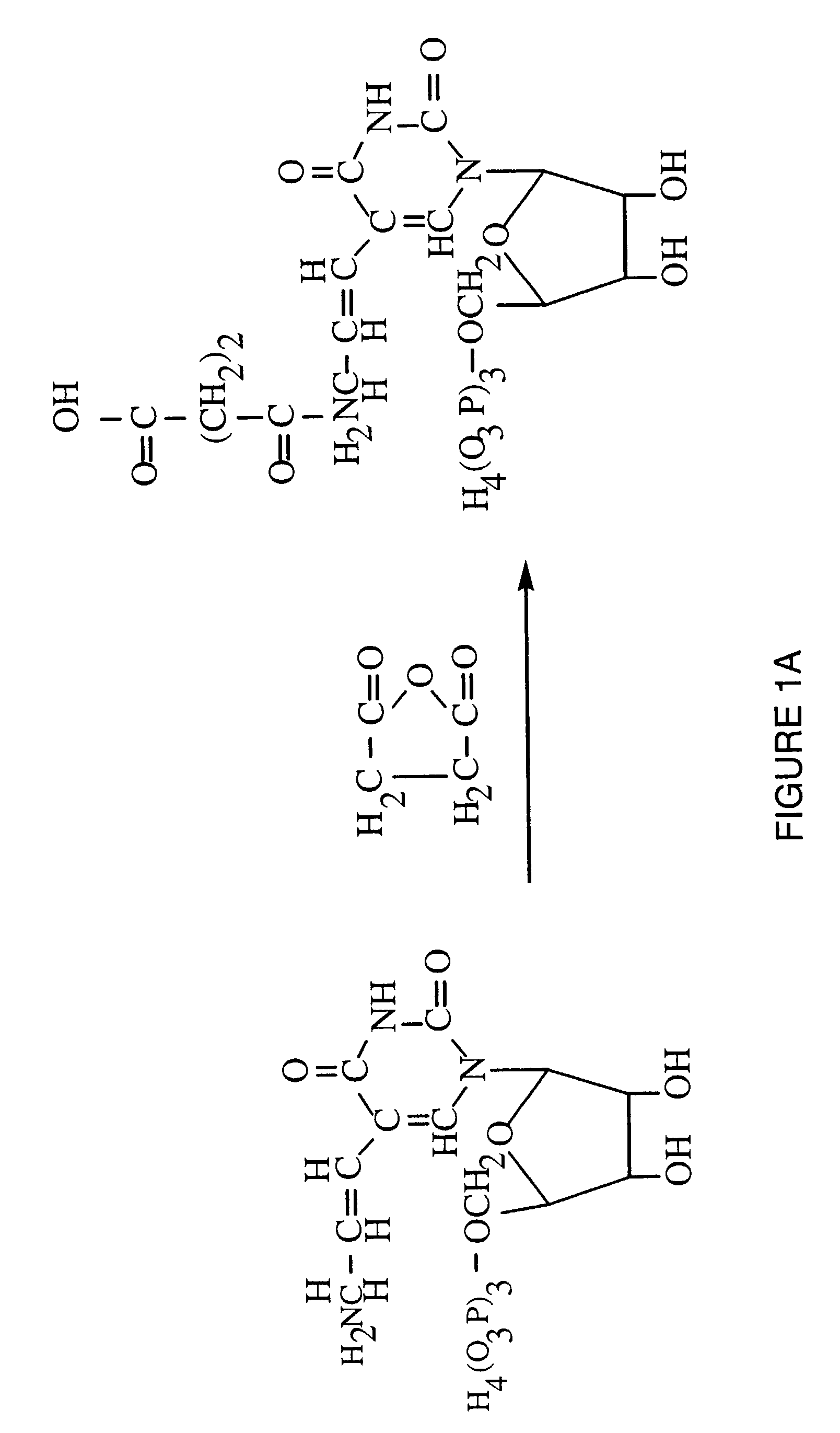
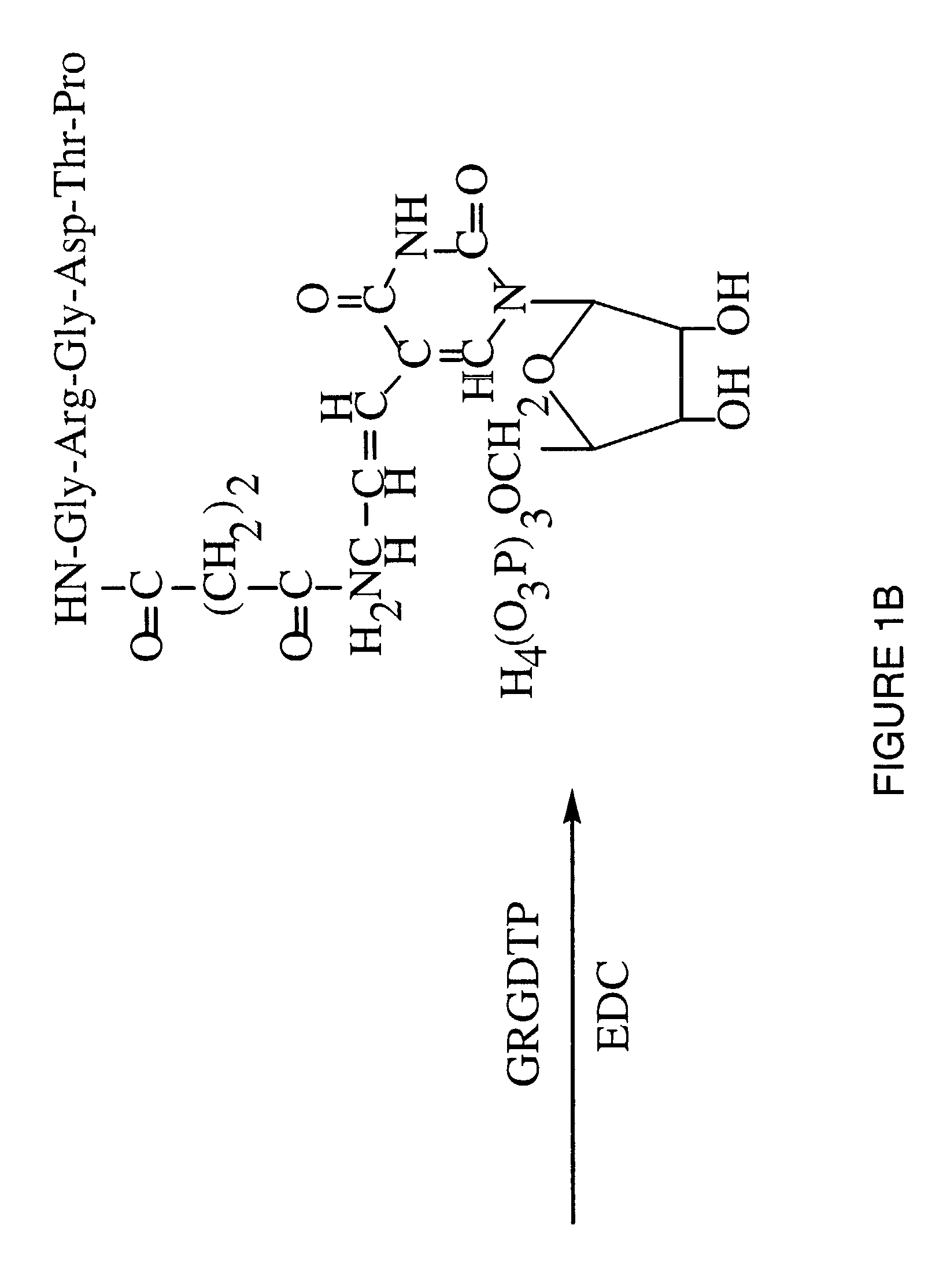
A method is described for generating blended nucleic acid ligands containing non-nucleic acid functional units. Specifically, a SELEX identified RNA ligand to the integrin gpIIbIIIa is conjugated to the peptide Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Thr-Pro (SEQ ID NO:1). This blended RNA ligand inhibits the biological activity of gpIIbIIIa with high specificity. Also described is a single-stranded DNA ligand to elastase coupled to N-methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-chloromethyl ketone (SEQ ID NO:2). This elastase blended nucleic acid ligand inhibits the biological activity of elastase.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Nucleic acid ligand binding site identification
InactiveUS6933116B2Easy to combineEfficient use ofPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsBinding siteBiology
This invention comprises nucleic acid ligand for use as a diagnostic reagent for detecting the presence or absence of a target molecule in a sample, and a diagnostic reagent to measure the amount of a target molecule in a sample. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acid ligands are identified by the method of the invention referred to as the Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment (SELEX), wherein a candidate mixture of nucleic acids are iteratively enriched in high affinity nucleic acids and amplified by further partitioning.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
A group of oligonucleotide sequences capable of identifying Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus synchronously and preparation method of the oligonucleotide sequences
ActiveCN102605075AImprove stabilityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle strandOligonucleotide
The invention discloses a group of oligonucleotide sequences capable of synchronous identification of Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus and a preparation method of the oligonucleotide sequences, and relates to identification and detection of Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus. The oligonucleotide sequences comprise SEQ ID No.1-4. