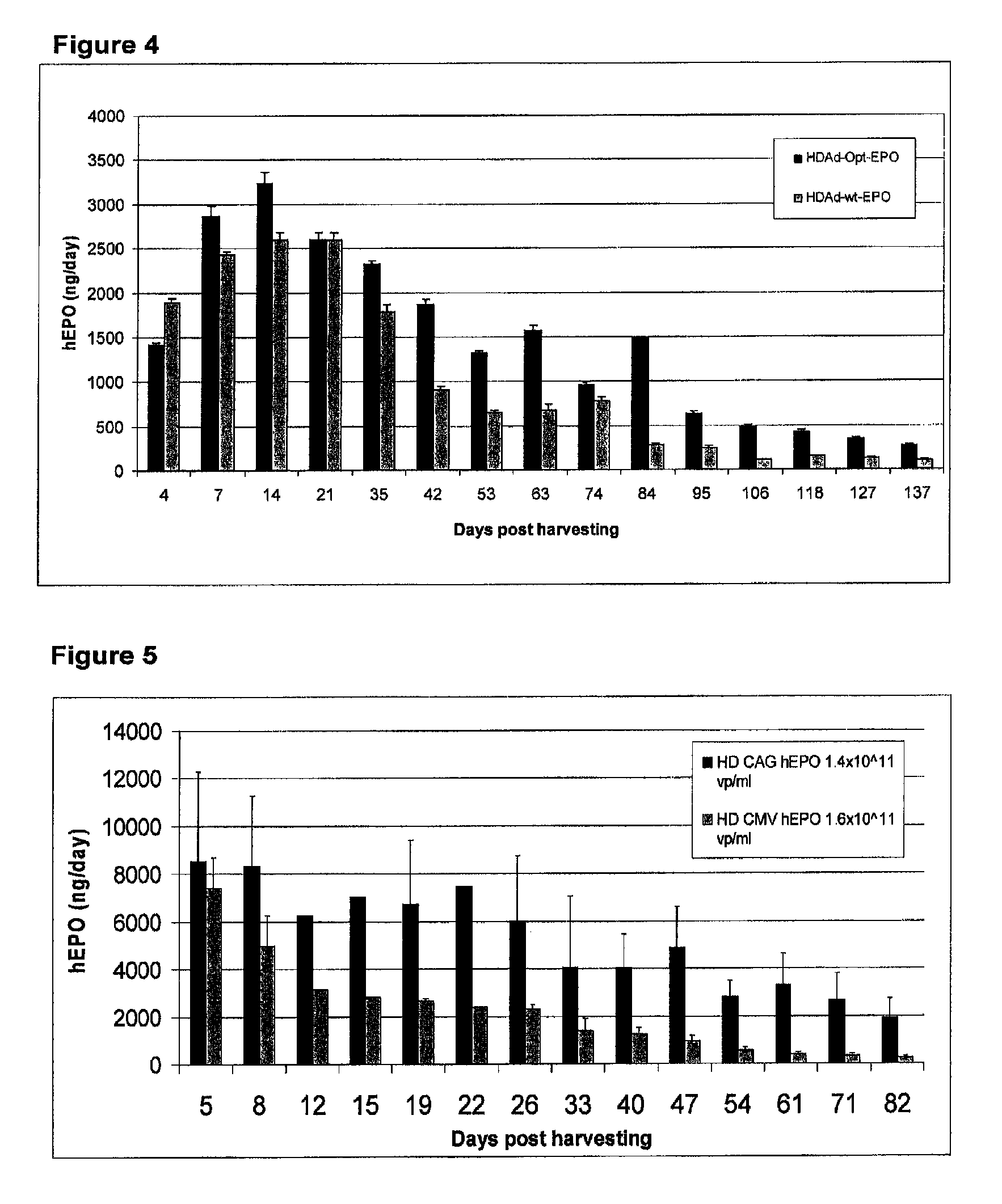
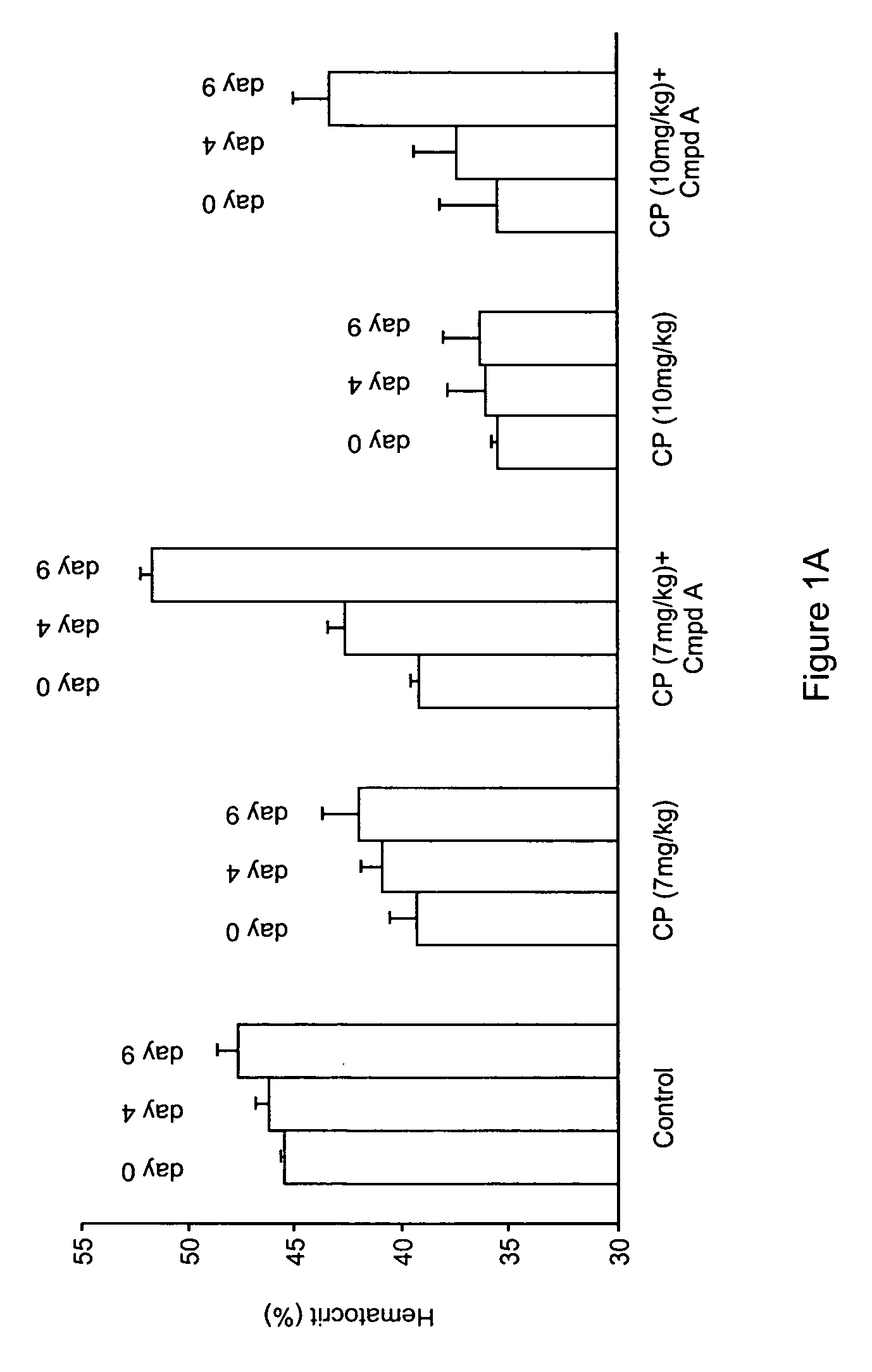
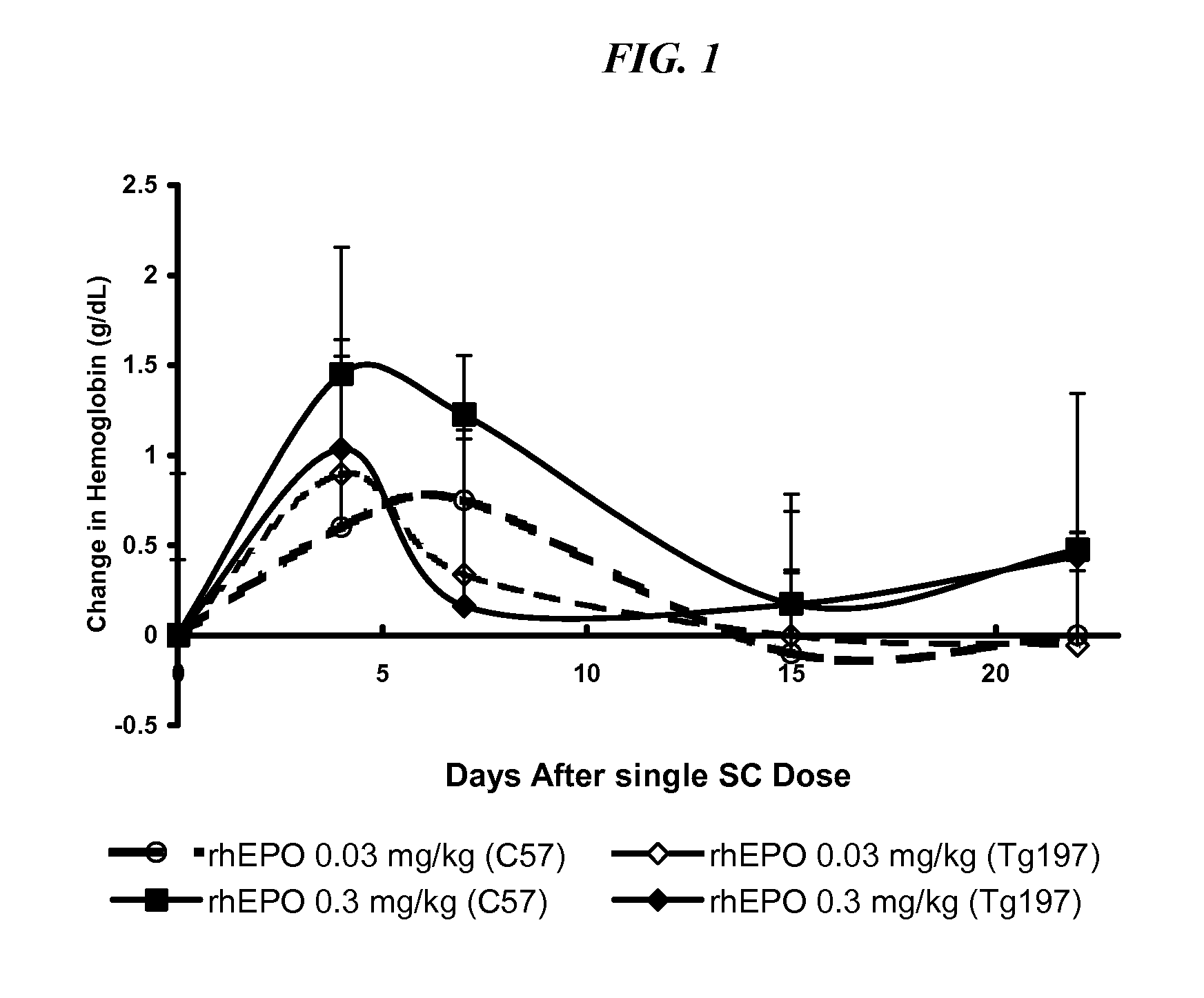
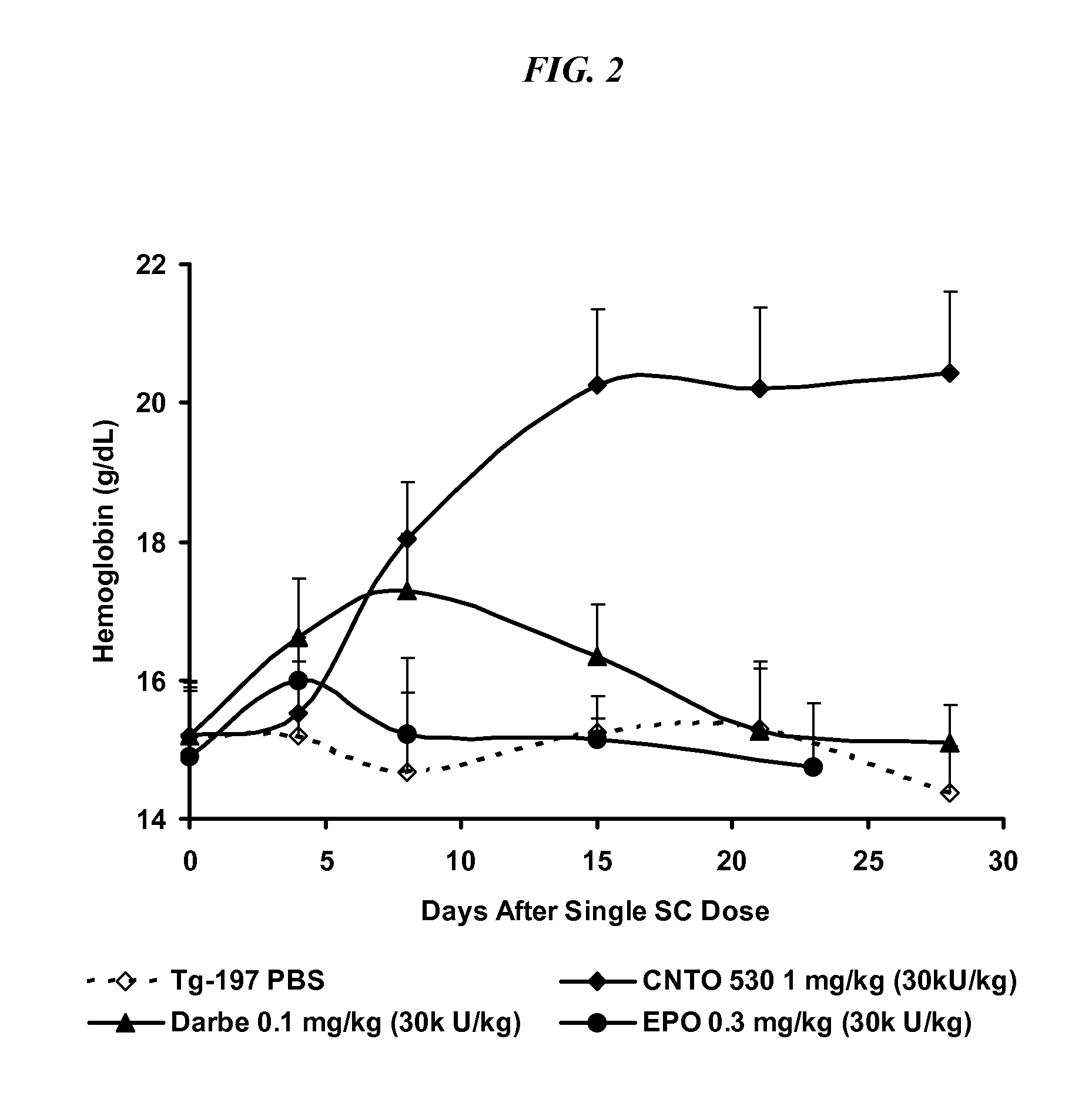
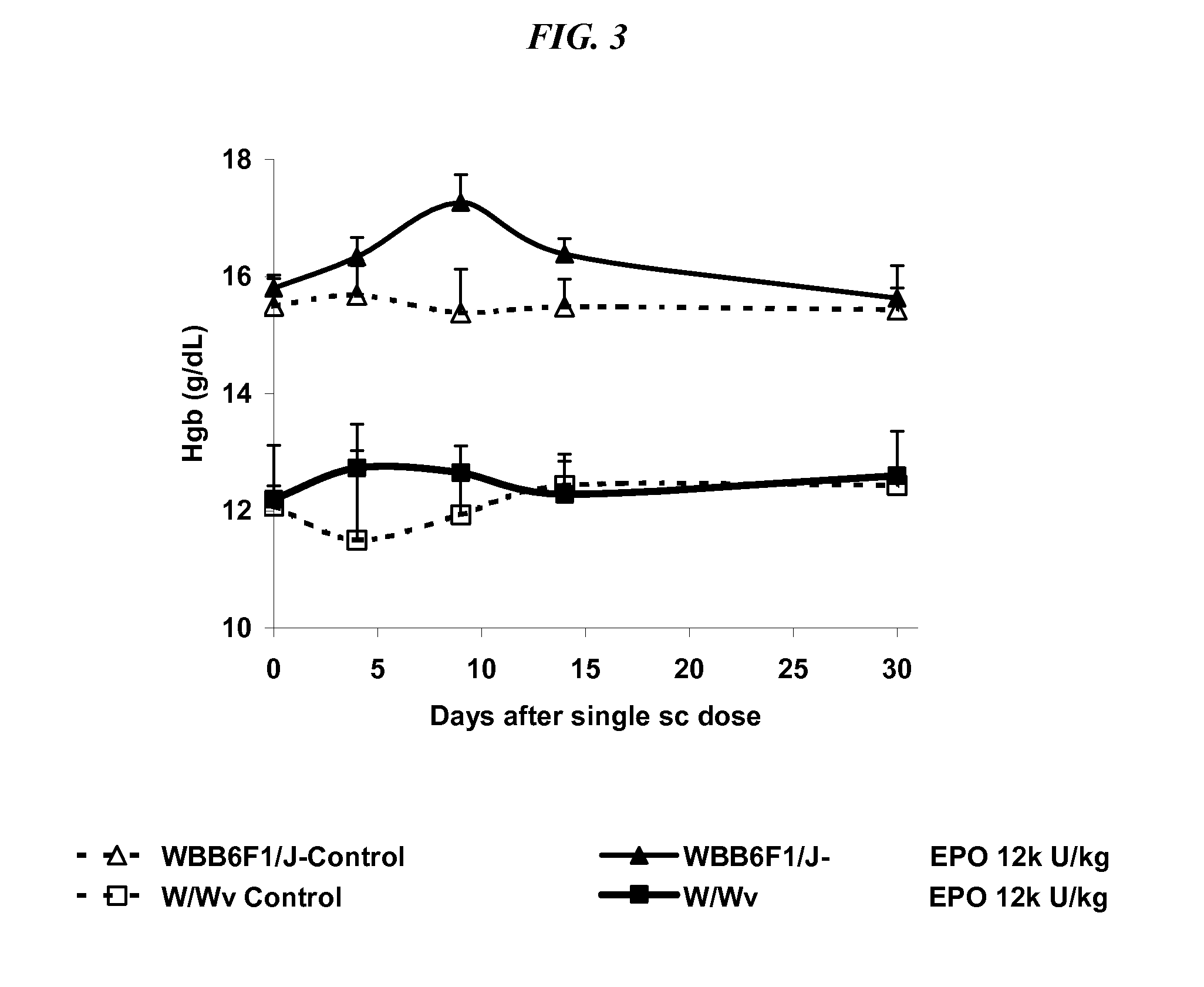
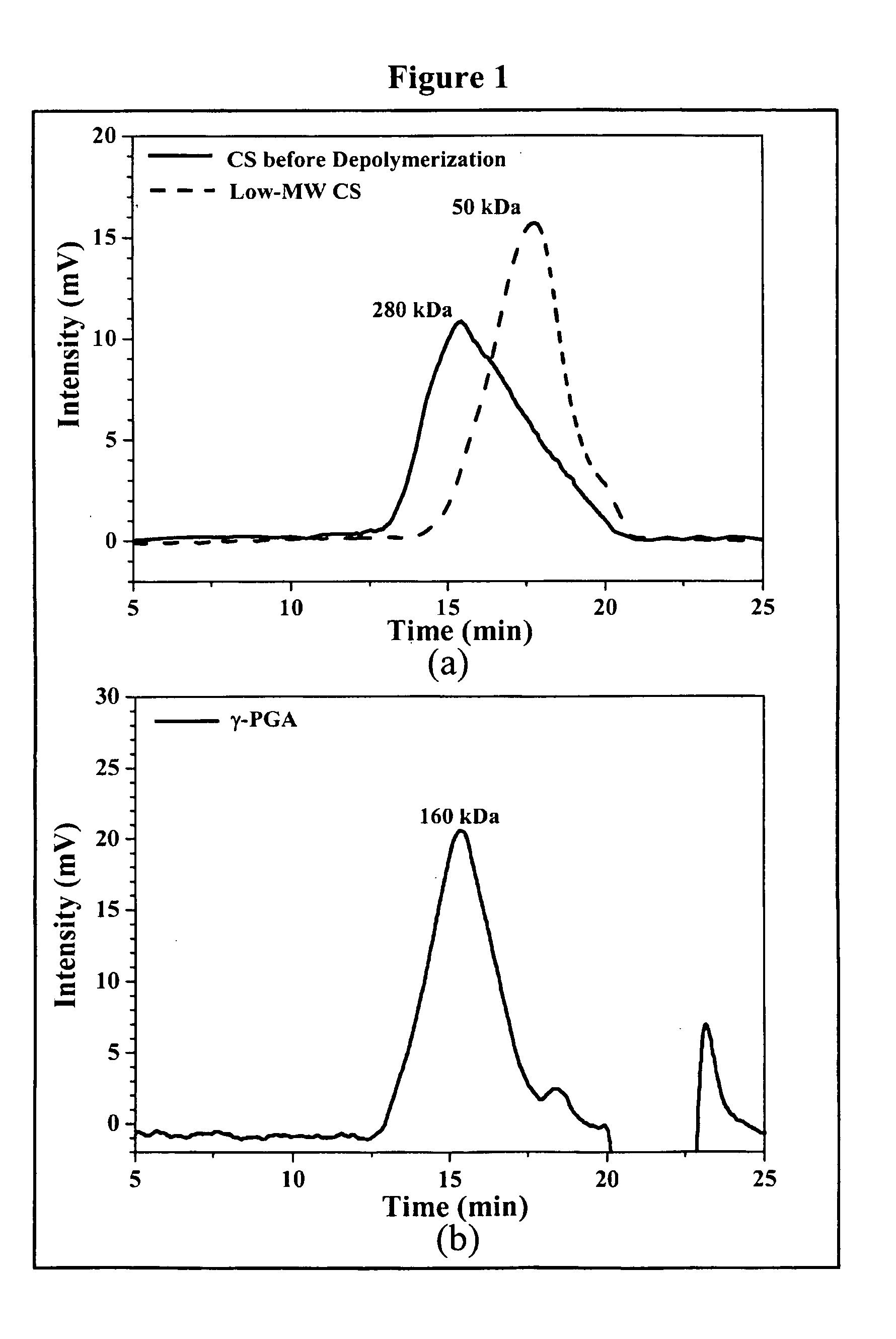
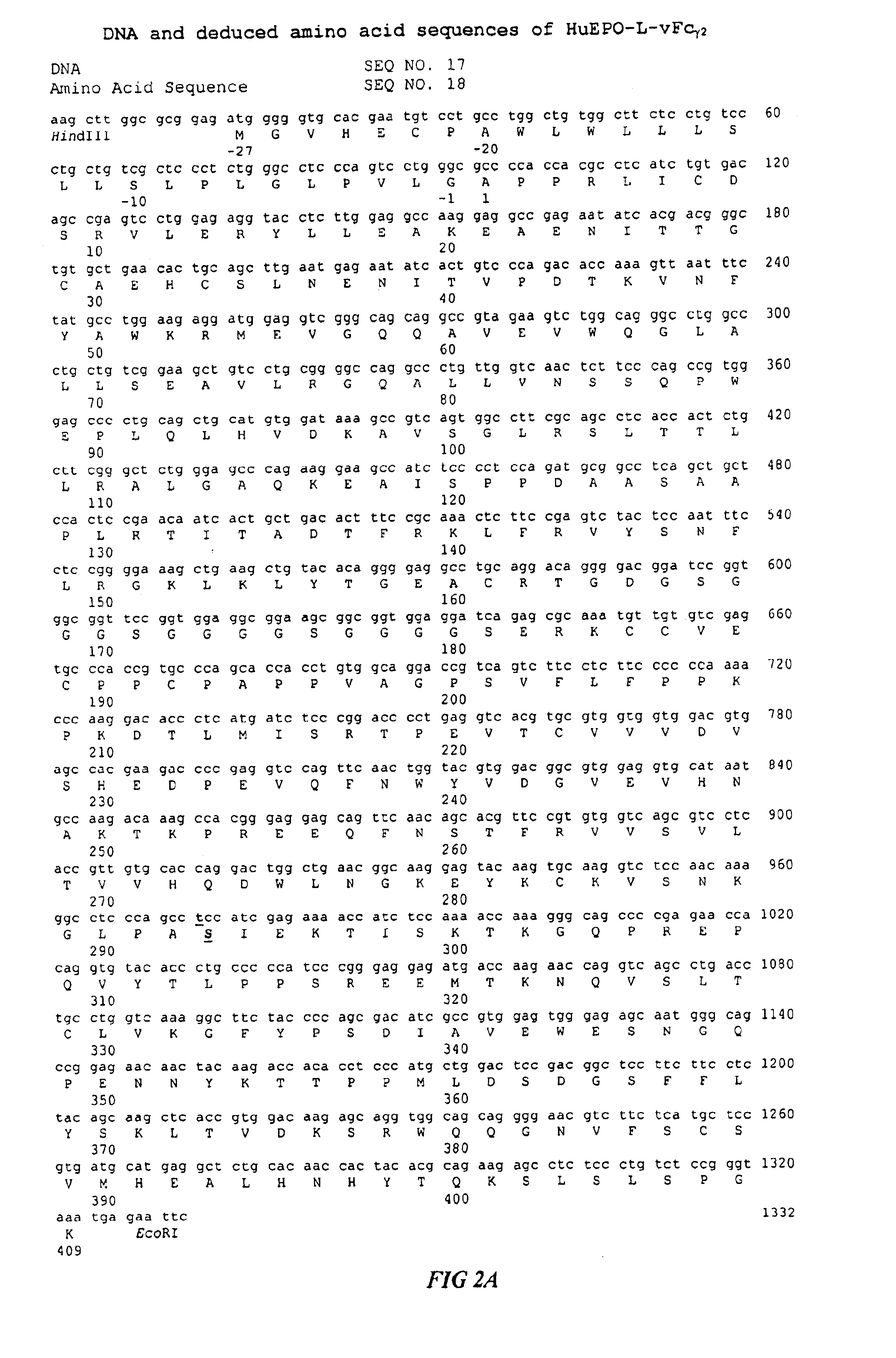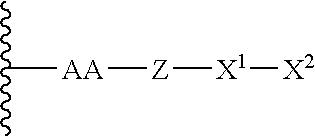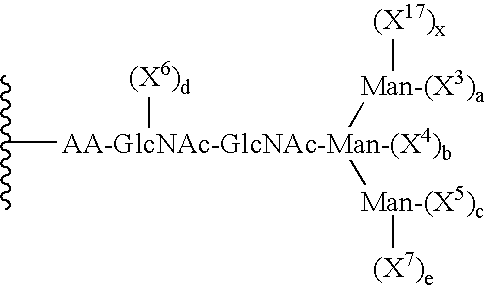Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
475 results about "Erythropoietin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
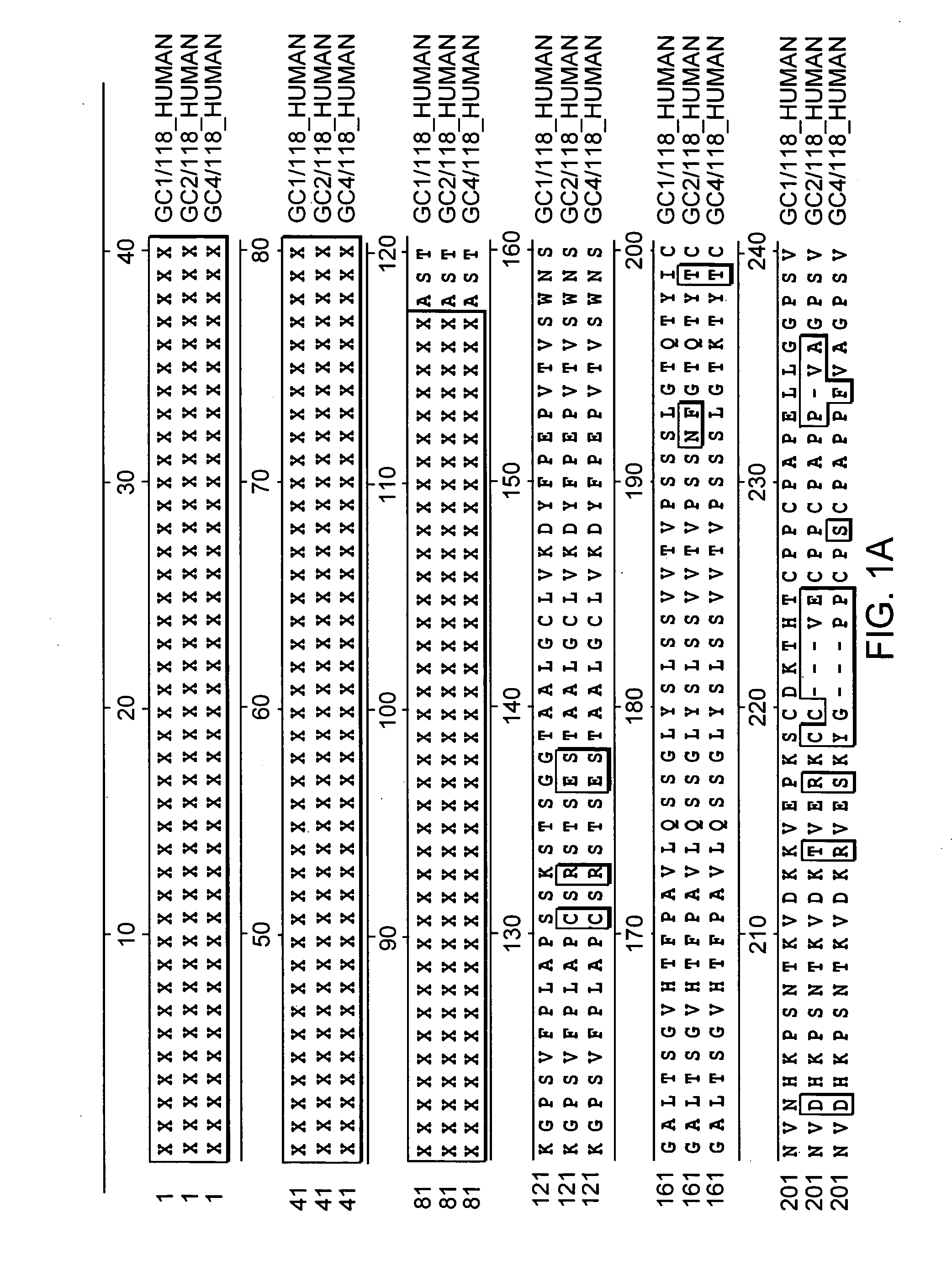
Erythropoietin (/ɪˌrɪθroʊˈpɔɪ.ɪtɪn, -rə-, -pɔɪˈɛtɪn, -ˈiːtɪn/; EPO), also known as haematopoietin or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted by the kidney in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bone marrow. Low levels of EPO (around 10 mU/mL) are constantly secreted sufficient to compensate for normal red blood cell turnover. Common causes of cellular hypoxia resulting in elevated levels of EPO (up to 10 000 mU/mL) include any anemia, and hypoxemia due to chronic lung disease.
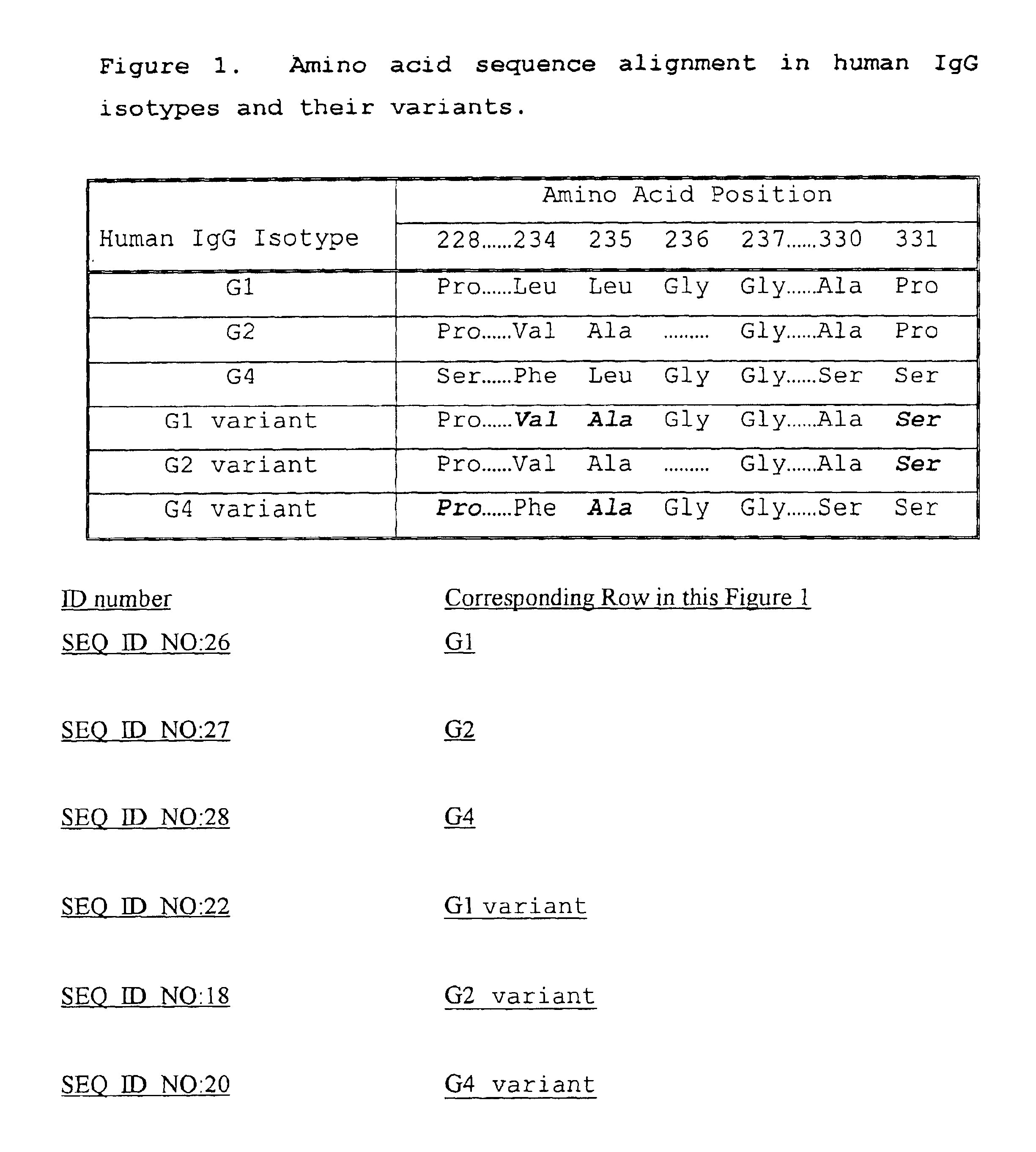
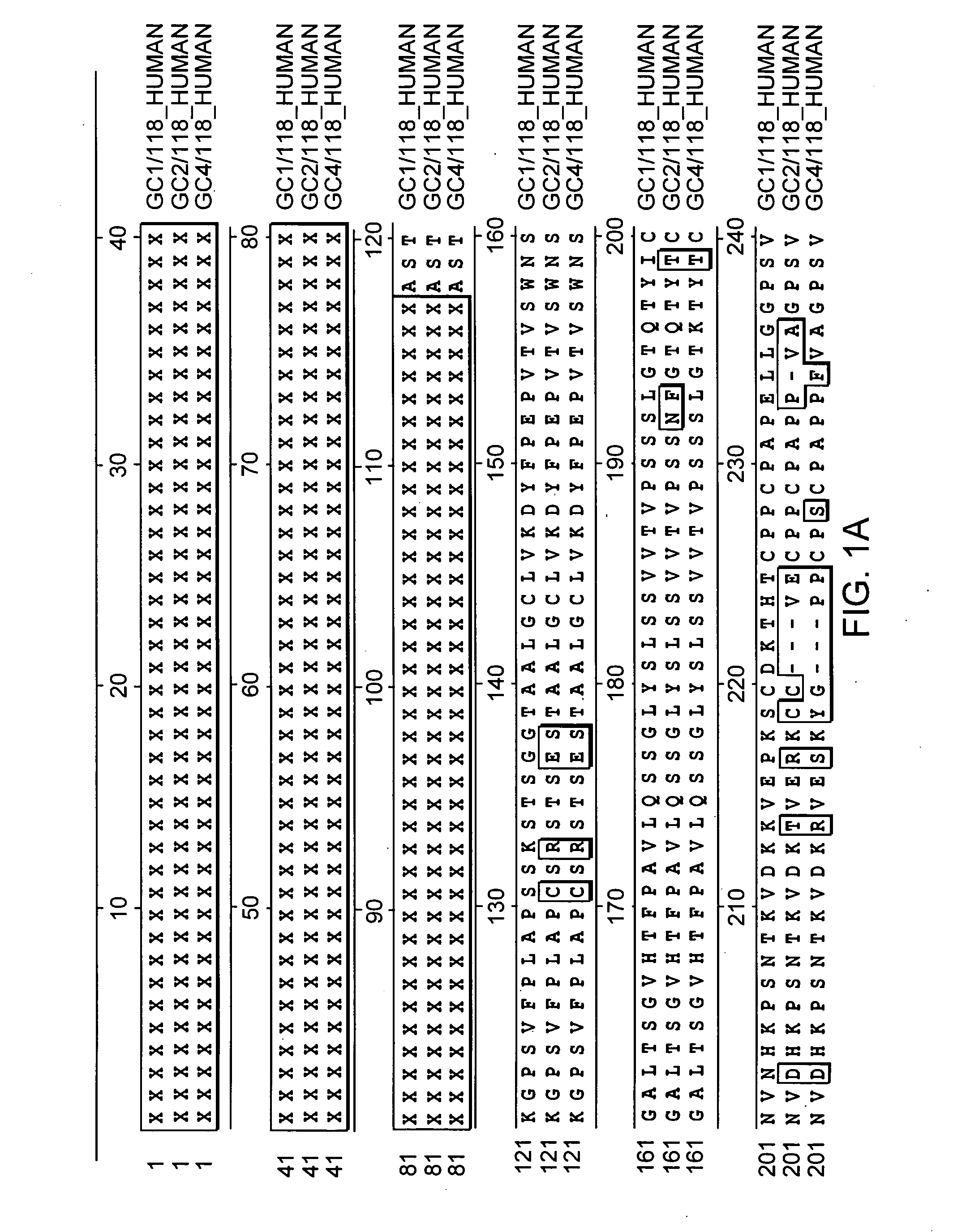
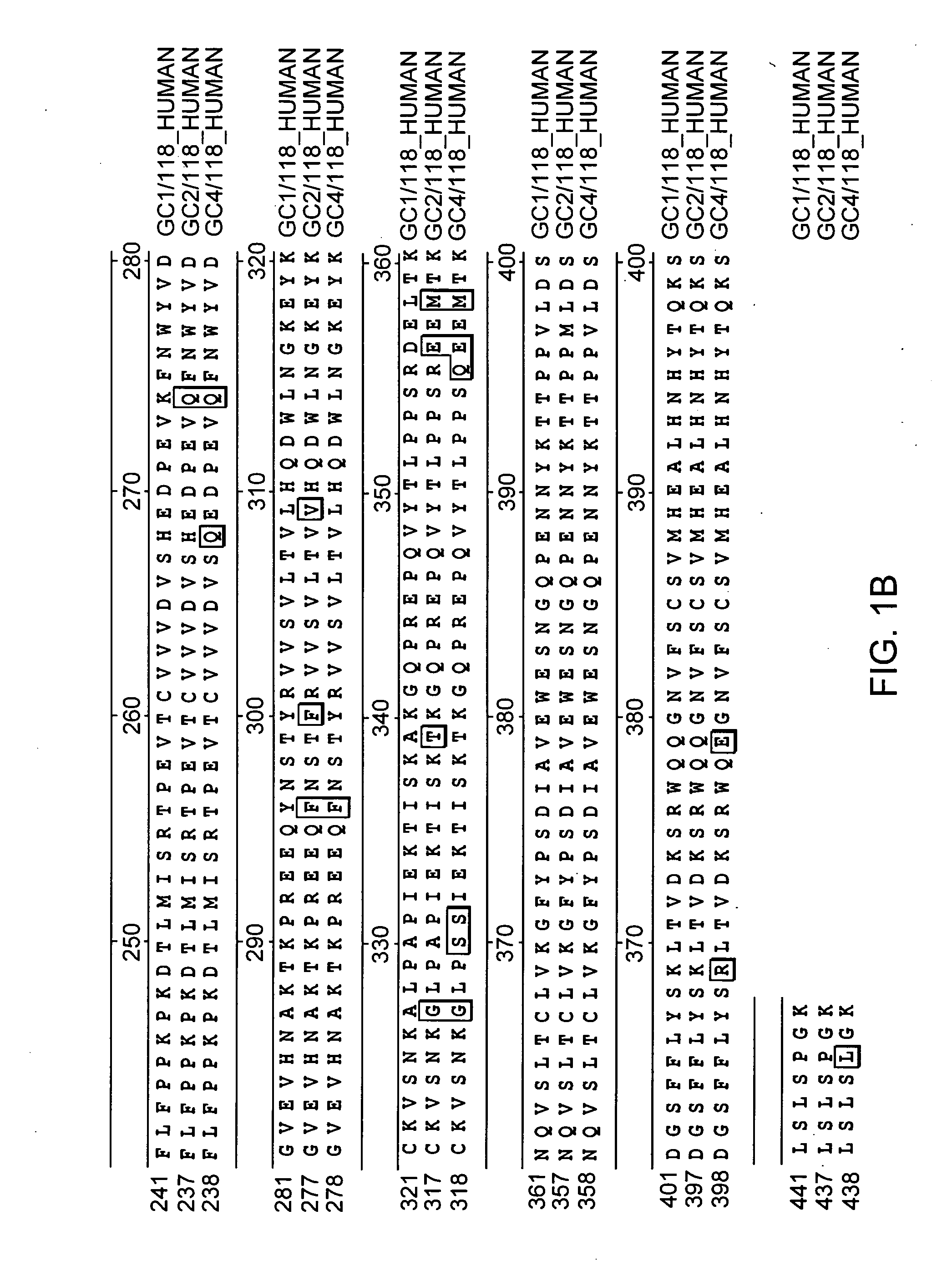
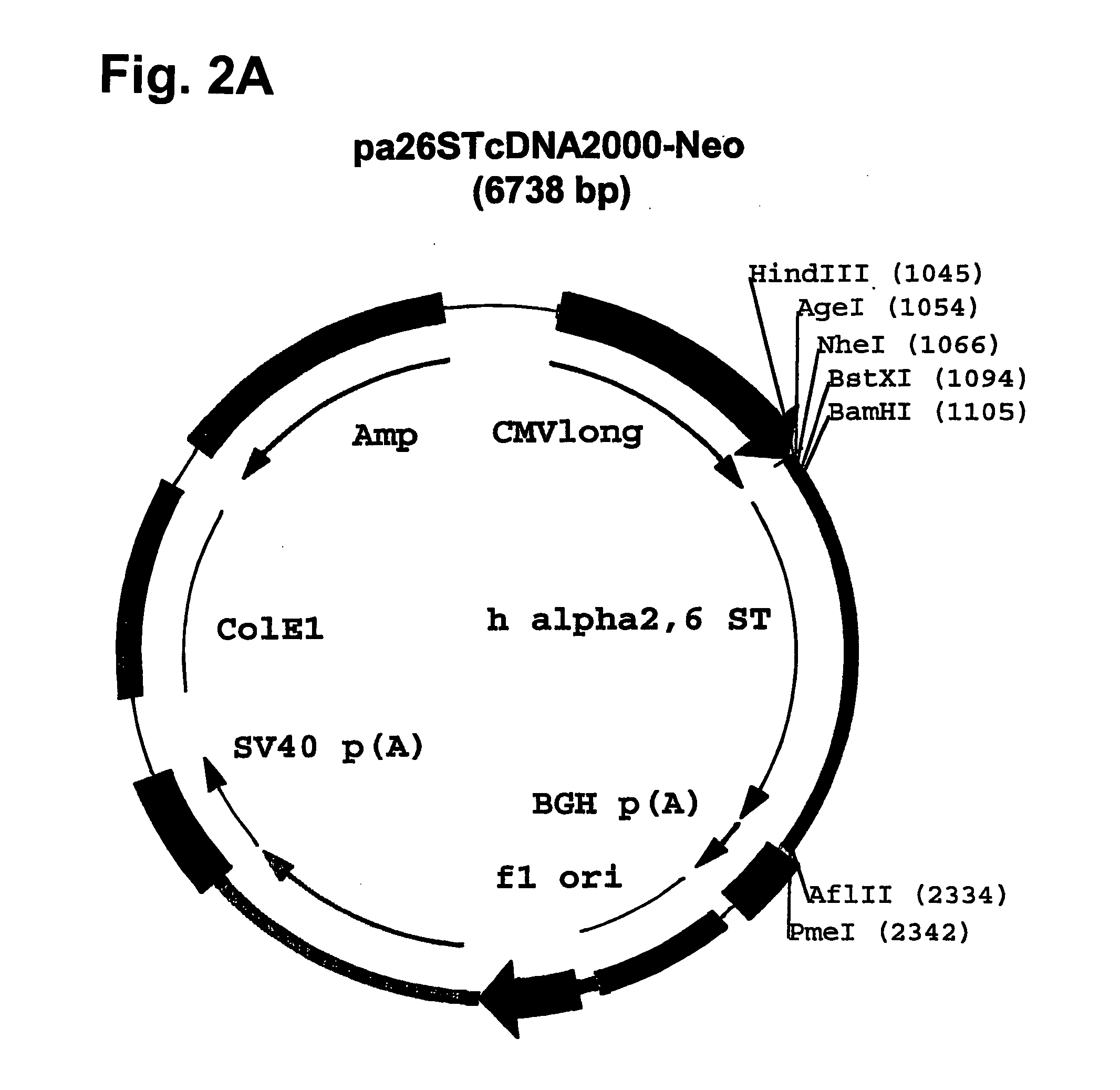
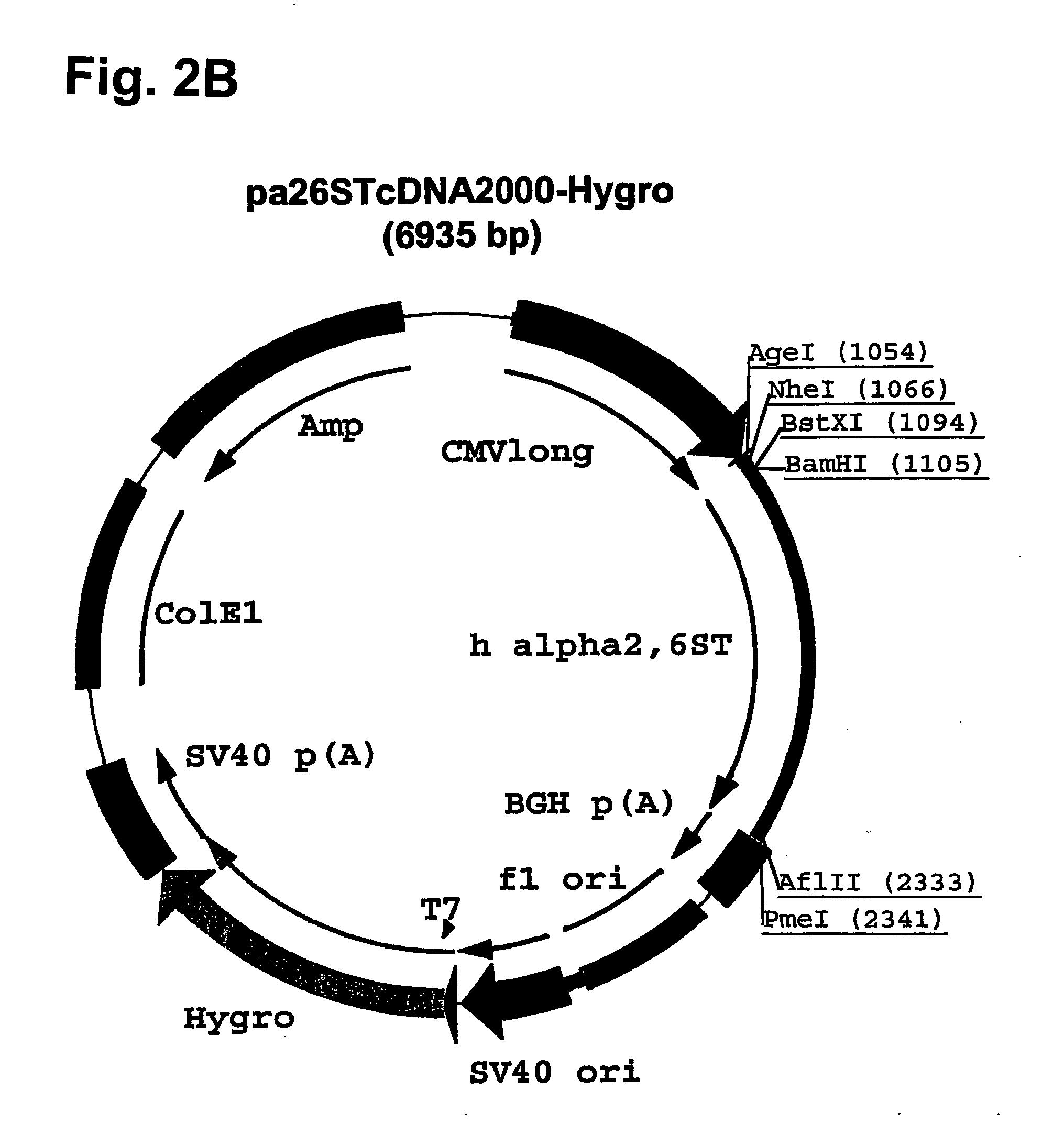
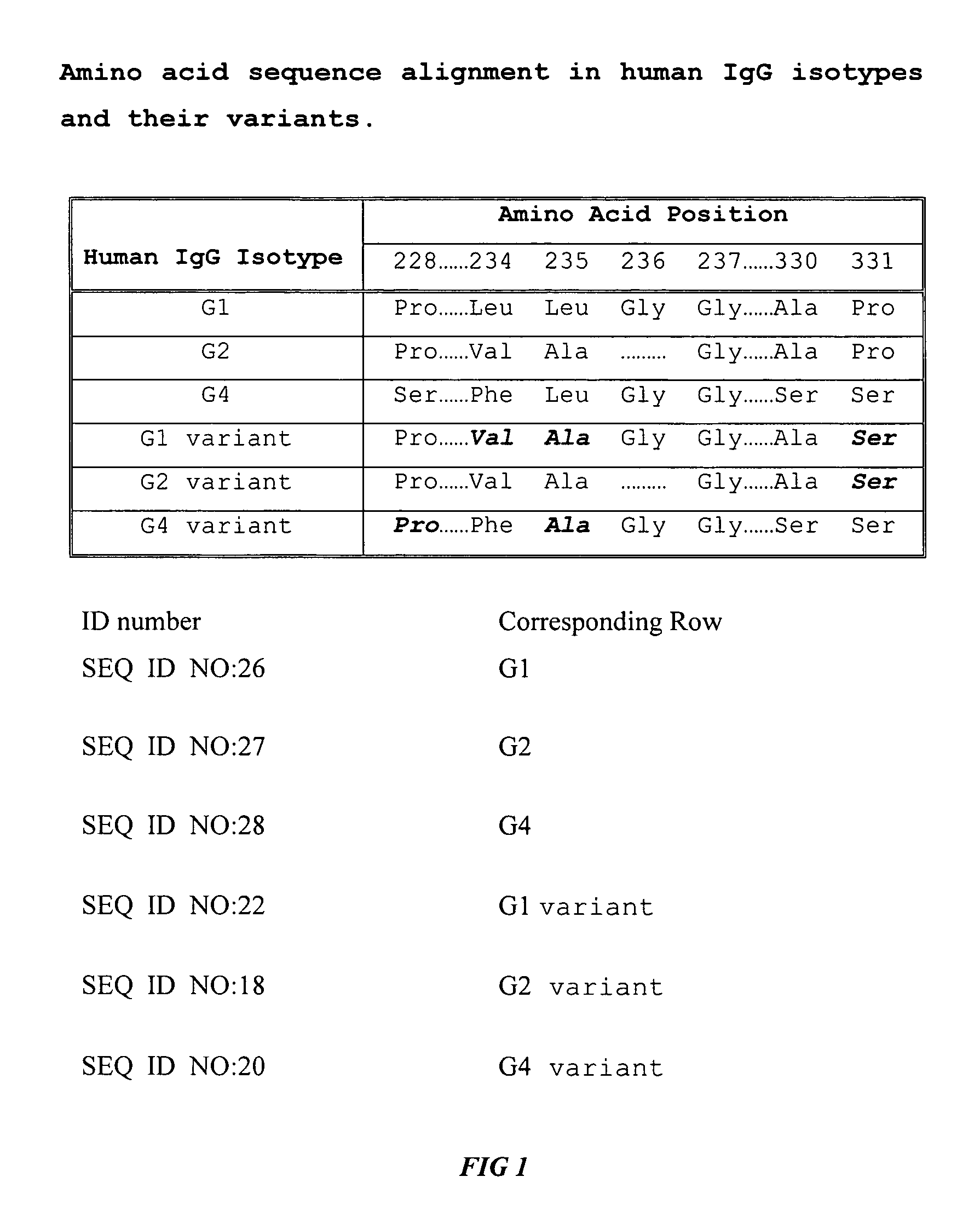
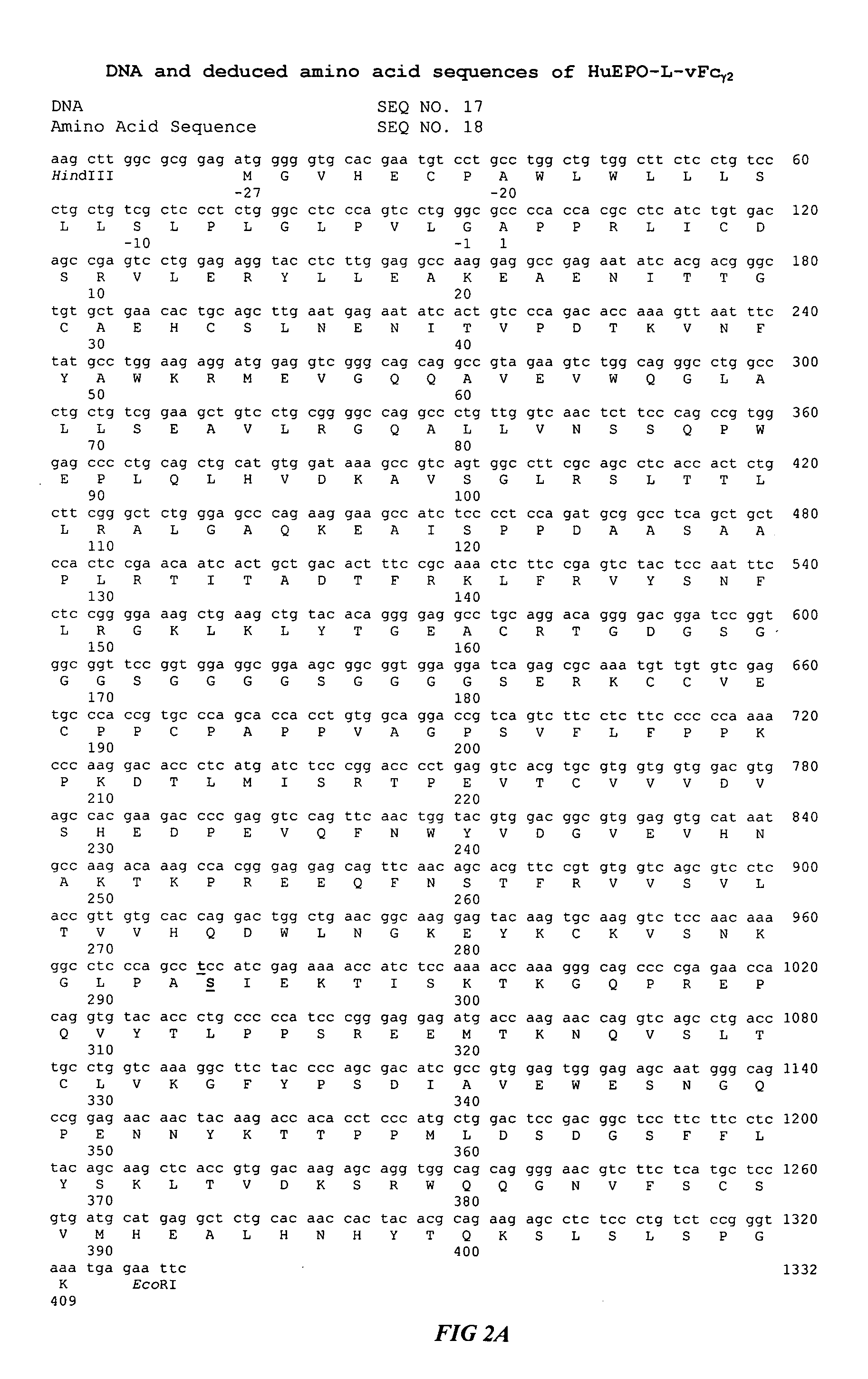
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS6900292B2Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:LONGBIO PHARM (SUZHOU) CO LTD
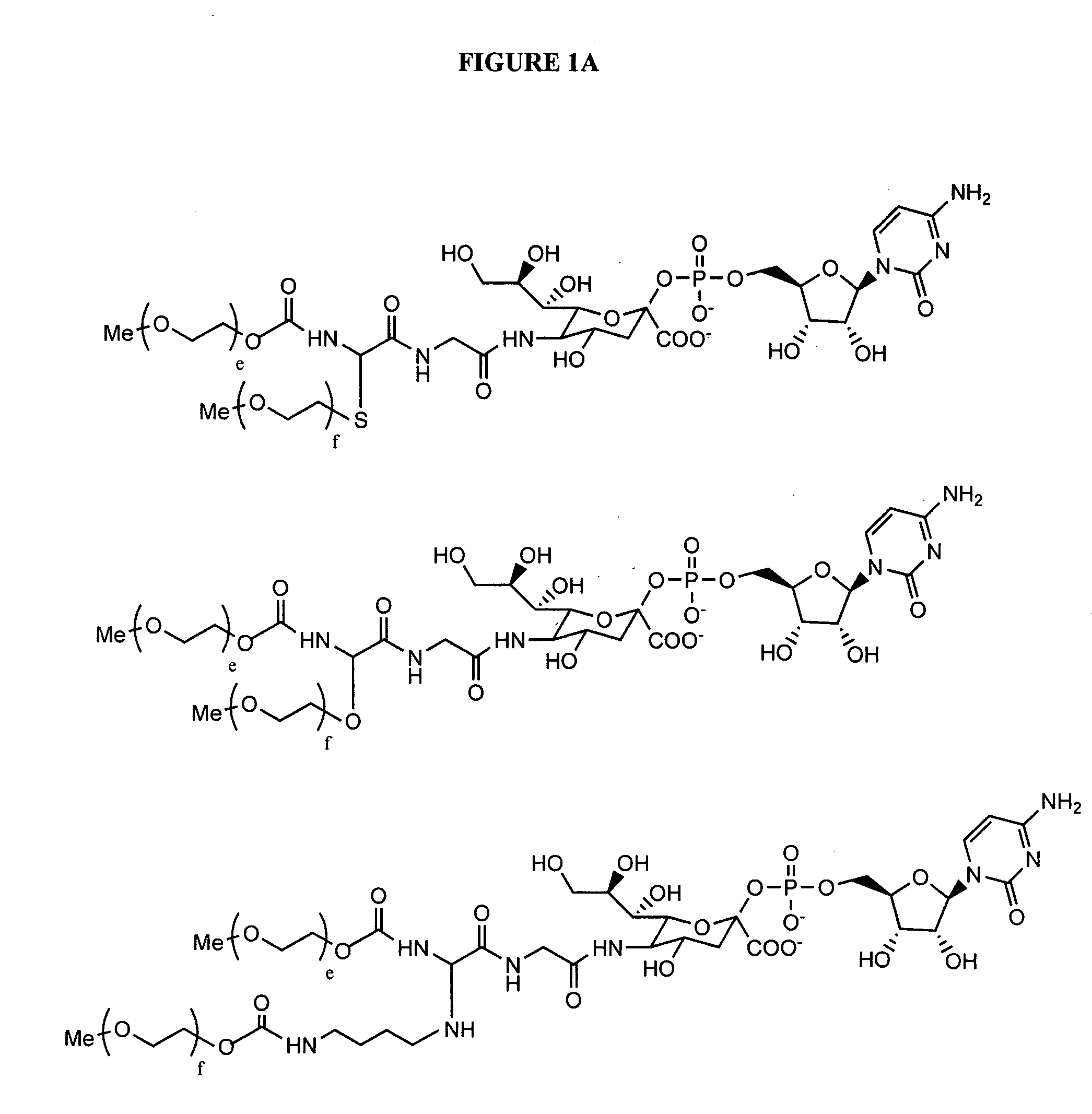
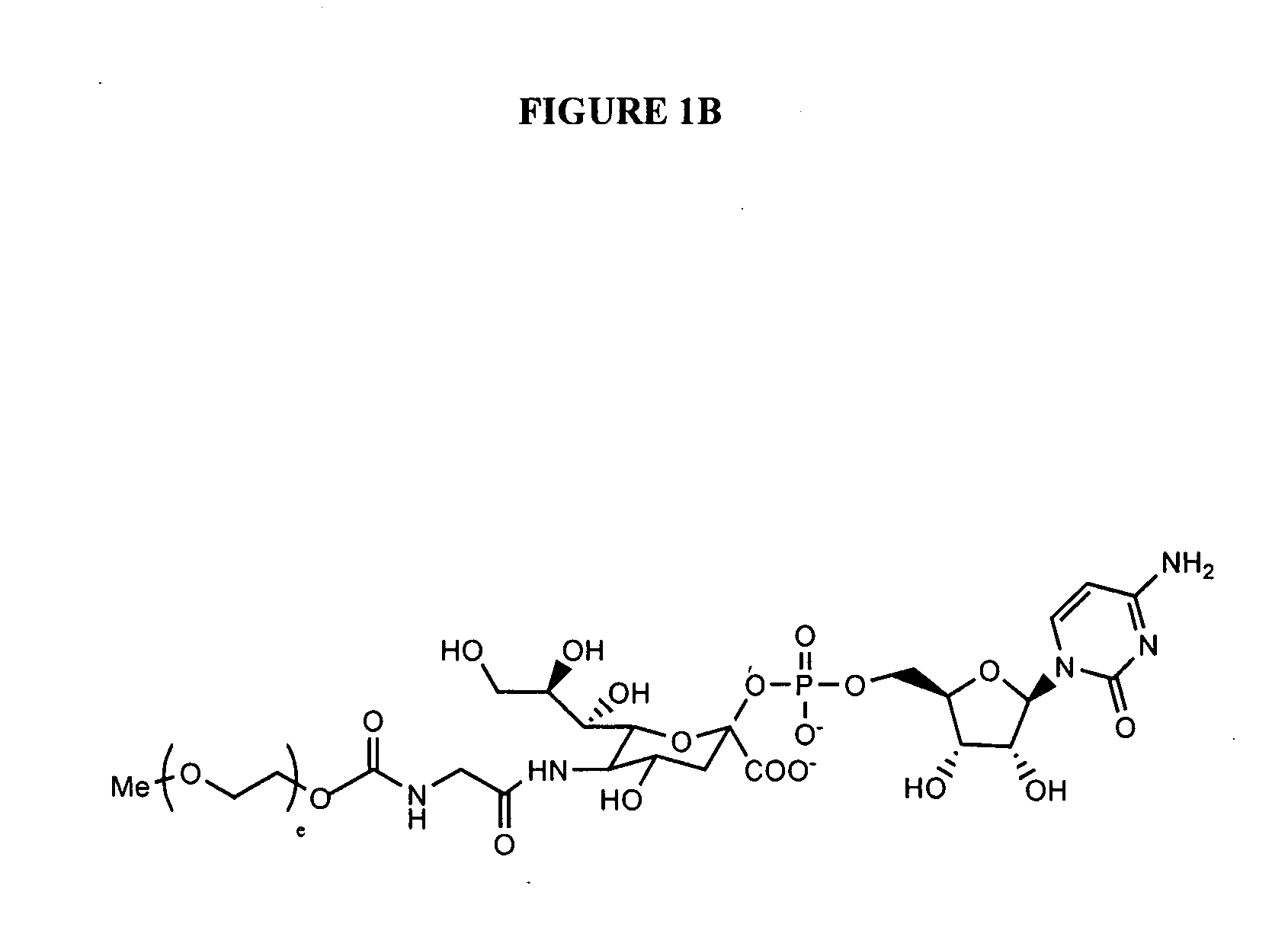
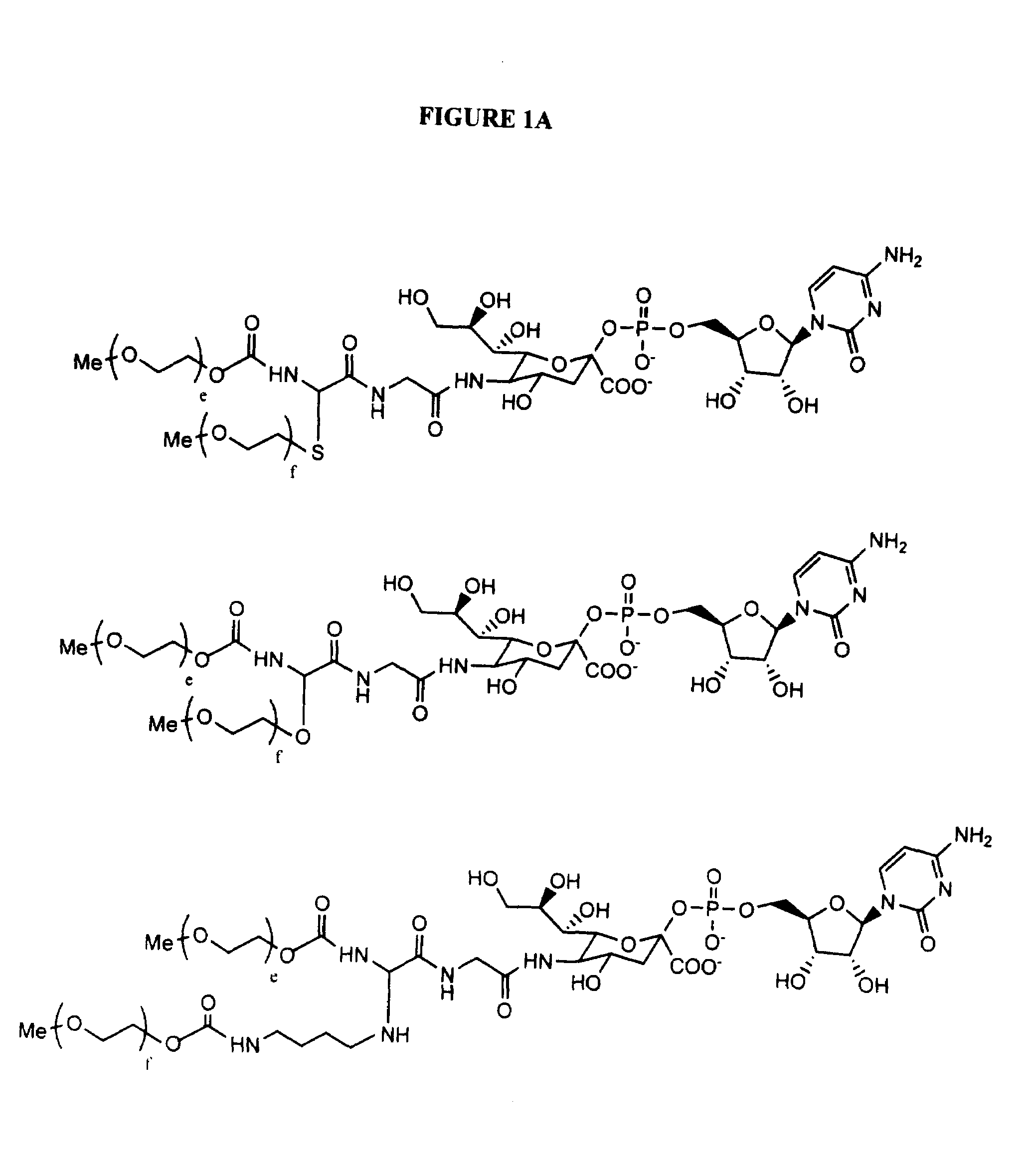
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20060111279A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost effectiveSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Erythropoietin: remodeling and glycoconjugation of erythropoietin
InactiveUS20060088906A1Increase hematocrit levelImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsErythropoiesisErythropoietin
Owner:NEOSE TECH