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) oligonucleotide library (5'-TCA GTC GCT TCG CCG TCT CCT TC----N35----GCA CAA GAG GGA GAC CCC AGA GGG-3') for screening; separately mixing the oligonucleotide library with Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus, and carrying out SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) screening; cloning and sequencing the aptamer-rich library; and selecting high-copy ssDNA in the sequencing result, verifying specificity of affinity, and obtaining the corresponding aptamers.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Bivalent binding molecules of 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors
Described herein are methods for identifying and preparing bivalent binding molecules to 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. The methods disclosed herein are based on the SELEX method for generating high affinity nucleic acid ligands. SELEX is an acronym for Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment. The methods of this invention combine two or more binding domains to two or more different epitopes of the same 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor. These bivalent binding molecules are useful as therapeutic and diagnostic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
A group of oligonucleotide aptamers for identifying clenbuterol hydrochloride, salbutamol and ractopamine with high specificity
ActiveCN105886512AEasy accessAccurate acquisitionBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerFluorescence
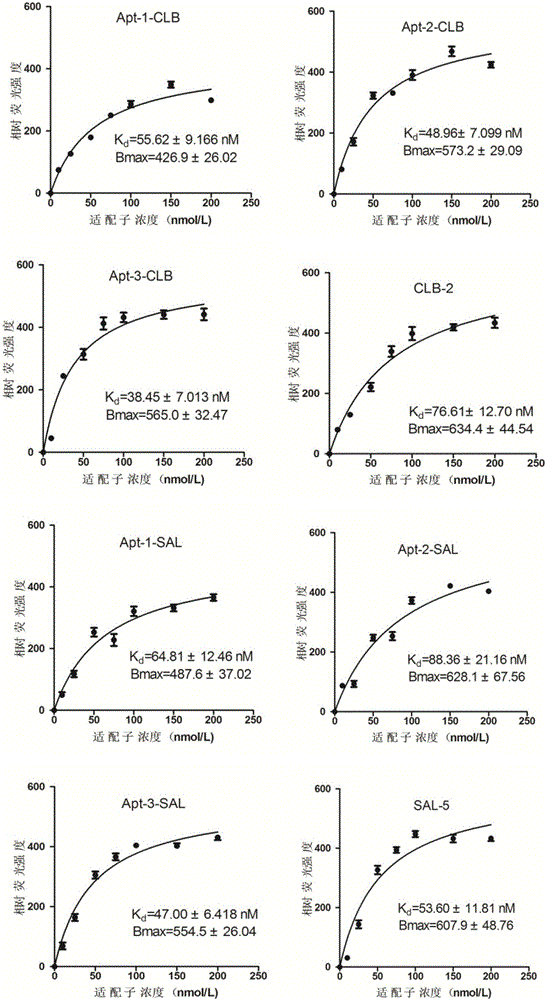
The invention provides a group of oligonucleotide aptamers Apt-1, Apt-2 and Apt-3 which are capable of simultaneously identifying clenbuterol hydrochloride and salbutamol, an oligonucleotide aptamer CLB-2 which is capable of identifying the clenbuterol hydrochloride with high specificity, an oligonucleotide aptamer SAL-5 which is capable of identifying the salbutamol with high specificity and two oligonucleotide aptamers RAC-5 and RAC-6 which are capable of identifying ractopamine with high specificity. Through an SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) technology based on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle separation, a random oligonucleotide library is immobilized on avidin-enveloped magnetic nanoparticles by virtue of a complementary chain of a biotinylation marker, and the oligonucleotide aptamers, which are high in specific affinity, are finally obtained by conducting screening by 16 turns. The aptamers are broad in application prospect; and the aptamers, by virtue of marker function genes or fluorescent dyes, are applicable to detection of the clenbuterol hydrochloride, the salbutamol and the ractopamine in food; therefore, a new choice is provided for existing detection methods which depend on antibodies.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
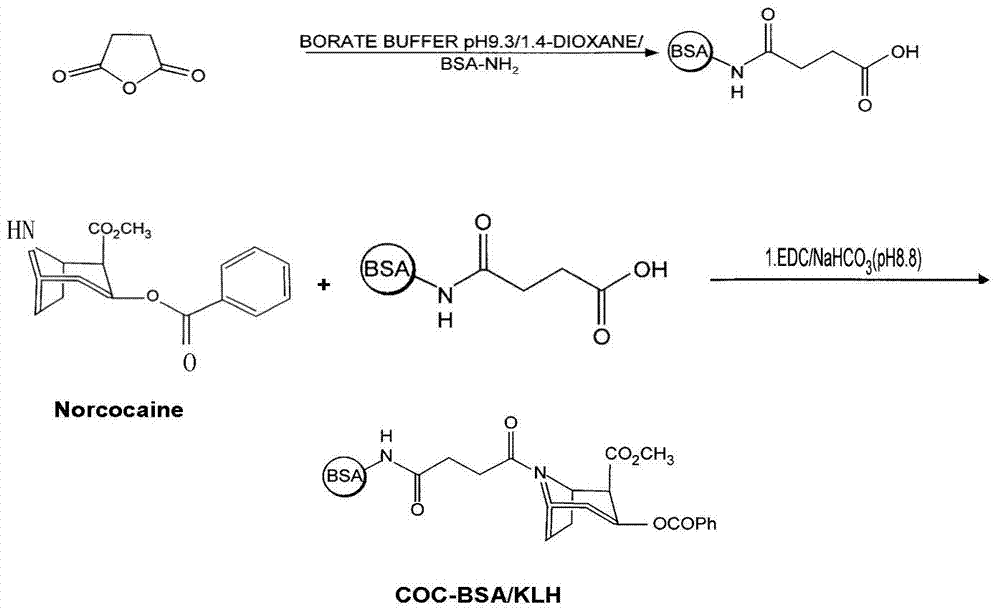
Cocaine aptamer, detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN104745586AStrong specificityBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationBiologySystematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment
The invention provides a cocaine aptamer, a detection kit and application thereof. In particular, based on a special structure ssDNA library, the inventor uses the SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology and successfully screens the aptamer with high affinity and specificity on cocaine. The aptamer provided by the invention is suitable for on-site rapid and sensitive detection of cocaine.
Owner:SHANGHAI CRIMINAL SCI TECH RES INST
Nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically recognizing Listeria monocytogenes, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN102010865AEasy to operateLower synthesis costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluoresceinScreening method
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically recognizing Listeria monocytogenes, a screening method and application thereof. By using the SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands By Exponential Enrichment) technology, a single-chain DNA oligonucleotide aptamer capable of specifically recognizing Listeria monocytogenes is obtained, and the aptamer can be transformed into a reporting aptamer by means of fluorescein labels and the like to be used for detecting Listeria monocytogenes. The sequence of the aptamer has wide application prospects in the aspect of accurately and fast detecting Listeria monocytogenes in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Oligonucleotide library classification and assessment method based on capillary zone electrophoresis