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050202538A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20050143292A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost-effectiveSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
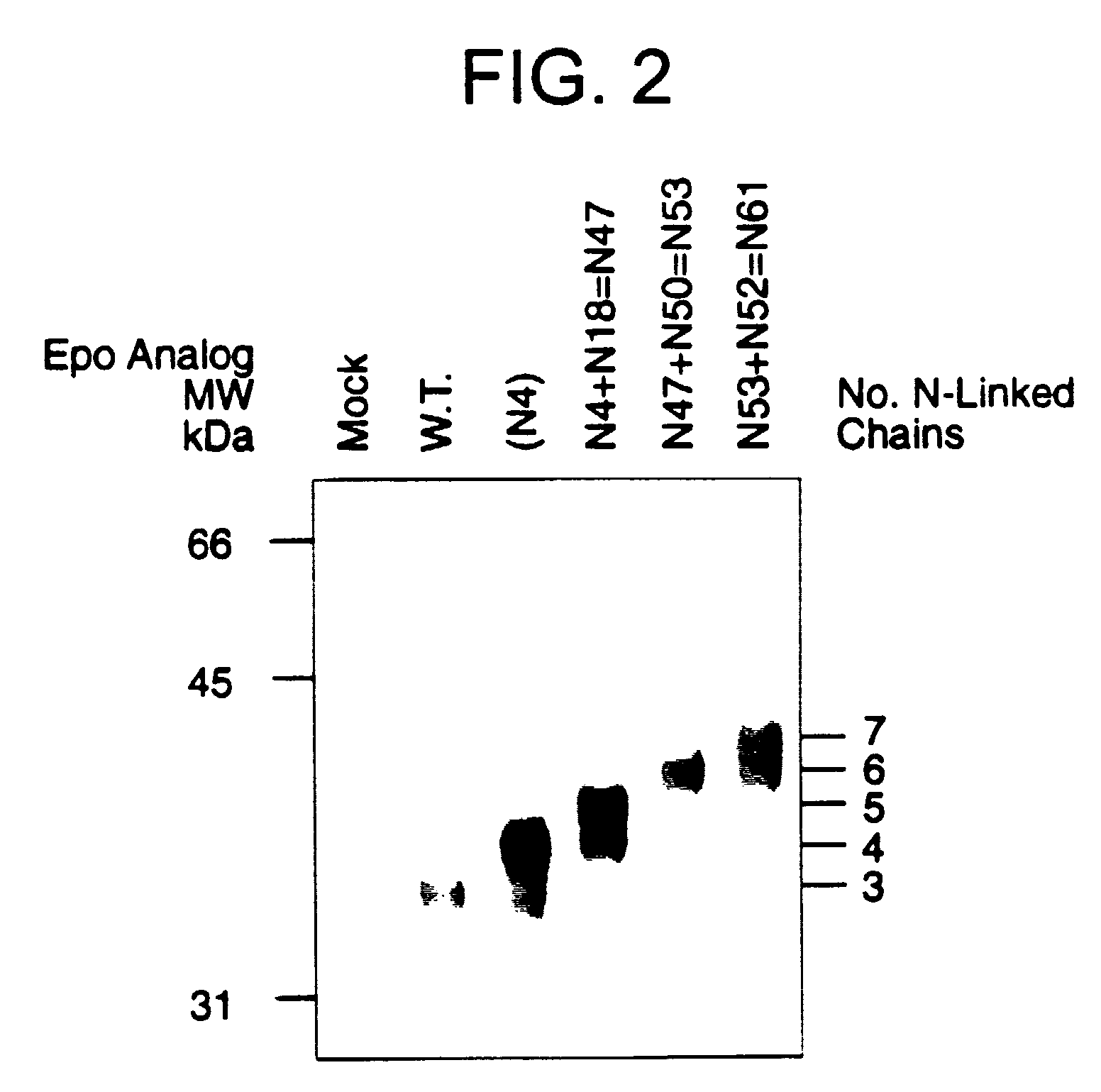
Glycosylation analogs of erythropoietin
ActiveUS7217689B1Increase the number ofHigh sialic acid contentPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue culturePlasmidDNA
Erythropoietin analogs having at least one additional site for glycosylation, or a rearrangement of at least one site for glycosylation are disclosed. The invention also relates to DNA sequences encoding said erythropoietin analogs, and recombinant plasmids and host cells for analog expression.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050192211A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
The present invention provides Fc-erythropoietin (“Fc-EPO”) fusion proteins with improved pharmacokinetics. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the production and practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