InactiveCN102636547AThe data processing method is simpleIntuitive approach to data processingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTime rangeCapillary electrophoresis
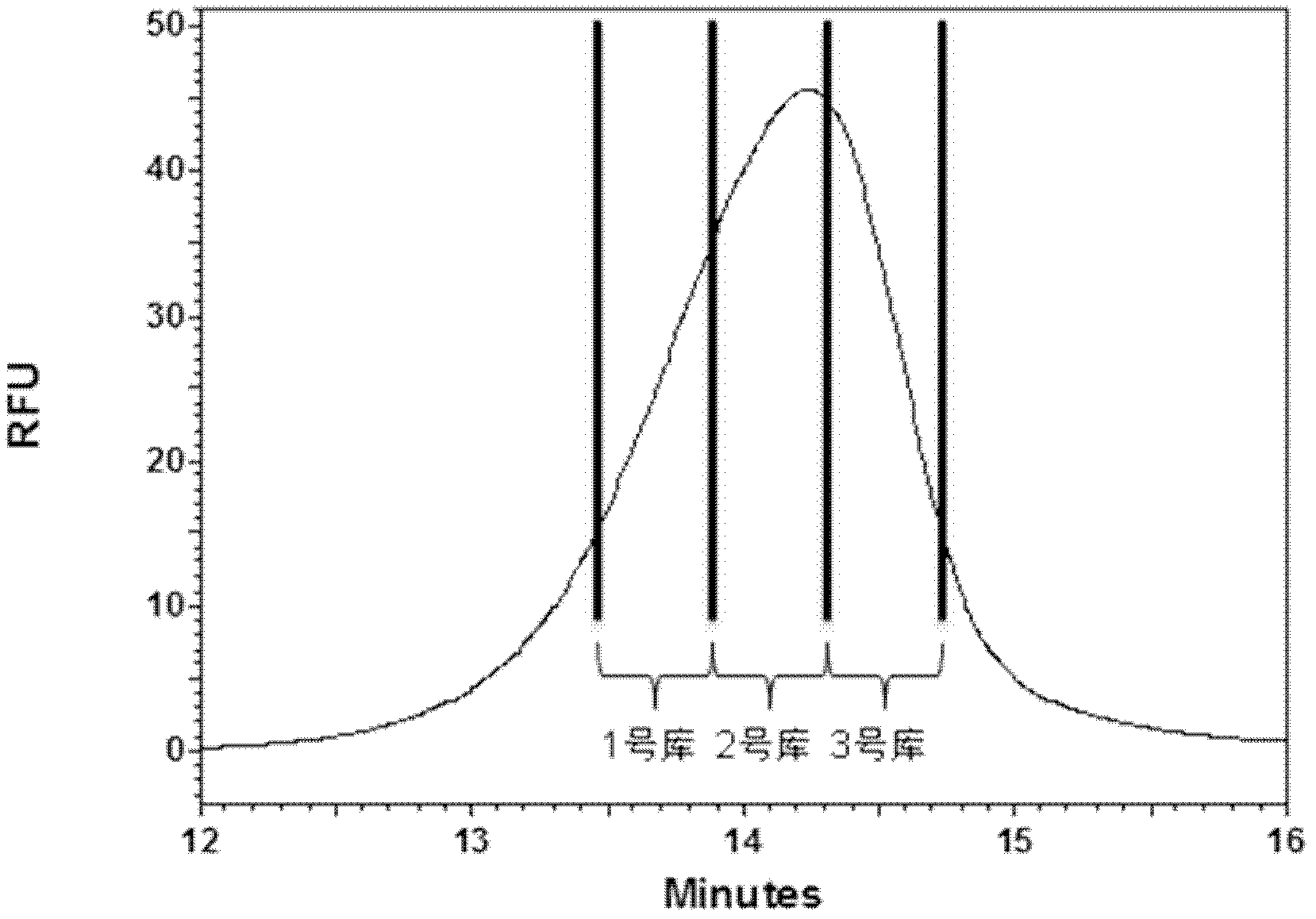
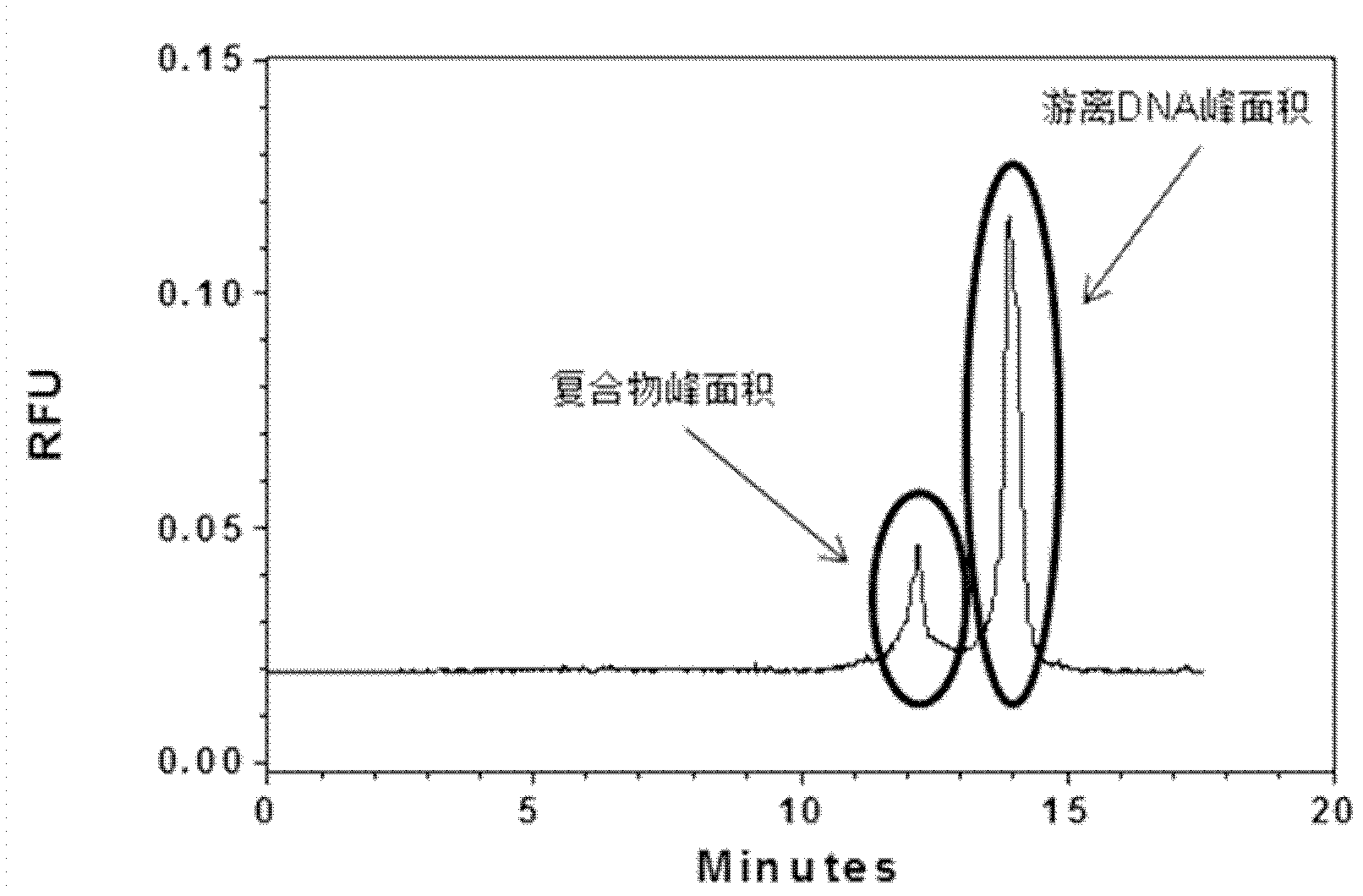
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide library classification and assessment method based on capillary zone electrophoresis, and belongs to the field of creature isolation analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: step one, carrying out capillary zone electrophoresis on an oligonucleotide library, and obtaining a secondary library within an oligonucleotide library electrophoresis time range according to transfer time slicing collection; and step two, respectively mixing each secondary library with a homogeneous target molecule, carrying out capillary zone electrophoresis, and comparing the strong or weak of each secondary library and target molecule interaction, thus obtaining the strongest secondary library of the target molecule combining capacity. The classification and assessment method can be used for realizing the fractionation of complicated constituent oligonucleotide library, and obtaining the strongest secondary library of the target molecule combining capacity; and the strongest secondary library of the combining capacity is utilized as a next CE (capillary electrophoresis)-SELEX(systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technical screening library, the screening range is reduced, and the screening period of an adaptation body is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Methamphetamine aptamer, detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN104745585AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerBiology
The invention provides a methamphetamine aptamer, a detection kit and application thereof. Specifically, based on an ssDNA library with a special structure, the inventor adopts the SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technique to successfully screen the aptamer with high affinity and specificity to methamphetamine. The aptamer provided by the invention can be used for on-site fast and sensitive detection of methamphetamine.
Owner:SHANGHAI CRIMINAL SCI TECH RES INST
Aptamers that bind abnormal cells
InactiveUS20090239762A1High affinityStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMixed cell cultureOn cells
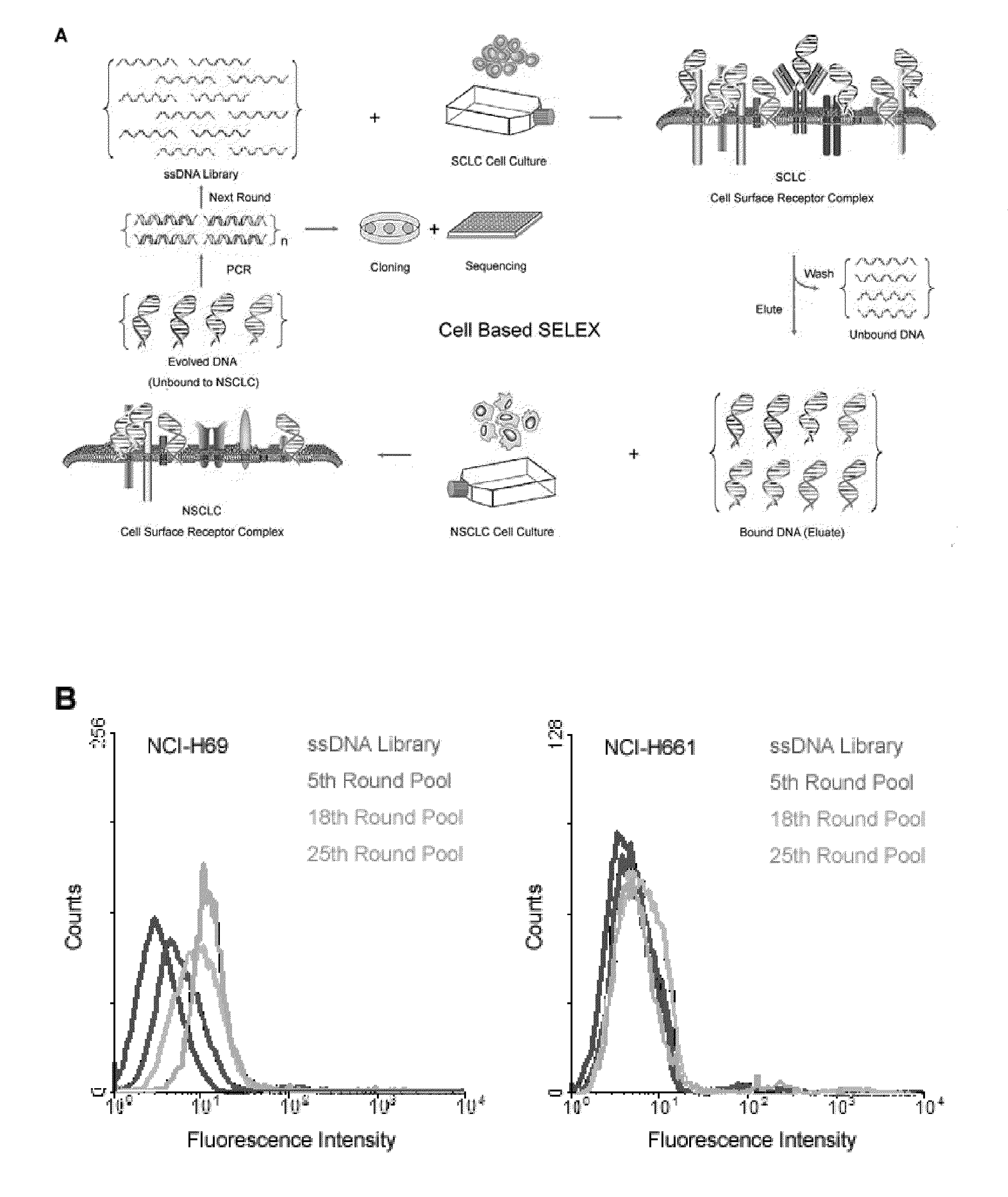
A new aptamer approach for the recognition of specific small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell surface molecular markers relies on cell-based systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (cell-SELEX) to evolve aptamers for whole live cells that express a variety of surface markers representing molecular differences among cancer cells. When applied to different lung cancer cells including those from patient samples, these aptamers bind to SCLC cells with high affinity and specificity in different assay formats. When conjugated with magnetic and fluorescent nanoparticles, the aptamer nano-conjugates could effectively extract SCLC cells from mixed cell media for isolation, enrichment, and sensitive detection.