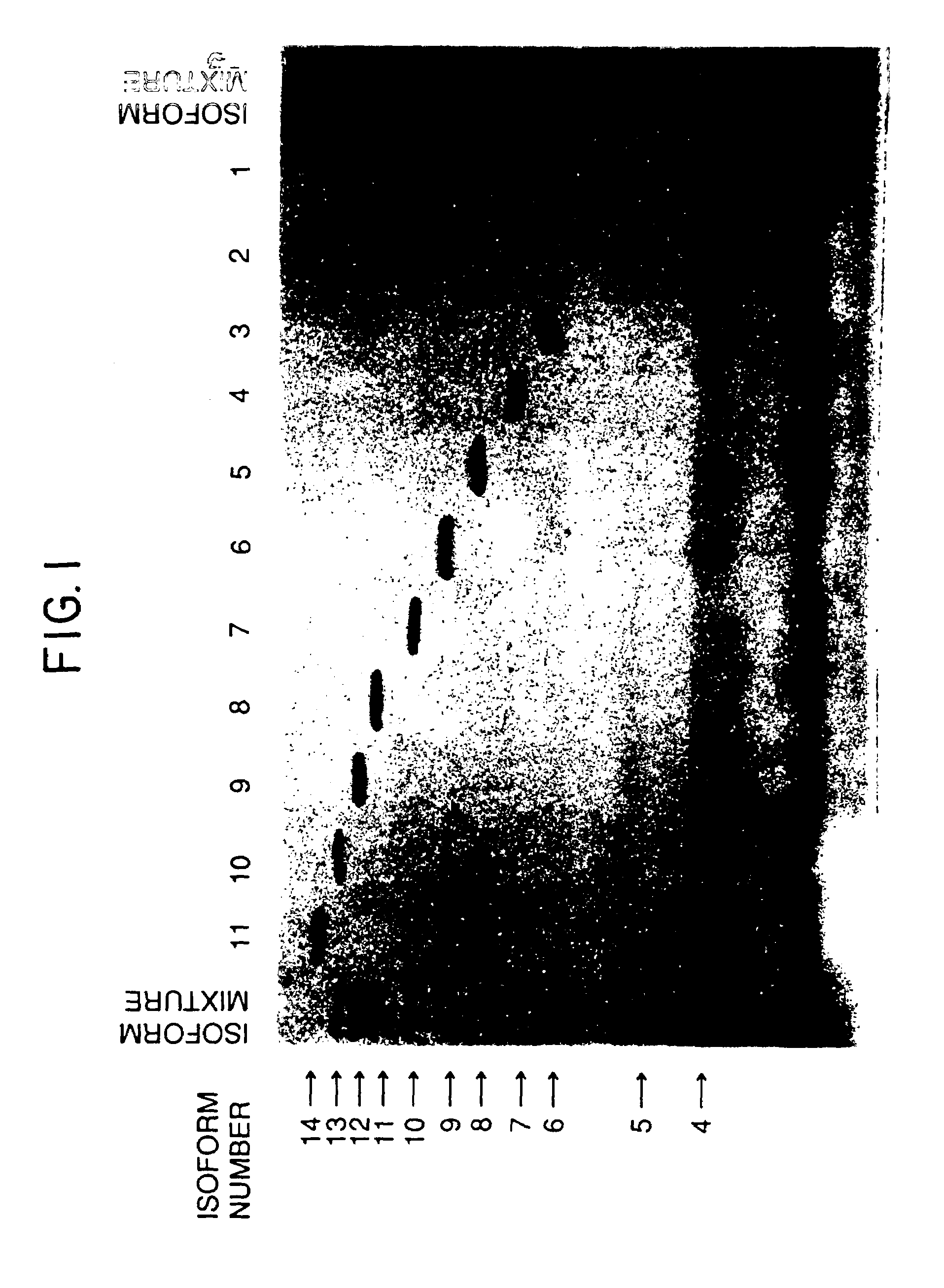
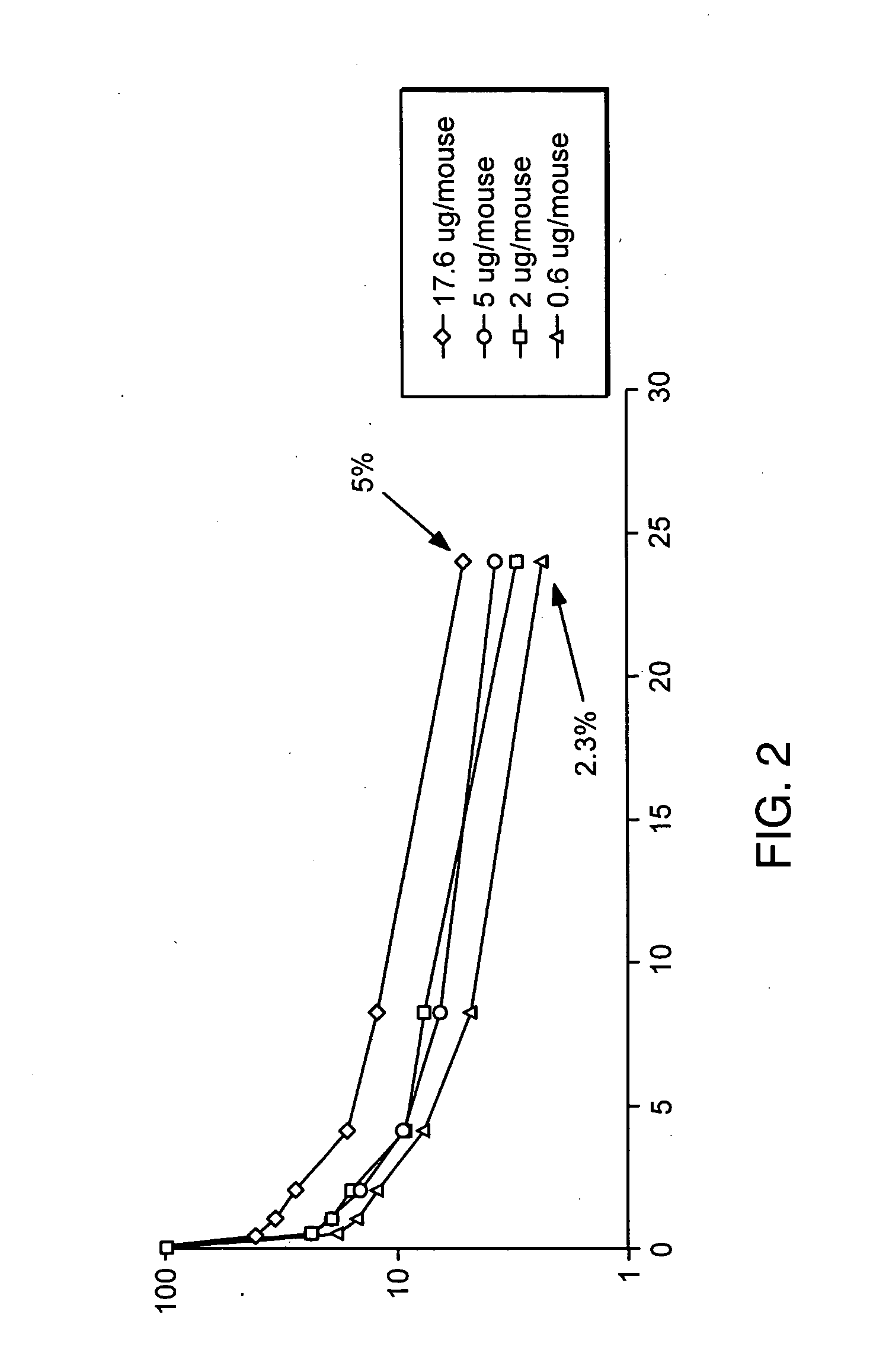
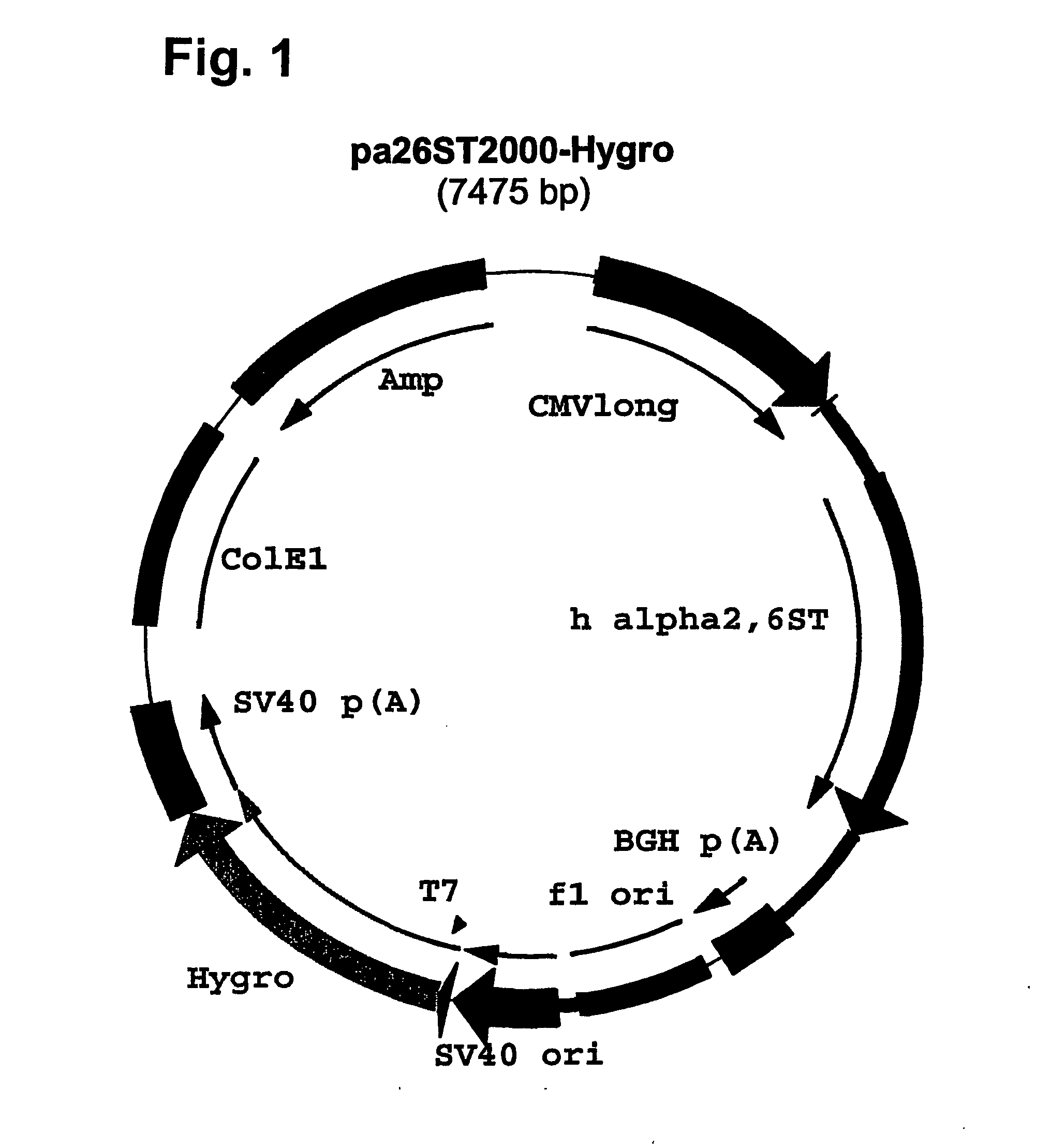
Compositions of erythropoietin isoforms comprising Lewis-X structures and high sialic acid content
InactiveUS20050181359A1Presence can be undesiredImprove system reliabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeterologousE1A Protein
Disclosed are immortalized human embryonic retina cells, having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein integrated into the genome of the cells, and further comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins, such as a sialyltransferase, wherein said nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins is under control of a heterologous promoter. Methods for producing recombinant proteins from such cells and obtaining such recombinant proteins having increased sialylation are provided as are novel compositions of isoforms of erythropoietin .