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
Set of aptamers specifically recognizing three marine toxins
ActiveCN107541516ALow costShorten the production cycleDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationStructural homologySingle strand
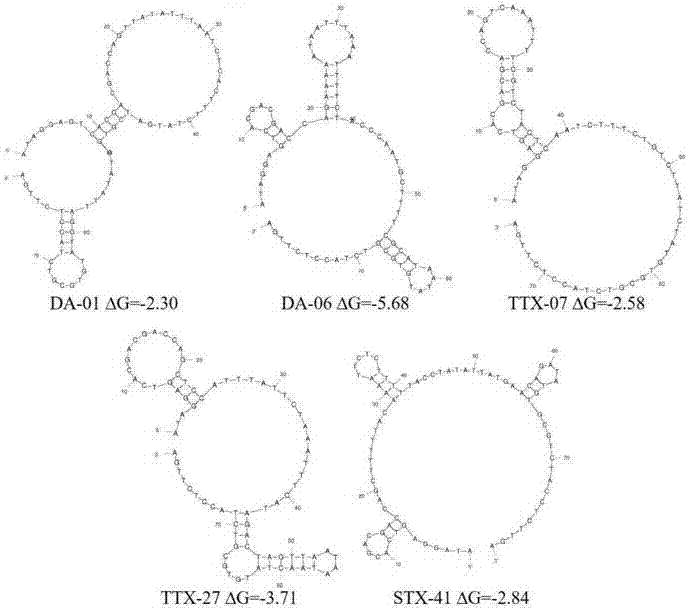
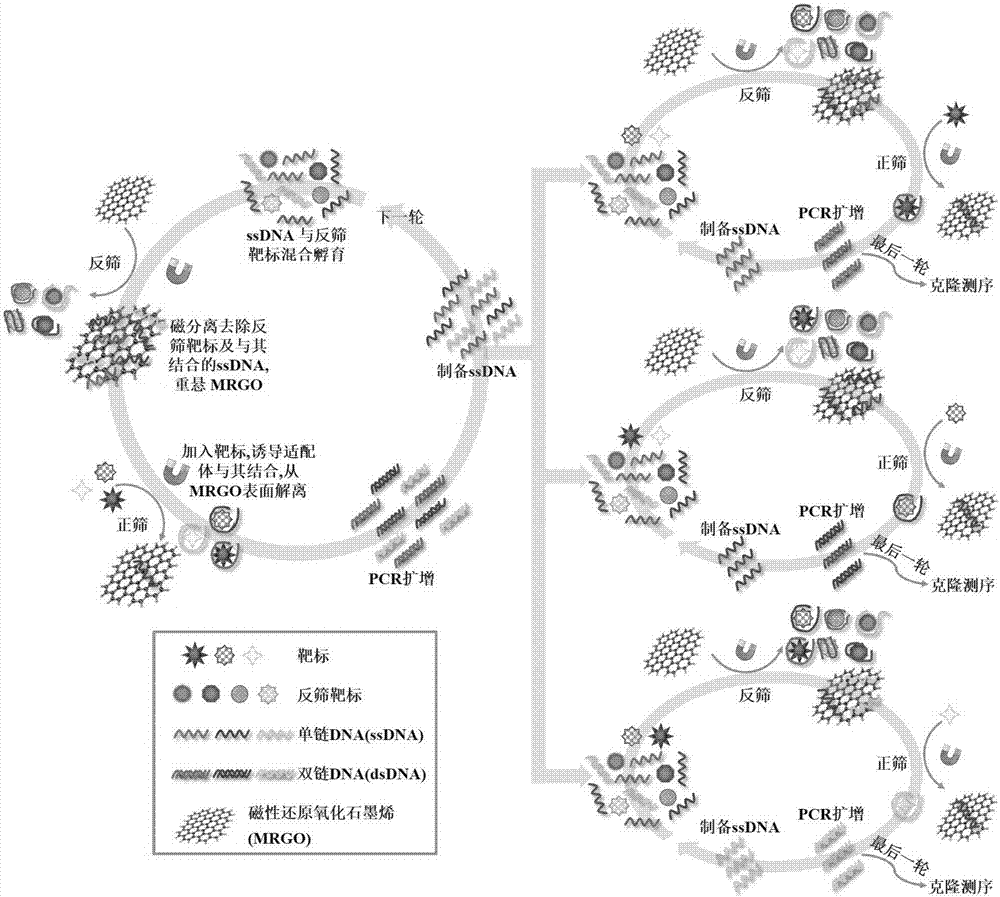
The invention provides a set of single stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamers DA-01 and TTX-27 which can simultaneously recognize domoic acid (DA) and tetrodotoxin (TTX), including one ssDNA aptamer DA-06 which specifically recognizes DA, one ssDNA aptamer TTX-07 which can specifically recognize TTX, and one ssDNA aptamer STX-41 which can specifically recognize saxitoxin (STX). According to the invention,magnetic reduced graphene oxide (MRGO) is adopted to assist in separated systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), properties of MRGO of being capable of adsorbing free ssDNA,but not adsorbing ssDNA combined with target molecules are utilized, and magnetic separation enrichment characteristics of MRGO are further used to separate ssDNA with affinity and without affinity to target toxins; primary structure homology and secondary structure similarity on obtained ssDNA are analyzed after 16 repeated rounds of incubation, separation, amplification and in-vitro screening for single-strand preparation, then the affinity and the specificity are measured, and finally one set of the aptamers with high affinity and specificity is obtained. The set of the aptamers has broadapplication prospects in the aspects of analysis, detection, separation, enrichment, removal and purification for DA, TTX and STX in aquatic products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting and identifying variety of snake venom by utilizing adaptor technology
The invention discloses a method for detecting and identifying the variety of snake venom by utilizing an adaptor technology, belonging to the field of biomedicine verification and relating to a method for detecting snake venom by utilizing the adaptor technology. Specific to the problems complex compositions of snake venom and poor specificity and sensitivity of the traditional snake bite detection method, the invention adopts a depletion SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) technology, and an adaptor with high-degree snake venom species specificity is obtained through screening and is converted into a report adaptor so as to establish a novel method for quickly detecting snake venom.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Aptamer AFB1-01 of aflatoxin B1 and application of aptamer AFB1-01
InactiveCN103695433AImprove stabilityEasy to storeFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerAflatoxin B
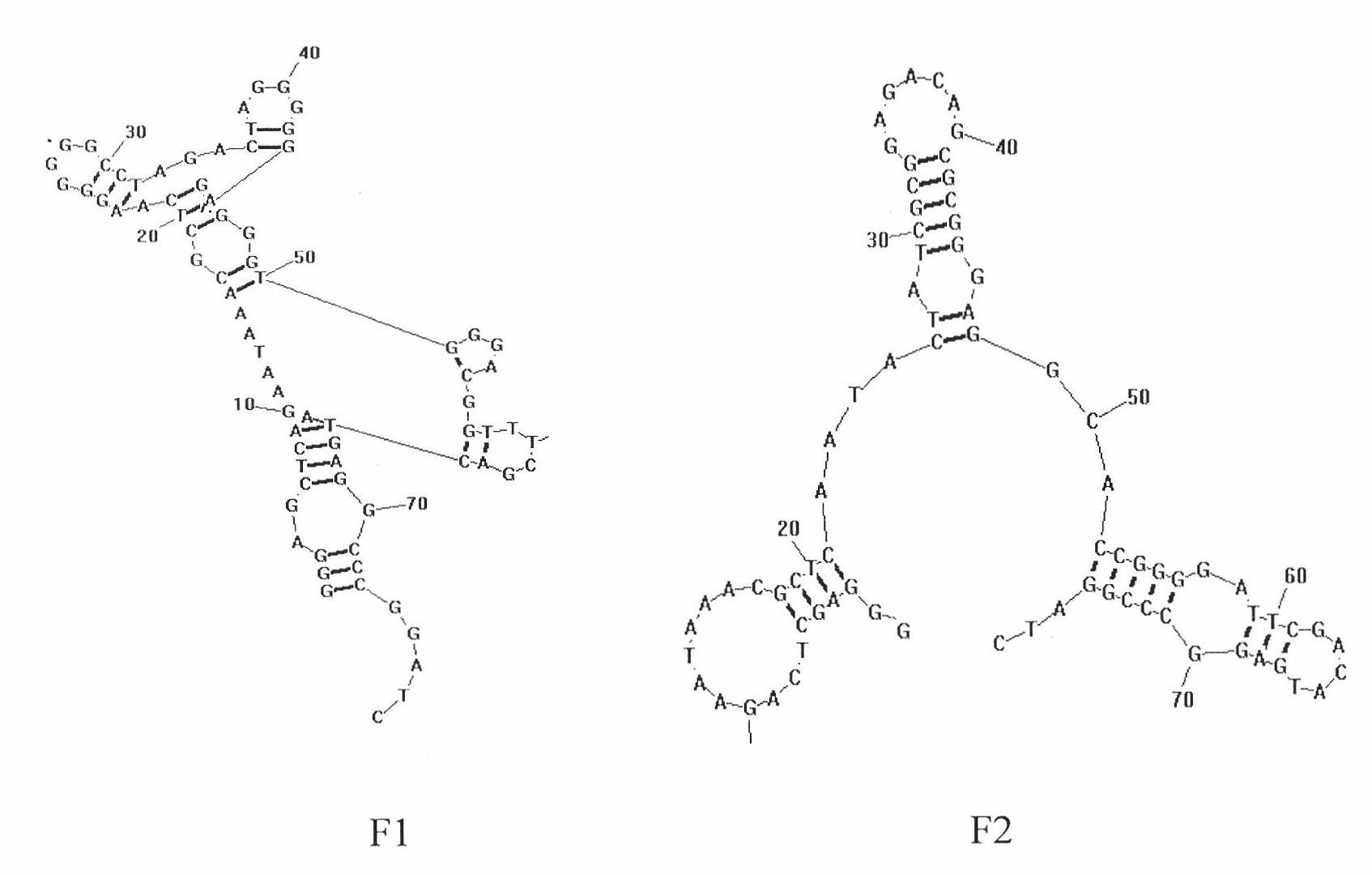
The invention discloses an aptamer AFB1-01 of aflatoxin B1 and an application of the AFB1-01, and relates to a nucleic acid. The aptamer AFB1-01 of the aflatoxin B1 is prepared by a systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) method based on agarose beads separation-flow cytometry analysis. The aptamer AFB1-01 of the aflatoxin B1 contains a G base, has a stem-and-loop structure, is high in affinity, good in stability, free of toxicity, and easy to synthetize and mark, and can be used as a potential detection reagent of the aflatoxin B1 in a sample.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Aptamer AFB1-20 of aflatoxin B1 and application thereof
InactiveCN103725686AImprove stabilityEasy to storeFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerAflatoxin B
The invention discloses an aptamer AFB1-20 of an aflatoxin B1 and application of the aptamer AFB1-20 and relates to nucleic acid. The invention also relates to a derivative of the aptamer including a truncated aptamer as well as a preparation method and application of the derivative. The aptamer AFB1-20 of the aflatoxin B1 is selectively prepared through an affinity SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) method based on agarose microbead separation-flow cytometry analysis. The aptamer AFB1-20 of the aflatoxin B1 and the derivative of the aptamer AFB1-20 are rich in G-base, have a stem-loop structure, high affinity, good stability and no toxicity, are easy to synthetize and label, and can be used as a potential separation, enrichment and detection reagent for the aflatoxin B1 in a sample.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Oligonucleotides aptamer special for distinguishing zearalenone
ActiveCN103013998AHigh affinityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a group of oligonucleotides aptamers special for distinguishing zearalenone, and belongs to the field of food safety testing. An SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology is combined with a magnetic bead with zearalenone coupled on the surface, and after 14 rounds of repeated incubation, cleaning, dissociation, amplification, gamma-exonuclease digestion are carried out to prepare a single-stranded secondary library, each oligonucleotides aptamer capable of being combined with the specificity of the zearalenone is screened out from a random single-stranded DNA library, after clone sequencing and 12 typical sequences are synthesized, the affinity is analyzed, and a specificity test is carried out to three aptamers with best affinity. The group of oligonucleotides aptamers (a nucleic acid sequence thereof selected from 1-3 in a sequence list) provides a new choice for developing a method which is for replacing the existing methods for detecting the zearalenone by depending on an antibody.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nucleic acid ligands to integrins
InactiveUS20070010473A1High affinity bindingInhibit bindingOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiagnostic agentIntegrin
Methods are described for the isolation of nucleic acid ligands to integrins using the SELEX process. SELEX is an acronym for Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment. The nucleic acid ligands of the present invention are useful as therapeutic and diagnostic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: Chemi-SELEX
InactiveUS20060088877A1Less laborReduce labor intensityOrganic chemistry methodsTransferasesCovalent InteractionSystematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment
This application provides methods for identifying nucleic acid ligands capable of covalently interacting with targets of interest. The nucleic acids can be associated with various functional units. The method also allows for the identification of nucleic acids that have facilitating activities as measured by their ability to facilitate formation of a covalent bond between the nucleic acid, including its associated functional unit, and its target.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Aptamer for osteosarcoma detection and kit for osteosarcoma detection
InactiveCN105755005AEasy to separateImprove efficiencyScreening processMaterial analysisAptamerBound property
The invention relates to an aptamer capable of binding osteosarcoma specifically.The aptamer is high in binding property and stability and is screened out from a random library by targeting the osteocarcinoma through application of a novel combinatorial chemistry technology SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment).The invention further relates to a kit for osteocarcinoma cell separation.The kit is capable of identifying osteocarcinoma cells quickly and is extremely high in application value.
Owner:曹帅
Bivalent binding molecules of 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors
InactiveUS20060147987A1Effective treatmentSure easyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEpitopeDiagnostic agent
Described herein are methods for identifying and preparing bivalent binding molecules to 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. The methods disclosed herein are based on the SELEX method for generating high affinity nucleic acid ligands. SELEX is an acronym for Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment. The methods of this invention combine two or more binding domains to two or more different epitopes of the same 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor. These bivalent binding molecules are useful as therapeutic and diagnostic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Nucleic acid ligands to integrins
InactiveUS7094535B2High affinity bindingInhibit bindingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesDiagnostic agentIntegrin
Methods are described for the isolation of nucleic acid ligands to integrins using the SELEX process. SELEX is an acronym for Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment. The nucleic acid ligands of the present invention are useful as therapeutic and diagnostic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Screening and application of oligonucleotide aptamer for specific recognition of Salmonella Typhimurium