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
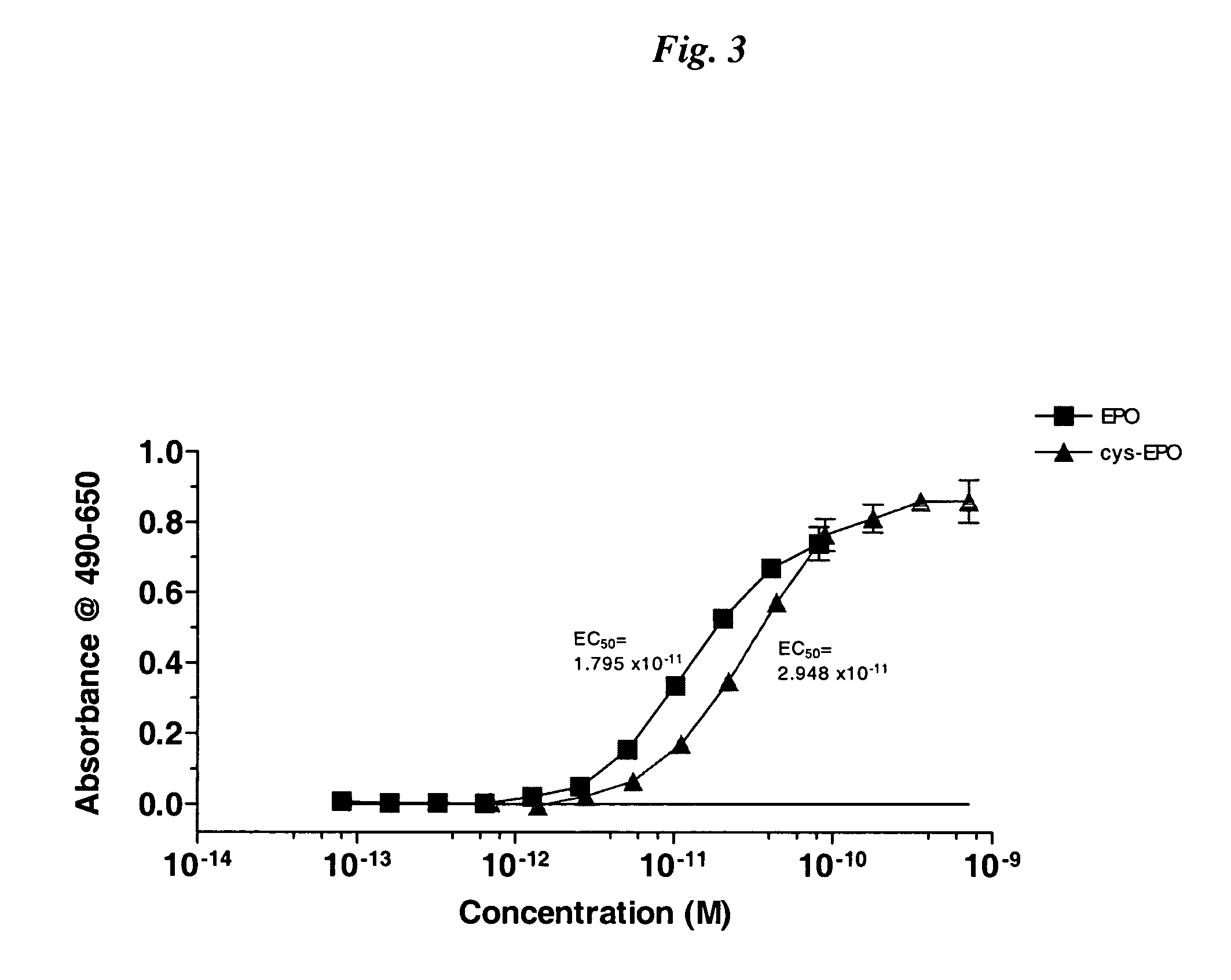
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS20050124045A1Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:SUN LEE HWEI K +2
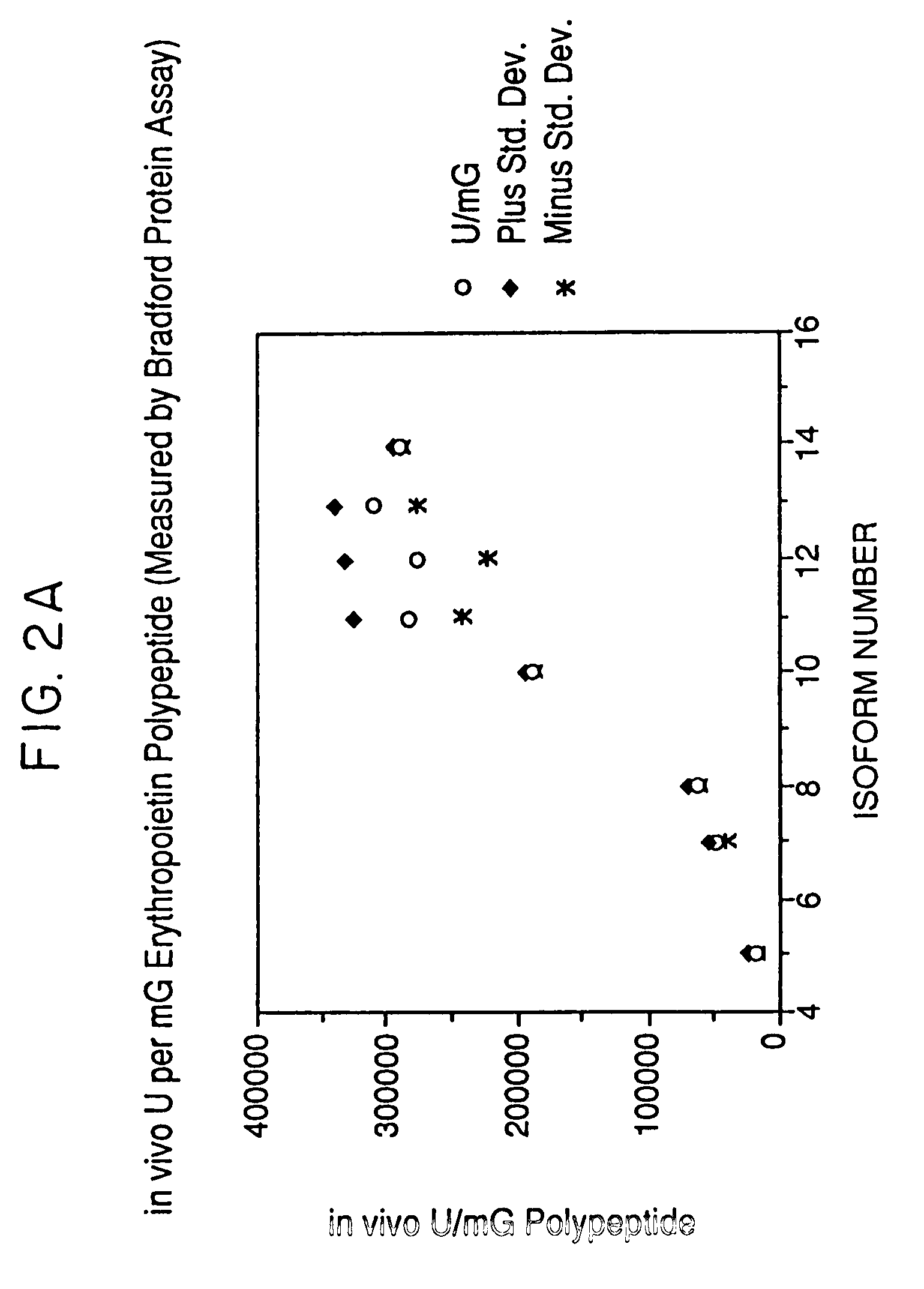
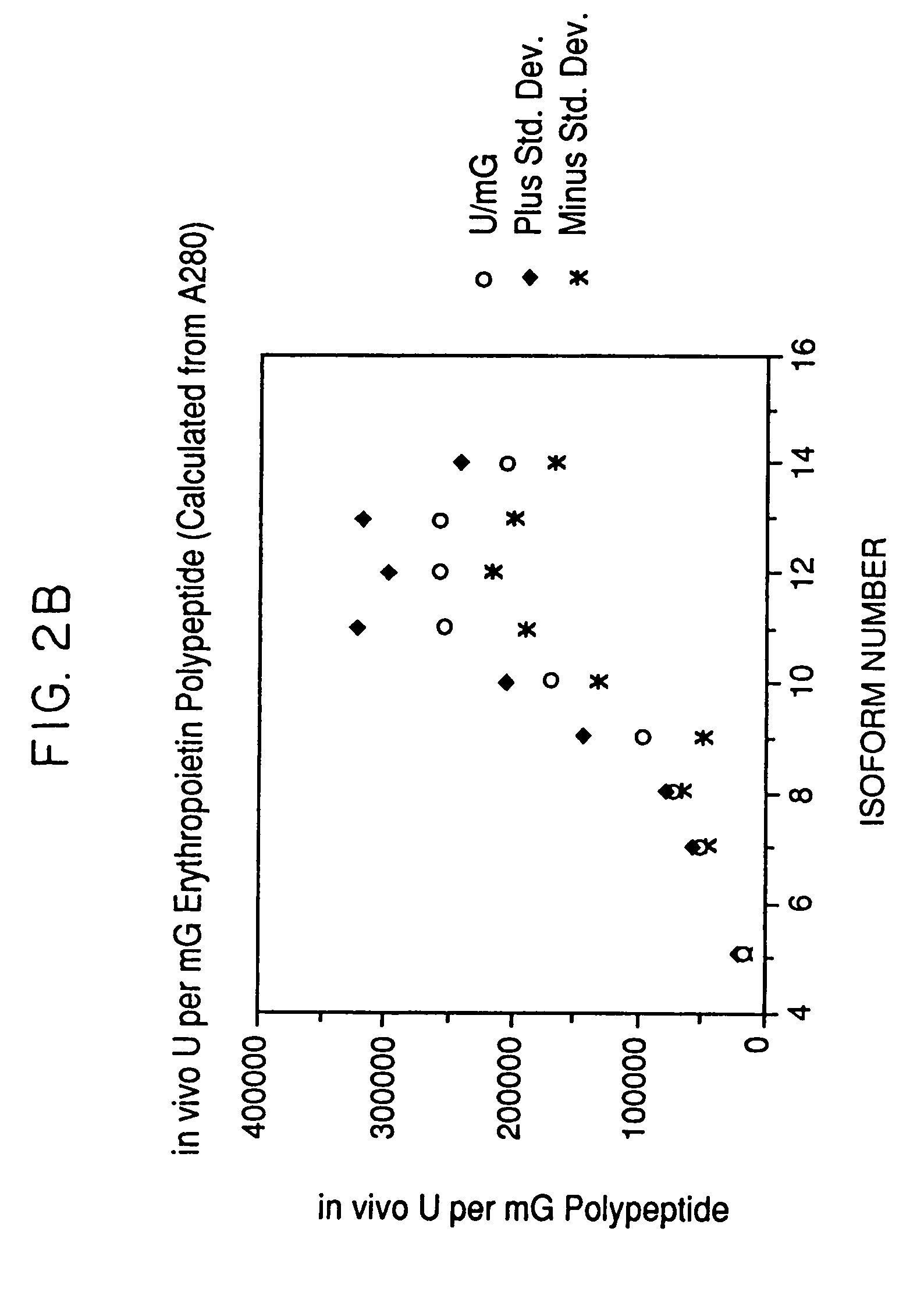
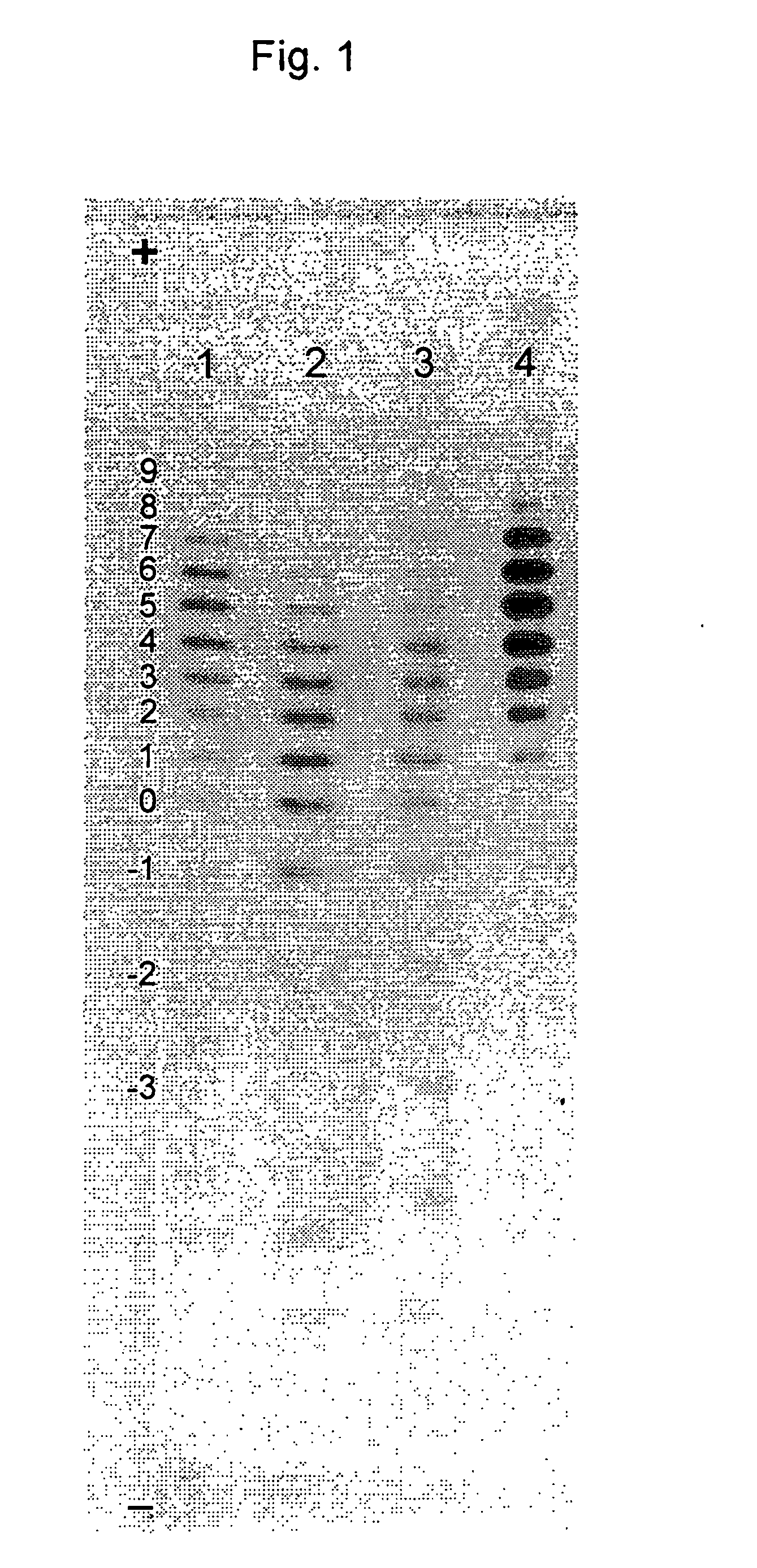
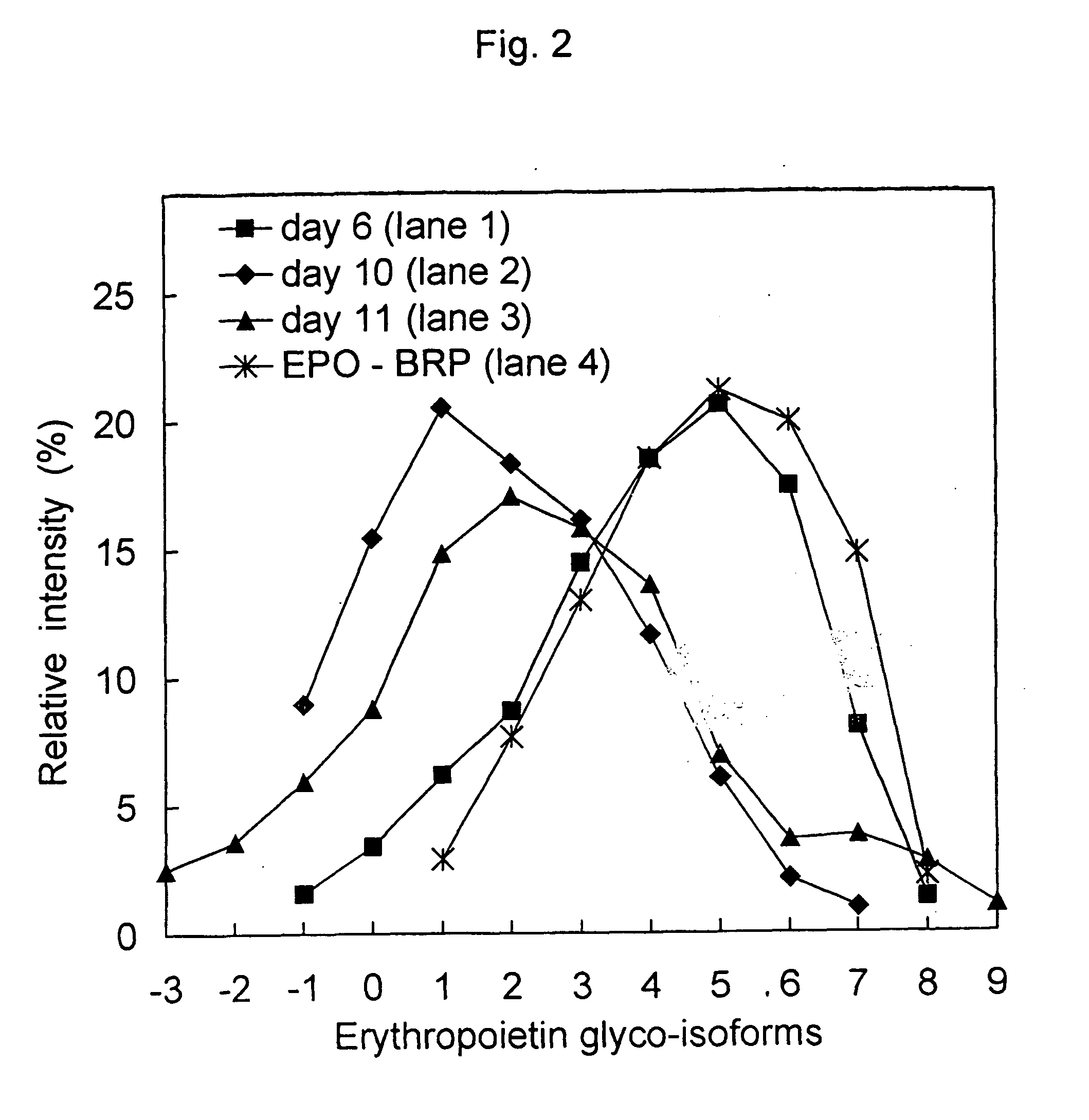
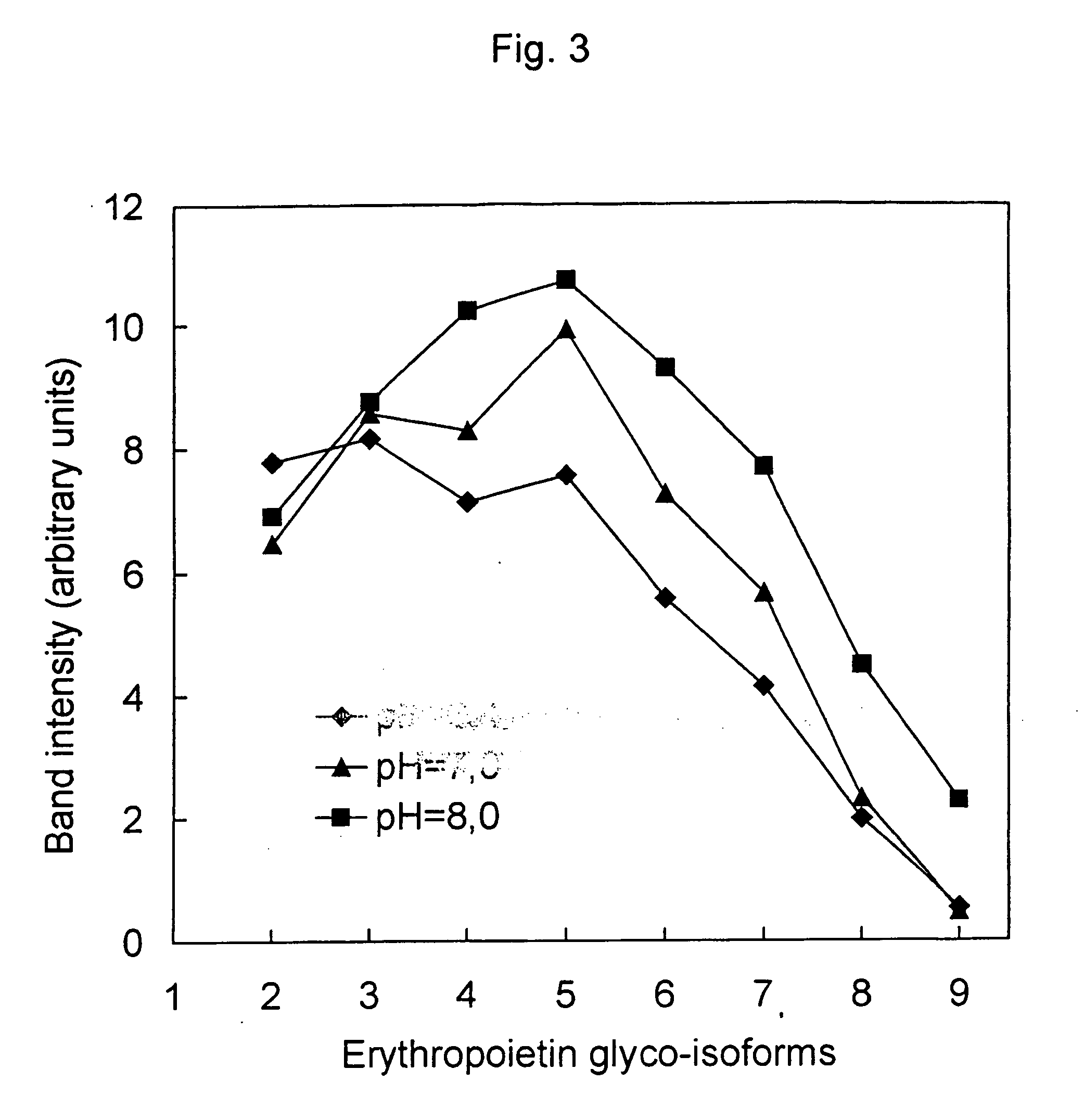
Process for the preparation of a desired erythropoietin glyco-isoform profile
InactiveUS20050153879A1High and uniform product specificityImprove product qualityPeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationFiltrationRed blood cell
The present invention provides a process for the production of erythropoietin (EPO) with high purity and with a desired profile of EPO glycol-isoforms by using a combination of specific chromatographic steps in such a manner that the starting EPO glycol-isoform profile is changed or modified. The applied chromatographic steps includes at least (a) dye affinity chromatography, and (b) hydrophobic chromatography and / or (c) anion-exchange chromatography. In a preferred embodiment, the process further includes (d) gel filtration chromatography. The present invention also provides a process for the determination of erythropoietin (EPO) glycol-isoform profile in an EPO containing composition.
Owner:SVETINA MONICA +4
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
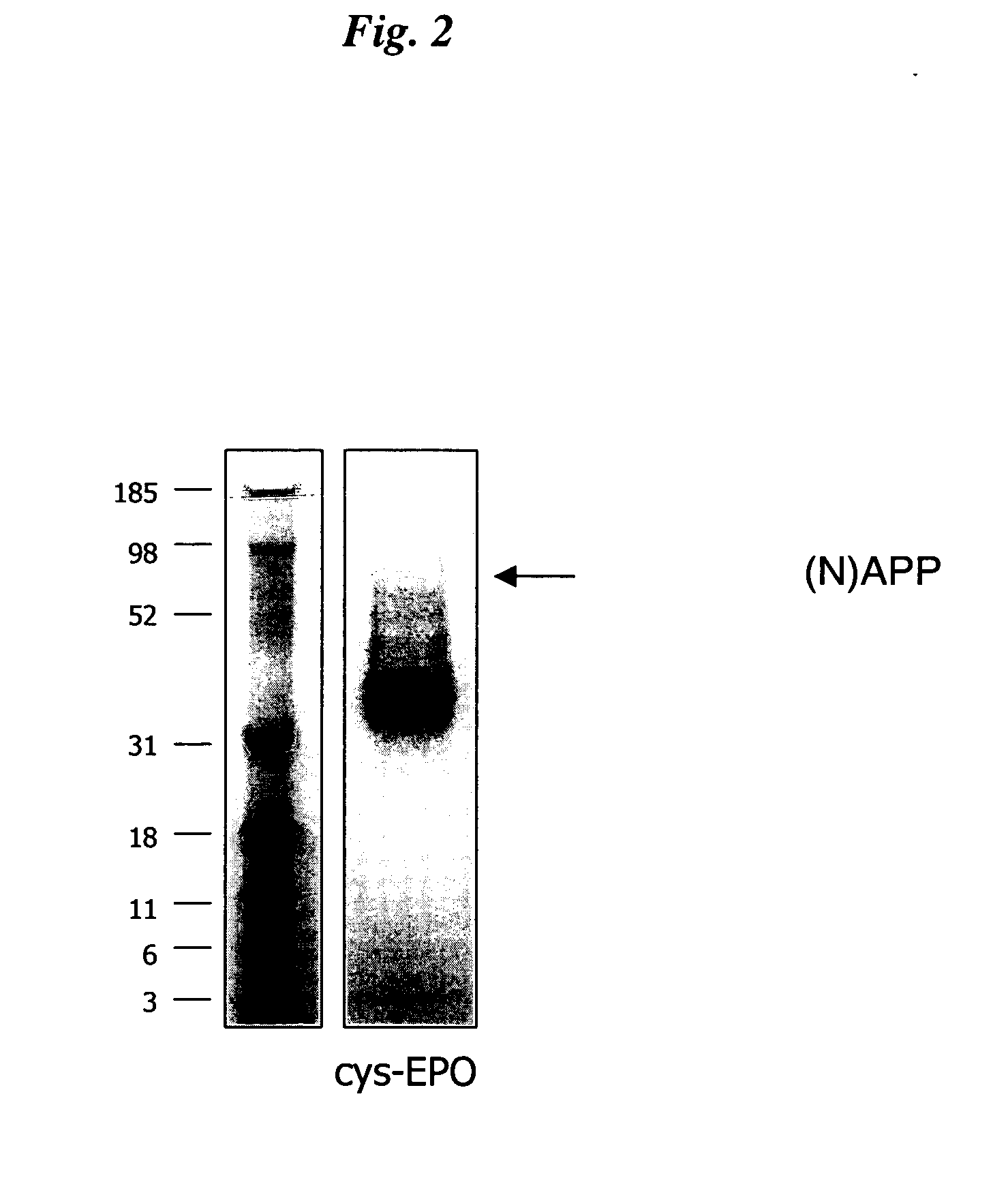
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
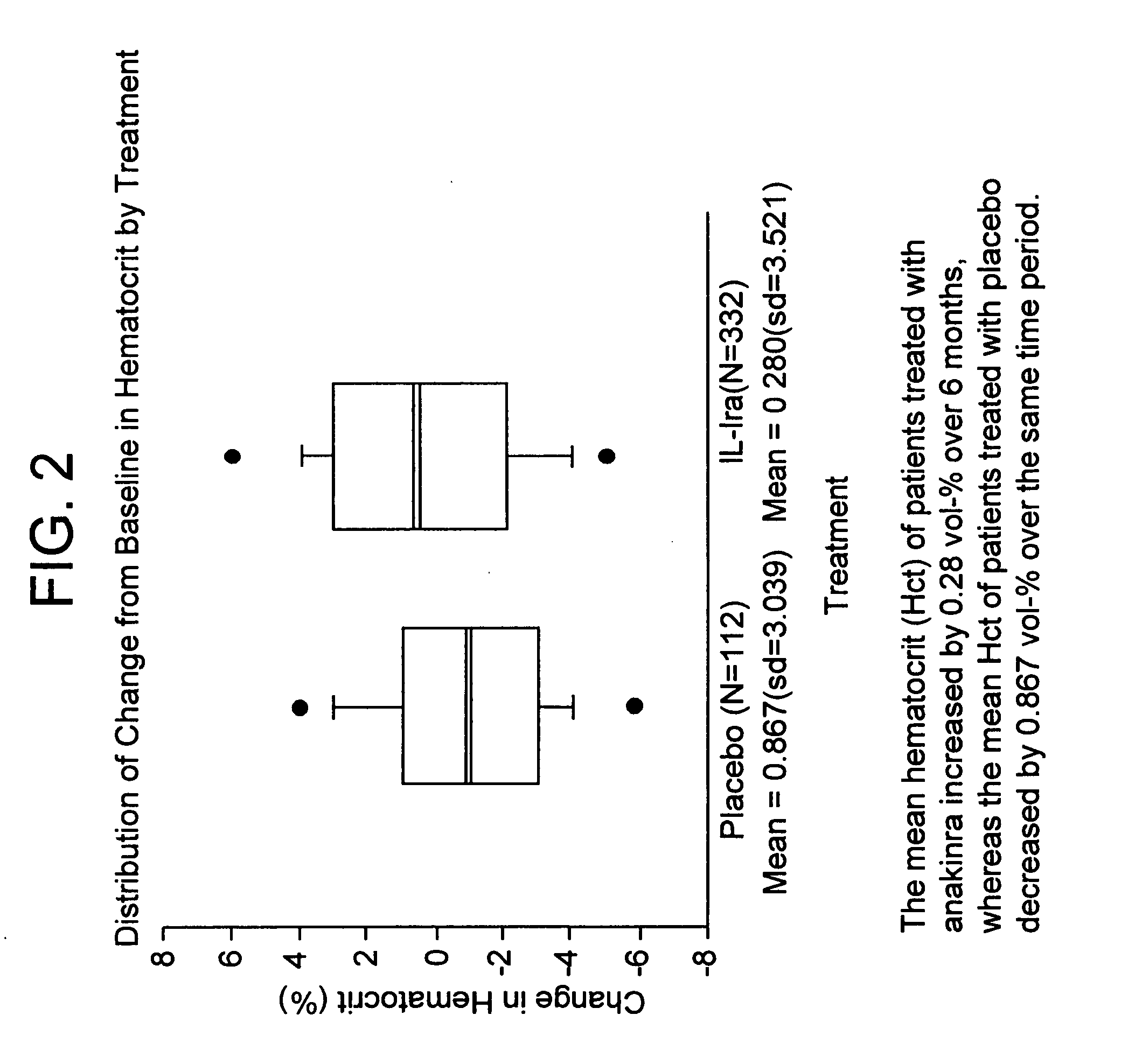
Method of treating blood disorders
InactiveUS20050106148A1Heavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseWhite blood cell
The invention relates to methods of treating a blood disorder in a mammal with an interleukin-1 (IL-1) inhibitor. The invention also relates to methods of treating a blood disorder in a mammal with an IL-1 inhibitor, a TNF inhibitor and an erythropoietin (EPO) receptor agonist. The invention also relates to compositions of an IL-1 inhibitor and compositions of an IL-1 inhibitor, a TNF inhibitor and an EPO receptor agonist.