ActiveCN103031305AShort synthesis cycleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyOligonucleotide
Belonging to the field of biotechnologies, the invention relates to screening and application of an oligonucleotide aptamer for specific recognition of Salmonella Typhimurium. Oligonucleotide aptamers able to specifically recognize Salmonella Typhimurium are obtained by a SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technique, and then a flow cytometer is employed to analyze the affinity and specificity of the aptamers, thus obtaining a Salmonella Typhimurium-recognizing oligonucleotide aptamer with the strongest affinity and the best specificity. The aptamer has wide application prospects in accurate, rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Group of oligonucleotide aptamers for specifically identifying aflatoxin B2
ActiveCN102952801ALower synthesis costReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerFluorescein
The invention discloses a group of oligonucleotide aptamers for specifically identifying aflatoxin B2. Single-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) aptamers capable of specifically identifying aflatoxin B2 are obtained through an SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology, and can be transferred to report aptamers through a fluorescein label and the like so as to be used for detect aflatoxin B2, and the aptamer sequences have wide application prospect in aspect of accurately and rapidly detecting aflatoxin B2 in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
One group of aptamers for specifically recognizing staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1
ActiveCN103243101AEasy to prepareLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesStaphylococcus aureus enterotoxinBioinformatics
The invention discloses one group of aptamers for specifically recognizing staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1, and belongs to the biological technical field of food safety. In order to overcome the defect of lacking aptamer of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1 in the prior art, one group of aptamers having good affinity and specificity on the staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1 is obtained by 12 turns of repeated screening through SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology and analysis and verification of affinity and specificity tests. The group of aptamers provides a specific and efficient recognition ligand for analyzing and detecting the staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1 in food or environment and provides a new selection for the existing method of detecting the staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1 through antibodies.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fusion protein aptamer screening method and kit
InactiveCN109321564AIntegrity guaranteedEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processAptamerScreening method
The invention provides a fusion protein aptamer screening method and kit in gene engineering, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The fusion protein aptamer screening method utilizes a two-way heat cycling subtraction systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), adopts fusion proteins in the gene engineering as a screening target, and epoxy (or carboxyl, NHS magnetic beads and streptomycin) agar magnetic beads as a vector, couples a fusion tag protein antibody (or biotinylated aptamer) onto the magnetic beads to form capturing magnetic beads so as to capture the fusion tag protein expressed in the gene engineering, and utilizes a random oligonucleotide library with large capacity to be combined with magnetic bead-tag protein antibody-tag protein-target protein to form a complex, thereby screening out the aptamer specifically combined with the target protein. The fusion protein aptamer screening method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, rapidness, high efficiency and the like, and has important significance in detection and medicine research for the secretion or intracellular expression gene engineering fusion protein of bacteria, yeast, insects and mammalian cells.
Owner:廖世奇
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com