Owner:AMGEN INC
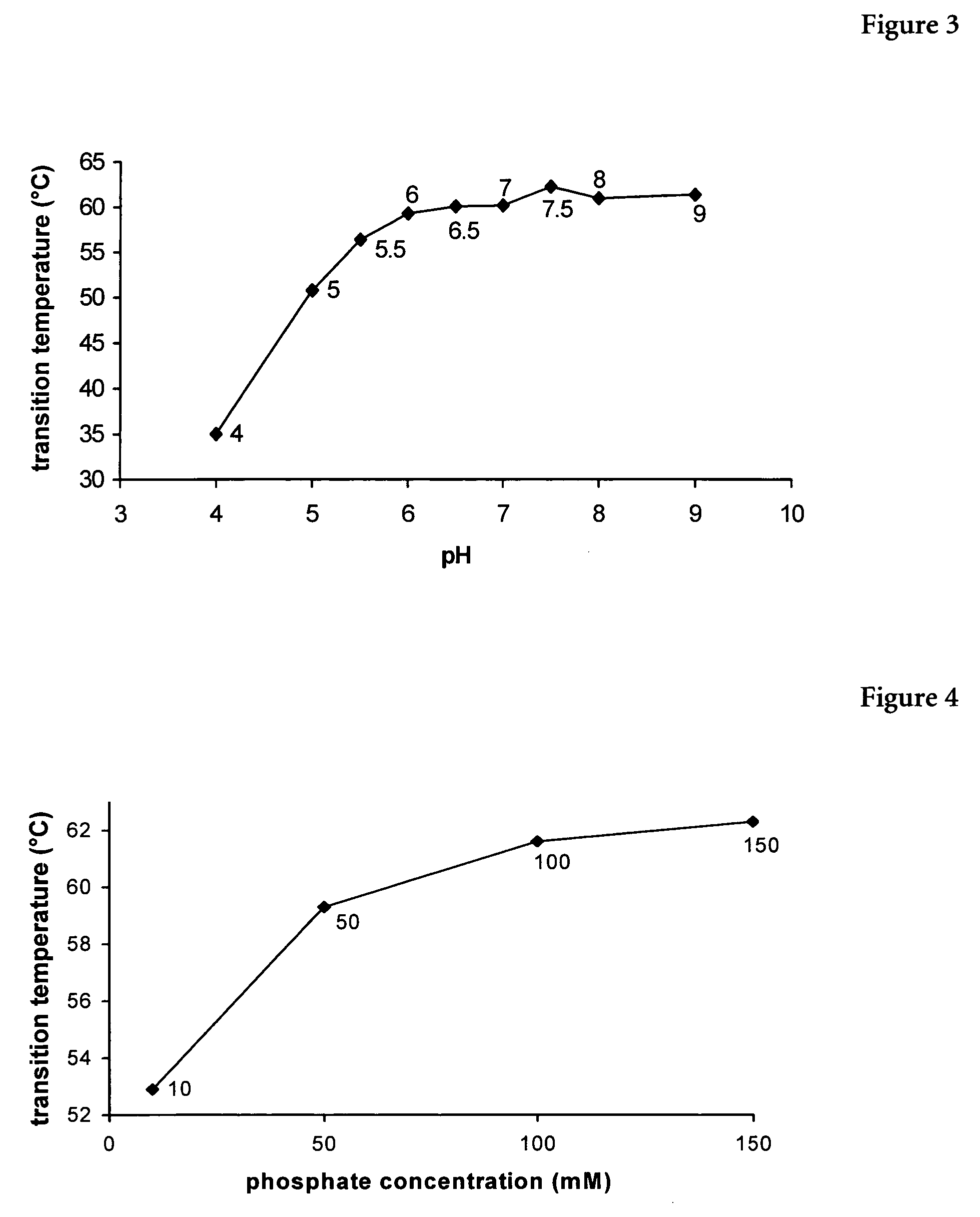
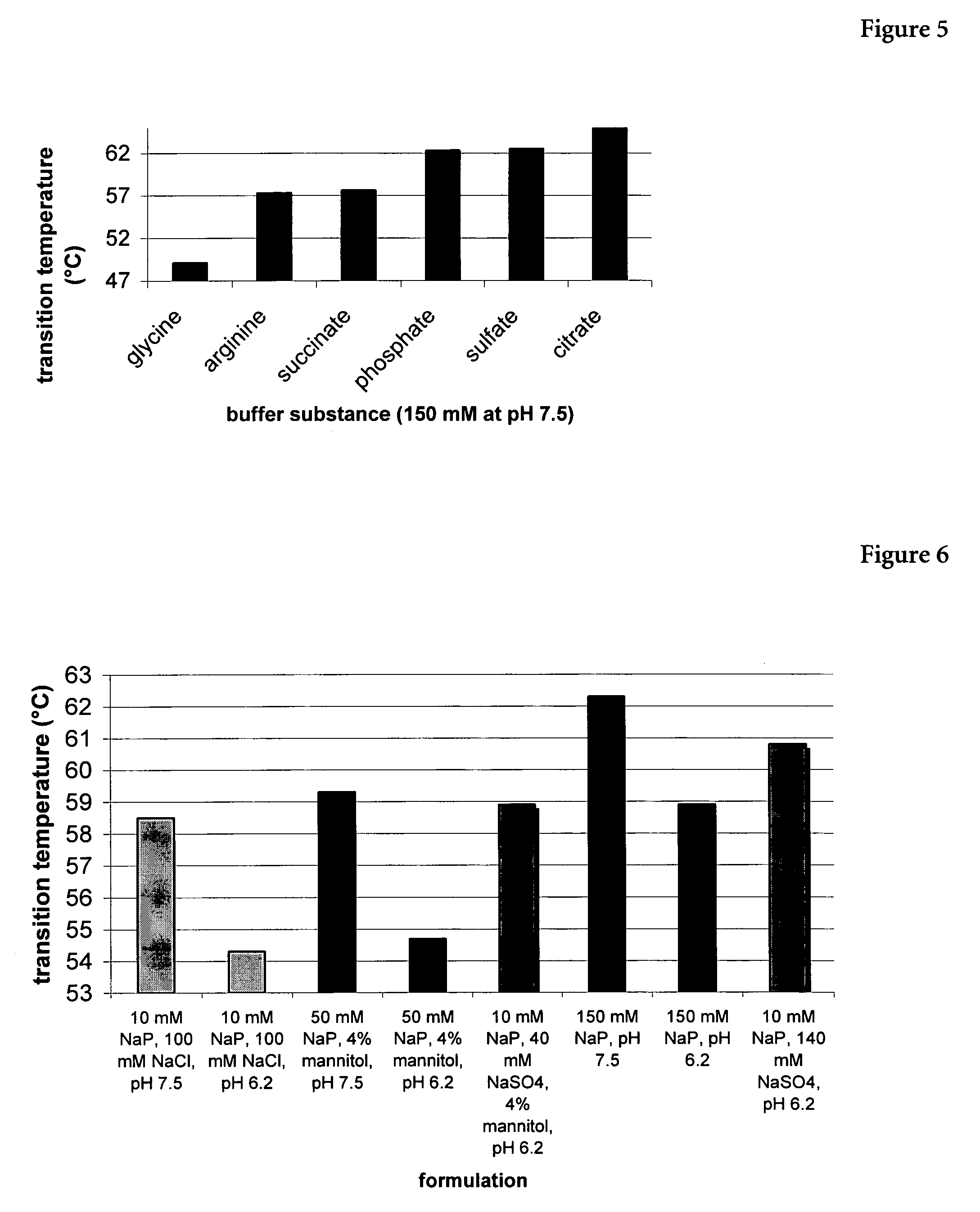
Erythropoietin composition
InactiveUS7202208B2Improve stabilityWithout loosingPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseErythropoiesis
The present invention relates to a liquid pharmaceutical composition consisting essentially of an erythropoietin protein, a multiple charged inorganic anion in a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer suitable to keep the solution pH in the range from about 5.5 to about 7.0, and optionally one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. This composition is especially useful for the prophylaxis and treatment of diseases related to erythropoiesis.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Tetrameric cytokines with improved biological activity
ActiveUS8034352B2Keep for a long timeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeHalf-life
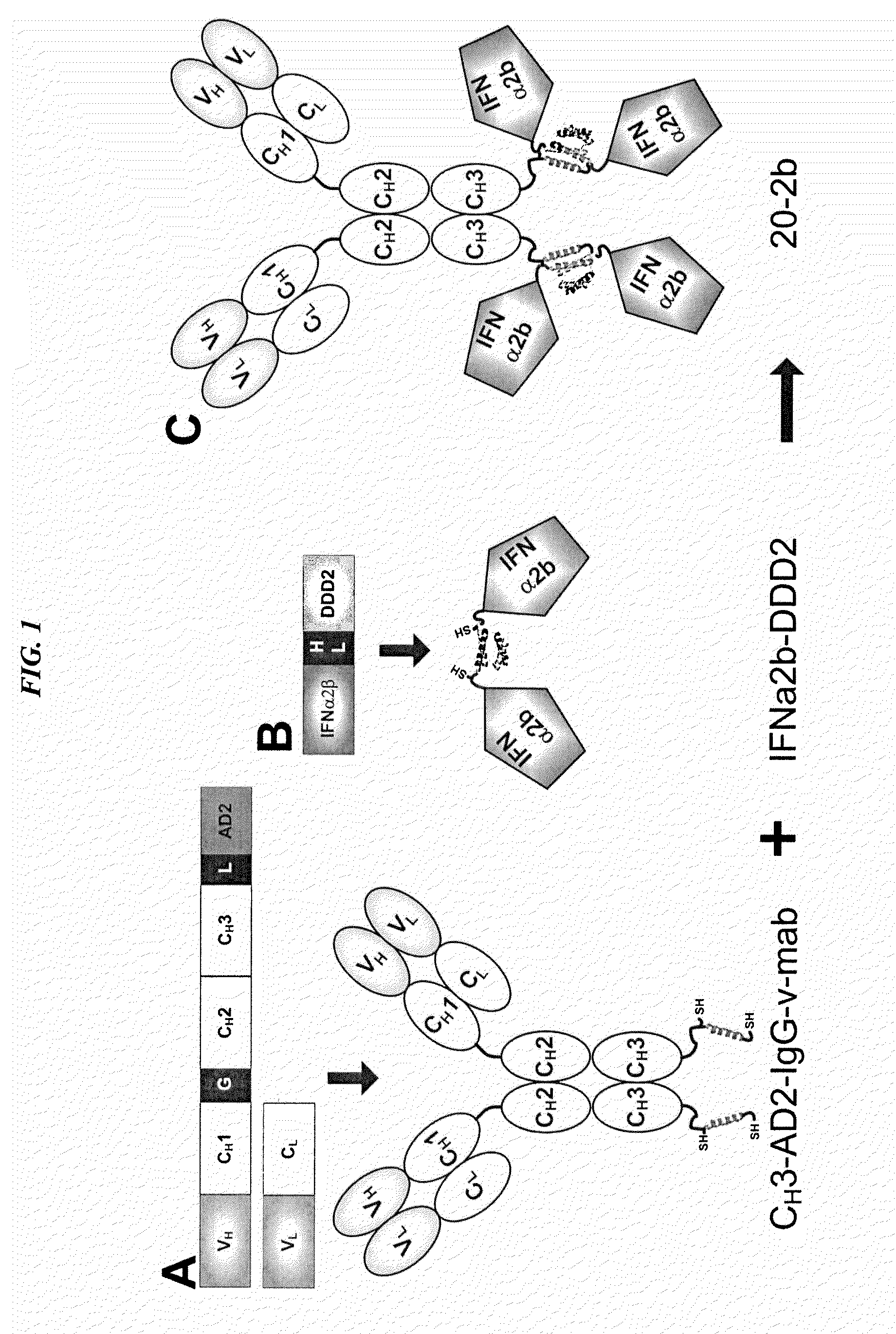
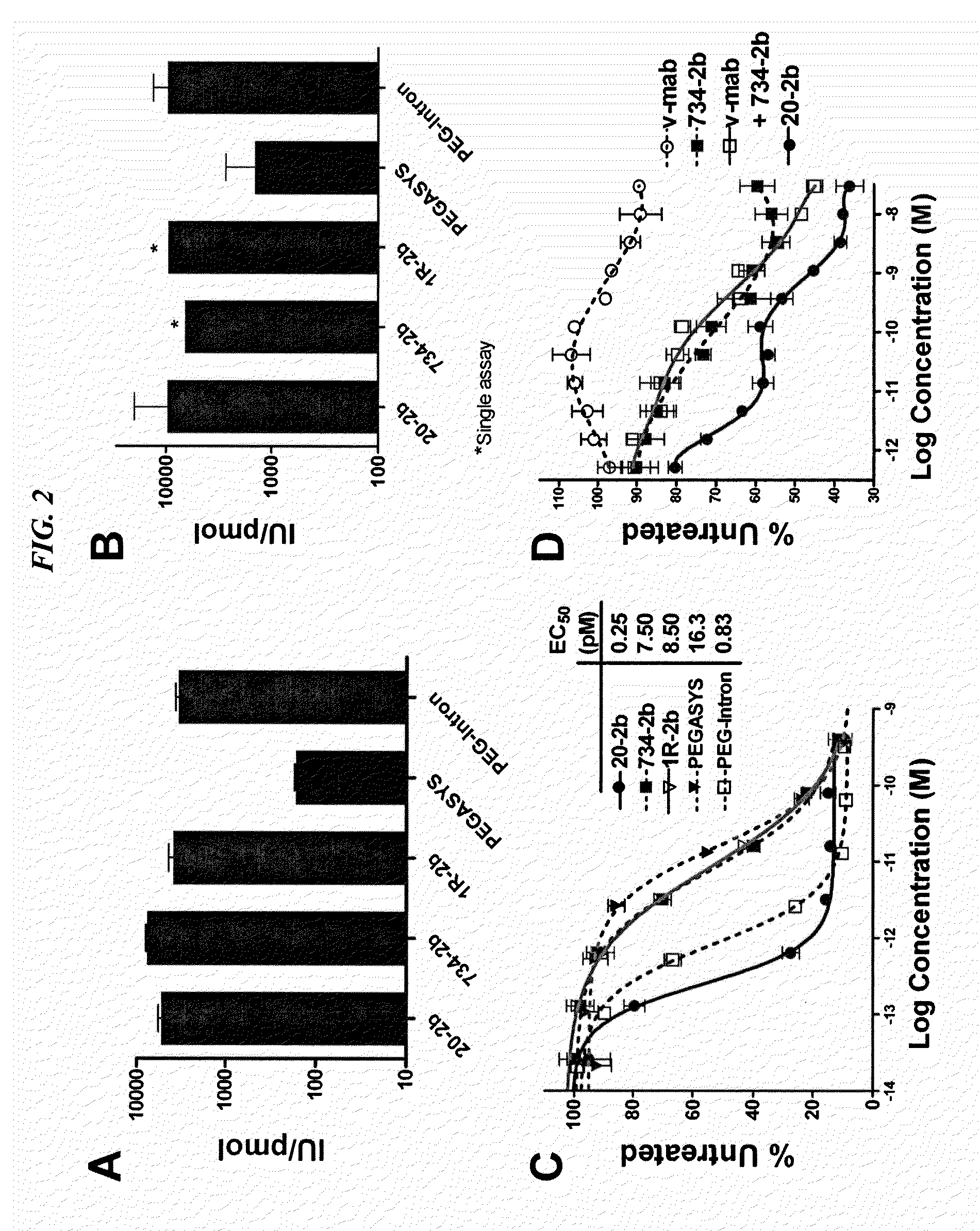
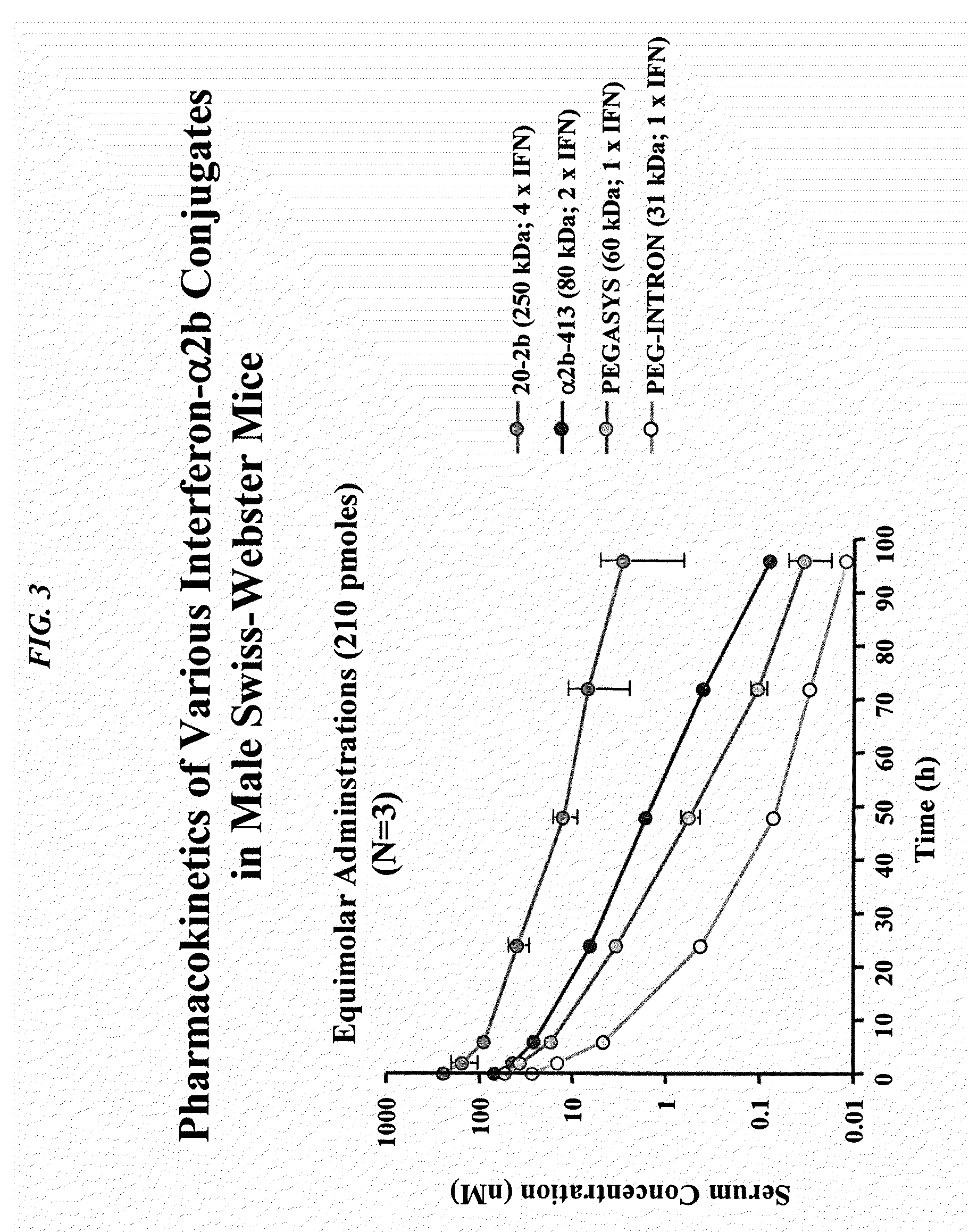
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In more preferred embodiment the cytokine is G-CSF, erythropoietin or INF-α2b.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Methods for treatment and prevention of neuromuscular and muscular conditions by peripherally administered erythropoietin
InactiveUS7309687B1Improve cognitive functionAvoid damageNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCentral neuron
Methods and compositions are provided for protecting or enhancing excitable tissue function in mammals by systemic administration of an erythropoietin receptor activity modulator, such as erythropoietin, which signals via an EPO-activated receptor to modulate the function of excitable tissue. Excitable tissues include central neuronal tissues, such as the brain, peripheral neuronal tissues, retina, and heart tissue. Protection of excitable tissues provides treatment of hypoxia, seizure disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, hypoglycemia, and neurotoxin poisoning. Enhancement of function is useful in learning and memory. The invention is also directed to compositions and methods for facilitating the transport of molecules across endothelial cell tight junction barriers, such as the blood-brain barrier, by association of molecules with an erythropoietin receptor activity modulator, such as an erythropoietin.
Owner:THE KENNETH S WARREN INST
Long lasting drug formulations
The present invention is directed to long-lasting erythropoietin therapeutic formulations and their methods of use wherein the formulation comprises a genetically modified micro-organ that comprises a vector which comprises a nucleic acid sequence operably linked to one or more regulatory sequences, wherein the nucleic acid sequence encodes erythropoietin.
Owner:MEDGENICS MEDICAL ISRAEL
Compounds and methods for treatment of chemotherapy-induced anemia
ActiveUS20070292433A1Reduce weight lossInhibitory activityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsGastroenterologyErythropoietin
The invention relates to methods and compounds for treating chemotherapy-induced anemia. In particular, methods for treating chemotherapy-induced anemia in subjects refractory to treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin are encompassed herein.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
Treatment of mitochondrial diseases with an erythropoietin mimetic
InactiveUS20090291092A1Stimulating erythropoiesisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRed blood cell
Methods of treating mitochondrial disorders that are not respiratory chain disorders using compositions comprising EPO mimetic compounds or compounds capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are disclosed. Methods of treating Friedreich's ataxia, Leigh's syndrome, or other disorders by increasing the expression of frataxin with an EPO mimetic compound or a compound capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are also disclosed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
Erythropoietin compositions
Methods and materials are provided for the production of compositions of erythropoietin protein, wherein said compositions comprise a pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Method of treating erythropoietin hyporesponsive anemias
InactiveUS20100266591A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHemoglobinopathyRed blood cell
The invention relates to methods of using compositions comprising EPO-mimetic peptides to treat anemia. The invention relates to methods of treating disorders characterized by the insufficient amounts of erythrocytes and hemoglobulin in the blood due to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or by hemoglobinopathies, such as alpha- or beta-thalessemia or sickle cell disease.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
Erythropoietin conjugates
InactiveUS7128913B2Easy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRed blood cellBone marrow cell
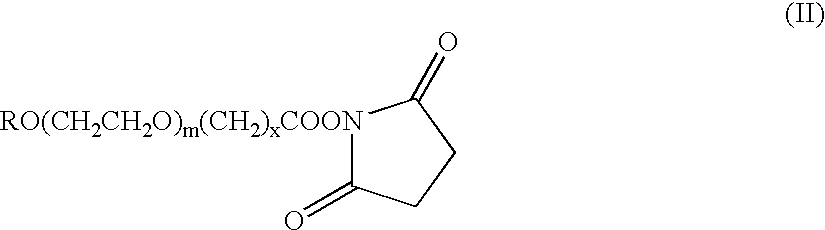
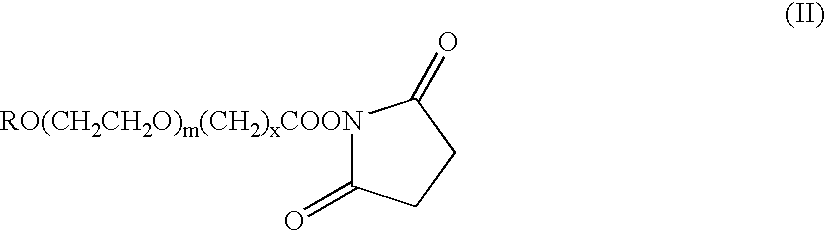
The present invention refers to conjugates of erythropoietin with poly(ethylene glycol) comprising an erythropoietin glycoprotein having an N-terminal α-amino group and having the in vivo biological activity of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of reticulocytes and red blood cells and selected from the group consisting of human erythropoietin and analogs thereof which have the sequence of human erythropoietin modified by the addition of from 1 to 6 glycosylation sites or a rearrangement of at least one glycosylation site; said glycoprotein being covalently linked to one poly(ethylene glycol) group of the formula—CO—(CH2)x—(OCH2CH2)m—ORwherein the —CO of the poly(ethylene glycol) group forms an amide bond with said N-terminal α-amino group; and wherein R is lower alkyl; x is 2 or 3; and m is from about 450 to about 1350.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
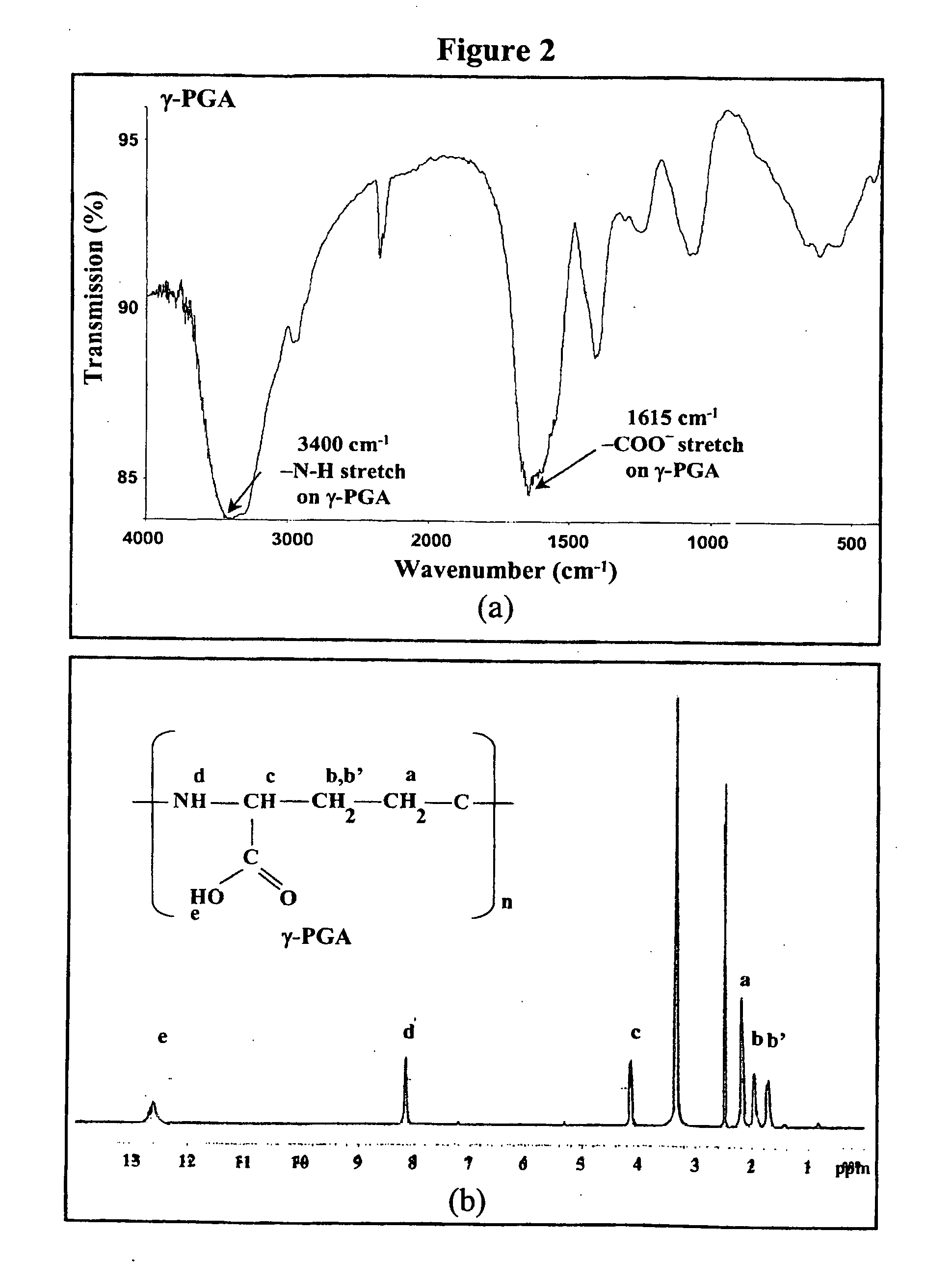
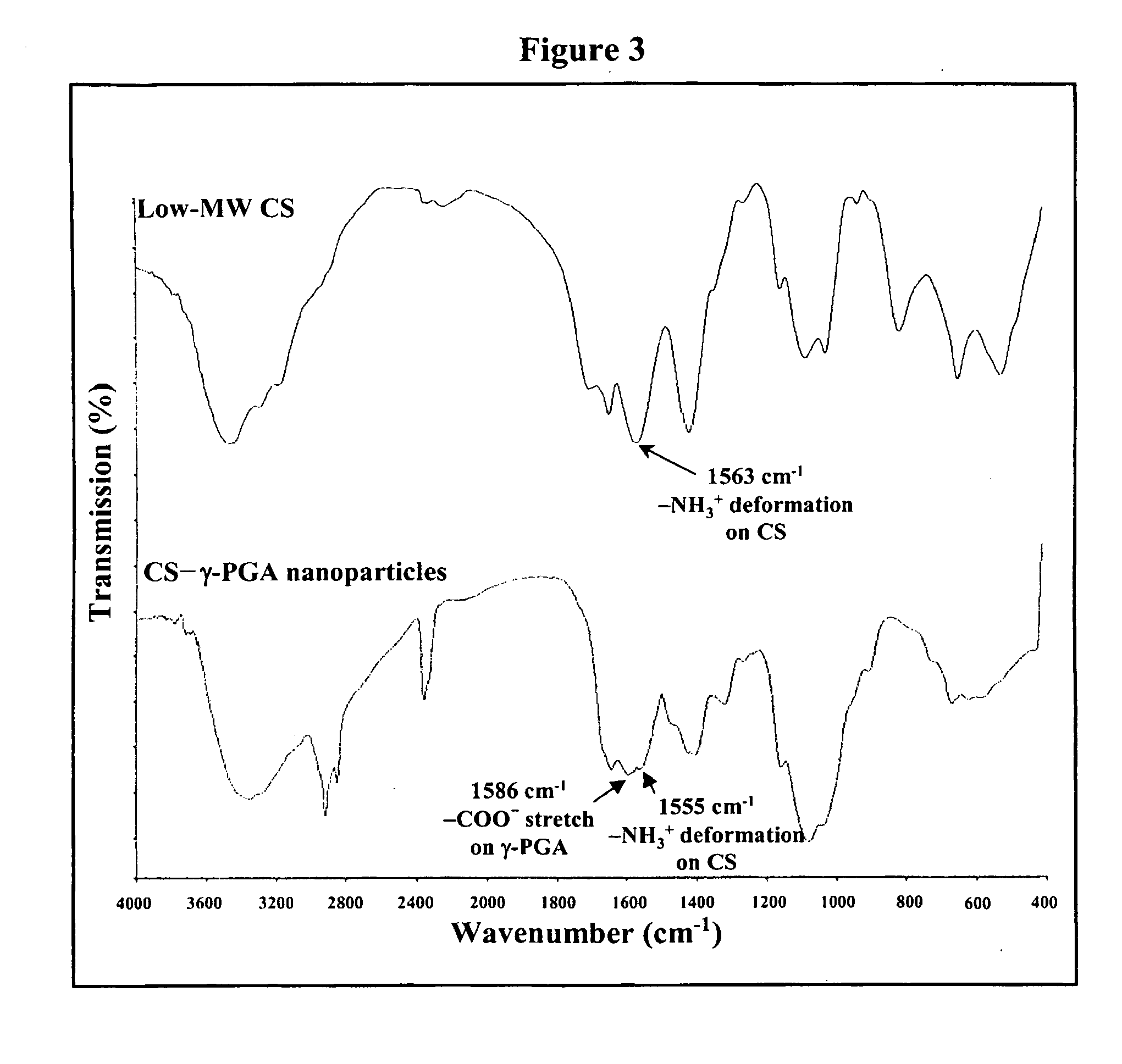
Nanoparticles for drug delivery
InactiveUS20070237827A1Sustained releaseReduce resistanceBiocidePowder deliveryHMG-CoA reductaseMedicine
The invention discloses the nanoparticles composed of chitosan, poly-glutamic acid, and at least one bioactive agent of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors or erythropoietin. The nanoparticles are characterized with a positive surface charge and their enhanced permeability for paracellular drug delivery.
Owner:NANOMEGA MEDICAL CORP
Treatment of neurological dysfunction comprising fructopyranose sulfamates and erythropoietin
InactiveUS6908902B2Increase neurite outgrowthBiocideNervous disorderErythropoietinFunctional disorder
Co-therapy for the treatment of neurological dysfunctions comprising administration of one or more fructopyranose sulfamates and erythropoietin.
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
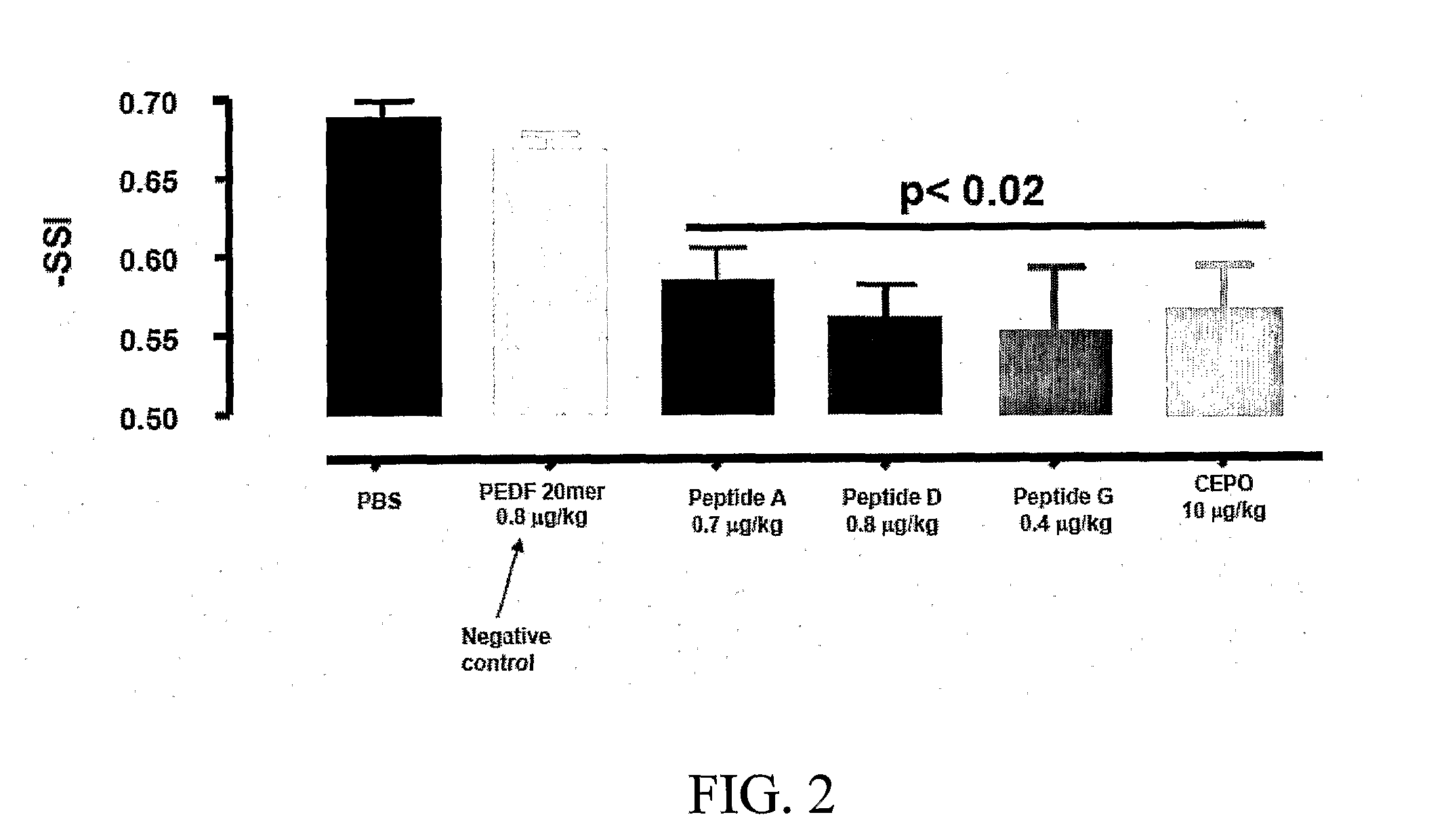
Tissue protective peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090221482A1Avoid damageFacilitate optimal expressionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue protection
The present invention is directed to novel tissue protective peptides. The tissue protective peptides of the invention may bind to a tissue protective receptor complex. In particular, the present invention is drawn to tissue protective peptides derived from or sharing consensus sequences with portions of cytokine receptor ligands, including Erythropoietin (EPO), that are not involved in the binding of the ligand to the receptor complex, e.g., to the EPO receptor homodimer. Accordingly, the tissue protective peptides of the invention are derived from the amino acid sequences of regions of cytokine receptor ligands that are generally located on or within the region of the ligand protein that is opposite of the receptor complex, i.e., are generally derived from amino acid sequences of regions of the ligand protein that face away from the receptor complex while the ligand is bound to the receptor. The invention is further directed to the consensus sequences for use in engineering a synthetic tissue protective peptide. These tissue protective peptides also include fragments, chimeras, as well as peptides designed to mimic the spatial localization of key amino acid residues within the tissue protective receptor ligands, e.g., EPO. The invention further encompasses methods for treating or preventing a disease or disorder using tissue protective peptides of the current invention. The invention also encompasses methods for enhancing excitable tissue function using tissue protective peptides of the current invention.
Owner:ARAIM PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of anemia
InactiveUS7304150B1Long half-lifeHigh activityHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesAnemiaErythropoietin
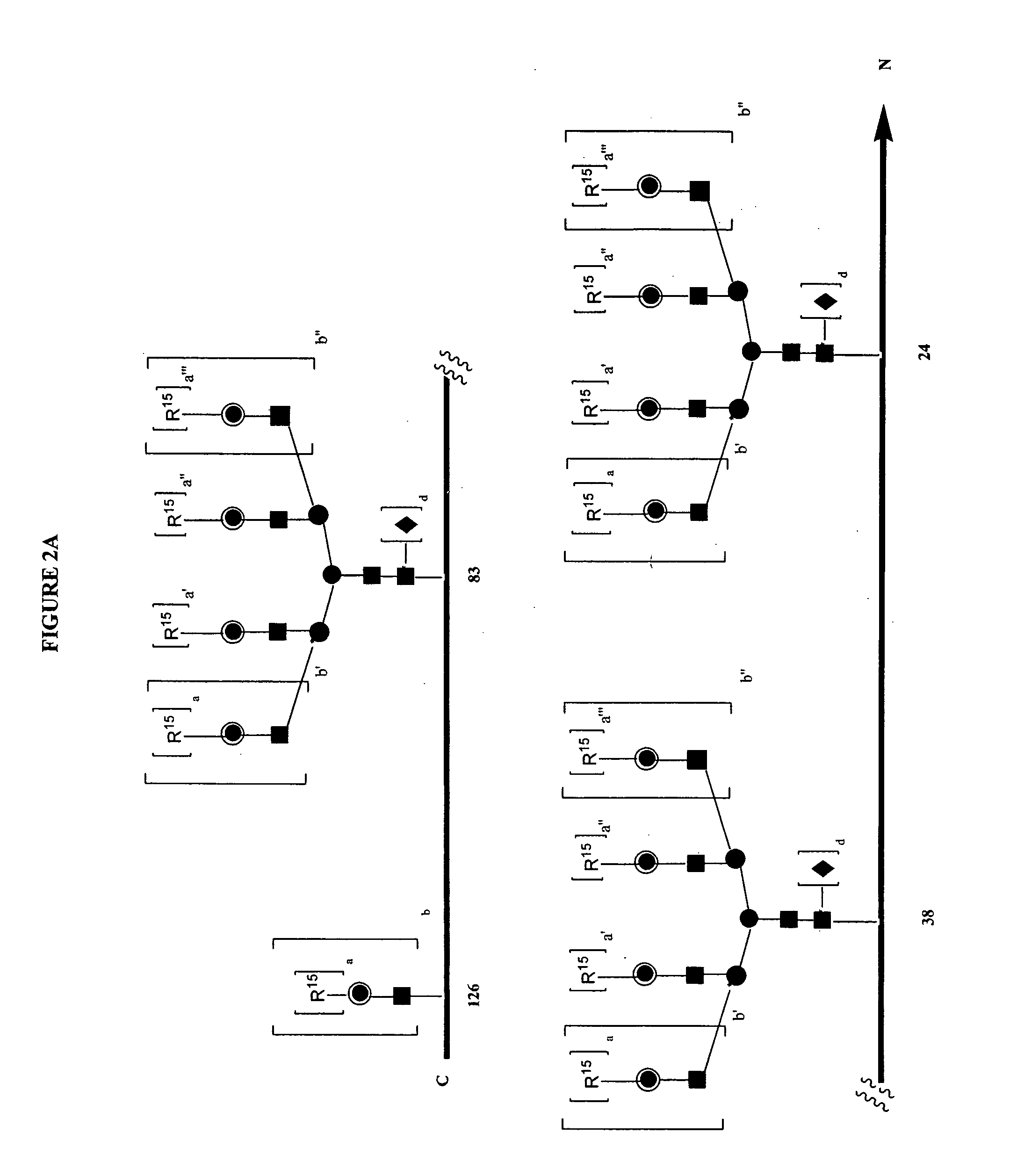
Methods for increasing and maintaining hematocrit in a mammal comprising administering a hyperglycosylated analog of erythropoietin are disclosed. An analog may be administered less frequently than an equivalent molar amount of recombinant human erythropoietin to obtain a comparable target hematocrit and treat anemia. Alternatively, a lower molar amount of a hyperglycosylated analog may be administered to obtain a comparable target hematocrit and treat anemia. Also disclosed are new hyperglycosylated erythopoietin analogs, methods of production of the analogs, and compositions comprising the analogs.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Pharmaceutical for prevention and treatment of demyelinating disease
A pharmaceutical for prevention and treatment of demyelination-associated neural function impairing diseases contains erythropoietin as an active ingredient, and protectively act on the survival of oligodendrocytes, which form a myelin sheath, in cerebrovascular dementia typified by multiple sclerosis and Binswanger disease, diseases involving demyelination. The pharmaceutical and method also promote maturation of undifferentiated oligodendrocytes present in the brain, activating remyelination. Through these mechanisms, the pharmaceutical and method can prevent and treat demyelination-associated neural function impairing diseases.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN FOUND FOR RES ON AGING & PROMOTION OF WELFARE +1
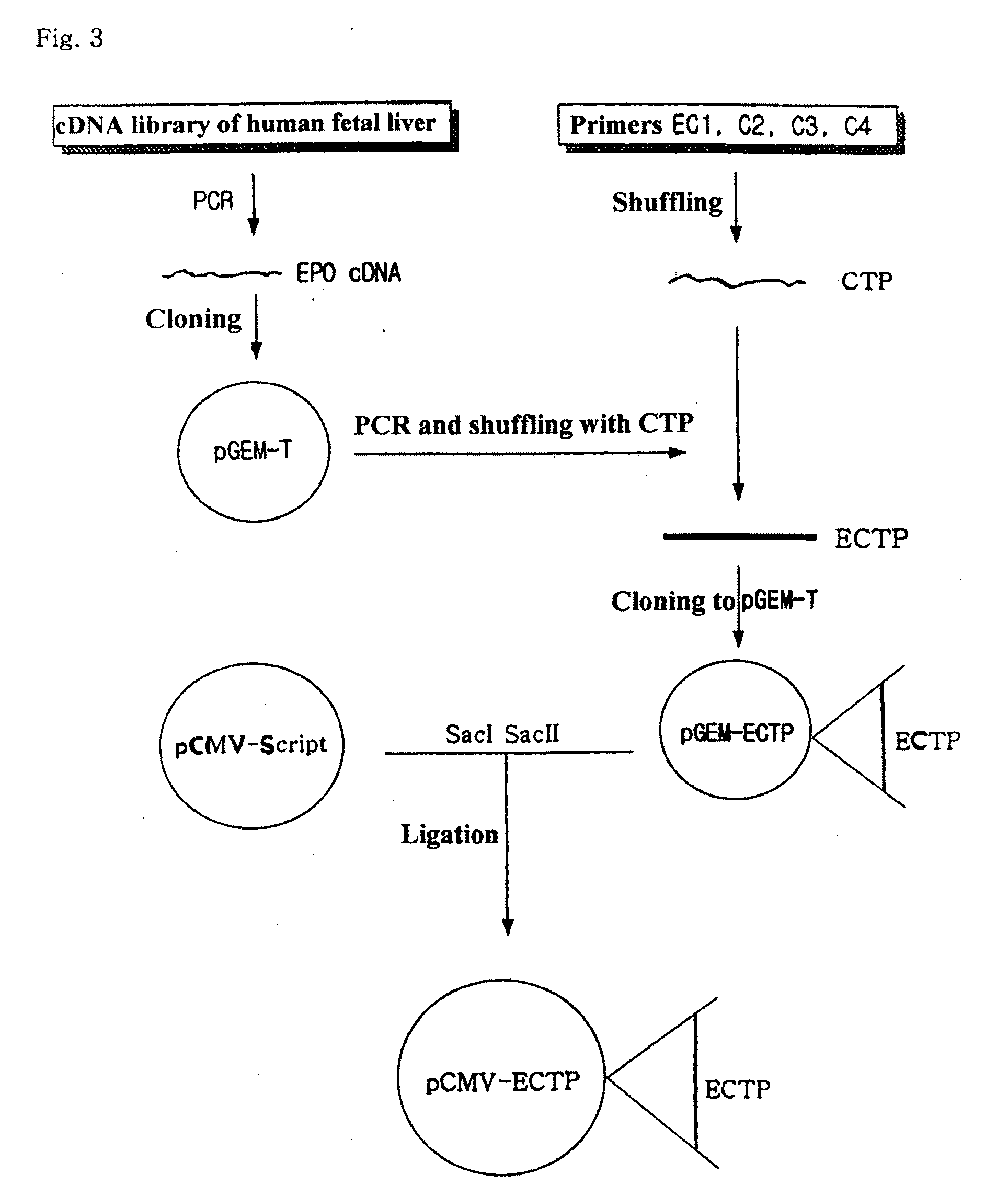
Fusion protein having the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin
InactiveUS20090221037A1High activityImprove in vivo activitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsΒ subunitRed blood cell
The present invention relates to a fusion protein in which a carboxy terminal of human erythropoietin (EPO) is fused with a carboxy terminal peptide fragment of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), to DNA encoding the fusion protein, and to a method for preparation of the fusion protein. The fusion protein has the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin.
Owner:CJ HEALTHCARE CORP
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20080305992A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost effectivePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com